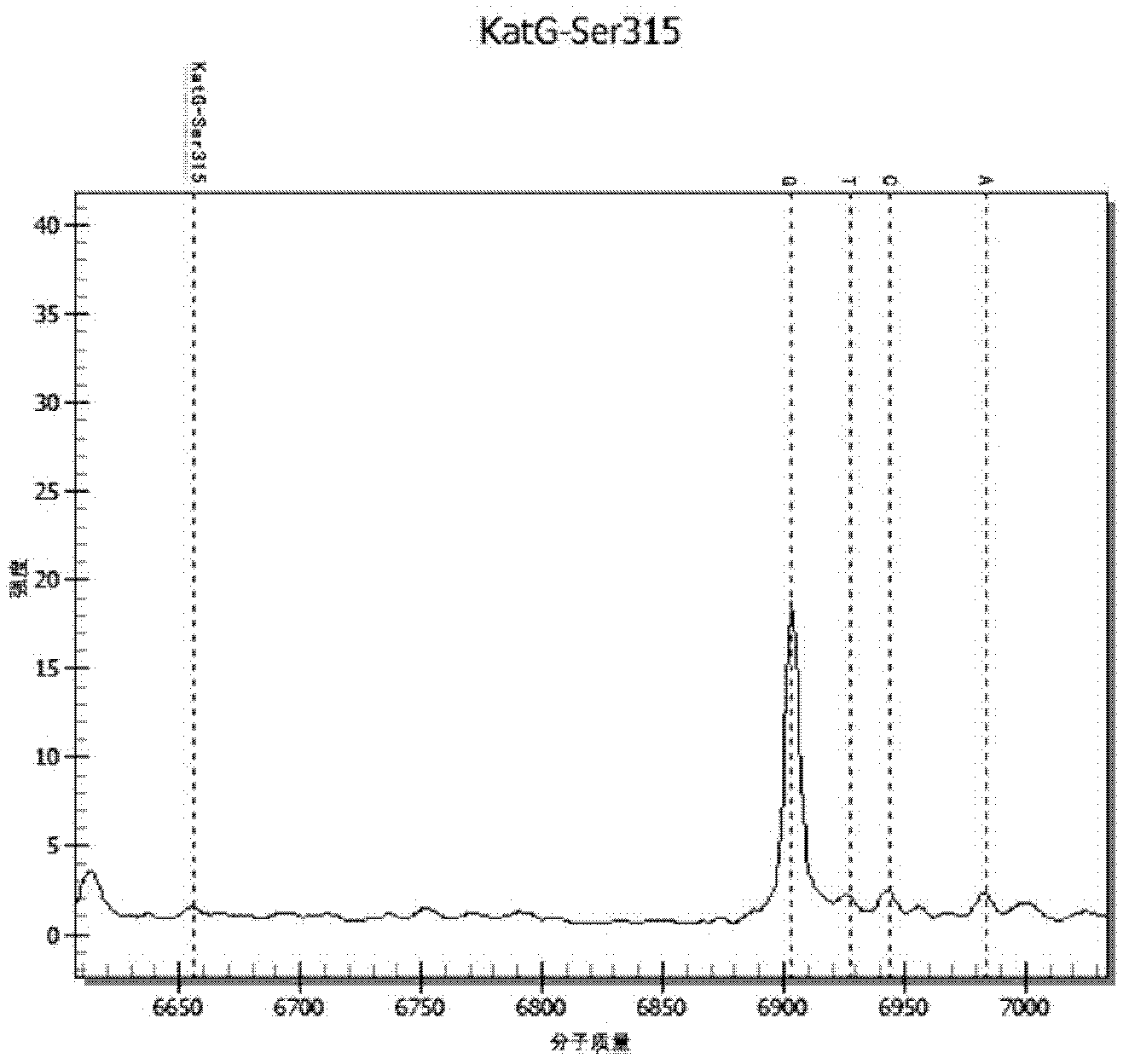
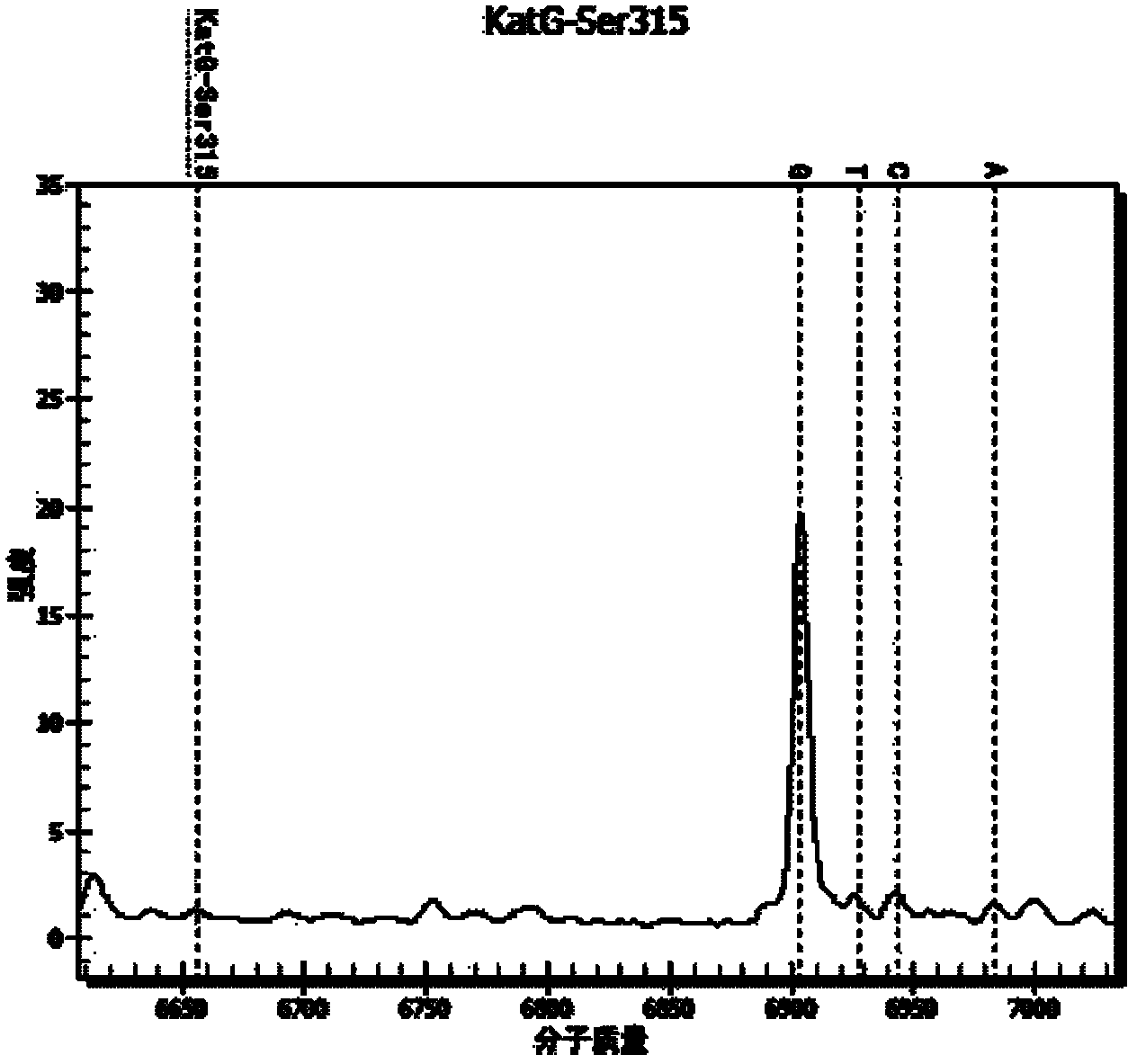
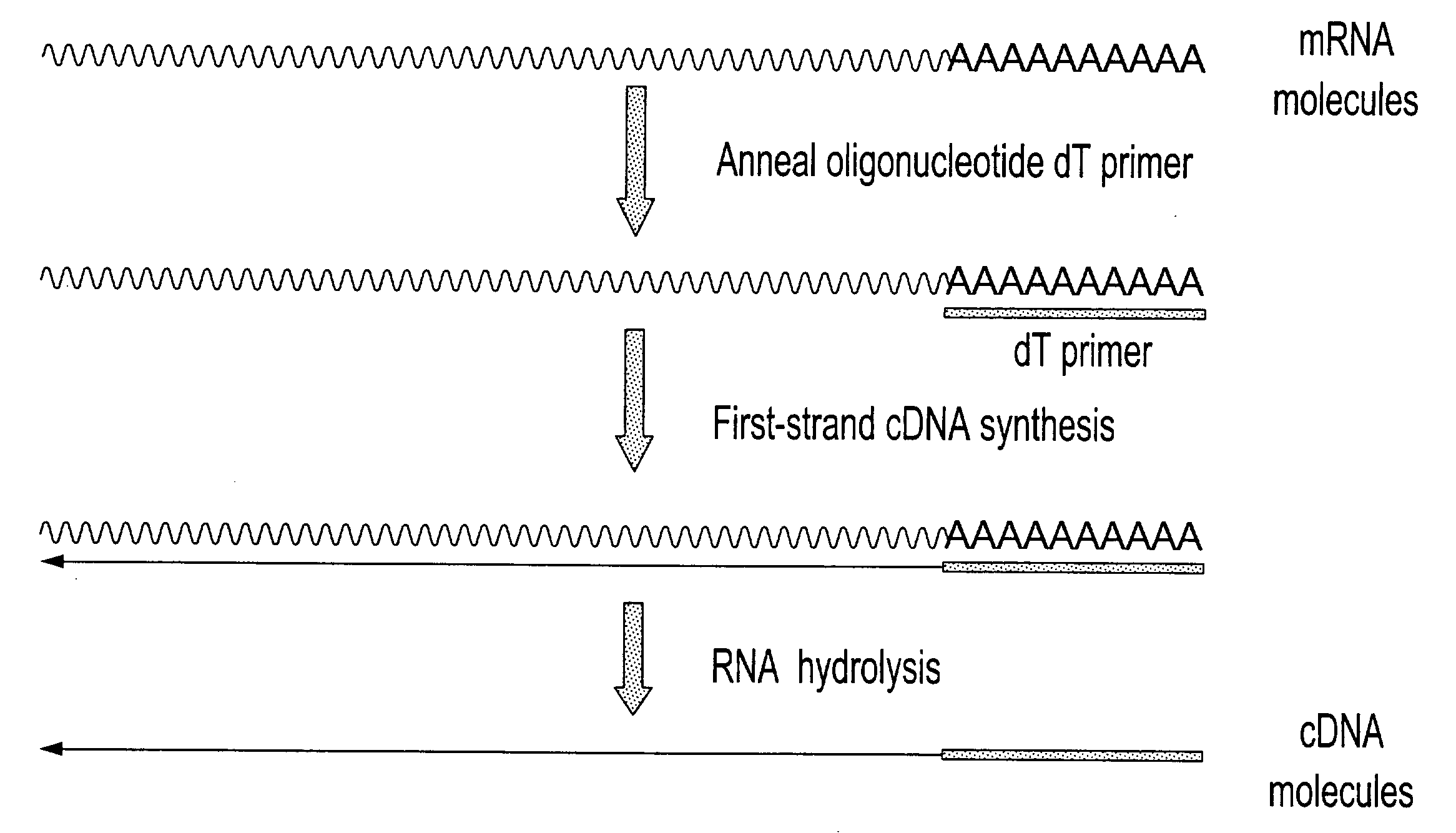
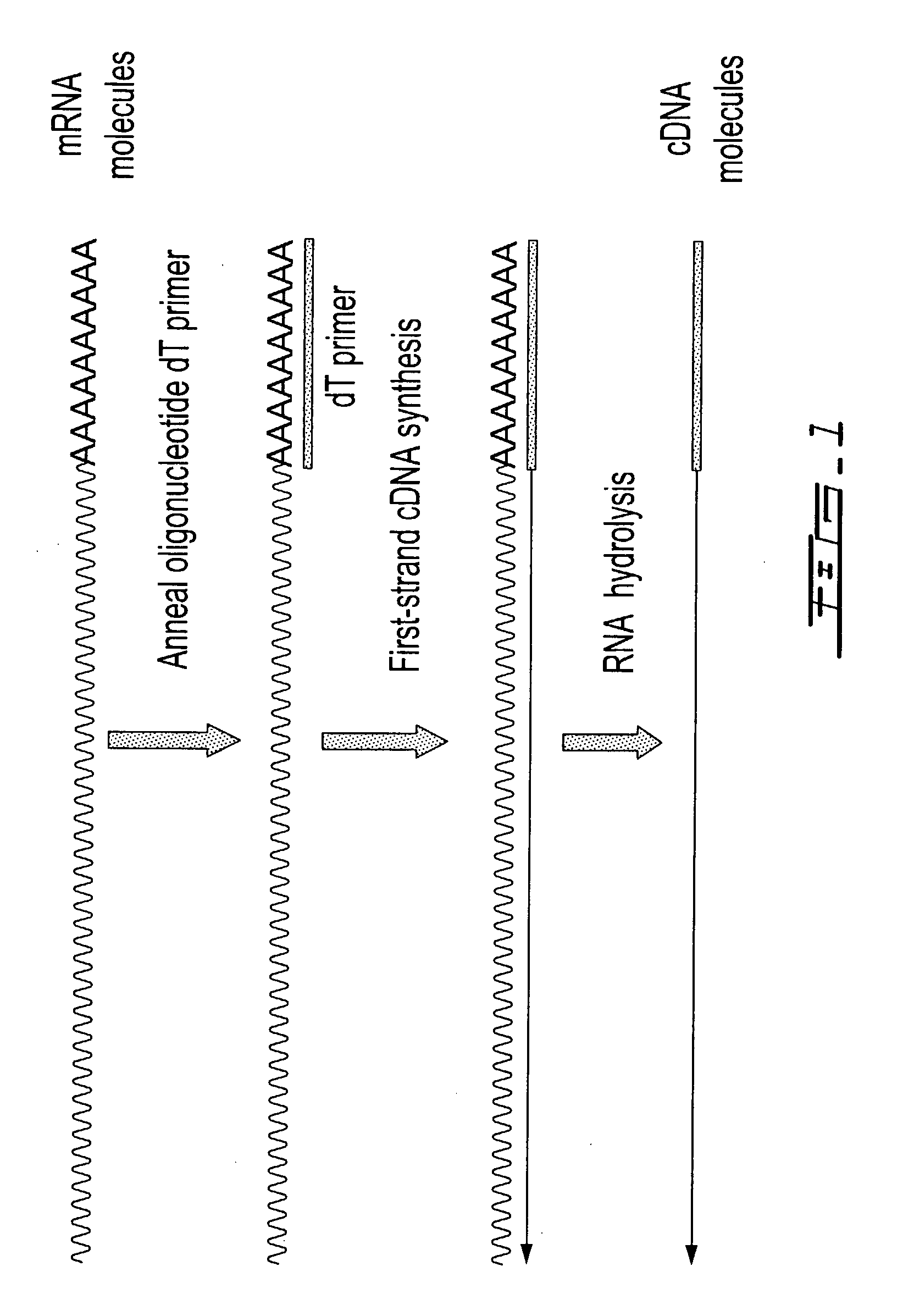
Patents
Literature
171 results about "Amplification dna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA amplification plays a role in cancer cells. A tumor cell amplifies, or copies, DNA segments as a result of cell signals and sometimes environmental events. Amplification can occur in vivo (in the living individual) or in vitro (literally "in glass", or in a plastic vessel in the laboratory).
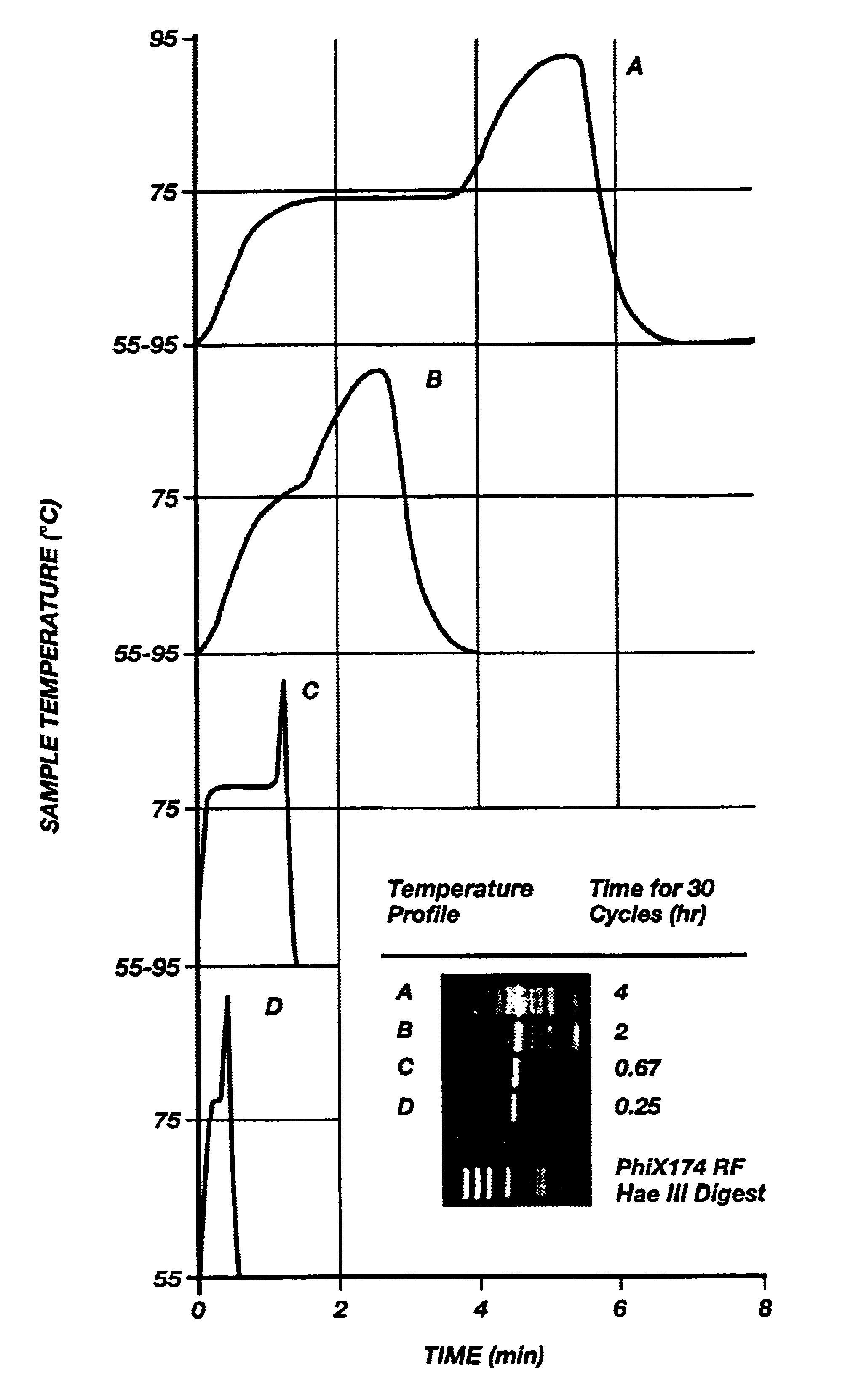
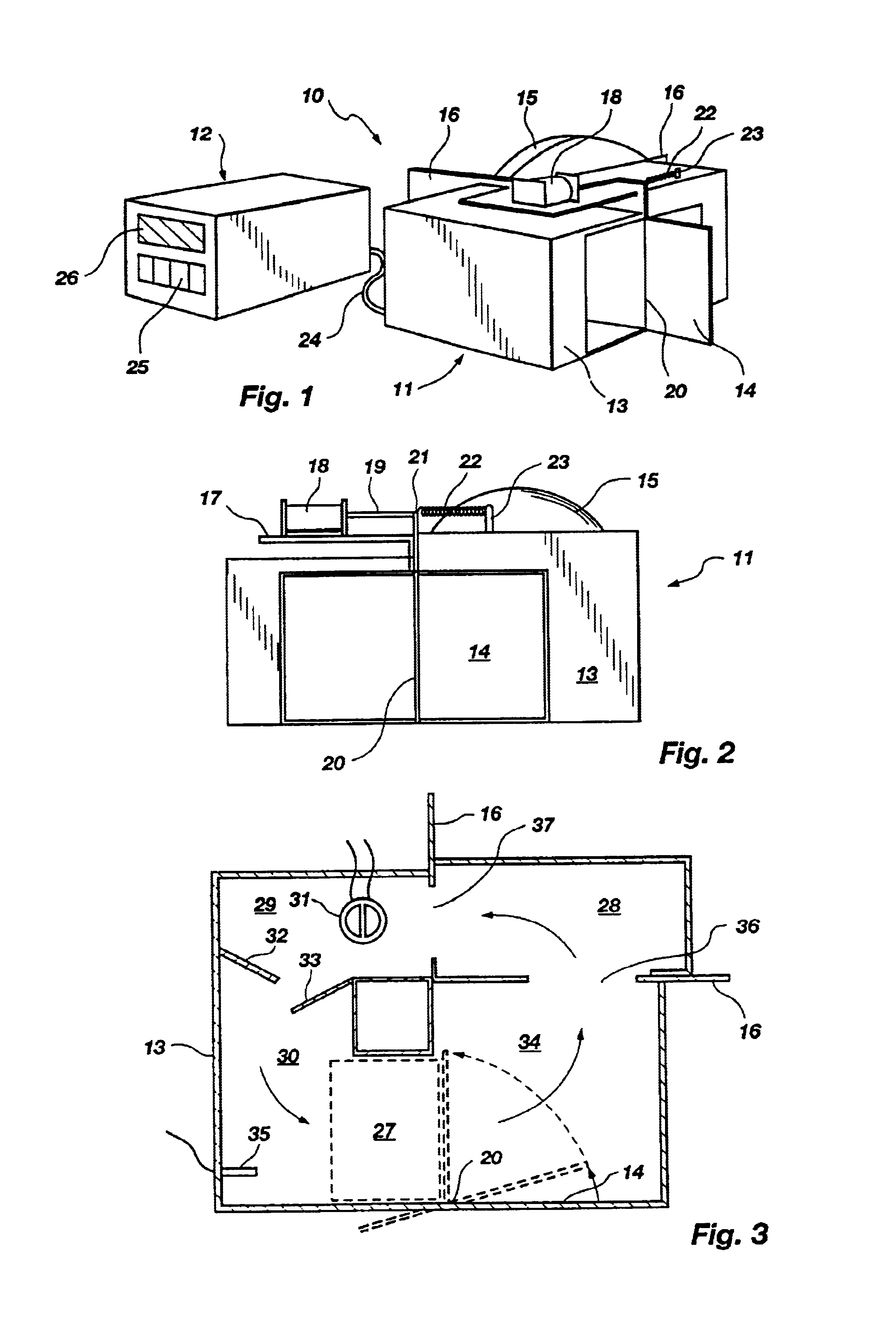
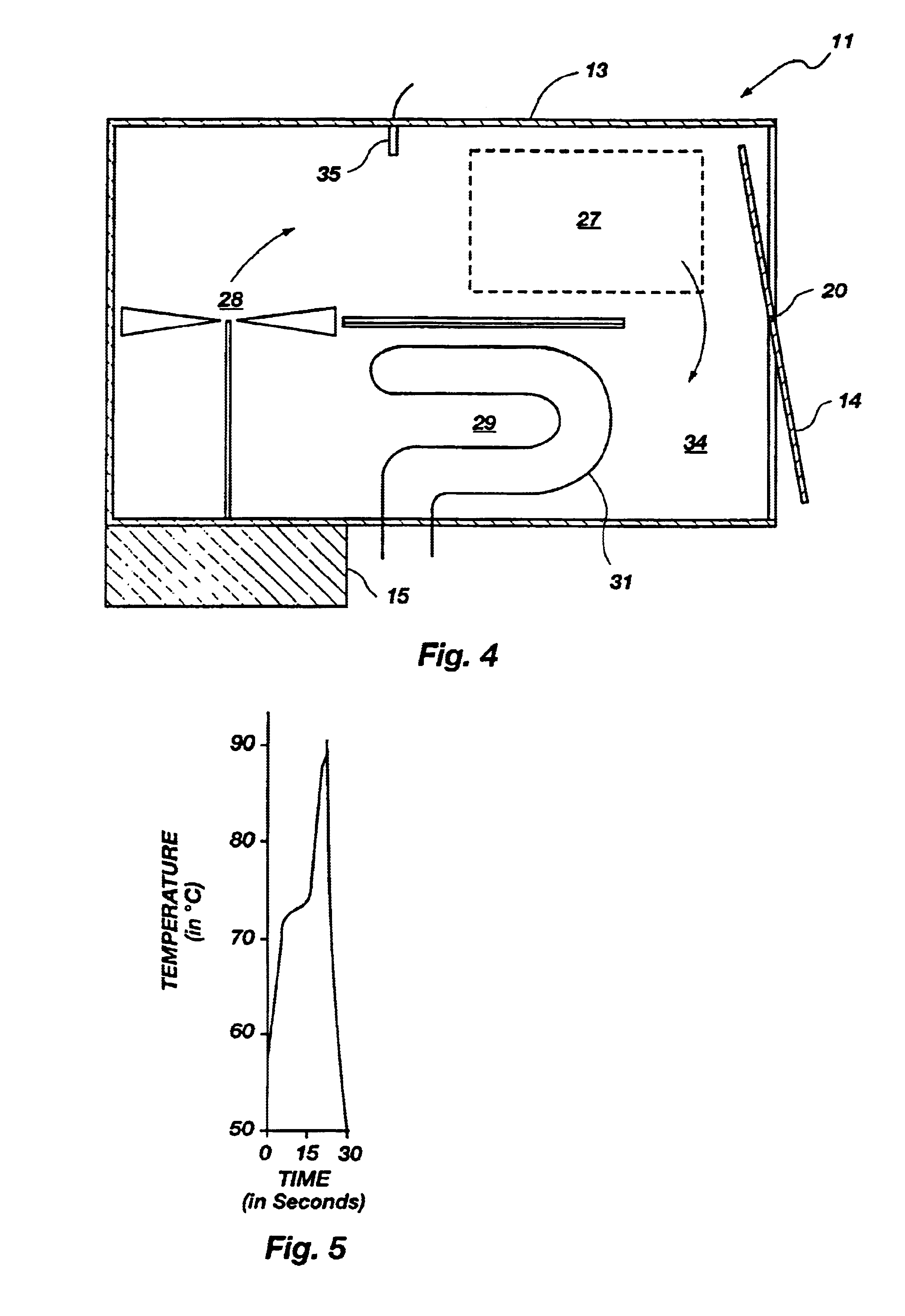
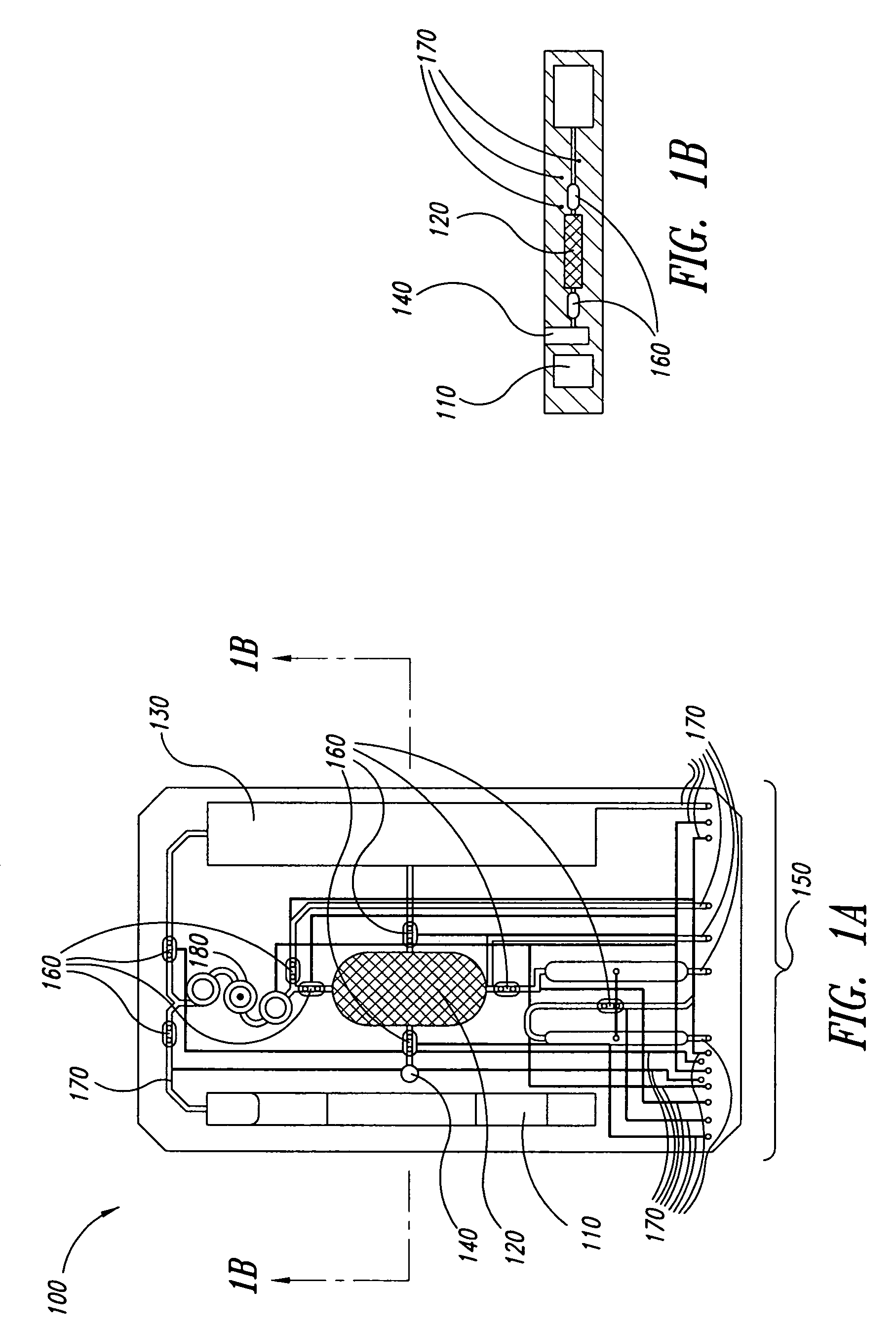
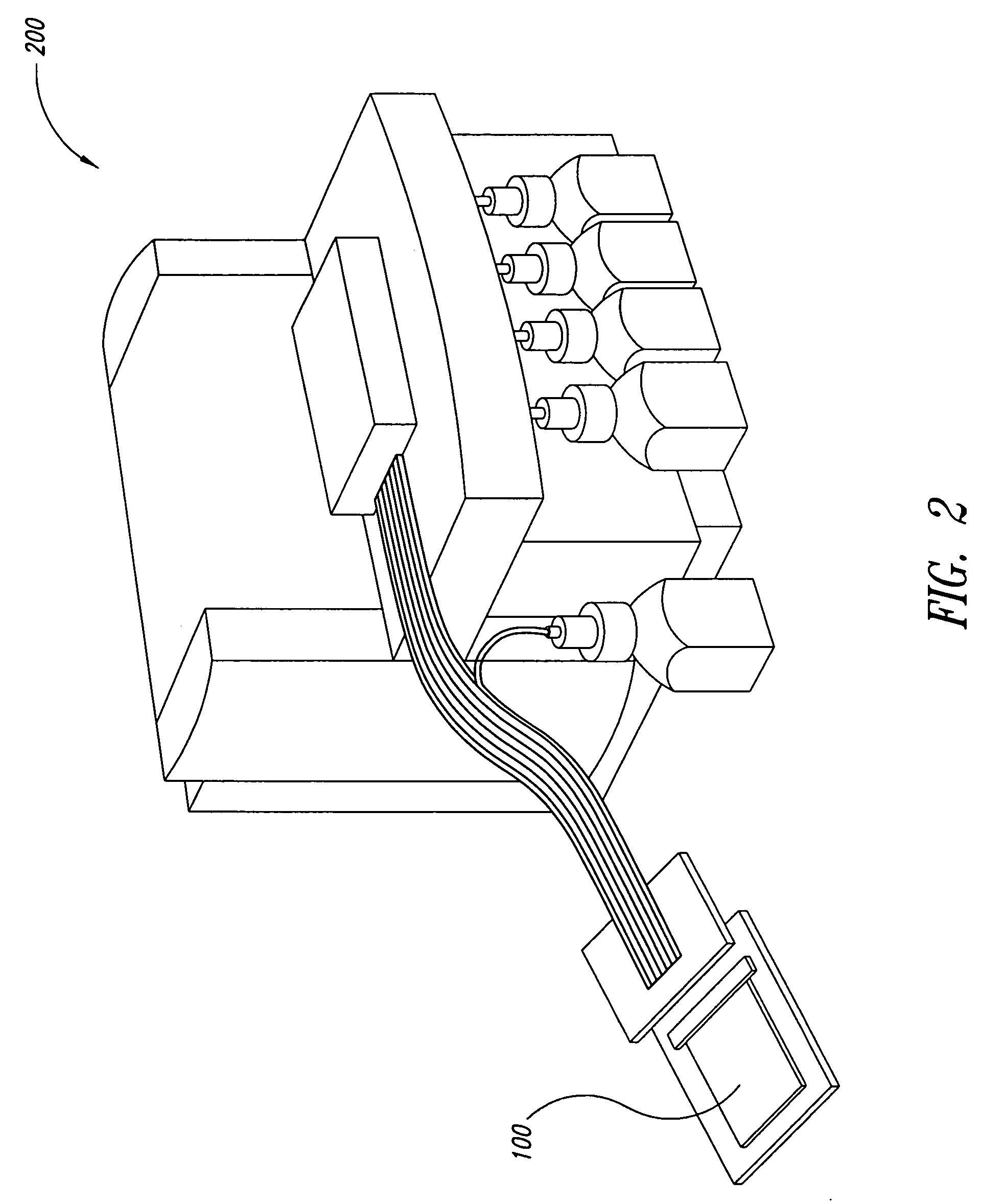
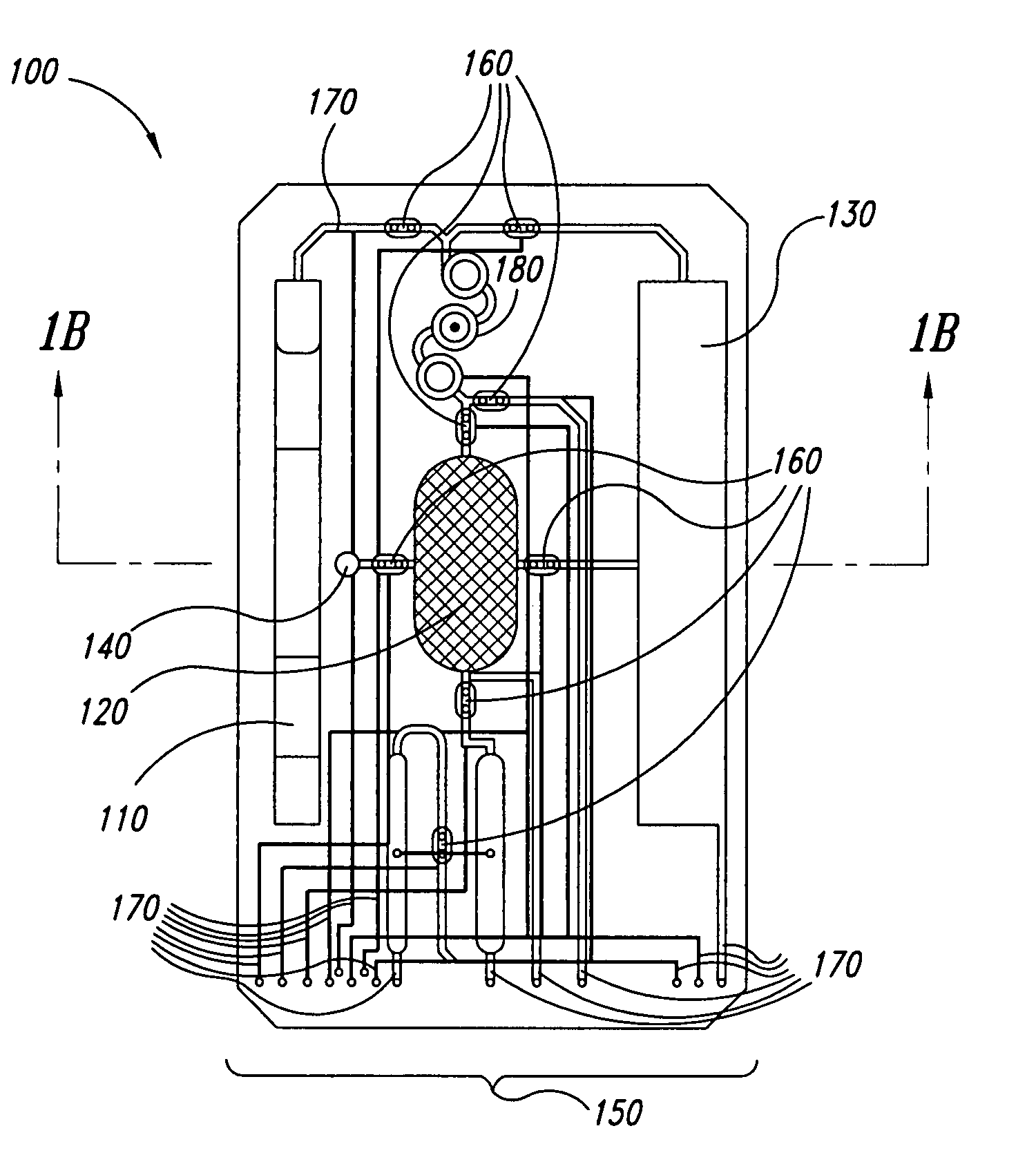
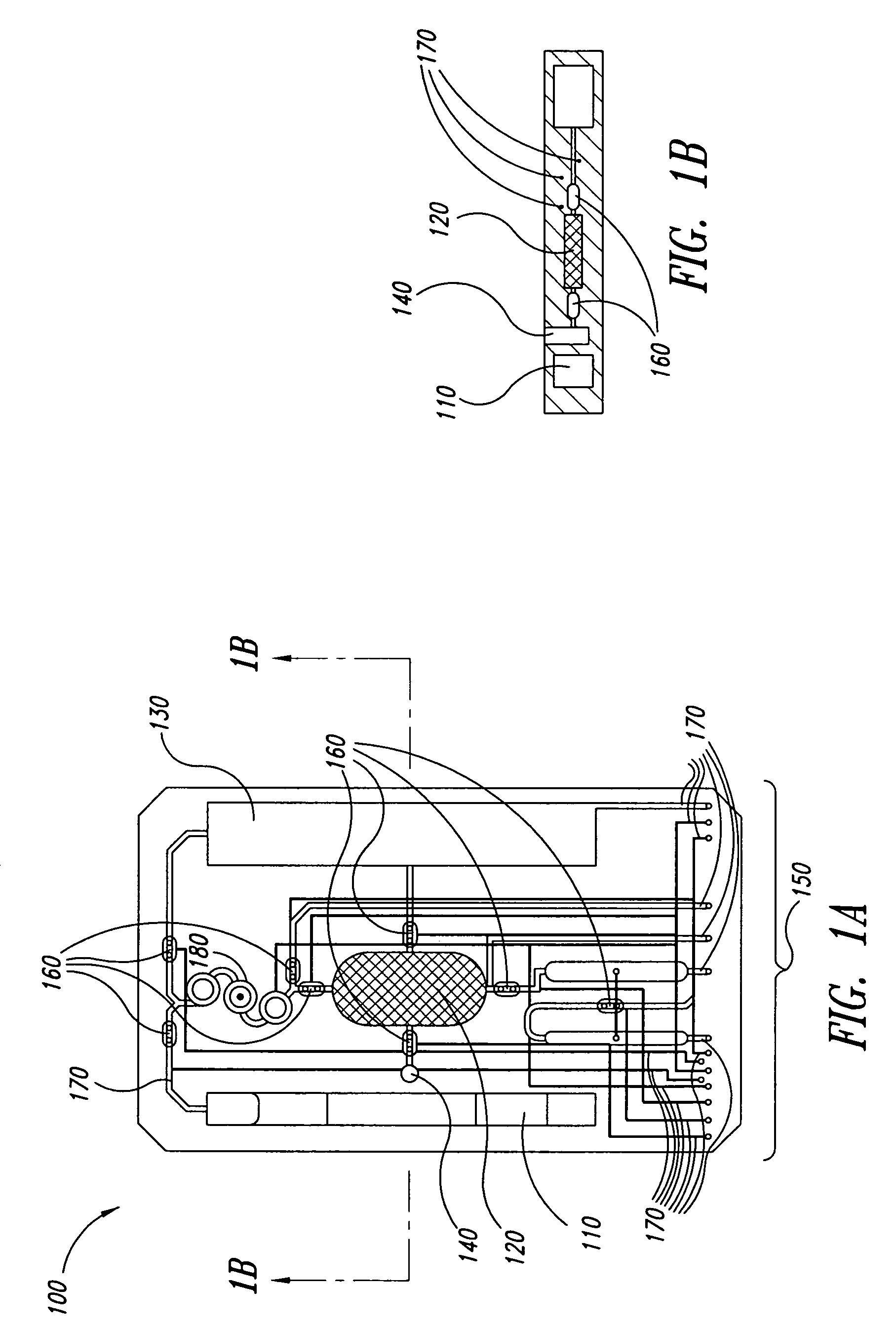
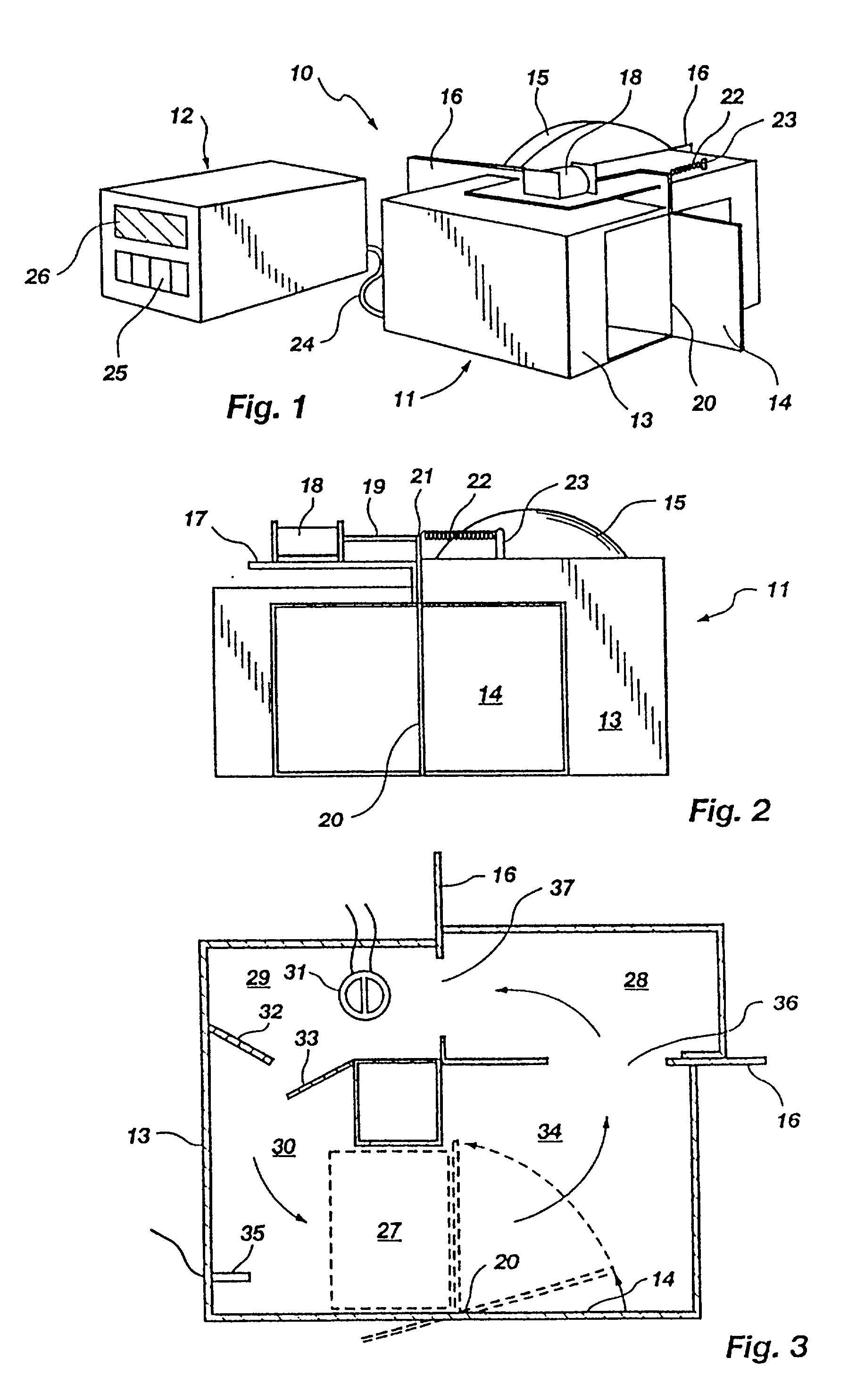
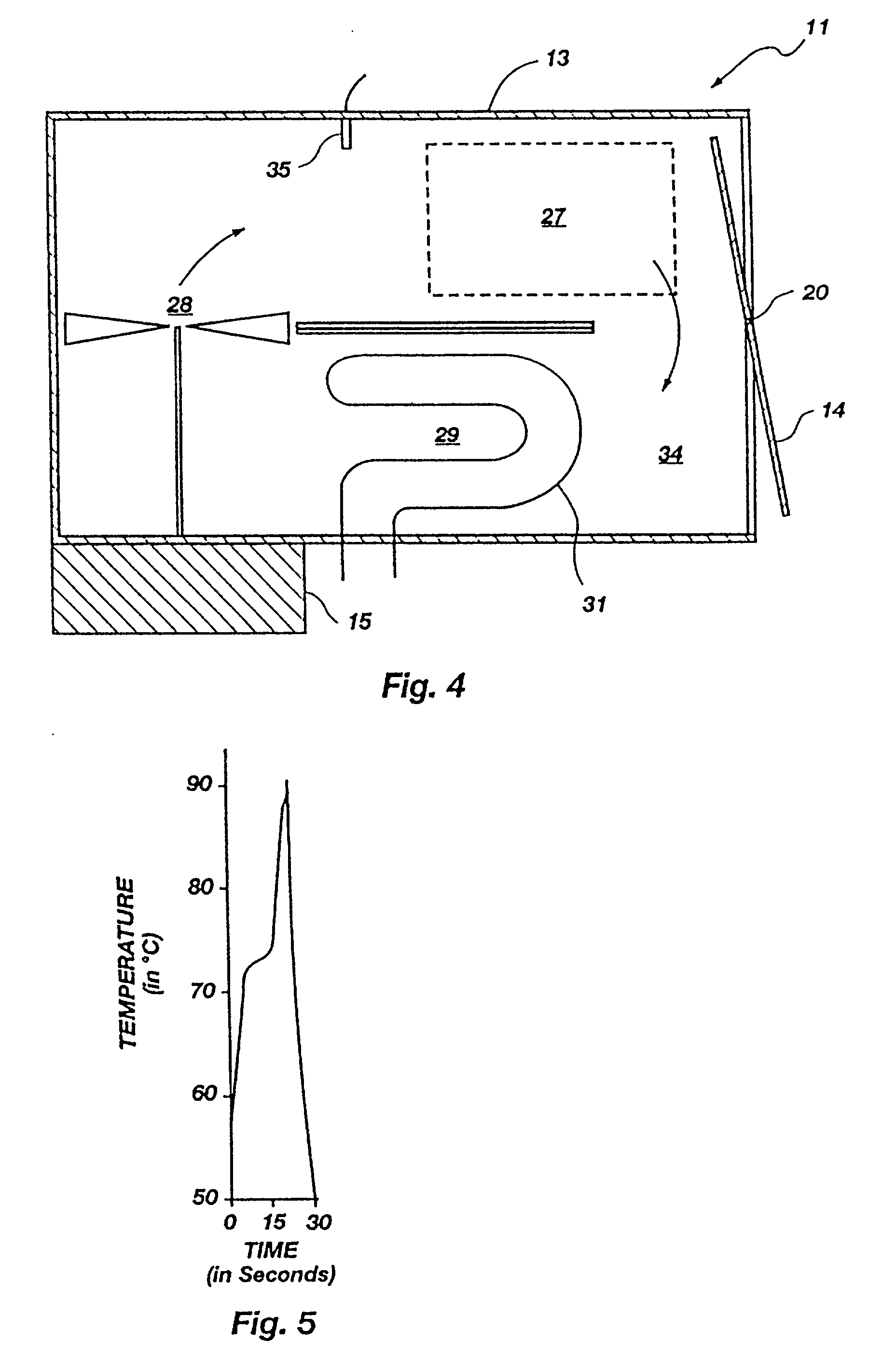
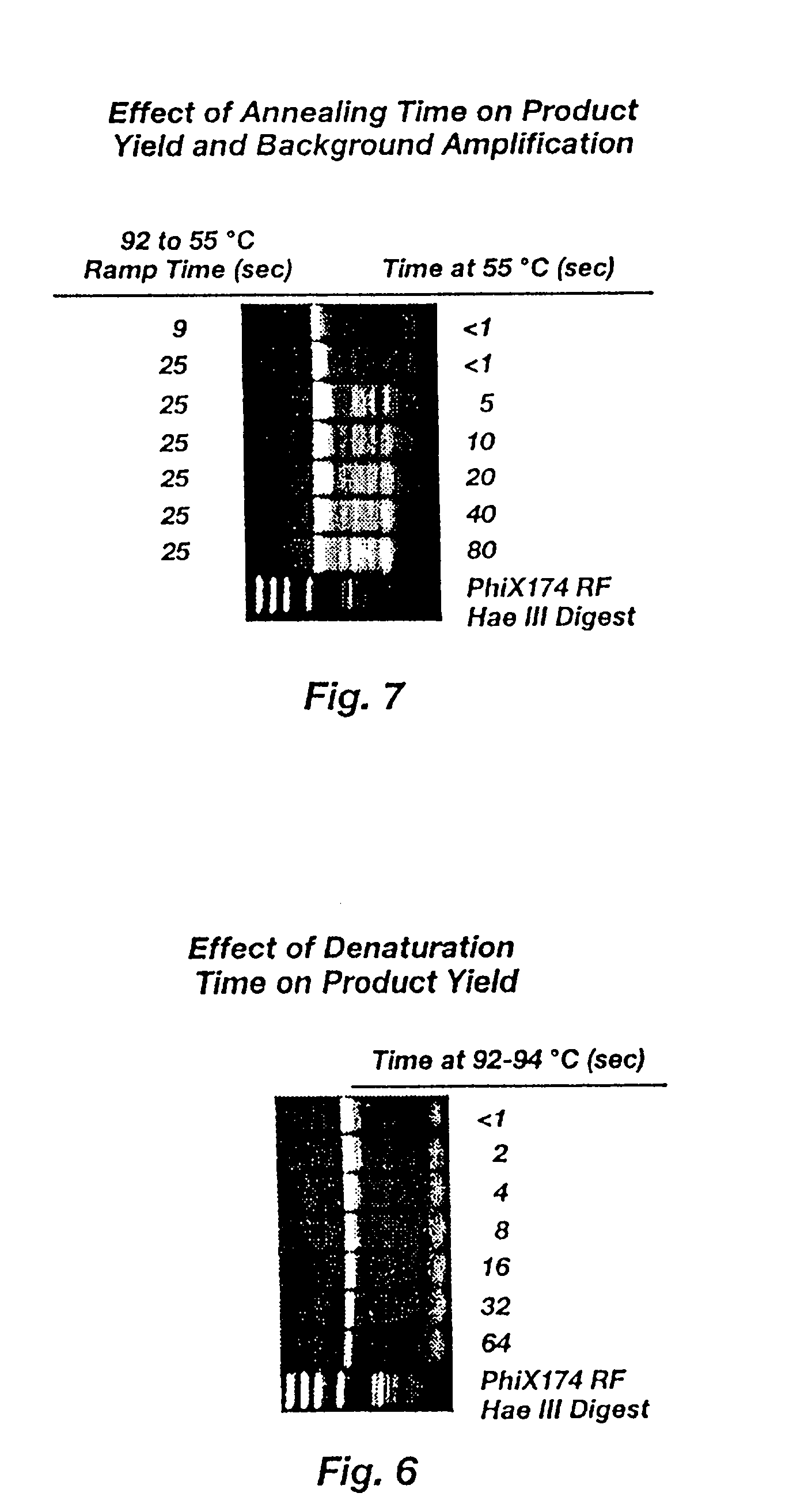
Method for rapid thermal cycling of biological samples
InactiveUS6787338B2Thermal massHigh yieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTime profileAmplification dna
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
Method and system for microfluidic manipulation, amplification and analysis of fluids, for example, bacteria assays and antiglobulin testing
A microfluidic system for isolation and amplification of DNA or RNA from aqueous solutions and detection of the DNA or RNA on a lateral flow detection strip, including a disposable microfluidic card for use in analysis of bacteria in platelets and an analysis of sexually transmitted diseases (STD) in urine. The card will include an embedded membrane that filters out cells and cellular debris. Any biological debris on the membrane will be lysed and the DNA or RNA amplified via PCR amplification protocol, including appropriate reagents and thermal cycling conditions. The amplified DNA or RNA are transferred to a lateral flow detection strip for a visual diagnostic read out. An alternate embodiment includes a microfluidic card for use in typing antiglobulin assays.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Methods and compositions for amplifying DNA clone copy number
A method for retrofitting DNA in a single-copy or high-copy vector, such as a fosmid or BAC, whereby an artificial transposon is used to introduce a conditional multi-copy origin of replication (“ori”) into the DNA in said vector. Following random in vitro or in vivo transposition of the ori-containing transposon into DNA in the single-copy or low-copy vector, the resulting insertion clones are introduced into a special host strain that contains a gene which encodes a polypeptide required for replication from the multi-copy ori. However, since the gene for this polypeptide is expressed from a tightly-regulated inducible promoter, the polypeptide is not expressed in the absence of inducer. On addition of inducer to the culture medium, the host cell synthesizes the polypeptide, which in turn activates replication from the multi-copy ori, thereby increasing the amount of clone DNA synthesized by the cell.
Owner:EPICENT TECH CORP
DNA amplification of a single cell
InactiveUS6673541B1Improve accuracyImprove comprehensive applicabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismComparative genomic hybridization
The present invention relates to a novel method for the amplification of DNA, this method being particularly useful for the amplification of the DNA or the whole genome of a single cell, chromosomes or fragments thereof. Described is also the use of the method in DNA analysis for medical, forensic, diagnostic or scientific purposes, like comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)-, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)-, polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-, single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP)-, DNA sequence-, "loss of heterozygosity" (LOH)-, fingerprint- and / or restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)-analysis.
Owner:AMGEN RES (MUNICH) GMBH
Electroluminescent-based fluorescence detection device
InactiveUS20100105035A1Quick identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityFluorescence
The present invention provides compositions providing and methods using fluorescence detection device, comprising an electroluminescent light (EL) source, for measuring fluorescence in biological samples. In particularly preferred embodiments, the present invention provides an economical, battery powered and Hand-held device for detecting fluorescent light emitted from reporter molecules incorporated into DNA, RNA, proteins or other biological samples, such as a fluorescence emitting biological sample on a microarray chip. Further, a real-time hand-held PCR Analyzer device comprising an EL light source for measuring fluorescence emissions from amplified DNA is provided.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Method and system for microfluidic manipulation, amplification and analysis of fluids, for example, bacteria assays and antiglobulin testing
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
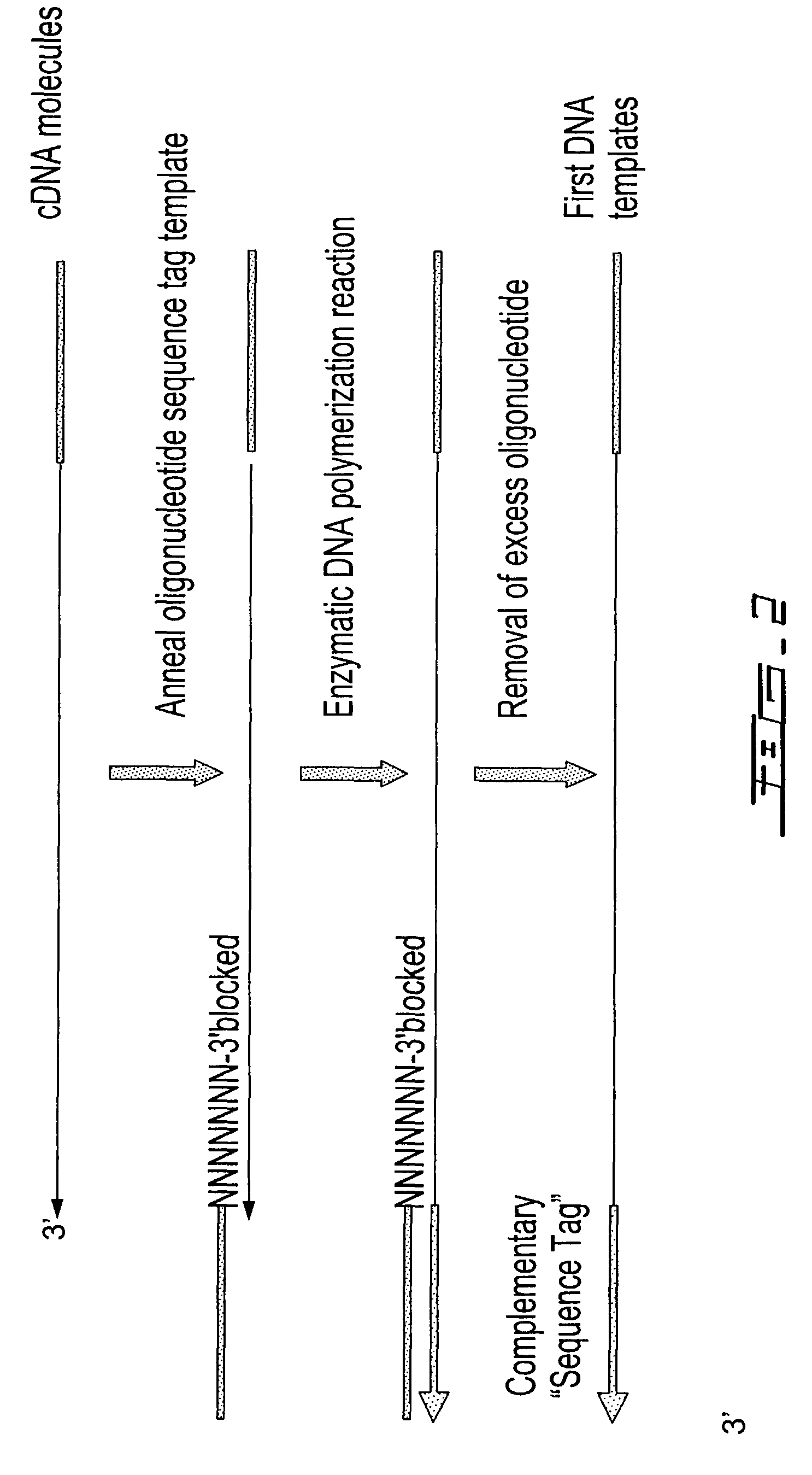
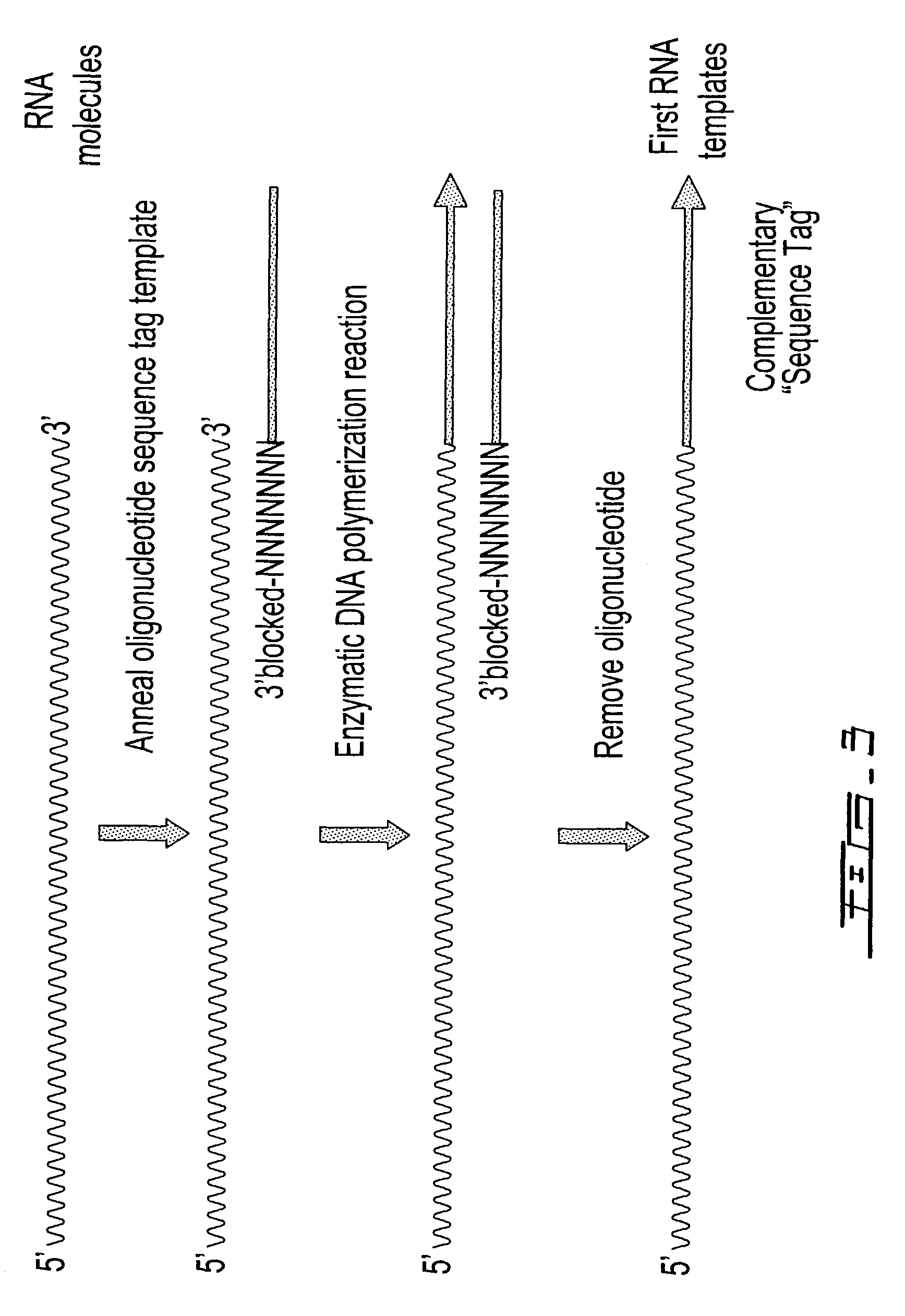
Selective terminal tagging of nucleic acids
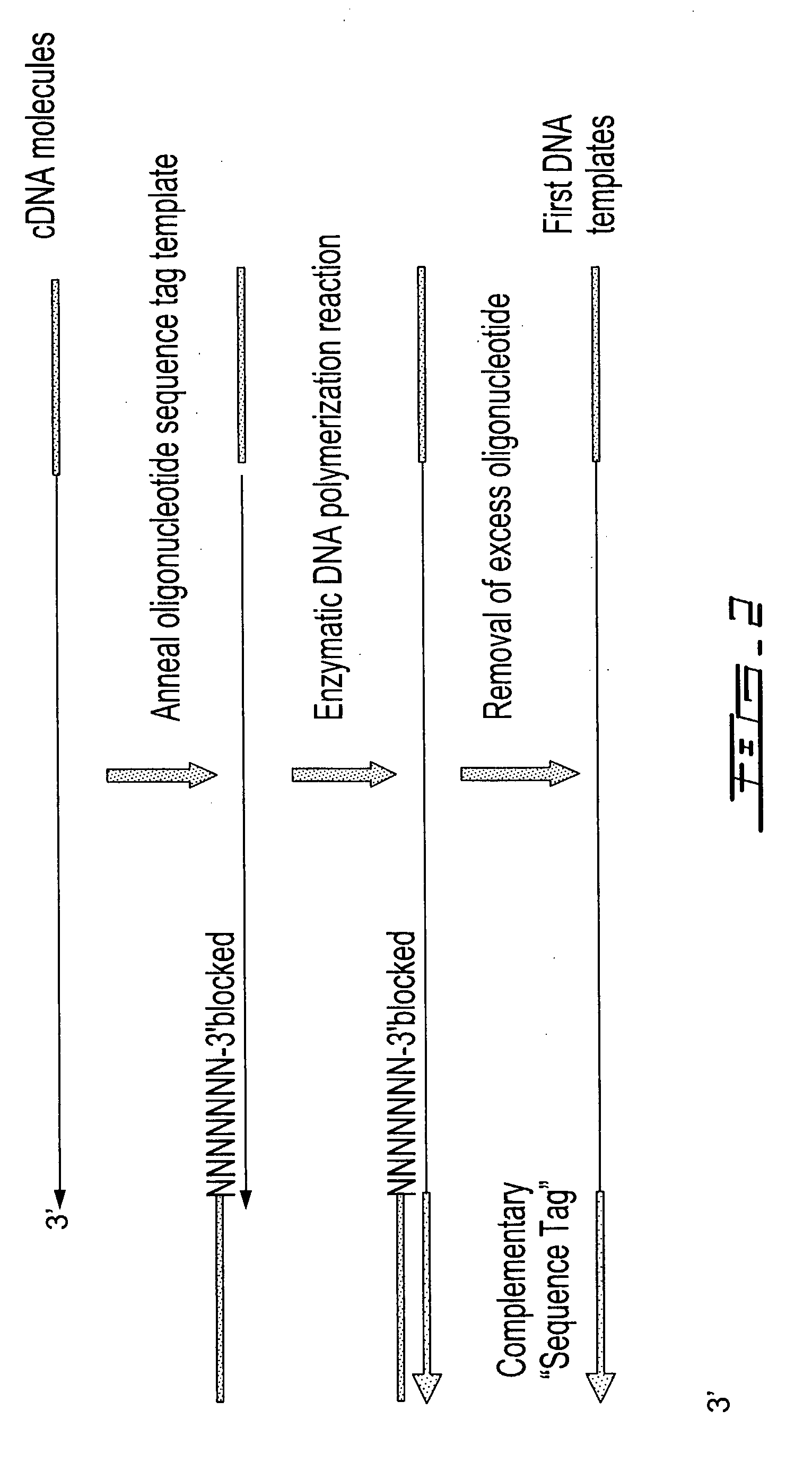
ActiveUS8304183B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification dnaComplete sequence
Methods are provided for adding a terminal sequence tag to nucleic acid molecules for use in RNA or DNA amplification. The tag introduced may be used as a primer binding site for subsequent amplification of the DNA molecule and / or sequencing of the DNA molecule and therefore provides means for identification and cloning of the 5′-end or the complete sequence of mRNAs.
Owner:CELLSCRIPT
Amplification and cloning of single DNA molecules using rolling circle amplification
ActiveUS8497069B2Easy to startMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCell freeAmplification dna
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
Dual Function Primers for Amplifying DNA and Methods of Use
InactiveUS20090068643A1Enabling detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceAmplification dna
The present invention provides novel nucleotide compositions that enable the detection of DNA synthesis products and methods for use thereof. In one embodiment, the method can be used in PCR and allows the progress of the reaction to be monitored as it occurs. In one embodiment, the invention employs at least one fluorescence-quenched oligonucleotide that can prime DNA extension reactions. In a second embodiment, the invention employs at least one fluorescence-quenched oligonucleotide that can function as a template for DNA extension reactions. In both embodiments, the oligonucleotide also functions as a probe for detecting the progress of successive extension reaction cycles. Signal detection is dependent upon DNA synthesis and can occur with or without probe cleavage.
Owner:INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES
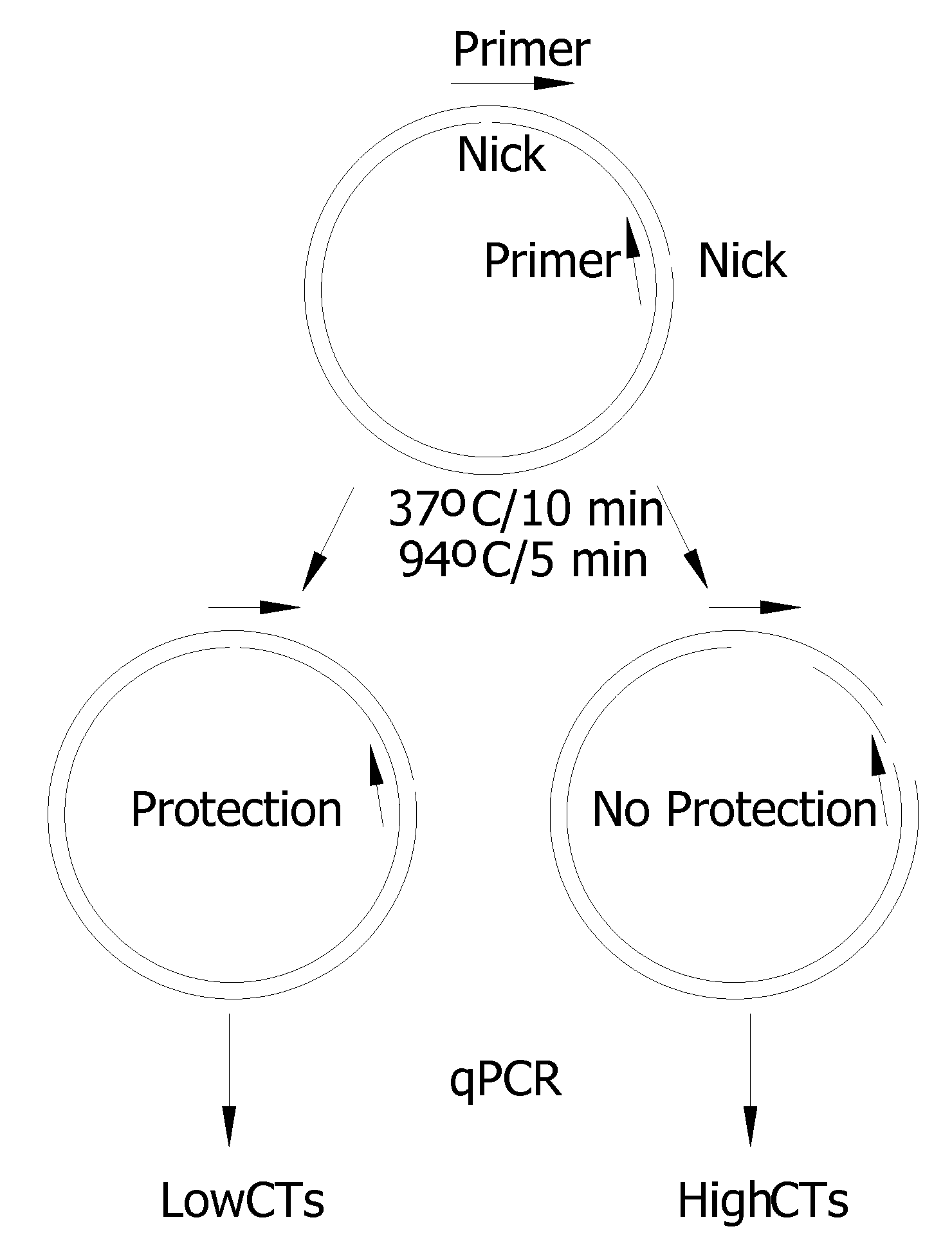
Recombinant Dna Nicking Endonuclease and Uses Thereof
Recombinant nicking endonucleases and associated methylases have been obtained and sequenced and their specificity has been defined. A mutant form of the nicking endonuclease has been cloned where the mutation includes deletion of amino acid sequences at the C-terminal end of the protein. The nicking enzymes have been used for a number of purposes including: amplifying DNA from as few cells as can be found in a single bacterial colony in the presence of a strand displacing polymerase; and for removing genomic DNA in a biological preparation where it is deemed to be a contaminant.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
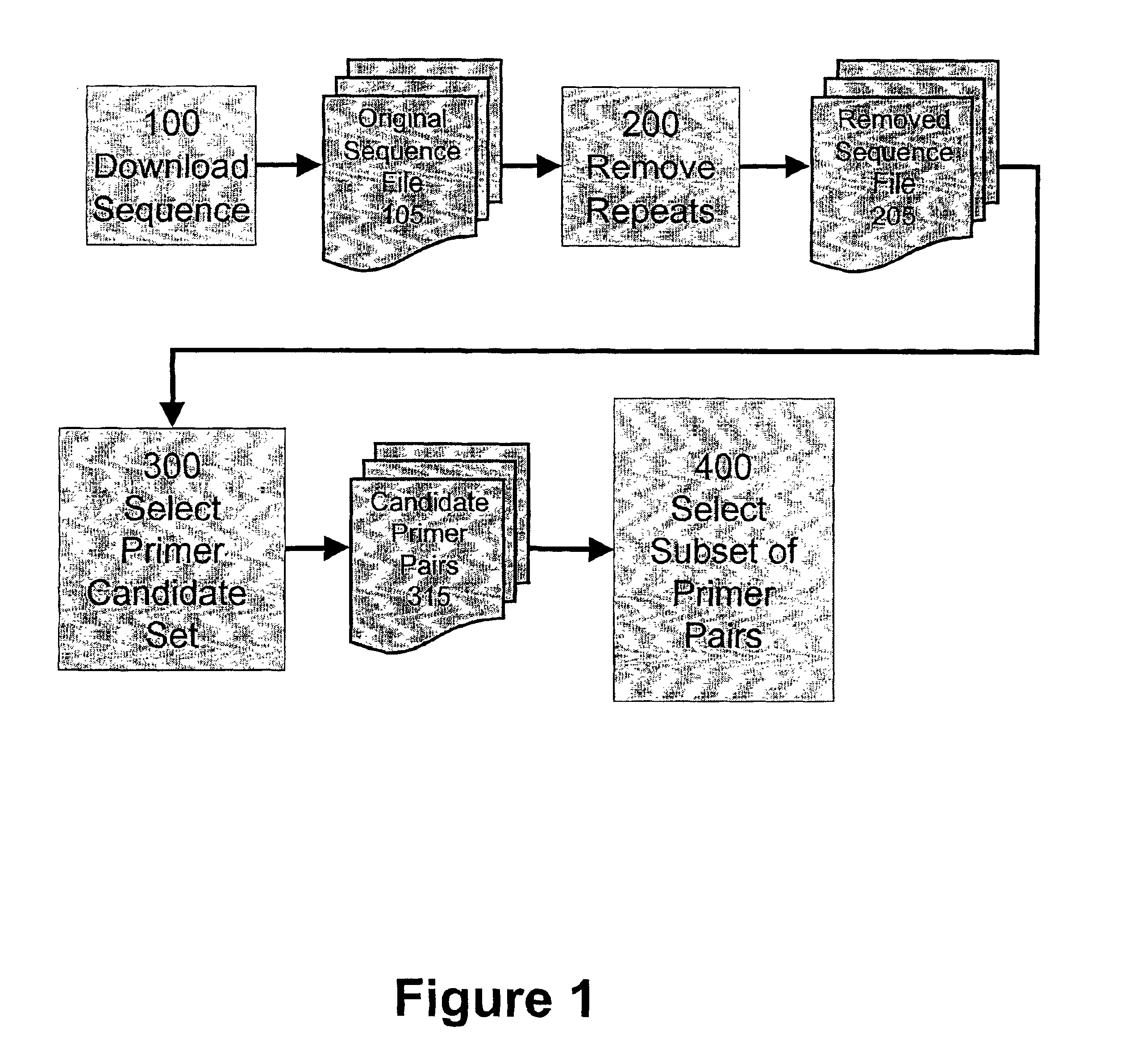
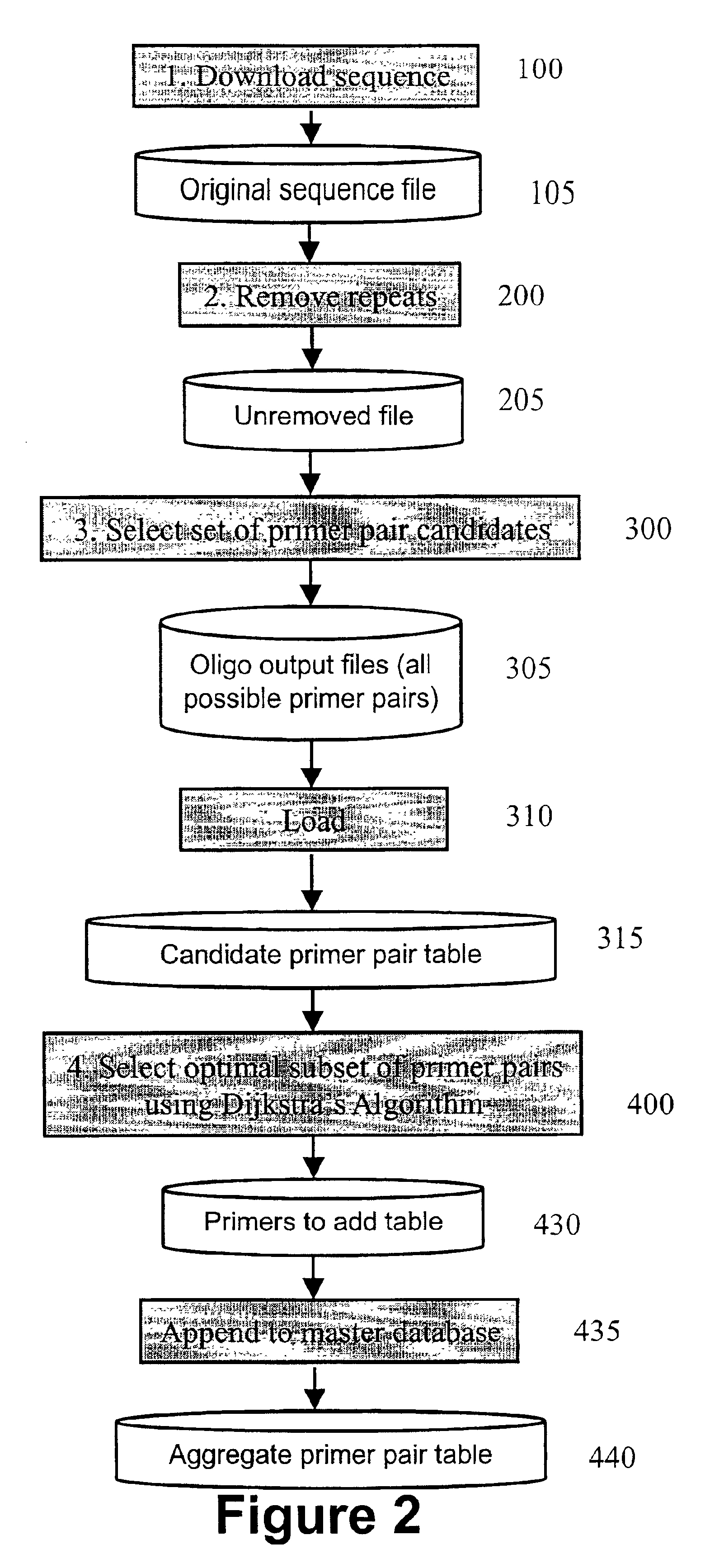
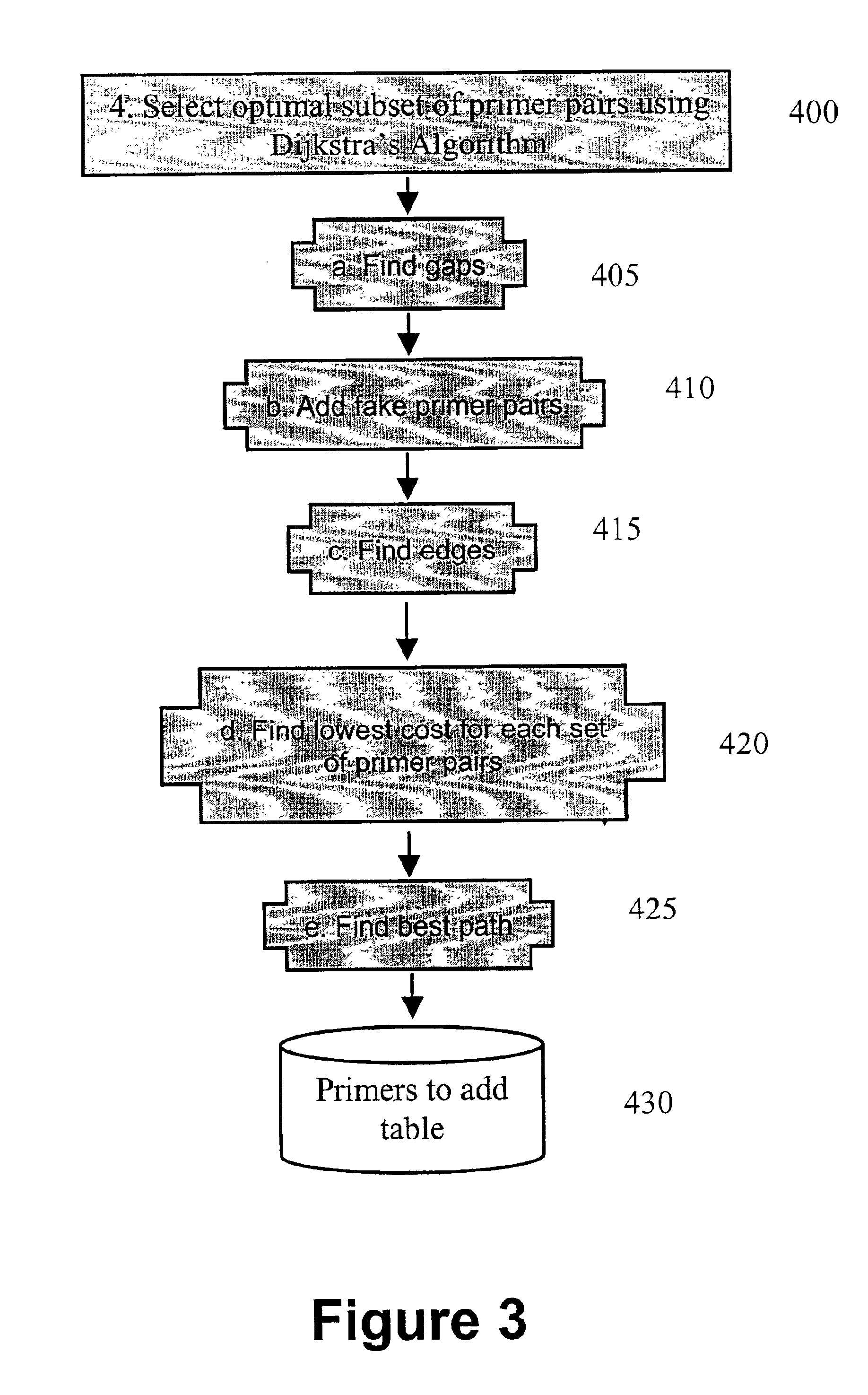
Algorithms for selection of primer pairs
InactiveUS6898531B2Robust methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAmplification dnaA-DNA
The presently claimed invention provides methods for amplifying a DNA target sequence. One embodiment of the present invention provides robust methods for amplification of target sequences. In a first aspect of the invention, a method for designing primer pairs for the amplification reaction is provided. In a further aspect of the invention, reagents and cycling parameters for the amplification reaction are provided.
Owner:PERLEGEN SCIENCES INC
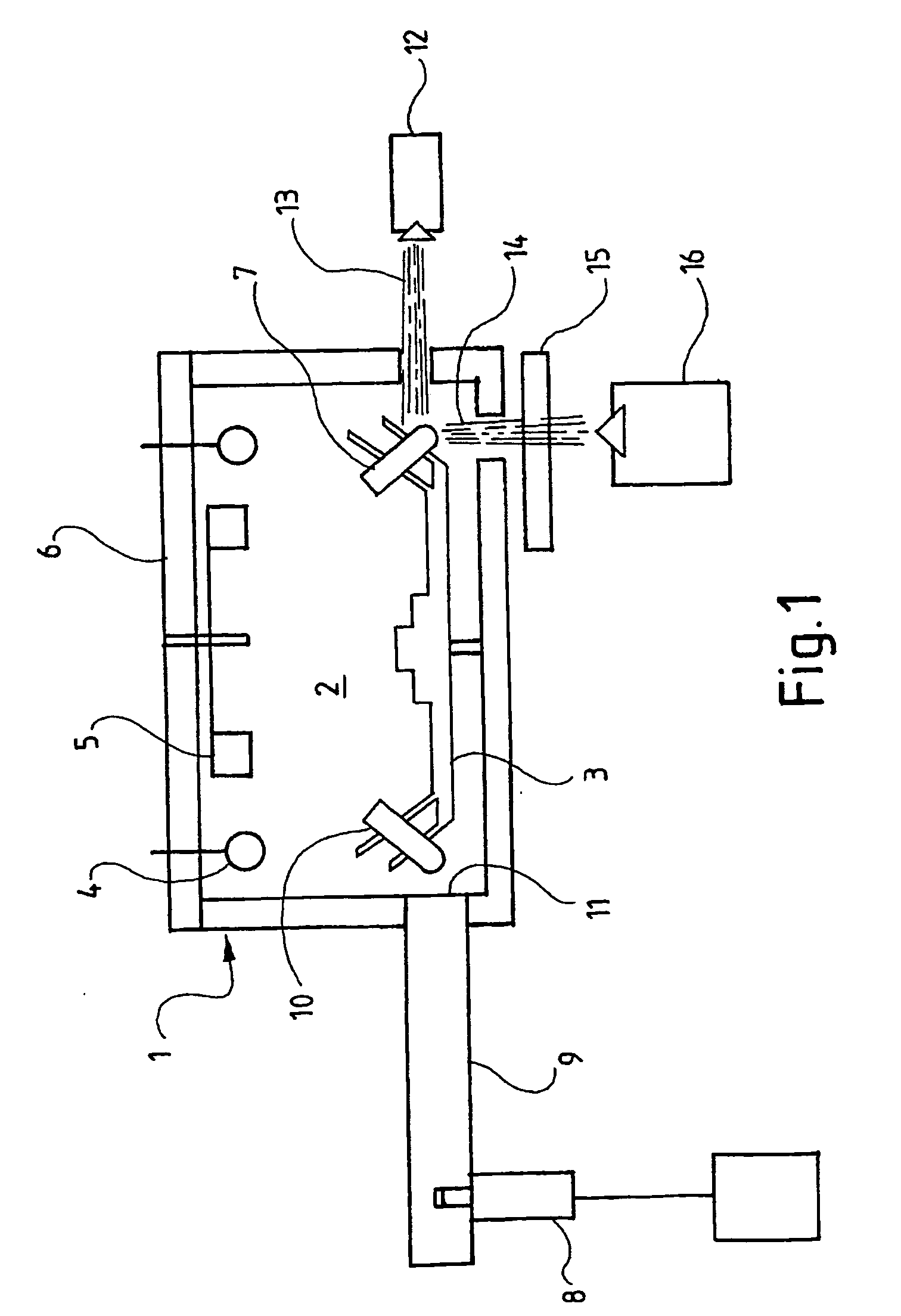
Device for the amplification of dna, comprising a microwave energy source
InactiveUS20050233324A1Shorten cycle timeFaster cycle timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrowaveAmplification dna
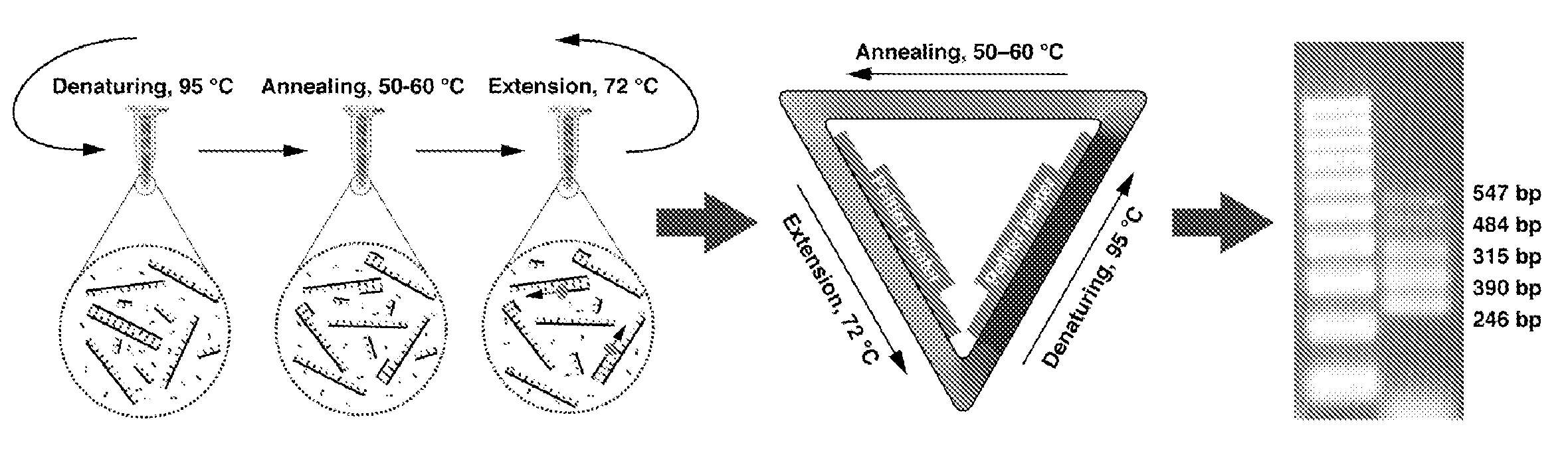
The invention relates to a device for the amplification of DNA in a reaction mixture, the device (1) comprising a heated chamber (2) including a rotor (3) for holding a plurality of reaction vessels for reaction mixtures, a drive means for the rotor, a microwave energy source (8) with means for controlled delivery of said energy to the reaction mixtures, and a system (14-16) for determining denaturation of double-stranded DNA. The invention also provides a method for the amplification of a nucleic acid strand. In the first step of the method, a reaction mixture is formed comprising the target nucleic acid strand, nucleotides, a primer, a thermostable nucleic acid polymerase, and, if necessary, a reagent for the detection of denaturation of double-stranded DNA. In the second step, the mixture is incubated at a temperature which allows synthesis of a nucleic acid strand complementary to the target nucleic acid strand. The third step comprises denaturing double-stranded DNA formed in the second step by microwave energisation of the reaction mixture with monitoring of the mixture to determine the denaturation end point. The reaction mixture is allowed to cool to a temperature at which primer anneals to the target nucleic acid strand in the fourth step. The second to fourth steps are repeated until a desired level of amplification is achieved.
Owner:CORBETT LIFE SCI
Kits for amplifying DNA
ActiveUS8183359B2Reduce appearance problemsMinimize and substantially eliminate emergenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification dnaA-DNA
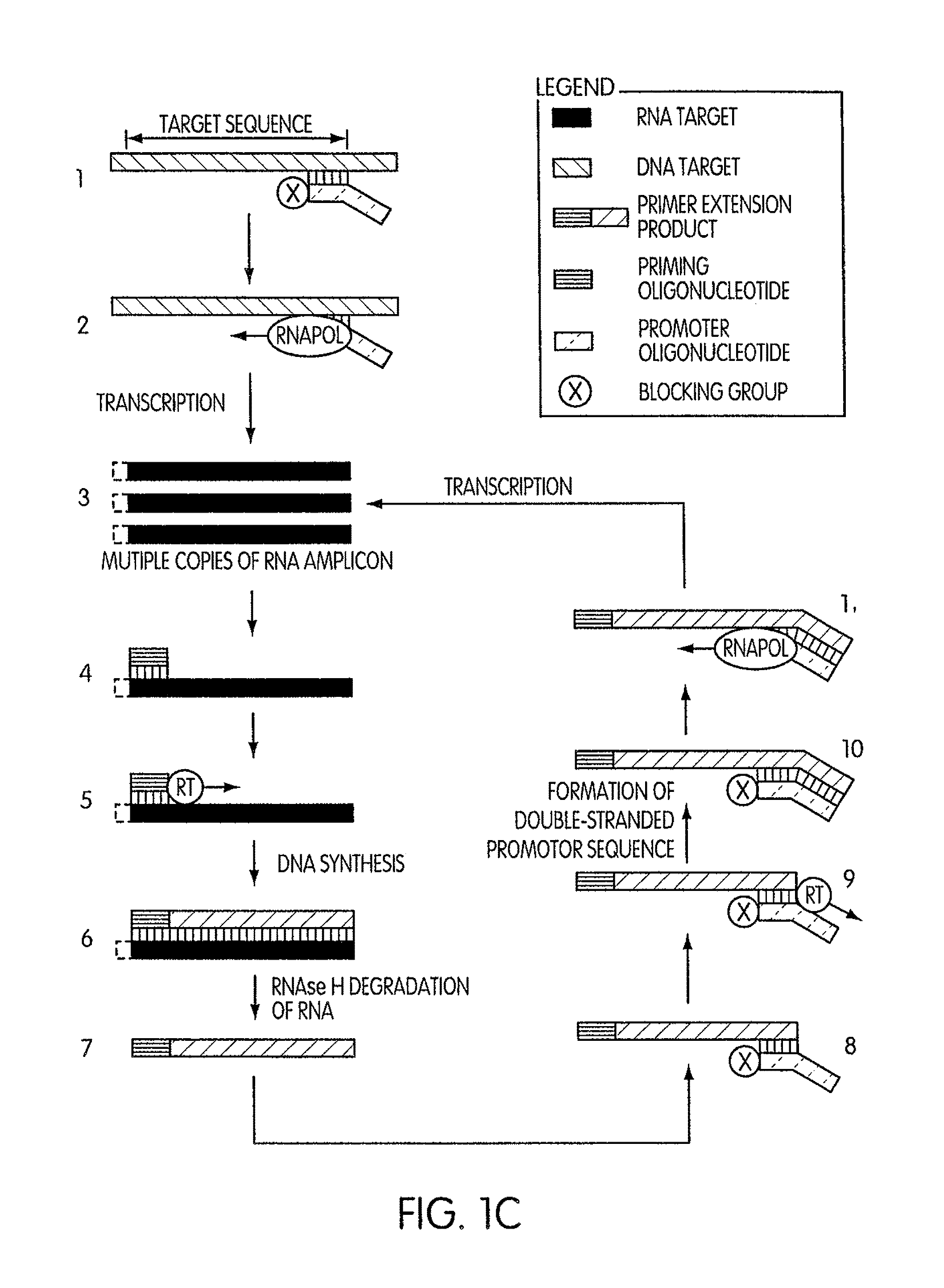
Kits for amplifying DNA which include a priming oligonucleotide that hybridizes to a 3′-end of a DNA target sequence, a displacer oligonucleotide that hybridizes to a target nucleic acid containing the DNA target sequence at a position upstream from the priming oligonucleotide, and a promoter oligonucleotide that includes a region that hybridizes to a 3′-region of a DNA primer extension product that includes the priming oligonucleotide and a promoter for an RNA polymerase. The priming oligonucleotide does not include an RNA region that hybridizes to the target nucleic acid and is selectively degraded by an enzyme activity when hybridized to the target nucleic acid. The kits do not include a restriction endonuclease and oligonucleotides that include a promoter for an RNA polymerase are all modified to prevent the initiation of DNA synthesis therefrom.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Method for detecting cell proliferative disorders
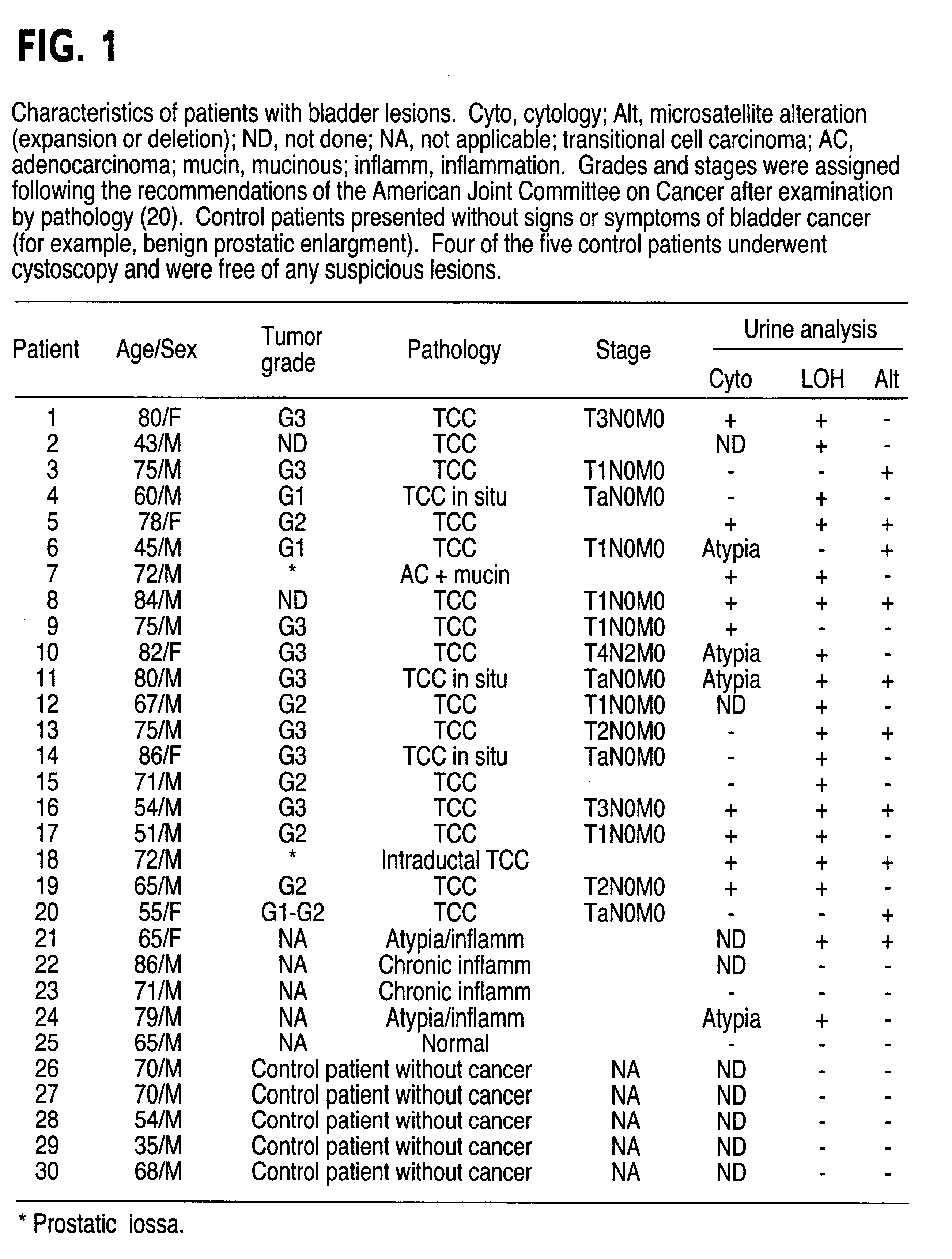
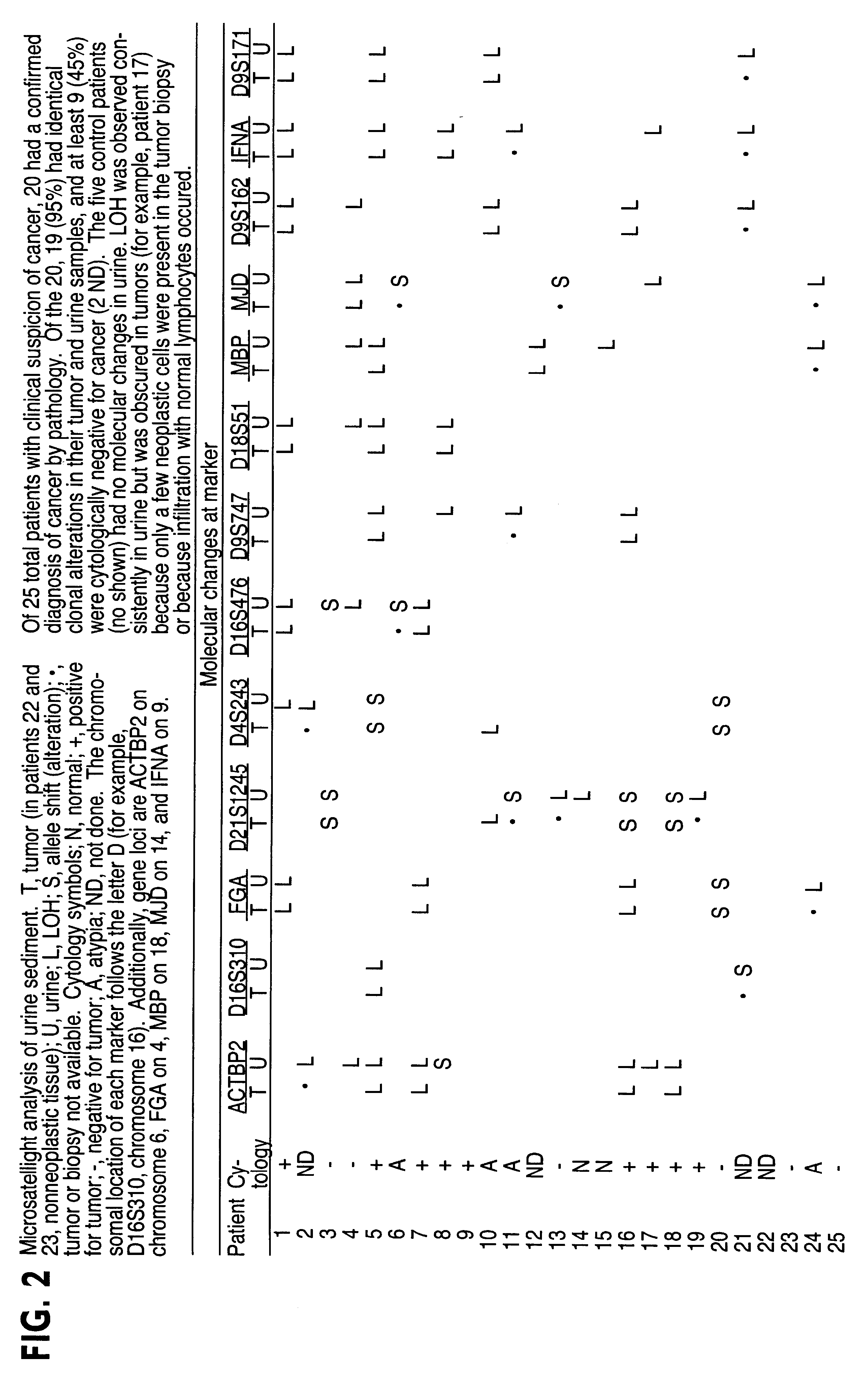
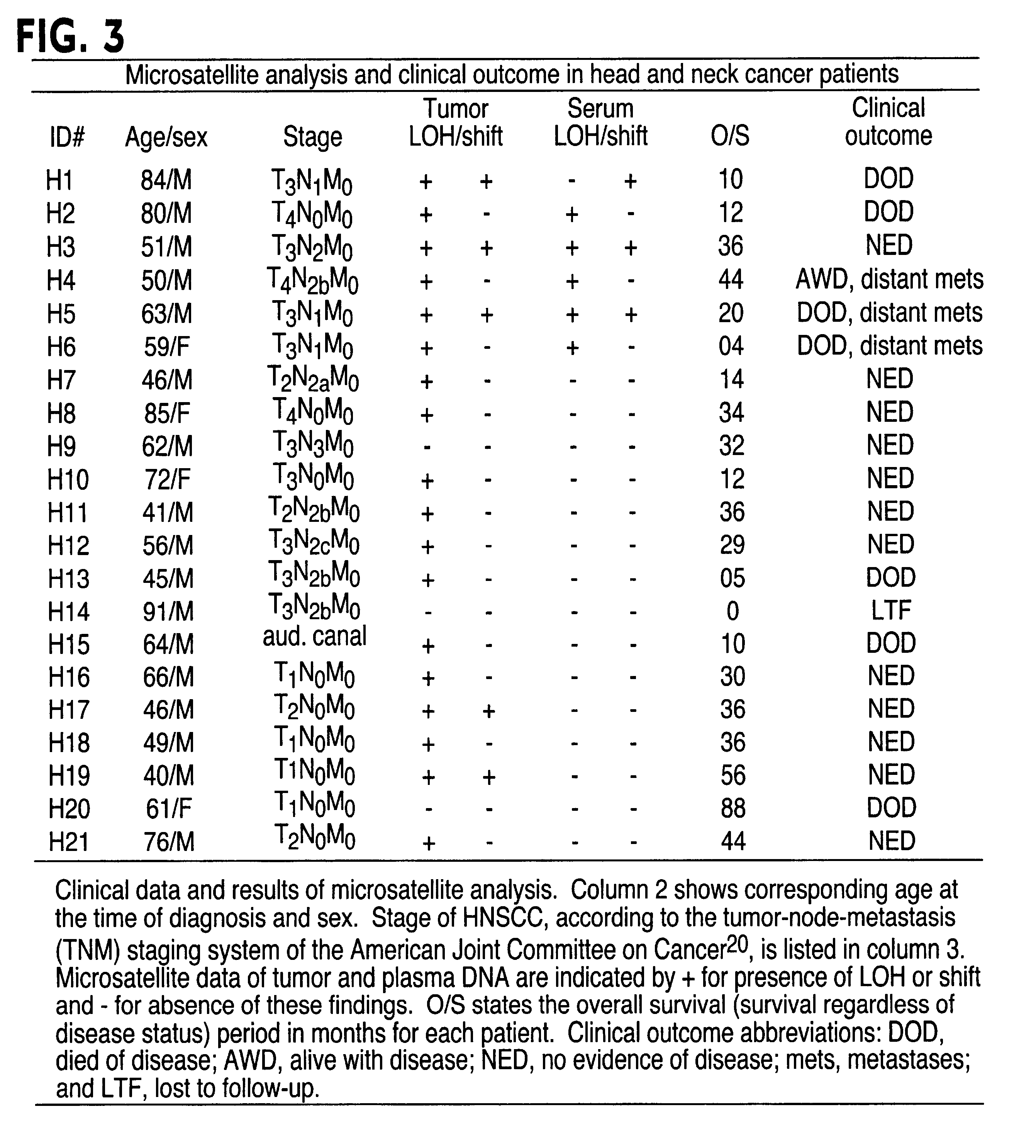
InactiveUS6291163B1Fast and reliable and sensitive and non-invasive screeningHigh copy numberSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCervical tissuePolymerase L
The present invention relates to the detection of a cell proliferative disorder associated with alterations of microsatellite DNA in a sample. The microsatellite DNA can be contained within any of a variety of samples, such as urine, sputum, bile, stool, cervical tissue, saliva, tears, or cerebral spinal fluid. The invention is a method to detect an allelic imbalance by assaying microsatellite DNA. Allelic imbalance is detected by observing an abnormality in an allele, such as an increase or decrease in microsatellite DNA which is at or corresponds to an allele. An increase can be detected as the appearance of a new allele. In practicing the invention, DNA amplification methods, particularly polymerase chain reactions, are useful for amplifying the DNA. DNA analysis methods can be used to detect such a decrease or increase. The invention is also a method to detect genetic instability of microsatellite DNA. Genetic instability is detected by observing an amplification or deletion of the small, tandem repeat DNA sequences in the microsatellite DNA which is at or corresponds to an allele. The invention is also a kit for practicing these methods.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
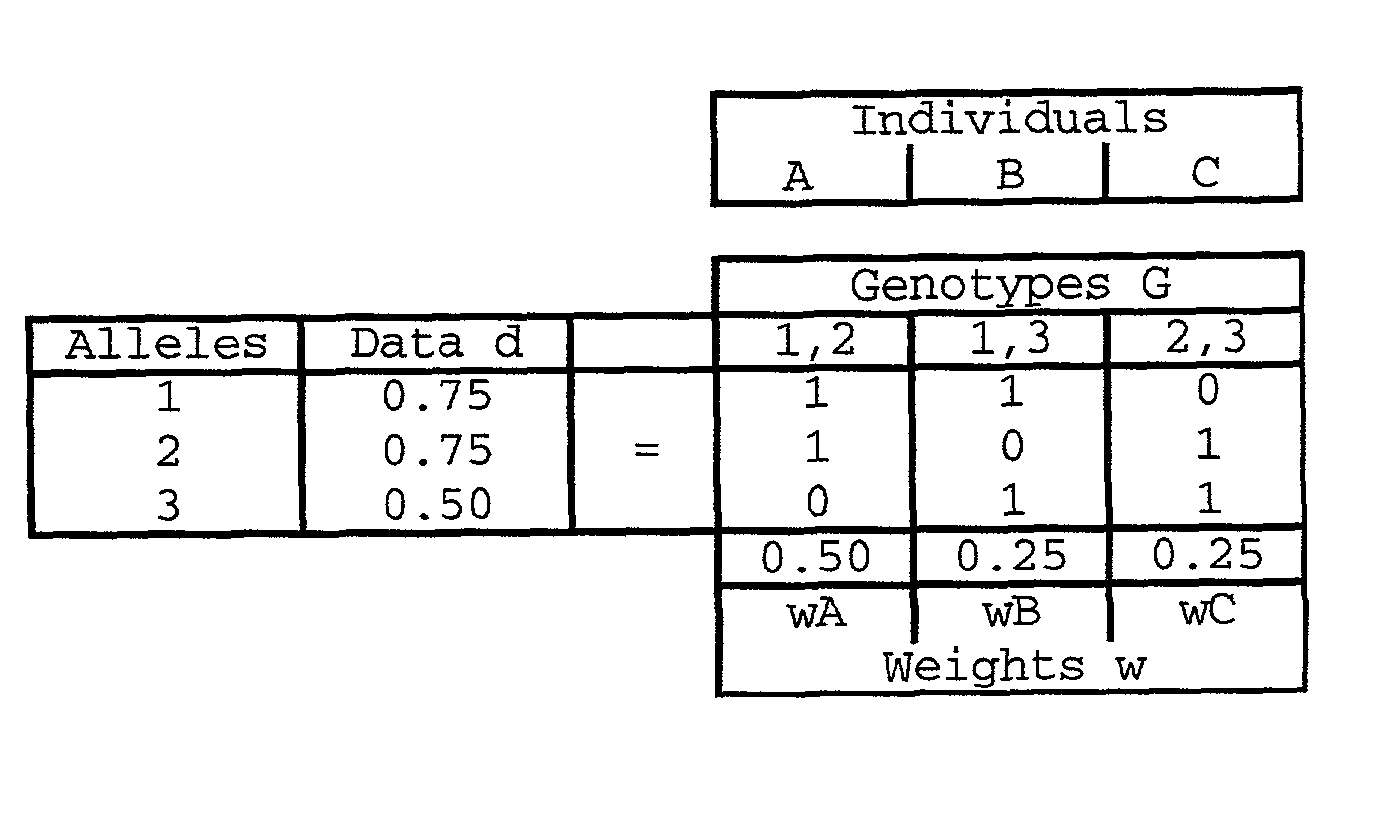
Method and system for DNA mixture analysis
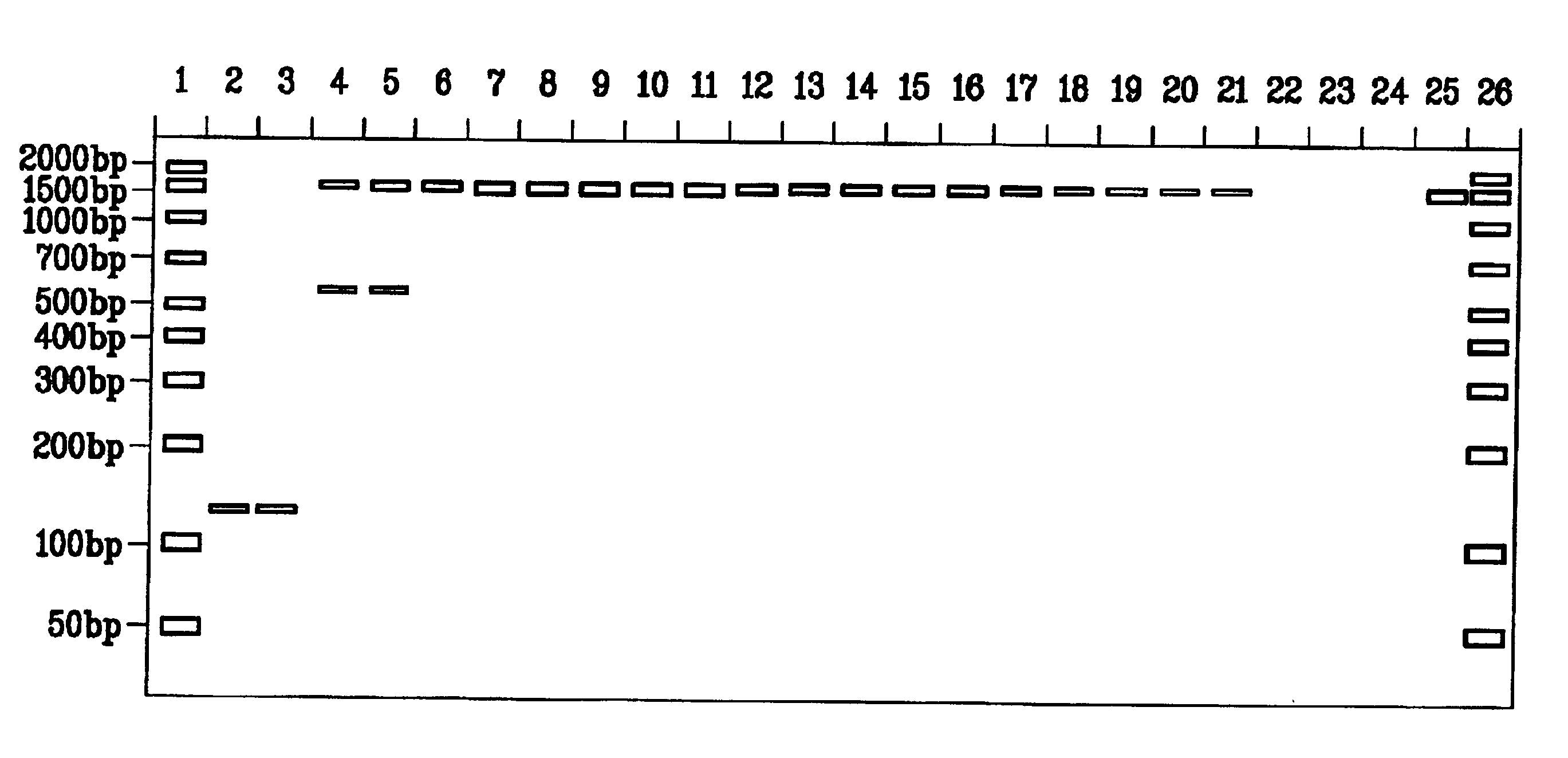
The present invention pertains to a process for automatically analyzing mixed DNA samples. Specifically, the process comprises the steps of obtaining a mixed DNA sample; amplifying the DNA sample to produce a product; detecting the product to produce a signal; and analyzing the signal to determine information about the composition of the mixed DNA sample. This DNA mixture analysis is useful for finding criminals and convicting them. This mixture analysis provides high quality estimates, and can determine genotypes, mixture weights, and likelihood ratios. This analysis provides confidence measures in the results it computes, and generates reports and intuitive visualizations. The process automates a tedious manual procedure, thereby reducing the cost, time, and effort involved in DNA forensic analysis. The system can greatly accelerate the rate of DNA crime analysis, and be used to exonerate innocent people.
Owner:CYBERGENETICS CORP
Method of reducing non-specific amplification in PCR
InactiveUS20030104395A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification dnaRibosomal DNA
The invention provides methods for reducing non-specific amplification DNA in a polymerase chain reaction comprising providing a sample comprising a target DNA sequence of interest; contacting the sample with at least one enzyme having nucleic acid polymerase activity; and incubating the sample with said enzyme for a time and under conditions sufficient to amplify the target DNA sequence, forming amplified target sequence; wherein the incubation is performed in the presence of an amount of sorbitol, or sorbitol and DMSO effective to reduce the non-specific amplification relative to the amount of non-specific amplification observed in the absence of sorbitol, or sorbitol and DMSO. The methods are suitable for amplification of ribosomal DNA, particularly from clinical samples. Compositions and kits containing sorbitol, or sorbitol and DMSO for reducing non-specific amplification are also provided.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
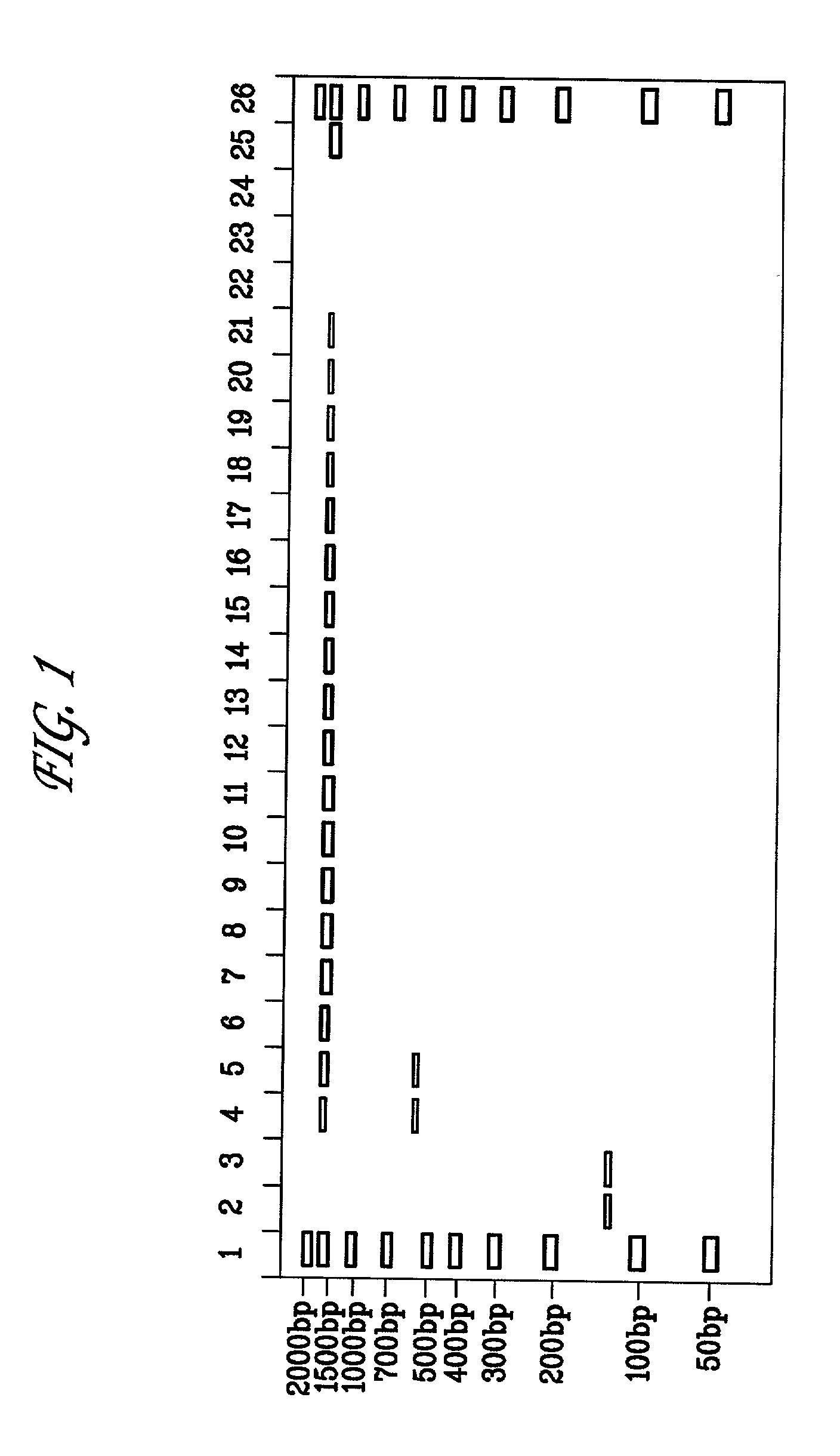
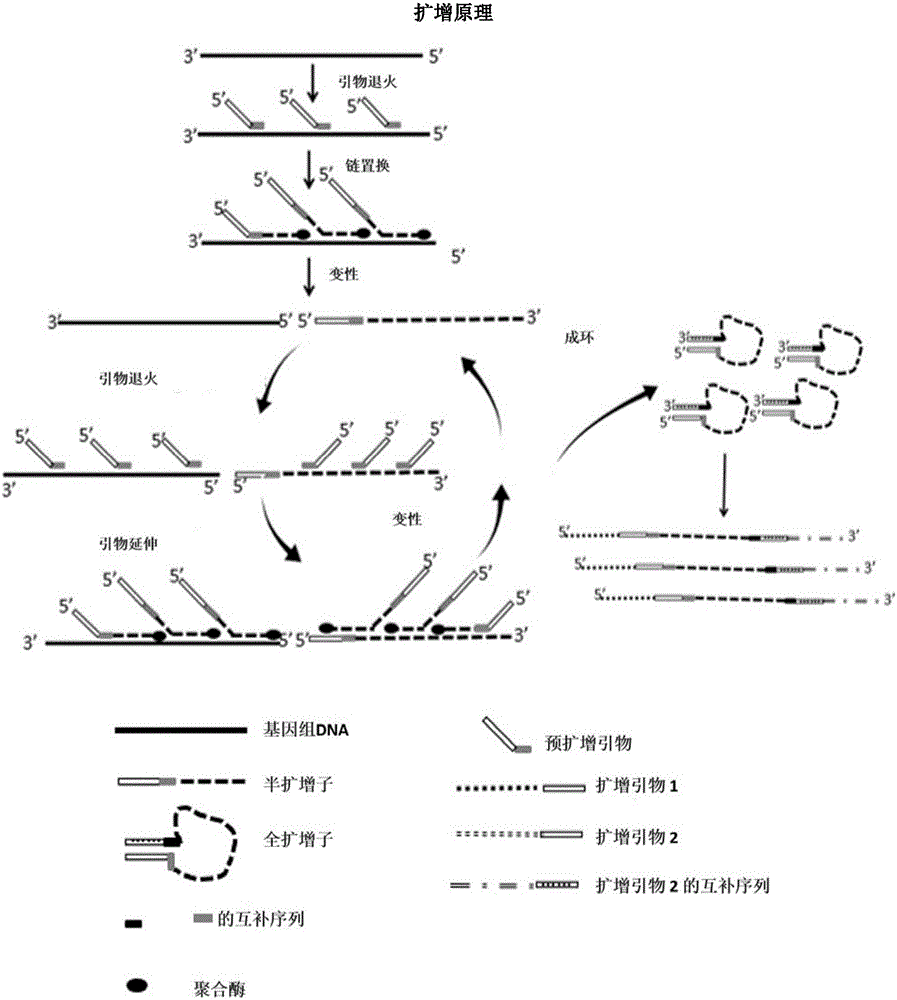
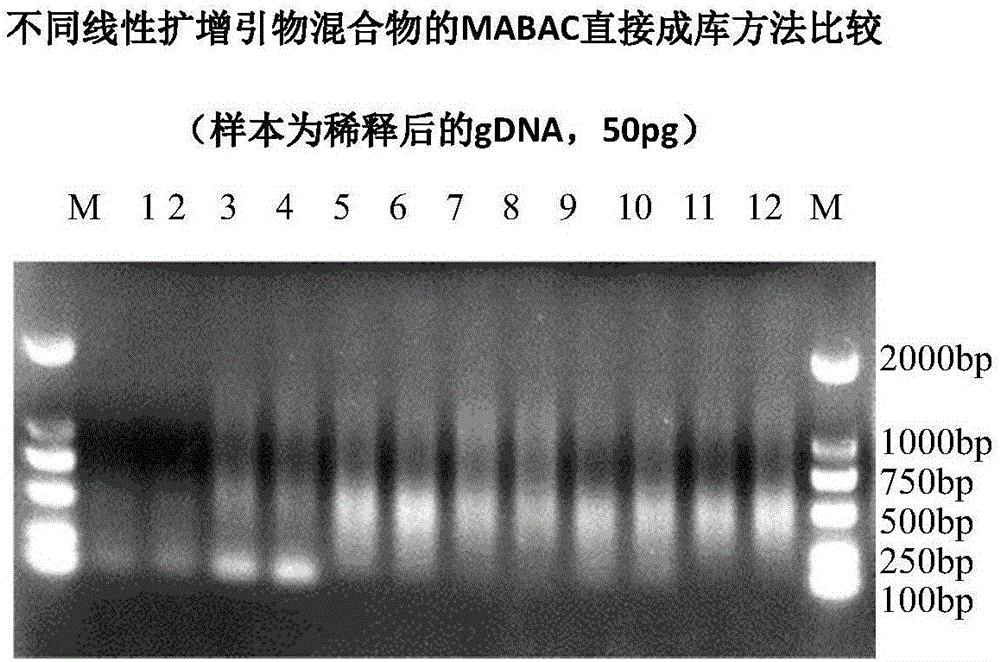
Method for amplifying DNA
The invention relates to a method for amplifying genome DNA, wherein the method comprises the following steps: (a) providing a first reaction mixture which includes a sample containing the genome DNA, a first primer, a nucleotide monomer mixture and nucleic acid polymerase, wherein from 5' terminal to 3' terminal, the first primer comprises a universal sequence and a first variable sequence including a first random sequence; (b) applying the first reaction mixture to a first temperature cyclic program, so that a pre-amplified product is obtained; (c) providing a second reaction mixture which includes the pre-amplified product, a second primer, a nucleotide monomer mixture and nucleic acid polymerase, wherein from 5' terminal to 3' terminal, the second primer comprises or is composed of a special sequence and the universal sequence; and (d) applying the second reaction mixture to a second temperature cyclic program, so that a amplified product is obtained. The invention also relates to a kit for amplifying the genome DNA.
Owner:XUKANG MEDICAL SCI & TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Portable buoyancy driven PCR thermocycler
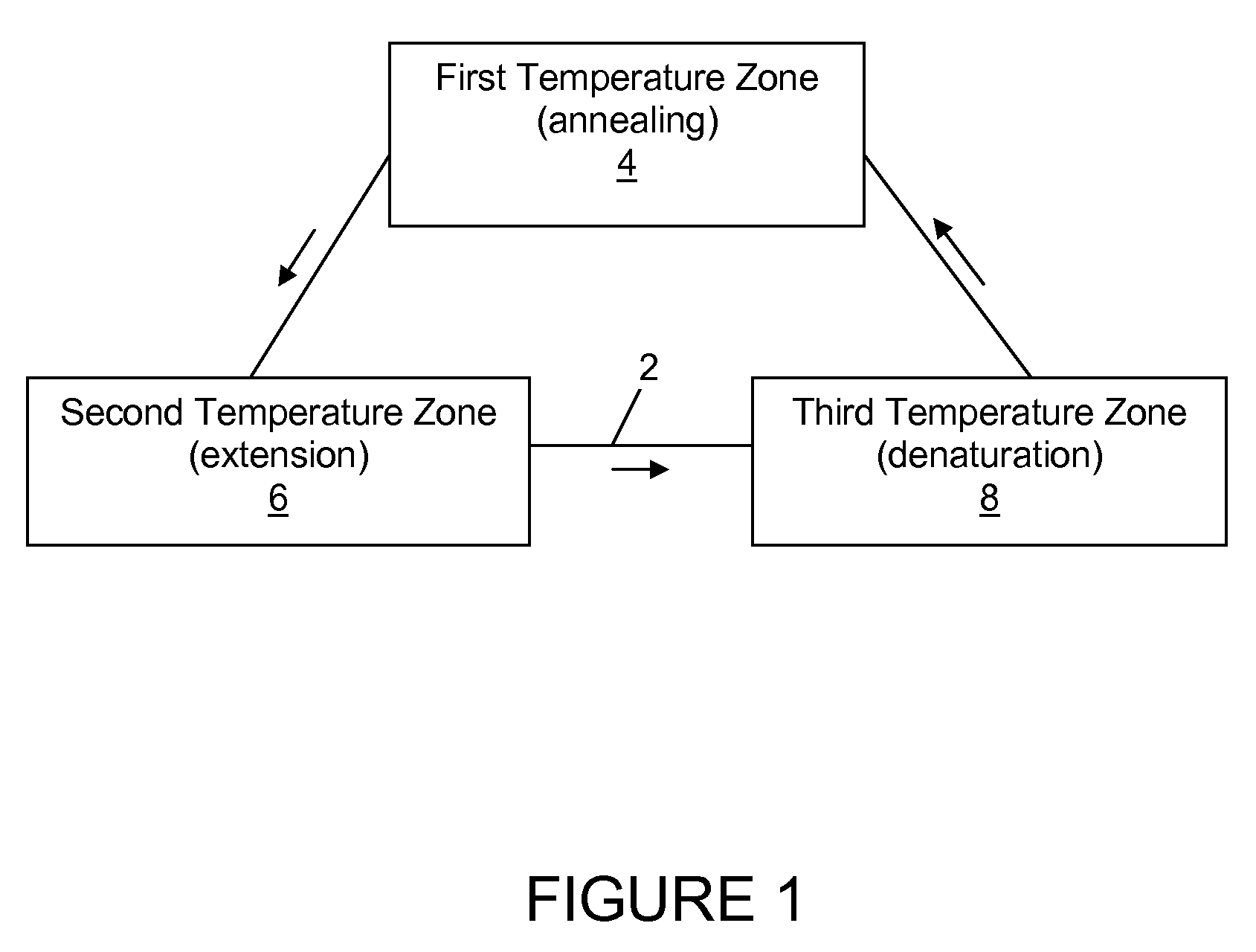
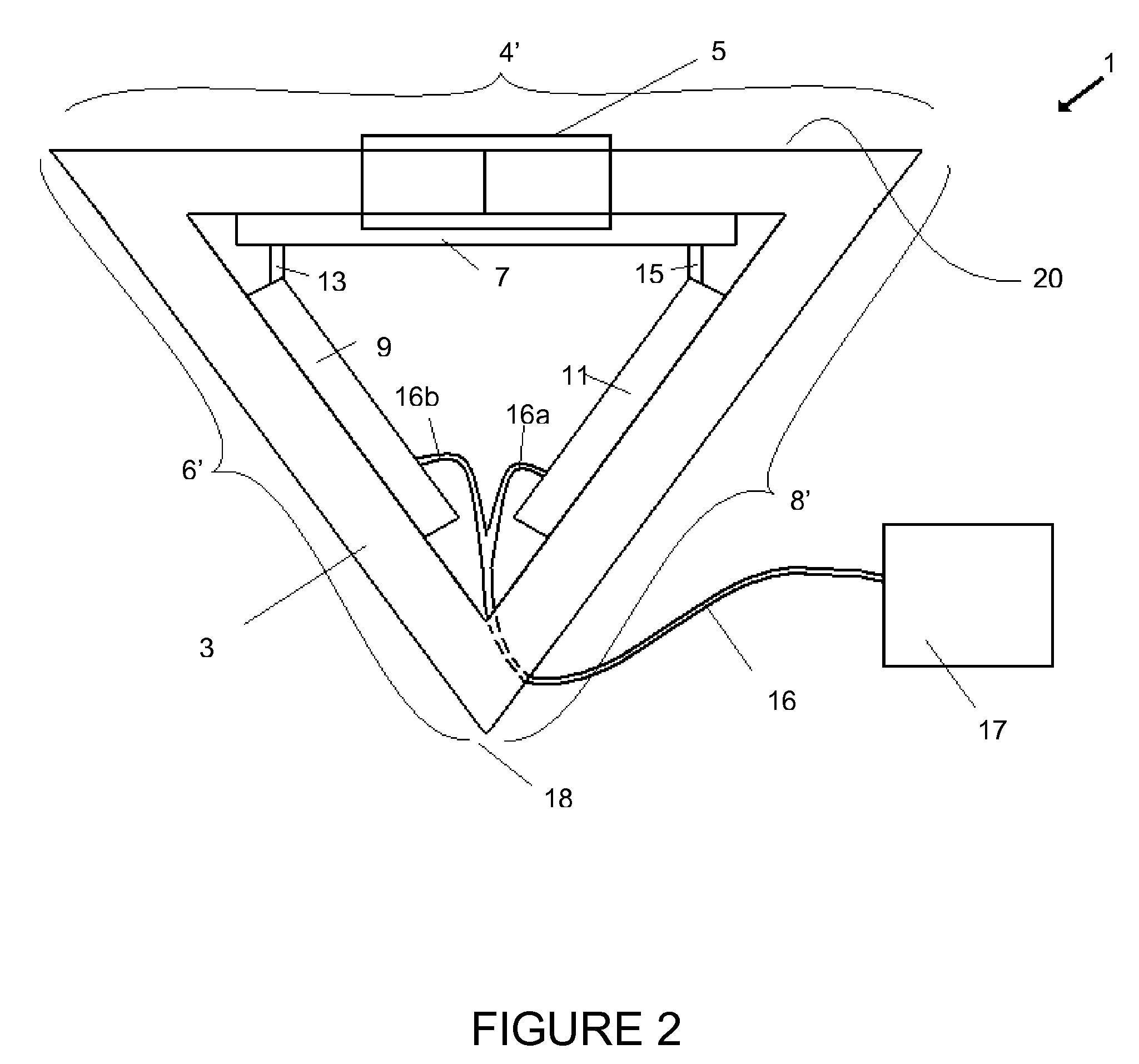
InactiveUS20080176292A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAmplification dnaClosed loop
A closed loop convective flow thermocycler for amplifying DNA sequences via polymerase chain reaction establishes buoyancy driven flow in response to an applied temperature gradient, so that PCR reagents are continuously cycled among temperature zones corresponding to denaturing, annealing and extension temperatures.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Method of reducing non-specific amplification in PCR
InactiveUS6783940B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification dnaPolymerase L
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Methods and Compositions for Identifying Sulfur and Iron Modifying Bacteria
ActiveUS20110104684A1Easy to controlSave moneySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification dnaSulfur
The invention relates to methods and compositions for identifying specific bacterial species, which are sulfur and iron oxidizers and / or reducers, from wall board (e.g., dry wall) and / or a patient tissue or body fluid. The method comprises the steps of extracting and recovering DNA of the bacterial species from the wall board and / or the patient tissue or body fluid, amplifying the DNA, hybridizing a probe to the DNA to specifically identify the bacterial species, and specifically identifying the bacterial species. Kits and nucleic acids for use in the methods are also provided. Methods for eliminating the sulfur and iron oxidizing and / or reducing bacteria from wall board using a zeolite are also provided.
Owner:ADVATECT DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Method and kit for directly amplifying DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segment from biological material
The invention discloses a method and kit for directly amplifying a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segment from a biological material. The kit disclosed by the invention comprises a lysis solution a, a lysis solution b, a lysis solution c and a neutralization solution, and can also comprise a 2*Taq PCR (polymerase chain reaction) mixed solution, wherein the lysis solution a comprises 50-70v% PEG (polyethylene glycol) 200 and 20-40mM KOH, and the pH value of the lysis solution a is 13.2-13.8; the lysis solution b comprises 5-10wt% chelex-100; the lysis solution c comprises 5-10wt% chelex-100 and 1-2wt% TritonX-100; and the neutralization solution comprises a 190-210 mmol / L Tris-HCl buffer of which the pH value is 6.8-7.5. The kit and method disclosed by the invention are applicable to many samples, such as bacteria, animal tissues, plant tissues, fungi, blood, saliva, hair and the like.
Owner:生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司
Production of closed linear DNA
ActiveUS20120282283A1Increase productionImprove machining productivityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAmplification dnaA-DNA
An in vitro process for the production of closed linear deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) comprises (a) contacting a DNA template comprising at least one protelomerase target sequence with at least one DNA polymerase in the presence of one or more primers under conditions promoting amplification of said template; and (b) contacting amplified DNA produced in (a) with at least one protelomerase under conditions promoting production of closed linear DNA. A kit provides components necessary in the process.
Owner:TOUCHLIGHT IP LTD
Method and kit for detecting drug resistance gene mutant type of tuberculous bacillus (TB)
InactiveCN103184270AReduce usageImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceMycobacterium
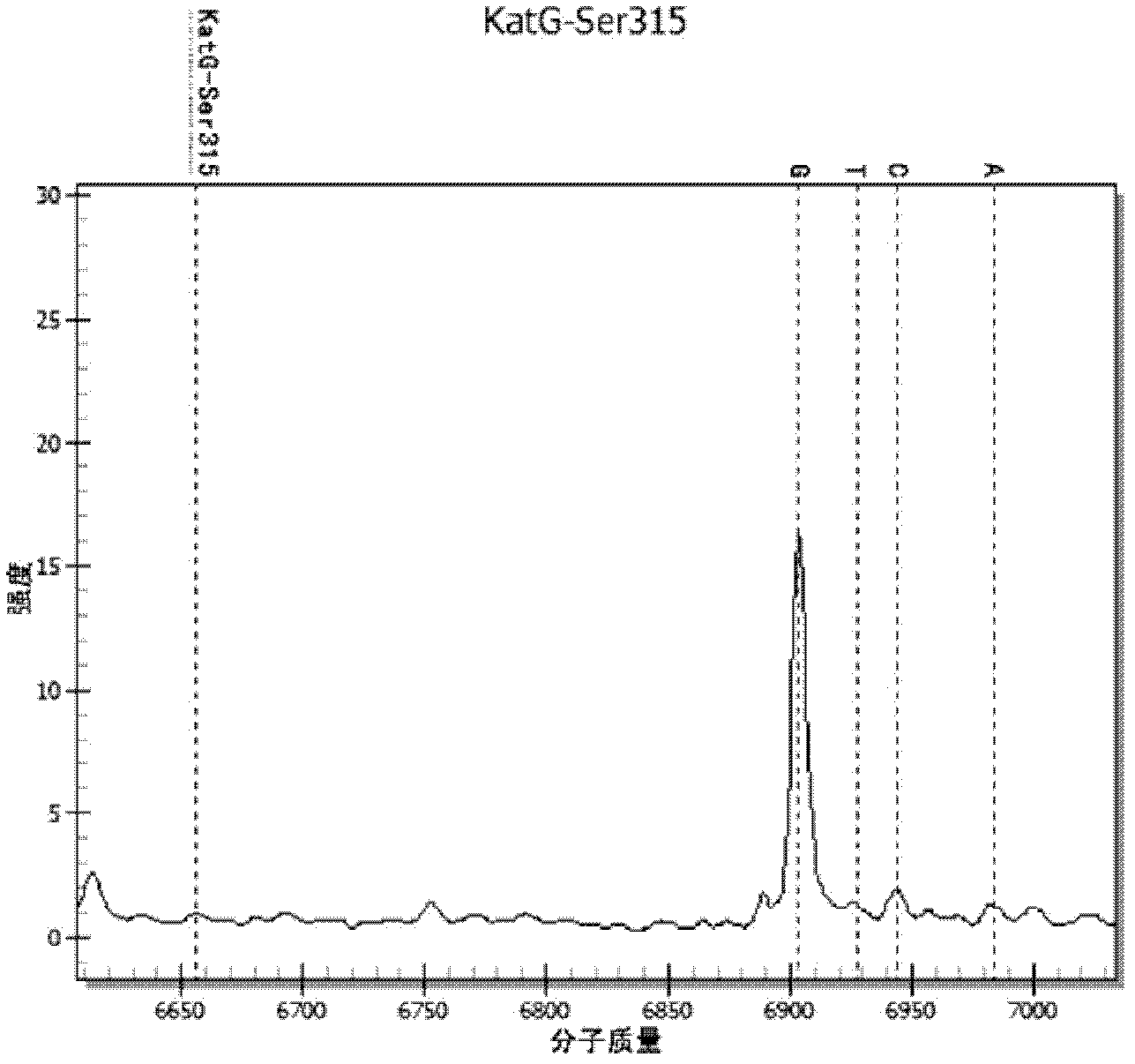
The invention provides a method and a kit for detecting a drug resistance gene mutant type of tuberculous bacillus (TB). Compared with the prior art, the invention has the following advantages: 1) reagents and consumables used in the invention are simple and stable, and expensive reagents like fluorescent dyes and special enzyme are not needed; 2) a reaction can be carried out in a microscale system, and usage of a sample and a variety of consumables is reduced; 3) since mass spectrometry is used for direct detection of molecular weight (a mass-to-charge ratio) of DNA and direct determination of types of bases (i.e., no need for signal conversion in any manner), it is theoretically practicable that identification can be realized as long as one copied amplified DNA fragment is amplified, so high sensitivity is obtained; and 4) since mass spectrometry also has the characteristics of automatic and high-flux detection and the like, combination of mass spectrometry and multi-primer extension enables a plurality of drug resistance sites to be simultaneously detected in one reaction system, thereby substantially reducing workload and increasing detection flux.
Owner:北京宏微特斯生物科技有限公司 +1
Selective terminal tagging of nucleic acids
ActiveUS20090227009A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionAmplification dna
Methods are provided for adding a terminal sequence tag to nucleic acid molecules for use in RNA or DNA amplification. The tag introduced may be used as a primer binding site for subsequent amplification of the DNA molecule and / or sequencing of the DNA molecule and therefore provides means for identification and cloning of the 5′-end or the complete sequence of mRNAs.
Owner:CELLSCRIPT
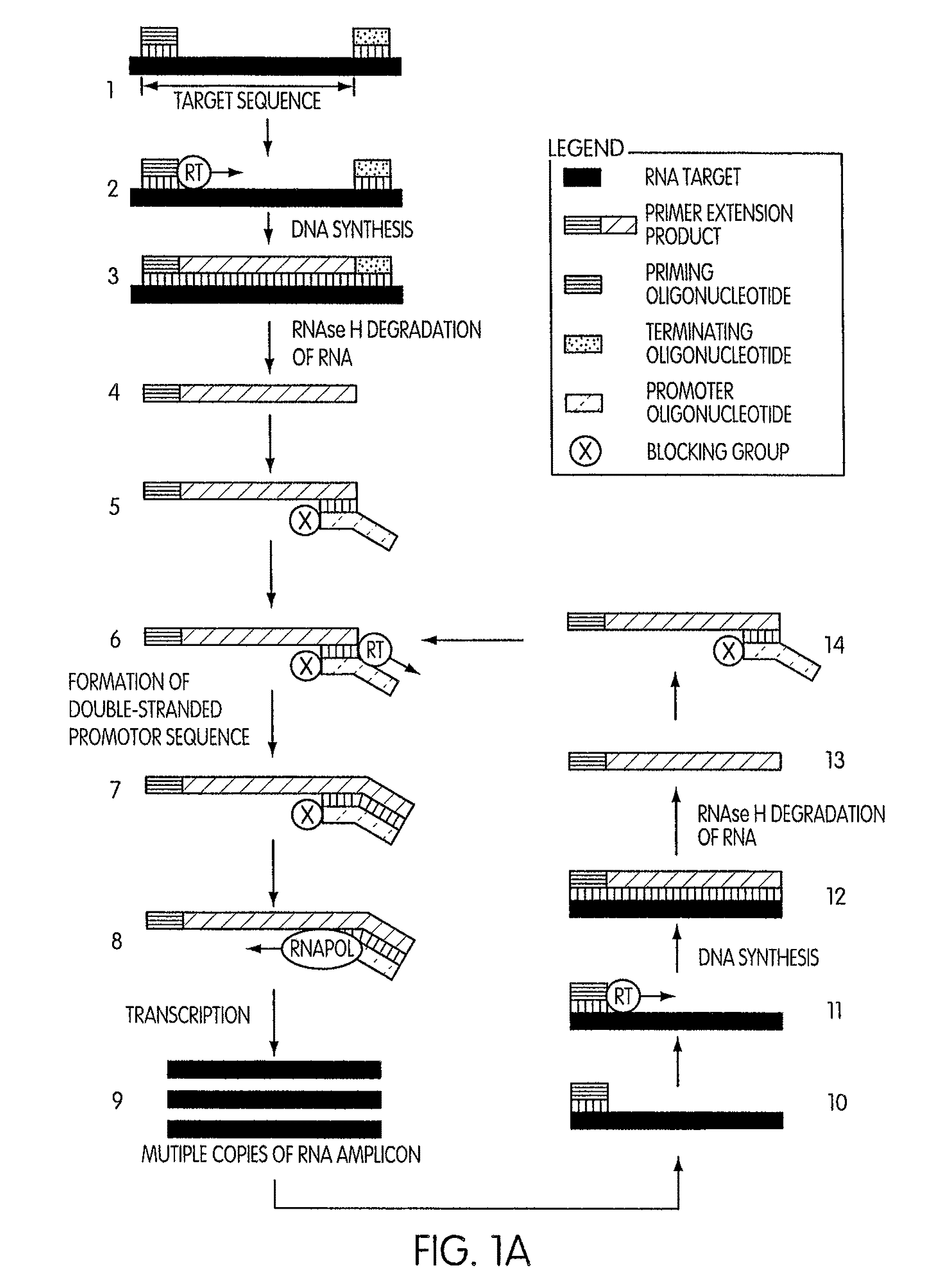
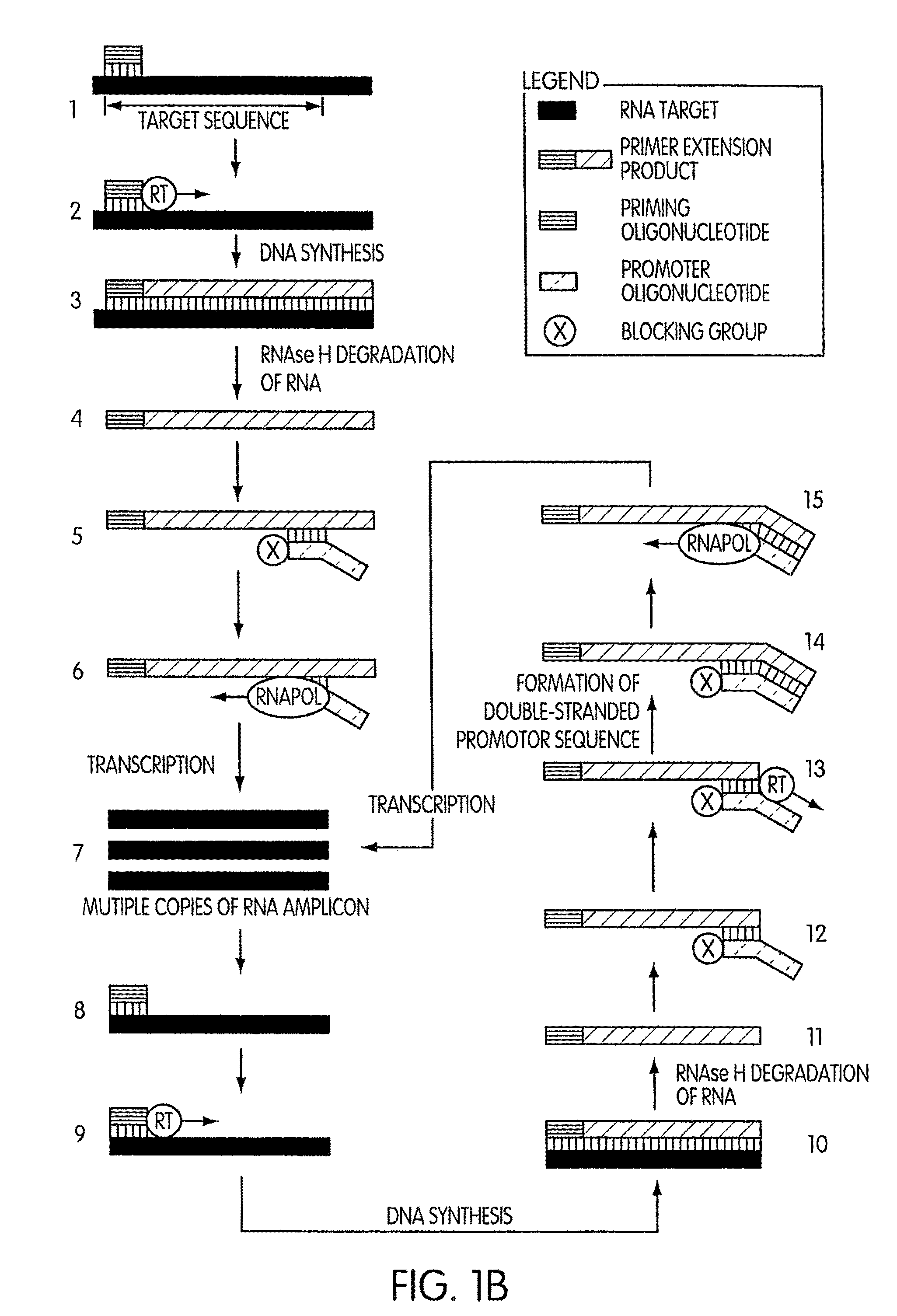
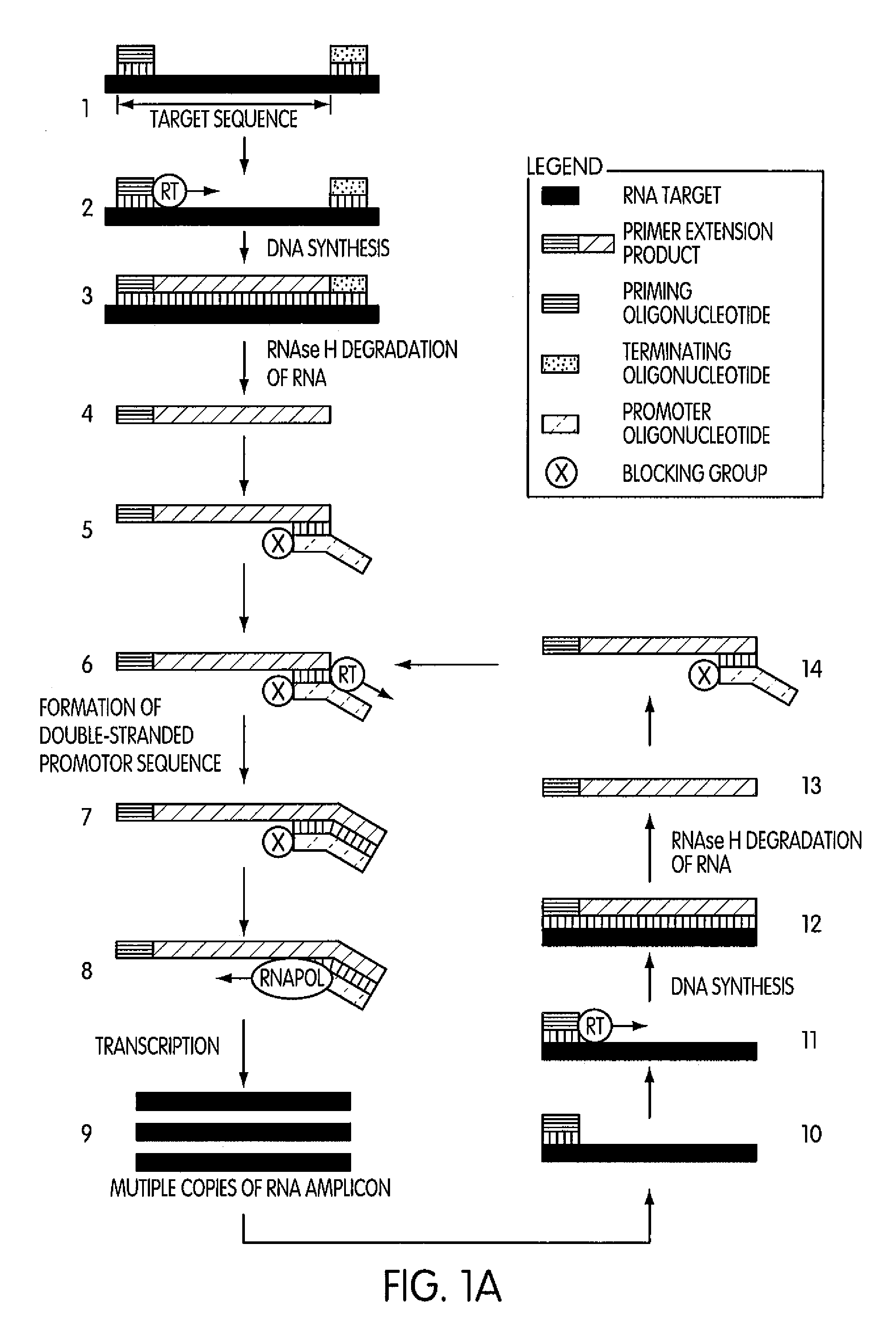
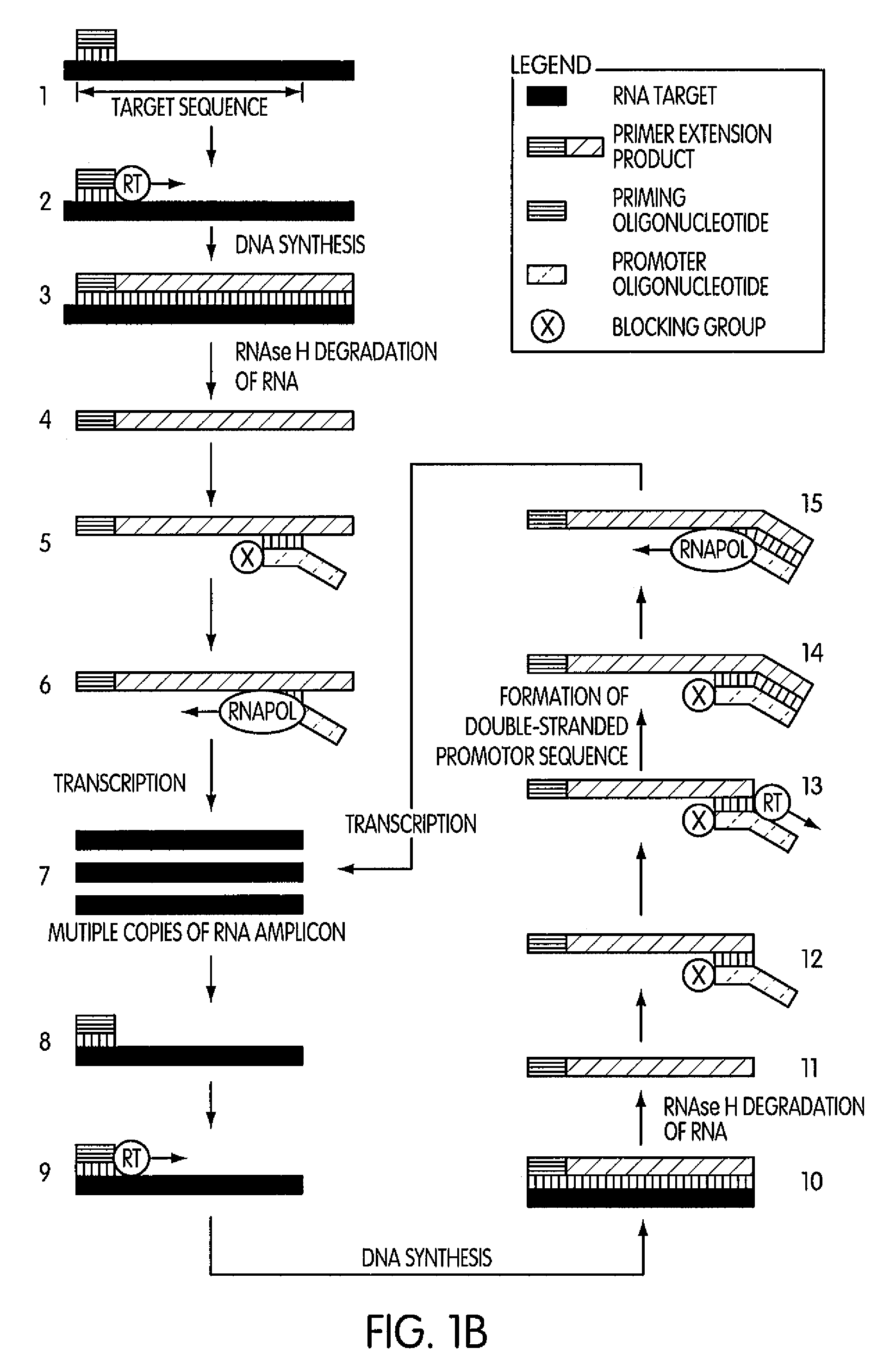
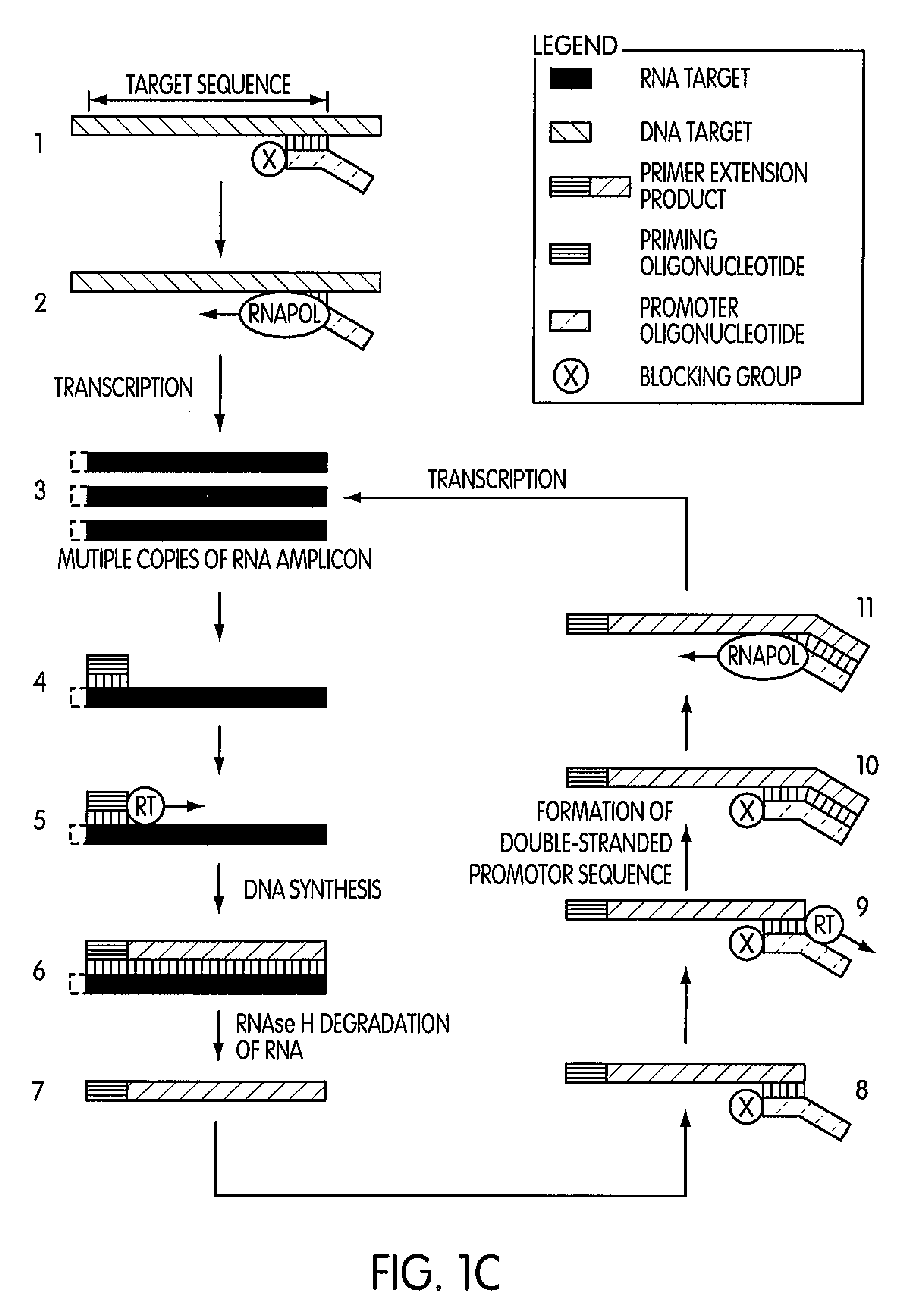
Methods and kits for amplifying DNA
ActiveUS7713697B2Reduce appearance problemsMinimize and substantially eliminate emergenceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAmplification dnaPolymerase L
Novel methods of synthesizing multiple copies of a target nucleic acid sequence which are autocatalytic are disclosed (i.e., able to cycle automatically without the need to modify reaction conditions such as temperature, pH, or ionic strength and using the product of one cycle in the next one). In particular, methods of nucleic acid amplification are disclosed which are robust and efficient, while reducing the appearance of side-products. In general, the methods use priming oligonucleotides that target only one sense of a target nucleic acid, a promoter oligonucleotide modified to prevent polymerase extension from its 3′-terminus and, optionally, a means for terminating a primer extension reaction, to amplify RNA or DNA molecules in vitro, while reducing or substantially eliminating the formation of side-pro ducts. The disclosed methods minimizes or substantially eliminate the emergence of side-products, thus providing a high level of specificity. Furthermore, the appearance of side-products can complicate the analysis of the amplification reaction by various molecular detection techniques. The disclosed methods minimize or substantially eliminate this problem, thus providing enhanced levels of sensitivity.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
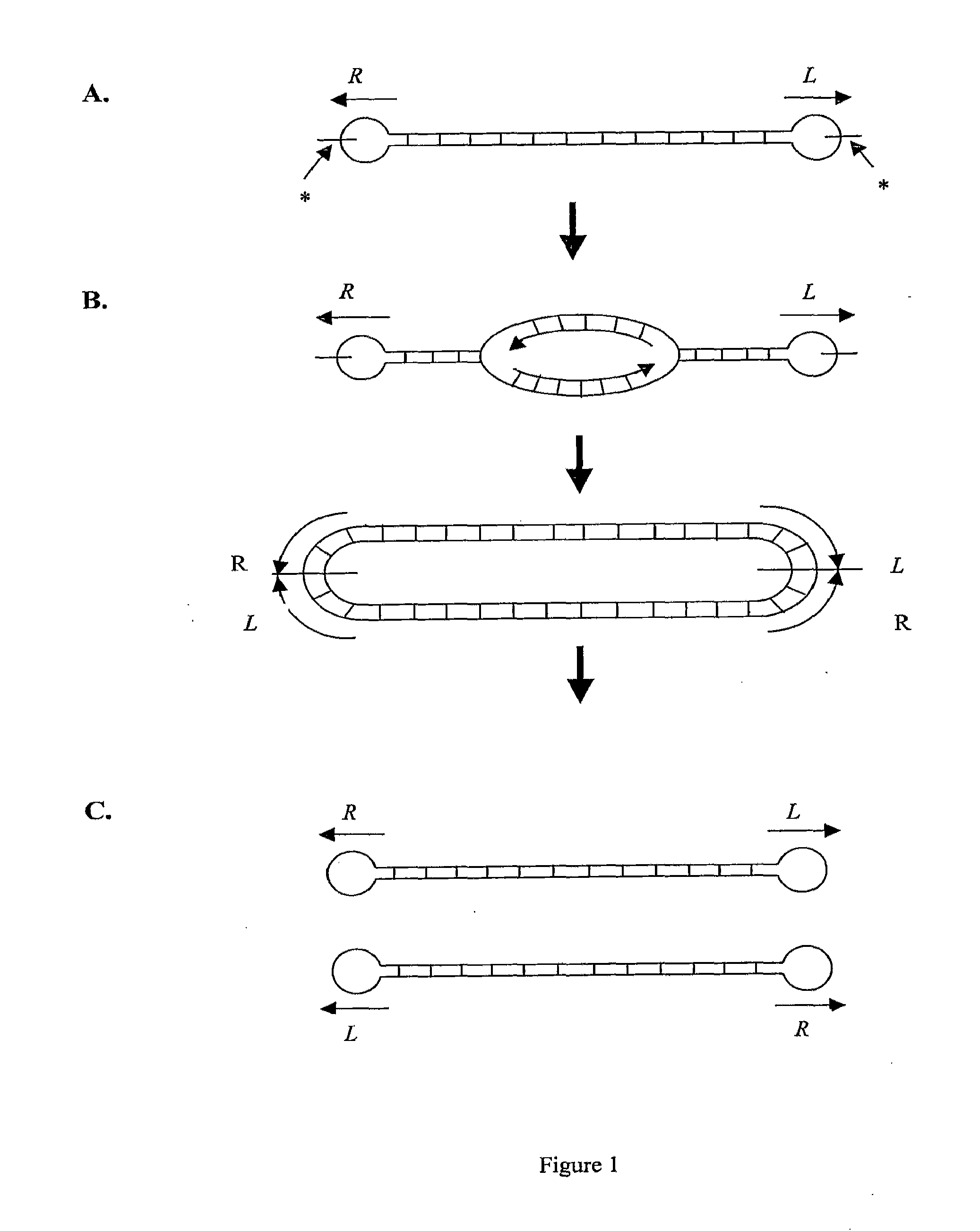
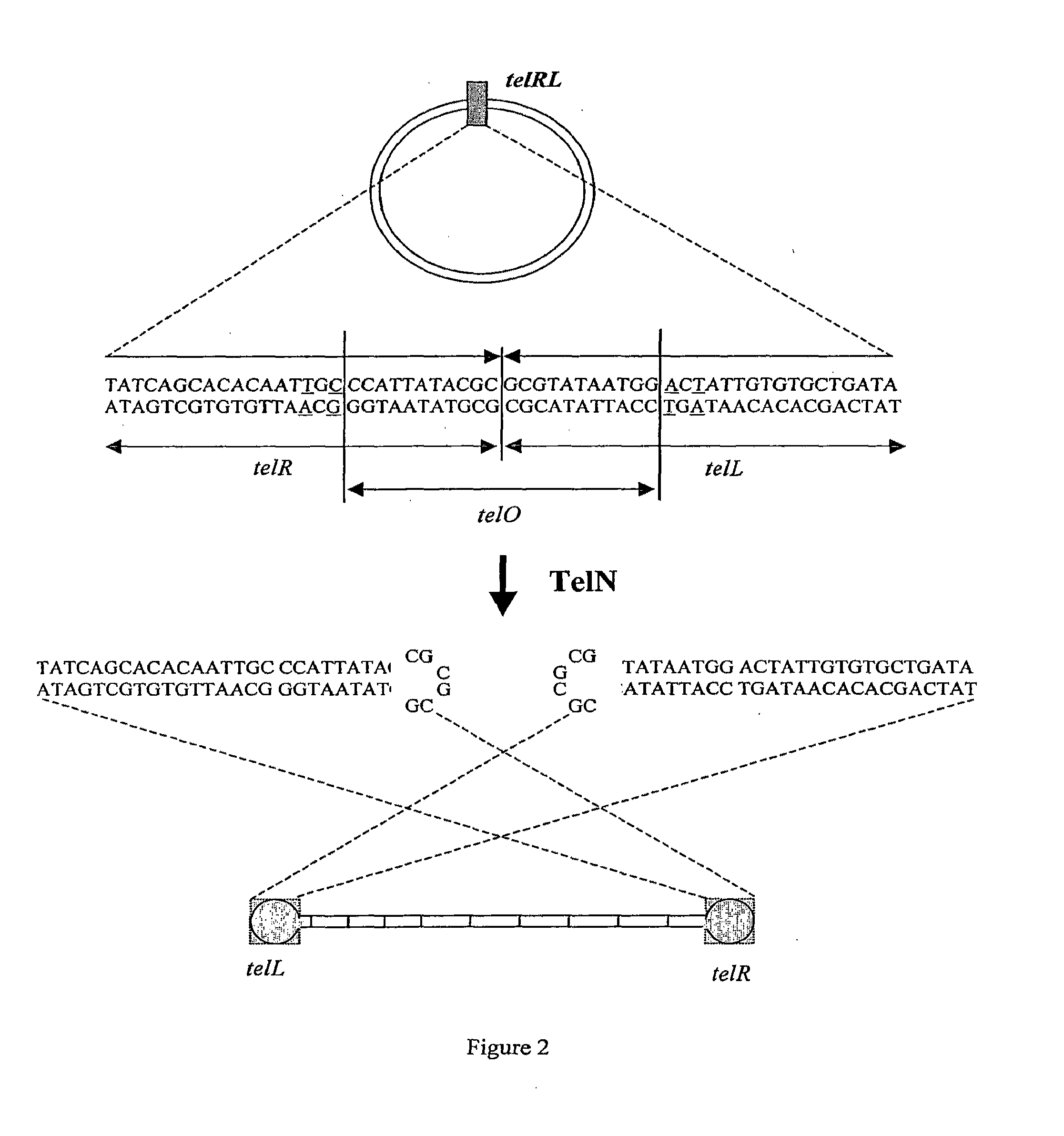
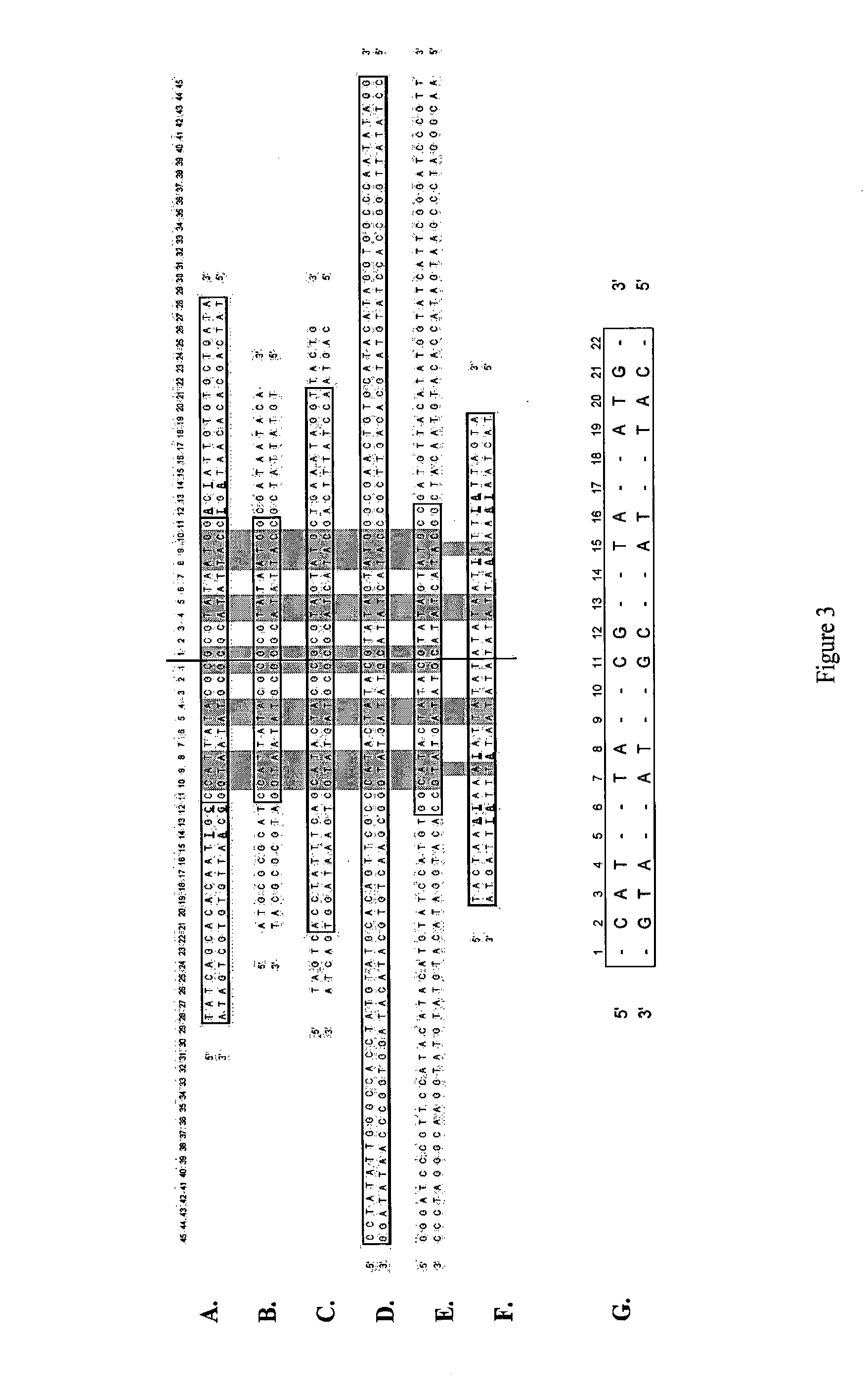
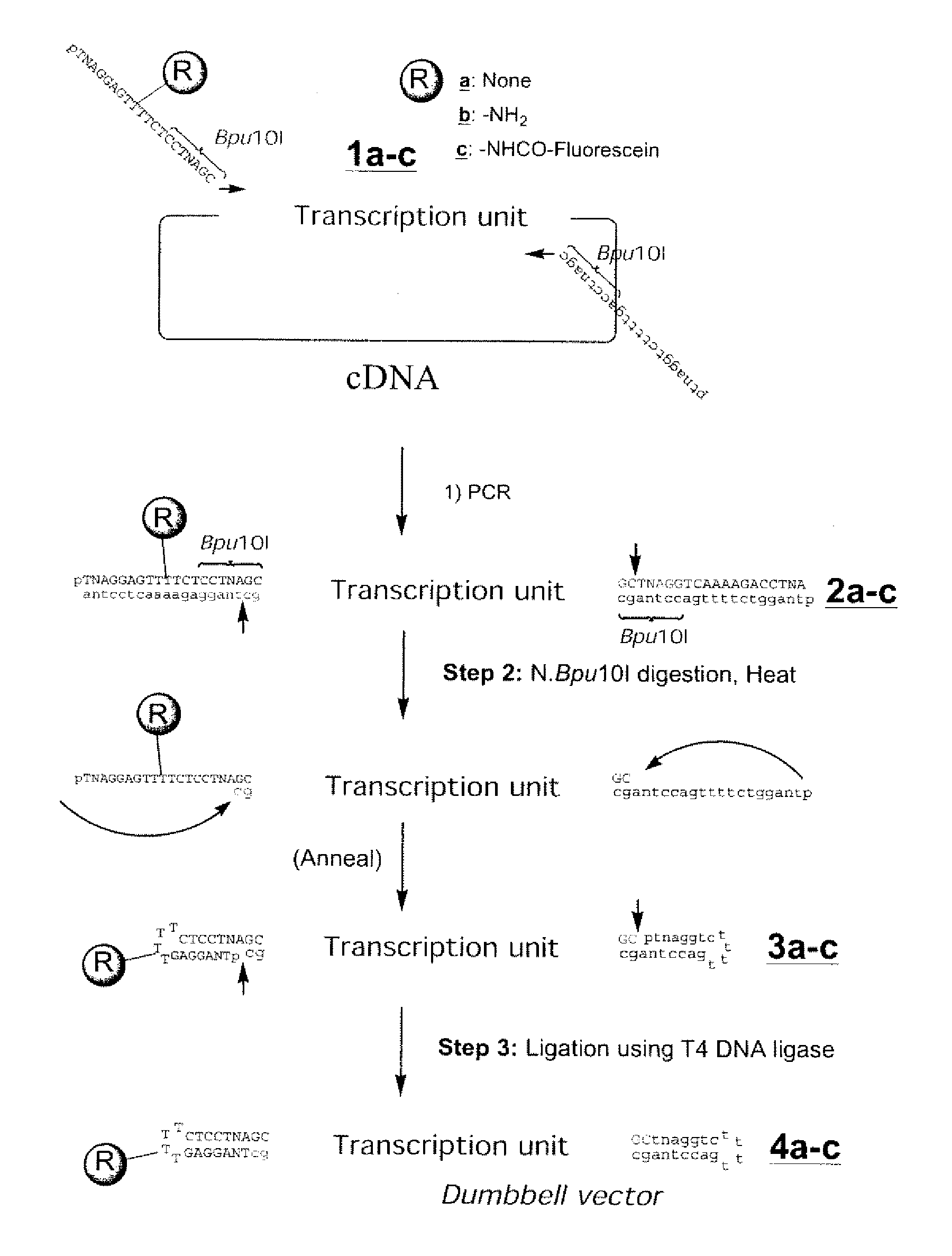
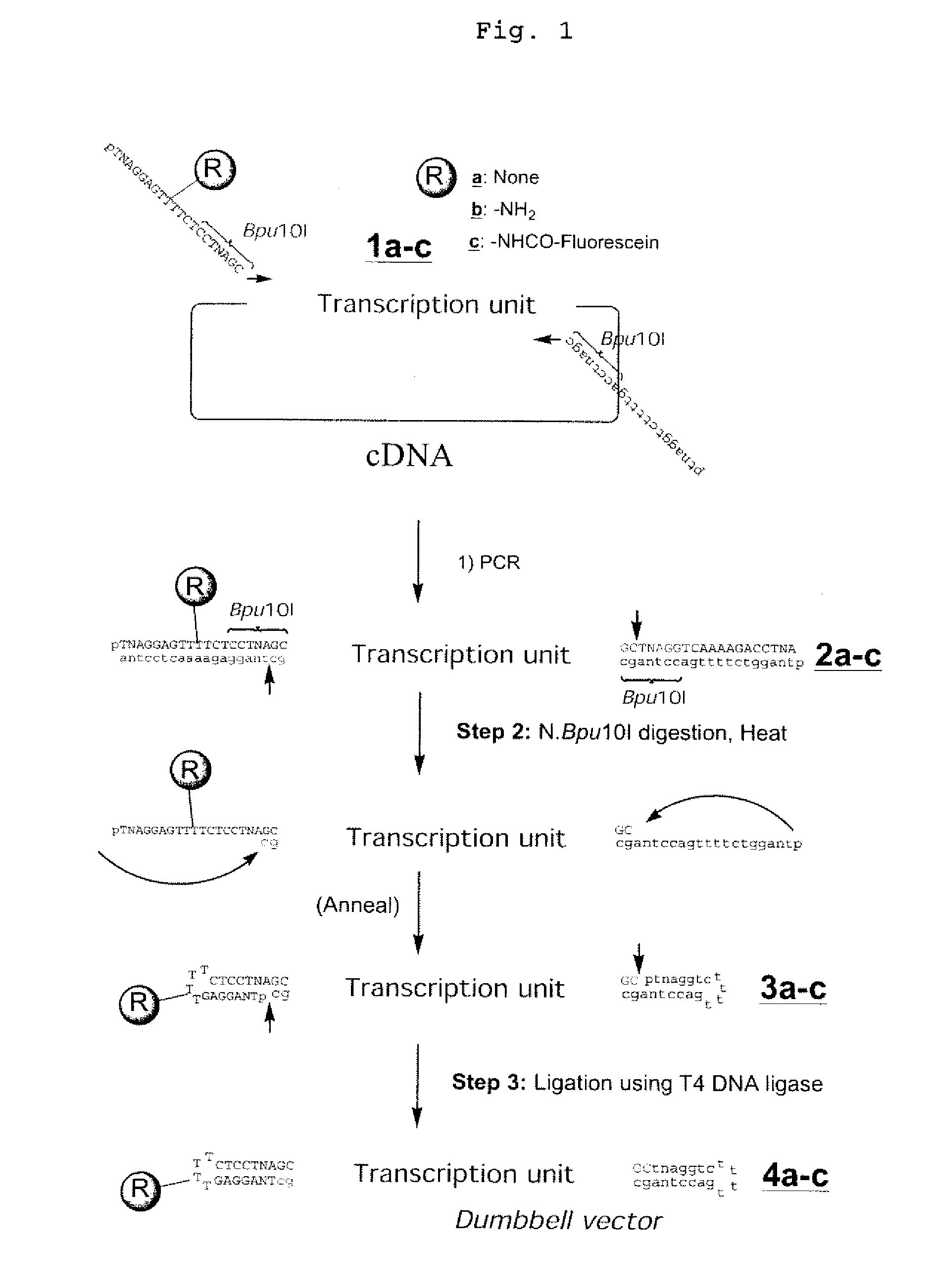
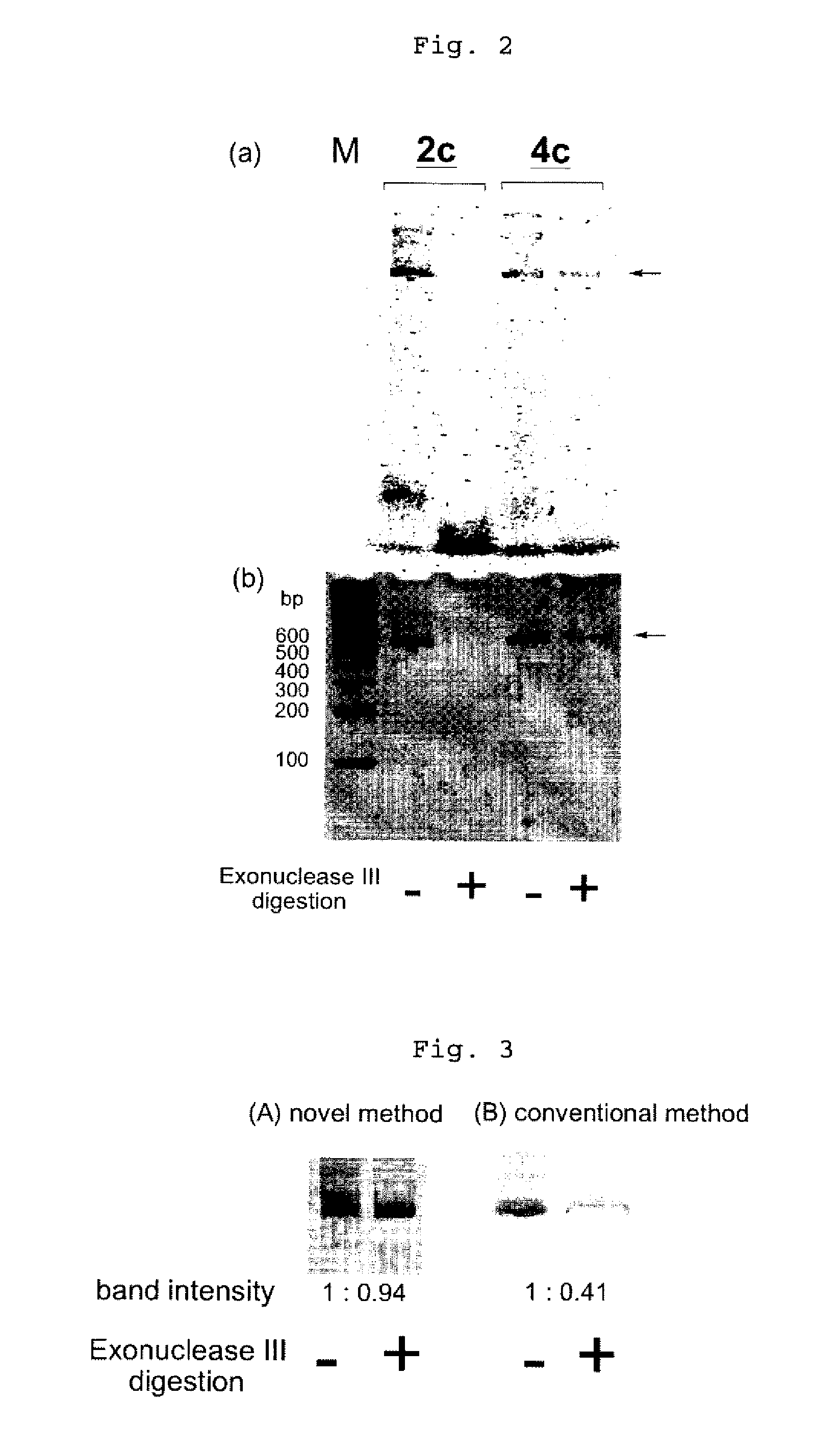
Efficient Process For Producing Dumbbell Dna
InactiveUS20080153763A1Simple methodOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesPhosphorylationAmplification dna
The present invention provides a simple method for producing a dumbbell-shaped DNA.A method for producing a dumbbell-shaped DNA, wherein each of sense and antisense strands is connected at both the 5′ and 3′ ends of a linear-shaped double stranded DNA by a single stranded DNA of loop structure, comprising the steps of;1) amplifying a target DNA in a template DNA by PCR using sense and antisense primers, wherein each of the sense and antisense primers contains the following sequence (a) at the 5′ end and also contains the following sequences (b), (c), and (d) in order from the 5′ end to the 3′ end,(a) a part of a sense sequence of a nickase recognition sequence, comprising the sequence of a region between the site where a nick is introduced by the action of a nickase and the 3′ end,(b) a sequence capable of forming a loop structure from a single strand,(c) the entire antisense sequence of the nickase recognition sequence (a),(d) a sequence complementary to all or part of the sequence of the target DNA;2) treating the amplified DNA product of step 1) with a nickase of (a);3) heating and then annealing the nickase treated amplified DNA product of step 2); and4) treating the heated and annealed amplified DNA product of step 3) with DNA ligase, wherein the sense and antisense primers used in step 1) are phosphorylated at the 5′ end, or the amplified DNA product is phosphorylated at the 5′ end after step 1) but before step 4).
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
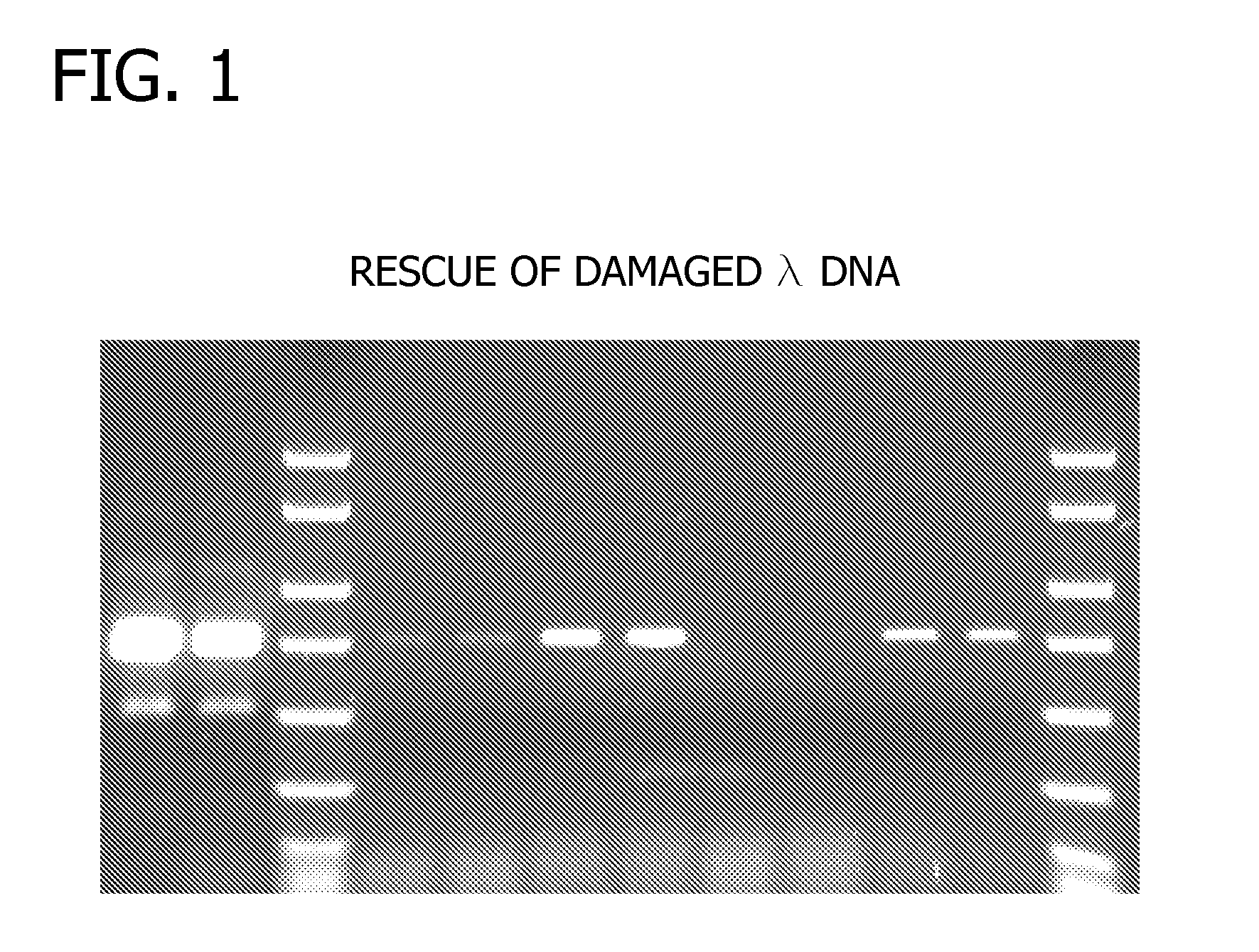
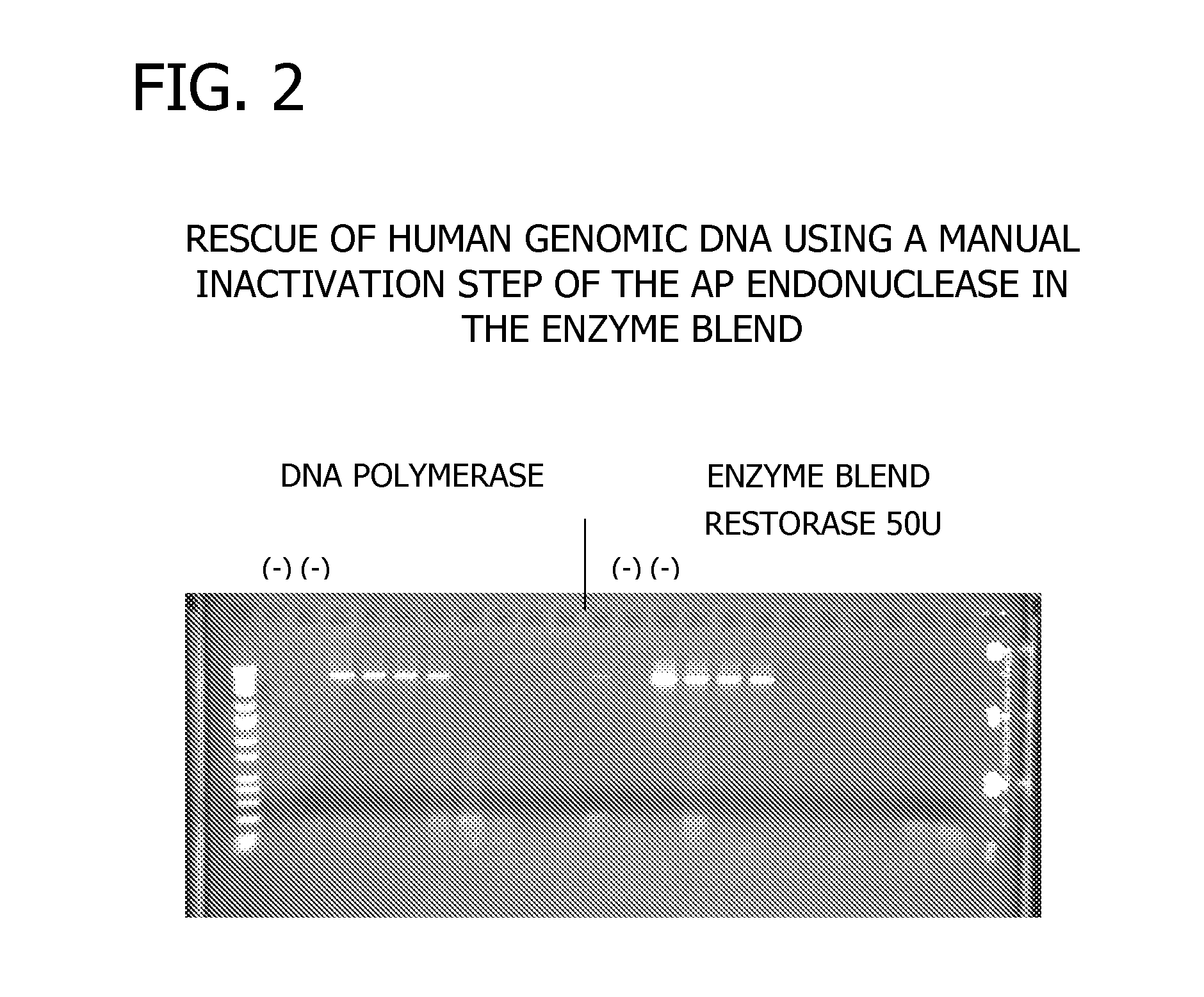
Methods and Compositions for Amplification of DNA
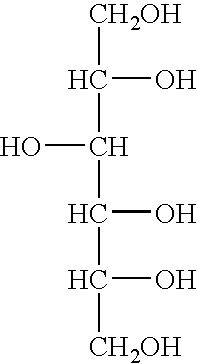
Compositions for the amplification of damaged nucleic acids are disclosed. The compositions generally comprise a mesophilc polymerase, a thermostable polymerase, and an AP endonuclease. Methods of using the same for the amplification of damaged DNA are also disclosed.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Method for identifying fast and slow feather molecules of chickens
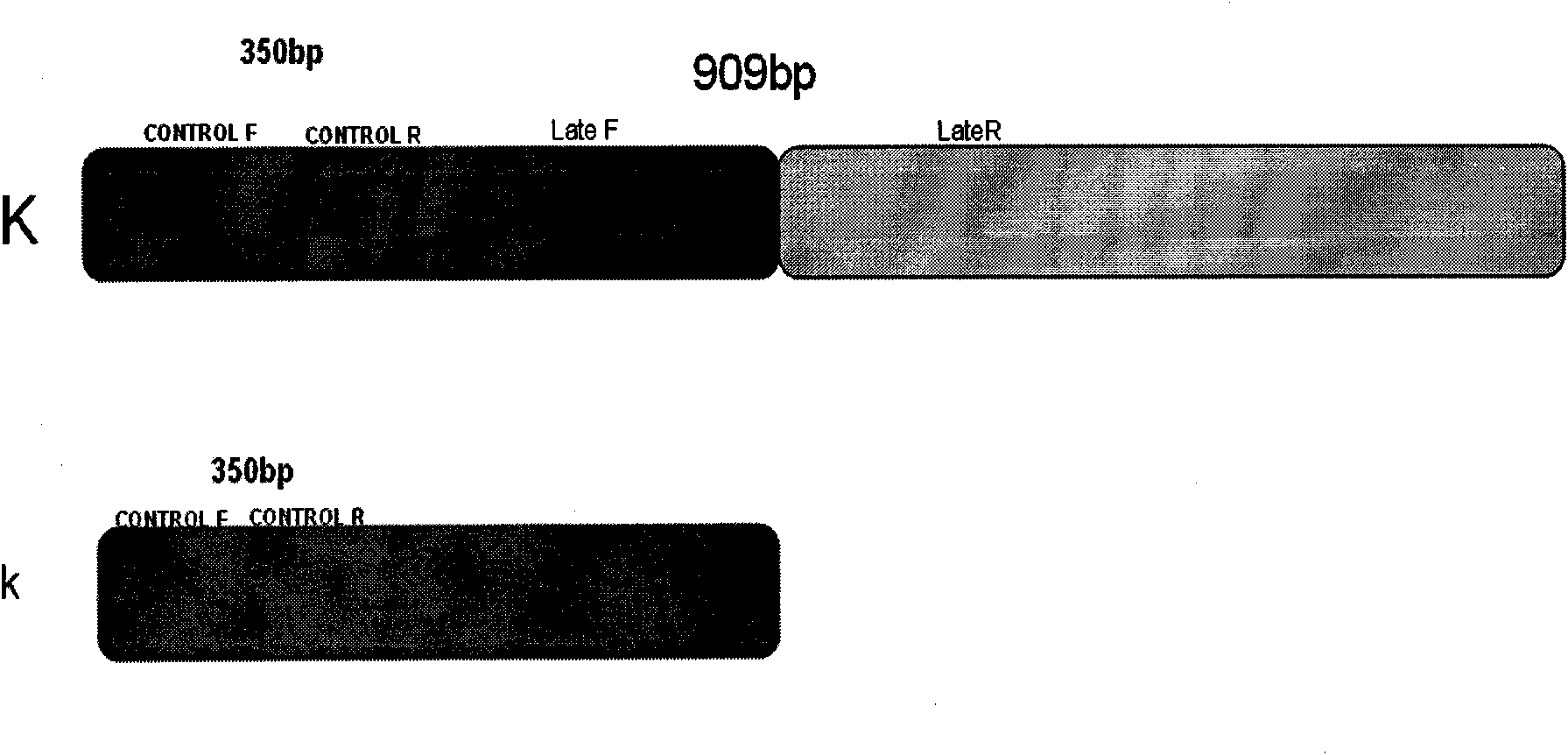
InactiveCN101619354AAccurate identificationShorten the establishment timeMicrobiological testing/measurementZ chromosomeDuplex pcr
The invention belongs to the technical field of animal breeding, in particular to a method for identifying fast feather type and slow feather type of chickens by applying double PCR. The method comprises the following steps: (1) designing two pairs of primers by utilizing a correlation sequence of a K gene locus found on a Z chromosome of a chicken according to structures of alleles of the fast and slow feather type; (2) extracting DNAs of chicken blood samples of the known fast and slow feather type to carry out a primer specificity test, and identifying the chicken to be a fast feather type or a slow feather type according to the size and the existence of an amplified DNA segment. When only one 350bp band is amplified, the chicken is judged to be a fast feather type, and when two bands of 350bp and 909bp are amplified, the chicken is judged to be a slow feather type. The invention also discloses a reliable checking method of the identifying method and applies the checking method to a breeding process of a self identification male and female matched system of the fast and slow feathers. The invention can shorten the breeding time of the self identification male and female matched system of the fast and slow feathers and save the breeding cost.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Methods And Compositions For Detecting Fungi And Mycotoxins
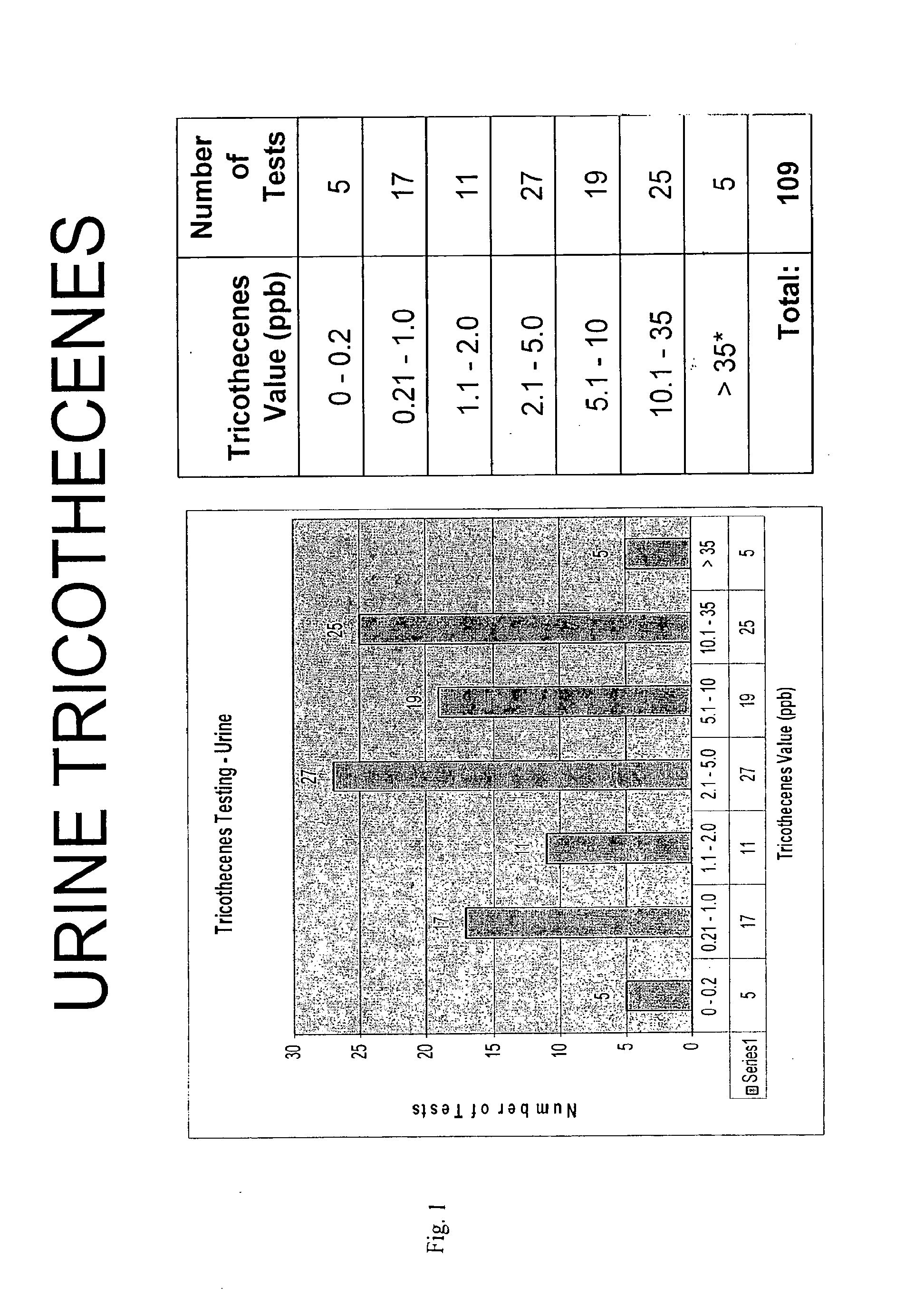
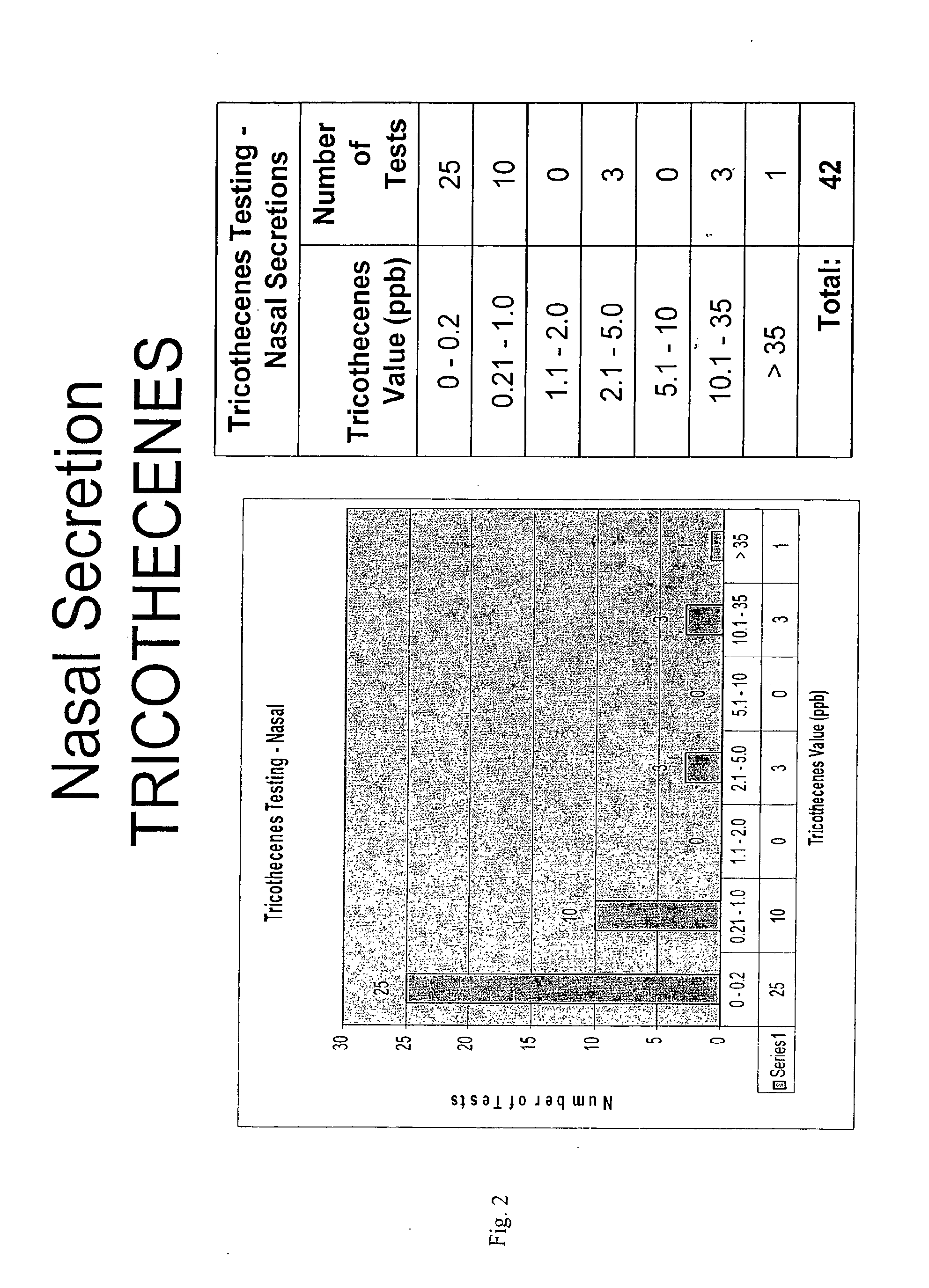
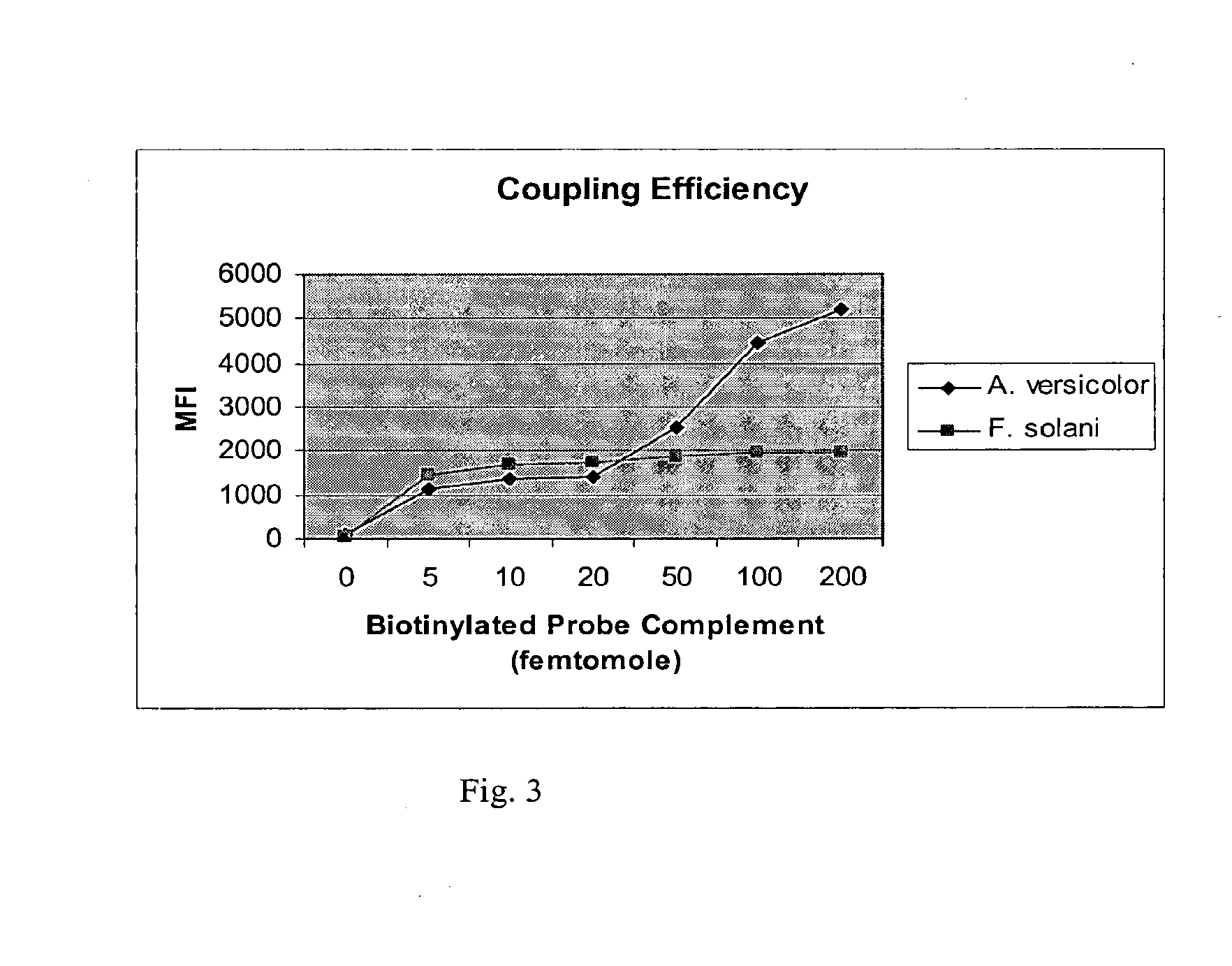
InactiveUS20130183697A1Increased susceptibilityReliable, sensitive, specific, and rapid methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMycotoxinRegimen
The invention relates to a method of identifying a specific fungal species in patient tissue or body fluid. The method comprises the steps of extracting and recovering DNA of the fungal species from the patient tissue or body fluid, amplifying the DNA, hybridizing a probe to the DNA to specifically identify the fungal species, and specifically identifying the fungal species. The invention also relates to a method of identifying a mycotoxin in patient tissue or body fluid. The method comprises the steps of extracting and recovering the mycotoxin from the patient tissue or body fluid, contacting the mycotoxin with an antibody directed against the mycotoxin, and identifying the myocotoxin. Both of these methods can be used to determine if a patient is at risk for or has developed a disease state related to a fungal infection, and to develop an effective treatment regimen for the patient.
Owner:ADVATECT DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Method for rapid thermal cycling of biological samples
InactiveUS20010007759A1Thermal massHigh yieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAmplification dnaTime profile
A thermal cycling method and device is disclosed. The device comprises a sample chamber whose temperature can be rapidly and accurately modulated over a range of temperatures needed to carry out a number of biological procedures, such a the DNA polymerase chain reaction. Biological samples are placed in glass micro capillary tubes and then located inside the sample chamber. A programmable controller regulates the temperature of the sample inside the sample chamber. Once a heating cycle is completed, the controller opens a door to the chamber for venting hot air out and cool ambient air is moved in. Temperature versus time profiles corresponding to optimum denaturation, annealing and elongation temperatures for amplification of DNA are achieved by the present invention.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com