Patents
Literature
69 results about "Primer binding site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
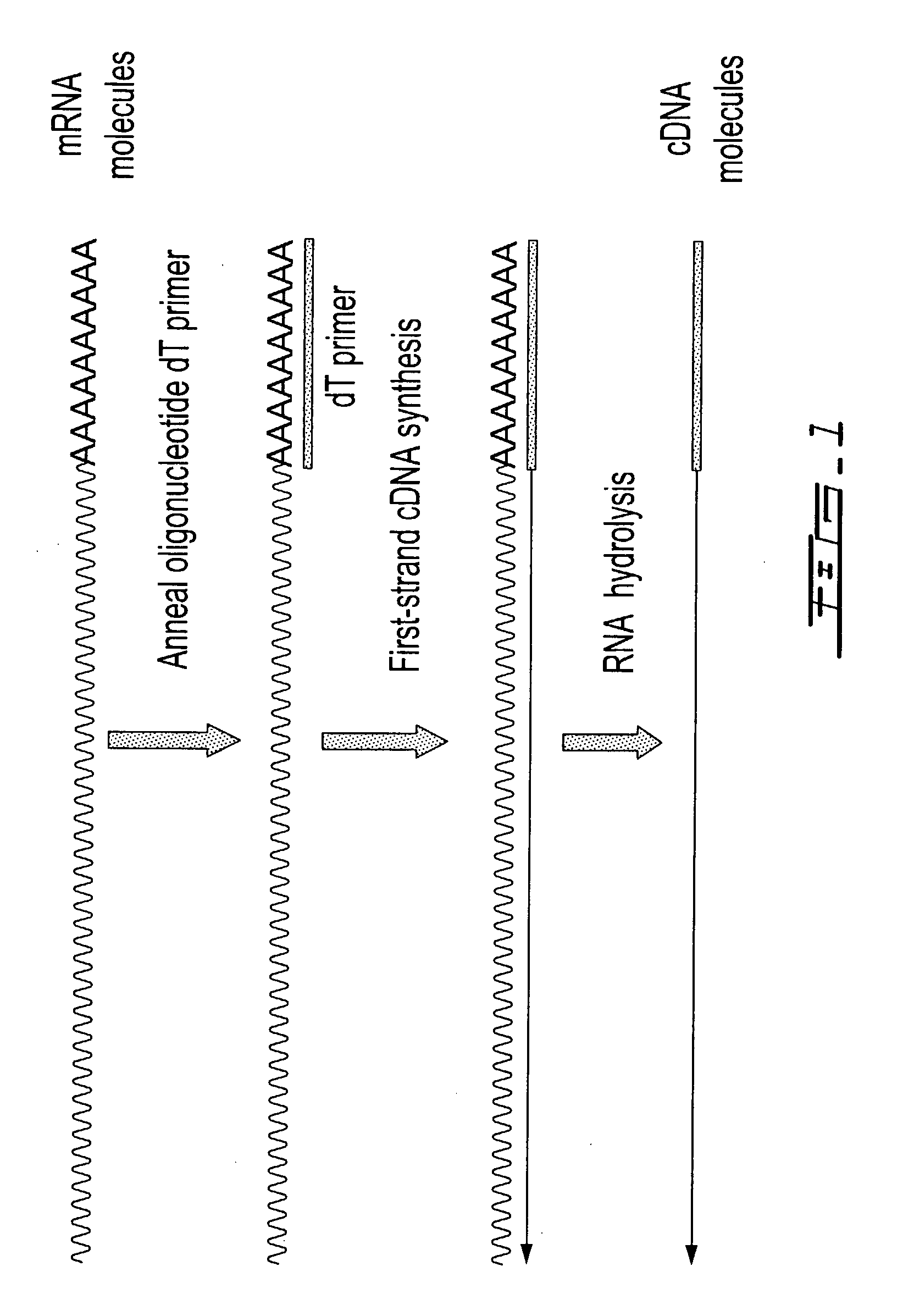
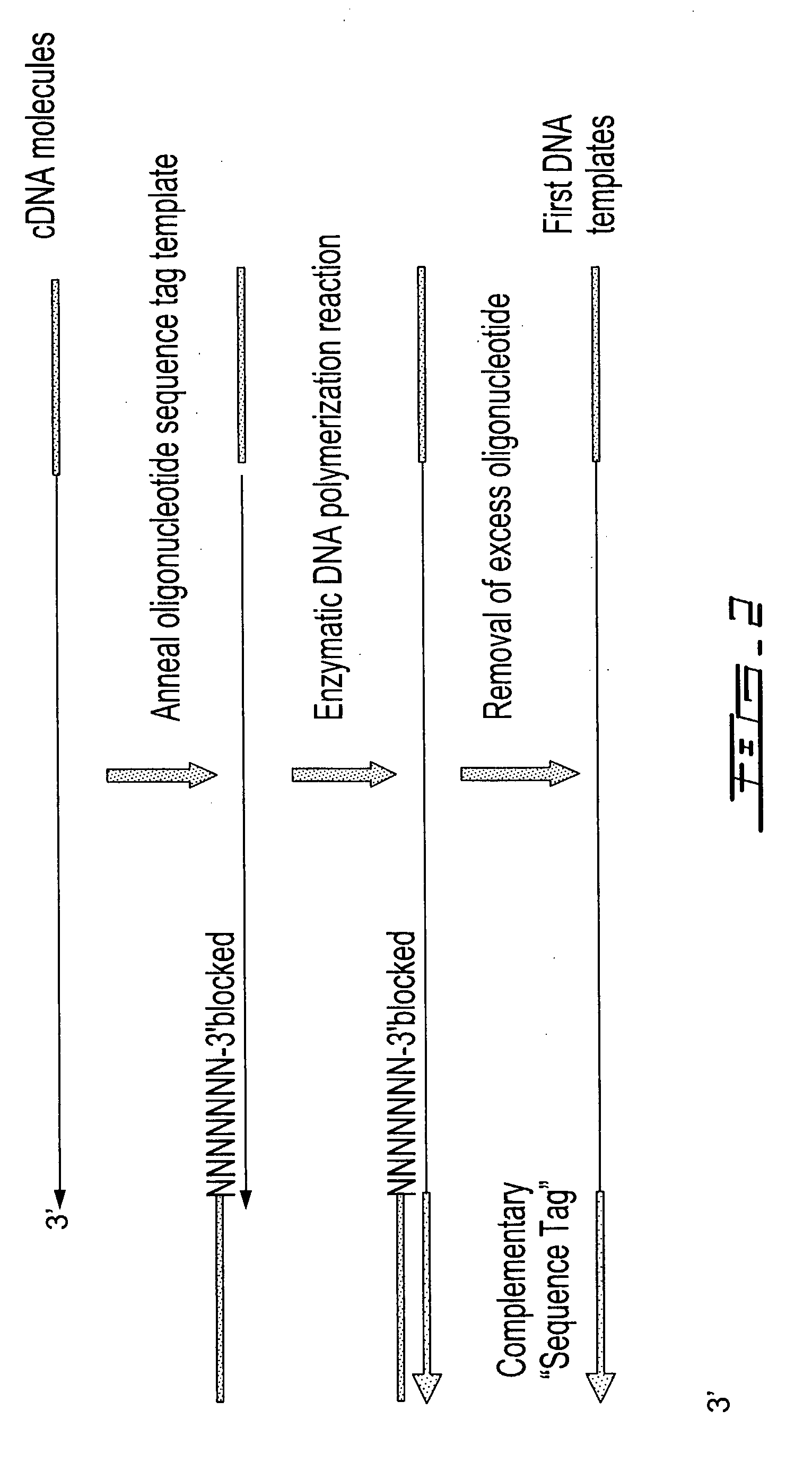
A primer binding site is a region of a nucleotide sequence where an RNA or DNA single-stranded primer binds to start replication. The primer binding site is on one of the two complementary strands of a double-stranded nucleotide polymer, in the strand which is to be copied, or is within a single-stranded nucleotide polymer sequence.
Ola-Based Methods for the Detection of Target Nucleic Avid Sequences
InactiveUS20070269805A1Low costSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical compoundGenomic clone
Owner:KEYGENE NV
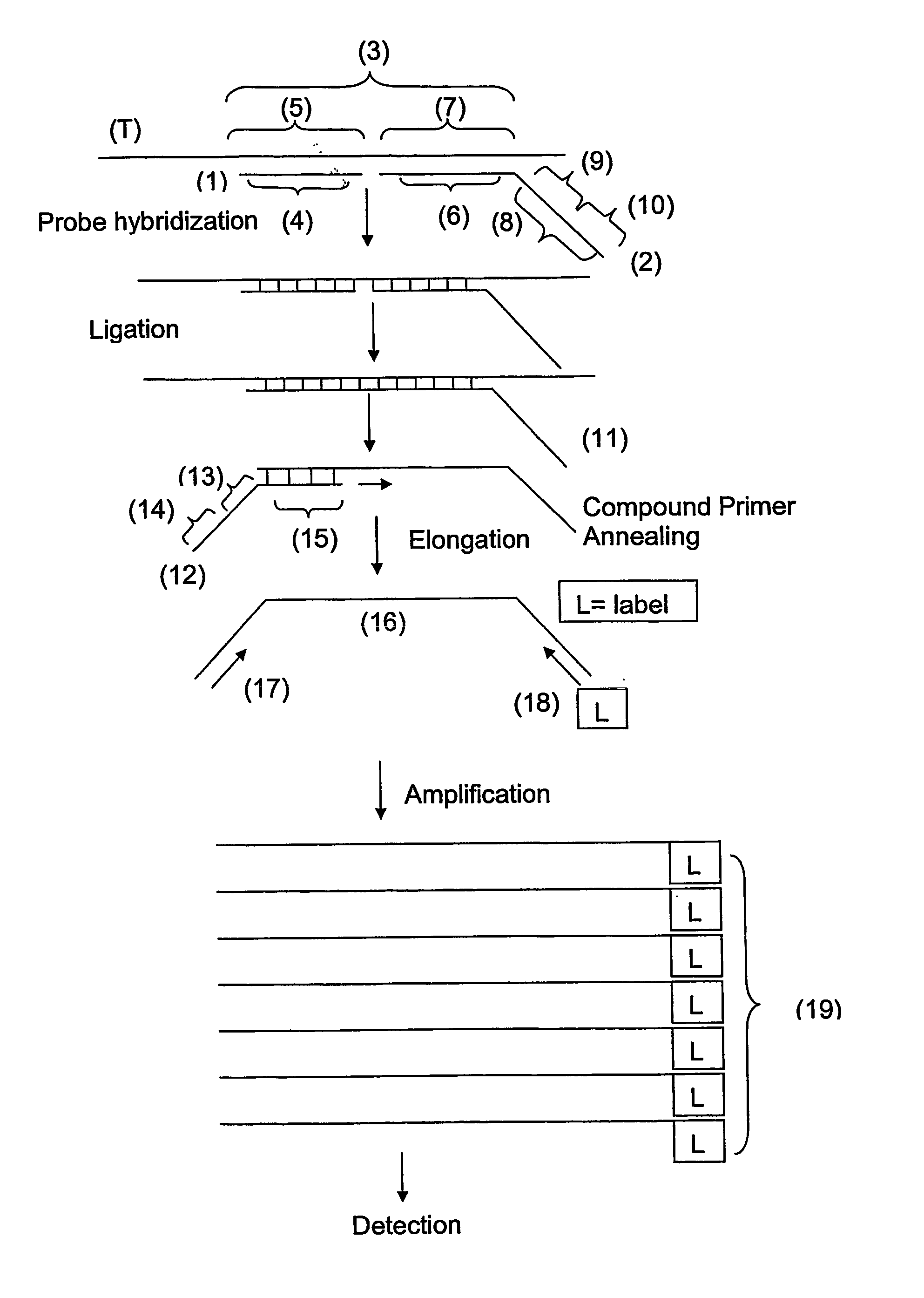
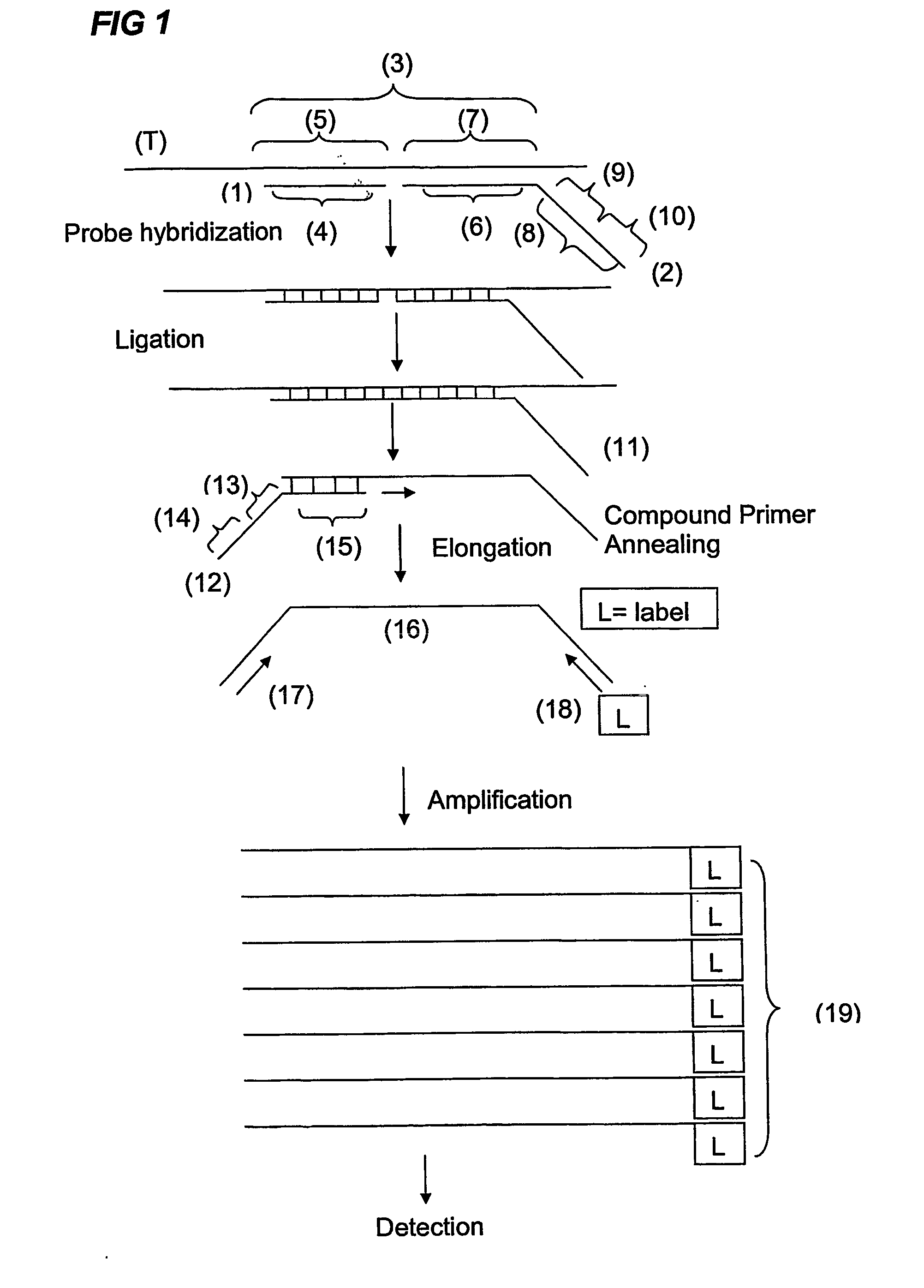
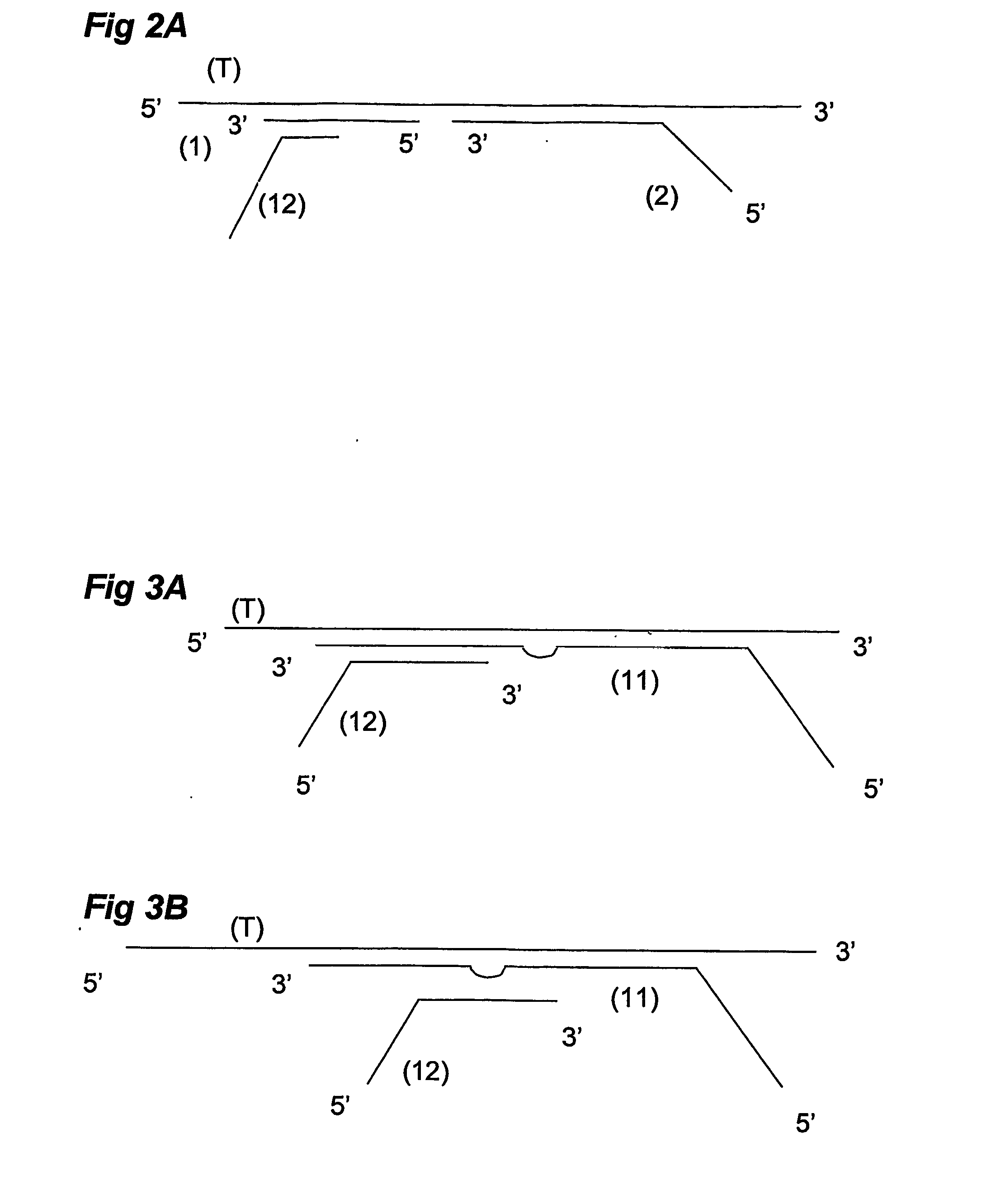
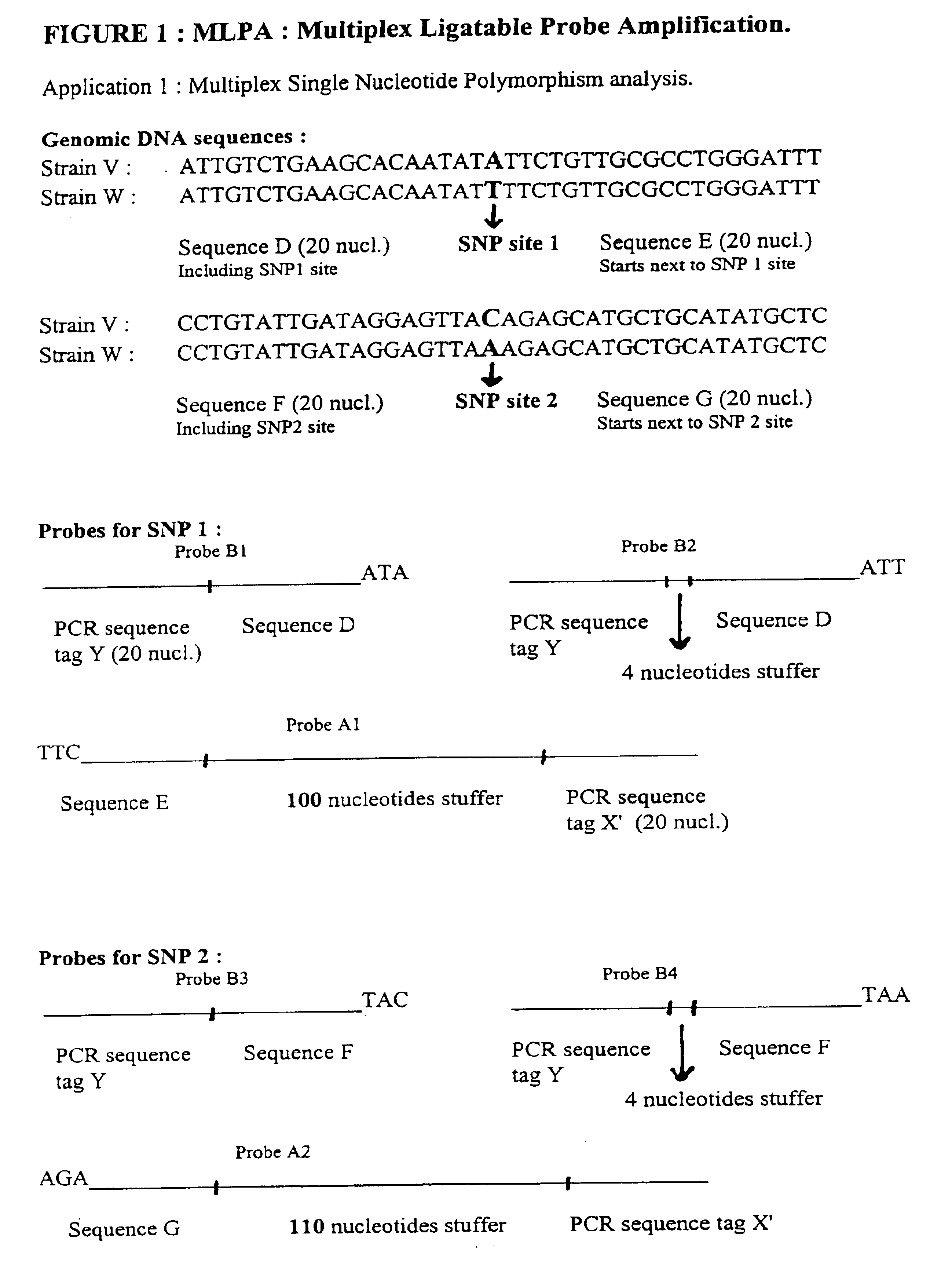
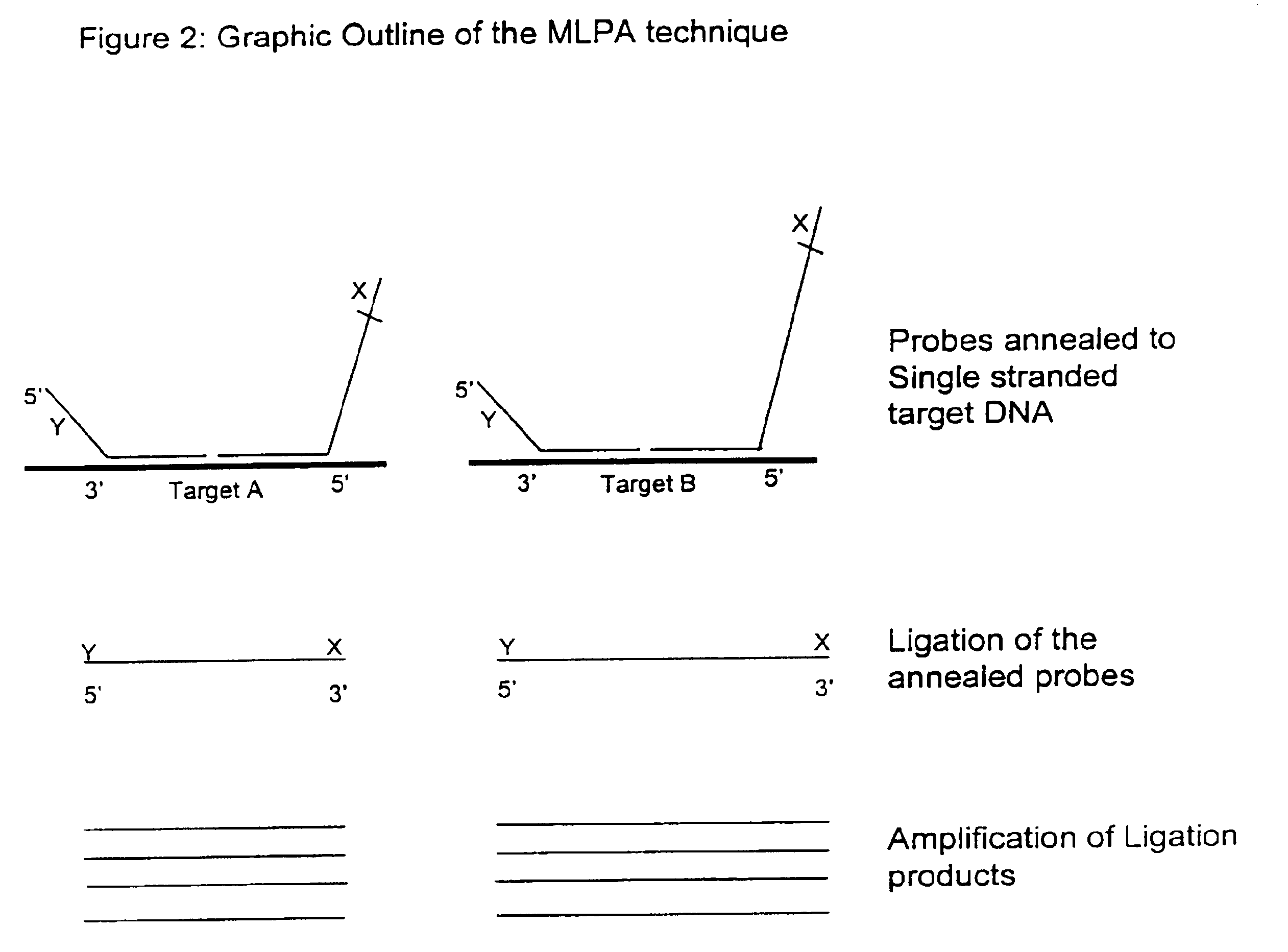
Multiplex ligatable probe amplification
InactiveUS6955901B2Reduce the amount requiredIncrease the molar ratioSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding siteNucleic acid sequencing
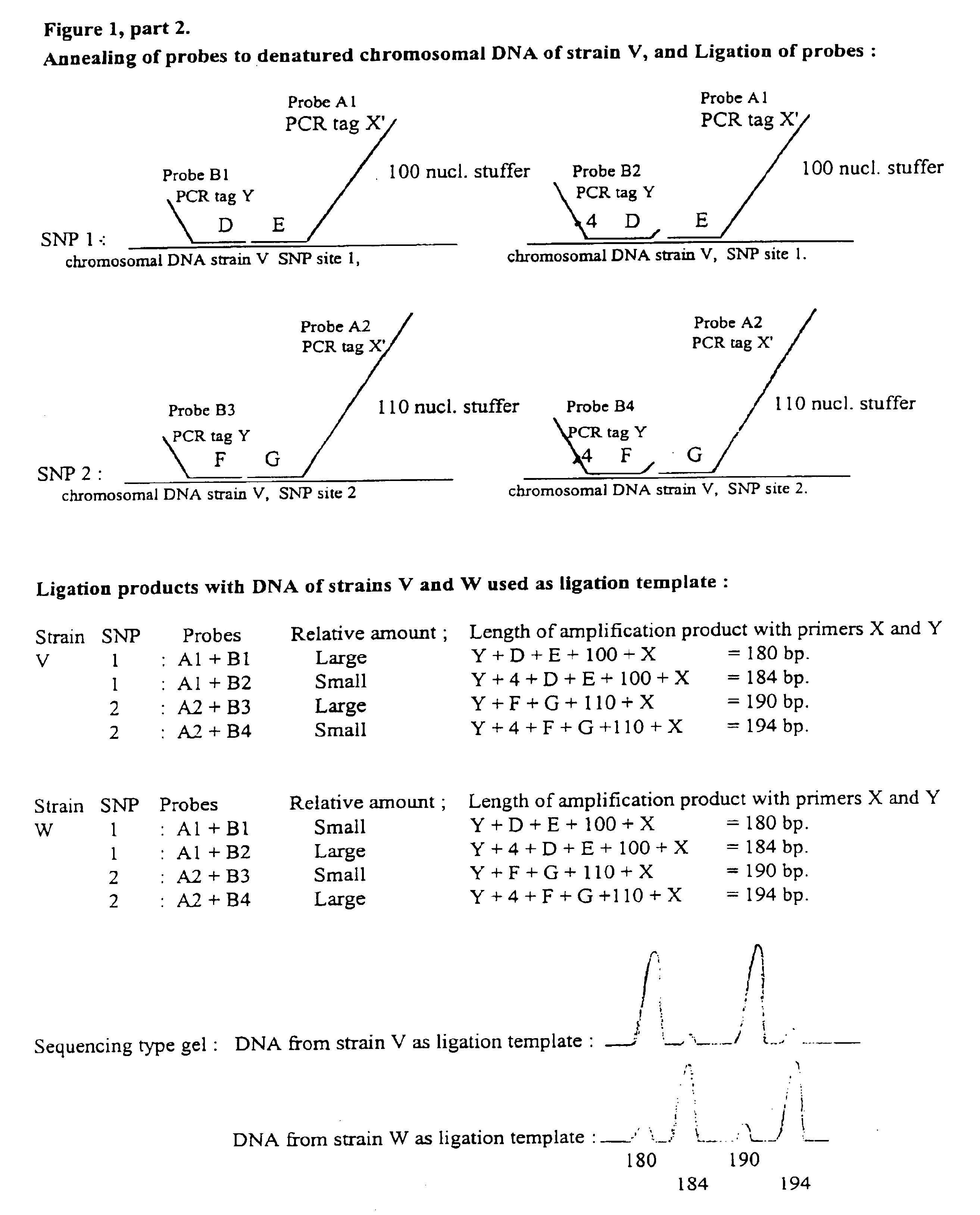
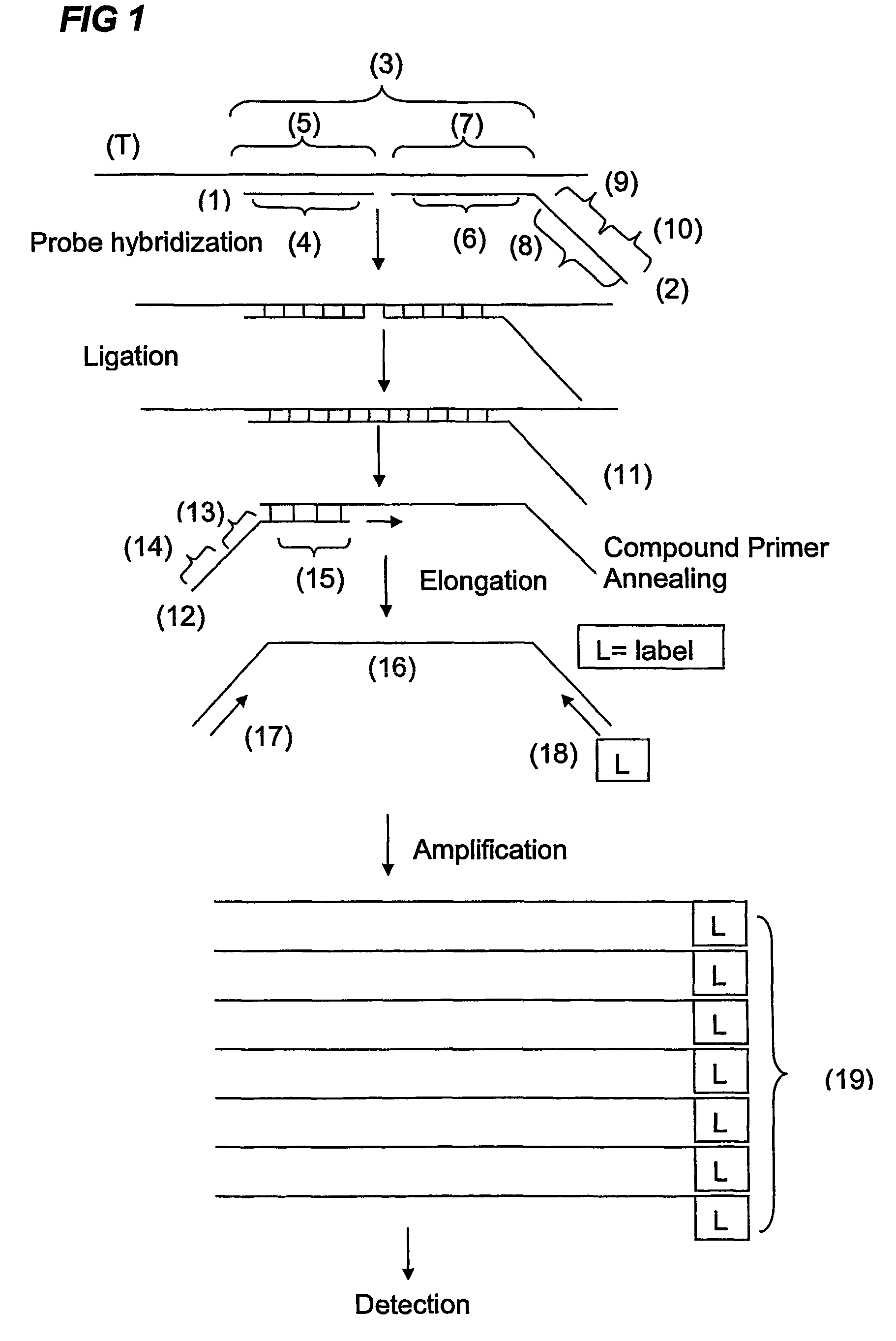
Described is an improved multiplex ligation-dependent amplification method for detecting the presence and quantification of at least one specific single stranded target nucleic acid sequence in a sample using a plurality of probe sets of at least two probes, each of which includes a target specific region and a non-complementary region comprising a primer binding site. The probes belonging to the same set are ligated together when hybridised to the target nucleic acid sequence and amplified by a suitable primer set. By using a femtomolar amount of the probes a large number of different probe sets can be used to simultaneously detect and quantify a corresponding large number of target sequences with high specificity.
Owner:DE LUWE HOEK OCTROOIEN
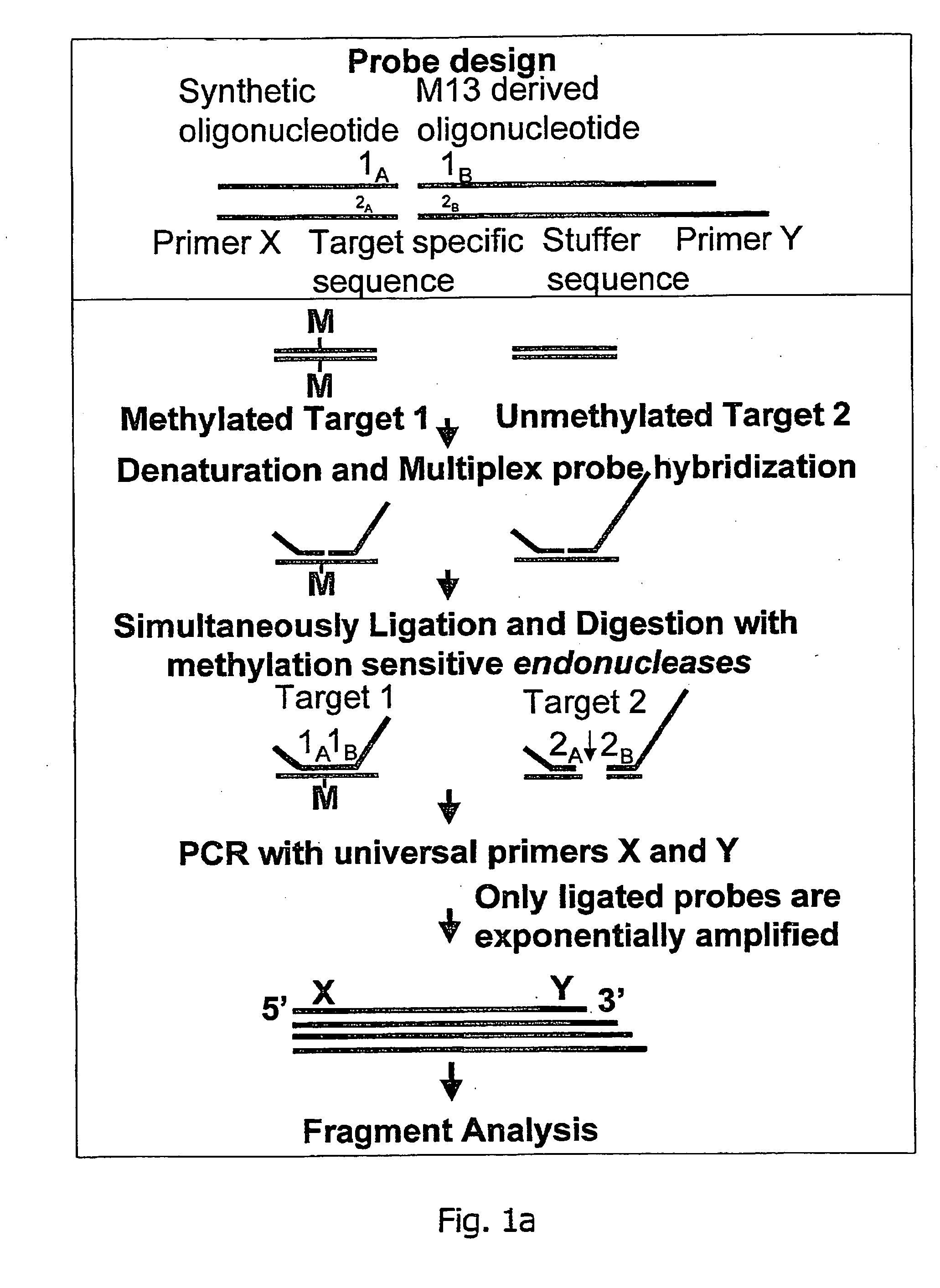
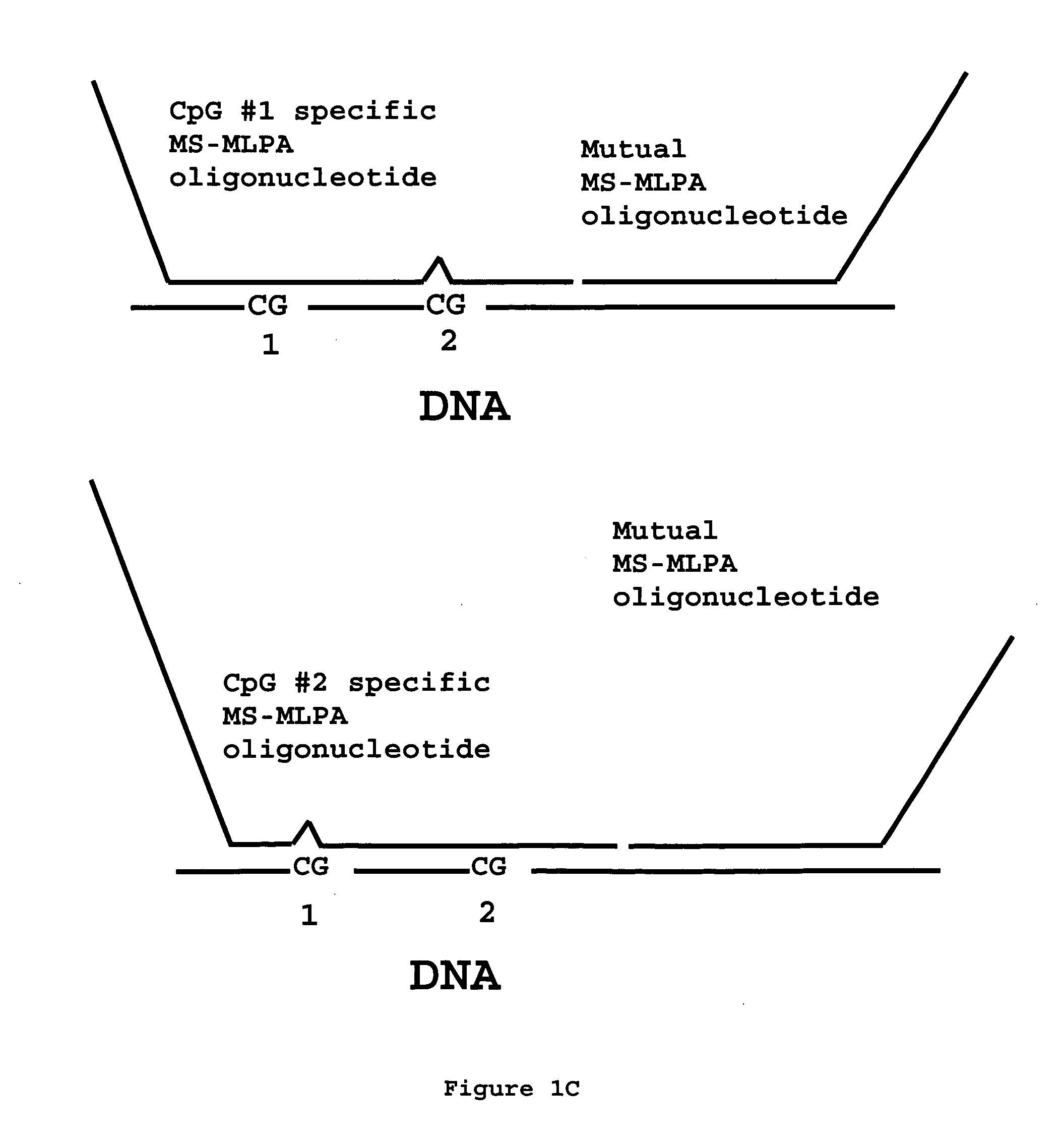
Methylation specific multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MS-MLPA)
InactiveUS20070092883A1Rapid and easy to applyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMultiplex ligation-dependent probe amplificationNucleic acid sequencing
An improved multiplex ligation-dependent amplification method is disclosed for detecting the presence of specific methylated sites in a single stranded target nucleic acid, while simultaneously, the quantification of the target nucleic acid sequence can be performed, using a plurality of probe sets of at least two probes, each of which includes a target specific region and non-complementary region containing a primer binding site. At least one of the probes further includes the sequence of one of the strands of a double stranded recognition site of a methylation sensitive restriction enzyme. The probes belonging to the same set are ligated together when hybridised to the target nucleic acid sequence, the hybrid is subjected to digestion by the methylation sensitive restriction enzyme, resulting in non-methylated recognition sites being cleaved. The probes of the uncleaved (methylated) hybrid are subsequently amplified by a suitable primer set.
Owner:DE LUWE HOEK OCTROOIEN
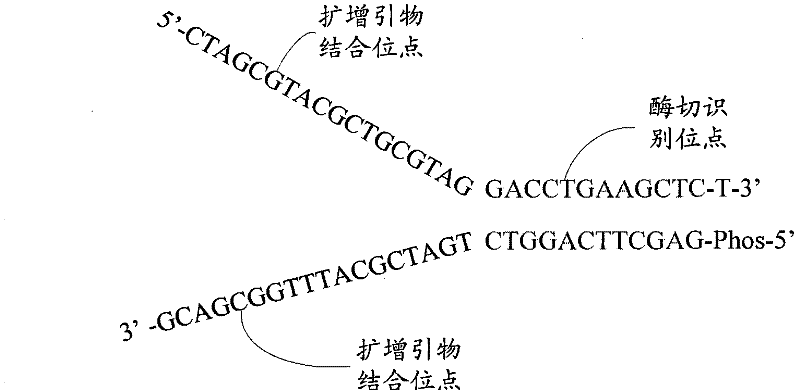
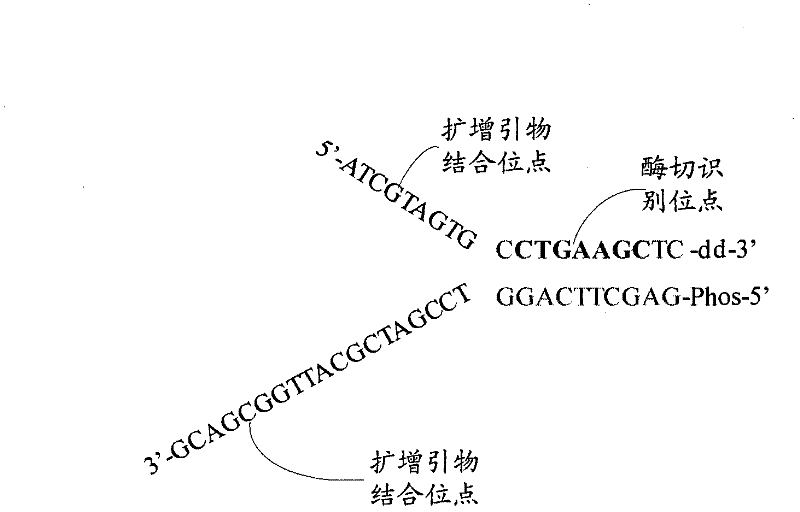
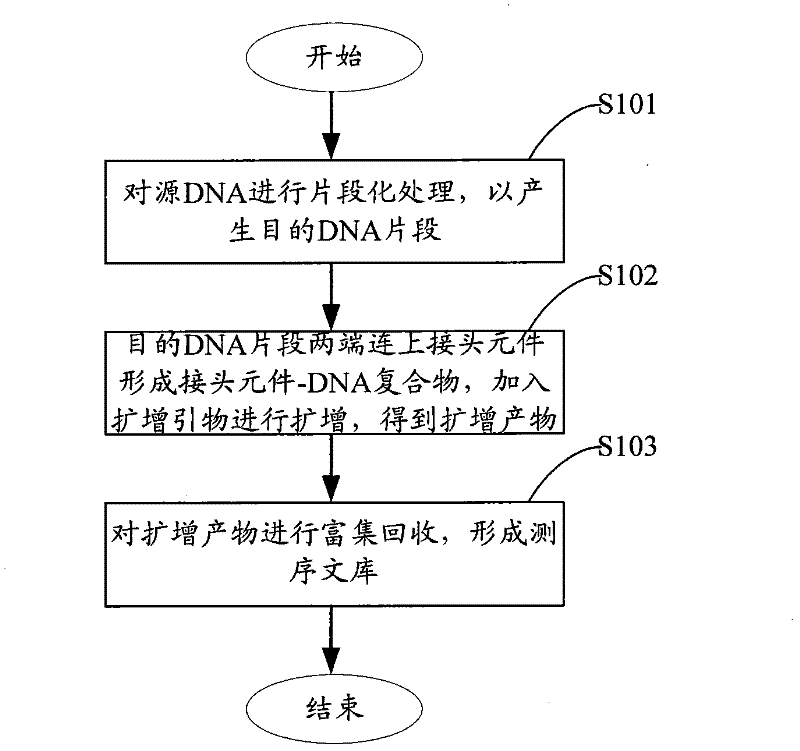
Systems and methods for constructing sequencing libraries
ActiveCN102296065AAvoid self-connectionEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBinding siteDNA fragmentation
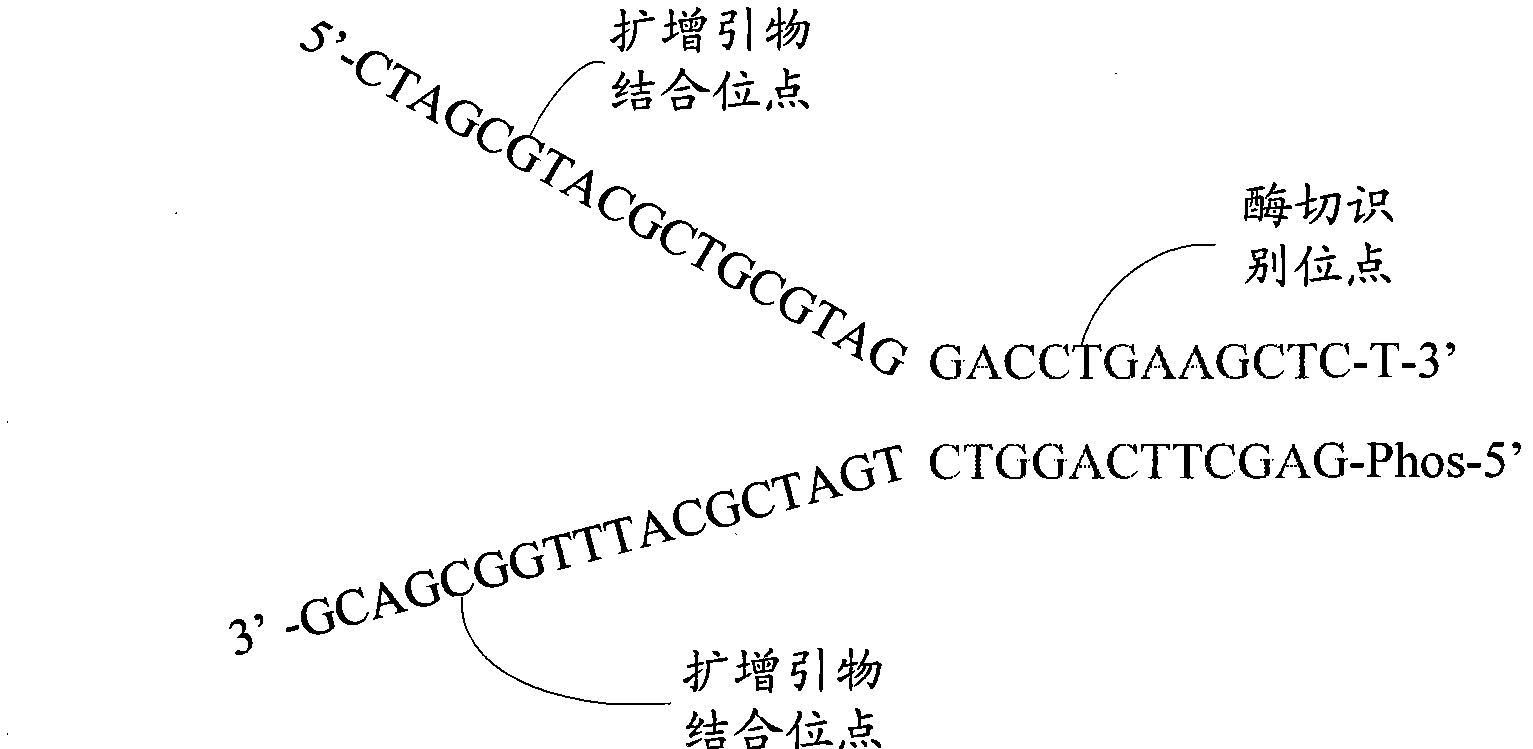
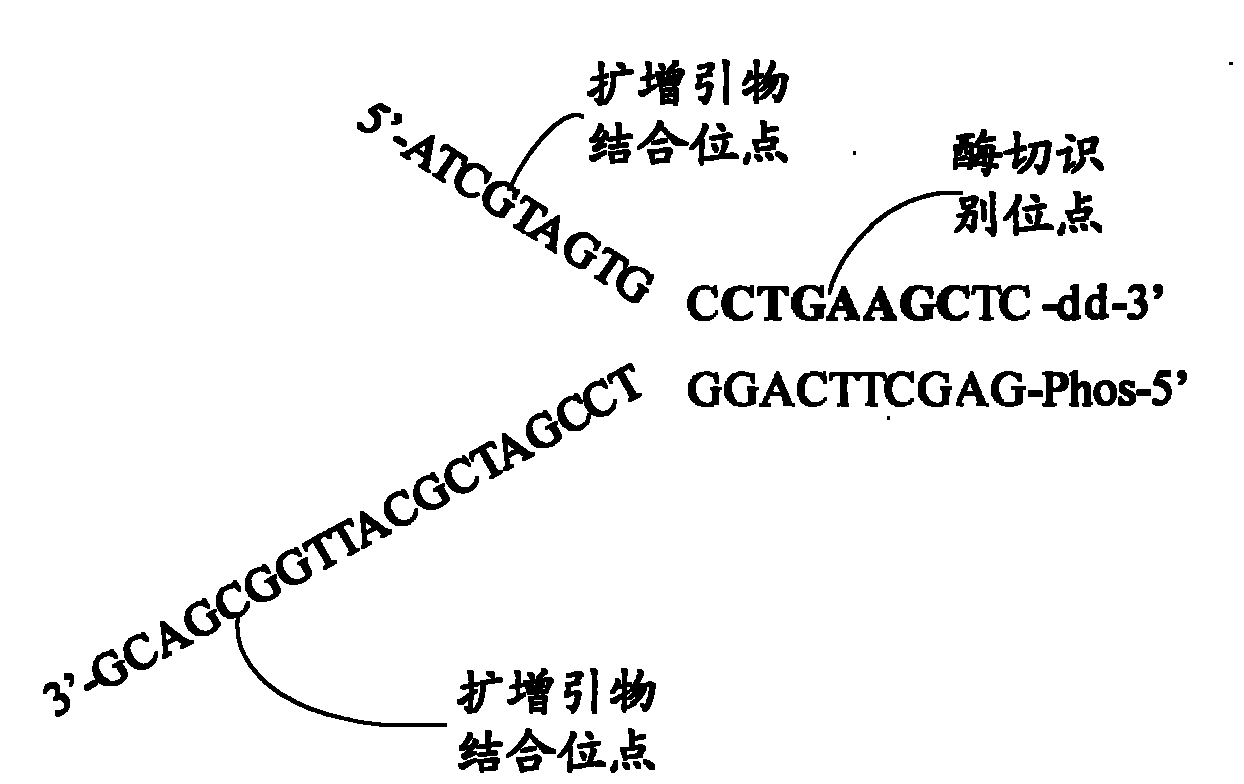
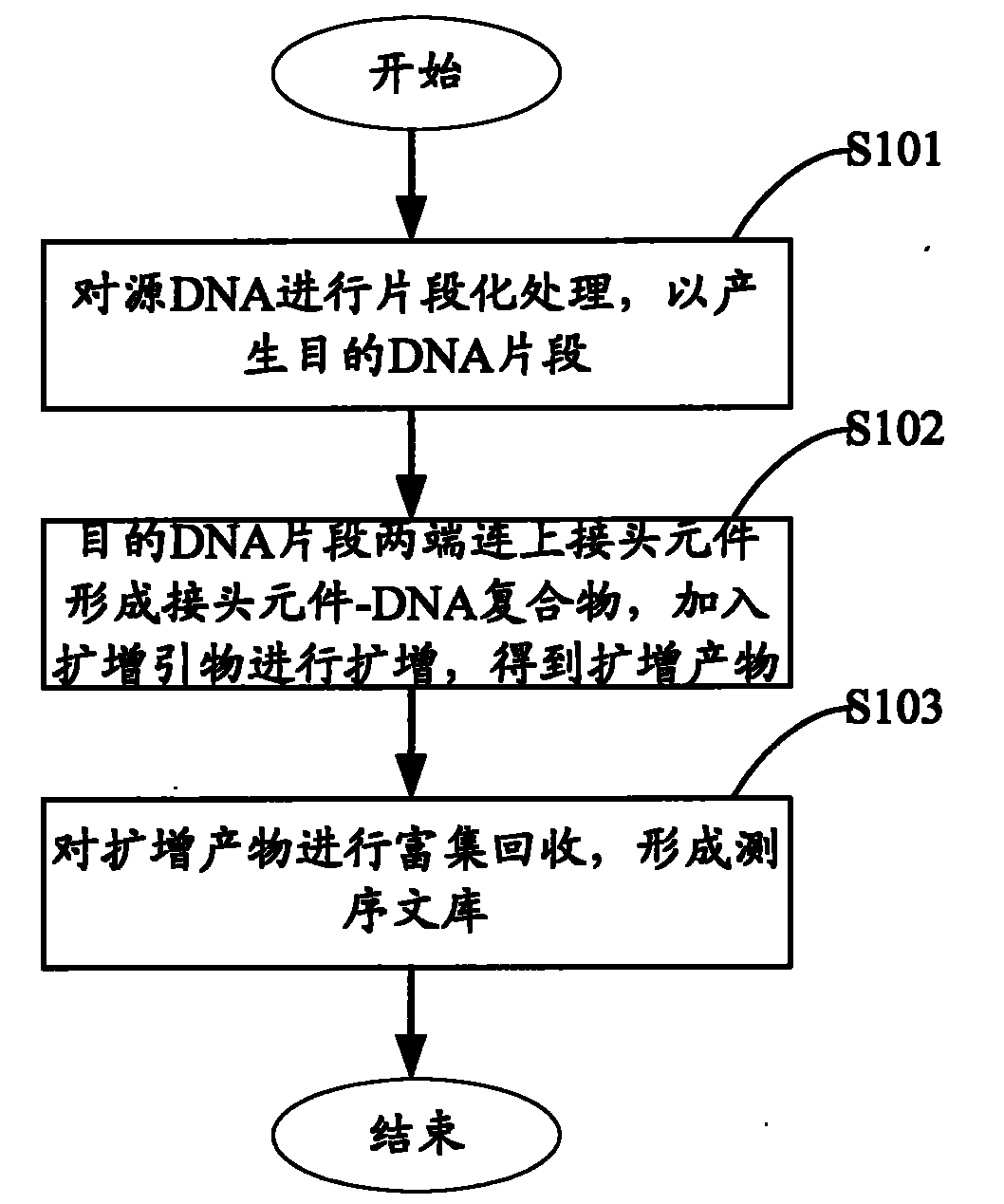
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, and provides a system and a method for constructing a sequencing library. The system and the method comprise a joint element and a method for applying the joint element to the construction of a sequencing library. The joint element is a bifurcate double-chain nucleic acid joint with a bifurcate region and a paired region orderly included at the 5' and the 3' ends, wherein two single chains of the bifurcate region respectively comprise at least one amplification primer binding site, and the paired region comprises at least one restrictionenzyme site. The joint element of the invention can prevent the self-connection phenomenon of the joint element and the occurrence of a non-object joint element-DNA fragment compound during the library construction.
Owner:WUHAN CONSIDERIN GENE & HEALTH TECH CO LTD
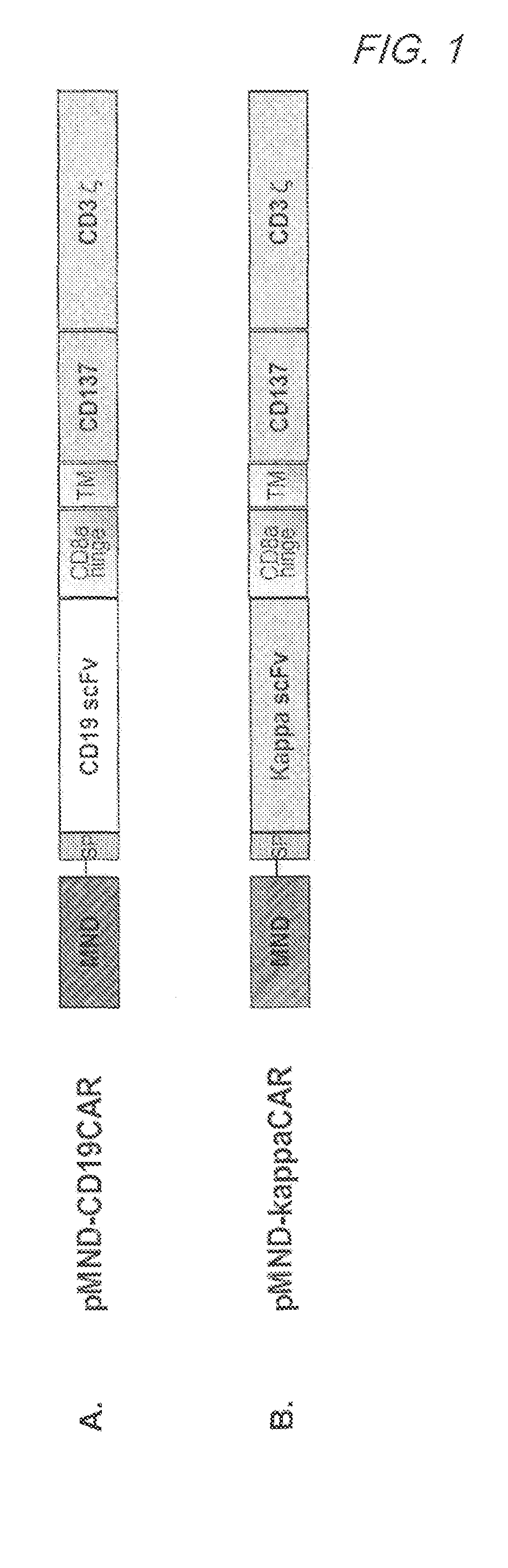
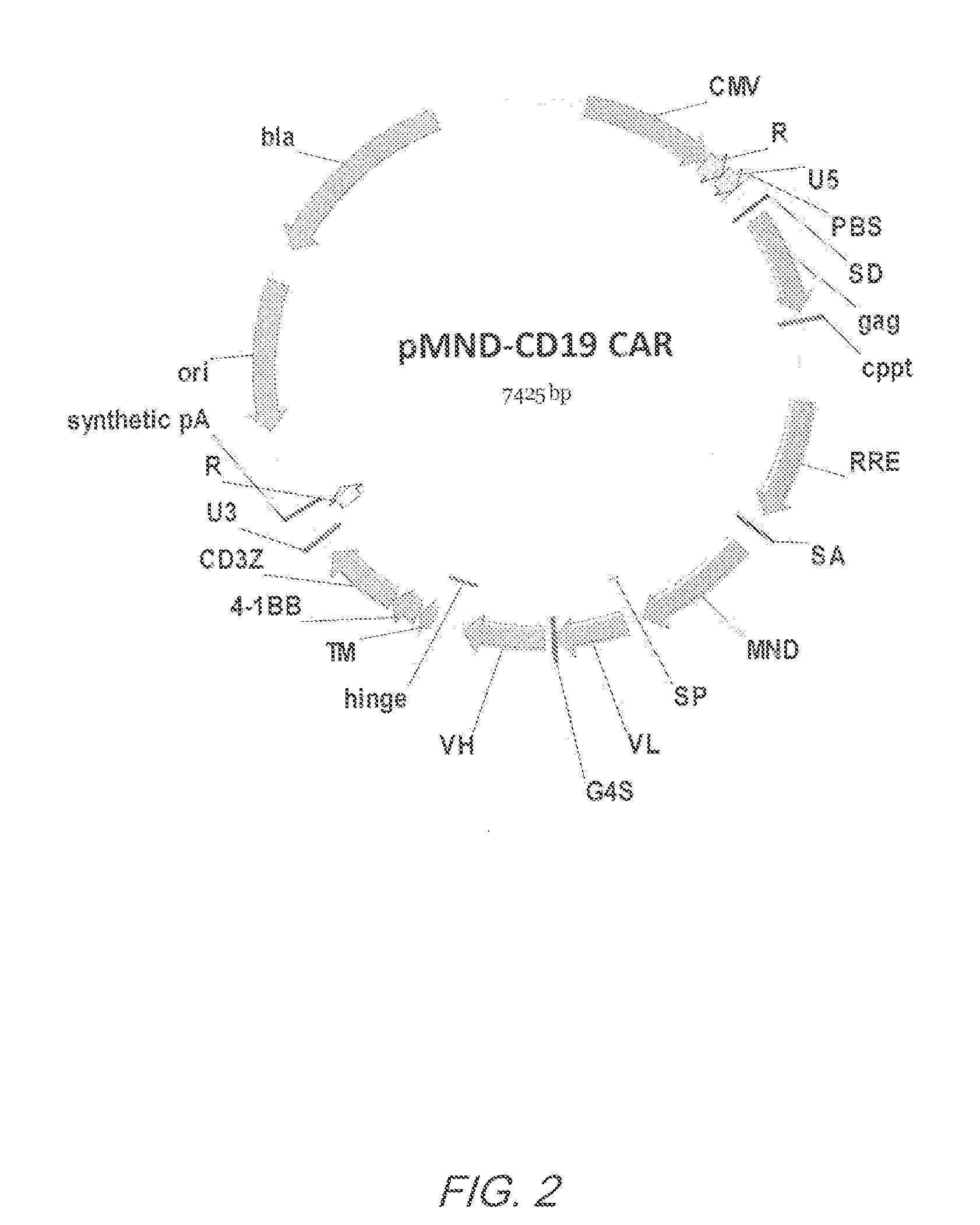
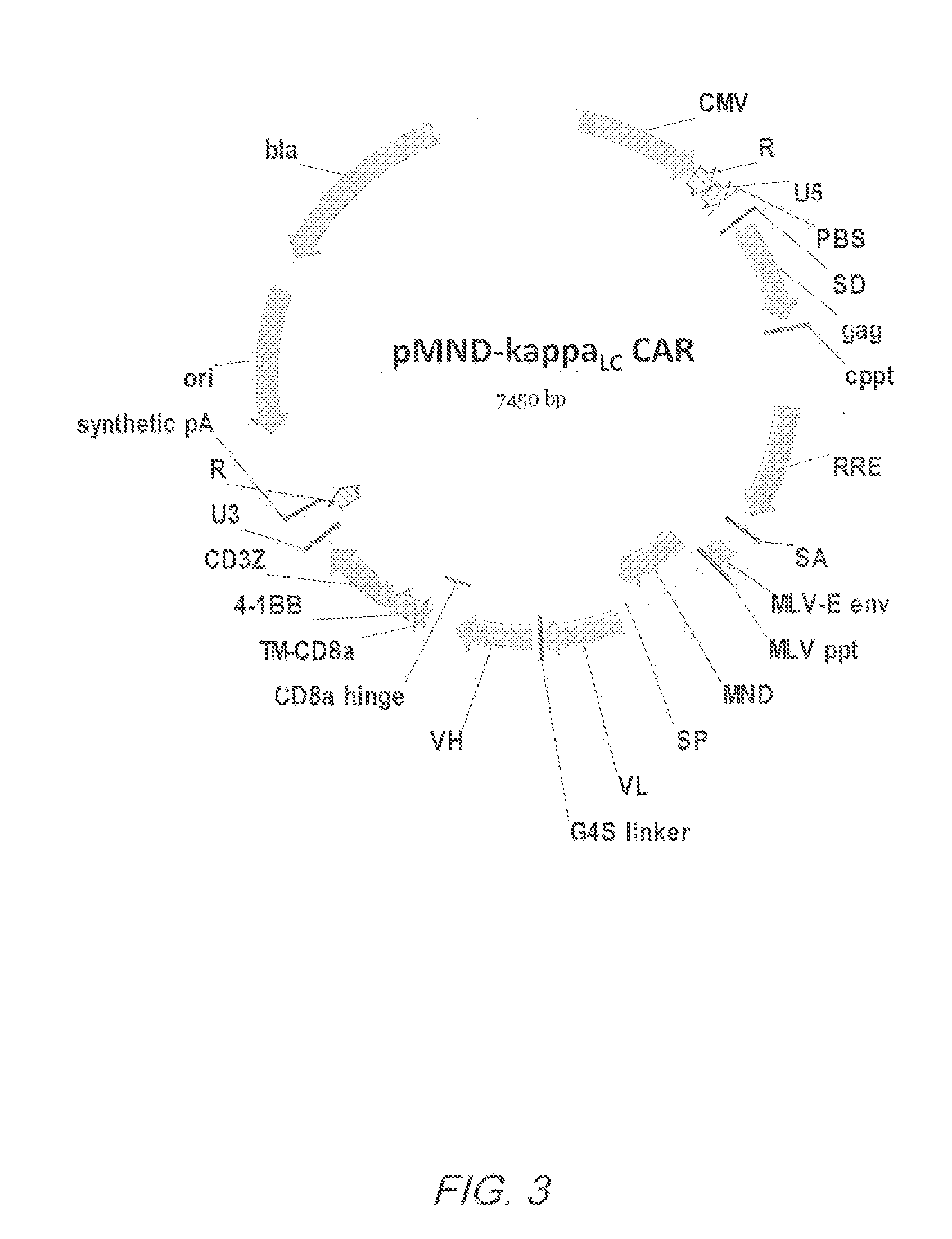
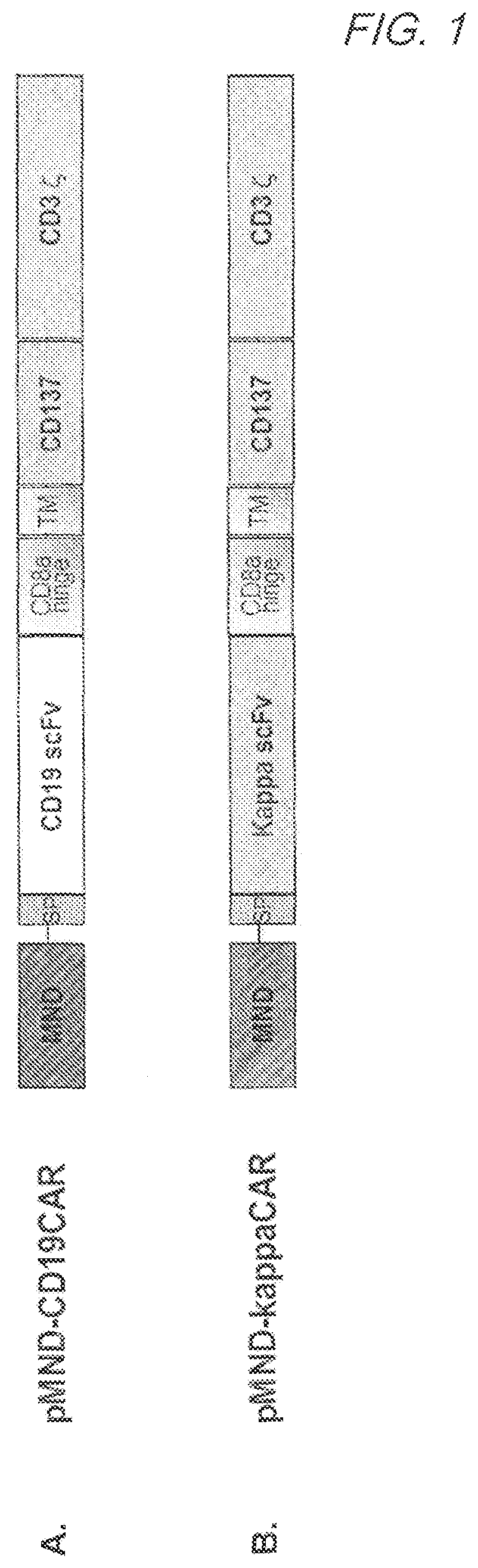
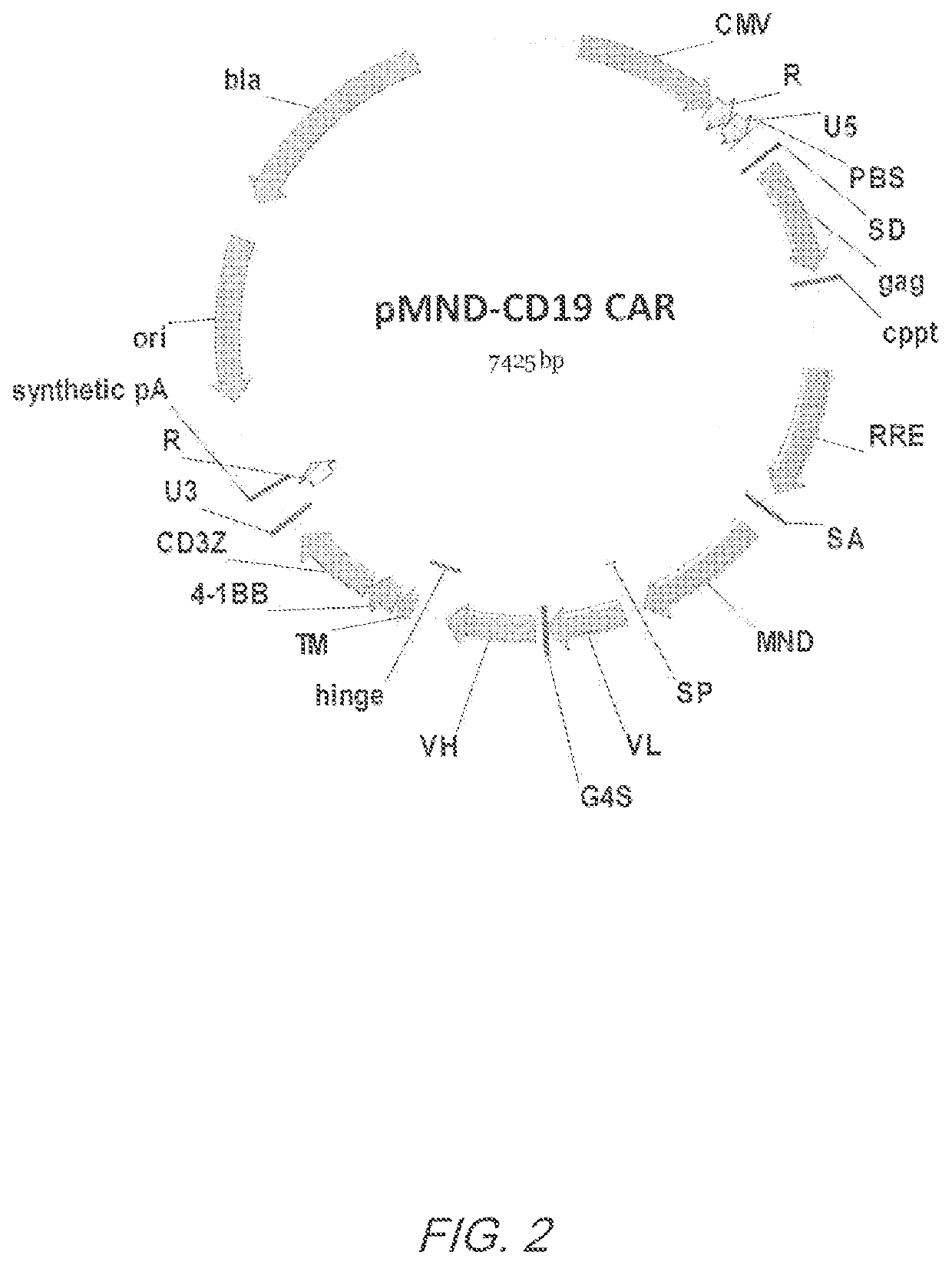
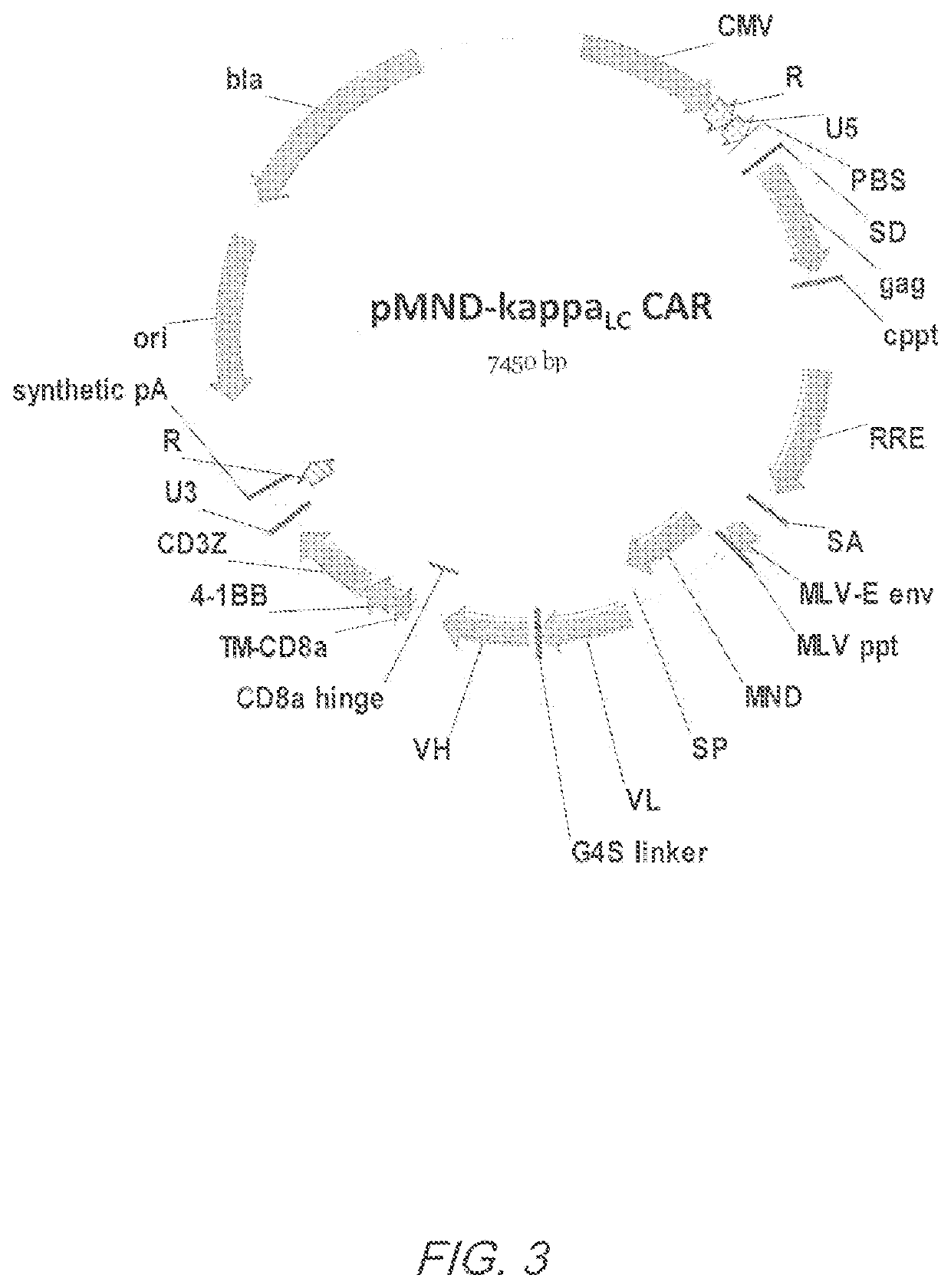
Mnd promoter chimeric antigen receptors
ActiveUS20170051308A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsBinding siteAntigen receptors
Vector compositions comprising a myeloproliferative sarcoma virus enhancer, negative control region deleted, dl587rev primer-binding site substituted (MND) promoter operably linked to a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) are provided.
Owner:2SEVENTY BIO INC
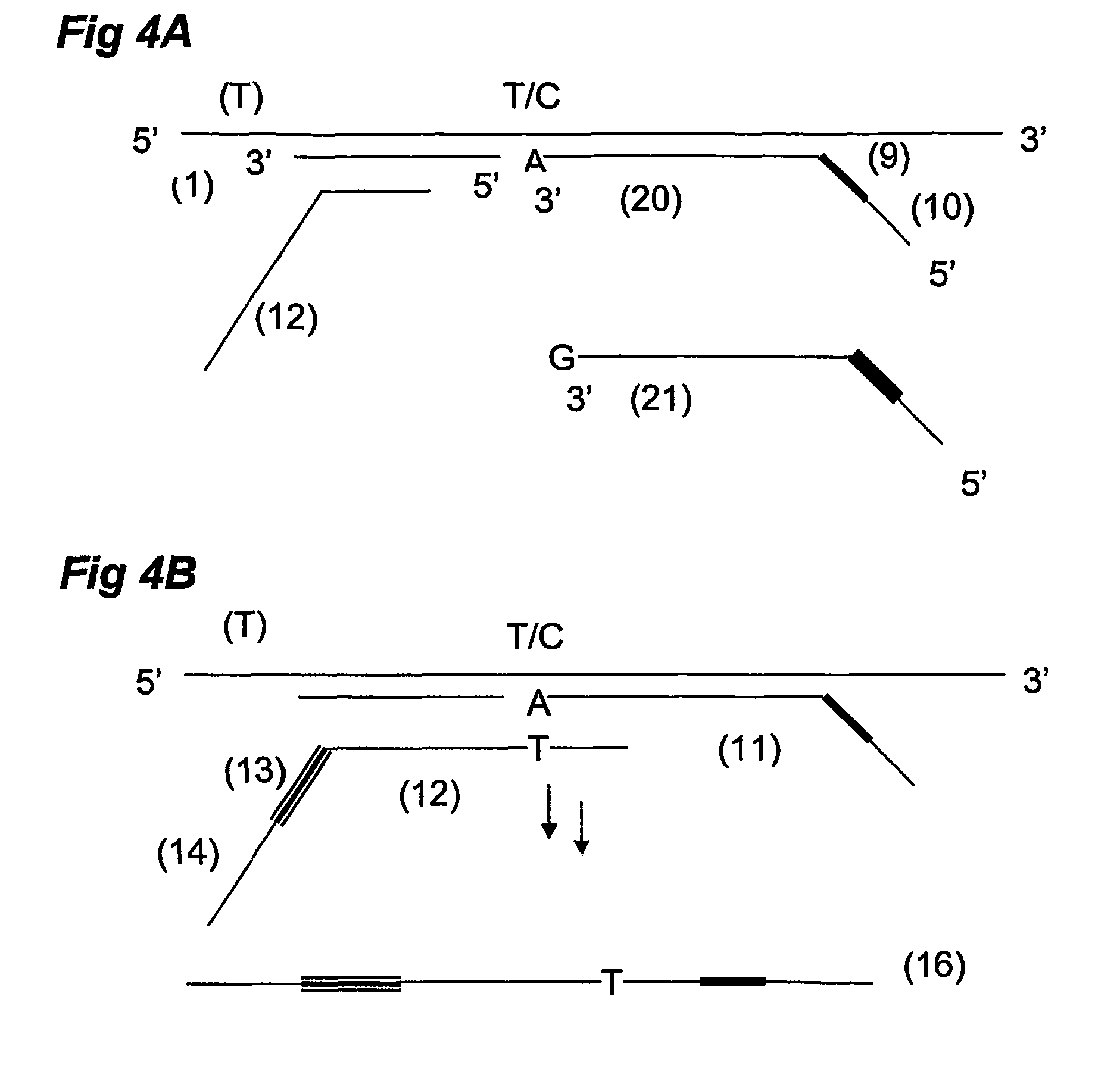
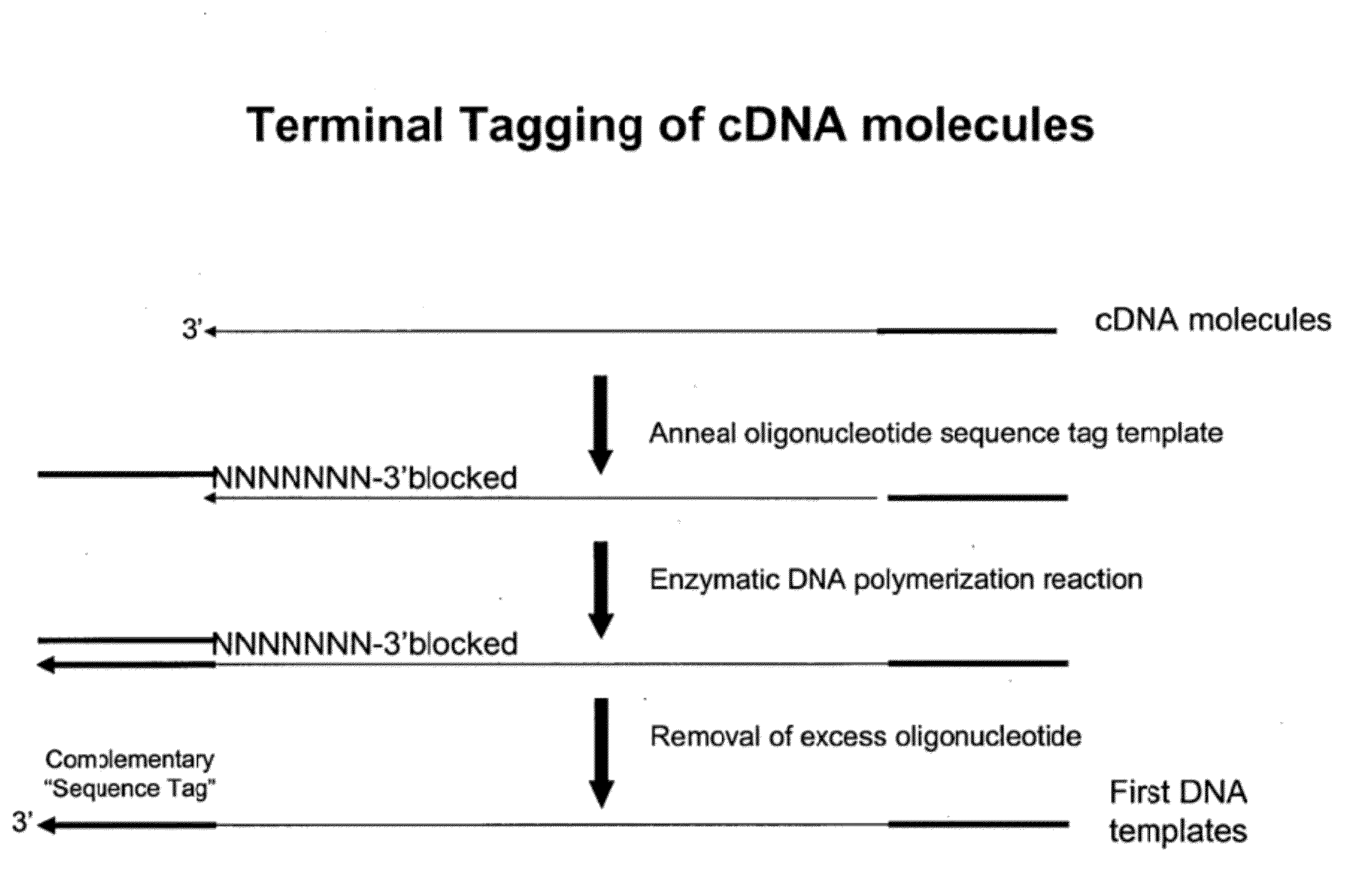
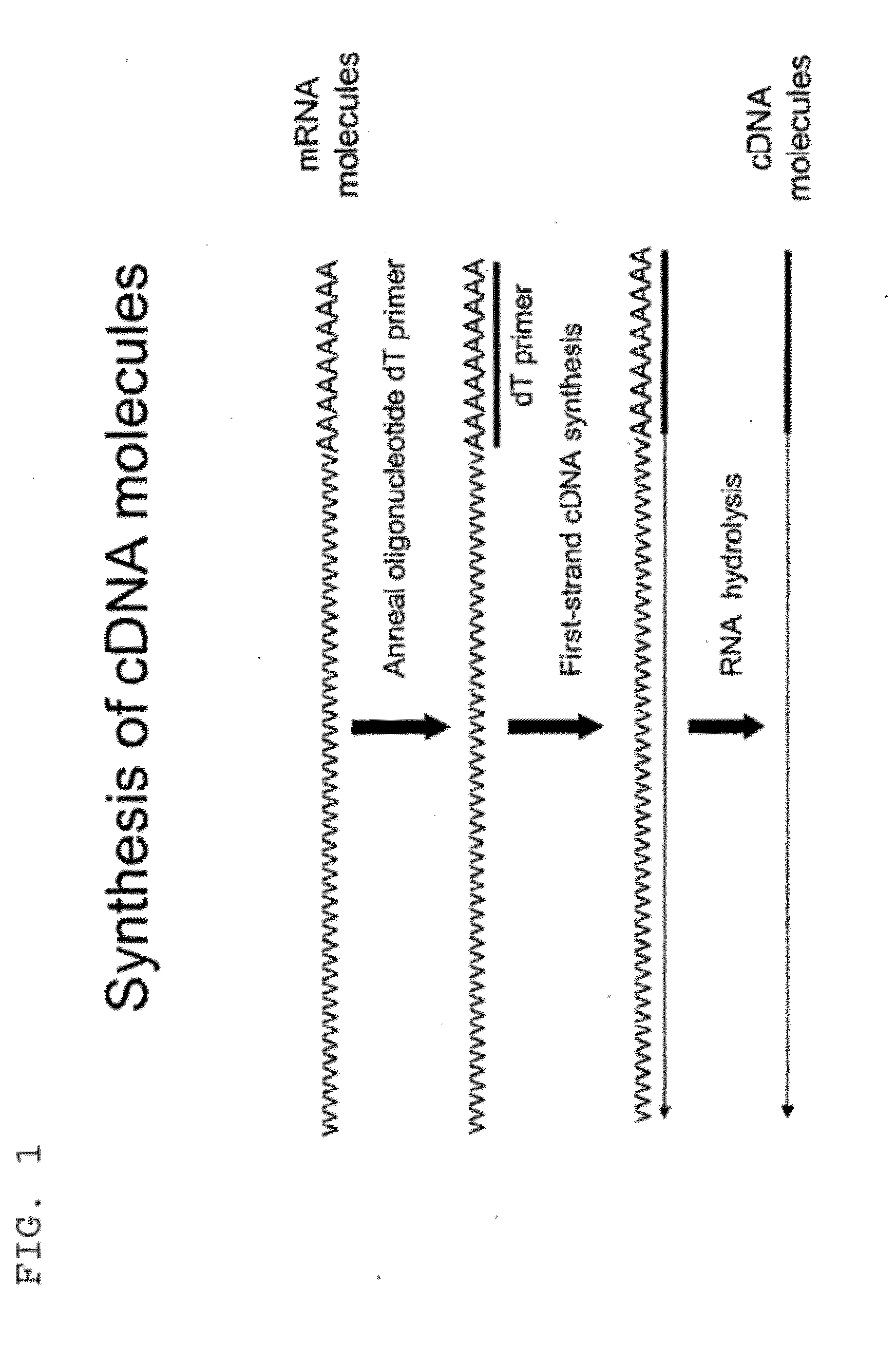
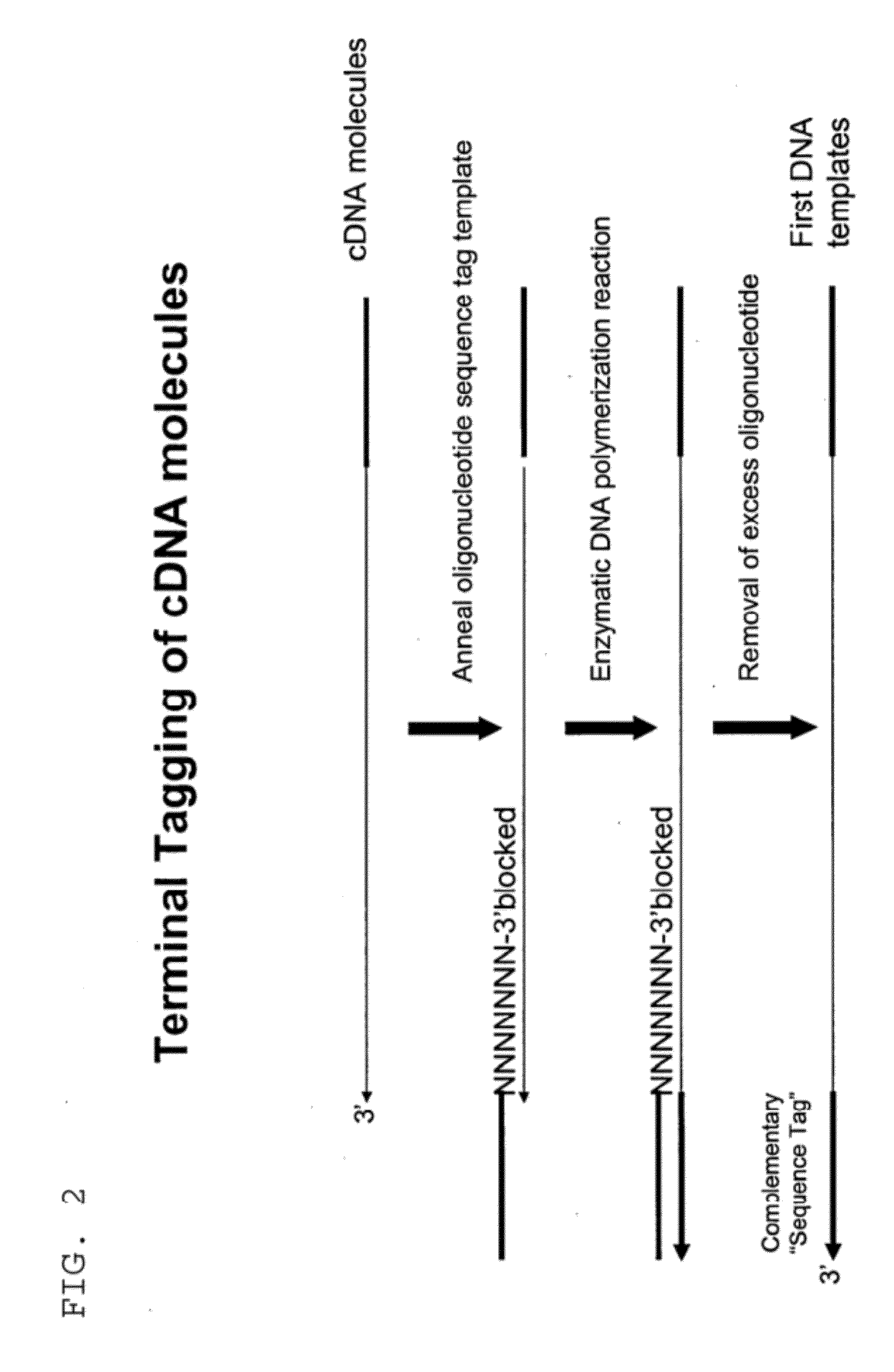
Selective terminal tagging of nucleic acids
ActiveUS8304183B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification dnaComplete sequence
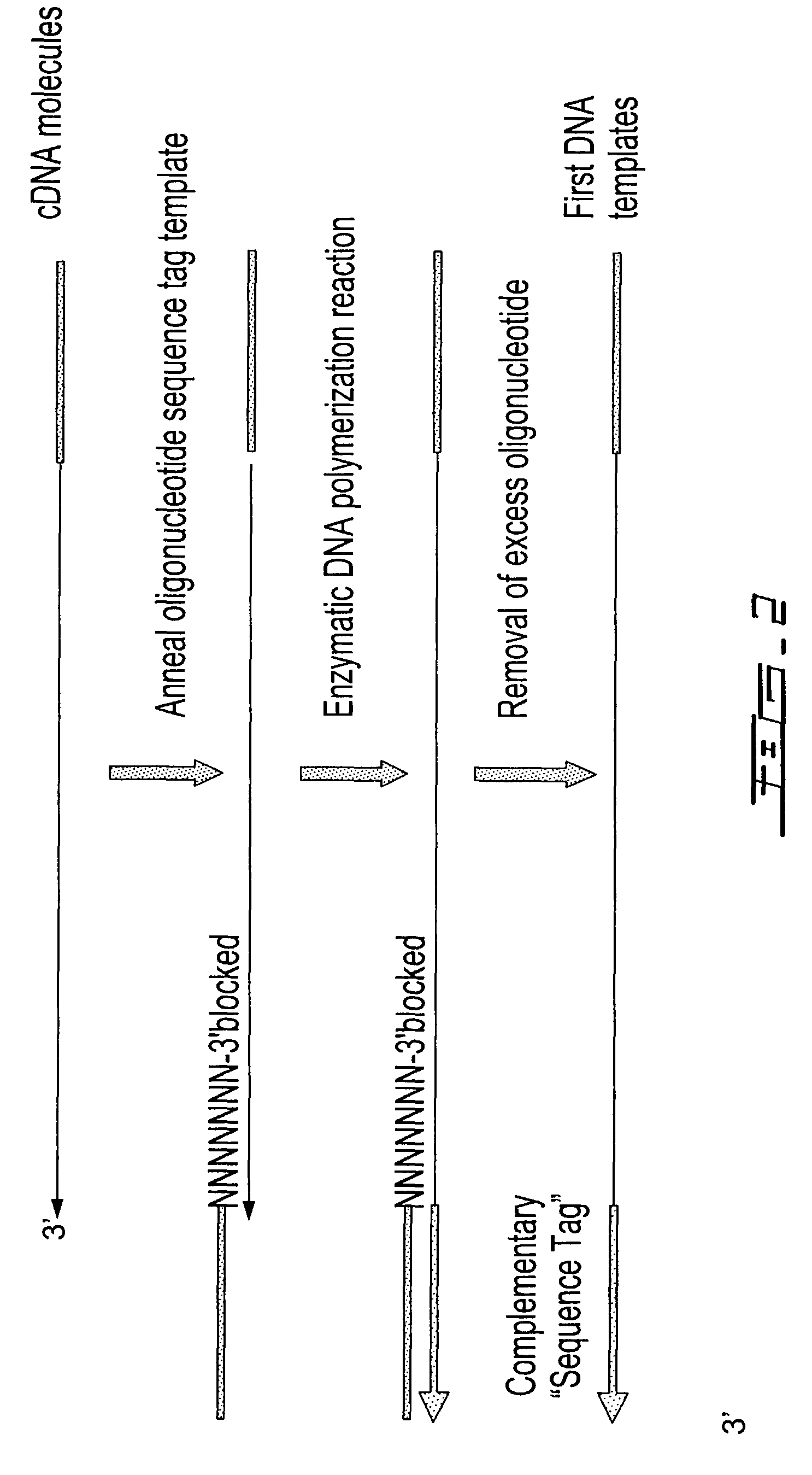
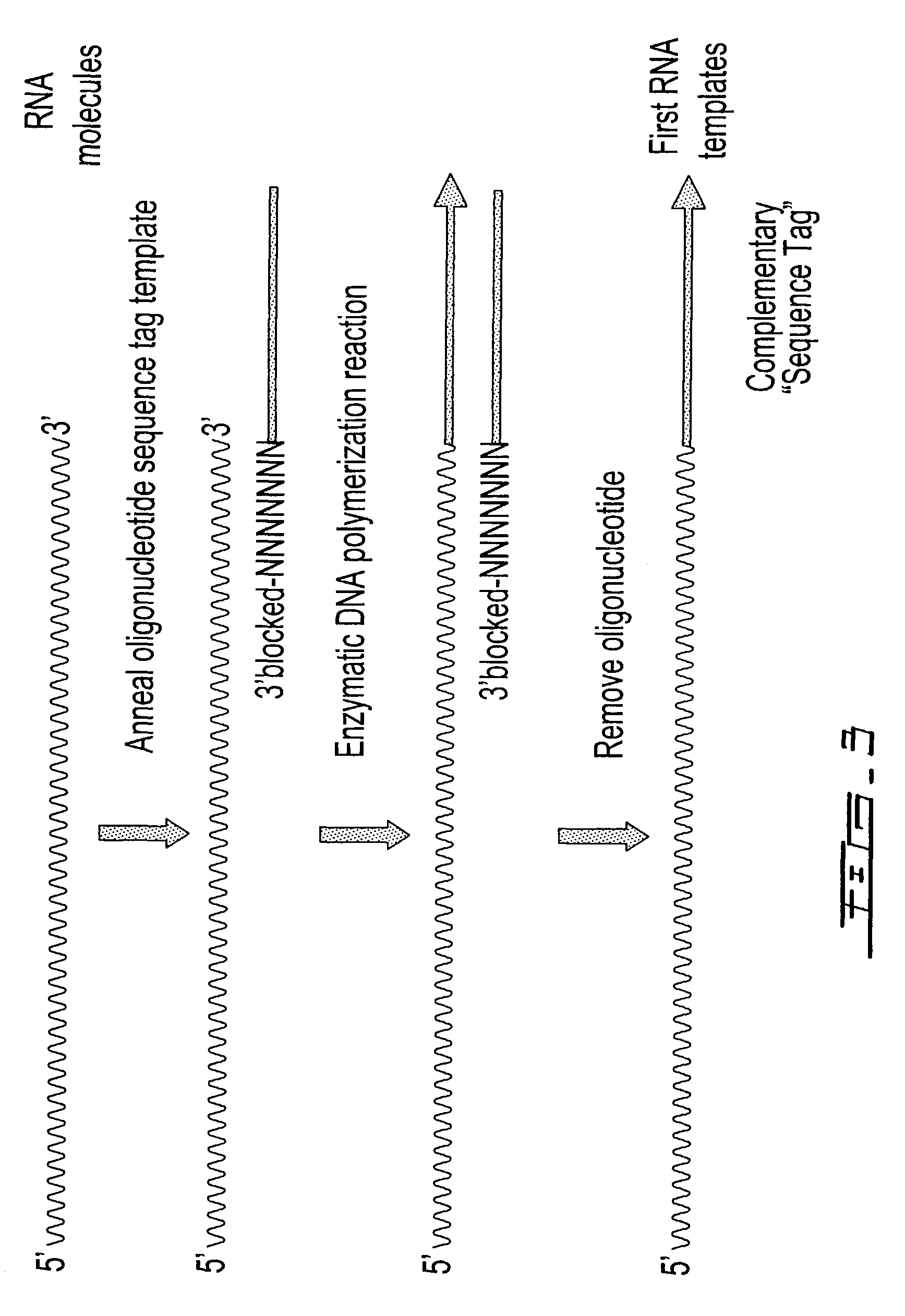
Methods are provided for adding a terminal sequence tag to nucleic acid molecules for use in RNA or DNA amplification. The tag introduced may be used as a primer binding site for subsequent amplification of the DNA molecule and / or sequencing of the DNA molecule and therefore provides means for identification and cloning of the 5′-end or the complete sequence of mRNAs.
Owner:CELLSCRIPT
Compositions and methods for co-amplifying subsequences of a nucleic acid fragment sequence
ActiveUS20140243242A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementEmulsionEmulsion polymerization
The present invention is related to genomic nucleotide sequencing. In particular, the invention describes a single reaction method to co-amplify multiple subsequences of a nucleic acid fragment sequence (i.e., for example, at least two read pairs from a single library insert sequence). Nucleic acid fragment sequences may include, but are not limited to, localizing library insert sequences and / or unique read pair sequences in specific orientations on a single emulsion polymerase chain reaction bead. Methods may include, but are not limited to, annealing, melting, digesting, and / or reannealing high throughput sequencing primers to high throughput sequencing primer binding sites. The compositions and methods disclosed herein contemplate sequencing complex genomes, amplified genomic regions, as well as detecting chromosomal structural rearrangements that are compatible with massively parallel high throughput sequencing platforms as well as ion semiconductor matching sequencing platforms (i.e., for example, Ion Torrent platforms).
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC
Methods of preparation of gene-specific oligonucleotide libraries and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060051789A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationOligoribonucleotidesRibonuclease
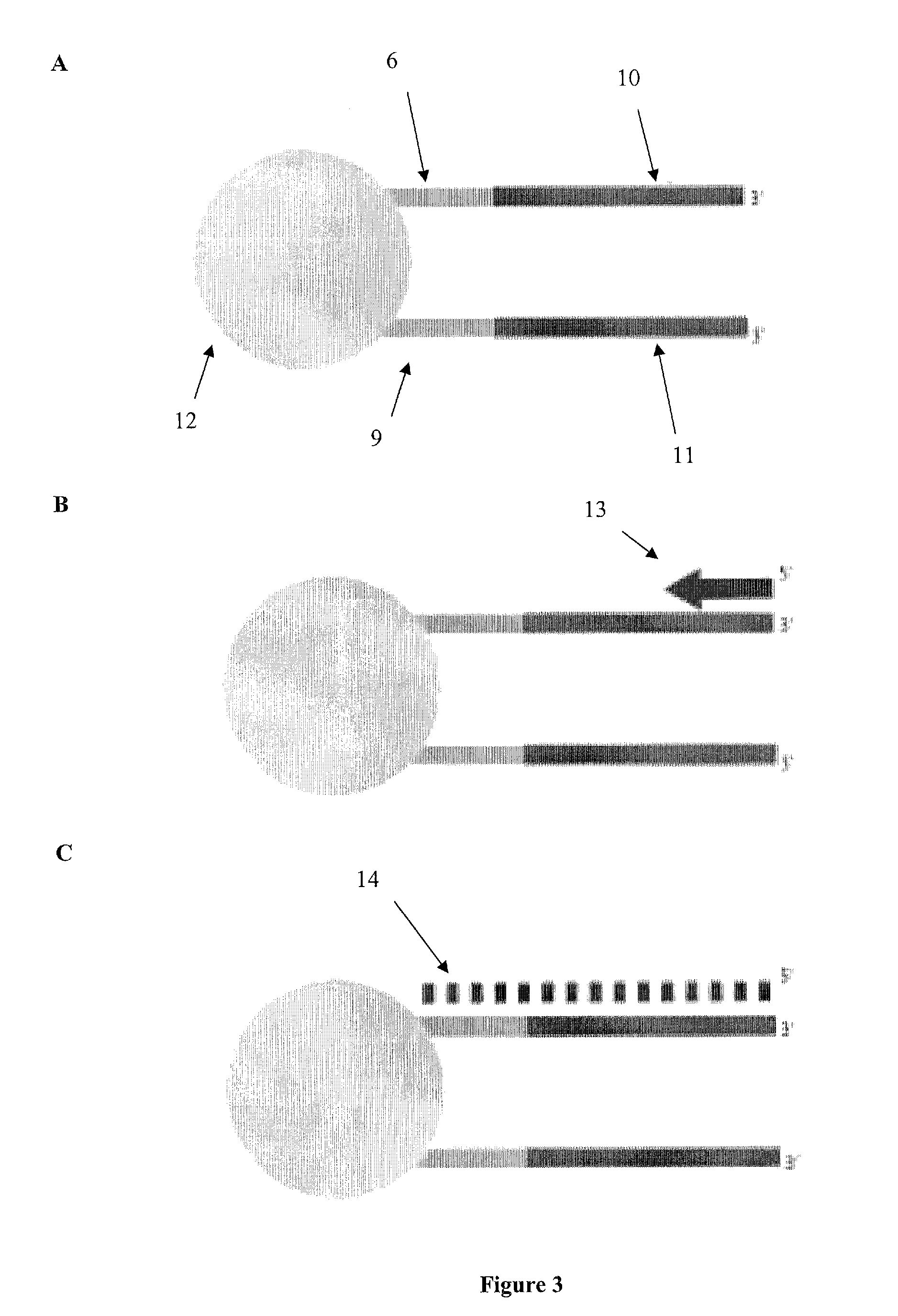
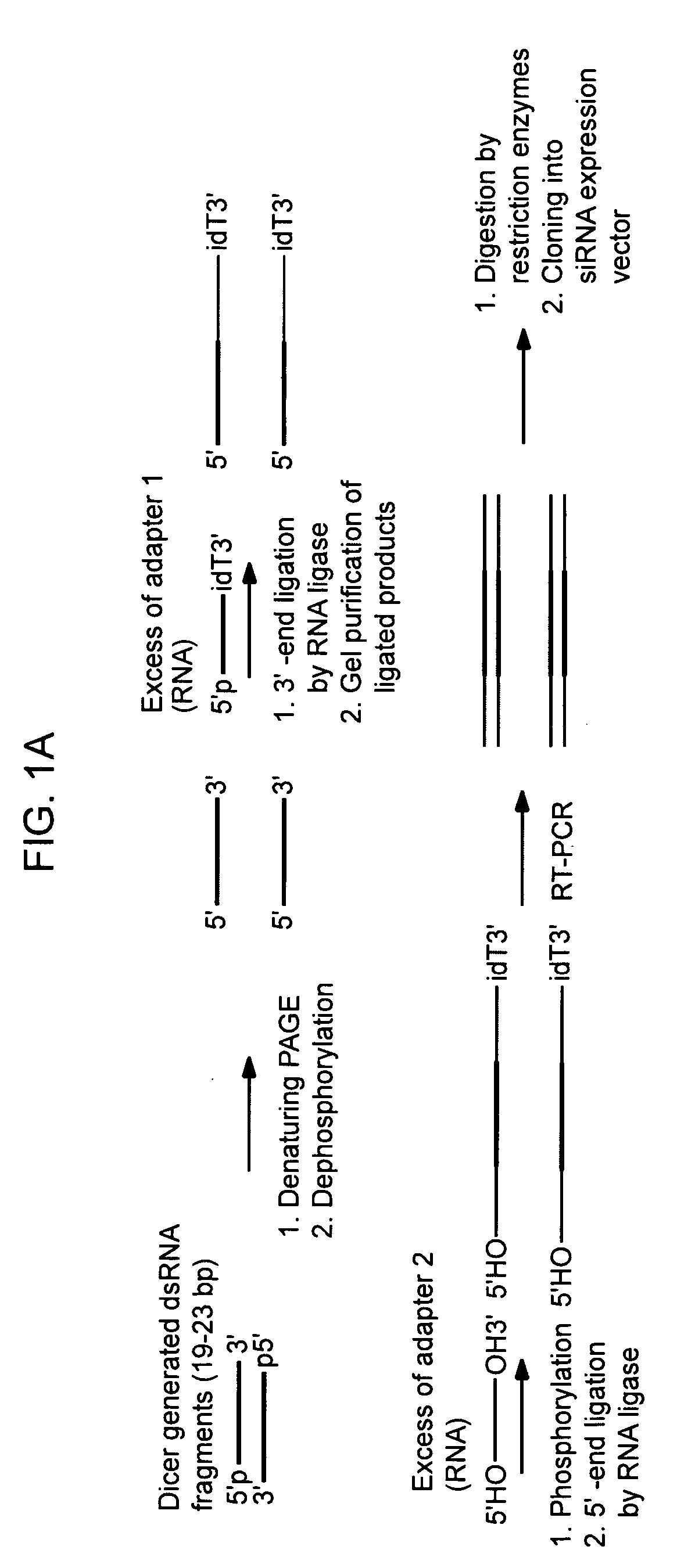
Methods of preparing gene-specific oligonucleotide libraries are disclosed. In one embodiment a double-stranded RNA corresponding to both sense and antisense strands of mRNA is digested by ribonuclease to produce short RNA fragments. In subsequent ligation steps, flanking oligoribonucleotides of defined sequences may be attached to the 3- and 5-ends of each fragment by RNA ligase (such as T4 RNA ligase). The products of ligation can be reverse transcribed and PCR amplified (RT-PCR) using the oligonucleotides attached to the gene-derived sequences as primer-binding sites. Various methods for incorporating libraries into expression vectors allowing expression of either siRNAs or shRNAs are also disclosed.
Owner:SOMAGENICS INC
Microbial population analysis
ActiveUS20170159108A1Increase diversityMicrobiological testing/measurementICT adaptationMicroorganismIts region
The present invention relates to a method of typing a microbiome for having a desirable or undesirable signature, comprising analyzing the composition of the population of microorganisms in said microbiome based on taxonomic variation in the DNA sequence of the microbial 16S-23S rRNA internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions in the genomic DNA of said microorganisms, wherein the sequences of conserved DNA regions comprised in the 16S and 23S rRNA sequences flanking said ITS region in the genome of said microorganisms comprise primer binding sites for amplification of said ITS regions.
Owner:IS DIAGNOSTICS
Selective terminal tagging of nucleic acids
ActiveUS20090227009A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionAmplification dna
Methods are provided for adding a terminal sequence tag to nucleic acid molecules for use in RNA or DNA amplification. The tag introduced may be used as a primer binding site for subsequent amplification of the DNA molecule and / or sequencing of the DNA molecule and therefore provides means for identification and cloning of the 5′-end or the complete sequence of mRNAs.
Owner:CELLSCRIPT
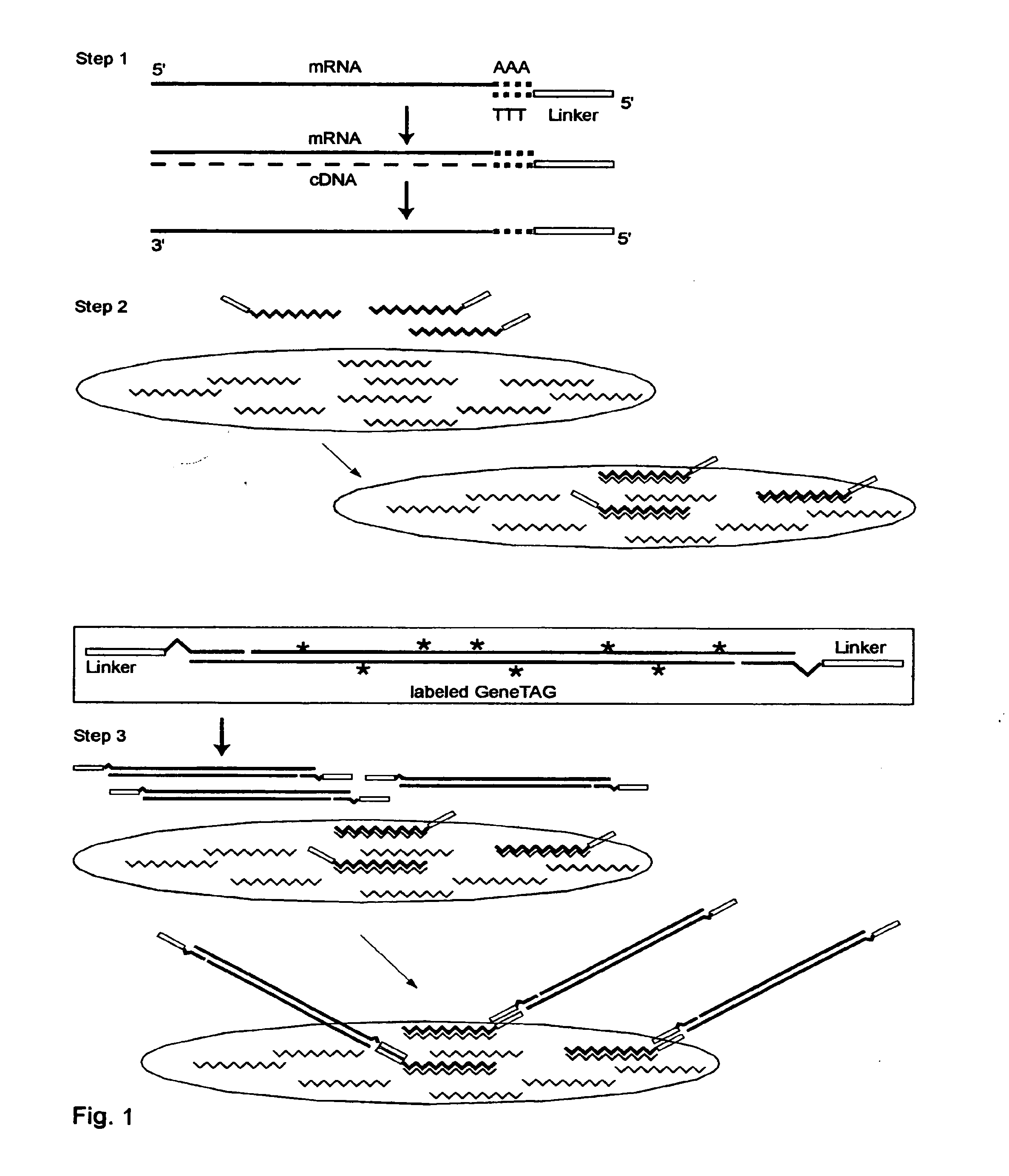
Systems and methods to quantify and amplify both signaling probes for cdna chips and genes expression microarrays
InactiveUS20040053275A1Excessive signalingGood signalSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCDNA MicroarraysGene Expression Array
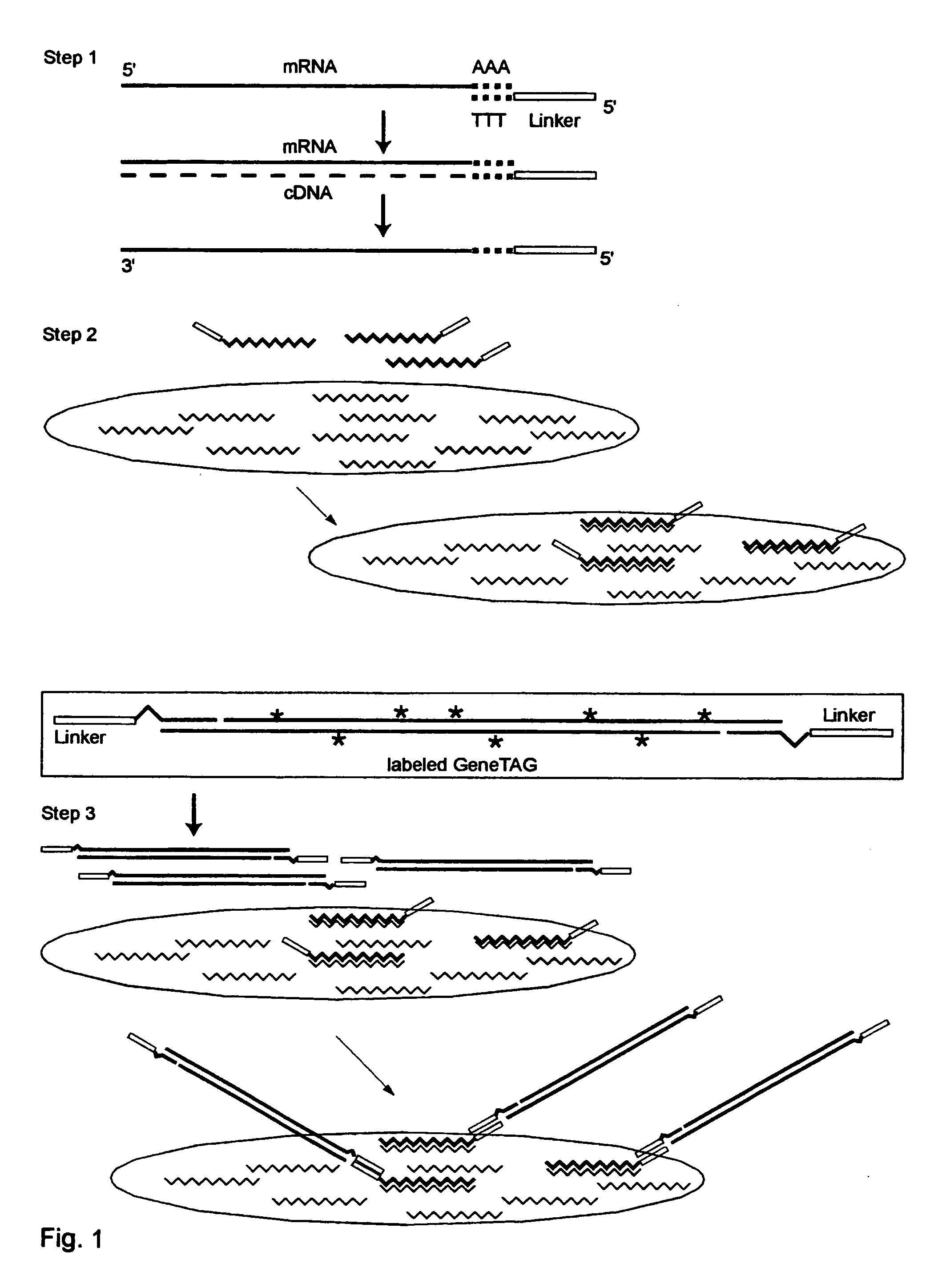
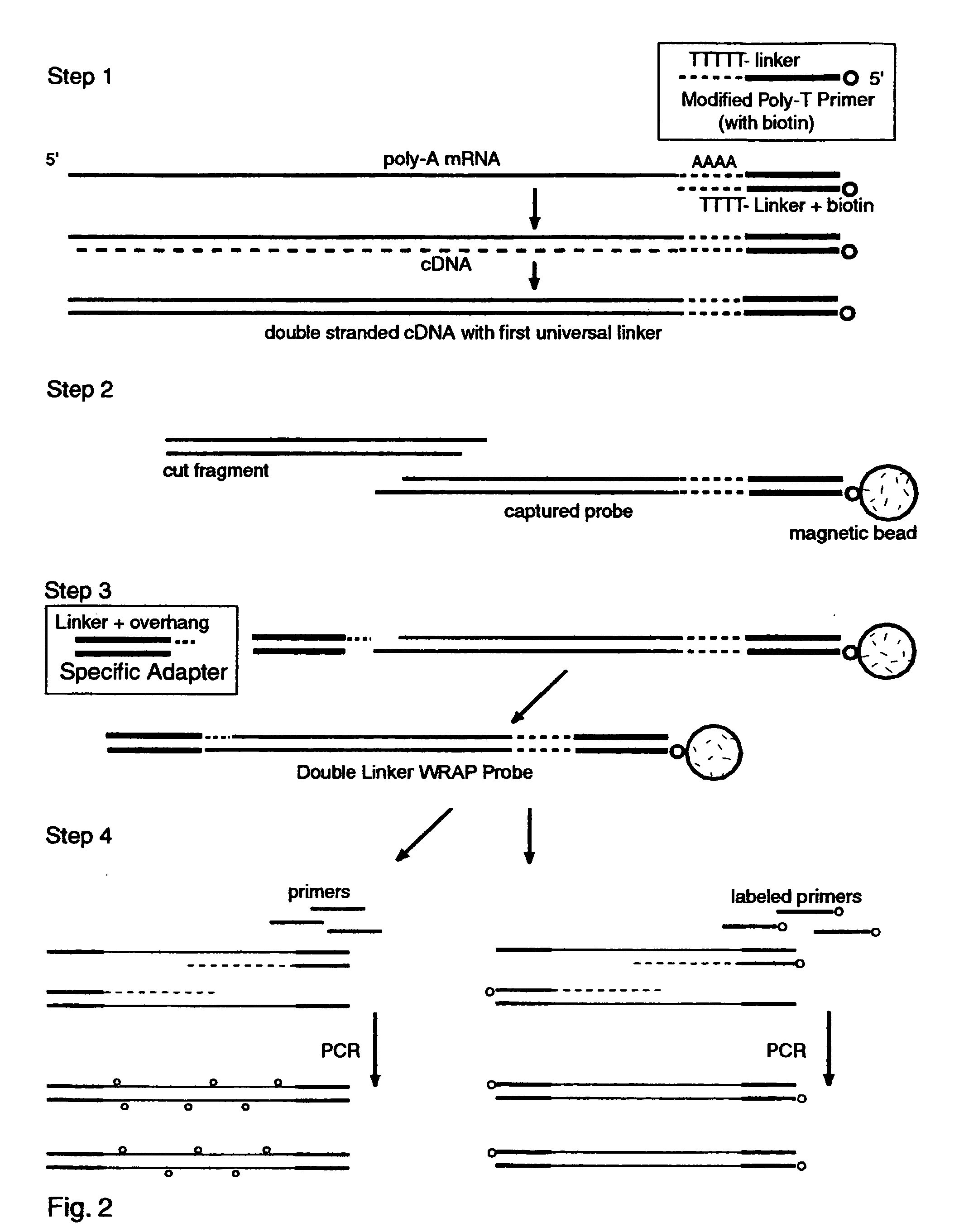
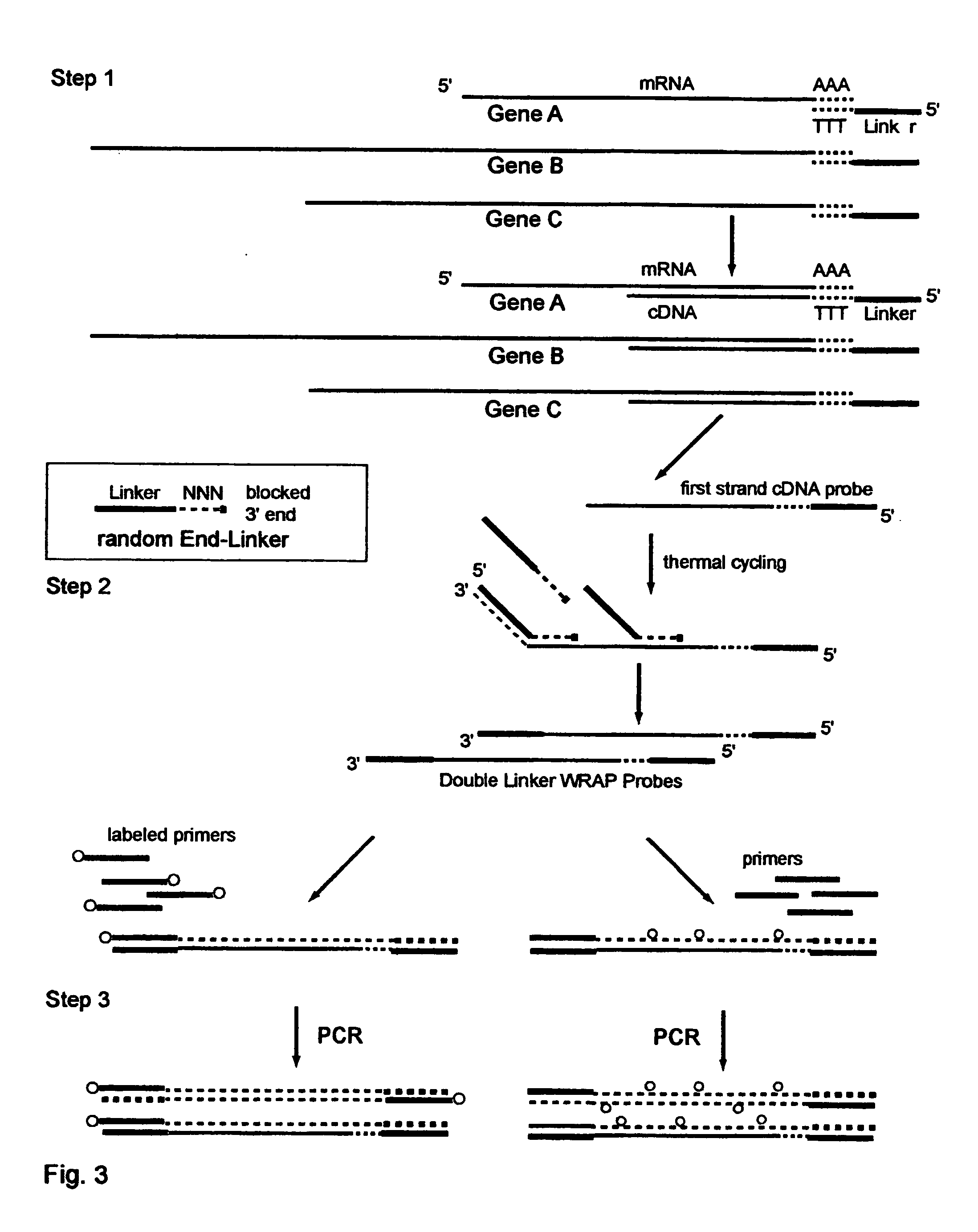
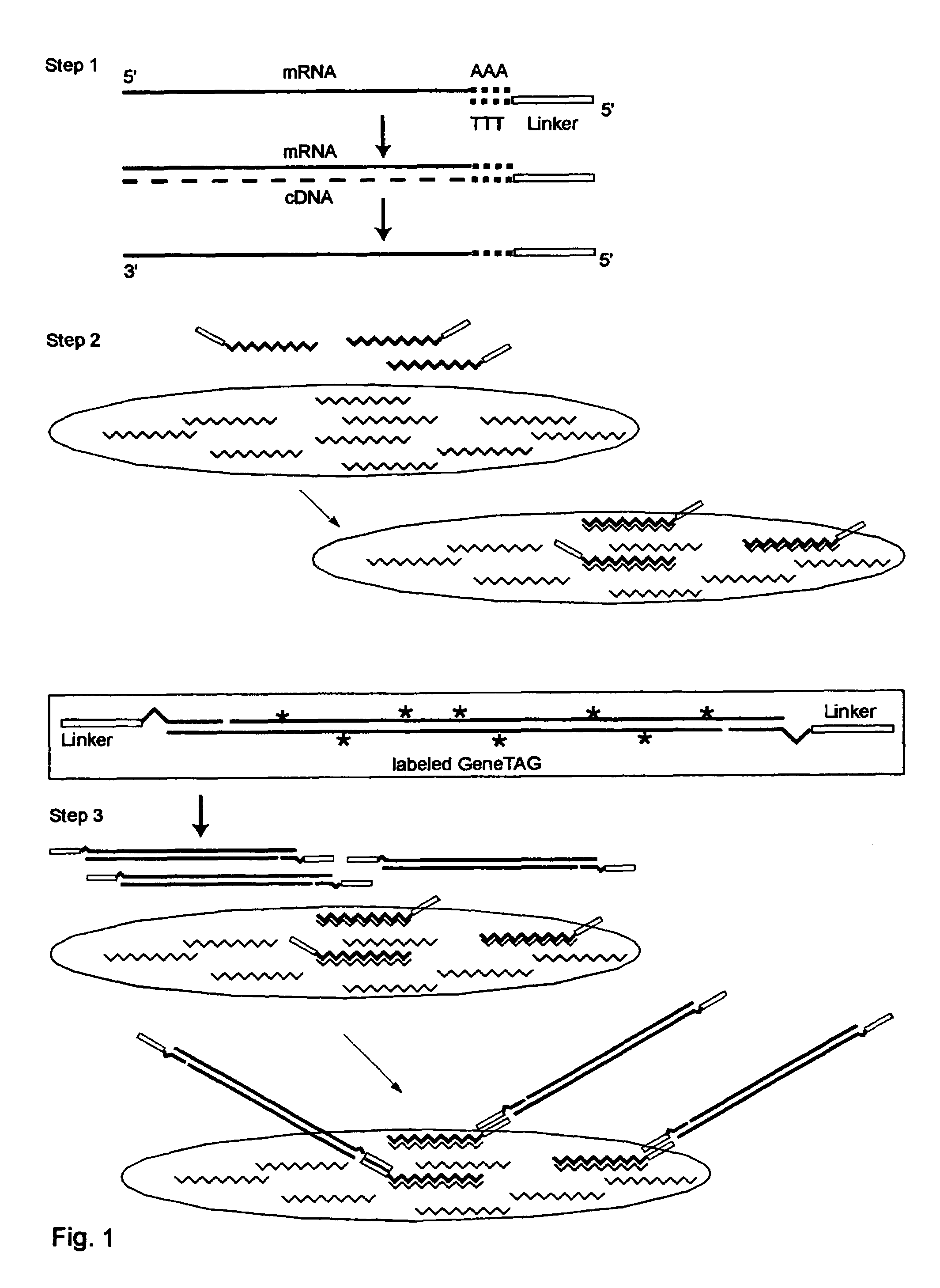
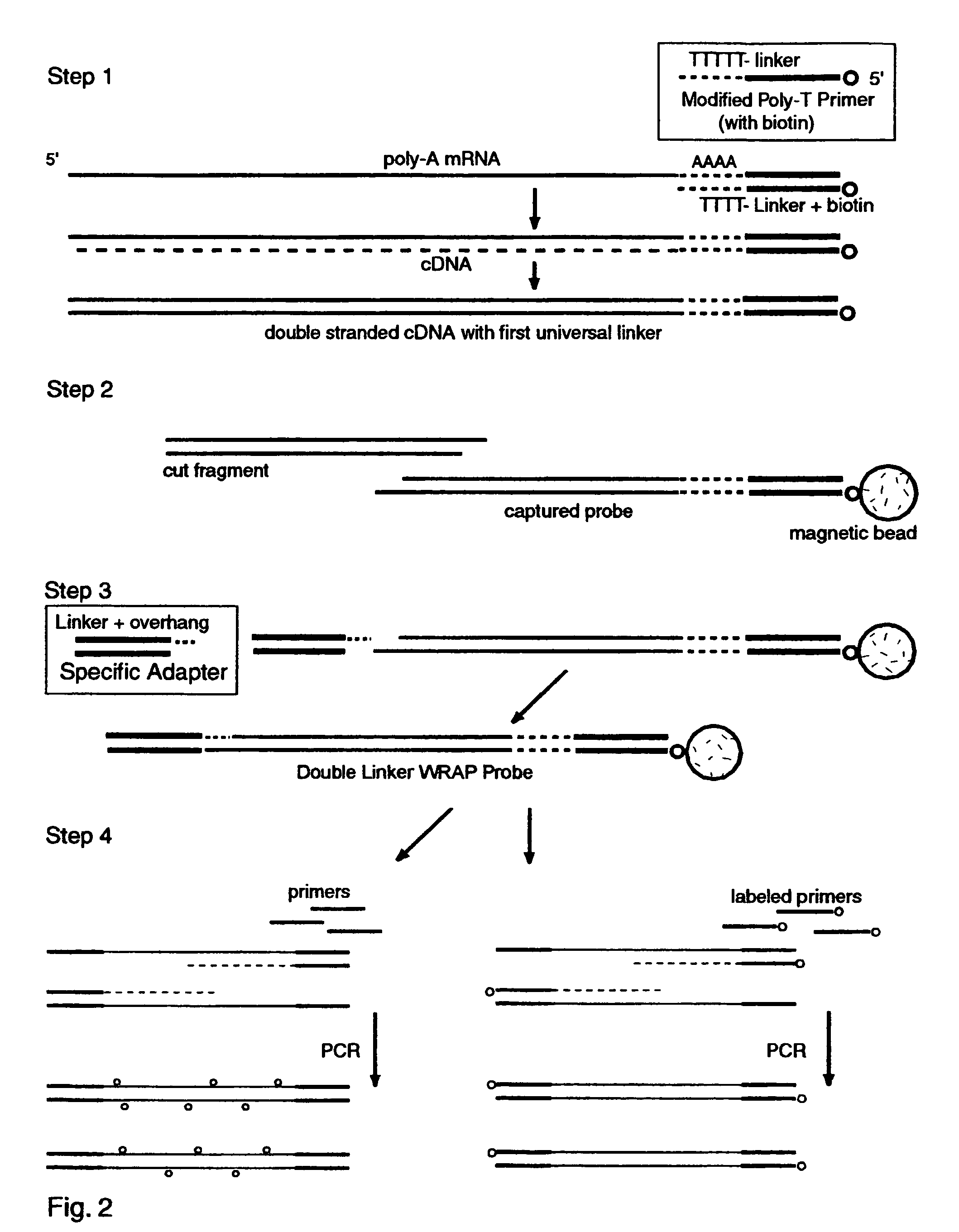
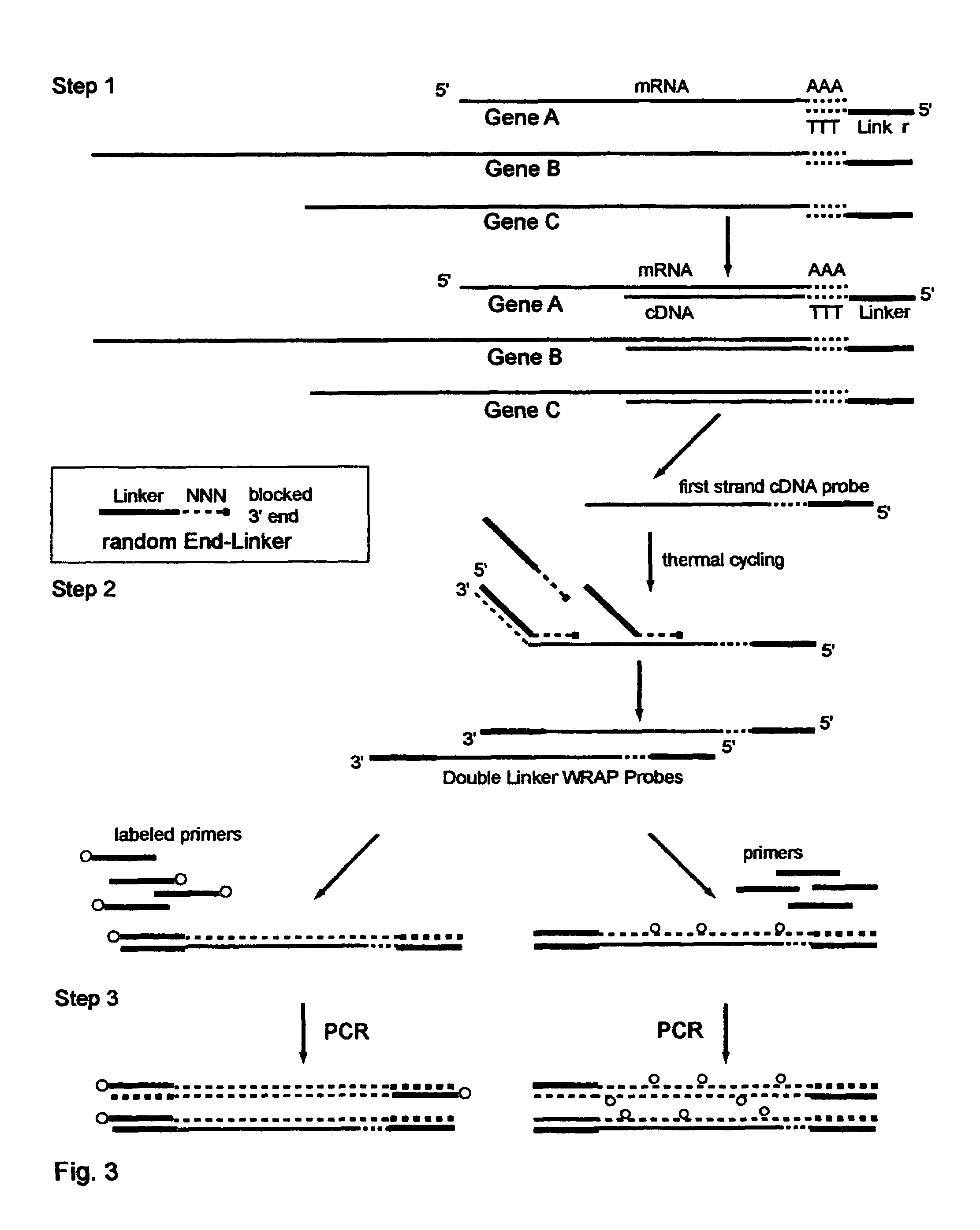
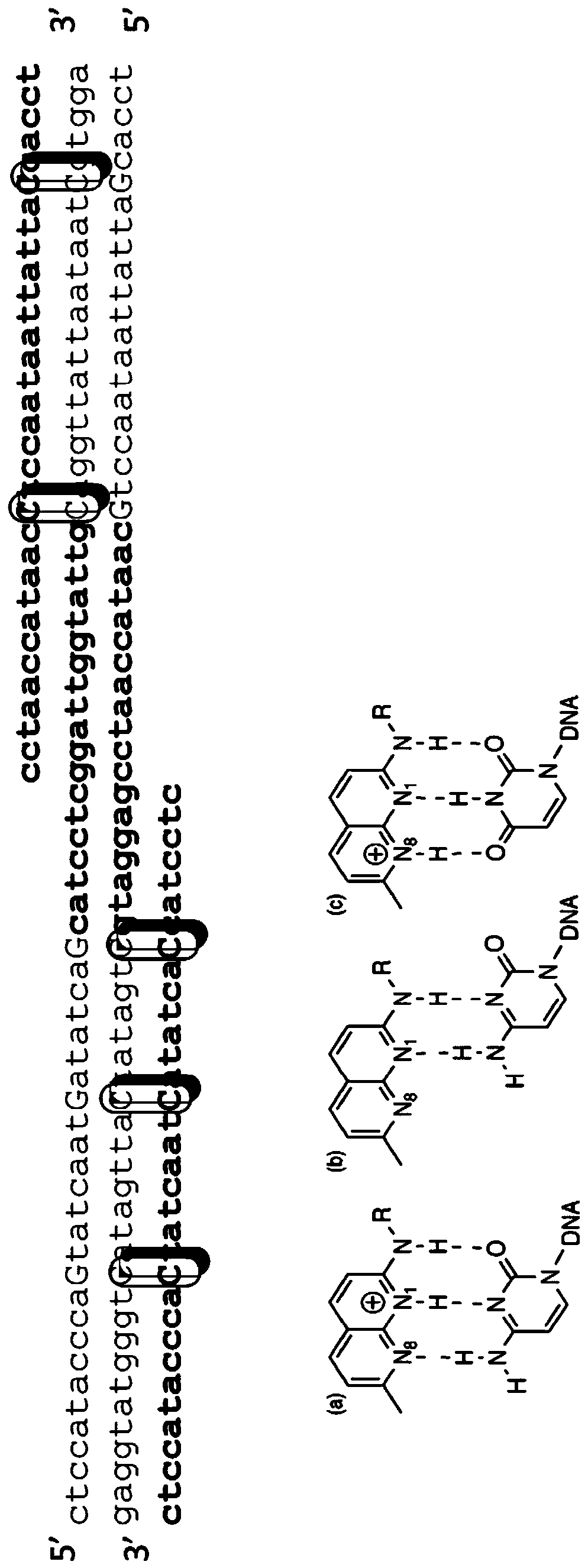
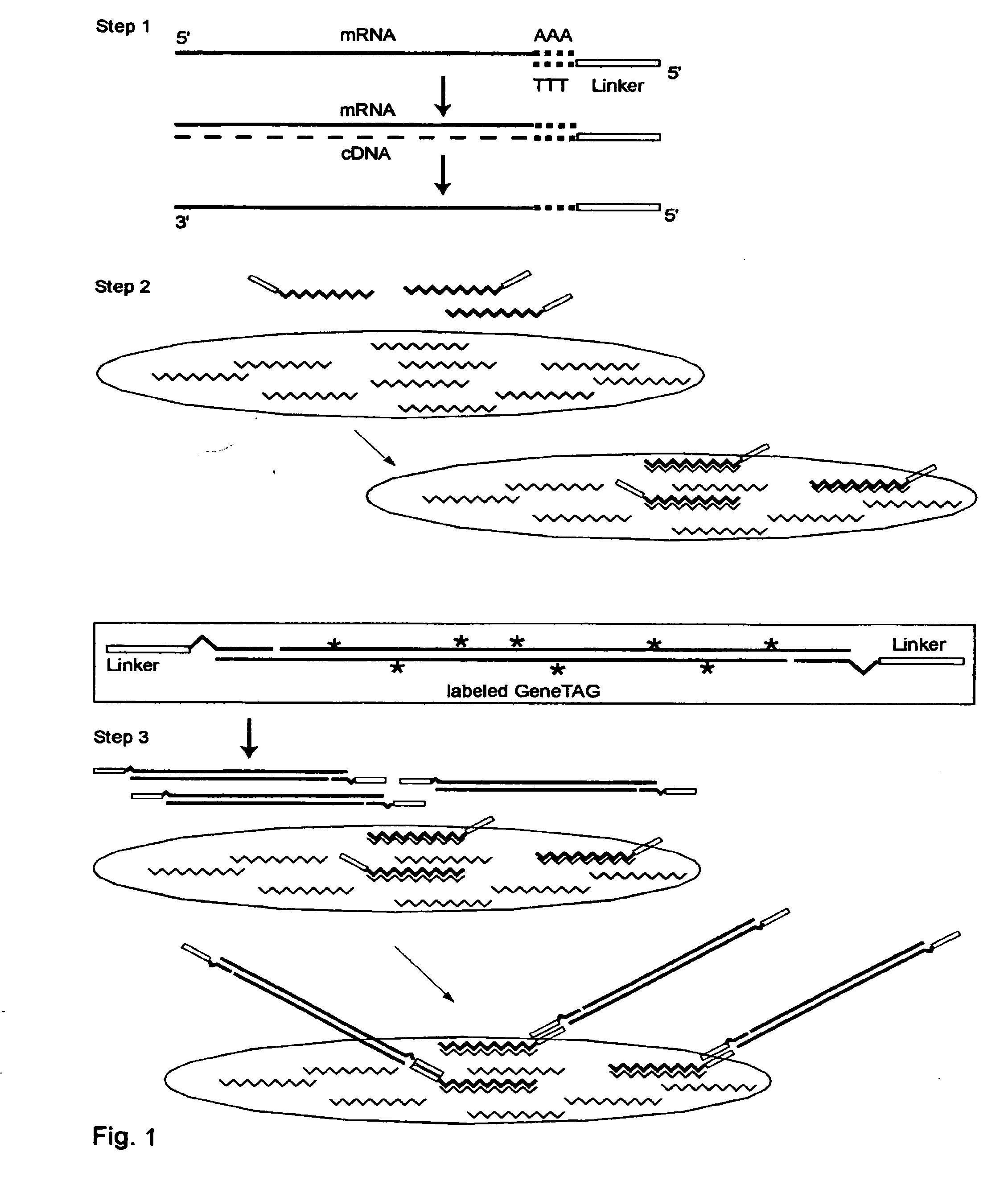
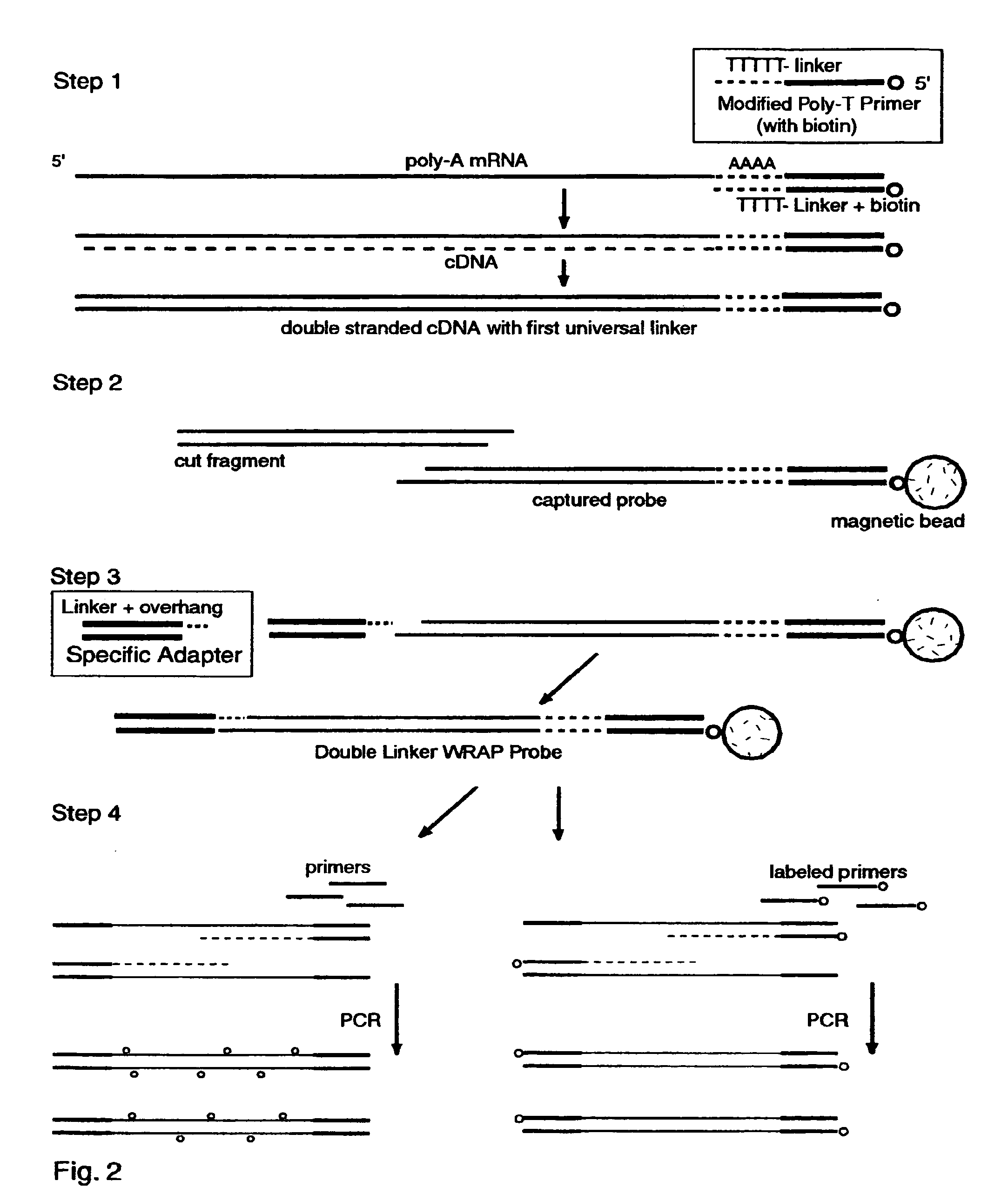
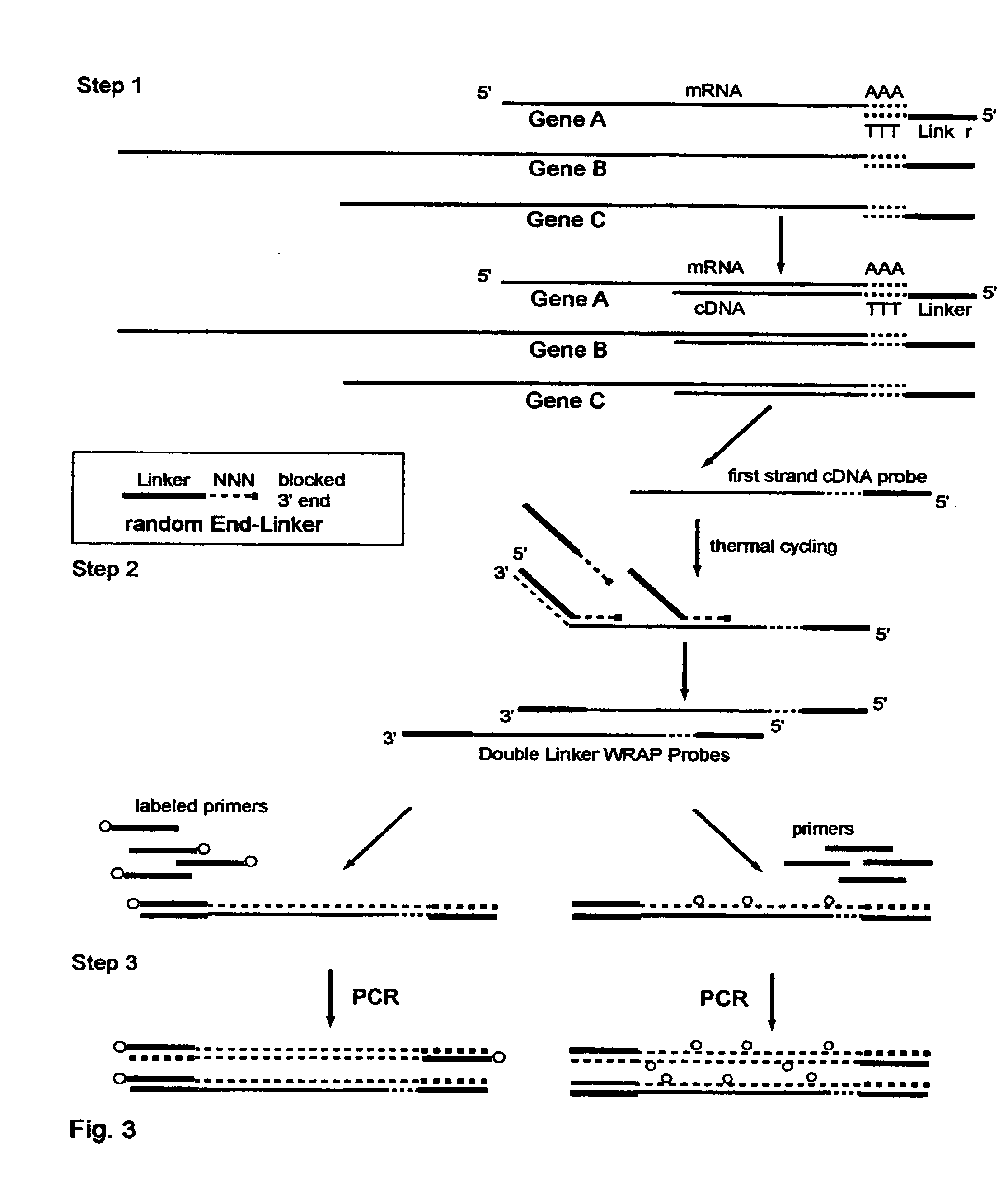
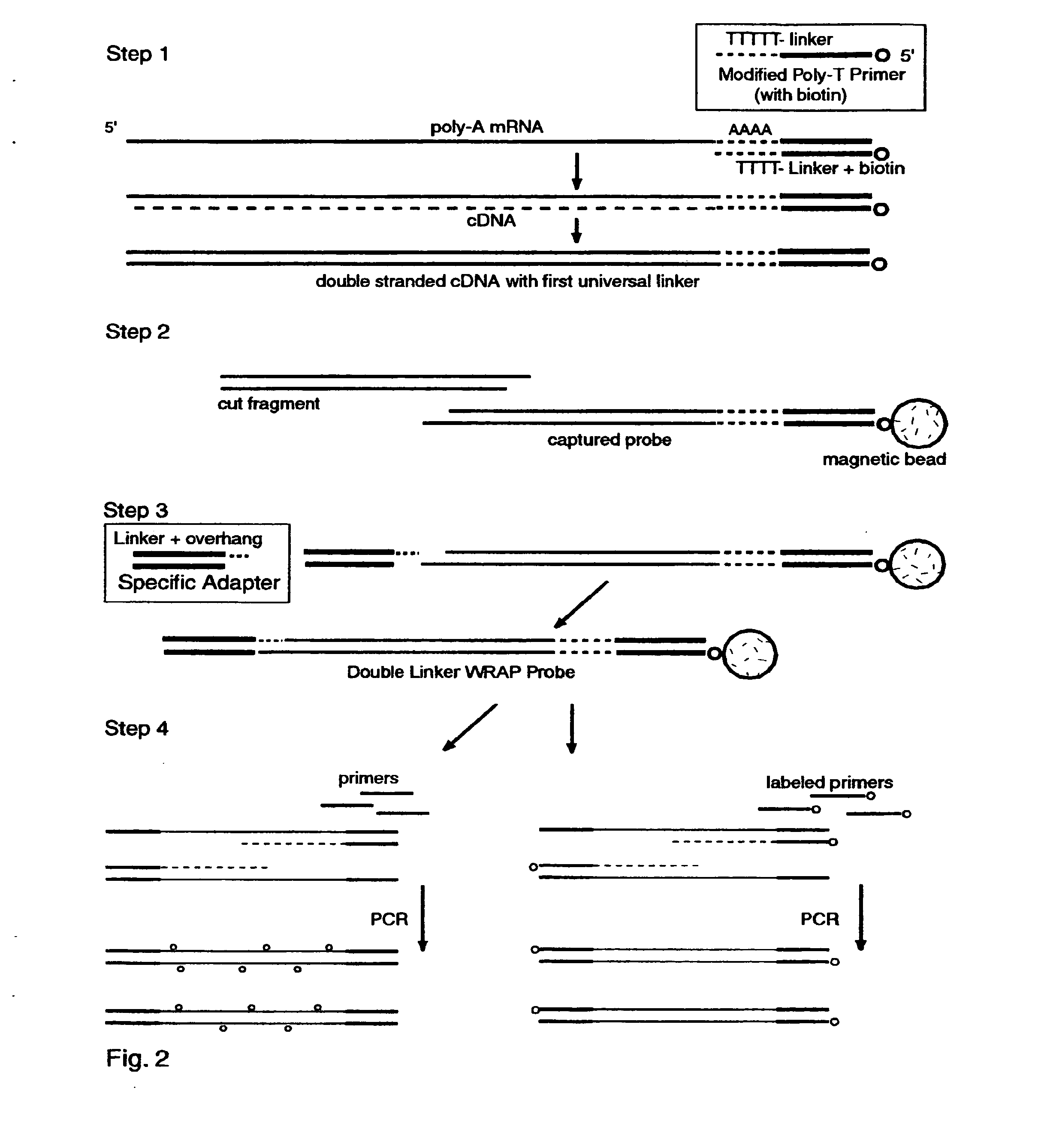
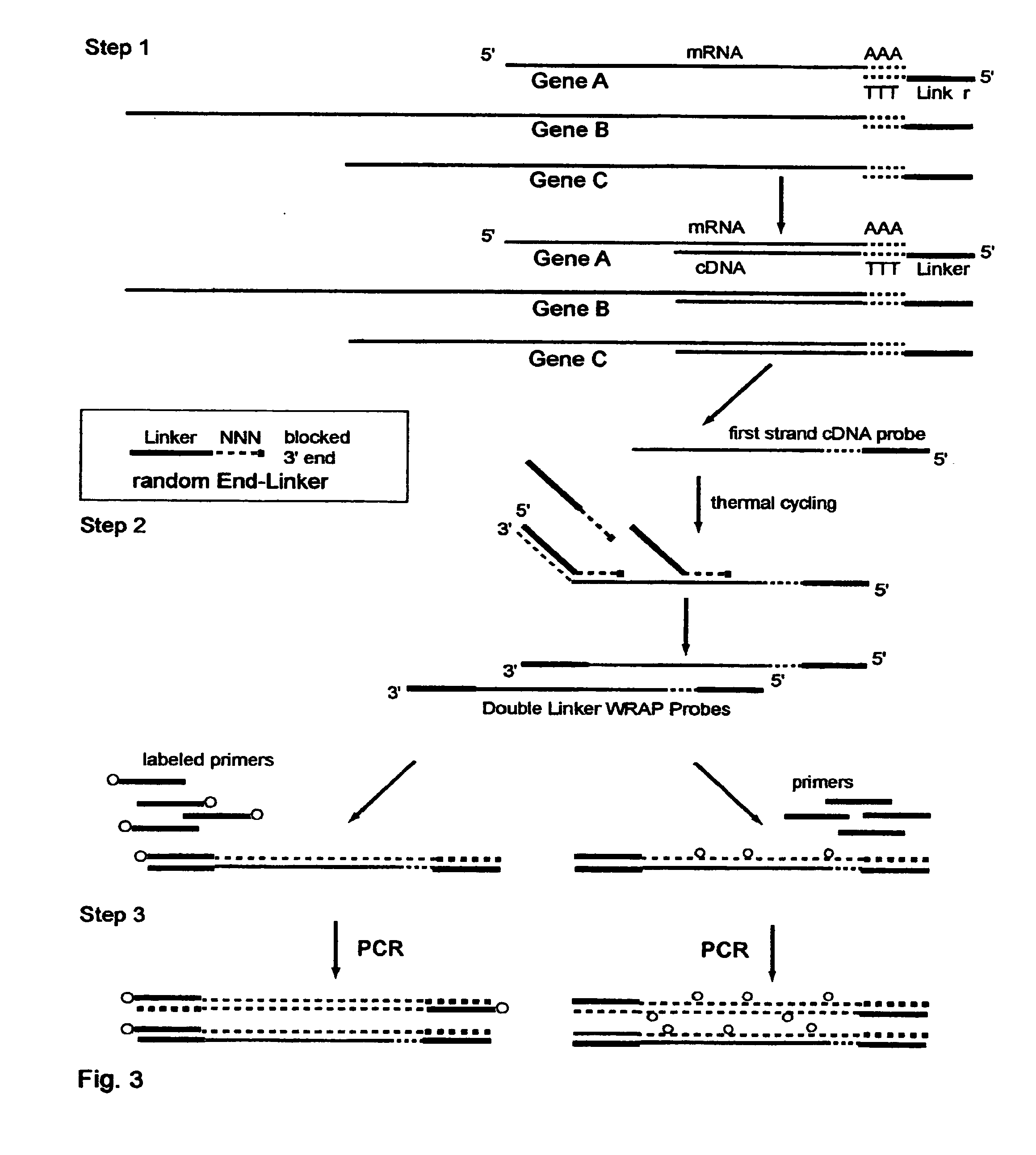
The invention provides a series of reagent compositions and methods for making and amplifying novel cDNA based probe sets from RNA samples to improve analysis with gene expression arrays. The methods globally produce probe sets with common universal linkers at one or both ends, called WRAP-Probes, wherein the linkers do not bind to the target sequences and they can efficiently bind added reporters to the probes. The universal linkers are also designed as primer binding sites for copying and amplifying the probes, either linearly with one linker, or exponentially with double linkers. The capacity to globally and exponentially amplify the probe set by PCR is a primary advantage. Adding reporters by terminal linkers also improves quantification since each probe gets equivalent signaling. The invention allows expression analysis of small research, clinical and forensic samples to enable improved diagnostics, drug discovery, therapeutic monitoring, and medical, agricultural and general research.
Owner:GENETAG TECH
Crispr effector system based diagnostics for virus detection
Provided herein is a nucleic acid detection system comprising: a CRISPR system comprising an effector protein and one or more guide RNAs designed to bind to corresponding target molecules; an RNA-based masking construct; and optionally, nucleic acid amplification reagents to amplify target RNA molecules in a sample. In another aspect, the embodiments provide a polypeptide detection system comprising: a CRISPR system comprising an effector protein and one or more guide RNAs designed to bind a trigger RNA, an RNA-based masking construct; and one or more detection aptamers comprising a masked RNApolymerase promoter binding site or a masked primer binding site. In some embodiments, the system may be used to detect viruses in samples.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
Template specific inhibition of PCR
InactiveUS20070031869A1Easy to identifyHighly reliable methodMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOligonucleotidePolymerase
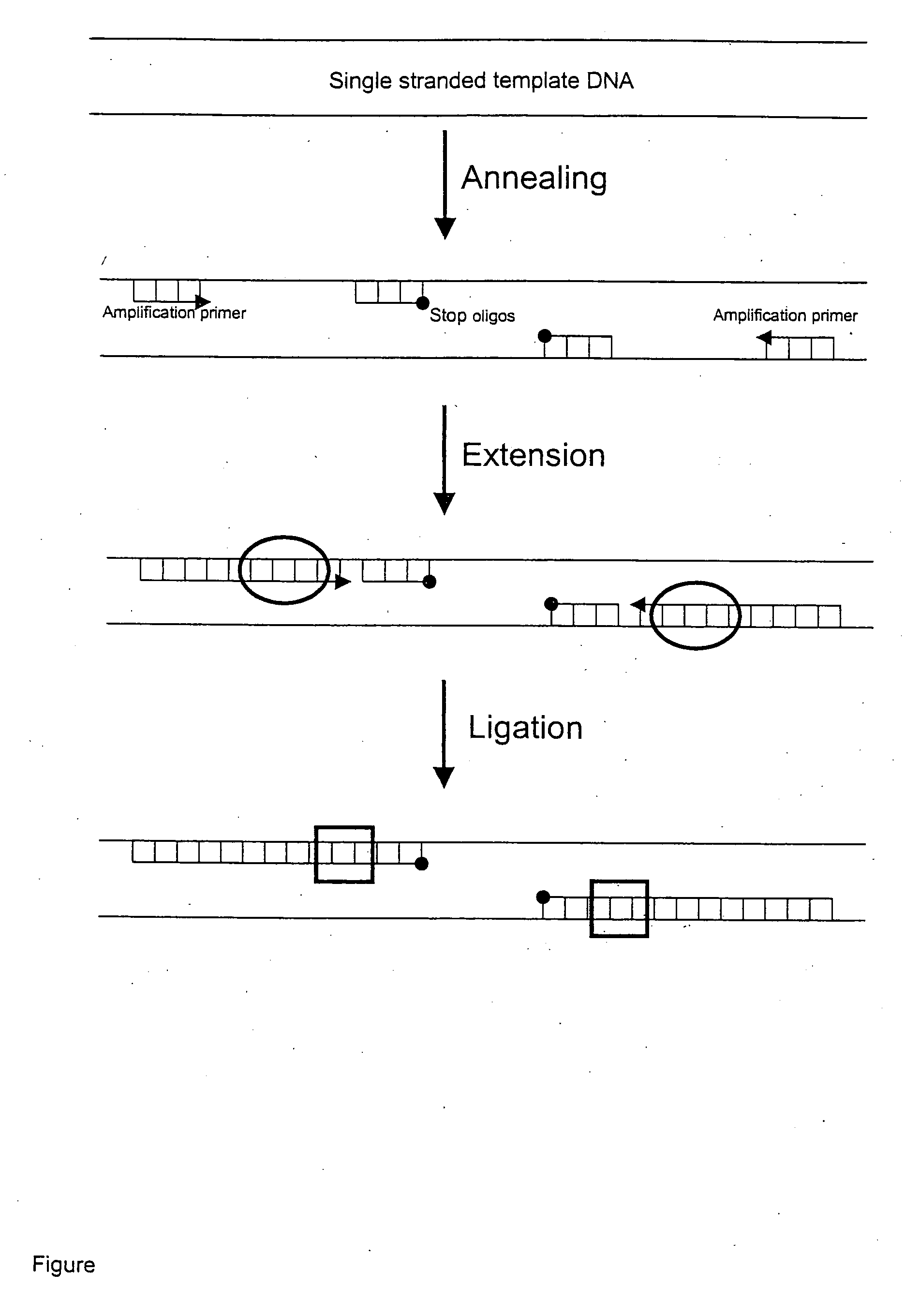
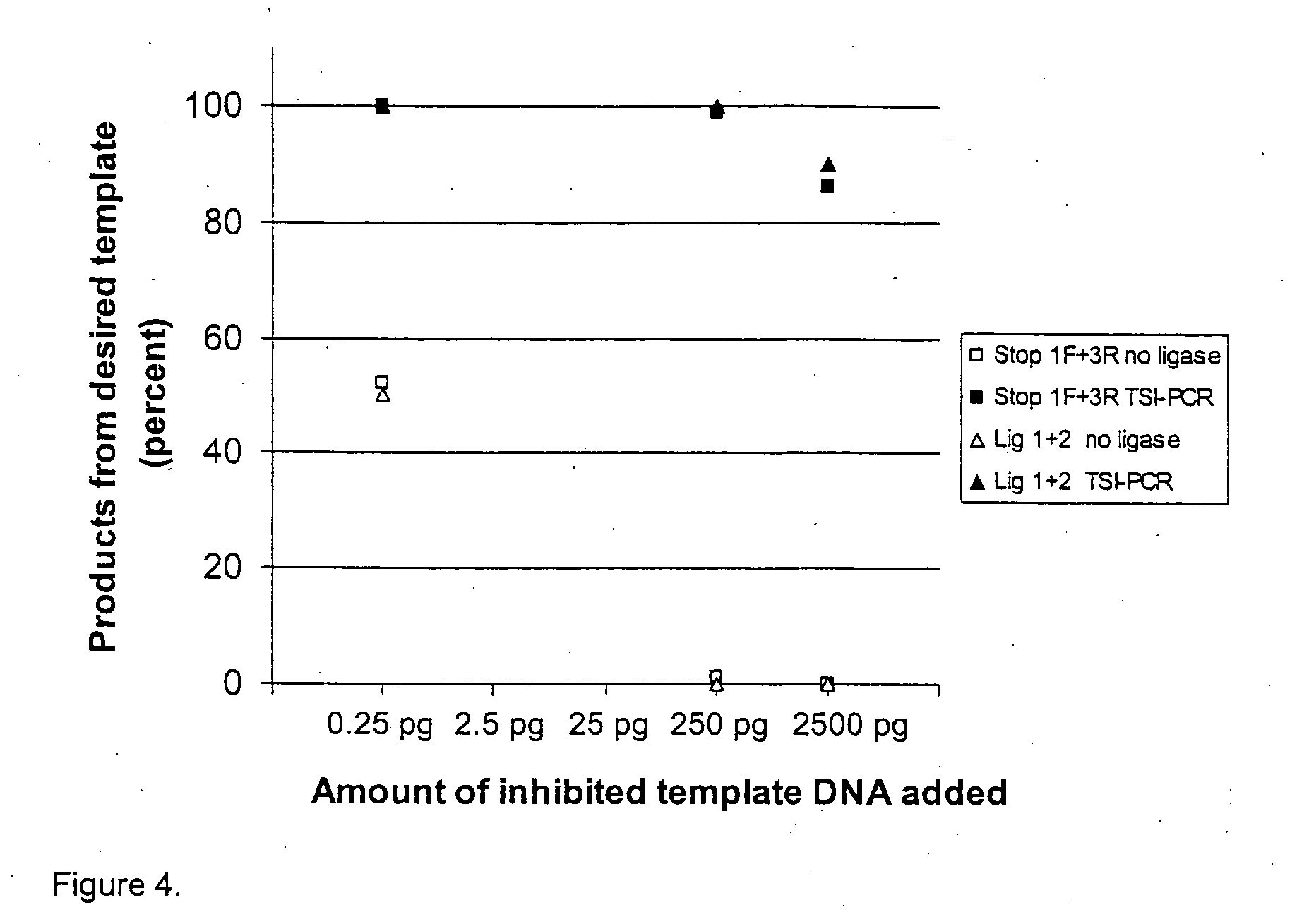
Template specific inhibition during PCR (TSI-PCR) allows specific inhibition of particular templates without disrupting the amplification of other templates that share amplification primer binding sites. TSI-PCR is achieved by ligation of stop oligos comprising a 3′ modification that prevents extension by DNA polymerases. Stop oligos hybridize to a region of the targeted amplicon downstream of the amplification primer. When the stop oligos are perfectly complementary to the target template, they are ligated onto the extending strand during the extension phase of the amplification cycle. This effectively truncates the extending strand at the site where the stop oligo binds and blocks further extension. The truncated products are not full-length and cannot be extended, and therefore do not serve as additional templates during sunsequent rounds of amplification. This results in substantial inhibition over multiple amplification cycles, but only for templates that match the stop oligos.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
MND promoter chimeric antigen receptors
ActiveUS10774343B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsBinding siteAntigen receptors
Vector compositions comprising a myeloproliferative sarcoma virus enhancer, negative control region deleted, dl587rev primer-binding site substituted (MND) promoter operably linked to a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) are provided.
Owner:2SEVENTY BIO INC
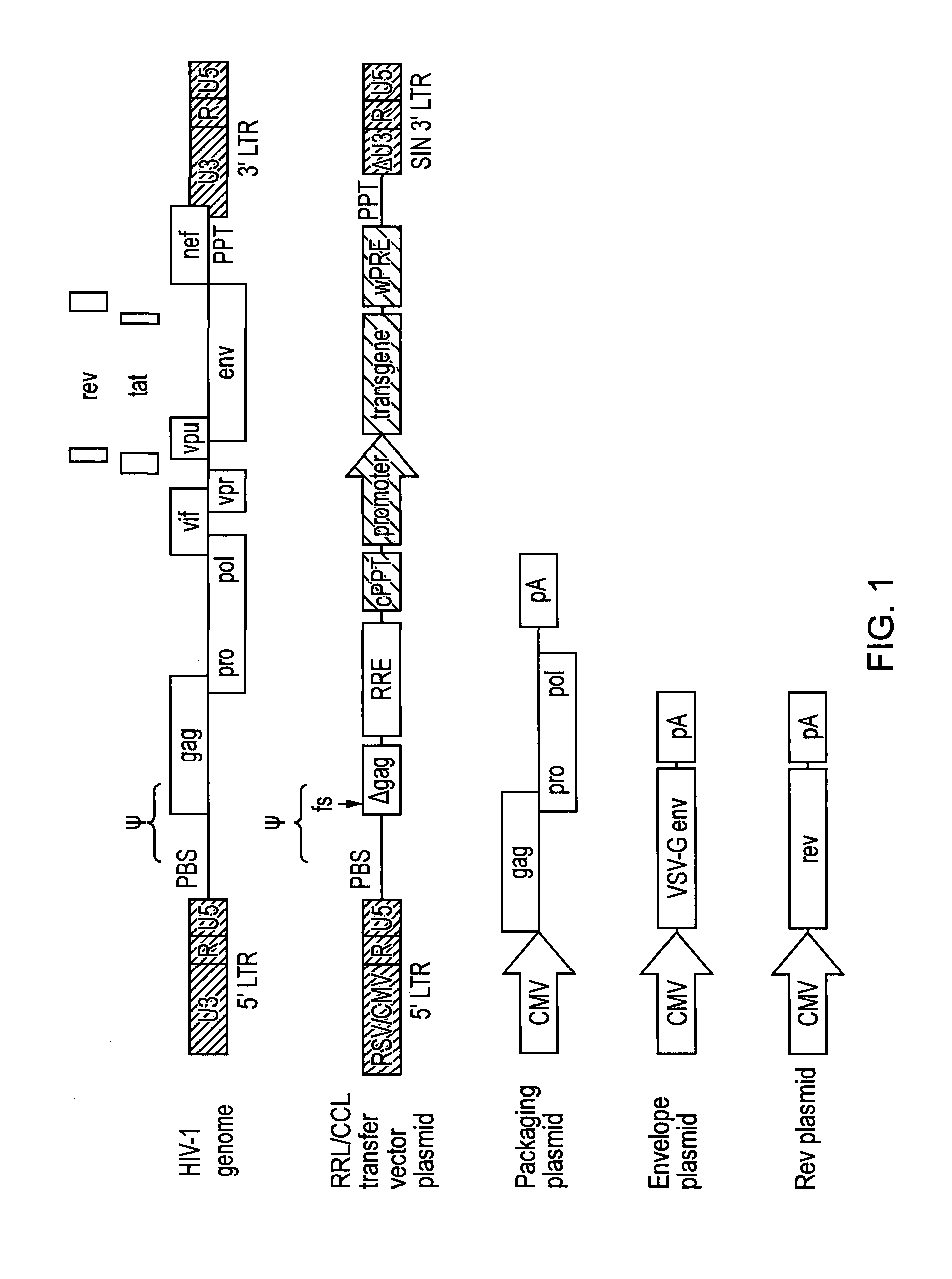
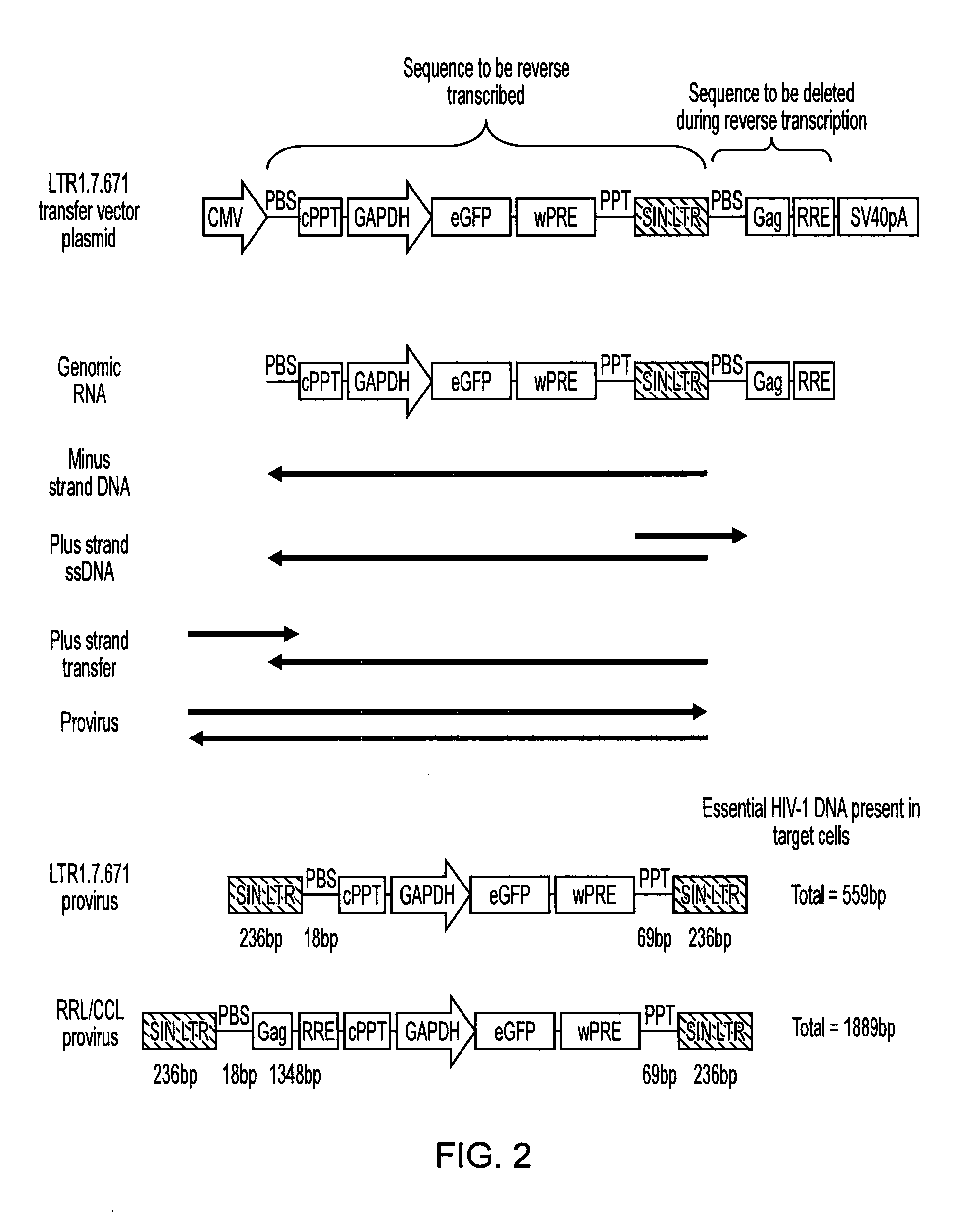
Single LTR lentivirus vector
The present invention provides an isolated nucleic acid comprising a single retroviral LTR, a polypurine tract, a packaging signal, a primer binding site and a rev responsive element. Further provided is an isolated nucleic acid comprising a heterologous nucleotide sequence, a single retroviral long terminal repeat (LTR), a packaging signal, a rev responsive element, a polypurine tract, a eukaryotic promoter, a primer binding site, a bacterial origin of replication and a bacterial selection marker. In addition, the present invention provides an isolated nucleic acid comprising a 5′ retroviral LTR and a 3′ retroviral LTR, a heterologous nucleotide sequence, a packaging signal, a rev responsive element, a polypurine tract, a eukaryotic promoter, a primer binding site, a bacterial origin of replication and a bacterial selection marker cassette, wherein the bacterial origin of replication and bacterial selection marker are located between the two LTRs.
Owner:KAFRI TAL +1
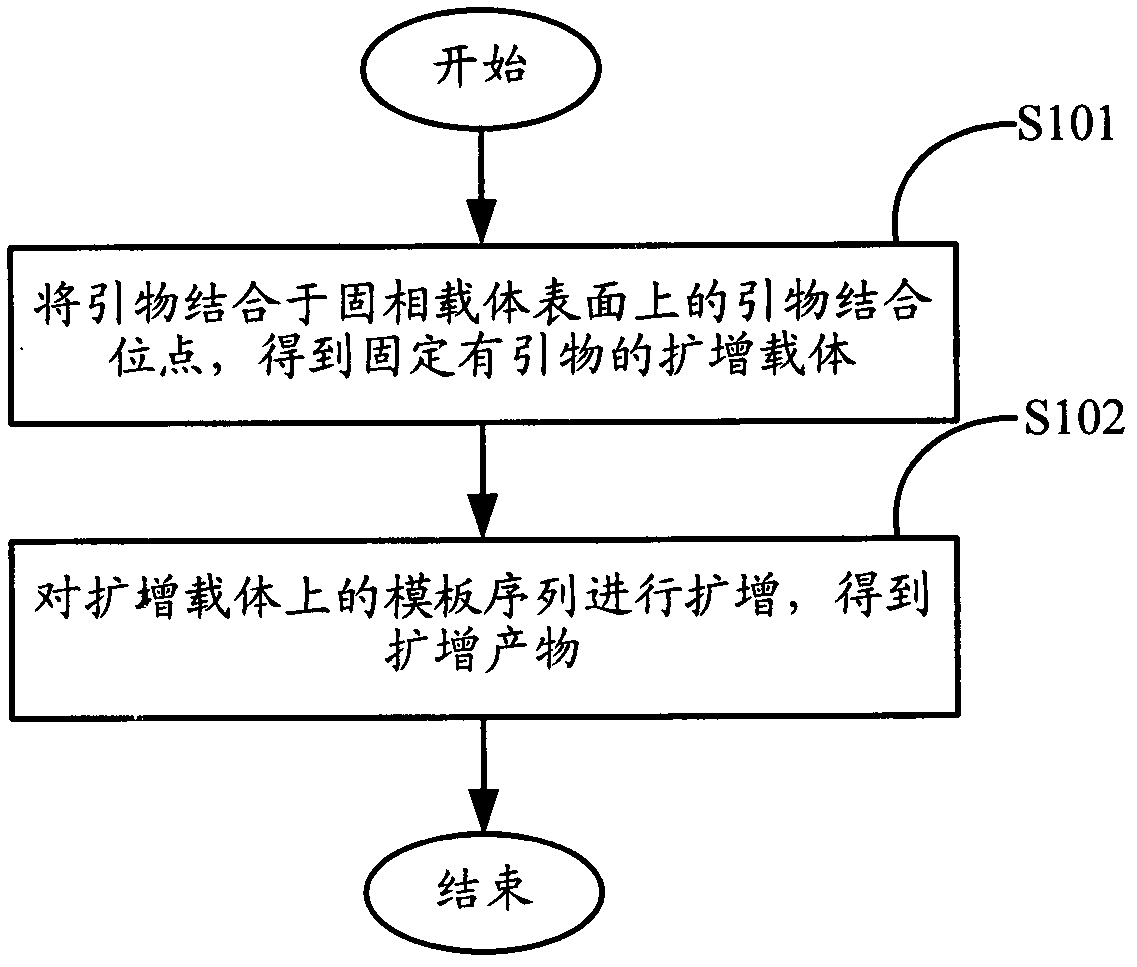
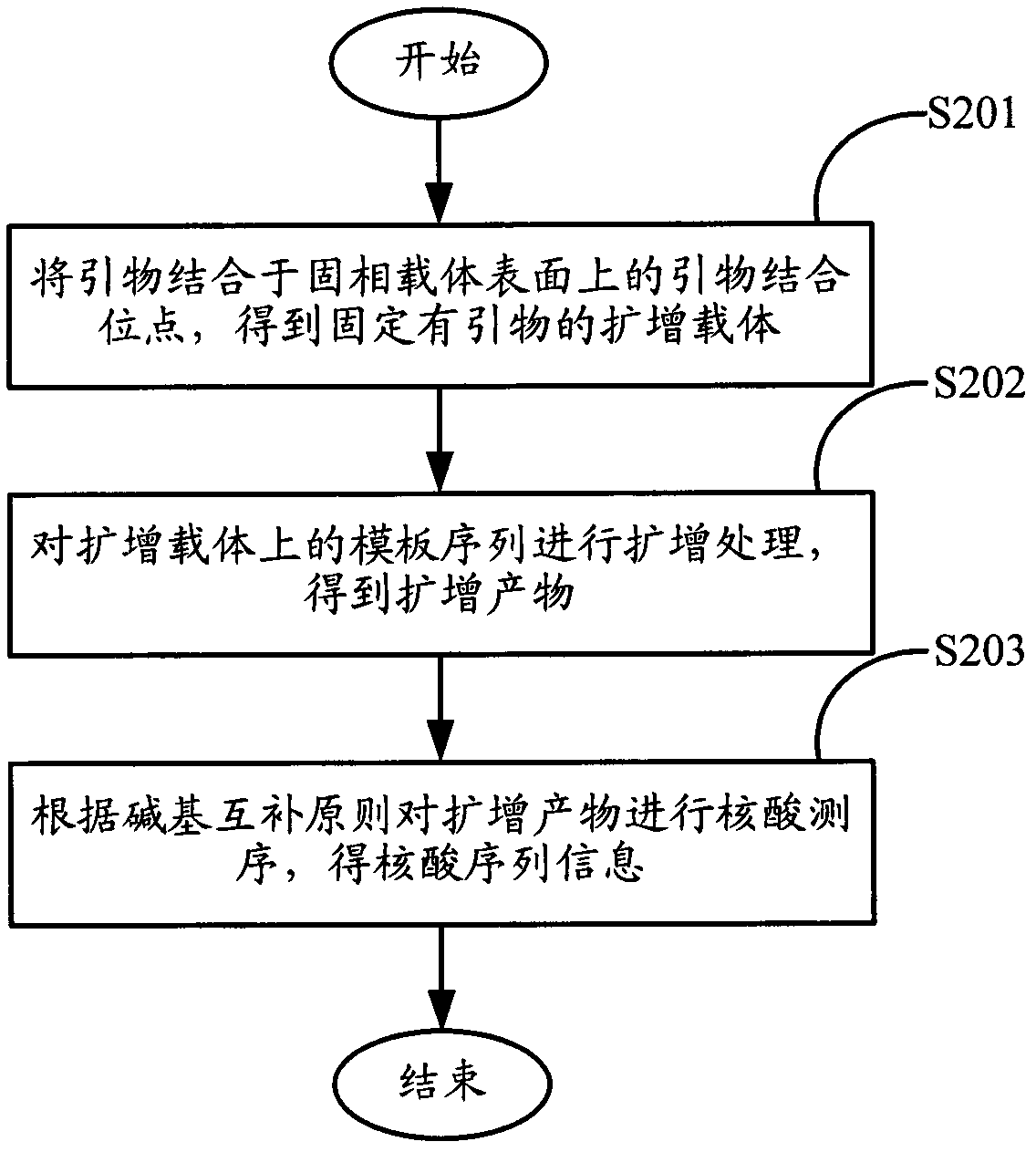
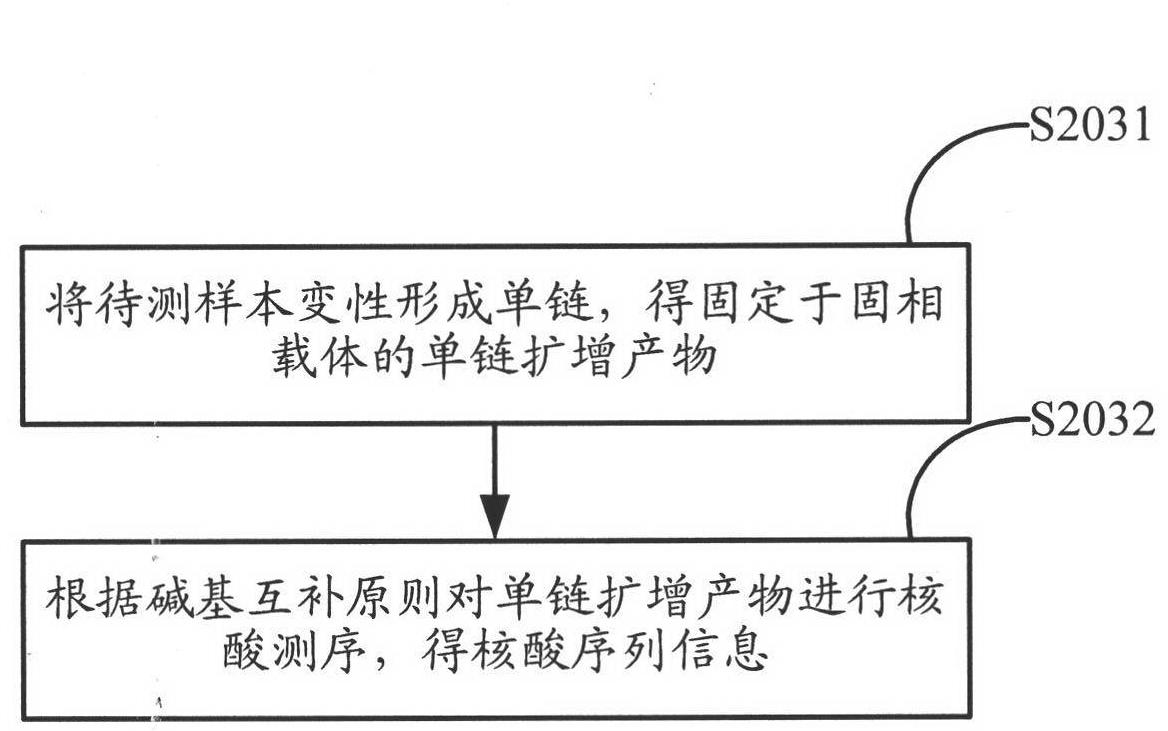
Method for amplifying and sequencing nucleic acid based on solid phase carrier
ActiveCN102604934AIncrease profitIncrease the amount of bindingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGene engineeringBiology
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, and provides a method for amplifying and sequencing nucleic acid based on a solid phase carrier. At least one template sequence is fixed at the surface of the solid phase carrier, and the method comprises the following steps: A, combining a primer with a primer binding site on the surface of the solid phase carrier to obtain an amplifying carrier fixed with the primer; and B, amplifying the template sequence on the amplifying carrier to obtain a amplifying product. The method is based on the solid phase carrier fixed with the template sequence on the surface to amplify, can fix the amplifying product on the surface of the solid phase carrier, and improves the combining amount of the amplifying product on the surface of the solid phase carrier; and in addition, the solid phase carrier obtained by the amplifying method is utilized to sequence, so that a detection signal of the sequencing is strengthened, the requirements on a detection instrument are reduced, and the accuracy of the sequencing is improved in equal detection conditions.
Owner:盛司潼
Nucleic acid preparation and analysis
InactiveCN106755451AAccurate sequencingImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding siteDouble chain
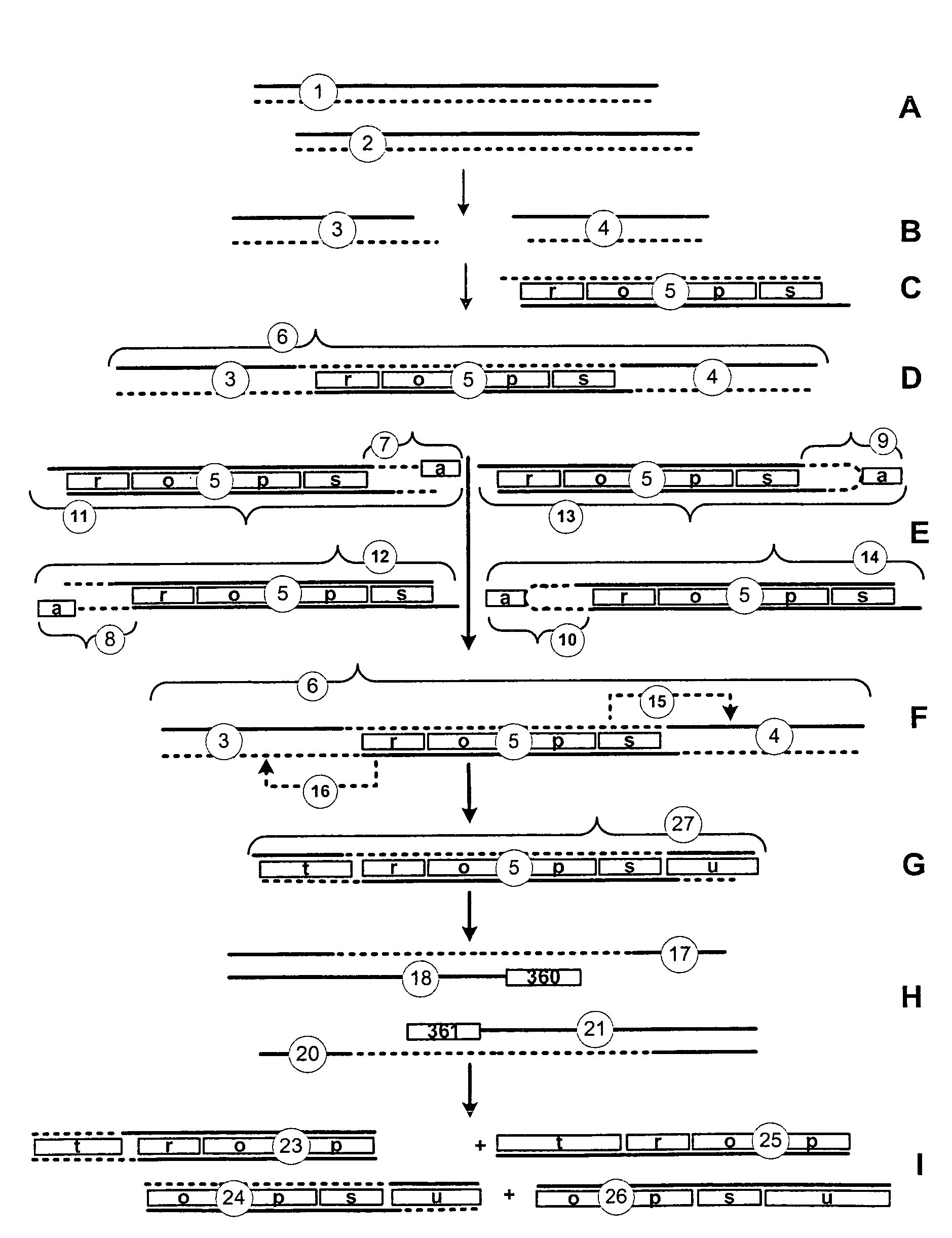
The invention discloses a method and system for preparing and analyzing nucleic acid. The method comprises the following steps: (a), connecting a linker to a single double-chain-target nucleic acid molecule, so as to enable the tail ends of the double-chain-target nucleic acid molecules to be connected, wherein the linker comprises (i) a pairing region and (ii) a non-pairing region; (b), providing (i) a linker primer which is mutually complementary with a primer binding site on a complementary chain of the on-pairing region, (ii) a target specific primer which is mutually complementary with a binding site of target nucleic acid; (c), performing amplified reaction to amplify the double-chain-target nucleic acid molecules with the tail ends being connected with each other in the presence of the linker primer and the target specific primer, so as to produce a first amplified molecule. The method has very high sensitivity for detecting nucleic acid variation, and the limit of detection (LOD) is about 0.01 to 0.001 percent in certain situations.
Owner:苏州艾达康医疗科技有限公司
Systems and methods to quantify and amplify both signaling probes for cDNA chips and genes expression microarrays
InactiveUS7482443B2Increase valueEnhanced signalSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGene Expression ArrayTherapeutic monitoring
The invention provides a series of reagent compositions and methods for making and amplifying novel cDNA based probe sets from RNA samples to improve analysis with gene expression arrays. The methods globally produce probe sets with common universal linkers at one or both ends, called WRAP-Probes, wherein the linkers do not bind to the target sequences and they can efficiently bind added reporters to the probes. The universal linkers are also designed as primer binding sites for copying and amplifying the probes, either linearly with one linker, or exponentially with double linkers. The capacity to globally and exponentially amplify the probe set by PCR is a primary advantage. Adding reporters by terminal linkers also improves quantification since each probe gets equivalent signaling. The invention allows expression analysis of small research, clinical and forensic samples to enable improved diagnostics, drug discovery, therapeutic monitoring, and medical, agricultural and general research.
Owner:GENETAG TECH
Fast and efficient construction method of normalized full-length cDNA library
ActiveCN102797044AAchieve captureConcise and efficient full-length mRNA screening functionLibrary creationProtein nucleotide librariesPhosphateNucleotide
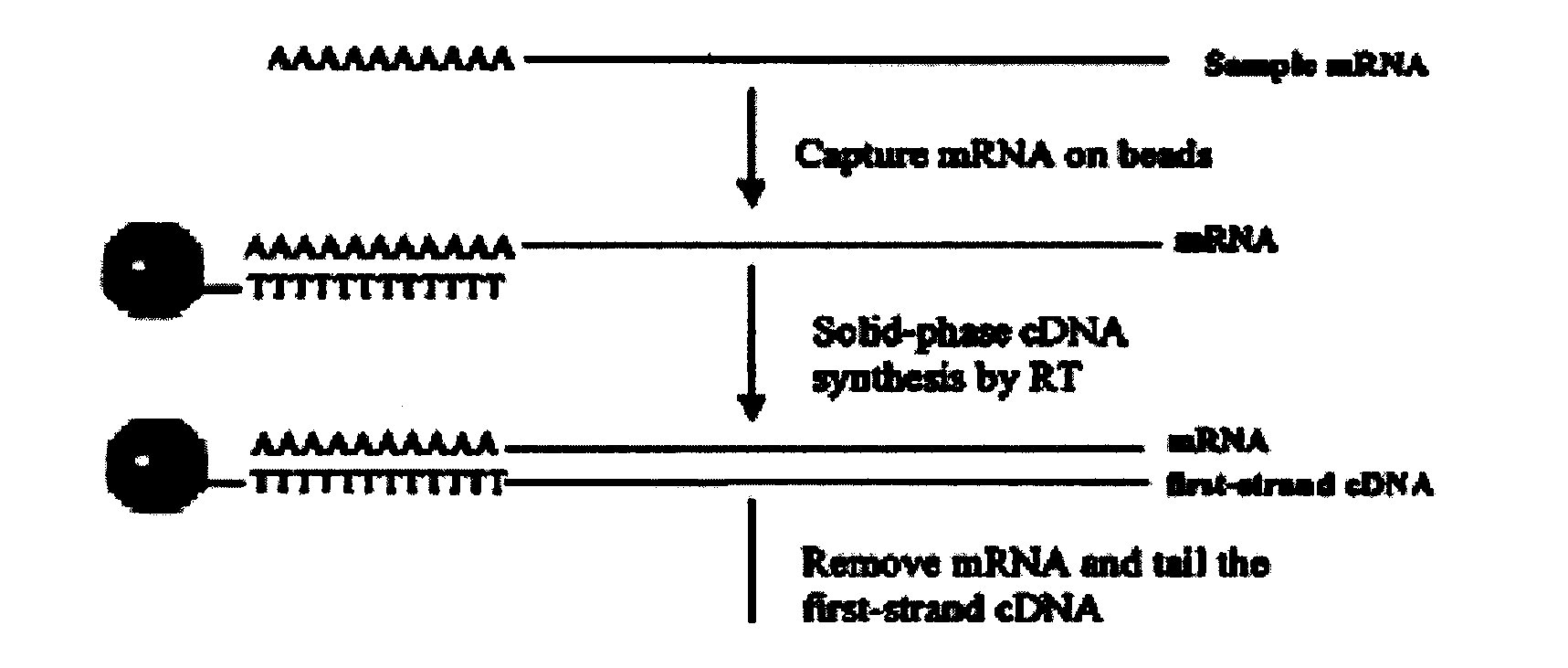
The invention relates to a fast and efficient construction method of a normalized full-length cDNA library. The method consists of: using specific 5-OH oligonucleotide to close non-full-length mRNA, then employing tobacco acid pyrophosphatase to remove a cap structure from the mRNA5' end to make a phosphate group at the cap structure of the mRNA5' end exposed, adopting an efficient RNA connection system to connect a section of optimized oligomeric RNA to the mRNA 5' end to serve as a primer binding site for triggering synthesis of second strand cDNA, finally conducting reverse transcription, two-strand synthesis as well as graded purification, and cloning the double-stranded DNA into a vector. The method can concisely and efficiently screen full-length mRNA, and realizes full-length mRNA capture of eukaryotes. The mRNA5' tail end contains a biotin label, which can be used for full-length mRNA separation. The used oligonucleotide primer contains optimized modification method and a nucleotide sequence, thus being able to realize full-length mRNA capture of eukaryotes, reverse transcription and DNA synthesis.
Owner:BEIJING VJT BIO CO LTD
Producing, cataloging and classifying sequence tags
InactiveUS7618778B2Overcome limitationsShortening the linear chimeric nucleic acid intermediatesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCatalogingDouble strand
Owner:KAUFMAN JOSEPH C
Digital amplification with primers of limited nucleotide composition
PendingCN111183229AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotide compositionNucleic acid
The invention provides methods of digital amplification using primers of limited nucleotide composition. Limited nucleotide composition means that the primers are underrepresented in at least one nucleotide type. Such primers have much reduced capacity to prime from each other or to extend initiated by mispriming from other than at their intended primer binding sites in a target nucleic acid.
Owner:ATILA BIOSYST
Systems and Methods to Quantify and Amplify Both Signaling and Probes for CDNA Chips and Gene Expression Microarrays
InactiveUS20090275029A1Increase valueEnhanced signalSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCDNA MicroarraysGene Expression Array
The invention provides a series of reagent compositions and methods for making and amplifying novel cDNA based probe sets from RNA samples to improve analysis with gene expression arrays. The methods globally produce probe sets with common universal linkers at one or both ends, called WRAP-Probes, wherein the linkers do not bind to the target sequences and they can efficiently bind added reporters to the probes. The universal linkers are also designed as primer binding sites for copying and amplifying the probes, either linearly with one linker, or exponentially with double linkers. The capacity to globally and exponentially amplify the probe set by PCR is a primary advantage. Adding reporters by terminal linkers also improves quantification since each probe gets equivalent signaling. The invention allows expression analysis of small research, clinical and forensic samples to enable improved diagnostics, drug discovery, therapeutic monitoring, and medical, agricultural and general research.
Owner:GENETAG TECH
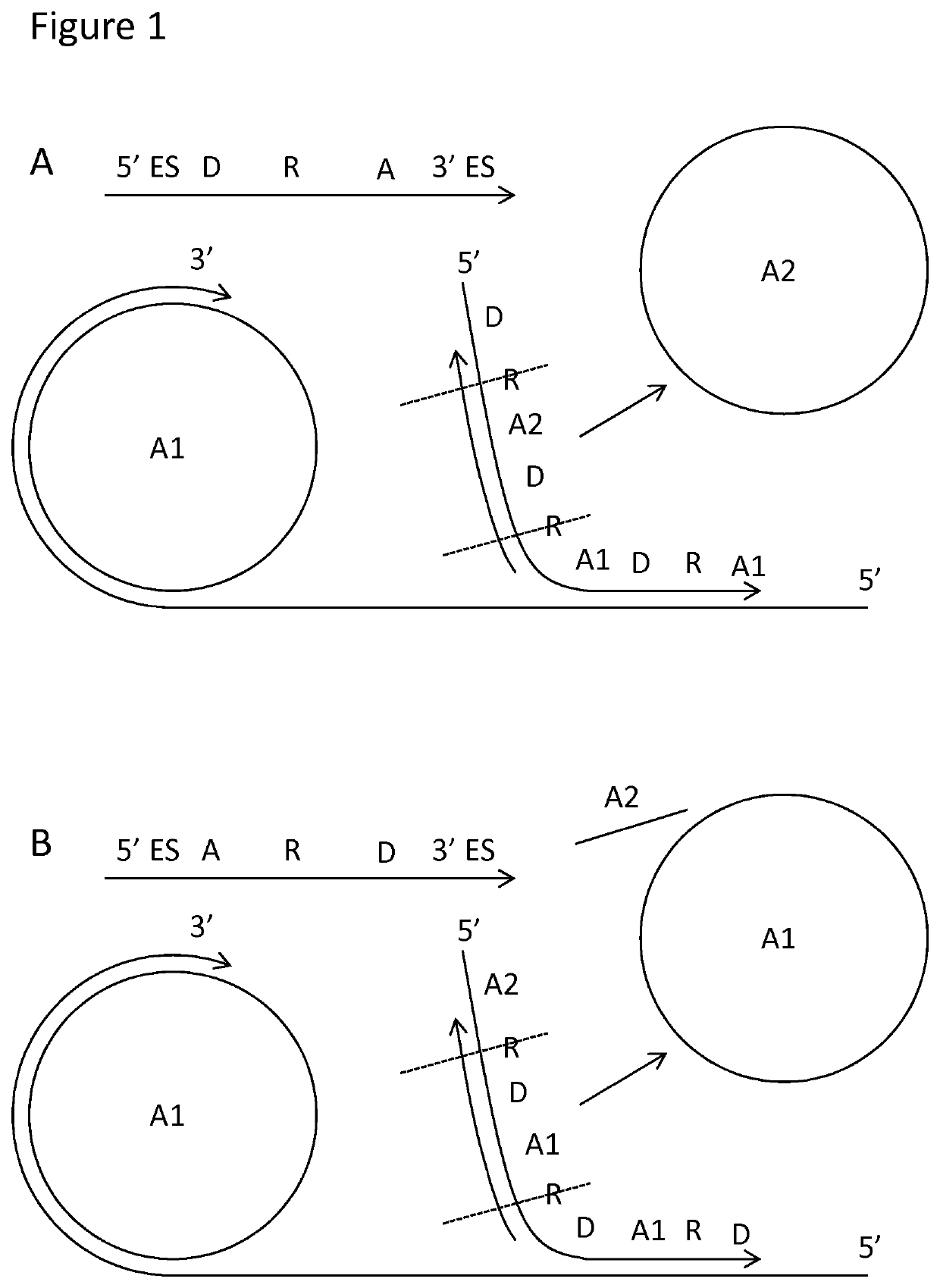
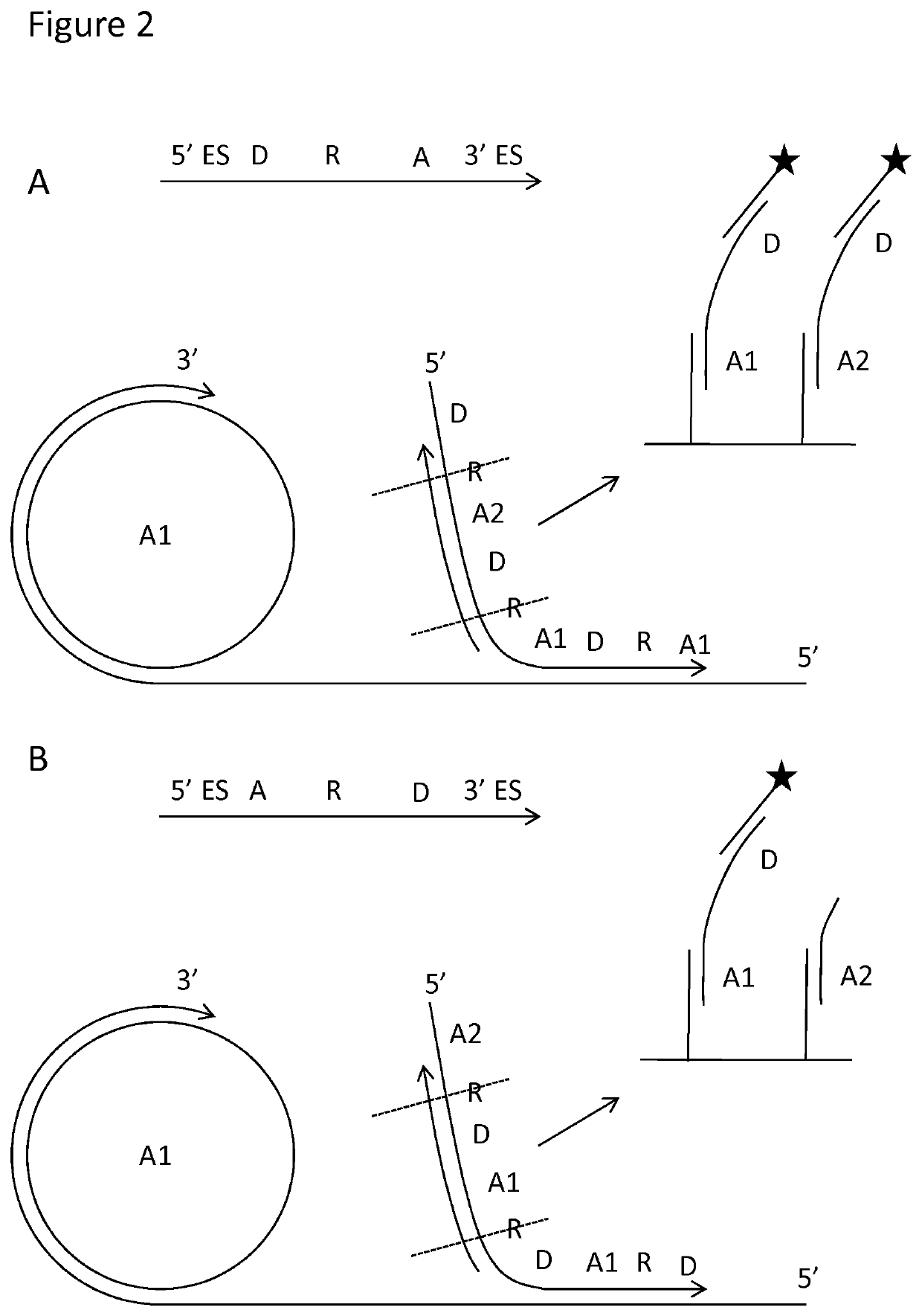
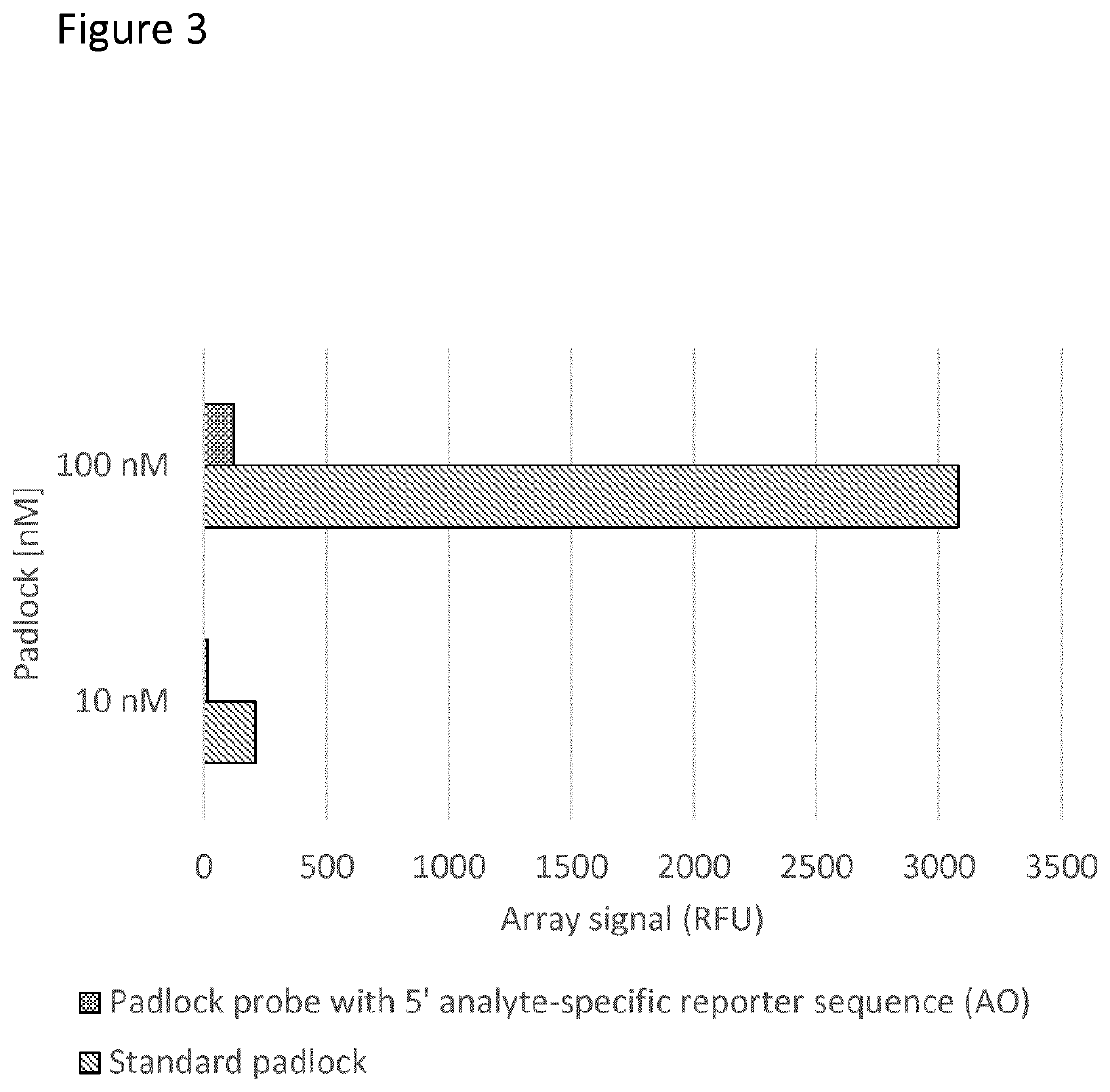
Padlock probe detection method
PendingUS20200040376A1Reduce background signalMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteBiochemistry
Multiplexed methods of detecting an analyte in a sample using two or more padlock probes each specific to a different target sequence are described. The target sequence is either part of an analyte or indicative of the presence of an analyte in the sample. Each padlock probe includes an analyte-specific reporter sequence, and either a restriction cleavage site located 3′ of the analyte-specific reporter sequence, and / or a first amplification primer binding site for an amplification reaction. Where the padlock probe includes a restriction cleavage site, cleavage at the restriction cleavage site occurs 3′ of the analyte-specific reporter sequence. Where the padlock probe includes a first amplification primer binding site for the further amplification reaction, it does not contain a second amplification primer binding site 5′ of the analyte-specific reporter sequence. Panels of probes and kits for the same are also described.
Owner:Q LINEA AB
System and Methods to Quantify and Amplify Both Signaling and Probes for cDNA Chips and Gene Expression Microarrays
InactiveUS20120157343A1Increase valueEnhanced signalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCDNA MicroarraysGene Expression Array
The invention provides a series of reagent compositions and methods for making and amplifying novel cDNA based probe sets from RNA samples to improve analysis with gene expression arrays. The methods globally produce probe sets with common universal linkers at one or both ends, called WRAP-Probes, wherein the linkers do not bind to the target sequences and they can efficiently bind added reporters to the probes. The universal linkers are also designed as primer binding sites for copying and amplifying the probes, either linearly with one linker, or exponentially with double linkers. The capacity to globally and exponentially amplify the probe set by PCR is a primary advantage. Adding reporters by terminal linkers also improves quantification since each probe gets equivalent signaling. The invention allows expression analysis of small research, clinical and forensic samples to enable improved diagnostics, drug discovery, therapeutic monitoring, and medical, agricultural and general research.
Owner:GENETAG TECH
Ola-based methods for the detection of target nucleic avid sequences
InactiveUS8808991B2Low costSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyNucleic acid sequence
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Selective terminal tagging of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20120156729A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionAmplification dna
Methods are provided for adding a terminal sequence tag to nucleic acid molecules for use in RNA or DNA amplification. The tag introduced may be used as a primer binding site for subsequent amplification of the DNA molecule and / or sequencing of the DNA molecule and therefore provides means for identification and cloning of the 5′-end or the complete sequence of mRNAs.
Owner:CELLSCRIPT
System and method for constructing sequencing library
ActiveCN102296065BEasy to buildAvoid the phenomenon of connecting the same connectorMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBinding siteDNA fragmentation
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, and provides a system and a method for constructing a sequencing library. The system and the method comprise a joint element and a method for applying the joint element to the construction of a sequencing library. The joint element is a bifurcate double-chain nucleic acid joint with a bifurcate region and a paired region orderly included at the 5' and the 3' ends, wherein two single chains of the bifurcate region respectively comprise at least one amplification primer binding site, and the paired region comprises at least one restrictionenzyme site. The joint element of the invention can prevent the self-connection phenomenon of the joint element and the occurrence of a non-object joint element-DNA fragment compound during the library construction.
Owner:WUHAN CONSIDERIN GENE & HEALTH TECH CO LTD
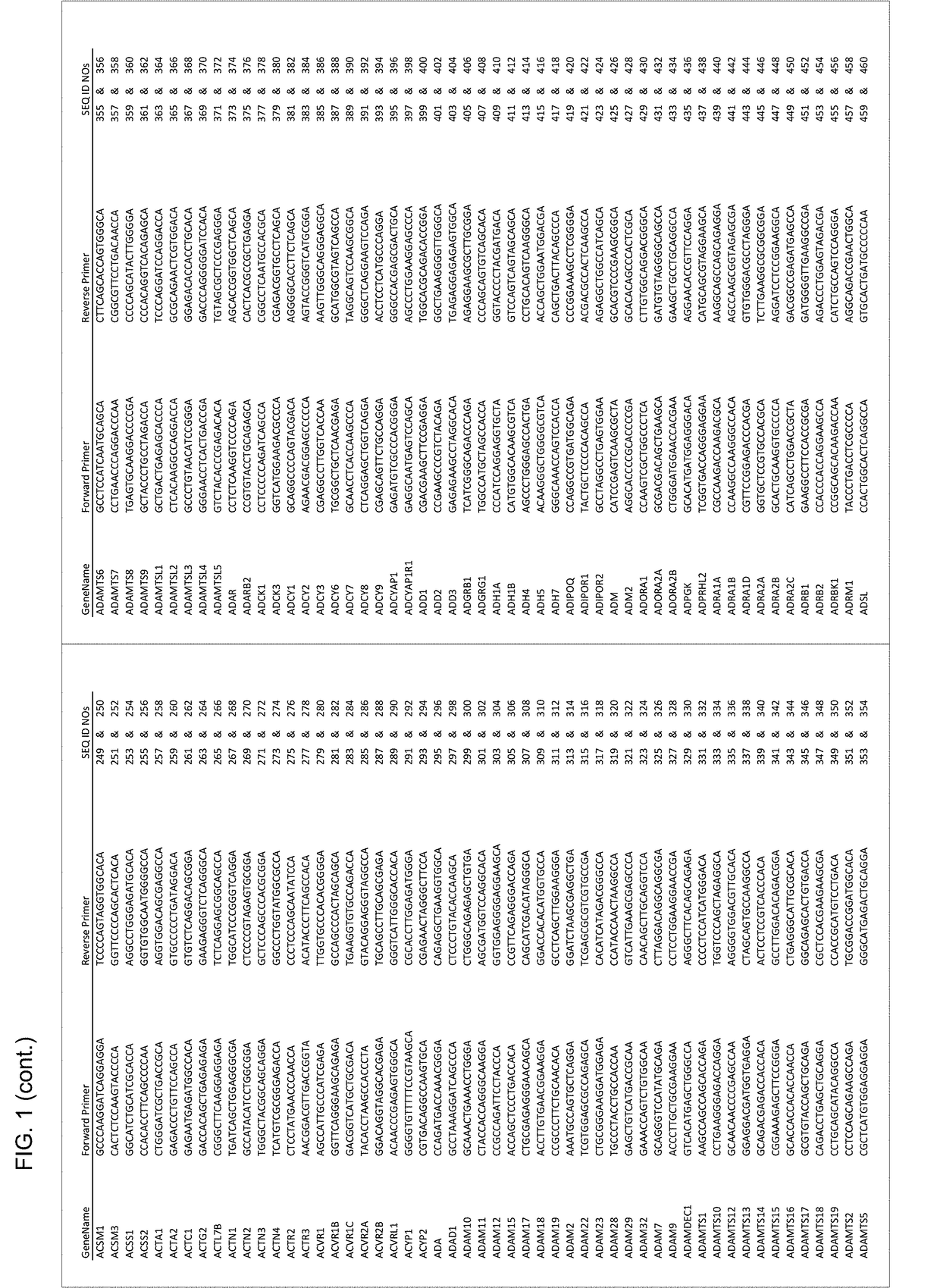
Experimentally Validated Sets of Gene Specific Primers for Use in Multiplex Applications
ActiveUS20180245164A1Minimizes primer dimerization and cross-reactivityImprove efficacyMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding siteHigh throughput sequence
Sets of experimentally validated gene specific primer pairs are provided. Embodiments of the sets include 10 or more gene specific primer pairs of forward and reverse primers. The forward and reverse primers of each primer pair include gene specific primers that are experimentally validated as suitable for use in a multiplex amplification assay. In some instances, each of the forward and reverse primers includes an anchor domain that includes a universal primer binding site. The sets find use in a variety of different applications, including high-throughput sequencing applications.
Owner:CELLECTA
Methods of Whole Genome Digital Amplification
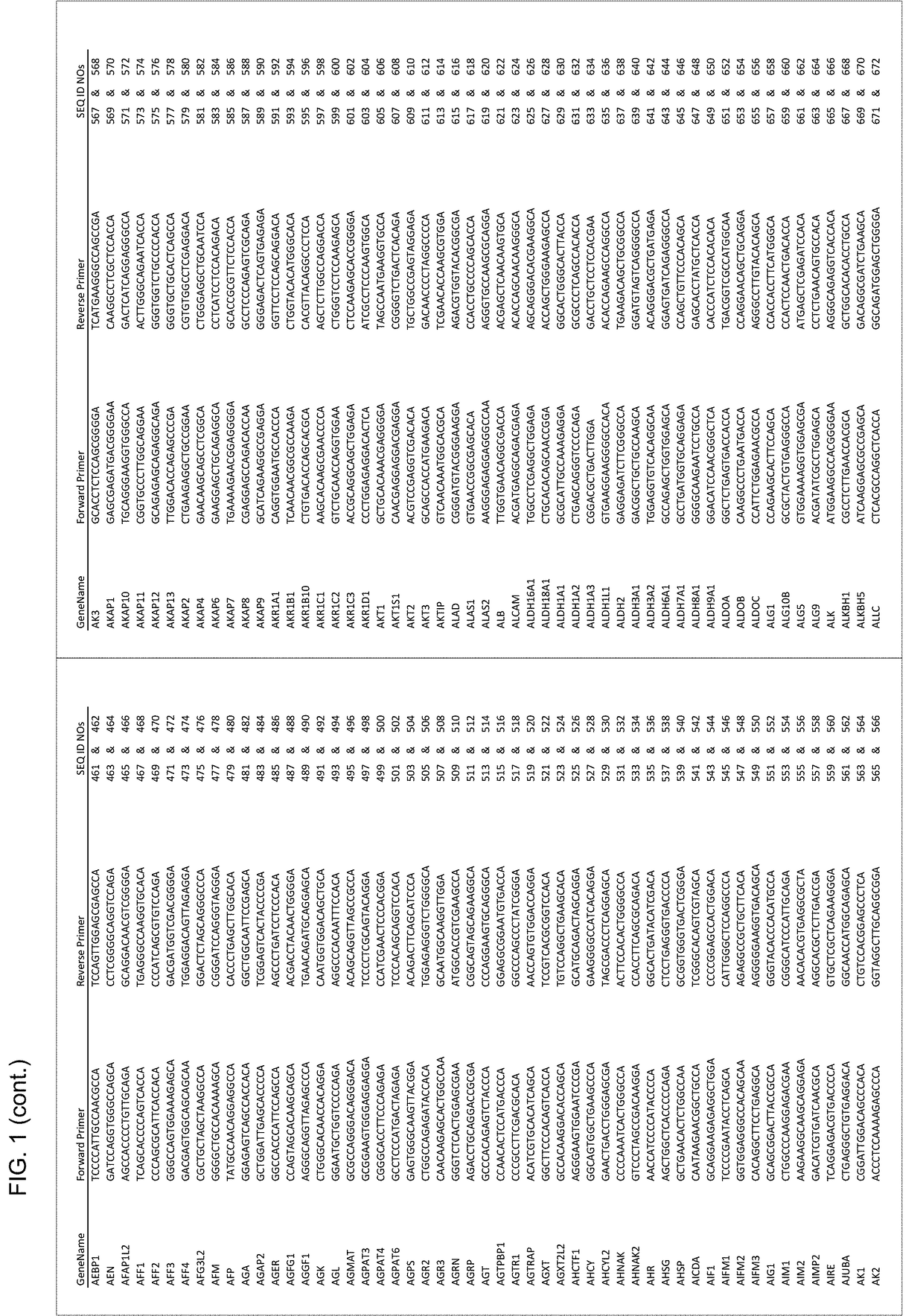
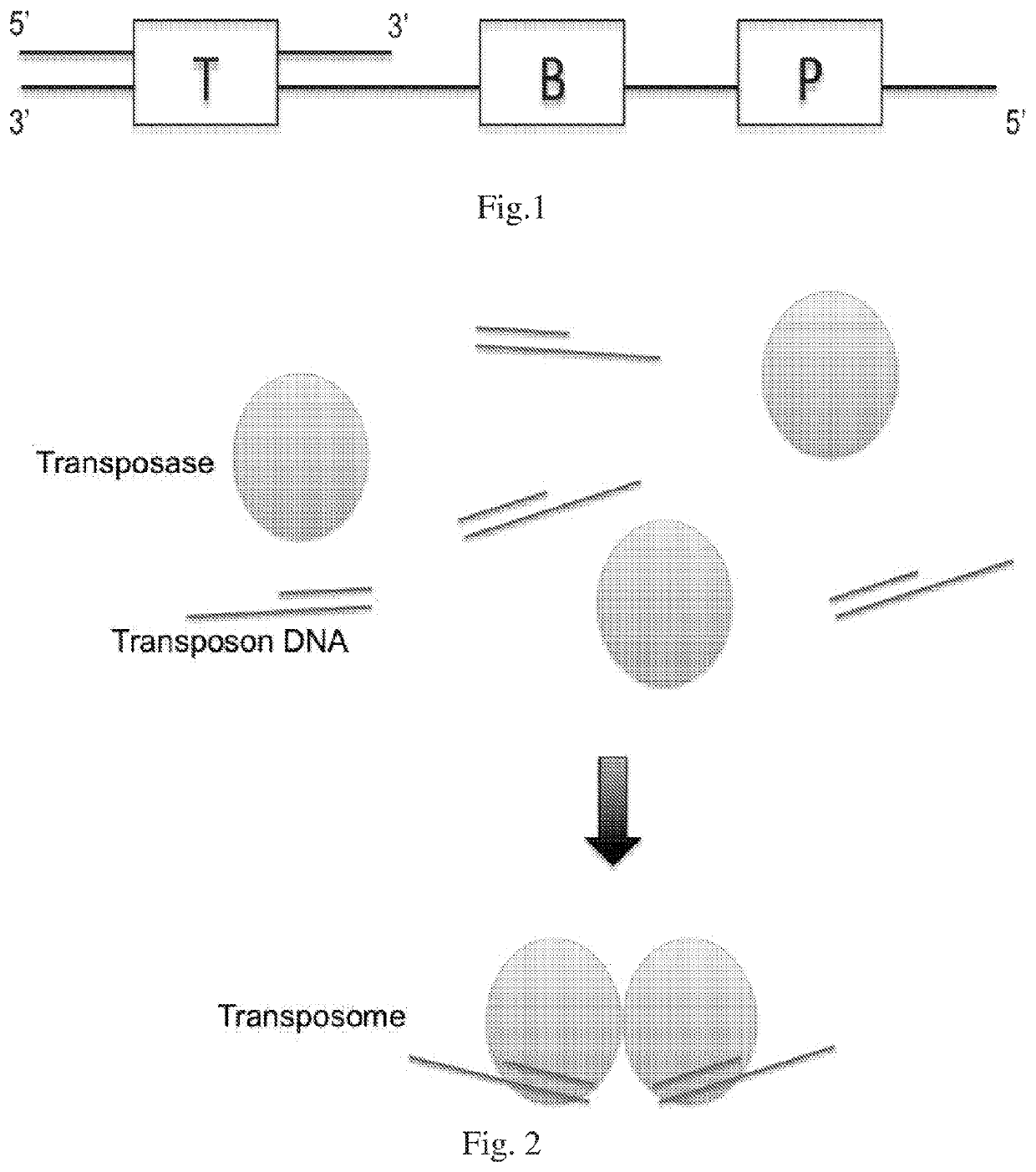
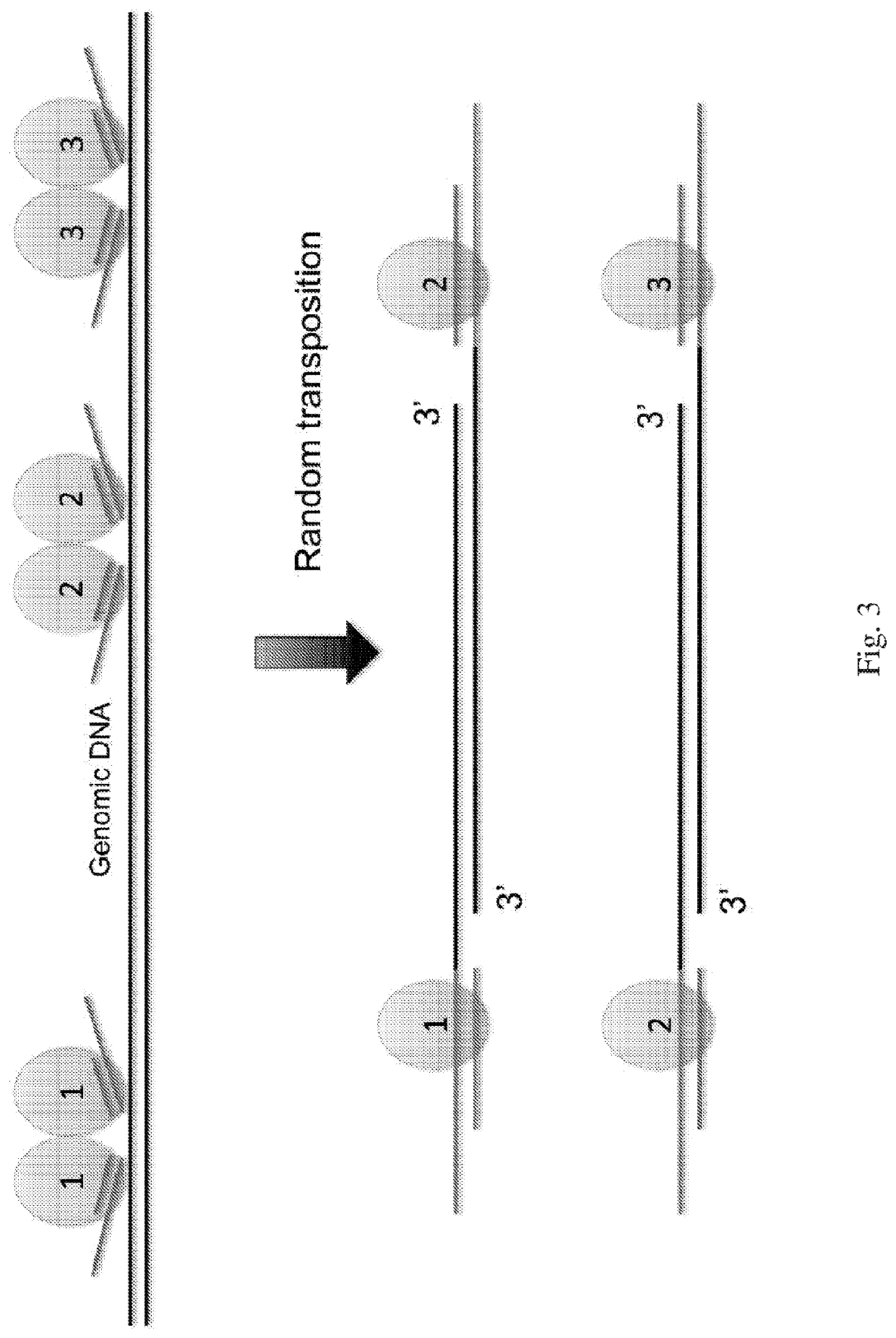
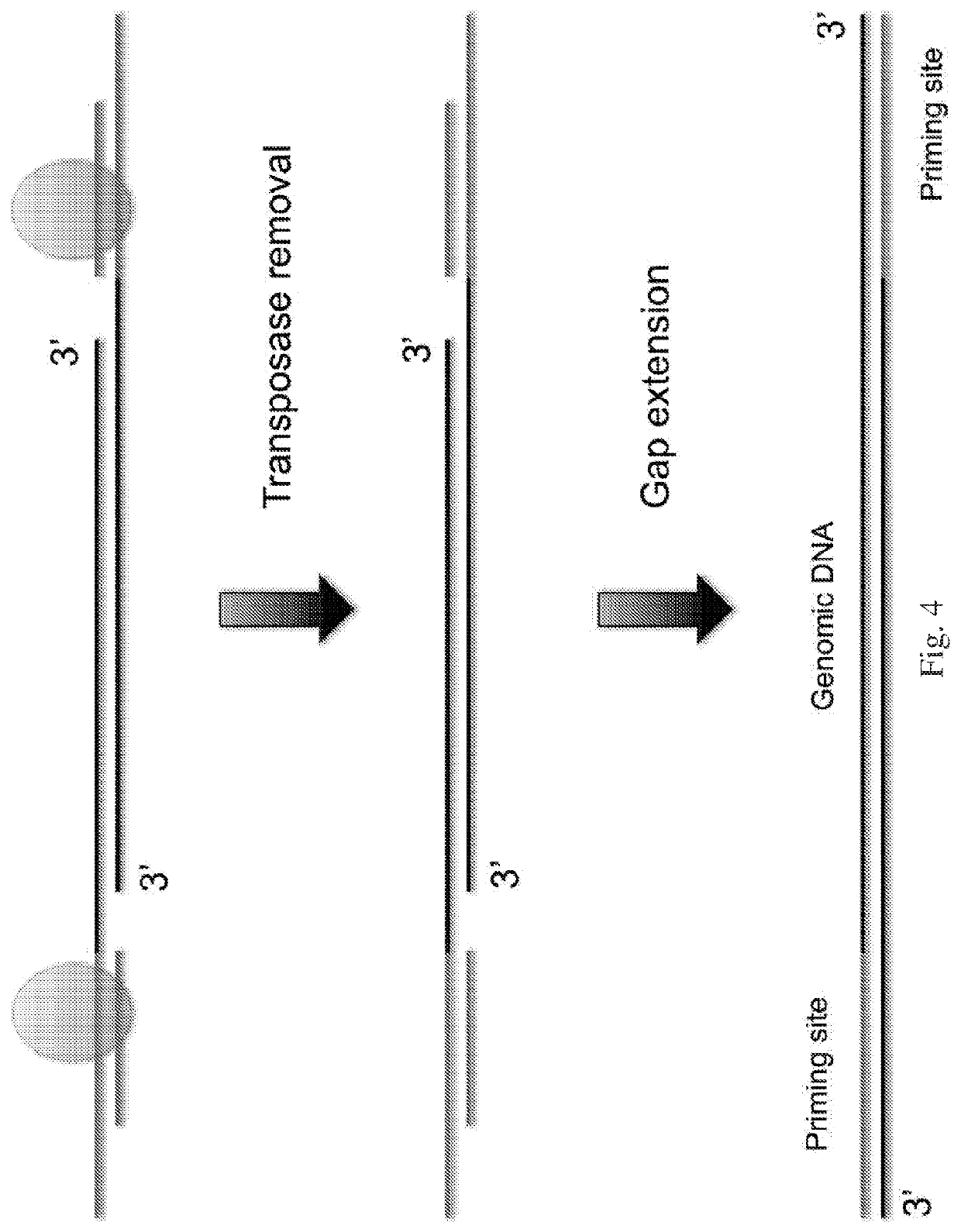
InactiveUS20210285038A1Large coverageImprove fidelityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentGenetics
The present disclosure provides a method for genomic DNA amplification, such as whole genome amplification, including using a transposase system to make fragments of the genomic DNA including primer binding sites, isolating in oil each fragment within its own aqueous microdroplet along with PCR amplification reagents, amplifying each fragment within its own aqueous microdroplet, demulsifying the microdroplets to obtain the amplicons and sequencing the amplicons.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
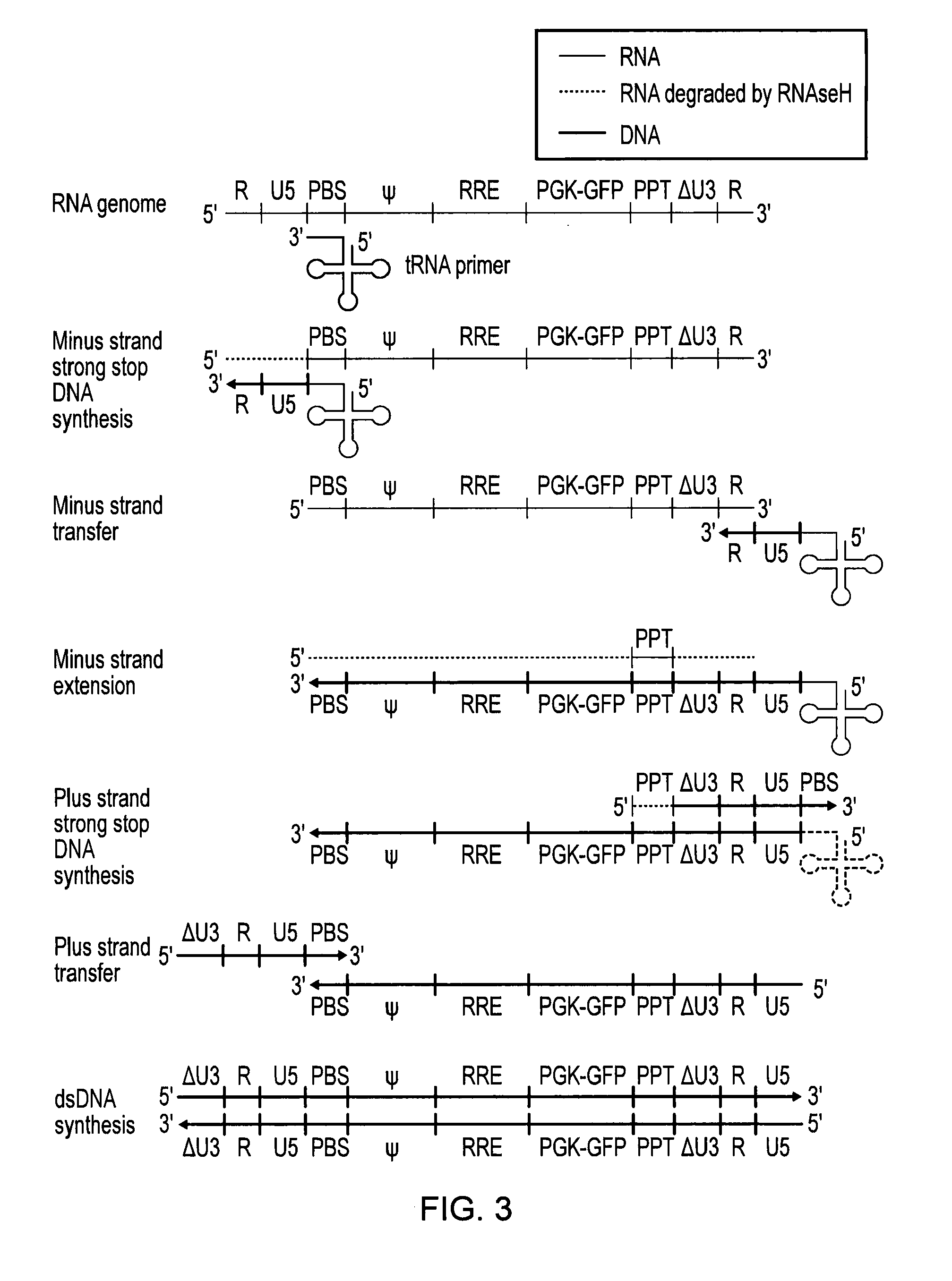
Retroviral vectors
ActiveUS20160230191A1Minimise ci elementReduce disadvantagesVectorsDrug compositionsBinding siteReverse transcriptase
There is disclosed a retroviral vector comprising a primer binding site, a long terminal repeat and an RNA packaging sequence, wherein the RNA packaging sequence is located 3′ of the long terminal repeat and no long terminal repeat is located 3′ of the RNA packaging sequence such that reverse transcription initiated at the primer binding site does not lead to reverse transcription of the RNA packaging sequence into vector DNA in a target cell. Also described is a host cell, a virion, a pharmaceutical composition, a method and uses including or involving the vector described above. Further, a cell or transgenic animal produced by using the vector is also described.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com