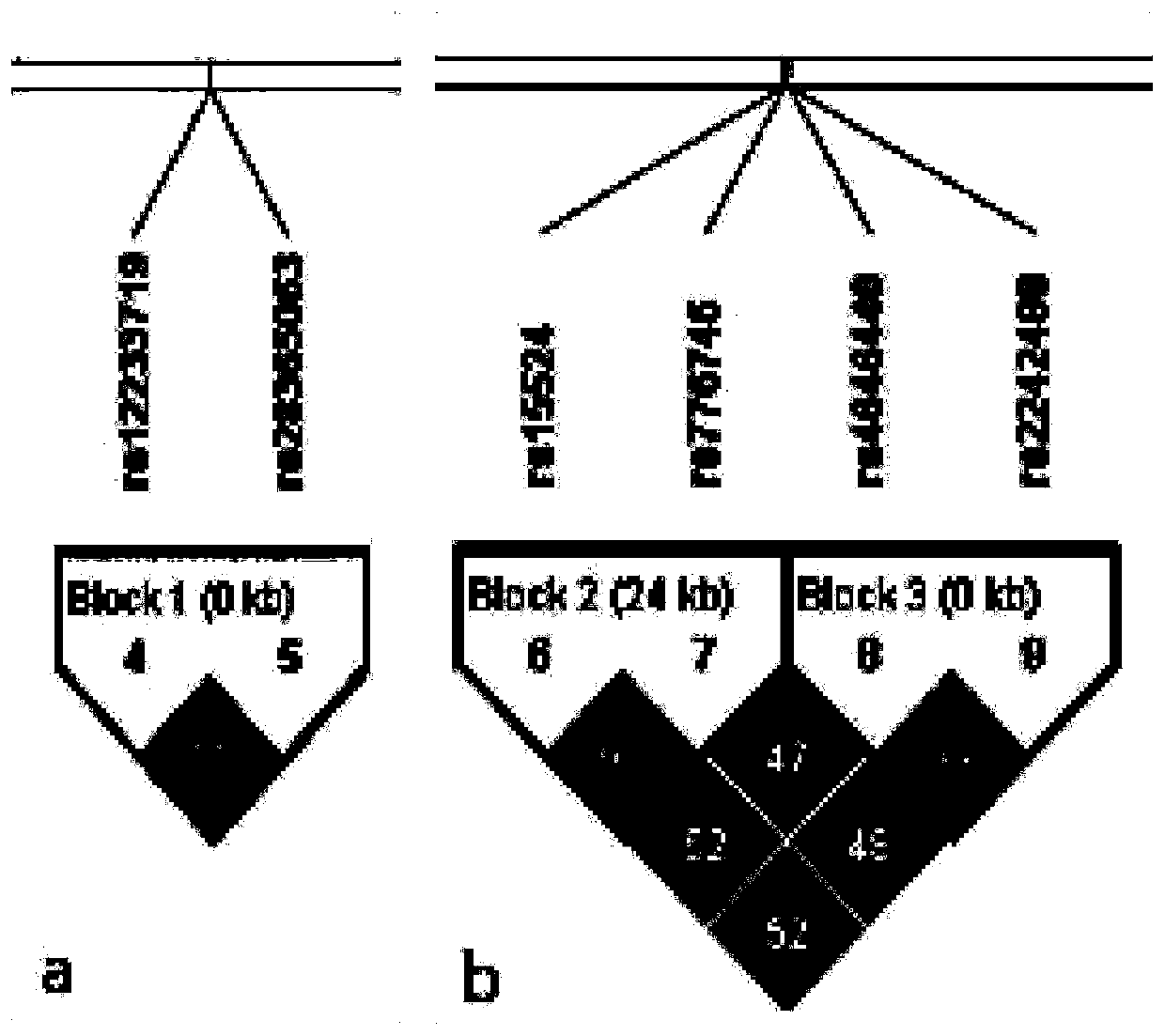
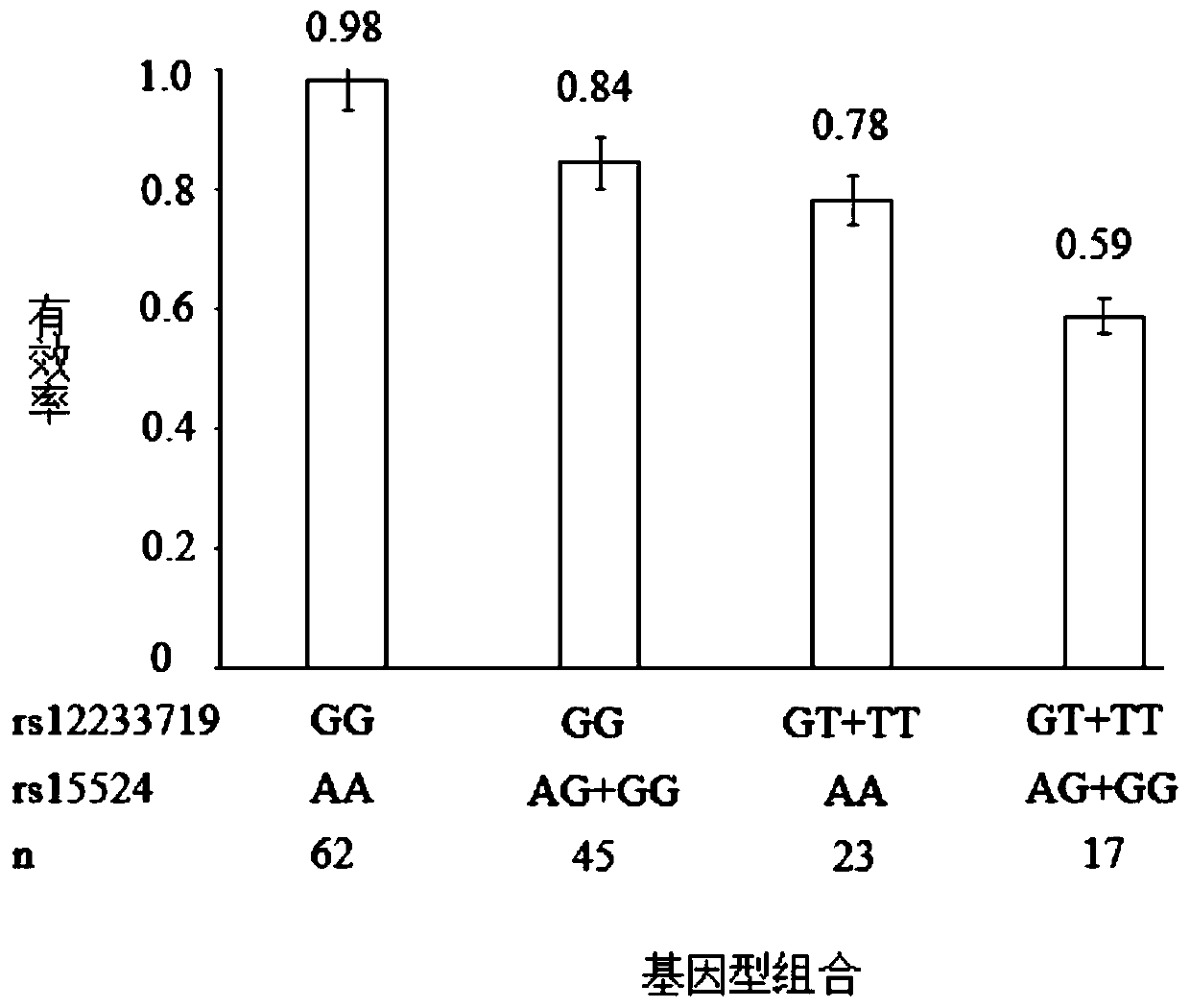
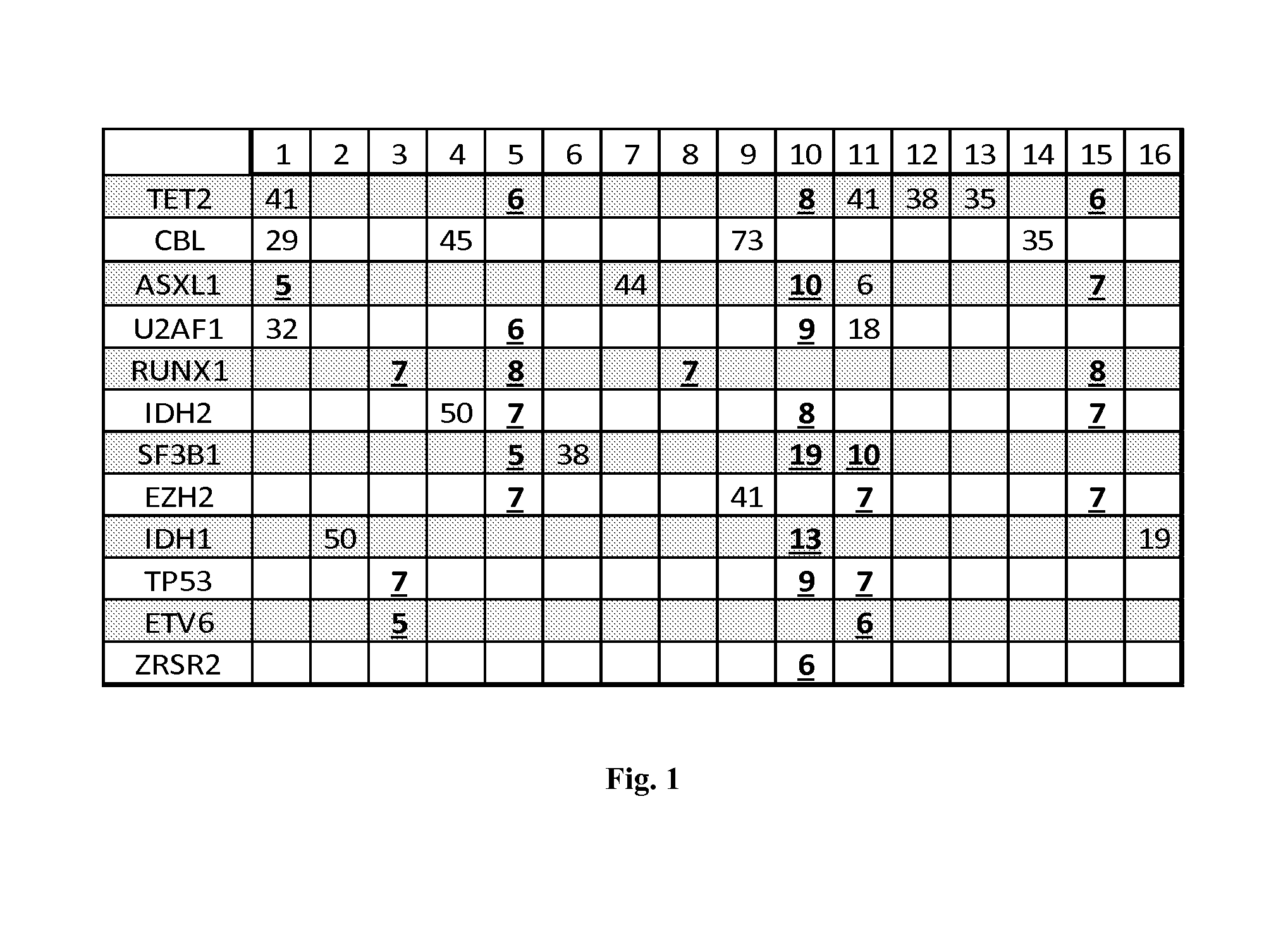
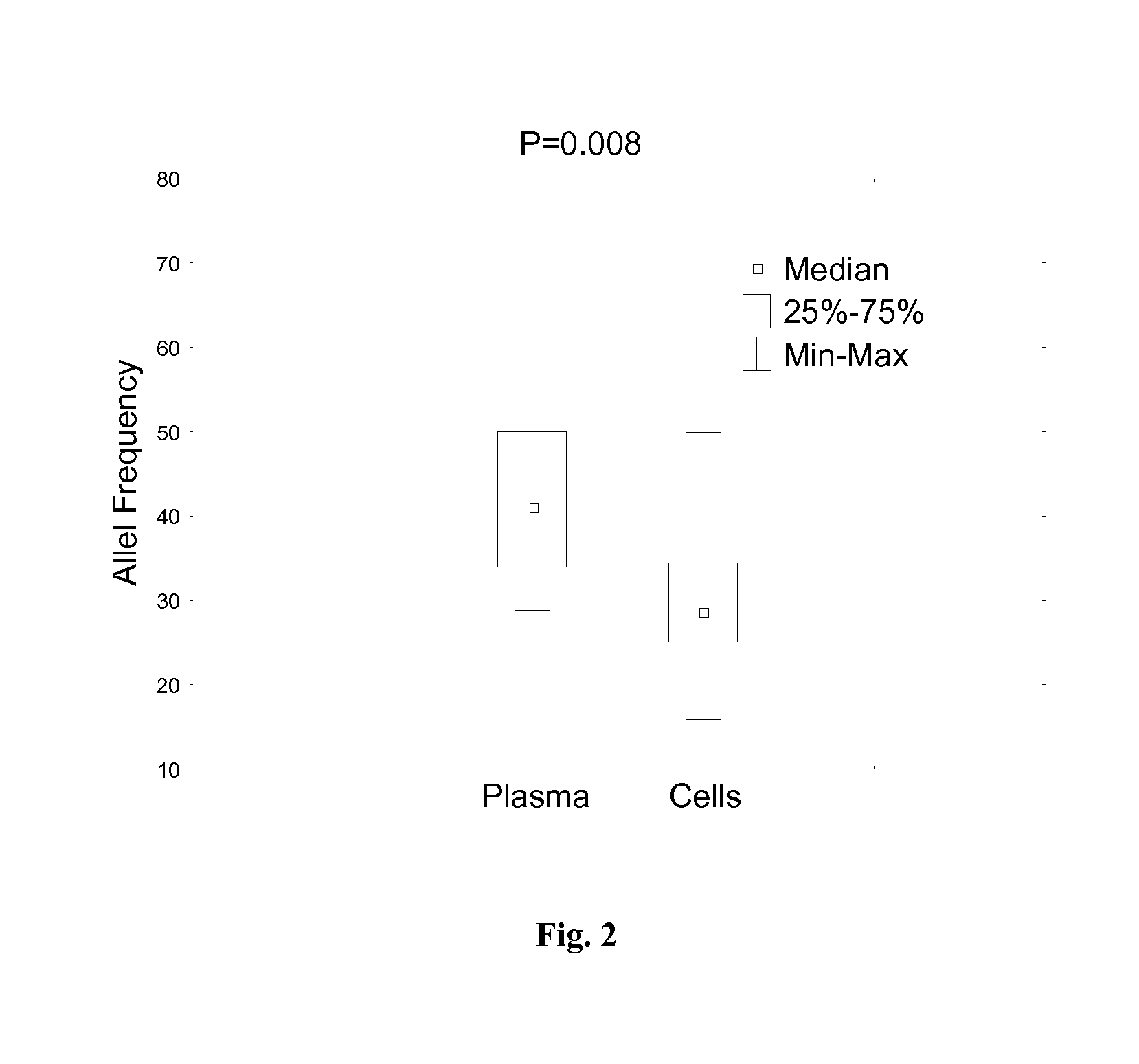
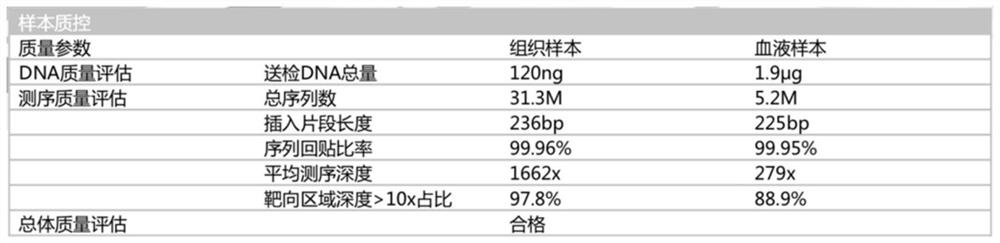
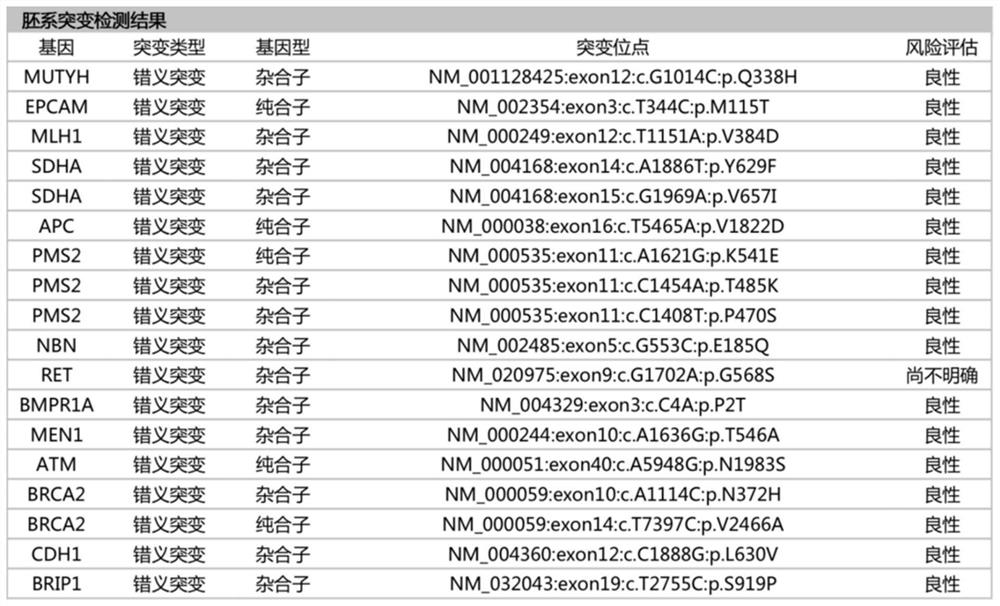
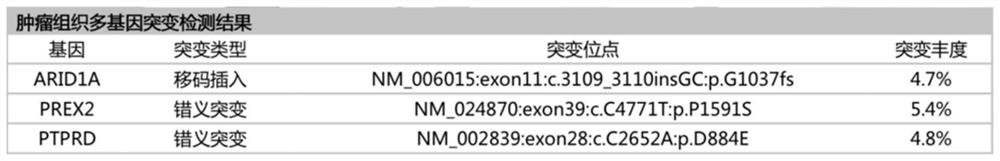
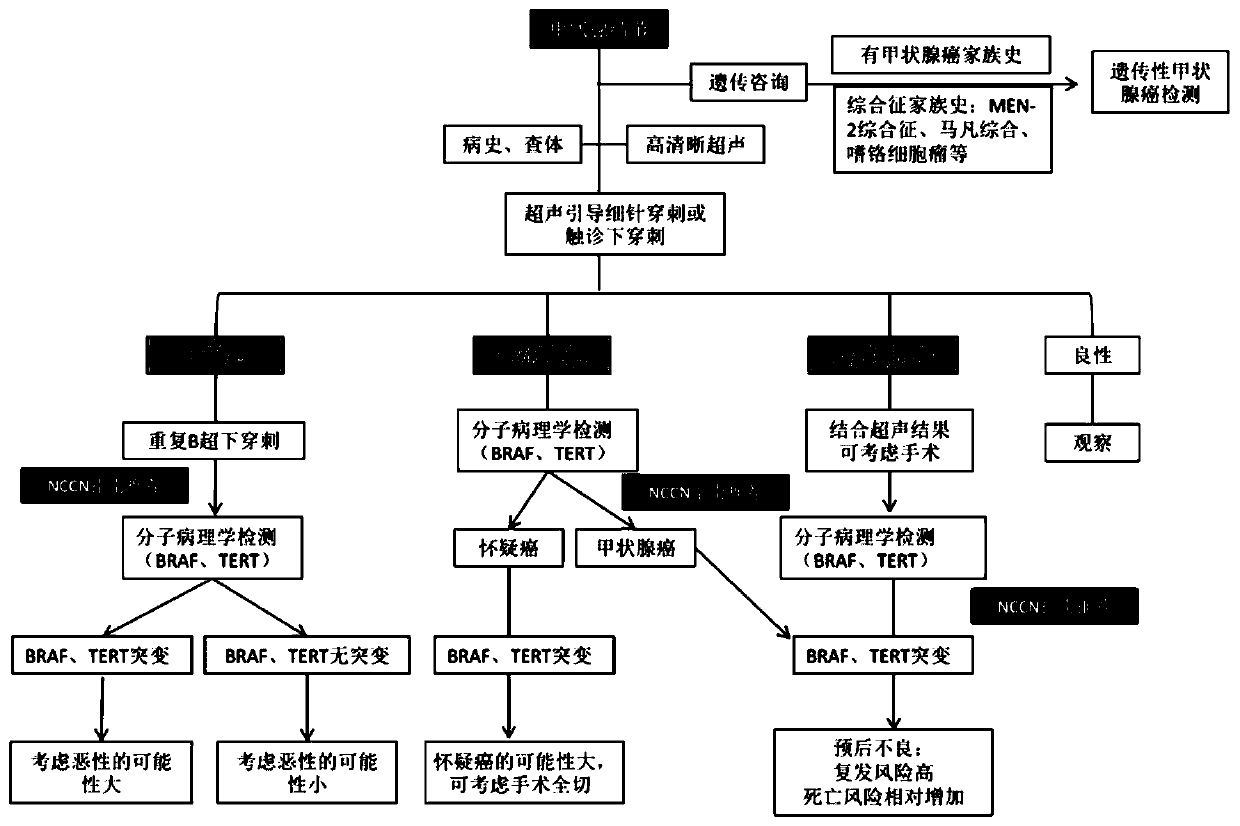
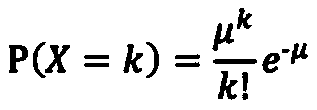Patents
Literature
168 results about "Deep sequencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
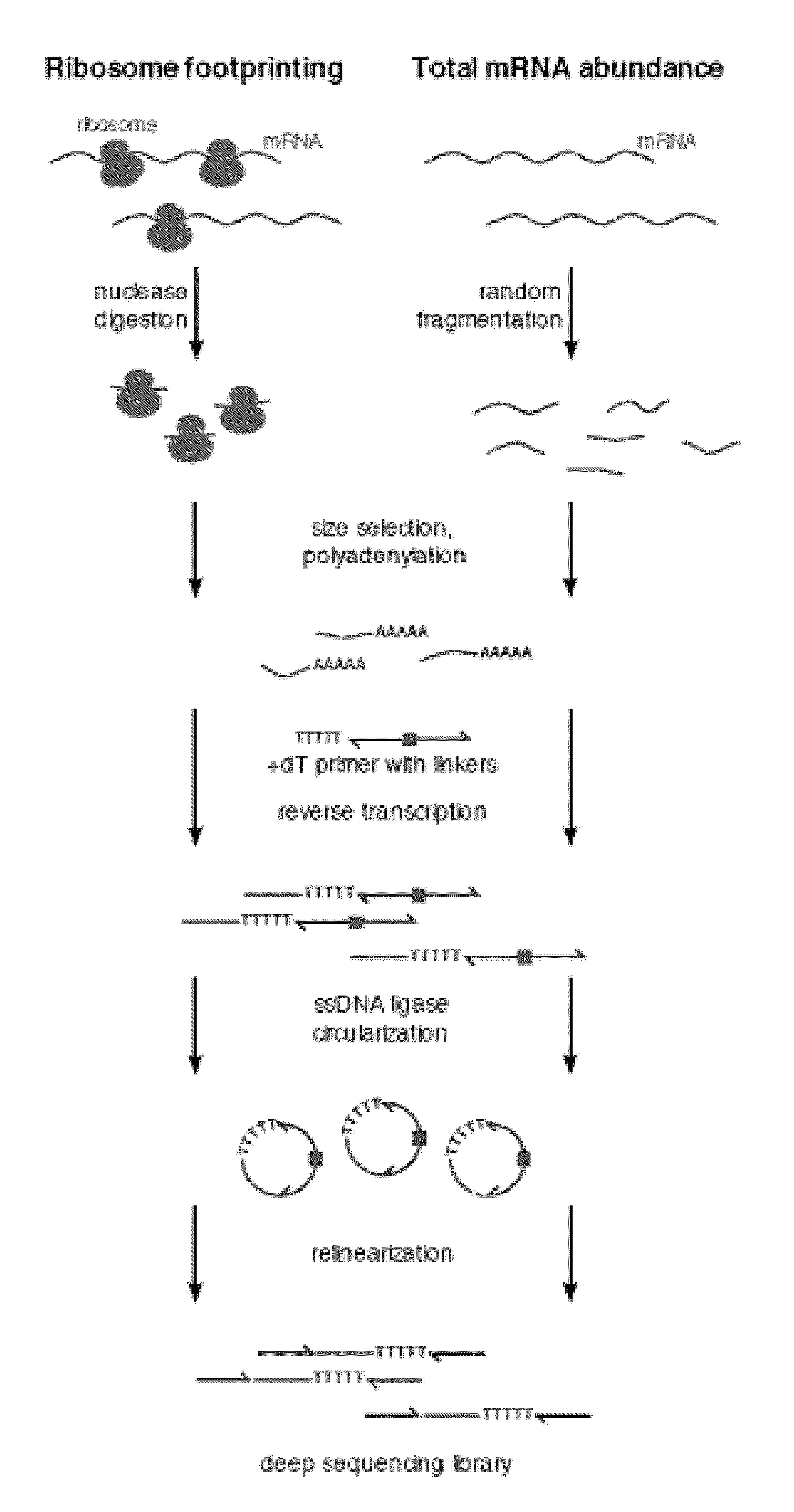
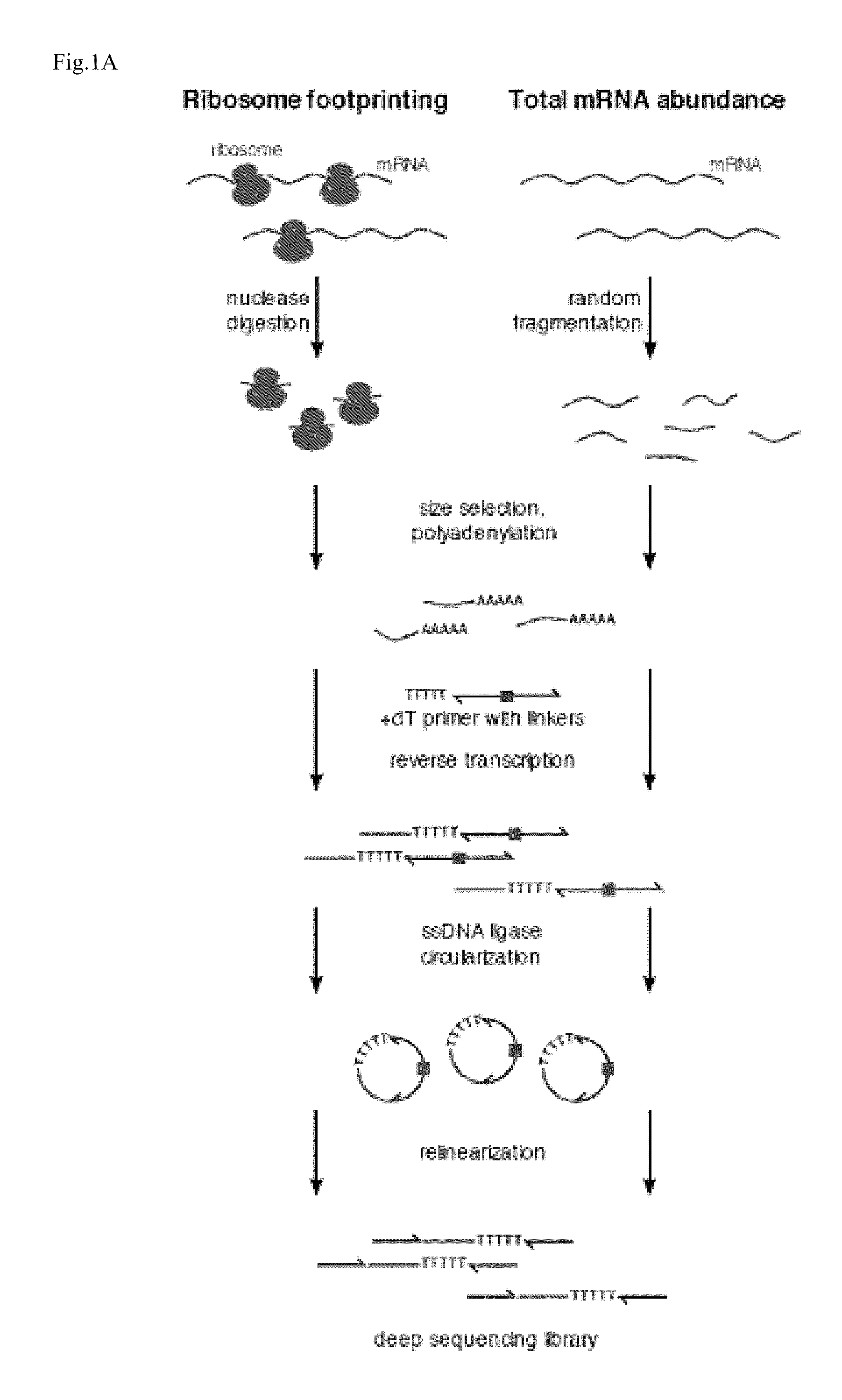
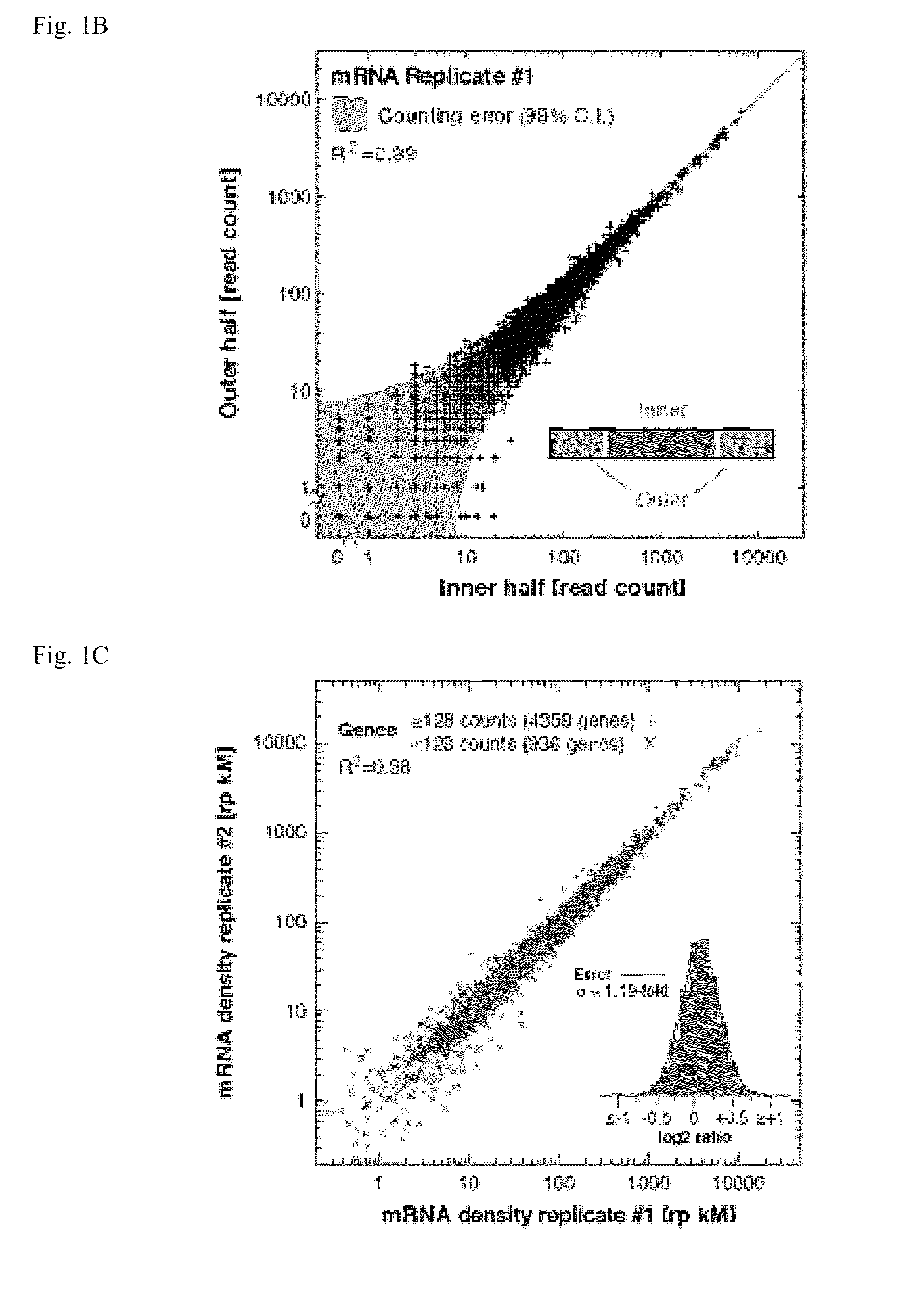
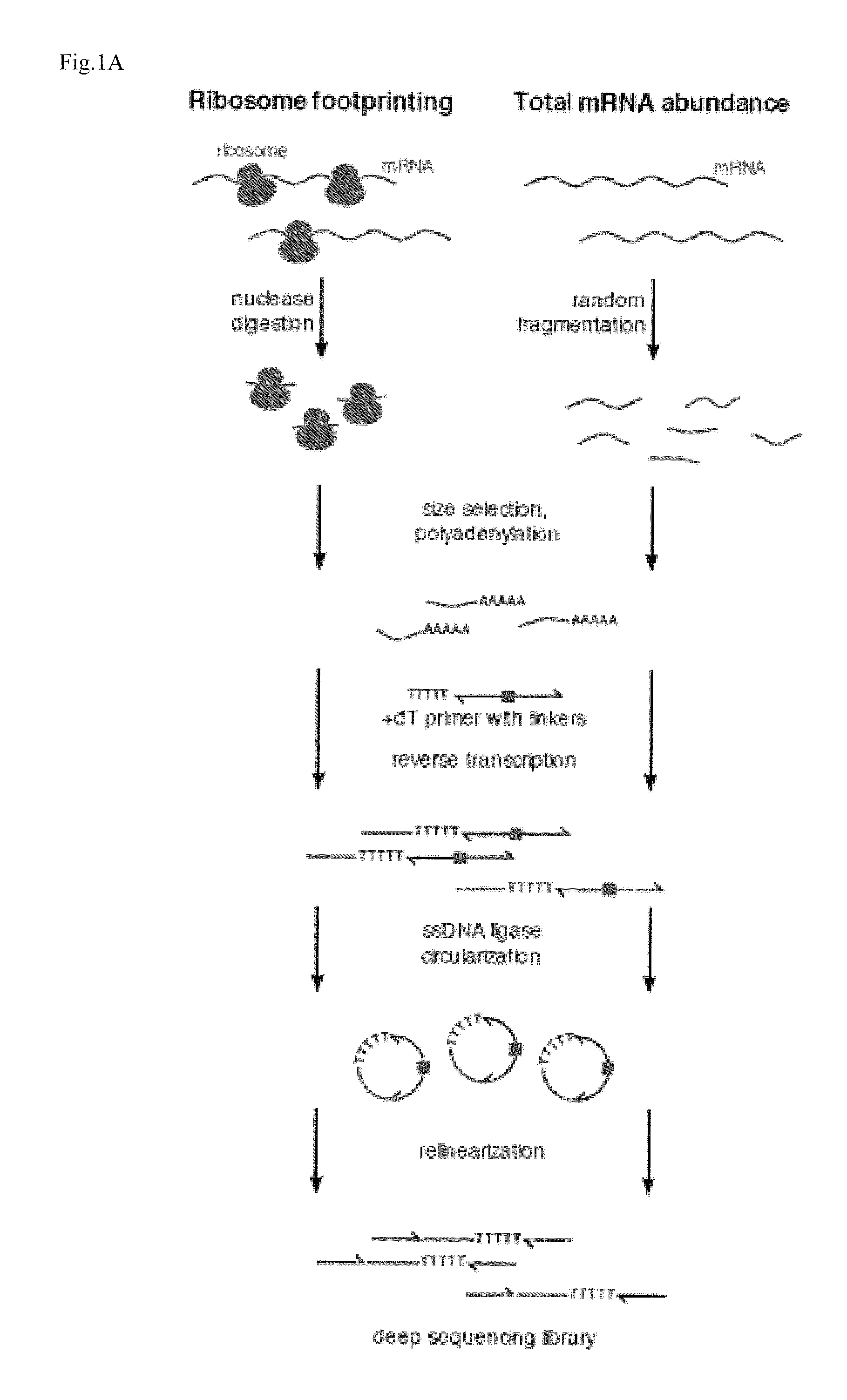
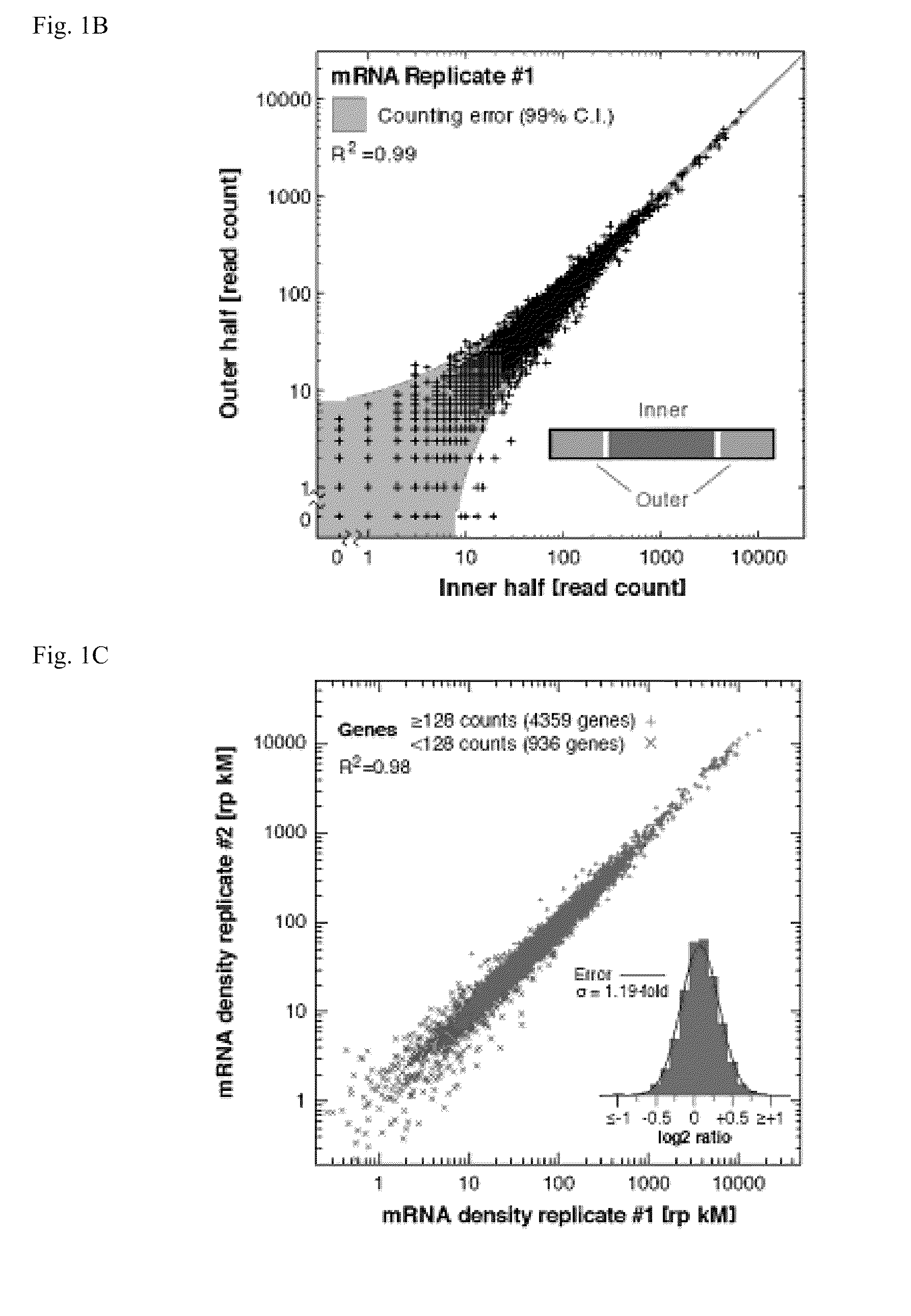
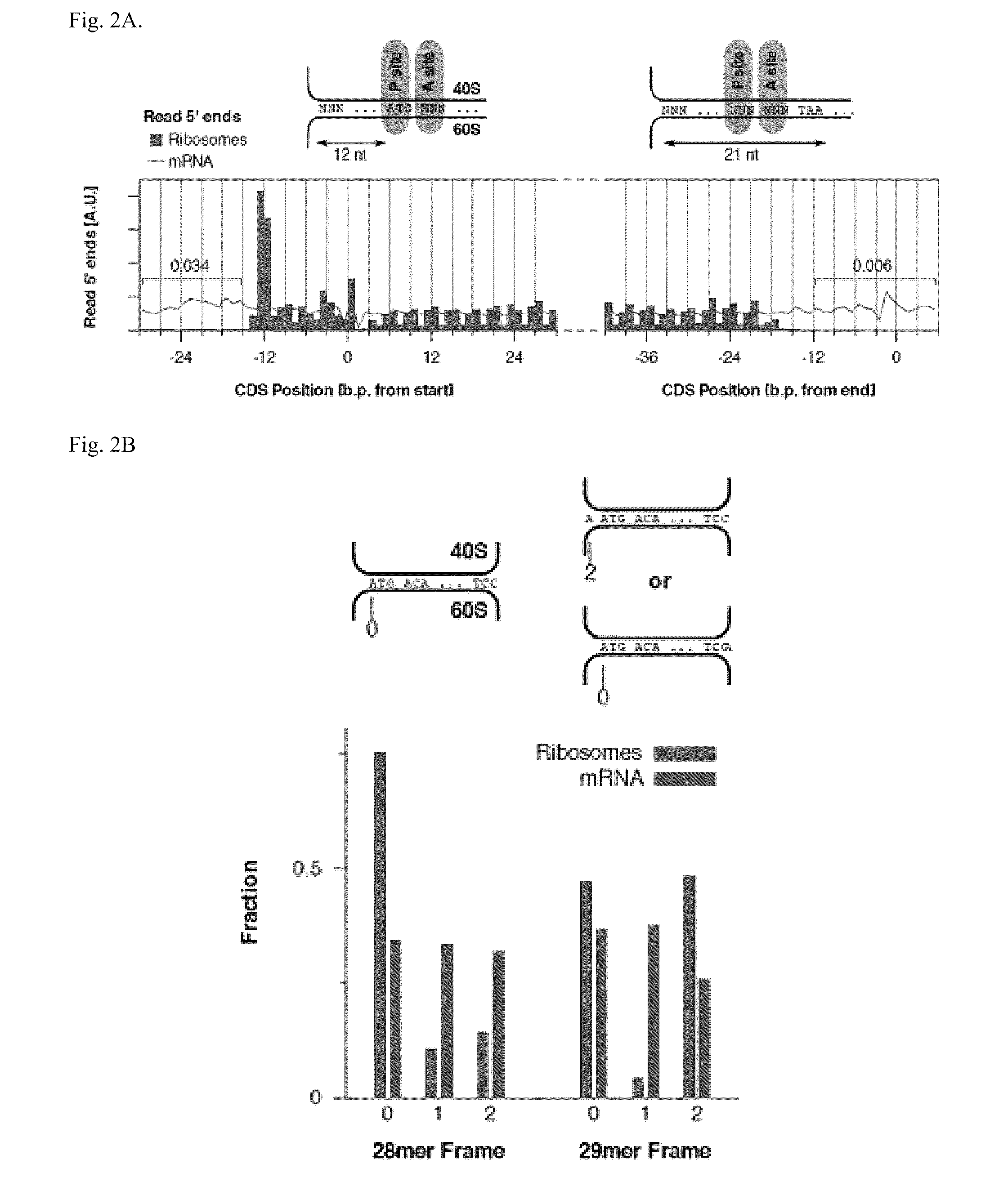
Coverage (or depth) in DNA sequencing is the number of unique reads that include a given nucleotide in the reconstructed sequence. Deep sequencing refers to the general concept of aiming for high number of unique reads of each region of a sequence.
Methods for Determining Sequence Variants Using Ultra-Deep Sequencing
InactiveUS20120264632A1Reduce and effort and lossReduce and and product lossMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningUltra deep sequencingDirect sequencing
The claimed invention provides for new sample preparation methods enabling direct sequencing of PCR products using pyrophosphate sequencing techniques. The PCR products may be specific regions of a genome. The techniques provided in this disclosure allows for SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) detection, classification, and assessment of individual allelic polymorphisms in one individual or a population of individuals. The results may be used for diagnostic and treatment of patients as well as assessment of viral and bacterial population identification.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Heterozygous genome processing method
ActiveCN104164479AAdvance researchPush forwardMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenome mapComputational biology
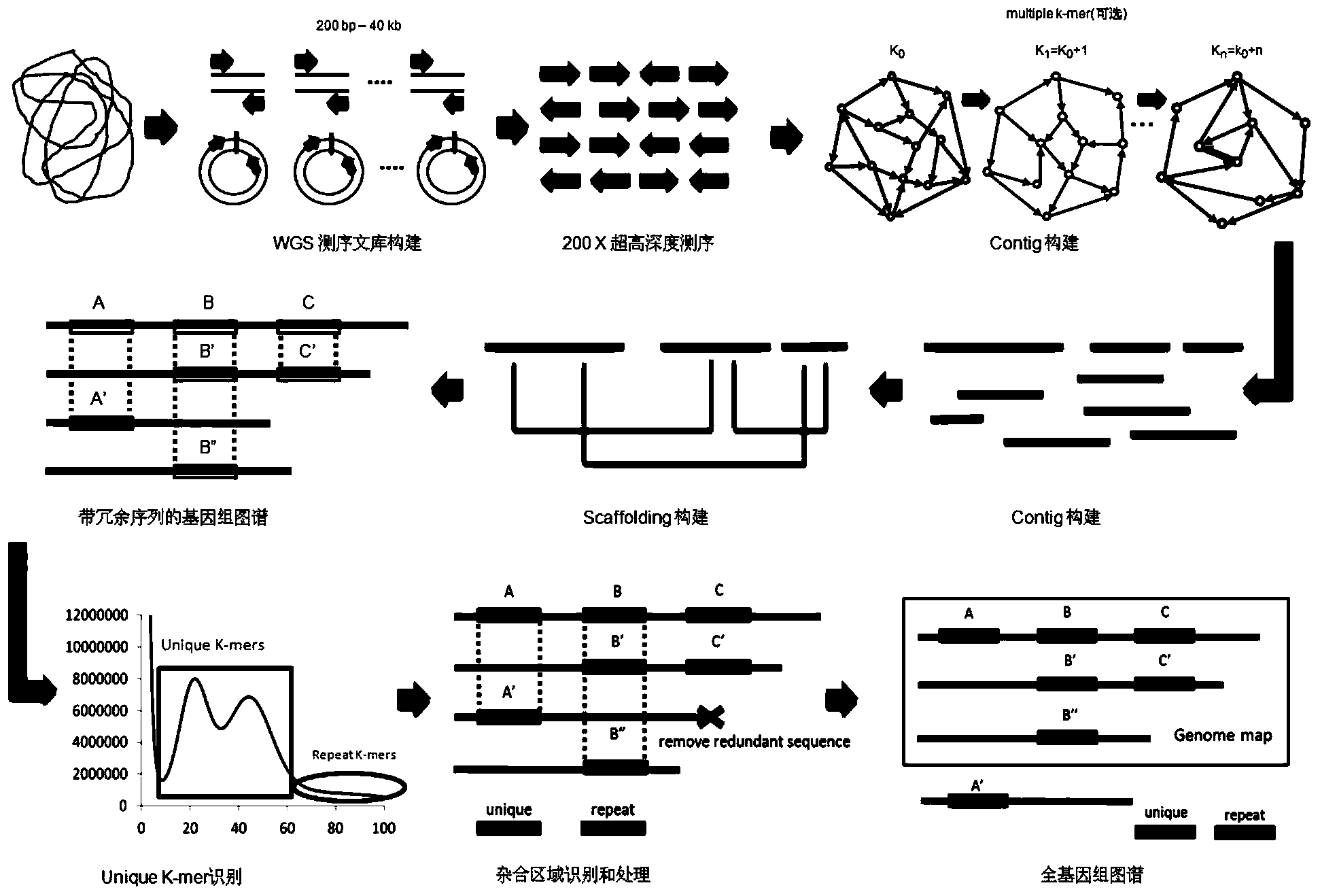
The invention discloses a heterozygous genome processing method. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out at least 200 times ultrahigh deep sequencing on target species by using a whole genome shotgun process to obtain an effective read length sequence Reads; carrying out scaffold sequence Scaffold assembling and construction on the effective Reads to obtain a genome map with a redundant sequence; and carrying out heterozygous recognition processing on the genome map with a redundant sequence to remove redundant Scaffold in a heterozygous region and reserve heterozygous region information in order to obtain a whole genome map. The method realizes the rapid assembling of the whole high-quality heterozygous genome map, and shortens the drafting cycle and cost.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Method for screening HRDs disease-causing mutation and gene chip hybridization probe designing method involved in same
ActiveCN103667438AClear relationshipScreening benefits are highMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDiseaseHybridization probe
The invention belongs to the field of biological medicines, and relates to a method for screening HRDs disease-causing mutation and a gene chip hybridization probe designing method involved in the same. The method for screening the HRDs disease-causing mutation comprises the steps of (1) establishing an HRDs genetic resource repository; (2) designing and synthesizing a gene chip hybridization probe of an HRDs disease-causing gene, and integrating the gene chip hybridization probe onto a gene chip; (3) capturing a target area by utilizing the prepared gene chip and executing the depth sequencing; (4) analyzing the sequencing data on the aspect of bioinformatics, and screening the candidate disease-causing gene; (5) functionally predicting a newly-discovered splicing gene mutation site. By establishing the high-efficient HRDs target gene capturing technology, adopting the depth sequencing as a means and confirming the efficiency of the HRDs capturing chip, a high-efficient credible biological information analysis model is established.
Owner:赵晨
Application of differential expression of gene in oral cancer diagnosis
ActiveCN105483246AHigh selectivitySimplify the process of quantitative detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsSquamous CarcinomasNormal tissue
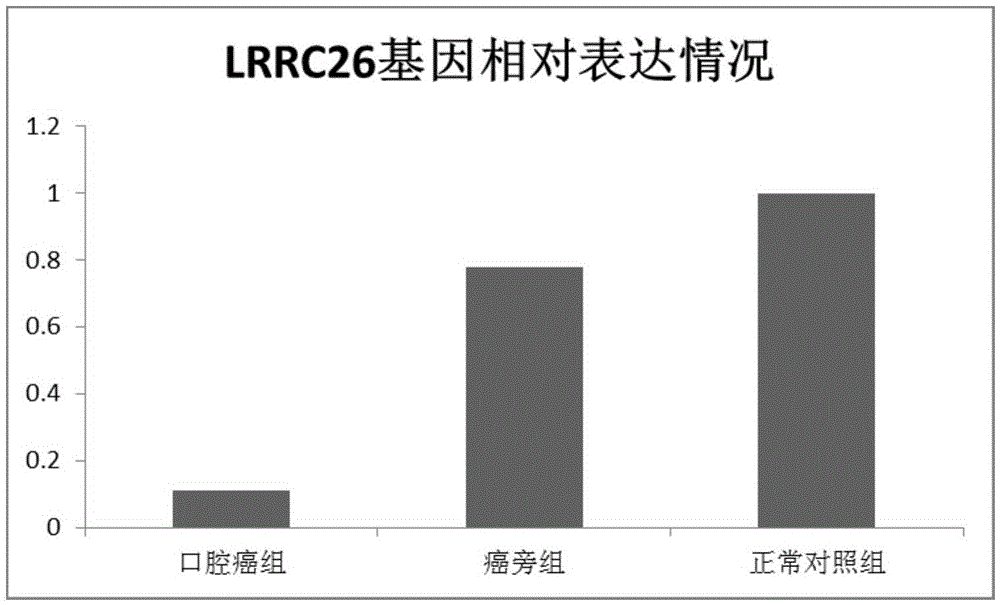
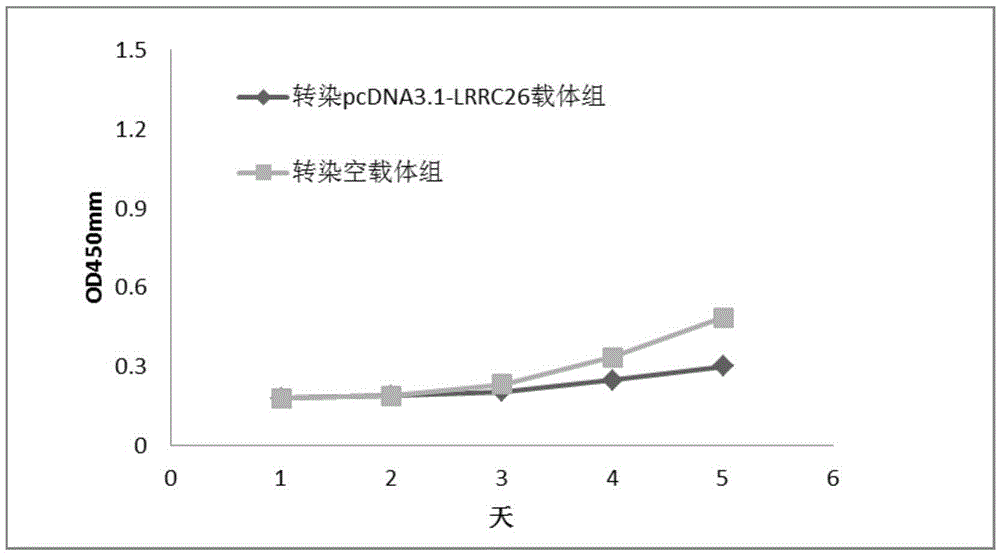
The invention relates to application of differential expression of a gene in oral cancer diagnosis, and particularly relates to application of differential expression of LRRC26 gene in oral squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis. Transcriptome deep sequencing analysis is performed by virtue of a high-throughput sequencing platform to preliminarily screen the gene LRRC26 with remarkable differential depression in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissues, para-carcinoma tissues and normal tissues; and the RT-PCR experiment further proves that the LRRC26 gene has low expression with oral squamous cell carcinoma tissues, can be used for preparing oral squamous cell carcinoma auxiliary diagnosis or prognosis preparations, and has an important clinical practical application value.
Owner:BEIJING MEDINTELL BIOMED CO LTD
Oral squarmous cell carcinomas pathogenic gene BPIFB2 and application thereof
InactiveCN104059982AGood correlationConvenient for clinical operationMicrobiological testing/measurementTumour tissuePcr method
The invention relates to an oral squarmous cell carcinomas pathogenic gene BPIFB2 and application of the oral squarmous cell carcinomas pathogenic gene BPIFB2. RNA is extracted from oral squarmous tissue, tissue adjacent to the oral squarmous cell carcinomas and normal tissue, deep sequencing and analyzing are performed on a transcriptome, the oral squarmous cell carcinomas relevant gene BPIFB2 is obtained through screening, an RT-PCR method is adopted for analyzing the expression conditions, on the carcinomas tissue and the tissue adjacent to the carcinomas of a patient with the oral squarmous cell carcinomas, of the screened BPIFB2, and the result shows that the obtained BPIFB2 through screening has good relevance to the oral squarmous cell carcinomas and can be used for preparing an oral squarmous cell carcinomas auxiliary diagnosis preparation or a pregnosis preparation. The invention further discloses a fluorogenic quantitative PCR kit and a using method of the fluorogenic quantitative PCR kit. The kit can detect the expression level of the BPIFB2 in oral squarmous cell carcinomas tissue sensitively, rapidly, quantitatively, accurately and stably and has good application prospects.
Owner:BEIJING MEDINTELL BIOMED CO LTD
Methods for detecting modification resistant nucleic acids
Methods are provided for, inter alia, detecting nucleic acid molecules resistant to degradation, such as a plurality of RNA molecules bound to a ribosome, using various technologies including deep sequencing.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
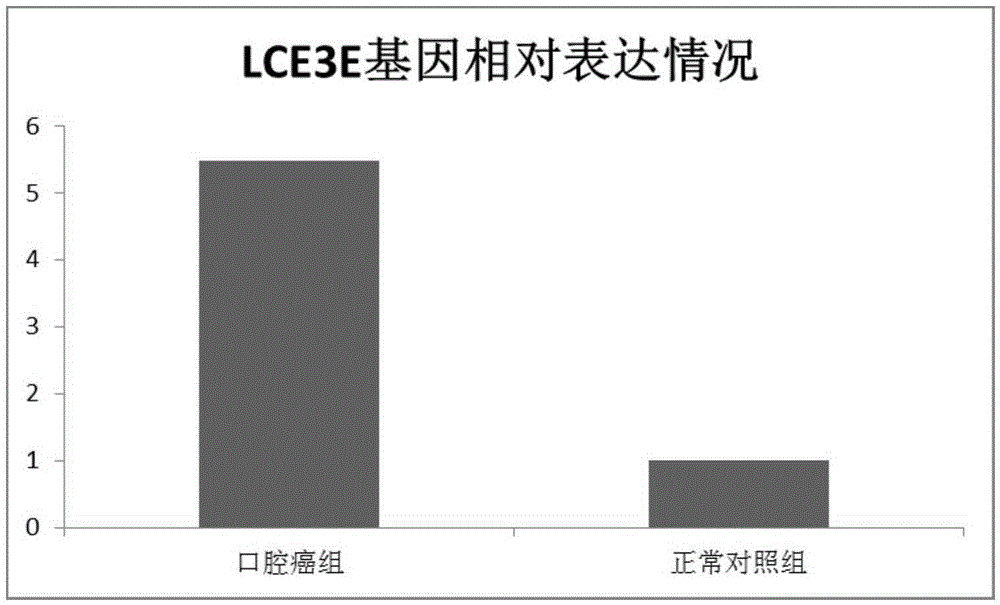
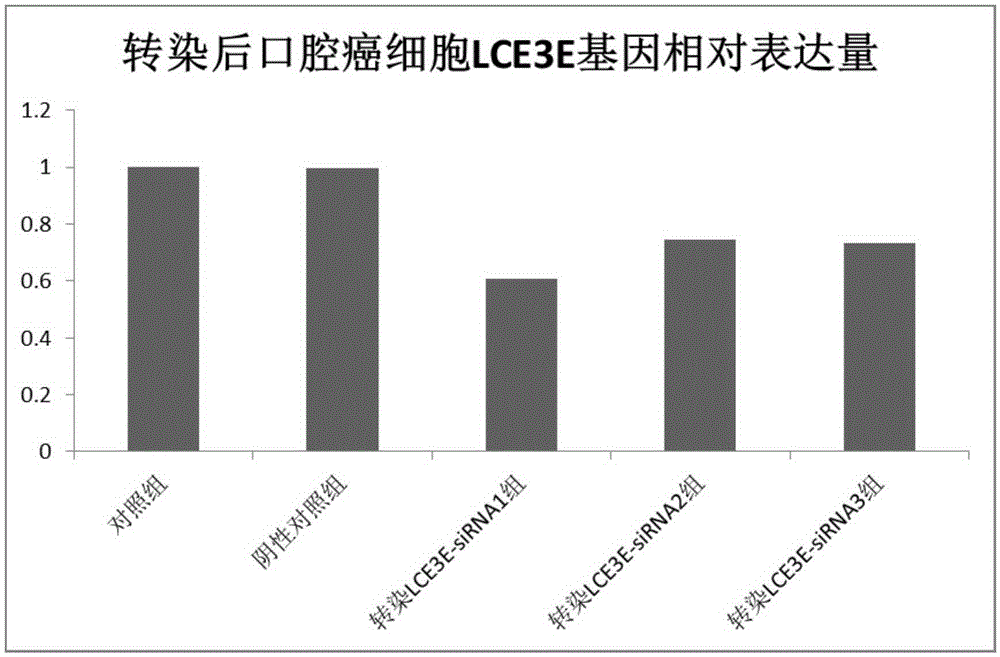
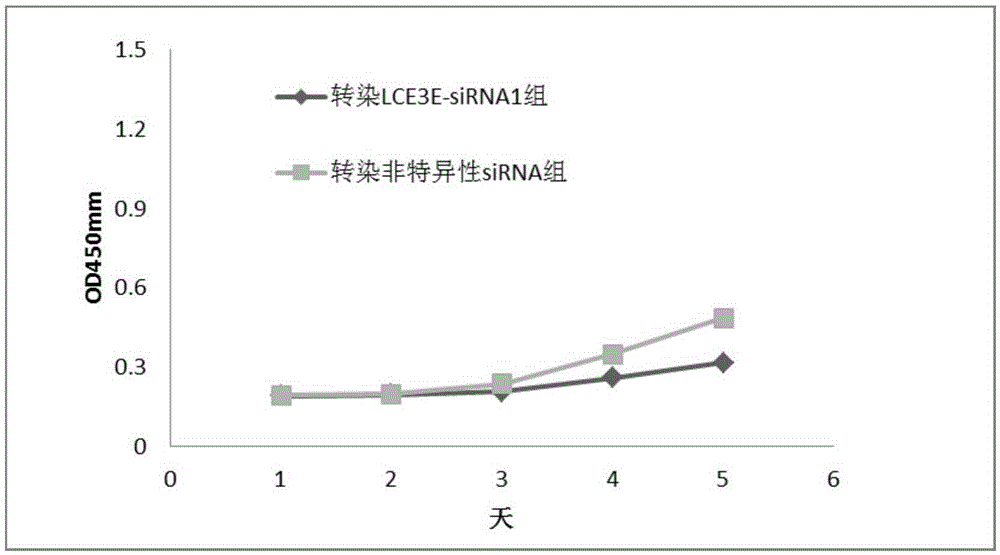
Application of LCE3E to diagnosis and treatment of oral cancer
ActiveCN105385781AHigh selectivitySimplify the process of quantitative detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSquamous CarcinomasNormal tissue
The invention relates to application of LCE3E to diagnosis and treatment of an oral cancer. According to the application, transcriptome deep sequencing analysis is performed through a high-throughput sequencing platform to preliminarily screen out LCE3E genes obvious in differential expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and normal tissue, a further RT-PCR experiment proves high expression of the LCE3E genes in the oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue, and an siRNA interference experiment shows that interference to expression of the LCE3E genes can effectively suppress proliferation of oral cancer cells. Oral cancer molecular markers in the application have significant clinical practical application value.
Owner:BEIJING MEDINTELL BIOMED CO LTD
Child glaucoma related gene chip, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108676865ARapid and efficient genetic diagnosisFast and Efficient Genetic CounselingNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDeep sequencingProbe target
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicines and relates to a gene chip hybridization probe for screening disease-causing gene mutations of child glaucoma, and a design method and application thereof. The invention provides a preparation method of a gene chip and the gene chip hybrid probe related to the disease-causing gene mutations of the child glaucoma, and the gene chip hybrid probe targets genes covering 289 pathogenic genes highly associated with the child glaucoma. The design method of the gene chip hybrid probe is as follows: designing and synthesizing a child glaucoma pathogenic gene hybrid probe, and integrating the child glaucoma pathogenic gene hybrid probe into a gene chip; using the prepared gene chip to capture a genome target region and performing deep sequencing; and performing bioinformatics analysis on screening data to screen candidate pathogenic genes and mutations. A high-efficiency screening technique for screening the disease-causing gene mutations of thechild glaucoma is established, and is helpful for clinically determining the mutant genes of the child glaucoma.
Owner:EYE & ENT HOSPITAL SHANGHAI MEDICAL SCHOOL FUDAN UNIV
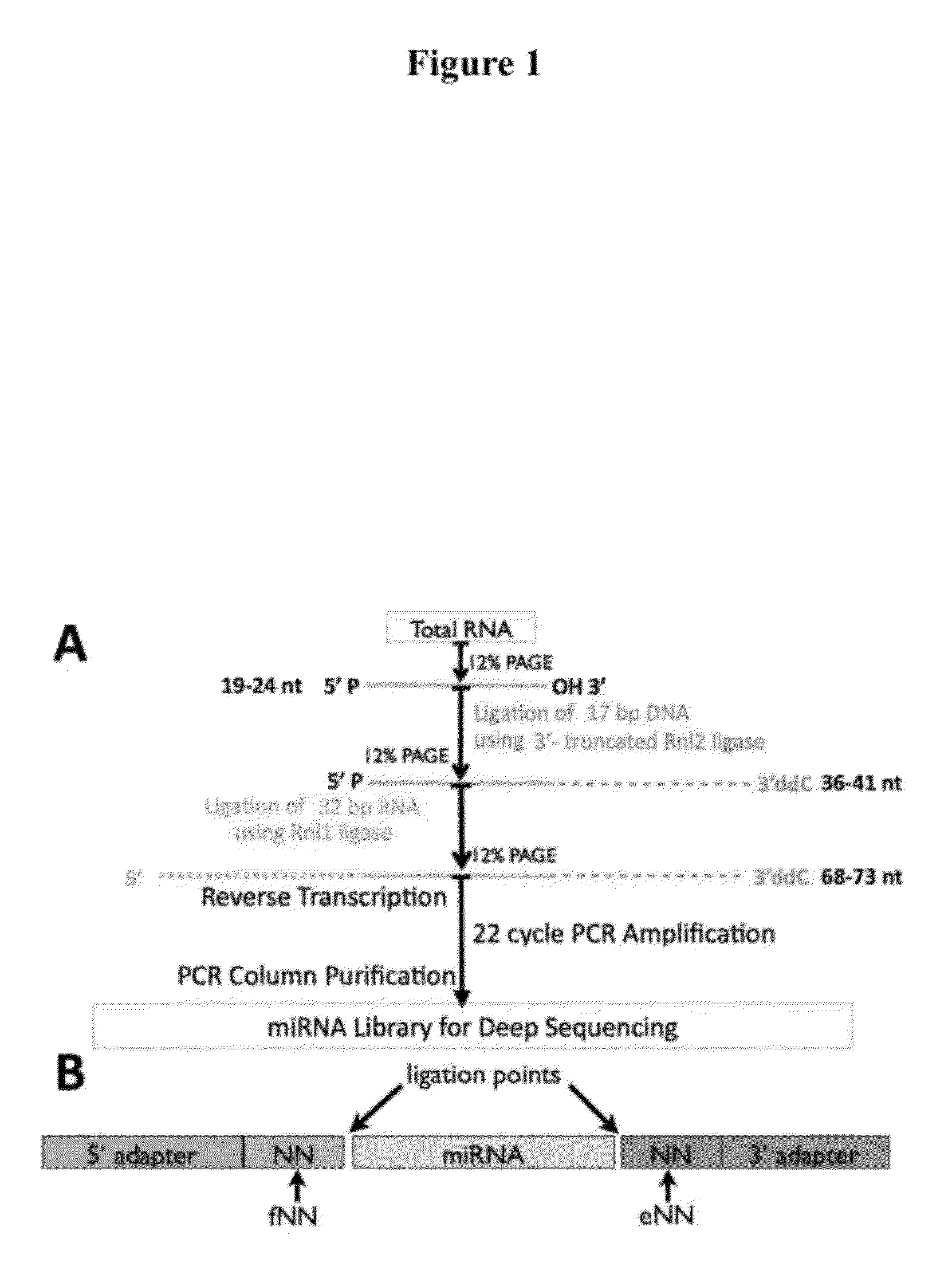
Pooled adapter strategy for reducing bias in small RNA characterization
ActiveUS20120322691A1Reduce biasAccurate contourNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologySmall RNA
Modified nucleic acid adapters are provided that collectively provide a mixture of nucleotides at the 3′ end of 5′ adapters and at the 5′ end of 3′ adapters such that at least one adapter in each set has any given nucleotide at position 1, i.e., the nucleotide position available for ligation to a small RNA, and has any given nucleotide at position 2 adjacent to position 1 for use in overcoming bias during nucleic acid manipulation, such as small RNA characterization and / or profiling by, e.g., deep sequencing, along with methods for use of the modified adapters in small RNA characterization. The modified adapters have at least two mixed nucleotides at the adapter terminus to be ligated to a nucleic acid such as a small RNA.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
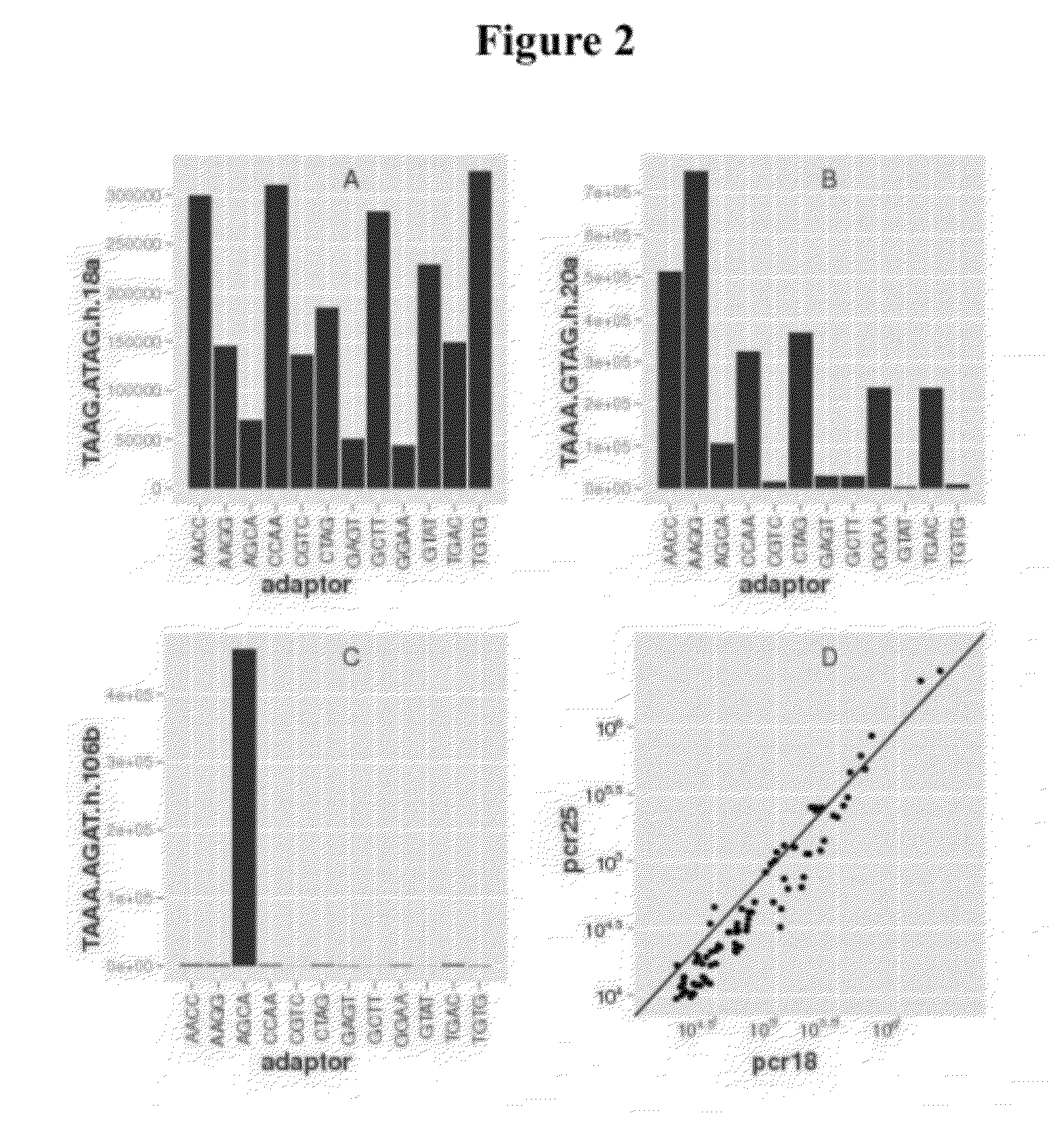
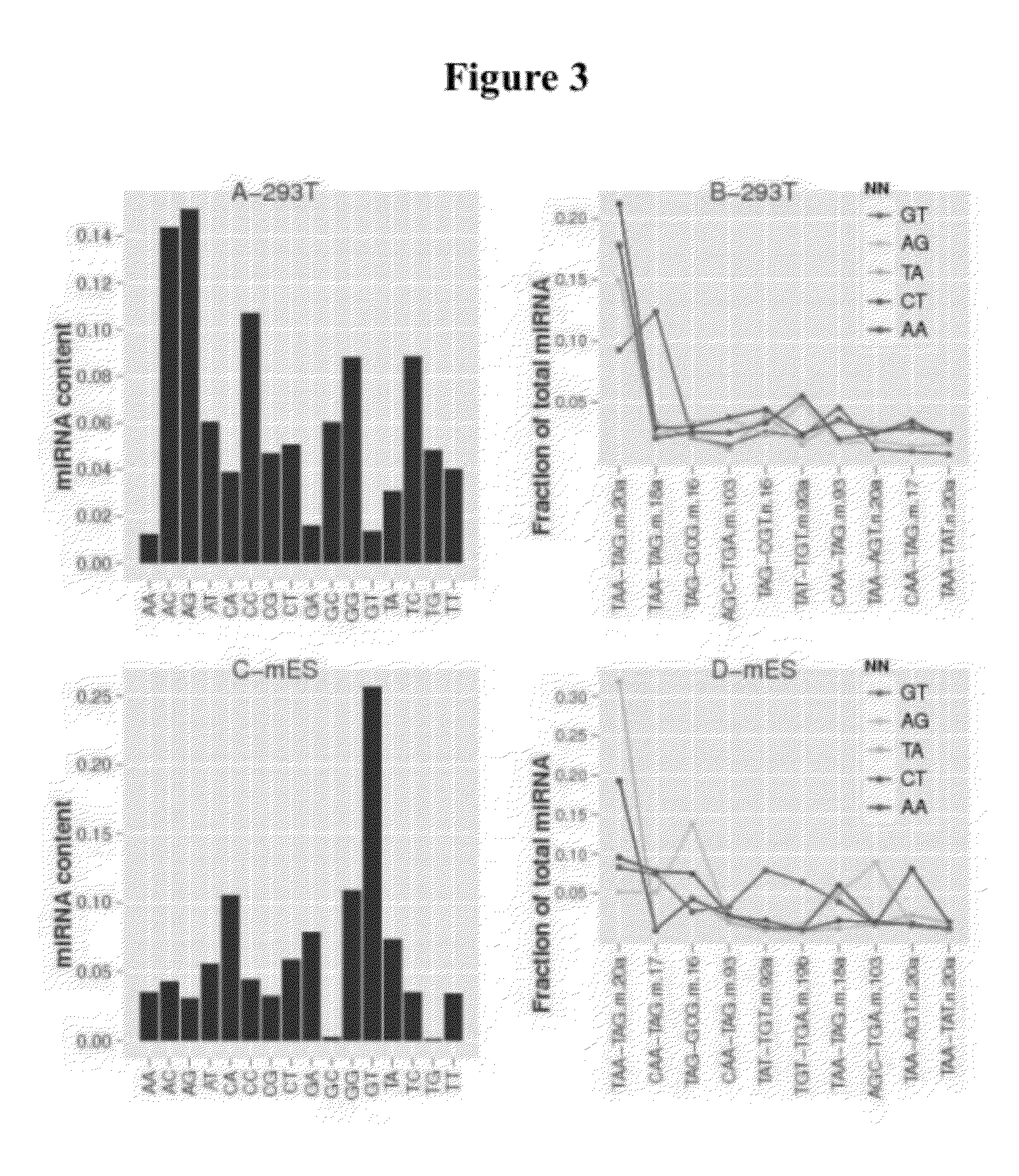
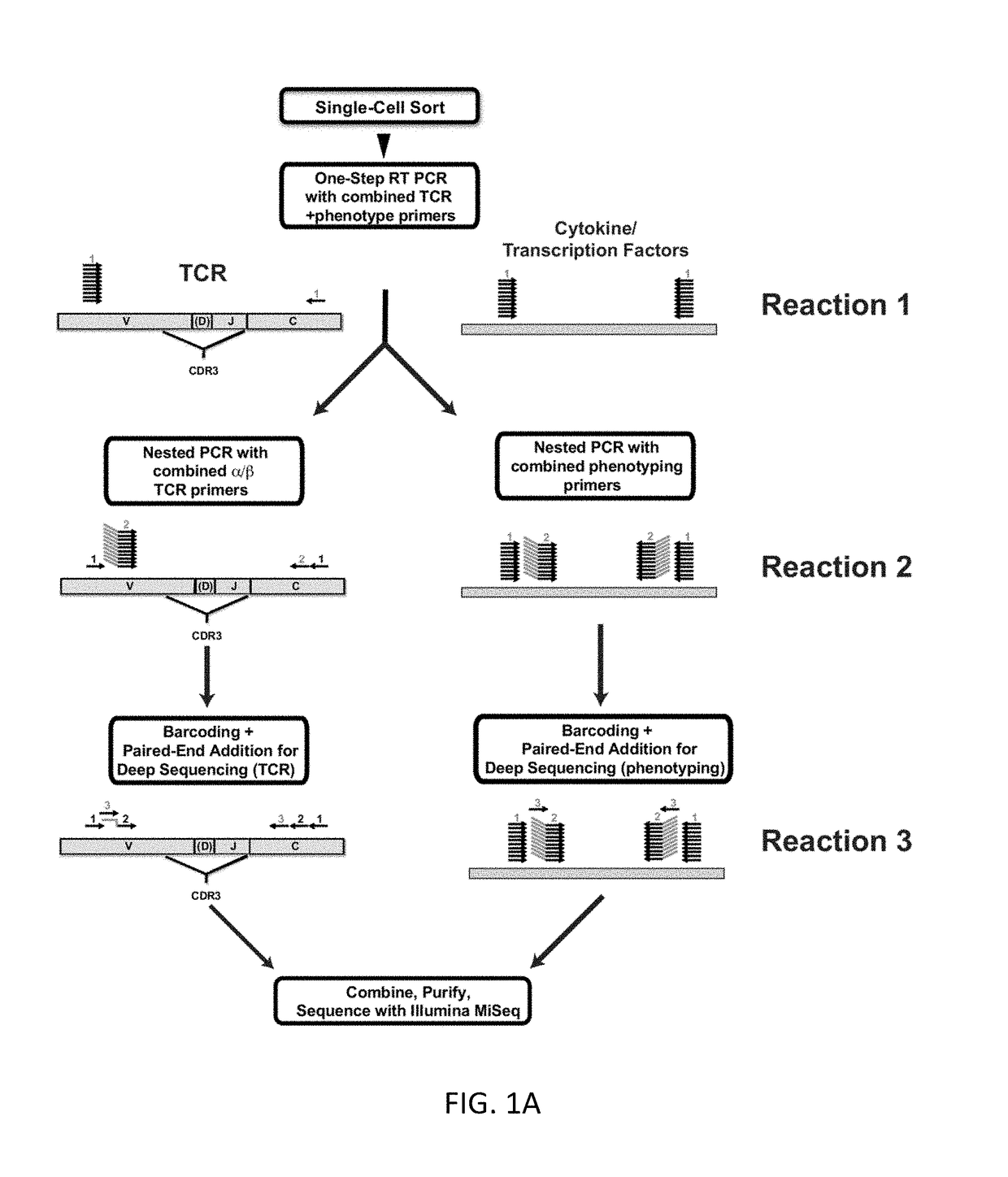
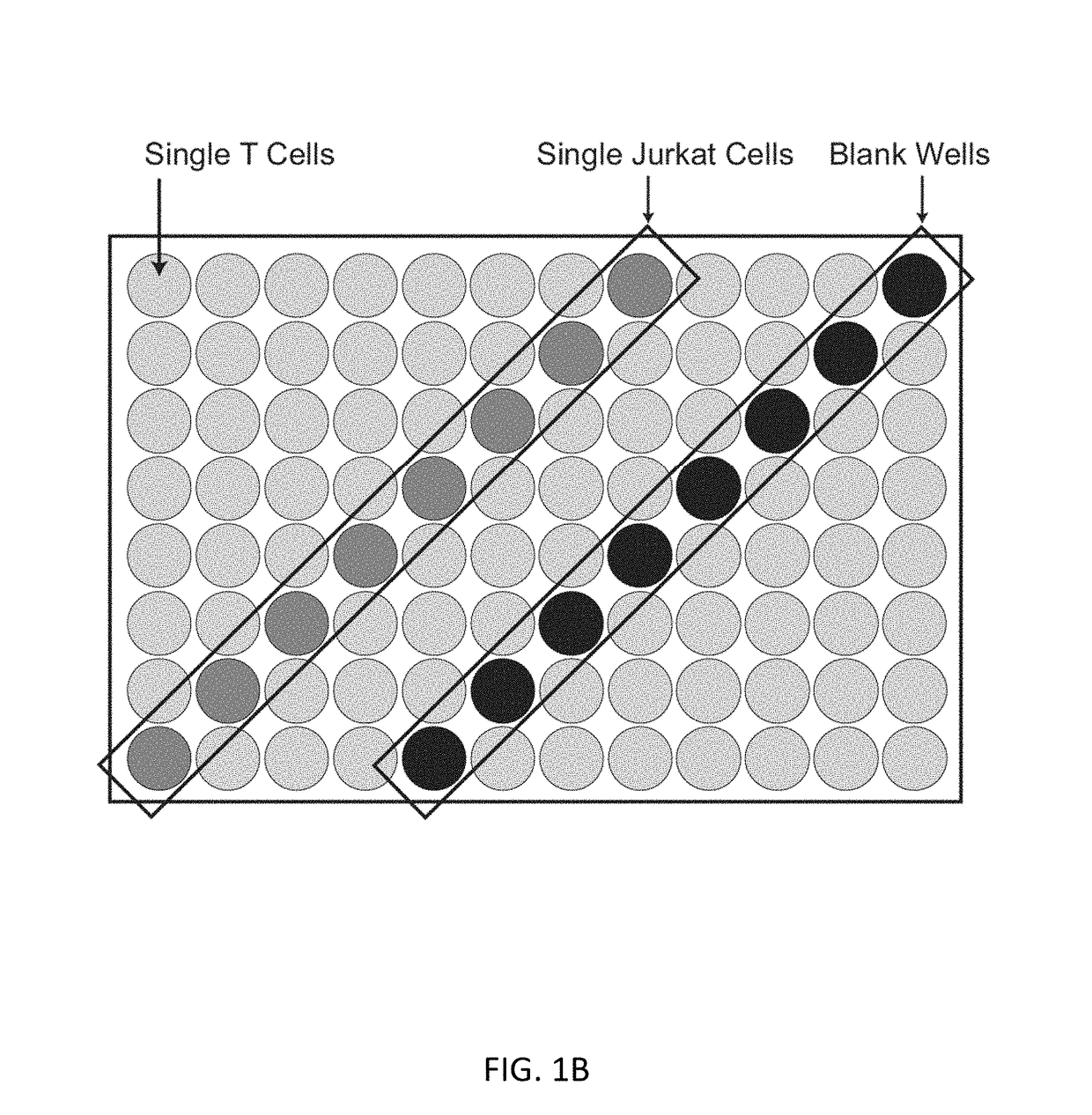
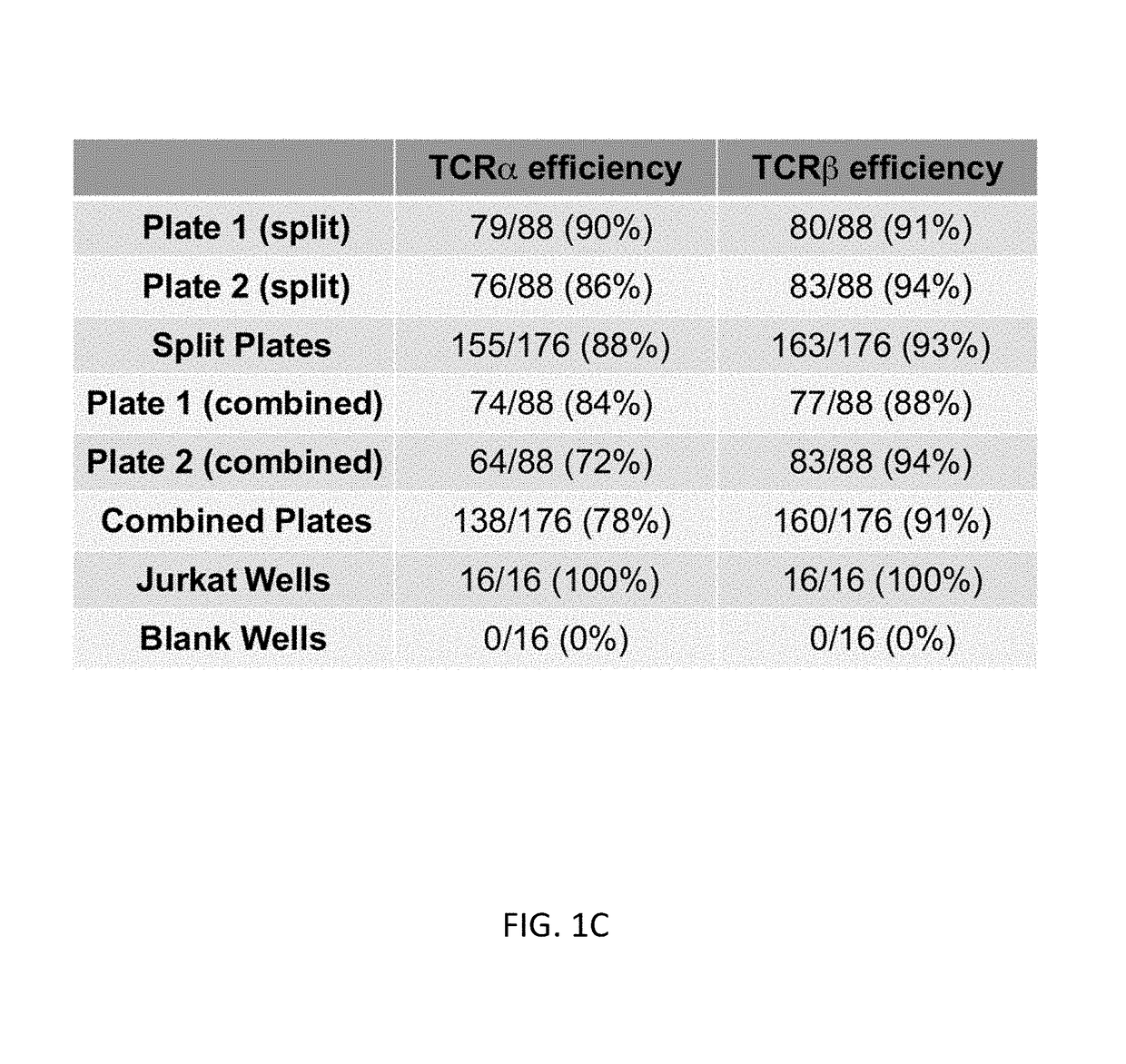
Single cell analysis of T cells using high-throughput multiplex amplification and deep sequencing
ActiveUS10202640B2Easy to produceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFunctional studiesOligonucleotide
Methods and oligonucleotide reagents for analyzing individual T cells are disclosed. In particular, the present disclosure provides methods for analyzing individual T cells using high-throughput multiplex amplification and deep sequencing of nucleic acids encoding T cell receptors (TCRs) and various other T cell phenotypic markers. The present disclosure further provides methods of reconstituting TCRs from individual T cells for functional studies, ligand discovery, or screening therapeutics.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
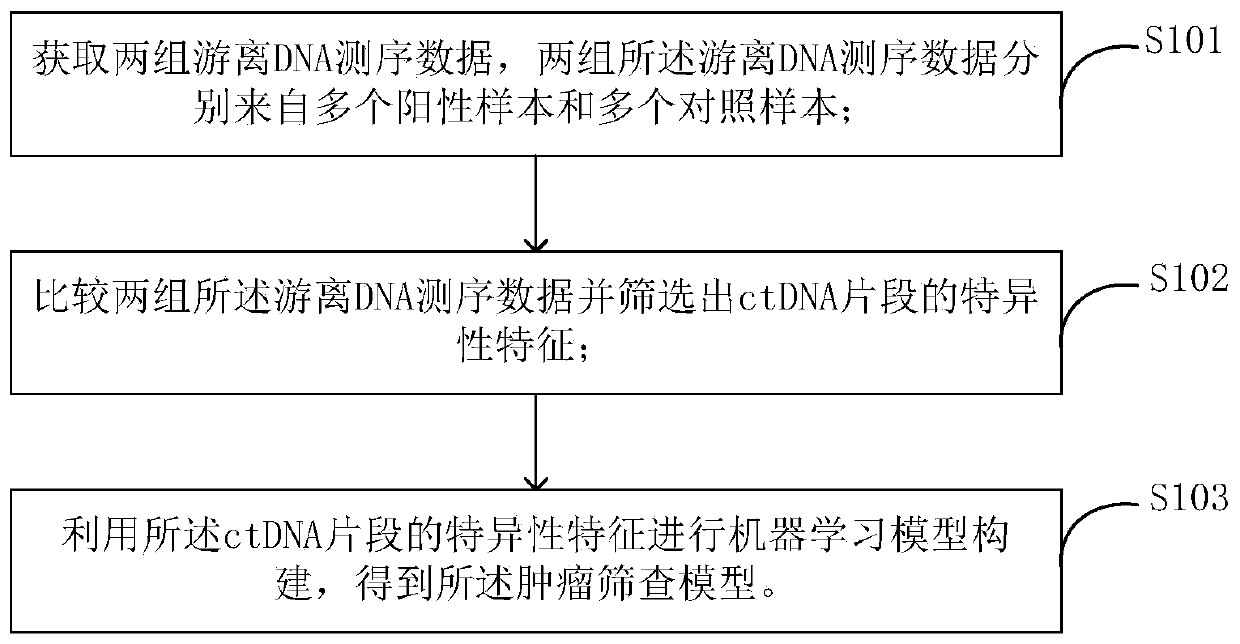
Tumor screening model and construction method and device thereof
ActiveCN111243673ARapid detectionImplement screening testsBiostatisticsMedical automated diagnosisPositive sampleComputer science
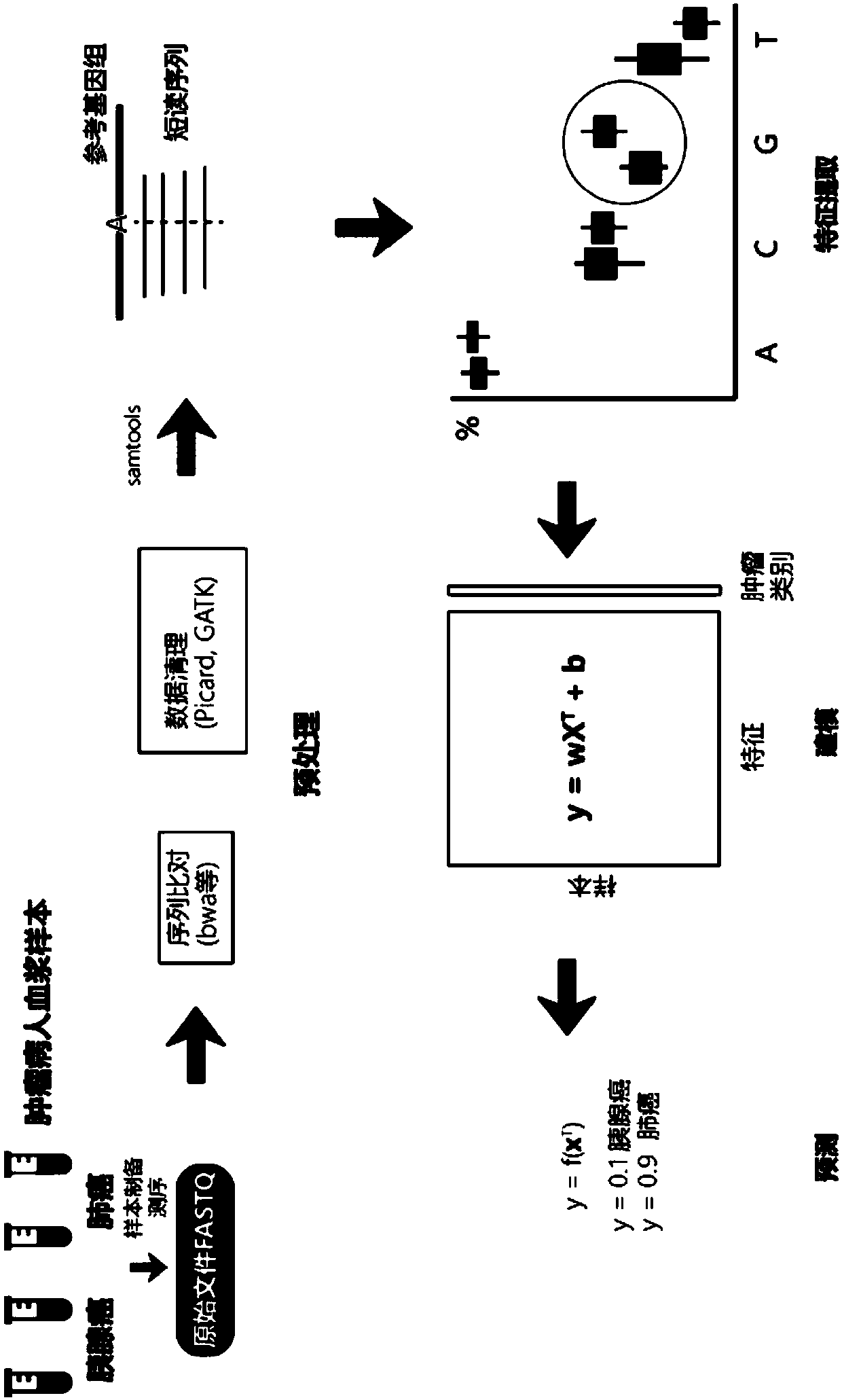
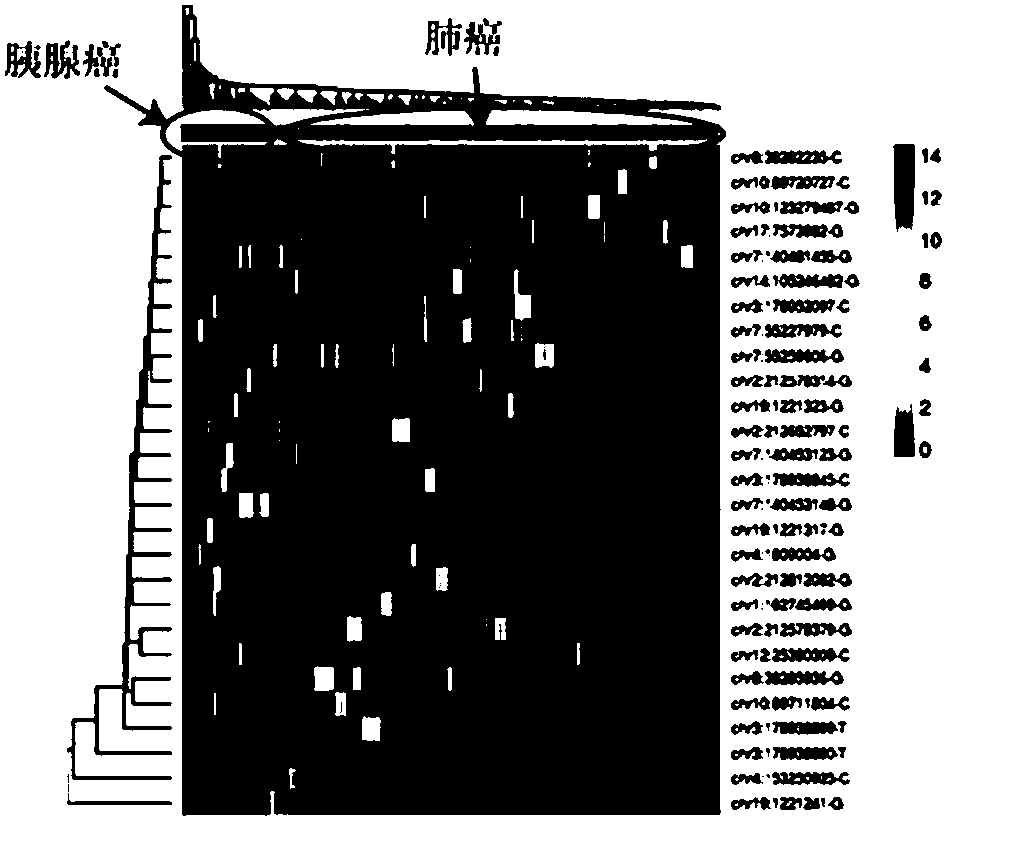
The invention provides a tumor screening model and a construction method and device thereof. The model construction method comprises the following steps: acquiring two groups of free DNA sequencing data from a plurality of positive samples and a plurality of control samples respectively; comparing the two groups of free DNA sequencing data and screening out specific characteristics of ctDNA fragments; and performing machine learning model construction by utilizing the specific characteristics of the ctDNA fragments to obtain a tumor screening model. According to that characteristic distribution of ctDNA fragments is obviously different from that of cfDNA, the method can be used for greatly improving ctDNA detection, ctDNA specificity characteristics are fully utilized, and the tumor screening model is constructed through machine learning. The tumor screening model has no strict requirement for the sequencing depth of a to-be-detected sample and can be realized by adopting conventionallow-depth sequencing, and thus, has great significance in research direction and clinical guidance for (early) screening of cancers.
Owner:北京橡鑫生物科技有限公司 +2
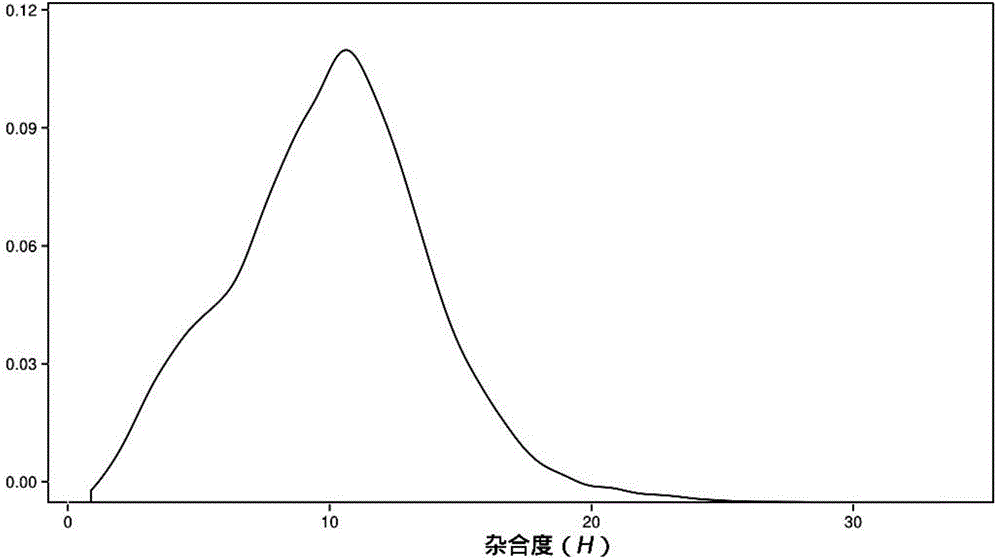
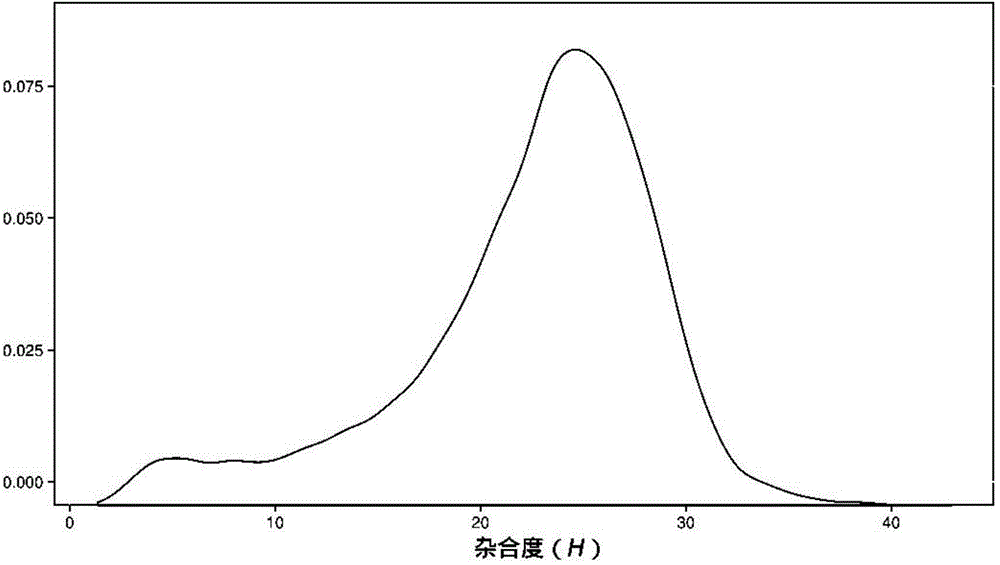
Method for identifying hybrid germplasm of actinidia based on genome heterozygosity
InactiveCN104630382AShorten the timeLower Sequencing CostsMicrobiological testing/measurementActinidiaGermplasm
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
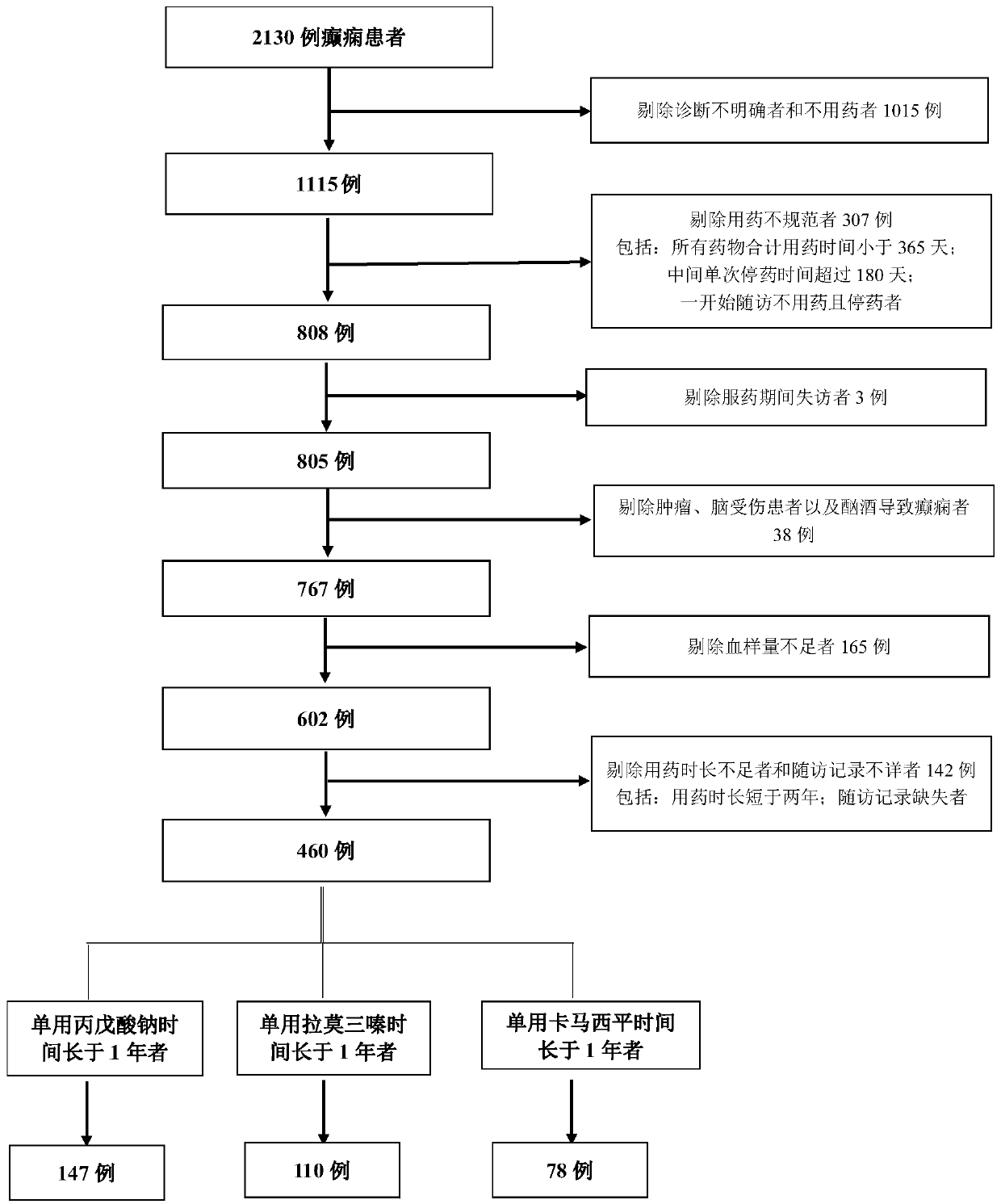
Epilepsy medication recommendation method and system
PendingCN111462921AHigh control rateShorten the timeBiostatisticsProteomicsAntiepileptic drugMetabolic enzymes
The invention provides an epilepsy medication recommendation method and system, and belongs to the technical field of biomedicine and data processing. According to the invention, deep sequencing is carried out on an antiepileptic drug metabolic enzyme gene, a transporter gene and a drug action target gene, related coding gene polymorphic sites are screened, a Bayesian accumulation regression treemodel and random forest regression are utilized to obtain a personalized medication scheme depending on individual genes, and a subset with high treatment effect is identified, so that clinical medication is guided in a targeted manner, the epilepsy control rate is improved, adverse reactions are reduced, the time for doctors and patients to explore the optimal treatment scheme is shortened, the diagnosis and treatment efficiency is improved, and the method has good practical application value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Deep sequencing of peripheral blood plasma DNA as a reliable test for confirming the diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome
ActiveUS20160130648A1Increase in bone marrow blastsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGackstroemiaHematologic malignancy
Methods are provided for treating, managing, diagnosing and monitoring myelodysplastic syndrome and other hematologic malignancies. These methods comprise the next generation sequencing analysis conducted on cell-free DNA from peripheral blood plasma or serum.
Owner:NEOGENOMICS LAB
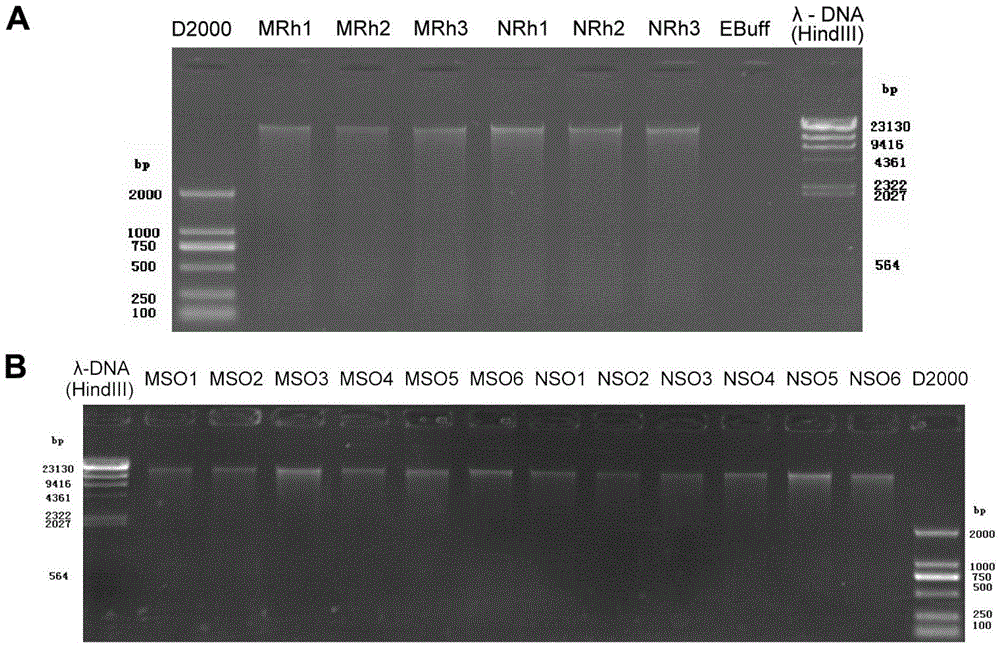
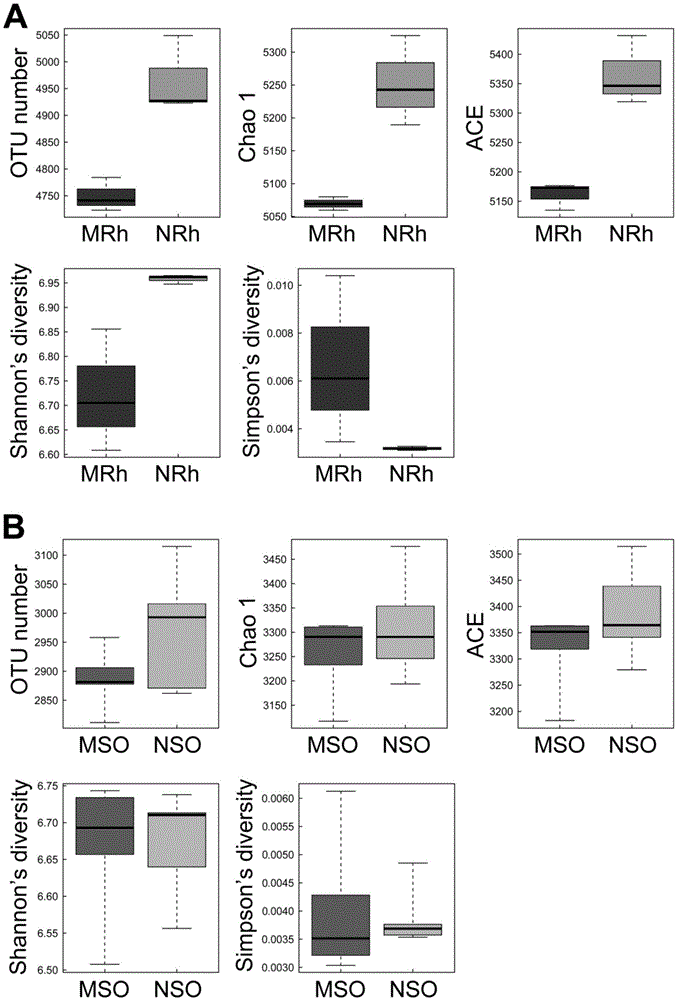
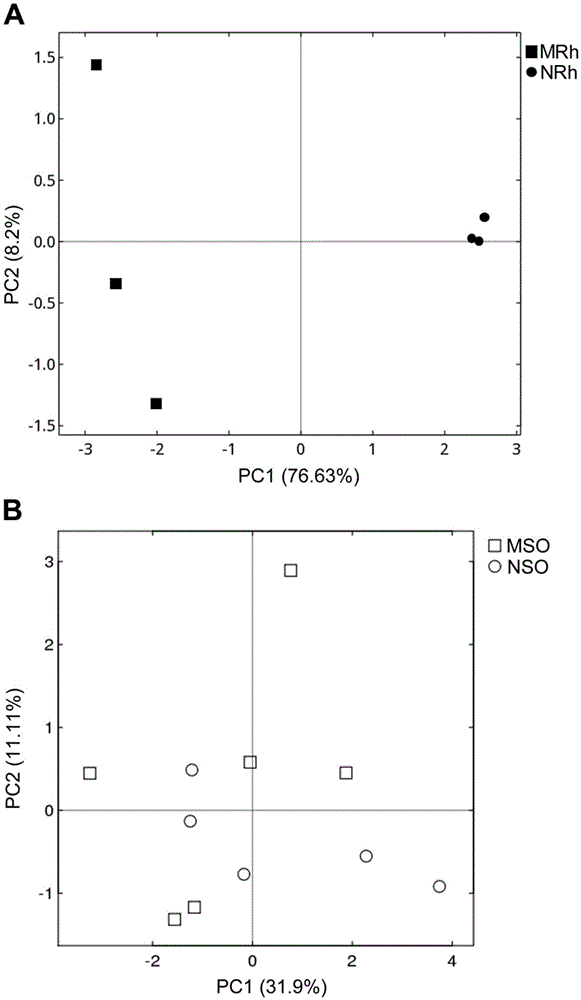
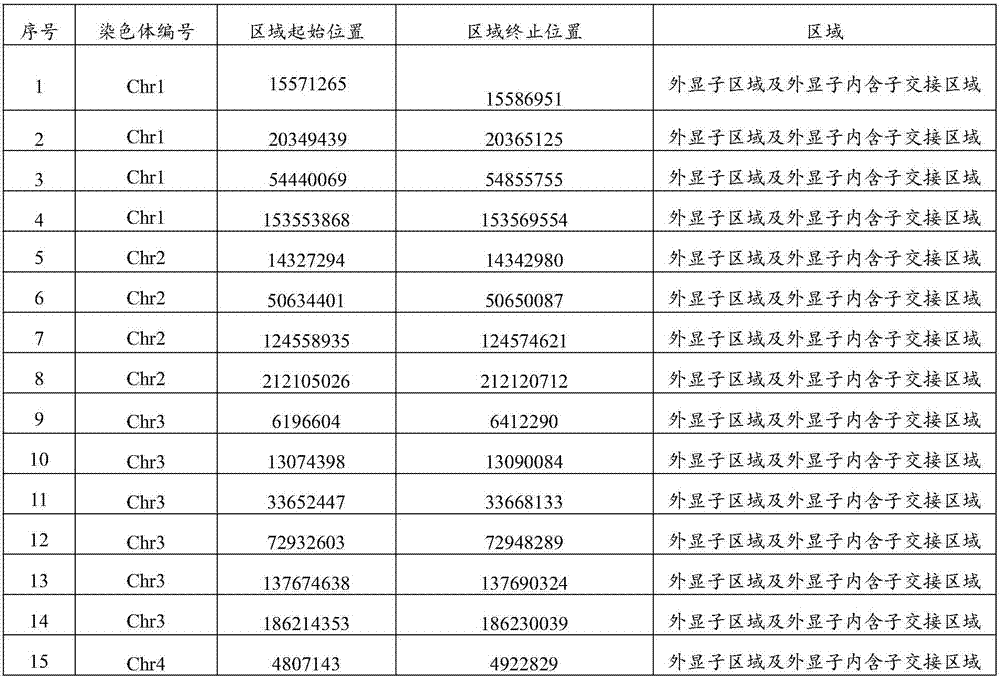
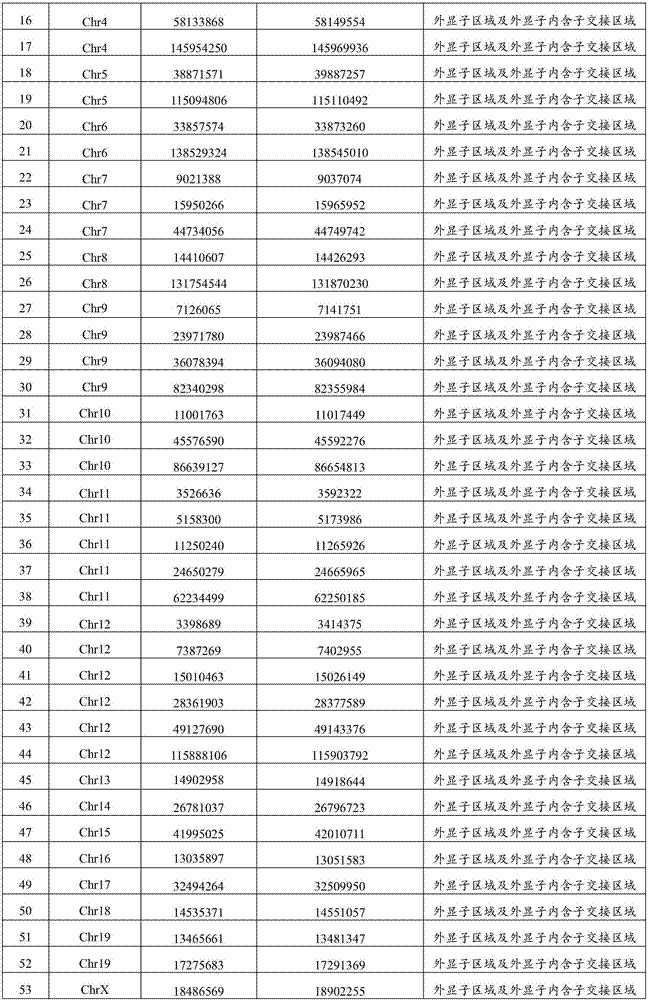
Method for detecting rhizosphere soil prokaryotic microorganisms of various soybeans based on 16SrDNA deep sequencing
InactiveCN105525025AComprehensive detectionImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismSoil microbiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil microbiology, and in particular relates to a method for detecting rhizosphere soil prokaryotic microorganisms of various soybeans based on 16SrDNA deep sequencing. The method comprises the following steps: 1. collecting root shook-off soil and rhizosphere soil of various soybeans in different development stages; 2. extracting microorganism metagenome DNA from the soil; 3. performing PCR amplification on a 16S rDNA fourth hypervariable region in the DNA by virtue of a dual-tag primer so as to construct a library; 4. simultaneously synthesizing and sequencing the qualified library by virtue of a Illumina Miseq platform in a mode of 250 nucleotides at dual ends, so that pure READS is obtained; 5. splicing: clustering at least 38000 effective tags generated from each sample into an operable classifying unit; 6. conducting significance analysis on species composition, structure, diversity and relative abundance difference; and 7. by taking the root shook-off soil as a control group of the system, accurately determining the composition, structure, diversity and relative abundance of a rhizosphere soil prokaryotic microorganism colony, and comparing the various soybeans.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
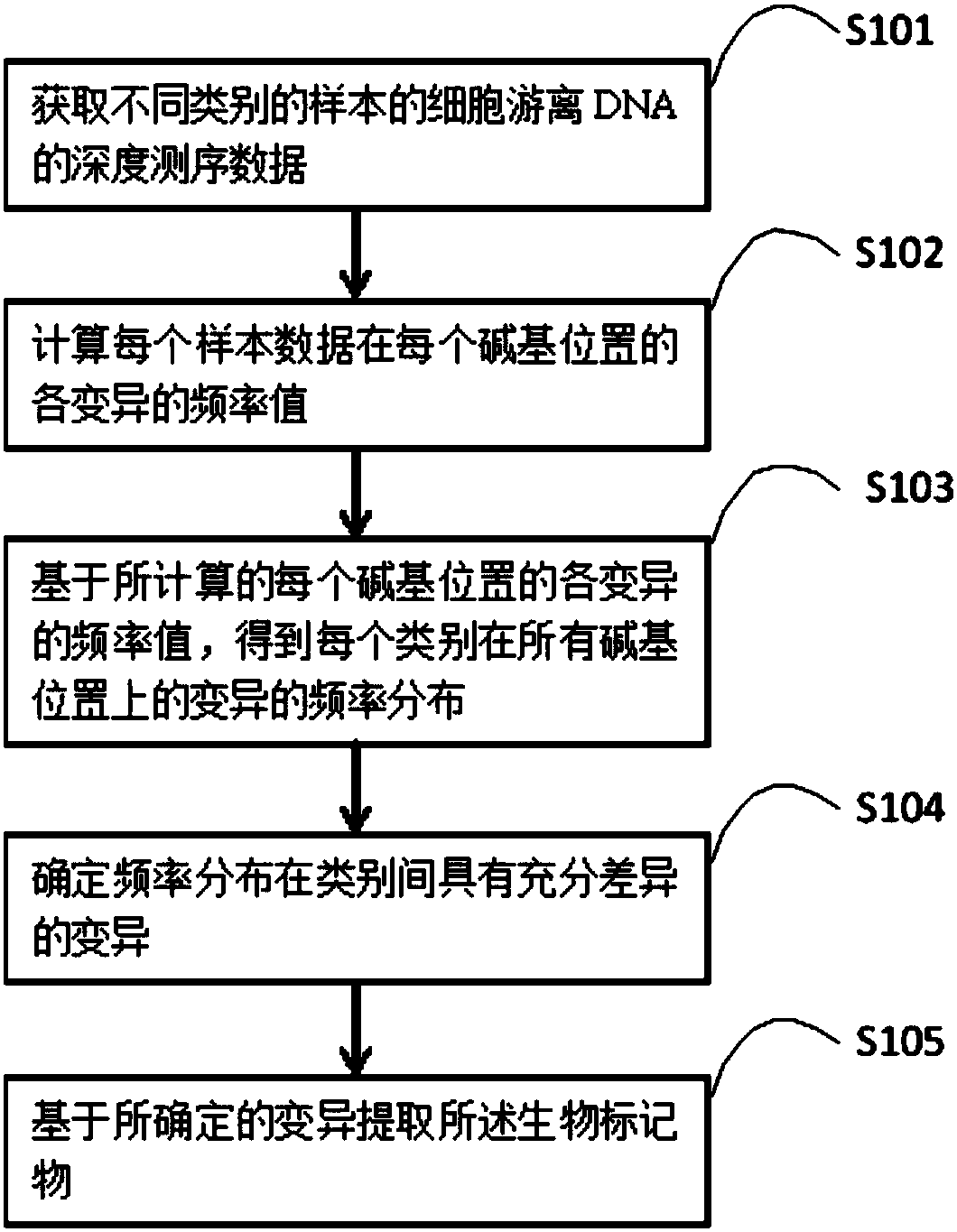
Method and device for extracting biomarker on basis of depth sequencing data of cell free DNAs
ActiveCN108021788ALimit excavationVariation is not limitedProteomicsGenomicsCell freeComputer science
The invention provides a method and a device for extracting a biomarker on the basis of depth sequencing data of cell free DNAs. The method comprises the following steps which are executed by a processor: the depth sequencing data of cell free DNAs of different types of samples are obtained; the frequency values of all variations of the data of each sample in each basic group position are calculated; the frequency distribution of the variations in all basic group positions of each type are obtained on the basis of the calculated frequency values of all variations in each basic group position;the variations whose frequencies differ greatly among the types are determined; the biomarker is extracted on the basis of the determined variations. According to the method, information in the cfDNAcan be excavated to the maximum.
Owner:BEIJING NEOCURNA BIOTECHNOLOGY CORP
Method for simple and rapid high-throughout extraction of plant genome DNA
The present invention provides a method for simple and rapid high-throughput extraction of plant genome DNA, and relates to the technical field of a plant complete gene DNA extraction method. A purpose of the present invention is to solve technical problems of high cost, complex operation, low throughput, long time consuming, low purity, easy pollution, and the like in the traditional and existing (2011) plant genome DNA extraction method. According to the present invention, self-preparing reagent formulas are adopted, and an enzyme reagent is not adopted, such that cost is low; liquid nitrogen grinding is not required, such that operation is simple; 384 samples can be performed in one time, such that throughout is high; an extraction process requires only 2.5 hours, such that a consumed time is short; only 0.5 mul of the extracted DNA is required to be adopted as a PCR template, such that purity is high; and a Parafilm film is adopted for sealing, such that characteristics of sealing, leakage resistance, cleaning, and no pollution are provided. In addition, the extracted plant complete genome DNA can be applicable for plant population genetics, phyletic evolution, molecular marker-assisted breeding, deep sequencing, and other researches, and suitable for industrial production and ordinary biological laboratory science researches.
Owner:匡贤彦 +2
Probe assembly, gene capturing chip, kit and application thereof
ActiveCN107090503ALow cost of treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHigh fluxGenic capture
The invention provides a probe assembly, a gene capturing chip, a kit and application. The assembly at least comprises a probe specifically combined to a target gene under the strict conditions. A special capturing probe is designed for a targeted chemotherapy medicine related gene on the basis of the DNA next generation sequencing method, a plurality of target gene segments are obtained at a time through a small number of samples, high-depth sequencing is achieved through a high-flux sequencing platform, the genetic polymorphism of chemotherapy medicine and various deviant forms such as point mutation, insertion / deletion and DNA copy number alteration in targeted medicine related gene can be detected at a time in parallel, and therefore all target gene mutations related to targeted chemotherapy treatment are detected at a time. Thus, options are provided for clinical doctors in a real sense, a more suitable treatment scheme can be obtained only through single detection, and treatment cost and time are saved for patients to a larger extent.
Owner:北京元码医学检验实验室有限公司
Method for recognizing contribution proportion of kiwi fruit hybrid patients on filial generation genome
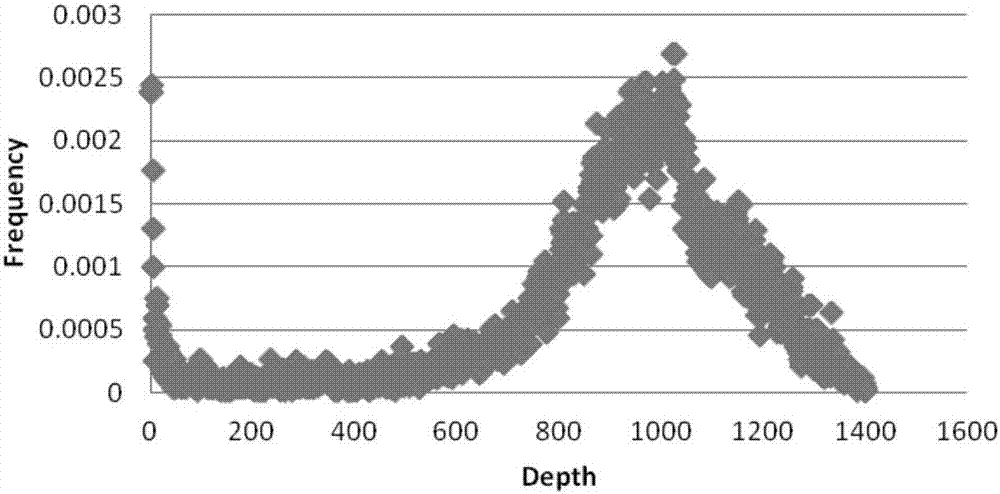
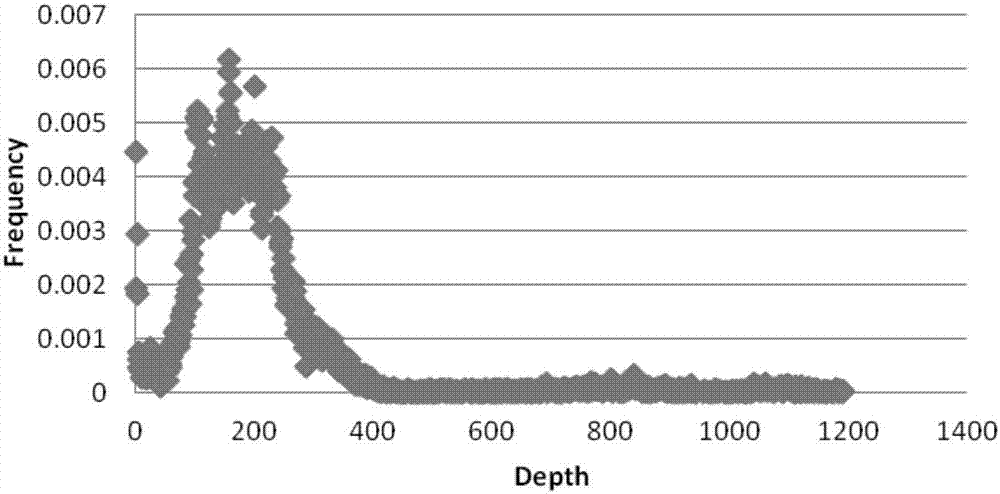
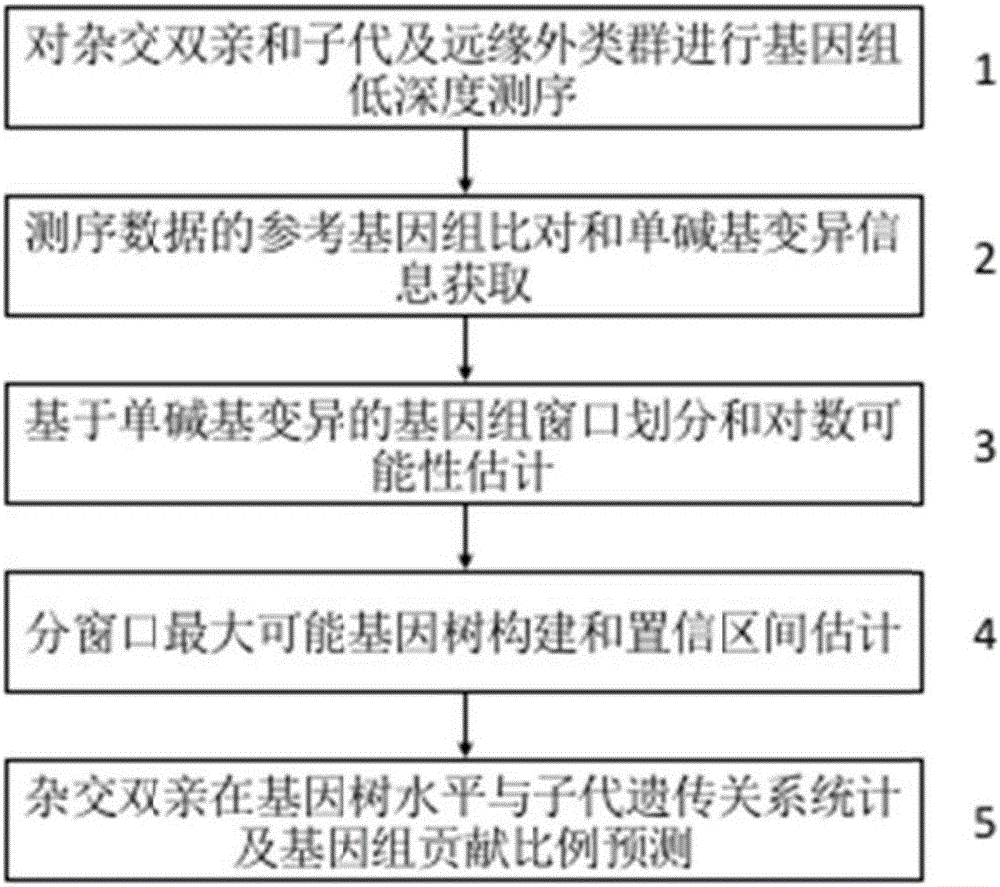
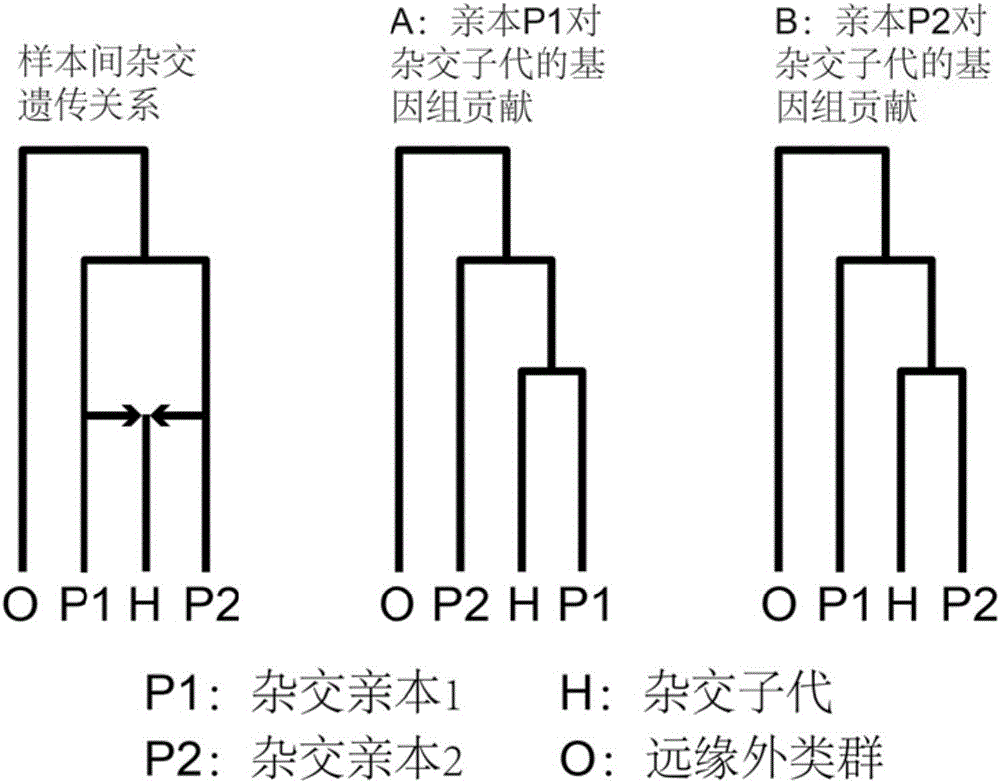
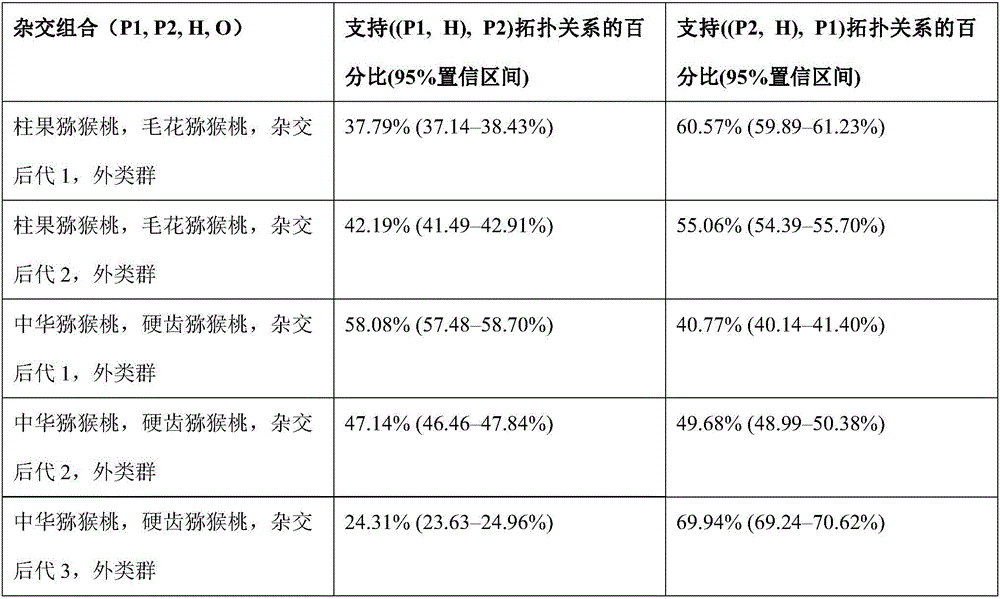
ActiveCN106755300AImprove accuracyFacilitate early screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationConfidence intervalKiwi fruit
The invention discloses a method for recognizing the contribution proportion of kiwi fruit hybrid patients on a filial generation genome. The method comprises the following steps of performing genome low-depth sequence testing on hybrid parents and filial generations and distant hybrid outgroup; performing sequence testing data reference genome comparison, and obtaining single basic group variation information; performing single basic group variation-based genome window division and log probability estimation; performing sub window maximum possible gene tree building and confidence interval estimation; performing gene tree level and filial generation genetic relationship statistics and genome contribution ratio prediction on the hybrid parents. The whole genome variation information is used for analyzing the evolution genetic relationship of the hybrid patients and the hybrid filial generation, so that the prediction of the hybrid filial generation characteristic properties realizes high accuracy; meanwhile, by using the method, the magnitude and the direction of the possibly existing phenotypic characteristic variation are predicted in the baby period of the hybrid filial generation formation; the early stage screening of the hybrid strains can be greatly promoted; the labor and material cost can be reduced; the resource mining and utilization efficiency can be greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Multiple primers, kit and method for high-throughput sequencing of enterovirus
InactiveCN110387438AComprehensive detection effectPerfect analysis techniquesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnterovirusGenotype
The invention discloses multiple primers and a kit for high-throughput detecting of a whole genome of enterovirus, and a high-throughput sequencing analysis method. Compared with the prior art, specific primers do not need to be used for detecting a certain generic type one by one in a targeted mode any more, but multiple PCR is utilized to conduct genomic amplification on various enterovirus subtypes through an experiment, the virus subtypes are accurately distinguished and identified, and the accuracy rate is higher, and repeatability is better; high-depth sequencing is adopted, the enough detection depth is ensured, and thus false positive is lower; and through the detection method, the gene types of the enterovirus are rapidly identified, genome variable site, diversity and recombination analysis of viruses can be further provided, and the important scientific basis of prevention and control over the enterovirus is provided.
Owner:广东省公共卫生研究院 +1
Gastric cancer detection panel based on next-generation sequencing technology and application of gastric cancer detection panel
PendingCN111996257ALow costAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenes mutationExon
The invention belongs to the technical field of polygene detection of gastric cancer, and discloses a gastric cancer detection panel based on a next-generation sequencing technology. According to theinvention, important exon regions and a part of intron regions of 557 genes are enriched by using a gene probe hybridization method, and high-depth sequencing is carried out, so events such as gene mutation, copy number variation and the like having clear clinical correlation with the gastric cancer can be accurately detected; and a multi-gene screening list is made into a probe, and high-risk genes are detected in a targeted mode through DNA sequencing, so gene mutation with guiding significance for diagnosis and treatment can be detected more efficiently, accurate typing of tumor patients are realized, and meanwhile, a plurality of tumor patients can be helped to participate in clinical tests.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT
Group of thyroid cancer markers and application thereof
ActiveCN110878358AIn-depth analysis of molecular level informationWide coverageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationOncologyMolecular typing
The invention provides a group of thyroid cancer markers and an application thereof. The markers comprise thyroid cancer molecular typing related genes, targeted medication related genes, chemotherapymedication related genes, operation prompt related genes, prognosis related genes and thyroid cancer heredity related genes. According to the invention, aiming at all exon regions of 44 genes relatedto thyroid molecular typing, targeted medication, chemotherapy medication, operation prompt, prognosis and heredity, high-depth sequencing is carried out; meanwhile, various variation types like SNV / Indel and gene fusion of genes are analyzed; and molecular level information of thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer is deeply analyzed. Aiming at a capture probe designed for the 44 genes, 558 targeting target regions are covered; the probe comprises 3633 sequences with a total size of 254.096 Kbp; and a prepared kit is wide in coverage, high in cost performance and high in effectiveness, can provide a reference basis for further molecular typing, medication prompt, genetic risk assessment and the like of a thyroid patient, and is applicable to clinical popularization and application.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOTECAN PHARMA +1
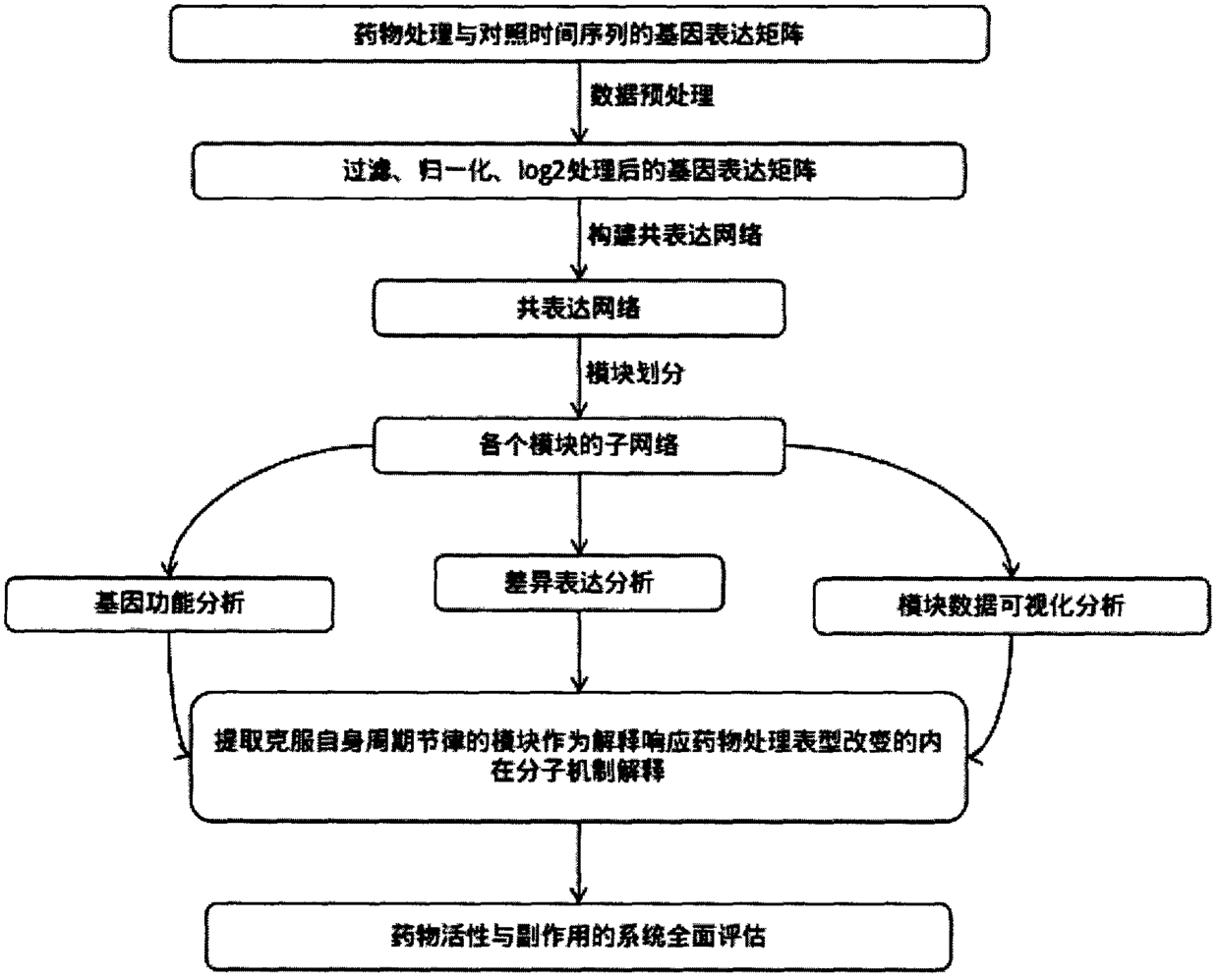
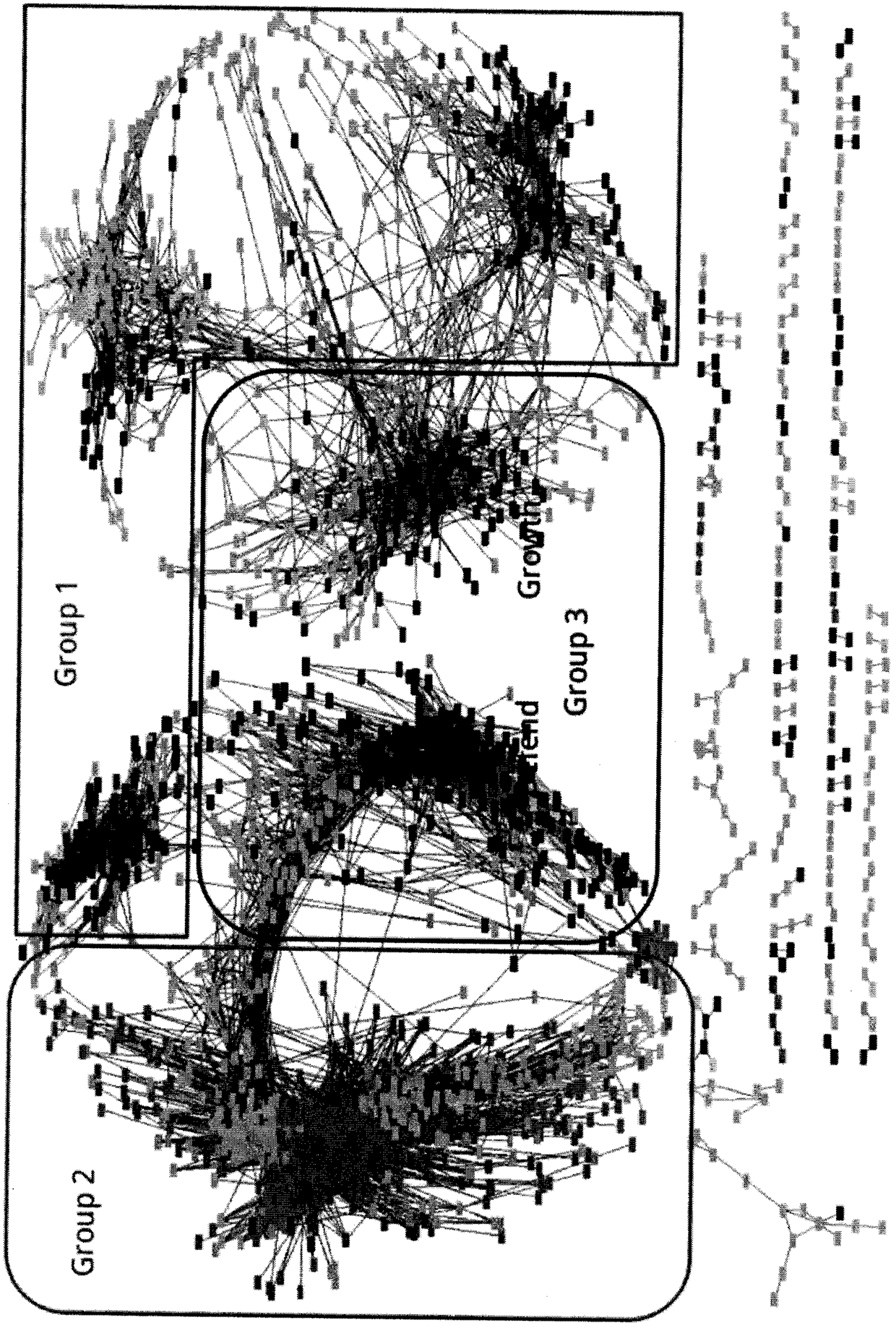
Application of transcriptomics for co-expressing cyclic circadian rhythm to discovery of drug action mechanism
InactiveCN109192252AInnovativeQuick identificationChemical property predictionMolecular entity identificationSide effectVeterinary Drugs
The invention provides a method for discovering a drug action mechanism by transcriptomics for co-expressing cyclic circadian rhythm. The method comprises the steps: successfully identifying a molecular mechanism of a drug action by analyzing deep sequencing circadian time sequence transcriptome data in combination with bioinformatics, coexpression analysis, machine learning and data visualizationtechnologies; and establishing an mRNA expression network by utilizing mRNA expression data, dividing modules, carrying out functional enrichment analysis on GO and KEGG of each module by utilizing hypergeometric distribution, extracting the module overcoming the cyclic rhythm of the module as a main explanation for an endogenous molecular mechanism of biological phenotype change related to corresponding drug treatment, and comprehensively explaining and assessing the molecular mechanism of a drug for a physiological function of a corresponding biological representation by utilizing data visualization in combination with phenotypic change and functional analysis after drug treatment. The invention further provides an application of the method to the research of an action mechanism of coronatine inhibiting growth and promoting defense and the discovery of action mechanisms and toxic / side effect mechanisms of pesticides, medicines, veterinary drugs and drugs for aquatic products.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
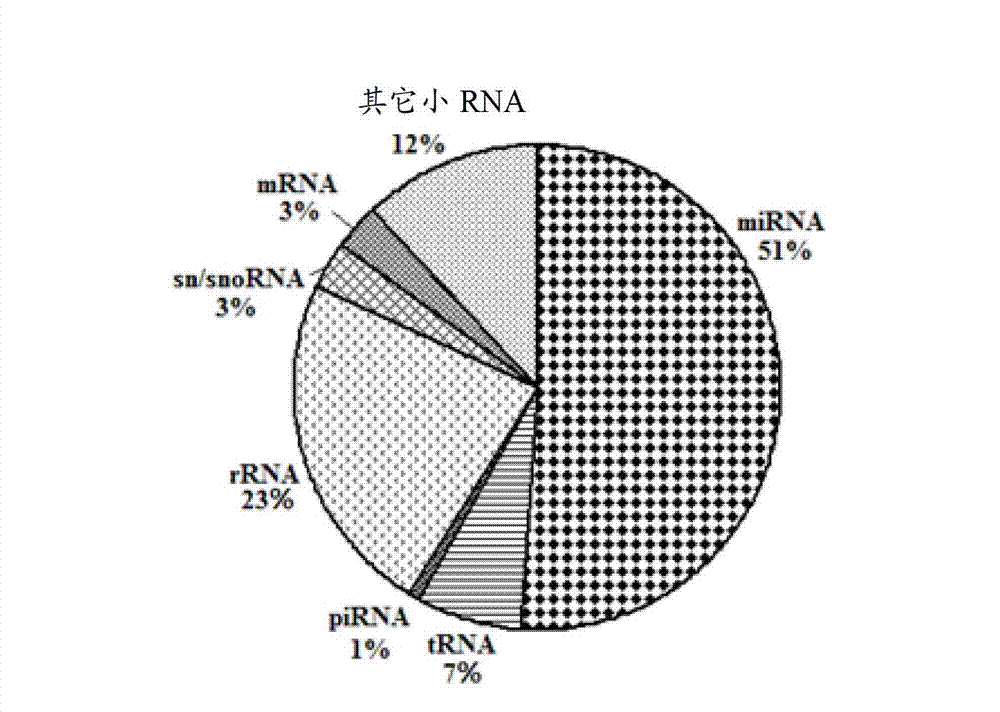
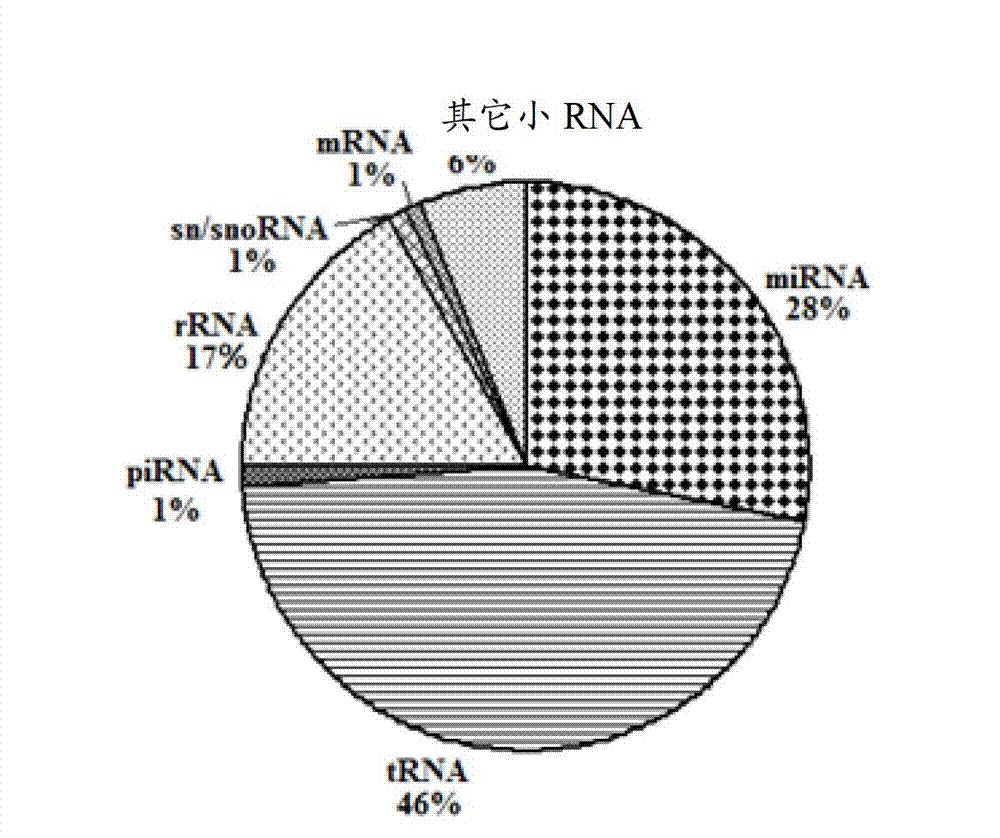
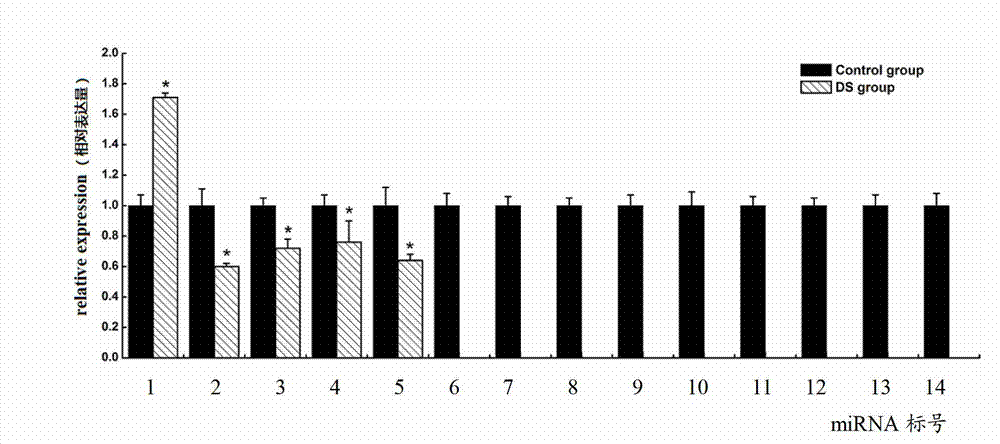
Down syndrome 21 chromosome miRNA differential expression map model, modeling method and application
ActiveCN103045736AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseDistribution characteristic
The expression map and the chromosome distribution characteristic of a DS (down syndrome) fetal genome-wide miRNAs are studied by an Illumina deep sequencing technology so as to obtain a down syndrome 21 chromosome-related miRNA differential expression map model, which consists of an up-regulated miRNA, four down-regulated miRNAs and 9 zero-expression miRNAs. miRNA molecules with significant difference and specific expression help to understand a molecular regulation mechanism for occurrence and development of a clinical phenotype of a DS disease and lay the foundation for further studying gene expression disorder of a DS patient genome-wide and a relationship between the gene expression disorder and relevant clinical symptoms.
Owner:徐勇
Capture probe set for dementia-related gene, kit, library construction method and use thereof
ActiveCN108753954AAccurate sequencing of target genesLower Sequencing CostsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationCoding regionRelated gene
The invention provides a capture probe set for a dementia-related gene, a kit, a library construction method and a use thereof and relates to the technical field of gene detection. The capture probe set contains coding regions of 95 genes and can capture aiming at a specific coding region and perform high-depth sequencing so that target gene sequencing is accurate and a sequencing cost is reduced.The capture probe set can efficiently enrich the target genes in construction of a library, reduce the sample size requirement and also better control the sequencing cost.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Methods for detecting modification resistant nucleic acids
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Liver cancer prognosis related serum miRNA markers and application of detection kit thereof
ActiveCN105647923AHigh clinical application valueBreakthrough innovationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationIndividualized treatmentSerum mirna
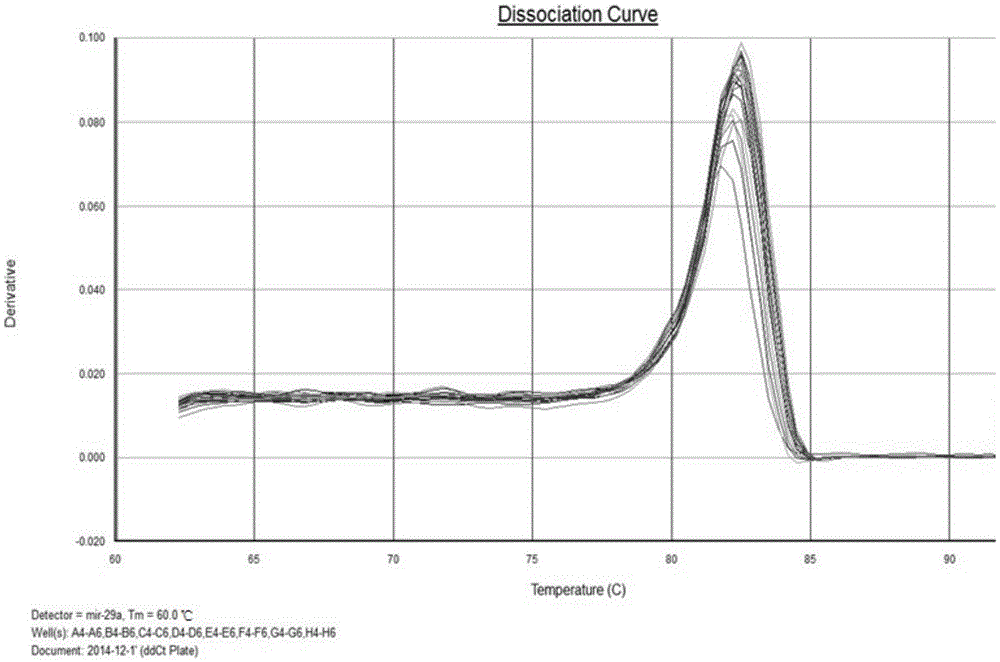
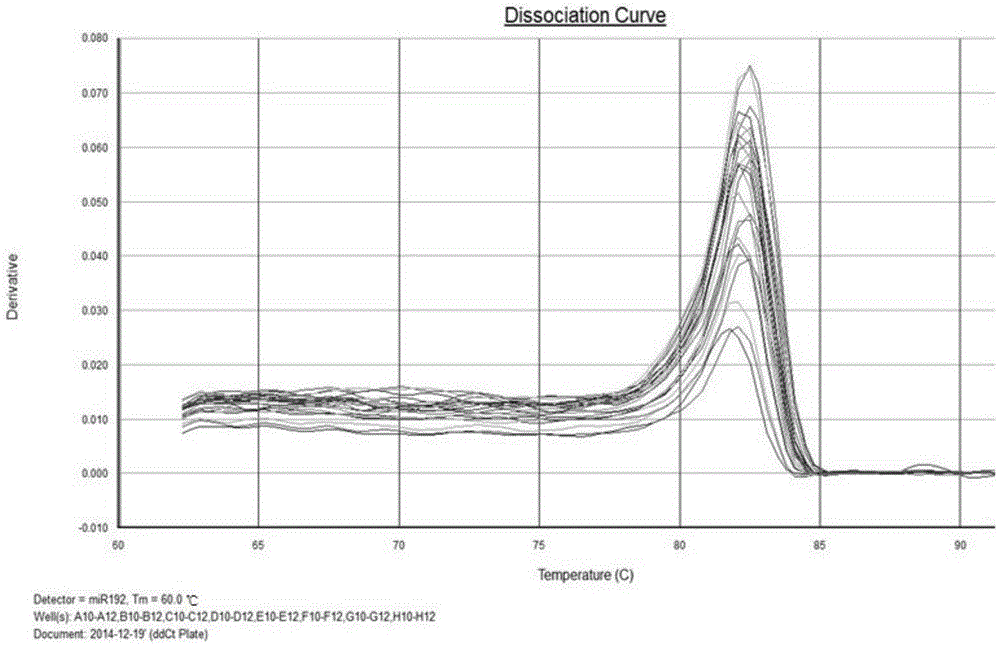
The invention discloses liver cancer prognosis related serum miRNA markers and an application of a detection kit thereof. The tumor markers are serum miR-29a-3p and miR-192-5p which are related with human liver cancer patients. According to preliminary work, liver cancer related serum miRNA expression profiles containing miR-29a-3p and miR-192-5p and having obvious expression difference are screened out through high-throughput deep sequencing, and qPCR (quantitative polymerase chain reaction) proves and finally confirms that miR-29a-3p and miR-192-5p are liver cancer risk (prognosis) related tumor markers. The markers and detection reagents can be used for preparing the rapid-detection pPCR kit, and the kit has the characteristics of rapidness and convenience in detection, high accuracy rate, no wound and the like; a prognostic model built through combination of miR-29a-3p, miR-192-5p and BCLC stage (Barcelona clinic liver cancer stage) can be applied to classification of risk degrees of the liver cancer patients, thereby guiding individualized treatment of the liver cancer patients.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT
Composite amplifying system of SNP-DIP micro haplotype domain for medico-legal individual recognition based on NGS subtyping
The invention belongs to the field of creative research and application of a medico-legal new technology, and particularly relates to and discloses a composite amplifying detection system of a micro haplotype domain consisting of SNP-DIP molecular genetic markers for medico-legal individual recognition. Based on SNP sites or DIP sites which are reported in the past, a research strategy of a microhaplotype domain is adopted, through a dbSNP library, whether flanking sequences (which are 100bp up and down) of the sites have other SNP or DIP heredity variations or not is consulted, and accordingto the combination type differences of heredity variations in each region, a molecular genetic marker similar to the micro haplotype domain is formed. The regions are deeply sequenced by a bibasic sequencing method, so that the simultaneous subtyping detection of a plurality of samples can be realized, and besides, the base sequence variation information of all SNP or DIP sites in each region canbe obtained. The 18 micro haplotype domains provided by the invention has higher accumulation individual recognition rate in East Asia groups, and can be used for application research of medico-legalindividual recognition.
Owner:西安交通大学口腔医院
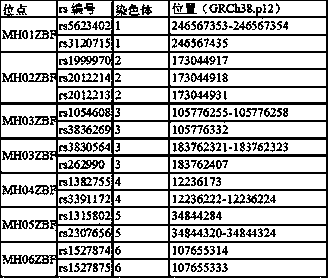
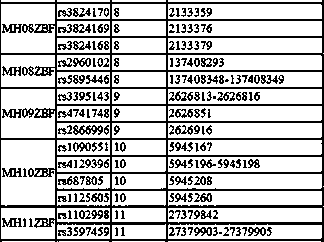
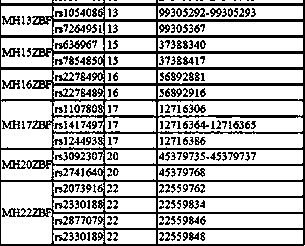
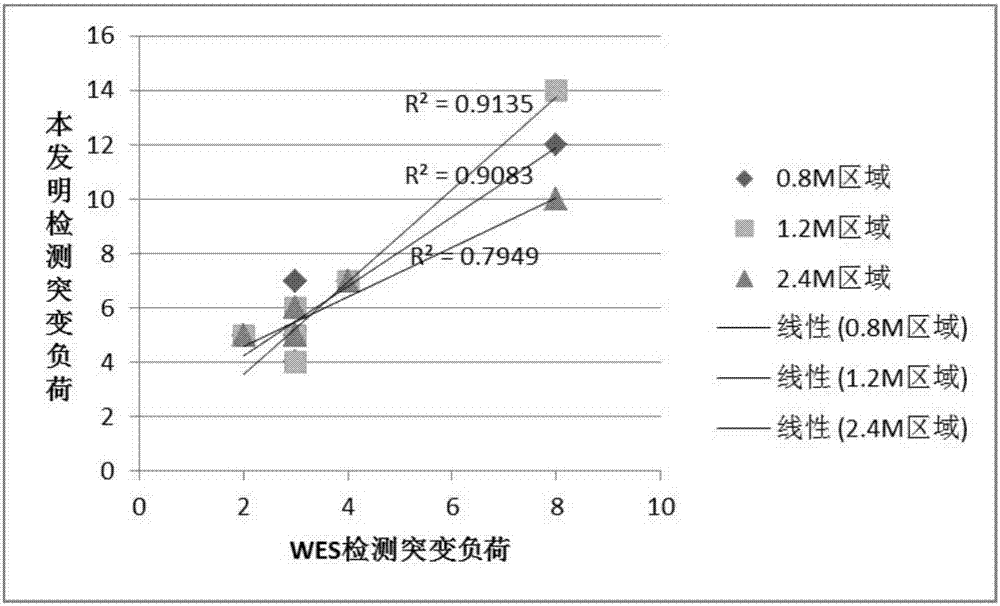
Method and kit for detecting mutational load of human genome based on high-throughput sequencing
PendingCN107338292AImprove consistencyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
Owner:3D BIOMEDICINE SCI & TECH CO LTD
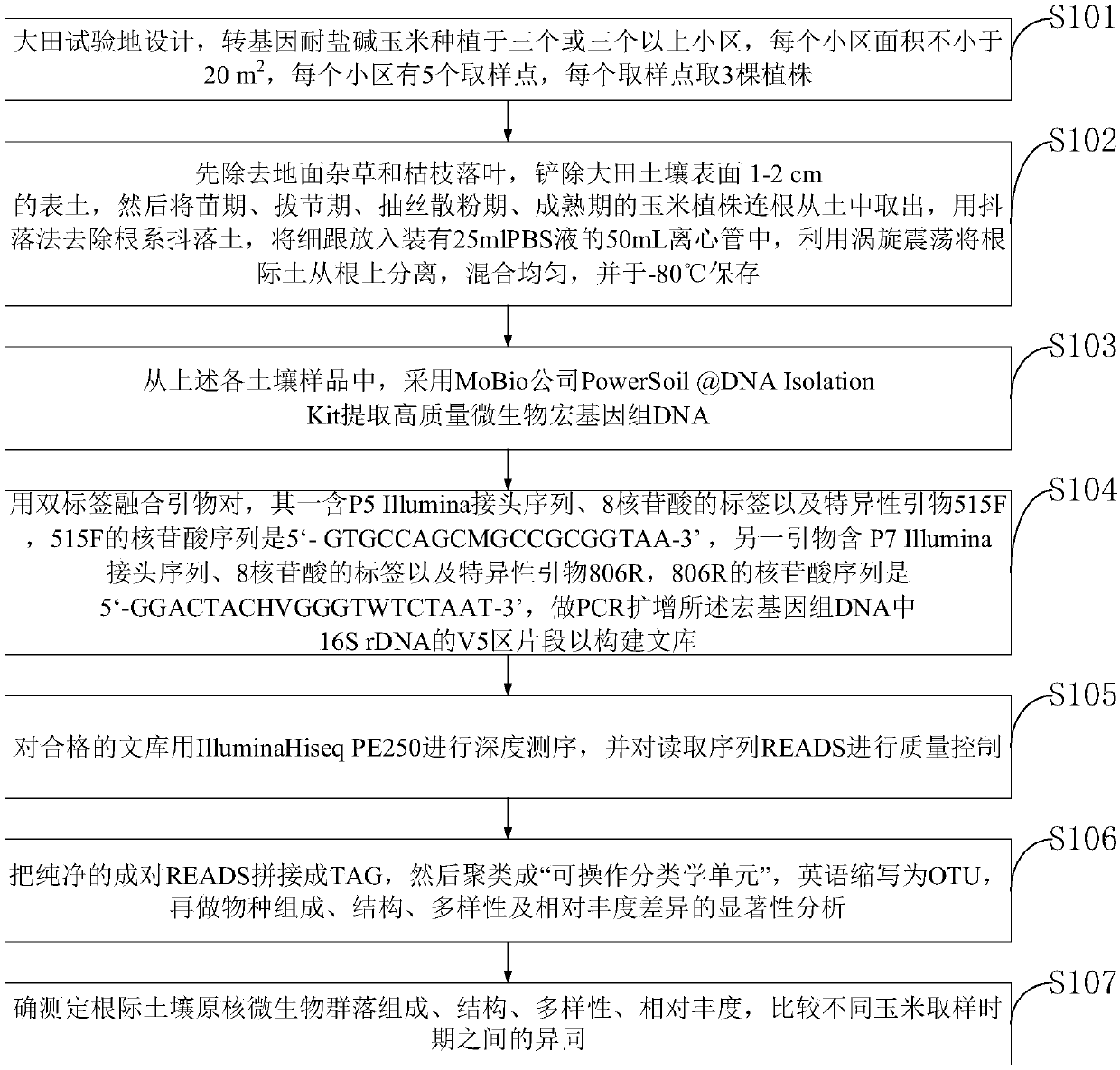
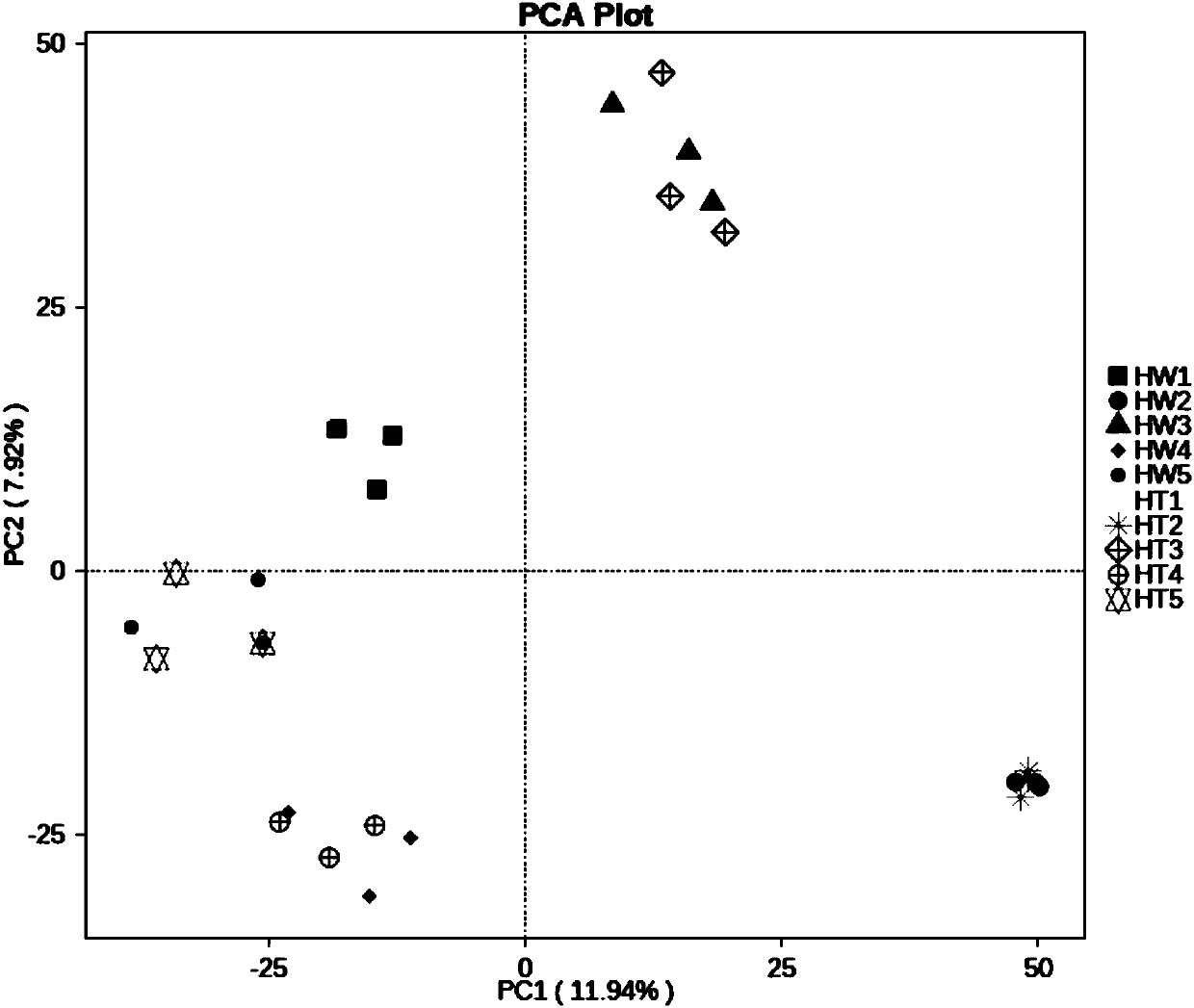
Method and system for detecting maize rhizosphere soil microorganisms based on deep sequencing
PendingCN107904296AImprove throughputLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismSoil microbiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil microbiology, and discloses a method and a system for detecting maize rhizosphere soil microorganisms based on deep sequencing. The method comprises the following steps: 1, collecting rhizosphere soil; 2, extracting high-quality microorganism genome DNA from the soil; 3, performing PCR to amplify a 16S rDNA V4 region in the DNA by using a double-tag primer, and constructing a library; 4, sequencing a qualified library to obtain pure READS; 5, splicing, wherein each sample produces at least 50 thousand effective TAG for clustering into operable taxons; 6, analyzing species composition, structure, diversity and relative abundance difference significance 7, determining the composition, the structure, the diversity and the relative abundanceof transgenic saline-alkaline-resistant maize rhizosphere soil prokaryotic microflorae. The method and the system for detecting the maize rhizosphere soil microorganisms based on deep sequencing aresupported by a major national genetic modification specific subject, namely, a national genetically modified corn wheat soybean environmental safety assessment technology (2016ZX08011003).
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com