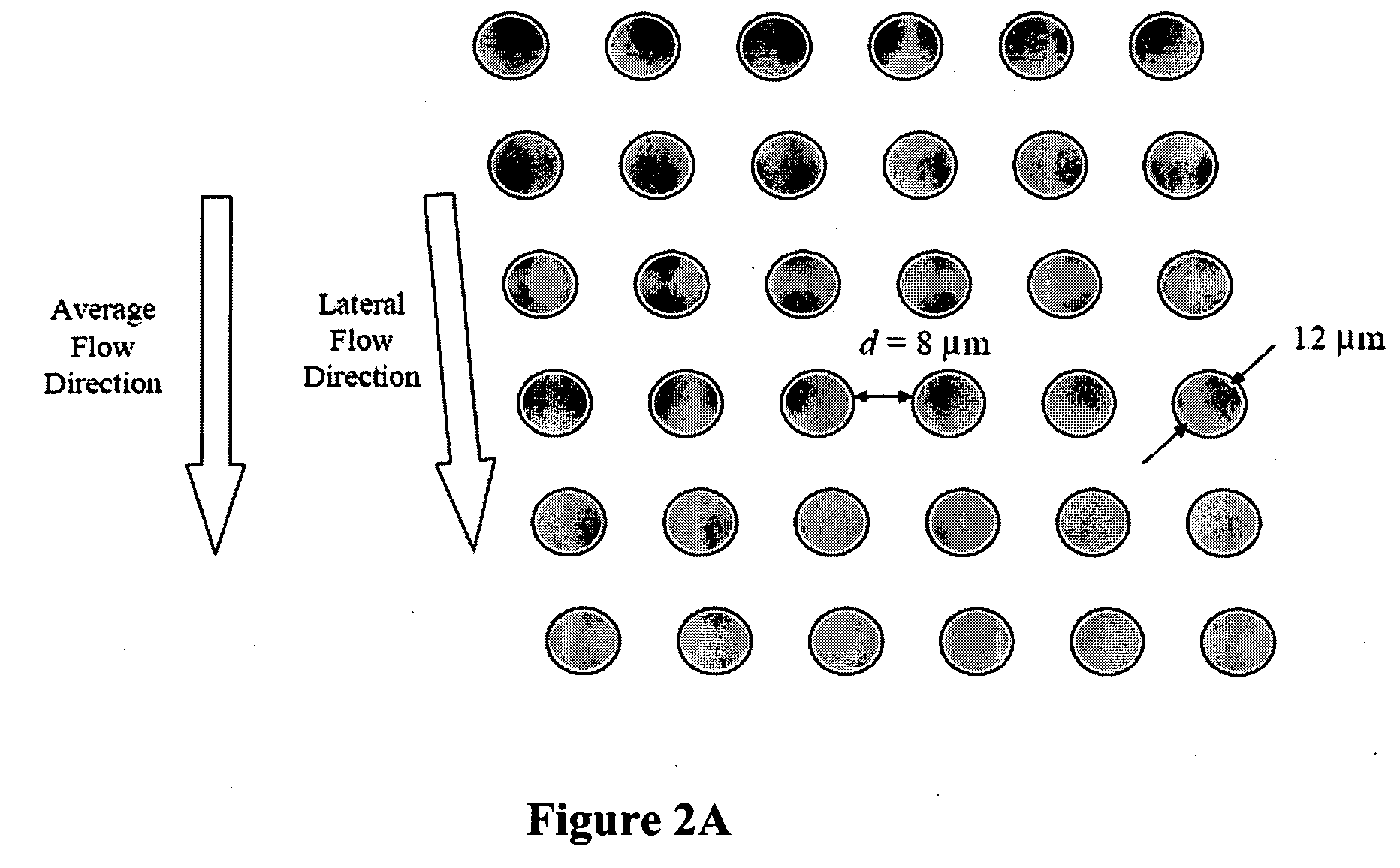
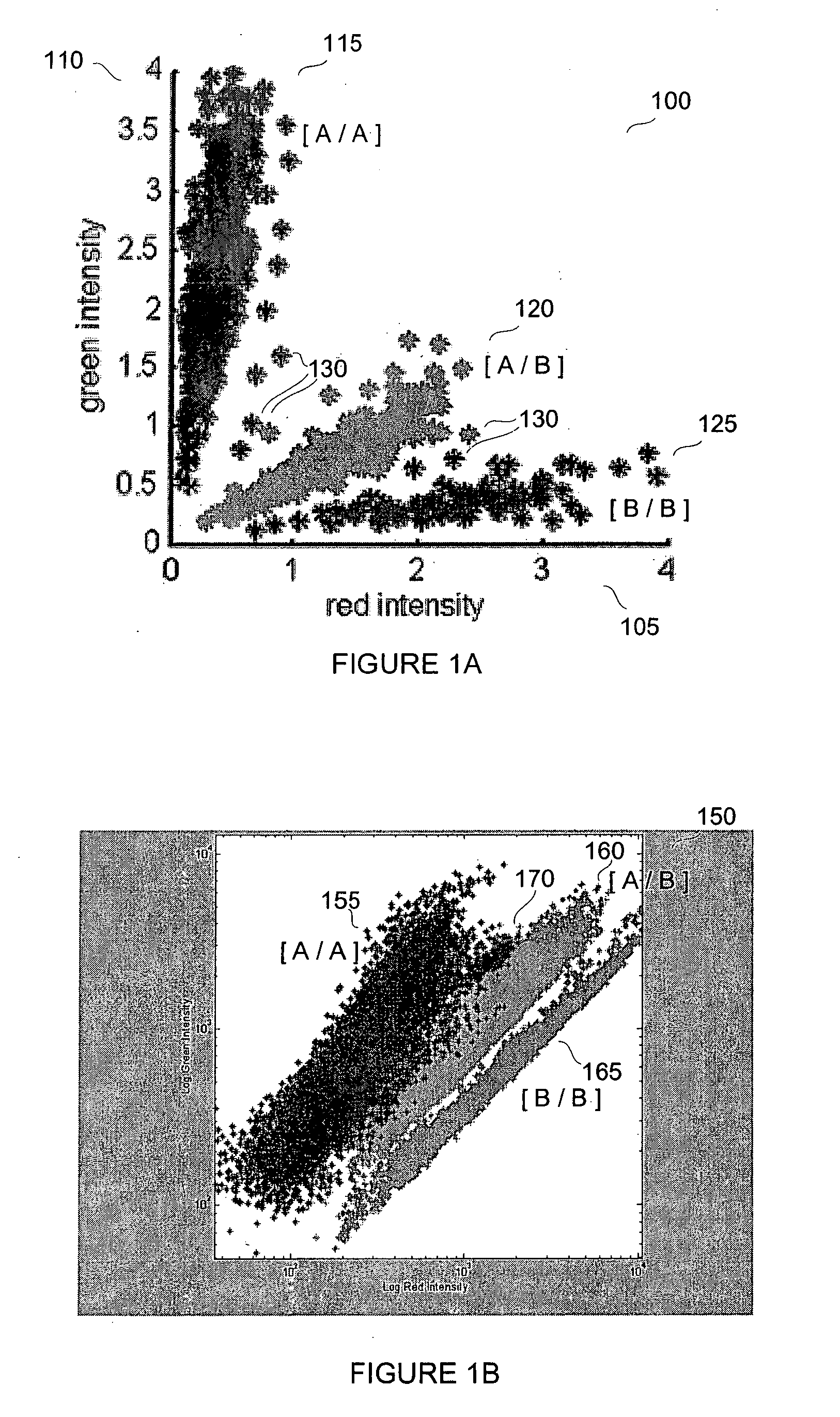
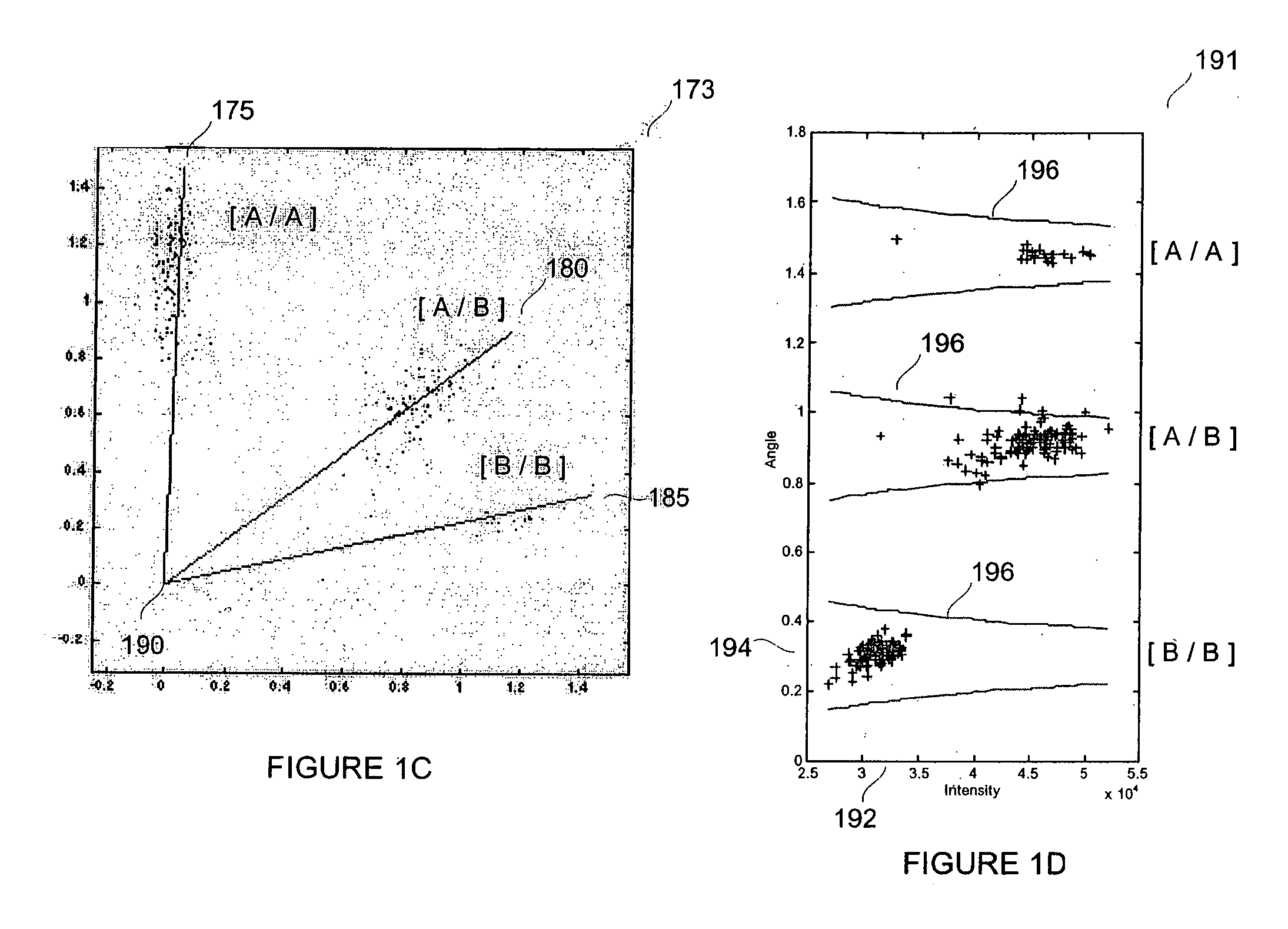
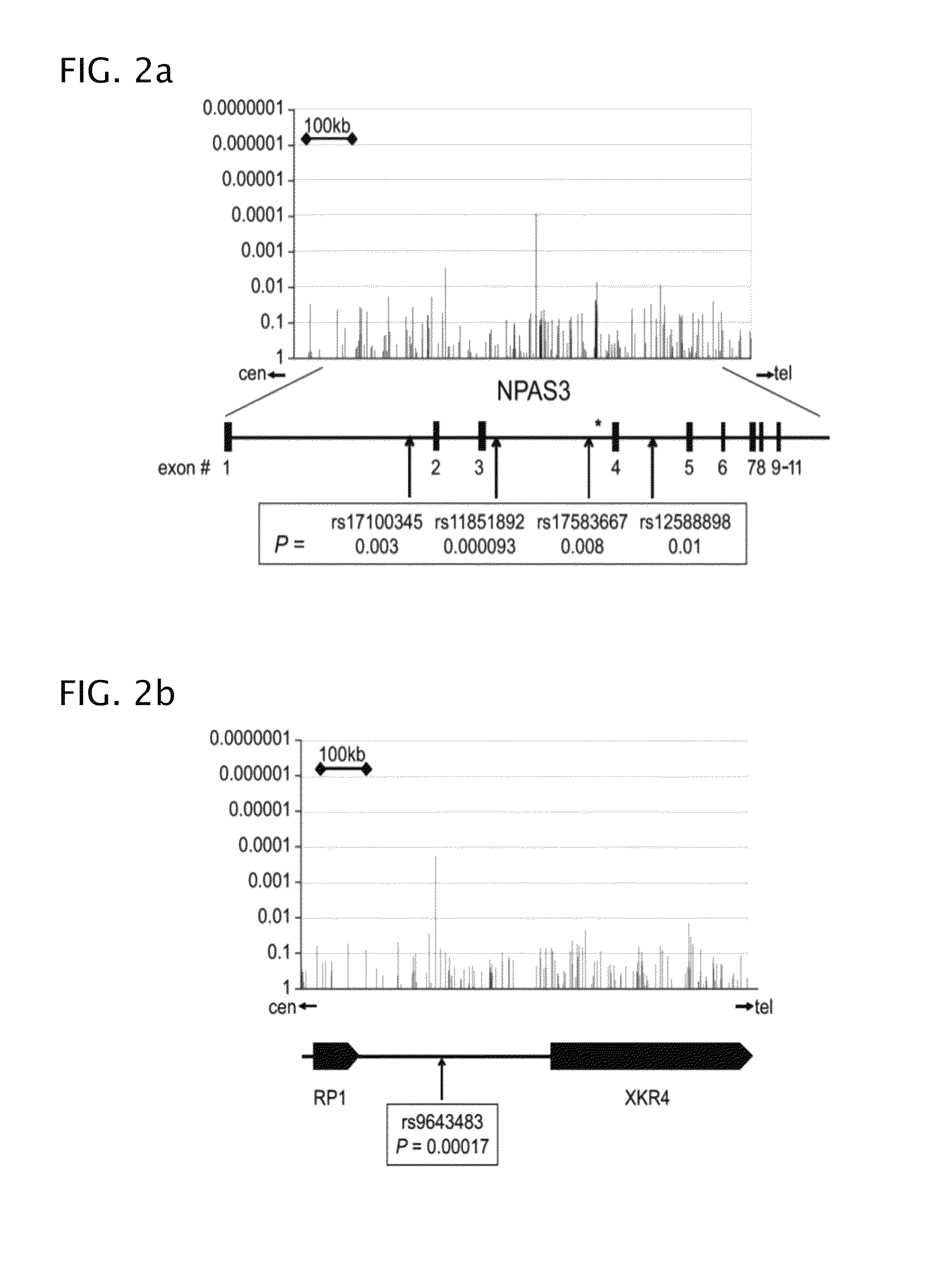
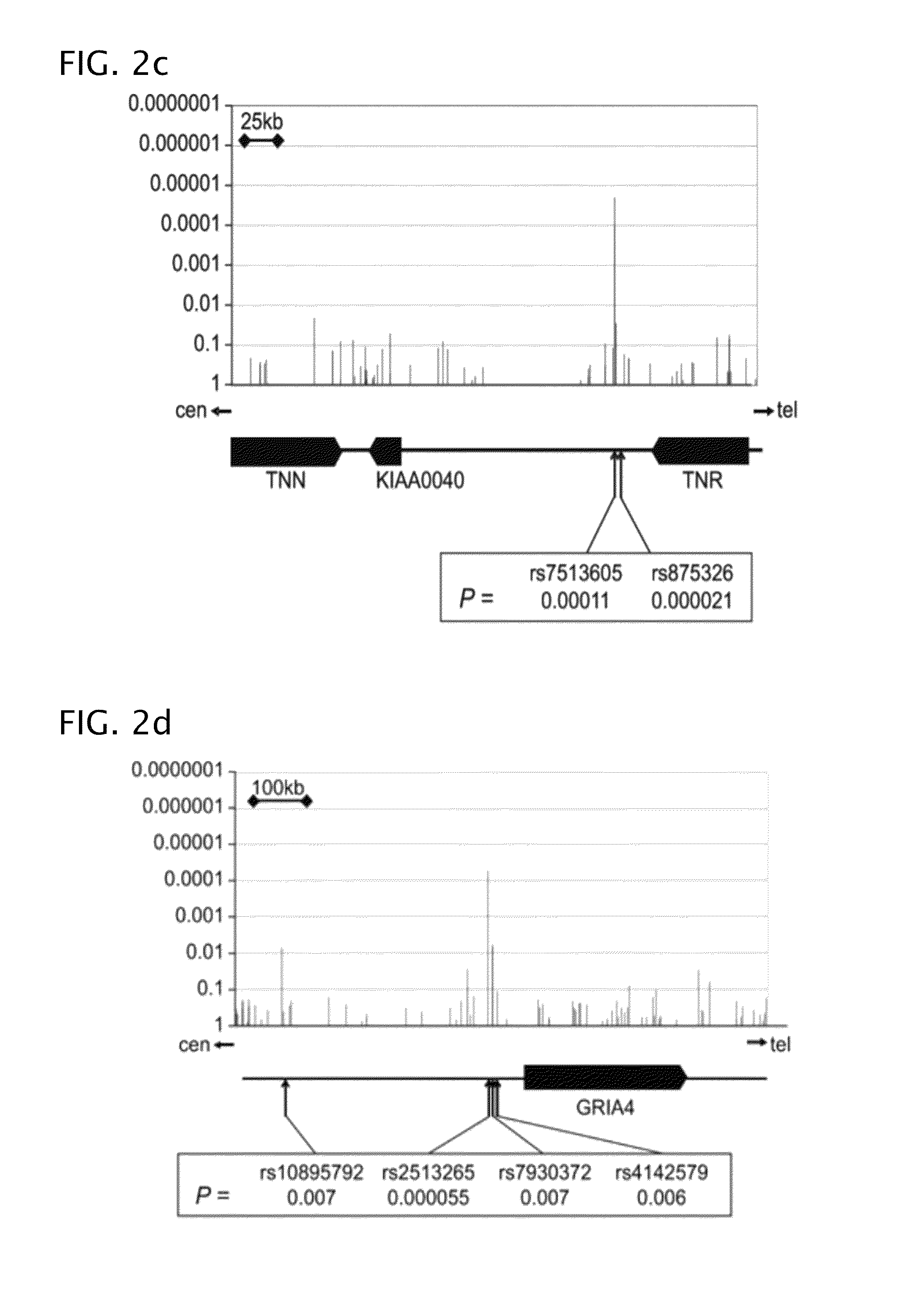
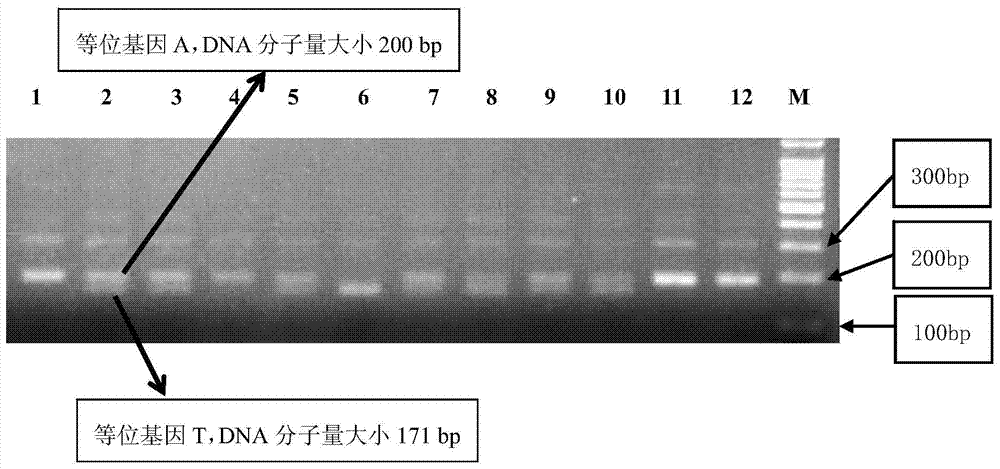
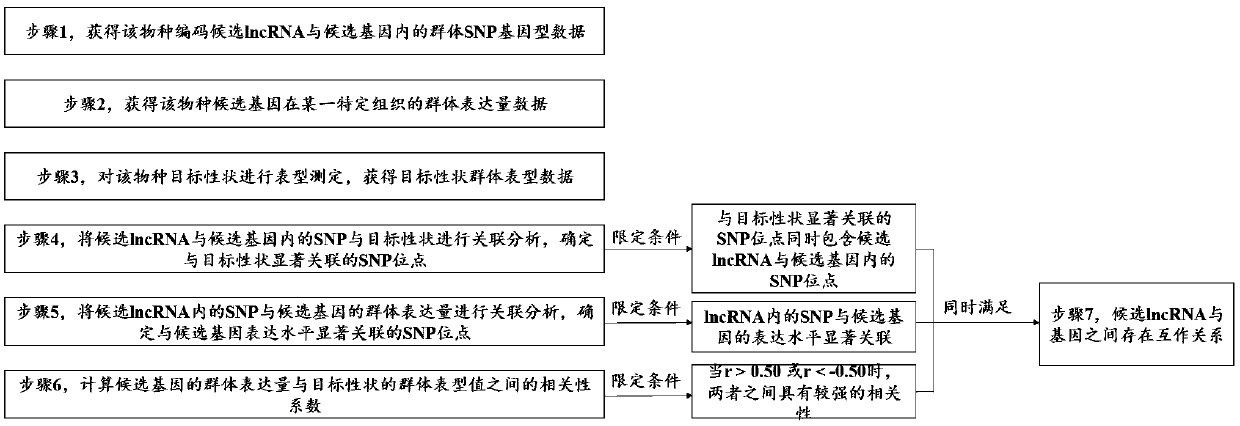
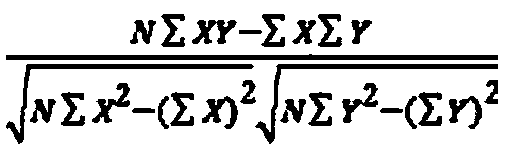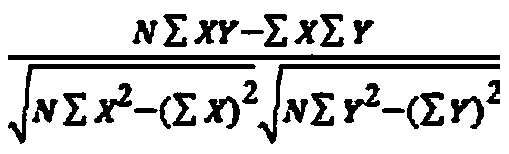Patents
Literature
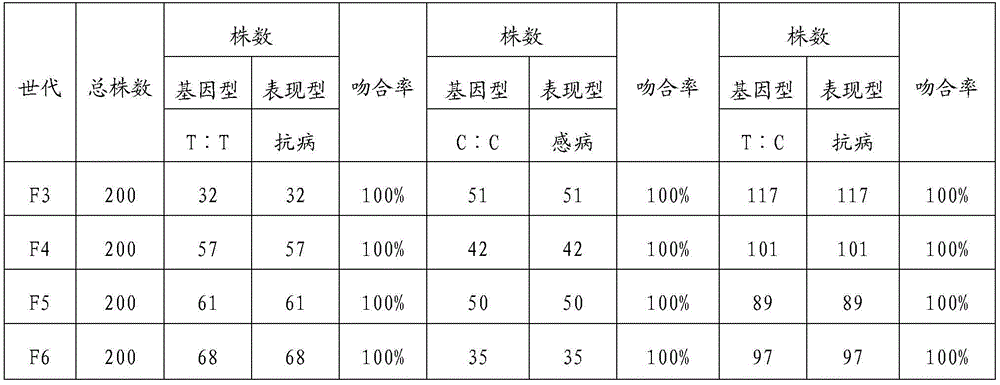
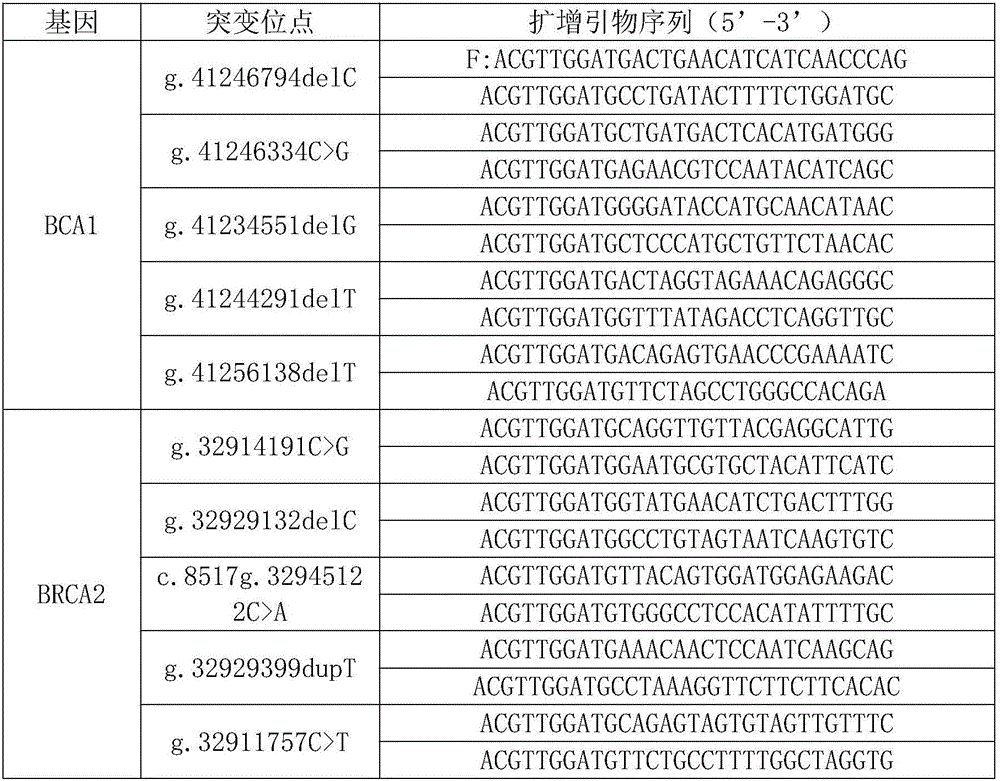
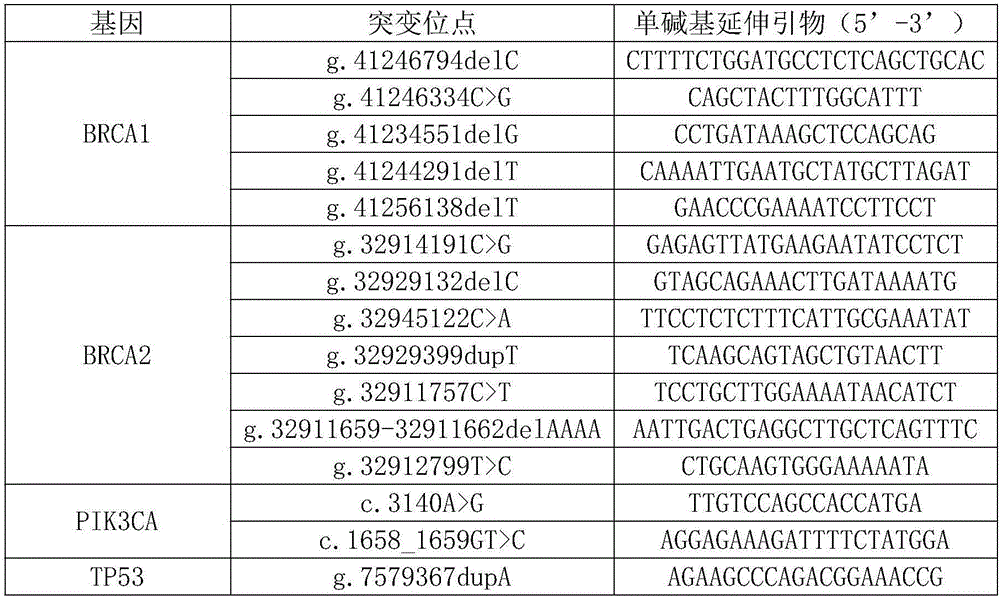
154 results about "SNP genotyping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. A SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is > 1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase of interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.
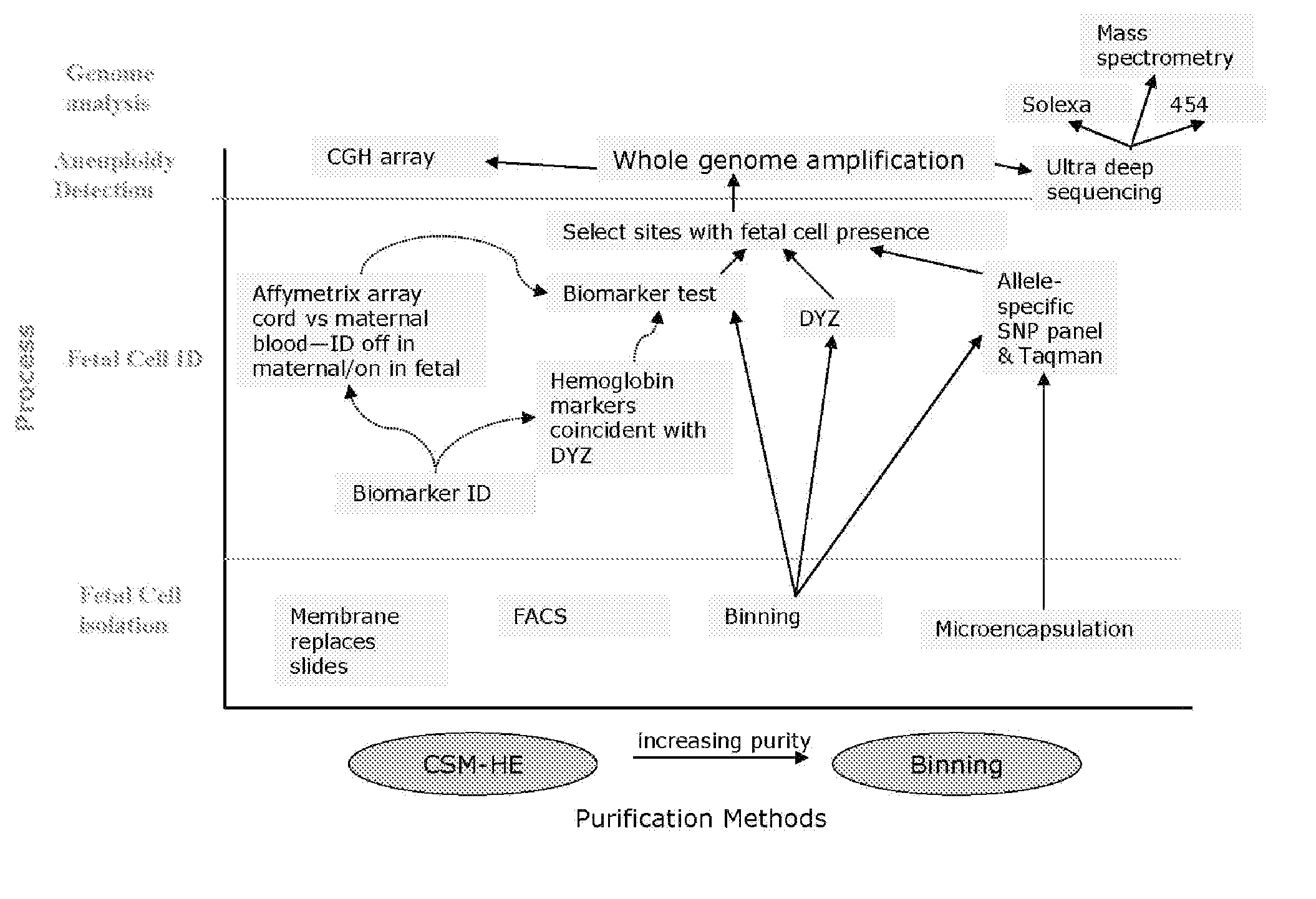
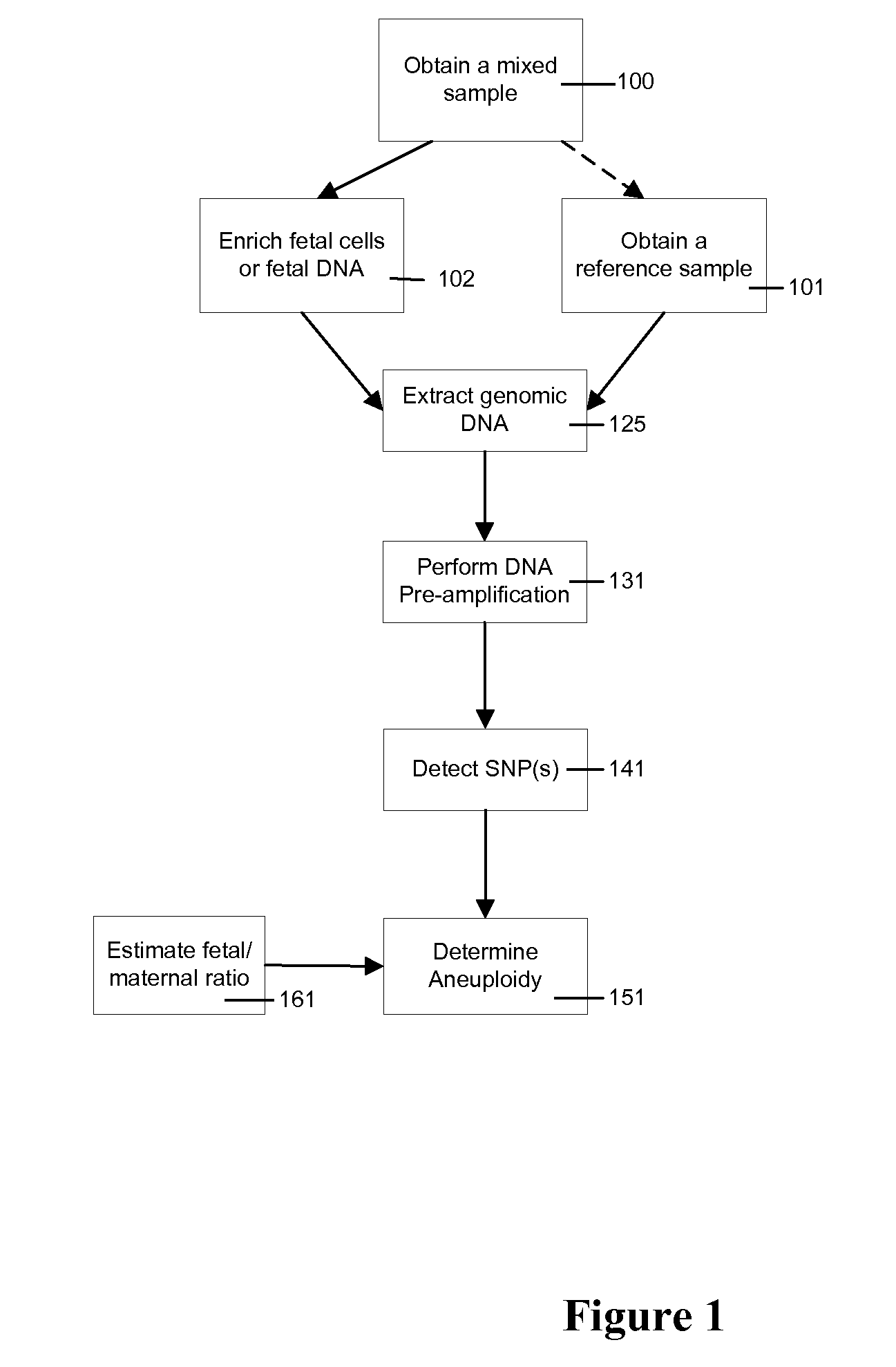
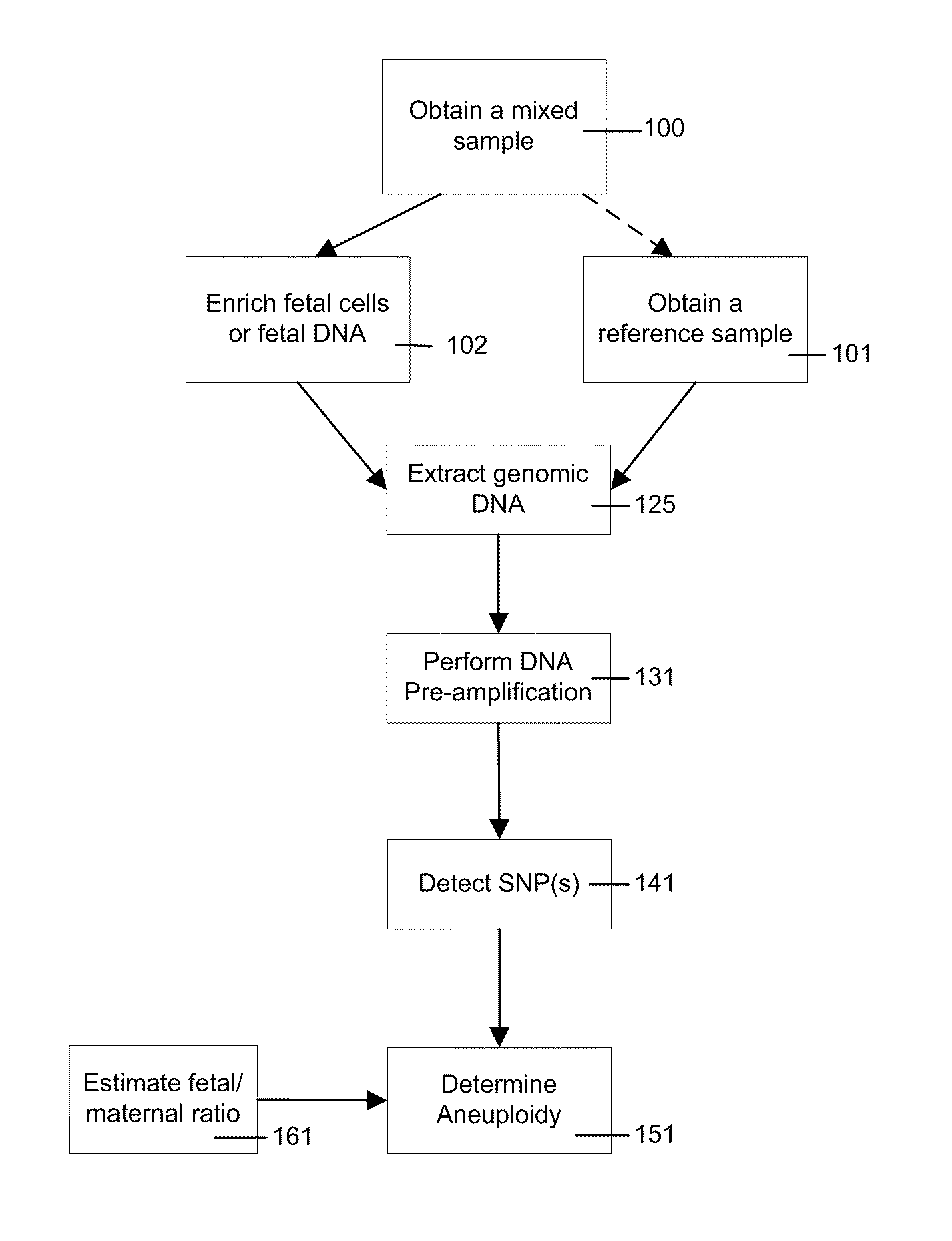
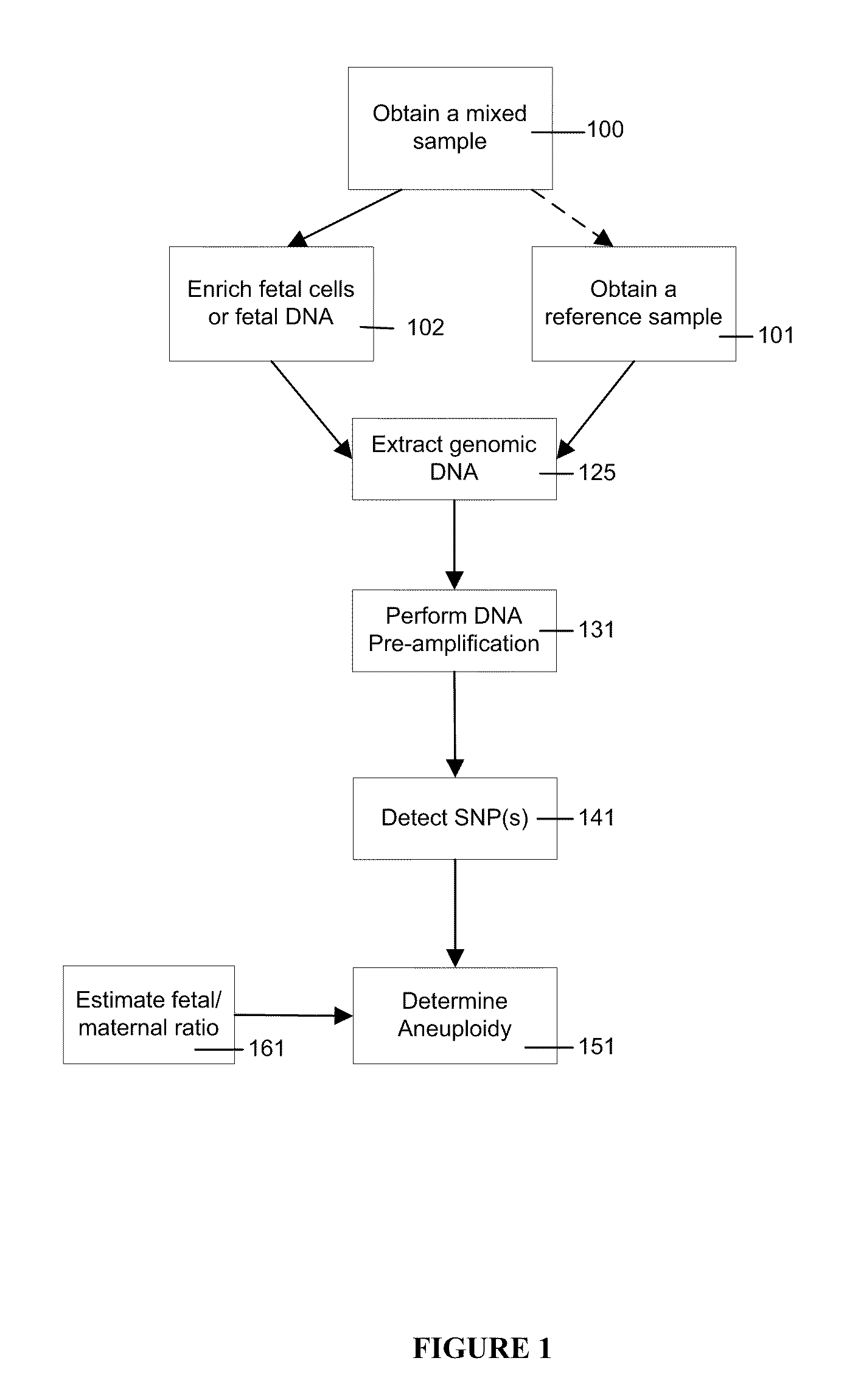
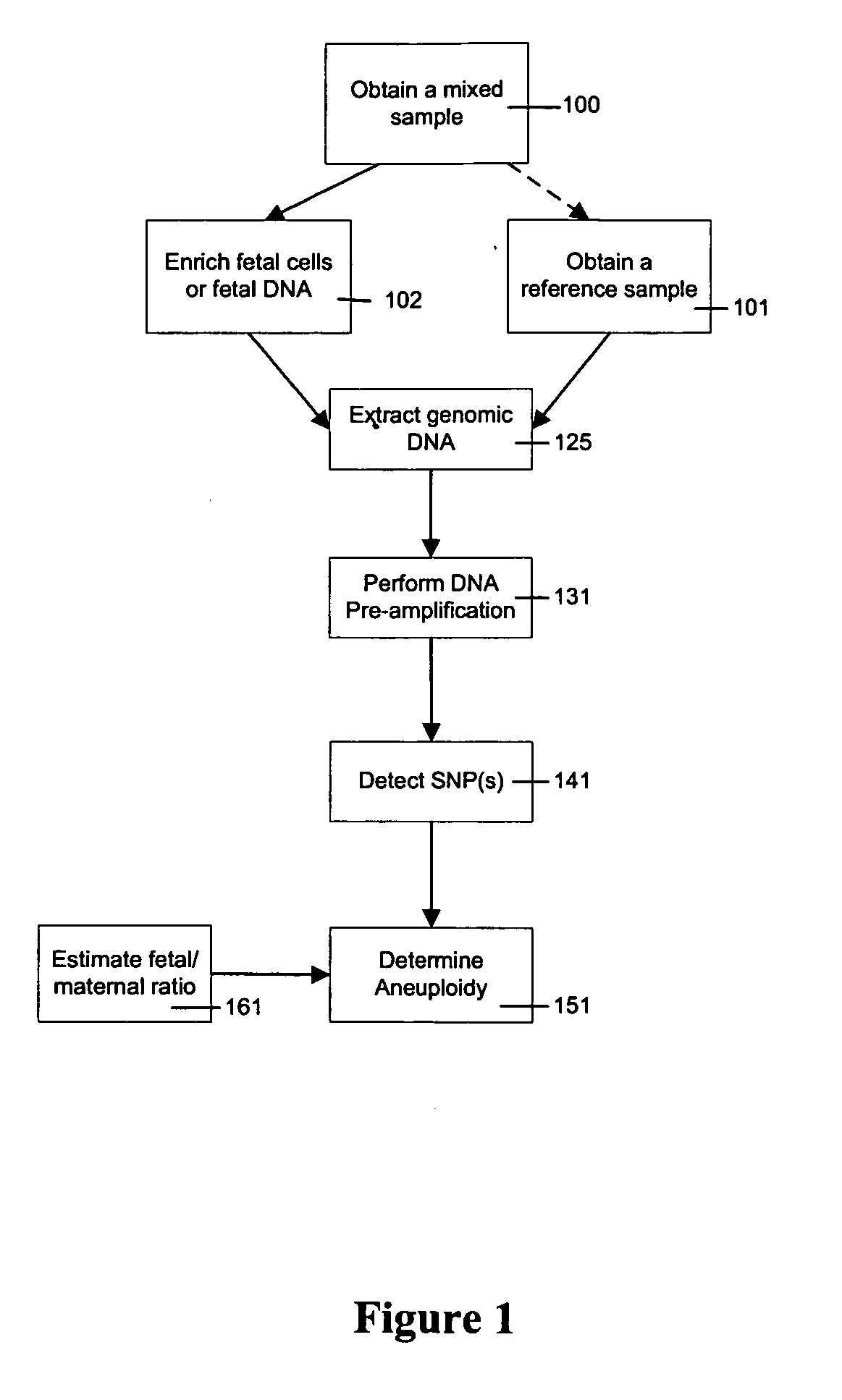
Use of highly parallel SNP genotyping for fetal diagnosis
InactiveUS20080070792A1Eliminate riskAnalysis time-consume and proneMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDiseaseBiology
The present invention provides apparatus and methods for enriching components or cells from a sample and conducting genetic analysis, such as SNP genotyping to provide diagnostic results for fetal disorders or conditions.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Fetal aneuploidy detection by sequencing
InactiveUS20100291572A1Eliminate riskAnalysis time-consume and proneMicrobiological testing/measurementFetal aneuploidyBiology
Owner:ARTEMIS HEALTH INC
Use of highly parallel SNP genotyping for fetal diagnosis
InactiveUS20090291443A1Eliminate riskAnalysis time-consume and proneMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyGenetic analysis
The present invention provides apparatus and methods for enriching components or cells from a sample and conducting genetic analysis, such as SNP genotyping to provide diagnostic results for fetal disorders or conditions.
Owner:STOUGHTON ROLAND +2
System and method for SNP genotype clustering
A system and methods for evaluating genetic information and biological data applying a clustering approach which may be used for allele calling and genotyping. Statistical analysis of sample data is performed at various levels to develop a model which associates individual data points with selected genotyping clusters and provides a relative indication of the call confidence. The methods provide a unified framework for allele-calling in many different contexts and may be applied to the data acquired from various identification methodologies.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Methods and products related to genotyping and DNA analysis
InactiveUS20090098551A1Improve throughputReduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenome ScanAllele-specific oligonucleotide
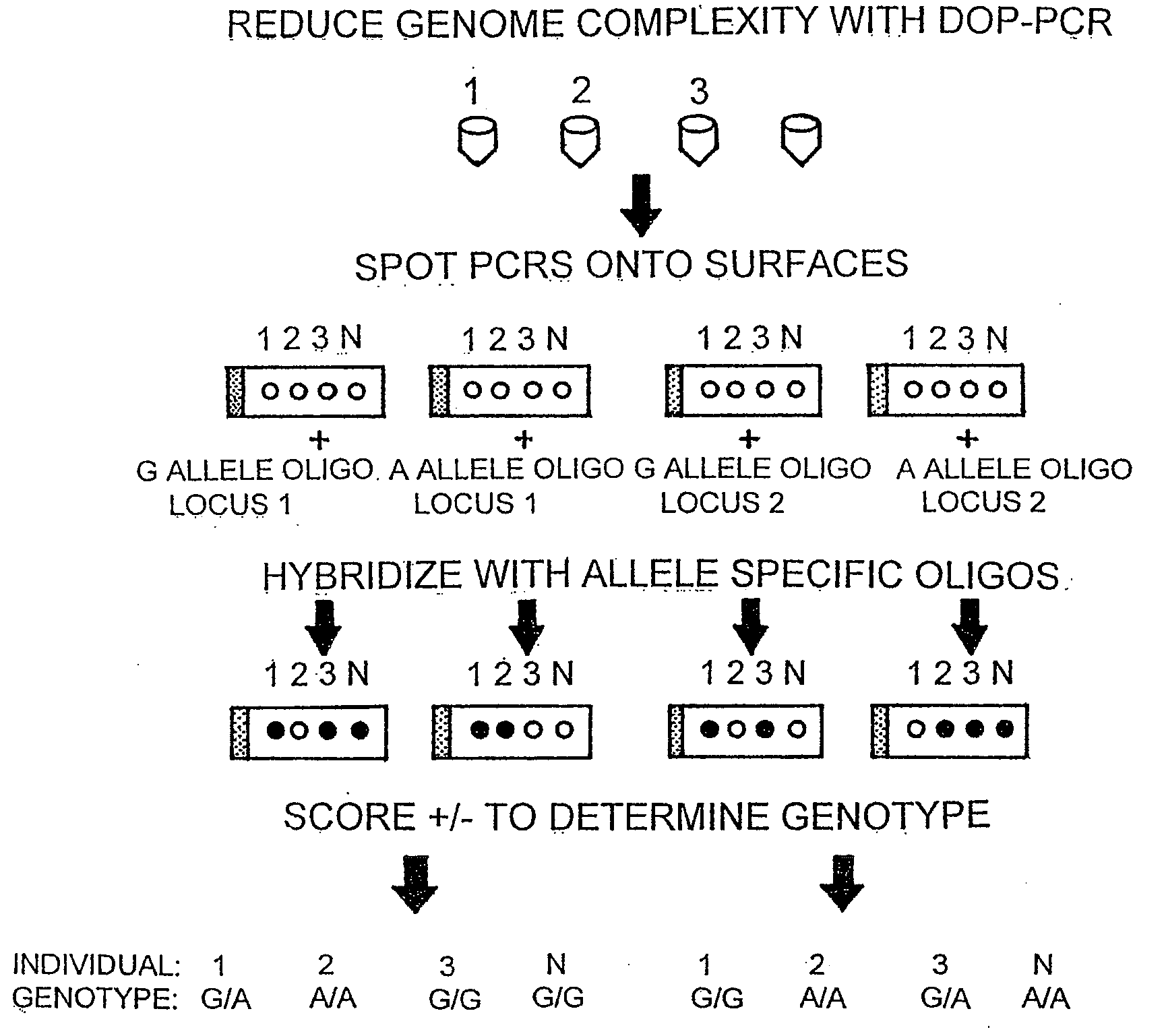
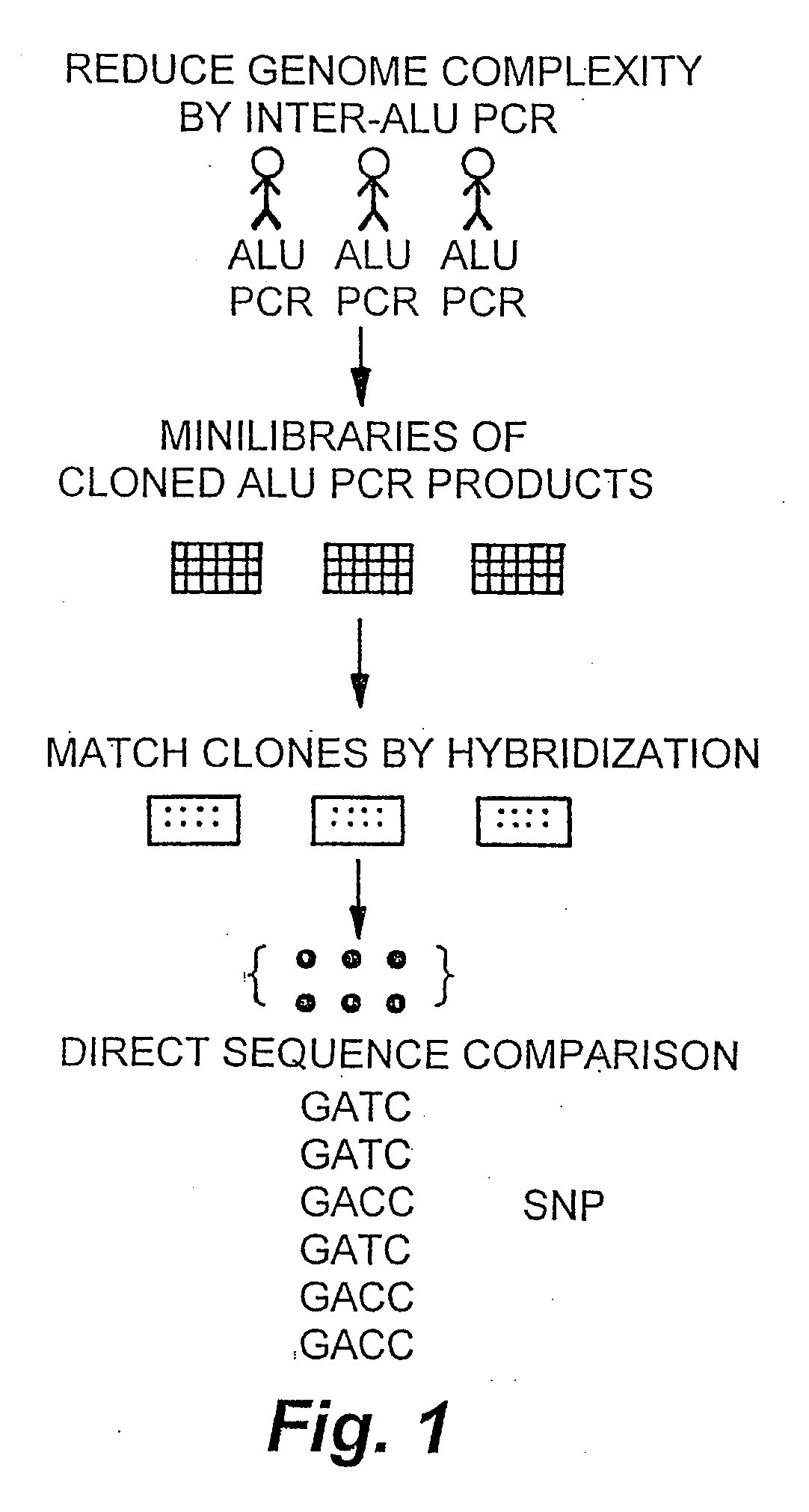
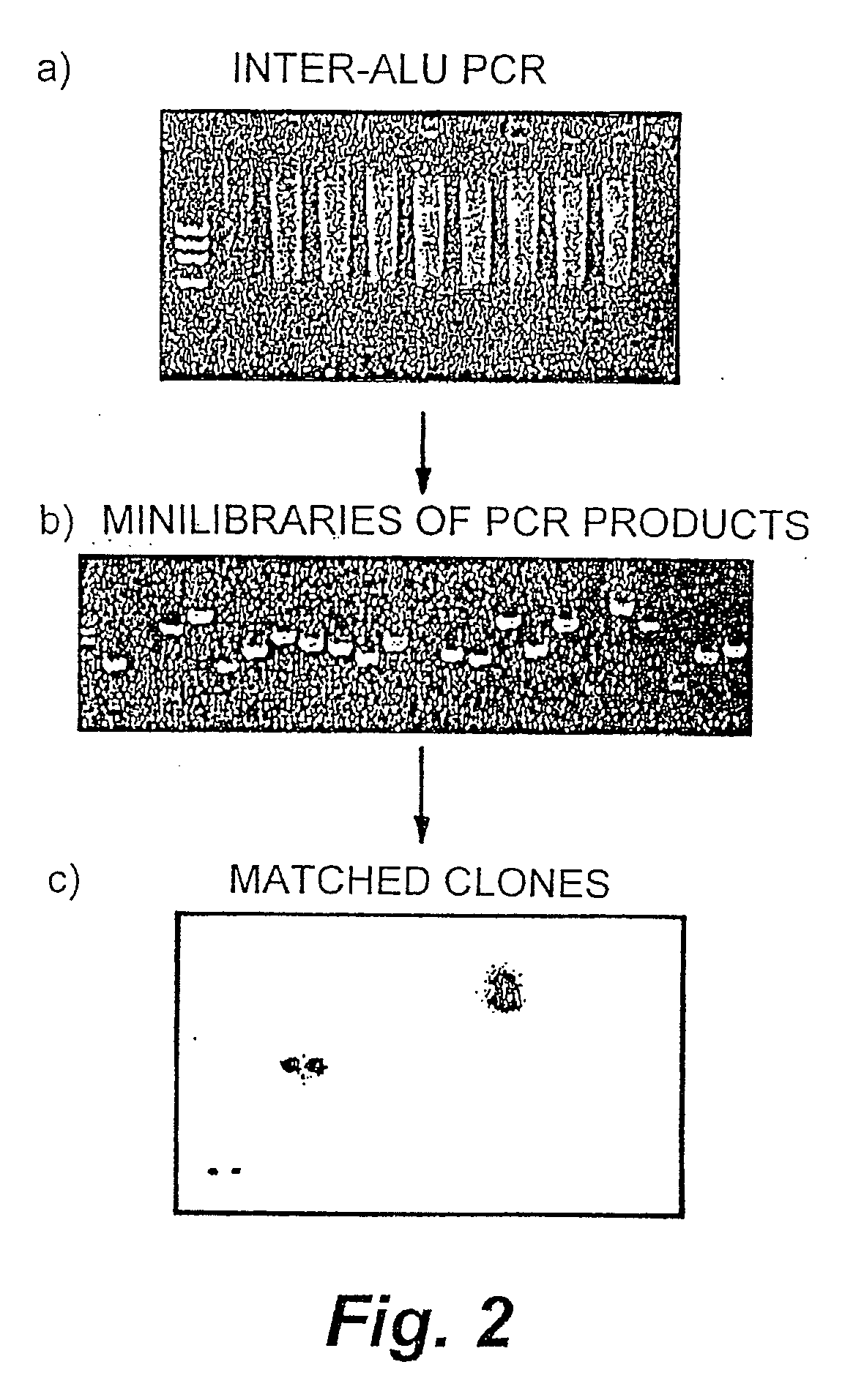
The invention encompasses methods and products related to genotyping. The method of genotyping of the invention is based on the use of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to perform high throughput genome scans. The high throughput method can be performed by hybridizing SNP allele-specific oligonucleotides and a reduced complexity genome (RCG). The invention also relates to methods of preparing the SNP specific oligonucleotides and RCGs, methods of fingerprinting, determining allele frequency for a SNP, characterizing tumors, generating a genomic classification code for a genome, identifying previously unknown SNPs, and related compositions and kits.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Using genetic polymorphisms of the bicd1 gene as a method for diagnosing and treating myopia
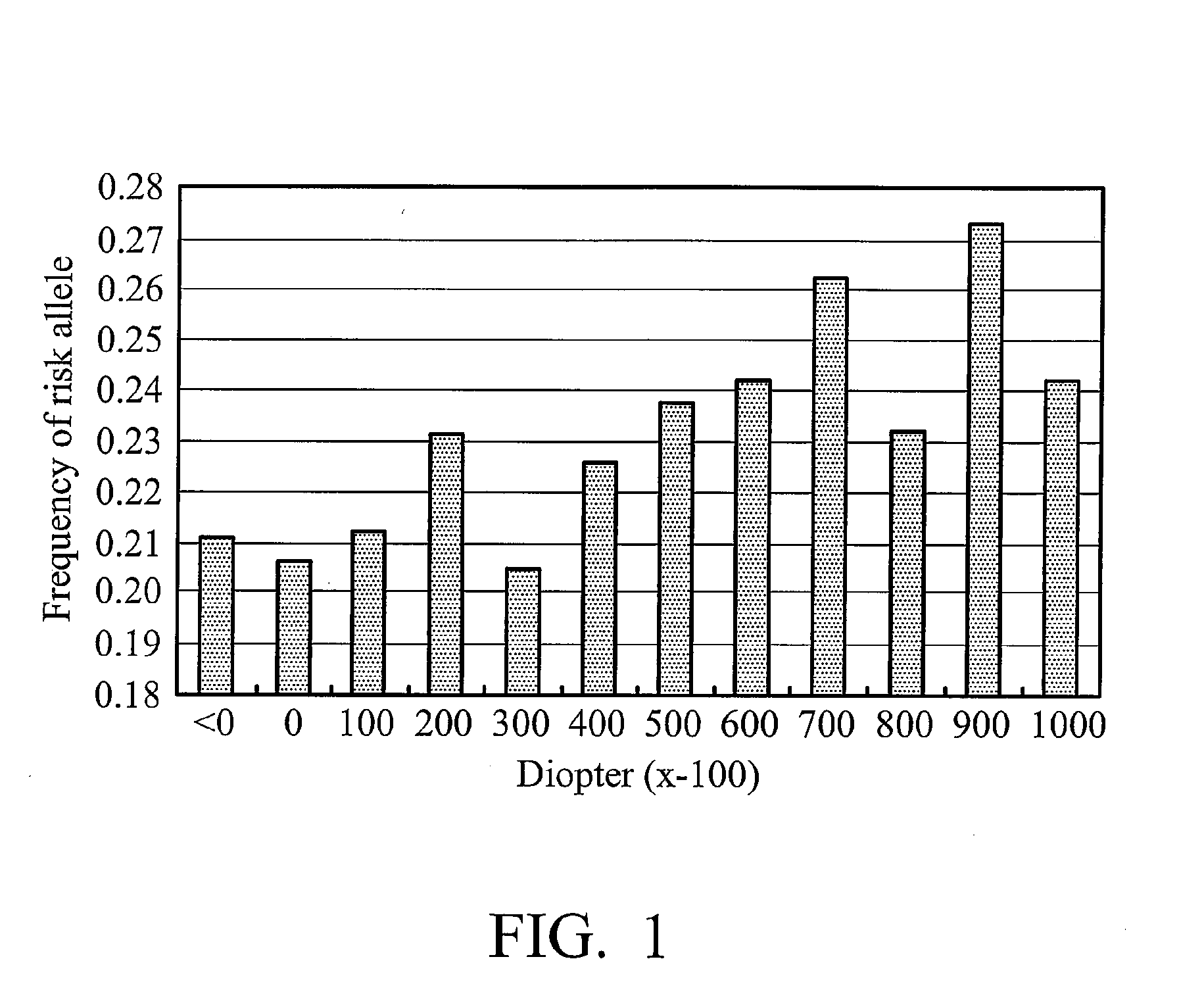
Using the BICD 1 gene as a method for diagnosing myopia and / or myopia related complications is provided. The method includes obtaining a biological sample from a subject, and determining at least one SNP genotype in the BICD1 gene in the biological sample, wherein the presence of the SNP genotype indicates that the subject is susceptible to myopia. The SNP genotype is selected from the group consisting of SNPs rs7966276, rs1151029, rs2650122, and rs10771923. In addition, the present invention also provides a method of screening a material for preventing, treating myopia, and a method of assessing a subject for probability of response to a myopia therapeutic agent.
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) marker combination and identification method of small Meishan pig and raw meat product
ActiveCN107699624AEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyRaw meat
The invention provides an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) marker combination and identification method of a small Meishan pig and a raw meat product. The method comprises the following steps: extracting a genome DNA of raw pork or a meat product, performing AGE (agarose gel electrophoresis) and Sanger sequencing after performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the genome DNA,and identifying the small Meishan pig and the meat product thereof according to an SNP genotype of a characteristic site of a sequencing result, wherein in the step of Sanger sequencing, peculiar mutation occurs at identified sites: SNP6, SNP12, SNP16, SNP71 and SNP79. According to the method, the problem that an identification method of the small Meishan pig and the meat product thereof does notexist in the prior art is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
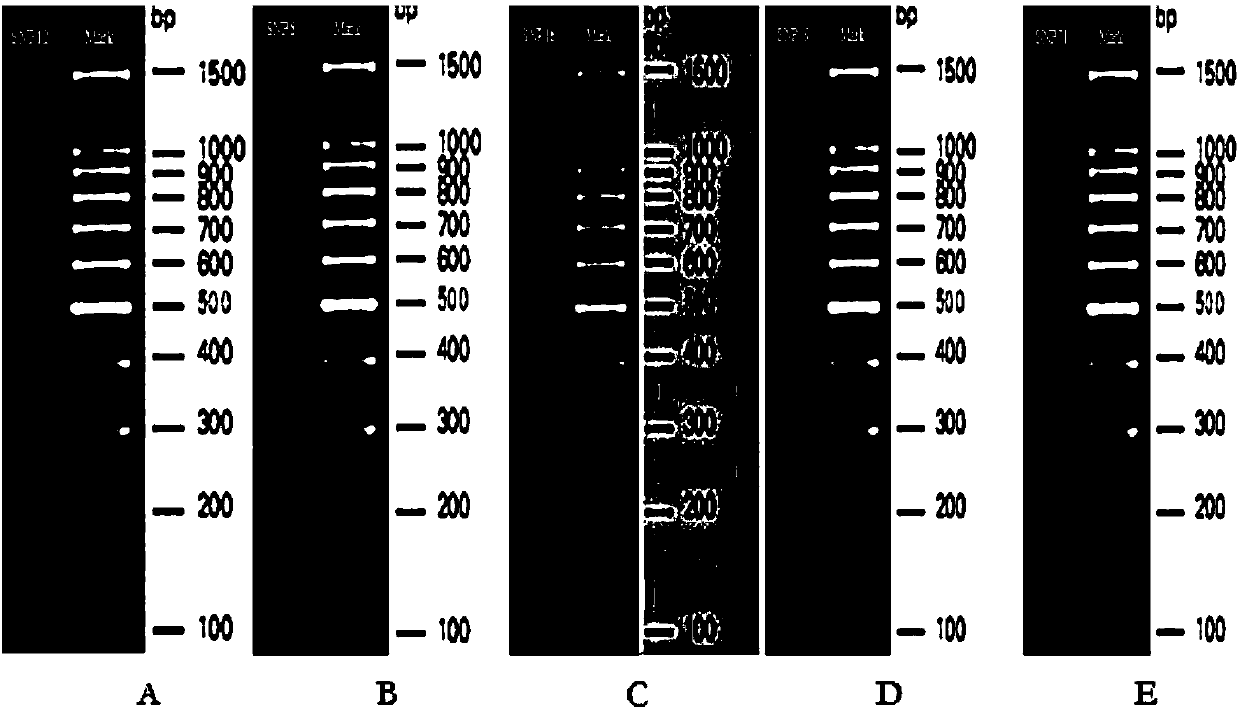
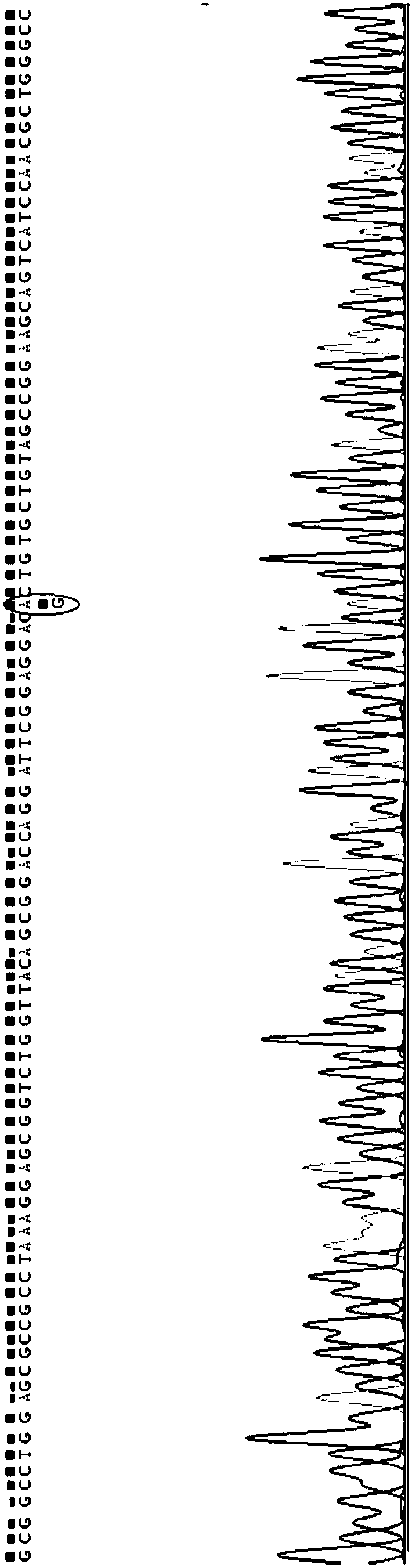
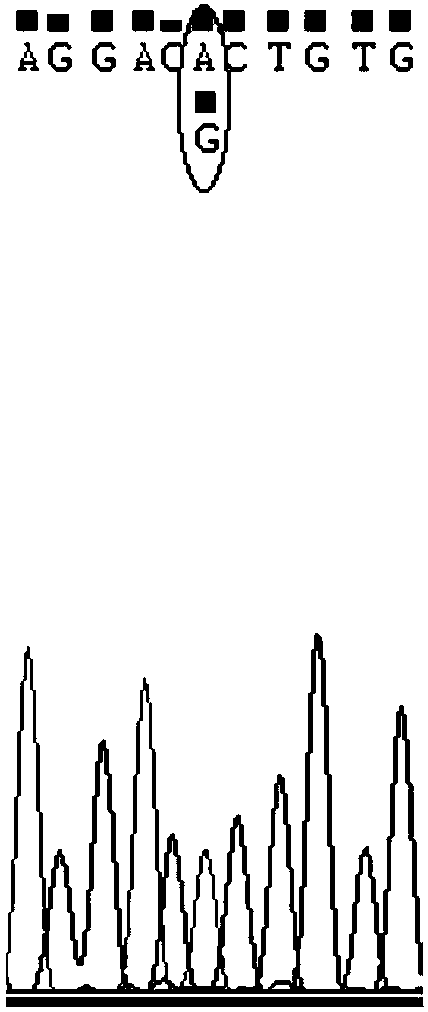
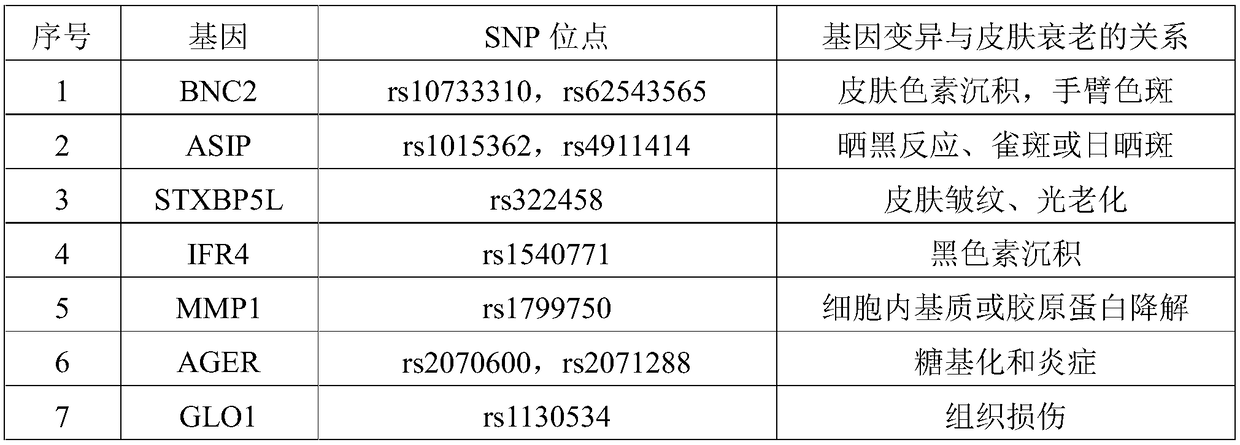
Complete-set primer applied to detecting of skin aging related susceptible genes SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) and application thereof
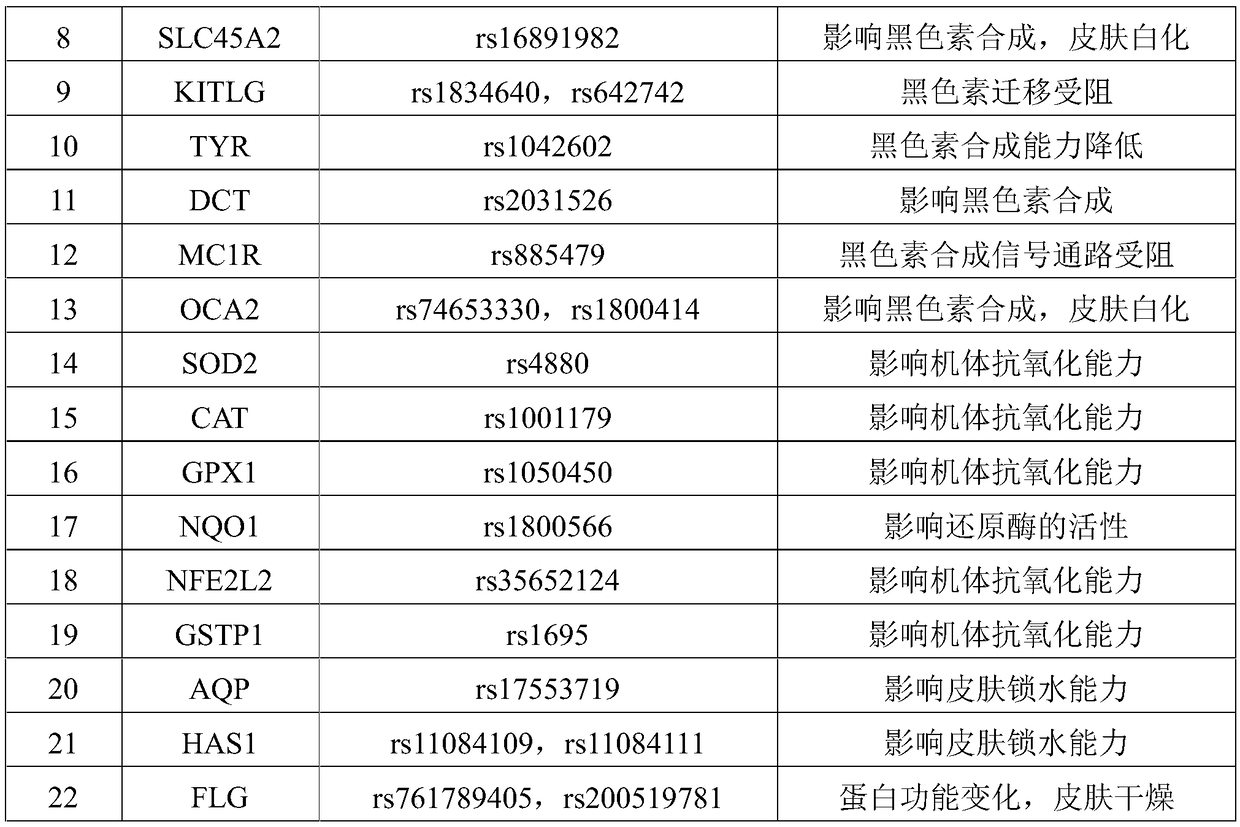
InactiveCN108251521AComprehensive Skin Genetic Testing ProgramReduce operational complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHuman DNA sequencingTime-of-flight mass spectrometry
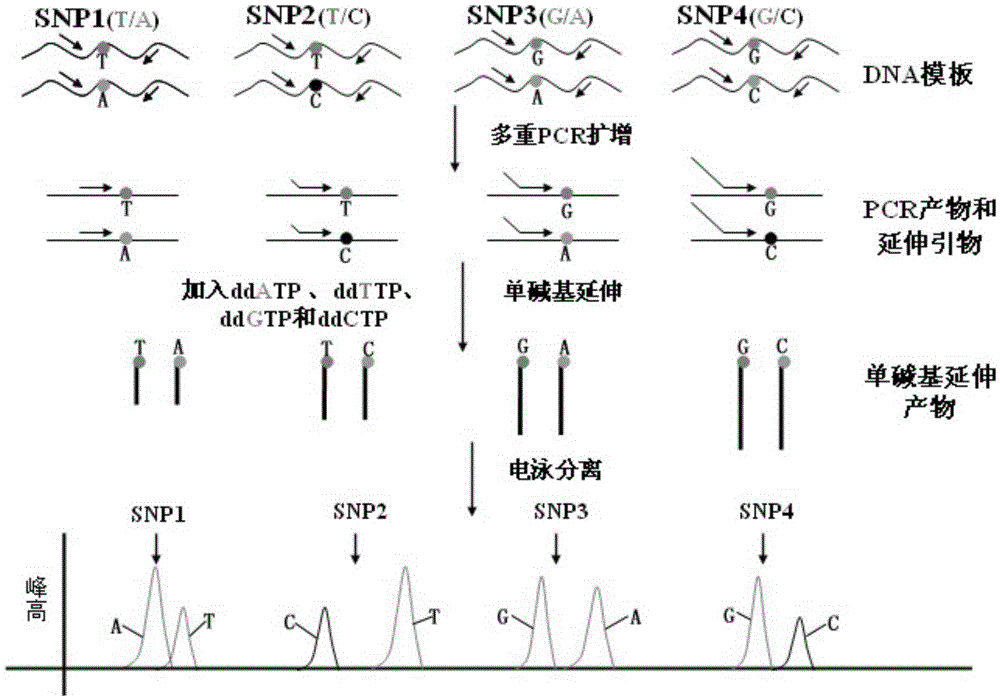
The invention relates to a complete-set primer applied to detecting of skin aging related susceptible genes SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) and application thereof. The complete-set primer is prepared from amplification primer pairs of 29 SNP sites of 22 skin aging related susceptible genes of human genome DNA and extension primers; a pair of multiple PCR amplification primers and a piece ofsingle-base extension primer are designed for each site respectively, and an MALDI-TOF MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry) method is utilized to detect SNP site genotyping of a sample to be detected. The skin aging related susceptible gene detecting method based on gene molecular subtyping disclosed by the invention can finish a plurality of SNP genotyping in the same reaction at the same time, so that accuracy, high efficiency and low cost are achieved. The gene detection disclosed by the invention can be applied to predicting of congenital agingresistance of the skin; thus, a scientific basis is provided for an external skin care scheme.
Owner:北京天平永达生物科技发展有限公司
Primers and method for detecting SNP gene typing of AhFAD2B genes of peanuts in high throughput
InactiveCN105385778AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiologySNP genotyping
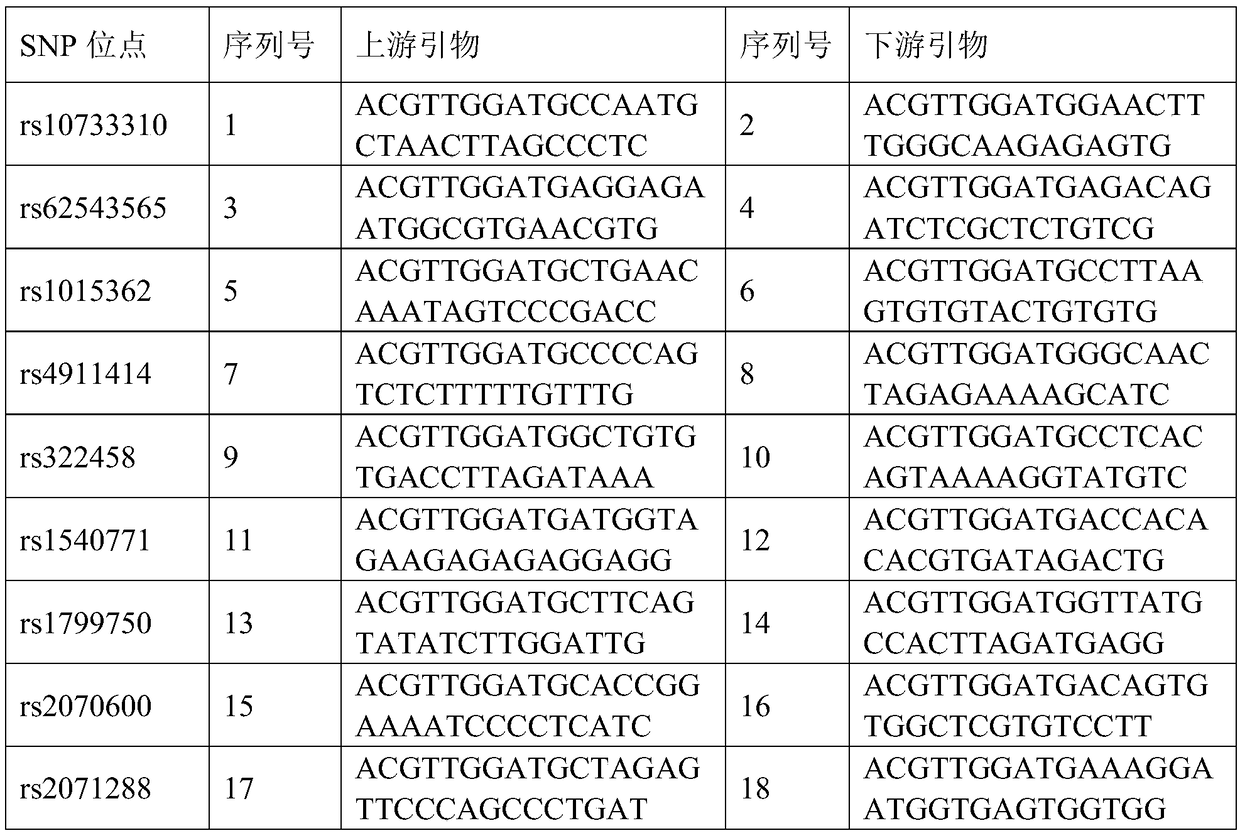
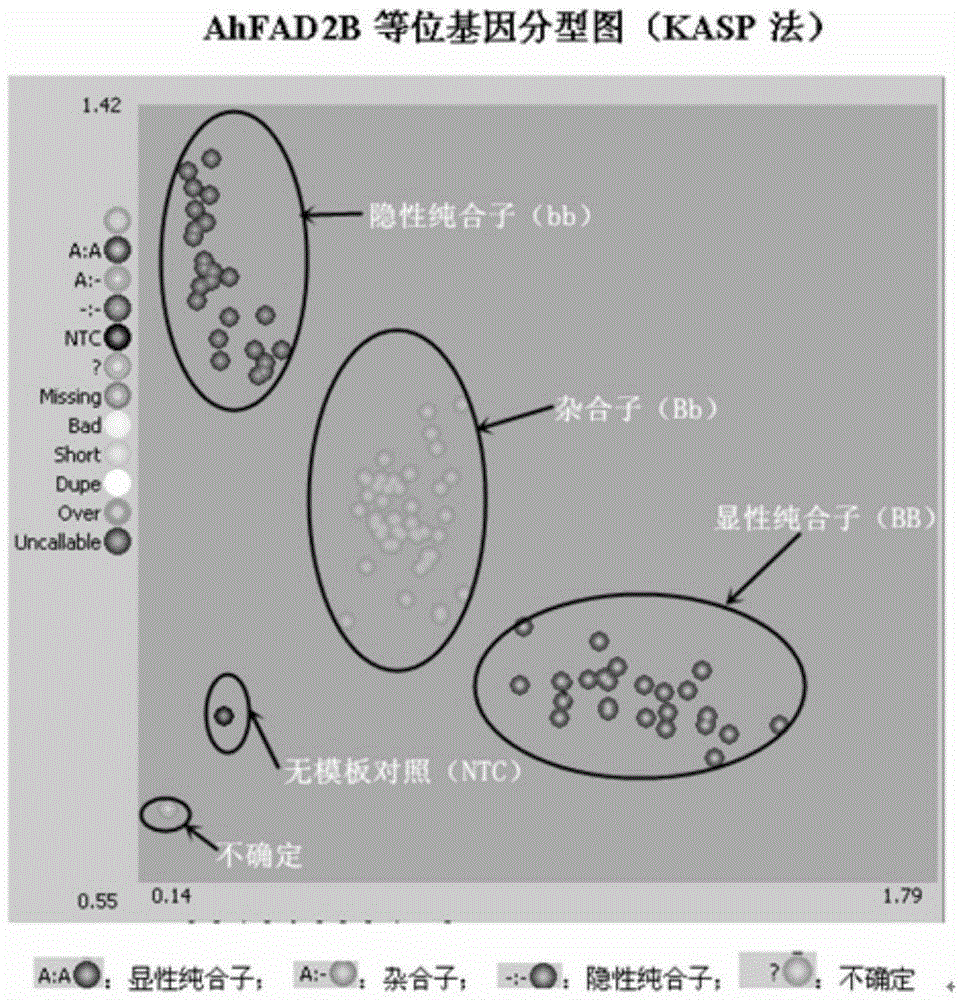
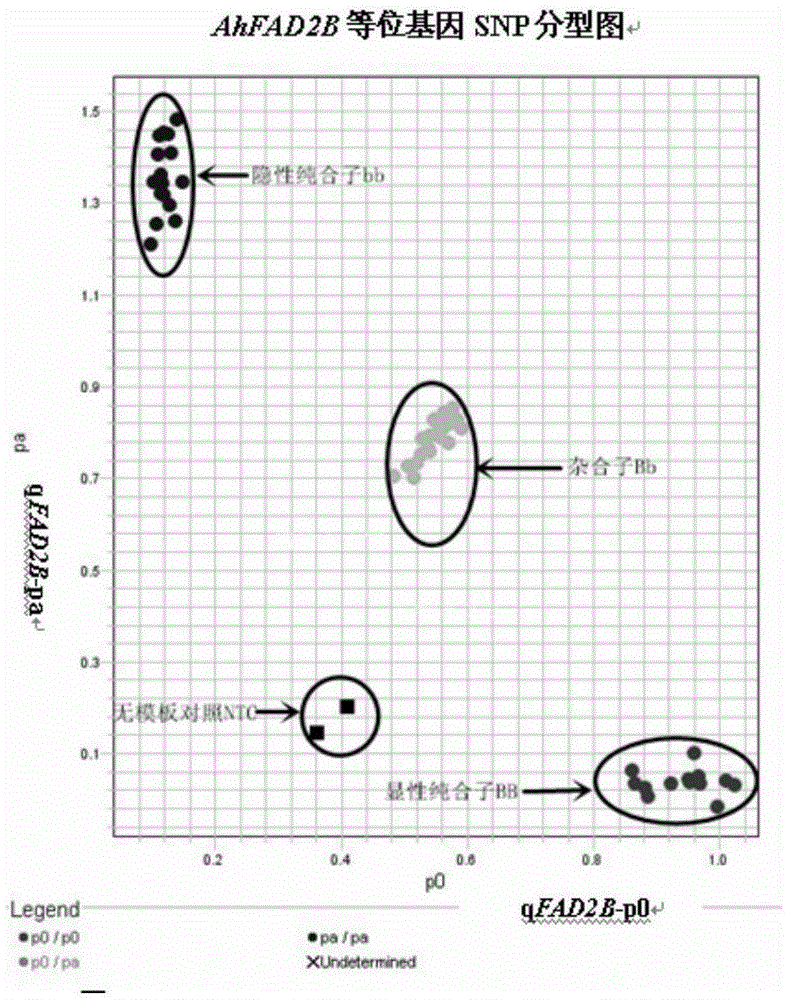
The invention relates to primers and a method for detecting SNP gene typing of AhFAD2B genes of peanuts in high throughput. The primers comprise the specific primer of which the nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2 and a universal prime of which the nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.3. According to the primers and method, the allelic variation condition of the AhFAD2B genes can be detected and identified in high throughput, the maximum sample quantity of one-time detection can reach 1536, the detection cost is low, rapidness and accuracy are achieved, and the efficiency and accuracy of peanut breeding selection are greatly improved.
Owner:BIOTECH RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
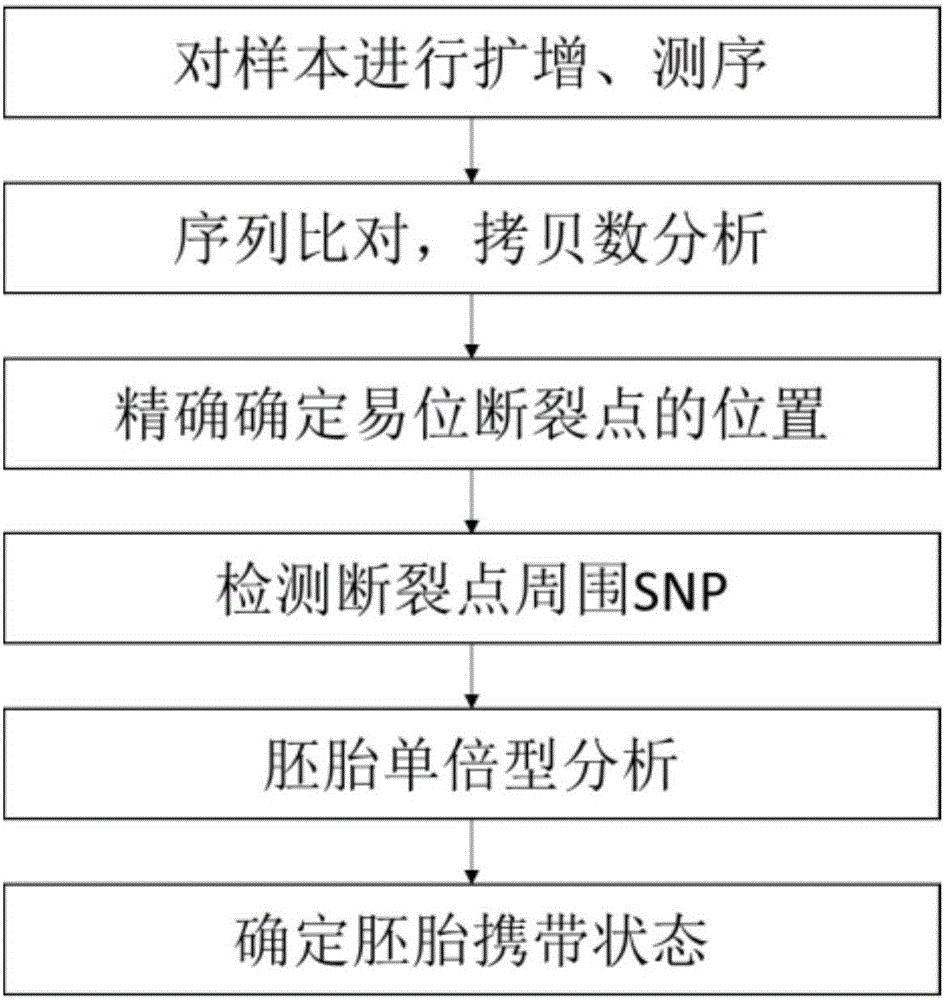
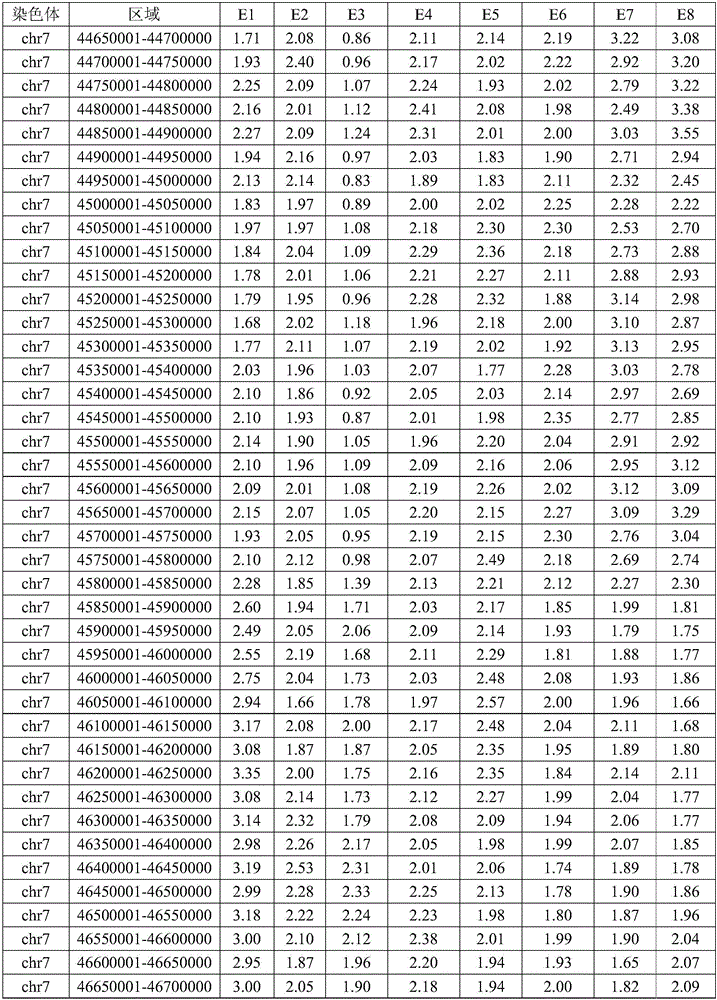
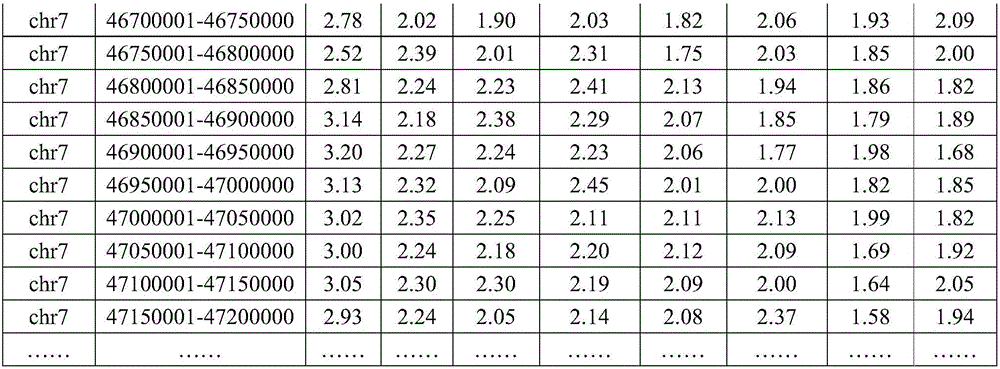
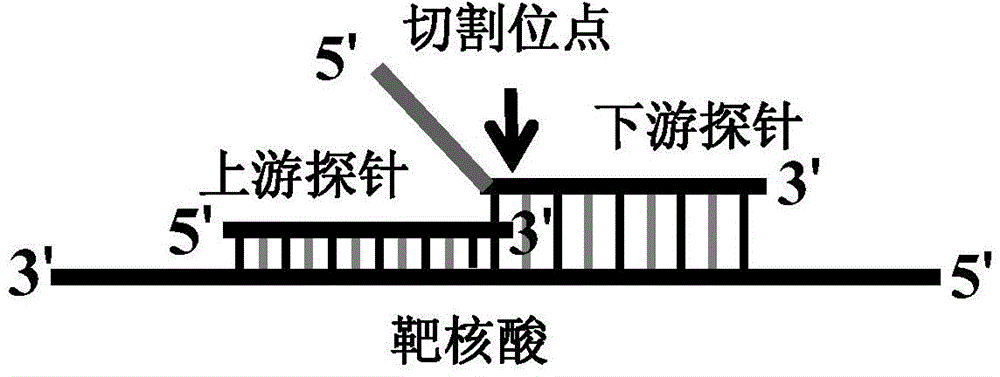
Method for identifying balanced translocation breaking point and balanced translocation carrying state of embryo
ActiveCN106834490AAccurate and effective detectionJudgment resolution improvedMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsSequence analysisCopy number analysis
The invention relates to the technical field of biotechnology and relates to the field of genome sequence analysis, and particularly relates a method for identifying a balanced translocation breaking point and a balanced translocation carrying state of an embryo. The method comprises the following steps: amplifying and sequencing a sample; comparing a sequencing sequence to a reference genome and analyzing a copy number; accurately determining a position of a translocation breaking point; detecting SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) at the periphery of the breaking point; carrying out SNP genotyping; carrying out embryo haplotype analysis; comprehensively judging a regular chromosome and a translocation chromosome haplotype; determining an embryo carrying state; and selecting an embryo without balanced translocation according to a haplotype. According to the method provided by the invention, the position of the balanced translocation breaking point can be accurately determined, and a few of SNP sites can also be used for accurately judging and typing; and the embryo without the balanced translocation is identified.
Owner:YIKON GENOMICS SHANGHAI CO LTD
Novel closed type nucleic acid visual detecting method for coupling nucleic acid amplification reaction, nucleic acid intrusive reaction and nano-particle chromogenic reaction
ActiveCN104561243AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoparticleNucleic acid sequencing
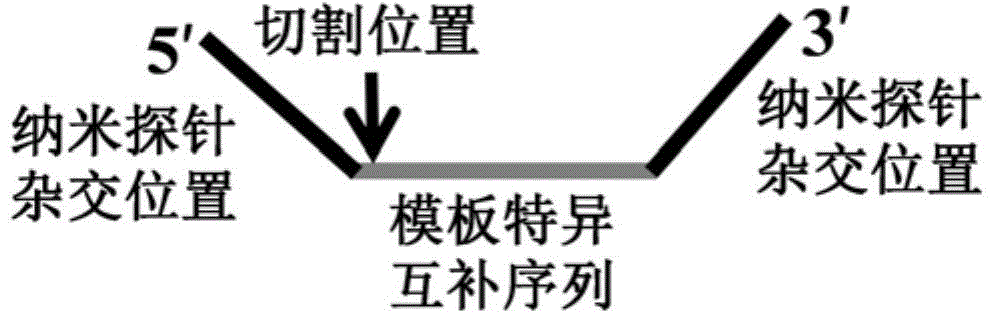
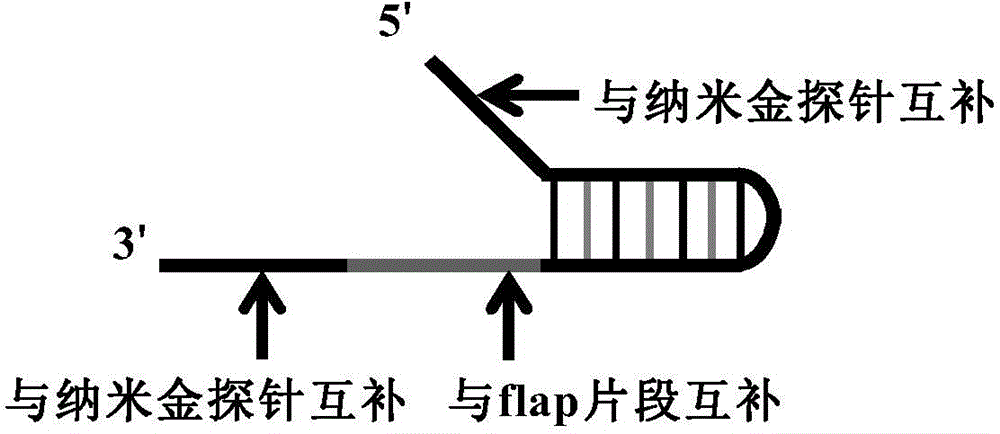
The invention discloses a novel closed type nucleic acid visual detecting method for coupling a nucleic acid amplification reaction, a nucleic acid intrusive reaction and a nano-particle chromogenic reaction. The detection method comprises the following steps: 1) target nucleic acid amplification and signal conversion phase: further amplifying the target nucleotide sequence, and converting the detection of the target nucleic acid to the detection of a hairpin probe fragment; 2) nanoprobe hybridization phase: after the amplification reaction, under the corresponding conditions, generating a gathering or dispersing phenomenon by the special nanoprobe, and utilizing the phenomenon to realize distinguishing detection to the target nucleic acid. With adoption of the detection method disclosed by the invention, the nucleic acid target sequence can be detected; furthermore, the nucleic acid intrusive reaction is high in specificity, and the nucleic acid sequence with single different basic groups near the intrusive loci can be distinguished and detected, so that the method not only can be used for detecting a template, but also can be used for single basic group distinguished SNP genotyping and gene mutation.
Owner:NANJING GENERAL HOSPITAL NANJING MILLITARY COMMAND P L A
Antipsychotic treatment based on SNP genotype
The present invention relates to the prediction of antipsychotic treatment efficacy based on a patient's genotype at one or more single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) loci and to the treatment of a patient based on such prediction.
Owner:VANDA PHARMA INC
Genetic marker for character of litter size of pig utilizing SLA-11 gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of manufacturing of animal genetic markers, and particularly relates to the technical field of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) detection at the 3908 bp of the third intron of the pig SLA-11 gene. A method for screening the genetic marker for character of litter size of the pig comprises the following steps: extracting a genome DNA from pig blood, designing a primer, performing PCR amplification, cloning PCR products, measuring sequence, comparing and analyzing the sequence, performing SNP detection, marking, conducting correlation analysis among the characters of litter sizes. According to the invention, the DNA sequence in the third intron zone of the pig SLA-11 gene, the SNP genotyping detection, and the genetic marker are obtained; the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1-10; base mutations (C / T) exist at the position of 68 bp in the sequence table of SEQ ID NO: 1-10, and lead to the polymorphism of the MspI-RFLP. The invention further discloses a manufacturing method and application of the genetic marker.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +1
Molecular marker identification method related to pig birth litter weight and fetal weight and application of molecular marker identification method
ActiveCN106011245AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAllele frequencyFetal weight
The invention discloses a molecular marker identification method related to pig birth litter weight and fetal weight and an application of the molecular marker identification method. The identification method comprises the following steps: collecting a sample; extracting and detecting pig genome DNA; then, conducting SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) chip genotype judgment and genotype data quality control: adding a PCR amplification primer pair and conducting a PCR amplification reaction by taking DNA of the sample as a template, purifying a reaction product and co-crystallizing the purified reaction product with a mass spectrum chip, conducting detection and typing by virtue of a flight mass spectrum method, detecting an SNP site of a target gene, computing an SNP genotype and an allele frequency by virtue of PopGene3.2, and conducting association analysis on the SNP and characters by virtue of SAS9.2 software; and finally, conducting data collating and analysis. The identification method disclosed by the invention, by determining the genotype of a pig individual, can assist identification of multiparous litter weight and fetal weight.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Antipsychotic treatment based on SNP genotype
The present invention relates to the prediction of antipsychotic treatment efficacy based on a patient's genotype at one or more single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) loci and to the treatment of a patient based on such prediction.
Owner:VANDA PHARMA INC
Method of determining genetic predisposition for deficiency in health functions using SNP analysis
InactiveUS20070254306A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingDNA methylationInherited Predisposition
A method of determining genetic predisposition for deficiency in a specific health function of a person using single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis is provided. The method includes performing a SNP genotyping assay of three or more genes using a sample obtained from the person, obtaining a SNP panel which includes predetermined identifier SNPs, comparing the SNP panel with a predetermined criterion defining the genetic predisposition for deficiency in a specific health function; and reporting presence of genetic predisposition for deficiency in this health function if the SNP panel meets the predetermined criterion. The health function includes glycation, inflammation, DNA methylation, oxidation or DNA repair.
Owner:GIAMPAPA VINCENT C
Genetic marker for character of litter size of pig utilizing WIF1 gene
A genetic marker for character of litter size of a pig utilizing WIF1 gene belongs to the technical field of genetic markers, and relates to the technical field of detection to single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) detection of the fifth intron of the encoding gene of a pig gene WIF1. A method for screening the genetic marker for character of litter size of the pig comprises the following steps: obtaining a genome DNA from pig blood, designing a primer, performing PCR amplification, cloning the PCR products, measuring sequence, comparing and analyzing the sequence, performing SNP detection, marking, conducting correlation analysis among the characters of litter sizes. The DNA sequence of the fifth intron of the pig gene WIF1 and the SNP genotyping detection and a genetic marker are disclosed; the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1-7; an allele mutation exists in the 133 bp position in the sequence table of SEQ ID NO:1-7, and leads to the polymorphism of Ase1-RFLP. The invention further discloses a manufacturing method and application of the genetic marker.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +1
SNP411871 marker associated to shell mould and weight of pinctada martensii, primer and application thereof
ActiveCN104711343AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceHinge line
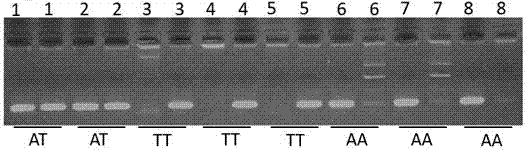
The invention discloses a SNP411871 marker associated to shell mould and weight of pinctada martensii, a primer and an application thereof. The primer comprises 411871FI: GGAAACGGAATTCACATTCATTATCTTTA; 411871RI: AATGTCAAGCTGGATATAATTTAGCTCTA; 411871FO: AAATTATTGAAACTATTTCACCGATTCG; and 411871RO: TTGTGATTTCATTTTCGTATCAATATTCTT. According to the invention, a specific SNP genotype site can be amplified by the primer, size of individual shell length and hinge line length as well as weight of soft part and adductor muscle can be visually compared according to a PCR electrophoretogram, nd the primer can be directly used for subsequent molecular mark assisted breeding.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for identifying plant lncRNA and gene interaction
ActiveCN109545278AAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsDiameter at breast heightCorrelation analysis
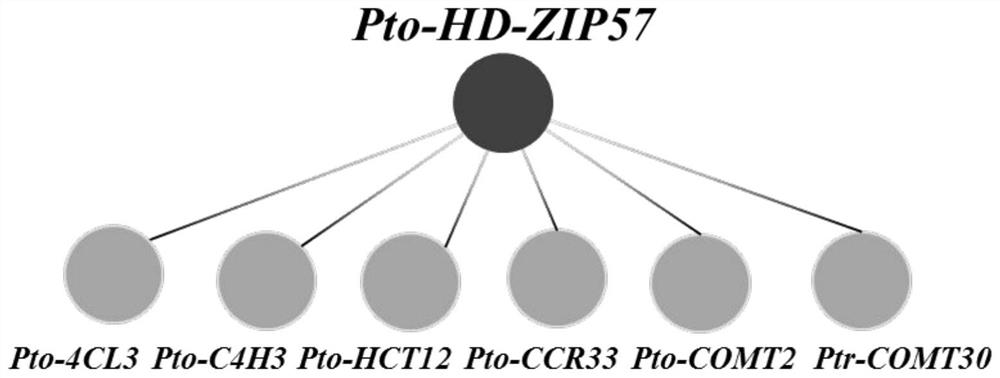
The present invention provides a method for identifying plant lncRNA and gene interaction, and relates to the technical field of molecular genetics. The method comprises the following steps: population SNP genotype data of lncRNA and gene are obtained; population expression data of the gene in a studied tissue are obtained; target trait population phenotypic data are obtained; the population SNP genotype data and target trait population phenotypic data are subjected to correlation analysis; the population SNP genotype data and population expression data are subjected to correlation analysis; acorrelation coefficient r of the population SNP genotype data and target trait population phenotypic data is calculated; when three limit conditions are met at the same time, the lncRNA interacts with the gene to commonly affect phenotypic variation of plant target traits. The method is used to accurately detect interaction between populus tomentosa lncRNA LNC-0052611 and gene Pto-COMT25, and theinteraction affects the phenotypic variation of diameter at breast height of populus tomentosa.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Kit for SNP genotyping of Chinese children short stature susceptibilty genes and utilization method of kit
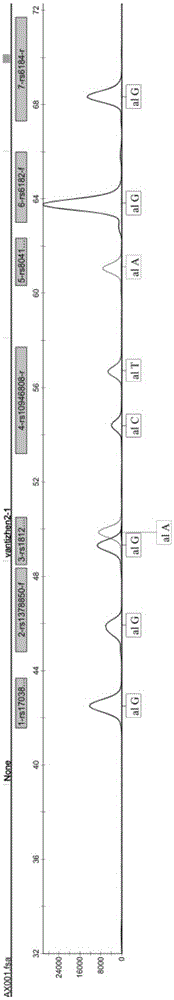
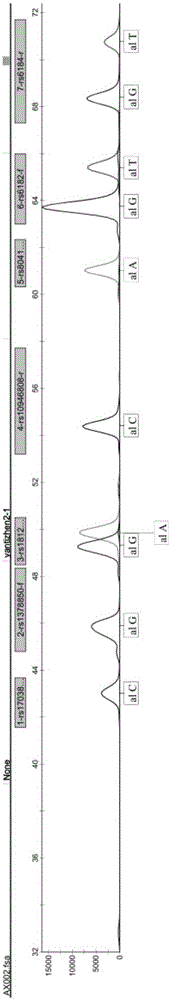
The invention relates to a kit for SNP genotyping of Chinese children short stature susceptibilty genes and a utilization method of the kit and particularly discloses a simultaneous qualitative and genotyping kit aiming at 12 SNP loci of 8 short stature susceptibilty genes of Chinese children and a utilization method of the simultaneous qualitative and genotyping kit. The method includes: taking a rs17038182 locus of an SPAG17 gene, a rs1378850 locus of a KBTBD gene, a rs1812175 locus of an HHIP gene, a rs10946808 locus of an HIST1H1D gene, a rs8041863 locus of an ACAN gene, a rs6182 locus of a GHR gene, a rs6184 locus of the GHR gene, a rs4410646 locus of the GHR gene, a rs12515480 locus of the GHR gene, a rs2940913 locus of the GHR gene, a rs1976667 locus of an IGF-1R gene and a rs3099 locus of an IHH gene as detection objects, respectively designing amplification primers and extension primers aiming at mutation of each SNP locus, performing multiplex PCR amplification and mark extension aiming at the 12 SNP loci, and performing capillary electrophoresis analysis to obtain genotypes of the 12 SNP loci at the same time. The kit for SNP genotyping has the advantages of convenience in use, simplicity in operation, low cost, high flux, directness and reliability of detection results and applicability to large-scale screening of SNP genotyping of the Chinese children short stature susceptibilty genes.
Owner:LIUZHOU CITY HEALTHCARE HOSPITAL FOR WOMEN & CHILDREN
Method for dividing breeding swine blood linkage based on whole genome SNP information
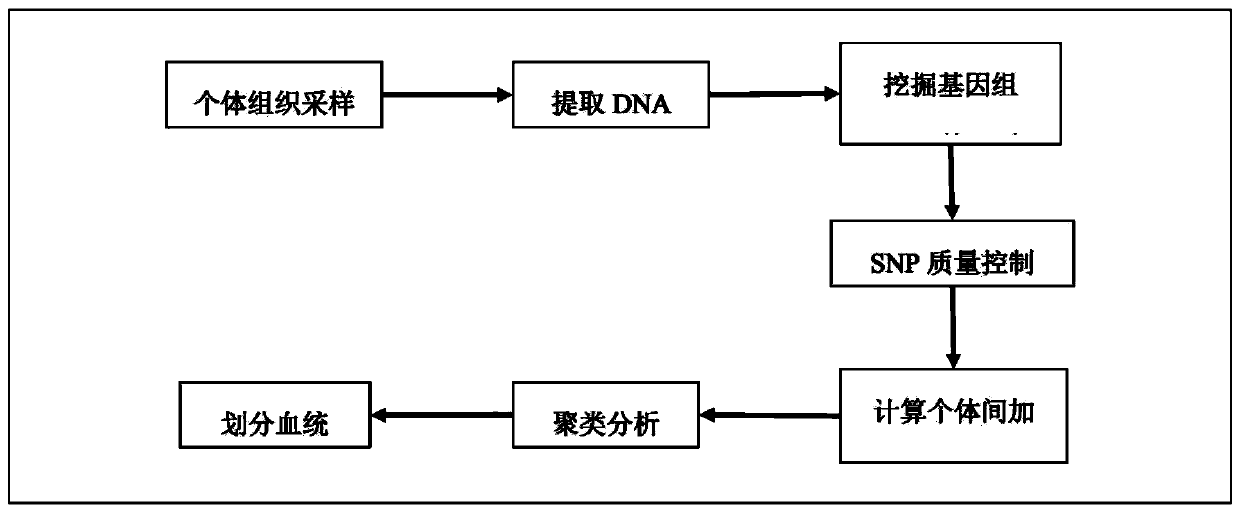
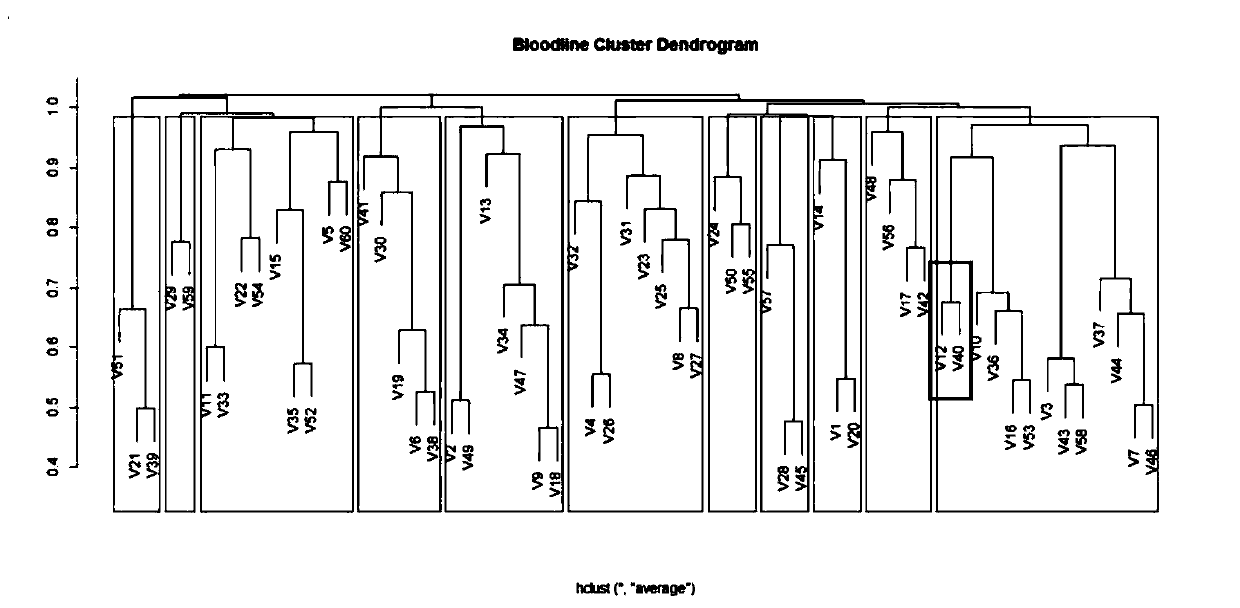
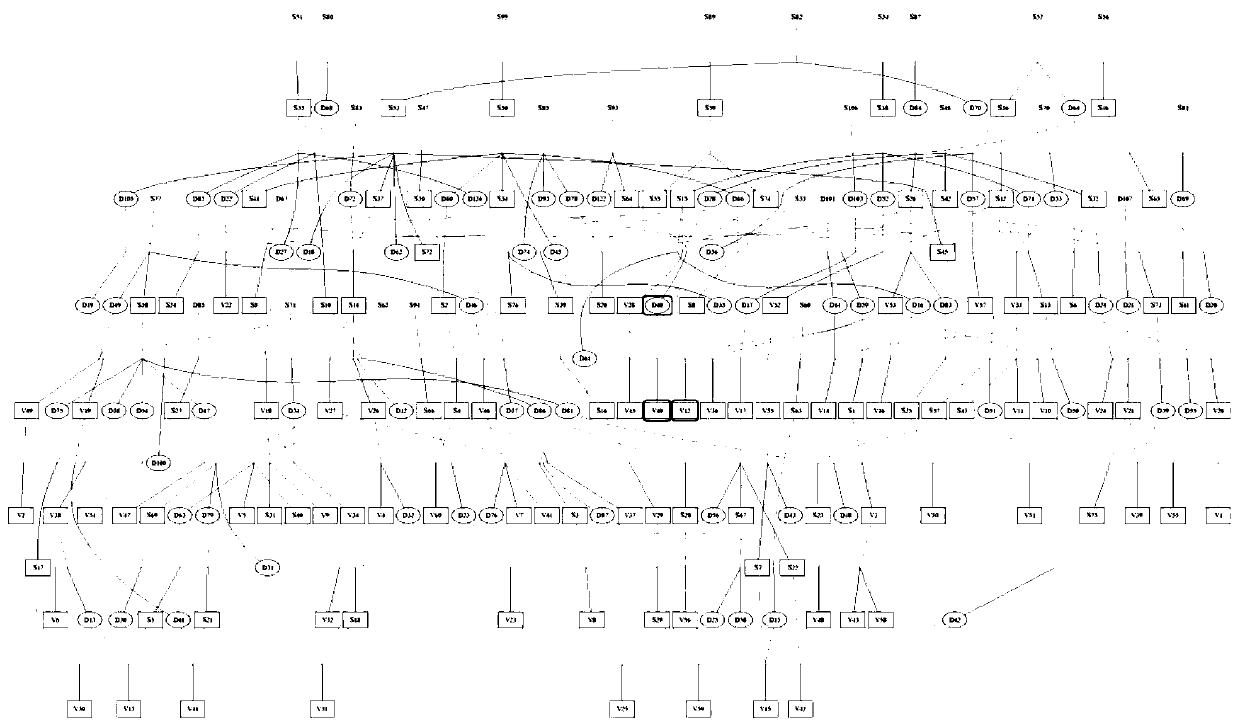
ActiveCN110176274AAccurate divisionAccurate predictionMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenotyping TechniquesHeredity
The invention discloses a method for dividing breeding swine blood linkage based on whole genome SNP information. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a body tissue of a dividing object, extracting the DNA, typing the genome SNP of each individual through a certain gene typing technique, and screening a qualified SNP site through quality control. calculating an additive heredity correlationvalue between individuals through the genome SNP genotype, then subtracting the additive heredity correlation value from one and using the obtained value as the distance between two individuals, thenperforming cluster analysis on the two individuals through an R-language hclust function, and using 0.9844 as a threshold for dividing the blood linkage. Compared with a traditional blood linkage dividing method, the method according to the invention has advantages of realizing a clear and concise obtained result, sufficiently reserving allele information which is transmitted from the parents, and realizing high reliability in blood linkage dividing.
Owner:WENS FOOD GRP CO LTD +1
Method for identifying marker of candidate gene related to milk production traits of buffaloes and application
ActiveCN112342302AImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsWater buffaloGenetic diversity
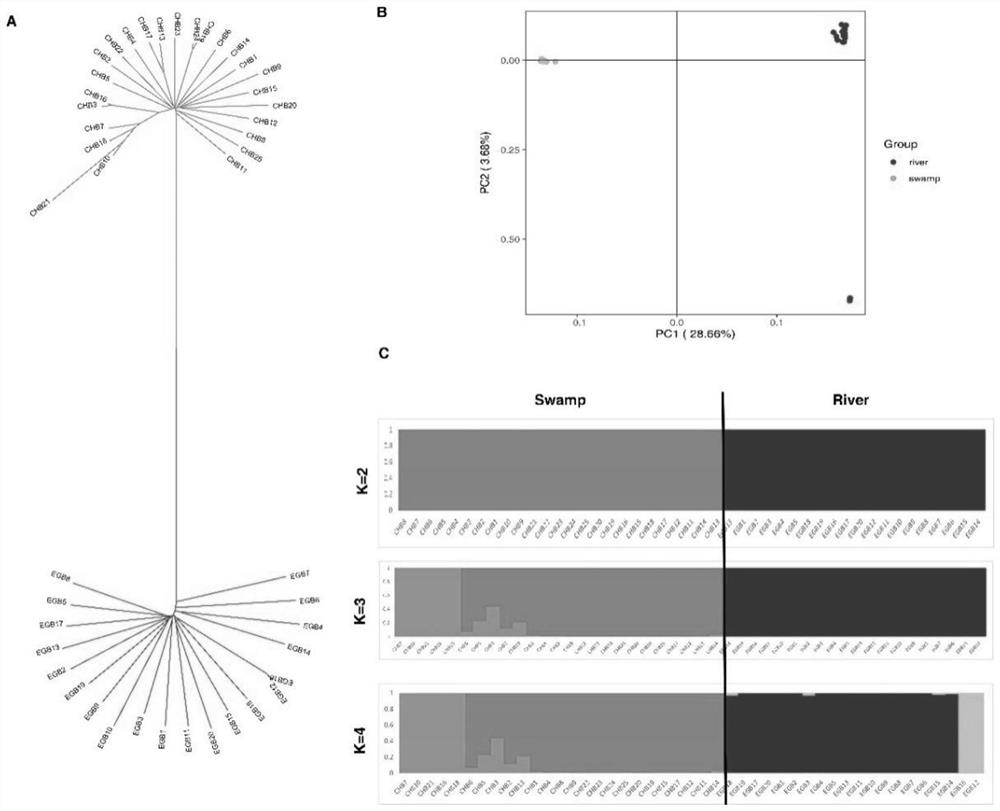
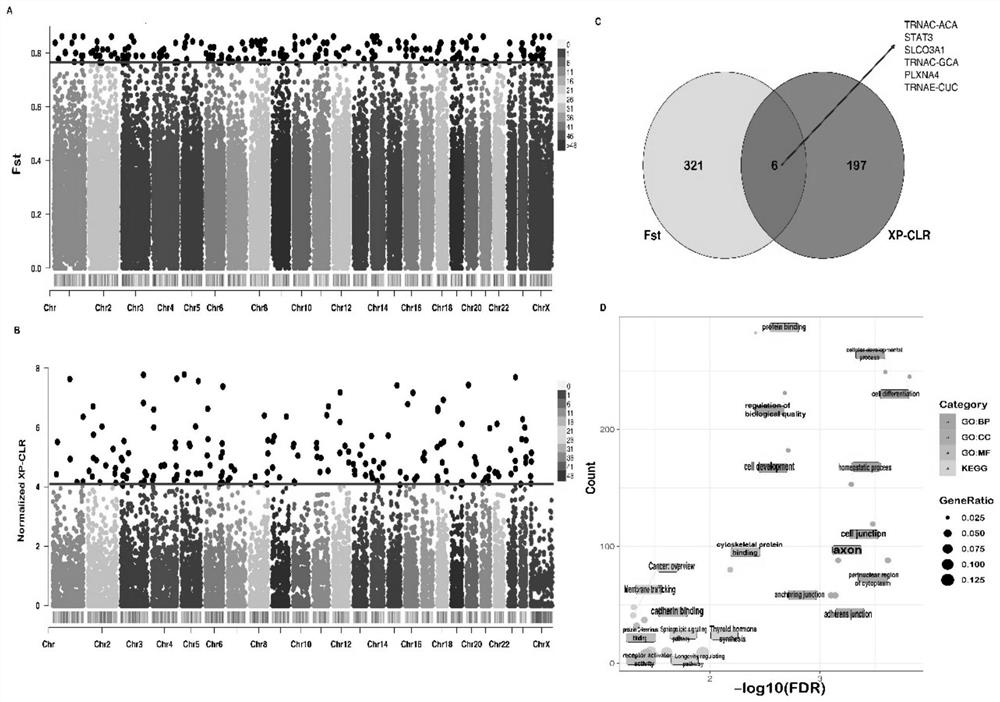
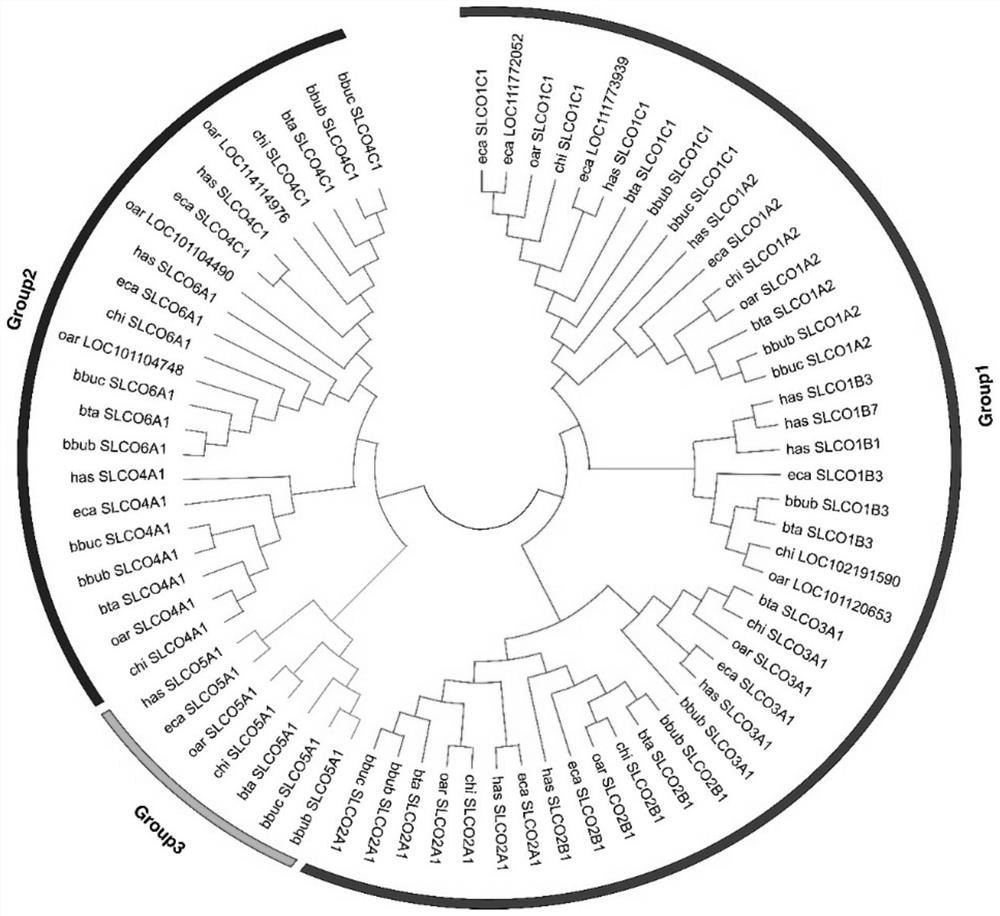
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular markers, and discloses a method for identifying a molecular marker of a candidate gene related to milk production traits of buffaloes. The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) obtaining SNP genotypes of 45 buffalo individuals by a dd-RAD method; (2) performing grouping based on population genetic diversity and population structures, further performing selection signal analysis by using Fst and XP-CLR strategies, and identifying the candidate gene related to the milk production traits; (3) using a comparative transcriptomestrategy to assist in verifying the relevance between the candidate gene and the milk production traits of the buffaloes; and (4) identifying the related molecular marker influencing the milk production traits of the buffaloes by using a marker-trait correlation analysis strategy. The candidate gene SCLO3A1 related to the milk production traits of the buffaloes and the molecular marker g.54621870G>T influencing the milk protein rate are identified by the method for the first time. The molecular marker can be used for breeding a buffalo population with high milk protein content.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION BUFFALO INST
High-flux molecular marker for identifying tomato leaf mold resistance, and marking method and application thereof
ActiveCN105624328AImprove throughputFully automatic operation processMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceResistant genes
The invention discloses a high-flux molecular marker for identifying tomato leaf mold resistance, and a marking method and application thereof. According to the molecular marker, a primer Cf-5-Al lele-F1, a primer Cf-5-Al lele-F2 and a primer Cf-5-R are designed according to the key specific sites of the target gene, and a primer tail end base is specifically matched with the target gene to carry out genotyping. A PCR (polymerase chain reaction)-based SNP Line platform is a high-flux molecular marker system, and thus, is capable of implementing the full-automatic operation procedure and lowering the human errors. The molecular marker has high analysis flux, can complete 0.5 million SNP genotyping every day, and is suitable for simultaneously detecting abundant samples. The high-detection-flux KASP molecular marker designed on the basis of tomato-leaf-mold-resistant gene Cf-5 is used for high-flux screening and identification of tomato-leaf-mold-resistant plants, can greatly save the time and labor cost, enhances the breeding efficiency of molecular marker assisted selection, has important meanings for culturing leaf-mold-resistant tomato leading varieties and effectively controlling hazards of tomato leaf mold, and is important breeding method innovation and technical innovation.
Owner:SHANDONG SHOUGUANG VEGETABLE SEED IND GRP CO LTD +1
Method of detecting breast cancer early diagnosis related genes based on nucleic mass spectrometry
InactiveCN107523646AEarly screening is accurateGood technical reproducibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBreast cancer susceptibility genesProtein mass spectrometry
The invention belongs to the field of gene detection, and in particular relates to a method for detecting genes related to early diagnosis of breast cancer based on nucleic acid mass spectrometry technology. The present invention provides a combined detection method for 15 breast cancer-related mutation sites of 4 genes and 18 breast cancer susceptibility SNP sites of 10 genes, and uses SequenomMassARRAYSNP genotype analysis technology to detect SNPs of breast cancer susceptibility genes Genotyping detection of loci and gene mutation loci associated with breast cancer. This method is more accurate for early screening of breast cancer, has good technical reproducibility, and is cost-effective; compared with TaqMan-PCR and SNP detection of second-generation platform sequencing, it has flexible design, high accuracy, and large sample size of detection sites , low cost and other advantages, hundreds to thousands of samples can be tested on dozens of SNP sites at the same time.
Owner:武汉赛云博生物科技有限公司
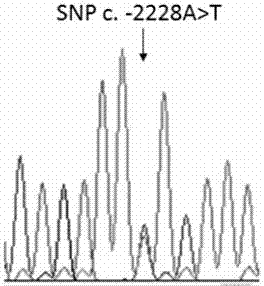
Application of skin color-associated SNP marker in genotyping of black-bone chickens
ActiveCN107988376AStrong specificitySingle detection bandMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTranscription initiation siteTyping
The invention provides an application of a skin color-associated SNP marker in genotyping of black-bone chickens. The SNP marker is located at 2228 bp upstream of a transcription initiation site in apromoter region of a TYR gene, and a base with polymorphism is adenine A or thymine T. The SNP genotype detection primer has high specificity, single detection band and accurate typing results. In combination with a provided detection method, the whole operation process is simpler and more efficient, and the cost is lower. Rapid and accurate individual screening is achieved, and a basis for breeding development and protection of black-bone chicken varieties is provided.
Owner:LESHAN NORMAL UNIV
Methods and SNP detection kits for predicting palm oil yield of a test oil palm plant
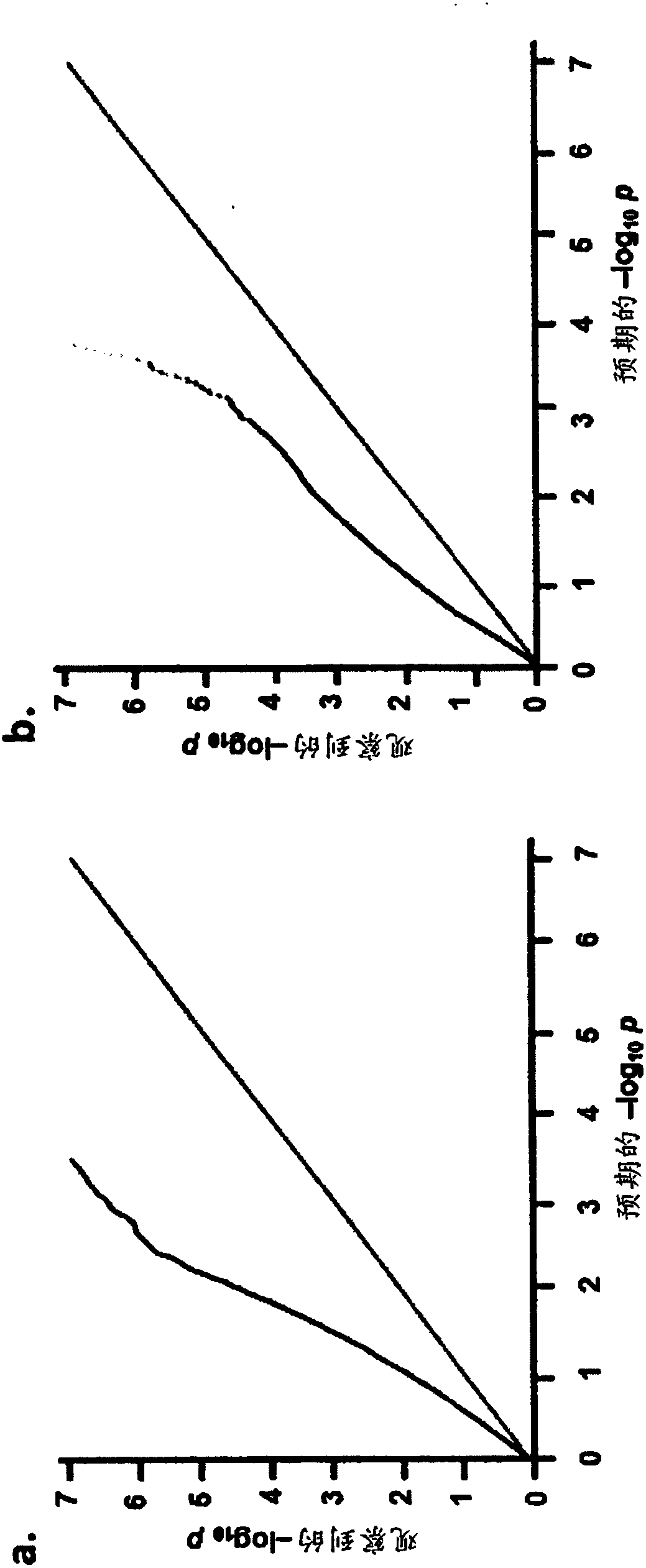
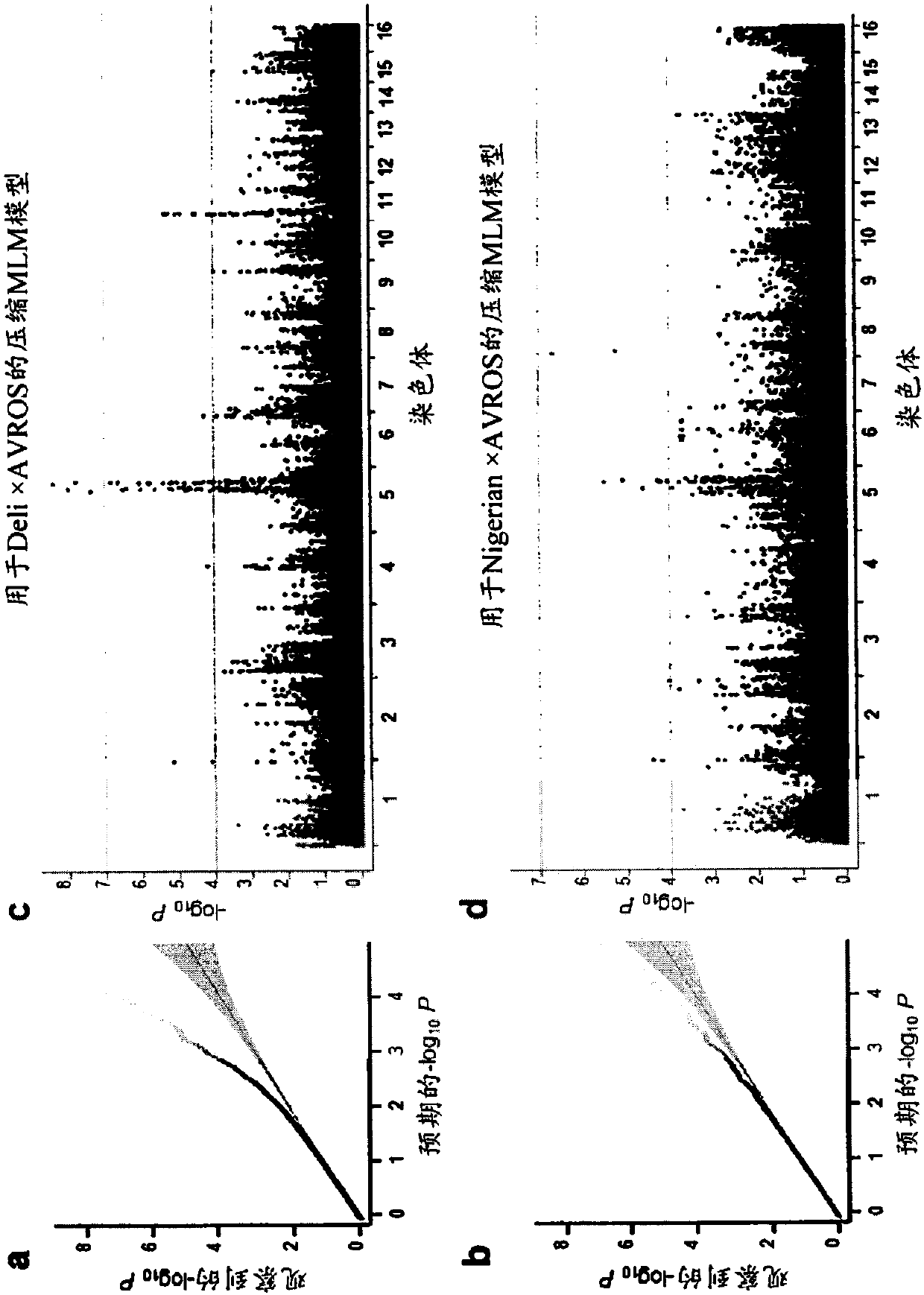
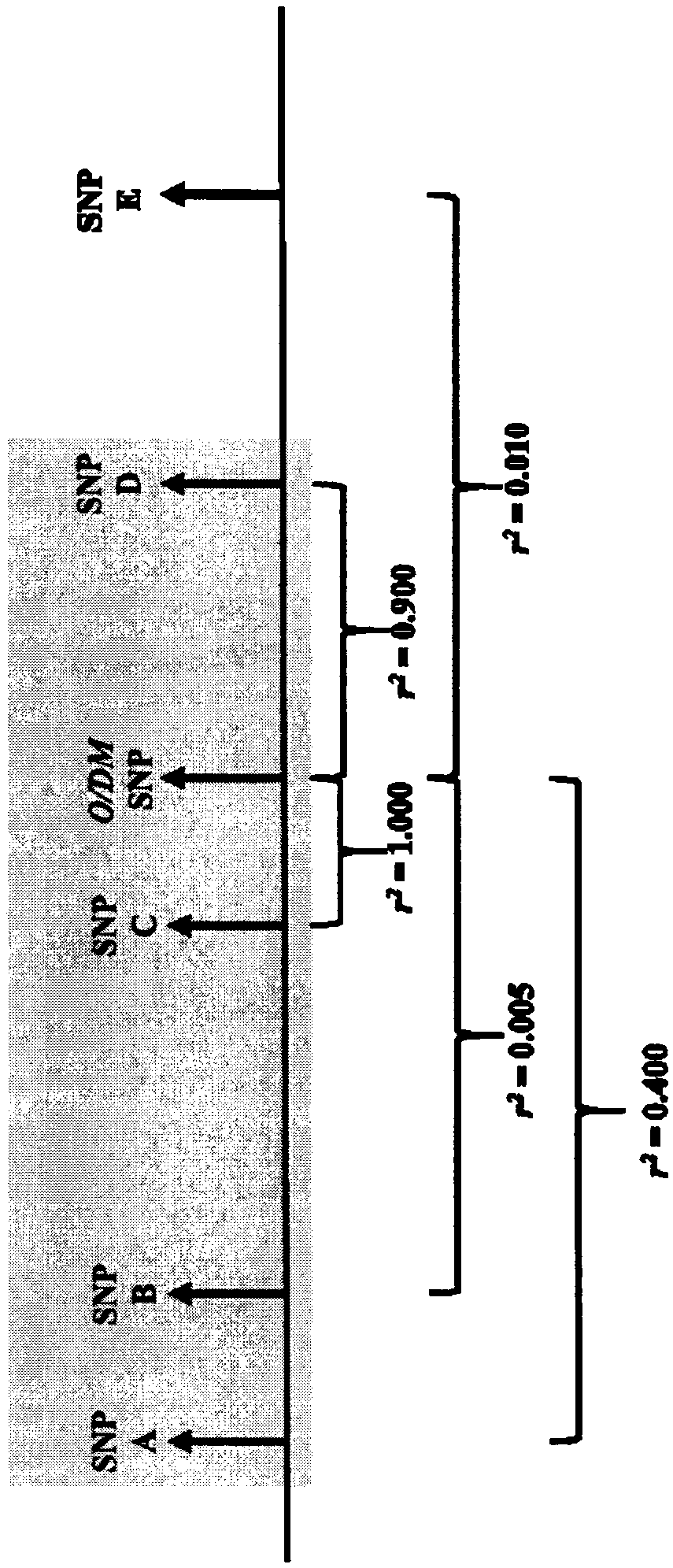
Methods for predicting palm oil yield of a test oil palm plant are disclosed. The methods comprise determining, from a sample of a test oil palm plant of a population, at least a first SNP genotype, corresponding to a first SNP marker, located in a first QTL for a high-oil- production trait and associated, after stratification and kinship correction, with the high-oil- production trait with a genome-wide -log10(p-value) of at least 4.0 in the population or having a linkage disequilibrium r2 value of at least 0.2 with respect to a first other SNP marker linked thereto and associated, after stratification and kinship correction, with the high-oil-production trait with a genome-wide -log10(p-value) of at least 4.0 in the population. The methods also comprise comparing the first SNP genotype to a corresponding first reference SNP genotype and predicting palm oil yield of the test plant based on extent of matching of the SNP genotypes.
Owner:SIME DARBY PLANTATION INTPROP SDN BHD
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) genotyping method and application thereof
InactiveCN103589797AOptimizing Kinds of WorkSimplify the development processMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman bodyPhylogenetic tree
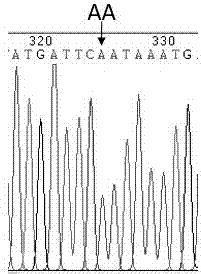
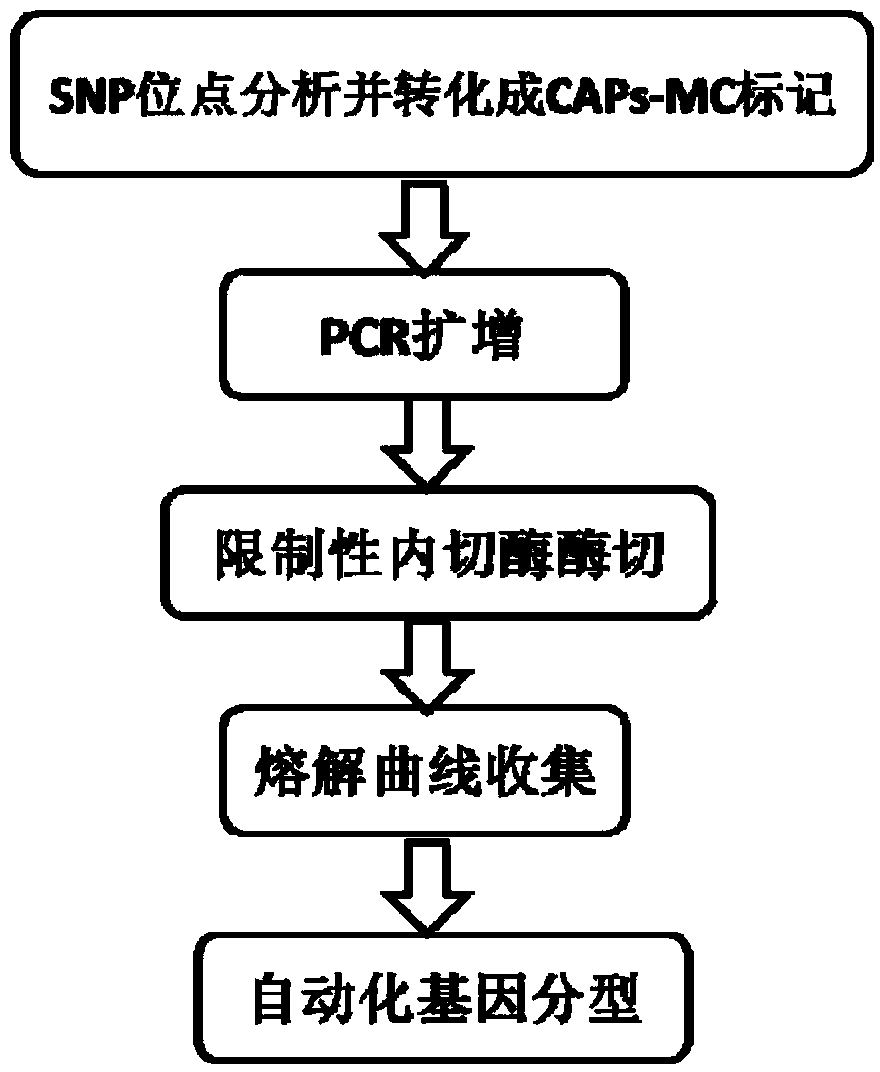
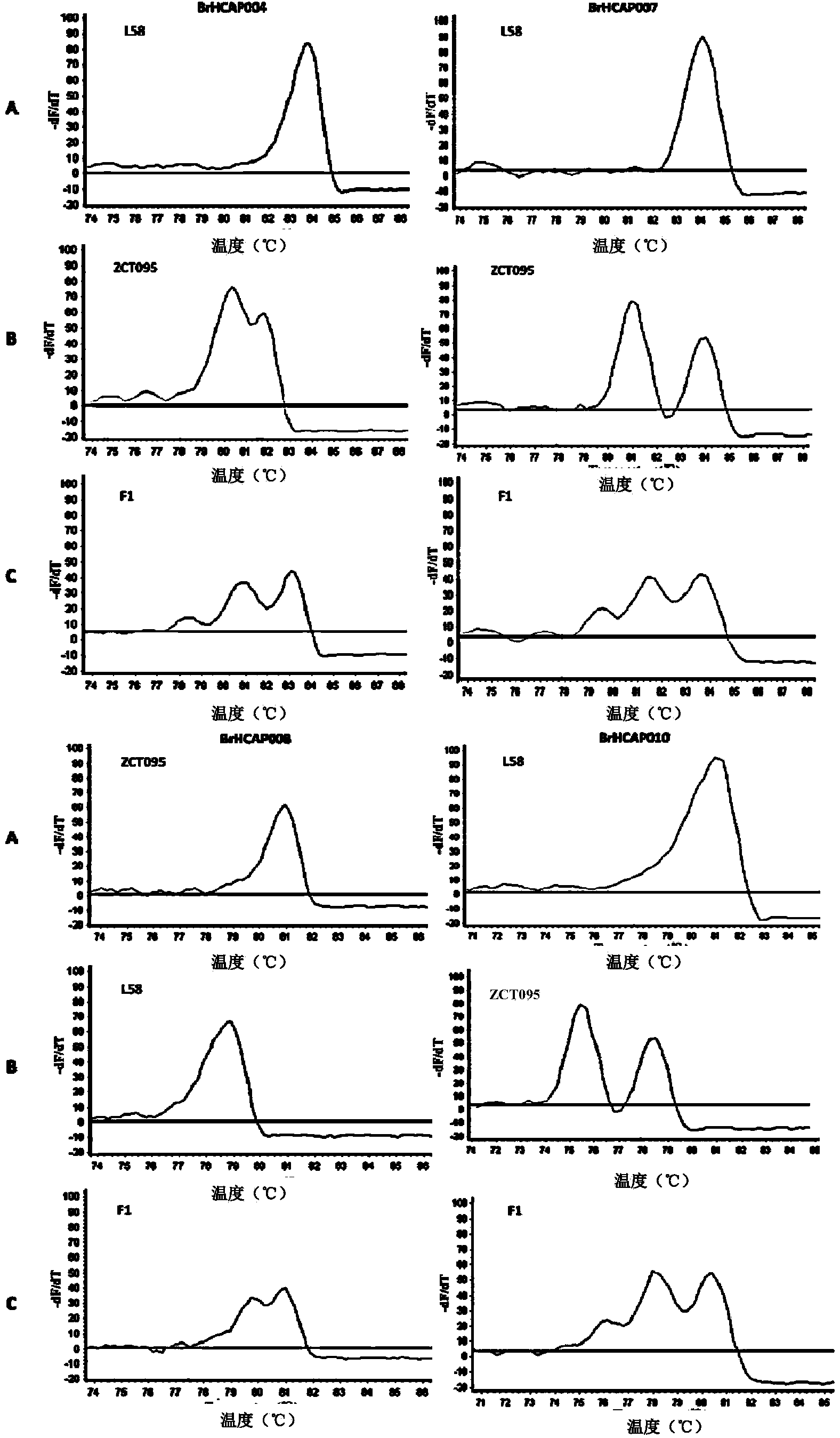
The invention provides an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) genotyping method and an application thereof, and relates to an SNP genotyping method. The SNP genotyping method is an SNP genotyping technology based on the combination of restriction endonuclease fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) and a melting curve. The method is high in accuracy, good in stability, fast, time-saving, high-throughput and safe, facilitates automatic operation and doesn't require gel electrophoresis, the operation process produces no harm to a human body, and the cost is low. The SNP genotyping method not only gains a great success in the aspects of plant SNP genotyping and breeding of Chinese cabbage, Chinese kale, tomatoes and the like, but also has a great application value in the aspects of establishment of a high-precision genetic map, fine mapping of genes, genome-wide association analysis, establishment of a phylogenetic tree and the like in biology.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
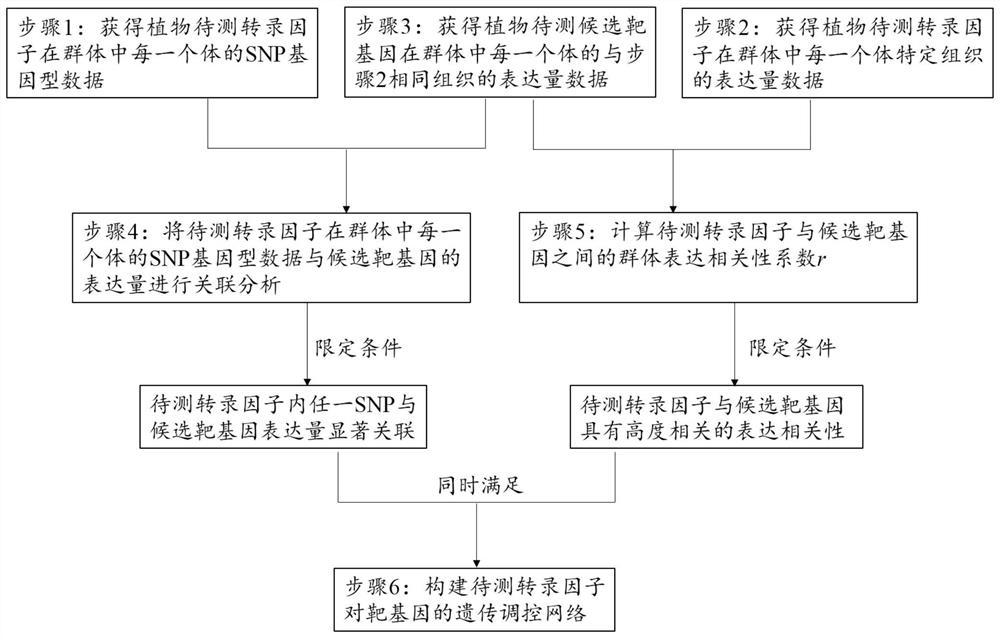
Method for constructing plant transcription factor-to-target gene genetic regulation network
The invention relates to a method for constructing a plant transcription factor-to-target gene genetic regulation network, and belongs to the technical field of molecular genetics. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining SNP genotype data of a plant transcription factor to be detected in each individual in a group, expression quantity data of a specific tissue of the plant transcription factor to be detected in each individual in the group, and expression quantity data of a same tissue of a plant candidate target gene to be detected in each individual in the group; determining SNPsignificantly associated with the candidate target gene expression quantity; determining candidate target genes highly related to the expression quantity of the transcription factor to be detected. When the determination conditions are met at the same time, it is indicated that the transcription factor to be detected regulates the expression of the candidate target genes, and a genetic regulationnetwork of the transcription factor to the target gene can be constructed accordingly. According to the method, the regulation relationship between a plant transcription factor and downstream target genes can be accurately identified in a high-throughput manner, and a genetic regulation network of the transcription factor to the target gene is constructed.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
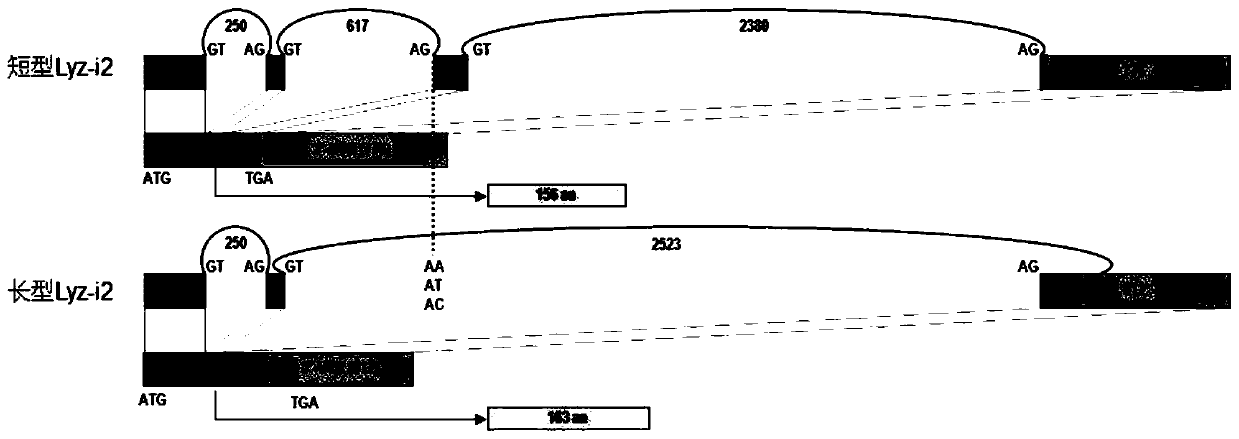
SNP marker for distinguishing ability of litopenaeus vannamei against vibrio harveyi infection and detection method thereof and application of SNP marker
ActiveCN110791571AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAntibiosisNucleotide
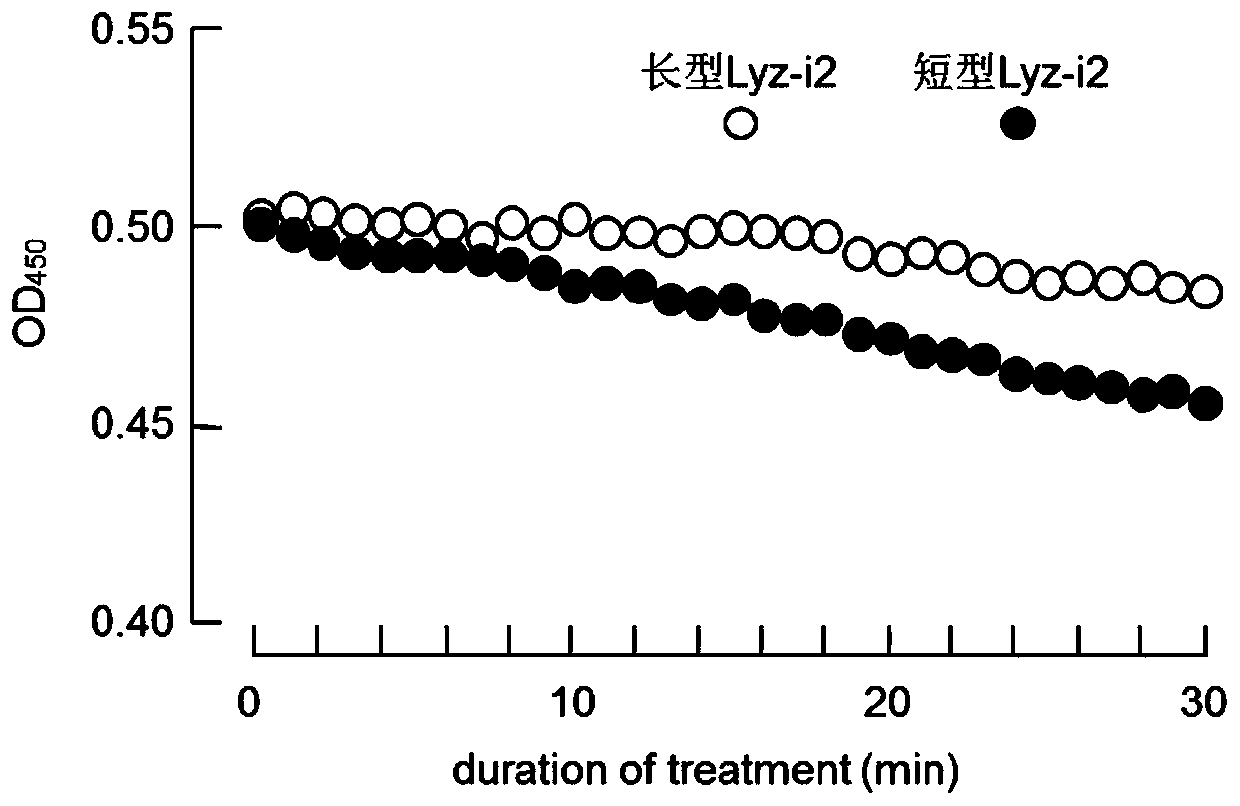
The present invention discloses a SNP marker for distinguishing ability of litopenaeus vannamei against vibrio harveyi infection and a detection method thereof and an application of the SNP marker. The SNP marker is located at the 1191th site of a Lyz-I2 gene sequence of litopenaeus vannamei, with mutation type comprising G homozygote, heterozygote of G and three other nucleotides, and homozygoteor heterozygote of three other nucleotides except for G. The invention provides a SNP site for distinguishing ability of litopenaeus vannamei against vibrio harveyi infection, and develops a tetra-primer for amplifying genotype of the SNP site and the detection method for detecting the SNP genotype. The method can simply, rapidly and accurately detects polymorphism forms of the site at low cost, thereby facilitating to rapidly screen individual litopenaeus vannamei and breeding group with high ability against vibrio harveyi, and to maintain antibacterial varieties of litopenaeus vannamei against vibrio harveyi.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Y haplogroup detection method
ActiveCN107153776AIncrease flexibilityImprove application breadthHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsHaplogroupData mining
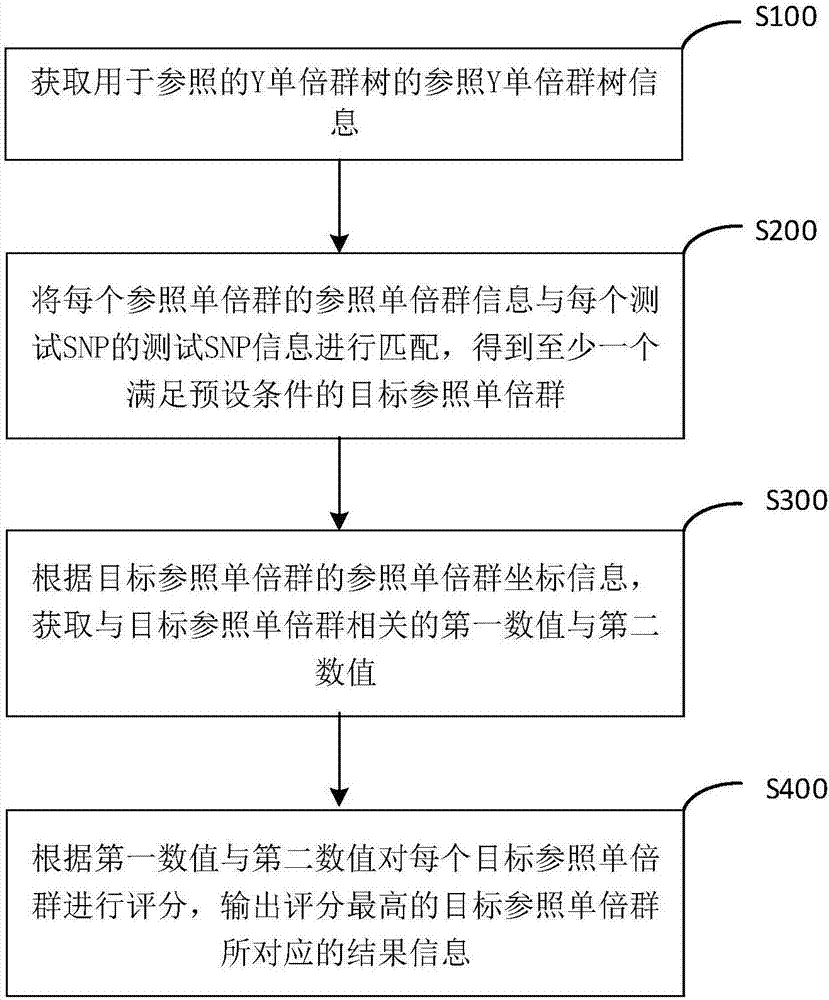
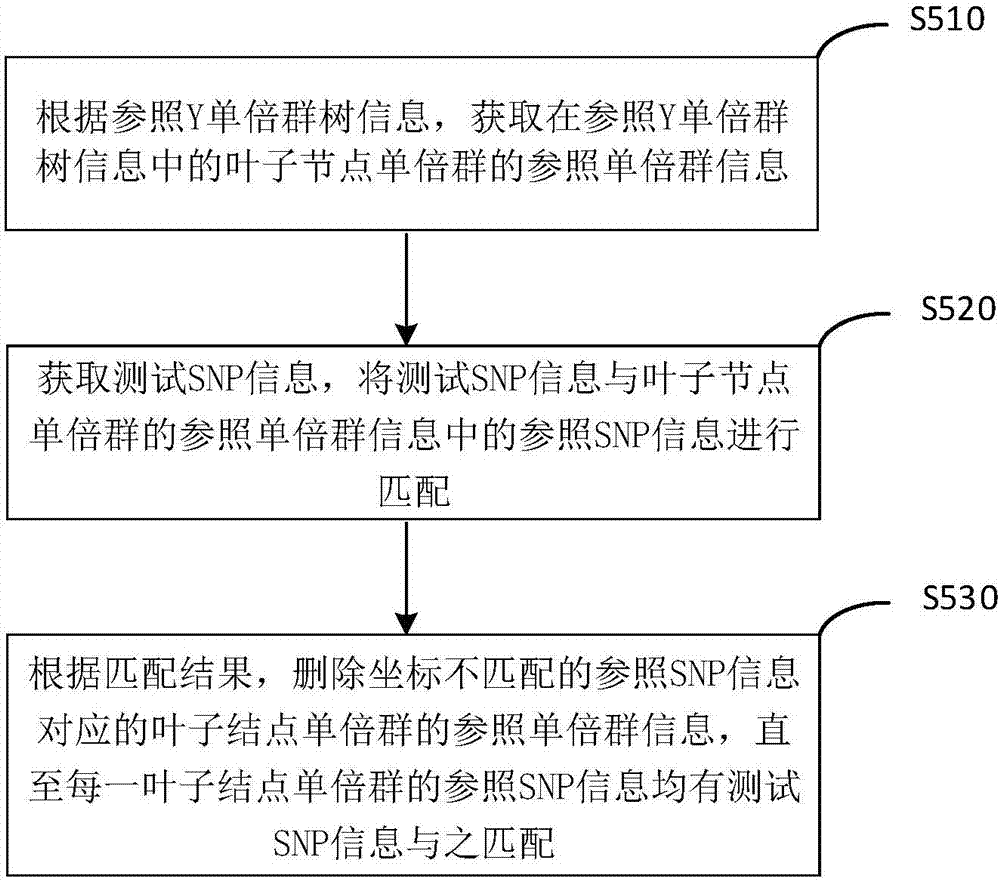
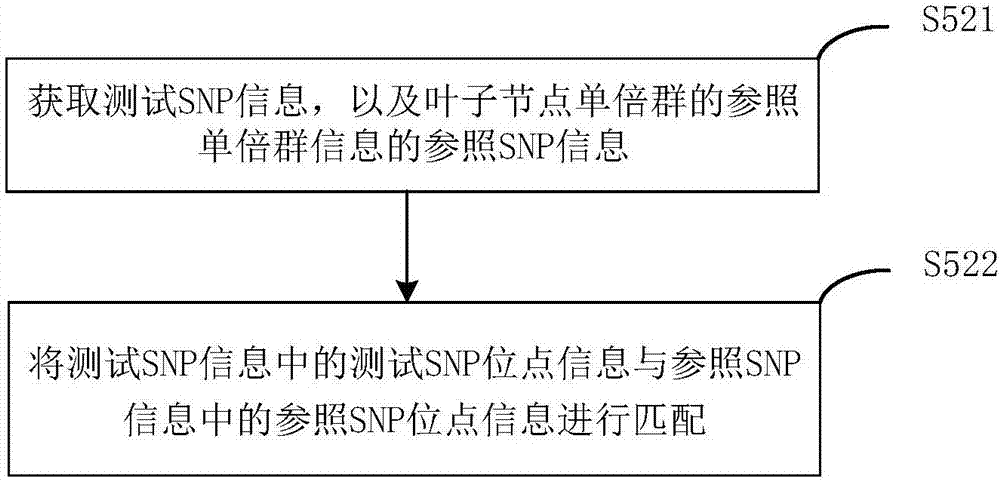
The invention relates to a Y haplogroup detection method. The method comprises the following steps that reference Y haplogroup tree information of Y haplogroup trees for reference is obtained, wherein the reference Y haplogroup tree information comprises reference haplogroup information of each reference haplogroup in the Y haplogroup trees; each piece of reference haplogroup information is matched with test SNP information to obtain at least one target reference haplogroup meeting the preset condition; according to reference haplogroup coordinate information of the target reference haplogroups, a first numerical value and a second numerical value related to the target reference haplogroups are obtained, each target reference haplogroup is scored, and result information corresponding to the target reference haplogroup with the highest score is output. According to the Y haplogroup detection method, the reference haplogroup and a test haplogroup are compared, the scoring system based on a path starting from a root node to the target haplogroups can adapt to a next-generation sequencing result and a high-throughput micro array SNP genotyping result at the same time, the detection applicability is higher, and the application range of detection means is enlarged.
Owner:深圳市早知道科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com