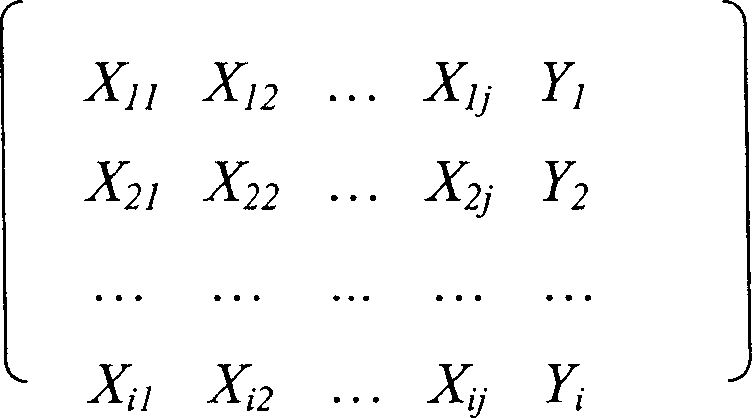Patents
Literature
315 results about "Ralstonia solanacearum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
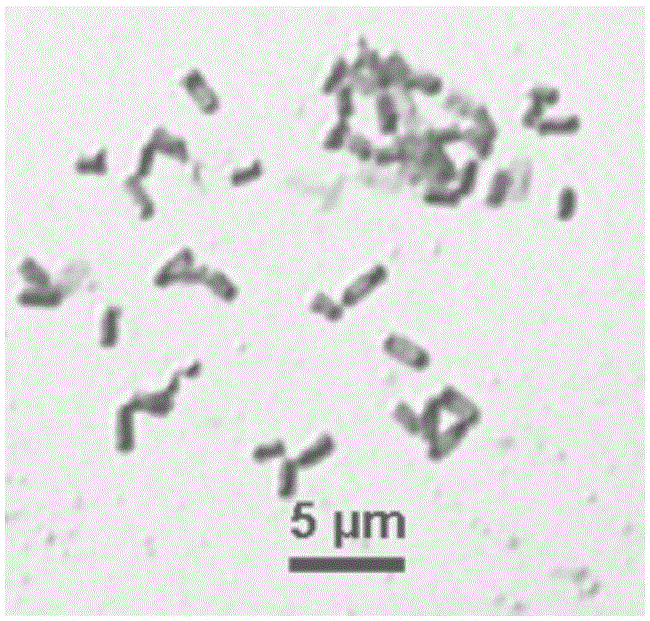
Ralstonia solanacearum is an aerobic non-spore-forming, Gram-negative, plant pathogenic bacterium. R. solanacearum is soil-borne and motile with a polar flagellar tuft. It colonises the xylem, causing bacterial wilt in a very wide range of potential host plants. It is known as Granville wilt when it occurs in tobacco. Bacterial wilts of tomato, pepper, eggplant, and Irish potato caused by R. solanacearum were among the first diseases that Erwin Frink Smith proved to be caused by a bacterial pathogen. Because of its devastating lethality, R. solanacearum is now of the more intensively studied phytopathogenic bacteria and bacterial wilt of tomato is a model system for investigating mechanisms of pathogenesis. Ralstonia was recently classified as Pseudomonas with similarity in most aspects, except that it does not produce fluorescent pigment like Pseudomonas. The genomes from different strains varies from 5.5 Mb up to 6 Mb, roughly being 3.5 Mb of a chromosome and 2 Mb of a megaplasmid. While the strain GMI1000 was one of the first phytopathogenic bacterias to have its genome completed, the strain UY031 was the first R. solanacearum to have its methylome reported. Within the R. solanacearum species complex, the four major monophyletic clusters of strains are termed phylotypes, that are geographically distinct: phylotypes I-IV are found in Asia, America, Africa, and Oceania, respectively.
Bacillus belesei BMF 03 and use and fermentation method thereof
A marine-derived Bacillus velezensis (Bacillus velezensis) BMF 03 having a deposit number of CCTCC NO: 2017374 is disclosed. BMF 03 strain and its aseptic fermentation broth have inhibitory effect onplant pathogenic fungi, including apple rot fungi, grape white rot fungi, mango anthracnose fungi and so on. The aseptic fermentation broth of BMF 03 strain can be used as an active ingredient to prepare an antibacterial drug, and the bacteria is selected from the group consisting of Keratinobacteria, Bacillus subtilis and Ralstonia solanacearum. The invention also discloses a fermentation methodof aseptic fermentation broth of BMF 03. The invention adopts a plate confrontation method and an Oxford cup method to screen a new marine bacterial strain BMF-03 with strong bacteriostatic effect andwide bacteriostatic spectrum, and adopts strain morphological observation, physiological and biochemical tests and 16S rDNA sequence analysis to determine the species relationship of excellent resistant strains. At that same time, the bacteriostatic substance produce by the strain, the sporulation fermentation medium and the shake flask fermentation conditions were also study, and the promoting effect of the strain fermentation broth and the solid fermentation product on the growth of the cucumber seedling was clarified, which laid a foundation for the application of the strain.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and microbial inoculum and application thereof
ActiveCN105132336AGrowth inhibitionWide range of sterilization applicationsBiocideBacteriaFusarium oxysporumMicroorganism
The invention discloses bacillus amyloliquefaciens and the microbial inoculum and application thereof. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens is a Latin name, the strain number is HC200, and the accession number in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center is CGMCC No.10371. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens has a selective antagonism effect on biocontrol bacteria and pathogenic bacteria and has a strong inhibiting effect on fusarium oxysporum, fusarium solani, phytophthora nicotianae and ralstonia solanacearum, and has a good synergetic antagonism effect on pathogenic bacteria by being matched with trichoderma viride H06.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Process of analyzing descending differentiated fatty acid type of Ralstonia solanacearum
InactiveCN101020921AEasy to set upComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementRalstonia solanacearumPathogenicity
The process of analyzing down differentiated fatty acid type of Ralstonia solanacearum includes screening Ralstonia solanacearum fatty acid laminating factor and establishing judgment models. By means of screening three characteristic factors, are established the following judgment models: Y1=-16.3353+0.0012X1+0.0056X9-0.0016X13, Y2=-3.4928+0.0002X1+0.0003X9+0.0025X13, and Y3=-9.1550-0.0003X1+0.0039X9+0.0042X13. The said analysis process can identify the fatty acid type of Ralstonia solanacearum and its pathogenicity, and provides theoretic foundation for the identification of the down differentiated fatty acid type of Ralstonia solanacearum related to pathogenicity.
Owner:BIOLOGICAL TECH INST OF FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Bacillusamyloliquefaciens subsp Lh-1 and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of microbial control, in particular to bacillusamyloliquefaciens subsp Lh-1 and application thereof. With a preservation number of CGMCC No.8548, the bacillusamyloliquefaciens subsp Lh-1 is applied in control of Verticillium dahliae, erwinia carotovora, ralstonia solanacearum, valsa leucostoma, Valsa Mali Miyabe et Yamada, Phytophthora capsici and phytophthora infestans. According to the invention, the bacillusamyloliquefaciens subsp Lh-1 and pesticide and chitosan oligosaccharide with dual effects of fertilizer and pesticide are combined into an Lh-1 microecological agent, the viable count is small, the dosage is small, the production process is simple, the cost is low, and the Lh-1 microecological agent has the dual functions of disease prevention and growth promotion. Nursery test proves that reduce the disease incidence of crop is reduced, especially for control of Verticillium dahliae, the disease incidence drops to 6%, and the control effect is significant. In addition, the Lh-1 microecological agent is a biological strain preparation, is completely free of a series of problems caused by use of chemical pesticides, thus being conducive to pollution-free production of crops, and farmers can have no need for pesticide or reduce the dosage of chemical pesticide, thus greatly saving the expenditure.
Owner:AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT OF SHANXI PROVINCE
Strain of efficient bacillus amyloliquefaciens, and bacterial agent and application thereof
ActiveCN108690821AGood inhibitory effectHigh inhibitory effectBiocideFungiDiseasePaecilomyces lilacinus
The invention discloses a strain of efficient bacillus amyloliquefaciens, and a bacterial agent and application thereof, wherein the Latin name of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens is Bacillus amyloliquefaciens; the strain number is HW05; the accession number of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center is CGMCC No. 10273. The efficient bacillus amyloliquefaciens provided by the invention has the obvious inhibition effects on fusarium oxysporum, phytophthora capsici, ralstonia solanacearum, pyricularia grisea, colletotrichum gloeosporioides and root-knot nematode. Through the single application of HW05, the efficient prevention and control effects can be achieved on leaf surface disease sweet melon powdery mildew, mango anthracnose diseases andmulberry red rust diseases; the HW05 and paecilomyces lilacinus can be matched for preventing and treating soil-borne banana wilting diseases and banana root-knot nematode diseases, and a good synergyeffect is achieved.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
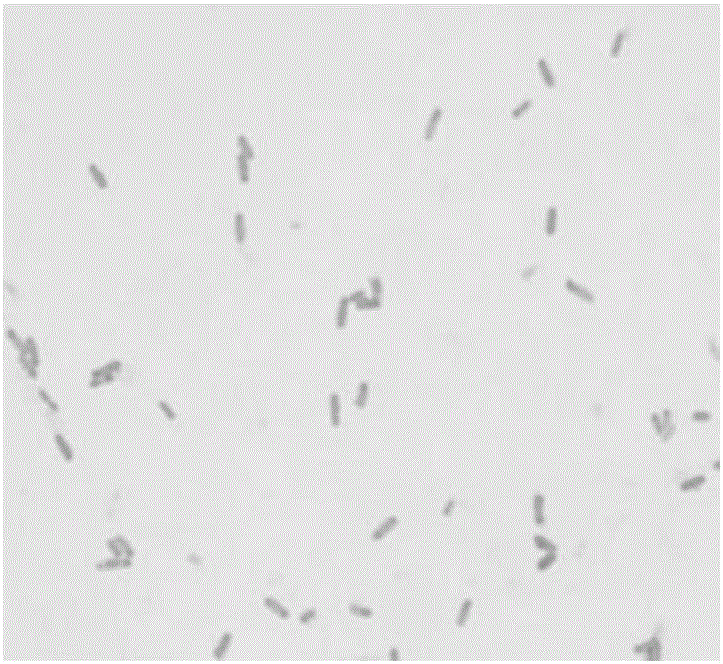
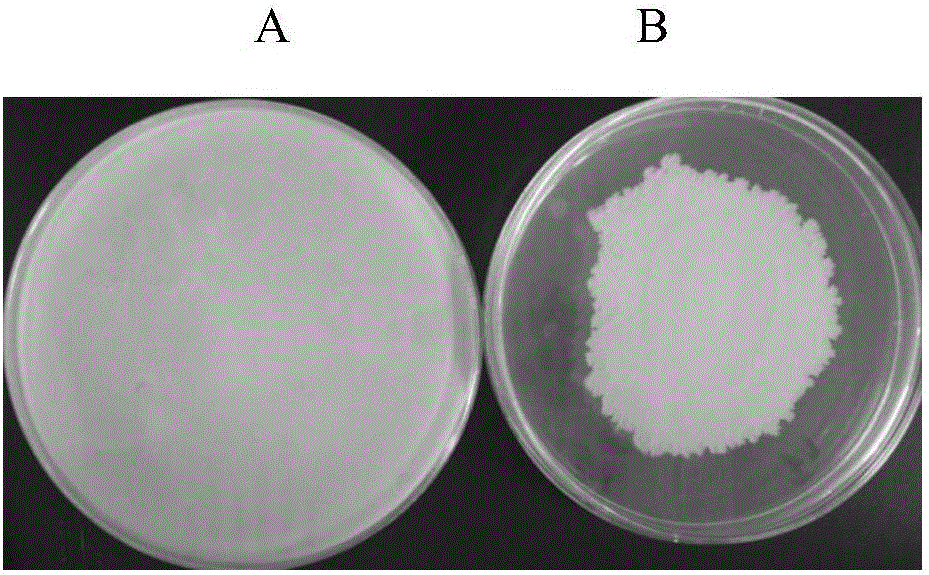
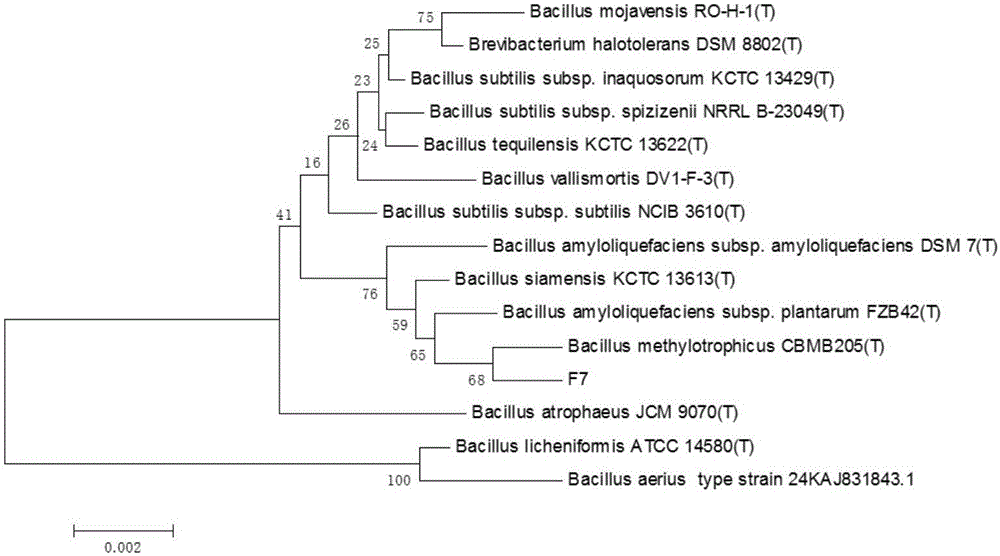
Bacillus methylotrophicus F7 and application thereof
PendingCN106754489AStrong antagonistic effectGood biological control effectPlant growth regulatorsBiocideRalstonia solanacearumPlant growth
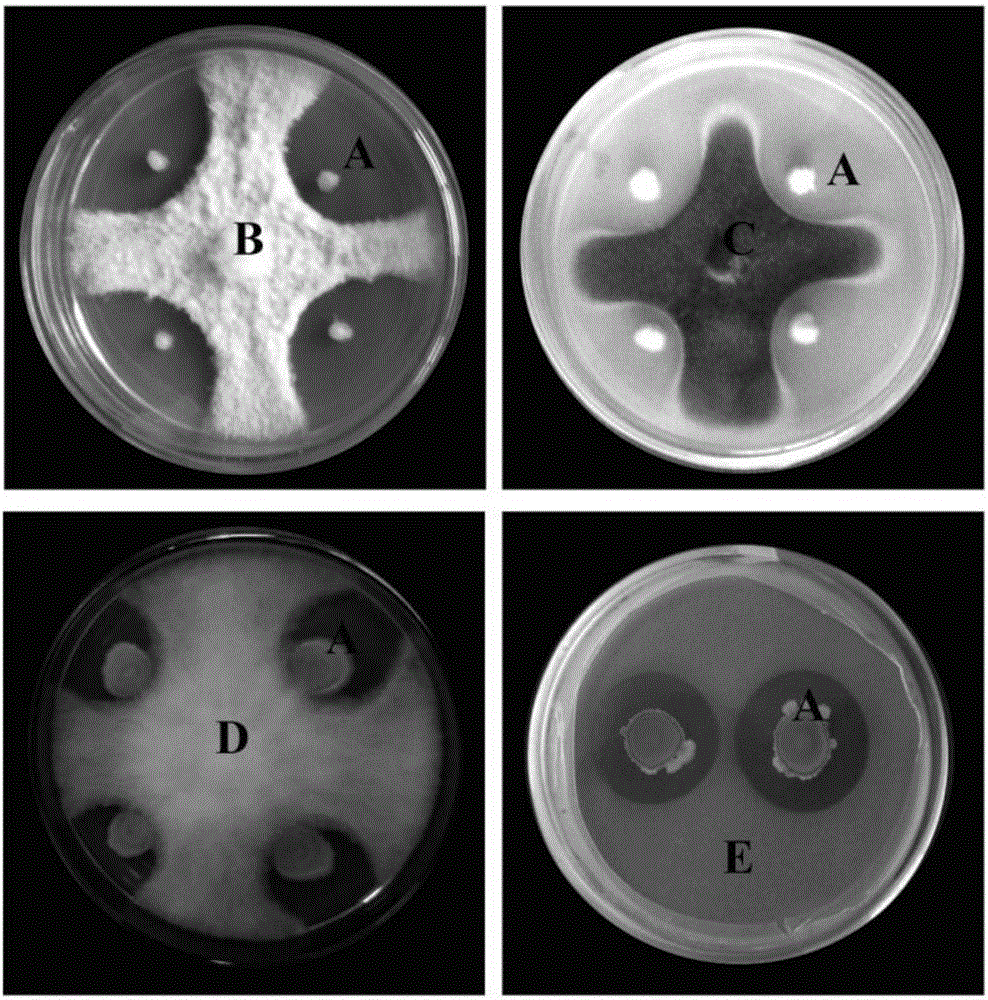
The invention discloses bacillus methylotrophicus F7 and an application thereof. The invention aims at providing a strain which has a plurality of beneficial properties, namely producing siderophore, cellulase and protease, producing auxin, producing ammonia and the like; the strain not only can be used for effectively inhibiting various pathogenic bacteria such as ralstonia solanacearum, fusarium oxysporum f.sp.cubense, colletotrichum gloeosporioides, fusarium oxysporum f.sp cucumerinum but also can promote plant growth. In accordance with the technical scheme, the bacillus methylotrophicus F7 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on February 1, 2016, with preservation number of CGMCC No.12124; in addition, five surfactin homologs, six fengycin homologs and three iturin homologs, which have an antibacterial effect, are extracted from fermentation liquid of the bacillus methylotrophicus F7; and the bacillus methylotrophicus F7 belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnology.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Paenibacillus polymyxa NSY50 with capabilities of promoting growth and preventing diseases
InactiveCN105734000AHas ACC deaminase activityEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsDiseaseRalstonia solanacearum
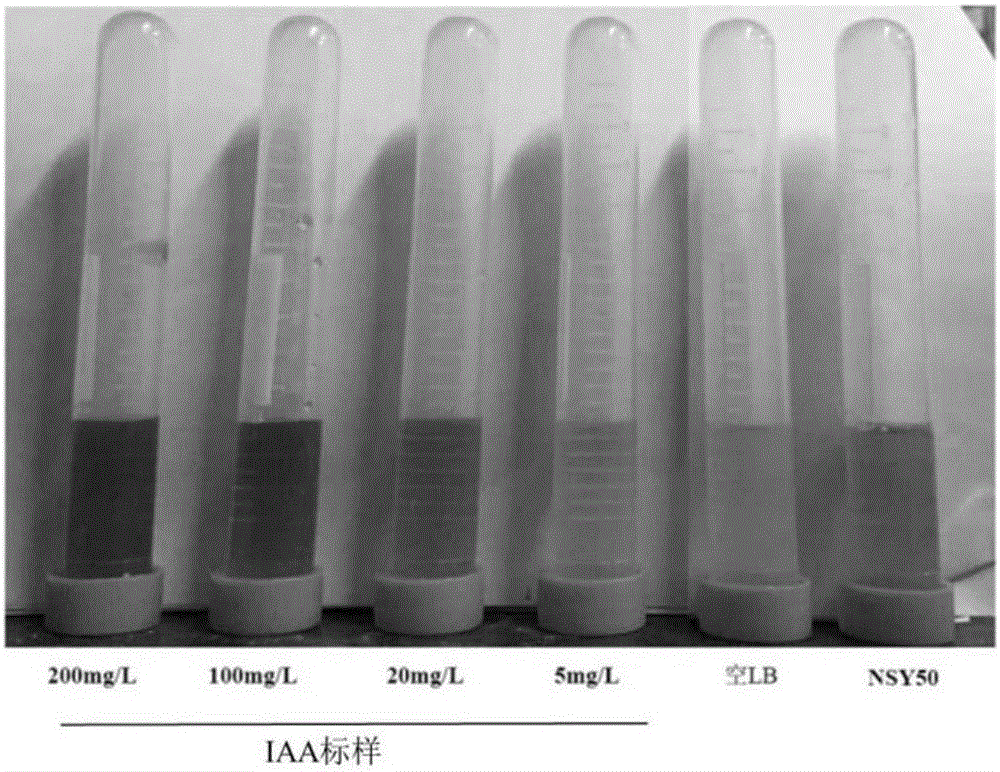
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a paenibacillus polymyxa NSY50 which is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on March 8, 2016 and has a preservation number of CGMCC NO. 12189. The invention also discloses a microbial inoculum containing the paenibacillus polymyxa NSY50. The strain disclosed by the invention can be used for synthesizing IAA, can generate protease and cellulase, has activity of ACC desaminase, and has a relatively good inhibitory effect on various plant pathogens of fusarium oxysporum f.sp.cucumberinu, didymella bryoniae, fusarium graminearum, ralstonia solanacearum and the like. A greenhouse experiment shows that the microbial inoculum prepared by using the strain can significantly promote the growth of cucumber seedlings and reduce the incidence of fusarium wilt of cucumber, and by adopting a bio-control microbial inoculum prepared by adopting the strain to perform root irrigation during transplantation, the bio-control effect on the fusarium wilt of cucumber under a room temperature condition reaches 75.90-82.83%.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
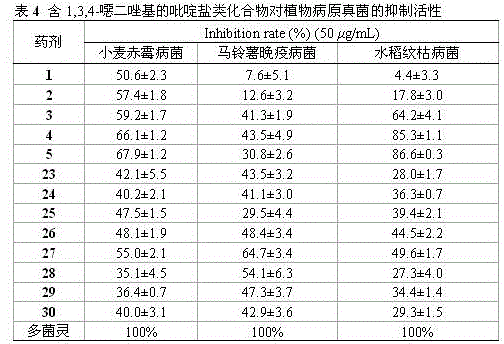
Pyridine salt compound containing 1,3,4-oxadiazolyl (thiadiazolyl) and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105541822AImprove biological activityEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideOrganic chemistryXanthomonas axonopodisRalstonia solanacearum
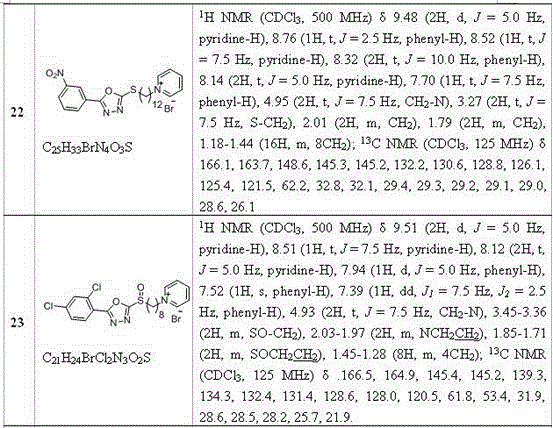
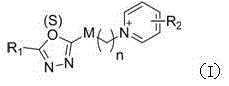
The invention disclose a pyridine salt compound containing 1,3,4-oxadiazolyl (thiadiazolyl) and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound is of the structure shown in the general formula (I). Based on the 1,3,4- oxadiazole (thiadiazole) thioether (sulfoxide or sulfone) compound, a pyridine base capable of improving the biological activity of the target compound is introduced into the system, and a series of 1,3,4- oxadiazole (thiadiazole) oxygen ether, thioether, sulfoxide or sulfone amphipathic molecules containing pyridine salt are synthesized. It is found that the compound has the good restraining effect on pathogenic bacteria and fungi such as Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, Ralstonia solanacearum, Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri, Gibberella zeae, Phytophythora infestans, Rhizoctonia solani, Borrytis cinerea, Fusarium oxysporum and Phytophythora infestans, and provides an important scientific foundation for new pesticide research, development and creation.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Microorganism plant vaccine capable of controlling tomato bacterial wilt disease
ActiveCN102978132AGood endogenous performanceDiffusion fastBiocideBacteriaMicroorganismRalstonia solanacearum
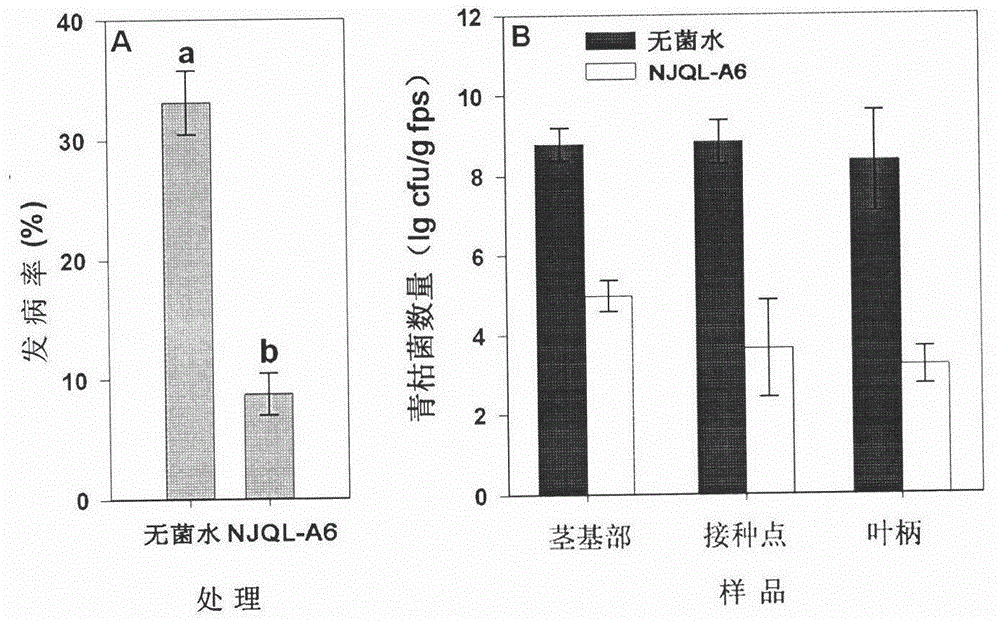
The invention relates to microorganism plant vaccine capable of controlling continuous tomato bacterial wilt disease, and belongs to the agricultural intensive production technology. According to the microorganism plant vaccine capable of controlling the tomato bacterial wilt disease, a ralstonia solanacearum sibling bacterium pearson ralstonia eutropha (Ralstoniapickettii) NJQL-A6 is isolated from the rhizosphere of a healthy tomato, and the ralstonia eutropha has a weaking inhibited impact on a bacterial wilt pathogenic bacteria ralstonia eutropha (Ralstonia solanacearum) panel. However, the ralstonia eutropha possesses powerful colonization capability on the tomato rhizosphere and inside a plant, and can inhibit the infection of the ralstonia eutropha to a tomato plant. Experiments show that after the vaccine is irrigated to be applied to soil, the vaccine can breed rapidly so that an advantage group is formed in the soil, and the biocontrol efficiency can be reached up to more than 70% in the soil where the tomato bacterial wilt disease is severe. By inoculating the biocontrol bateria on the tomato plant with the root being infected by the bacterial wilt on the overground part, the further development of the disease can be effectively controlled.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Paenibacillus polymyxa and application thereof
The invention discloses a Paenibacillus polymyxa strain for preventing and controlling plant bacterial wilt, which is named Paenibacillus polymyxa ZJU0901 through identification and is conserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) positioned in Wuhan University, Luojia Hill, Wuhan. The conservation date of the strain is July 19th, 2009, and the conservation number of the strain is CCTCC NO:M209157. The strain can produce inhibiting effect on the growth of different biochemical types of strain of ralstonia solanacearum under in vitro conditions and can effectively prevent and control plant bacterial wilt.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Insertion sequence element derived from ralstonia solanacearum
InactiveUS20030009026A1Useful industriallyReduce pathogenicitySugar derivativesHydrolasesRalstonia solanacearumInsertion sequence
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI
Screening method of pseudomonas solanacearum bacteriophage resource
InactiveCN104560891AMake up for the lack of conservation resourcesEfficient separationMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesBiotechnologyRalstonia solanacearum
The invention discloses a screening method of a pseudomonas solanacearum bacteriophage resource. The screening method comprises the following steps: S1, taking a soil sample, treating the sample, and filtering by a filter membrane to obtain a filtrate; S2, culturing a pseudomonas solanacearum strain to obtain a pseudomonas solanacearum liquid; S3, co-culturing the filtrate in the S1 and the pseudomonas solanacearum in the S2; and S4, selecting and storing bacteriophage plaque, wherein the used material comprises sterile water, the pseudomonas solanacearum strain, a CPG culture medium, agar powder and low-melting-point agar. The CPG culture medium comprises a CPG solid culture medium and a CPG liquid culture medium. The method can be applied to screening the pseudomonas solanacearum bacteriophage resource from tobacco-planting soil, bacterial wilt soil and sewage and providing and collecting the pseudomonas solanacearum bacteriophage resource for researching prevention and control of tobacco bacterial wilt by using the pseudomonas solanacearum bacteriophage.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI RES INST
Acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis CLP-7, and applications thereof
The invention discloses an acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 which is capable of preventing diseases and promoting growth, and can be used for biocontrol. The acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is preserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, on 27th, October, 2016, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.13204. The antibacterial spectrum of the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is relatively large; the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of inhibiting growth of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae, Ralstonia solanacearum, and Alternaria alternata Keissler; the antagonistic activity under acidic conditions is high, the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of producing siderophore, possesses protease and glucanase activity, and potassium releasing capacity. The results of biocontrol pot experiment show that the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of preventing under acidic soil conditions, and promoting growth and chlorophyll synthesis of tobacco seedlings in acidic soil, so that the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 and microorganism bacterium agents of the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 can be used for preventing tobacco fungi and bacterial root and stem diseases under continuous cropping or acidic soil conditions effectively, and is high in application value.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD +1
Phage for preventing and controlling soil-borne bacterial wilt, and application thereof
The invention discloses a phage for preventing and controlling soil-borne bacterial wilt, and an application thereof. The phage is a special Ralstonia solanacearum phage NN-742, and the special Ralstonia solanacearum phage NN-742 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on March 6, 2018 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M 2018102, and is named Podoviridae phage. The pathogen-specific phage can efficiently lyse bacteria to make the bacteria dead when used in biological control, and is nontoxic to the environment; and the phage has a strong specificity, does not destroy other normal florae, and can keep soil microbes balanced. The phage can specifically lyse bacterial wilt pathogens, and can be used to prevent and control tomato soil-borne bacterial wilt .
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Two ralstonia-solanacearum-resistant endophytic bacillus velezensis strains and application thereof
ActiveCN107779420AExcellent field control effectStrong colonization abilityBiocideBacteriaNicotiana tabacumPlant roots
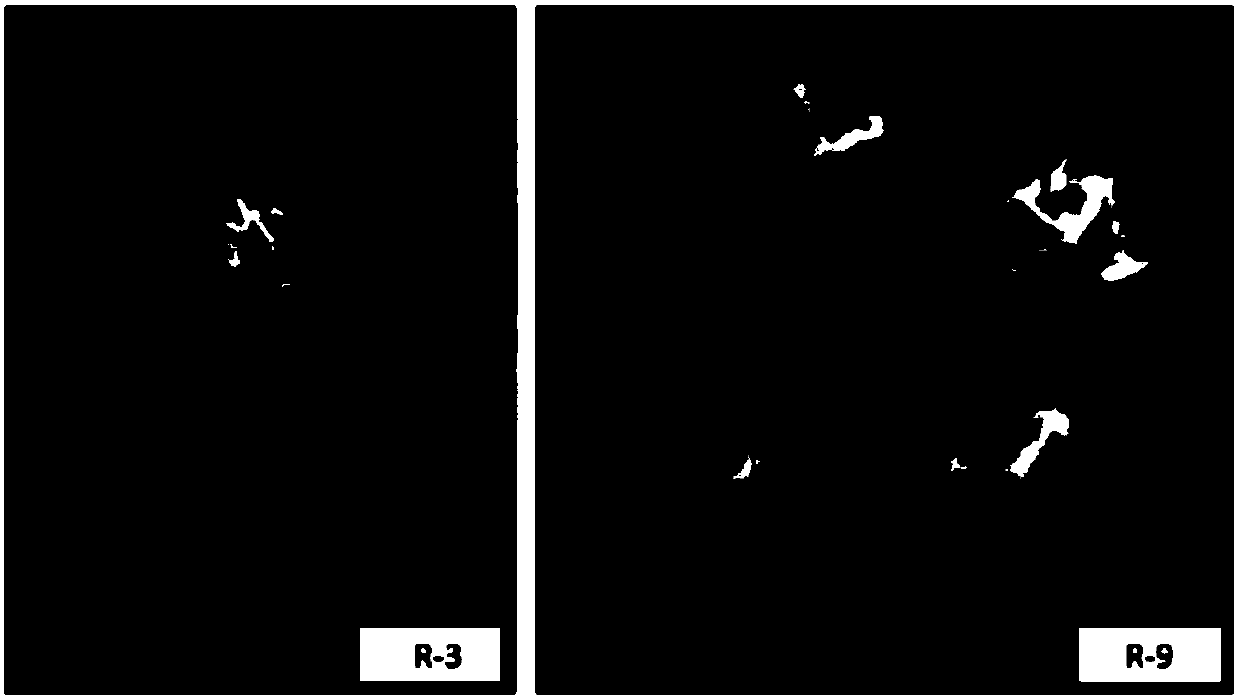
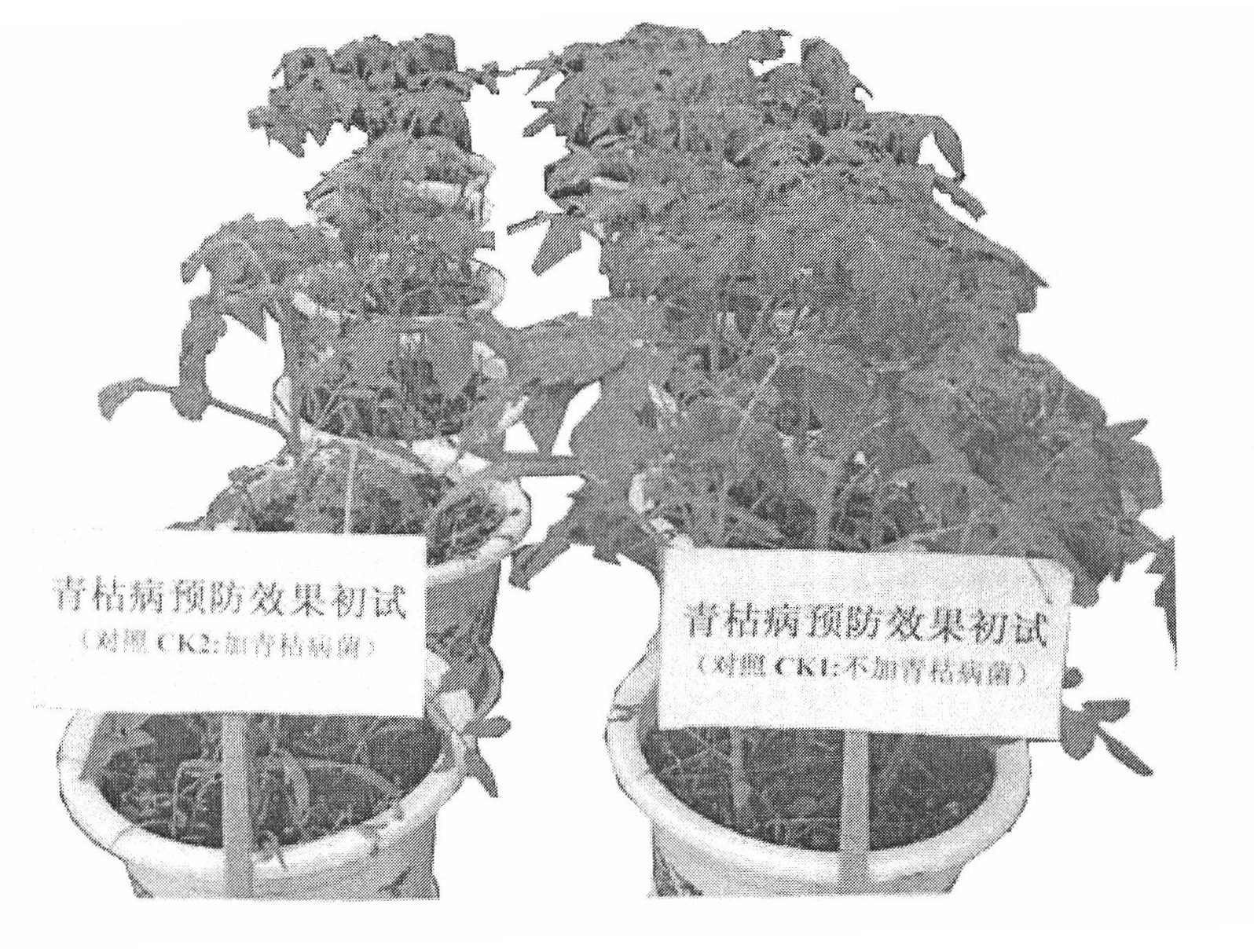
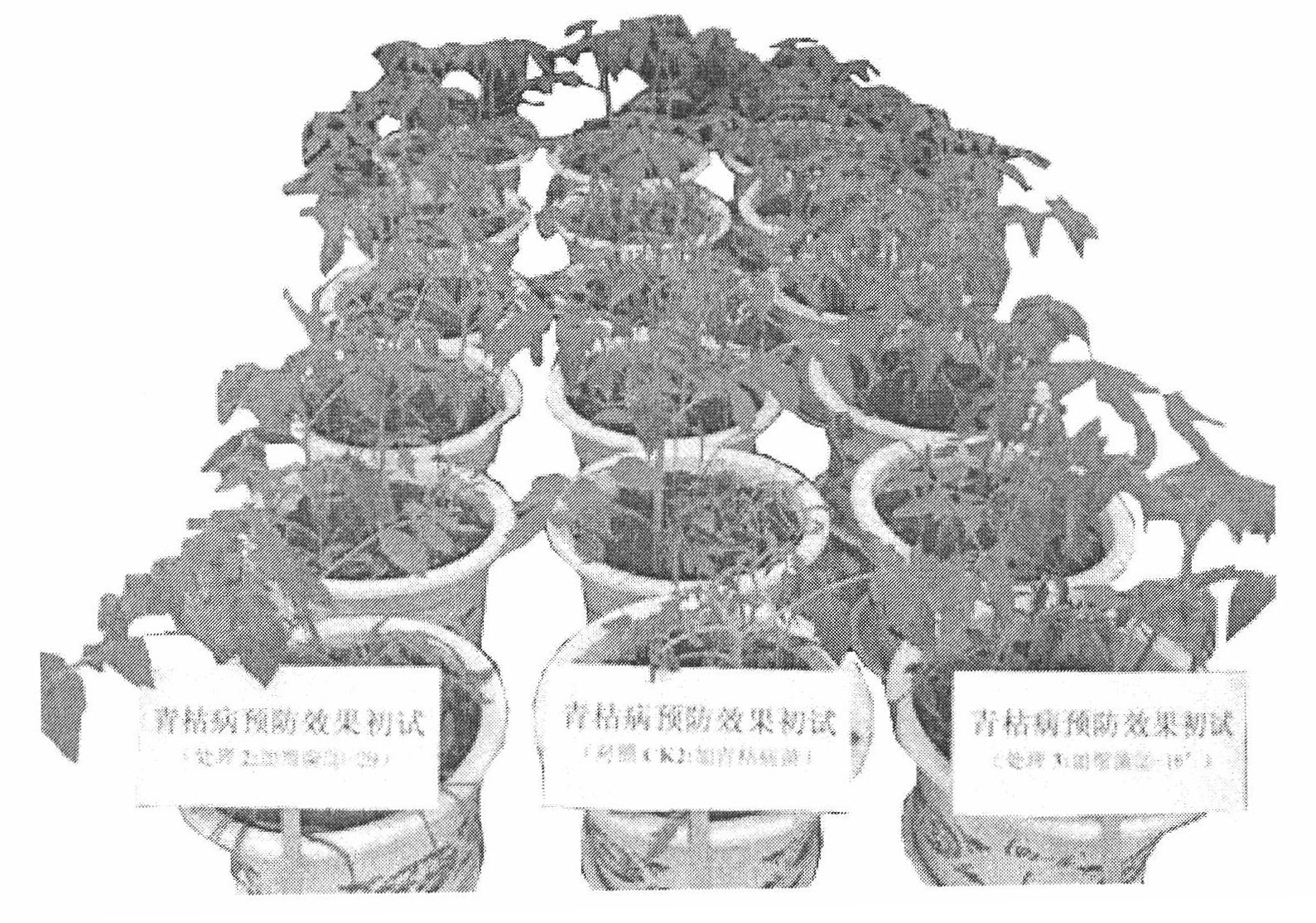
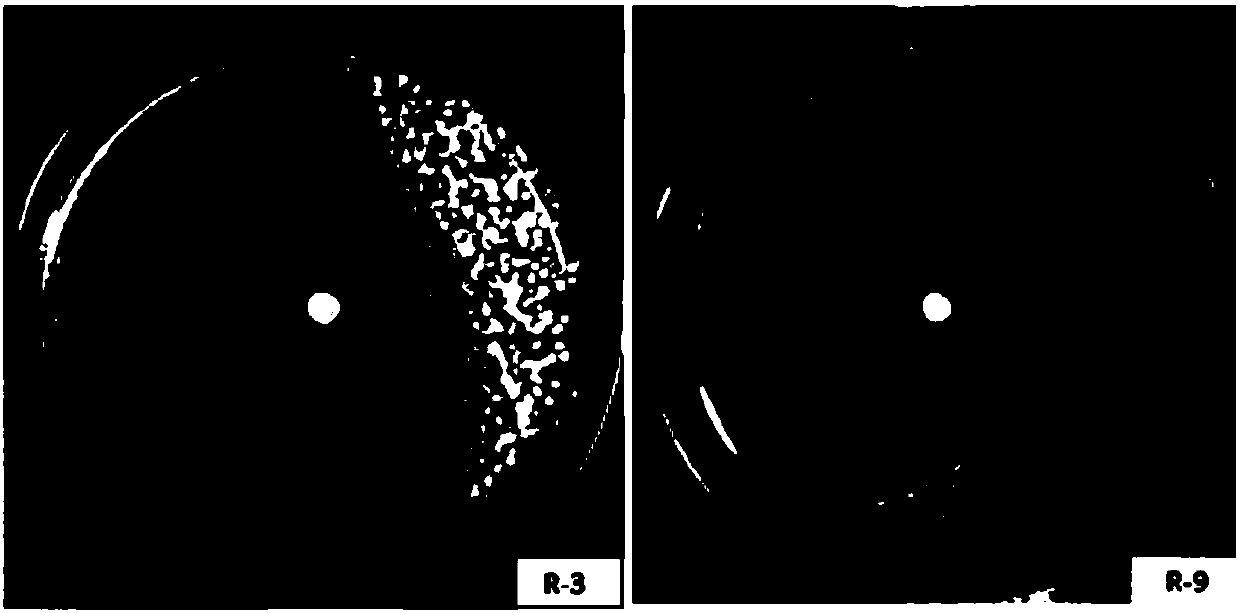
The invention relates to two ralstonia-solanacearum-resistant endophytic bacillus velezensis strains and application thereof. By separation, screening and purification in roots of healthy tobacco plants in a ralstonia solanacearum occurrence area of the Enshi Prefecture, two biocontrol bacillus endophyticus strains R-3 and R-9 are obtained, have evident resistance effects on ralstonia solanacearumand are both capable of generating high-temperature-resistant ralstonia-solanacearum-resistant substances. By gyrB gene sequence identification and phylogenetic tree construction, results show that the R-3 and R-9 are both bacillus velezensis; by potted plant root irrigation experimental verification, the bacilli R-3 and R-9 have great colonization performance in tobacco roots and can enter stemsthrough root transmission; by field experimental verification, bacillus velezensis R-3 and R-9 are effective in ralstonia solanacearum prevention and treatment, remarkably superior to chemical agentkasugamycin and free of pollution. The biocontrol endophyte research field is further enriched by researching on the bacilli R-3 and R-9, and a guiding significance to ralstonia solanacearum prevention and treatment is achieved.
Owner:湖北省烟草公司恩施州公司
Biological control bacillus subtilis for crop bacterial wilt
InactiveCN1884481AStrong plate antagonistic abilityDelayed onsetBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
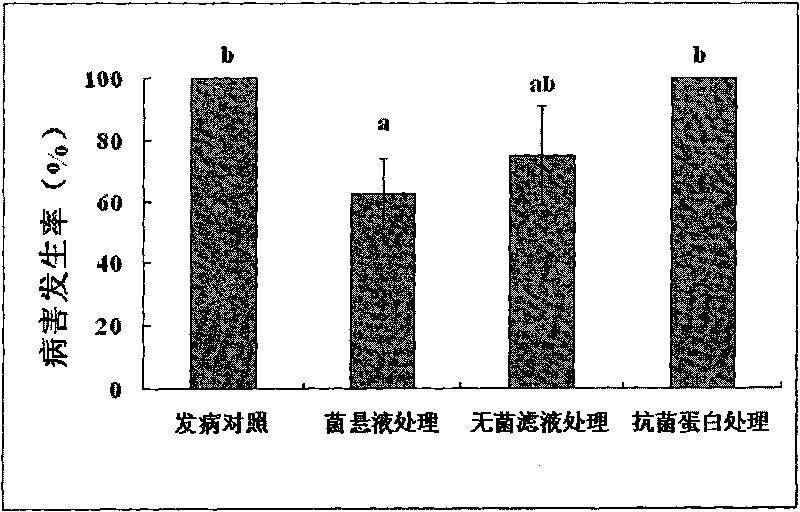
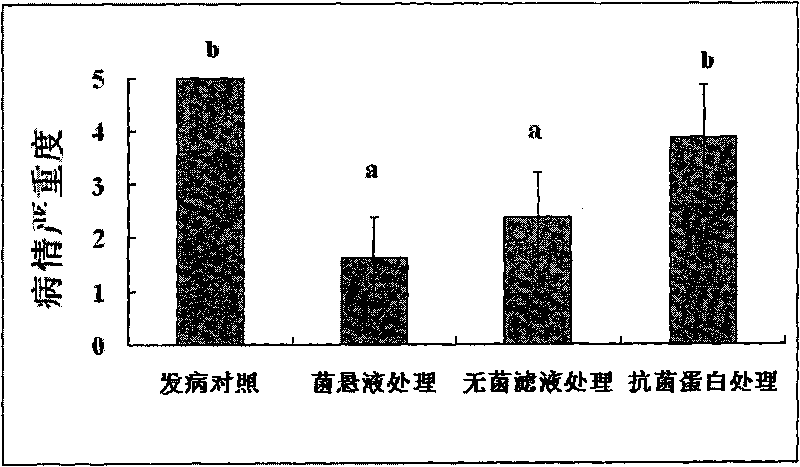
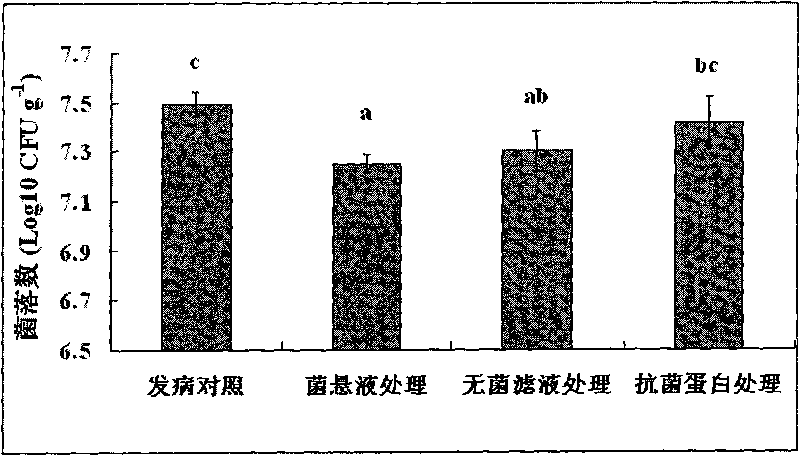
The invention provides a crop Pythium biological control bacillus subtilis strain and belongs to the biotechnological sphere. The invention relates to a crop Pythium bacillus subtilis strain and its biological crop preserved number is CGMCC1732. The said strain can reduce the growth of Ralstonia solanacearum and the biological control experiment indicates that it can prevent and cure the Granville wilt. Simultaneously the invention also provides an antagonistic protein blend obtained from the said strain and the blend has higher application value in crop Pythium biological control.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Lysing bacteriophage and application thereof in prevention and control of tobacco soil-borne bacterial wilt
ActiveCN112831475AReduce disturbanceInhibition of bacterial wiltBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMicroorganism
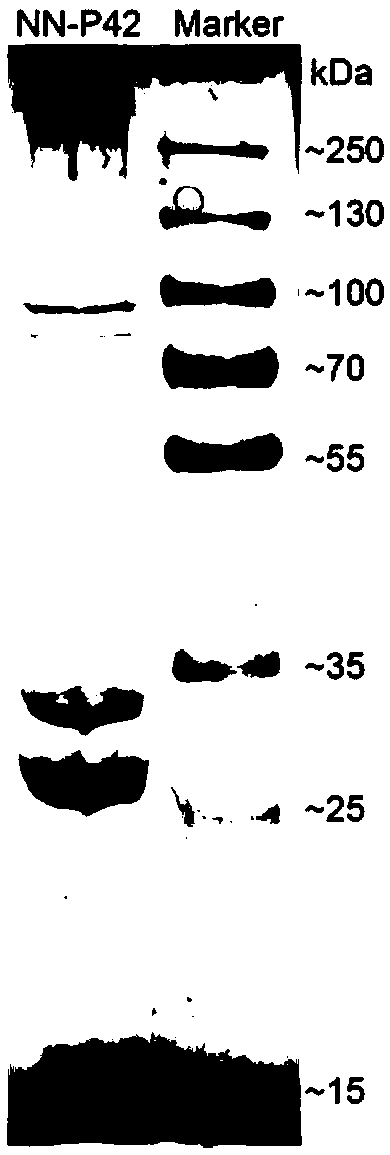
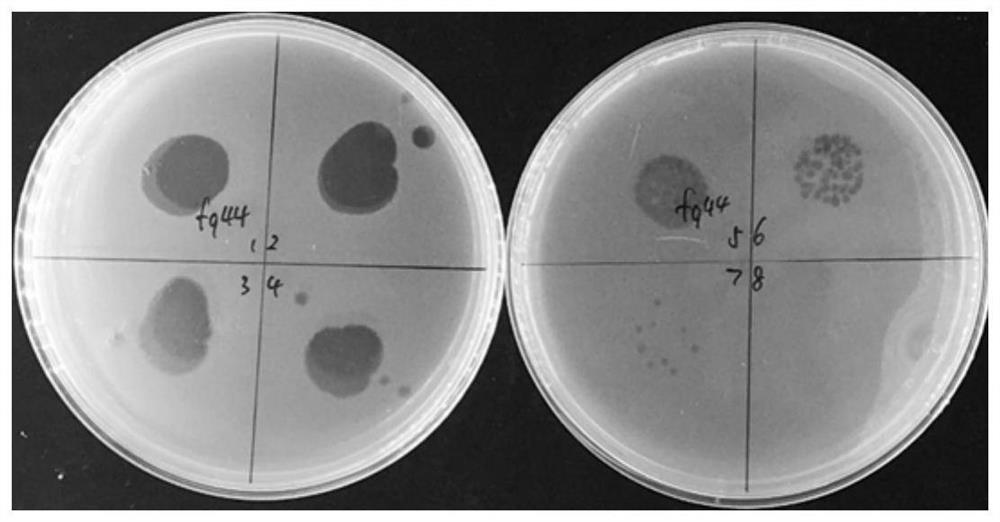
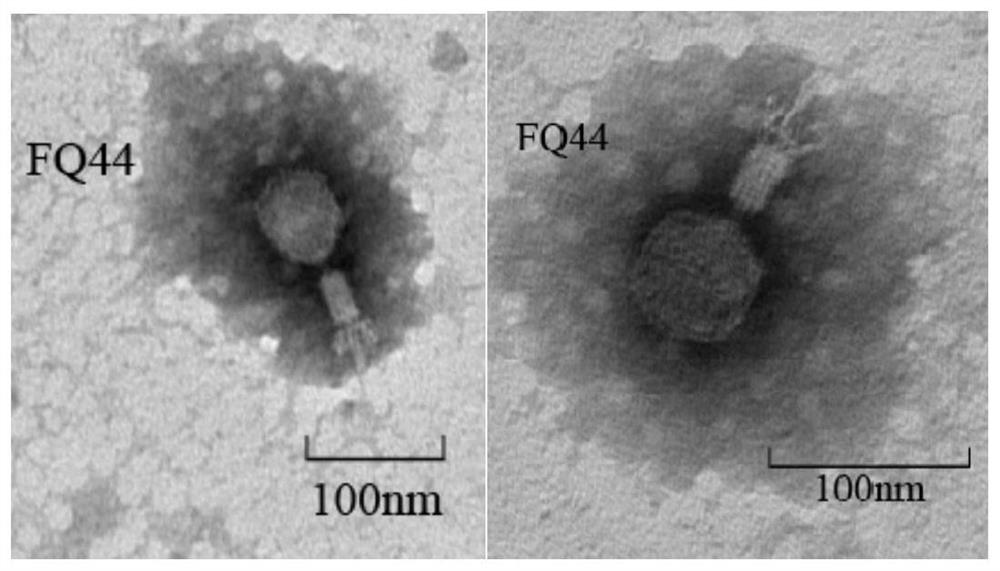
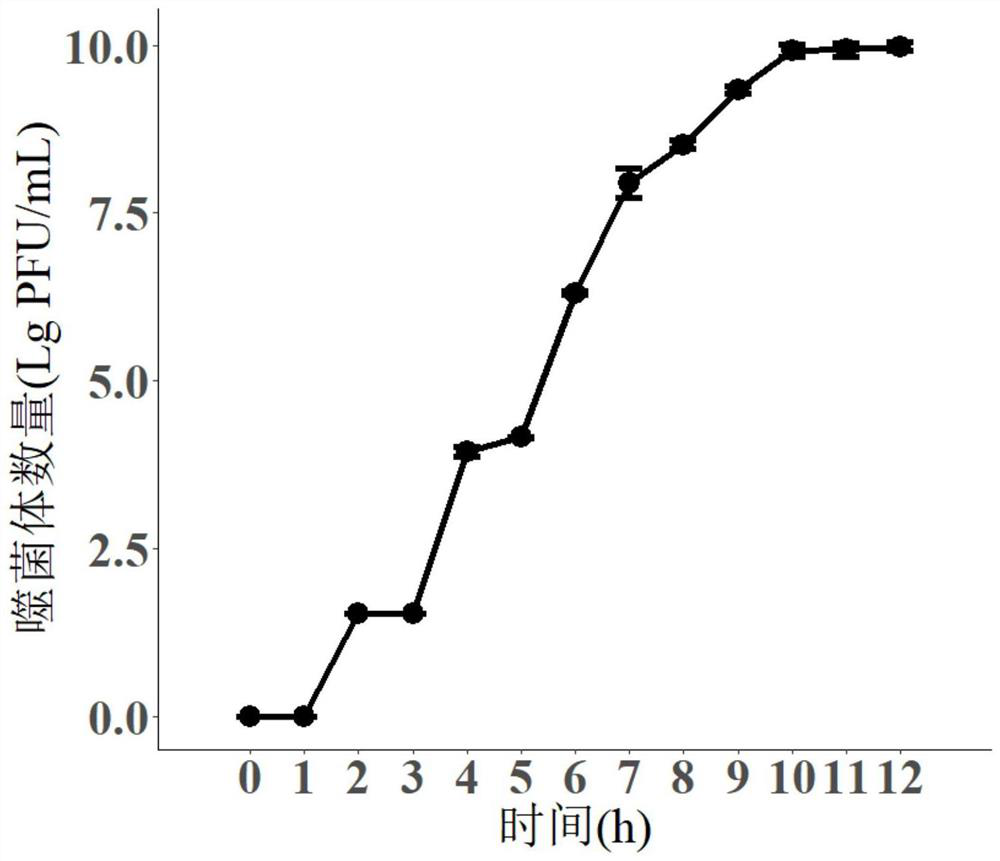
The invention discloses a lytic bacteriophage FQ44, which is classified and named as a lauraceae bacteriophage, and is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on September 29, 2020, and the preservation number of the bacteriophage is CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO: M2020560. The invention also discloses an application of the bacteriophage FQ44 in prevention and control of tobacco soil-borne bacterial wilt, and the bacteriophage is applied into soil by adopting a root irrigation method. According to the invention, the ralstonia solanacearum obligate bacteriophage is used for inhibiting tobacco soil-borne bacterial wilt, so that damage to common microbial communities in soil is avoided while the soil-borne bacterial wilt is prevented and controlled. Indoor related experiments show that the bacteriophage FQ44 belongs to muscular tail bacteriophage, can effectively inhibit the growth of part of tobacco ralstonia solanacearum, and has the best effect when being applied according to the optimal infection complex number (MOI 1-10); and field experiment results show that the bacterial wilt can be effectively inhibited, and the bacterial wilt inhibitor has a wide prospect.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus methylotrophicus AR3, bacillus subtilis AR4 and bacillus amyloliquefaciens AR10 and application thereof
The invention provides three biocontrol bacilli namely bacillus methylotrophicus AR3, bacillus subtilis AR4 and bacillus amyloliquefaciens AR10 and application thereof to preparation of a crop ralstonia solanacearum resistant bacteria agent. According to the invention, three biocontrol bacilli namely bacillus methylotrophicus AR3, bacillus subtilis AR4 and bacillus amyloliquefaciens AR10 are obtained through soil sample taking, screening, analysis and cultivation in a healthy tobacco field in the Xuan'en county, results of plenty of field experiments prove that when being used separately or used in a mixed manner, the three biocontrol bacilli have the good effect of preventing and controlling crop ralstonia solanacearum, are highly targeted and low in pollution, and can be stored for a long term and conveniently used in the field after being prepared into the bacteria agent, so that the achievement of the bacilli in the field of biocontrol bacterium research is enriched and guiding significance on later related research work is realized.
Owner:武汉华恩绿农生物科技有限公司
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain capable of controlling Ralstonia solanacearum effectively and promoting capsicum annuum growth
ActiveCN108624543AEnhance disease preventionGood growth promoting effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicroorganismNicotiana tabacum
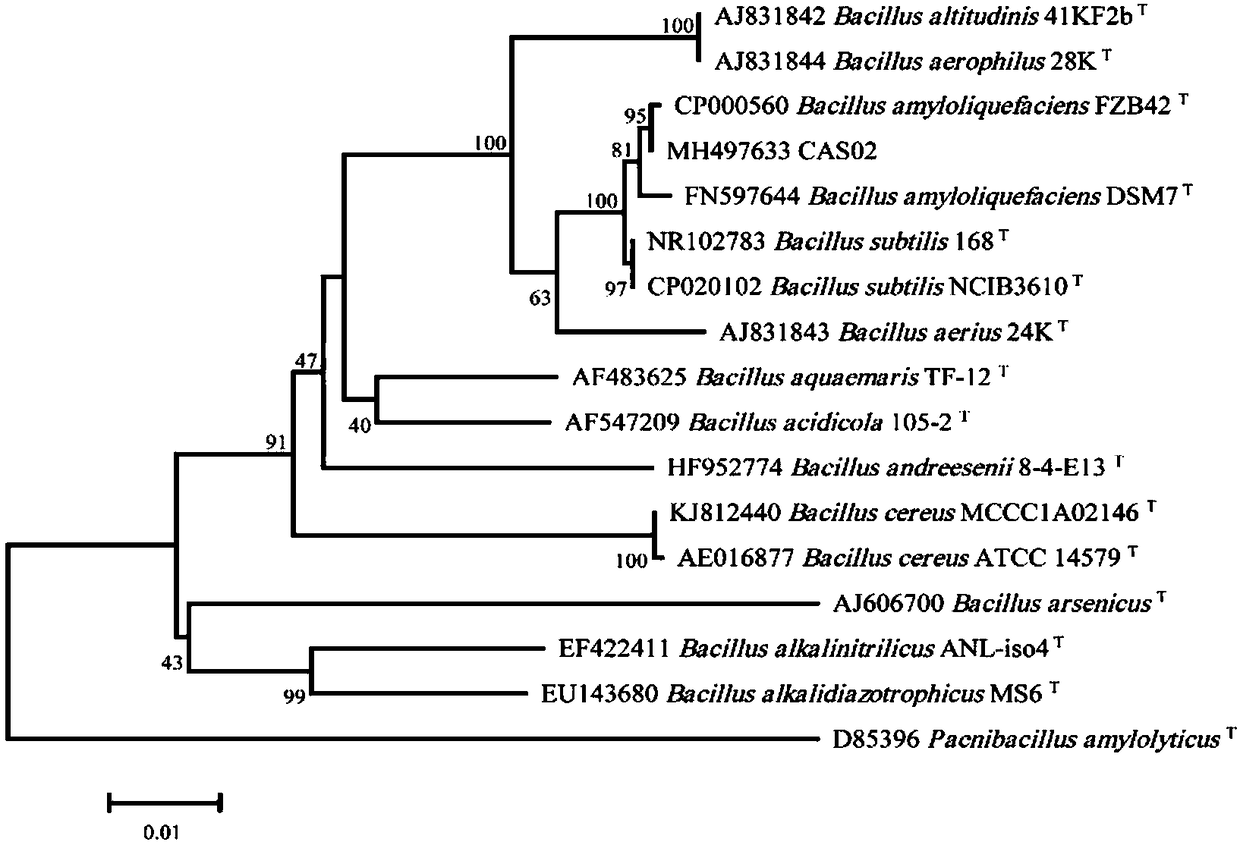
The invention provides a bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain capable of controlling Ralstonia solanacearum effectively and promoting capsicum annuum growth, and belongs to the technical field of microorganism. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain CAS02 is isolated from tobacco roots, is preserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on 26th, March, 2018, and the biological preservation number is CGMCC NO.15514. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain CAS02 is capable of promoting capsicum annuum growth, inhibiting growth of a plurality of pathogens such as capsicum annuum Pseudomonas solanacearum, and is promising in application prospect.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
Agent for Preventing Bacterial Wilt Disease, and Method for Preventing Bacterial Wilt Disease
ActiveUS20140044679A1Avoid developmentPreventing bacterial wilt diseaseBiocideBacteriaDiseaseFragaria
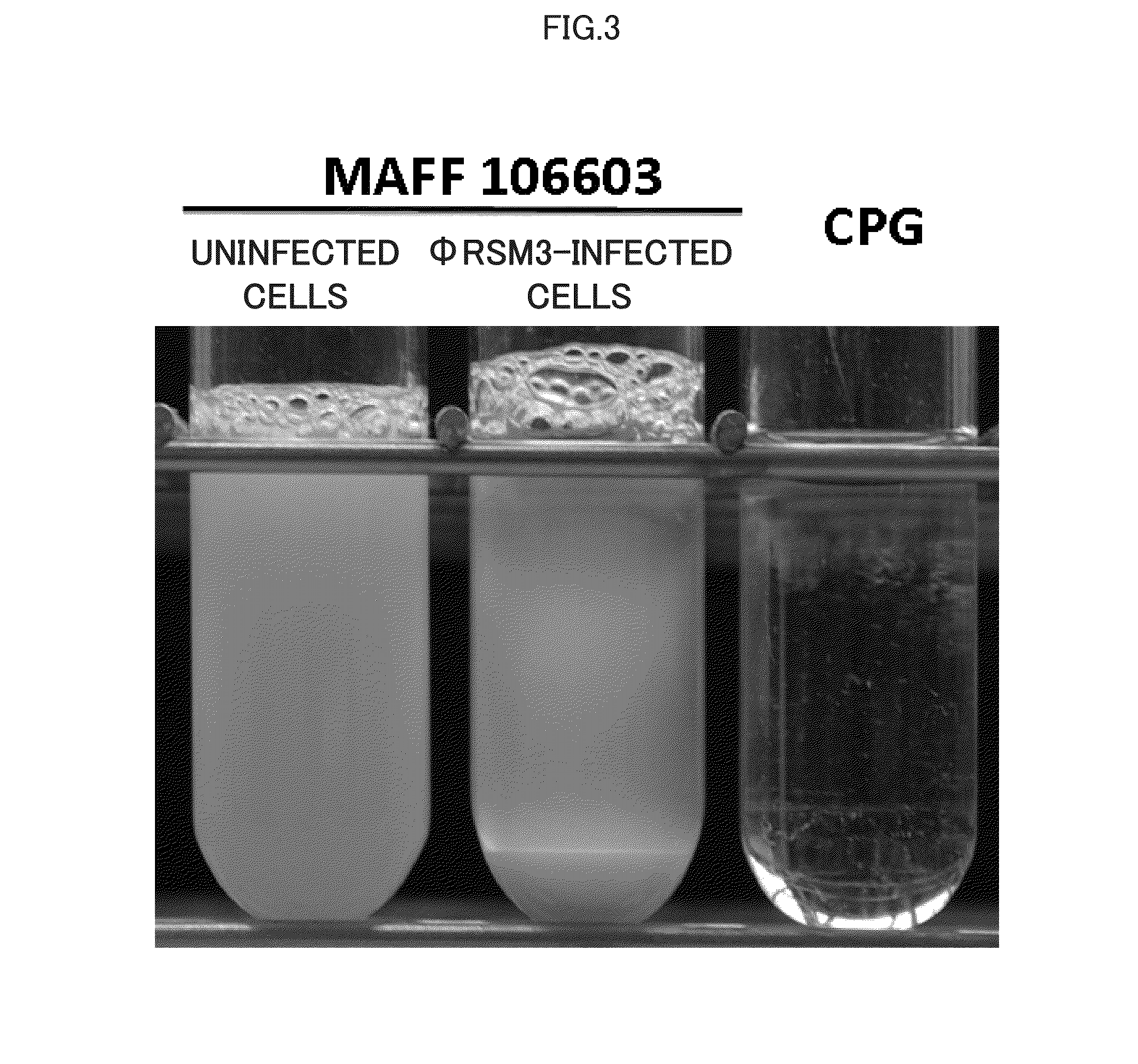
Provided are: an agent for preventing bacterial wilt disease, which agent can prevent the development of bacterial wilt disease caused by various different bacterial wilt disease strains, that is, the development of bacterial wilt disease in various different plant varieties; and a method for preventing bacterial wilt disease utilizing the agent for preventing bacterial wilt disease. The agent for preventing bacterial wilt disease comprises as an active ingredient a wilt bacterium (Ralstonia solanacearum) infected with the φRSM1-type filamentous phage and / or the φRSM3-type filamentous phage. The method for preventing bacterial wilt disease comprises the step of inoculating the agent for preventing bacterial wilt disease to a plant. The plant is preferably any one of tomato, potato, green pepper, eggplant, tobacco, capsicum, Japanese basil, Japanese radish, strawberry, banana, marguerite, chrysanthemum and sunflower.
Owner:HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY
Method for high-flux identification of ralstonia solanacearum resistance
InactiveCN104082055AGuaranteed reliabilityPromote resultsCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a method for high-flux identification of ralstonia solanacearum resistance. The method comprises the following steps: sterilizing quartz sand with particle size ranging from 2 mm to 4 mm at high temperature of 121 DEG C for 30 minutes, cooling, and spreading into an aseptic 12-pore cell culture plate, wherein each pore is filled with 10 g of the quartz sand and 4 ml of aseptic water; sowing flue-cured tobacco seeds to be tested onto the quartz sand of the 12-pore cell culture plate, after sowing, and culturing by the 12-pore cell culture plate under the conditions of 25 DEG C, RH of more than 80% and alternative 16-hour lighting and 8-hour shading; after the flue-cured tobacco seeds germinate, adding a Hoagland's nutrient solution into the 12-pore cell culture plate for culturing the flue-cured tobacco seeds under the aseptic condition, continuously culturing under the conditions of 25 DEG C, RH of more than 80% and alternative 16-hour lighting and 8-hour shading, and identifying the disease resistance of the flue-cured tobacco seeds each with 5-6 leaves, wherein each pore is filled with 2 ml of the Hoagland's nutrient solution; preparing inoculating liquid and inoculating; investigating and grading the disease states. According to the method, the ralstonia solanacearum resistance can be identified with high flux and high efficiency and a large amount of flue-cured tobacco varieties can be identified in one time.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI RES INST
Bio-derived compositions for use in agricultural and environmental remediation
ActiveUS20150223470A1Effective, inexpensive, and environmentally appropriate compositionsPromote growthBiocideUnknown materialsDiseaseLasiodiplodia theobromae
This invention pertains to a composition, which is a natural and organic pesticide, specifically for mitigating, controlling and treating fungicidal, virucidal and bactericidal pathogenic microorganisms in agricultural products such as root crops, fruits and vegetables. Examples of such disease-causing microorganisms are Mycosphaerella fijensis causing black Sigatoka disease in Cavendish (banana), Ralstonia solanacearum causing Moko disease in Cavendish (banana), Lasiodiplodia theobromae causing soft rot or fruit rot in crops and fruits, Fusarium oxysporum causing Panama wilt in fruits and crops, and many others. The composition is a fermented product of tropical plants, carbon source, protein (nitrogen) source, and a carrier agent. The fermented product may help strengthen the plant's immune system to fight pathogenic diseases. Since all the major constituents of the composition are generally regarded as safe, this natural pesticide is found to be non-toxic and safe to humans and animals, and environmentally benign.
Owner:IBEX BIONOMICS
LRR-RLK (leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase) gene in arachis hypogaea.L and application thereof to bacterial wilt resistance of tobaccos
InactiveCN104480118AIncreased bacterial wilt disease resistanceImprove disease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to an LRR-RLK (leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase) gene AhRLK6 associated with bacterial wilt resistance of arachis hypogaea.L and a construction method of an over-expression vector of the gene and in particular relates to an application of the gene AhRLK6 in arachis hypogaea.L to tobacco bacterial wilt resistant gene engineering, belonging to the technical field of plant gene engineering. The gene contains nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID No.1. The over-expression vector is constructed to transform Cuibi-1 tobaccos, the transgenic plants are inoculated with ralstonia solanacearum through molecular detection, and over-expression of the over-expression vector in the tobaccos can conduce to obviously improving the resistance of the transgenic tobaccos to bacterial wilt, thereby indicating that AhRLK6 possibly participates in the defence reaction of the plants to ralstonia solanacearum, which lays the foundation for bacterial wilt resistant genetic breeding of the plants and strongly promotes the development and application of the tobacco bacterial wilt resistant gene engineering.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
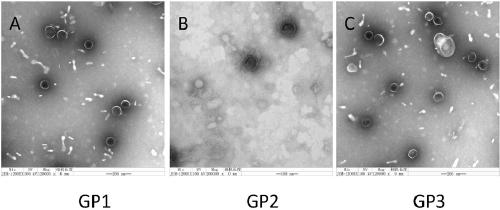
Novel ralstonia solanacearum phages and compositions and application thereof
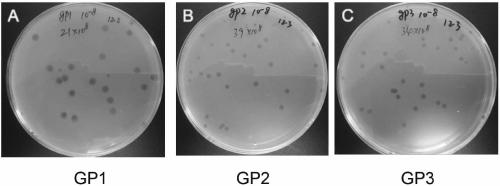
ActiveCN109136194ANon-toxicBroad cracking spectrumBiocideVirus peptidesMicroorganismRalstonia solanacearum
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, in particular to a ralstonia solanacearum phage GP1 with the preservation number of CCTCC M 2016633, a ralstonia solanacearum phage GP2 with the preservation number of CCTCC M 2016634 and a ralstonia solanacearum phage GP3 with the preservation number of CCTCC M 2016635. The phages have the advantages that the phages are strict virulent phagesand can effectively kill ralstonia solanacearum of different plant host sources, especially the ralstonia solanacearum causing ginger blast; the phages are non-toxic to normal microbial flora, DNAs ofthe phages cannot encode virulence genes, and the stability is high under the pH of 5-9; there is no magnitude change in titer at 4 DEG C after preservation for one year; bacteria can be effectivelyinhibited and killed under low titer. The phages can be used for prevention and treatment of crop bacterial wilt caused by ralstonia solanacearum, especially ginger blast, excellent strain resources are provided for developing novel bio-pesticide resistant to bacterial wilt, and a good application and development prospect is achieved.
Owner:PHAGELUX (NANJING) BIO-TECH CO LTD
Broth for preventing and treating ralstonia solanacearum and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106465734AImprove efficacyStrong targetingBiocideDead animal preservationNicotiana tabacumRalstonia solanacearum
The invention discloses a broth for preventing and treating ralstonia solanacearum and a preparation method thereof. According to the invention, different biocontrol fungus are combined, then mixed according to different proportions and fermented, and a stable and effective combination is screened, the screened combination can effectively control the ralstonia solanacearum through a root watering application method; the broth for preventing and treating ralstonia solanacearum is prepared by fermenting streptomyces pluricolorescens seed liquid, streptomyces recifensis seed liquid, a bacillus safensis broth, a brevibacilluscentrosporus broth, trichoderma rufobrunneum seed liquid, cane molasses, soybean molasses, cottonseed meal powder, composite amino acid raw powder, potassium fulvic acid, calcium carbonate, magnesium sulfate, and 800 parts of water.
Owner:FOSHAN YANHUI BIOTECH CO LTD
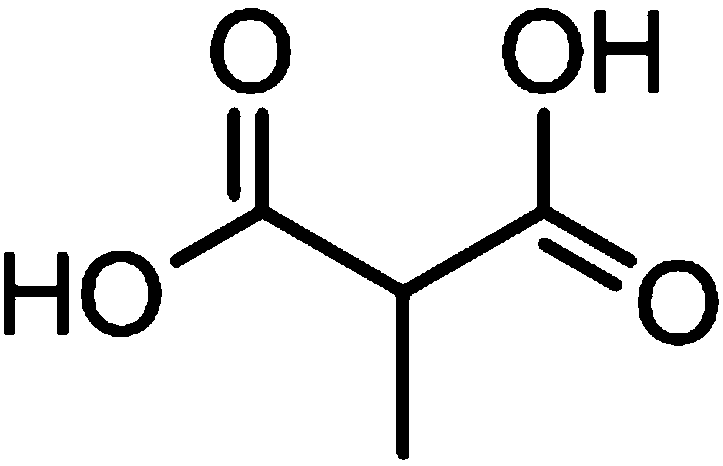
Application of methylmalonic acid in preparation of nematode pesticide
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural microbiology, and specifically relates to an application of methylmalonic acid in preparation of a nematode pesticide. Through determination of the fatality rate of meloidogyne incognita and caenorhabditis elegans, it finds that the methylmalonic acid has a good insecticidal effect on nematodes; LC50 of the methylmalonic acid to the meloidogyne incognita and the caenorhabditis elegans is separately 13.11 and 1.20; and after the methylmalonic acid and betaine are compounded, the LC50 of the methylmalonic acid to the meloidogyne incognita and the caenorhabditis elegans is separately 2.85 and 0.27; and at the same time, the methylmalonic acid has an inhibition effect on ralstonia solanacearum and erwinia carotovora. The preparationprovides new selectivity for the preparation of biocontrol preparations of meloidogyne.
Owner:HUBEI BIOPESTICIDE ENG RES CENT
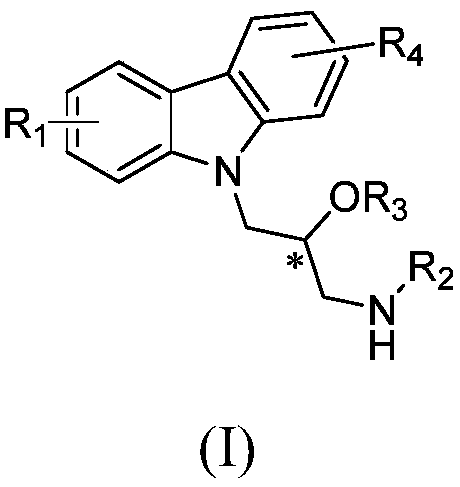
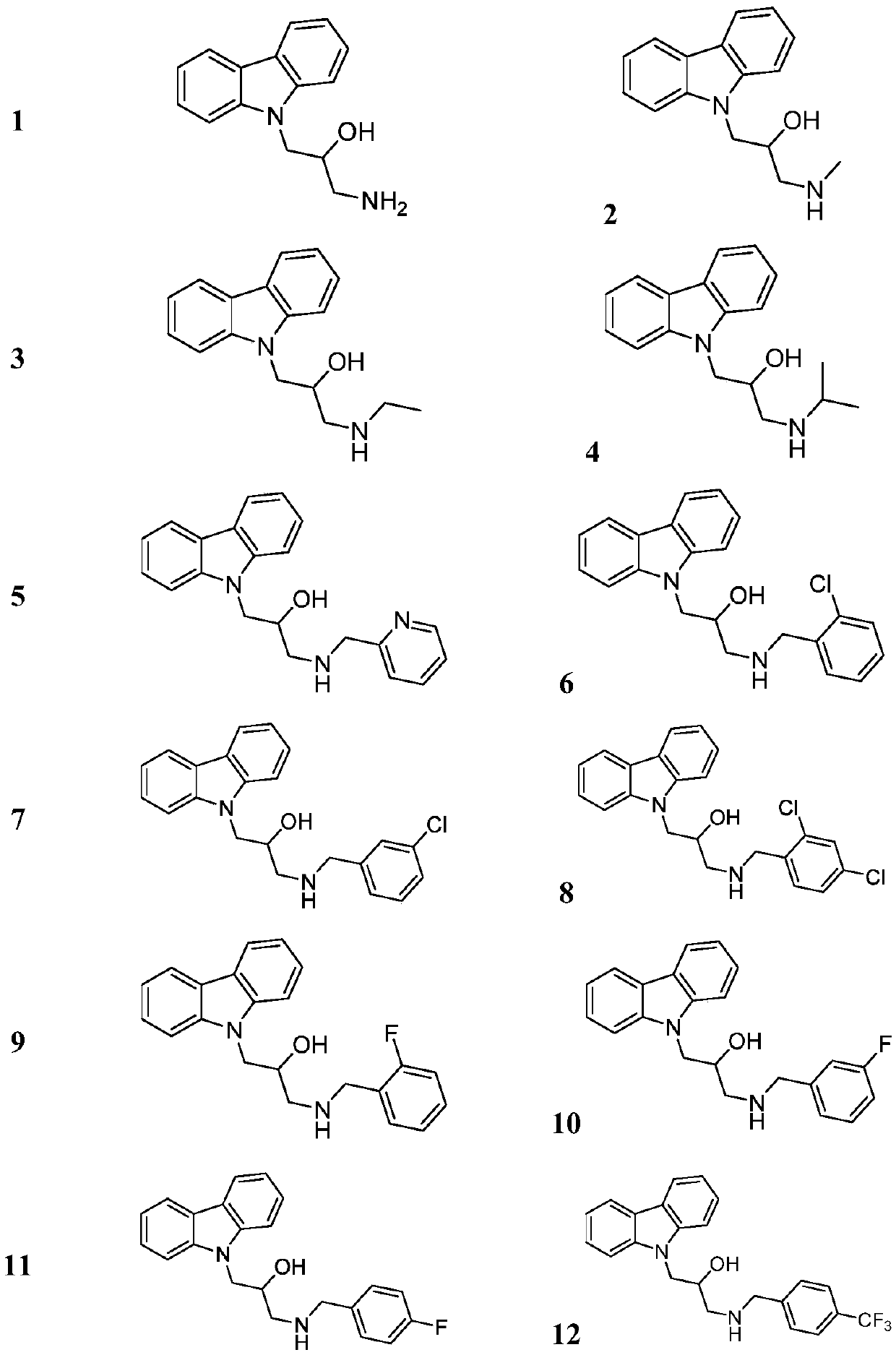
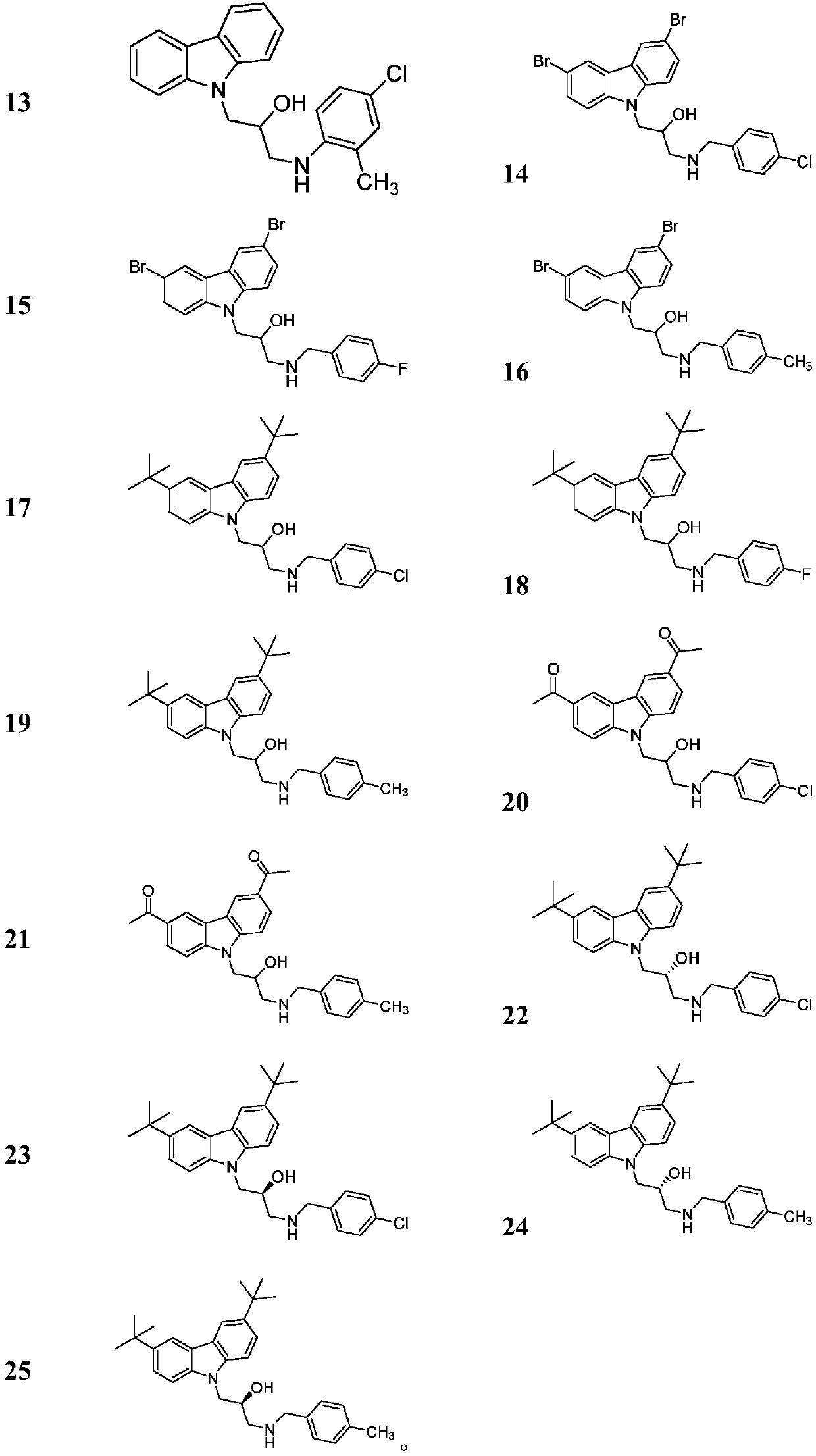
Preparation method for carbazolylv isopropanolamine derivative with chiral center and application
ActiveCN109627206AImprove biological activityStrong inhibitory activityBiocideOrganic chemistry methodsKiwi fruitRalstonia solanacearum
The invention relates to a preparation method for a carbazolylv isopropanolamine derivative with the chiral center and application. The structure of the compound is shown in the formula (I), and the compound achieves the better effect of inhibiting xanthomonas oryzae, ralstonia solanacearum, cucumber xanthomonas oryzae, konjak xanthomonas oryzae, xanthomonas citri, grape ulcer bacteria, tomato ulcer bacteria, kiwi fruit ulcer bacteria, apple ulcer bacteria, cucumber botrytis cinerea, chili blight bacteria, sclerotinia sclerotiorum, wheat gibberella saubinetii, potato late blight, blueberry root rotting bacteria and the like.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Application method of rastonia solanacearum bacteriophage
ActiveCN104542717AReduce the amount of applicationPromote absorptionBiocideDisinfectantsDiseaseVascular bundle
The invention discloses an application method of rastonia solanacearum bacteriophage. The application method comprises the following steps: placing rastonia solanacearum bacteriophage into a sterile syringe needle diagonally inserted in a tobacco plant stem, then covering the rastonia solanacearum bacteriophage with sterile mineral oil so as to prevent evaporation and pollution, so that the rastonia solanacearum bacteriophage directly enters the tobacco plant stem through the sterile syringe needle. According to the characteristic that the rastonia solanacearum is typical bacterial vascular bundle disease, the application method for utilizing the bacteriophage resources to prevent rastonia solanacearum disease is designed, and the method is applied to prevention and control of bacterial wilt of crops, the application amount of the rastonia solanacearum bacteriophage can be reduced, the influence of the outside factors such as sunshine, ultraviolet rays, and rainwater can be avoided, and the resistance on the bacteriophage obtained through the coevolution of the pathogen rastonia solanacearum and the rastonia solanacearum bacteriophage due to long-time contact can be avoided.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI RES INST
Method of quickly identifying bacterial wilt resistance in tobacco varieties in seedling stage
PendingCN107211861AMake sure to enterReduce harmCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
A method of quickly identifying bacterial wilt resistance in tobacco varieties in seedling stage comprises the main steps of A, raising seedlings of a tobacco variety under test in nutrient pots according to a floating seedling raising method; B, subjecting tobacco plants infected by bacterial wilt and collected from a field to isolation purification culture for 3-5 days via a TTC (triphenyl tetrazolium chloride) medium to obtain purified Ralstonia solanacearum; inoculating the Ralstonia solanacearum subjected to purification culture to NA (nutrient agar) medium, and culturing for 12 h to obtain an inoculation bacterial liquid; C, sucking the inoculation bacterial liquid with an injector, selecting tobacco seedlings growing with 3-4 true leaves in the nutrient pots in step A, and injecting 2-4 mu L of the inoculation bacterial liquid obliquely into a stalk of each selected tobacco seedling from its axil; D, culturing the inoculated tobacco seedlings in a sunlight culture room for 10 days, observing and recording disease attack conditions of the tobacco seedlings on 10th day of culture, calculating a disease index, and judging the bacterial wilt resistance of the tobacco variety under test. The method is simple to perform, high in measuring speed, good in results accuracy and good in result uniformity.
Owner:四川省农业科学院经济作物育种栽培研究所 +2
Pseudomonas sp. strain and use thereof
InactiveCN101928683AReduce usageReduce pollutionBiocideBacteriaAgricultural pollutionRalstonia solanacearum
The invention provides a pseudomonas sp. strain 2-29, which belongs to the class of pseudomonas sp. and was collected with a collection number of CGMCC No.3331 in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (abbreviated as CGMCC) of Institute of Microbiology Chinese Academy of Sciences located on Datun road in Chaoyang district of Beijing, on October 2009. The invention also provides the use of the pseudomonas sp. strain 2-29 in the prevention and control of tomato ralstonia solanacearum. For solving the problem that an effective chemical for treating tomato ralstonia solanacearum lacks at present and the problem that pseudomonas sp. is susceptible to generating medicament resistance to chemical pesticide, a strain having an antagonistic effect on tomato ralstonia solanacearum is screen through screening tomato ralstonia solanacearum antagonists and the test of the control effect of the tomato ralstonia solanacearum antagonists; on this basis, field tests can be further performed for developing a mature microbial fertilizer; and thus, the pseudomonas sp. strain 2-29 has a great significance for reducing the use of a large amount of fertilizer and pesticide and reducing agricultural pollution sources.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com