Patents
Literature
181 results about "First principle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A first principle is a basic proposition or assumption that cannot be deduced from any other proposition or assumption. In philosophy, first principles are from First Cause attitudes and taught by Aristotelians, and nuanced versions of first principles are referred to as postulates by Kantians. In mathematics, first principles are referred to as axioms or postulates. In physics and other sciences, theoretical work is said to be from first principles, or ab initio, if it starts directly at the level of established science and does not make assumptions such as empirical model and parameter fitting.
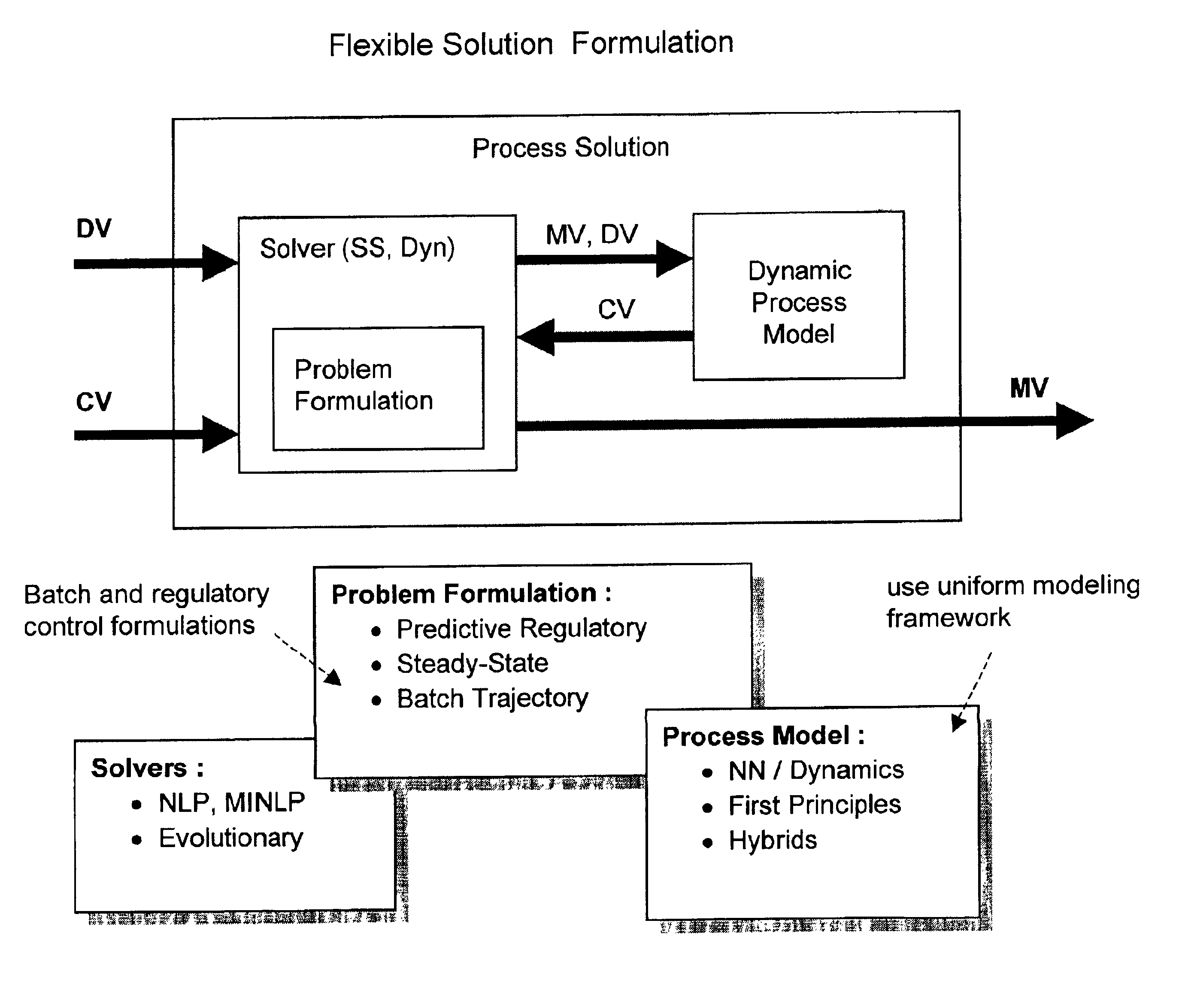
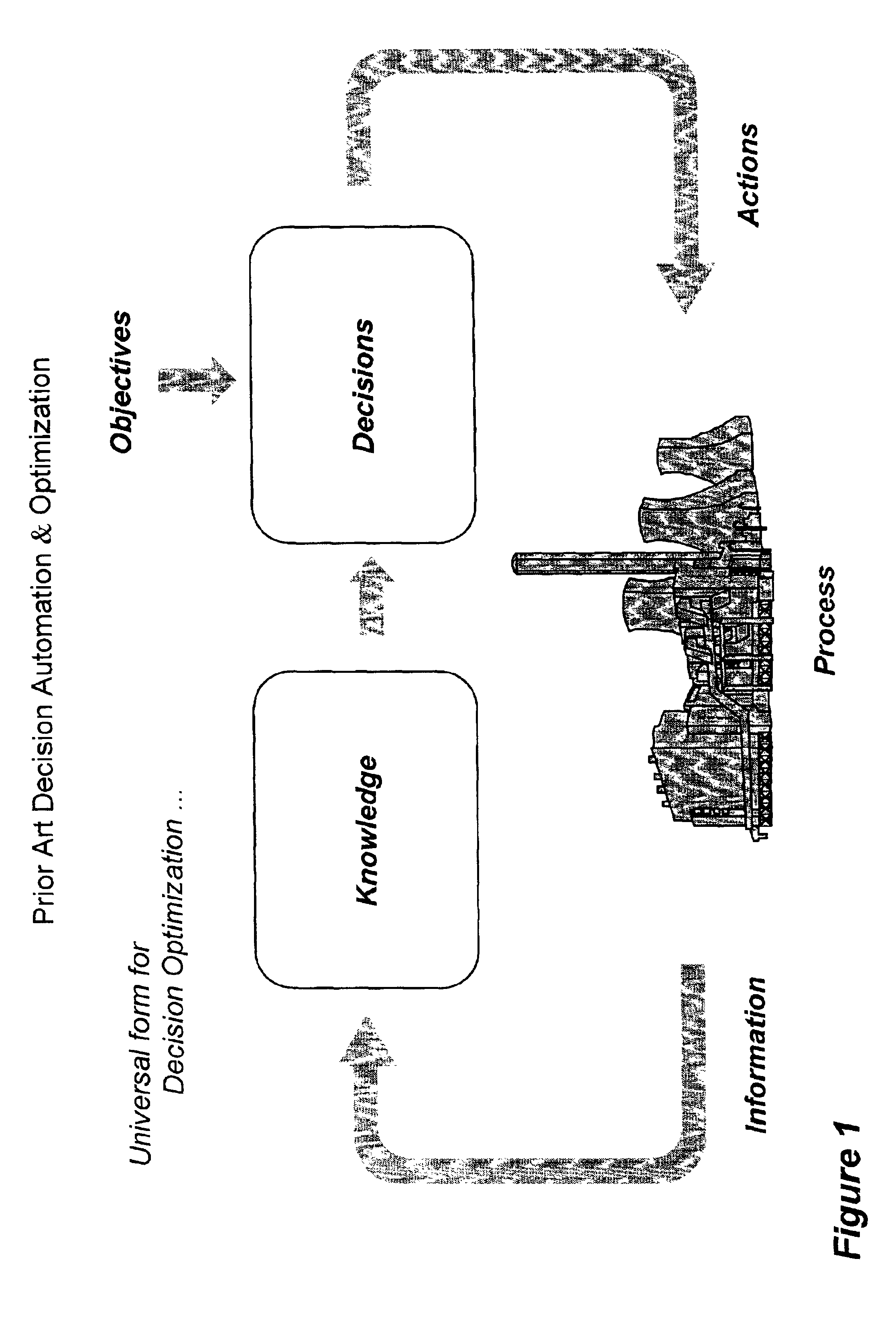
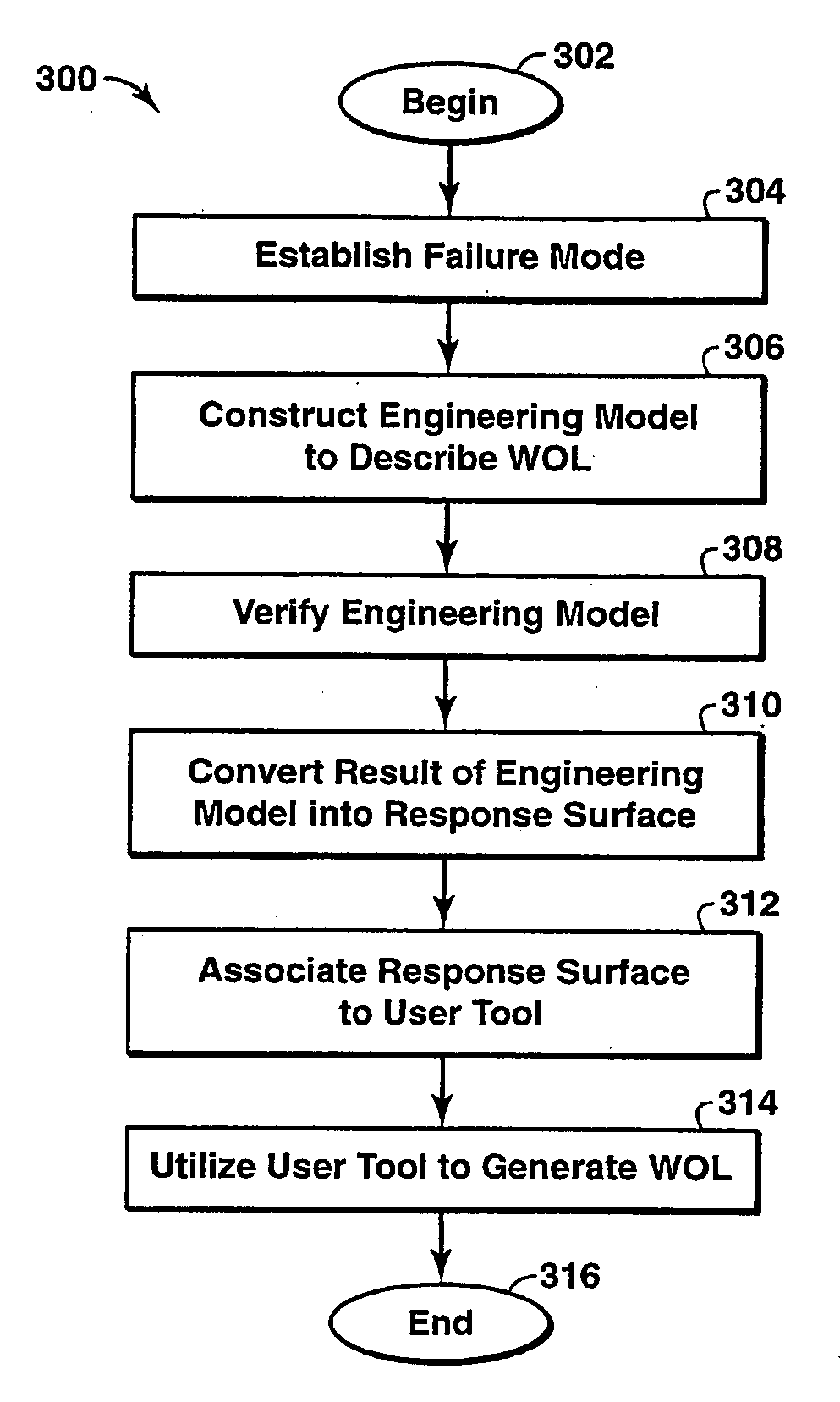
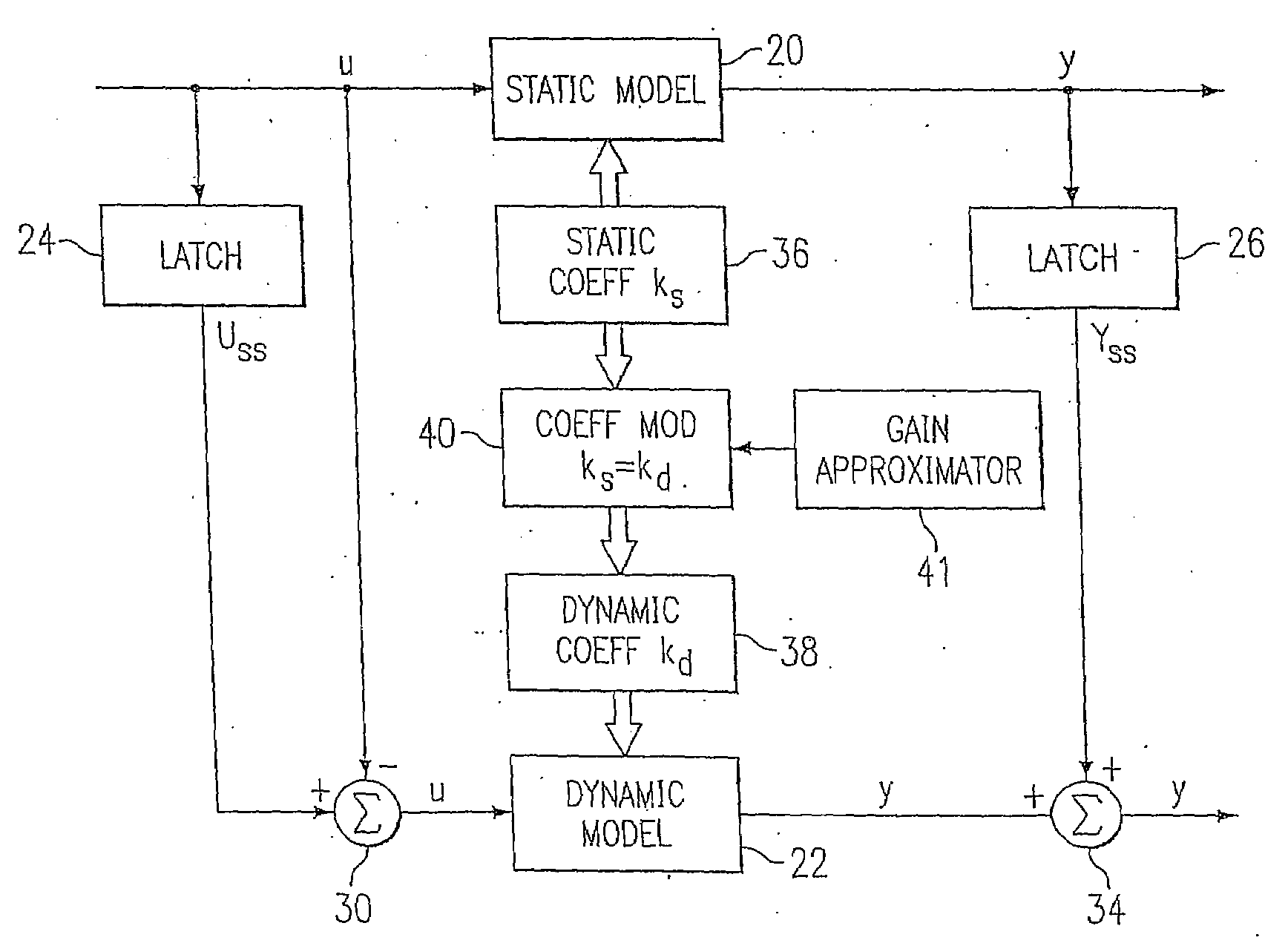
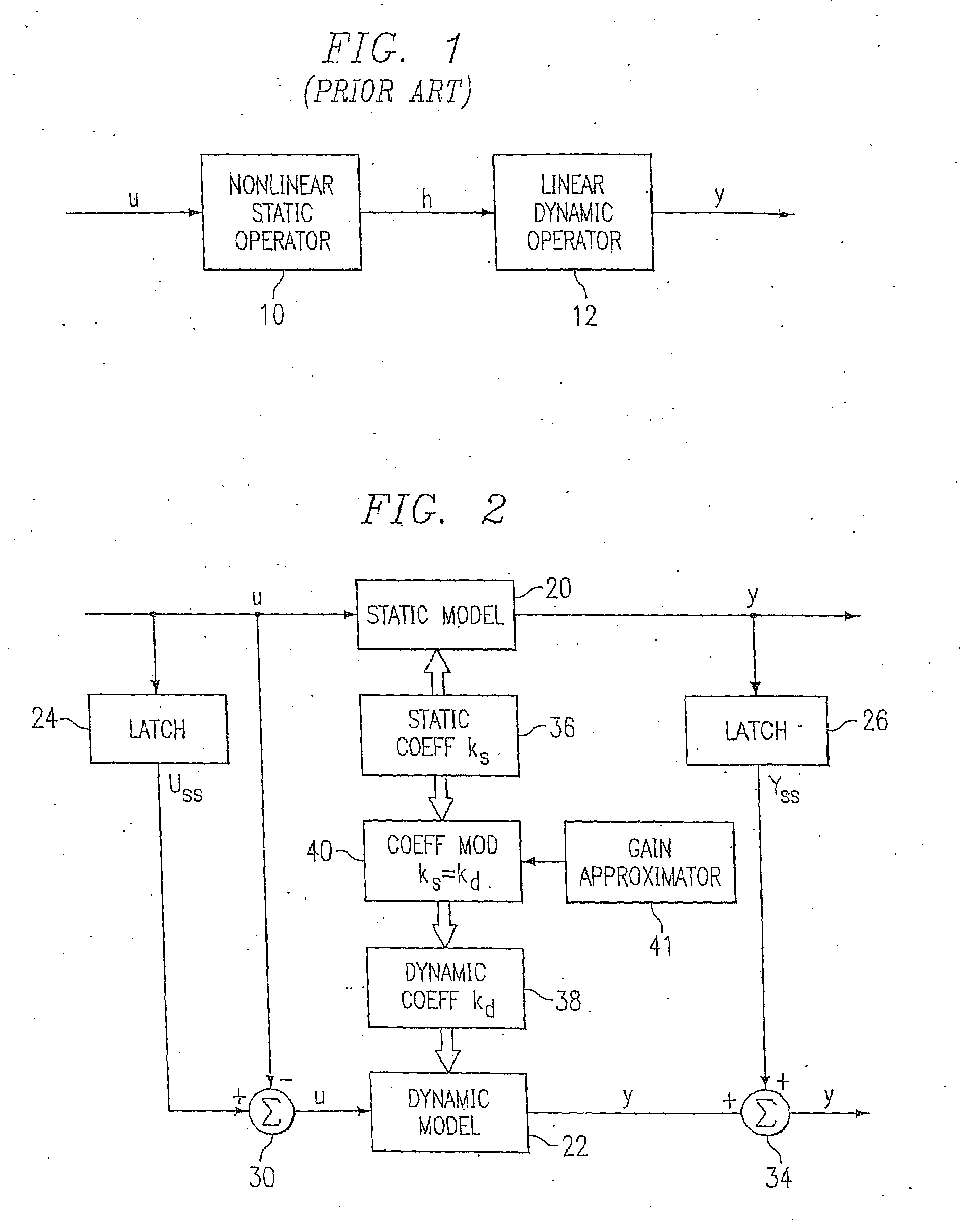
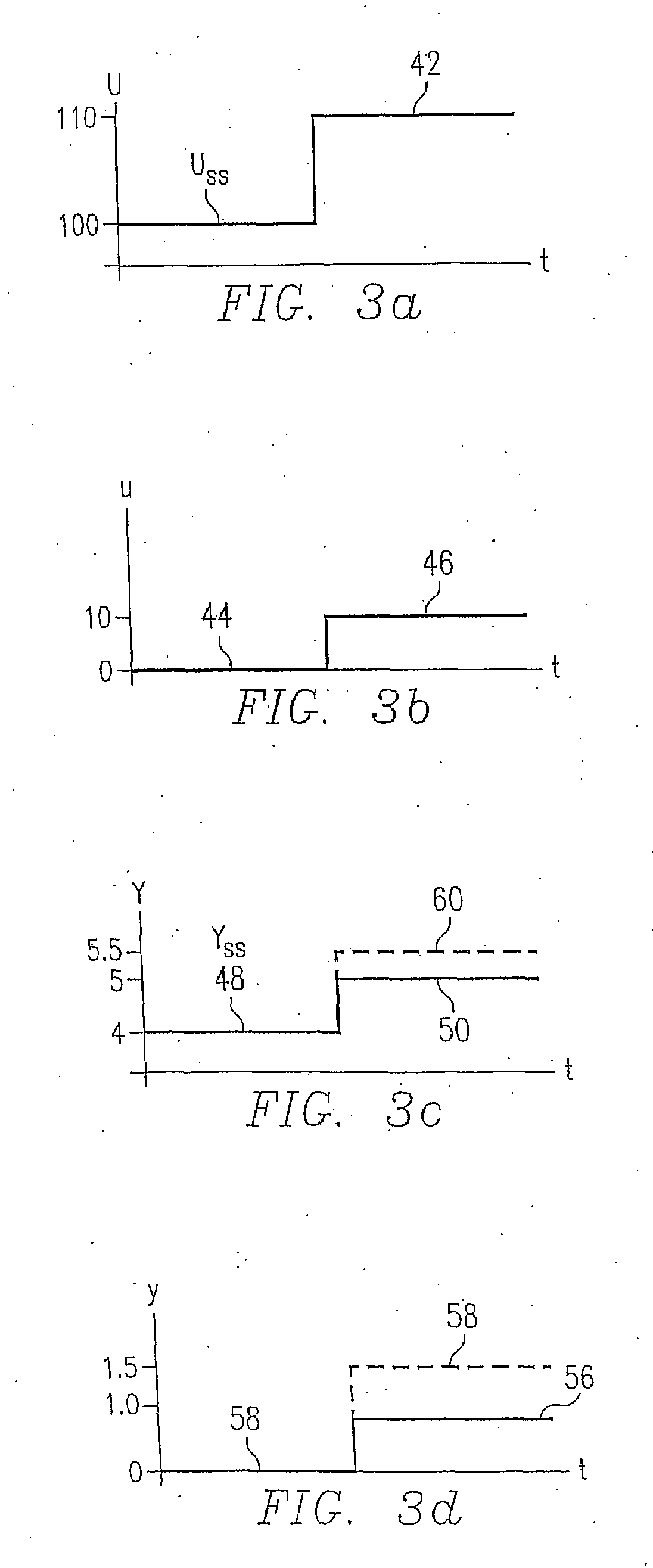
System and method for enterprise modeling, optimization and control
InactiveUS6934931B2Increase flexibilityImprove powerForecastingResourcesEnterprise modellingOptimal scheduling
A system and method for performing modeling, prediction, optimization, and control, including an enterprise wide framework for constructing modeling, optimization, and control solutions. The framework includes a plurality of base classes that may be used to create primitive software objects. These objects may then be combined to create optimization and / or control solutions. The distributed event-driven component architecture allows much greater flexibility and power in creating, deploying, and modifying modeling, optimization and control solutions. The system also includes various techniques for performing improved modeling, optimization, and control, as well as improved scheduling and control. For example, the system may include a combination of batch and continuous processing frameworks, and a unified hybrid modeling framework which allows encapsulation and composition of different model types, such as first principles models and empirical models. The system further includes an integrated process scheduling solution referred to as process coordinator that seamlessly incorporates the capabilities of advanced control and execution into a real time event triggered optimal scheduling solution.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
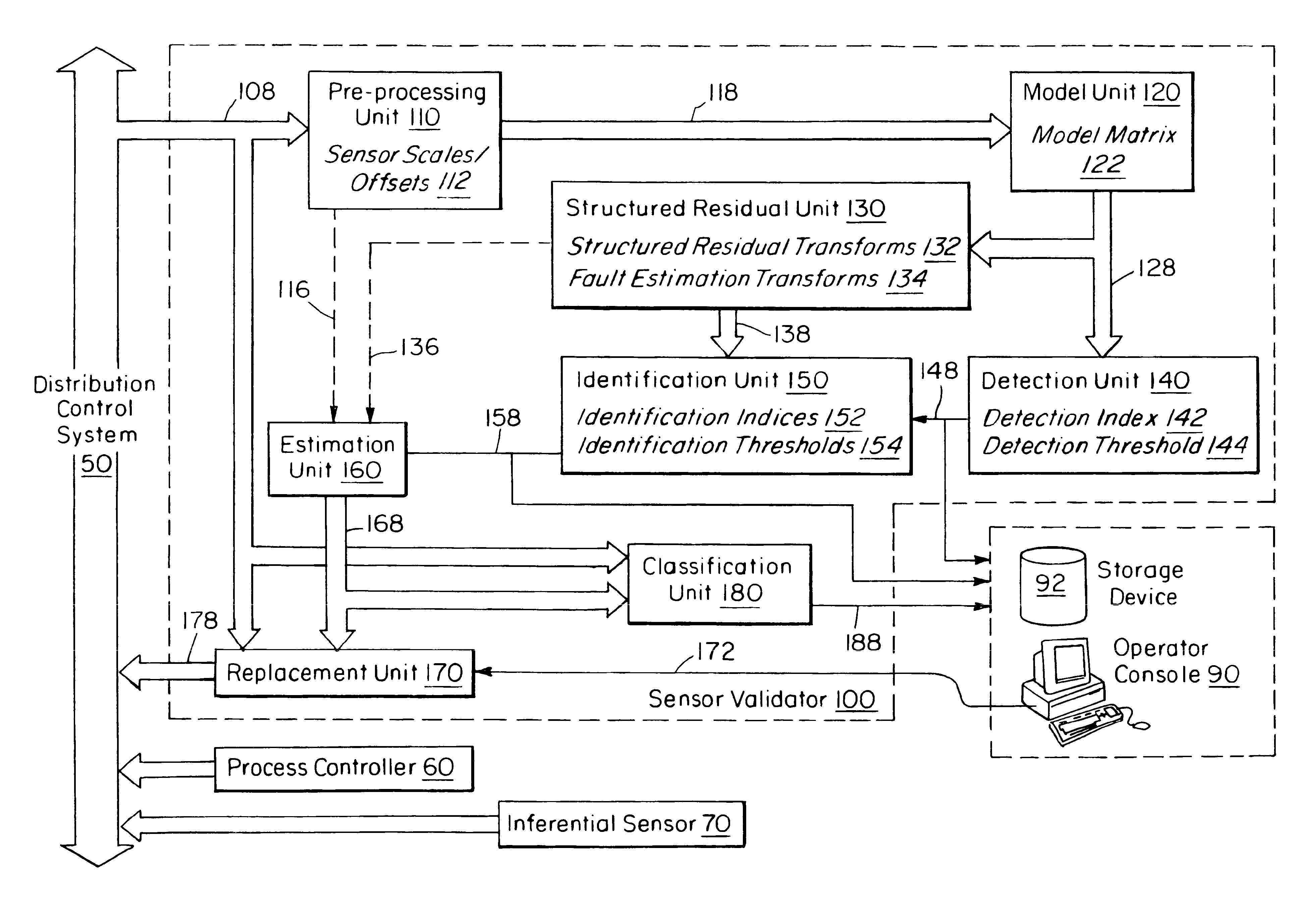
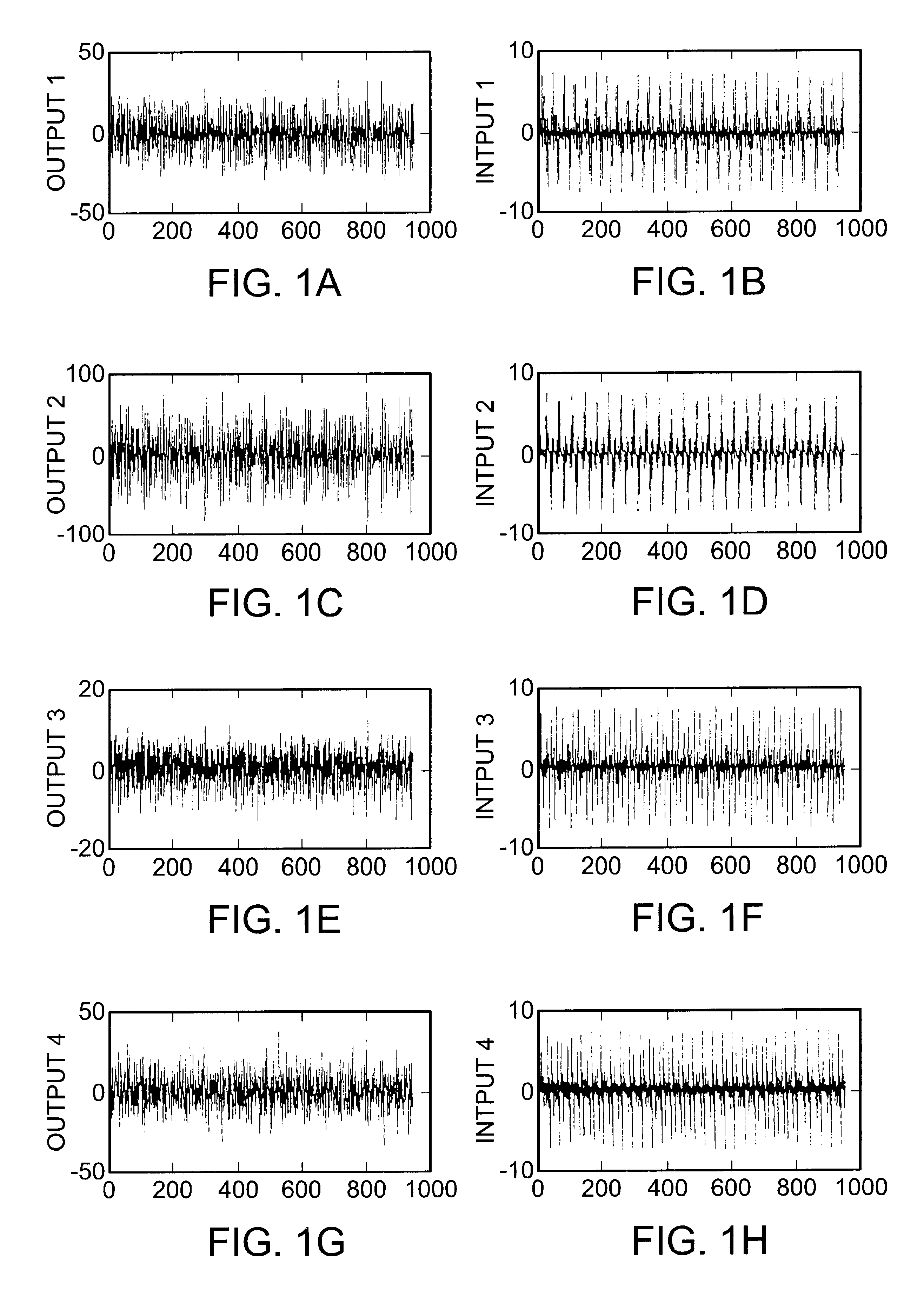
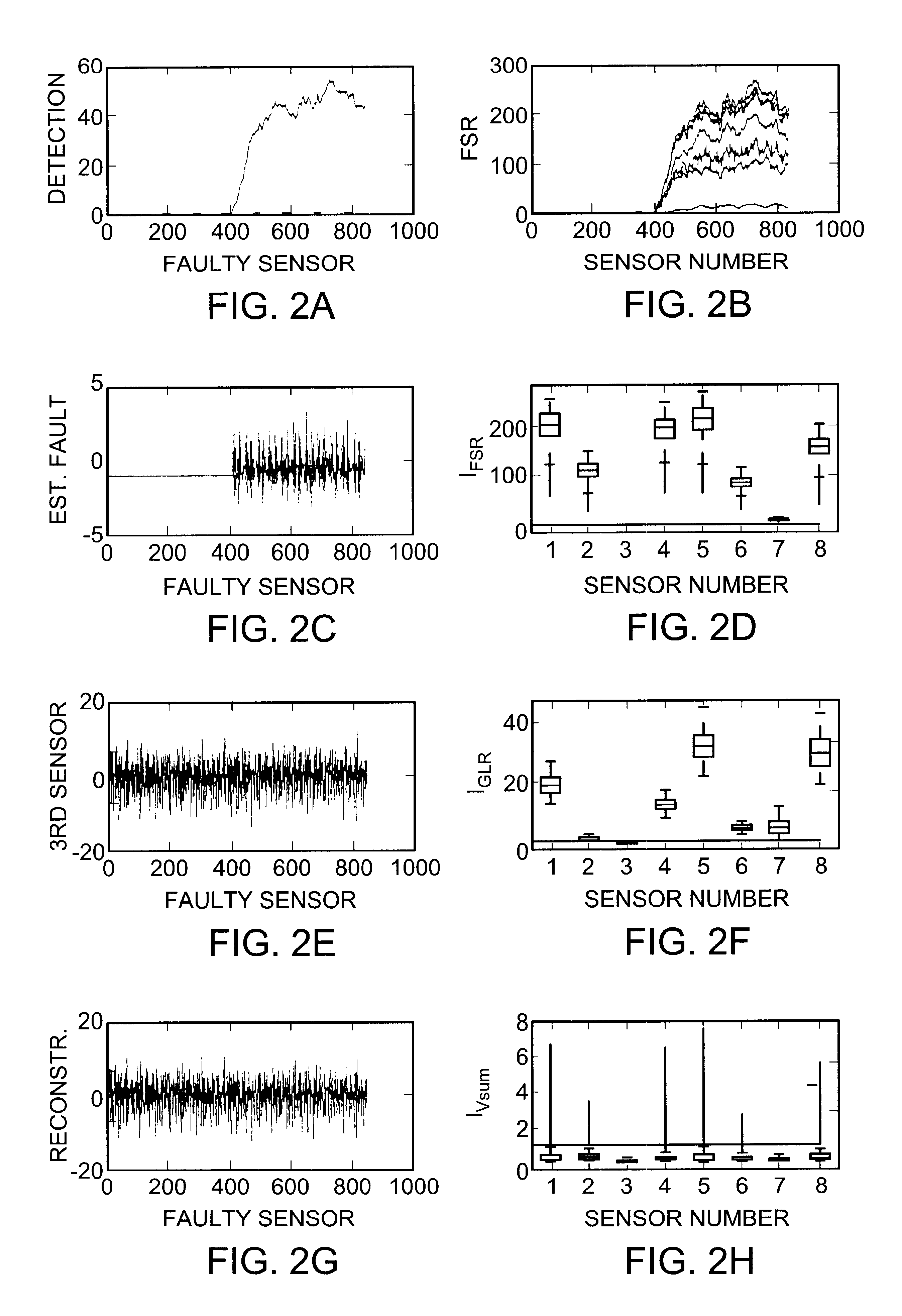
Sensor validation apparatus and method
An apparatus and method is disclosed for detecting, identifying, and classifying faults occurring in sensors measuring a process. A variety of process models can be used such as first principles models, dynamic multivariable predictive control models, from data using statistical methods such as partial least squares (PLS) or principal component analysis. If faults are identified in one or more sensors, the apparatus and method provide replacement values for the faulty sensors so that any process controllers and process monitoring systems that use these sensors can remain in operation during the fault period. The identification of faulty sensors is achieved through the use of a set of structured residual transforms that are uniquely designed to be insensitive to specific subsets of sensors, while being maximally sensitive to sensors not in the subset. Identified faults are classified into one of the types Complete Failure, Bias, Drift, Precision Loss, or Unknown.
Owner:ASPENTECH CORP
System and method for enterprise modeling, optimization and control
A system and method for performing modeling, prediction, optimization, and control, including an enterprise wide framework for constructing modeling, optimization, and control solutions. The framework includes a plurality of base classes that may be used to create primitive software objects. These objects may then be combined to create optimization and / or control solutions. The distributed event-driven component architecture allows much greater flexibility and power in creating, deploying, and modifying modeling, optimization and control solutions. The system also includes various techniques for performing improved modeling, optimization, and control, as well as improved scheduling and control. For example, the system may include a combination of batch and continuous processing frameworks, and a unified hybrid modeling framework which allows encapsulation and composition of different model types, such as first principles models and empirical models. The system further includes an integrated process scheduling solution referred to as process coordinator that seamlessly incorporates the capabilities of advanced control and execution into a real time event triggered optimal scheduling solution.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
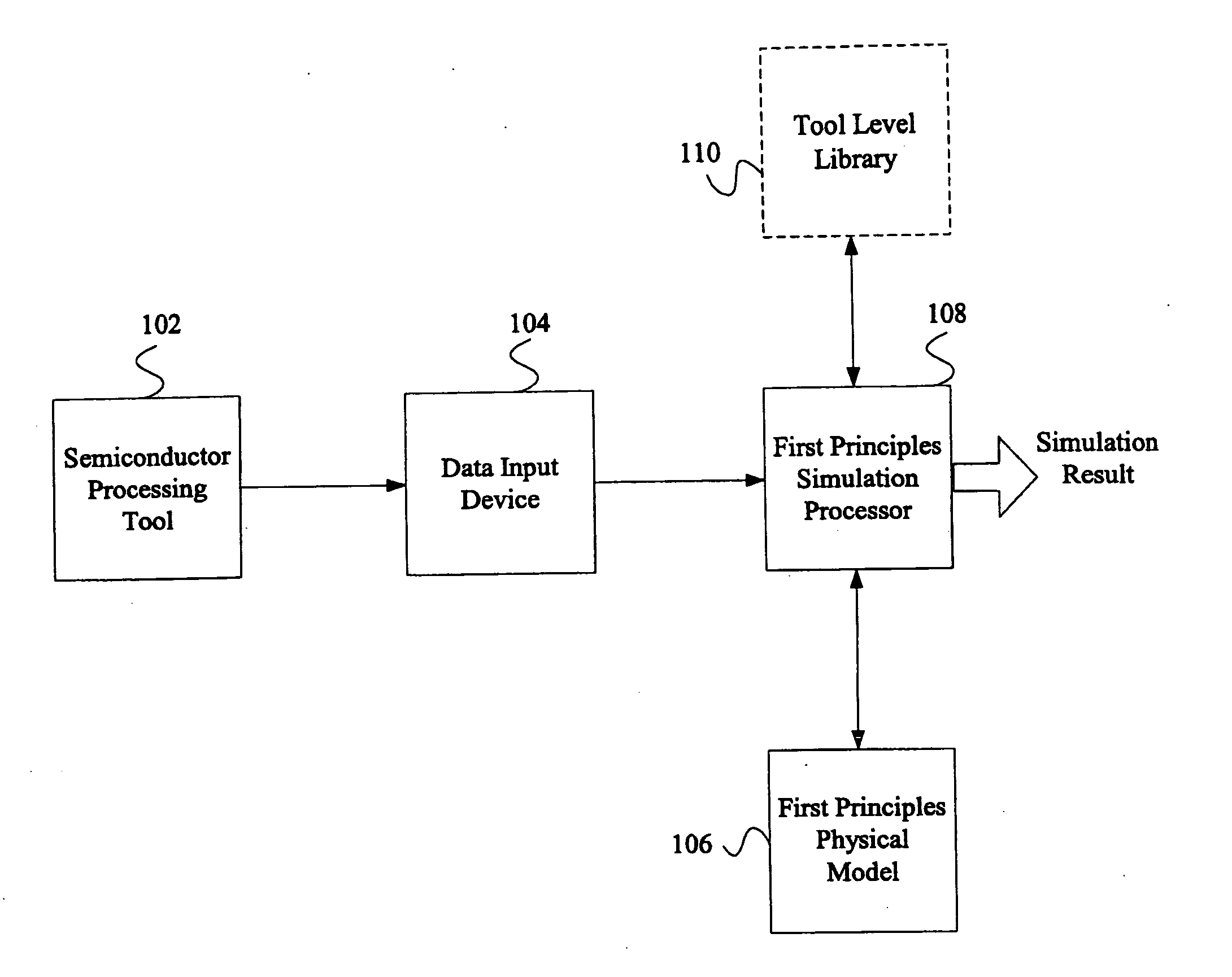
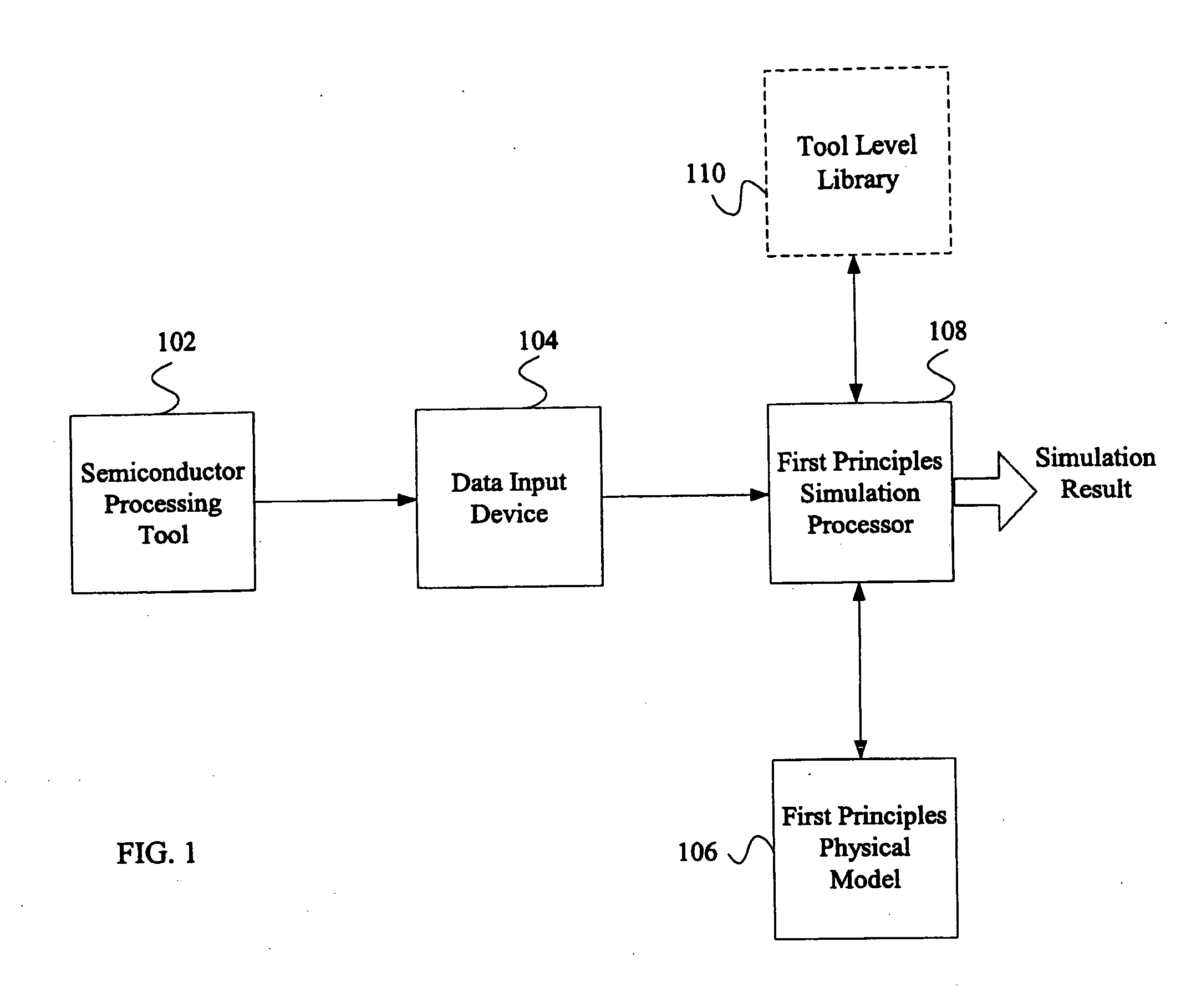
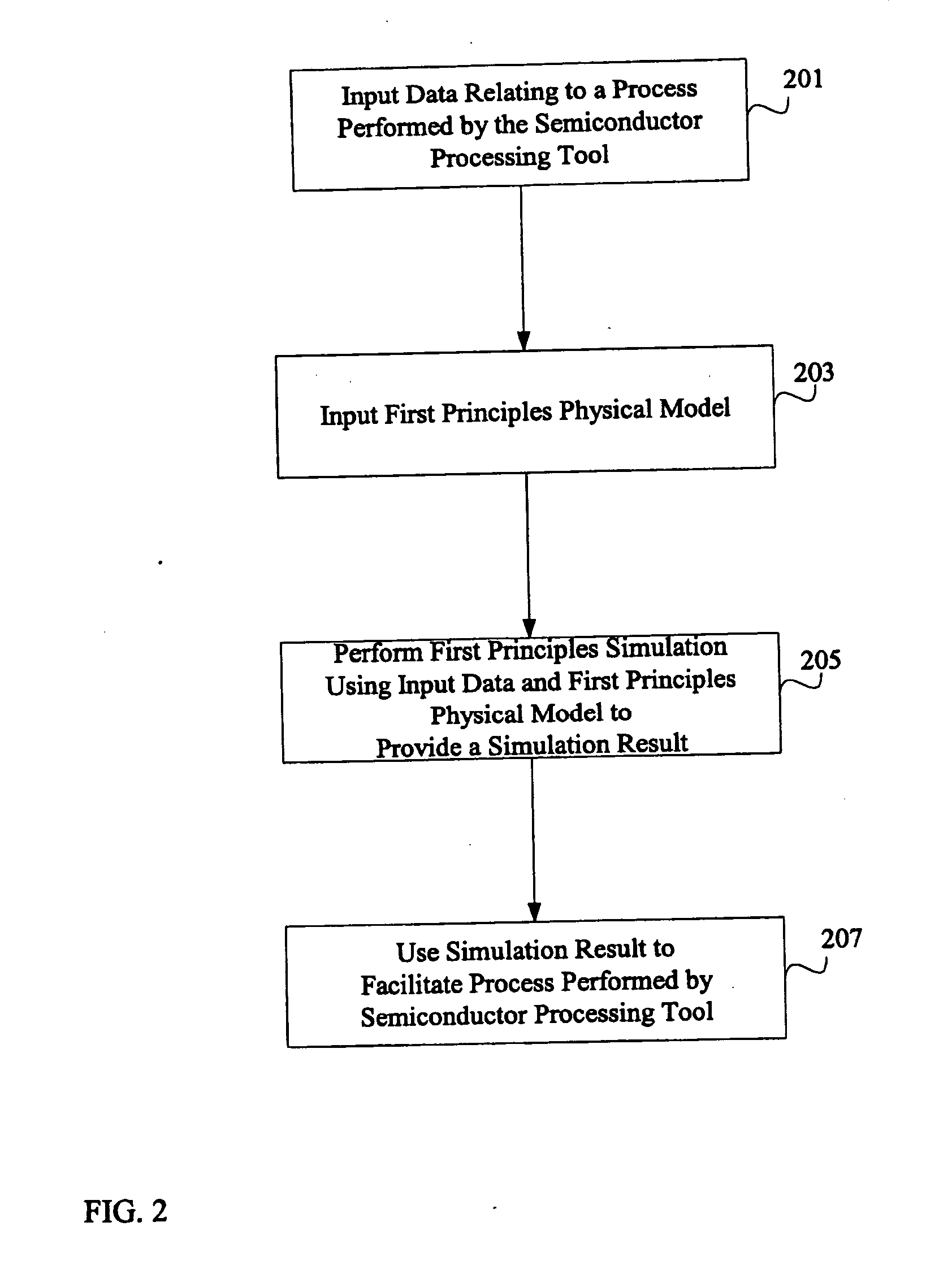
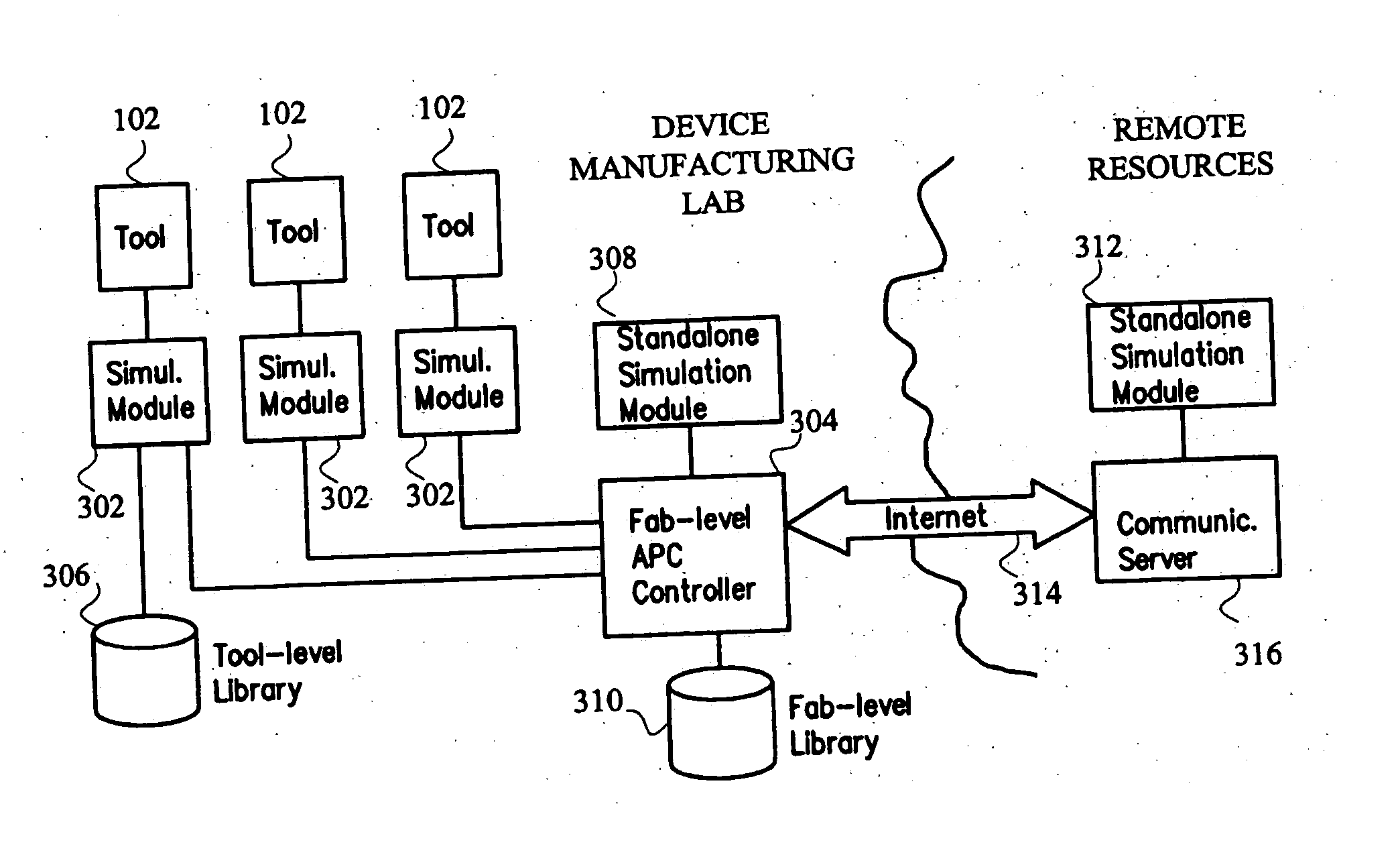
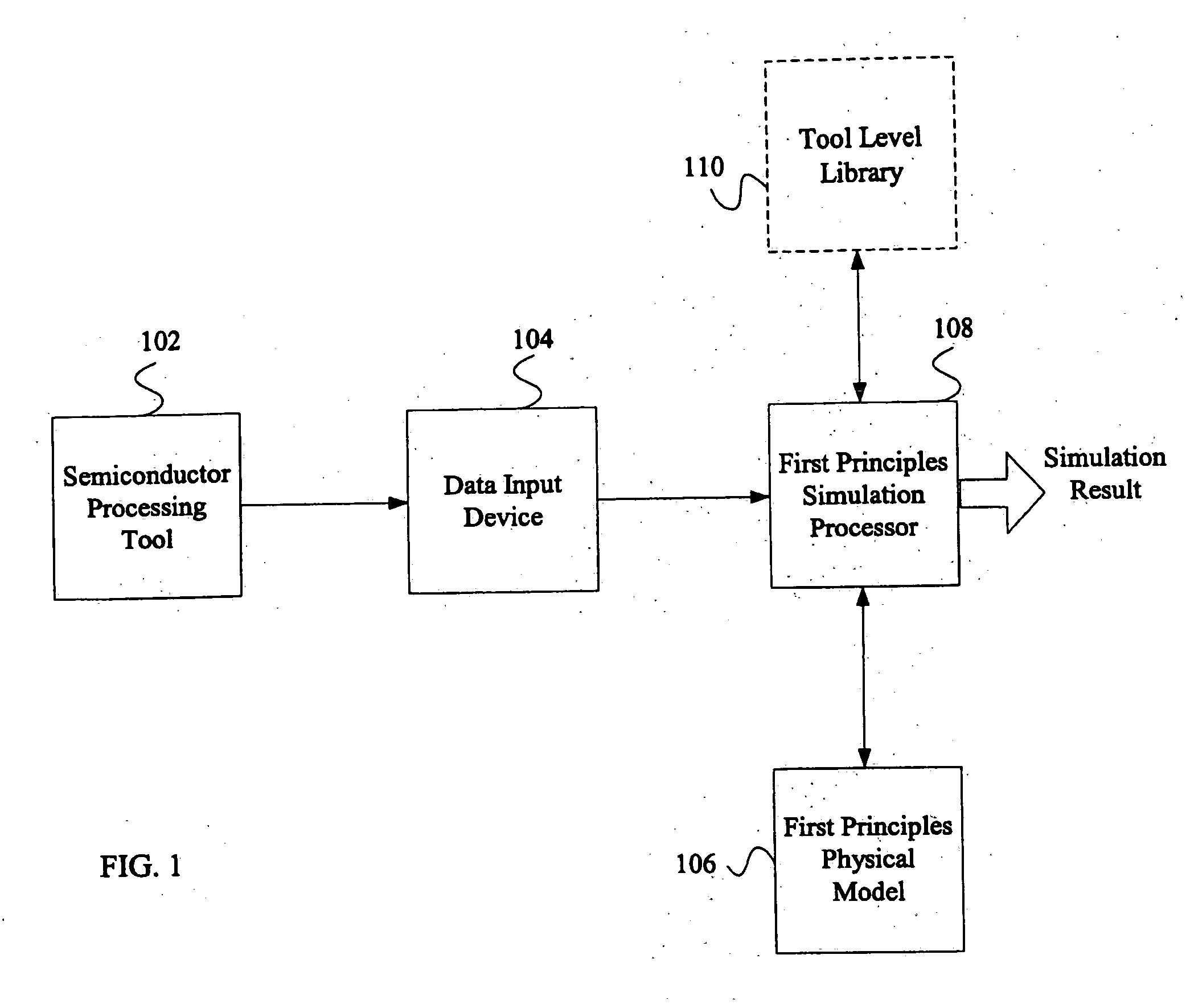
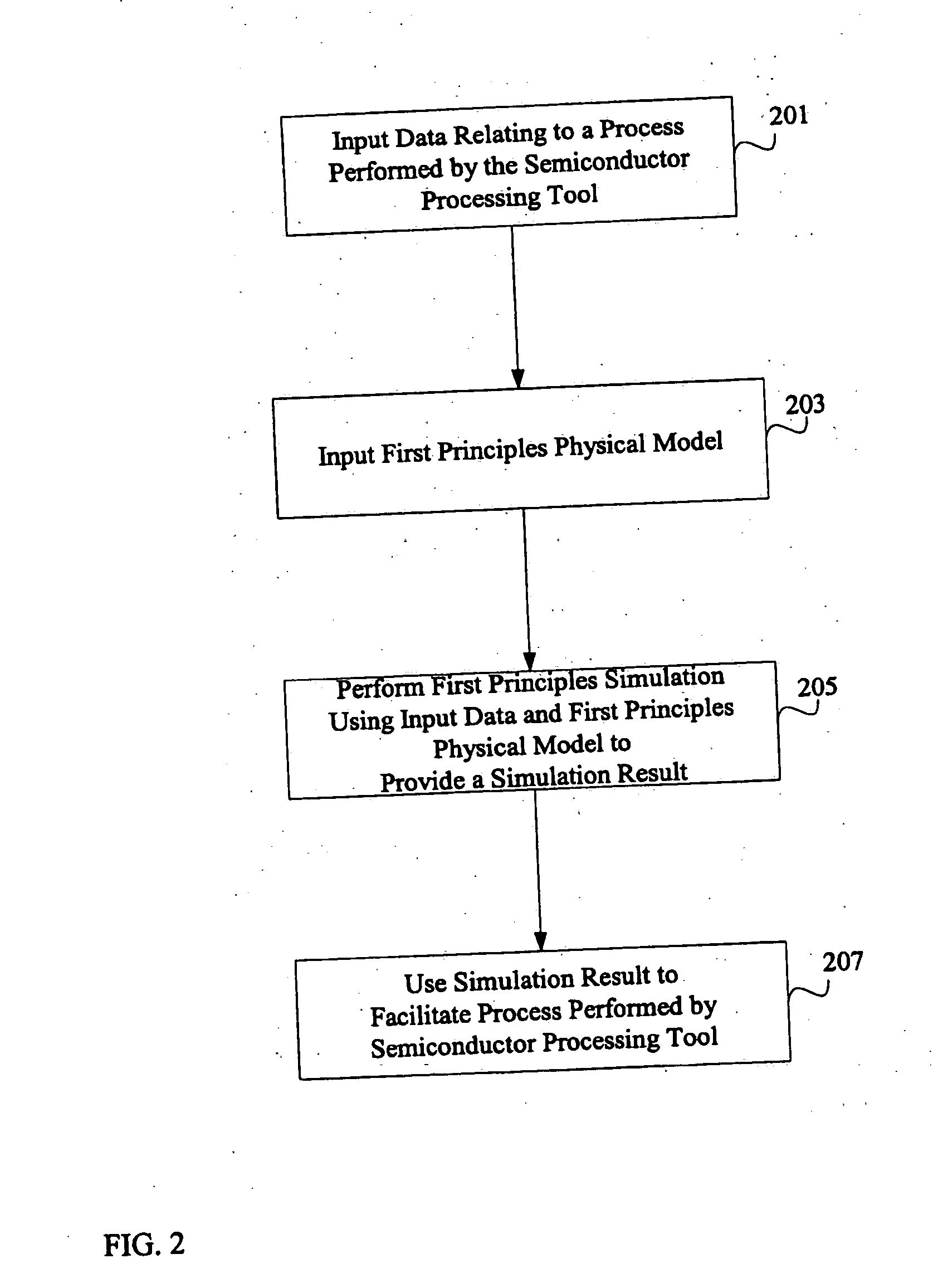
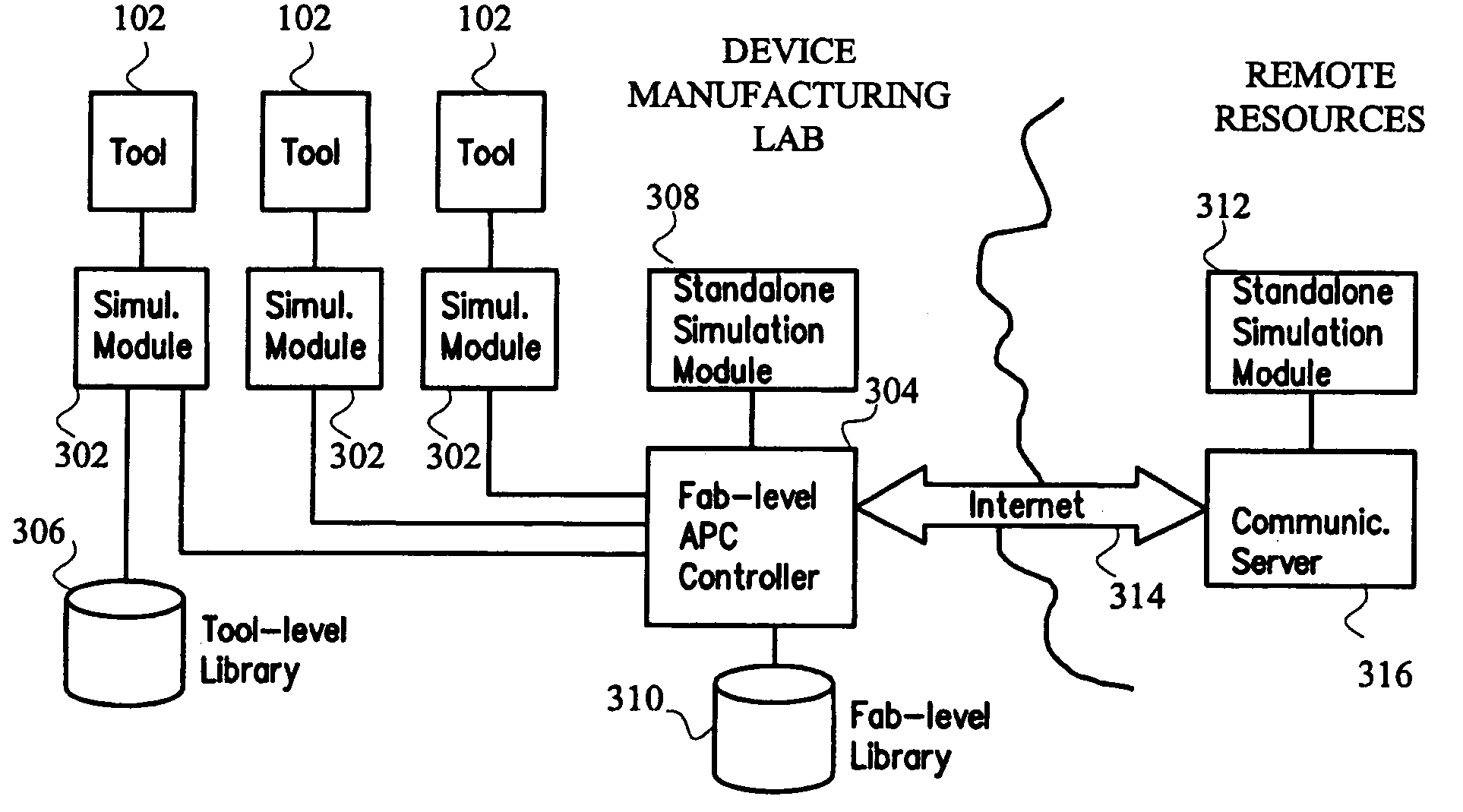
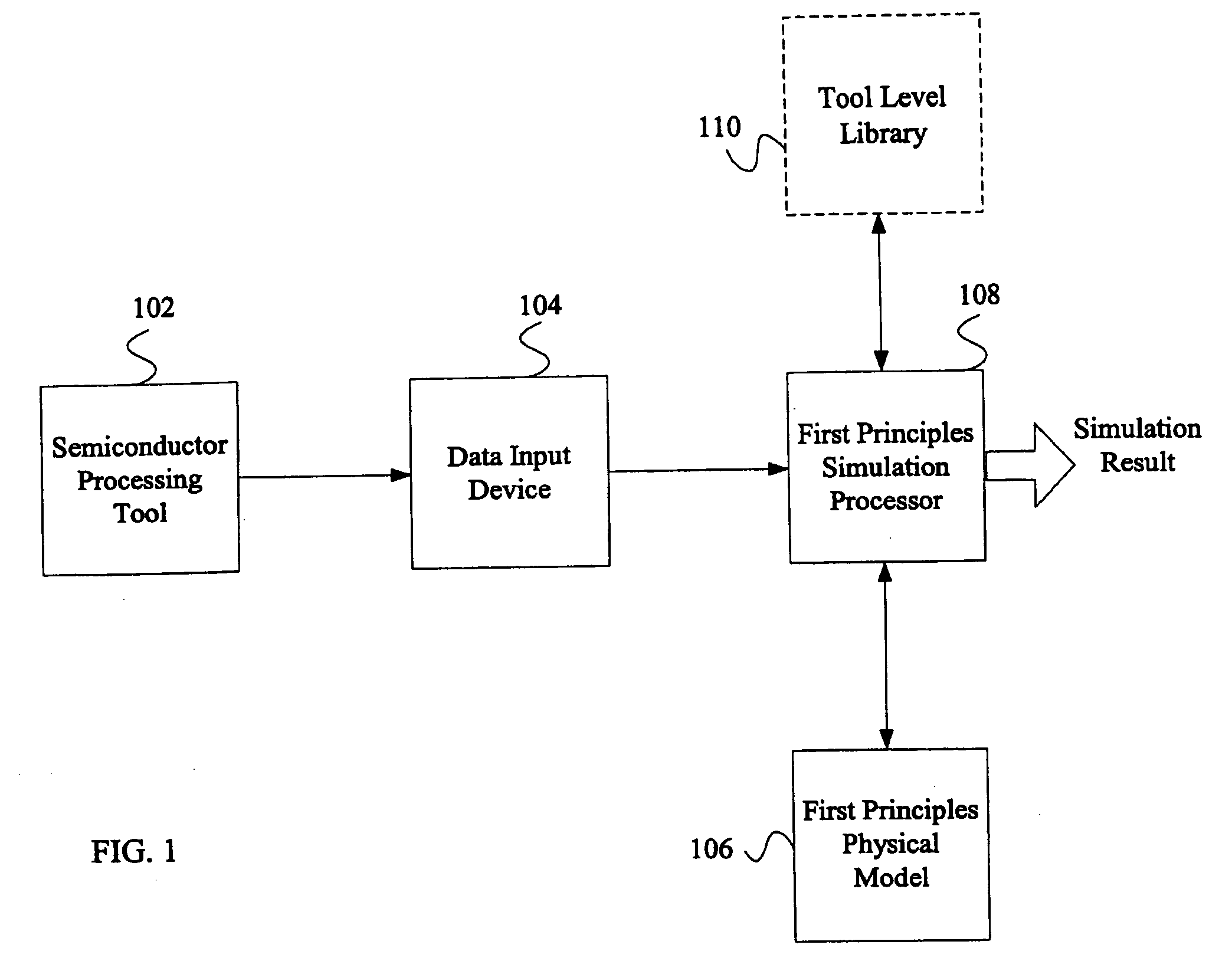
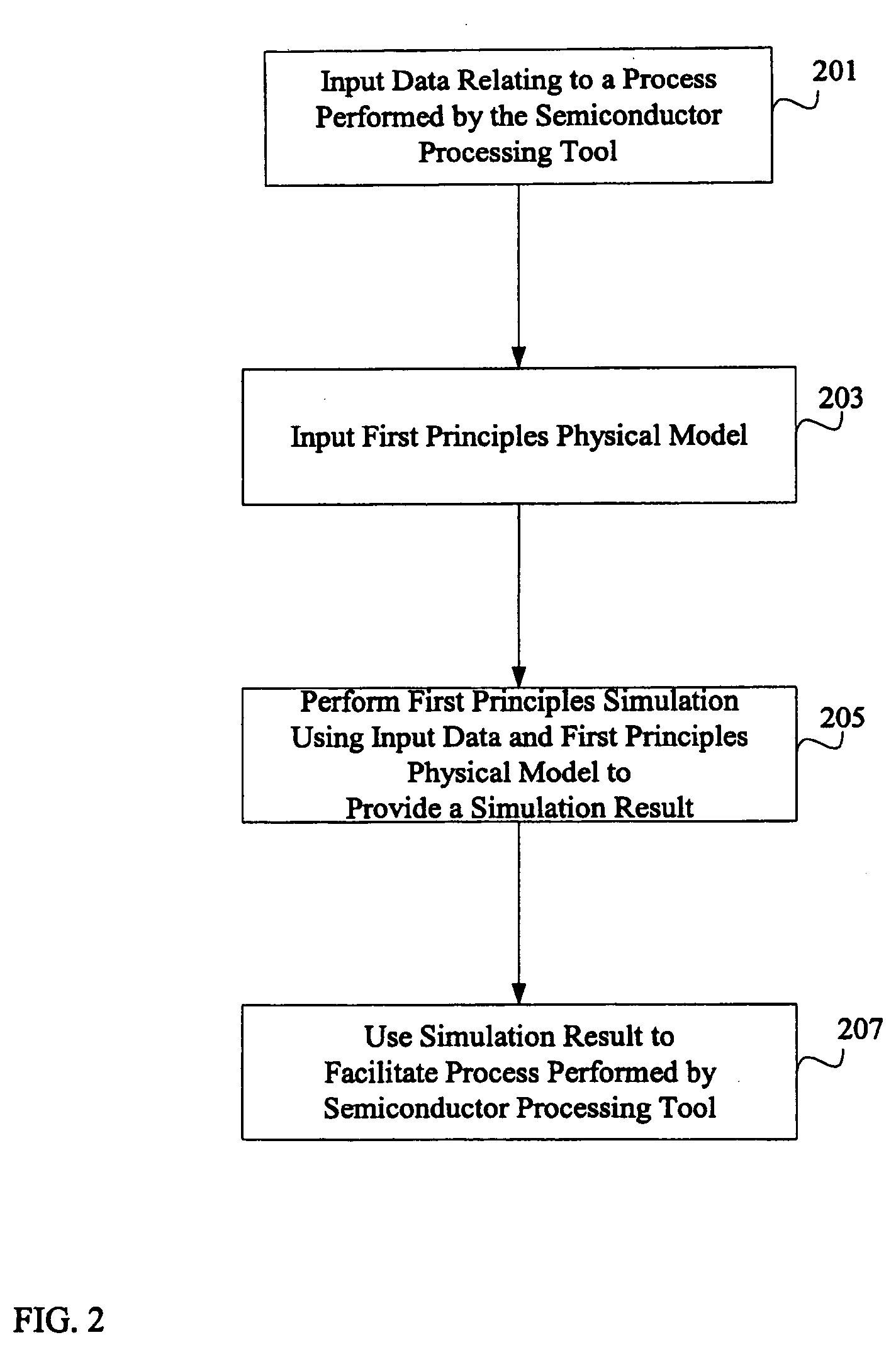
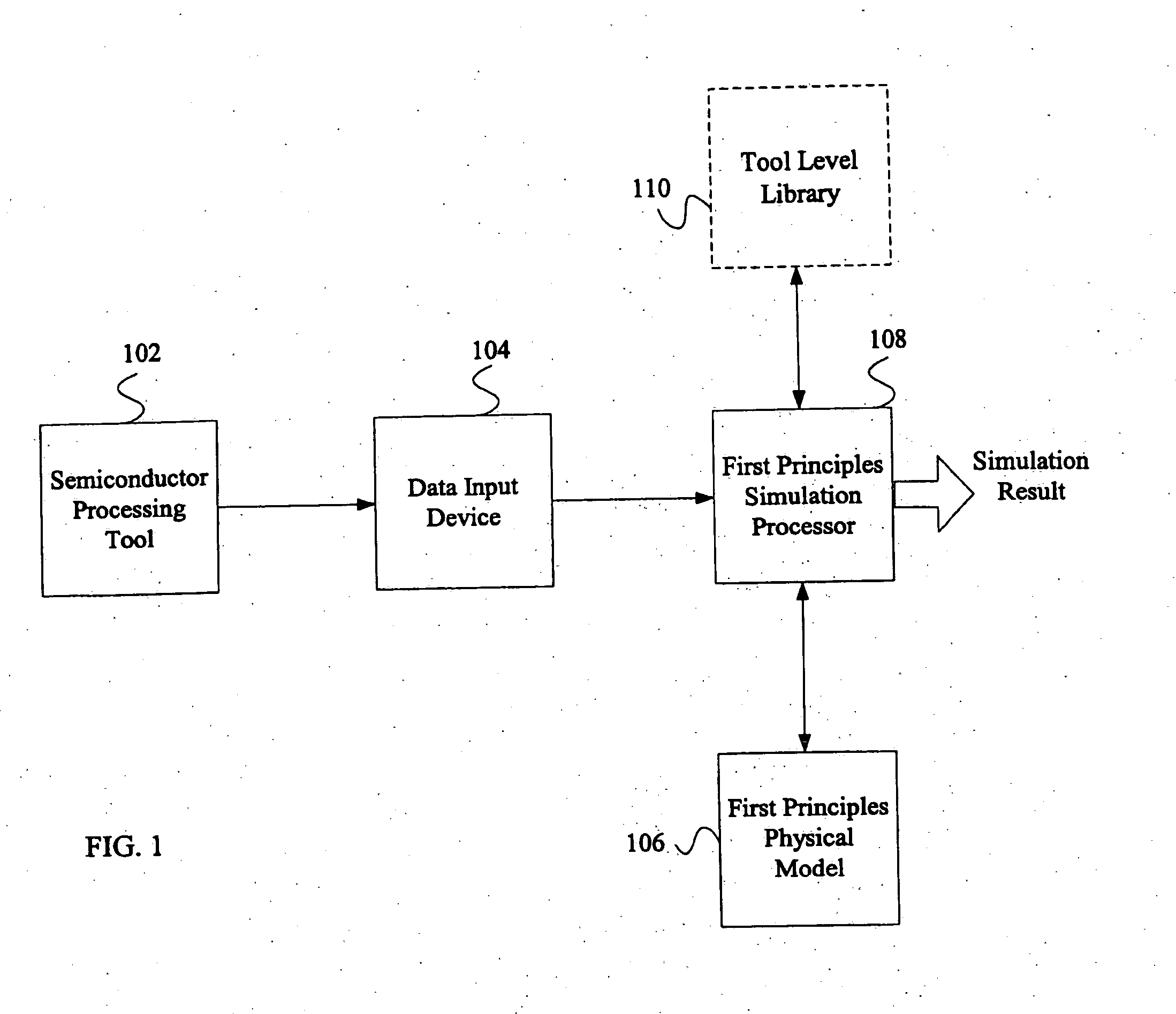
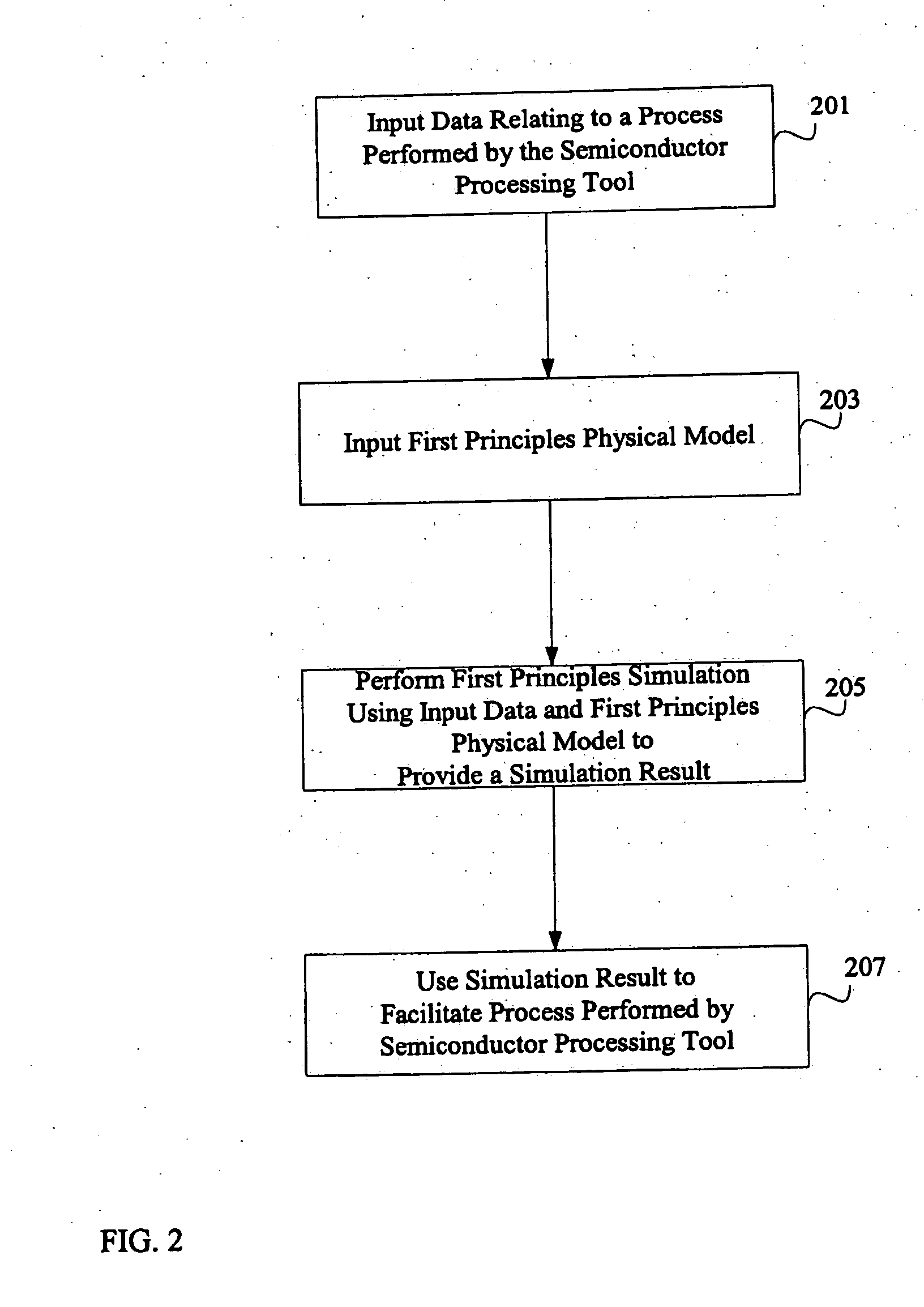
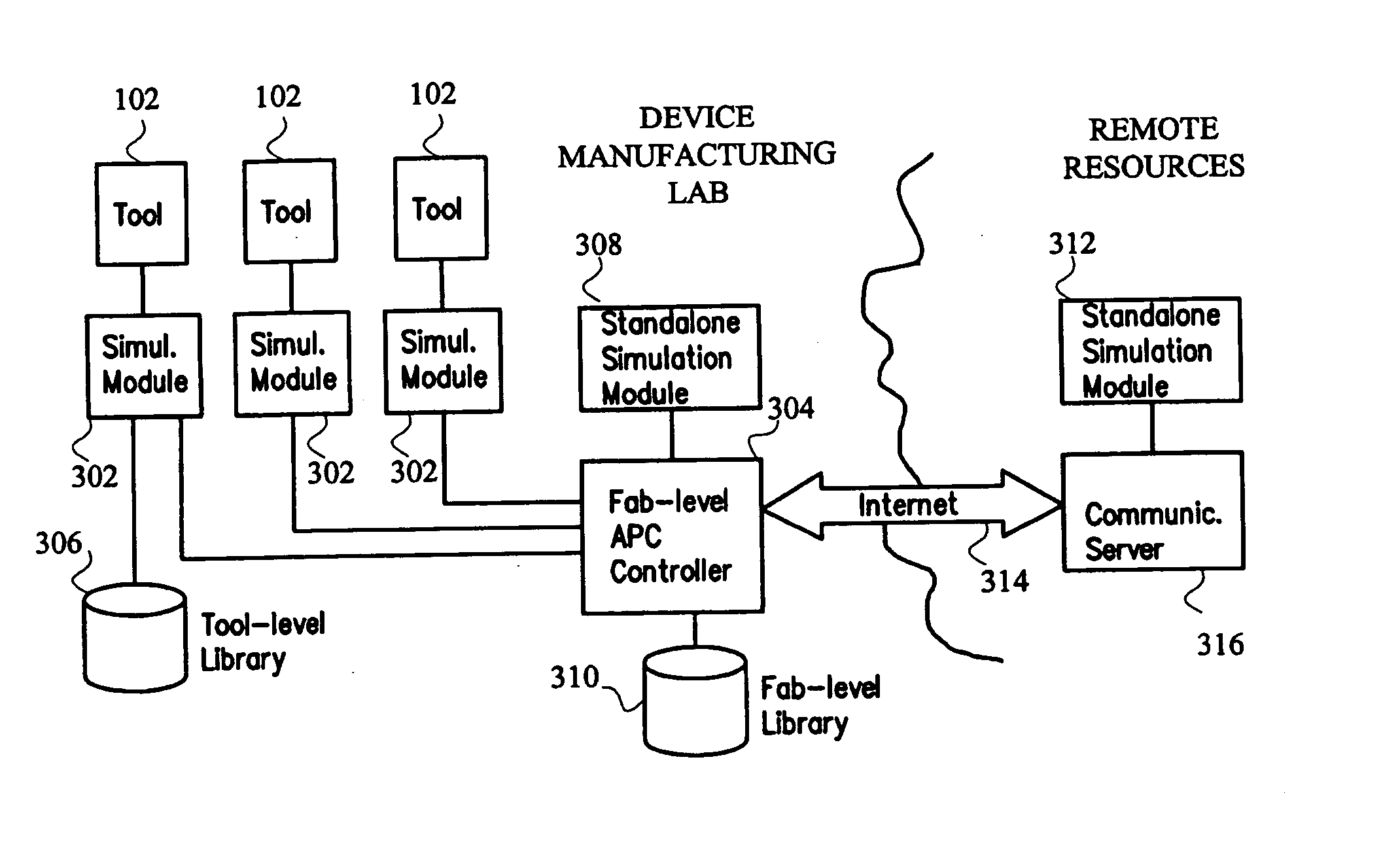
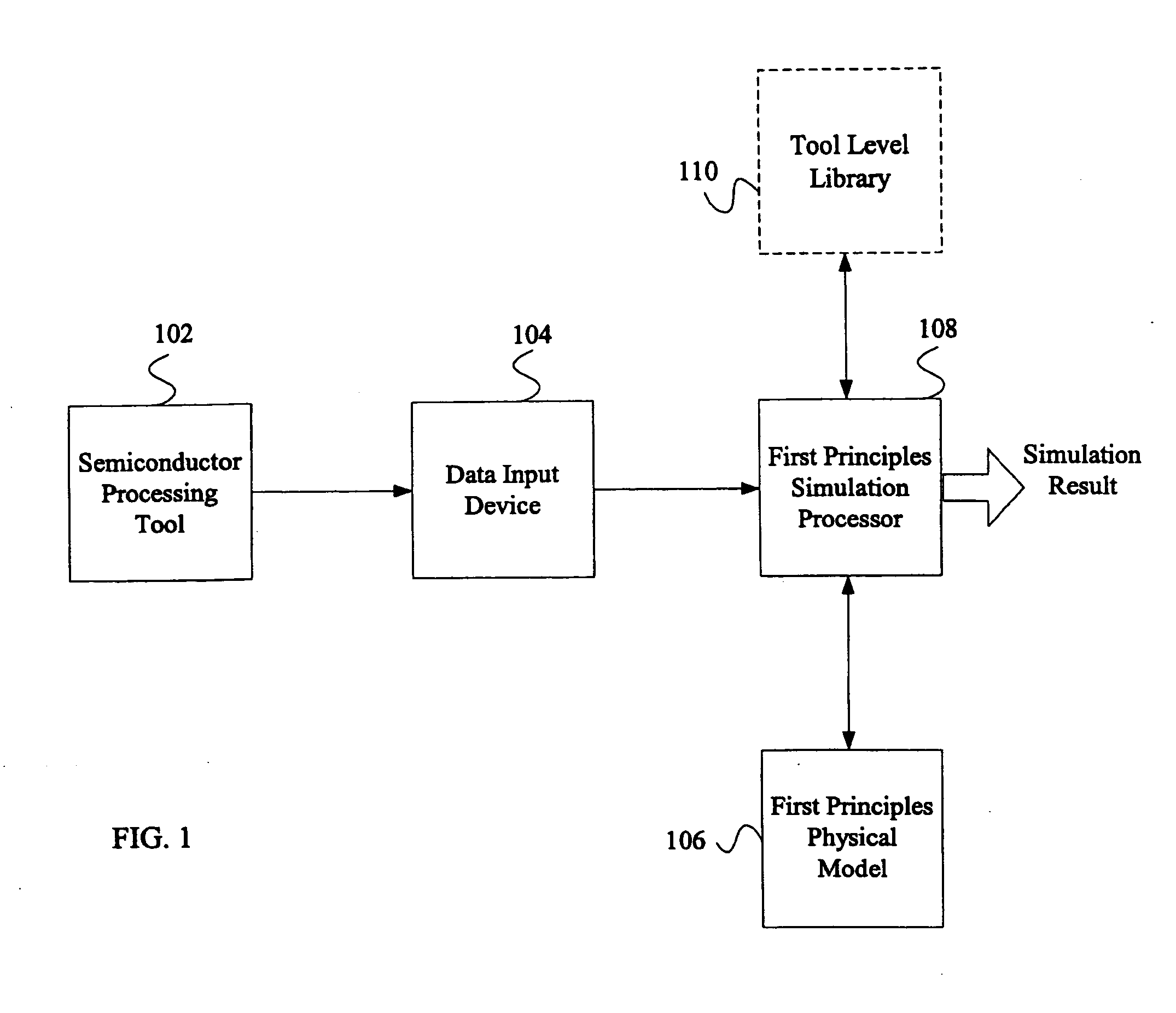
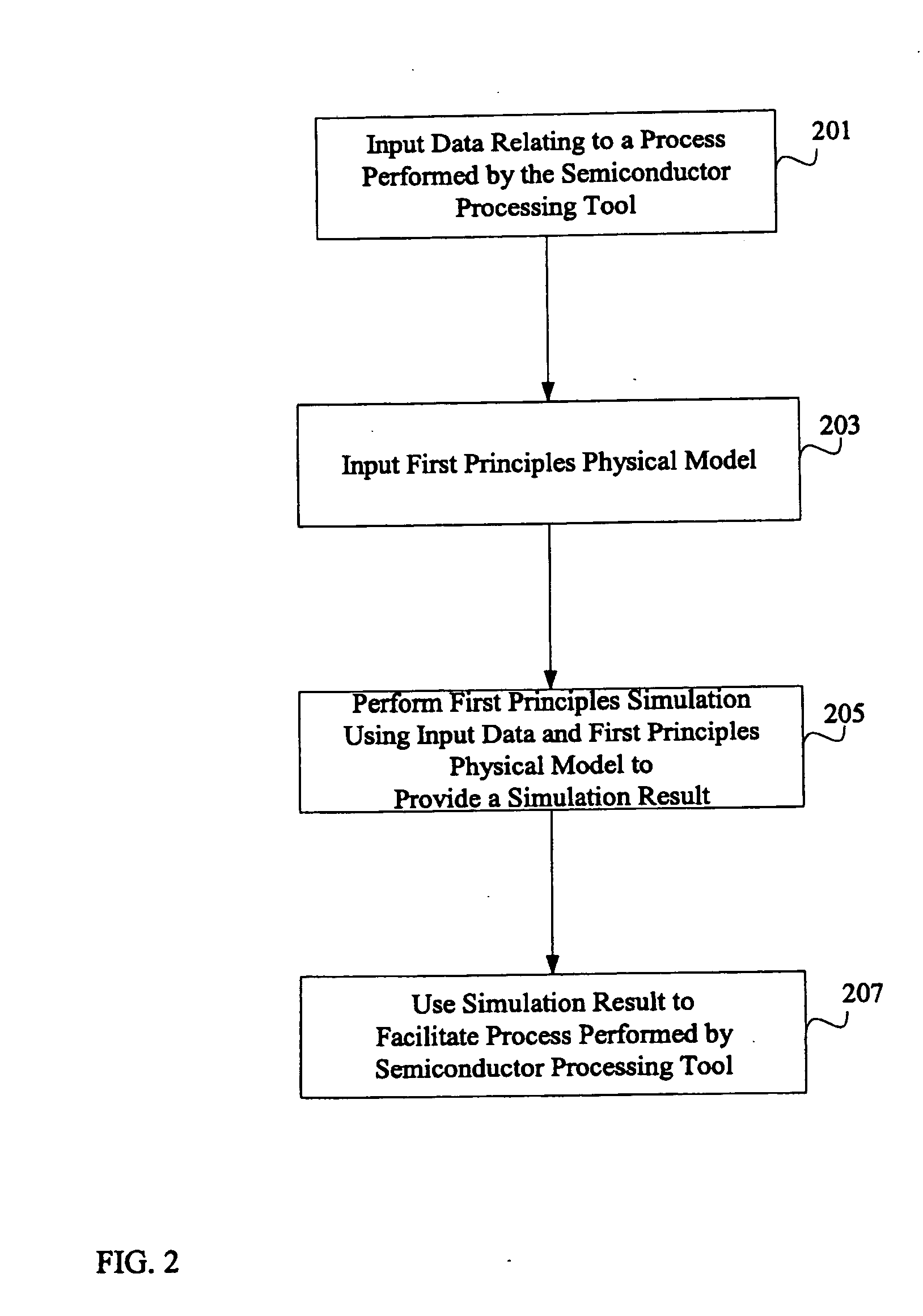
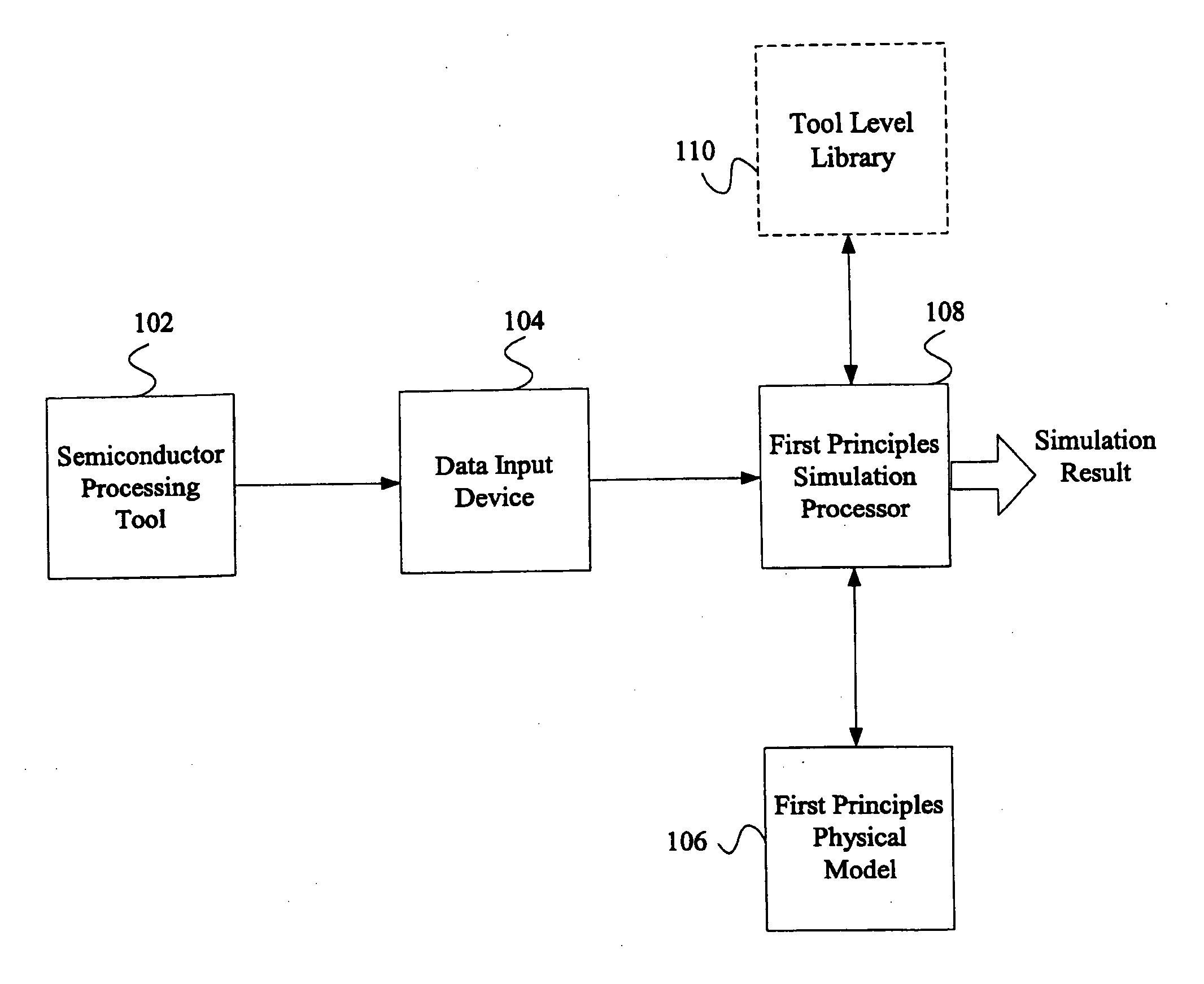
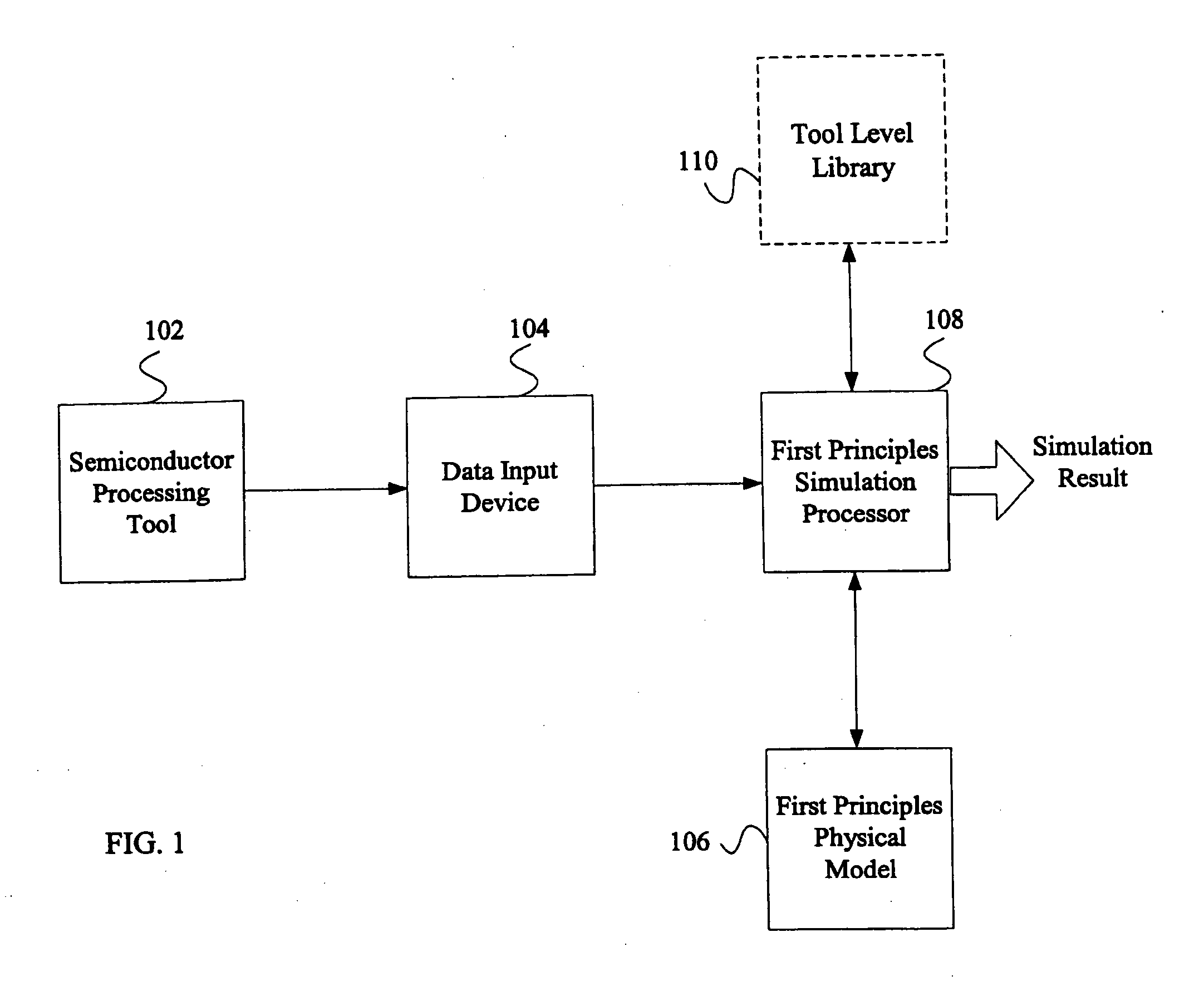
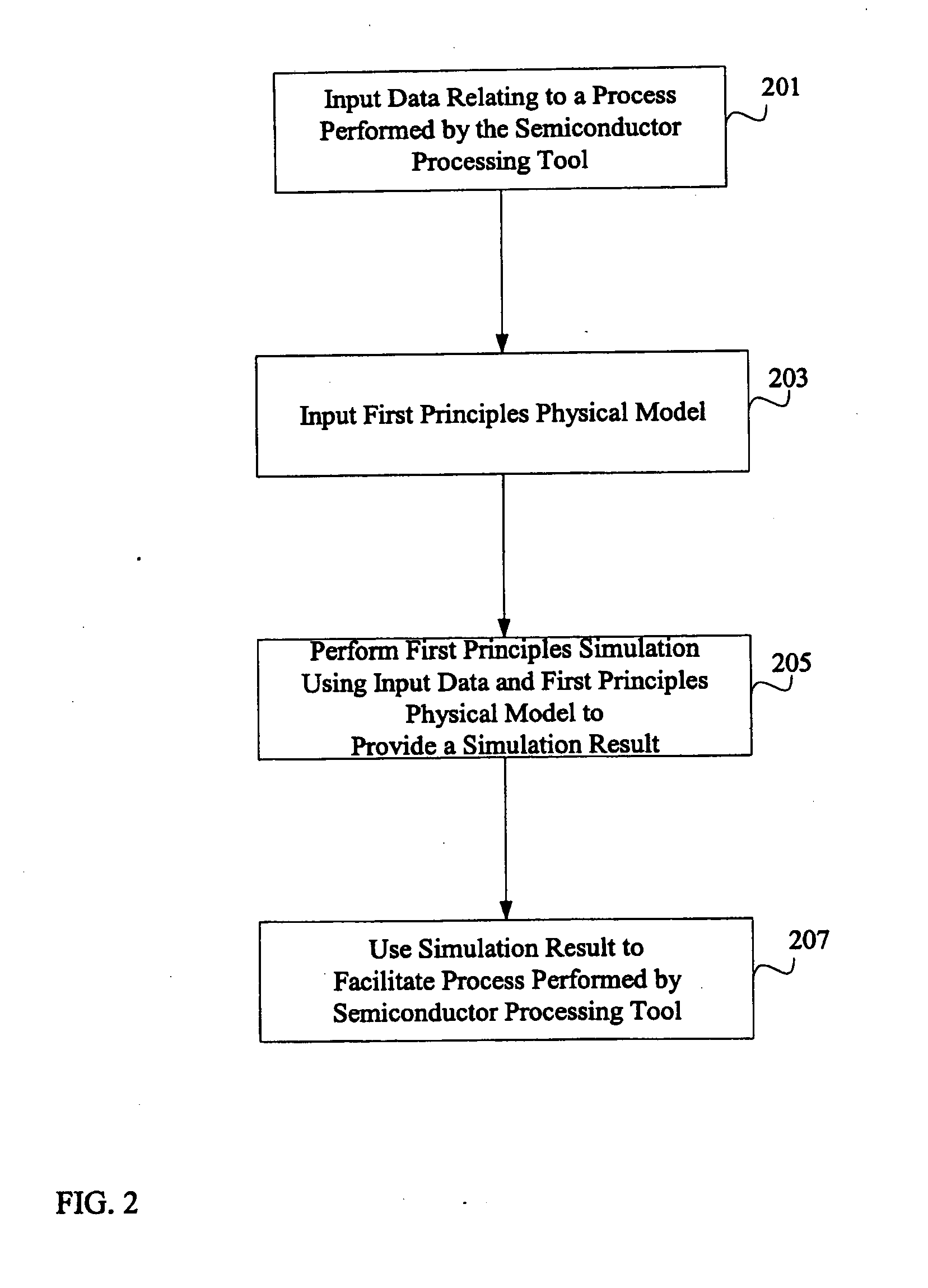
System and method for using first-principles simulation to provide virtual sensors that facilitate a semiconductor manufacturing process
InactiveUS20050071039A1Easy to processEasy to implementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDigital data processing detailsPhysical modelFirst principle
A method, system, and computer readable medium for facilitating a process performed by a semiconductor processing tool. The method includes inputting data relating to a process performed by the semiconductor processing tool, and inputting a first principles physical model relating to the semiconductor processing tool. First principles simulation is performed using the input data and the physical model to provide a virtual sensor measurement relating to the process performed by the semiconductor processing tool, and the virtual sensor measurement is used to facilitate the process performed by the semiconductor processing tool.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
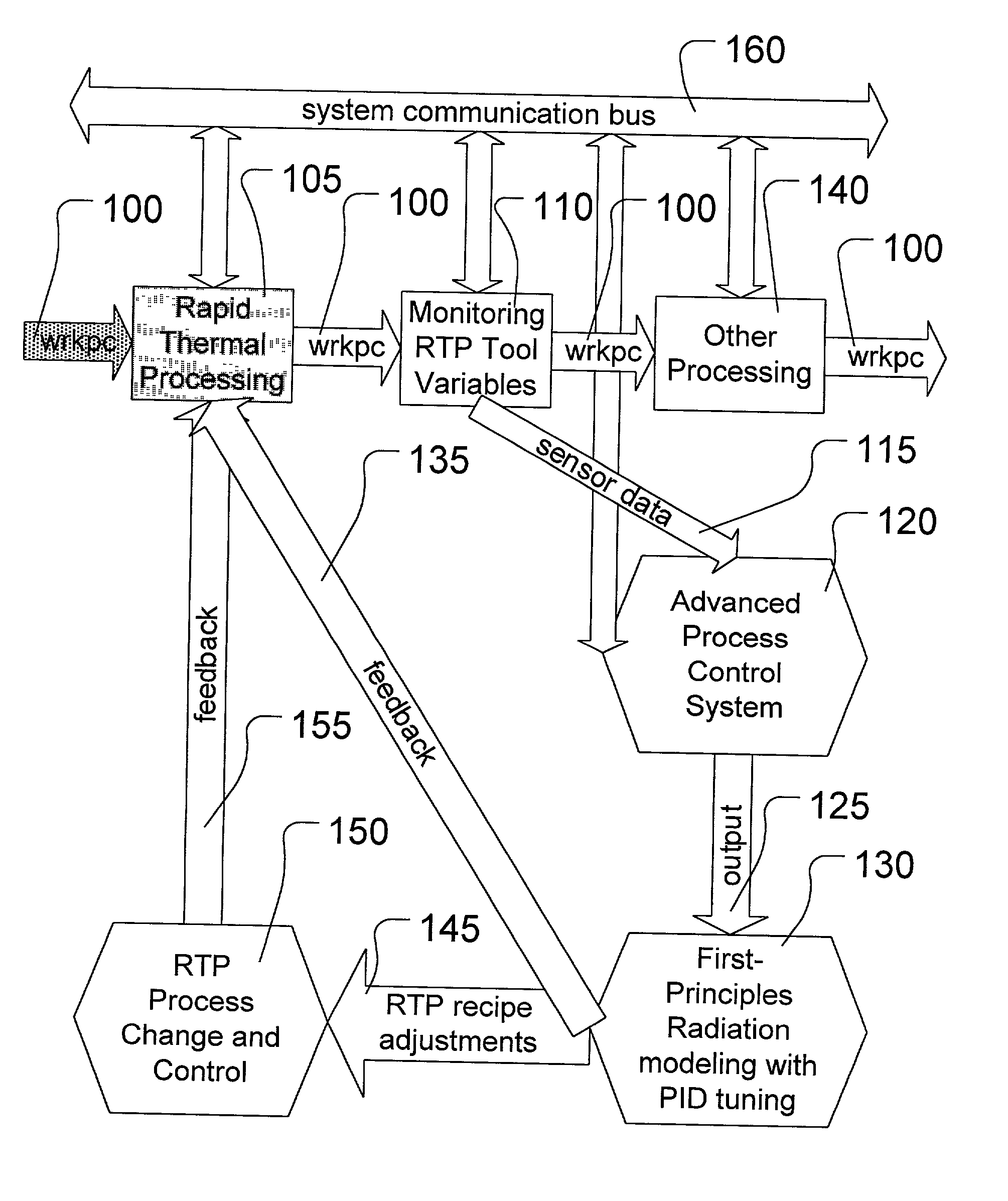
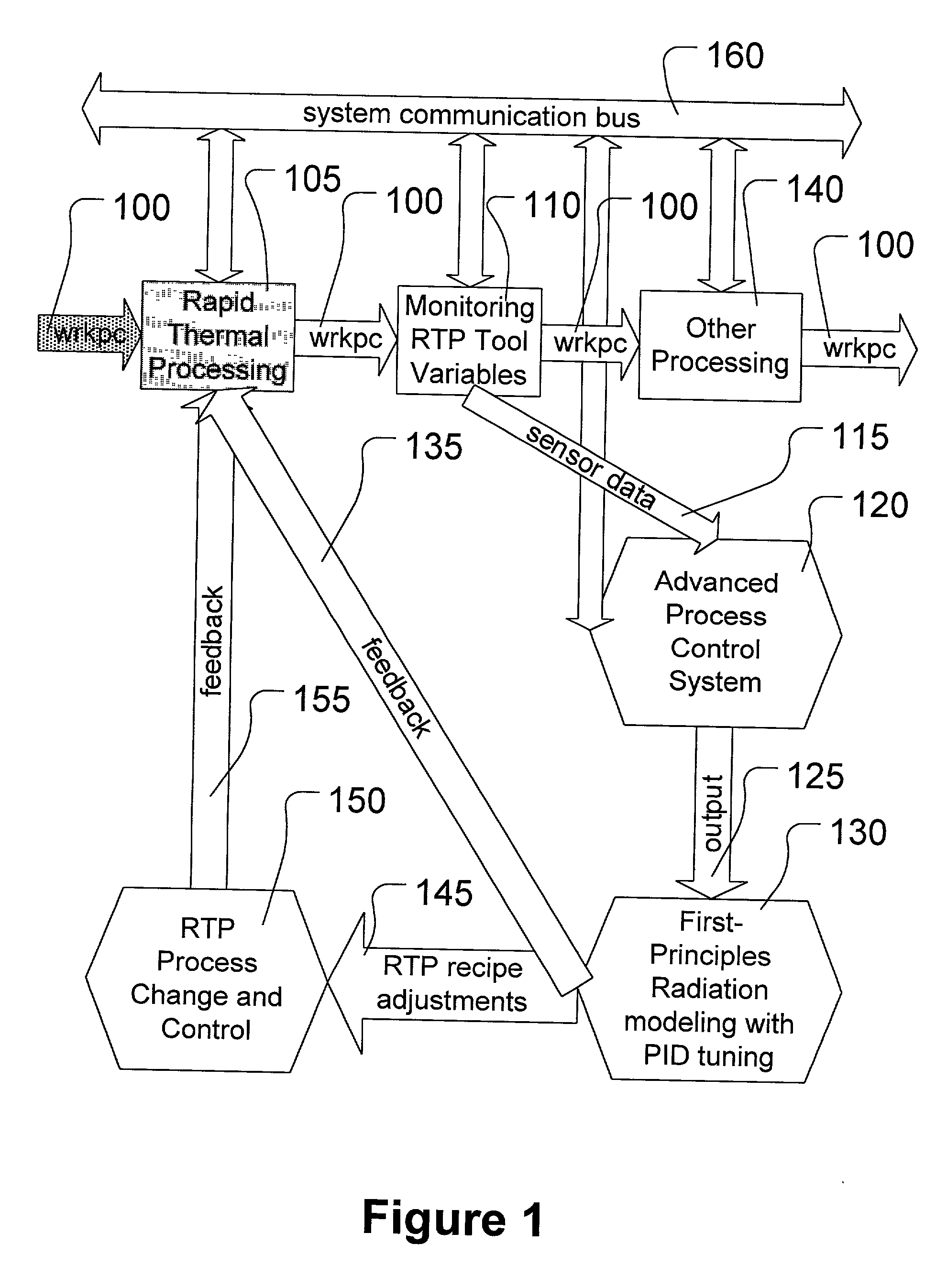
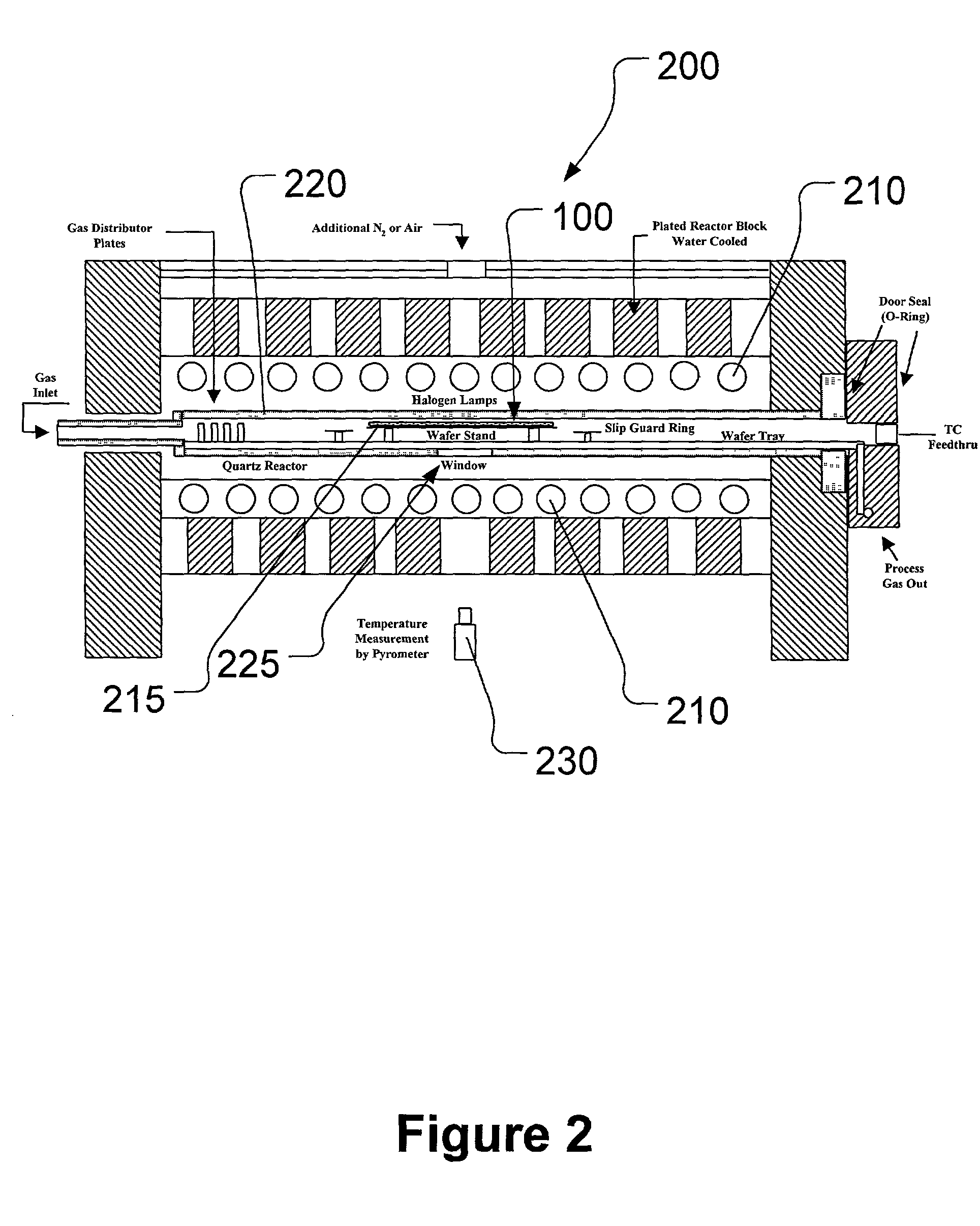
Run-to-run control method for proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller tuning for rapid thermal processing (RTP)
InactiveUS20020107604A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermodynamicsFirst principle
A method is provided, the method comprising measuring at least one parameter characteristic of rapid thermal processing performed on a workpiece in a rapid thermal processing step, and modeling the at least one characteristic parameter measured using a first-principles radiation model. The method also comprises applying the first-principles radiation model to modify the rapid thermal processing performed in the rapid thermal processing step.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
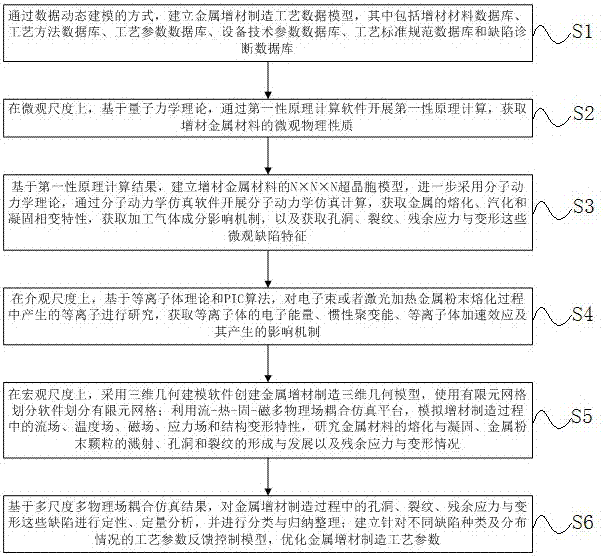
Multi-scale multiphysics coupling simulation method of metal additive manufacturing
ActiveCN107368642AOptimizing manufacturing process parametersImprove manufacturing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsManufacturing technologyFirst principle
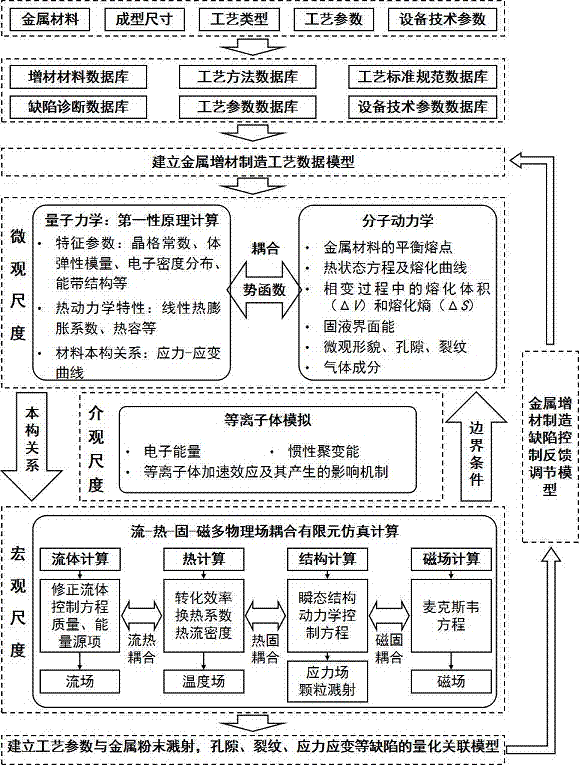
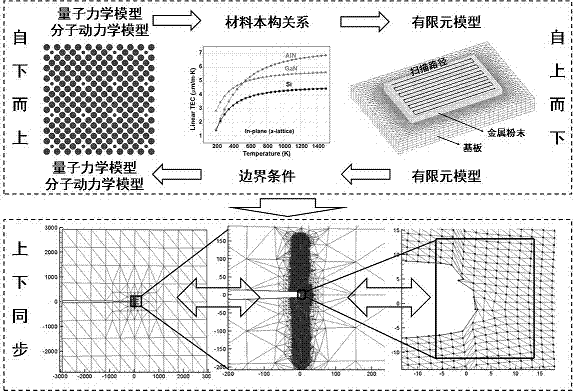
The invention provides a multi-scale multiphysics coupling simulation method of metal additive manufacturing. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a metal additive manufacturing technology data model; S2, carrying out first-principles calculation by calculation software on a microscale through first principles to acquire micro physical properties of additive metal material; S3, establishing an NxNxN super-cell model of the additive metal material, and carrying out molecular dynamics simulation calculation through molecular dynamics simulation software; S4, studying plasma, which is generated in a melting process of metal powder heated by an electron beam or a laser, on a mesoscale; S5, utilizing a flow-heat-solid-magnet multiphysics coupling simulation platform for simulation calculation; and S6, establishing a technology parameter feedback control model for different types and distribution situations of defects, and optimizing metal additive manufacturing technology parameters. The method forms a macro-micro-integration metal additive manufacturing product quality prediction system by means of multi-scale multiphysics coupling simulation.
Owner:湖南珞佳智能科技有限公司
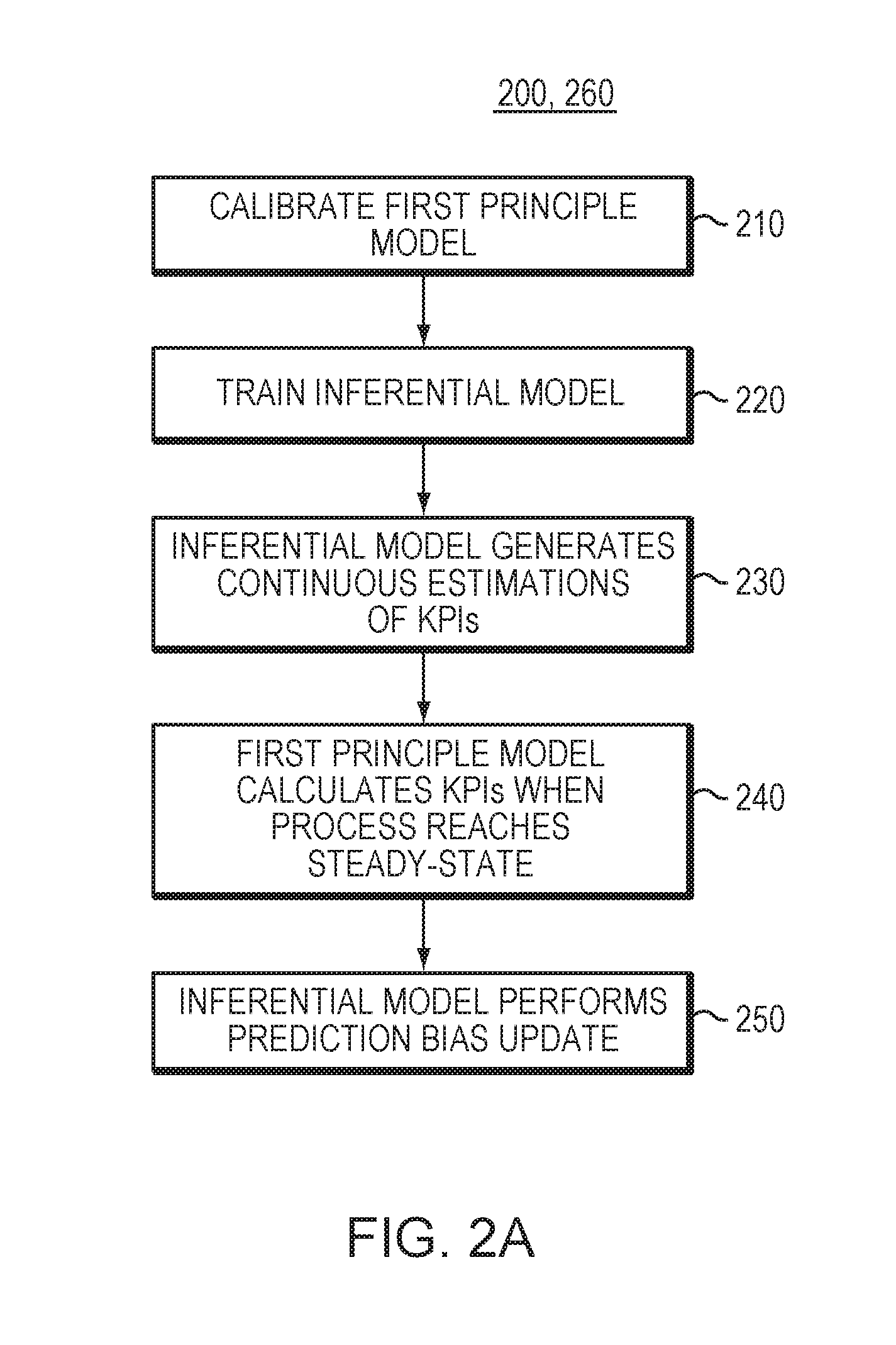
Computer System And Method For Causality Analysis Using Hybrid First-Principles And Inferential Model
ActiveUS20160320768A1Reduce riskReduce economic lossProgramme controlComputer controlData variabilityFirst principle
The present invention is directed to computer-based methods and system to perform root-cause analysis on an industrial process. The methods and system load process data for an industrial process from a historian database and build a hybrid first-principles and inferential model. The methods and system then executes the hybrid model to generate KPIs for the industrial process using the loaded process variables. The methods and system then selects a subset of the KPIs to represent an event occurring in the industrial process, and divides the data for the subset into multiple subset of time series. The system and methods select time intervals from the time series based on the data variability in the selected time intervals and perform a cross-correlation between the loaded process variables and the selected time interval, resulting in a cross-correlation score for each loaded process variable. The methods and system then select precursor candidates from the loaded process variables based on the cross-correlation scores and execute a parametric model for performing quantitative analysis of the selected precursor candidates, resulting in a strength of correlation score for each precursor candidate. The methods and system select root-cause variables from the selected precursor candidates based on the strength of correlation scores for analyzing the root-cause of the event.
Owner:ASPENTECH CORP
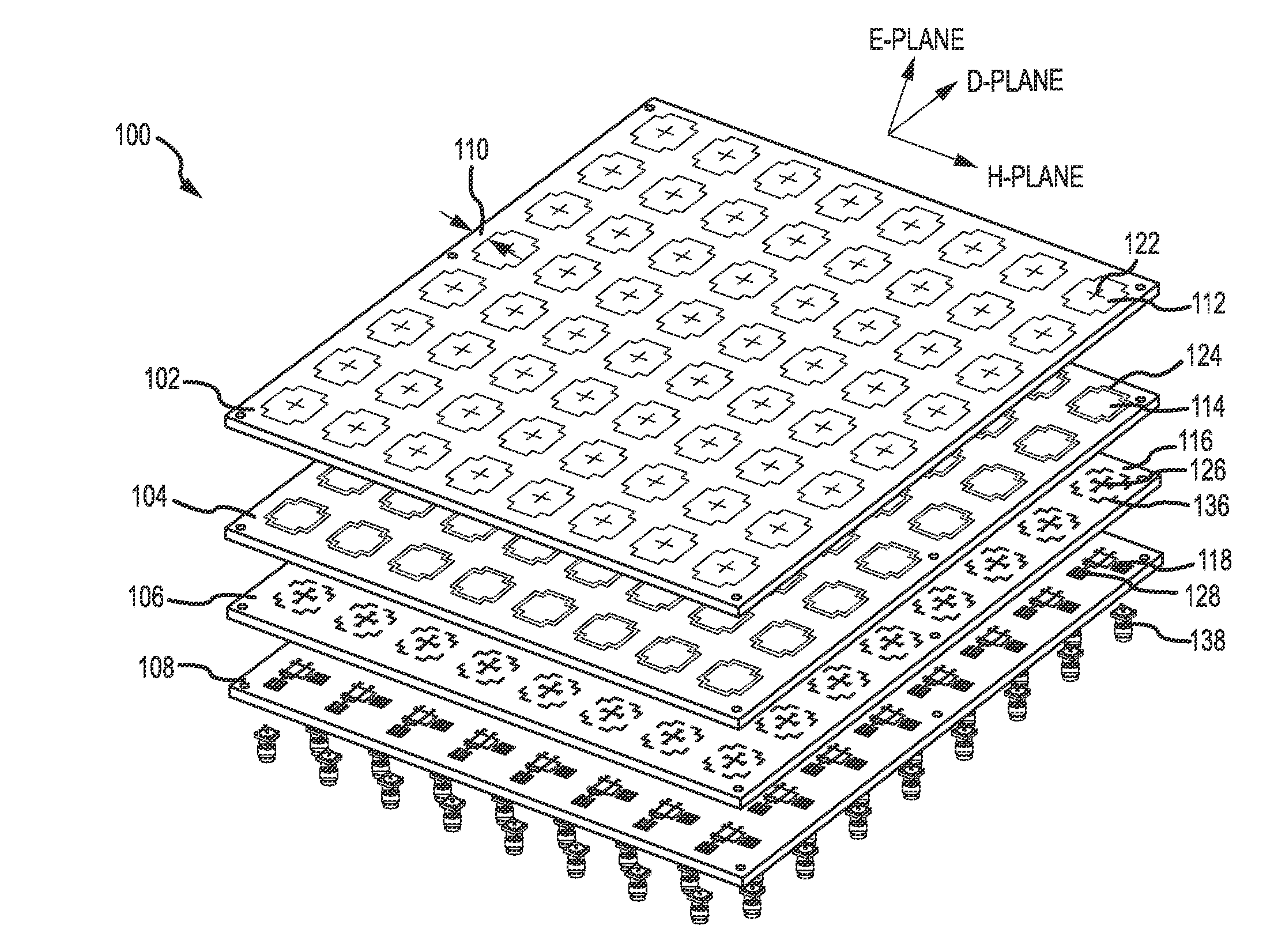
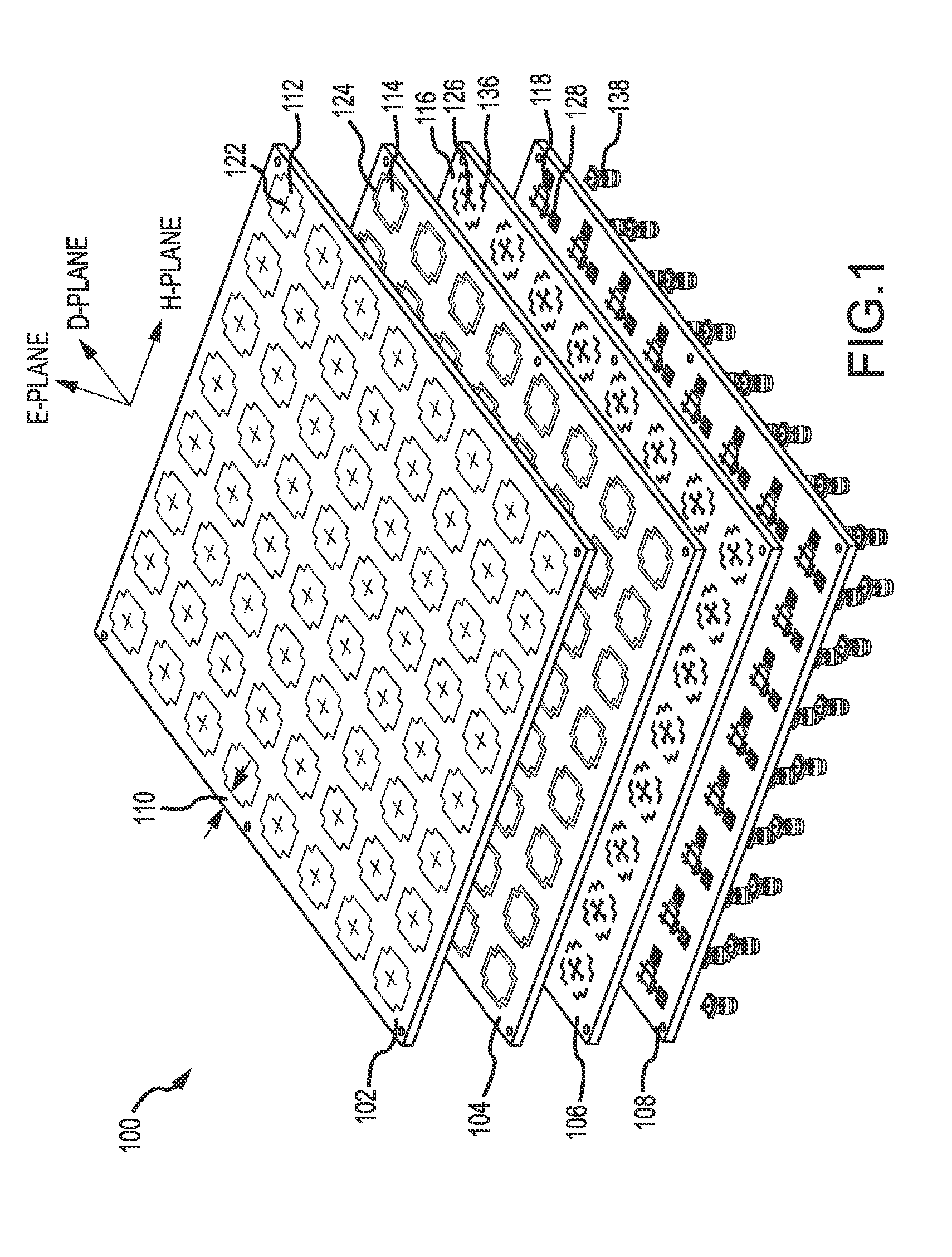
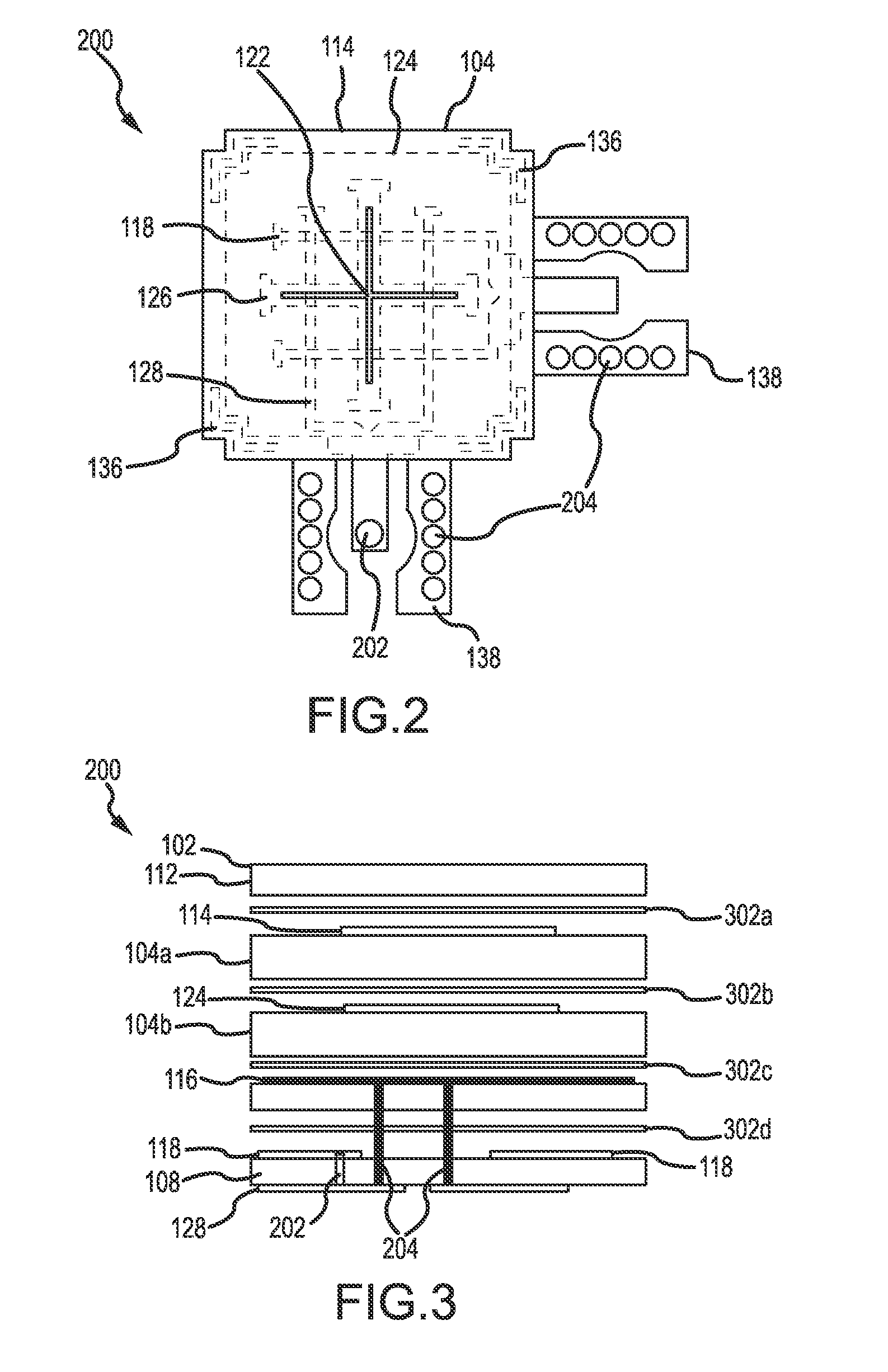
Dual-polarized radiating patch antenna
A dual-polarized patch antenna, an dual-polarized patch antenna array, and a method for forming the same are provided. The dual-polarized patch antenna comprises a radome, a horizontal feed and a vertical feed, a first cross-shaped patch, and a ground plane including a cross aperture. The dual-polarized patch antenna may include a cross patch and a cross aperture to increase the isolation in a cross-polarization between a horizontal polarized signal and a vertical polarized signal in a first principle plane and to decrease a mismatch in co-polarizations between the horizontal polarized signal and the vertical polarized signal in a second principle plane.
Owner:UNIV FOR ATMOSPHERIC RES
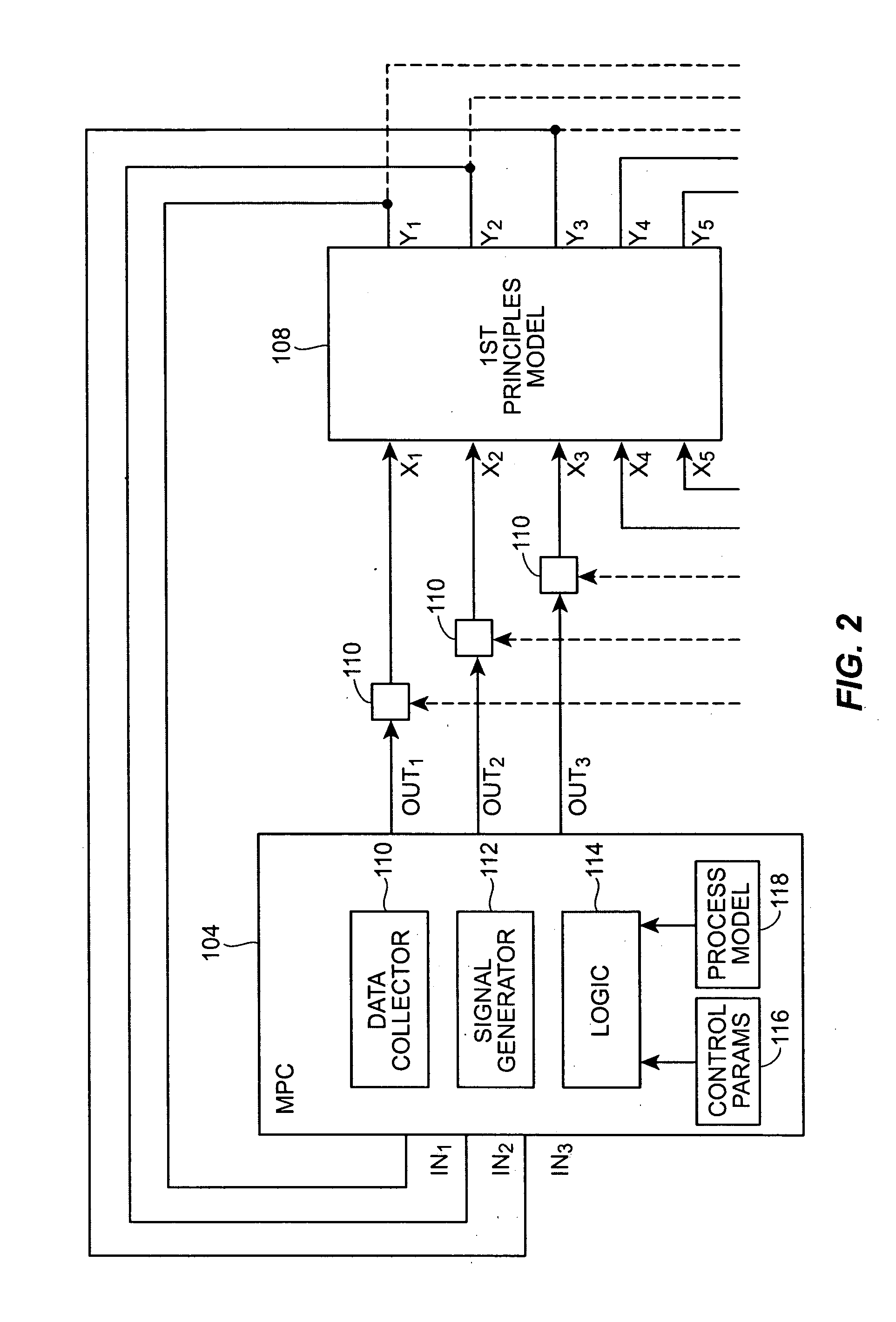
System and method for using first-principles simulation to control a semiconductor manufacturing process
InactiveUS20050071038A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFirst principlePhysical model
A method, system and computer readable medium for controlling a process performed by a semiconductor processing tool includes inputting data relating to a process performed by the semiconductor processing tool, and inputting a first principles physical model relating to the semiconductor processing tool. First principles simulation is then performed using the input data and the physical model to provide a first principles simulation result, and the first principles simulation result is used to control the process performed by the semiconductor processing tool.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
System and method for using first-principles simulation to control a semiconductor manufacturing process
InactiveUS20050071035A1Programme controlAnalogue computers for electric apparatusPhysical modelFirst principle
A method, system and computer readable medium for controlling a process performed by a semiconductor processing tool. The method includes inputting data relating to a process performed by the semiconductor processing tool, inputting a first principles physical model relating to the semiconductor processing tool, performing first principles simulation using the input data and the physical model to provide a first principles simulation result. The first principles simulation result is used to build an empirical model, and at least one of the first principles simulation result and the empirical model is selected to control the process performed by the semiconductor processing tool.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
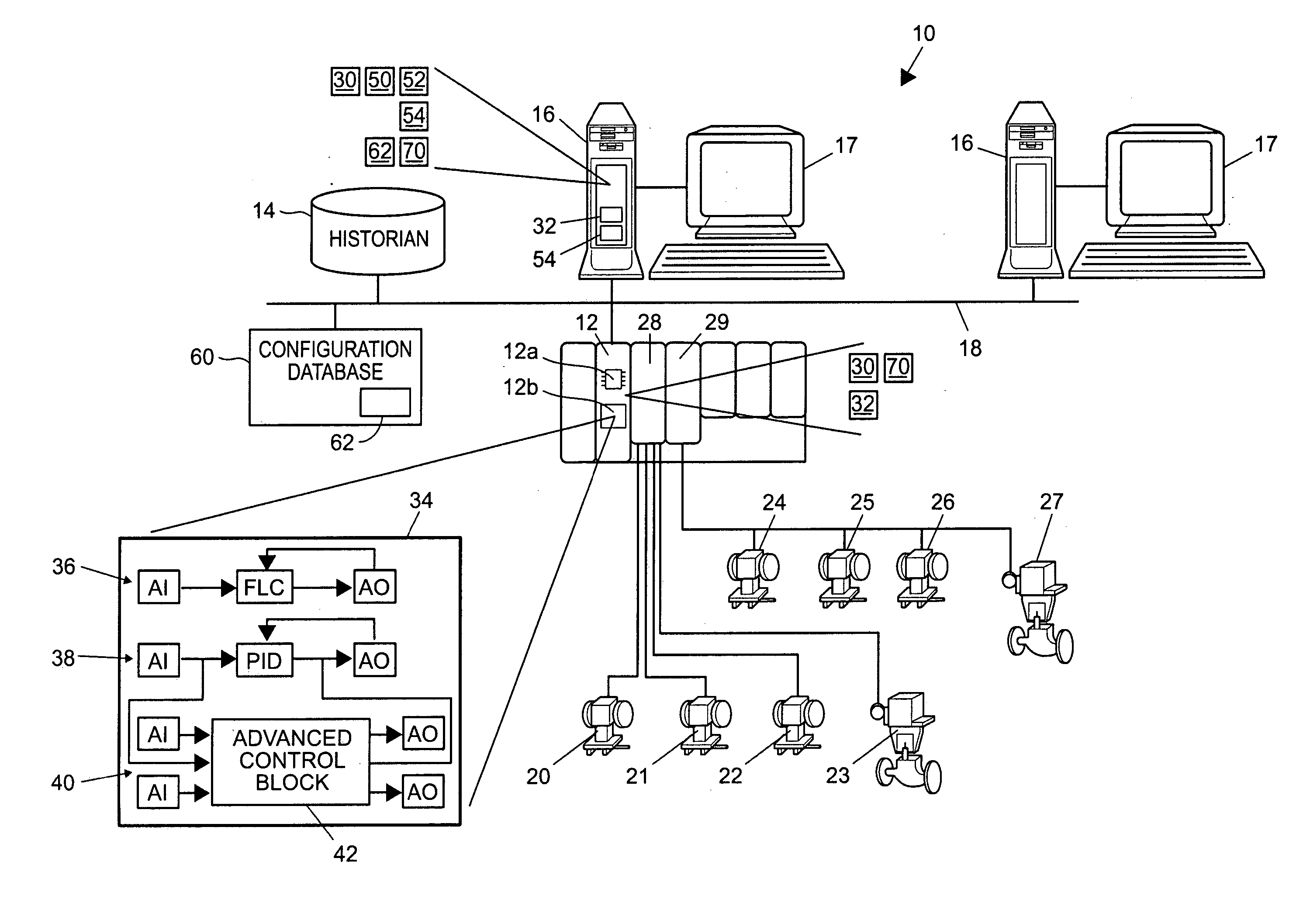
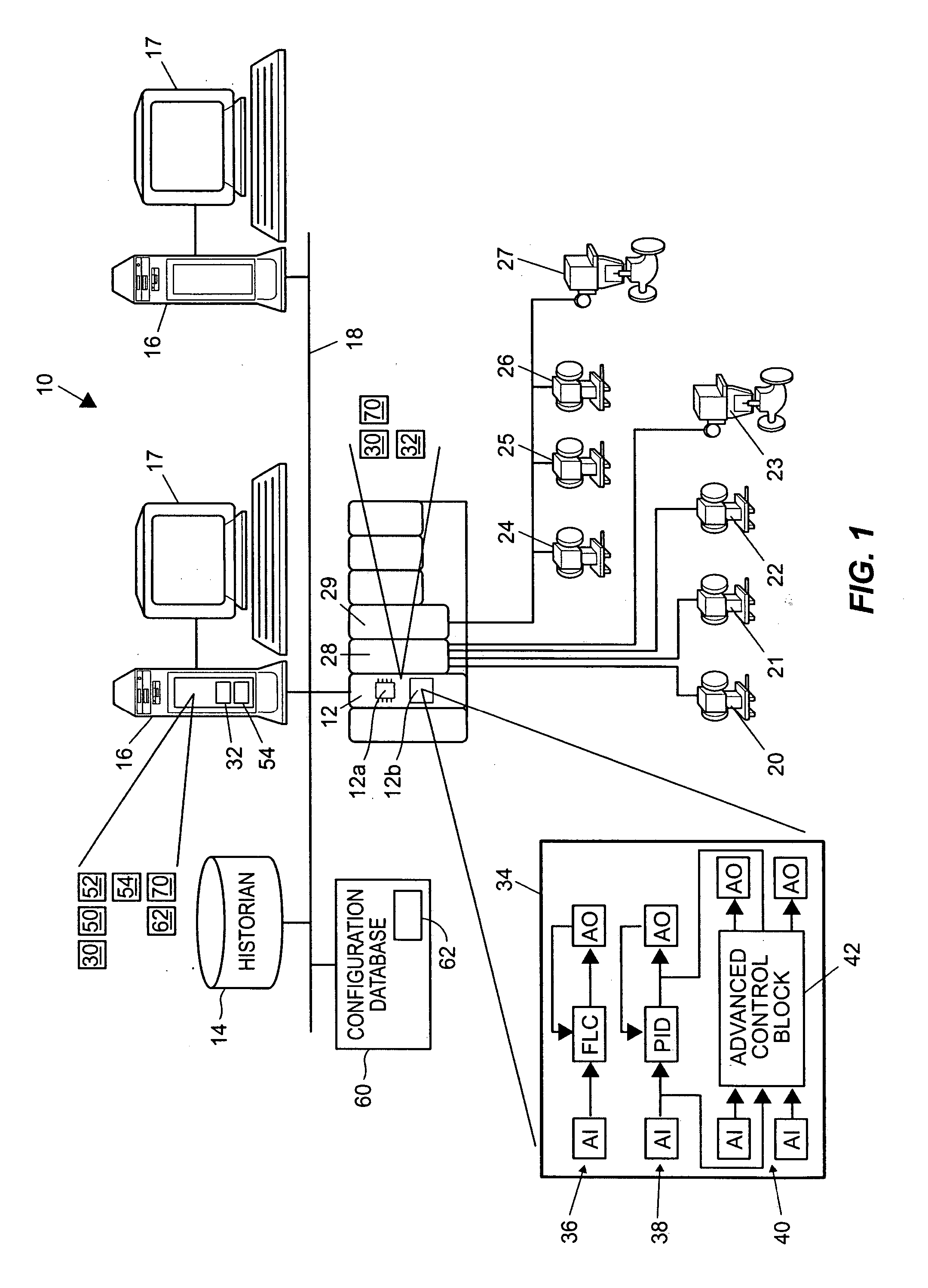
Method and system for controlling a batch process
ActiveUS20070078530A1Easy to controlSimulator controlElectric controllersProduction rateBatch processing
A first principles model may be used to simulate a batch process, and the first principles model may be used to configure a multiple-input / multiple-output control routine for controlling the batch process. The first principles model may generate estimates of batch parameters that cannot, or are not, measured during operation of the actual batch process. An example of such a parameter may be a rate of change of a component (e.g., a production rate, a cell growth rate, etc.) of the batch process. The first principles model and the configured multiple-input / multiple-output control routine may be used to facilitate control of the batch process.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
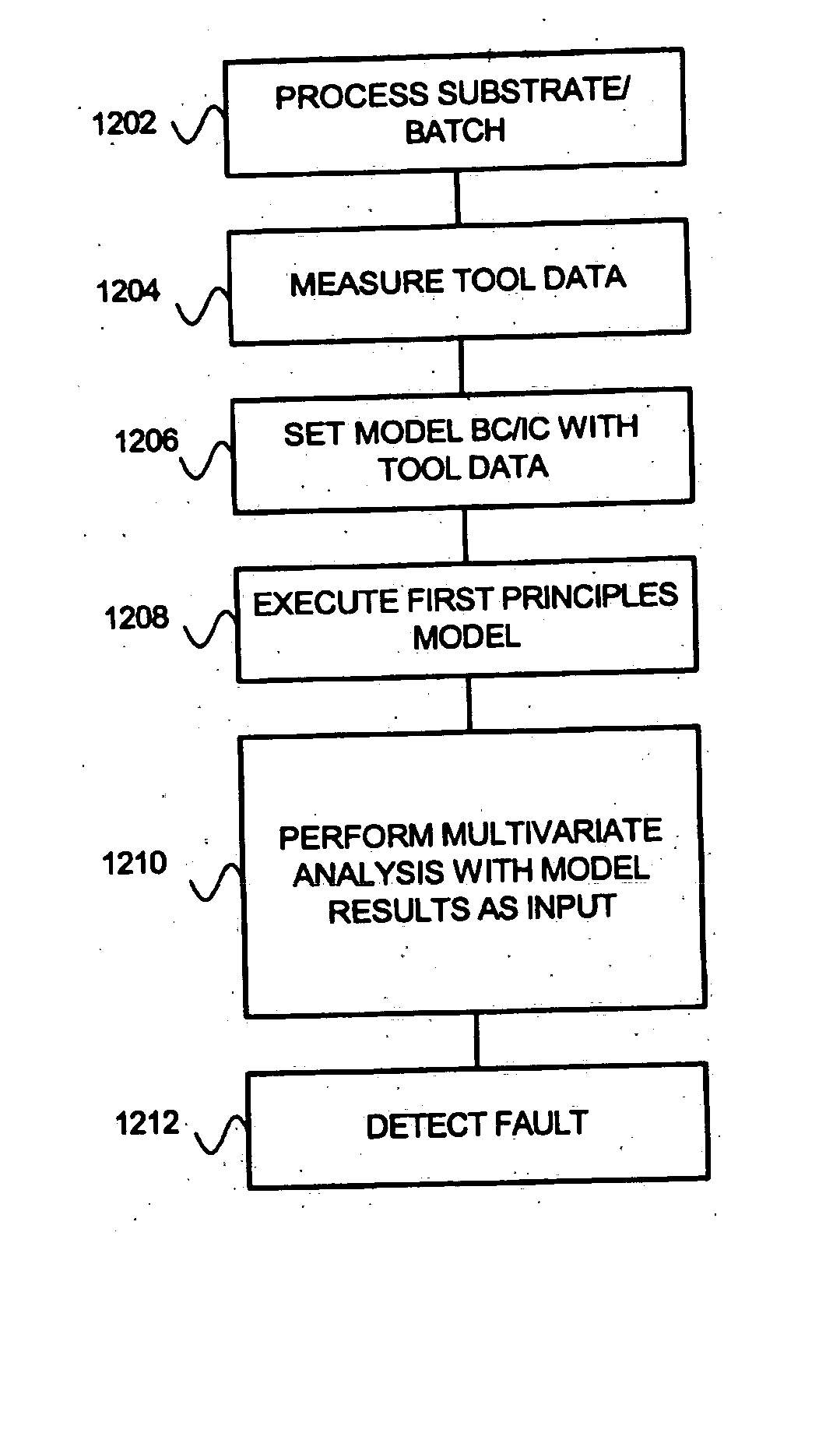
System and method for using first-principles simulation to analyze a process performed by a semiconductor processing tool
InactiveUS20050071037A1Programme controlAnalogue computers for electric apparatusPhysical modelFirst principle
A method, system and computer readable medium for analyzing a process performed by a semiconductor processing tool. The method includes inputting data relating to a process performed by the semiconductor processing tool, and inputting a first principles physical model relating to the semiconductor processing tool. First principles simulation is performed using the input data and the physical model to provide a first principles simulation result; and the first principles simulation result is used to determine a fault in the process performed by the semiconductor processing tool.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
System and method for using first-principles simulation to characterize a semiconductor manufacturing process
InactiveUS20050071036A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDigital data processing detailsData setPhysical model
A method, system and computer readable medium for facilitating a process performed by a semiconductor processing tool. The method includes inputting data relating to a process performed by the semiconductor processing tool, and inputting a first principles physical model relating to the semiconductor processing tool. First principles simulation is then performed using the input data and the physical model to provide a simulation result for the process performed by the semiconductor processing tool, and the simulation result is used as part of a data set that characterizes the process performed by the semiconductor processing tool.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
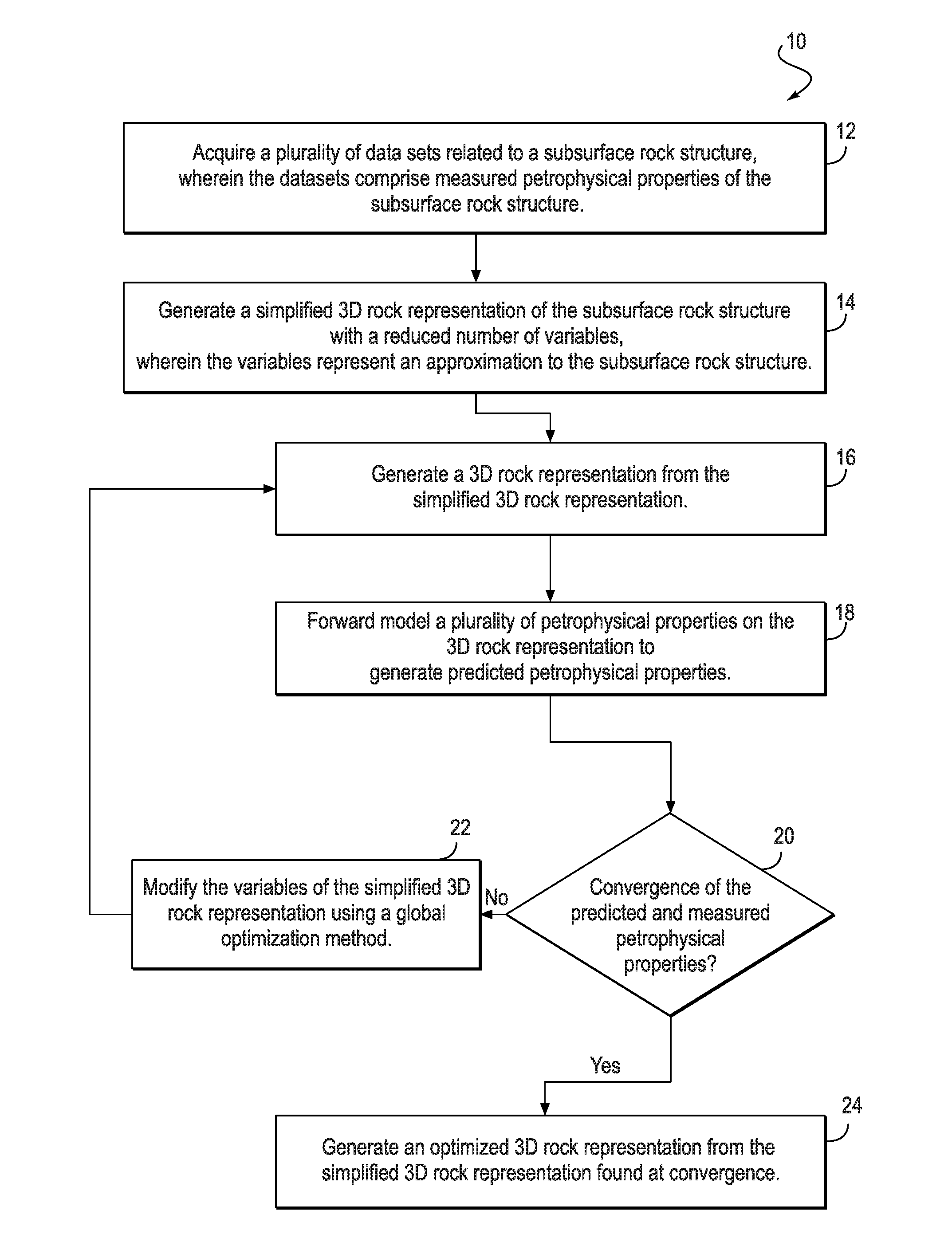
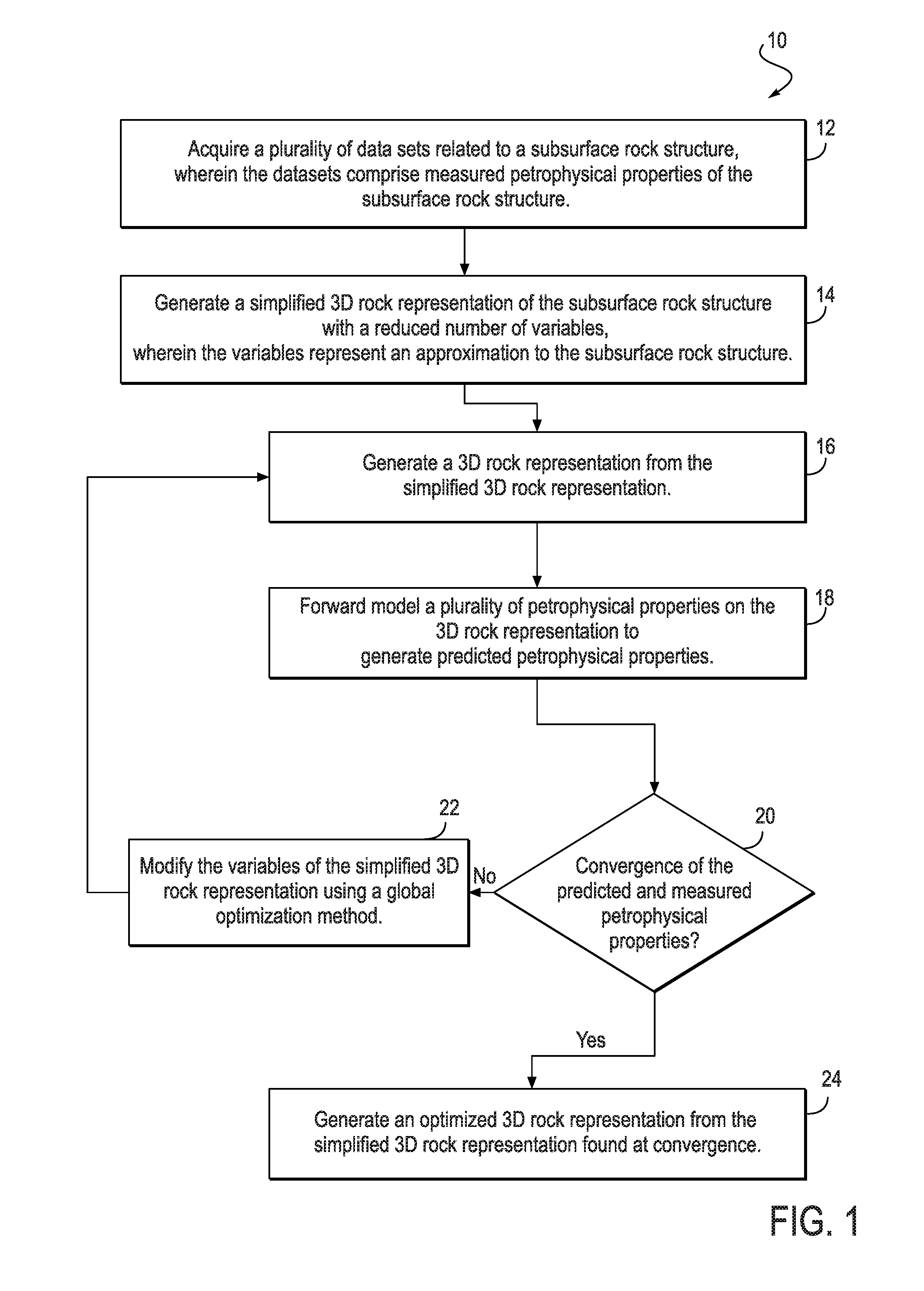
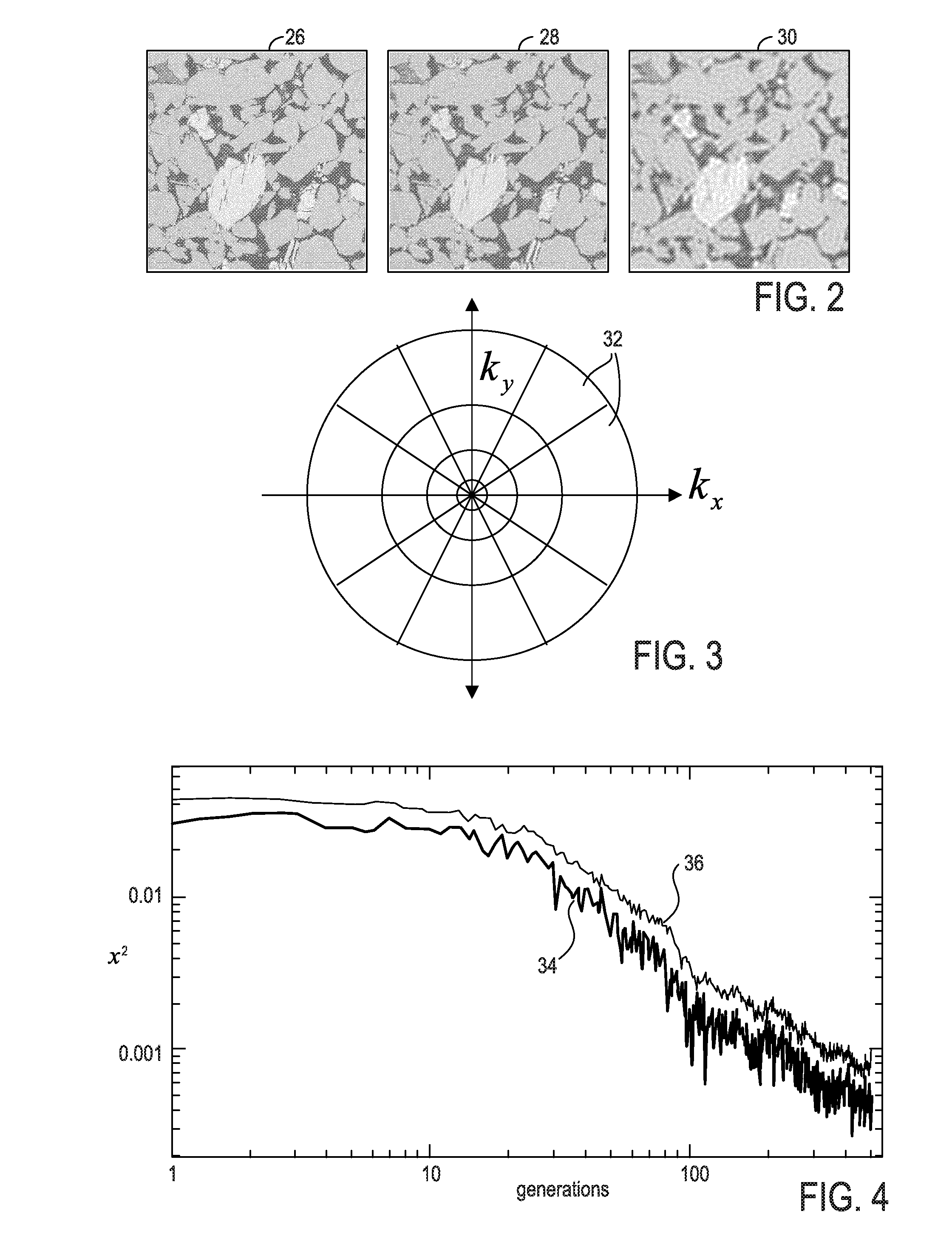
Method for creating a 3D rock representation using petrophysical data
The present invention enables the use of a global optimization method for performing joint-inversion of multiple petrophysical data sets, using forward models based on first principle of physics, to generate a 3D rock representation of a subsurface rock structure. The resulting 3D rock representation captures the internal structure, and honors the measured petrophysical properties, of the subsurface rock structure. The 3D rock representation can then be used to predict additional properties not considered in the inversion, to further characterize the subsurface rock structure.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
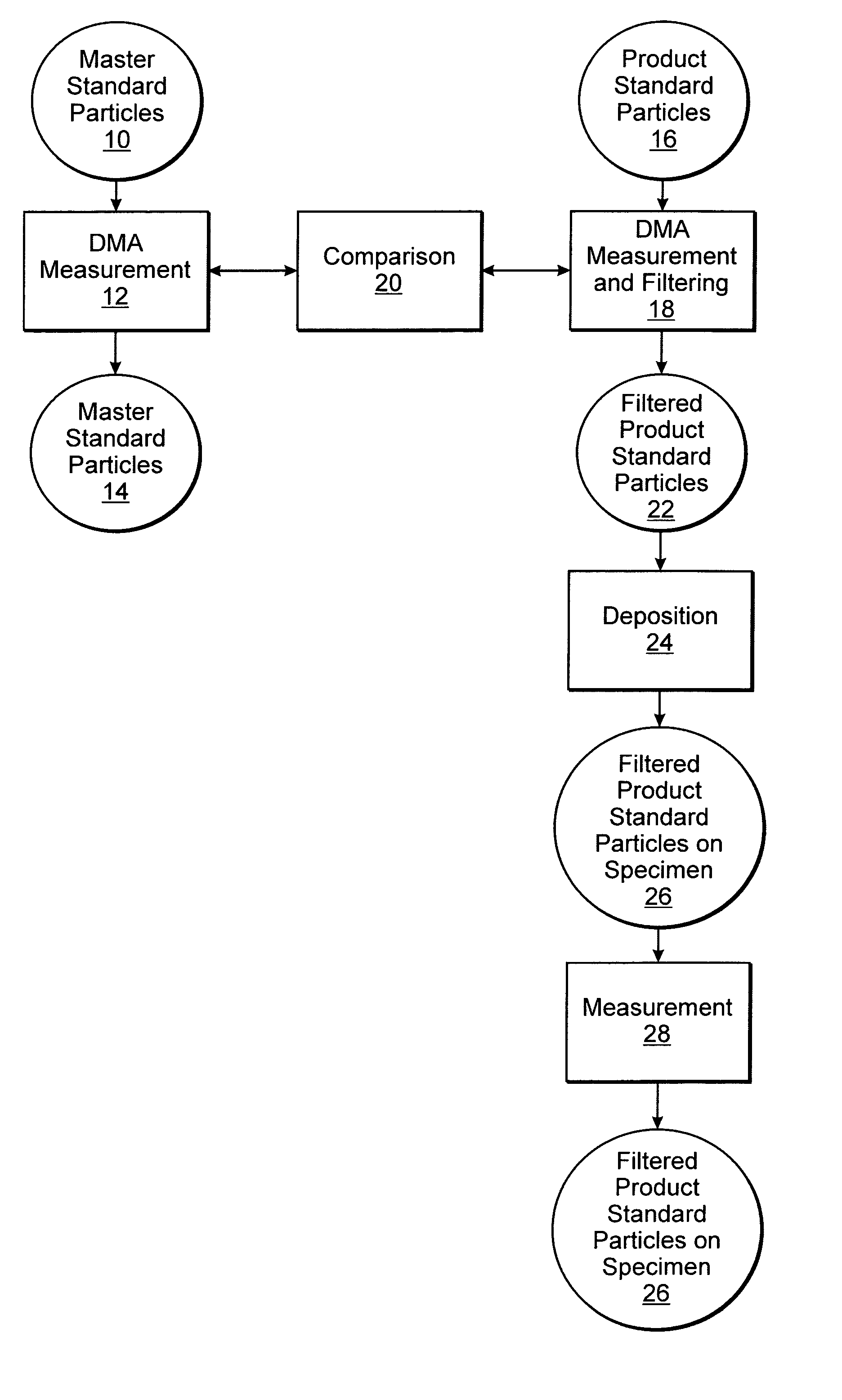
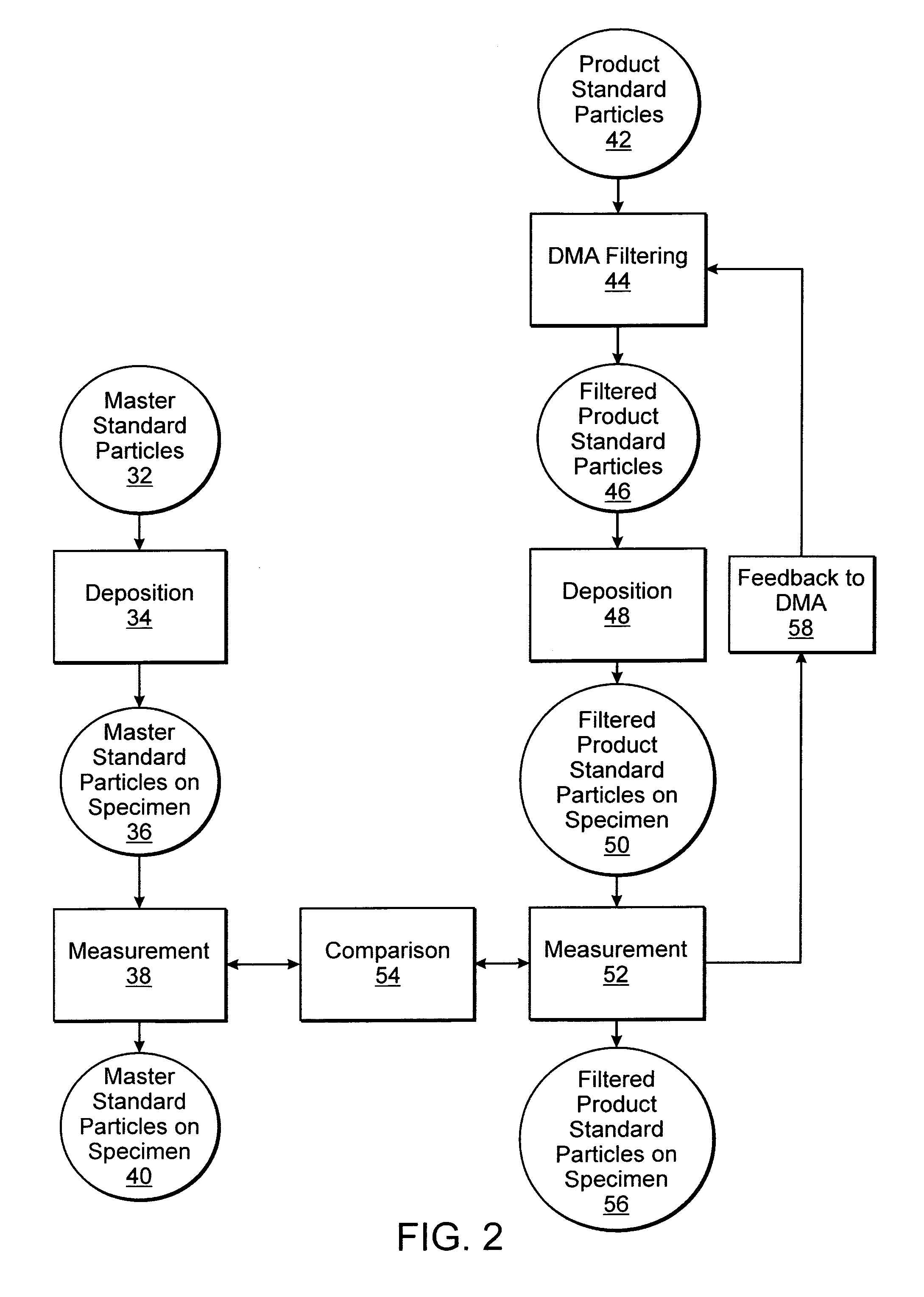
Methods for forming a calibration standard and calibration standards for inspection systems
InactiveUS7027146B1Size accuracy is loweredRemove uncertaintyPhotometry using reference valueOptically investigating flaws/contaminationFull width at half maximumFirst principle
Methods for forming calibration standards for an inspection system and calibration standards are provided. One method includes scanning a first and a second specimen with an optical system. Master standard particles having a lateral dimension traceable to a national or international authority or first principles measurements are deposited on the first specimen. Product standard particles are deposited on the second specimen. In addition, the method includes determining a lateral dimension of the product standard particles by comparing data generated by scanning the two specimens. One calibration standard includes particles having a lateral dimension of less than about 100 nm deposited on a specimen. A distribution of the lateral dimension has a full width at half maximum of less than about 3%. The uncertainty of the lateral dimension is less than about 2%. Therefore, the standard meets the requirements for the 130 nm technology generation of semiconductor devices.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
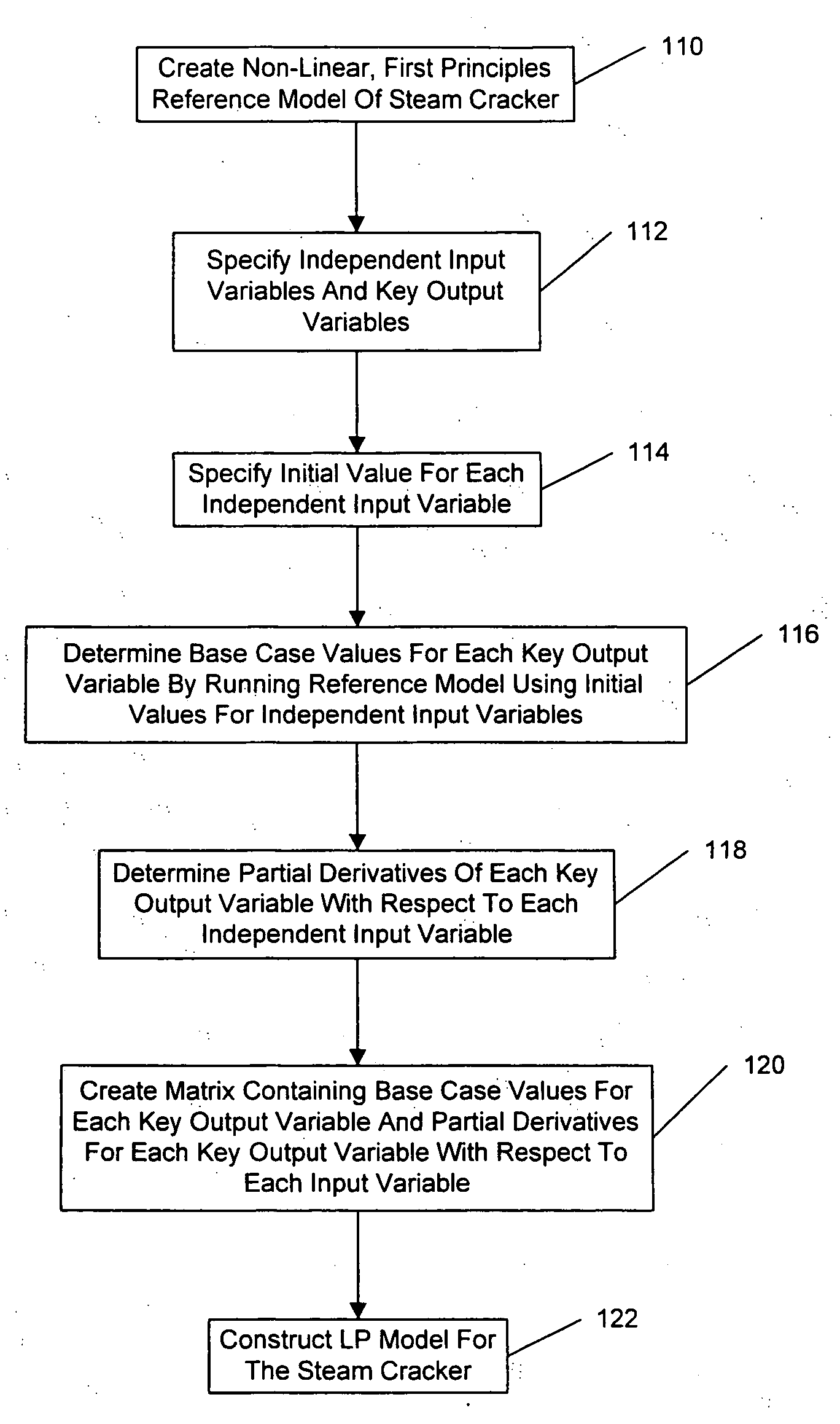
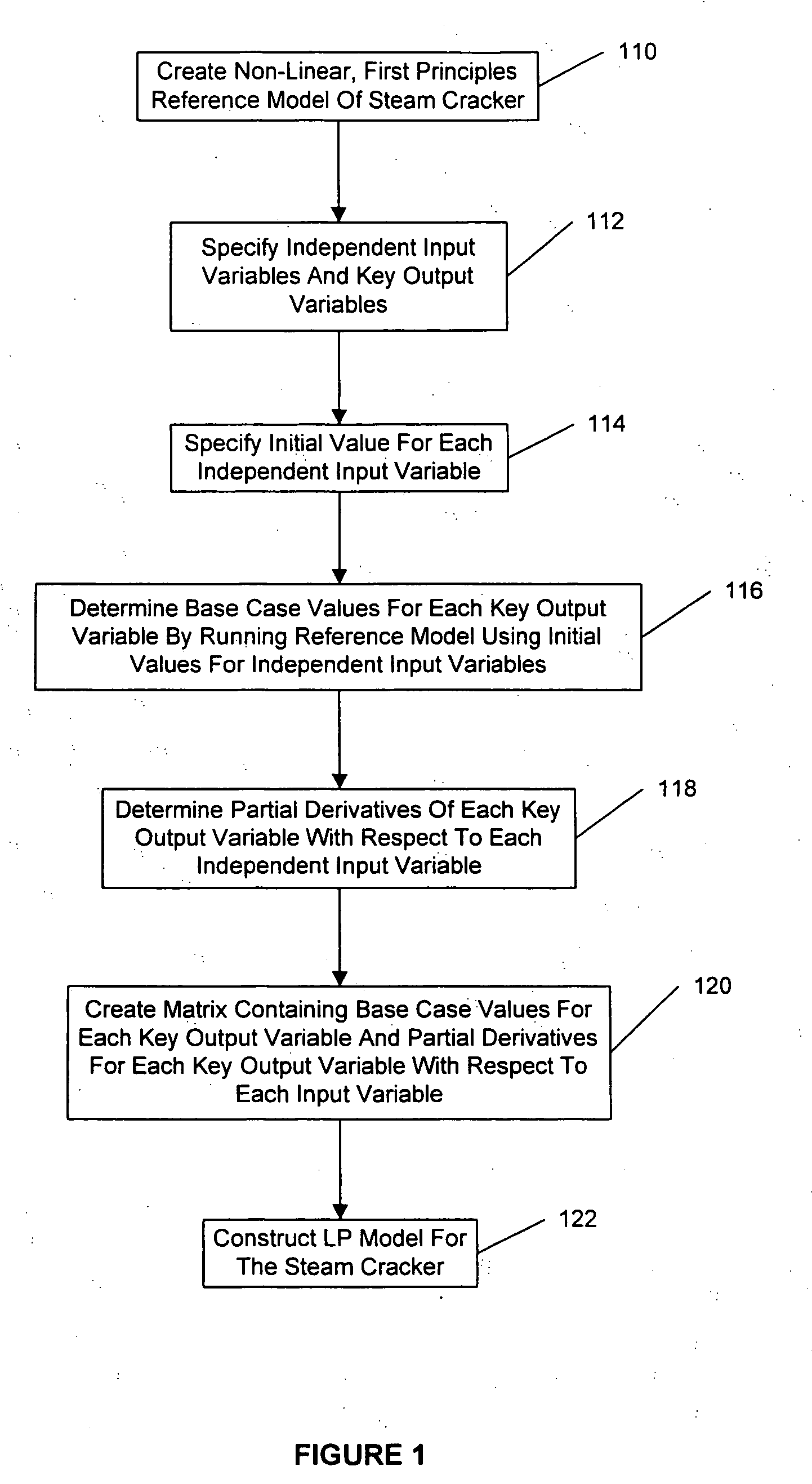
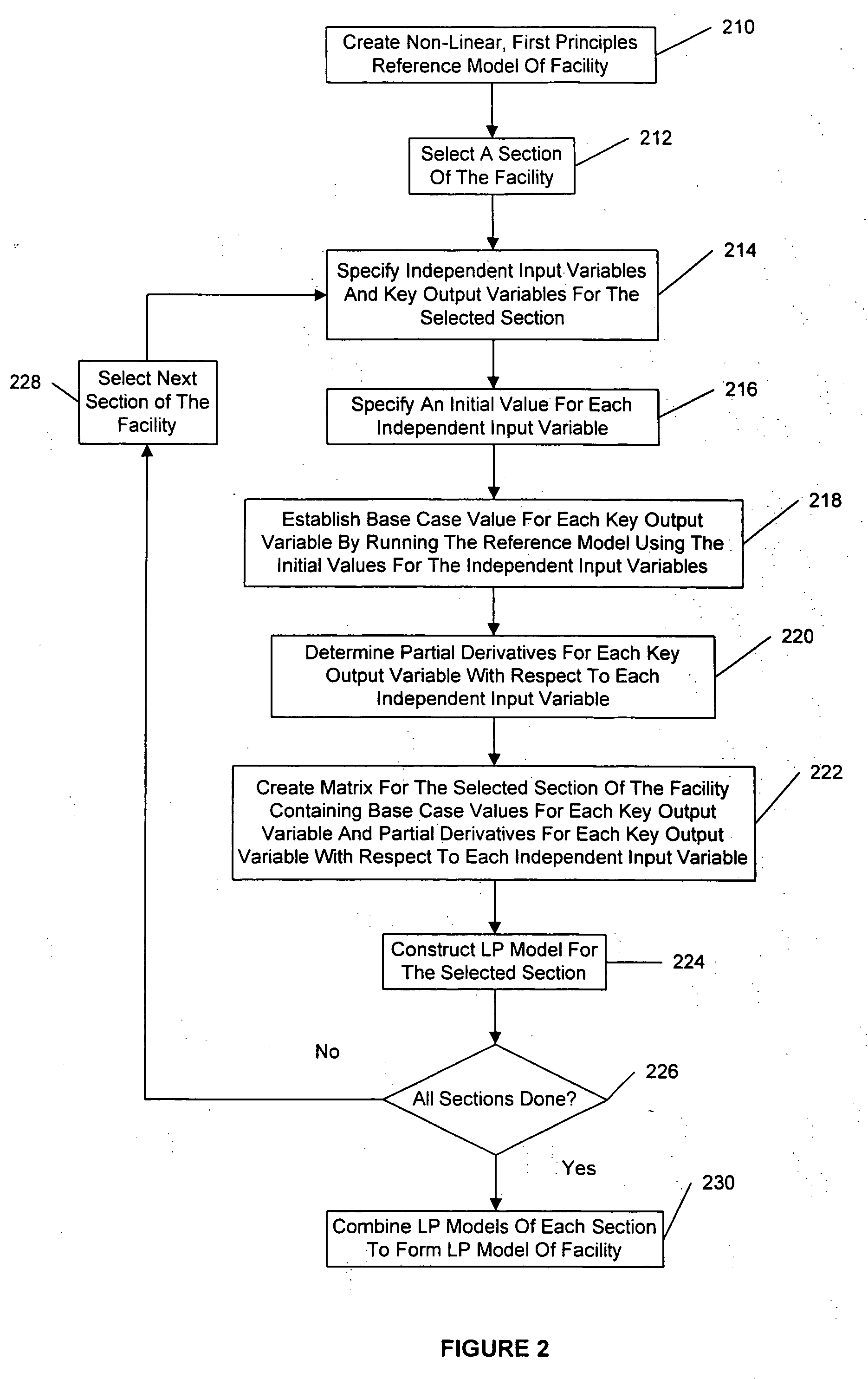
Method for creating a linear programming model of an industrial process facility
ActiveUS20060184254A1Simplify the development processEliminate needSolidificationLiquefactionReference modelFirst principle
A method for creating a linear programming (LP) model of an industrial process facility is disclosed. The model may be used for interactively simulating and / or optimizing the operation of the facility to facilitate feedstock selection and / or other economic analyses. According to the inventive method, a first principles reference tool is used to create a non-linear reference model of the entire facility. Then, independent input variables and key output variables are specified, and initial values for the independent input variables are specified. Base case values for each key output variable are determined by running the non-linear reference model using the specified initial values for the independent input variables. Next, partial derivatives for each key output variable with respect to each independent input variable are determined. A matrix is constructed containing the base case values and partial derivatives. The matrix serves as the depiction of the industrial process facility in the final LP, which may also include prices, availabilities, and other external constraints.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
System and method for using first-principles simulation to facilitate a semiconductor manufacturing process
InactiveUS20050071034A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFirst principlePhysical model
A method, system and computer readable medium for facilitating a process performed by a semiconductor processing tool. The method includes inputting data relating to a process performed by the semiconductor processing tool and inputting a first principles physical model relating to the semiconductor processing tool. First principles simulation is then performed using the input data and the physical model to provide a first principles simulation result, and the first principles simulation result is used to facilitate the process performed by the semiconductor processing tool.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
Semiconductor memory device and USB memory device using the same
InactiveUS20070066102A1Final product manufacturePrinted electric component incorporationElectrical conductorFirst principle
A USB terminal having a conductor layer to be an input / output terminal of a USB connector is formed on a first principle surface of a circuit board. A memory element is mounted on a second principle surface at an opposite side of a terminal forming surface of the circuit board, and the memory element is sealed with a sealing resin. A semiconductor memory device as a USB memory main body is constituted by them. A USB memory is constituted by housing the USB memory main body inside of a USB connector case.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
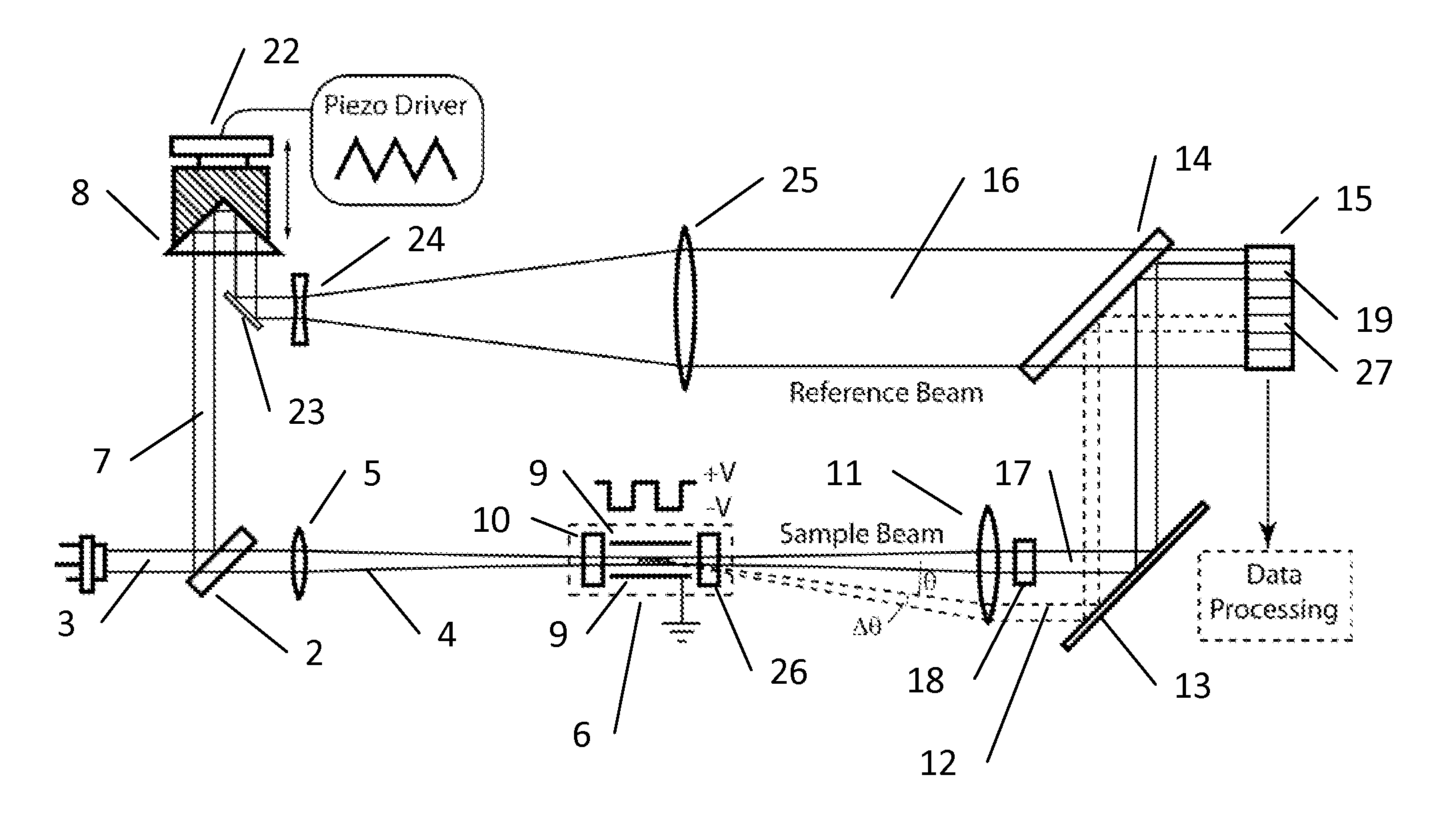
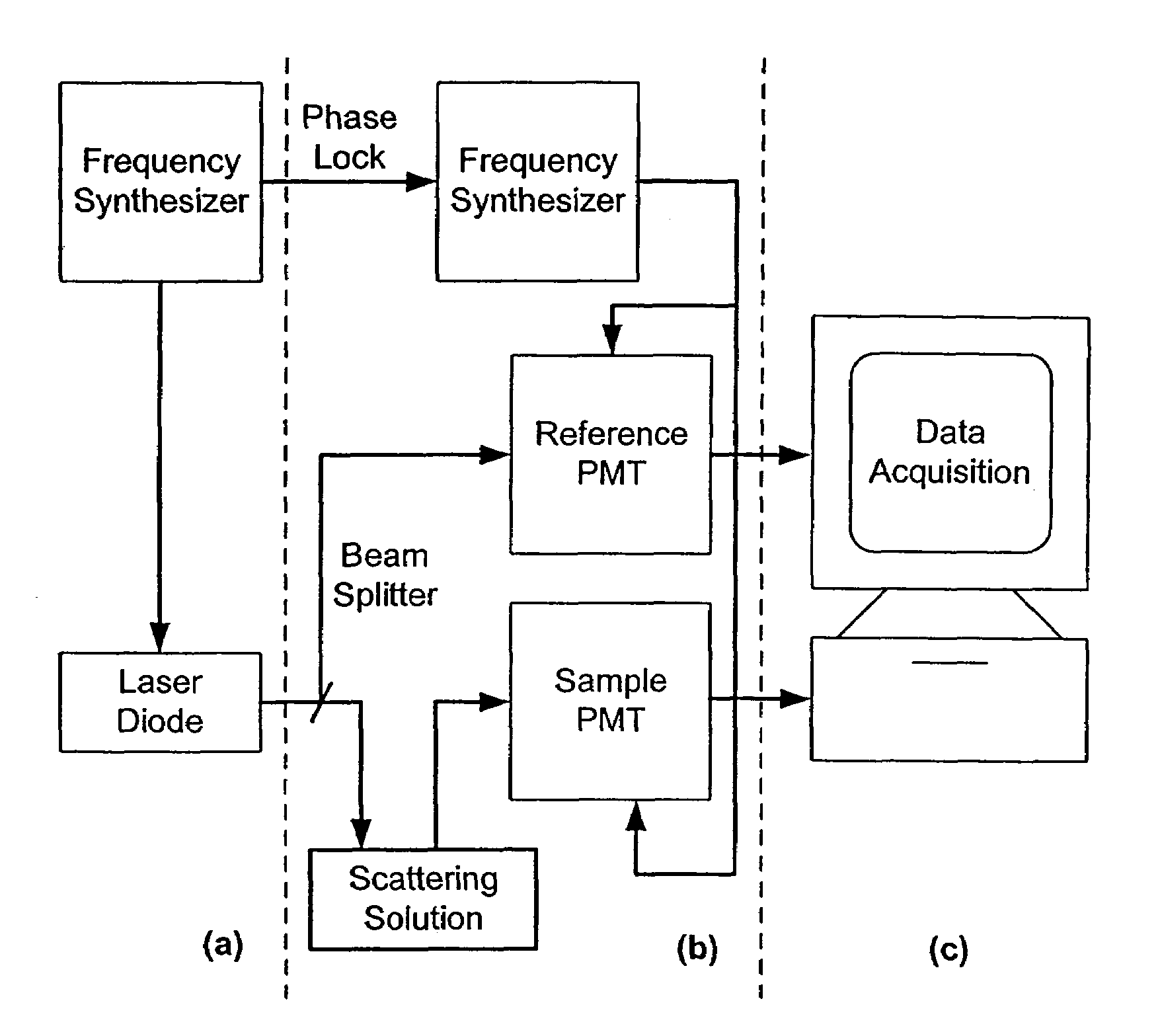
Method and apparatus to measure particle mobility in solution
ActiveUS20110210002A1Reduce harmMinimizing electrochemical degradationSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementPhotodetectorFree solution
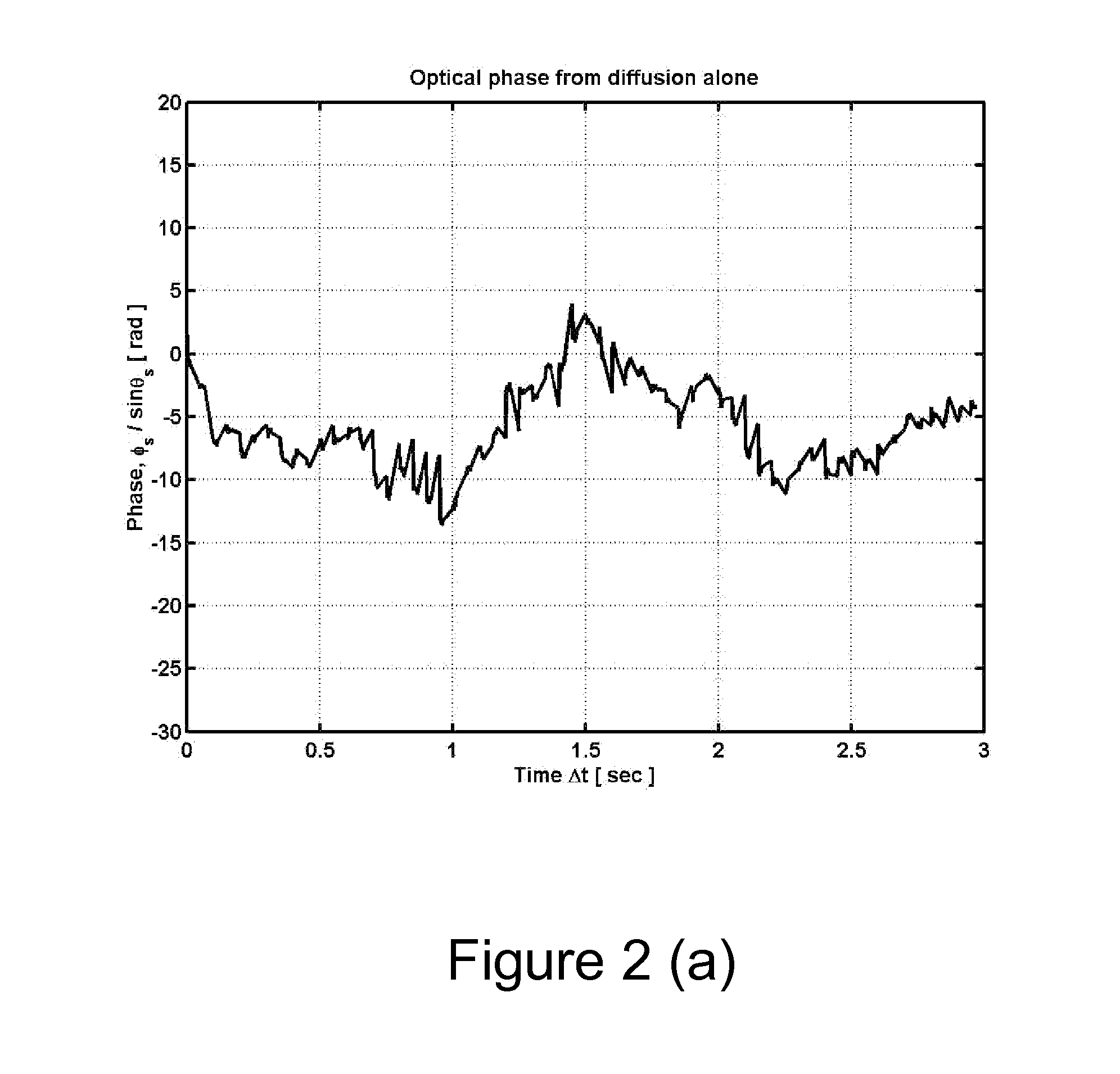
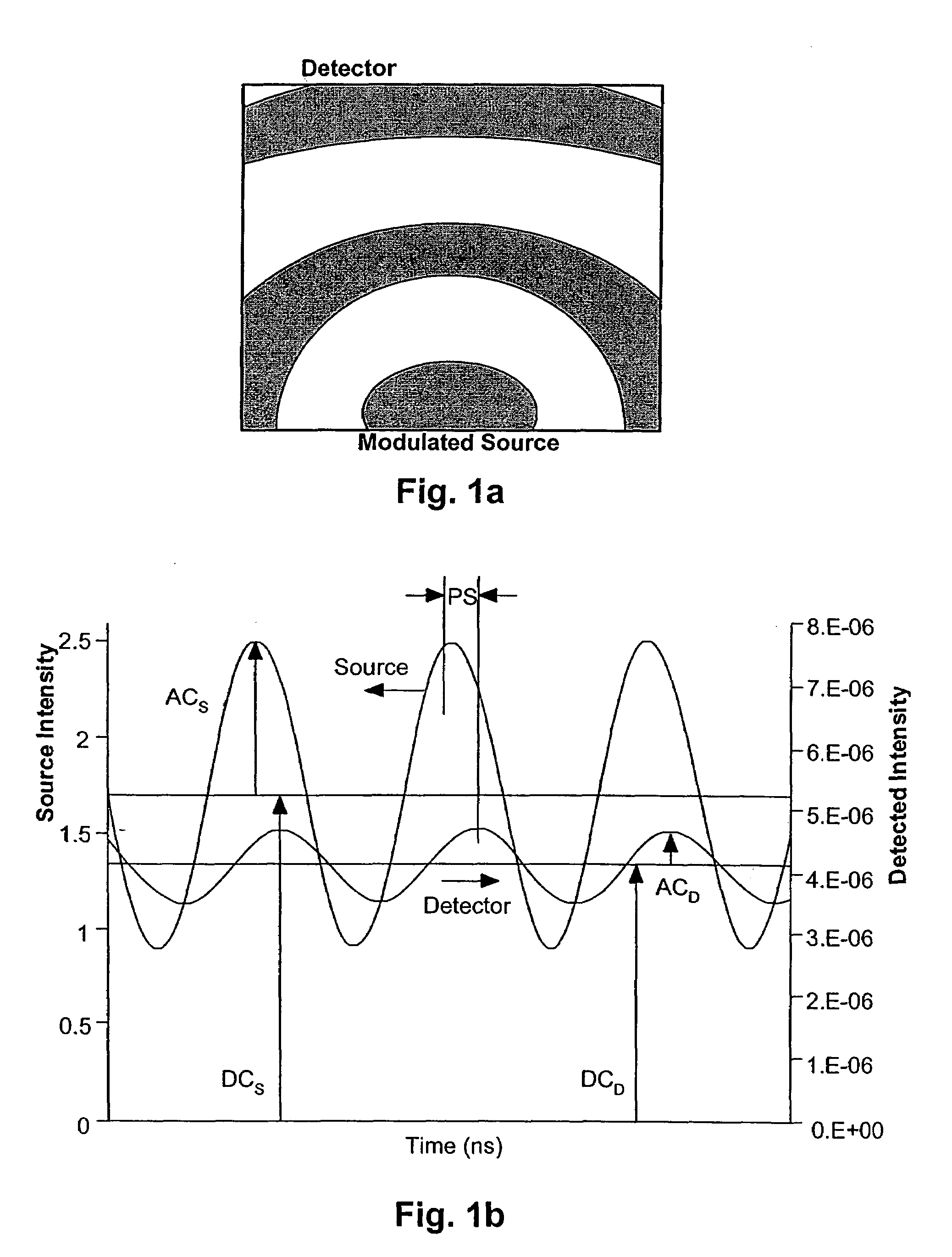
A method and apparatus is disclosed for measurement of the electrophoretic mobility of particles and molecules in solution. A sample of particles is placed in a cell containing two electrodes that apply an alternating electric field. A monochromatic light beam passes through the sample. Light scattered by the particles, along with the unscattered beam, is collected and collimated as it exits the cell. This beam is combined in free space with a phase modulated reference beam. The interference forms a frequency modulated speckle pattern, which is detected by a photodetector array. Each array element collects a narrow range of well-defined scattering angles. The signal from each is demodulated to extract the optical phase information providing a first-principle measurement of the electrophoretic mobility of the scattering particles. Each detector element provides a simultaneous independent measurement. This inherent parallelism drastically increases the amount of information available in a given time. The resulting increased sensitivity extends the mobility measurement to particles below one nanometer, reduces the required concentration and electric field compared to previous methods. This minimizes damage to fragile samples, increases the electrode useful life, and reduces joule heating. Electrophoretic mobility is a critically important parameter for predicting the stability of nanoparticle suspensions and pharmaceutical formulations such as protein therapeutics. This invention enables reliable free-solution phase measurement of these samples.
Owner:WYATT TECH
Electronic component and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20130155639A1Increase flexibilityReduce manufacturing costPrinted circuit assemblingMagnetic/electric field screeningFirst principleEngineering
An electronic component includes a substrate, first electronic components mounted on a first principle surface of the substrate, a first resin layer that covers the first principal surface of the substrate and the first electronic components, a second electronic component mounted on a second principle surface of the substrate, a second resin layer that covers the second principal surface of the substrate and the second electronic component, an electrically conductive shield layer, and a ground electrode arranged in the substrate so as to reach a side surface of the substrate. The shield layer is a single continuous layer that covers the first resin layer, the side surface of the substrate, and a portion of the second resin layer adjacent to the substrate. The shield layer is in contact with and electrically connected to the ground electrode.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
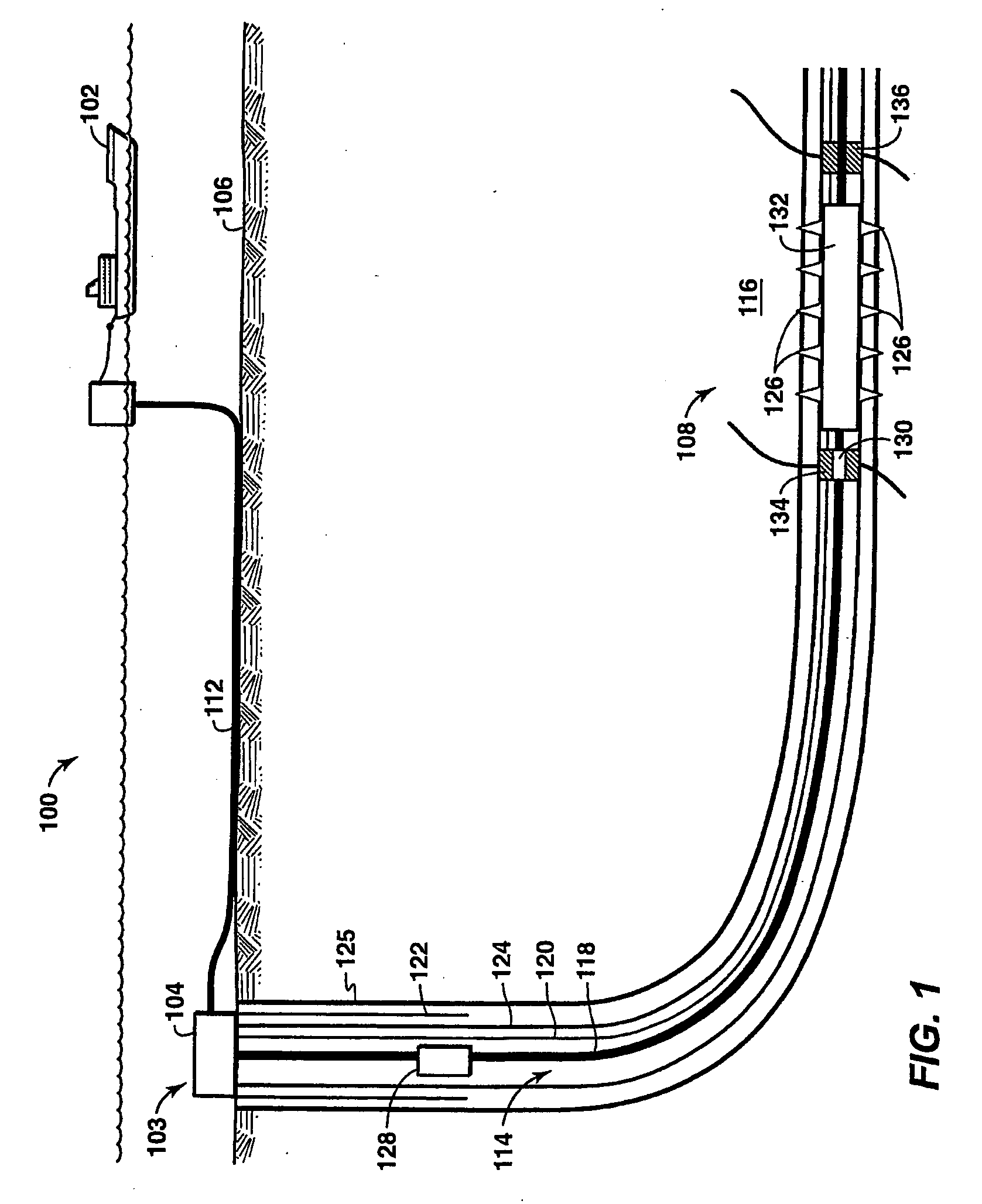
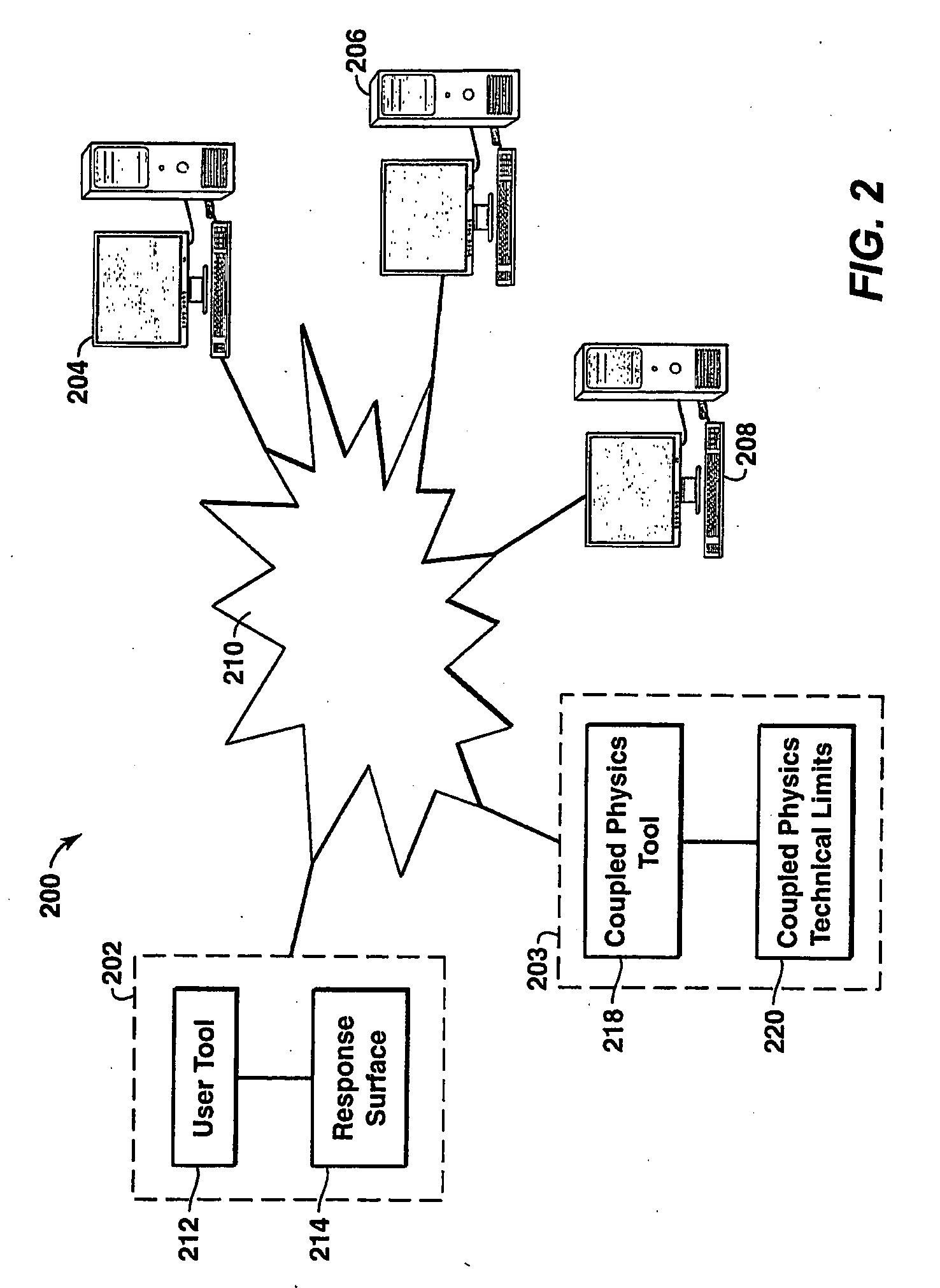
Well Modeling Associated With Extraction of Hydrocarbons From Subsurface Formations
InactiveUS20090216508A1Fluid removalSpecial data processing applicationsFirst principleLaws of thermodynamics
A method and apparatus for associated with various phases of a well completion. In one embodiment, a method is described that includes identifying first principle physical laws governing performance of a well completion and parameters associated with the first principle physical laws or the well. A coupled physics simulator is selected based on the first principle physical laws. Then, a coupled physics limit is generated based upon the coupled physics simulator that incorporates the first principle physical laws and the parameters.
Owner:DALE BRUCE A +3
Method of designing and modifying lithium ion battery cathode materials
InactiveUS20170293707A1Improve accuracyCalculation speedFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsPhysical modelFirst principle
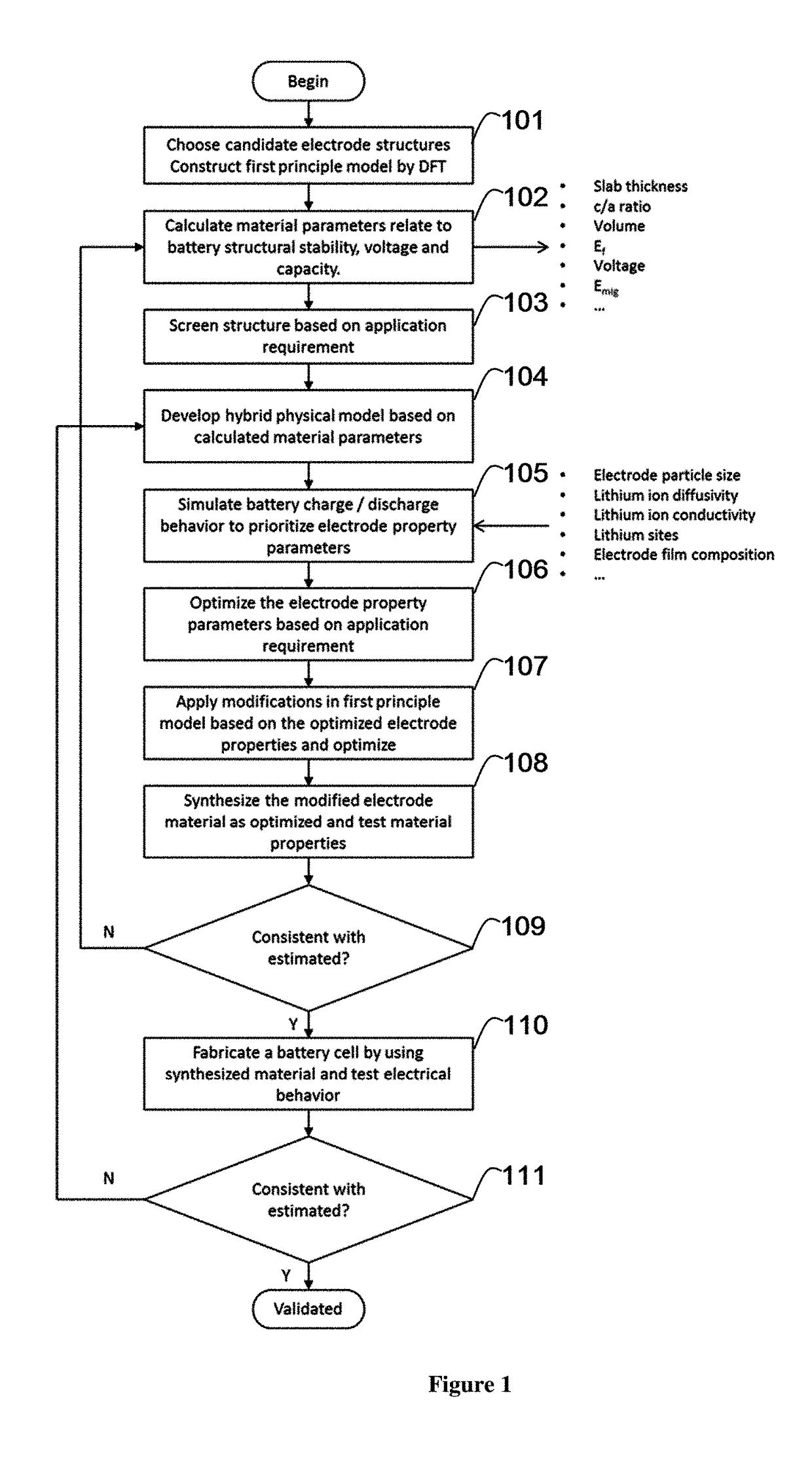
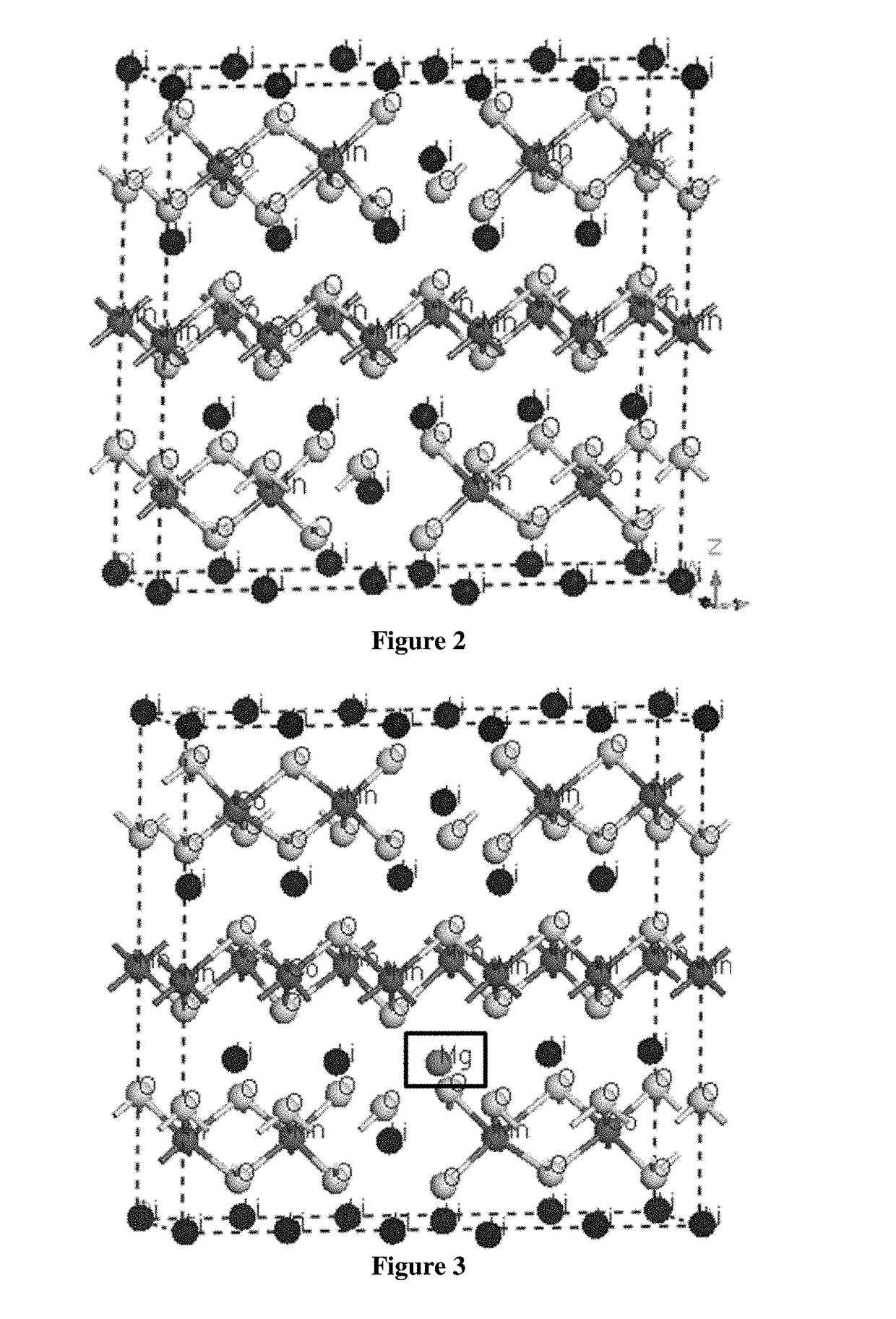
A method of designing and modifying electrode materials for a battery device is disclosed in this invention. The method includes constructing a first principle model for battery electrode material properties estimation and screening. The method also includes applying a structural and compositional modification on the first principle model. In some embodiments, the method includes developing a hybrid physical model to estimate the battery cell cycling behavior with the calculated and experimental parameters. The method and the simulation models have the advantage that both atomic level and physical structure will be considered for the battery electrode and its modified derivatives with small compositional or structural changes. Therefore, both the time consumption and accuracy for battery electrode material designing and modification for specific application requirements can be improved.
Owner:NANO & ADVANCED MATERIALS INST
Electronic circuit module with built-in antenna and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090051606A1Improve productivityStable and constant distanceLoop antennas with ferromagnetic corePrinted electric component incorporationFirst principleSemiconductor
An electronic circuit module with a built-in antenna (1) includes the following elements: a mounting module having a wiring board (2), a passive component, and a semiconductor device; a resin sheet substrate (11) having an antenna pattern (12) formed on a first principle surface of a base thereof; and a magnetic layer interposed between the mounting module and the resin sheet substrate (11). These elements are housed in a case (16).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
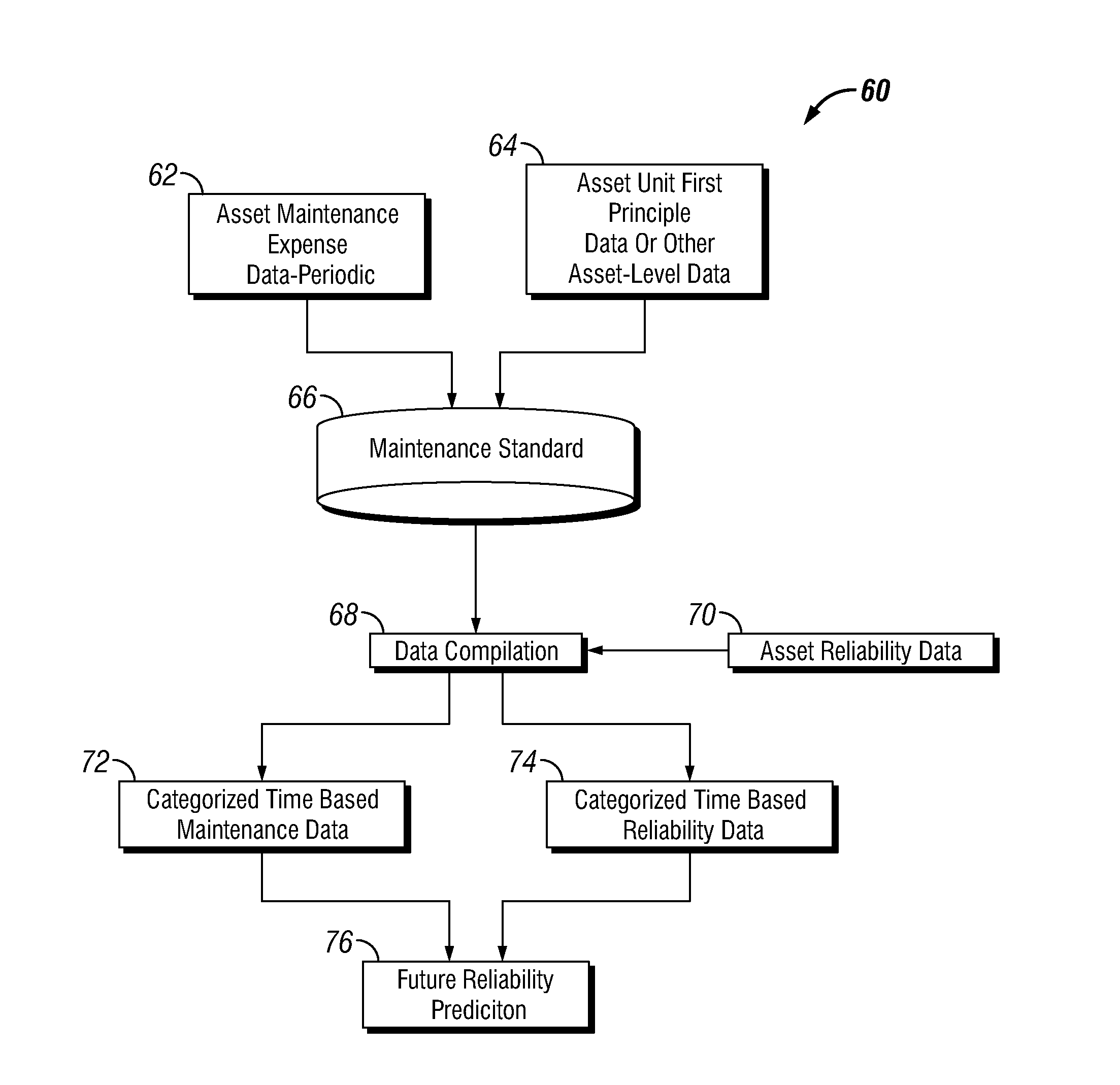
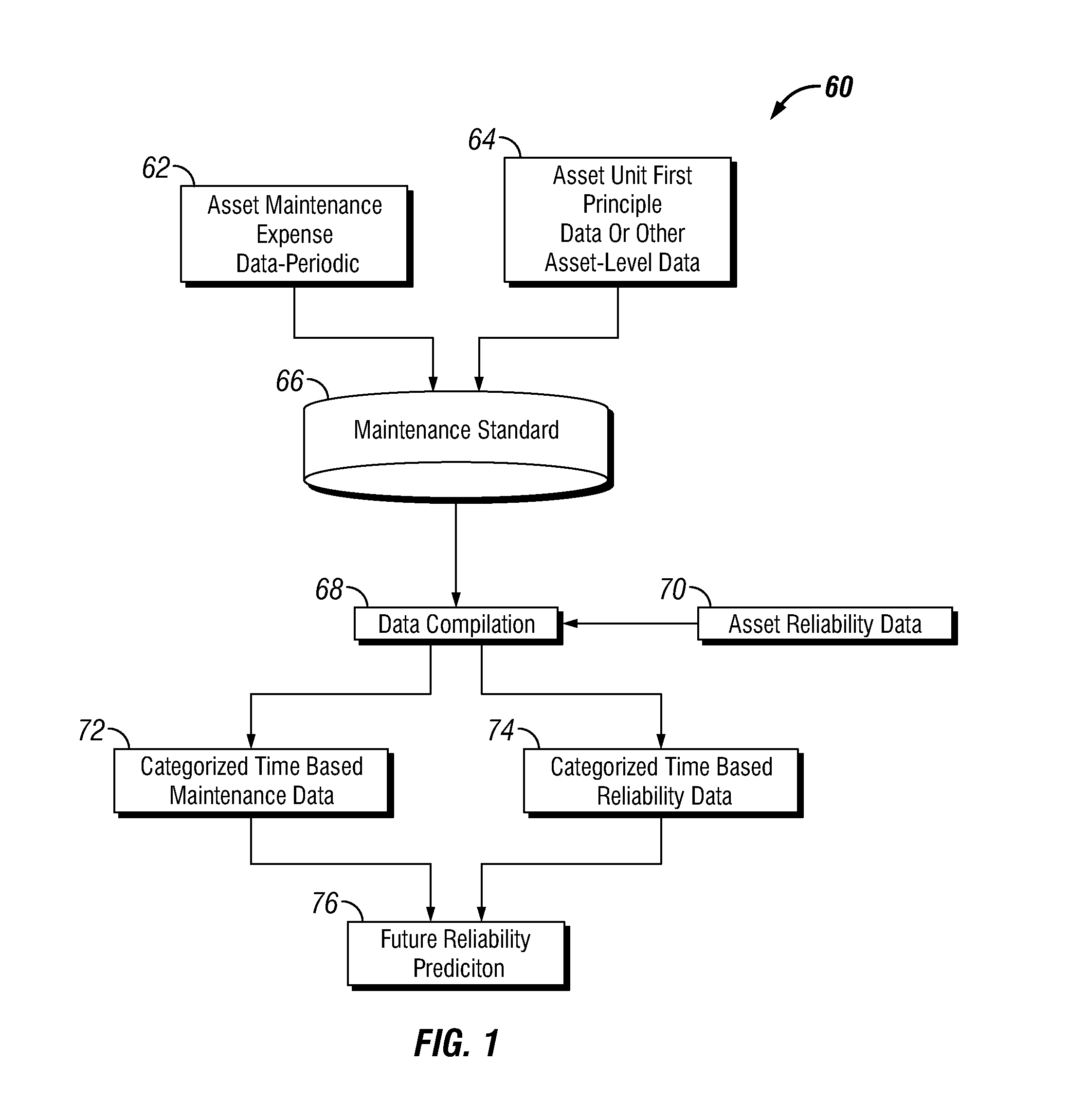
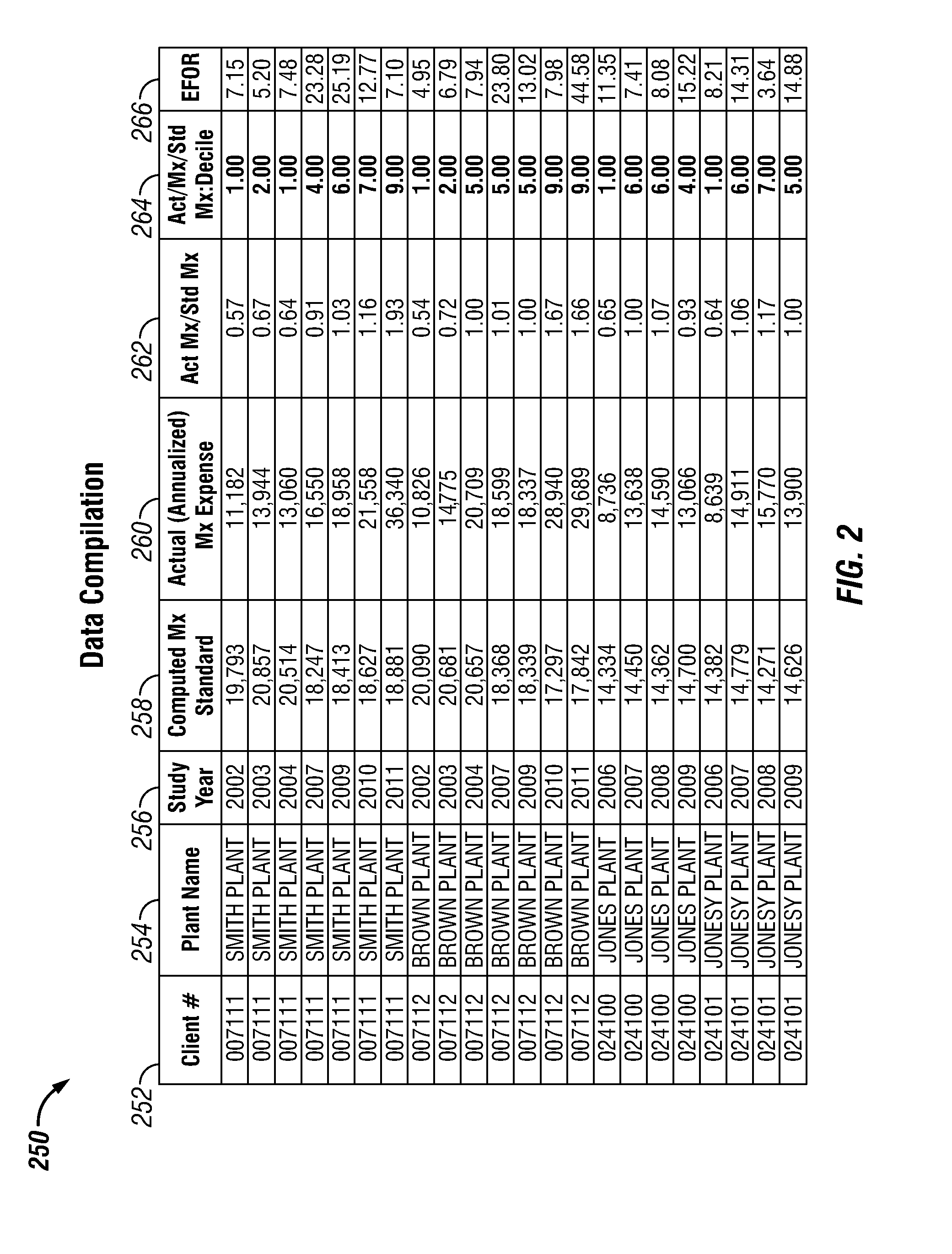
Future Reliability Prediction Based on System Operational and Performance Data Modelling
ActiveUS20150294048A1Technology managementComputation using non-denominational number representationData modelingFirst principle
Systems, methods, and apparatuses for improving future reliability prediction of a measurable system by receiving operational and performance data, such as maintenance expense data, first principle data, and asset reliability data via an input interface associated with the measurable system. A plurality of category values may be generated that categorizes the maintenance expense data by a designated interval using a maintenance standard that is generated from one or more comparative analysis models associated with the measureable system. The estimated future reliability of the measurable system is determined based on the asset reliability data and the plurality of category values and the results of the future reliability are displayed on an output interface.
Owner:HARTFORD STEAM BOILER INSPECTION & INSURANCE
Dynamic Controller Utilizing a Hybrid Model
ActiveUS20080065241A1Minimize error valueOutput errorSimulator controlComputation using non-denominational number representationFirst principleLinear model
A system and method for predicting operation of a plant or process receive an input value from the plant or process. An integrity of a non-linear model corresponding to a local input space of the input value may be determined. The non-linear model may include an empirical representation of the plant or process. If the integrity is above a first threshold, non-linear model may be used to provide a first output value. However, if the integrity is below the first threshold, a linearized first principles model may be used to provide a second output value. The linearized first principles model may include an analytic representation of the plant or process. Additionally, the analytic representation of the plant or process may be independent of the empirical representation of the plant or process. The first output value and / or the second output value may be usable to manage the plant or process.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
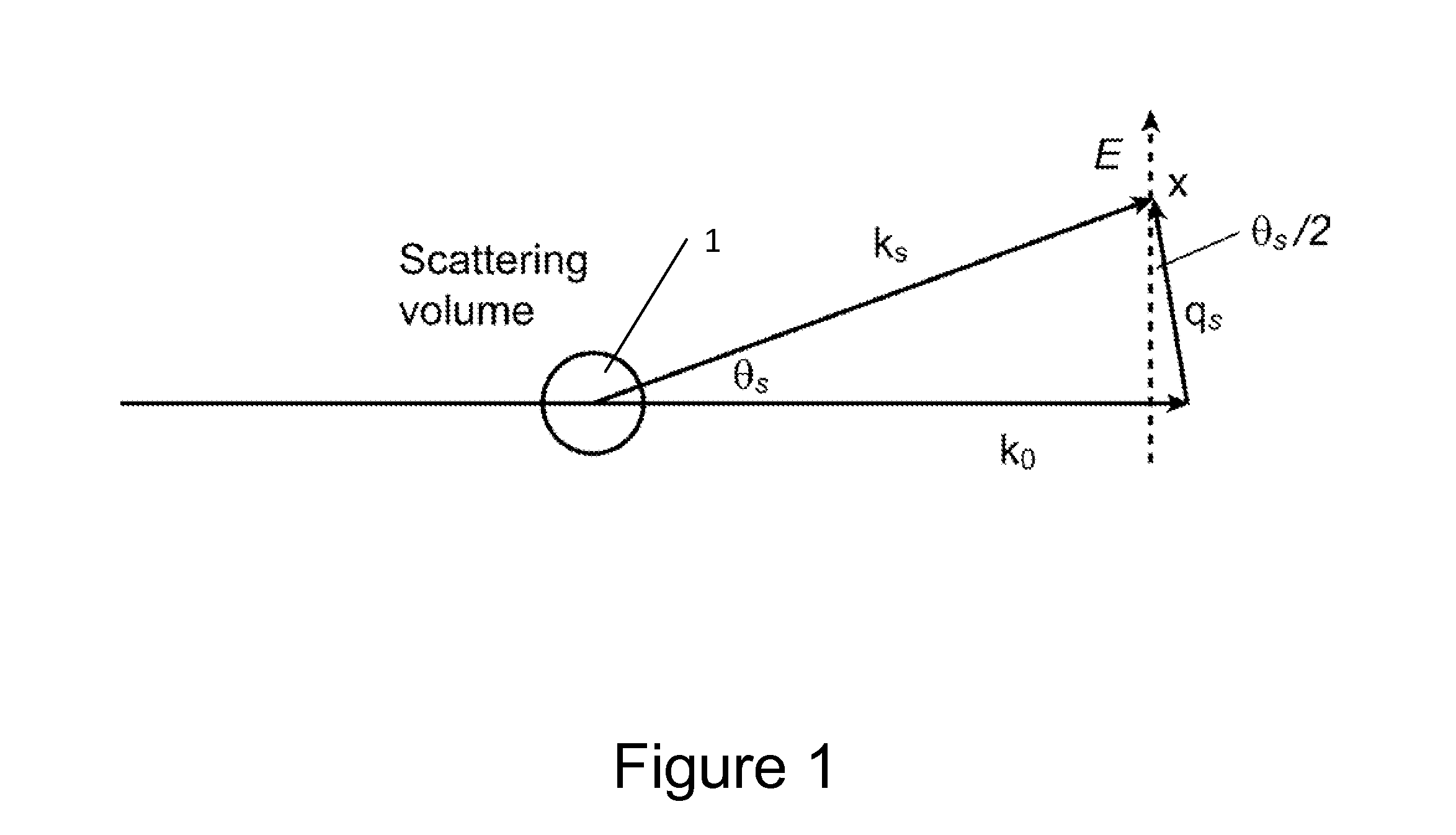
Method for characterising particles in suspension from frequency domain photon migration measurements
InactiveUS7268873B2Scattering properties measurementsParticle size analysisFirst principleLinear regression
Methods are provided for measuring isotropic scattering coefficients of suspensions using multiply scattered radiation that is modulated in amplitude at selected modulation frequencies. The radiation may be light. Quantities describing diffusion of the multiply scattered radiation are preferably measured at a plurality of distances between source and receiver and a plurality of frequencies. Linear regression techniques are provided for maximizing accuracy of the scattering data at a selected wavelength of a radiation. Methods are provided for inversing an integral equation so as to determine a calculated value of scattering coefficient. Parameters are varied to minimize the difference between the calculated and measured scattering coefficients and thereby to determine volume fraction, particle size distribution and interparticle force between the particles in a suspension. By incorporating a first principles model to account for interparticle force, the measurements can be used to determine a parameter governing interparticle forces in a suspension. The suspension may be in a liquid or a gas.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Photoacoustic Spectrometer with Calculable Cell Constant for Quantitative Absorption Measurements of Pure Gases, Gaseous Mixtures, and Aerosols
InactiveUS20120118042A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis using microwave meansFirst principleIntensity modulation
A photoacoustic spectrometer that is intensity-modulated, laser-driven and with a calculable cell constant. The axially symmetrical photoacoustic spectrometer combines first-principles models of acoustic wave propagation with high-resolution spectroscopic measurements, and takes into account molecular relaxation. The spectrometer includes a duct and two chambers disposed at the end of the duct. Inlet and exit tubes, which are disposed in substantially the location of acoustic pressure nodes, permit the gas, gaseous mixture or aerosol to enter and exit the spectrometer. The absolute response of the spectrometer may be modeled and measured. A detailed theoretical analysis of the system and its predicted response may be predicted as a function of gas properties, resonance frequency and sample energy transfer relaxation rates.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TEHCNOLOGY
Methods and Apparatus for Optical Amplitude Modulated Wavefront Shaping
Owner:PARKER DAVID H
Software definable block adaptive decision feedback equalizer
InactiveUS7010030B2Easy to useMultiple-port networksData representation error detection/correctionAlgorithmFirst principle
A block decision feedback equalizer is designed by deriving, from first principles, a block exact decision feedback equalizer and then systematically applying simplifying assumptions to obtain several block approximate decision feedback equalizers, each suitable for multipath channel equalization and having error convergence insensitive to filter length. The resulting block decision feedback equalizer is software definable may be dynamically adapted by choosing whether to update error correction coefficients.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Finite-difference simulation and visualization of elastodynamics in time-evolving generalized curvilinear coordinates
InactiveUS7574338B1Facilitate autonomous updatingWide applicabilityVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingSystems designStructural health monitoring
Modeling and simulation of free and forced structural vibrations is essential to an overall structural health monitoring capability. In the various embodiments, a first principles finite-difference approach is adopted in modeling a structural subsystem such as a mechanical gear by solving elastodynamic equations in generalized curvilinear coordinates. Such a capability to generate a dynamic structural response is widely applicable in a variety of structural health monitoring systems. This capability (1) will lead to an understanding of the dynamic behavior of a structural system and hence its improved design, (2) will generate a sufficiently large space of normal and damage solutions that can be used by machine learning algorithms to detect anomalous system behavior and achieve a system design optimization and (3) will lead to an optimal sensor placement strategy, based on the identification of local stress maxima all over the domain.
Owner:NASA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com