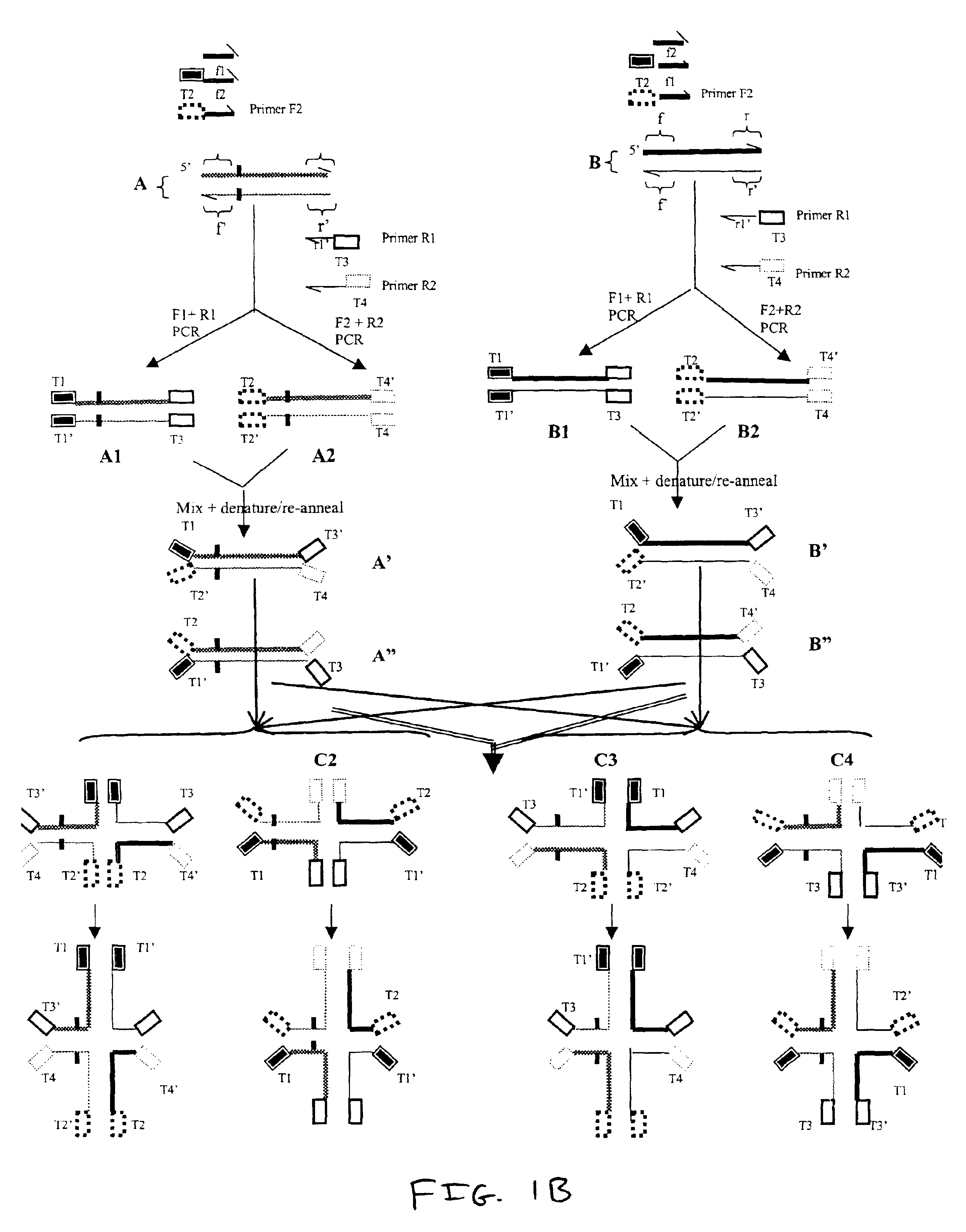
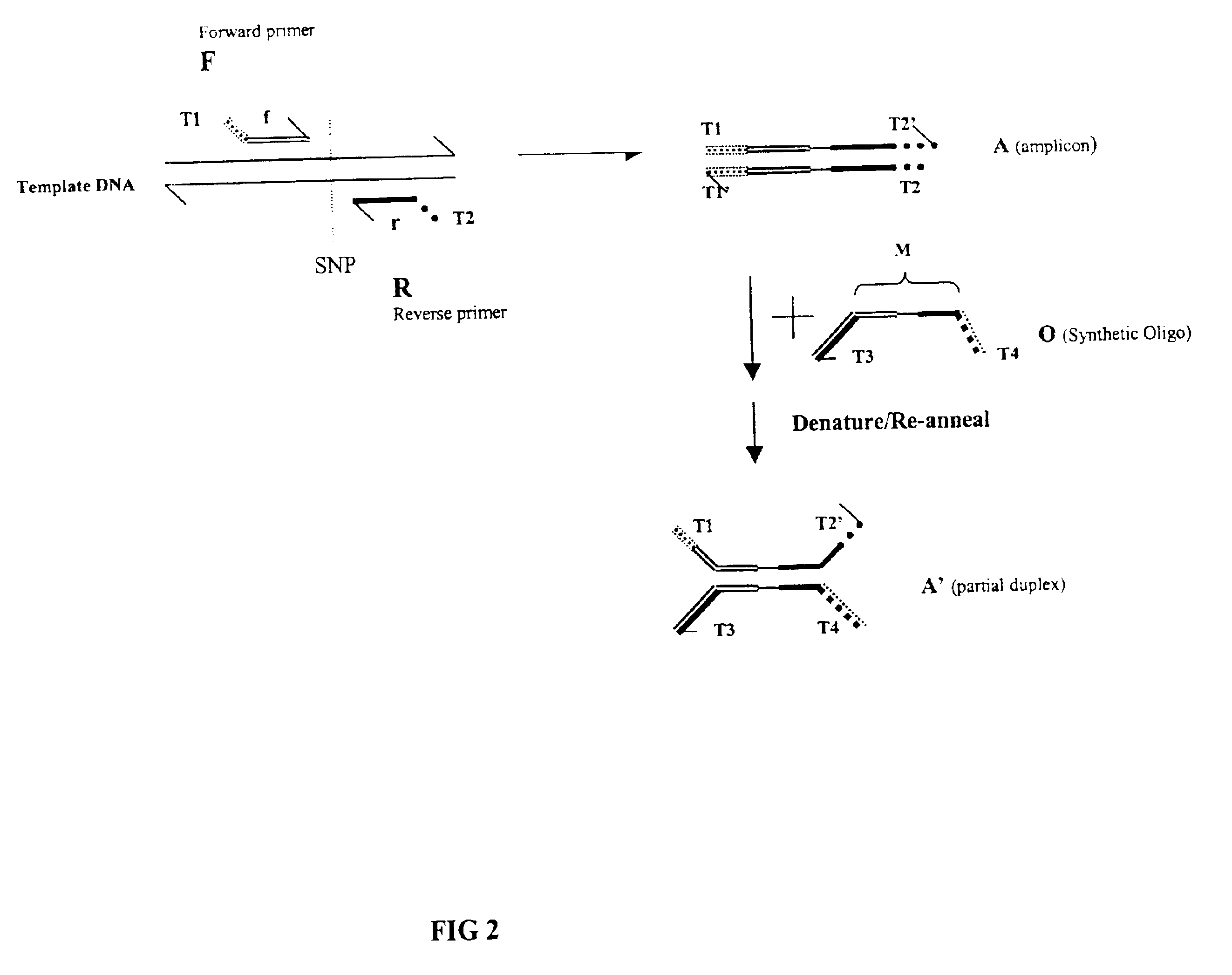
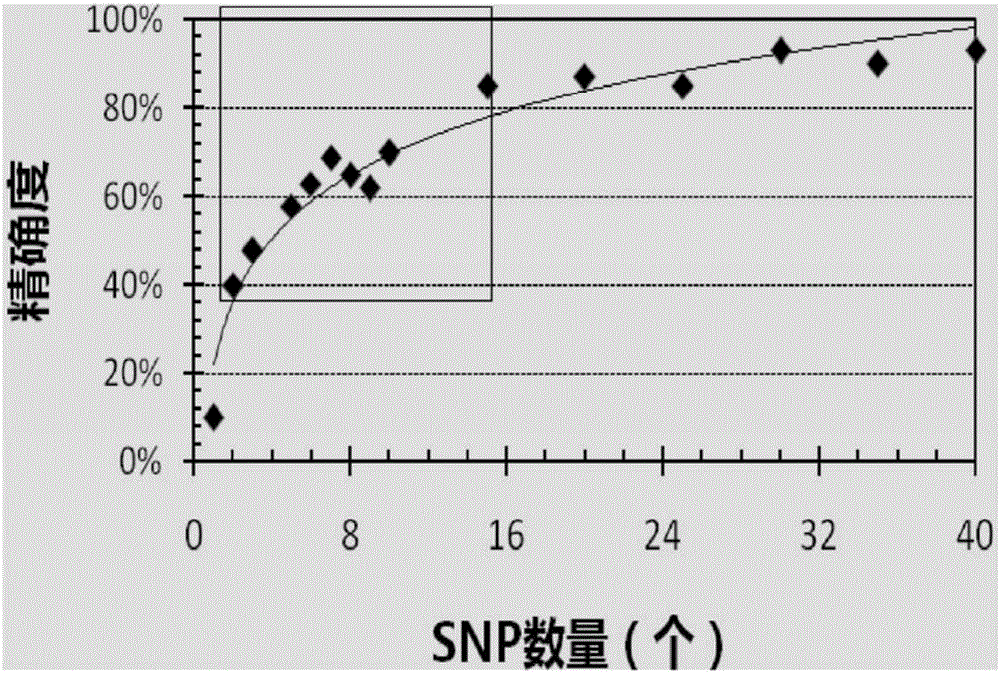
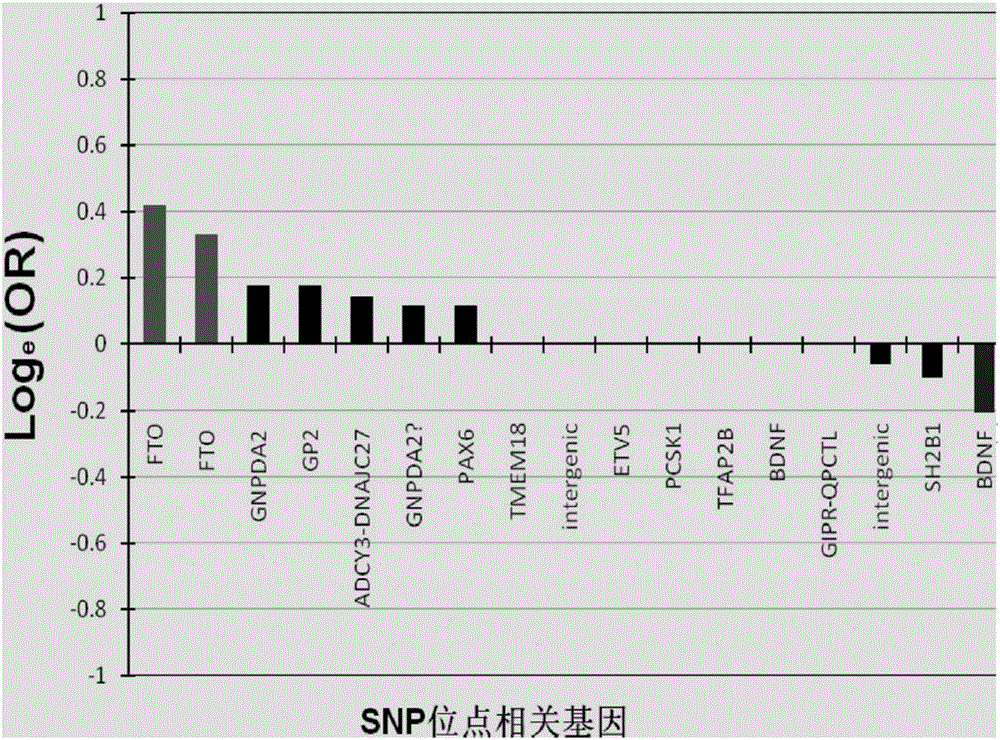
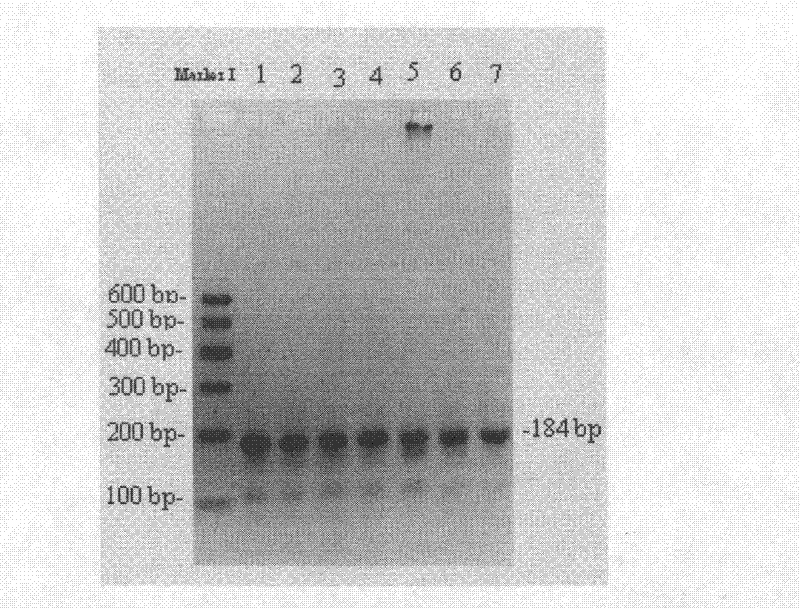
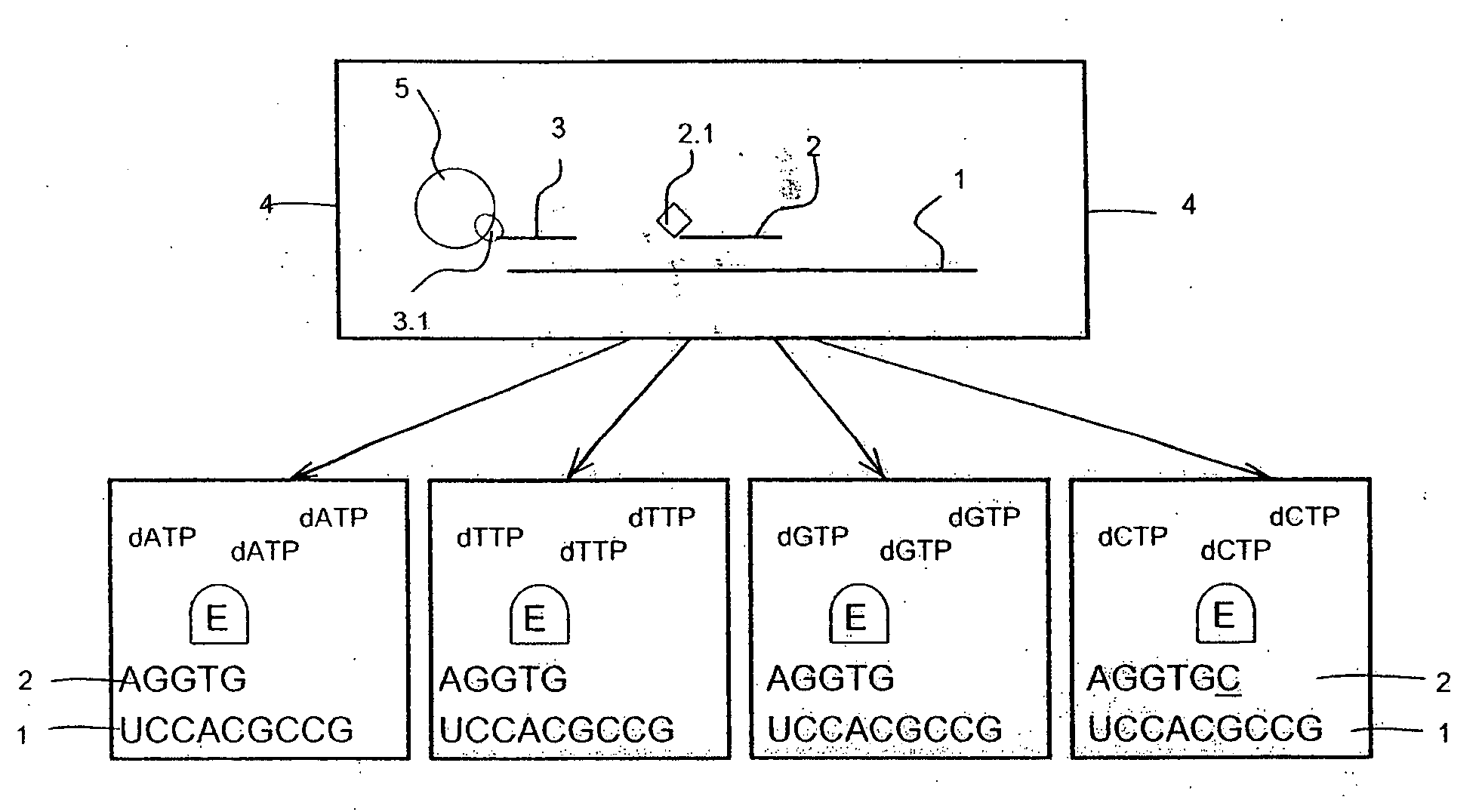
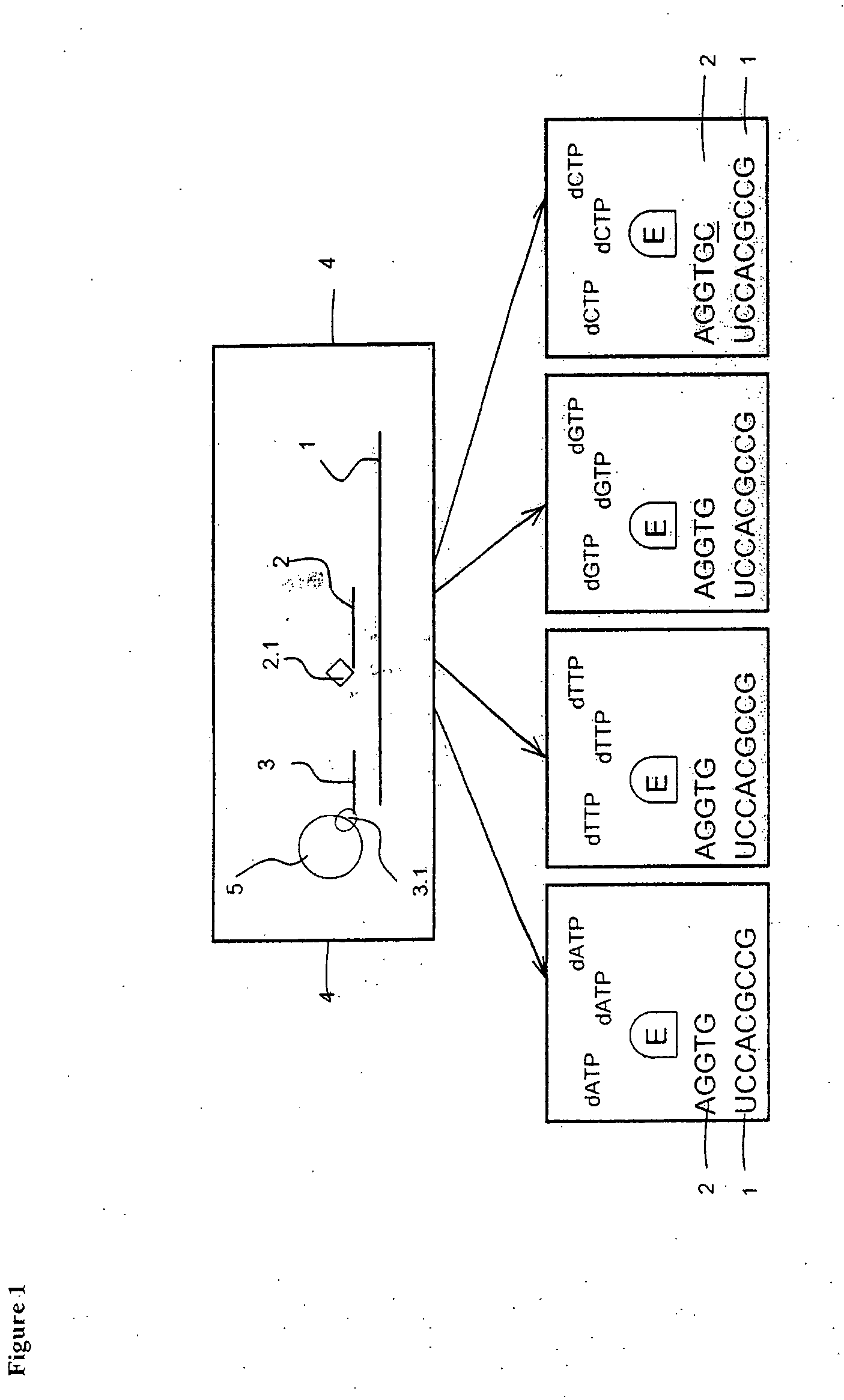
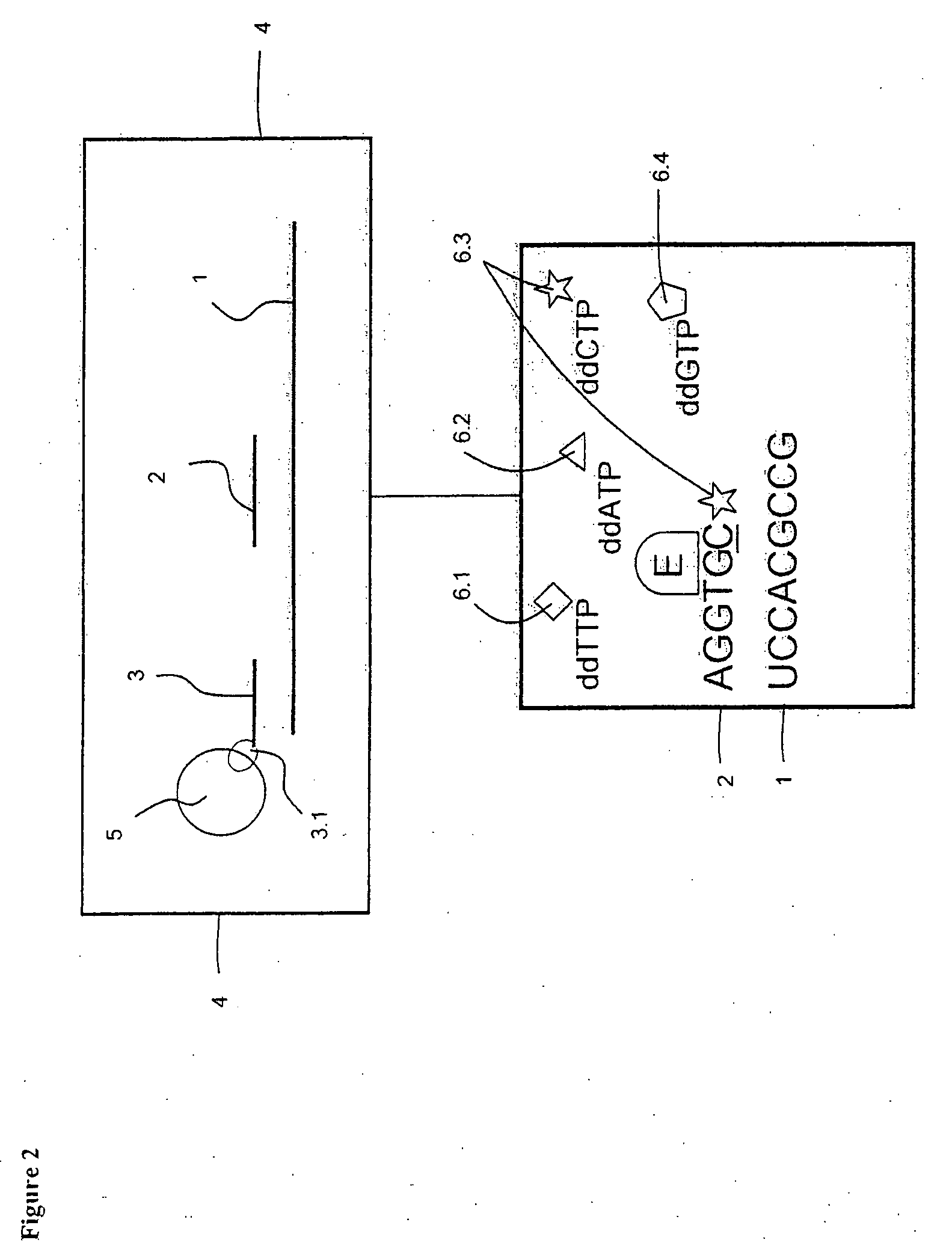
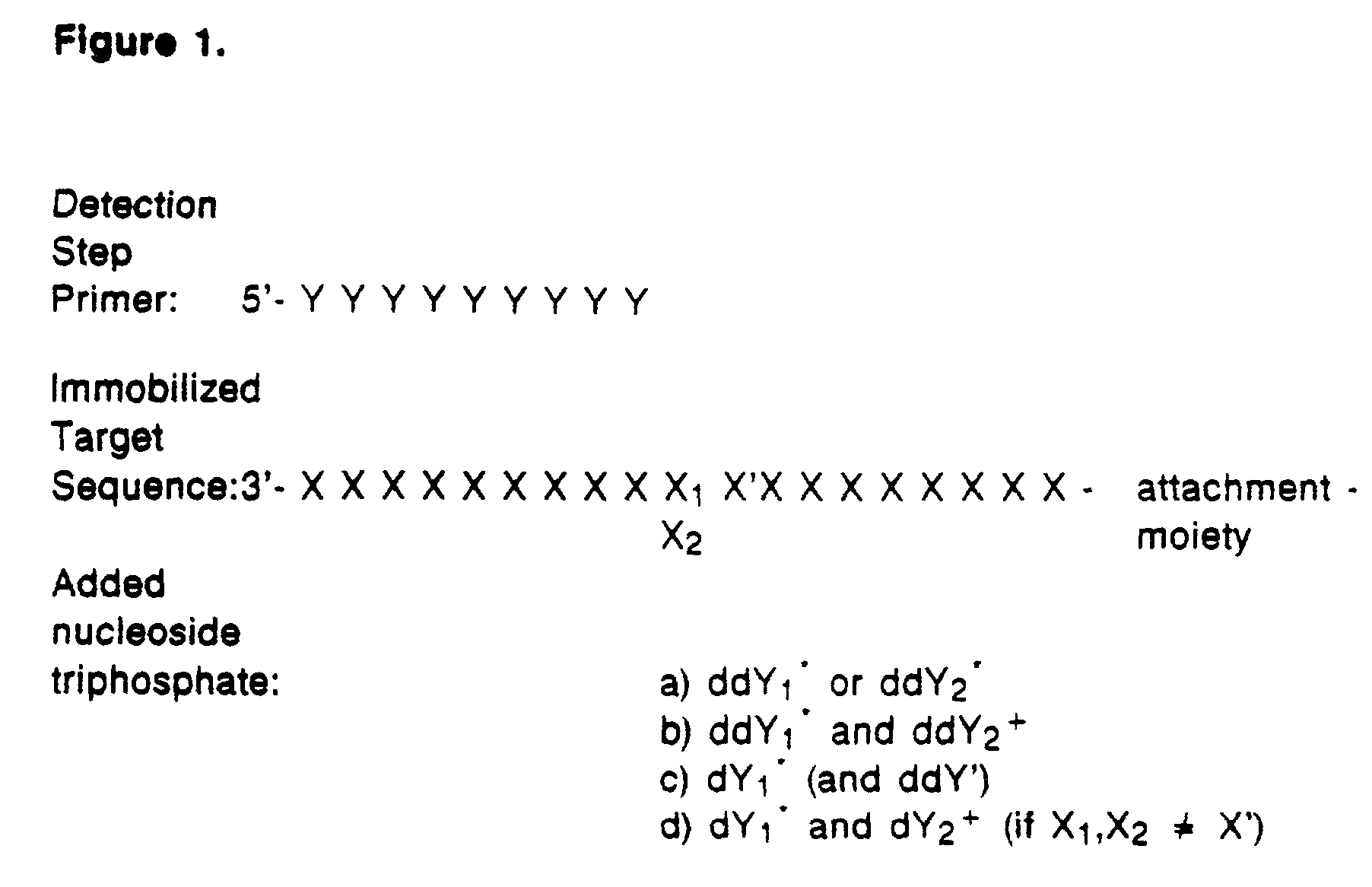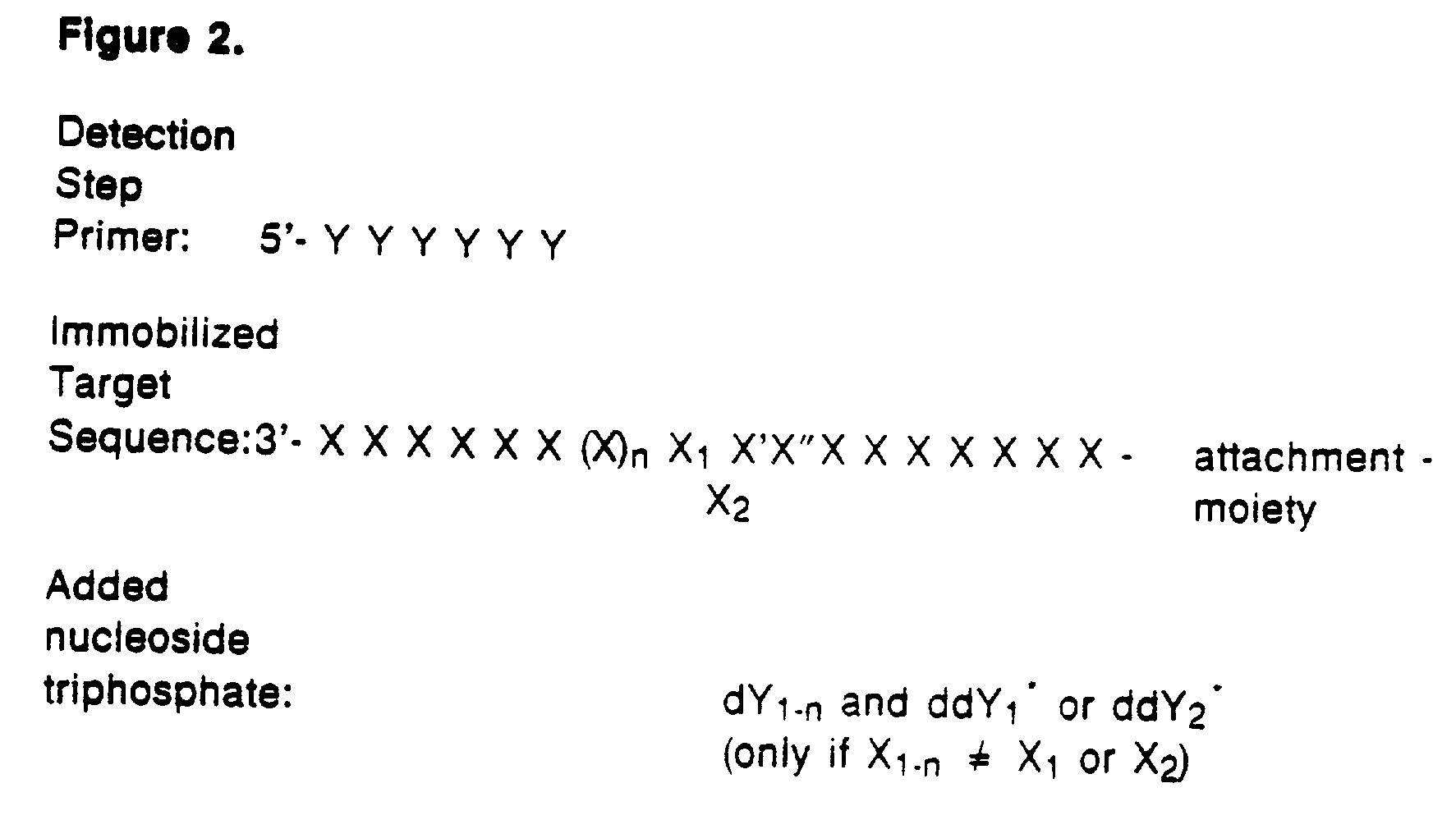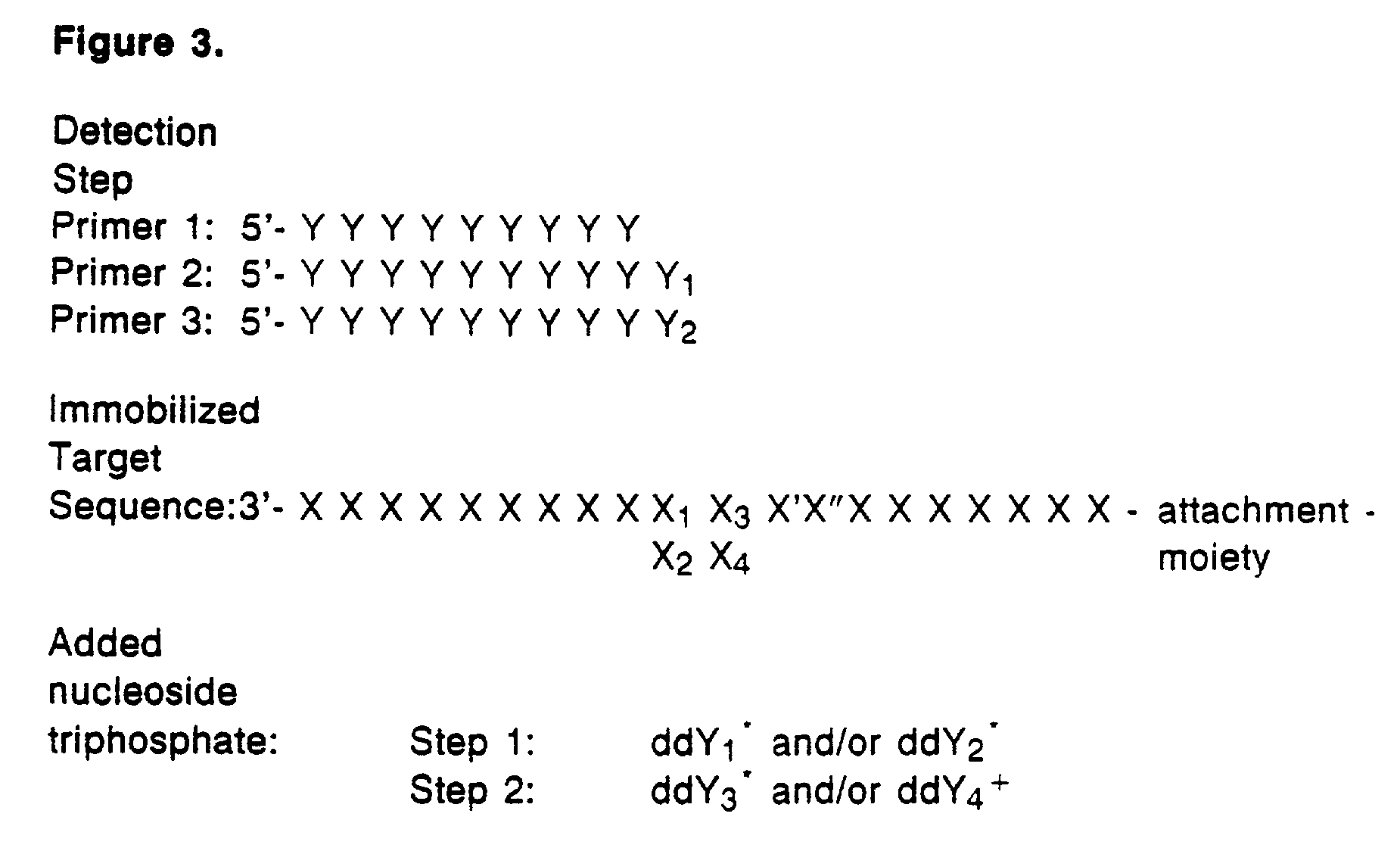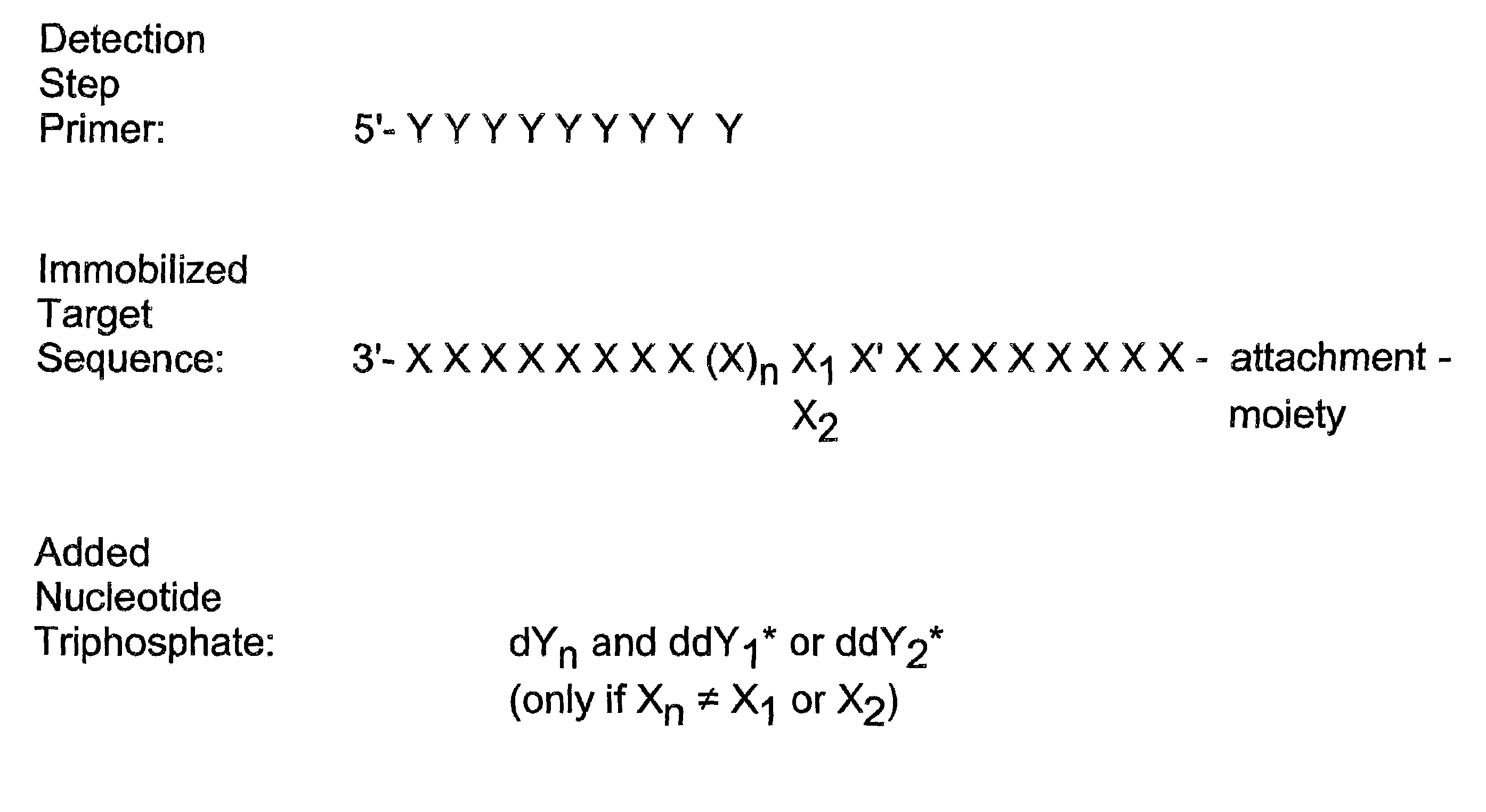Patents
Literature
84 results about "Nucleotide variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A single-nucleotide polymorphism, often abbreviated to SNP (/snɪp/; plural /snɪps/), is a substitution of a single nucleotide that occurs at a specific position in the genome, where each variation is present to some appreciable degree within a population (e.g. > 1%).
Methods for cancer detection and monitoring
PendingUS20190316184A1Minimize dimer formationHealth-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementLymphatic SpreadEarly Relapse
The invention provides methods for detecting single nucleotide variants in breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer. Additional methods and compositions, such as reaction mixtures and solid supports comprising clonal populations of nucleic acids, are provided. For example, provided here is a method for monitoring and detection of early relapse or metastasis of breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer, comprising generating a set of amplicons by performing a multiplex amplification reaction on nucleic acids isolated from a sample of blood or urine or a fraction thereof from a patient who has been treated for a breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer, wherein each amplicon of the set of amplicons spans at least one single nucleotide variant locus of a set of patient-specific single nucleotide variant loci associated with the breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer; and determining the sequence of at least a segment of each amplicon of the set of amplicons that comprises a patient-specific single nucleotide variant locus, wherein detection of one or more patient-specific single nucleotide variants is indicative of early relapse or metastasis of breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer.
Owner:NATERA
Methods and kits for the detection of nucleotide mutations using peptide nucleic acid as both PCR clamp and sensor probe
Disclosed herein is a method for determining whether a target polynucleotide sequence contained in a nucleic acid sample has nucleotide variation(s) in a selected region thereof, the steps of which involve the use of a pair of primers that allows the formation of a PCR product having a sequence covering that of the selected region of the target polynucleotide sequence via a PCR process, and a peptide nucleic acid (PNA) that acts as a PCR clamp as well as a sensor probe. Also disclosed herein is a kit for use in determining the presence of nucleotide variation(s) in the target polynucleotide sequence, which includes the pair of primers and the PNA.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
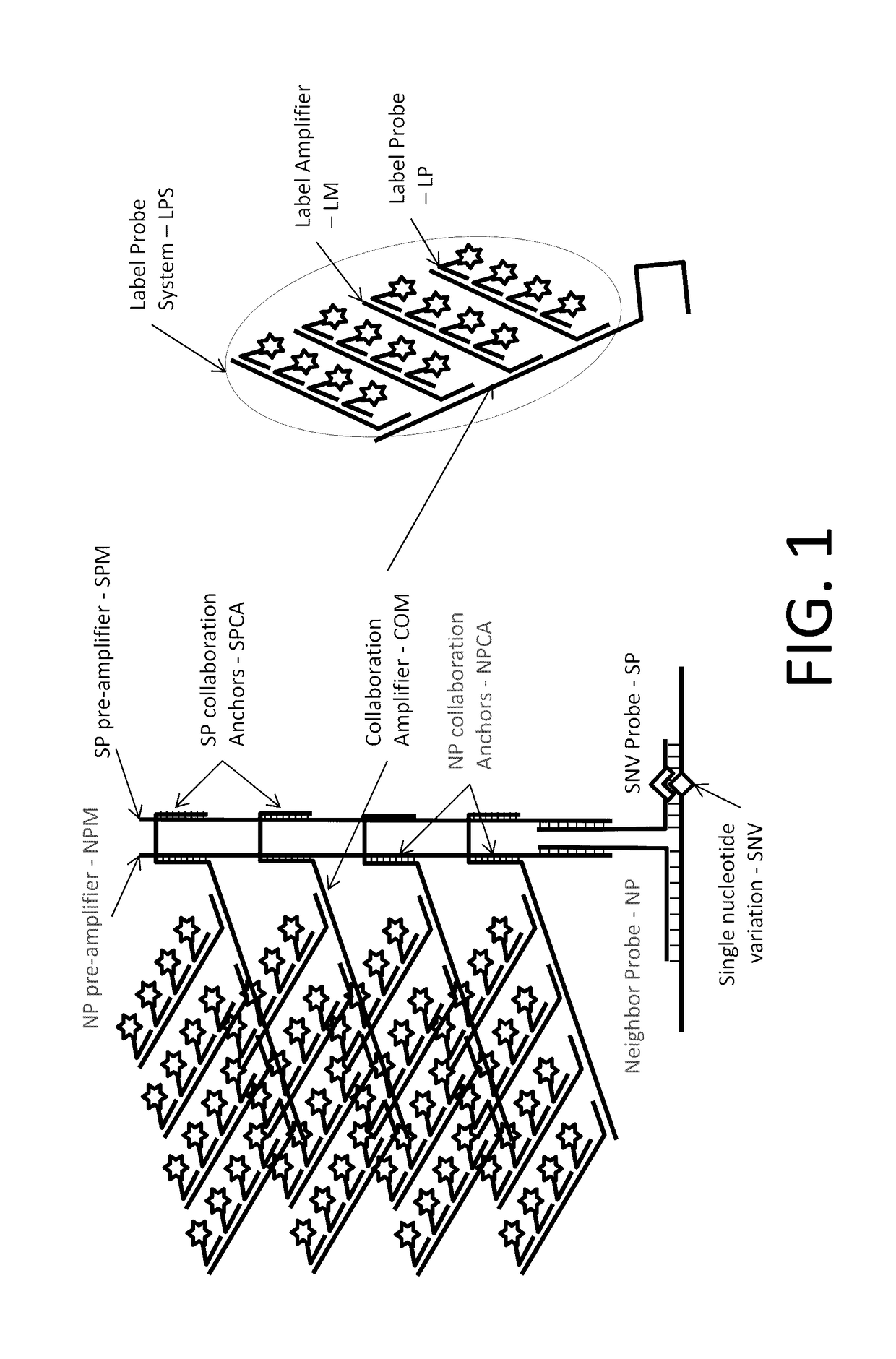
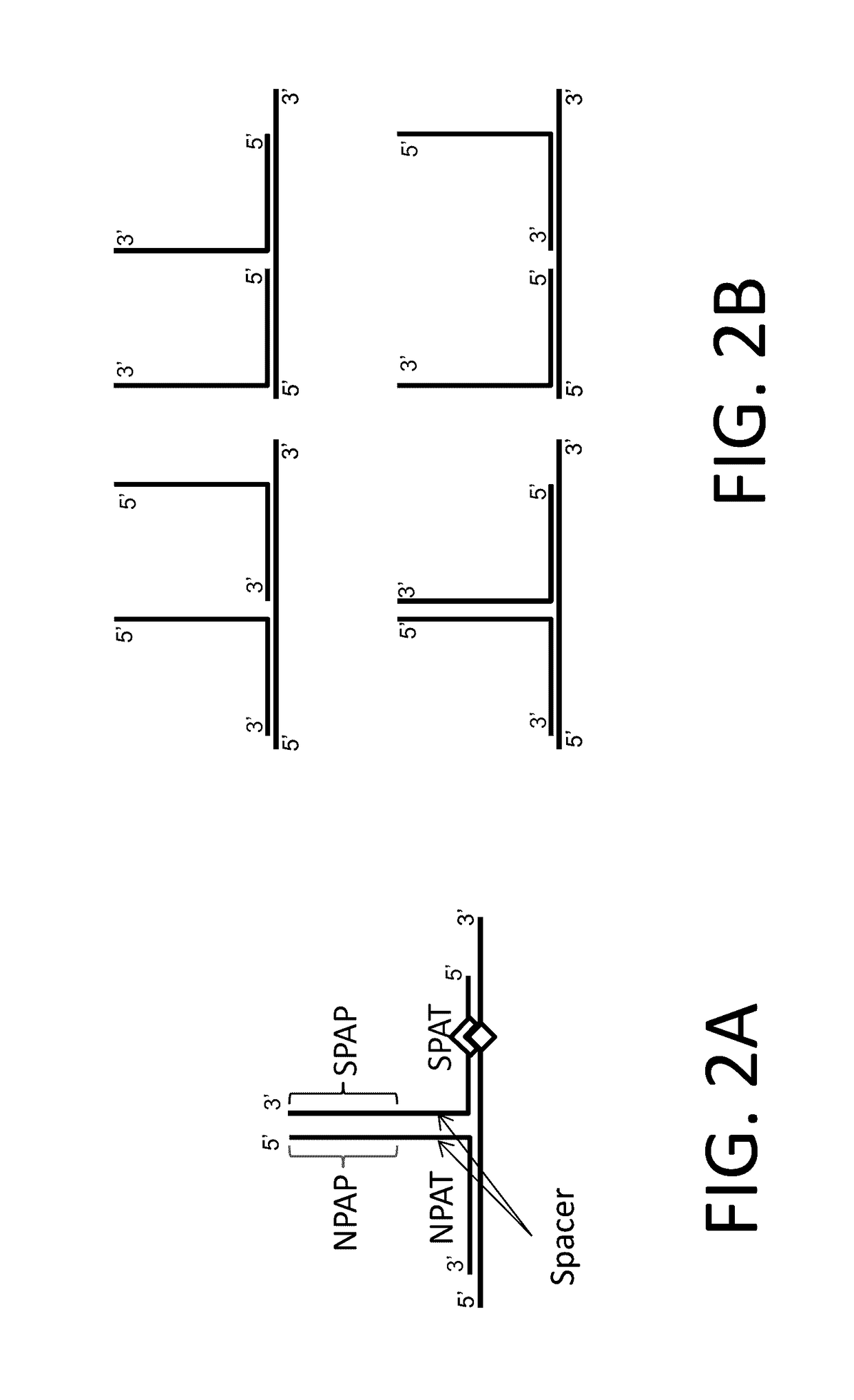
In situ detection of nucleotide variants in high noise samples, and compositions and methods related thereto
The invention relates to methods of in situ detection of a nucleic acid variation of a target nucleic acid in a sample, including single nucleotide variations, multi-nucleotide variations or splice sites. The method can comprise the steps of contacting the sample with a probe that detects the nucleic acid variation or splice site and a neighbor probe; contacting the sample with pre-amplifiers that bind to the nucleic acid variation probe or splice site probe and neighbor probe, respectively; contacting the sample with a collaboration amplifier that binds to the pre-amplifiers; and contacting the sample with a label probe system, wherein hybridization of the components forms a signal generating complex (SGC) comprising a target nucleic acid with the nucleic acid variation or splice site, the probes and amplifiers; and detecting in situ signal from the SGC on the sample. The invention also provides samples, tissue slides, and kits relating to detection of nucleic acid variations, including single nucleotide variations, multi-nucleotide variations or splice sites, of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL DIAGNOSTICS INC
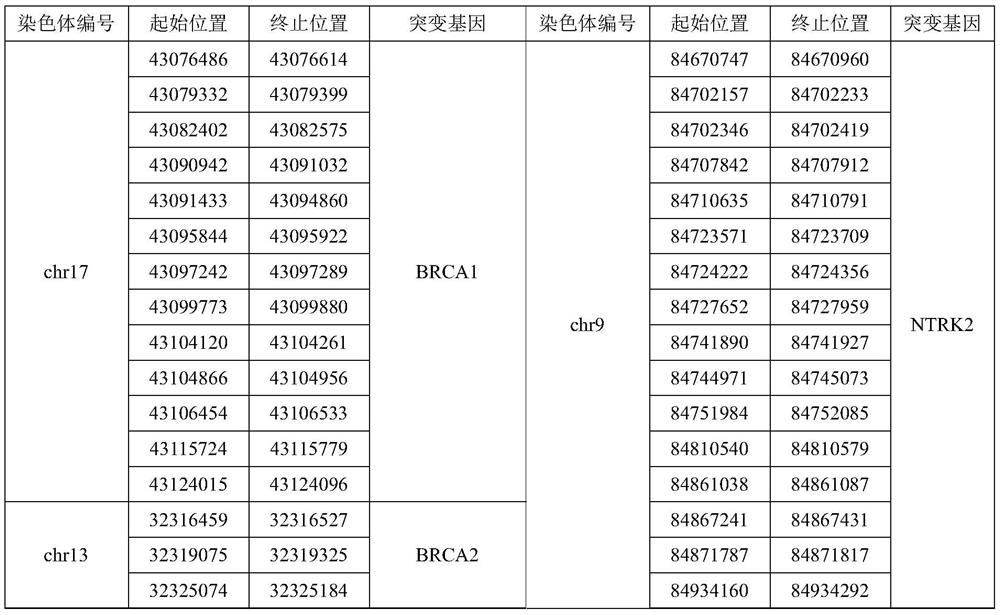
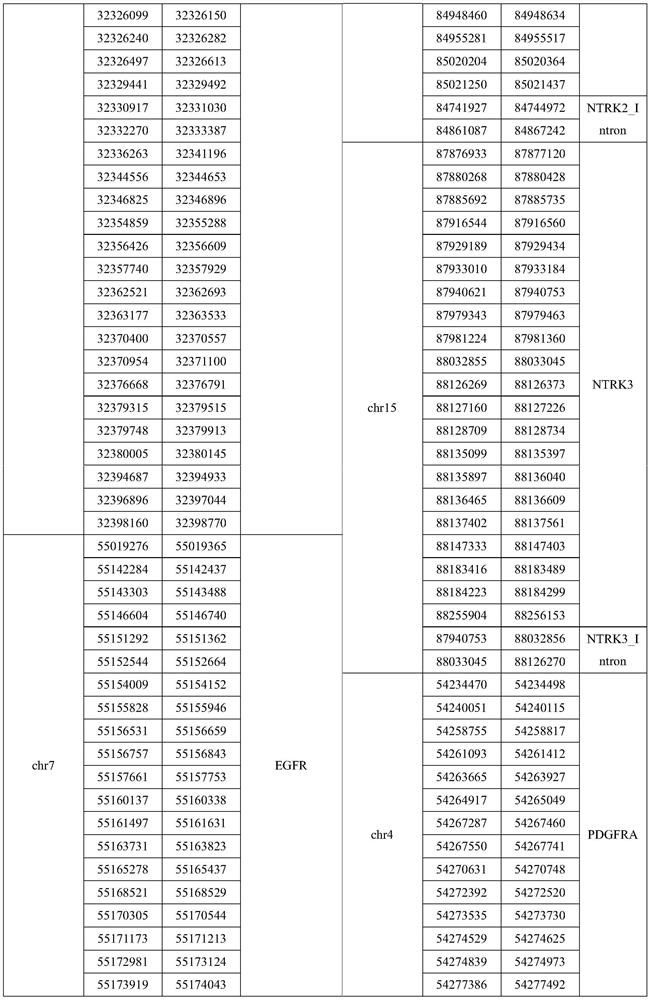
Gene panel used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation, detection method used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation and application of gene panel
InactiveCN111647648AComprehensive immunotherapyComprehensive treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
The invention relates to a gene panel used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation, and a detection method and application of the gene panel. The panel disclosed by the invention comprises 54419 pieces of targeted DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) probes. The targeted DNA comprises the exon regions of 445 pieces of genes on the human genomes, 2573 pieces of MSI (microsatellite instability) sites and 566 position intervals used for detecting gene fusion. The detection method in the invention can be used for detecting SNV (single nucleotide variation), Indel (Insertion and Deletion), CNV (Copy Number Variation), Fusion, MSI, TMB (Tumor Mutational Burden), HLA (human leucocyte antigen) parting and the like of a tumor somatic cell multi-site DNA mutation. An optimal individual treatment medicine and scheme can be conveniently selected according to the genome features of patients in a breast cancer immunotherapy process.
Owner:北斗生命科学(广州)有限公司 +1
Methods and compositions for detecting differences between nucleic acids
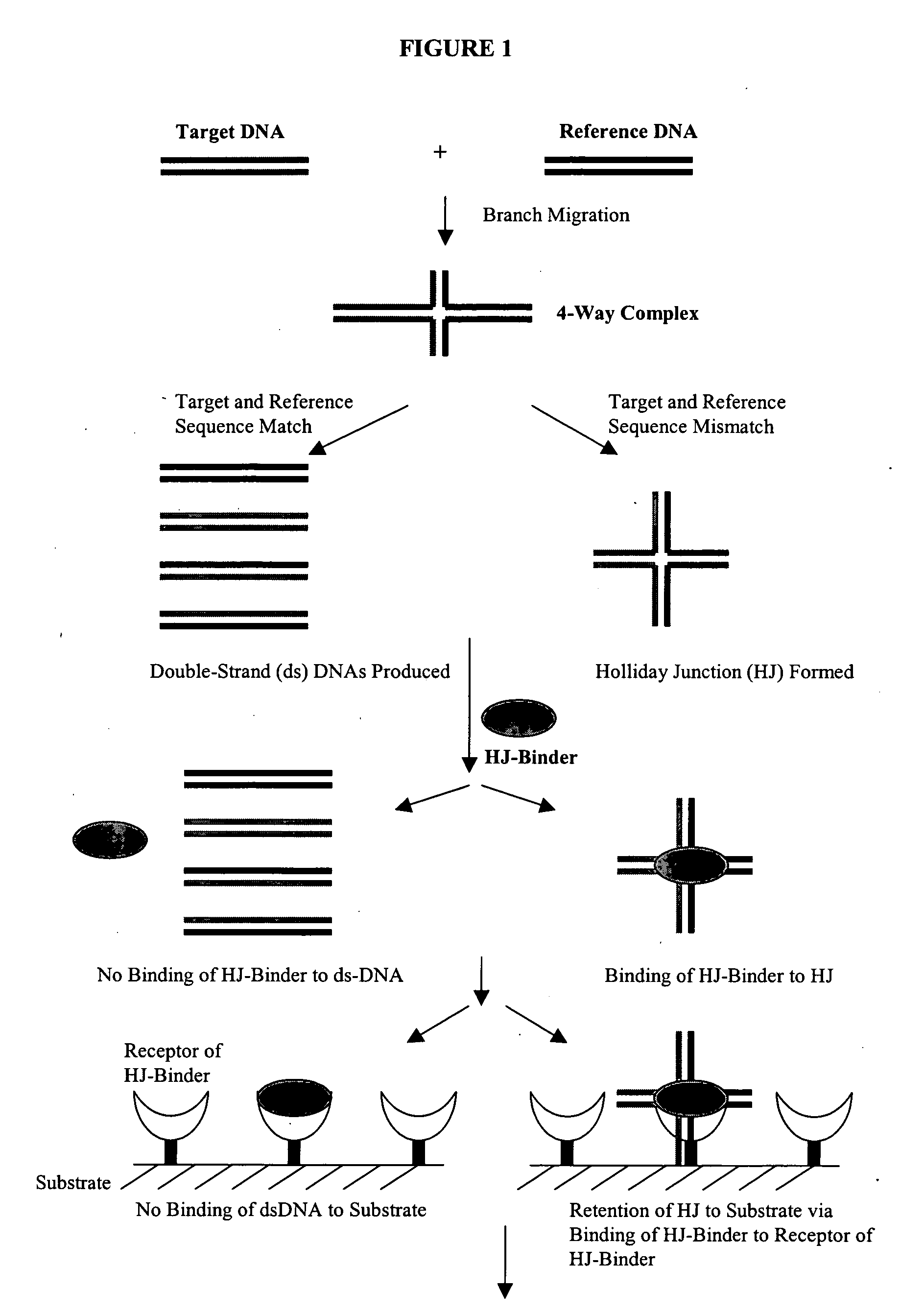
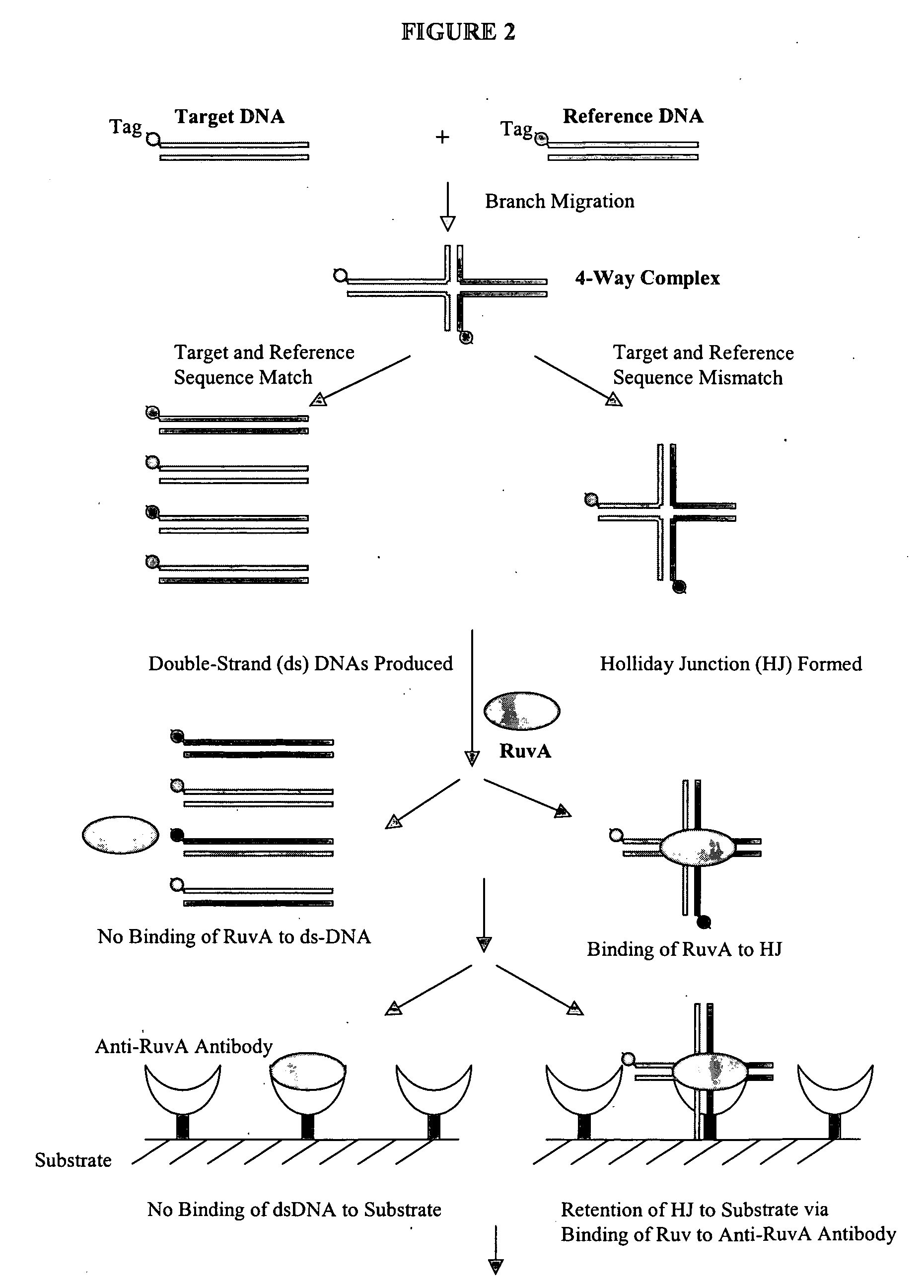
The present invention provides sensitive methods for detecting the presence or absence of a difference between related nucleic acid sequences. In one aspect of the invention, a method is provided for detecting a difference in the sequence of two nucleic acid molecules. The method includes the steps of: contacting two nucleic acids under conditions that allow the formation of a four-way complex and branch migration; contacting the four-way complex with a tracer molecule and a detection molecule under conditions in which the detection molecule is capable of binding the tracer molecule or the four-way complex; and determining binding of the tracer molecule to the detection molecule before and after exposure to the four-way complex. Competition of the four-way complex with the tracer molecule for binding to the detection molecule indicates a difference between the two nucleic acids. The methods disclosed can be used for detecting nucleotide variations or mutations of an organism, for example, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), which leads to identification of genetic traits associated with diseases or other phenotypic characteristics.
Owner:PANOMICS
Personalized genetic typing guidance body building and weight losing method and equipment application thereof
InactiveCN105821136AEasy to useHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationPersonalizationHuman DNA sequencing
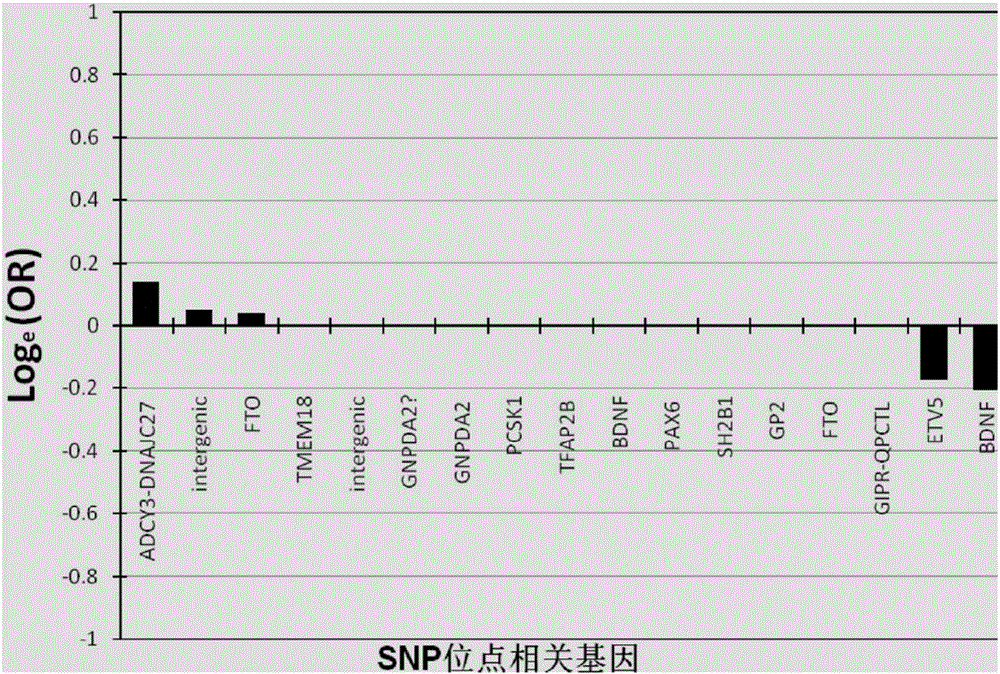
The invention relates to data related to influences of different kinds of fat intake on obesity and influences of different types of sports on weight reduction and blood glucose reduction in disclosed human genome single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) data. According to genetic differences between individuals, a method suitable for determining main reasons of obesity and making personalized diet schemes or giving suggestions about lifestyles is built, and the method is applied to development of wearable mobile devices and application software. The invention further relates to preparation and application of genetic chips related to detection. The personalized weight losing and body building schemes can reasonably, efficiently and selectively use modern sports exercise means and diet regulation according to personal gene characteristics, so that individuals achieve the aims of diet regulation and exercise planning more scientifically and more quickly.
Owner:SHANGHAI MIJIAN BIOTECH CO LTD
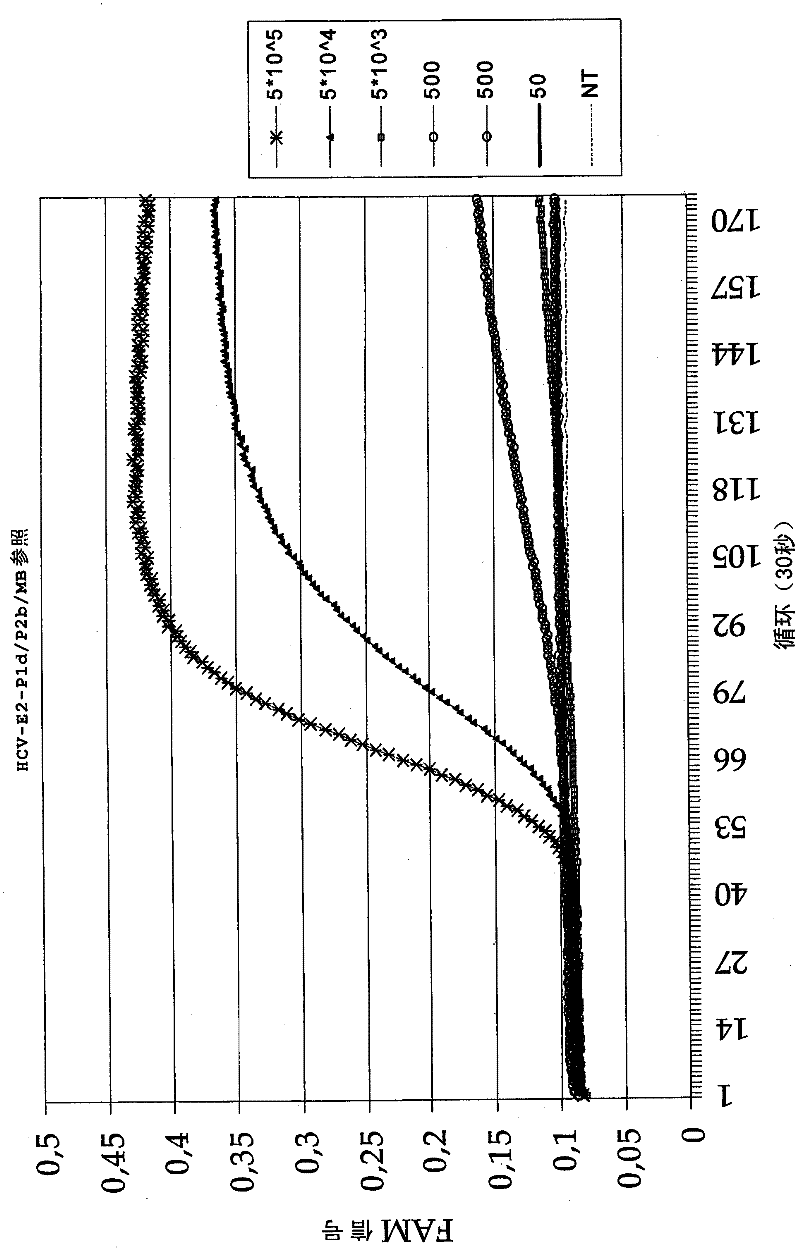
NS5A nucleotide sequence variation as a marker for interferon response
InactiveUS20050260567A1Raise the possibilitySustained responseSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementInterferon therapyNucleotide variation
Methods and reagents for determining a nucleotide variation at position 937 of the HCV-1a NS5A gene useful in predicting an individual's response to interferon treatment are presented.
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
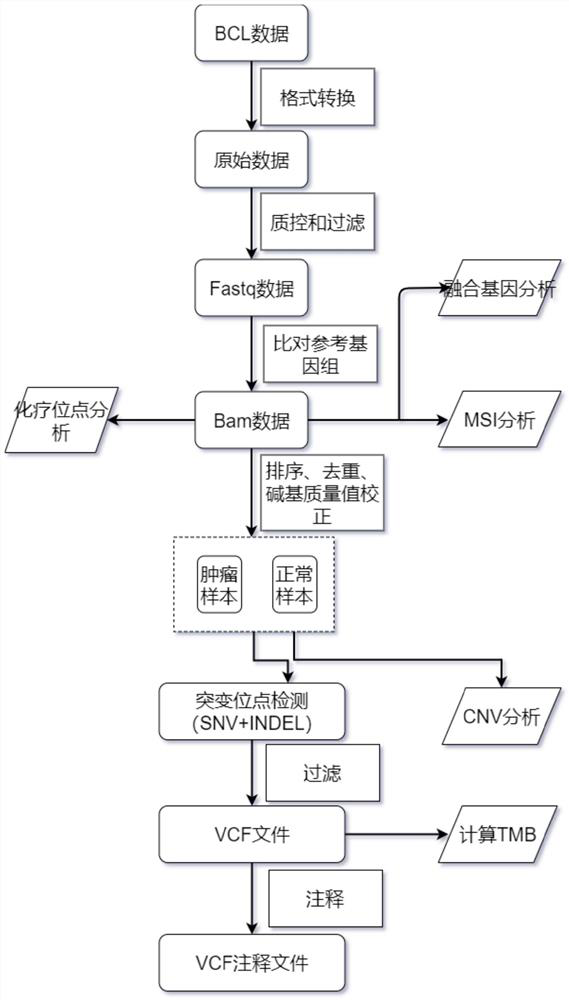
High-flux sequencing data analysis method and device
ActiveCN109767810AAccurate calculationVariation detection is fastProteomicsGenomicsInsertion deletionReference genome sequence
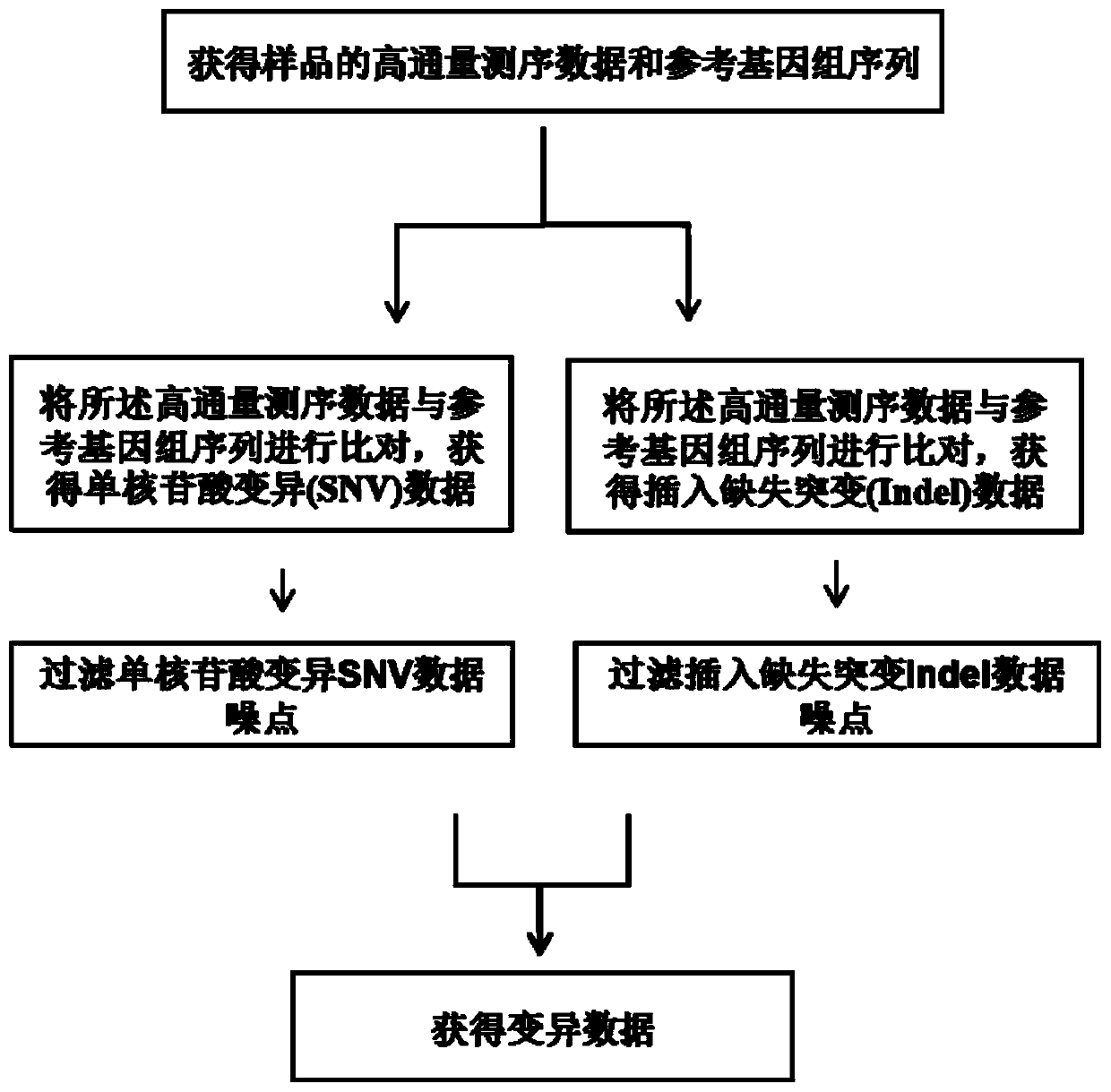
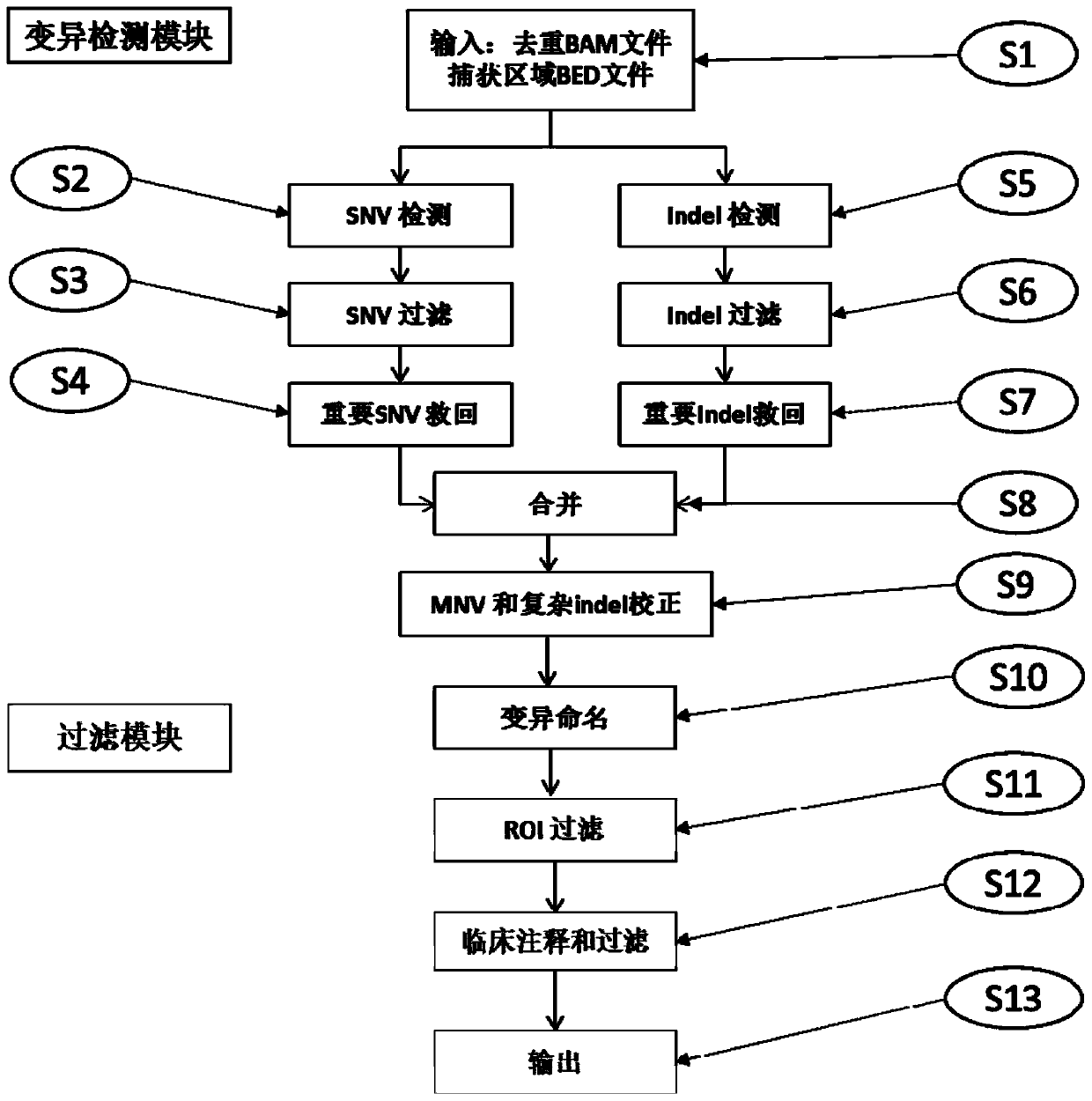
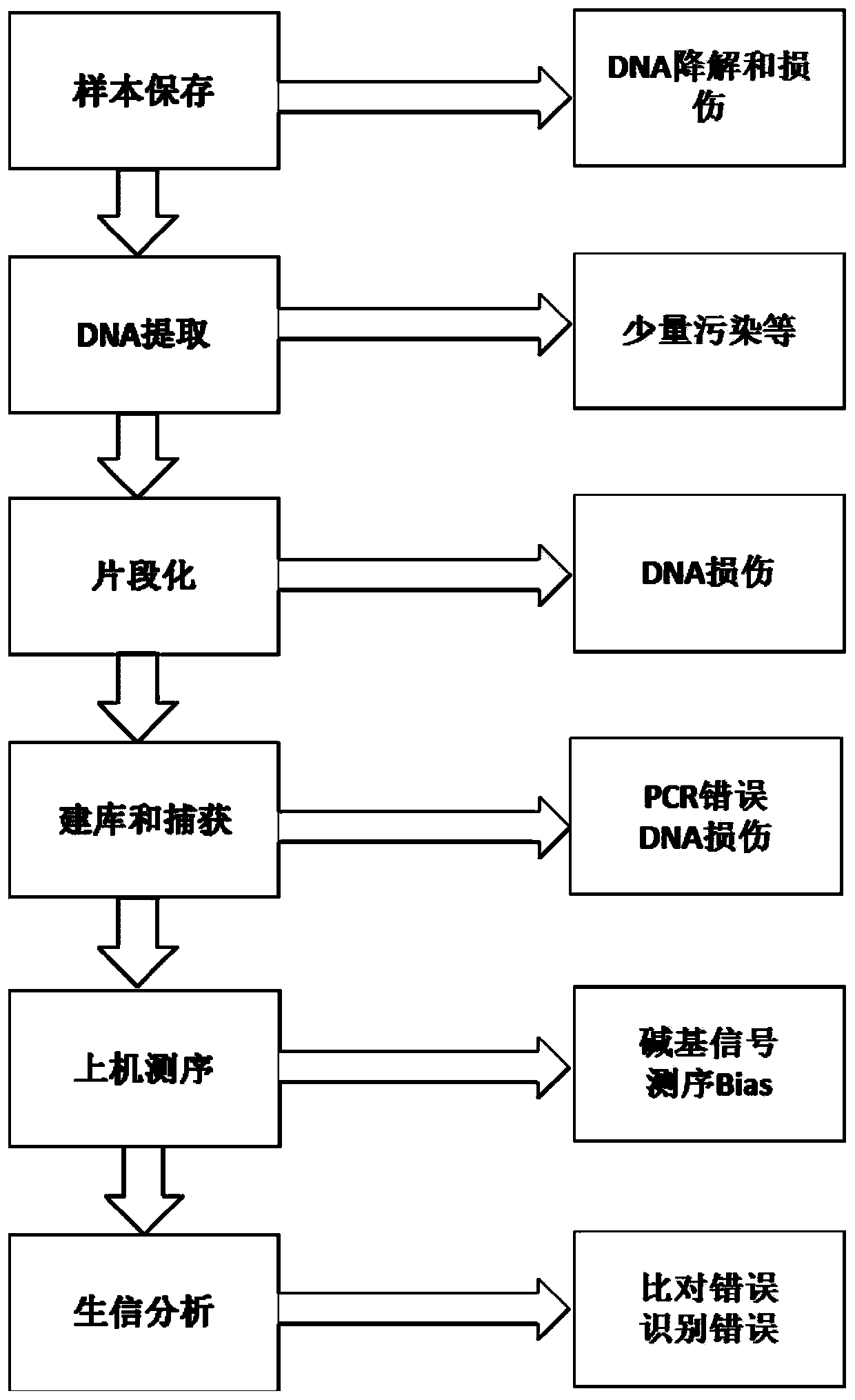
The invention relates to a high-flux sequencing data analysis method and a device. The high-flux sequencing data analysis method comprises the steps of acquiring high-flux sequencing data of a sampleand a reference genome sequence, comparing the high-flux sequencing data with the reference genome sequence, and respectively acquiring locus data of single nucleotide variation (SNV) and locus data of insertion deletion mutation (Indel), and respectively filtering noise points of the SNV data and the Indel data through comparing the difference substantial degrees of the variation and the background, thereby obtaining the variation data. The invention further provides a device for analyzing the high-flux sequencing data and a computer-readable storage medium for storing instructions.
Owner:3D BIOMEDICINE SCI & TECH CO LTD
Model construction method for identifying tumour purity sample and application thereof
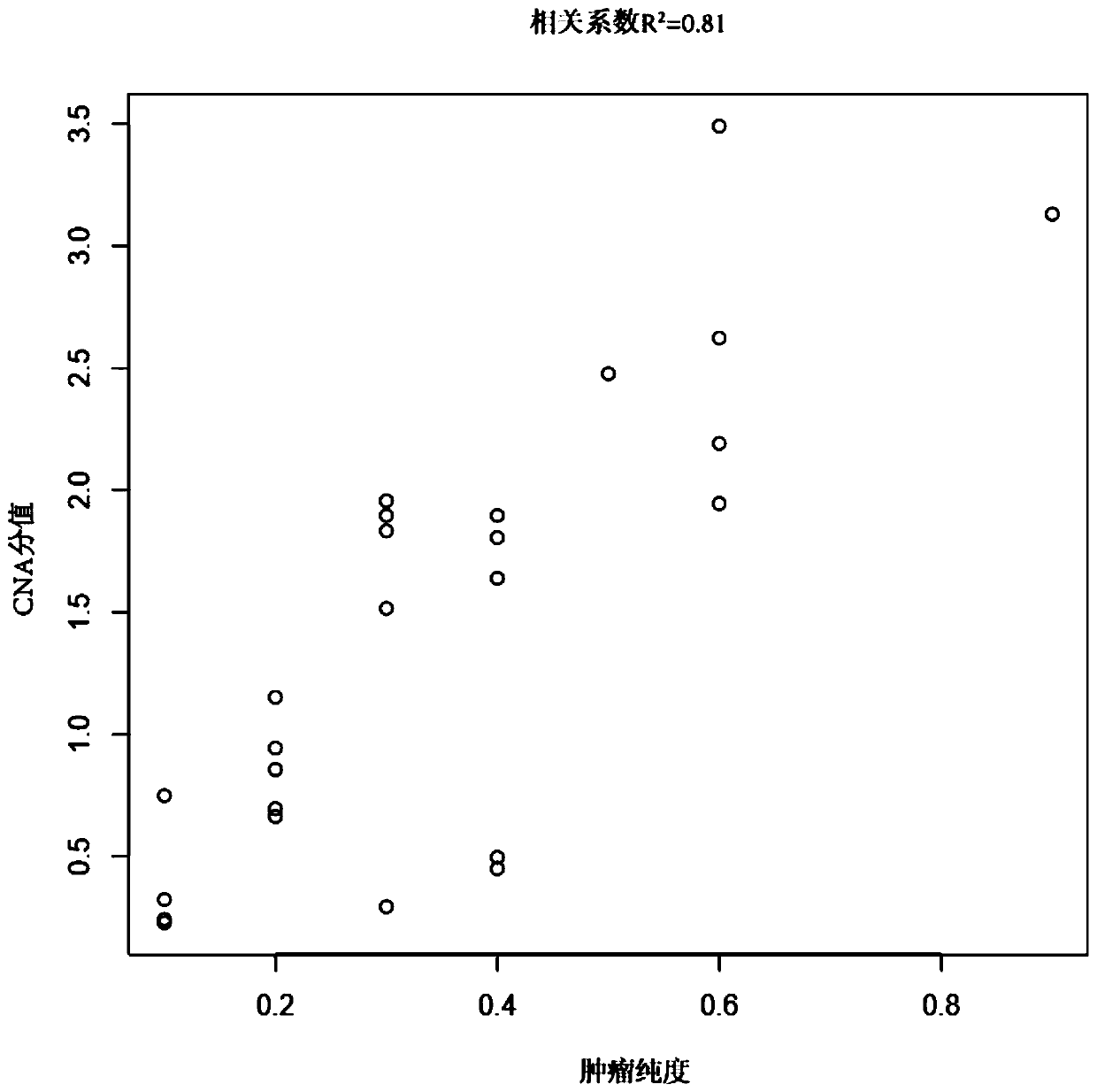
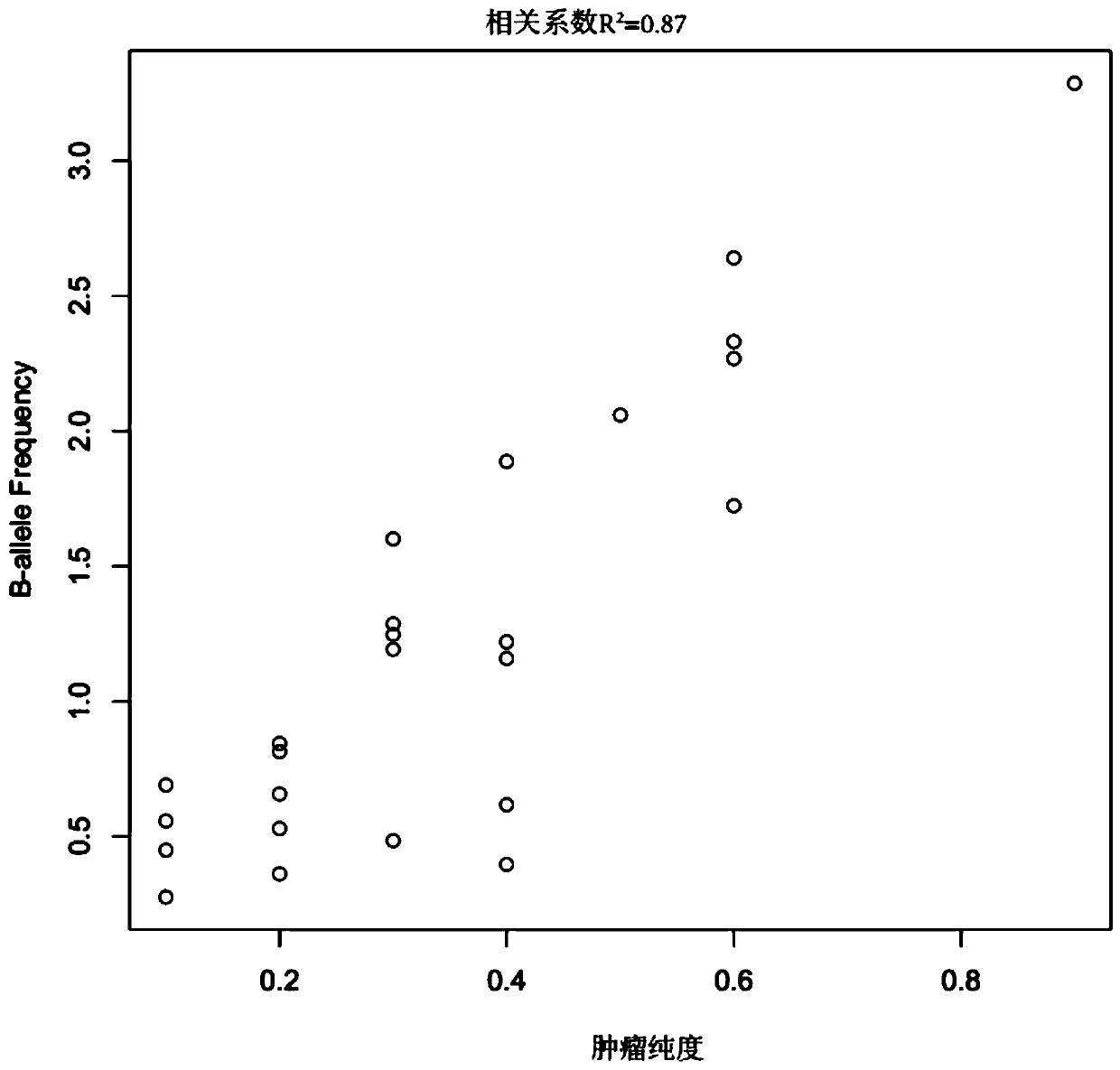
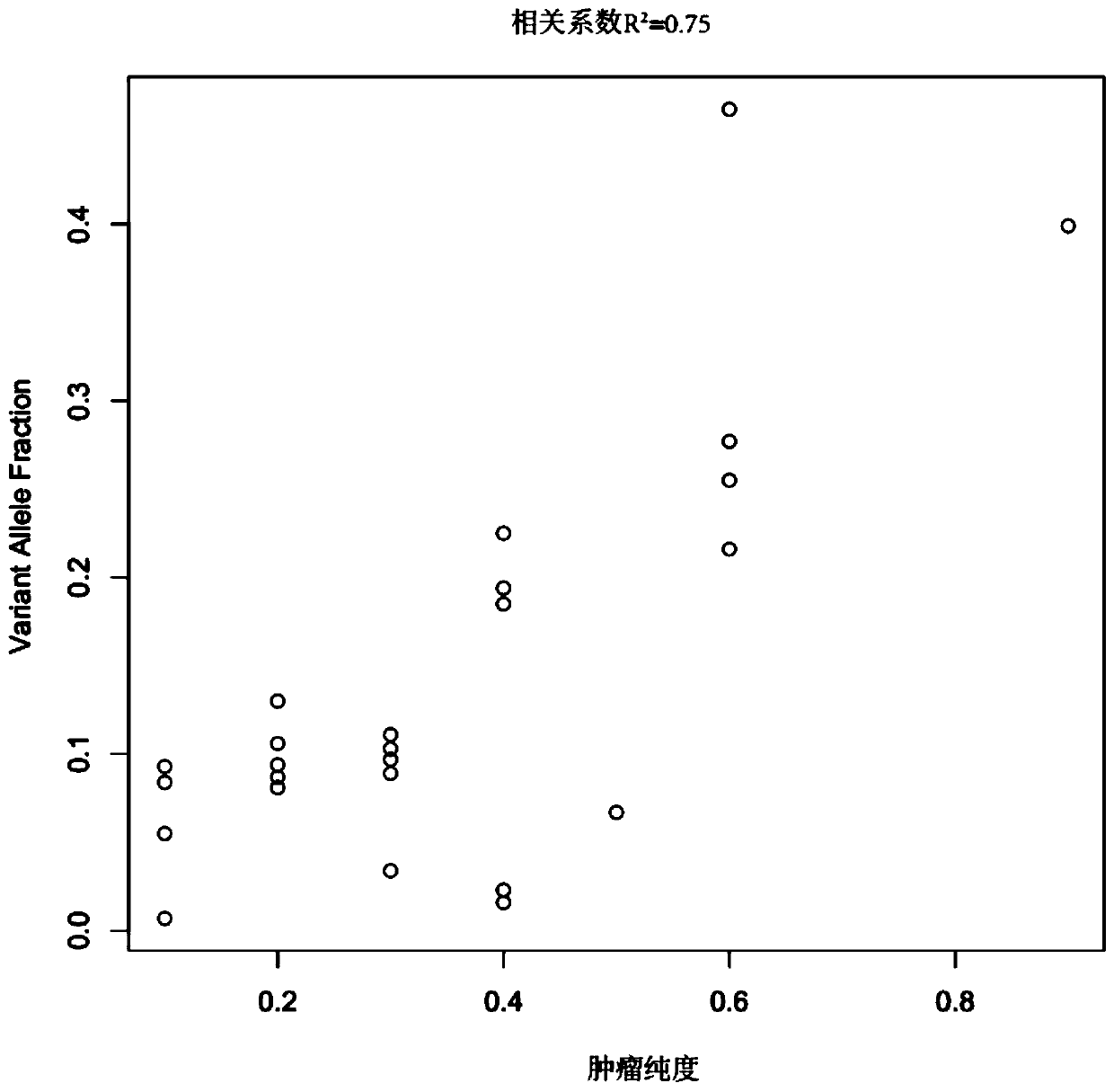
ActiveCN110808081ASolve the problem of difficult identification of tumor purityAccurate identificationProteomicsGenomicsTarget captureNucleotide variation
The invention belongs to the field of tumor purity detection, and especially relates to a model construction method for identifying a tumour purity sample and application thereof. The method comprisesthe steps of: based on targeted capture sequencing data of a tumor sample with known tumor purity, acquiring index data including a somatic cell copy number variation amplitude, heterozygote germlinemononucleotide variation and a somatic cell allele variation fraction; and associating the index data with the tumor purity of the tumor sample with known purity to construct an identification model.In the method, somatic mutation and germ cell variation are combined, the index data such as the somatic cell copy number variation amplitude, the heterozygote germline mononucleotide variation, themodel constructed by integrating the index data such as the somatic cell allele variation fraction and the like is used to solve the problem that the purity of tumors is difficult to identify due to few mutation sites in interval chip capture sequencing such as panel sequencing is solved, low-purity samples can be accurately identified, multiple cross confirmation among different indexes is achieved, and the reliability is high.
Owner:SHENZHEN GENEPLUS CLINICAL LAB
Method and device for detecting gene mutation and expression quantity
ActiveCN112397144AEfficient enrichmentApplicable developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsNucleotideRelated gene
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting gene mutation and expression quantity. The method comprises the following steps: S1, extracting RNA, interrupting, and carrying out reversetranscription to obtain cDNA; S2, constructing a gene library by adopting cDNA; S3, capturing and enriching a target gene from the gene library by utilizing specific hybridization of a capture probe and the target region; S4, sequencing by using a high-throughput sequencer to obtain RNA targeted sequencing data; S5, analyzing changes of gene mutation and expression quantity in the RNA targeted sequencing data, wherein the step S5 specifically comprises the following substeps: S51, analyzing the gene expression quantity; S52, analyzing gene overexpression; S53, carrying out gene fusion analysis; S54, carrying out the fusion mutation expression quantity analysis; S55, carrying out the single nucleotide variation analysis; S56, analyzing the expression quantity of the mononucleotide variationmutation. RNA transcripts expressed by tumor-related genes can be efficiently enriched, and the expression quantity and mutation conditions of the tumor genes in tumor tissues are analyzed.
Owner:ZHENYUE BIOTECHNOLOGY JIANGSU CO LTD
Method and kit for detecting mutation or nucleotide variation of organism
InactiveUS20050106575A1Efficient migrationMicrobiological testing/measurementSolid-state devicesDiseaseNucleotide
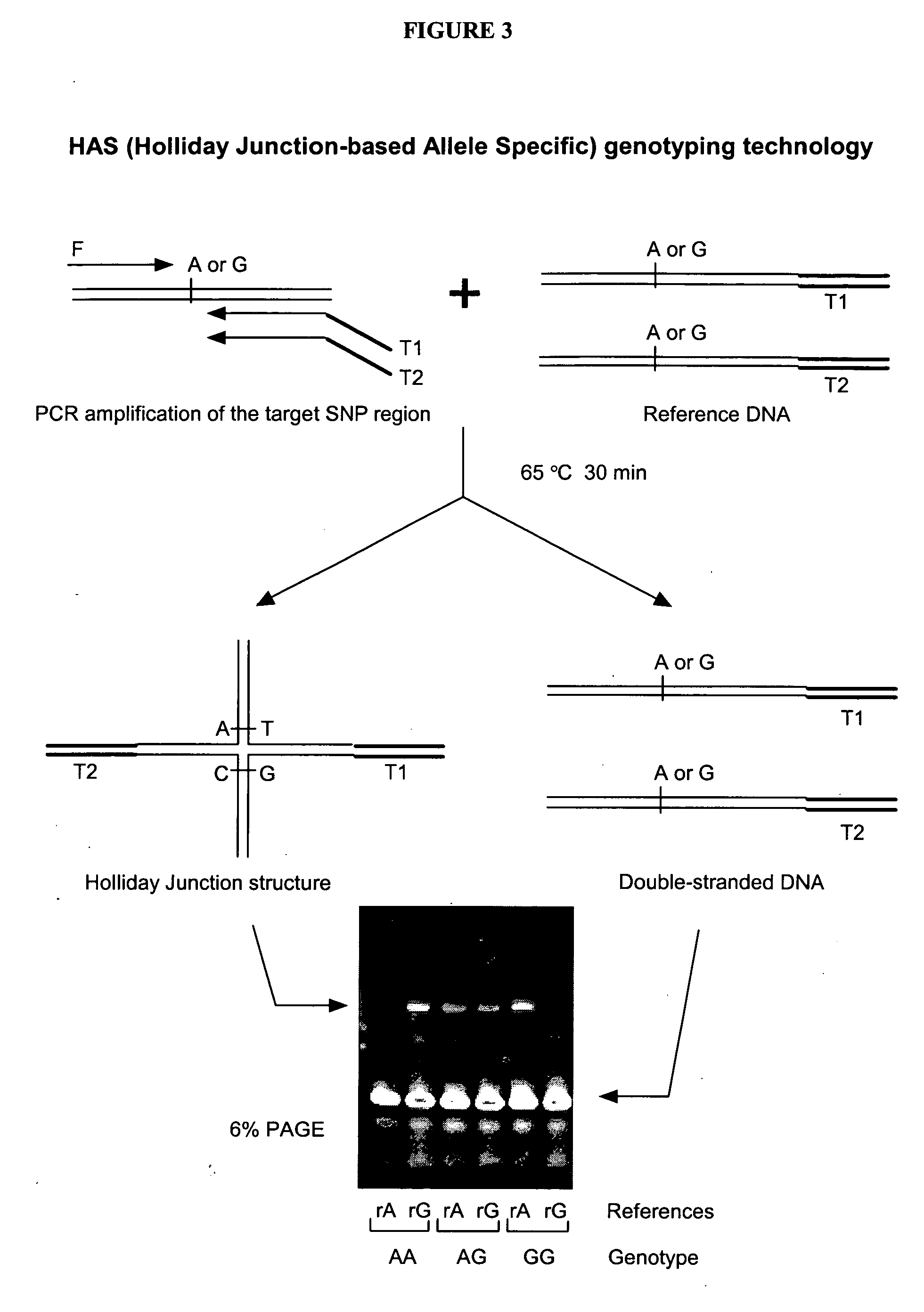
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for highly efficient, high throughput detection of mutation or nucleotide variation of an organism. By exploiting the molecular interactions between strands of nucleic acid and between nucleic acid and protein, assays have been developed to detect nucleotide variation, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in various biological samples including human genomic DNA and virus. In preferred embodiments, immunoassays are developed to specifically capture a nucleic acid-protein complex formed between a 4-way nucleic acid structure called Holliday junction and a protein that specifically recognizes the Holliday junction. These assays can be used in a wide variety of applications such as diagnostics, genotyping, genetic profiling, mutation detection, disease prevention, therapeutic treatment, and screening for therapeutic targets or therapeutics.
Owner:PANOMICS
Methods for cancer detection and monitoring by means of personalized detection of circulating tumor DNA
The invention provides methods for detecting single nucleotide variants in breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer. Additional methods and compositions, such as reaction mixtures and solidsupports comprising clonal populations of nucleic acids, are provided. For example, provided here is a method for monitoring and detection of early relapse or metastasis of breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer, comprising generating a set of amplicons by performing a multiplex amplification reaction on nucleic acids isolated from a sample of blood or urine or a fraction thereof from a patient who has been treated for a breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer, wherein each amplicon of the set of amplicons spans at least one single nucleotide variant locus of a set ofpatient-specific single nucleotide variant loci associated with the breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer; and determining the sequence of at least a segment of each amplicon of the setof amplicons that comprises a patient-specific single nucleotide variant locus, wherein detection of one or more patient-specific single nucleotide variants is indicative of early relapse or metastasis of breast cancer, bladder cancer, or colorectal cancer.
Owner:NATERA
A method for functional prediction of single nucleotide genomic variation in a non-coding region
ActiveCN109033751ALow sequencing depth requirementAvoid time costSpecial data processing applicationsGenomic mutationNucleotide
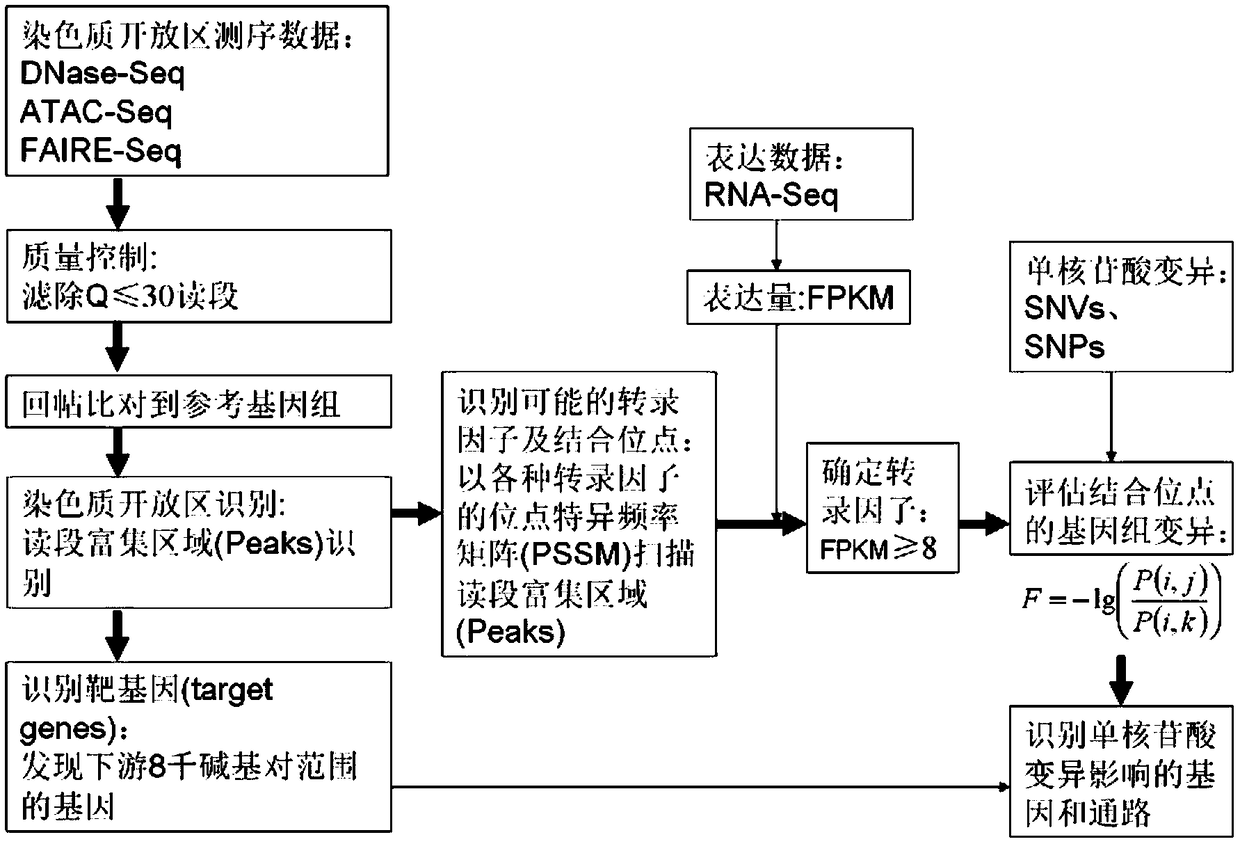
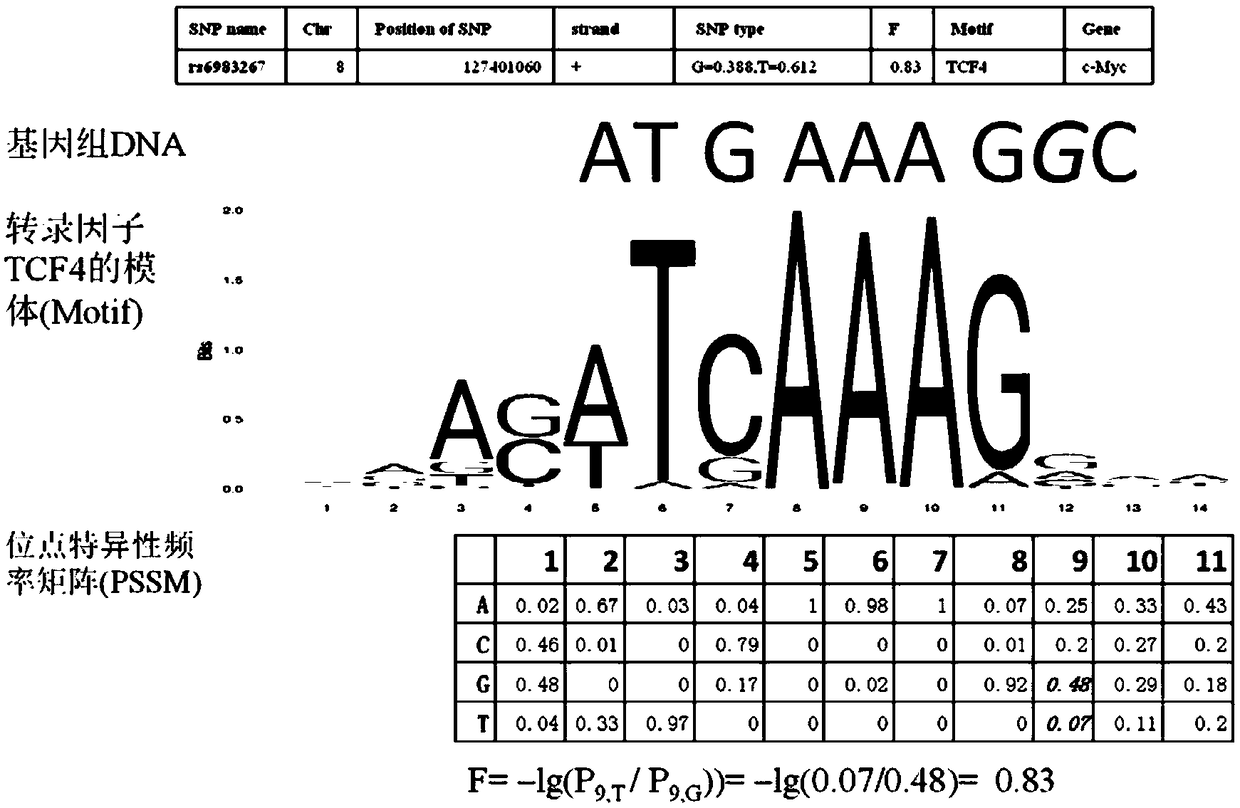
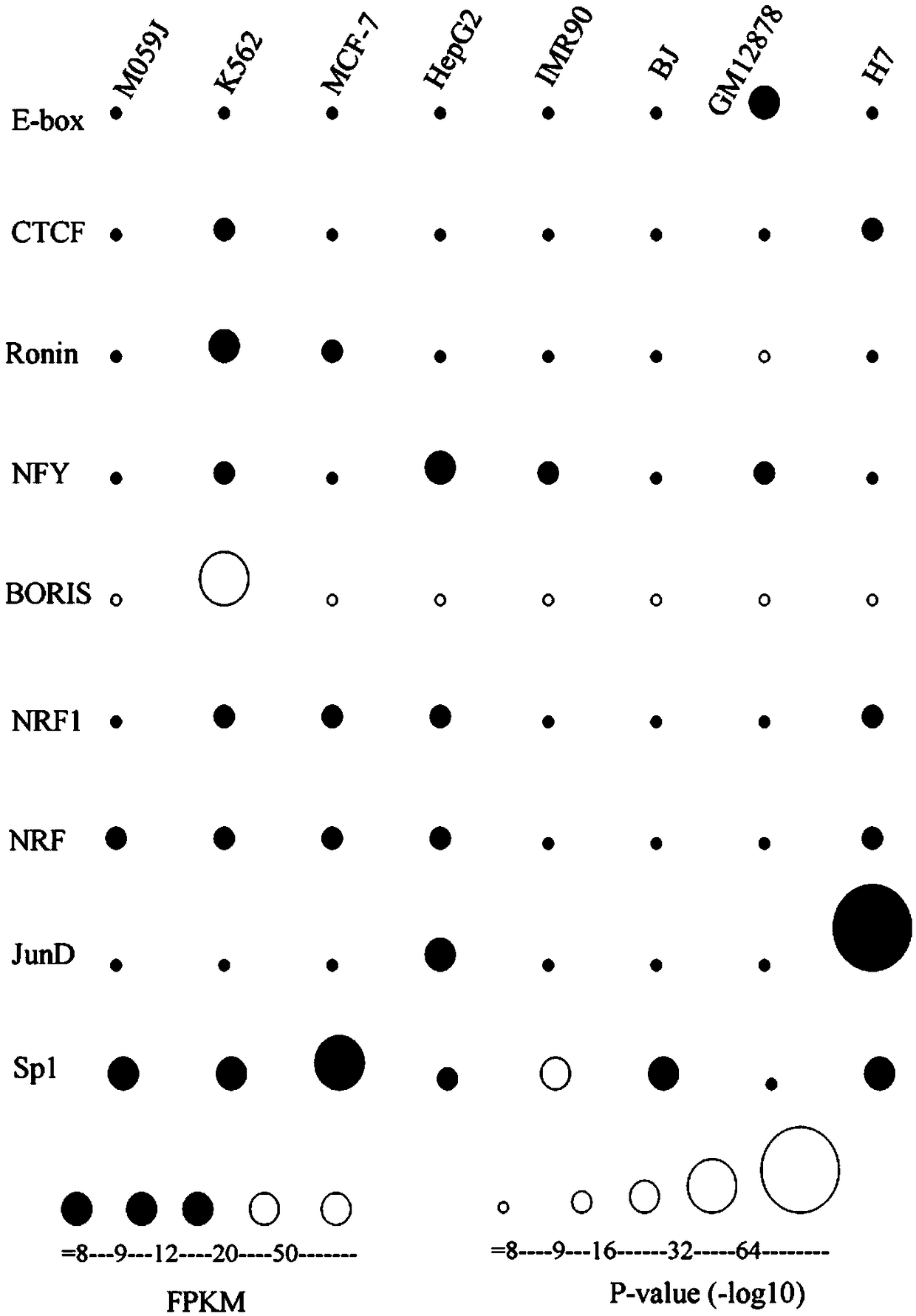
The invention discloses a method for functional prediction of single nucleotide genomic variation in a non-coding region, which comprises the following steps: 1) identifying a chromatin open region; 2) identifying transcription factor bin sites; 3) assessing the role of single nucleotide variations: Based on the site-specific frequency matrix of transcription factors, the effect of single nucleotide variations in the transcription factor binding site region on transcription factor binding is calculated, and the single nucleotide variations that significantly change the binding capacity of transcription factors are identified; the role of single nucleotide variations is further evaluated by viewing the biological pathway of the target gene of the transcription factor. The method recognizesa variety of transcription factors and their binding sites at one time through chromatin open region information and gene expression information, and realizes the functional annotation of non-coding region genomic mutation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
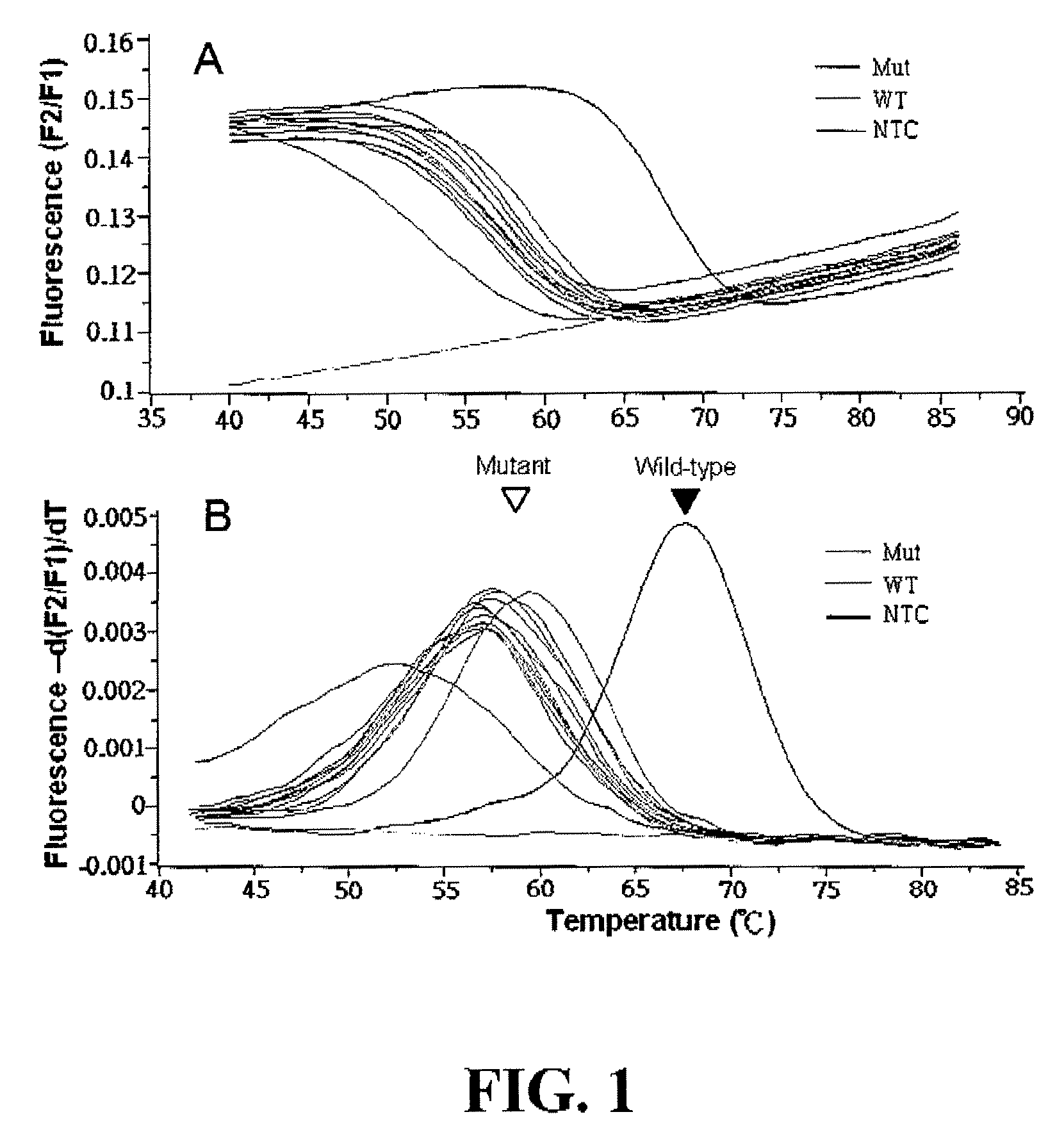
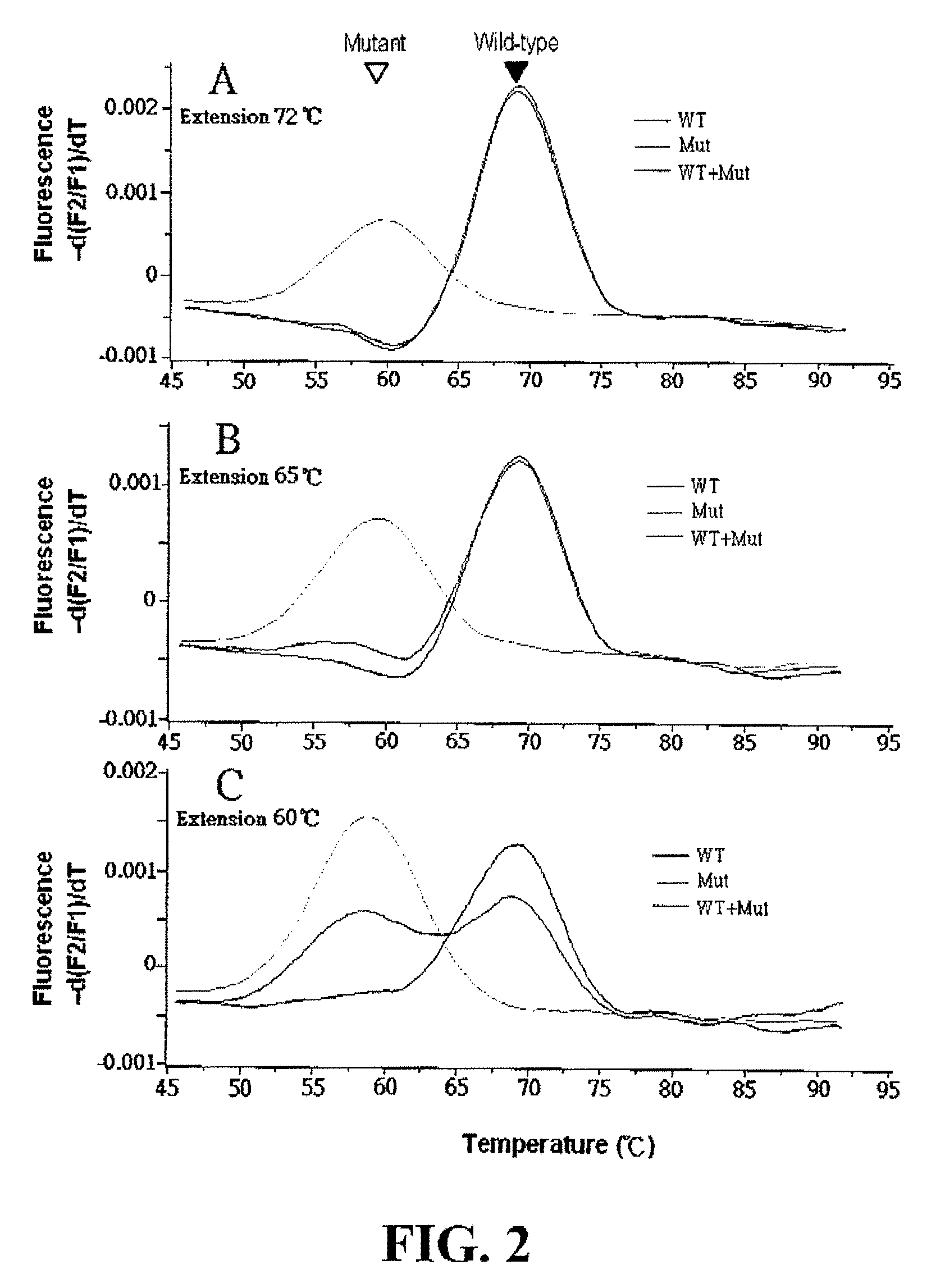
Method for the Detection of Multiple Single Nucleotide Variations or Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in a Single Tube
ActiveUS20120141995A1Easily contaminatedVariation is detectedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleotide variation
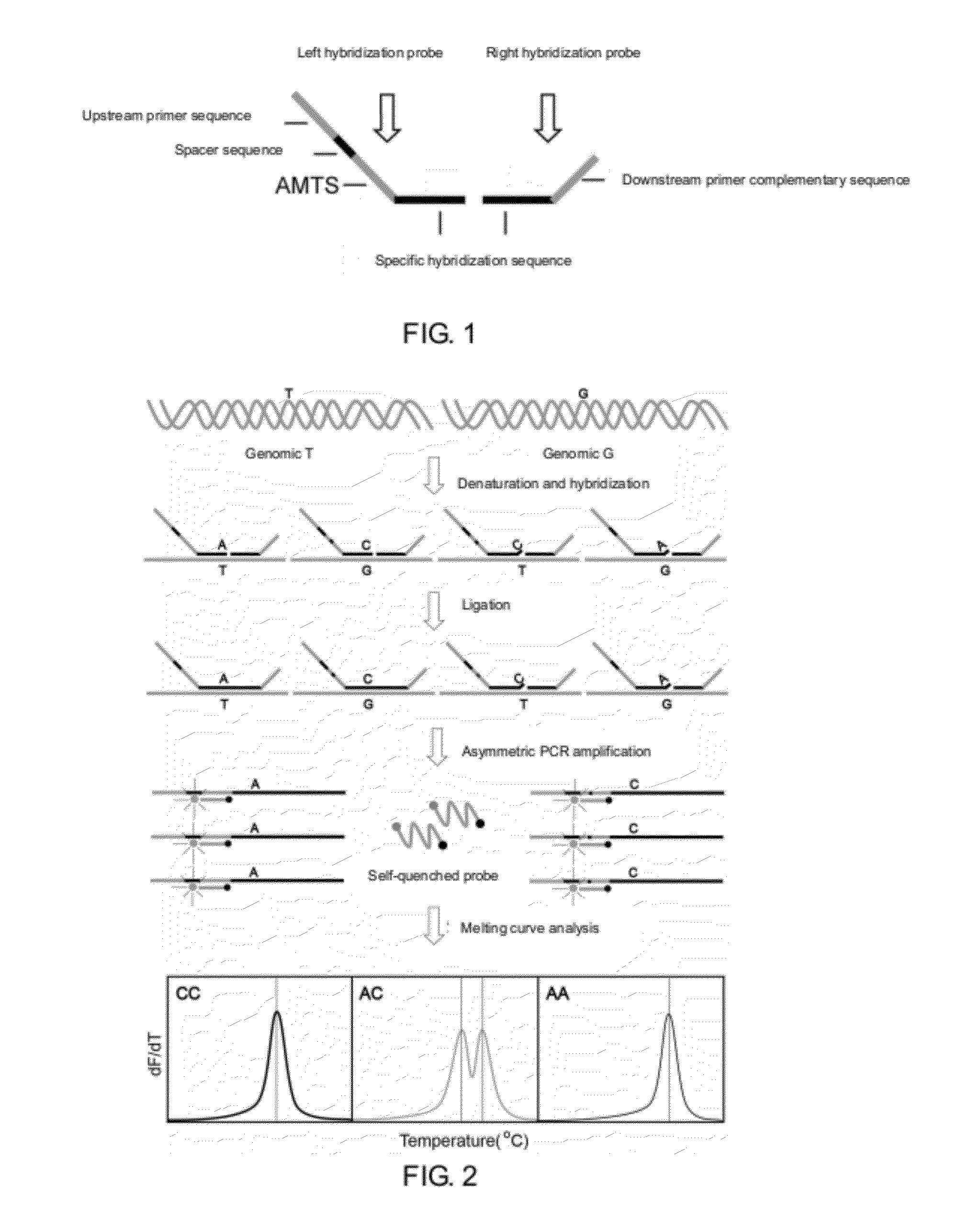
The present invention discloses a method for detecting multiple single nucleotide variations or polymorphisms in a single reaction tube, and the oligonucleotide, the probe, the set of probes, the kit used, as well as the use thereof. Specifically, it relates to a method for identifying the genotype of multiple single nucleotide variation or SNP sites from the melting temperature of a kind of artificial melting temperature tag sequence (AMTS) and the type of fluorescence labels.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for lowering the dependency towards sequence variation of a nucleic acid target in a diagnostic hybridization assay
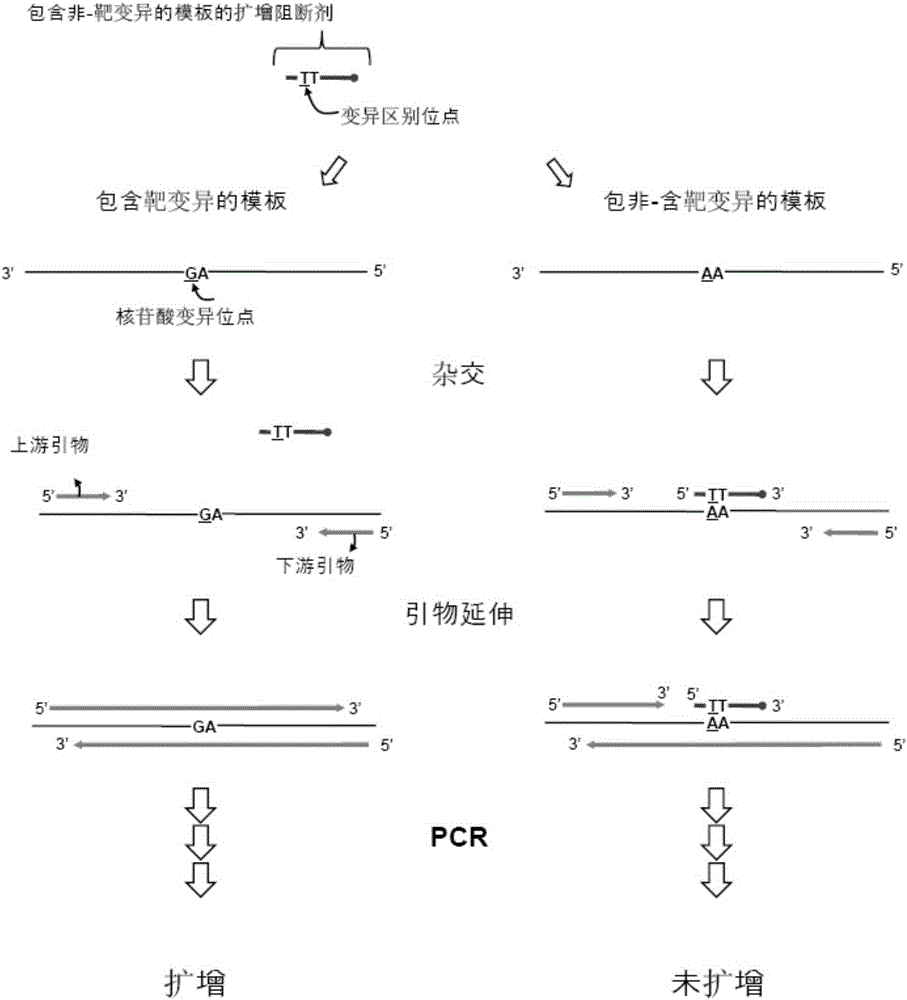
The present invention provides primer or / and probe, this target sequence containing at least one variation, defined as either one non-conserved nucleotide, called genotype variation, or one nucleotide variation within one and the same genotype, wherein the primer or / and probe comprises a nucleic acid sequence that is complementary to said target sequence except for the at least complementary base of the variation(s), which is not present in the primer or / and probe. The present invention is especially useful in methods for diagnostic, preventive and therapeutic applications.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX SA
Gene data system for clinical diagnosis and prediction
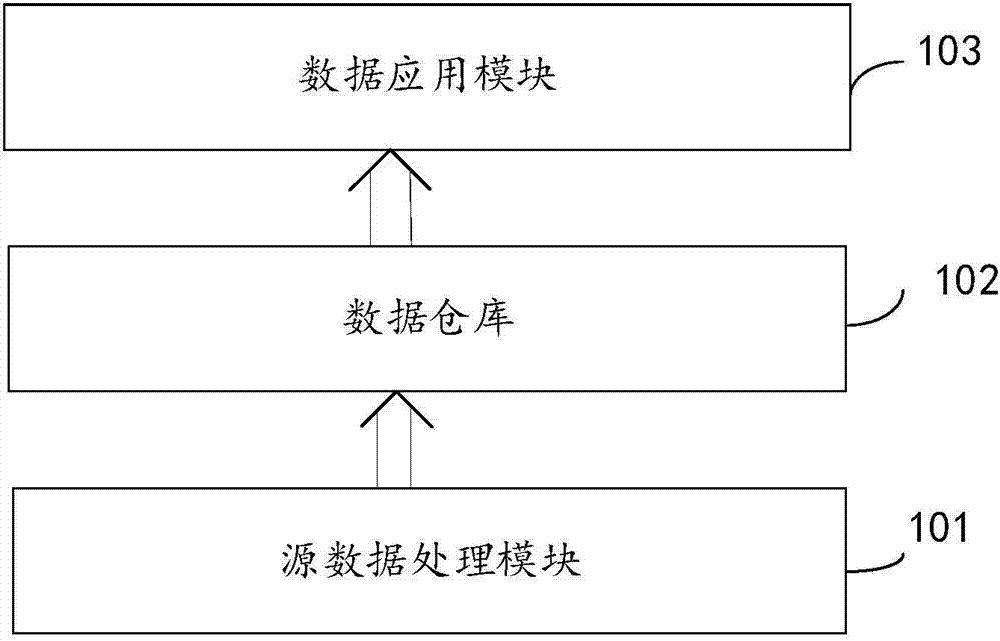
InactiveCN107247890AReliable data supportHigh degree of automationData visualisationBiostatisticsData warehouseData system
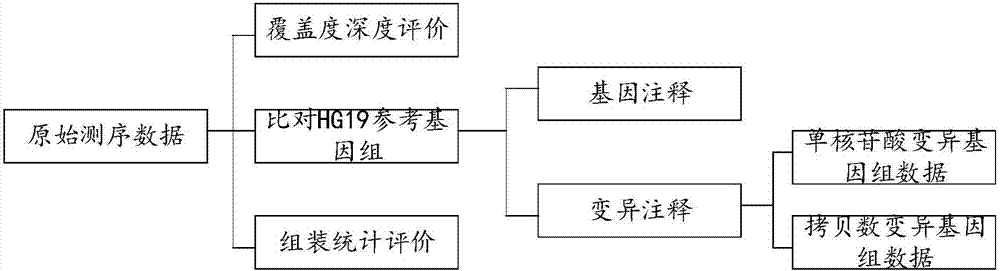
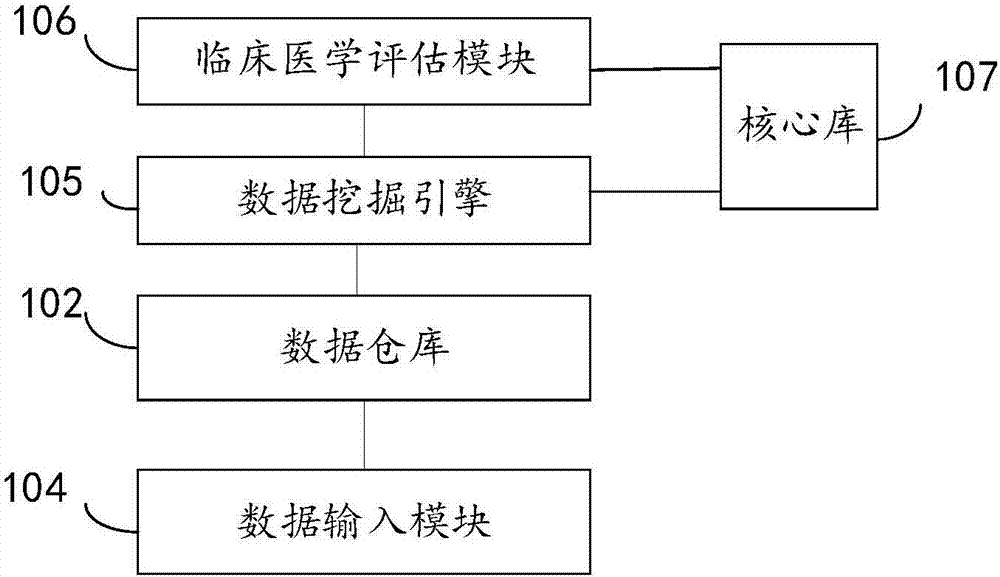
The invention discloses a gene data system for clinical diagnosis and prediction. The system comprises a source data processing module, a data warehouse and a data application module, wherein the source data processing module is used for receiving original sequencing data, conducting sort processing on the original sequencing data according to a preset rule, and generating single nucleotide variation genome data and copy number variation genome data; the data warehouse is used for storing the single nucleotide variation genome data and the copy number variation genome data; the data application module is used for receiving control commands, acquiring related data from the data warehouse according to the control commands and disposing and outputting the related data; the system further builds the data architecture of normal variation and pathogenicity variation of the human gene, can conduct analysis and management on the data and provides reliable data support for clinical diagnosis and prediction.
Owner:张巍
Method for measuring drug fast variation of hepatitis b virus to Adefovir
InactiveCN101004415AIncreased sensitivityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrophoresisNucleotide variation
A method for determining adfuwei tolerance variation of hepatitis B virus includes designing specific primer, carrying out amplification by set of PCR means, using BgII and BseDI to carry out enzyme cut reaction electrophoresis on amplified product then carrying out restrictive section length polymorphism analysis.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
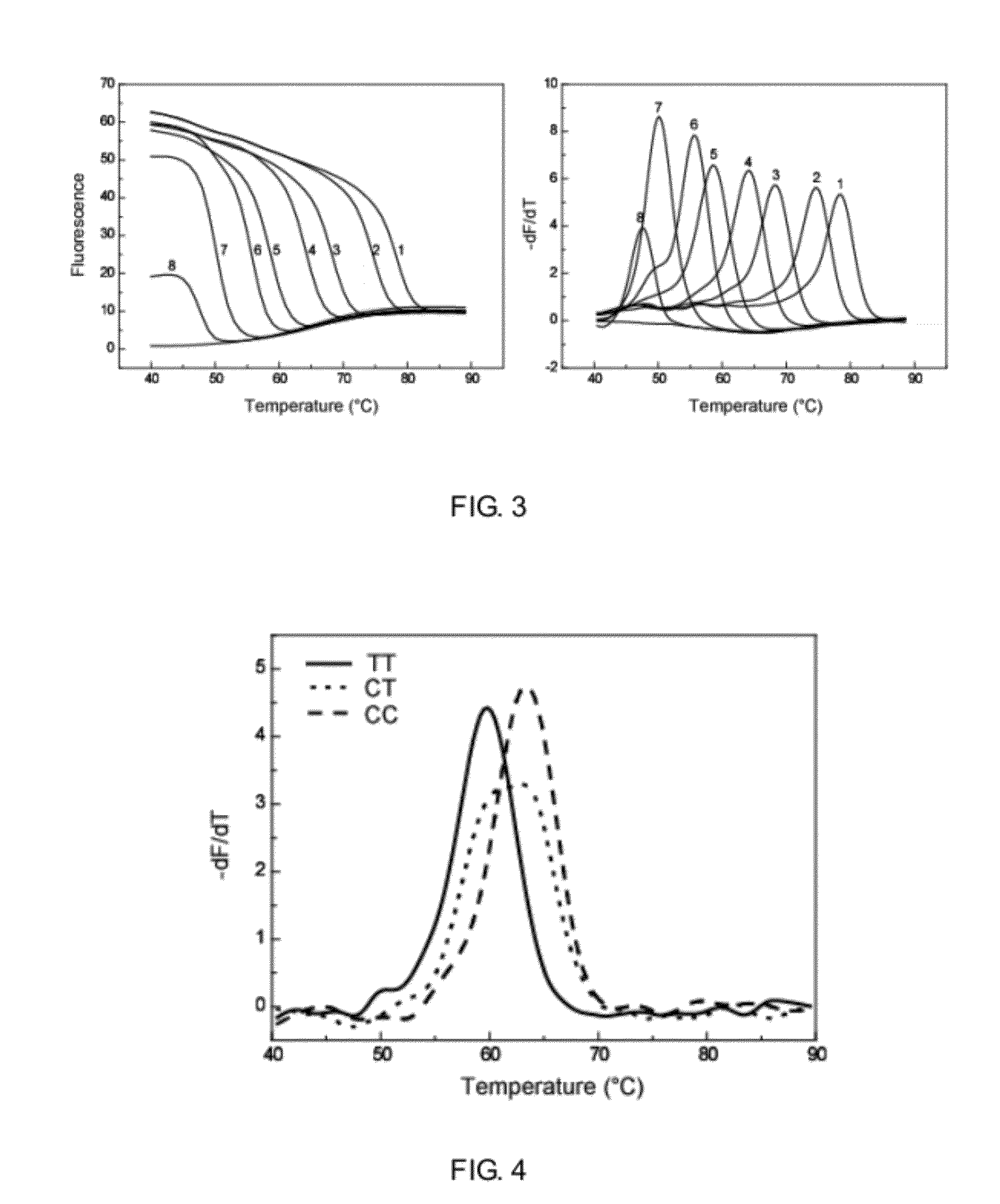
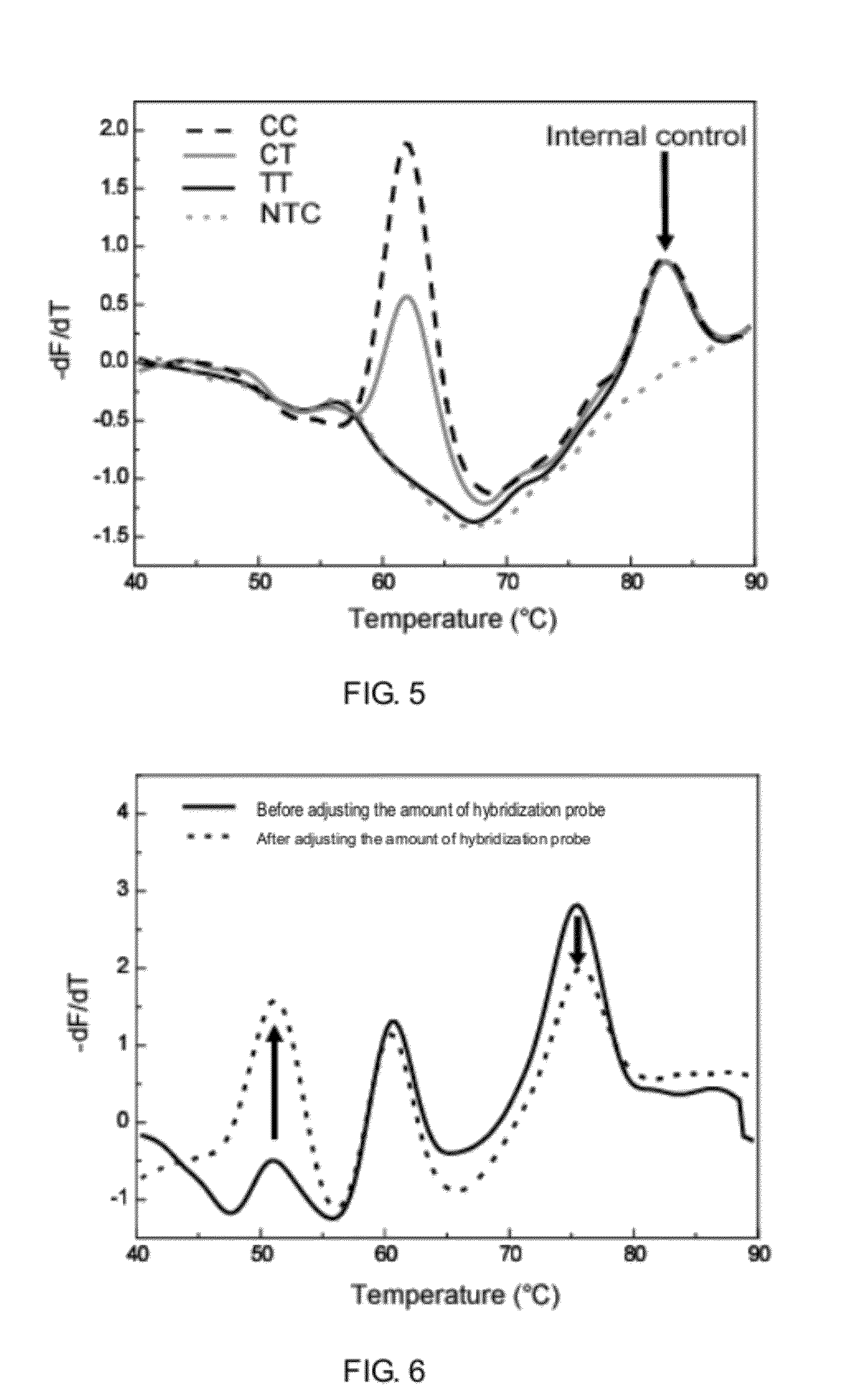
A method for rapid detection of goat six6 gene single nucleotide polymorphism and its application
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of goat homeobox 6 (six6) gene, using the whole genome DNA of the goat to be tested containing the Six6 gene as a template, and using a primer pair P as Primers, PCR amplified goat Six6 gene; after the PCR product was digested with restriction endonuclease PstI, agarose gel electrophoresis was carried out; the genotype at position 232 of the goat Six6 gene was identified according to the electrophoresis results (with sequence Accession No.NM_001104993. 1 for reference); in animal production practice, since the Six6 gene single nucleotide variation or SNP has important effects on the formation of embryos, regulation of growth hormone and promotion of pituitary hormone secretion, the different genotypes of the site are related to growth and development Association analysis of trait data. The results showed that the tube circumference of CT genotype individuals was significantly larger than that of CC genotype individuals (P=0.047), indicating that CT genotype can be used as a molecular genetic marker to increase tube circumference in goats. Therefore, the detection method for rapid detection of Six6 gene SNP provided by the present invention is conducive to the rapid establishment of goat populations with excellent genetic resources in the marker-assisted selection (MAS) breeding of Chinese goat growth traits.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method and test kit for detecting nucleotide variations
InactiveUS20090011944A1Detect presenceMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationNucleotide variationSingle strand
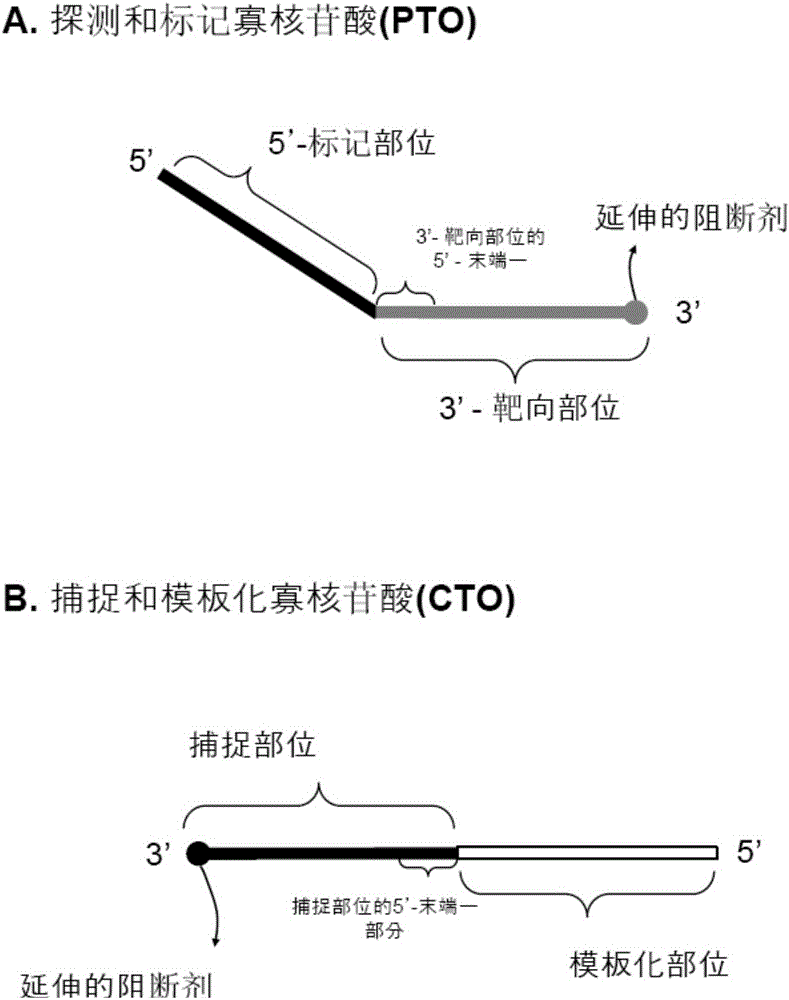
The present invention is related to a method for a simultaneous determination of the relative amounts of more than one target polynucleotide sequence and nucleotide variations in said targets. The method is carried out by separating and recording single-stranded probes, which have hybridized to the targets and which are determined and distinguished by their defined properties including size and optional detectable label. The probes are complementary to a region in the target that has a sequence being contiguous to the nucleotide variations to be determined. After being hybridized with affinity-tagged targets, the probes are attached to a solid support and purified. The target probe hybrids are elongated using enzyme-assisted elongations. The elongated probes are recorded after release from the solid supports and the amount of each of the targets and their nucleotide variations and the ratio of modified and modified target polynucleotide sequences are calculated from the recorded results. Also disclosed is a test kit, which kit comprises in a packaged form devices equipments and reagents as well as instructions for carrying out the method. The method is useful for several diagnostic purposes.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
SNP mark related to weight of eriocheir sinensis and application of SNP mark
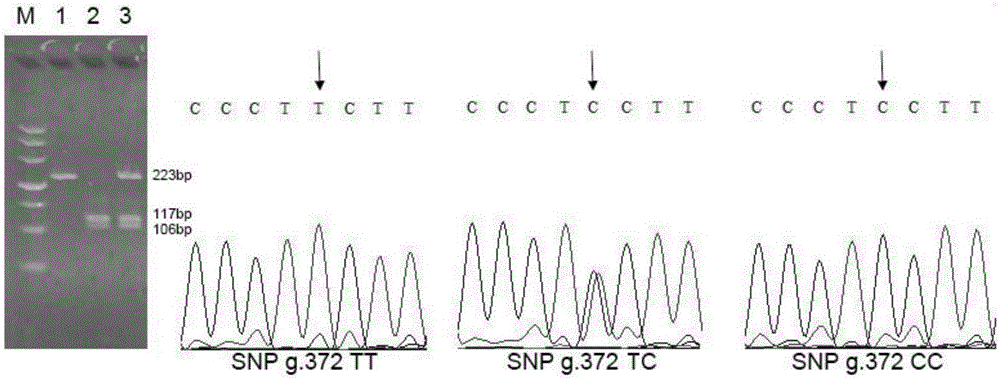
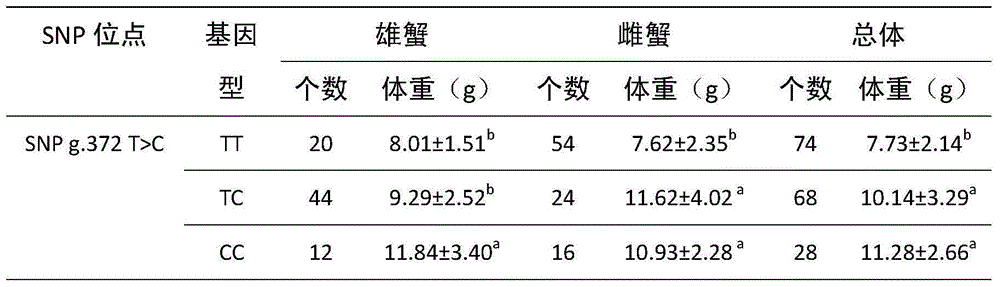
ActiveCN105002171AIncrease weightMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotide variationGene type
The invention discloses an SNP mark related to the weight of eriocheir sinensis and application of the SNP mark. The SNP mark related to the weight of the eriocheir sinensis is located on the5'- side wing area of an MIH gene, the specific position is the 372bp part of the MIH gene, and nucleotide variation information is SNP g.372T>C. Obvious relevance exists between the SNP position point and the weight trait of the eriocheir sinensis species, and the average weight of the CC gene type individual is obviously higher than the average weight of the TT gene type individual. SNP g.372T>C genetic typing is carried out on a river crab breeding colony and morphology characteristic analysis is combined so that the individual with the gene type of CC can be preferably selected as a breeding parent, and the research has the significant guiding meaning on breeding of a novel large-specification river crab variety.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES INSITUTE OF JIANGSUPROVINCE +1
Detection of nucleotide variation on target nucleic acid sequence
ActiveCN105358710AEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyMutation detectionNucleotide variation
Owner:SEEGENE INC
SNP locus significantly relevant to precocious puberty trait of eriocheir sinensis and application
ActiveCN108753995AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPrecocious pubertySarcocheilichthys sinensis
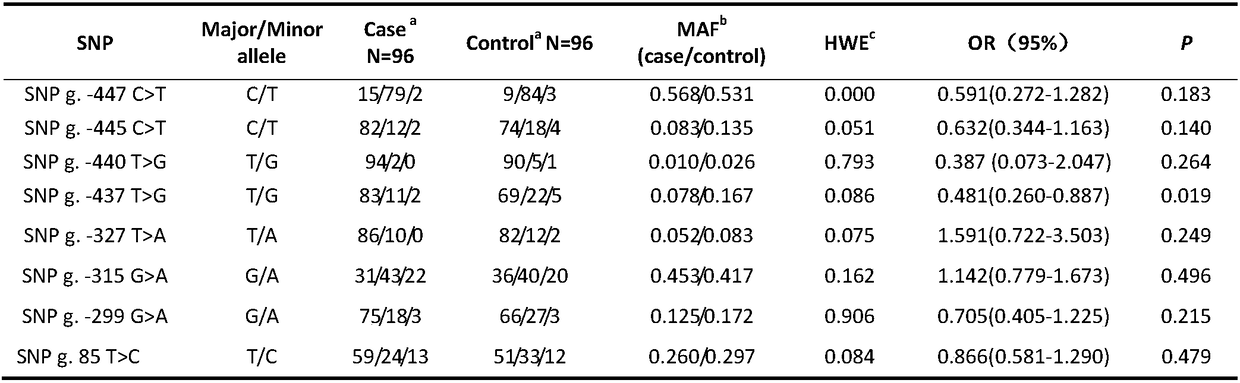
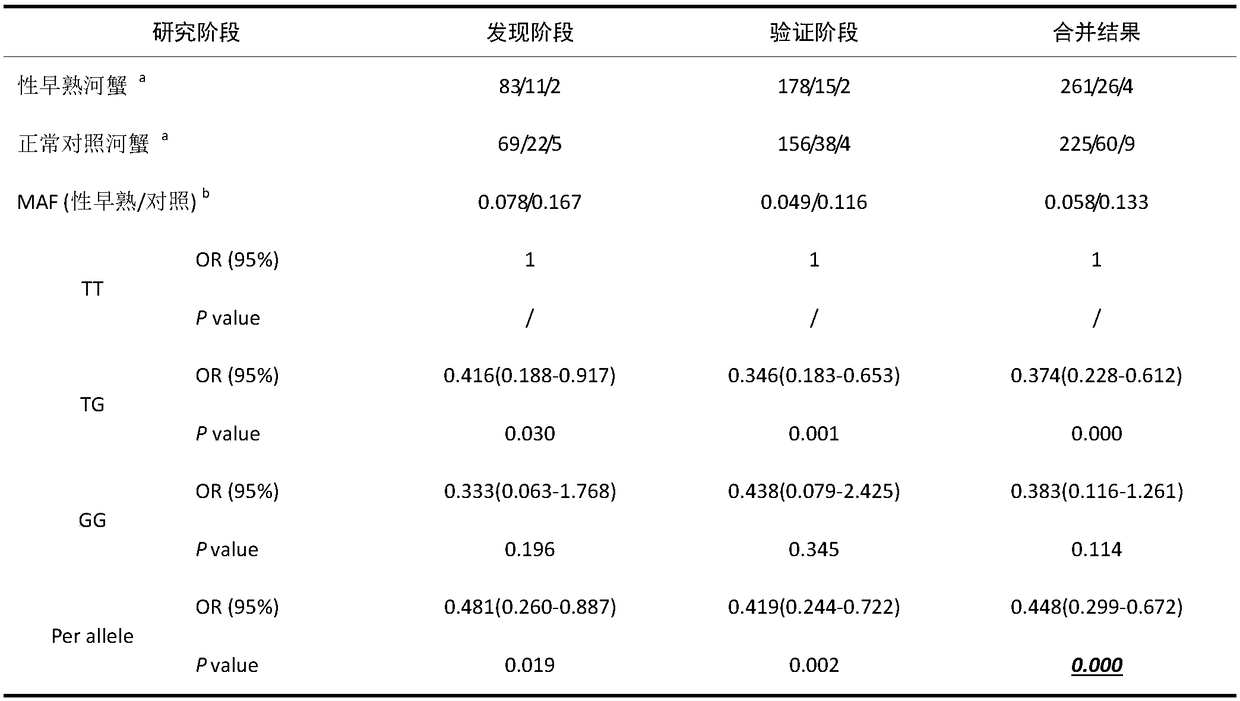
The invention discloses an SNP locus significantly relevant to the precocious puberty trait of eriocheir sinensis and the application. The SNP locus is positioned in a Vg gene 5'-flanking region-437bpposition of the eriocheir sinensis, and nucleotide variation information is SNP g.-437T) G. PCR primer used for detecting the SNP locus is SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2, and restriction enzyme is MboI.The SNP locus has significant correlation with precocious puberty of the eriocheir sinensis, and the risk of precocious puberty trait of GG gene eriocheir sinensis individual is obviously smaller than that of precocious puberty trait of TT gene individual. The SNP locus and the PCR primer used for genetic typing are applied to the predication of the risk of precocious puberty of the eriocheir sinensis and / or the variety breeding of the eriocheir sinensis.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES INSITUTE OF JIANGSUPROVINCE
Specific primersand detection method of Tibetan mastiff molecular marker
ActiveCN109988851AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotide variationMicrosatellite
The invention relates to the technical field of specific primers and a detection method of single nucleotide variation and microsatellite markers of a dog variety of Tibetan mastiff. The method comprises the following steps: 1) extracting Tibetan mastiff genome DNA and other dog genome DNA; 2) taking the genome DNA extracted in the step (1) as a template, and respectively carrying out PCR amplification by using SNP molecular marker primers or primer groups; 3) sequencing a PCR amplification product by using a sequencer; 4) detecting the variation condition of single nucleotide polymorphic sites. The specific primers for the Tibetan mastiff molecular marker has a detailed detection method, and has an important application value for analyzing genetic characteristics, pedigree geographic patterns, population structures of Tibetan mastiff dogs and scientific protection and utilization of germplasm resources.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for establishing risk prediction model of gastric cancer
InactiveCN108504732AImprove early diagnosis rateImprove clinical outcomesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleotide variation
The invention relates to a method for establishing a prediction model for predicting the risk of gastric cancer, belonging to the technical field of molecular biological technology for tumors. According to the invention, the prediction model for predicting the risk of gastric cancer is established by determining a plurality of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites in collected biological samples; the established model is used for comparing and analyzing SNP sites so as to determine the gastric cancer catching risk of a population and to predict correlation of the diagnosis of gastric cancer of subjects to gastric cancer occurrence risks. The method provided by the invention is based on the established prediction model and biological samples collected from subjects, analyzes statistically-significant single nucleotide variation by contrasting a normal population and patients with gastric cancer and taking the frequency of genovariation into consideration, and determines the correlation of the diagnosis of gastric cancer of the subjects to gastric cancer occurrence risks, so an early diagnosis rate and clinical outcome are improved. The risk prediction model is applicable to prediction of the gastric cancer catching risks of people.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV +1
Variety identification-encoding system and encoding method using the same
ActiveUS20160196382A1Improve competitivenessEasy to identifyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotide variationRegion analysis
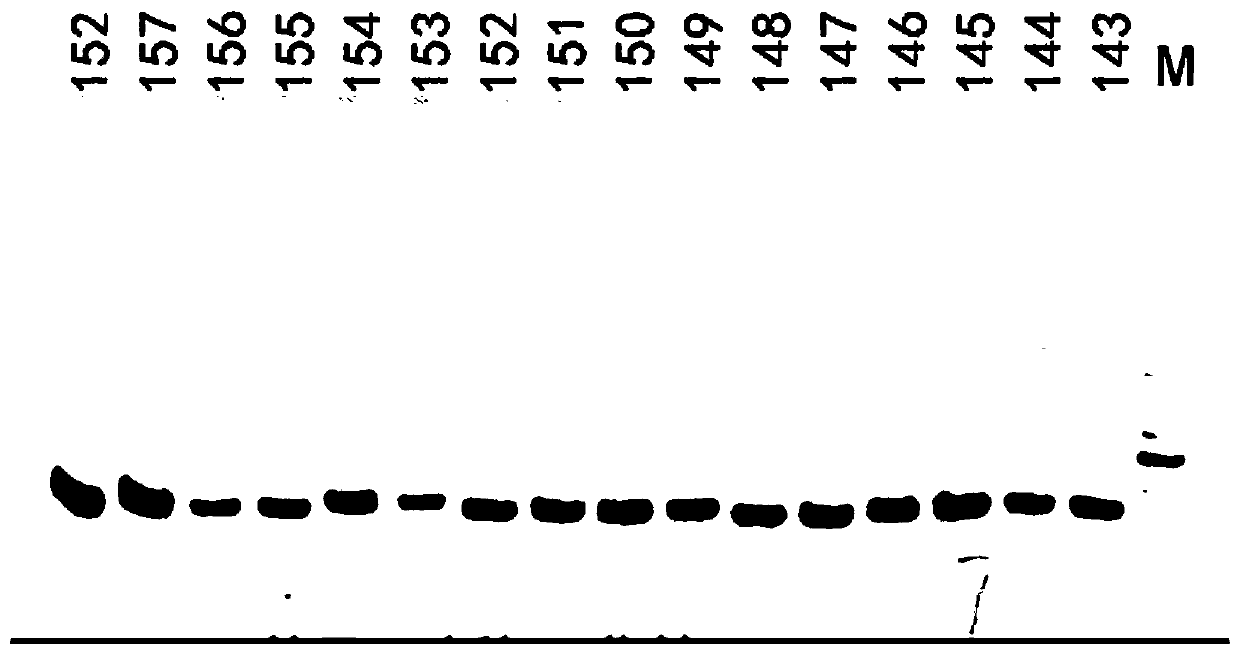
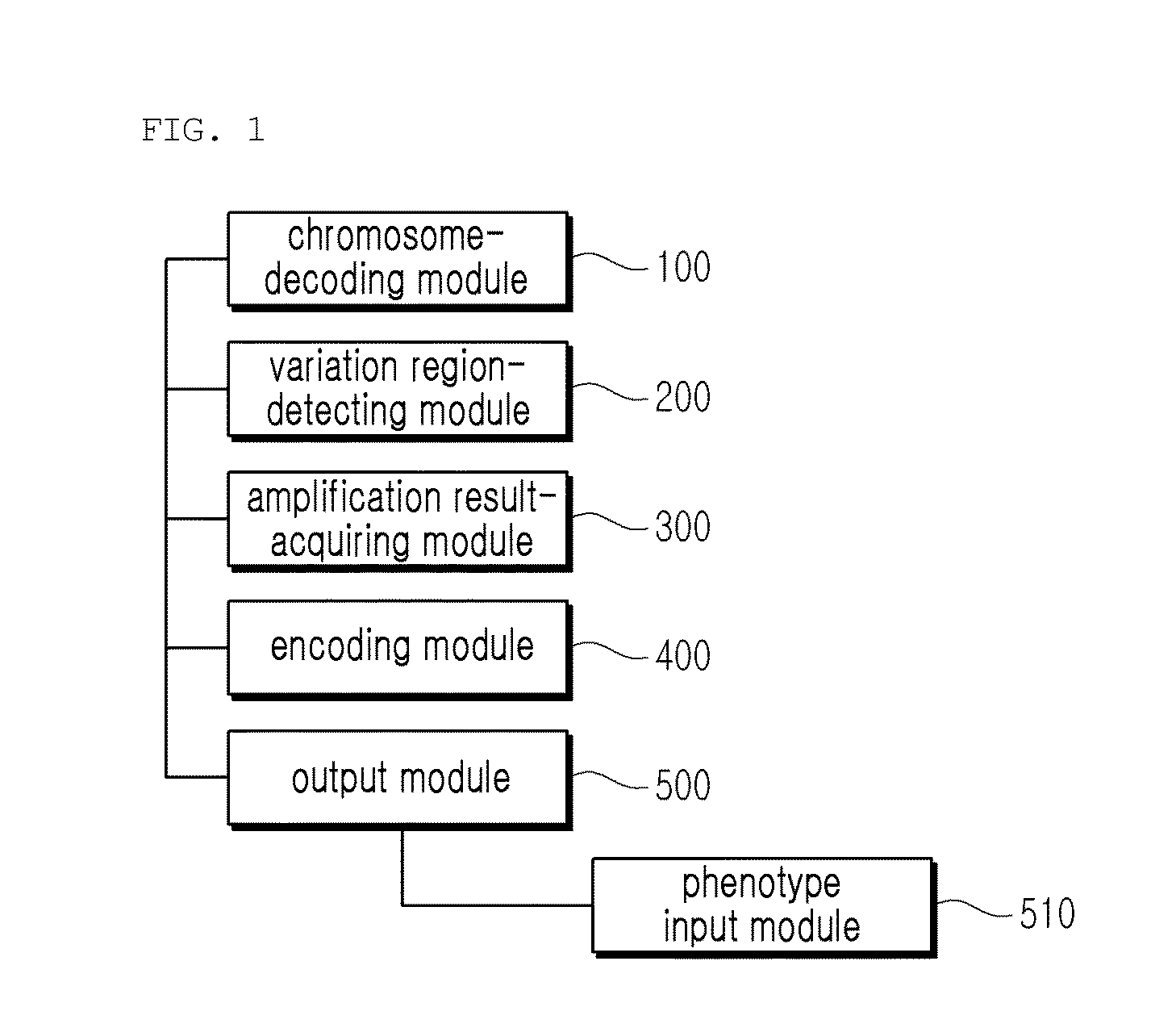
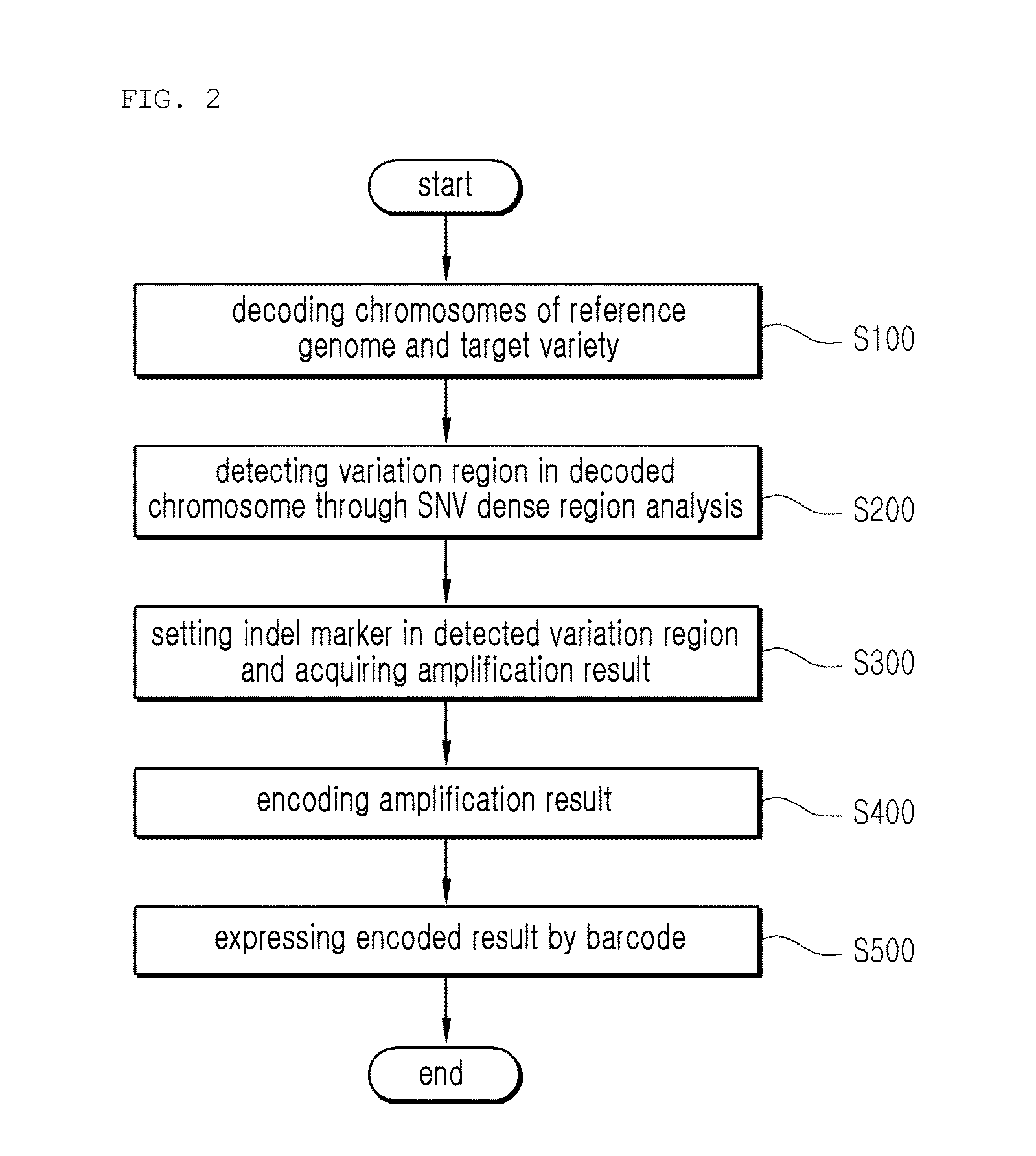
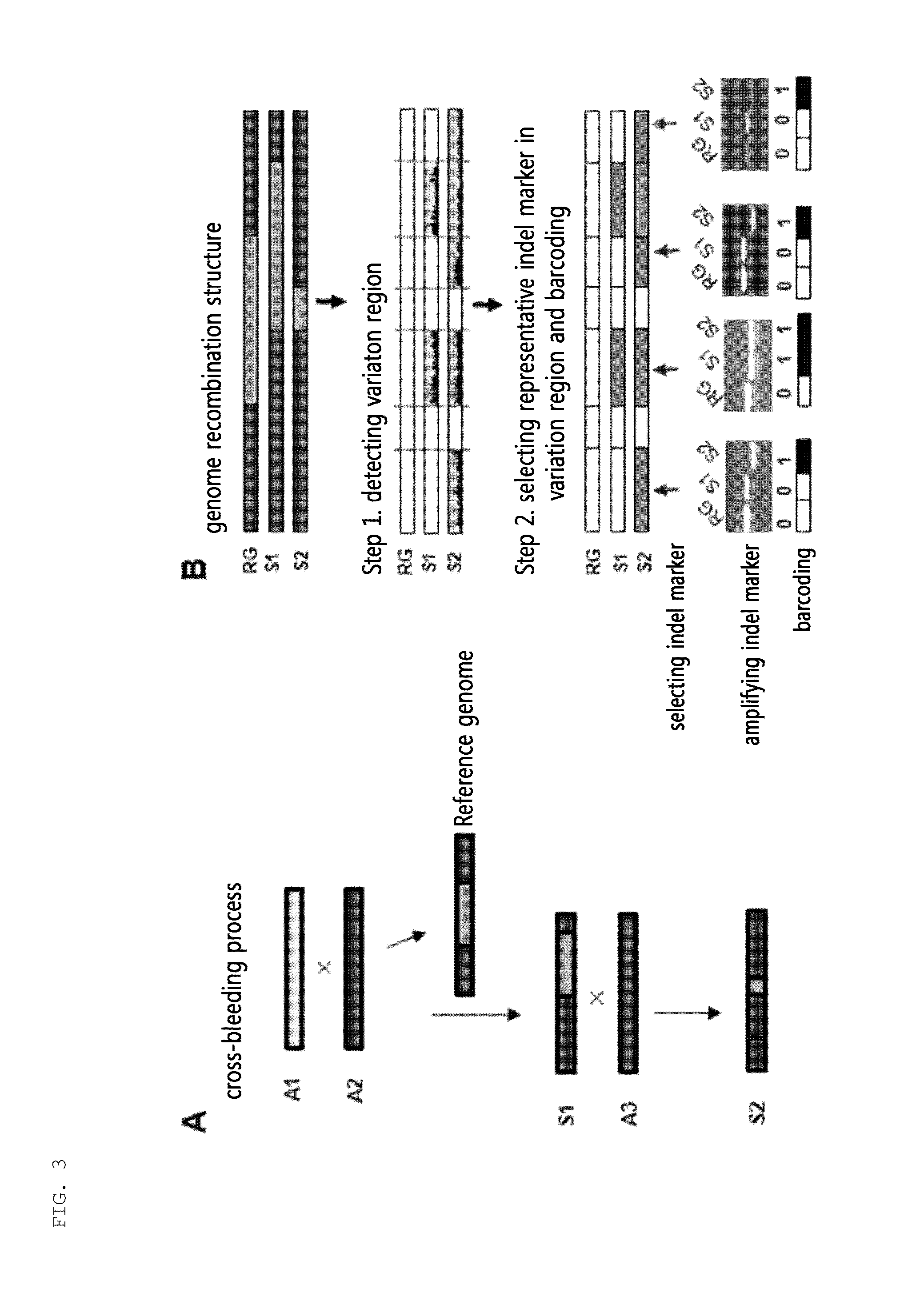
Provided is a variety identification-encoding system, including: a chromosome-decoding module decoding a chromosome of a reference genome variety and a chromosome of a target variety; a variation region-detecting module detecting a variation region in the decoded chromosome through single nucleotide variation dense region analysis; an amplification result-acquiring module setting an indel marker in the detected variation region and amplifying the indel marker by a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to acquire an amplification result; and an encoding module encoding the amplification result.
Owner:REPUBLIC OF KOREA (MANAGEMENT RURAL DEV ADMINISTRATION)
Universal primer set for amplifying whole genome sequence of canine distemper viruses and use thereof
PendingCN108998572AClarify the variationPromote amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVirulent characteristicsCanine distemper virus CDV
The invention discloses a universal primer set for amplifying a whole genome sequence of canine distemper viruses and a use thereof. The primer set is composed of 11 pairs of primers. Each pair of theprimers are composed of an upstream primer and a downstream primer. The nucleotide sequences of the 11 pairs of primers are respectively shown in the formulas of SEQ ID NO. 1-22. The whole genome sequences of 23 canine distemper virus strains published in GenBank are compared and 11 pairs of specific universal primers are designed according to a conserved region. The research result shows that the 11 pairs of universal primers can conveniently and accurately amplify the whole genome sequences of a wild canine distemper virus strain and a vaccine strain, significantly improve the efficiency ofacquiring whole genome sequences of different strains of canine distemper viruses, and shorten the acquisition time of the whole genome sequences of other unknown canine distemper virus strains. Through the universal primer set, the viral nucleotide variation before and after the adaptation of wild canine distemper viruses to cells is determined and the technological means for understanding the pathogenic mechanism of wild canine distemper viruses and finding a key virulence site for wild canine distemper viruses are provided.
Owner:INST OF SPECIAL ANIMAL & PLANT SCI OF CAAS
Reagent kit for determining specific nucleotide variations
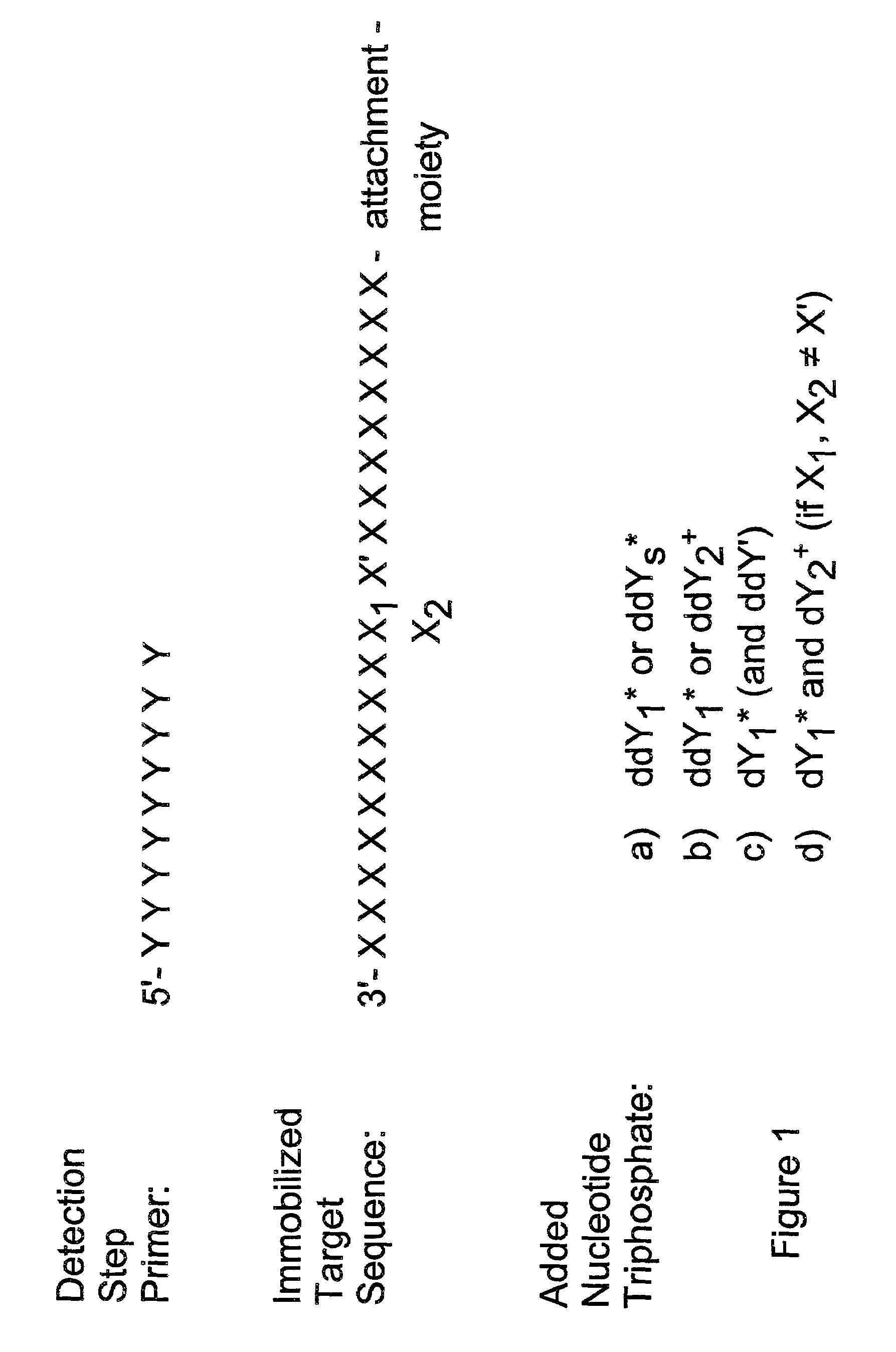
InactiveUS7132235B2Improve automationFew and easily procedureSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotide variationNucleotide sequencing
Detection of variable nucleotide(s) is based on primer extension and incorporation of detectable nucleoside triphosphates. By selecting the detection step primers from the region immediately adjacent to the variable nucleotide, this variation can be detected after incorporation of as few as one nucleoside triphosphate. Labelled nucleoside triphosphates matching the variable nucleotide are added and the incorporation of a label into the detection step primer is measured. The selection of the detection step primer is important to the method according to this invention and is dependent on the nucleotide sequence of interest. The detection step primers are preferably selected so as to span the region immediately toward the 3′ end from the variable nucleotide to be detected. The detection step primers can also be complementary to a sequence beginning several nucleotides removed from the variable nucleotide. The only limitation concerning the position of the detection step primers is that the sequence between the 3′ end of the detection step primer and the variable nucleotide to be detected must not contain a nucleotide residue of the same type as the one to be detected. The detection step primers can equally well be chosen to be complementary to either the coding or non-coding strands of the nucleotide sequence of interest.
Owner:ORCHID CELLMARK INC
Epitaxial probe type qPCR detection method for SNV
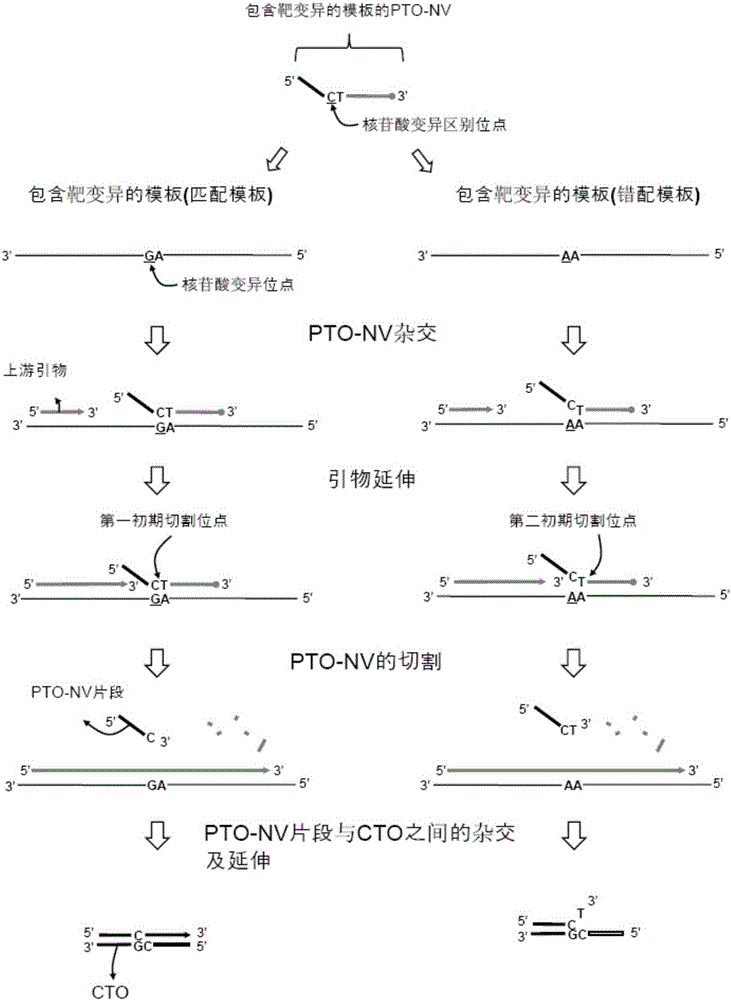
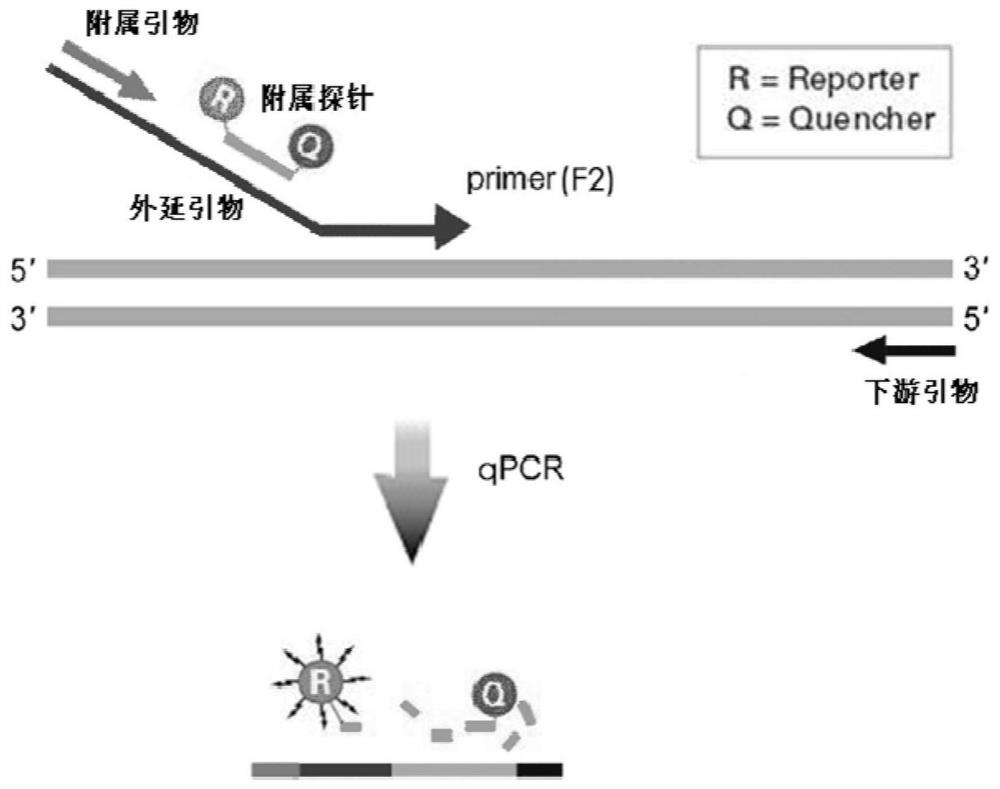
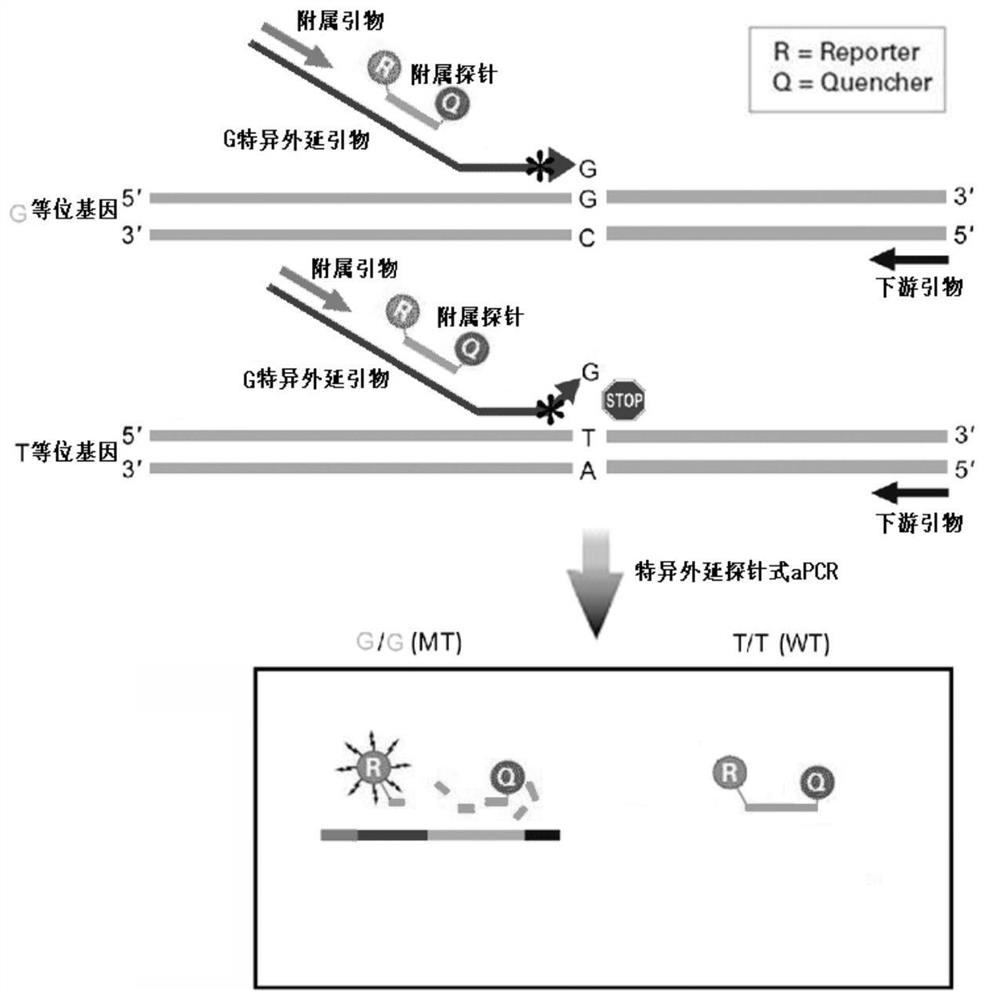
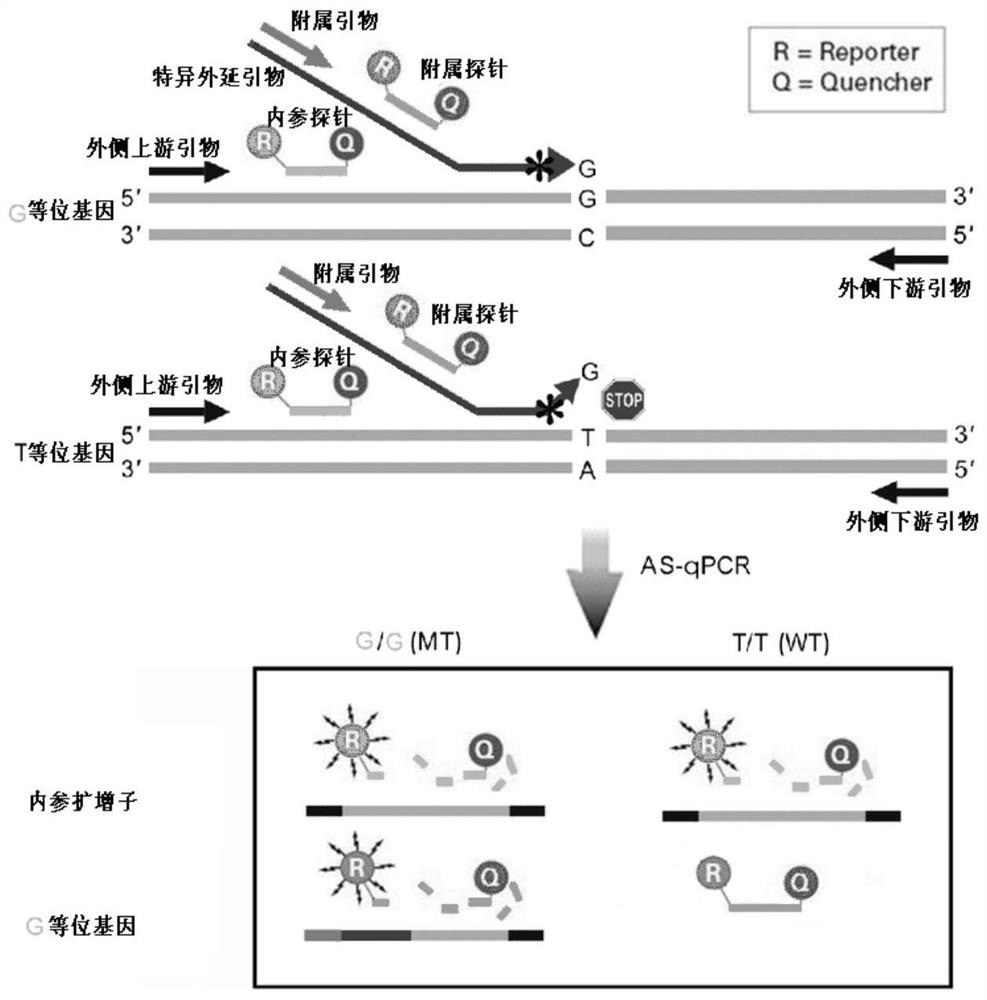
PendingCN113846147AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesNucleotide variationGenetics
The invention discloses an epitaxial probe type qPCR detection method for single nucleotide variation (SNV). Four primers are designed according to known single nucleotide variation sites, two of the four primers are outer side primers, the other two primers are specific primers, bases at the 3' ends of the specific primers are respectively complementary with bases of a mutation template and a normal template, mismatch can be introduced or not introduced into bases near the 3' ends, epitaxy of a segment of artificial sequence is carried out from the 5' end of each specific primer, a homodromous affiliated primer is designed on the 5' segment of each artificial sequence, an affiliated probe is designed on the 3' segment of each artificial sequence, and in the amplification of the specific primers and downstream primers, the affiliated probes on the specific primers are degraded and emits light in the extension of the affiliated primers so as to indicate the amplification efficiency of the specific primers. If only one genotype of the single nucleotide variation sites is detected, the two outer side primers, one specific primer, the affiliated primer of the specific primer and the probes can be used. The method still has a plurality of implementation modes, and compared with probe type AS-PCR, the method has higher sensitivity and lower cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Method for determining specific nucleotide variations
InactiveUS7026117B2Improve automationFew and easily procedureSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotide variationNucleotide sequencing
Detection of variable nucleotide(s) is based on primer extension and incorporation of detectable nucleoside triphosphates. By selecting the detection step primers from the region immediately adjacent to the variable nucleotide, this variation can be detected after incorporation of as few as one nucleoside triphosphate. Labelled nucleoside triphosphates matching the variable nucleotide are added and the incorporation of a label into the detection step primer is measured. The selection of the detection step primer is important to the method according to this invention and is dependent on the nucleotide sequence of interest. The detection step primers are preferably selected so as to span the region immediately toward the 3′ end from the variable nucleotide to be detected. The detection step primers can also be complementary to a sequence beginning several nucleotides removed from the variable nucleotide. The only limitation concerning the position of the detection step primers is that the sequence between the 3′ end of the detection step primer and the variable nucleotide to be detected must not contain a nucleotide residue of the same type as the one to be detected. The detection step primers can equally well be chosen to be complementary to either the coding or non-coding strands of the nucleotide sequence of interest.
Owner:LAB OF AMERICA HLDG
Identification method of group of genomic characteristic mutation fingerprints associated with homologous recombination repair defects
The present invention discloses a genomic characteristic mutation fingerprint related to hHRD type homologous recombination repair defects and comprises a combination characteristic of a single nucleotide variation (SNV) and insertion deletion (Indel) genomic fingerprint, and an identification method thereof. The fingerprint characteristics can be subjected to high-throughput whole-genome resequencing, bioinformatics software analysis and statistical correlation analysis and are used to identify infectious diseases or tumors with the characteristic mutation fingerprints, especially hepatitis Bvirus infection and related diseases, including liver cirrhosis, liver fibrosis and liver cancer. The mutation fingerprint can also be used to guide methods and uses of treatments of targeted drugs targeting the homologous recombination defects on a variety of the various tumors with the hHRD homologous recombination repair defects, including but not limited to breast cancer, ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, endometrioid carcinoma, ovarian clear cell carcinoma, prostate cancer, gastric cancer, skin cancer, hepatitis B virus infection or related liver cirrhosis, liver cancer and bile duct cell cancer.
Owner:THE WEST CHINA SECOND UNIV HOSPITAL OF SICHUAN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com