Patents
Literature
1289 results about "Electrophoresis band" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
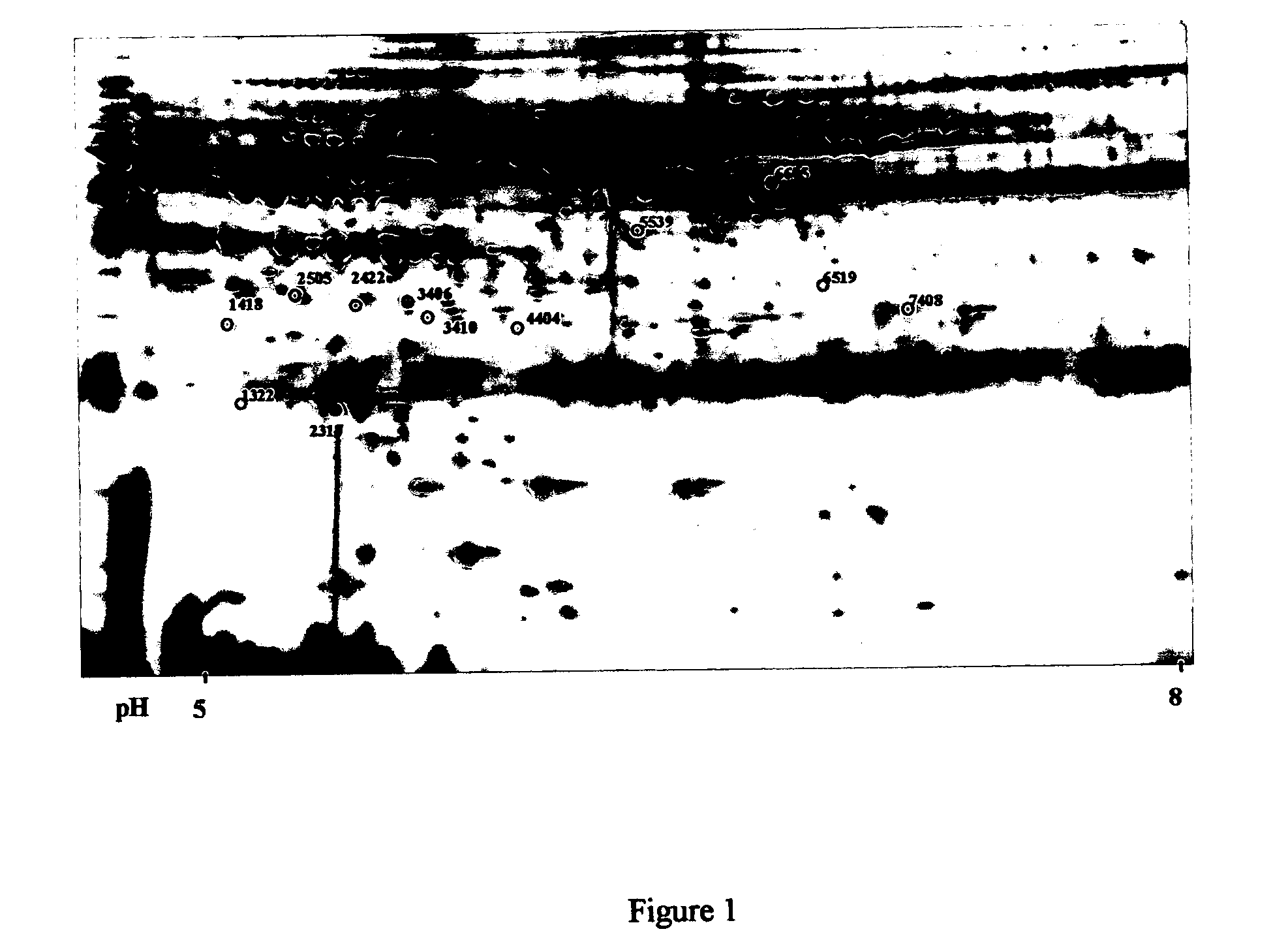
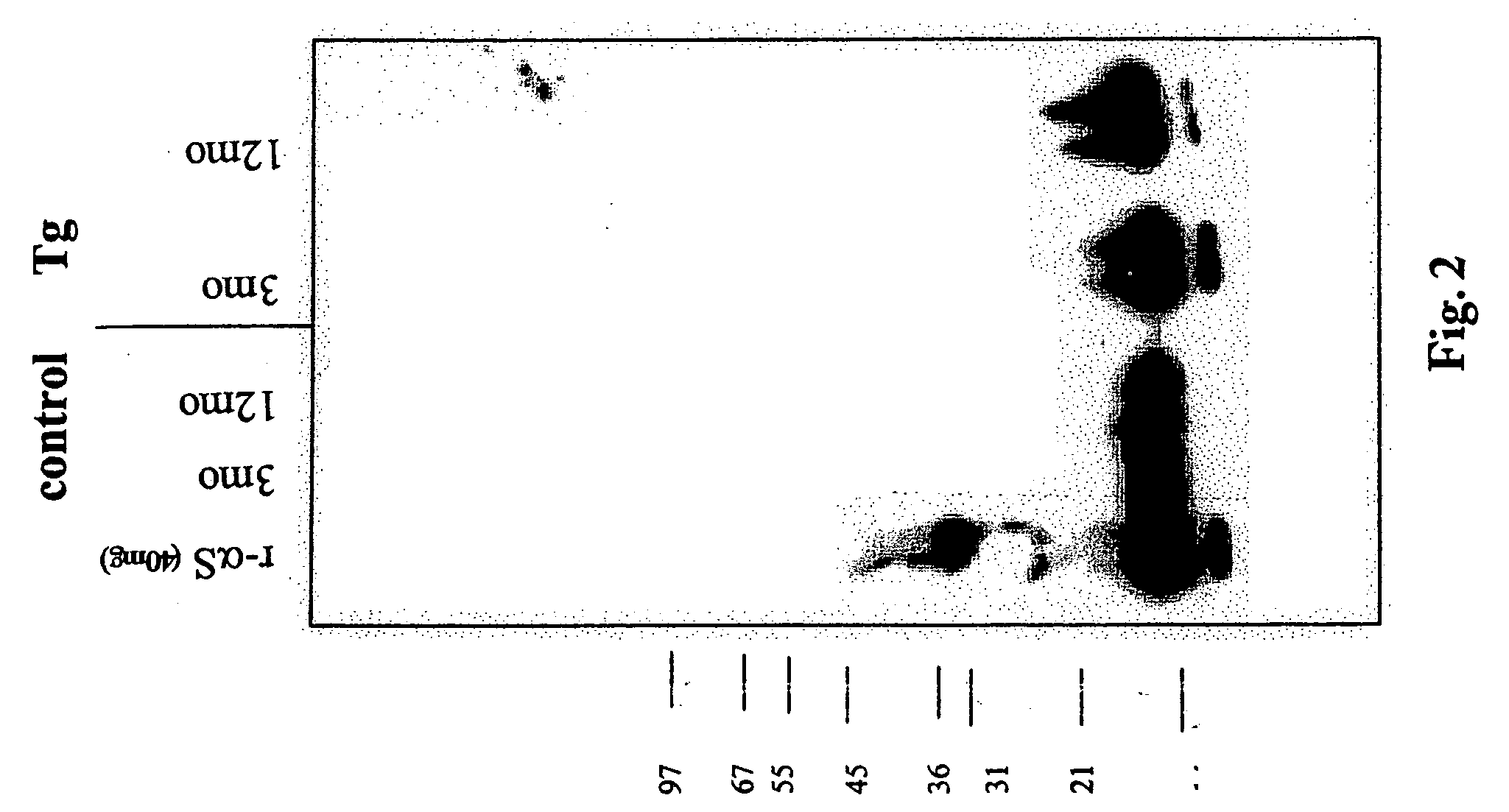
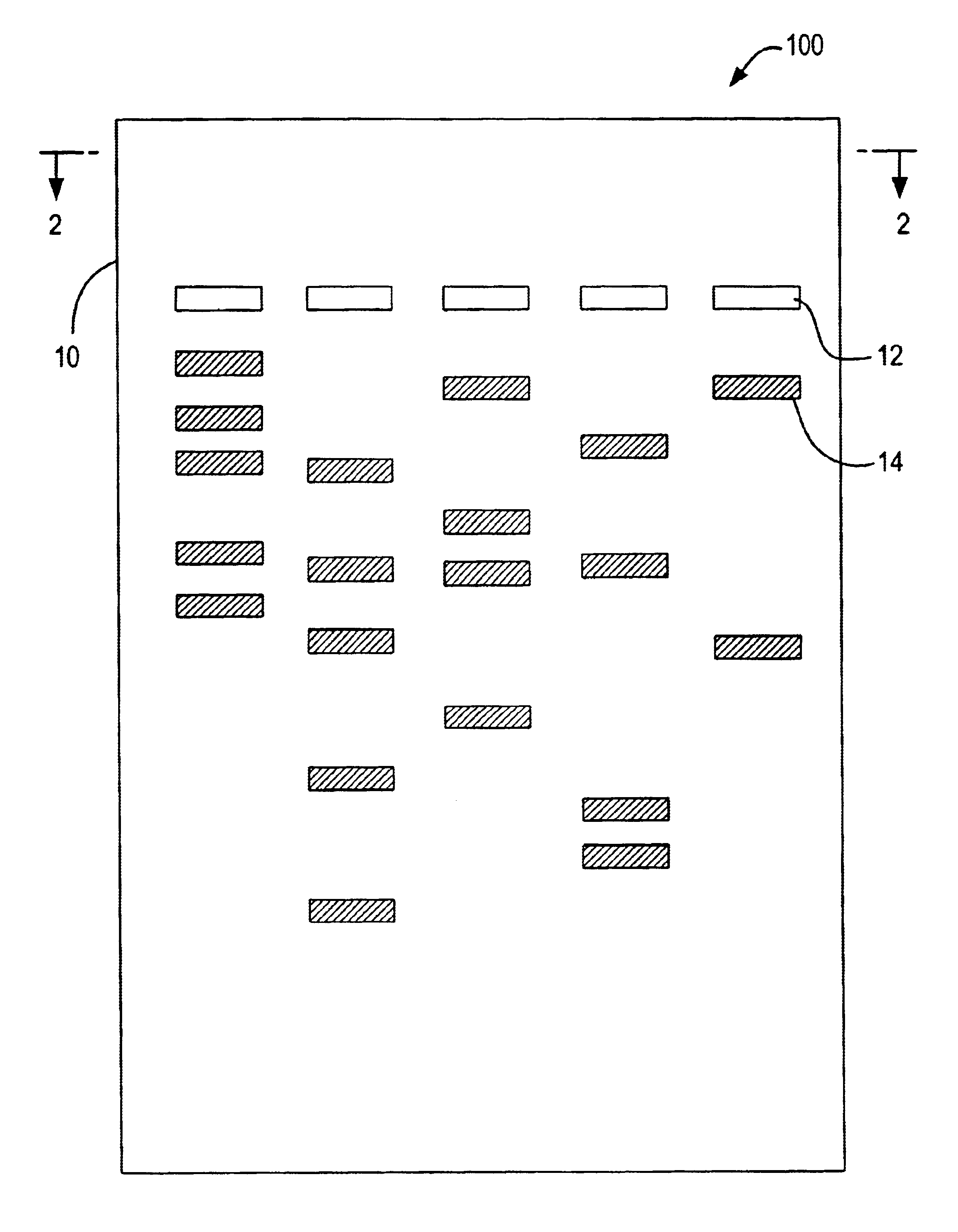
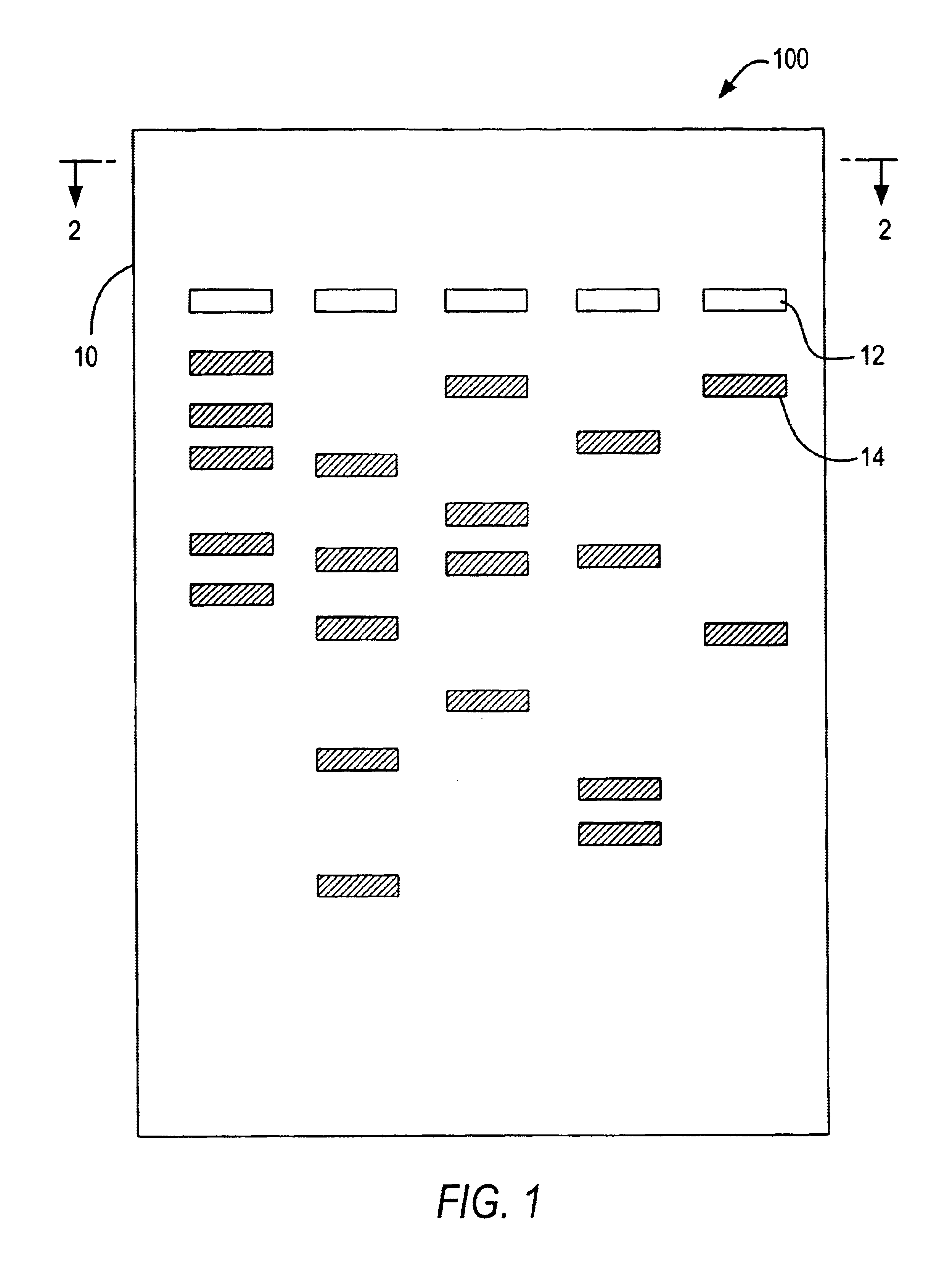
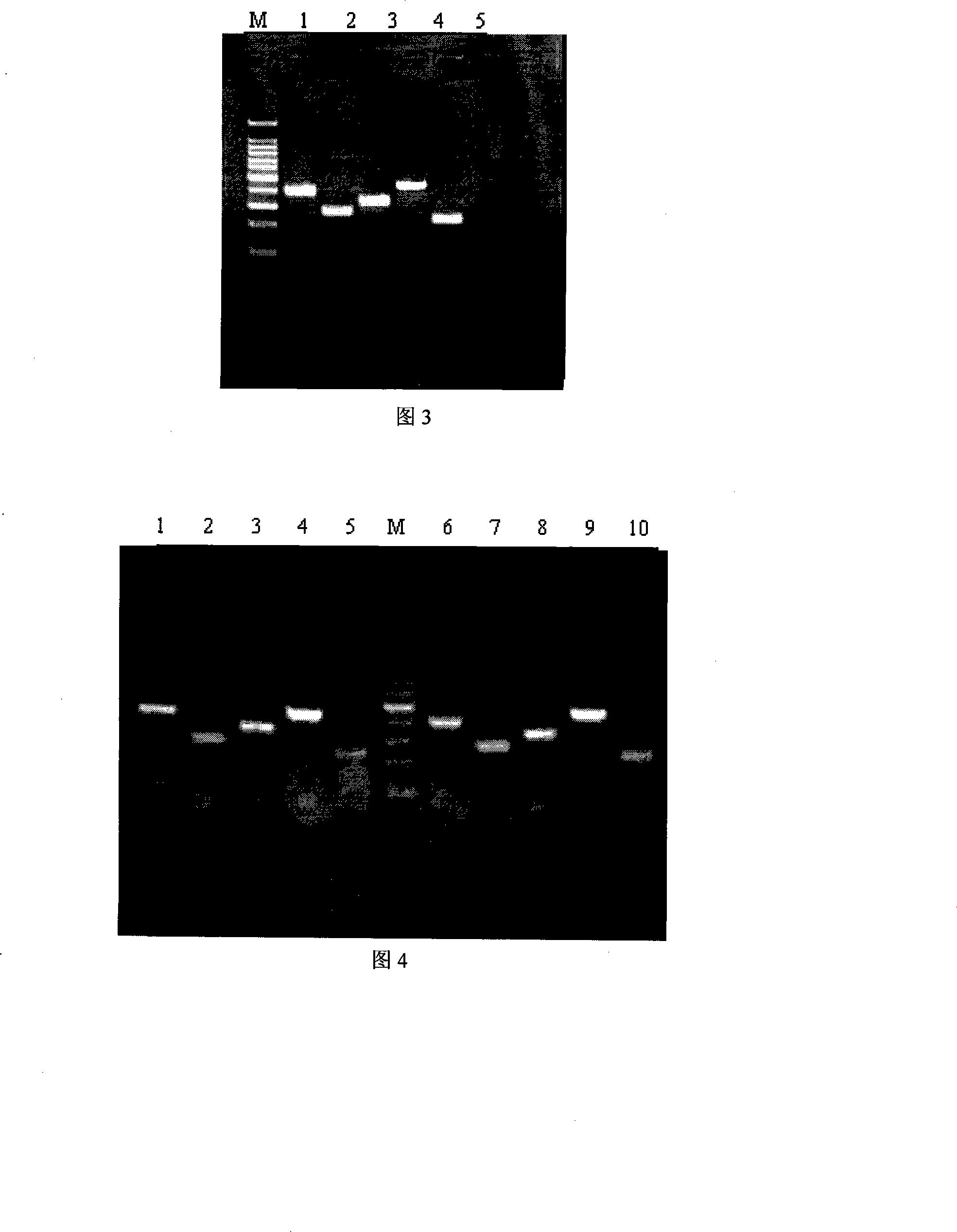
4) Electric current applied to the gel. 5) DNA bands are separated by size. 6) DNA bands are stained. Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of macromolecules (DNA, RNA and proteins) and their fragments, based on their size and charge.
Microfluidic treatment method and device
InactiveUS20050161326A1Easily compiled into databaseAccurate gradientShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersSludge treatmentGel electrophoresisMicrochip Electrophoresis
The present invention relates to a microchip apparatus using liquids. More specifically, the invention provides a liquid mixing apparatus comprising at least two microchannels for introducing liquids and a mixing microchannel that connects to the at least two liquid-introducing microchannels, wherein the liquids are transported from the respective liquid-introducing microchannels toward the mixing microchannel, the apparatus further comprising means for enhancing the mixing of the liquids that converge in the mixing microchannel. The invention also provides an electrophoretic apparatus and a microchip electrophoretic apparatus for denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis.
Owner:EBARA CORP
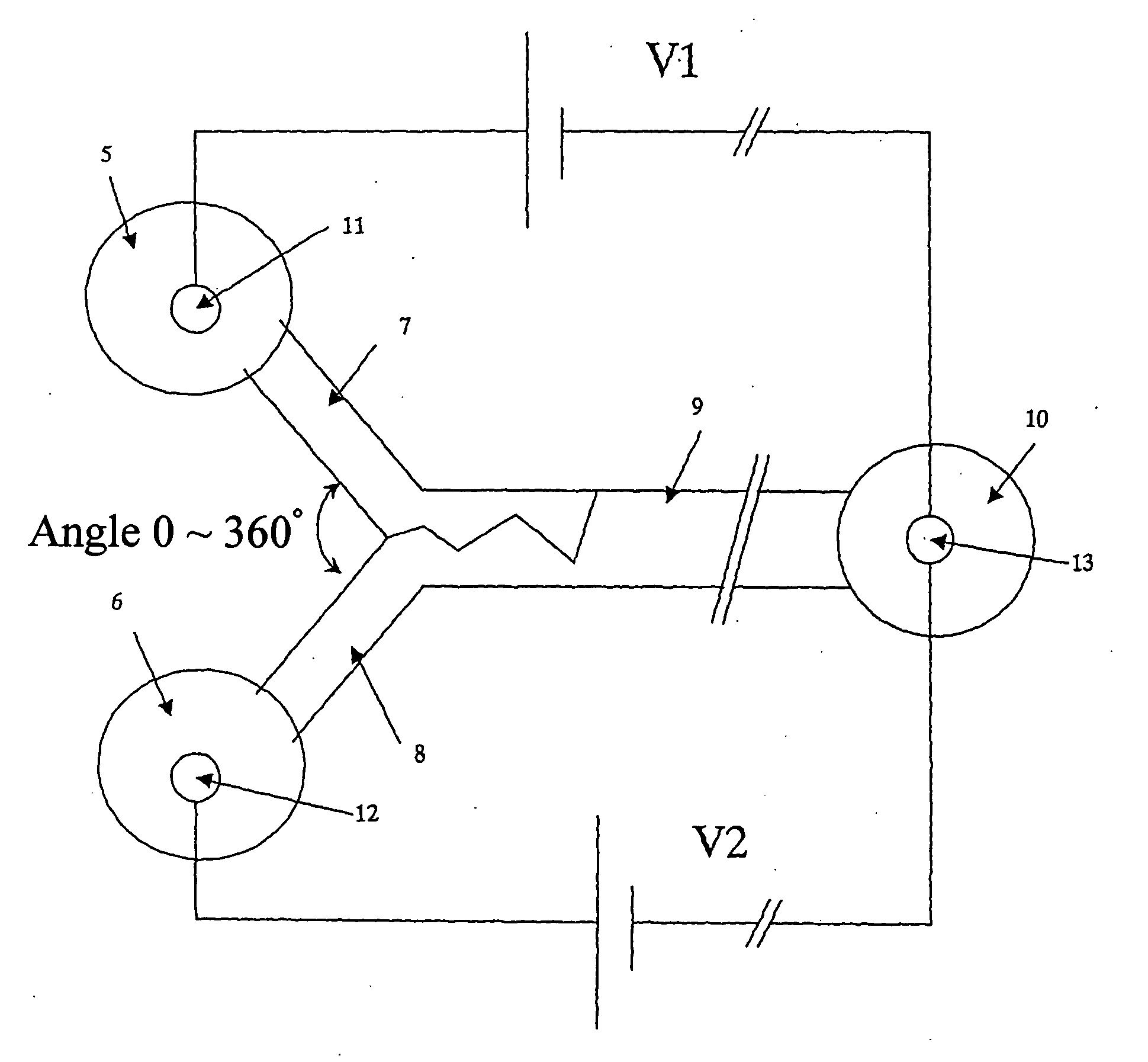
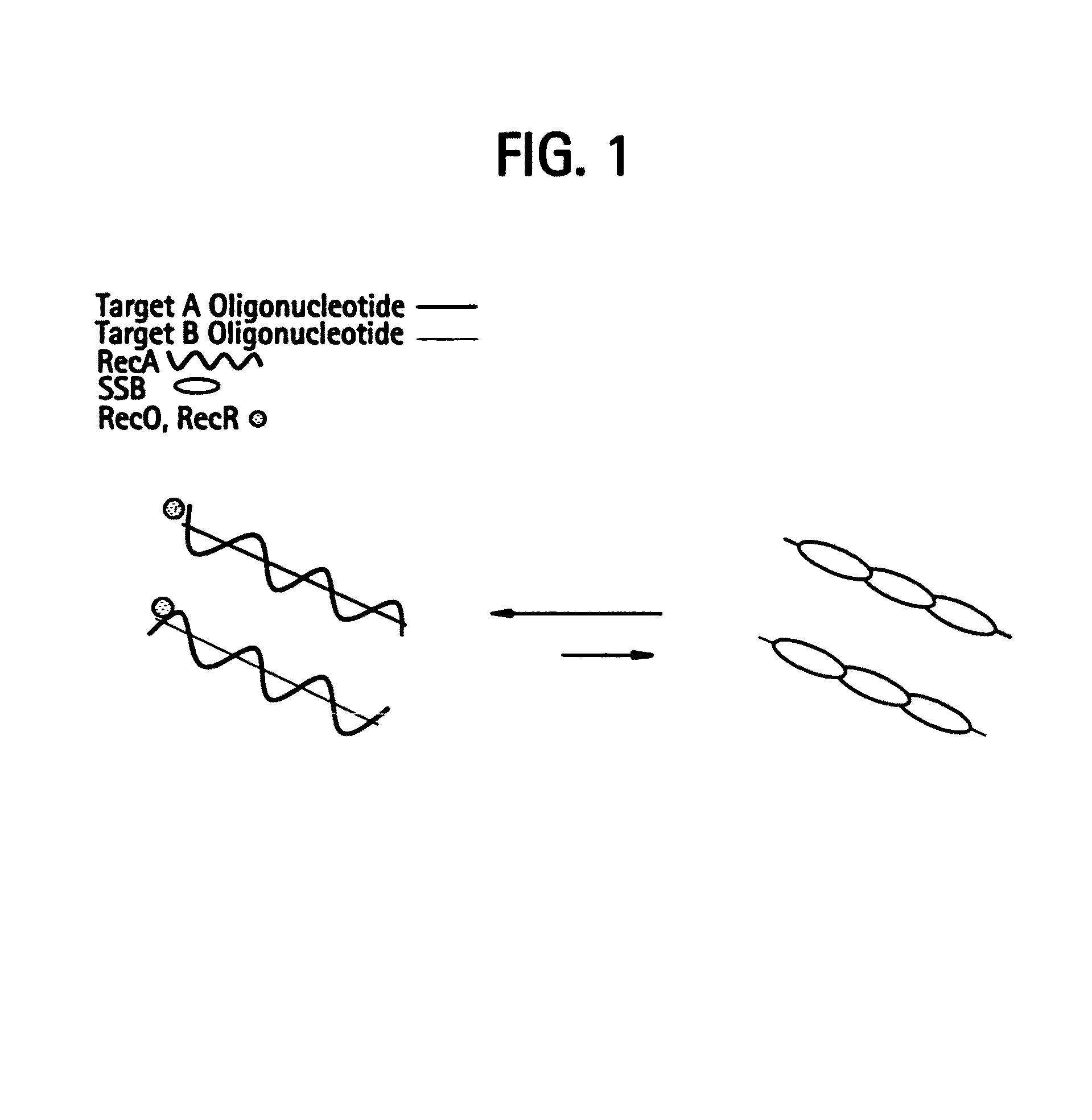
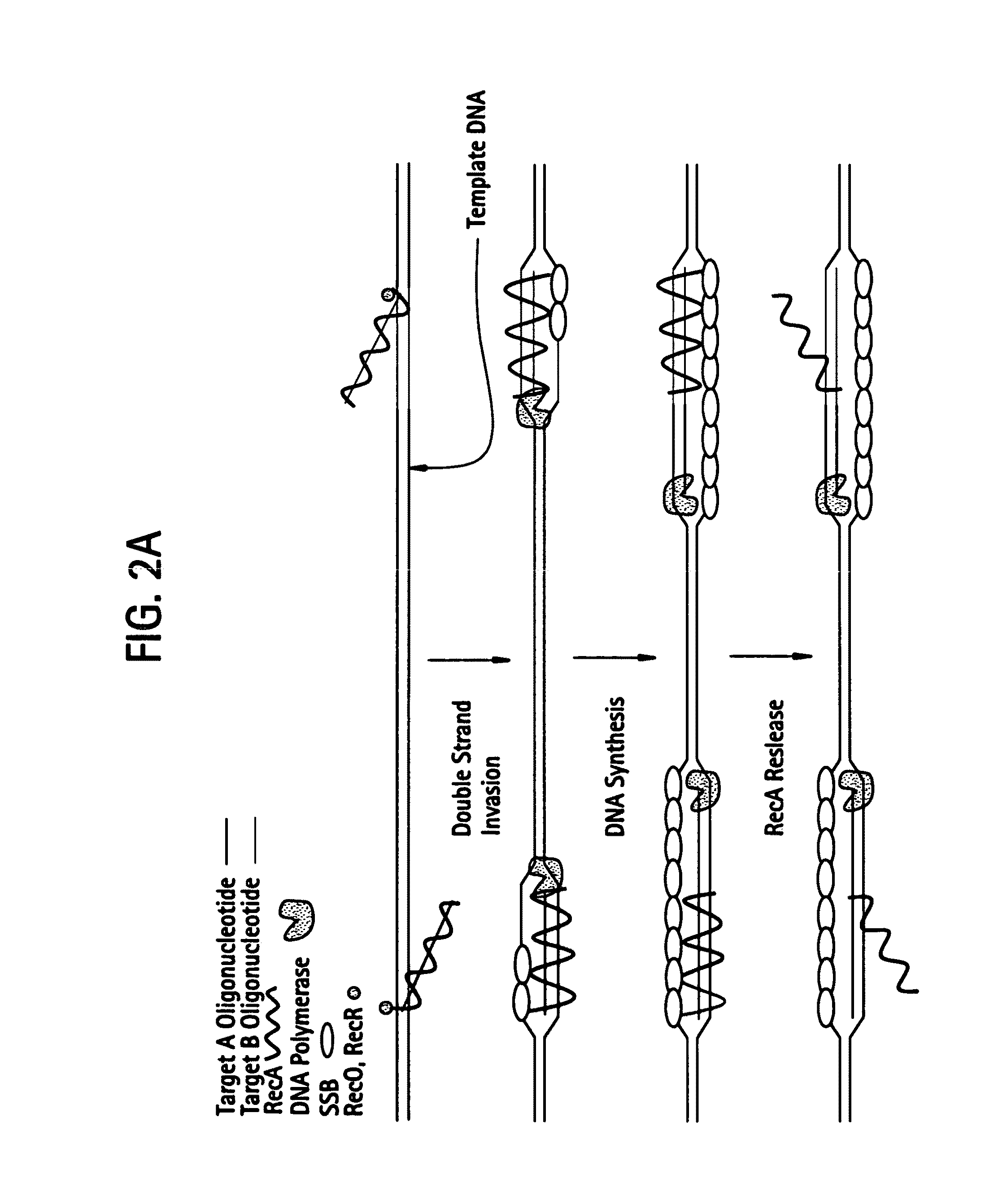
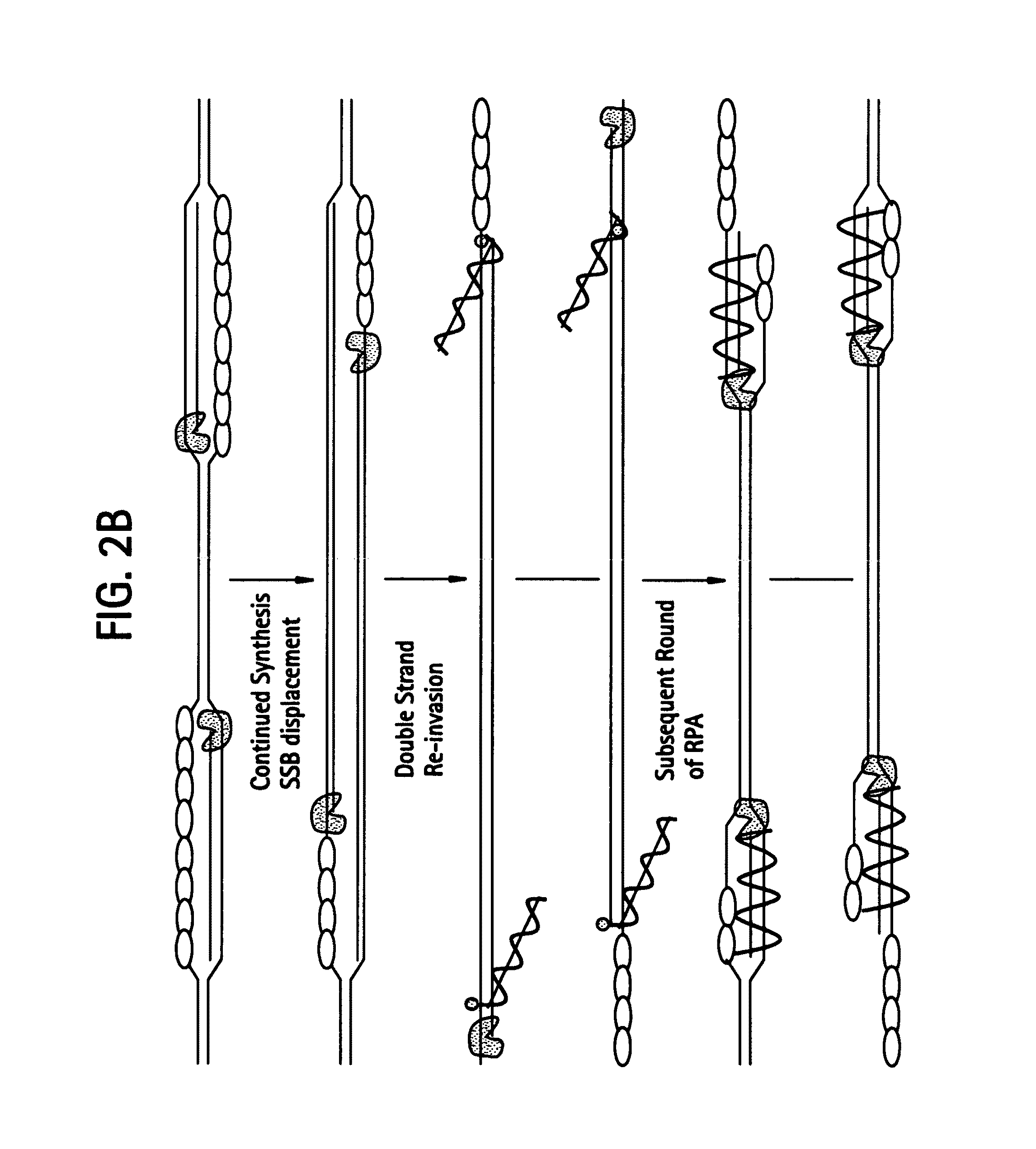
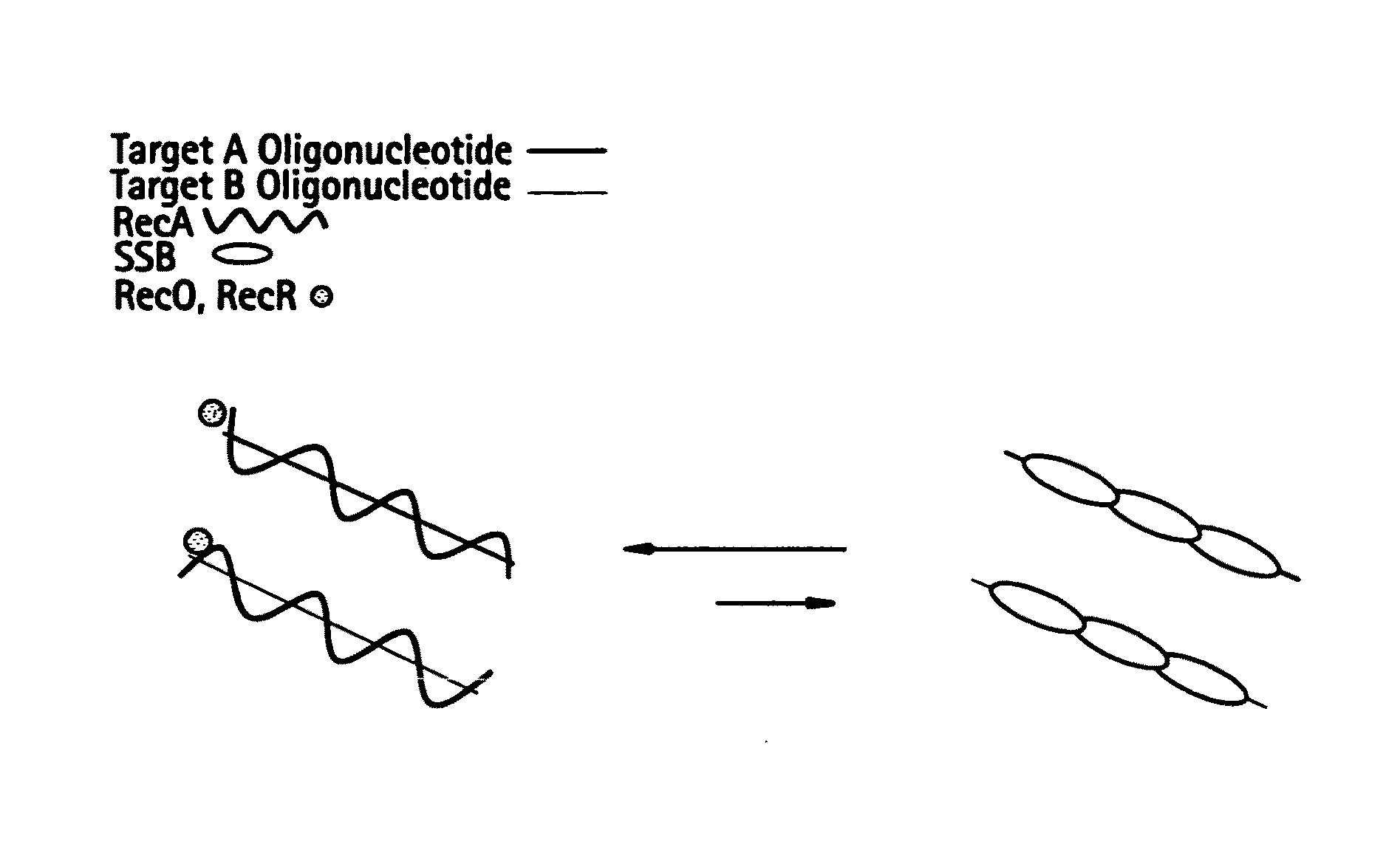
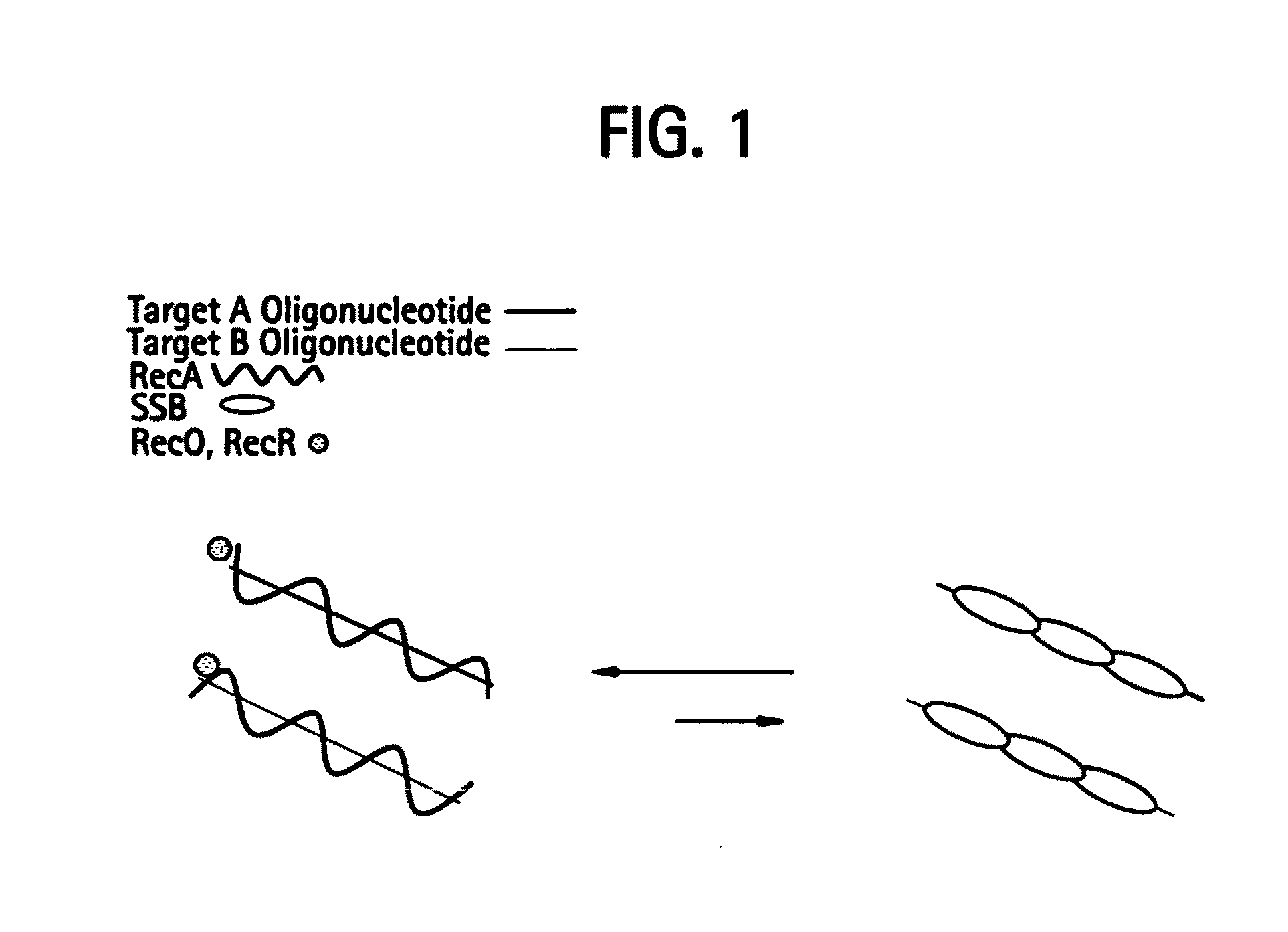
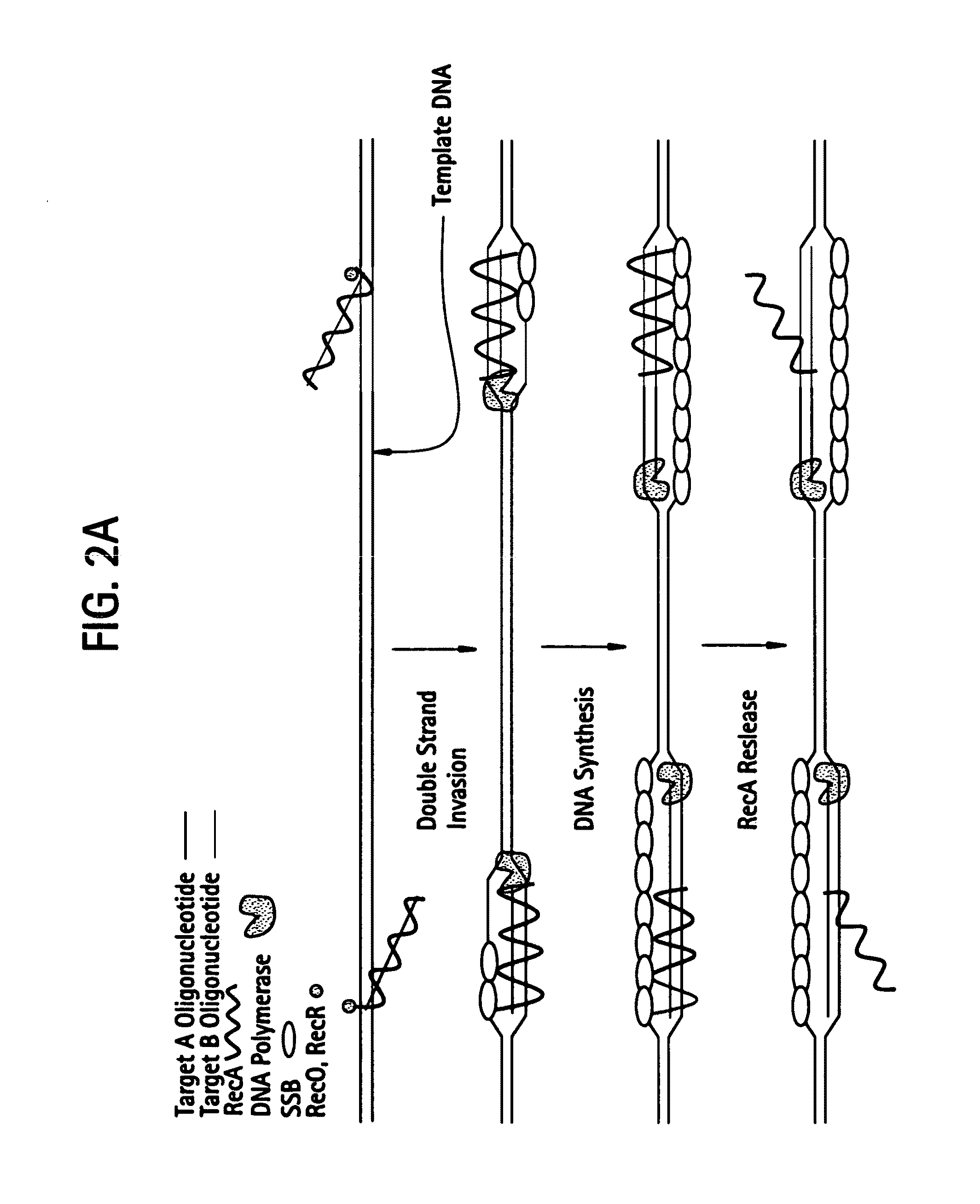
Recombinase polymerase amplification
This disclosure describes related novel methods for Recombinase-Polymerase Amplification (RPA) of a target DNA that exploit the properties of recombinase and related proteins, to invade double-stranded DNA with single stranded homologous DNA permitting sequence specific priming of DNA polymerase reactions. The disclosed methods have the advantage of not requiring thermocycling or thermophilic enzymes, thus offering easy and affordable implementation and portability relative to other amplification methods. Further RPA reactions using light and otherwise, methods to determine the nature of amplified species without a need for gel electrophoresis, methods to improve and optimize signal to noise ratios in RPA reactions, methods to optimize oligonucleotide primer function, methods to control carry-over contamination, and methods to employ sequence-specific third ‘specificity’ probes. Further described are novel properties and approaches for use of probes monitored by light in dynamic recombination environments.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
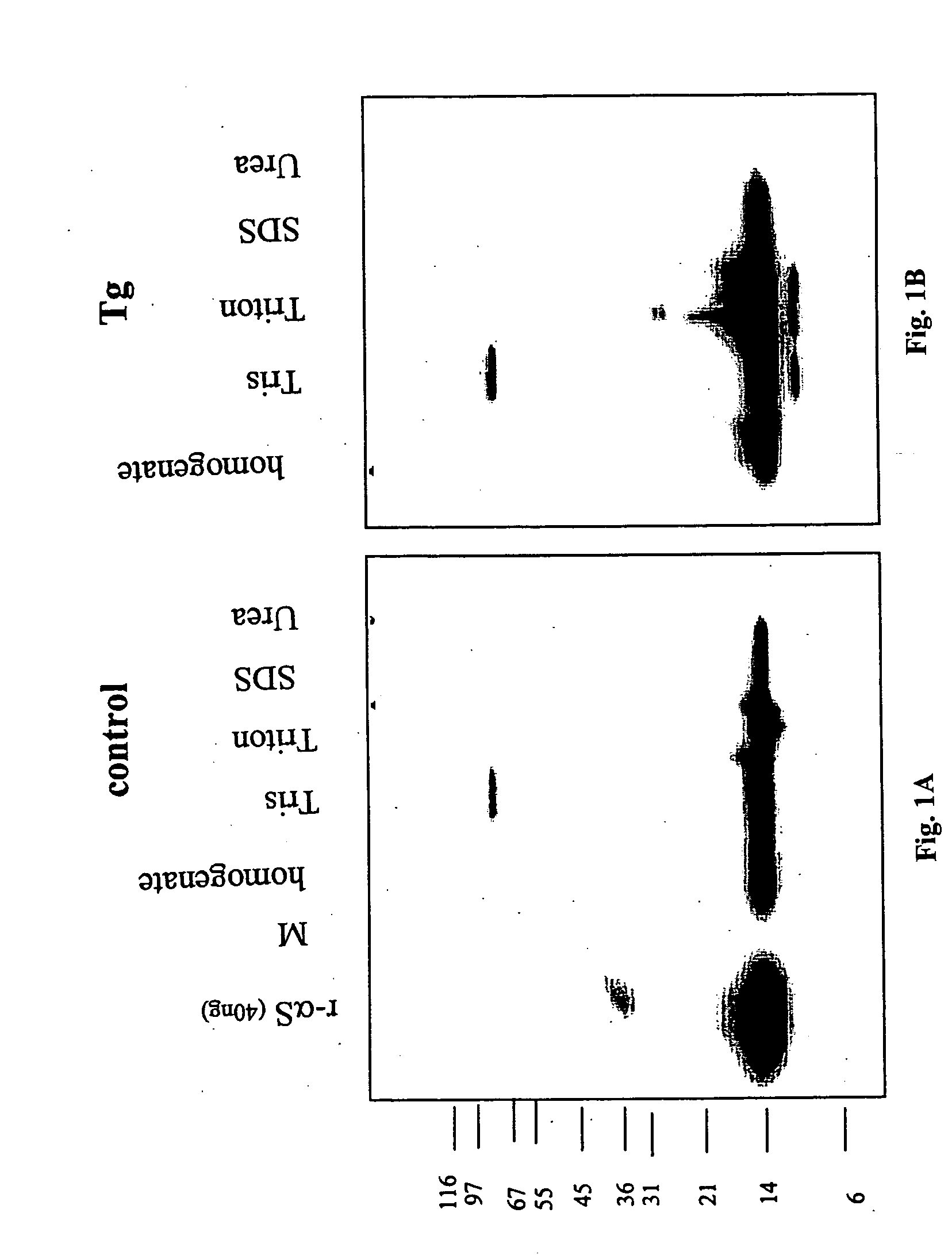
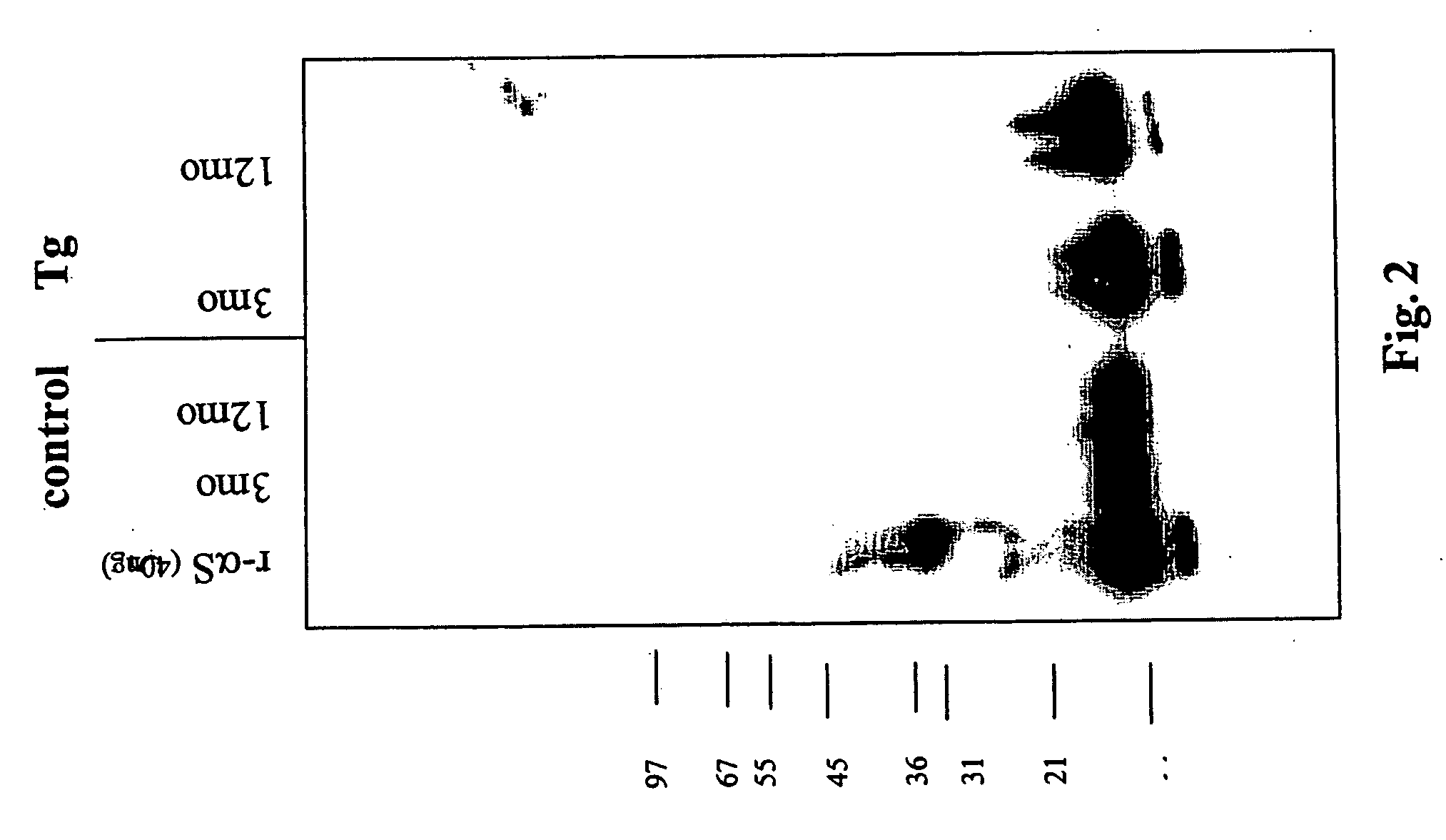
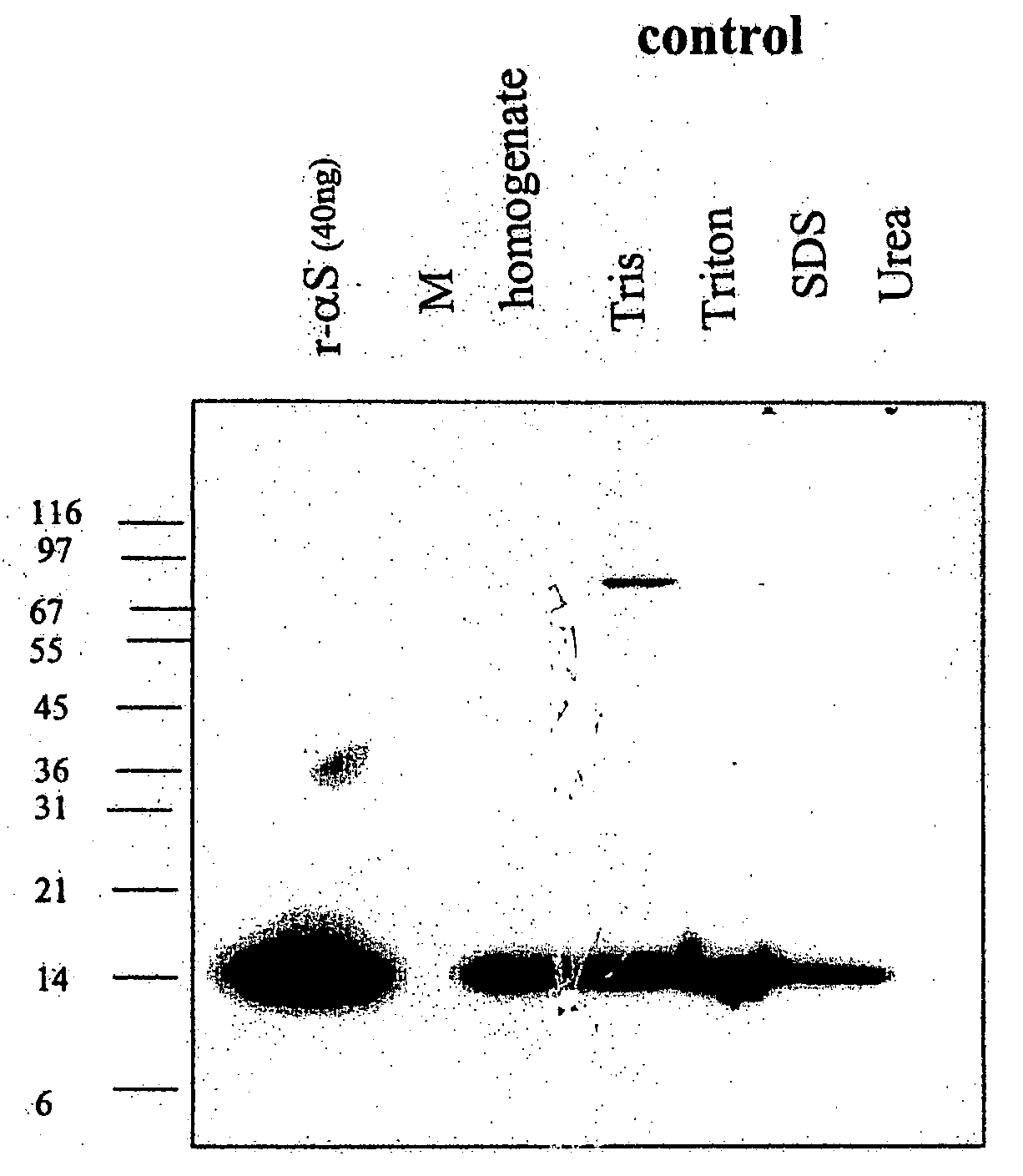
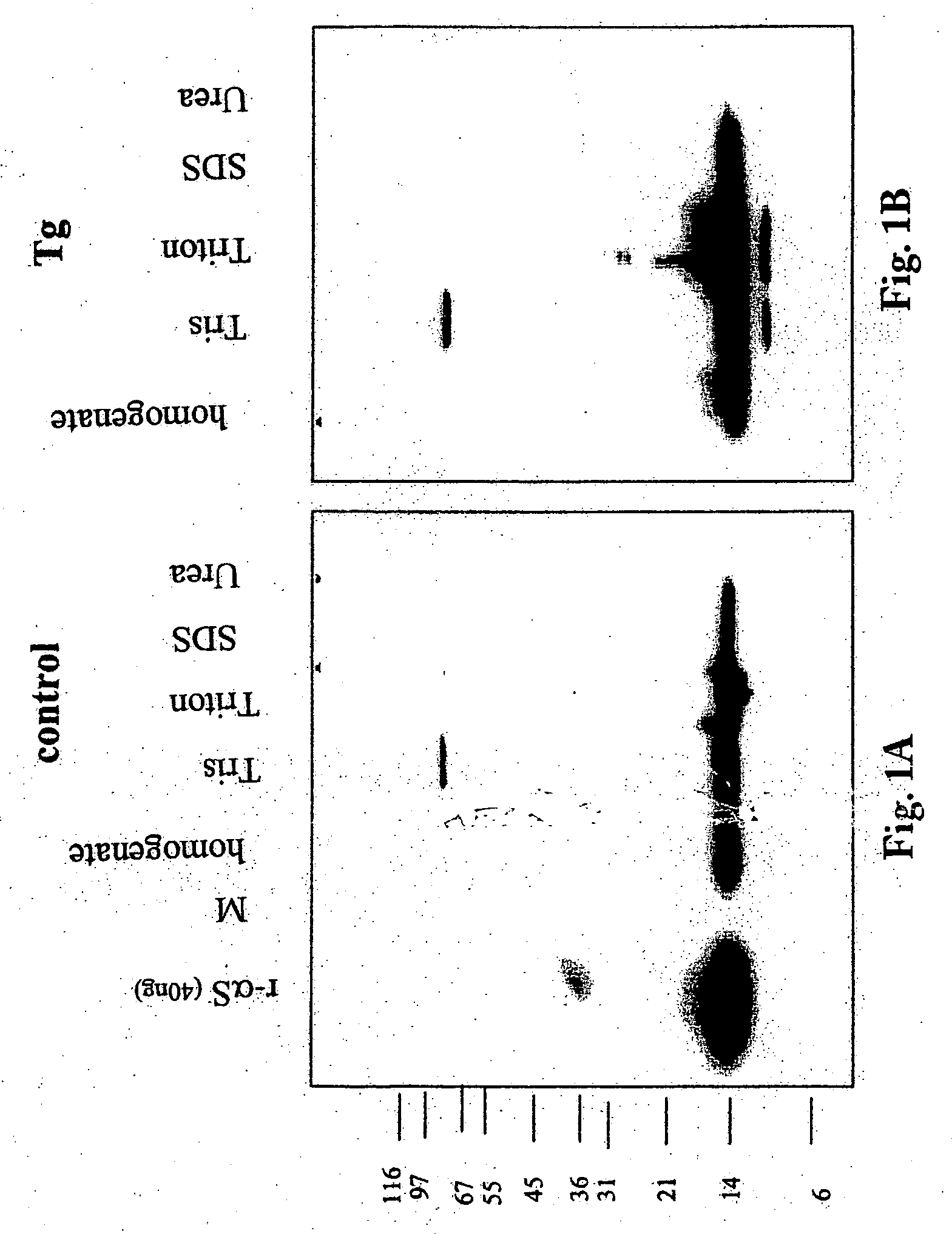
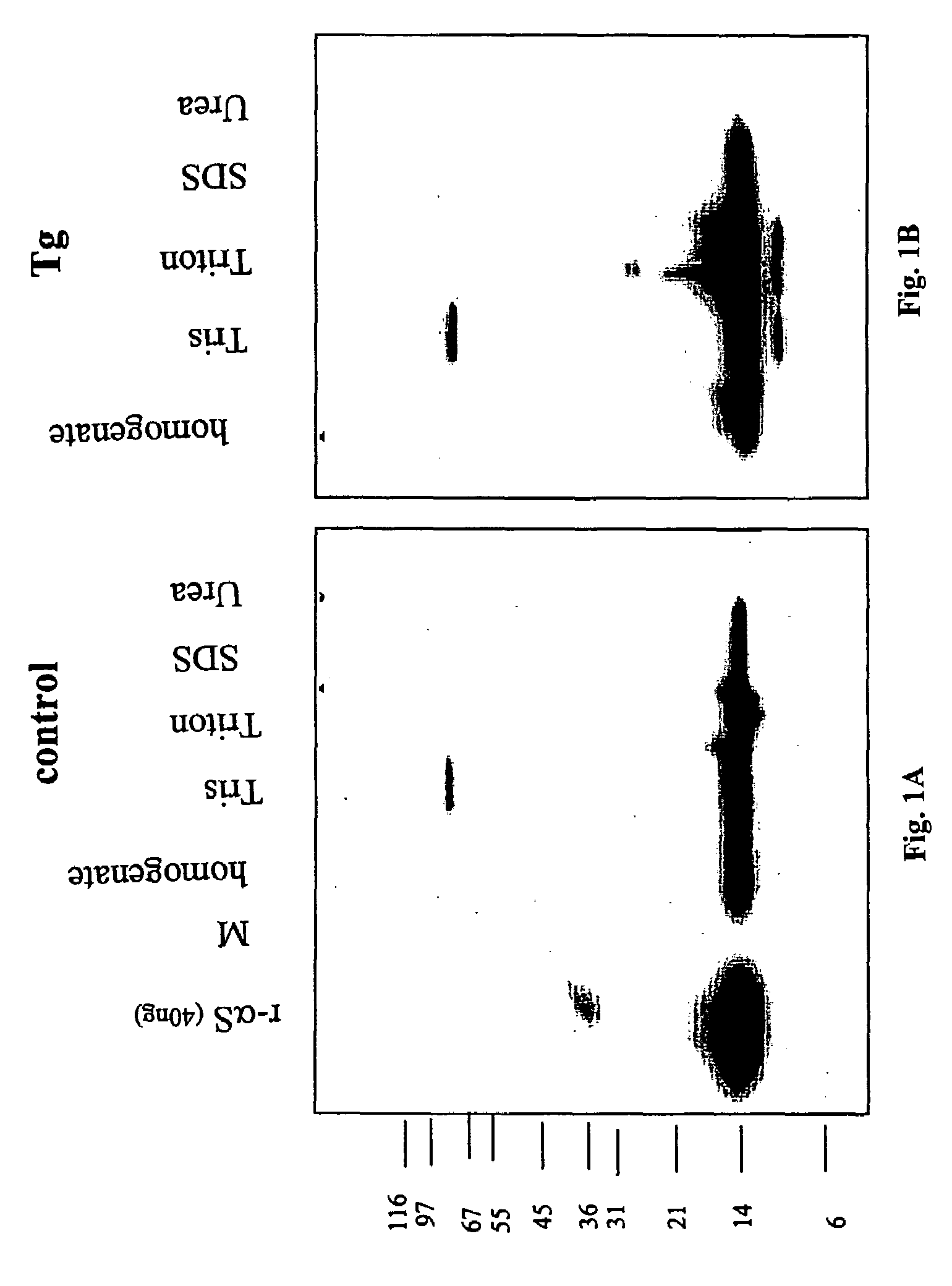
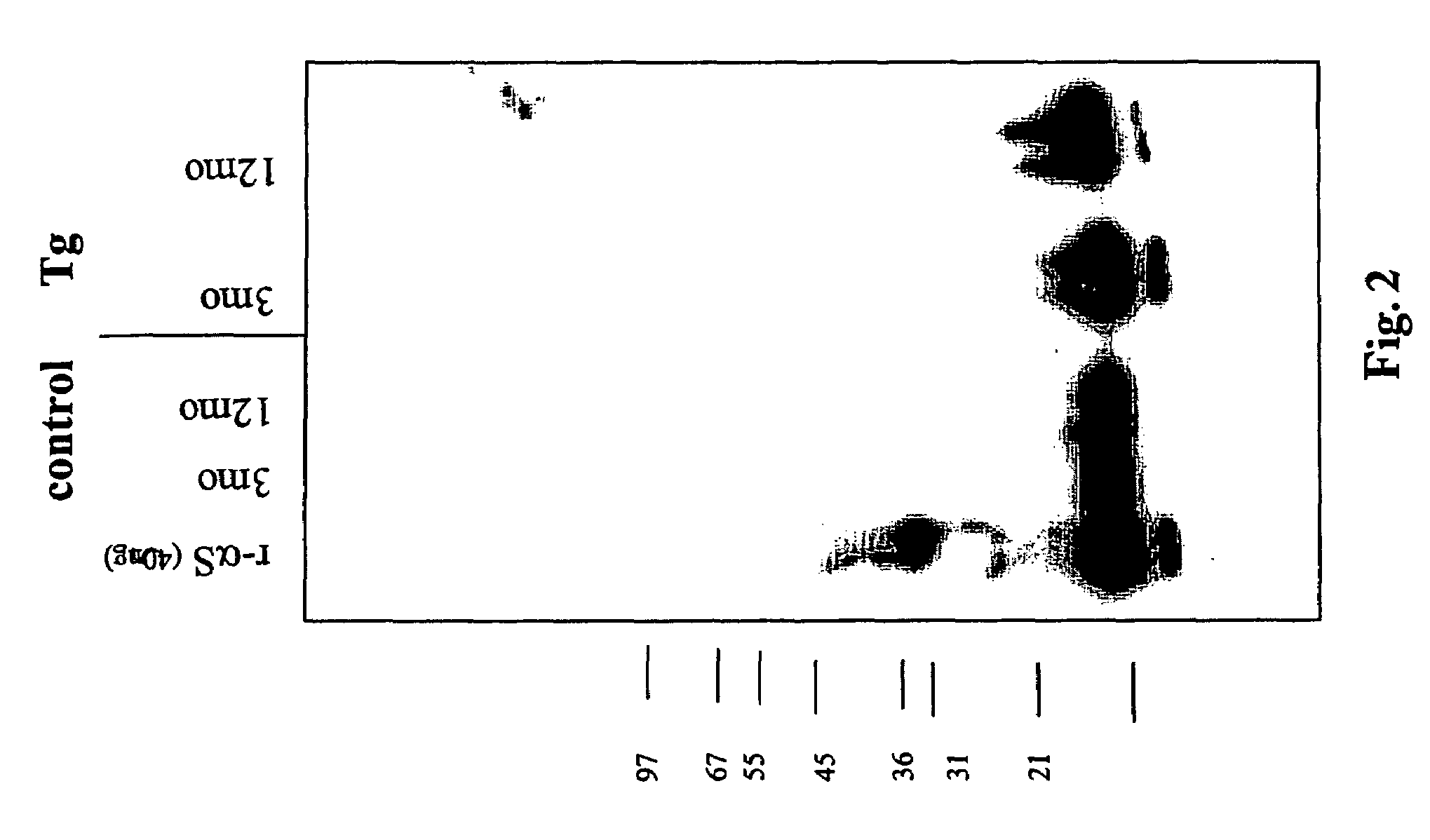
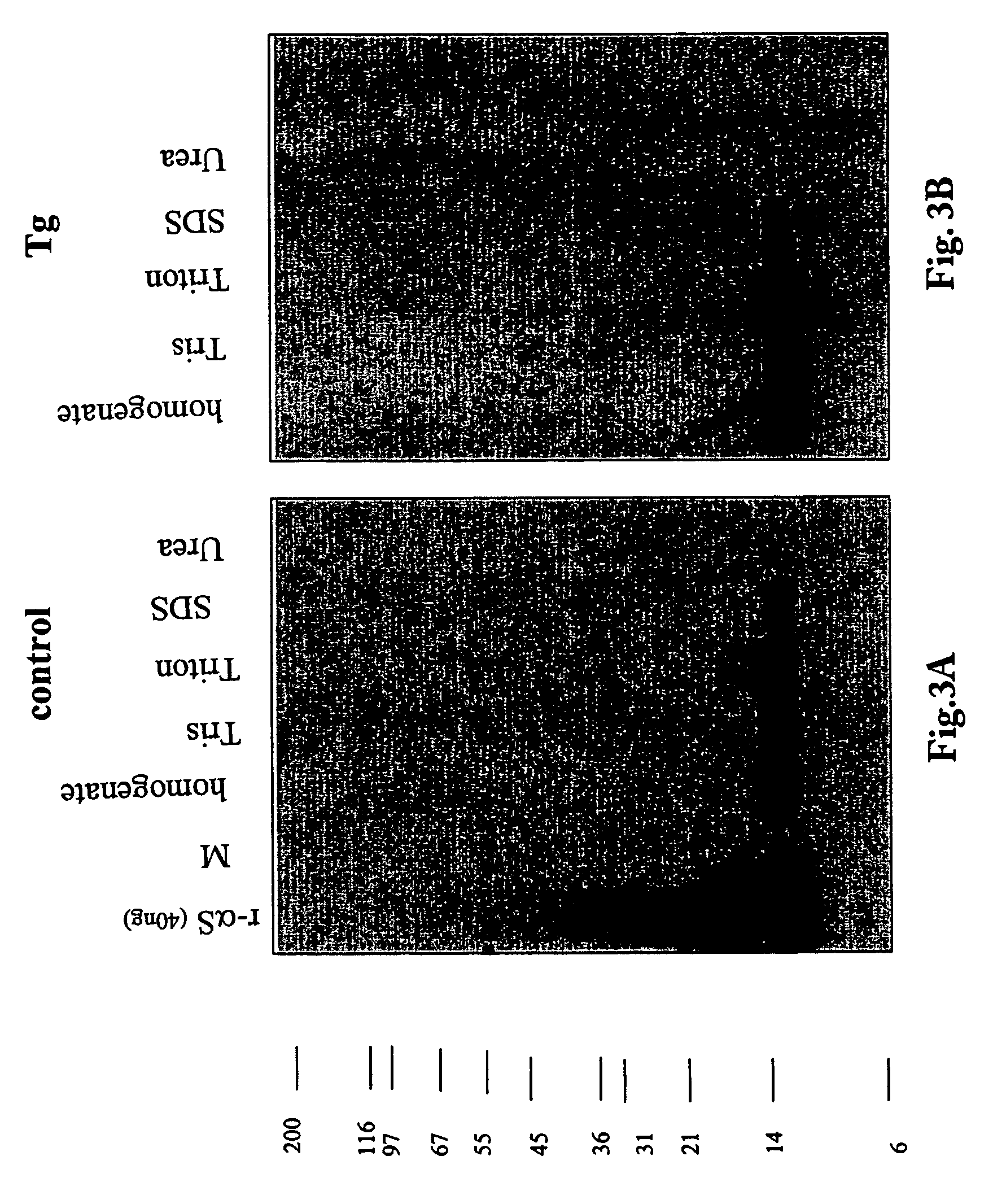
Truncated fragments of alpha-synuclein in Lewy body disease
ActiveUS20050198694A1Useful pharmacological activityBiocideNervous disorderGel electrophoresisC-terminus
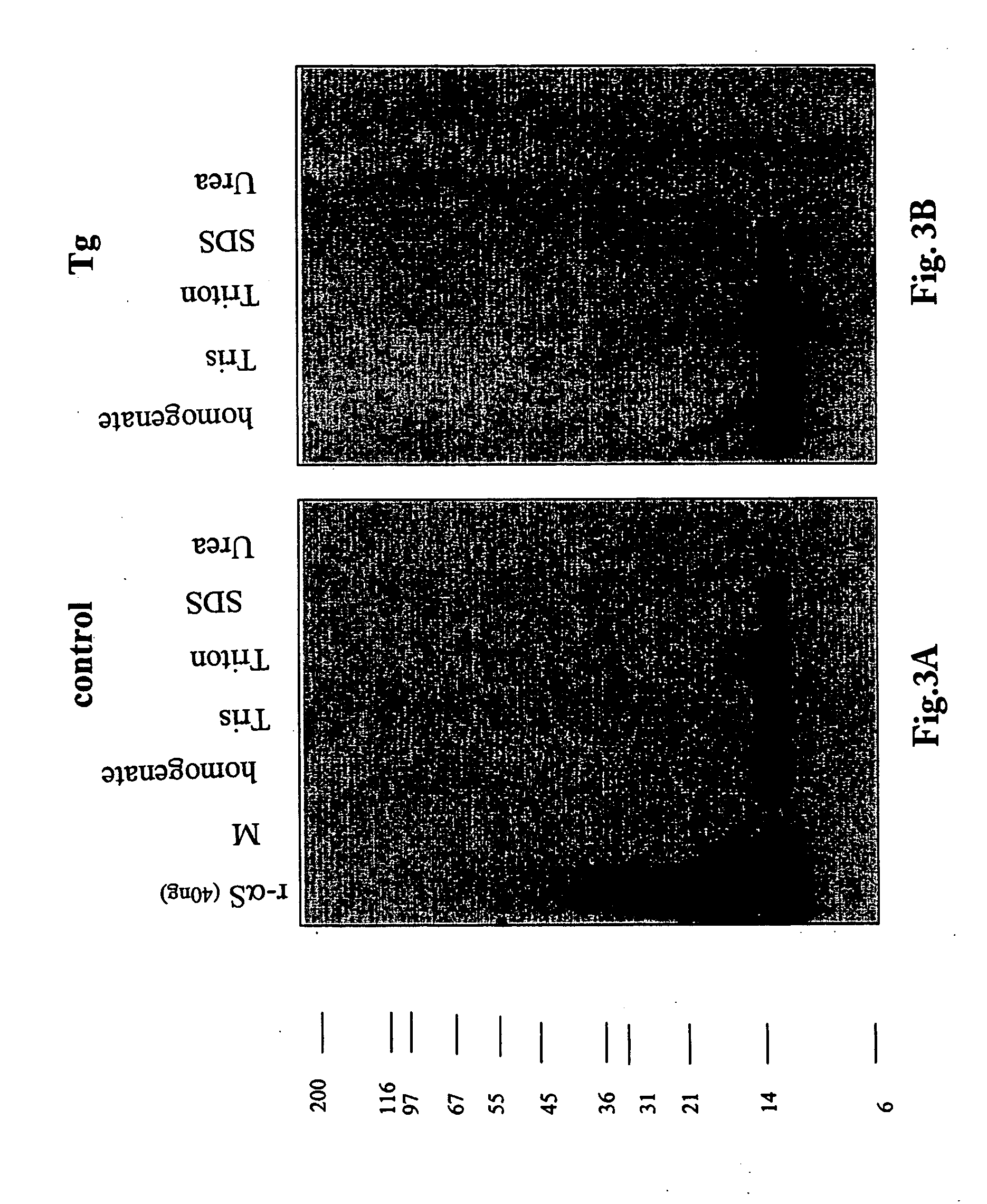
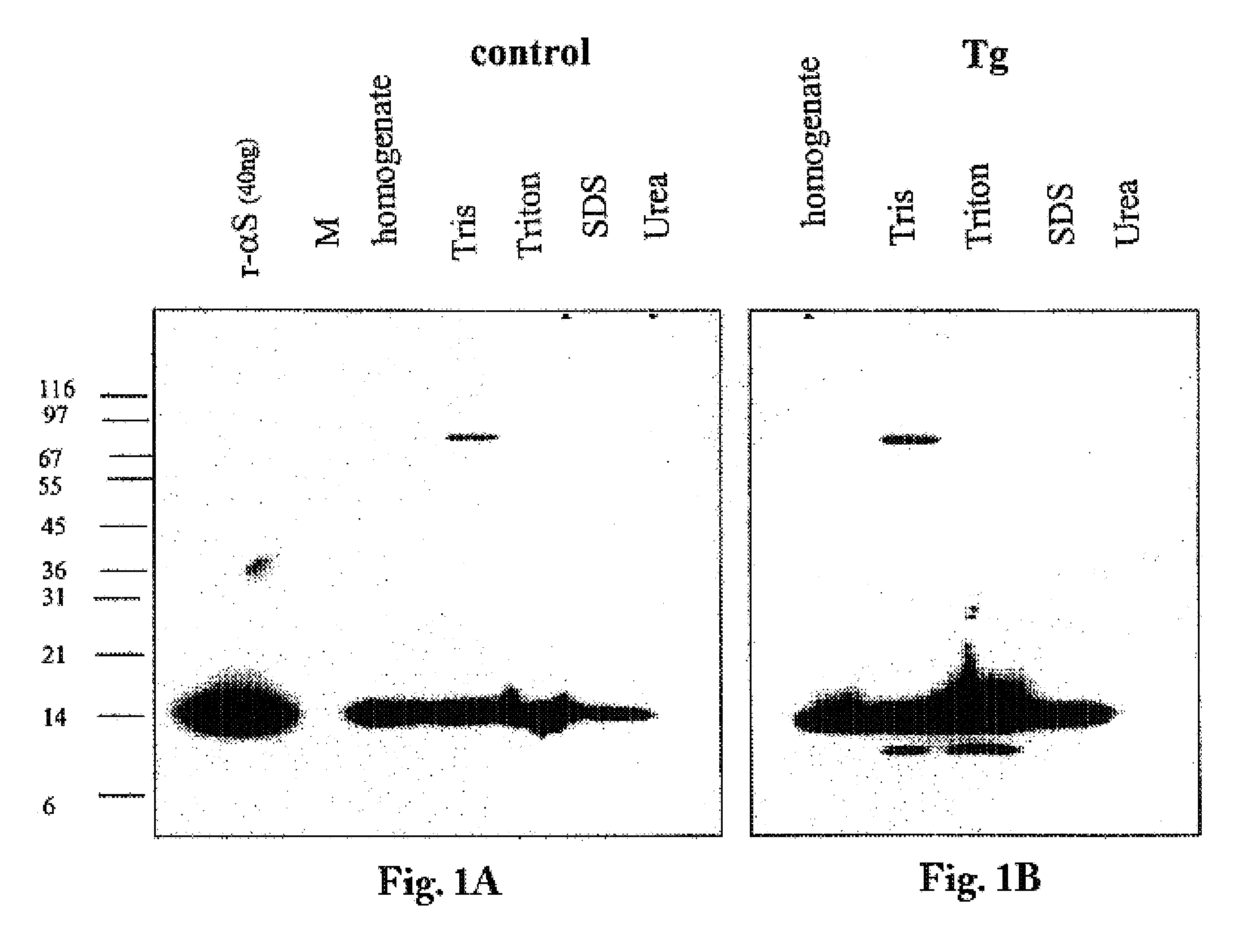
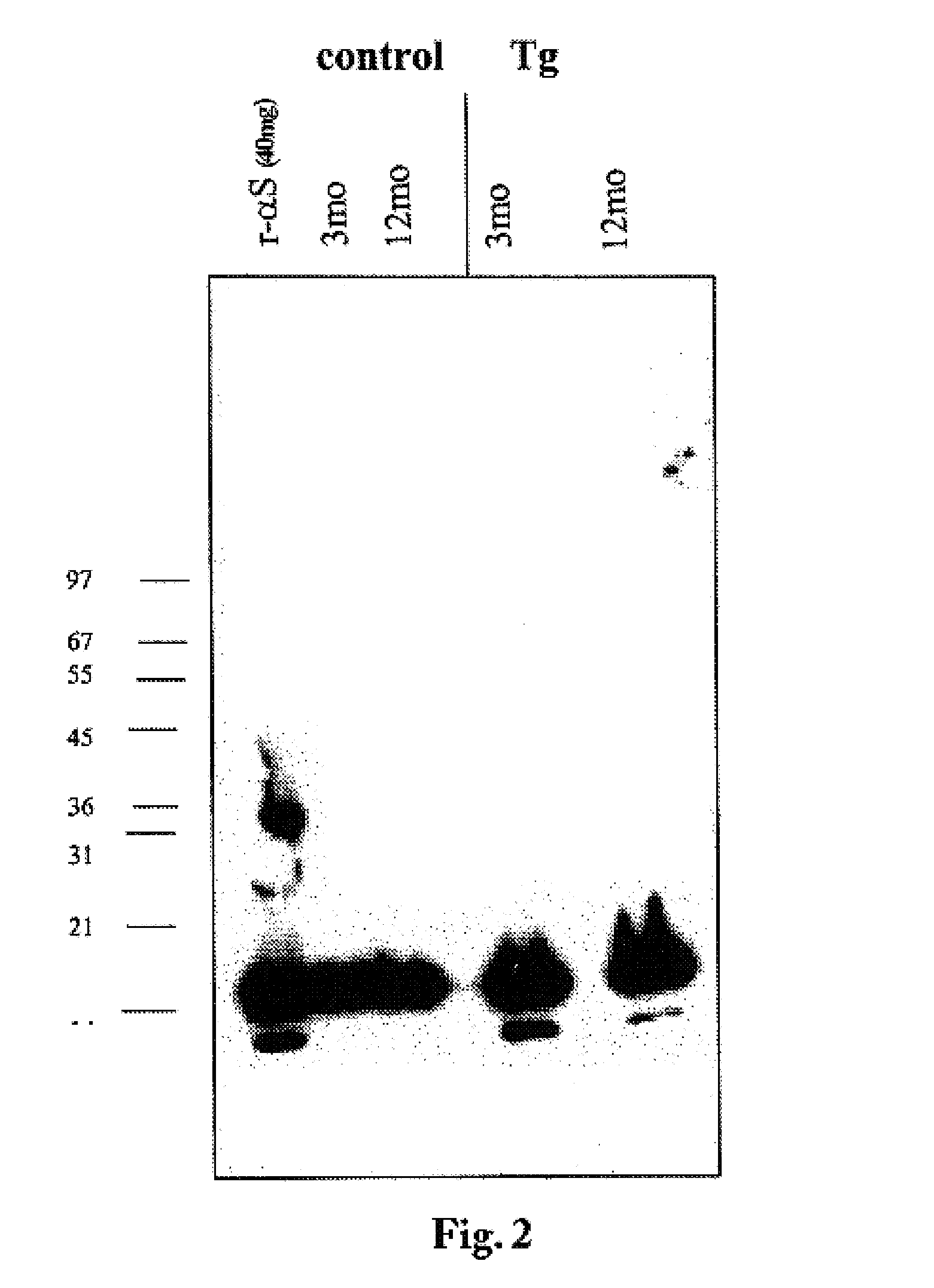
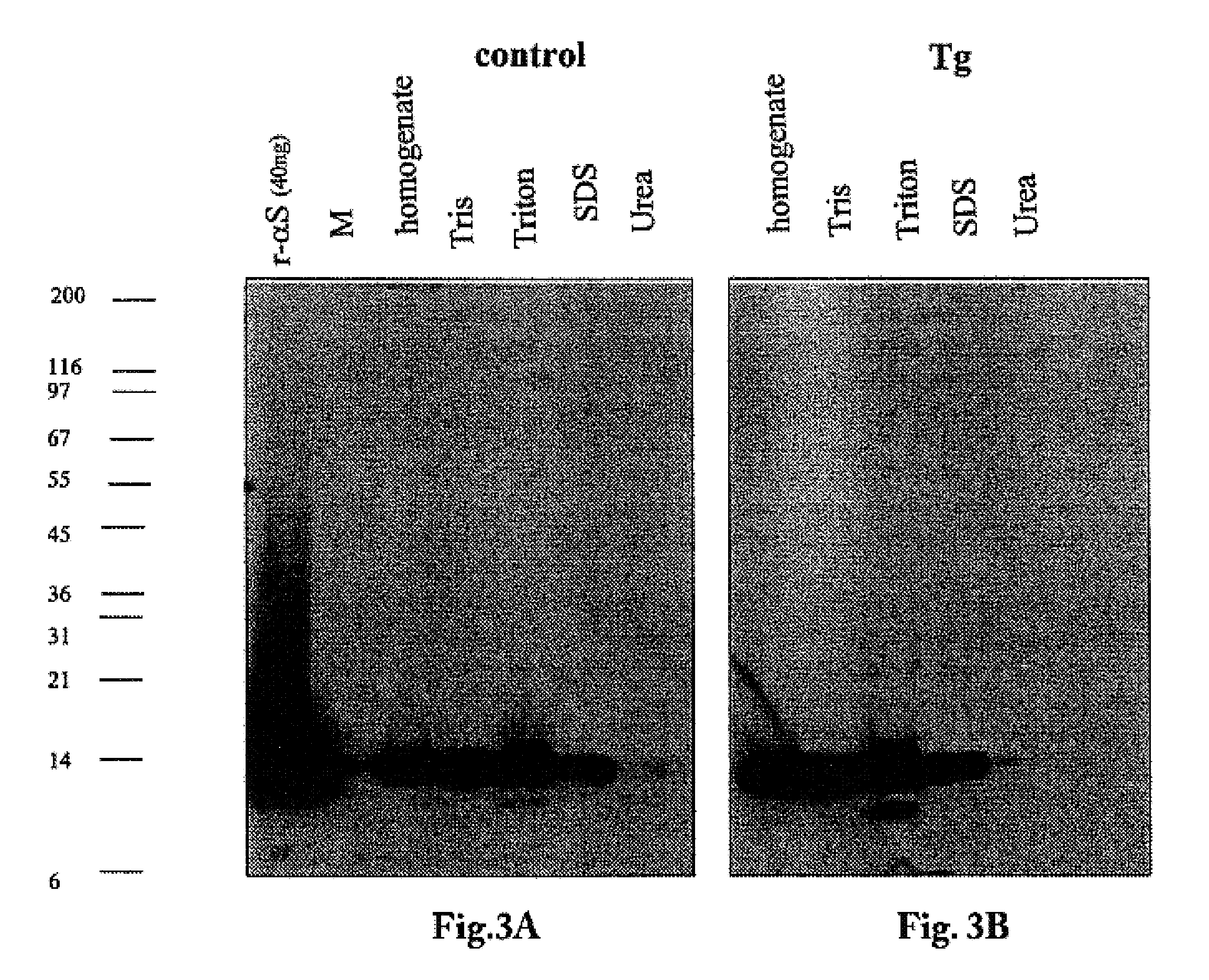
The application identifies novel fragments of alpha-synuclein in patients with Lewy Body Disease (LBD) and transgenic animal models thereof. These diseases are characterized by aggregations of alpha-synuclein. The fragments have a truncated C-terminus relative to fill-length alpha-synuclein. Some fragments are characterized by a molecular weight of about 12 kDa as determined by SDS gel electrophoresis in tricine buffer and a truncation of at least ten contiguous amino acids from the C-terminus of natural alpha-synuclein. The site of cleavage preferably occurs after residue 117 and before residue 126 of natural alpha-synuclein. The identification of these novel fragments of alpha-synuclein has a number of application in for example, drug discovery, diagnostics, therapeutics, and transgenic animals.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF FLINDERS UNIV +2
Process for analyzing protein samples
InactiveUS7045296B2Reduce disulfide bondEasy labelingSamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein expression profileUnit operation
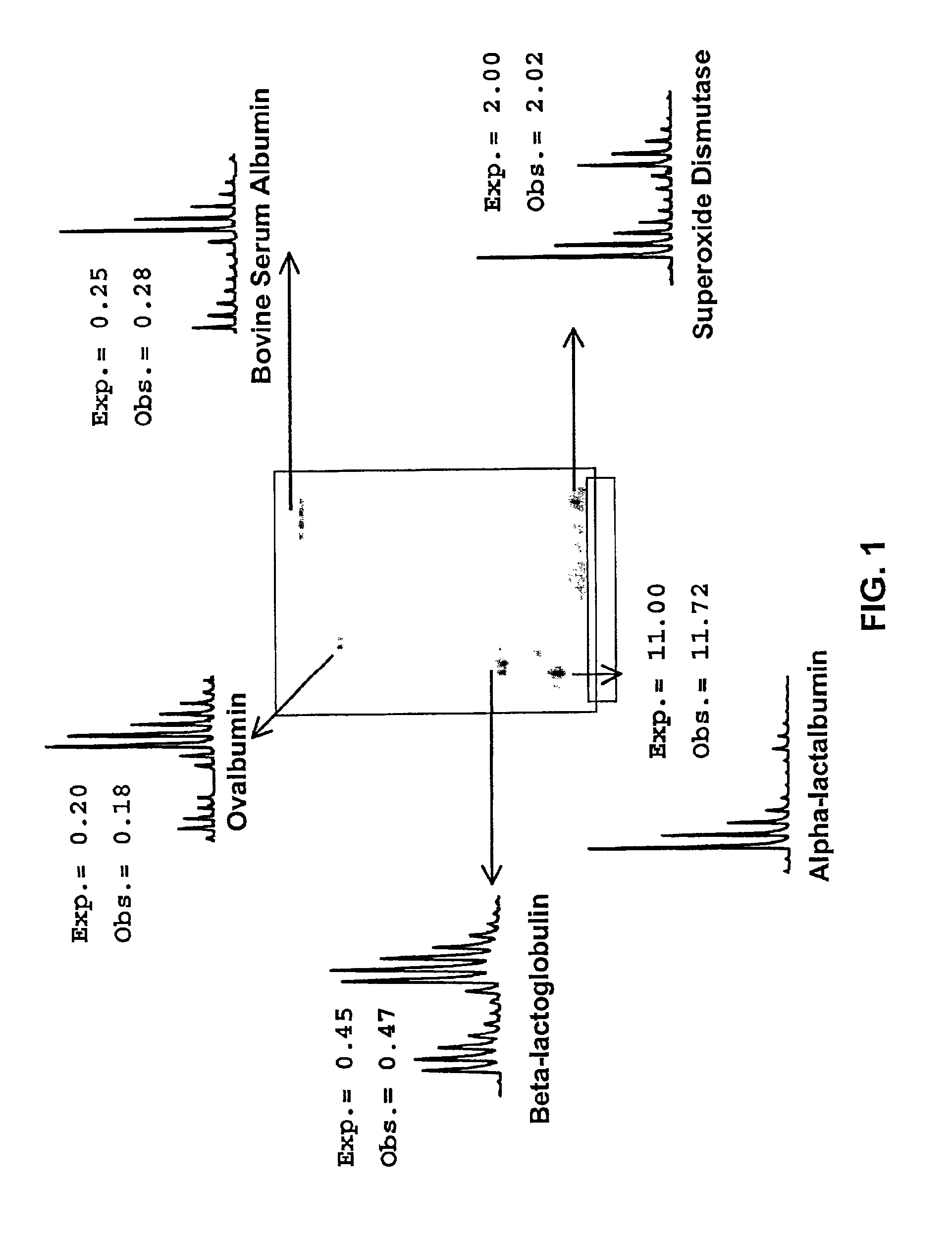
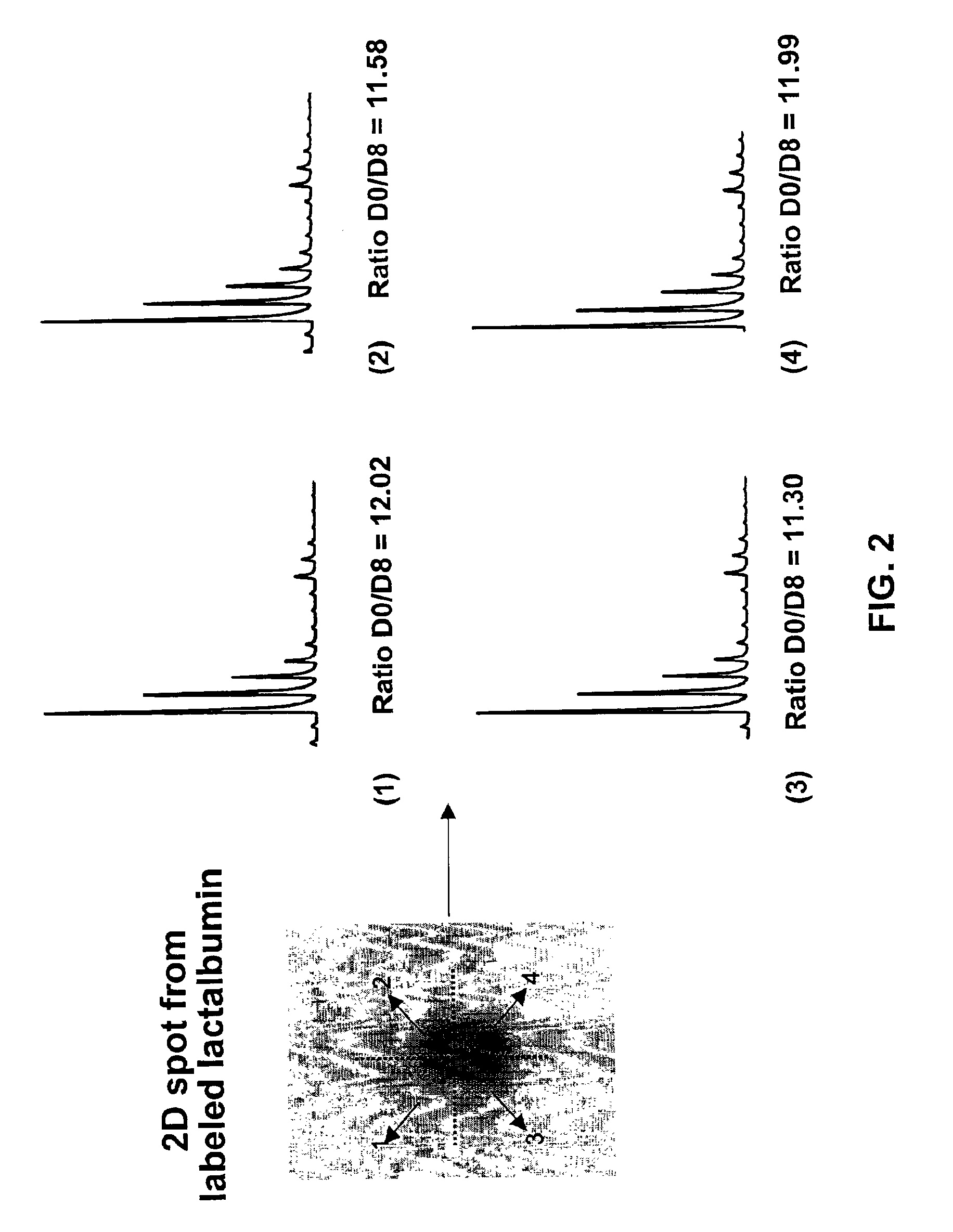
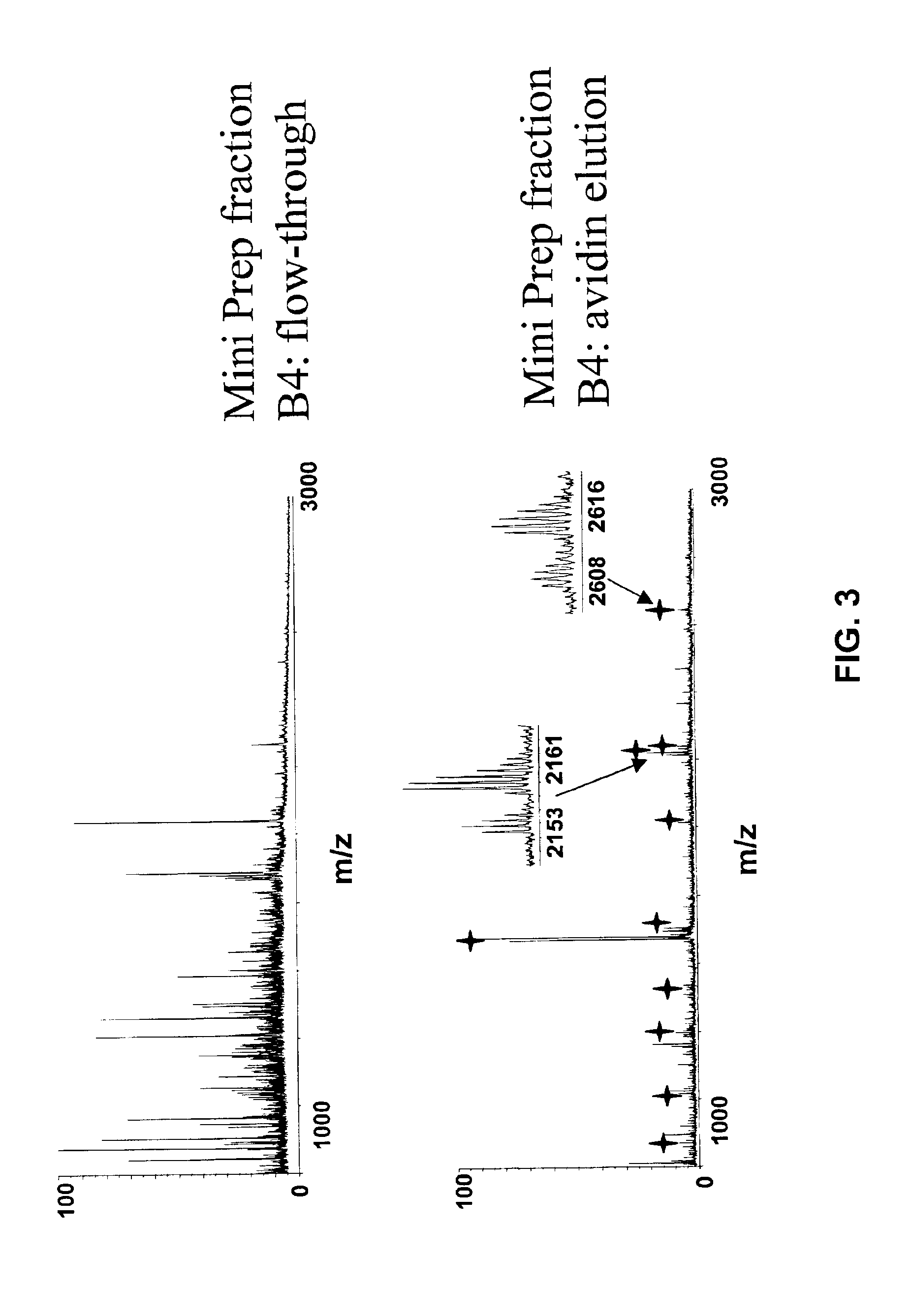
Methods using gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry for the rapid, quantitative analysis of proteins or protein function in mixtures of proteins derived from two or more samples in one unit operation are disclosed. In one embodiment the method includes (a) preparing an extract of proteins from each of at least two different samples; (b) providing a set of substantially chemically identical and differentially isotopically labeled protein reagents; (c) reacting the extract of proteins from different samples of step (a) with a different isotopically labeled reagent from the set of step (b) to provide two or more sets of isotopically differentially labeled proteins; (d) mixing each of the two or more sets of isotopically labeled proteins to form a single mixture of isotopically differentially labeled proteins; (e) electrophoresing the mixture of step (d) by an electrophoresing method capable of separating proteins within the mixture; (f) digesting at least a portion of one or more separated proteins of step (e) and (g) detecting the difference in the expression levels of the proteins in the two samples by mass spectrometry based on one or more peptides in the sample of labeled peptides. The analytical method can be used for qualitative and particularly for quantitative analysis of global protein expression profiles in cells and tissues, i.e. the quantitative analysis of proteomes.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE +1
Recombinase polymerase amplification
InactiveUS20100311127A1High activitySimple designHeating or cooling apparatusHydrolasesOligonucleotide primersSingle strand
This disclosure describes related novel methods for Recombinase-Polymerase Amplification (RPA) of a target DNA that exploit the properties of recombinase and related proteins, to invade double-stranded DNA with single stranded homologous DNA permitting sequence specific priming of DNA polymerase reactions. The disclosed methods have the advantage of not requiring thermocycling or thermophilic enzymes, thus offering easy and affordable implementation and portability relative to other amplification methods. Further RPA reactions using light and otherwise, methods to determine the nature of amplified species without a need for gel electrophoresis, methods to improve and optimize signal to noise ratios in RPA reactions, methods to optimize oligonucleotide primer function, methods to control carry-over contamination, and methods to employ sequence-specific third ‘specificity’ probes. Further described are novel properties and approaches for use of probes monitored by light in dynamic recombination environments.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
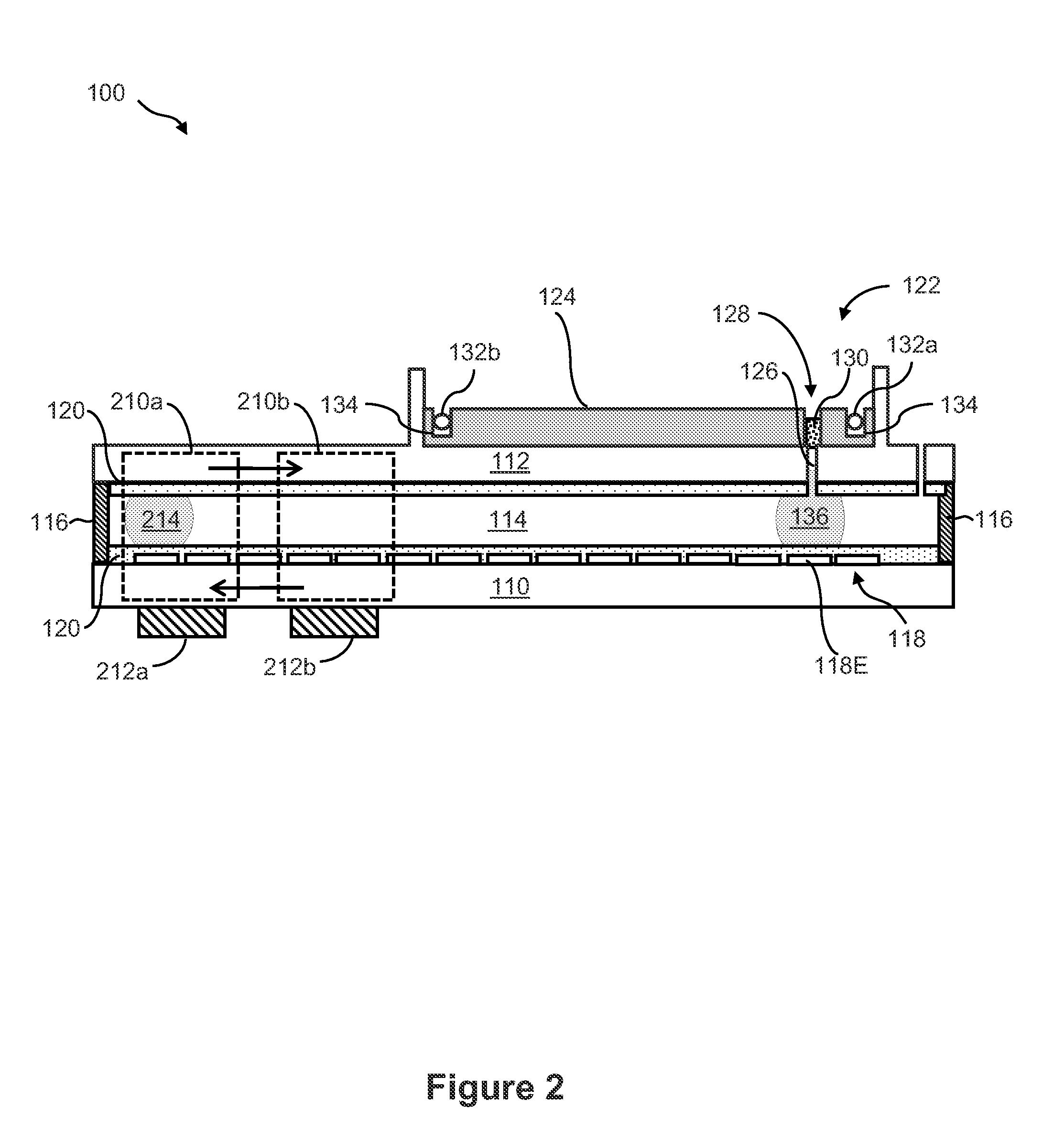
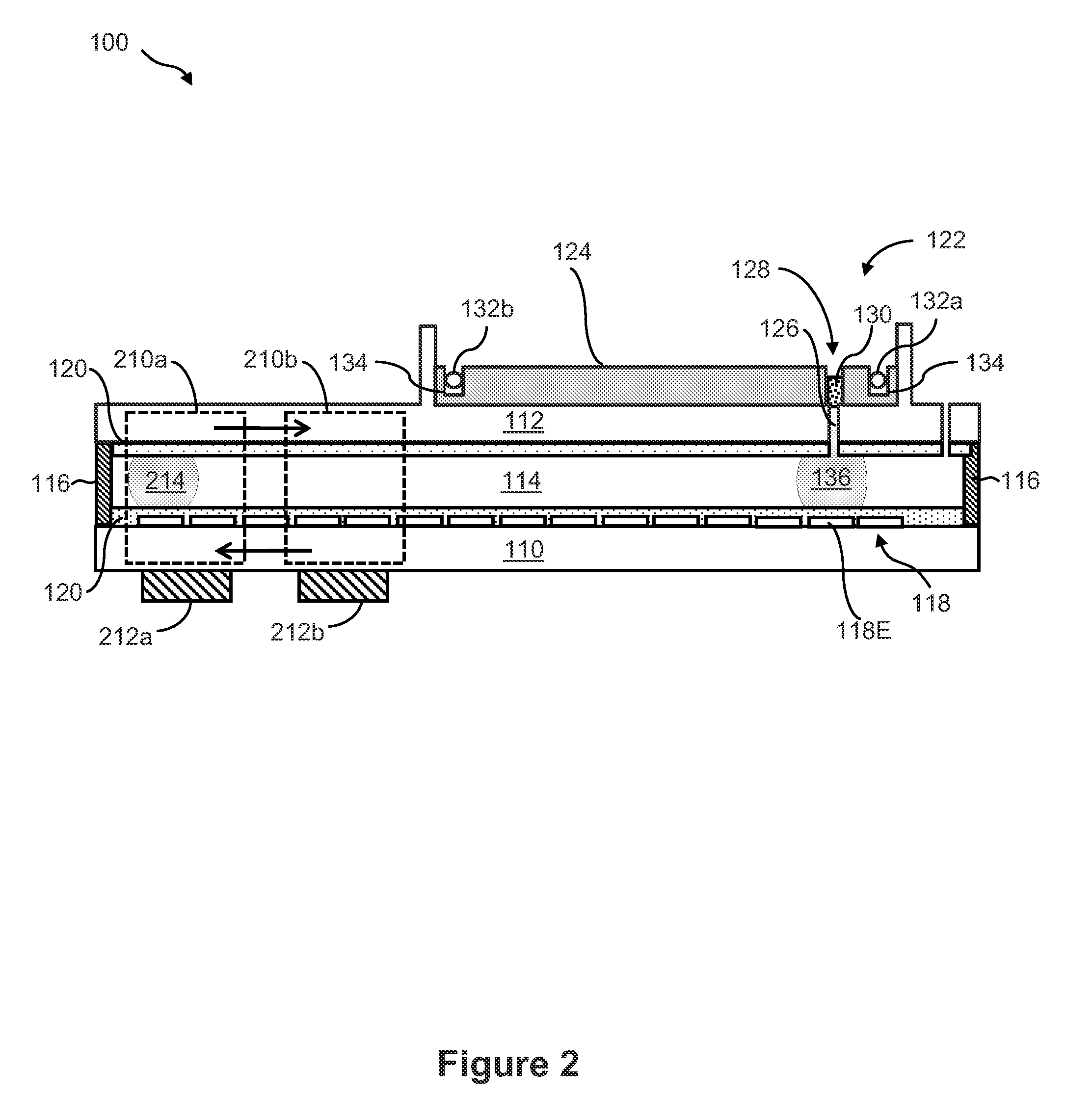
Integrated Droplet Actuator for Gel; Electrophoresis and Molecular Analysis
InactiveUS20130059366A1Easy to useFacilitates of propertyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusMolecular analysisEngineering
The invention is directed to a droplet actuator device and methods for integrating gel electrophoresis analysis with pre or post-analytical sample handling as well as other molecular analysis processes. Using digital microfluidics technology, the droplet actuator device and methods of the invention provide the ability to perform gel electrophoresis and liquid handling operations on a single integrated device. The integrated liquid handling operations may be used to prepare and deliver samples to the electrophoresis gel, capture and subsequently process products of the electrophoresis gel or perform additional assays on the same sample materials which are analyzed by gel electrophoresis. In one embodiment, one or more molecular assays, such as nucleic acid (e.g., DNA) quantification by real-time PCR, and one or more sample processing operations such as sample dilution is performed on a droplet actuator integrated with an electrophoresis gel. In one embodiment, an electrophoresis gel may be integrated on the top substrate of the droplet actuator.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
Truncated fragments of alpha-synuclein in Lewy Body Disease
The application identifies novel fragments of alpha-synuclein in patients with Lewy Body Disease (LBD) and transgenic animal models thereof. These diseases are characterized by aggregations of alpha-synuclein. The fragments have a truncated C-terminus relative to full-length alpha-synuclein. Some fragments are characterized by a molecular weight of about 12 kDa as determined by SDS gel electrophoresis in tricine buffer and a truncation of at least ten contiguous amino acids from the C-terminus of natural alpha-synuclein. The site of cleavage preferably occurs after residue 117 and before residue 126 of natural alpha-synuclein. The identification of these novel fragments of alpha-synuclein has a number of application in for example, drug discovery, diagnostics, therapeutics, and transgenic animals.
Owner:PROTHENA BIOSCI LTD
Dispersion of carbon nanotubes by nucleic acids
Carbon nanotubes dispersed by a stabilized solution of nucleic acid molecules formed separated nanotube-nucleic acid complexes and were separated according to standard chromatographic methods, including gel electrophoresis, two phase solvent systems and ion exchange chromatography.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Gel electrophoresis training aid and training kit
InactiveUS6866514B2Durable and reusableMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEducational modelsElastomerGel electrophoresis
A gel electrophoresis training aid is provided. The training aid includes a substantially transparent elastomeric body having at least one series of spaced-apart wells. The elastomeric body is adapted with a plurality of spaced-apart bands extending in the same direction from the wells. Each of the spaced-apart bands are positioned substantially parallel to one spaced-apart well. A training kit including the training aid is also provided.
Owner:VON ENTERPRISES
Method for extracting keratin from feather
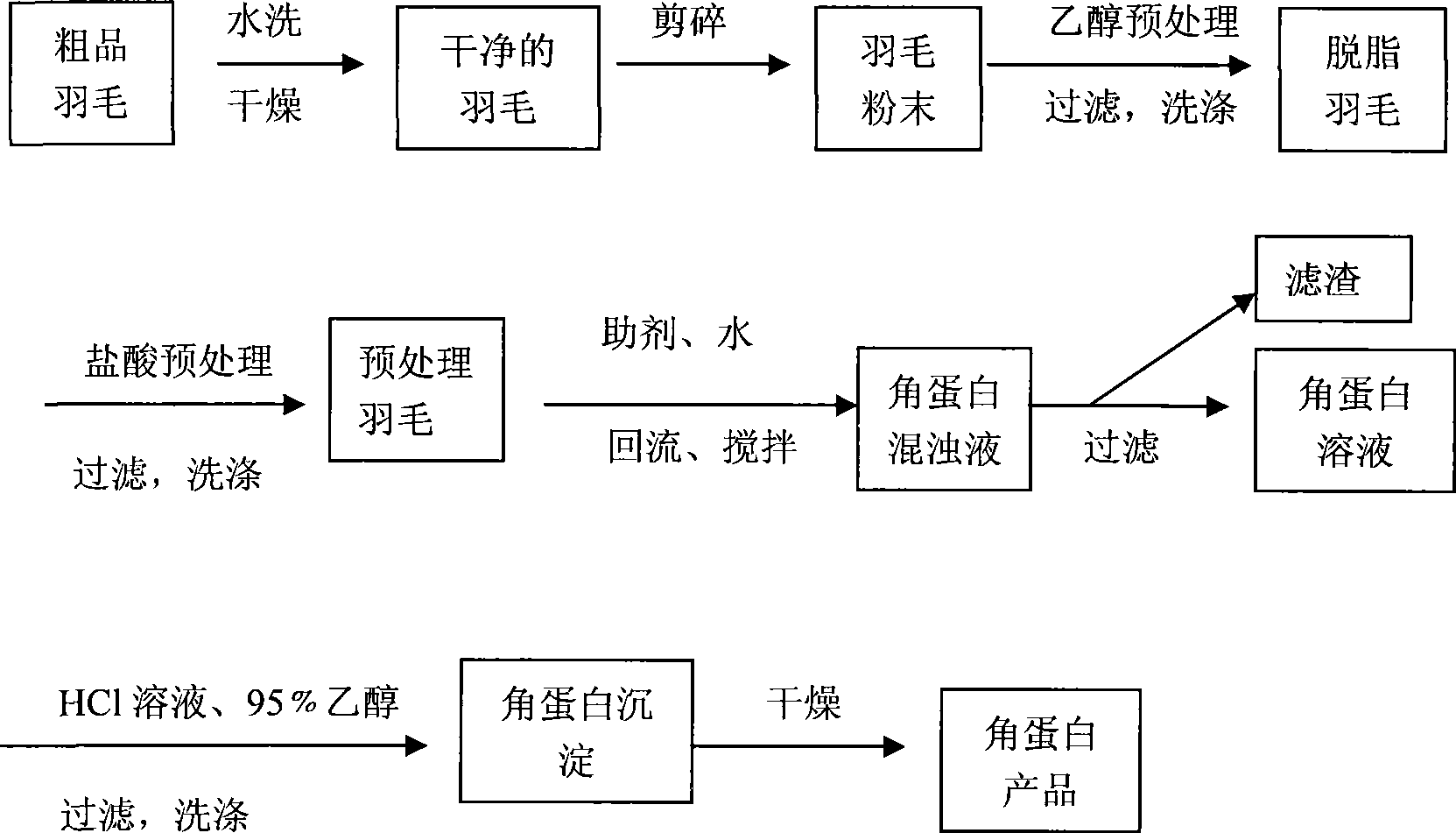
InactiveCN101372503AHigh yieldReduce extraction timePeptide preparation methodsInfraredGel electrophoresis
The invention provides a method for extracting keratin from feather, comprising the steps that after being crashed, clean feather is pretreated by ethanol and hydrochloric acid; by adopting mercaptoethanol reduction method, the pretreated feather is deacidized to obtain keratin solution of the feather, and then clean sand white keratin solid powder is obtained through acid coprecipitate, washing and drying. The extracted keratin is analyzed and represented by the methods such as ultraviolet-visible spectrum, infrared spectrum, SDS-gel electrophoresis, elementary analysis, etc. The results shows that the keratin extracted by the method mainly contains the elements such as C, H, N, O, S, the total content of which reaches over 99%, and the purity is higher; the molecular weight of the keratin mainly ranges from 5 to 20 kD and 40 to 80kD.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for treating systemic bacterial, fungal and protozoan infection
ActiveUS8431123B2Low-toxicLower Level RequirementsHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesProtozoa
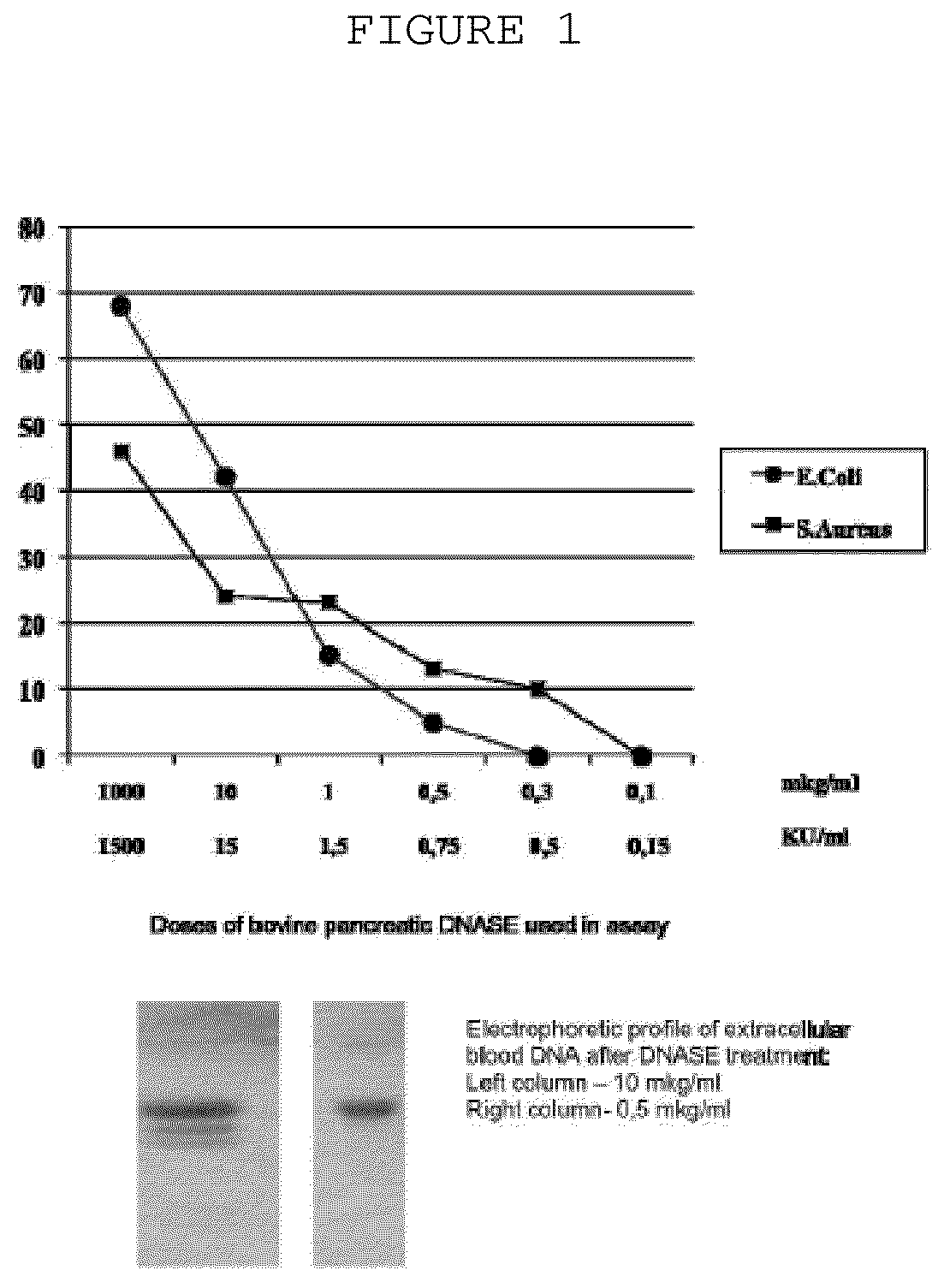
The invention is directed to a treatment of diseases that are accompanied by quantitative and / or qualitative changes of blood extracellular DNA and, more particularly, to a treatment of systemic bacterial, fungal and protozoan infections. The inventive method comprises introducing a treatment agent into a circulating blood system of a patient diagnosed with systemic infection caused by bacteria, fungi or protozoa, wherein said treatment agent destroys extracellular DNA in said blood of said patient and wherein said treatment agent used to destroy said extracellular DNA is a DNase enzyme: said agent being administered in doses and regimens which are sufficient to decrease the average molecular weight of circulating extracellular blood DNA in the blood of said patient; such decrease in the average molecular weight can be measured by gel electrophoresis of extracellular blood DNA fraction from the blood of said patient. A DNase enzyme may be applied in a dose and regimen that provide a DNase DNA hydrolytic activity measured in blood plasma that exceeds 1.5 Kunitz units per 1 ml of blood plasma for more than 12 hours within a period of 24 hours.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Cell line gene knock-out method for obtaining large fragment deletion through CRISPR/Cas9 system
ActiveCN107435051AEasy accessImprove knockout productivityVectorsStable introduction of DNAFluorescenceLarge fragment
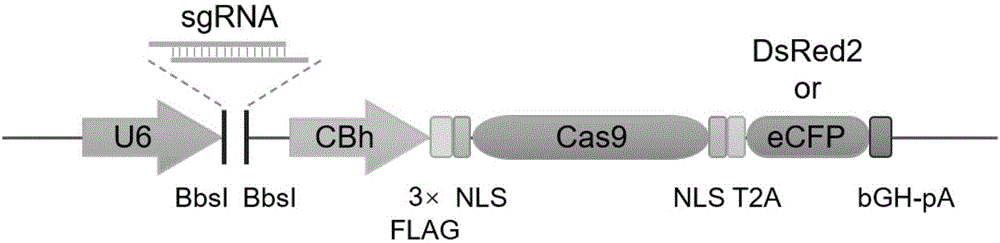
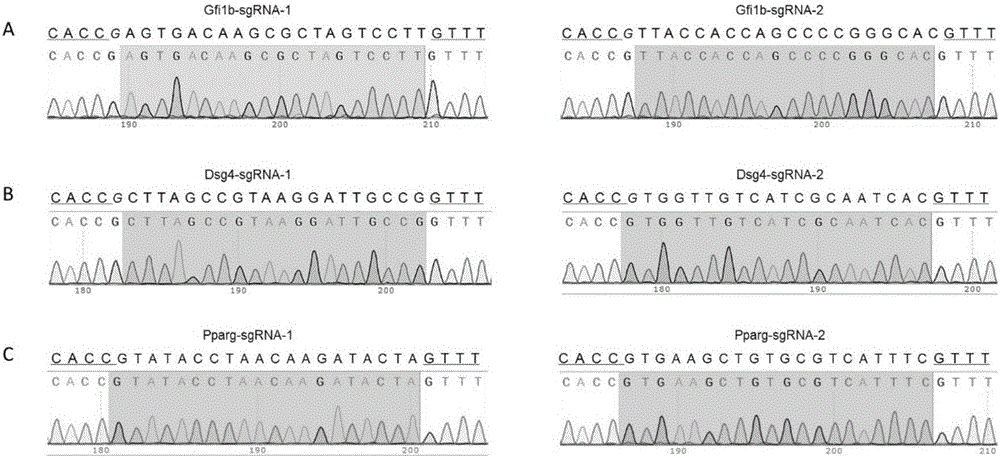
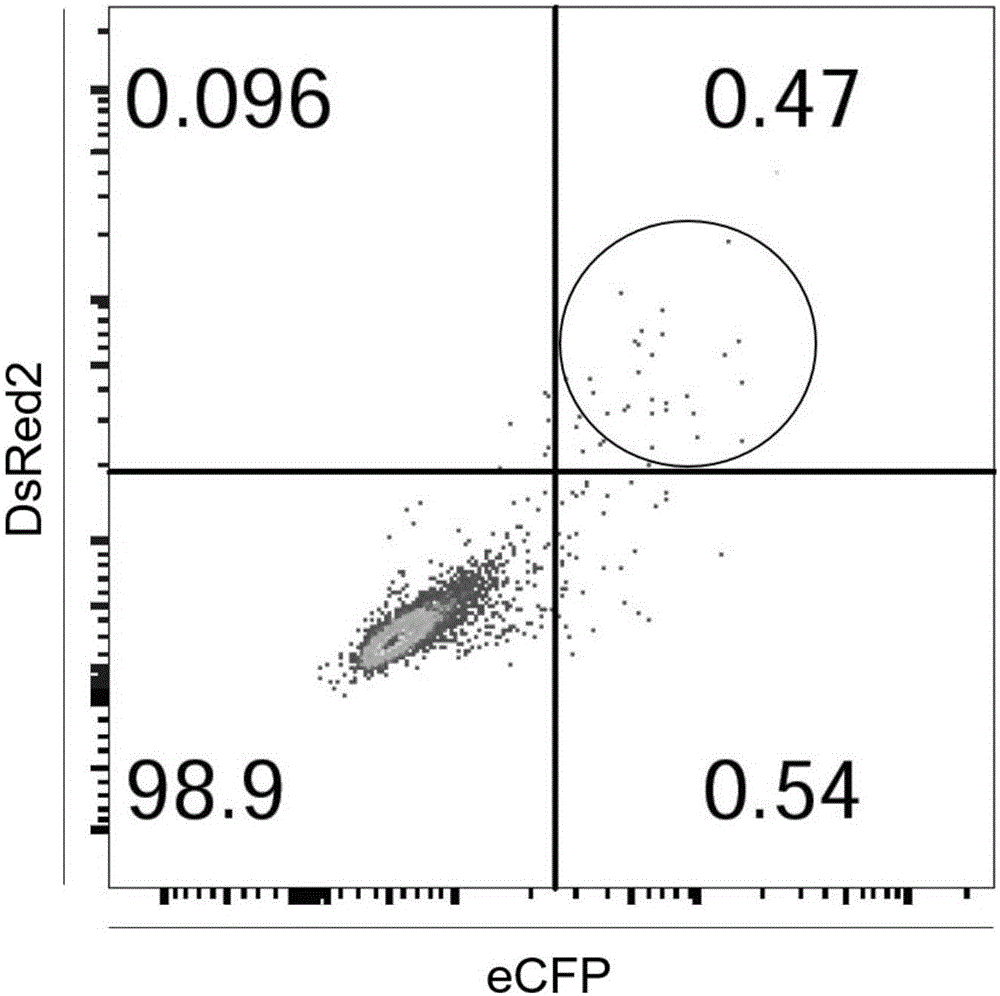
The invention relates to a cell line gene knock-out method for obtaining large fragment deletion through a CRISPR / Cas9 system, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and genetic modification. A pX458 vector is modified, so that the pX458 vector is provided with DsRed2 and ECFP (Enhanced Cyan Fluorescence Protein); then, a plurality of specific sgRNA sites are designed by aiming at a target gene and are connected into the modified vector; after the cell line transfection, cell groups are sorted by a flow cytometry; single cells subjected to genome editing can be very fast obtained; then, a single-cell DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence is subjected to PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification; and single cells with large fragment deletion can be picked out from the single cells through gel electrophoresis. The CRISPR / Cas9 system, the flow cytometry single-cell sorting and fluorescent protein screening on the expression vector are combined, so that the positive monoclonal cells with the large fragment deletion can be obtained in a short time; and the work efficiency of the cell line gene knock-out is greatly improved.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Truncated fragments of alpha-synuclein in Lewy body disease
The application identifies novel fragments of alpha-synuclein in patients with Lewy Body Disease (LBD) and transgenic animal models thereof. These diseases are characterized by aggregations of alpha-synuclein. The fragments have a truncated C-terminus relative to full-length alpha-synuclein. Some fragments are characterized by a molecular weight of about 12 kDa as determined by SDS gel electrophoresis in tricine buffer and a truncation of at least ten contiguous amino acids from the C-terminus of natural alpha-synuclein. The site of cleavage preferably occurs after residue 117 and before residue 126 of natural alpha-synuclein. The identification of these novel fragments of alpha-synuclein has a number of application in for example, drug discovery, diagnostics, therapeutics, and transgenic animals.
Owner:PROTHENA BIOSCI LTD
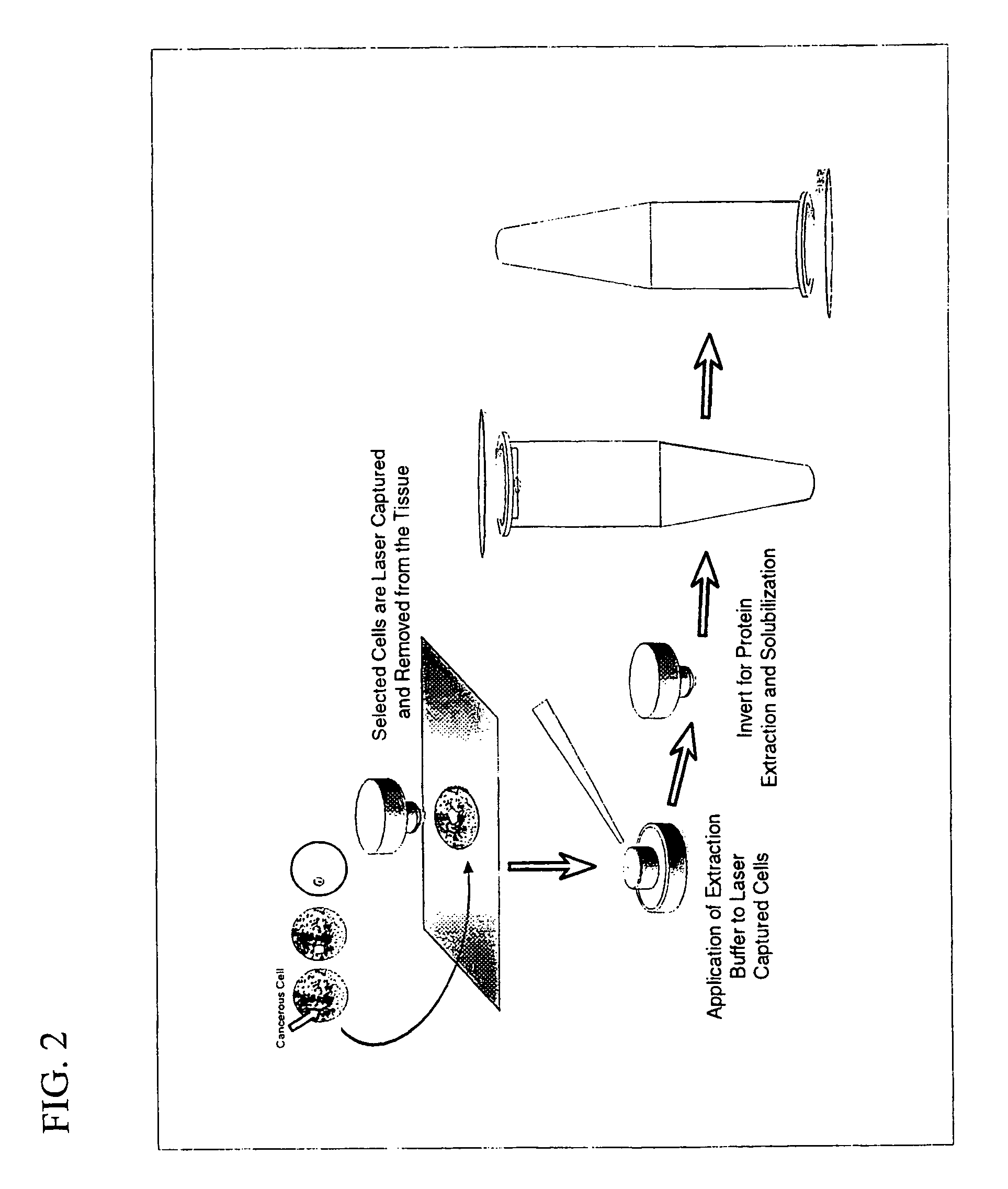
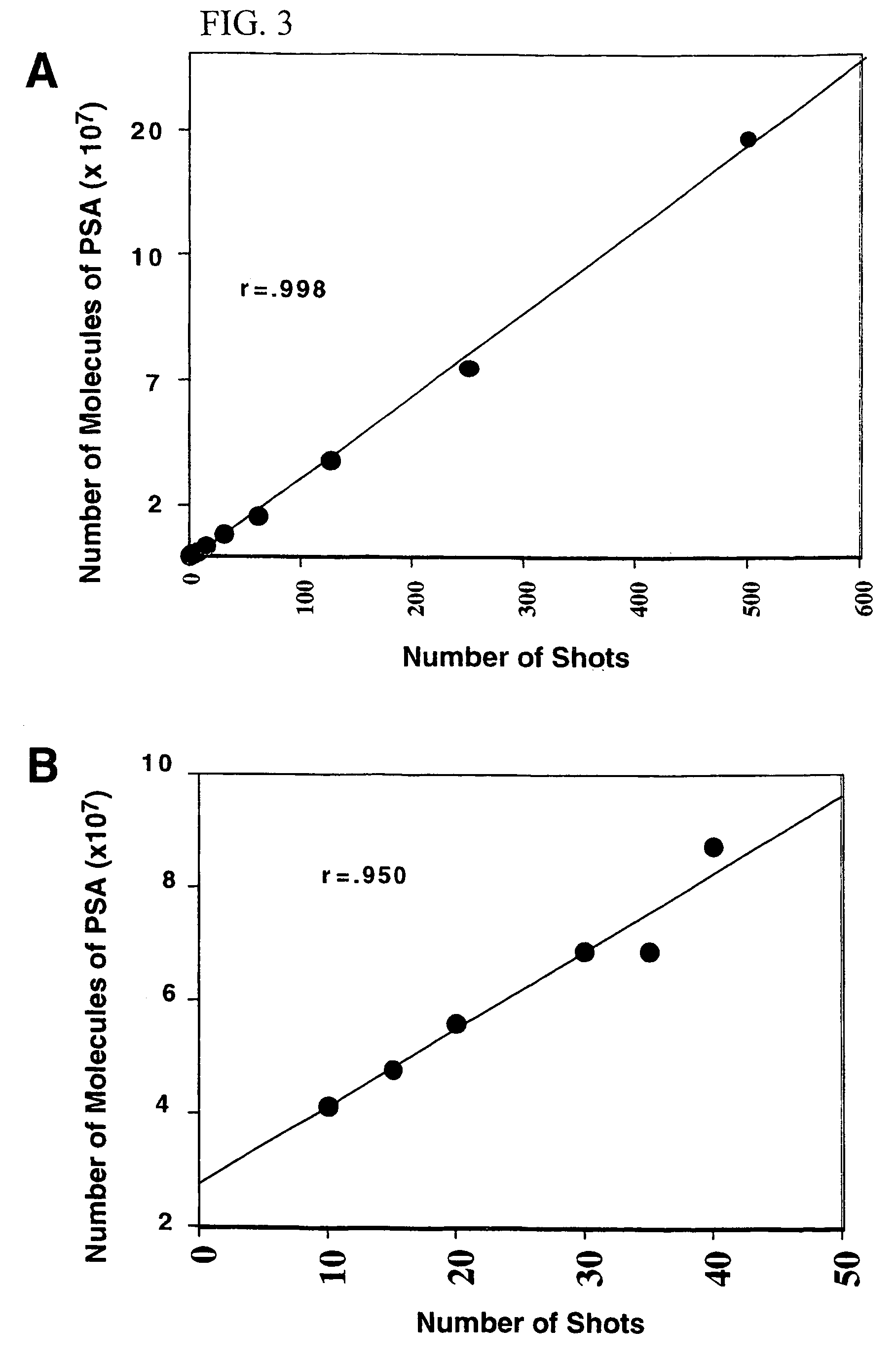
Methods for the isolation and analysis of cellular protein content
InactiveUS6969614B1Rapid and reliable to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementWithdrawing sample devicesLymphatic SpreadPresent method
The present invention describes devices and methods for performing protein analysis on laser capture microdissected cells, which permits proteomic analysis on cells of different populations. Particular disclosed examples are analysis of normal versus malignant cells, or a comparison of differential protein expression in cells that are progressing from normal to malignant. The protein content of the microdissected cells may be analyzed using techniques such as immunoassays, 1D and 2D gel electrophoresis characterization, Western blotting, liquid chromatography quadrapole ion trap electrospray (LCQ-MS), Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization / Time of Flight (MALDI / TOF), and Surface Enhanced Laser Desorption Ionization Spectroscopy (SELDI). In addition to permitting direct comparison of qualitative and quantitative protein content of tumor cells and normal cells from the same tissue sample, the methods also allow for investigation of protein characteristics of tumor cells, such as binding ability and amino acid sequence, and differential expression of proteins in particular cell populations in response to drug treatment. The present methods also provide, through the use of protein fingerprinting, a rapid and reliable way to identify the source tissue of a tumor metastasis.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Method for treating systemic DNA mutation disease
ActiveUS8388951B2Lower Level RequirementsGood treatment effectPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDiseaseA-DNA
A treatment for systemic DNA mutation diseases accompanied with development of somatic mosaicism and elevation of blood extracellular DNA and, more particularly, to a treatment of diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. The inventive method consist from introducing a treatment agent into a circulating blood system of a patient diagnosed with systemic DNA mutation diseases when said treatment agent destroys extracellular DNA in said blood of said patient and wherein said treatment agent used to destroy said extracellular DNA is a DNASE enzyme: said agent might be administered in doses and regimens which sufficient to decrease number average molecular weight of circulating extracellular blood DNA in the blood of said patient; such decrease of number average molecular weight might be measured by gel electrophoresis of extracellular blood DNA fraction from the blood of said patient. A DNASE enzyme may be further applied in a dose and regime that provide a DNA hydrolytic activity measured in blood plasma exceeding 1.5 Kunitz units per 1 ml of blood plasma for more than 12 hours within a period of 24 hours.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Environment DNA identification method for fish community structure researching
ActiveCN104531879AProtected speciesSave human and financial resourcesMicrobiological testing/measurementCommunity structureNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to an environment DNA identification method for fish community structure researching. The method is characterized by comprising the steps that 1, water samples are collected according to the size of the water area where a fish community is located; 2, the water samples are processed, and total environment DNA of the processed water samples is extracted; 3, a 16s r DNA sequence with nucleotide sequences being SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 is adopted as a universal primer to carry out PCR amplification on the total environment DNA, and a PCR product is obtained; 4, gel electrophoresis is carried out on the PCR product, and gel with DNA is obtained; 5, gel cutting and clone sequencing are carried out on the gel with the DNA, and then blast comparison is carried out through GENBANK so as to determine whether the DNA is a fish sequence or not; 6, after it is determined that the DNA is the fish sequence, the next-generation sequencing technology is adopted for analyzing composition conditions of the PCR product on a large scale, and therefore the environment DNA fish composition and community structure are determined. The environment DNA identification method is quite easy, convenient and efficient and has the practical value.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Identification method for animal derived materials
ActiveCN101196463AHigh detection sensitivityLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansFood ComponentAgricultural science
An identification method of animal source character component is provided, which relates to an identification method of food component. The invention overcomes that the current identification method of animal source character component has the defects of low testing sensitivity and unable to test the heat-processed manufactured meat. The animal source character component is identified by the following method: extracting the source character sample DNA of the animal for testing, PCR testing and gel electrophoresis, and then identifying the component of animal source character. The method in the invention has high testing sensitivity, and the identification number limit can be below 1 percent. The identification method in the invention can test the heat-processed manufactured meat, and mix manufactured meat and bone meal product. The identification number limit also can reach below 1 percent. The identification method in the invention doesn't use liquid nitrogen in identification process, which not only lowers the cost, but also improves the safety of the operation.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Gel electrophoresis dyeing device
ActiveCN103575584AEasy to put inEasy to take outPreparing sample for investigationHazardous substanceElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a gel electrophoresis dyeing device, which is characterized by comprising a liquid storage device (1), a dyeing box (2) and a drive device (4), wherein the liquid storage device is used for storing a liquid reagent used in the dyeing process and is provided with a liquid pouring port and a liquid outlet port; the top of the dyeing box is sealed by a dyeing box cover plate (20); a liquid outlet port is formed on the dyeing box cover plate (20); a gel plate fixing device (3) used for fixing a plurality of gel plates is arranged in the dyeing box (2); the drive device is connected with the dyeing box (2) to drive the dyeing box to shake; the liquid inlet port is connected with the liquid outlet port by a liquid inlet conduit; and a liquid inlet valve is installed on the liquid inlet conduit. By utilizing the gel electrophoresis dyeing device, the plurality of gel plates can be dyed simultaneously, loading and unloading of the gel plates are convenient, crush of the gel plates is avoided, contact of an operator with a hazardous substance is reduced simultaneously, and time and labor are saved. The gel electrophoresis dyeing device is safe and convenient.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
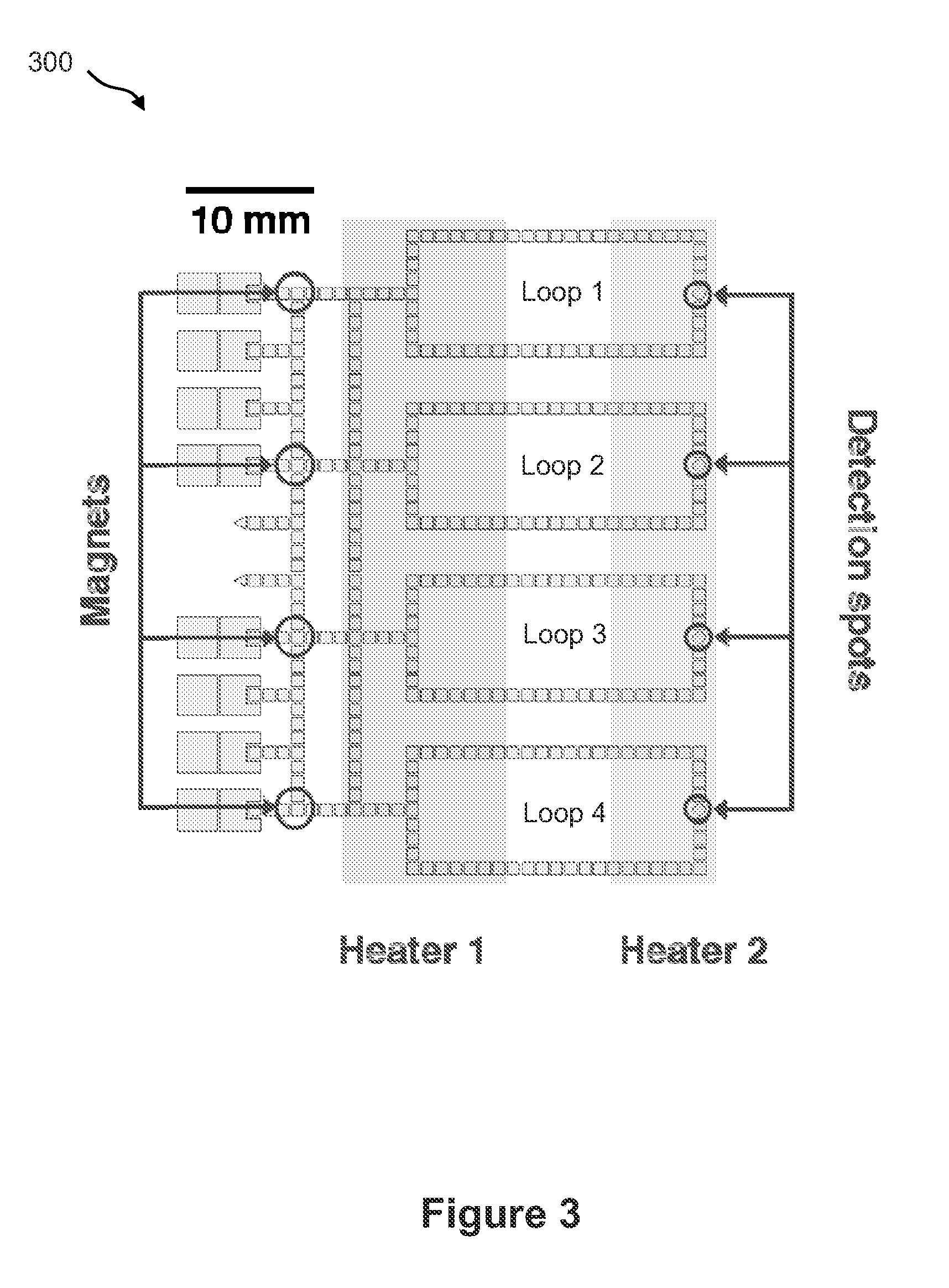
Distributed multi-segmented reconfigurable traveling wave grids for separation of proteins in gel electrophoresis
ActiveUS7156970B2Reduce processing timeIncrease field strengthElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentElectrophoresisEngineering
Various traveling wave grids and electrophoretic systems, and electrode assemblies using such grids, are disclosed. A configuration in which a voltage potential is used to load a biomolecule sample against a grid is disclosed. A unique strategy of using multiple, reconfigurable grids in such systems is also described. The strategy involves initially conducting a broad protein separation and then selectively tailoring one or more grids, and conducting one or more secondary processing operations. Related strategies and specific methods are additionally disclosed for separating samples of biomolecules and components thereof using the noted systems, assemblies, and grids.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Deafness susceptibility gene screen test kit
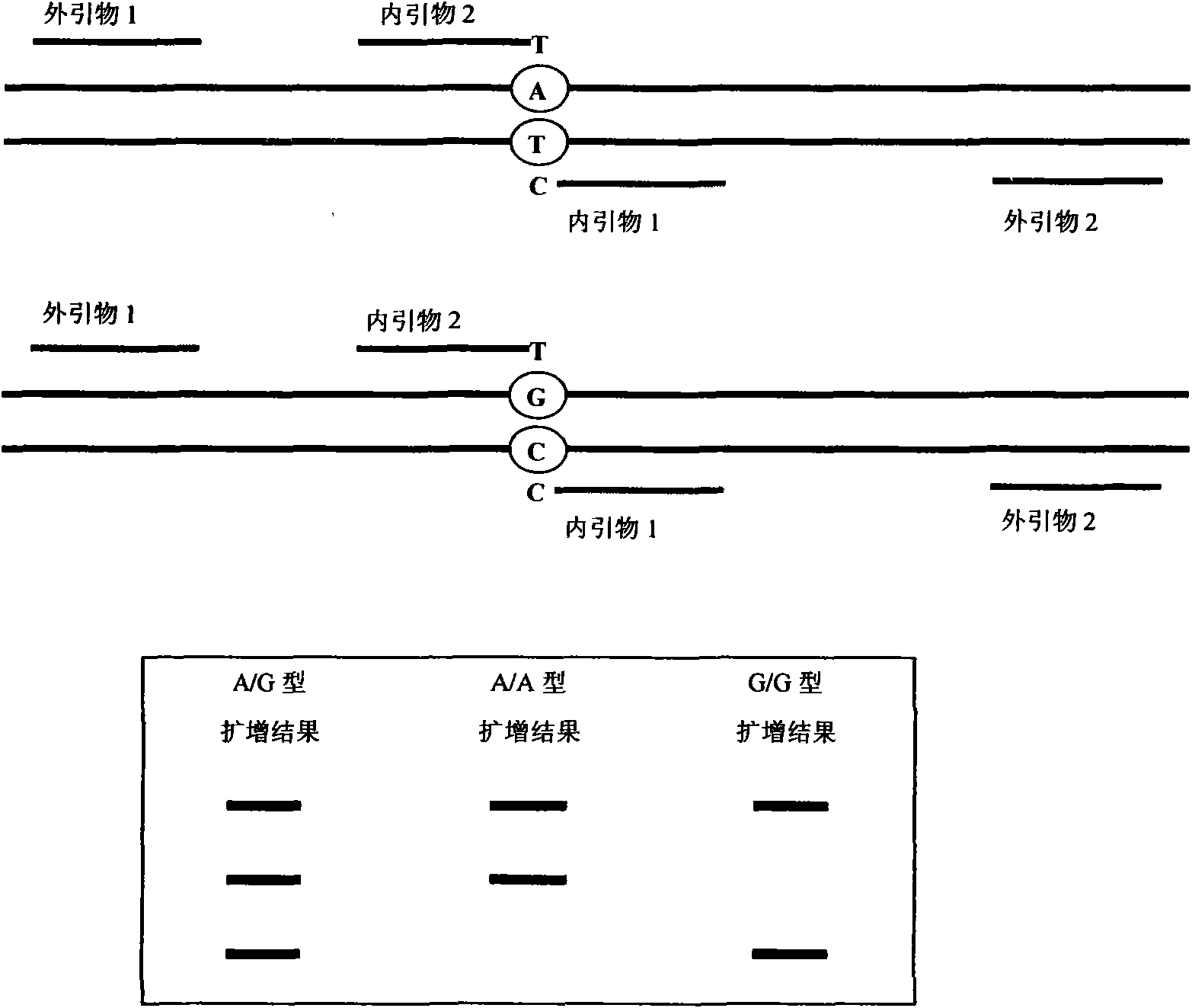
The invention relates to a hereditable deafness susceptibility gene screen test kit. The kit uses mutation from C to T of 1,494 locus of a 12s rRNA gene, mutation from A to G of 1,555 locus of the 12srRNA gene, mutation from A to G of IVS7(-2) locus of an SLC26A4 gene and C(+ / -) of 235 locus of a GJB2 gene as detecting objects, designs and optimizes a set of specific primers respectively againsteach locus to be tested according to the PCR technical principle of a tetra-primer amplification refractory mutation system, amplifies the whole set of the primers in the same reaction tube, and performs primary multiple PCR amplification and primary gel electrophoresis on the four reaction tubes to obtain gene types of four loci simultaneously.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Integrated droplet actuator for gel; electrophoresis and molecular analysis
InactiveUS9091649B2Easy to useFacilitates of propertyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusElectrophoresisEngineering
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
Truncated fragments of alpha-synuclein in Lewy body disease
The application identifies fragments of alpha-synuclein in patients with Lewy Body Disease (LBD) and transgenic animal models thereof. These diseases are characterized by aggregations of alpha-synuclein. The fragments have a truncated C-terminus relative to full-length alpha-synuclein. Some fragments are characterized by a molecular weight of about 12 kDa as determined by SDS gel electrophoresis in tricine buffer and a truncation of at least ten contiguous amino acids from the C-terminus of natural alpha-synuclein. The site of cleavage preferably occurs after residue 117 and before residue 126 of natural alpha-synuclein. The identification of these novel fragments of alpha-synuclein has a number of application in for example, drug discovery, diagnostics, therapeutics, and transgenic animals.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF FLINDERS UNIV +2
Transilluminator base and scanner for imaging fluorescent gels, charging devices and portable electrophoresis systems
ActiveUS8562802B1Facilitating electrophoresisAvoid spreadingSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisFluorophore
Cassette electrophoresis systems that allow viewing of molecules during the electrophoresis run are disclosed. Cassette electrophoresis bases that reversibly engage light sources, such as light source bases are disclosed. Also disclosed are visible light transillumination systems for viewing a pattern of fluorescence emitted by fluorophores comprising a cassette housing fluorophore-containing material and a base unit to support the cassette. In some aspects the base unit that includes a power supply also houses a light source having output in the visible wavelength region and a filter placed between the light source and the fluorophores. The system is constructed and arranged such that patterns of fluorescence emitted by the fluorophores are viewable. Also described are charging devices for providing charge to gel electrophoresis systems, portable gel electrophoresis systems and methods of use thereof.
Owner:LIFE TECH ISRAEL
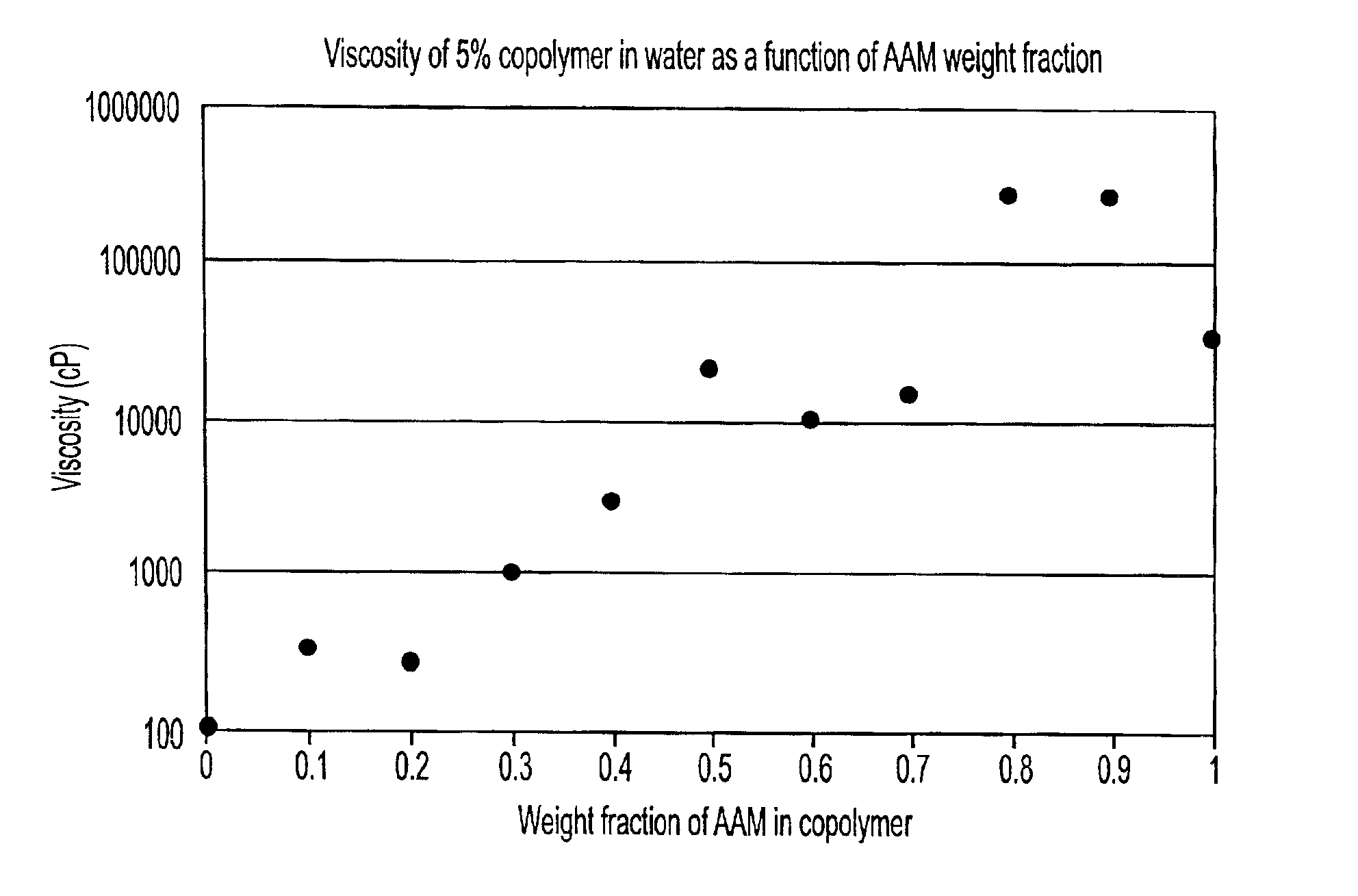
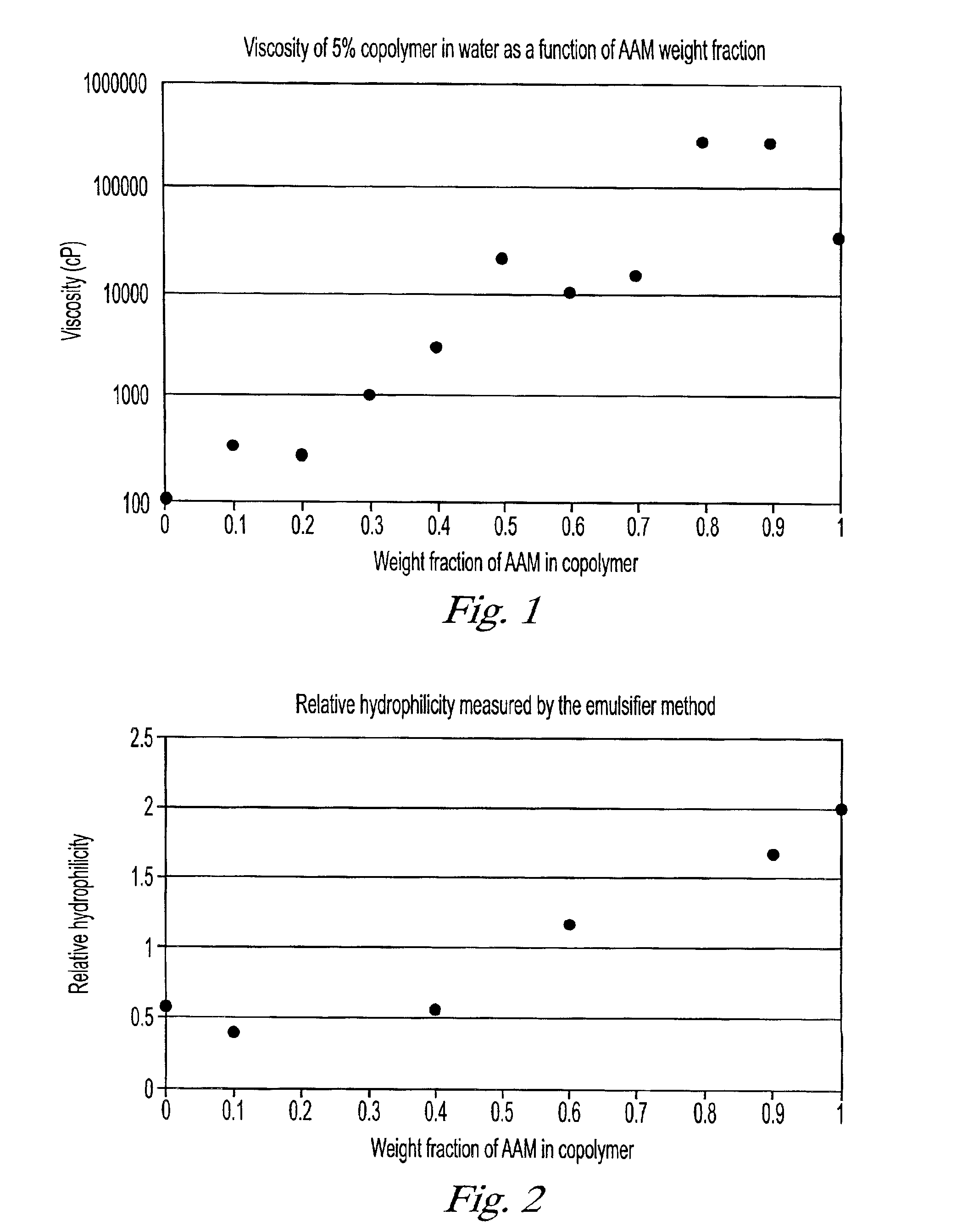
Copolymers for capillary gel electrophoresis
InactiveUS6926815B2Facilitates high level of separation performanceEnsure solubilitySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
This invention relates to an electrophoresis separation medium having a gel matrix of at least one random, linear copolymer comprising a primary comonomer and at least one secondary comonomer, wherein the comonomers are randomly distributed along the copolymer chain. The primary comonomer is an acrylamide or an acrylamide derivative that provides the primary physical, chemical, and sieving properties of the gel matrix. The at least one secondary comonomer imparts an inherent physical, chemical, or sieving property to the copolymer chain. The primary and secondary comonomers are present in a ratio sufficient to induce desired properties that optimize electrophoresis performance. The invention also relates to a method of separating a mixture of biological molecules using this gel matrix, a method of preparing the novel electrophoresis separation medium, and a capillary tube filled with the electrophoresis separation medium.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Twelve (12) protein biomarkers for diagnosis and early detection of breast cancer
InactiveUS20090035801A1More sensitiveMonitor responseMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisDisease severityGel electrophoresis
The invention relates to 12 identified protein biomarkers for diagnosis, determination of disease severity, and therapeutic response monitoring of patients with breast cancer. The method is based on the use of 2-dimensional (2D) gel electrophoresis to separate the complex mixture of proteins found in blood serum, the quantitation of up to 12 protein biomarkers, and statistical analysis of the concentration of the protein biomarkers.
Owner:NEOGENOMICS INC
Method for detecting potential inherent toxicity of organic pollutants in water body
InactiveCN101570785AHigh enrichment factorProtect healthMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansResearch ObjectGel electrophoresis
The invention discloses a method for detecting potential inherent toxicity of organic pollutants in a water body, which comprises the following steps: using resin to perform enrichment of water samples first; and applying a comet assay of Euglena gracilis to research the inherent toxicity of the organic pollutants in the water body. The key technique lies in the innovation of glue manufacturing process, namely adopting fractioning at a first layer, then adopting the conventional 'sandwich' glue manufacturing method, and manufacturing the glue by using a normal melting point glue with a higher melting point at a third layer, thus the defect that a rubber plate in the conventional method is easy to damage is overcome. By performing optimization research on cracking time and electrophoresis conditions of algae comets, a perfect image result is obtained. At present, the method for detecting the potential inherent toxicity of the organic pollutants in the water body through algae single cell gel electrophoresis (SCGE) is not reported, and algae are applied to the SCGE to widen the research objects of the SCGE.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Special primer for aided-identifying strains of lactobacillus and application thereof
InactiveCN101818147AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationIntestinal wallsAquatic animal
The invention claims a special primer for aided-identifying strains of lactobacillus and the application thereof. The special primer is composed of a primer pair A and a primer pair B; the primer pair A is composed of the DNA of the sequences 13 and 14 in the sequence table; and the primer pair B is composed of the DNA of the sequences 15 and 16 in the sequence table. The PCR amplification is carried out on the total DNA of the strain to be detected by using the special primer; if the PCR product can be amplified by the primer pair A or the primer pair B, the strain to be detected is the candidate strain of lactobacillus; if no PCR product is amplified by the primer pair A or the primer pair B, the strain to be detected is the candidate strain of non-lactobacillus. In combination with the denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) or the sequencing technology, the invention further determines that the strain to be detected is the specific strain of lactobacillus. By adopting the special primer of the invention and combining with the PCR and the DGGE, the planting condition of the probiotics on the intestinal wall of aquatic animal can be directly identified. The method is the fastest, simplest, most convenient and effective method at present.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
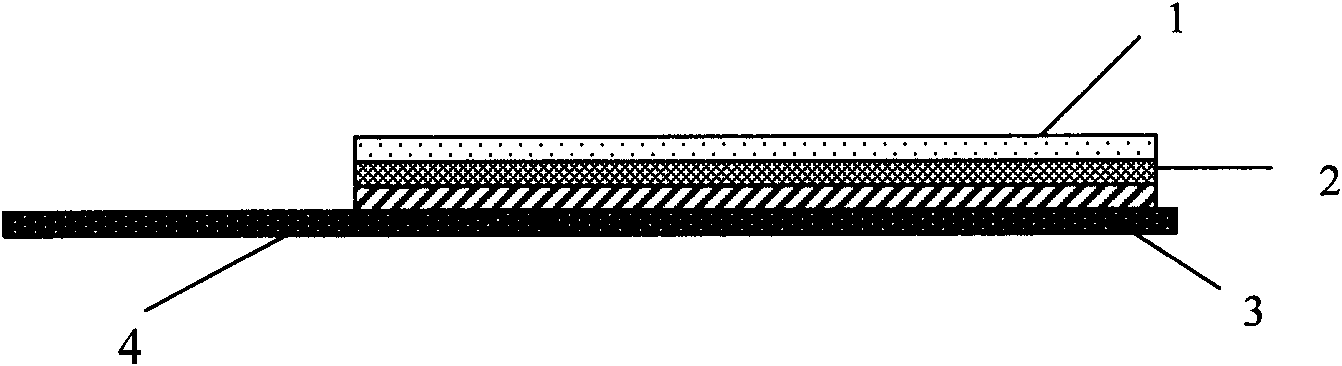
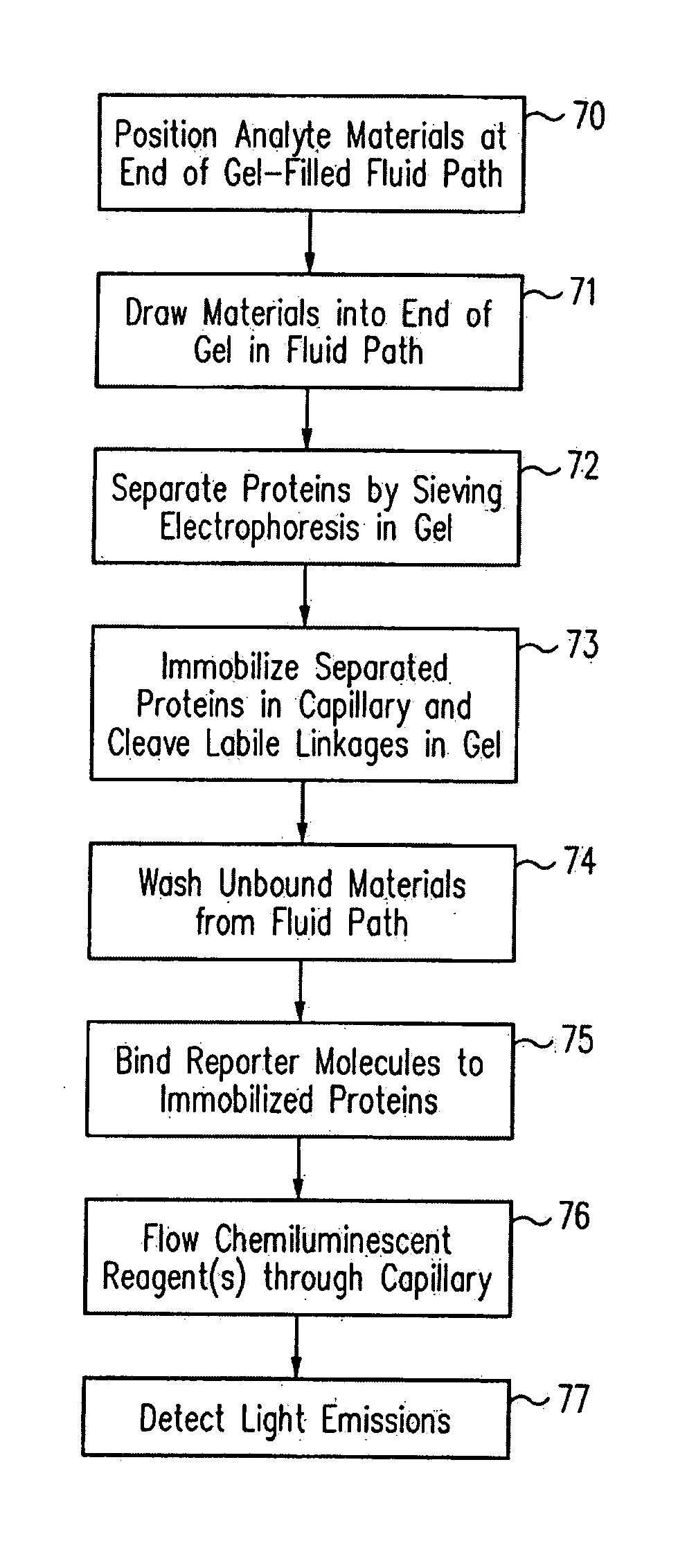
Methods and devices for analyte detection
ActiveUS20080009078A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteBiological activation
Methods and apparatus are provided to resolve analytes within a fluid path using isoelectric focusing, gel electrophoresis, or other separation means. Materials within the fluid path that are compatible with these separation means are used to attach resolved analytes to the wall of the fluid path. Attachment results from a triggerable event such as photoactivation, thermal activation, or chemical activation. In accordance with a further aspect of the present invention, the material in the capillary may also be disrupted, by either the triggerable event or a subsequent event such as melting or photocleavage. Thus, an open lumen or porous structure may be created within the fluid path, allowing unbound analyte materials to be washed from the fluid path, and detection agents to be washed into the fluid path. The separation-compatible materials may be polymerizable monomers, gels, entangled polymers or other materials.
Owner:PROTEINSIMPLE
Method for gel electrophoresis separation of serum lipoprotein and quantization detection thereof
InactiveCN1699406AAchieve metabolic homeostasisImprove performanceApolipeptidesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrophoresisGel electrophoresis of proteins
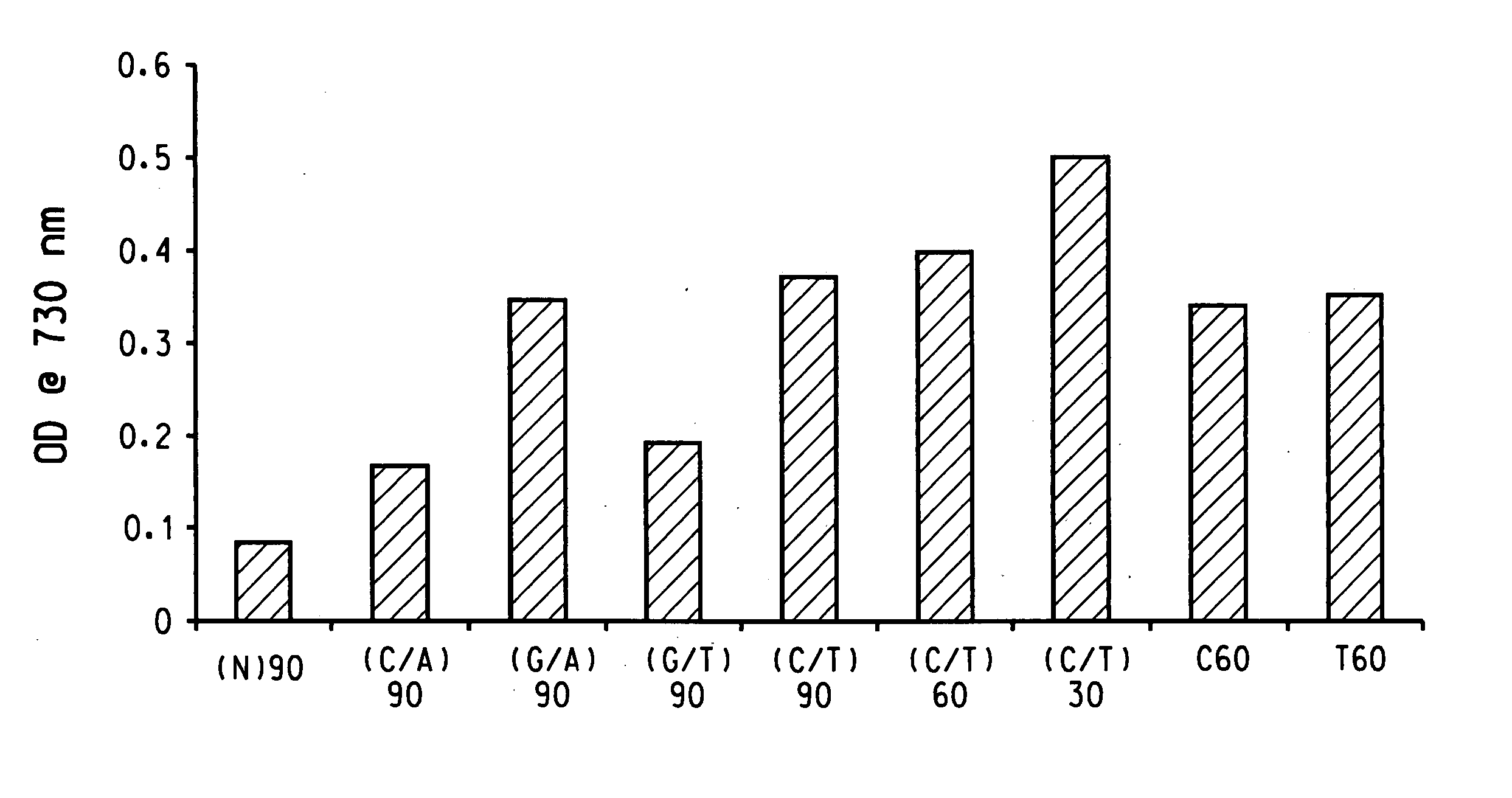
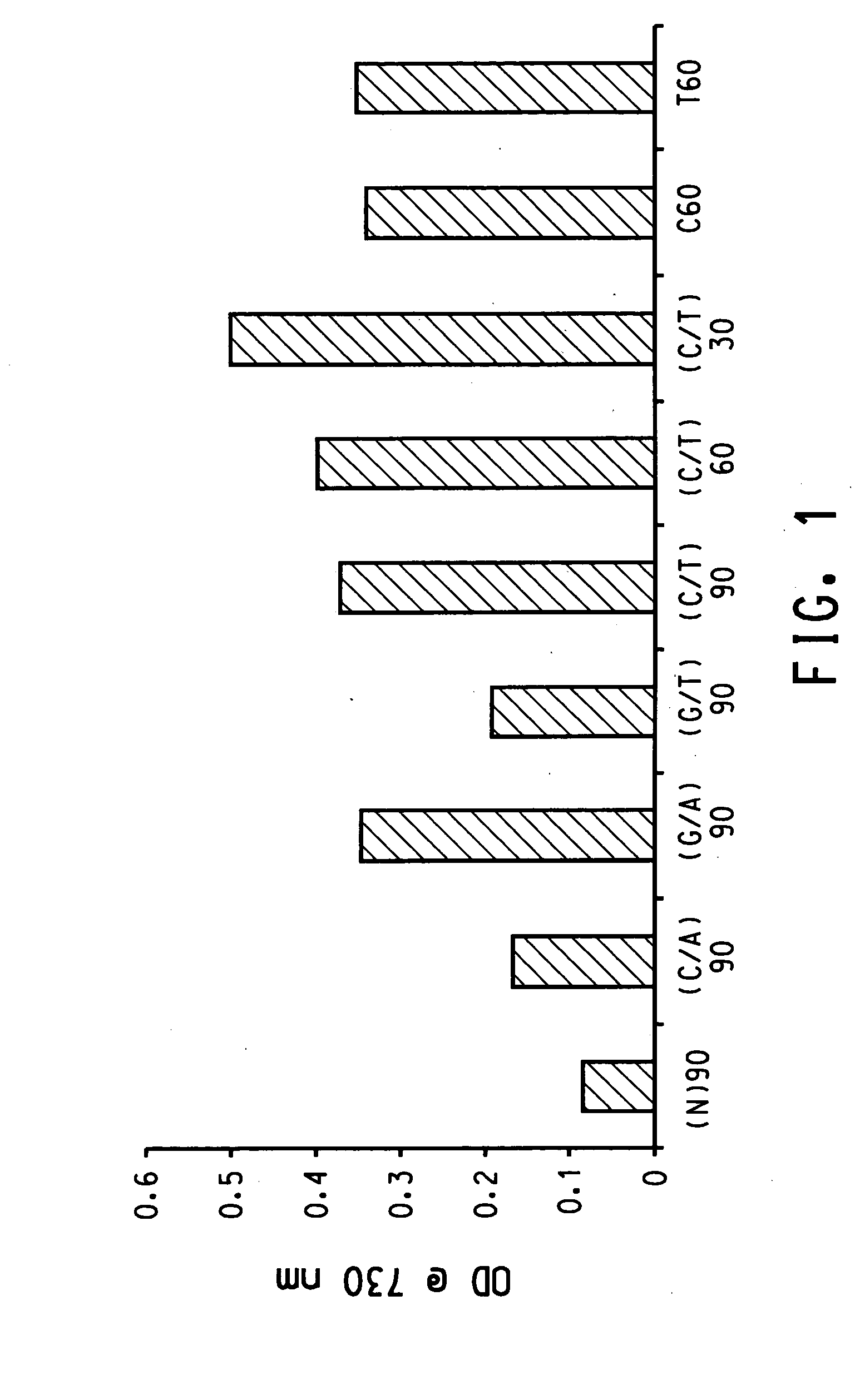
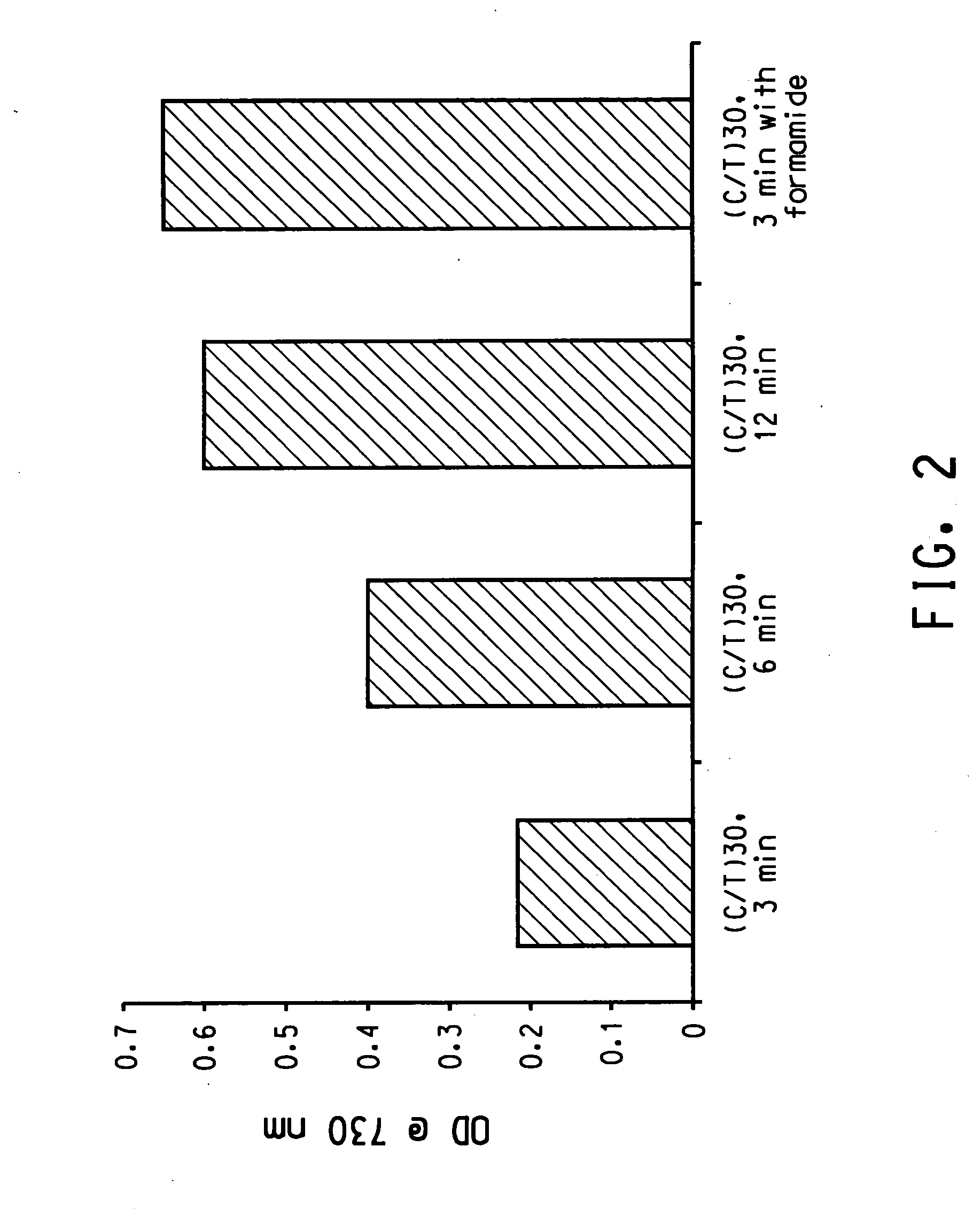
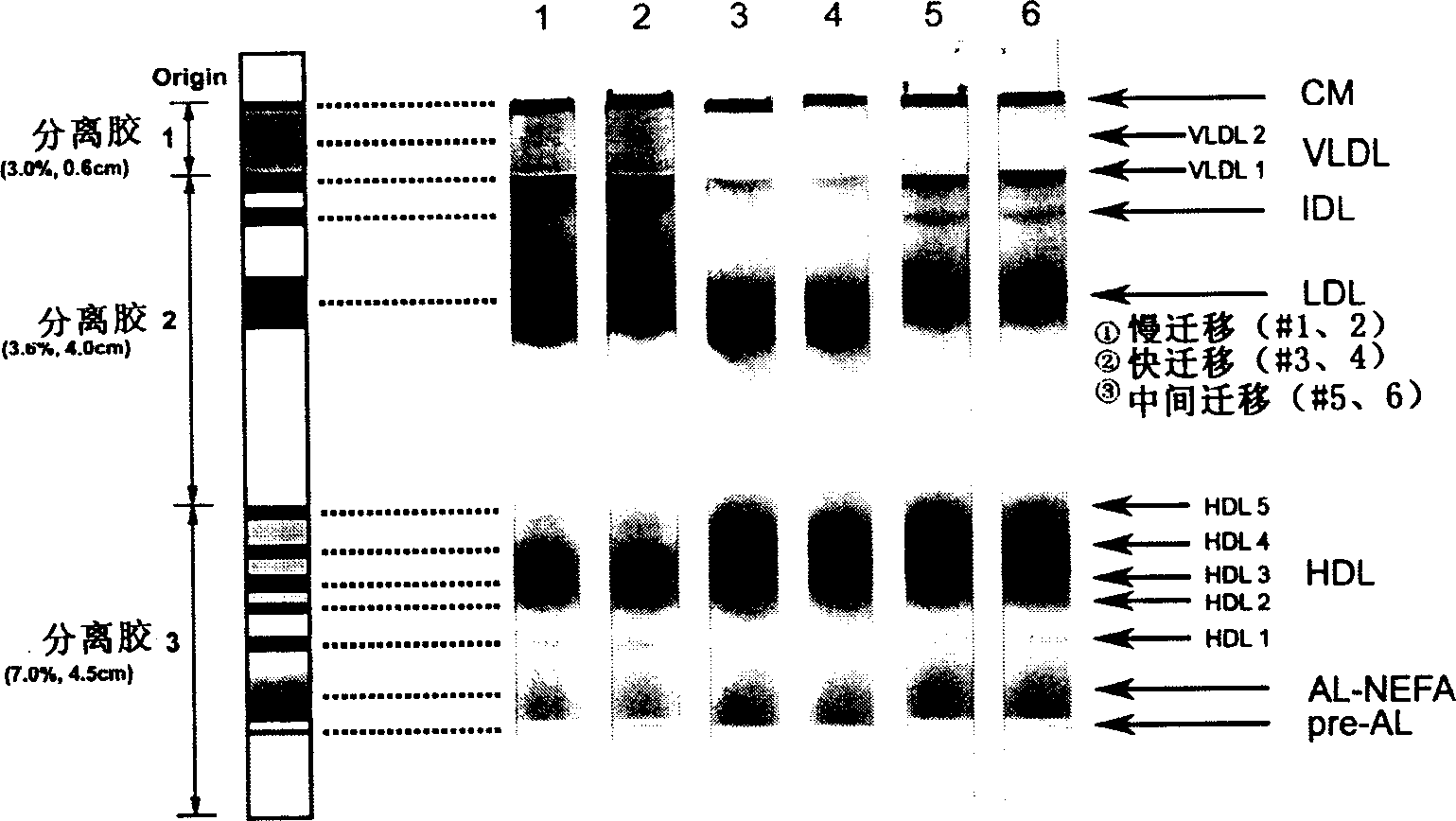
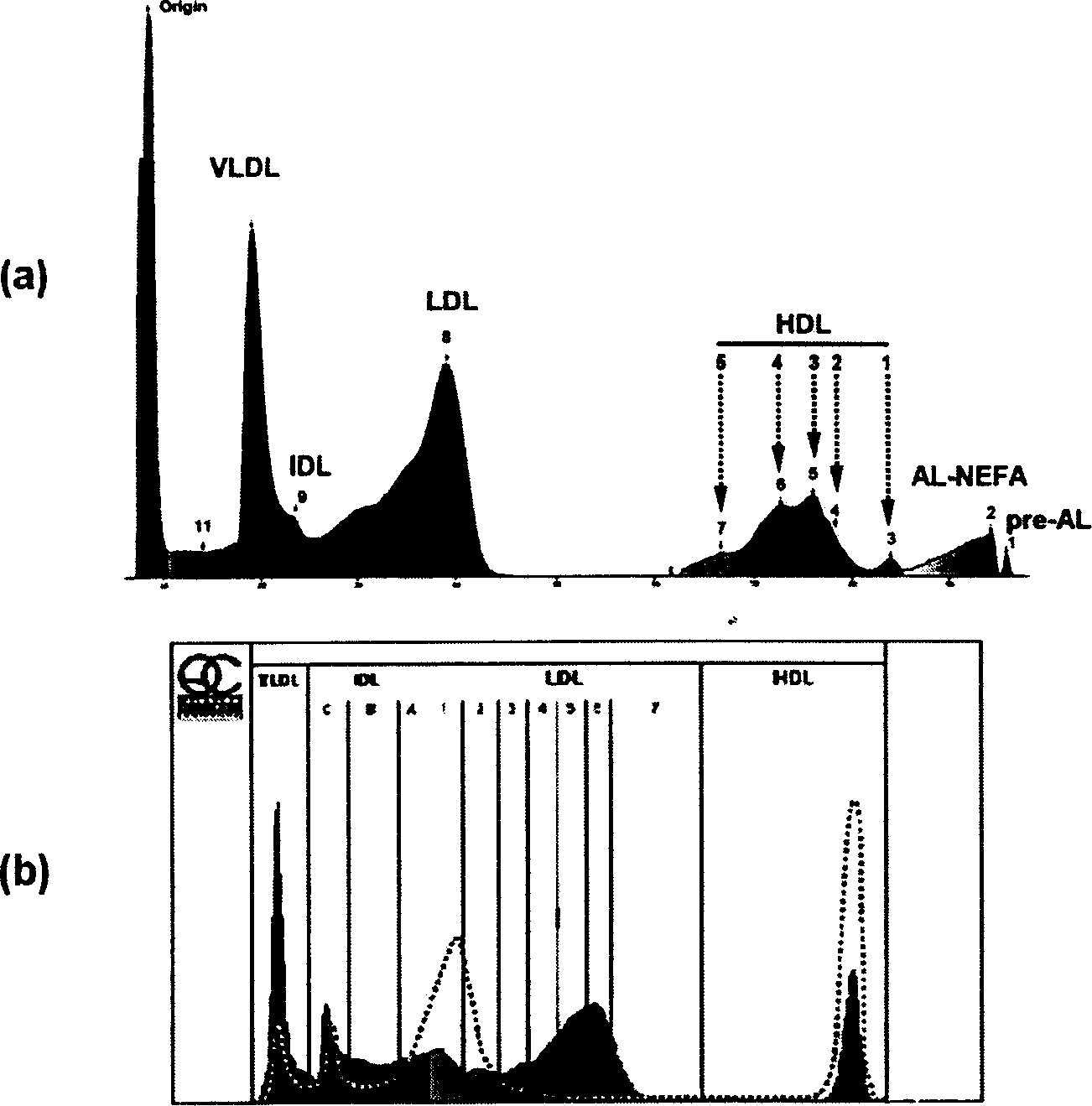
The invention discloses a method for gel electrophoresis separation of serum, wherein sectionalized polyacrylamide gels with three different concentrations are used as electrophoresis carrier for forming temperature gradient in the electrophoresis tank, so as to achieve synchronous electrophoretic separation for serum lipoprotein and its subcomponents, wherein the concentrations of the polyacrylamide gel being separation gel 1 3.0%, separation gel 2 3.6%, separation gel 3 7.0%.
Owner:陈允钦 +1
Methods, cassettes, gels and apparatuses for isolation and collection of biomolecules from electrophoresis gels
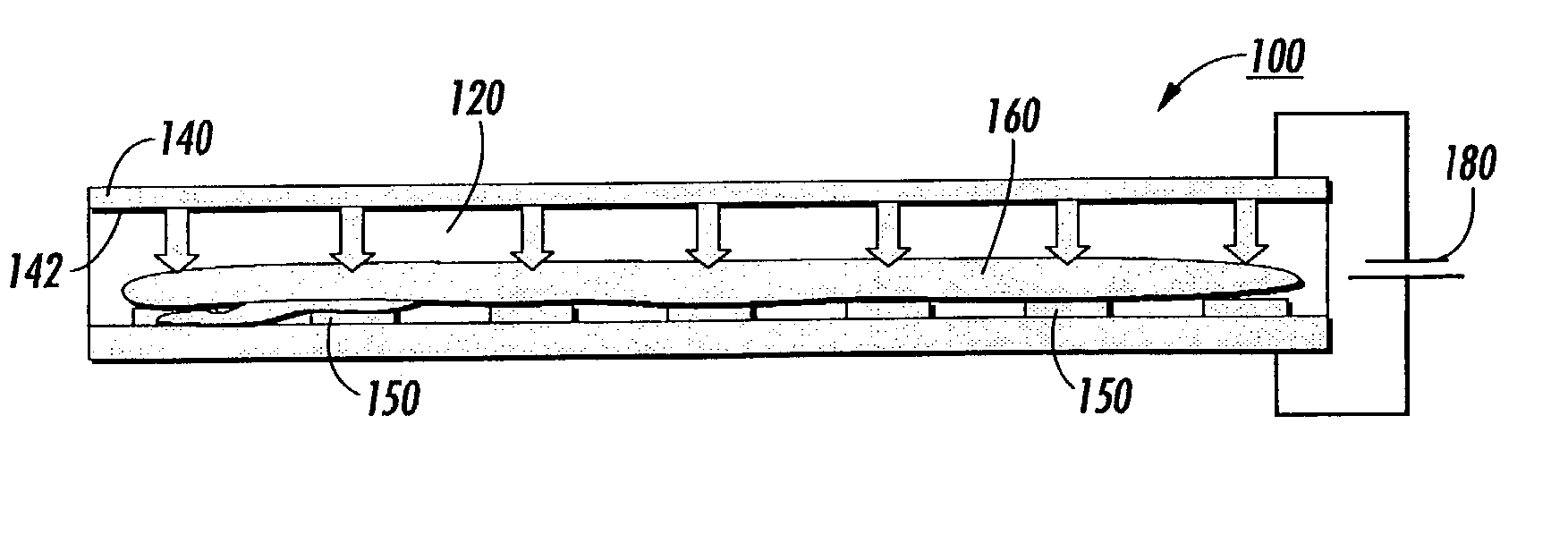
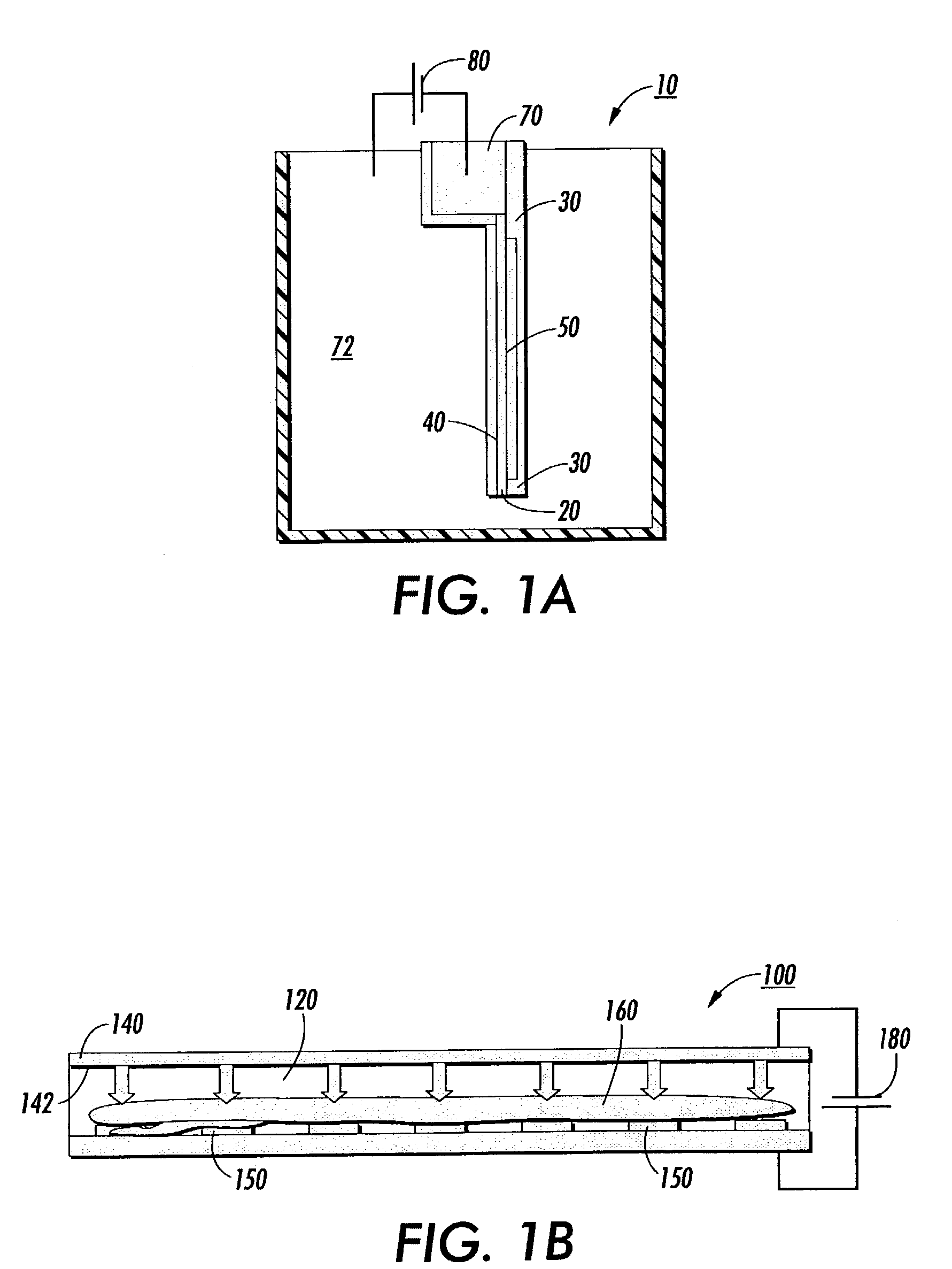
InactiveUS20080057557A1Efficient methodImprove efficiencyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentElectrophoresisGel electrophoresis
Electrophoresis systems, assemblies, cassettes and methods for easily, and more effectively and efficiently, isolating a biomolecule band from an electrophoretic gel are provided. The methods use an electrophoresis cassette with at least one loading well and at lest one collection well. A sample containing the biomolecule of interest is placed into at least one loading well and buffer or water is placed in at lest one collection well. An electric field is then applied to drive migration and separation of the sample into different component bands within the gel. When the component of interest is located within at least one collection well, the electric field is terminated and the buffer or water in the collection well is removed, thereby isolating and collecting the sample component of interest.
Owner:LIFE TECH ISRAEL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com