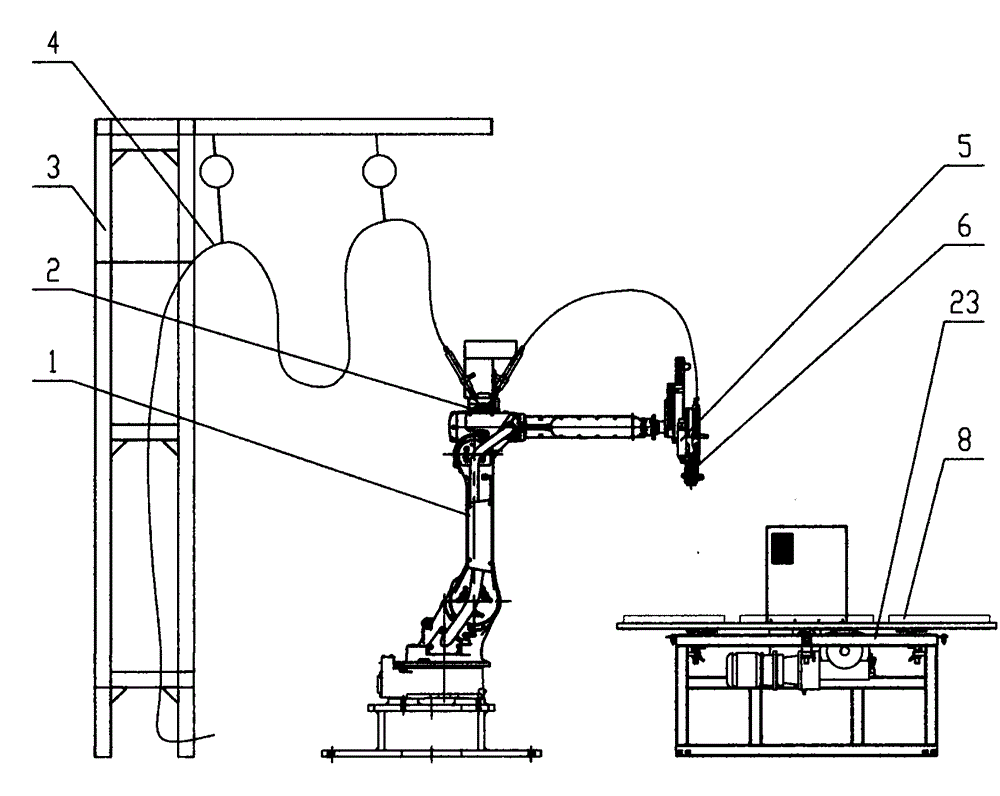
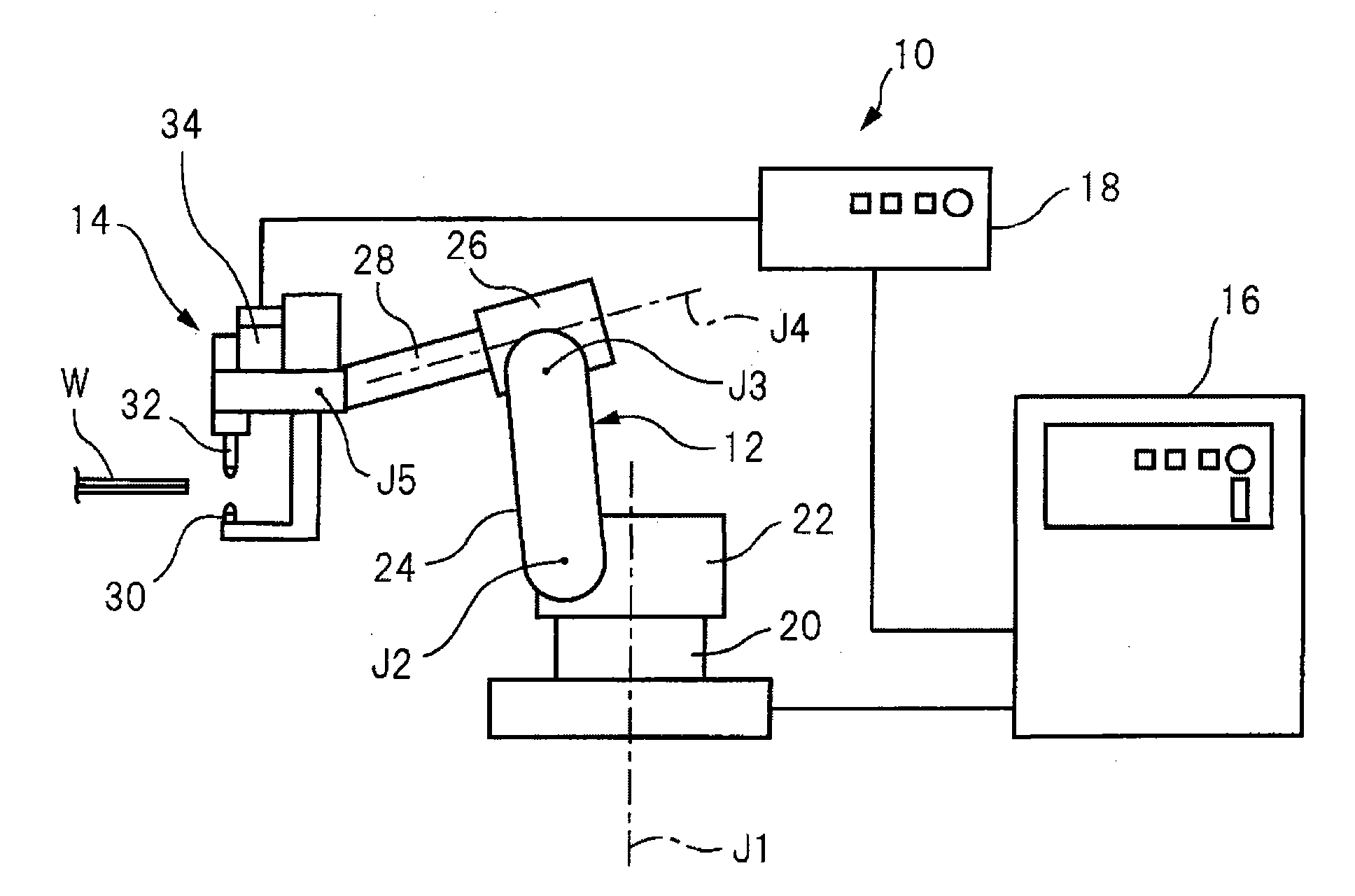
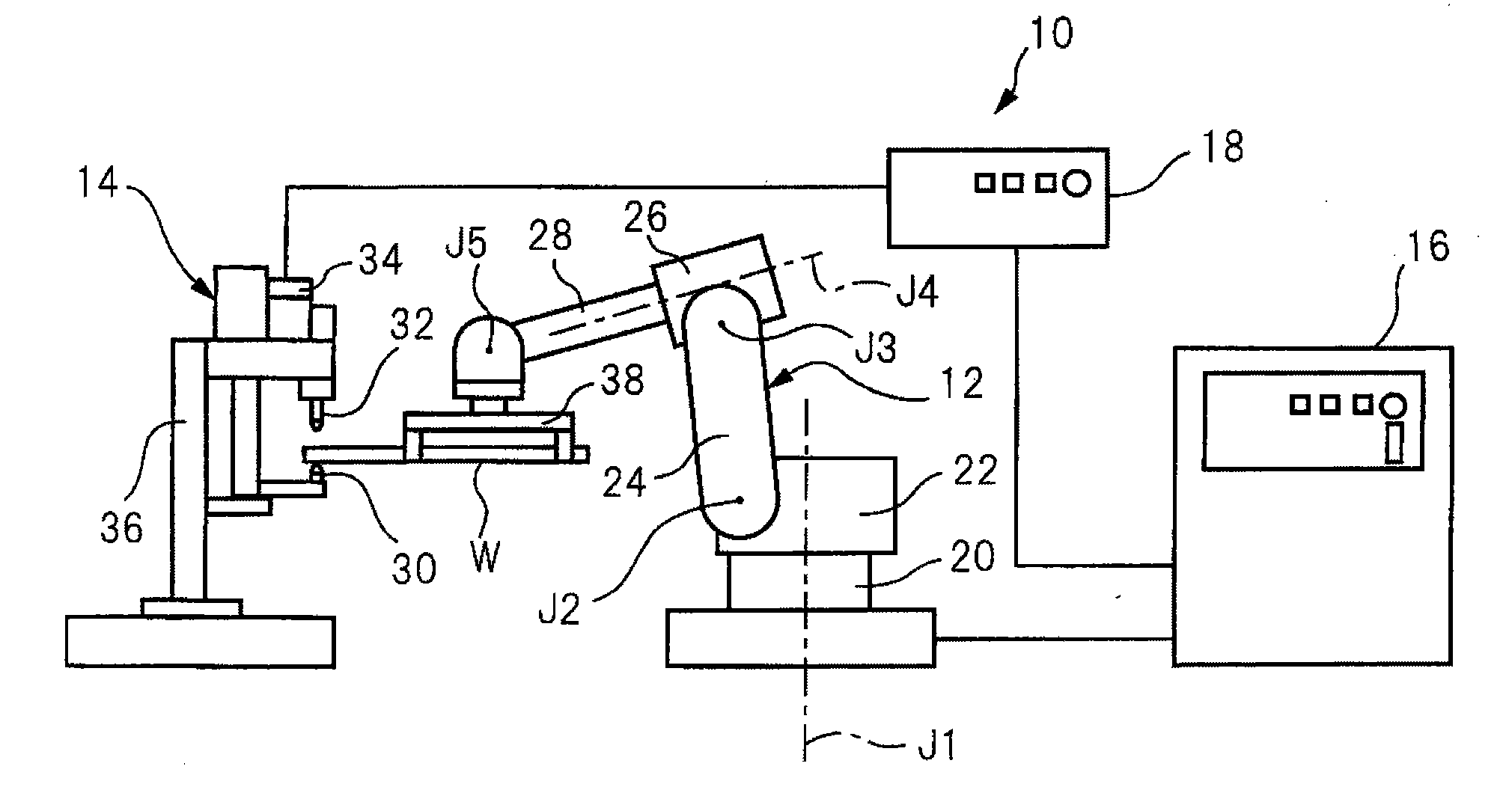
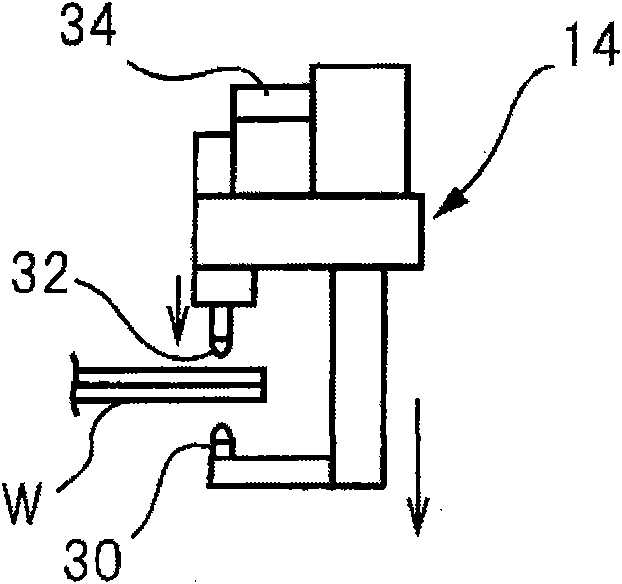
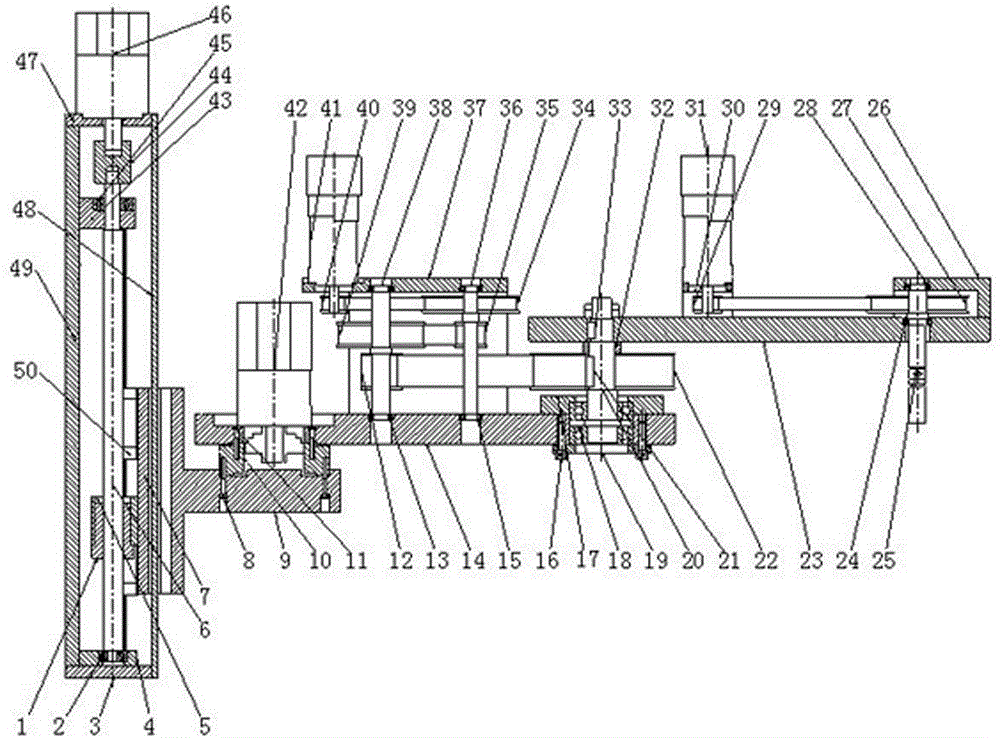
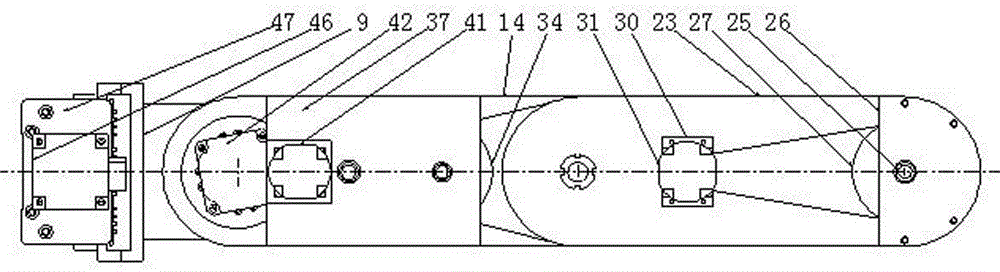
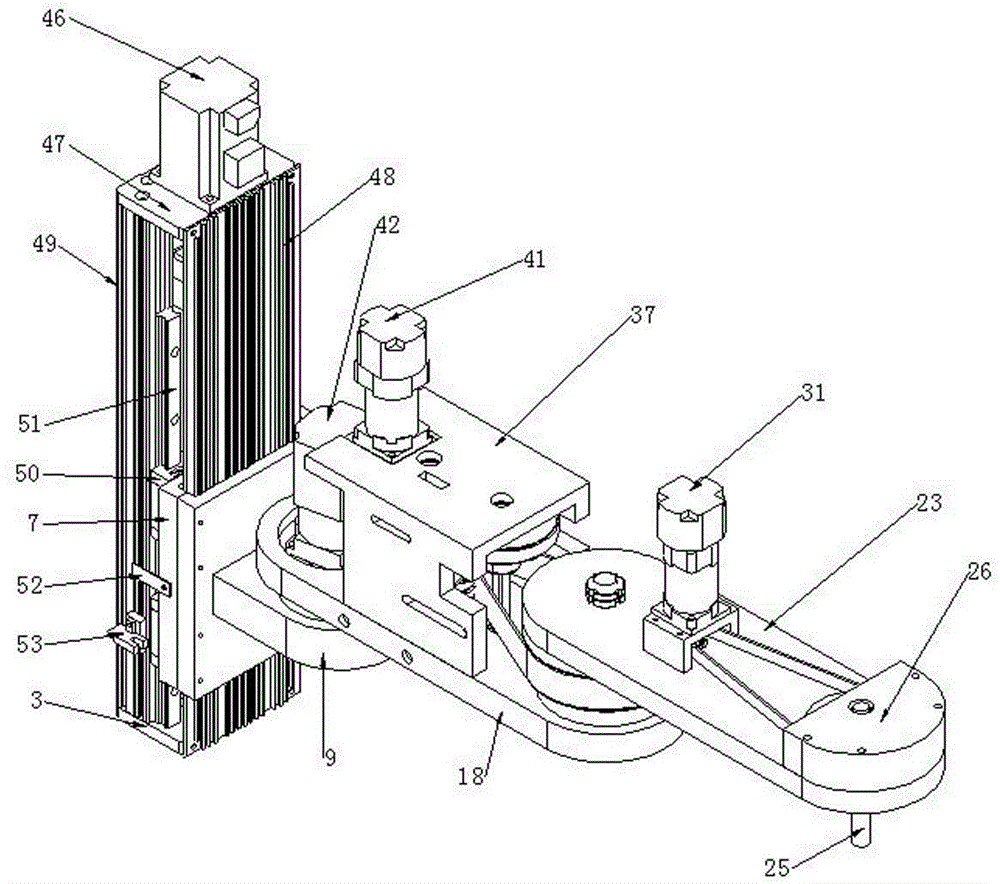
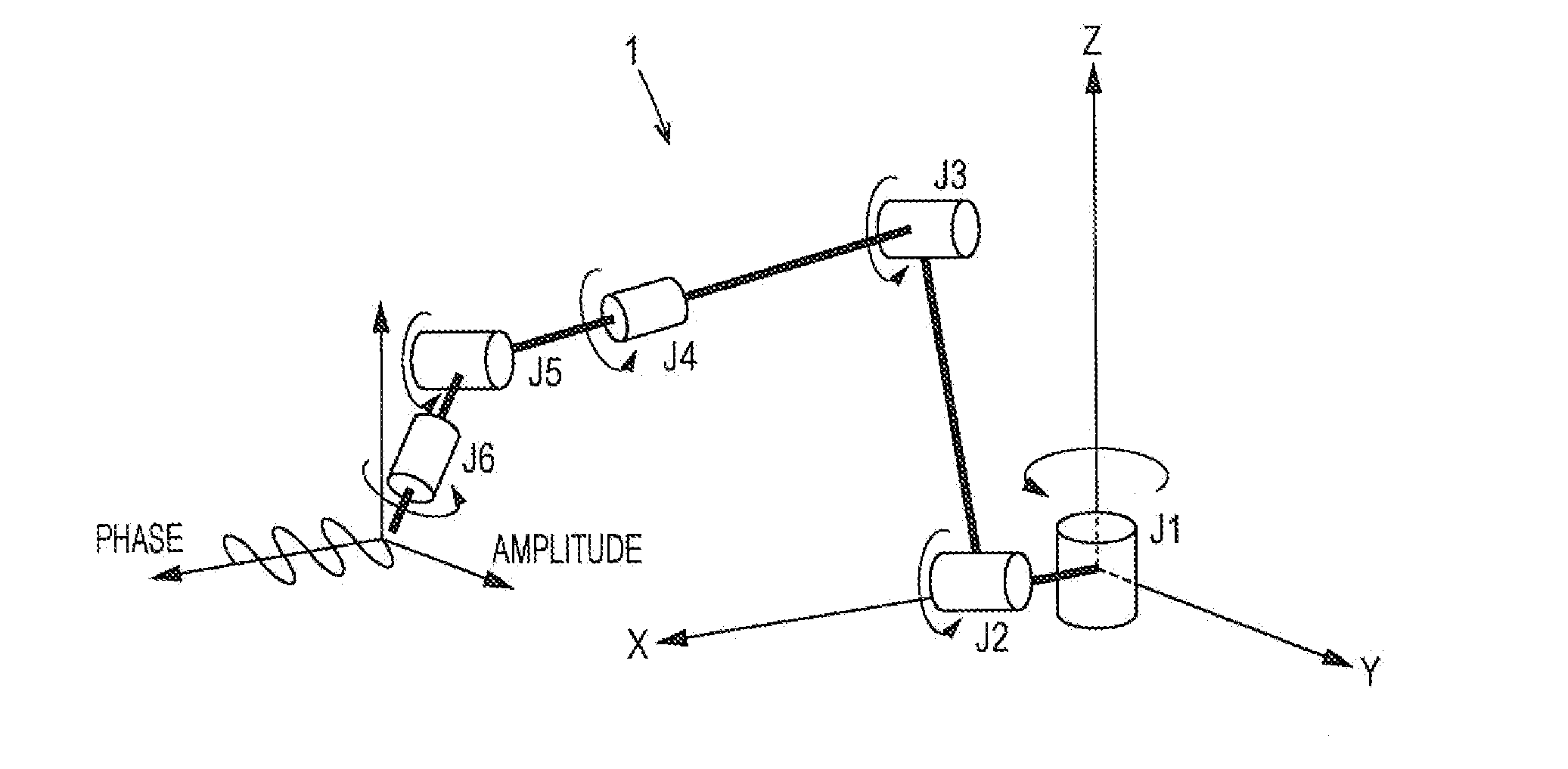
Patents
Literature
393 results about "Arthrobotrys" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Arthrobotrys is a genus of mitosporic fungi in the family Orbiliaceae. There are 71 species. They are predatory fungi that capture and feed on nematode worms. Rings that form on the hyphae constrict and entrap the worms, then hyphae grow into the worm and digest it.
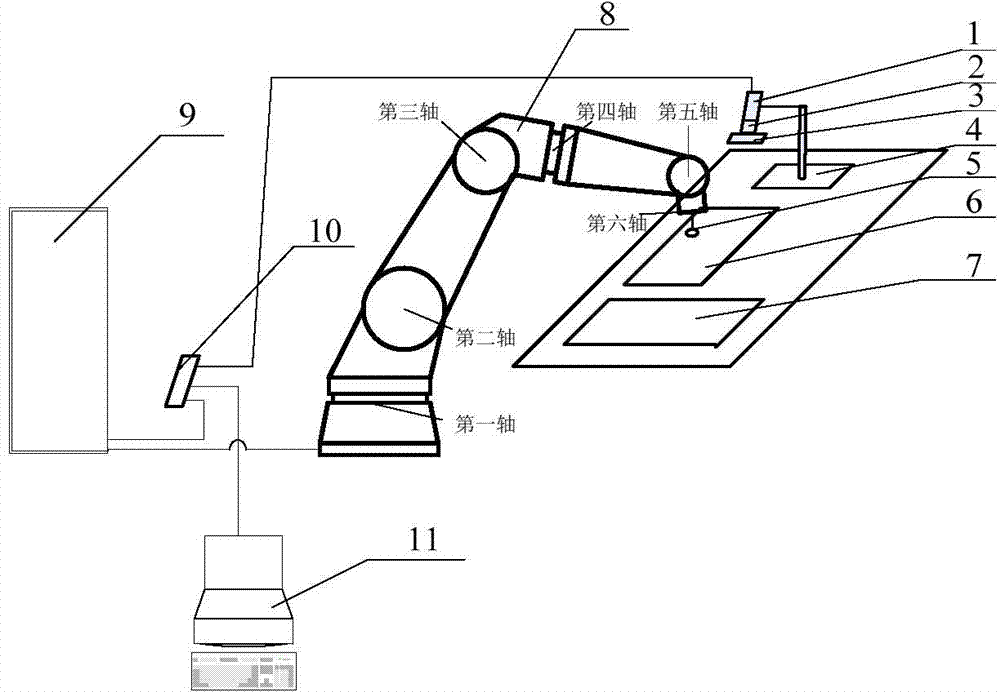
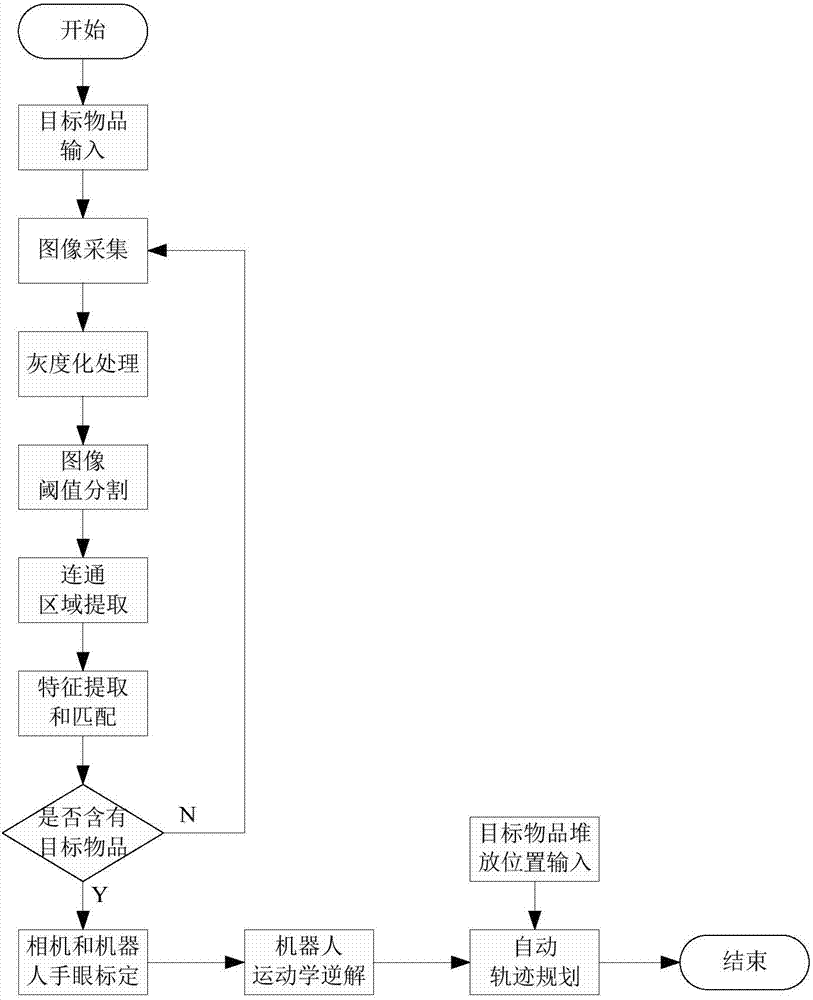
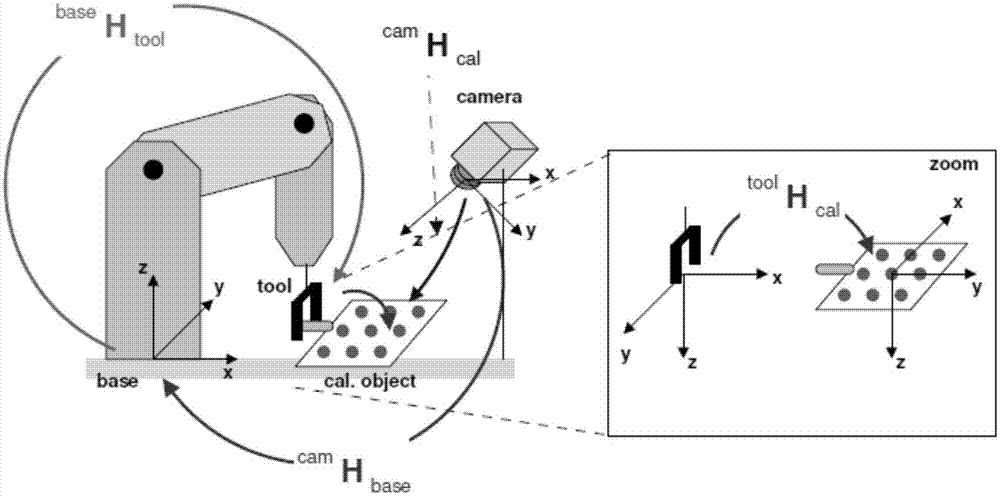
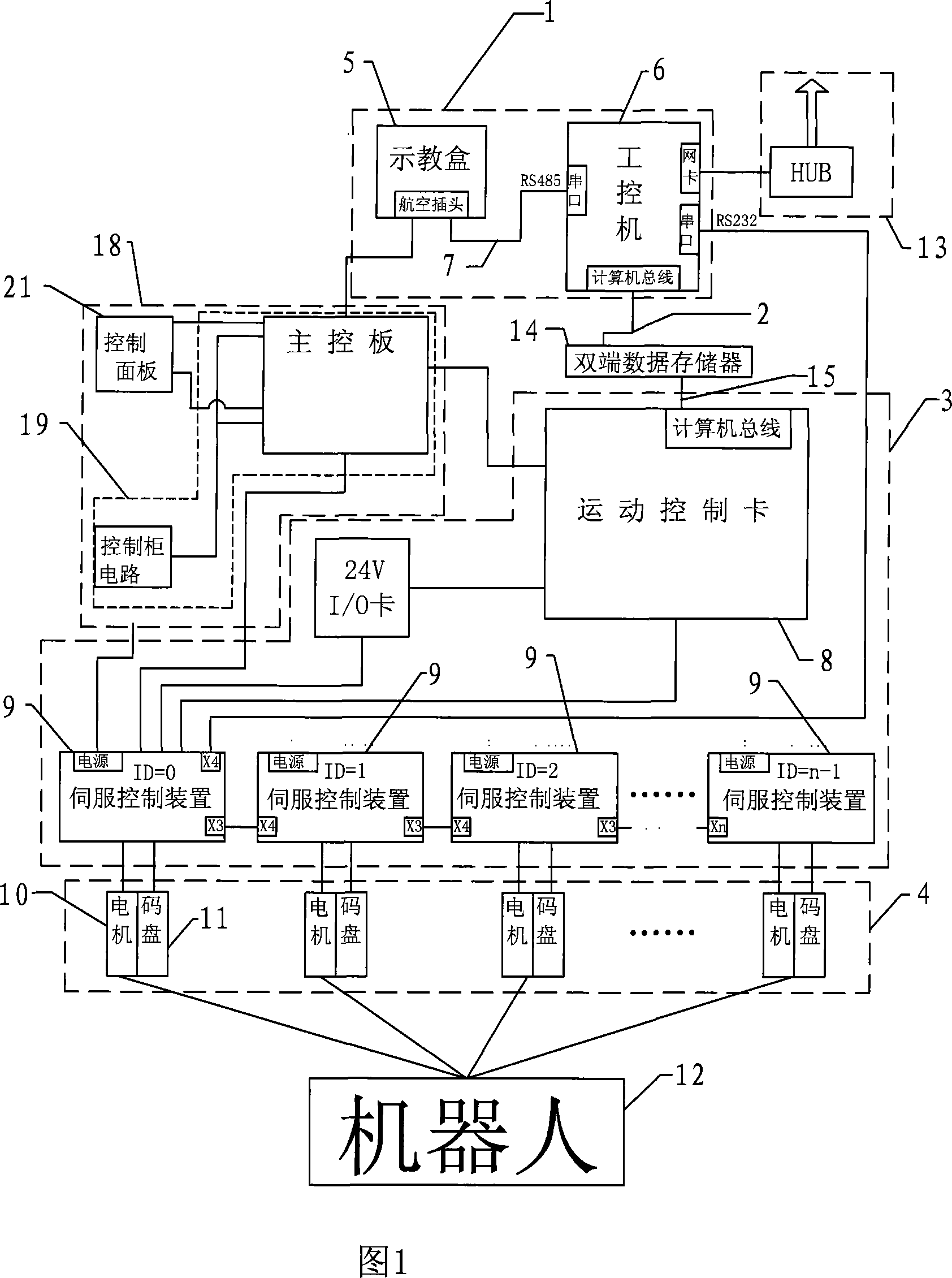
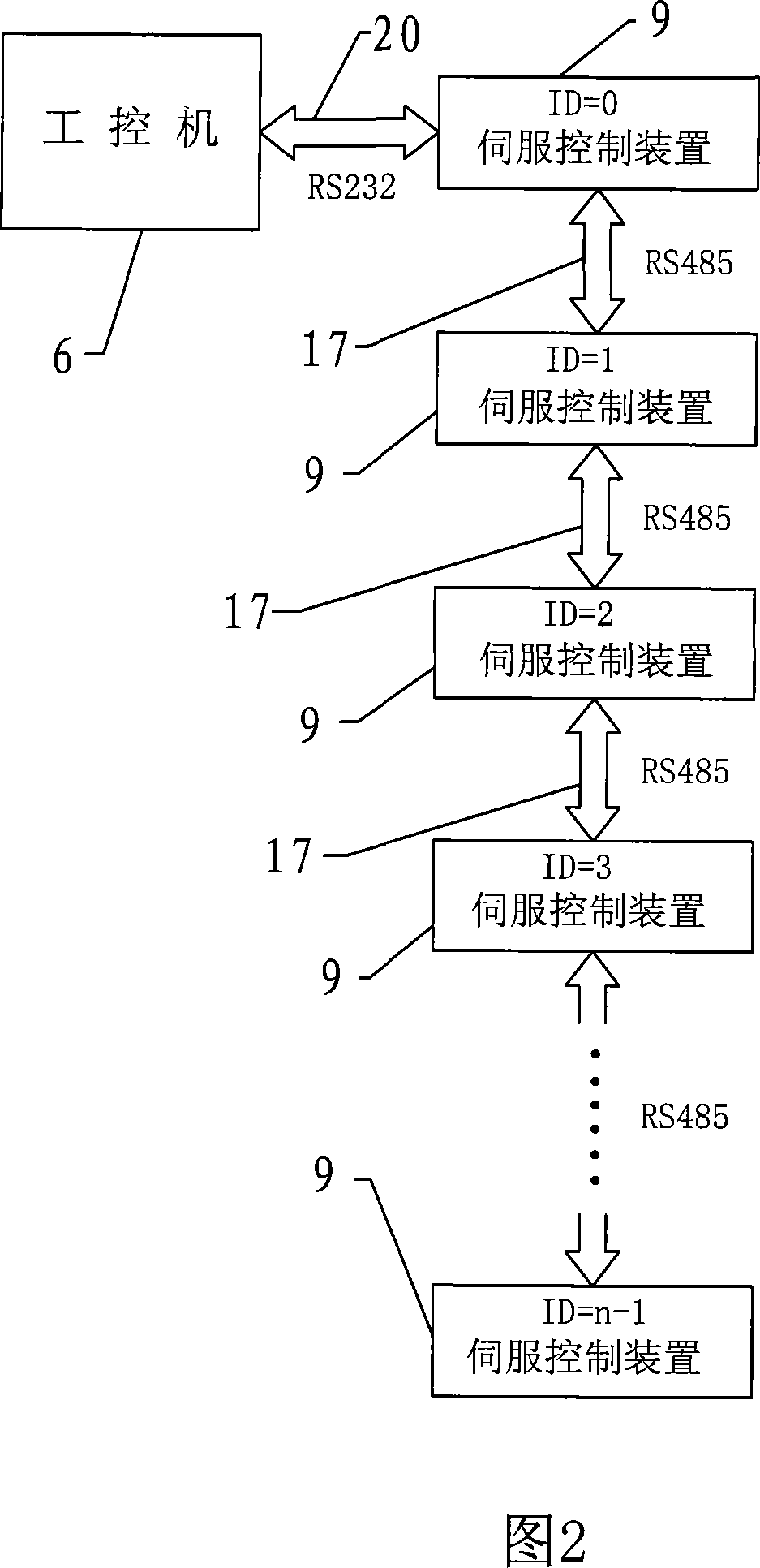
System and method for machine vision-based robot sorting
The invention discloses a system and a method for machine vision-based robot sorting. The system comprises a CCD digital camera, a camera lens, a light source, a six-axle joint robot main body, an electrical control cabinet and a vacuum sucker. The CCD digital camera is connected to an industrial computer by a switch. The six-axle joint robot main body is connected to the electrical control cabinet. The electrical control cabinet accesses the switch. The vacuum sucker is rigidly fixed to the tail end of the six-axle joint robot main body. The camera unit is used for making a photo of an object to be sorted, collecting data and transmitting the data to the industrial computer by the switch. The industrial computer is used for treating the acquired photo of the object to be sorted, carrying out accurate positioning and then transmitting a control signal to the electrical control cabinet by the switch. The electrical control cabinet is used for controlling the six-axle joint robot main body to carry out corresponding sorting processes according to the received control signal. The system and the method improve work efficiency, reduce operation workers and reduce a production cost in sorting.
Owner:716TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
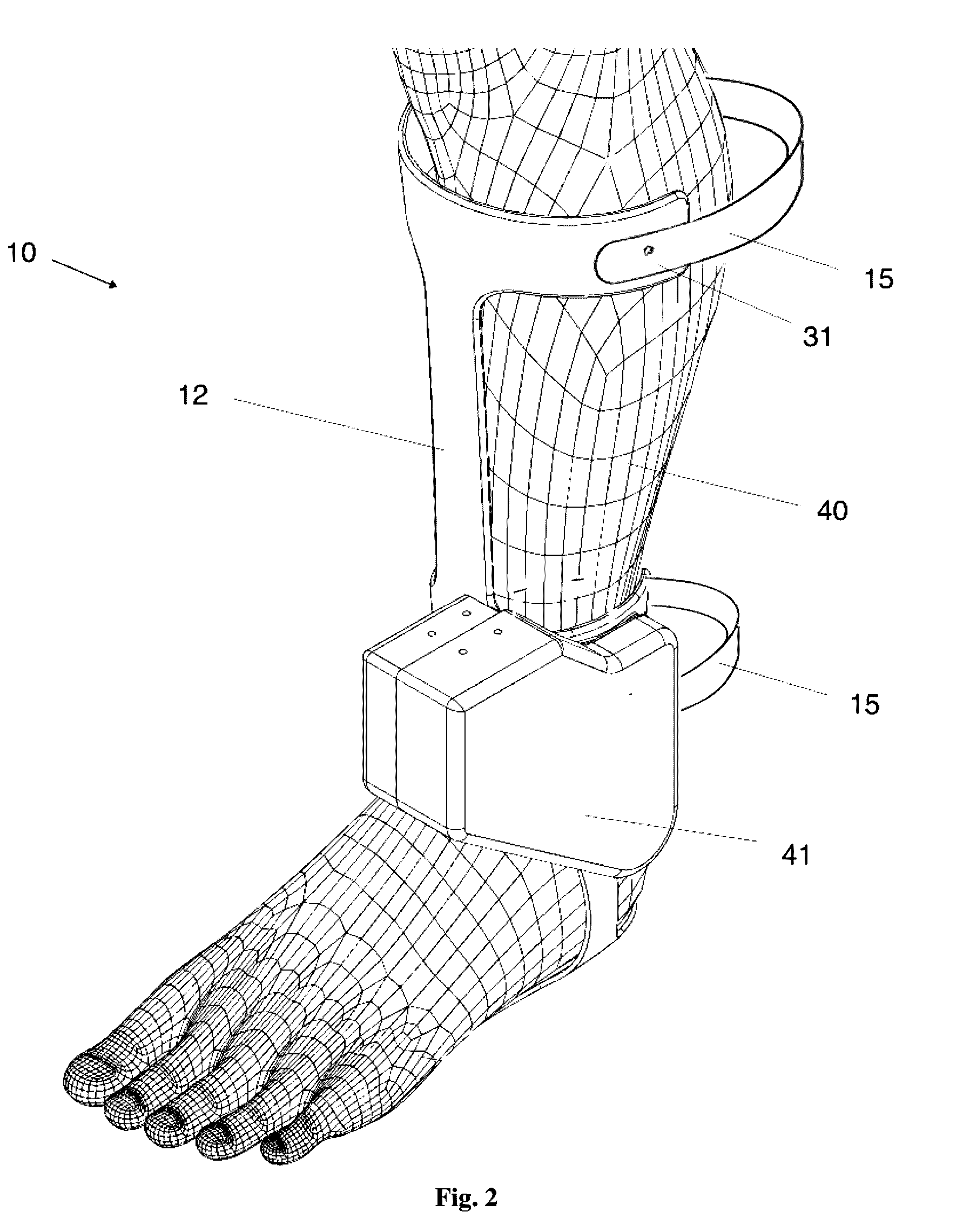
Exoskeleton Ankle Robot
ActiveUS20160331557A1Less cumbersomeDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesTruncal muscle weaknessJoint problem
A portable electrical motor-driven exoskeleton ankle joint robot with gear transmission and control system which is intended to provide walking assistance in different speed and walking conditions to persons with disability in walking or muscle weakness or joint problem.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
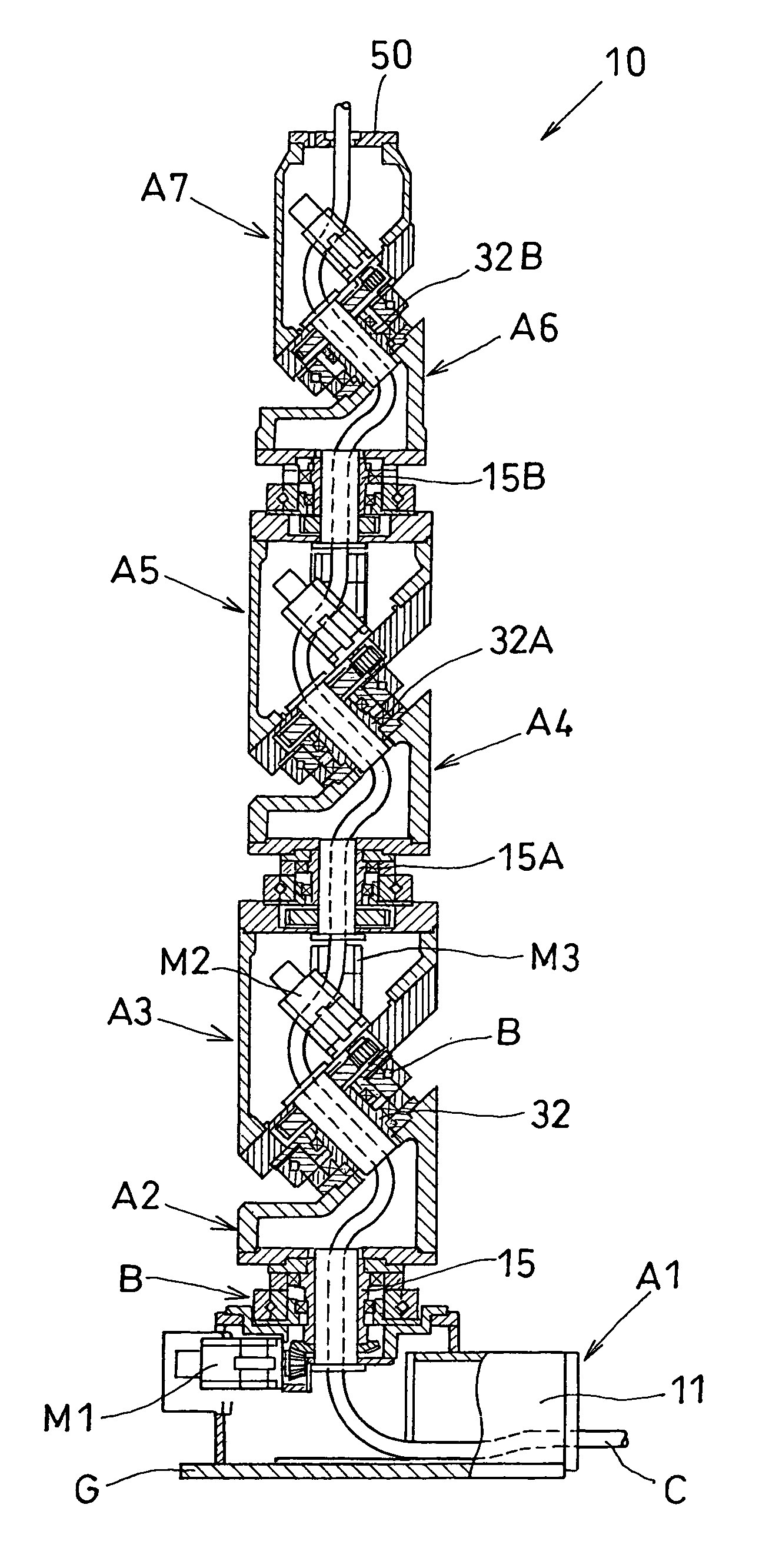
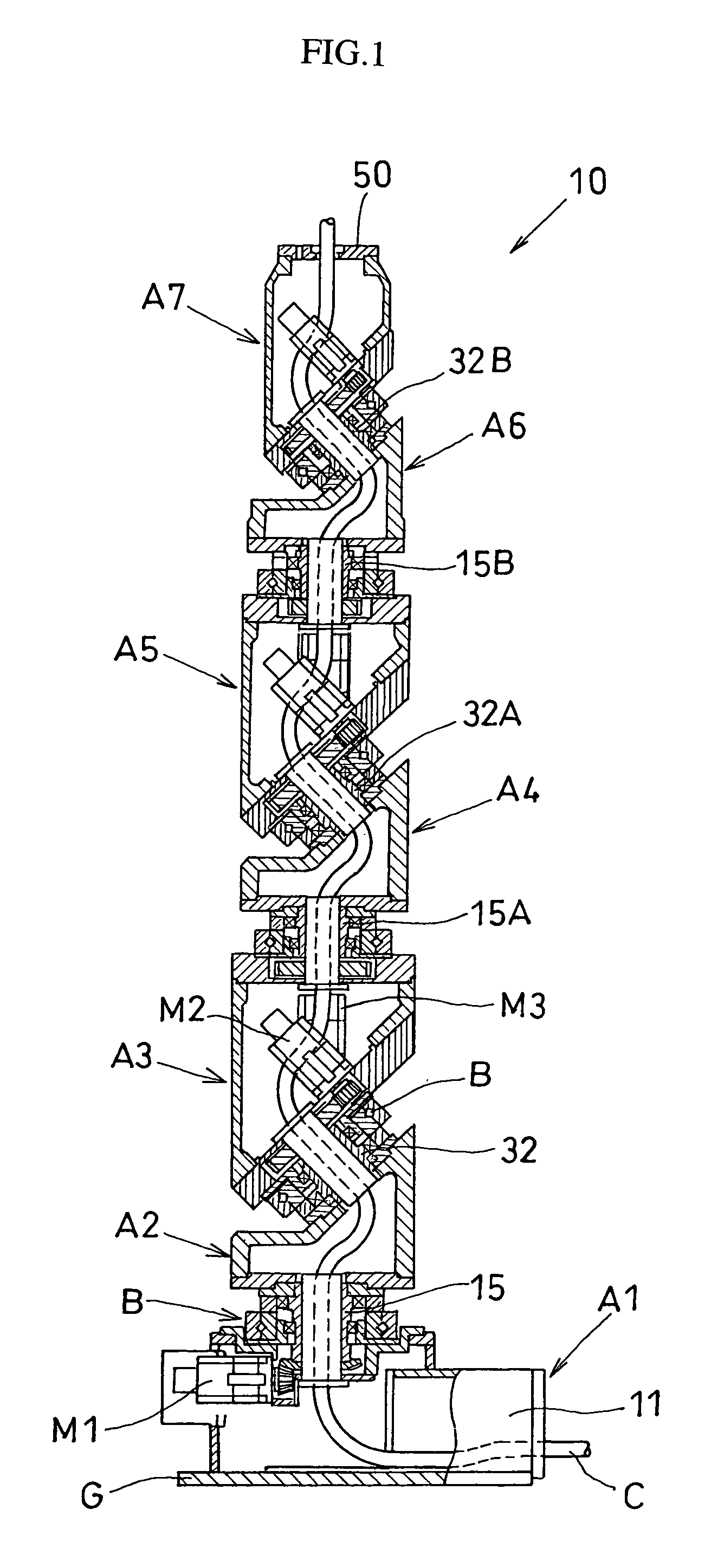
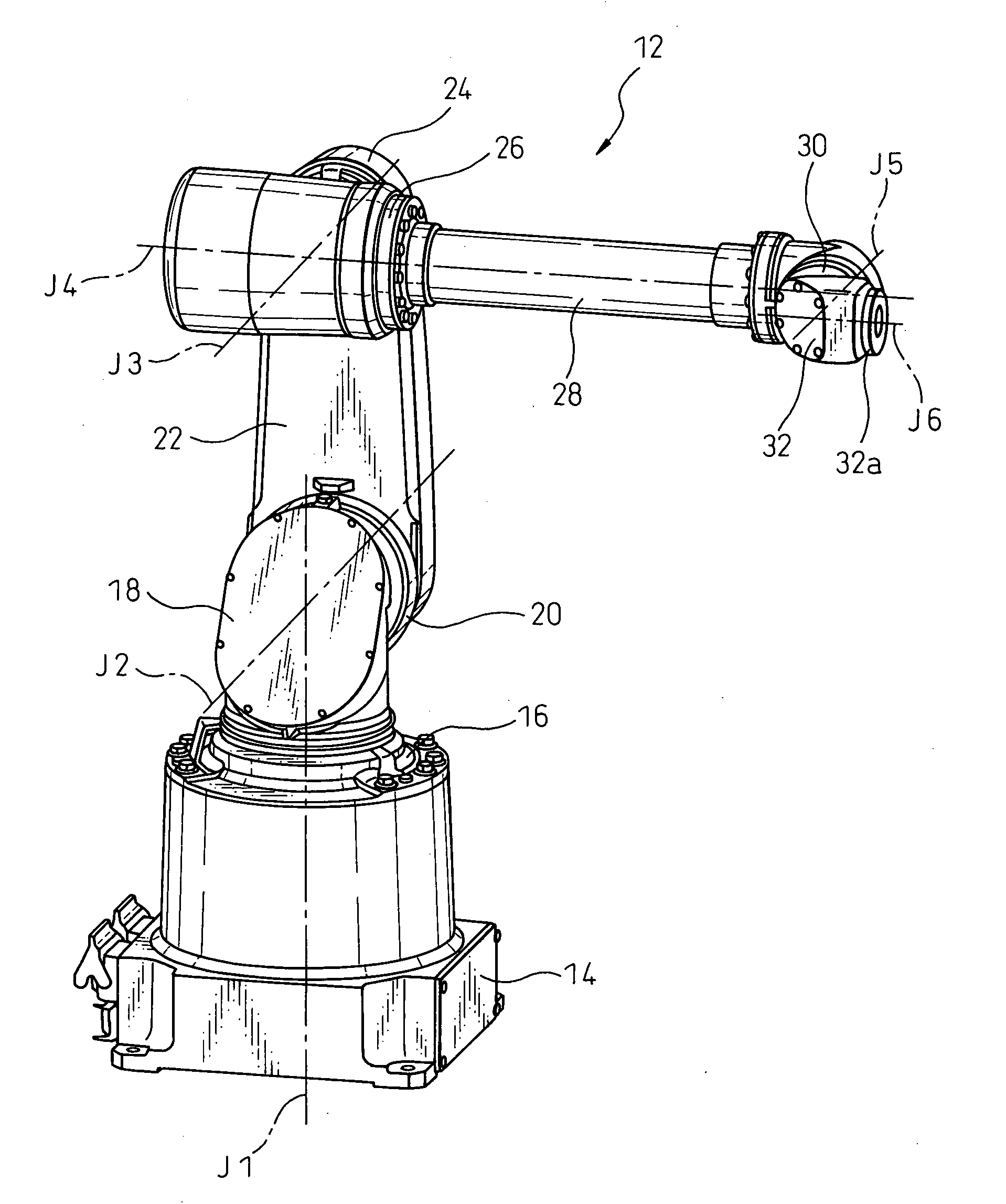
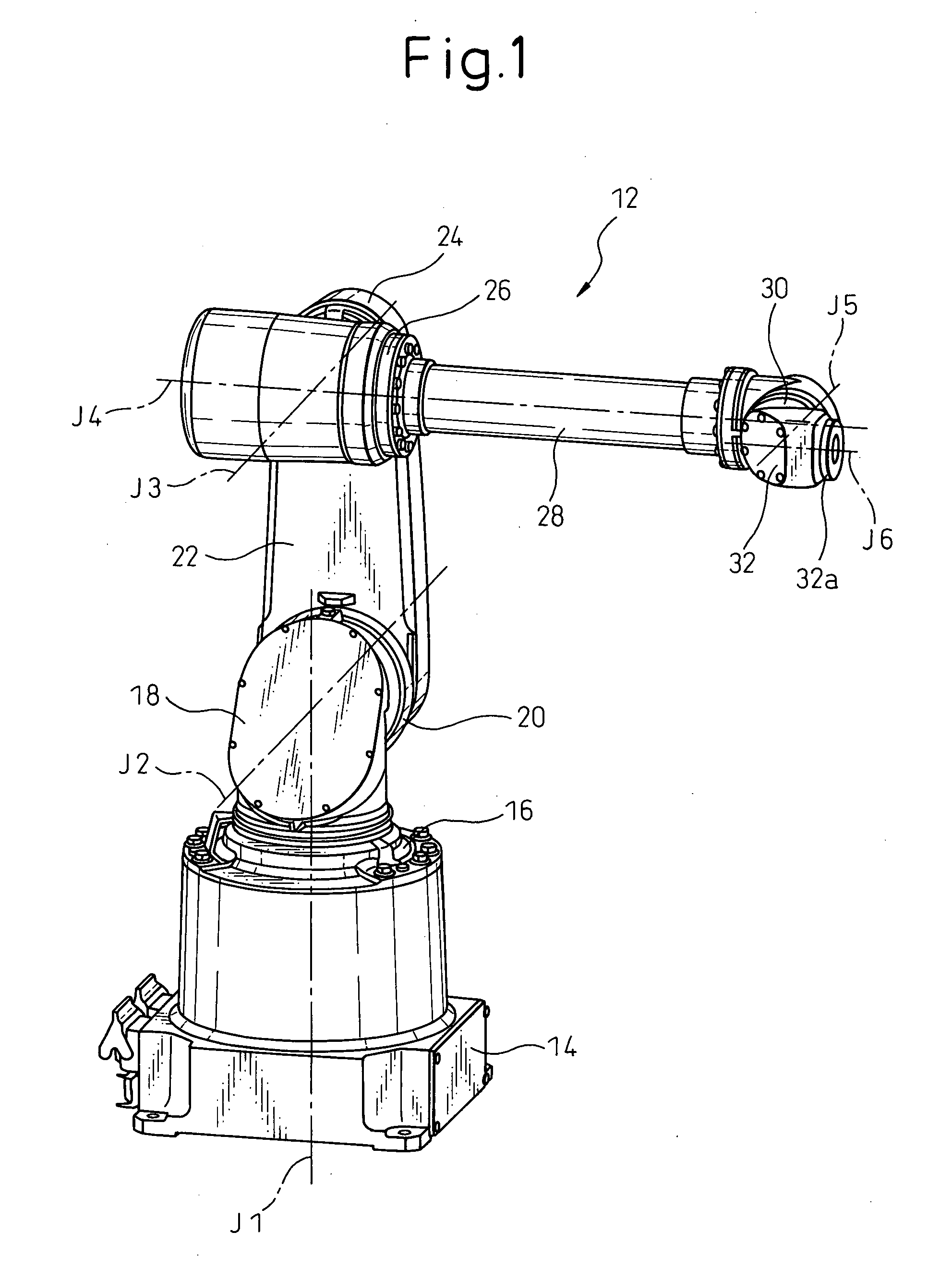
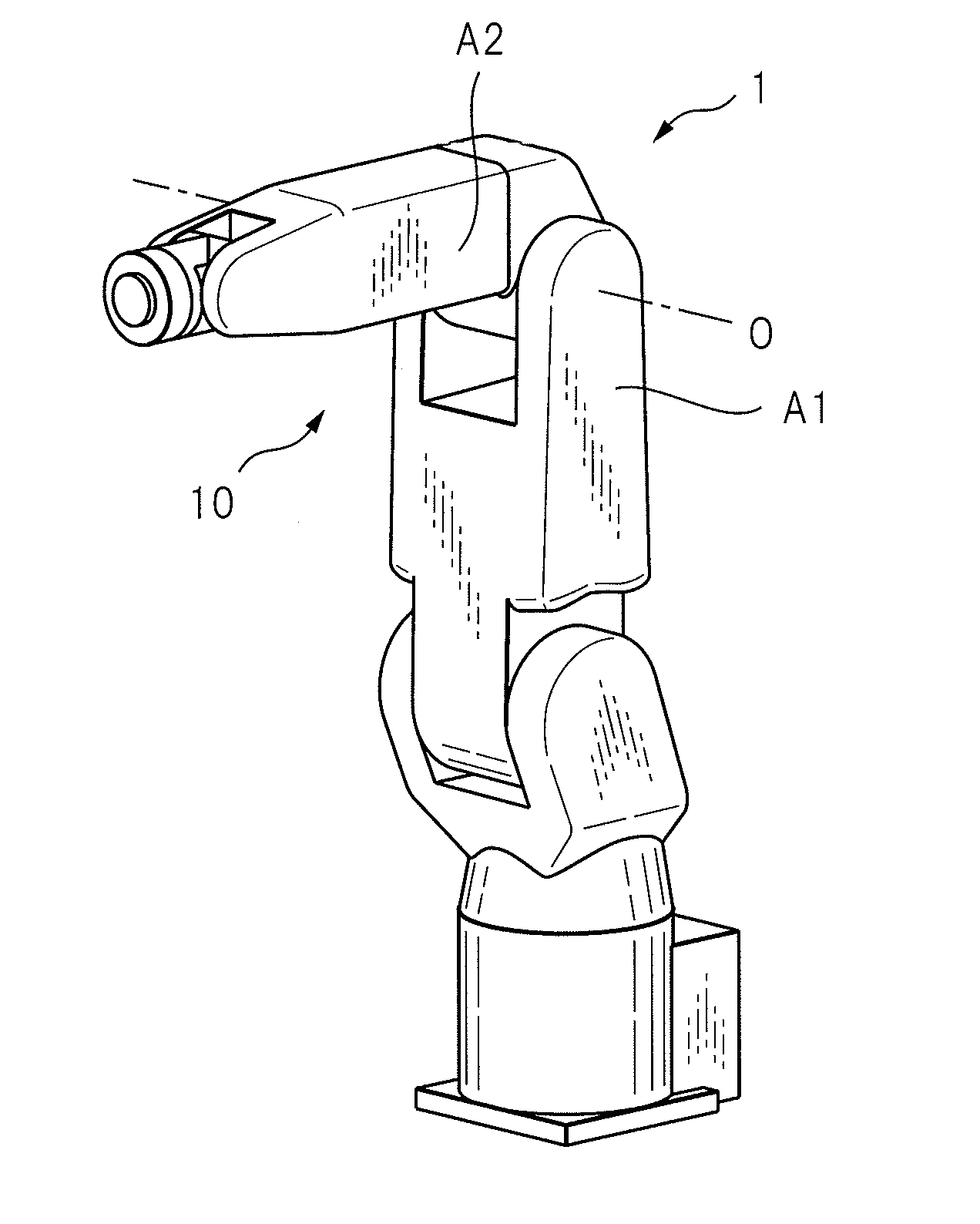
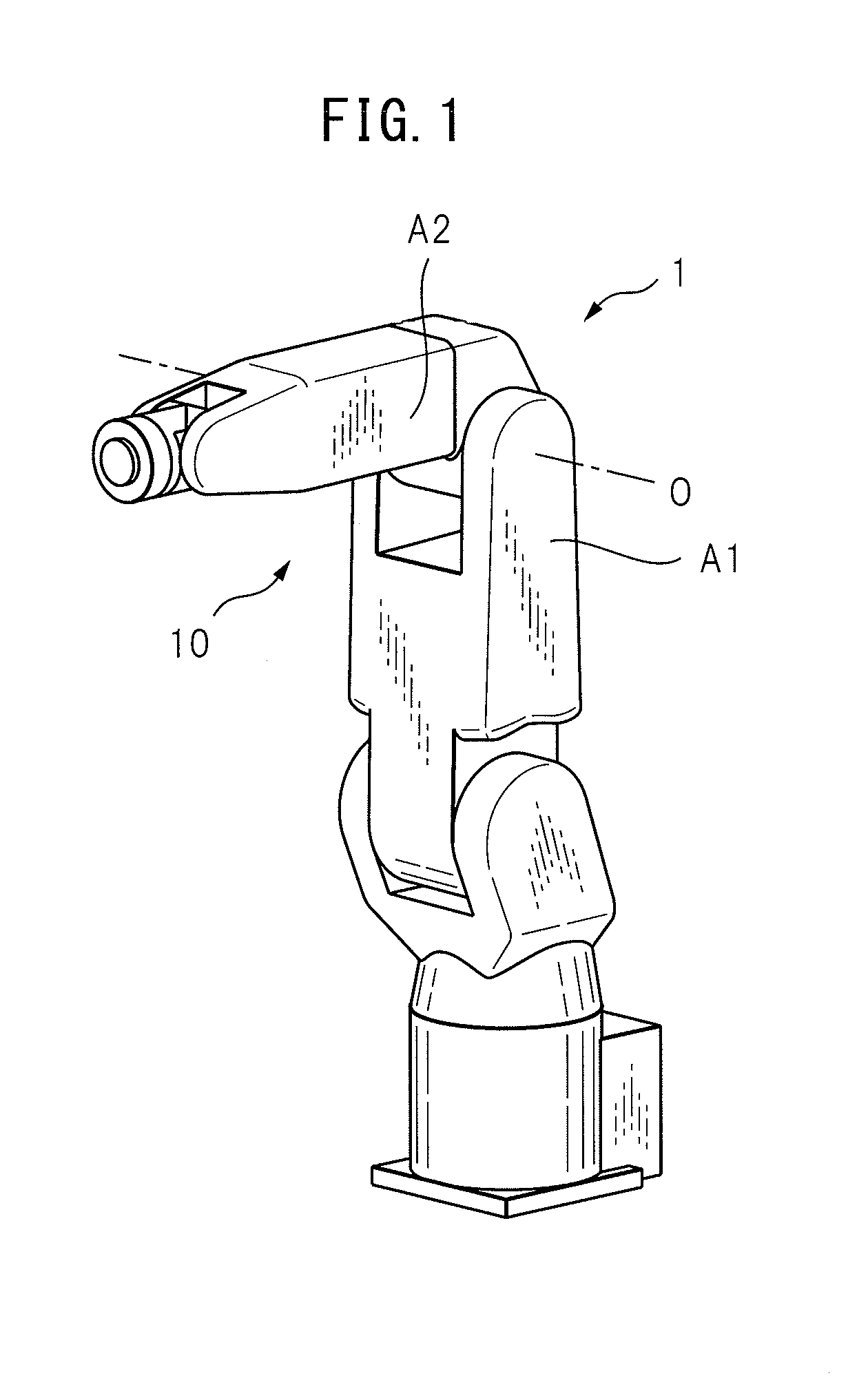
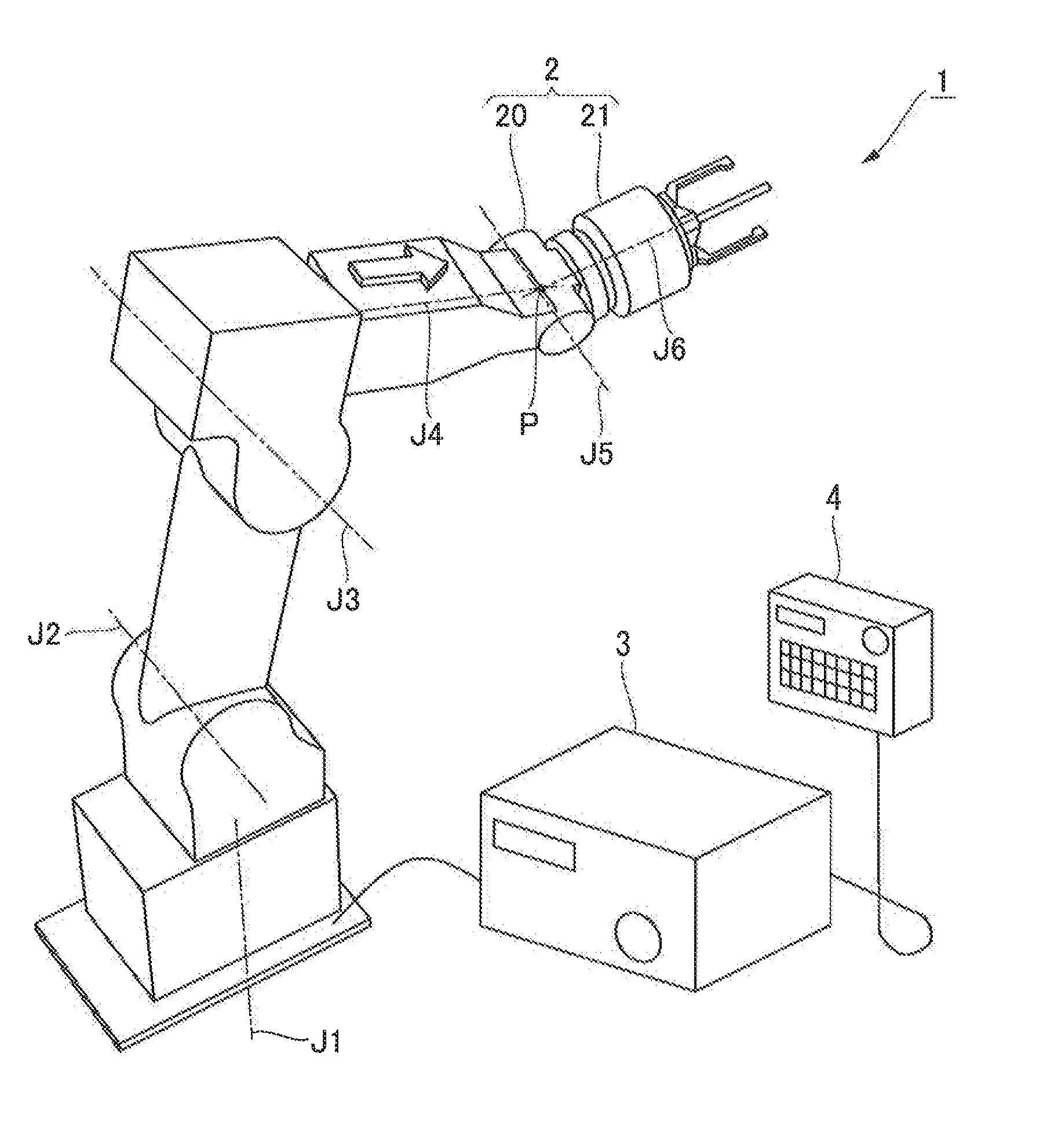
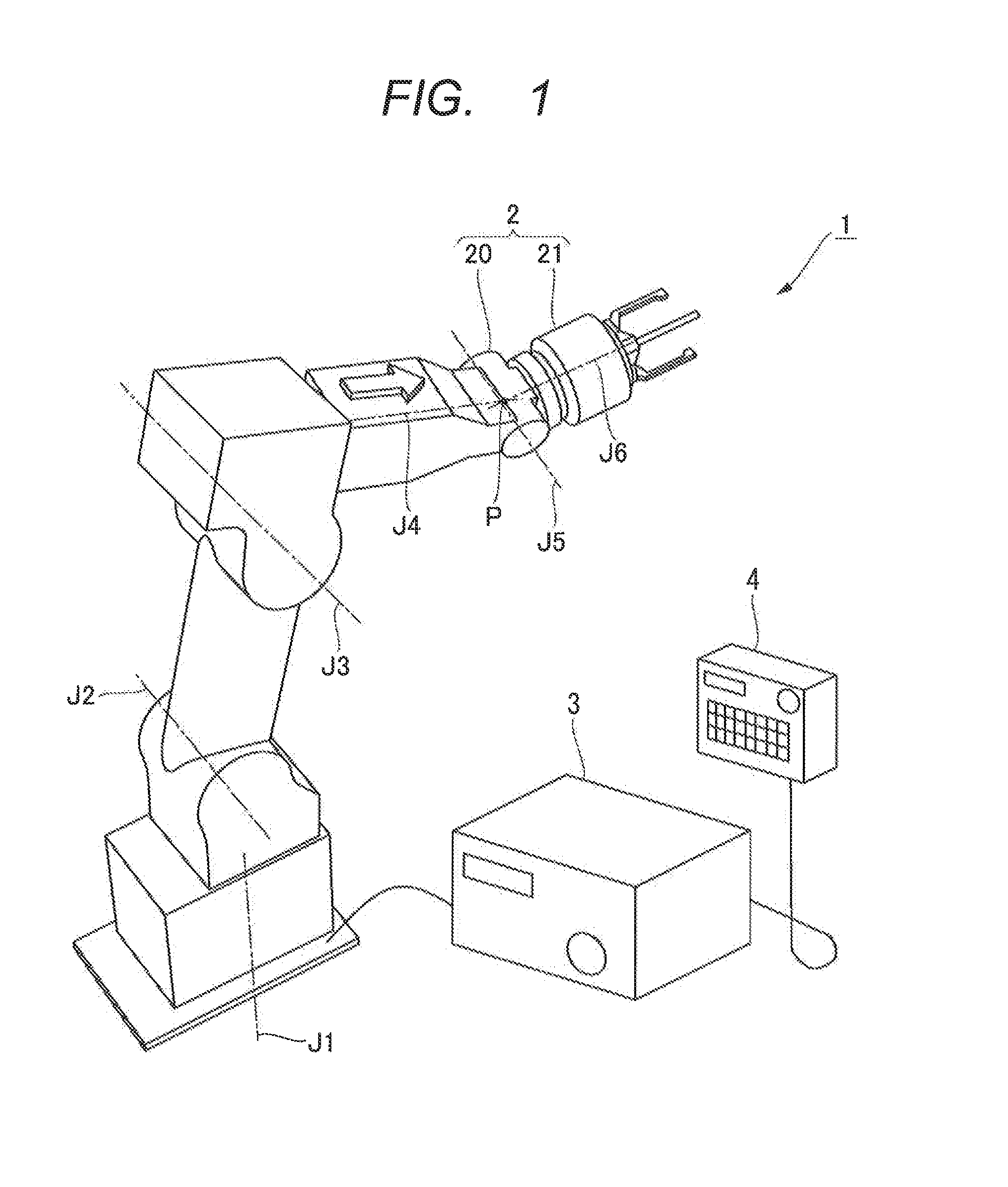
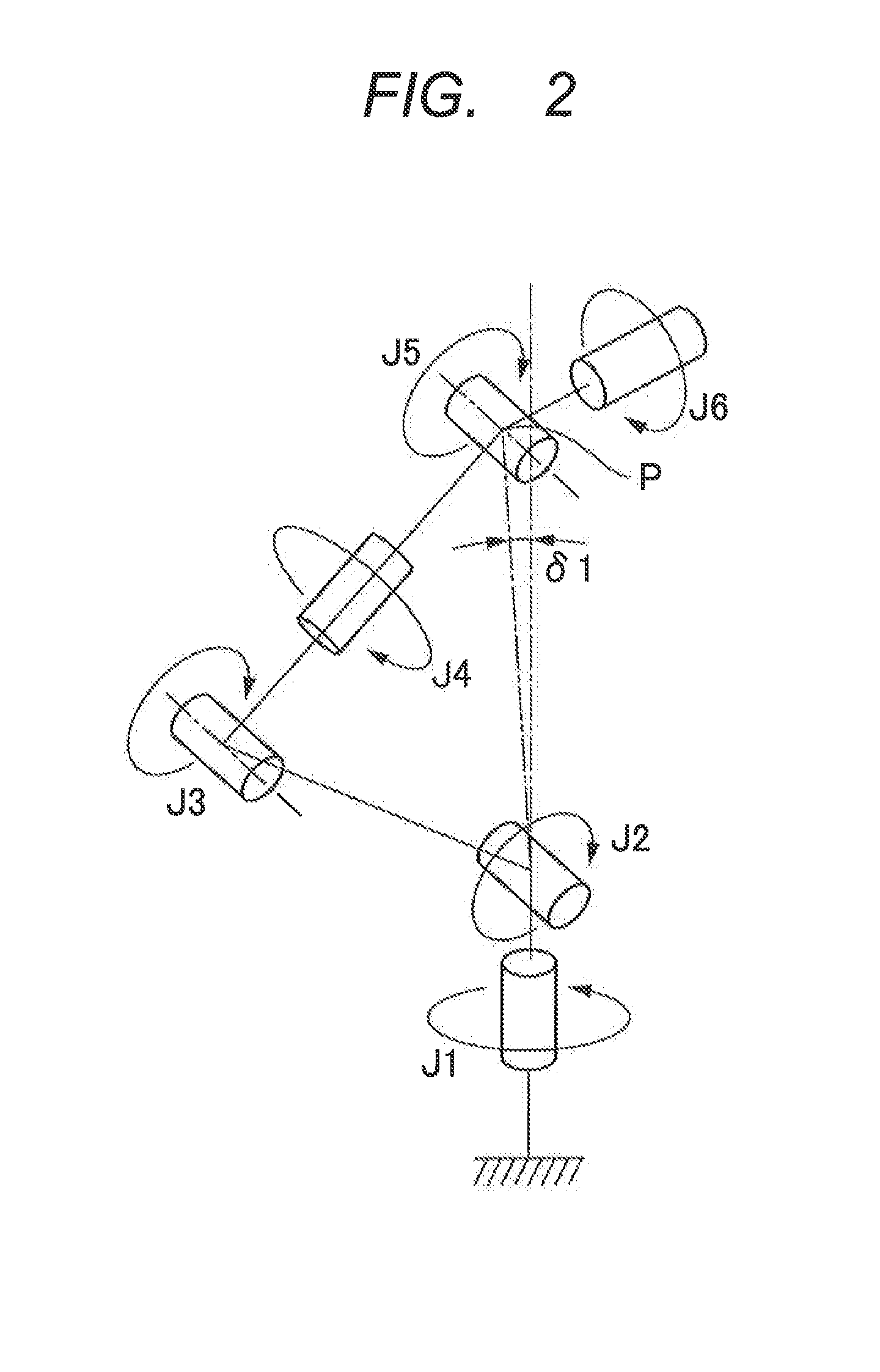
Articulated robot
ActiveUS20040149064A1Programme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusElectric power transmissionRotational axis
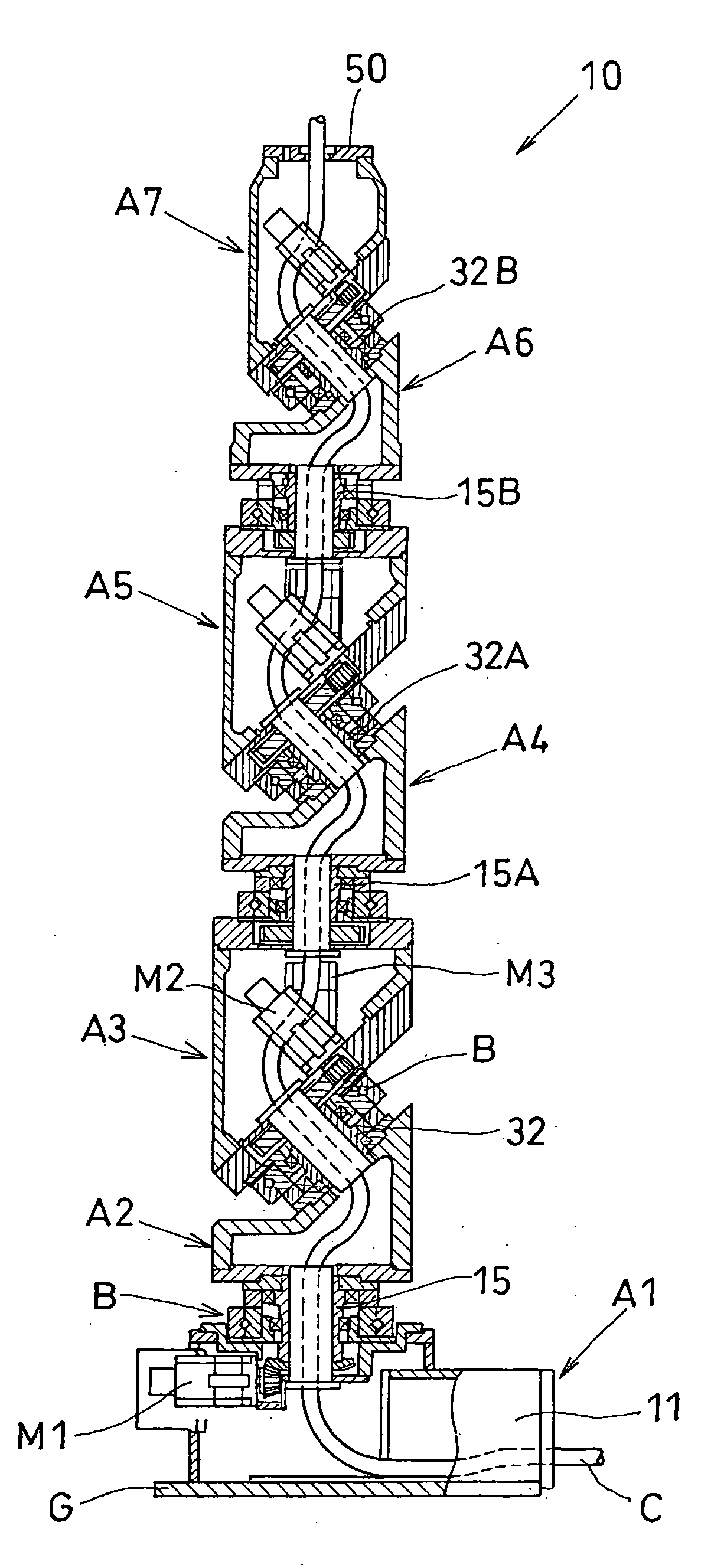
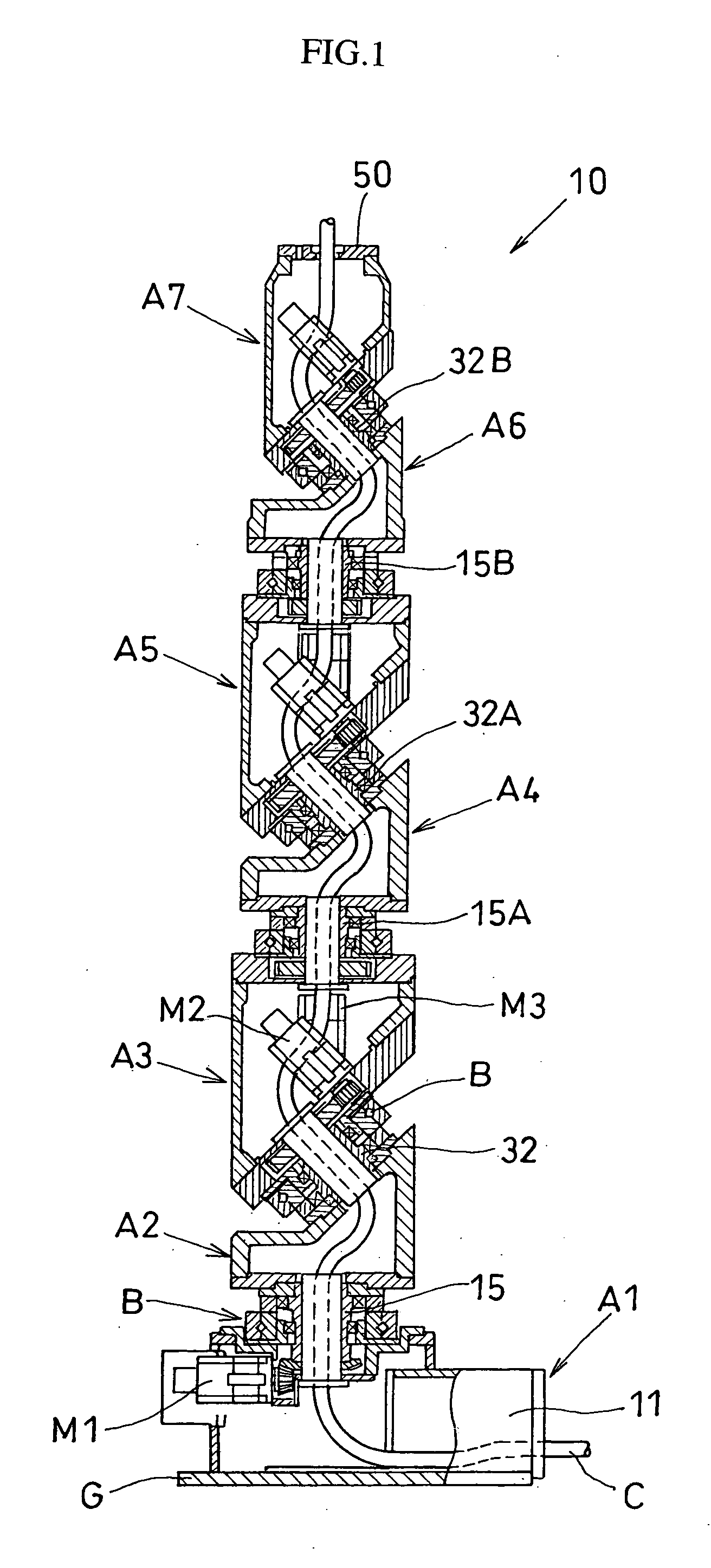
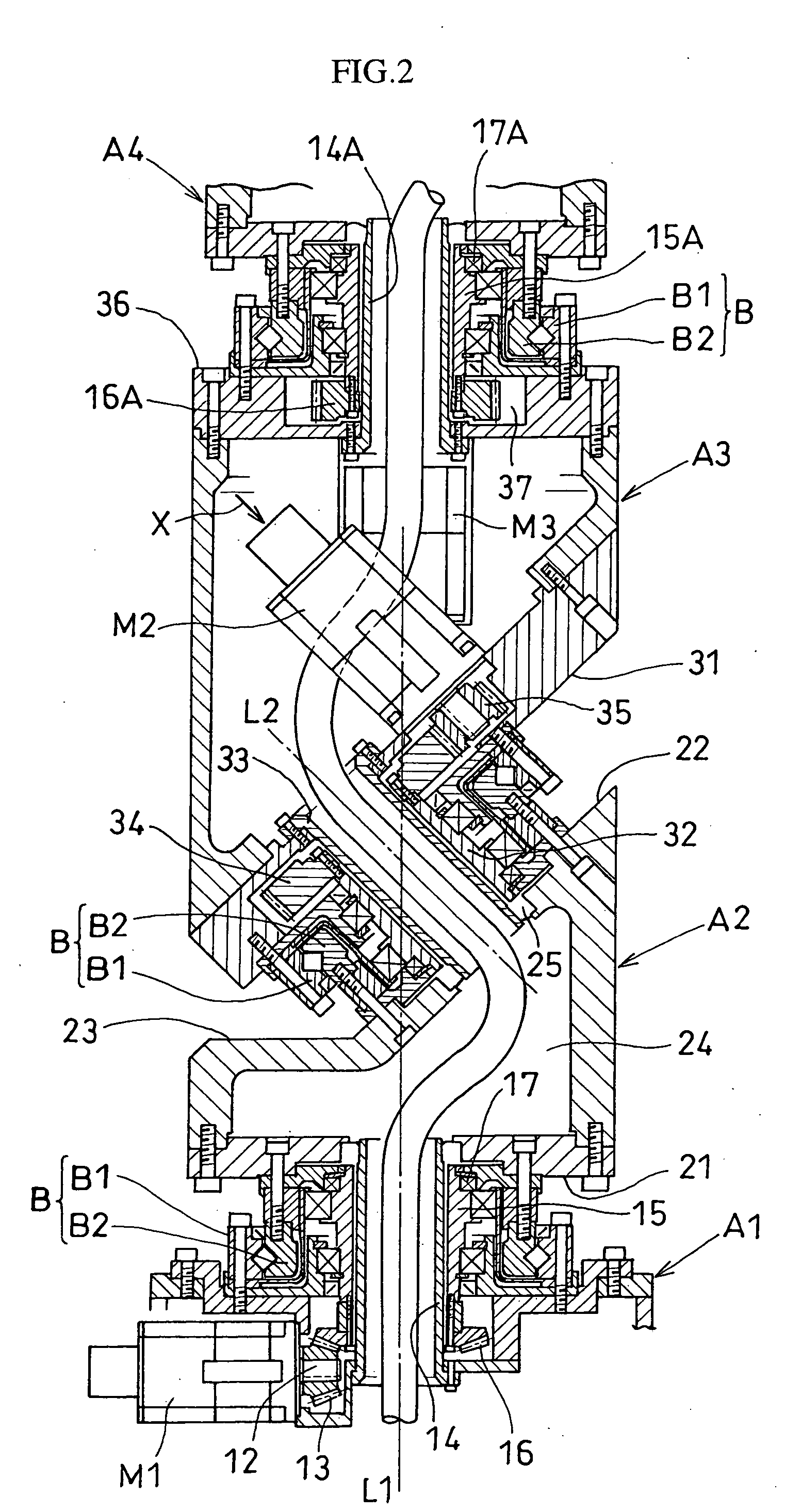
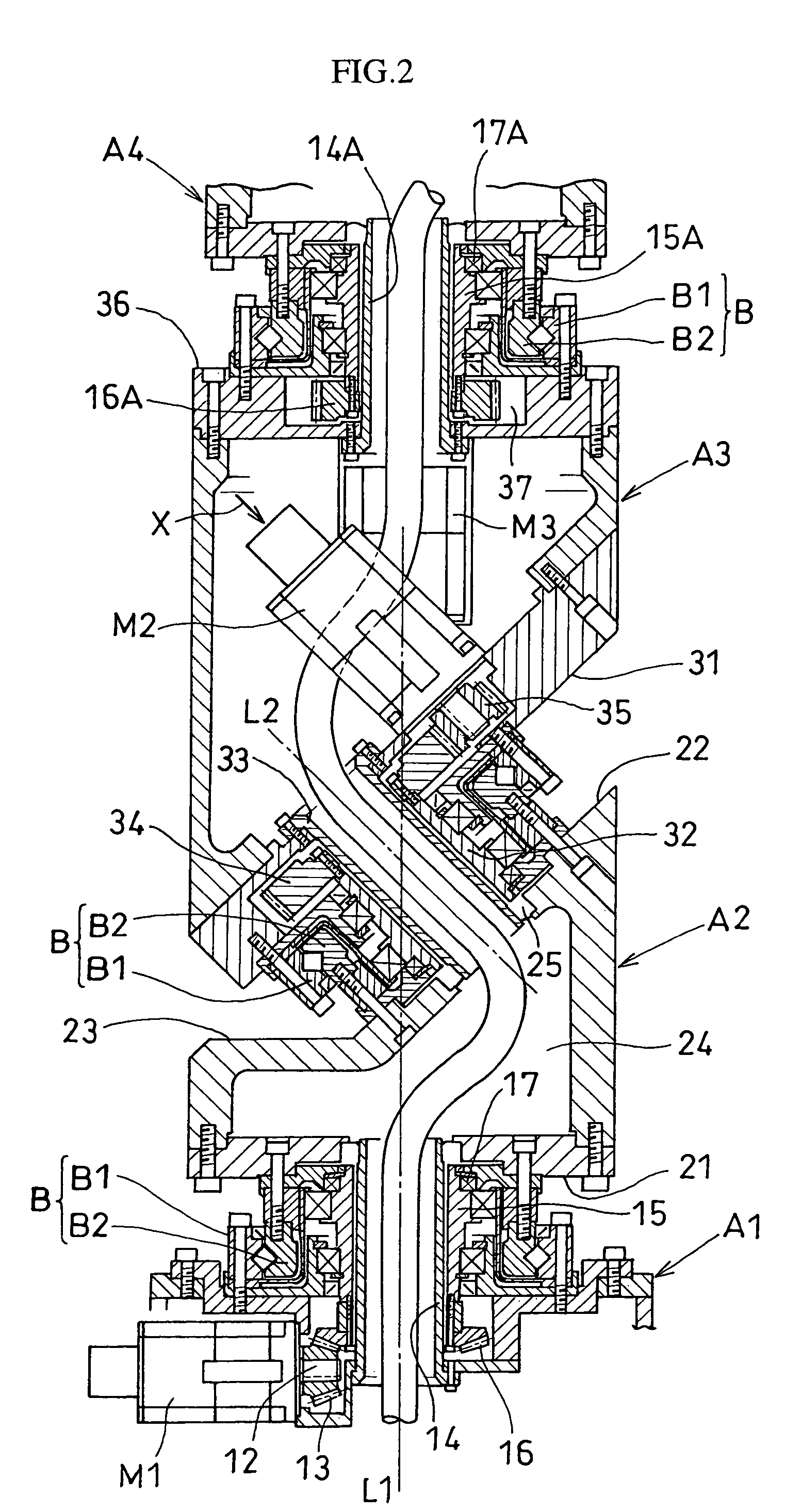
An articulated robot capable of reducing dead space while maintaining a wide operating area and simplifying a power transmission system necessary for moving each joint. A plurality of joint arms A1 to A7 are connected via first rotating shafts 15, 15A, and 15B as horizontal rotating shafts and via second rotating shafts 32, 32A, and 32B as inclined rotating shafts alternately. A motor M for driving the rotating shaft and a speed-reducing mechanism are provided for each rotating shaft.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
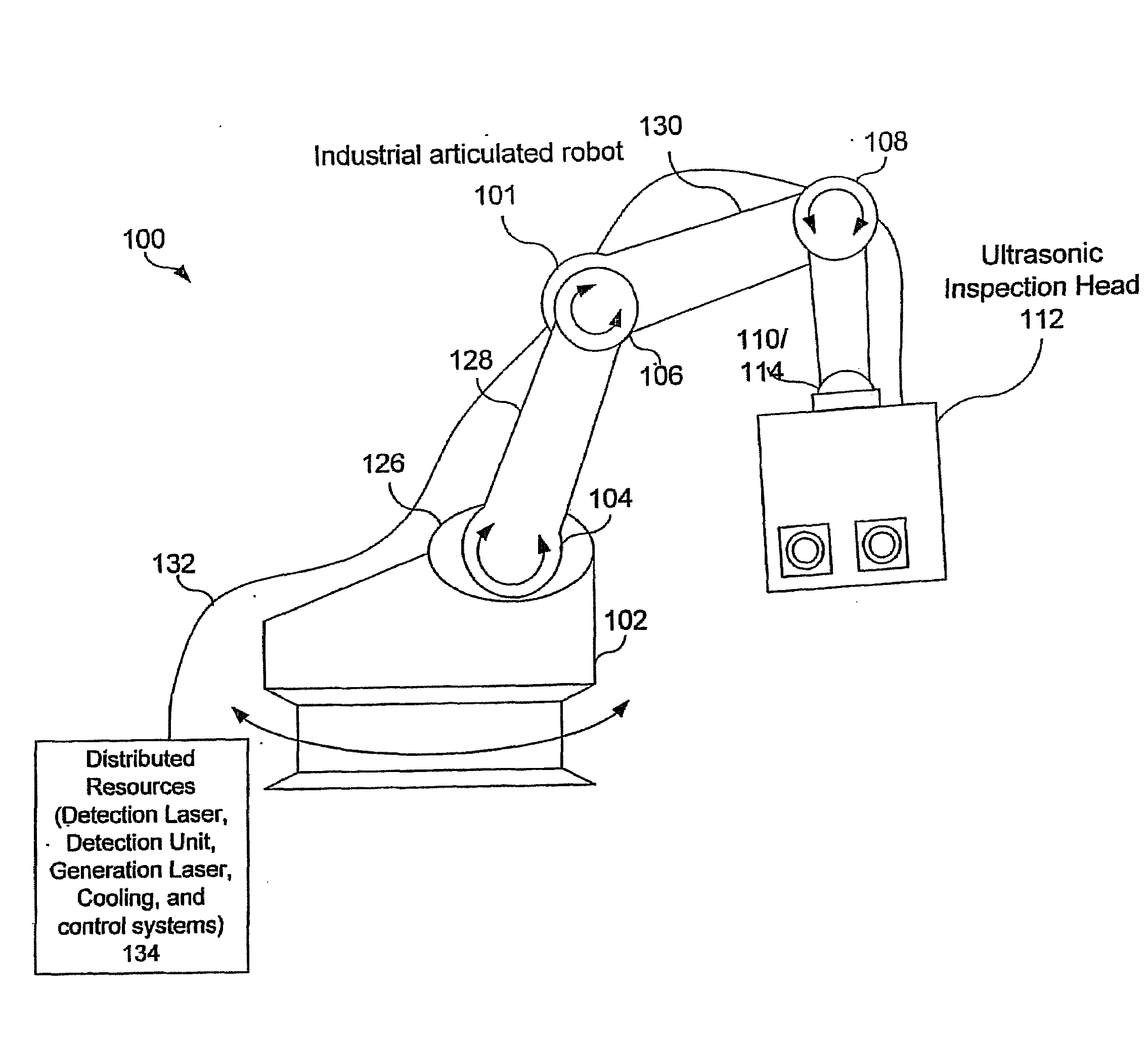
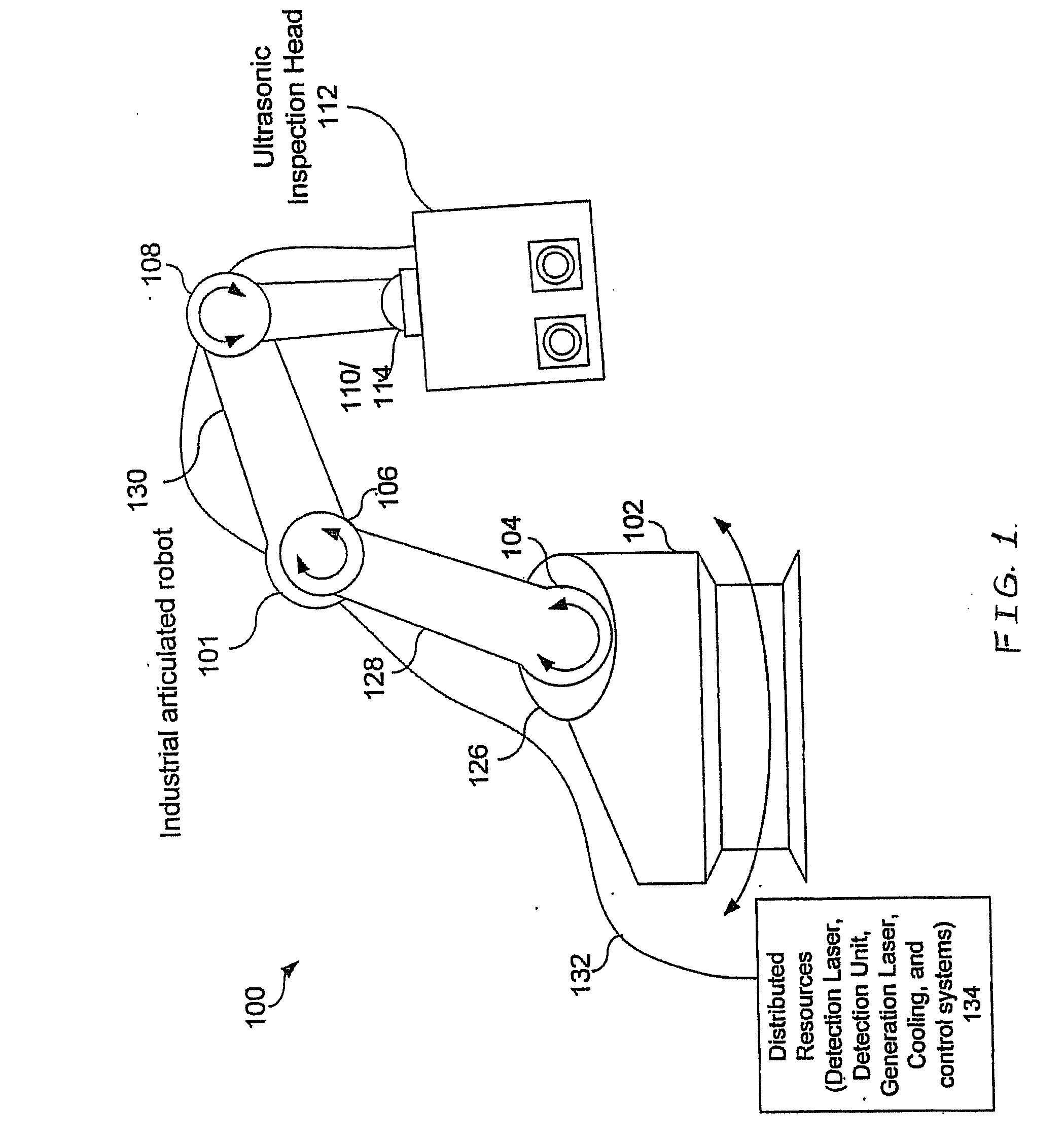
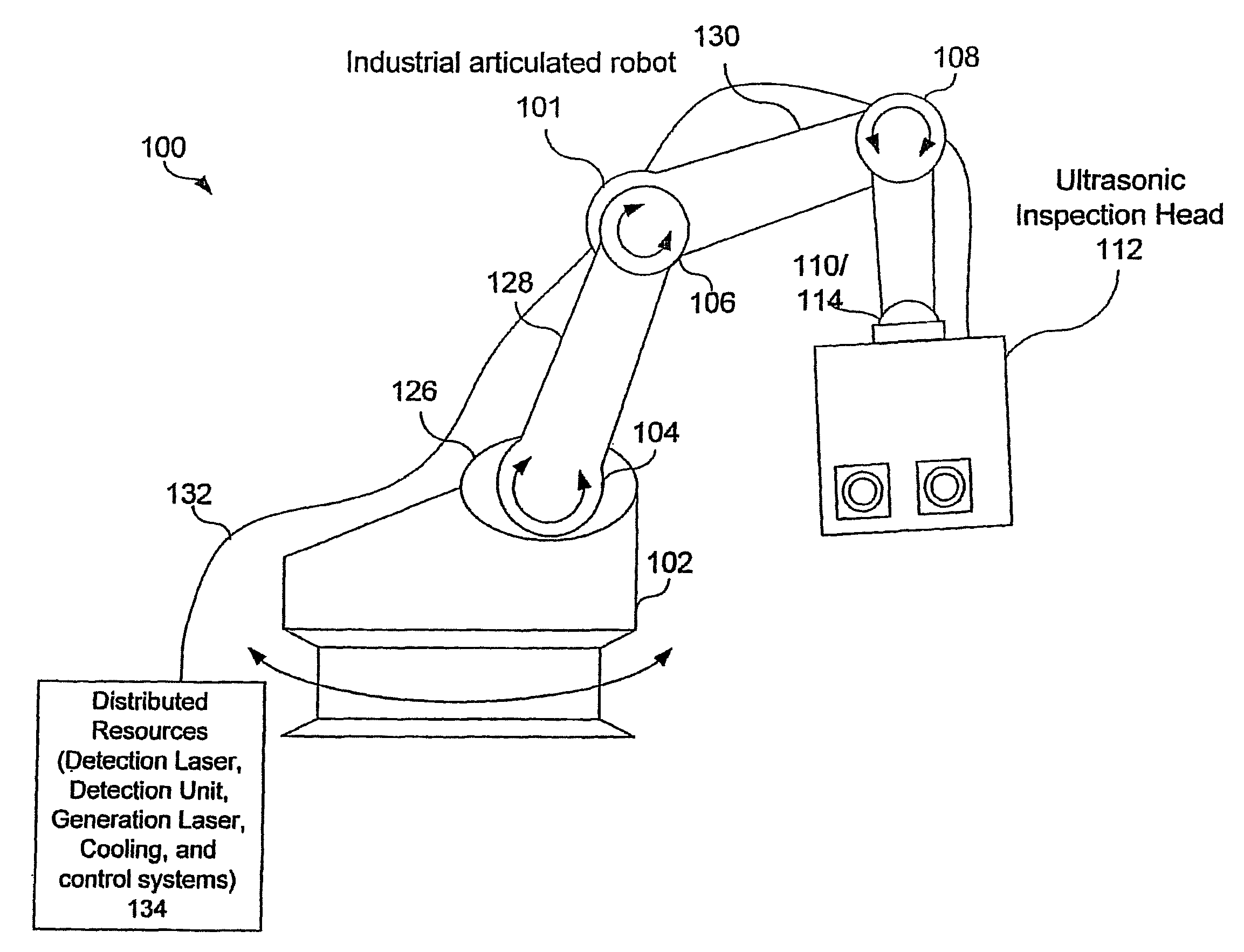
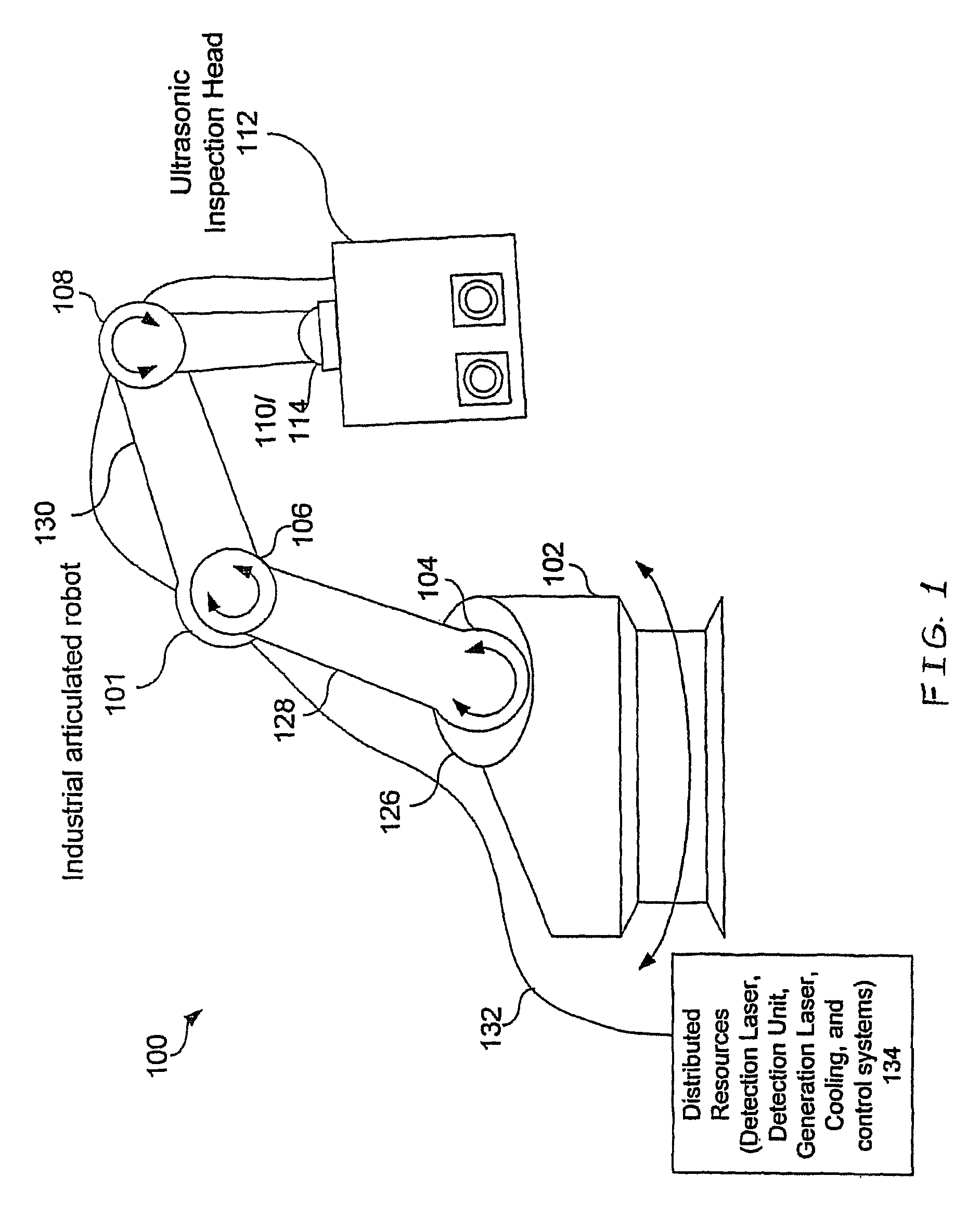
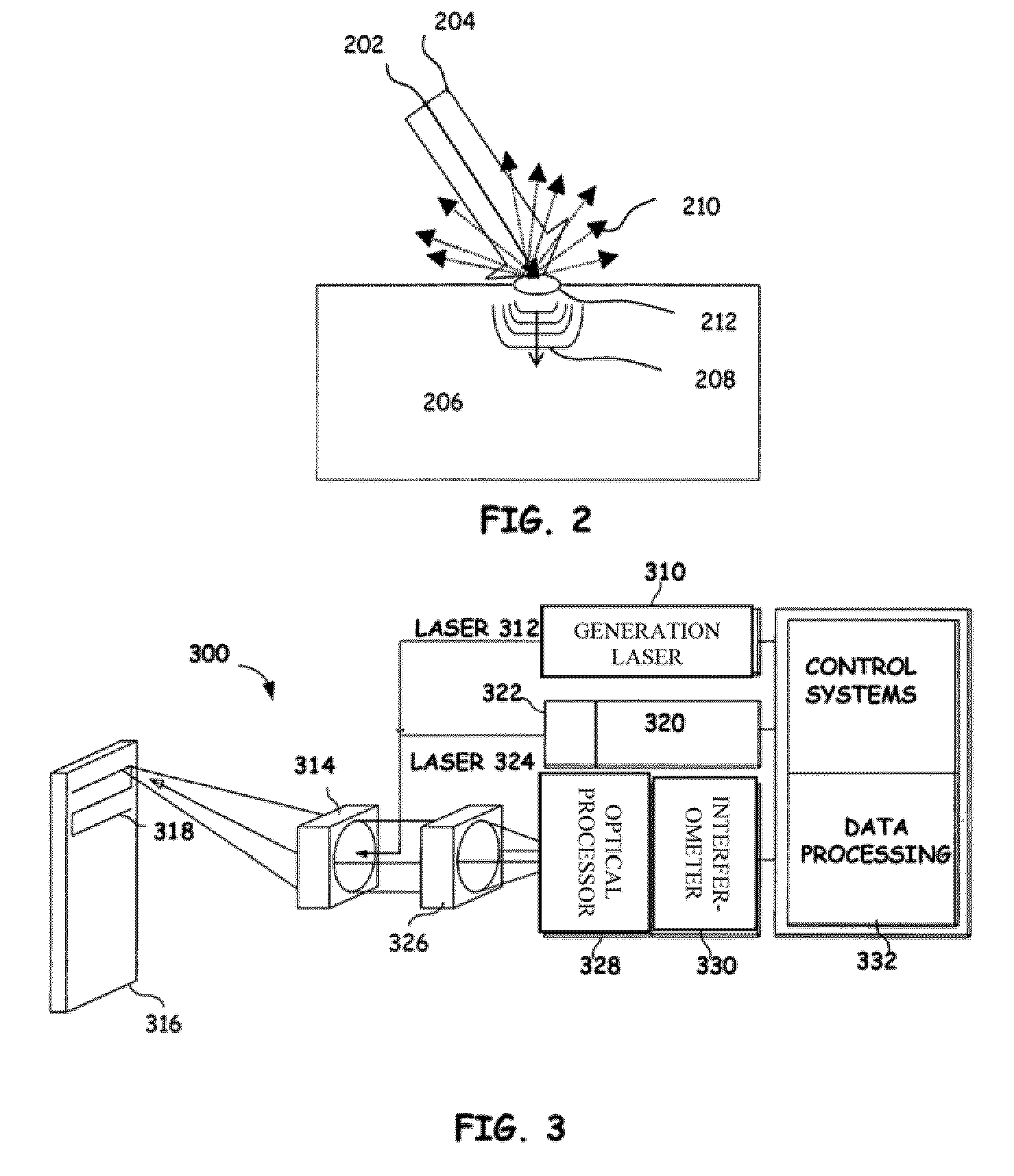
Articulated robot for laser ultrasonic inspection
ActiveUS20090010285A1Cost-effectiveMore compact robotsLaser using scattering effectsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveUltrasound sonography
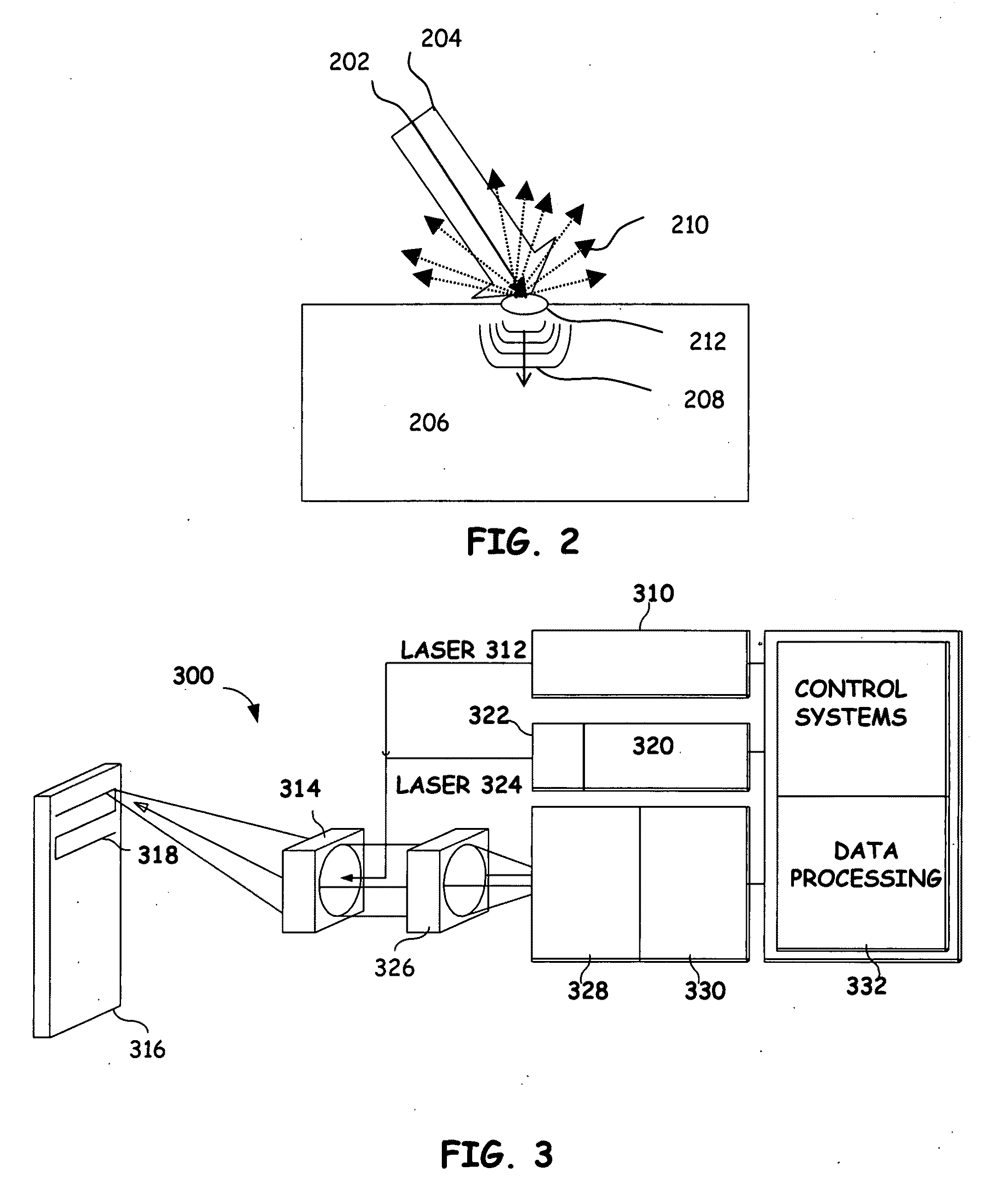
An ultrasonic non-destructive evaluation (NDE) system operable to inspect target materials is provided. This ultrasonic NDE system includes an articulated robot, an ultrasound inspection head, a processing module, and a control module. The ultrasound inspection head couples to or mounts on the articulated robot. The ultrasound inspection head is operable to deliver a generation laser beam, a detection laser beam, and collect phase modulated light scattered by the target materials. The processing module processes the phase modulated light and produces information about the internal structure of the target materials. The control module directs the articulated robot to position the ultrasound inspection head according to a pre-determined scan plan.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Novel intelligent universal high-speed screwing assembly robot
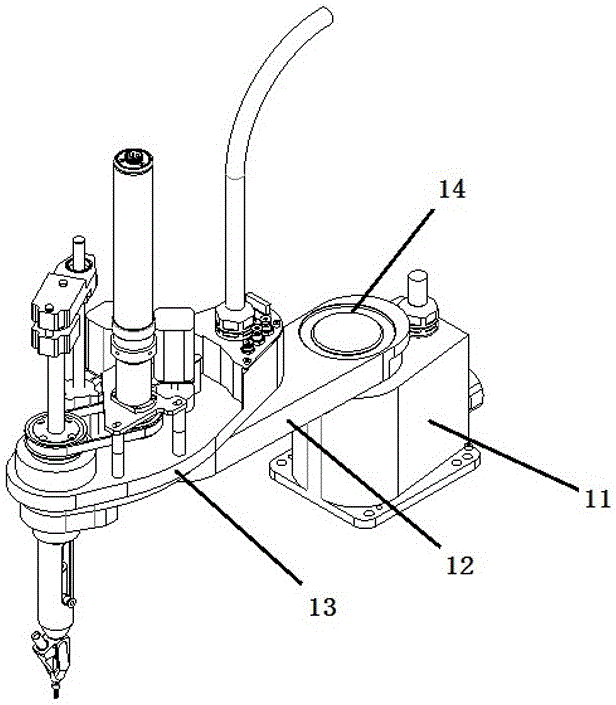
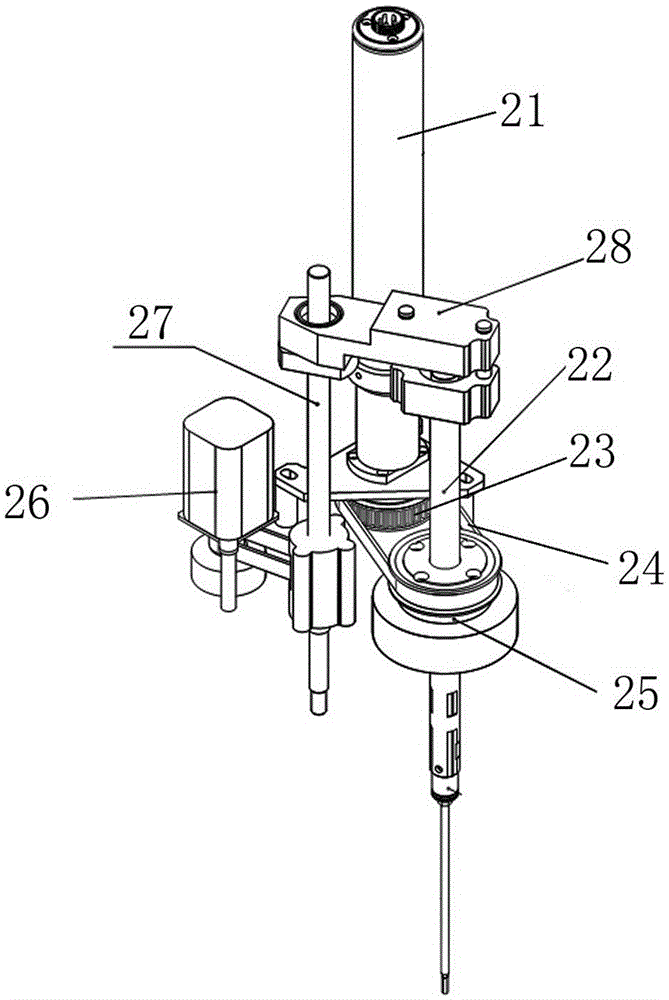
ActiveCN105081757AAchieve lockingAchieve positioningMetal working apparatusManipulatorSimulationArthrobotrys
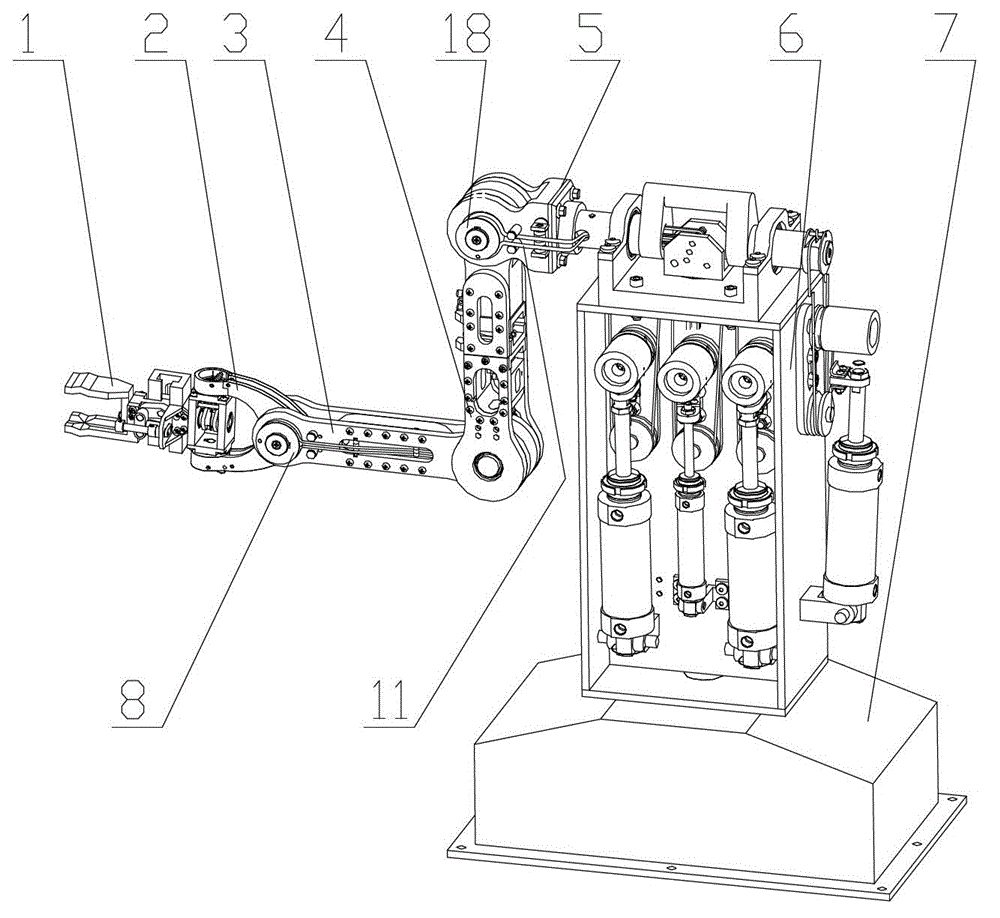
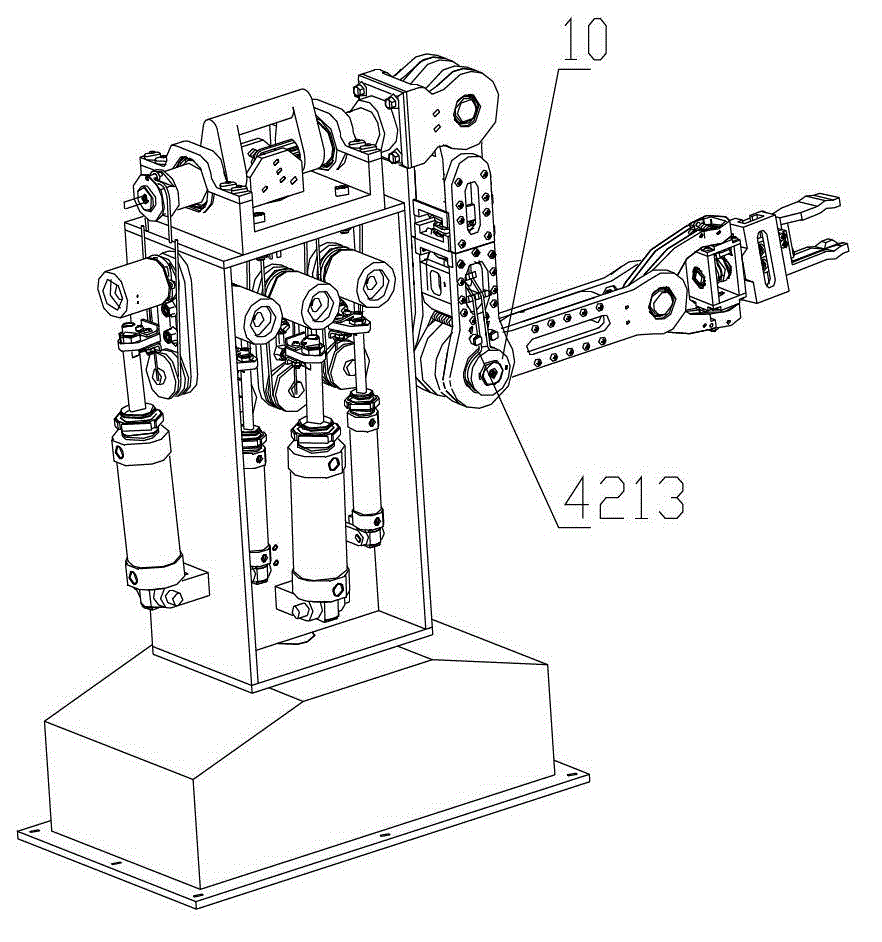
The invention discloses a novel intelligent universal high-speed screwing assembly robot. The novel intelligent universal high-speed screwing assembly robot comprises a horizontal joint robot base which comprises a locking device and an ejection device. The horizontal joint robot base realizes position adjustment in the horizontal X direction and Y direction. The locking device realizes movement and rotation in the Z direction through a spline assembly to finish the locking movement of a screw. The ejection device enables the screw to be attached to the lower end of a lever, and the screw locking accuracy is improved. The novel intelligent universal high-speed screwing assembly robot is based on the prototype of a horizontal joint robot, the locking device is realized by ingeniously using the spline assembly structure in the horizontal joint robot, and the novel intelligent universal high-speed screwing assembly robot is good in universality and high in stability.
Owner:苏州博思特装配自动化科技有限公司
Rope-driving multi-joint robot
InactiveCN102941573ALow costHigh transmission precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsDegrees of freedomControl theory
The invention belongs to the field of joint robots, and particularly relates to a rope-driving multi-joint robot which is used for solving the transmission and arrangement problems of a multi-joint steel wire rope. The rope-driving multi-joint robot comprises hands, wrists, forearms, upper arms, shoulders, a waist and a base, wherein the waist is arranged on the base and is connected with the shoulders through crankshaft assemblies, the shoulders are connected with the upper arms through rotary joint shafts, the upper arms are connected with the forearms through driven gear components II on the rotary joint shafts, the forearms are connected with the wrists through driven gear assemblies I on the rotary joint shafts, the wrists are connected with the hands through the rotary joint shafts, all the parts are connected with one another so as to form a plurality of joints, a rope-driving unit of the joints is connected with one or more than two of the waist, the shoulders, the upper arms, the forearms, the wrists and the hands through flexible ropes, so that the rope-driving multi-joint robot is formed. The robot has eight degrees of freedom in total, and can fully exert the advantages of steel wire rope transmission, such as high transmission precision, and easiness in distribution.
Owner:庄德胜
Multi-joint robot and control program thereof
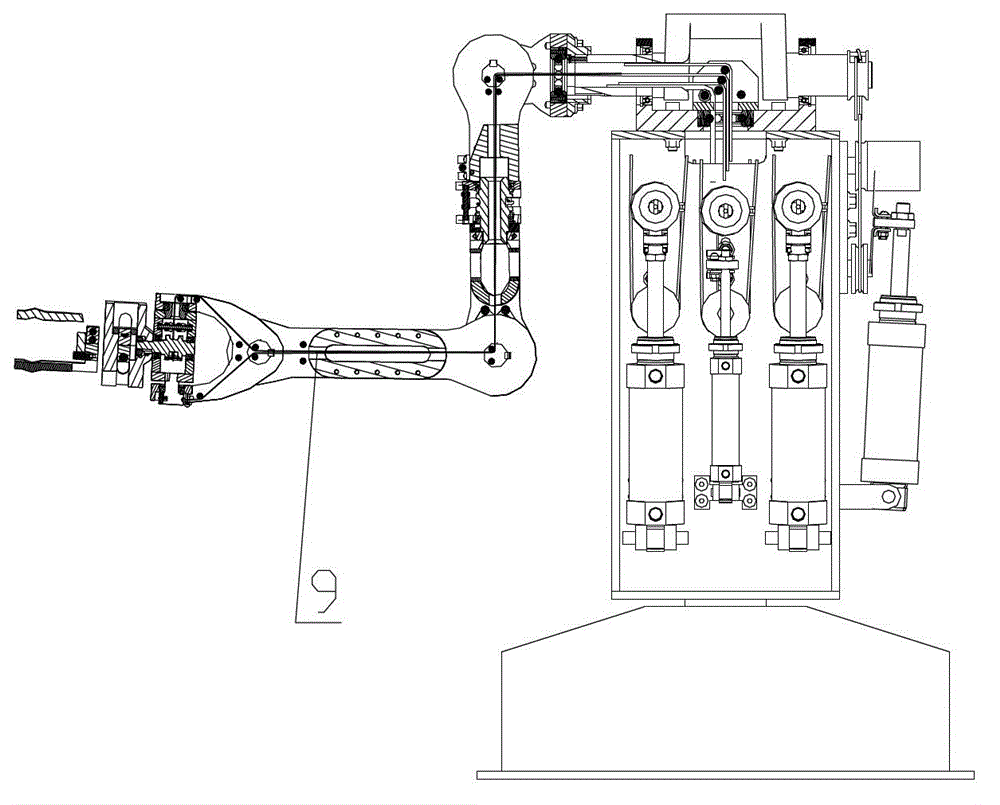
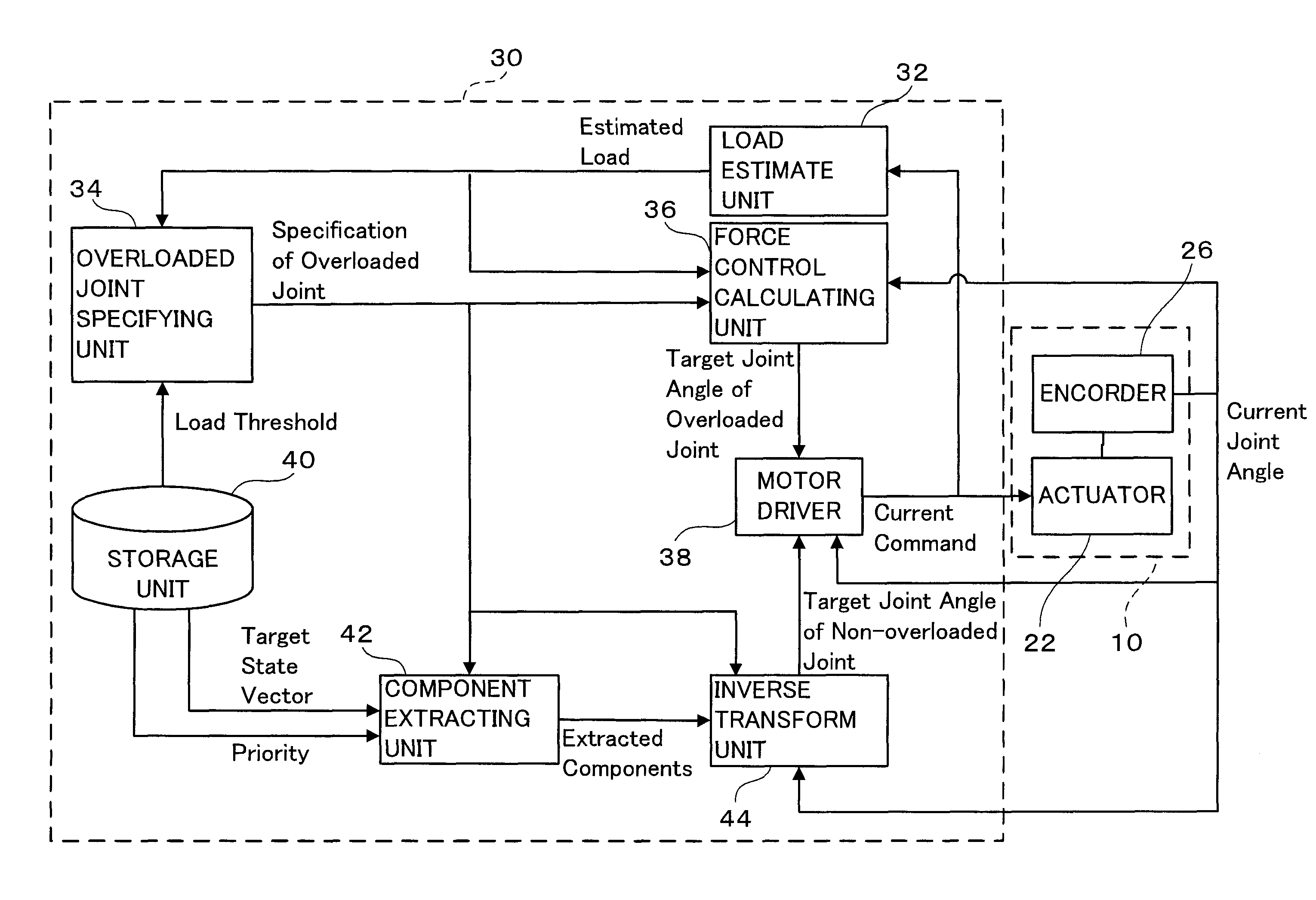
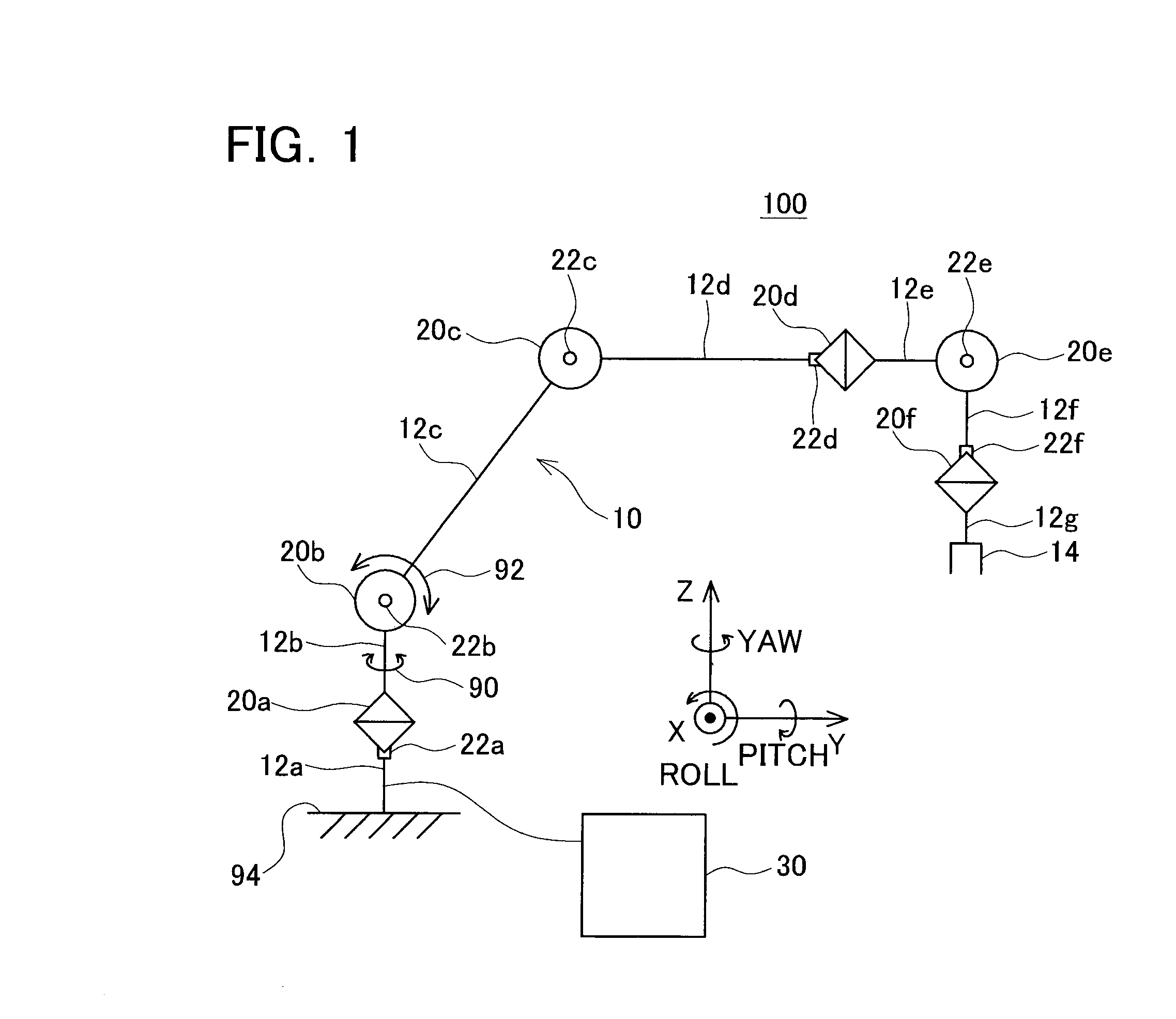
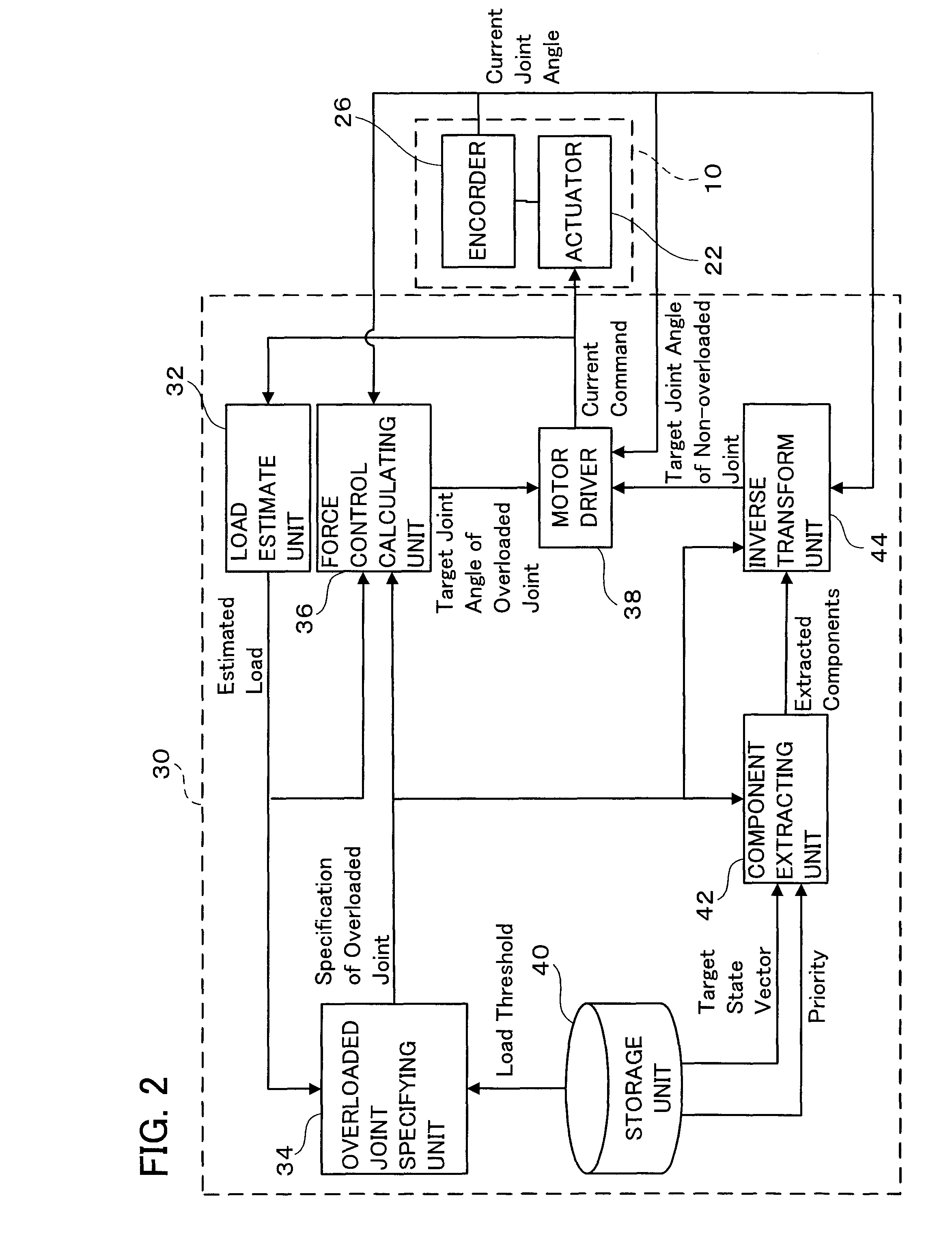
InactiveUS20100234999A1Easing overloaded stateFollow exactlyProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorTransformation unitArthrobotrys
The present invention provides a multi-joint robot that, when the loads acting on some of joints are overloaded, controls the joints so as to continue the work as far as possible while easing the overloaded state. The load estimate unit (32) estimates the load acting on each joint, and the overloaded joint specifying unit (34) specifies an overloaded joint of which the estimated load is greater than a threshold. The storage unit (40) stores a target state vector of an end link of the robot and stores a predetermined priority with respect to the components of the vector. The component extracting unit (42) extracts the same number of components as that of non-overloaded joints from the target state vector in order of a higher priority. The force control calculating unit (36) determines the target drive quantity for driving the overloaded joint in the same direction as that of the load. The inverse transformation unit determines the target drive quantities with respect to the non-overloaded joints so as to realize the extracted components. Thus, the non-overloaded joints can be controlled so as to follow the target state vector as far as possible, while the overloaded joints are controlled in a direction to reduce the load.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Surgical robotic systems and methods thereof
ActiveUS20170071685A1Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceSupporting systemEngineering
An automated medical system and method for using the automated medical system. The automated medical system may comprise a robot support system. The robot support system may comprise a robot body. The robot support system may further comprise a selective compliance articulated robot arm coupled to the robot body and operable to position a tool at a selected position in a surgical procedure. The robot support system may further comprise an activation assembly operable to transmit a move signal to the selective compliance articulated robot arm allowing an operator to move the selective compliance articulated robot arm. The automated medical system may further comprise a camera tracking system and an automated imaging system.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
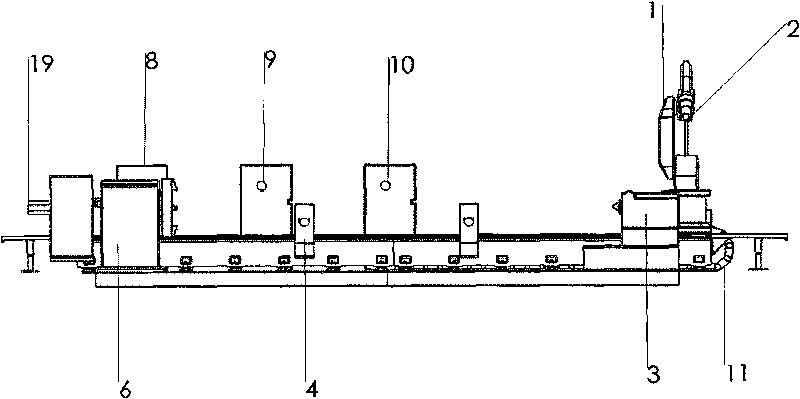
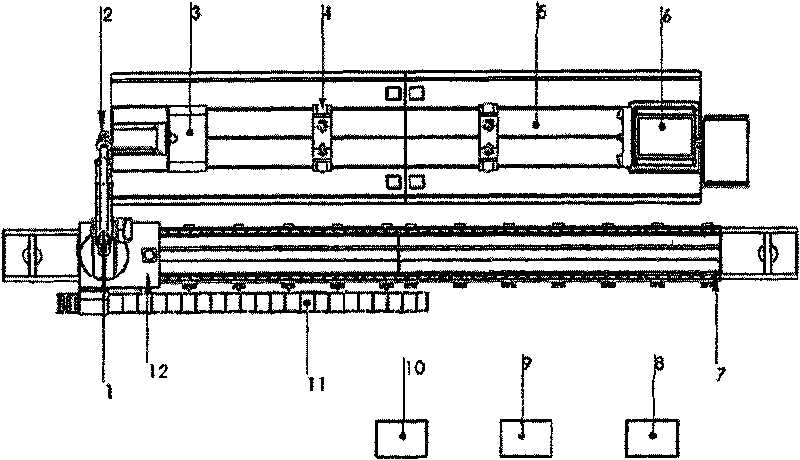
Multi-axis linkage numerical control laser processing system
InactiveCN101690993AOvercoming complexityDifficult to overcome controlLaser beam welding apparatusNumerical controlLaser processing
The invention provides a multi-axis linkage numerical control laser processing system, which is structurally characterized in that a workbench is provided with a linear guide rail, two ends of the guide rail are provided with a workbench tail seat and a headstock respectively, and two open center brackets are movably arranged on the guide rail and are positioned between the workbench tail seat and the headstock; a guide rail stand is arranged beside the workbench, the guide rail stand is provided with another parallel guide rail, and a movable sliding stand is movably arranged on the guide rail; a robot is fixed on the movable sliding stand, and a laser processing head is arranged at the tail end of a last joint of the robot; and a controller is connected with the robot and the movable sliding stand through control wires respectively so as to control the robot and control the movable sliding stand to drive the robot to move on the guide rail stand. The system solves the problem that a joint robot laser processing system has a small processing range, and can meet the numerical control laser processing requirements of parts of large size and super-large size.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Articulated robot
ActiveUS7597025B2Reduce dead spaceWide areaProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusElectric power transmissionRotational axis
An articulated robot capable of reducing dead space while maintaining a wide operating area and simplifying a power transmission system necessary for moving each joint. A plurality of joint arms A1 to A7 are connected via first rotating shafts 15, 15A, and 15B as horizontal rotating shafts and via second rotating shafts 32, 32A, and 32B as inclined rotating shafts alternately. A motor M for driving the rotating shaft and a speed-reducing mechanism are provided for each rotating shaft.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
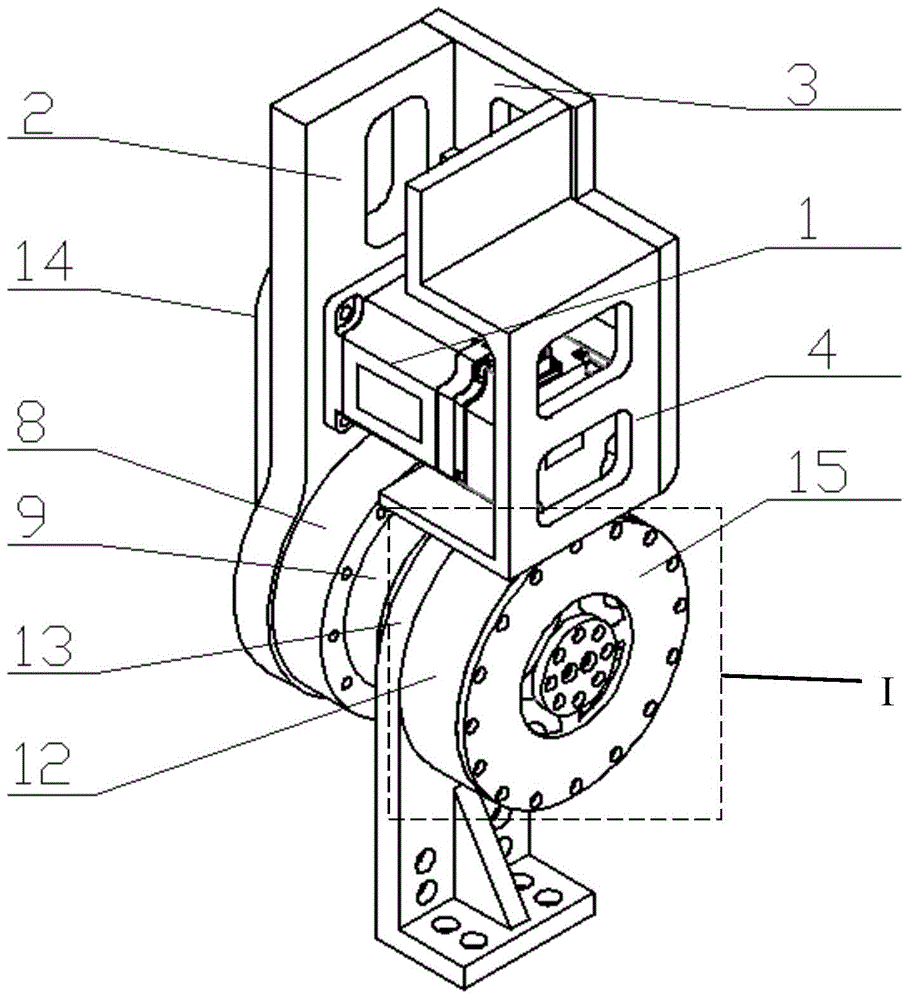
Crosshead shoes driving reducer for multi-joint robot
ActiveCN104964011ACompact structureReduce noiseGearing detailsFriction gearingsMechanical wearReducer
The invention relates to a crosshead shoes driving reducer for a multi-joint robot. The crosshead shoe driving reducer for the multi-joint robot comprises input shafts, output shafts, reducer bodies, crosshead shoes, transmission balls, track controllers and drive balls. The input shafts, the crosshead shoes, the track controllers and the output shaft are installed in the reducer bodies. Transmission tracks used for the installation of the transmission balls are arranged in the crosshead shoes. The transmission balls move in the transmission tracks to convey the movement of the input shafts to the track controllers. Moving track used for the installation of the drive balls are arranged on the lower surfaces of the track controllers. The track controllers adjust the output of the output shafts through the drive balls. According to the crosshead shoe driving reducer for the multi-joint robot, automatic adjustment for complete consistency of movement and eccentric magnitude of an eccentric shaft is achieved, the tracks of the transmission balls and the tracks of the track controllers of the reducer are completely consistent, the output of the reducer is stable, and the mechanical wear rate is low.
Owner:中正数据技术有限公司
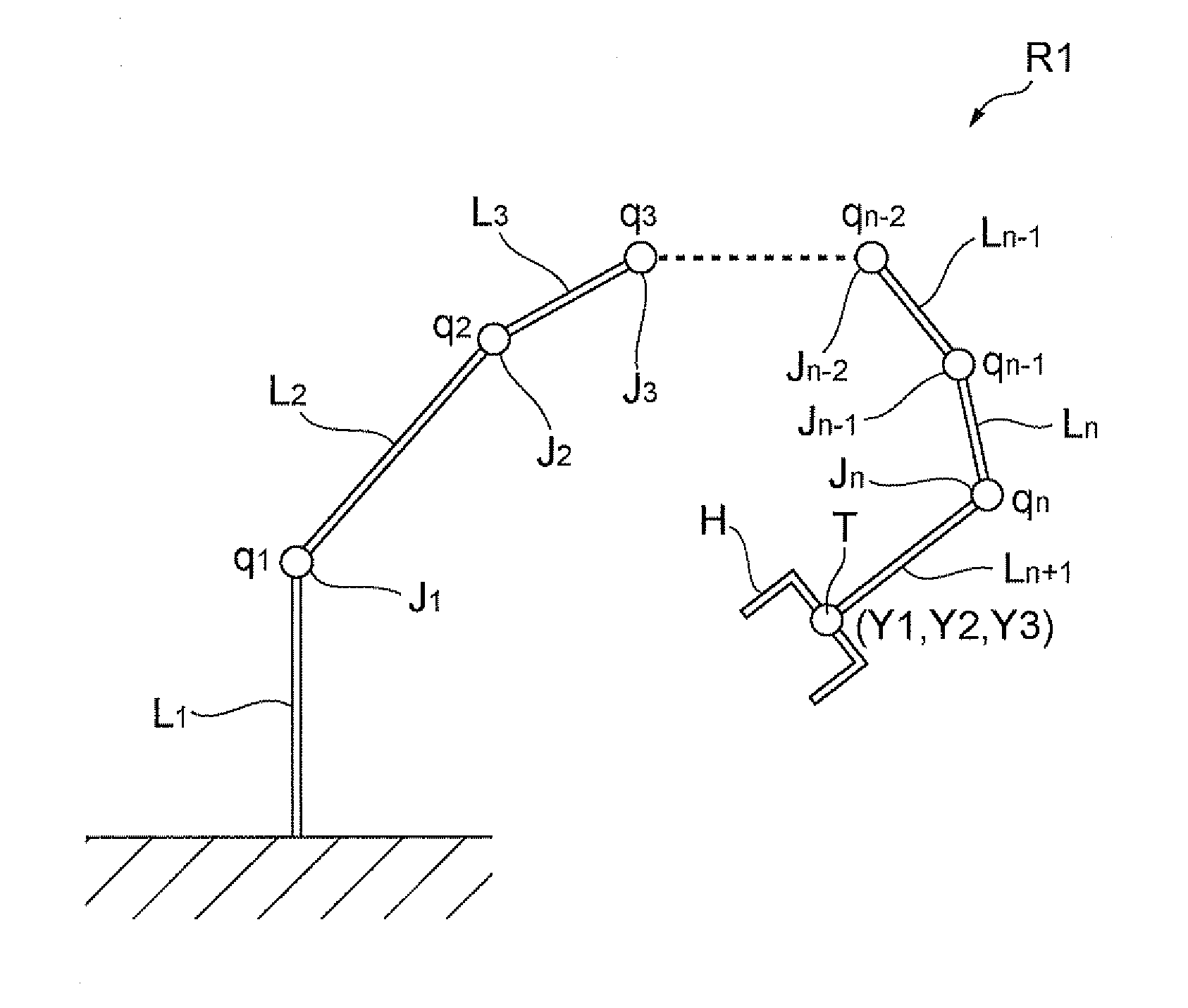
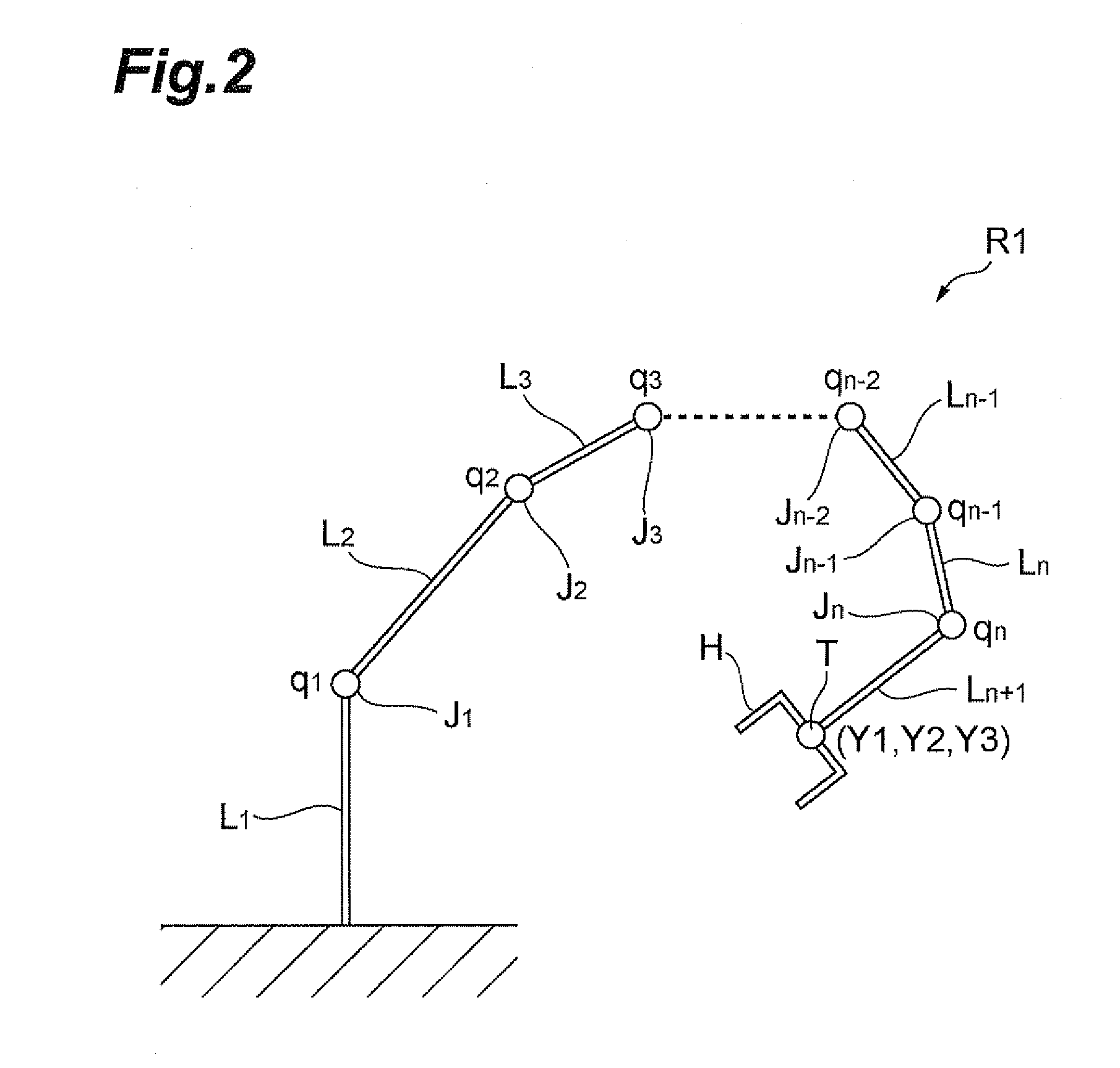
Movement path generation device for robot
InactiveUS20100204828A1Improve search efficiencyValid choiceProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpecial data processing applicationsPath generationEngineering
A movement path generating device for a robot is provided which can generate a movement path of a jointed robot satisfying a constraint condition and accomplishing optimization of various estimation conditions. The movement path generating device for a robot generating a movement path of a jointed robot with a dynamic constraint includes: constraint condition acquiring means for acquiring a constraint condition of the robot; estimation condition acquiring means for acquiring an estimation condition of the robot; posture generating means for generating a plurality of postures of the robot satisfying the constraint condition; posture estimating means for estimating the plurality of postures generated by the posture generating means on the basis of the estimation condition; posture selecting means for selecting one posture out of the plurality of postures generated by the posture generating means on the basis of the estimation result by the posture estimating means; and movement path generating means for generating the movement path of the robot using the posture selected by the posture selecting means.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
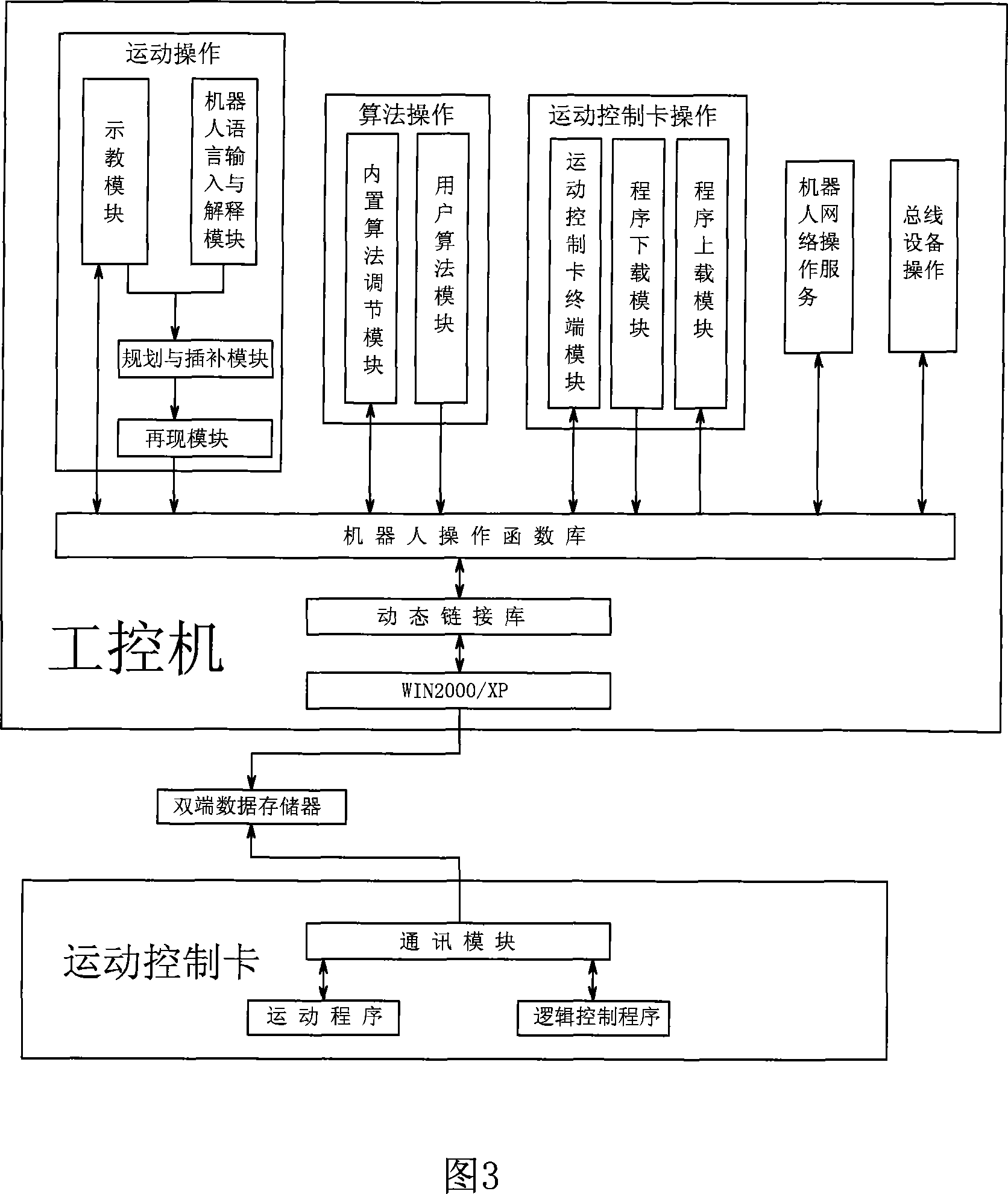
Open robotic system
ActiveCN101200064AImprove scalabilityGood configurabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorExtensibilityRobotic systems
The invention relates to an opening robot system, which comprises a multi-joint robot body and a controller for controlling the multi-joint robot body. The controller comprises a main control module, a motion control module communicated with the main control module through a first bus and a body control module communicated with the motion control module and controlling the multi-joint robot body. The controller can extend other function modules easily, such as a network control module for remote operation, and can integrate various external sensors. In different application situations, the users can modify the design of the controller or change the relevant module. As the opening robot system is in good expansibility, configurability and portability, the opening robot system has strong adaptability to different tasks.
Owner:KUSN HUAHENG ENG TECH CENT
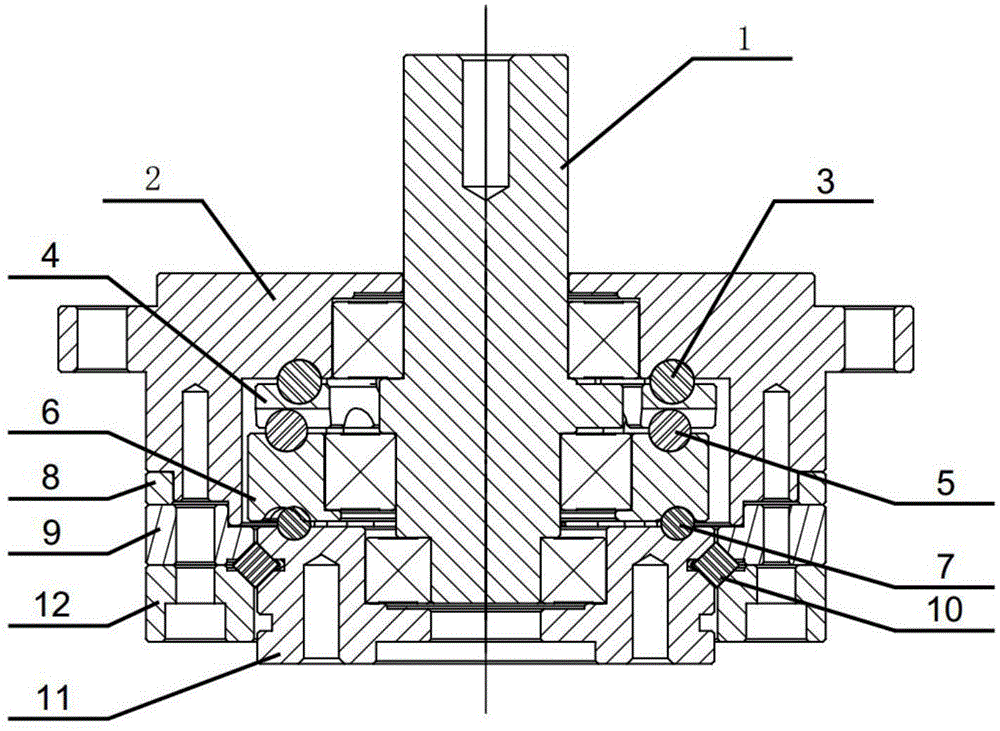
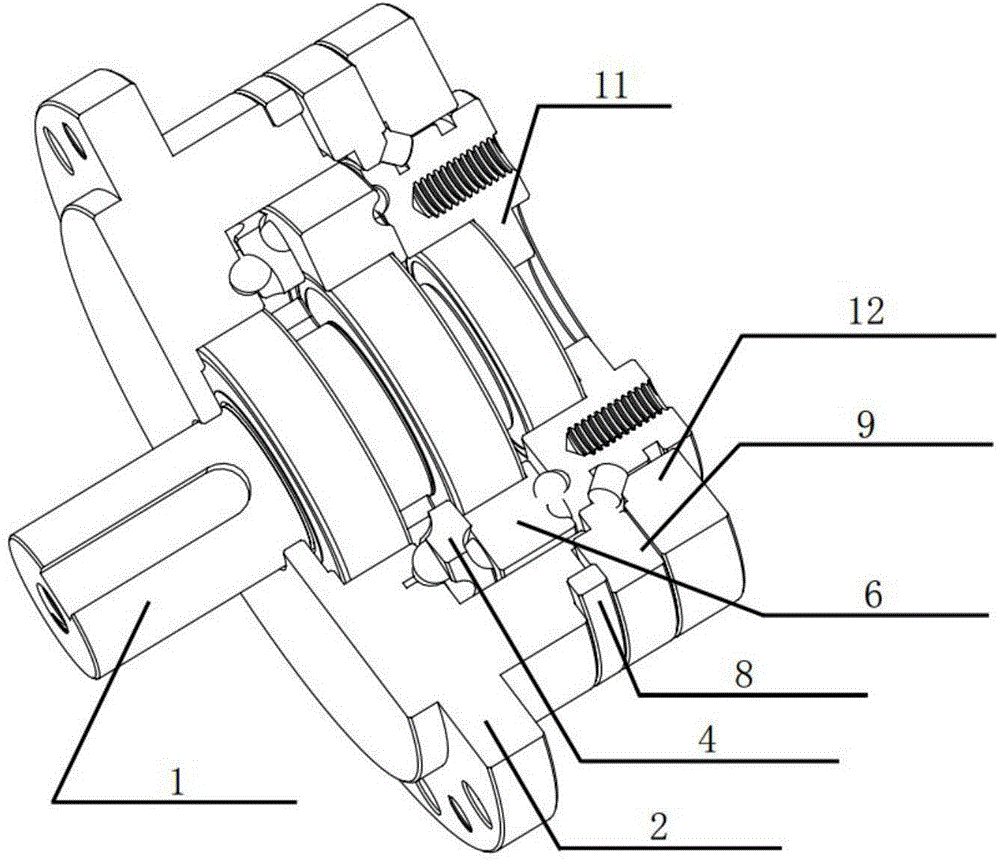
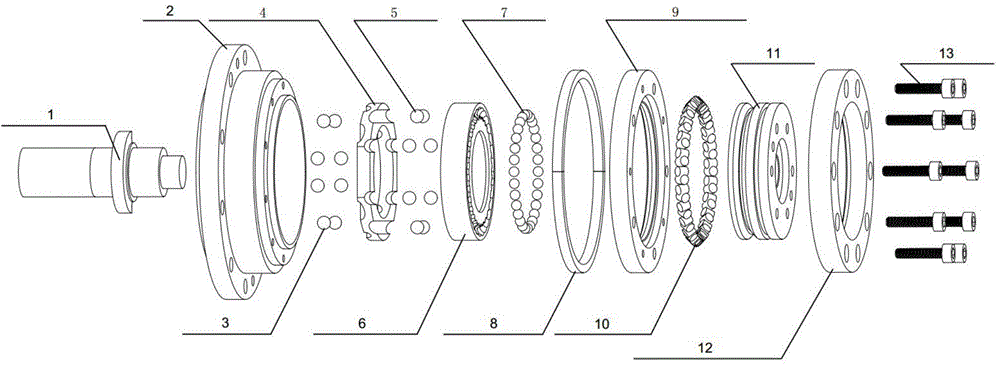
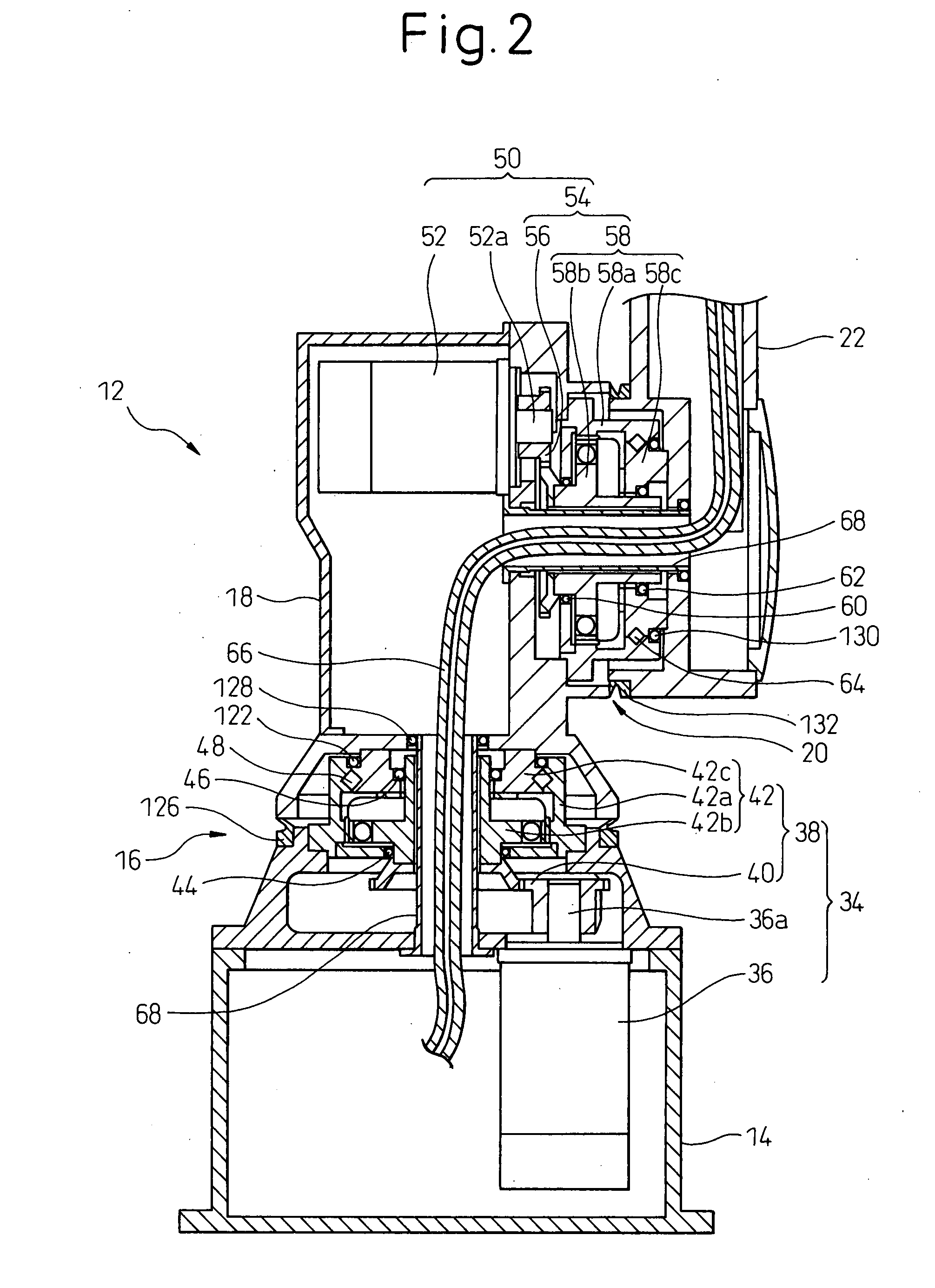
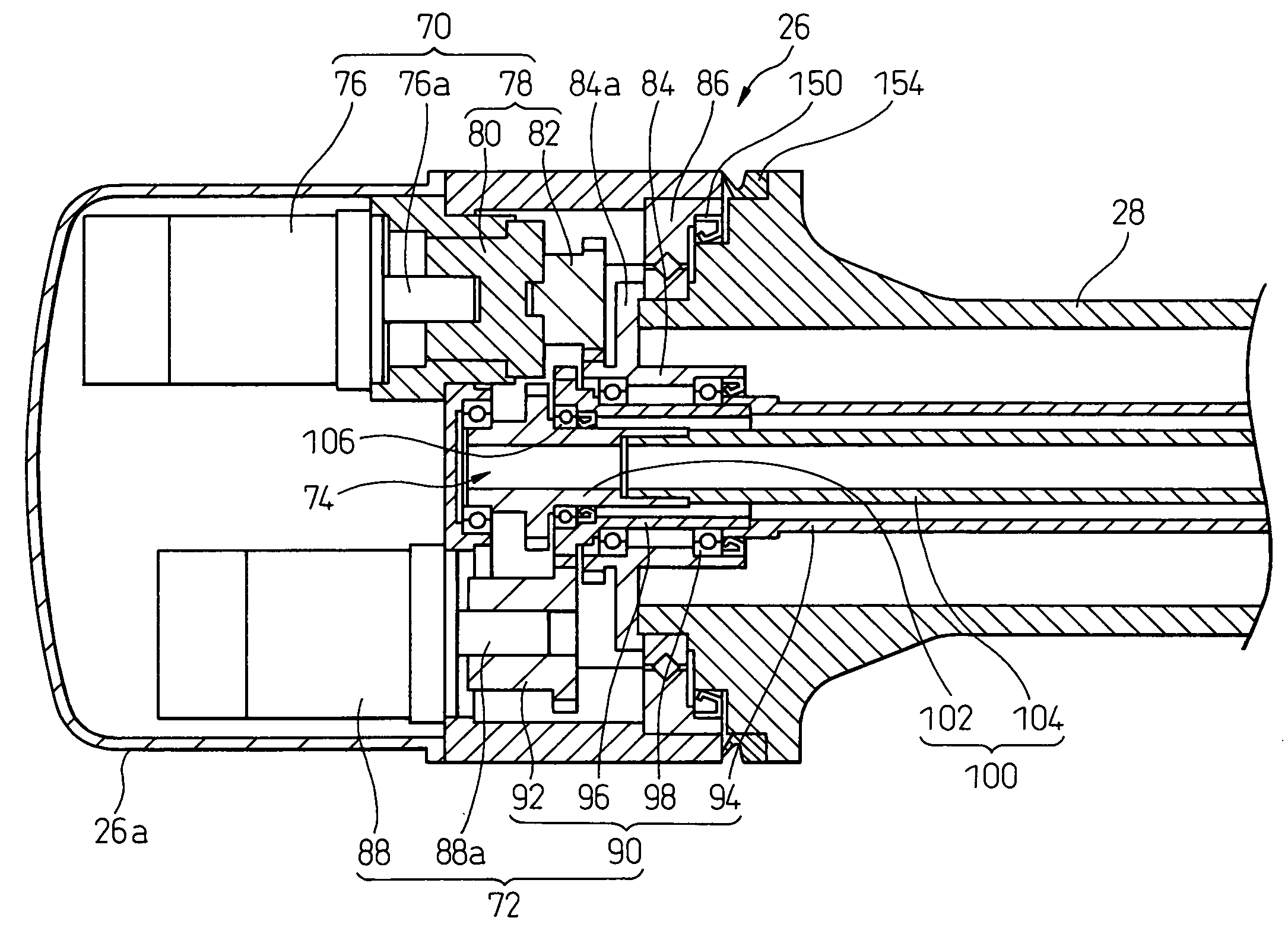
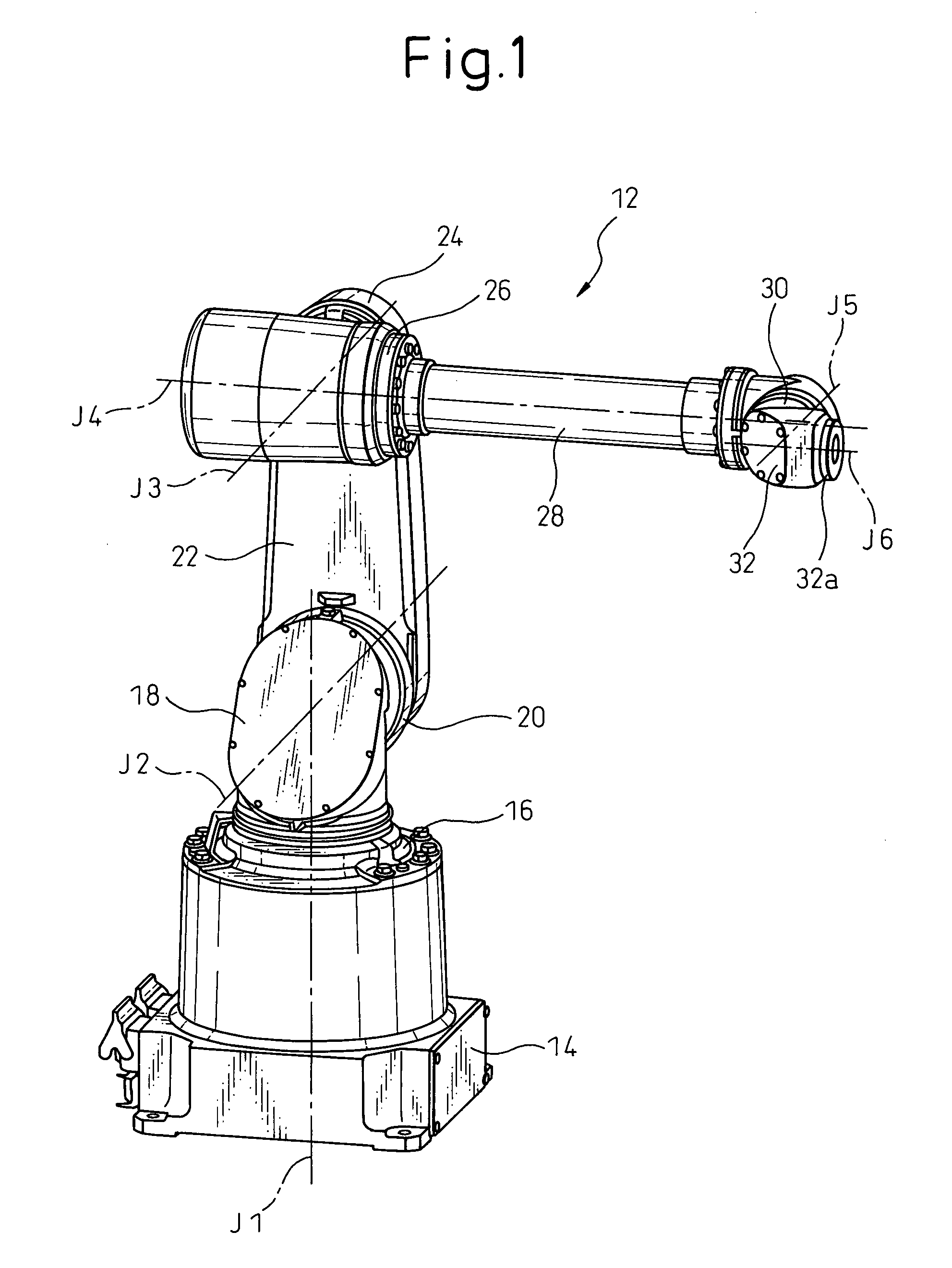
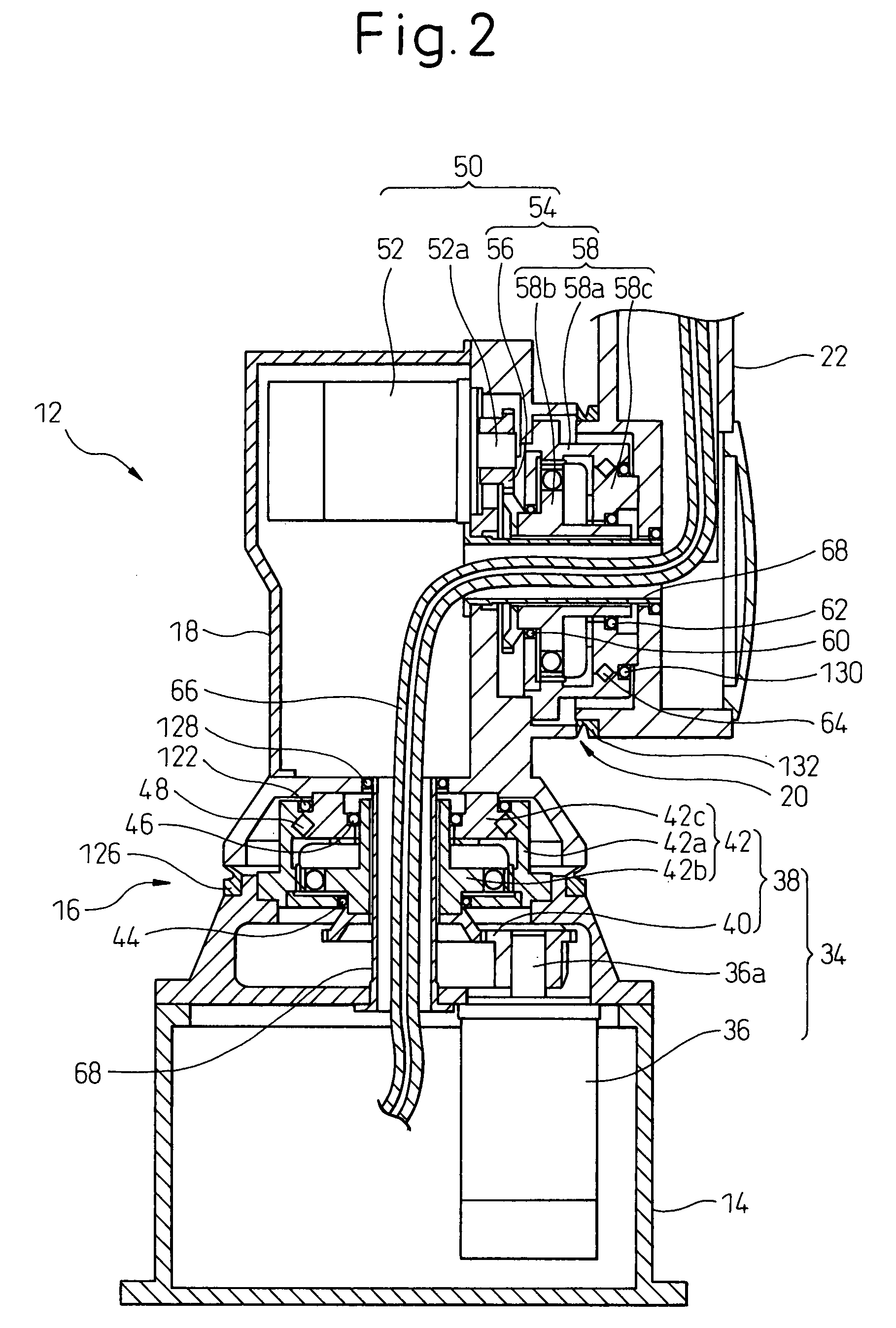
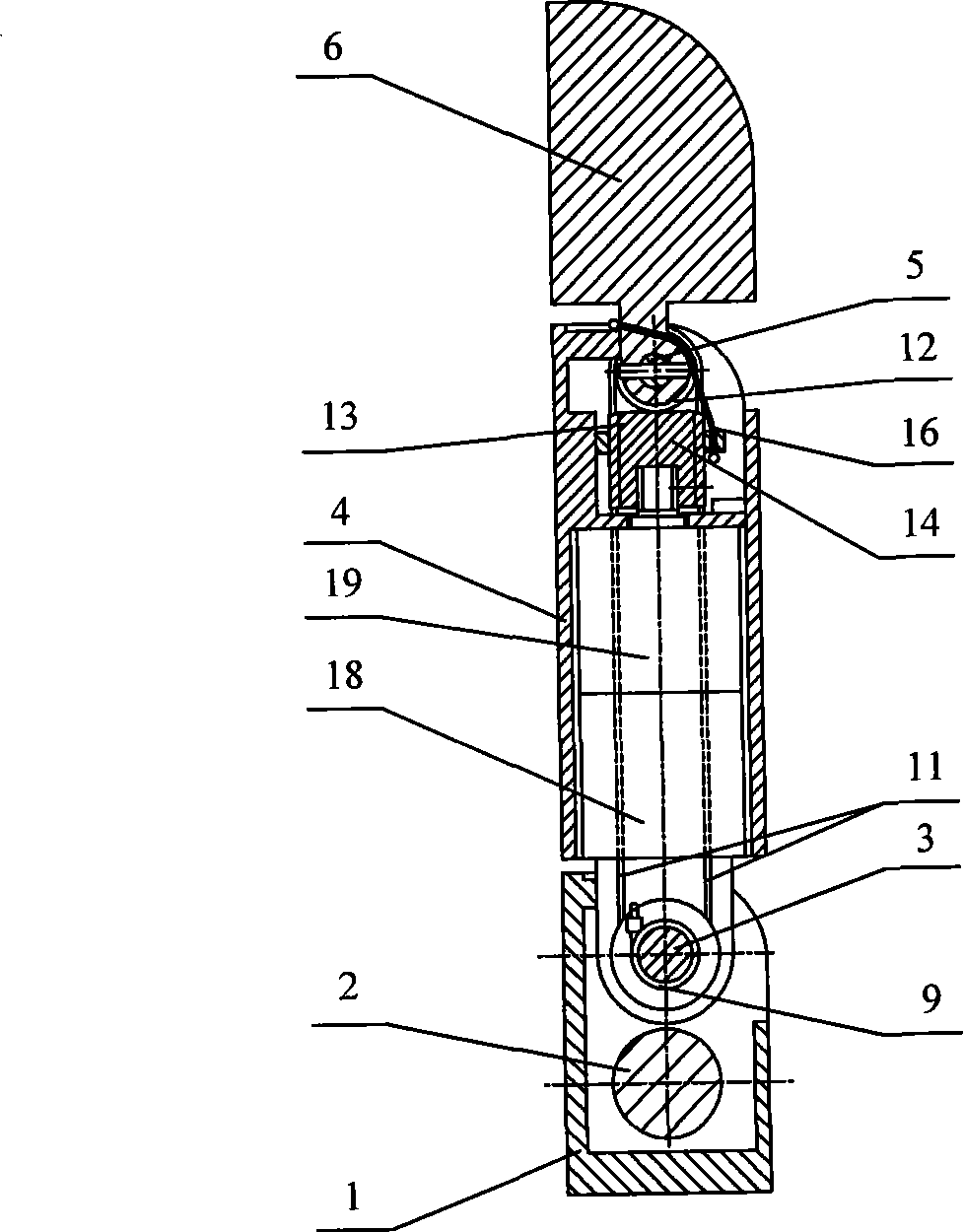
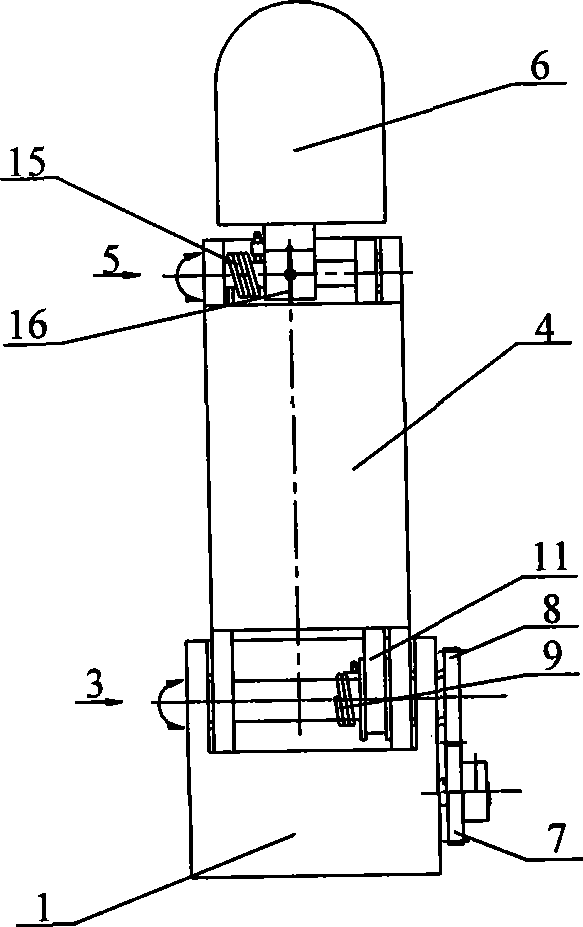
Sealing device for joint section of robot and articulated robot having the same
A sealing device provided to a joint section of a robot. The sealing device includes overlapped seal portions having a multi-stage configuration, provided for a driving mechanism incorporated into the joint section. The overlapped seal portions include a first seal portion including a first contact seal element sealing a first inter-member gap defined adjacent to a lubricant retaining section provided in the driving mechanism; and a second seal portion arranged outside the first seal portion and including a second contact seal element sealing a second inter-member gap defined in a circumferential wall of the joint section, the circumferential wall defining an accommodation space for accommodating the driving mechanism.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Synchronous spraying device for large machine
InactiveCN105772293ARealize simultaneous sprayingEnsure consistencySpraying apparatusArthrobotrysMechanical engineering
The invention provides a synchronous spraying device for a large machine. The synchronous spraying device comprises a plurality of movable bases (1), wherein a six-axis joint robot is installed on each movable base (1), and a spray gun is installed at the tail end of each six-axis joint robot; a steel plate (2) is arranged at the front end of each movable base (1), a piston cylinder (3) is further horizontally arranged at the front end of each movable base (1), the outer end of a piston rod of each piston cylinder (3) is level with the outer side of the corresponding steel plate (2) while retracting, and an electrically-controlled magnetic attraction device (4) is arranged at the rear end of each movable base (1); and the movable bases (1) attract the electrically-controlled magnetic attraction devices (4) through the steel plates (2) and are sequentially connected in series to form an integrated movable platform. According to the synchronous spraying device provided by the invention, the integrated movable platform formed by sequentially connecting the plurality of movable bases (1) in series is provided, and synchronous spraying of all the six-axis joint robots can be realized; and moreover, the problem of interference is avoided, and the consistency of the spraying quality of parts of the large machine can be ensured.
Owner:李富平
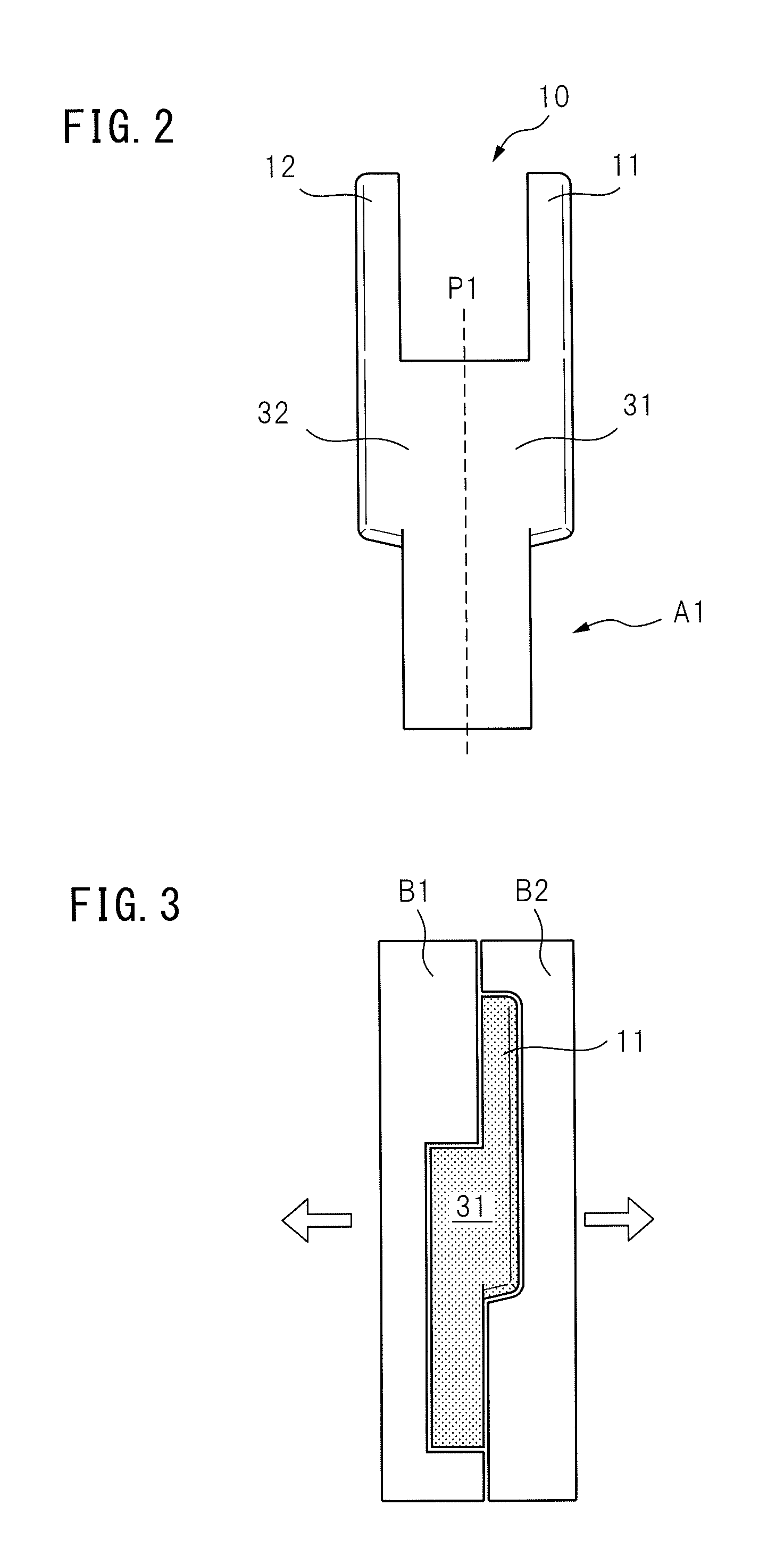
Multi-joint robot with both-side supported arm member
InactiveUS20140047940A1Programme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusRotational axisControl theory
In a multi-joint robot (1) including a first arm member (A1) providing a U-shaped portion (10) composed of two protrusion units (11, 12) parallel with each other, and including a second arm member (A2) connected to two protrusion units of the U-shaped portion so as to be rotated and such that both sides of the second arm member are supported by two protrusion units, the first arm member is formed by two half form portions (31, 32) that are divided between the two protrusion units of the U-shaped portion and are divided on a plane perpendicular to a rotational axis of the second arm member. Moreover, the first arm member includes a coupling unit (45a, 45b) for coupling two half form portions to each other.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Articulated robot for laser ultrasonic inspection
ActiveUS7784348B2Cost-effectiveMore compact robotsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesLaser using scattering effectsNon destructiveUltrasound sonography
An ultrasonic non-destructive evaluation (NDE) system operable to inspect target materials is provided. This ultrasonic NDE system includes an articulated robot, an ultrasound inspection head, a processing module, and a control module. The ultrasound inspection head couples to or mounts on the articulated robot. The ultrasound inspection head is operable to deliver a generation laser beam, a detection laser beam, and collect phase modulated light scattered by the target materials. The processing module processes the phase modulated light and produces information about the internal structure of the target materials. The control module directs the articulated robot to position the ultrasound inspection head according to a pre-determined scan plan.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Full-automatic robot gluing equipment and process technology
The invention relates to the technical field of gluing, in particular to full-automatic robot gluing equipment and a process technology which are used for two-component polyurethane gluing. The full-automatic robot gluing equipment is characterized in that the equipment comprises a three-axis robot or a four-axis robot or a five-axis robot or a six-axis robot, a glue supply device, a two-component gluing head, a two-station automatic gluing workbench or a multi-station automatic rotary gluing workbench, plasma treatment equipment, a waste cleaning solution recovery device and an intelligent control system. The three-axis robot or the four-axis robot is of a gantry type or cantilever type structure. The two-component gluing head and a plasma treatment head are fixed to the three-axis robot or the four-axis robot and can be linked in the X axis, the Y axis and the Z axis. The five-axis robot or the six-axis robot is an articulated robot, and five-axis linkage or six-axis linkage of the two-component gluing head and the plasma treatment head can be achieved. According to the novel polyurethane gluing equipment and the process technology, the proportion is precise, glue tape performance is stable, and the sealing effect is good.
Owner:DALIAN HUAGONG INNOVATION TECH
Method of detection of welding workpiece position using movable electrode
A method of detection of a welding workpiece position using a movable electrode, in a spot welding system, a welding workpiece and a spot welding gun are moved relatively by a multi-articulated robot, such that the movable electrode is closed to the welding workpiece or the movable electrode is separated from the welding workpiece, simultaneously, a current or torque of a servo motor is monitored, and a surface position of the welding workpiece is detected from the position of the movable electrode and the position of the multiarticulated robot when the trend of the current or torque changes.The spot welding system comprises: the spot welding gun having the movalbe electrode driven by the servo motor and a counter electrode arranged facing the movable electrode, and the multiarticulated robot for holding one of the welding workpiece and the spot welding gun. Thereby, the precision of detection of the surface position of the welding workpiece by the movable electrode in the spot welding system can now be improved without lengthening the time required for detection of the surface position of the welding workpiece.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Novel four-degree-of-freedom articulated robot structure
ActiveCN104385260ACompact structureConvenient ArrangementProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsDegrees of freedomEngineering
The invention discloses a novel four-degree-of-freedom articulated robot structure. The novel four-degree-of-freedom articulated robot structure comprises a base, a lifting seat, a first mechanical arm, a Y-axis cover, a second mechanical arm, and an operation main shaft, wherein the lifting seat vertically moves in the direction of a Z-axis under the limiting actions of a lead screw, a lead screw, and a guide rail pair, the first mechanical arm can rotate around an X-axis parallel to the Z-axis to be installed on the lifting seat, the Y-axis cover is installed on the first mechanical arm, bears a first Y-axis speed reduction device shaft and a second Y-axis speed reduction device shaft, and is provided with through holes for a Y-axis servo motor shaft, the first Y-axis speed reduction device shaft and the second Y-axis speed reduction device shaft to penetrate, the second mechanical arm can rotate around the Y-axis parallel to the X-axis to be installed on the first mechanical arm, and the operation main shaft can rotate around an R-axis parallel to the Y-axis to be installed on the second mechanical arm. The novel four-degree-of-freedom articulated robot structure is simple in structure, low in cost, large in operation space, and high in operation accuracy.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Elastic-deformation-compensation control device and control method for articulated robot
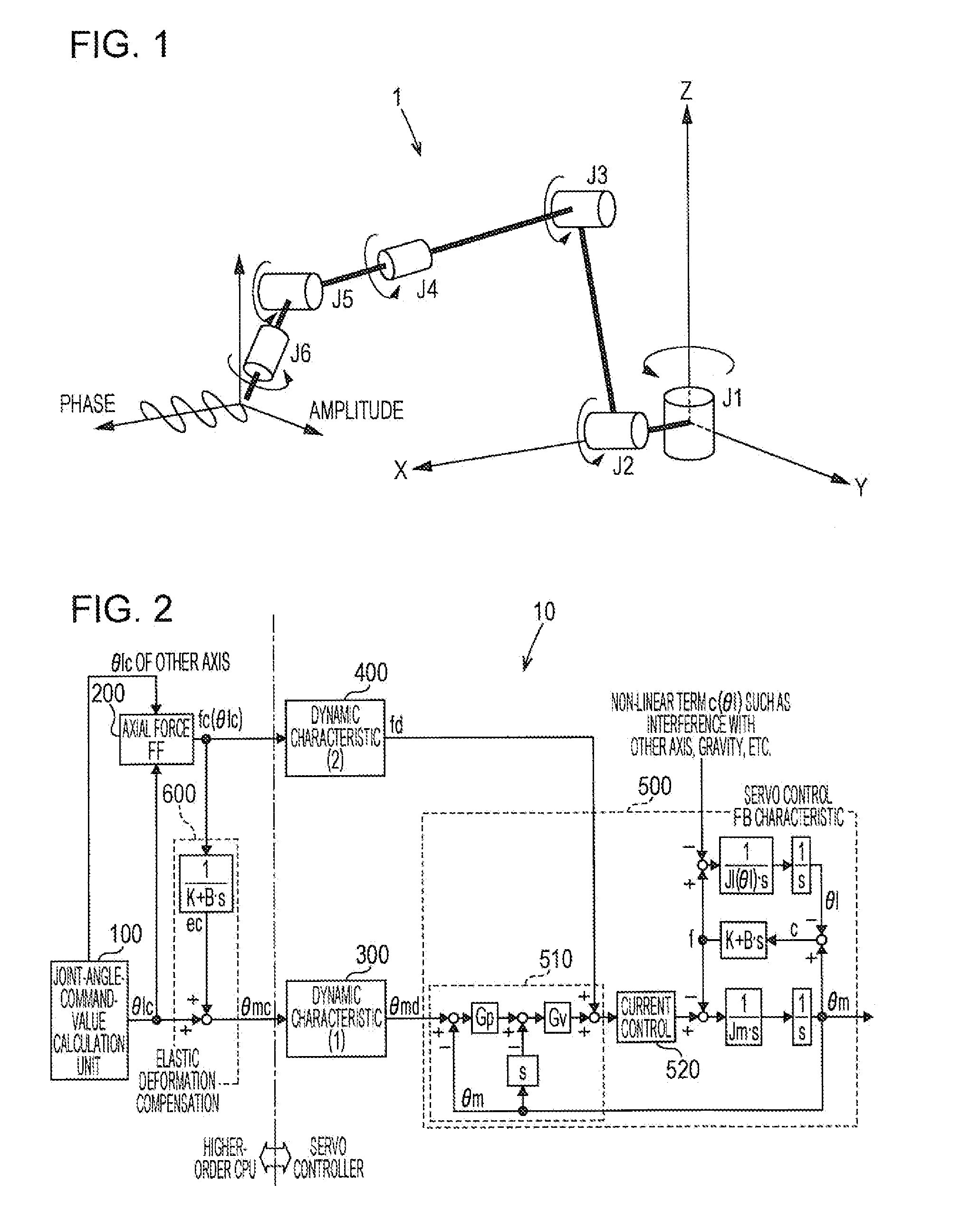
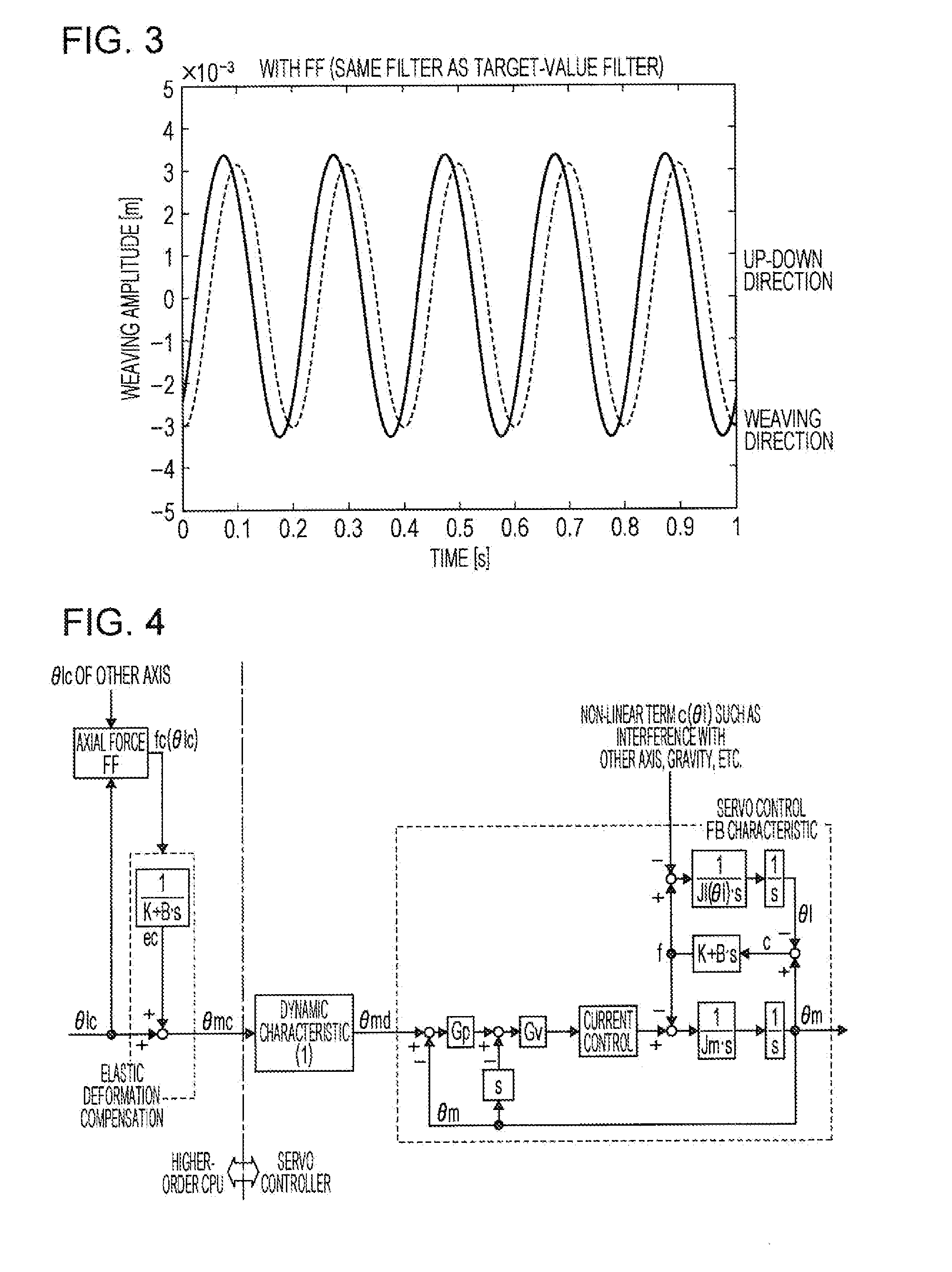
ActiveUS20150105905A1Improve trajectory accuracyImprove accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlAxial forceControl theory
In an elastic-deformation-compensation control device (10), a first dynamic characteristic calculation unit (300) performs filtering processing with respect to a motor-angle command value (θmc) outputted from a motor-angle-command-value calculation unit (600), and outputs a processed motor-angle target value (θmd). A second dynamic characteristic calculation unit (400) is provided with a high-frequency cutoff characteristic having a cutoff frequency which is lower than that of the first dynamic characteristic calculation unit (300), performs filtering processing with respect to the output from an axial force torque calculation unit (200), and outputs a processed axial force torque compensation value (fd).
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Sealing device for joint section of robot and articulated robot having the same
A sealing device provided to a joint section of a robot. The sealing device includes overlapped seal portions having a multi-stage configuration, provided for a driving mechanism incorporated into the joint section. The overlapped seal portions include a first seal portion including a first contact seal element sealing a first inter-member gap defined adjacent to a lubricant retaining section provided in the driving mechanism; and a second seal portion arranged outside the first seal portion and including a second contact seal element sealing a second inter-member gap defined in a circumferential wall of the joint section, the circumferential wall defining an accommodation space for accommodating the driving mechanism.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Connection rod key slot type coupling under-actuated double-joint robot finger device
A connection rod key slot type coupling under-actuated double-joint robot finger device belongs to the technical field of personification robot hand design. The device comprises a base, a motor, a speed reducer, a first finger section, a second finger section, a far joint shaft, a near joint shaft and a coupling transmission mechanism. The coupling transmission mechanism comprises a connection rod, a push rod and a connection shaft. The device comprehensively achieves effective blending of coupling grabbing effect and self-adapting under-actuated grabbing effect in the mode of key slot transmission and spring decoupling. The device only adopts two connection rods to form the transmission mechanism, is simple in structure and achieves the coupling self-adapting grabbing effect through only one spring. The appearance of the fingers and action for grabbing objects are similar to human fingers. The device is low in requirement for a control system and is suitable for serving as fingers of common personification robot hands.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Hybrid type industrial robot
The invention relates to a hybrid type industrial robot. The hybrid type industrial robot is composed of three linear motion shafts X, Y and Z, a swing shaft C and two rotary shafts A and B. Primary forms of the linear motion shafts are cantilever type (ox-head type) rectangular coordinate manipulators. The rotary shaft B is connected with the tail end of the shaft Z which does up-down linear motion. The swing shaft C and the rotary shaft A are arranged under the rotary shaft B and driven by the same. The rotary shaft A at the tail end is connected to the tail end of the swing shaft C through a connecting side plate and drives loading motion. The rotary shafts and the swing shaft actually are motion shafts at the tail end of a joint robot. Thus the hybrid type industrial robot is composed of the rectangular coordinate manipulators and the motion shafts at the tail end of the joint robot. By the hybrid type industrial robot, rapid and highly difficult reclaiming motion is achieved, load ratio is increased, use efficiency of an injection molding machine is improved, and space for mounting is smaller.
Owner:NINGBO WELLLIH ROBOTS TECH CO LTD
Displacement under-actuated two-articulated robot finger device based on flexible piece
The invention discloses a displacement shift underactuated two-joint robot finger device based on a flexible piece, which pertains to the technical field of anthropomorphic robots and comprises a base, a first motor, a near joint shaft, a middle finger section, a far joint shaft, an end finger section, a first transmission mechanism and a first spring piece, as well as a second motor, the flexible piece and a second spring piece. The second motor is fixedly connected with the middle finger section, two ends of the flexible piece are respectively connected with the output shaft of the second motor and the end finger section, and the second spring piece is connected to a driving chain from the near joint shaft to the far joint shaft in series. The device uses the motors, the transmission mechanism, the flexible piece and the spring pieces to comprehensively realize the special effect of variable original configuration and self-adapting grabbing of fingers. The device leads the middle joint to bend so as to achieve good grabbing preparation posture before grabbing, and grabs the object in the self-adapting underactuated manner during grabbing. The device has the grabbing action which more approaches to the hands of human, and can stably grab and automatically adapt to objects of various shapes and sizes, thus being applicable to robot hands.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
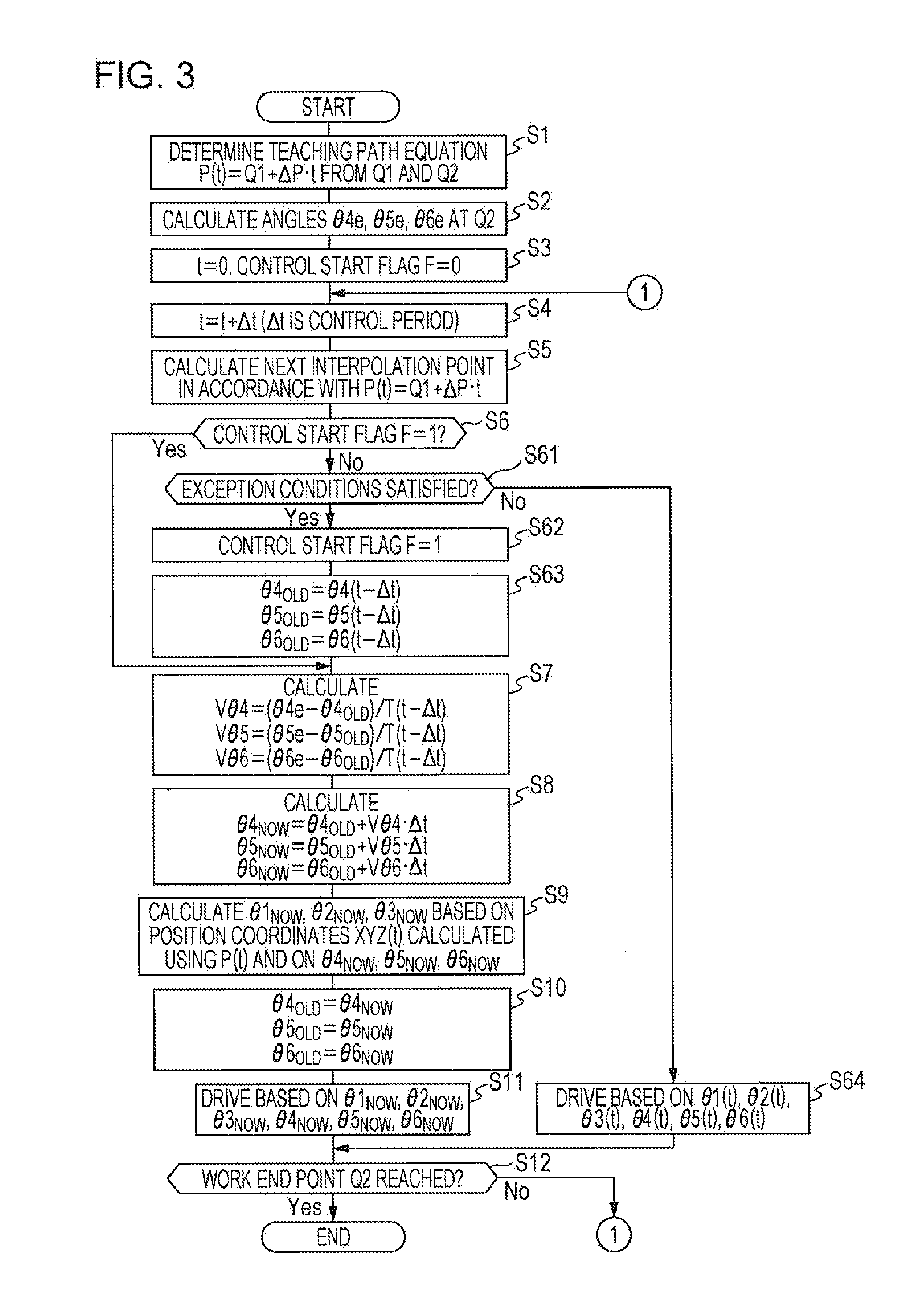
Control device, control method, and control program for articulated robot
ActiveUS20130345868A1Reliably reachProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlDrive shaftSituated computing
The purpose of the present invention is to have the angles of each of the drive shafts of the first articulated drive system infallibly reach the angle of the work completed position, while maintaining the rate of movement and position of the working parts of an articulated robot. If exception conditions are not satisfied, the drive shafts of first and second articulation drive systems are driven individually (S64) on the basis of interpolated points calculated in step 5 (S5). After exception conditions are satisfied (Yes side of S61), until the working parts reach the work completed position (No side of S12), the angle of each of the drive shafts of the first articulated drive system required to vary each of the drive shafts of the first articulated drive system in a linear manner with the angle at the work completed position as a target is calculated (S8), and the angle of each of the drive shafts of the second articulated drive system is calculated on the basis of the position of the working part at the interpolated point calculated in step 5 (S5) and the angle of each of the drive shafts of the first articulated drive system as calculated (S9), and the drive shafts of the first and second articulated drive systems are driven according to said calculation results (S11).
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Planar multi-joint robot
ActiveCN104249366AEasy to moveAdapt to the needs of battery replacementProgramme-controlled manipulatorAutomotive batteryPush pull
The invention provides a planar multi-joint robot which comprises a rotary table mechanism, a lifting mechanism, a rotating mechanism and a push-pull mechanism, wherein the lifting mechanism is arranged on the rotary table mechanism; the lifting direction of the lifting mechanism is perpendicular to a rotating plane of the rotary table mechanism; the rotating mechanism is connected with the lifting mechanism in a pivoting manner; the rotating plane of the rotating mechanism is perpendicular to the lifting direction of the lifting mechanism; the push-pull mechanism is connected with the rotating mechanism and is provided with a space for containing an automobile battery. The push-pull mechanism for loading and unloading the automobile battery can realize multi-rotation through rotation of the rotary table mechanism and rotation of the rotating mechanism; by lifting of the lifting mechanism on the rotary table mechanism, the push-pull mechanism can move up and down, and multi-dimensional movement of the push-pull mechanism in the space is realized. According to the planar multi-joint robot, the flexibility of battery exchange is improved; a requirement on automobile battery exchange can be met, so that the battery can be accurately replaced on an automobile at different positions.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
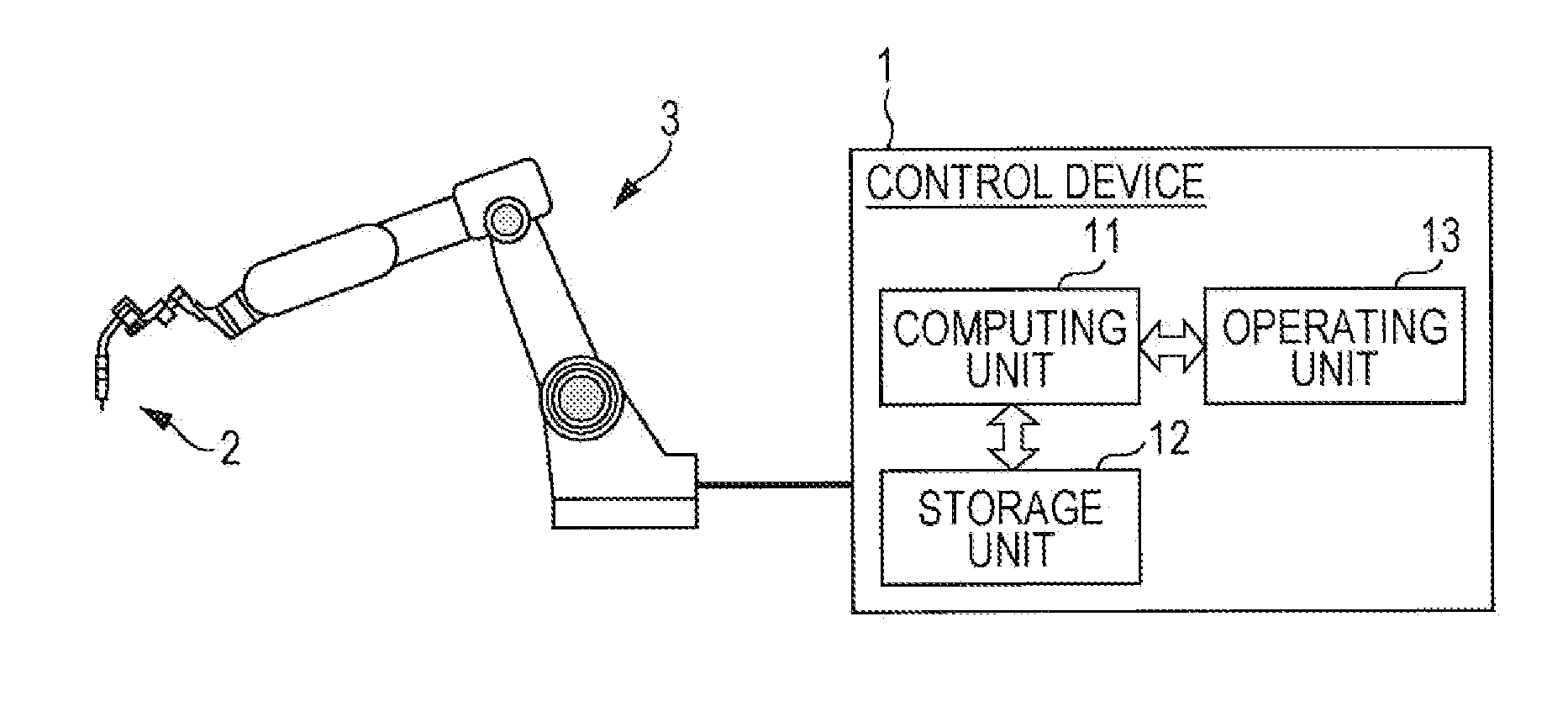
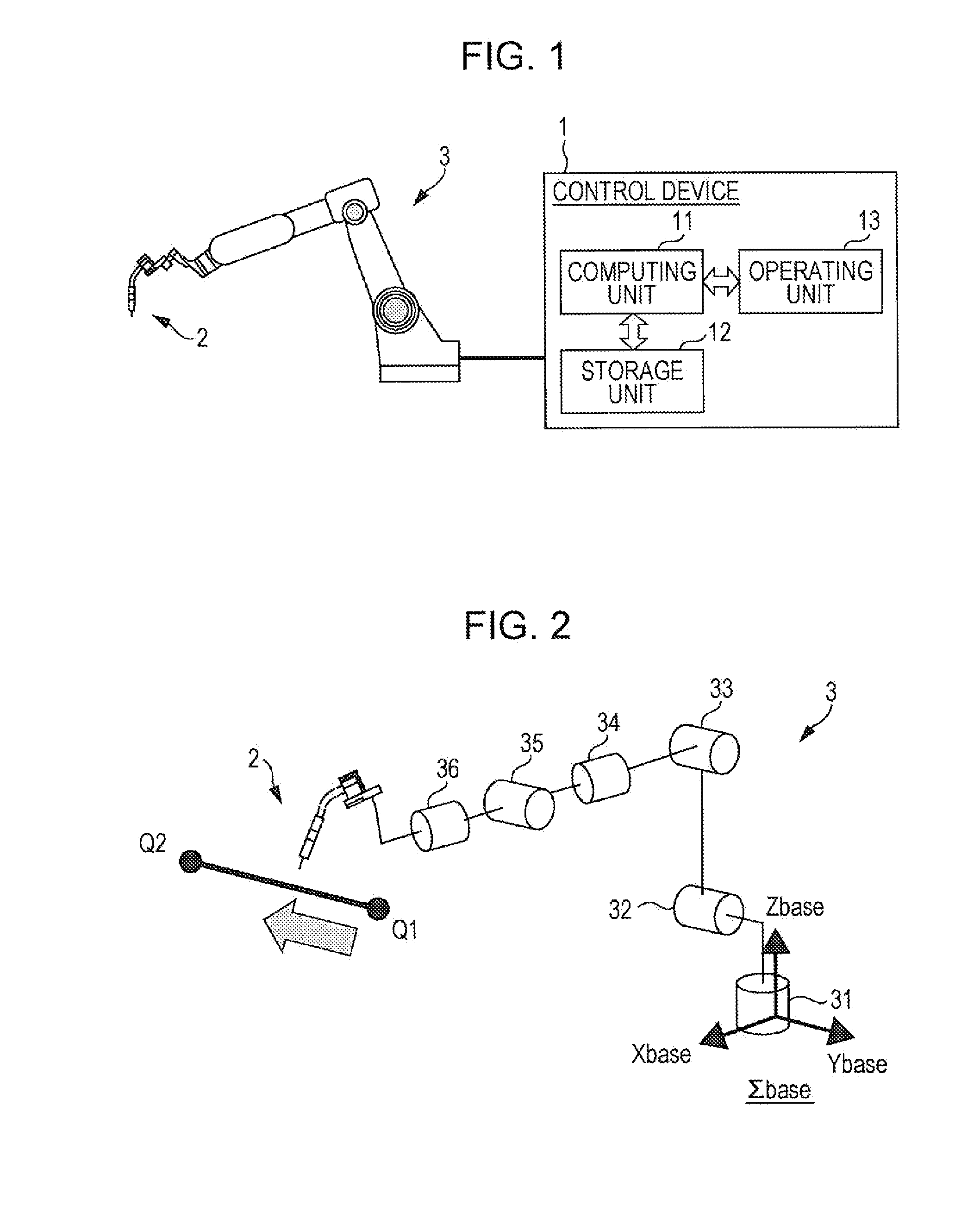
Robot apparatus and robot controlling method
A robot apparatus 1 includes: a multi-articulated robot 2; and a controller 3 that drive-controls the multi-articulated robot 2 based on an input motion command. The controller 3 includes: a joint angle computing unit 32 that computes each joint angle command for driving the multi-articulated robot 2 based on the motion command; a servo controlling apparatus 30 that moves the multi-articulated robot 2 by rotationally driving each rotational joint based on the joint angle command computed by the joint angle computing unit 32; a singular point calculating unit 51 that calculates a distance between the multi-articulated robot 2 and a singular point of the multi-articulated robot 2; and a maximum joint angle deviation adjusting unit 52 that limits a maximum rotation speed of a rotational joint specified in advance based on a singular point type, if the singular point distance becomes smaller than a predetermined value.
Owner:CANON KK
Rotary type flexible joint
ActiveCN104385293AExtended service lifeFully embodies the principle of bionicsJointsVehiclesLinear motionReducer
The invention discloses a rotary type flexible joint. The flexible joint comprises a motor, a motor frame, a mounting plate, a first connecting plate, a first synchronous pulley, a first synchronous pulley cover plate, a synchronous belt, a reducer, a reducer flange, a spring mounting rack, a spring output rack, an output disk, a second connecting plate, a synchronous belt end cover, a third connecting plate, a crossed roller bearing, a bearing outer ring baffle, a bearing inner ring baffle, a first flat key, a reducer flange end cover, a spring, a second flat key, a third flat key, a second synchronous pulley and a second synchronous pulley cover plate. The flexible joint solves the problem that the flexible joint only can generate linear motion, and a foundation is laid for designing a joint robot which is high in flexibility, can span certain barriers and pits and has high adaptive capacity to environment.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Teaching data preparing method for articulated robot
ActiveUS7248012B2Smoothly moving the articulated robotShorten exercise timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlData preparationEngineering
Set the first temporary attitude of an end effector for a plurality of work points (step S3). Determine the attitude of an articulated robot at one-end first work point out of a plurality of work points (step S4). Determine the attitude of an articulated robot at the other-end final work point out of a plurality of work points (step S5). Set the second temporary attitudes of an end effector respectively for the other work points so that the attitude of an end effector gradually changes from the first work point toward the final work point (step S6). Correct the first temporary attitude with the second temporary attitude (step S7).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com