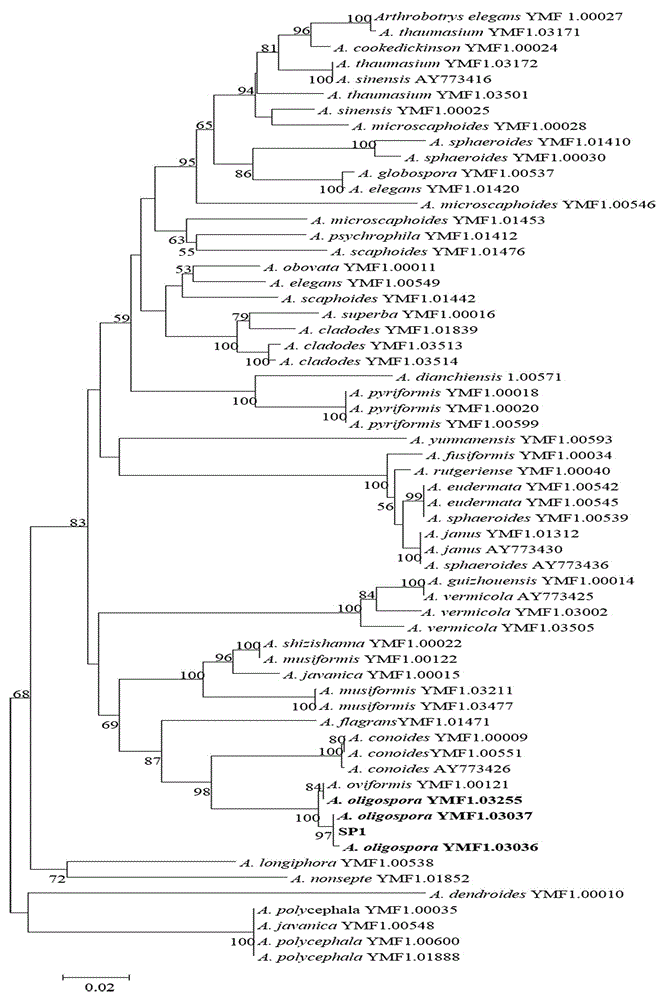
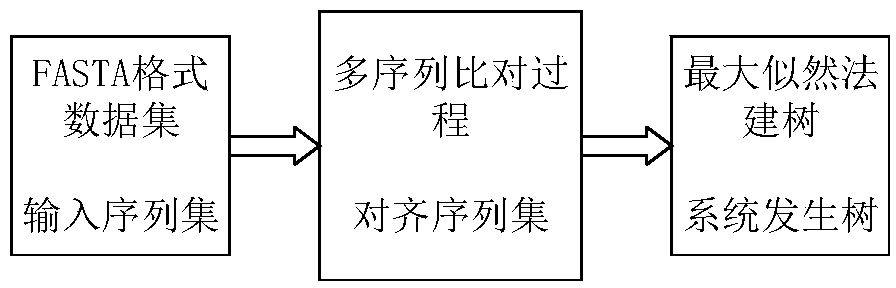
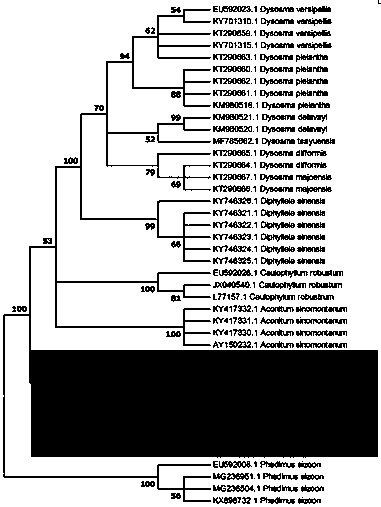
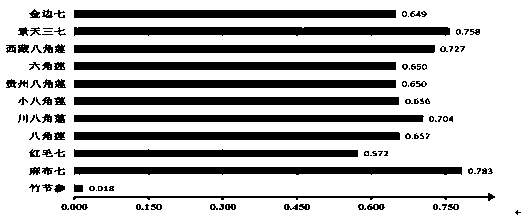
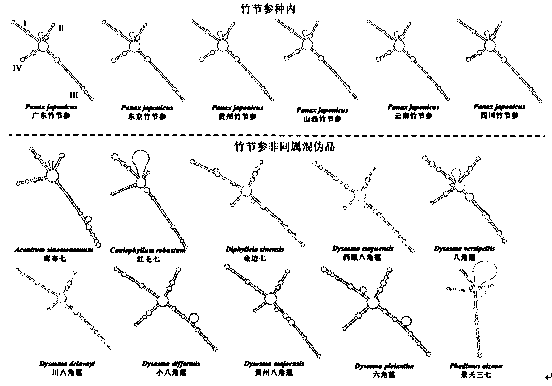
Patents
Literature
116 results about "Phylogenetic tree" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A phylogenetic tree or evolutionary tree is a branching diagram or "tree" showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities—their phylogeny (/faɪˈlɒdʒəni/)—based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics. All life on Earth is part of a single phylogenetic tree, indicating common ancestry.
Browsable database for biological use
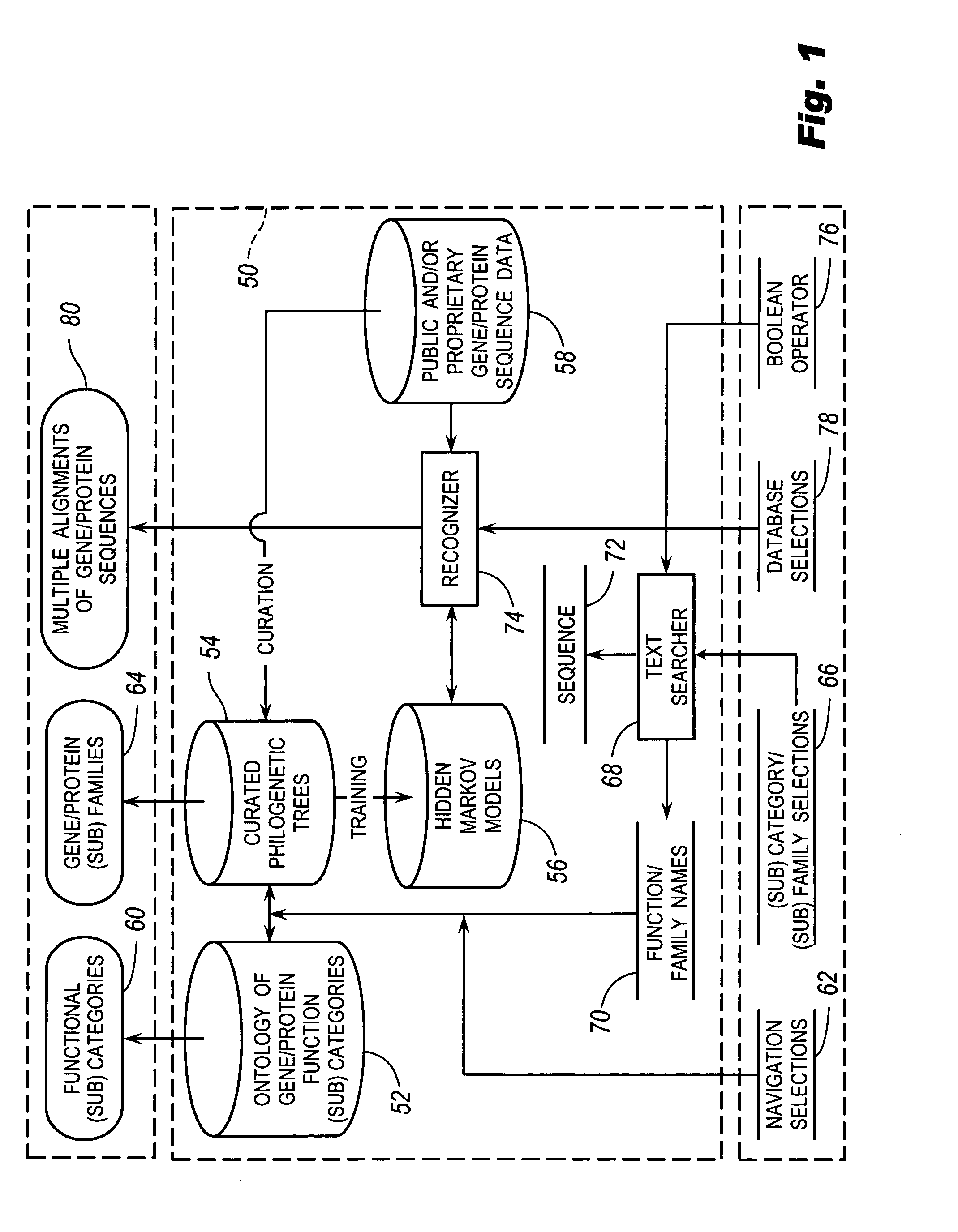
The browsable database can allow for high-throughput analysis of protein sequences. One helpful feature may be a simplified ontology of protein function, which allows browsing of the database by biological functions. Biologist curators may have associated the ontology terms with Hidden Markov Models (HMMs), rather than individual sequences, so that they can be applied to additional sequences. To ensure accurate functional classification, HMMs may be constructed not only for families, but for curator-defined subfamilies, whenever family members have divergent functions or nomenclature. Multiple sequence alignments and phylogenetic trees, including curator-assigned information, can be available for each family. Various versions of the browsable database may include training sequences from all organisms in the GenBank non-redundant protein database, and the HMMs can be used to classify gene products across the entire genomes of human, and Drosophila melanogaster.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Rapid analysis method and system for genomes of pathogenic microorganisms
ActiveCN106886689AHigh resolutionAccurate distinctionSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsGenomicsVirulent characteristics
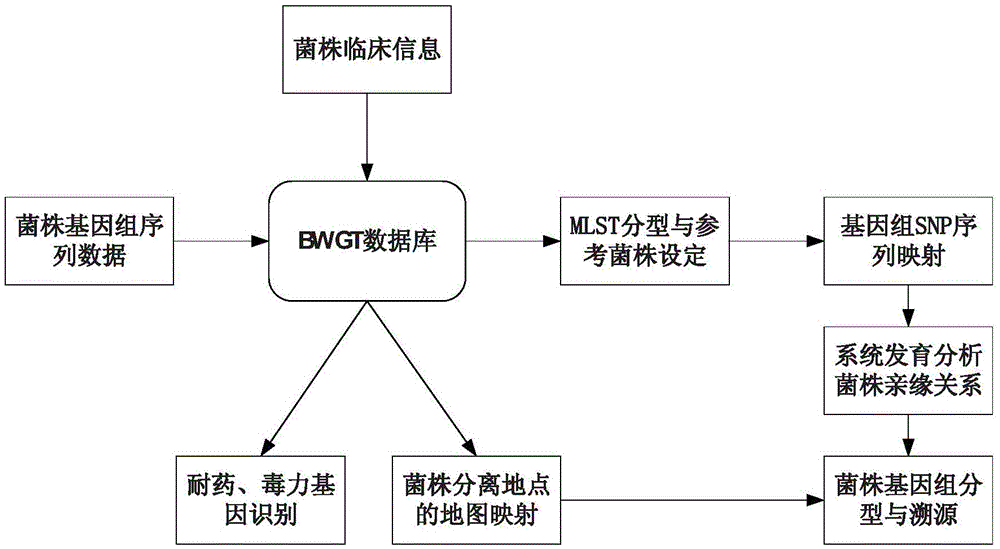
The invention discloses a rapid analysis method for genomes of pathogenic microorganisms and a data analysis platform. The method provides typing and source-tracing functions of bacterial genome sequences based on a bacterial strain database system. A user can only set simple parameters and upload bacterial strain genome sequences. The system can feed back the MLST parting result of bacterial strains, medicine resistance and distribution of virulence genes within the shortest time and make reference to names of bacterial strains and provide phylogenetic trees of all bacterial strains which are uploaded by a user and arranged in a database. The method is suitable for the establishment of a data analysis platform for pathogeny microbiology which integrates study of genetics, genomics and phylogenetics. Compared with the conventional typing technology, the rapid analysis method and system for genomes of pathogenic microorganisms have the following beneficial effects: higher resolution is obtained; bacterial strains of the same clone can be accurately detected; the feedback speed of results is high; and the technology of efficient reference strain setting and genome SNP sequence mapping, data analysis results can be quickly obtained by a user, thereby facilitating real-time tracking and fast source-tracing of clonal spreads in pathogenic microorganisms.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Nucleic acid molecules for detecting bacteria and phylogenetic units of bacteria
InactiveUS7202027B1Sure easyEasy to compareSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesPhylogenetic tree
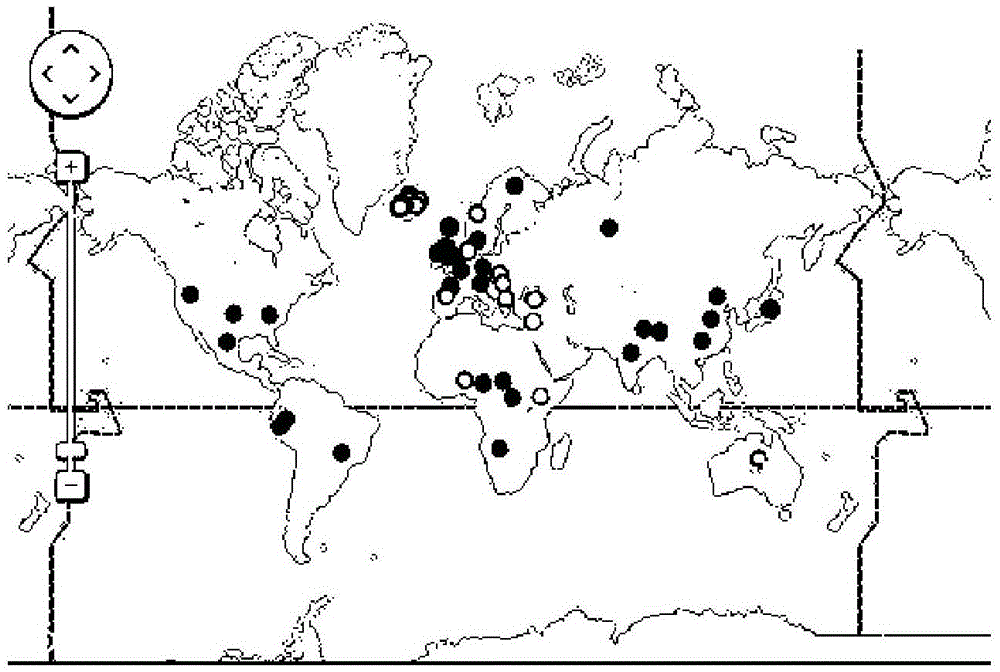
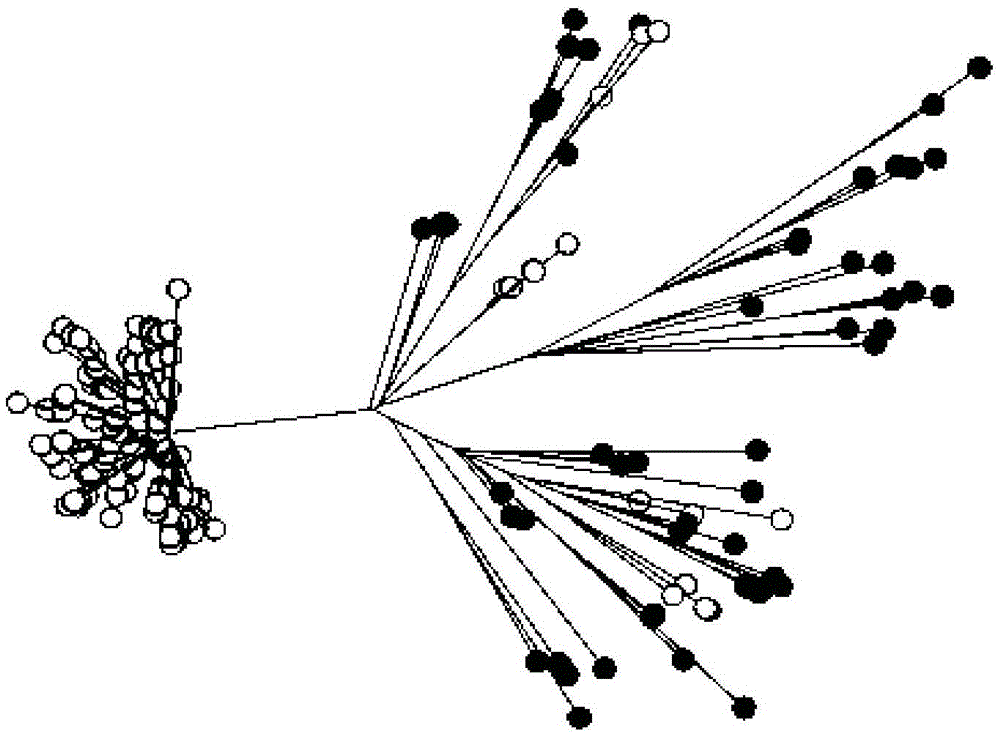
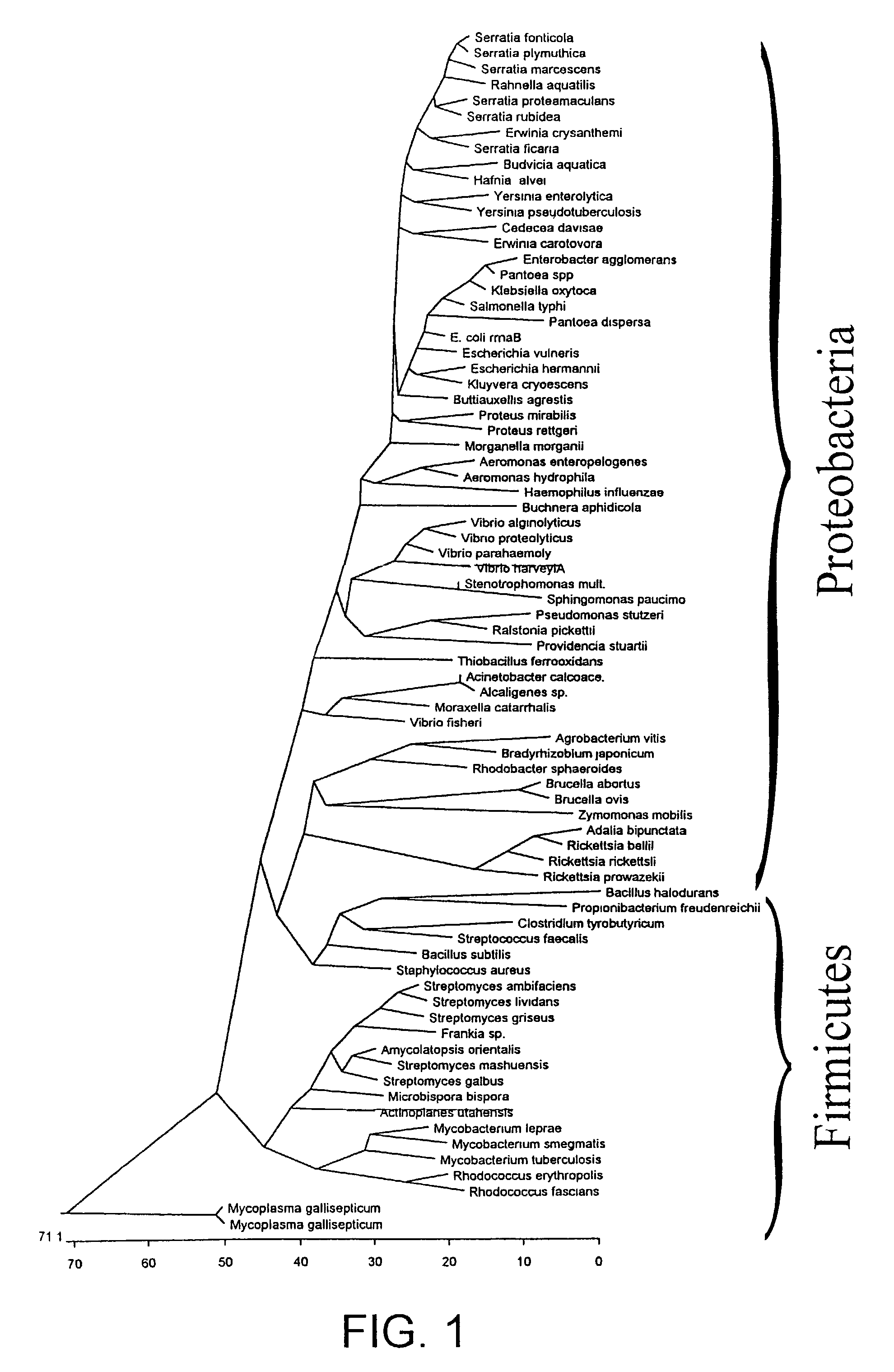
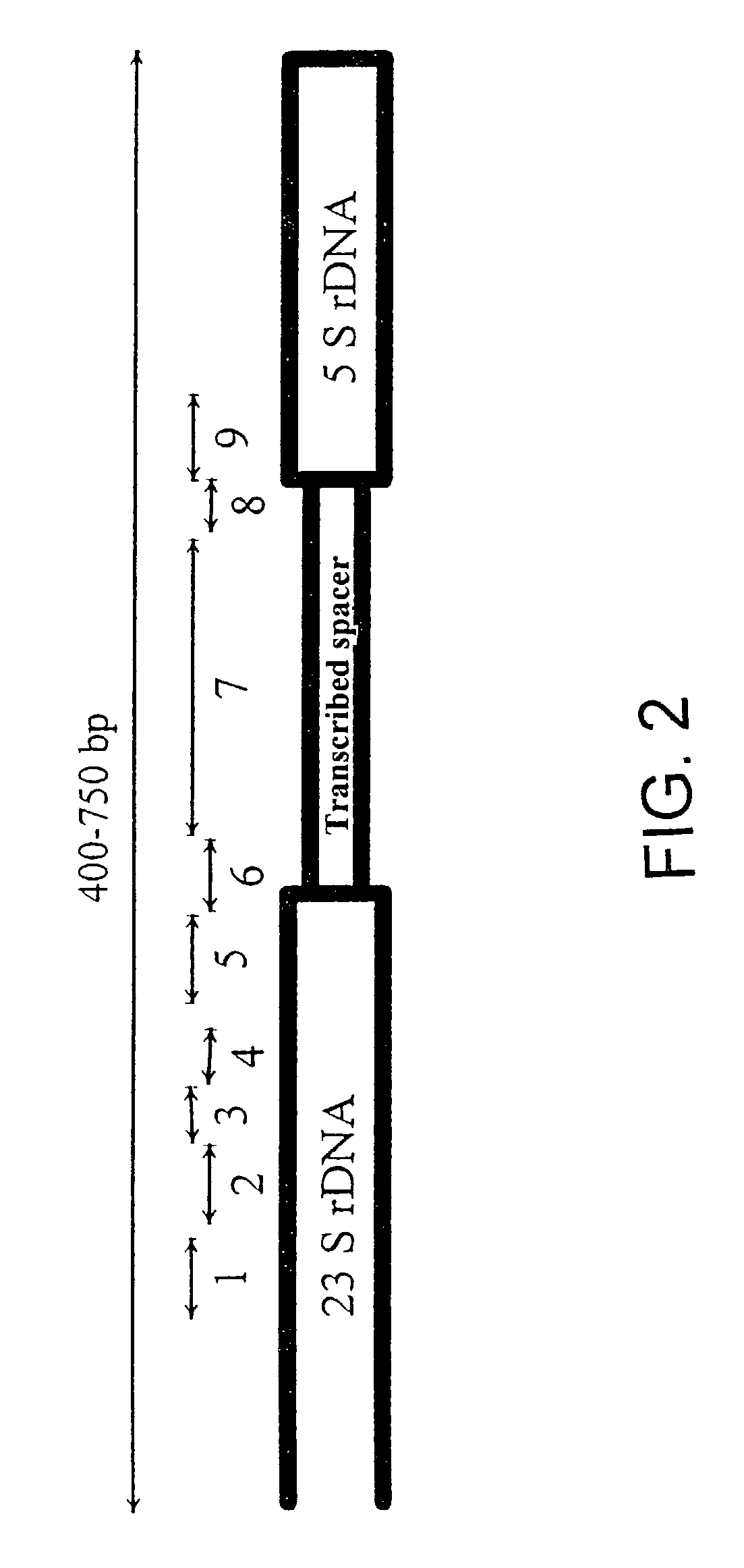
The present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules which allow the identification of bacteria or groups of bacteria. For detection, the region of the bacterial genome containing the 23 S / 5 S rRNA is used as the target sequence for the bacterial detection.
Owner:BIOTECON DIAGNOSTICS
Method for identifying predator nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys through DNA bar codes
InactiveCN105063761AEasy to expandEasy to compareLibrary creationSpecial data processing applicationsDNA barcodingGermplasm
The invention provides a method for identifying predator nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys through DNA bar codes and belongs to the field of fungus species identification. According to the method, RPB2 genes serve as target DNA bar code genes for identifying the predator nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys, combined arthrobotrys sample experiment data and target fungus data merged strategy is adopted to establish a high-cavity database, meanwhile, RPB2 genes to be identified are compared with a gene library, an identifying rule is established based on a system generation tree method of genetic distance method and clustering analysis of the Kimura-2-parameter probability to identify species. The method has the advantages that the RPB2 genes serve as the DNA bar codes most suitable for identifying the nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys, and the method is universal and easy to amplify and compare. The identifying efficiency and the reliability and accuracy of the identifying method are greatly superior to those of a conventional DNA bar code method, and the method makes up for the blank of the nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys DNA bar code molecular markers and the method provides a useful research tool for researches on germplasm resource excavation, biocontrol application and genetic diversity of nematophagous hyphomycete.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
System and Method for Sequence Distance Measure for Phylogenetic Tree Construction
ActiveUS20070225918A1Quick identificationSugar derivativesBiological testingRapid identificationPhylogenetic tree
The present invention permits identification of biological materials following recovery of DNA using standard techniques by comparing a mathematical characterization of the unknown sequence with the mathematical characterization of DNA sequences of known genera and species. The clinical identification of infectious organisms is required for accurate diagnosis and selection of antimicrobial therapeutics. The invention allows an ab initio approach with the potential for rapid identification of biological materials of unknown origin. The approach provides for identification and classification of emergent or new organisms without previous phenotypic identification. The technique may also be used in monitoring situations where the need exists for classification of material into broad categories of bacteria which could have an immediate impact on bio-terrorism prevention.
Owner:NUTECH VENTURES
Method, oligonucleotide and kit for detecting high-risk HPV (human papilloma viruses)
ActiveCN105603121AReduce usageGuaranteed SensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesTrue positive ratePhylogenetic tree
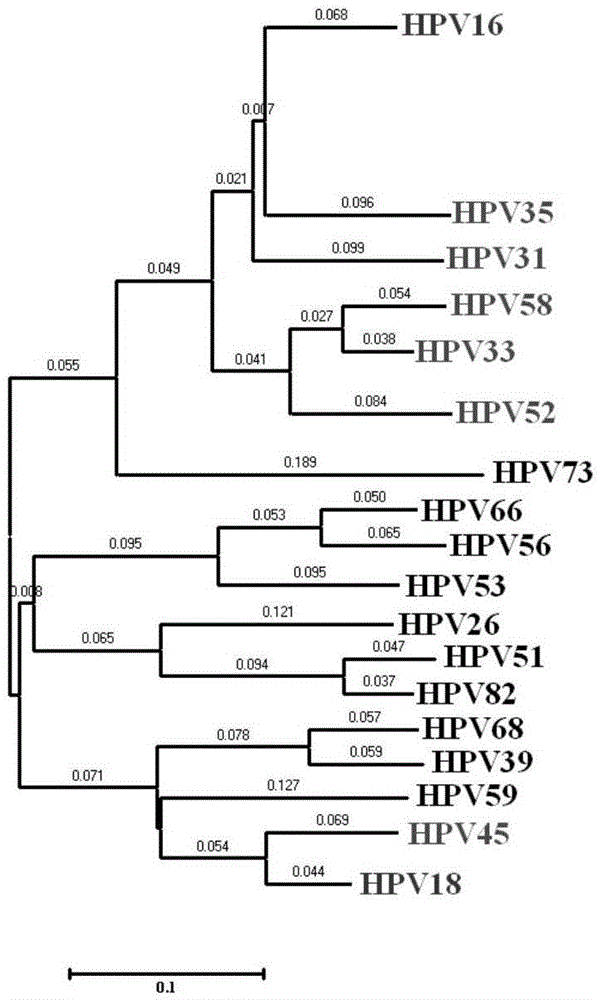
The invention provides a method, oligonucleotide and kit for detecting common high-risk HPV (human papilloma viruses). A fluorescence PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology is adopted, HPV16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68, 26, 53, 66, 73 and 82 which possibly exist in a sample are subjected to initial detection and type identification. By the method, oligonucleotide and kit for detecting the common high-risk HPV, 18 high-risk types can be detected simultaneously, and the HPV 16 and 18 can be subjected to genetic typing simultaneously. On the basis of 18 types of high-risk HPV and affinity of other types on a phylogenetic tree, a high-risk HPV primer and a probe are designed, a background fluorescence value is reduced remarkably while detection accuracy, sensitivity and specificity are guaranteed, detection flux is increased remarkably, and detection cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:ACON BIOTECH (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
Two ralstonia-solanacearum-resistant endophytic bacillus velezensis strains and application thereof
ActiveCN107779420AExcellent field control effectStrong colonization abilityBiocideBacteriaNicotiana tabacumPlant roots
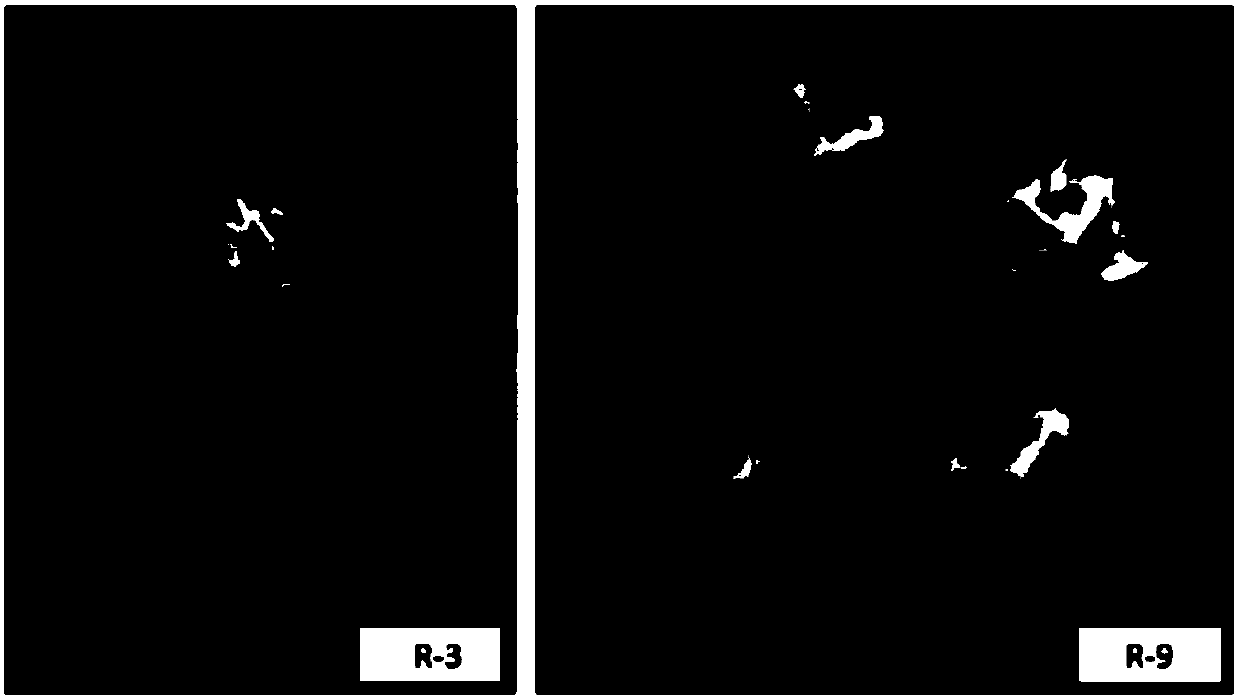
The invention relates to two ralstonia-solanacearum-resistant endophytic bacillus velezensis strains and application thereof. By separation, screening and purification in roots of healthy tobacco plants in a ralstonia solanacearum occurrence area of the Enshi Prefecture, two biocontrol bacillus endophyticus strains R-3 and R-9 are obtained, have evident resistance effects on ralstonia solanacearumand are both capable of generating high-temperature-resistant ralstonia-solanacearum-resistant substances. By gyrB gene sequence identification and phylogenetic tree construction, results show that the R-3 and R-9 are both bacillus velezensis; by potted plant root irrigation experimental verification, the bacilli R-3 and R-9 have great colonization performance in tobacco roots and can enter stemsthrough root transmission; by field experimental verification, bacillus velezensis R-3 and R-9 are effective in ralstonia solanacearum prevention and treatment, remarkably superior to chemical agentkasugamycin and free of pollution. The biocontrol endophyte research field is further enriched by researching on the bacilli R-3 and R-9, and a guiding significance to ralstonia solanacearum prevention and treatment is achieved.
Owner:湖北省烟草公司恩施州公司
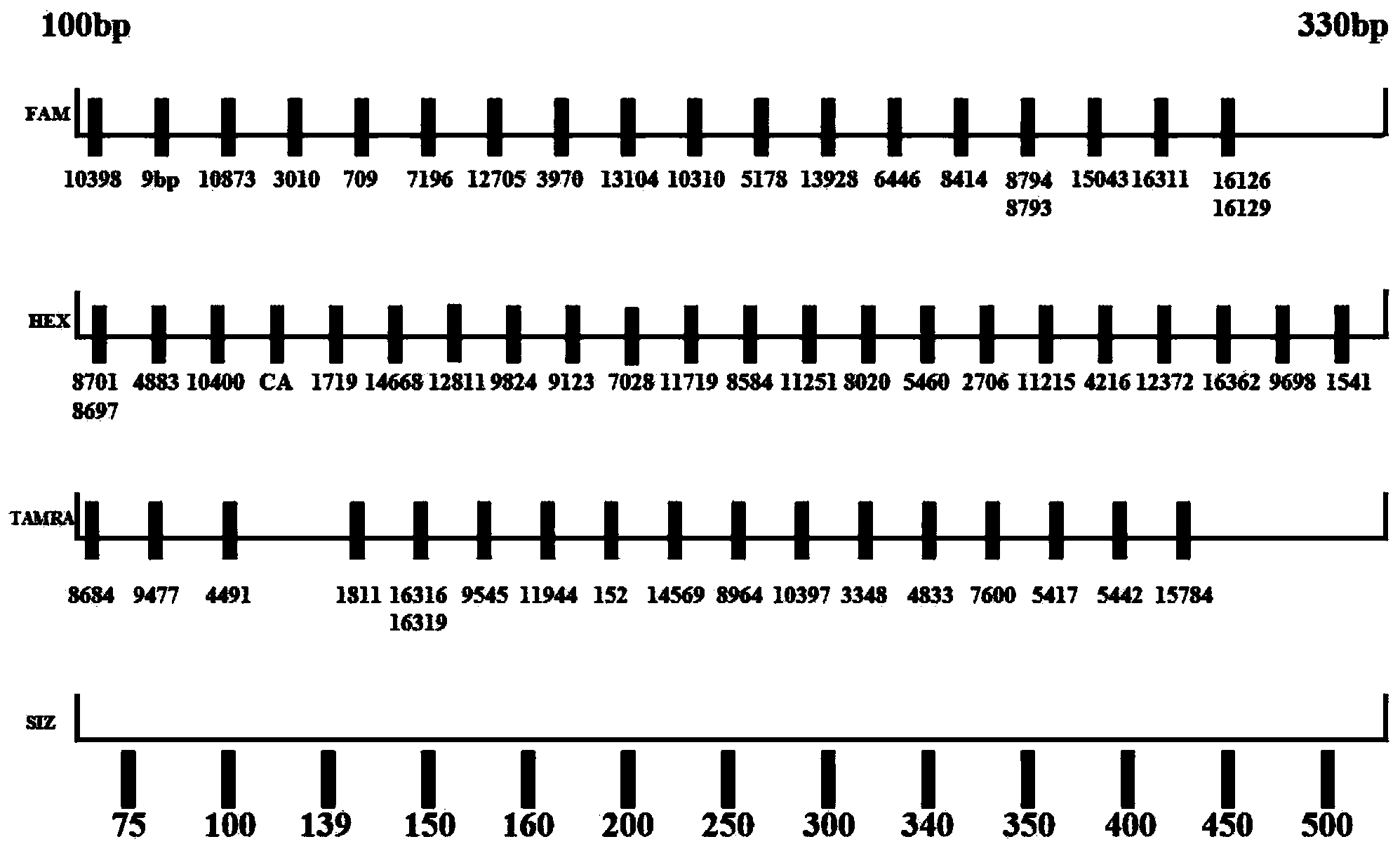
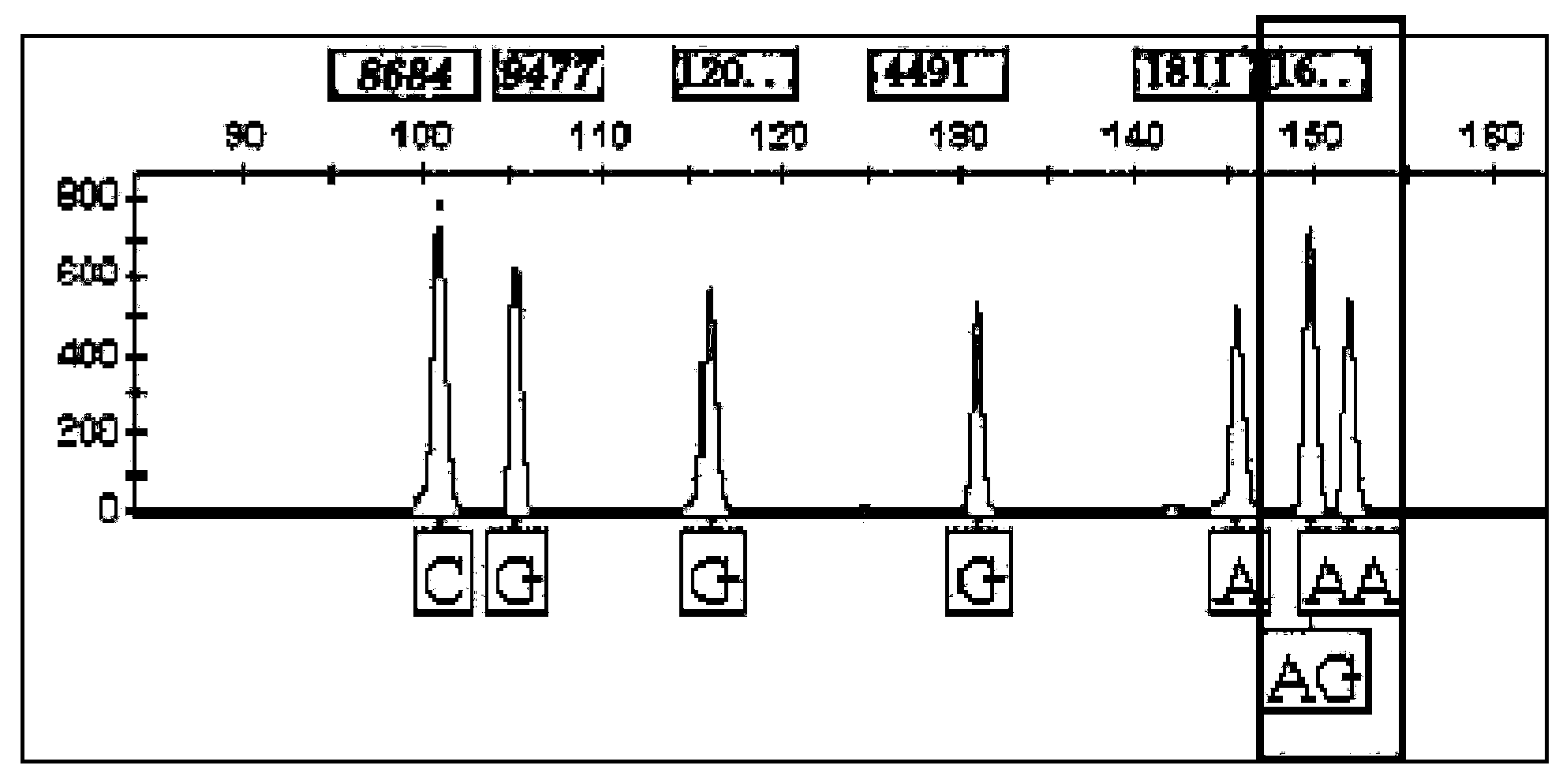
Mitochondria SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) fluorescence-labeling multiple amplification kit and application thereof
ActiveCN103898226AMeet the skill levelEfficient mtDNA haplotyping strategyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceElectrophoresis
The invention relates to a mitochondria SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) fluorescence-labeling multiple amplification kit capable of detecting 61 SNP loci at the same time. According to a mitochondria phylogenetic tree, based on genetic characteristics of Chinese populatio, 61 SNP loci which are high in polymorphism, low in mutation rate and strong in parting capacity are selected, wherein the 61 SNP lotuses comprise 54 loci in a coding region, 7 loci in a control region; the kit can be used for detecting the 61 SNP loci by virtue of specific primers. The kit which is used as a mitochondria detecting system is capable of carrying out amplification in three tubes at the same time and performing electrophoresis at the same time, so that haplotype diversity reaches 98.6%, and therefore, the mitochondria SNP fluorescence-labeling multiple amplification kit can be used as a kit for identifying the same maternal line, after autosome STR and Y chromosome STR.
Owner:SHANG HAI GENE BIO TECH +2
DNA bar code technology for identifying rosewood and rosewood product, and application method thereof
InactiveCN104404131ALarge capacityReduce dependenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA barcodingPhylogenetic tree
The invention discloses a DNA bar code technology for identifying rosewood and rosewood products and an application method thereof. The technology is as below: constructing a high capacity database through a strategy by merging database of rosewood samples experiment data and a target plant; sequencing a DNA bar code sequence of the rosewood samples; merging the sequencing sequences with homologous sequences published in the Genbank database to construct a rosewood DNA bar code gene database with wide range of data sources; and establishing an algorithm and decision rules for the identification database by using matK+rbcL genes as the target DNA bar code gene for rosewood identification, and using a search tool method of a local alignment algorithm based on frequency, a genetic distance method based on Kimura-2-parameter probability and a phylogenetic tree method based on clustering analysis. The DNA bar code technology for identifying rosewood and rosewood products and the application method thereof establish an accurate and quick rosewood DNA bar code identification technology.
Owner:NANJING INST OF PROD QUALITY INSPECTION
Equipment state overhaul management module for EAM system of power plant
The invention relates to an equipment state overhaul management module for an EAM system of a power plant, which comprises a state monitoring point tracking submodule for obtaining detection data from state monitoring points, comparing the monitoring data with judgment conditions preset by the system and generating an exception report when exceptional data appear; a recording submodule used for recording the obtained detection data; and an overhaul item generating submodul used for generating the overhaul items of corresponding equipment when the detection data meet the set conditions. State overhaul is an equipment maintenance and management measure which tracks and analyzes the state monitoring points of the equipment and determines an equipment overhaul countermeasure according to a set overhaul policy in accordance with the comprehensive state of the equipment. The equipment uses a phylogenetic tree structure tissue for displaying, by collecting, analyzing and consulting exception information and variation trend data of relative state points, an equipment manager masters the equipment state in management range conveniently and an auxiliary decision tool for deciding the equipment overhaul countermeasure is provided.
Owner:国能浙江北仑第三发电有限公司
Method and system for building a phylogeny from genetic sequences and using the same for recommendation of vaccine strain candidates for the influenza virus
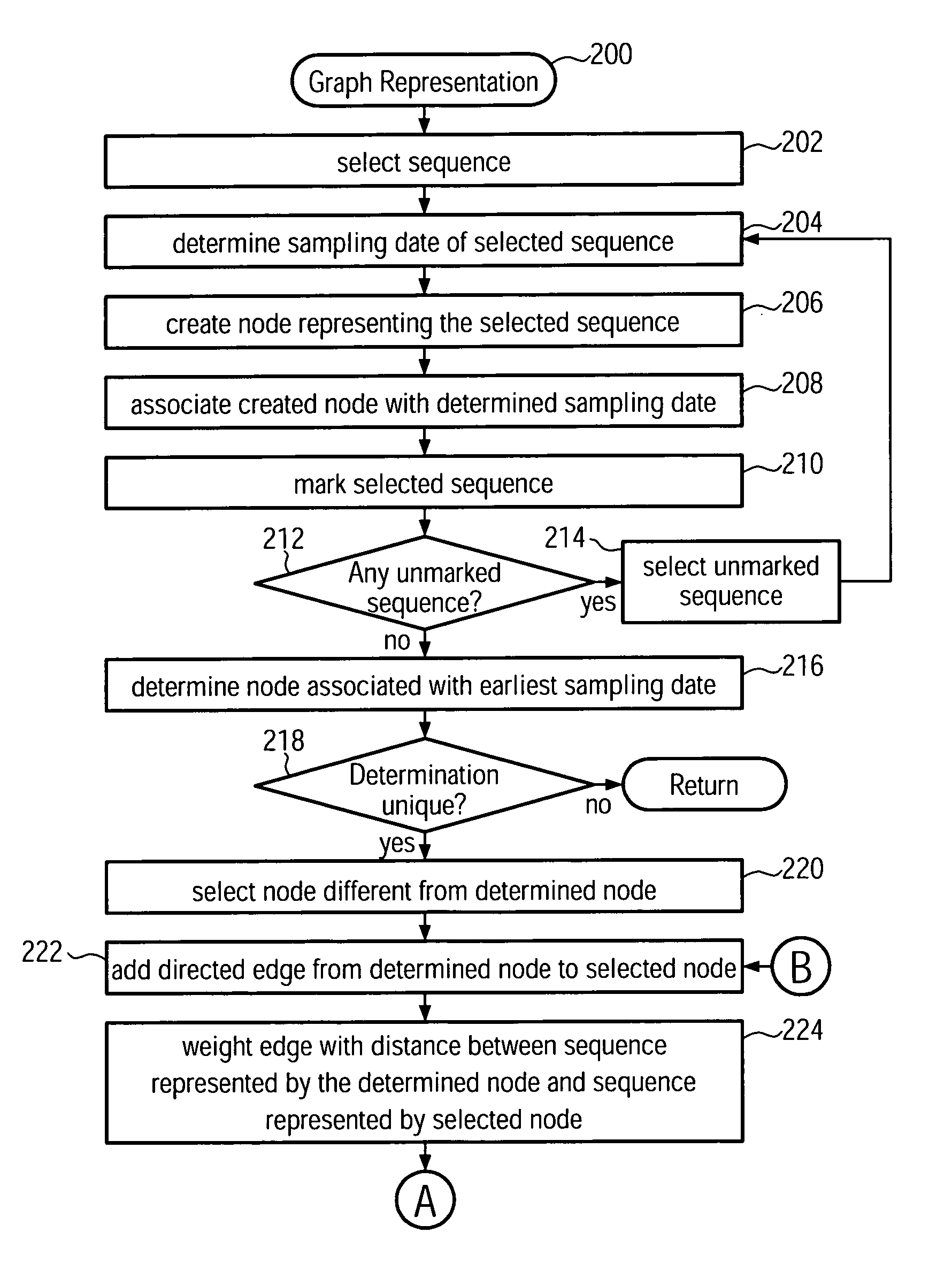
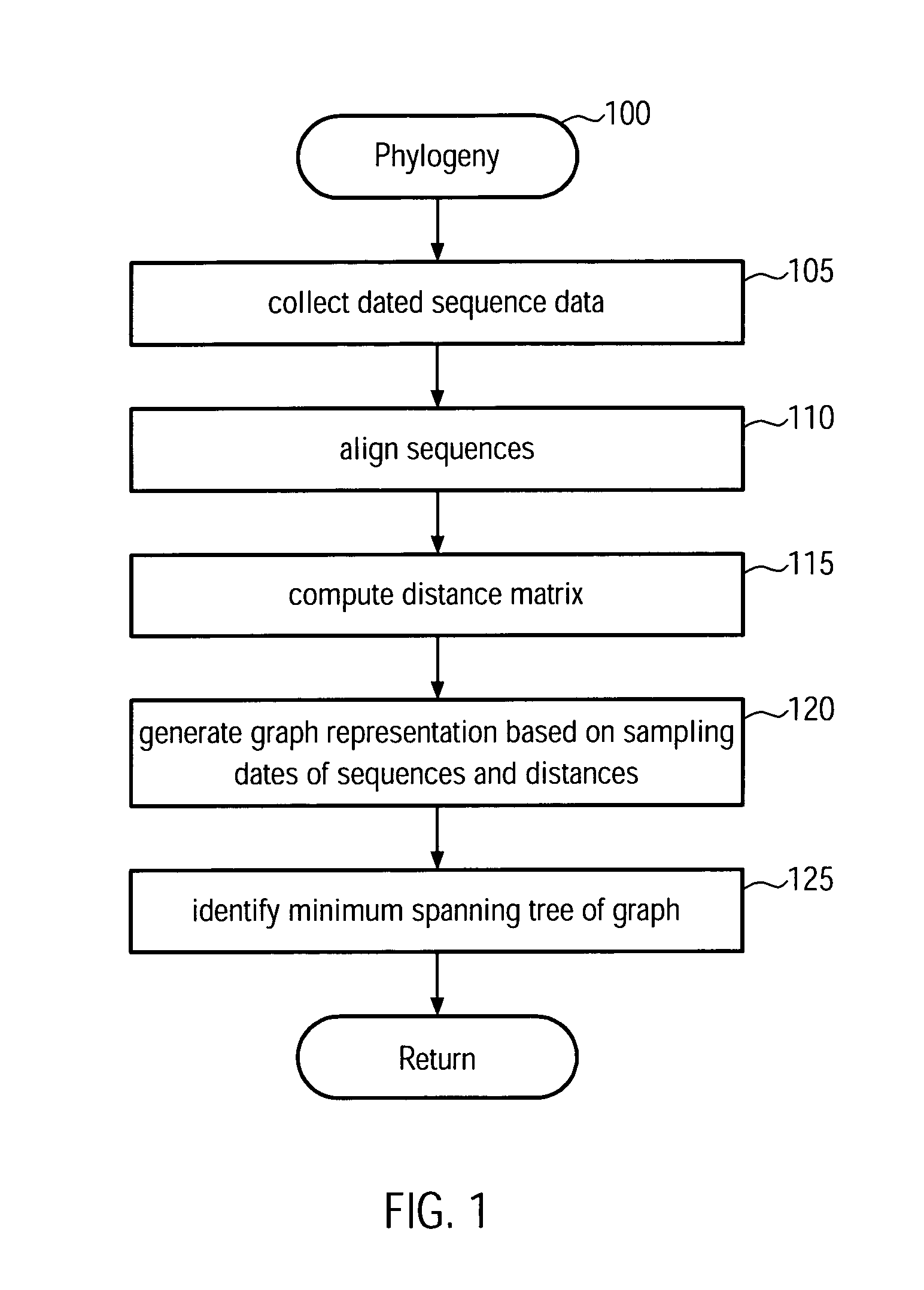
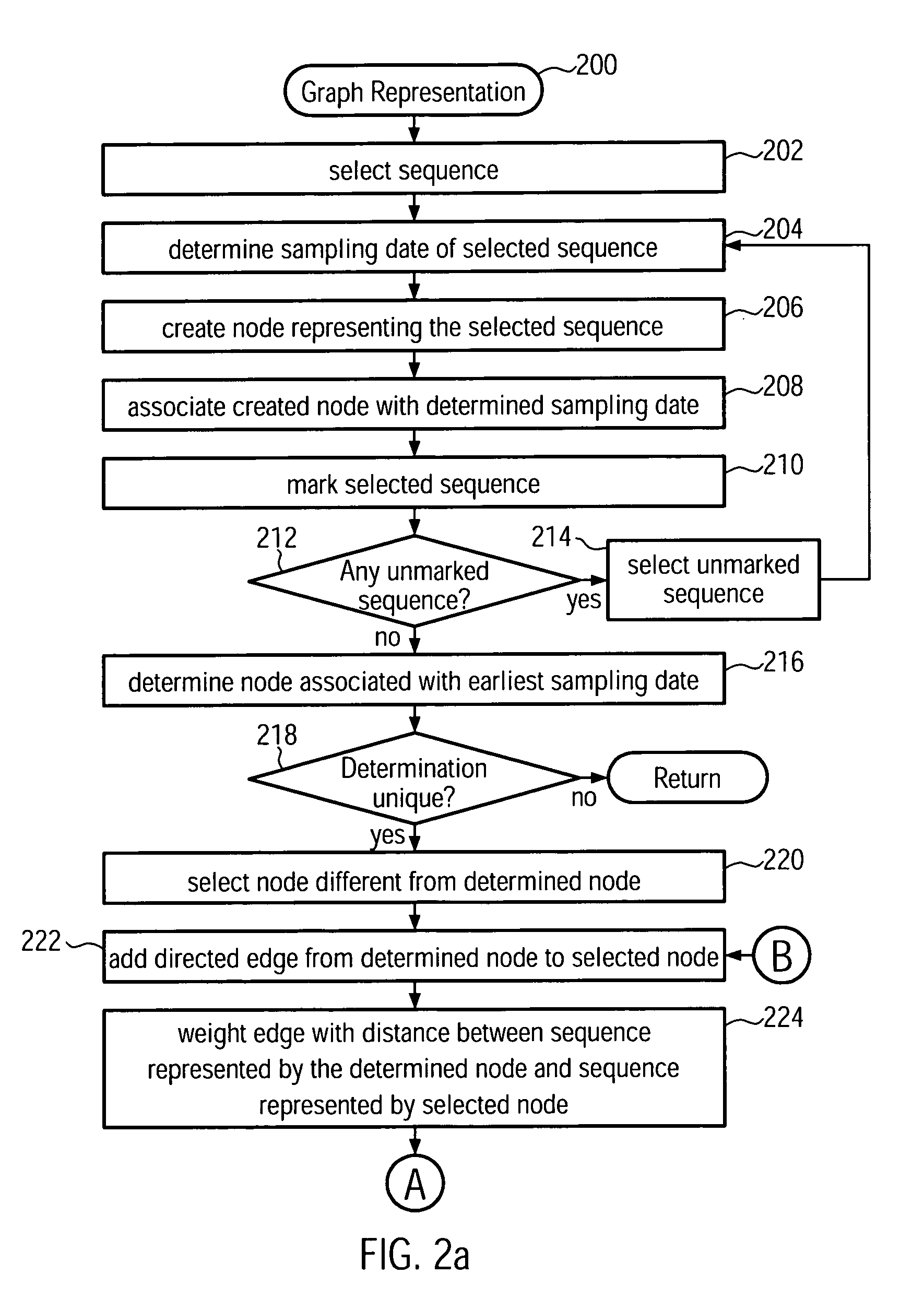
A computer-implemented method and a computer system for identifying a phylogenetic tree from a plurality of biological sequences is provided. Each biological sequence is associated with a sampling date. First, the plurality of biological sequences is aligned and a distance matrix is obtained. Then, a subset of these sequences without any duplicated sequences is selected and a directed graph representation of the subset of biological sequences is generated based the associated sampling dates. Then, a minimum spanning tree is computed from the weighted directed graph representation. Then, in an iterative procedure, the sequences of unsampled evolutionary intermediates are inferred from mutation patterns that reflect the difference in sequence between the nodes in the minimum spanning tree. The new sequences are added with associated time stamps to the sequence set. Then, sets of identical sequences are removed. Then, an optimum branching is recomputed. This step is repeated until no new intermediates are found. In the final step, the sequences that have been set aside in the initializing step are added to the plurality of sequences derived in the update step. From this plurality of sequences an optimum branching is computed and identified as the phylogenetic tree. Amino acid changes repeatedly occurring on the internal branches of the obtained tree can be used to identify sequences and associated viral isolates suitable as vaccine strains for the following influenza season.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Population genetic evolution map and construction method thereof
ActiveCN110910959AGenetic relationship is clearBuild accuratelySequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsCold spotGenetics
The invention provides a population genetic evolution map and a construction method thereof. The construction method comprises the following steps: selecting a recombined cold spot region; constructing a phylogenetic tree by utilizing the SNP sites of the recombined cold spot region; performing clustering analysis on the phylogenetic tree, and determining an evolution relationship between speciesso as to obtain a population genetic evolution map. According to the method, the phylogenetic tree is constructed by selecting SNP sites of the recombined cold spot region (such as a centromere region); on one hand, due to low recombination occurrence rate and stable inheritance between parents and filial generations, the genetic evolution relationship is clear, the constructed phylogenetic tree is more accurate, and on the other hand, the number of SNP sites in the selected sequence is smaller than that of whole genome sequences and is more and more comprehensive than that of SNP sites in a haplotype analysis method. Therefore, the phylogenetic tree can be quickly and accurately constructed.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Preparation method for burkholderia cepacia, and application in high-performance phosphate-dissolving microbial fertilizer by using the same
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
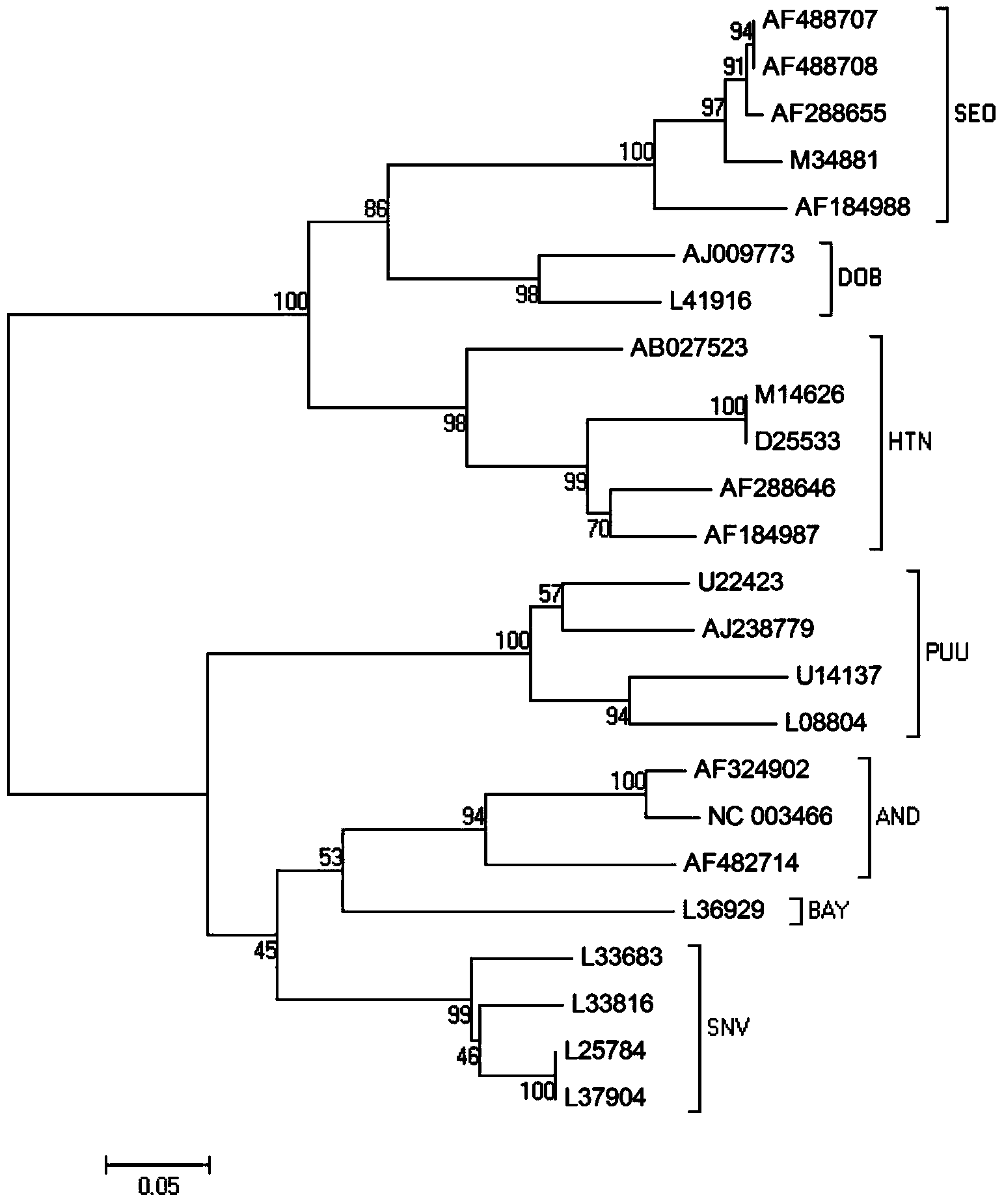
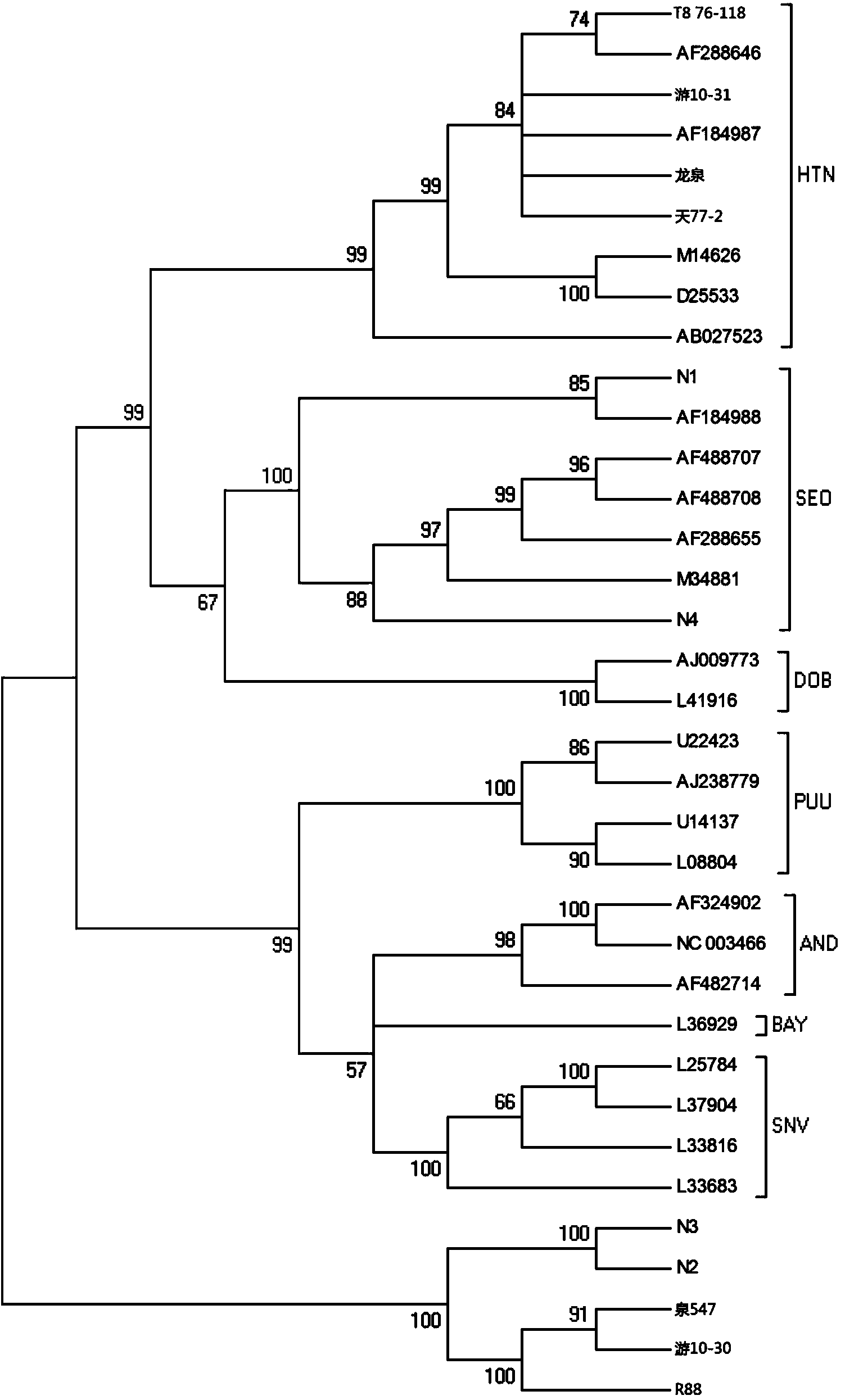
Primer, kit and method for conducting genetic typing on hantavirus by means of PCR direct sequencing method
ActiveCN103484566AEasy and fast genotypingMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesTotal rnaDirect sequencing
The invention discloses a primer, kit and method for conducting genetic typing on the hantavirus by means of a PCR direct sequencing method. The primer comprises an upstream primer: ATTAGCCCWGTCATGAGTGT, and a downstream primer: CTTTGACTCYTTTGKYTCCA, wherein the Y is a C or a T, the W is an A or a T, and the K is a G or a T. The method comprises the steps of extracting a total RNA of a virus sample to be tested, conducting reverse transcription to obtain a cDNA, using the cDNA as a template, utilizing the primer for conducting PCR amplification, conducting sequencing on an amplified target fragment, constructing a phylogenetic tree by using corresponding fragments of known genotype representative strains as a reference on the basis of sequence information of the target fragment, and conducting the genetic typing on the virus sample to be tested according to the phylogenetic tree. When the primer is used, a specificity sequence of an S gene of the hantavirus can be obtained by only conducting one-time PCR amplification, and the genetic typing can be easily, conveniently and rapidly carried out on the hantavirus by utilizing the specificity sequence.
Owner:嘉兴实践医学科技有限公司
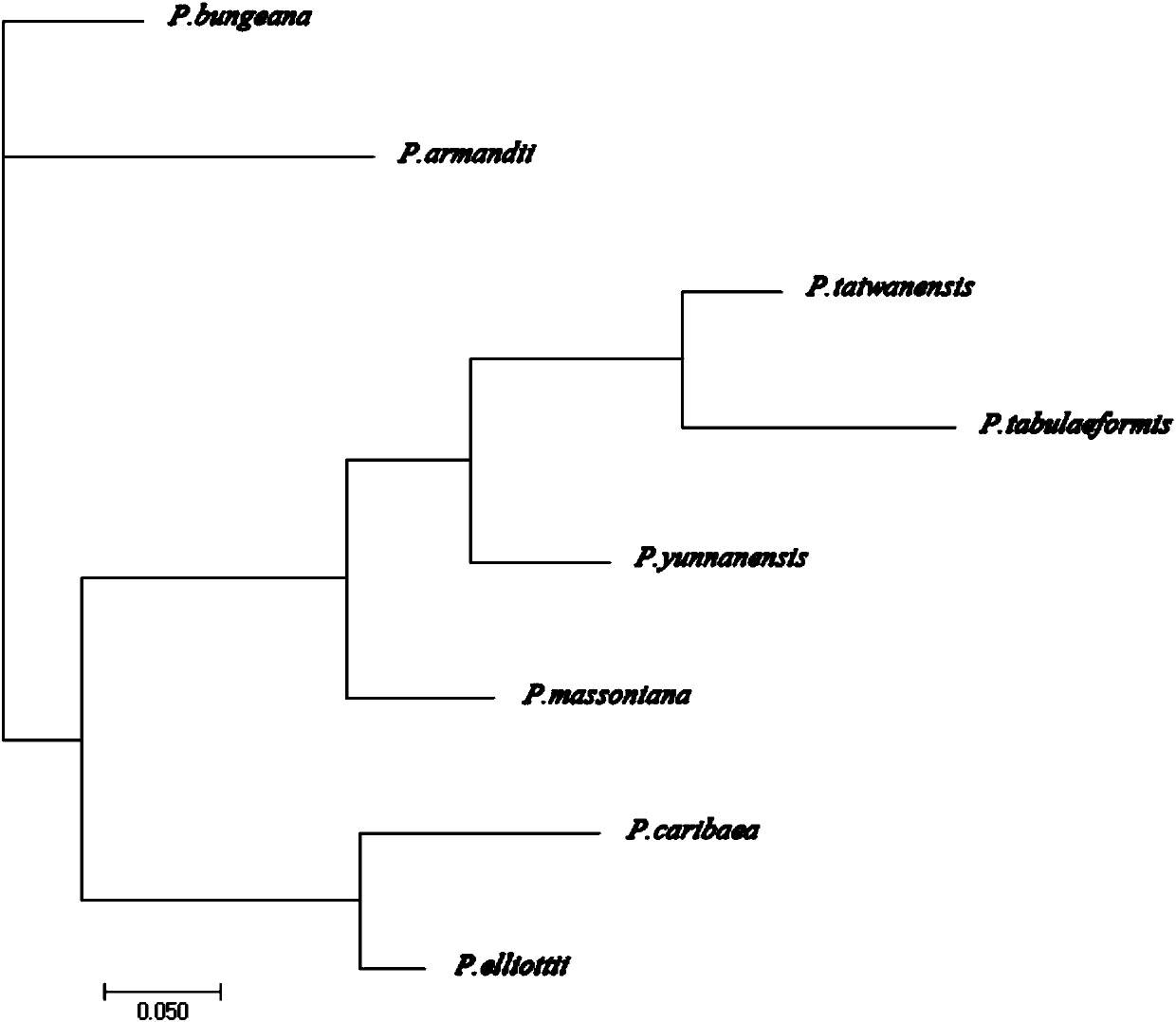
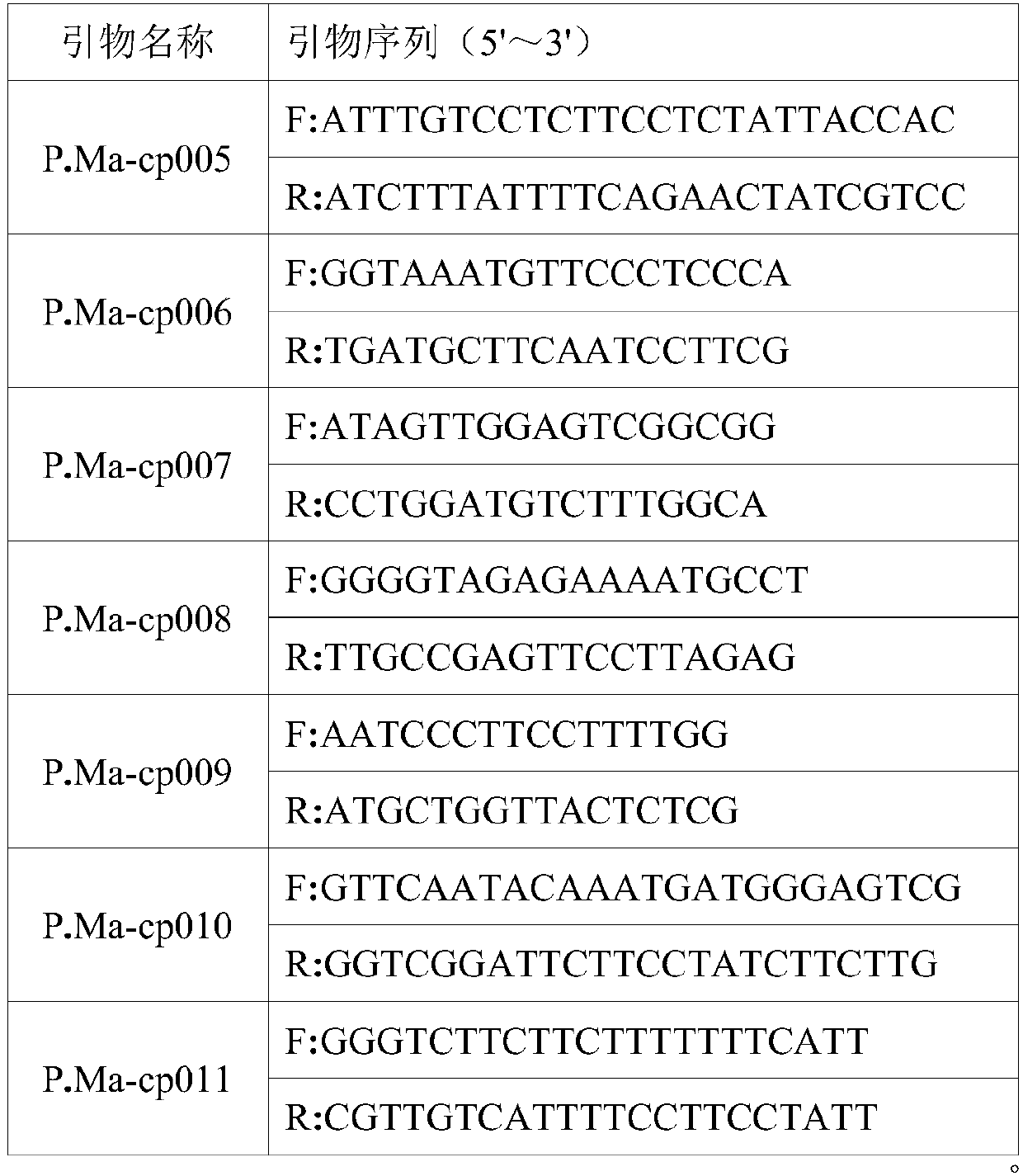
Pinus massoniana cpSSR polymorphism primer and identification method of pine sibling species of primer
ActiveCN107557362ALess prone to recombinationMultiple copies smallMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCapillary electrophoresisPhylogenetic tree
The invention discloses a pinus massoniana cpSSR polymorphism primer and an identification method of pine sibling species of the primer. According to design of a chloroplast genome of pinus massoniana, 16 pairs of cpSSR primers are obtained, further, 7 pairs of primers which are stable in difference and good in polymorphism are screened from the 16 pairs of cpSSR primers, and through utilization of the 7 pairs of primers, a finger print and phylogenetic tree of 8 kinds of pine sibling species are successfully established. Based on the 7 pairs of cpSSR primers, a PCR amplification reaction is carried out. Capillary electrophoresis technology is used to analyze a PCR product, 8 kinds of pine sibling species trees can be accurately identified. The primer and method are efficient, accurate, and convenient and are not prone to be affected by the environment. The polymorphism primer and an identification method thereof can reflect the genetic information of the 8 kinds of pine plasmons, andcan be used for research of identification of 8 kinds of pine sibling species and genetic relationship.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for rebuilding species system generation tree based on alignment of multiple metabolic pathways
ActiveCN106909805ASimplify comparison workSystems biologySpecial data processing applicationsNODALNode clustering
The invention discloses a method for rebuilding a species system generation tree based on alignment of multiple metabolic pathways. The method comprises the following steps: building a combined graph of the multiple metabolic pathways through global alignment of the multiple metabolic pathways, then building mapping between functional modules of all the metabolic pathways through node clustering of the combined graph, further analyzing a relation among the metabolic pathways according to the mapping of the functional modules, and building the system generation tree among species. The method has the beneficial effects that by the implementation of the method, the alignment work of the metabolic pathways is simplified, and a researcher only needs to do simple operation to quickly and accurately generate the system generation tree among the species.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
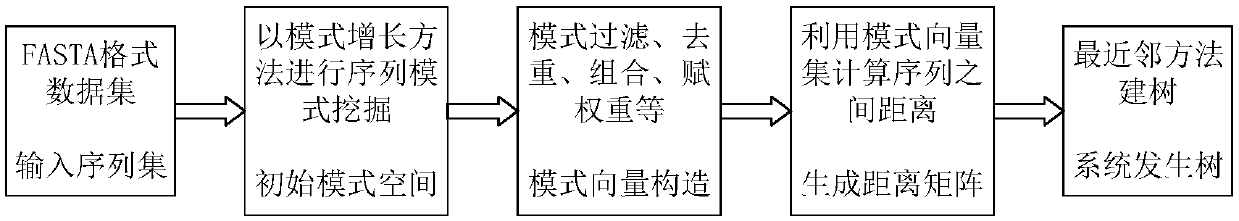
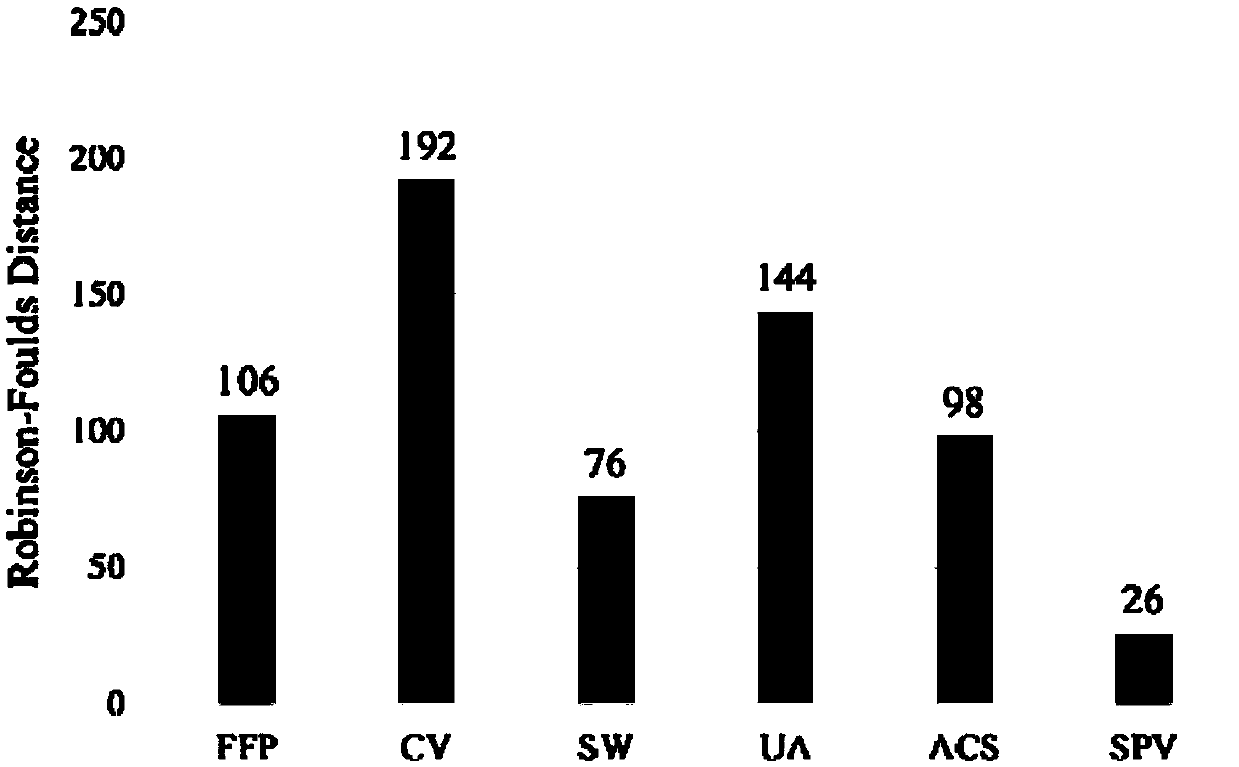
Phylogenetic tree construction method based on sequence pattern mining algorithm
ActiveCN109545283AAvoid redundant patternsQuick buildBiostatisticsSequence analysisPhylogenetic treePattern vector
The invention relates to a phylogenetic tree construction method based on a sequence pattern mining algorithm. The phylogenetic tree construction method based on the sequence pattern mining algorithmcomprises the following steps: mining a specific pattern which is hidden in a sequence set and can be used for measuring sequence similarity to obtain an initial pattern set; filtering an unclosed frequent pattern in the initial patter set to acquire an optimized pattern set capable of representing the sequence set; and constructing a patter vector set and calculating the distance between numericvectors so as to construct a distance matrix for producing a phylogenetic tree. The sequence pattern which frequently appears in the sequence set is extracted by a sequence patter mining algorithm, the sequence set is converted into binary system by the filtered pattern set or the distance matrix is calculated in the form of giving weight information to the pattern vector set, and then the phylogenetic tree is constructed. For the large-scale and low-similarity sequence set, the more representative pattern in the sequence set can be mined by utilizing a pattern growth strategy, so that the extraction of a redundancy pattern which is useless for measuring sequence similarity is voided and measurement on the similarity among the sequences within the global range is optimized.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
PCV2d (porcine circovirus type 2) virus-like particle vaccine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108355131ADoes not affect formDoes not affect sizeViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesEscherichia coliPhylogenetic tree
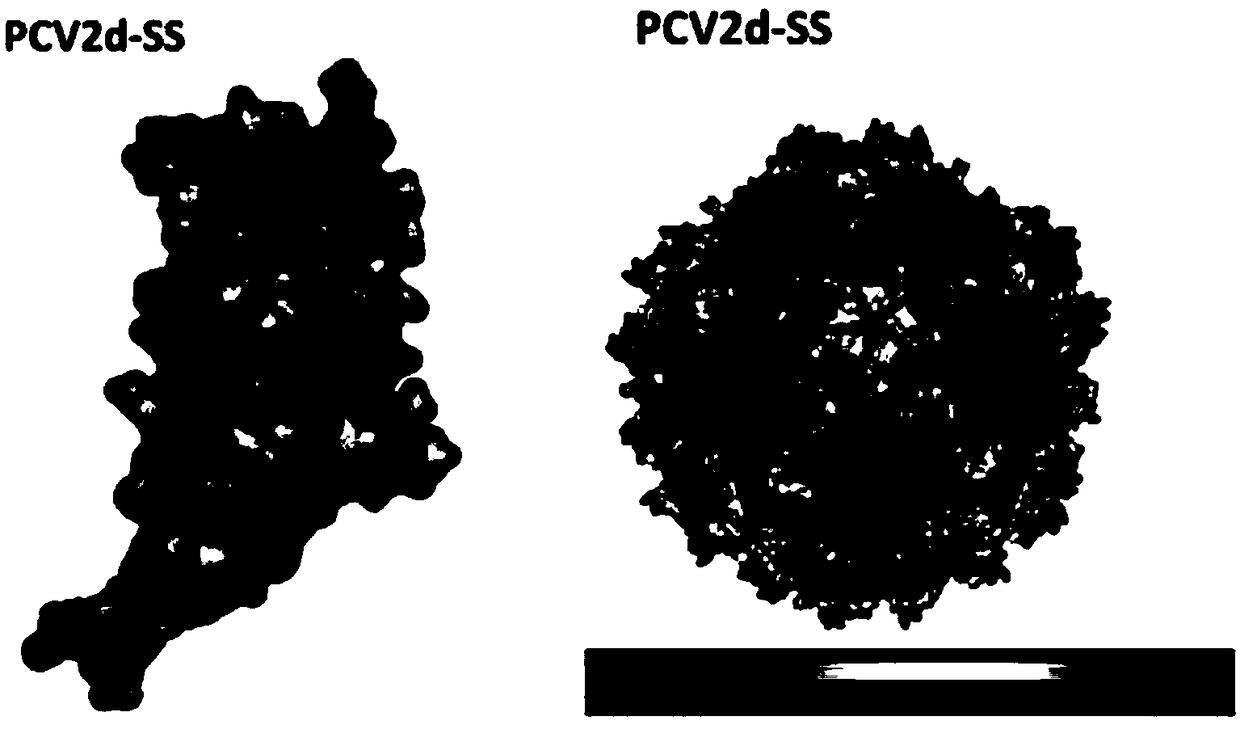
The invention relates to a PCV2d (porcine circovirus type 2) virus-like particle vaccine and a preparation method thereof. By means of epidemiological analysis for PCV2d strains of China, comparison of amino acid sequence information of a large quantity of collected strains as well as phylogenetic tree analysis, a Cap gene of a currently epidemic PCV2d strain in China is selected, PCV2d Cap protein is effectively expressed by an Escherichia coli prokaryotic expression system through codon sequence optimization, PCV2d virus-like particles are prepared successfully by purification and assembly in an in-vitro assembly and dialysis buffer solution, and form, size and concentration of the virus-like particles are not affected when the virus-like particles are placed for 6 months in a storage buffer solution at 4 DEG C and subzero 20 DEG C; the prepared PCV2d virus-like particle vaccine immunizes 21-day-old piglets, and a PCV2d challenge test proves that the vaccine has a good protecting effect for the piglets.
Owner:JIANGSU NANNONG HI TECH +1
Methods for determining the genetic affinity of microorganisms and viruses
InactiveUS8214153B1Particle separator tubesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesIsotopic labeling
Selecting which sub-sequences in a database of nucleic acid such as 16S rRNA are highly characteristic of particular groupings of bacteria, microorganisms, fungi, etc. on a substantially phylogenetic tree. Also applicable to viruses comprising viral genomic RNA or DNA. A catalogue of highly characteristic sequences identified by this method is assembled to establish the genetic identity of an unknown organism. The characteristic sequences are used to design nucleic acid hybridization probes that include the characteristic sequence or its complement, or are derived from one or more characteristic sequences. A plurality of these characteristic sequences is used in hybridization to determine the phylogenetic tree position of the organism(s) in a sample. Those target organisms represented in the original sequence database and sufficient characteristic sequences can identify to the species or subspecies level. Oligonucleotide arrays of many probes are especially preferred. A hybridization signal can comprise fluorescence, chemiluminescence, or isotopic labeling, etc.; or sequences in a sample can be detected by direct means, e.g. mass spectrometry. The method's characteristic sequences can also be used to design specific PCR primers. The method uniquely identifies the phylogenetic affinity of an unknown organism without requiring prior knowledge of what is present in the sample. Even if the organism has not been previously encountered, the method still provides useful information about which phylogenetic tree bifurcation nodes encompass the organism.
Owner:TECH LICENSING CO LLC
Method for identifying Gaoyou duck varieties by utilizing molecular bioinformatics
InactiveCN101812500AAccurate identificationReflect germplasm differencesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhylogenetic treeGenetic distance
The invention relates to a method for identifying Gaoyou duck varieties by utilizing molecular bioinformatics, belonging to the technical filed of biological variety identification. In the invention, the sequences of gene b of cytochrome of mitochondrial DNA of a Gaoyou duck and the duck variety to be tested are accurately obtained on the basis of gene cloning and DNA sequencing technologies, a plurality of bioinformatics software is utilized to accurately figure out the haplotype, variation locus, haplotype diversity, average nucleotide difference, nucleotide ramification degree, pure genetic distance, Kimura dual-parameter genetic distance among varieties, variety colony cluster result images and haplotype phylogenetic trees of each variety, and the genetic information difference among the varieties is utilized to identify the true and false of the Gaoyou duck varieties through software precise calculation and analysis results.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF POULTRY SCI
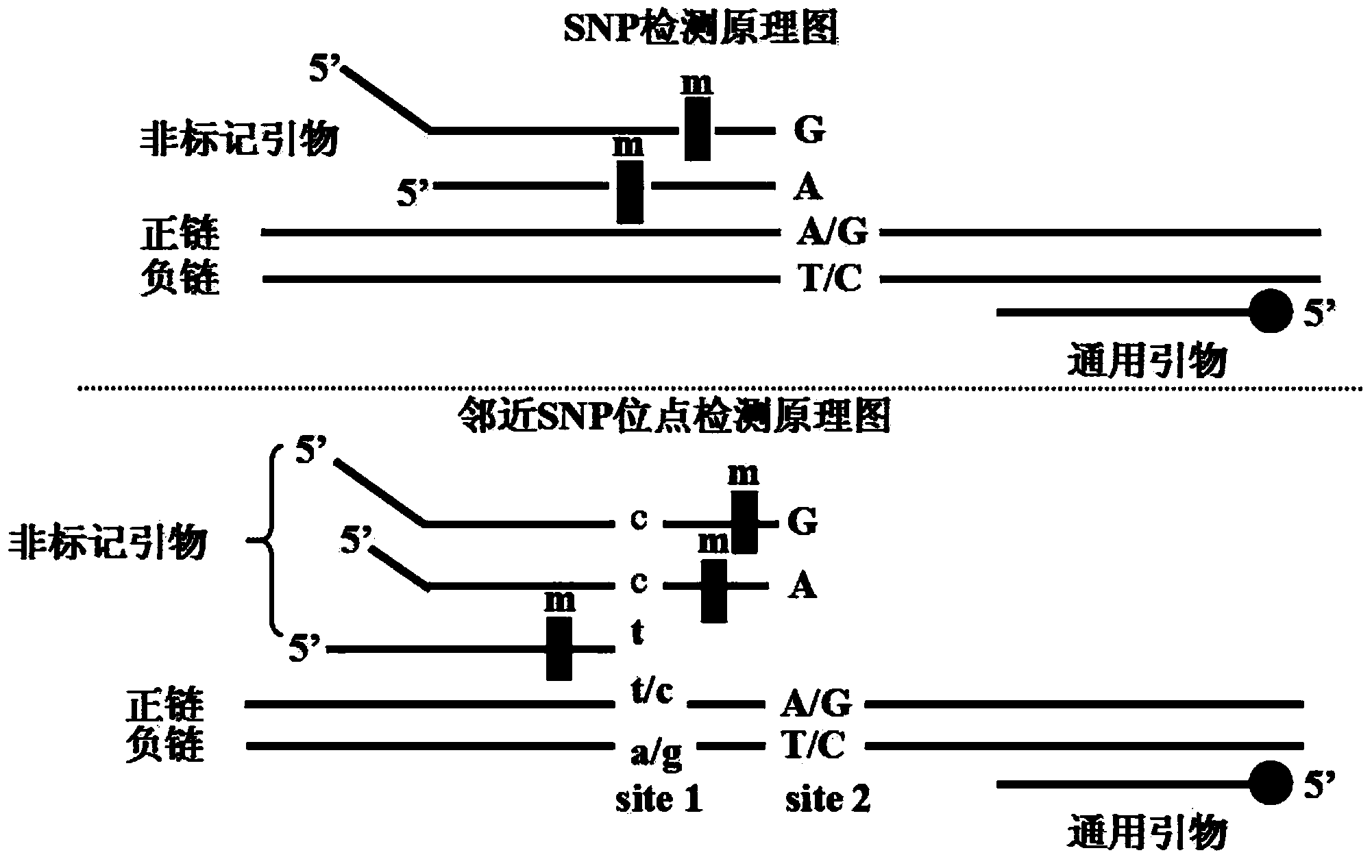
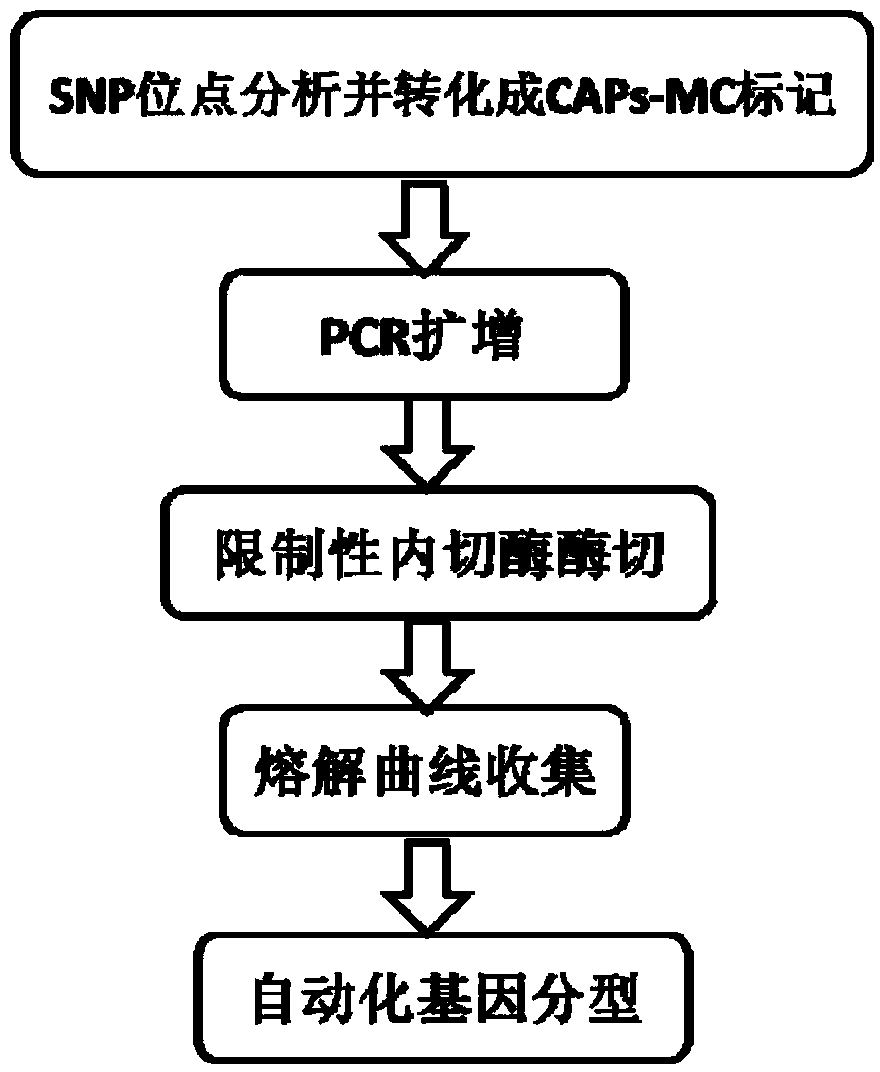
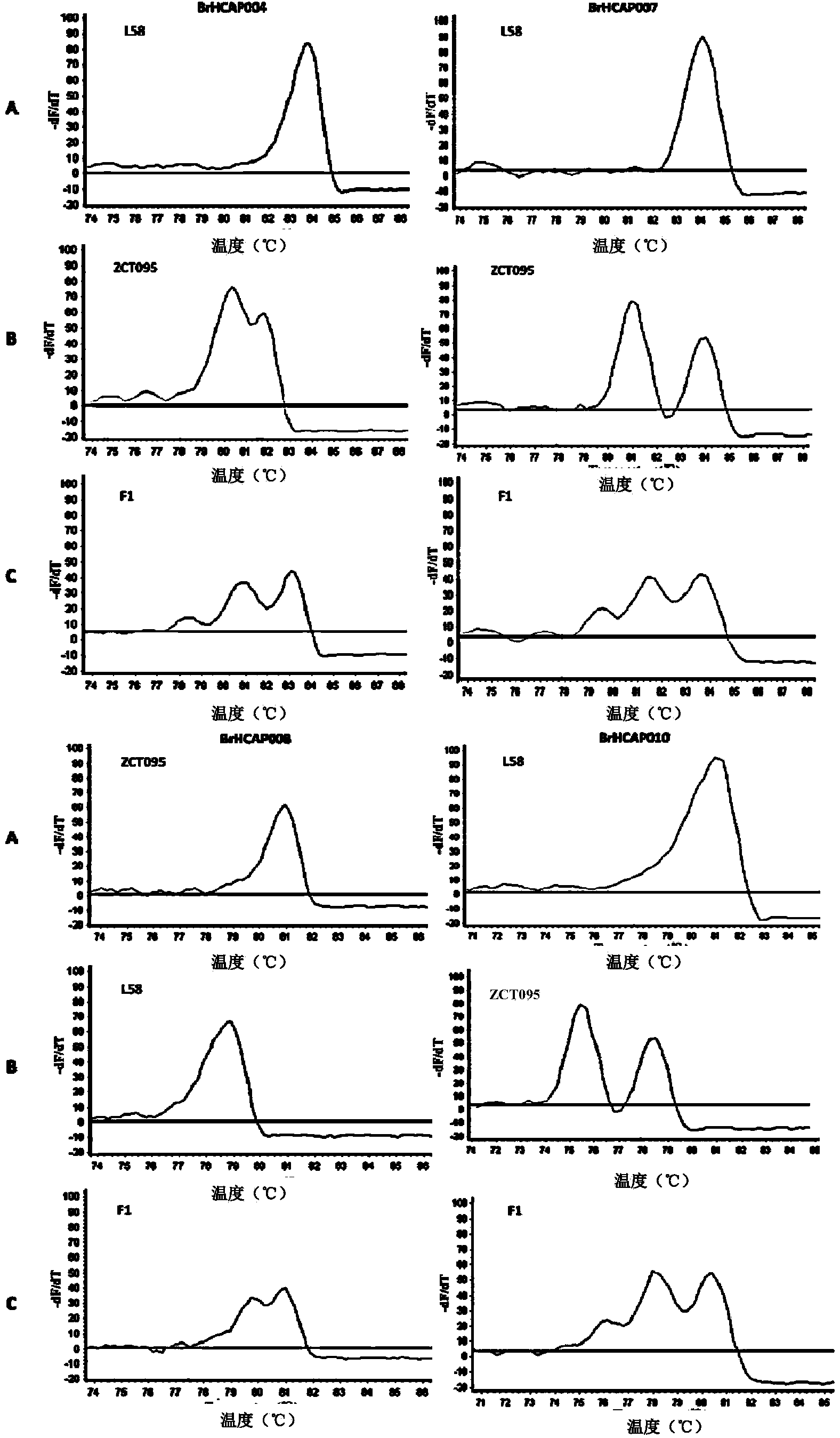
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) genotyping method and application thereof
InactiveCN103589797AOptimizing Kinds of WorkSimplify the development processMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman bodyPhylogenetic tree
The invention provides an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) genotyping method and an application thereof, and relates to an SNP genotyping method. The SNP genotyping method is an SNP genotyping technology based on the combination of restriction endonuclease fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) and a melting curve. The method is high in accuracy, good in stability, fast, time-saving, high-throughput and safe, facilitates automatic operation and doesn't require gel electrophoresis, the operation process produces no harm to a human body, and the cost is low. The SNP genotyping method not only gains a great success in the aspects of plant SNP genotyping and breeding of Chinese cabbage, Chinese kale, tomatoes and the like, but also has a great application value in the aspects of establishment of a high-precision genetic map, fine mapping of genes, genome-wide association analysis, establishment of a phylogenetic tree and the like in biology.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
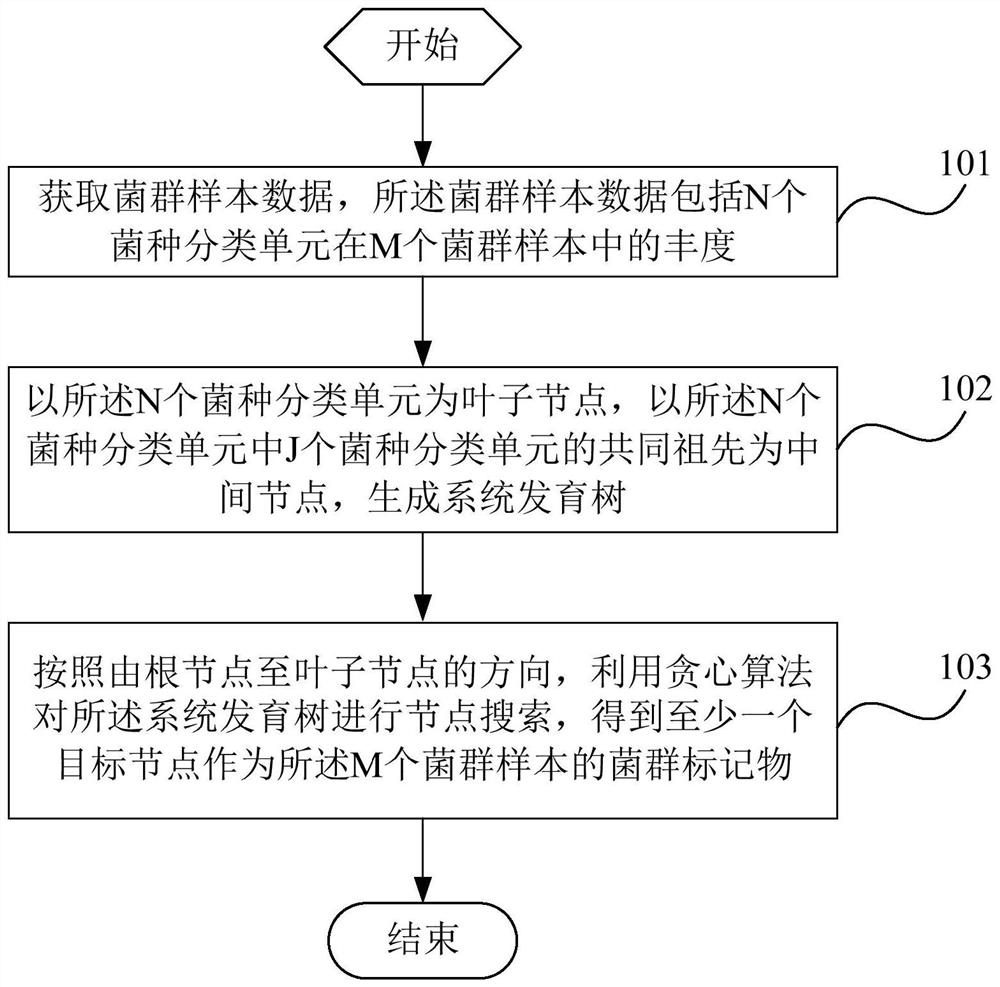
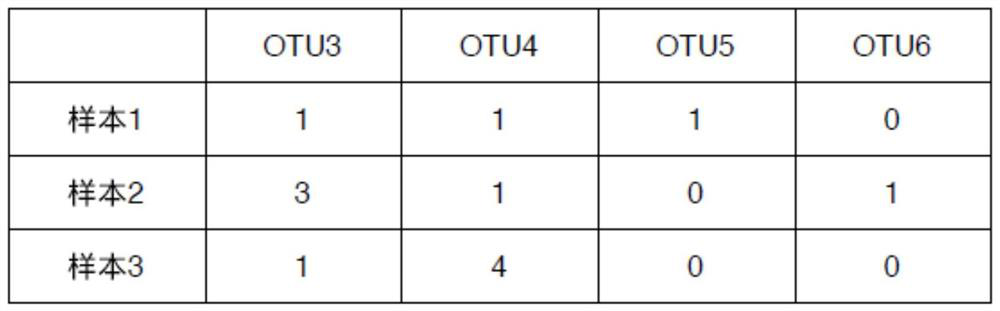
Flora marker obtaining method and device, terminal and storage medium
ActiveCN111710364ARealize OKReduce computational complexityBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation complexityGreedy algorithm
The invention is applicable to the technical field of biology, and provides a flora marker obtaining method and device, a terminal and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining flora sample data, wherein the flora sample data comprises abundance of N strain classification units in M flora samples, and N and M are positive integers; generating a phylogenetic tree by taking the N strain classification units as leaf nodes and taking the common ancestor of the J strain classification units in the N strain classification units as an intermediate node; and according to the direction from the root node to the leaf nodes, performing node search on the phylogenetic tree by utilizing a greedy algorithm to obtain at least one target node as the flora marker of the M florasamples. According to the scheme, the calculation complexity of high-dimensional flora sample data can be reduced, the target flora marker can be determined efficiently, and the calculation amount isreduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
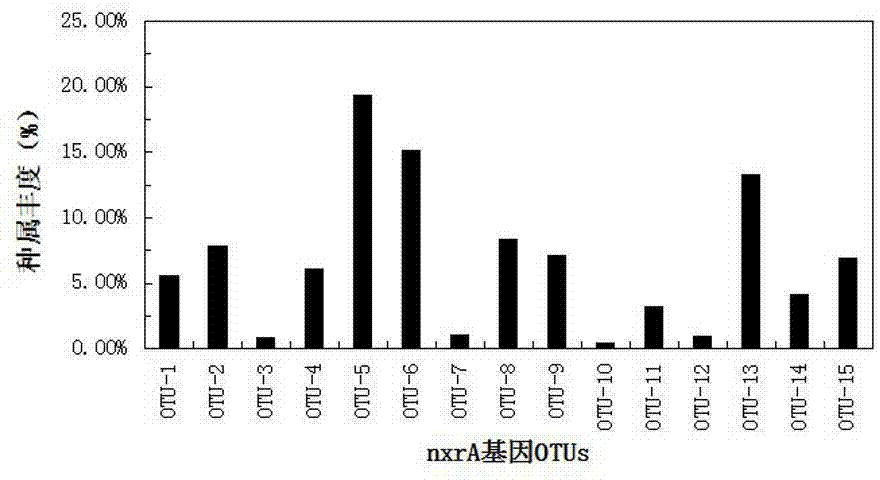
Method for detecting community structures and abundance of nitrite oxidizing bacteria in wastewater
InactiveCN104745684AStrong specificityReal-time monitoring of denitrification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementActivated sludgeCommunity structure
The invention discloses a method for detecting the community structures and abundance of nitrite oxidizing bacteria in wastewater. The method comprises the concrete steps as follows: (a) extracting the whole-genome DNA of activated sludge in the wastewater; (b) performing PCR amplification of a gene nxrA and a gene nxrB; (c) sequencing amplification products respectively by a Roche 454 pyrosequencing method; (d) dividing the OTUs (Operational Taxonomic Units) of sequencing results; and (e) selecting OTUs sequences with the similarity of 97%, performing BLASTn comparison between the OTUs sequences, and dividing the phylogenetic trees of the gene nxrA and the gene nxrB respectively by using MEGA software, wherein the phylogenetic trees are the community structures of the nitrite oxidizing bacteria in the wastewater, and the relative abundance of the different OTUs of the gene nxrA and the gene nxrB is the abundance of the nitrite oxidizing bacteria in the wastewater. The method is simple and convenient to operate, has a wide detection range, can be applied to detection and analysis in a laboratory and can also realize real-time detection of the nitrogen removal efficiency of a wastewater treatment plant.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for identifying Japanese ginseng rhizomes and non-generic confusion or counterfeit species of Japanese ginseng rhizomes based on ITS2
InactiveCN108715904AEasy to identifyRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPhylogenetic treeConfusion
The invention relates to a method for identifying Japanese ginseng rhizomes and non-generic confusion or counterfeit species of the Japanese ginseng rhizomes based on ITS2, and discloses a method foridentifying the Japanese ginseng rhizomes and the non-generic confusion or counterfeit species of the Japanese ginseng rhizomes according to DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) level. The method includes thesteps: 1) extracting Japanese ginseng rhizome DNA of a sample to be measured; 2) taking the DNA of the sample to be measured as a template and performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplificationon fragments of an ITS2 sequence; 3) positively sequencing a PCR product and performing ITS2 database shearing to obtain the ITS2 sequences of the Japanese ginseng rhizomes; 4) building an NJ phylogenetic tree, analyzing intraspecific and interspecific average genetic distances and comparing secondary structural features. Results indicate that the ITS2 sequences of the Japanese ginseng rhizomes are clustered together, the intraspecific average genetic distances of the Japanese ginseng rhizomes are remarkably shorter than the interspecific average genetic distances of the non-generic confusionor counterfeit species of the Japanese ginseng rhizomes, secondary structures of the Japanese ginseng rhizomes widely differ from those of the non-generic confusion or counterfeit species, and the ITS2 sequences are used for rapidly and accurately identifying the Japanese ginseng rhizomes and the non-generic confusion or counterfeit species of the Japanese ginseng rhizomes. The method is simple tooperate, high in resolution ratio and strong in applicability and repeatability, and the Japanese ginseng rhizomes and the non-generic confusion or counterfeit species of the Japanese ginseng rhizomes can be rapidly and accurately identified.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEDICAL UNIV
Laccase protein gene and cloning and sequencing method thereof
The invention discloses an Antrodia camphorate <{EN0}>Laccase protein gene and a cloning and sequencing method thereof, belonging to the technical field of molecular biology. The Antrodia camphorate <{EN0}>Laccase protein gene is a gene of laccase; specifically, the nucleotide sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and codes polypeptide with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. The invention further provides a cloning and sequencing method for the Antrodia camphorate <{EN0}>Laccase protein gene. The method comprises the following steps: tissue isolation; isolation of total RNA; and cloning and sequencing of a full-length cDNA sequence. The nucleic acid sequence and variety of the gene can be confirmed by analyzing sequencing results with molecular biology software and constructing a phylogenetic tree.
Owner:SHANGHAI QINSHENGYUAN BIOTECH
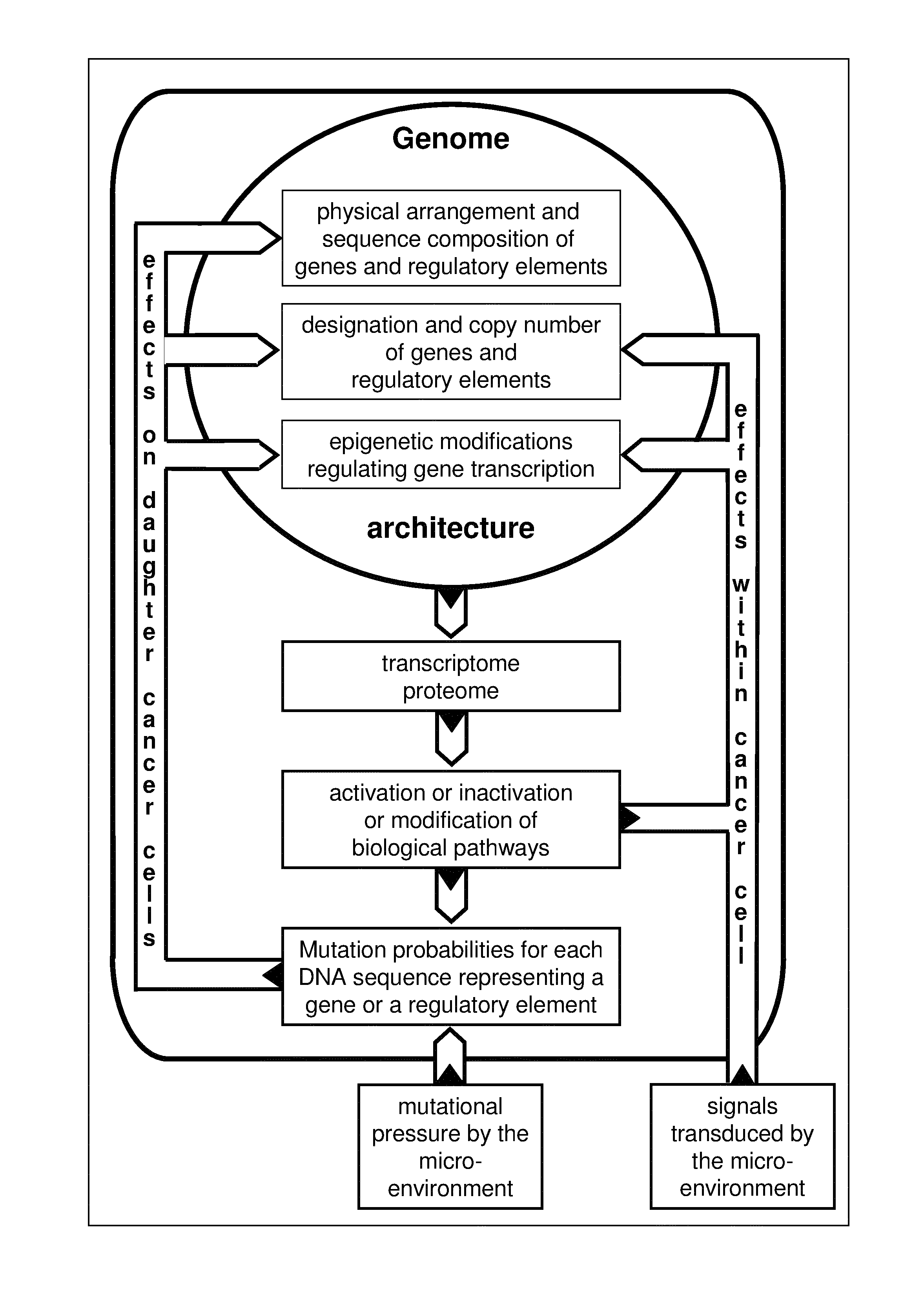
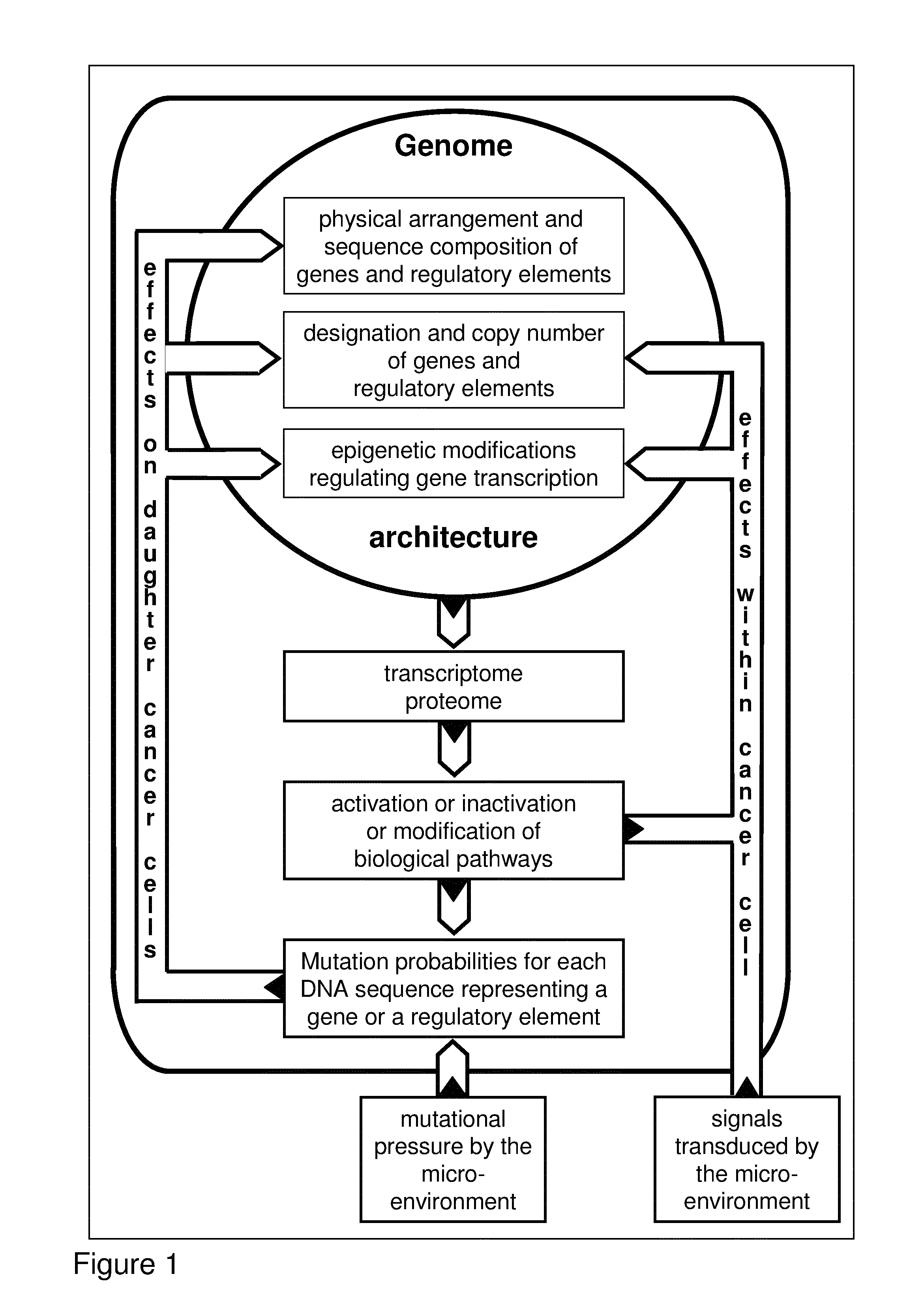
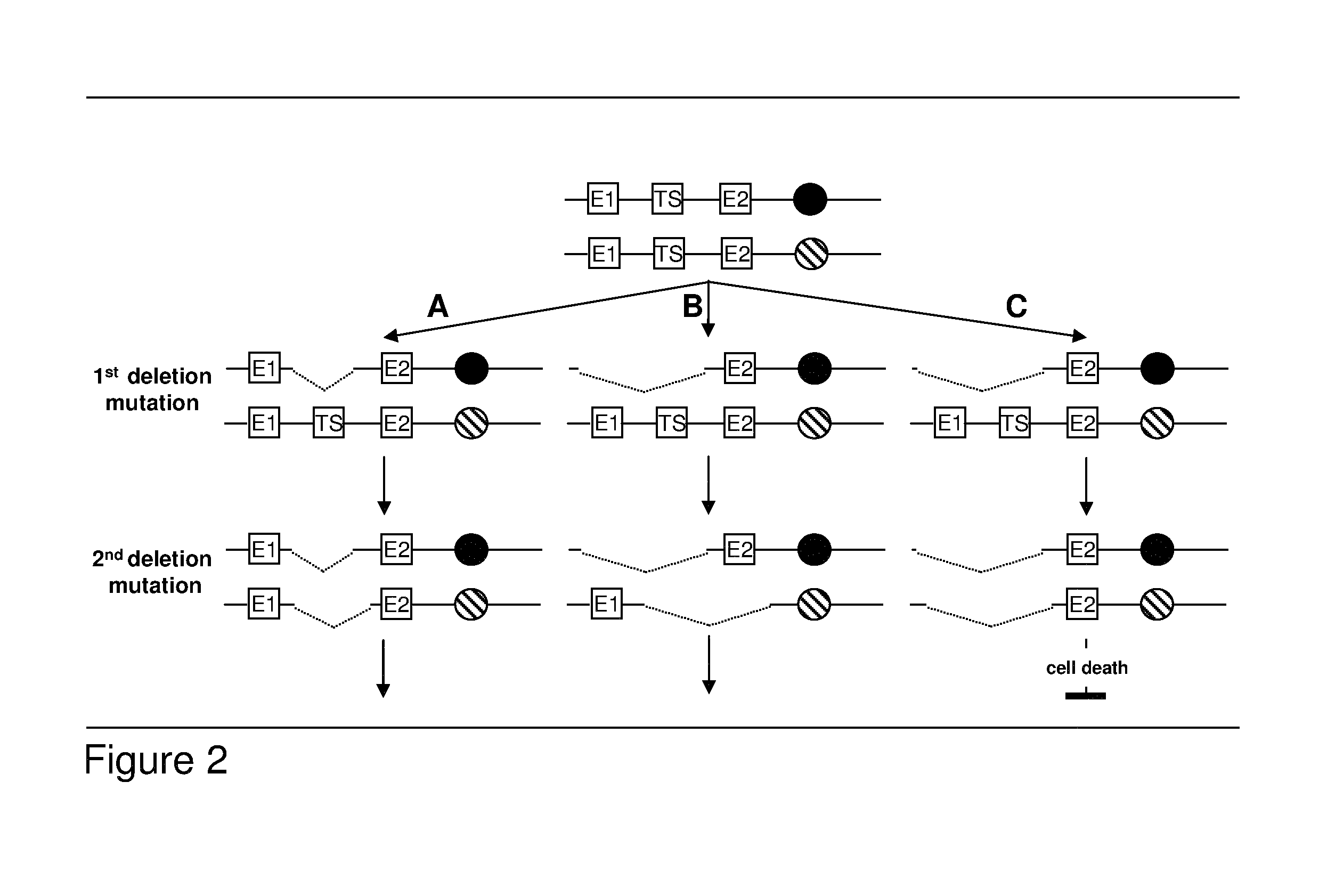
Algorithm for modification of somatic cancer evolution
Owner:RUBBEN ALBERT
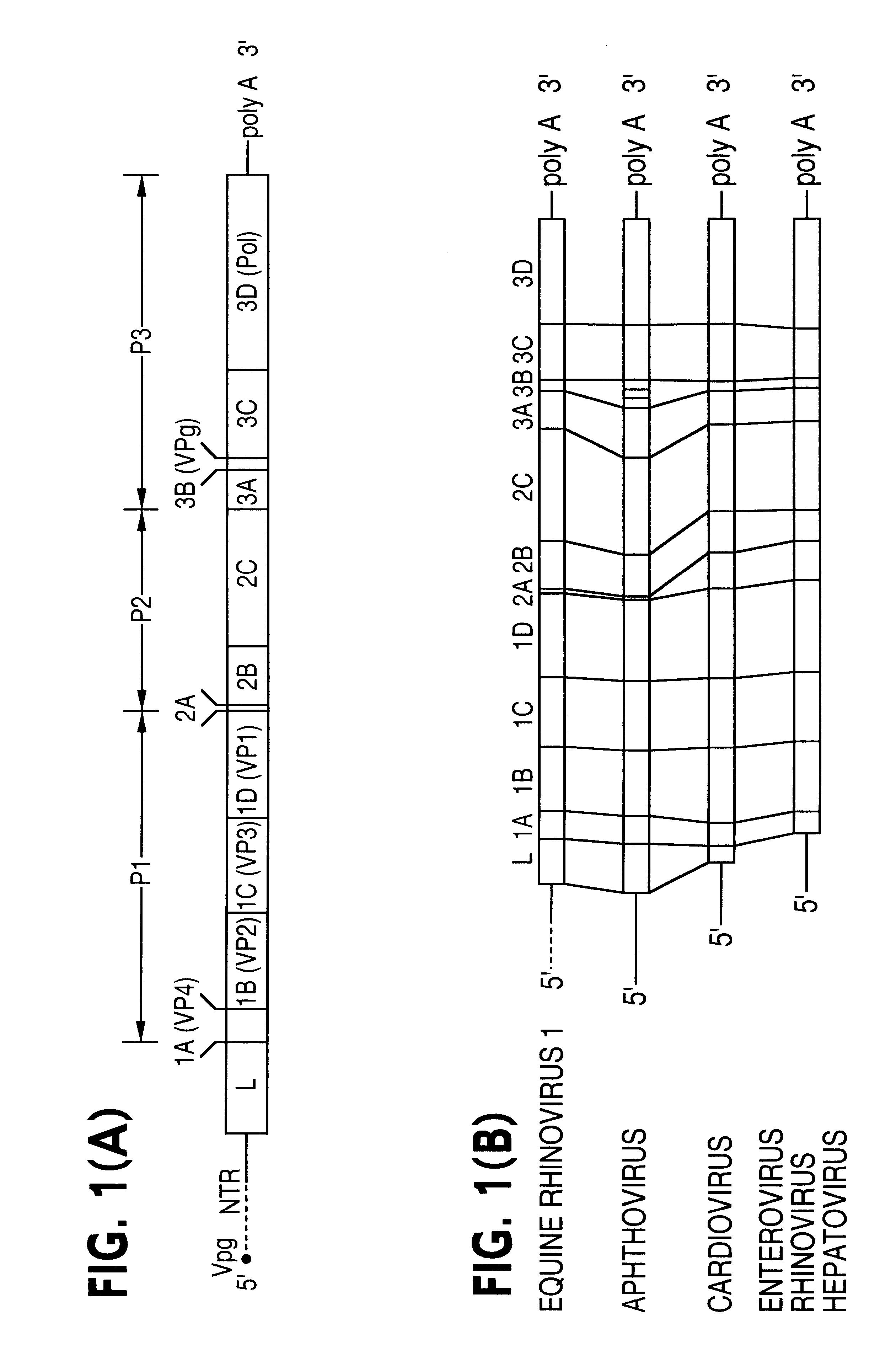
Equine rhinovirus 1 proteins
Equine rhinovirus 1 (ERhV1) is a respiratory pathogen of horses which has an uncertain taxonomic status. The nucleotide sequence of the ERhV1 genome and amino acid sequence have been substantially determined (FIG. 2). The predicted polyprotein was encoded by 6,741 nucleotides and possessed a typical picornavirus proteolytic cleavage pattern, including a leader polypeptide. The genomic structure and predicted amino acid sequence of ERhV1 were more similar to those of foot-and-mouth disease viruses (FMDV), the only members of the aphthovirus genus, than other picornaviruses. Nucleotide sequences coding for the complete polyprotein, the polymerase, and VP1 were analyzed separately. The phylogenetic trees confirmed that ERhV1 was more closely related to aphthoviruses than to other picornaviruses. Virion proteins and virus-like particles are described and probes, primers, antigens, vectors, diagnostics and tests developed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
Method for isolating and identifying effective degrading fungi for corn stalks
PendingCN110129407AImprove accuracyThe identification result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention discloses a method for isolating and identifying effective degrading fungi for corn stalks. The method includes: selecting samples, performing inoculated culture, screening and culturingthe fungi, through four screening and culturing mediums including a fungus screening and culturing medium, a Congo red cellulose screening and agar culturing medium, a seed culturing medium and an effective corn stalk degrading liquid state fermentation culturing medium, culturing the fungi obtained from multiple times of activation, preliminarily screening cellulose degrading fungi, observing growth form of the cellulose degrading fungi, performing molecular biological identification, subjecting fungus strains obtained from morphological identification to PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection, and establishing a phylogenetic tree for obtained results so that to-be-tested fungus strains can be identified more correctly. The fungus screening and culturing medium is utilized to screen the effective corn stalk degrading fungi, and the Congo red cellulose screening and agar culturing medium, the seed culturing medium and the effective corn stalk degrading liquid state fermentation culturing medium are utilized to screen the effective degrading fungi. By utilizing different screening and culturing mediums to culture, the required fungi can be obtained more accurately, and accuracyof an experiment can be improved. Through strict sterilization during purification, identification results are enabled to be more accurate.
Owner:HONGHE COLLEGE
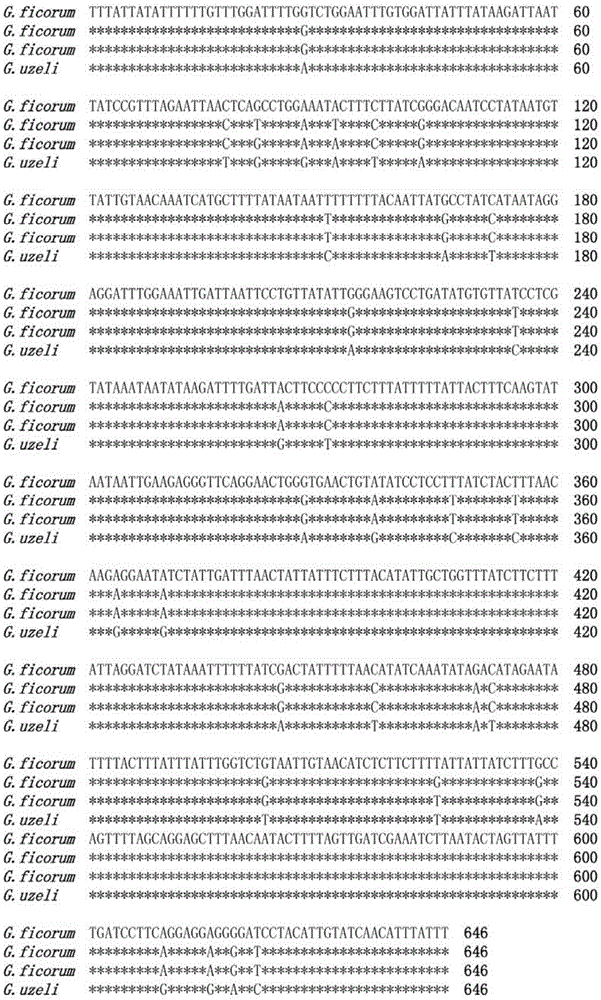
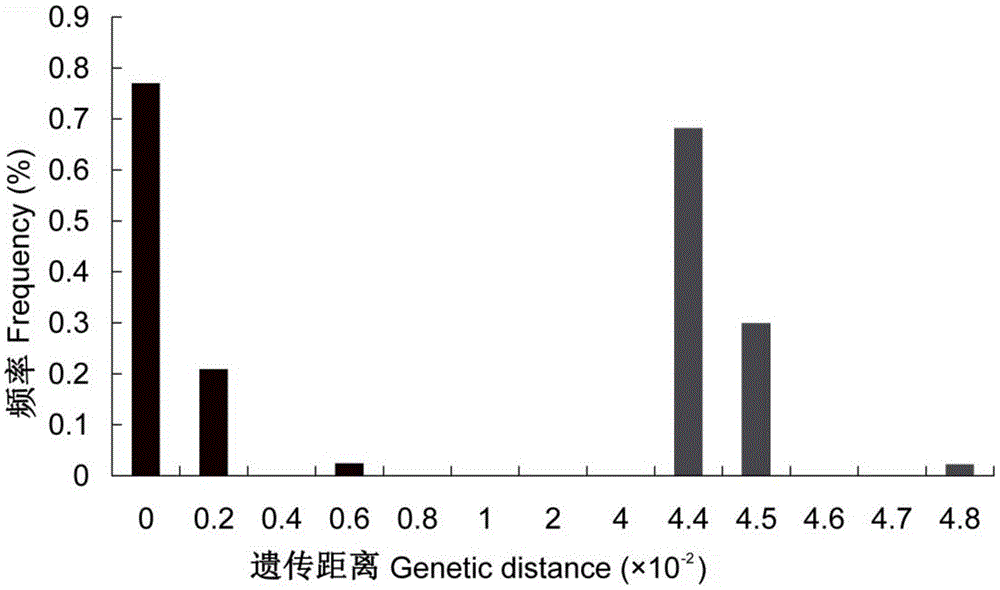
Molecular method capable of identifying gynaikothrips ficorum and gynairothrips uzeli zimmerman
InactiveCN105420365AAccurate identificationOvercome small sizeMicrobiological testing/measurement3-deoxyriboseGynaikothrips ficorum
The invention provides a molecular method capable of identifying gynaikothrips ficorum and gynairothrips uzeli zimmerman. The molecular method comprises the following steps: (1) extracting DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of a sample to be identified; (2) taking the DNA extracted by the step (1) as a template, carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by using a primer pair and purifying an amplified product; (3) sequencing the PCR amplified product purified by the step (2), and accurately distinguishing two seeds through a basic group variation site, a genetic distance and a phylogenetic tree. The invention provides a method for identifying the gynaikothrips ficorum and the gynairothrips uzeli zimmerman through molecular biology; the method is simple to operate and accurate in identification and can be widely popularized.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for establishing mycobacterium abscessus RUO database and subtype super map
ActiveCN106483188AImprove identification efficiencyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhylogenetic treeFlight time
The invention discloses a method for establishing a mycobacterium abscessus RUO database and a subtype super map. The method is characterized by including the following steps of mycobacterium abscessus strain collecting and DNA extracting; 2, gene library preparing and illumine HiSeq sequencing; 3, genome establishing and phylogenetic tree establishing; 4, sample preparing and strain detecting; 5, accuracy confirming. According to the method, mycobacterium abscessus subspecies are analyzed and determined; ionization-flight-time mass-spectrometric-detection subspecies information is desorbed in the mode that a matrix assists in laser, the RUO database and the established super map are established, the sensitivity and the specificity are detected through strain blind testing, the operation procedure and the diagnostic standard for subspecies-level laboratory identification are formulated, a work chain of the microbial standard in-vitro-diagnosis procedure is added, and the efficiency of all microbiological labs on mycobacterium abscessus subtype identification is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI PULMONARY HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com