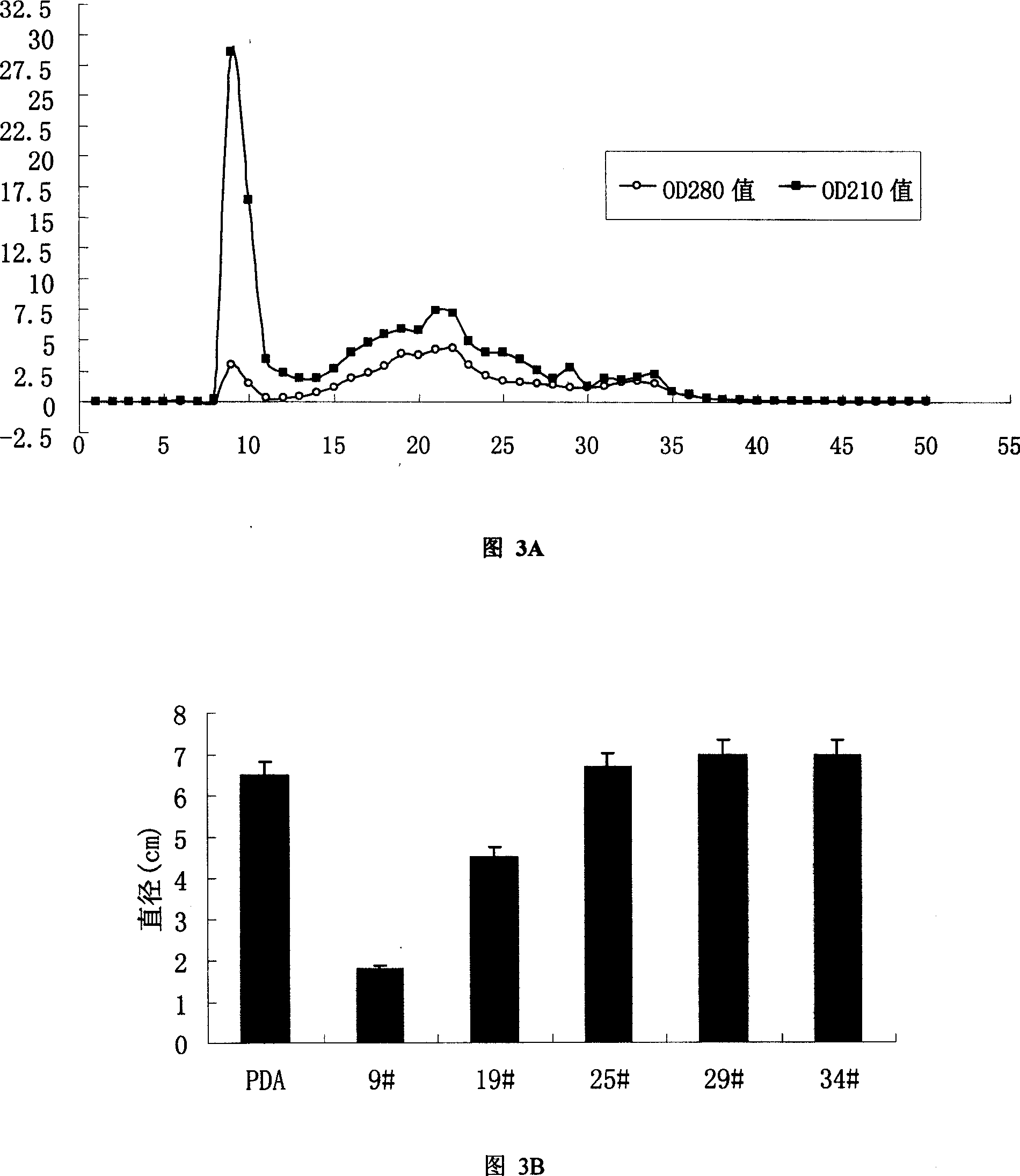
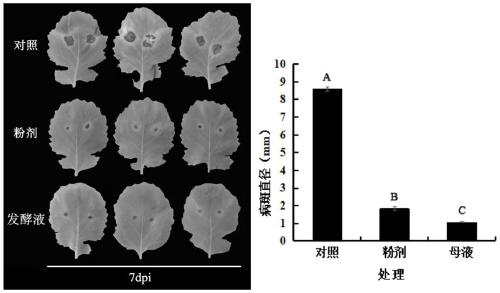
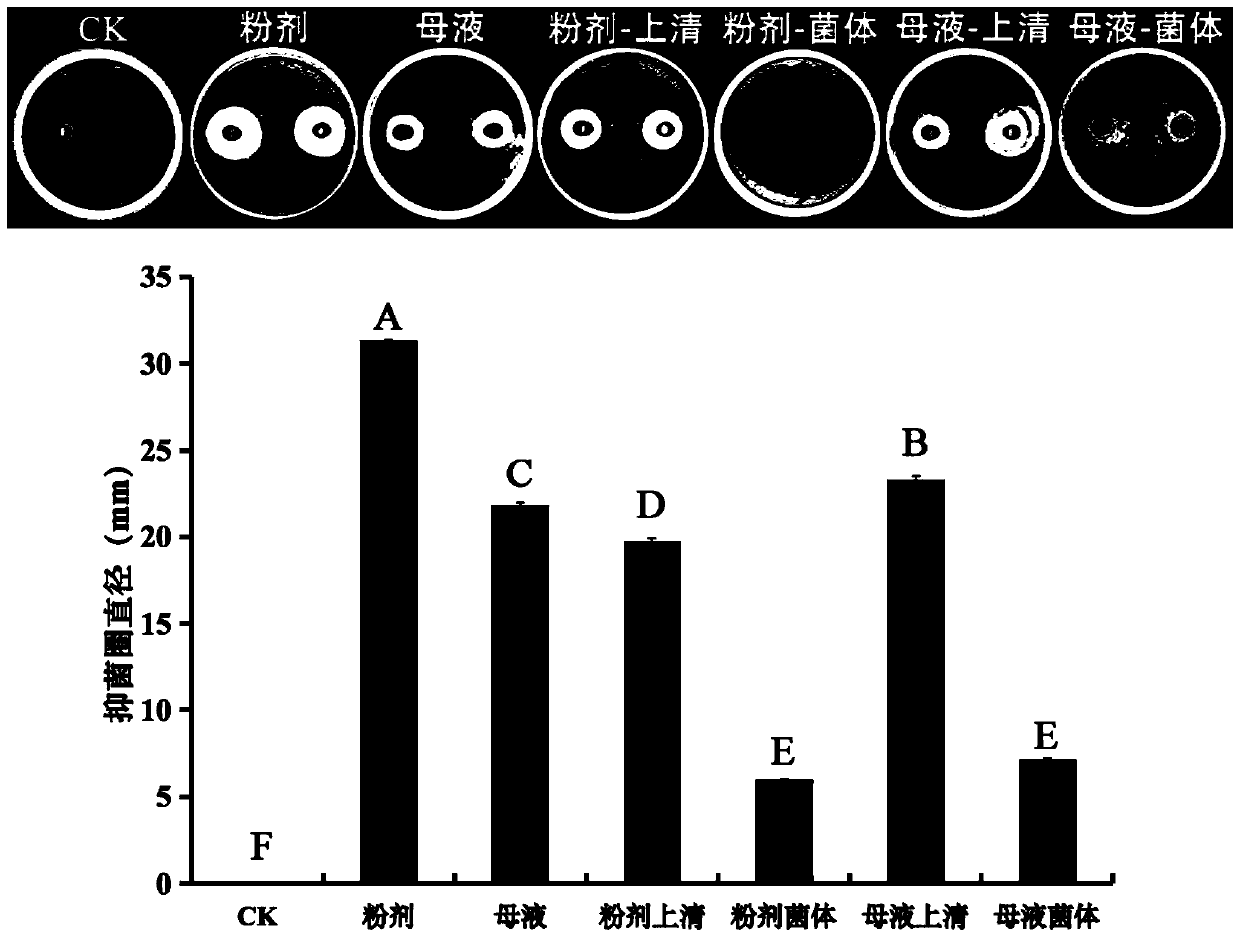
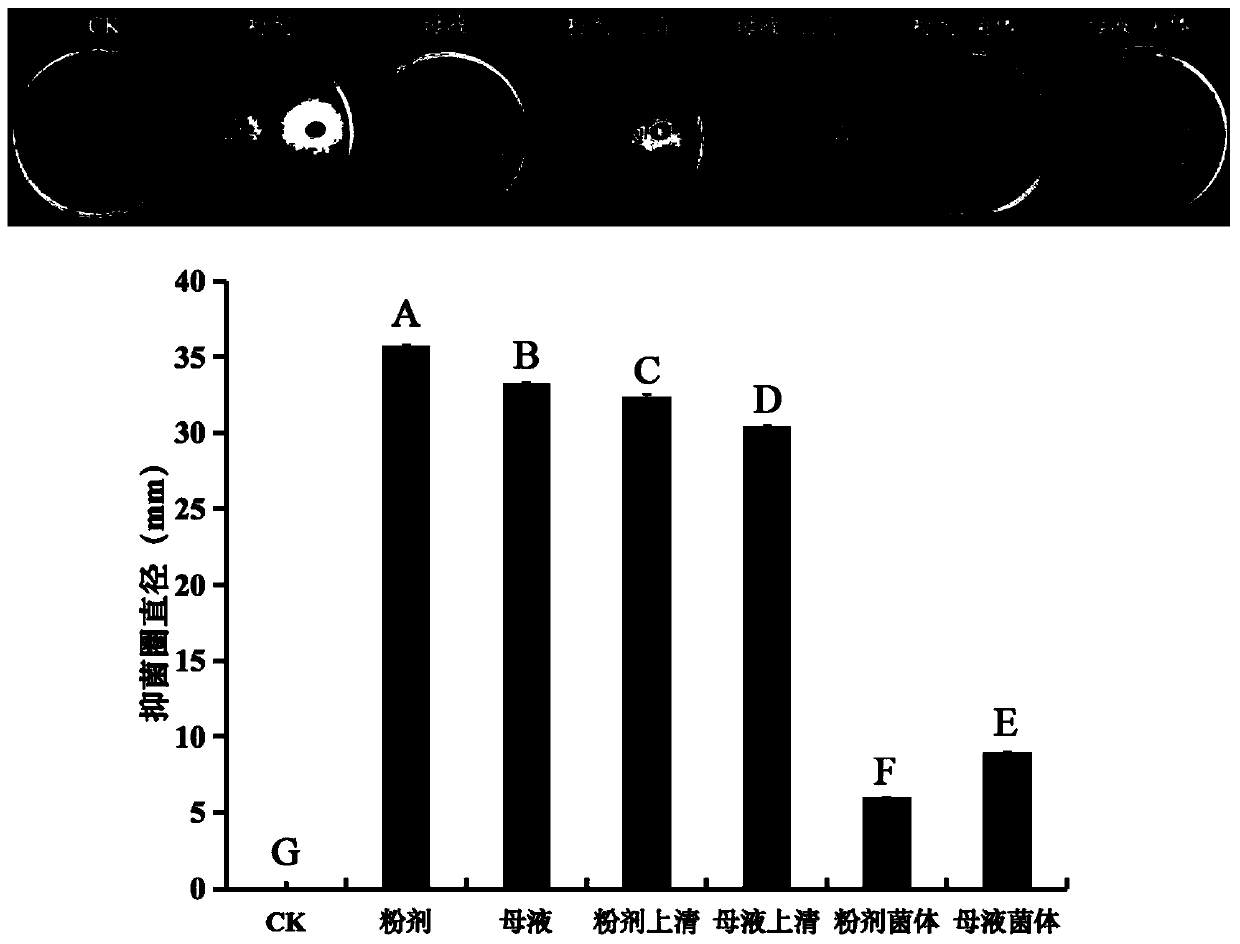
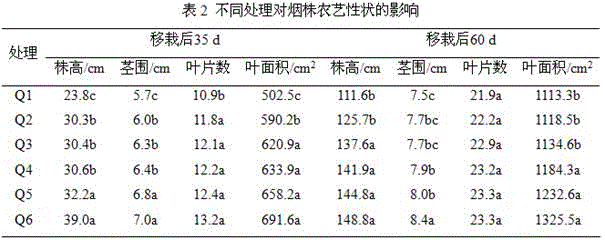
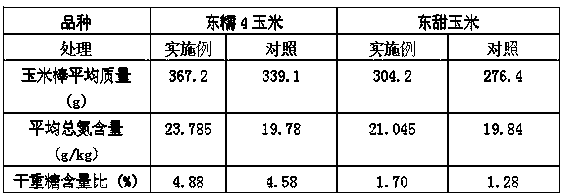
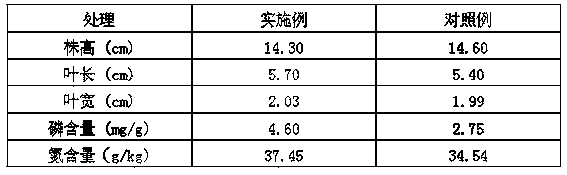
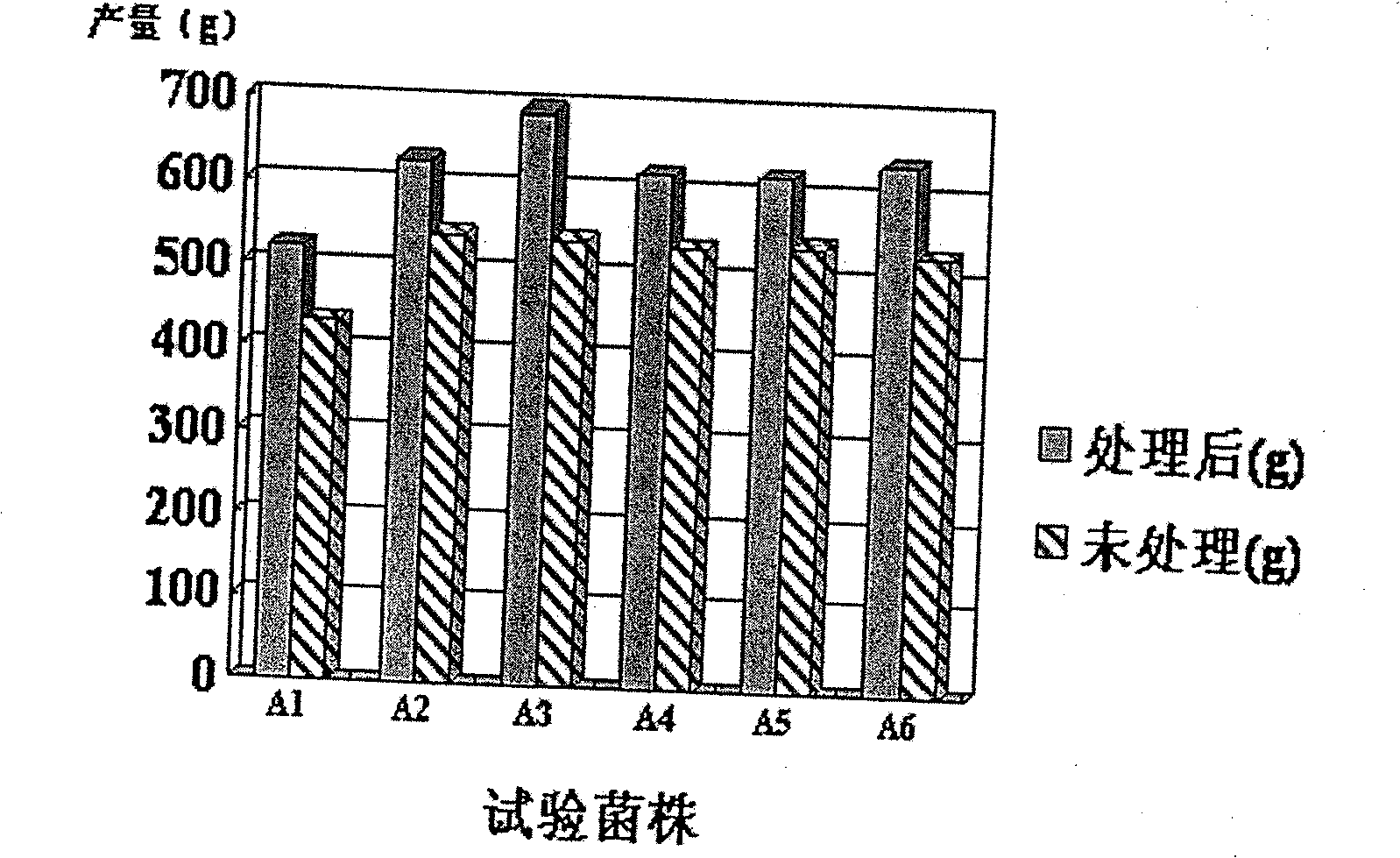
Patents
Literature
75 results about "Agricultural microbiology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Agricultural microbiology is a branch of microbiology dealing with plant-associated microbes and plant and animal diseases. It also deals with the microbiology of soil fertility, such as microbial degradation of organic matter and soil nutrient transformations. Done by Alpha B S Conteh of Njala University.
Lactobacillus plantarum for food fermentation and applications thereof
InactiveCN101691551AShort fermentation timeGood fermentation propertiesFungiBacteriaMicroorganismLactobacillus
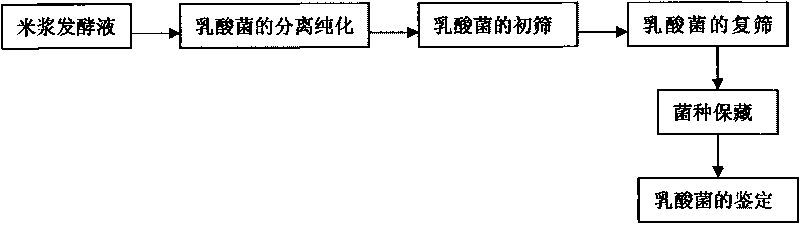
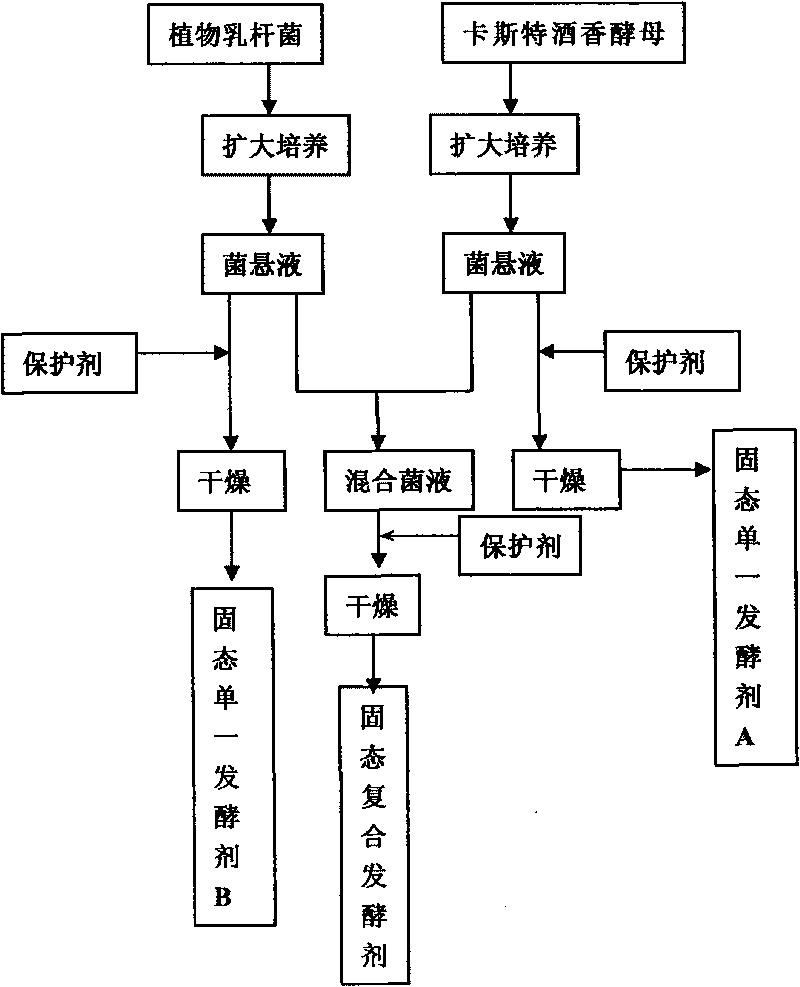
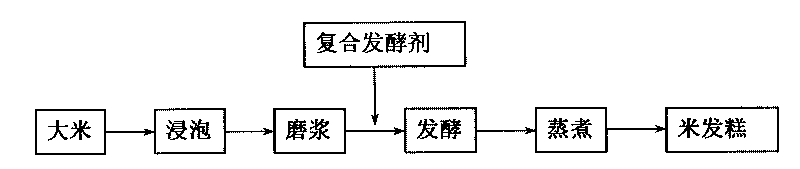
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology and food processing, particularly to a bacterial strain as a microbial starter, comprising a composite starter of the bacterial strain and Brettanomyces custersii and applications. The invention is characterized in that Lactobacillus-plantarum for rice cake fermentation is obtained by separating and screening. The bacterial strain is stored in CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Colletion), and the CCTCC number is M209127. The microbial composite starter is produced by utilizing Lactobacillus-plantarum ZSM-002 bacterial strain and Brettanomyces custersii ZSM-001. The microbial composite starter can be applied to rice fermented products, including the application thereof in the rice cake products. The microbial composite starter has good fermenting property, and is easy for industrialized production. In addition, the products have typical sweet and sour flavor.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN103146610AIncrease profitImprove utilization efficiencyBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlant rootsPhosphate
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural microbiology, and relates to plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and an application thereof. The plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (Pseudomonas fluorescens Y1) was collected in the General Microbiological Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee on January 11th, 2013, and is named Pseudomonas fluorescens in a classified manner, and the collection number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO. 7130. The strain utilizes insoluble phosphate as a phosphorus source for strong growth ability, can improve the utilization ratio of the fertilizer, promotes the development of plant roots and uptake of a fertilizer and increases the phosphorus content of the plant. The plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria disclosed by the invention has a good growth promoting effect for peanuts, and the efficient phosphate solubilisation of the strain promotes the growth and the development of the peanuts and the utilization ratio of a phosphorus fertilizer.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens producing lipopeptide to promote fungi apoptosis and lipopeptide prepared by the same and use
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology, and relates to the fields of biochemistry and molecular biology simultaneously. Through separation, a bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain CH1 for producing a growth-promoting fungus apoptosis lipopeptide is obtained, which is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) with the preserving number of CCTCC: M208127. A bioactive substance is obtained from a culture of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain CH1 and is characterized as the growth-promoting fungus apoptosis lipopeptide. The molecular weight of the lipopeptide is 1,065 or a homologue thereof. The lipopeptide has an infrared spectrum as shown in Figure 6 in the instruction and consists of 9 carbon alkyls and 8 amino acids, wherein the seventh alkyl carbon and the last amino acid form a cyclic peptide through an oxygen atom. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain and the lipopeptide prepared from the same are tested on the biological application prospect in apoptosis.
Owner:武汉光谷世傲生物科技有限公司
Bacillus velenzensis and application thereof to biological control
ActiveCN111254086AGrowth inhibitionReduce diseasePlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyAMARANTHUS CAUDATUS SEED
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms, in particular to Bacillus velenzensis and application thereof to biological control. The Bacillus velenzensis disclosed bythe invention is Bacillus velezensis Bv-6, and a preservation number is CCTCC NO:M20191106. The Bacillus velenzensis fermented solutions or powder can effectively inhibit growth of mycelia of important pathogens (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum(Lib.)de Bary, Botrytis cinerea Pers. and Blackleg) on rapes, and germination of conidiophores and ascospores; and through seed soaking treatment of the fermentedsolutions, the seeds of the rapes can be normally germinated and grown, and the edisease resistance of plants can be improved. In addition, the Bacillus velenzensis has the characteristics of being high in proliferation speed, high in stability, high in temperature resistance and free of toxicity. Therefore, the Bacillus velezensis strain Bv-6 has the potential of developing and utilizing the function of the biological control.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
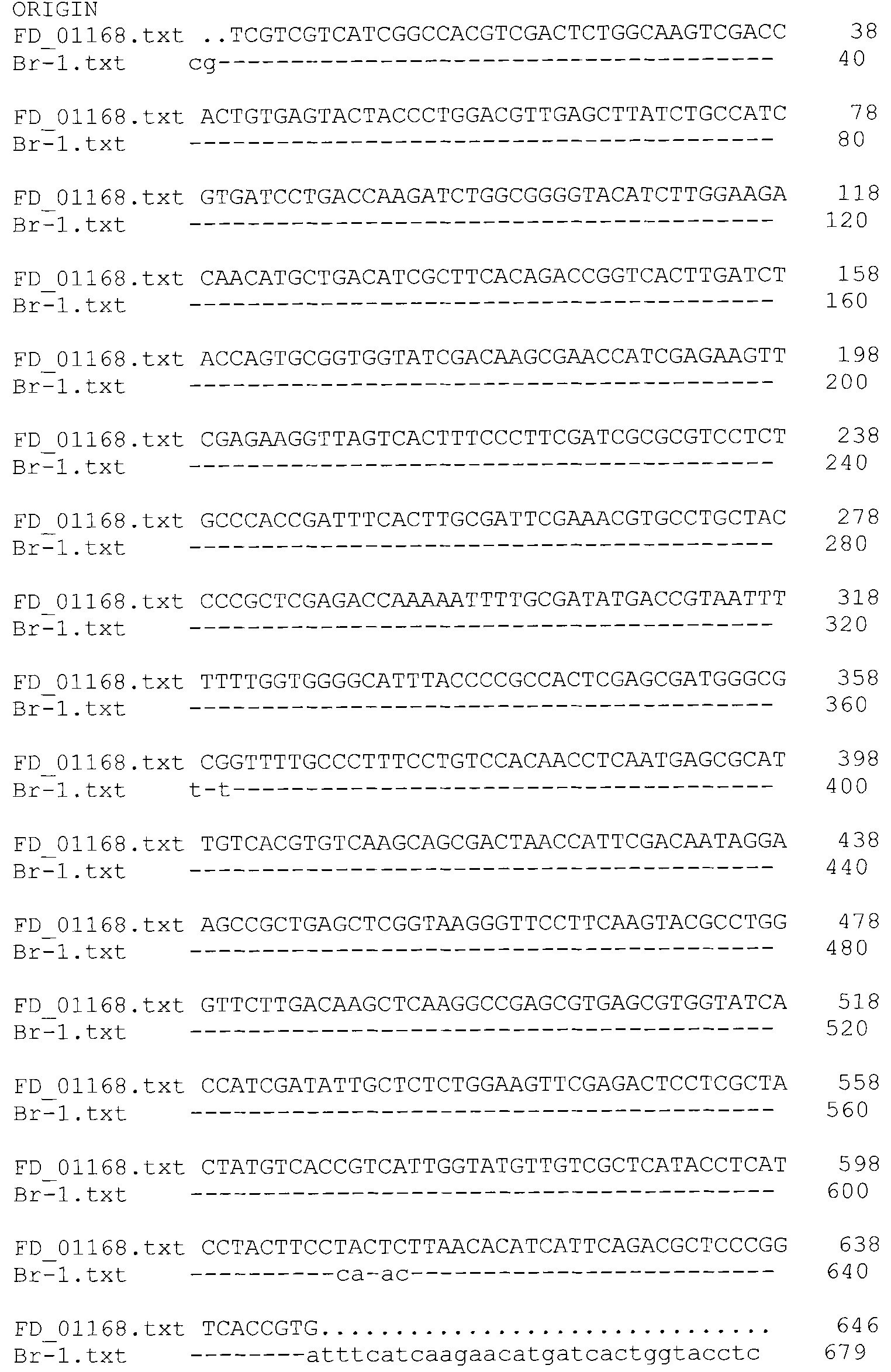
Fusarium proliferatum, and bacterium agent and application thereof
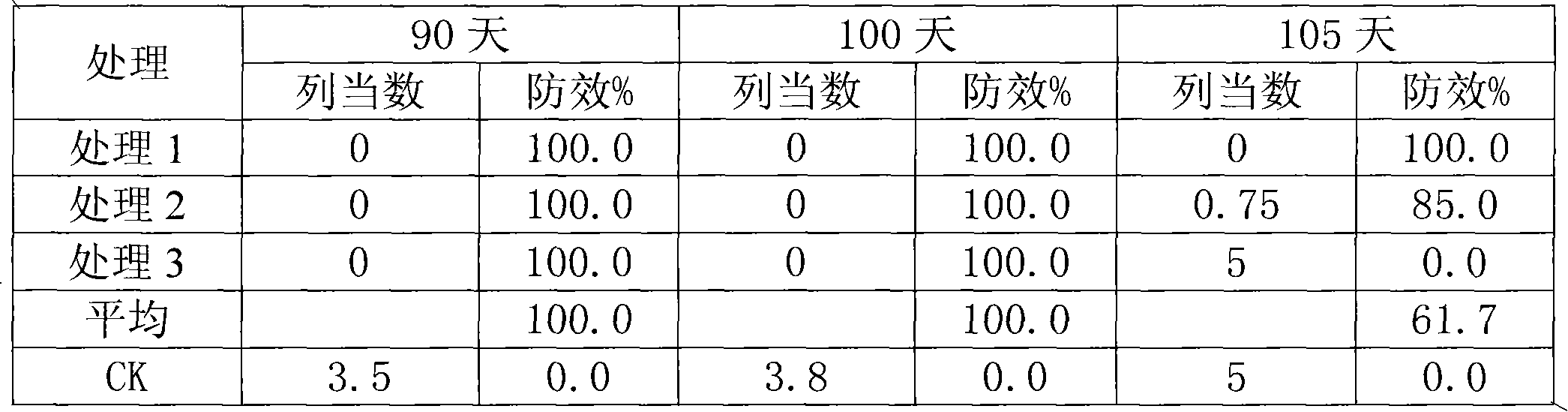
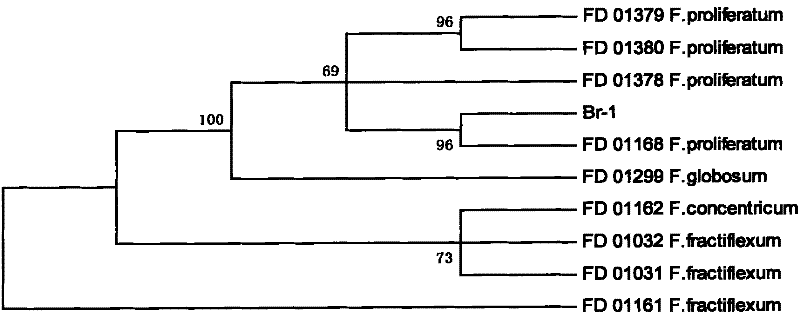
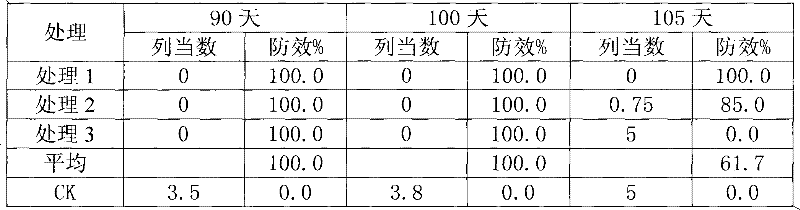
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural microbiology and discloses a fusarium proliferatum strain Br-1 with the preserved number of CGMCC No. 3759. The invention also discloses a microbiological bacterium agent prepared by using the Br-1. The fusarium proliferatum strain Br-1 and the bacterium agent thereof have good inhibiting effect for orobanche cumana wallr, and the control effect in fields reaches 61.7-82.0%; and secondarily, a preparation method of the microbiological bacterium agent is simple, and has low cost and easy promotion and application. In addition, the invention belongs to a biological control method, has no pollution, no nuisance and low residue and is environment-friendly.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Pretreatment fungicide for xylose residue or furfural residue, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102154108AFast startup timeEasy to degradeFungiMicroorganism based processesDry weightBiogas production
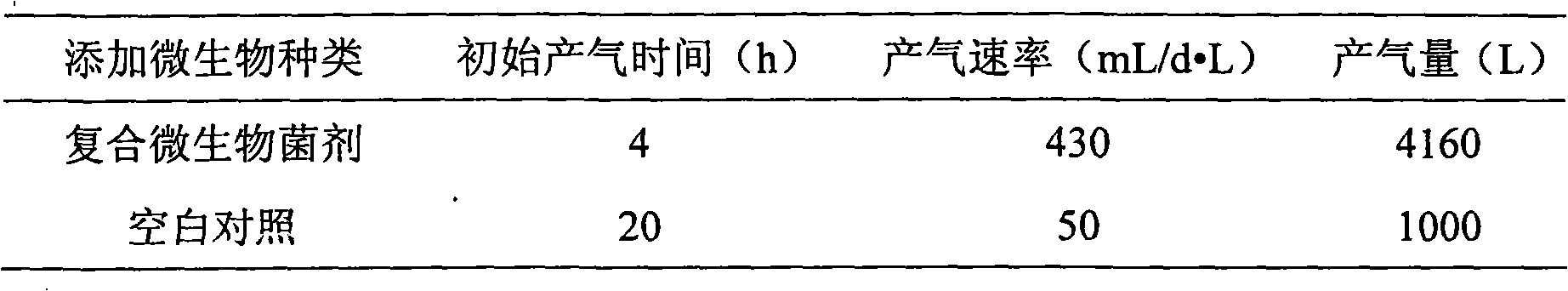
The invention relates to a pretreatment fungicide for xylose residue or furfural residue, a preparation method and an application thereof, belonging to the technical field of agricultural microbiology. The invention relates to a microbial composite fungicide specially used for promoting the xylose residue or the furfural residue to degrade and improving the production efficiency of methane. The invention firstly adopts liquid fermentation technology to purely breed and ferment all components of the microbial fungicide, and then the components are compounded. The preparation method of the pretreatment fungicide comprises: 0.20-0.40 parts by weight of trichoderma viride liquid, 0.10-0.15 parts by weight of phanerochaete chrysosporium liquid, 0.05-0.10 parts by weight of aspergillus niger liquid, 0.08-0.16 parts by weight of aspergillus oryzae liquid and 0.05-0.10 parts by weight of trametes versicolor liquid, and the dry weight of fermentation hyphae is more than 20g / L. The composite fungicide can be used for improving the composite fungicide speed of the xylose residue or the furfural residue as well as the methane production efficiency; the methane production efficiency is improved by 30-60%; the fermentation time is shortened; the start period is shortened by 3-10 days; and the invention is also good in the effects on the aspects of pretreatment of smashed straws, and methane production.
Owner:ENERGY RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
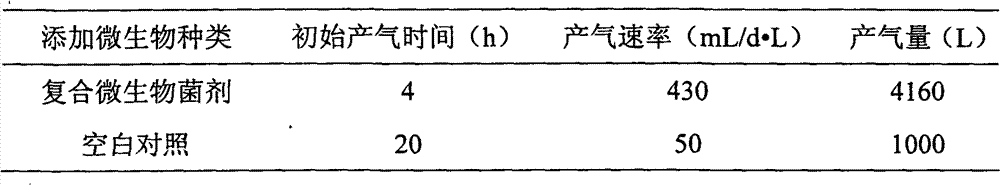
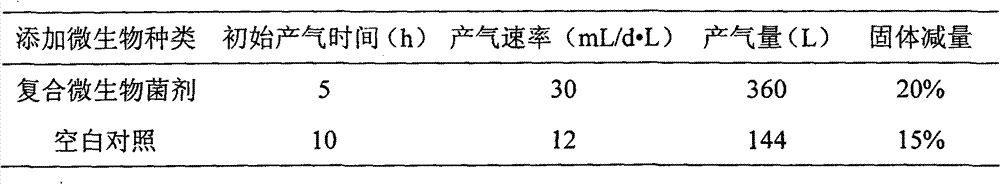
Complex bacterial preparation and application thereof
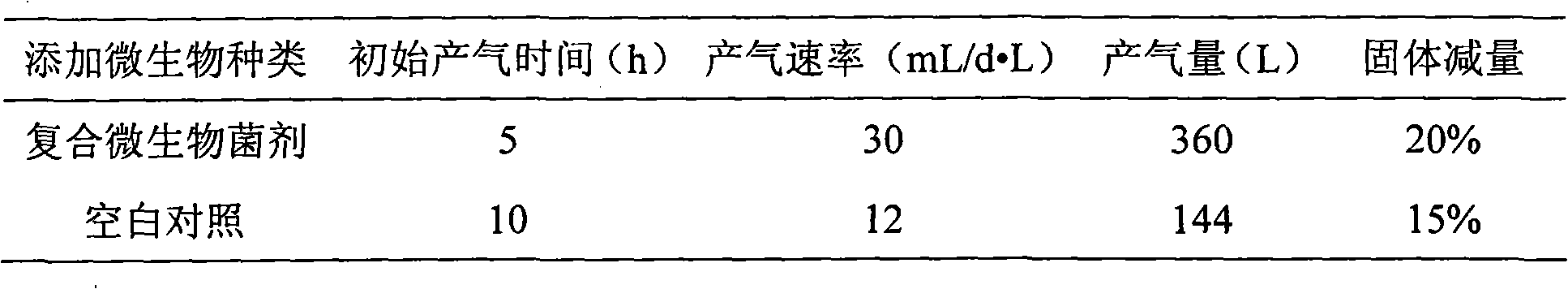
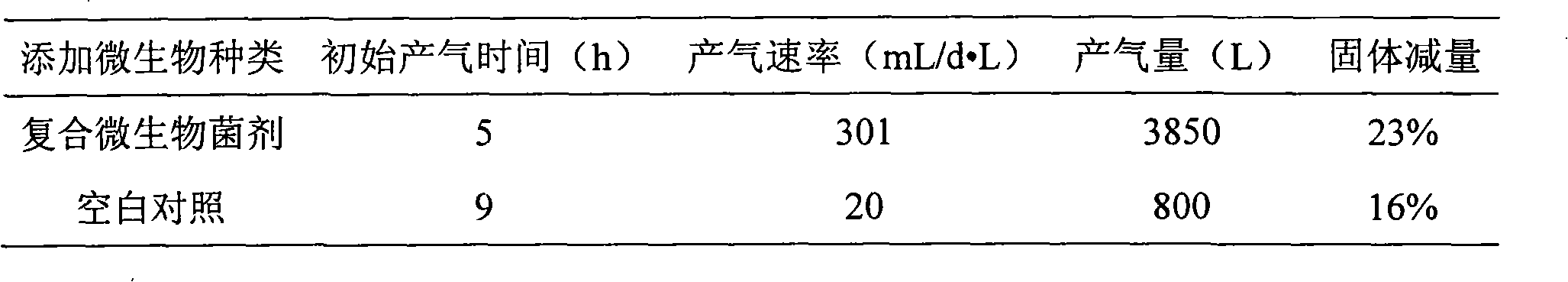
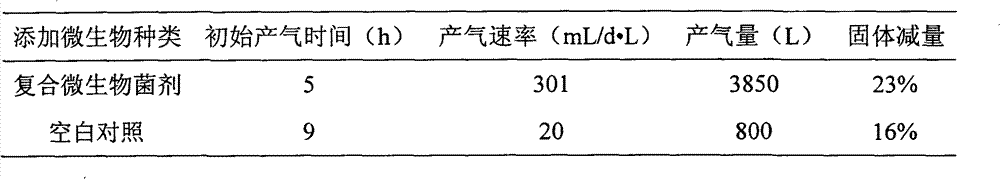
The invention belongs to the technical field of the agricultural microbiology and discloses a complex bacterial preparation and application thereof. The complex bacterial preparation is prepared by mixing the following components: 1 to 3 parts of fermentation liquor of Escherichia.coli, 2 to 3 parts of fermentation liquor of Trichoderma virens, 1 to 4 parts of fermentation liquor of Pseudomonas fluorescens and 4 to 6 parts of fermentation liquor of Bacillus subtilis. The complex bacterial preparation provided by the invention not only can improve the methane yield of straws and cow dung and improve the methane generating speed, but also can further reduce content of solid waste by 30 percent. The method has the advantages of quick response, low cost, simple using method, easy popularization and the like and can be popularized and used.
Owner:江苏加德绿色能源有限公司
Multiple-effect plant growth-promoting bacteria and isolation and screening method thereof
ActiveCN110484470AObvious nutrient conversion effectEasy to colonizeBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementGrowth plantRhizobacteria
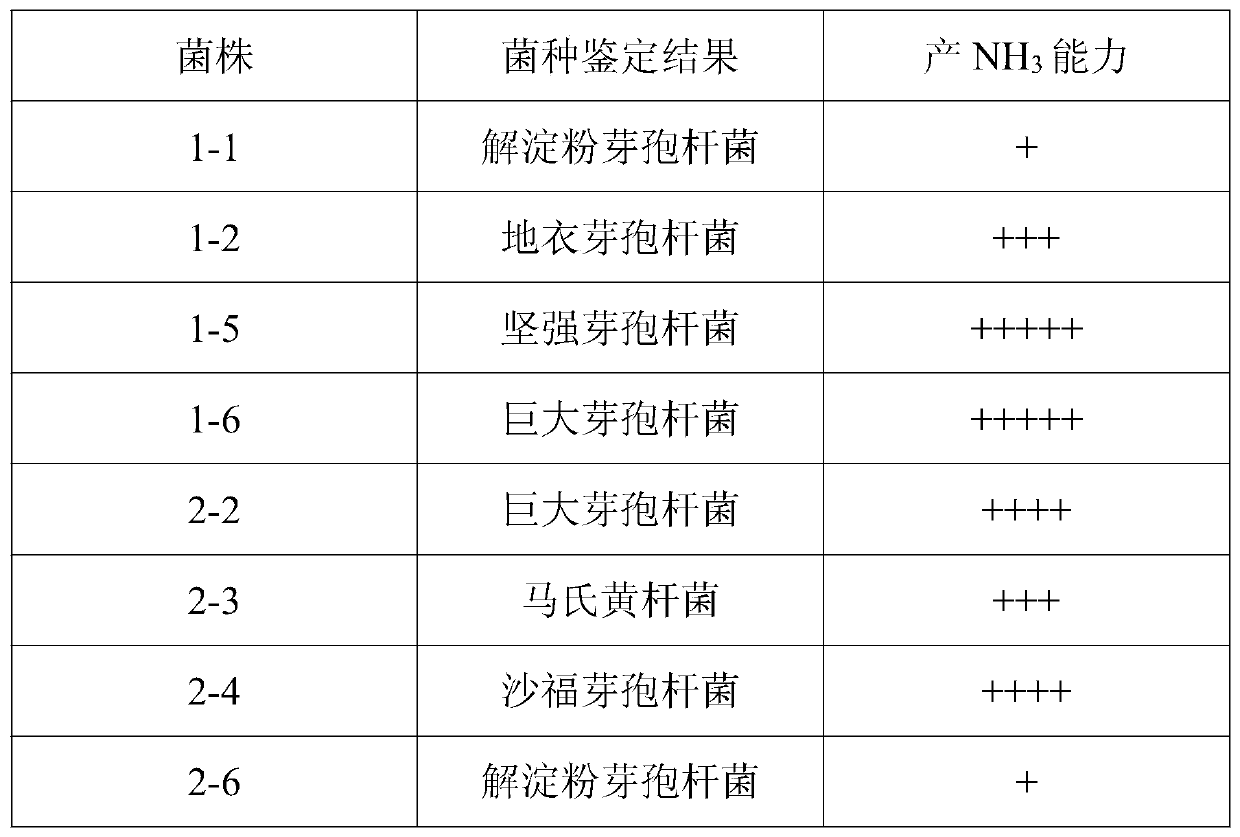
Multiple-effect plant growth-promoting bacteria and an isolation and screening method are disclosed. The invention belongs to the field of agricultural microbiology and specifically relates to multi-effect plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria with phosphorus-solubilizing, NH3-producing, plant growth hormone-producing and siderophore-producing effects. The preservation number of the multi-effect plant growth-promoting bacteria is CGMCC No. 14664. The multiple-effect plant growth-promoting bacteria are applied to fertilizers and microbial inoculants. The isolation and screening method of the invention includes sampling, cultivation of strains, identification and selection of strains, preliminary selection of strains, re-selection of strains, signing of strain performance and identification of multi-effect strains.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES +1
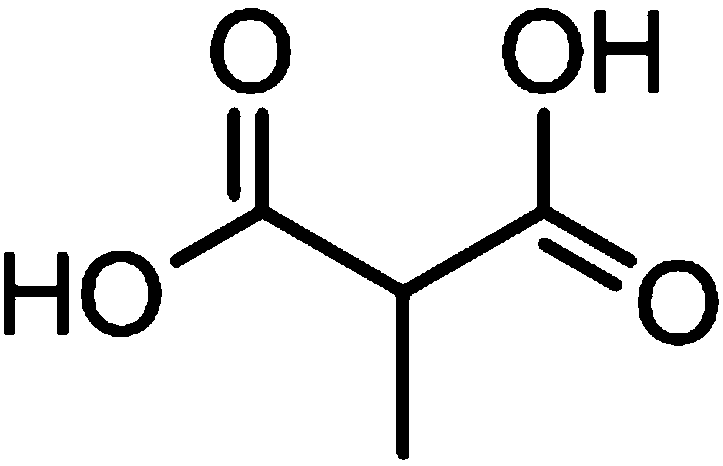
Application of methylmalonic acid in preparation of nematode pesticide
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural microbiology, and specifically relates to an application of methylmalonic acid in preparation of a nematode pesticide. Through determination of the fatality rate of meloidogyne incognita and caenorhabditis elegans, it finds that the methylmalonic acid has a good insecticidal effect on nematodes; LC50 of the methylmalonic acid to the meloidogyne incognita and the caenorhabditis elegans is separately 13.11 and 1.20; and after the methylmalonic acid and betaine are compounded, the LC50 of the methylmalonic acid to the meloidogyne incognita and the caenorhabditis elegans is separately 2.85 and 0.27; and at the same time, the methylmalonic acid has an inhibition effect on ralstonia solanacearum and erwinia carotovora. The preparationprovides new selectivity for the preparation of biocontrol preparations of meloidogyne.
Owner:HUBEI BIOPESTICIDE ENG RES CENT
Culture medium using waste loquat branches as matrix as well as preparation and cultivation method of culture medium
InactiveCN103449928AAchieve recyclingIncrease economic incomeHorticultureFertilizer mixturesSaccharumSucrose
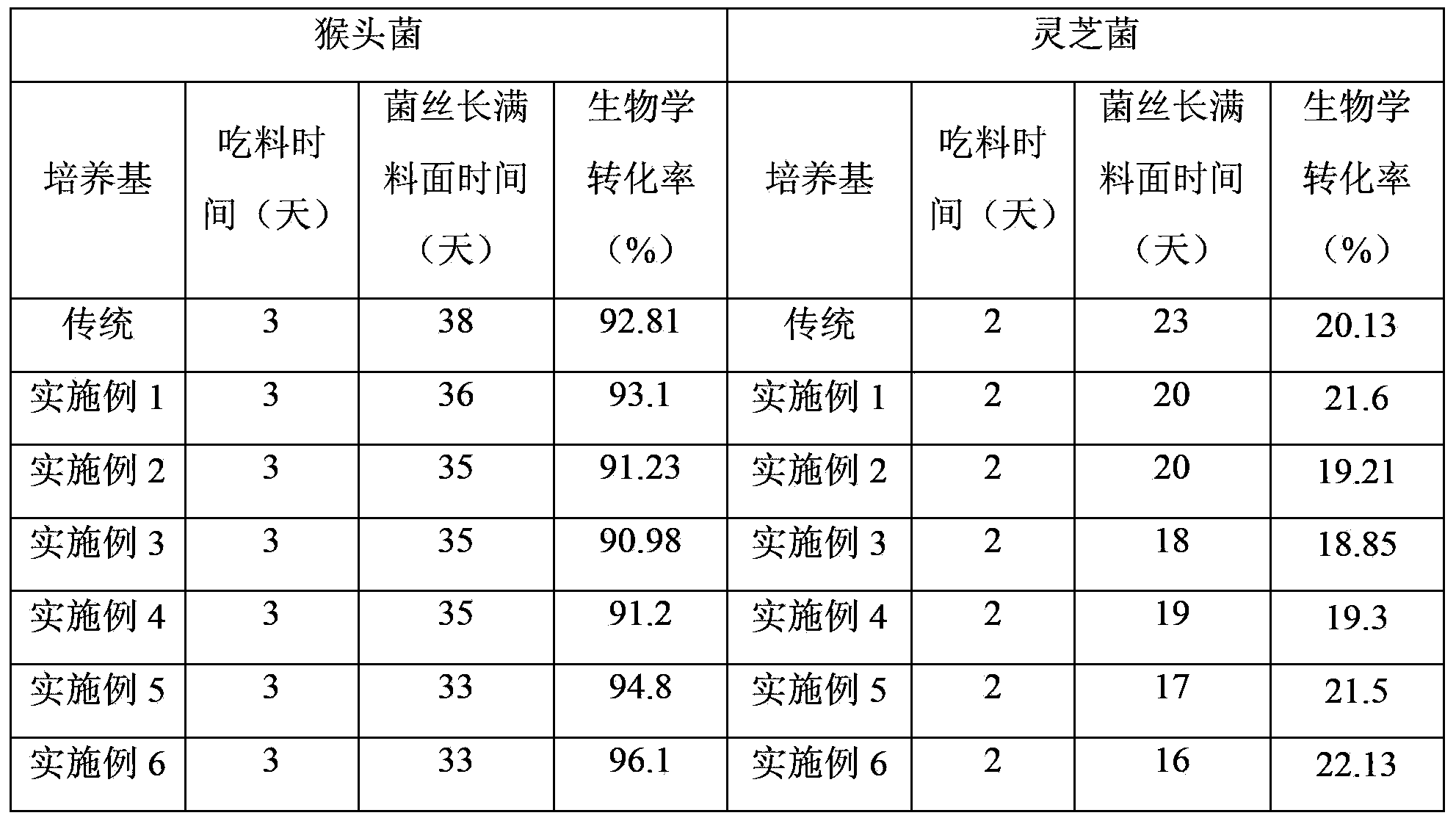
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural microbiology, and specifically relates to a culture medium using waste loquat branches as matrix as well as a preparation and a cultivation method of the culture medium, aiming at solving the technical problem that existing edible fungus is short of cultivation resources, and an existing method for producing the edible fungus by the loquat branches is complex to operate and high in cost. The culture medium comprises the following materials in ratio: 38%-68% of loquat branches, 0%-20% of corncobs, 10%-20% of distilled grains, 3%-8% of oil cakes, 8%-15% of wheat bran, 0.5%-1% of ammonium sulfate, 0.5%-1% of sucrose, 1% of quick lime, 1% of plaster and 1% of zymocyte. According to the invention, the waste loquat branches are fermented and treated for cultivating hericium erinaceus and ganoderma lucidum, so that the operation method is simple and easy to implement and the production cost can be lowered, and therefore, a new resource is provided for edible fungus cultivation.
Owner:攀枝花市农林科学研究院
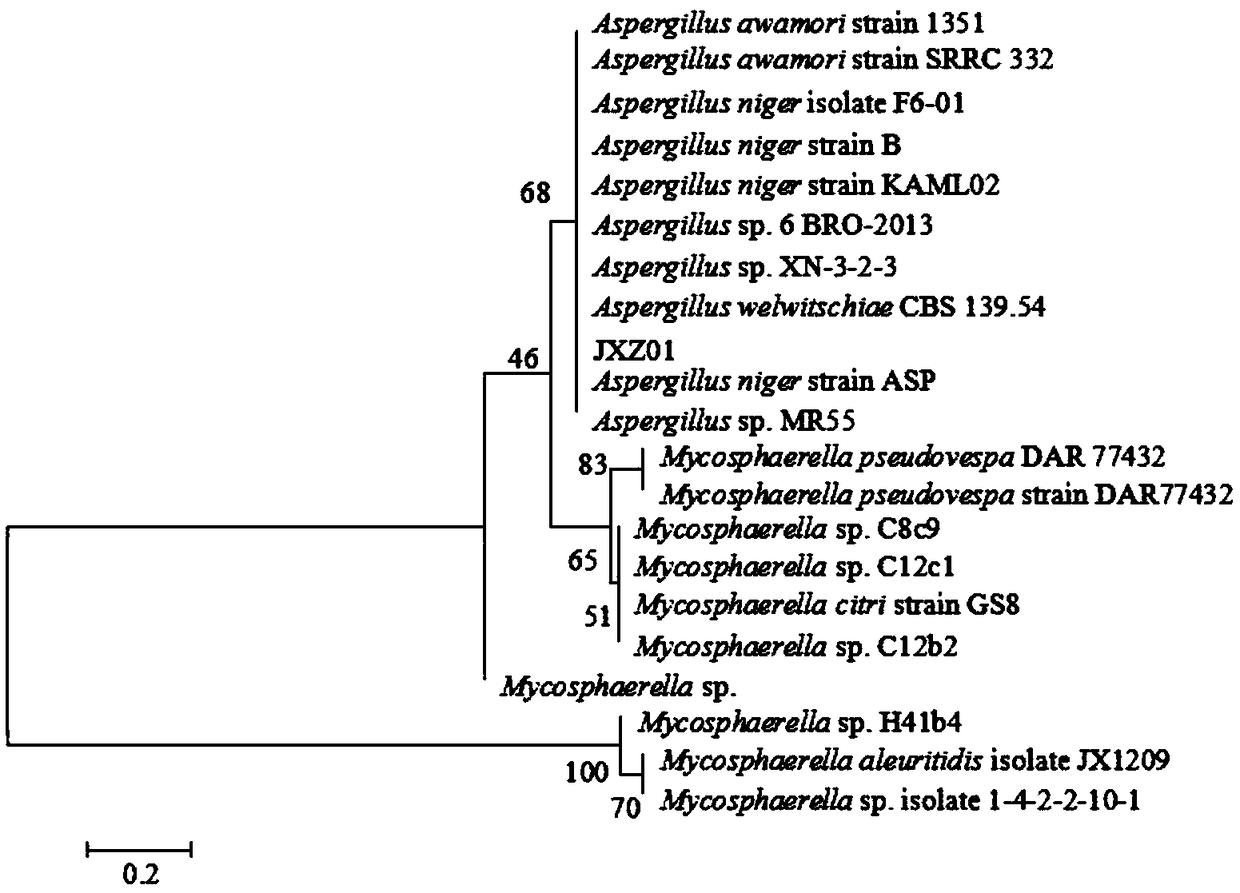
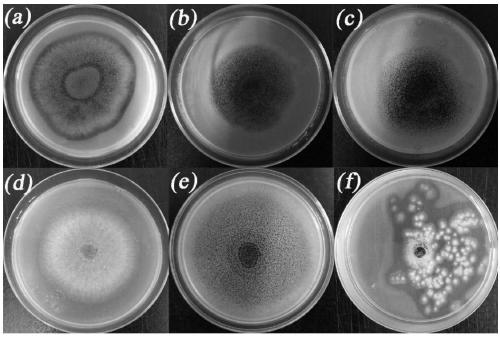
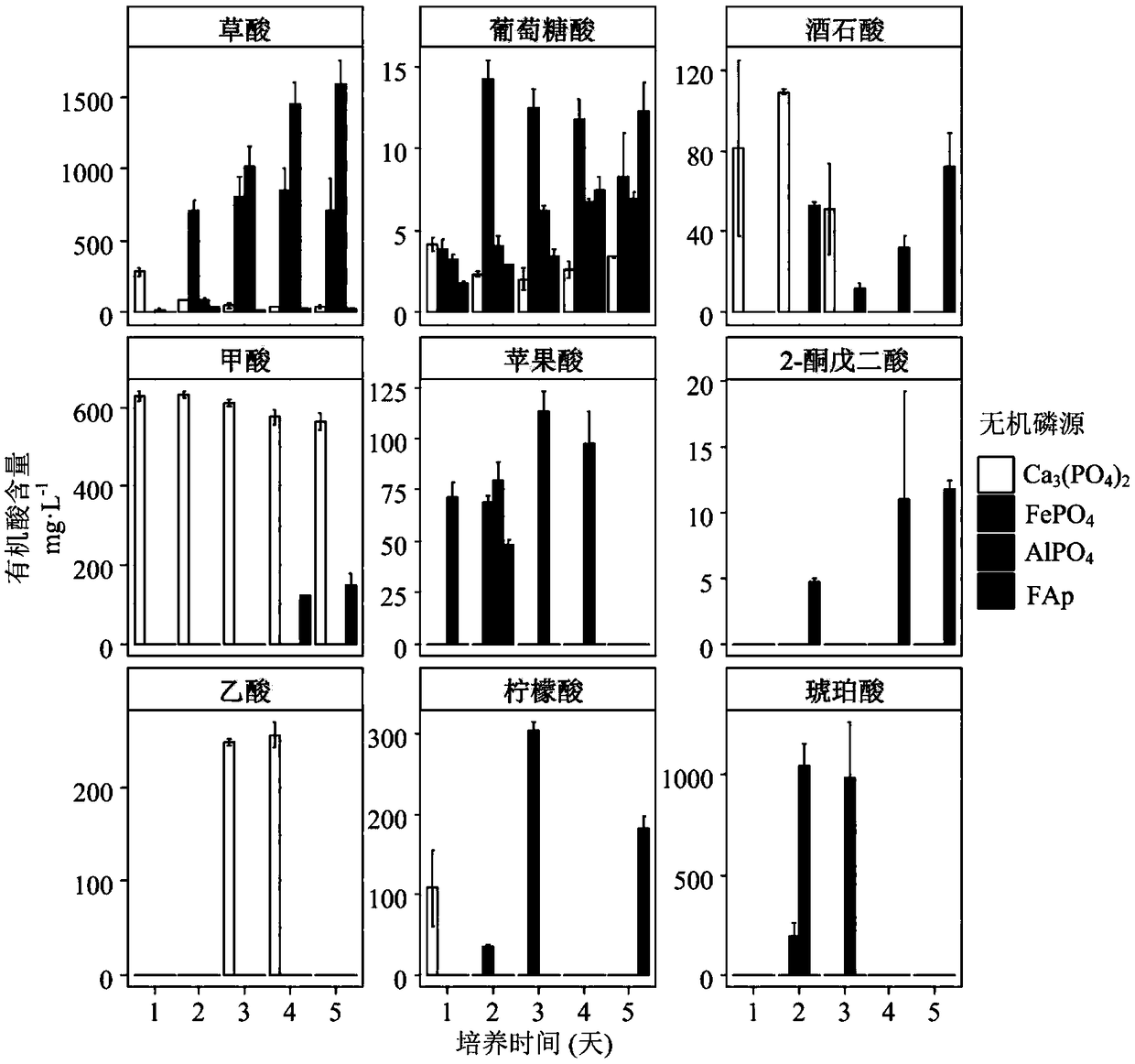
Separation and application of aspergillus niger JXZ01 with decomposition capability of various difficult-to-dissolve phosphorous sources
ActiveCN109182136AImprove toleranceImprove repair effectFungiContaminated soil reclamationPhytaseDecomposition
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural microbiology and discloses a fungus with a good phosphorous decomposition capability and application thereof to heavy metal pollution remediation. Aclassified name of the fungus is aspergillus niger with the strain number of JXZ01. The strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on July 19, 2018 and thepreservation number is CGMCC_No. 15994. The strain not only can secrete various organic acids to realize the aim of decomposing tricalcium phosphate, iron phosphate, aluminum phosphate and rock phosphate and releasing soluble phosphate, also can be used for secreting acidic phosphatase and phytase to realize the effects of decomposing lecithin and calcium phytate and simultaneously releasing the soluble phosphate. The strain has good tolerance capability and repairing effect on heavy metal including Cu, Pb, Cr, Zn and the like, and has a potential of being applied to the field of the heavy metal pollution remediation of soil.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus composition for control of panax ginseng and American ginseng black spot disease and botrytis cinerea and use thereof
InactiveCN107242249AQuality is not affectedPrevent No Pesticide ResiduesBiocideDead animal preservationDiseaseGinseng family
Belonging to the field of agricultural microbiology, the invention in particular discloses three new bacillus strains, a bacillus composition and use thereof in control of panax ginseng and American ginseng black spot disease and botrytis cinerea. The bacillus combined inoculums provided by the invention can effectively control panax ginseng and American ginseng black spot disease and botrytis cinerea lesions, and has the characteristics of good field planting effect, long duration, lasting effect, and control effect superior to that of traditional chemical pesticides.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
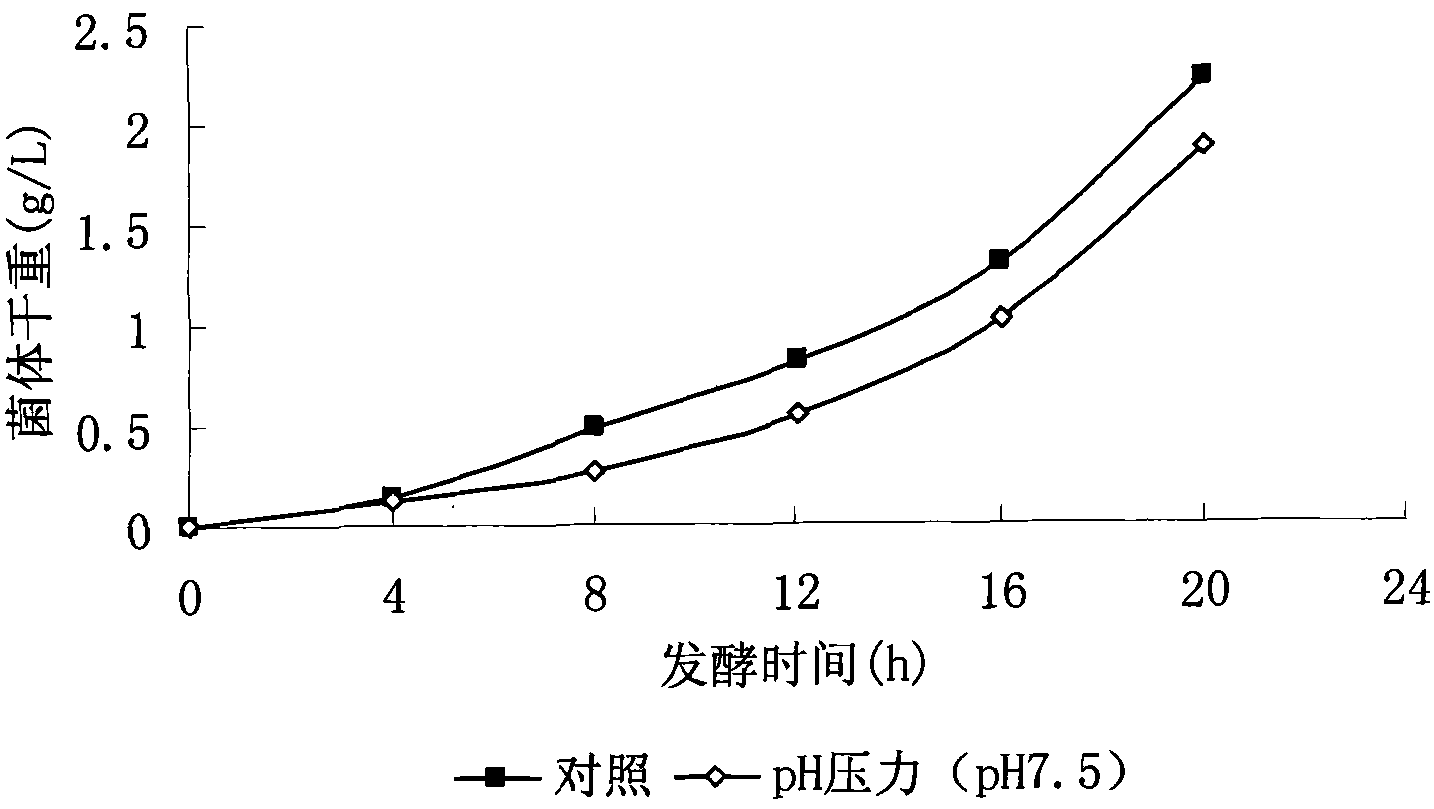
Method for enhancing yield of bacillus fermentation poly-gamma-glutamate by utilizing environmental pressure
InactiveCN101875950ARegulating pHSimple fermentation operationMicroorganism based processesFermentationBacillus licheniformisMicroorganism
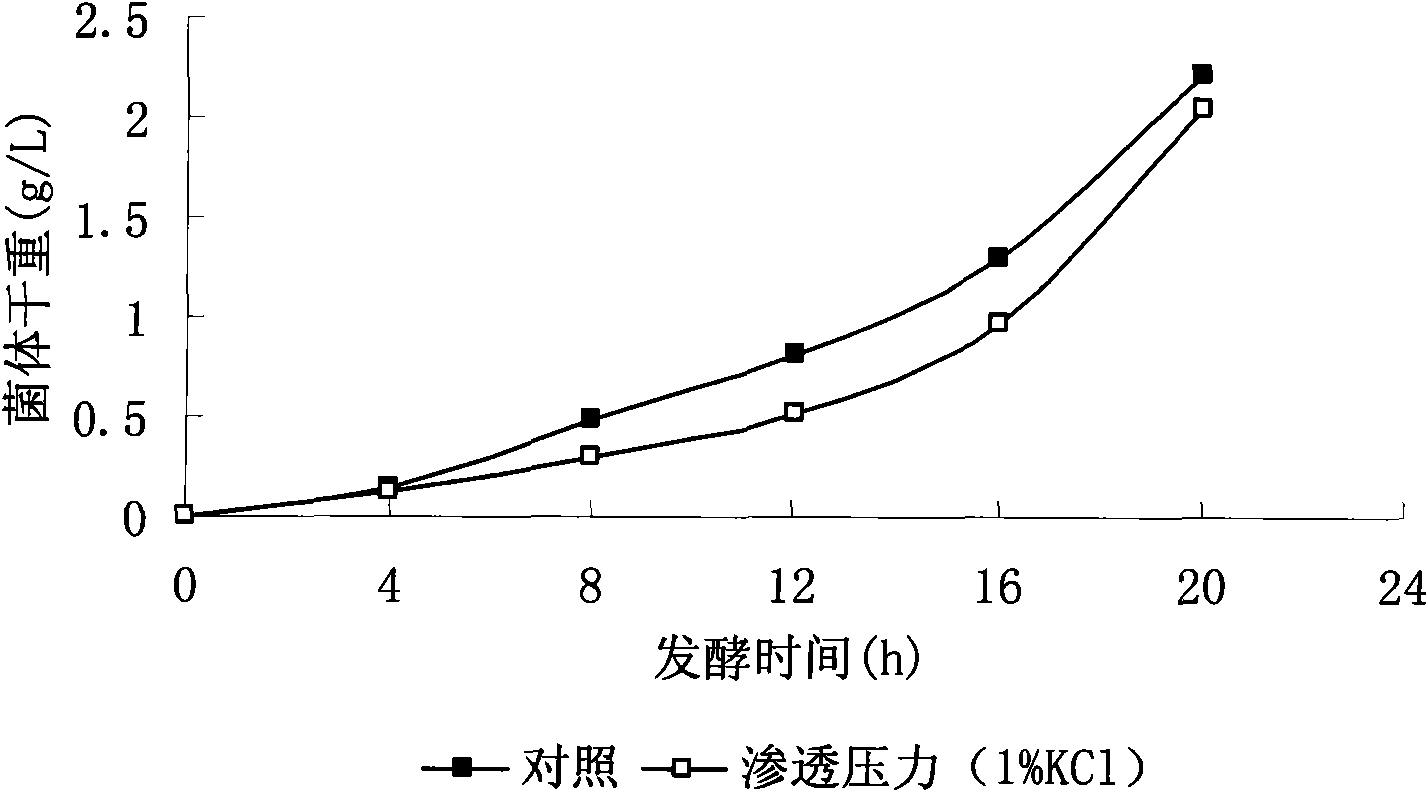
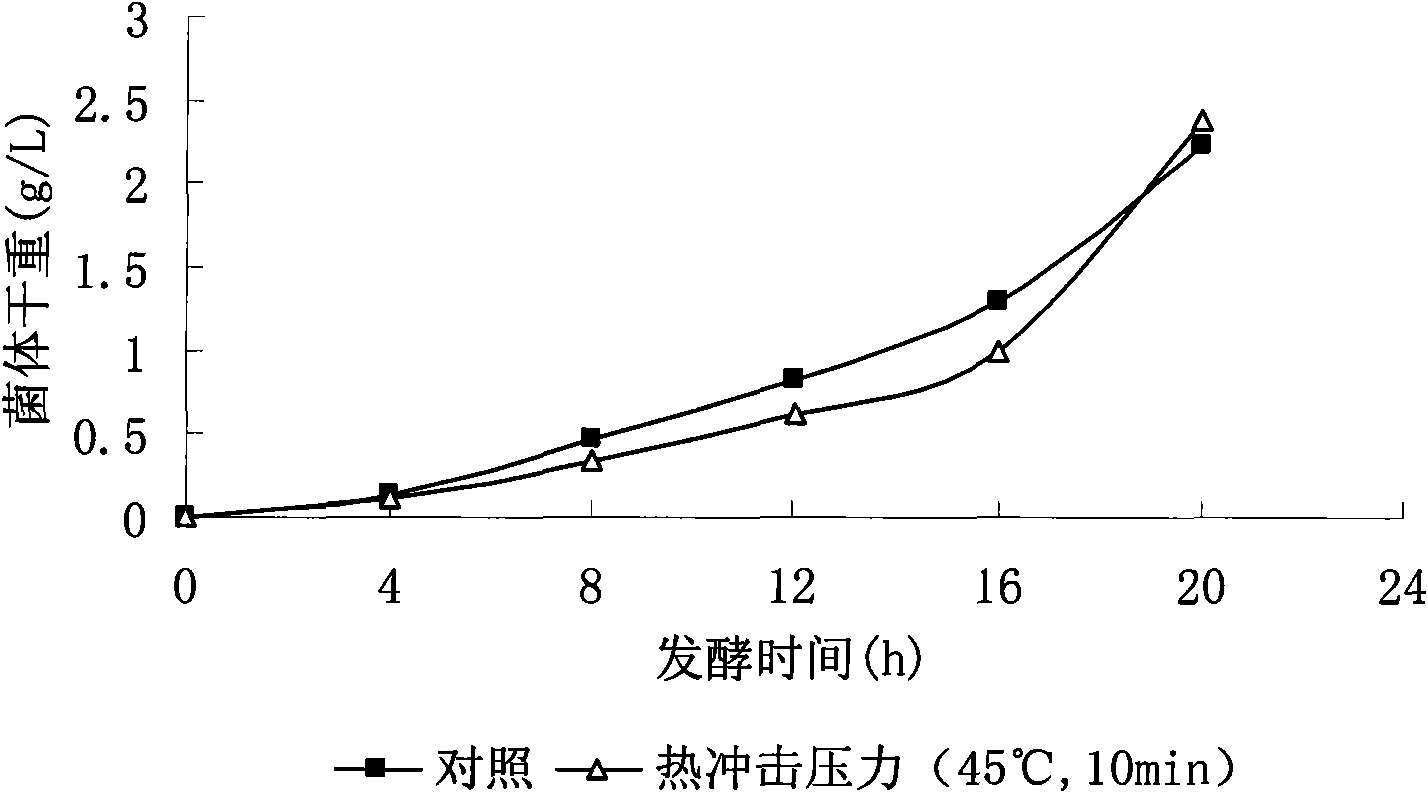
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology application and particularly relates to a method for enhancing the yield of bacillus fermentation poly-gamma-glutamate by utilizing environmental pressure. The method is characterized in that in the fermentation process, the yield of the poly-gamma-glutamate is enhanced through the seepage pressure or / and the hot impact pressure or / and the pH pressure of potassium ion mediate. The invention also relates to microbiology bacillus licheniformis WX-02 for fermentation production. The strain is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection and has a preserving number of CCTCC M208065.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for recycling spartina alterniflora
ActiveCN104396569AFruiting period is shortenedEliminate growthBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationBiotechnologyActivated carbon
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology, and particularly relates to a method for recycling spartina alterniflora. The method for recycling the spartina alterniflora includes: firstly, processing the spartina alterniflora after being harvested through a desalting technology, and partially removing salinity of the spartina alterniflora; then, composting and fermenting the spartina alterniflora with bran, corn flour and activated carbon so as to obtain compost; using the compost for cultivating a salt tolerance edible bacterial strain which is yellow oyster mushroom. The method for recycling the spartina alterniflora achieves recycling application of the spartina alterniflora, turns harm into good, and not only creates economic benefit, but also generates good ecological benefit.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Bacillus subtillis for preventing and controlling cole sclerotium and antibioticsubstance separation
InactiveCN101270344AStrong ability to inhibit Sclerotinia sclerotiorumBiocideBacteriaSclerotiniaAntibacterial activity
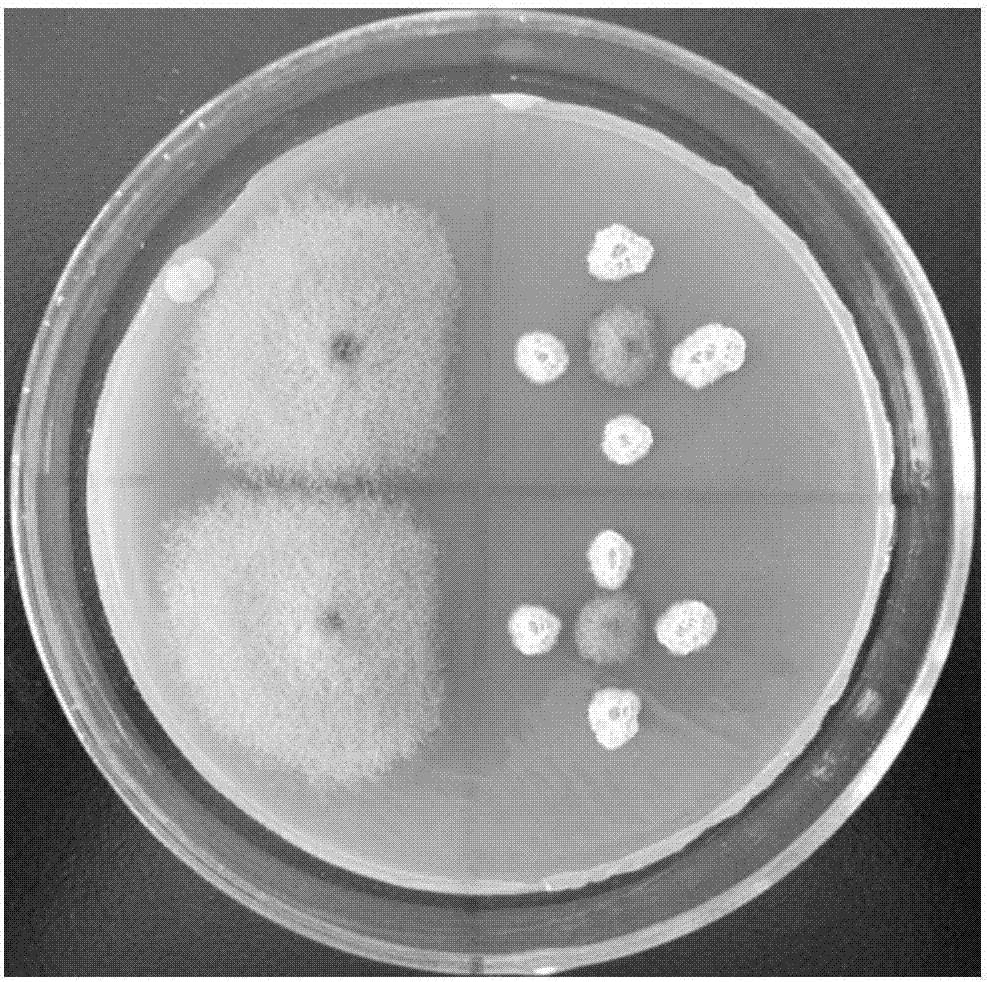
The invention belongs to the technical field of agromicrobiology, in particular relates to separation and screening of an antagonistic bacterial strain X-01 which can inhibit sclerotinia sclerotiorum,and separation and application of antibacterial active substance. The bacterial strain X-01 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with the preservation number of CCTCC No. M208067. The bacterial strain X-01 is identified as bacillus subtilis through morphologic observation, biophysical and biochemical study, and 16S rDNA autoploidy study. The bacterial strain can secrete a lipopeptid antibiotic, iturin A. The molecular weight of the lipopeptid antibiotic is 1042.9Da. The invention further discloses a method for preparing the lipopeptid antibiotic, iturin A, by the bacterial strain X-01. According to the biological control test in vitro, the lipopeptid antibiotic, iturin A, has significant inhibitory effect on the sclerotinia sclerotiorum. When the concentration of the lipopeptid antibiotic iturin A is 100 Mu g / ml, the effect to control the sclerotinia sclerotiorum can reach 100 percent; when the concentration is 10 Mu g / ml, the effect to control the sclerotinia sclerotiorum can reach 40.7 percent.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Bacillus liquid compound microbial fertilizer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109320363AFacilitated releaseIncrease the number of live sporesCalcareous fertilisersBio-organic fraction processingBacterial strainFermentation
The invention discloses bacillus liquid compound microbial fertilizer and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology. The bacillus liquid compound microbial fertilizer is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 40-60% of Bacillus subtilis SEM-9 bacterial liquid, 20-40% of a nutrient complex, 1-3% of manganese sulfate, 4-8%of sodium methylene bis-naphthalene sulfonate and the balance of water. Bacillus subtilis SEM-9 bacterial strains in the bacillus liquid compound microbial fertilizer are derived from silkworm excrement, meanwhile through fermentation of the Bacillus subtilis SEM-9 bacterial strains, silkworm excrement liquid biologic fertilizer is produced, a growing environment approximating to the original ecology can be provided for the Bacillus subtilis SEM-9 bacterial strains to increase the number of live spores, and release of various nutrient substances in the silkworm excrement can also be better facilitated; and the compound microbial fertilizer is used for crops such as green cucumbers and cabbages, and can remarkably increase the yield of the crops and improve the resisting capacity to fusarium wilt.
Owner:GUANGDONG GEOLONG BIOTECH
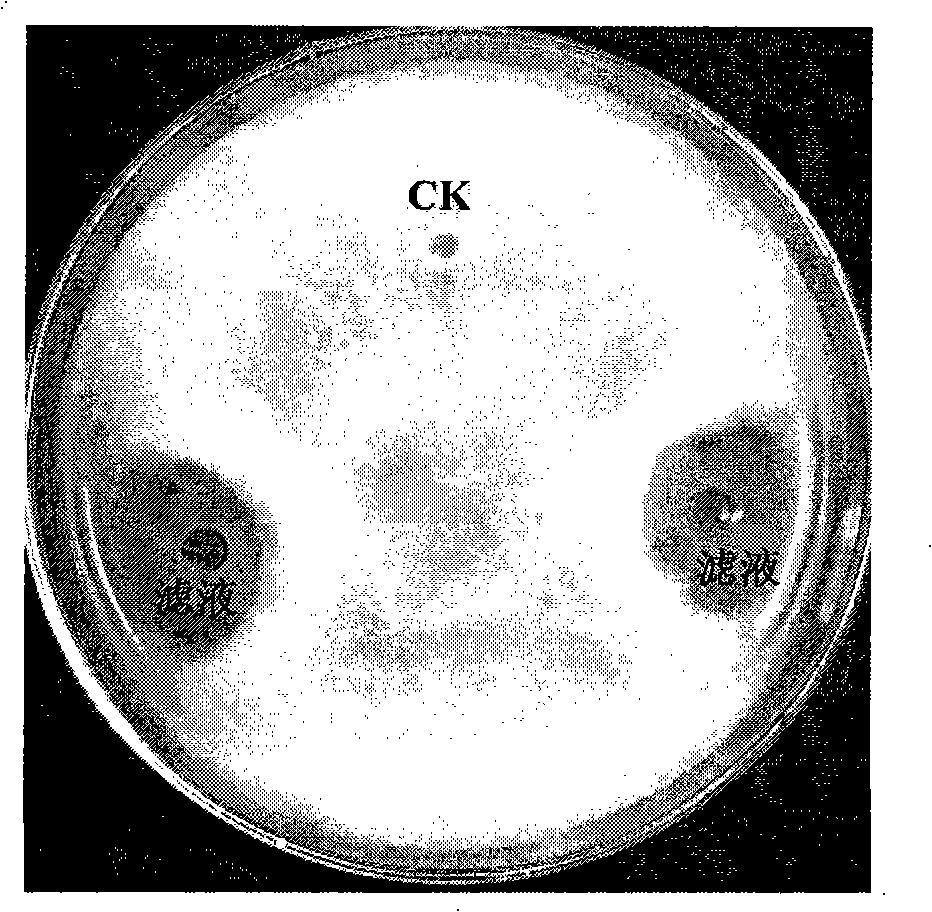
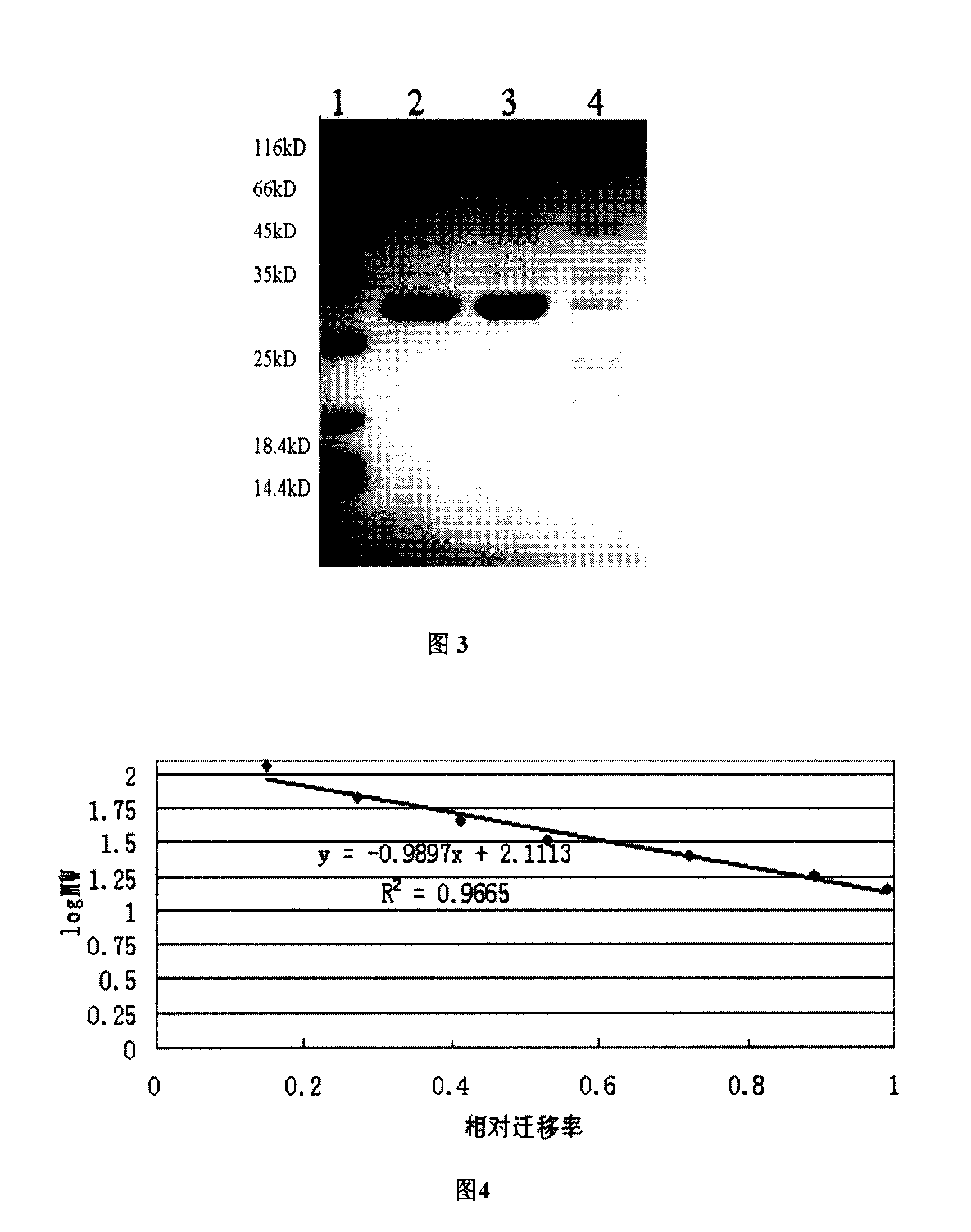
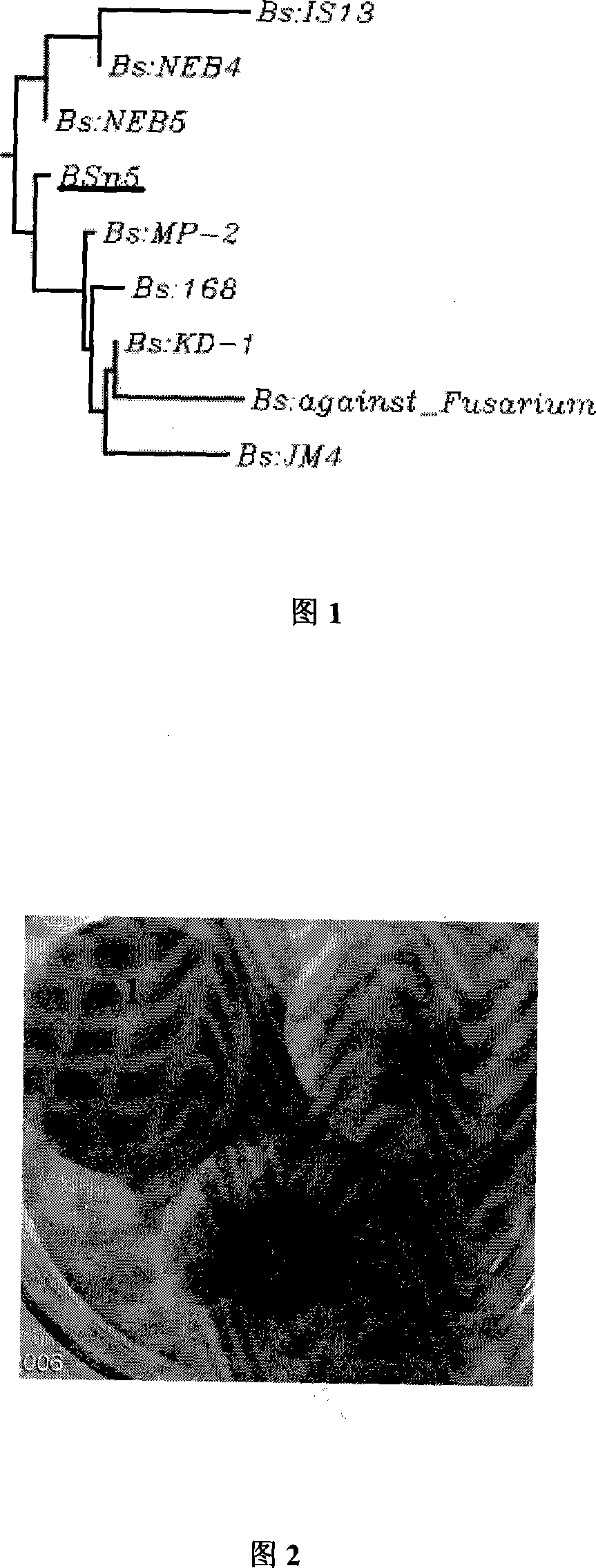
Bacillus subtilis BSn5 with bacteriostasis active to carrot soft rot Erwinia and bacteriostasis protein APn5
The present invention belongs to the field of agricultural microbiological technology, and discloses Bacillus subtilis BSn5 possessing bacteriostasis activity on carrot soft rot erwinia and the bacteriostatic protein APn5. Bacillus subtilis BSn5 in the preservation number of CCTCC No. M207124 is separated from the callus of bacteria infected konjaku. Bacillus subtilis BSn5 has bacteriostasis activity on carrot soft rot erwinia, and the bacteriostatic protein APn5 has molecular weight of 31.6 kDa.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Special composite microbial fertilizer with functions of strengthening seedlings and promoting roots for tobaccos, and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology, and discloses a special composite microbial fertilizer with the functions of strengthening seedlings and promoting roots for tobaccos. The special composite microbial fertilizer is prepared through adding, by dry weight, 1-4% of Bacillus thuringiensis bacterial solution and 1-4% of Paecilomyces lilacinus(Thorn.)Samson bacterial powder in a common tobacco seedling-raising substrate, wherein the abovementioned '%' represents the millilitre of the bacterial solution or the gram of the bacterial powder added per 100g of the common tobacco seedling-raising substrate, by dry weight. According to the special composite microbial fertilizer disclosed by the invention, specific tobacco rhizosphere functional bacteria are selected with regard to the tobaccos, and added into the common tobacco seedling-raising substrate in an activity-keeping manner, thus the raised seedlings can be strengthened, the root development can be promoted, high-quality seedlings with lots of active functional microbes in rhizospheres can be raised, the growth of the raised seedlings during a post-cultivation process can be promoted, the yield of the tobaccos can be increased and the quality of the tobaccos can be improved.
Owner:INST OF PLANT NUTITUION & RESOURCE ENVIRONMENT HENAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Application of AM (arbuscularmycorrhizal) fungi to increasing crop yields and method for applying AM fungi to increasing crop yields
ActiveCN103782817AIncrease productionIncrease the absorption areaHorticulture methodsMicroorganismOrganic fertilizer
The invention discloses a method for applying AM (arbuscularmycorrhizal) fungi to increasing crop yields, and belongs to the field of agricultural microbiology application technologies. The method includes 1), sowing crop seeds into cultivation pots; 2), inoculating the AM fungi on the surfaces of the crop seeds; 3), transplanting crop seedlings infected by the AM fungi to experimental fields 10-15 days after seedlings of the sown seeds emerge; 4), applying compound fertilizers to the root of each seedling 15-20 days after the seedlings are transplanted to the experimental fields, paying attention to preserving soil moisture thereafter and properly performing ridging; 5), harvesting crops after the crops are ripe. The method has the advantages that symbionts are set up among the AM fungi and root systems of the crops, so that absorption areas of the root systems of the crops can be expanded, inorganic and organic fertilizers in soil can be sufficiently utilized, loss of the fertilizers and environmental pollution can be reduced, operation is facilitated, the agricultural cost is low, harden soil can be rehabilitated, the crop yields can be obviously increased as known from contrast experiments, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving growth rate and yield of oyster mushroom
InactiveCN101352126AAvoid harmDoes not compromise food safetyFungiSaving energy measuresMicroorganismAgricultural science
The invention relates to a method for improving the growth speed and the yield of mushroom and belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology; the method comprises the following steps: the mushroom hypha is processed by magnetization by the magnetic field; the magnetizing post culture is carried out; then the existing and skilled technology is adopted to carry out transferring of original seeds, cultivated seeds and produced seeds; and a bag cultivation mode is adopted to complete the fruiting in plastic tents. The method for improving the growth speed and the yield of mushroom of the invention can improve the production trait by controlling the intensity of the magnetic field and the processing time quantitatively.
Owner:INST OF SOIL & FERTILIZER SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
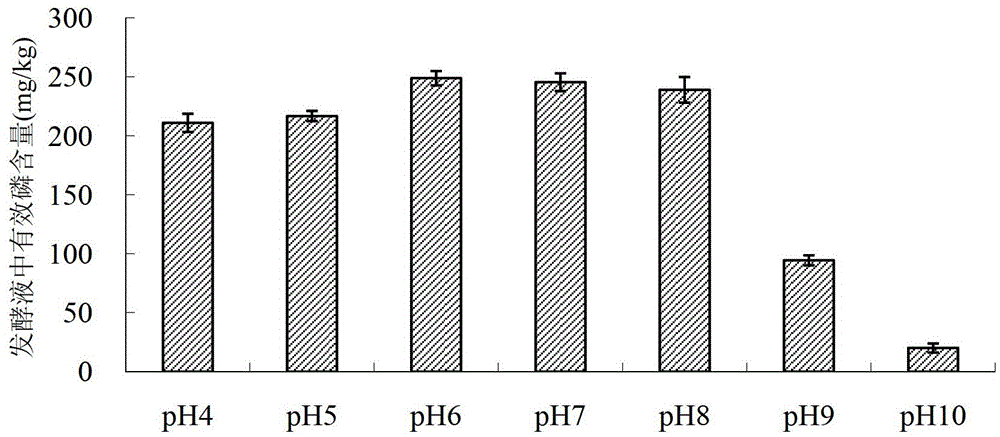
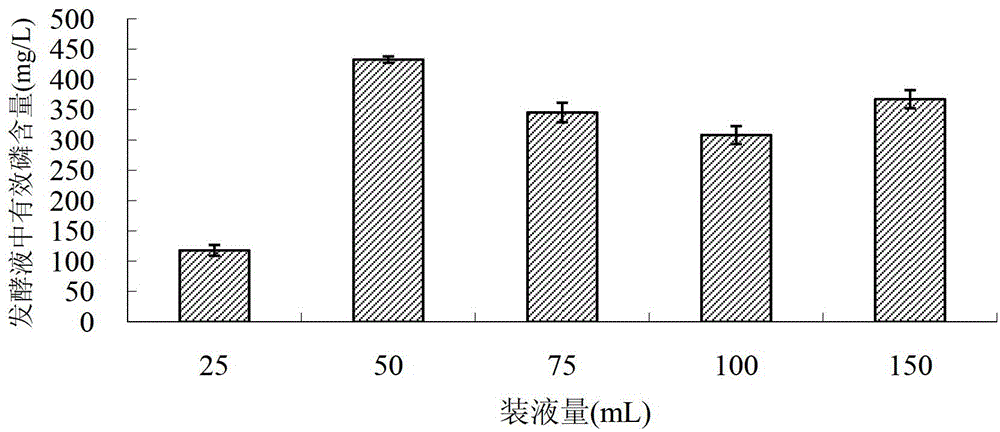
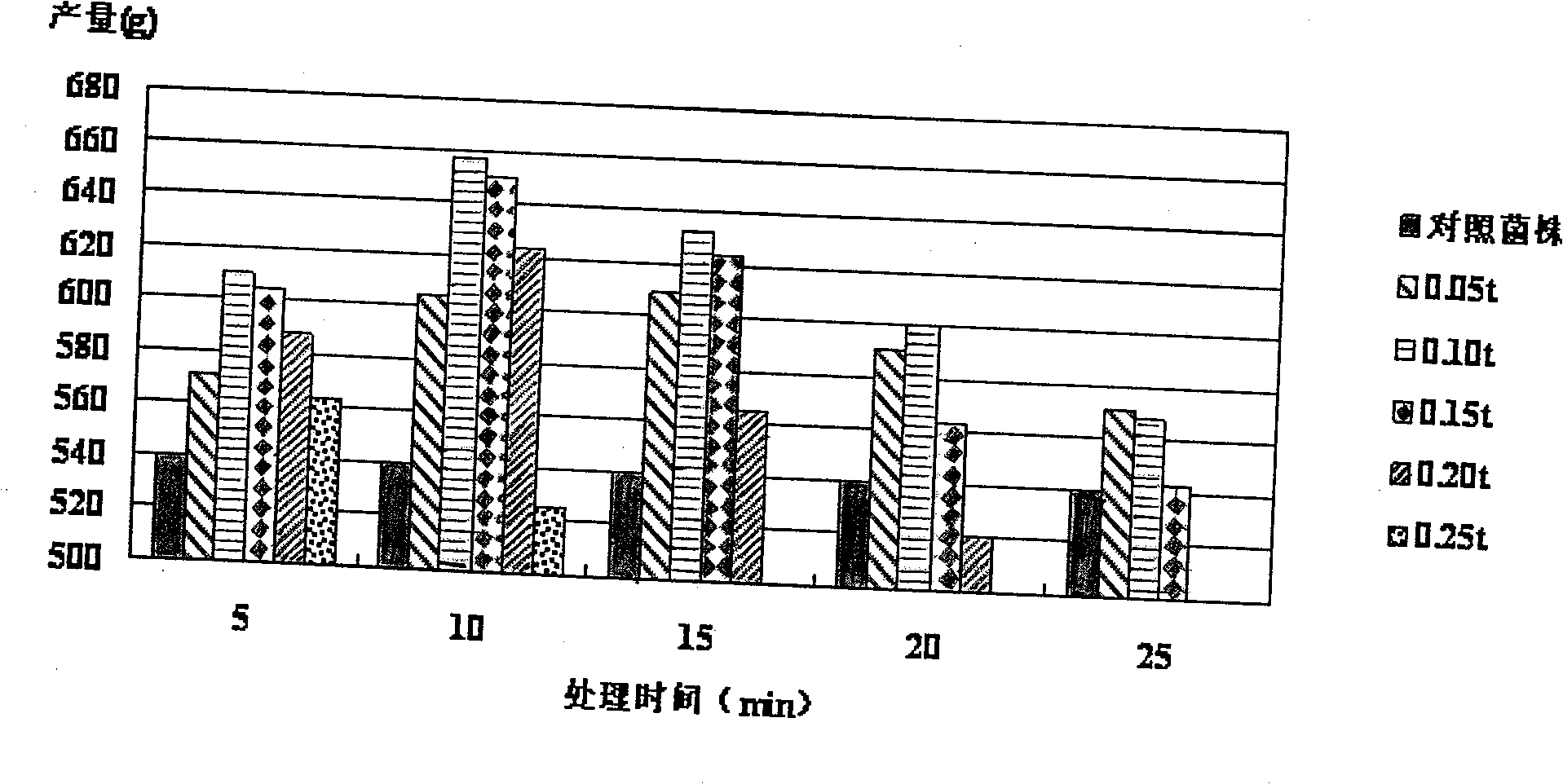
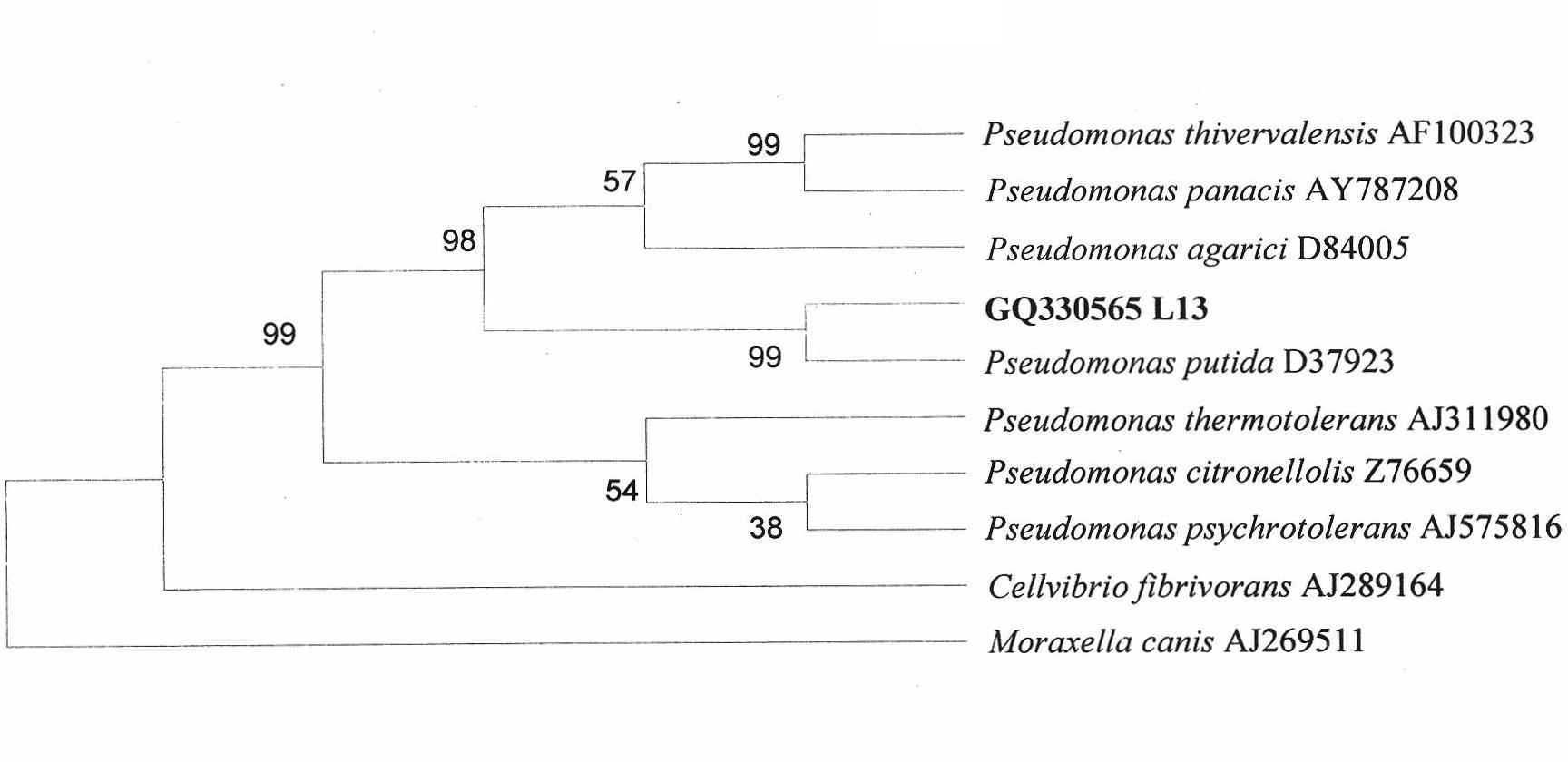
Phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida L13 and fermentation process thereof
InactiveCN102649941APromote growthImprove micro-ecological environmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphatePseudomonas putida
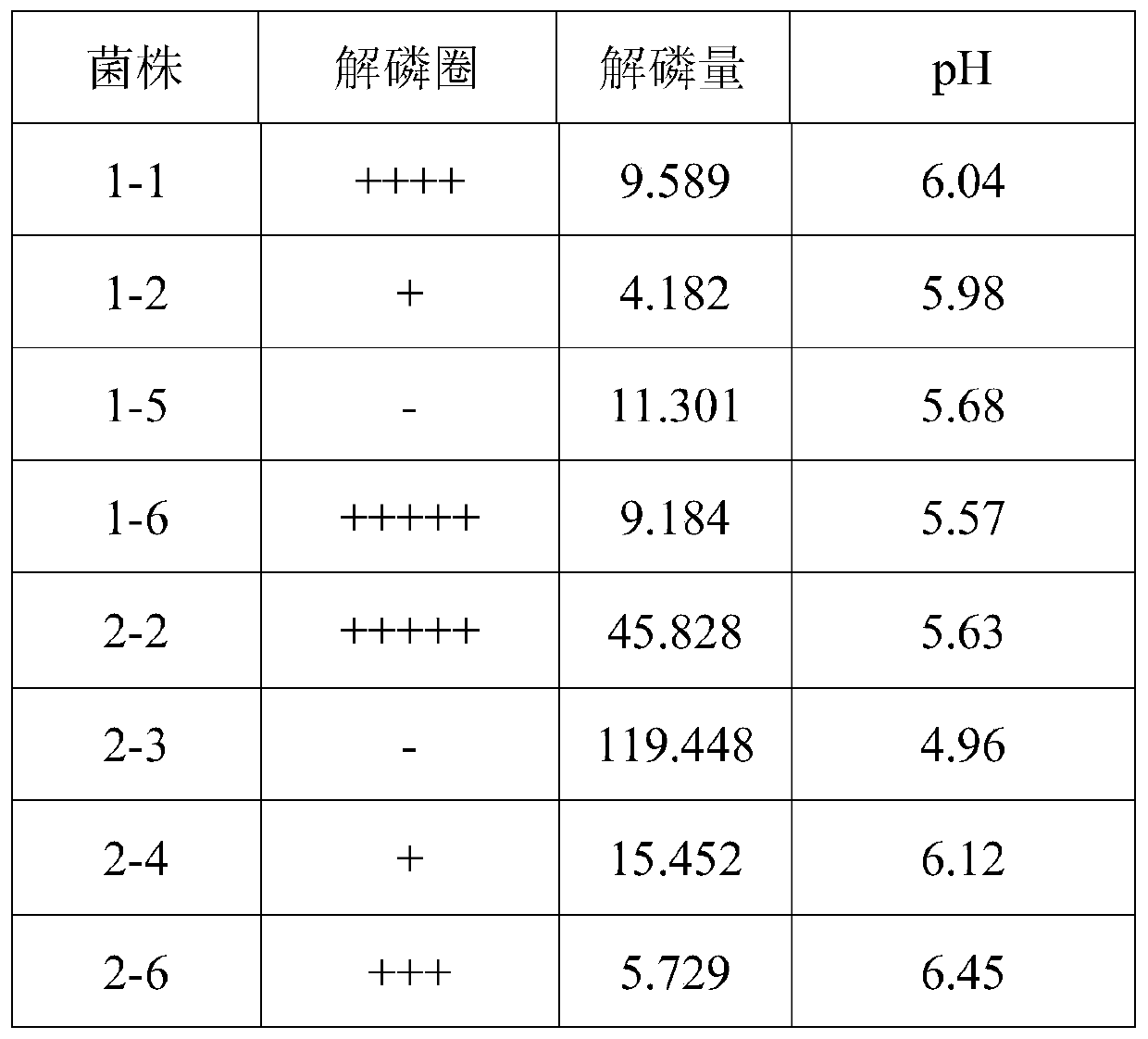
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology, and particularly relates to the separation screening and fermentation cultivation of phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida L13. A phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida L13 strain with the capacity of dissolving phosphorus is obtained through separation, and the preservation No. is CCTCC No.2010342. The fermentation process comprises the following steps of: (1) taking L13 bacterial strain slope seeds for streak cultivation on an LB (lysogeny broth) culture medium flat plate to obtain first-level seeds; (2) inoculating a first-level seed single bacterial colony into an LB culture medium shake flask to make OD (optical density) 600 be 2.0 to obtain second-level seeds; (3) inoculating the second-level seeds into a shake flask for fermentation cultivation to obtain the pseudomonas putida; or inoculating the second-level seeds into a fermentation tank so as to obtain the pseudomonas putida through optimized cultivation. The pseudomonas putida strain disclosed by the invention grows rapidly, the yield of the pseudomonas putida is high, and the viable count can reach more than 10 billions. The phosphorus-dissolving amount of the phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida in a PKO (Pikovskaya') culture medium in which 1-3g / L of calcium phytate is the unique phosphorus source can reach 120-220mg / L, and the phosphorus-dissolving amount of the phosphorus-dissolving pseudomonas putida in a PKO culture medium in which 4-6g / L of tricalcium phosphate is the unique phosphorus source can reach 300-500mg / L.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST OF HUBEI PROVINCE +2
Compound microorganism agent and application thereof
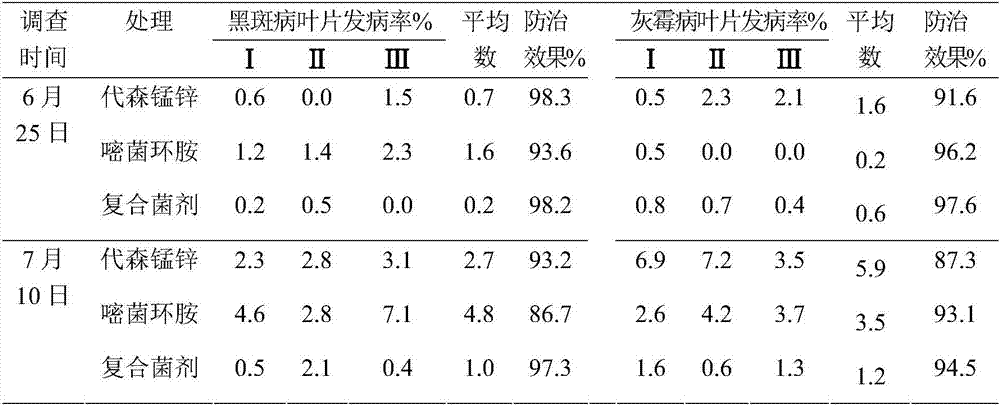
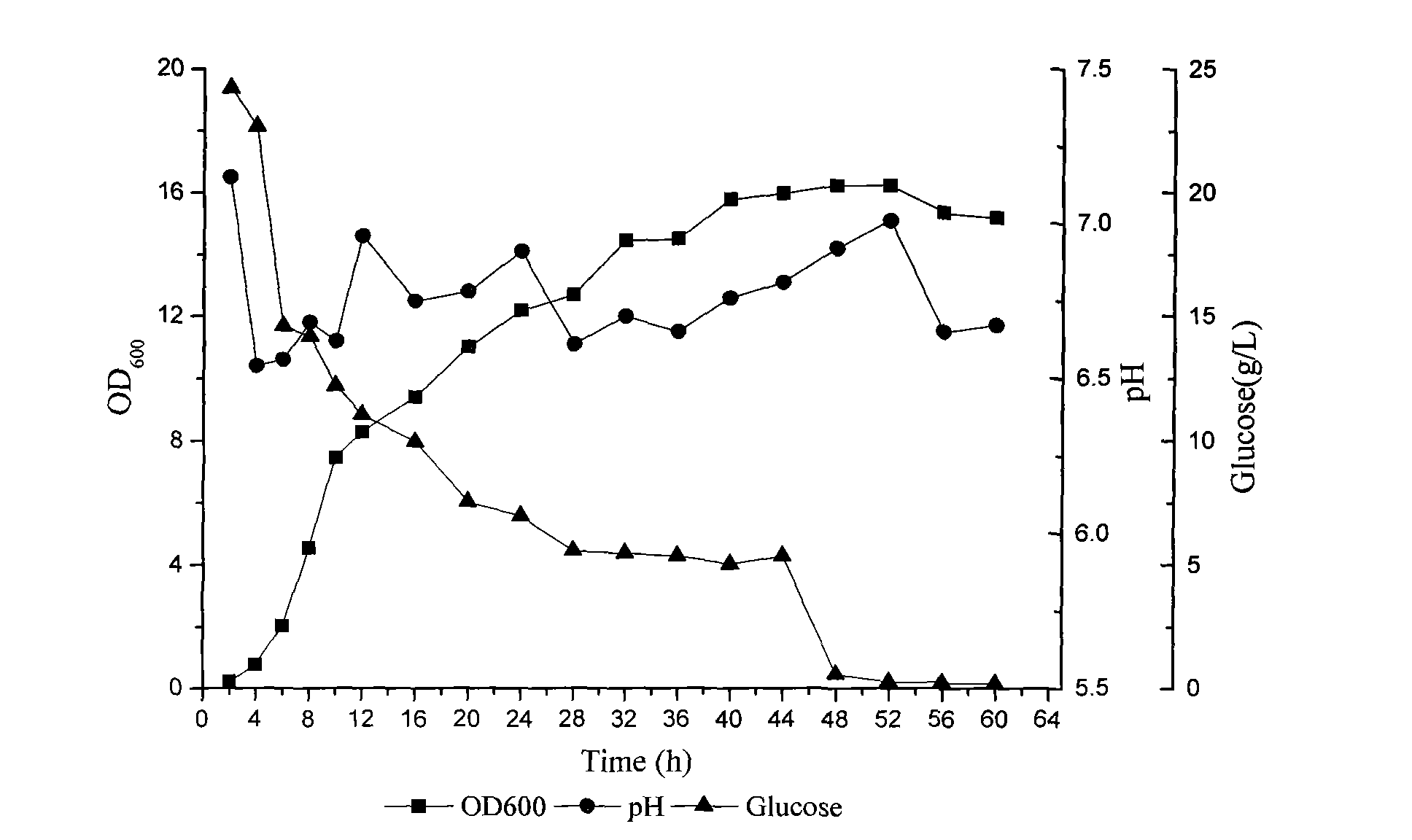
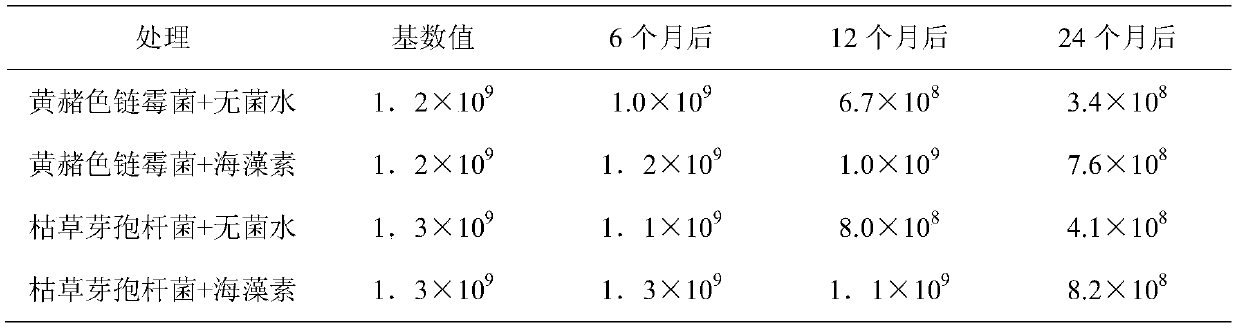
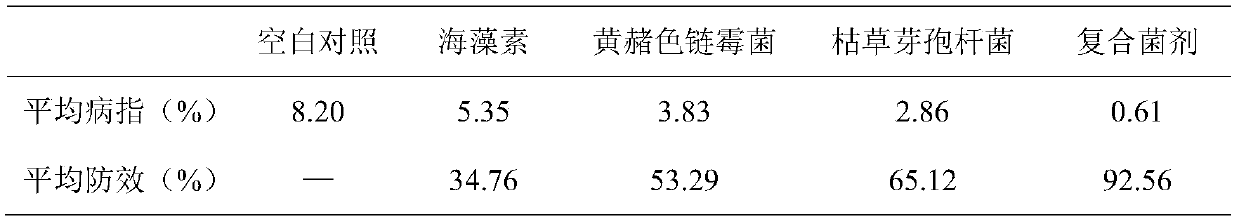
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology, and discloses a compound microorganism agent and application thereof. The compound microorganism agent is formed by compounding a seaweed element, a yellow-ochre streptomyces fermentation culture solution and a bacillus subtilis fermentation culture solution in a ratio of (2-3):(3-5):(3-5), preferentially 2:4:4. The compound microorganism agent is capable of not only prolonging the decaying time of microorganism living bacteria, but also improving the prevention and control effect to plant diseases, and can reach prevention efficiency of 90% or above to various diseases.
Owner:海南博士威生物科技有限公司
Preparation method of iturinA micro capsule
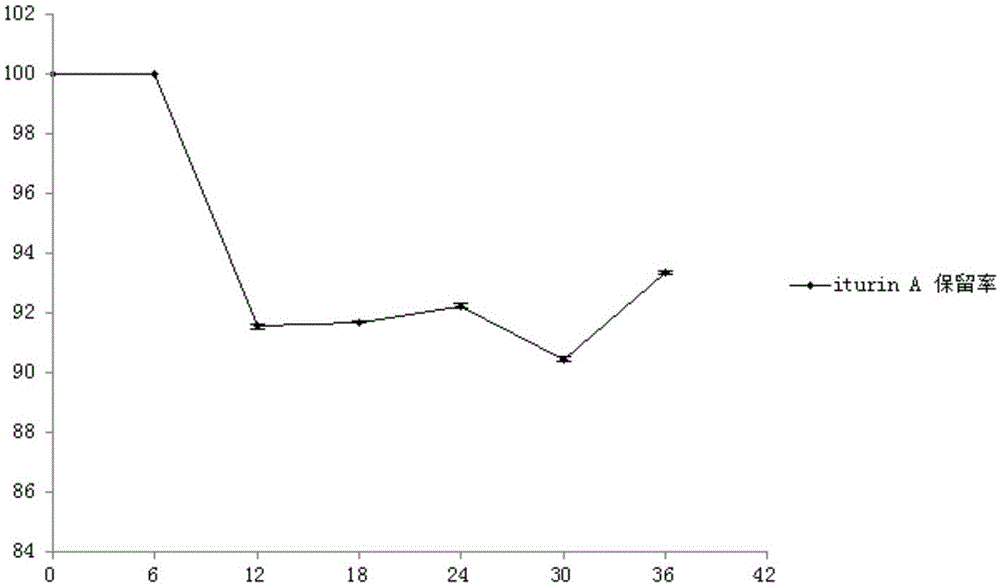
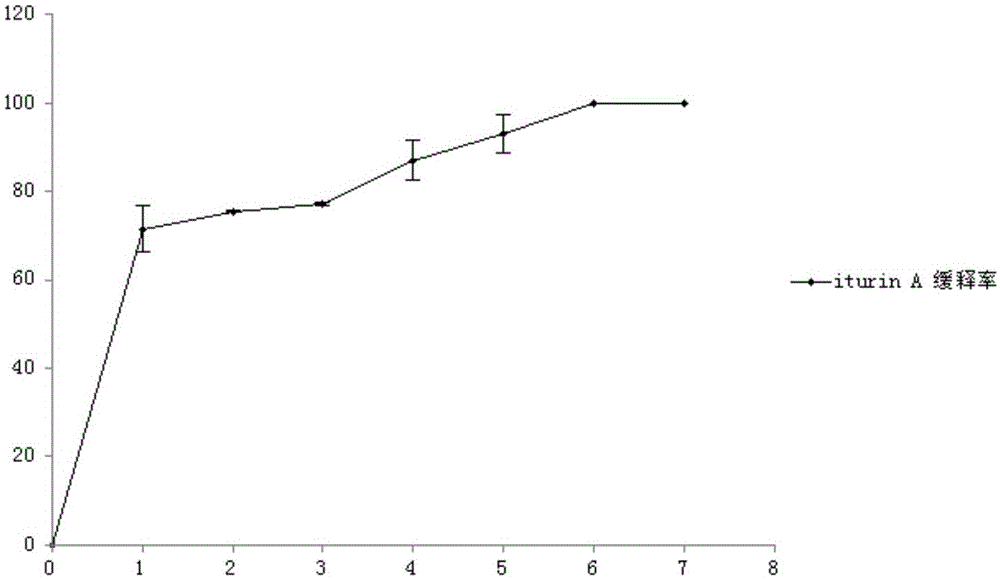
InactiveCN104997756AImprove stress resistanceBlock adverse effectsAntimycoticsCyclic peptide ingredientsUltravioletDrug biological activity
The invention discloses a preparation method of iturinA micro capsule, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology. The iturin A micro capsules employs an aqueous solution of an active substance iturin A as core material, and sodium alginate and gamma-polyglutamic acid as wall materials; the aqueous solution of the core material and the aqueous solution of the wall materials are uniformly mixed by stirring, high pressure homogenization is carried out for 15 minutes, a stable emulsion is obtained, the iturin A micro capsule is prepared by a spray drying technology. The micro capsule prepared by the invention can effectively prevent influences of extraneous ultraviolet ray, temperature and other adverse environments to the biological activity of iturin A, has good slow controlled releasing effect and storage stability, and has good application prospect in the field of biological pesticide.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Streptomyces hygroscopicus Sh-43 strain, its fermentation solution production method and application
InactiveCN102732460AStrong antagonistic effectStable antagonistic effectBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention, belonging to the technical field of agricultural microbiology, specifically relates to an anti-Rhizoctonia solani Streptomyces hygroscopicus Sh-43 strain, its fermentation solution production method and application. Streptomyces hygroscopicus Sh-43 strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University under accession Number of CCTCC NO: M2012172 on May18, 2012. The Streptomyces hygroscopicus Sh-43 strain of the invention has the advantages of significant anti-Rhizoctonia solani effect, wide antimicrobial spectrum, stable resistance effect, simple culture conditions, and good control effect on rice sheath blight, and has wide application prospect in the field of biological control of plant diseases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
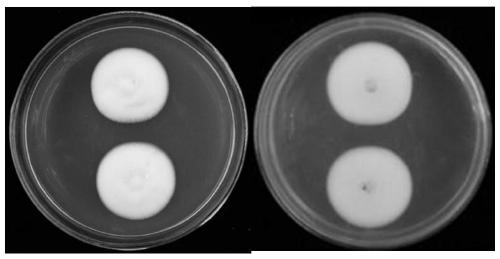
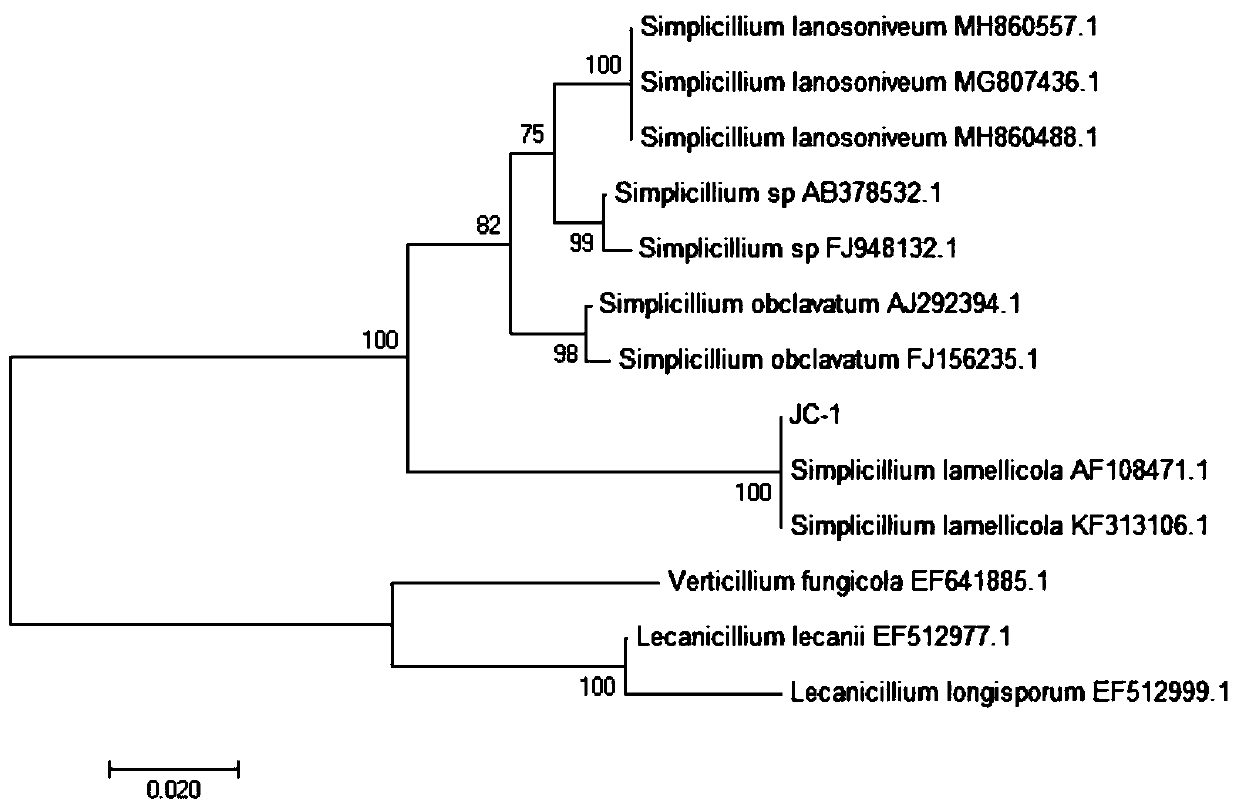
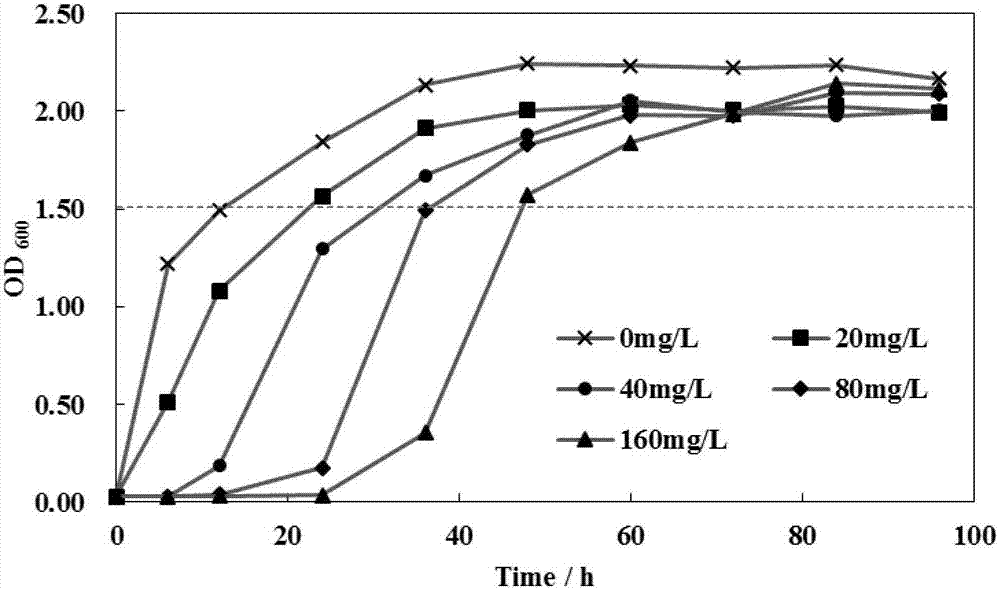
Biocontrol bacterium Simplicillium lamellicola JC-1 and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology, and discloses a biocontrol bacterium Simplicillium lamellicola JC-1 and an application thereof. The preservation number of the biocontrol bacterium Simplicillium lamellicola JC-1 is CCTCC NO:M2019246. A Simplicillium lamellicola strain or fermentation substance filtrate thereof can effectively restrain growth of mycelia ofimportant pathogenic bacteria (sclerotinia scleroterum, botrytis cinerea, rhizoctonia solani and leptosphaeria biglobosa) on rape. Compared with chemically-synthesized pesticides which are used for control at present, the biocontrol bacterium Simplicillium lamellicola JC-1 has the advantages of being efficient, low in toxicity, free from environment pollution, and the like, and drug resistance isnot liable to cause because that the biocontrol bacterium Simplicillium lamellicola JC-1 is from natural environment, and the biocontrol bacterium Simplicillium lamellicola JC-1 has great applicationprospects.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Biocontrol strain HW2 for preventing and treating cucumber green mottle mosaic virus and application of biocontrol strain HW2
InactiveCN105219673AReduce dosageConducive to pollution-free productionPlant growth regulatorsBiocideGrowth promotingPlant disease
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural microbiology, and relates to a biocontrol strain HW2 for preventing and treating cucumber green mottle mosaic virus and an application of the biocontrol strain HW2. Through authentication, the biocontrol strain HW2 belongs to stenotrophomonas maltophilia, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on June 29, 2015, wherein the preservation number of the biocontrol strain HW2 is CGMCC NO.11024. Meanwhile, the greenhouse experimental result shows that the biocontrol strain HW2 can obviously reduce the disease severity of the cucumber green mottle mosaic virus, and has an obvious effect in preventing and treating cucumber green mottle mosaic virus, the control effect is within 53.85%-57.02%, the microbial inoculum has a very good growth promoting effect for cucumber, the biomass increase can achieve 42.76%, and the content of chlorophyll of the cucumber leaf is obviously increased. Therefore, the strain and the microbial inoculum prepared by the strain can be applied to the prevention and treatment of the cucumber green mottle mosaic virus and growth promotion.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
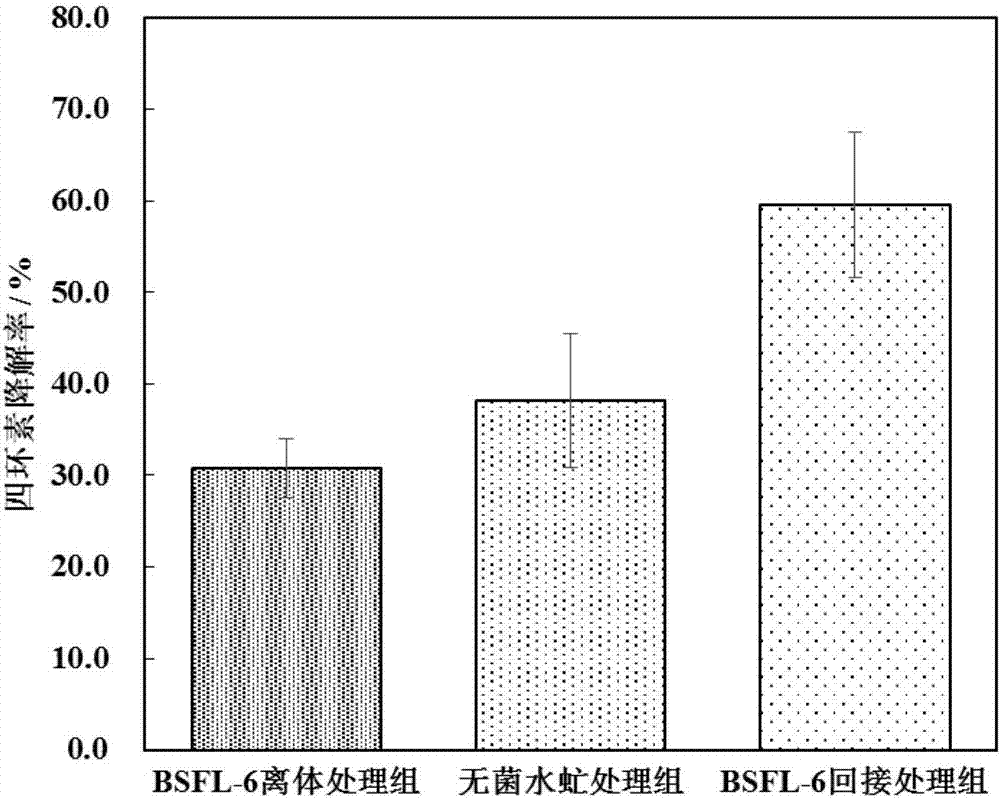
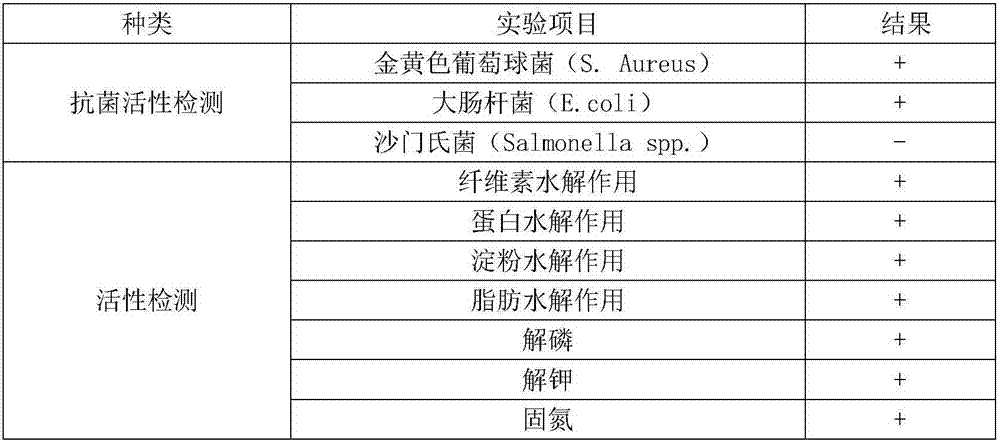
Insect stratiomyiid intestinal tract derived serratia marcescens BSFL06 and application thereof
InactiveCN106987543APromote growthPotential for antibiotic degradation applicationsAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliSerratia species
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology, and in particular discloses insect stratiomyiid intestinal tract derived serratia marcescens BSFL06 and application thereof. The serratia marcescens is serratia marcescens BSFL06, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2017073. The serratia marcescens BSFL06 provided by the invention can effectively degrade antibiotic tetracycline, enhances the tetracycline resisting and degrading capabilities of the stratiomyiid in the material transformation process, has bacteriostatic activity on harmful bacteria staphylococcus aureus (S.Aureus) and scherichia coli (E.coli), is stratiomyiid intestinal tract probiotics and can be used for promoting the stratiomyiid to perform transformation on tetracycline polluted waste.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Complex bacterial preparation and application thereof
Owner:江苏加德绿色能源有限公司
Fusarium proliferatum, and bacterium agent and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural microbiology and discloses a fusarium proliferatum strain Br-1 with the preserved number of CGMCC No. 3759. The invention also discloses a microbiological bacterium agent prepared by using the Br-1. The fusarium proliferatum strain Br-1 and the bacterium agent thereof have good inhibiting effect for orobanche cumana wallr, and the control effect in fields reaches 61.7-82.0%; and secondarily, a preparation method of the microbiological bacterium agent is simple, and has low cost and easy promotion and application. In addition, the invention belongs to a biological control method, has no pollution, no nuisance and low residue and is environment-friendly.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
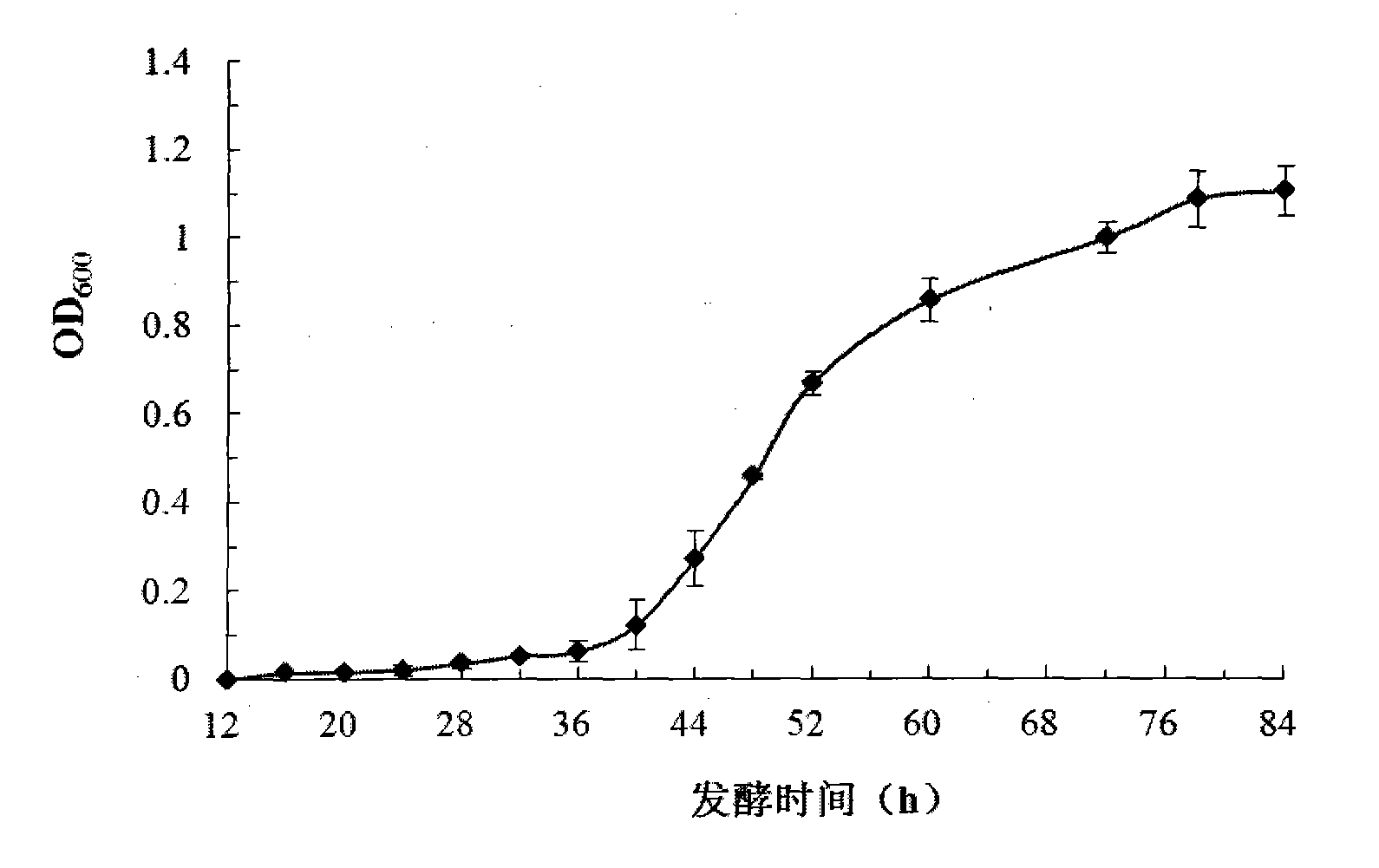
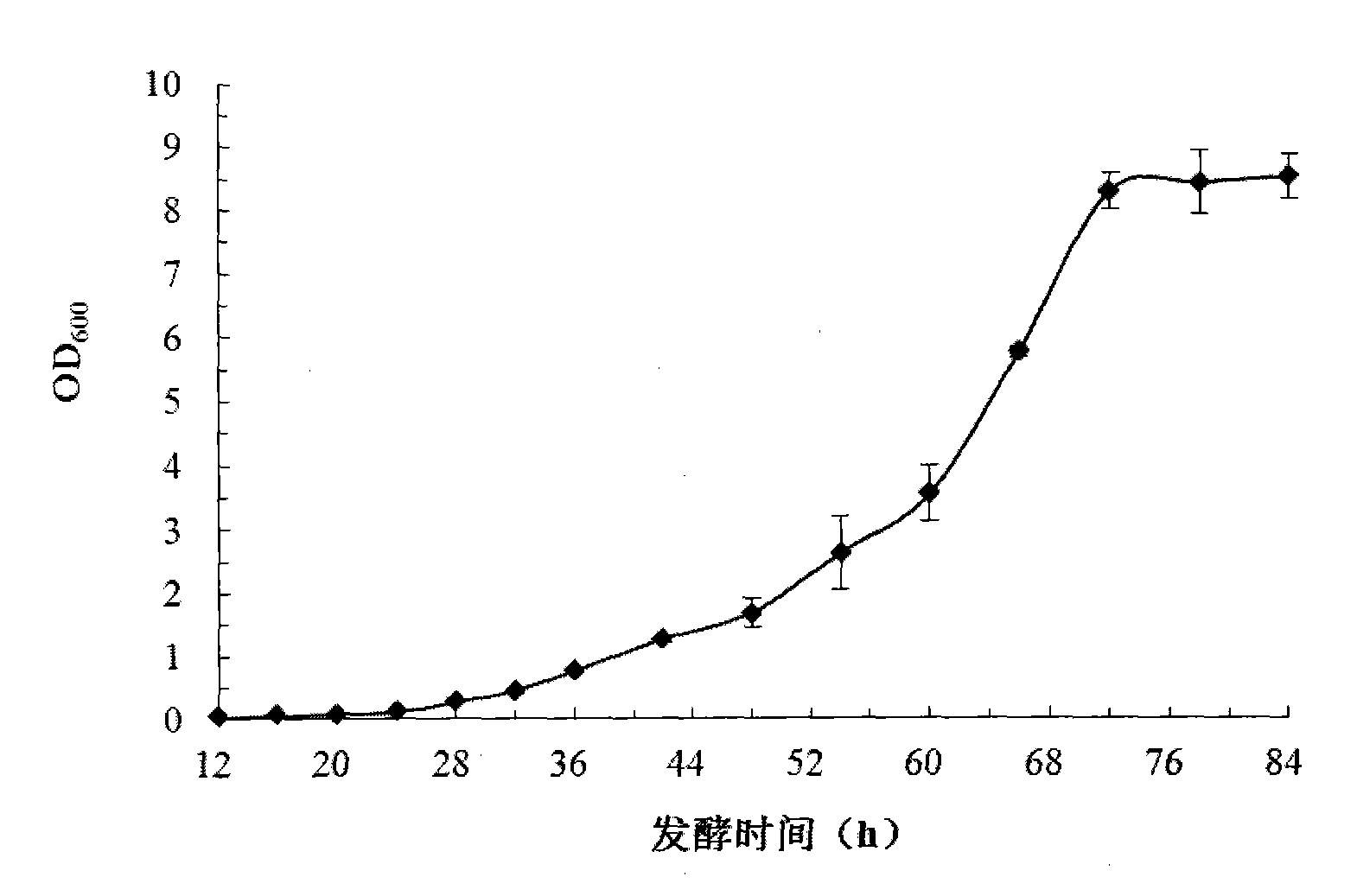
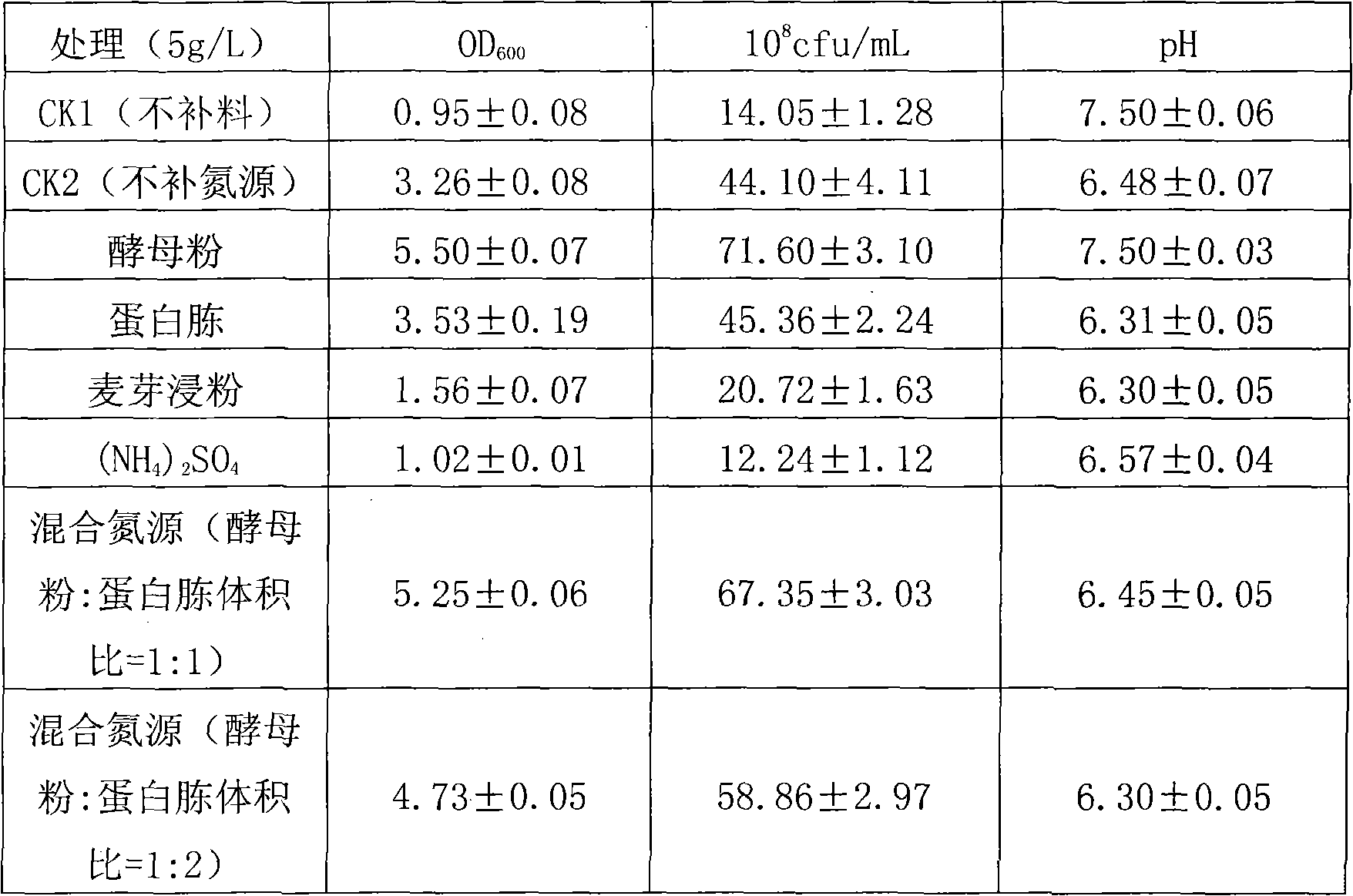
High-density fermentation process of rhizobium huakuii
InactiveCN102649942AIncrease biomassSimple ingredientsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microbiology, and particularly relates to a high-density fermentation process of rhizobium huakuii, which is carried out for obtaining highest biomass, in particular to a fermentation method in which C and N sources different from the original fermentation culture medium are replenished. The biomass of the rhizobium huakuii obtained by the process disclosed by the invention can reach more than 13 billions / mL. According to the process method disclosed by the invention, seeds growing to the late period of logarithm are inoculated intoa YM (Yeast Manitol) culture medium, liquid content in a fermentation tank is 40-60%, the inoculum size is 1-6%, the temperature of the tank is controlled to be 26-30 DEG C, the rotate speed is 400-800rpm, the first time of material replenishment is carried out after 24-48 hours of fermentation, the second time of material replenishment is carried out after 48-72 hours of growing, fermentation iscontinued to 60-84 hours after the second time of material replenishment is completed, and then the fermentation is ended. The replenished material comprises glucose of which the final concentration is 0.5-1.5 g / L, yeast powder of which the final concentration is 1-4g / L and peptone of which the final concentration is 1-4g / L. The process disclosed by the invention is simple, the efficiency is superior to that of the prior art, and the production cost is lower.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com