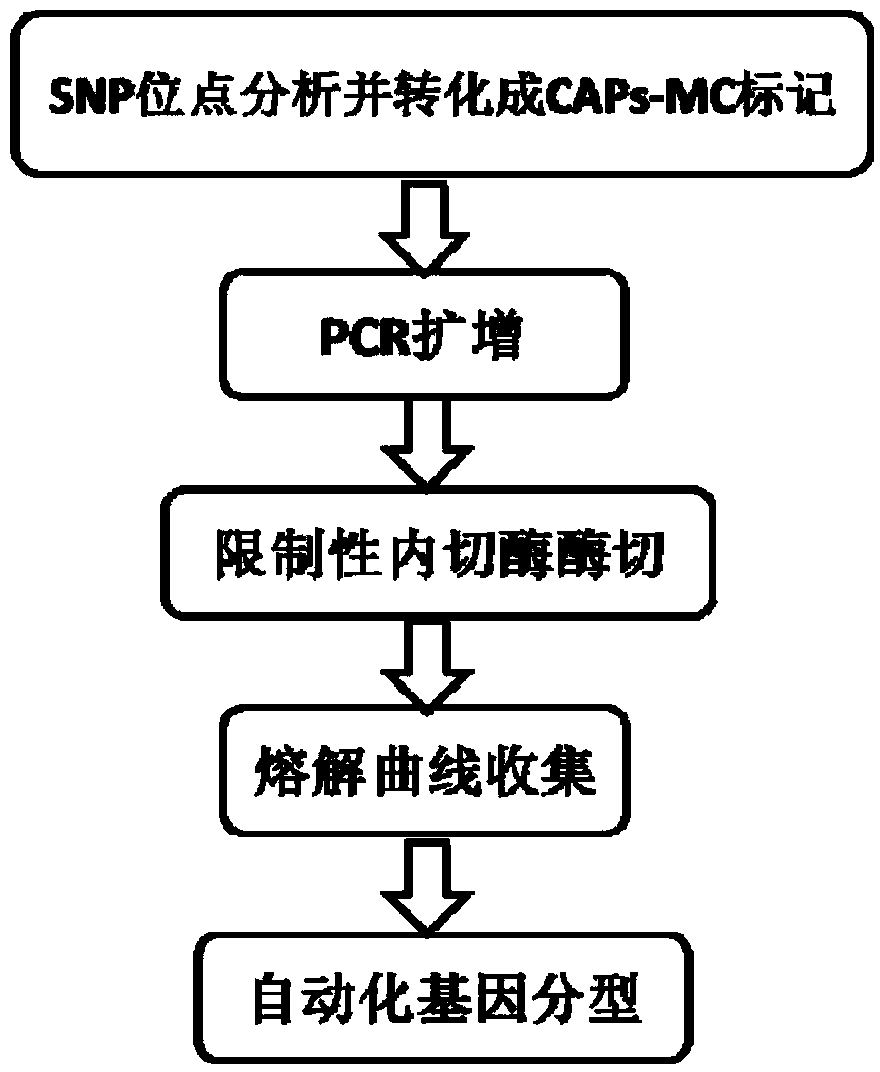
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) genotyping method and application thereof
A single nucleotide polymorphism and typing method technology, applied in the field of single nucleotide polymorphism typing, can solve the problems of high cost and popular application, high reagent requirements, low degree of automation, etc., and achieve high accuracy , cost reduction, high degree of mechanization effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
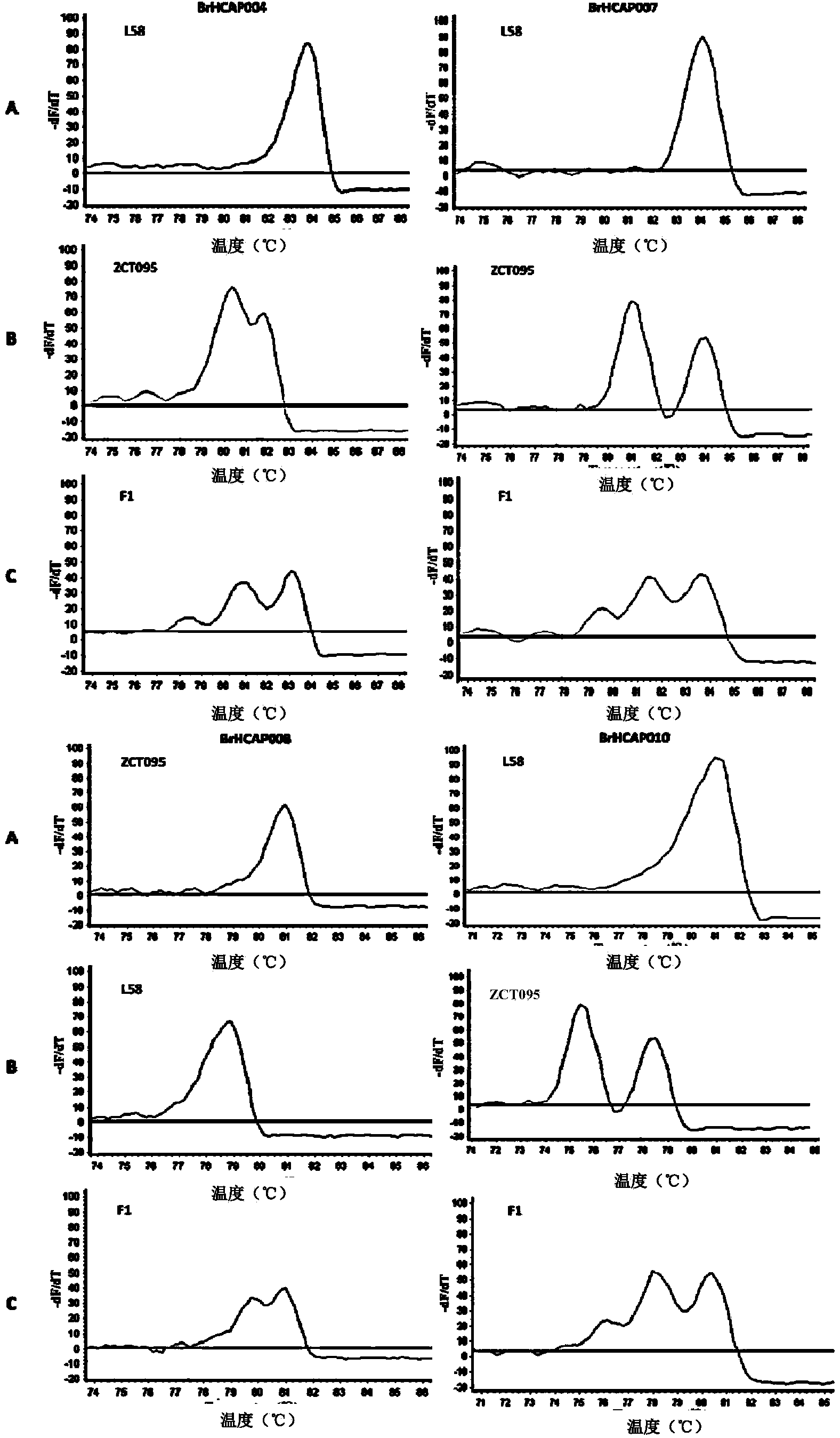
[0056] Example 1: Taking cabbage as an example, 4 SNP sites were randomly selected in the whole genome, and the CAPS-MC technology was used to detect 3 genotypes
[0057] (1) Analysis of SNP sites
[0058] Analyze the SNP variation sites of the two parental Dicer recognition sequences of the parent 'L58' (Chinese cabbage) and the parent 'ZCT095' (Laver stalk), using the published Chinese cabbage genome reference sequence as a bridge, through the parent 'L58' (Chinese cabbage) The resequencing data were compared with the cabbage reference genome sequence, and the SNP variation sites between the two were extracted; the resequencing data of another parent 'ZCT095' (Laver stalk) was compared to the extracted SNP site; the parent 'ZCT095 The sites identical to the reference genome sequence were considered to be polymorphic sites between the parent 'ZCT095' and the parent 'L58'.
[0059] Similarly, by comparing the resequencing data of the parent 'ZCT095' with the reference genome ...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Example 2: Taking the plant kale as an example, the application of this technology to screen male sterile individual plants in the kale BC7 population
[0093] (1) Analysis of SNP sites and conversion into CAPS-MC markers
[0094] Based on the resequencing data of the parents "kale M1" and "kale M2", predict the SNP site of the restriction endonuclease AluI recognition base sequence (AGC^T), take one of the SNP sites as an example, and Transformed into CAPS-MC markers, 8 lines were randomly selected from the population for SNP detection. The sequence of the forward primer of this marker is (5’-3’) TCTAACGCATGTAATGATTTCACAT; the sequence of the reverse primer is (5’-3’) AACCTTAAACACAAATCCAAATTTA. The size of the PCR target fragment is 175bp, and the size after AluI digestion is 90bp and 85bp.
[0095] (2) PCR amplification and digestion
[0096] Genomic DNA of 8 selected strains were extracted respectively, and PCR amplification was carried out using labeled primers. ...
Embodiment 3
[0101] Example 3: Taking tomato as an example, the detection of the SNP site of the X gene.
[0102] (1) SNP site analysis and conversion into CAPS-MC markers
[0103] Such as Figure 5 As shown, there is a SNP (T136G) polymorphism in the 136bp of the tomato X gene. Search the restriction endonuclease site according to the polymorphic sequence, and find that the polymorphic site is located in the base recognized by the endonuclease HpyCH4IV (A^CGT). When the SNP site is G, it can be cut by the enzyme , if the SNP site is T, it cannot be cut by the enzyme. For the upstream and downstream sequences of this site, CAPS-MC markers were developed, and forward and reverse primers (5'-3') were designed: AATTTCTGATTCCACCATTGC, AAGCCCTACGTCAAAGACCA. The size of the PCR target fragment is 232bp, and the size after HpyCH4IV digestion is 134bp and 98bp.
[0104] (2) PCR amplification and digestion
[0105] The genomic DNA of the 6 samples to be tested was extracted respectively, and P...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com