Cell line gene knock-out method for obtaining large fragment deletion through CRISPR/Cas9 system
A gene knockout and large fragment technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering and genetic modification, can solve problems such as unavailable bases, deletions, time-consuming and labor-intensive problems, and achieve the effect of improving work efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
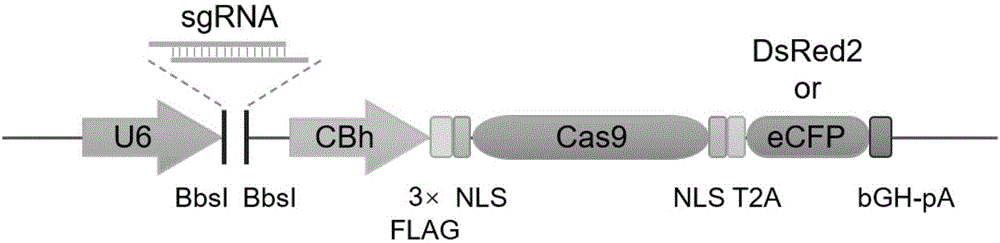
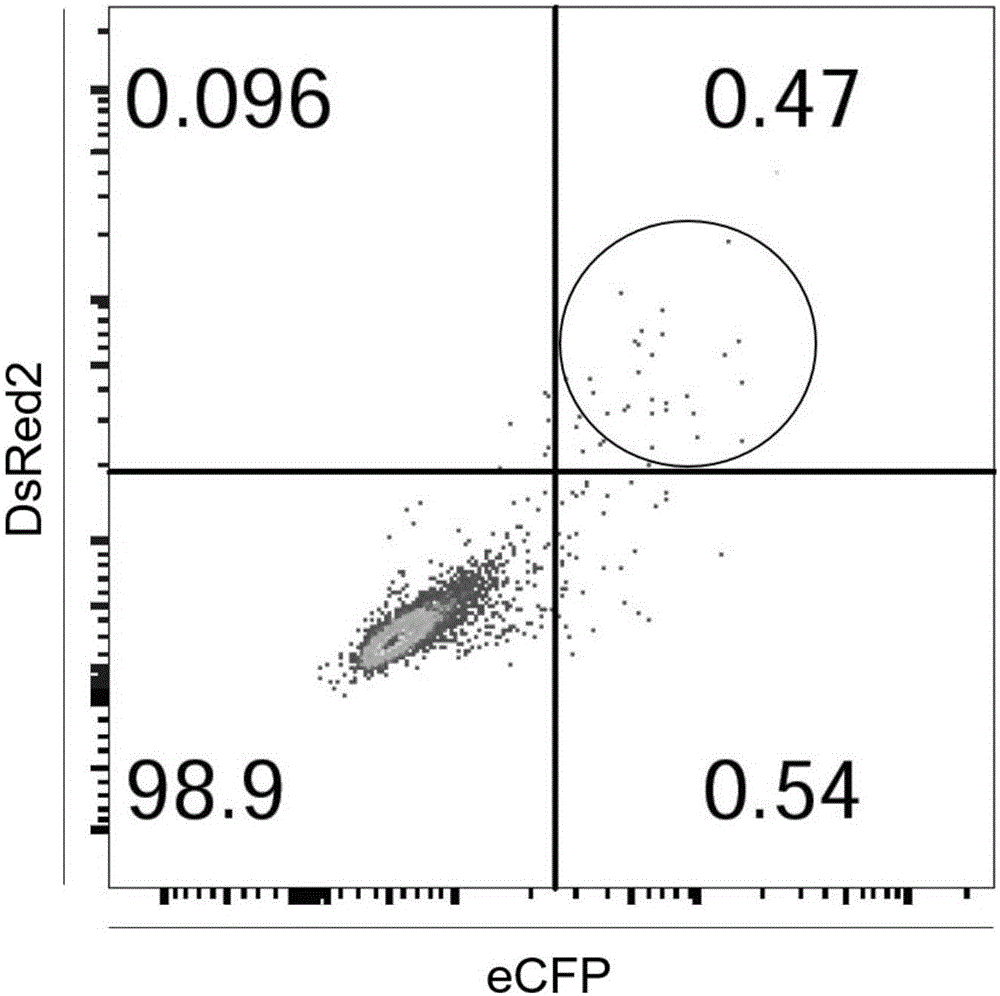
[0056] The all-in-one CRISPR / Cas9 system vector was transformed to obtain expression vectors with DsRed2 and ECFP respectively.
[0057] (1) The parent vector pX458 was purchased from addgene (ID: 48138). After expanding the culture, the vector DNA was linearized with the restriction enzyme EcoRI (NEB). The specific steps are: add 1 μg pX458 vector to a 1.5ml centrifuge tube in turn DNA; 3 μl of 10×NEB Buffer 2.1; 1 μl of EcoRI (NEB) and finally replenished with water to a total volume of 30 μl, and incubated at 37°C for 2 hours. After the digestion was completed, the digestion product was purified using QIAquick PCR Purification Kit and recovered into 30 μl ddH2O.
[0058] (2) The DNA sequences of DsRed2 (as shown in SEQ ID NO. 25) and ECFP (as shown in SEQ ID NO. 26) were submitted to the company for synthesis (Shanghai Bailiger Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), at the 5' end of the sequence Add the EcoRI restriction site and T2A sequence, and clone into the pUC57 vector; then dige...
Embodiment 2
[0061] A method to rapidly obtain the Gfi1b gene knockout in RAW264.7 cell line with large deletion by CRISPR / Cas9 system.
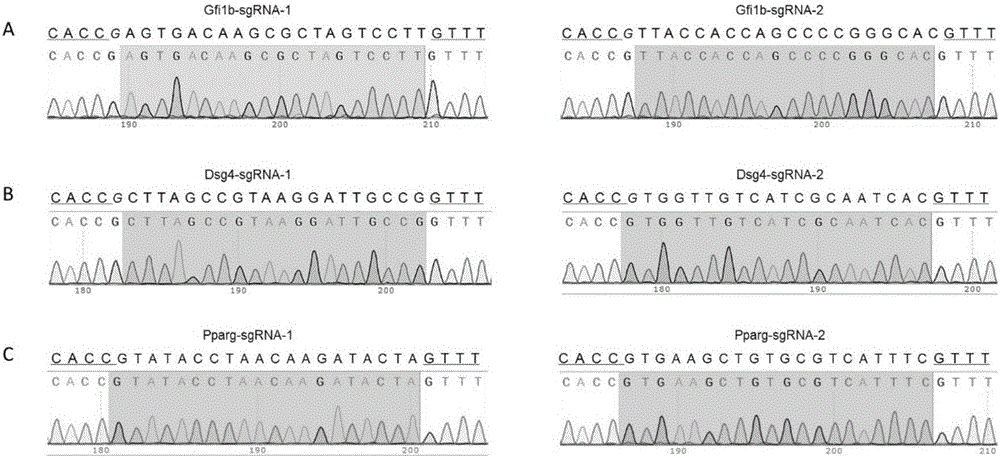
[0062] (1) Determine the specific target sites sgRNA1 and sgRNA2 of the gene to be knocked out Gfi1b (Gene ID: 1276578): find the mouse Gfi1b gene DNA sequence in the mouse genome database ensembl (http: / / asia.ensembl.org) (Transcript ID: ENSMUST00000028156.7), and then use the online design software CRISPOR (http: / / crispor.tefor.net / crispor.cgi) to determine the target sites of intron1-2 and exon2 in the mouse Gfi1b gene (exon ID: ENSMUSE00001307648) selected two specific sites as the target sequence of sgRNA, the two target sequences were: sgRNA1 (SEQ ID NO.1): 5'-AGTGACAAGCGCTAGTCCTTTGG-3', sgRNA2 (SEQ ID NO.2): 5'-TTACCACCAGCCCCGGGCACAGG-3'.
[0063] (2) Design primers: According to the sgRNA target sequence in step (1), design 2 pairs of 4 primers (Shanghai Bailiger Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), and add a BbsI restriction site at the 5' end of the prim...
Embodiment 3
[0080] A rapid knockout method of the Pparg gene in the RAW264.7 cell line with a large deletion by the CRISPR / Cas9 system.
[0081] (1) Determine the specific target sites sgRNA1 and sgRNA2 of the mouse gene Pparg (Gene ID: 97747) to be knocked out: find the mouse Pparg gene in the mouse genome database ensembl (http: / / asia.ensembl.org) DNA sequence (Transcript ID: ENSMUST00000171644.7), then use the online design software CRISPOR
[0082] (http: / / crispor.tefor.net / crispor.cgi), it is determined to select two specific sites in the target site intron2-3 of the mouse Pparg gene as the target sequence of the sgRNA, and the two target sequences are respectively :
[0083] sgRNA1 (SEQ ID NO.9): 5'-GTATACCTAACAAGATACTA TGG-3';
[0084] sgRNA2 (SEQ ID NO. 10): 5'-GTGAAGCTGTGCGTCATTTC AGG-3'.
[0085] (2) Design primers: According to step (1) sgRNA target sequence, design 2 pairs of 4 primers (Shanghai Bailig Biotechnology Co., Ltd., and add a BbsI restriction site at the 5' end o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com