Separation and application of aspergillus niger JXZ01 with decomposition capability of various difficult-to-dissolve phosphorous sources
An insoluble and phosphorus source technology, applied in the field of agricultural microorganisms, can solve the problems of unstable benefits and single species, and achieve high tolerance and repair ability, low pathogenicity, good colonization ability and phosphorus dissolving ability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
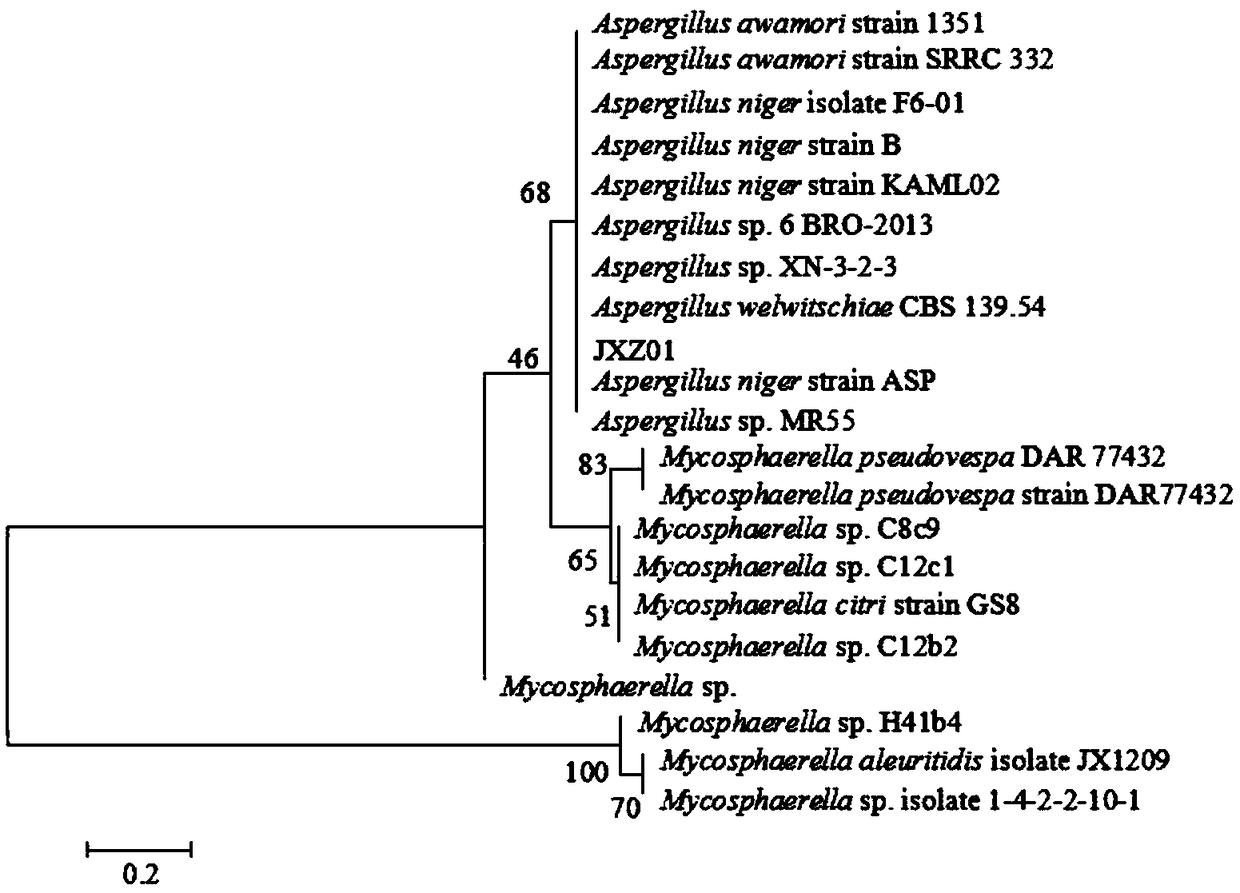
[0032] The separation and identification of embodiment 1 phosphate-dissolving bacteria
[0033] First prepare the following three media:
[0034] PDA medium: glucose 10.00g, potato 200.00g, agar 18.00-20.00g, distilled water 1000.00mL.
[0035] PVK inorganic phosphorus medium: glucose 10.00g, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 0.50g, MnSO 4 4H 2 O 0.03g, KCl 0.30g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.30g, FeSO 4 4H 2 O 0.03g, NaCl 0.3g, inorganic phosphorus source (Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 / FePO 4 / AlPO 4 / FAp) 10.00g, agar 18.00~20.00g, distilled water 1000.00mL, pH 7.00~7.50.
[0036] PVK organophosphate medium: glucose 10.00g, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 0.50g, MnSO 4 4H 2 O 0.03g, KCl 0.30g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.30g, FeSO 4 4H 2 O 0.03g, NaCl 0.30g, organic phosphorus source (lecithin / calcium phytate) 2.00g, agar 18.00-20.00g, distilled water 1000mL, pH 7.00-7.50.
[0037] The sterilizing condition of the above-mentioned culture medium is high-pressure steam sterilization at 115° C. for 30 minutes. The agar was...
Embodiment 2
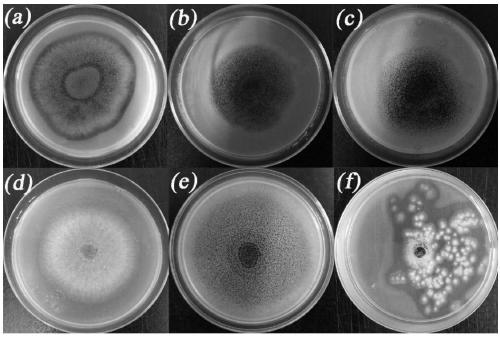
[0040] Example 2 JXZ01 Decomposition Ability Determination of Different Insoluble Phosphorus Sources
[0041] In order to measure the ability of the bacterial strain JXZ01 of the present invention to dissolve insoluble phosphorus sources, firstly use an inoculation loop to spot a single colony on a solid PVK plate under different phosphorus source conditions, culture at a constant temperature of 30°C for 3 to 4 days, and observe whether there is phosphorus dissolution. The formation of circles can be used to qualitatively judge the phosphorus-dissolving ability of the screened phosphorus-dissolving microorganisms. The growth of JXZ01 on PVK plates under different phosphorus source conditions is as follows: figure 2 As shown, in Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 , FAp, lecithin and calcium phytate as phosphorus sources can produce obvious phosphorus-dissolving circle; in addition, although FePO 4 and AlPO 4 When it was used as phosphorus source, there was no obvious phosphorus-dissolving ci...
Embodiment 3
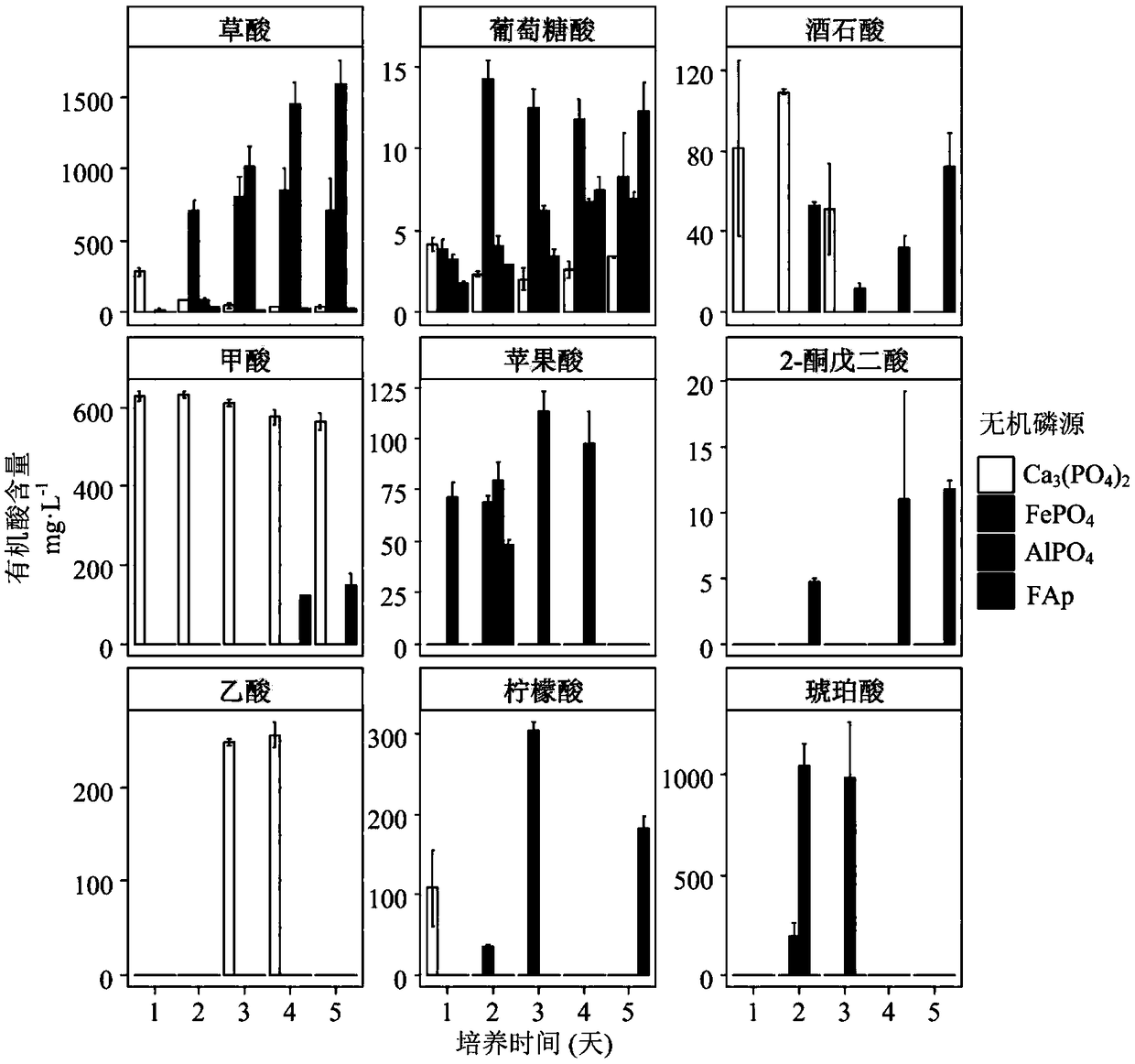
[0052] Example 3 Determination of JXZ01 Secreting Organic Acids Under Inorganic Phosphorus Source Conditions
[0053] The mechanism of the bacterial strain JXZ01 of the present invention to dissolve inorganic phosphate is mainly to secrete organic acid. The types and concentrations of organic acids secreted by JXZ01 under different inorganic phosphorus sources were separated and determined by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
[0054] The specific method is as follows:
[0055] Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 、FePO 4 , AlPO 4 , FAp is the single phosphorus source PVK liquid fermentation broth sample centrifuged at 12000rpm for 10min, the supernatant is filtered through a 0.22μm filter membrane and packed into a brown sampling bottle, and the organic acid is determined by high performance liquid chromatography for subsequent use. The detected organic acids include oxalic acid, gluconic acid, tartaric acid, formic acid, acetic acid, malic acid, α-ketoglutaric acid, citric acid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com