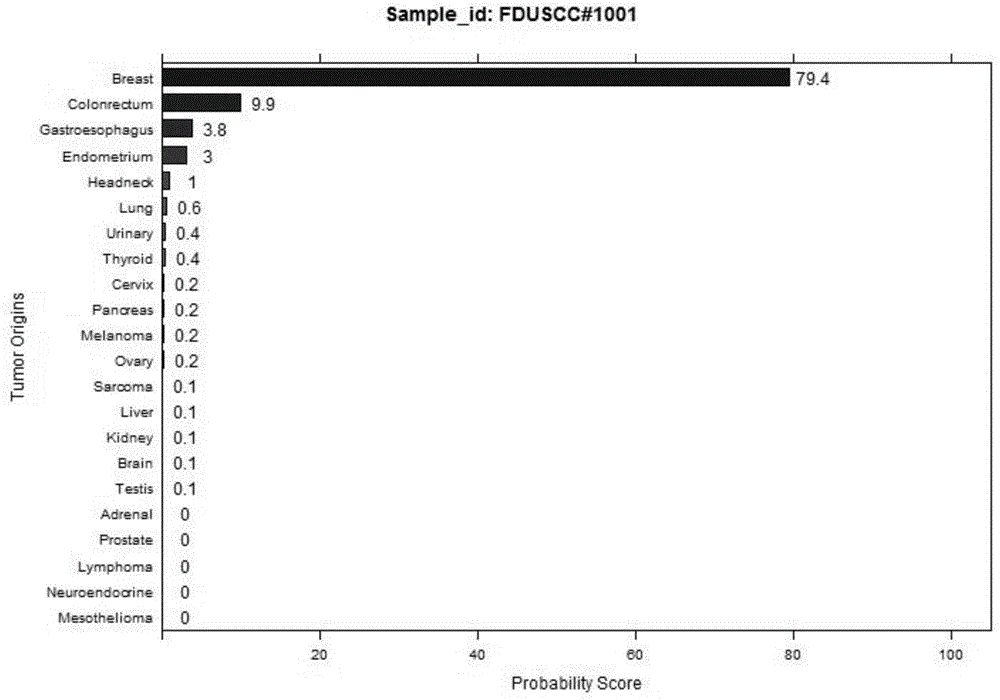
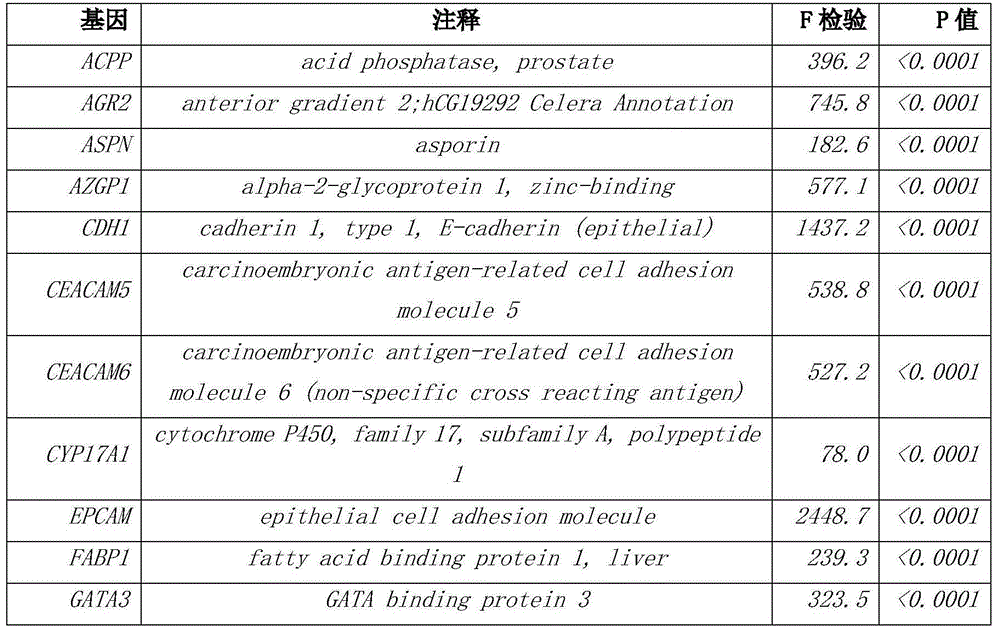
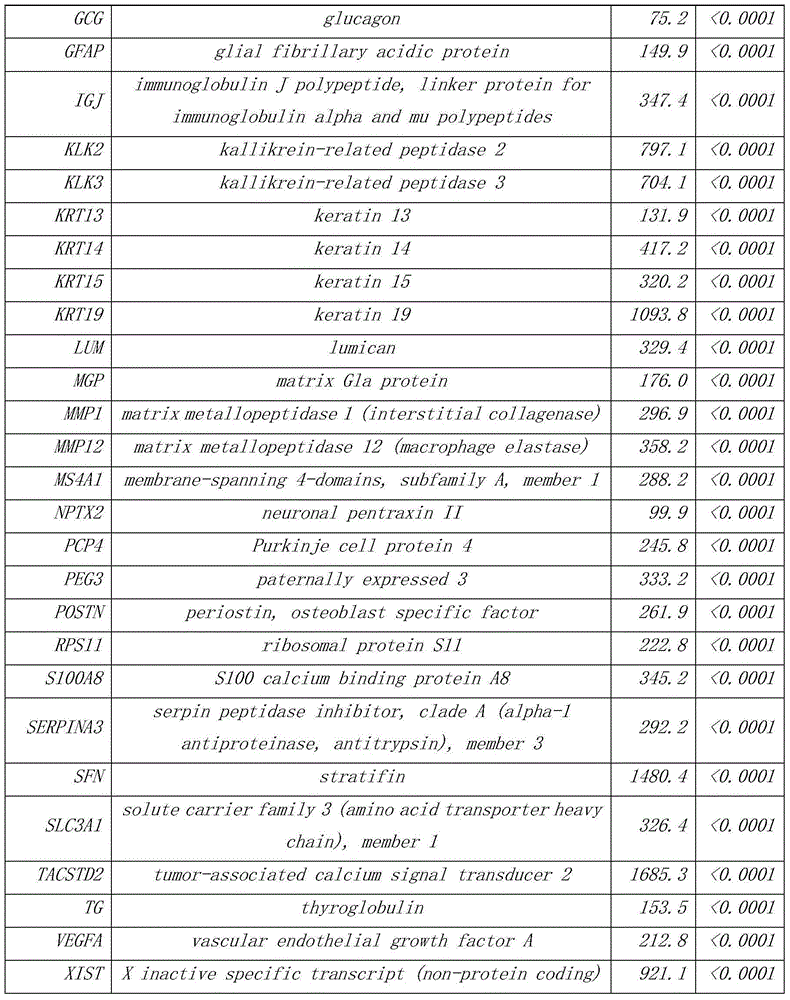
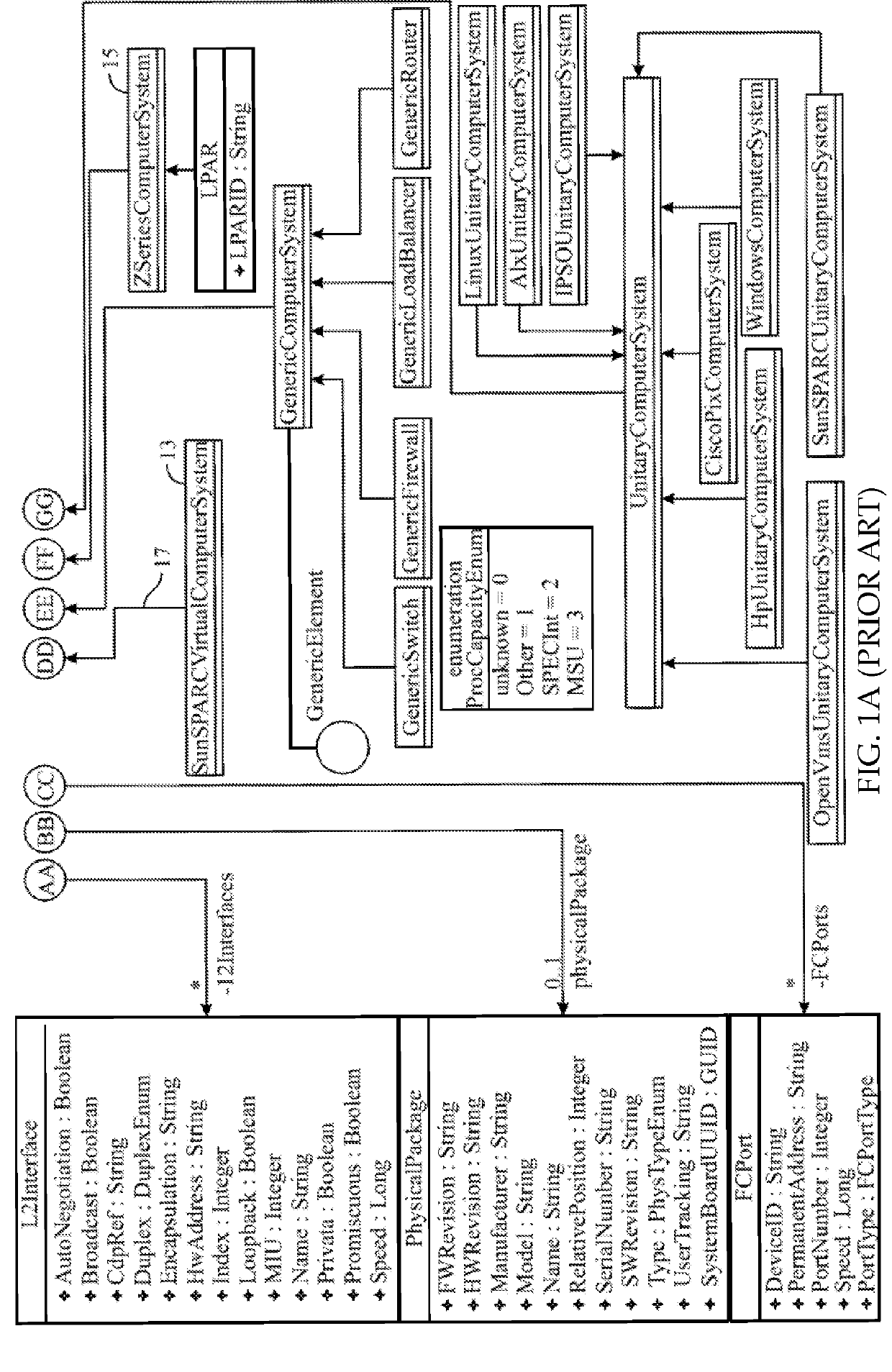
Patents
Literature
69 results about "Subtyping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
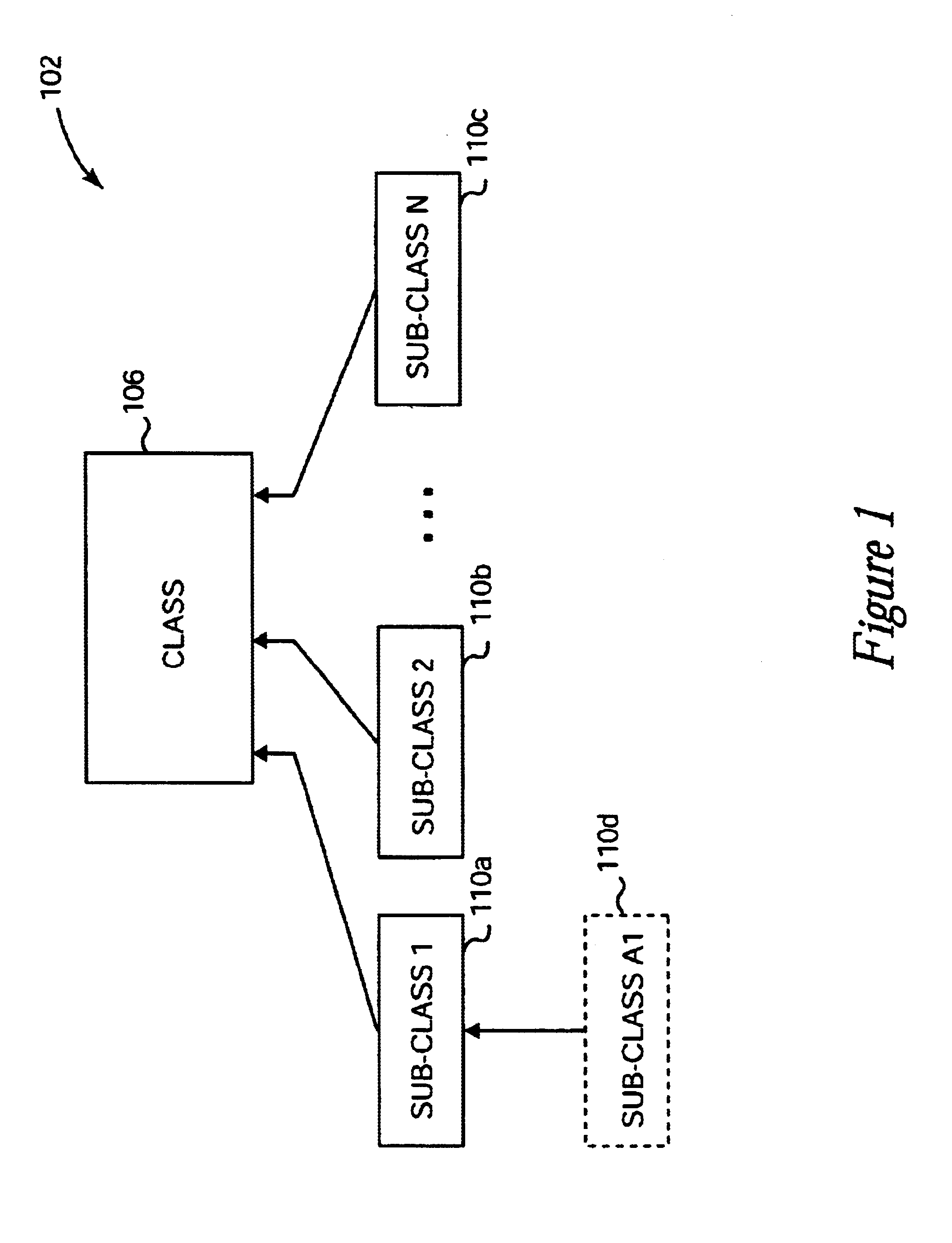
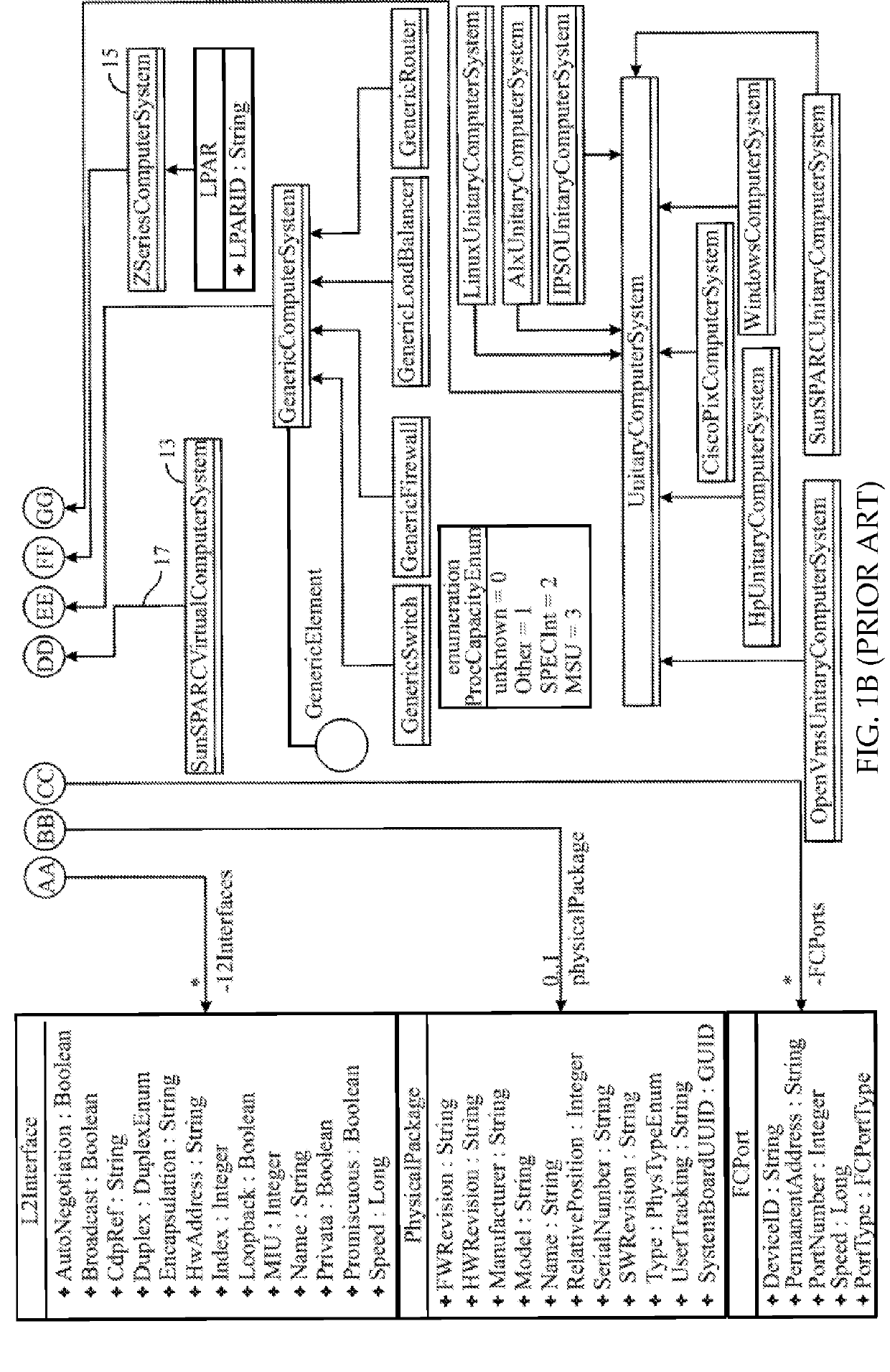
In programming language theory, subtyping (also subtype polymorphism or inclusion polymorphism) is a form of type polymorphism in which a subtype is a datatype that is related to another datatype (the supertype) by some notion of substitutability, meaning that program elements, typically subroutines or functions, written to operate on elements of the supertype can also operate on elements of the subtype. If S is a subtype of T, the subtyping relation is often written S <: T, to mean that any term of type S can be safely used in a context where a term of type T is expected. The precise semantics of subtyping crucially depends on the particulars of what "safely used in a context where" means in a given programming language. The type system of a programming language essentially defines its own subtyping relation, which may well be trivial should the language support no (or very little) conversion mechanisms.
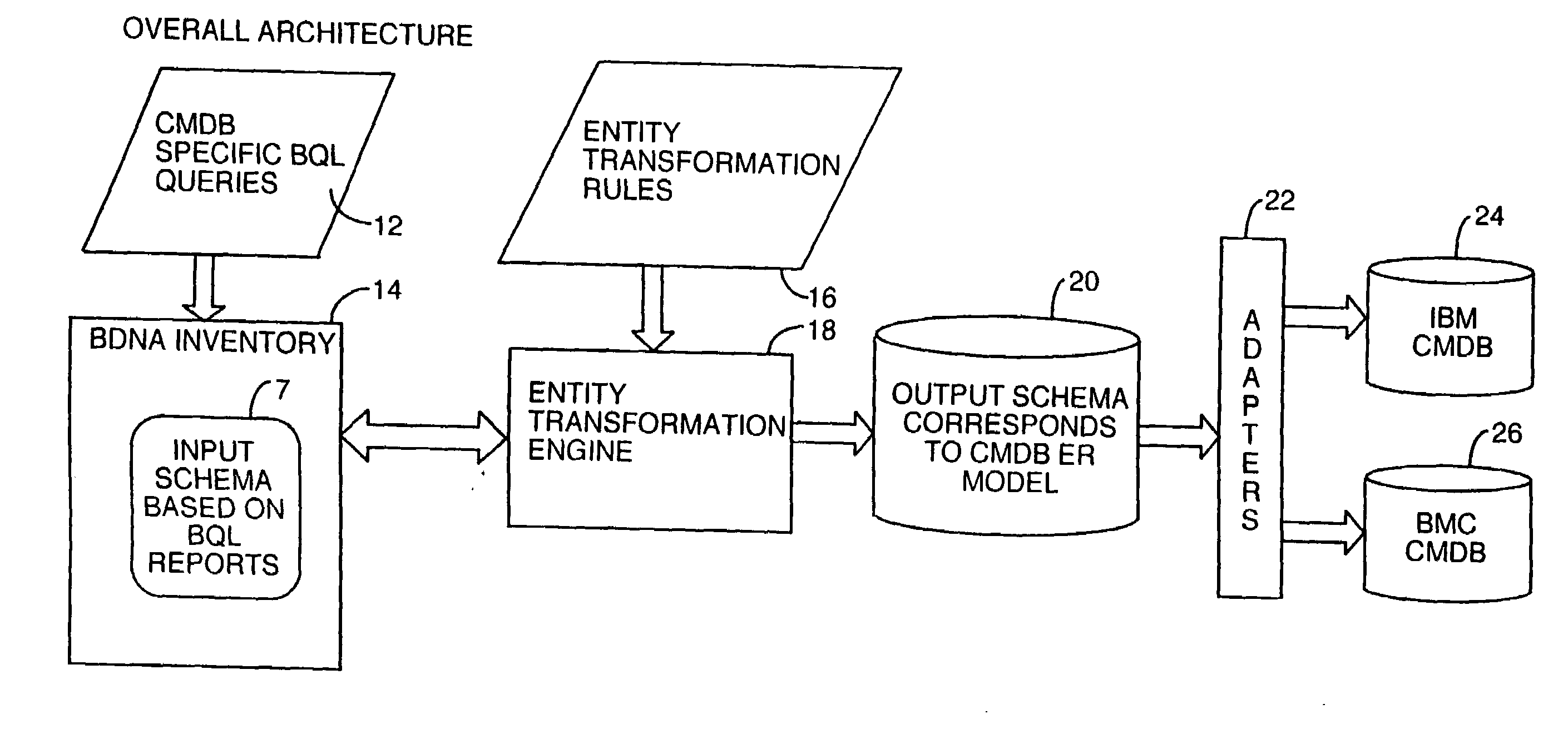
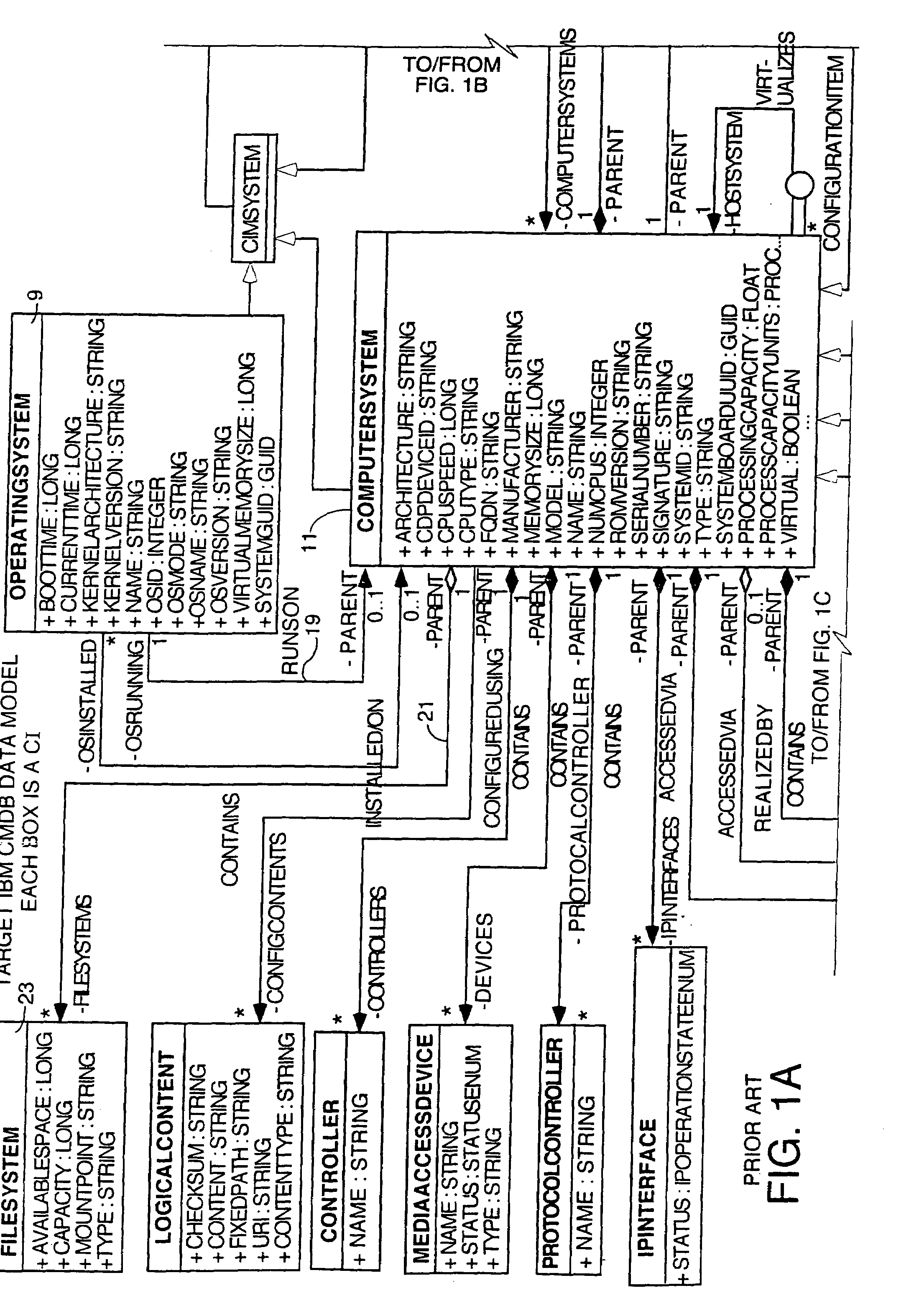
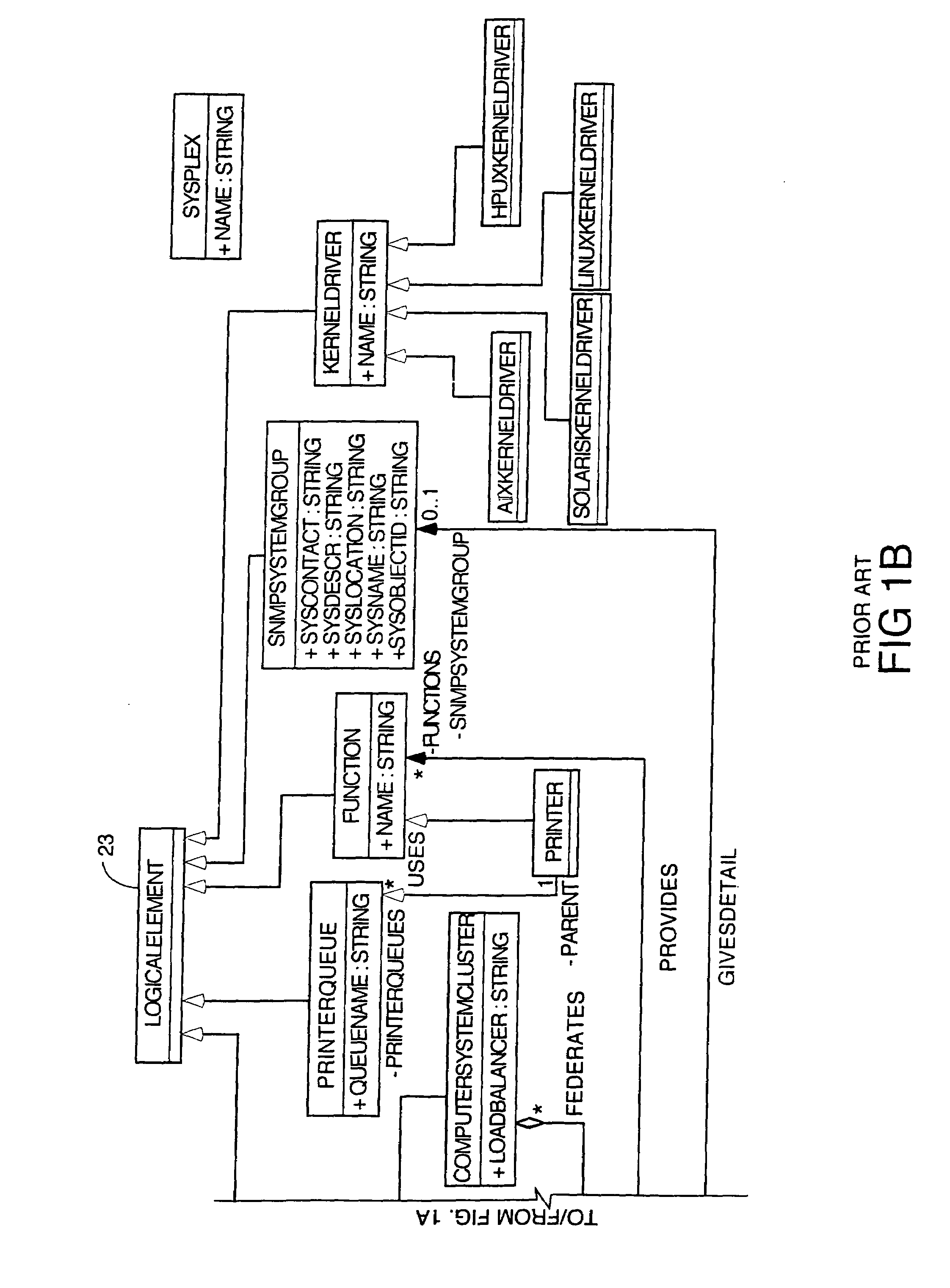
External system integration into automated attribute discovery
InactiveUS20090144319A1Database management systemsObject oriented databasesEntity–relationship modelEntity type
Owner:PANWAR RAJENDRA BHAGWATISINGH +1
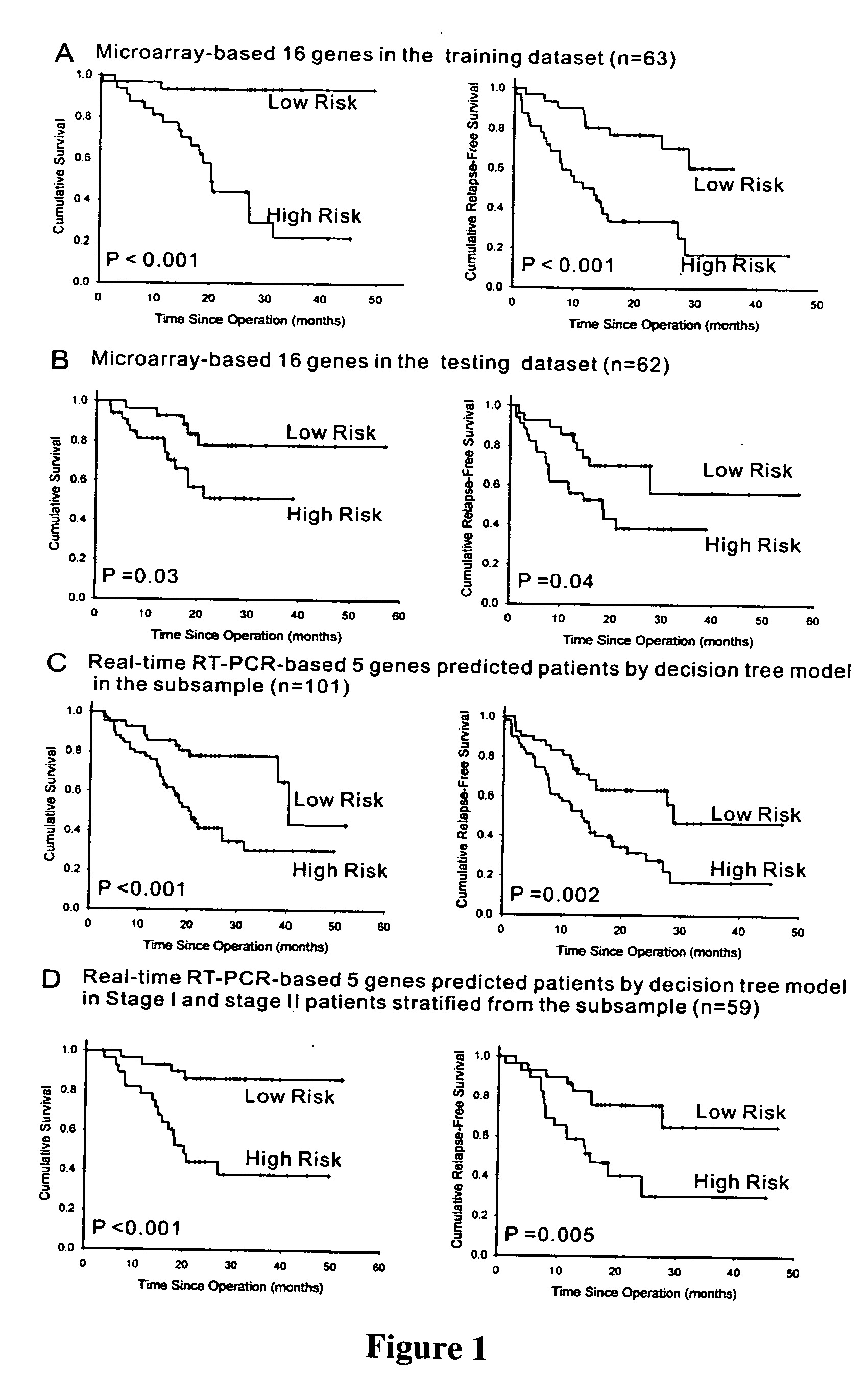
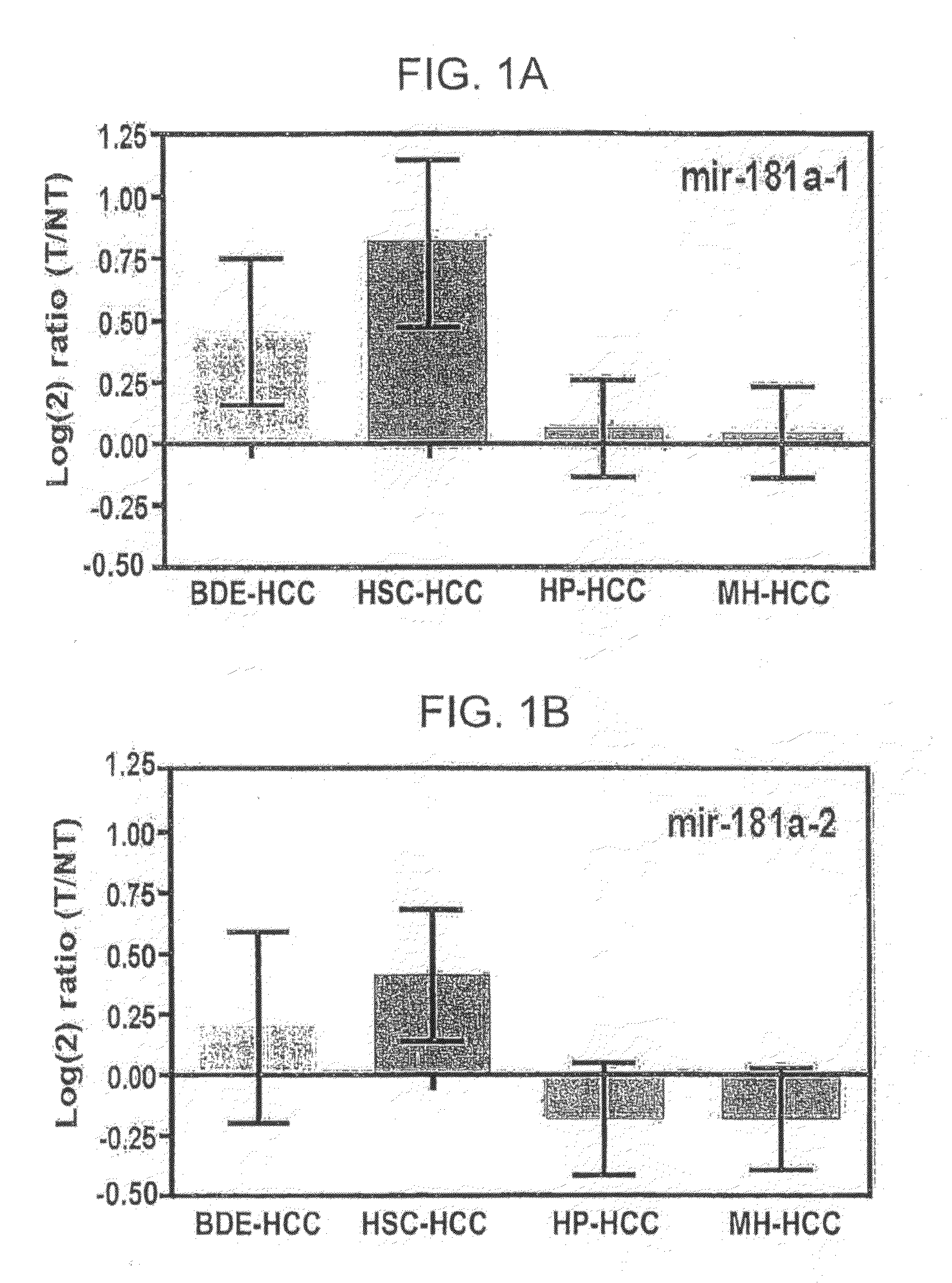
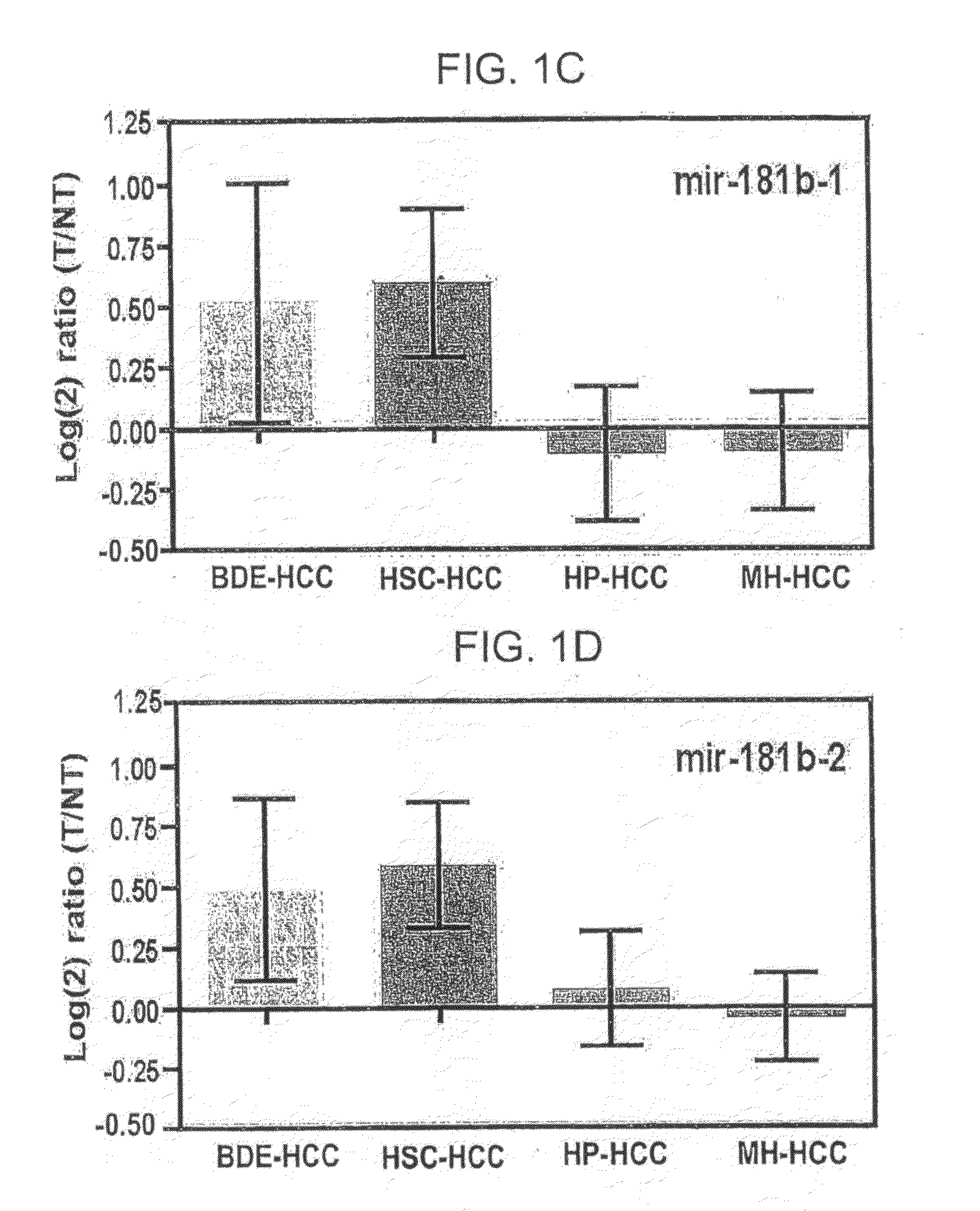
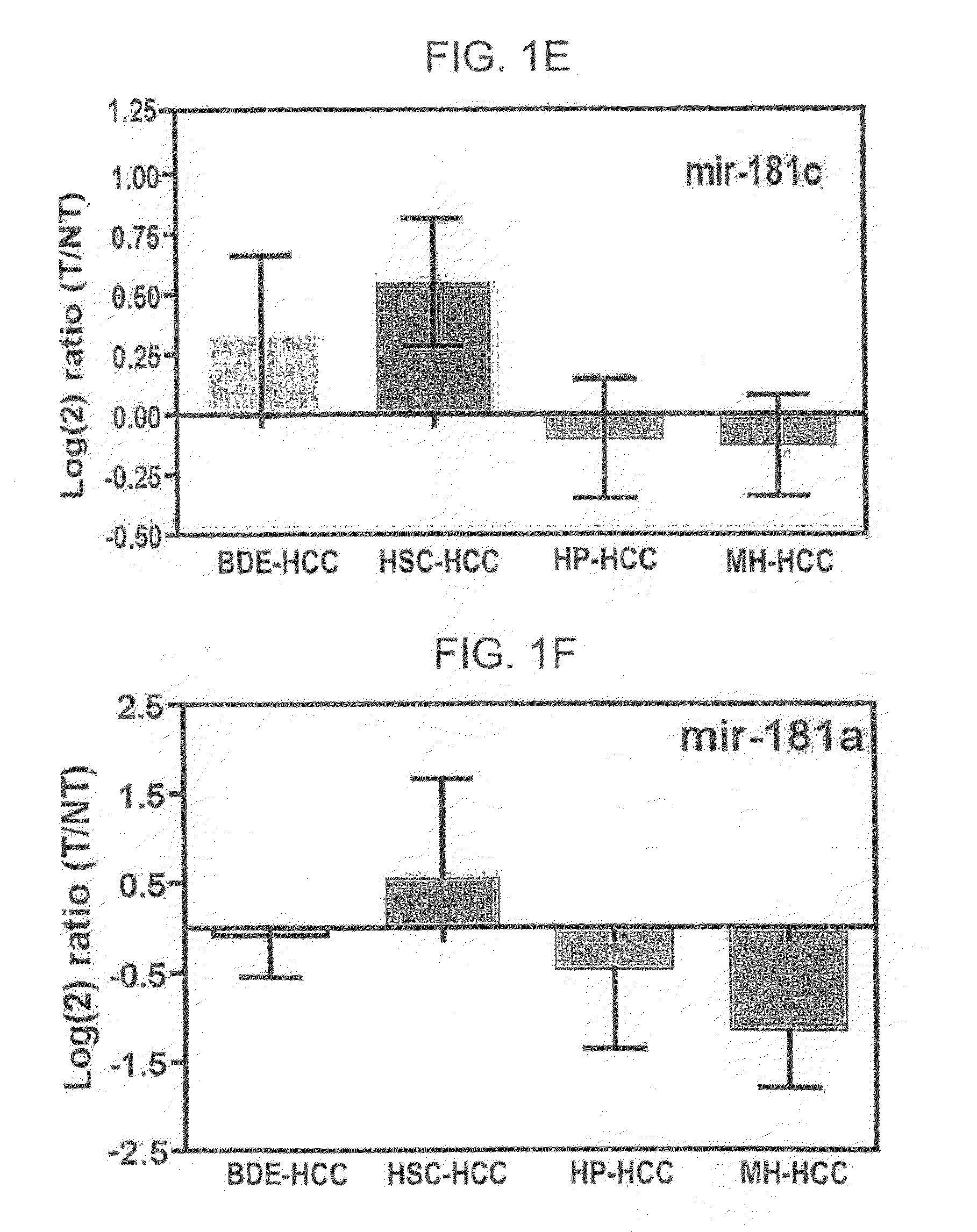
Metastasis-associated gene profiling for identification of tumor tissue, subtyping, and prediction of prognosis of patients
InactiveUS20060211036A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAbnormal tissue growthReal-Time PCRs
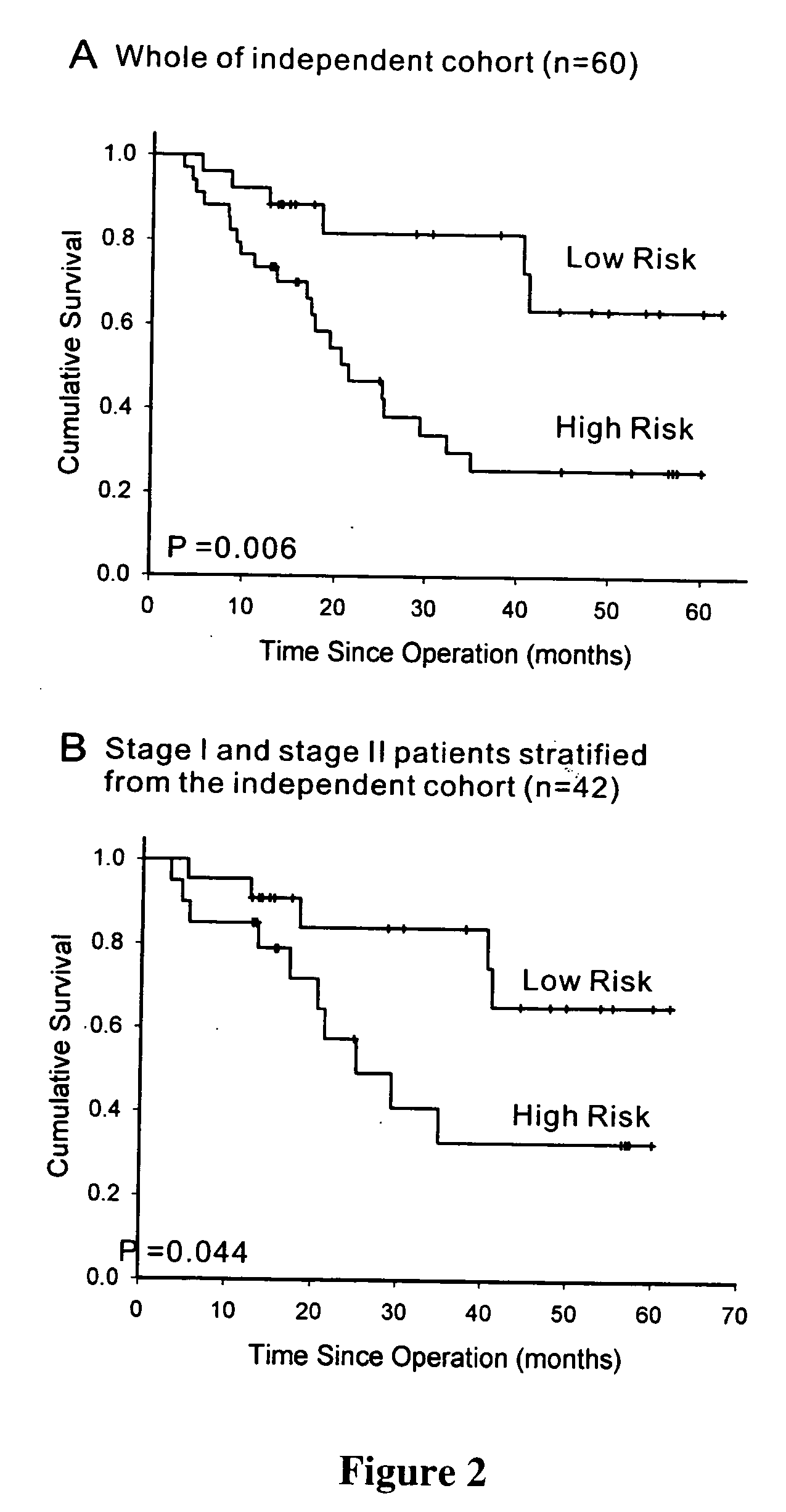
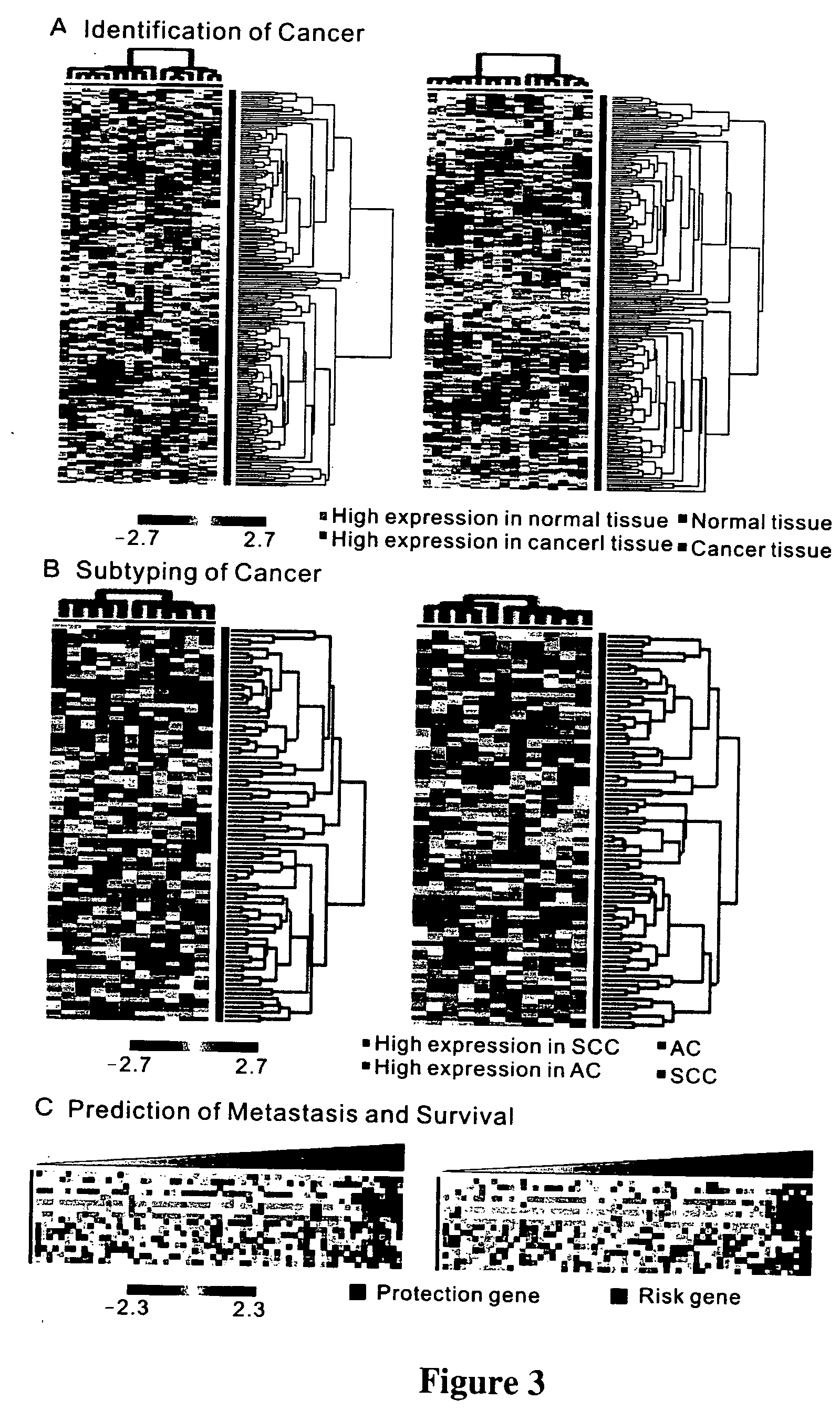
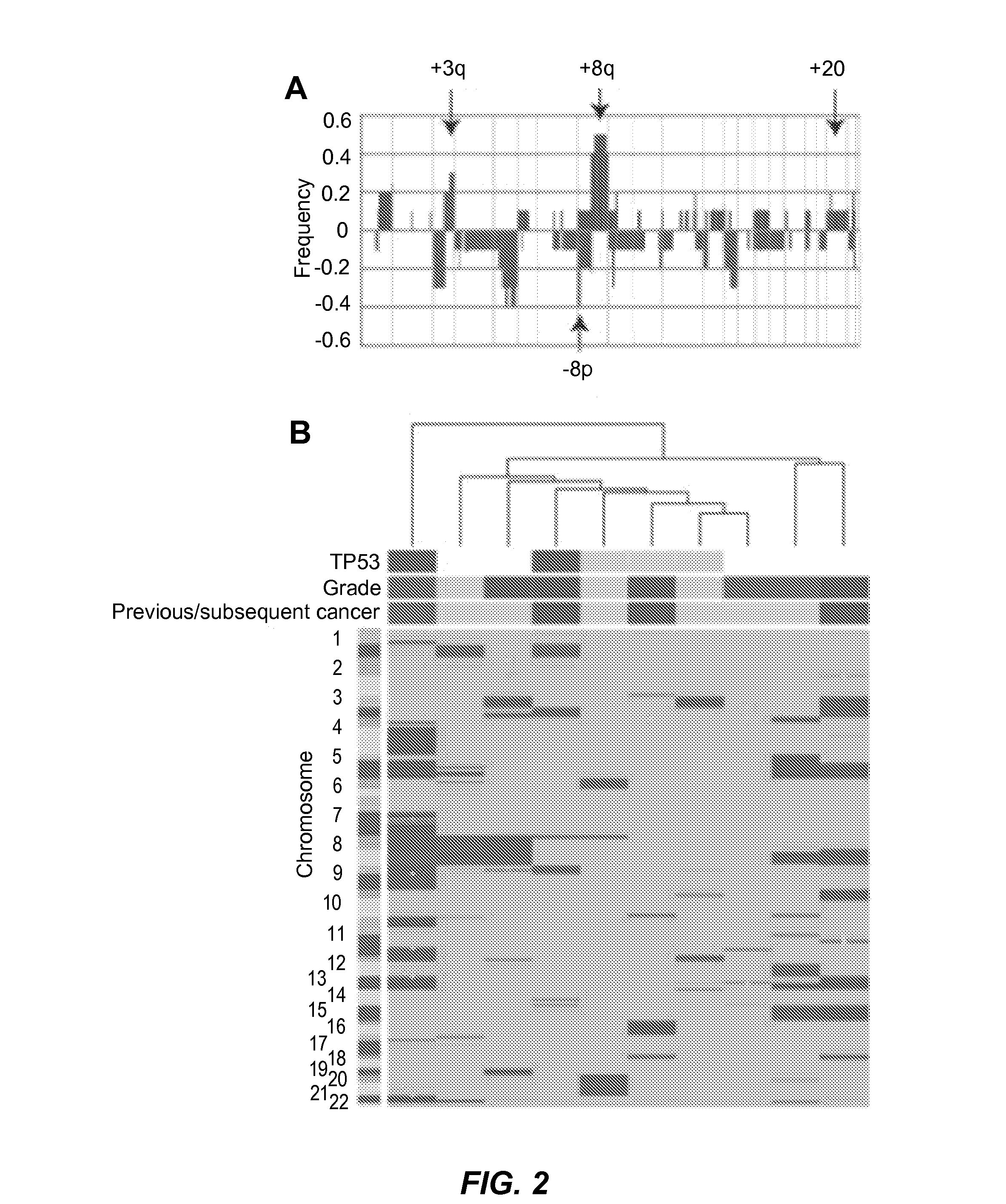
The present invention provides methods using a gene expression profiling analysis (1) to determine whether a human sample is a tumor using a gene set containing nucleic acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 1-7, 8-17 or 1-17; (2) to identify whether a tumor tissue is an adenocarcinoma (using a gene set containing nucleic acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 15, and 18-21) or a squamous cell carcinoma (using a gene set containing nucleic acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 22-27); and (3) to predict the prognosis of survival and metastasis in humans with tumor (using a gene set containing nucleic acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS:19, and 28-42 or SEQ ID NOS: 19, 29, 31, 40, and 42), particularly for those humans who are at the early stage of lung cancer. The gene expression profiling is preferably performed by cDNA microarray-based techniques and / or Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (Real-Time RT-PCR), and analyzed by statistical means.
Owner:ADVPHARMA
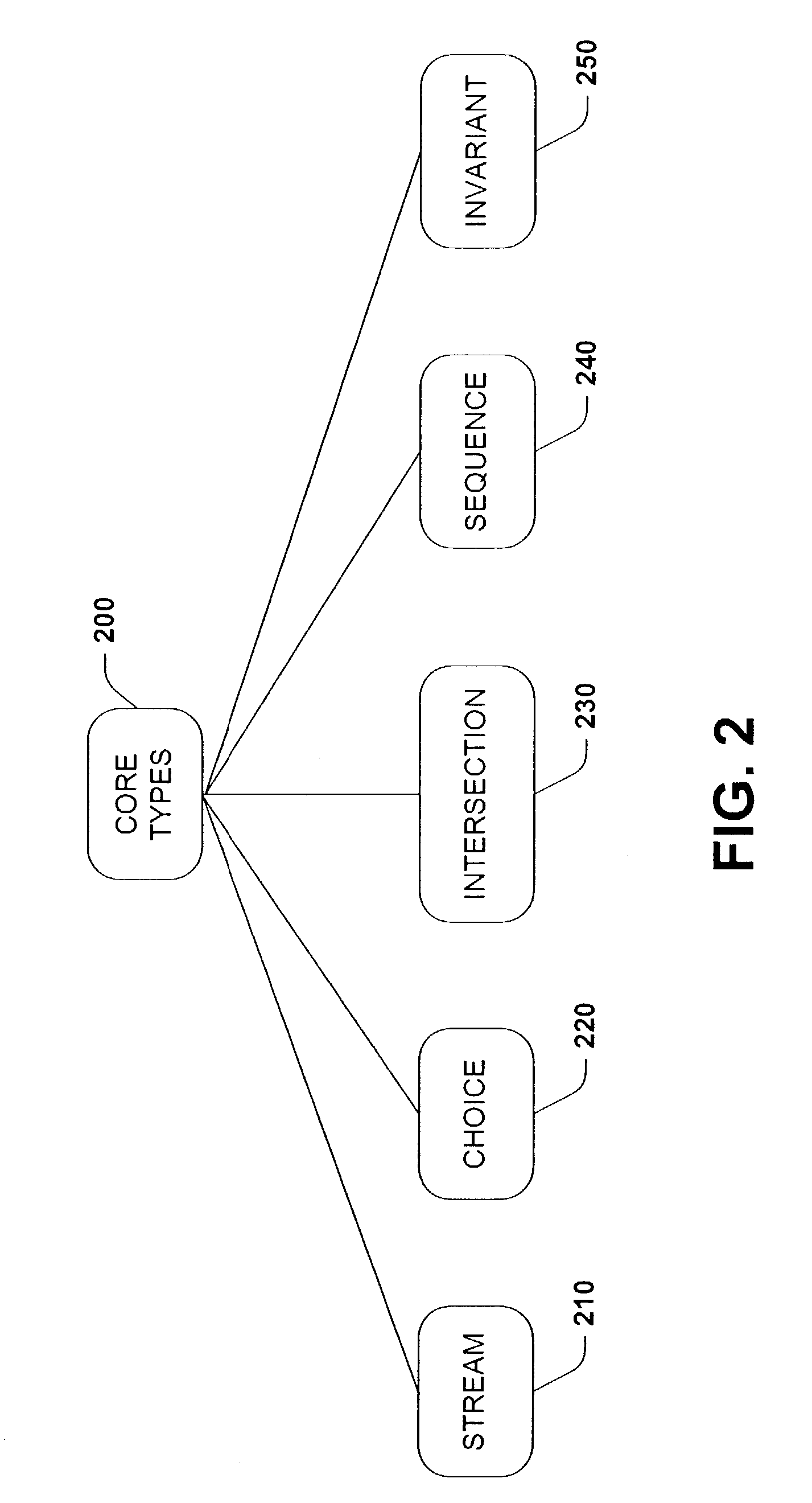
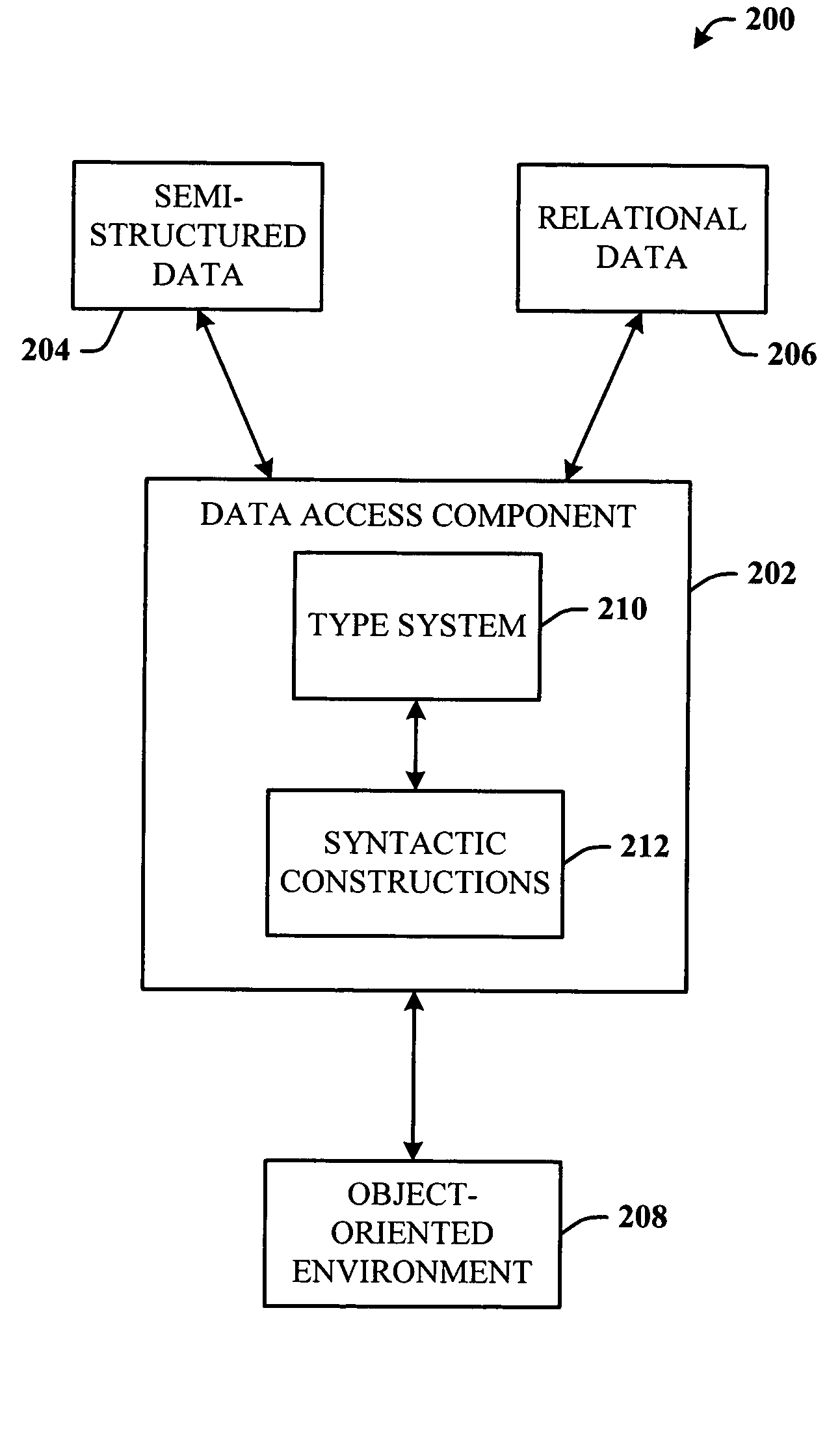
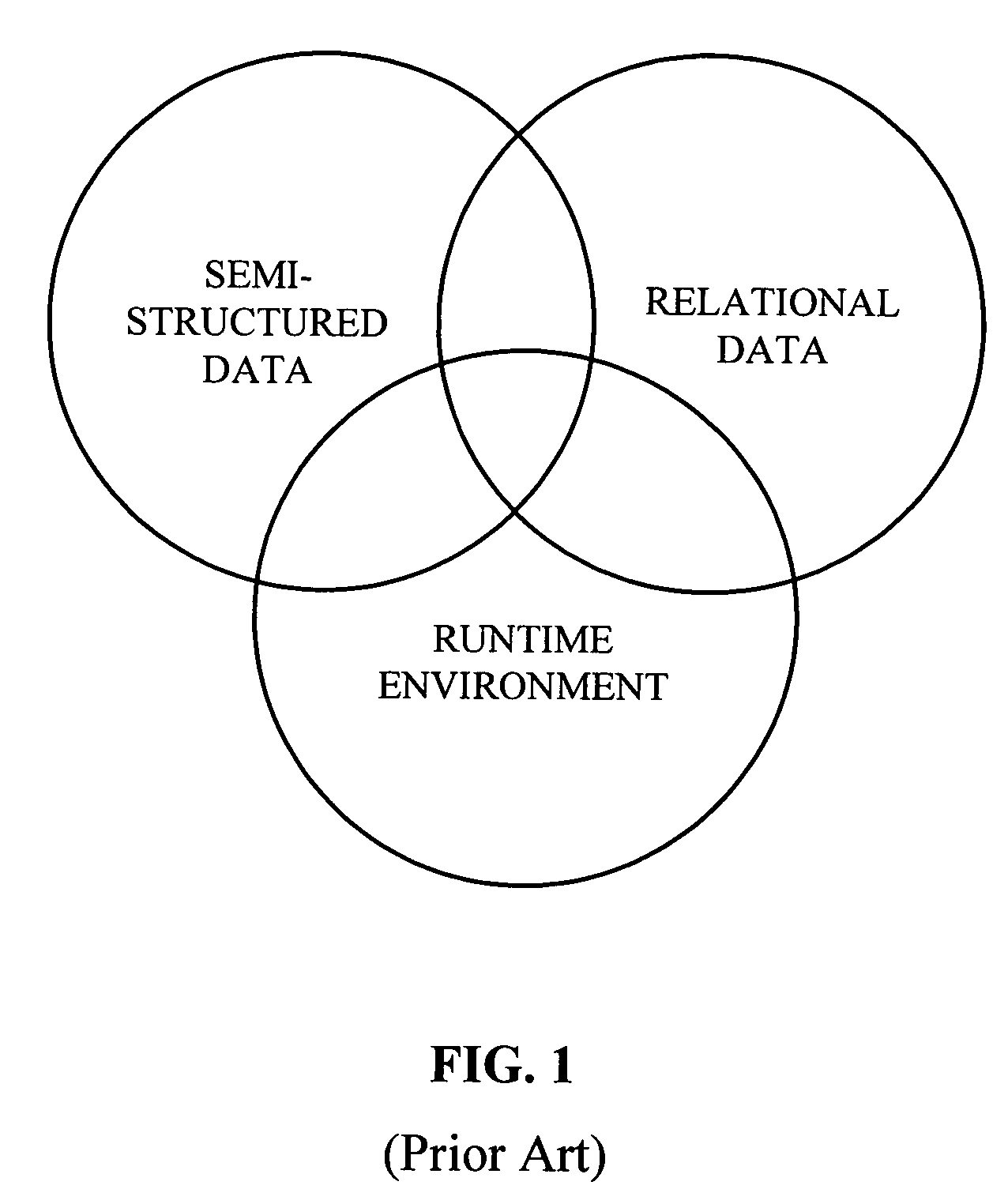
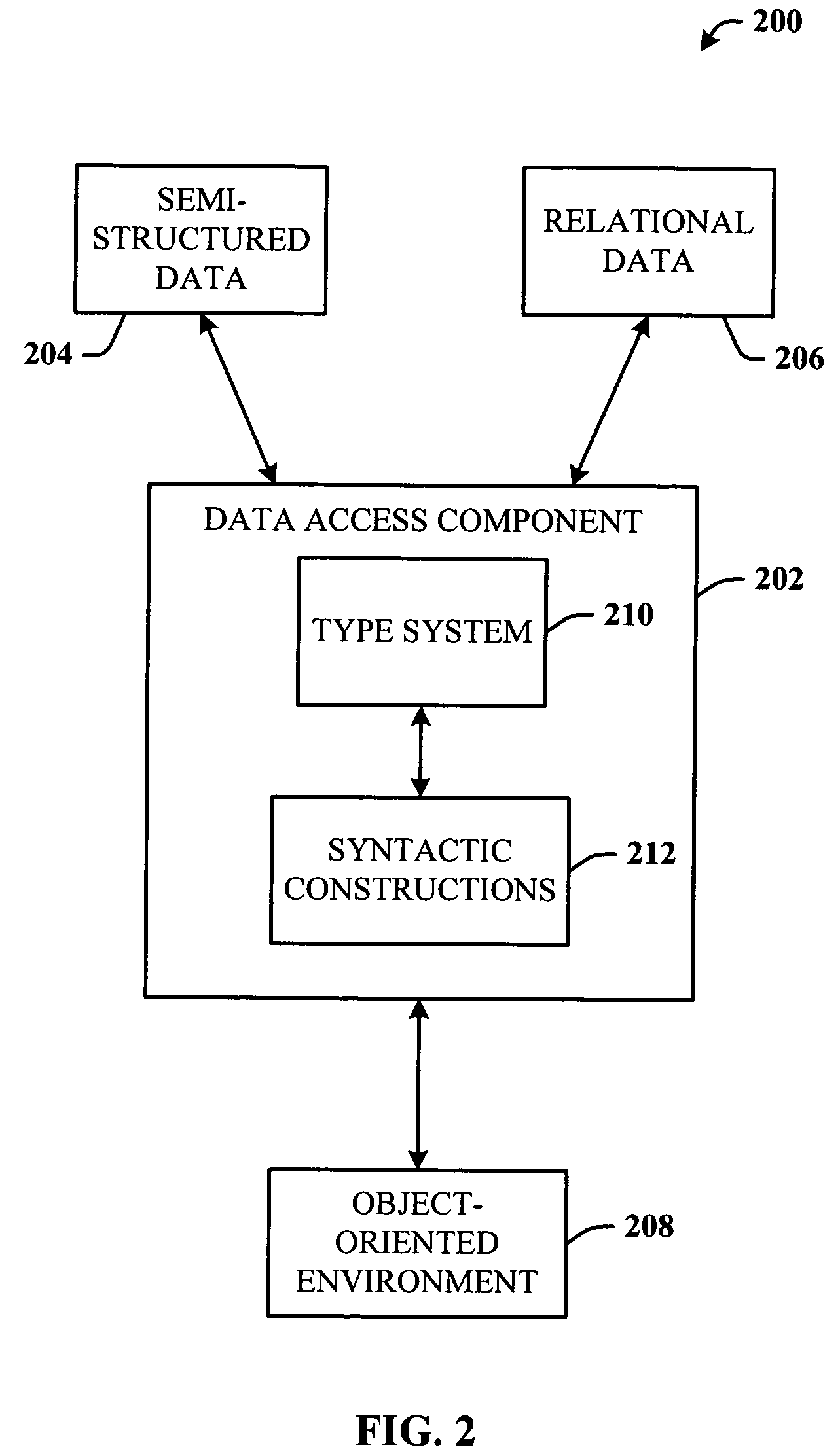
Core object-oriented type system for semi-structured data
InactiveUS7389498B2Improve abilitiesEnhance layeringError preventionSoftware engineeringSemi-structured dataValidation methods
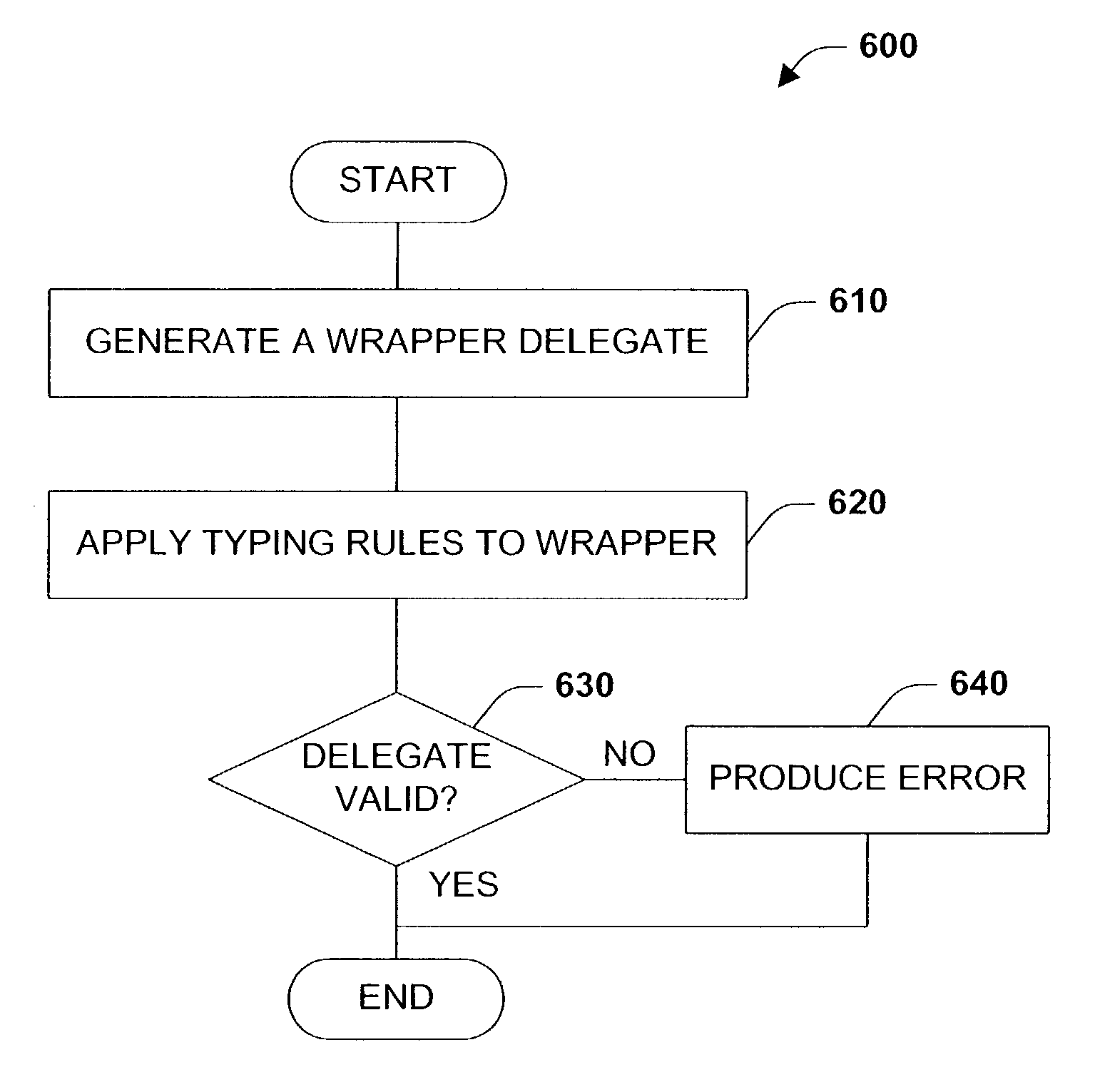
A type system employing structural subtyping is disclosed herein. A core type system supports several structural types, such as stream, choice, intersection and sequence. Also part of the core type system is a new invariant type, which denotes values whose dynamic type is the same as its static type, and type restrictions for limiting a range of a base type. Furthermore, a streamlined structural version of delegates, called structural delegates and a validation method thereof are introduce into the type system. To further facilitate type safety, strict statically checked interface casts are introduced.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods for Determining Heptocellular Carcinoma Subtype and Detecting Hepatic Cancer Stem Cells
InactiveUS20100197770A1Increased and decreased expressionOrganic active ingredientsElectrolysis componentsBiomarker (petroleum)Hepatic Cancers
The invention provides a method of determining an HCC subtype in a subject comprising a) obtaining a sample from the subject, b) assaying the sample to detect the expression of 1 or more biomarkers, and c) correlating the expression of the biomarkers with an HCC subtype in a subject. The invention further provides methods of detecting HCC stem cells in a sample. Additionally, the invention provides methods and compositions for treating subjects with HCC that take advantage of the biomarkers associated with HCC stem cells.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND +2
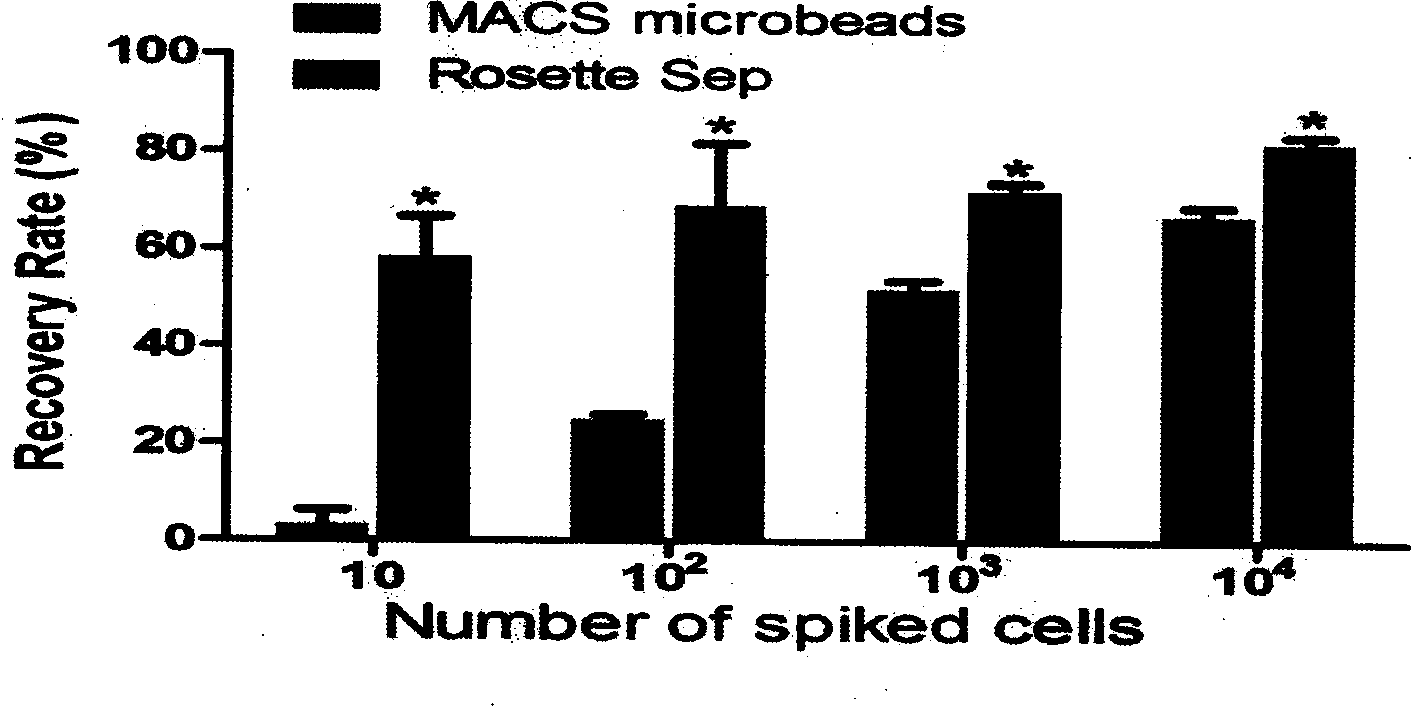
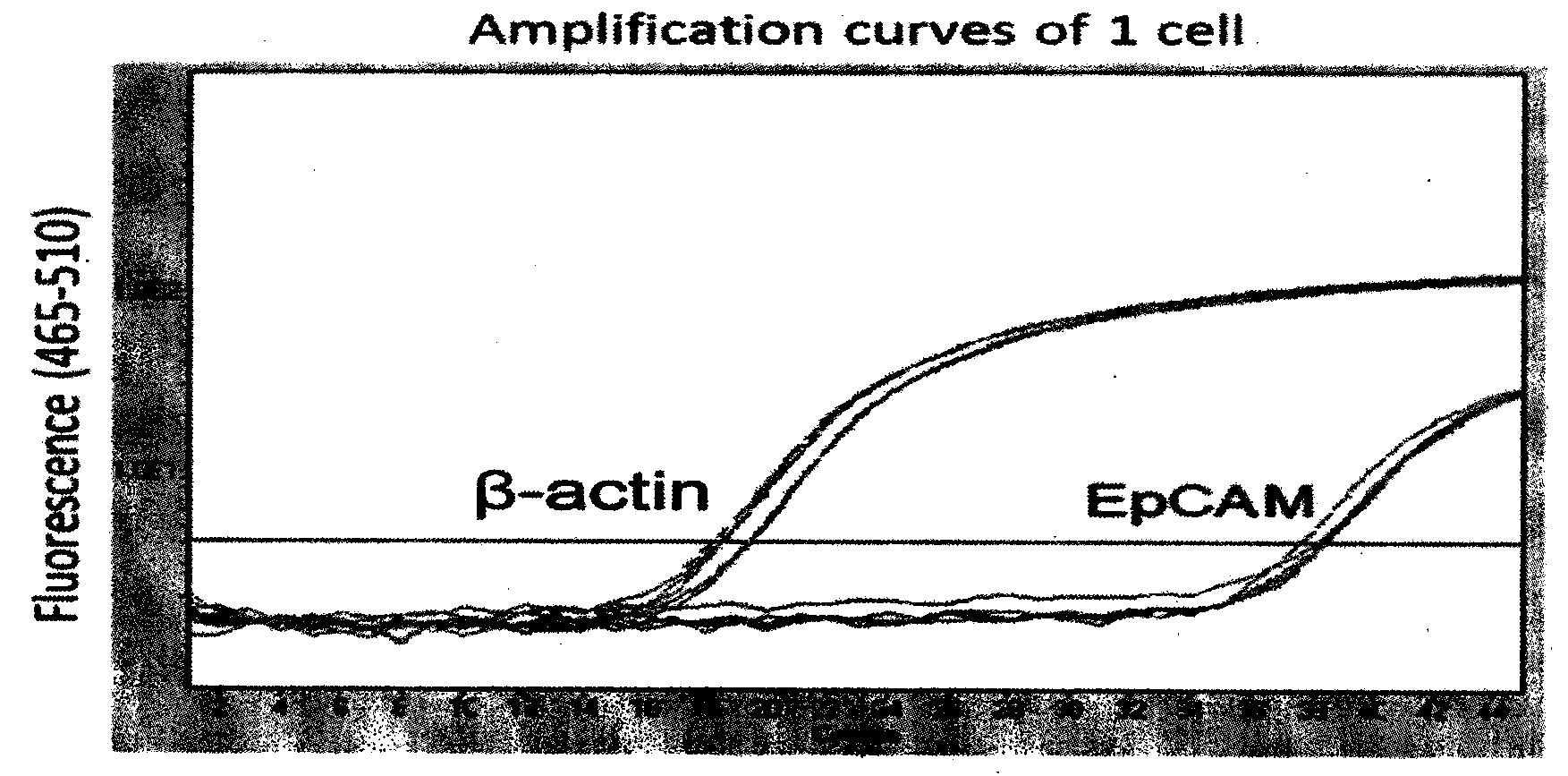
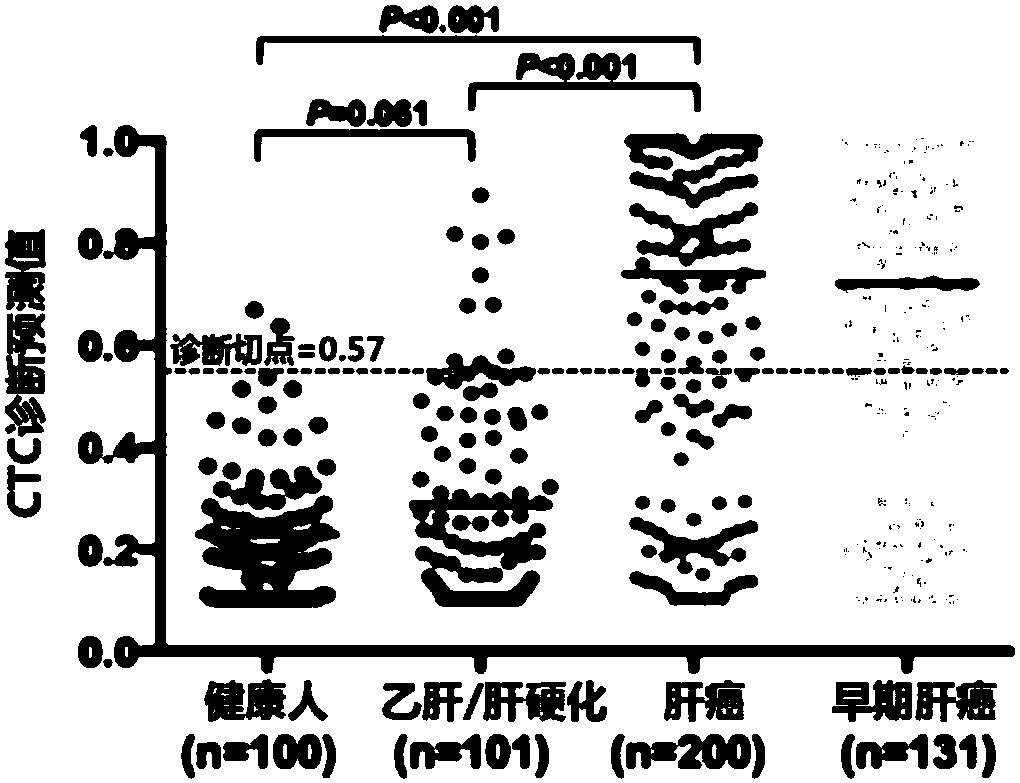
Circulating tumor cell detection kit and application thereof
InactiveCN105785005AAccurate detectionEfficient enrichmentMaterial analysisLymphatic SpreadFluorescence
The invention relates to a circulating tumor cell detection kit and application thereof. The circulating tumor cell detection kit comprises a chip, sample diluent, a cell separation fluid, a cell trapping agent, a cell cleaning solution, a cell fixing agent, antibody diluent, a cell penetration agent and a fluorescence dye. The application method of the circulating tumor cell detection kit mainly comprises the several steps of separation of circulating tumor cells, trapped antibody coating, trapping of the circulating tumor cells and immuno-fluorescent staining of the circulating tumor cells. The circulating tumor cell detection kit is mainly used for tumor prognosis, reappear, metastasis, curative effect monitoring, early diagnosis and early warning, monitoring of curative effect and tumor progression situation, and utilizes the molecular subtyping, screening specificity and other characteristics of the circulating tumor cells to conduct targeted research on circulating tumor cell sensitive drug so as to supplement tumor metastasis, relapse and drug resistance mechanisms and guide individualized medical treatment.
Owner:杭州华得森生物技术有限公司
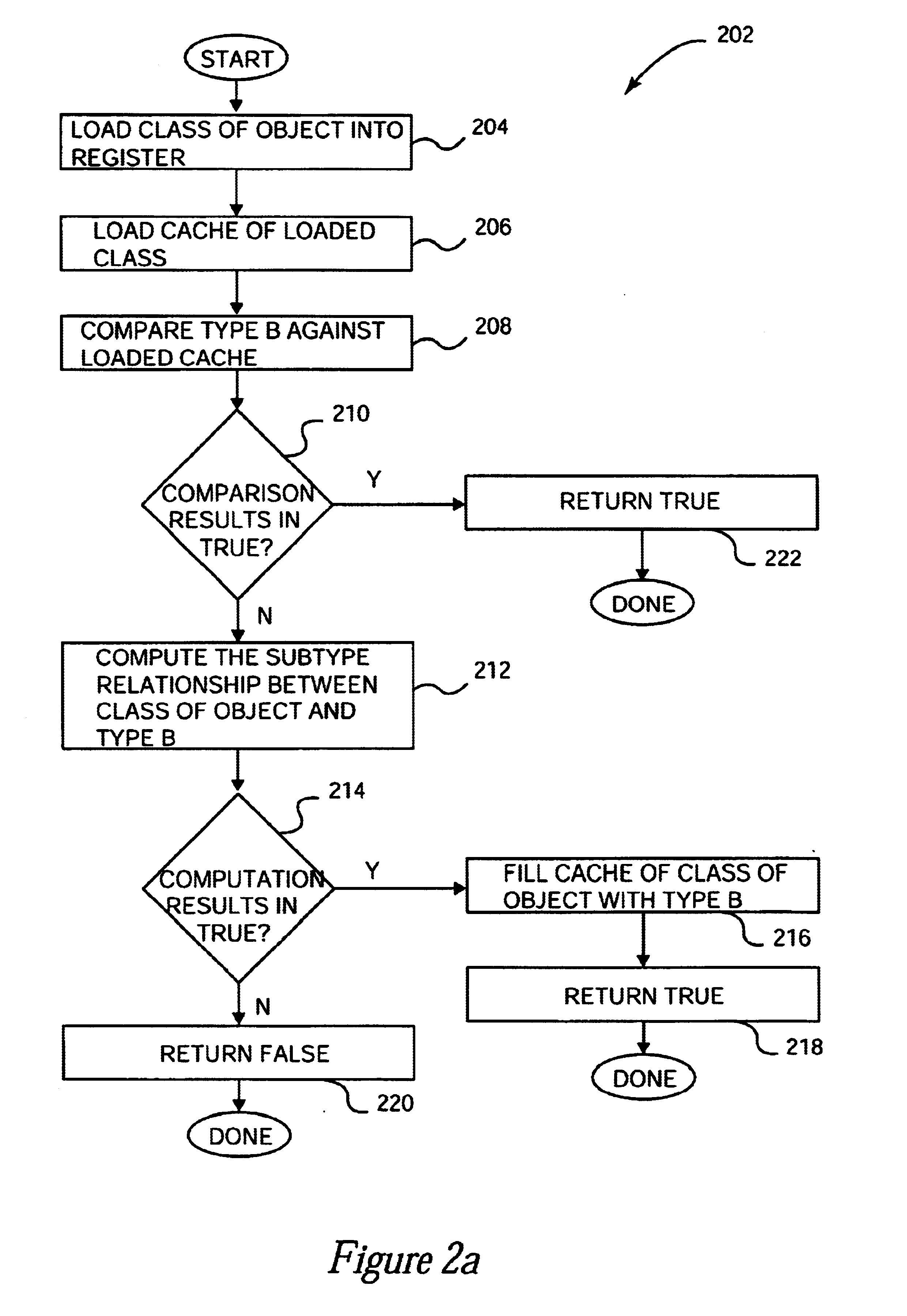
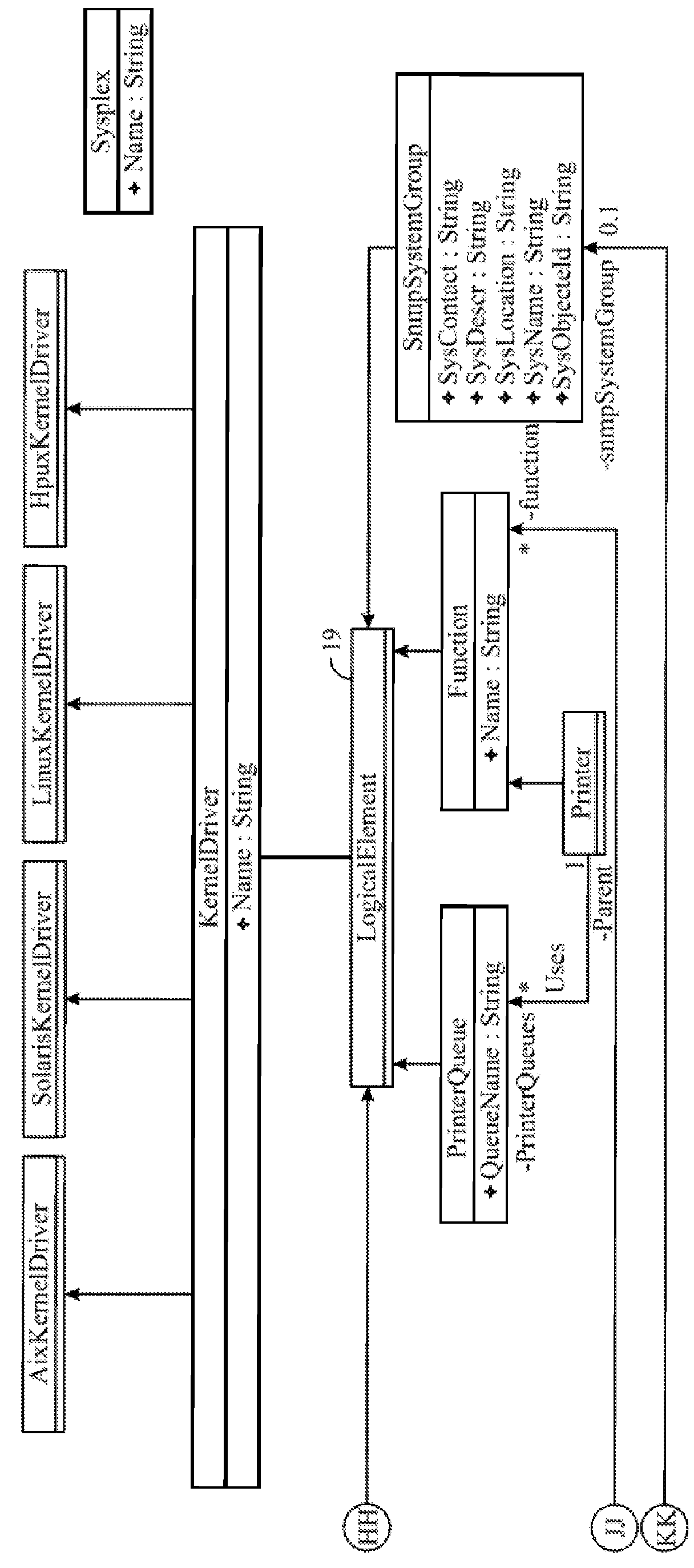
Method and apparatus for implementing fast subclass and subtype checks
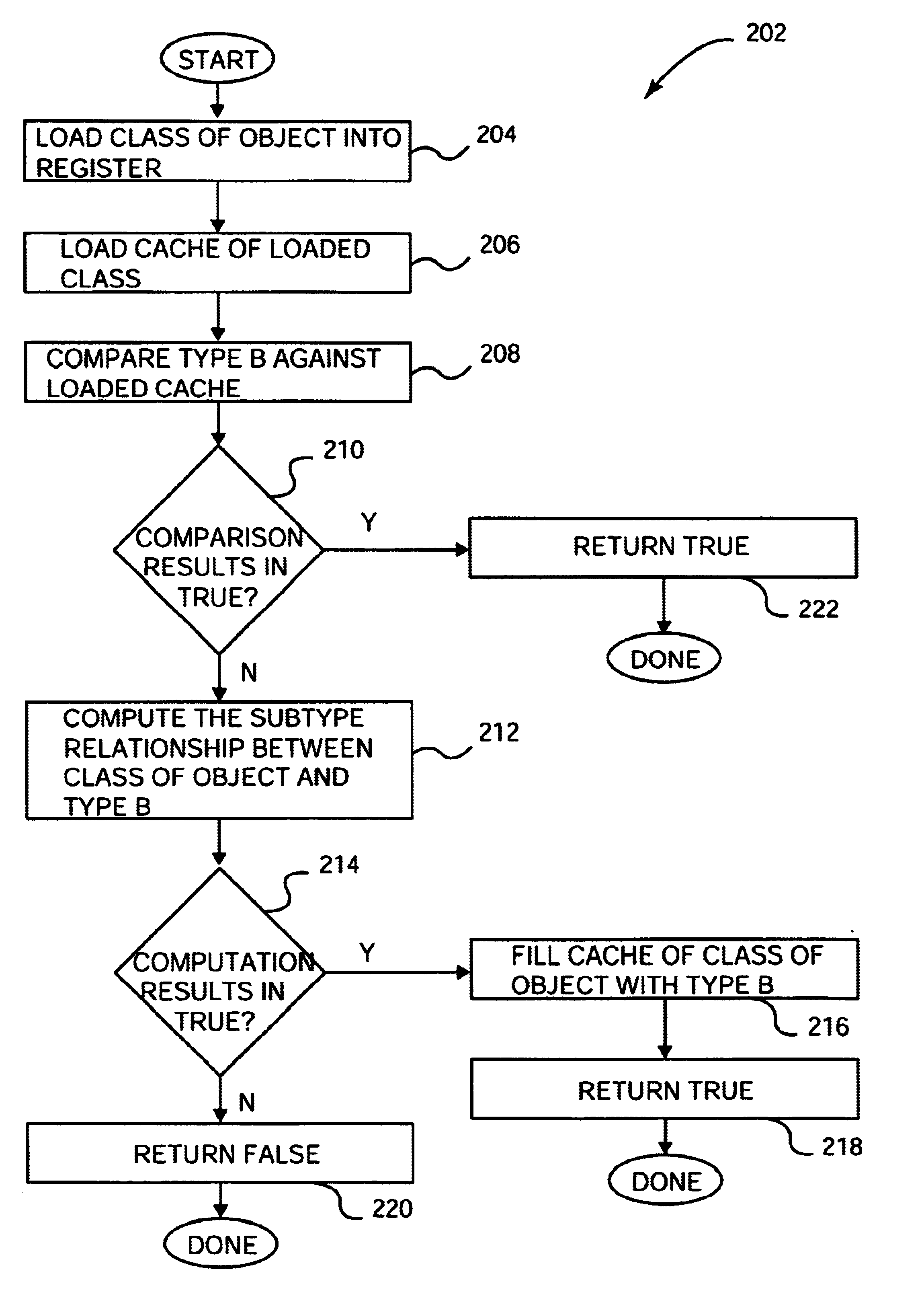
Methods and apparatus for performing fast subtype checks during program execution are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a method for determining whether a class associated with an object that is a part of an object-based computing system is a subtype of another type includes obtaining a candidate type from a dynamic storage location that is associated with a class which is associated with the object, and comparing the candidate type against a first type that is potentially the same as the candidate type. A determination is then made as to whether the candidate type is substantially equal to the first type. When the determination is that the candidate type is substantially equal to the first type, an indication that the candidate type is a subtype of the first type is provided. In one embodiment, the candidate type obtained from the dynamic storage location is obtained from a cache element in the class associated with the object.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Type-system extensions for object-oriented language based on coercive subtyping with restrictions
InactiveUS7774376B1Prevent problematic instantiationSoftware engineeringDigital data processing detailsIdentity transformSemi-structured data
A type system that facilitates seamless integration of data access to relational and semi-structured data in an object oriented host language. A data access component includes the type system and corresponding set of syntax constructions that facilitates coercive subtyping and restricts covariance to identity conversions.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Group of genes for tumor molecular subtyping and application thereof
ActiveCN105087568AImprove living conditionsRealize personalized medicineNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementAGR2Cancer type
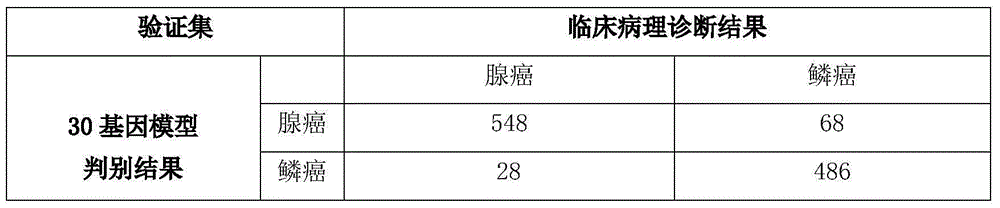
The invention discloses a group of genes for tumor molecular subtyping. The group of genes includes 38 genes such as an ACPP gene and an AGR2 gene. Moreover, the invention further discloses a kit for tumor molecular subtyping and application of the kit. The group of genes is beneficial to the recognition of the tissue sources of tumors. After a tumor sample is obtained, the tissue source and cancer type of the tumor sample can be judged objectively and accurately through detection and conjoint analysis of the gene group, so that a patient can be treated specifically.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUANQING BIOTECH CO LTD
External system integration into automated attribute discovery
Methods and apparatus to transform attribute data about assets in a source system data model into attribute data about the same assets in a target system data model. The first step is to extract the necessary attribute data from attribute data collected about inventory assets of a business entity needed to populate the attributes in objects representing those inventory assets in a target system data model. Transformation rules are written which are designed to make all conversions necessary in semantics, units of measure, etc. to transform the source system attribute data into attribute data for the target system which has the proper data format. These transformation rules are executed on a computer on the extracted attribute data and the transformed attribute data is stored in an ER model. In the preferred embodiment, the transformation rules are object-oriented in that transformation rules for subtypes can be inherited from their parent types or classes. An export adapter which is capable of invoking the application programmatic interface of the target system CMDB is then used to export the transformed attribute data stored in the ER model to the target system CMDB.
Owner:BNDENA
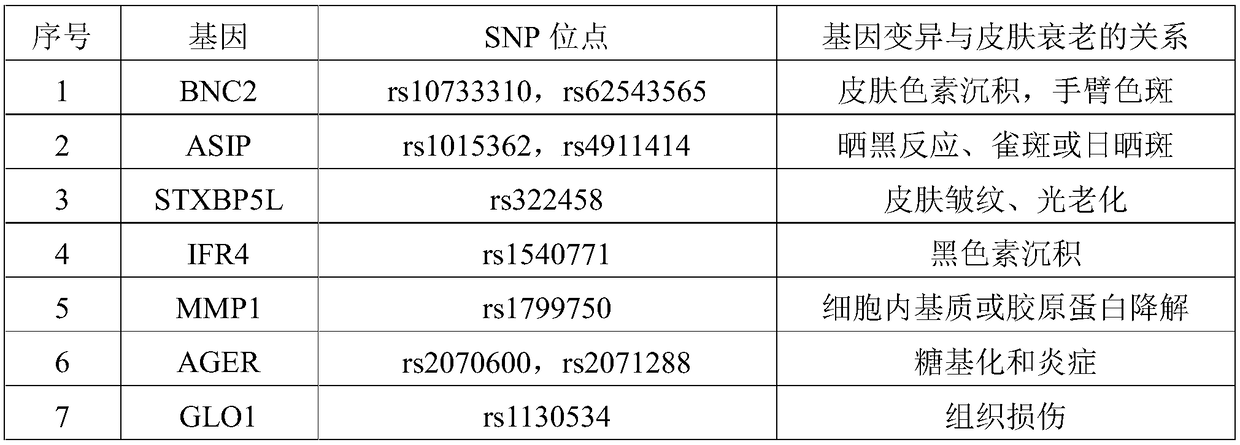
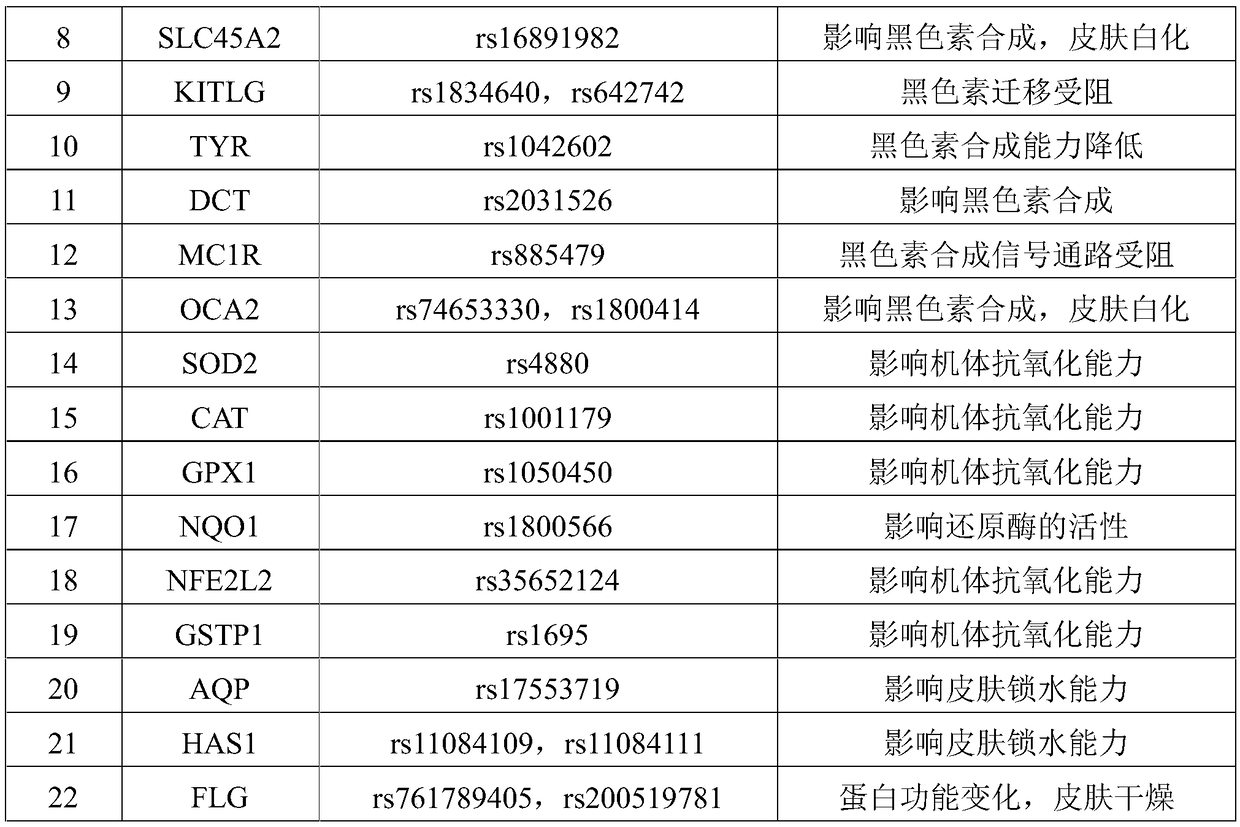
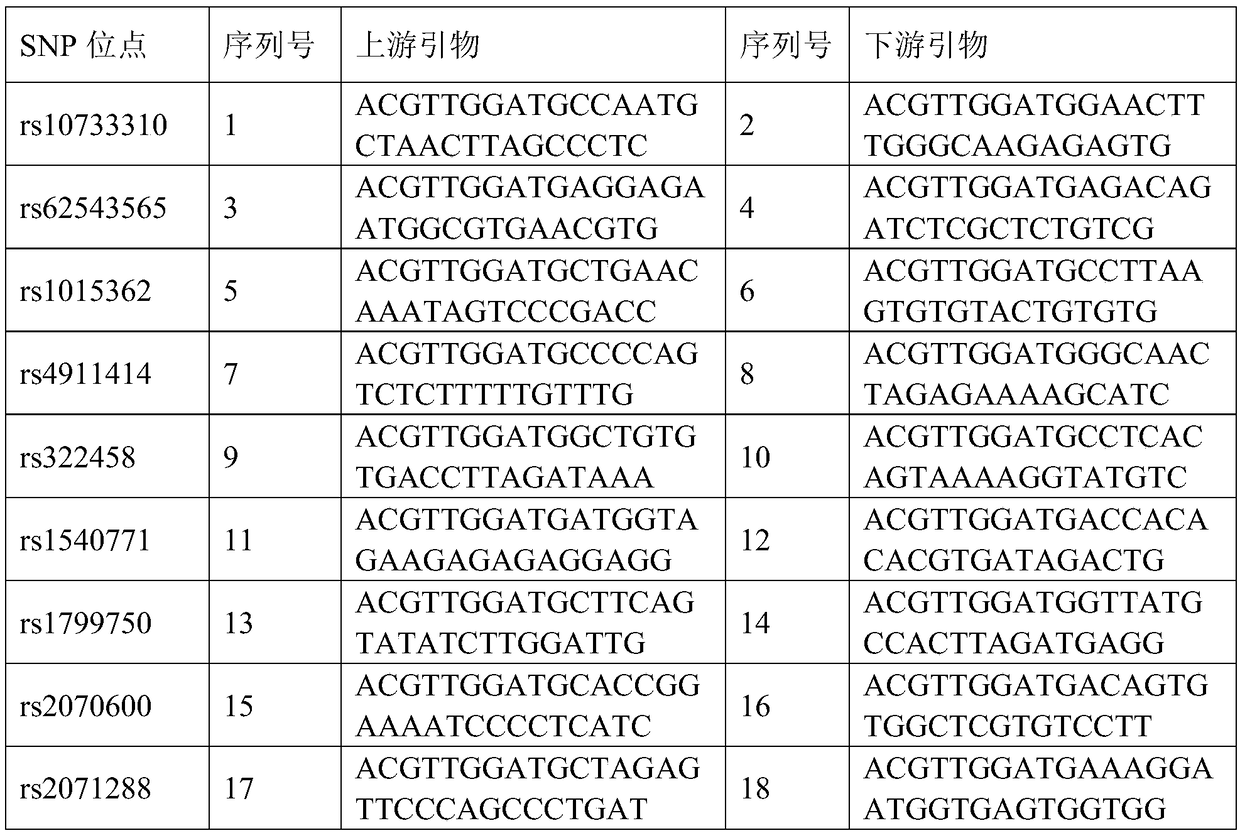
Complete-set primer applied to detecting of skin aging related susceptible genes SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) and application thereof
InactiveCN108251521AComprehensive Skin Genetic Testing ProgramReduce operational complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHuman DNA sequencingTime-of-flight mass spectrometry
The invention relates to a complete-set primer applied to detecting of skin aging related susceptible genes SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) and application thereof. The complete-set primer is prepared from amplification primer pairs of 29 SNP sites of 22 skin aging related susceptible genes of human genome DNA and extension primers; a pair of multiple PCR amplification primers and a piece ofsingle-base extension primer are designed for each site respectively, and an MALDI-TOF MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry) method is utilized to detect SNP site genotyping of a sample to be detected. The skin aging related susceptible gene detecting method based on gene molecular subtyping disclosed by the invention can finish a plurality of SNP genotyping in the same reaction at the same time, so that accuracy, high efficiency and low cost are achieved. The gene detection disclosed by the invention can be applied to predicting of congenital agingresistance of the skin; thus, a scientific basis is provided for an external skin care scheme.
Owner:北京天平永达生物科技发展有限公司
Circulating tumor cell detection kit and application thereof
ActiveCN103866016AAvoid interferenceUse less bloodMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividualized treatmentFluorescence
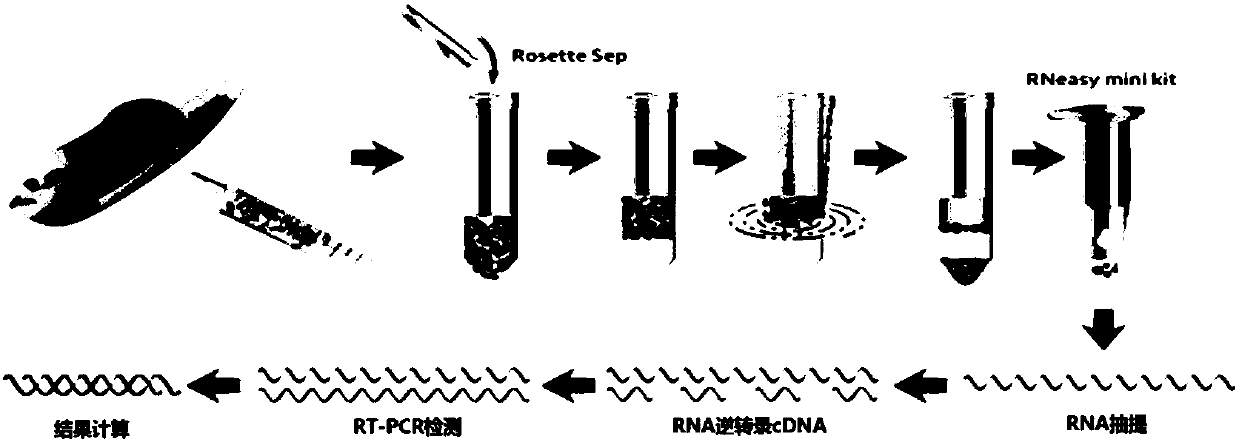
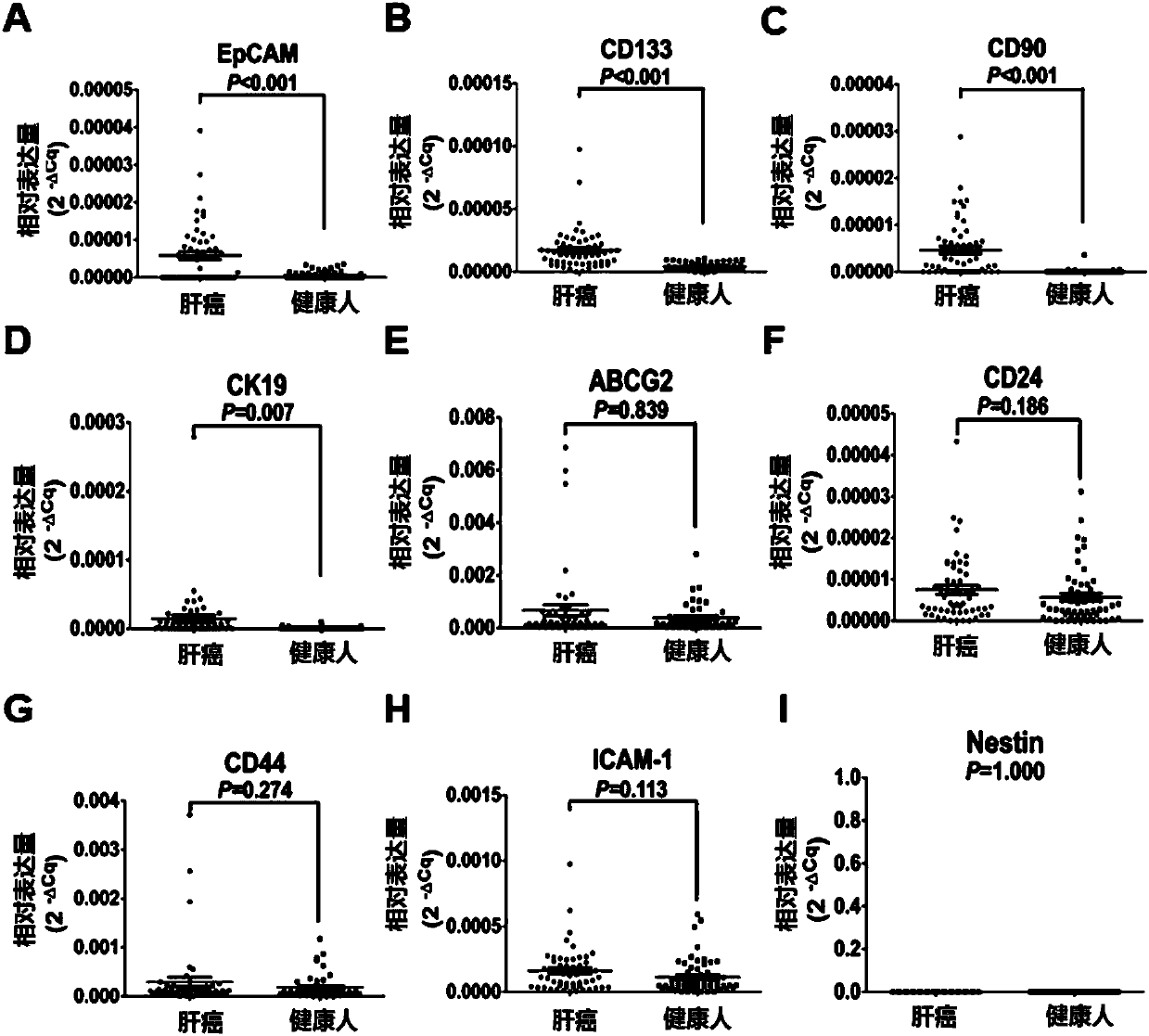
The invention provides a circulating tumor cell detection kit and an application thereof. The circulating tumor cell detection kit is characterized by comprising a RosetteSep rare cell enriching reagent, an RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) extraction reagent, an RNA reverse transcription reagent, a fluorescence labeling Taqman probe, a specific primer and a qPCR (Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) reaction system reagent. The kit can be applied to tumor patient minimally invasive liquid biopsy, early diagnosis and early warning on tumor metastasis and reappearance are achieved, the curative effect in antineoplaston and the tumor development situation are monitored, molecular subtyping based on circulating tumor cells is achieved, and sensitive medicines which specifically aim at the circulating tumor cells are selected, understanding about tumor metastasis, replase and relevant medicine resistance mechanisms is improved, and individualized treatment on tumor patients is guided, so that the total survival of tumor patients is remarkably improved, and great clinical significance is achieved.
Owner:上海顿慧医疗科技发展有限公司 +1
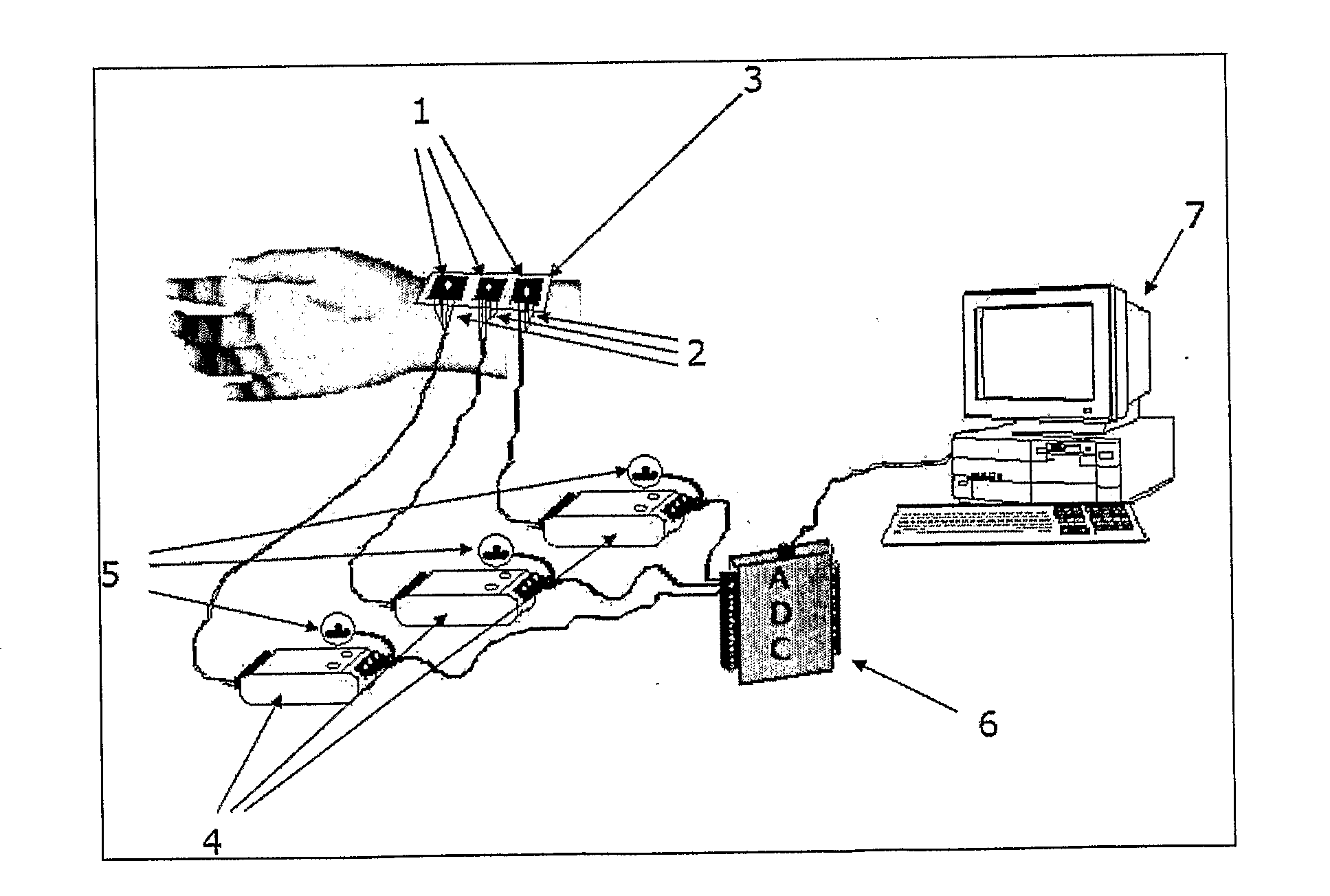
Non-invasive device nadi tarangini useful for quantitave detection of arterial nadi pulse waveform
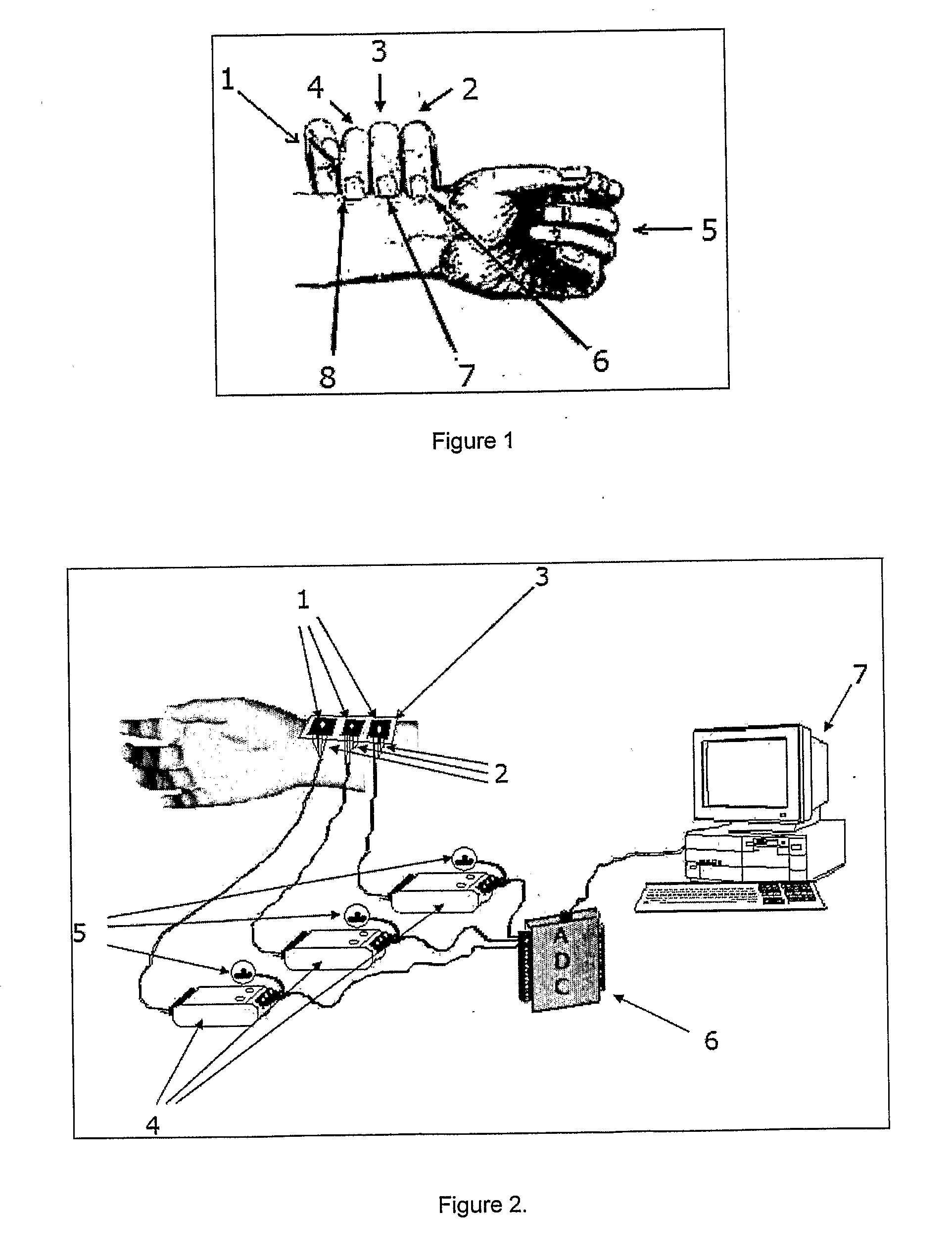
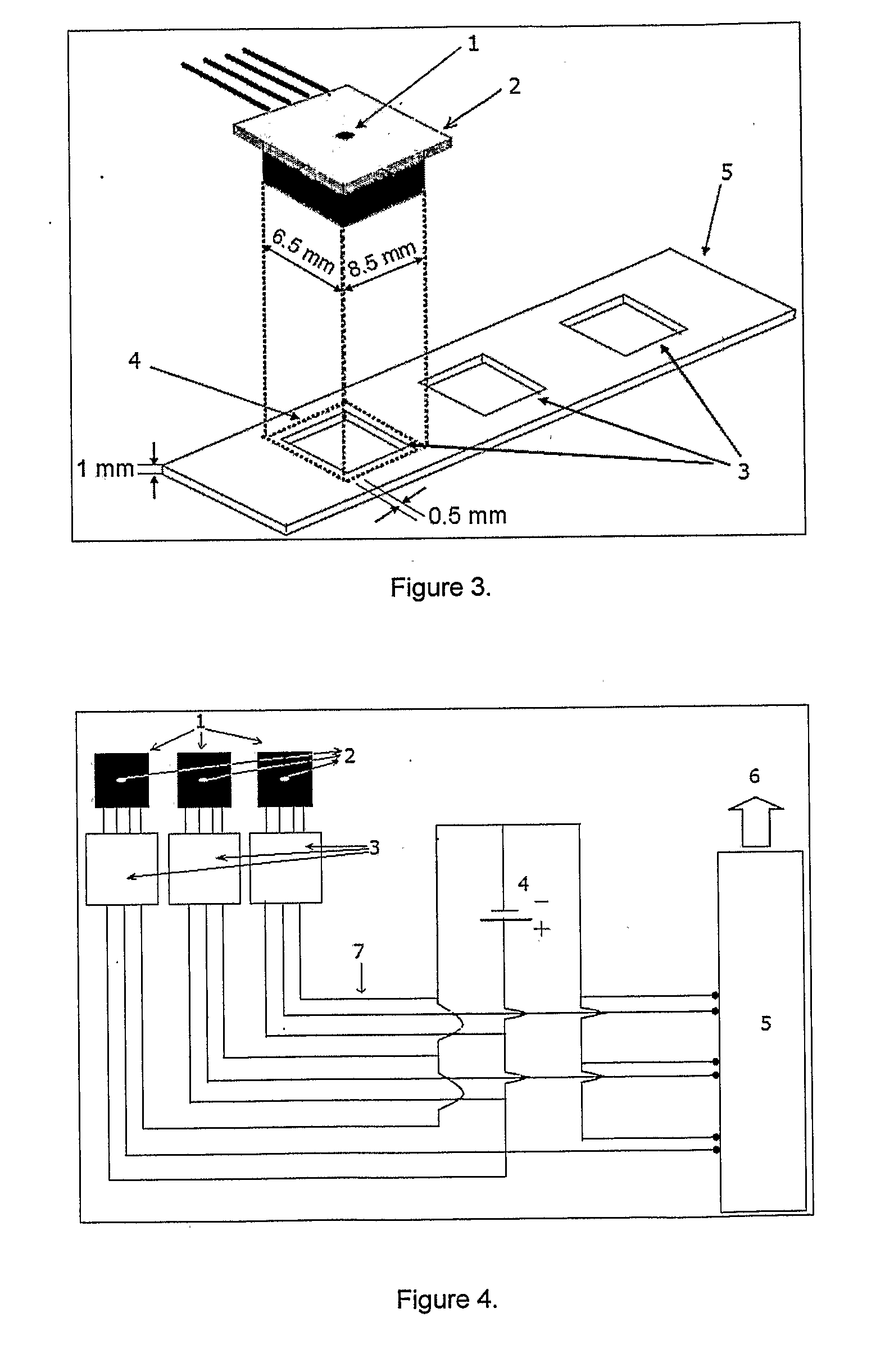
InactiveUS20100152594A1Inexpensive and convenientEliminate errorsEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterSpiritual HealthNon invasive
The present invention discloses the procedure for obtaining complete spectrum of the Nadi pulses, as a time series and capable of detecting the major types and the subtypes of the Nadi pulses. The device of this invention involves three diaphragm elements equipped with strain gauge, three transmitters cum amplifiers, and a digitizer for quantifying analog signal. The system acquires the data with 12-bit accuracy with practically no electronic and / or external interfering noise. The pertaining proofs are given which clearly shows the capability of delivering the accurate spectrums, with repeatability of the pulses from the invented system. ‘Nadi-Nidan’ is a prominent method in Ayurveda (Ayurveda is a Sanskrit word derived from ‘Ayus’ and ‘vid’, meaning life and knowledge respectively. It is a holistic science encompassing mental, physical and spiritual health), which is known to dictate all the salient features of a human body. Nadi-Nidan is a specialty of ‘Vaidyas’ (Ayurvedic physicians) and hence the present system would enable the diagnosis accurately, quantitatively and independent of any human errors.
Owner:BHAT ASHOK +5
Molecular subtyping of oral squamous cell carcinoma to distinguish a subtype that is unlikely to metastasize
InactiveUS20130225420A1Significant likelihoodMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningSquamous CarcinomasDentistry
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Group of genes for lung cancer molecular subtyping and application thereof
ActiveCN105154542APrecision therapyImprove survival rateNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementJoint analysisGenome
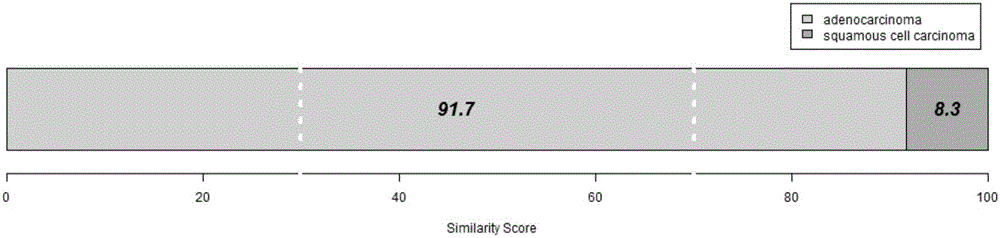
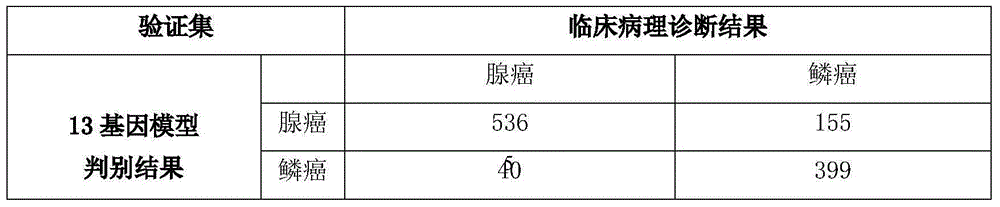
The invention discloses a group of genes for lung cancer molecular subtyping. The group of genes for lung cancer molecular subtyping comprises thirteen genes such as a COMP gene and an FXYD3 gene. Besides, the invention further discloses a kit for lung cancer molecular subtyping and application thereof. The genes, the kit and the application thereof can facilitate differential diagnosis of lung cancer subtypes, the subtypes of lung cancers can be objectively and accurately discriminated by performing detection and joint analysis to the gene group after lung cancer samples are obtained, and thereby pertinent treatment can be performed to patients.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUANQING BIOTECH CO LTD
Gene chip for detection and typing of bird flu virus
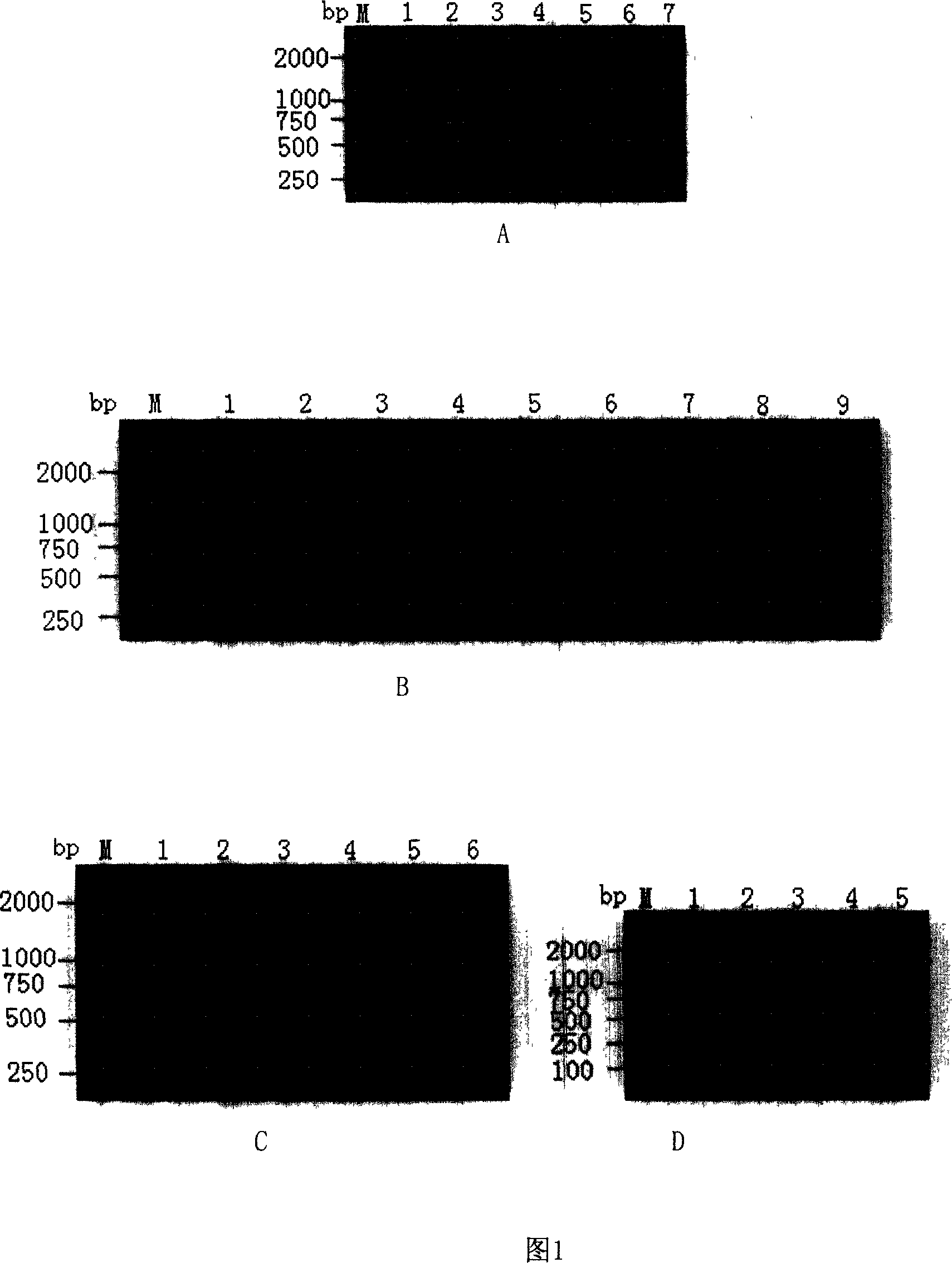
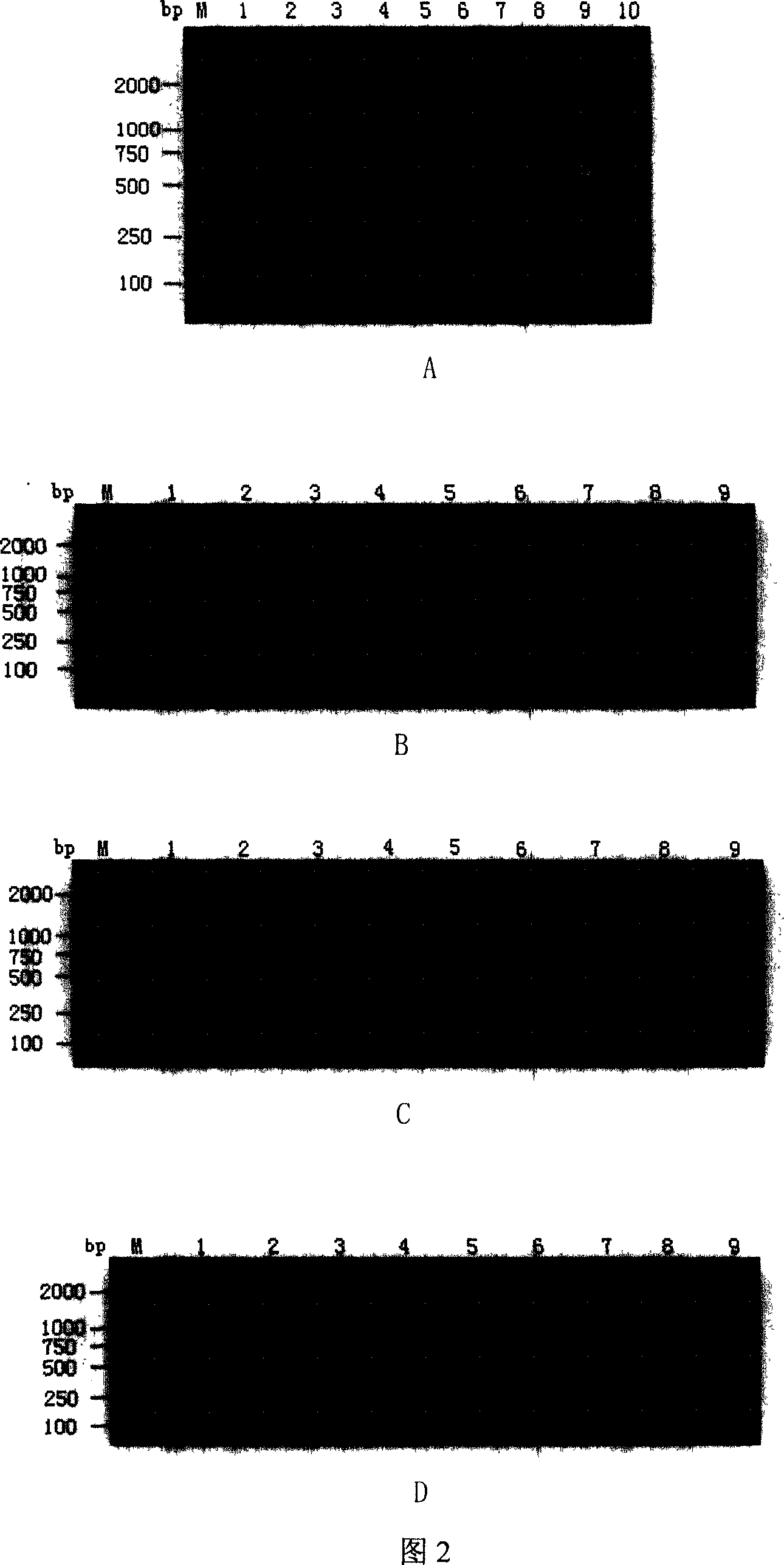
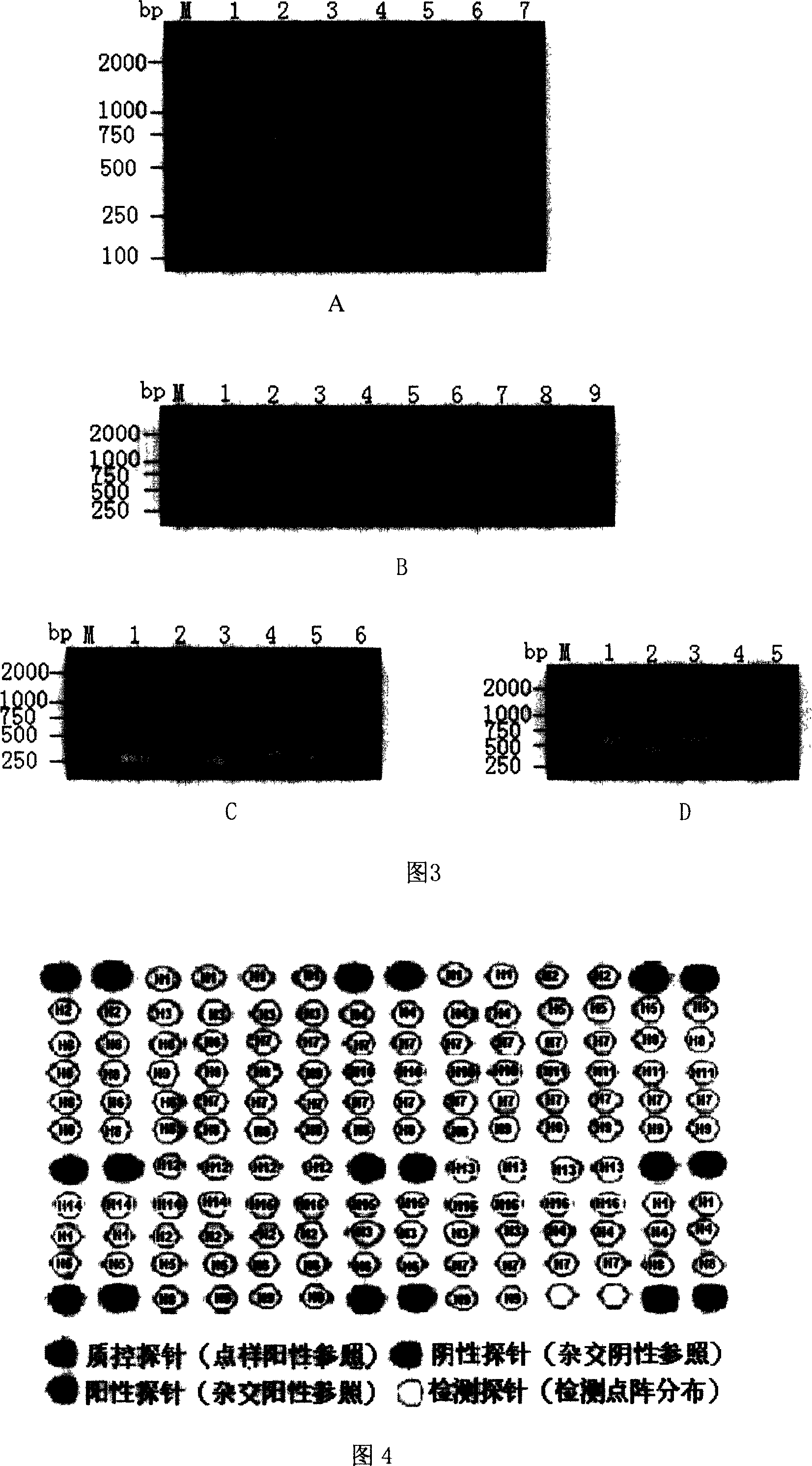
The present invention relates to gene chip for the detection and subtyping of bird flu virus. The present invention establishes gene chip with high specificity, high sensitivity and great practicability for detection and subtyping of bird flu virus through designing and screening 50 pairs of specific primers, 2 universal primers, 52 specific probes and 3 quality control probes for the multiple RT-PCR subtyping detection of bird flu virus genes based on the gene sequences of different bird flu virus subtypes Genebank reports; and performing the effectiveness test, specificity test, sensitivity test and condition optimization of gene chip detection. The present invention establishes also the detection and subtyping process with the chip and gives the initial application.
Owner:中国检验检疫科学研究院动植物检疫研究所
Method for the amplification of HLA class I alleles
InactiveUS20020197613A1Simple methodImprove methodMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationForward primerIntein
The present invention relates to a method and to specific primers for the locus-specific, separate amplification of exon 2, exon 3 and / or exon 4 of HLA-A, HLA-B or HLA-C alleles, making use of at least one primer set wherein: for the amplification of exon 2, the reverse primer specifically hybridizes to a locus-specific target sequence in intron 2 of respectively HLA-A, HLA-B or HLA-C; for the amplification of exon 3, the forward primer specifically hybridizes to a locus-specific target sequence in intron 2 of respectively HLA-A, HLA-B or HLA-C and / or the reverse primer specifically hybridizes to a locus-specific target sequence in intron 3 of respectively HLA-A, HLA-B or HLA-C; for the amplification of exon 4, the forward primer specifically hybridizes to a locus-specific target sequence in intron 3 of respectively HLA-A, HLA-B or HLA-C. In accordance, the present invention provides an improved method for the typing or subtyping of HLA Class I alleles making use of the amplification method of the invention.
Owner:INNOGENETICS NV
A group of genes for molecular subtyping of renal cell carcinoma and application of genes
ActiveCN107723368AImprove survival ratePrecision medicineMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFOSBSERPINA5 gene
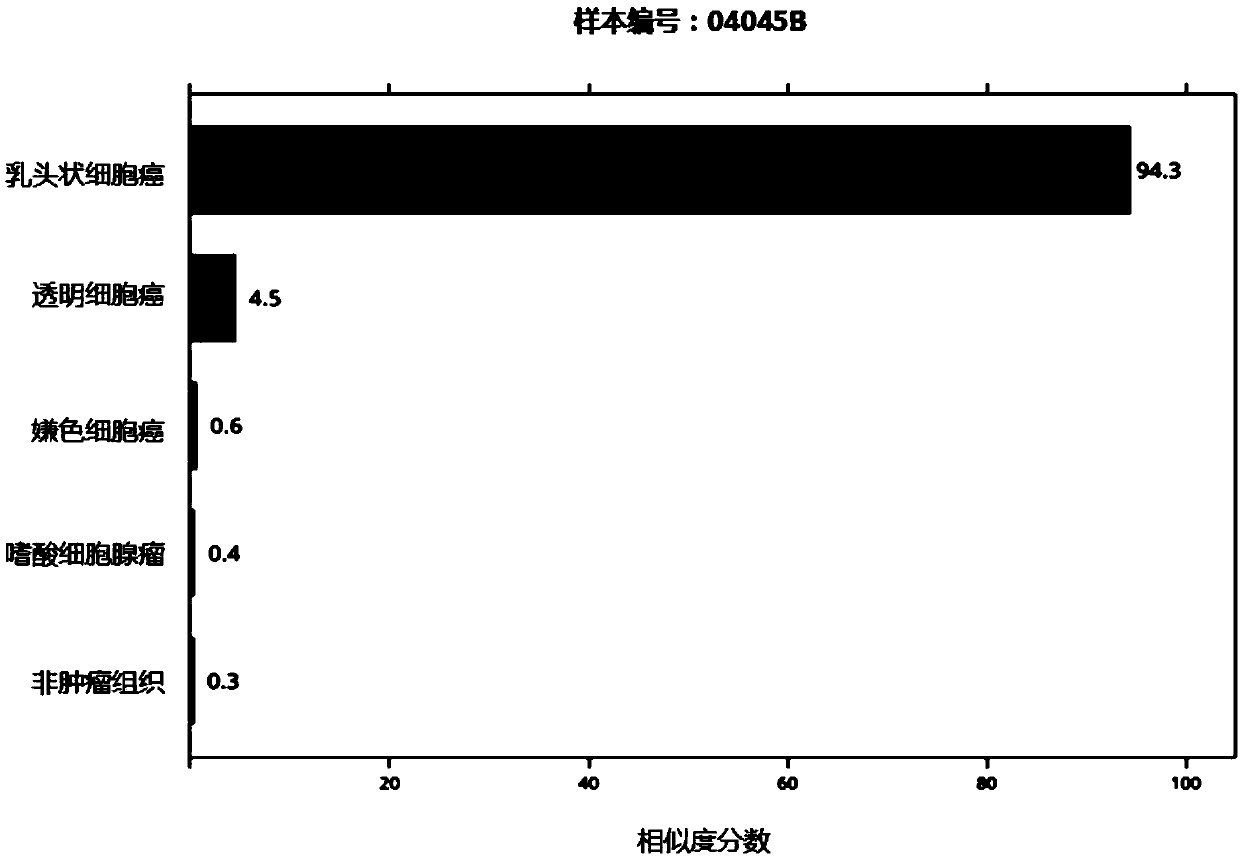
The invention discloses a group of genes for molecular subtyping of renal cell carcinoma and an application of the genes. The group of genes include 44 genes as follows: RHCG gene, RNF128 gene, TMEM255A gene, PCP4 gene, DHRS2 gene, CLDN8 gene, AQP6 gene, SLC18A2 gene, KRT7 gene, SERPINA5 gene, SFTPB gene, DEFB1 gene, MAL gene, ANGPTL4 gene, LCN2 gene, PLIN2 gene, ZNF395 gene, TACSTD2 gene, NDUFA4L2 gene, NNMT gene, HILPDA gene, UMOD gene, SLC12A1 gene, CALB1 gene, C7 gene, S100A2 gene, ASS1 gene, MT1G gene, ABCA8 gene, FOSB gene, MAOB gene, STAP1 gene, TFPI2 gene, AKR1C2 gene, IGFBP6 gene, VCAN gene, FLRT3 gene, MMP7 gene, GSTA1 gene, CRYAB gene, PAH gene, IGFBP1 gene, ATP6V0A4 gene and ALDOB gene. Based upon verification, it is proved that the genes can be used for accurately distinguishing oncocytic adenom, clear cell carcinoma, papillary cell carcinoma chromophobe renal carcinoma; the genes are broad in application scope, high in accuracy rate and short in experimental cycle; and the genes can achieve an important clinical significance for the precise treatment of a patient.
Owner:HANGZHOU CANHELP GENOMICS TECH CO LTD
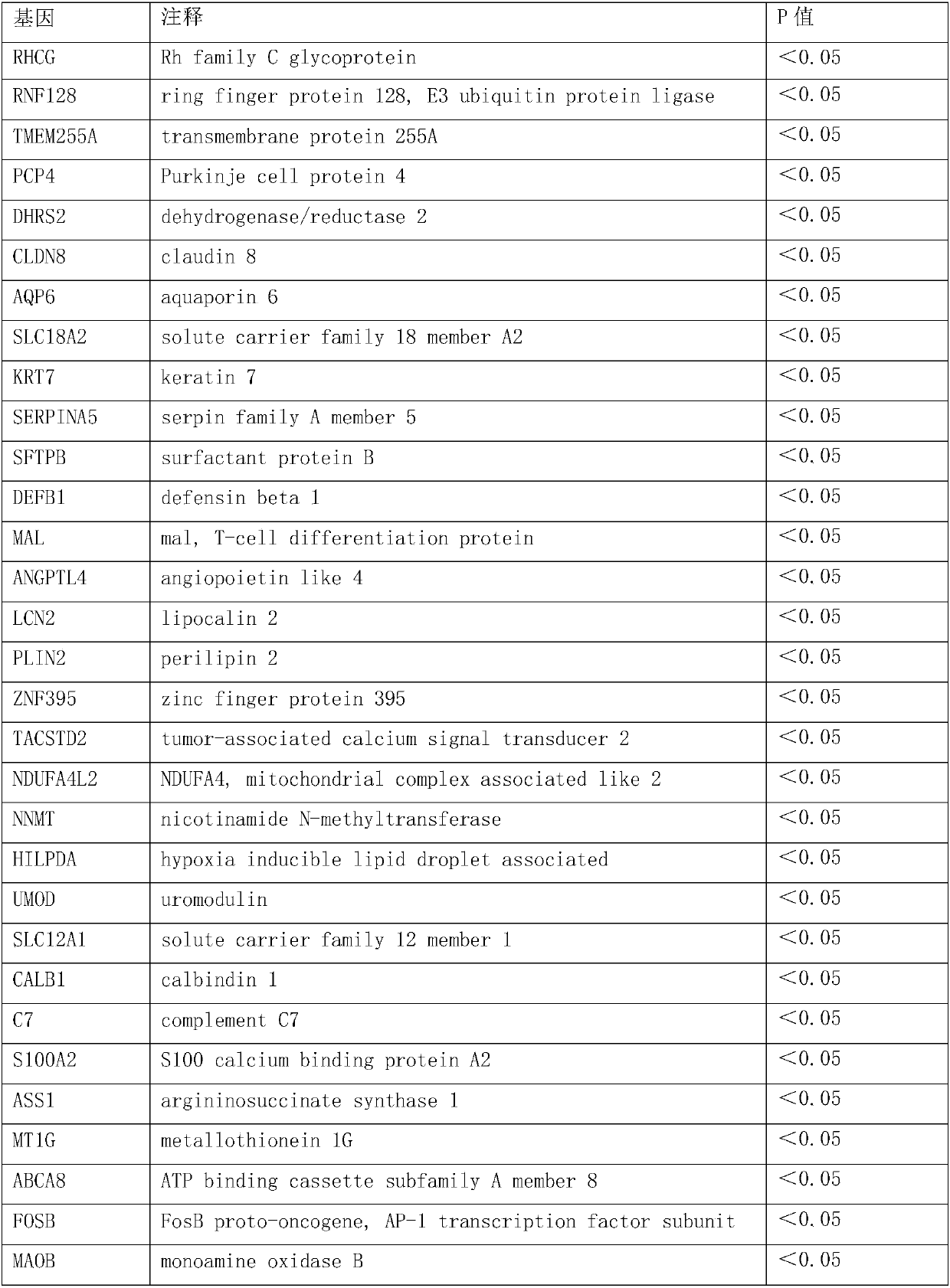
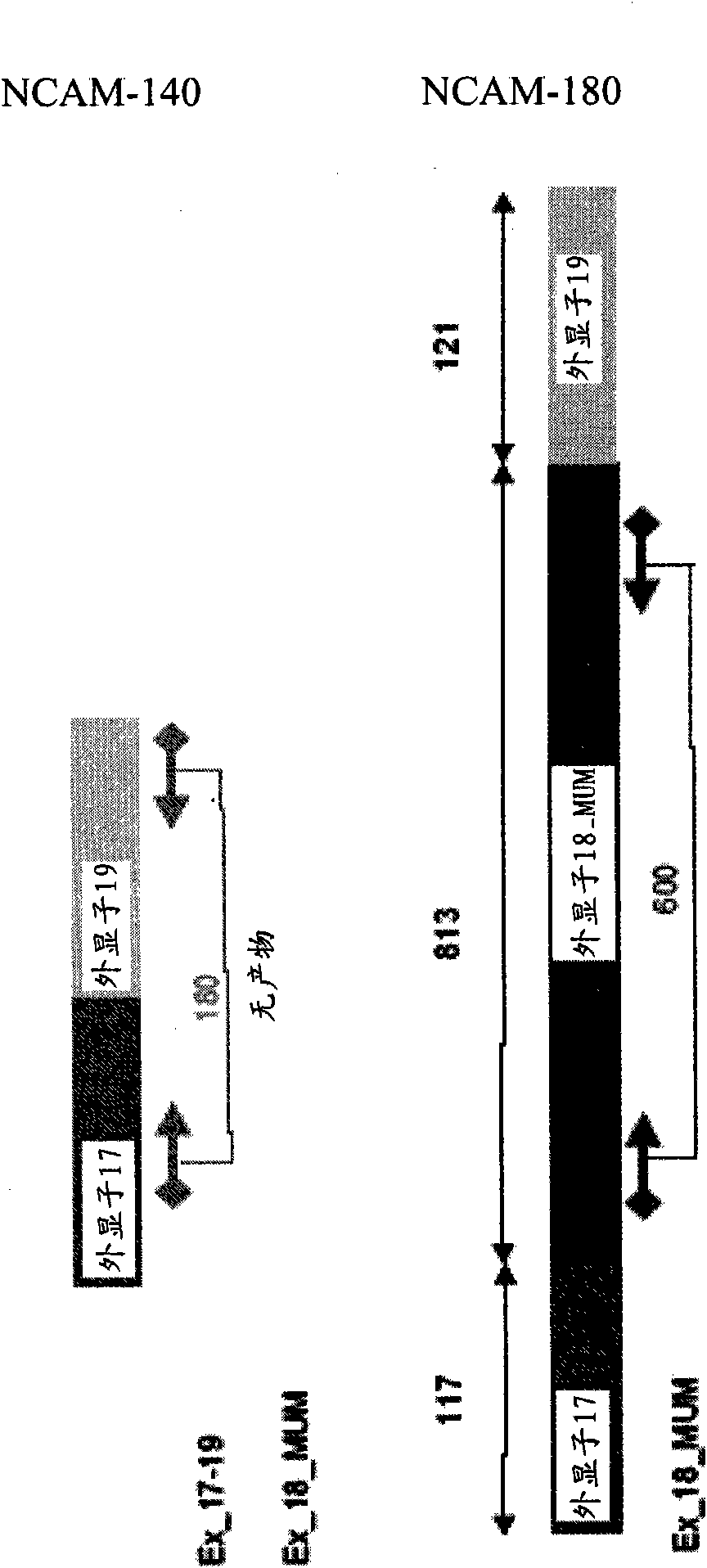
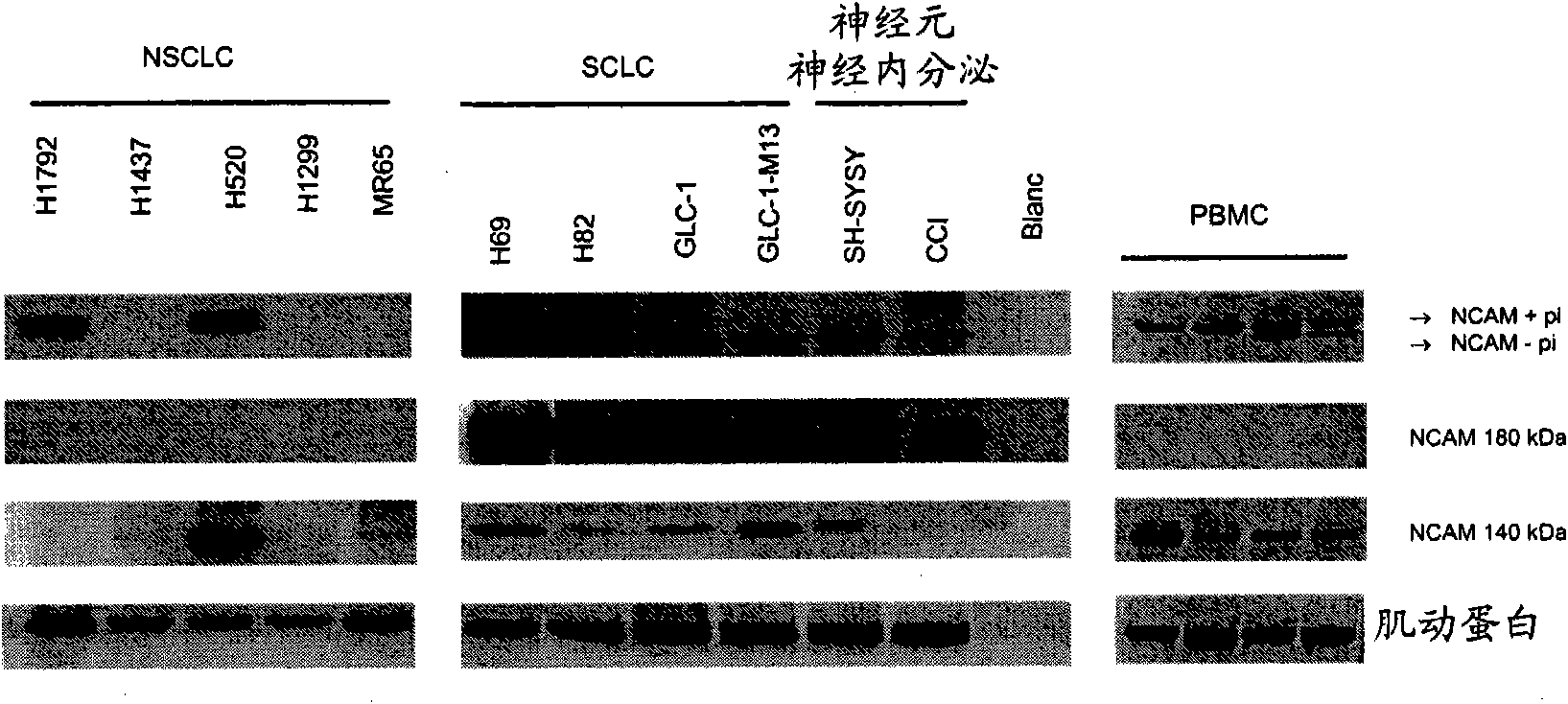
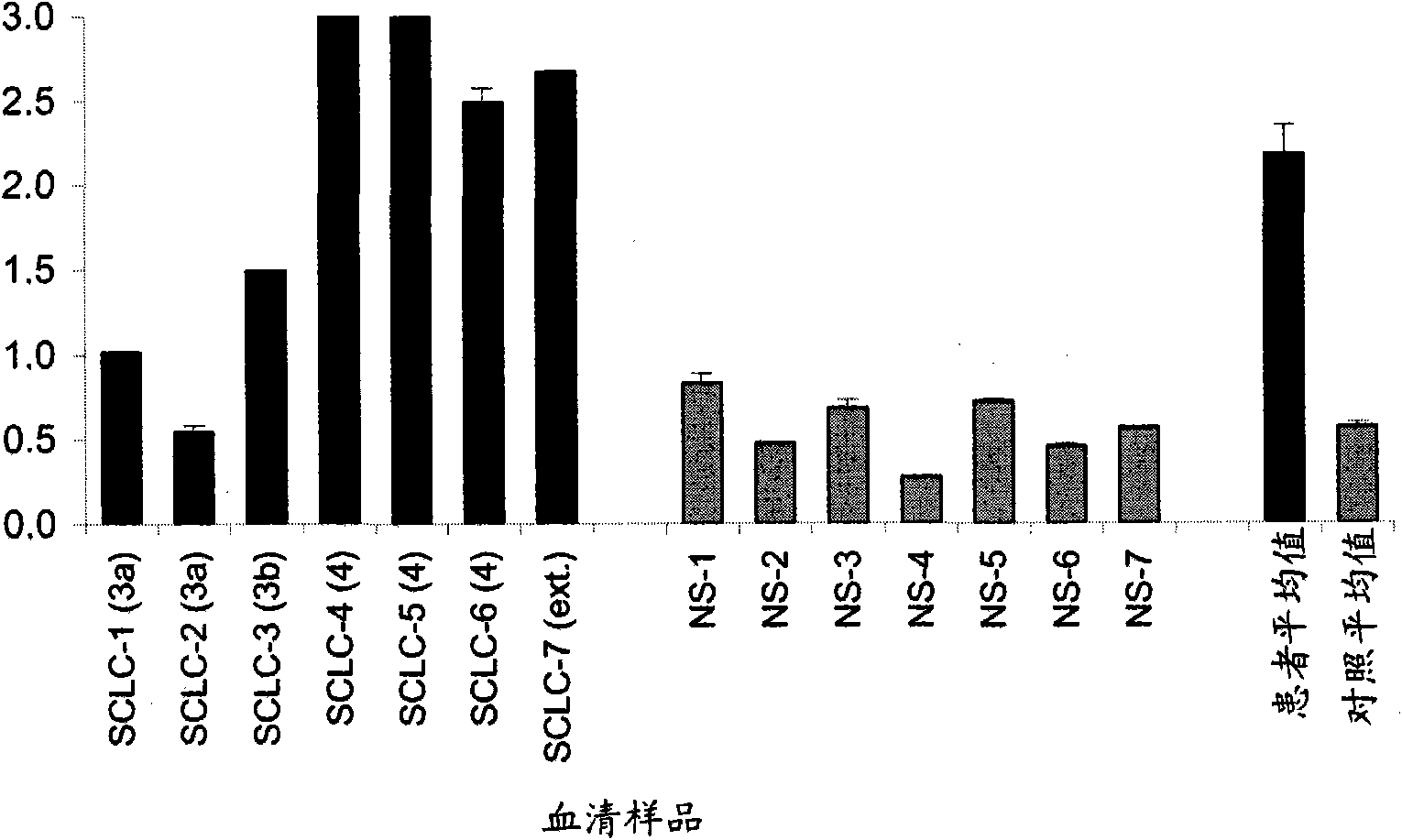
Small cell lung carcinoma biomarker panel
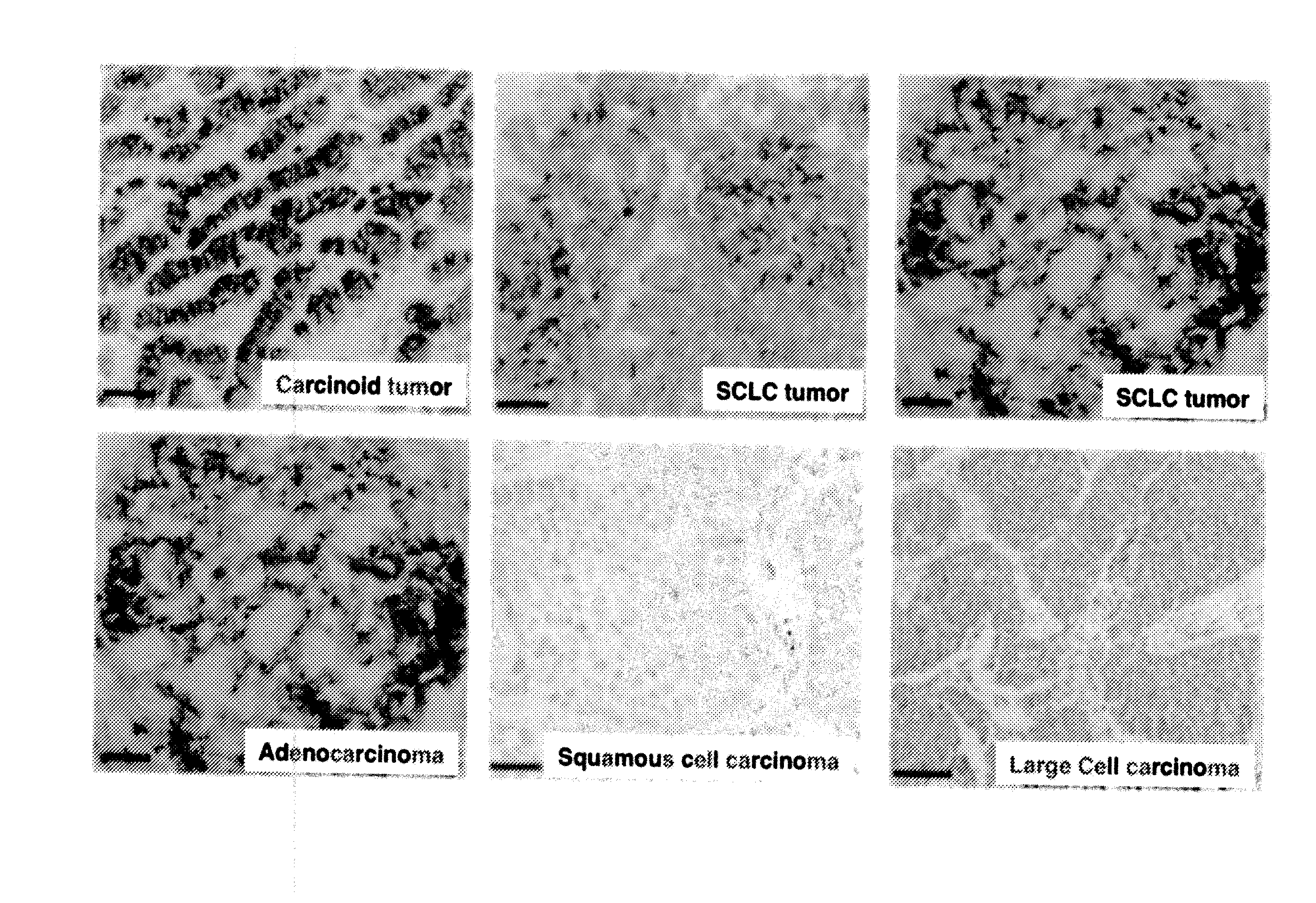
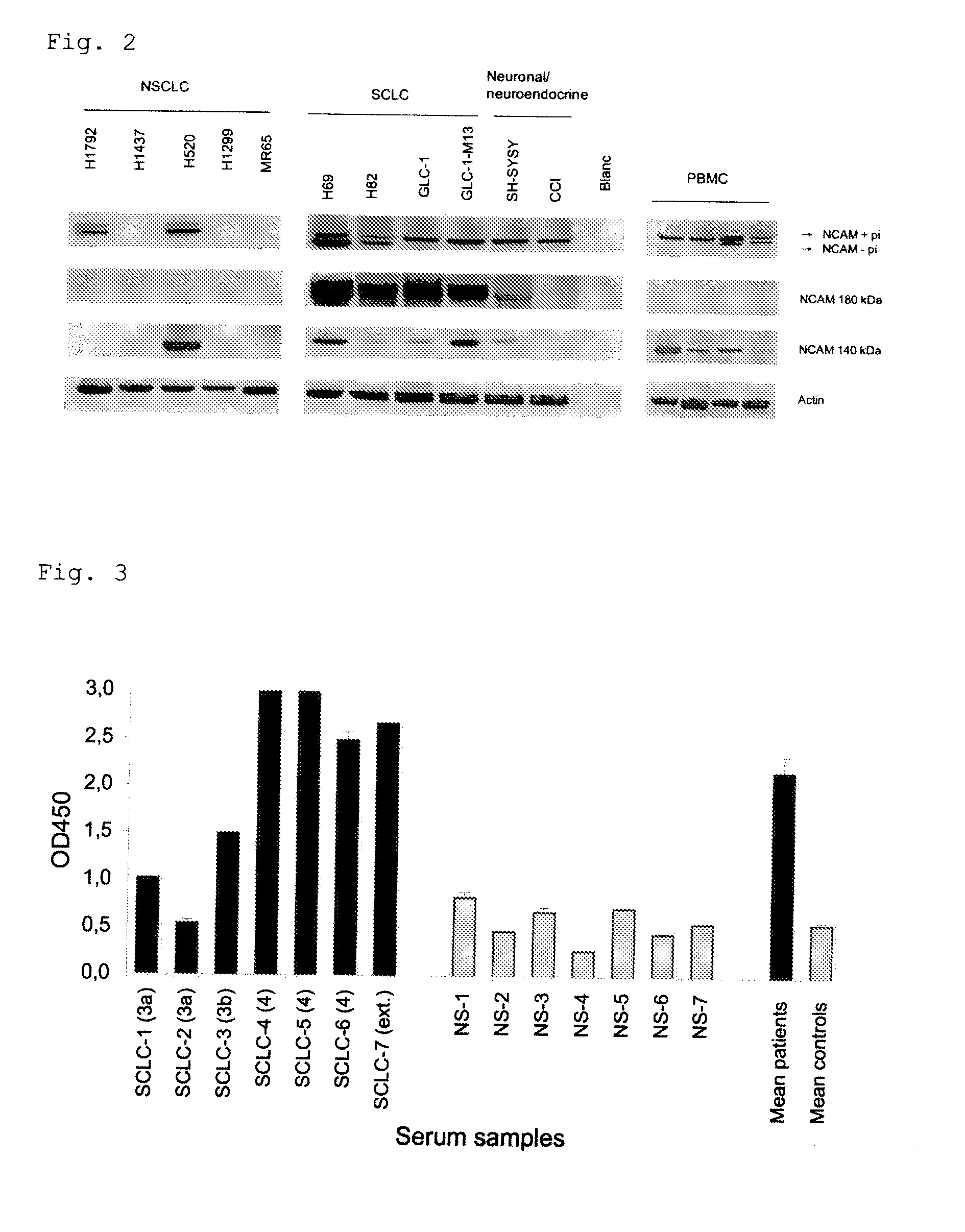
The invention relates generally to the field of cancer detection, diagnosis, subtyping, staging, prognosis, treatment and prevention. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods for the detection, and / or diagnosing and / or subtyping and / or staging of lung cancer in a patient. Based on a particular panel of biomarkers, the present invention provides methods to detect, diagnose at an early stage and / or differentiate small cell lung cancer (SCLC) from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and within NSCLC to differentiate between squamous cell carcinomas (SCC), adenocarcinomas (AC), within SCC to discriminate G2 and G3 stage and within lung cancer to differentiate for lung cancers with or without neuroendocrine origin. It further provides the use of said panel of biomarkers in monitoring disease progression in a patient, including both in vitro and in vivo imaging techniques. The in vitro imaging techniques typically include an immunoassay detecting protein or antibody of the biomarkers on a sample taken from said patient, e.g. serum or tissue sample. The in vivo imaging techniques typically include chest radiographs (X-rays), Computed Tomography (CT) imaging, spiral CT, Positron Emission Tomography (PET), PET-CT and scintigraphy for molecular imaging and diagnosis and to monitor disease progression and treatment response in patients. It is accordingly a further aspect to provide a kit to perform the aforementioned diagnosing and / or subtyping and / or staging assay and the imaging techniques, comprising reagents to determine the gene expression or protein level of the aforementioned panel of biomarkers for in vitro and in vivo applications.
Owner:MUBIO PRODS BV
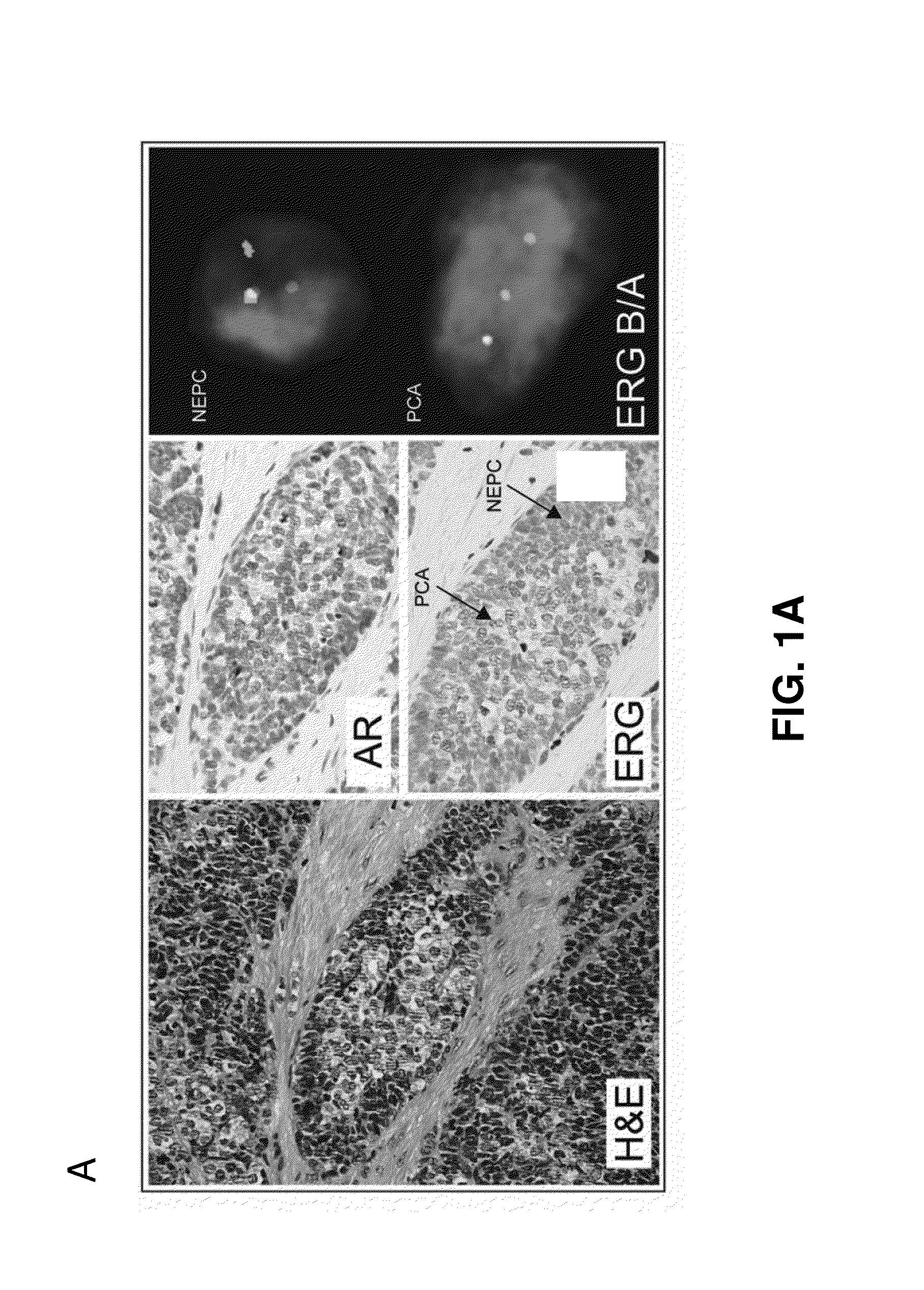
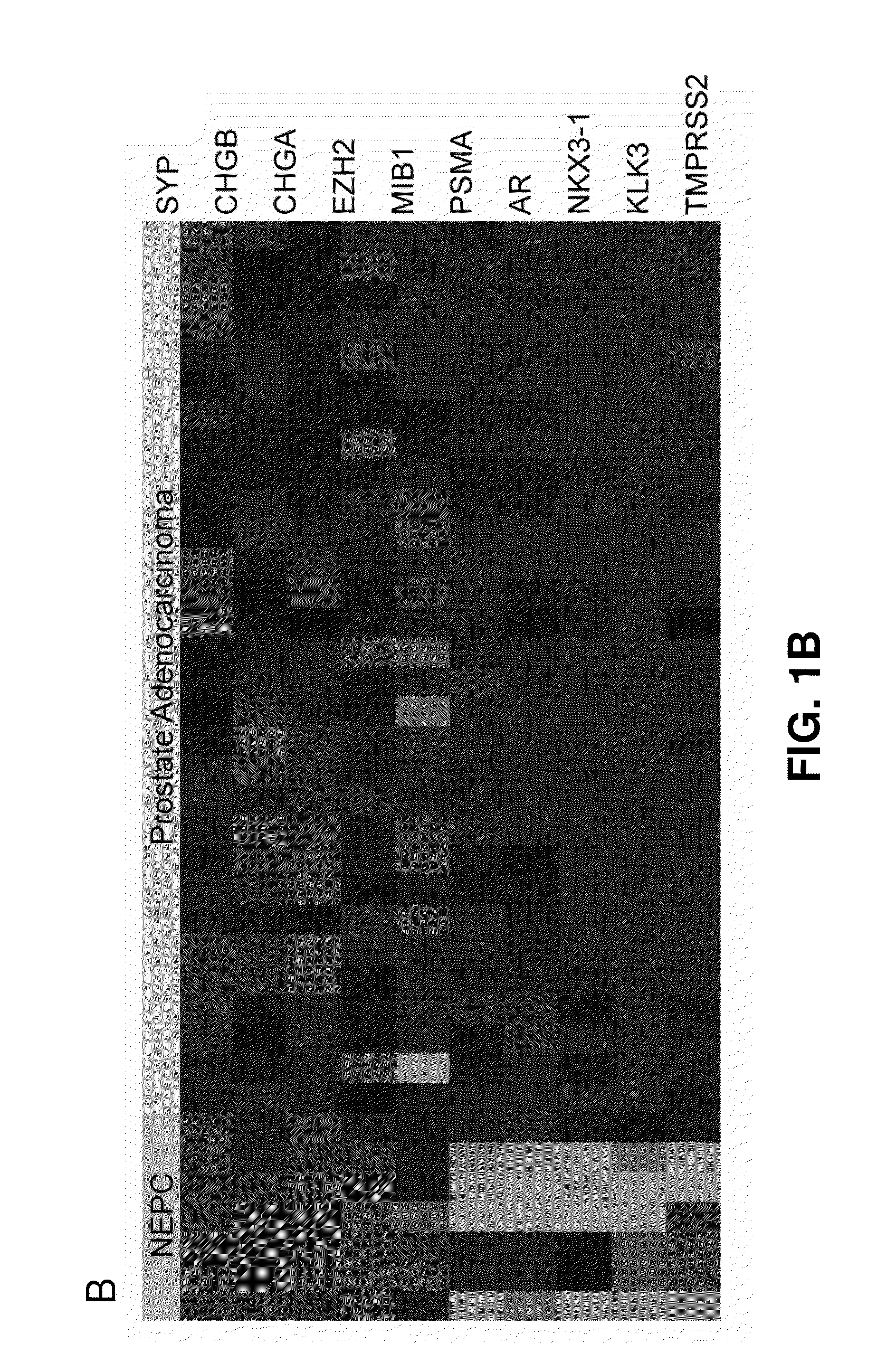
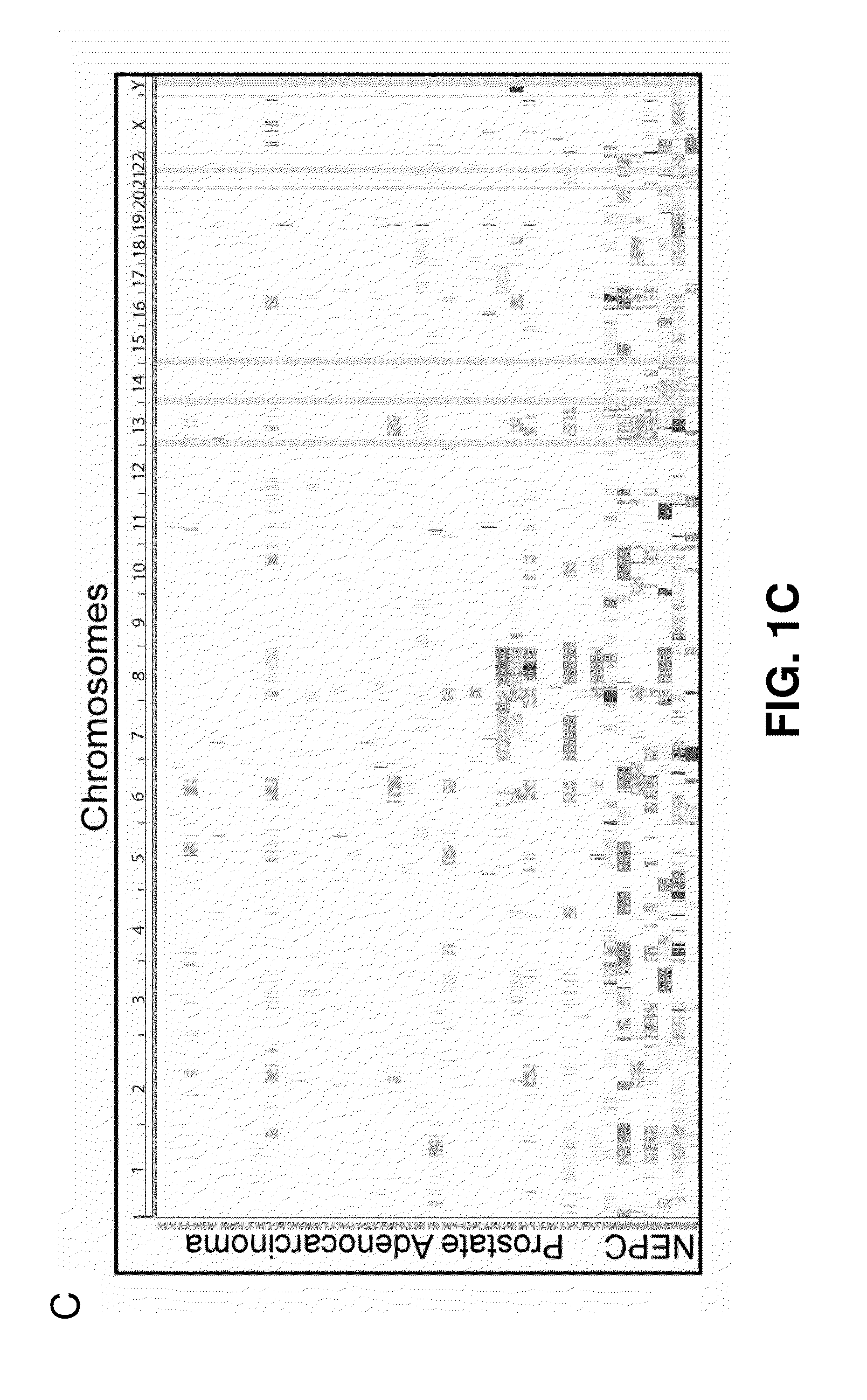
Molecular subtyping, prognosis and treatment of prostate cancer
Disclosed herein are new prognostic molecular markers for prostate cancer. More specifically, the invention has identified that overexpression or amplification of at least one of AURKA or MYCN define a distinct subgroup of prostate cancer that is predisposed to the development of lethal NEPC, who will benefit from early intervention.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Small cell lung carcinoma biomarker panel
InactiveUS20110053156A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomarker panelCompanion animal
The invention relates generally to the field of cancer detection, diagnosis, subtyping, staging, prognosis, treatment and prevention. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods for the detection, and / or diagnosing and / or subtyping and / or staging of lung cancer in a patient. Based on a particular panel of biomarkers, the present invention provides methods to detect, diagnose at an early stage and / or differentiate small cell lung cancer (SCLC) from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and within NSCLC to differentiate between squamous cell carcinomas (SCC), adenocarcinomas (AC), within SCC to discriminate G2 and G3 stage and within lung cancer to differentiate for lung cancers with or without neuroendocrine origin. It further provides the use of said panel of biomarkers in monitoring disease progression in a patient, including both in vitro and in vivo imaging techniques. The in vitro imaging techniques typically include an immunoassay detecting protein or antibody of the biomarkers on a sample taken from said patient, e.g. serum or tissue sample. The in vivo imaging techniques typically include chest radiographs (X-rays), Computed Tomography (CT) imaging, spiral CT, Positron Emission Tomography (PET), PET-CT and scintigraphy for molecular imaging and diagnosis and to monitor disease progression and treatment response in patients. It is accordingly a further aspect to provide a kit to perform the aforementioned diagnosing and / or subtyping and / or staging assay and the imaging techniques, comprising reagents to determine the gene expression or protein level of the aforementioned panel of biomarkers for in vitro and in vivo applications.
Owner:MUBIO PRODS BV
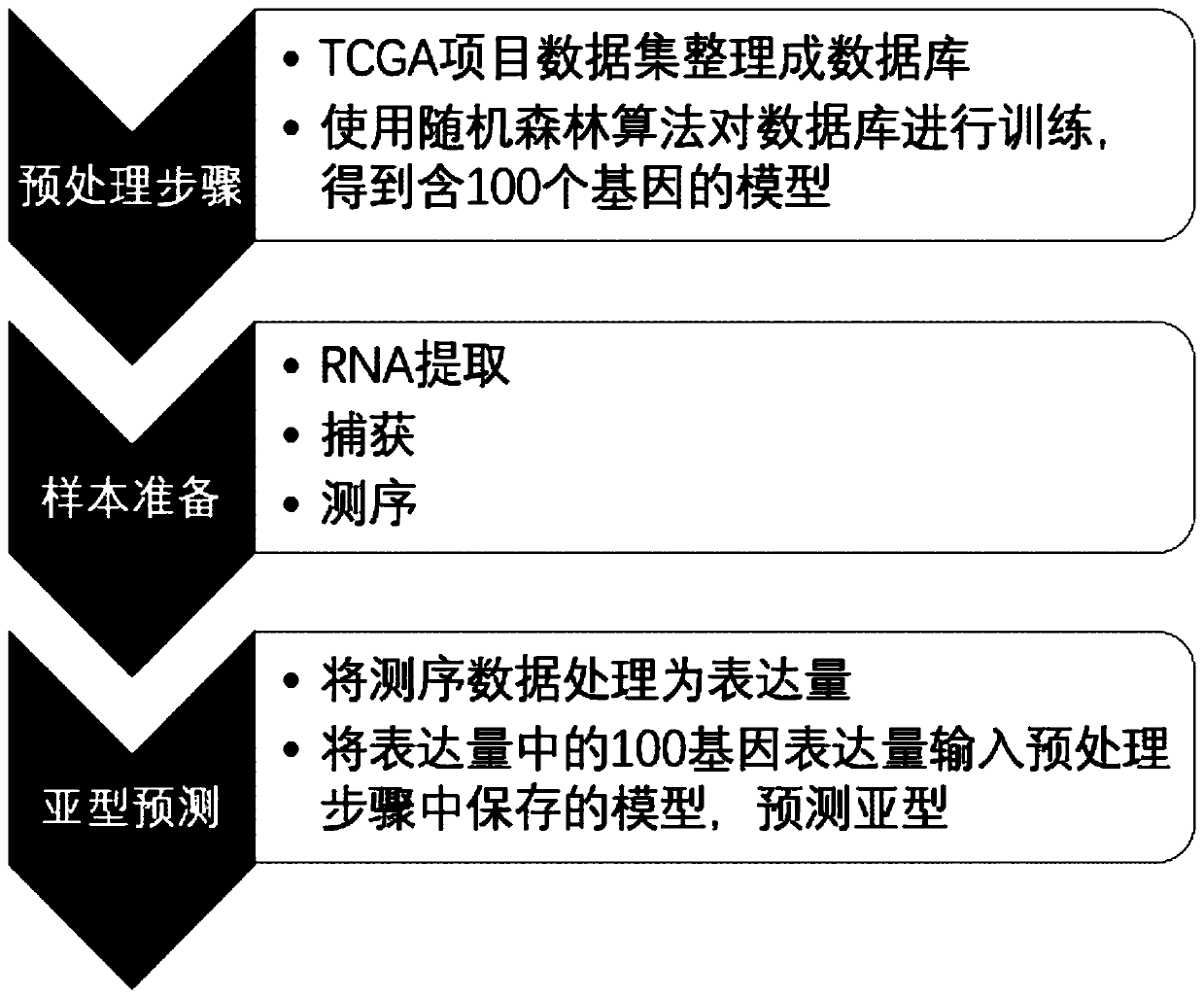
Cancer subtyping method and device based on RNA targeted sequencing and machine learning
InactiveCN110400601AImprove accuracyEfficient enrichmentMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsTypingLung cancer
The invention discloses a cancer subtyping method and a device based on RNA targeted sequencing and machine learning. According to the method, through RNA targeted sequencing technology, a target genearea is concentrated efficiently. Through steps of inverse transcription, database establishing and sequencing, second-generation sequencing data of the target area are obtained. Furthermore a randomforest algorithm is used for training on a TCGA dataset for obtaining a tumor typing predicting model, thereby accurately performing cancer subtyping. The method according to the invention can obtaina model for realizing lung cancer and renal cell carcinoma typing with high accuracy. The method according to the invention can reduce typing cost. Furthermore the typing speed, precision and the typing result accuracy are better than that of a traditional method.
Owner:元码基因科技(无锡)有限公司
Joint detection kit for multiple markers on CTCs (circulating tumor cells) and application of kit
InactiveCN107586839AAvoid interferenceUse less bloodMicrobiological testing/measurementLymphatic SpreadHepatocellular carcinoma
The invention provides a joint detection kit for multiple stem cell markers on surfaces of CTCs (circulating tumor cells) and an application of the kit. The joint detection kit for multiple stem cellmarkers on surfaces of CTCs comprises 1) a peripheral blood CTC enrichment reagent; 2) an RNA extraction reagent; 3) an RNA reverse transcription reagent; 4) a fluorescence labeled Taqman probe and aspecific primer; 5) a qPCR reaction system reagent and a hepatocellular carcinoma prediction formula. The kit can be used for biopsy of minimally invasive fluids of tumor patients, early diagnosis andearly warning of tumor metastasis and relapse are realized, the anti-tumor therapy effect and the tumor progression condition are monitored, molecular subtyping based on CTCs and screening of specific sensitive drugs for the CTCs are realized, so that knowledge about tumor metastasis, relapse and drug resistance related mechanisms is improved, individualized medical treatment of tumor patients isguided, the overall survival of the tumor patients is significantly improved, and the kit has great clinical significance.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
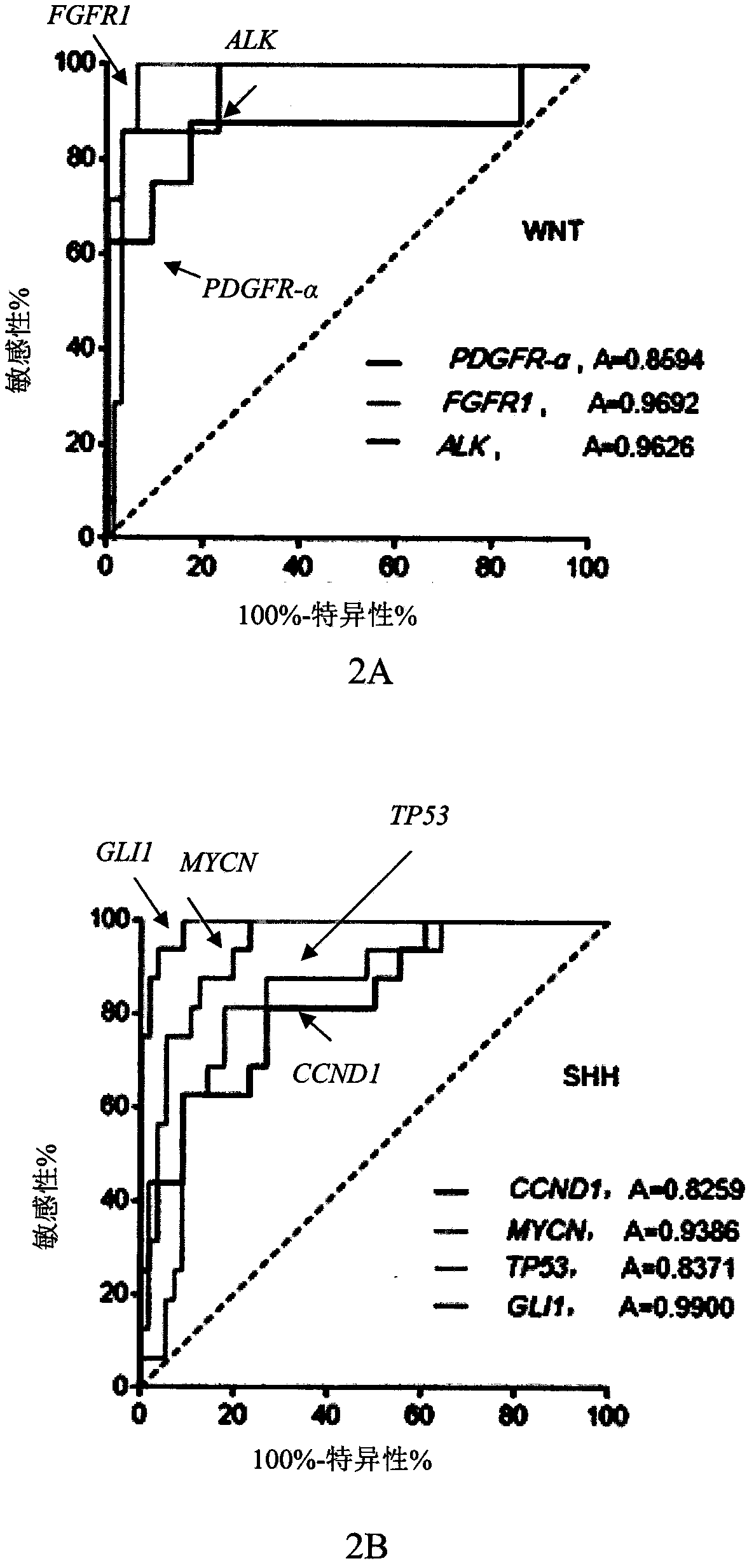
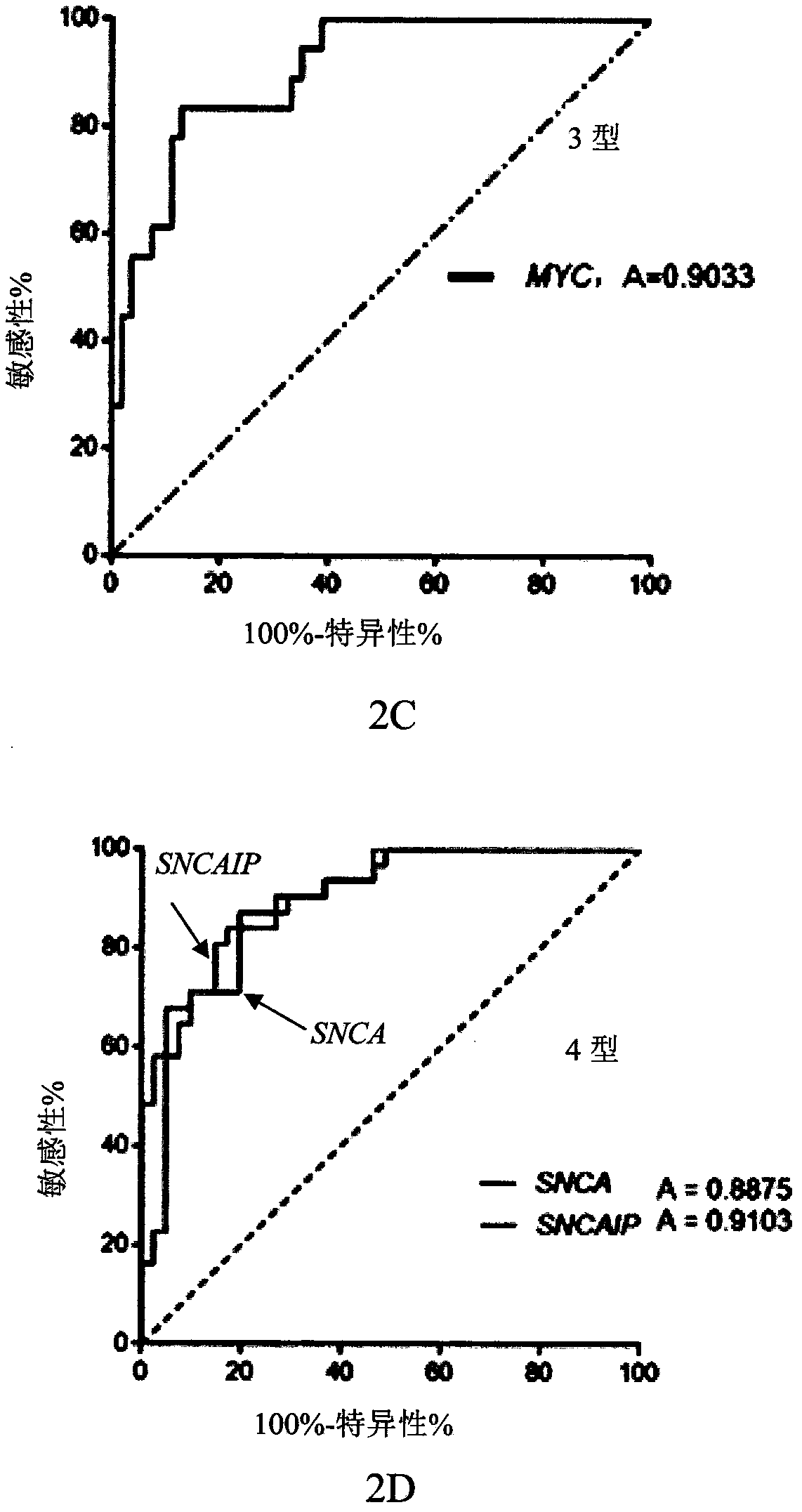
Genetic group for molecular subtyping of medulloblastoma and use of SNCA gene as biomarker of 4-type medulloblastoma
ActiveCN108728533AAbility to inhibit invasionInduce apoptosisMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringPediatric MedulloblastomaFhit gene
The invention discloses a genetic group for molecular subtyping of medulloblastoma. The genetic group is formed on one or more of 32 genes in total. The invention further discloses a kit for molecularsubtyping of medulloblastoma and use of the genetic group in the preparation of a reagent for molecular subtyping of medulloblastoma. Besides, the invention further provides use of an SNCA gene for diagnosis or as a diagnosis marker of 4-type medulloblastoma.
Owner:常青
Methods for typing of lung cancer
Methods and compositions are provided for the molecular subtyping of lung cancer samples. Specifically, a method of assessing whether a patient's lung cancer subtype is adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, or a neuroendocrine (encompassing both small cell carcinoma and carcinoid) is provided herein. A method for assessing whether a patient's lung cancer subtype is adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, small cell carcinoma or carcinoid lung cancer is also provided. The methods provided herein entail probing the levels of the classifier biomarkers of Table 1-Table 6 or a subset thereof at the nucleic acid level, in a lung cancer sample obtained from the patient. Based in part on the levels of the classifier biomarkers, the lung cancer sample is classified as a particular lung cancer subtype.
Owner:GENECENTRIC THERAPEUTICS INC +1
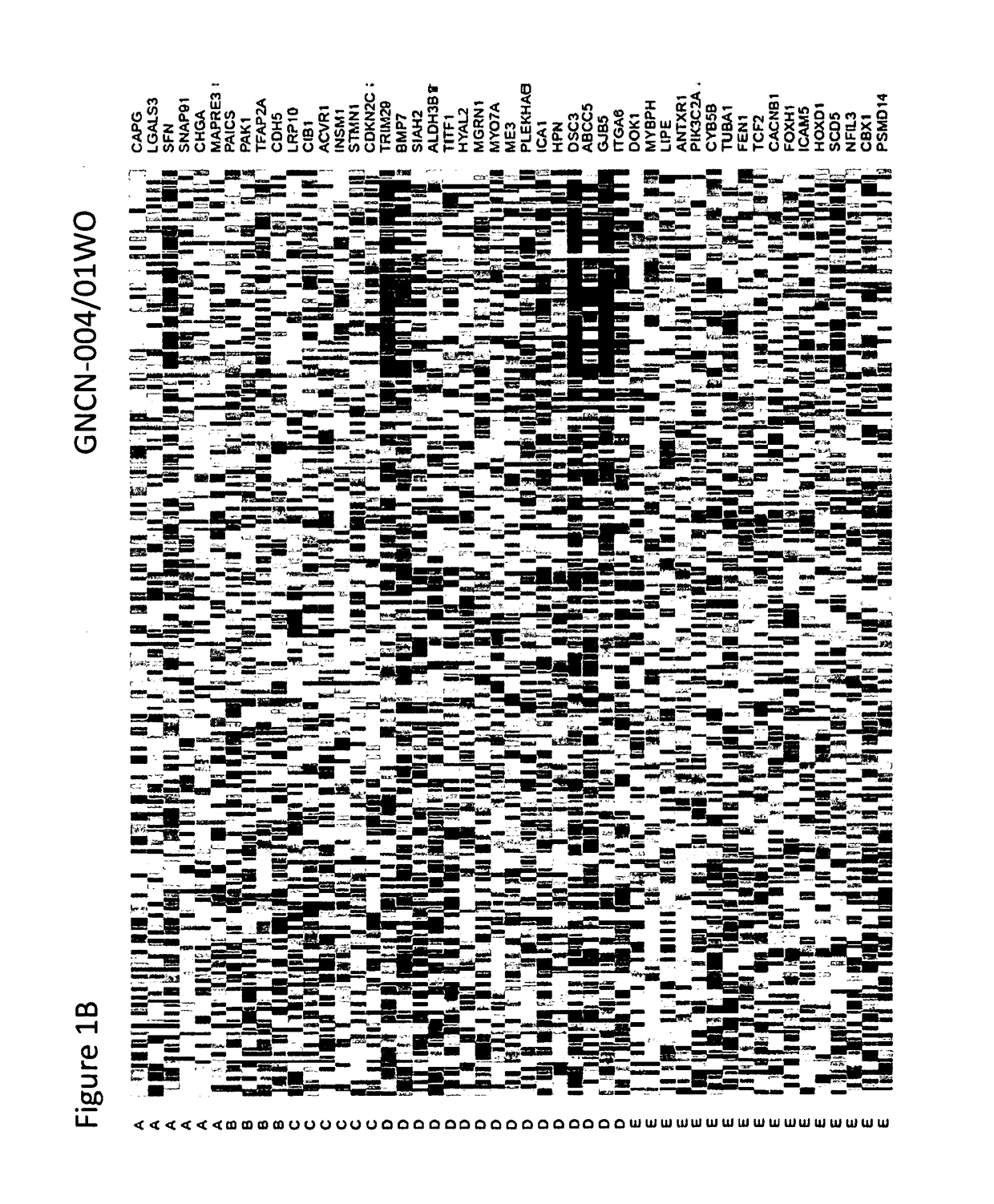
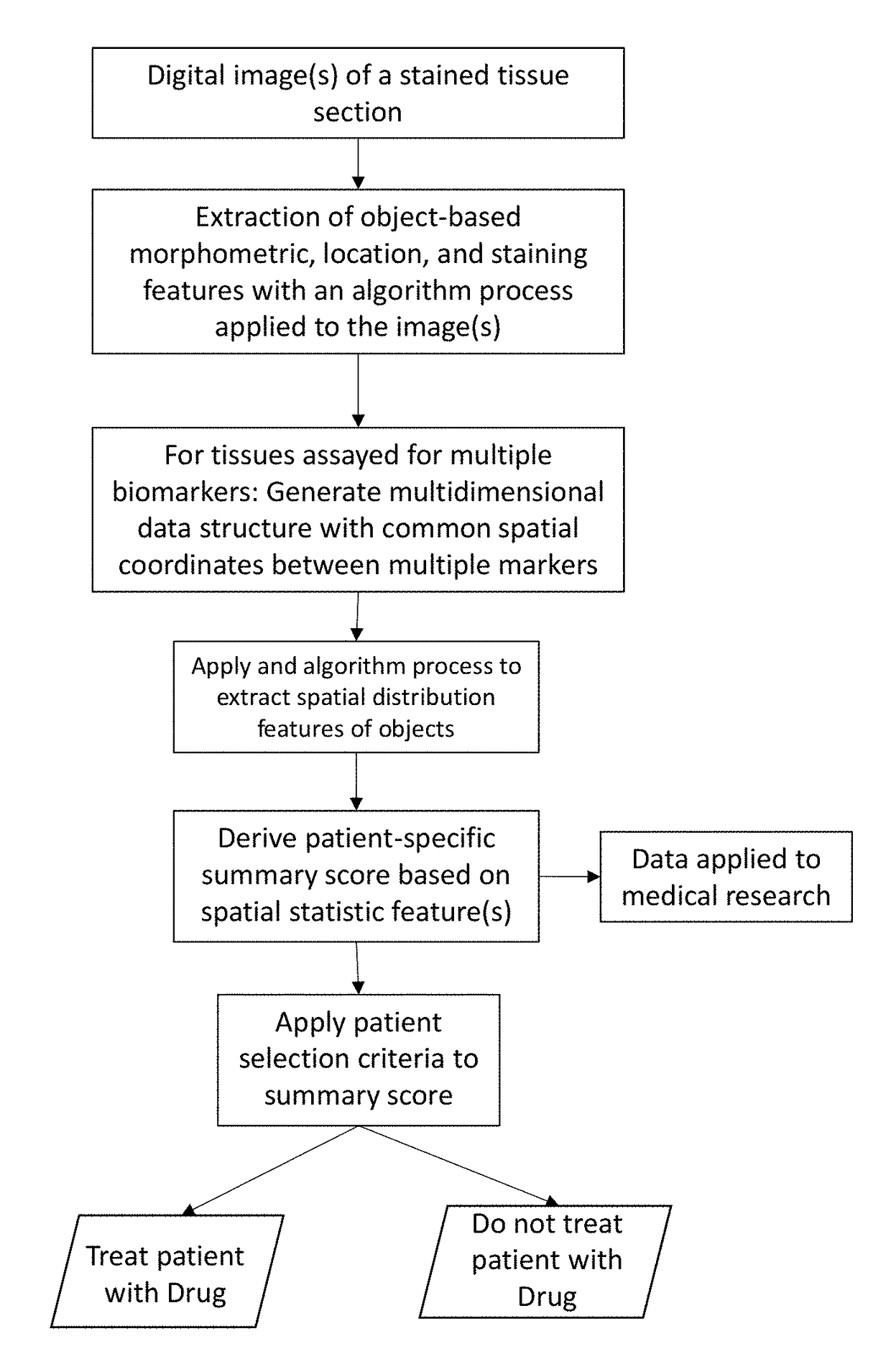
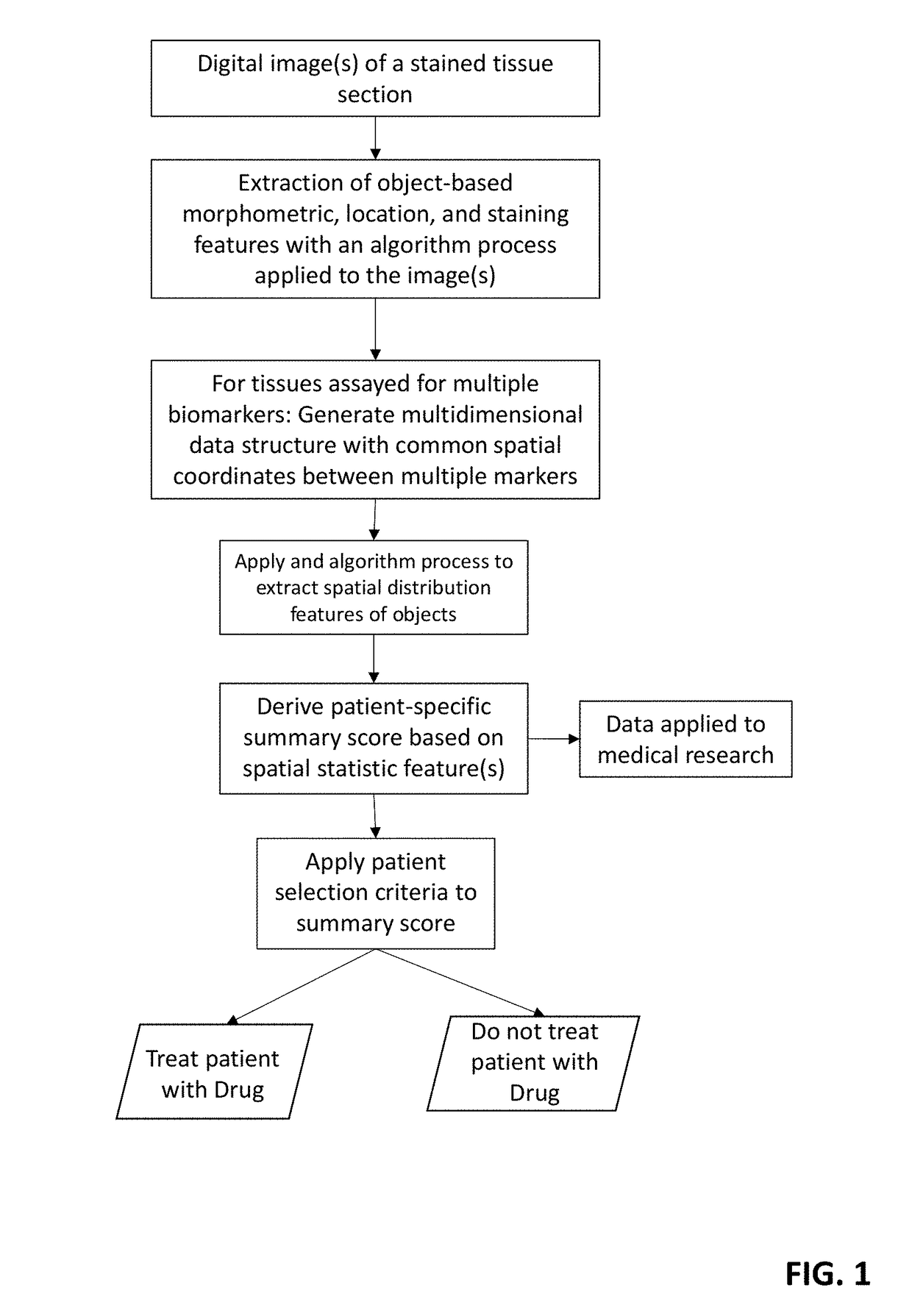
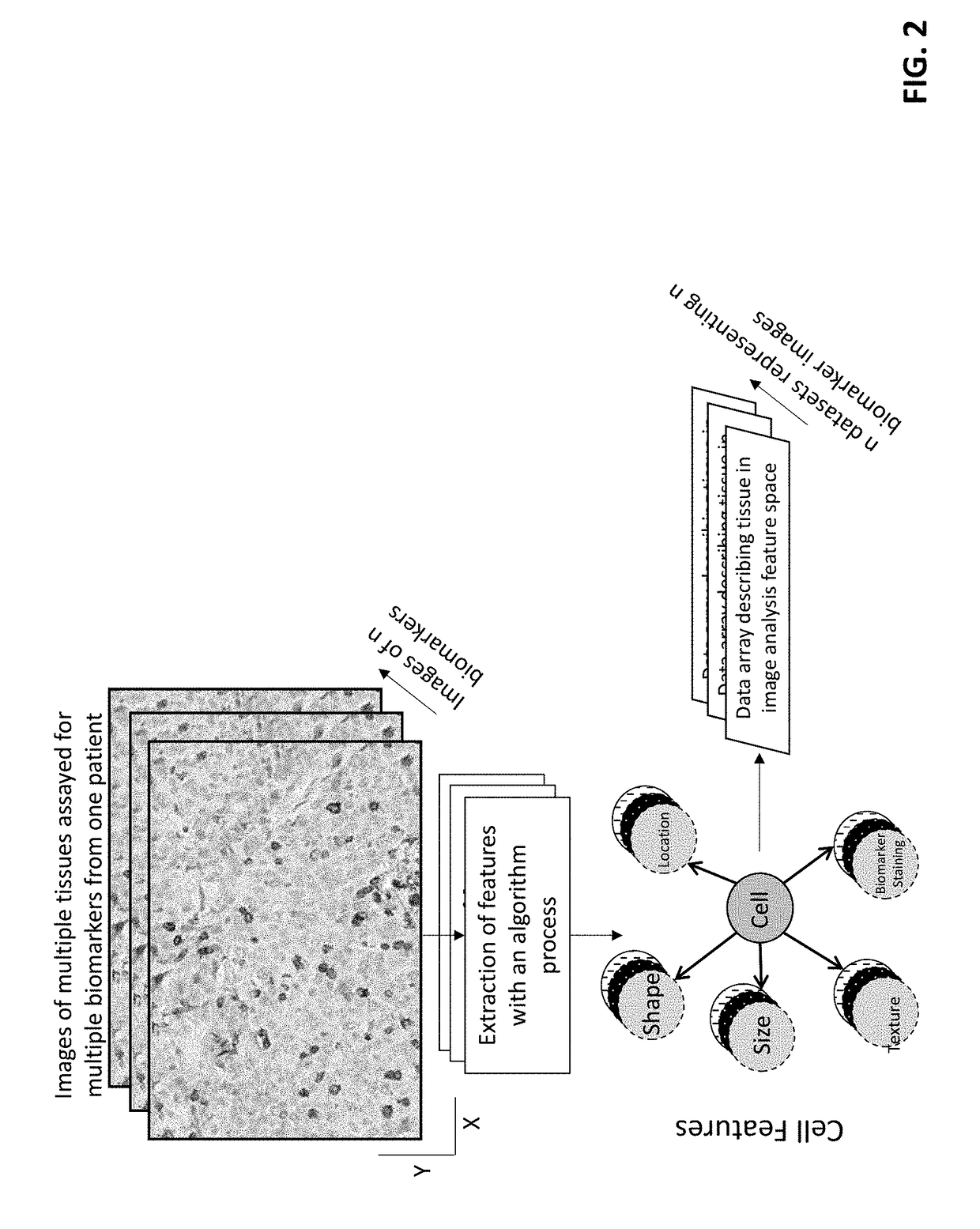
Method for scoring pathology images using spatial analysis of tissues
The disclosure concerns a method for extracting spatial distribution statistics from patient tissue samples assayed with a tissue-based test for the purpose of scoring the patient tissue samples and guiding treatment based on the score(s). The method described herein utilizes digital image analysis of an image of one or more tissue sections to extract object-based (e.g., cells) features. The object-based features within the image of the tissue section is further processed using one or more algorithm processes to extract sophisticated spatial distribution features of one or more object type or sub-type in the tissue. Statistics describing the spatial distribution features are summarized to generate a patient-specific diagnostic score, and this score can be evaluated to guide patient treatment decisions.
Owner:FLAGSHIP BIOSCI
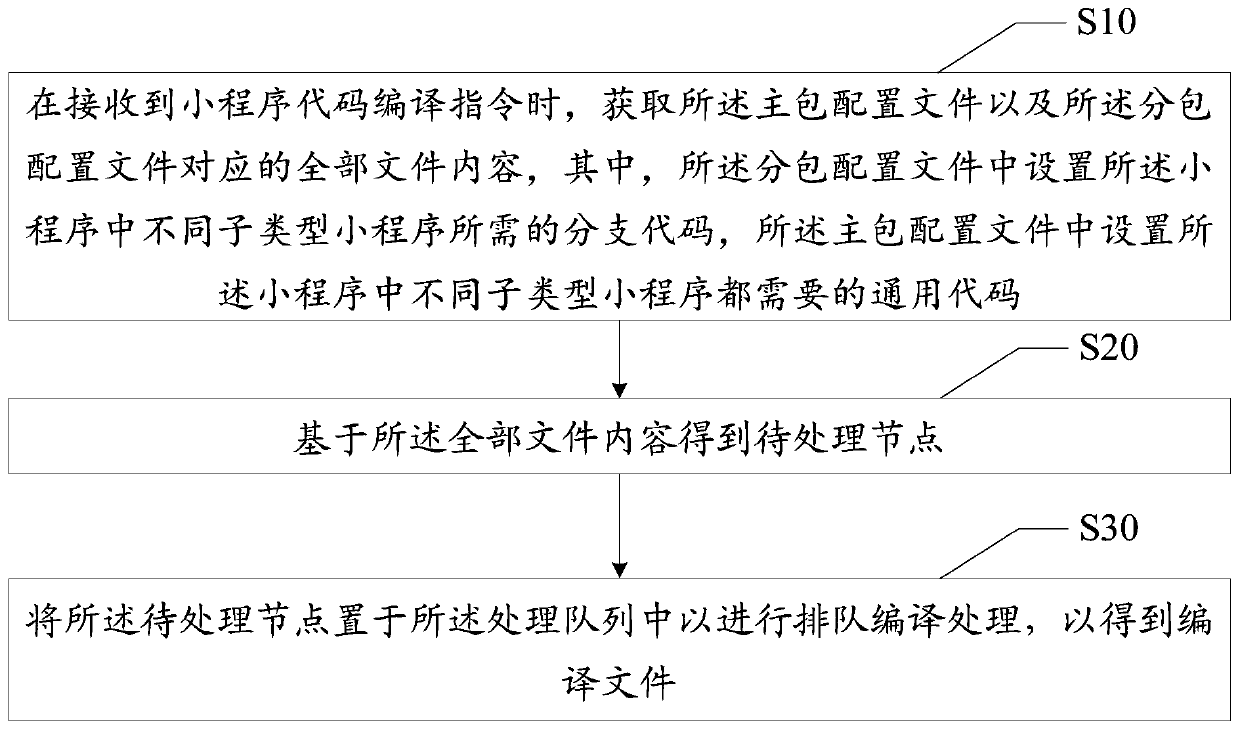
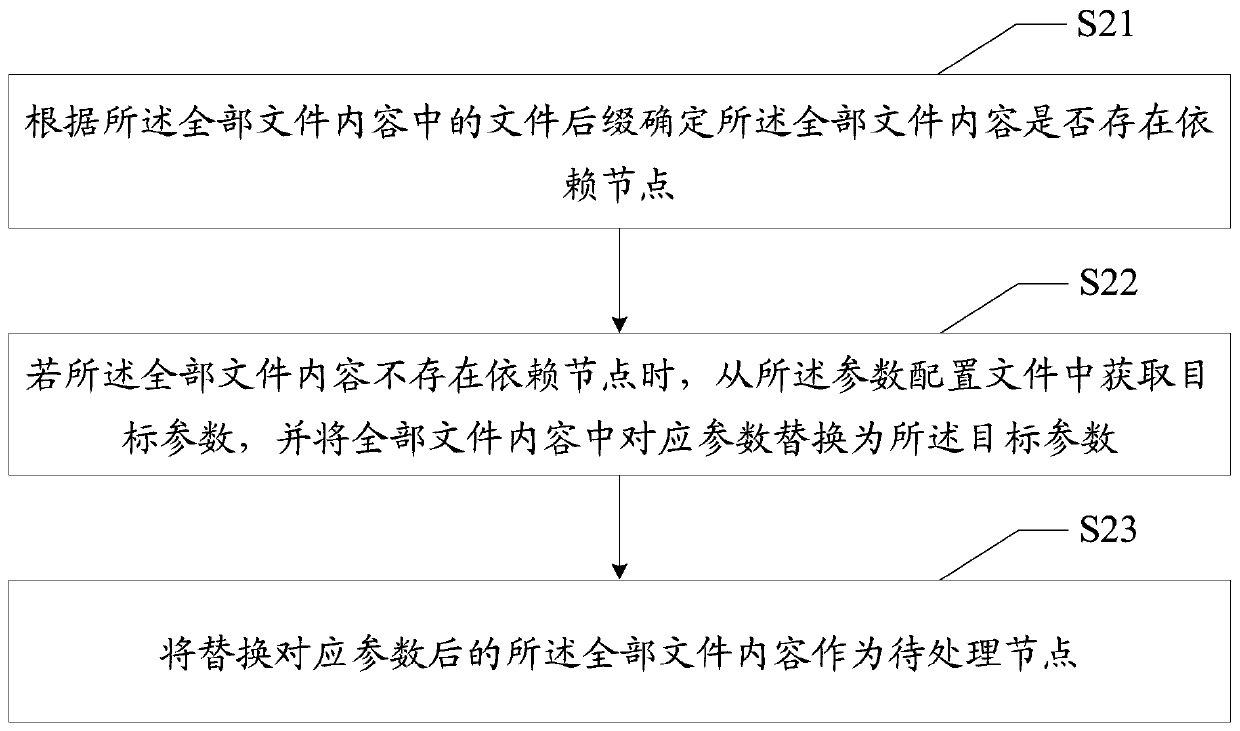
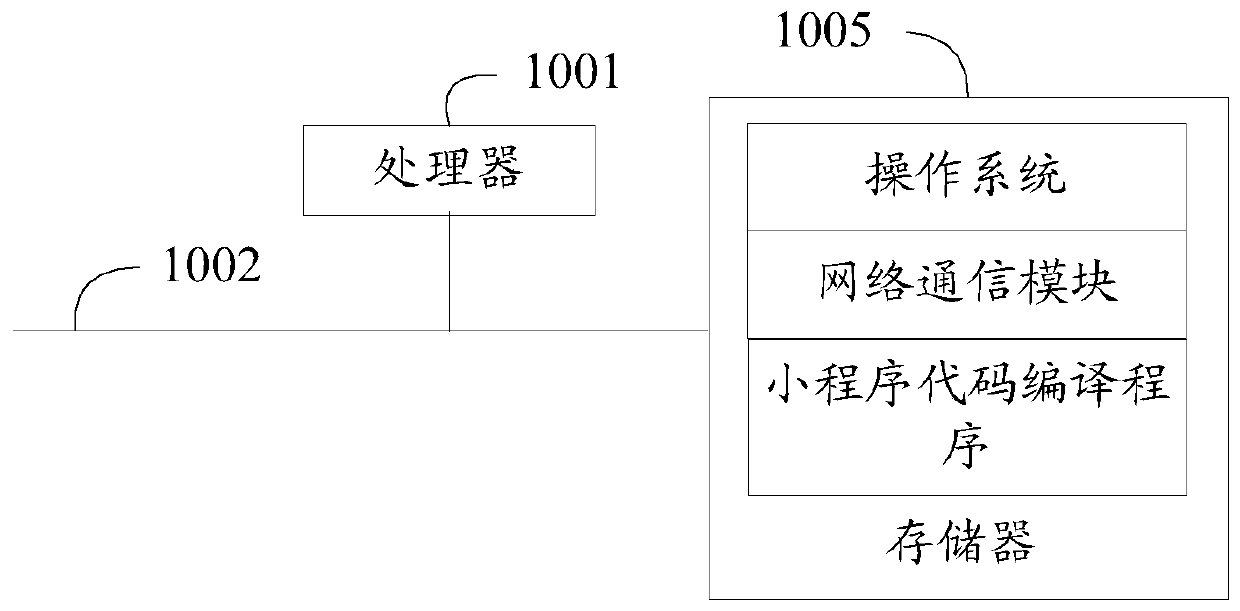
Small program code compiling method and device, equipment and medium
PendingCN111045683AImprove reusabilityImprove maintainabilityCode compilationMaintainabilityReusability
The invention discloses a small program code compiling method and device, equipment and a medium and relates to the technical field of financial science and technology, the method is applied to the applet code compiler, wherein a main package configuration file is set in the compiler; subpackaging configuration files and processing queues, the applet code compiling method comprises the following steps: compiling applet codes; when a small program code compiling instruction is received; obtaining all file contents corresponding to the main package configuration file and the sub-package configuration file, setting branch codes required by different sub-type small programs in the small programs in the sub-package configuration file, and setting universal codes required by different sub-type small programs in the small programs in the main package configuration file; obtaining a to-be-processed node based on all the file contents; and placing the to-be-processed node in the processing queue to perform queuing compilation processing to obtain a compiled file. The technical problems that in existing applet code compiling, maintainability is poor, and code reusability is poor are solved.
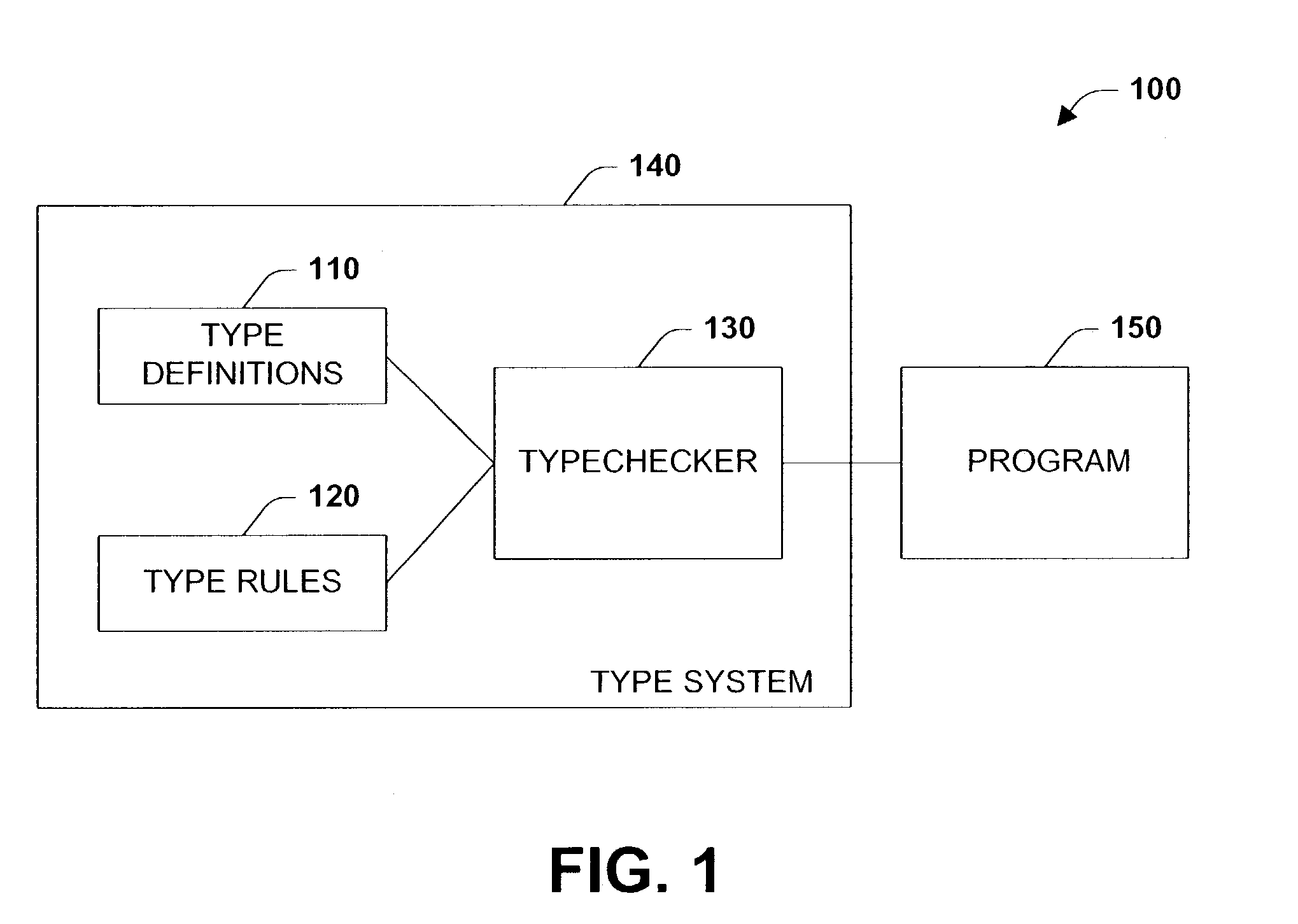
Owner:WEBANK (CHINA)
Methods and kits for the molecular subtyping of tumors
The present invention relates to an in vitro method of identifying a molecular subtype of a tumor in a cancer patient and to a method of stratifying a cancer patient for tumor treatment. The present invention further relates to kits that are useful for identifying a molecular subtype of a tumor in a cancer patient.
Owner:BIONTECH DIAGNOSTICS +1
Methods for enhancing type reconstruction
InactiveUS20050081194A1Program documentationSpecific program execution arrangementsSystems approachesProgram analysis
Systems, methods, and structures are discussed that enhance type reconstruction for programs. Whereas previous methods insufficiently provide the set of types necessary for program analysis, the embodiments of the present invention can accept any verifiable bytecode programs and produce a set of types needed for program analysis. The embodiments of the present invention provide a technique called subtype completion that transforms a subtyping system by extending its type hierarchy to a lattice. However, such transformation inserts only a minimal amount of elements so as to enhance the computation of reconstructed types.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
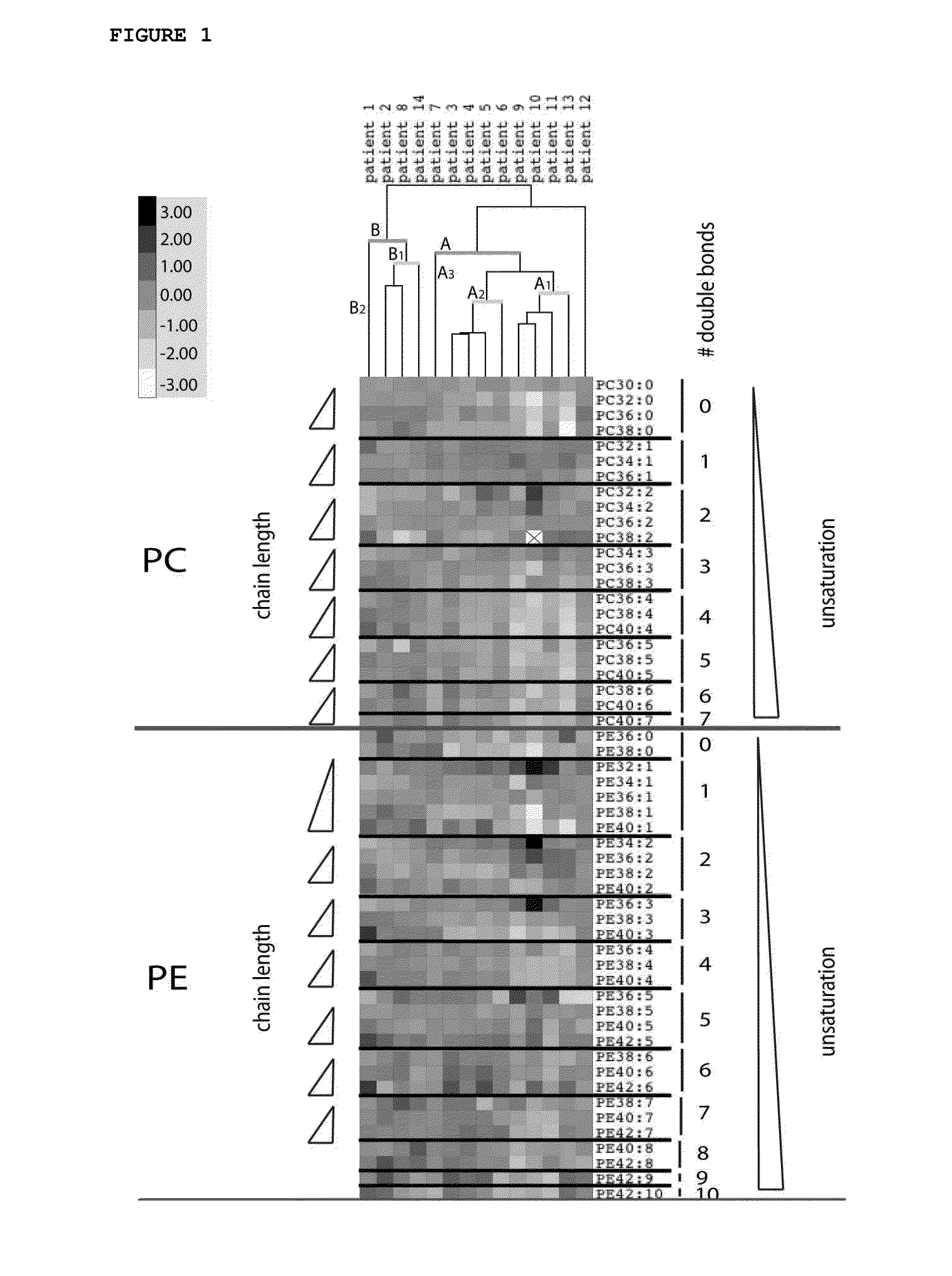
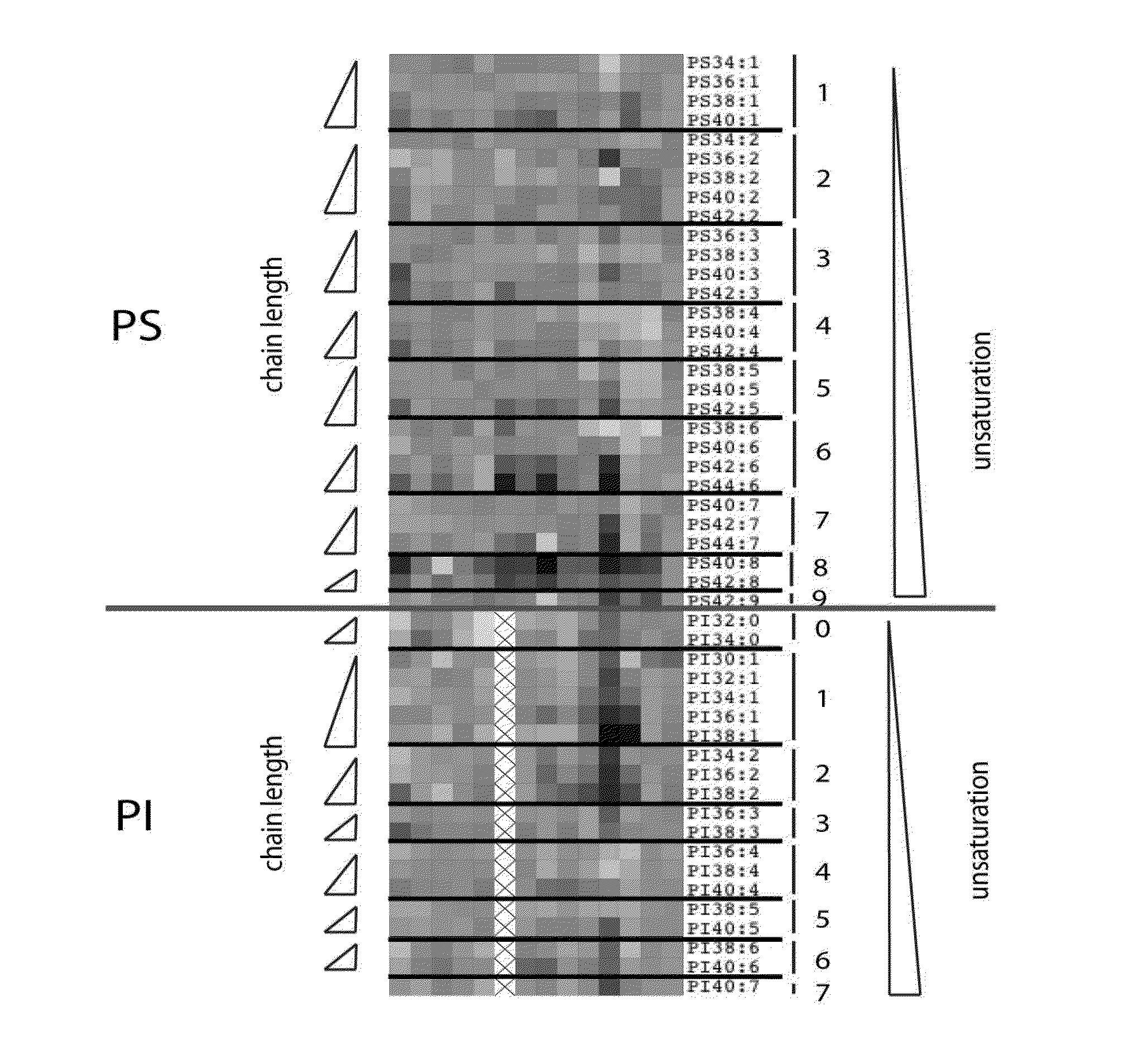
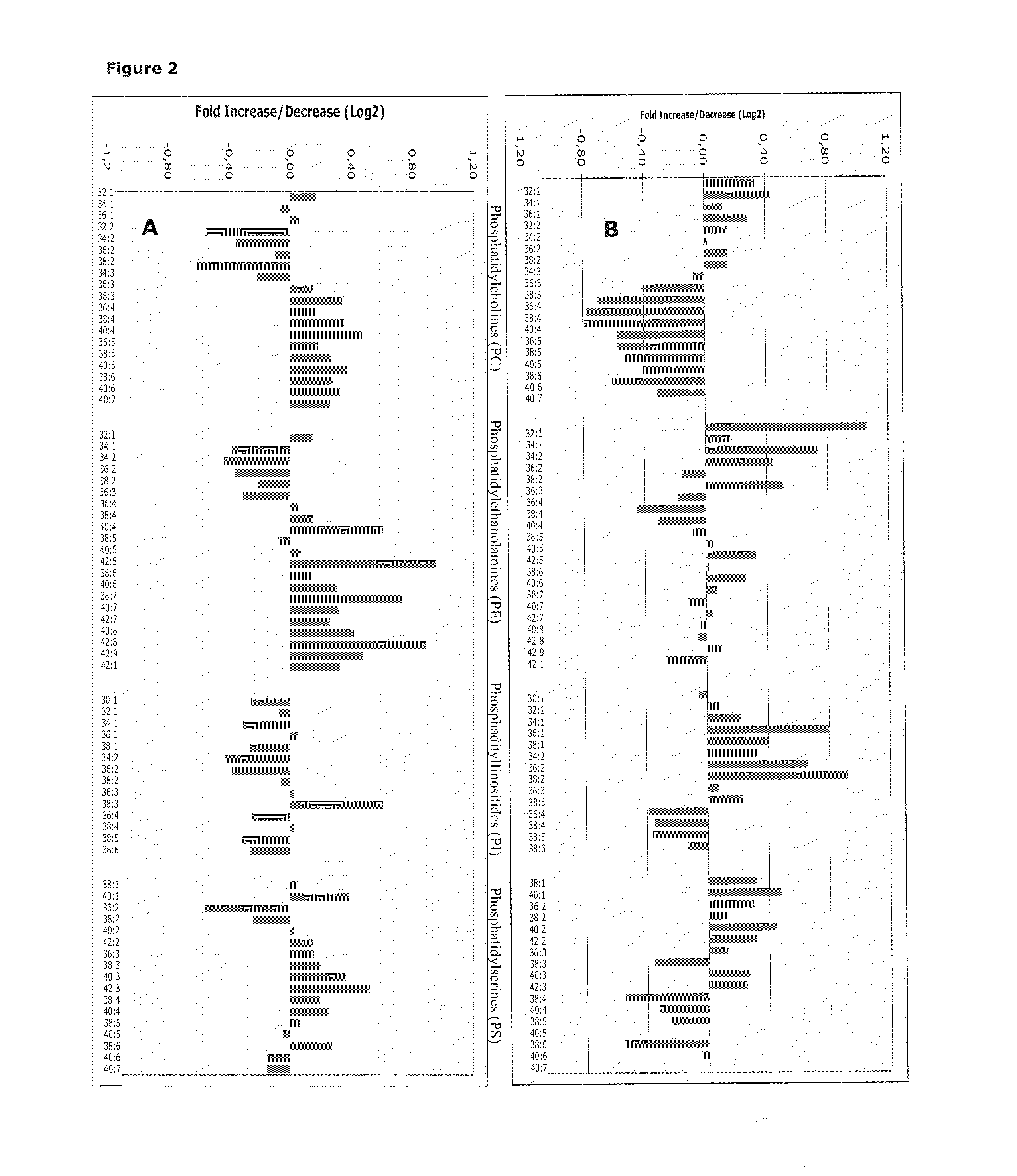
Cancer phospholipidome
ActiveUS20140220613A1Aggressive elongation phenotypeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAbnormal tissue growthPredictive methods
In general, the present invention relates to identification of lipidome biomarkers for cancer analysis and it provides prognostic and predictive methods and kits for cancer diagnosis and subtyping and for diagnosing and / or predicting the evolution of a tumor and its response to lipid metabolism-targeted or other types of therapy in a subject, by making use of phospholipid (PL) profiling, wherein changes in the combined acyl chain length of intact body fluid-derived or tumor-derived phospholipid species is indicative of an elongation phenotype.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
A protein combination used for assessing glioblastoma prognosis and applications thereof
InactiveCN108169490AImprove survival rateHigh sensitivityDisease diagnosisBiological testingLIN28Immunohistochemistry technique
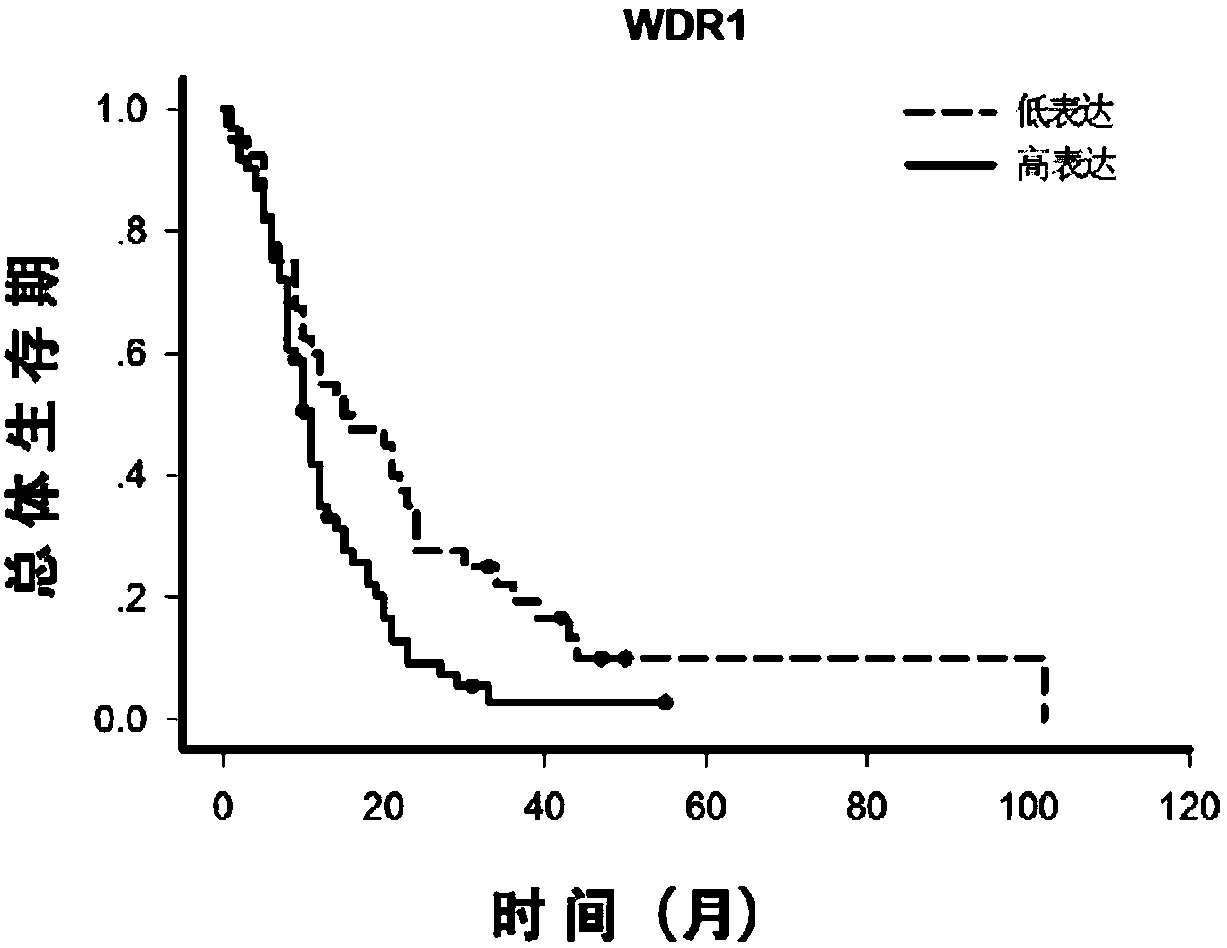
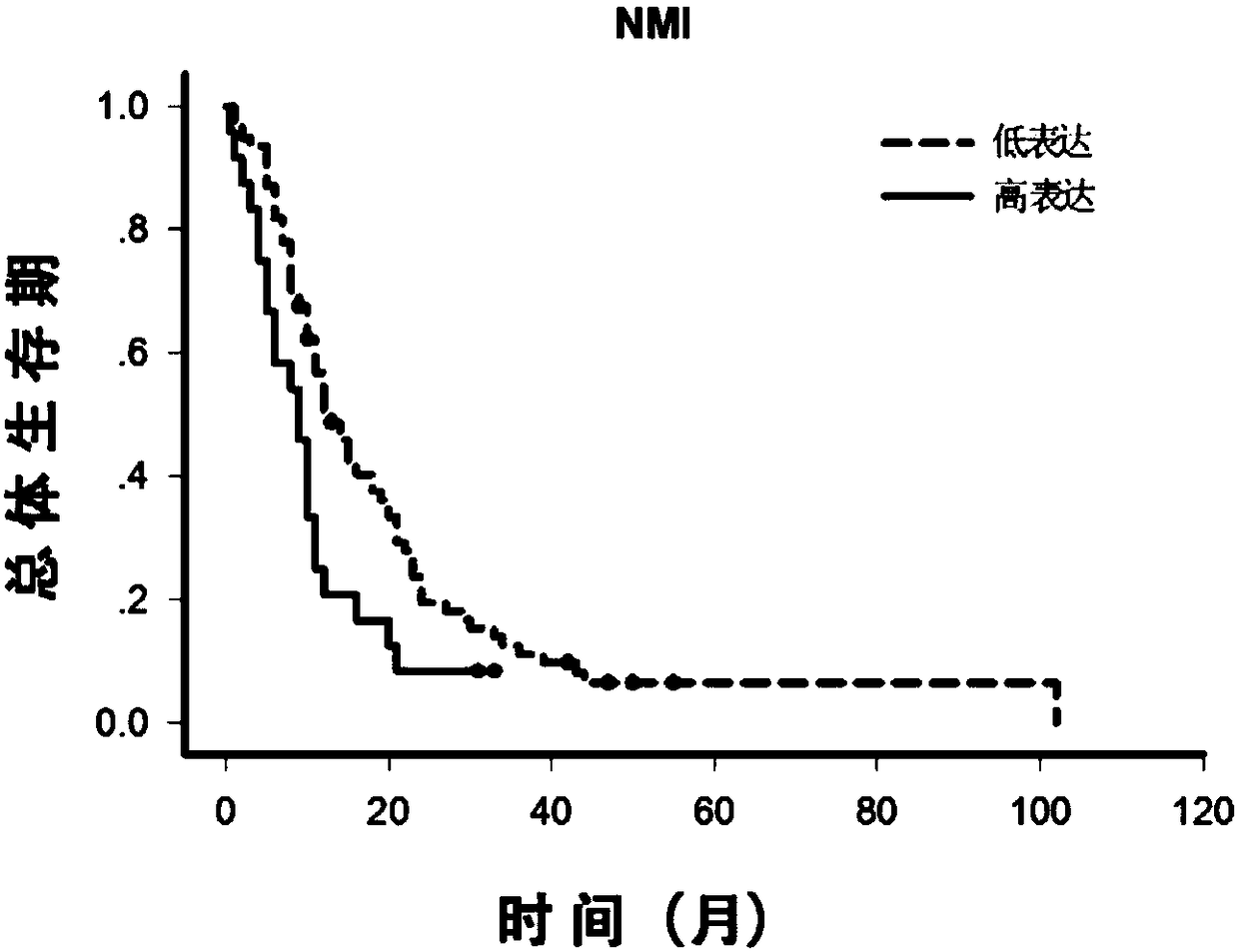
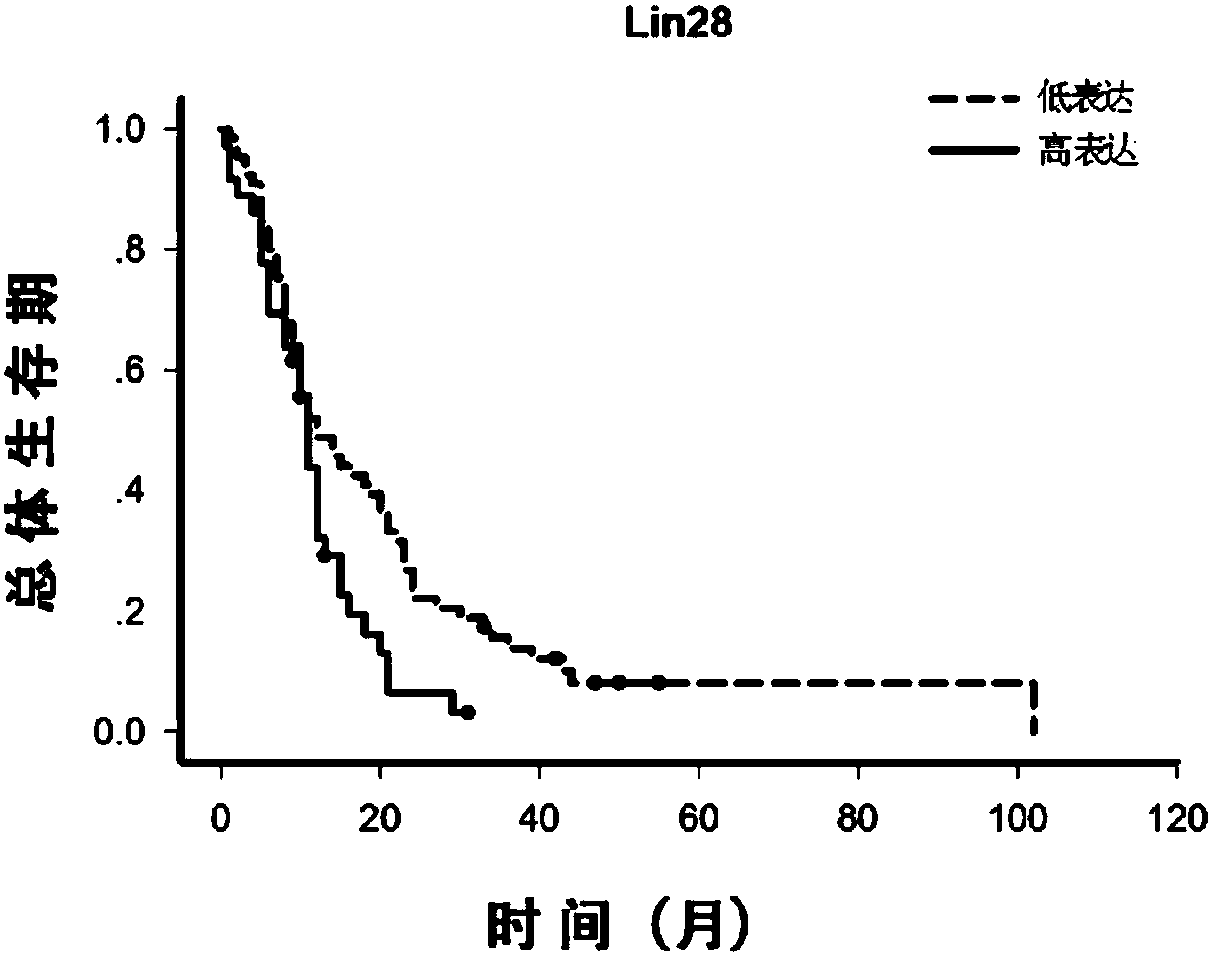
The invention relates to the technical field of medical biological detection and provides novel uses of WDR1, NMI and LIN28 proteins, particularly an application in preparation of a kit for assessingbrain glioblastoma prognosis. The invention further provides a kit and detection method performing brain glioblastoma prognosis assessing through quantitative detection of the WDR1, NMI and LIN28 proteins by adopting an immunohistochemical method. Expression levels of the WDR1, NMI and LIN28 proteins in brain glioblastoma tissues are measured by utilizing an immunohistochemical technique and system scoring, and it is determined that the expression levels of the WDR1, NMI and LIN28 proteins are related with prognosis of patients with brain glioblastoma after operations by combination with postoperative follow-up observation information. The combination of the WDR1, NMI and LIN28 proteins can be used for preparing a protein molecular marker for determining prognosis of patients with brain glioblastoma, and is of great directive significance for brain glioblastoma molecular subtyping, postoperative monitoring of patients and sequential therapy.
Owner:SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com