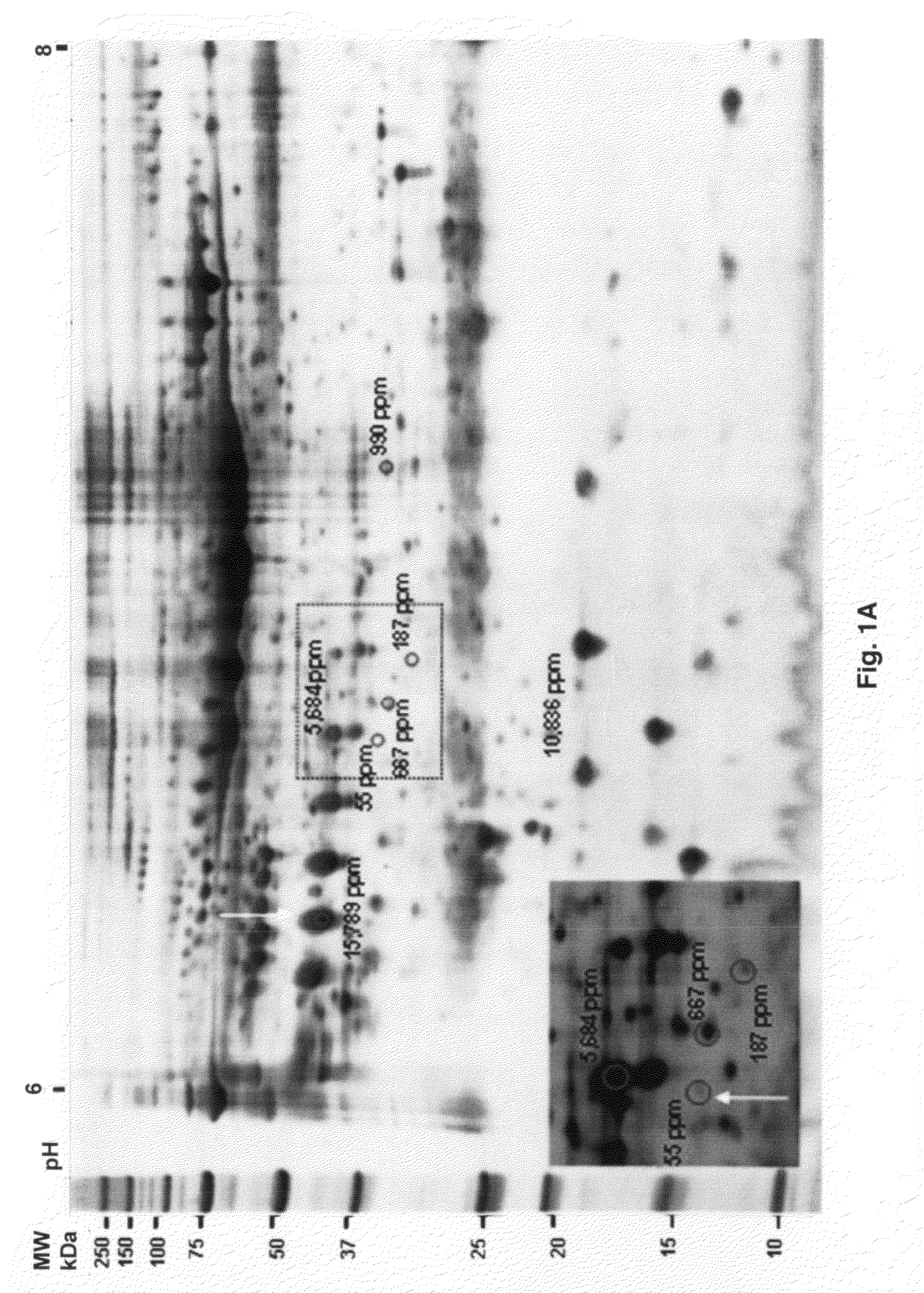Patents
Literature
145 results about "Disease severity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Disease severity refers to the presence and extensiveness of a disease in the body. It is objectively evaluated through diagnostic testing and physiological examination of the impaired biological organs or tissues, in cases in which disease severity can be distinguished from other realms of health, as in heart disease.
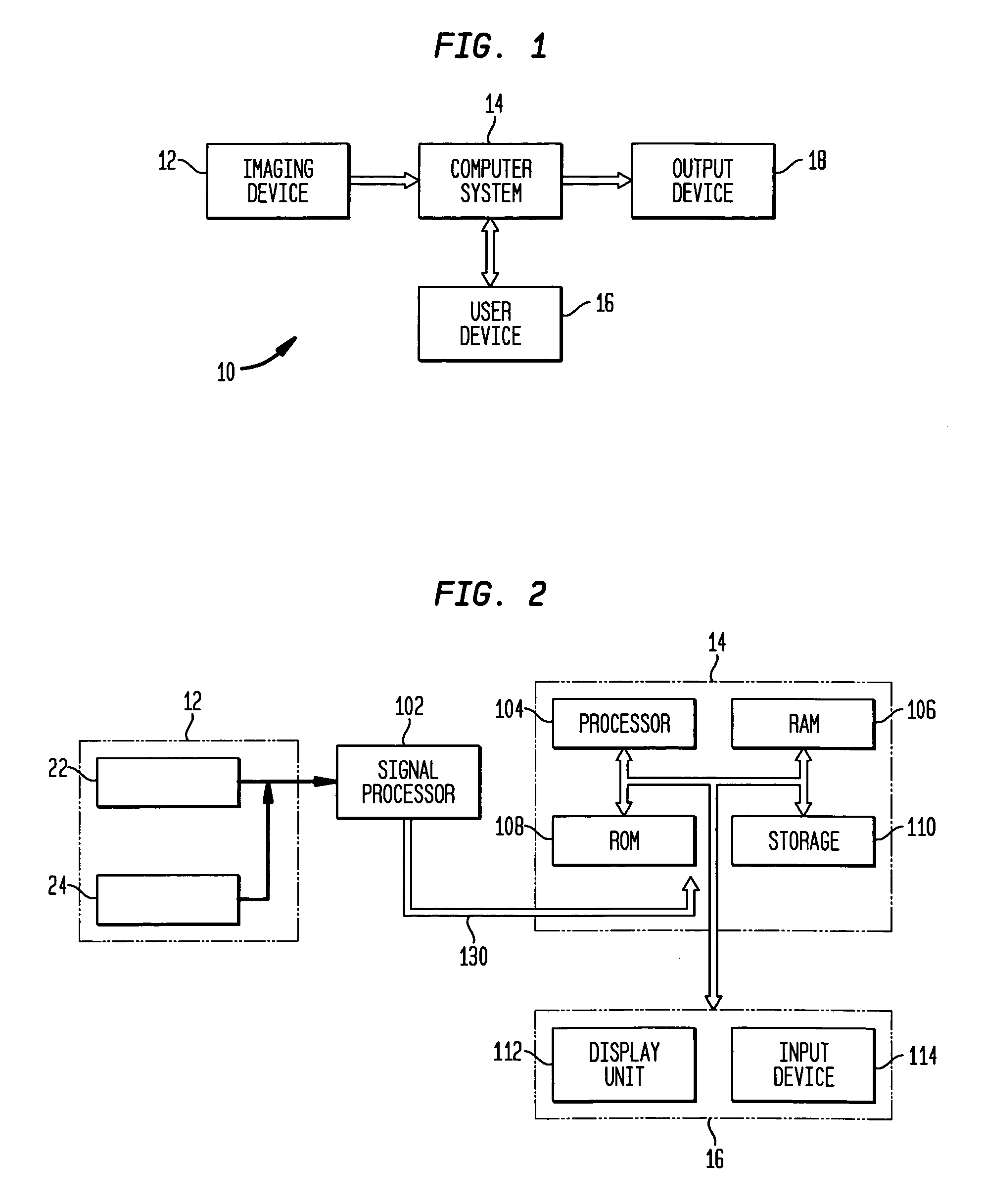
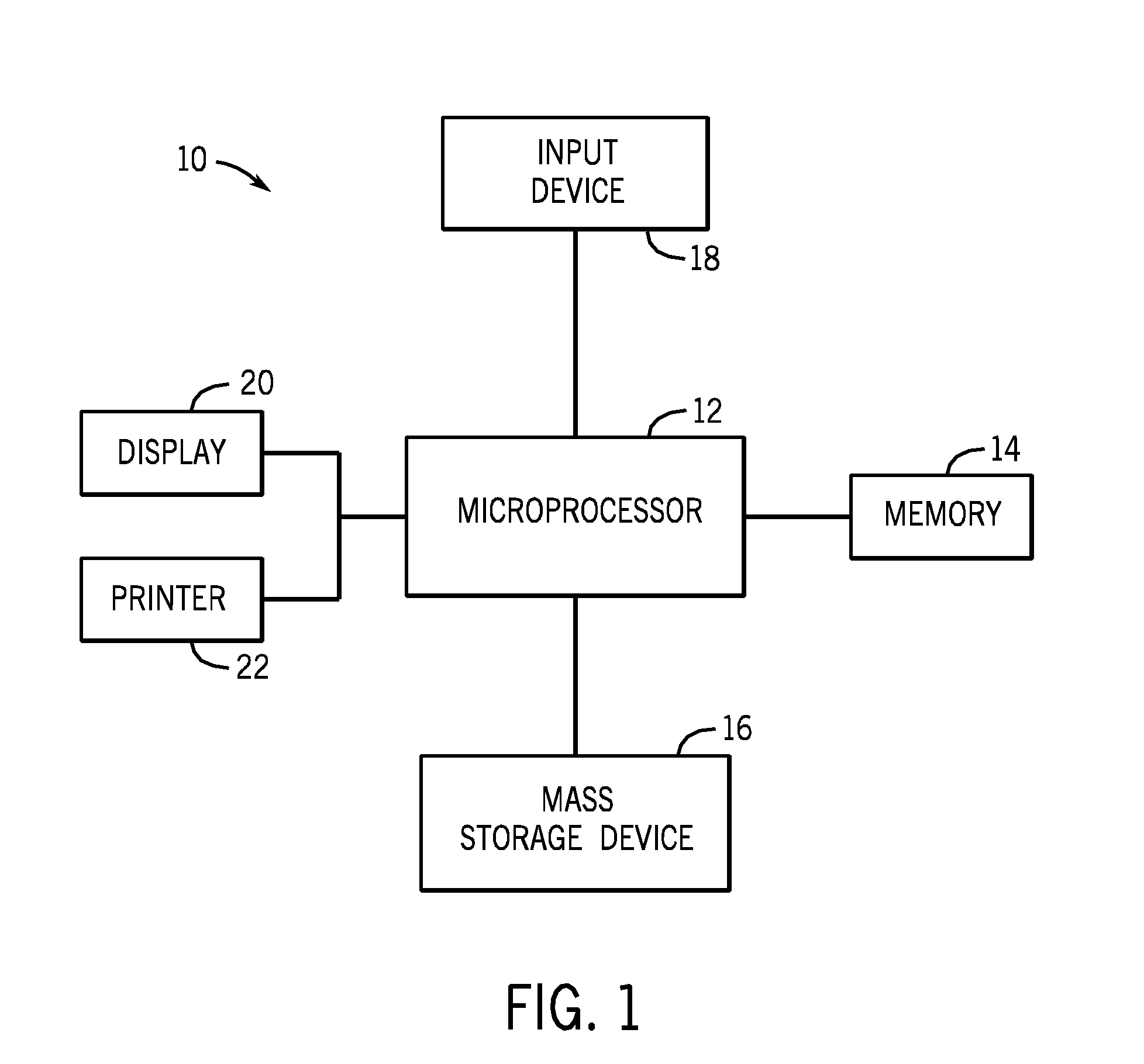
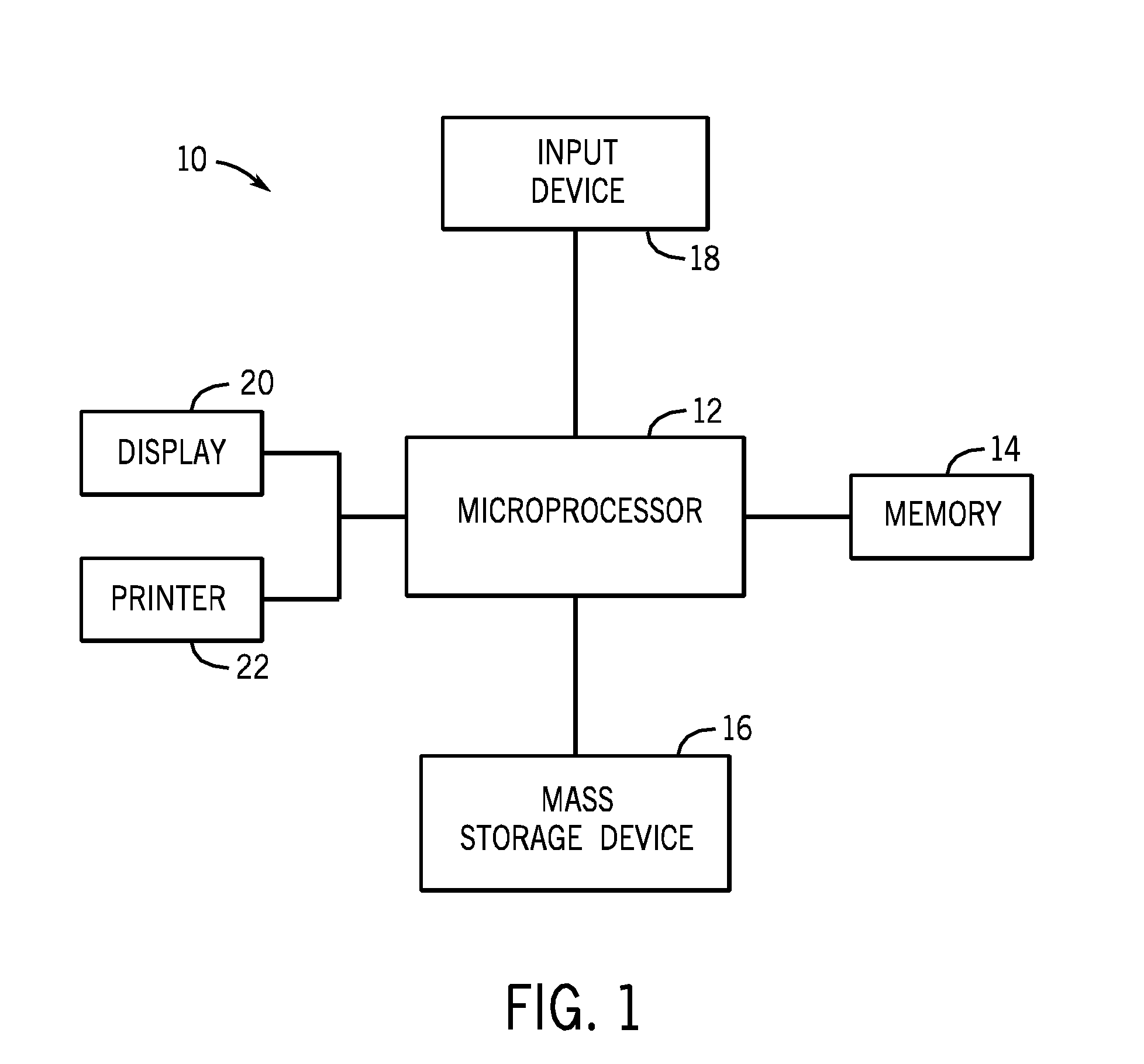
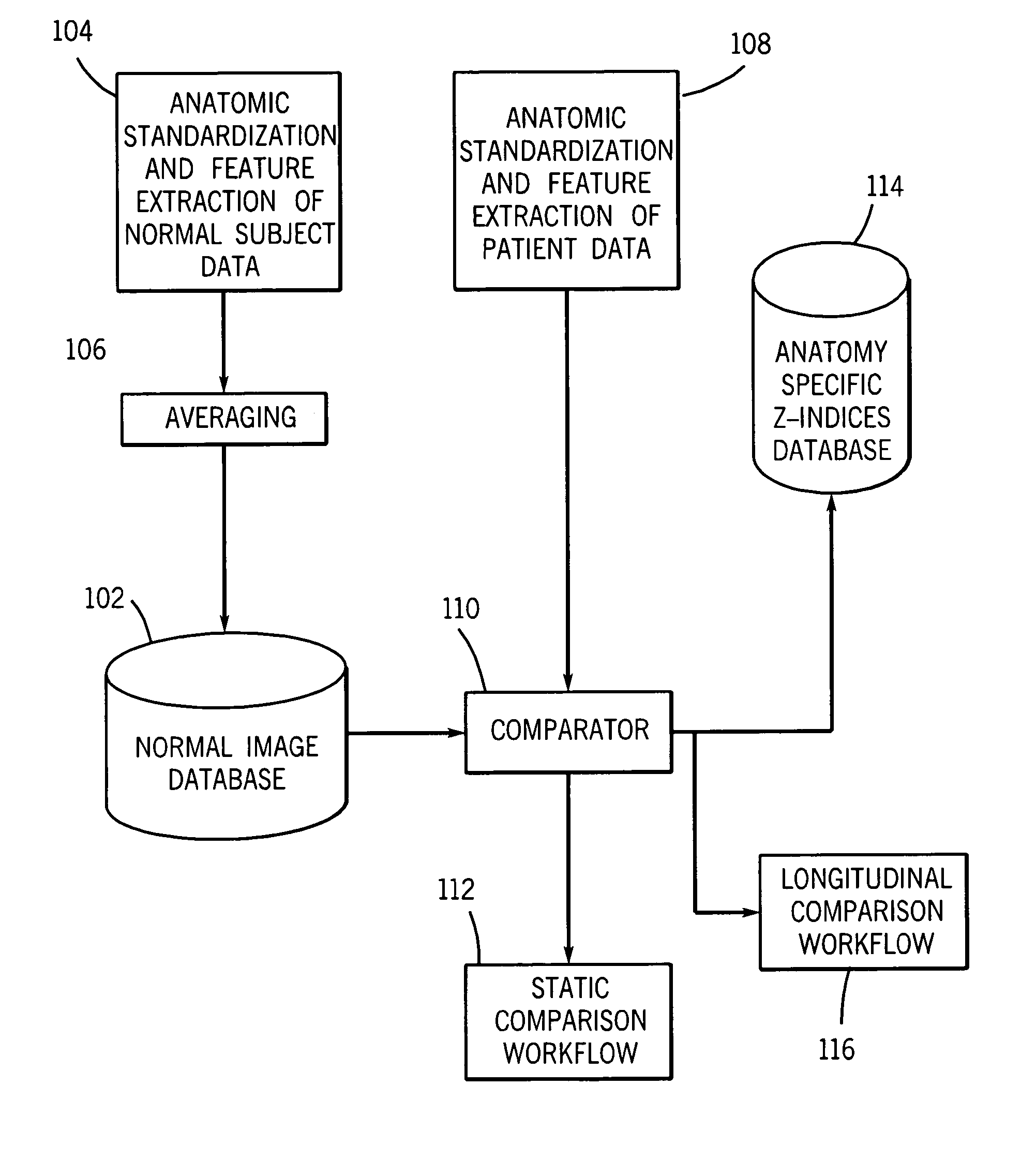
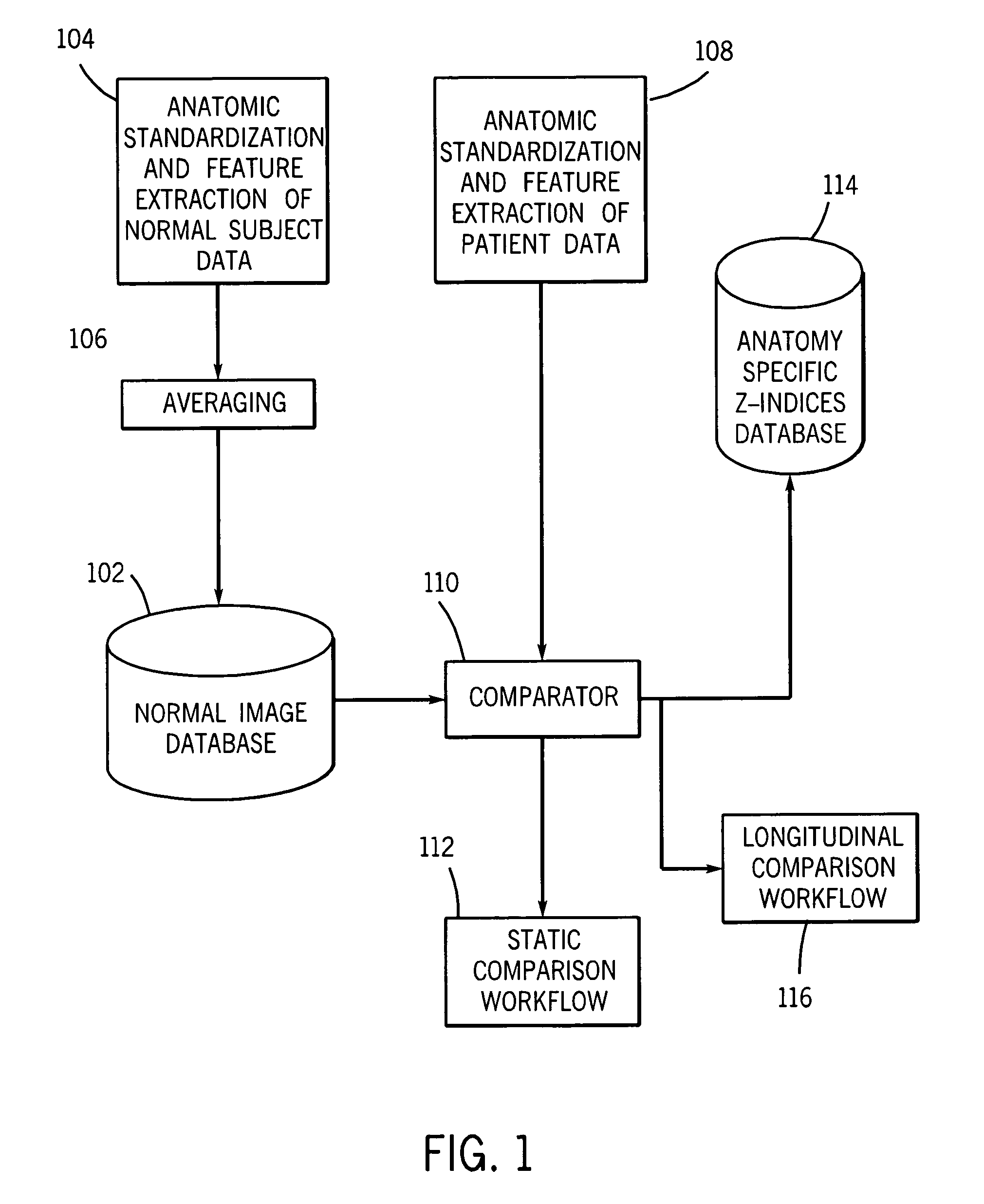
System and method of measuring disease severity of a patient before, during and after treatment
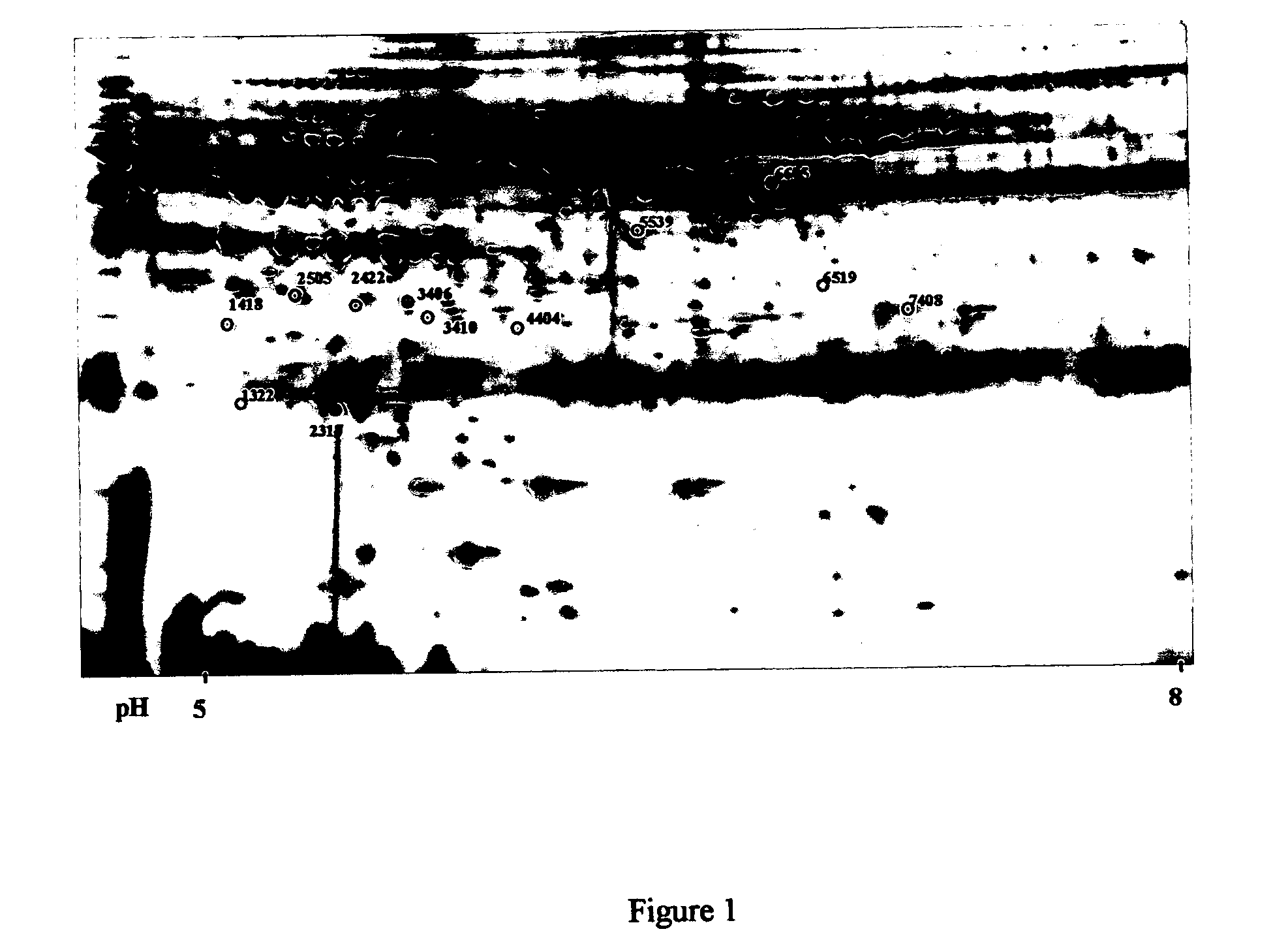
ActiveUS20050065421A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationImage analysisData setImaging data
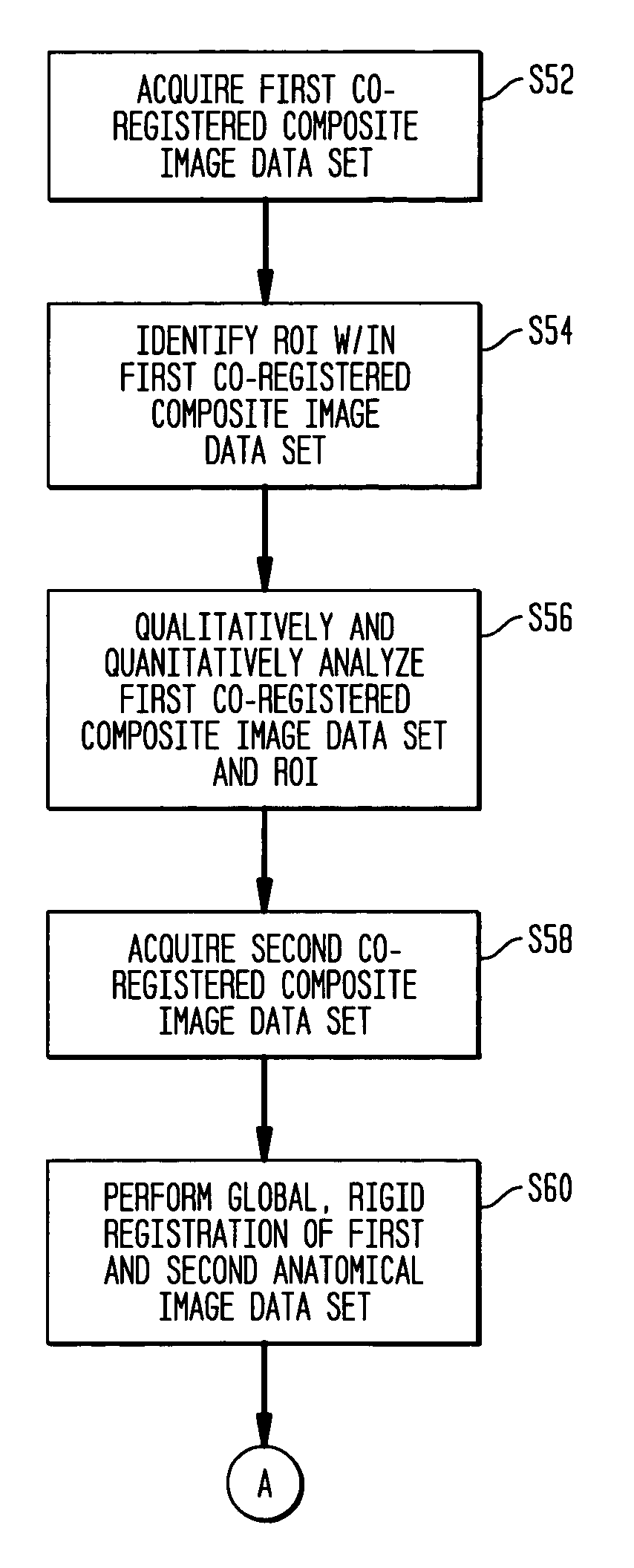
A system and method of obtaining serial biochemical, anatomical or physiological in vivo measurements of disease from one or more medical images of a patient before, during and after treatment, and measuring extent and severity of the disease is provided. First anatomical and functional image data sets are acquired, and form a first co-registered composite image data set. At least a volume of interest (ROI) within the first co-registered composite image data set is identified. The first co-registered composite image data set including the ROI is qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed to determine extent and severity of the disease. Second anatomical and functional image data sets are acquired, and form a second co-registered composite image data set. A global, rigid registration is performed on the first and second anatomical image data sets, such that the first and second functional image data sets are also globally registered. At least a ROI within the globally registered image data set using the identified ROI within the first co-registered composite image data set is identified. A local, non-rigid registration is performed on the ROI within the first co-registered composite image data set and the ROI within the globally registered image data set, thereby producing a first co-registered serial image data set. The first co-registered serial image data set including the ROIs is qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed to determine severity of the disease and / or response to treatment of the patient.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
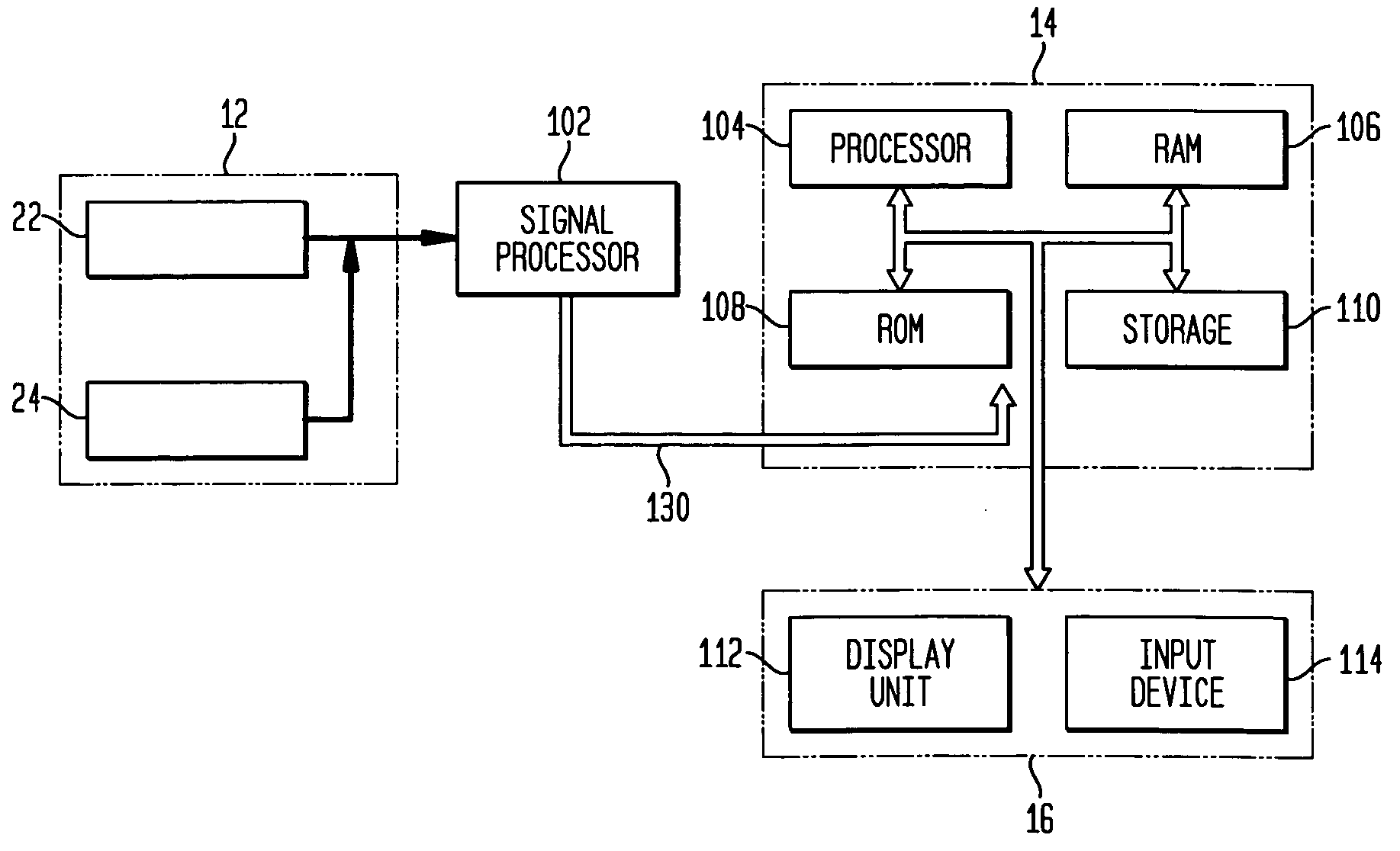
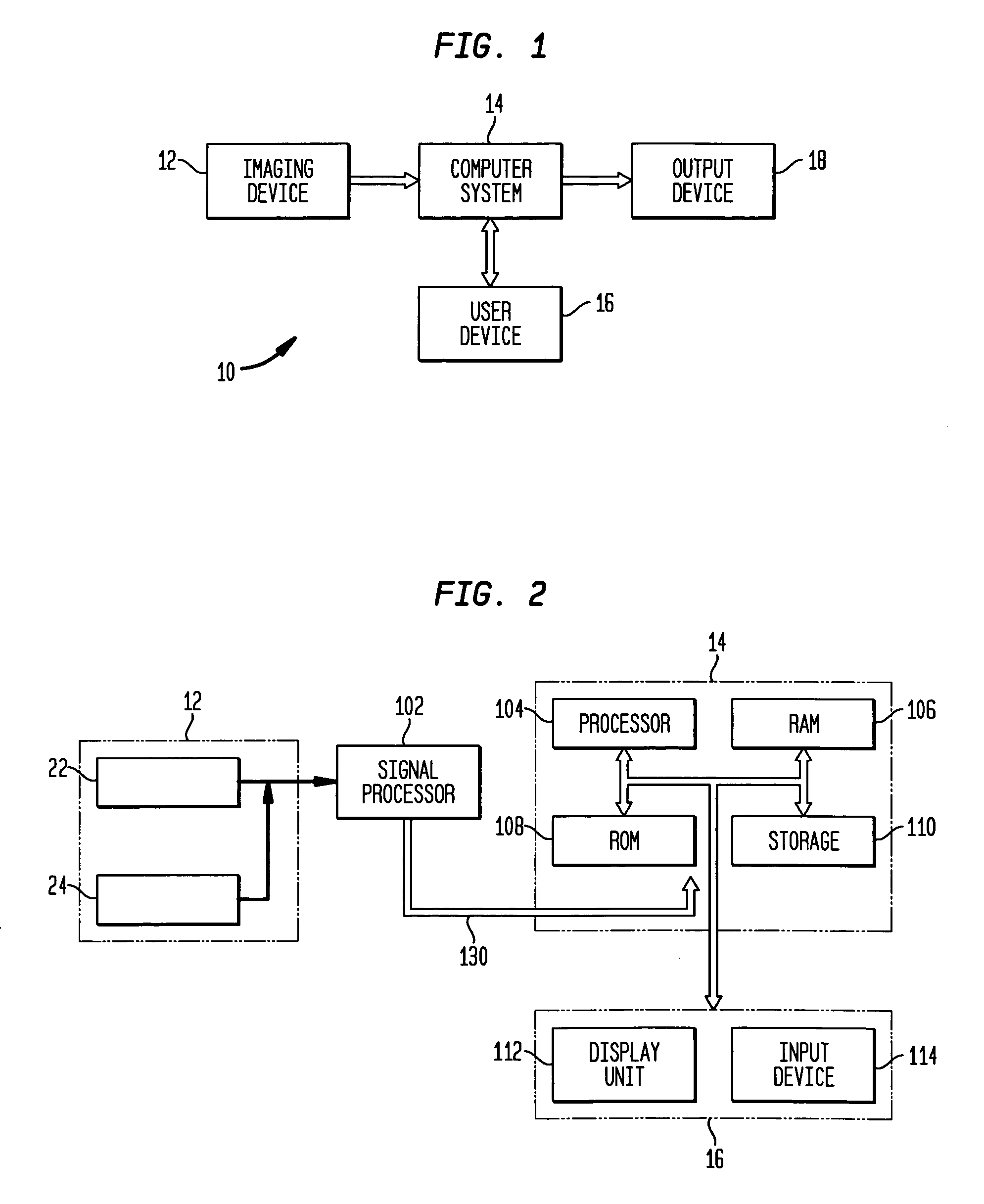
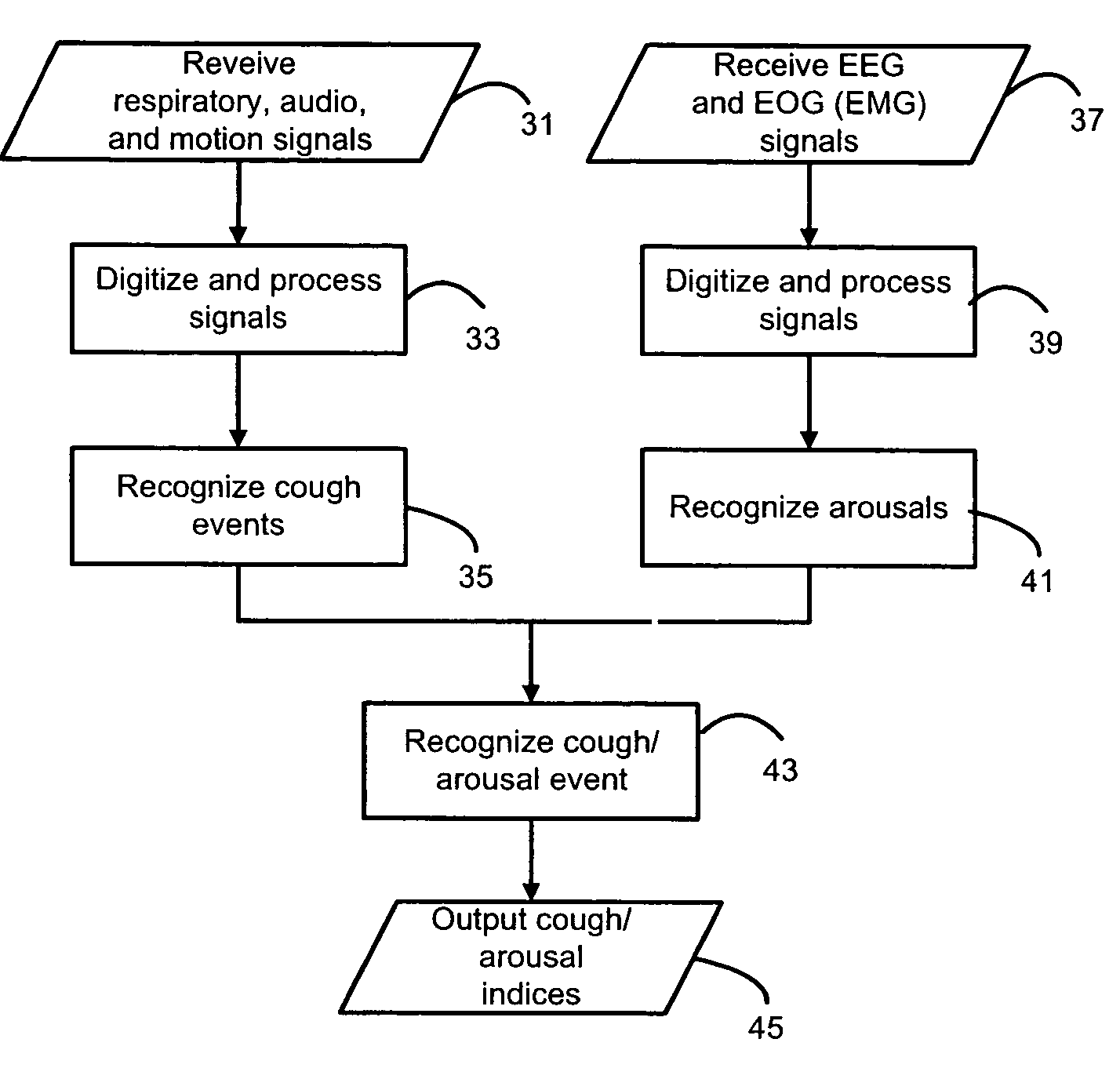
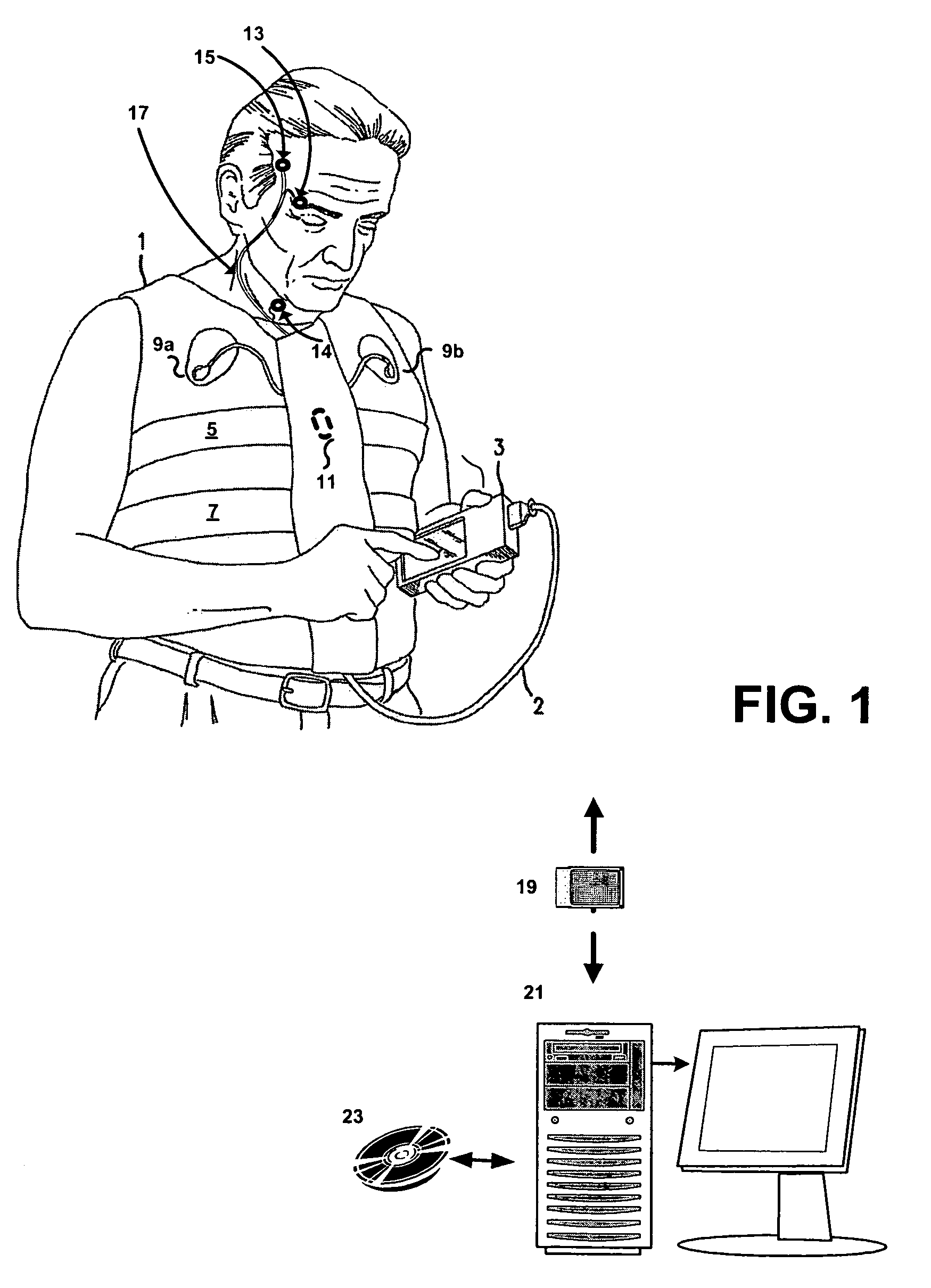
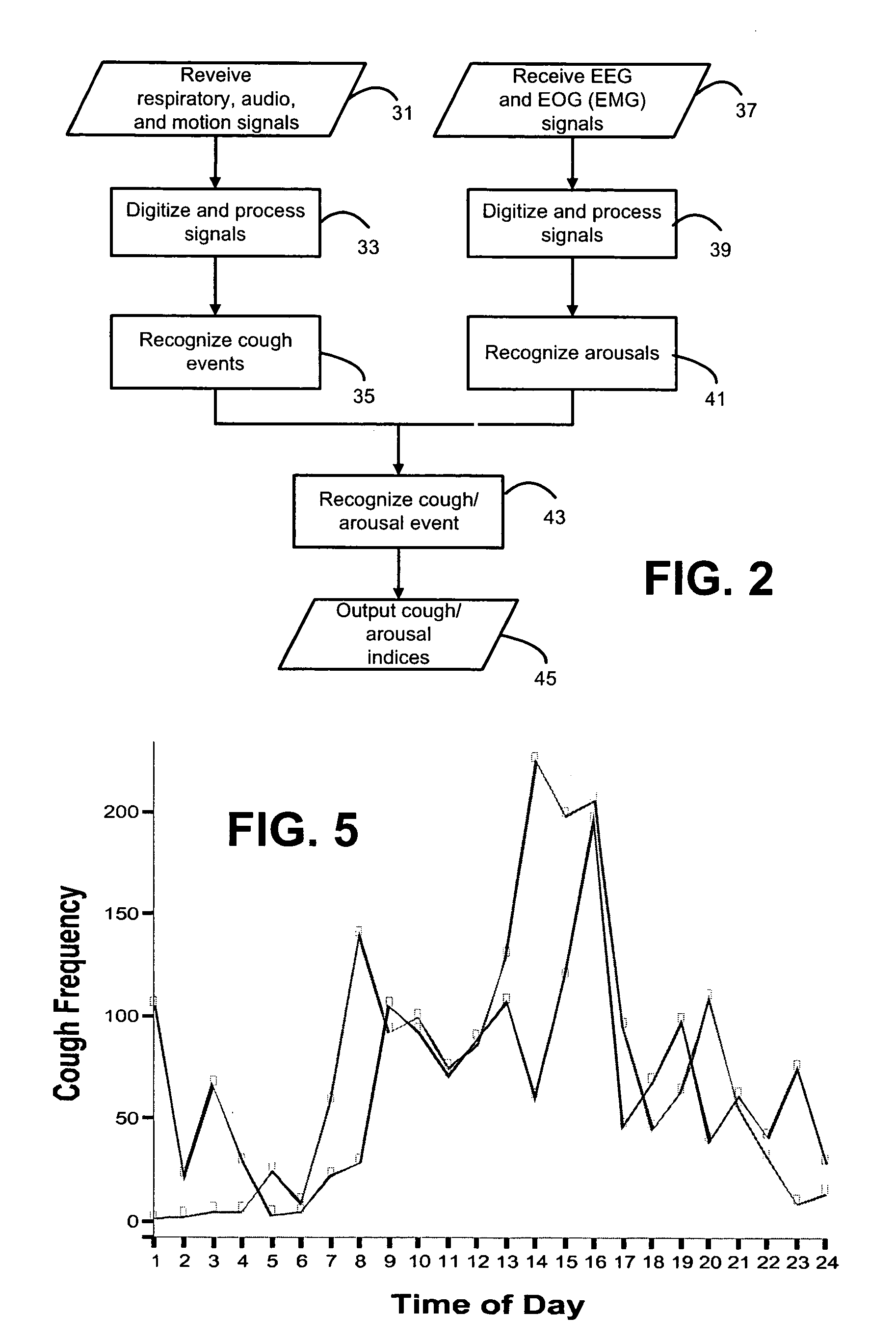
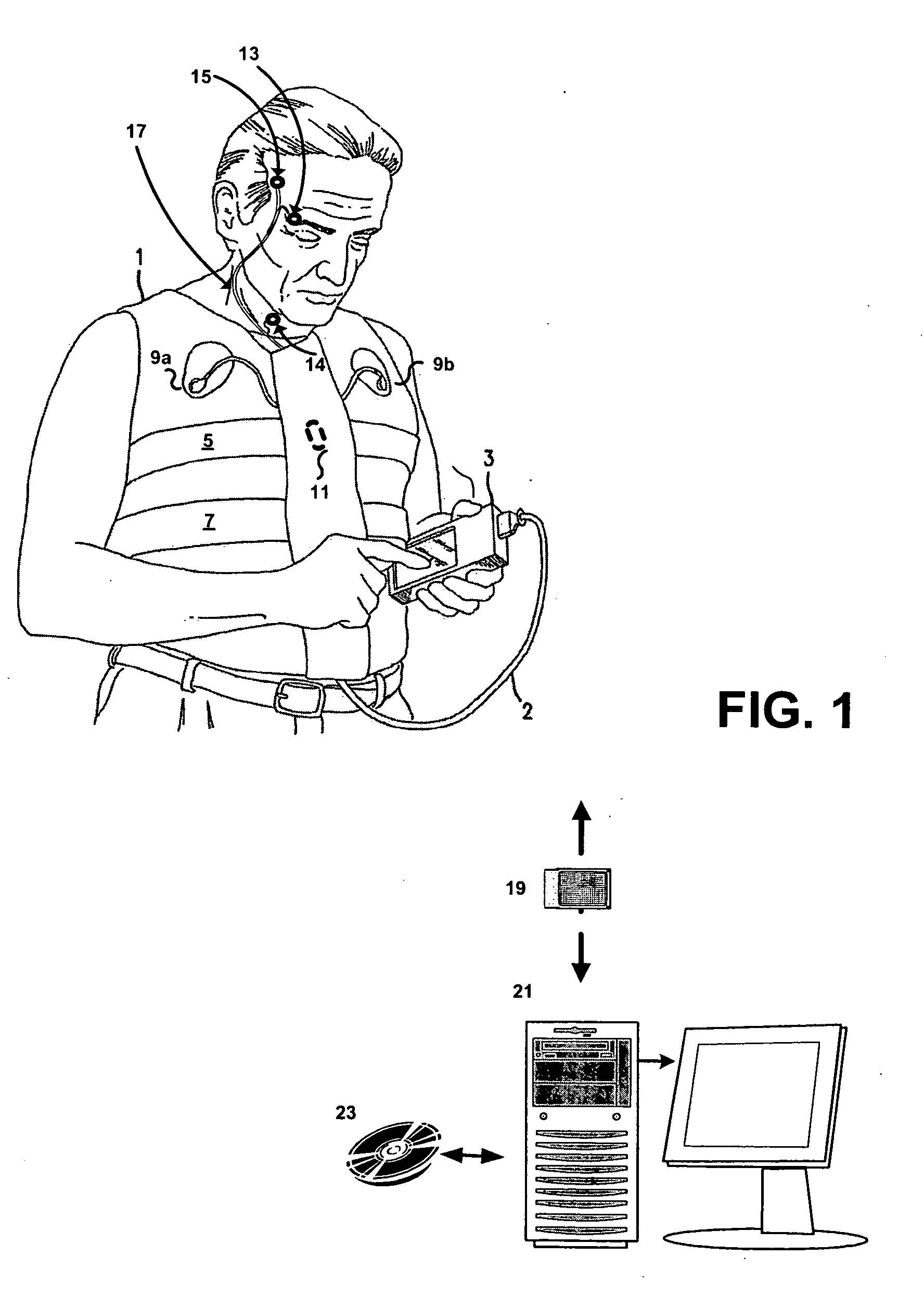
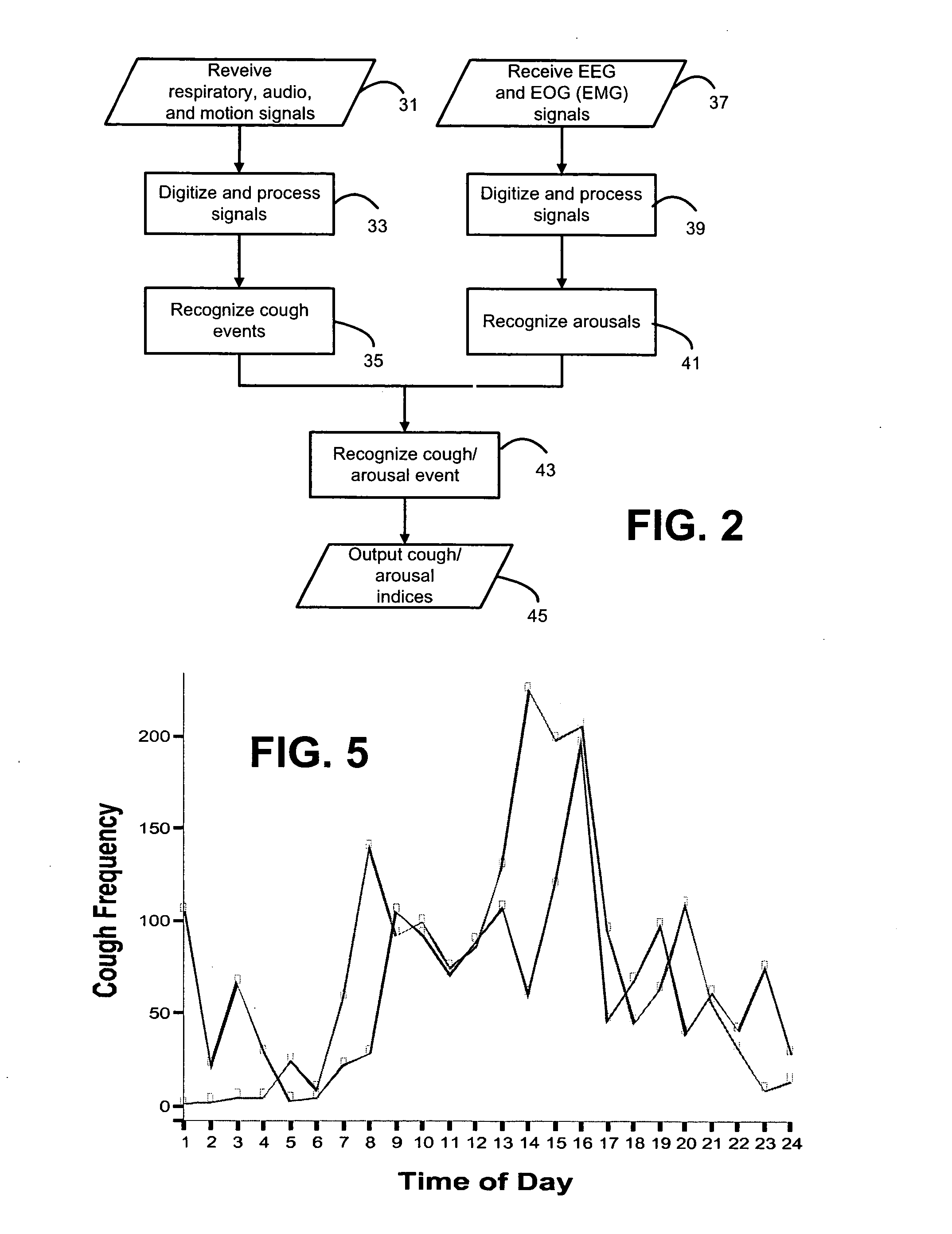
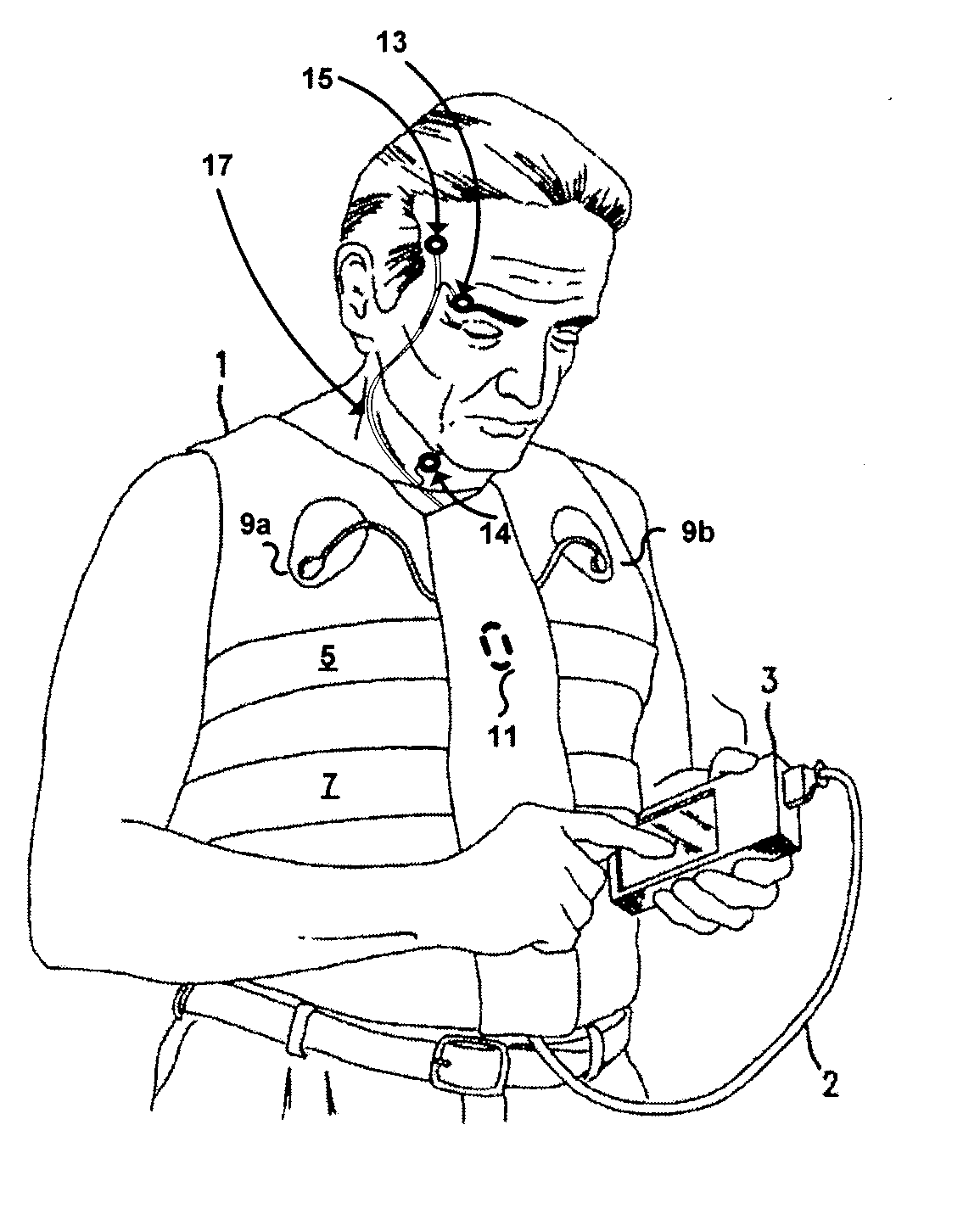
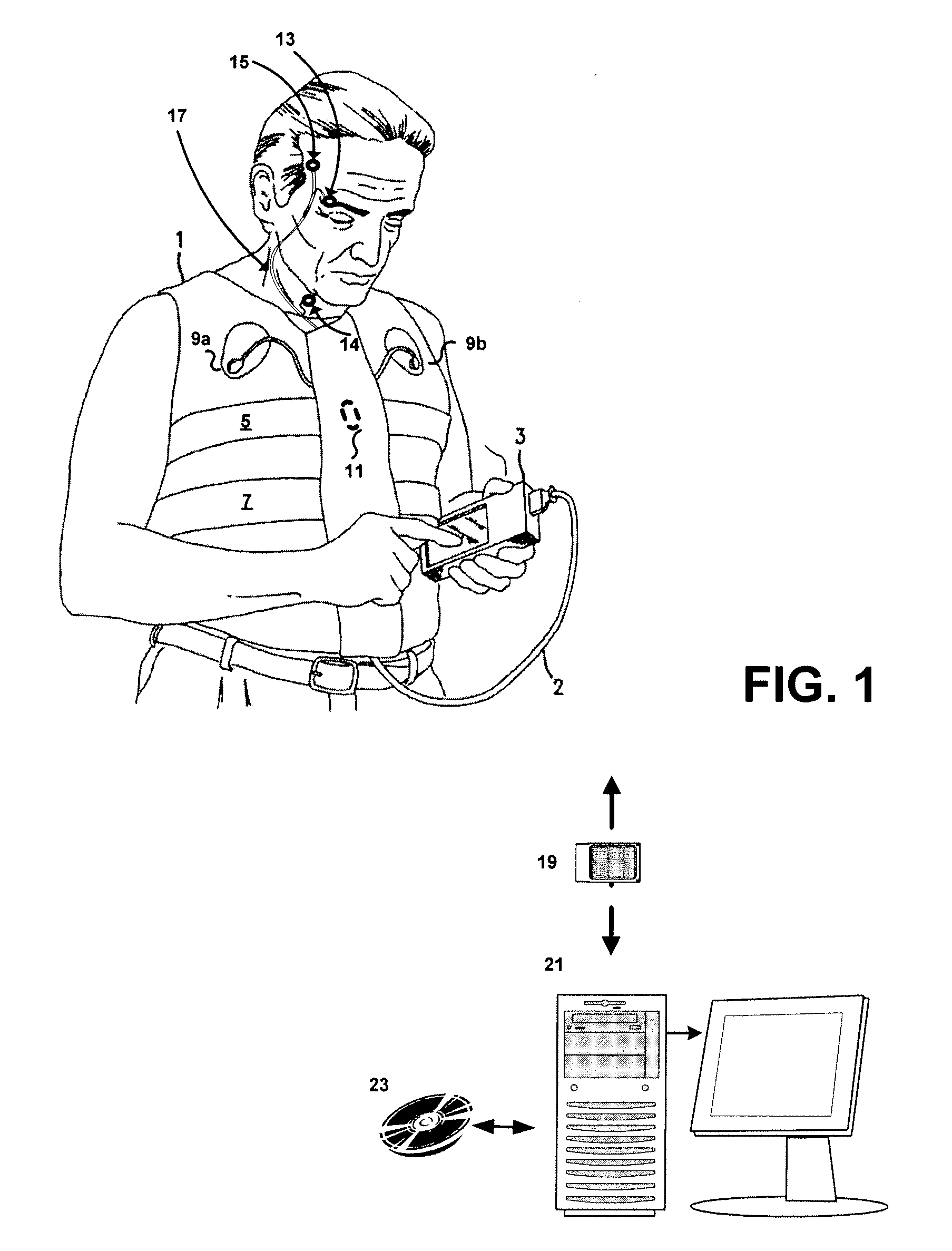
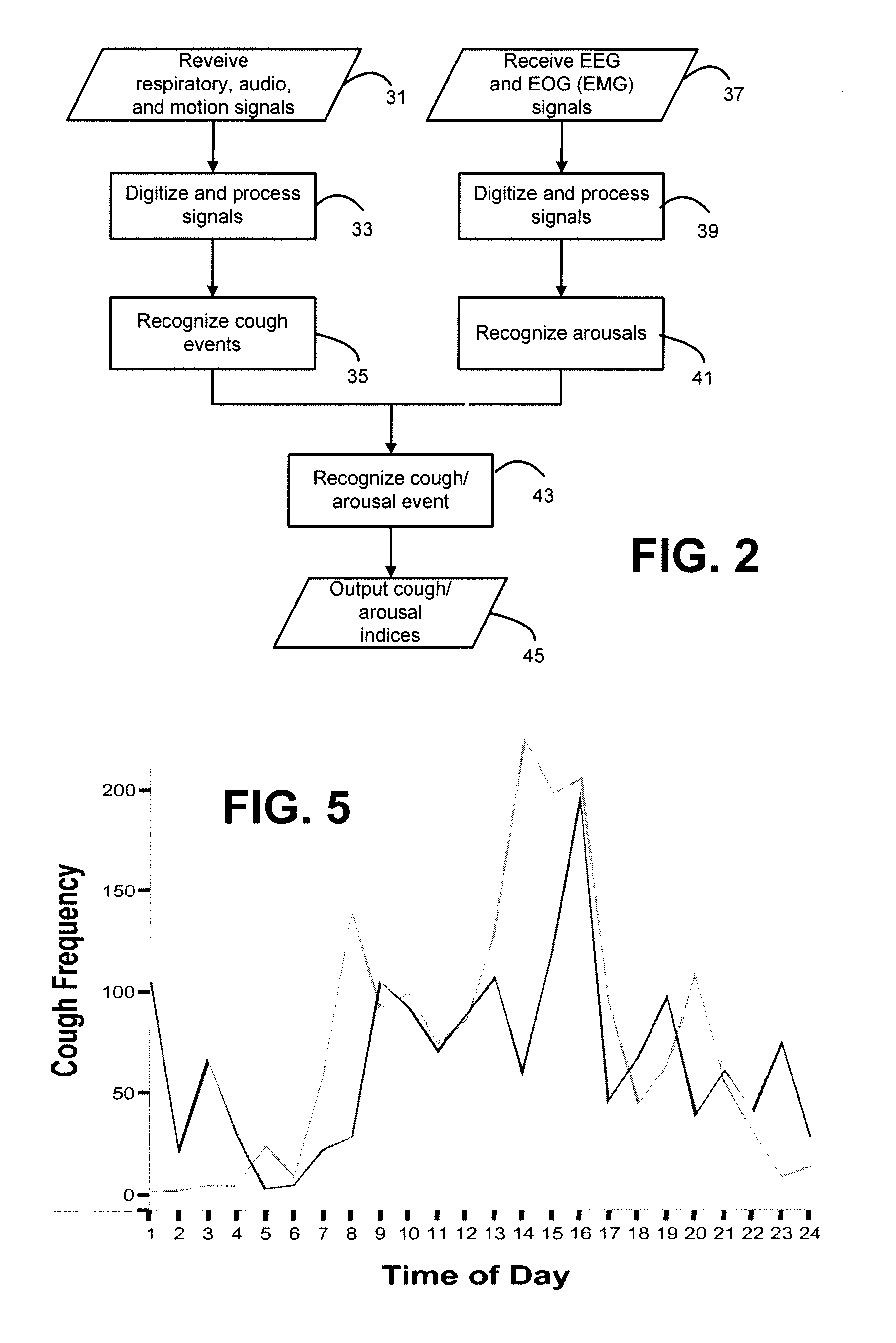
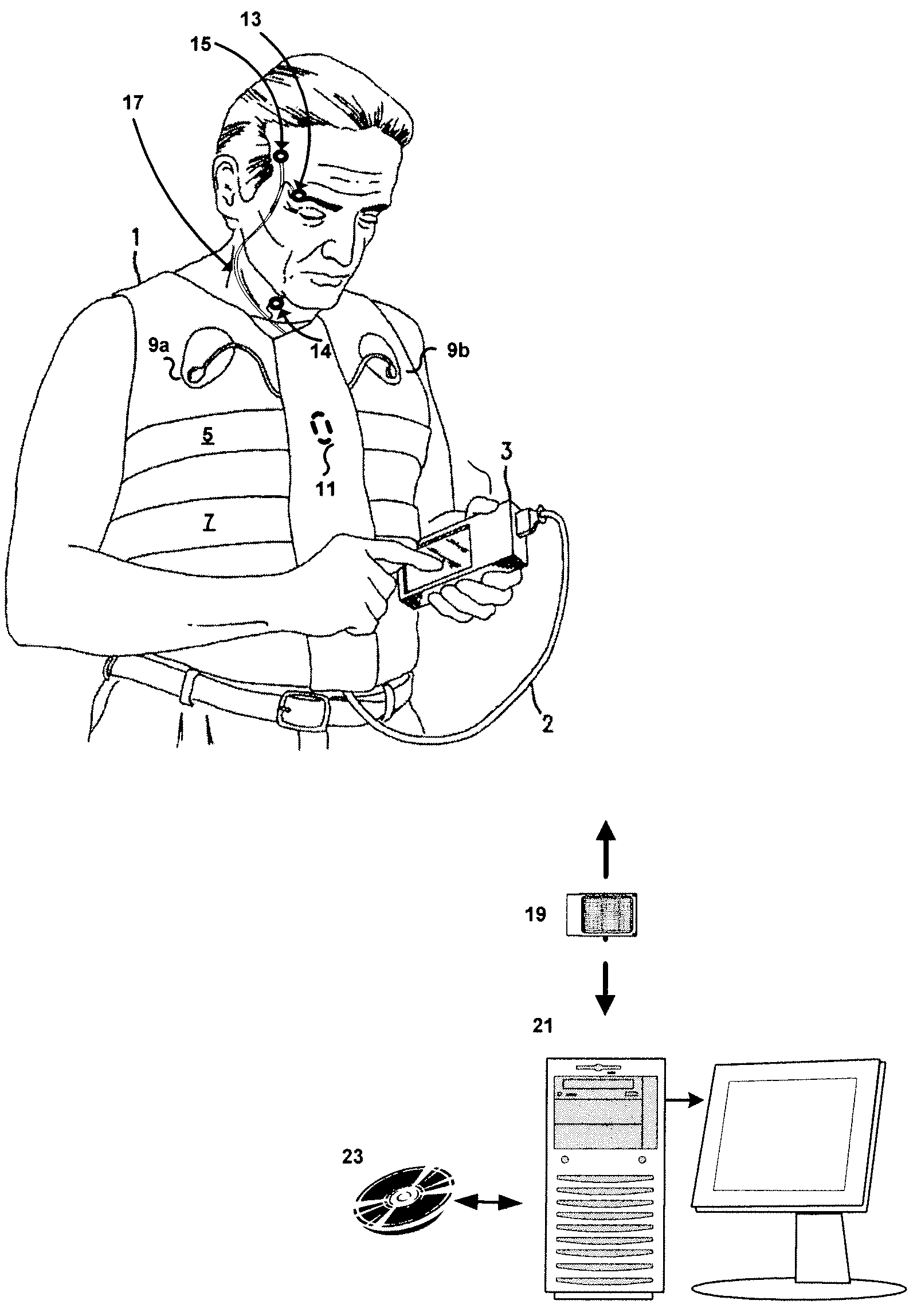
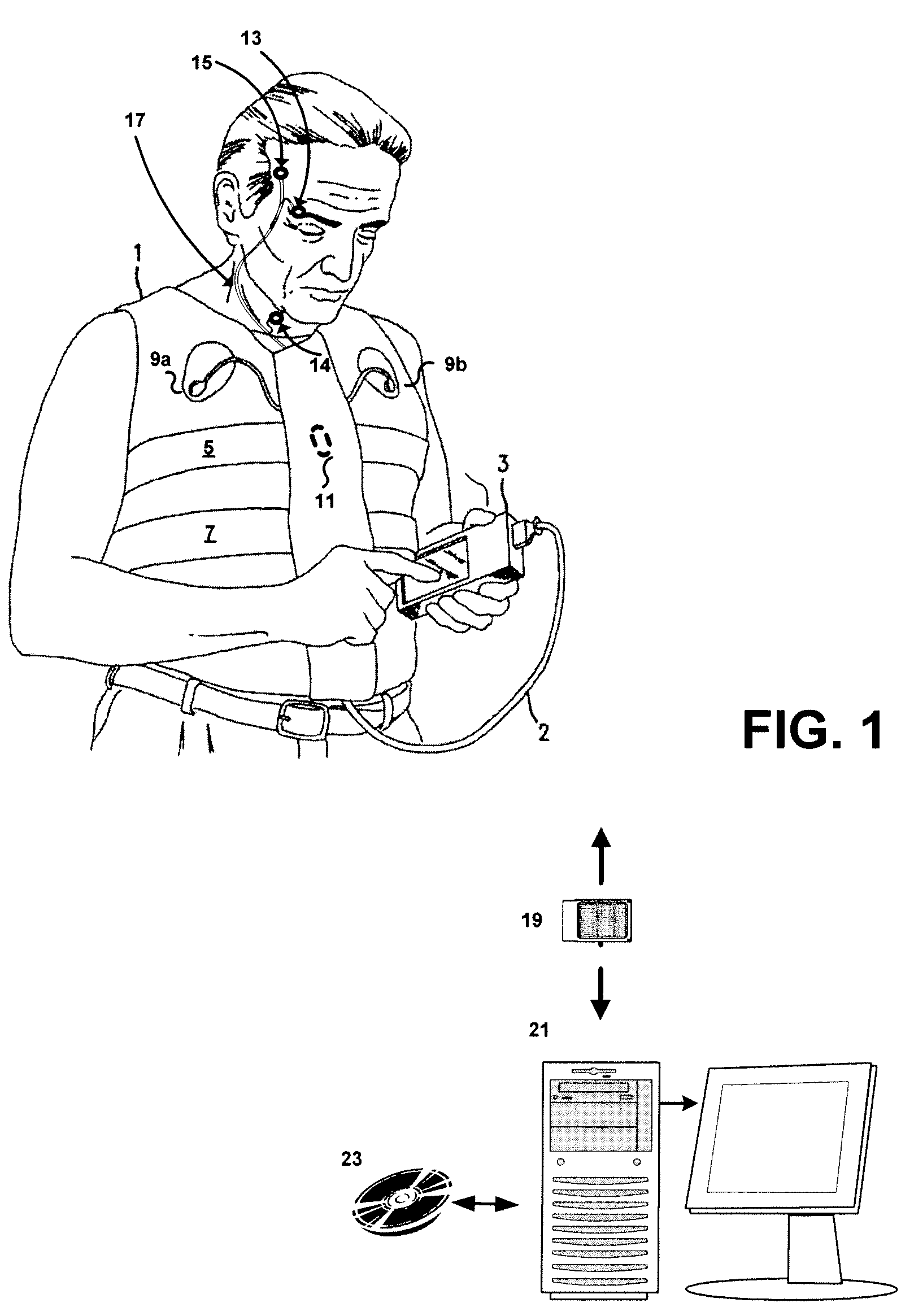
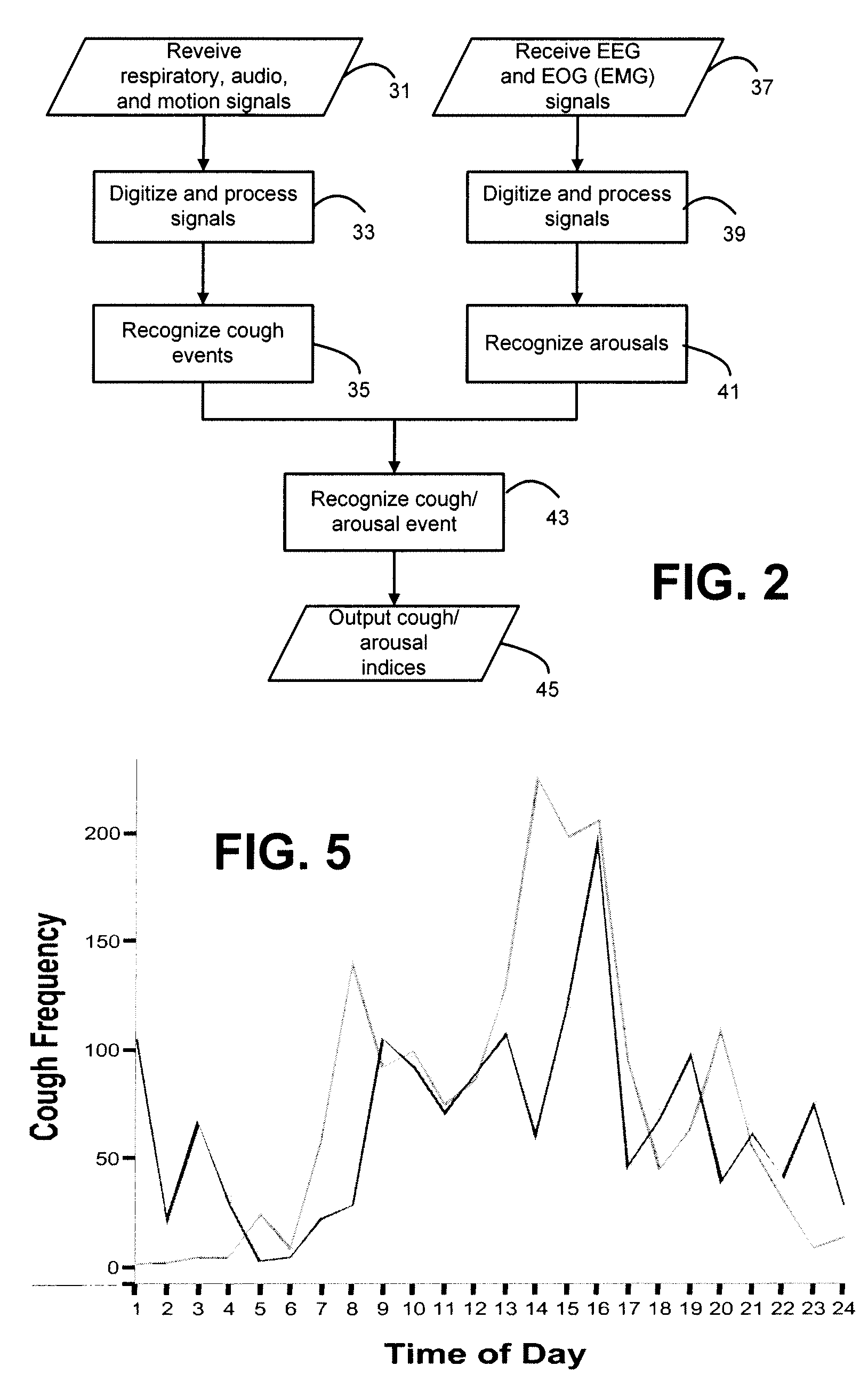
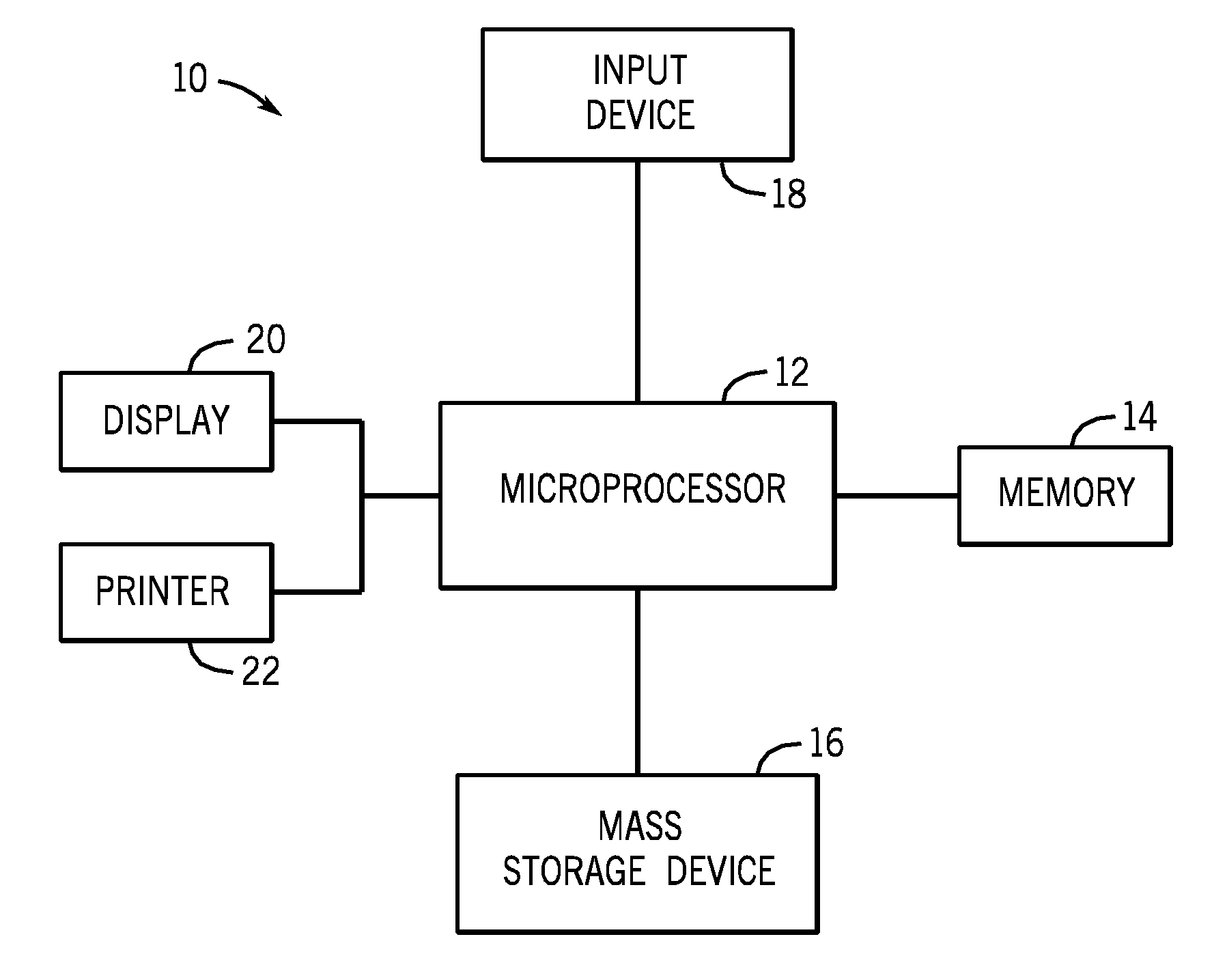
Systems and methods for monitoring cough
The present invention provides systems and methods for monitoring subjects, especially during sleep. Respiratory and sound data are recorded and coughs arousal are recognized as joint events in both of these signals having selected characteristics. Further, cough-arousal events during sleep are recognized when a likely cough occurs in association with a recognized EEG arousal. Cough arousal events are combined into a cough arousal index that reflects disease severity and sleep disruption due to cough. The methods of this invention are computer-implemented and can be provided as a program product including a computer readable medium. Measurements and indices provided by this invention can be used to monitor and to treat respiratory diseases.
Owner:ADIDAS
Systems and methods for monitoring cough
The present invention provides systems and methods for monitoring subjects, especially during sleep. Respiratory and sound data are recorded and coughs arousal are recognized as joint events in both of these signals having selected characteristics. Further, cough-arousal events during sleep are recognized when a likely cough occurs in association with a recognized EEG arousal. Cough arousal events are combined into a cough arousal index that reflects disease severity and sleep disruption due to cough. The methods of this invention are computer-implemented and can be provided as a program product including a computer readable medium. Measurements and indices provided by this invention can be used to monitor and to treat respiratory diseases.
Owner:ADIDAS
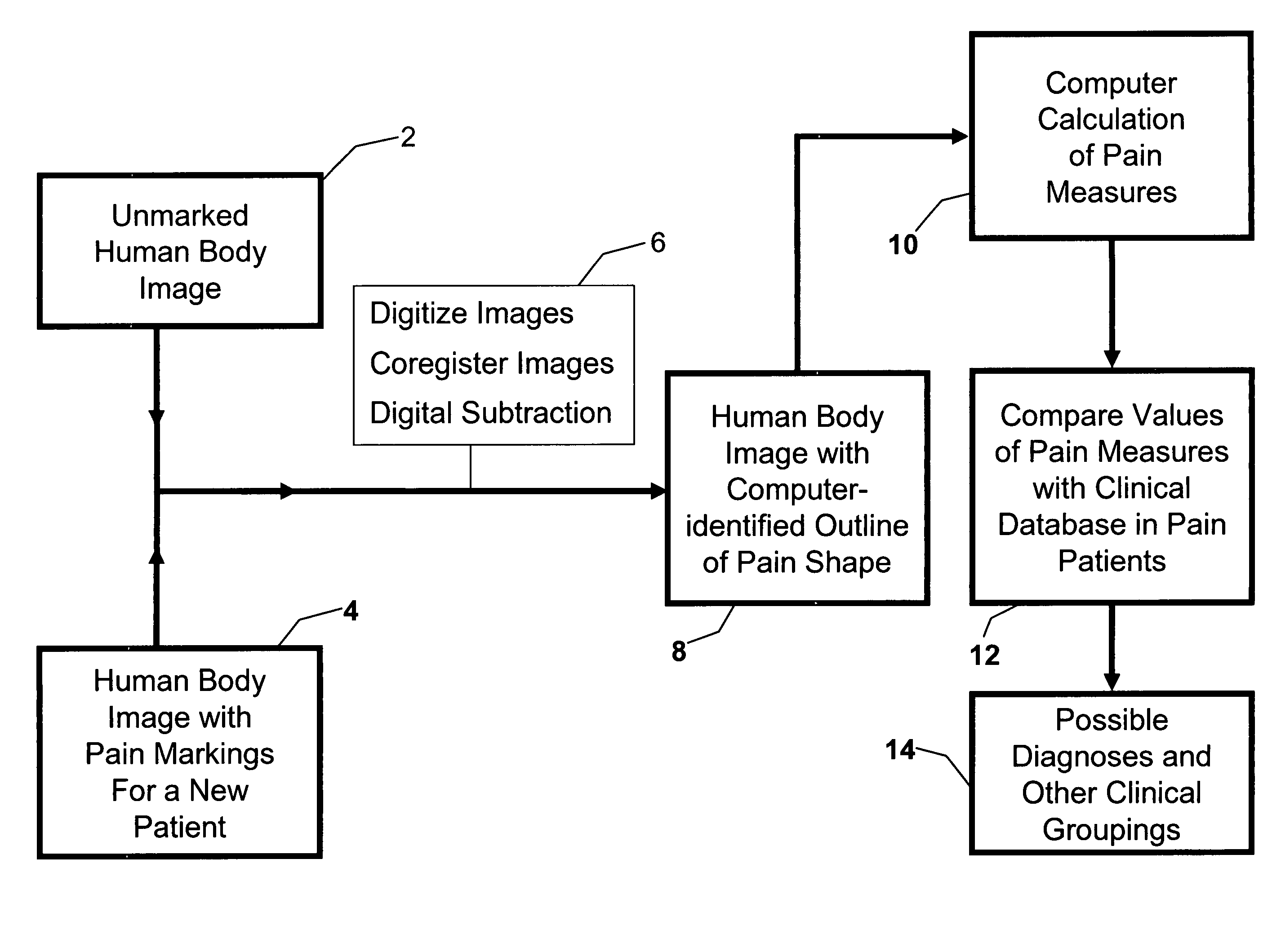
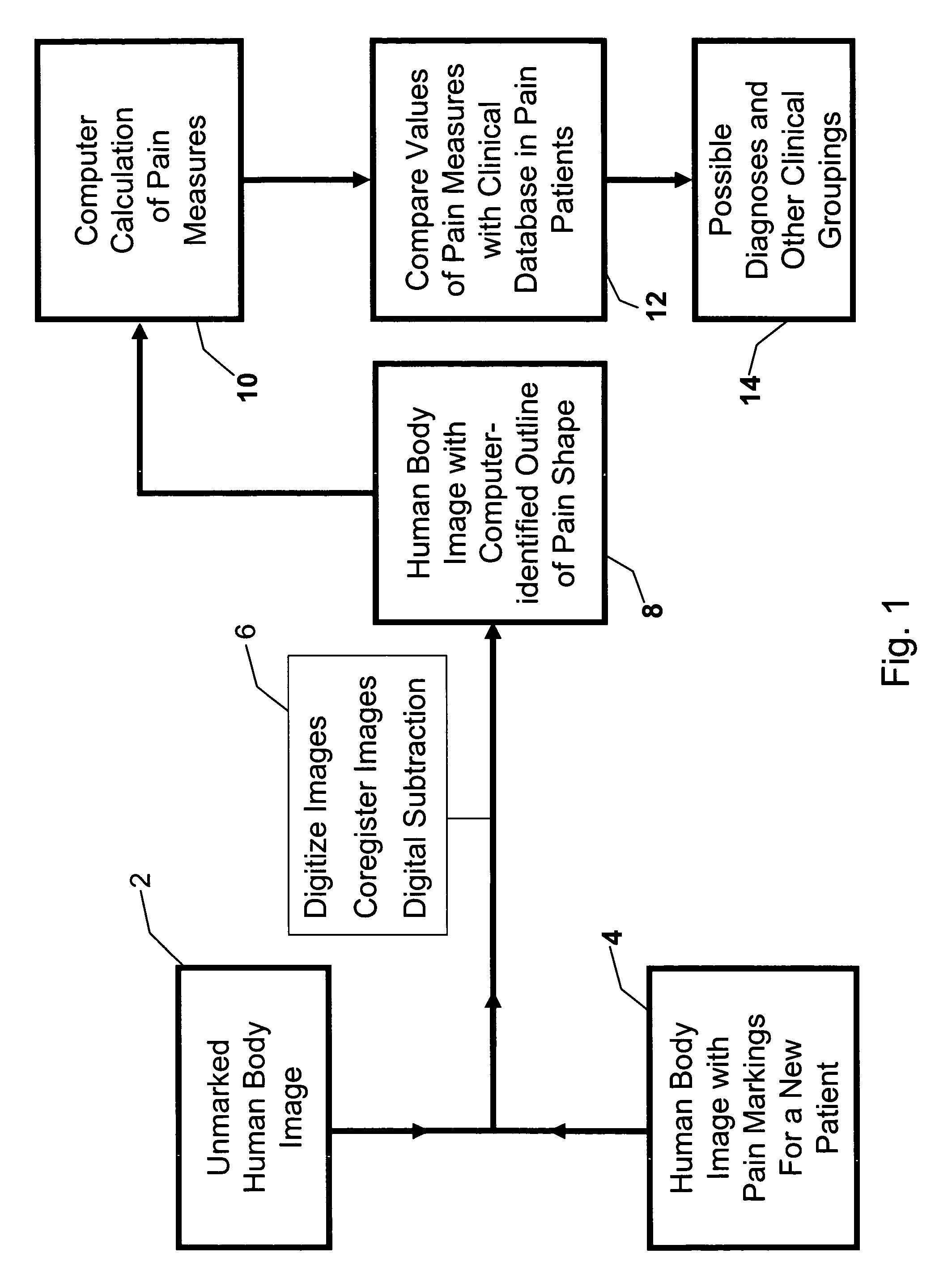
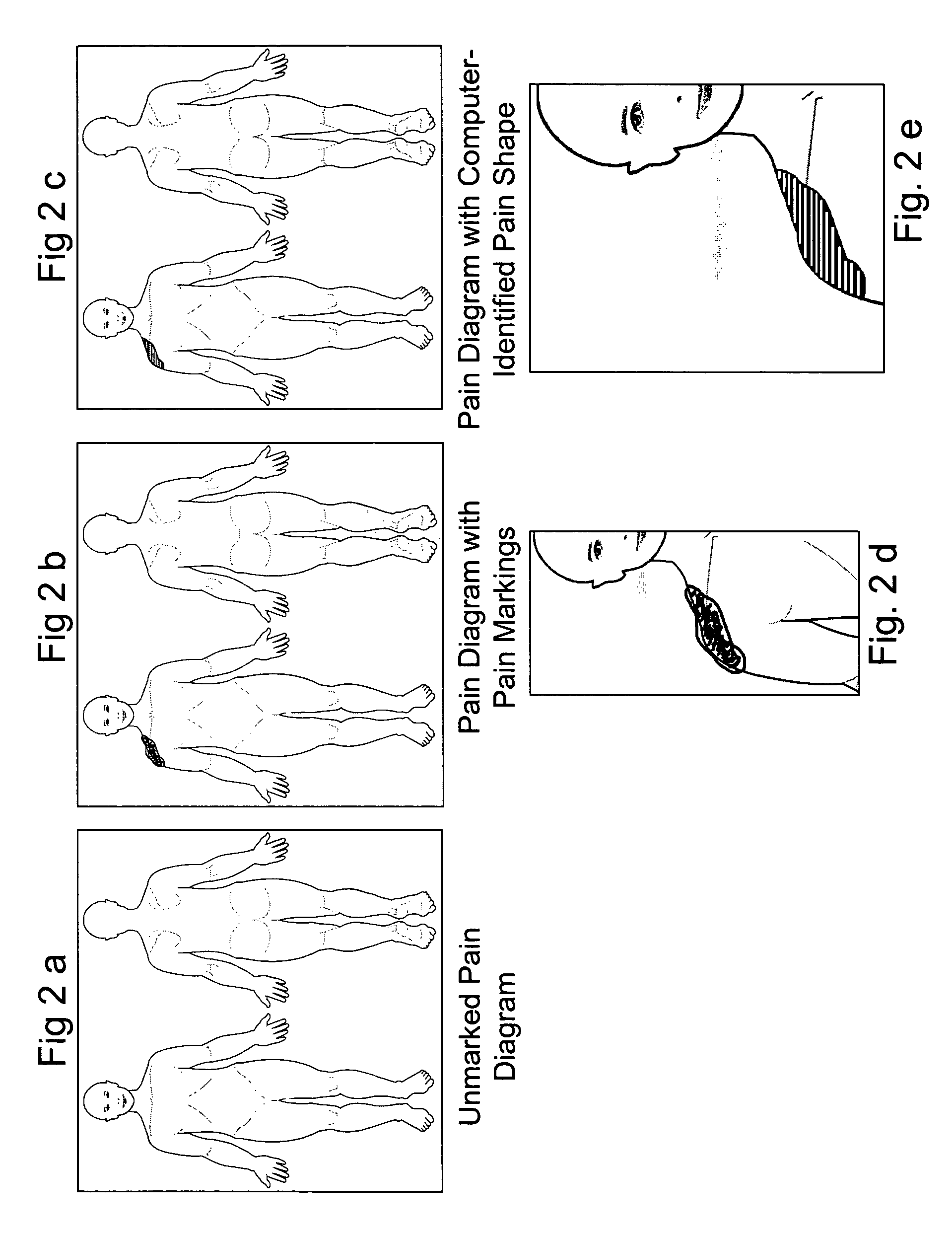
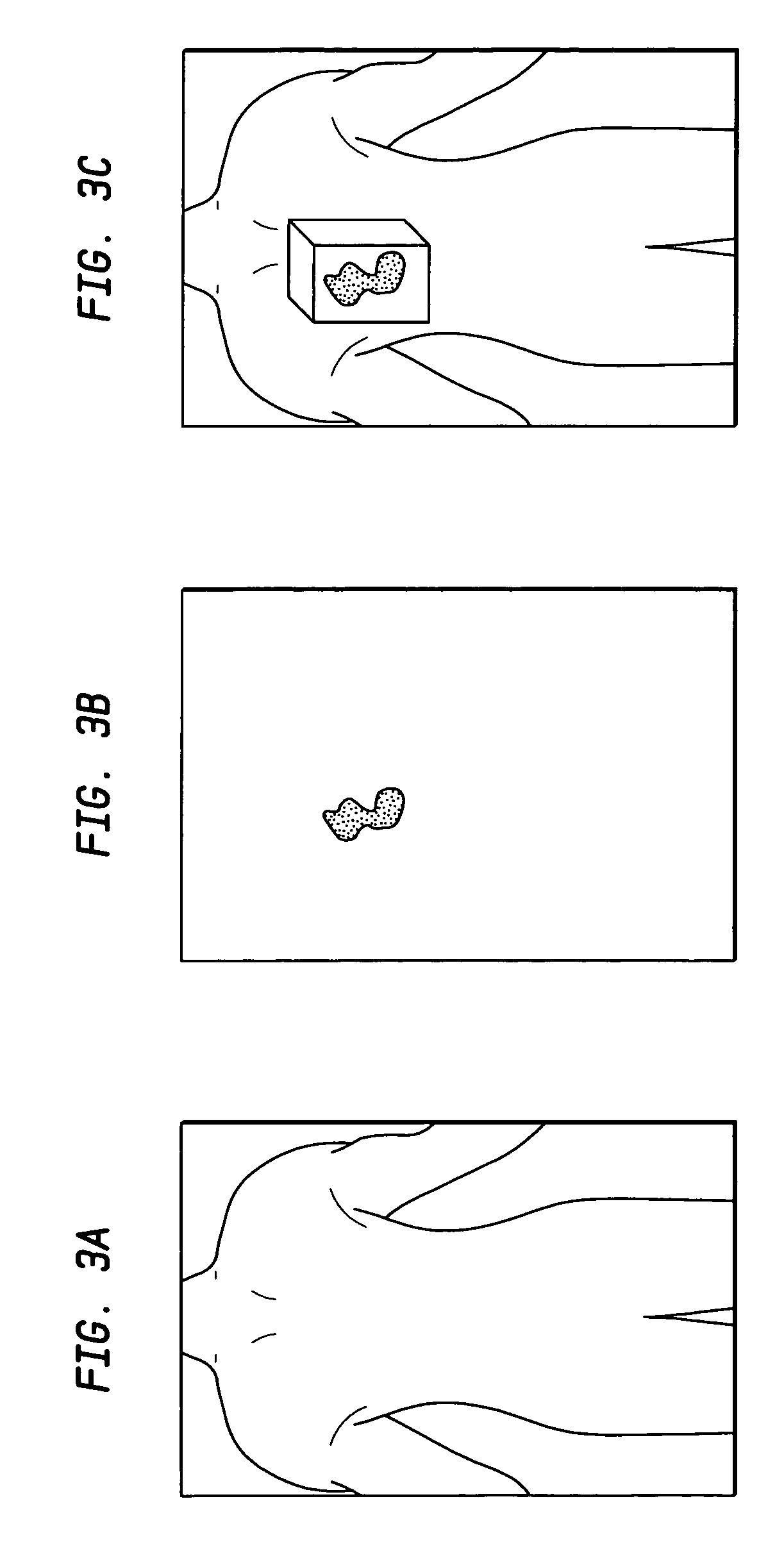
Method for analysis of pain images
A method uses body images and computer hardware and software to collect and analyze clinical data in patients experiencing pain. Pain location information is obtained by the drawing of an outline of the pain on a paper copy or electronic display of the body image. Composite images are generated representing aggregate data for specified patient groups. The coordinates of common anatomic landmarks on differently designed body images are mapped to each other, permitting integrated analysis of pain data, e.g., pain shape, centroid, meta centroid, from multiple body image designs and display of all pain data on a single body image design. Differences and similarities between groups of patients are displayed visually and numerically, and are used to assign the probability of a given patient belonging to a particular diagnostic group or category of disease severity.
Owner:TAYLOR MICROTECH
Systems and methods for monitoring cough
The present invention provides systems and methods for monitoring subjects, especially during sleep. Respiratory and sound data are recorded and coughs arousal are recognized as joint events in both of these signals having selected characteristics. Further, cough-arousal events during sleep are recognized when a likely cough occurs in association with a recognized EEG arousal. Cough arousal events are combined into a cough arousal index that reflects disease severity and sleep disruption due to cough. The methods of this invention are computer-implemented and can be provided as a program product including a computer readable medium. Measurements and indices provided by this invention can be used to monitor and to treat respiratory diseases.
Owner:ADIDAS
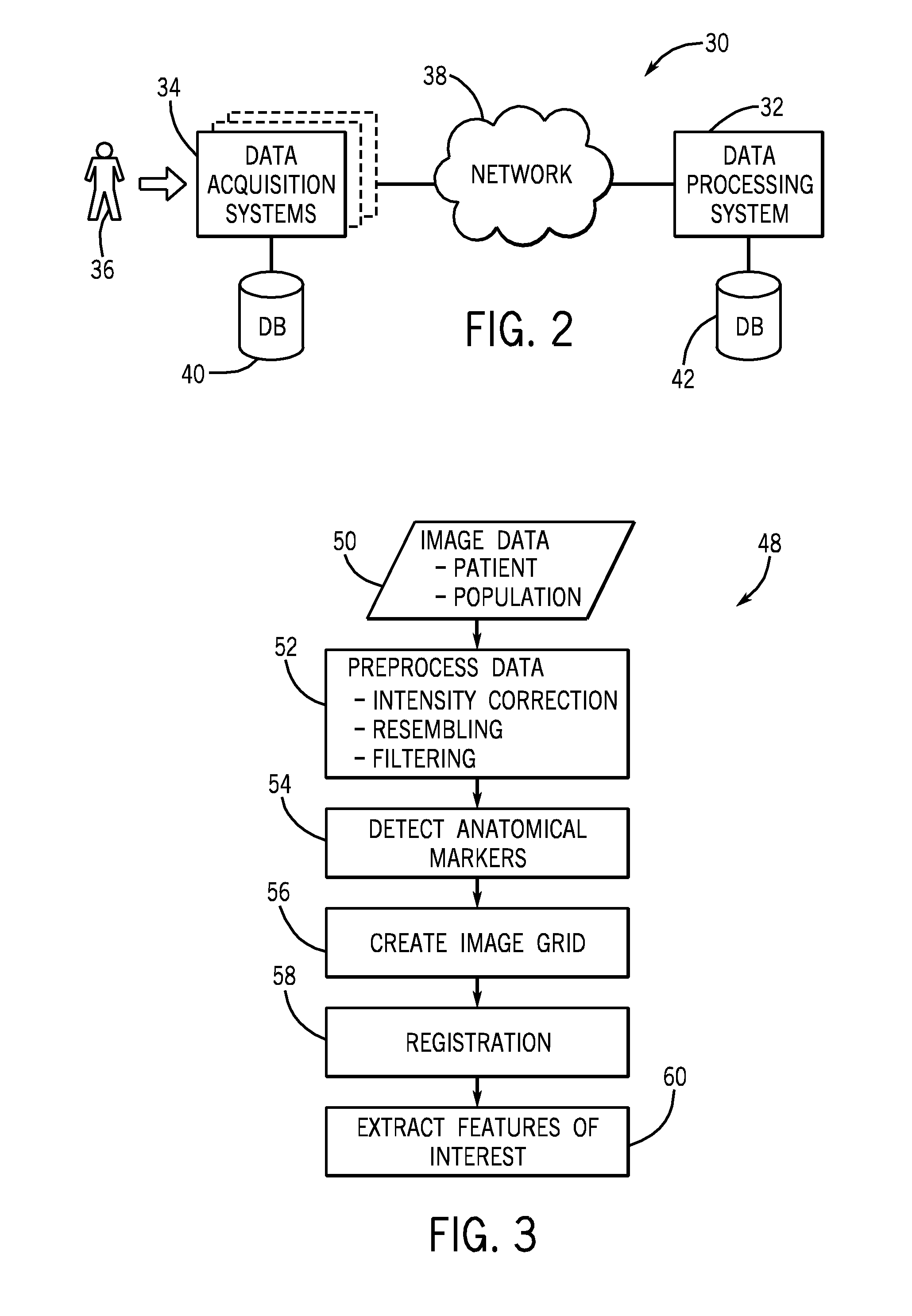
System and method of measuring disease severity of a patient before, during and after treatment
ActiveUS7935055B2Image analysisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData setAfter treatment
A system for obtaining serial biochemical, anatomical or physiological in vivo measurements of disease from one or more medical images of a patient before, during and after treatment, and measuring extent and severity of the disease is provided. First anatomical and functional image data sets are acquired, and form a first co-registered composite image data set. At least a volume of interest (VOI) within the first co-registered composite image data set is identified. The first co-registered composite image data set including the VOI is qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed to determine extent and severity of the disease. Second anatomical and functional image data sets are acquired, and form a second co-registered composite image data set. A global, rigid registration is performed on the first and second anatomical image data sets, such that the first and second functional image data sets are also globally registered.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
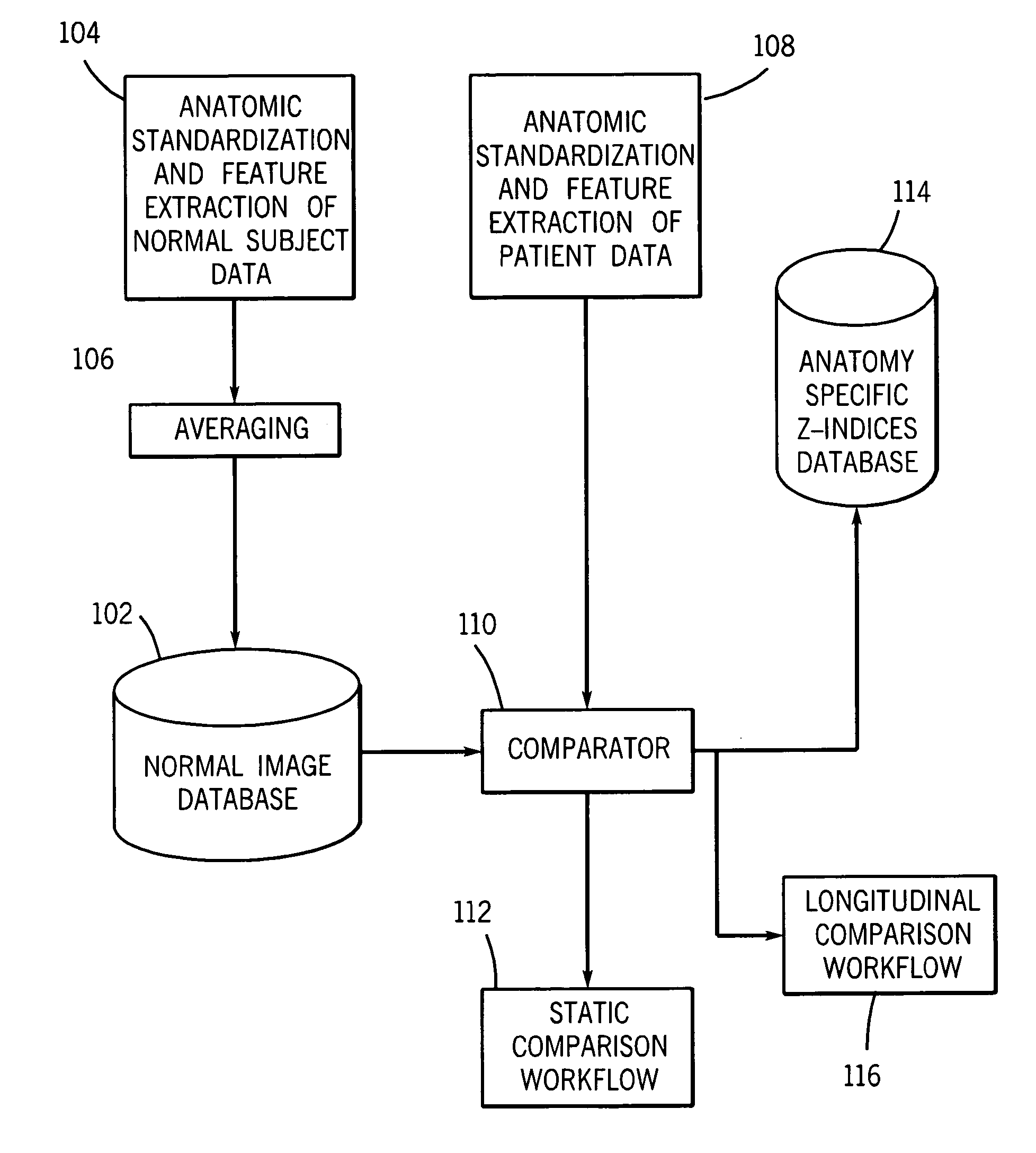
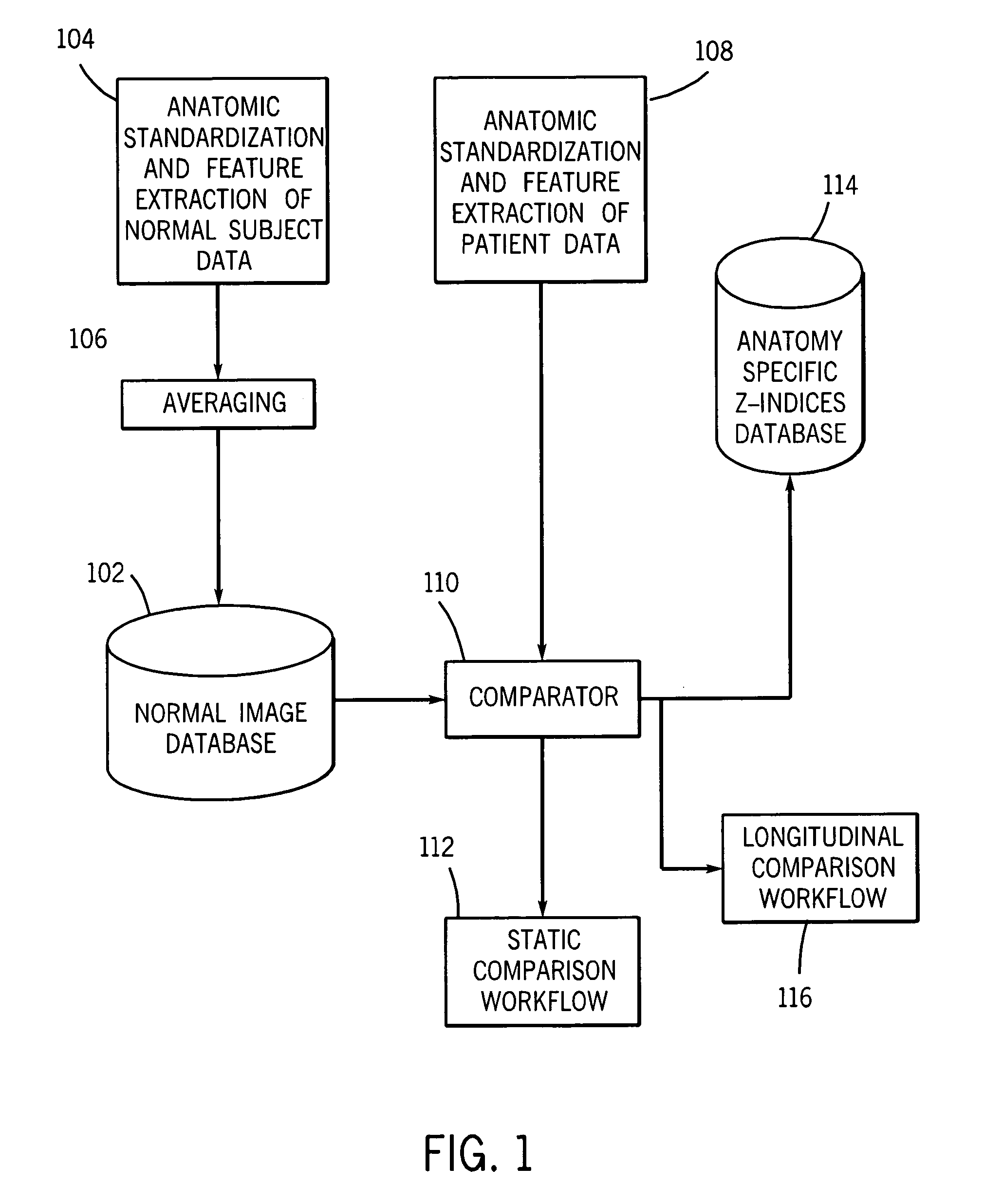
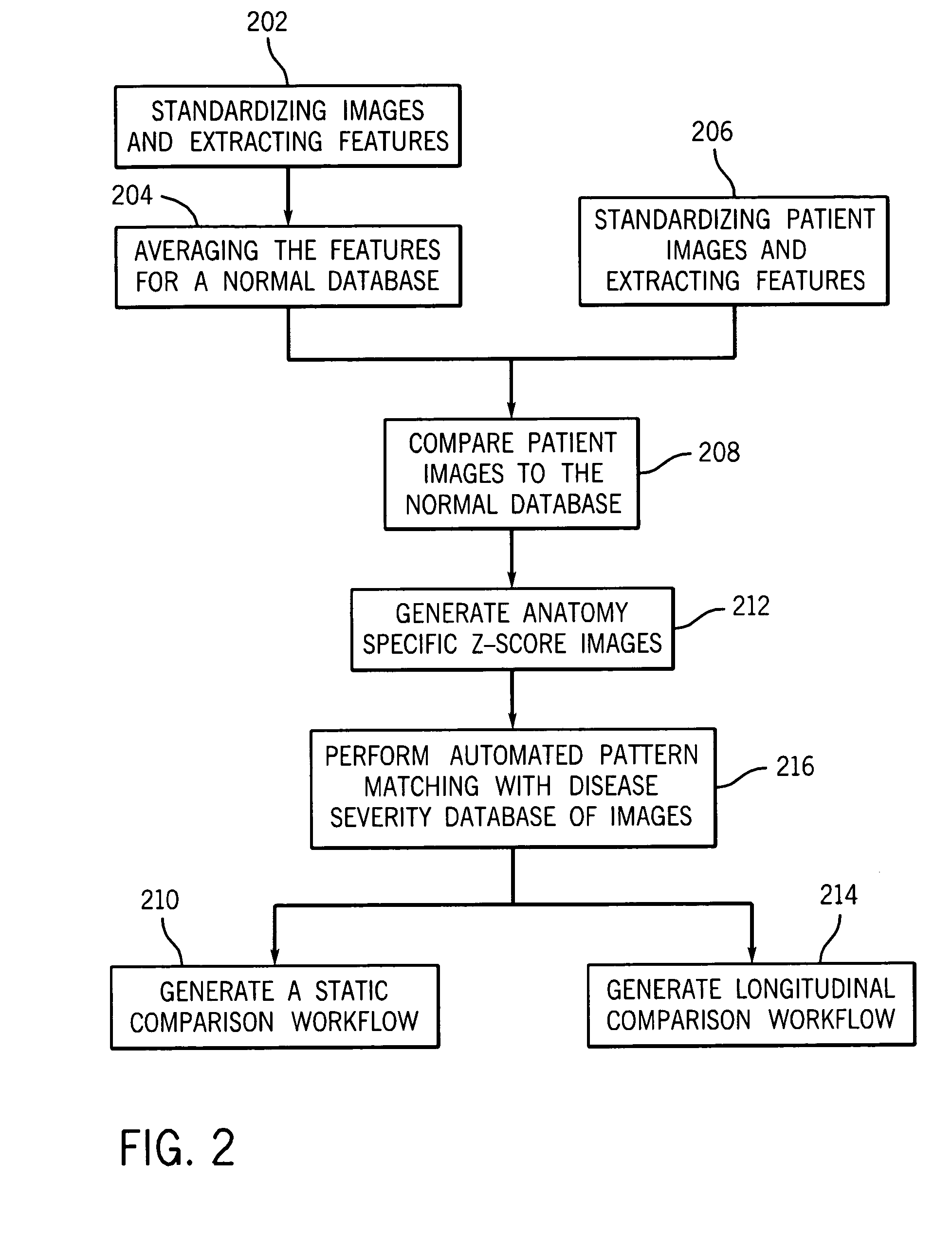
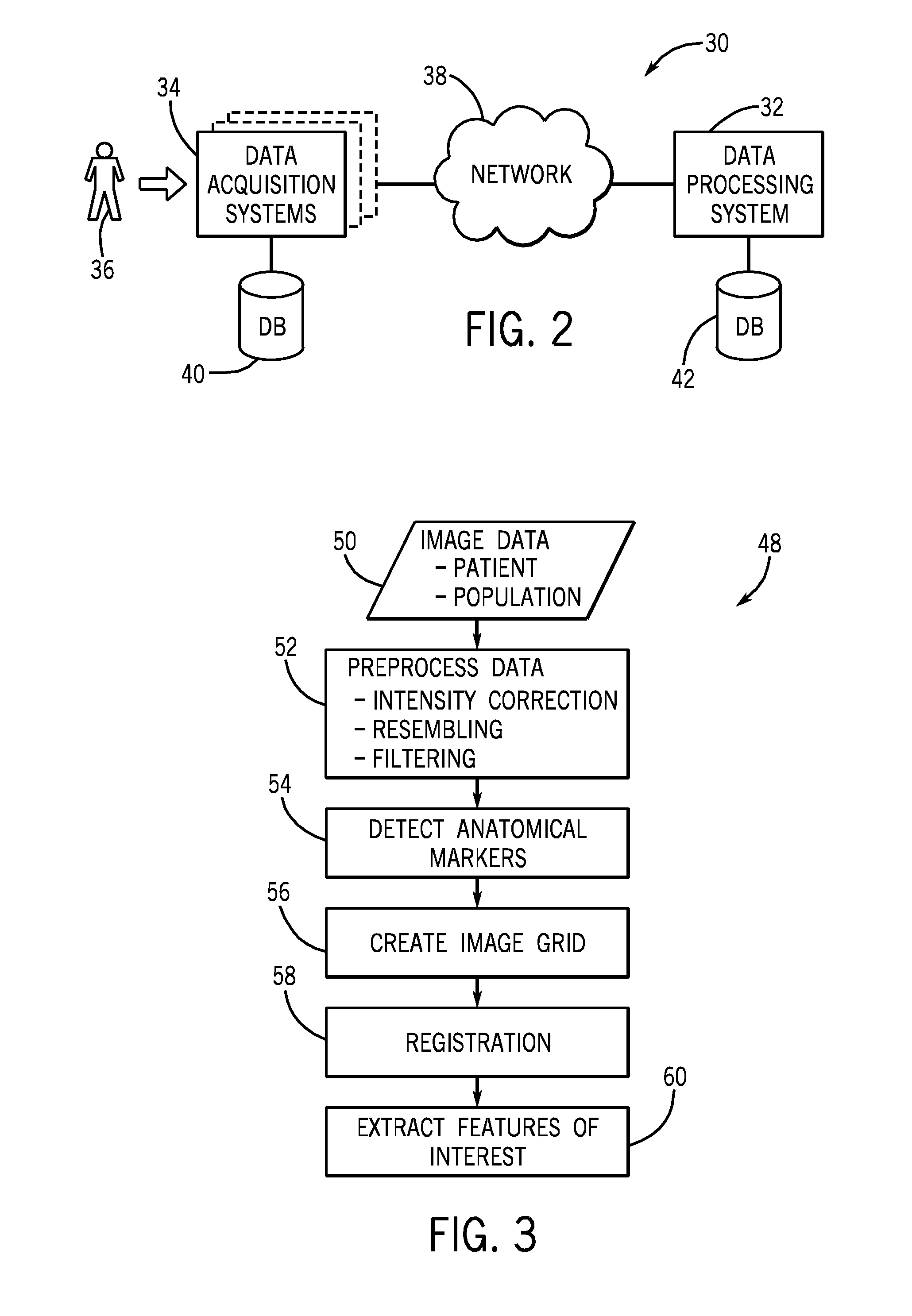
Method and system for automatically generating a disease severity index
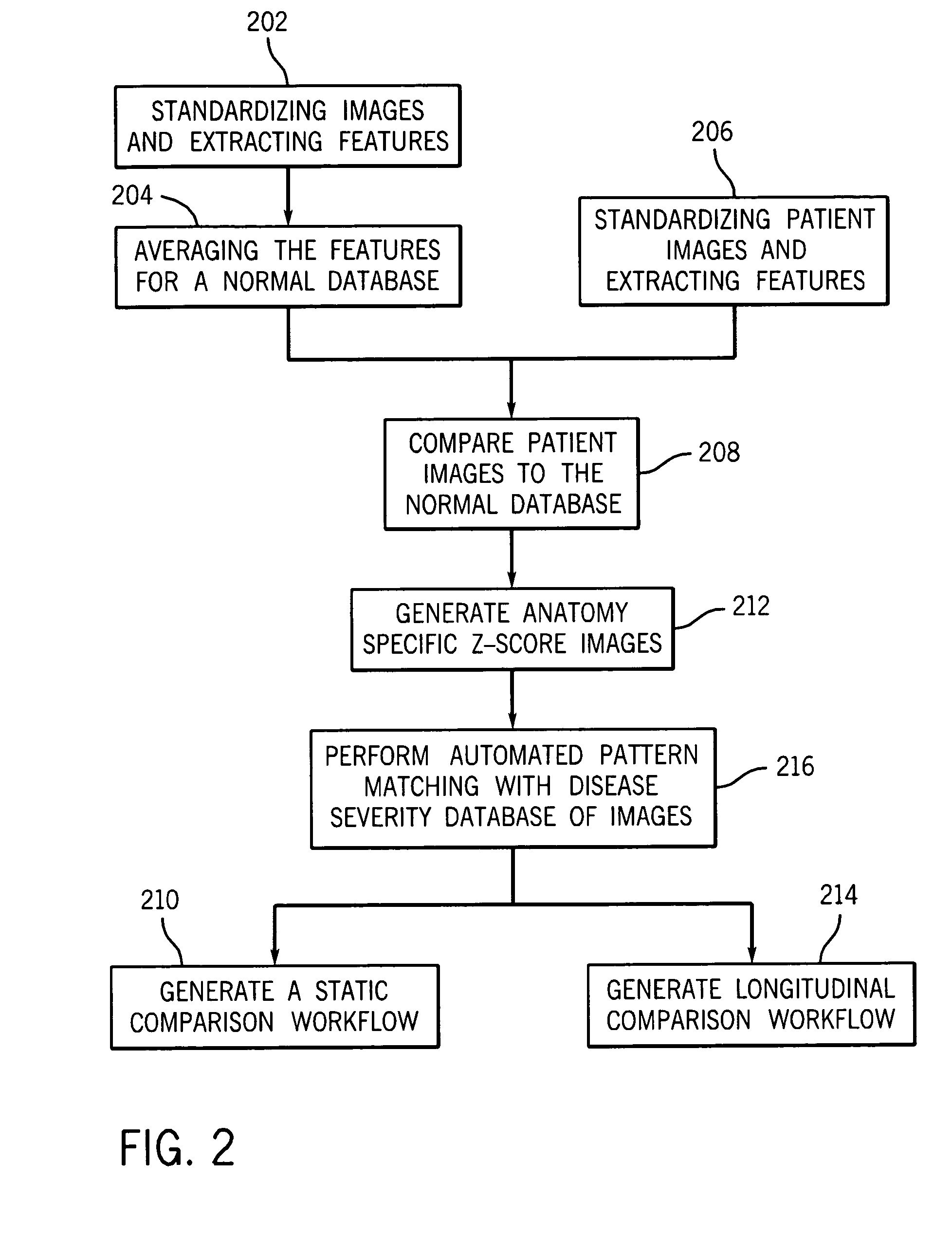
Methods and systems for automatically generating a severity index for images of anatomical features of a patient are provided. In an exemplary embodiment, an image of an anatomical feature of a patient is compared with a normal, standardized image of the same anatomical feature. Based on this comparison, a deviation image for the anatomical feature is generated that represents the degree and manner the acquired image deviates from normal for that anatomical feature. The deviation image is automatically pattern matched against multiple images of known disease severity for the anatomical feature. Based on the automated pattern match, a known disease severity, such as in the form of a severity index, is provided as corresponding anatomical feature for the patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Respiratory disease monitoring system
ActiveUS8758262B2Minimizing compromiseInfluence health outcomes in asthmaStethoscopeRespiratory organ evaluationAccelerometerFrequency spectrum
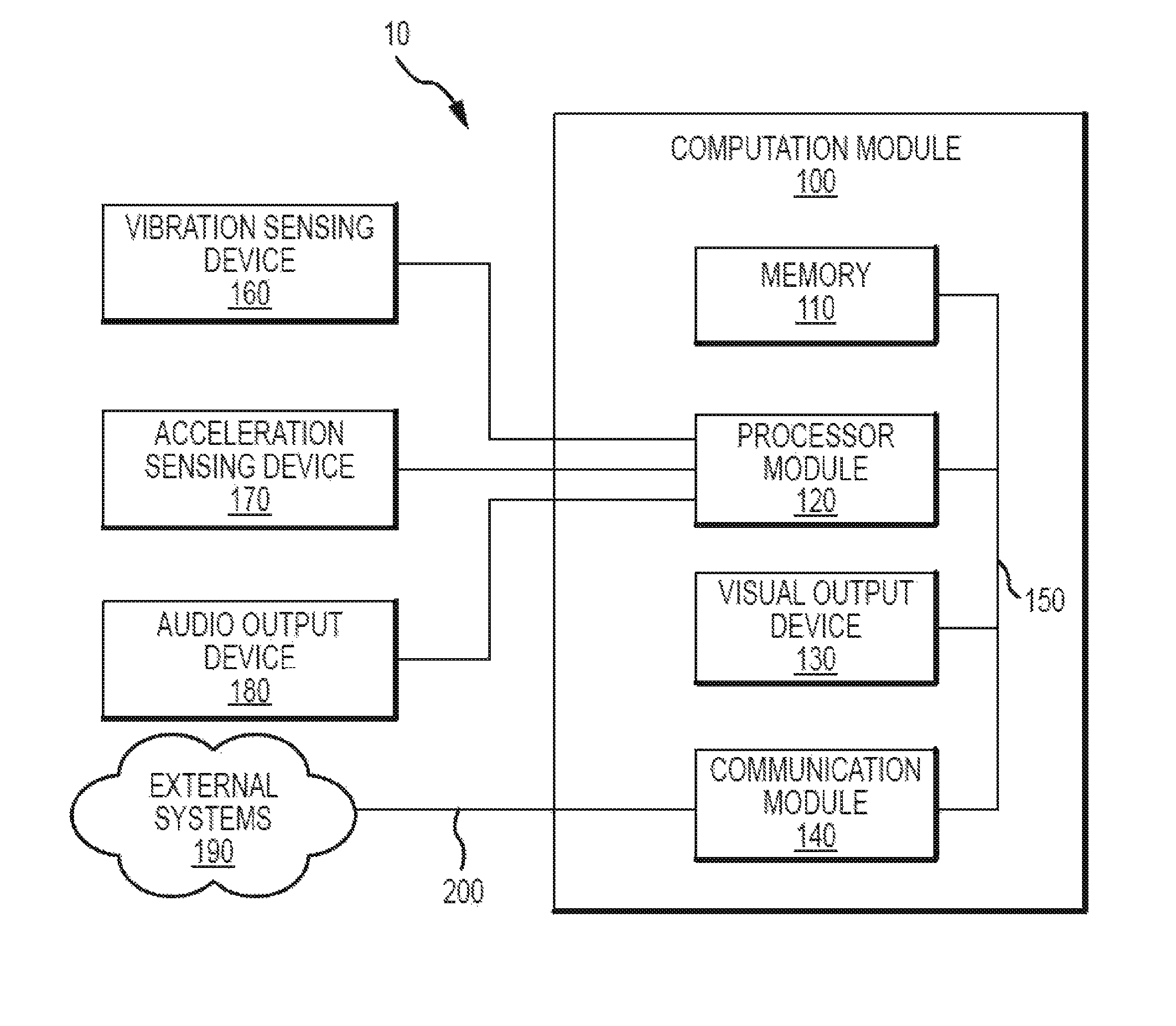
An automated system for monitoring respiratory diseases, such as asthma, provides noninvasive, multimodal monitoring of respiratory signs and symptoms that can include wheeze and cough. Some embodiments employ a mobile device, such as a cell phone, in which raw data from a microphone and an accelerometer are processed, analyzed, and stored. Data can be collected continuously. Time domain and frequency domain analyses of signals to determine, e.g., energy, duration, and spectral content of candidate sounds can be employed to discriminate symptoms of interest from background sounds and to establish significance. Accelerometer signals are analyzed to determine activity levels. Analyses of a user's symptoms and activity level prior to, during, and after an event can provide meaningful determinations of disease severity and predict future respiratory events. The system can provide a summary of data, as well as an alarm when symptom severity reaches a threshold.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Systems and methods for monitoring cough
Owner:ADIDAS
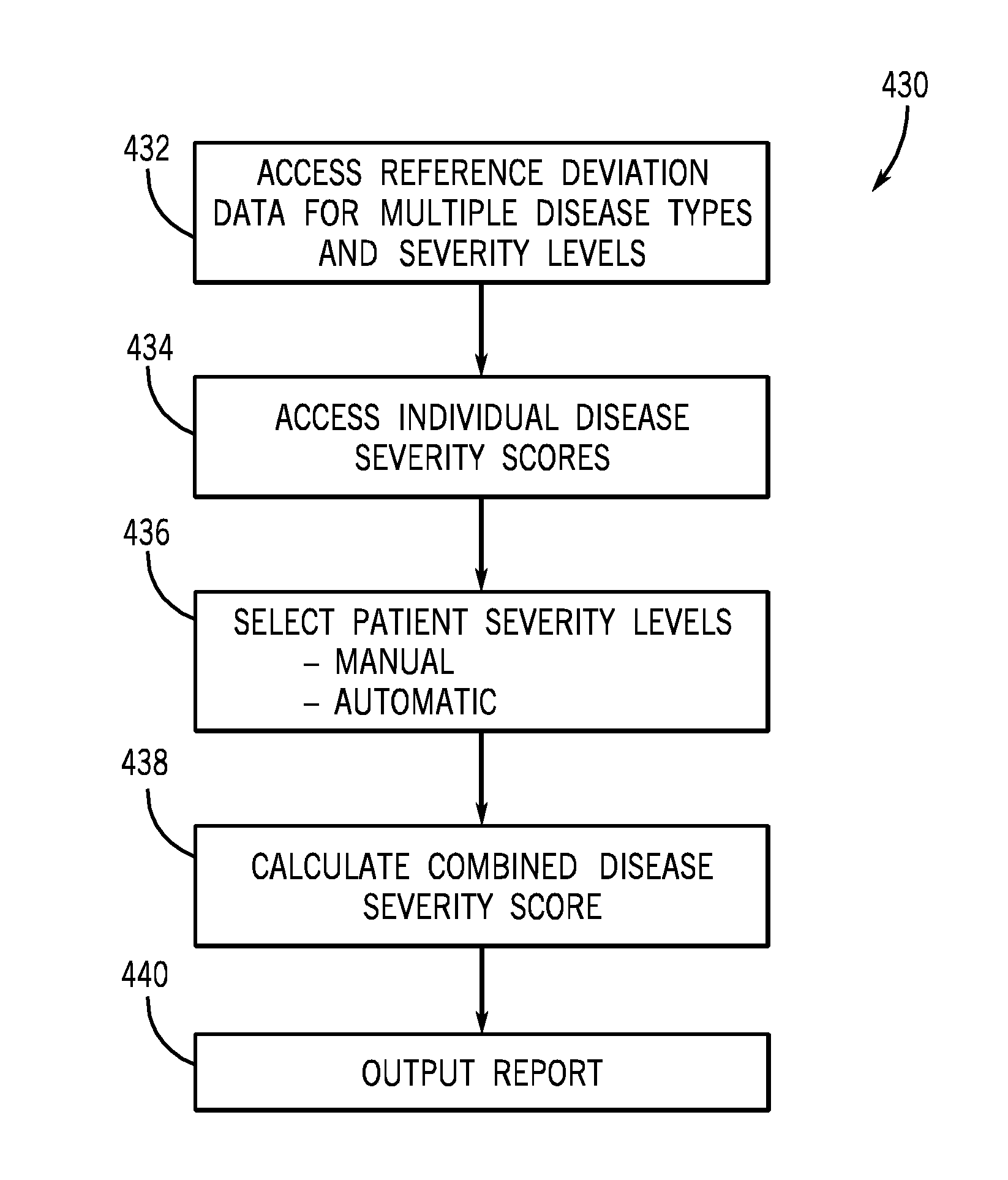
System and Method for Analysis of Multiple Diseases and Severities
A data processing technique is provided. In one embodiment, a computer-implemented method includes accessing reference deviation maps for a plurality of disease types. The reference deviation maps may include subsets of maps associated with severity levels of respective disease types, and a disease severity score may be associated with each severity level. The method may include selecting patient severity levels for multiple disease types based on the subsets of reference deviation maps. Also, the method may include automatically calculating a combined patient disease severity score based at least in part on the disease severity scores associated with the selected patient severity levels, and may include outputting a report based at least in part on the combined patient disease severity score. Additional methods, systems, and manufactures are also disclosed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
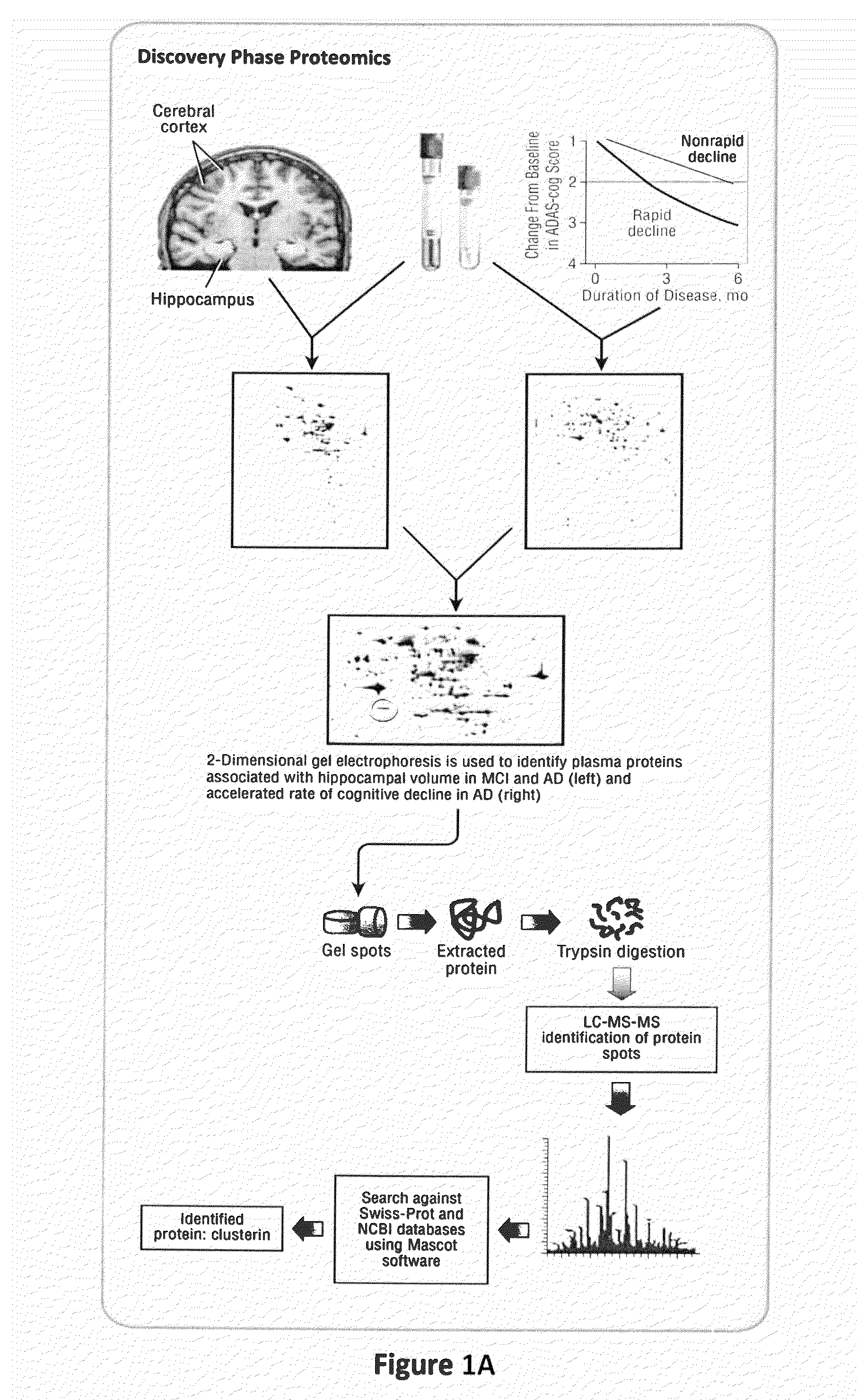
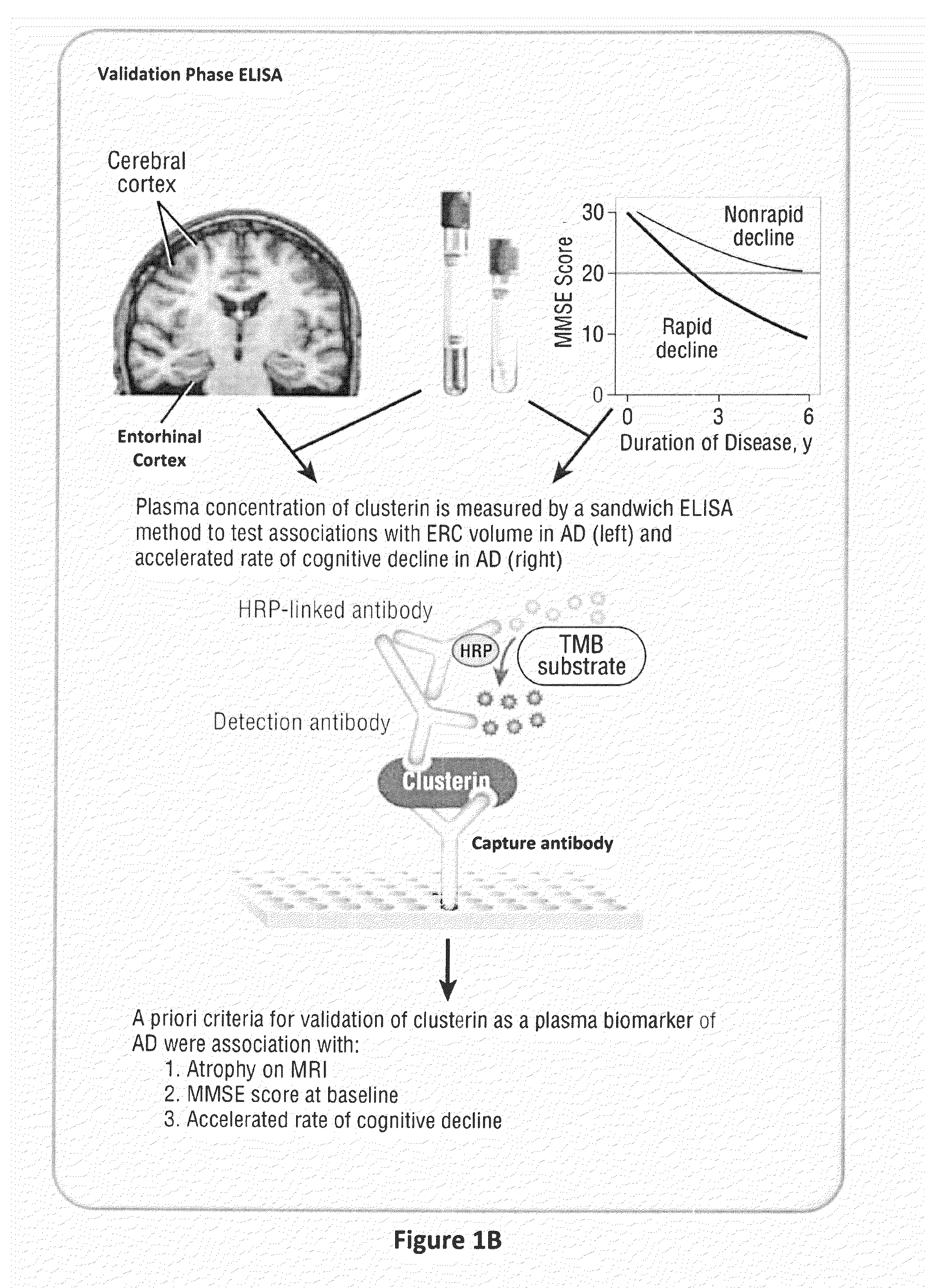
Multiple forms of Alzheimer's disease based on differences in concentrations of protein biomarkers in blood serum
The present invention relates to identification and uses of biomarkers for neurodegenerative disease, including Alzheimer's disease, and the related diseases. More specifically, the present invention relates to the identification of protein biomarkers useful for the screening, diagnosis, and differentiation of Alzheimer's disease from Parkinson's disease, other neurodegenerative diseases, and normal controls, and in the monitoring of Alzheimer's disease severity and disease mechanisms in patients.
Owner:NEOGENOMICS INC
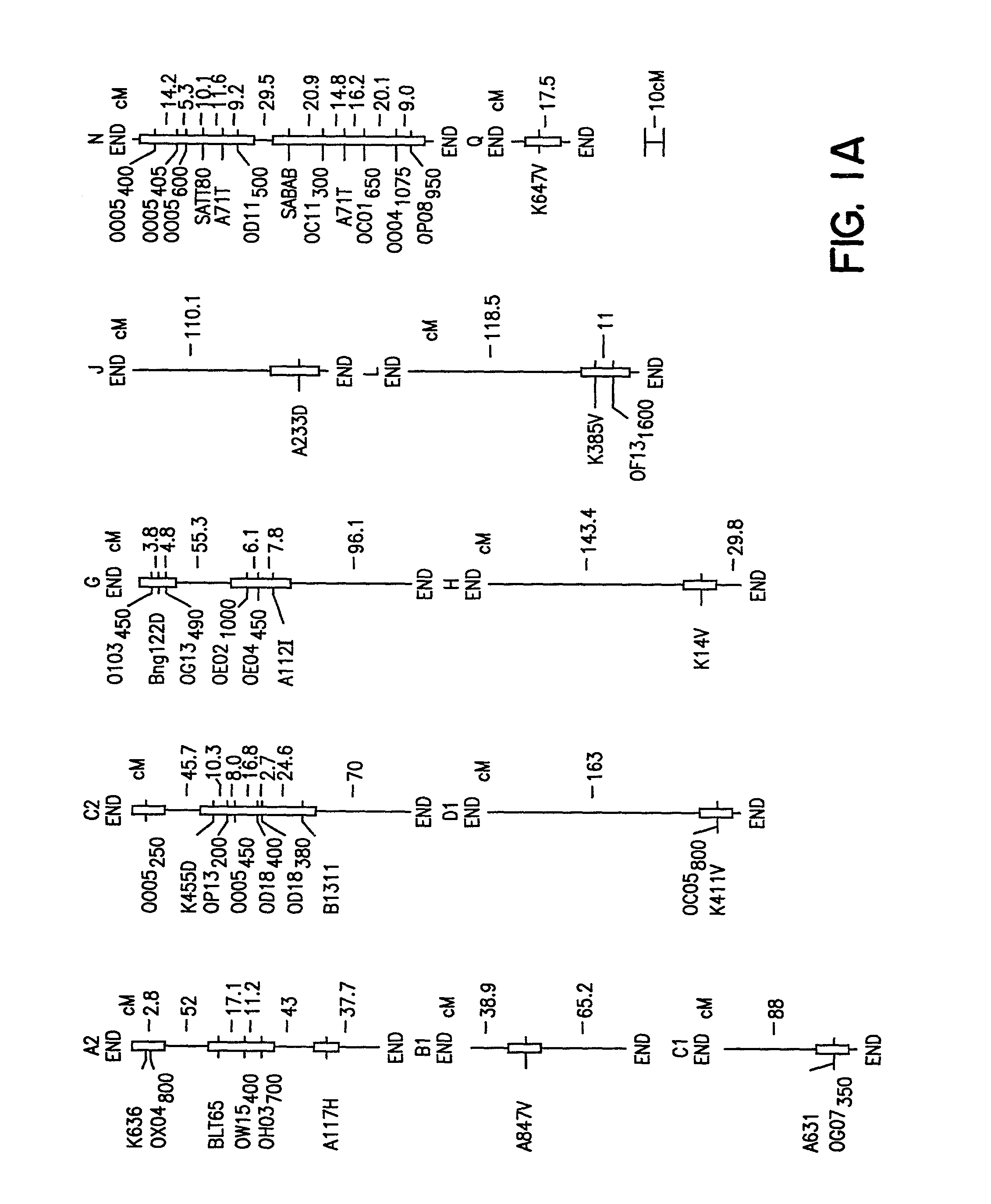
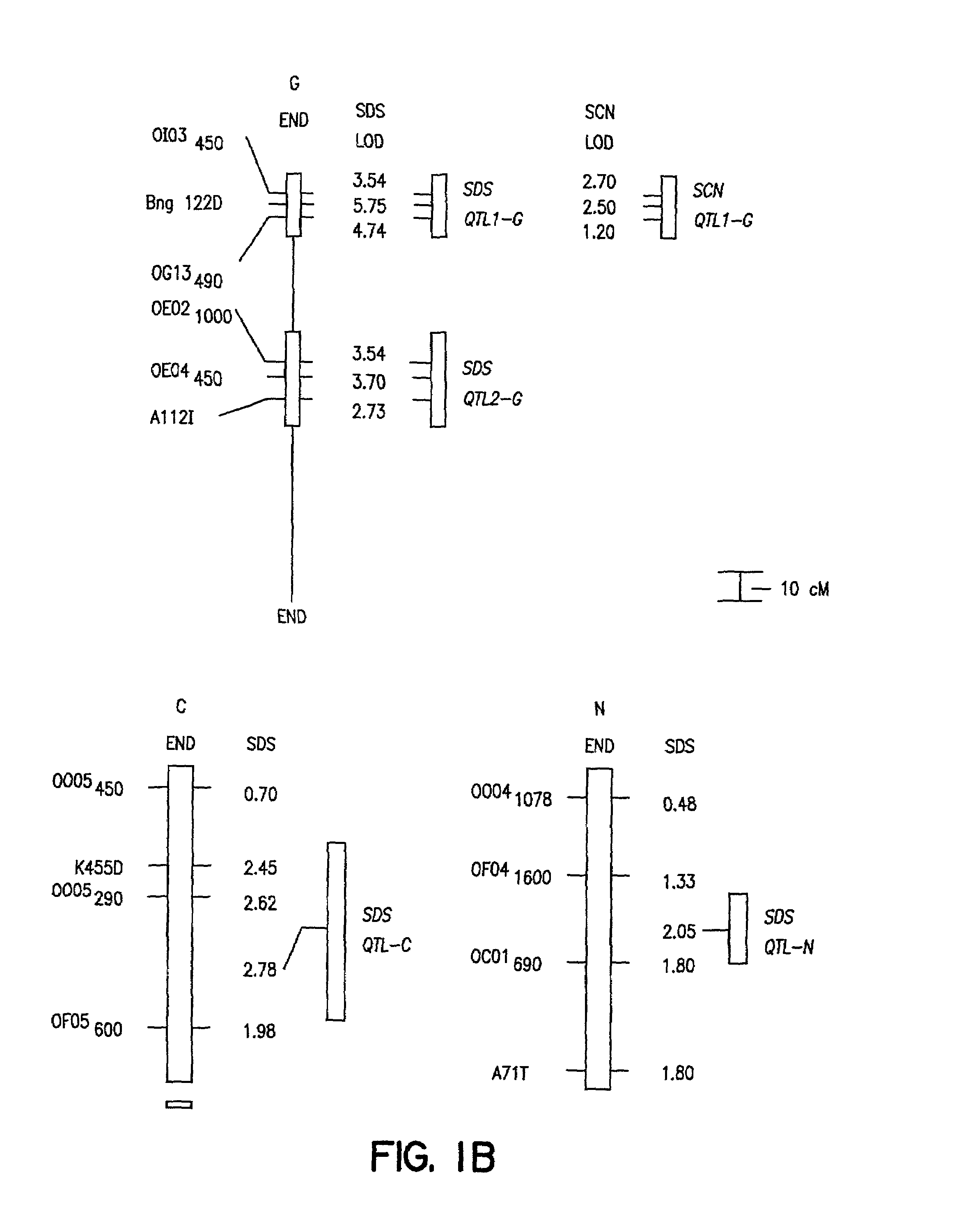
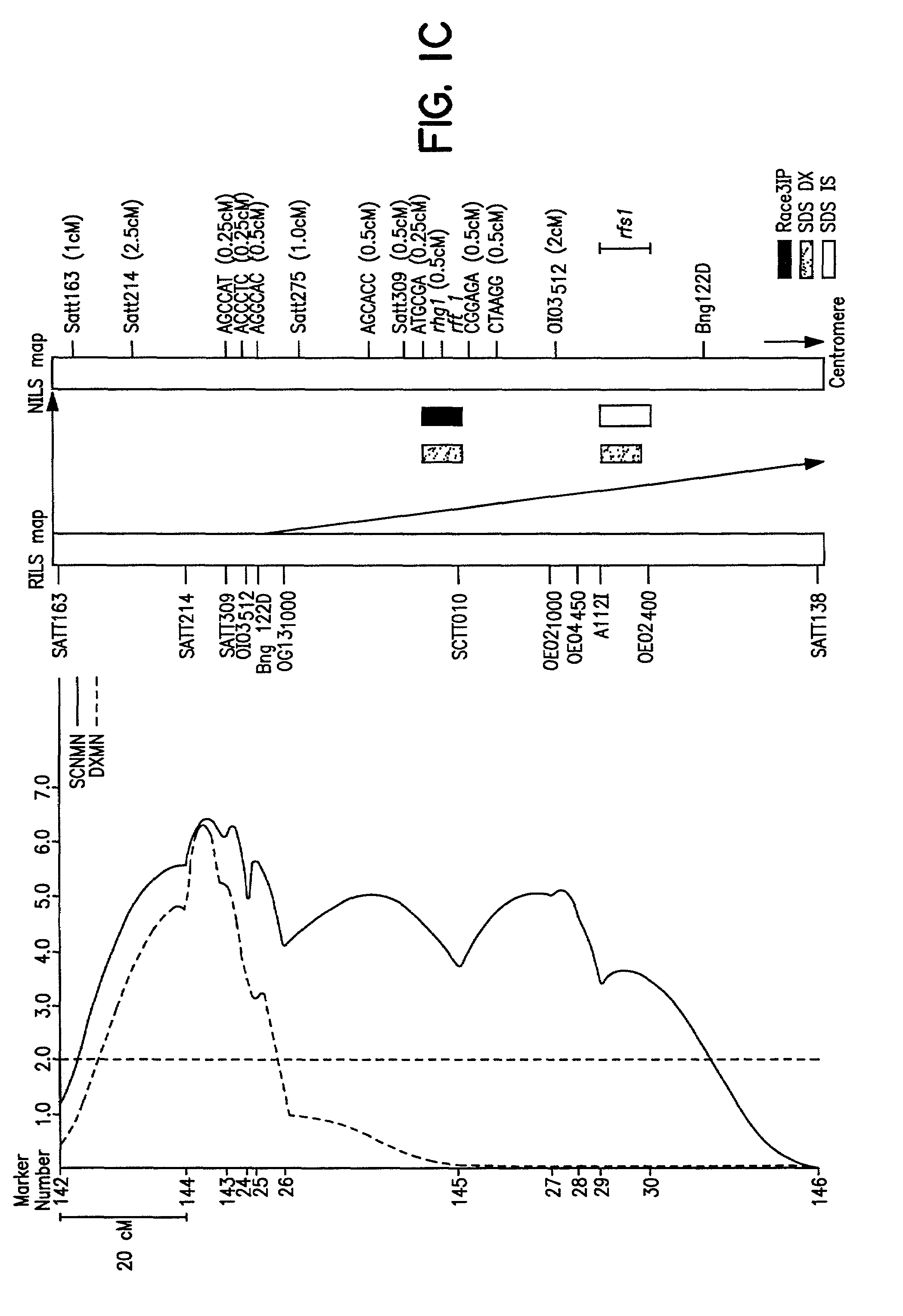
Method of determining soybean sudden death syndrome resistance in a soybean plant
InactiveUS7288386B2Solves the problem quickly and cheaply selecting resistant cultivarsImprove selection for SDS and SCN resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCell culture mediaBacterial growth
A method of determining the presence of soybean sudden death syndrome resistance in the soybean plant in a greenhouse setting, the method comprising the steps of: (a) inoculating soil with a low density inoculum of Fusarium solani; (b) planting a soybean plant in said inoculated soil; (c) growing said plant in said soil in a greenhouse; (d) isolating Fusarium solani-infected tissue from said plant; (e) culturing said infected tissue for a period of time sufficient to allow for fungal colony forming unit growth; (f) scoring at least one of disease severity and infection severity in said plant using the number of said fungal colony forming units; and (g) correlating at least one of said disease severity and said infection severity to at least one of disease severity and infection severity data from genetic markers associated with soybean sudden death syndrome resistance to identify a correlation, wherein a statistically significant correlation indicates presence of soybean sudden death syndrome resistance in said soybean plant. Also provided is a method of characterizing resistance to soybean sudden death syndrome in a soybean plant, the method comprising the steps of: (a) isolating roots from a soybean plant infected by Fusariurn solani; (b) culturing the root on a culture plate including a restrictive growth medium that provides for slow fungal growth and restricted bacterial growth; (c) determining root infection severity by statistically evaluating the number of Fusarium solani colony forming units on said culture plate; and (d) characterizing resistance to soybean sudden death syndrome in said soybean plant based on said determined root infection severity.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
System and method for analysis of multiple diseases and severities
A data processing technique is provided. In one embodiment, a computer-implemented method includes accessing reference deviation maps for a plurality of disease types. The reference deviation maps may include subsets of maps associated with severity levels of respective disease types, and a disease severity score may be associated with each severity level. The method may include selecting patient severity levels for multiple disease types based on the subsets of reference deviation maps. Also, the method may include automatically calculating a combined patient disease severity score based at least in part on the disease severity scores associated with the selected patient severity levels, and may include outputting a report based at least in part on the combined patient disease severity score. Additional methods, systems, and manufactures are also disclosed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
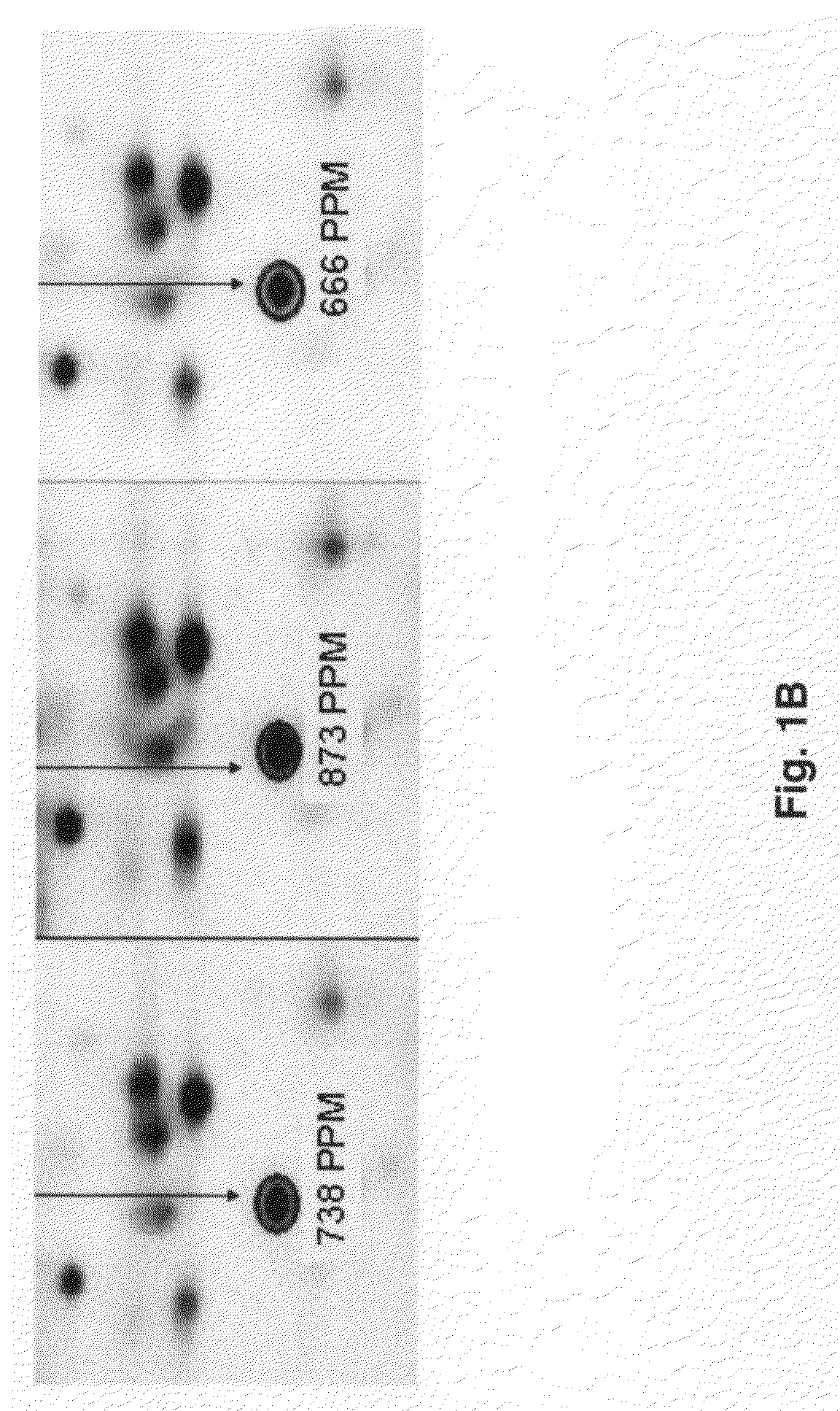
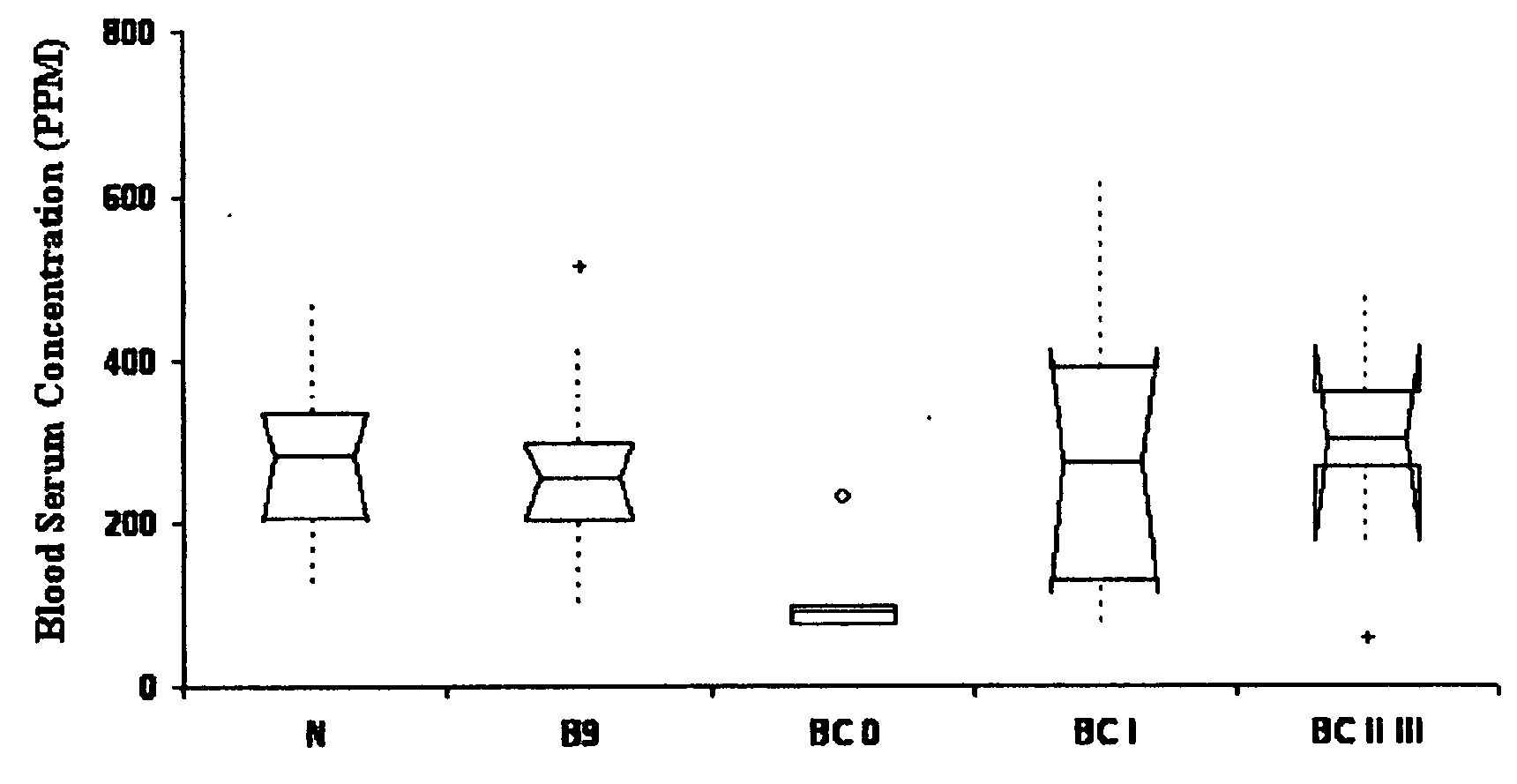
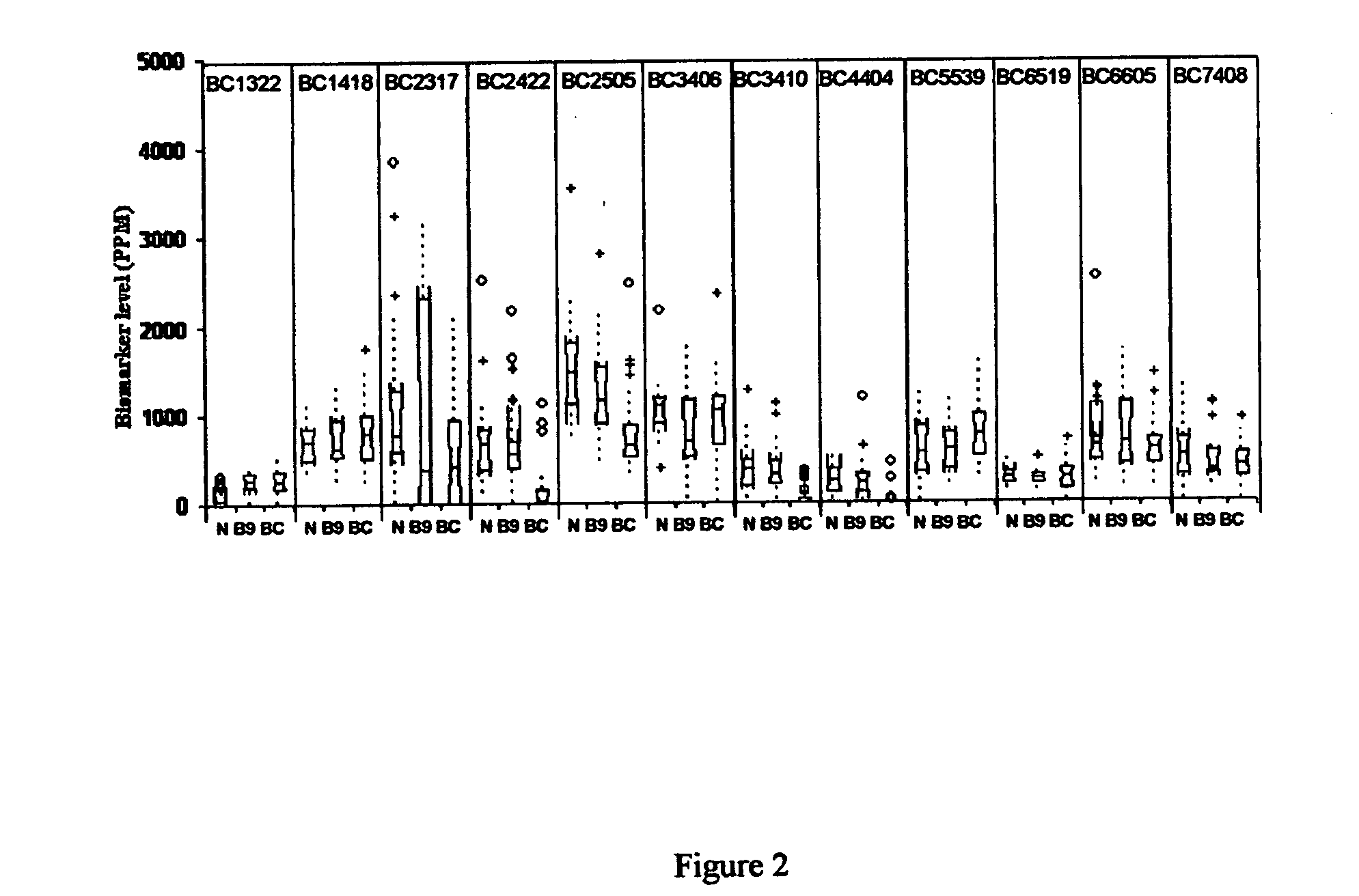
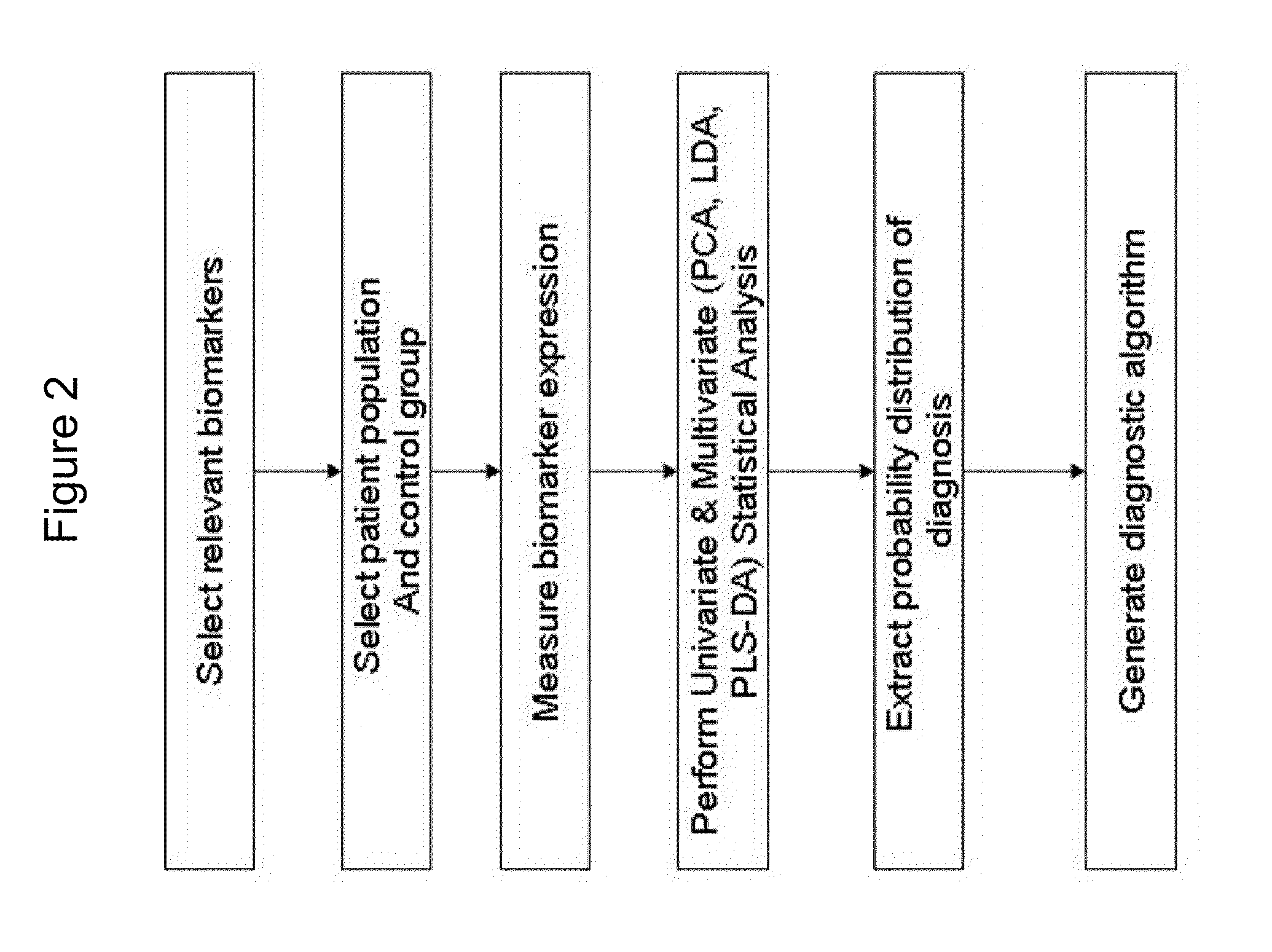
Twelve (12) protein biomarkers for diagnosis and early detection of breast cancer
InactiveUS20090035801A1More sensitiveMonitor responseMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisDisease severityGel electrophoresis
The invention relates to 12 identified protein biomarkers for diagnosis, determination of disease severity, and therapeutic response monitoring of patients with breast cancer. The method is based on the use of 2-dimensional (2D) gel electrophoresis to separate the complex mixture of proteins found in blood serum, the quantitation of up to 12 protein biomarkers, and statistical analysis of the concentration of the protein biomarkers.
Owner:NEOGENOMICS INC
Inhaler and driving method for same
InactiveUS20100089394A1Efficient managementReduce errorsRespiratorsMedical devicesDisease severityIntensive care medicine
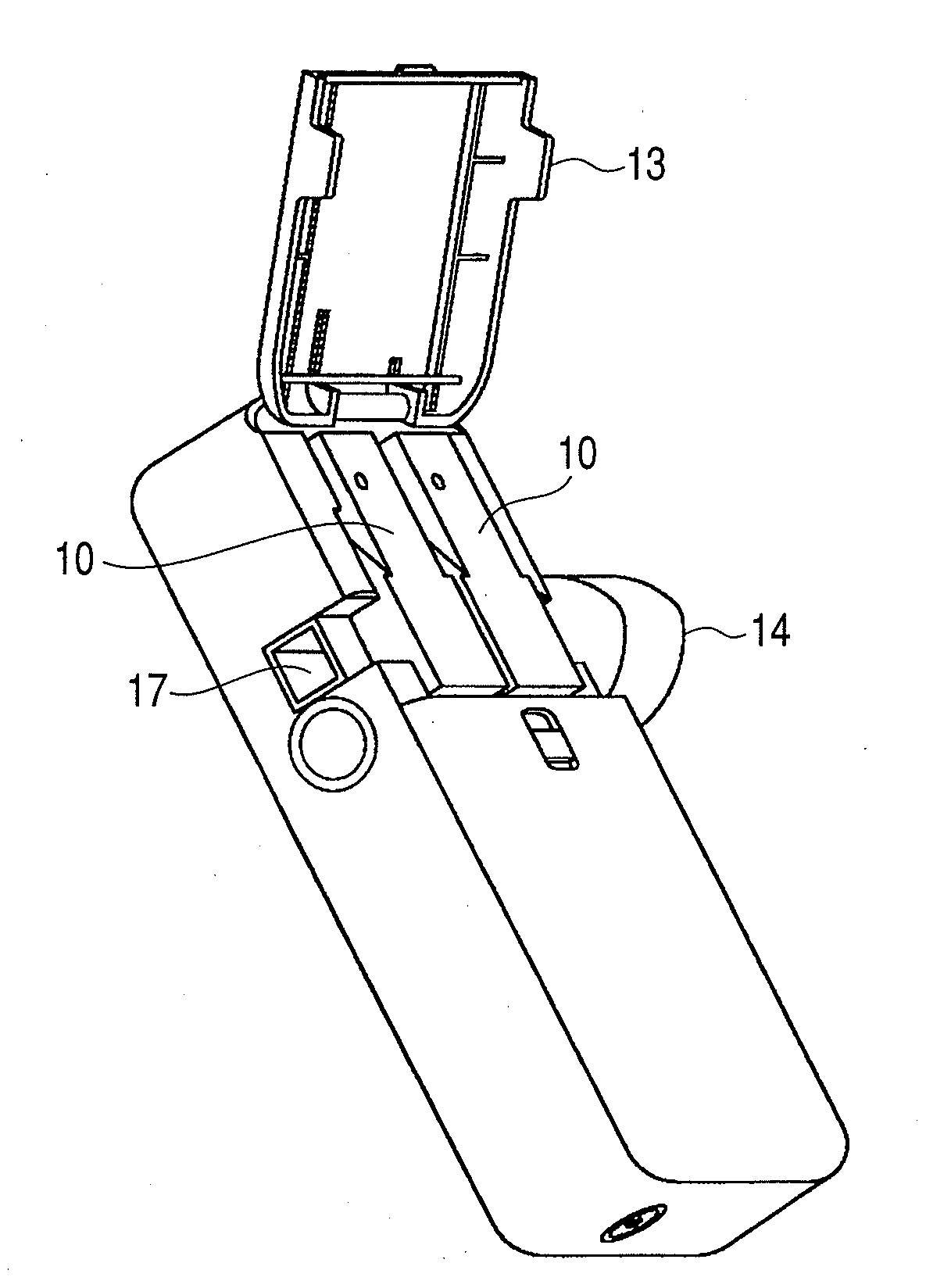
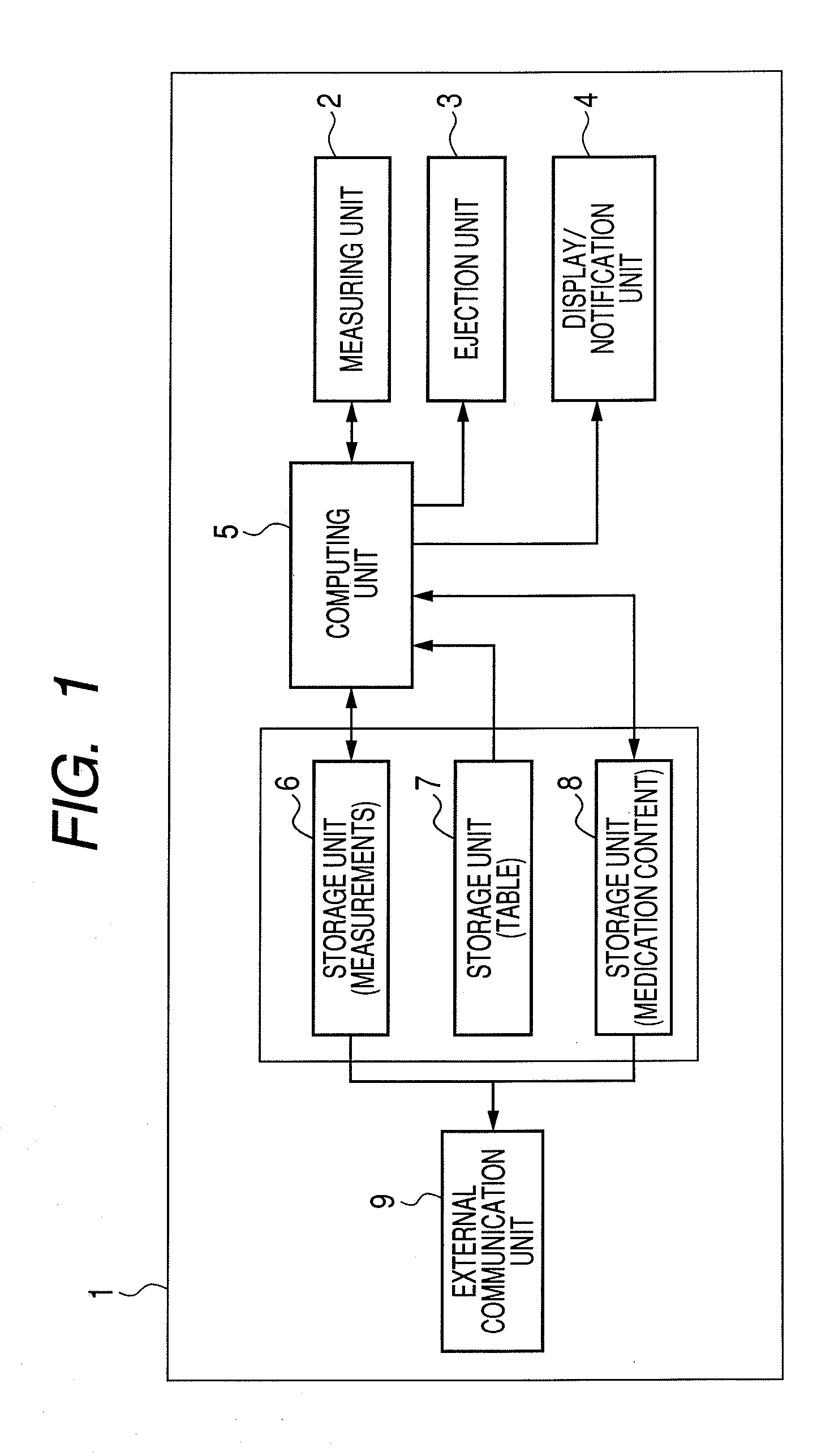
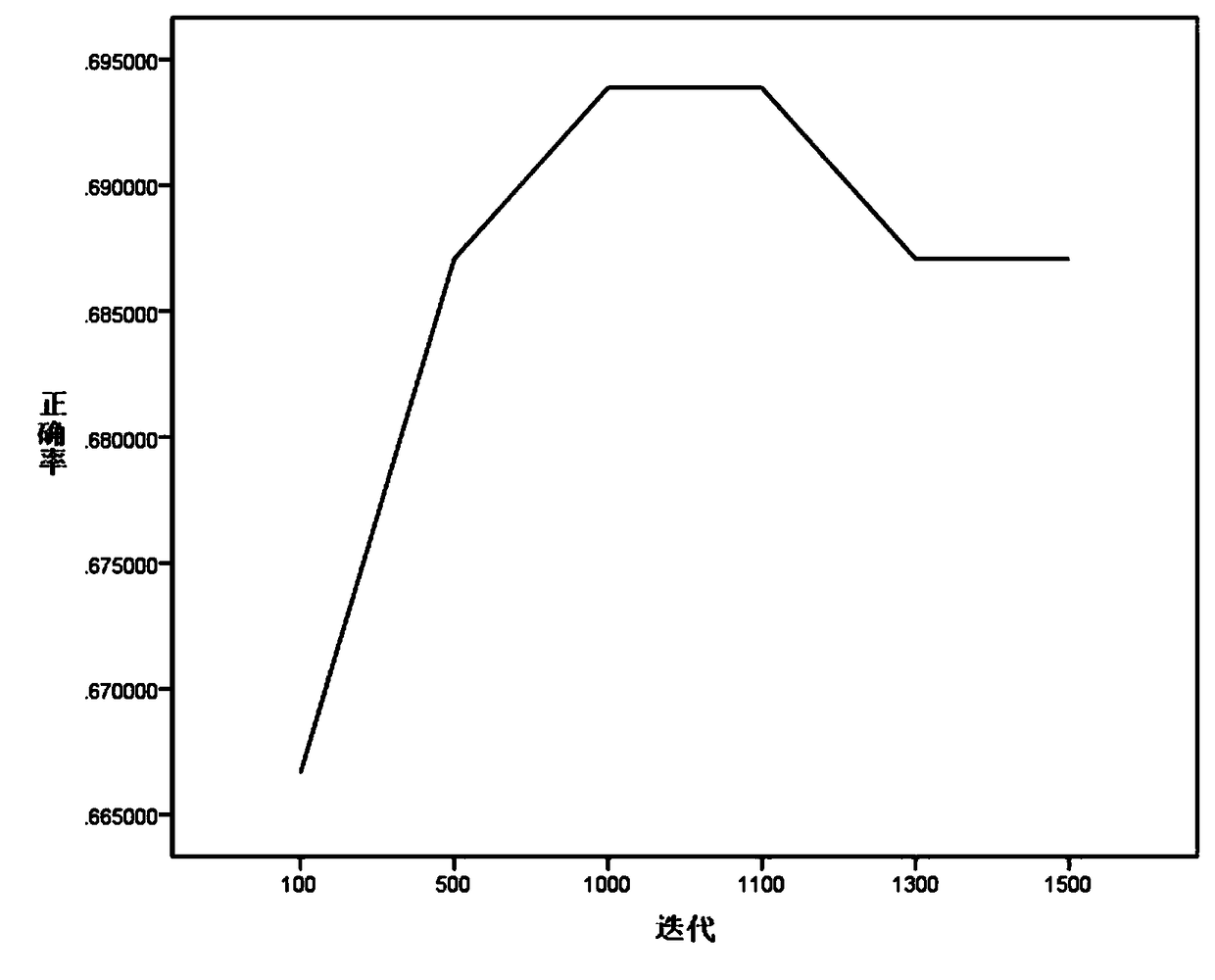
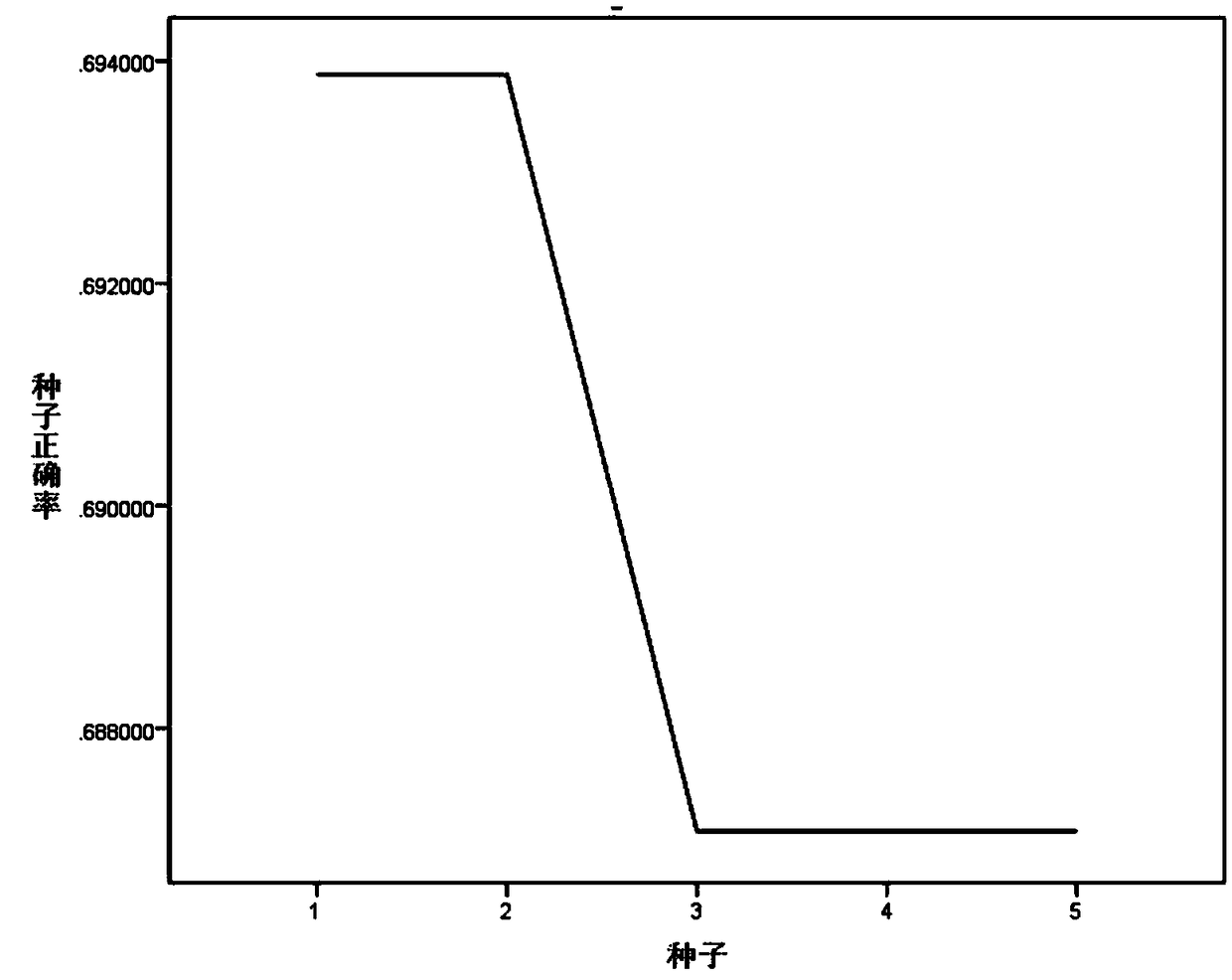
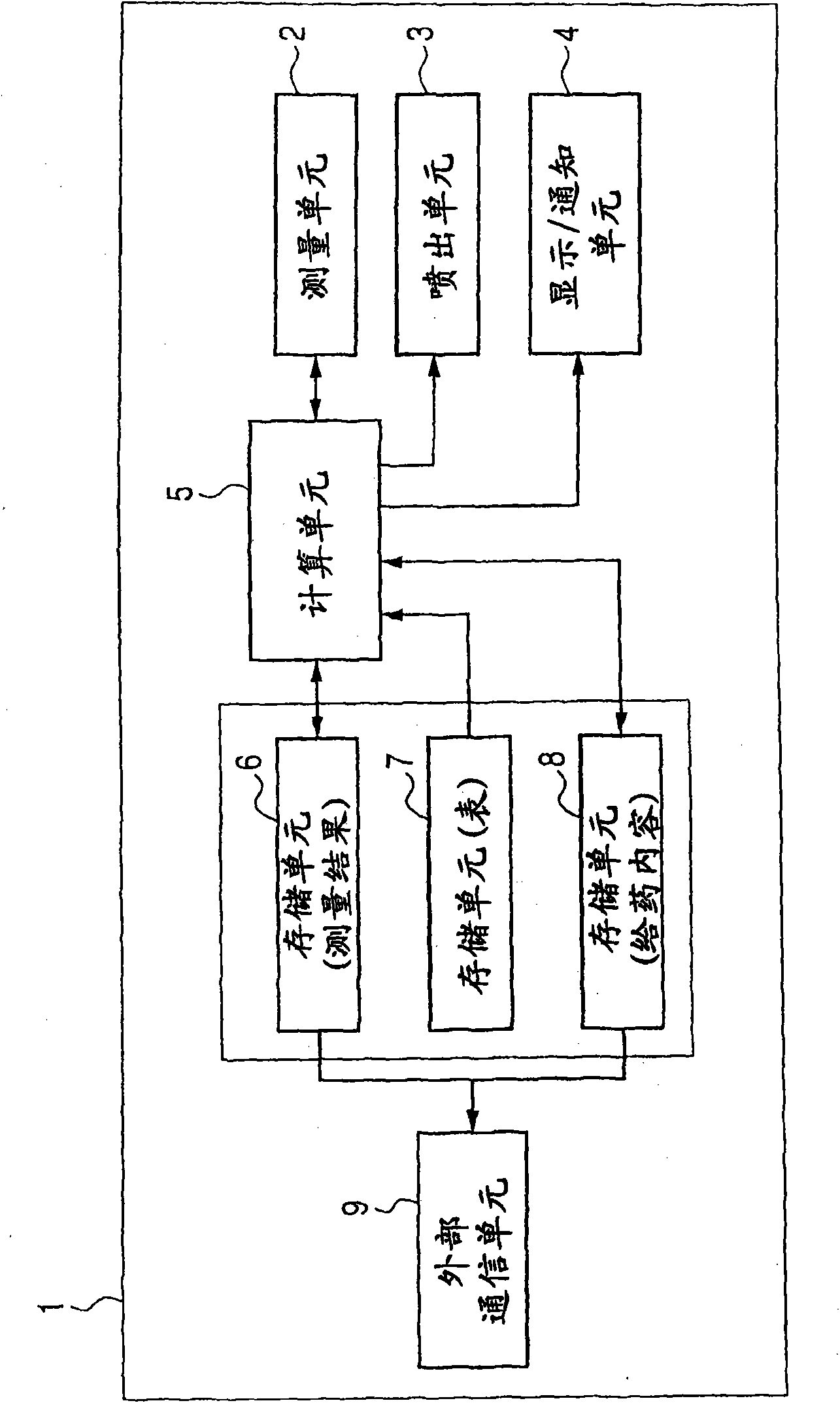
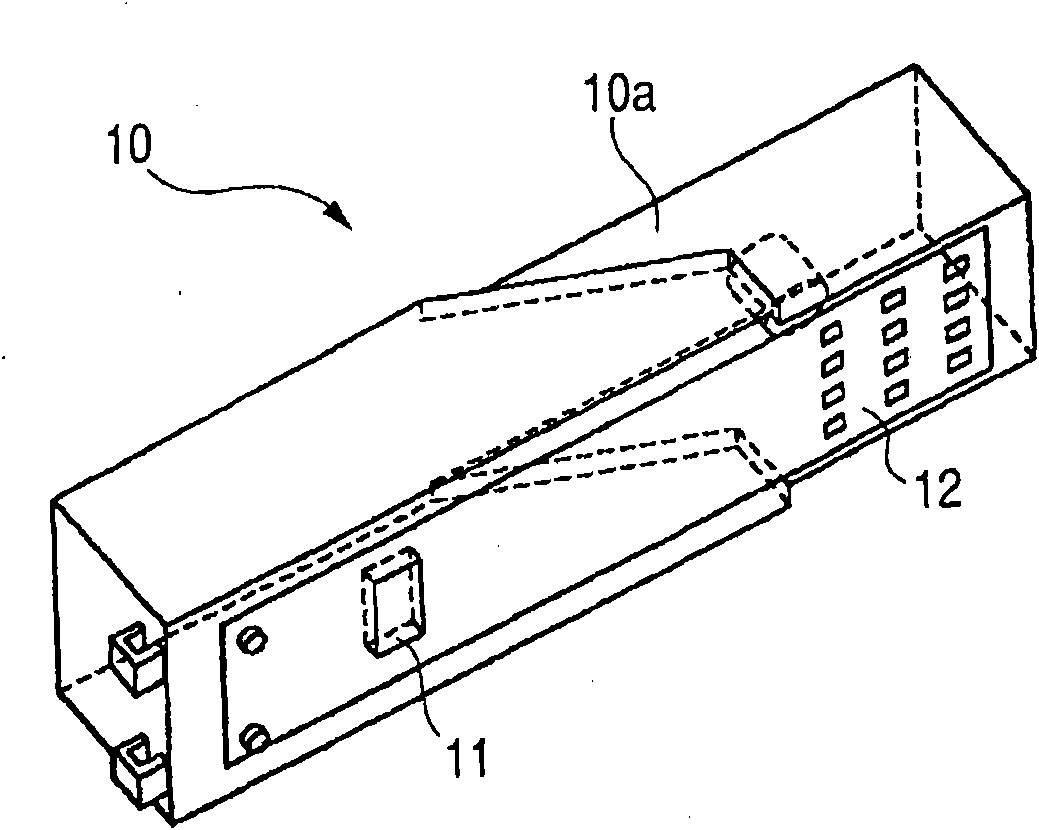
The present invention provides an inhaler capable of measuring lung function, feeding back the measurements, and administering medicine suitable for a lung condition in a single use. The inhaler 1 of the present invention includes a lung function measuring unit 2 having a spirometer for measuring lung function, and, using a computing unit 5, compares the lung function measurements with a medication pattern table stored in a storage unit 7 and determines a disease severity and a diseased region of the lung. Based on the determination results, the computing unit further selects types and particle diameters of medicines suitable for the lung condition, and controls an ejection unit 3 including a plurality of ejection portions to eject the medicines required for treatment in a single use.
Owner:CANON KK
Systems for clinical trials
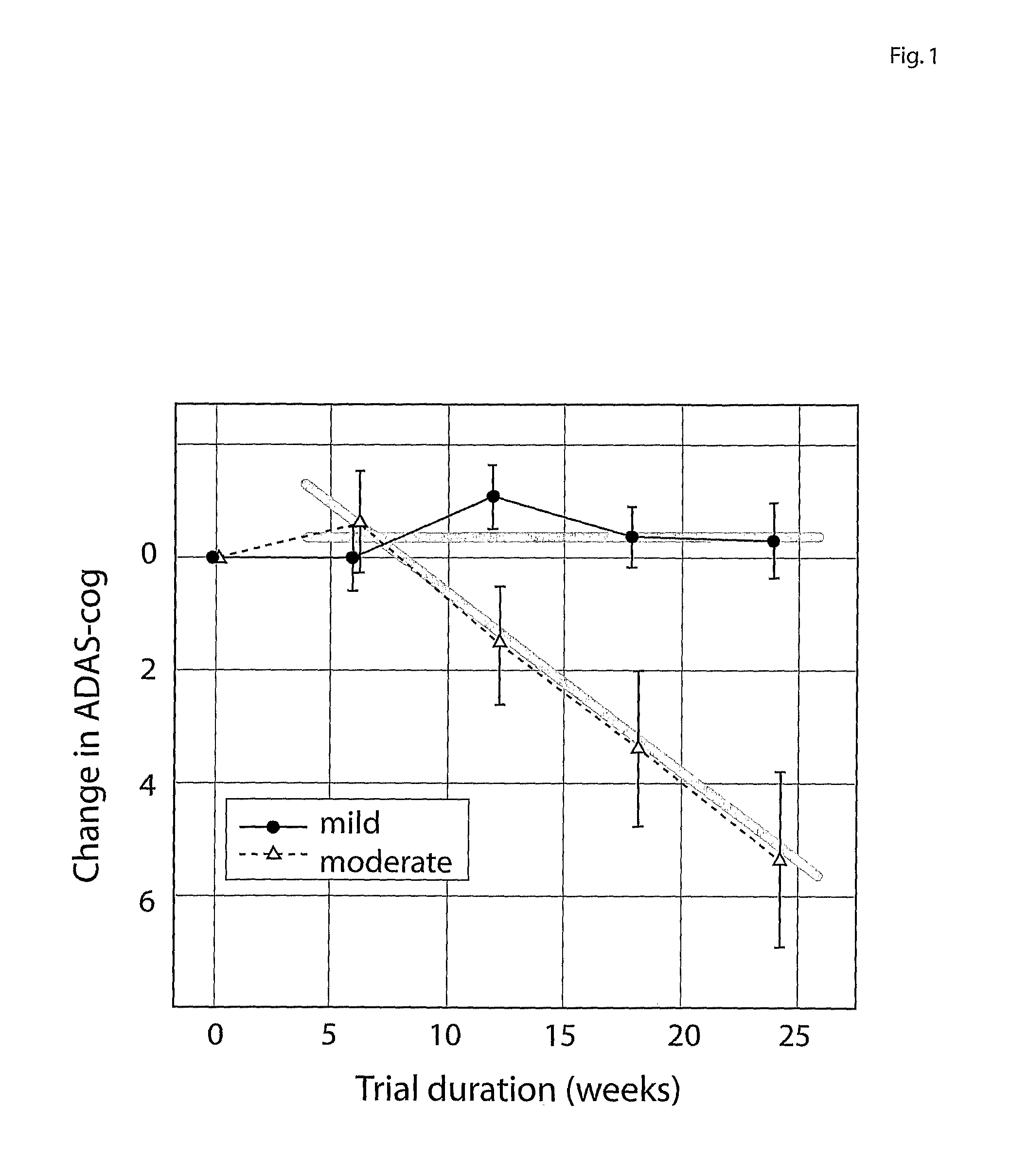
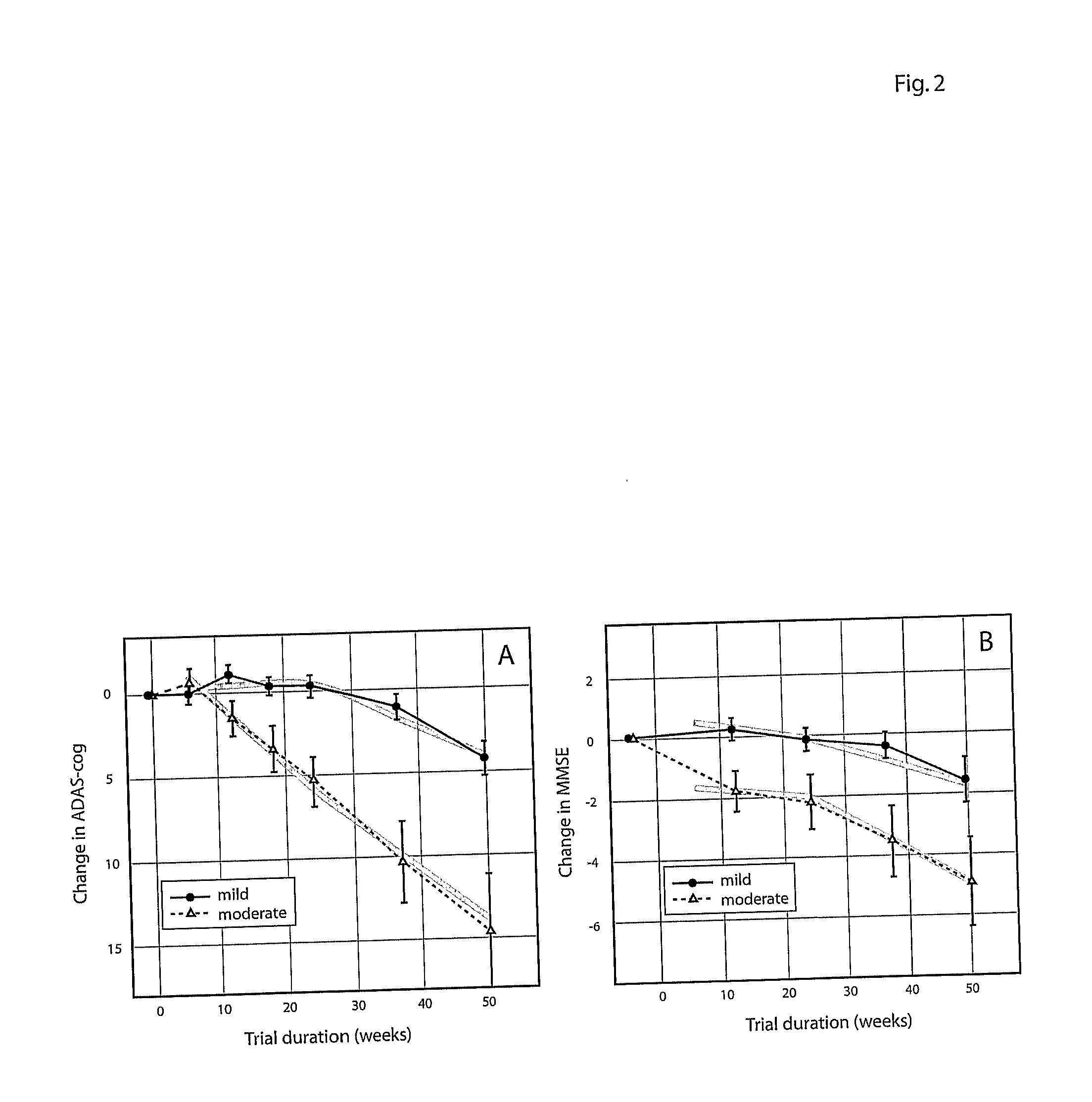
InactiveUS20100280975A1Medical simulationData processing applicationsBaseline IndicatorTreatment Arm
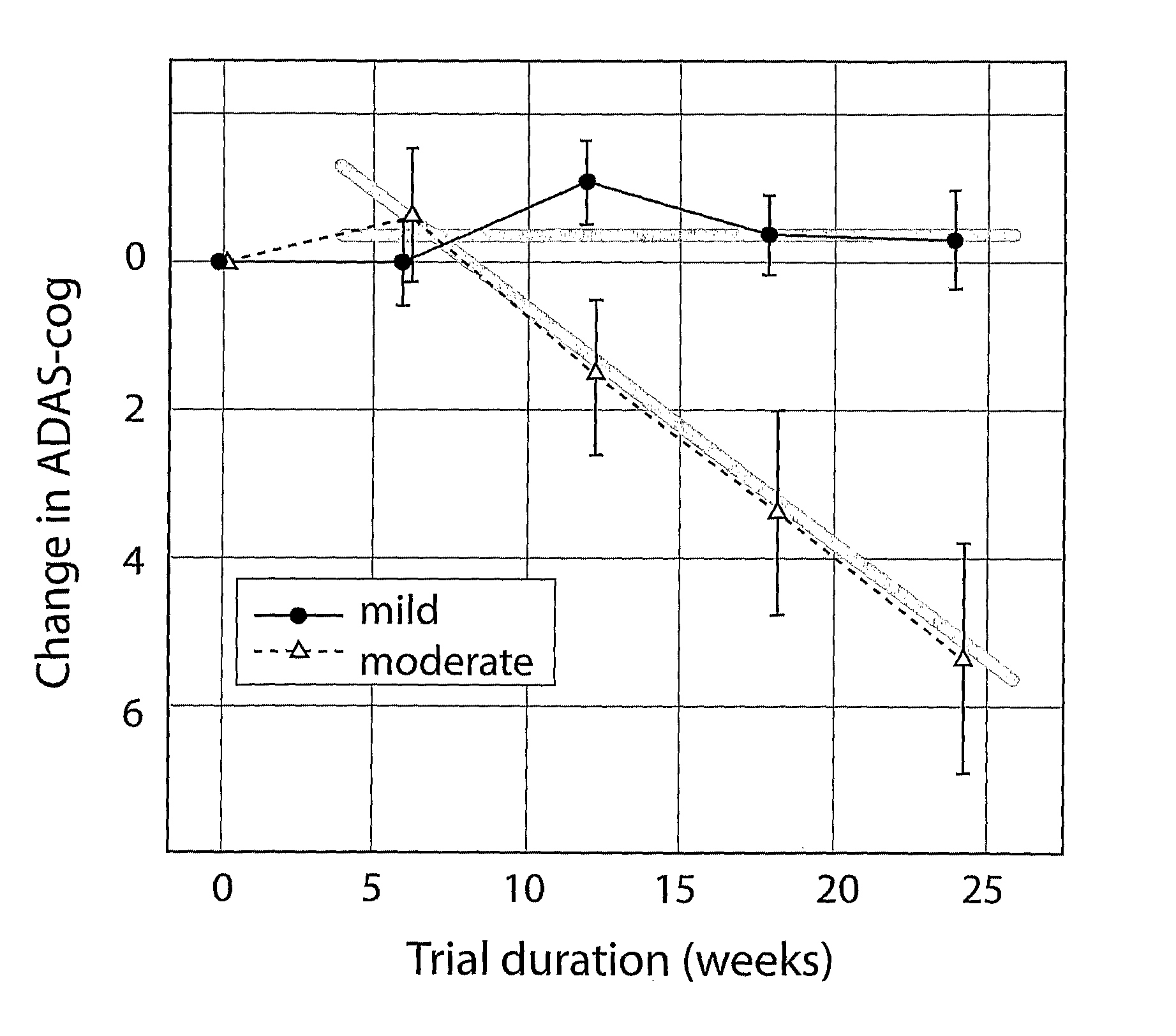
The invention provides methods and systems for assessing the efficacy of a pharmaceutical which is putatively disease modifying of a cognitive disorder, for use in the treatment or prophylaxis of that cognitive disorder, the method comprising the steps of: (1) stratifying a subject group into at least 2 sub-groups according to a baseline indicator of likely disease progression, (2) treating members of each subject group with the pharmaceutical for a treatment time frame, (3) deriving psychometric and optionally physiological outcome measures for each treated patient group, (4) comparing the outcomes at (3) with a comparator arm of said sub-groups which is optionally a placebo or minimal efficacy comparator arm, (5) using the comparison in (4) to derive an efficacy measure for the pharmaceutical. The methods and systems of the invention address problems such as low rate of decline over the treatment time-frame of patients who have mild-disease severity at baseline and biased withdrawal, particularly in the placebo / comparator treatment arm.
Owner:WISTA LAB LTD
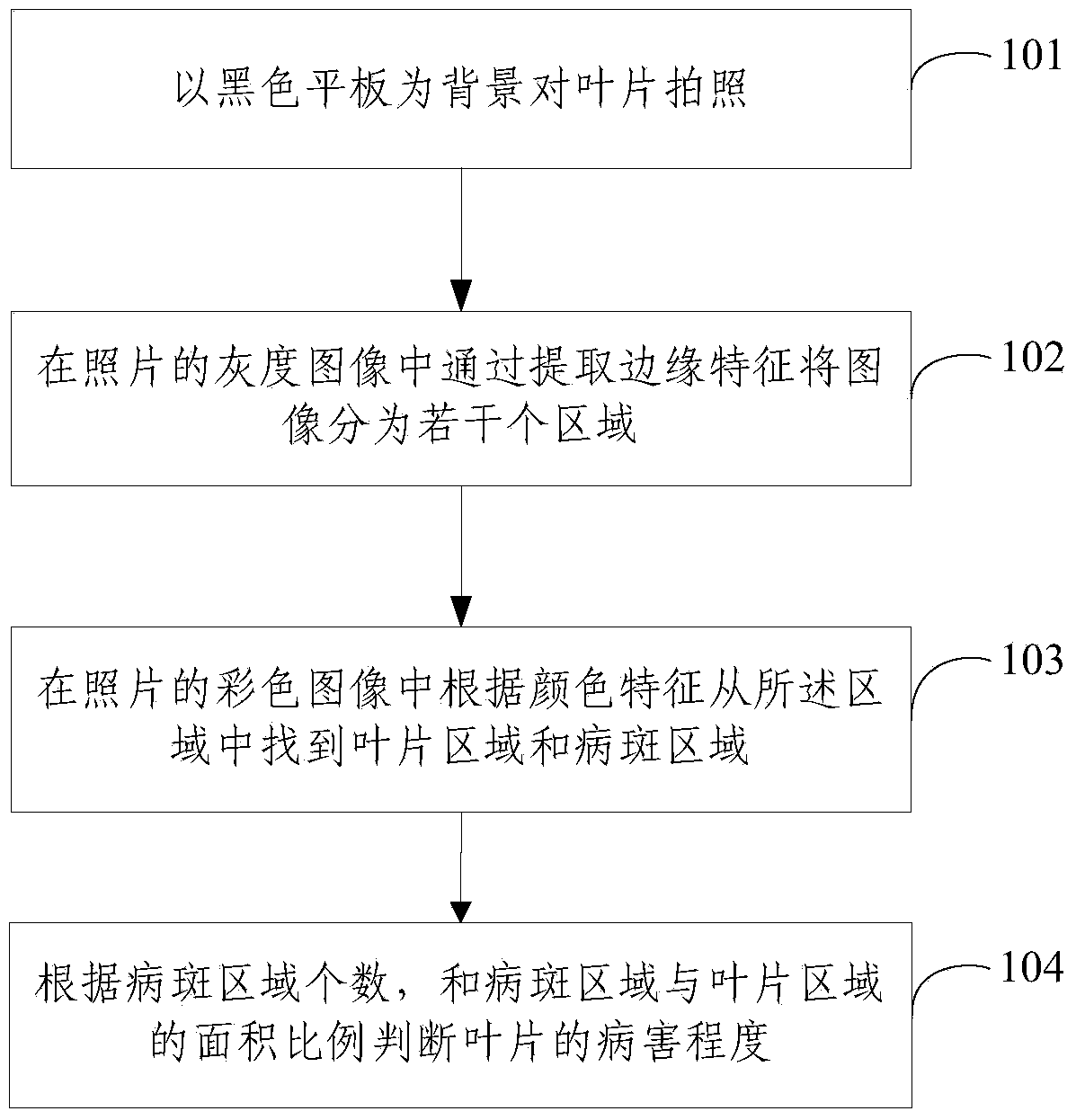
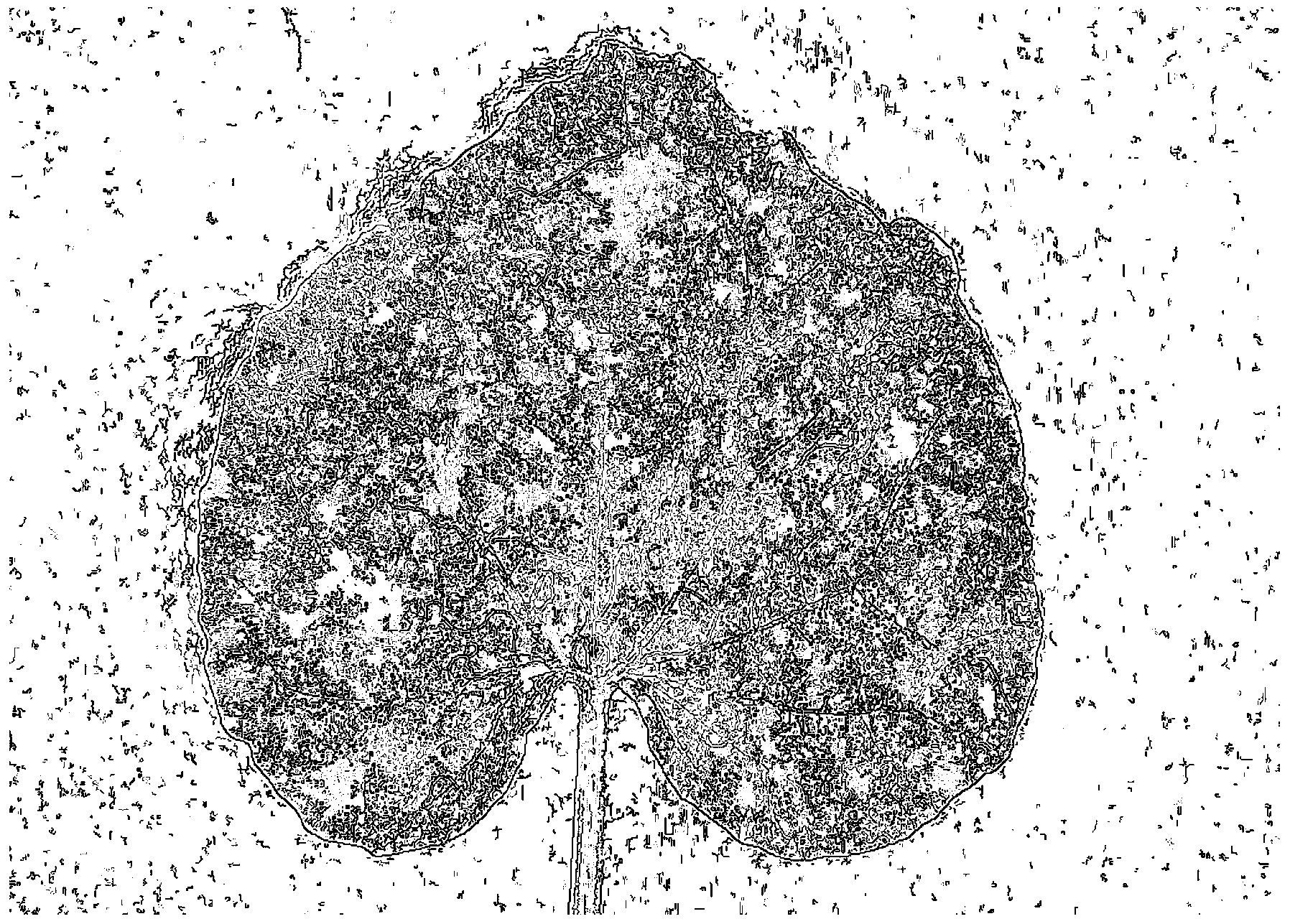
Method and system for acquiring disease severity of leaf under open field environment
ActiveCN103778628AAvoid inaccurate resultsReduce labor intensityImage analysisColor imageAcquired diseases
The invention relates to agricultural engineering and particularly relates to a method and a system for acquiring the disease severity of a leaf under an open field environment. The method comprises the following steps: taking a picture of a leaf against a black flat plate; extracting edge features in a gray image of the picture to divide the image into a plurality of regions; finding out leaf regions and diseased spot regions from the regions according to color features in a color image of the picture; and judging the disease severity of the leaf according to the number of the diseased spot regions and the area ratio of the diseased spot regions to the leaf regions. The disease severity of a leaf can be accurately calculated under an open field environment.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
Method and system for automatically generating a disease severity index
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
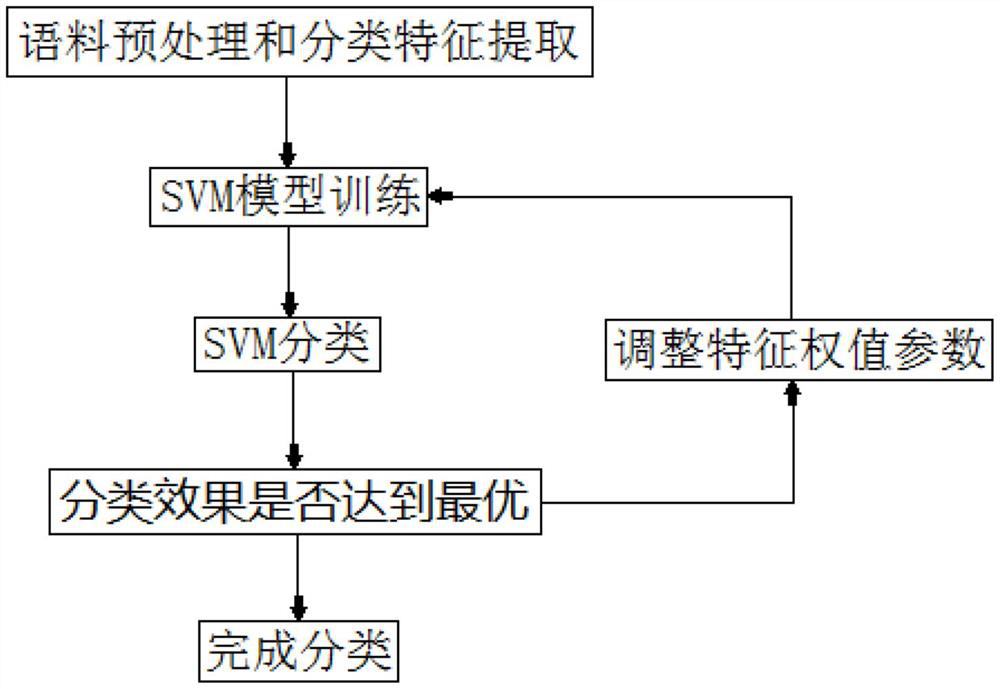
Semi-supervised self-learning driven medical text disease identification method
PendingCN112735597ASimple methodImprove featuresMedical data miningSemantic analysisFeature extractionText annotation
Disclosed is a semi-supervised self-learning driven medical text disease identification method provided by the invention, feature classification of the medical text is mainly realized, the features include disease object types, disease progression, whether diseases occur, disease severity, disease condition, disease uncertainty and the like, and by identifying and classifying features, unstructured medical texts are structured and can be directly processed and used in further information mining; based on the features of few medical text annotation texts and many unannotated texts, the invention is developed from the aspects of feature extraction and classification model optimization; experimental results show that the method well makes up for the defects and deficiencies of few tagged texts, and since similar data and wrong classification data are easily introduced into the self-learning method, the effect of the semi-supervised SVM in the aspect of utilizing untagged data is better than that of the semi-supervised SVM, and the feasibility and high efficiency of the method are proved.
Owner:荆门汇易佳信息科技有限公司
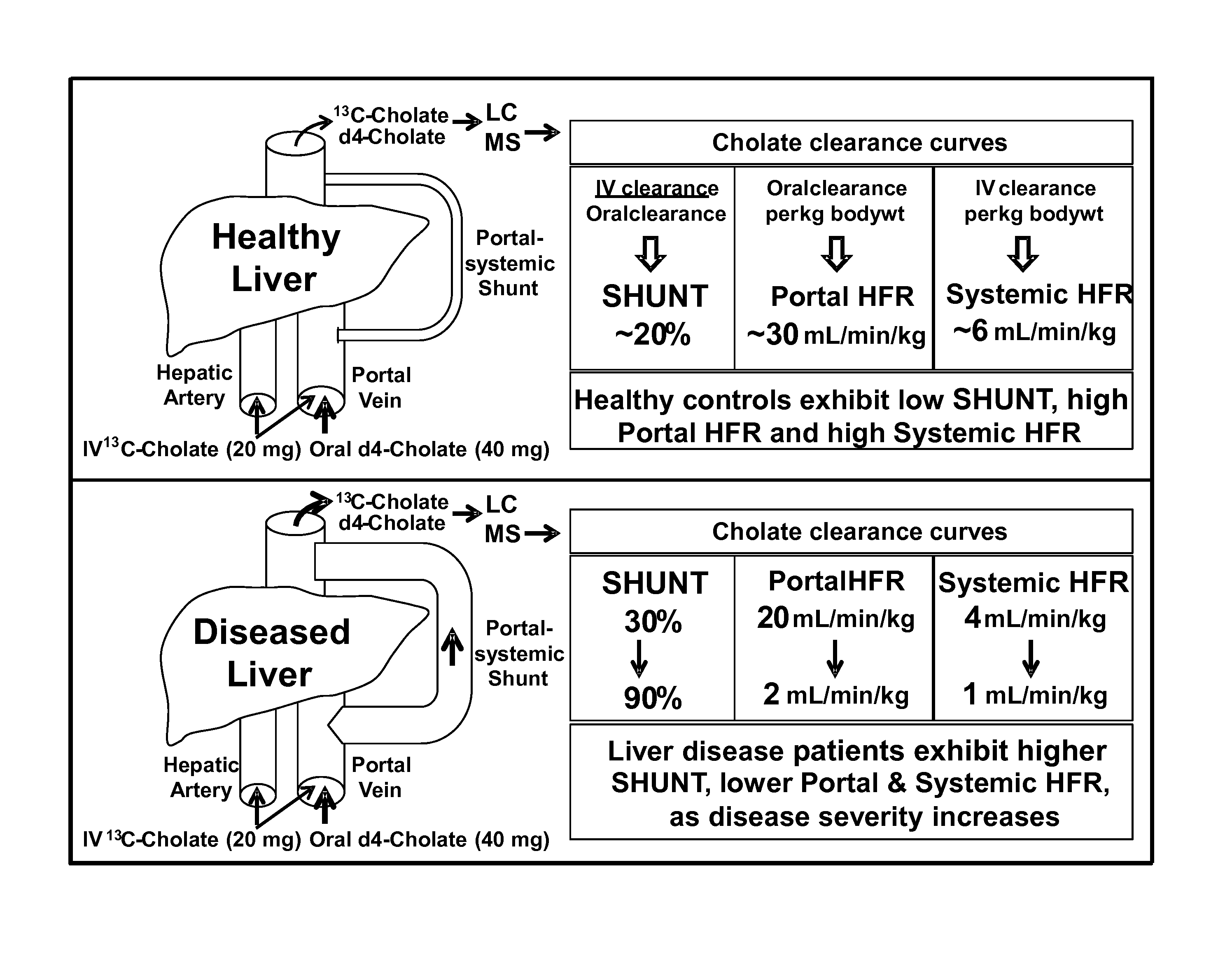
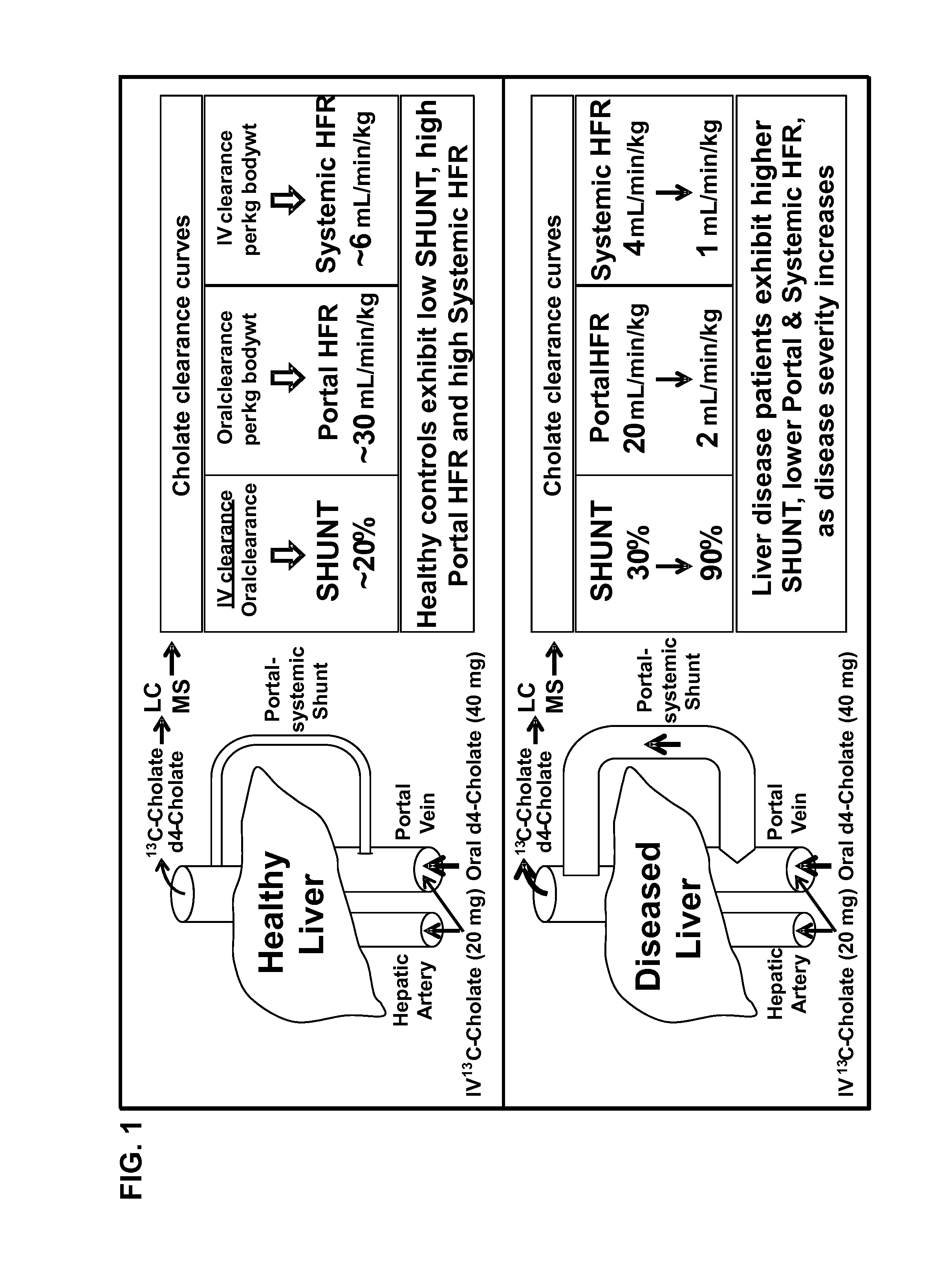
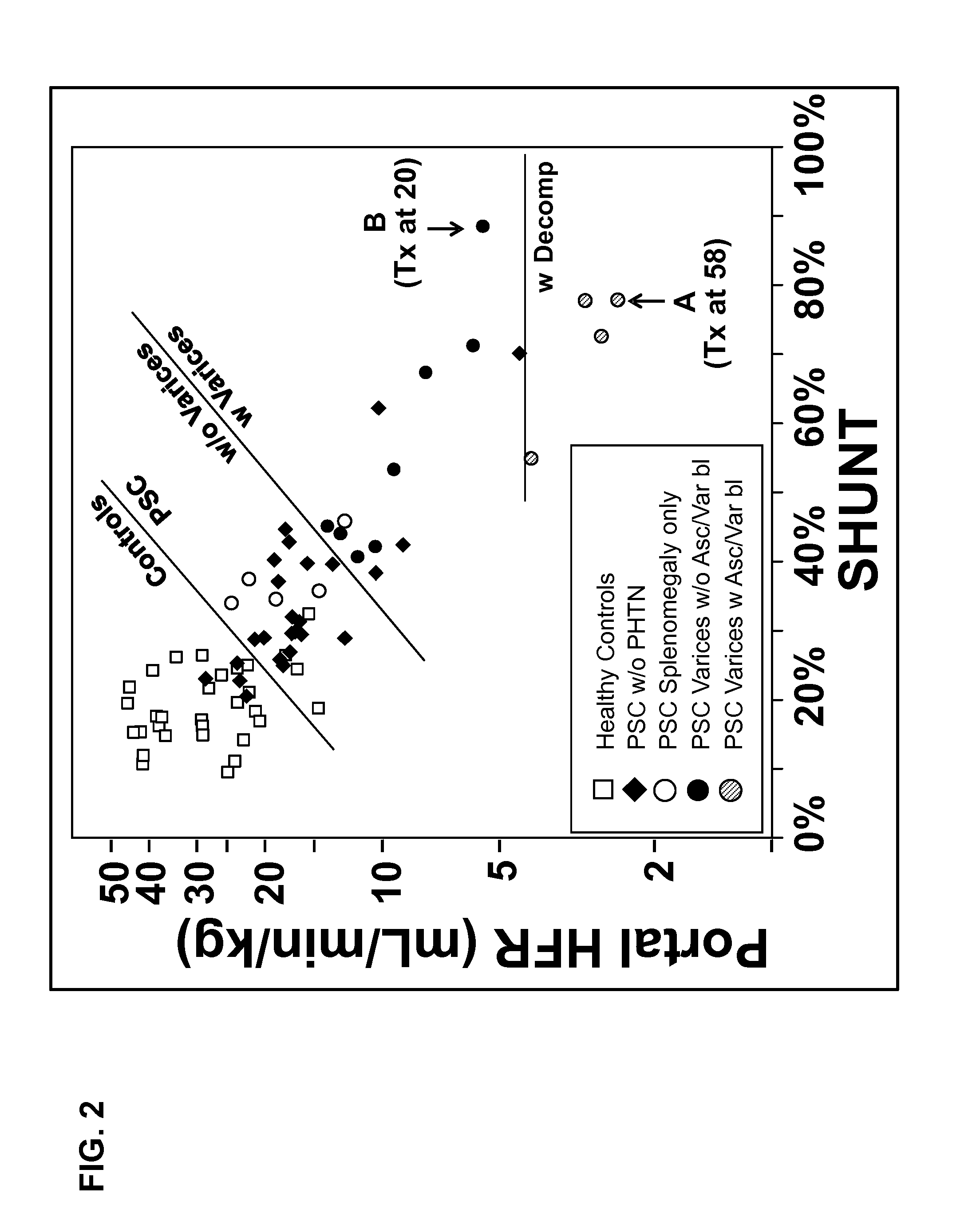
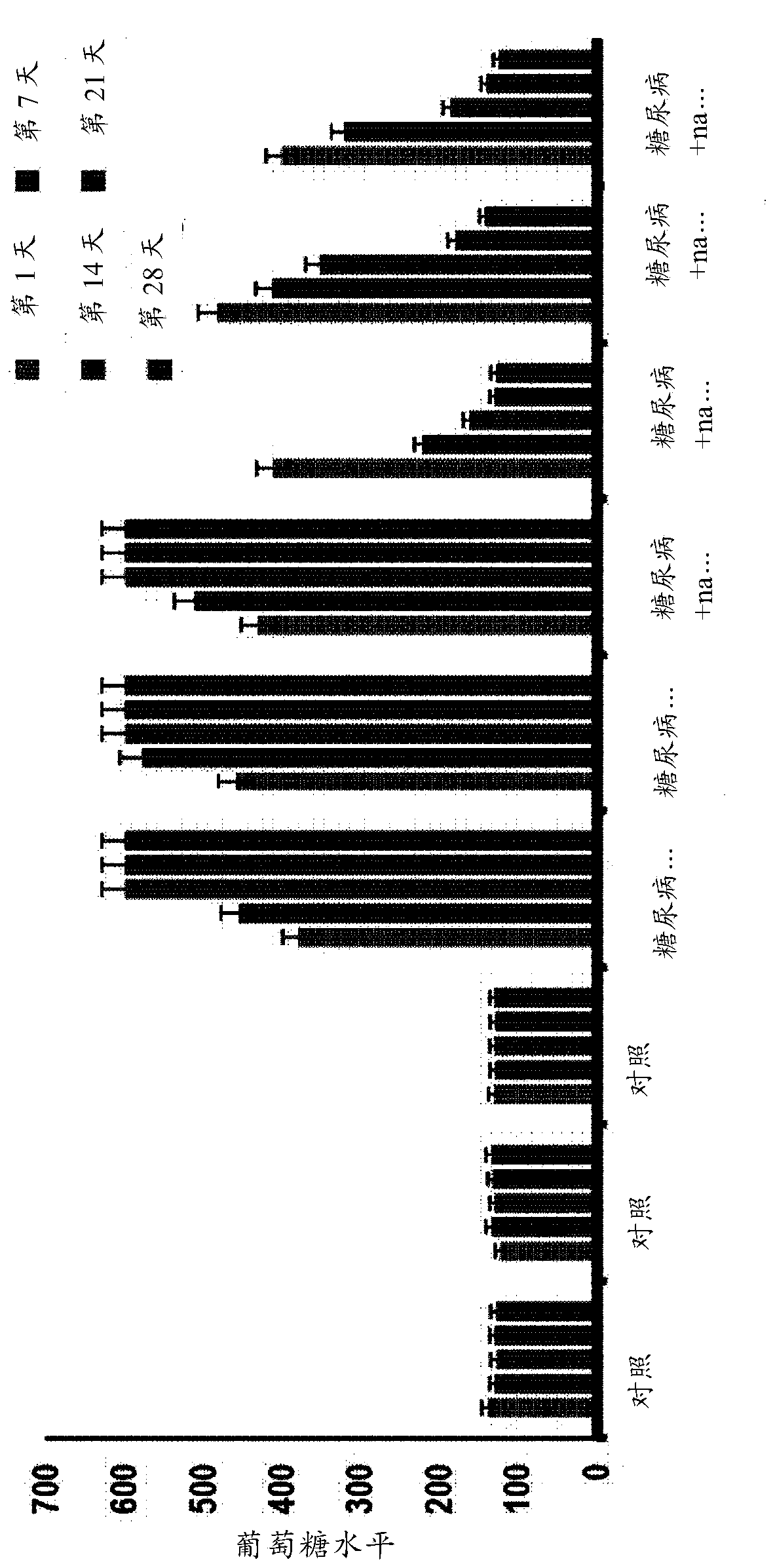
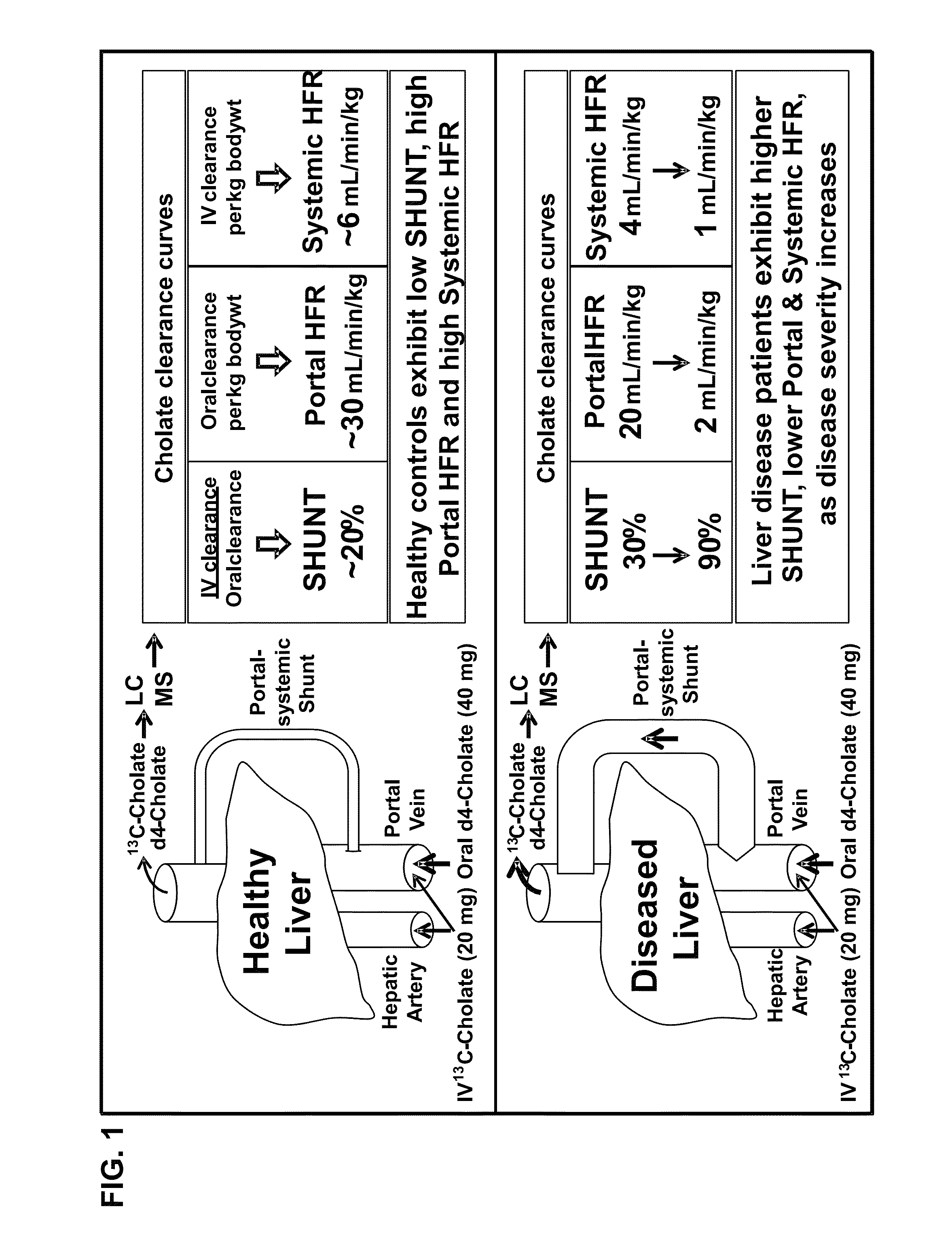
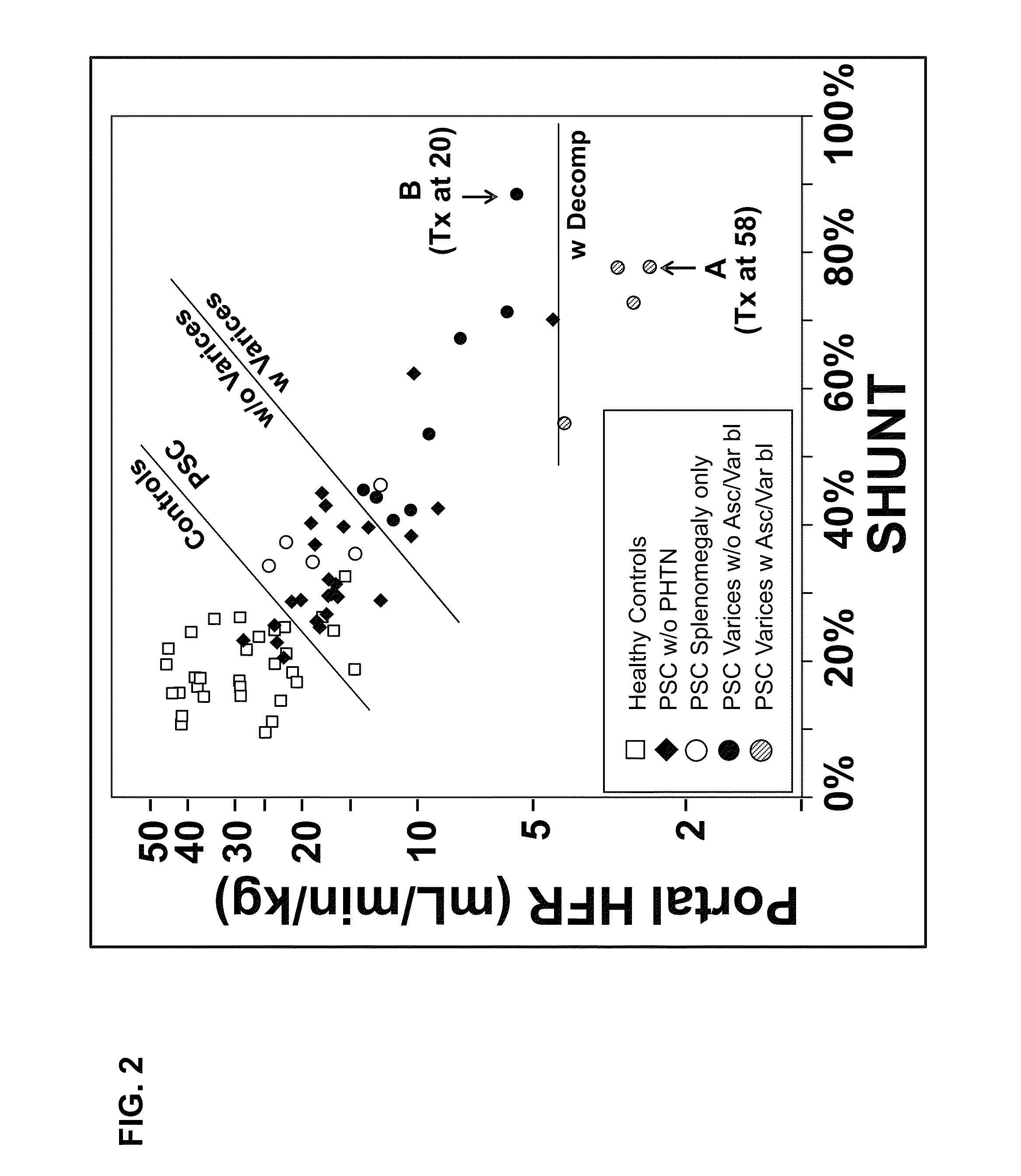
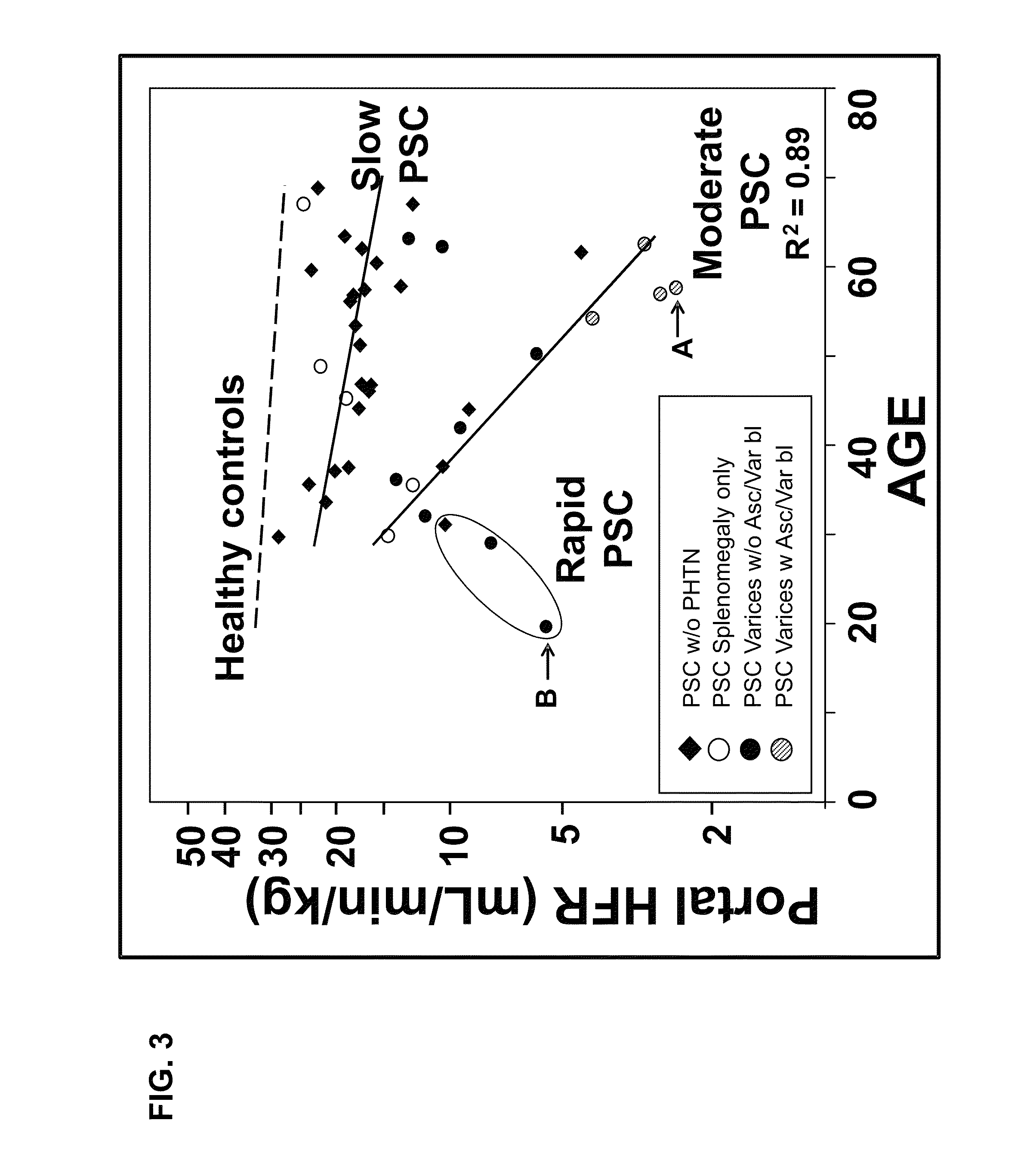
Disease severity index for assessment of chronic liver disease and method for diagnosis of three distinct subtypes of primary sclerosing cholangitis
ActiveUS20140147875A1Low indexOrganic active ingredientsHealth-index calculationDisease severityNon invasive
A Disease Severity Index (DSI) is provided for assessment of chronic liver disease in a patient using non-invasive liver function test results. A DSI was derived from non-invasive liver function test results based on hepatic blood flow. The DSI is used in methods for prediction of clinical outcomes, prediction of response to antiviral treatment, and assessment of progression of chronic liver diseases. Non-invasive methods to diagnose three distinct categories of patients with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) are provided. The methods can be used to diagnose PSC patients as Slow Progressors, Moderate Progressors and Rapid Progressors.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Multiple Biomarker Panels to Stratify Disease Severity and Monitor Treatment of Depression
InactiveUS20110213219A1Accurately stratify disease severityMonitor responseDisease diagnosisDiagnostic recording/measuringBiomarker panelDisease severity
Materials and Methods for stratifying disease severity and for monitoring major depressive disorder are provided.
Owner:RIDGE DIAGNOSTICS
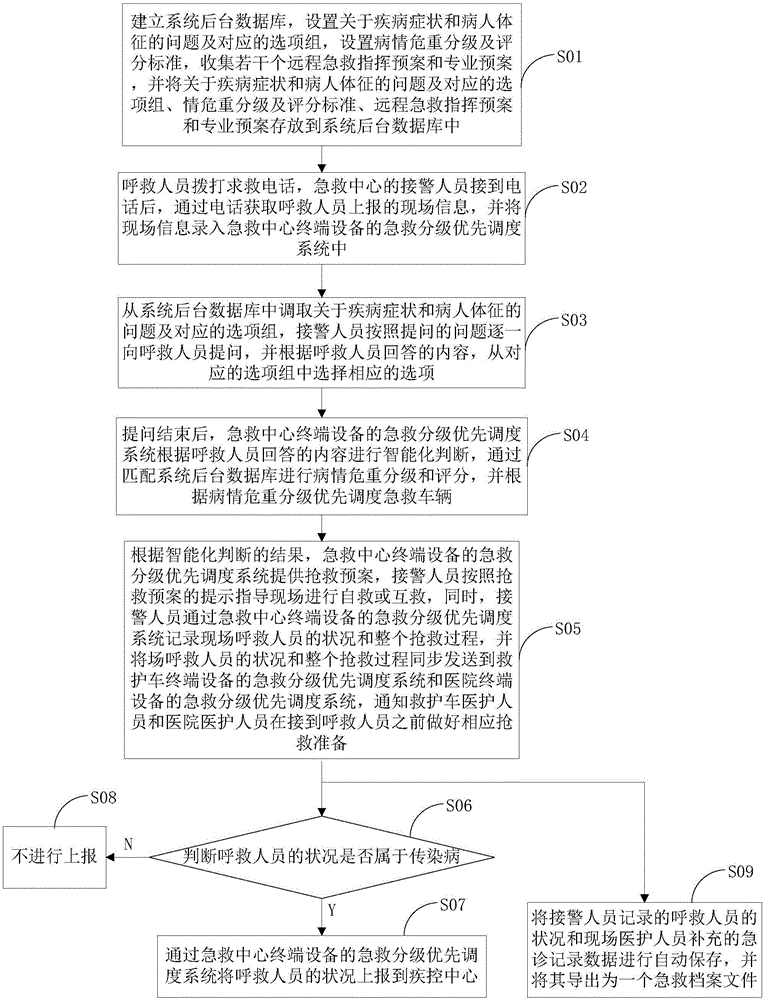
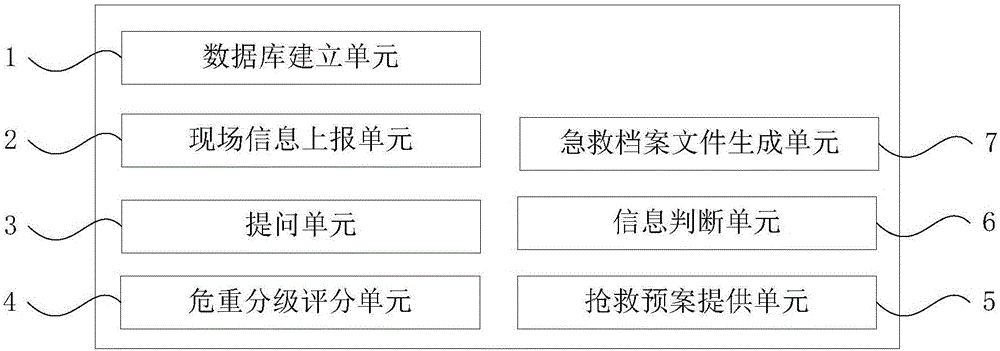
Medical priority dispatch method and apparatus
A medical priority dispatch method and apparatus. The method comprises: establish a system background database; a person who calls for help makes a call for help, and an alarm receiver of an emergency center acquires scene information by means of the call, and records same into a medical priority dispatch system; the alarm receiver asks the person who calls for help some questions according to questions prompted by the system, and checks answers; the medical priority dispatch system performs disease severity classification and scoring according to the answers of the person who calls for help, and dispatches an emergency vehicle by priority according to the disease severity classification; and provide a rescue plan, the alarm receiver guides, according to an instruction of the rescue plan, people on the scene to save themselves or each other, and moreover, the medical priority dispatch system records the condition of the person who calls for help on the scene and the whole rescue process, and synchronously sends same to an ambulance and a hospital. The medical priority dispatch method and apparatus have the following beneficial effects: before an ambulance arrives at the scene, people who call for help can save themselves or each other according to the guidance of an alarm receiver.
Owner:SHENZHEN EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE INFORMATION TECH
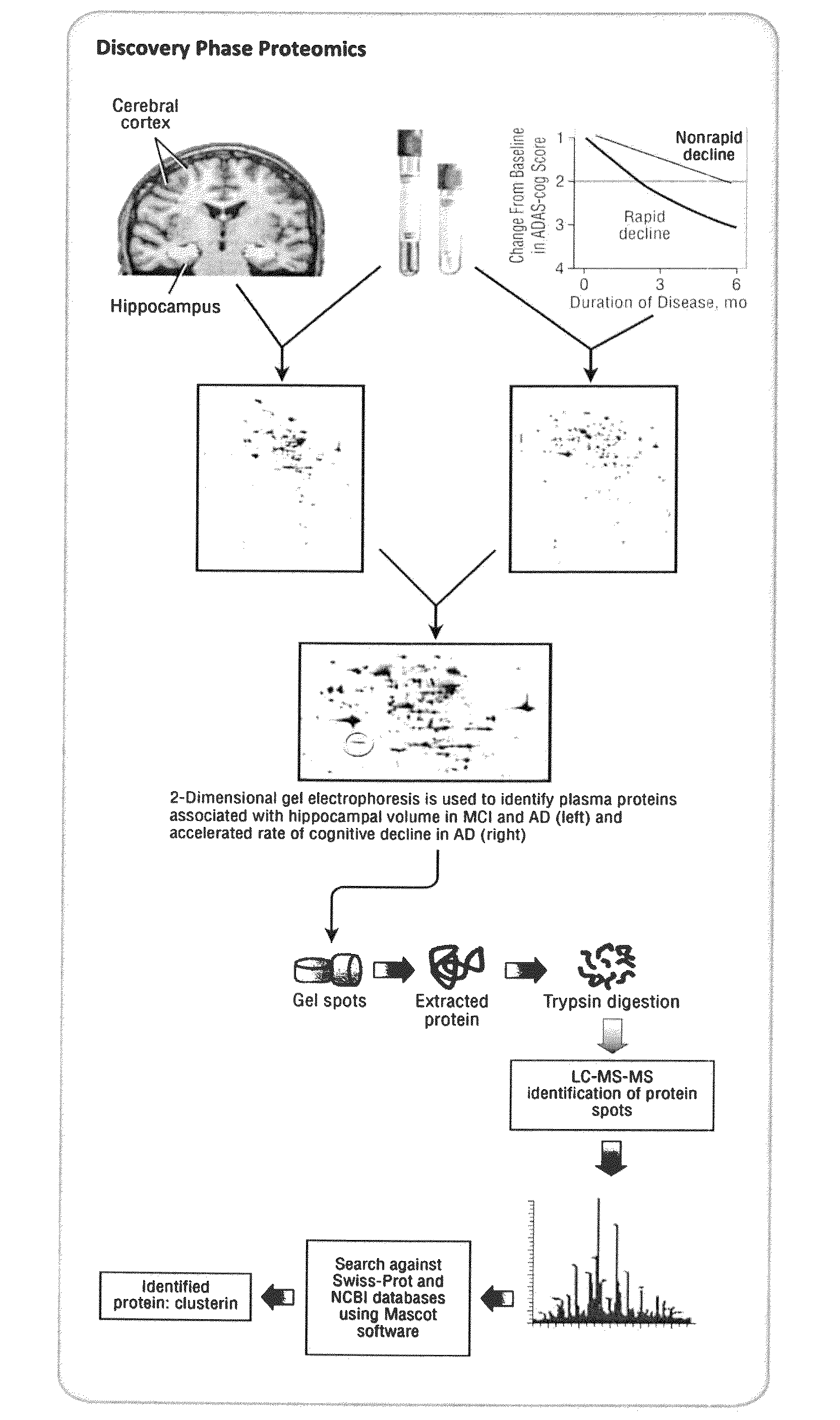
Markers and methods relating to the assessment of alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS20110082187A1Pronounced clinicalPronounced pathological stateCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsDisease severityClusterin
Owner:KING'S COLLEGE LONDON +1
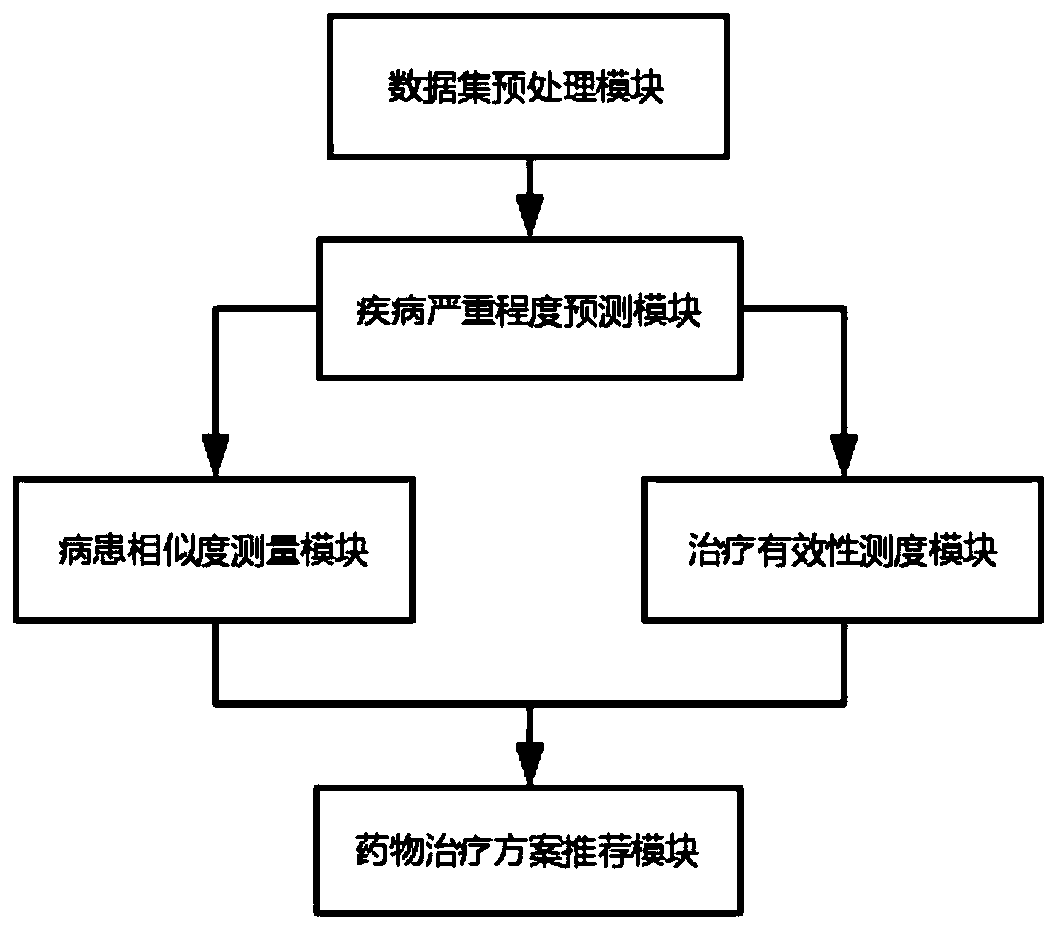
Large-scale medical data knowledge mining and treatment scheme recommendation system
ActiveCN110880362ATreatment refinementDrug Therapy UpdatesMedical data miningDrug and medicationsMedical recordData set
The invention discloses a large-scale medical data knowledge mining and treatment scheme recommendation system. The system comprises a data set preprocessing module which is used for obtaining real electronic medical record data and carrying out preprocessing on the electronic medical record data composed of a plurality of types of heterogeneous data sources; a disease severity prediction module which is used for obtaining disease severity scores of each patient in the treatment process; a treatment effectiveness measurement module which is used for obtaining effective treatment measurement information; a patient similarity measurement module which is used for constructing a similarity measurement relationship of patients; and a drug therapy scheme recommendation module which is used for obtaining drug therapy scheme recommendation of the next stage. According to the invention, the severity degree of the illness state of the patient is judged and predicted through the multitask bidirectional heterogeneous LSTM, the effectiveness measure of treatment is defined, the fine grit similarity of the patient is calculated, and the treatment scheme of the next stage is recommended accordingto the historical treatment records of the patient and the effective treatment schemes of other patients with high pathology similarity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
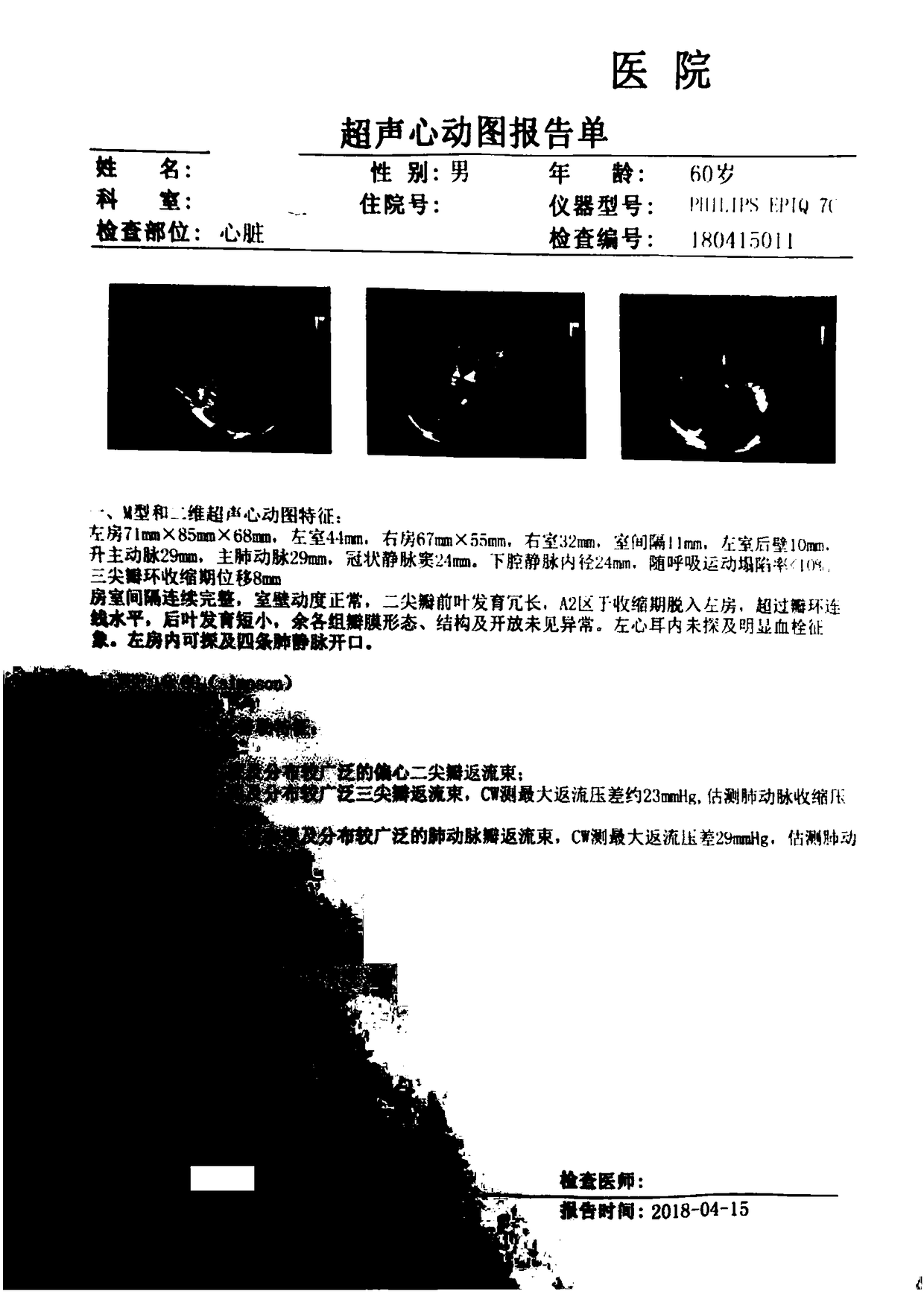
Intelligent evaluation and diagnosis method and system for heart disease types and severity degrees
InactiveCN109009222AAble to learnImprove forecast accuracyOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsData dredgingNaive Bayes classifier
The invention discloses an intelligent evaluation and diagnosis method and a system for heart disease types and severity degrees. The method comprises the steps of acquiring disease characteristic data and demographic characteristic data, and analyzing the acquired ultrasonic echocardiogram report data and the patient demographic characteristic data by utilizing a learning model to obtain a modelevaluation index, a heart disease type and a heart disease severity. According to the invention, a data mining method is adopted, so that data preprocessing, data screening and other operations are carried out on data through the data mining correlation method. The method is adopted for selecting a noise ratio during the characteristics selection process. A random forest model is adopted for carrying out the classification prediction of the heart disease severity. Meanwhile, an effective research method is obtained through comparing and analyzing the algorithm performances and the learning effects of the random forest model, a naive Bayes classifier, a decision tree model and a BP neural network model. Moreover, a standard for the severity classification of heart disease patients and a prediction method for predicting the treatment risk of the heart disease operation are provided.
Owner:杨成伟
Inhaler and driving method for same
InactiveCN101678184AReduce the amount of applicationSmall burdenRespiratorsMedical devicesDisease severityDrug product
The present invention provides an inhaler capable of measuring lung function, feeding back the measurements, and administering medicine suitable for a lung condition in a single use. The inhaler 1 ofthe present invention includes a lung function measuring unit 2 having a spirometer for measuring lung function, and, using a computing unit 5, compares the lung function measurements with a medication pattern table stored in a storage unit 7 and determines a disease severity and a diseased region of the lung. Based on the determination results, the computing unit further selects types and particle diameters of medicines suitable for the lung condition, and controls an ejection unit 3 including a plurality of ejection portions to eject the medicines required for treatment in a single use.
Owner:CANON KK
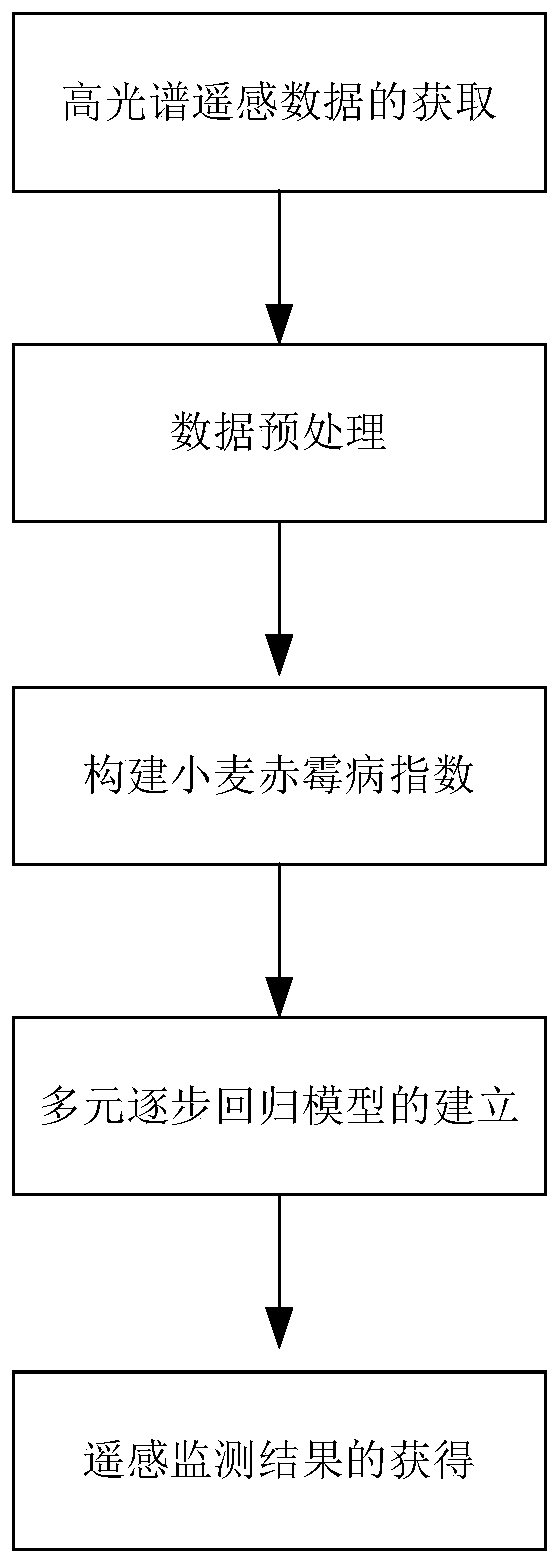
Winter wheat head blight hyperspectral remote sensing monitoring method based on wheat ear scale analysis
ActiveCN110132860AEffective monitoringGood correlationColor/spectral properties measurementsSensing dataStepwise regression
The invention relates to a winter wheat head blight hyperspectral remote sensing monitoring method based on wheat ear scale analysis, and compared to the prior art, overcomes the defect that remote sensing monitoring on the head blight does not aim at wheat ear scale analysis. The winter wheat head blight hyperspectral remote sensing monitoring method comprises the following steps of: acquiring hyperspectral remote sensing data; carrying out data preprocessing; constructing a wheat head blight index; establishing a multiple stepwise regression model; and obtaining a remote sensing monitoring result. According to the invention, after the head blight index is constructed by utilizing a normalization ratio of a first-order differential sum in sensitive wavebands, unary linear regression and multiple stepwise regression models of the head blight index and disease severity are established, so as to implement effective monitoring on the wheat head blight and provide ideas and bases for noninvasive diagnosis on the head blight of infected wheat on the canopy scale and the field scale.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Biomarker sbp1 for early diagnosis of renal diseases, and use thereof
PendingCN109890981AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisKidney abnormalitiesRenal filtrate
A biomarker and a technology for utilizing the same, of the present invention, can be useful in the early diagnosis, in urine, of a renal function abnormality due to diabetes and drugs and in the prediction and evaluation of disease severity, and, further, can accurately determine, with high sensitivity and specificity, a renal function abnormality due to diabetes and exposure to drugs, and enablethe early and effective diagnosis of kidney abnormality symptoms through a relatively simple method, thereby being widely usable in various fields, such as in clinical experiments essential for new drug development and in diagnosing drug-causing acute / chronic renal failure, which can frequently occur in the clinical treatment process.
Owner:SERGENTECH GMBH
Pharmaceutical composition for preventing and treating rheumatoid arthritis
InactiveCN101700249AInhibition of clinical onsetOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticChlorogenic acidEarly rheumatoid arthritis
The invention discloses a pharmaceutical composition for preventing and treating rheumatoid arthritis. The traditional Chinese medicine raw materials for constituting active ingredients of the pharmaceutical composition by weight are as follows: 5.5-6.0mg of berberine, 0.3-0.4mg of palmatine, 1.5-2.0mg of jatrorrhizine, 1.5-1.8mg of magnoflorine, 0.1-0.2mg of phellodendrine, 0.2-0.3mg of coptisine, 55-60mg of baicalin, 1.5-2.0mg of baicalein, 5.0-7.0mg of wogonoside, 0.03-0.05mg of wogonin, 20-25mg of geniposide, 0.1-0.2mg of crocin and 0.25-0.3mg of chlorogenic acid. The results of pharmacological tests show that the pharmaceutical composition can significantly reduce the disease severity of CIA mice with the rheumatoid arthritis, significantly improve the inflammation and the immune injury situation at lesion sites in comparison with a control group and be used for preparing drugs for preventing and treating the rheumatoid arthritis.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Disease severity index for assessment of chronic liver disease and method for diagnosis of three distinct subtypes of primary sclerosing cholangitis
ActiveUS9091701B2Low indexOrganic active ingredientsHealth-index calculationDisease severityChronic liver disease
A Disease Severity Index (DSI) is provided for assessment of chronic liver disease in a patient using non-invasive liver function test results. A DSI was derived from non-invasive liver function test results based on hepatic blood flow. The DSI is used in methods for prediction of clinical outcomes, prediction of response to antiviral treatment, and assessment of progression of chronic liver diseases. Non-invasive methods to diagnose three distinct categories of patients with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) are provided. The methods can be used to diagnose PSC patients as Slow Progressors, Moderate Progressors and Rapid Progressors.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com