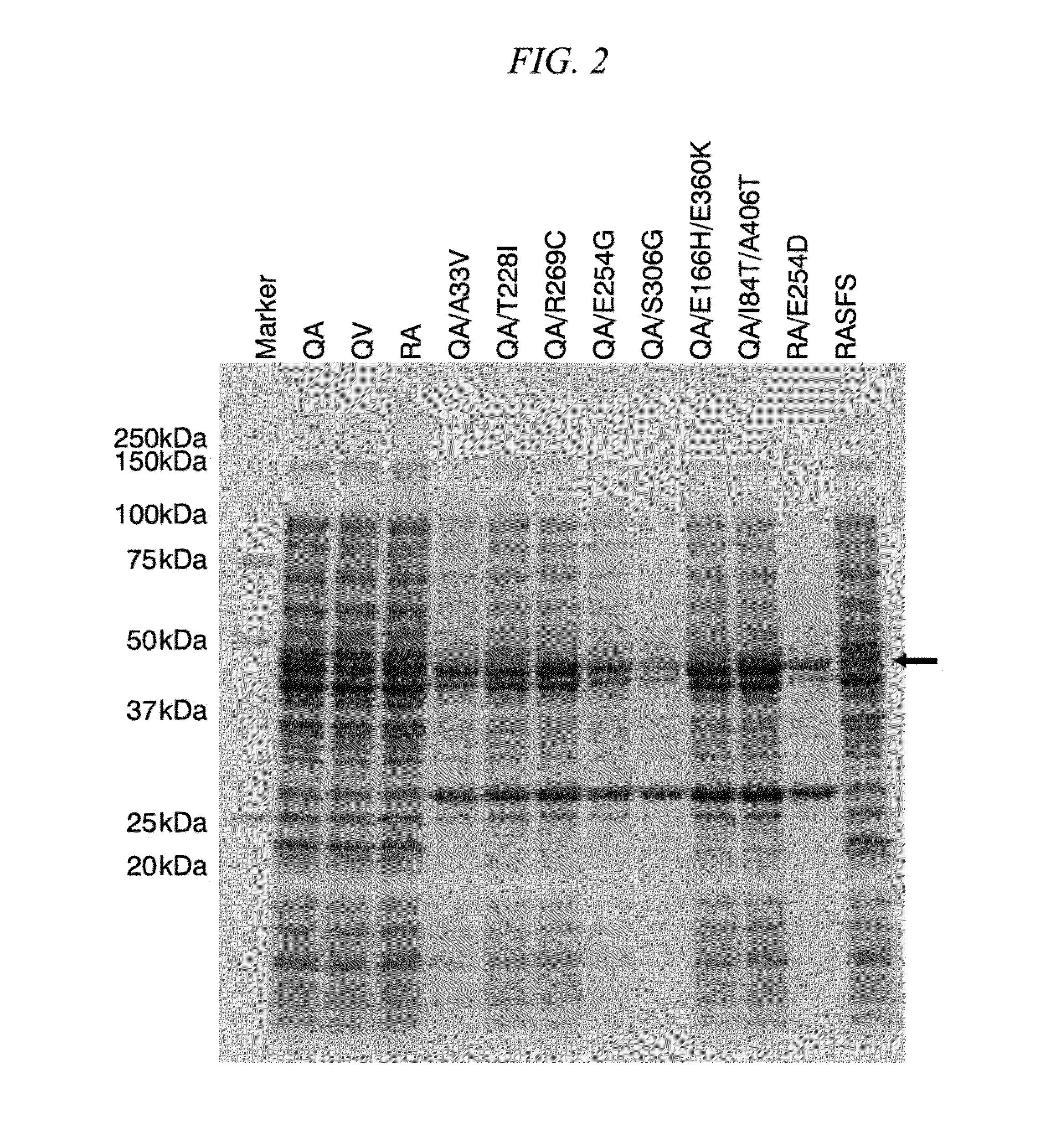
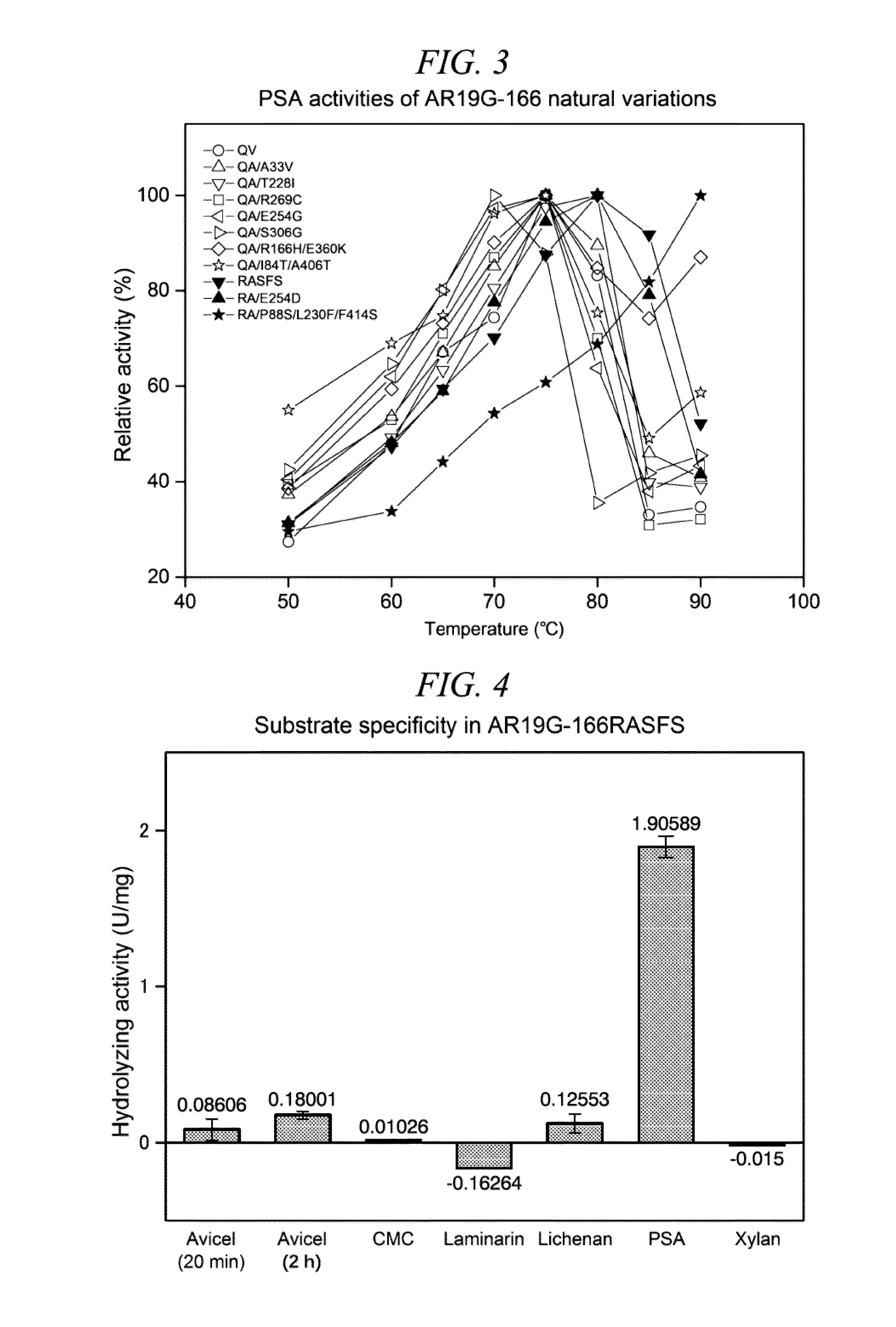
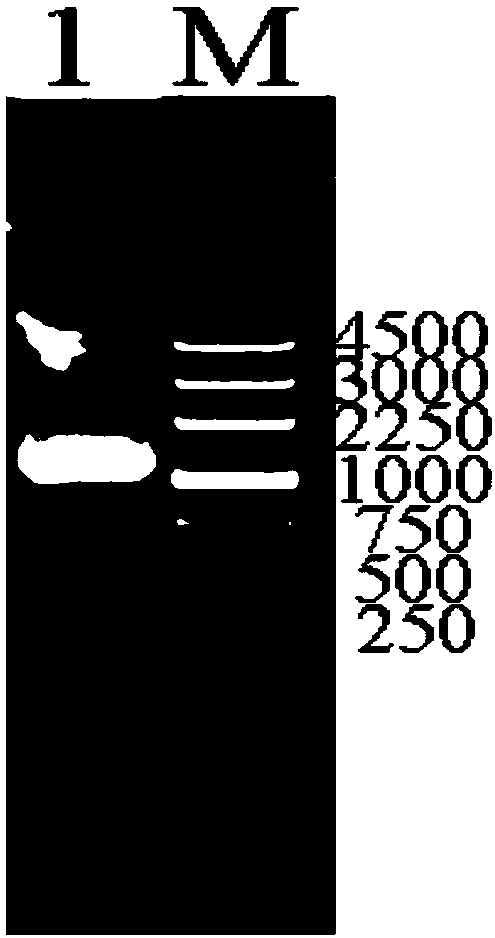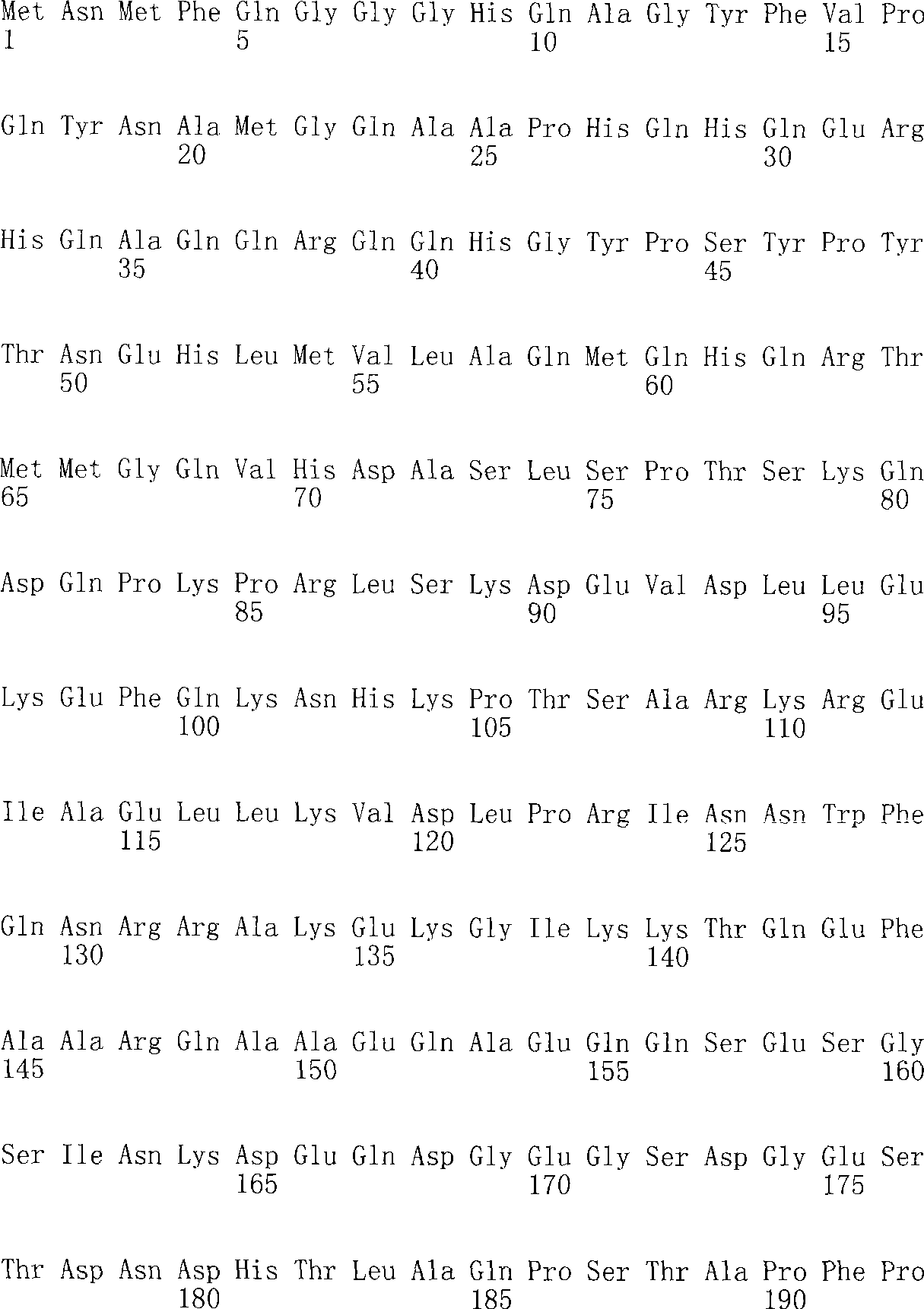Patents
Literature
74 results about "Genome database" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical Definition of Genome Database. Genome Database: The Genome Database (GDB) is the official central repository for genomic mapping data resulting from the Human Genome Initiative. It was established at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland, USA in 1990.
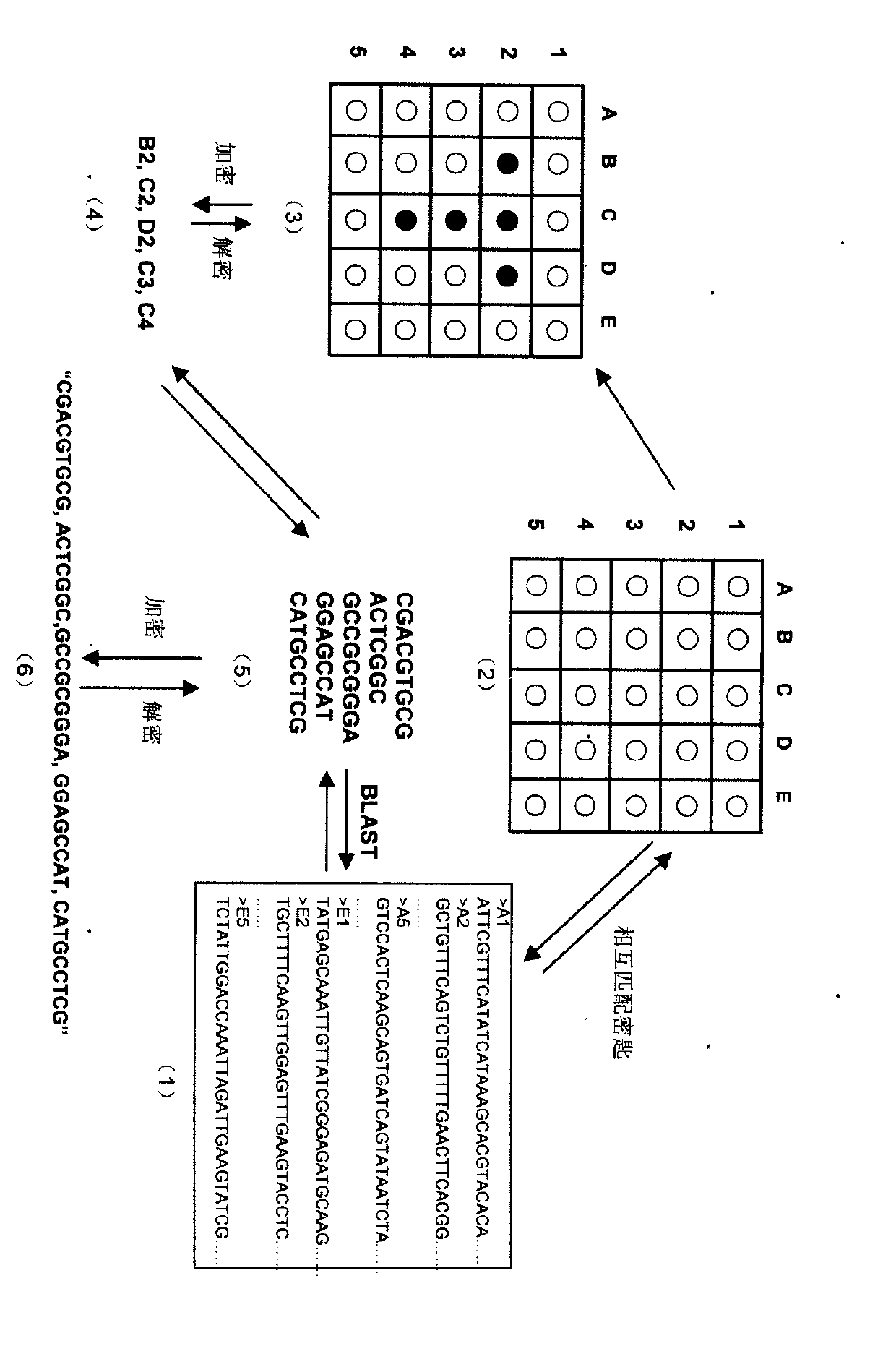
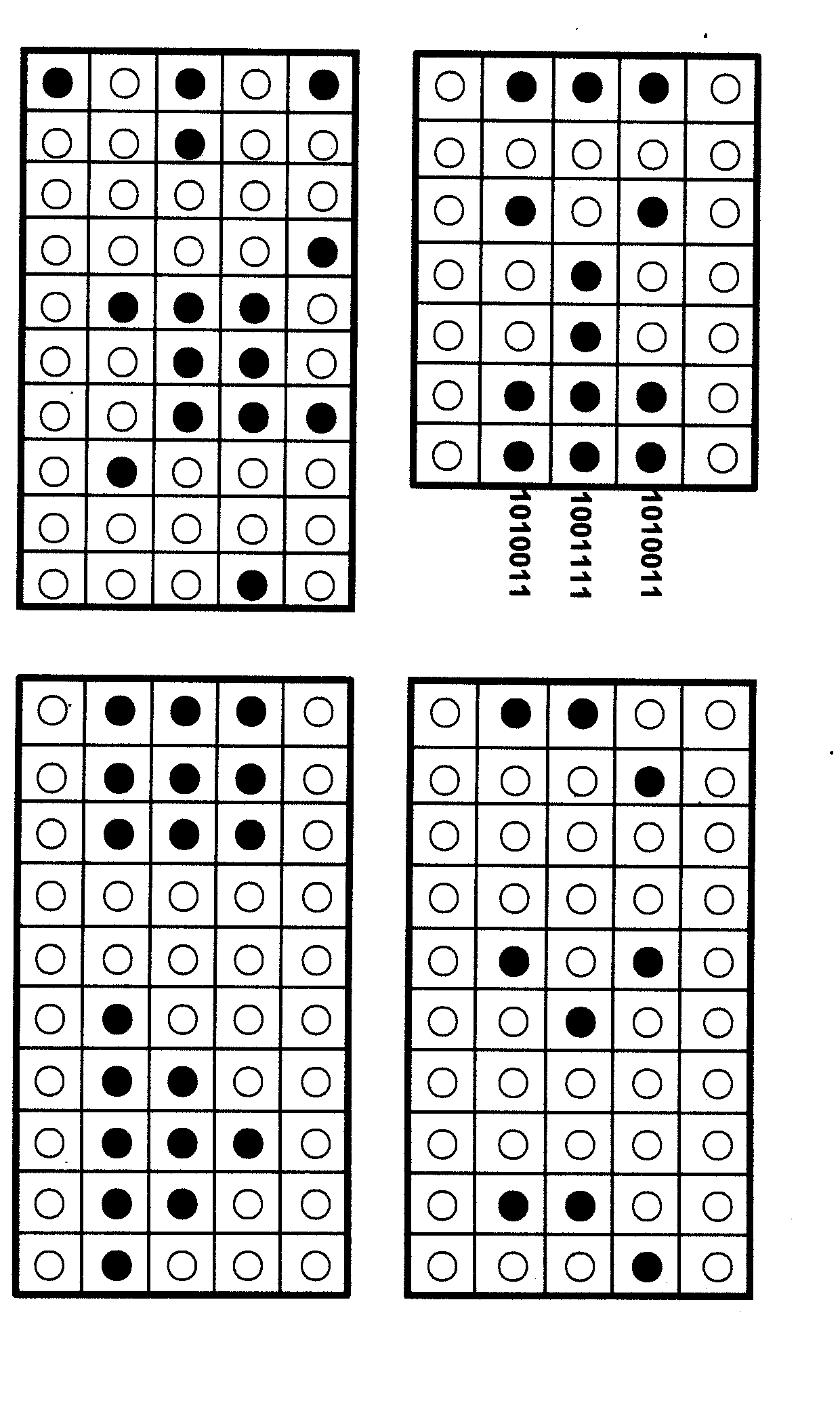
Virtual genome-based cryptosystem (VGC)
InactiveCN102025482ASolve the first sharing problemHuge key spaceGenetic modelsSecuring communicationPlaintextDNA Microarray Chip
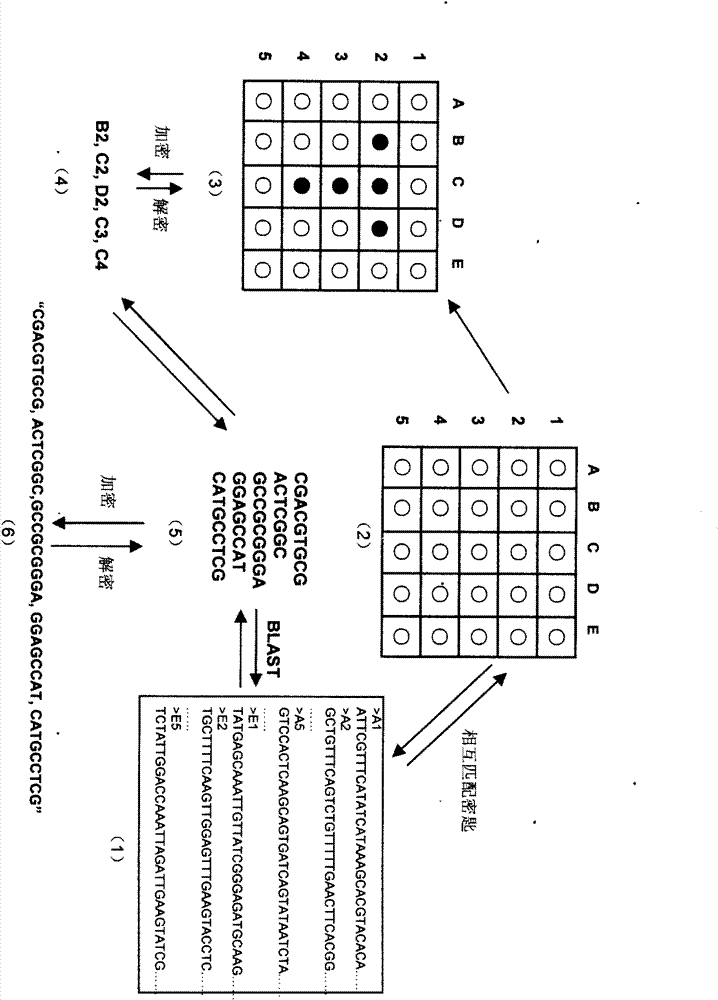
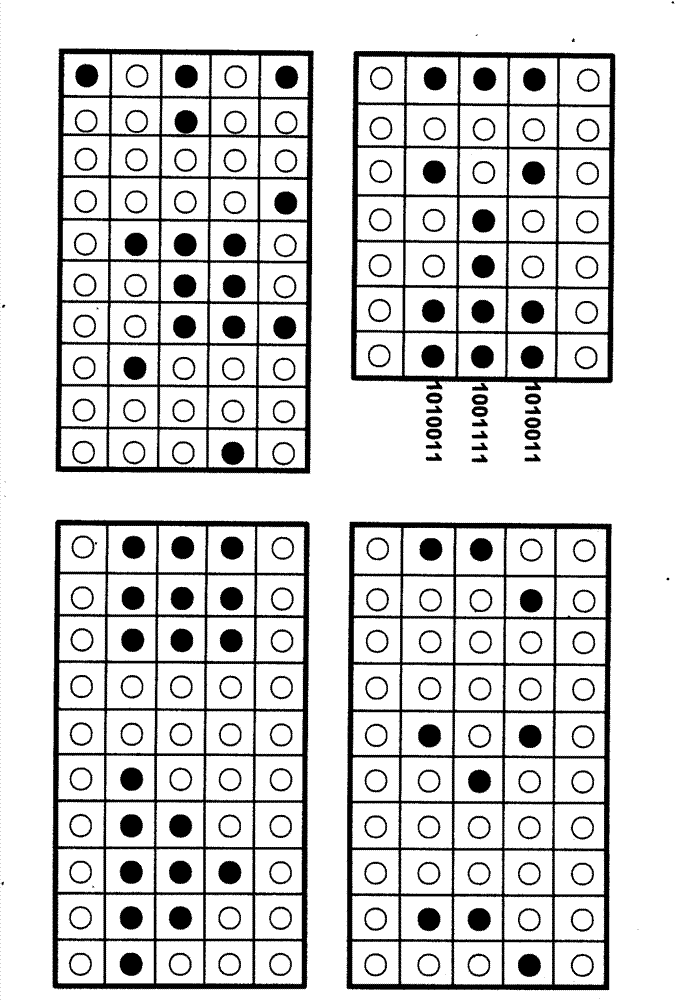
The invention relates to information security technology, in particular to a virtual genome-based cryptosystem (VGC). The cryptosystem is provided with two matched keys, of which one is a virtual genome database (VGDB) consisting of random deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequences and the other one is a position table that virtual genes of the VGDB are randomly distributed in a two-dimensional microarray, namely a virtual DNA microarray chip (VDMC). Any plaintext information can be freely written on the VDMC, namely points for forming the plaintext information are selected from the VDMC microarray. The selected points correspond to the virtual genes in the VGDB; small segments of DNA sequences are randomly selected from the virtual genes; and the uniqueness of the small segments of DNA sequences in the VGDB is determined by using a common tool of the bioinformatics, namely a basic local alignment search tool (BLAST), or other character string search algorithms such as a Knuth-Morris-Pratt (KMP) algorithm and the like. A cipher text is combined by the small segments of DNA sequences. The small segments of DNA sequences need only to perform BLAST on the VGDB during decryption, namely the points for forming the plaintext information can be discovered, and the plaintext information can be restored according to the VDMC. Any non-VGDB sequence can be randomly inserted into the cipher text and does not have any influence on the encryption. Thus, the VGC is an excellent information hiding system. In addition, the VGC key can be updated automatically so as to realize an indecipherable one-time-pad system. The cryptosystem is used for real-time quick secret information communication, digital signature and identity authentication.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Pathogenic microorganism genome database and establishment method thereof
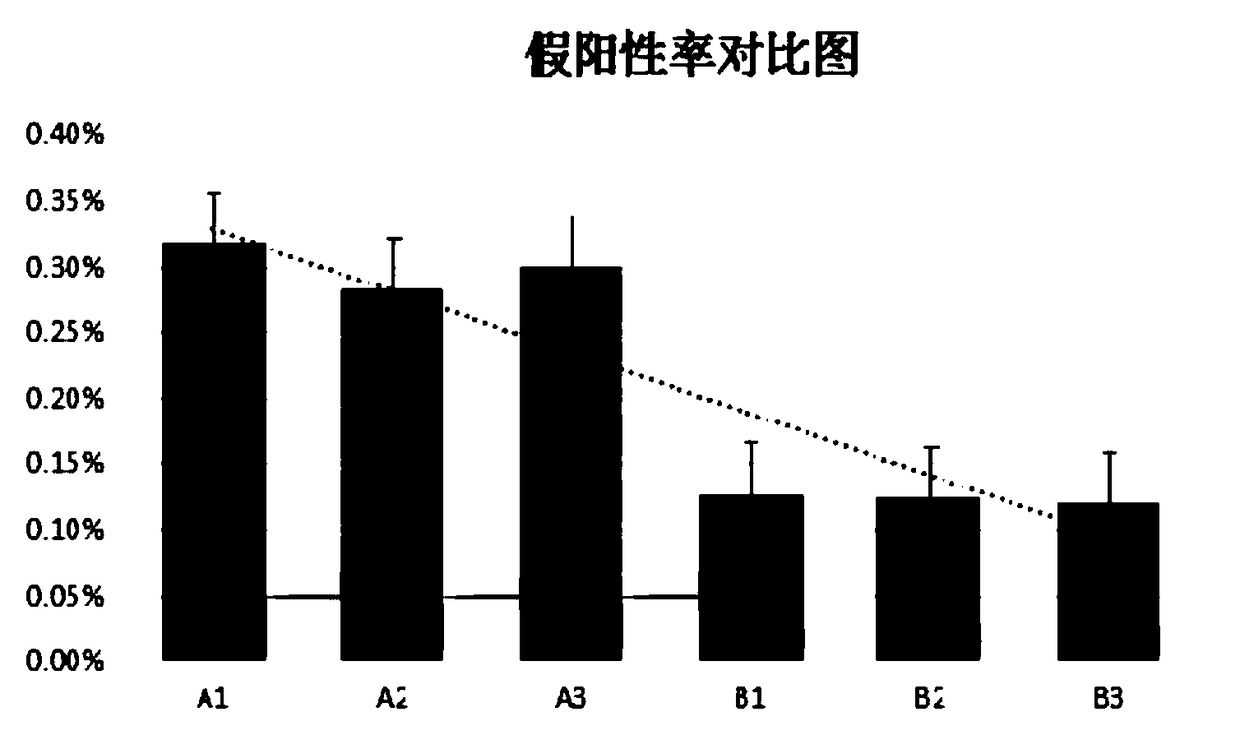
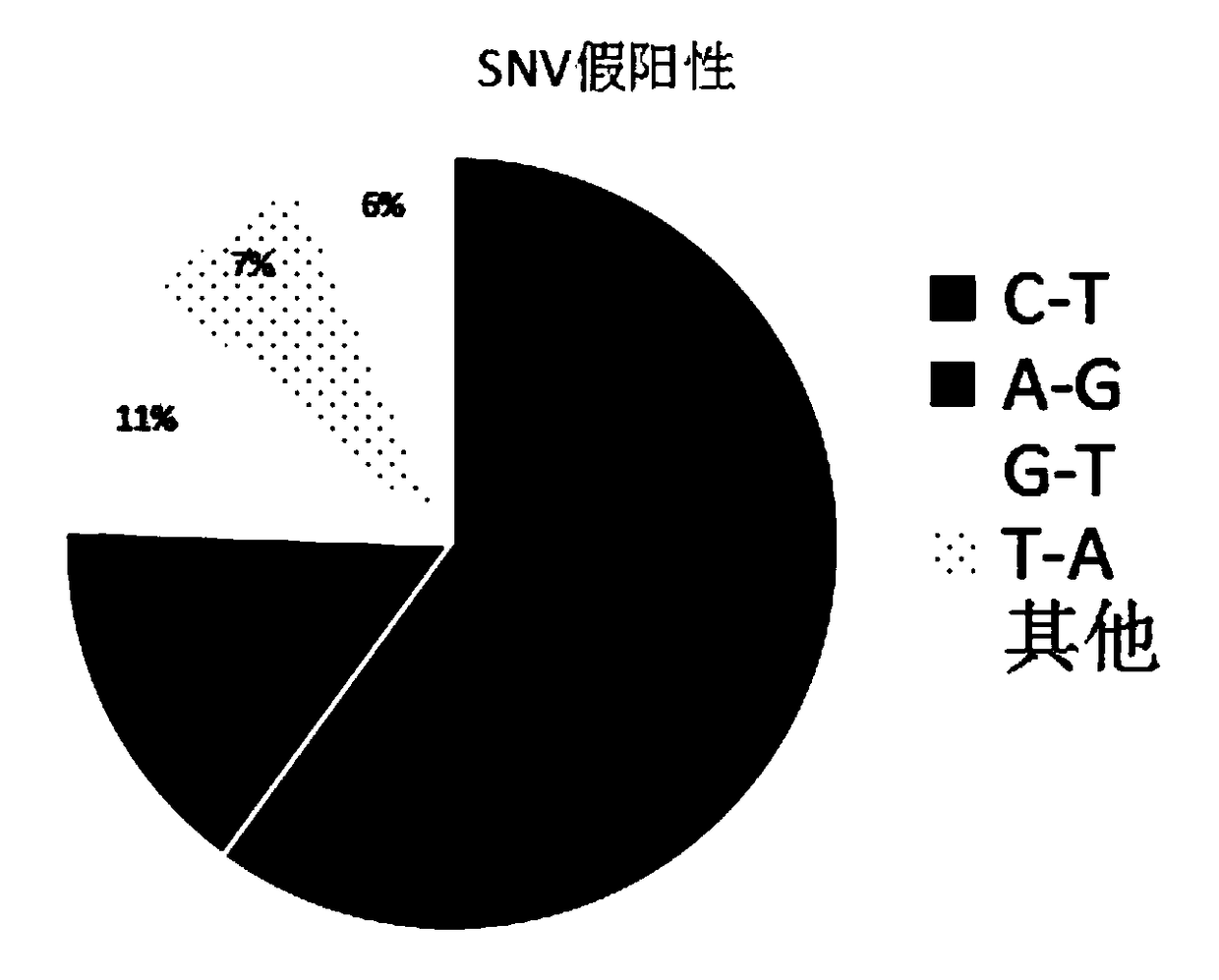
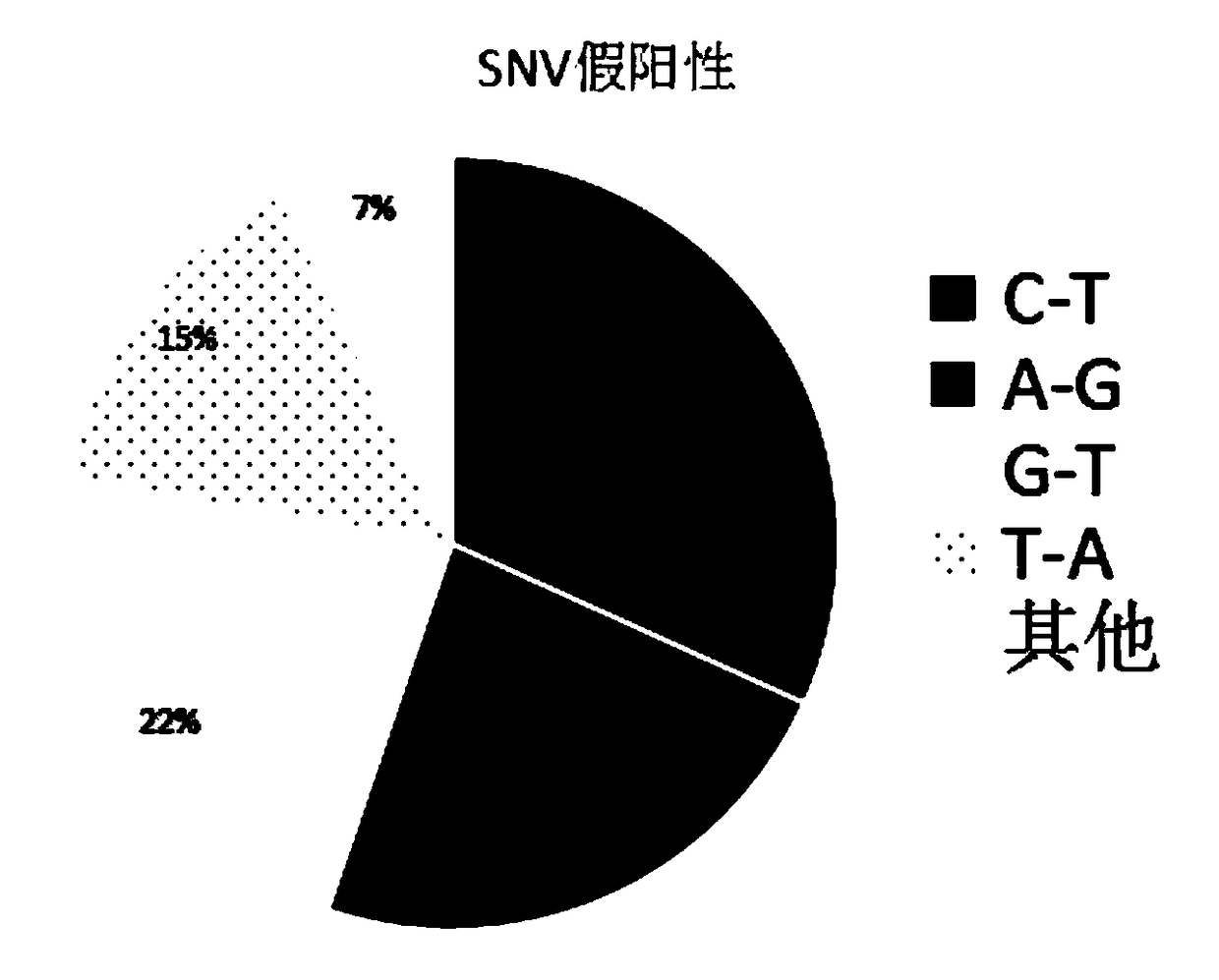
ActiveCN110473594AReduce data volumeAvoid false positivesBioinformaticsInstrumentsPathogenic microorganismHemidesmosome assembly
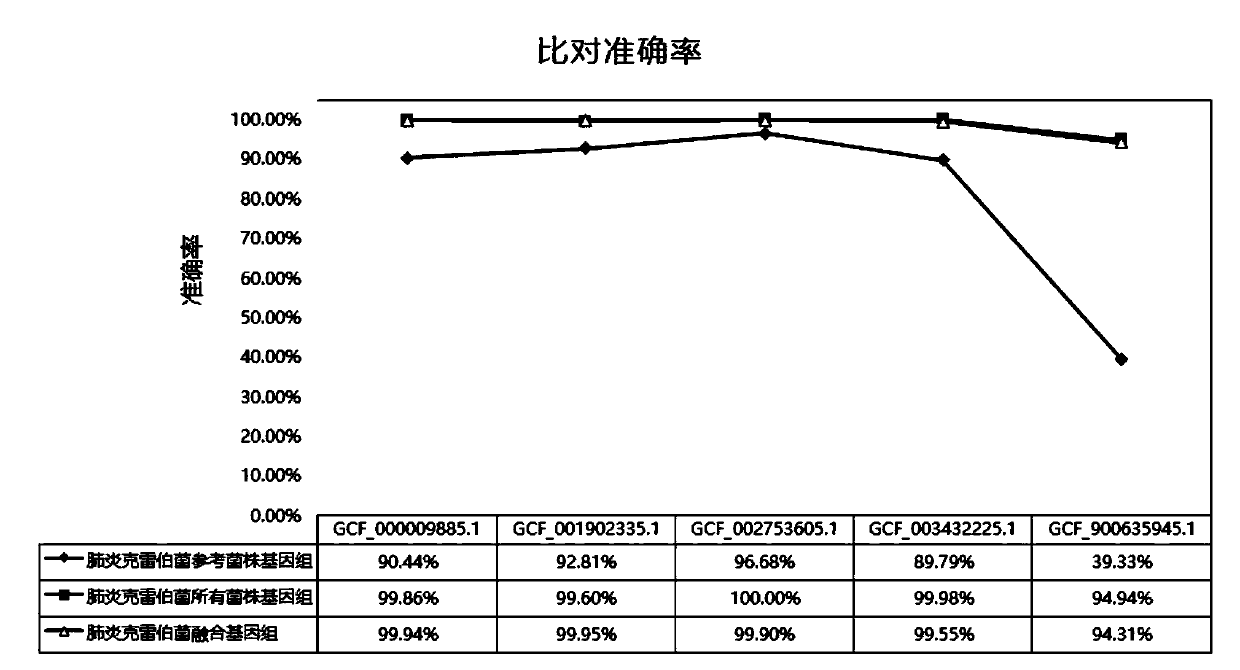
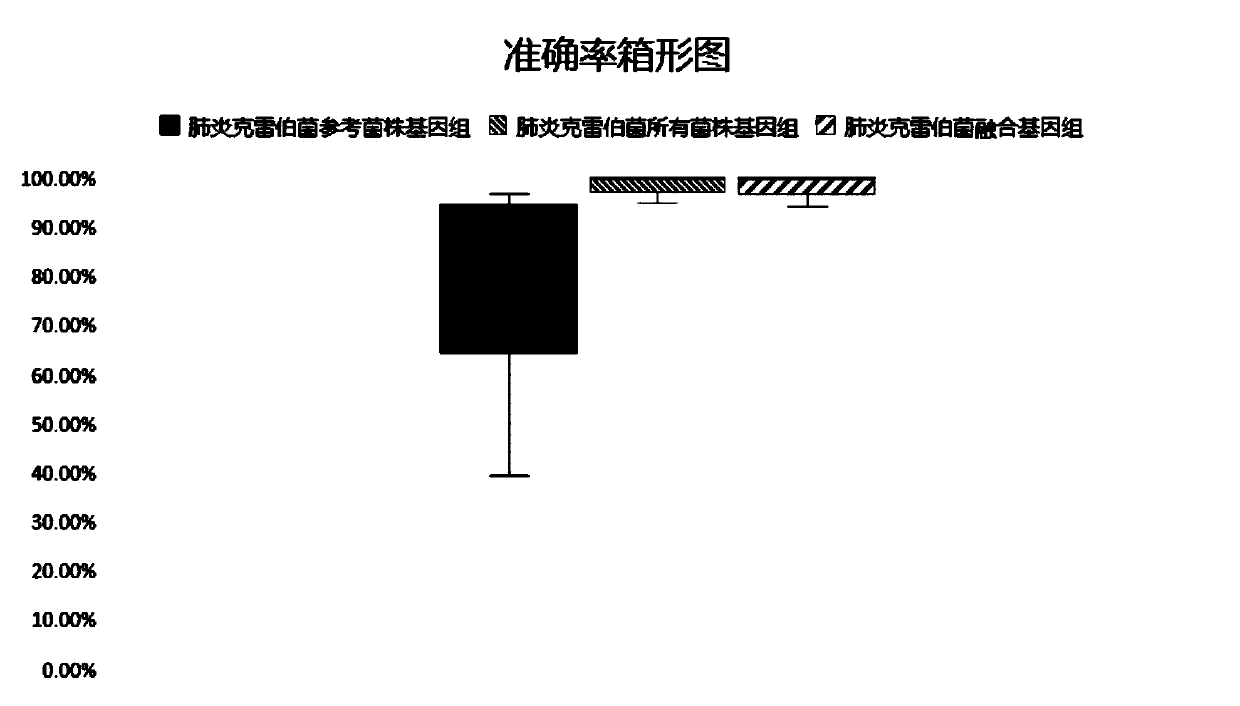
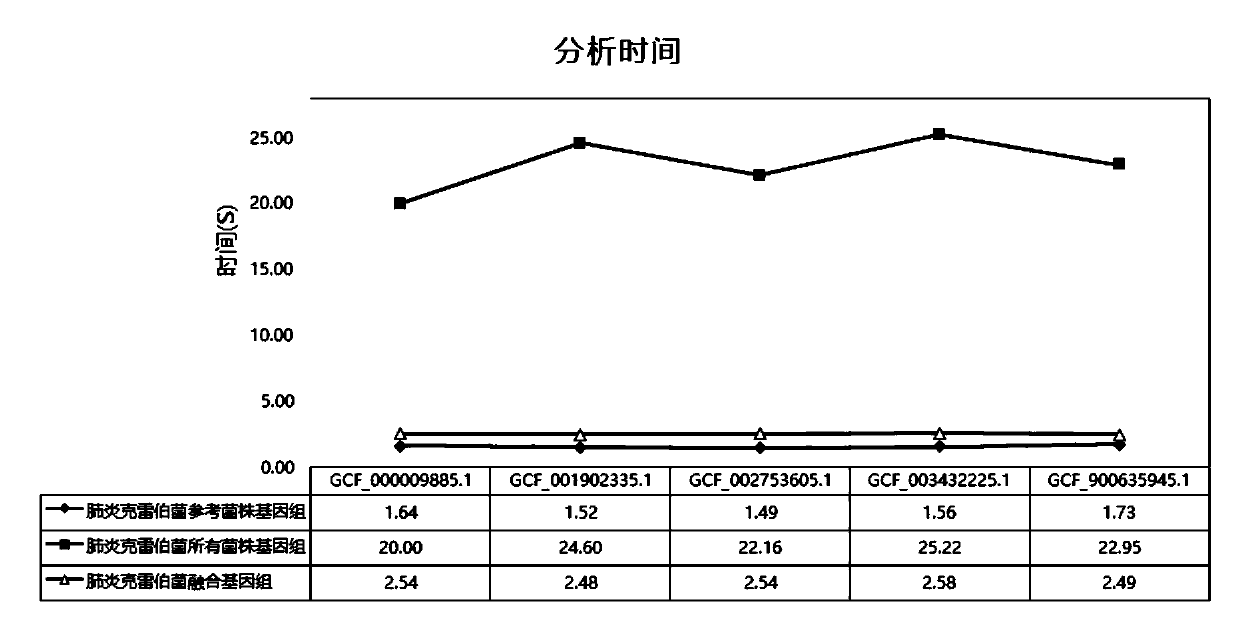
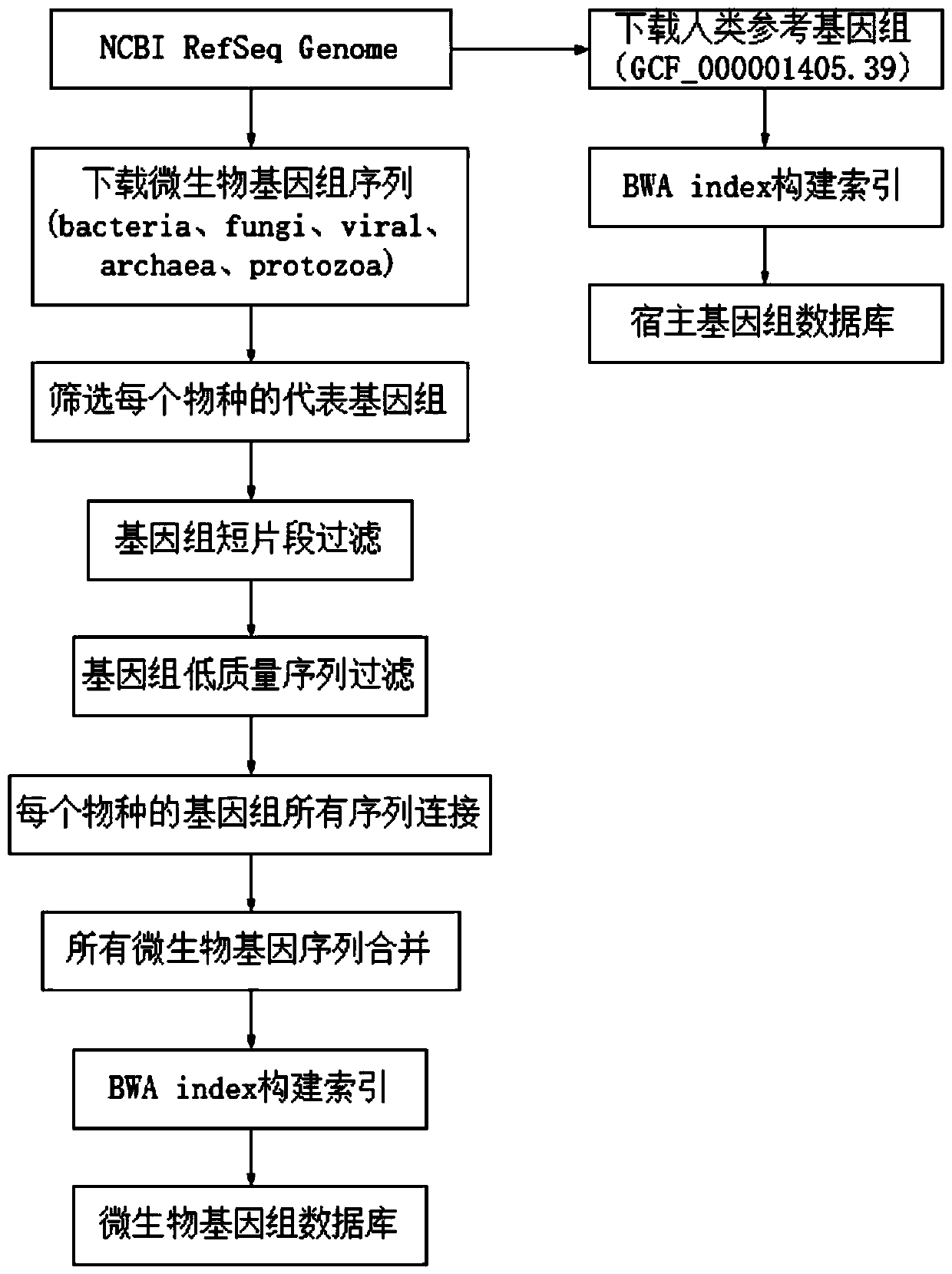
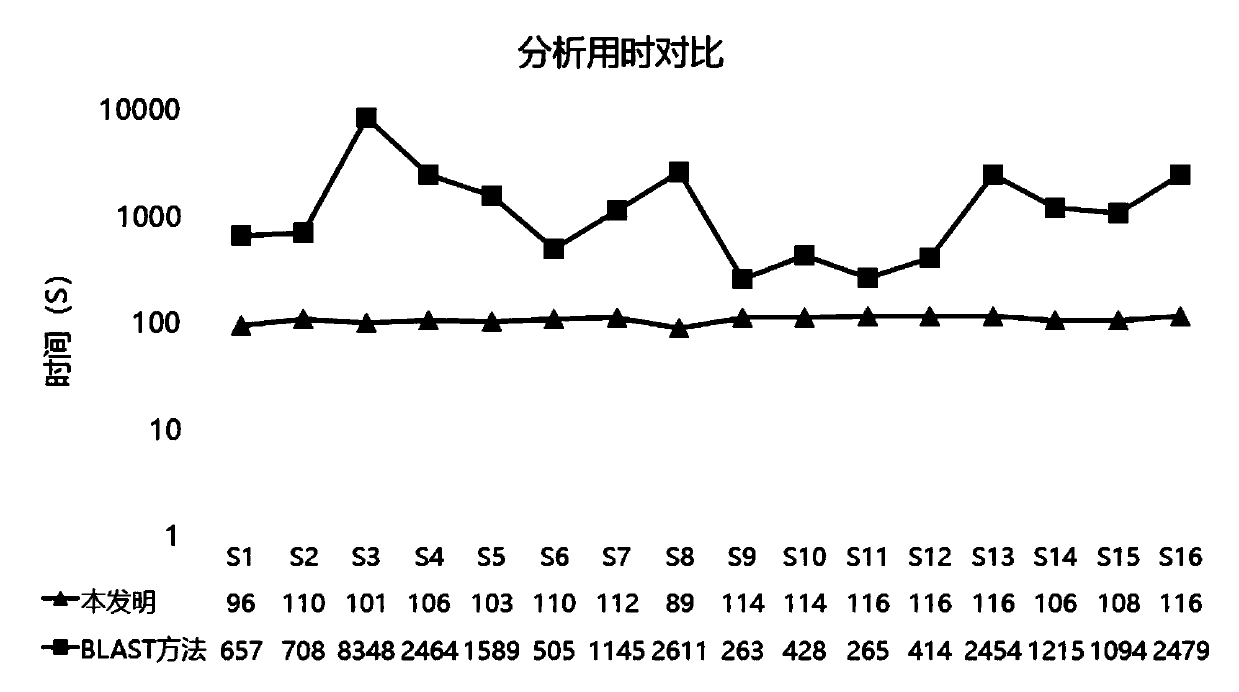
The invention relates to a pathogenic microorganism genome database and an establishment method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of meta-genomes. The method comprises the following steps ofdata acquisition, wherein pathogenic microorganism genome data is obtained; strain genome screening, wherein species strain genomes are selected according to a predetermined screening rule; plasmid sequence removal, wherein plasmid sequences existing in the strain genomes obtained in the last step are removed; filtration, wherein according to a predetermined filtering rule, strains with incorrectlabeling information, incomplete chromosome assembly and incorrect classification are removed to obtain a reference strain genome of the species; fusion genome construction, wherein the reference strain genome is interrupted, redundancy is removed, reassembly is performed, and the sequences are reassembled to obtain a fusion genome of the species; database assembly, wherein the above steps are repeated to obtain the fusion genome of the predetermined species, summary is performed, and the pathogenic microorganism genome database is obtained. The genome database has the advantages of not onlyhaving a high precision rate, but also having short analysis time and reducing the cost.
Owner:GZ VISION GENE TECH CO LTD +4
Evolutionary Architectures For Evolution of Deep Neural Networks
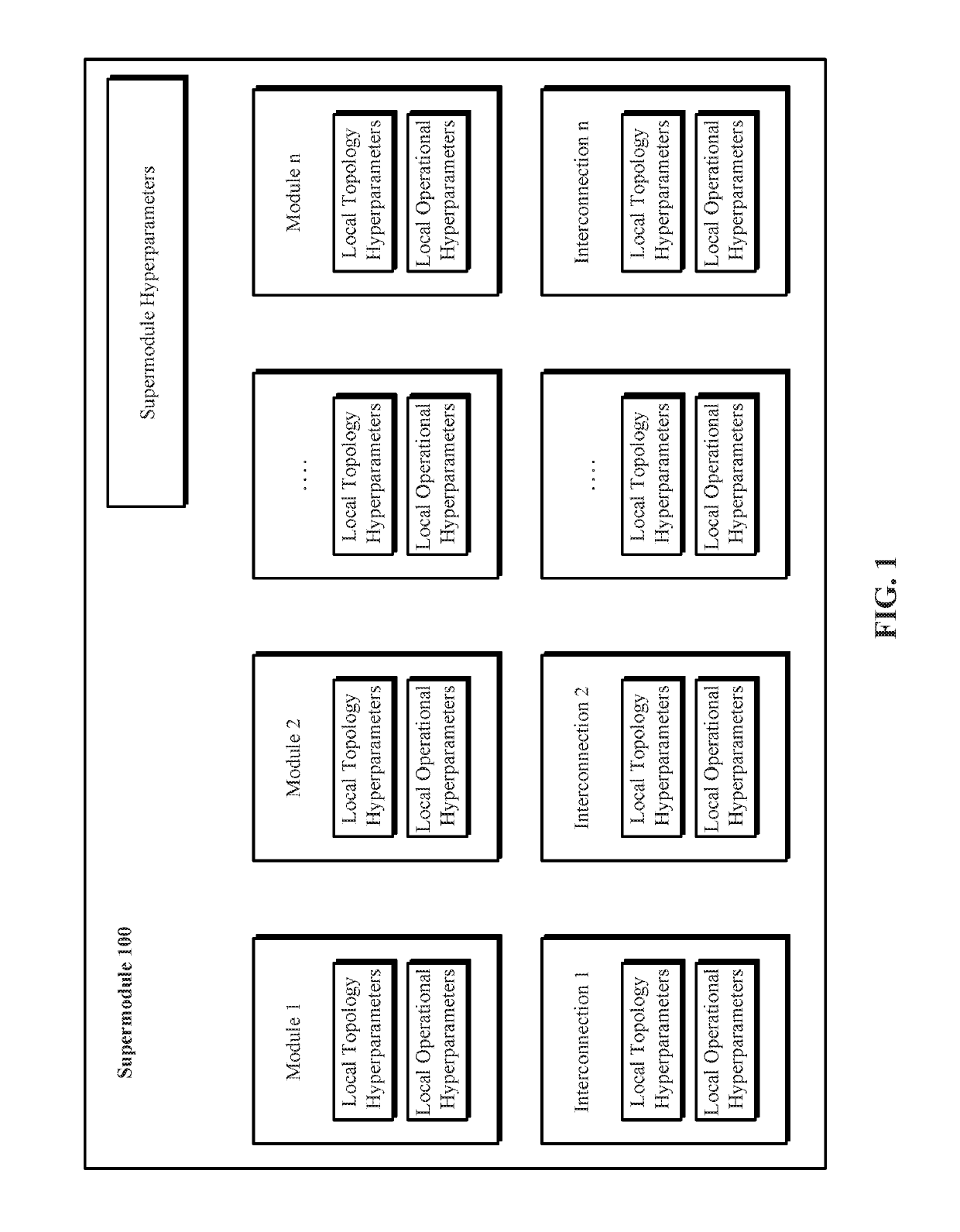
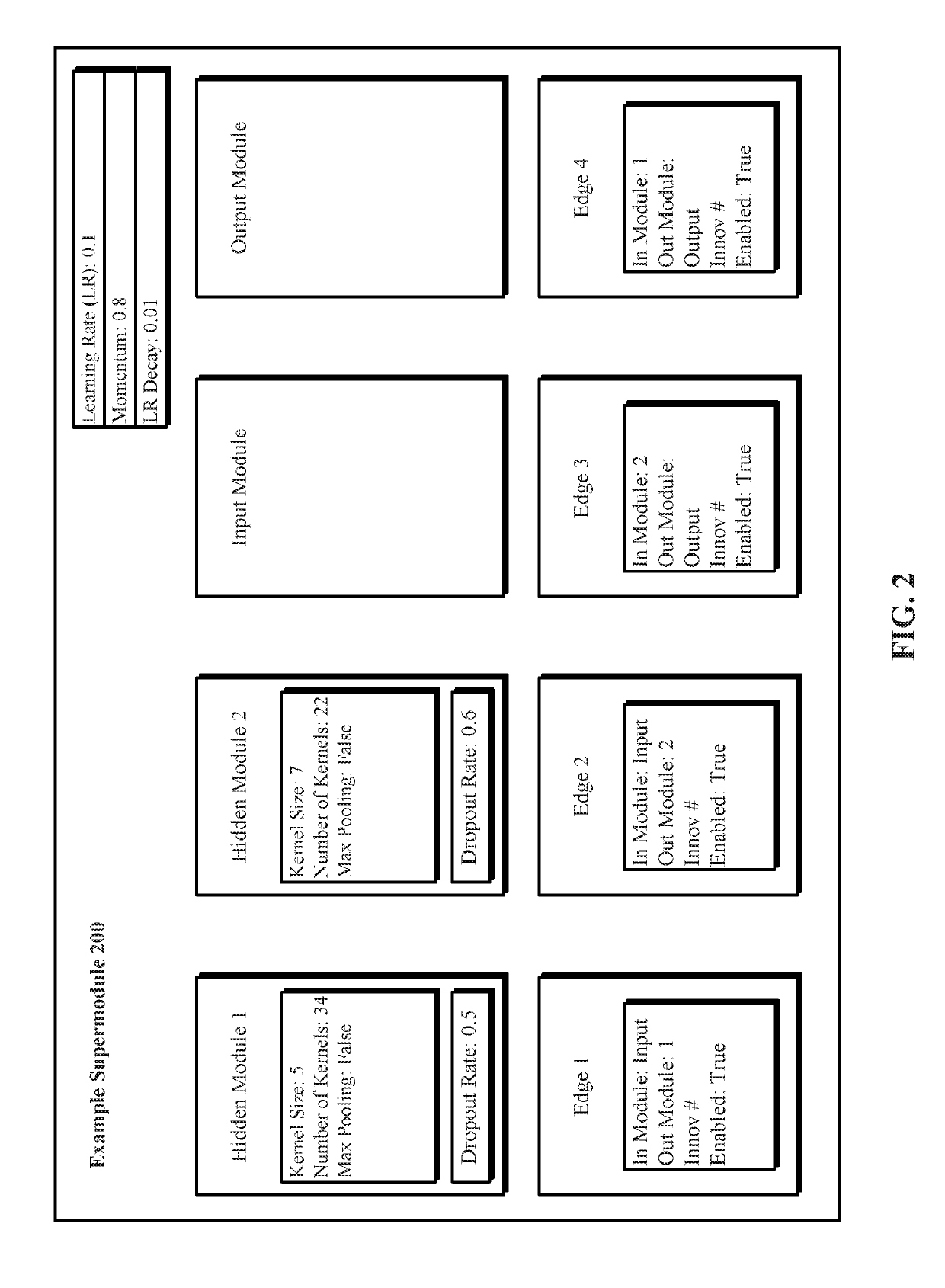
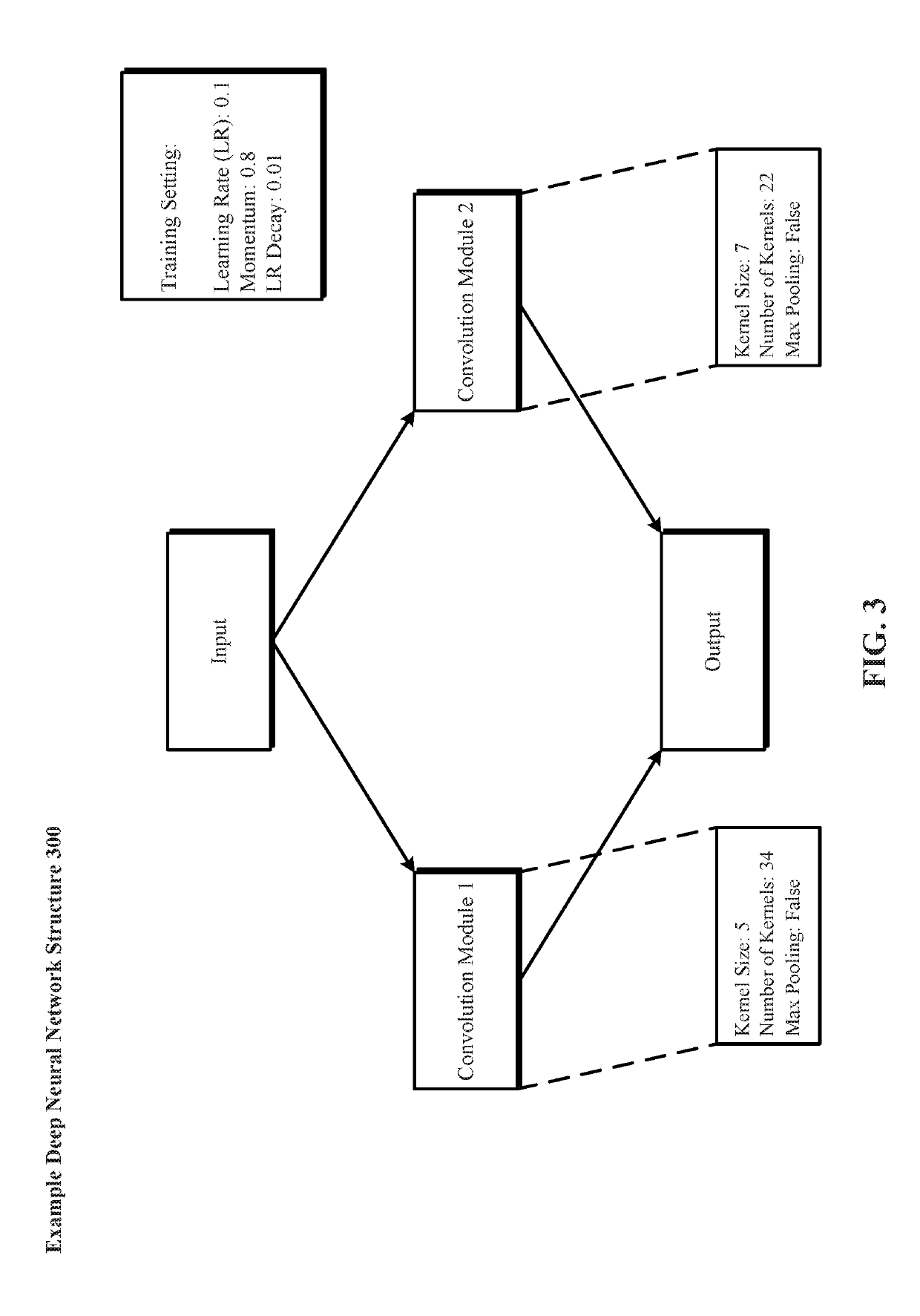
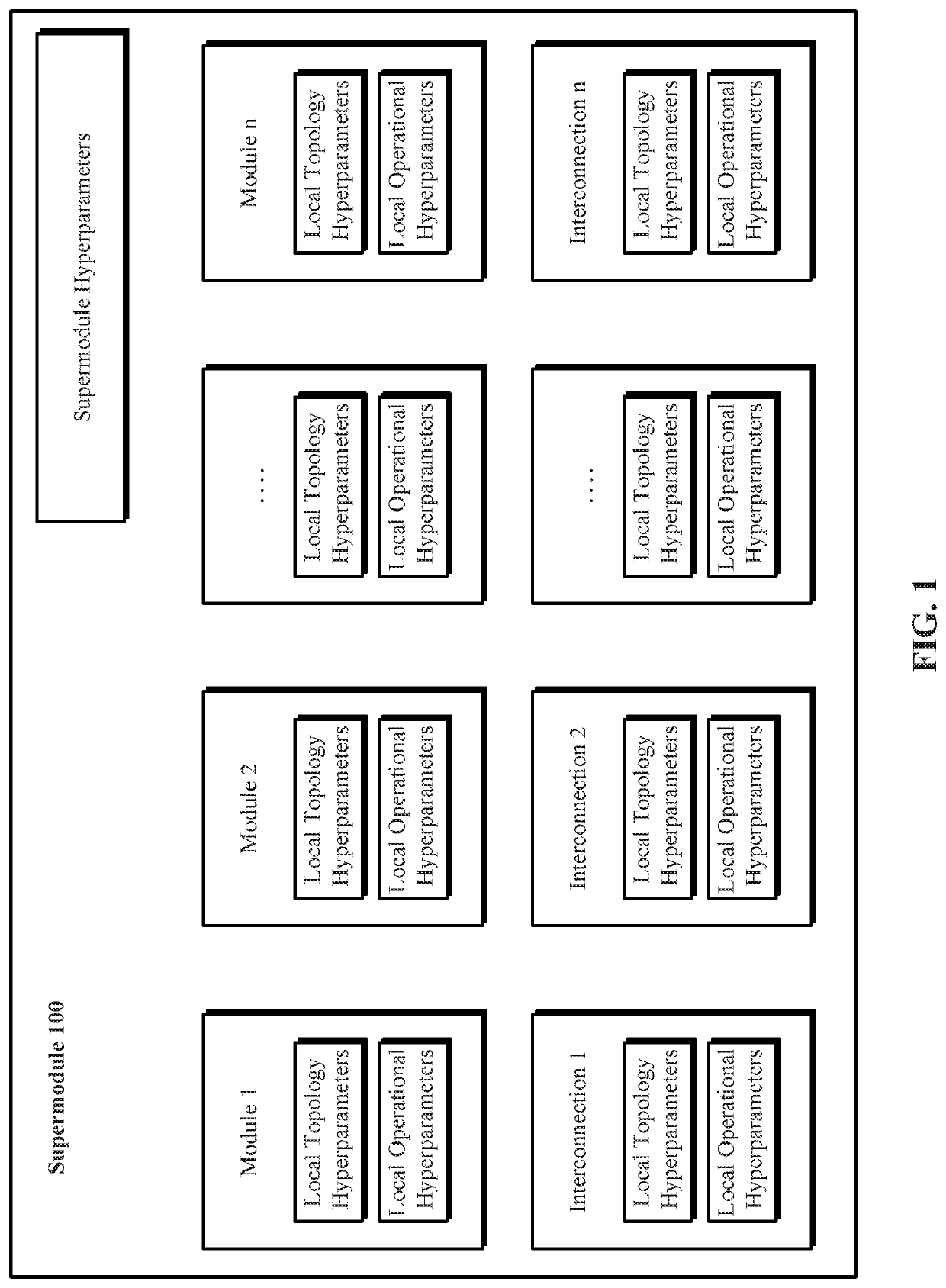
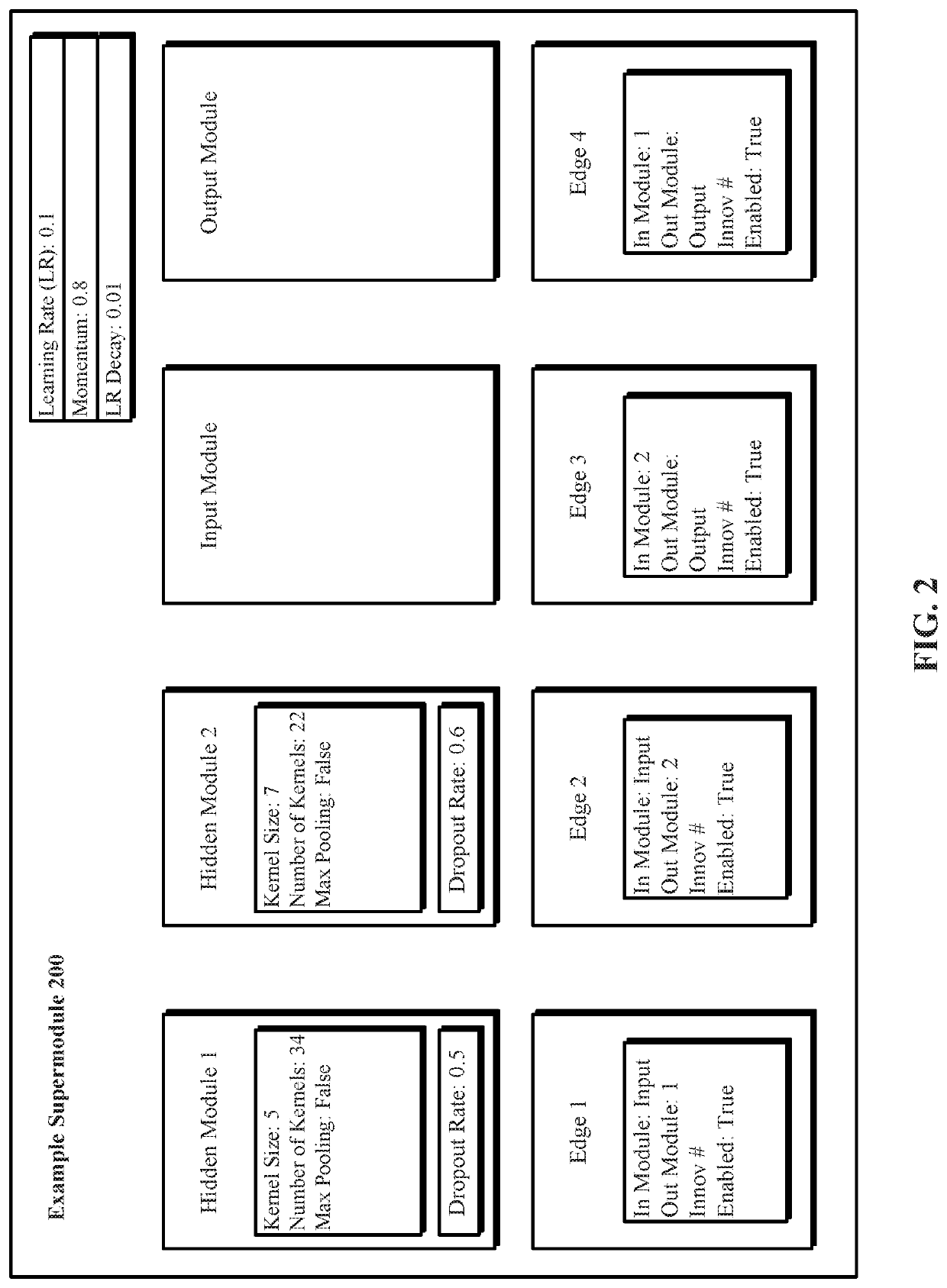
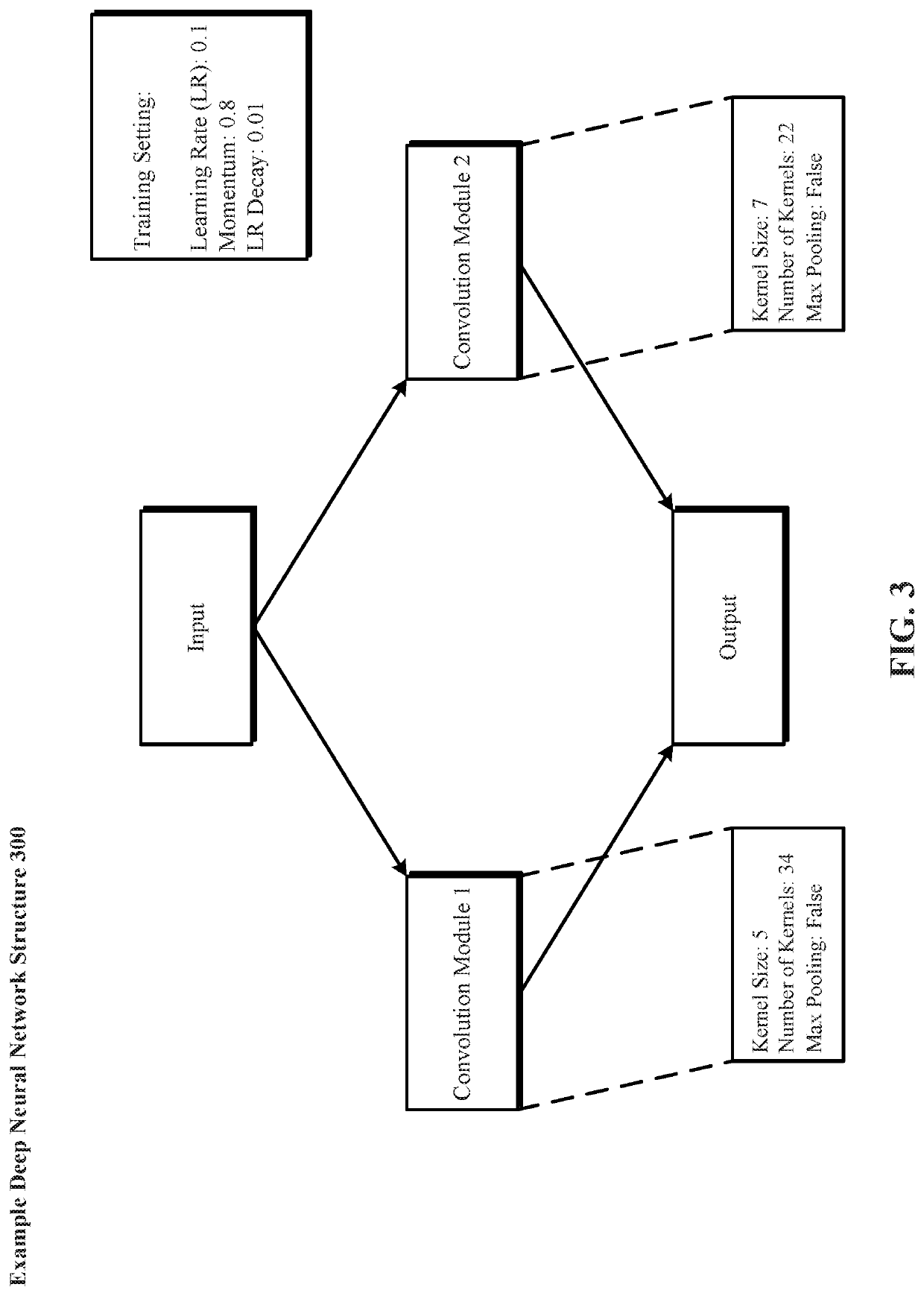
A system and method for evolving a deep neural network structure that solves a provided problem includes: a memory storing a candidate supermodule genome database having a pool of candidate supermodules having values for hyperparameters for identifying a plurality of neural network modules in the candidate supermodule and further storing fixed multitask neural networks; a training module that assembles and trains N enhanced fixed multitask neural networks and trains each enhanced fixed multitask neural network using training data; an evaluation module that evaluates a performance of each enhanced fixed multitask neural network using validation data; a competition module that discards supermodules in accordance with assigned fitness values and saves others in an elitist pool; an evolution module that evolves the supermodules in the elitist pool; and a solution harvesting module providing for deployment of a selected one of the enhanced fixed multitask neural networks, instantiated with supermodules selected from the elitist pool.
Owner:COGNIZANT TECH SOLUTIONS U S CORP
Pathogenic microorganism analysis and identification system and application thereof
ActiveCN111462821AImprove accuracyReduce mistakesSequence analysisInstrumentsMicrobial profilingOrganism
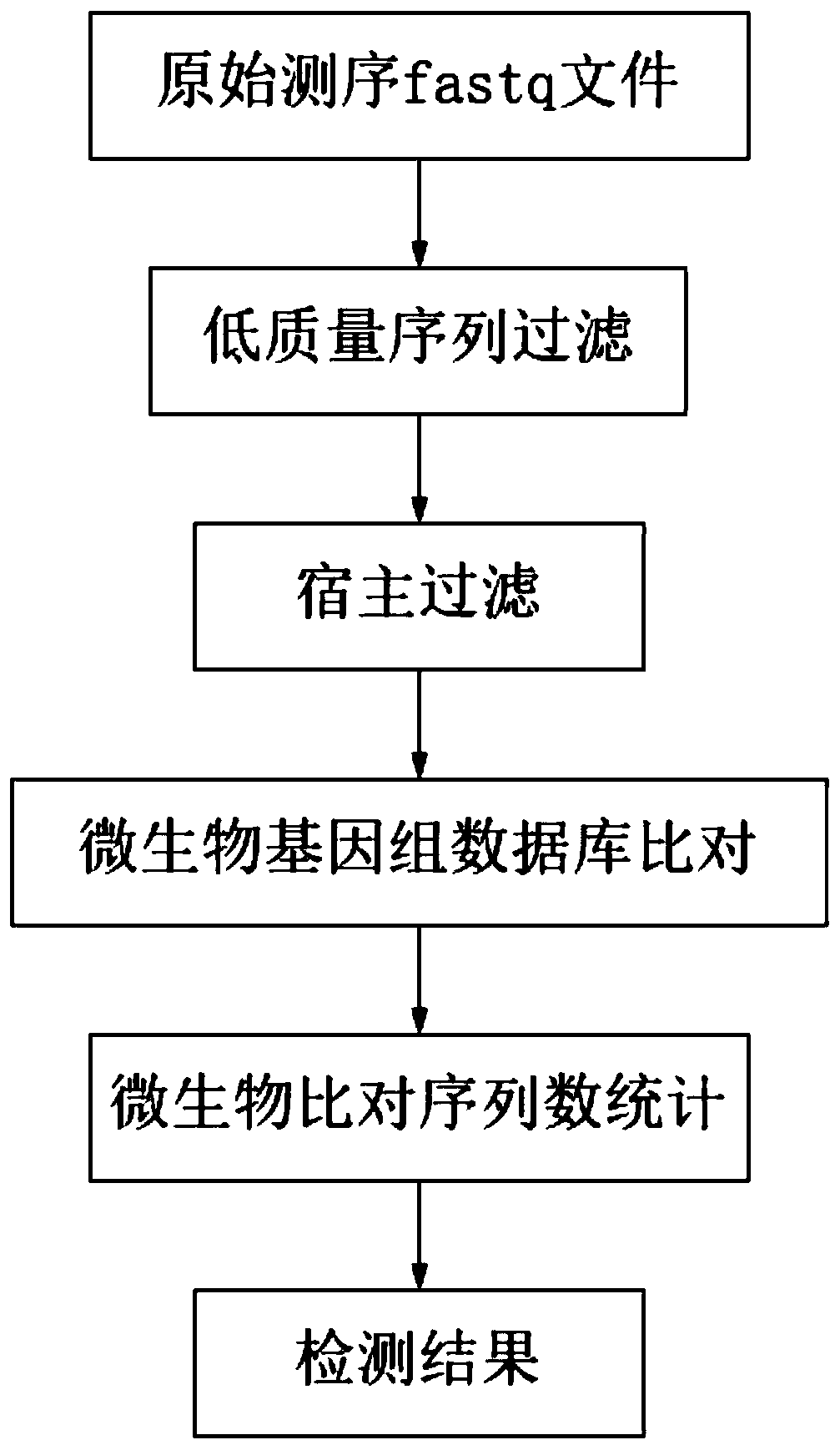
The invention relates to a pathogenic microorganism analysis and identification system and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene detection and analysis. The pathogenic microorganism analysis and identification system comprises: a data acquisition module used for acquiring gene sequencing data obtained by high-throughput sequencing; a data filtering module used for performing low-quality sequence filtering and host sequence filtering in sequence; a data comparison module used for comparing sequences to a pathogenic microorganism genome database; a species comparison module used for counting to-be-analyzed sequences; a data analysis module used for calculating the similarity S and the average similarity value SMSi of each species on each sequence comparison in the common comparison sequence set; a species sequence module used for calculating the total comparison sequence number SNTi of the species; and a result output module used for carrying out bioinformaticsanalysis to obtain a pathogenic microorganism analysis and identification result. The pathogenic microorganism analysis and identification system has the advantages of short analysis time and high accuracy, and can accurately detect mixed infection and obtain specific pathogen information.
Owner:广州微远医疗器械有限公司 +3
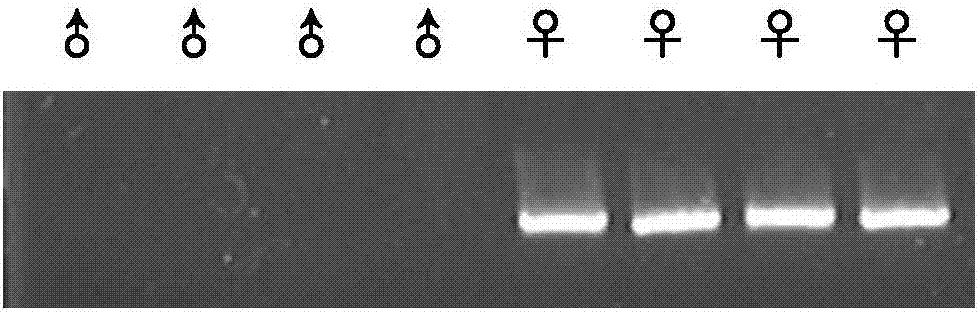
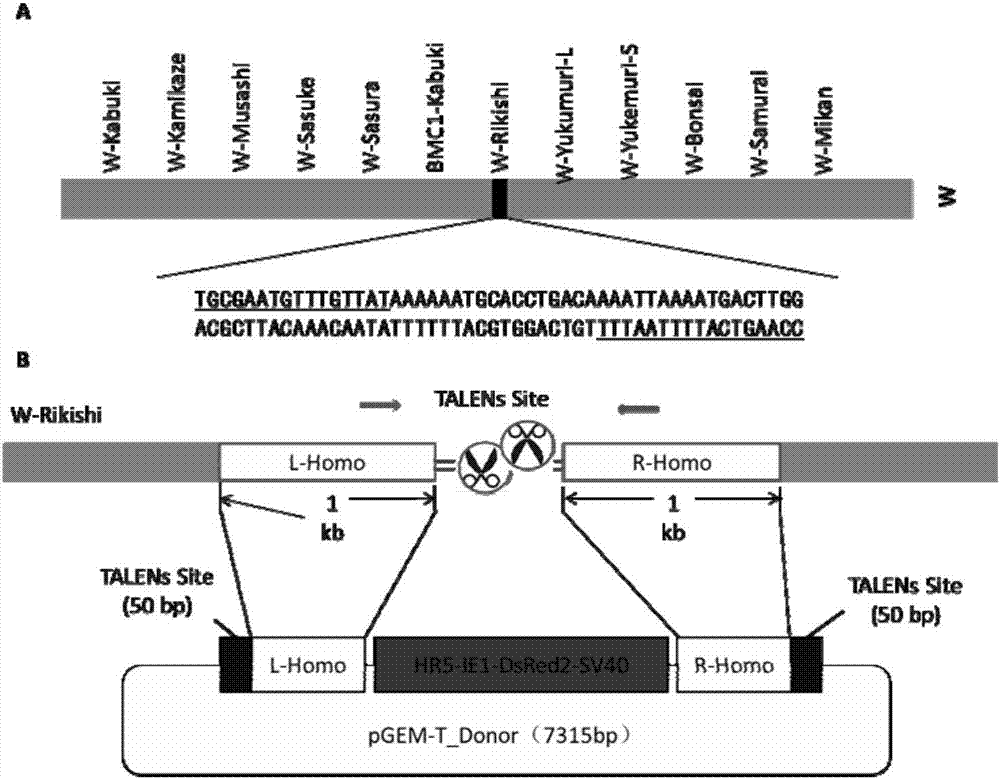
Method for inserting exogenous genes into W chromosomes of bombyx mori in fixed-point mode
ActiveCN107384967AAccurate resolutionGuaranteed hybridization rateHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAFluorescent proteinMrna expression
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology (genome editing), and relates to a method for inserting exogenous genes into W chromosomes of bombyx mori in a fixed-point mode through mediating of transcriptional activator-like nuclease, and application of the method to bombyx mori sex discrimination. The method for inserting exogenous genes into W chromosomes of bombyx mori in the fixed-point mode specifically comprises the steps that W chromosome molecular markers in a bombyx mori genome database are analyzed, a TALENs targeting site is screened, TALENs mRNA expression plasmid is designed and obtained by synthesis, homologous recombinant carrier plasmid for expressing exogenous (reporter) genes (such as red fluorescent protein) is constructed, the microinjection technique is used for injecting the TALENs mRNA expression plasmid and the homologous recombinant (donor) carrier plasmid into eggs of the bombyx mori Nistara strain, the exogenous genes are inserted into the W chromosomes of bombyx mori in the fixed-point mode, the exogenous genes are only expressed in female individuals, and thus the purpose of rapid and efficient sex discrimination is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
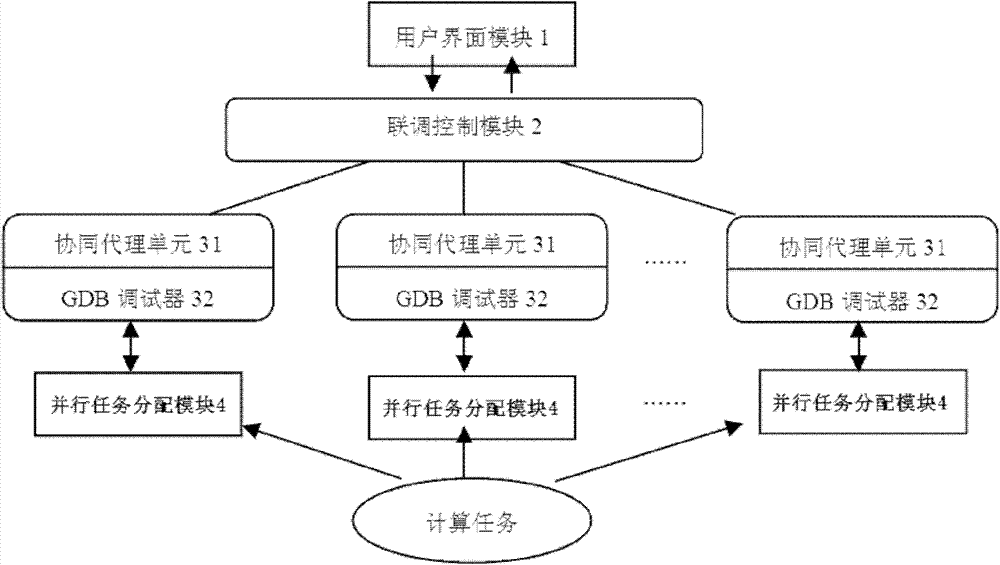
GDB (genome database) based heterogeneous computing and debugging environment realizing system
InactiveCN102902620AEasy to masterEasy to operateSoftware testing/debuggingGenome databaseUser interface
The invention relates to a GDB (genome database) based heterogeneous computing and debugging environment realizing system comprising a user interface module, a joint debugging control module, heterogeneous node debugging modules and parallel task distributing modules which are connected sequentially. The user interface module is used for interacting with users and receiving debugging operation commands from the users in a command line manner and feeding back the debugging result information. The joint debugging control module is used for starting and stopping the heterogeneous node debugging modules, distributing debugging tasks and recovering debugging results, and debugging and controlling parallel subtasks synchronously or asynchronously. The heterogeneous node debugging modules are used for executing debugging commands transmitted by the joint debugging control module; and the parallel task distributing modules are used for partitioning a computing task into a plurality of parallel subtasks and distributing and dispatching the parallel subtasks to execute on the corresponding heterogeneous node debugging modules. Compared with the prior art, the GDB based heterogeneous computing and debugging environment realizing system has the advantages of simplicity in operation, fast deployment and low cost and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
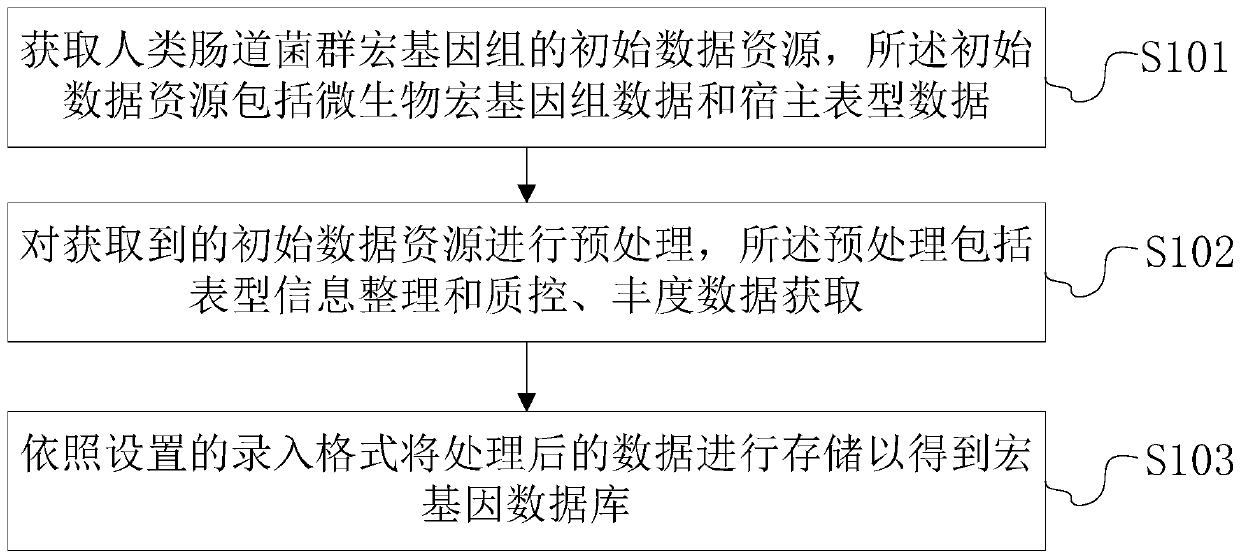
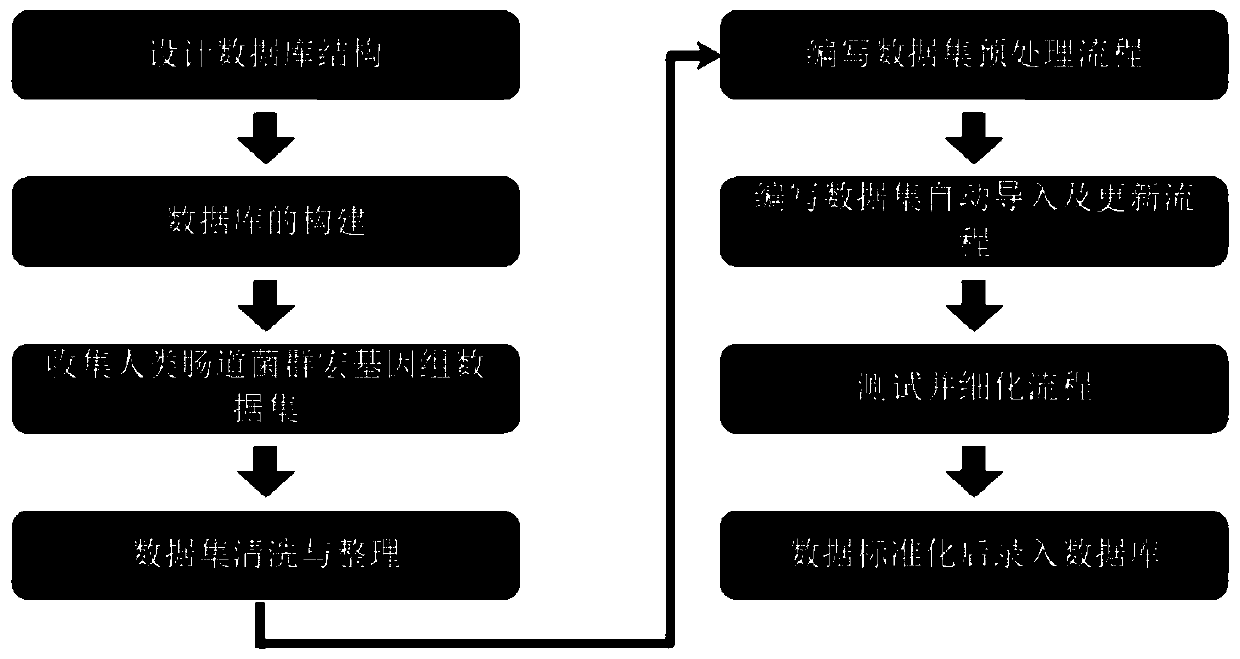
Intestinal flora metagenome database construction method and device and intestinal flora metagenome database analysis method and device
The invention discloses an intestinal flora metagenome database construction method which comprises the following steps: acquiring initial data resources of a human intestinal flora metagenome, the initial data resources comprising microbial metagenome data and host phenotype data; preprocessing the acquired initial data resources, wherein the preprocessing comprises phenotypic information arrangement and quality control and abundance data acquisition; and storing the processed data according to a set entry format to obtain a metagene database. The invention further discloses an analysis method and system based on the intestinal flora metagenome database, and a storage medium. According to the intestinal flora metagenome database construction method, screening and unified standard processing are carried out on original data, so that obtained database information is accurate, reliable and standard, and information transmission, database management and database data interaction are facilitated.
Owner:康美华大基因技术有限公司
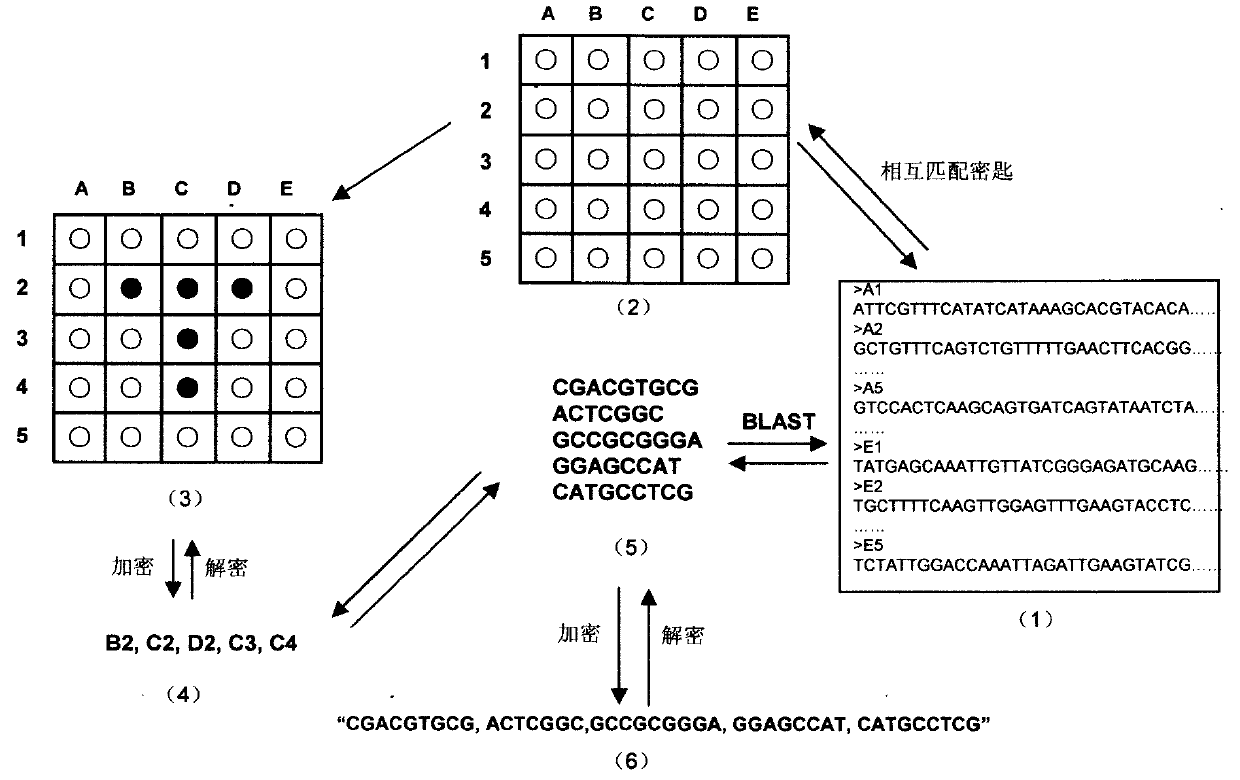
Construction method of virtual genome-based cryptosystem (VGC)
InactiveCN102025482BHuge key spaceSolve the first sharing problemGenetic modelsSecuring communicationPlaintextDNA Microarray Chip
The invention relates to information security technology, in particular to a virtual genome-based cryptosystem (VGC). The cryptosystem is provided with two matched keys, of which one is a virtual genome database (VGDB) consisting of random deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequences and the other one is a position table that virtual genes of the VGDB are randomly distributed in a two-dimensional microarray, namely a virtual DNA microarray chip (VDMC). Any plaintext information can be freely written on the VDMC, namely points for forming the plaintext information are selected from the VDMC microarray. The selected points correspond to the virtual genes in the VGDB; small segments of DNA sequences are randomly selected from the virtual genes; and the uniqueness of the small segments of DNA sequences in the VGDB is determined by using a common tool of the bioinformatics, namely a basic local alignment search tool (BLAST), or other character string search algorithms such as a Knuth-Morris-Pratt (KMP) algorithm and the like. A cipher text is combined by the small segments of DNA sequences. The small segments of DNA sequences need only to perform BLAST on the VGDB during decryption, namely the points for forming the plaintext information can be discovered, and the plaintext information can be restored according to the VDMC. Any non-VGDB sequence can be randomly inserted into the cipher text and does not have any influence on the encryption. Thus, the VGC is an excellent information hiding system. In addition, the VGC key can be updated automatically so as to realize an indecipherable one-time-pad system. The cryptosystem is used for real-time quick secret information communication, digital signature and identity authentication.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Simplified representative unicellular whole-genome database creating method and application thereof
InactiveCN108148830AReduce error rateMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGenome databaseSmall cell
The invention provides a better and suitable simplified representative unicellular whole-genome database creating method and application thereof. On one hand, the method can be effectively applied totrace samples or samples with smaller cell population to perform simplified genome database creation by optimizing primers and amplifying steps; on the other hand, by means of enzyme correction treatment, an enzyme treating step capable of specifically resecting uridine monophosphate can be applied to a simplified genome unicellular sample amplifying method, and amplification error rate can be remarkably reduced. Compared with the prior art, the method creatively applies an optimized and improved unicellular database creating scheme to simplified genome database creation of the trace samples or the samples with the smaller cell population; meanwhile, compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of higher efficiency, simpleness, practicability, accuracy, small loss, low cost,good method repeatability, low error rate, great suitability for the simplified genome unicellular whole-genome amplification of the trace samples or the samples with the smaller cell population and ability in widening sample application ranges; meanwhile, the error rate is reduced, and detection accuracy is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAJORBIO BIO PHARM TECH
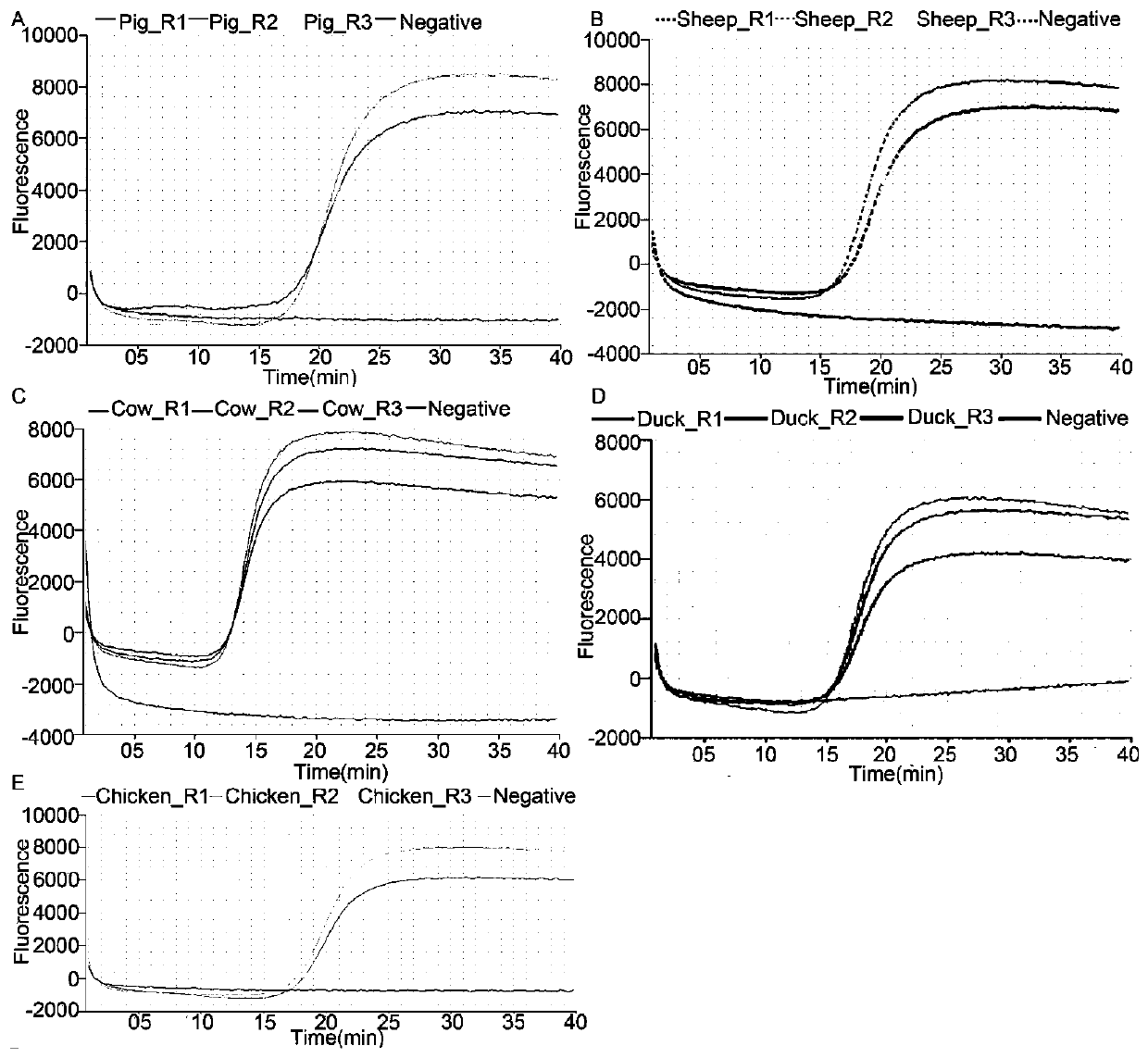
Multi-animal-derived adulteration identification method based on whole genome sequencing technology
ActiveCN110982888AQualitative and quantitative contentMicrobiological testing/measurementWhole genome sequencingPharmaceutical industry
The invention discloses a multi-animal-derived adulteration identification method based on a whole genome sequencing technology. The multi-animal-derived adulteration identification method comprises the following steps: 1) constructing a mitochondrial genome database, comparing sequencing data with the mitochondrial genome database, and extracting mitochondrial sequences obtained by comparison; 2)reassembling mitochondrial genomes of various species in the mitochondrial sequences extracted in the step 1); 3) comparing the mitochondrial sequences extracted in the step 1) to a recombined mitochondrial genome in the step 2), and extracting the sequences compared to the recombined mitochondrial genome in the step 2); and 4) dividing the sequences compared to the recombined mitochondrial genome in the step 3) into two classes, extracting the sequences compared to the recombined mitochondrial genome of a single species, and analyzing the species composition of a mixture according to the number of the sequences. The method provided by the invention can qualitatively and quantitatively determine the content of various biological components in a complex meat sample, and has extensive application prospect in food and pharmaceutical industries.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Method for obtaining natural variant of enzyme and super thermostable cellobiohydrolase
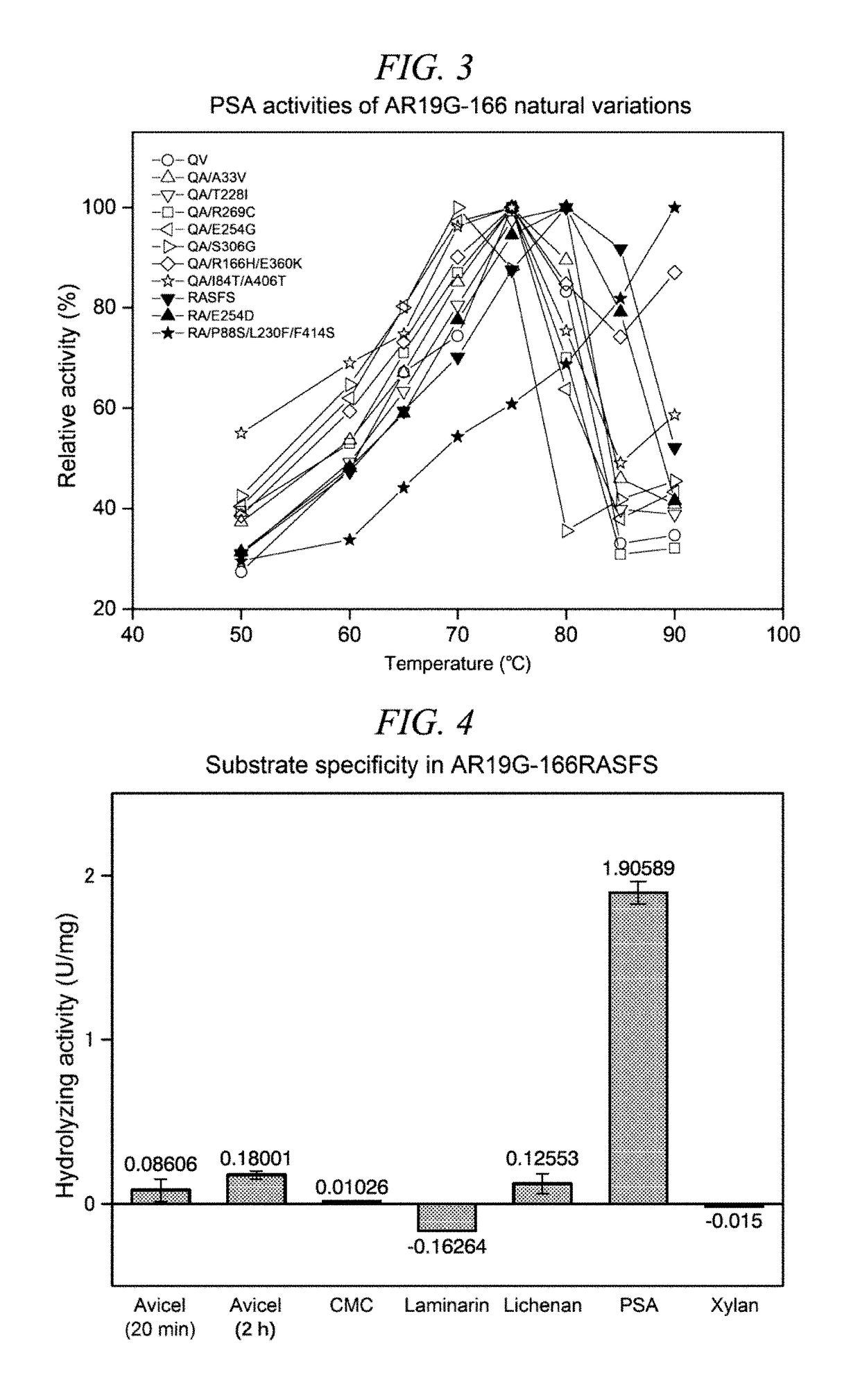
InactiveUS20150259659A1Efficiently obtainedIncrease enzyme activityMicroorganismsLibrary screeningGenome databaseEnzyme
A method for selectively obtaining a natural variant of an enzyme having activity includes (1) a step of detecting an ORF sequence of a protein having enzyme activity from a genome database including base sequences of metagenomic DNA of environmental microbiota; (2) a step of obtaining at least one PCR clone including the ORF sequence having a full length, a partial sequence of the ORF sequence, or a base sequence encoding an amino acid sequence which is formed by deletion, substitution, or addition of at least one amino acid residue in an amino acid sequence encoded by the ORF sequence, by performing PCR cloning on at least one metagenomic DNA of the environmental microbiota by using a primer designed based on the ORF sequence; (3) a step of determining a base sequence and an amino acid sequence which is encoded by the base sequence for each PCR clone obtained in the step (2); and (4) a step of selecting a natural variant of an enzyme having activity by measuring enzyme activity of proteins encoded by each PCR clone obtained in the step (2).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
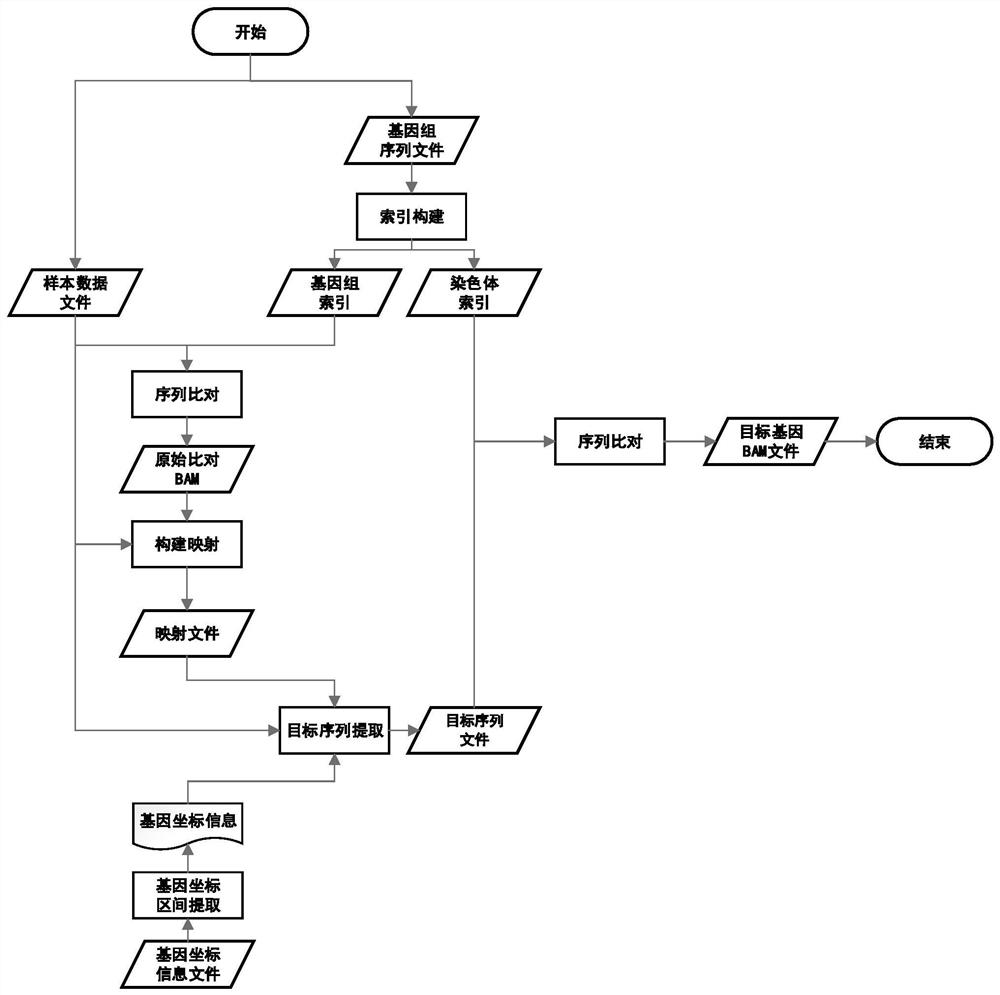
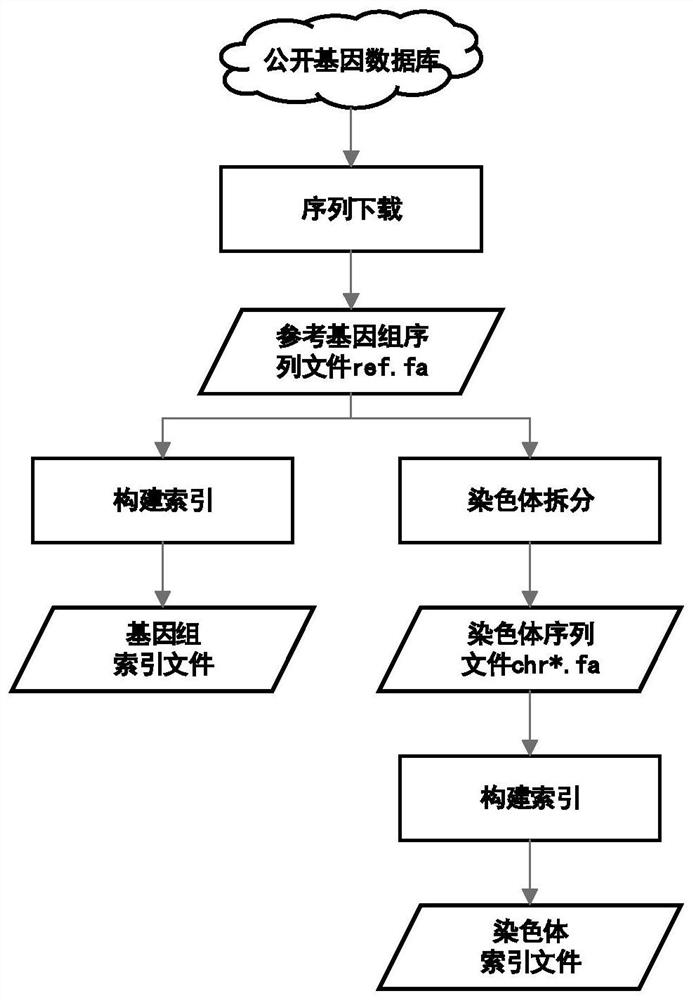
Method for quickly acquiring comparison result data of target genome region
PendingCN113488106AQuick extractionQuick comparisonSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsReference genome sequenceTarget gene
The invention discloses a method for quickly acquiring comparison result data of a target genome region. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a reference genome sequence file and coordinate information files of all genes by using a public genome database on the basis of sample original sequencing data, and constructing a reference genome index file and a chromosome index file; constructing a mapping relationship between the sequence line number of the sample original sequencing data and genome comparison coordinates, and quickly reconstructing sample original sequencing data of a target gene sequence by using the mapping relationship; and carrying out sequence comparison by utilizing the chromosome index file and the sample original sequencing data of the target gene sequence to obtain an original comparison data file of the target gene sequence, and carrying out sequencing and duplicate removal to obtain final comparison result data of a target genome region. The method has the characteristics of simplicity in deployment, convenience in operation, high efficiency, high throughput and wide application range. Compared with an original secondary data BAM file, the obtained result basically has no information loss.
Owner:SUZHOU SMK GENE TECH LTD
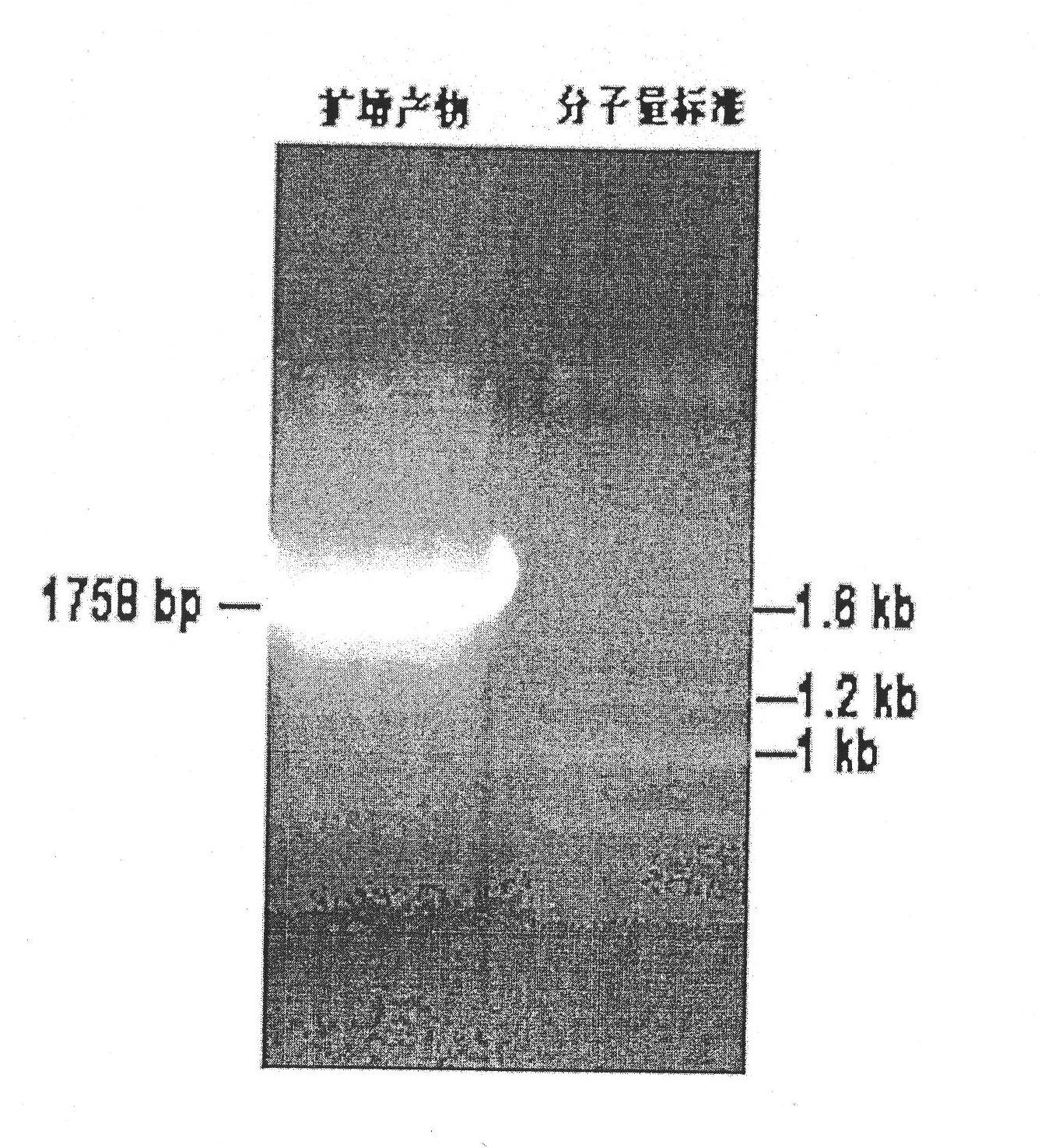
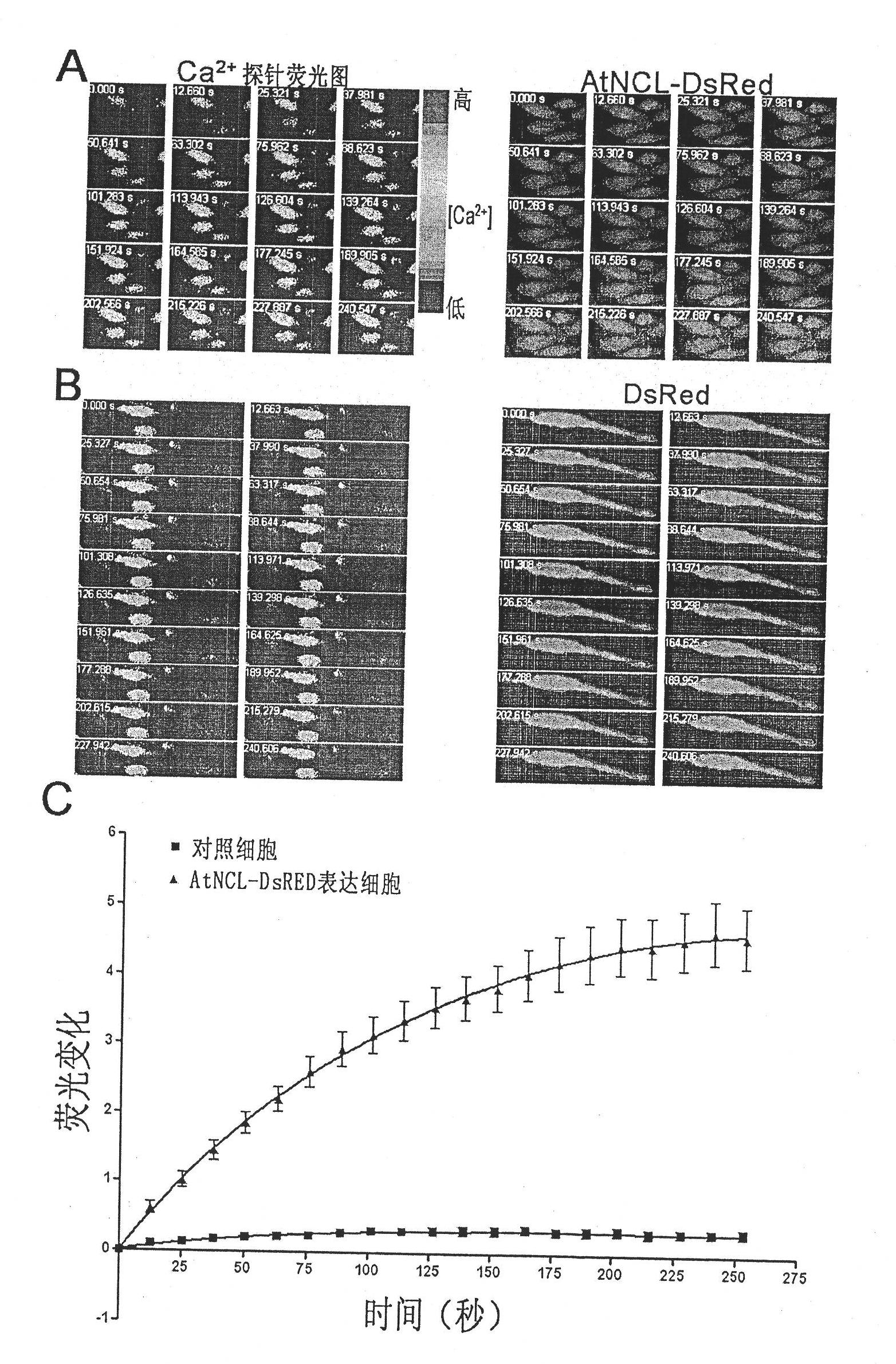
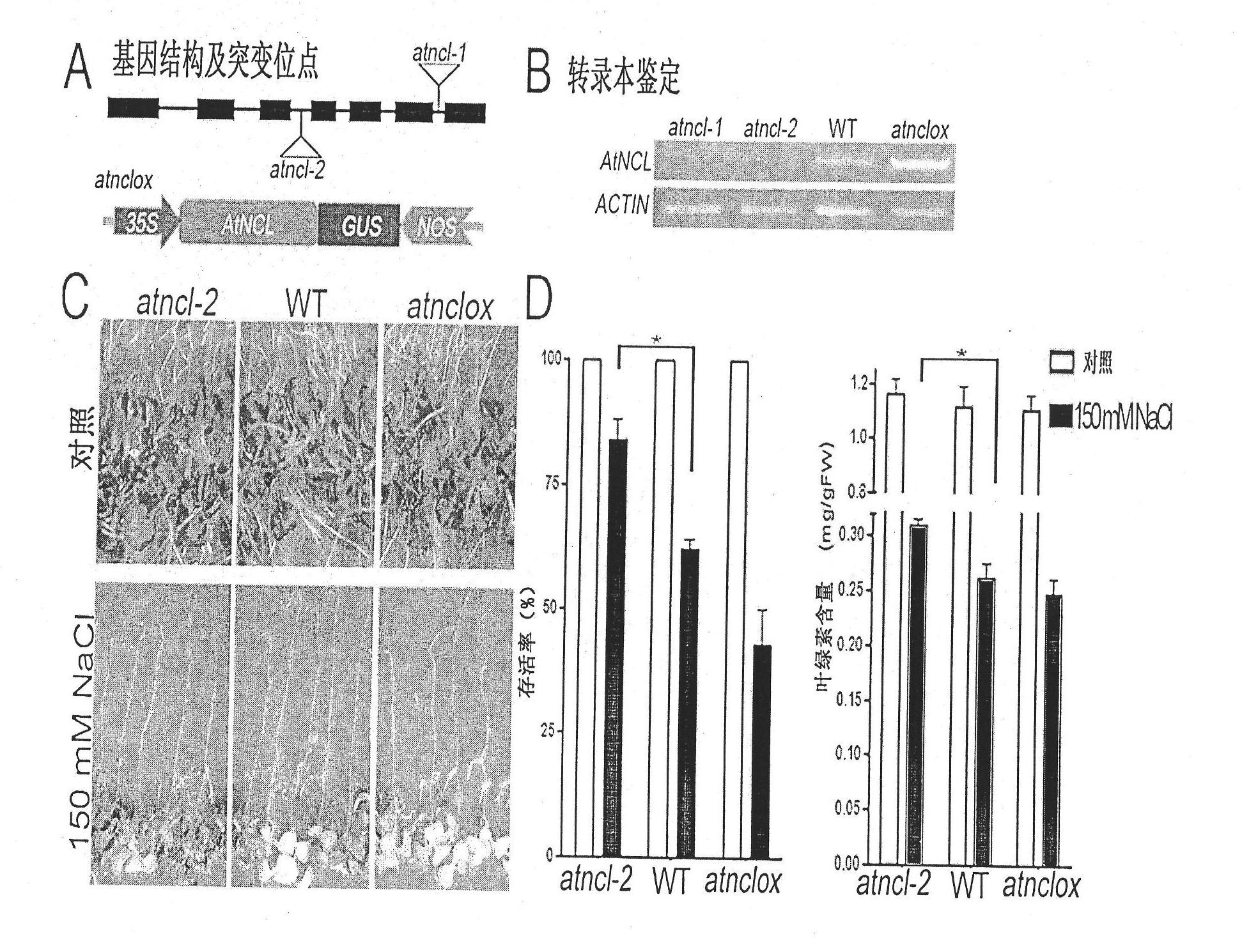
Application of plant sodium-calcium exchanger gene (AtNCL)
InactiveCN101955947AImprove salt tolerancePlant peptidesGenetic engineeringTransport systemOpen reading frame
The invention discloses a plant sodium-calcium exchanger gene (AtNCL) and application of the sodium-calcium transport activity of the coding protein thereof in breeding salt-resistant variety of crop. The number of a model plant Arabidopsis thaliana sodium-calcium exchanger gene (AtNCL) in an Arabidopsis thaliana genome database (TAIR) is Atlg53210; the total length of the open reading frame of the gene is 1,758bp, and protein consisting of 585 amino acid residues is coded. Experiments prove that AtNCL participates in the elimination process of calcium signals of plant response to salt stress, and that a new ion transport system exists in the plant. By regulating the expression of the plant sodium-calcium exchanger gene through the crop transgenic technology according to the characteristics of AtNCL, a new crop variety with improved salt resistance can be obtained.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIV
Evolutionary architectures for evolution of deep neural networks
A system and method for evolving a deep neural network structure that solves a provided problem includes: a memory storing a candidate supermodule genome database having a pool of candidate supermodules having values for hyperparameters for identifying a plurality of neural network modules in the candidate supermodule and further storing fixed multitask neural networks; a training module that assembles and trains N enhanced fixed multitask neural networks and trains each enhanced fixed multitask neural network using training data; an evaluation module that evaluates a performance of each enhanced fixed multitask neural network using validation data; a competition module that discards supermodules in accordance with assigned fitness values and saves others in an elitist pool; an evolution module that evolves the supermodules in the elitist pool; and a solution harvesting module providing for deployment of a selected one of the enhanced fixed multitask neural networks, instantiated with supermodules selected from the elitist pool.
Owner:COGNIZANT TECH SOLUTIONS U S CORP
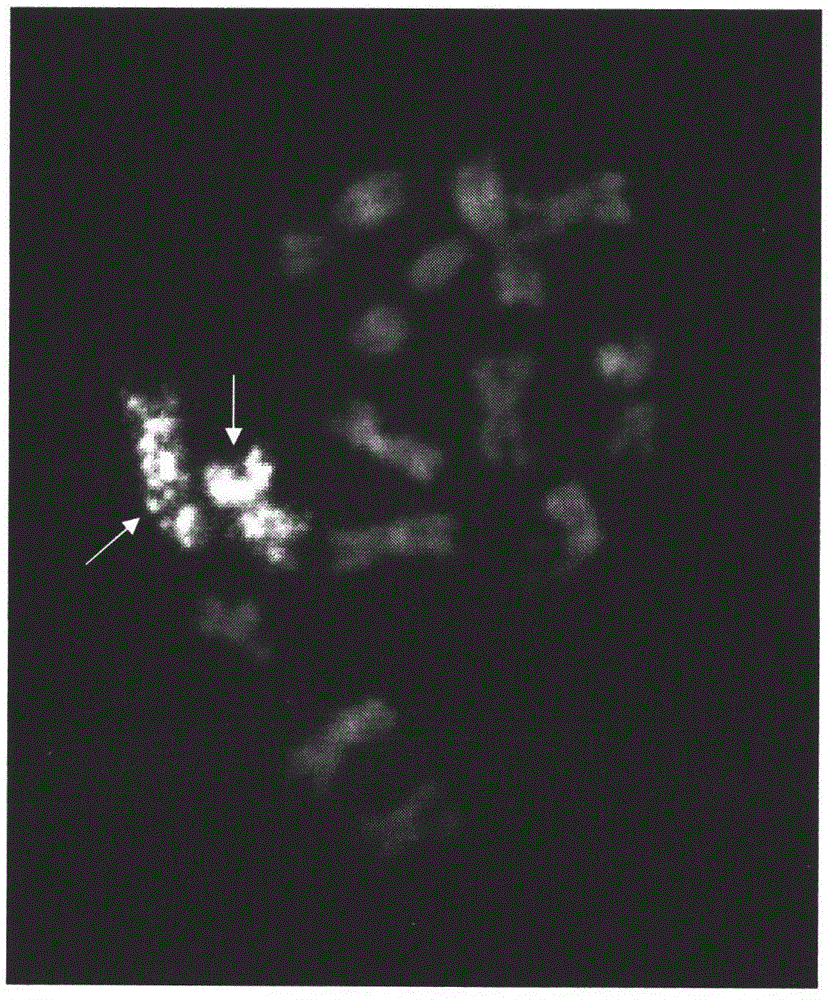
Preparation method and application of Cucumis sativus. L chromosome-6 probe
InactiveCN104593508ASimplicity guaranteedAvoid interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationFluorescenceGenome database
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a Cucumis sativus. L chromosome-6 probe. According to the method, on the basis of a Cucumis sativus. L genomic sequence, a DNA sequence containing no repetitive sequence is selected through RepeatMasker and Cucumis sativus. L genome database BLAST analysis, and primer design is performed through Primer Premier 5.0. A PCT product covering single chromosomes is obtained through PCR amplification, the PCT product is purified in agarose gel electrophoresis, the concentration is measured with a nucleic acid concentration measurement instrument, then equal amounts of products of all pairs of primers are mixed, and a probe is marked by a nick translation method and is hybridized to a chromosome flake by a FISH (Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization) technology so as to complete the preparation, detection and application of the single-chromosome probe. Through the application of the method, Cucumis sativus. L single chromosomes and a probe of any chromosome region can be obtained quickly, and precise analysis and research on a single chromosome and the morphological structure of any chromosome can be performed.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
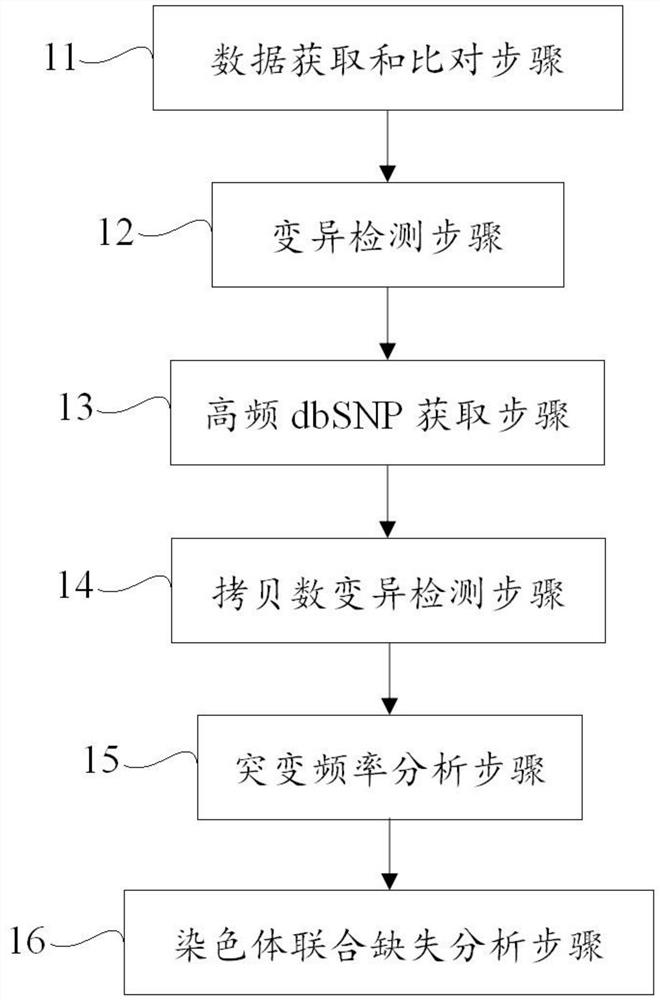
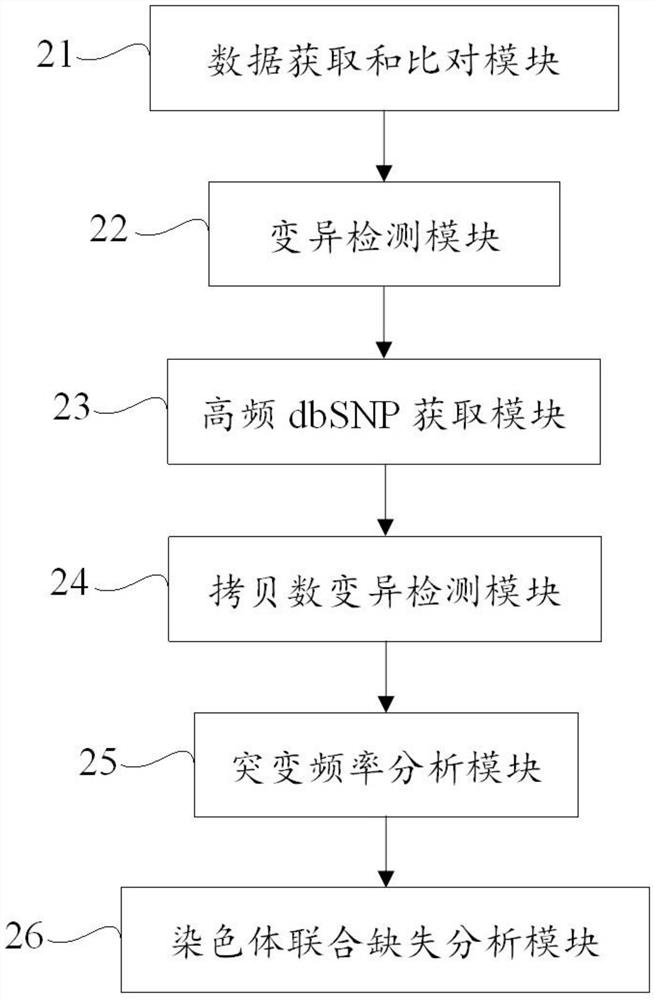
Method and device for detecting chromosome joint deletion and storage medium
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting chromosome joint deletion and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: performing SNP analysis on deduplicated data by adopting variation detection software to obtain variation information; reading dbSNP site information of which the crowd frequency is higher than 0.01 in a thousand-person genome database in 1p and 19q capture regions; acquiring copy number variation information in 1p and 19q regions by adopting copy number variation detection software; acquiring mutation frequency information of a normal control sample and mutation frequency of a tumor tissue sample; and analyzing 1p / 19q joint deletion based on the point mutation frequency and the copy number change. 1p / 19q chromosome joint deletion is analyzed through point mutation frequency and copy number change of high-throughput sequencing data; the blank of analyzing and detecting 1p / 19q chromosome joint deletion by high-throughput sequencing data is filled; variation detection such as point mutation, insertion and deletion and fusion can be carried out; and the sequencing data use efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN HAPLOX BIOTECH
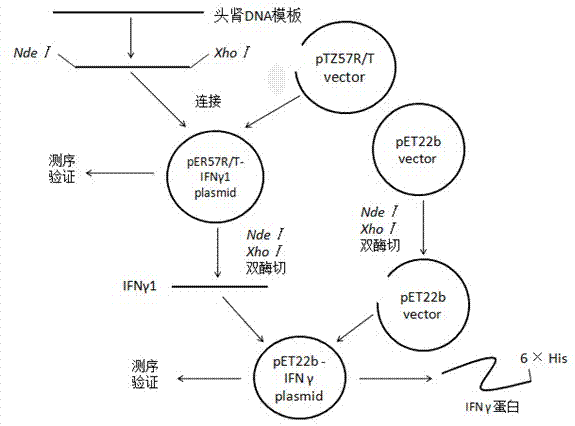
Epinephelus coioides interferon IFNgamma1 and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103243106AEnriching System Signaling Pathway TheoryMicroorganism based processesAntibody medical ingredientsNucleotideEpinephelus bruneus
The invention relates to an epinephelus coioides interferon IFNgamma1 gene, a protein coded by the gene and an application of the protein in preparing a novel immunopotentiator. According to the invention, an opened reading frame of the IFNgamma1 gene is cloned from head-kidney RNAs (Ribonucleic Acid) of epinephelus coioides through a method of screening a genome database and designing specific primer amplification. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQIDNO:2. The amino acid sequence of the protein coded is shown as SEQIDNO:1. Through initial verification, the epinephelus coioides interferon IFNgamma1 protein can induce associated expression of immunogenes and can be developed to natural immunopotentiators or immunologic adjuvants for fishes.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
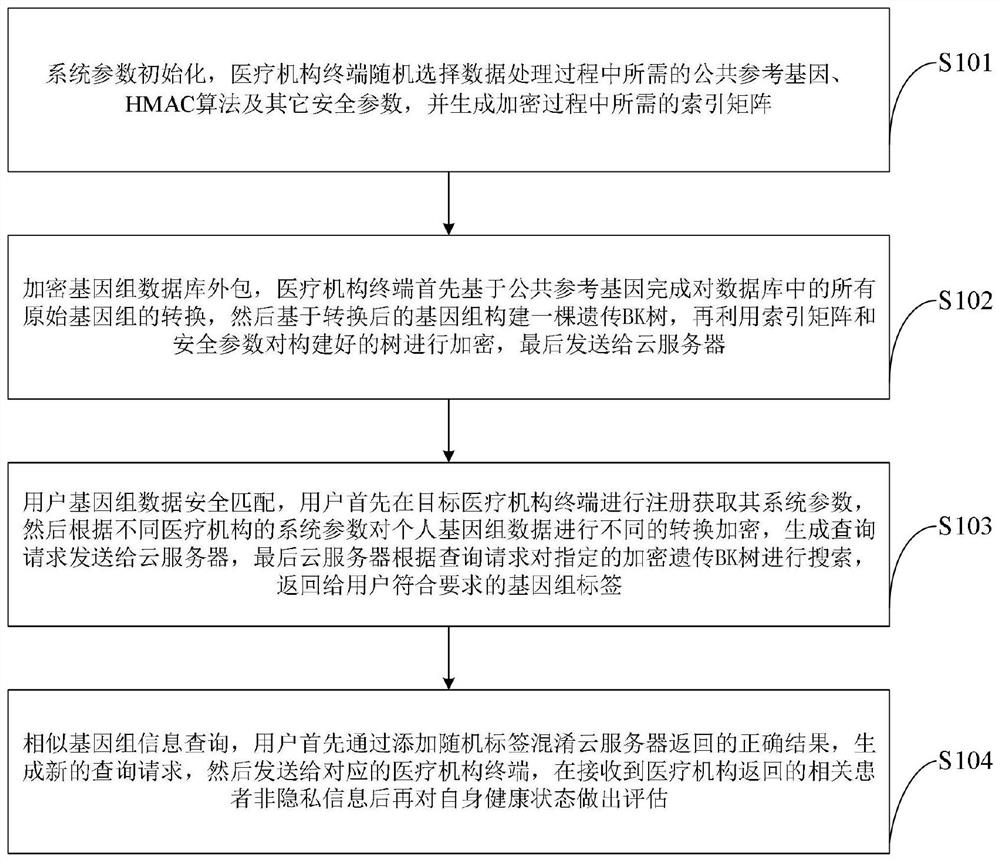
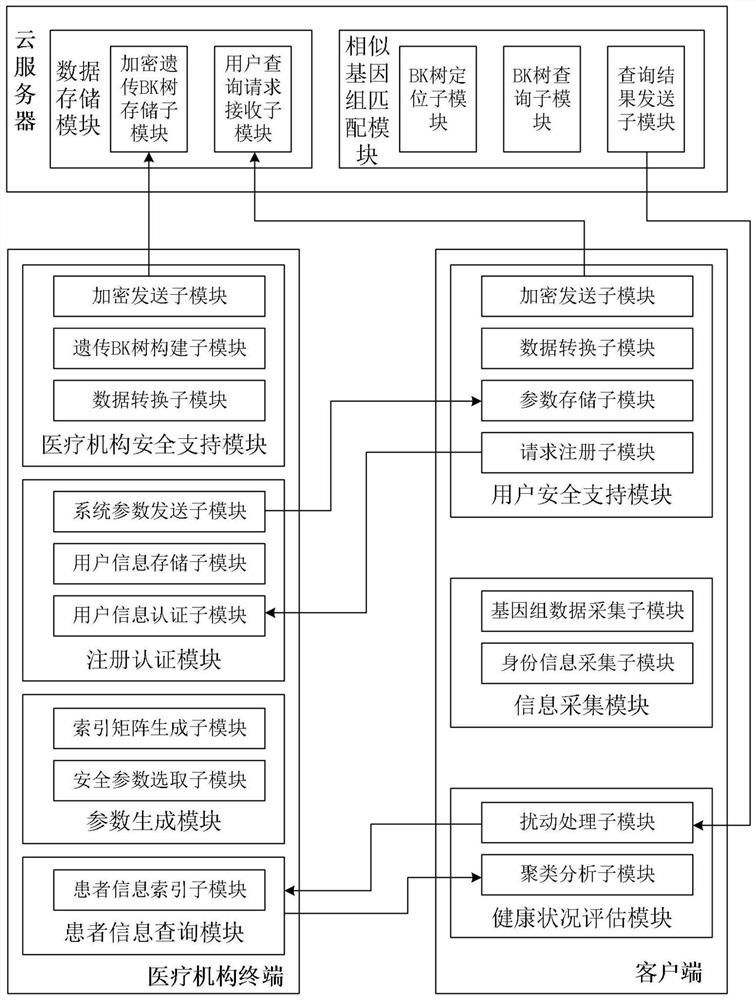
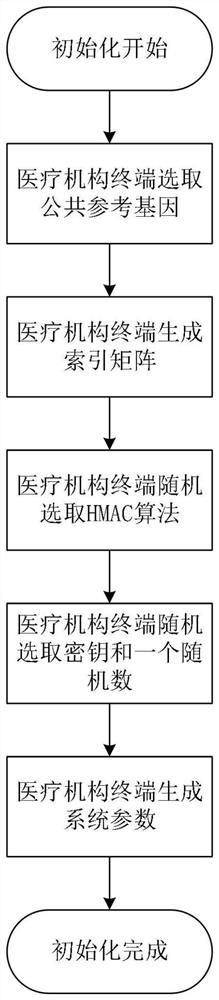
Genome data similarity-oriented efficient matching and privacy protection method and system
ActiveCN111967048ARealize privacy protectionImprove privacyHealth-index calculationBiostatisticsData privacy protectionCiphertext
The invention belongs to the technical field of information security, and discloses a genome data similarity-oriented efficient matching and privacy protection method and system. The client converts and encrypts personal genome data by using the acquired system parameters, generates a query request, sends the query request to the cloud server to request for searching similar genomes, confuses received similar genome tags, sends the similar genome tags to the medical institution terminal to request for similar patient information and evaluates the health condition of the client; the medical institution terminal generates system parameters and provides registration service for the client, and outsources the genome database stored locally to the cloud service to provide similar genome query service for the user; and the cloud server stores an encrypted genetic BK tree outsourced by the medical institution terminal, performs calculation search on the ciphertext tree, and returns a label set of similar genomes to the user. Privacy protection of original genome data of a medical institution terminal and a user is achieved, and the matching efficiency of similar genomes is improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
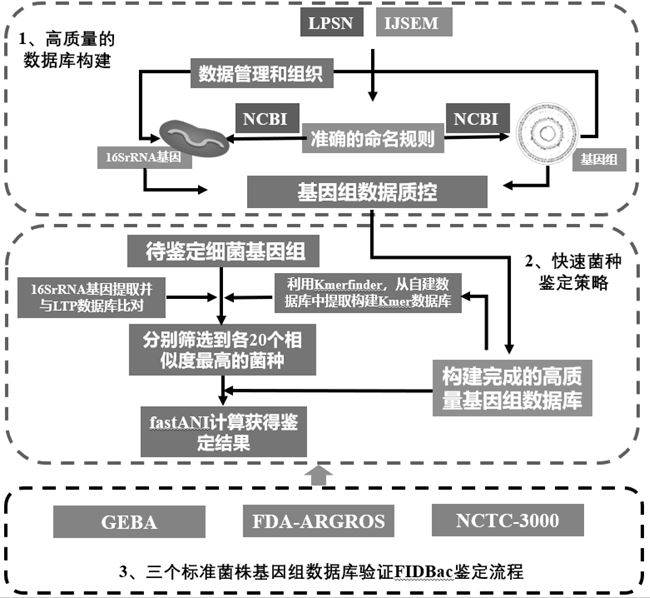
Bacteria identification and typing analysis genome database and identification and typing analysis method
ActiveCN112863606AImprove accuracyRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBioinformaticsBacteria identificationFood industry
The invention discloses a bacterial identification and typing analysis genome database and an identification and typing analysis method. A high-quality bacterial identification and typing analysis genome database is created by deleting erroneous tags and assembling low-quality genomes. Based on the database, a bacterial identification and typing analysis method based on genome information is provided, and a set of rapid bacterial genome identification and identification platform (FIDBac) is developed. The accuracy rate of FIDBac identification reaches 97% or above, and is obviously higher than that of other identification systems or software of the same kind. The single, coherent and automatic bacterial genome identification working process has important significance in the fields of food industry, pharmaceutical industry, clinical diagnosis, microbial resource development and the like.
Owner:杭州微数生物科技有限公司
SNP molecular marker related to Cucumis sativus L multiple-trichome character, and application of SNP molecular marker
ActiveCN112322769AAccurate genetic lociEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenome databaseCucumber family
The invention discloses an SNP molecular marker related to a Cucumis sativus L multiple-trichome character, and application of the SNP molecular marker. The SNP molecular marker is a primer designed by taking each 400bp of DNA sequence before and behind a Chr6:27397366 site in a "Chinese Long v2" Cucumis sativus L genome database as a template, a genome sequence obtained by amplification is disclosed by SEQ ID NO:1, and from a 5' terminal, A / C polymorphism, i.e., an SNP site, is in the presence on the 401st site of the sequence. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention is tightly linkedwith a Cucumis sativus L multiple-trichome gene, is reliable, is quick in detection, can be used for the directional genetic breeding of Cucumis sativus L multiple-trichome related characters, and has an important theoretical and practical guidance meaning for quickening the genetic improvement progress of a Cucumis sativus L variety and improving breeding selection efficiency.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for analyzing metabolism regulation mechanism of carotenoid in maize grains based on dynamic correlation between co-expression patterns of gene pairs
ActiveCN107058526AImprove qualityBest gene combinationMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationGenomicsCorrelation analysis
The invention belongs to the field of functional genomics and particularly relates to a method for analyzing a metabolism regulation mechanism of carotenoid in maize grains based on dynamic correlation between co-expression patterns of gene pairs. The method comprises the following steps: downloading 13 key genes in a carotenoid metabolism pathway from a maize genome database maizeGDB; collecting grain transcripts obtained after pollinating maize inbred lines for 15 days, and sequencing to obtain gene expression level data, and extracting expression level data of the 13 key genes; building a dynamic correlation analysis LA model; and analyzing and identifying a regulation relation between the key genes in the pathway utilizing a dynamic correlation analysis. The method is capable of excavating the regulation relation between the 13 key genes in the carotenoid metabolism pathway based on dynamic correlation analysis, analyzing the regulation mechanism of synthesis and accumulation of carotenoid in grains and providing optimal gene combination for molecular-marker assistant breeding, and has important significance for increasing carotenoid in maize and improving maize quality.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
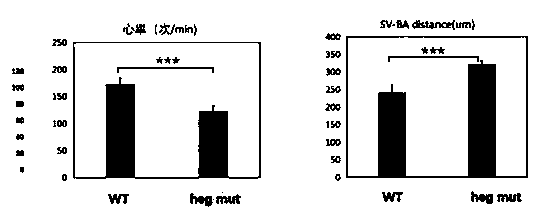
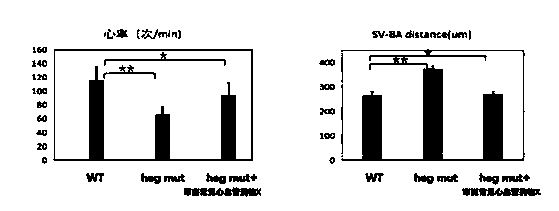
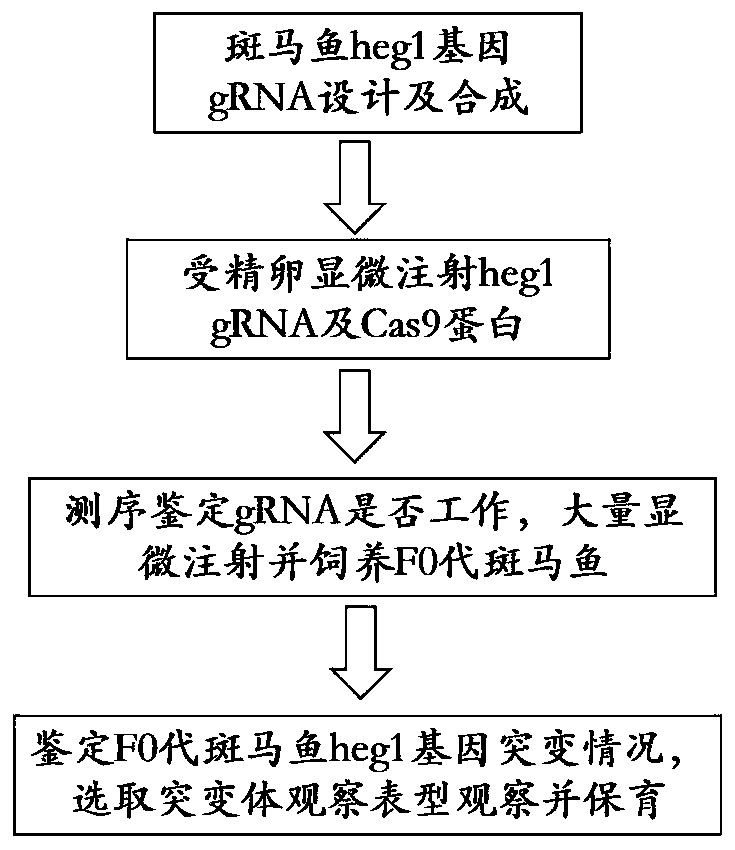
Construction method of zebra fish animal model for cardiovascular disease drug screening
ActiveCN111471718ASmall and transparentPhenotype stableCompounds screening/testingCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiotechnologyFish embryo
The invention discloses a construction method of a zebra fish animal model for cardiovascular disease drug screening, and specifically relates to the field of animal model construction methods. The method comprises the following specific steps: selecting a gRNA target site of a zebra fish heg1 gene and synthesizing gRNA in vitro; in order to obtain the target site, firstly, downloading genome dataof the target gene heg1 from a zebra fish genome database; and selecting a 529bp long target sequence near a first exon of the heg1 gene and inputting the sequence into a target point website to obtain a target point primer. According to the invention, a cardiovascular malformation zebra fish mutant with genetic stability can be obtained; by using the zebra fish embryo transparency and the autonomous oxygen dissolving property, the mutant can be used for screening and verifying the influence of different cardiovascular drugs on cardiovascular development; and the zebra fish animal model construction method provides important physiological significance and specificity for screening of cardiovascular disease treatment drugs.
Owner:华芯微鱼(苏州)生物科技有限公司
Method for obtaining natural variant of enzyme and super thermostable cellobiohydrolase
InactiveUS9944914B2Efficiently obtainedIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaLibrary screeningGenome databasePcr cloning
A method for selectively obtaining a natural variant of an enzyme having activity includes (1) a step of detecting an ORF sequence of a protein having enzyme activity from a genome database including base sequences of metagenomic DNA of environmental microbiota; (2) a step of obtaining at least one PCR clone including the ORF sequence having a full length, a partial sequence of the ORF sequence, or a base sequence encoding an amino acid sequence which is formed by deletion, substitution, or addition of at least one amino acid residue in an amino acid sequence encoded by the ORF sequence, by performing PCR cloning on at least one metagenomic DNA of the environmental microbiota by using a primer designed based on the ORF sequence; (3) a step of determining a base sequence and an amino acid sequence which is encoded by the base sequence for each PCR clone obtained in the step (2); and (4) a step of selecting a natural variant of an enzyme having activity by measuring enzyme activity of proteins encoded by each PCR clone obtained in the step (2).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
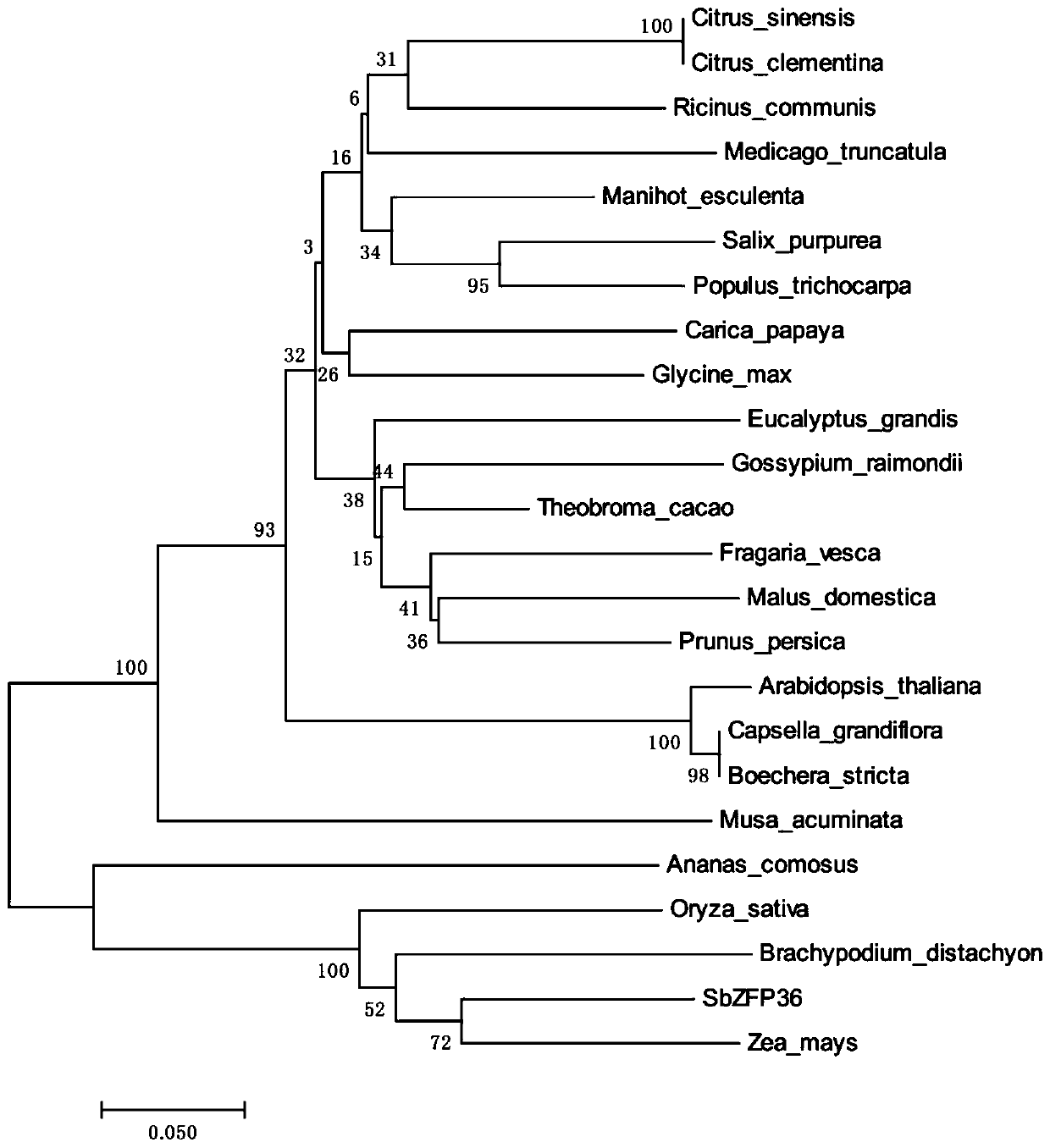
Sorghum C2H2 zinc finger protein gene SbZFP36 and recombinant vector and expression method thereof
InactiveCN109971770AImprove stress resistanceHigh expressionPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses a sorghum C2H2 zinc finger protein gene SbZFP36. The nucleotide sequence of the sorghum C2H2 zinc finger protein gene SbZFP36 is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. The invention also discloses a protein encoded by the sorghum C2H2 zinc finger protein gene SbZFP36, and the amino acid sequence of the protein is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention also discloses a recombinant vector containing the sorghum C2H2 zinc finger protein gene SbZFP36 and an expression method. According to the invention, a sorghum homologous gene SbZFP36 is obtained from a sorghum genome database through theprotein sequence of a rice ZFP gene, the full length of the gene is 711bp, a prokaryotic expression vector is constructed according to the gene, a protein purification system is used for purifying theprokaryotic expression vector, the result lays a foundation for further researching the protein crystal structure and biological characteristics, and a basis is further provided for improving the disease resistance of sorghum through a gene editing method.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV +1
Method for screening SNP markers of Liriodendron genome
ActiveCN108754005AQuality improvementValid statement accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementF1 generationLiriodendron tulipifera
The invention discloses a method for screening SNP markers of a Liriodendron genome. F1-generation individuals obtained from Liriodendron tulipifera 'NK' and Liriodendron 'LS' by hybridization are taken as a material, a Liriodendron reference genome obtained by sequencing is taken as the basis, PCR amplification primers are designed by Primer 5.0 software, amplification efficiency and specificityof the primers are verified, 27 candidate SNP loci are selected for primer design, a screening result is detected by agarose gel electrophoresis after PCR amplification, provenance material are verified, and finally, the SNP markers of the Liriodendron genome are obtained. 27 SNP loci are selected from a Liriodendron genome database for primer synthesis, products are subjected to PCR amplificationdetection and sent out for sequencing, a result shows that all the loci are real SNP loci, which means that the SNP loci are reliable in quality, used standards are better, and the obtained high-quality SNP markers can be applied to follow-up work such as genetic linkage maps and the like.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Chicken coccidiosis ATG (Autophagy Related Protein) Etatg6 encoding gene sequence and acquiring method thereof
The invention discloses a chicken coccidiosis ATG (Autophagy Related Protein) Etatg6 encoding gene sequence and an acquiring method thereof. An encoding gene of a homolog of autophagy related ATG6 isdiscovered through bioinformatics analysis on an E.tenella genome database, clinically isolated E.tenella is used as a model, amplification is successfully realized by utilizing a molecular biologicalmethod, an Etatg6 ORF gene sequence of which the overall length is 1356bp is acquired, and the ATG of which the encoding length is 451 amino acids is discovered through the bioinformatics analysis carried out on the acquired gene sequence, so that data is firstly accumulated for chicken coccidiosis autophagy, and new basis is provided for further screening novel anticoccidial drug targets.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HEALTH GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Homeobox gene HTF1 capable of regulating conidium germination of Magnaporthe grisea of and use thereof
InactiveCN101532022ASharply reduce the number of groupsInhibitionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesHomeobox ProteinsMutant strain
The invention provides a homeobox gene HTF1 capable of regulating conidium germination of Magnaporthe grisea of and use thereof. Gene clone shows that the homeobox gene HTF1 is same to HTF1 sequence (MGG_00184.5) published by the Magnaporthe grisea genome database and comprises the typical structure domain of homeobox protein. The gene knock-out mutant losses the capability of generating conidium and conidiophore increases, and the rice inoculated by hypha block generates pathogenicity. The gene knock-out mutant restores the capability of generating conidium after function complementation test. The homeobox structure domain sequence is knocked out from the HTF1 gene therefore the Magnaporthe grisea can not generate conidium. The HTF1 gene can be used as the molecule target of the new pesticide design. The HTF1 mutant strain can be produced into engineering bacteria, thereby gradually reducing the stock number of the natural Magnaporthe grisea and playing important role in preventing and treating rice blast.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
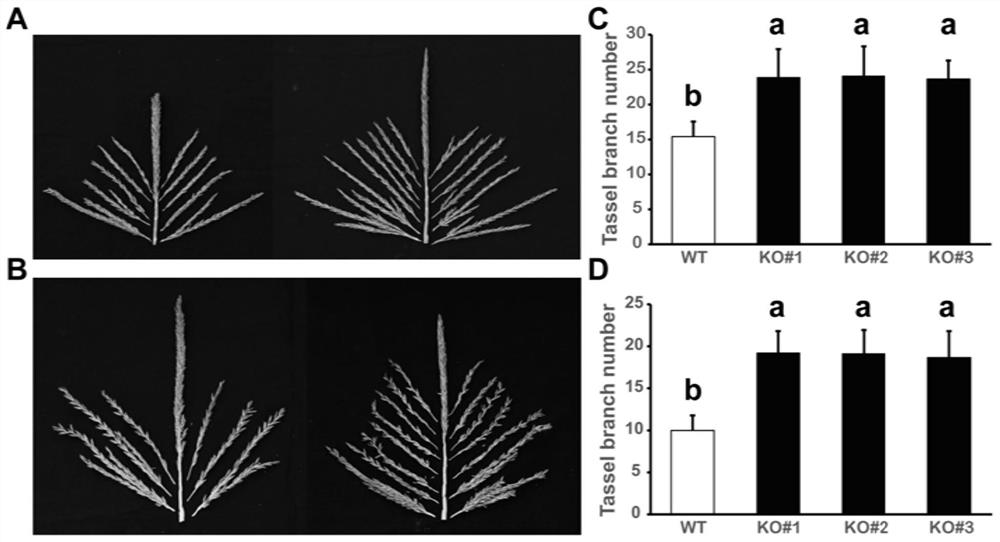
Application of ZmELF3.1 protein and function deletion mutant thereof in regulation and control of crop tassel branch number
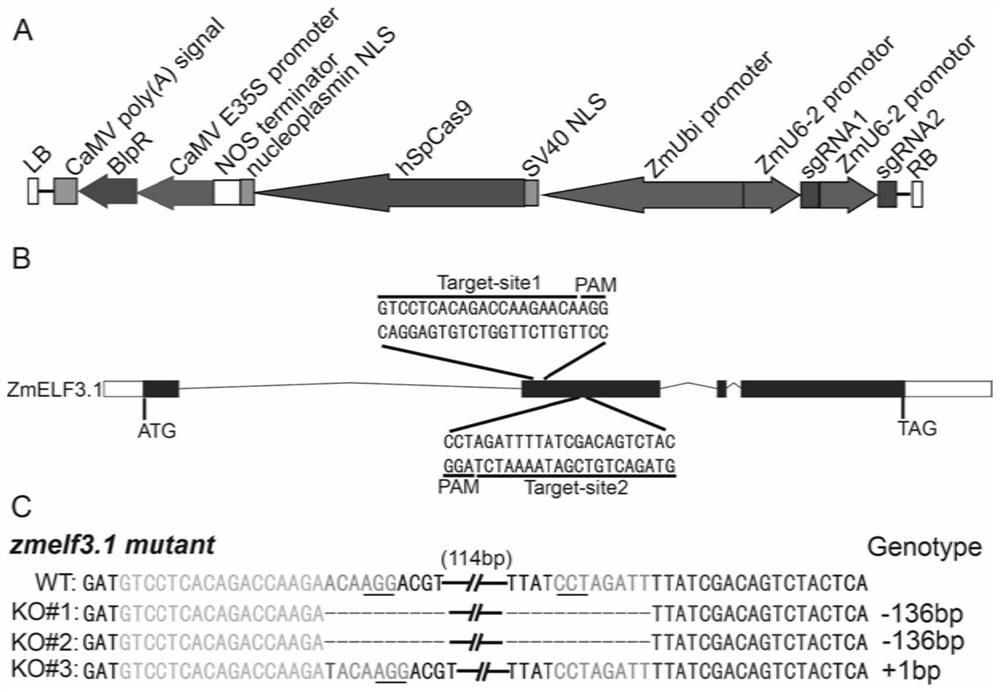
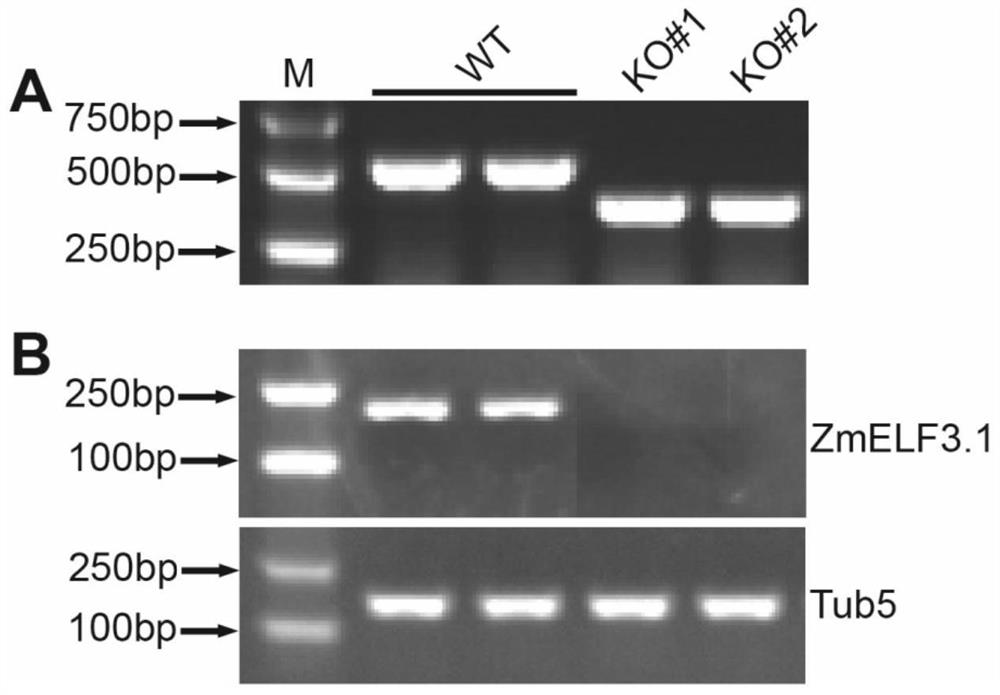
The invention discloses application of a ZmELF3.1 protein and a function deletion mutant thereof in regulation and control of a Zea mays L. tassel branch number. On the basis of the protein sequence of Arabidopsis thaliana ELF3, the ELF3 genes of two pieces of Zea mays L. are obtained through homologous comparison in a Zea mays L. genome database, wherein the two ELF3 genes are respectively named as ZmELF3.1 and ZmELF3.2. After the Zea mays L. ZmELF3.1 gene is mutated by further utilizing an RISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology, the function deletion mutant of the Zea mays L. ZmELF3.1 gene shows a phenotype that the tassel branch number is increased under long-day and short-day conditions, and therefore, a situation that the Zea mays L. ZmELF3.1 gene plays a crucial role in the regulation and control of the increase of the Zea mays L. tassel branch number is determined. The invention has an application prospect in the regulation and control of the increase of the Zea mays L. tassel branch number, and also can be applied to Zea mays L. inbred line improvement and cross breeding.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
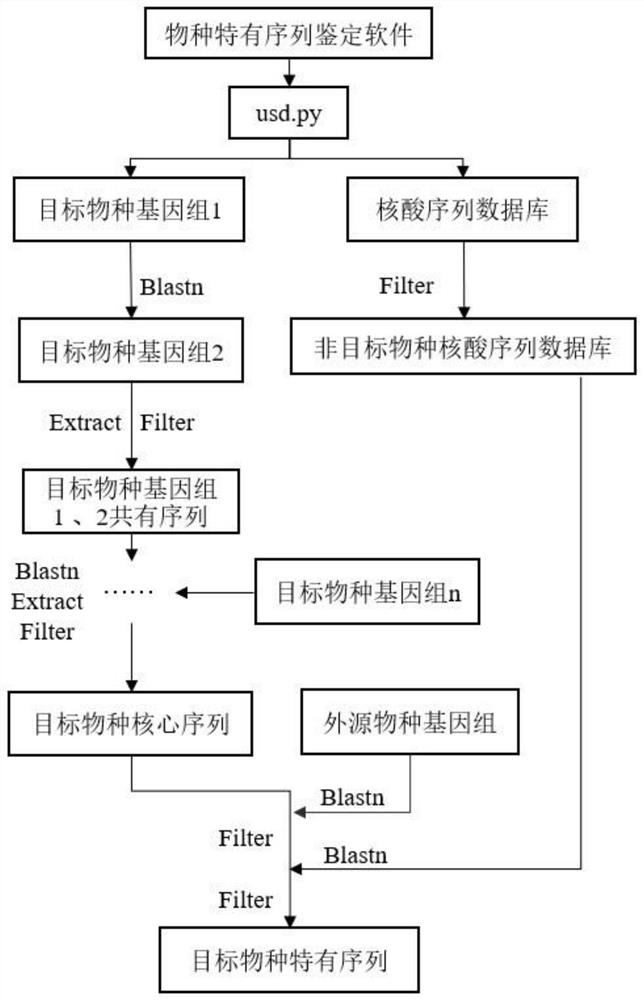
Target species specific sequence acquisition method and target species detection method
ActiveCN112331268ASimple methodImprove reliabilitySequence analysisInstrumentsGenome databaseNucleic acid sequencing
The invention relates to a target species specific sequence acquisition method and a target species detection method; the target species specific sequence acquisition method comprises the following steps: selecting all whole genome sequences of a target species in a genome database, and screening out a target species core sequence by comparing all whole genome sequences of the target species; filtering out all nucleic acid sequences of the target species in a nucleic acid database to obtain a non-target species nucleic acid sequence database; and comparing the core sequence of the target species with a non-target species nucleic acid sequence database, and filtering out the nucleic acid sequence obtained by comparison in the core sequence of the target species to finally obtain a specificsequence of the target species. By means of the method, the specific sequence of the target species can be obtained, the method is simple and high in reliability, and the target species and the classification status of the organism can be determined by identifying whether the specific sequence of the target species exists in the sample or not. Therefore, the existence of the target species or theclassification status of the target species can be identified only by amplifying the specific sequence of the target species obtained by the method for obtaining the specific sequence of the target species.
Owner:成都基因坊科技有限公司
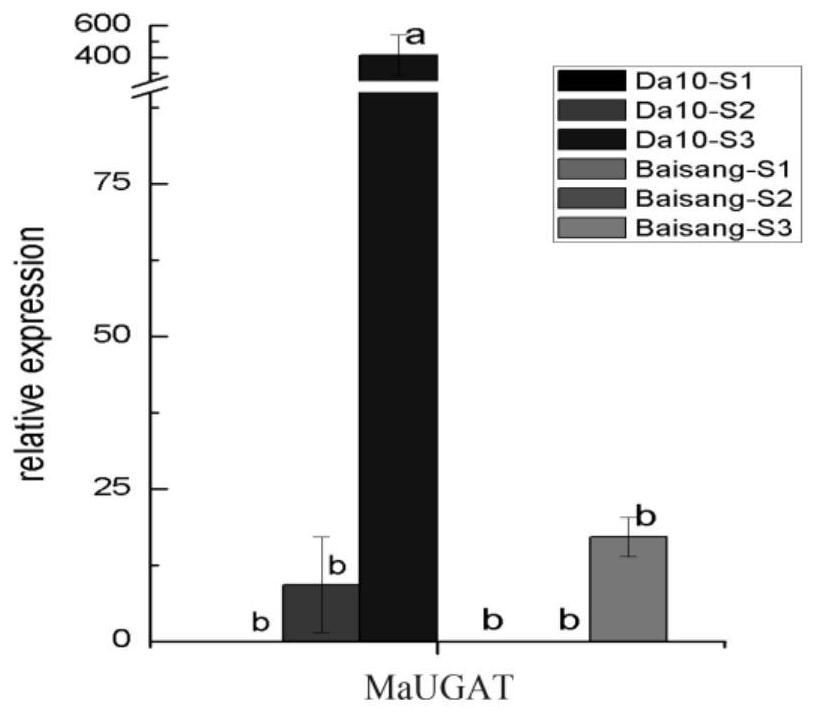
Cloning method and application of mulberry anthocyanin-3-O-glucoside-2-O-glucuronic acid transferase gene
InactiveCN112501160AImprove qualityComprehensive dataFermentationGlycosyltransferasesEnzyme GeneTotal rna
The invention discloses a cloning method and application of a mulberry anthocyanin-3-O-glucoside-2-O-glucuronic acid transferase gene. The cloning method comprises the following steps: extracting total RNA of a mulberry test sample and synthesizing a cDNA first chain; cloning a mulberry MaUGAT gene. The invention further discloses application of the mulberry anthocyanin-3-O-glucoside-2-O-glucuronic acid transferase gene cloned by the method in a mulberry germplasm cultivation process. One anthocyanin-3-O-glucoside-2-O-glucuronic acid transferase gene is compared and identified from a Sichuan mulberry genome database, and the gene is cloned from Yueshengda 10 mulberries by designing a specific primer. The method enriches related data in the mulberries and even moraceae plants, provides candidate genes for genetic improvement of the mulberries, promotes improvement of the quality of the mulberries, and better serves industrialization of fruit mulberries.
Owner:SICHUAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI SERICULTURE INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com