Nucleic acid preparation and analysis
A target nucleic acid and molecular technology, applied in the field of gene mutation detection, can solve the problems of underrepresentation, overrepresentation, population deviation, etc., and achieve the effect of accurate sequencing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
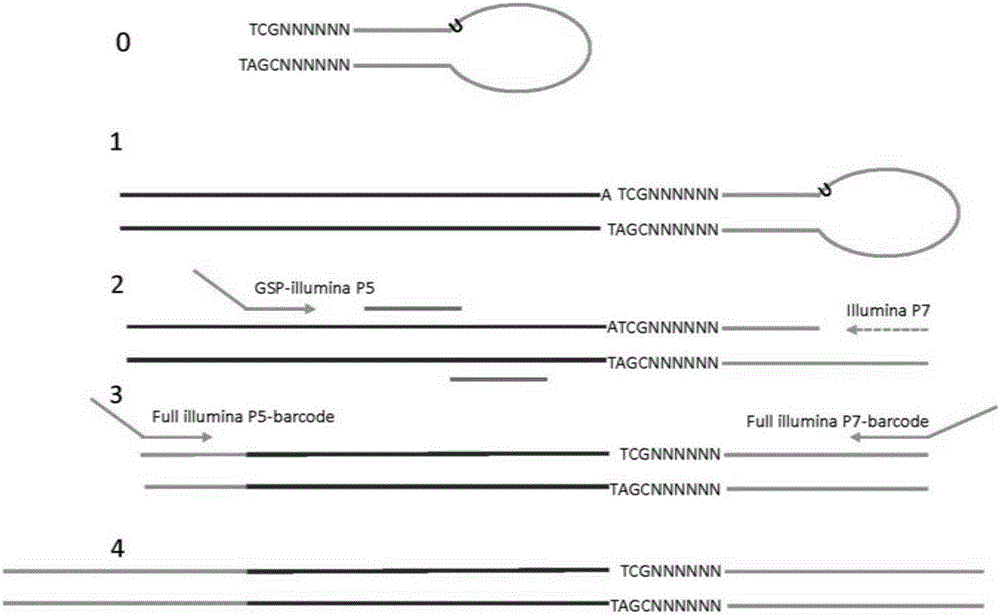
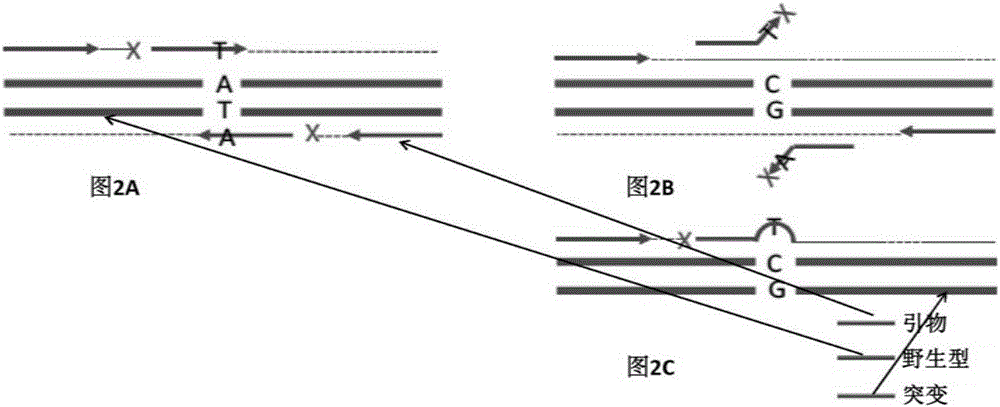
[0169] In this embodiment, the method disclosed above is implemented by taking six mutation hotspots EGFR T790, L858R, E19_del, KRAS G12V, Q61H, and BRAFV600E as examples. The method will be described in detail below using EGFR T790 as the double-stranded target nucleic acid template.
[0170] (1) The connector structure used is a universal U-shaped Illumina universal connector:
[0171]
[0172] The position of the short line is the connection point of the linker, that is (the 12nt on the right (GCTCTTCCGATC in linker sequence 1 and the CGAGAAGGCTAG fragment in linker sequence 2) is the pairing region) pairing region; other parts are non-pairing regions; the non-pairing of this linker structure The region forms a U-joint structure.
[0173] The linker structure is a U-shaped linker formed by pairing both ends of a nucleic acid sequence: 5'P-GATCGGAAGAGCACACGTCTGAACTCCAGTC-U-ACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATC*T3'. After digestion, the linker sequence 1 used: 5'ACACTCTTTCCCT...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com