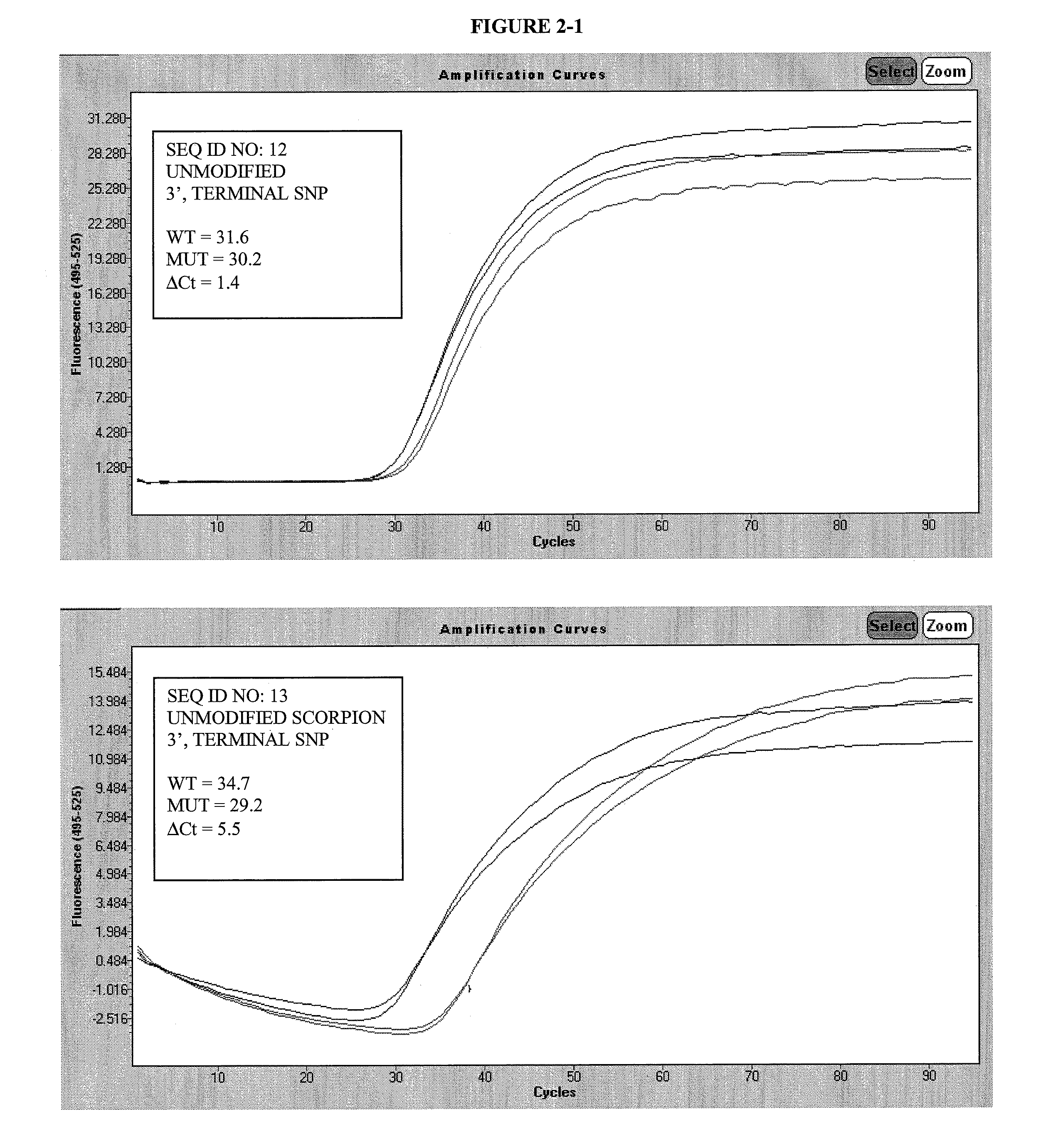
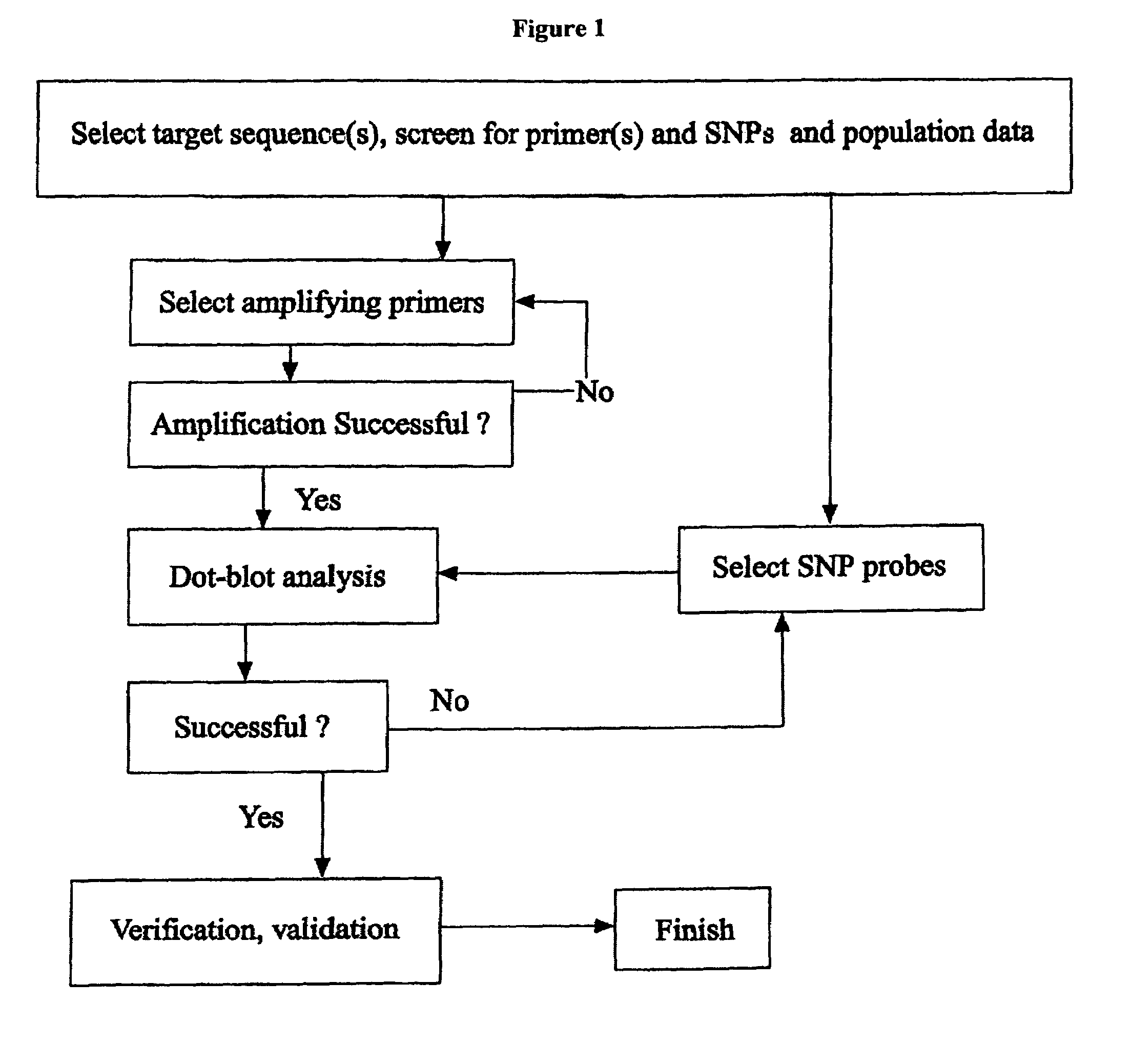
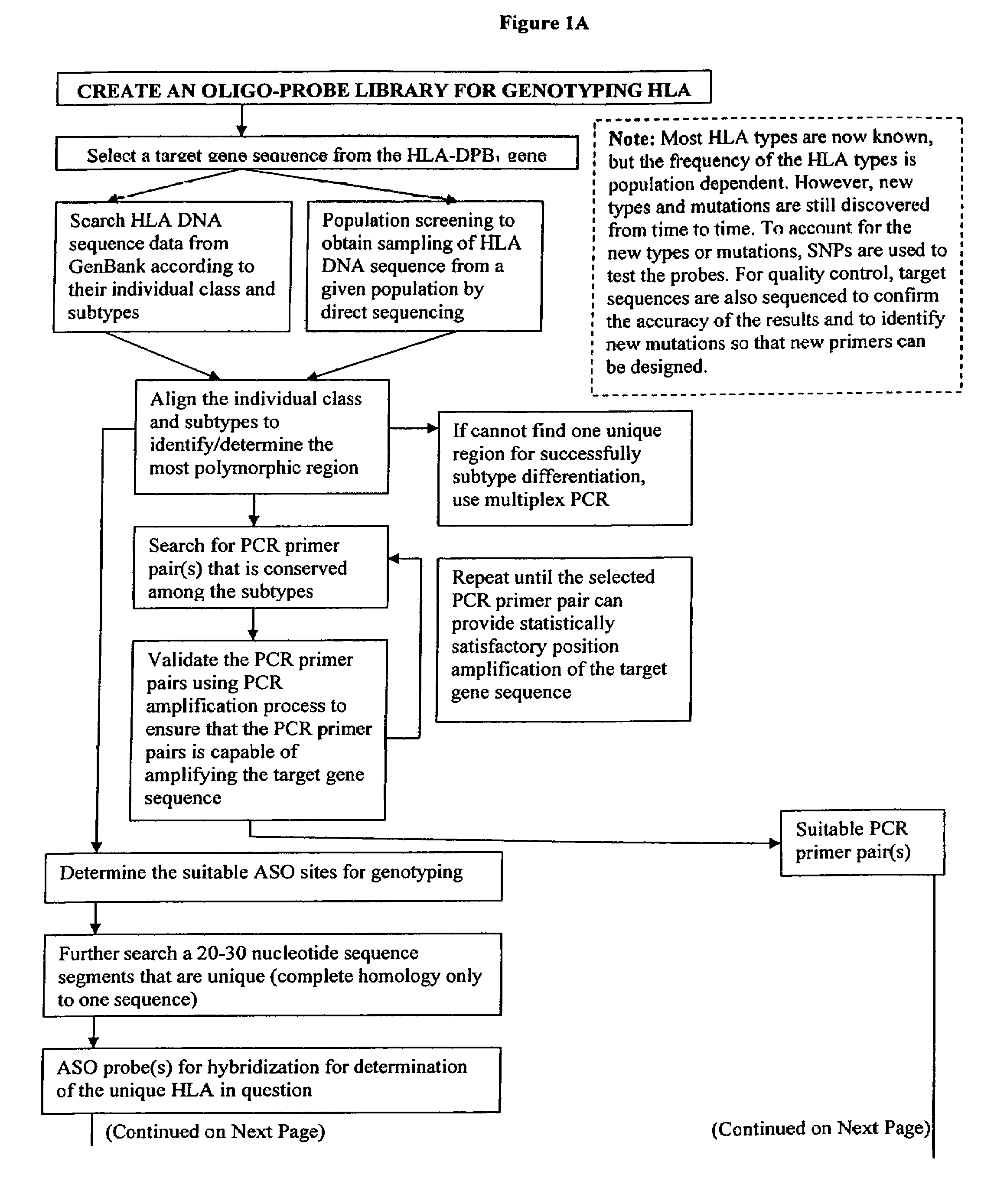
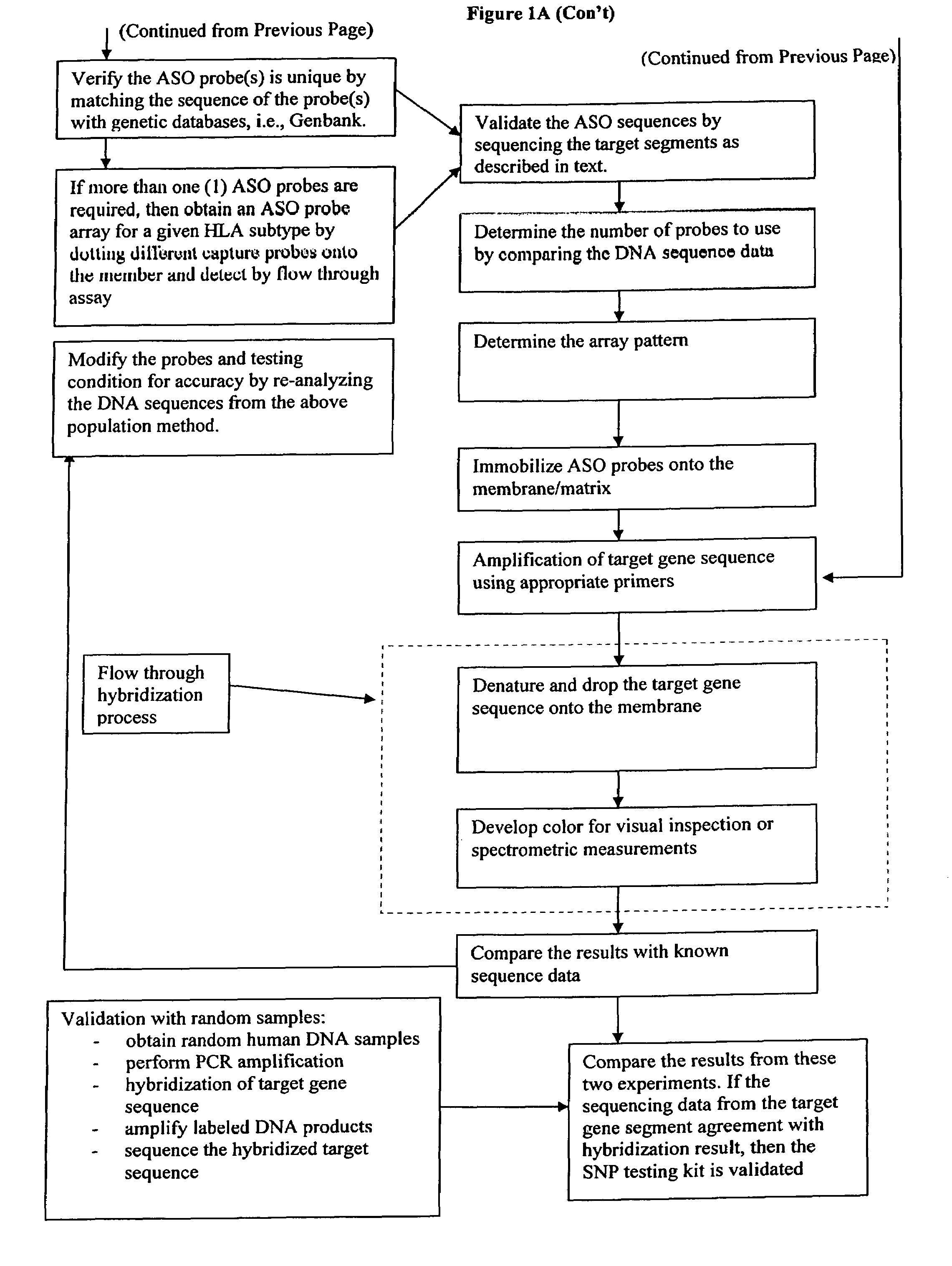
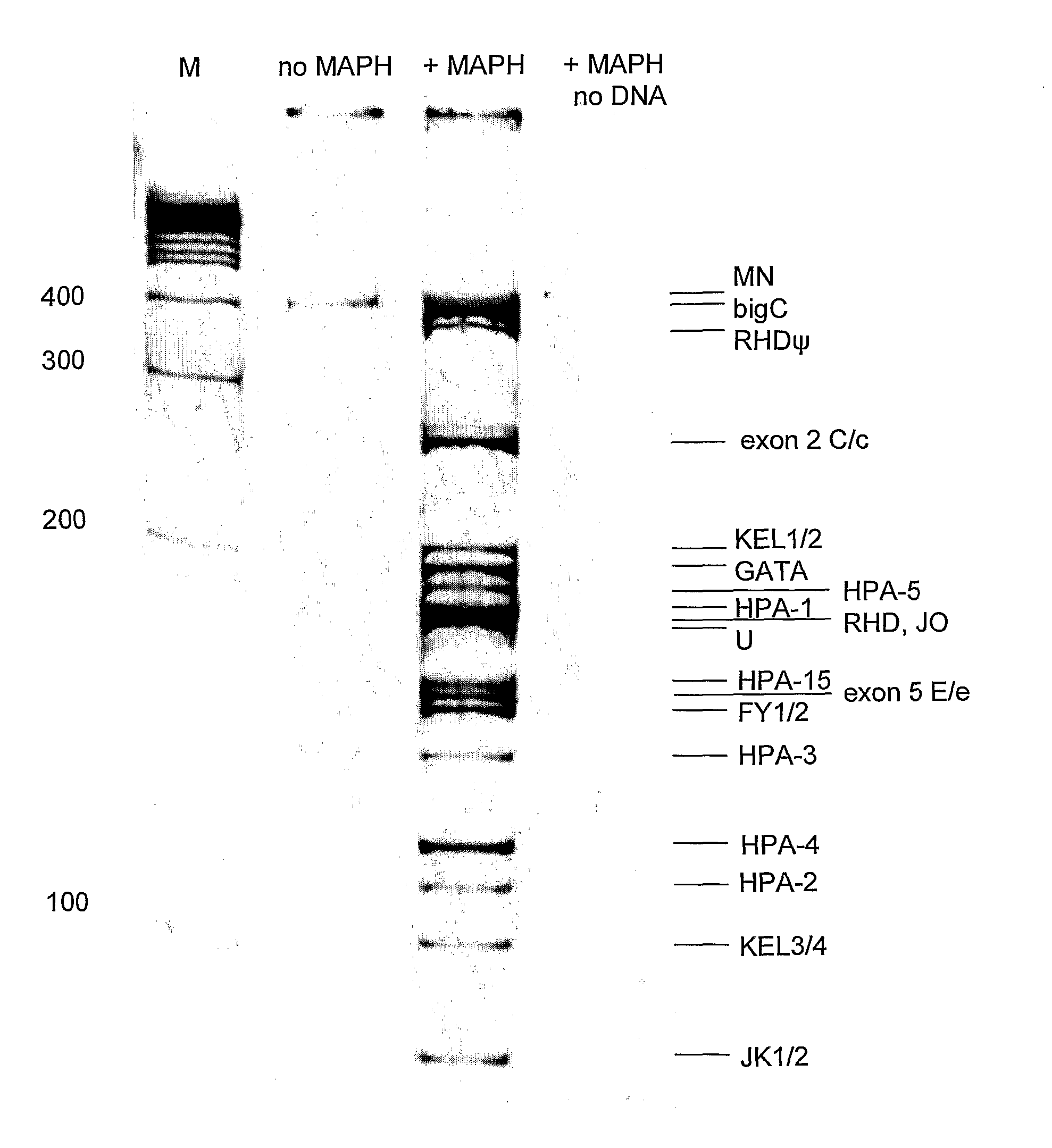
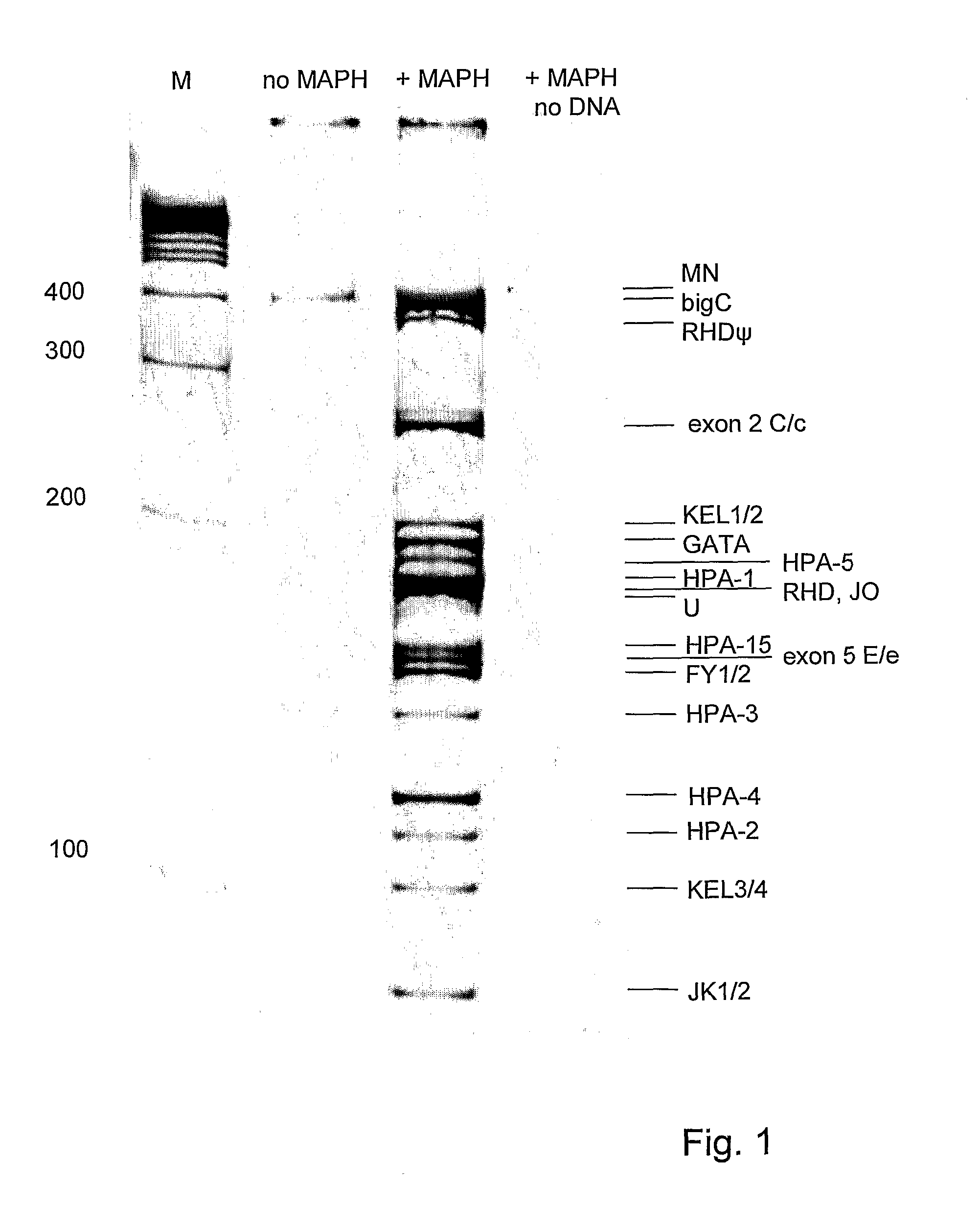
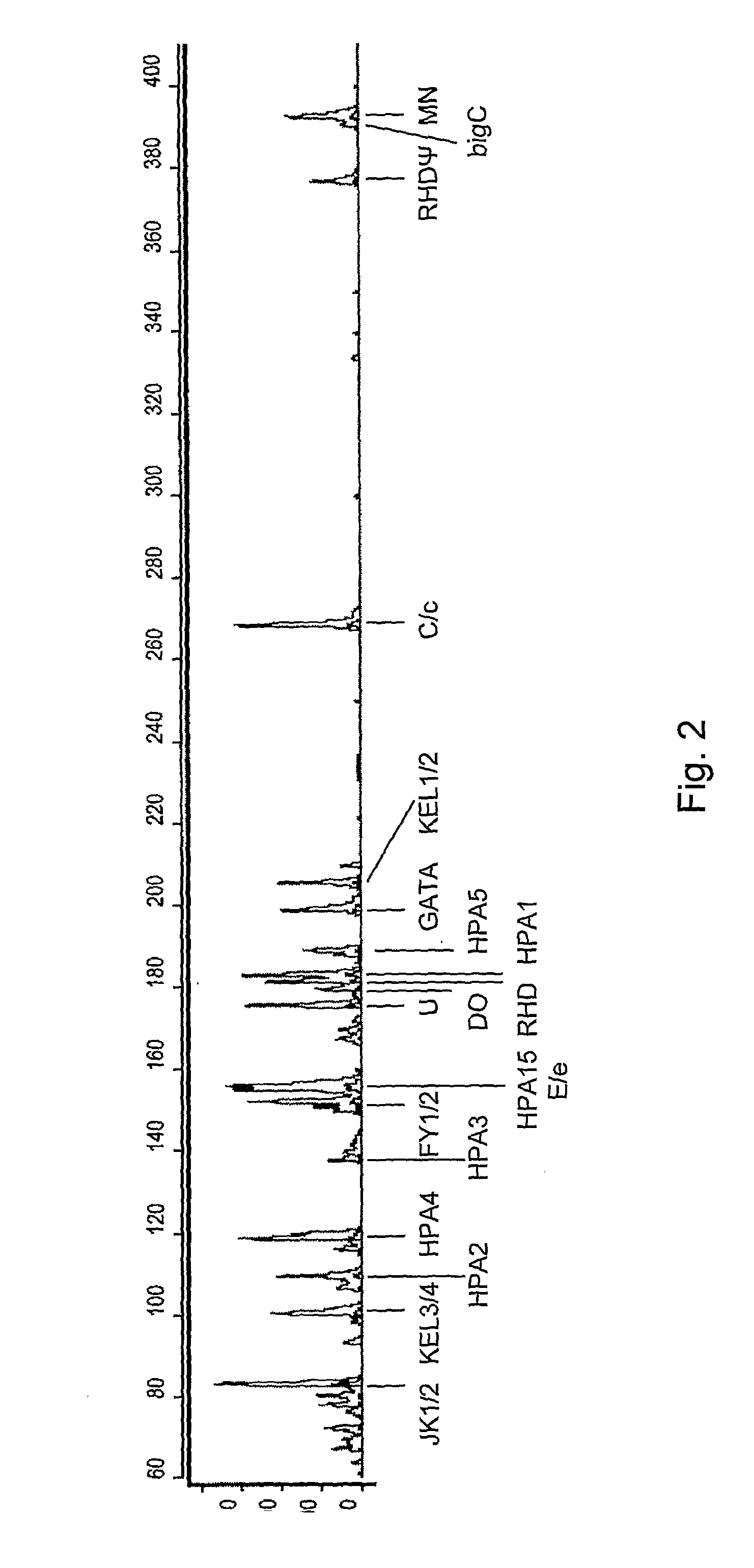
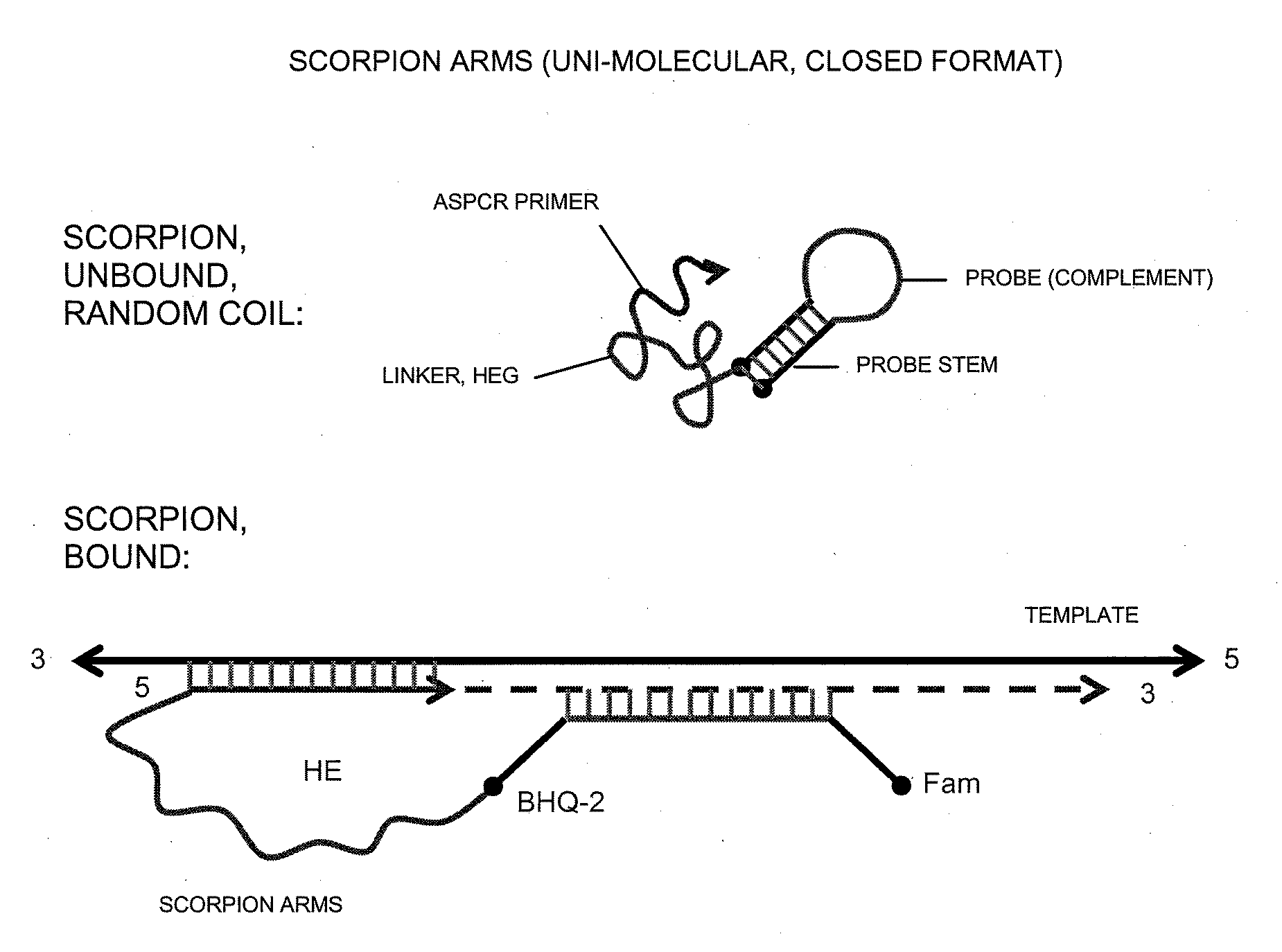
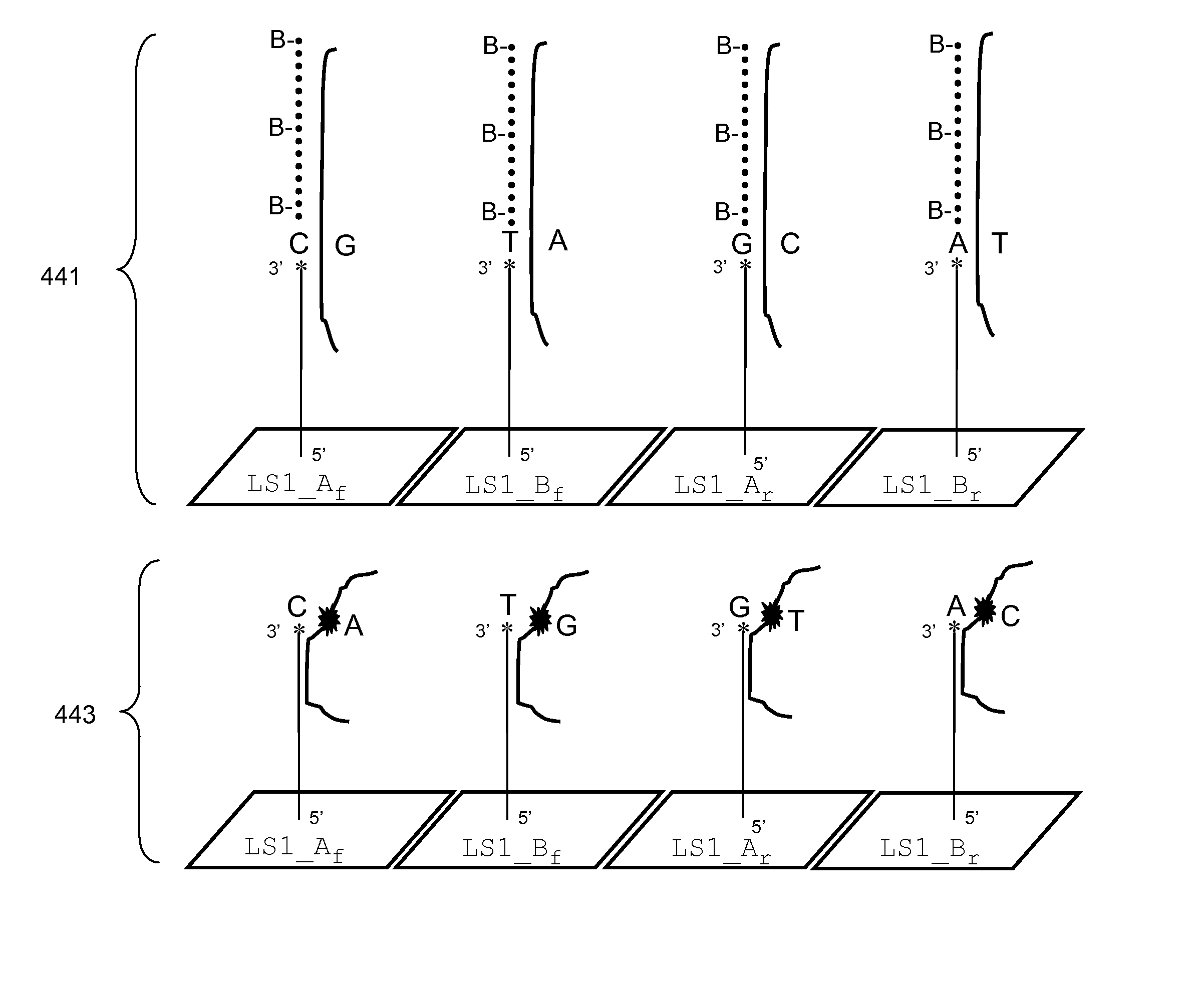
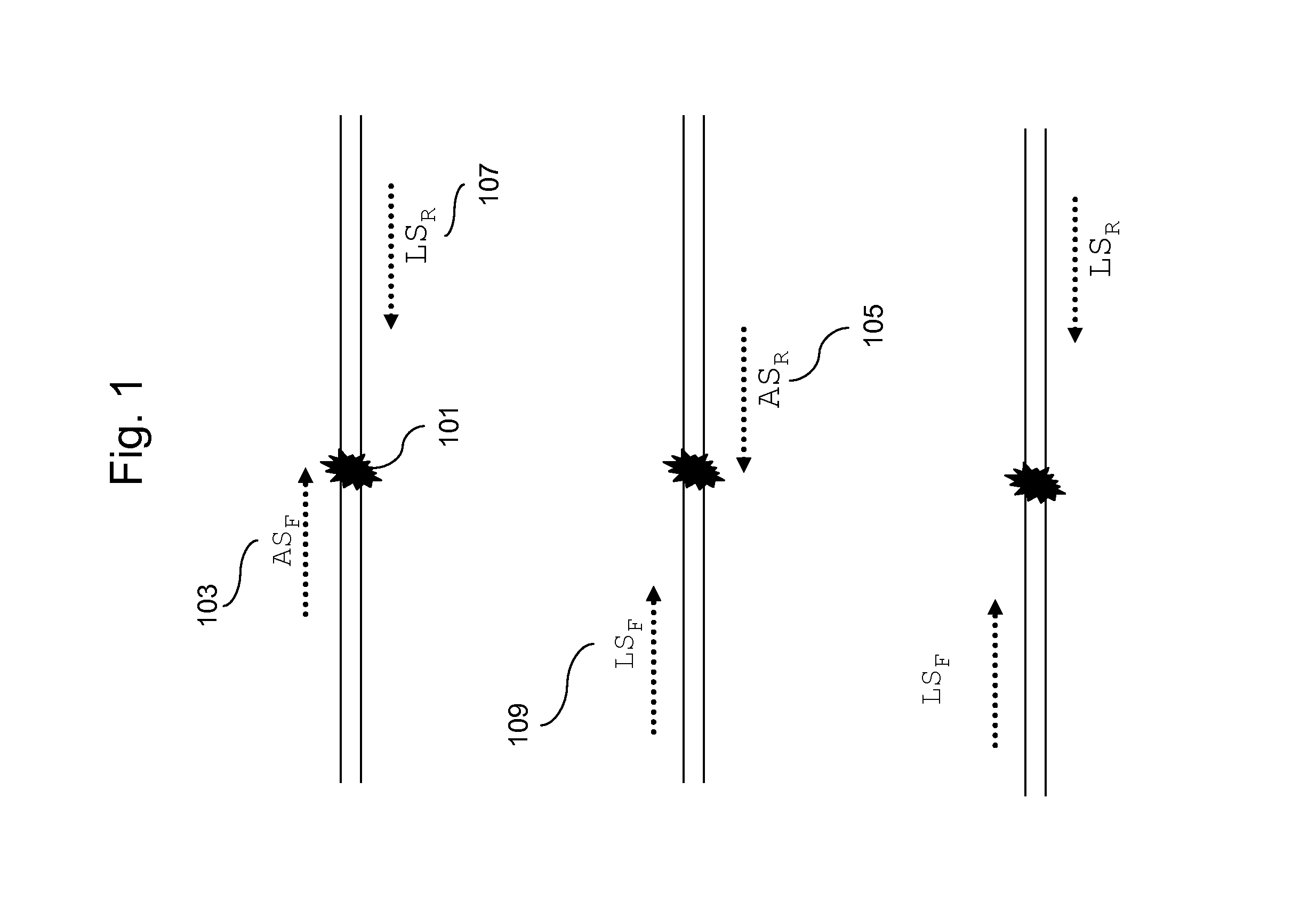
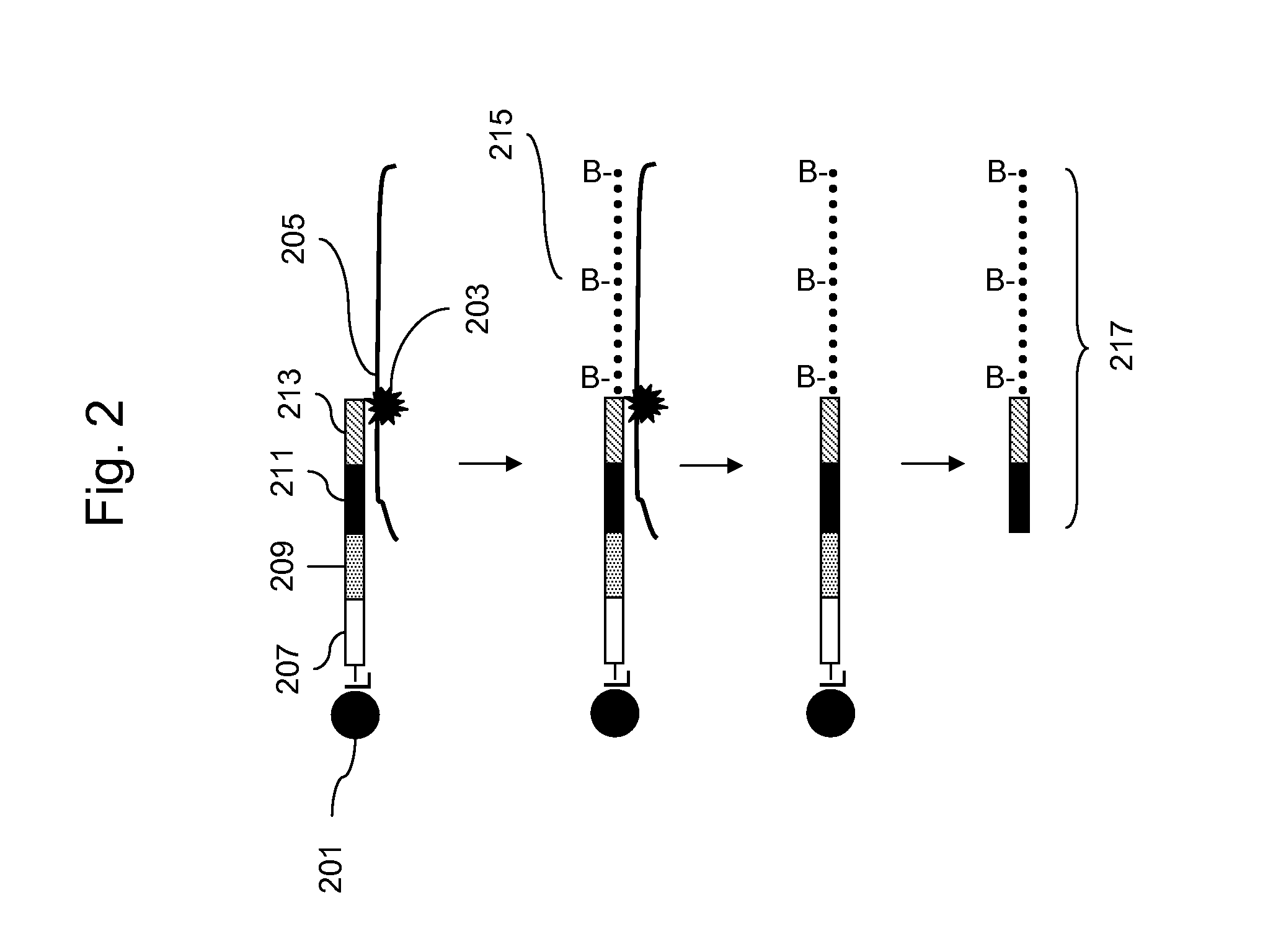
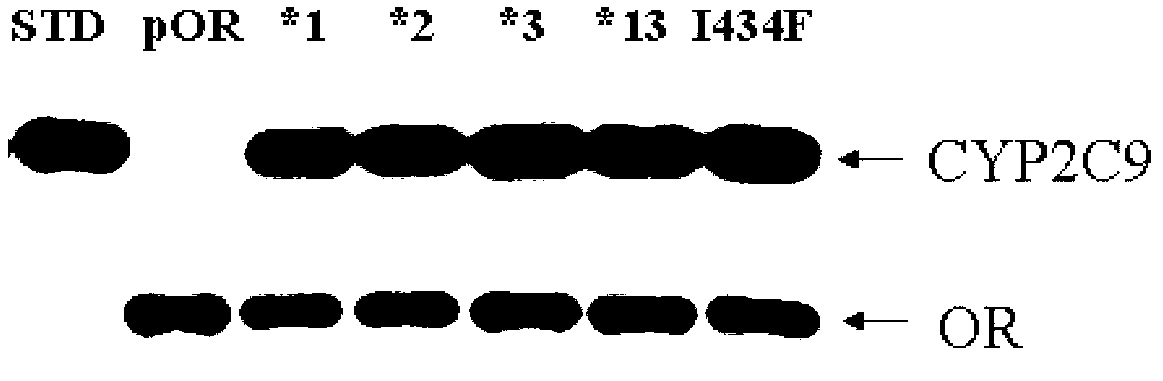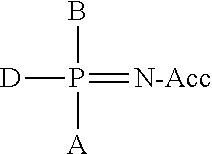Patents
Literature
58 results about "Allele-specific oligonucleotide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
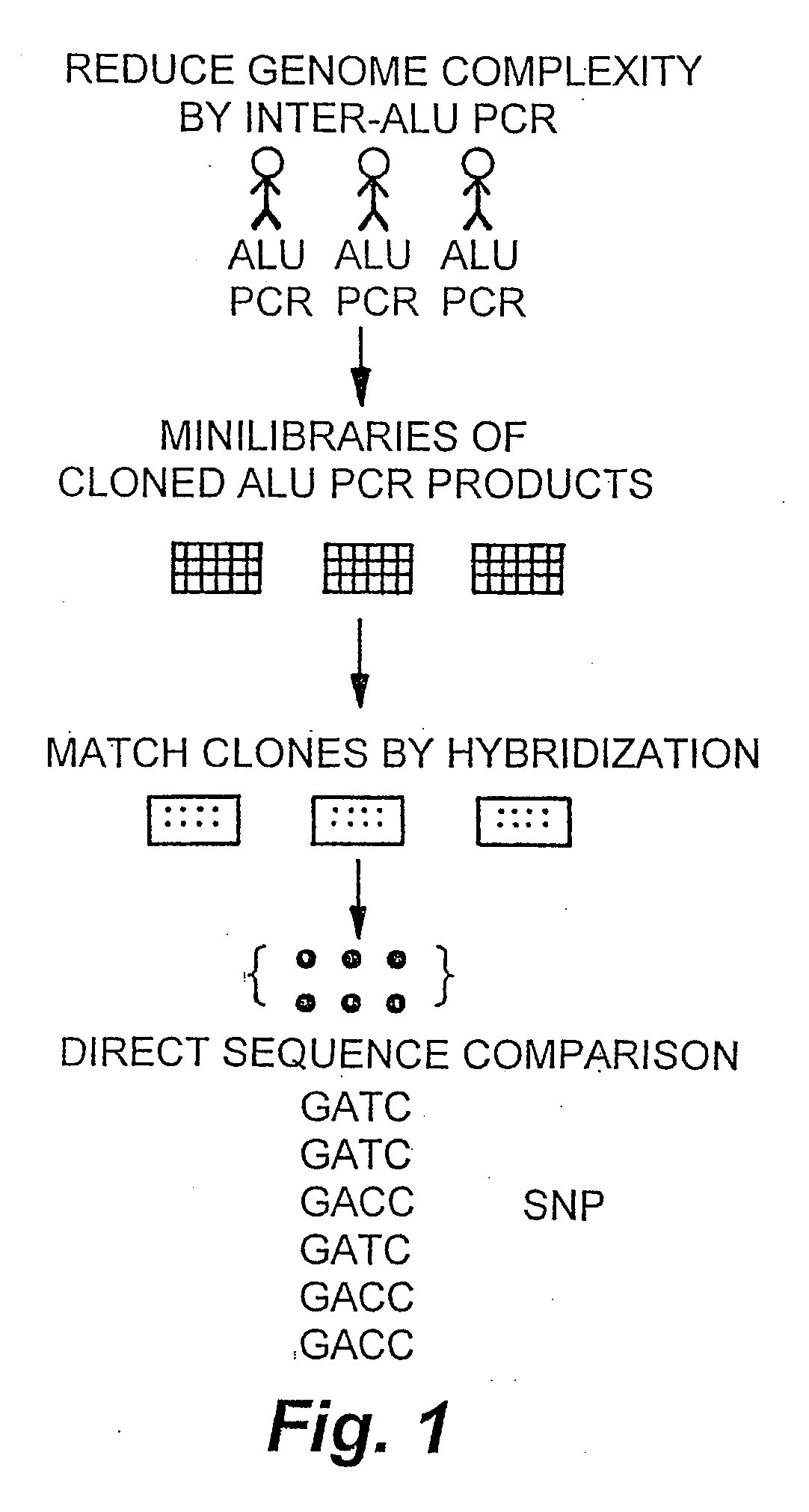
An allele-specific oligonucleotide (ASO) is a short piece of synthetic DNA complementary to the sequence of a variable target DNA. It acts as a probe for the presence of the target in a Southern blot assay or, more commonly, in the simpler Dot blot assay. It is a common tool used in genetic testing, forensics, and Molecular Biology research.
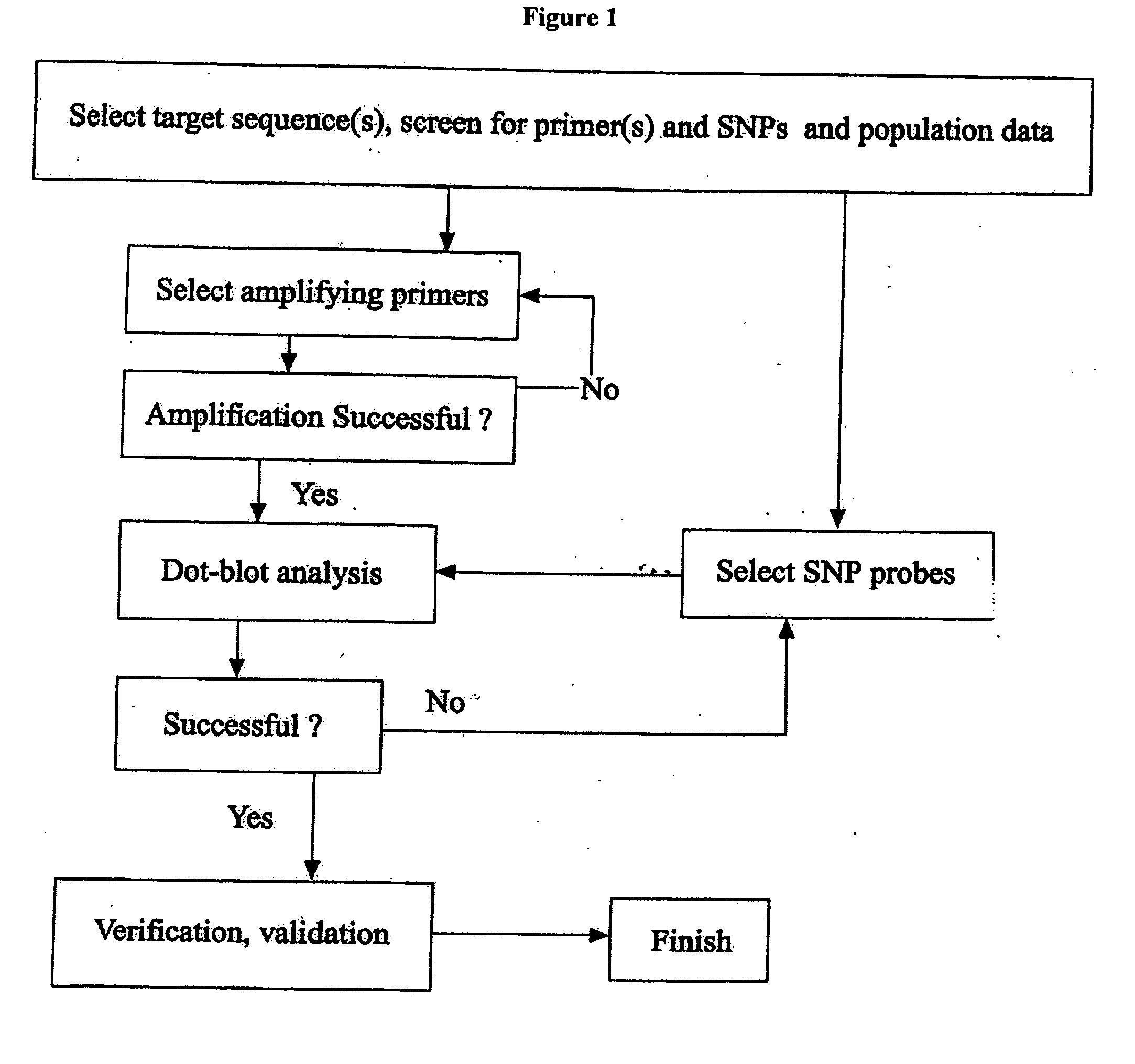
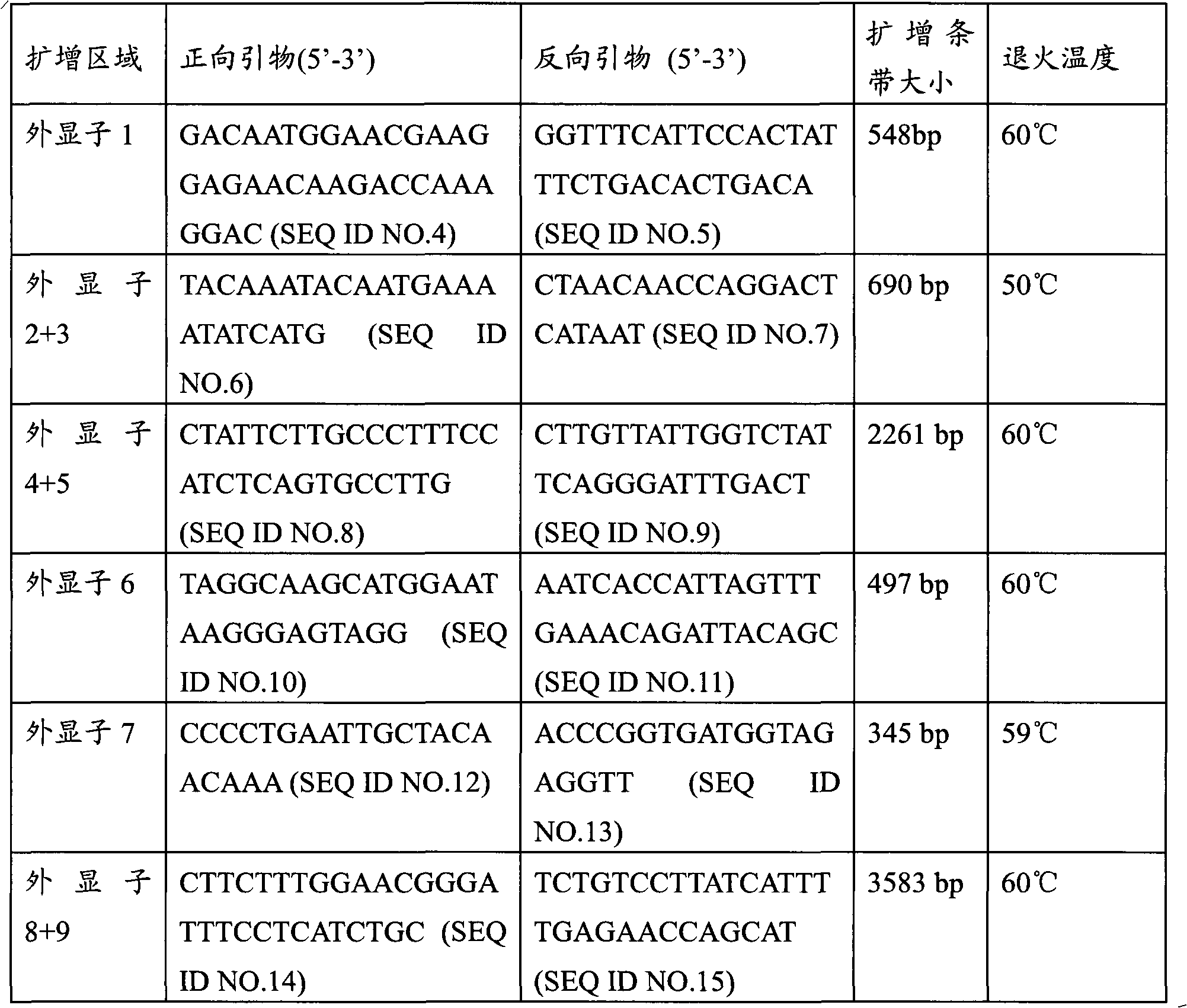
Methods for Genotyping
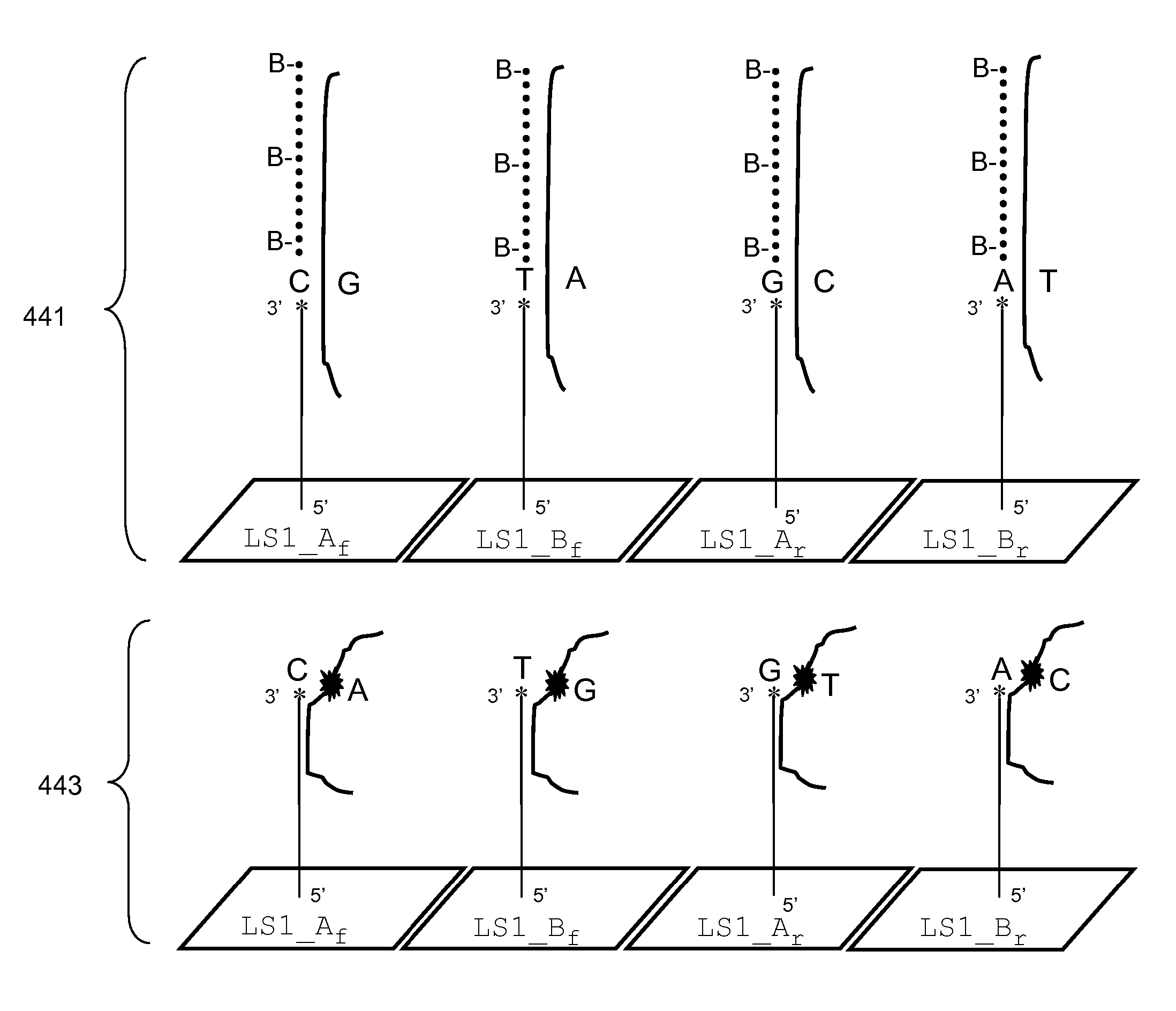
InactiveUS20070269817A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementAllele-specific oligonucleotidePolymerase L
The present invention provides for methods for discriminating between alleles at polymorphic positions in a genome. In general the methods employ allele specific extension of oligonucleotides that are complementary to one of the alleles at the 3′ end of the oligonucleotide. The allele specific oligonucleotides are resistant to proof reading activity from a polymerase and may be extended in an allele specific manner by a DNA polymerase with a functional 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity. The allele specific oligonucleotides may be attached to a solid support such as a chip or a bead.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Allele-Specific Amplification
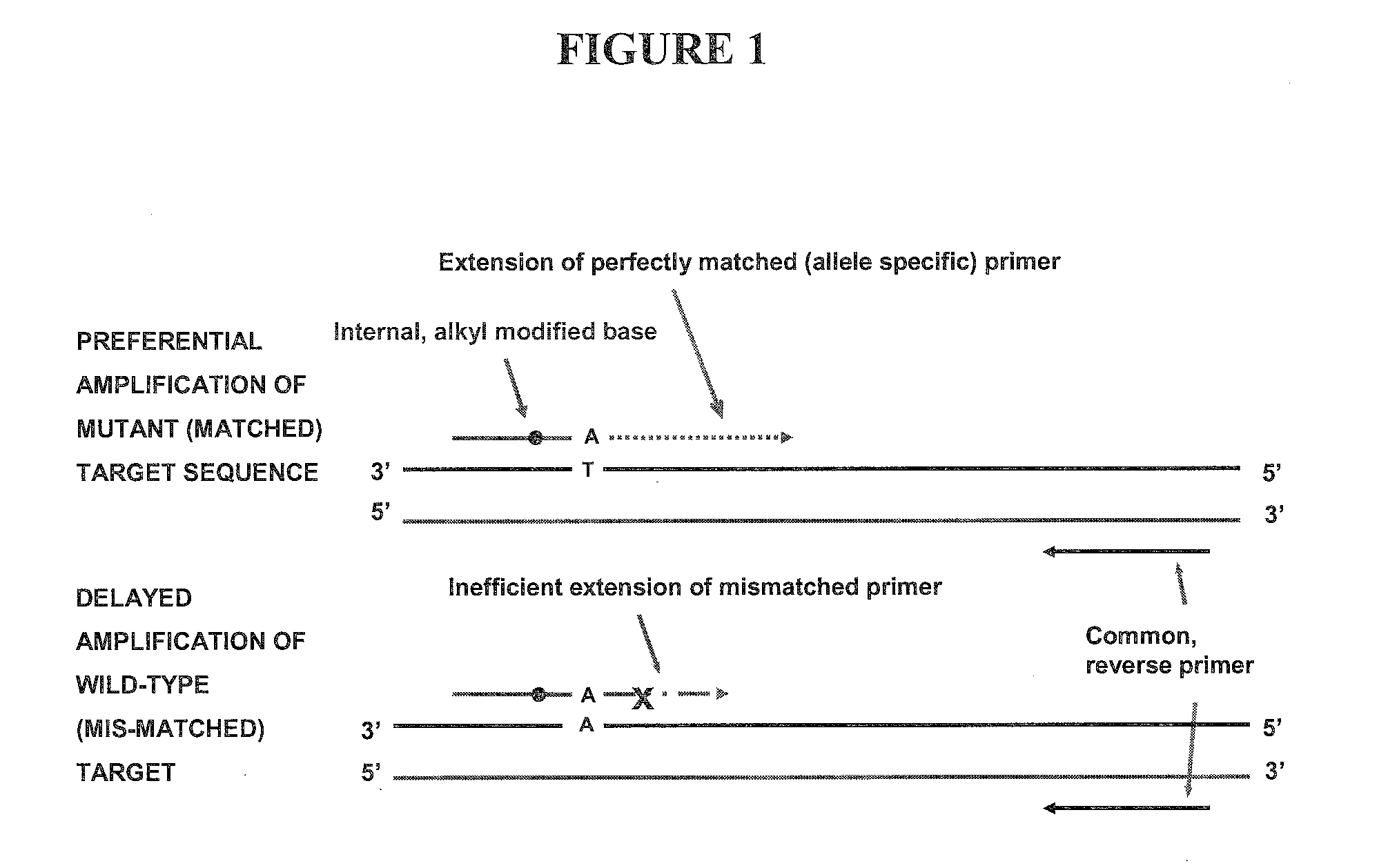
ActiveUS20100099110A1Simple methodSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAllele-specific oligonucleotideGenetics
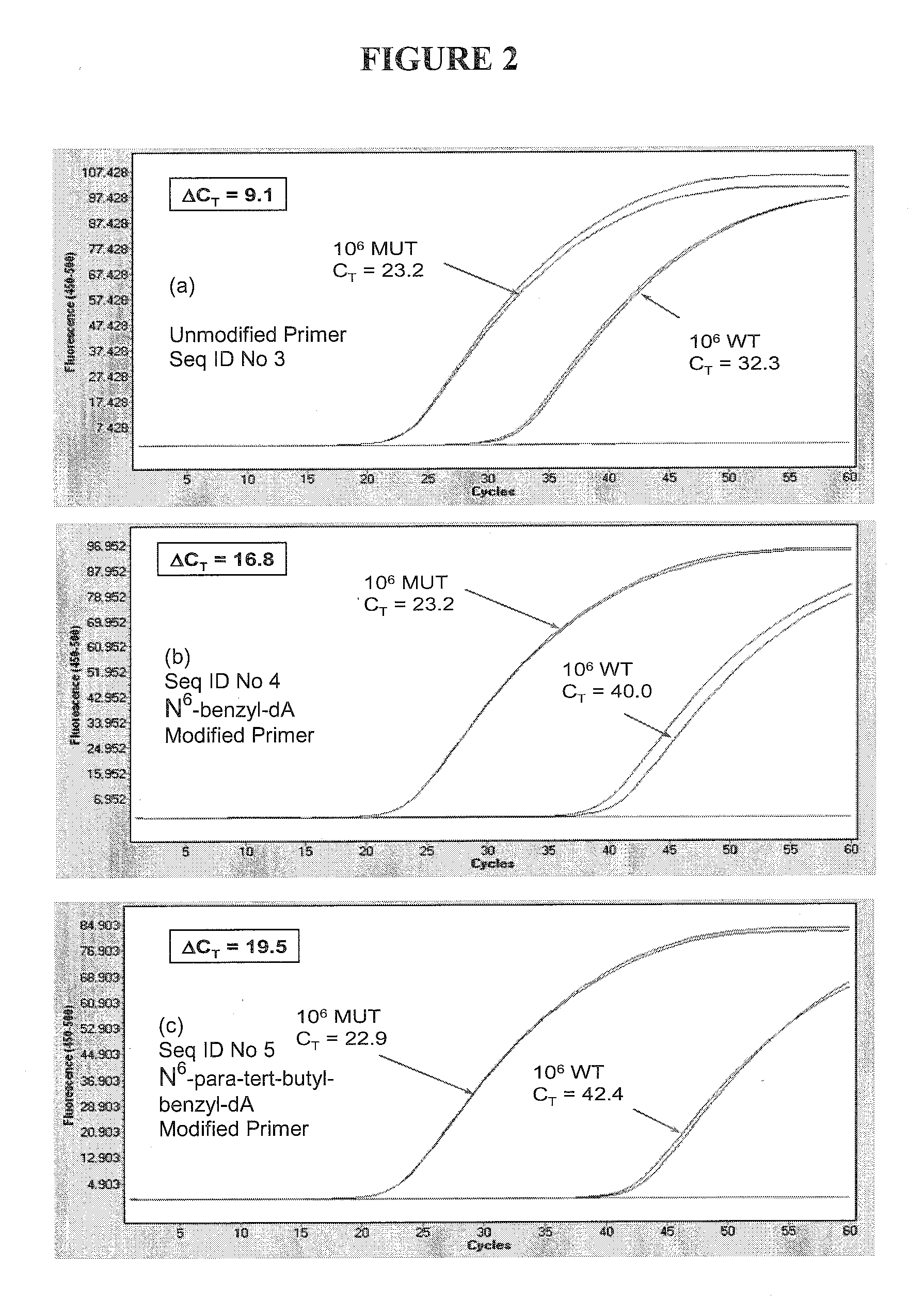
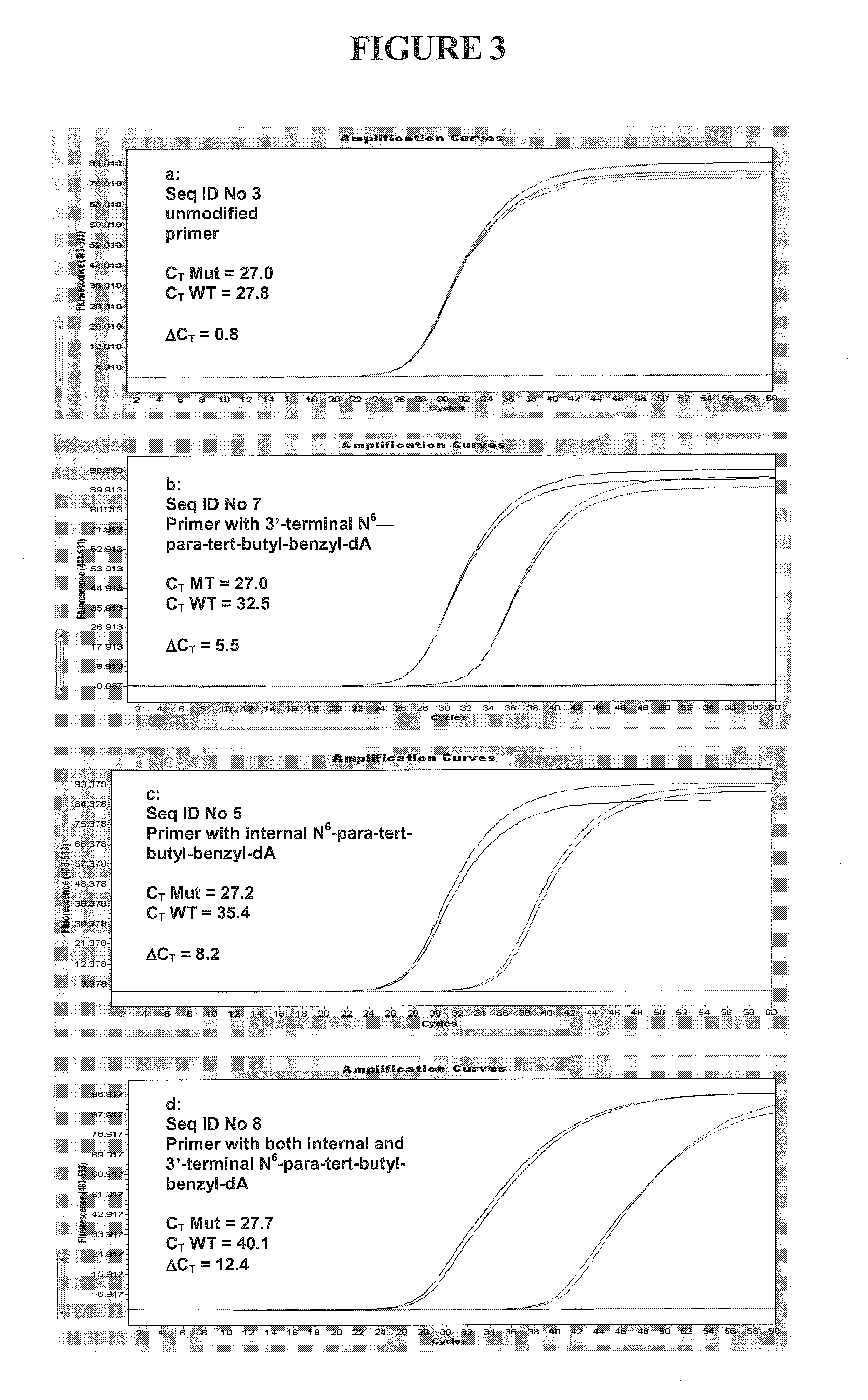
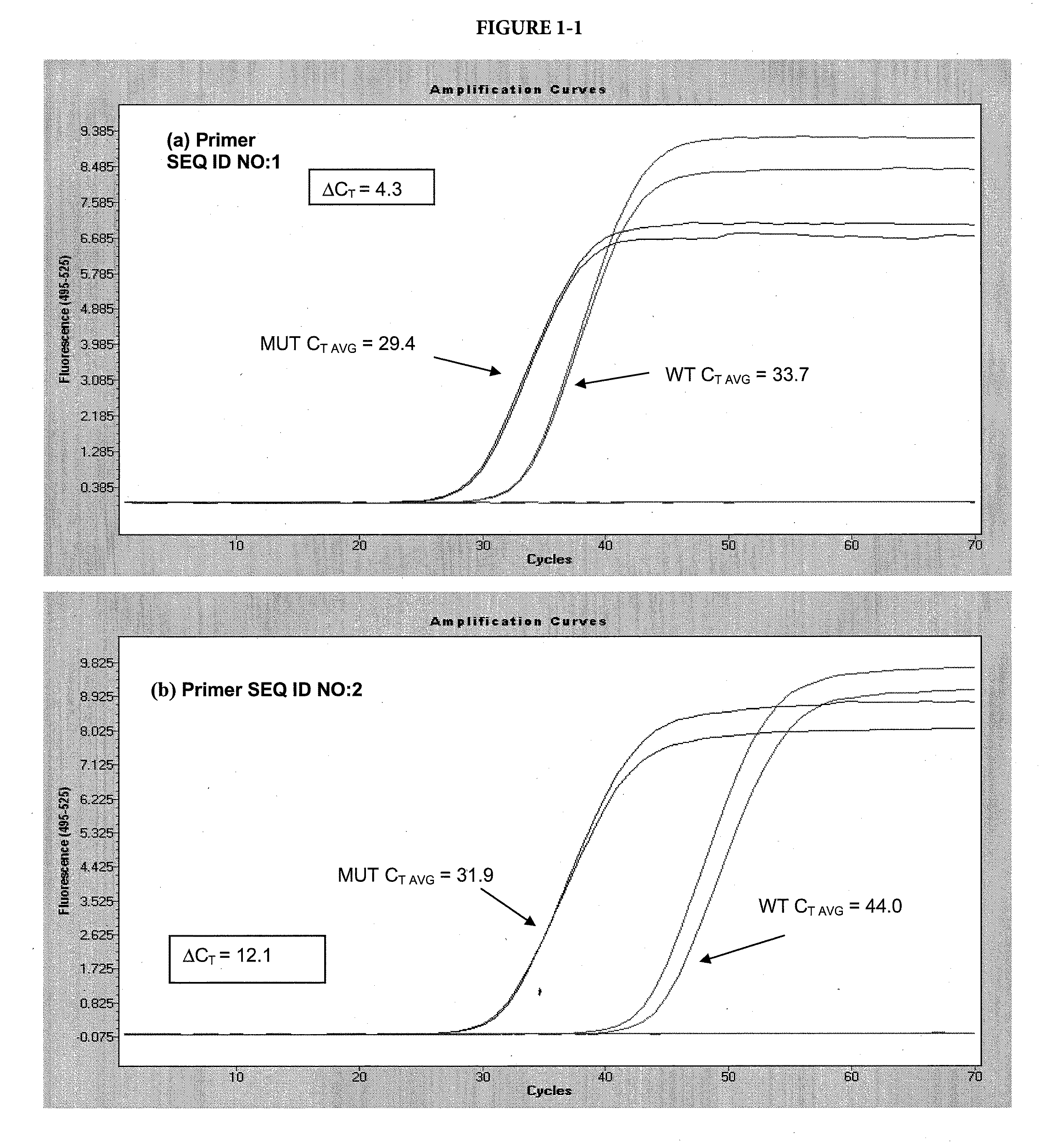
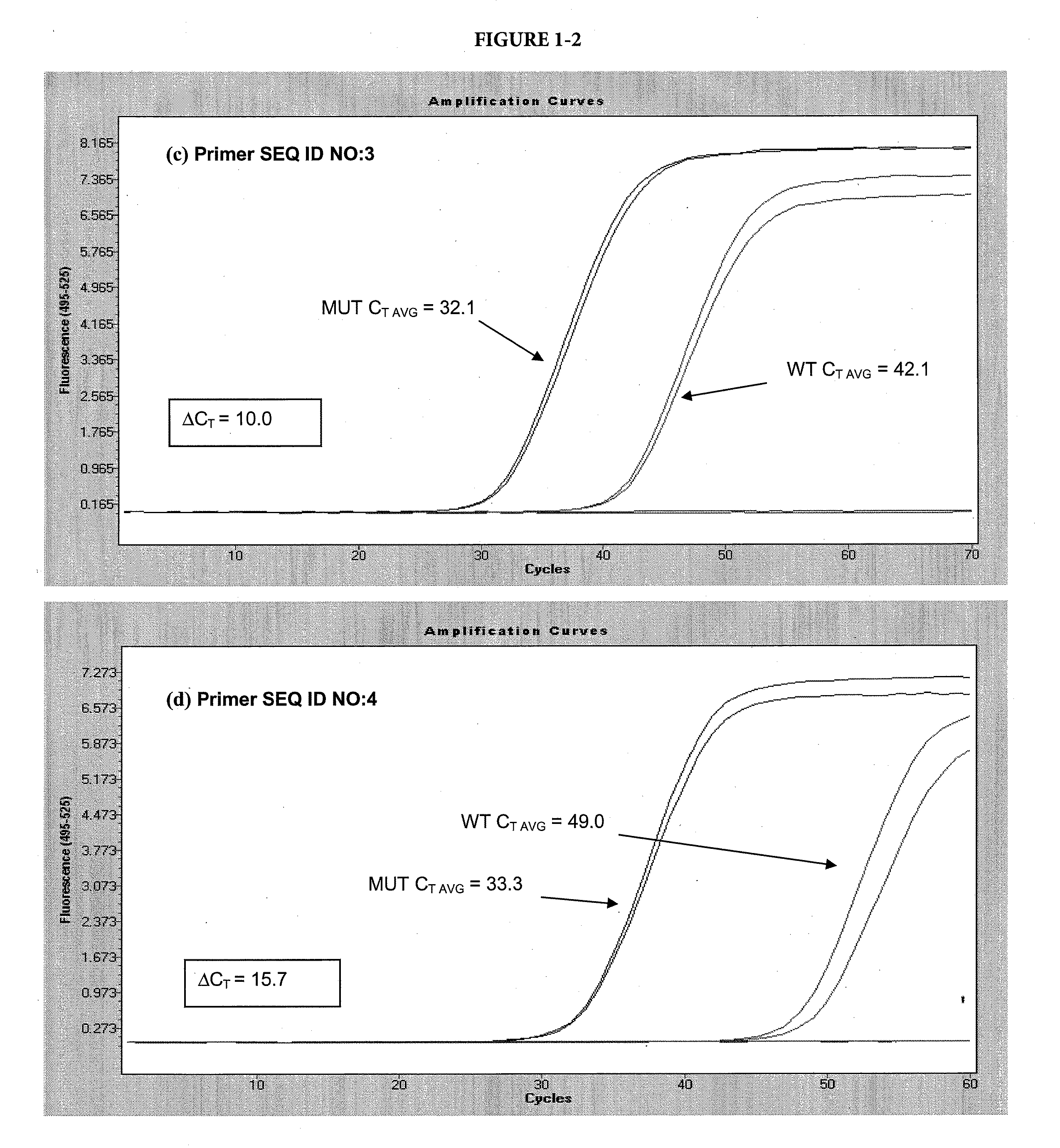
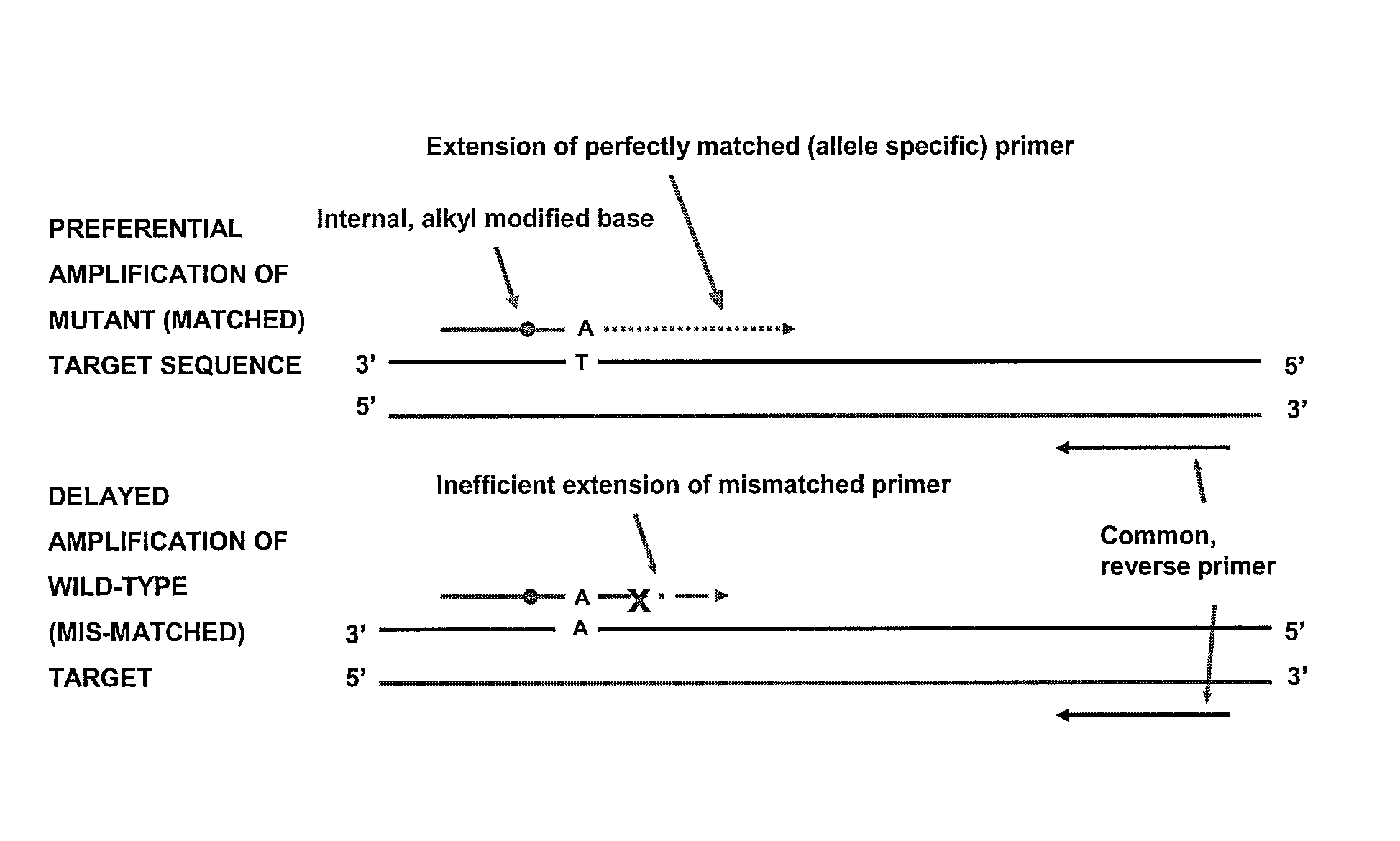
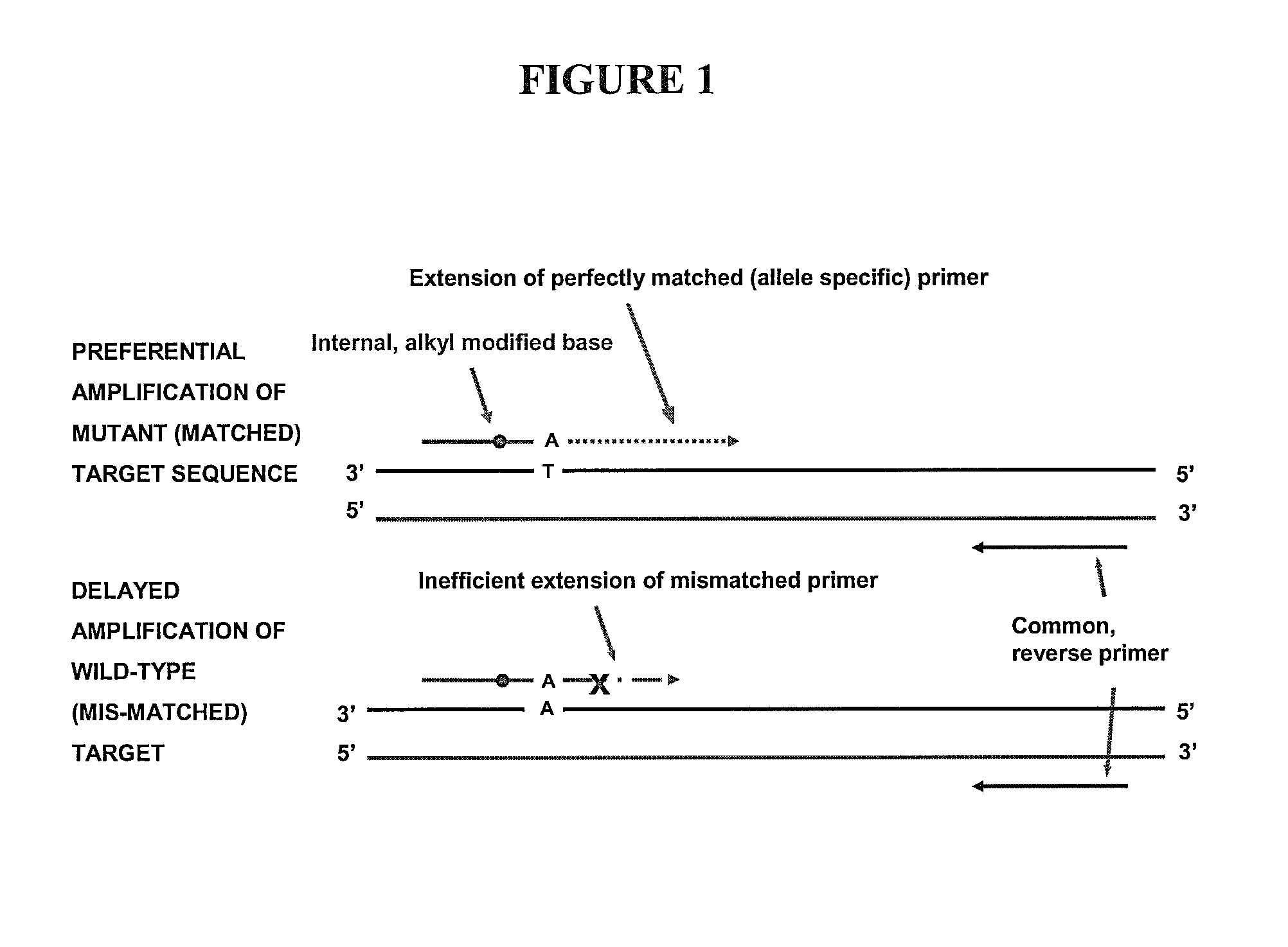
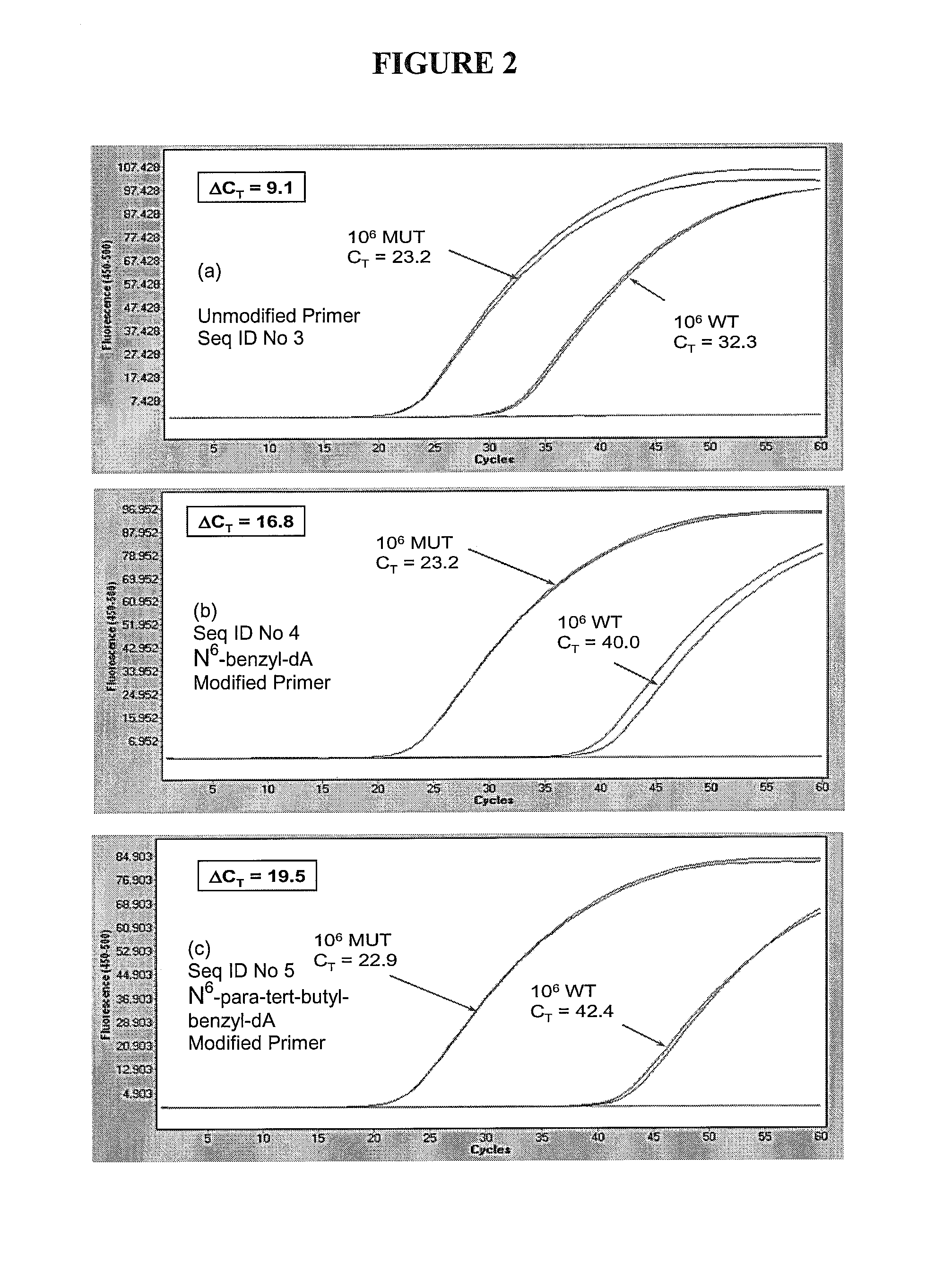
The present invention includes a method of allele-specific amplification, utilizing an allele-specific oligonucleotide, at least partially complementary to more than one variant of the target sequence, but having a 3′-terminal nucleotide complementary to only one variant of the target sequence and having at least one nucleotide with a base covalently modified at the exocyclic amino group, wherein the allele-specific oligonucleotide is extended by a nucleotide-incorporating biocatalyst predominantly when hybridized to the variant of the target sequence for which it has said complementary 3′-terminal nucleotide.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Methods and products related to genotyping and DNA analysis
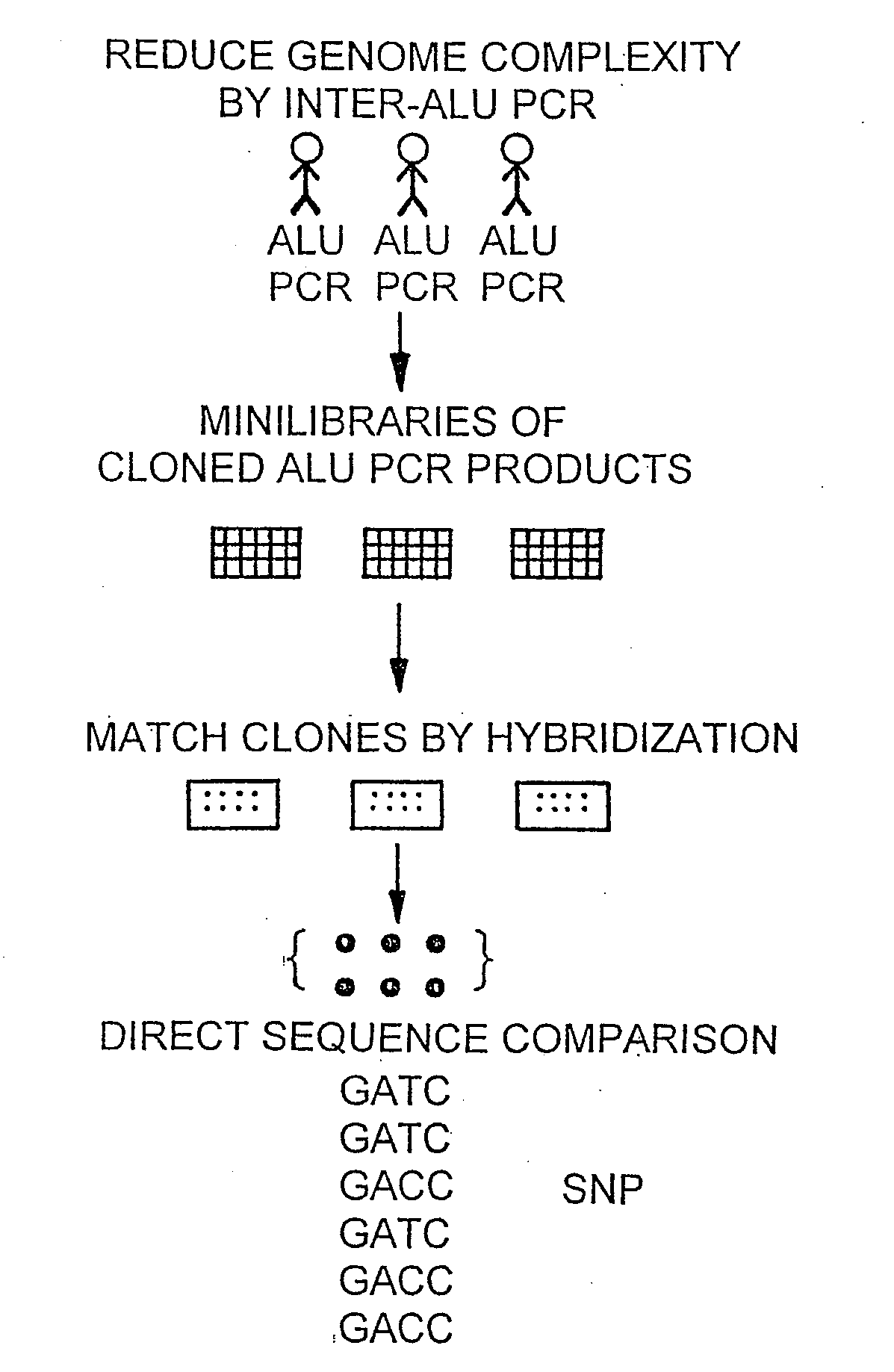
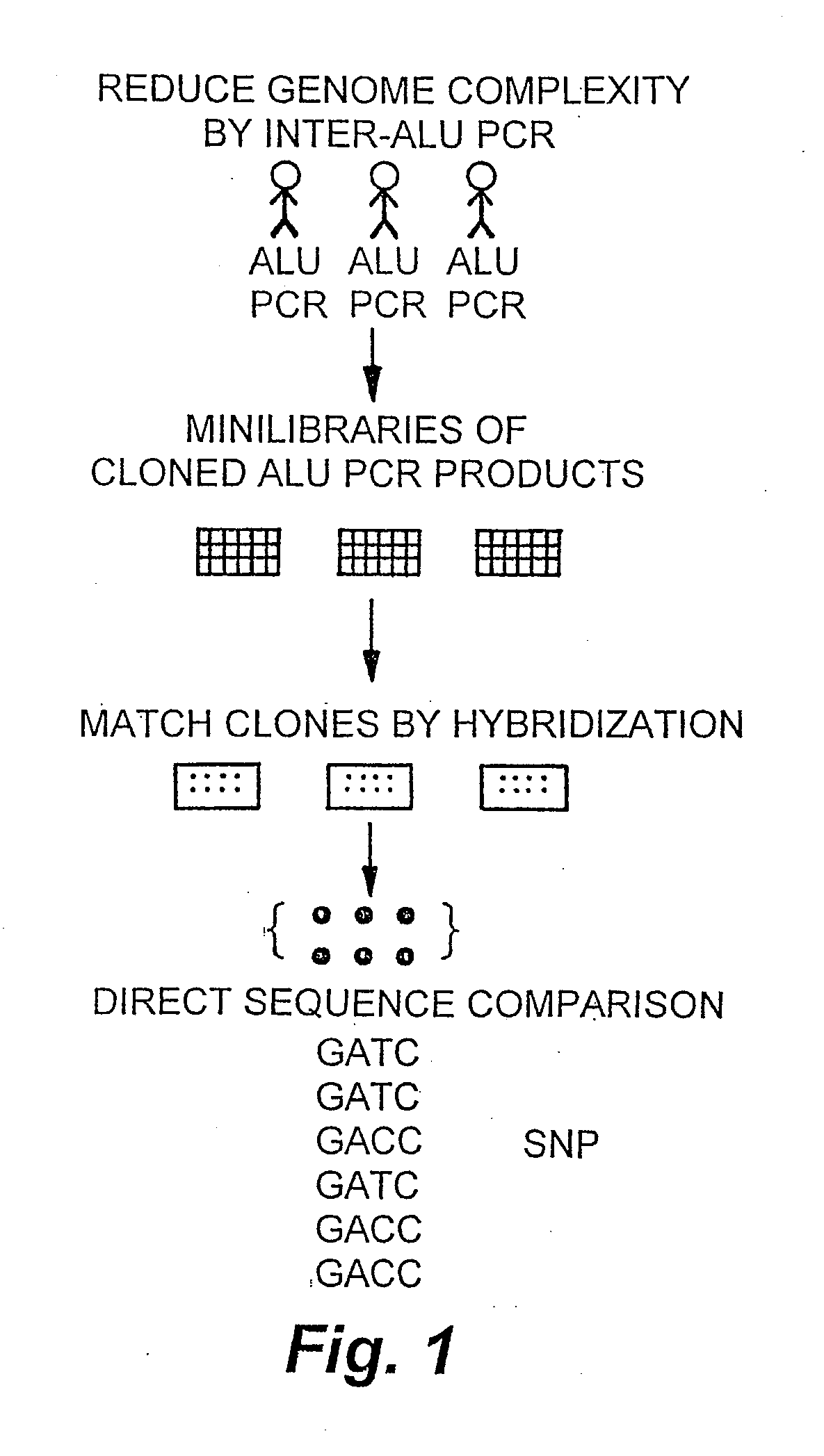
InactiveUS20090098551A1Improve throughputReduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenome ScanAllele-specific oligonucleotide
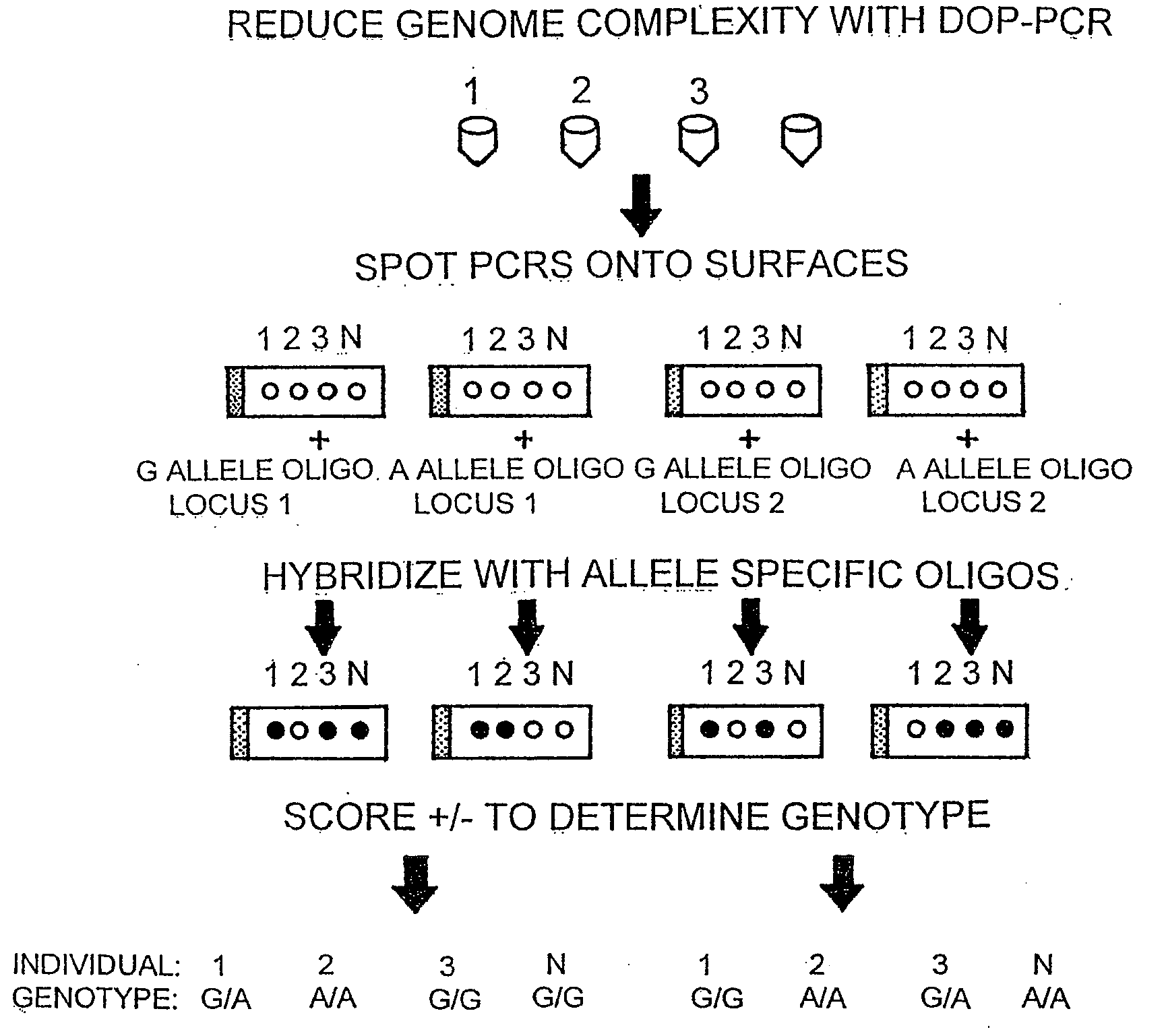
The invention encompasses methods and products related to genotyping. The method of genotyping of the invention is based on the use of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to perform high throughput genome scans. The high throughput method can be performed by hybridizing SNP allele-specific oligonucleotides and a reduced complexity genome (RCG). The invention also relates to methods of preparing the SNP specific oligonucleotides and RCGs, methods of fingerprinting, determining allele frequency for a SNP, characterizing tumors, generating a genomic classification code for a genome, identifying previously unknown SNPs, and related compositions and kits.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Rapid genotyping analysis and the device thereof
InactiveUS20060292601A1Accuracy is compromisedFacilitate SNP genotypingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSensitive analysisDot blotting
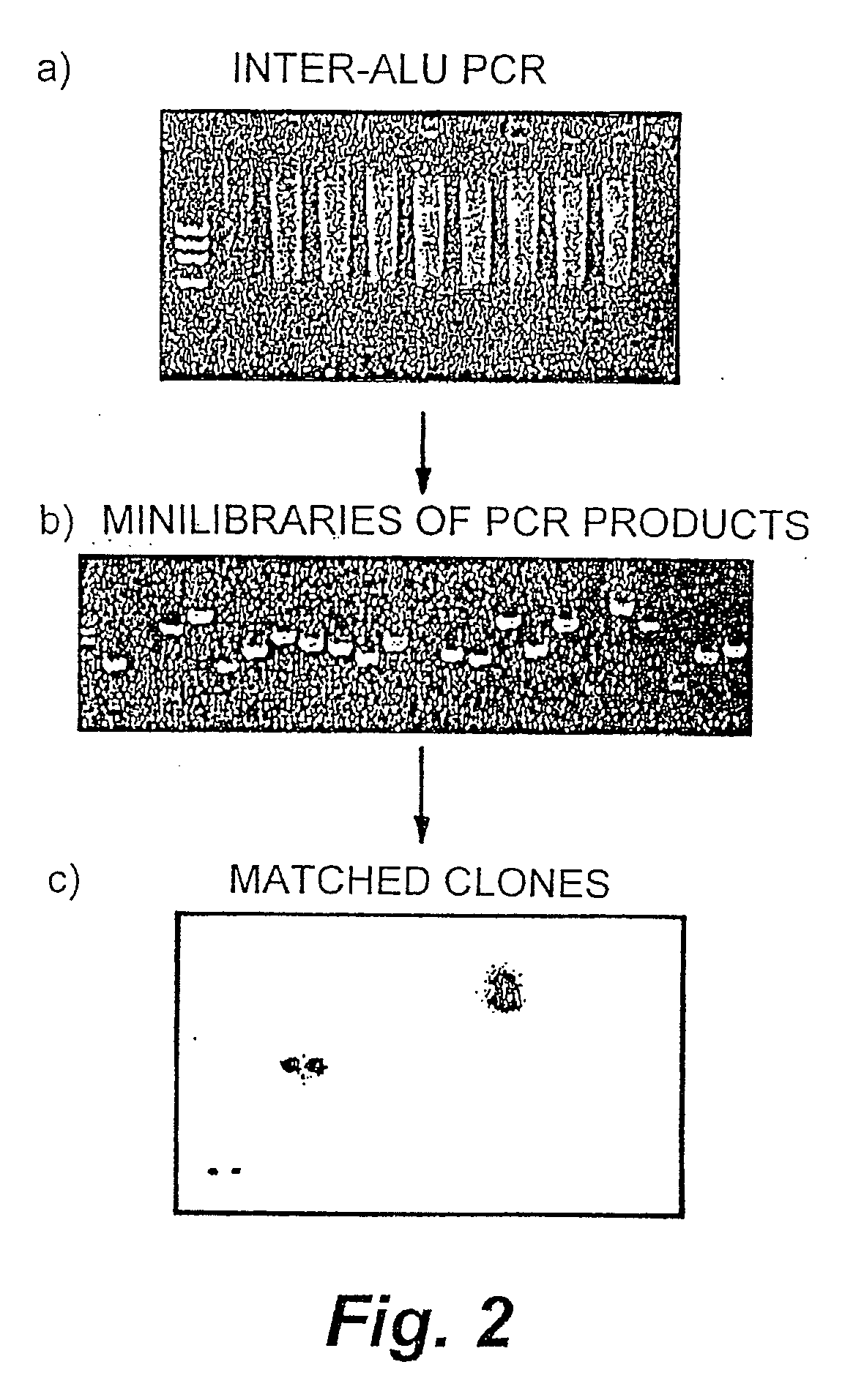
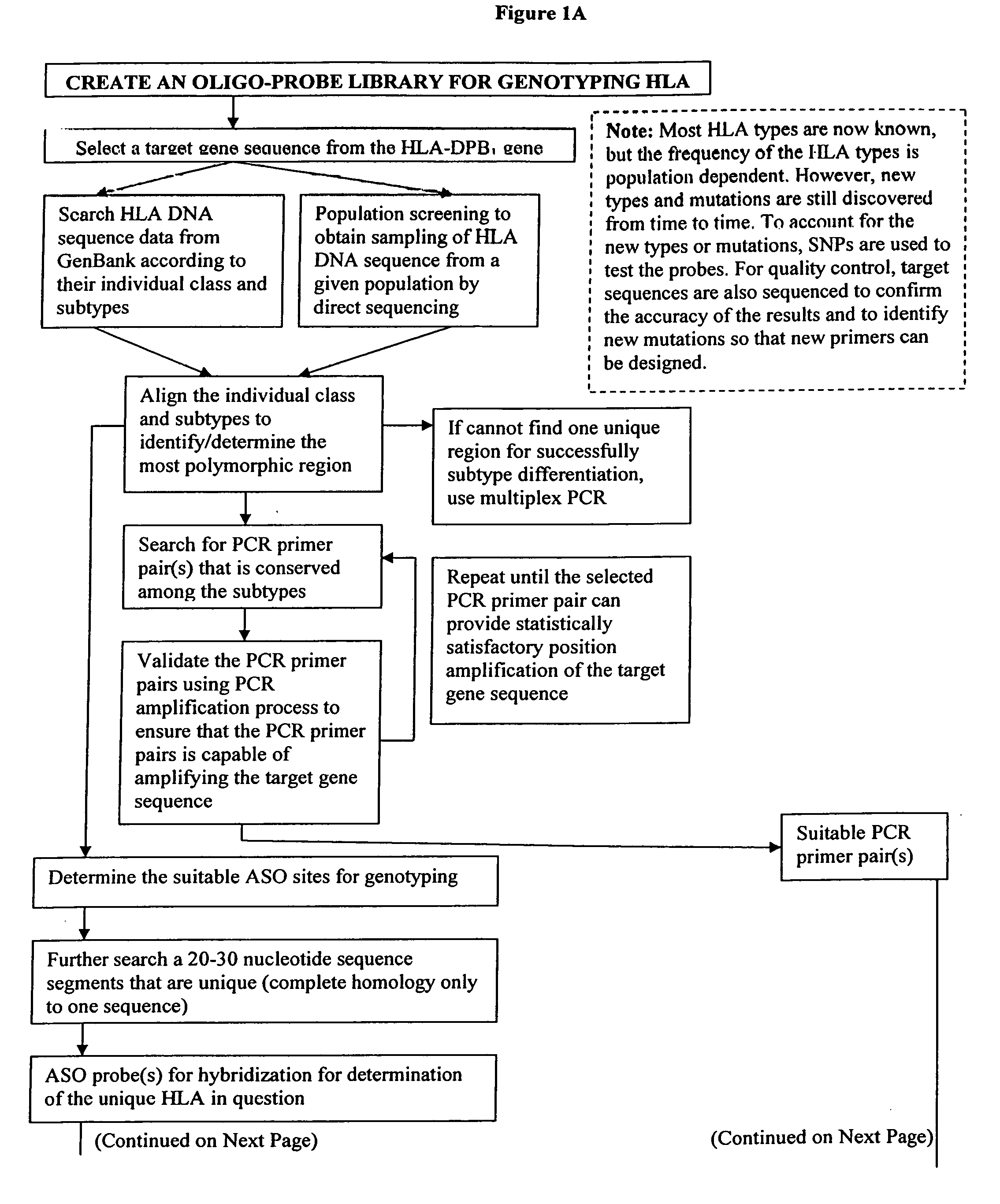
The present invention discloses the use of Allele-Specific-oligonucleotide (ASO) as a detection assay for human HLA classification. Using Reversed-Dot-Blotting format and flow through hybridization process, more efficient, faster and less expensive HLA classification can be achieved. A simplified procedure for HLA genotyping is also described. This invention further provides a Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)-based DNA fingerprining method for rapid and accurate genotyping, identification as well as DNA analyses of genetic data from human beings and different organisms. In addition this invention also discloses a new device for rapid and sensitive analyses of nucleic acids, proteins and other analysts for diagnosis.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAIGAO MEDICAL LAB CO LTD
DNA fingerprinting using allelic specific oligonucleotide reversed dot blot (ASO-RDB) flow through hybridization process and device
InactiveUS20050079493A1Accuracy is compromisedEasy to identifyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPresent methodAllele-specific oligonucleotide
The present invention disclosed the use of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) as the detection assay for human identification. Using the reversed dot-blot format and the flow through hybridization process, the process can be more efficient, less expensive and with similar or better power of exclusion in definitive identification. The present method can be applied to any other organisms.
Owner:TAM JOSEPH
A method of genotyping blood cell antigens and kit suitable for genotyping blood cell antigens
A method of genotyping blood cell antigens comprising subjecting DNA from an individual of a mammalian species to a multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) to amplify and detectably label a region of the locus of at least two different blood cell antigens which contains the site of nucleotide polymorphism of said blood cell antigen and using the thus amplified and labeled DNA fragments to determine the genotype for each of said blood cell antigens. The multiplex PCR comprises the use of at least one pair of blood cell antigen-specific chimeric primers for each blood cell antigen to be genotyped and at least one detectably labeled universal primer, preferably a pair of detectably labeled universal primers. The universal primer(s) have a unique sequence not occurring in the DNA of said mammalian species. Each chimeric primer pair comprises a left chimeric primer and a right chimeric primer, each of them comprising a blood cell antigen-specific part at the 3' end and a universal part at the 5' end. The base sequence of the universal part of the chimeric primers corresponds to the base sequence of said at lea st one universal primer. The blood cell antigen-specific parts of the chimeric primer pair enclose a region of the locus of the blood cell antigen which contains the site of nucleotide polymorphism of said blood cell antigen. A k it for genotyping blood cell antigens by this method. A set of blood cell antig en- specific chimeric primer pairs and a set of blood cell antigen allele-specif ic oligonucleotide probes.
Owner:桑昆血液供给基金会
Allele-specific amplification of nucleic acids
ActiveUS9238832B2Eliminating allele-specificityMinimize exonuclease activity of enzymeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAllele-specific oligonucleotideNucleotide
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Primers with modified phosphate and base in allele-specific PCR
ActiveUS9382581B2Effective expansionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAllele-specific oligonucleotideNucleotide
The present invention includes a method of allele-specific amplification, utilizing an allele-specific oligonucleotide, at least partially complementary to more than one variant of the target sequence, but having at least one selective nucleotide complementary to only one variant of the target sequence and incorporating both a nucleotide with a base covalently modified at the exocyclic amino group and a modified phosphate.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Rapid genotyping analysis and the device thereof
InactiveUS7732138B2Accurate measurementNot require expensiveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSensitive analysisAllele-specific oligonucleotide
The present invention discloses the use of Allele-Specific-Oligonucleotide (ASO) as a detection assay for human HLA classification. Using Reversed-Dot-Blotting format and flow through hybridization process, more efficient, faster and less expensive HLA classification can be achieved. A simplified procedure for HLA genotyping is also described. This invention further provides a Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)-based DNA fingerprining method for rapid and accurate genotyping, identification as well as DNA analyses of genetic data from human beings and different organisms. In addition this invention also discloses a new device for rapid and sensitive analyses of nucleic acids, proteins and other analysts for diagnosis.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAIGAO MEDICAL LAB CO LTD
Method of Genotyping Blood Cell Antigens and Kit Suitable for Genotyping Blood Cell Antigens
InactiveUS20080050727A1Practical and rapid and reliable genotypingGood choiceMicrobiological testing/measurementAllele-specific oligonucleotideNucleotide
A method of genotyping blood cell antigens comprising subjecting DNA from an individual of a mammalian species to a multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) to amplify and detectably label a region of the locus of at least two different blood cell antigens which contains the site of nucleotide polymorphism of said blood cell antigen and using the thus amplified and labeled DNA fragments to determine the genotype for each of said blood cell antigens. The multiplex PCR -comprises the use of at least one pair of blood cell antigen-specific chimeric primers for each blood cell antigen to be genotyped and at least one detectably labeled universal primer, preferably a pair of detectably labeled universal primers. The universal primer(s) have a unique sequence not occurring in the DNA of said mammalian species. Each chimeric primer pair comprises a left chimeric primer and a right chimeric primer, Each of them comprising a blood cell antigen-specific part at the 3′ end and a universal part at the 5′ end. The base sequence of the universal part of the chimeric primers corresponds to the base sequence of said at least one universal primer. The blood cell antigen-specific parts of the chimeric primer pair enclose a region of the locus of the blood cell antigen which contains the site of nucleotide polymorphism of said blood cell antigen. A kit for genotyping blood cell antigens by this method. A set of blood cell antigen-specific chimeric primer pairs and a set of blood cell antigen allele-specific oligonucleotide probes.
Owner:STICHTING SANQUIN BLOEDVOORZIENING
Allele-Specific Amplification of Nucleic Acids
ActiveUS20110311968A1Less extensionEliminating allele-specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAllele-specific oligonucleotideNucleotide
The present invention includes a method of allele-specific amplification, utilizing an allele-specific oligonucleotide, at least partially complementary to more than one variant of the target sequence, having an internally-placed selective nucleotide complementary to only one variant of the target sequence wherein the allele-specific oligonucleotide is extended by a nucleic acid polymerase predominantly or exclusively when hybridized to the variant of the target sequence for which it has said complementary selective nucleotide.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Allele-specific amplification
ActiveUS8586299B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAllele-specific oligonucleotideNucleotide
The present invention includes a method of allele-specific amplification, utilizing an allele-specific oligonucleotide, at least partially complementary to more than one variant of the target sequence, but having a 3′-terminal nucleotide complementary to only one variant of the target sequence and having at least one nucleotide with a base covalently modified at the exocyclic amino group, wherein the allele-specific oligonucleotide is extended by a nucleotide-incorporating biocatalyst predominantly when hybridized to the variant of the target sequence for which it has said complementary 3′-terminal nucleotide.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Use of G-Clamp for Improved Allele-SpecificPCR
ActiveUS20130078630A1Effective expansionLess extensionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAllele-specific oligonucleotideGenetics
The present invention includes a method of allele-specific amplification, utilizing an allele-specific oligonucleotide, at least partially complementary to more than one variant of the target sequence, but having at least one selective nucleotide complementary to only one variant of the target sequence and incorporating at least one “G-clamp” nucleotide.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Flight mass spectrometry genotyping detection method
InactiveCN111041079AReduce dosageEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEnzyme digestionAllele-specific oligonucleotide
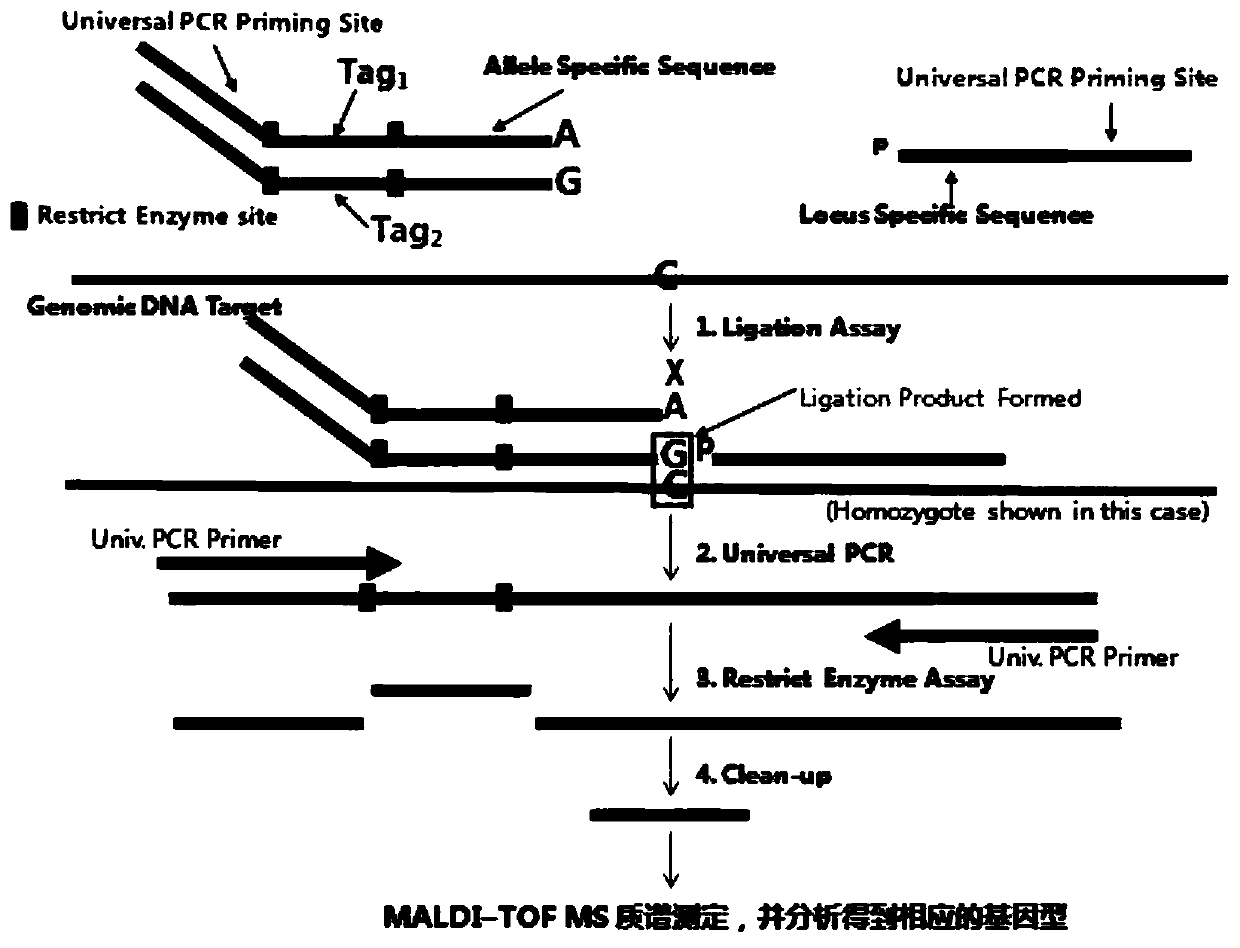
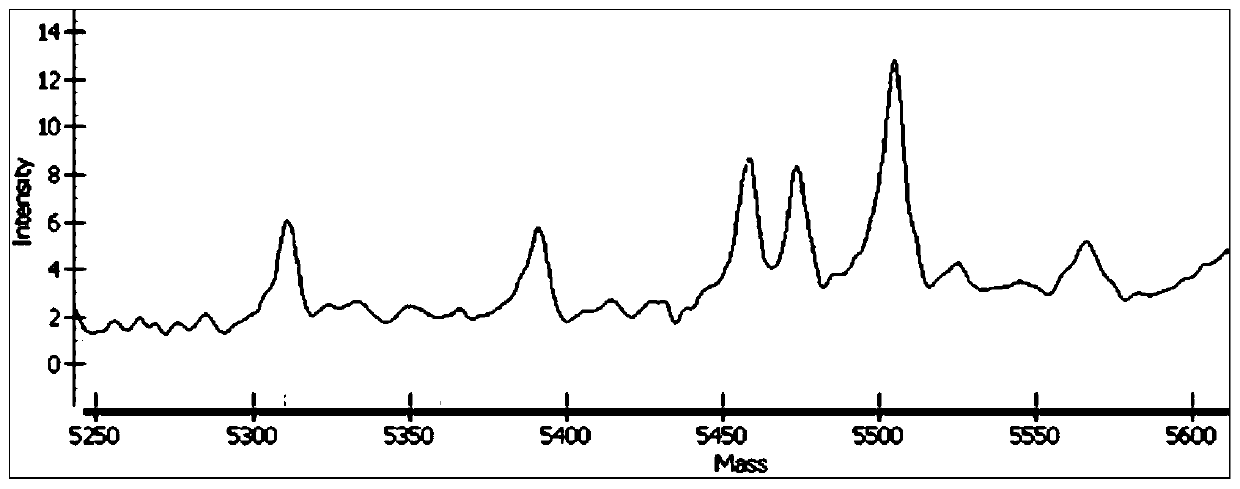
The invention discloses a flight mass spectrometry genotyping detection method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) designing three oligonucleotide probes for a SNP site, wherein the 3 / endsof a first probe and a second probe are respectively two allelic genes, i.e., allele-specific oligos (ASOs) of a pre-selected SNP site, (2) when the sequence is completely matched with the target sequence, preparing a connection product, (4) carrying out enzyme digestion on the PCR product by using restriction endonuclease, and purifying the product by using streptavidin-coated beads, and (5) transferring the purified product to a 384-well chip. SNP site typing is carried out by adopting MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, and SNP typing is provided by adopting the method which is simple to operate,low in cost and high in resolution ratio.
Owner:博淼生物科技(北京)有限公司
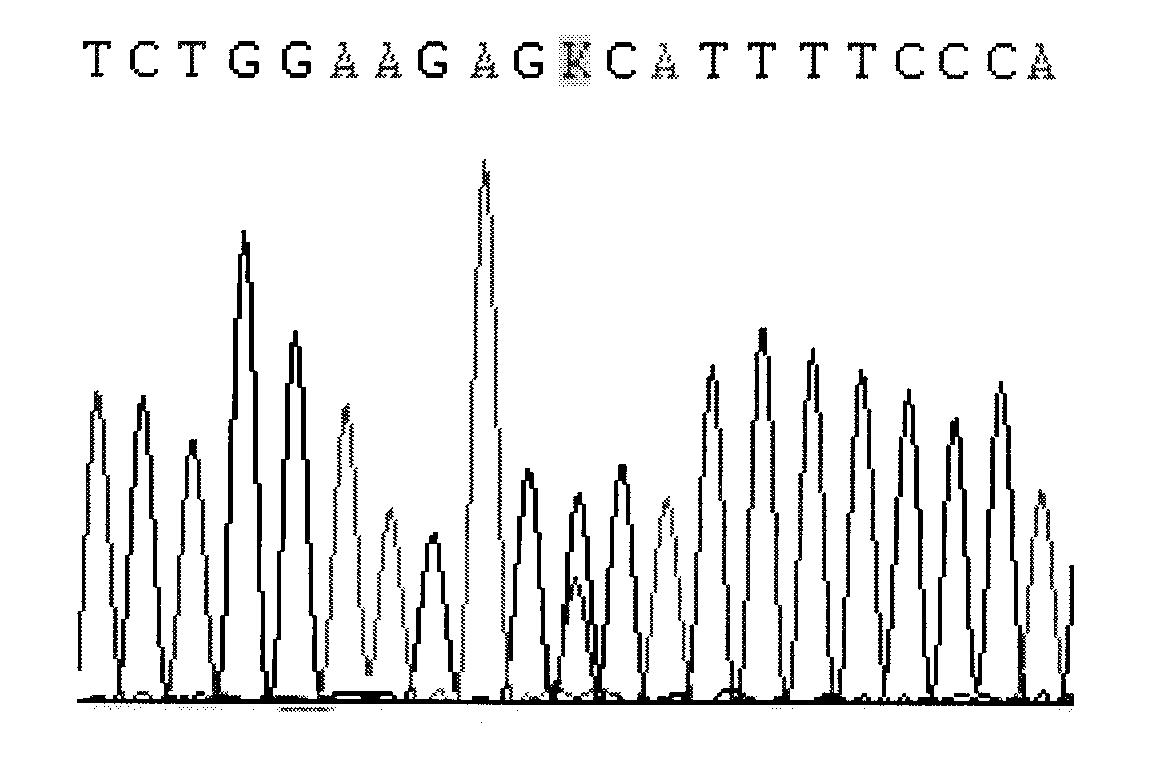
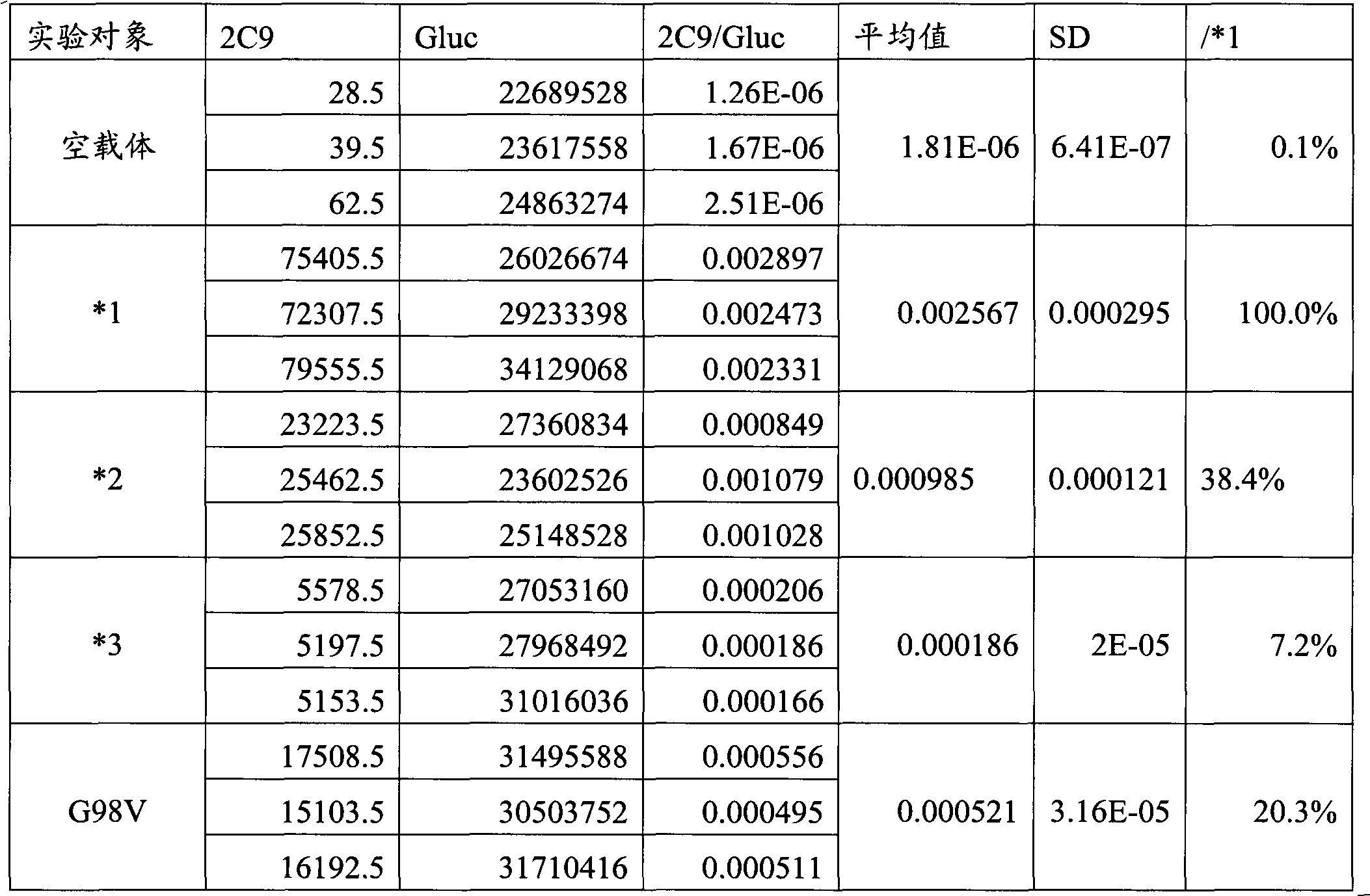
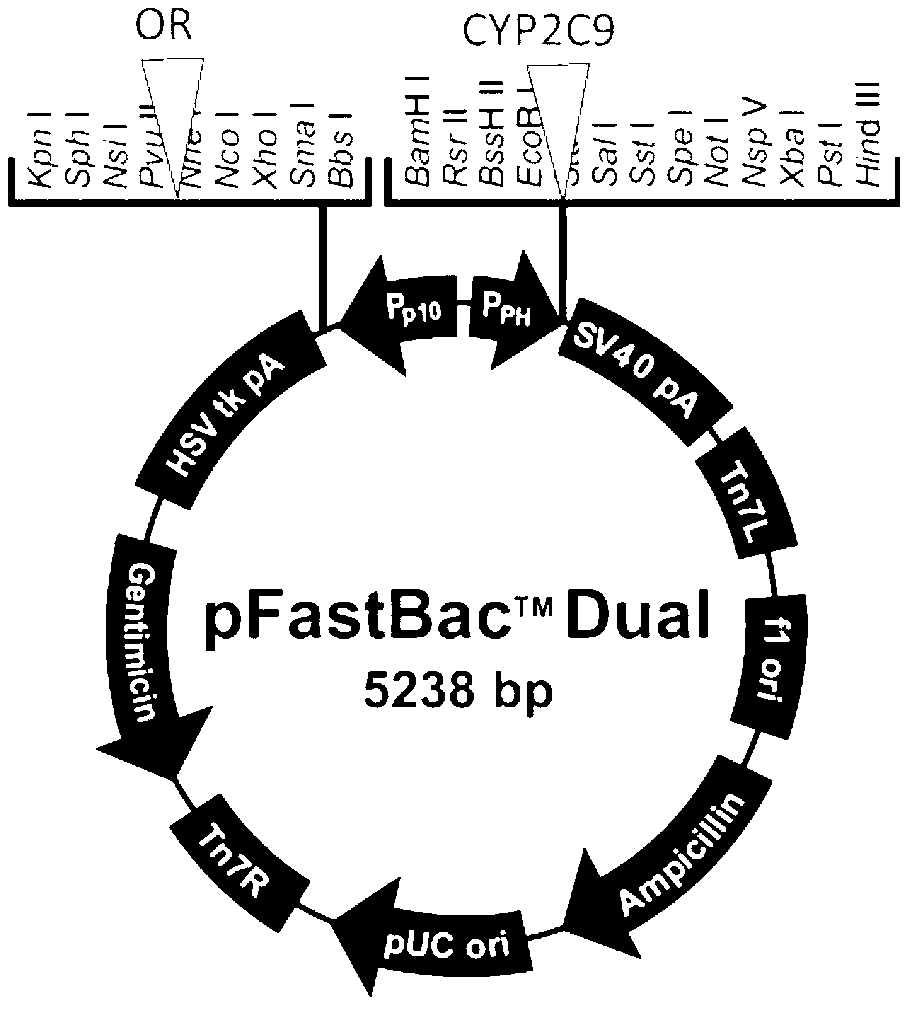
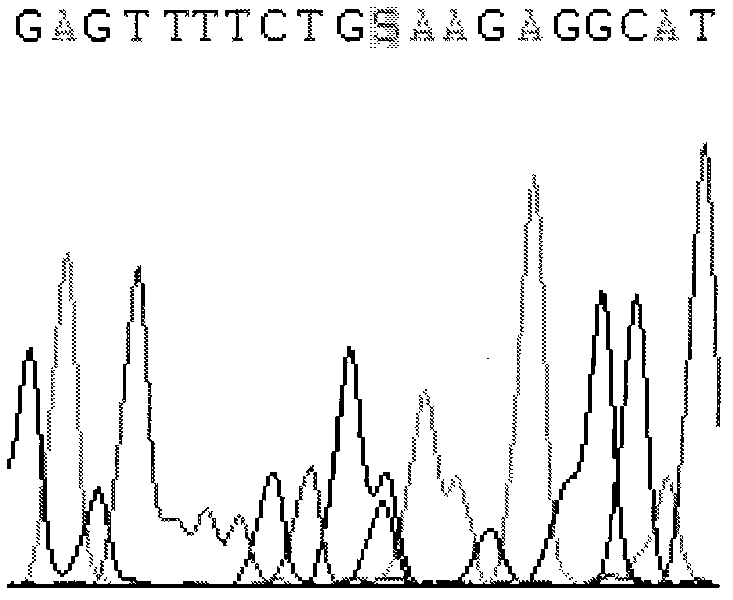
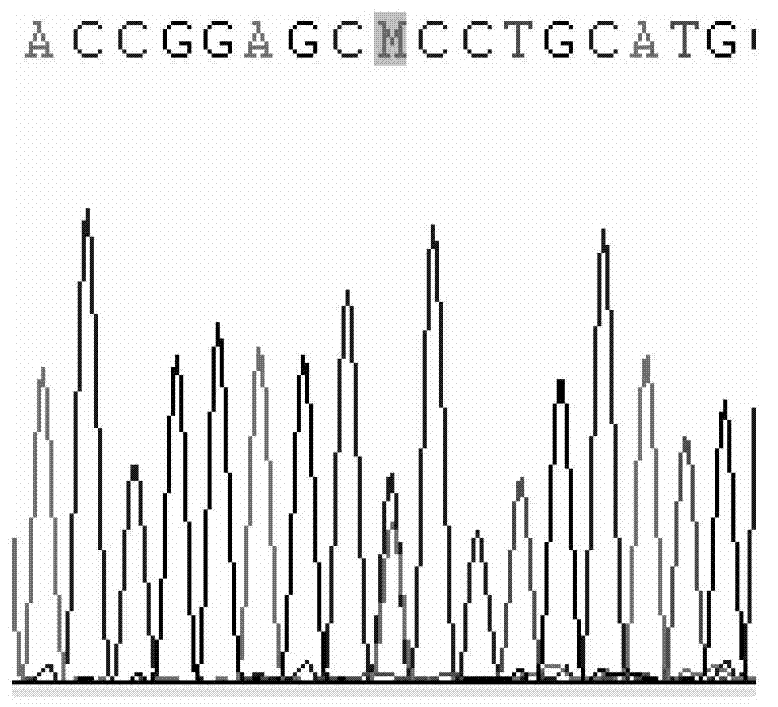
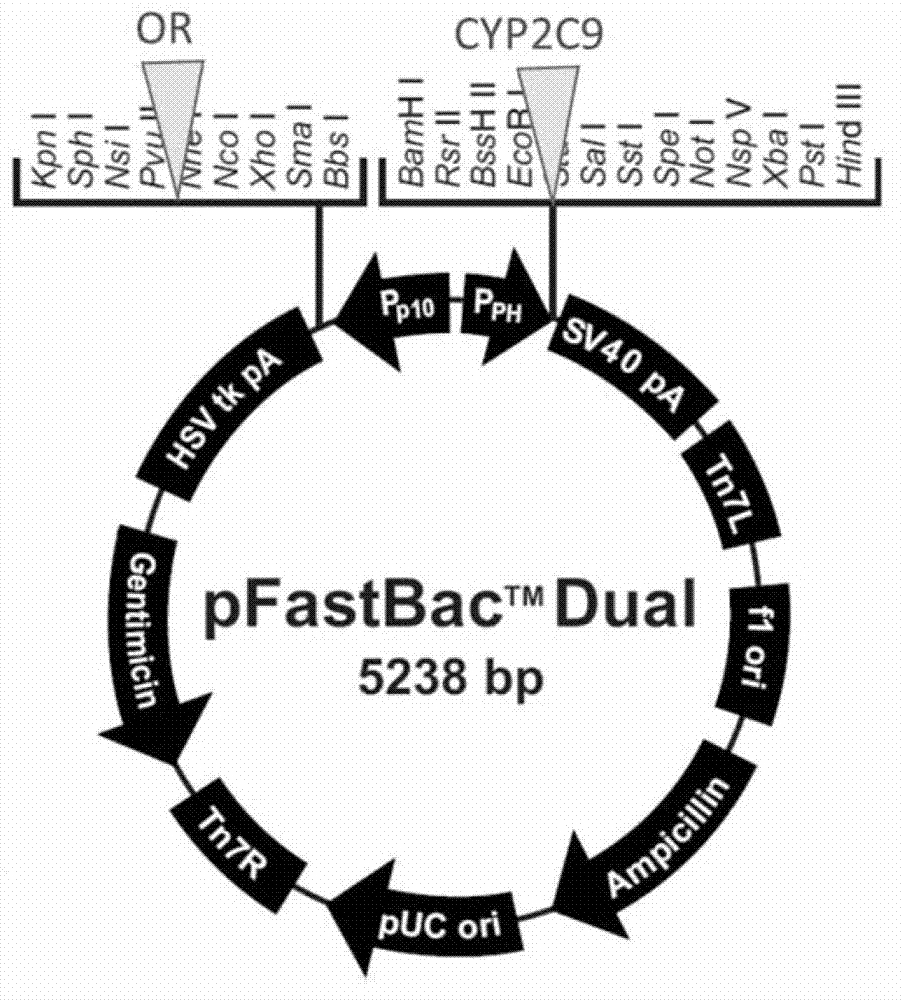
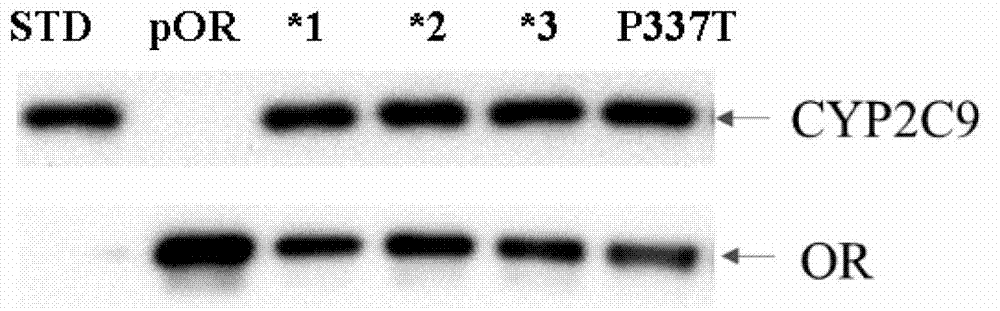
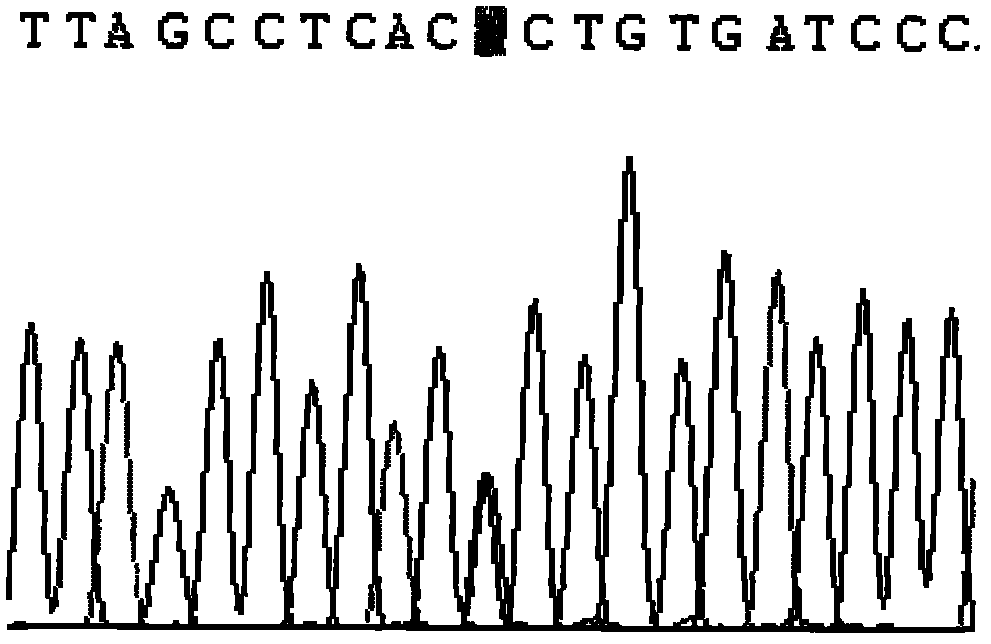
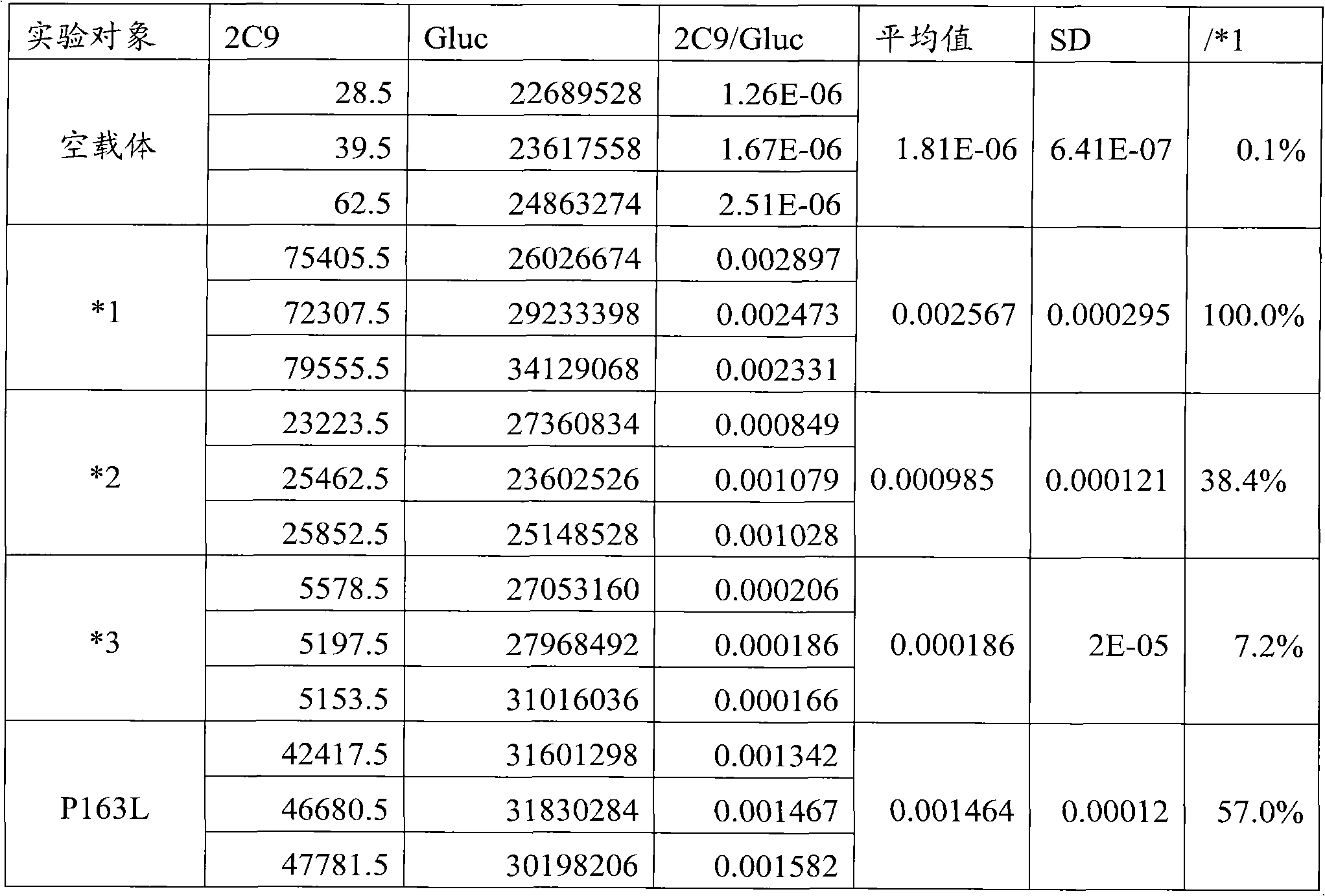
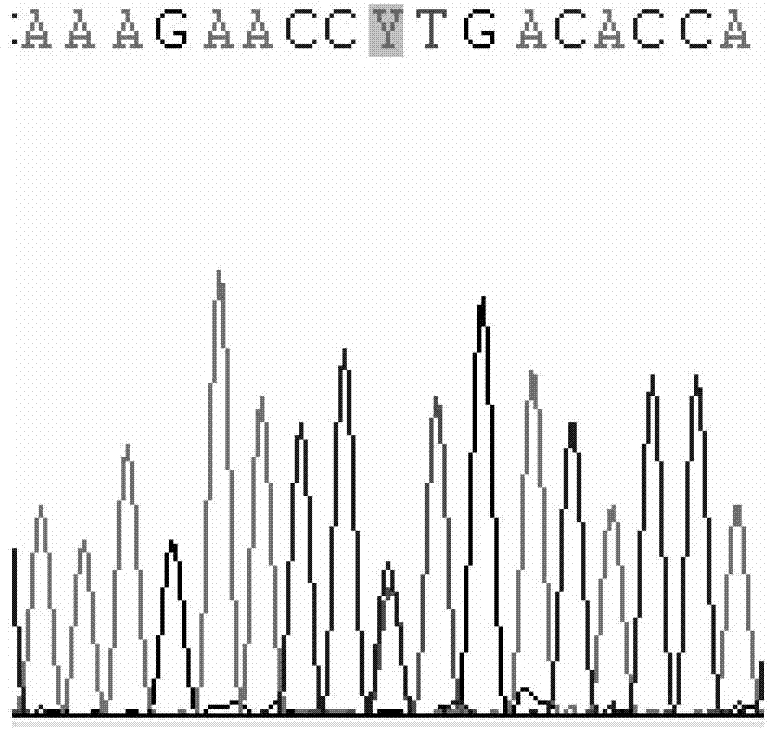
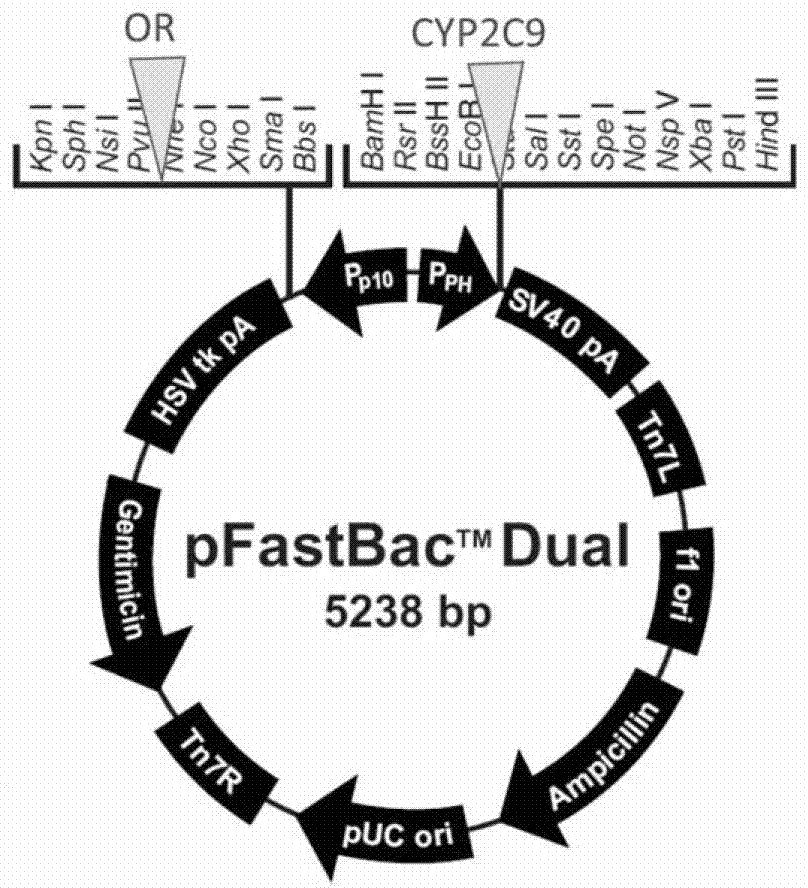
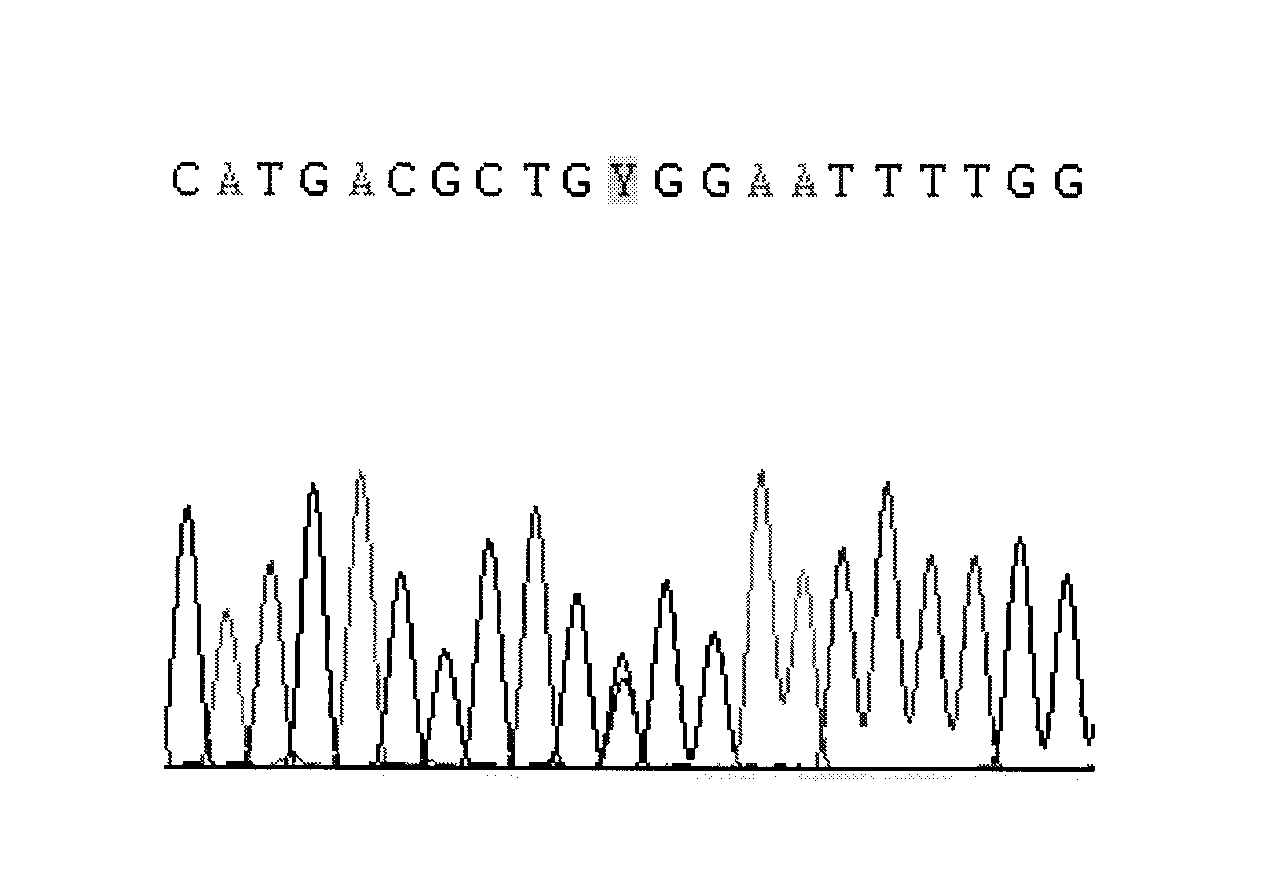
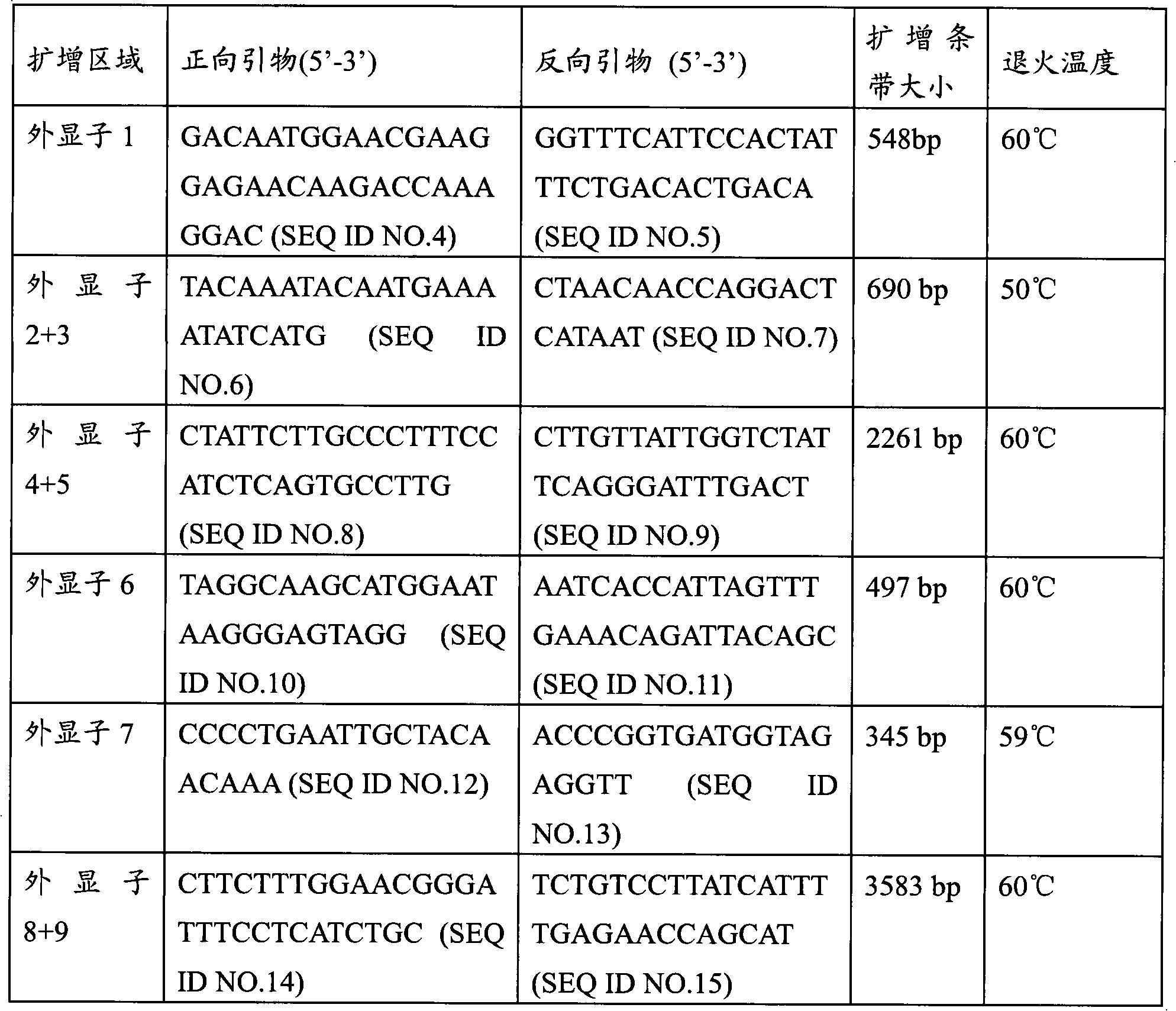
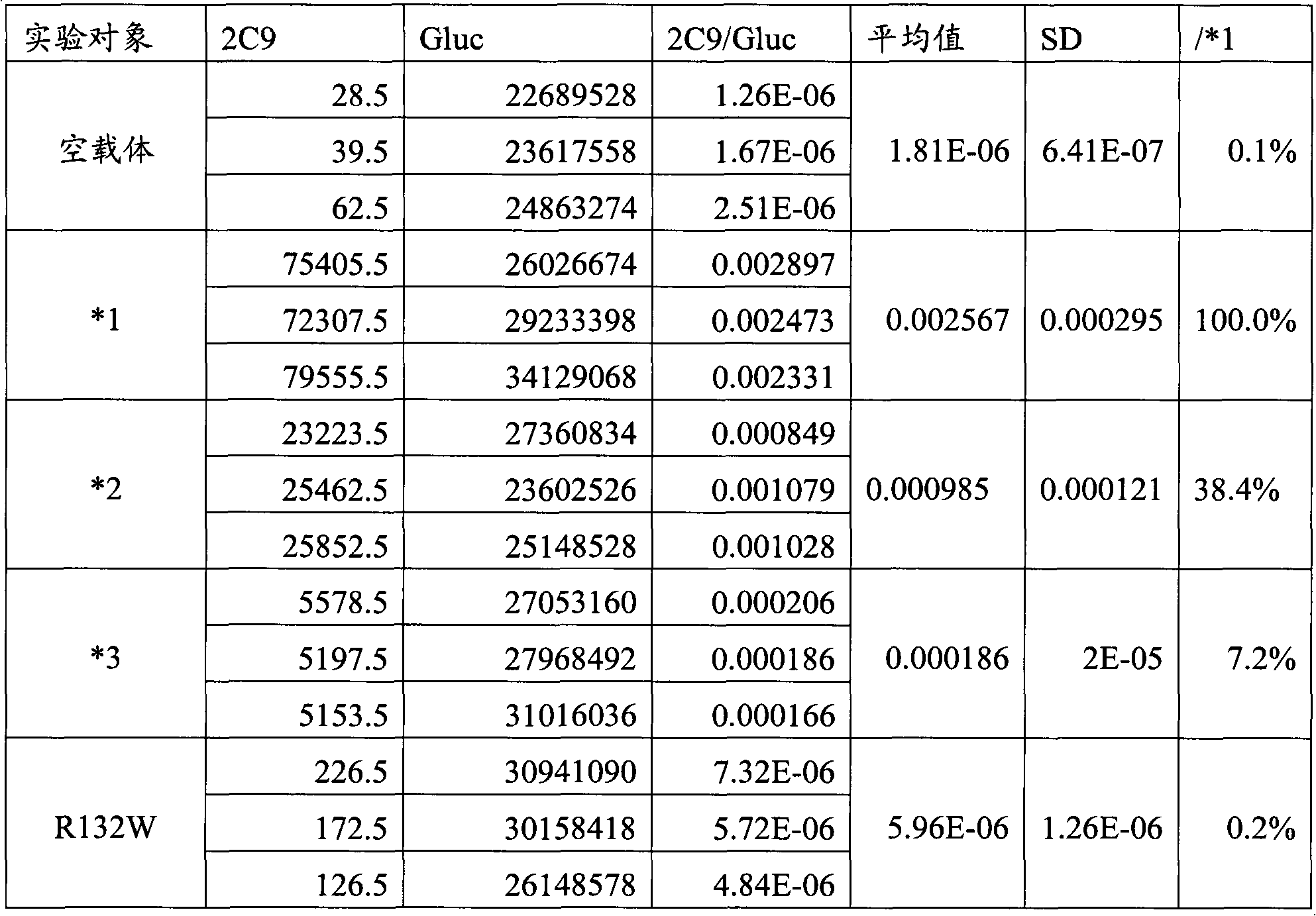
CYP2C9 gene segment comprising 293G>T, coded protein segment and application thereof
ActiveCN103045619AReduced metabolic activityMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesAllele-specific oligonucleotideWild type
The invention belongs to the field of biology, and relates to single base mutation. More particularly, the invention relates to a mutation site of a 293th site of SEQ ID NO.2 corresponding to a CYP2C9 gene, wherein the mutation site is mutated into T from wild type G. The invention also relates to a nucleic acid segment, a coded protein segment and application thereof. The invention also provides an allele-specific oligonucleotide, kit and method for detecting the mutation site.
Owner:蔡剑平
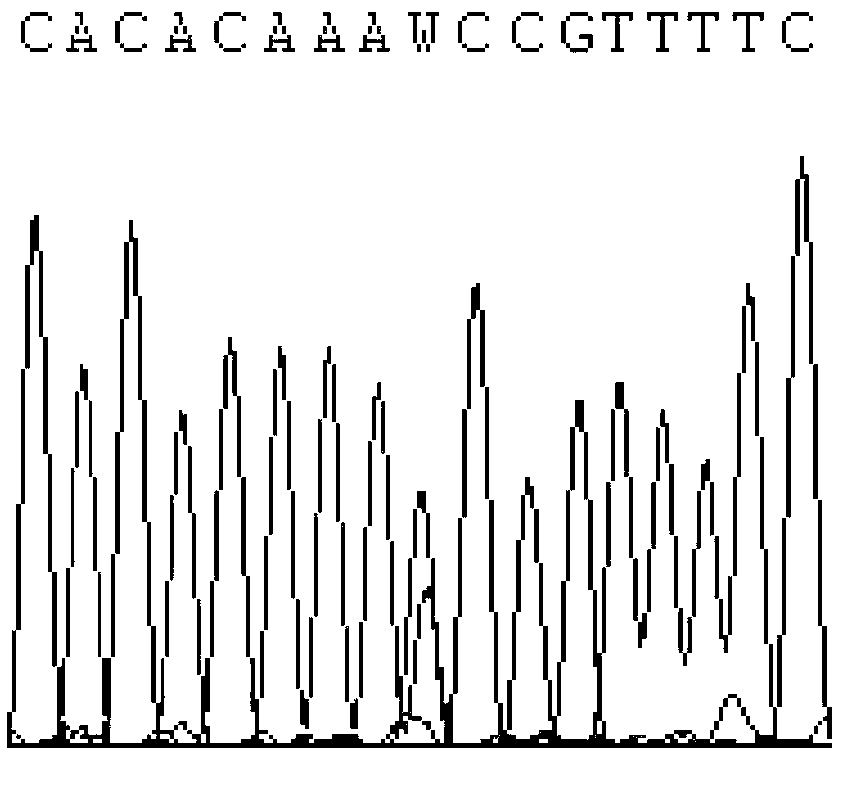
CYP2C9 gene fragment containing 1300A>T mutation, protein fragment encoded through same and application thereof
ActiveCN103173443AMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesBase JAllele-specific oligonucleotide
The invention belongs to the field of biology, relates to single-base mutation and particularly relates to a 1300th bit mutation site of a CYP2C9 gene corresponding to SEQ ID NO.2. The 1300th bit mutation site is mutated from wild type A into T. The invention relates to a nucleic acid fragment containing the 1300th bit mutation site, a protein fragment encoded through the same and application thereof. The invention also provides allelomorphic gene specific oligonucleotide for detecting the 1300th bit mutation site, a kit and a detection method.
Owner:BEIJING HOSPITAL
Methods and products related to genotyping and DNA analysis
InactiveUS20140243229A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenome ScanAllele-specific oligonucleotide
The invention encompasses methods and products related to genotyping. The method of genotyping of the invention is based on the use of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to perform high throughput genome scans. The high throughput method can be performed by hybridizing SNP allele-specific oligonucleotides and a reduced complexity genome (RCG). The invention also relates to methods of preparing the SNP specific oligonucleotides and RCGs, methods of fingerprinting, determining allele frequency for a SNP, characterizing tumors, generating a genomic classification code for a genome, identifying previously unknown SNPs, and related compositions and kits.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
CYP2C9 gene segment comprising 679C>T, coded protein segment and application thereof
ActiveCN103031311AMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesAllele-specific oligonucleotideProtein insertion
The invention belongs to the field of biology, and relates to single base mutation. More particularly, the invention relates to a mutation site of a 679th site of SEQ ID NO.2 corresponding to a CYP2C9 gene, wherein the mutation site is mutated into T from wild type C. The invention also relates to a nucleic acid segment, a coded protein segment and application thereof. The invention also provides an allele-specific oligonucleotide, kit and detection method for detecting the mutation site.
Owner:蔡剑平
CYP2C9 gene segment comprising 287G>C, coded protein segment and application thereof
ActiveCN103031317AMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesAllele-specific oligonucleotideWild type
The invention belongs to the field of biology, and relates to single base mutation. More particularly, the invention relates to a mutation site of a 287th site of SEQ ID NO.2 corresponding to a CYP2C9 gene, wherein the mutation site is mutated into C from wild type G. The invention also relates to a nucleic acid segment, a coded protein segment and application thereof. The invention also provides an allele-specific oligonucleotide, kit and detection method for detecting the mutation site.
Owner:蔡剑平
CYP2C9 gene segment containing 1009C>A mutation, protein segment coded by same and application thereof
ActiveCN103194463AMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesAllele-specific oligonucleotideProtein insertion
The invention belongs to the field of biology, relates to single-base mutation, and in particular relates to a CYP2C9 gene which is corresponding to the mutation site mutated from wild type C into A on the 1009th bit of SEQ ID NO.2, a nucleic acid segment containing the mutation site, a protein segment coded by the nucleic acid segment and application thereof. The invention also provides allele specific oligonucleotide, a kit and a detection method for detecting the mutation site.
Owner:卫生部北京医院
CYP2C9 gene segment comprising 448C>T, coded protein segment and application thereof
ActiveCN103031312AMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesAllele-specific oligonucleotideProtein insertion
The invention belongs to the field of biology, and relates to single base mutation. More particularly, the invention relates to a mutation site of a 448th site of SEQ ID NO.2 corresponding to a CYP2C9 gene, wherein the mutation site is mutated into T from wild type C. The invention also relates to a nucleic acid segment, a coded protein segment and application thereof. The invention also provides an allele-specific oligonucleotide, kit and detection method for detecting the mutation site.
Owner:蔡剑平
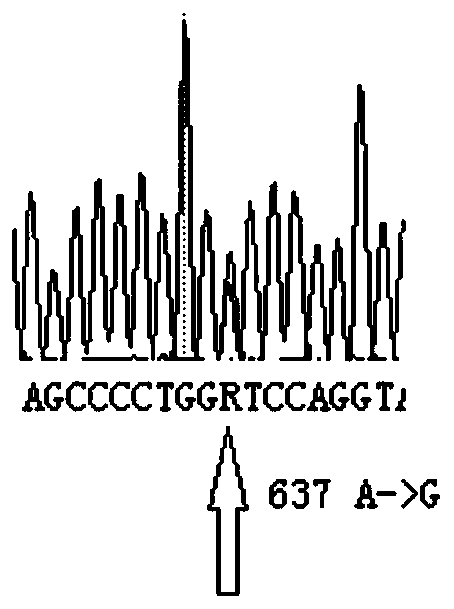
CYP2C9 gene segment comprising 637A> G mutation, encoded protein segment and application thereof
ActiveCN111004811AImprove metabolic activityMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesBase JAllele-specific oligonucleotide
The invention belongs to the field of biology, and relates to single base mutation, and more specifically, the invention relates to a mutation site, corresponding to the 637th site of SEQ ID NO.2, ofCYP2C9 gene, the site is mutated from wild type A into G, a nucleic acid fragment containing the mutation site, a protein fragment coded by the nucleic acid fragment and application of the nucleic acid fragment are disclsoed. The invention also provides allele-specific oligonucleotides, kits and detection methods for detecting the mutation site.
Owner:BEIJING HOSPITAL
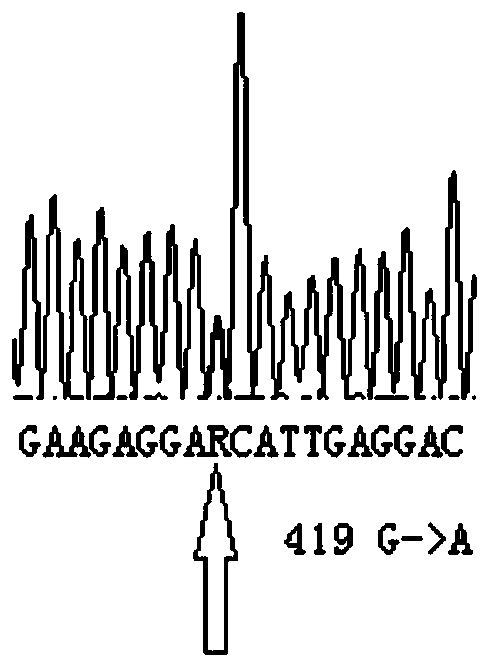
CYP2C9 gene segment comprising 419G> A mutation, encoded protein segment and application thereof
ActiveCN111004810AImprove metabolic activityMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesBase JAllele-specific oligonucleotide
The invention belongs to the field of biology, and relates to single base mutation, and more specifically, the invention relates to a mutation site, corresponding to the 419th site of SEQ ID NO.2, ofCYP2C9 gene; the site is mutated into A from wild-type G, a nucleic acid fragment containing the mutation site, a protein fragment coded by the nucleic acid fragment and application of the nucleic acid fragment are disclosed. The invention also provides allele-specific oligonucleotides, kits and detection methods for detecting the mutation site.
Owner:BEIJING HOSPITAL
CYP2C9 gene segment containing 1400T>C mutation, protein segment coded by same and application thereof
ActiveCN103194464AMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesAllele-specific oligonucleotideWild type
The invention belongs to the field of biology, relates to single-base mutation, and in particular relates to a CYP2C9 gene which is corresponding to the mutation site mutated from wild type T into C on the 1400th bit of SEQ ID NO.2, a nucleic acid segment containing the mutation site, a protein segment coded by the nucleic acid segment and application thereof. The invention also provides allele specific oligonucleotide, a kit and a detection method for detecting the mutation site.
Owner:BEIJING HOSPITAL
Primers with Modified Phosphate and Base in Allele-Specific PCR
ActiveUS20140170650A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAllele-specific oligonucleotidePhosphate
The present invention includes a method of allele-specific amplification, utilizing an allele-specific oligonucleotide, at least partially complementary to more than one variant of the target sequence, but having at least one selective nucleotide complementary to only one variant of the target sequence and incorporating both a nucleotide with a base covalently modified at the exocyclic amino group and a modified phosphate.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Methods for Genotyping
InactiveUS20110217710A9Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementAllele-specific oligonucleotideGenetics
The present invention provides for methods for discriminating between alleles at polymorphic positions in a genome. In general the methods employ allele specific extension of oligonucleotides that are complementary to one of the alleles at the 3′ end of the oligonucleotide. The allele specific oligonucleotides are resistant to proof reading activity from a polymerase and may be extended in an allele specific manner by a DNA polymerase with a functional 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity. The allele specific oligonucleotides may be attached to a solid support such as a chip or a bead.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
CYP2C9 gene segment comprising 394C>T, coded protein segment and application thereof
ActiveCN103045618AMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesAllele-specific oligonucleotideWild type
The invention belongs to the field of biology, and relates to single base mutation. More particularly, the invention relates to a mutation site of a 394th site of SEQ ID NO.2 corresponding to a CYP2C9 gene, wherein the mutation site is mutated into T from wild type C. The invention also relates to a nucleic acid segment, a coded protein segment and application thereof. The invention also provides an allele-specific oligonucleotide, kit and method for detecting the mutation site.
Owner:蔡剑平
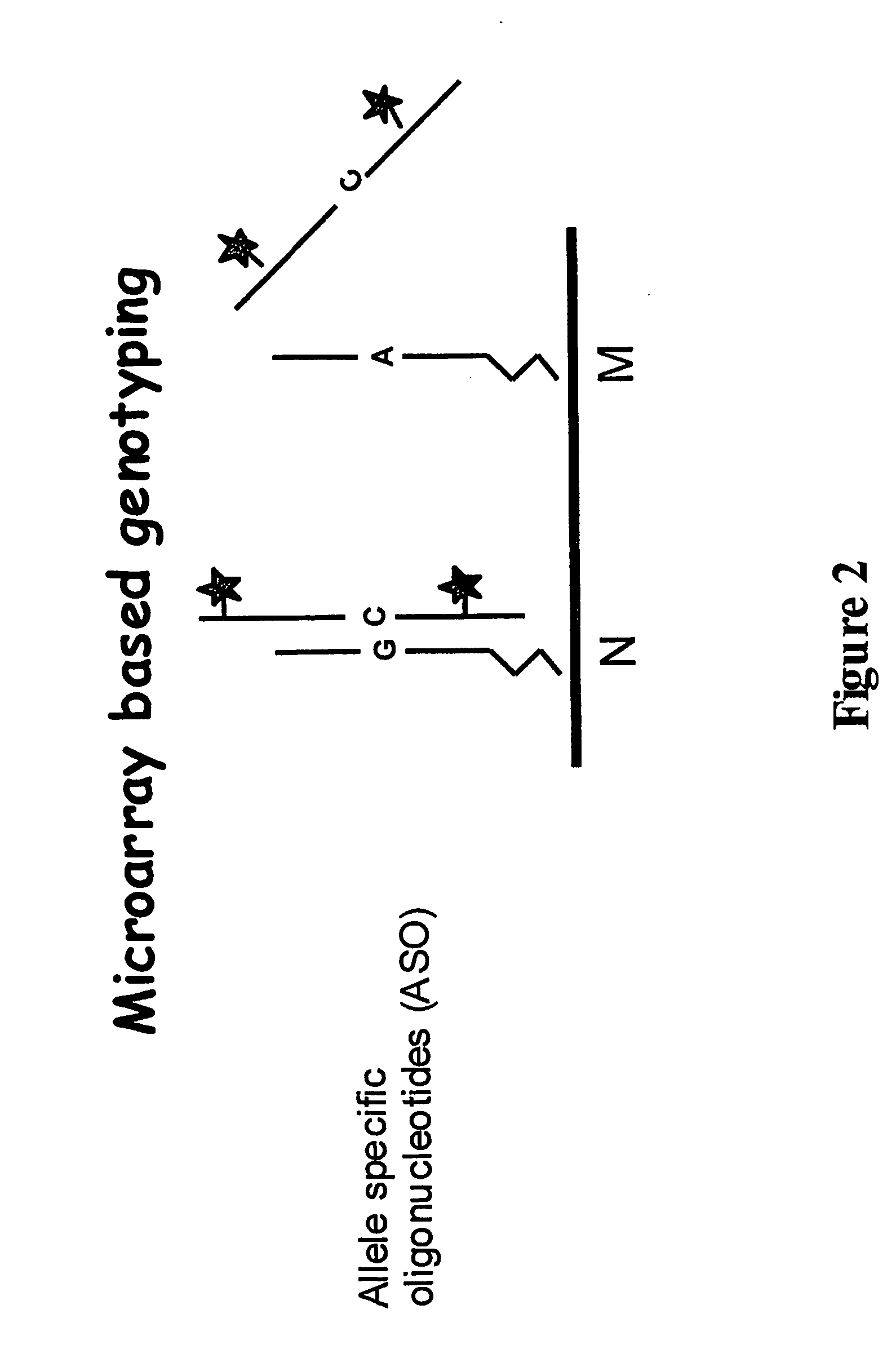
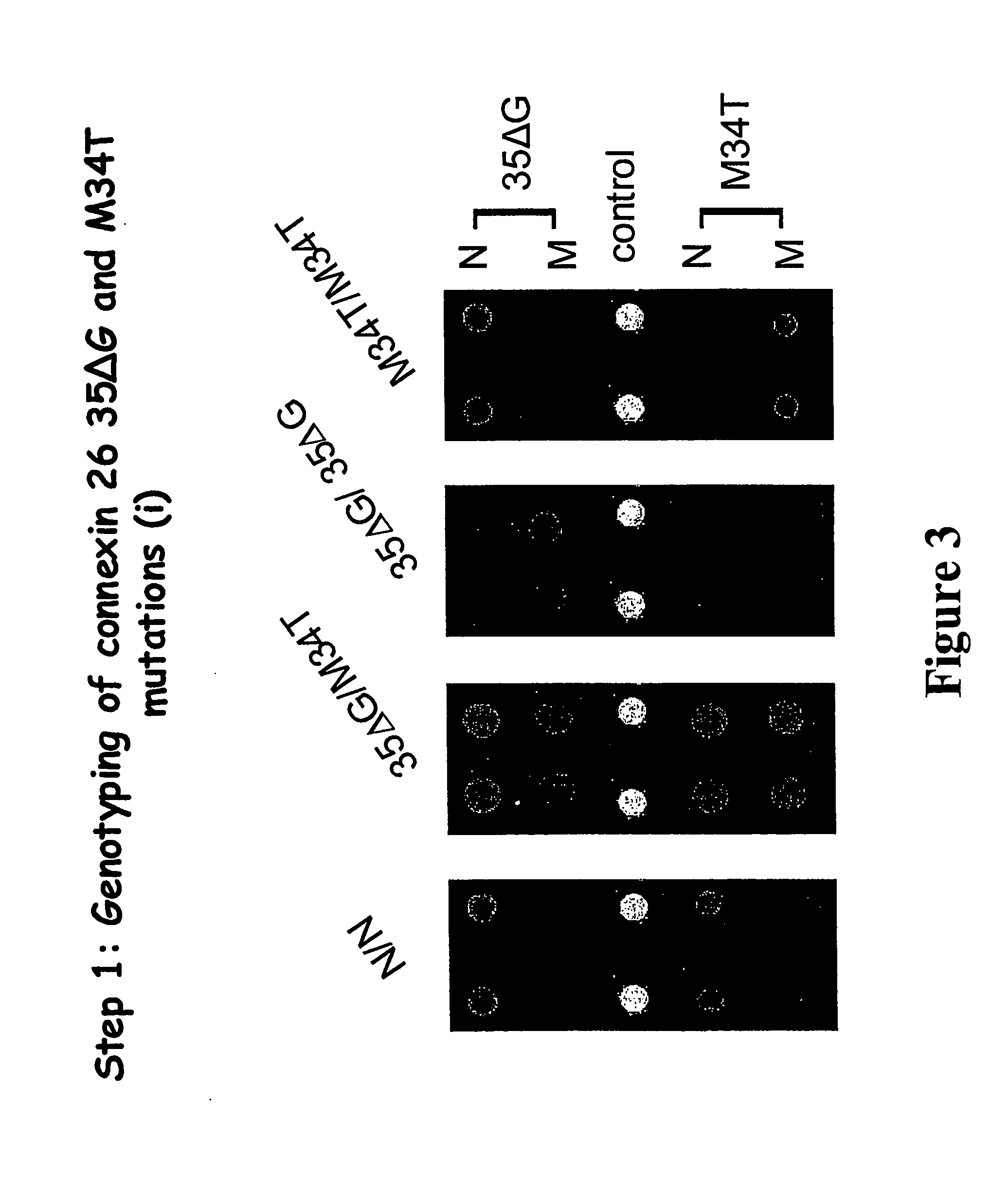
Genotyping of deafness by oligonucleotide microarray analysis
InactiveUS20070009887A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-Stranded RNATotal Deafness
A method for genotyping a subject with respect to a gene or target nucleic acid sequence associated with a pathological condition, said method comprising contacting an allele specific oligonucleotide immobilized to a solid support with a single-stranded from of RNA or DNA from a subject to be tested labeled directly or indirectly with a reporter molecule capable of giving an identifiable signal under conditions which permit hybridization of single stranded RNA or DNA which is exactly complementary to the immobilized allele specific oligonucleotide but substantially less or no hybridization of non-complementary single-stranded RNA or DNA molecules and then screening for the presence or absence or level of reporter molecule which provides an indicator of the genetic identity of the single-stranded RNA or DNA molecule which in turn provides the genotype of the subject.
Owner:MURDOCH CHILDRENS RES INST
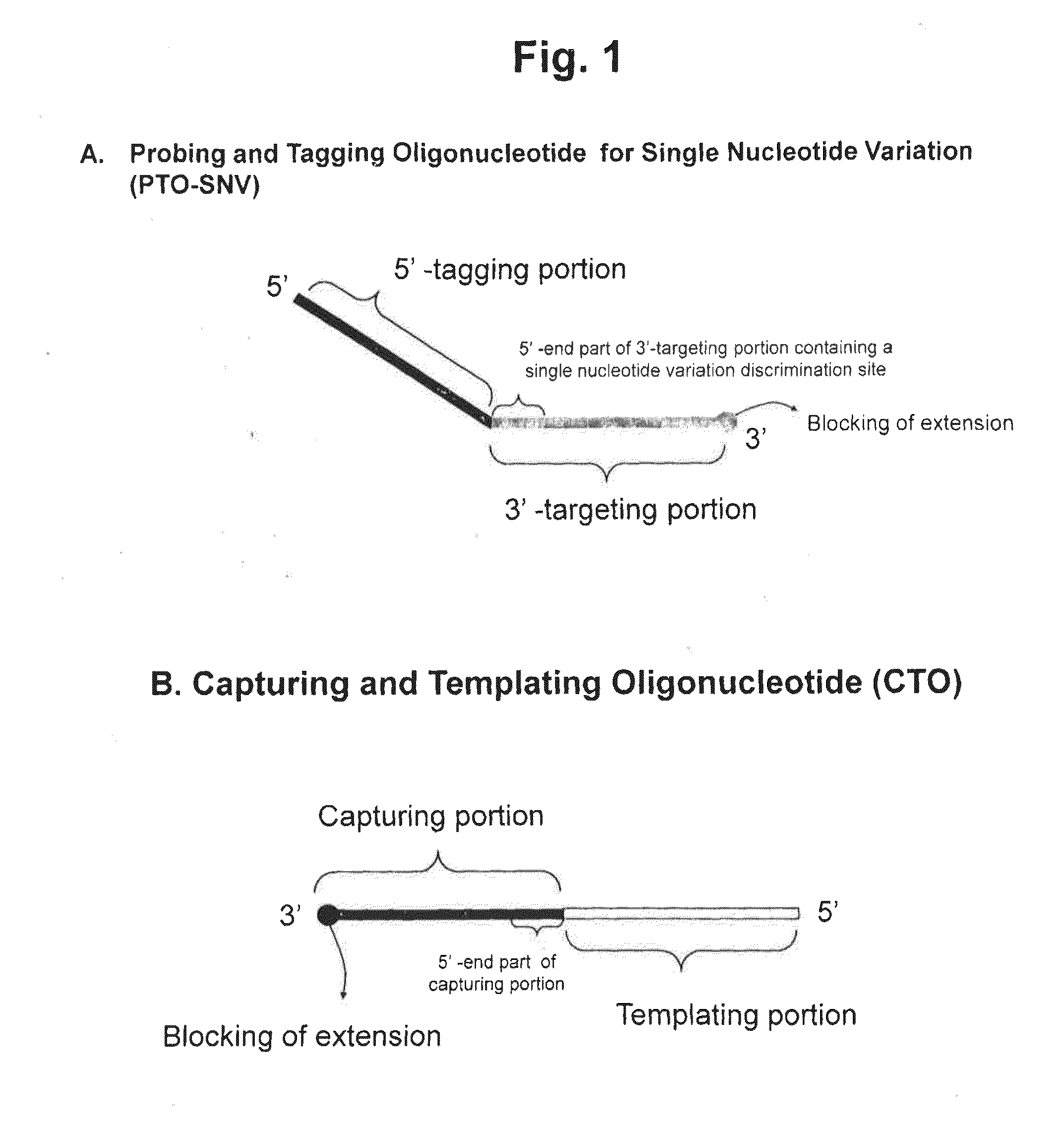
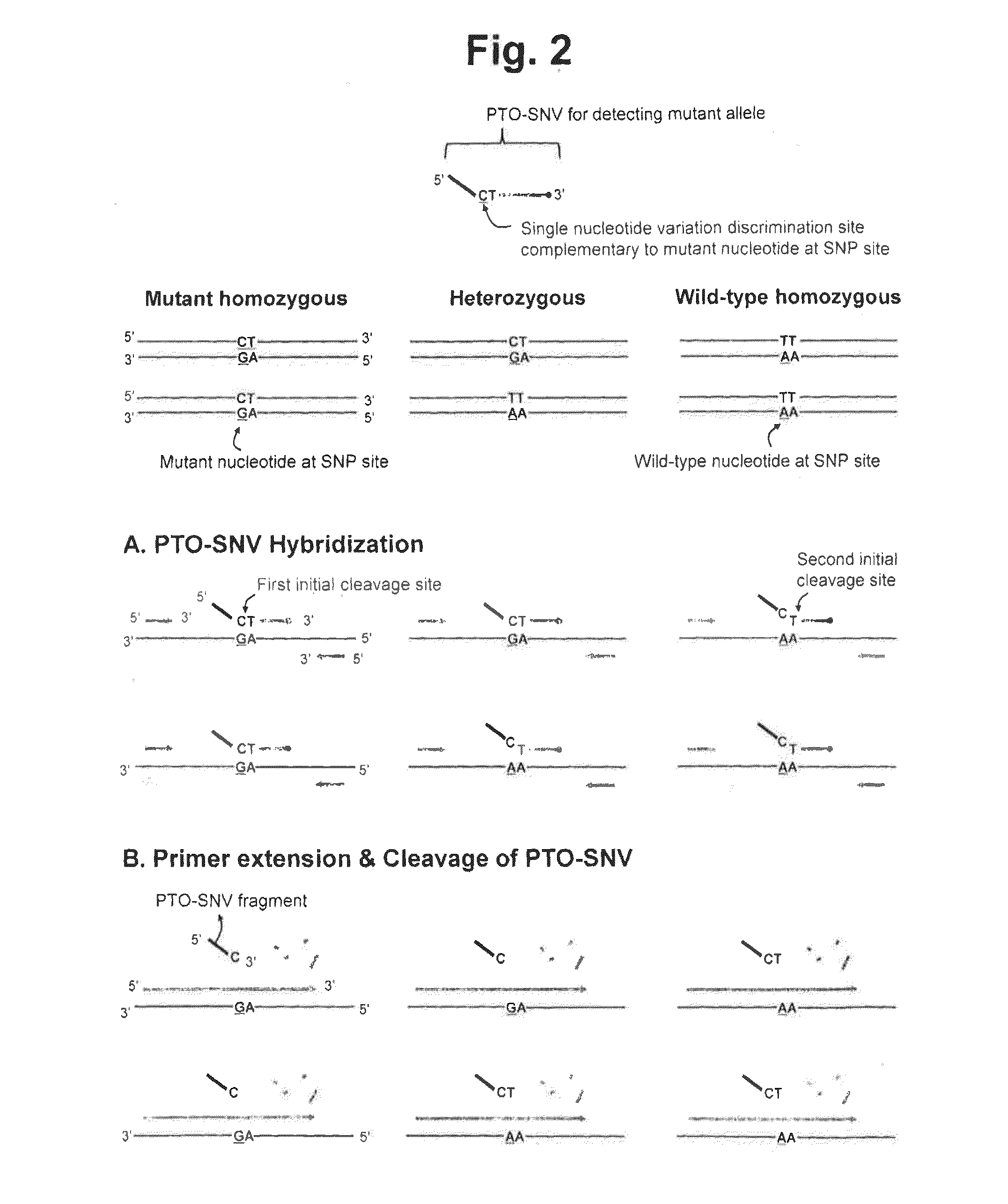
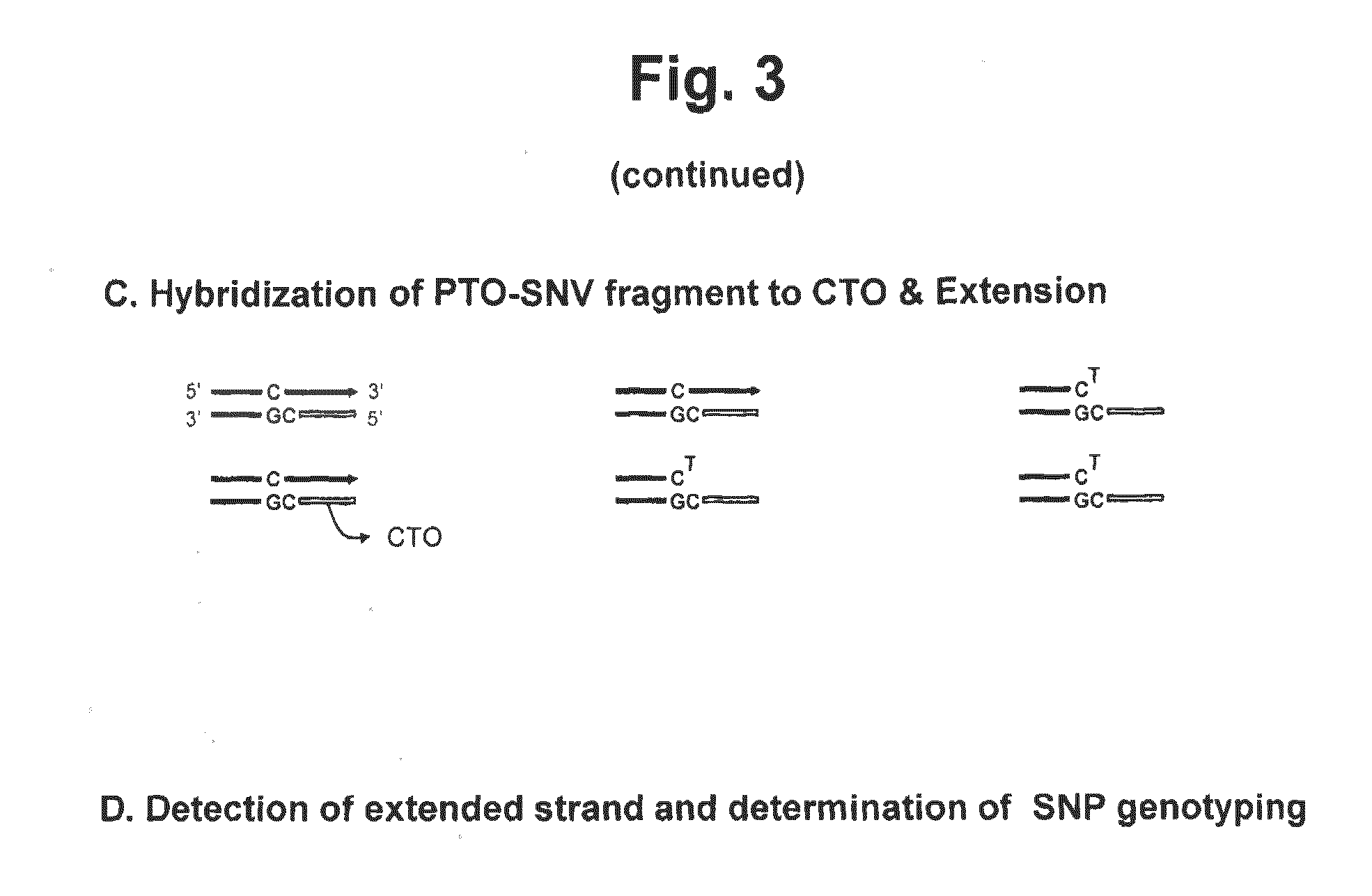
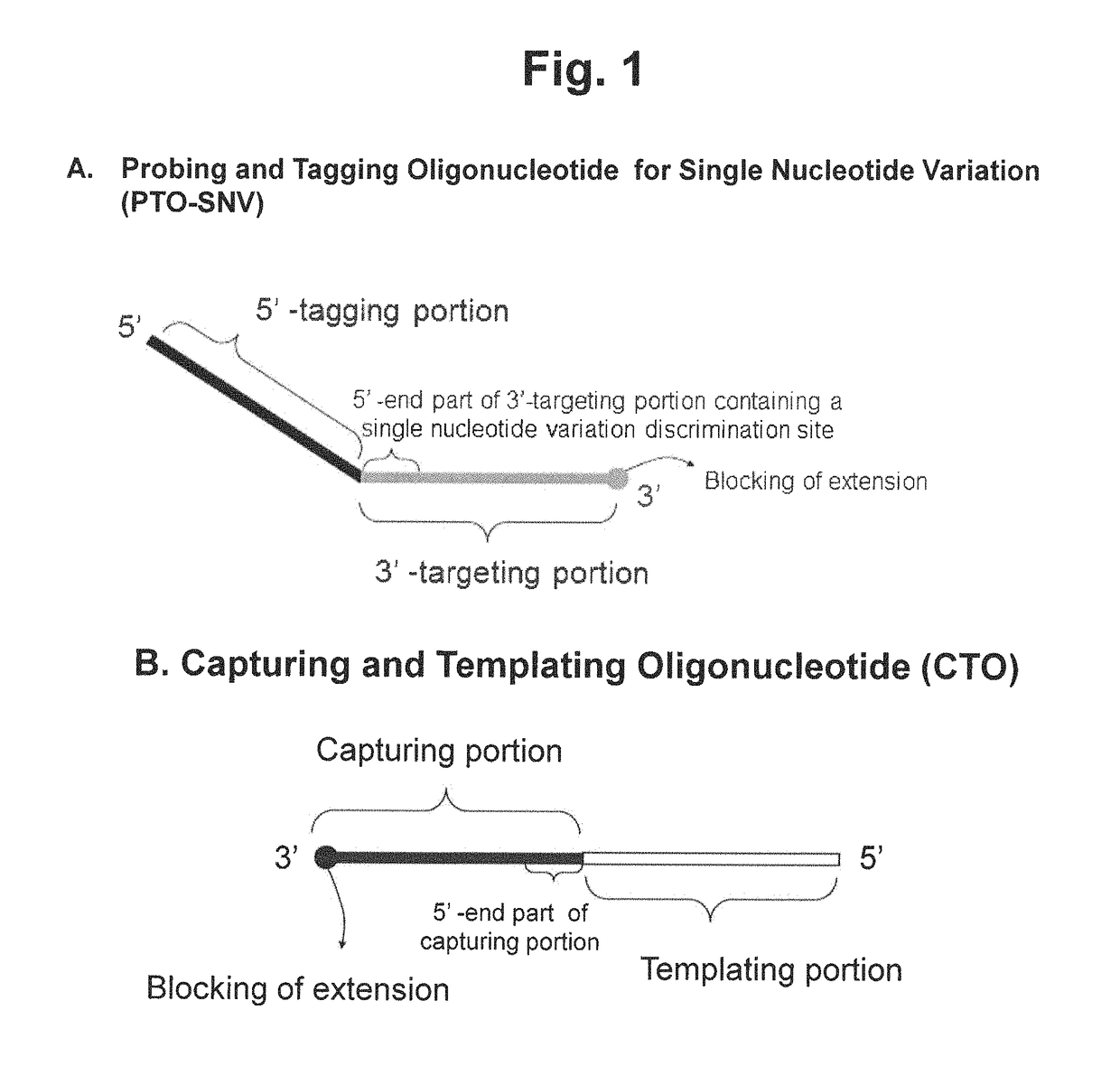
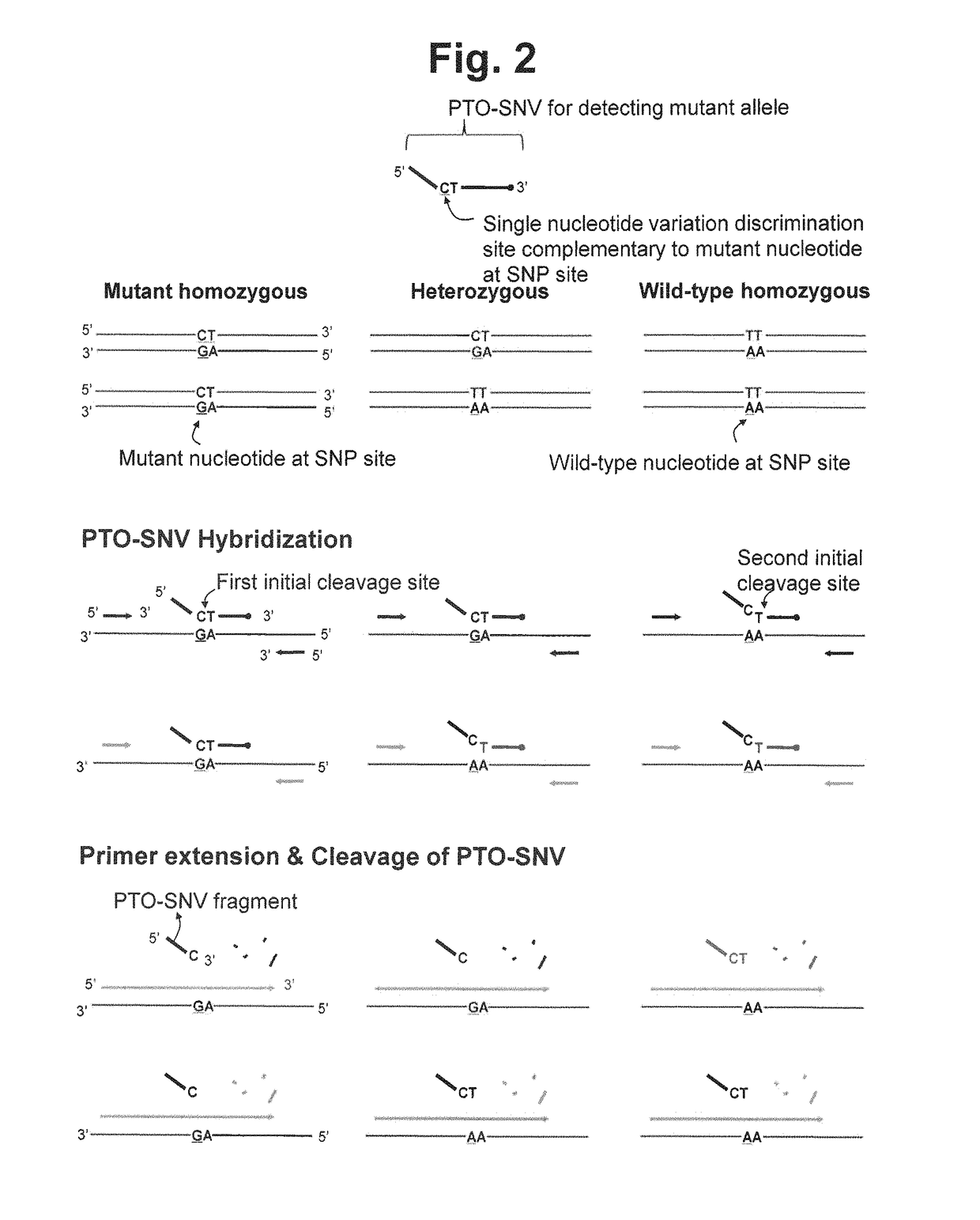
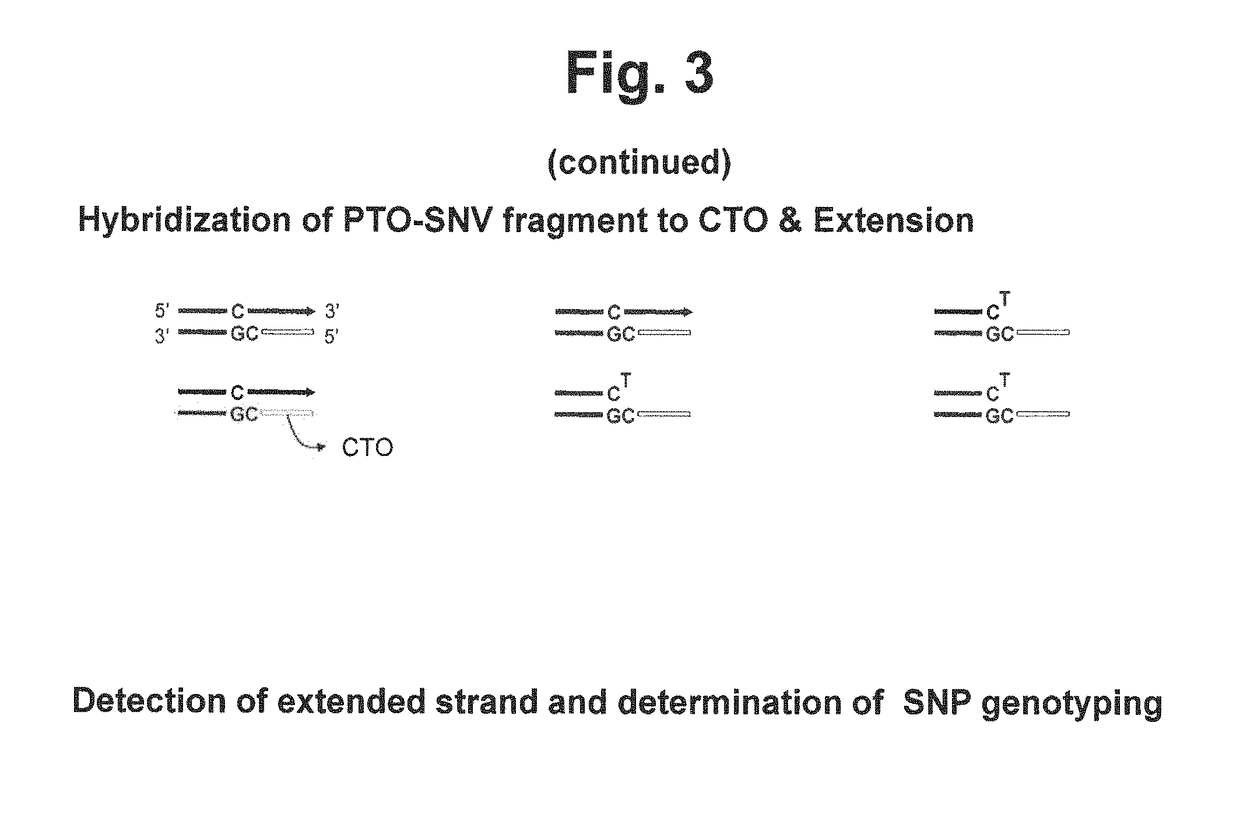
Method for determining SNP genotype
ActiveUS20160273041A1Microbiological testing/measurementAllele-specific oligonucleotideNucleotide variation
The present invention is generally drawn to a novel method for determining a SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) genotype using a PTO-SNV (Probing and Tagging Oligonucleotide for Single Nucleotide Variation). The present invention provides novel protocols for SNP genotyping in which only one allele-specific oligonucleotide permits in a SNP genotyping reaction to determine whether a target nucleic acid sequence to be analyzed is homozygous or heterozygous for the SNP allele of interest or has no SNP allele of interest.
Owner:SEEGENE INC
Method for determining SNP genotype
Owner:SEEGENE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com