Bacillus composition for control of panax ginseng and American ginseng black spot disease and botrytis cinerea and use thereof
A technology of spores and compositions, which is applied in the field of spores compositions for the prevention and treatment of ginseng and American ginseng black spot and gray mold, can solve the problems of poor effect, survival, and large variation of strains, and achieve the prevention of no pesticide residues , Strong adaptability and strong adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Isolation, cultivation and identification test of ginseng dominant spores
[0041] 1. Obtain the material of ginseng dominant spore species
[0042] In August 2015, ginseng leaves were collected at the ginseng planting bases in Qing'an and Heihe, Heilongjiang Province, and multiple plants and leaves were selected.
[0043] 2. Bacillus isolation method
[0044] Cut ginseng leaves into 1-2cm pieces with sterile scissors, put them into conical flasks filled with 50mL sterile normal saline, vibrate at 120rpm for 1h (so that the bacteria fall off the leaves and disperse evenly in the normal saline), place in Incubate in a 63°C incubator for 4 hours (maintain at 63°C for 4 hours to kill various non-spores, molds, and pathogenic fungi, but the spores basically do not die), as samples to be separated.
[0045] Prepare sterilized CPDA medium to make a culture plate. Draw 0.5 mL of the above-mentioned heat-treated sample and evenly spread it on the CPDA medium cultur...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2 strain screening test
[0055] 1. Materials
[0056] 87 strains of Bacillus subtilis, 60 strains of B. tequilensis and 62 strains of B. velezensis were isolated by the applicant from ginseng leaves. The pathogens of ginseng black spot and gray mold were provided by Shenyang Agricultural University.
[0057] 2. Method
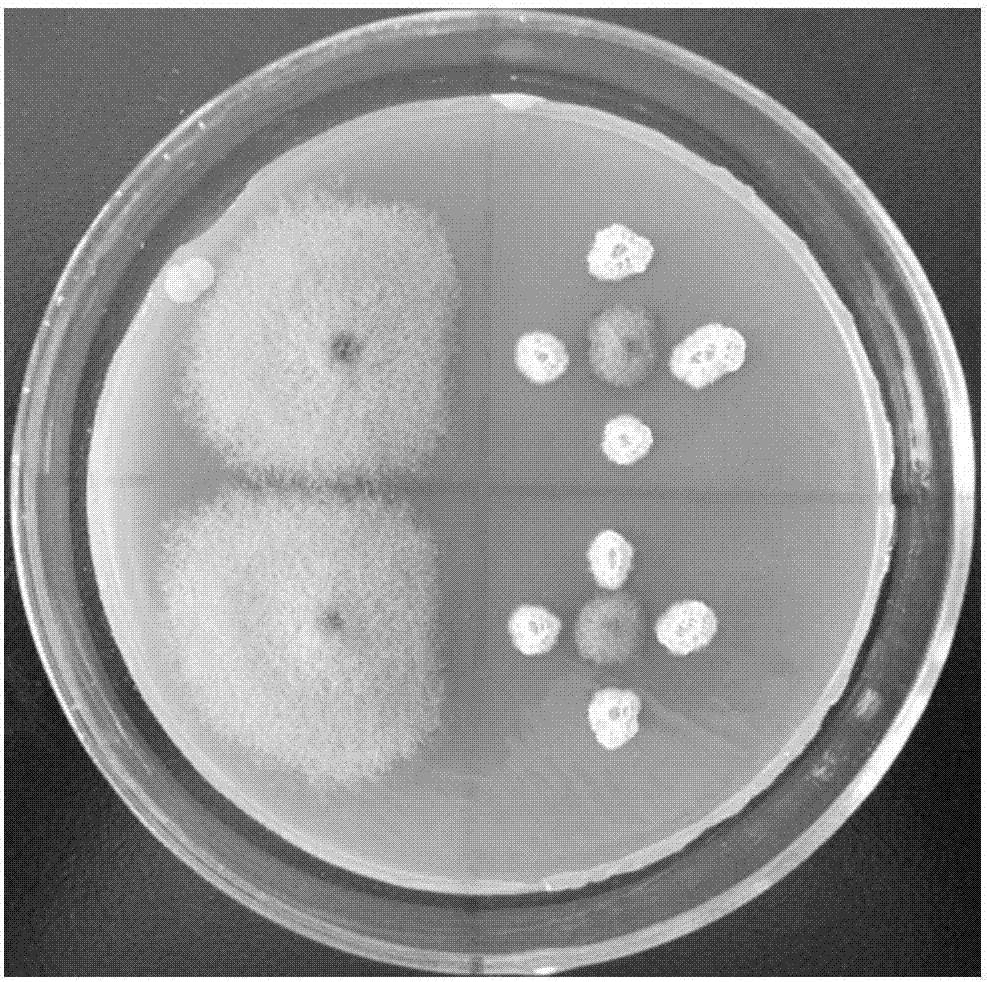
[0058] The pathogenic bacteria of black spot and gray mold were purely cultured respectively. The culture conditions were to use CPDA agar medium plate and place it in a constant temperature incubator at 25°C for 3-4 days. The spores were used as the inoculated samples for the antagonistic experiments.
[0059] Bacillus subtilis, B. tequilensis, and B. velezensis were purely cultured respectively. The culture conditions were to use CPDA agar medium plates and place them in a constant temperature incubator at 25°C for 2 days to form visible to the naked eye. Small colonies were then inoculated into conical flasks equipped with liquid CPDA med...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Embodiment 3 field experiment
[0068] 1. Materials
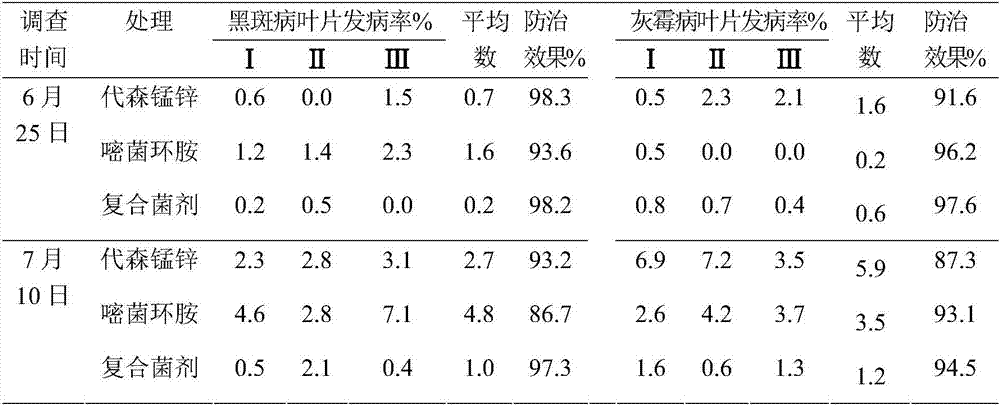
[0069] According to the theory of biological invasion, the more complex the population of the community, the less likely it is for alien species to invade. Alien species are easy to invade a single population, and the single strain used is usually difficult to survive on the leaves for a long time, and the effect is not good in practical application. The compound bacterial agent is a good method. In order to ensure the stable colonization of spores, according to the ratio of the dominant bacteria in the natural state, the ratio of the above three antagonistic bacteria is: Bacillus subtilis: Bacillus tequila: Bacillus Velez = 1.5: 1: 1 composite bacteria agent for field trials.
[0070] The chemical fungicide is 80% mancozeb wettable powder; 50% cyprodinil water dispersible granule.
[0071] 2. Method
[0072] The field test was carried out at the ginseng planting base of Qinghe Forestry Bureau, Heilongjiang Provi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com