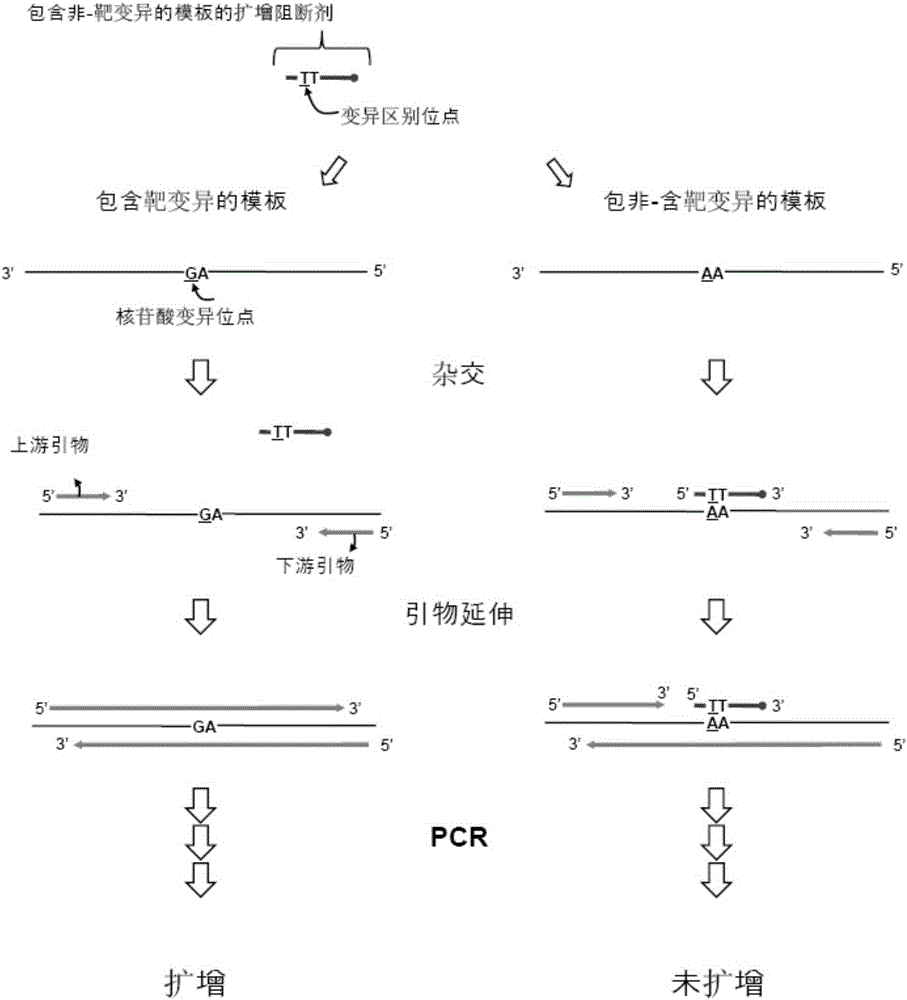
Detection of nucleotide variation on target nucleic acid sequence
A target nucleic acid sequence and target nucleotide technology, which is applied in the determination/testing of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, recombinant DNA technology, etc., and can solve the problem of inability to completely block the amplification of wild-type alleles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0217] [Example 1 (Interchain Interactivity-Dual Labeling)]
[0218] In Example 1 of the interactive dual labeling system, the first fragment or capture and template oligonucleotides have an interactive dual label comprising a reporter molecule and a quencher molecule, the extension dimerization in step (e) above The melting of the substance induces a change in the signal from the interacting dual label to provide the target signal in step (e). exist Figure 5 Example 1 of an interactive dual labeling system is shown diagrammatically in . Example 1 was named Interchain Interactivity-Dual Labeling.
example 1-1
[0219] [Example 1-1 (Interstrand Interactivity on Capture and Templated Oligonucleotides—Dual Labeling)]
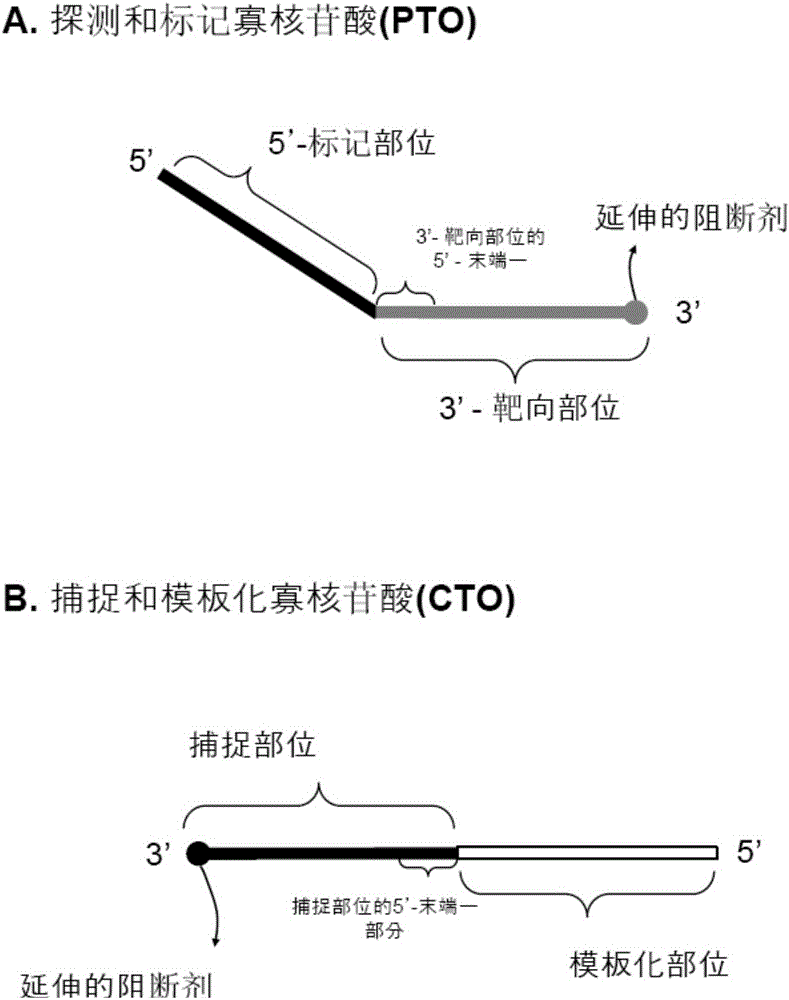
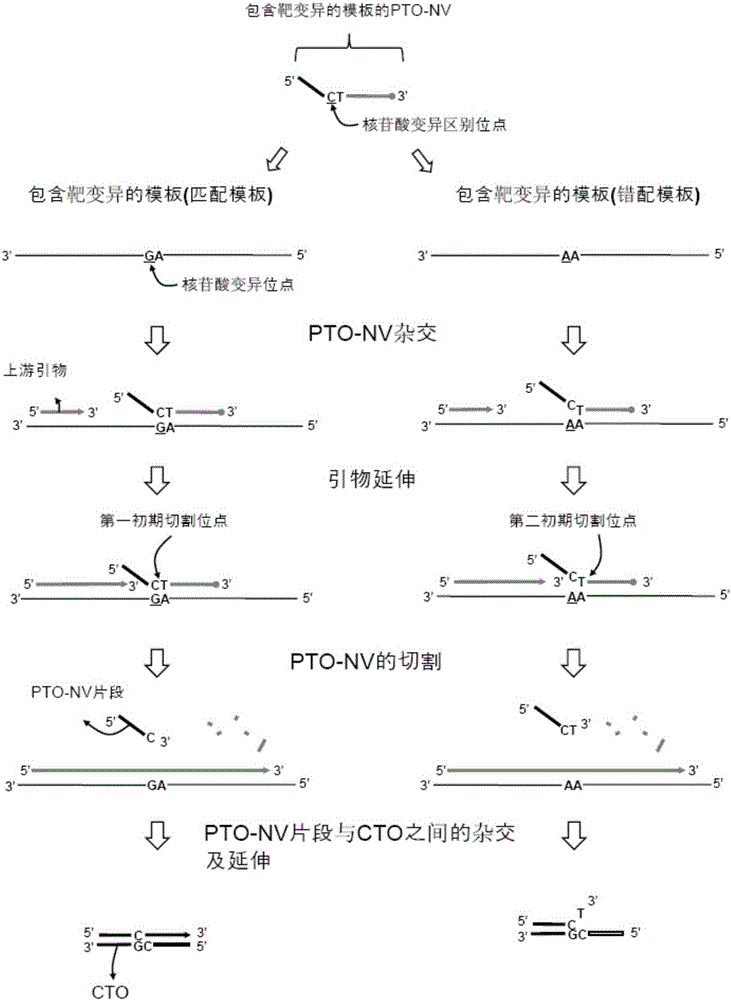
[0220] refer to Figure 5 , to illustrate the illustrated example. The templated sites of the capture and template oligonucleotides have reporter and quencher molecules. Probing and labeling oligonucleotide-nucleotide variants that hybridize to the target nucleic acid sequence are cleaved and a first fragment is released, and the first fragment is hybridized to the capture site of the capture and templated oligonucleotides and extended to form extended dimer.
[0221] In the case where the extended dimer is formed in step (d) above, the reporter and quencher molecules of the capture and template oligonucleotides are structurally separated from each other such that the quencher molecule does not interfere with the reporter molecule from the reporter molecule. The signal is quenched, and in the case where the extension dimer is unchained in step (e), the reporter molecul...
example 1-2
[0234] [Example 1-2 (Detection and Labeling of Oligonucleotides - Interstrand Interactivity on Nucleotide Variations - Dual Labeling)]
[0235]The 5'-labeling sites that detect and label oligonucleotide-nucleotide variations can have reporter and quencher molecules. The probe and label oligonucleotide-nucleotide variants that hybridize to the target nucleic acid sequence are cleaved to release a first fragment comprising a 5'-labeled site with reporter and quencher molecules. The first fragment described above hybridizes to the capture site of the capture and templated oligonucleotides.
[0236] In the case of forming the extended dimer in the above-mentioned step (d), the reporter molecule and the quenching molecule on the above-mentioned first fragment are structurally separated from each other, so that the quenching molecule does not quench the signal from the reporter molecule, and in the In the case where the extension dimer is melted in step (e), the reporter ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com