Tumor screening model and construction method and device thereof
A technology for tumor screening and construction methods, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, medical automated diagnosis, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to achieve low-cost tumor screening, and achieve the effect of efficient screening and detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
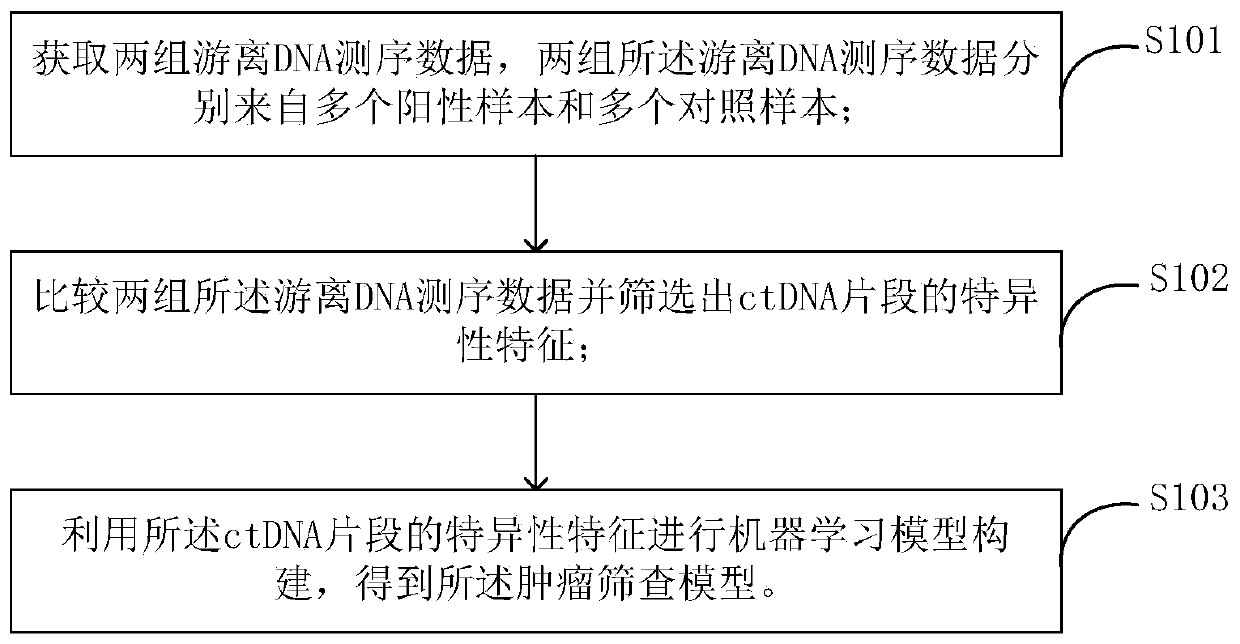
[0039] In a preferred embodiment of the present application, a method for constructing a tumor screening model is provided, figure 1 is a flowchart of a method for constructing a tumor screening model according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown, the method includes:
[0040] Step S101, obtaining two sets of cell-free DNA sequencing data, the two sets of cell-free DNA sequencing data are respectively from multiple positive samples and multiple control samples;
[0041] Step S103, comparing two sets of cell-free DNA sequencing data and screening out the specific characteristics of ctDNA fragments;
[0042] Step S105, using the specific features of ctDNA fragments to construct a machine learning model to obtain a tumor screening model.
[0043] The above-mentioned method of the present application can be used to greatly improve the detection of ctDNA according to the characteristic distribution of ctDNA fragments which are obviously different from cfDNA, and f...
Embodiment 2
[0069] In a preferred embodiment of the present application, a more specific method for constructing a tumor screening model is provided, the method comprising:
[0070] 1. The input data is the raw data of next-generation sequencing off-machine, and the data format is fastq.
[0071] 1) Preprocess the original off-machine data, including removing adapters and low-quality data.
[0072] 2) Compare and sort the processed original off-machine data with the reference genome, and obtain the comparison results, and the data format is bam.
[0073] 3) Perform duplication reads identification on the bam file, and remove duplication reads.
[0074] 2. Feature selection:
[0075] A) Compare the cell-free DNA sequencing data of the two groups of samples and screen out the specific characteristics of the ctDNA fragments according to the following principles:
[0076] 1) Extract the absolute position of the end of all read pairs in the tumor sample, that is, the physical position corre...
Embodiment 3
[0106] In an optional embodiment, a tumor screening model is also provided, and the tumor screening model is constructed by any of the above methods.
[0107] In another optional embodiment, there is also provided a tumor screening device, which contains the above-mentioned tumor screening model.
[0108] The tumor screening model or tumor screening device can be used to greatly improve the detection of ctDNA according to the characteristic distribution of ctDNA fragments that are significantly different from cfDNA, and further screen out the unique characteristics of ctDNA, and make full use of the specificity of ctDNA in positive samples. Sexual characteristics, constructed by machine learning, can be relatively accurate and efficiently screen the samples to be tested. Moreover, the tumor screening model does not require high sequencing depth of the samples to be tested, and can be realized by conventional low-depth sequencing, providing important research directions and cli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com