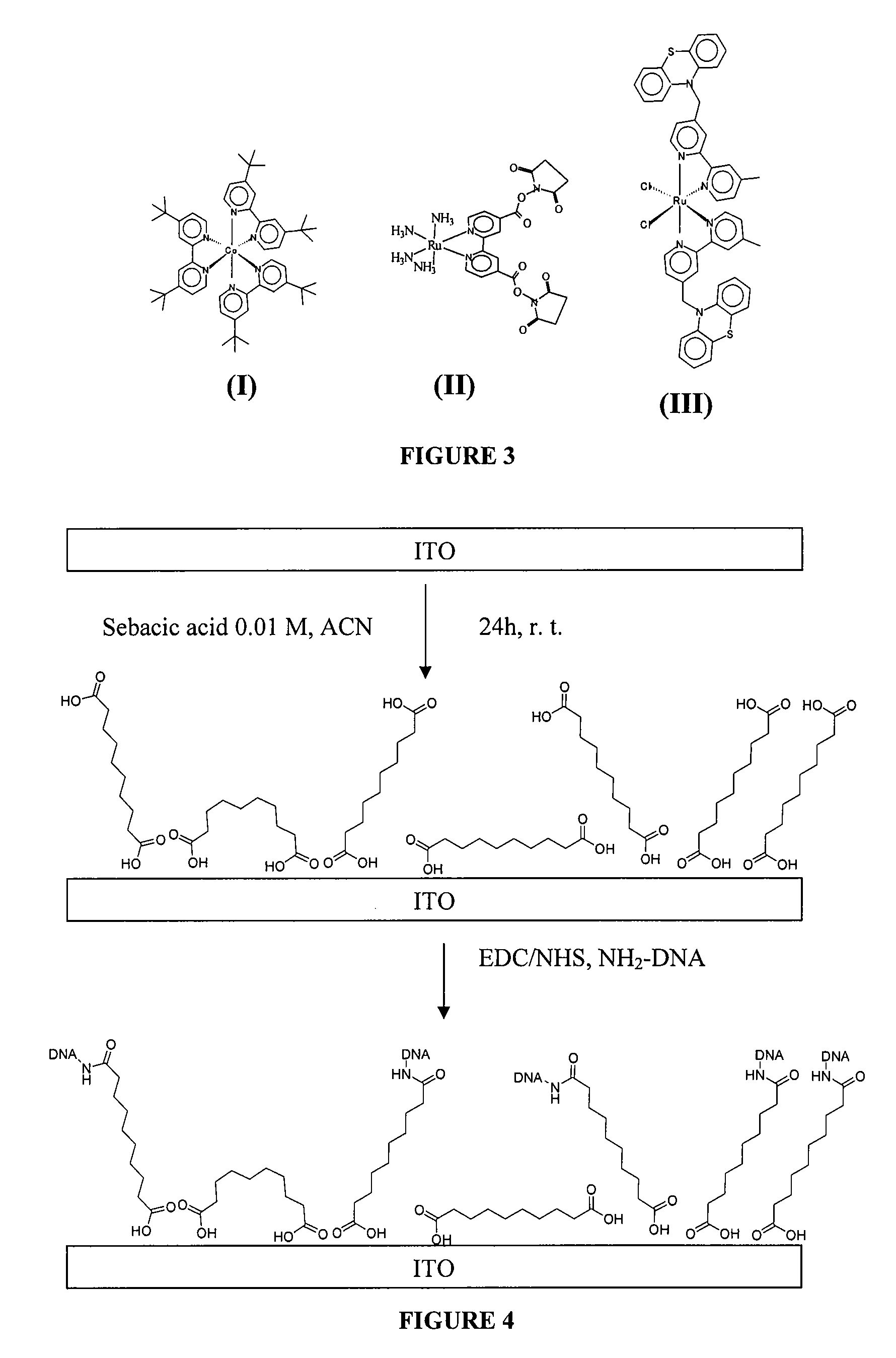
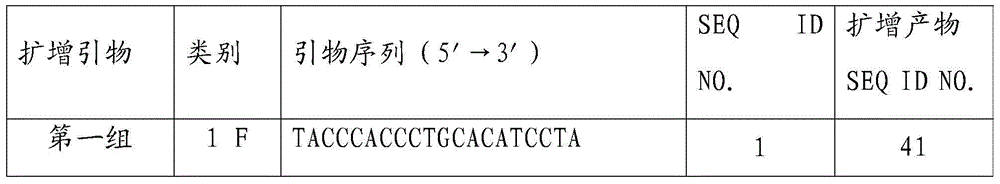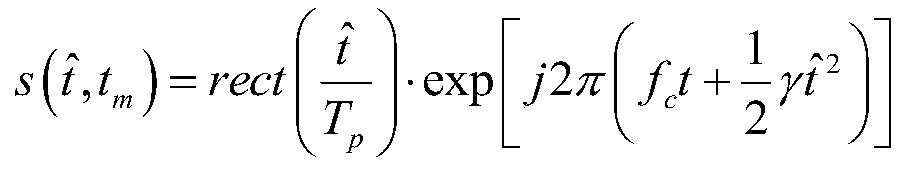Patents
Literature
264 results about "Probe target" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
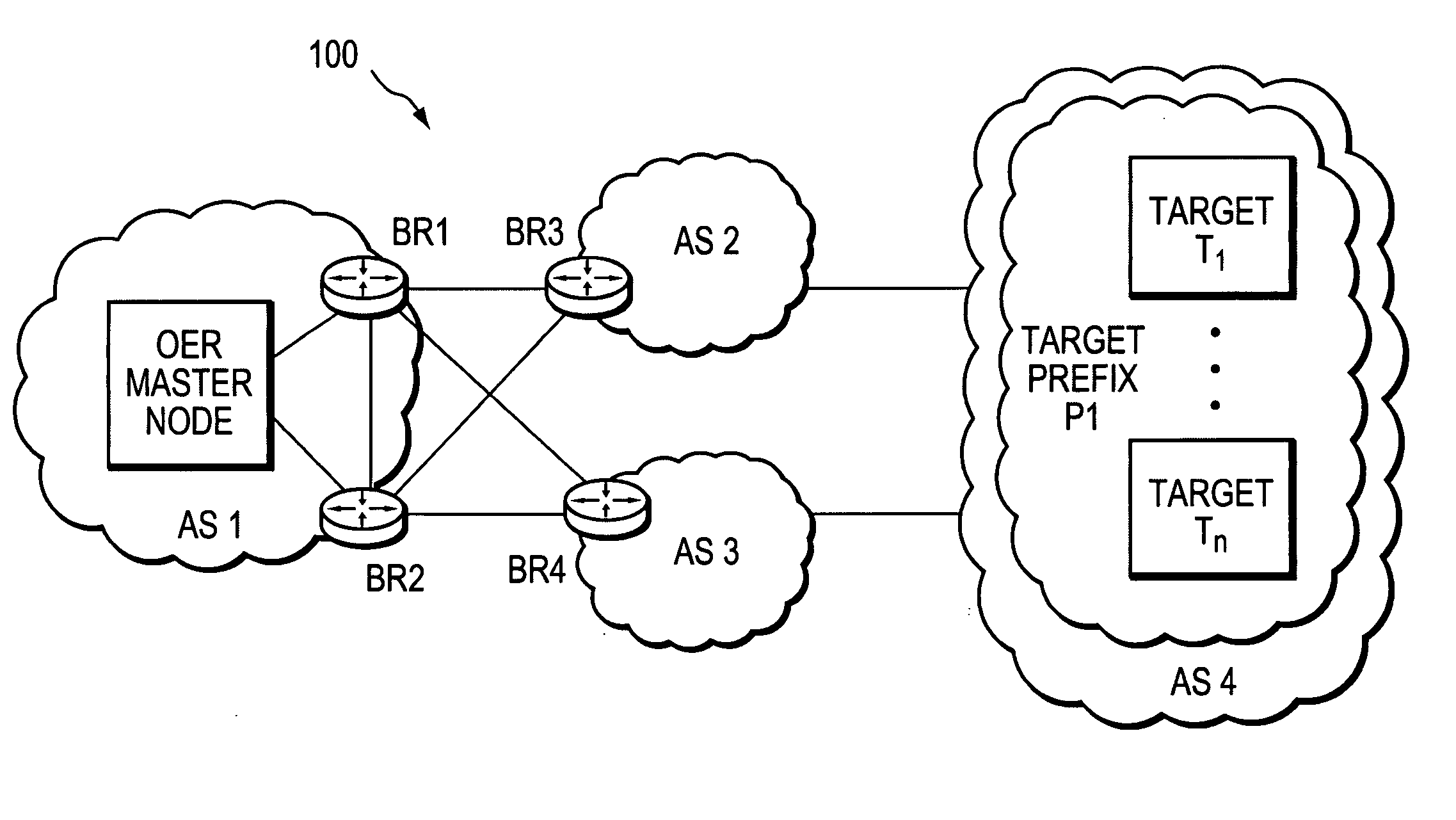
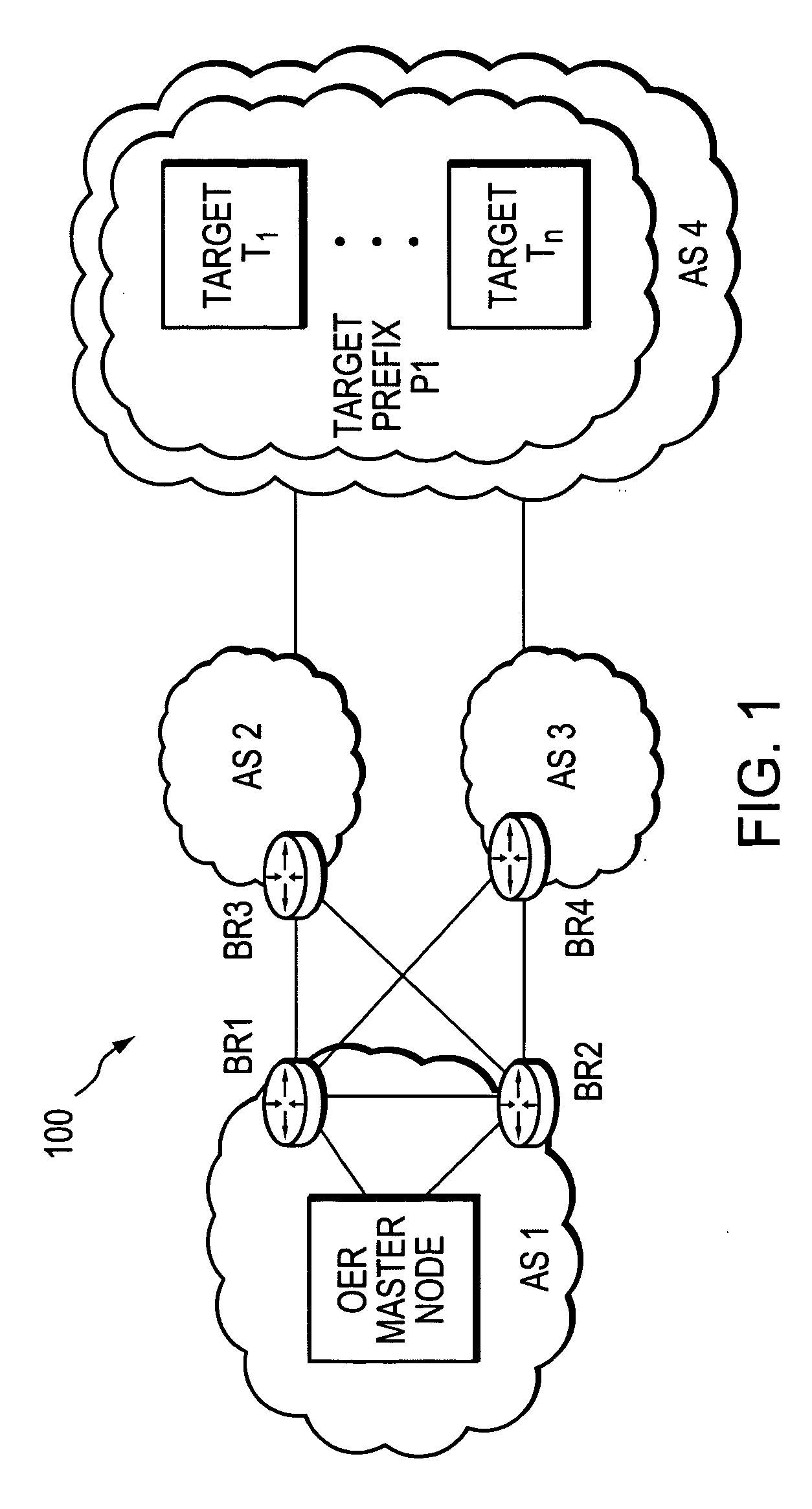
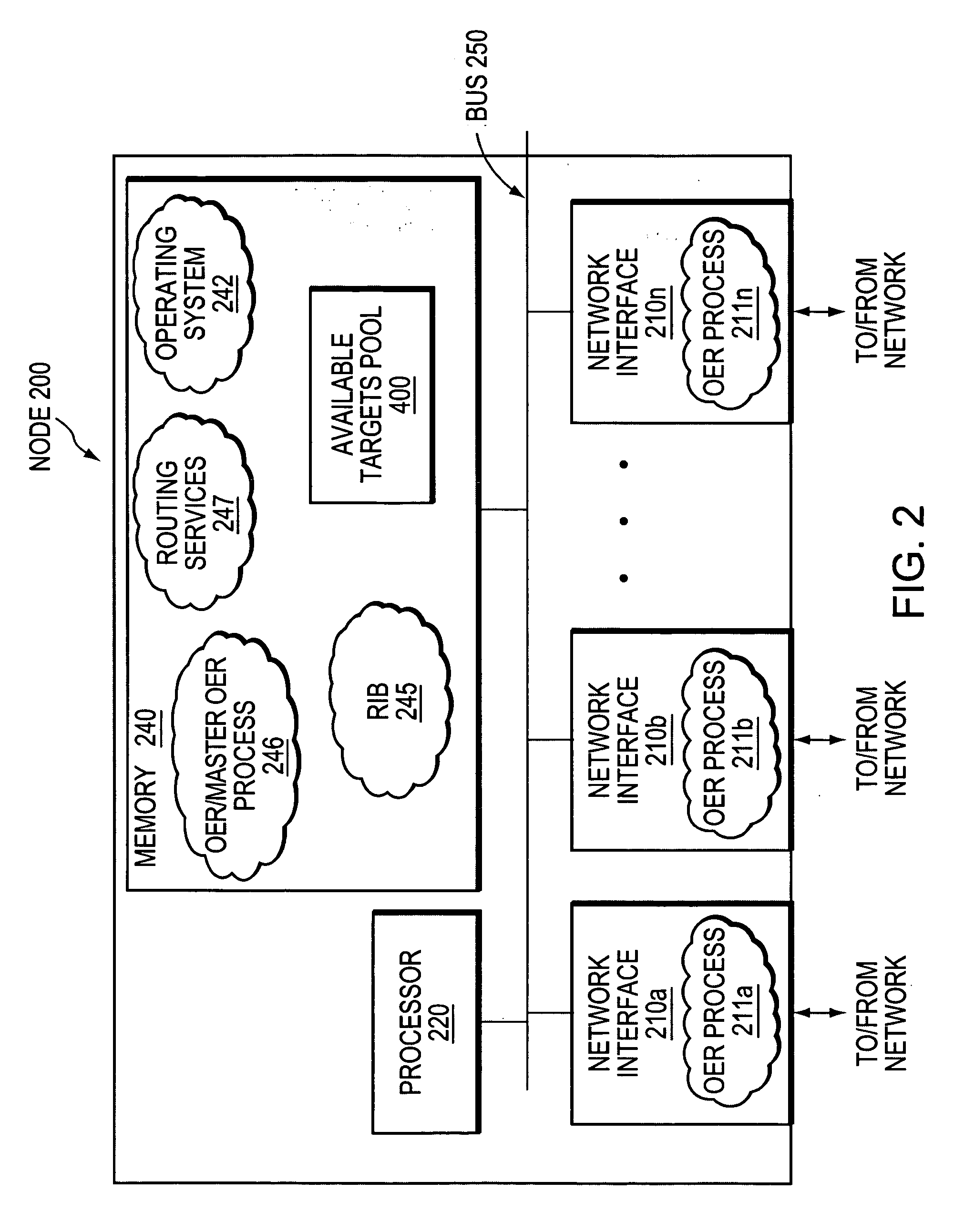
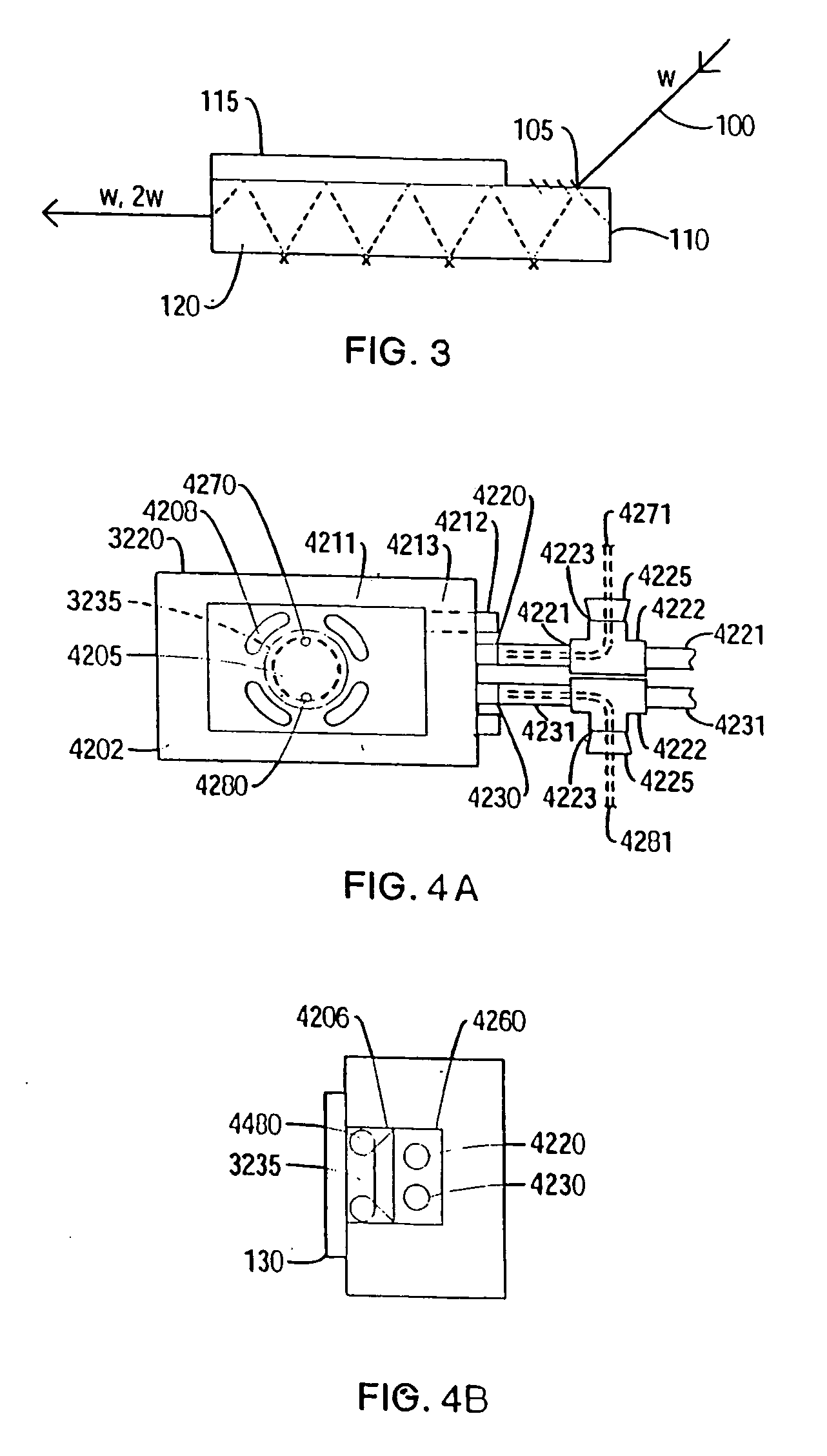
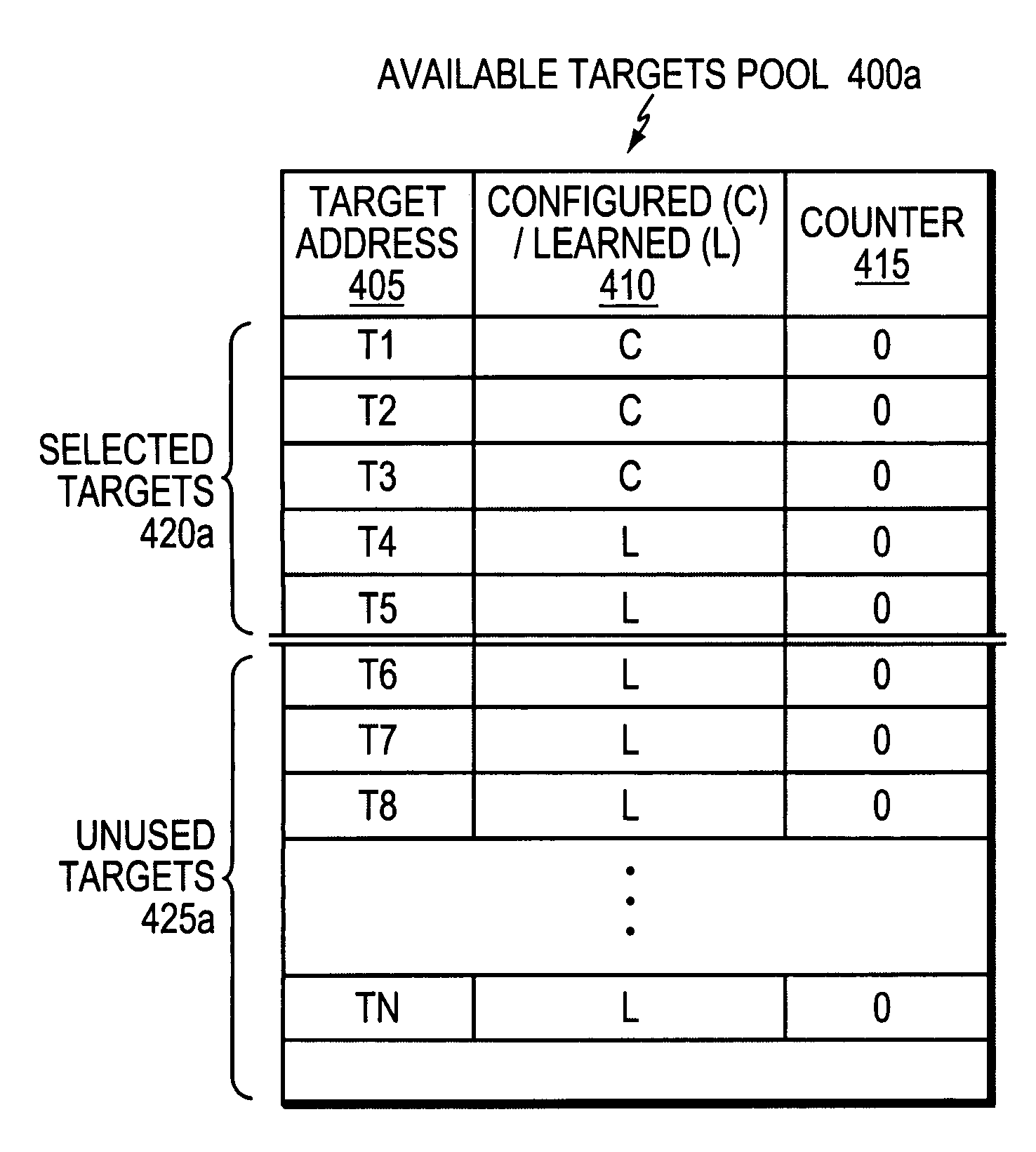
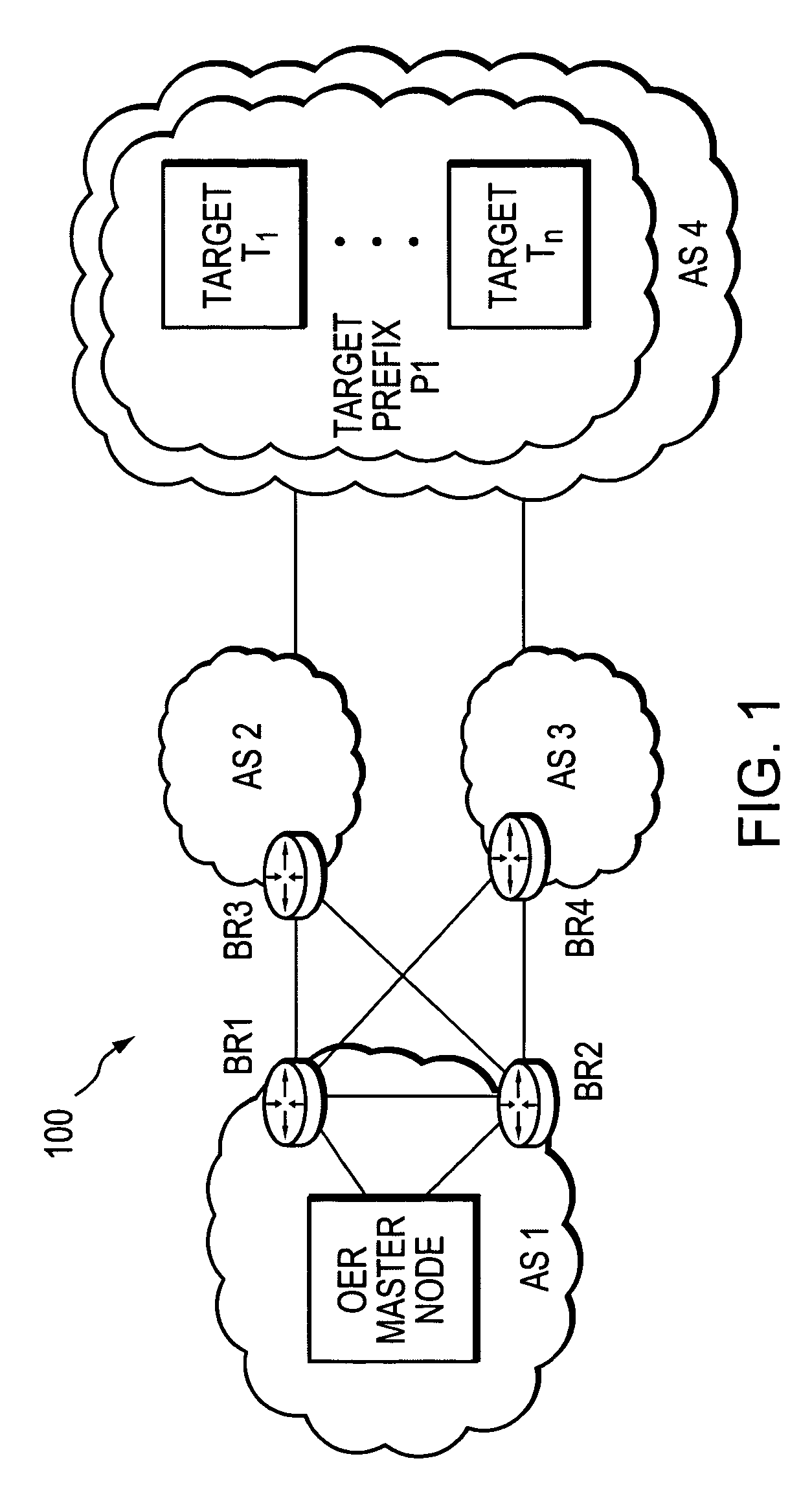
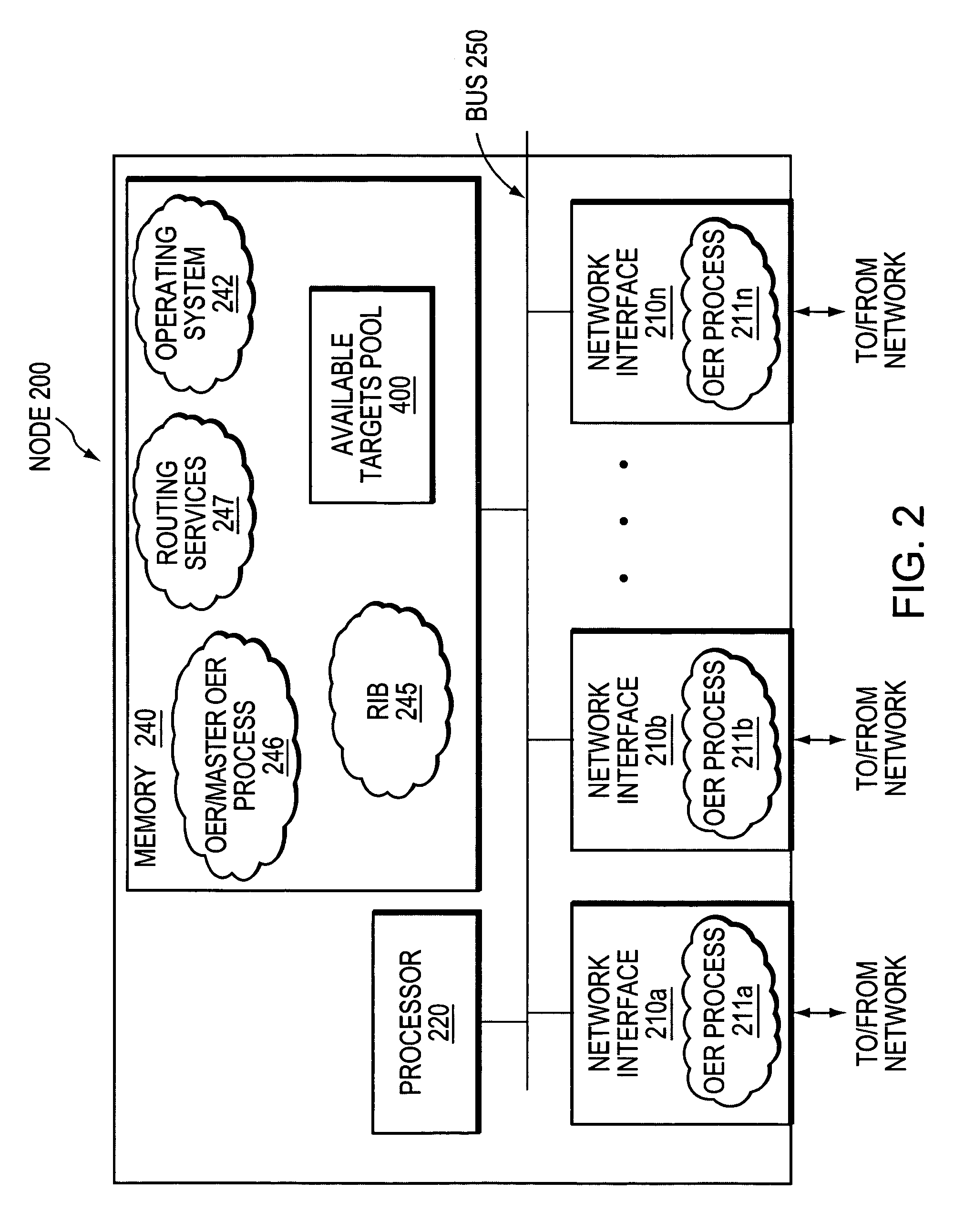
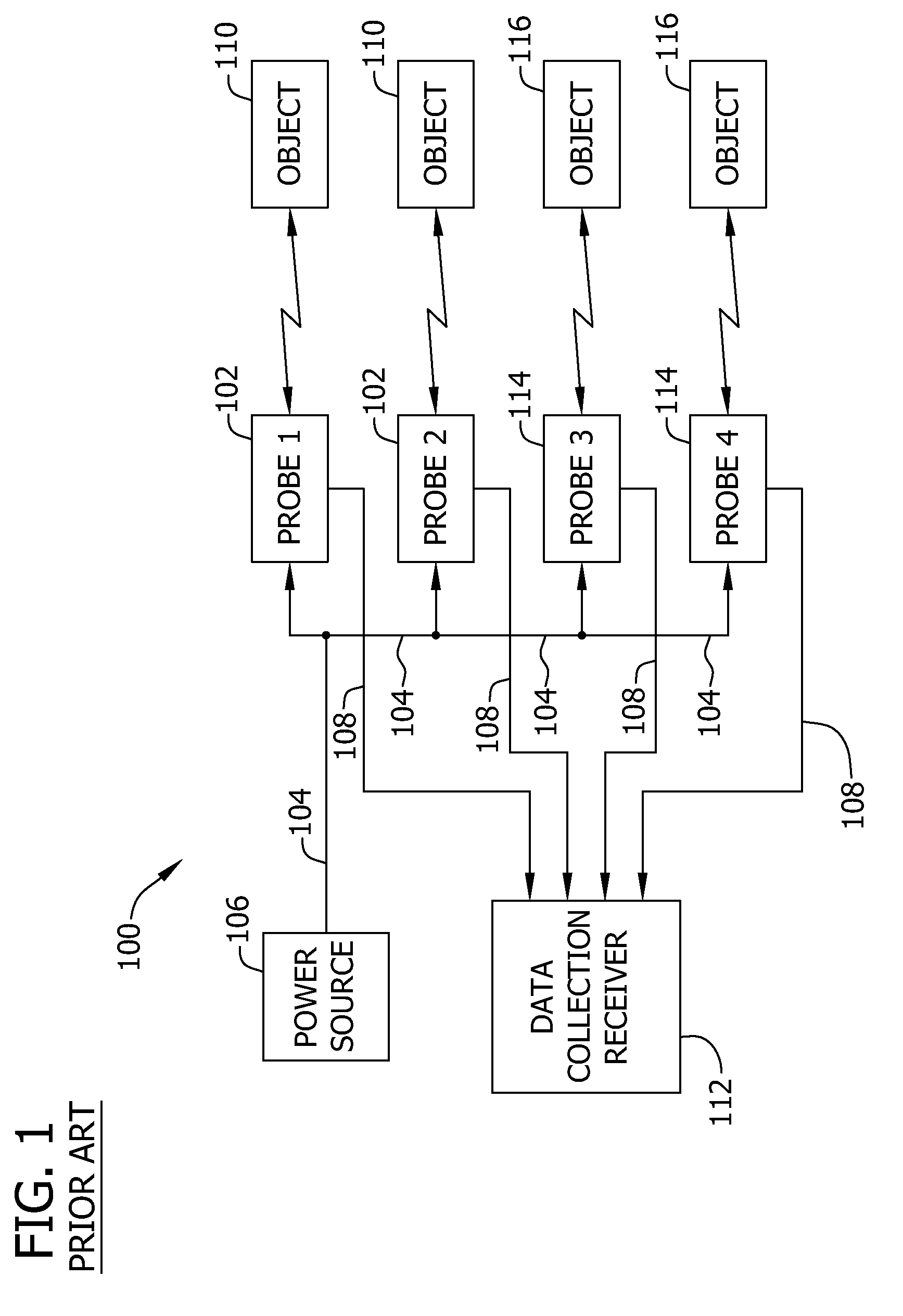
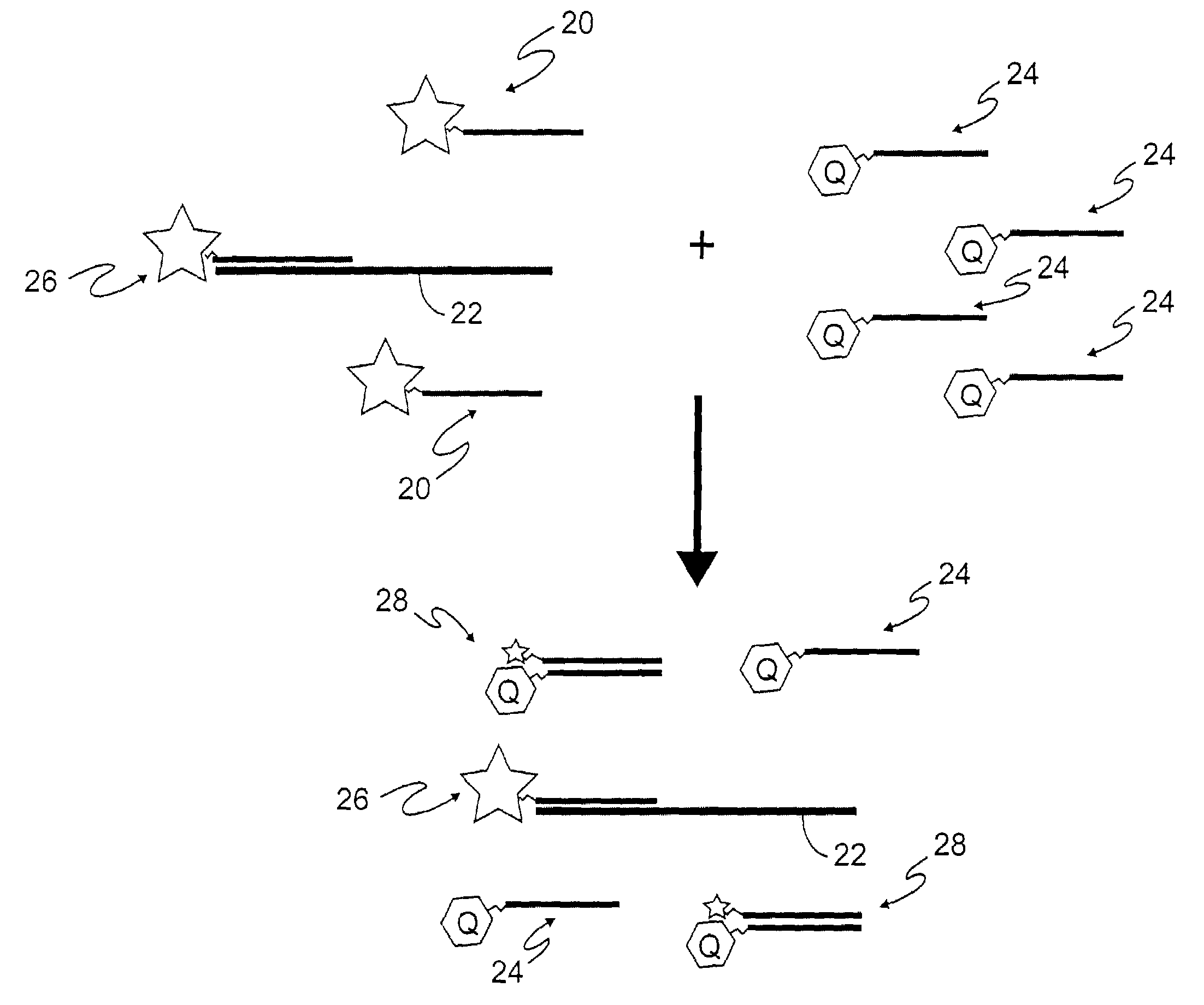
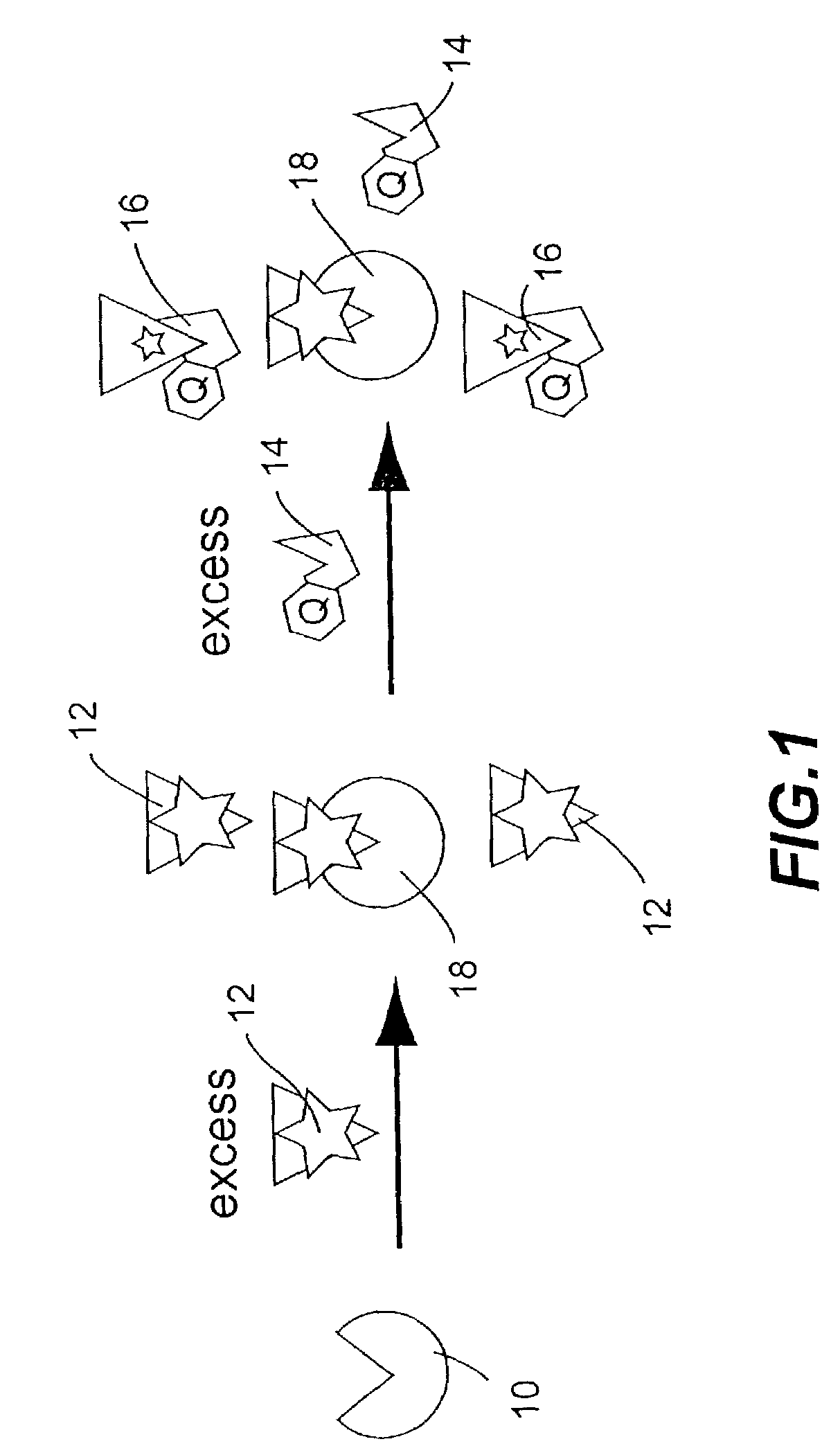
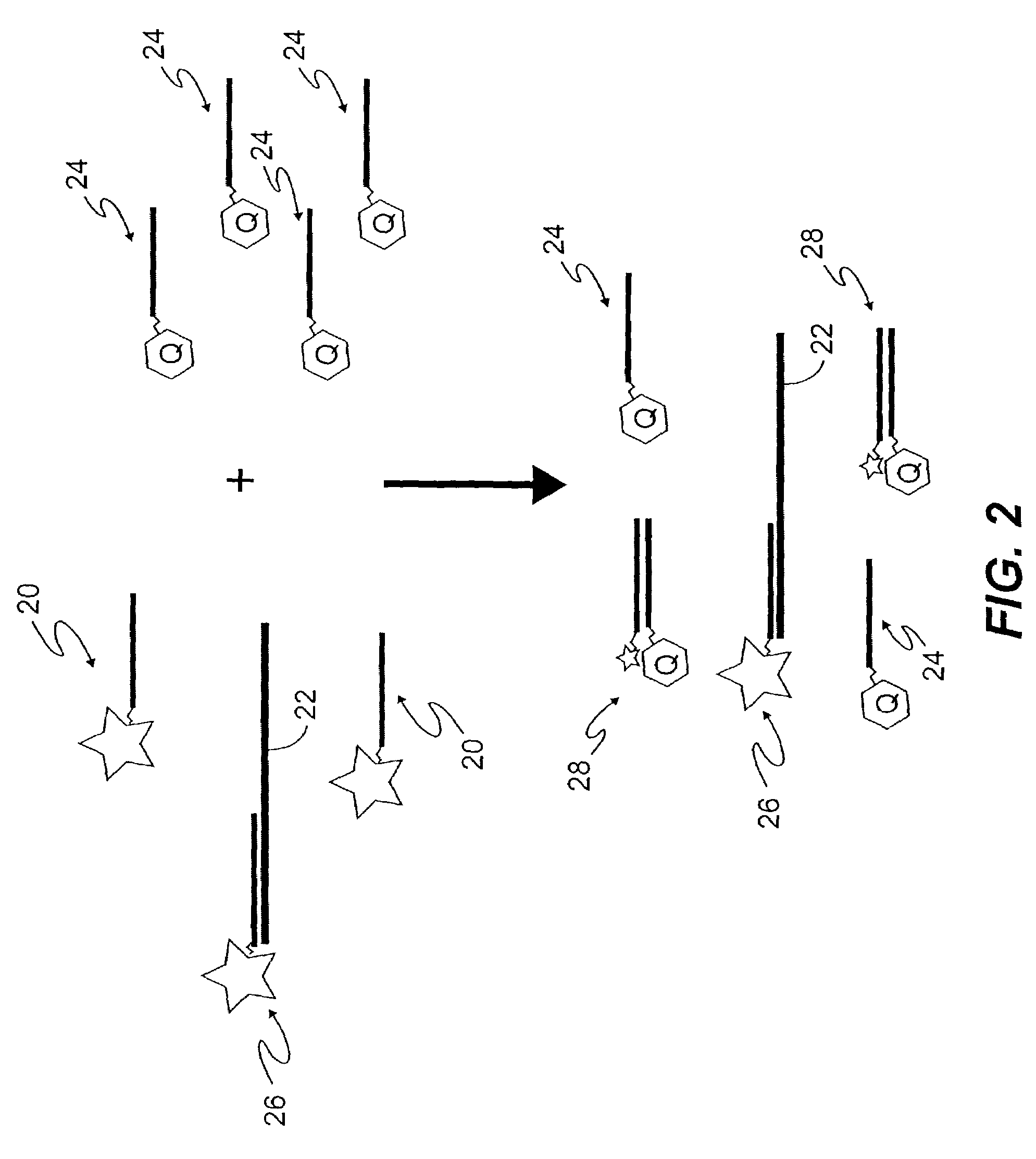
Active probe target management
ActiveUS20060239201A1Efficient managementError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsProbe targetEvaluation period
A technique manages targets to which probe packets are sent from a source of a computer network. The novel target management technique dynamically selects an optimal set of valid targets for a particular (monitored) prefix of the computer network. Specifically, one or more targets are selected from a pool of possible learned and configured targets to be used as representatives of the monitored prefix. Probe packets are sent from the source to the selected targets for the duration of an evaluation period. Targets that do not respond to the probe packets during the evaluation period are invalid and deselected, and if available, an unused target is selected from the pool of possible targets to replace each non-responding target for a next evaluation period. Invalid learned targets are discarded, while invalid configured targets are returned to the pool of possible targets for potential re-selection in a later evaluation period.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Security for WAP servers
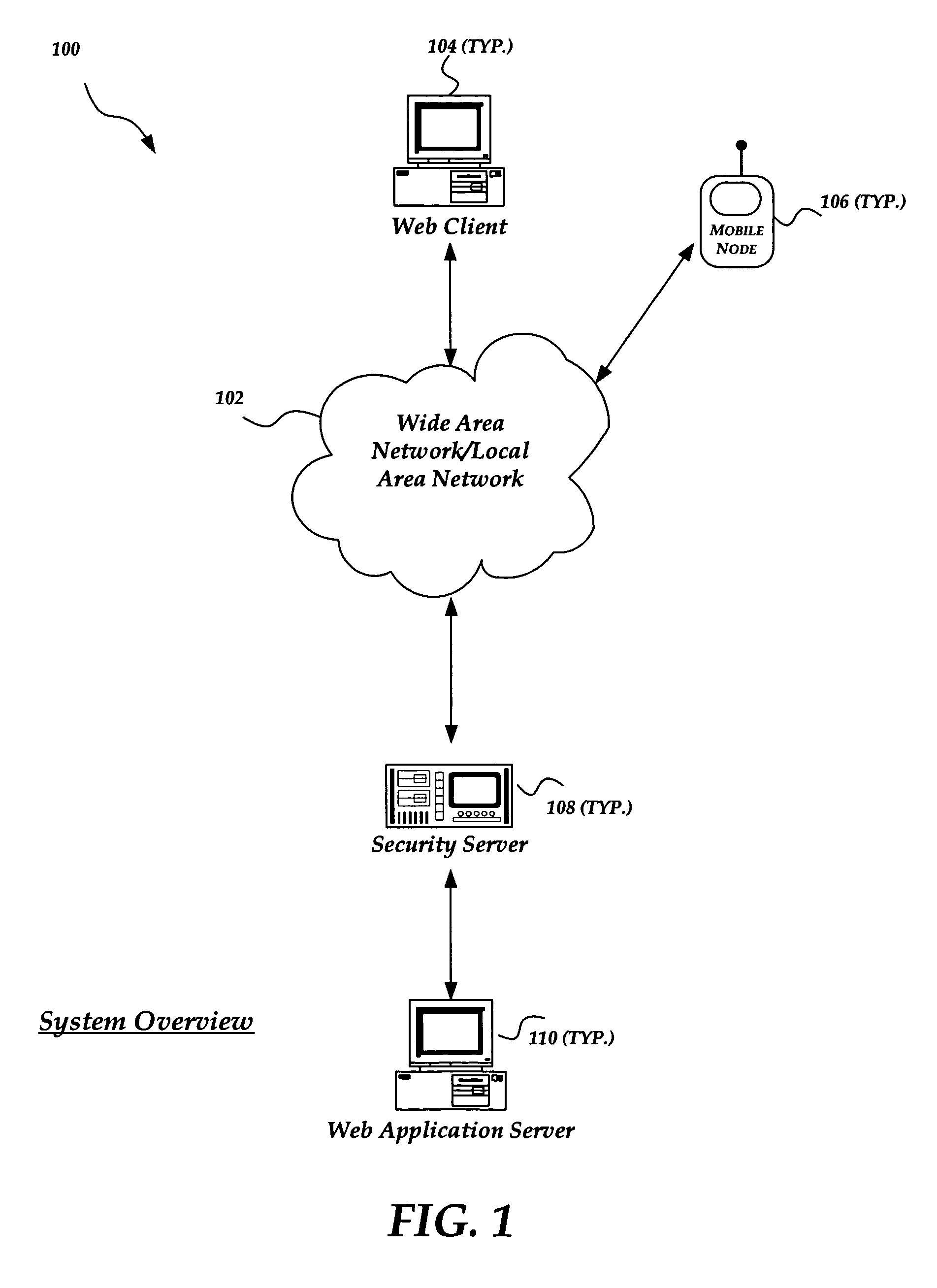
ActiveUS7472413B1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsApplication serverWeb application
A method and system for improving the security and control of internet / network web application processes, such as web applications. The invention enables validation of requests from web clients before the request reaches a web application server. Incoming web client requests are compared to an application model that may include an allowed navigation path within an underlying web application. Requests inconsistent with the application model are blocked before reaching the application server. The invention may also verify that application state data sent to application servers has not been inappropriately modified. Furthermore, the invention enables application models to be automatically generated by employing, for example, a web crawler to probe target applications. Once a preliminary application model is generated it can be operated in a training mode. An administrator may tune the application model by adding a request that was incorrectly marked as non-compliant to the application model.
Owner:F5 NETWORKS INC
Method using a nonlinear optical technique for detection of interactions involving a conformational change
InactiveUS20060228725A1No need for labor and time-consuming washing stepLow backgroundCompound screeningMaterial nanotechnologyThird harmonicFrequency generation
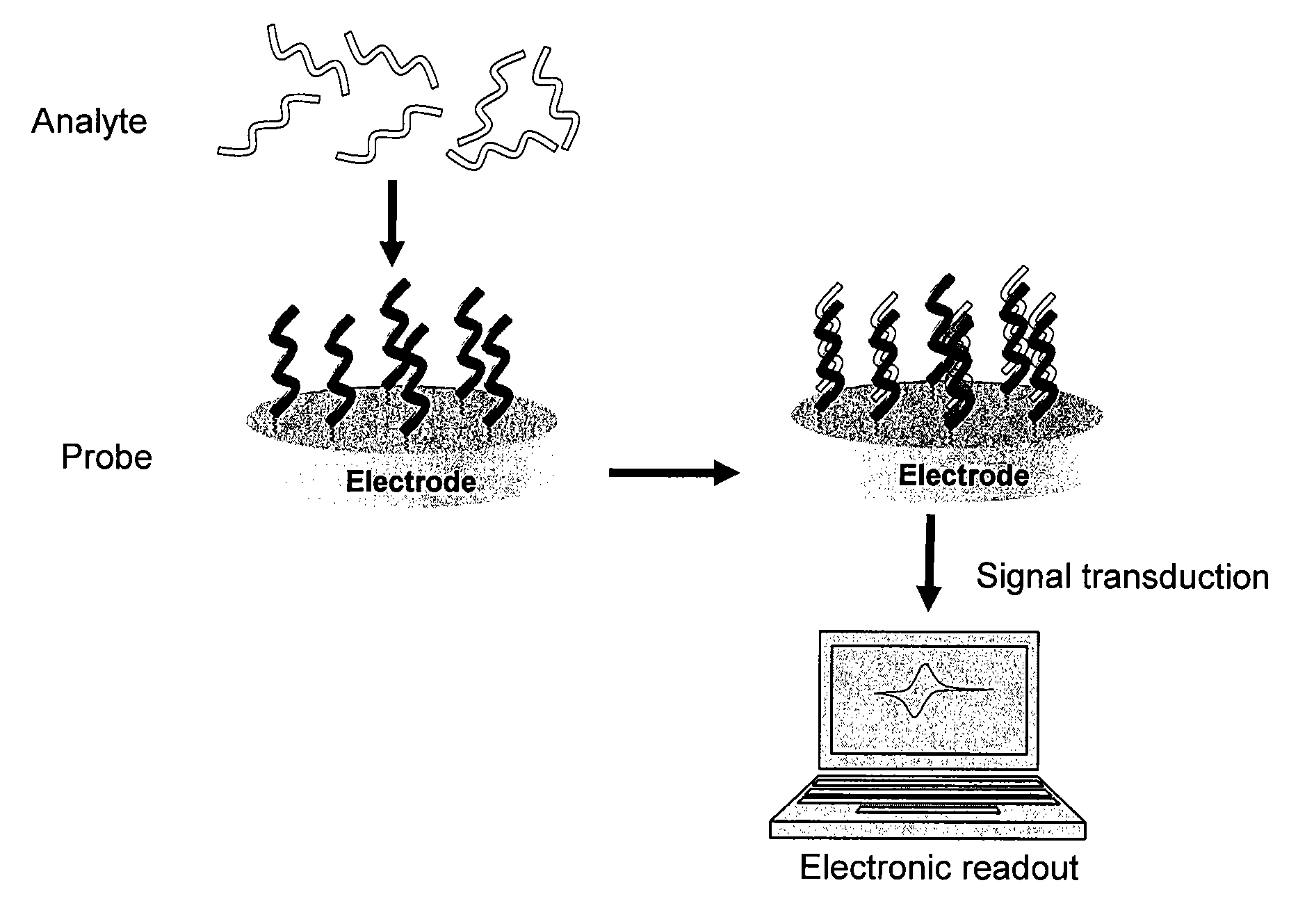
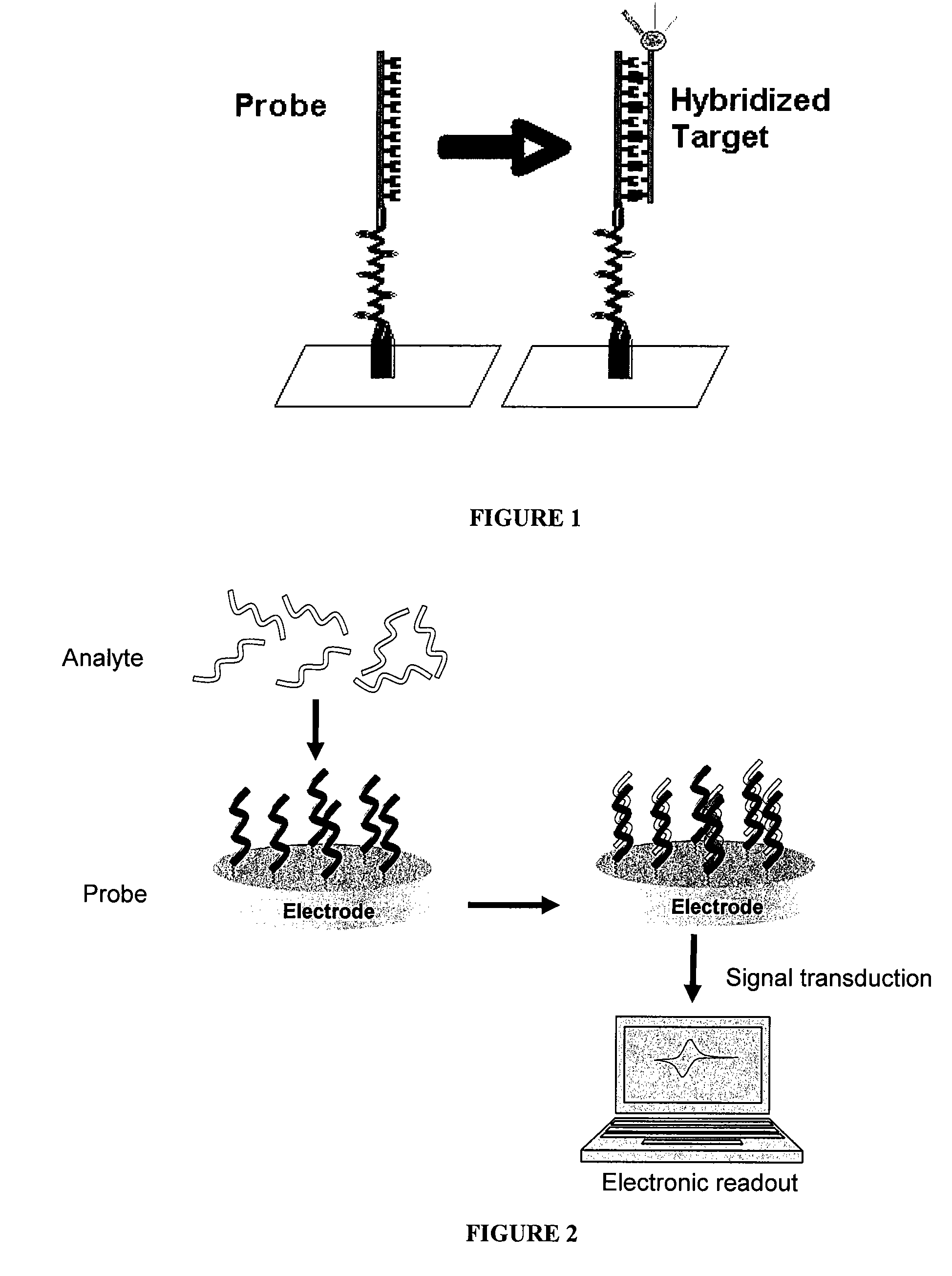
A nonlinear optical technique, such as second or third harmonic or sum or difference frequency generation, is used to detect binding interactions, or the degree or extent of binding, that comprise a conformational change. In one aspect of the present invention, the nonlinear optical technique detects a conformational change in a probe due to target binding. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate probes by detecting a conformational change due to a probe-target interaction. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate modulators of a probe-target interaction by detecting a conformational change in the presence of the modulator.
Owner:BIODESY
Active probe target management
ActiveUS7675861B2Efficient managementError preventionTransmission systemsProbe targetEvaluation period
A technique manages targets to which probe packets are sent from a source of a computer network. The novel target management technique dynamically selects an optimal set of valid targets for a particular (monitored) prefix of the computer network. Specifically, one or more targets are selected from a pool of possible learned and configured targets to be used as representatives of the monitored prefix. Probe packets are sent from the source to the selected targets for the duration of an evaluation period. Targets that do not respond to the probe packets during the evaluation period are invalid and deselected, and if available, an unused target is selected from the pool of possible targets to replace each non-responding target for a next evaluation period. Invalid learned targets are discarded, while invalid configured targets are returned to the pool of possible targets for potential re-selection in a later evaluation period.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Immobilization of biopolymers to aminated substrates by direct adsorption
InactiveUS6861214B1Rapid and convenient methodExpensive productMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiopolymerPolypropylene
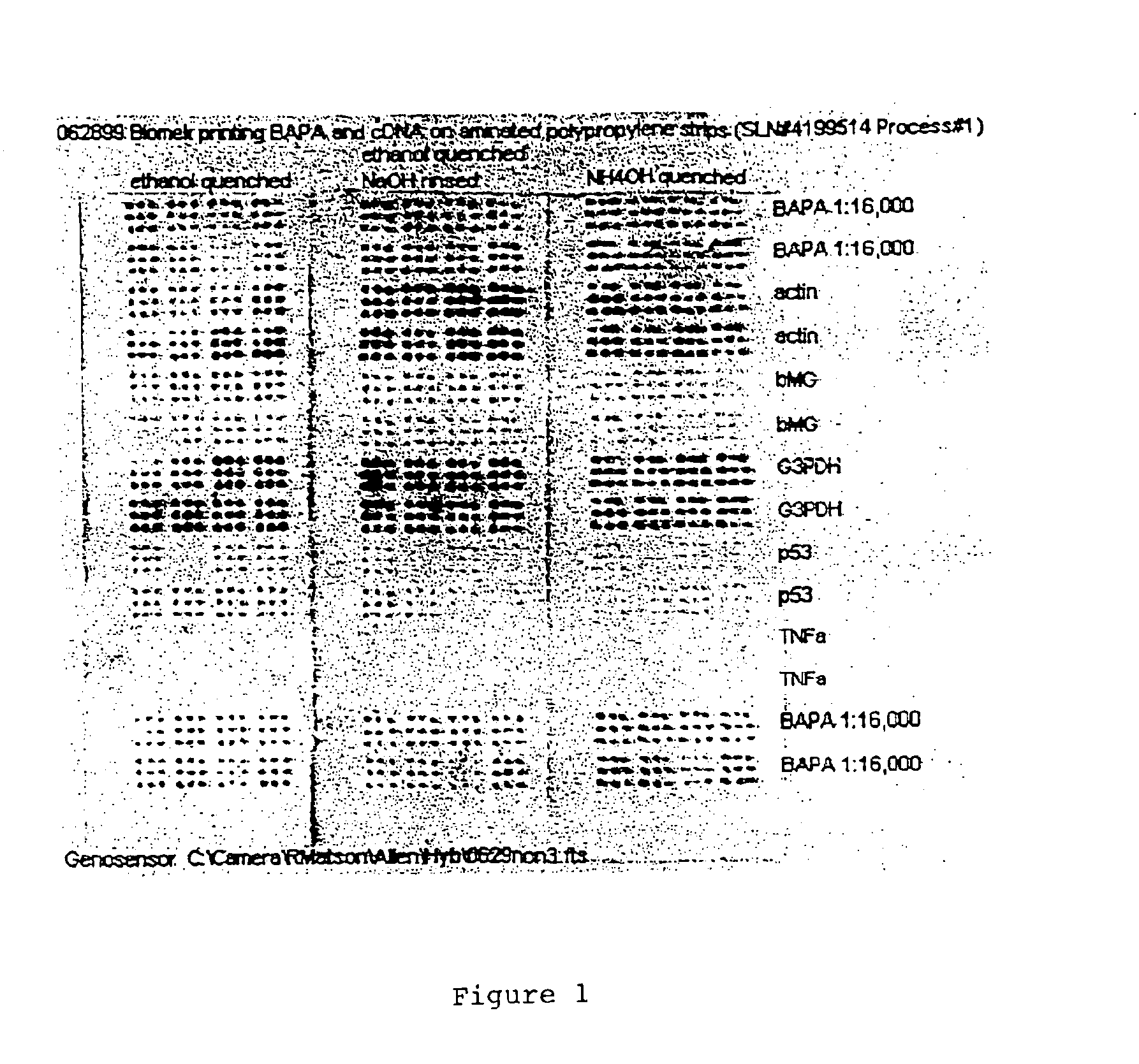
An assay article for detection biopolymers contained in a sample is described. The assay article includes a substrate and a biopolymer directly adsorbed on the surface of the substrate. A plurality of biopolymers may be adsorbed on the surface of the substrate to form an array. Also disclosed is a method of making the assay article. In the preferred method, an aminated polypropylene substrate is used. A biopolymer is contacted with the aminated substrate under a condition sufficient for direct adsorption of the biopolymer on the surface of the substrate. A method of detecting a target biopolymer contained in a sample is also disclosed. In this method, a substrate is contacted with either a probe or target biopolymer under a condition sufficient for a direct adsorption of either the probe or target biopolymer on the substrate to form a probe assay article or a target assay article. Then, the probe assay article is contacted with the target biopolymer, or the target assay article is contacted with the probe biopolymer under a condition that allows the formation of a probe-target complex. Finally, the complex is detected and the presence of the complex is used as a measurement for the presence or the amount of the biopolymer target contained in the sample.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Electrochemical Detection of Substrates
InactiveUS20080081329A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRedox catalystSurface binding
The present invention provides a method for detecting probe-target substrate binding. In particular, the present invention provides a method for detecting a surface bound target complex by detecting the redox reaction of a redox transition metal complex that is catalyzed by a redox-catalyst complex.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF FERRARA +1
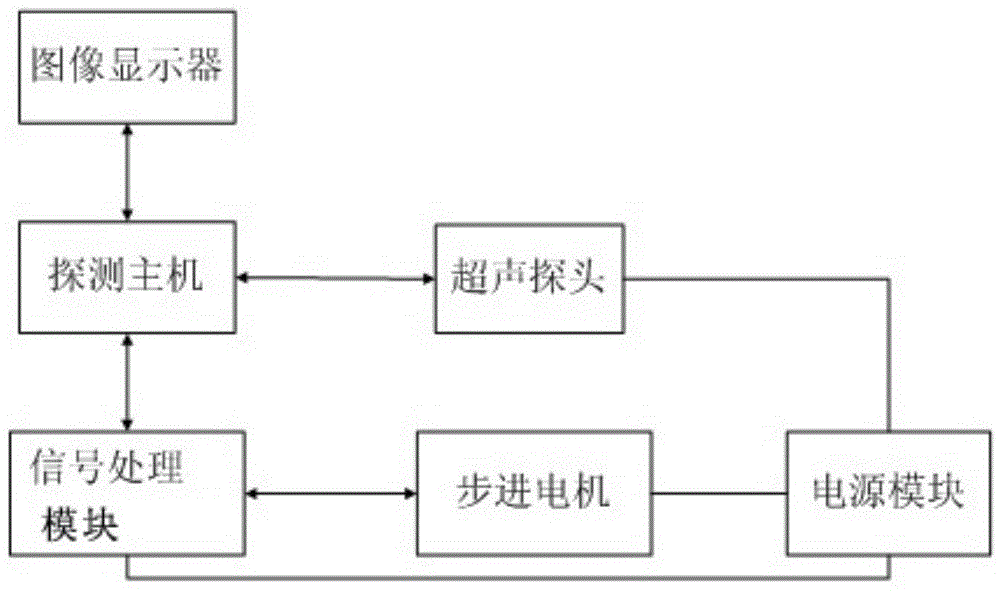
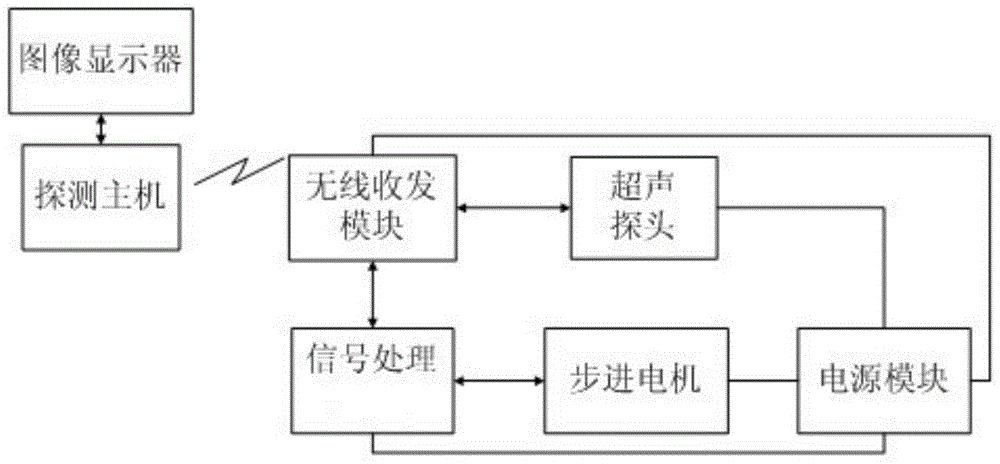
Ultrasonic detection imaging method and device
InactiveCN103954966ASolve splicing difficultiesFlexibleUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsEcho detectionMotor drive
The invention discloses an ultrasonic detection imaging method. The method includes the following steps that first, a stepping motor drives a foldable multi-stage rotating ultrasonic probe, an ultrasonic probe body of the foldable multi-stage rotating ultrasonic probe transmits an ultrasonic signal, and an ultrasonic echo detection signal is collected and transmitted to a detection host; second, a signal processing module positions and calculates the position of the ultrasonic probe body, and position information is transmitted to the detection host; third, the ultrasonic echo detection signal picked by the detection host is imaged through the detection host, image splicing is performed according to the position information, and an image of a detected target is obtained; fourth, an image display displays the image. The invention further discloses a device for implementing the ultrasonic detection imaging method. The device comprises a sucker, the image display, the detection host, a power module, a signal processing module and the foldable multi-stage rotating ultrasonic probe. The device has the advantages of being simple in structure, easy to operate, convenient to control, high in accuracy and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Detector emission method employing force-borrow mechanism to select space detection target
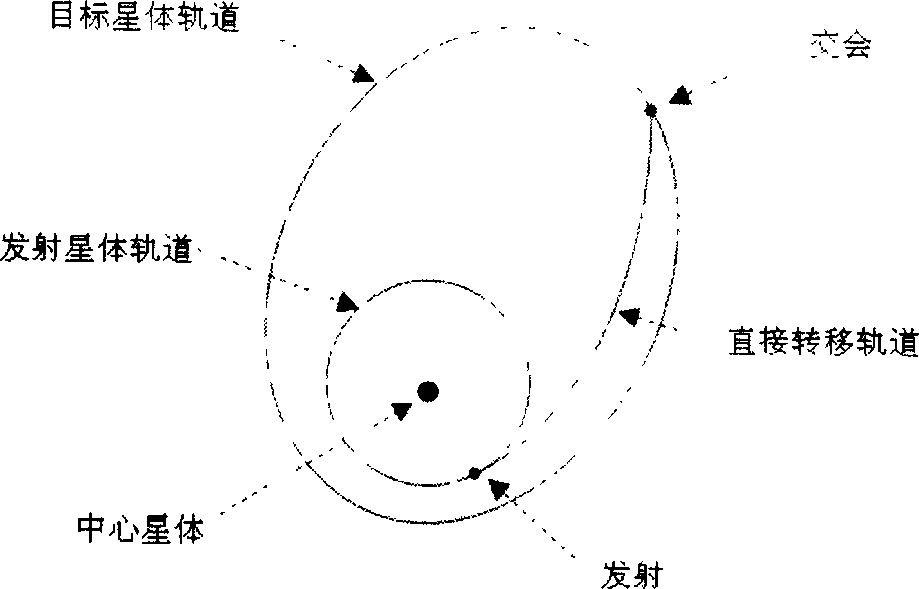
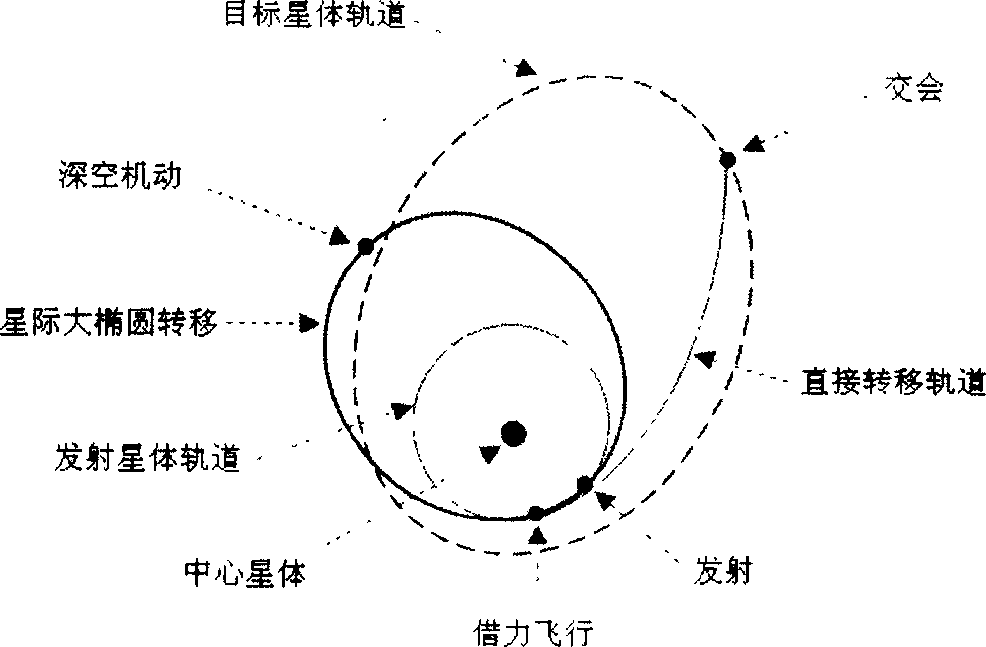
The invention relates to a method for emitting detector which can select the detected target via swing-by mechanism, belonging to the technique of deep space detecting rail transfer. It can solve the problems of approachability evaluation of detected target with long semi long axis or large eccentric rate. The inventive method comprises: calculating optimized dual impulse transfer track; selecting swing-by track type; and assembling the swing-by tracks. First calculating the optimized dual impulse transfer track from the target star to emitting star; using the emitting star as swing-by star; using the parameter of dual impulse transfer at the emitting star as the match parameter in swing-by flying; using the heliocentric large-ellipse orbit whose period is several times of the revolution period of emitting star and the deep space device at aphelion, to search for the emitting parameter of said match condition. The invention guides in the swing-by mechanism to realize the expansion of former dual impulse transfer, to improve the approachability of the target with long semi long axis or large eccentric rate.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Ratiometric fluorescent probe of targeting mitochondria for sulfur dioxide
InactiveCN108912085AHigh recognition sensitivityStrong specificityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceSulfite
The invention provides a ratiometric fluorescent probe targeting mitochondria for detecting sulfur dioxide / sulfite (hydrosulphite). The ratiometric fluorescent probe has a structural formula as shownin the specification. The ratiometric fluorescent probe for detecting the sulfur dioxide provided by the invention has high recognition sensitivity, eliminates the interference of background, environment and concentration at the same time, is resistant to interference of various ions, amino acids and active oxygen, and has good specificity and potential application value for detecting the sulfur dioxide in environmental and biological systems. The probe provided by the invention has the advantages of simple and practicable synthetic process, cheap and easily-available raw materials, low preparation cost and easy popularization.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Atomic force microscope as an analyzing tool for biochip
InactiveUS20090048120A1Easy to adaptHigh sensitivityLibrary screeningNanotechnologyAtomic force microscopyMagnetic force microscope
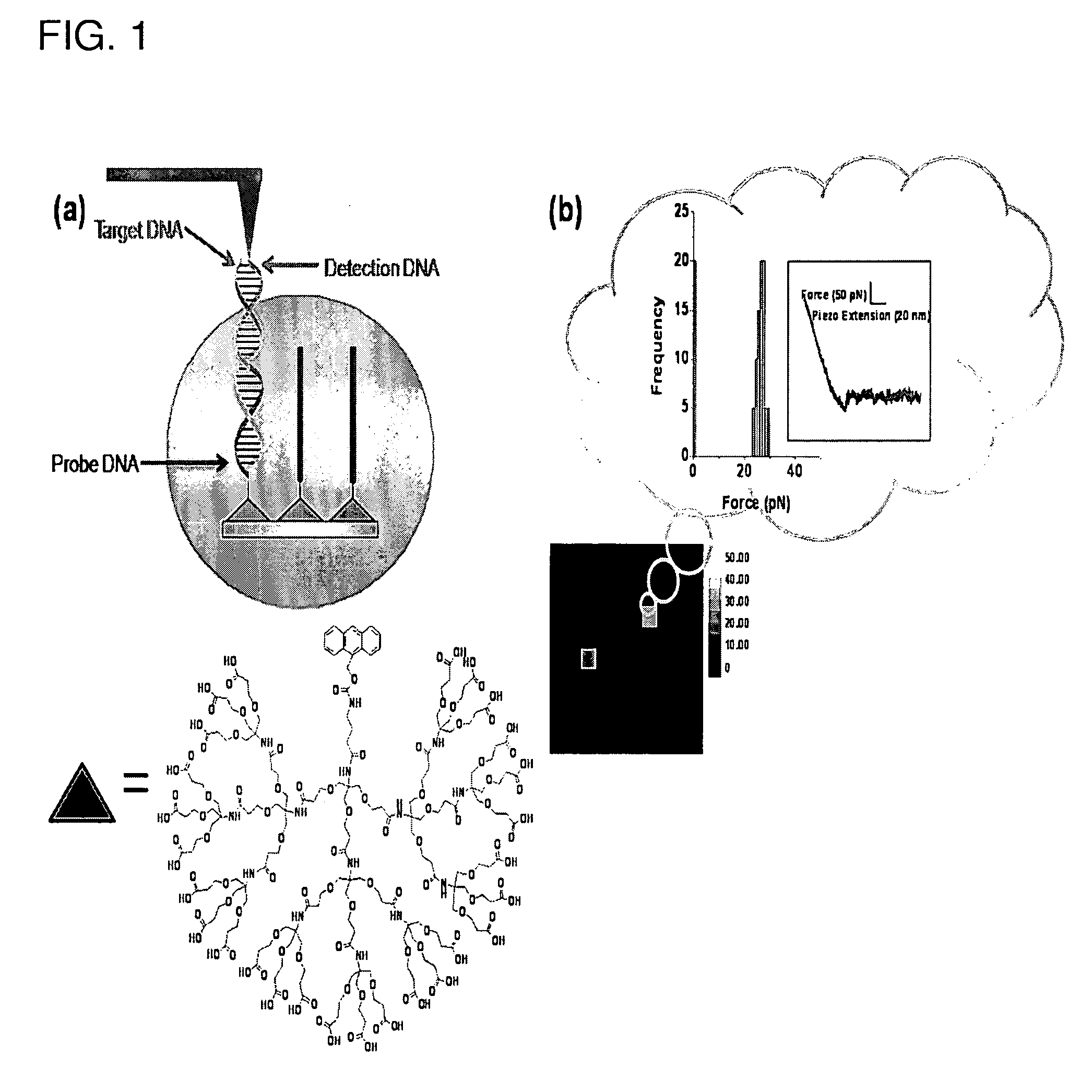
The present application discloses a method for detecting a presence of target ligand in a fluid medium which includes the steps of: (i) contacting the fluid medium with a solid substrate that includes an array of dendrons on its surface, wherein each of the dendron includes a central atom, a probe that is attached to the central atom optionally through a linker, and a base portion attached to the central atom and having a plurality of termini that are attached to the surface of the solid support; and (ii) determining the presence of a probe-target ligand complex by measuring binding force between the bound ligand and detection molecule tethered to the tip of an atomic force microscope (“AFM”), which detection molecule has affinity for the ligand, wherein measurement of an increase in force between the probe-target ligand complex and the detection molecule by AFM indicates the presence of the probe-target ligand complex.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
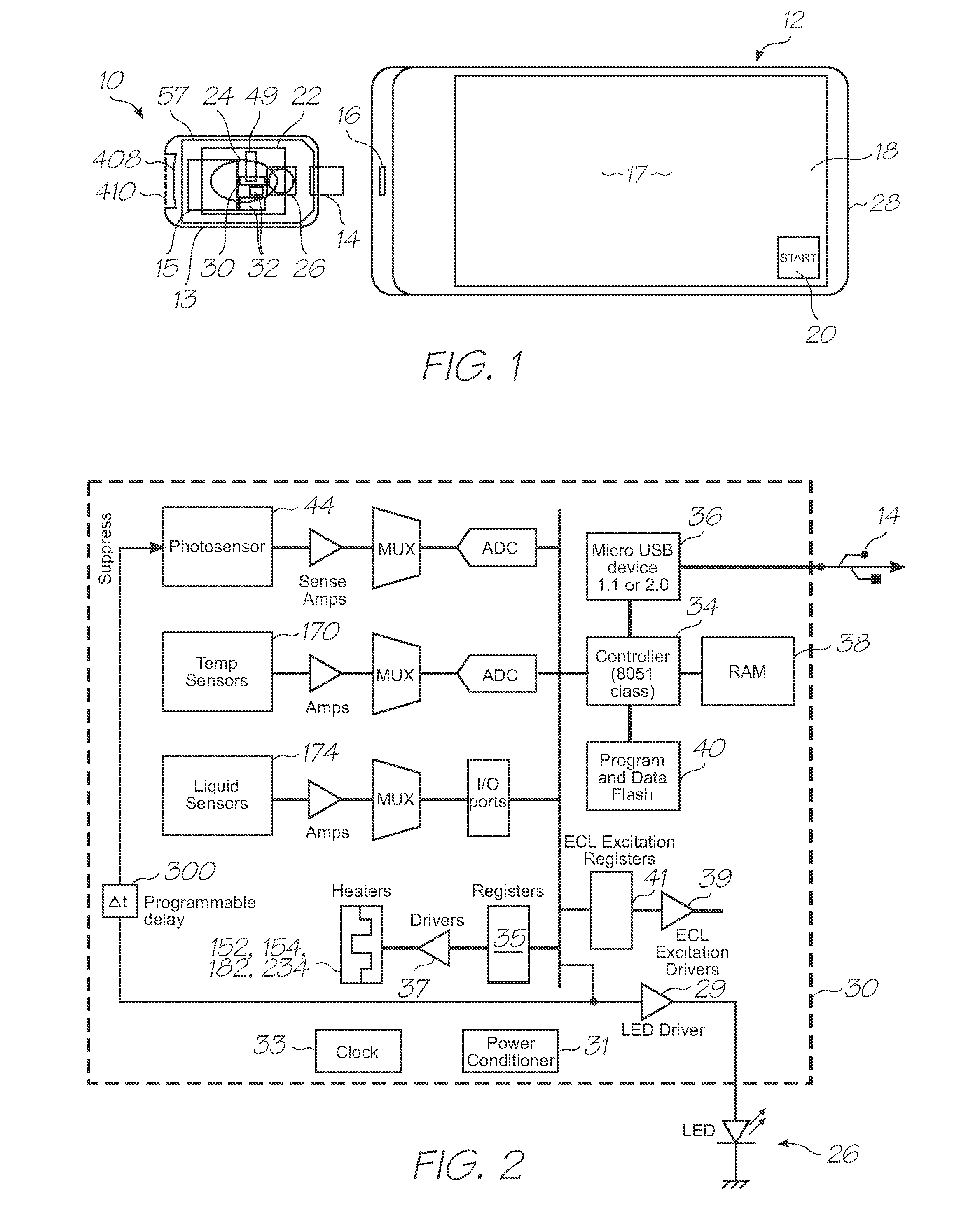
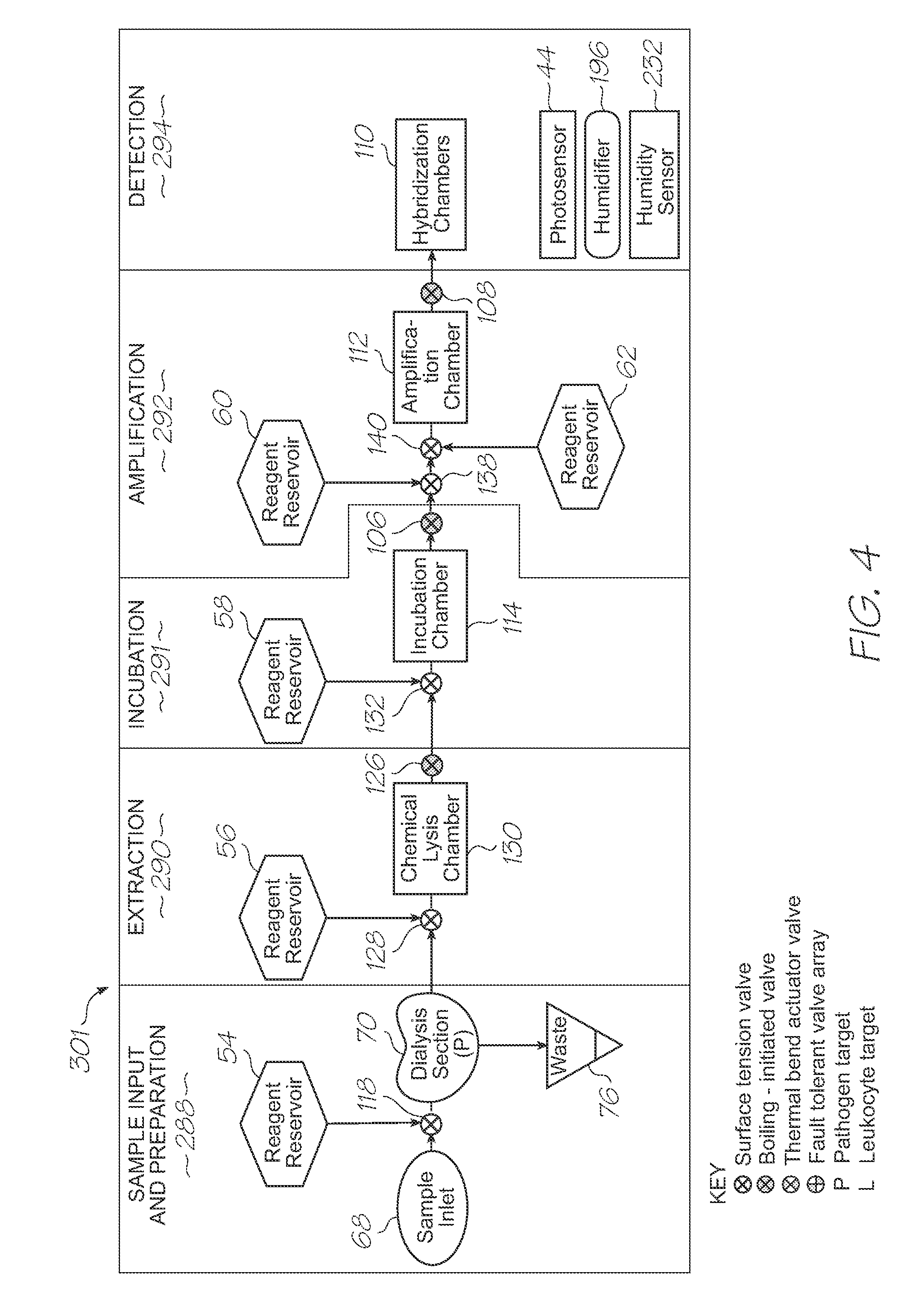
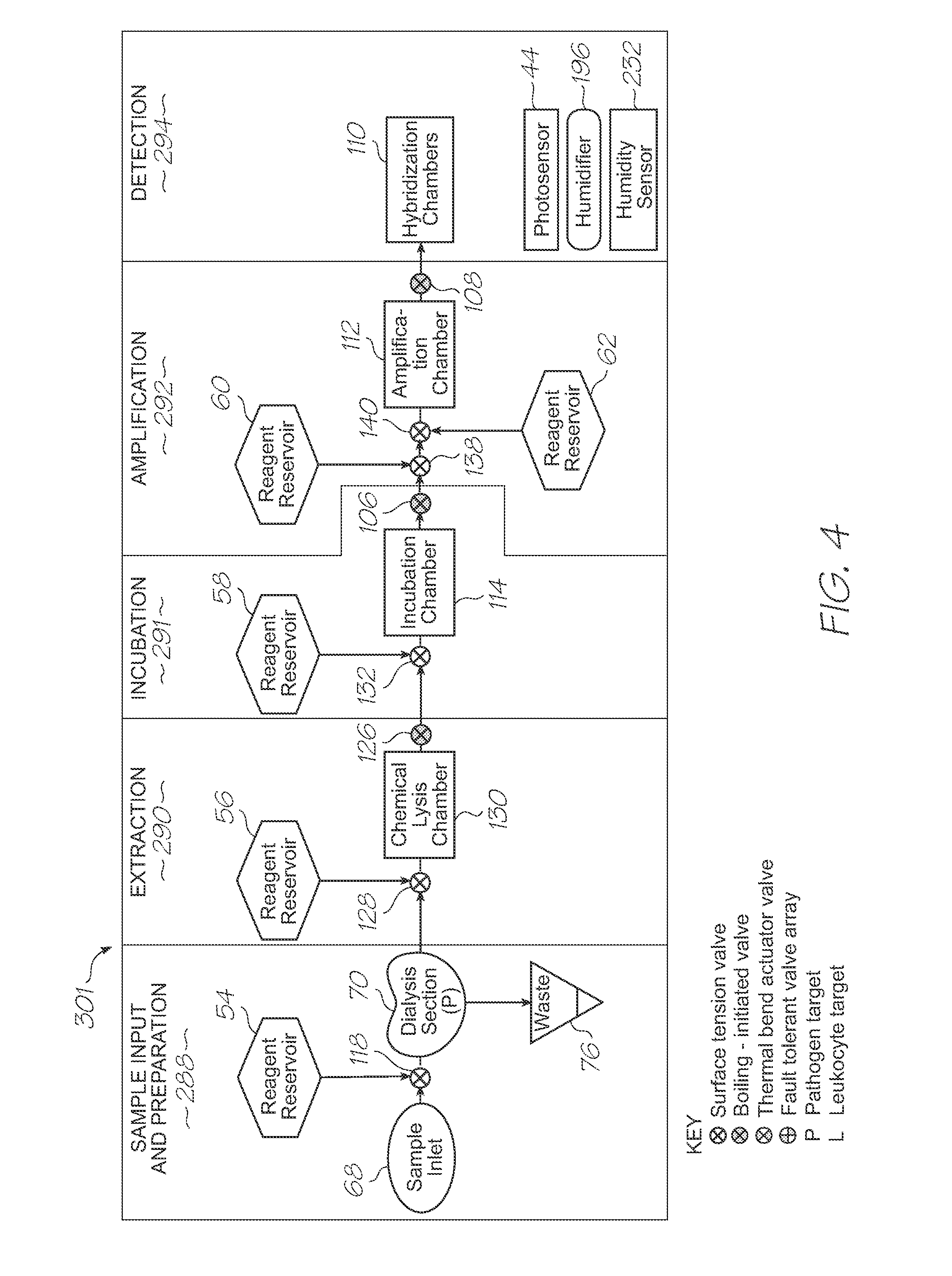
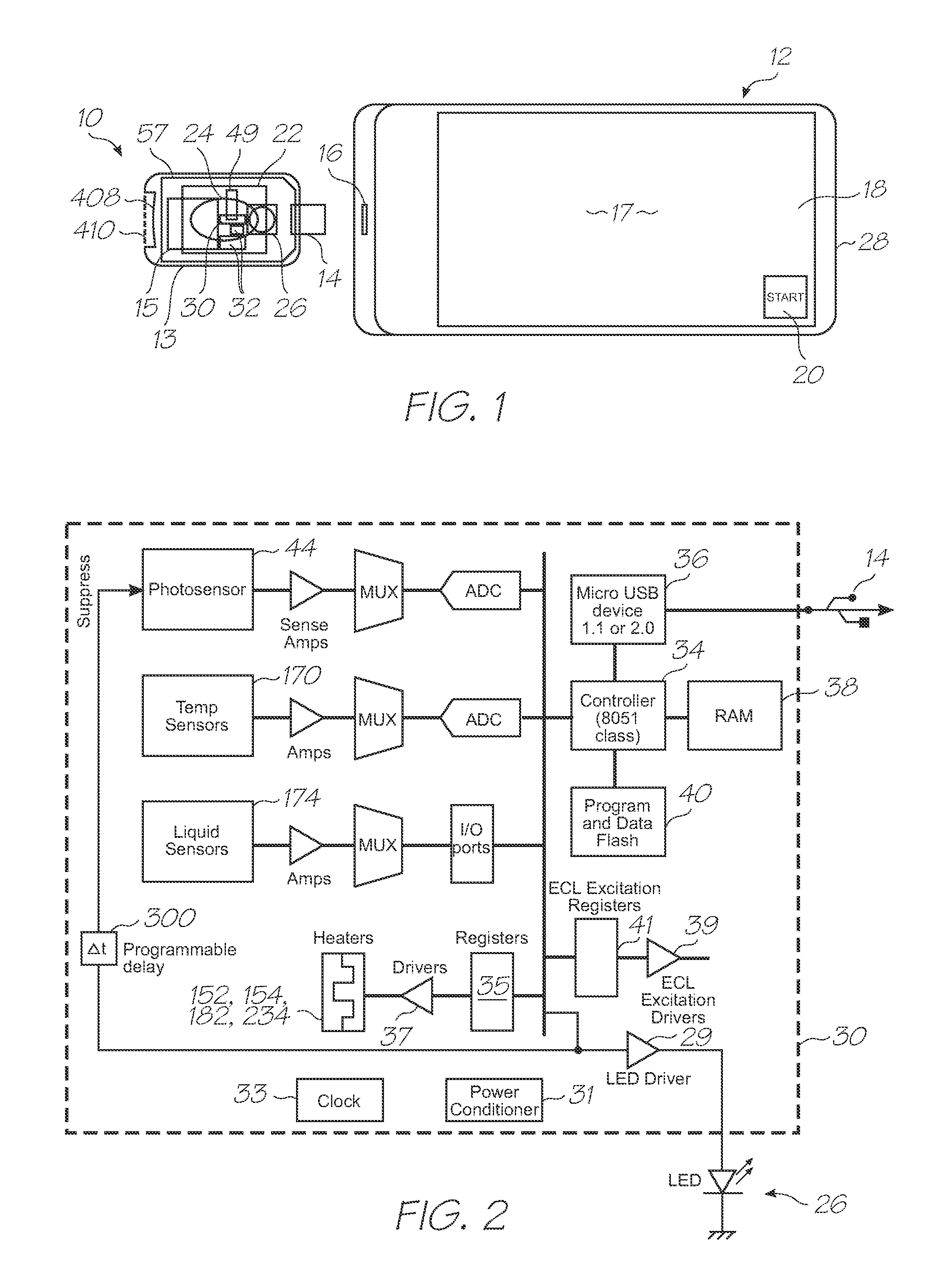
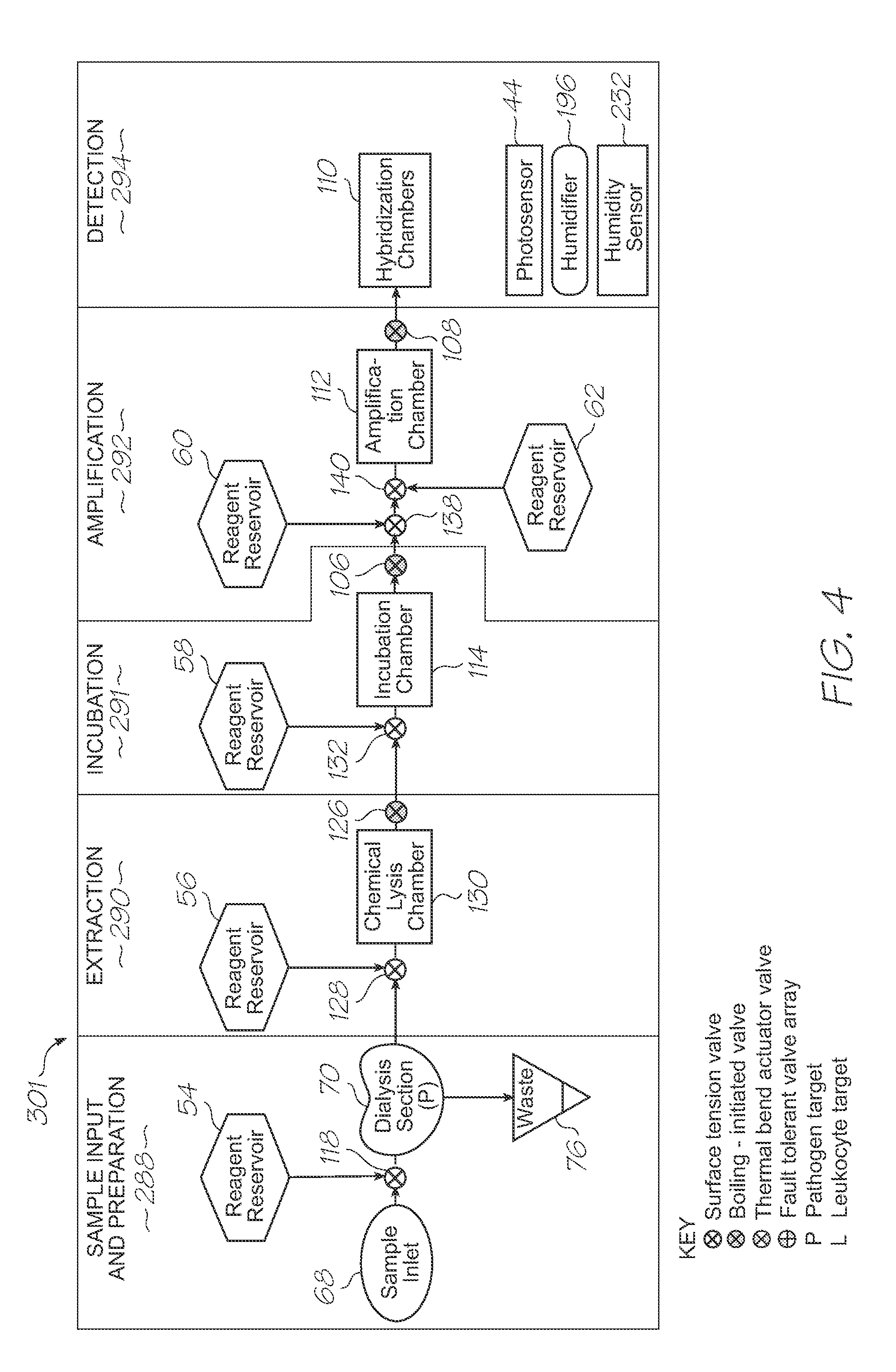
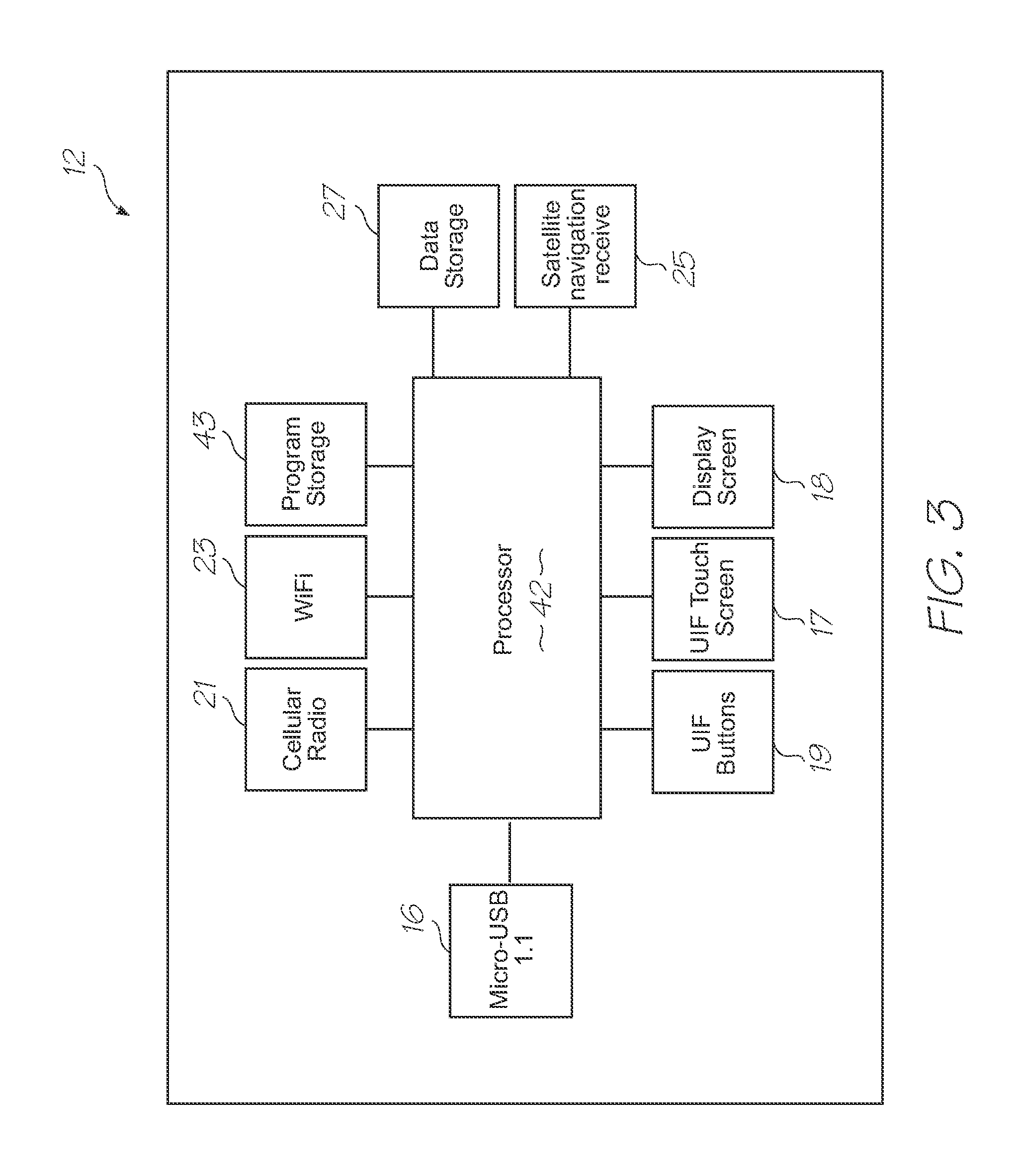
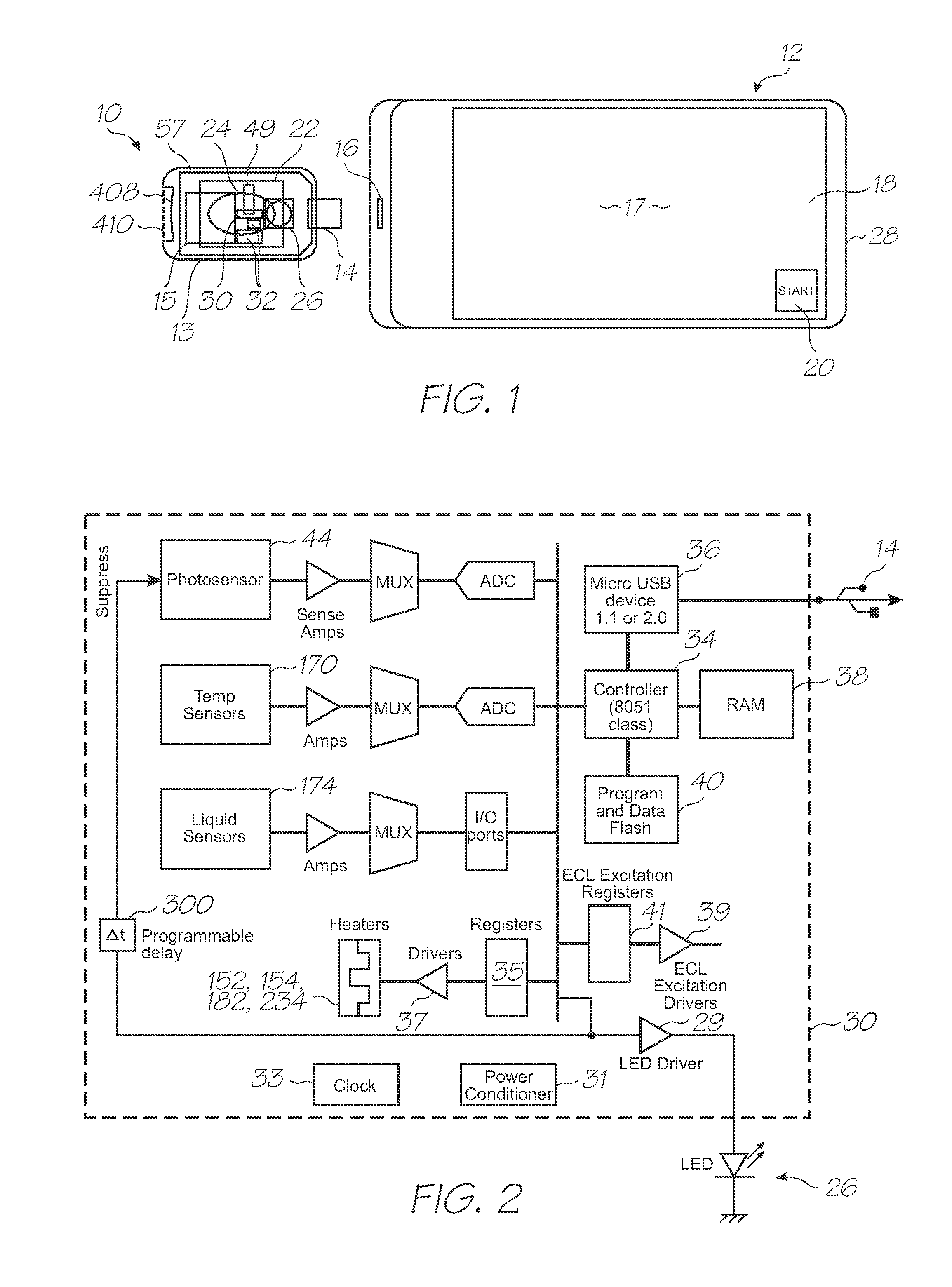
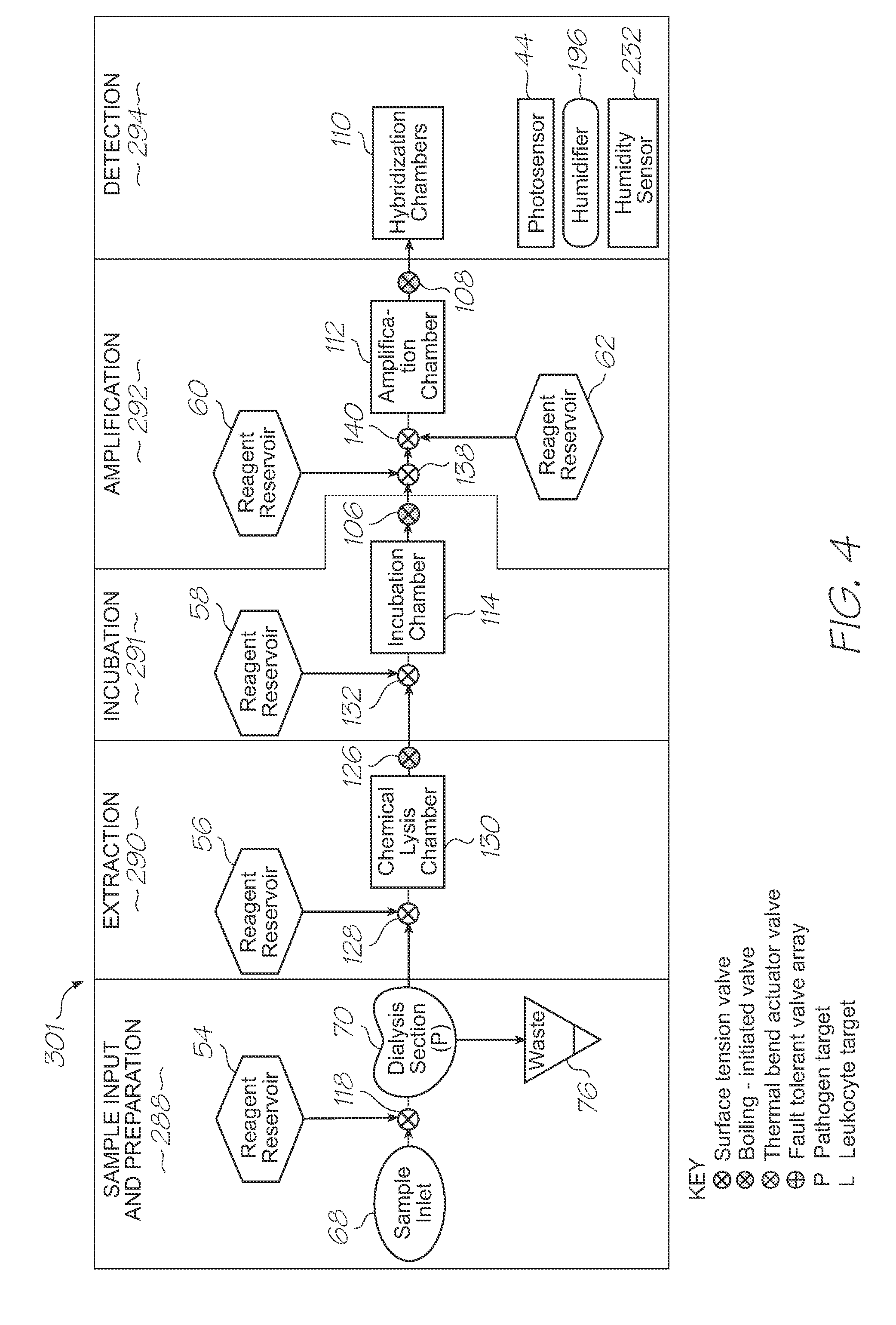
Microfluidic test module with low mass of probes
InactiveUS20110312793A1Lower the volumeLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsValve arrangementsNucleic acid sequencingBiology
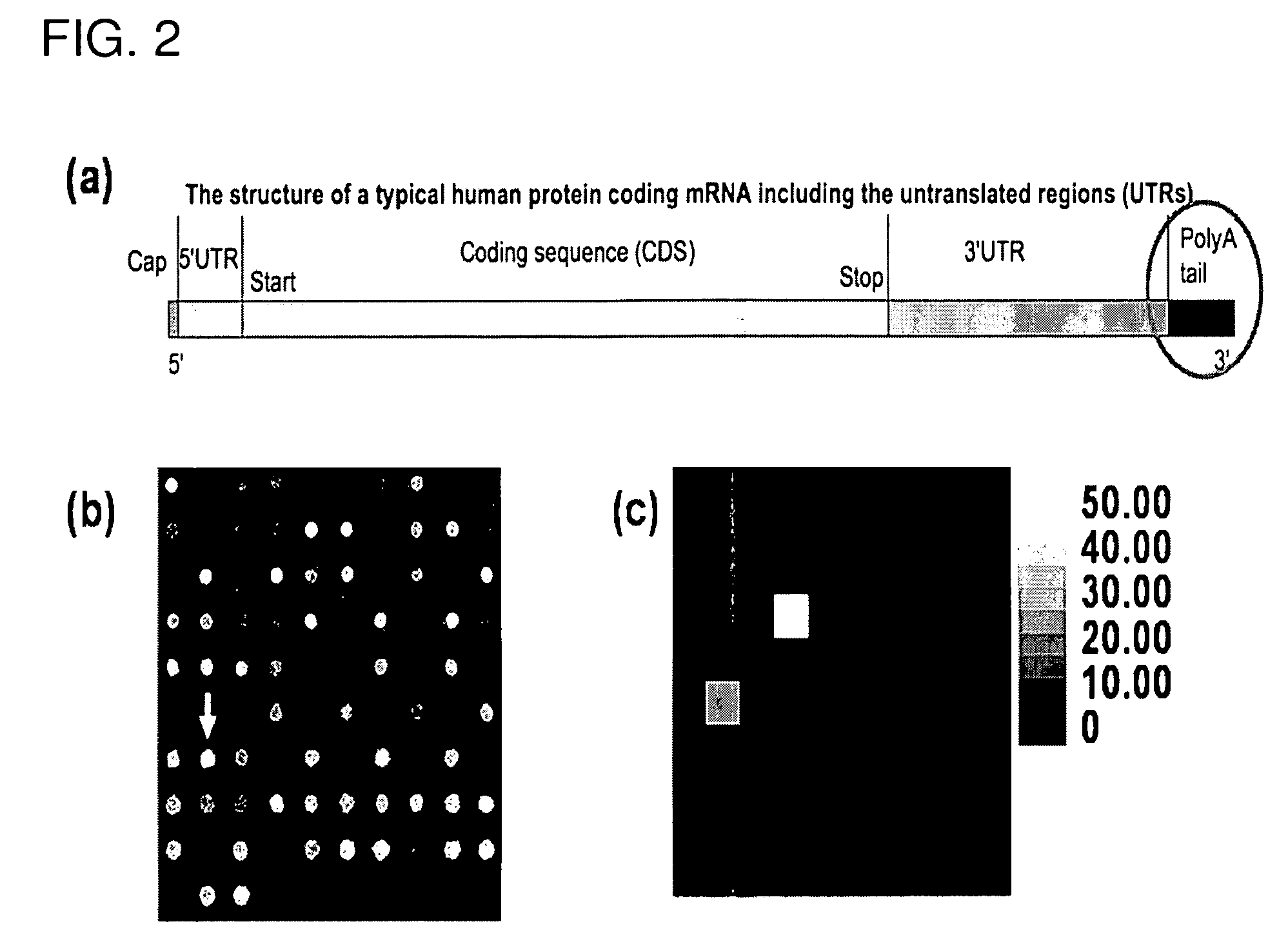
A microfluidic test module having an outer casing having an inlet for receiving a biological sample containing a target nucleic acid sequence, and, a hybridization chamber mounted in the casing, the hybridization chamber holding a volume of fluid containing probes, the probes each having a nucleic acid sequence for hybridization with the target nucleic acid sequence to form probe-target hybrids, wherein, the mass of the probes in each of the hybridization chambers is less than 270 picograms.
Owner:GENEASYS
Child glaucoma related gene chip, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108676865ARapid and efficient genetic diagnosisFast and Efficient Genetic CounselingNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDeep sequencingProbe target
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicines and relates to a gene chip hybridization probe for screening disease-causing gene mutations of child glaucoma, and a design method and application thereof. The invention provides a preparation method of a gene chip and the gene chip hybrid probe related to the disease-causing gene mutations of the child glaucoma, and the gene chip hybrid probe targets genes covering 289 pathogenic genes highly associated with the child glaucoma. The design method of the gene chip hybrid probe is as follows: designing and synthesizing a child glaucoma pathogenic gene hybrid probe, and integrating the child glaucoma pathogenic gene hybrid probe into a gene chip; using the prepared gene chip to capture a genome target region and performing deep sequencing; and performing bioinformatics analysis on screening data to screen candidate pathogenic genes and mutations. A high-efficiency screening technique for screening the disease-causing gene mutations of thechild glaucoma is established, and is helpful for clinically determining the mutant genes of the child glaucoma.
Owner:EYE & ENT HOSPITAL SHANGHAI MEDICAL SCHOOL FUDAN UNIV
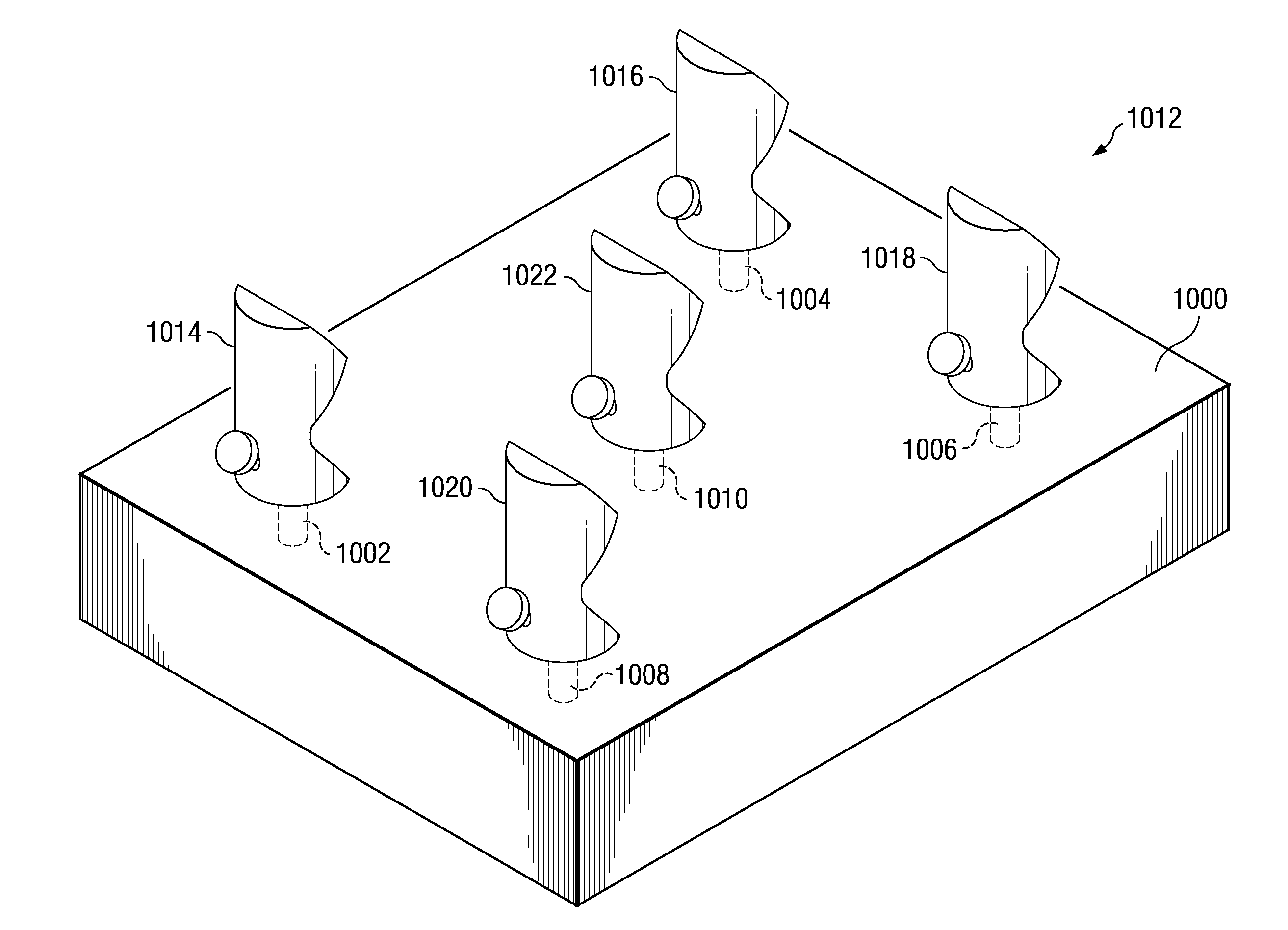
Variable shaft sizing for measurement targets
A measurement targeting apparatus comprises a target body, a vessel with a channel, a fluid located within the channel in the vessel, and a pressurization system. The target body is selected from one of a photogrammetry target, a theodolite target, a construction ball, a touch probe target, a coordinating measurement machine probe target, a laser tracker target, and a laser projector target. The vessel has a centerline, has a substantially cylindrical portion capable of being received in a hole in a part, and is comprised of a material selected from steel, aluminum, and plastic. The vessel is capable of expanding when the fluid within the channel in the vessel is pressurized. The pressurization system is capable of pressurizing the fluid within the channel to cause the vessel to expand around the centerline.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
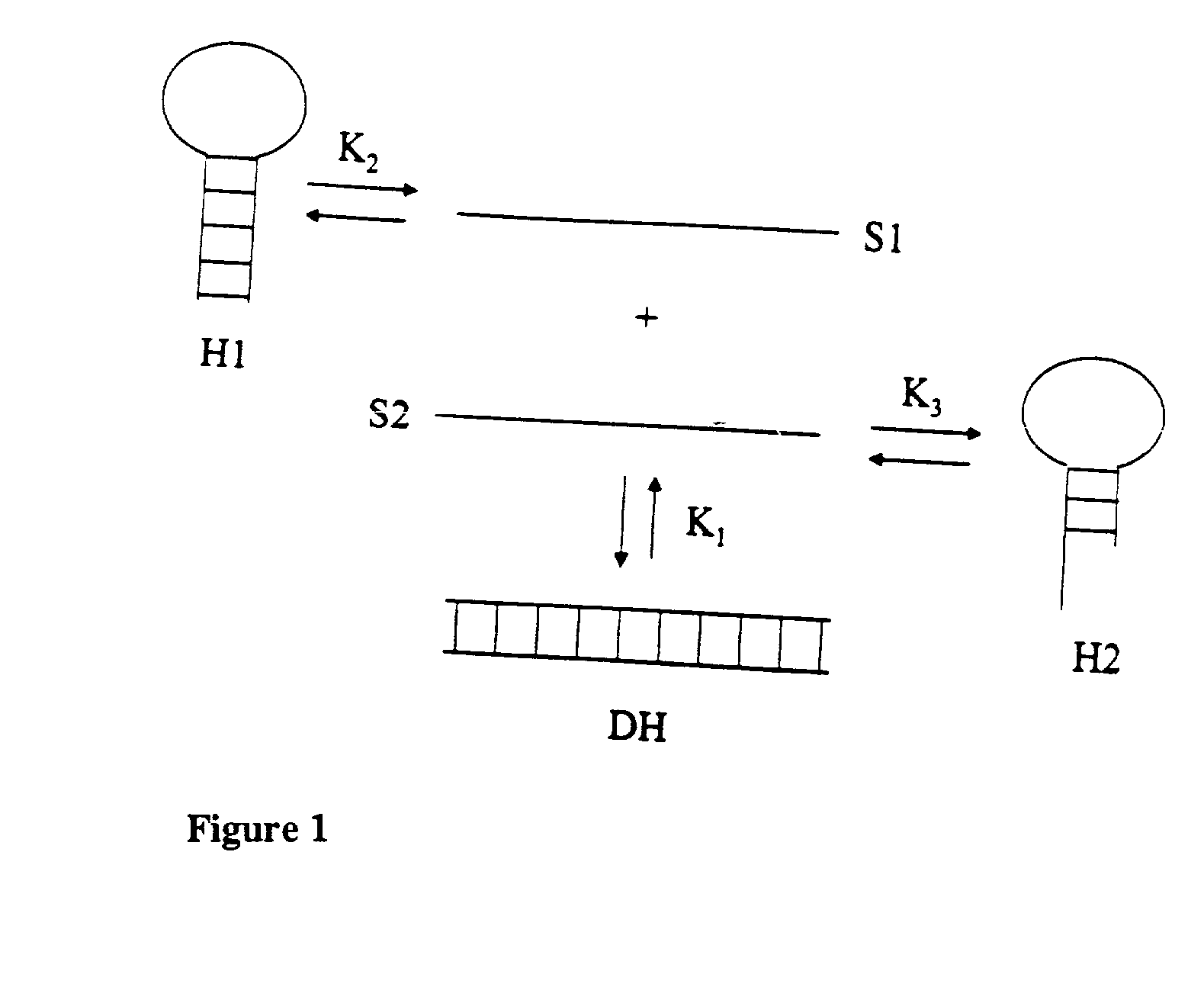
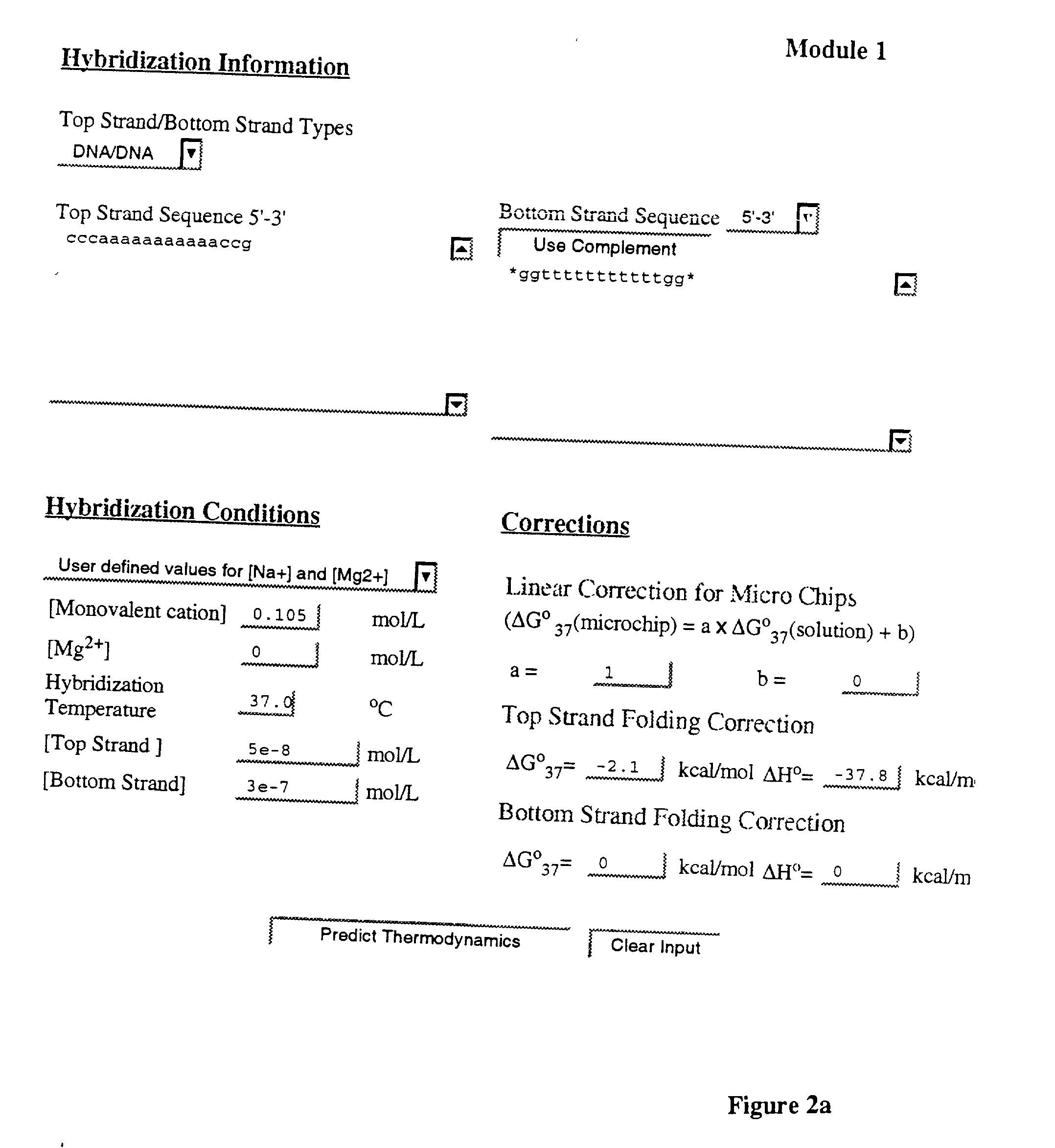
Method and system for predicting nucleic acid hybridization thermodynamics and computer-readable storage medium for use therein
InactiveUS20030224357A1Accurately predict not only the Tm for hybridizationNumerical stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesBinding siteUser interface
Method and system to predict and optimize probe-target hybridization are provided. The method may be implemented using six interactive, interrelated, software modules. Module 1 predicts the hybridization thermodynamics of a duplex given the two strands. Module 2 finds the best primer of a given length binding to a given target. Module 3 executes a primer walk to find alternative binding sites of a given primer on a given target. Module 5 is a combination of Modules 2 and 3. Module 6 finds the alternative binding sites of a given primer on a given target (Module 3) and calculates the concentration of target with primer bound at primary and alternative sites. Module 7 is a combination of Modules 2 and 5 and also calculates the various concentrations. The six modules can be operated either through an interactive user interface or using batch file submission as provided by Module 4. The program is suited to predict DNA / DNA, RNA / RNA, and RNA / DNA systems.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Single-use test module for detection of hybridization of targets with oligonucleotide probes
InactiveUS20110312810A1Easily usable, mass-producible, inexpensive, compactValve arrangementsHeating or cooling apparatusFluorescenceHand held
A single-use test module having an outer casing dimensioned for hand-held portability, the outer casing having an inlet for receiving a biological sample containing a target nucleic acid sequence, probes in the outer casing for hybridization having a nucleic acid sequence for hybridization with a target nucleic acid sequence to form a probe-target hybrid, the probe-target hybrid being configured to generate a fluorescence signal in response to an excitation light, and, a photosensor to detect the fluorescence signal.
Owner:GENEASYS
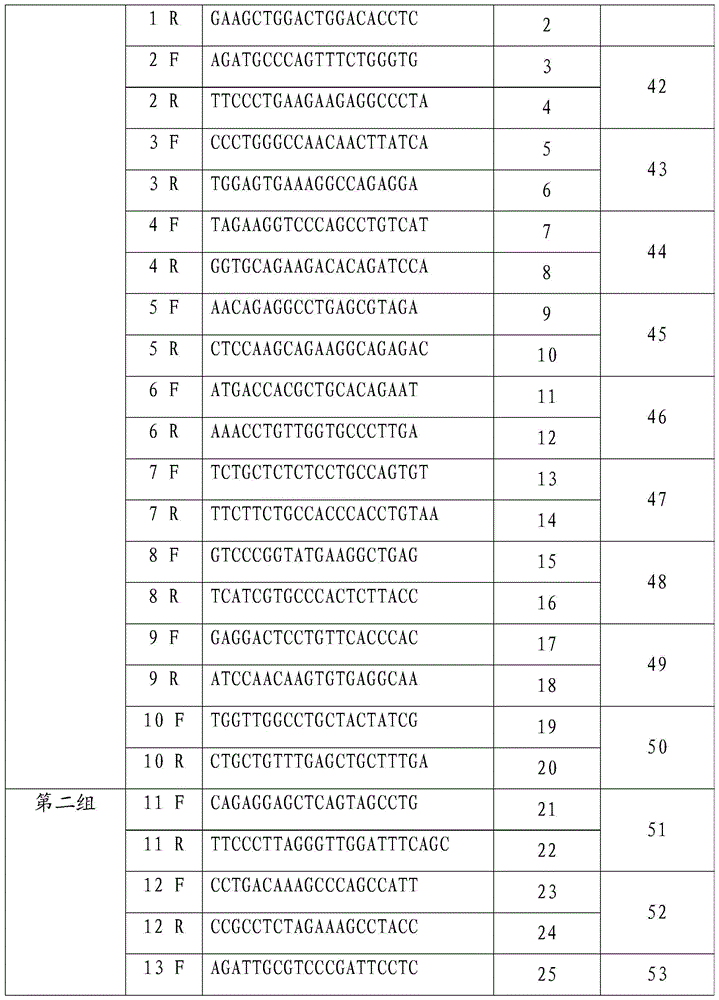
HER2 gene amplification detection probe, kit and method
InactiveCN104561361AHigh coincidence rateAvoid cross reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceBiology
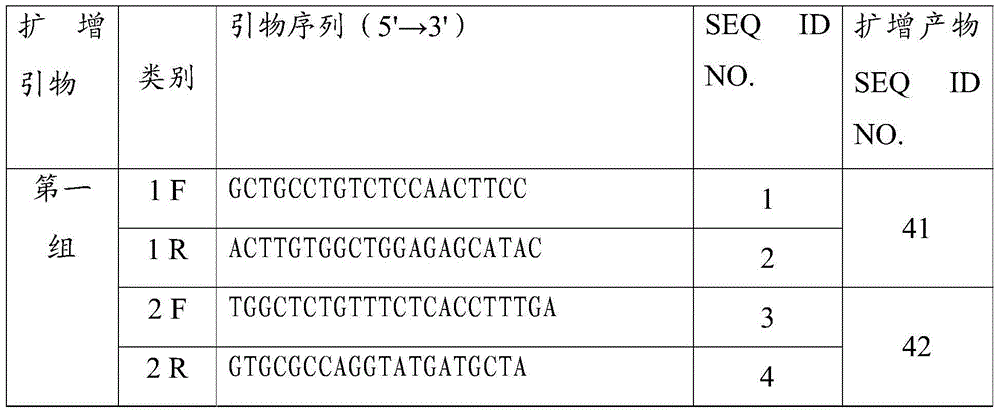
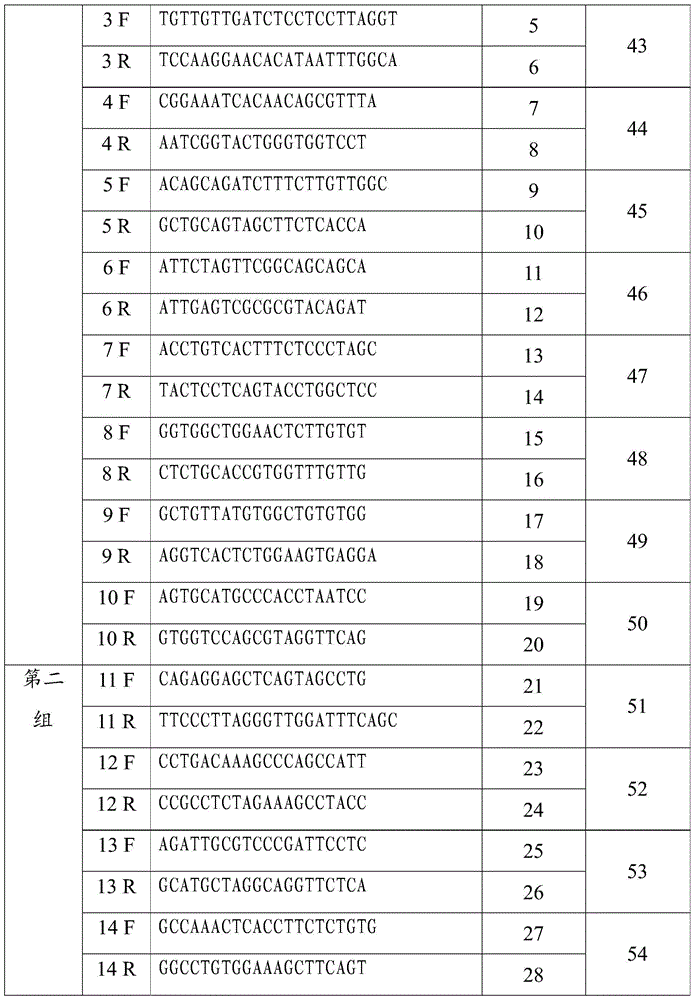
The invention discloses an HER2 gene amplification detection probe, a kit and a method. The detection probe comprises a first group of probes for labeling fluorescent dye and targeted to an HER2 gene, and a second group of probes targeted to the centromere region of human chromosome 7, wherein the first group of the probes are selected from at least one of probes as shown in SEQ ID NO.41-SEQ ID NO.50; the second group of the probes are selected from at least one of probes as shown in SEQ ID NO.51-SEQ ID NO.60; and the fluorescent dyes labeled by the two groups of the probes are different in color. A FISH probe in the HER2 gene amplification detection kit provided by the invention is free from a repeated sequence, and capable of avoiding a cross reaction and undergoes hybridization recognition with an HER2 target detection fragment in the chromosome; and the probe has the advantages of high accuracy, good specificity and low false positive rate.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
Microfluidic device with triggered photodetection of fluorescing probe-target hybrid
InactiveUS20110312666A1Accurate sensor timingHigh sensitivityValve arrangementsHeating or cooling apparatusFluorescenceNucleic acid sequencing
A microfluidic device having a probe for hybridization with a target nucleic acid sequence to form a probe-target hybrid, the probe-target hybrid having a reporting fluorophore for emitting a fluorescence signal in response to an excitation light, a detection photodiode for exposure to the excitation light and the fluorescence signal, and, a trigger photodiode for exposure to the excitation light, the trigger photodiode being configured to activate the detection photodiode after the excitation light has been extinguished.
Owner:GENEASYS
Superconductive cyclotron extraction region beam measurement detection target head
ActiveCN107329166AGuaranteed uptimeHigh resolutionMagnetic resonance acceleratorsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSignal onRadial position
The invention discloses a superconductive cyclotron extraction region beam measurement detection target head, which comprises a probe target head and a fixation structure. The probe target head is formed by a multi-wire probe, a ceramic block and a connecting rod. One end of each tungsten wire passes through a through hole in the ceramic block and extends into the connecting rod; each tungsten wire is fixedly arranged in the ceramic block through welding; and the ceramic block is fixedly arranged in one end of the connecting rod through welding. The fixation structure comprises an aluminum alloy connecting piece and a drive rod. The connecting rod and the drive rod are connected through the aluminum alloy connecting piece. The detection target head can carry out measurement based on intensity of electrical signals on different wires and through a point motion mode of the drive rod to obtain axial and radial position information of the beam, so that beam debugging can be carried out, and stable and effective operation of an accelerator is realized; and the detection target head has the advantages of high resolution, high precision, simple measurement and capable of replacing the probe without opening the cavity.
Owner:HEFEI CAS ION MEDICAL & TECHNICAL DEVICES CO LTD
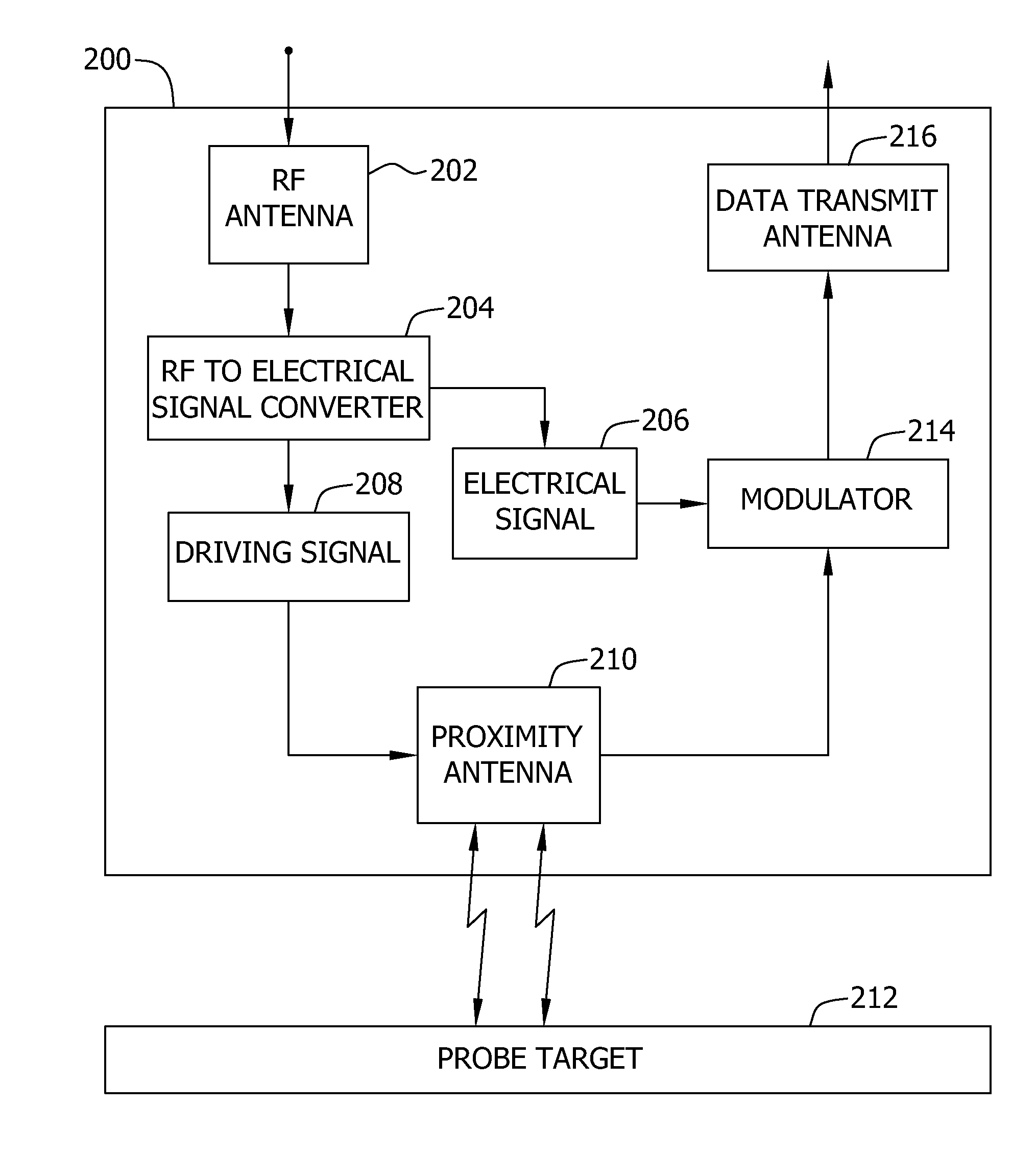
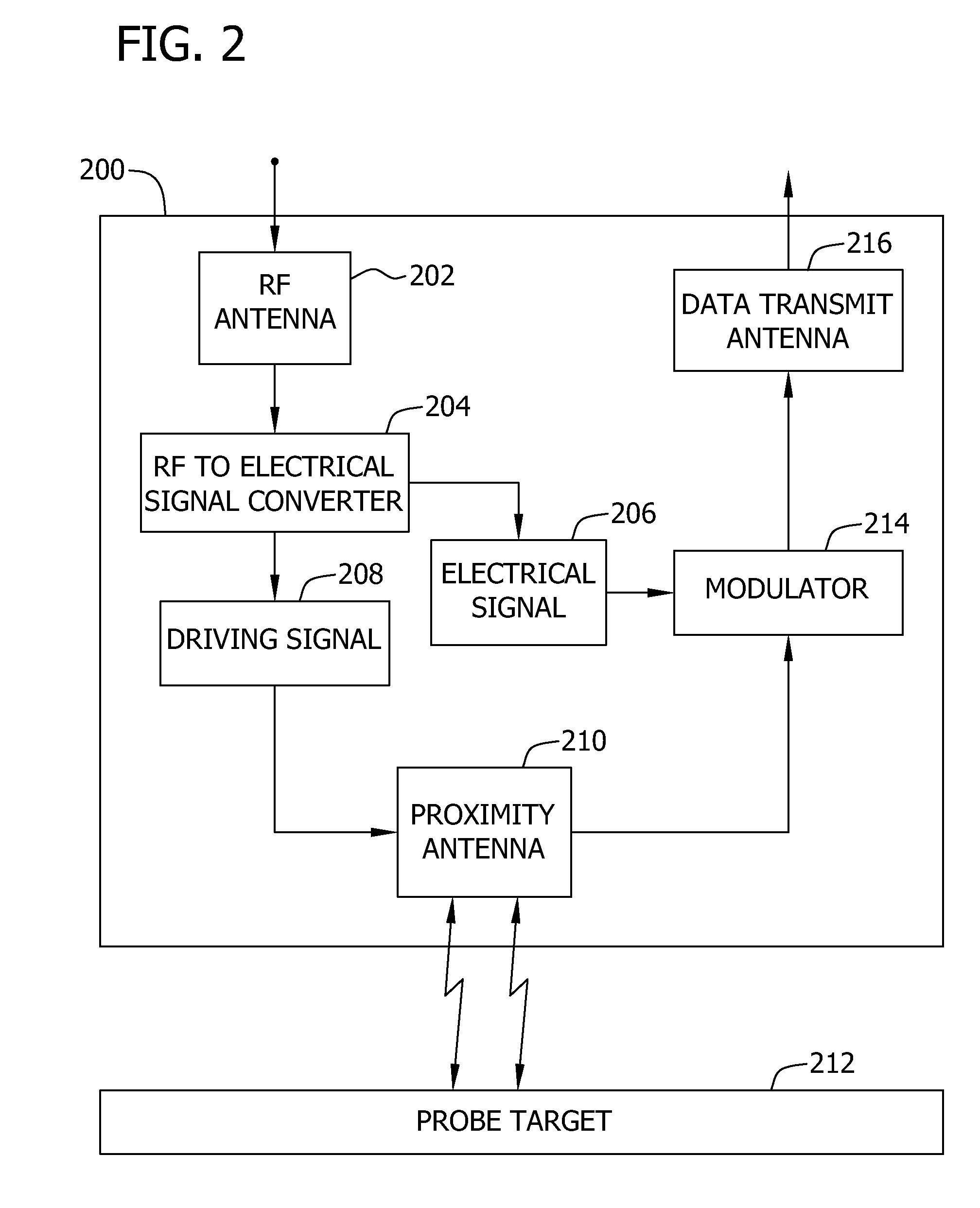
Wireless proximity probe and method of operating same
ActiveUS8159396B2Direction finders using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadio frequency signalEngineering
A proximity probe, for use in determining a distance to a probe target, includes a first antenna configured to wirelessly receive a radio-frequency signal at a first predetermined frequency and a converter configured to convert the received signal to a driving signal and to an electrical signal. The proximity probe also includes a second antenna configured to receive power via the driving signal and to generate a signal indicative of a distance from the proximity probe to the probe target, and a third antenna configured to transmit the generated signal.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Sonar detecting method for large yellow croaker escaping from deep water net cage and special equipment thereof
InactiveCN101493524AQuantity knownKnow fat and thinAcoustic wave reradiationDigital signal processingEcho signal
The invention discloses a device specially used for sonar-detecting whether large yellow croakers escape from a deepwater net-cage, comprising a computer, a probe which is arranged closely to the net-cage, and a digital to analog adaptive device which is connected with the computer; wherein, the probe is arranged at the external side of the net-cage; the probe comprises a sonar transducer and a flowmeter probe; the digital to analog adaptive device is connected with the probe and can convert the analog signal of the probe into the digital signal and send the signal to the computer; the computer receives the digital signal of the digital to analog adaptive device, processes the digital signal and judges whether the fish escapes or not according to the coupling result of the echo signal scanned by the flowing speed and sonar. The invention also discloses a sonar detection method which utilizes the device to detect whether the fish escapes from the deepwater net-cage simultaneously. The device and the method has the advantages that the device is not affected by water quality, the detection distance is far, the result is exact, the target objects can be intuitively and effectively monitored and detected, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
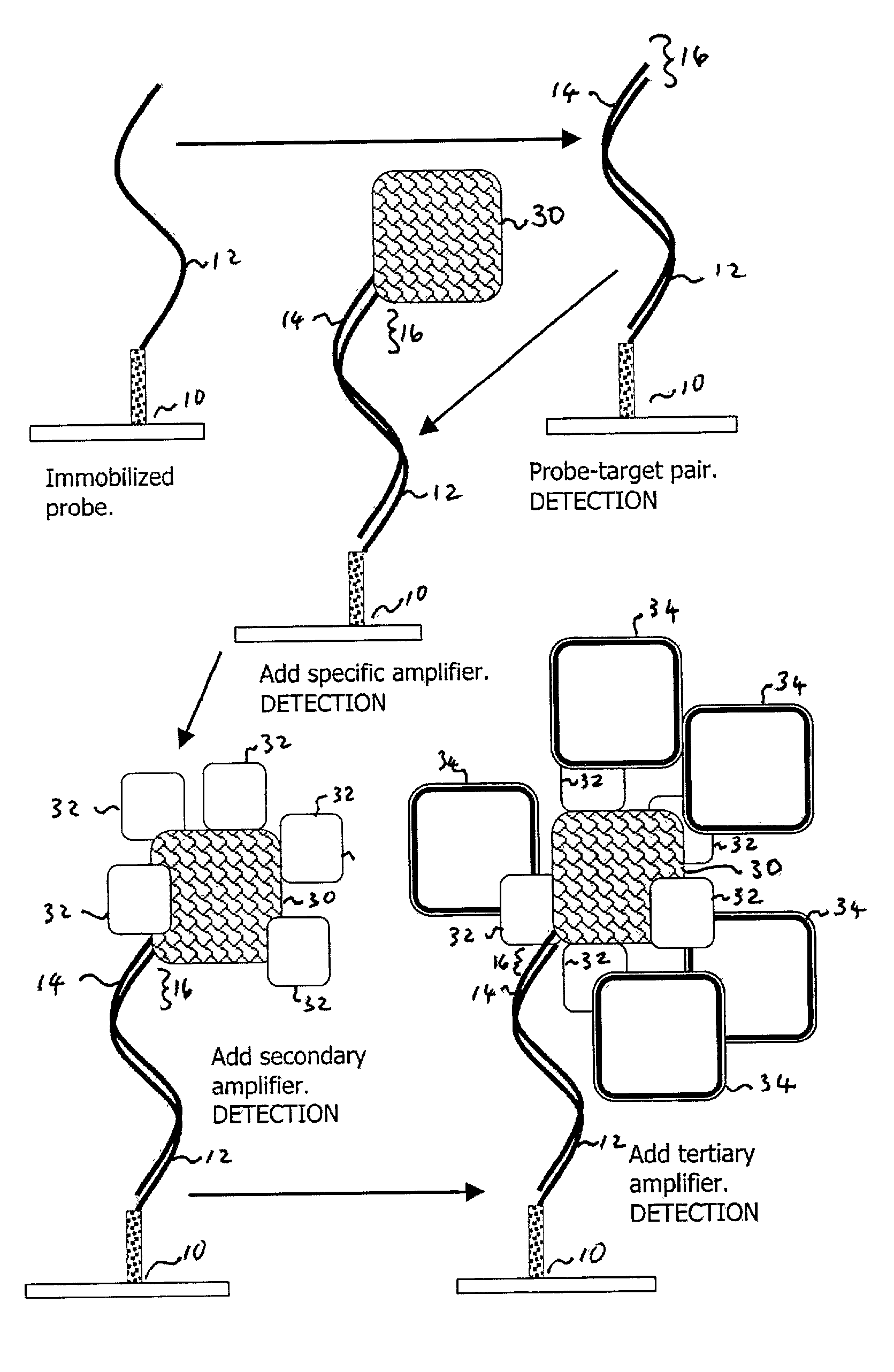
Method and apparatus for recognizing molecular compounds
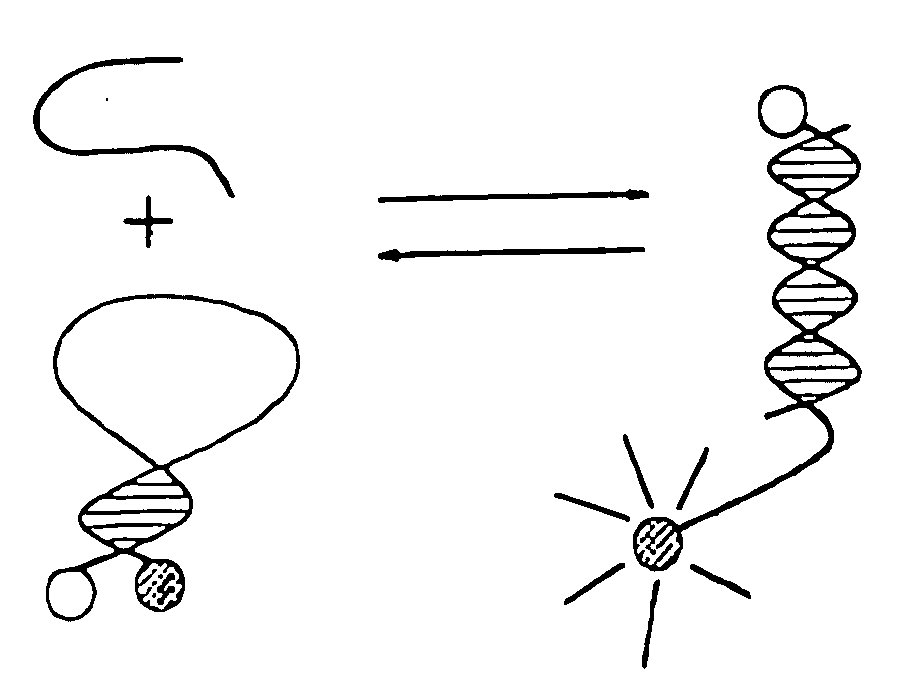
InactiveUS20030224370A1Easy to detectEnlarged and enhanced probe-target combinationRadiation pyrometryNucleotide librariesBiotin-streptavidin complexCompound a
A probe-target reaction is made more recognizable by the provision of a mass-enhancing and / or evanescent-field-perturbing amplifier element which reacts uniquely with and binds to the probe-target pair to provide increased mass. Where the probe-target pair is hybridized dsDNA, a suitable mass-enhancing amplifier is anti-double stranded DNA mouse IgM. In examples with sufficient sequence pairs in the probe-target combination, a sequence-specific minor-groove-binding polyamide can be used that carries biotin which can be amplified by streptavidin in a suitable carrier. In a preferred embodiment, a plurality of probes are immobilized at the sites of a microarray, each probe being specific to a different target. Optics utilizing total internal reflection are described for observing perturbation of the evanescent field.
Owner:MAVEN TECH
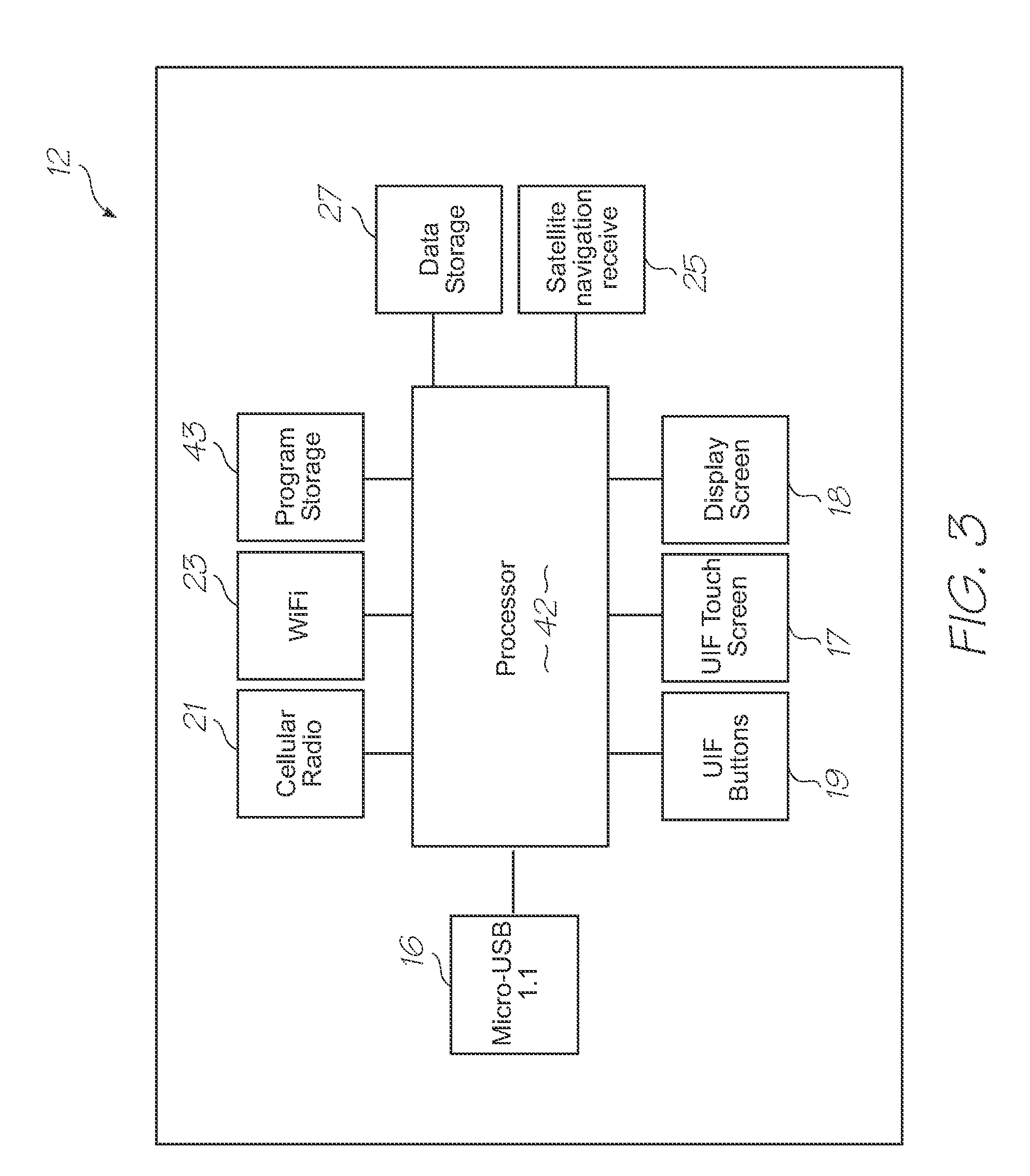
Microfluidic device for simultaneous detection of multiple conditions in a patient
InactiveUS20110312644A1Fast detection timeLow costValve arrangementsHeating or cooling apparatusBiological materialsProbe target
Owner:GENEASYS
Microfluidic device for detection of mitochondrial DNA via fluorescence modulated by hybridization
InactiveUS20110312751A1High sensitivityImprove fidelityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsValve arrangementsEnergy transferLysis
A microfluidic device for analysis of mitochondrial DNA in a sample, the microfluidic device having an inlet for receiving a sample of biological material having cells with mitochondria containing mitochondrial DNA, a lysis section for lysing the mitochondria to release the mitochondrial DNA, fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) probes for hybridization with target nucleic acid sequences in the mitochondrial DNA to form probe-target hybrids, and, a photosensor for detecting the probe-target hybrids.
Owner:GENEASYS
Quenching methods for background reduction in luminescence-based probe-target binding assays
InactiveUS7202036B2Reduce luminance of backgroundLuminous efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisQuenchingAdduct
Background luminescence is reduced from a solution containing unbound luminescent probes, each having a first molecule that attaches to a target molecule and having an attached luminescent moiety, and luminescent probe / target adducts. Quenching capture reagent molecules are formed that are capable of forming an adduct with the unbound luminescent probes and having an attached quencher material effective to quench luminescence of the luminescent moiety. The quencher material of the capture reagent molecules is added to a solution of the luminescent probe / target adducts and binds in a proximity to the luminescent moiety of the unbound luminescent probes to quench luminescence from the luminescent moiety when the luminescent moiety is exposed to exciting illumination. The quencher capture reagent does not bind to probe molecules that are bound to target molecules and the probe / target adduct emission is not quenched.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
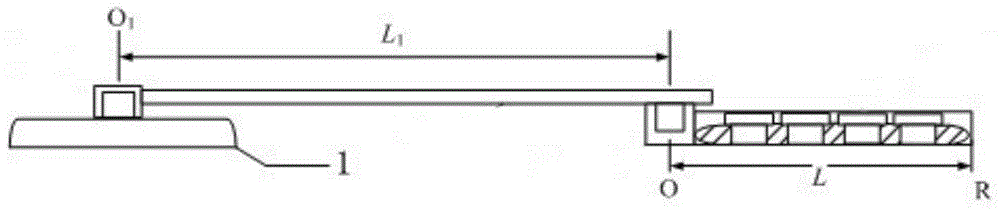
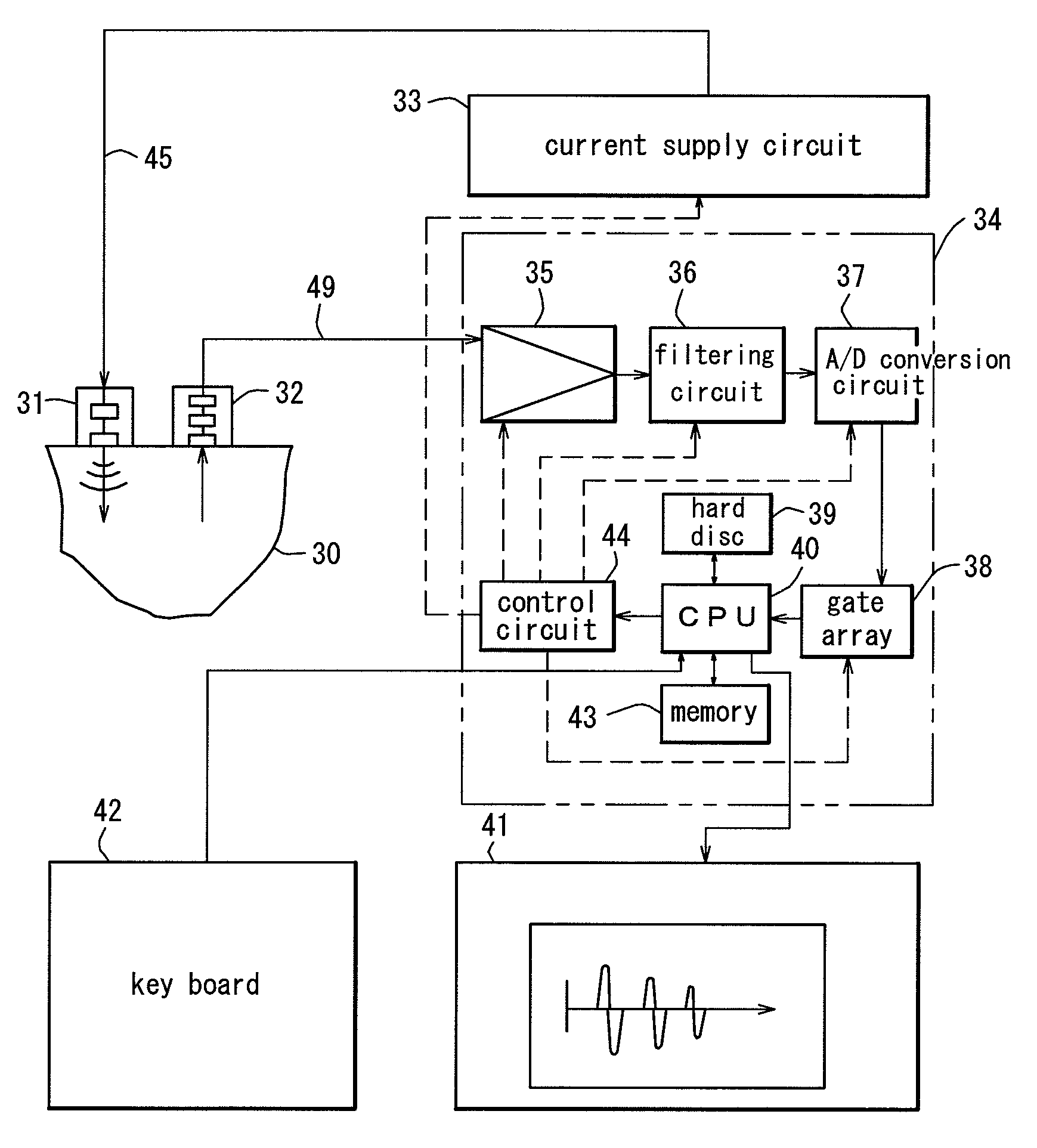
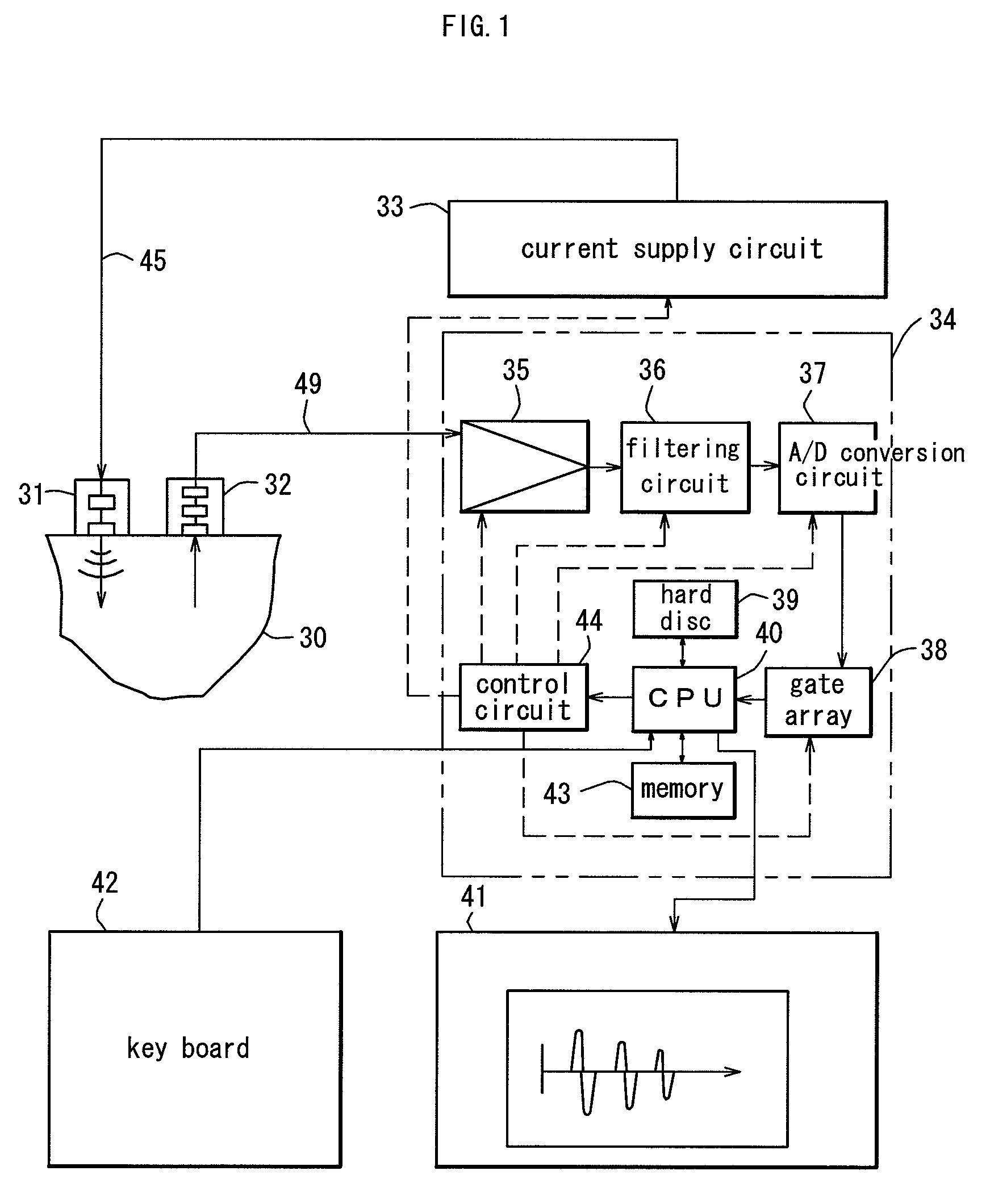
Ultrasonic probing method and apparatus therefor utilizing resonance phenomenon
InactiveUS7600442B2High precisionImprove accuracyVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFrequency spectrumSize measurement
A flaw Z with a long probing length inside a probing target is allowed to be probed. The waves other than the probing target waves are removed or reduced, so that the individual difference in the sizing result due to the ability of the measuring personnel is eliminated to improve the precision of the probing. A transmission probe 31 and a receiving probe 32 for transmitting and receiving a wide band ultrasonic wave are included. Each time the positions of the probes 31 and 32 are moved, a received wave Gj(t) is obtained. From a spectrum Fj(f) corresponding to the received wave Gj(t), a narrowband spectrum FAj(f) is extracted. A component wave GAj(t) corresponding to the narrow band spectrum FAj(f) is obtained by inverse Fourier transformation. The component wave GAj(t) is provided for a comparative display using a predetermined sizing coefficient. The position of a flaw Z is determined inside a probing target 30 right below the line segment connecting the centers of the transmission probe 31 and the receiving probe 32, based on at which of the measurement points a wave is generated on the comparative display screen.
Owner:H&B SYST +2
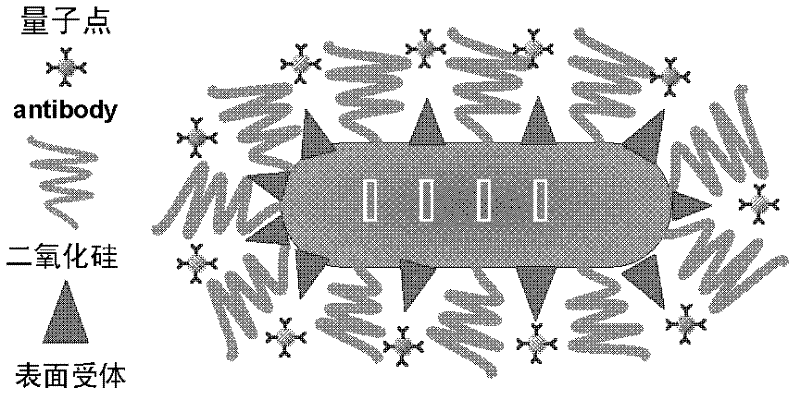
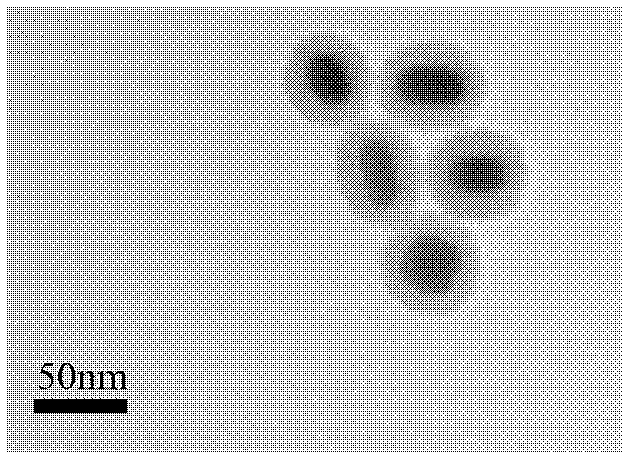
Application of a core-shell nanoparticle
InactiveCN102258793ASolve the problem of water solubilityHigh quantum yieldInorganic non-active ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsTreatment effectCancer cell
The invention provides an application of core-shell nanoparticles for preparing biological imaging agents, molecular biological probes and targeted drug-carrying carriers. The core-shell nanoparticle is that the inner core material is gold nanorod; the middle layer is silicon dioxide and surface acceptor; the outer shell is a coupling body of water-based CdTe quantum dots and biomolecules. The core-shell nanoparticle has low toxicity and low cost, solves the problem of water solubility of the nanoparticle, and improves the biocompatibility of the composite nanoparticle. The core-shell nanoparticles have strong fluorescence characteristics, and the surface receptors have spectral signals, and the fluorescence signals are observed through the biological imaging system to obtain the information of the lesion. Utilizing the strong fluorescent properties of the core-shell nanoparticles, they can be combined with cells in living organisms as biological probes for early diagnosis of diseases. The complex of drug and core-shell nanoparticles will successfully reside on the surface of cancer cells, and the drug will reach the cancer cells to achieve therapeutic effect.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
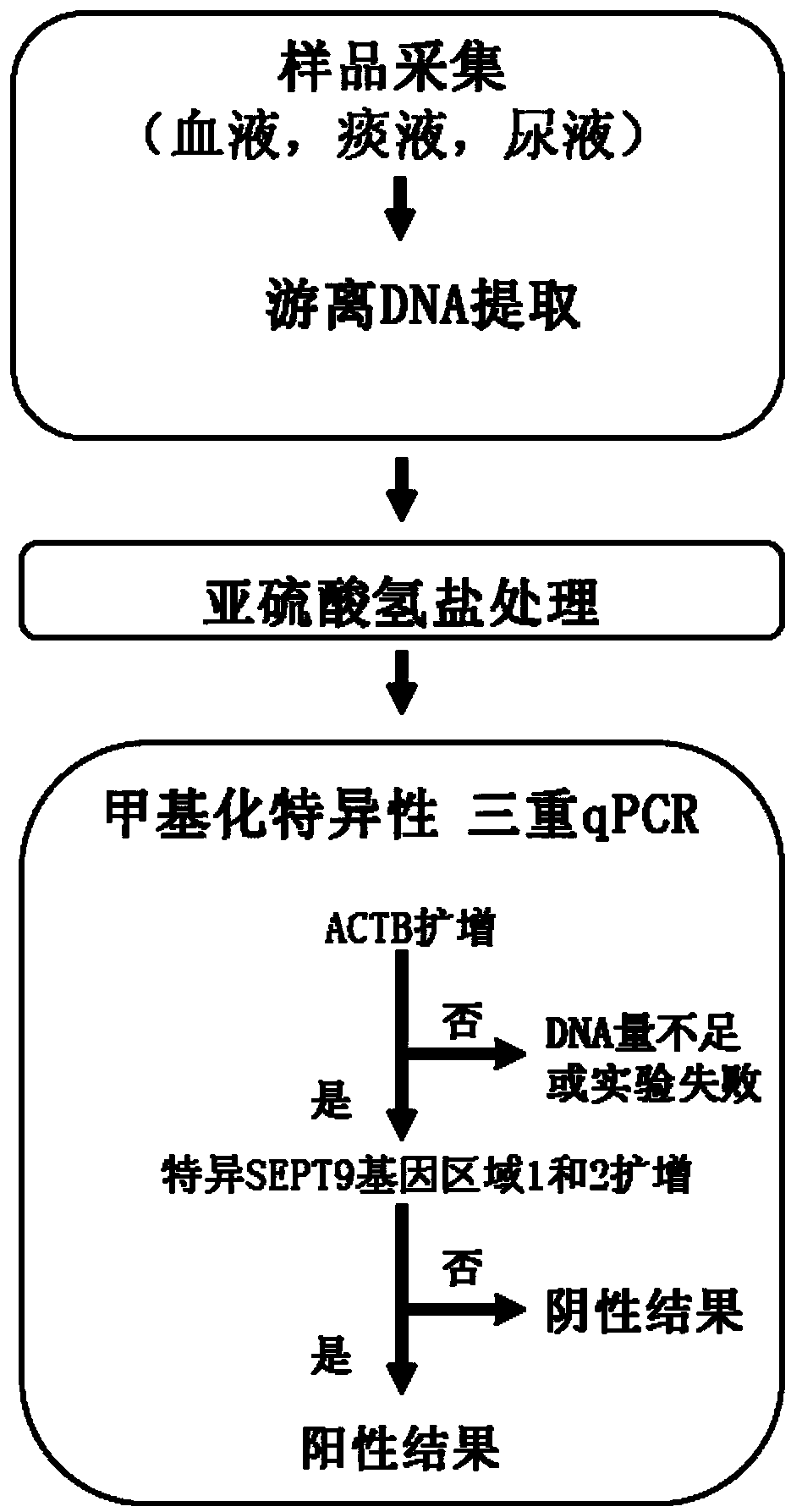
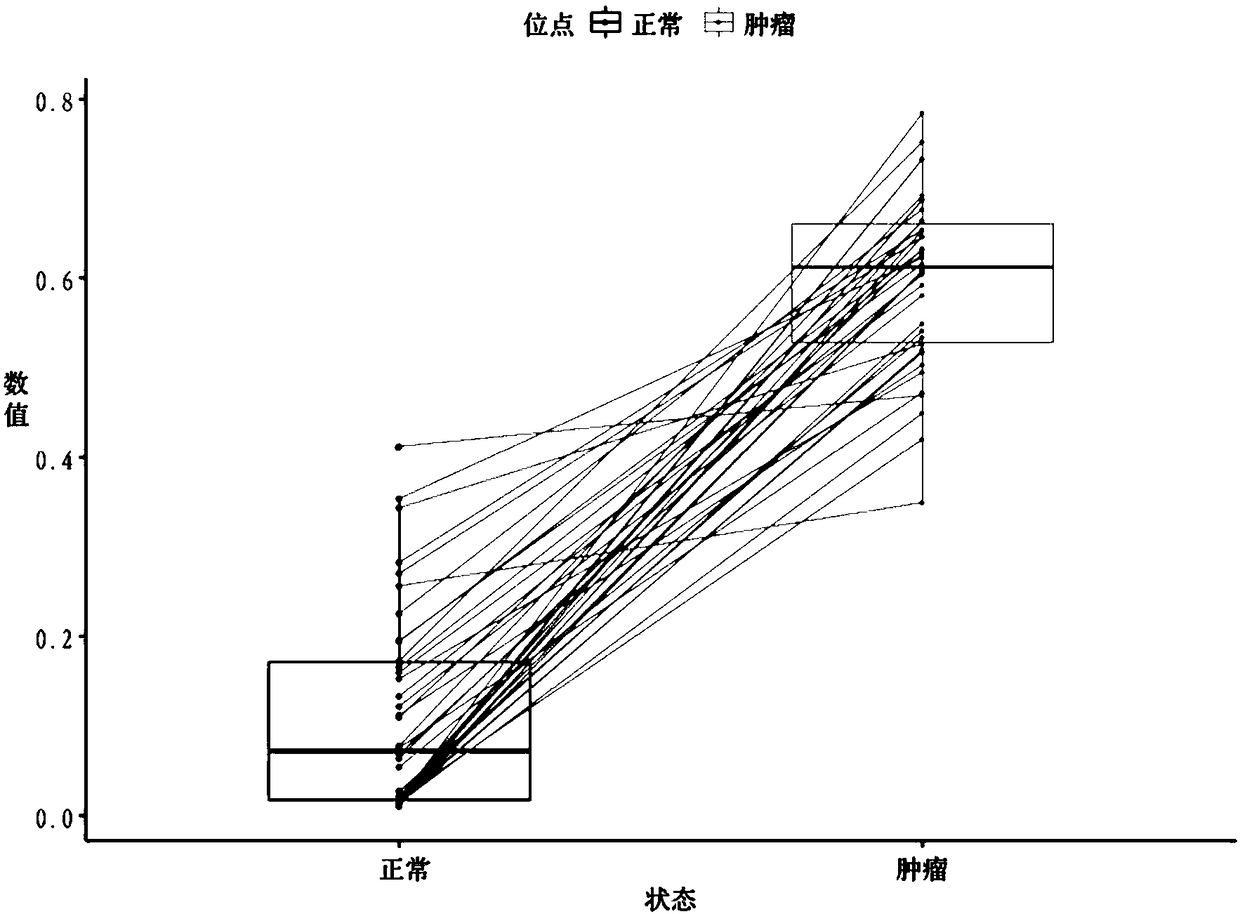
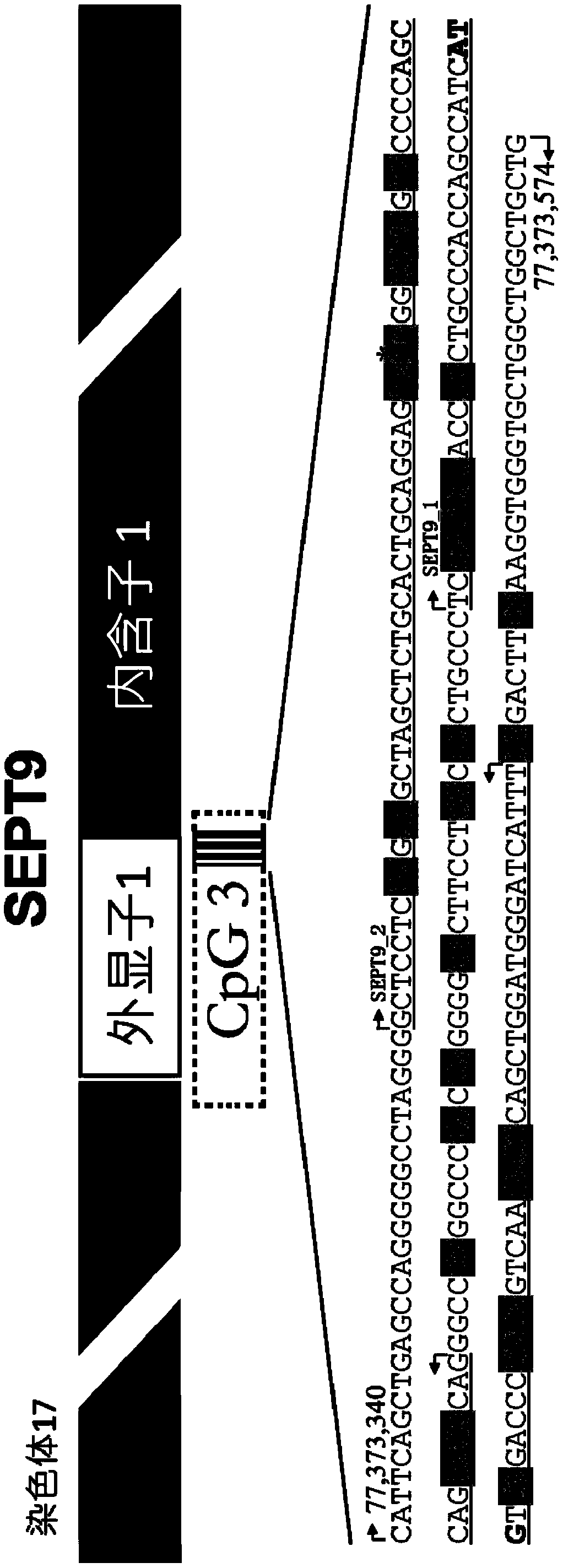
Kit and method for detecting DNA methylation by triplex qPCR assay
The present disclosure provides a kit and method for detecting DNA methylation by a triplex qPCR assay. The kit includes a combination of three sets of primers and probes, wherein two sets of primersand probes are combined to target two regions selected from the sequence of the human SEPT9 gene. Another set of primers and probes targets an internal reference. The kit described in the present disclosure is capable of more sensitive and accurate determination of the DNA methylation level or status in a particular region.
Owner:深圳市新合生物医疗科技有限公司
Nucleic acid array with releaseable nucleic acid probes
InactiveUS20090286694A1Heating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesNucleic acid hybridisation
A process is provided for identifying a complementary target nucleic acid. The process includes the hybridization of a nucleic acid probe to a carrier to form a nucleic acid probe-carrier complex. The complex is placed in a compartment bounded by a media permeable to the nucleic acid probe and exclusive of both the carrier and the complex. The complex is then denatured, with the nucleic acid probe transported through the media and into contact with the target nucleic acid. The nucleic acid probe hybridizes to the complementary target nucleic acid to yield a probe-target double stranded complex. A non-complementary nucleic acid probe, independent probe-target complex is returned to the compartment and given an opportunity to rehybridize to the carrier. A determination as to whether at least one of the complementary target nucleic acid or the carrier is present as a complex provides information as to probe sequences complementary to the target nucleic acid.
Owner:ZAINIEV GAFUR +1
TOP2A gene abnormality detection probe, kit and method
InactiveCN104561360AHigh coincidence rateAvoid cross reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceTOP2A Gene
The invention discloses a TOP2A gene abnormality detection probe, a kit and a method. The detection probe comprises a first group of probes for labeling fluorescent dye and targeted to a TOP2A gene, and a second group of probes targeted to the centromere region of human chromosome 7, wherein the first group of the probes are selected from at least one of probes as shown in SEQ ID NO.41-SEQ ID NO.50; the second group of the probes are selected from at least one of probes as shown in SEQ ID NO.51-SEQ ID NO.60; and the fluorescent dyes labeled by the two groups of the probes are different in color. A FISH probe in the TOP2A gene abnormality detection kit provided by the invention is free from a repeated sequence, and capable of avoiding a cross reaction and undergoes hybridization recognition with a TOP2A target detection fragment in the chromosome; and the probe has the advantages of high accuracy, good specificity and low false positive rate.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
Method for generating broadband dechirp echoes based on sweep frequency data
ActiveCN110850384ASmall frequency intervalReduce computationWave based measurement systemsEngineeringRadar signal processing
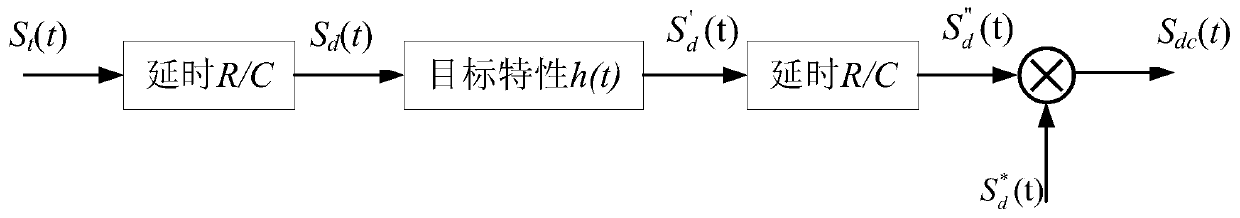
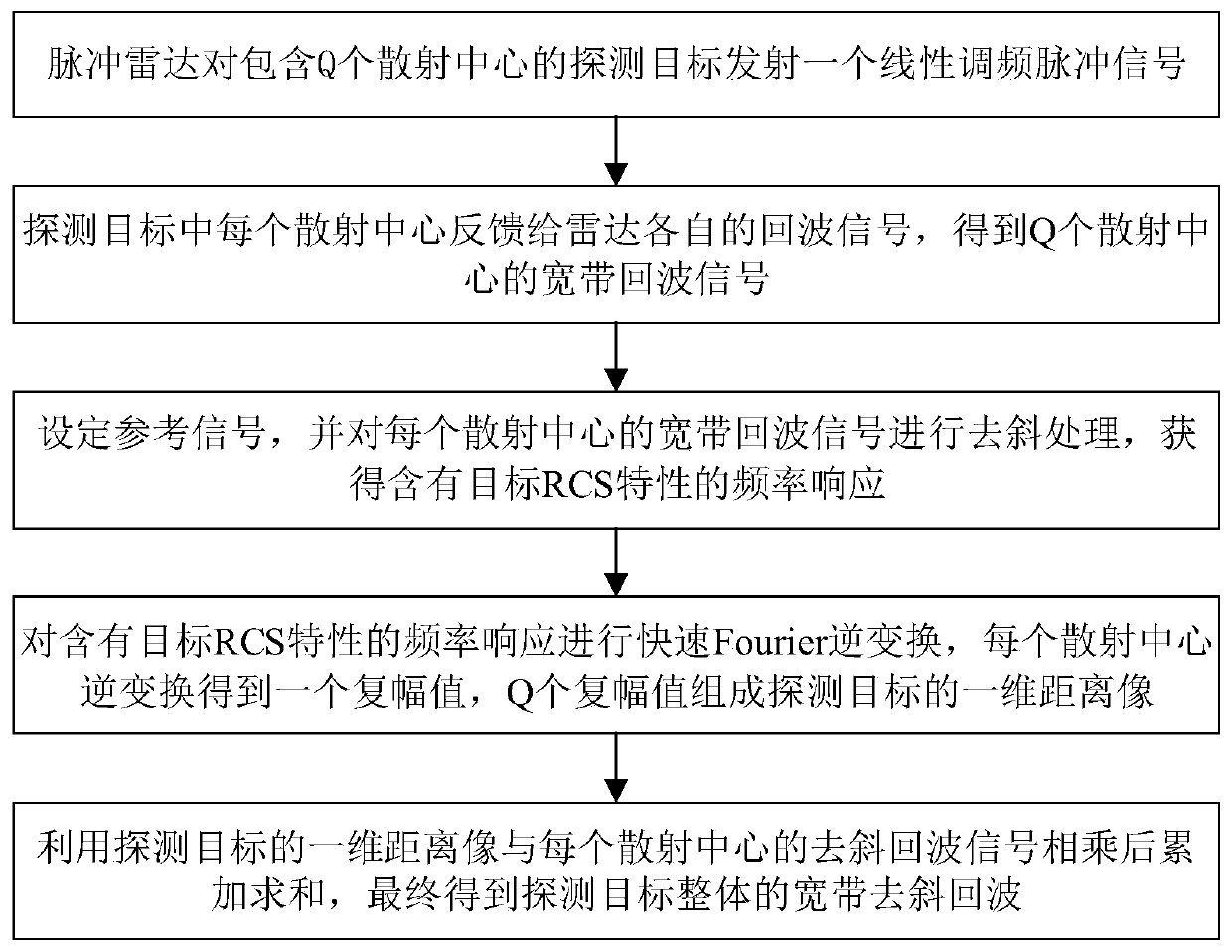
The invention discloses a method for generating broadband dechirp echoes based on sweep frequency data, and belongs to the technical field of radar signal processing. The method comprises the steps: enabling a pulse radar to send a linear frequency modulation pulse signal to a detection target comprising Q scattering centers; enabling each scattering center in the detection target to feed back signals to the radar to obtain broadband echo signals of Q scattering centers; setting a reference signal, and performing dechirping processing on the broadband echo signal of each scattering center to obtain a frequency response containing a target RCS characteristic; carrying out fast Fourier inverse transformation on the frequency response containing the RCS characteristics of the target, carryingout inverse transformation on each scattering center to obtain a complex amplitude, and forming a one-dimensional range profile of the detection target by Q complex amplitudes; multiplying the one-dimensional range profile of the detection target by the dechirping echo signal of each scattering center, and performing accumulating and summing to finally obtain the broadband dechirping echo of thewhole detection target. According to the method, the operand is greatly reduced, and meanwhile, the precision and the accuracy which are the same as those of convolution operation are ensured.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com