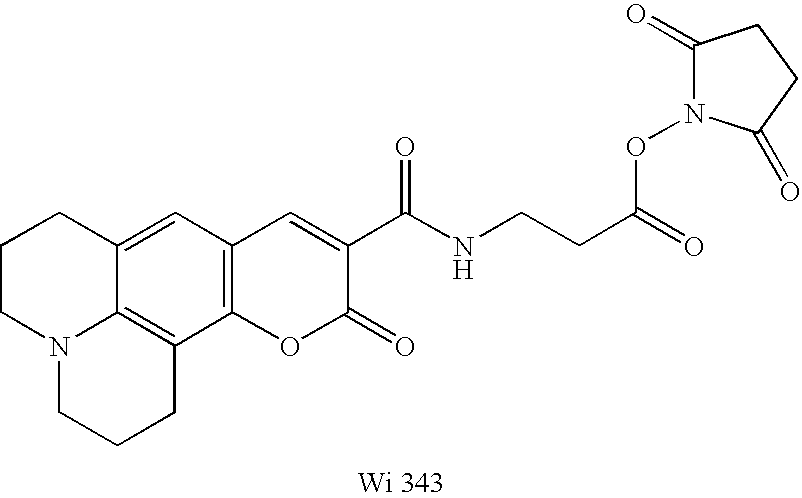
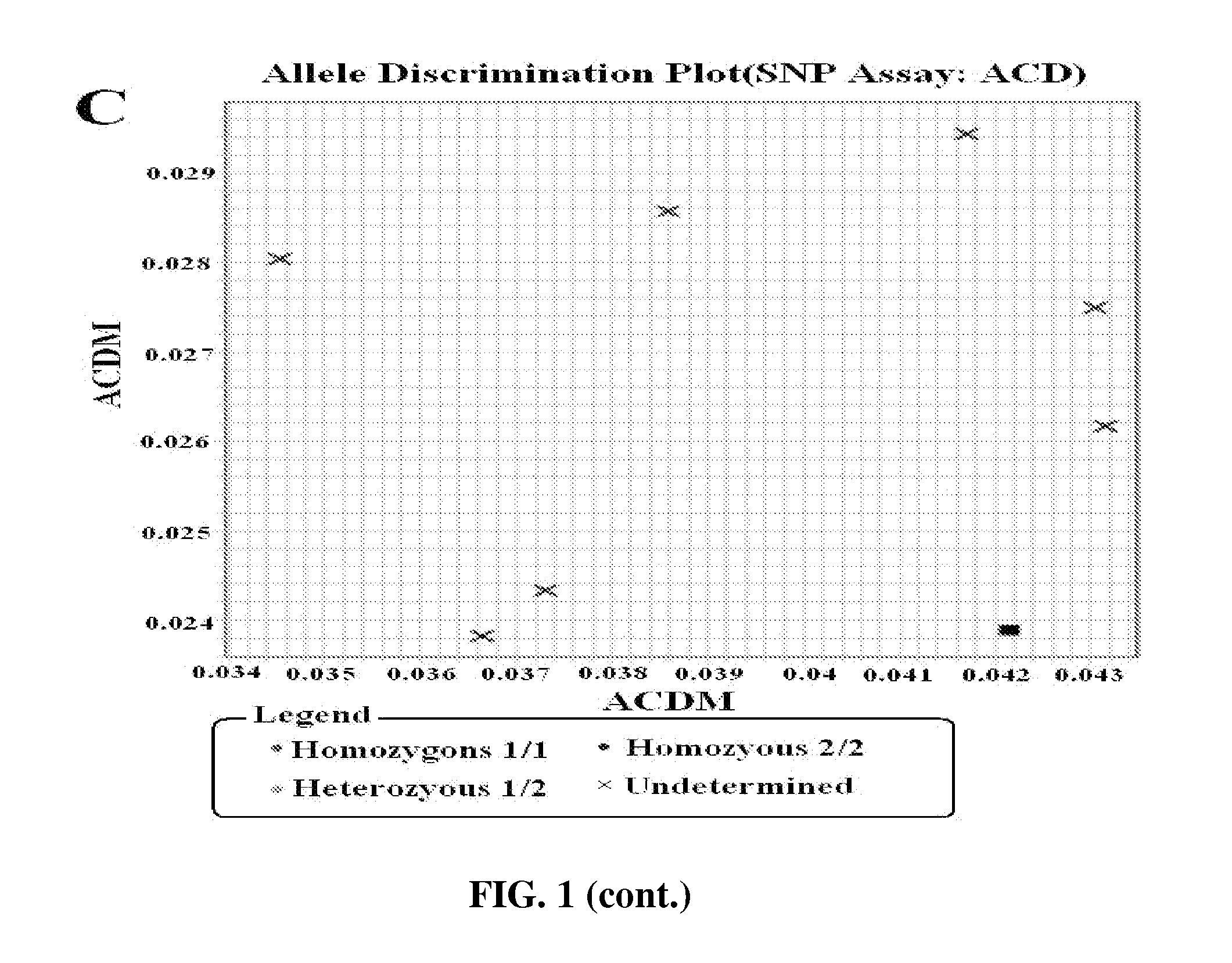
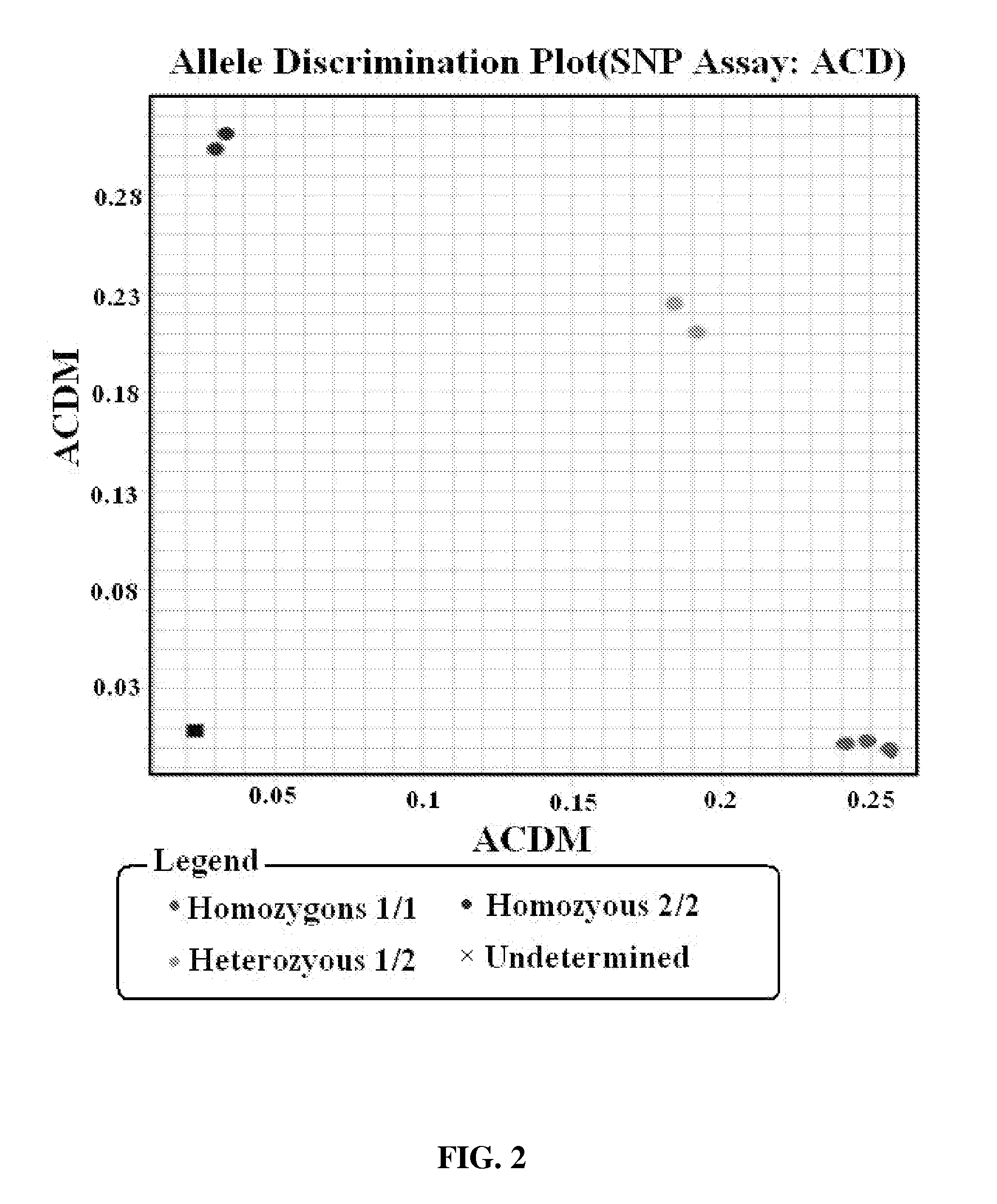
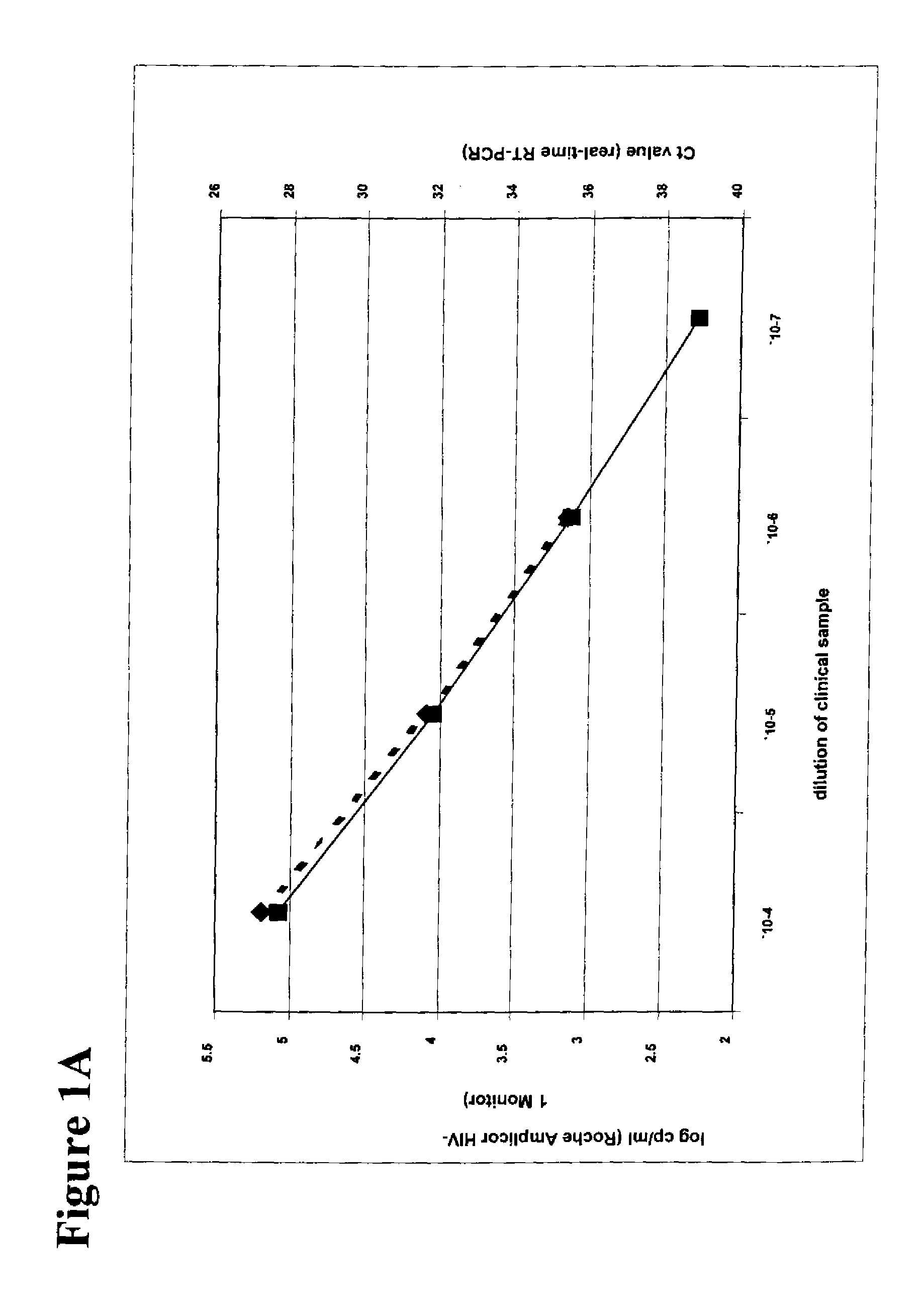
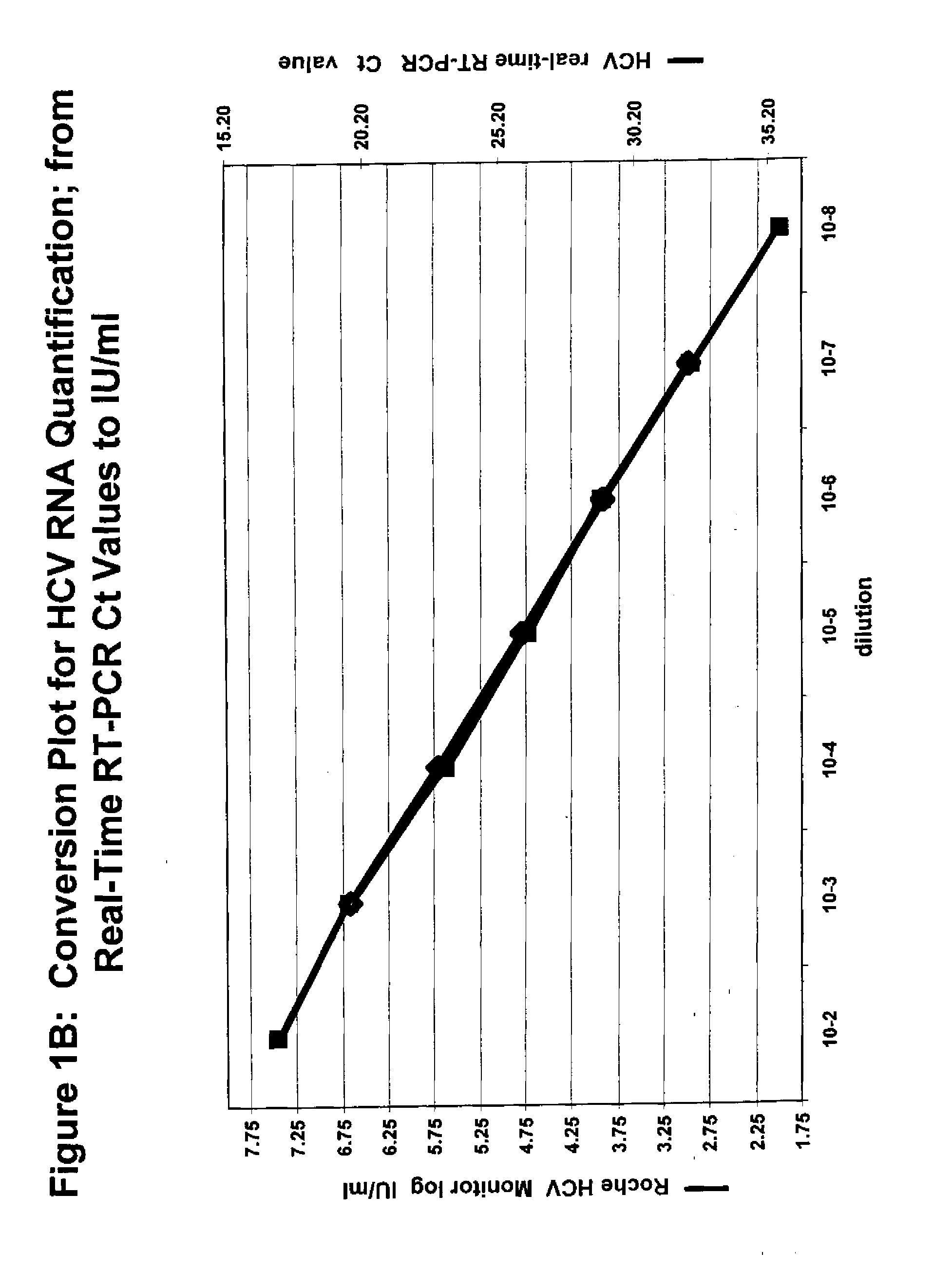
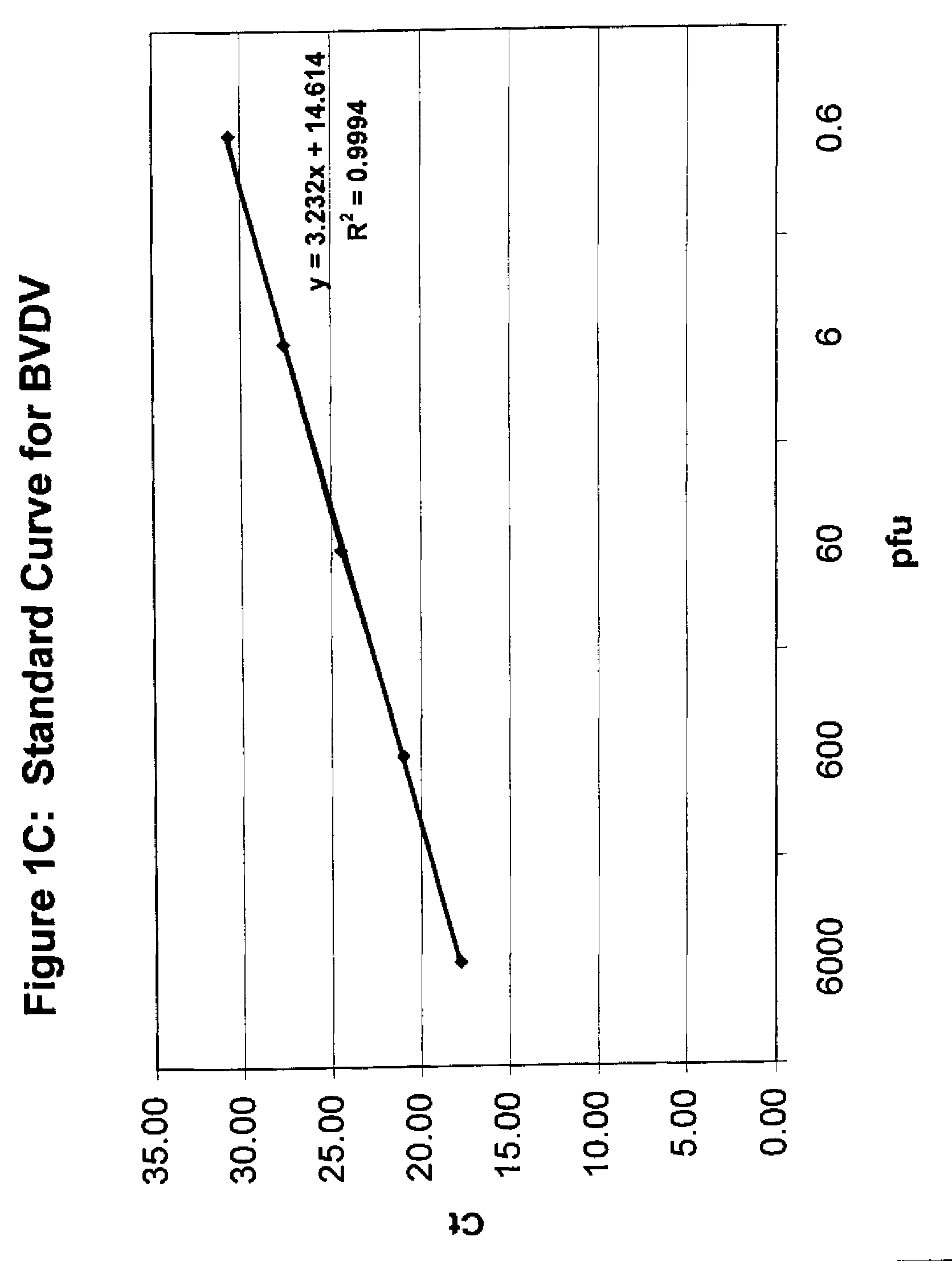
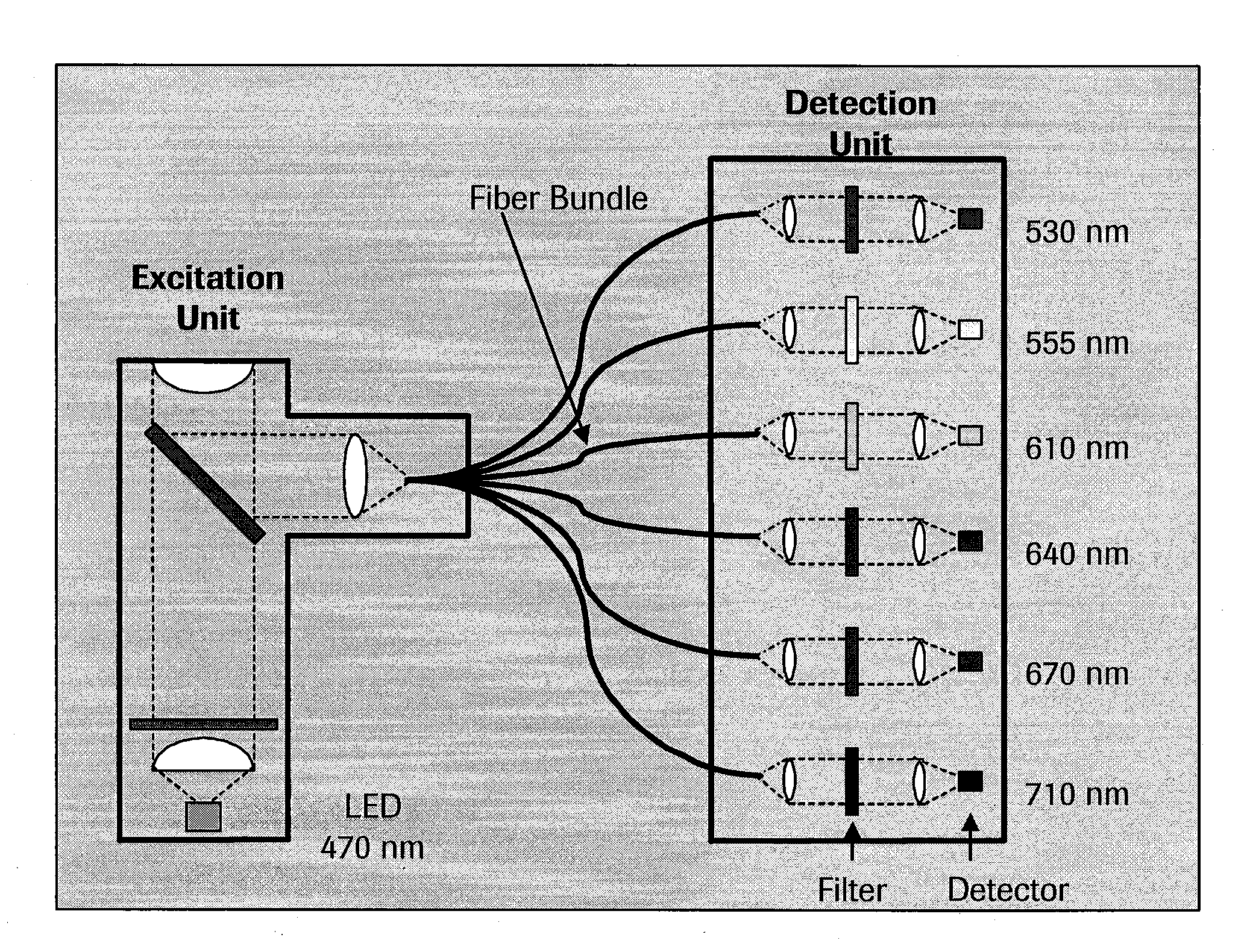
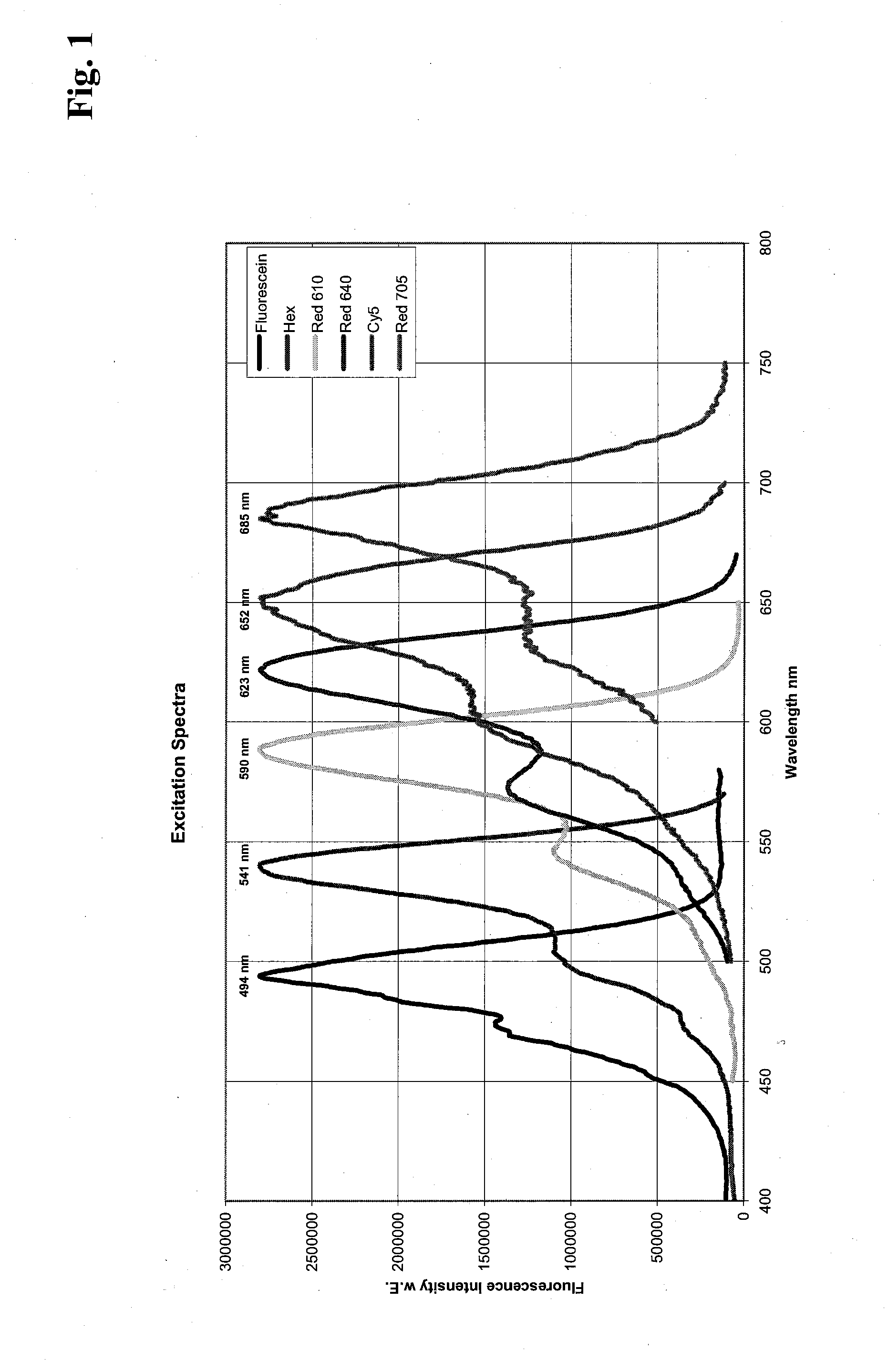
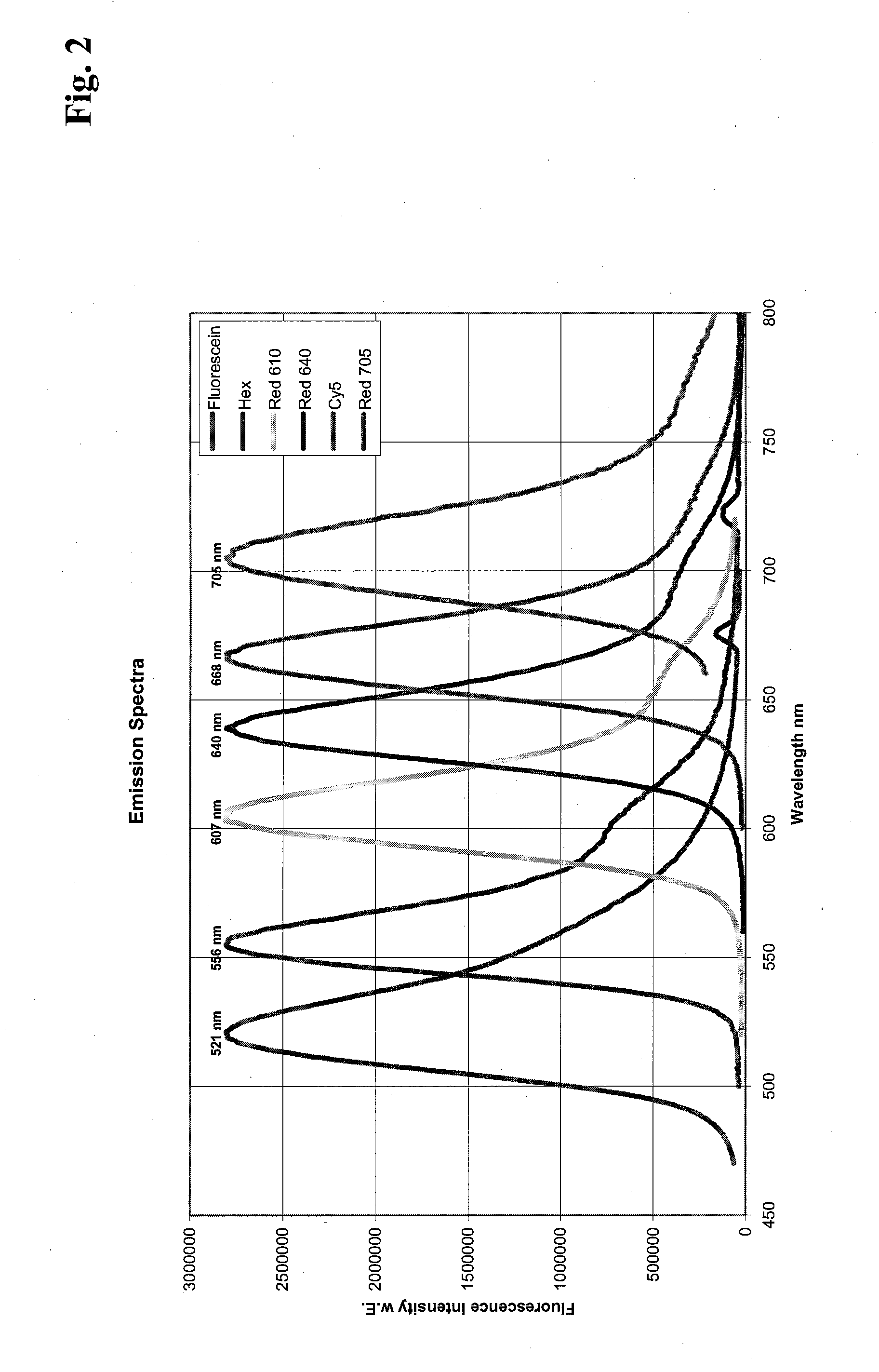
Patents
Literature
82 results about "Real-Time PCRs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A real-time polymerase chain reaction (Real-Time PCR), also known as quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR, i.e. in real-time, and not at its end, as in conventional PCR.
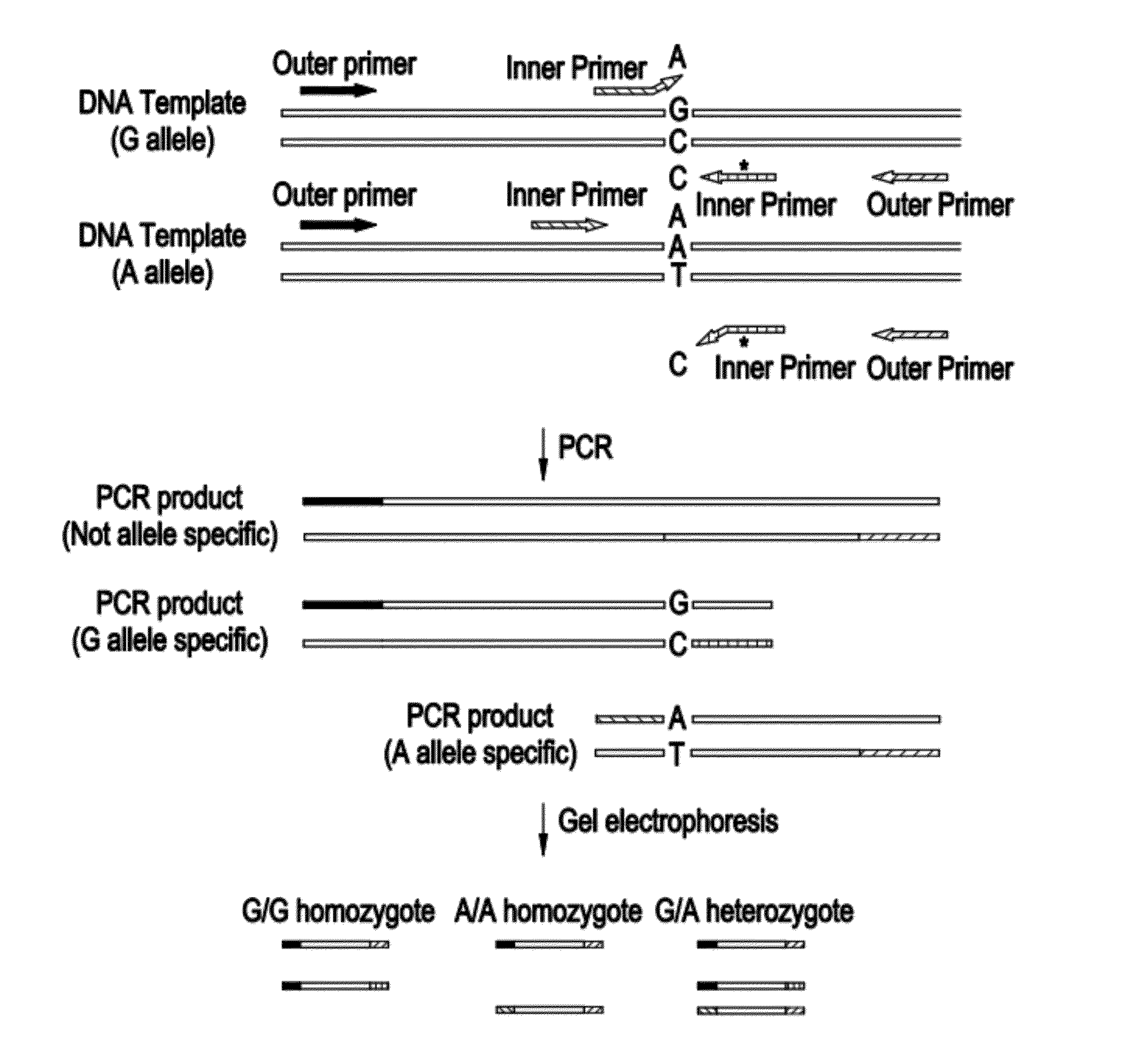
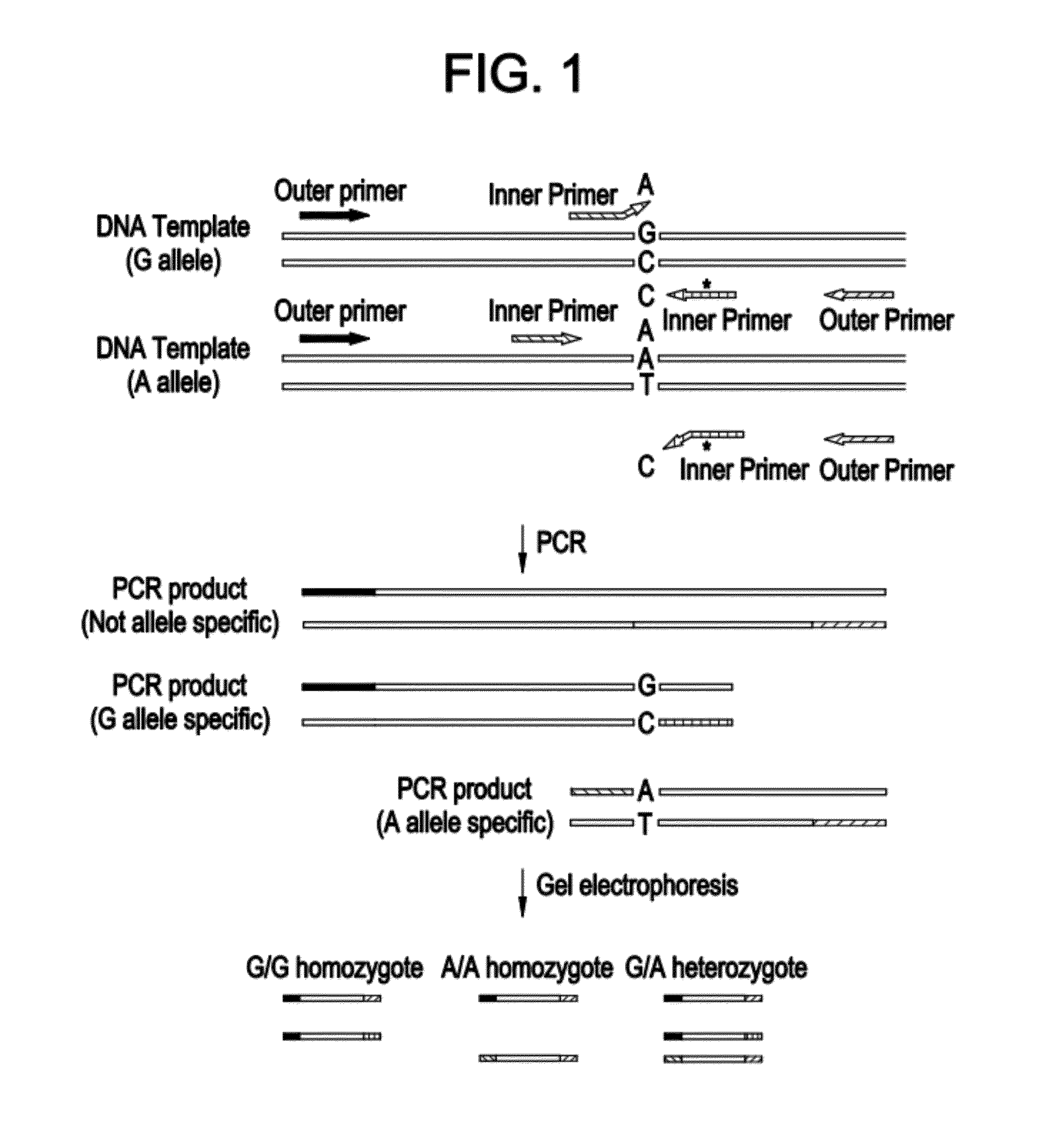
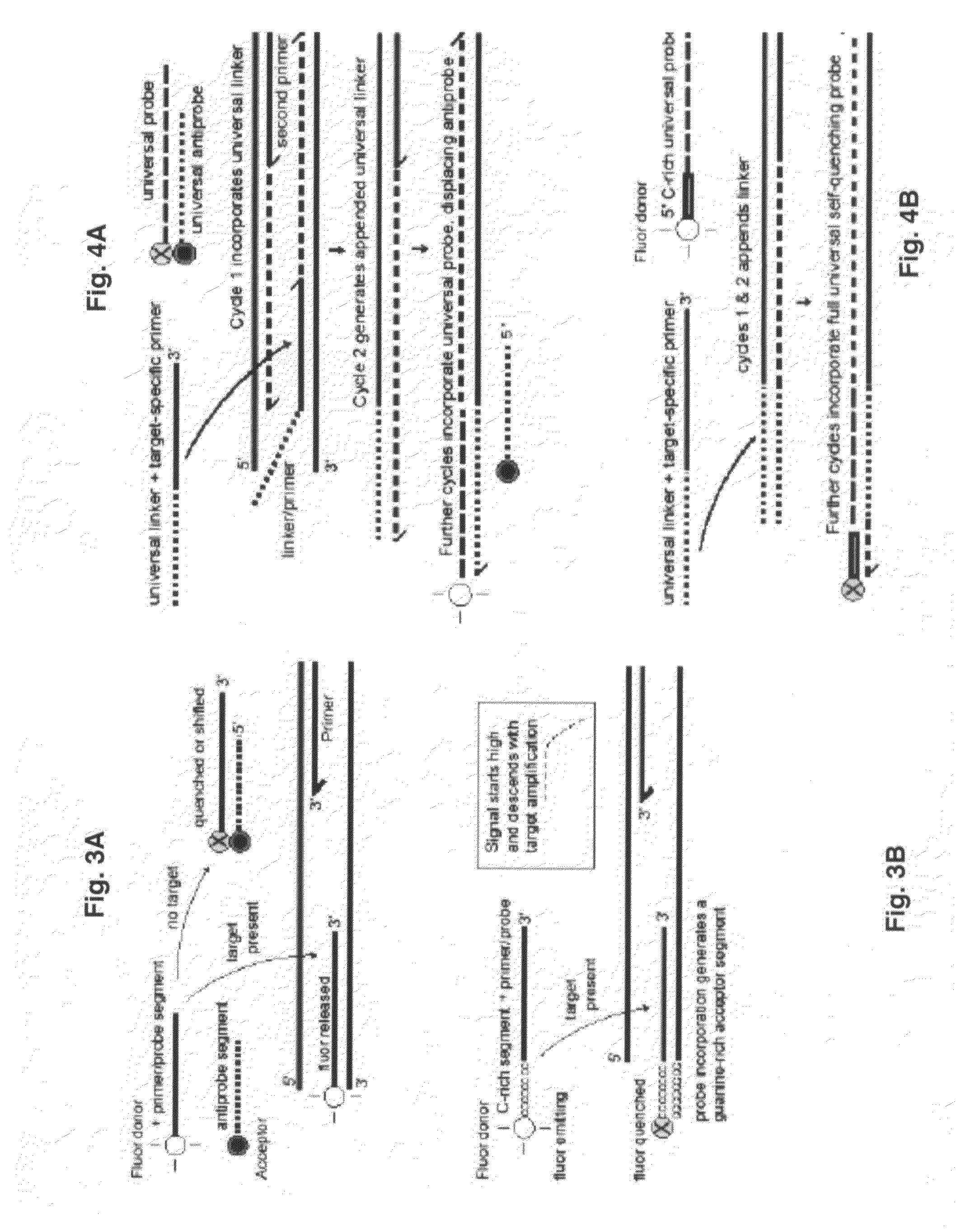
Double stranded linear nucleic acid probe and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050227257A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementReal-Time PCRsNucleic Acid Probes
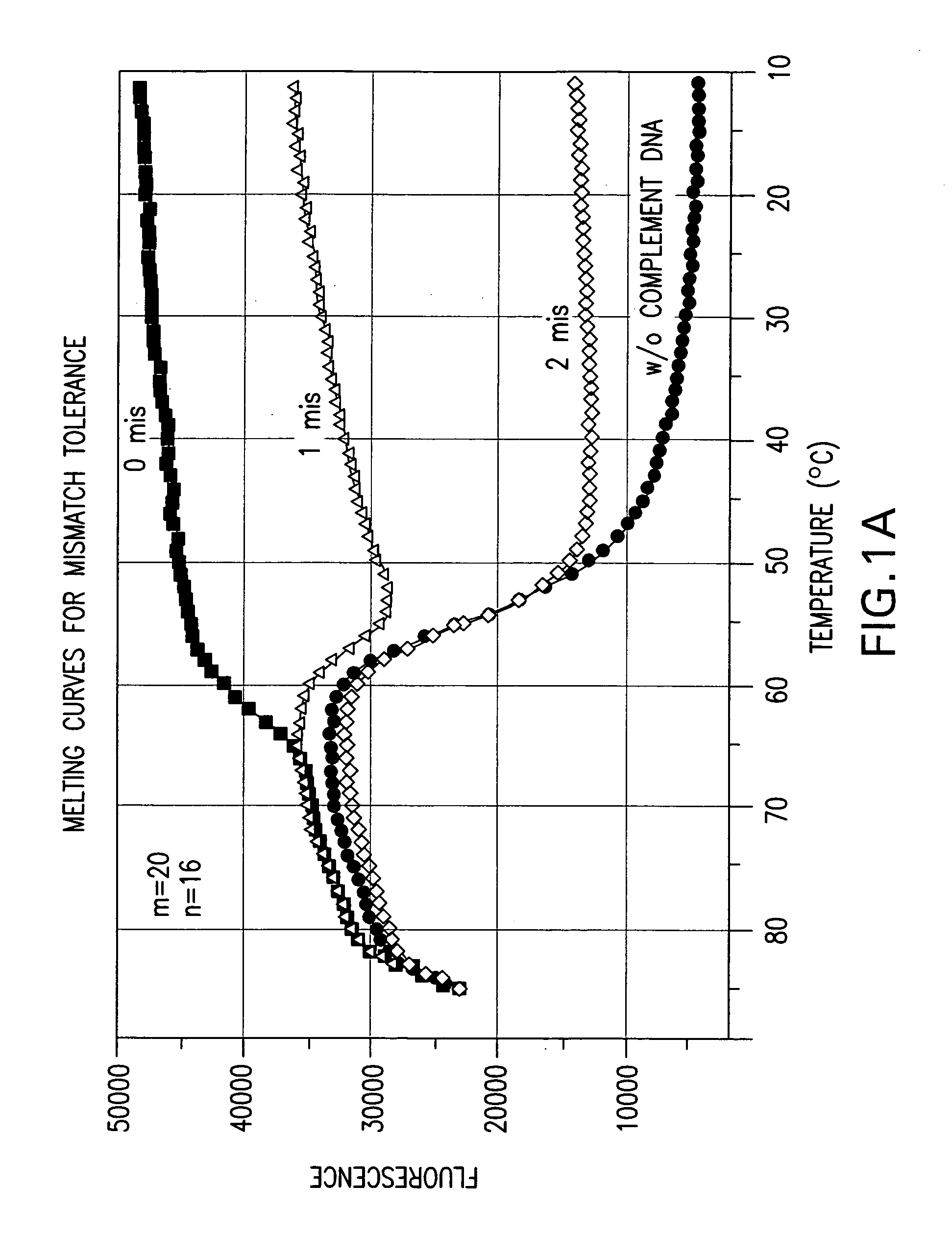
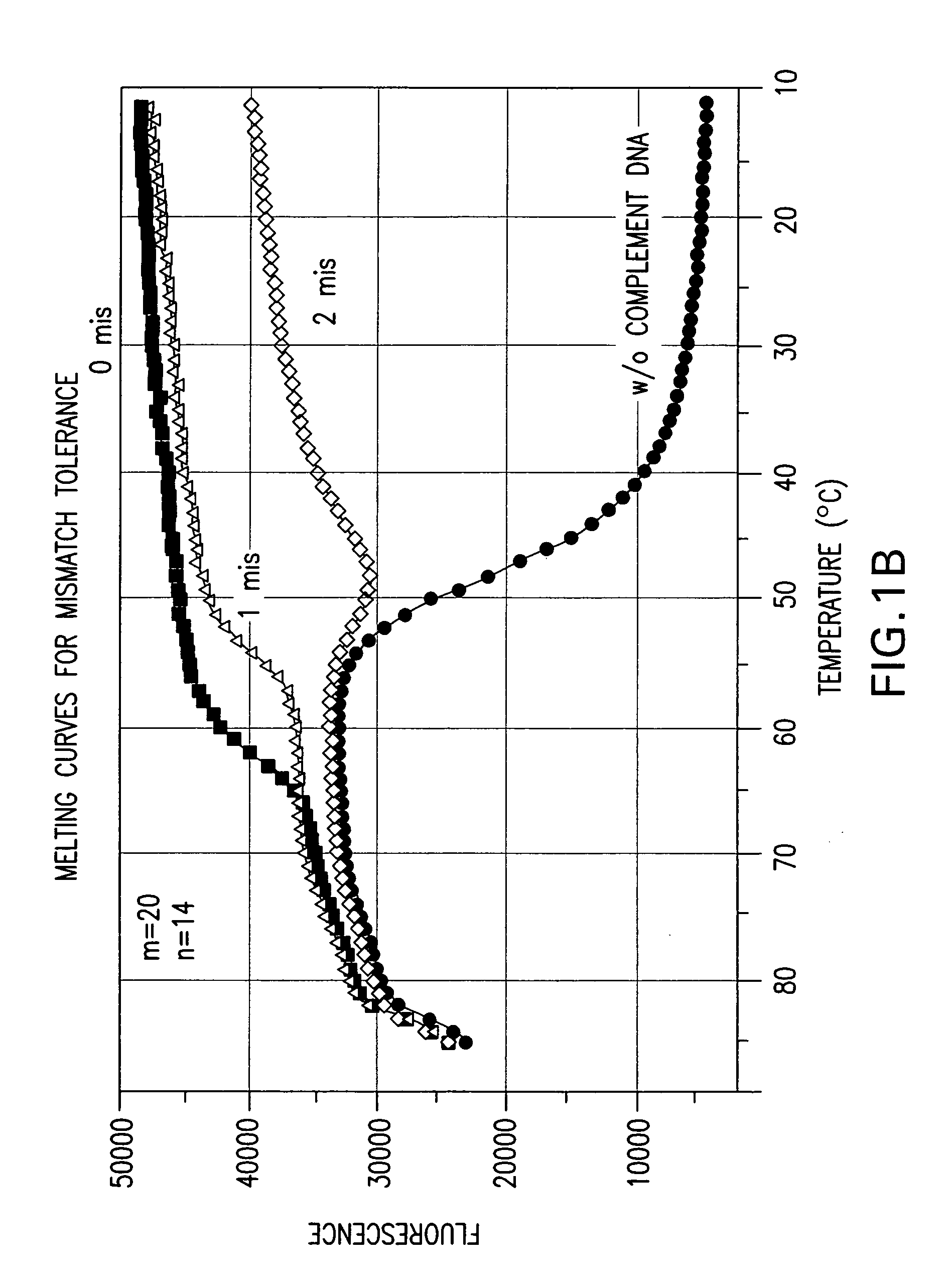
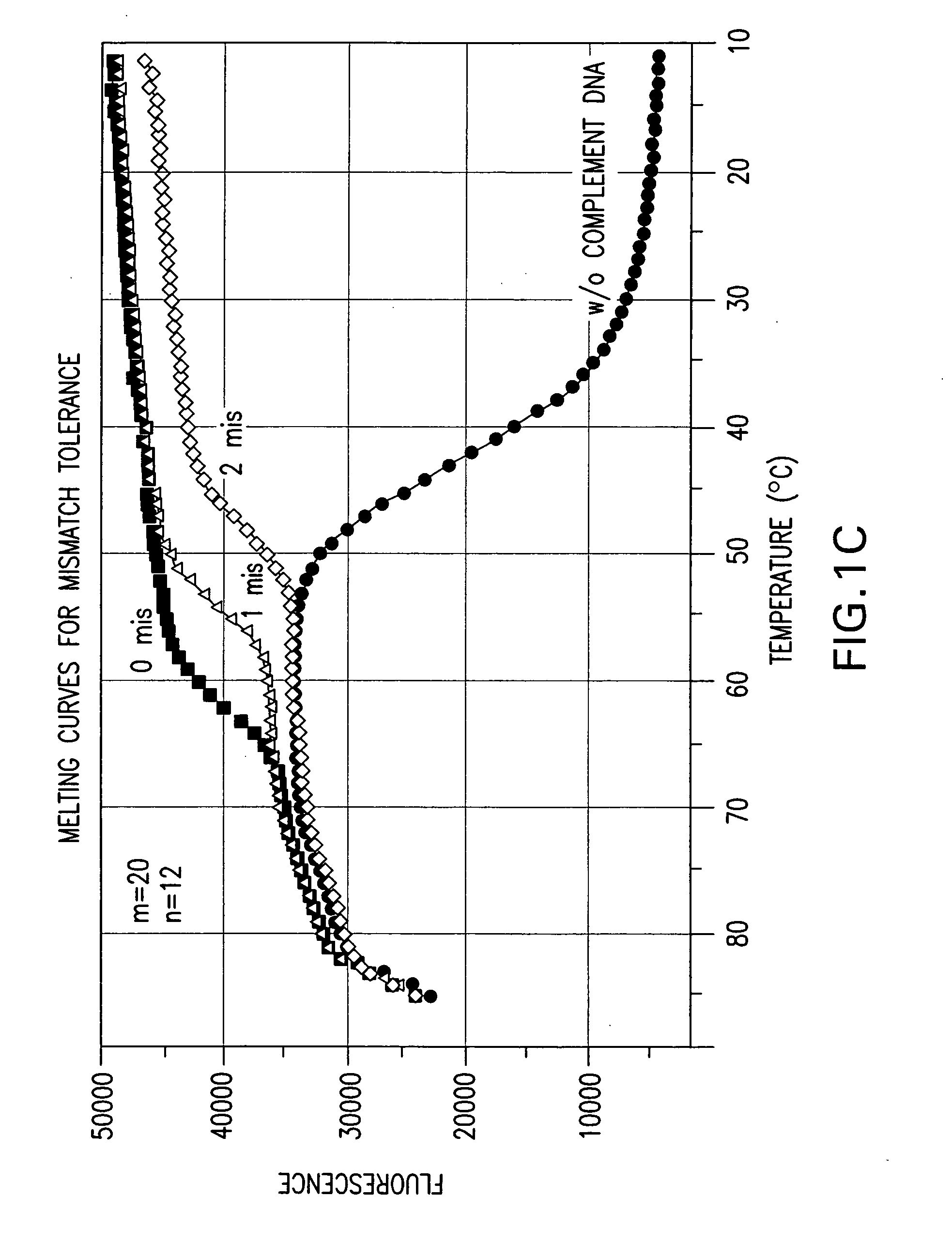
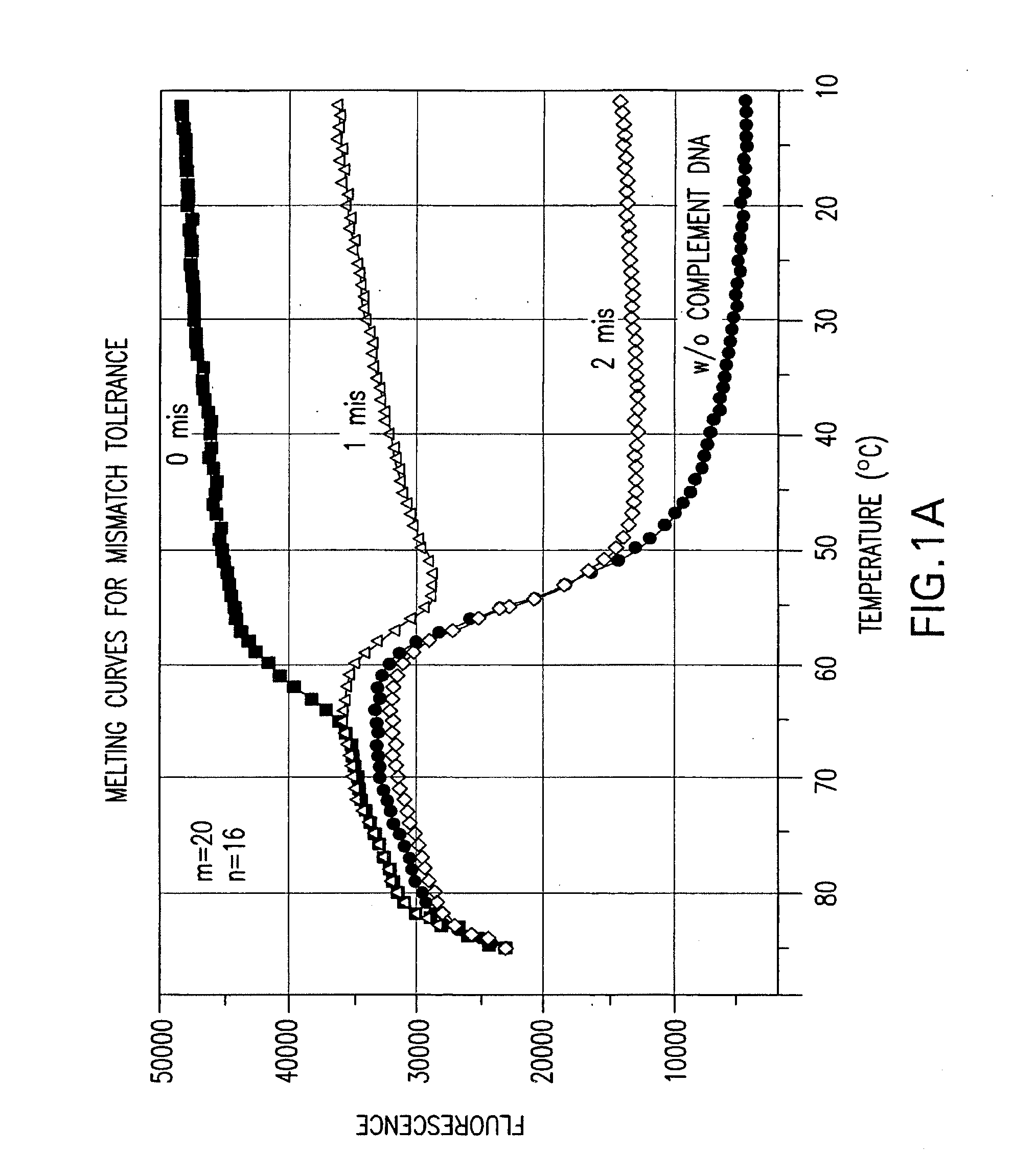
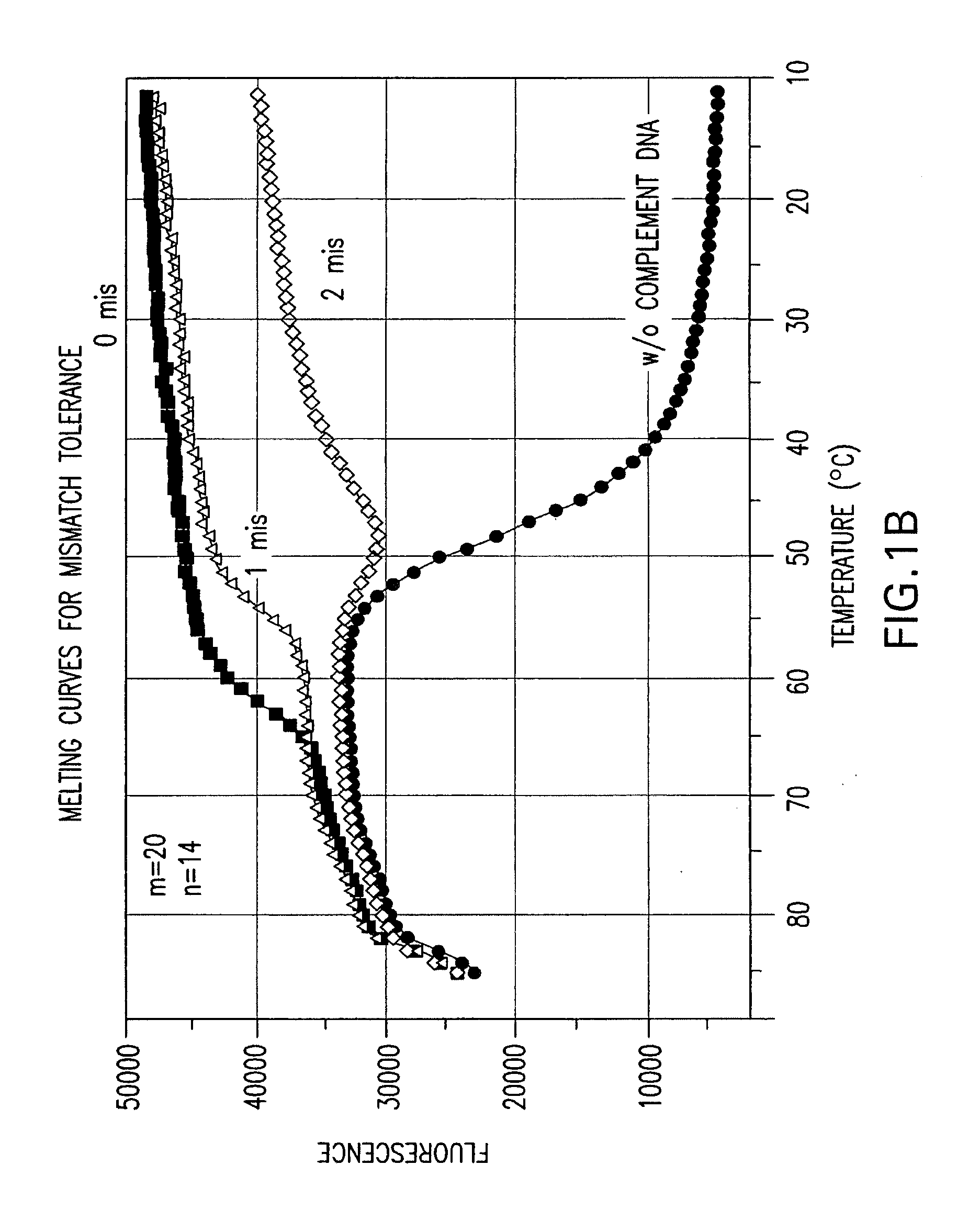
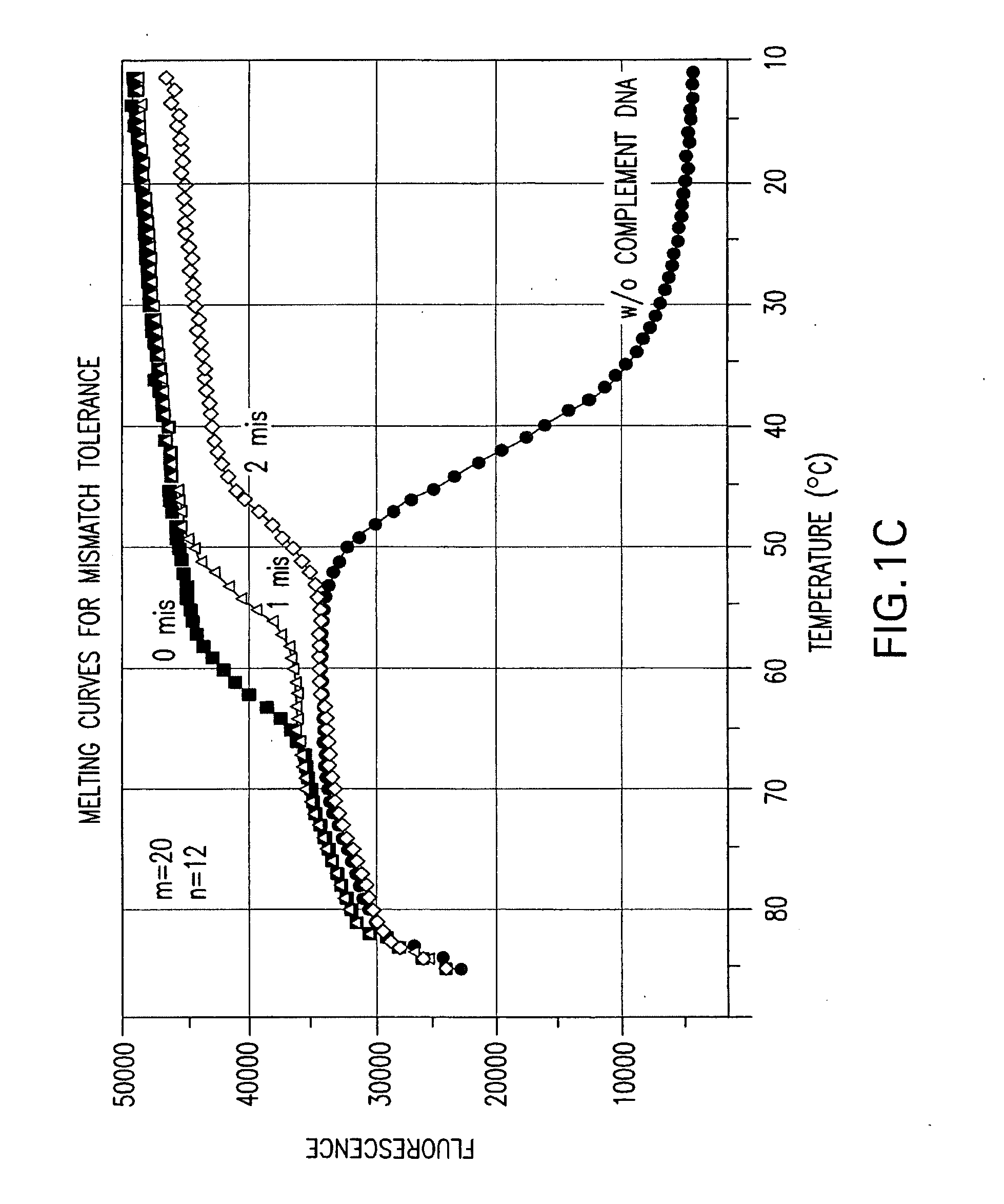
A double-stranded nucleic acid hybridization probe and methods of using the same are described. The probe described is particularly suited for real-time RT-PCR reactions and has high tolerance to mismatches.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Multiplex digital PCR
InactiveUS20130178378A1Low costEasy to controlNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplexingReal-Time PCRs
Embodiments of the claimed subject matter are directed to the ability to further multiplex in the digital regime using combinatorial color, temporal, and intensity encoding of probe sequences for a greater number of total signal readouts. A digital PCR solution is provide which enables the unique ability to identify a greater number of fluorescent probe sequences by using multiple color, temporal, and intensity combinations to encode each unique probe sequence. Furthermore, less expensive real-time PCR amplification indicators such as PicoGreen can be used to achieve multiplexed digital PCR based on temporal cues, intensity cues, or intensity and temporal cues combined, thus distinguishing primer pairs at greater degrees with significant cost reductions. These can also be used to enhance controls and normalize results for greater accuracy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Metastasis-associated gene profiling for identification of tumor tissue, subtyping, and prediction of prognosis of patients
InactiveUS20060211036A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAbnormal tissue growthReal-Time PCRs
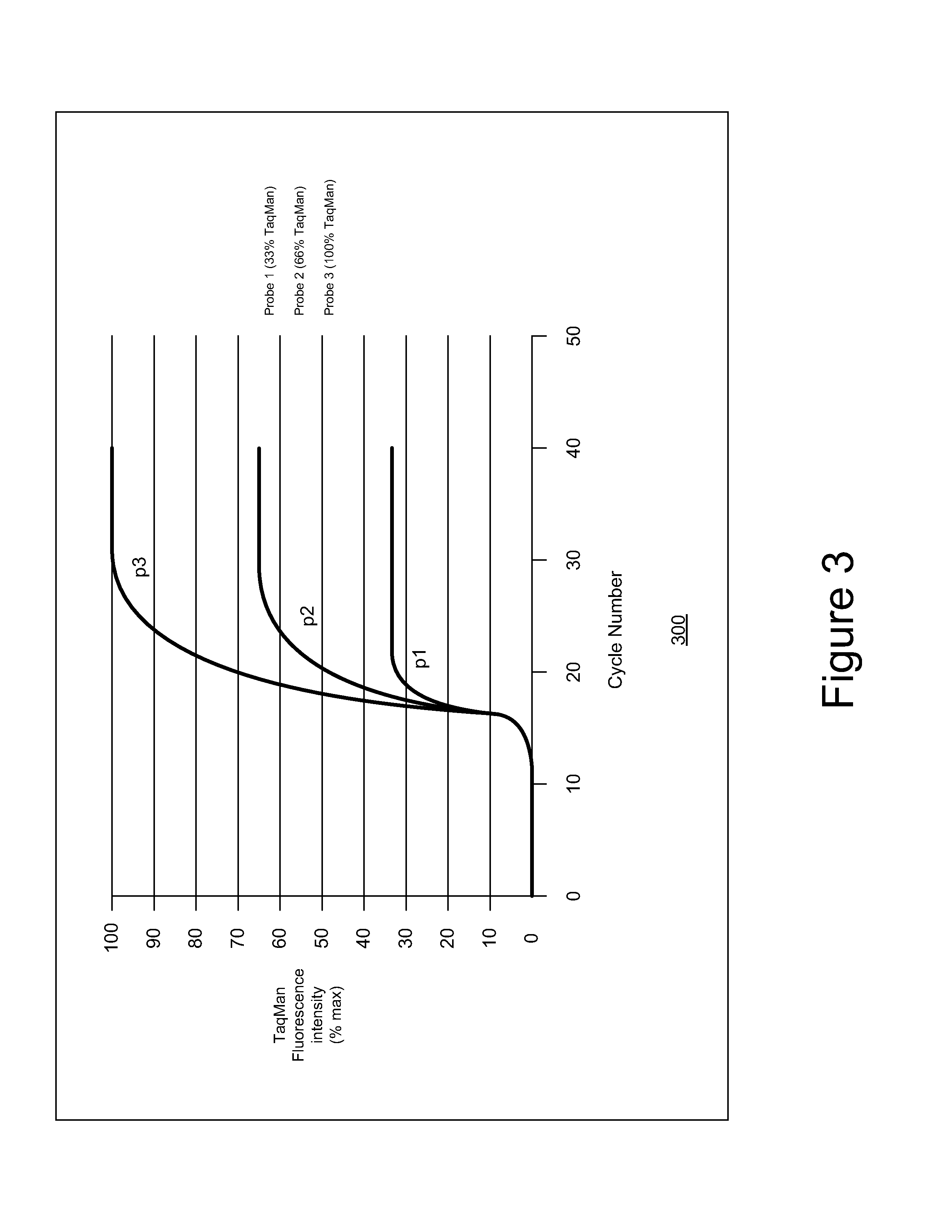
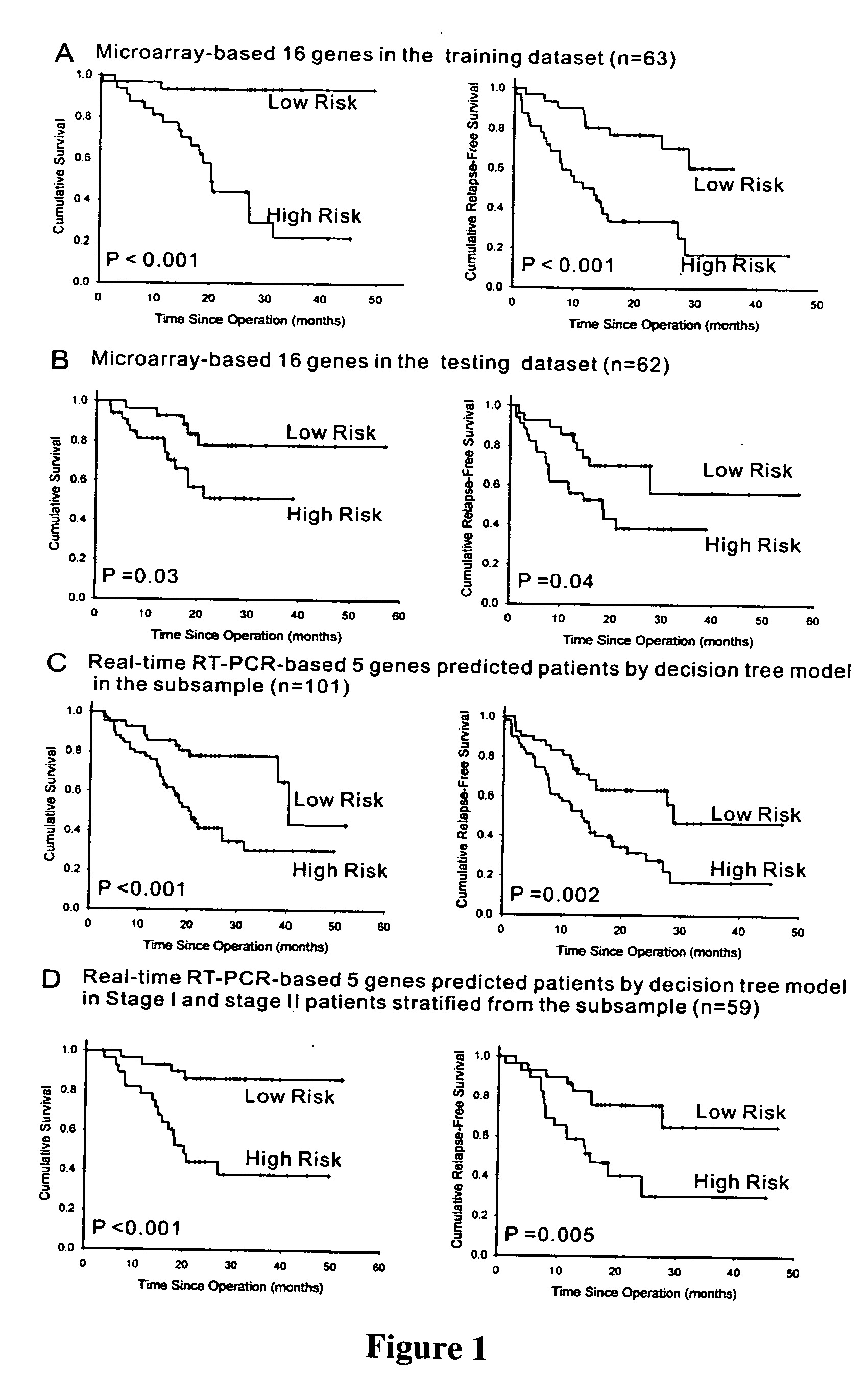
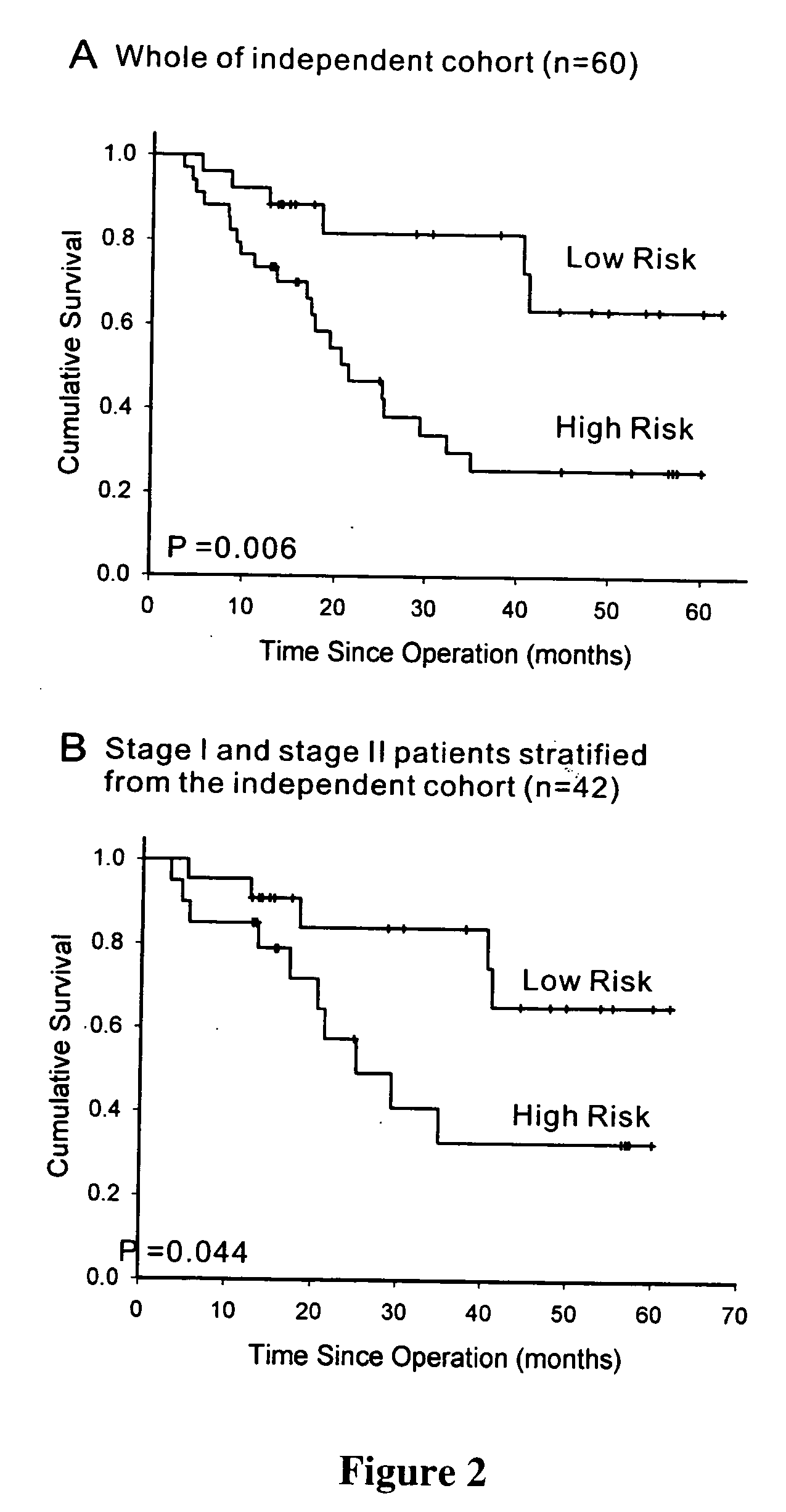
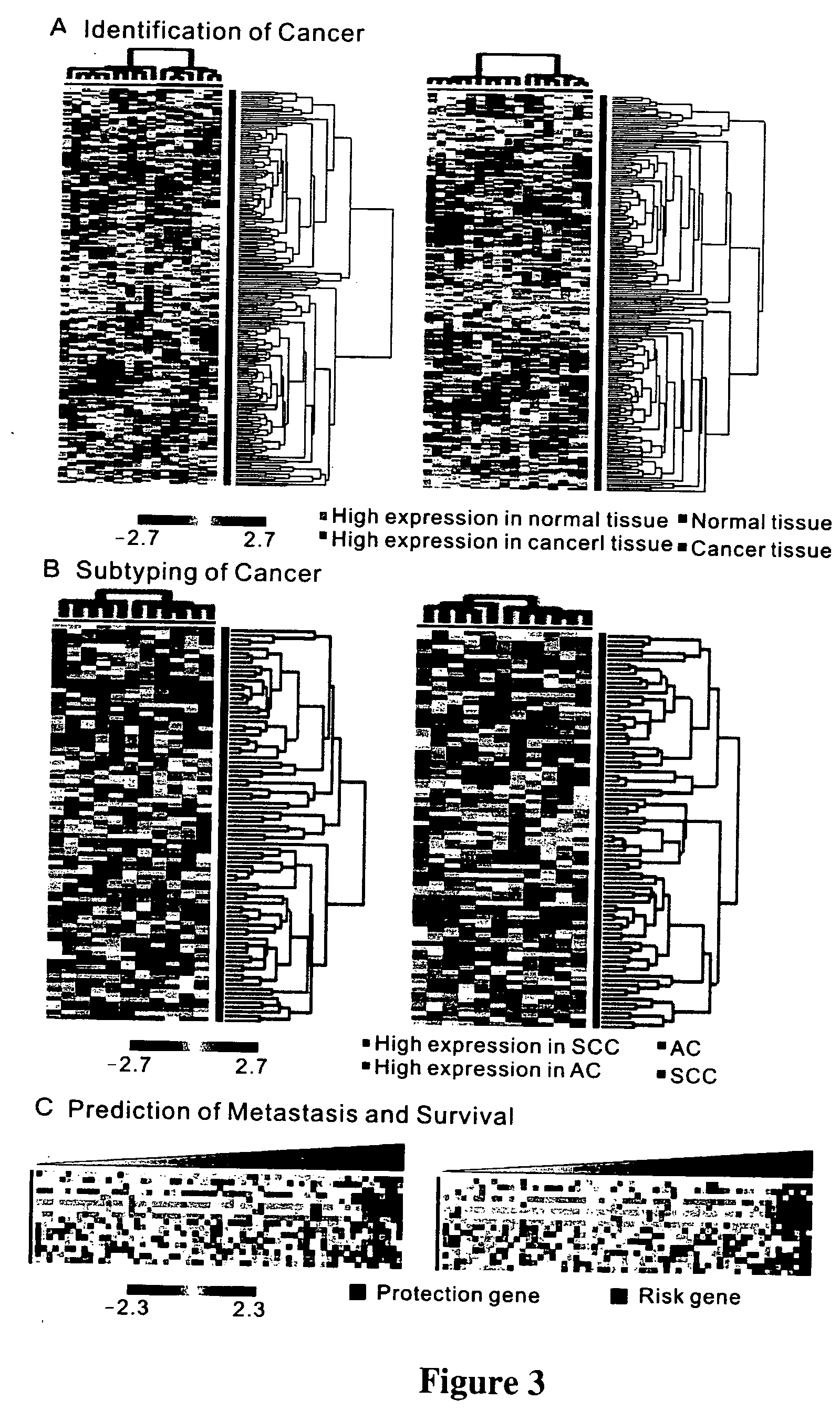
The present invention provides methods using a gene expression profiling analysis (1) to determine whether a human sample is a tumor using a gene set containing nucleic acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 1-7, 8-17 or 1-17; (2) to identify whether a tumor tissue is an adenocarcinoma (using a gene set containing nucleic acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 15, and 18-21) or a squamous cell carcinoma (using a gene set containing nucleic acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 22-27); and (3) to predict the prognosis of survival and metastasis in humans with tumor (using a gene set containing nucleic acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS:19, and 28-42 or SEQ ID NOS: 19, 29, 31, 40, and 42), particularly for those humans who are at the early stage of lung cancer. The gene expression profiling is preferably performed by cDNA microarray-based techniques and / or Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (Real-Time RT-PCR), and analyzed by statistical means.
Owner:ADVPHARMA
System for multi color real time pcr
ActiveUS20060269922A1Enhanced signalLess-expensive setupBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReal-Time PCRsHybridization probe
The invention is directed to a system for performing multi-color real time PCT, comprising a flexible real time PCT instrument and a specific composition or reaction mixture for performing multiplex PCR: In particular, the present invention is directed to a composition or reaction mixtuer which comprises at least 3, preferably 4-5 and most preferably exactly 4 pairs of FRET hybridization probes. Each pair of said hybridization probes consists of a FRET donor probe carrying a FRET donor moiety and a FRET acceptor probe carrying a FRET acceptor moiety having an emission maximum between 550 and 710 nm.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
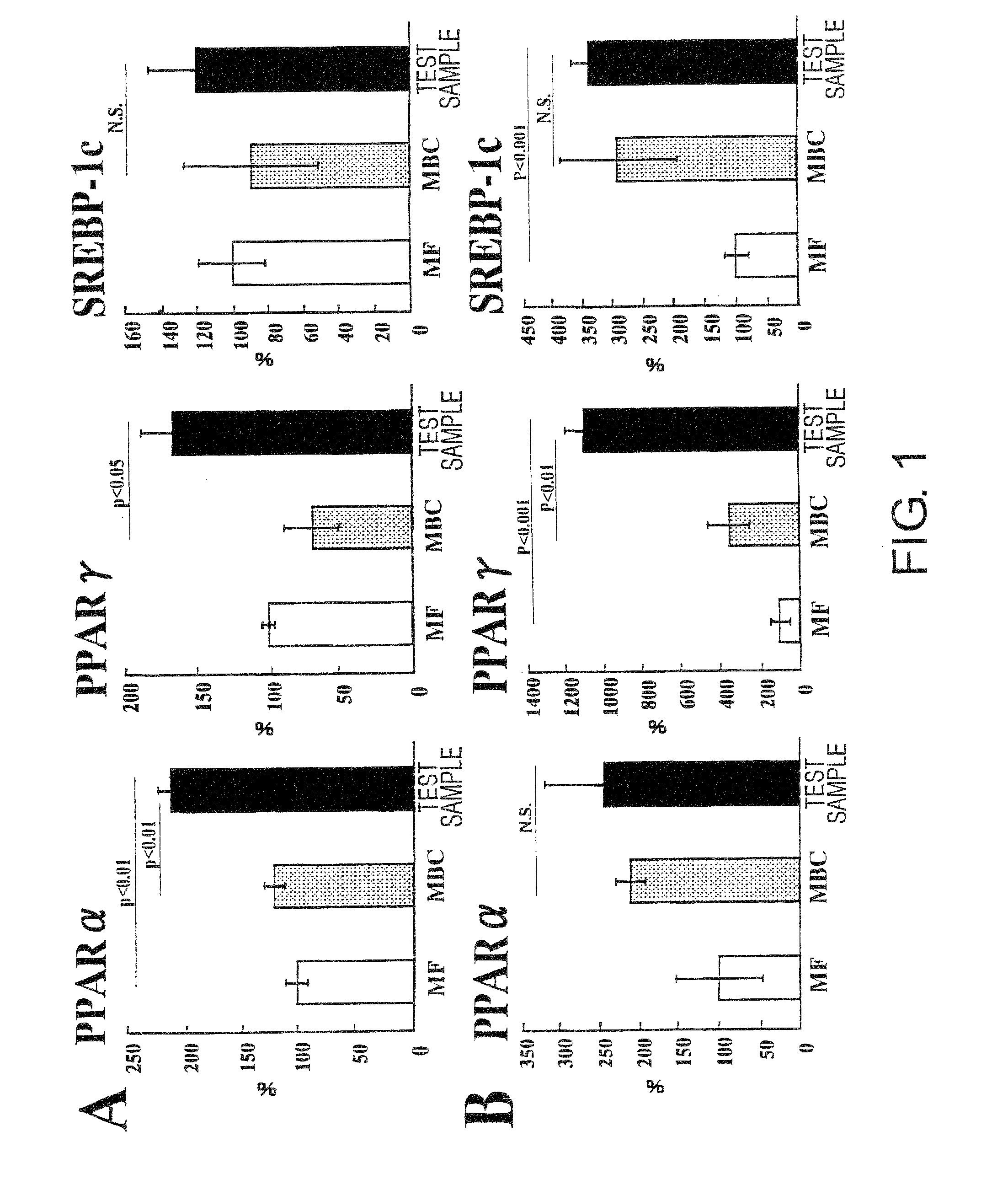
Compositions for Enhancing the Production of PPAR and/or PPAR-Associated Factors
InactiveUS20110178008A1Increase productionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsReal-Time PCRsD-Glucose
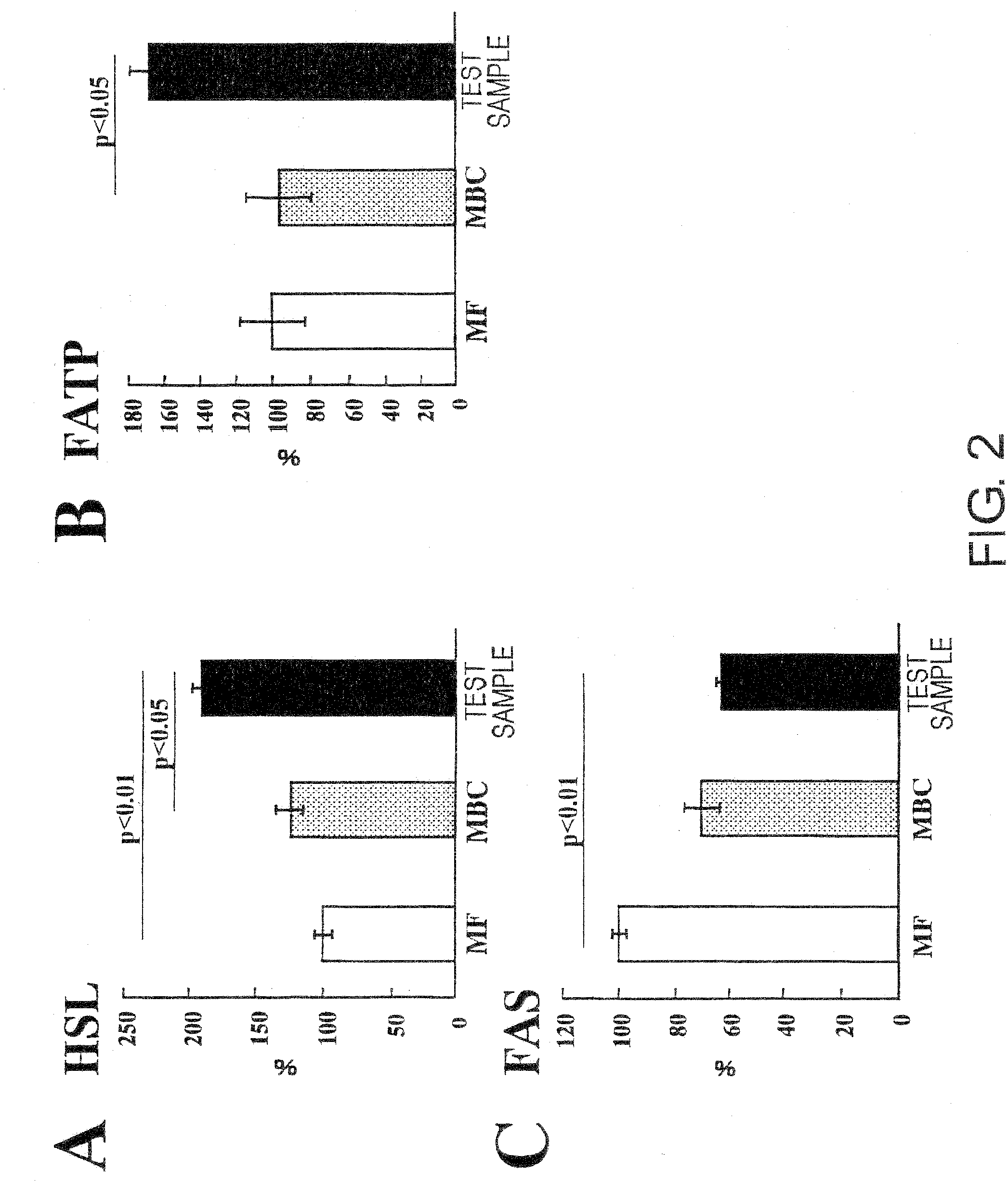
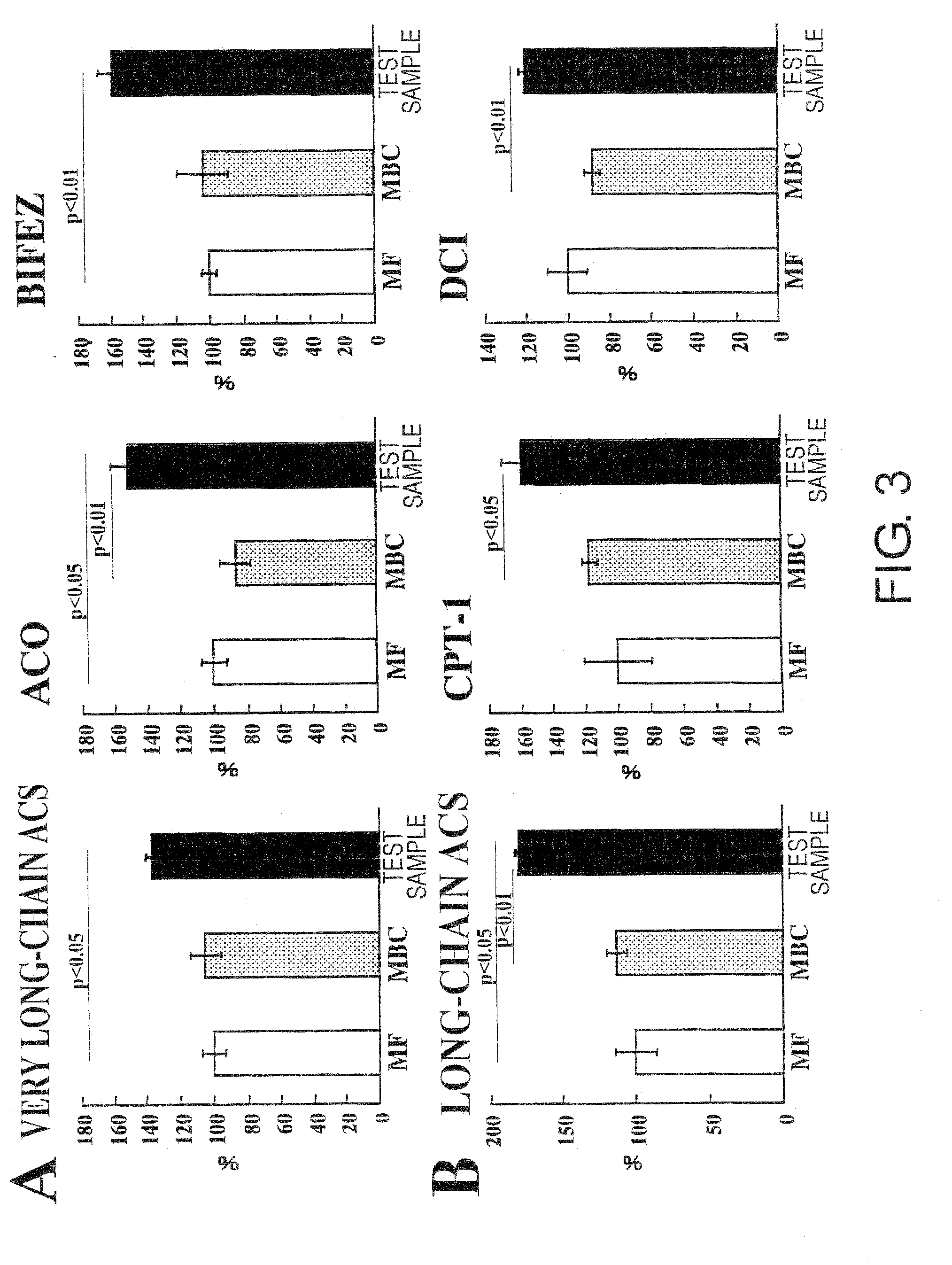
The present inventors focused on certain nutritional compositions known to have activity of controlling blood glucose levels. These foods were administered to rats for long periods, and real-time PCR was used to analyze the expression of genes associated with lipid metabolism in the liver and adipose tissues. As a result, the present inventors found that the expression of the PPARα gene is enhanced by these foods, and that this is accompanied by suppressed expression of fatty acid synthase and enhanced expression of a group of PPARα target genes associated with fatty acid metabolism. The present inventors also confirmed the effect of these foods in enhancing the expression of PPARγ and adiponectin, and discovered that these foods have the activity of enhancing the production of PPAR and PPAR-associated factors.
Owner:MEIJI CO LTD
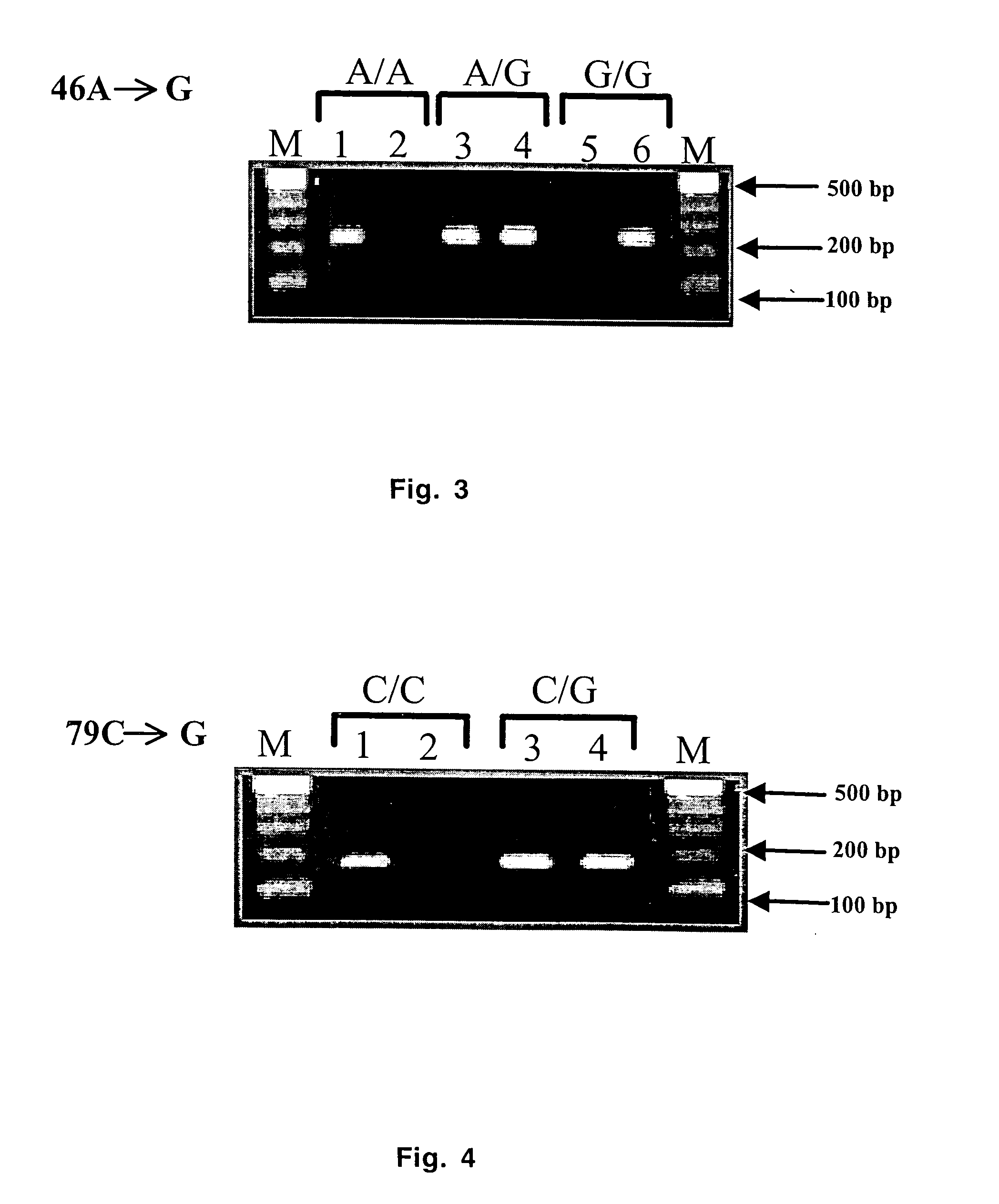
Real-time polymerase chain reaction-based genotyping assay for beta2-adrenergic receptor single nucleotide polymorphism
InactiveUS20050153353A1Rapid and inexpensive and robust chain reactionGrowth inhibitionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotype AssayReal-Time PCRs
The present invention provides fluorescence-based real-time PCR assays for the rapid detection of β2-adrenergic receptor single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The genotyping assay can be used to detect SNPs of human β2-adrenergic receptor (β2-AR) single nucleotide polymorphisms A46G and C79G.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
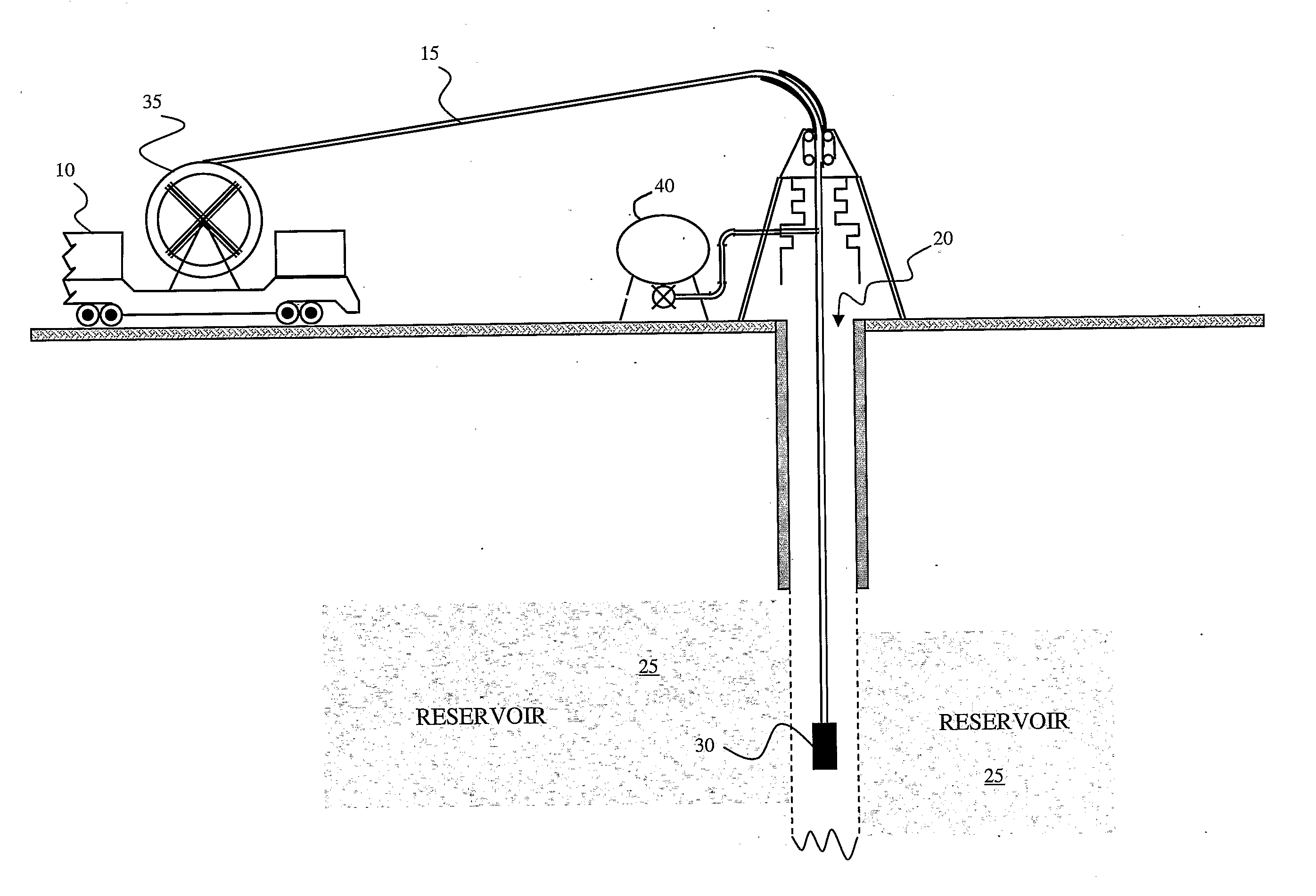
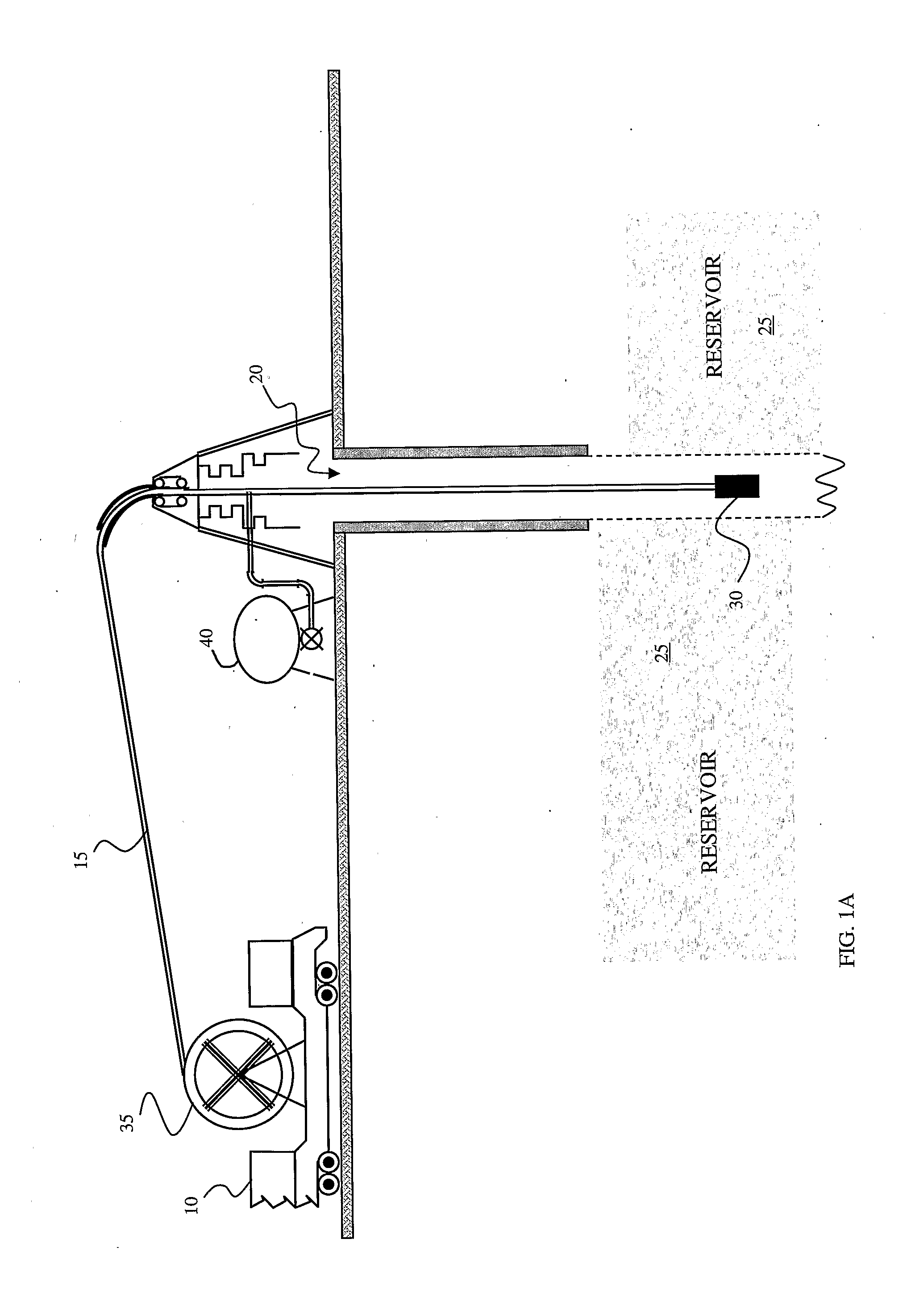
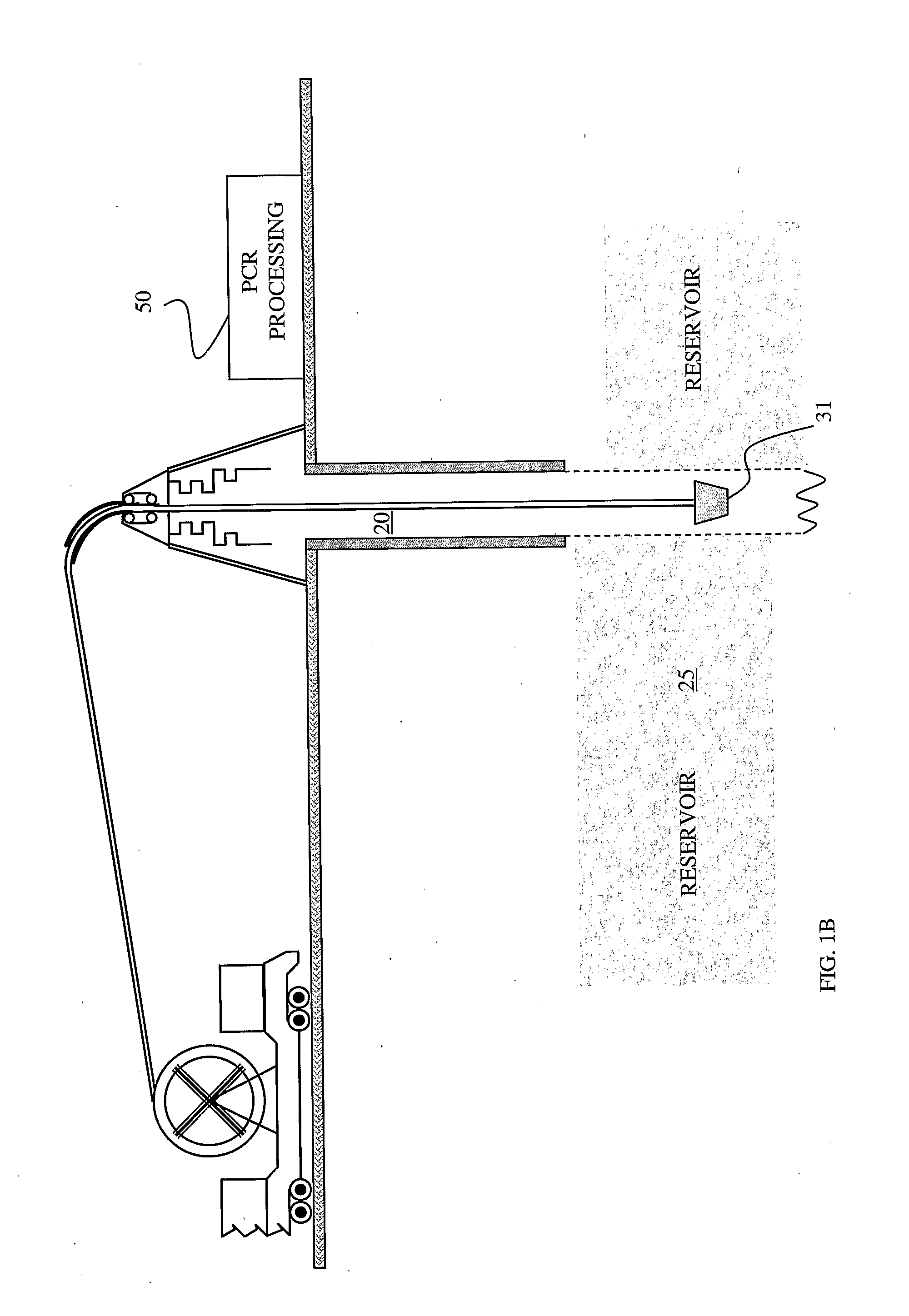
Methods and systems for evaluation of hydrocarbon reservoirs and associated fluids using biological tags and real-time PCR
InactiveUS20100015612A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsSurveyReal-Time PCRsHydrocotyle bowlesioides
This invention relates in general to characterizing hydrocarbon reservoirs and / or determining flow properties of fluids associated with the reservoir-including fluids introduced into the reservoir to provide for hydrocarbon extraction-using biological tags and real-time polymerase chain reactions for tag detection. In embodiments of the present invention, one or more biological tags may be added to one or more liquids associated with the hydrocarbon reservoir and subsequently one or more liquid samples may be taken from locations associated with the hydrocarbon and the presence of the one or more biological tag may be qualitatively and / or quantitatively tested for in the samples using real-time PCR.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Non-invasive detection of fish viruses by real-time PCR
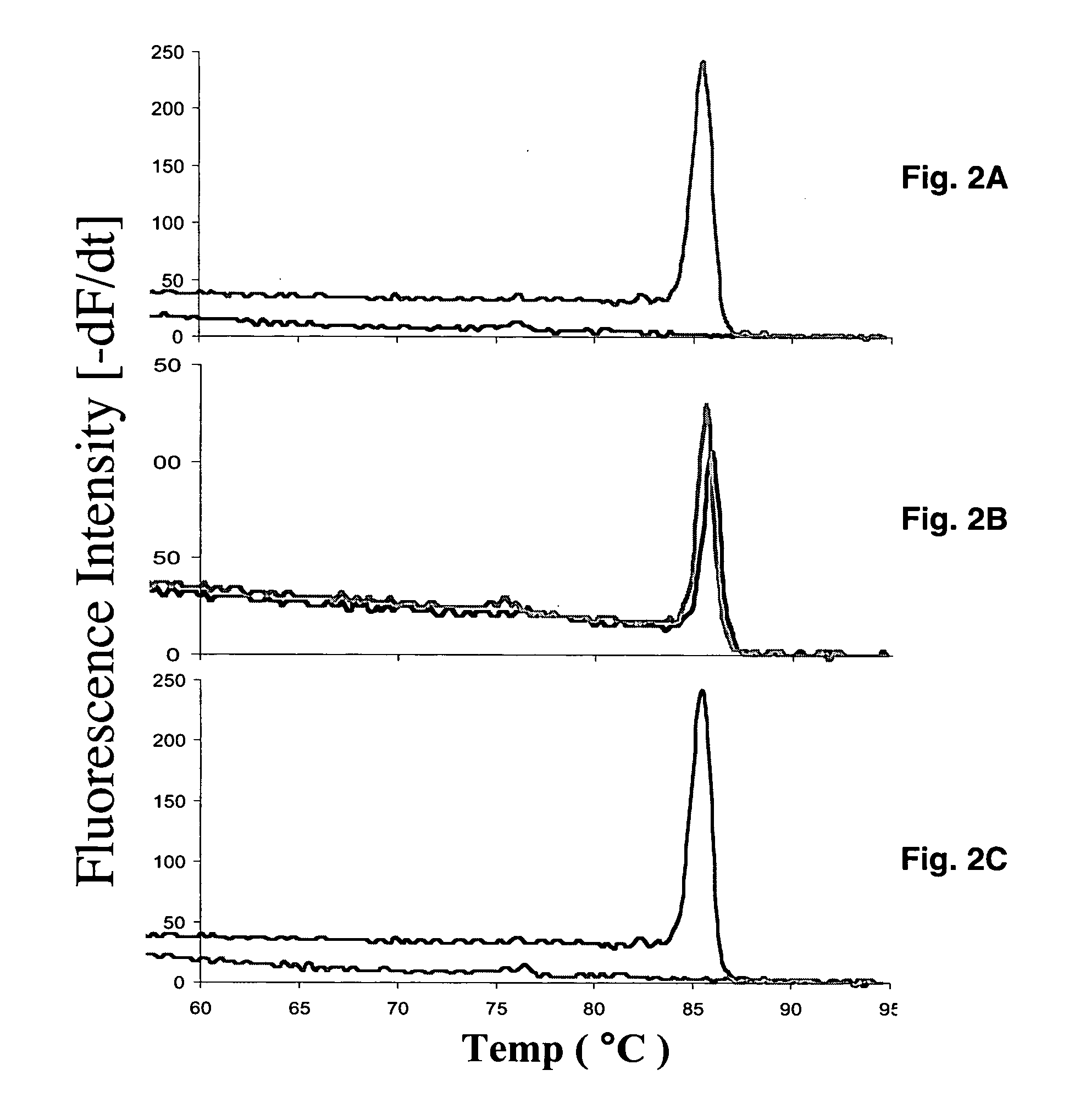
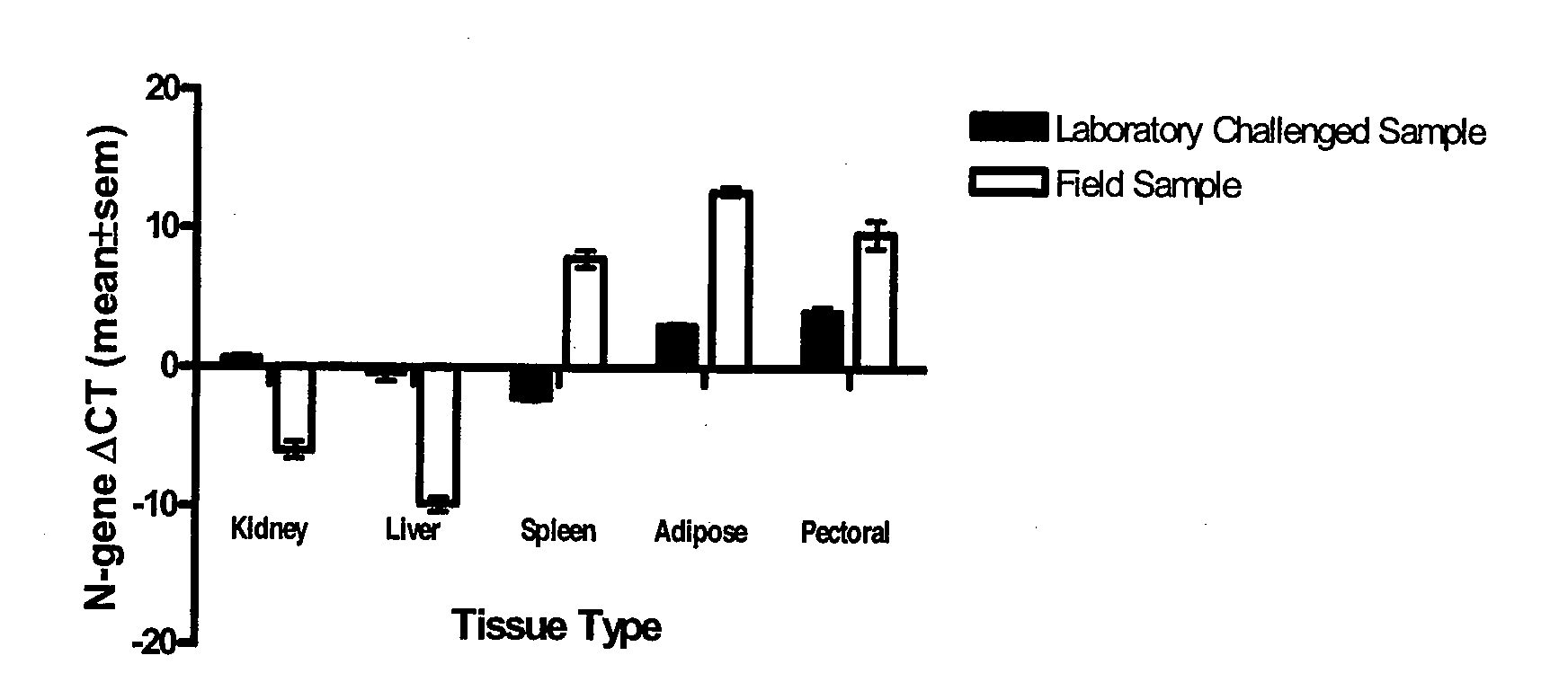
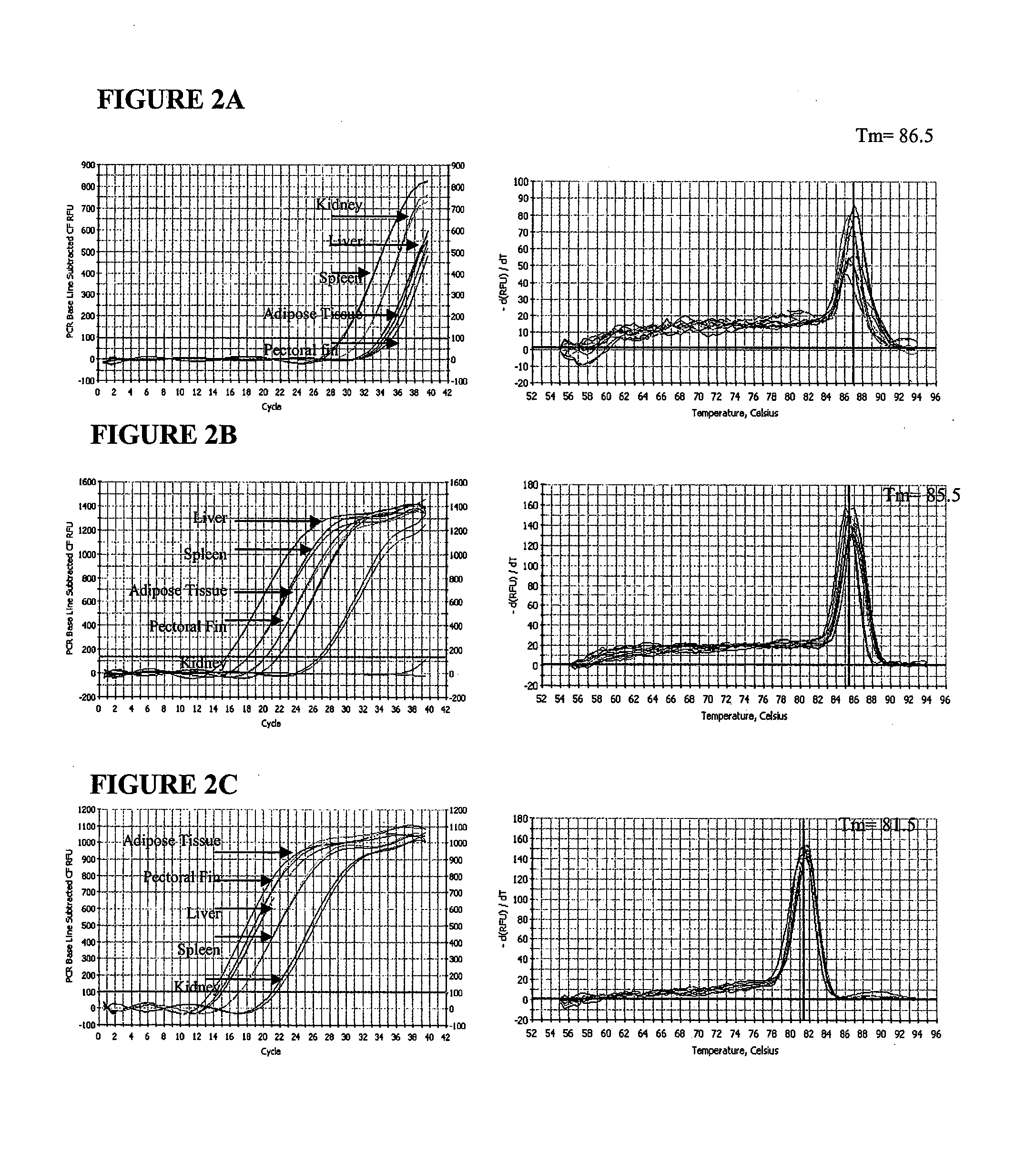
A real-time assay coupled with a non-invasive tissue sampling was developed for the detection and quantification of fish viruses. As a proof of principles, data were presented for the detection and quantification of infectious hypodermal necrosis virus (IHNV) in trout. The primers were designed for IHNV nucleocapsid (N), and surface glycoprotein (G) genes, and trout &bgr;-actin and elongation factor-l&agr; (EF-I &agr;) were used as internal control for the assay. The reaction conditions for the real-time RT-PCR were optimized using cDNA derived from IHNV-infected Epithelioma papulosum cyprinid (EPC) cells. Using both N- and G-gene primers, IHNV was successfully detected in liver, kidney, spleen, adipose tissue and pectoral fin samples of laboratory-challenged and wild samples. The dissociation curves with a single melting peak at expected temperature (85° C. for the N-gene and 86.5° C. for the G-gene) confirmed the specificity of the N- and G-gene amplicons. The IHNV N- and the G-gene expression levels in different tissues of laboratory challenged samples were in the order of spleen, liver, kidney, adipose tissue and pectoral fin, however in the field-collected samples the order of gene expression was liver, kidney, pectoral fin, adipose tissue, and spleen. The N- and G-gene expressions in spleen were found to be dramatically lower in the field-collected samples compared to the laboratory-challenged samples indicating a potential difference in the IHNV replication in the laboratory as opposed to field conditions. The real-time PCR assay was found to be rapid, highly sensitive, and reproducible. Based upon the ability to detect the virus in pectoral fins a non-invasive detection method for IHNV and other fish viruses is developed. Such a non-invasive tissue sampling coupled with real-time PCR assay is very valuable for large-scale virus screening of fish in aquaculture facilities as well as for epidemiological studies.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONUTRITION CORP
Primers for diagnosing avellino corneal dystrophy
InactiveUS20120077200A1Efficiently and accurately diagnosingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementReal-Time PCRsCornea dystrophy
The present invention relates to a real-time PCR primer pair and probe for diagnosing Avellino corneal dystrophy, and more particularly to a real-time PCR primer pair and probe for diagnosing Avellino corneal dystrophy, which can accurately diagnose the presence or absence of a mutation in exon 4 of BIGH3 gene, which is responsible for Avellino corneal dystrophy. The use of the primer pair and probe according to the invention can diagnose Avellino corneal dystrophy in a more rapid and accurate manner than a conventional method that uses a DNA chip or PCR.
Owner:AVELLINO
Simultaneous quantification of nucleic acids in diseased cells
InactiveUS20070196824A1Assess potential side-effectsLow variabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementReal-Time PCRsAntiviral drug
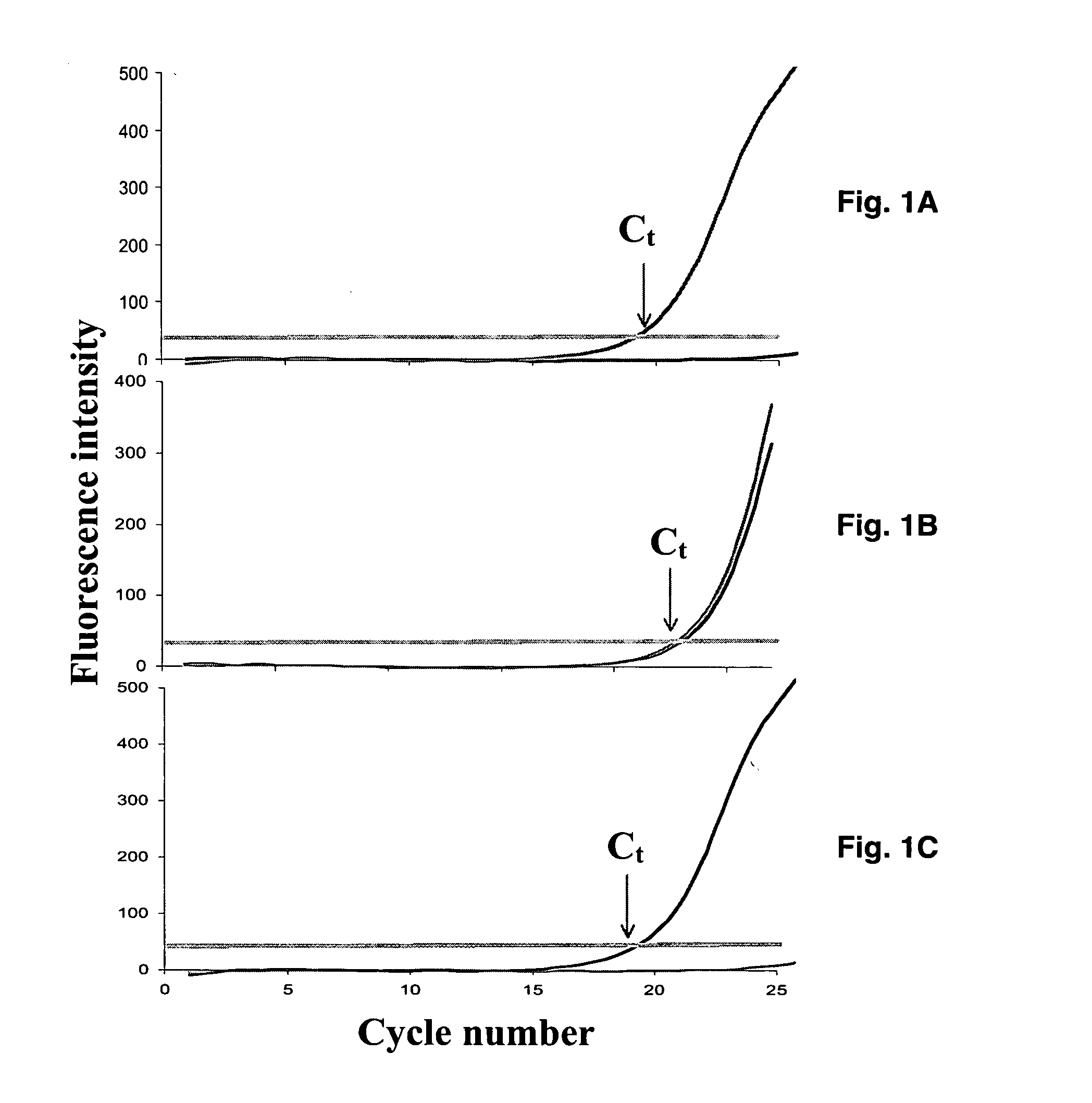
Processes and methods for the simultaneous quantification of nucleic acids in diseased cells that are based on real-time PCR are provided. The real-time PCR protocol is an excellent tool for reliable quantification of in vitro drug screening and evaluation protocols to determine the efficacy of potential anti-viral agents. Quantification using these simultaneous PCR cycle threshold (Ct) detection techniques during one-step real-time RT-PCR (Applied Biosystems, CA) eliminates the variability resulting from quantification of end-point RT-PCR products. In addition, the mitochondrial toxicity assay is an added tool to assess potential side-effects for these chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:GILEAD PHARMASSET LLC
System For Multi Color Real Time PCR
InactiveUS20110151550A1Enhanced signalLess-expensive setupBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReal-Time PCRsHybridization probe
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Methods, systems and devices for multiple single-cell capturing and processing using microfluidics
InactiveUS20130302884A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusReal-Time PCRsMRNA Sequencing
Methods, systems, and devices are described for multiple single-cell capturing and processing utilizing microfluidics. Tools and techniques are provided for capturing, partitioning, and / or manipulating individual cells from a larger population of cells along with generating genetic information and / or reactions related to each individual cell. Different capture configurations may be utilized to capture individual cells and then processing each individual cell in a multi-chamber reaction configuration. Some embodiments may provide for specific target amplification, whole genome amplification, whole transcriptome amplification, real-time PCR preparation, copy number variation, preamplification, mRNA sequencing, and / or haplotyping of the multiple individual cells that have been partitioned from the larger population of cells. Some embodiments may provide for other applications. Some embodiments may be configured for imaging the individual cells or associated reaction products as part of the processing. Reaction products may be harvested and / or further analyzed in some cases.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
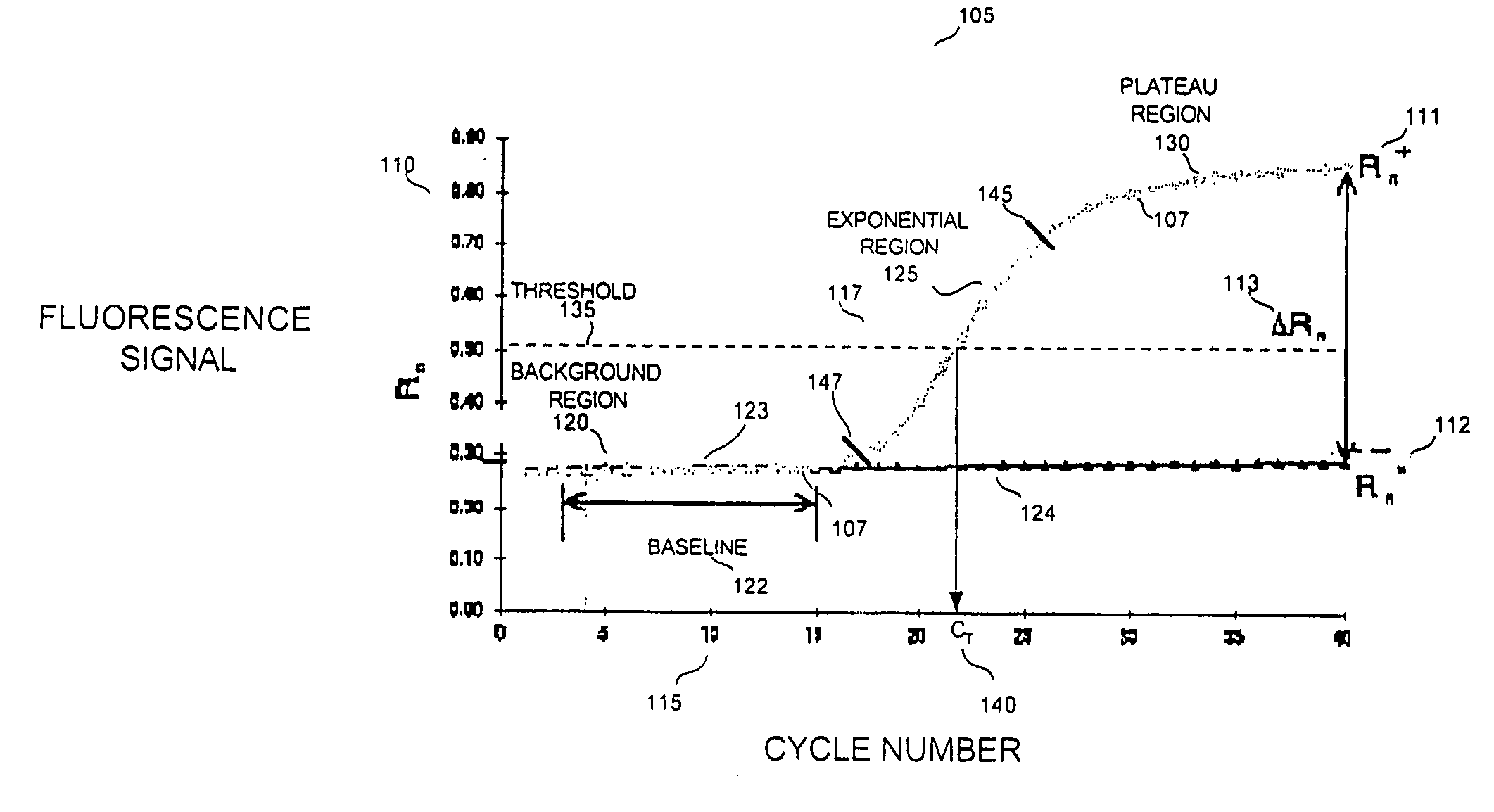
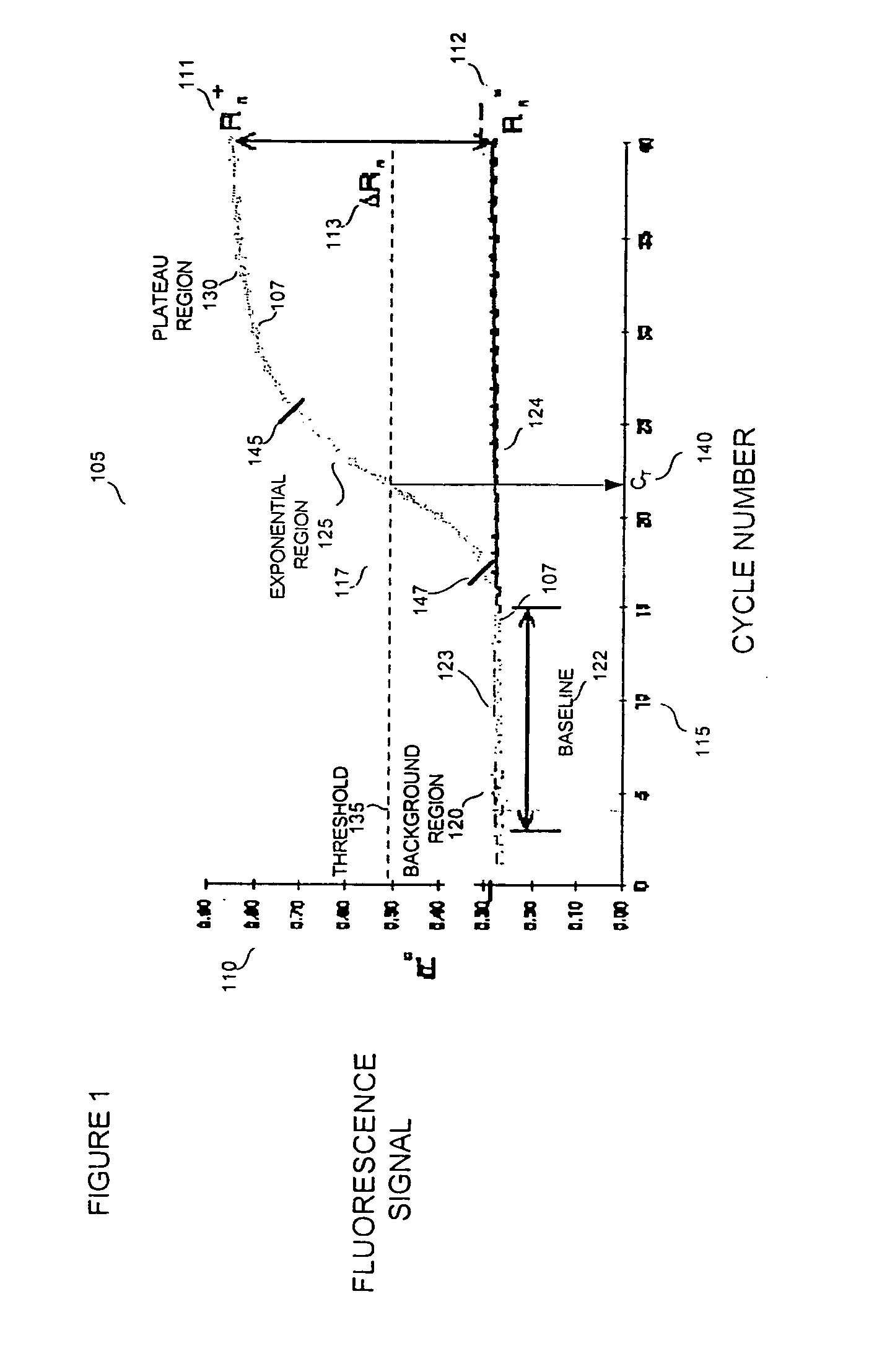
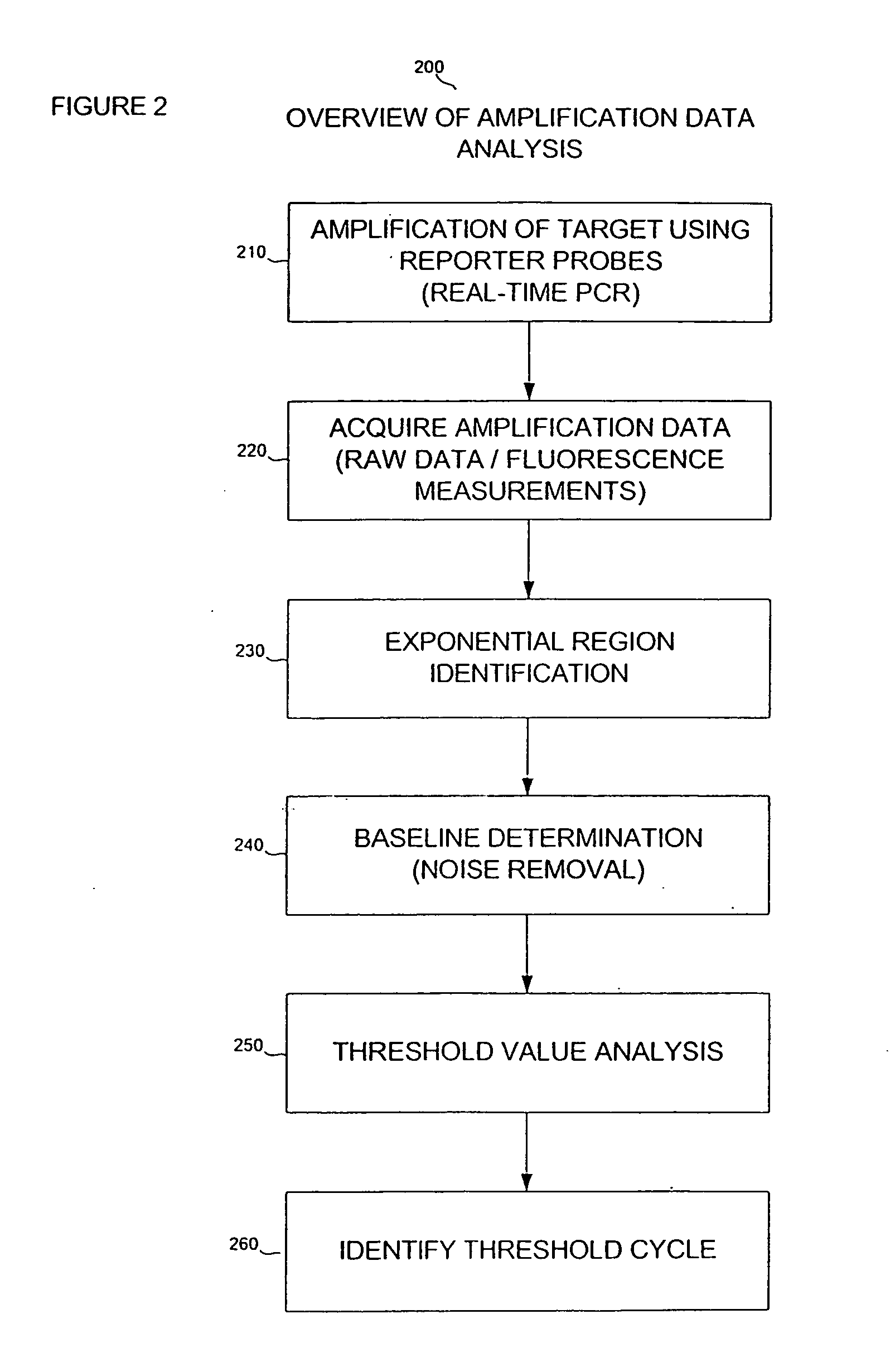
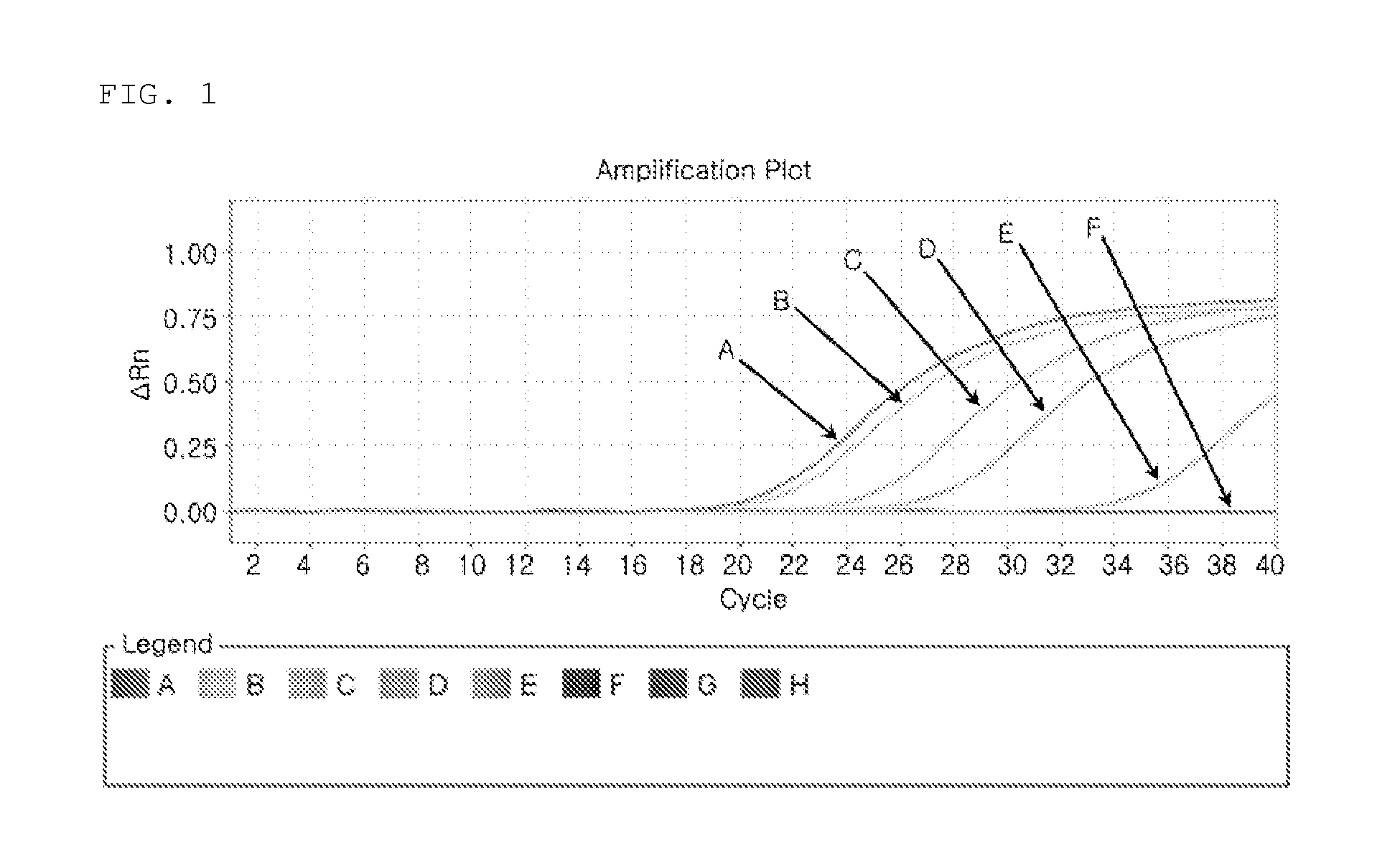
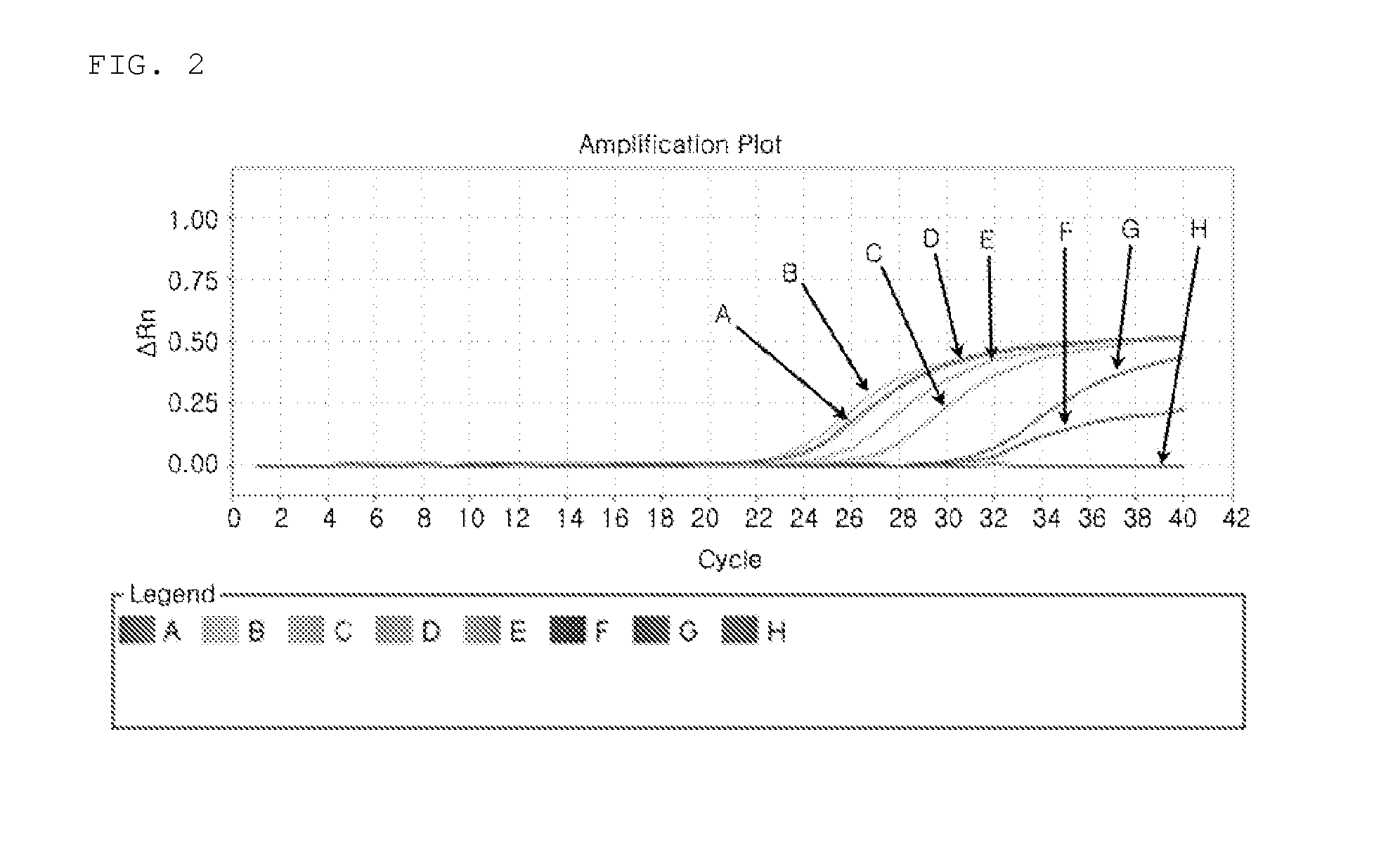
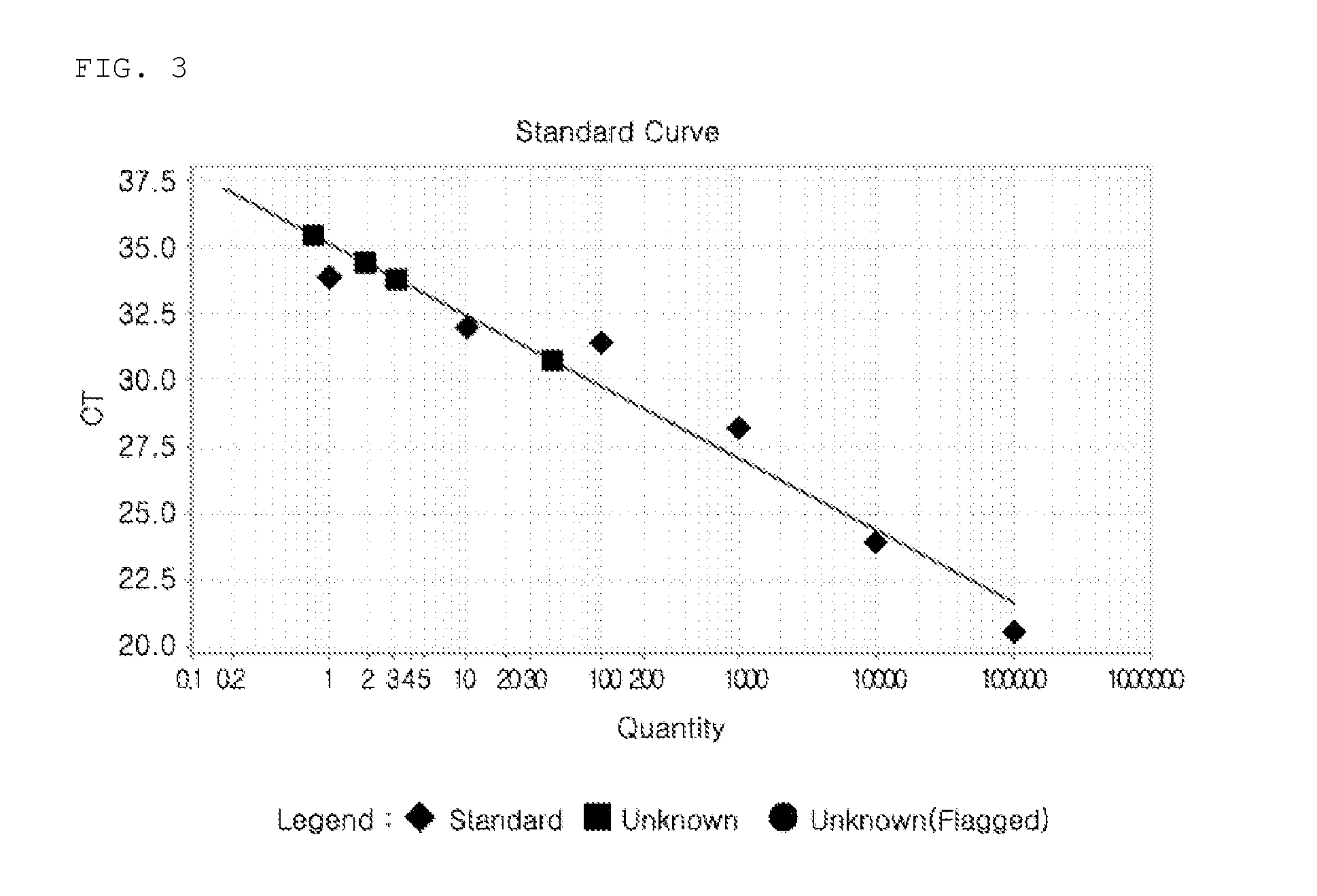
Automatic threshold setting and baseline determination for real-time PCR
InactiveUS20070124088A1Microbiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionReal-Time PCRsSimulation
The invention discloses a system and methods for quantitating the presence of nucleic acid sequences by evaluation of amplification data generated using real-time PCR. In one aspect, the methods may be adapted to identify a threshold and threshold cycle for one or more reactions based upon evaluation of exponential and baseline regions for each amplification reaction. The methodology used in the analysis may be readily automated such that subjective user interpretation of the data is substantially reduced or eliminated.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
One-step method of elution of DNA from blood samples
Described are reagents, methods, and kits for eluting, and amplifying and / or characterizing DNA from liquid and dried blood samples. A one-step DNA elution buffer has been developed that simplifies purification of DNA from blood samples. The purified DNA is suitable for use in subsequent widely used techniques such as enzymatic DNA amplification and quantitative analysis such as real-time PCR.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method of detection of classical swine fever
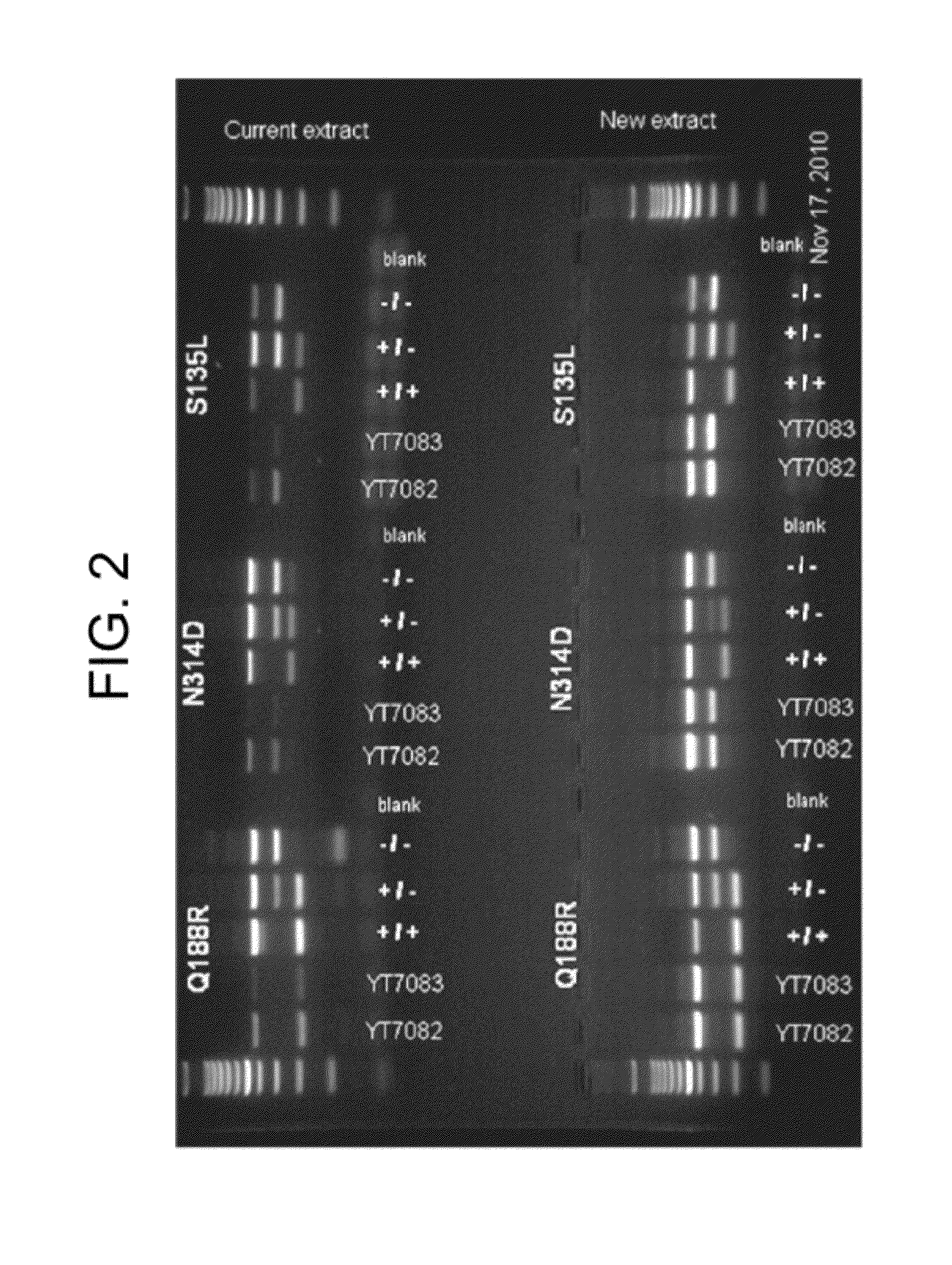
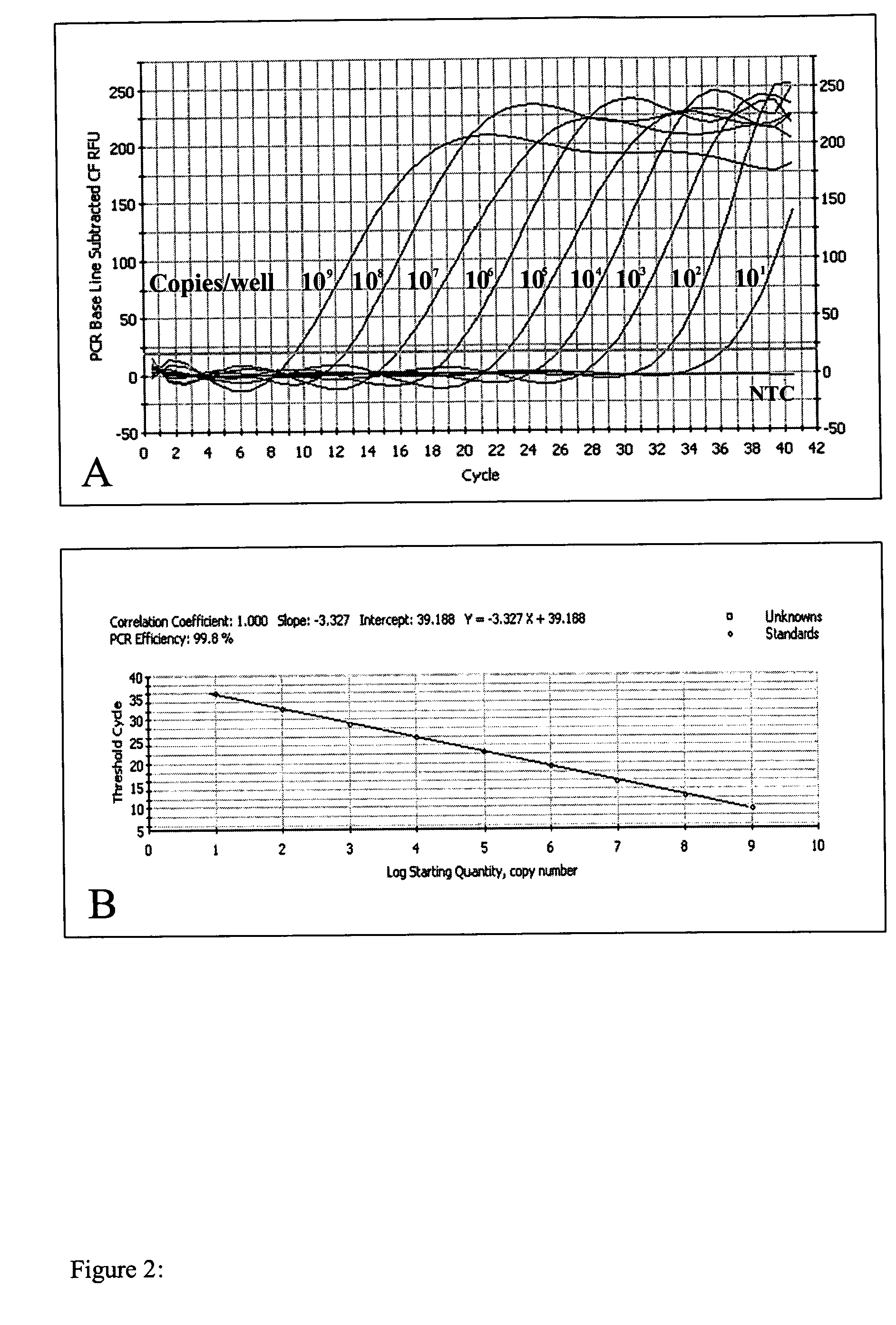
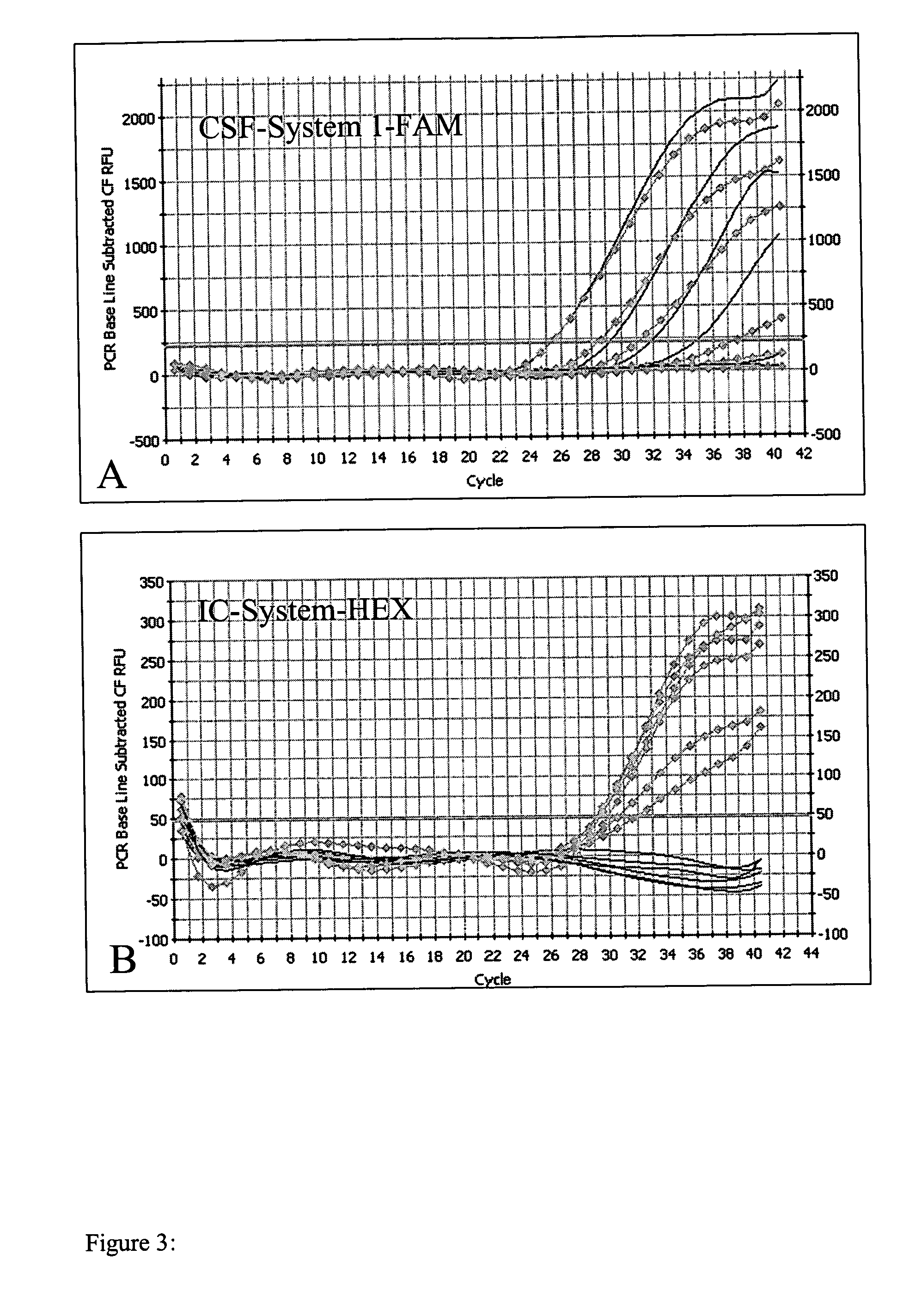
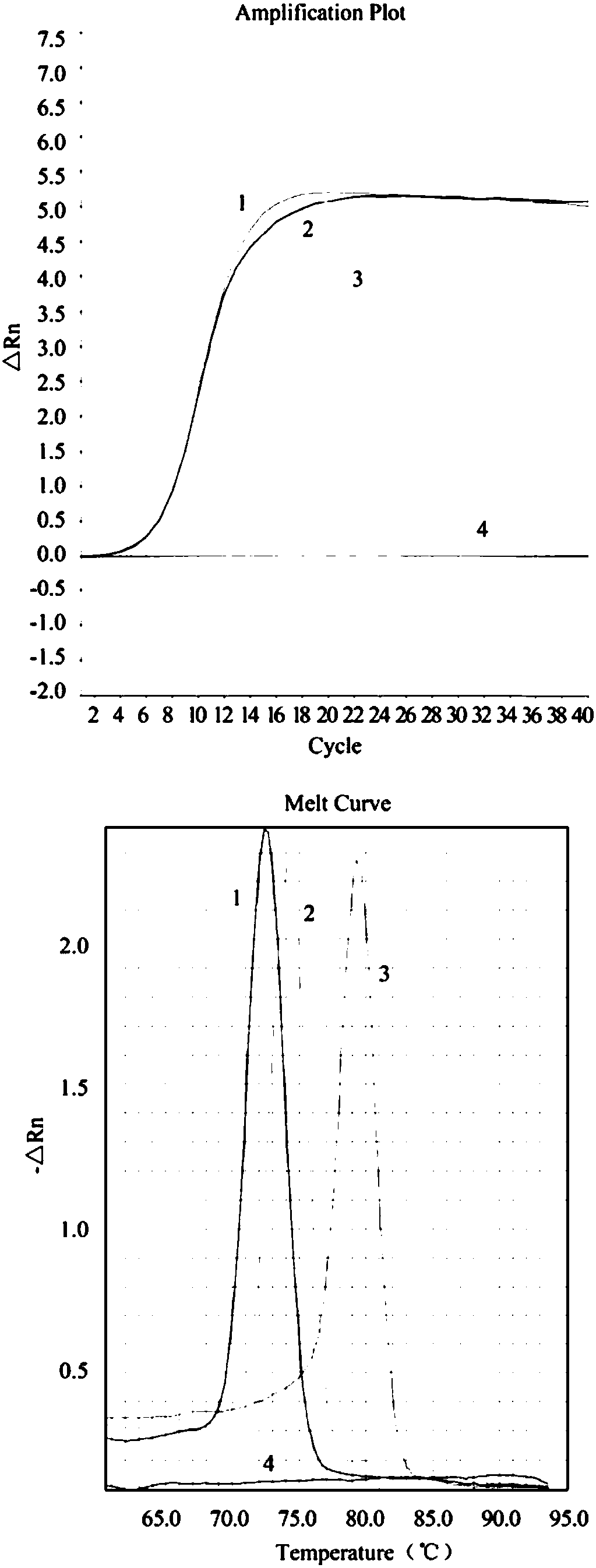
The invention relates to a multiplex real-time RT-PCR assay with a heterologous internal control system (i.e., EGFP-RNA) for the simple and fast diagnosis of classical swine fever virus (CSFV). Primers and FAM-labeled TaqMan probes, specific for CSFV were selected by analyzing the consensus sequence of the 5′-non translated region of various CSFV strains. For determining the analytical sensitivity an in vitro transcript (T7-PC3Alf) of the 5′ NTR was constructed and tested. Furthermore, a primer-probe system for the detection of the internal control sequence was established, and a multiplex assay using CSF-System 1 and the IC real-time PCR could be performed as a one-tube assay without loss of sensitivity or specificity.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
DPO (Dual Priming Oligonucleotide) primer group for porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus and porcine rotavirus detection and application of DPO primer group
ActiveCN108060269ALarge annealing temperature rangeStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReal-Time PCRsPorcine rotavirus
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Primer and probe sequence for human metapneumovirus nucleonic acid detection
InactiveCN102031314AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReal-Time PCRsPcr method
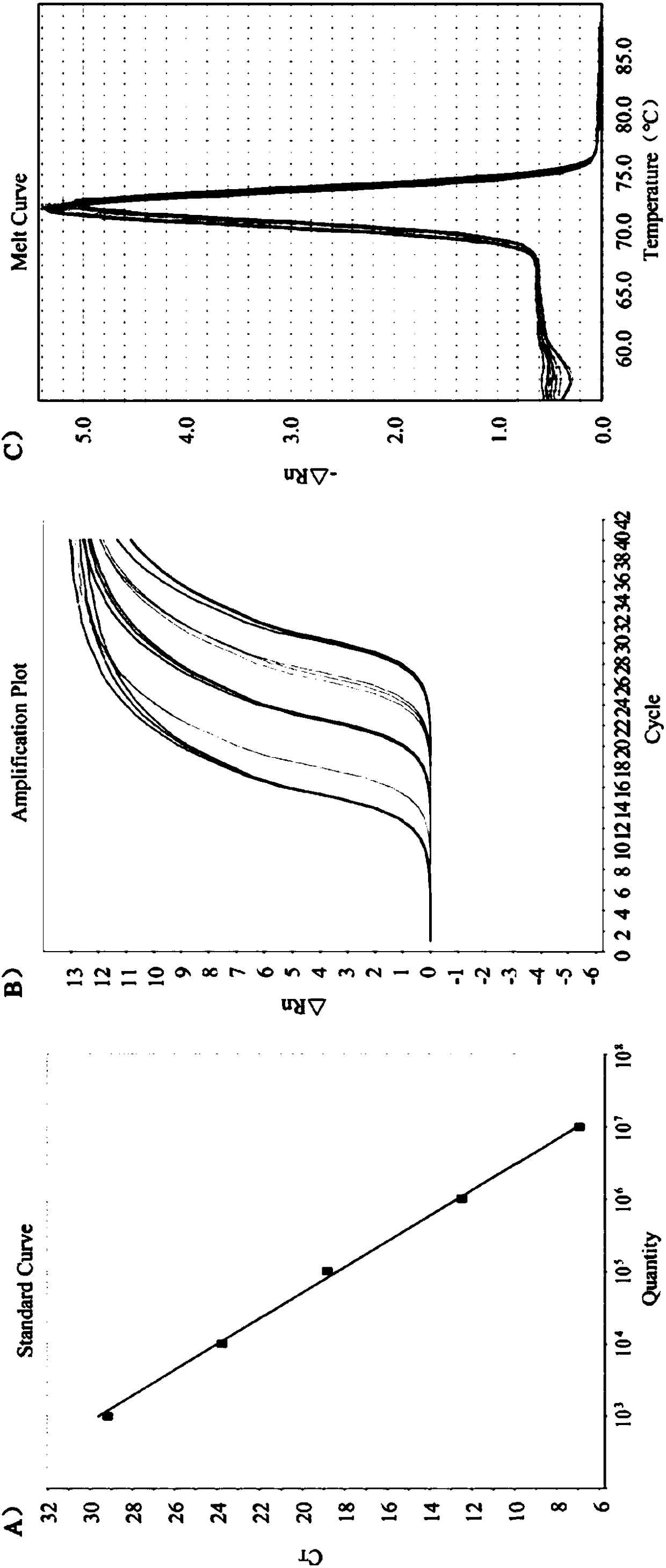
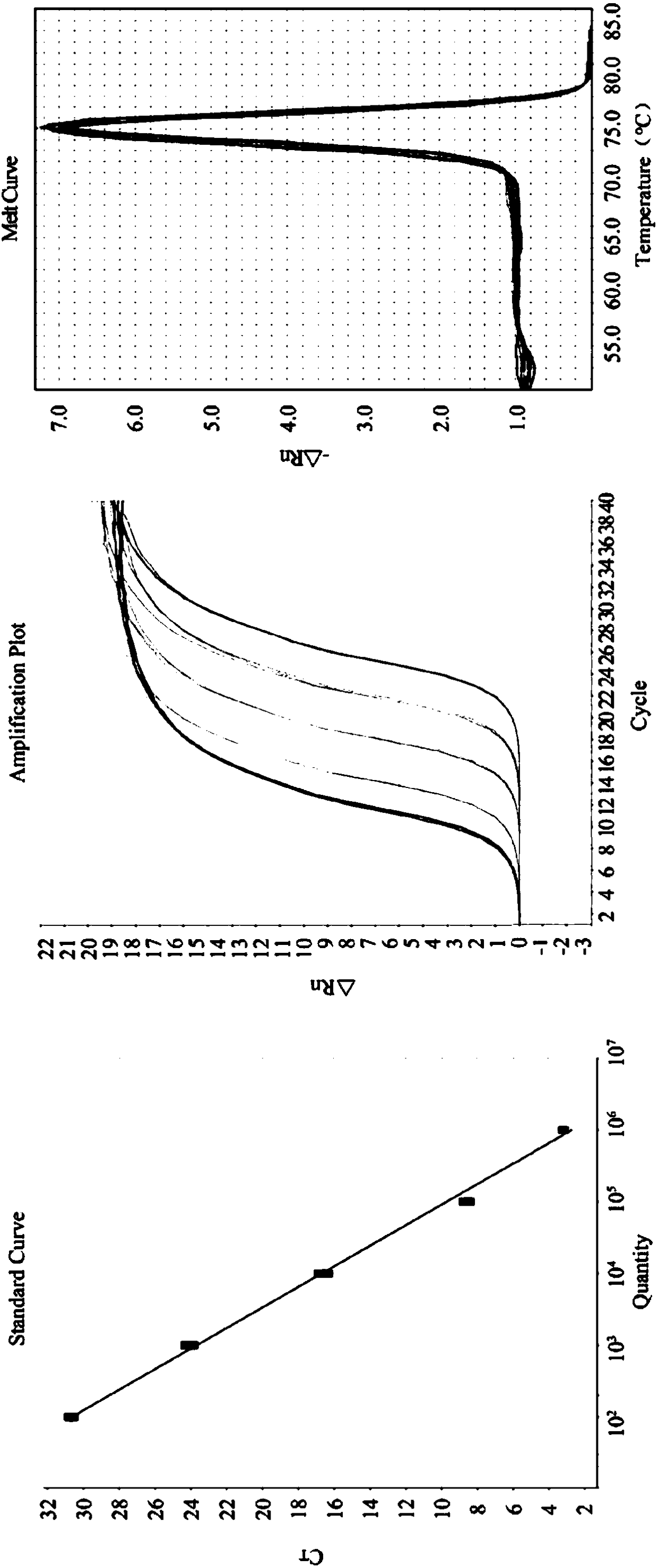
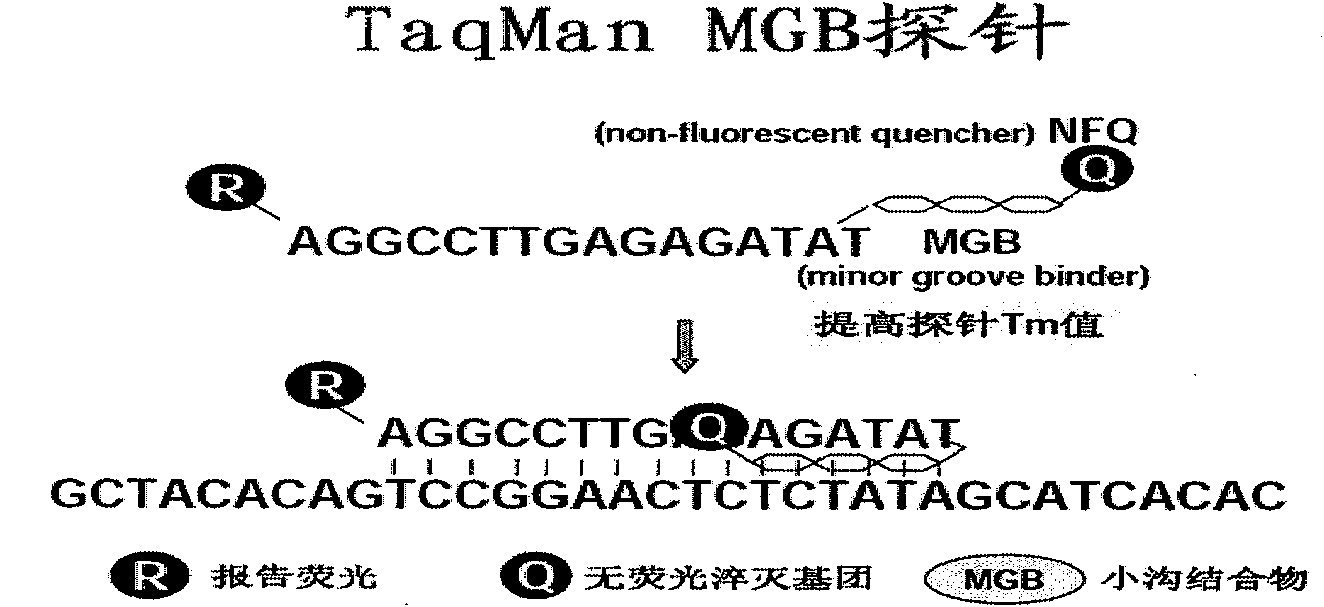
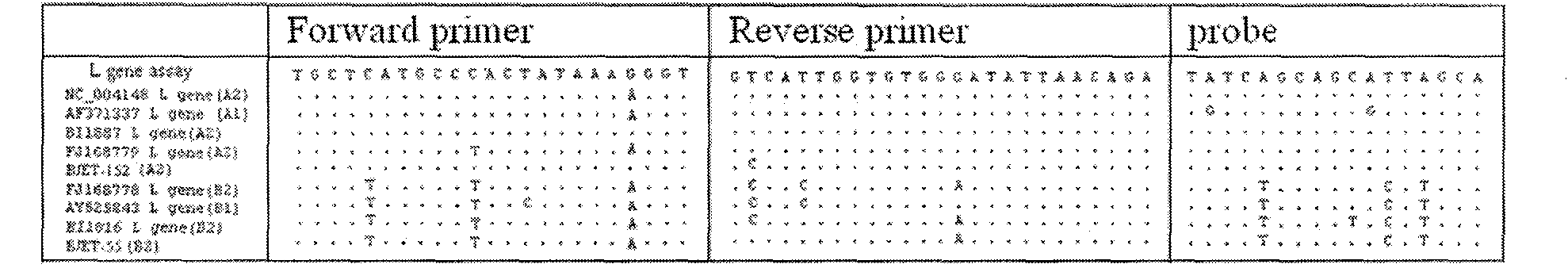
The invention relates to the technical field of primer and probe sequences for detecting nucleonic acid of human metapneumovirus: a biotechnology and a virus detection technology and provides a primer and MGB (Myohaemoglobin) probe sequence for real-time RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection of human metapneumovirus nucleonic acid. The sequence is a primer and probe sequence which is designed and synthesized by carrying out sequence detection and analysis on an N gene and an L gene of known hMPV (human Metapneumovirus) and takes the L gene as a target. The sequence is researched and verified by 200 clinical samples detected with the real-time RT-PCR method, and the degenerate base group of the sequence includes the variation rule of 4 genetic subtypes of the hMPV, therefore, the sequence can be used for the research and the development of detection technology of nucleonic acid infected by the hMPV.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所
Single-cell mRNA quantification with real-time rt-pcr
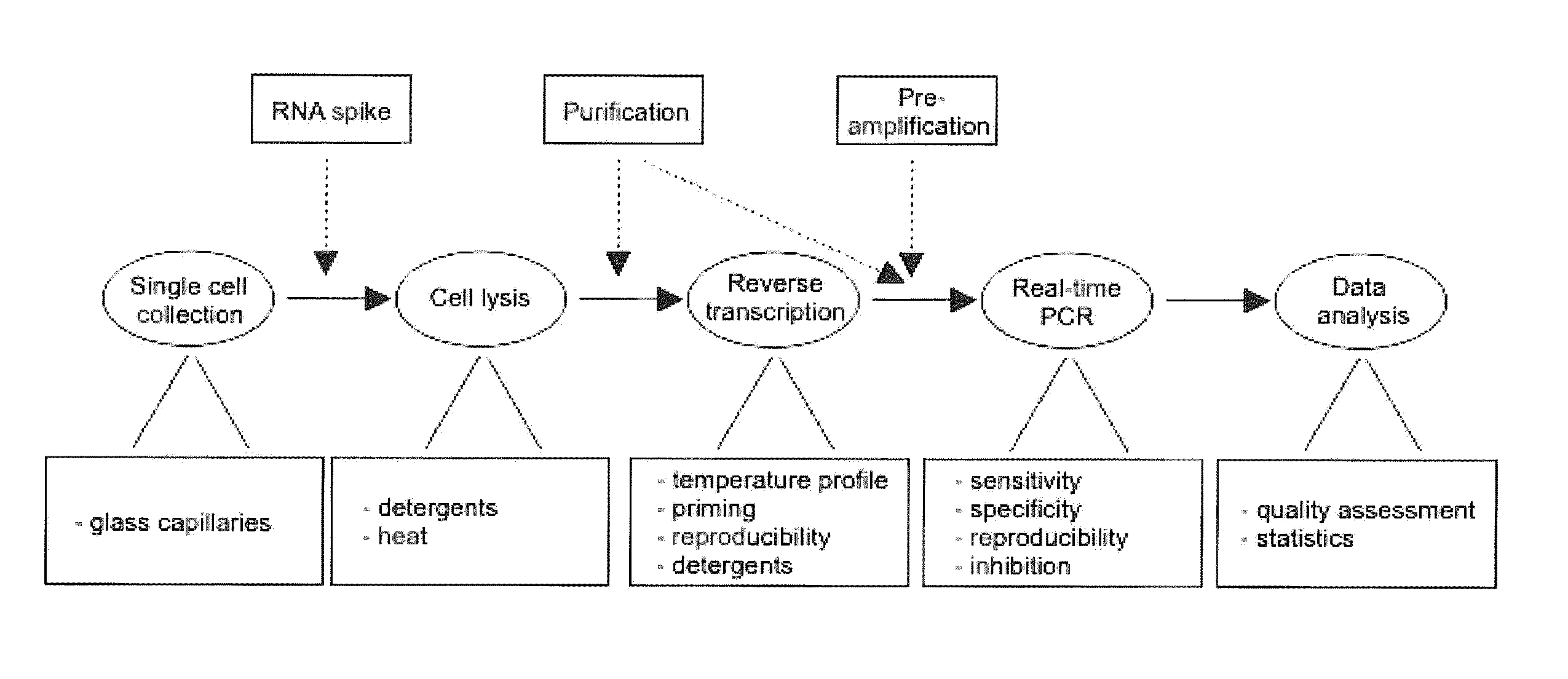
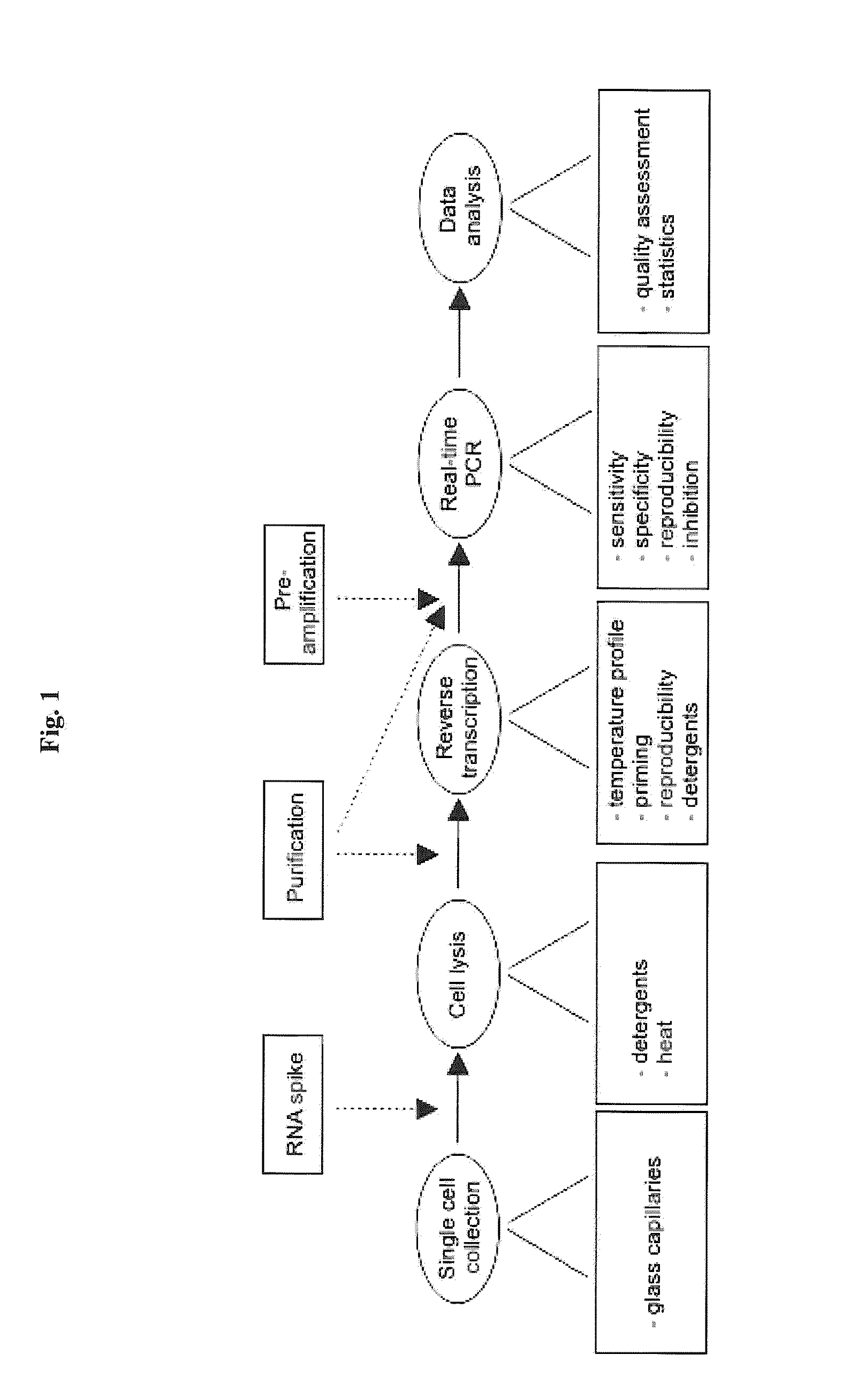
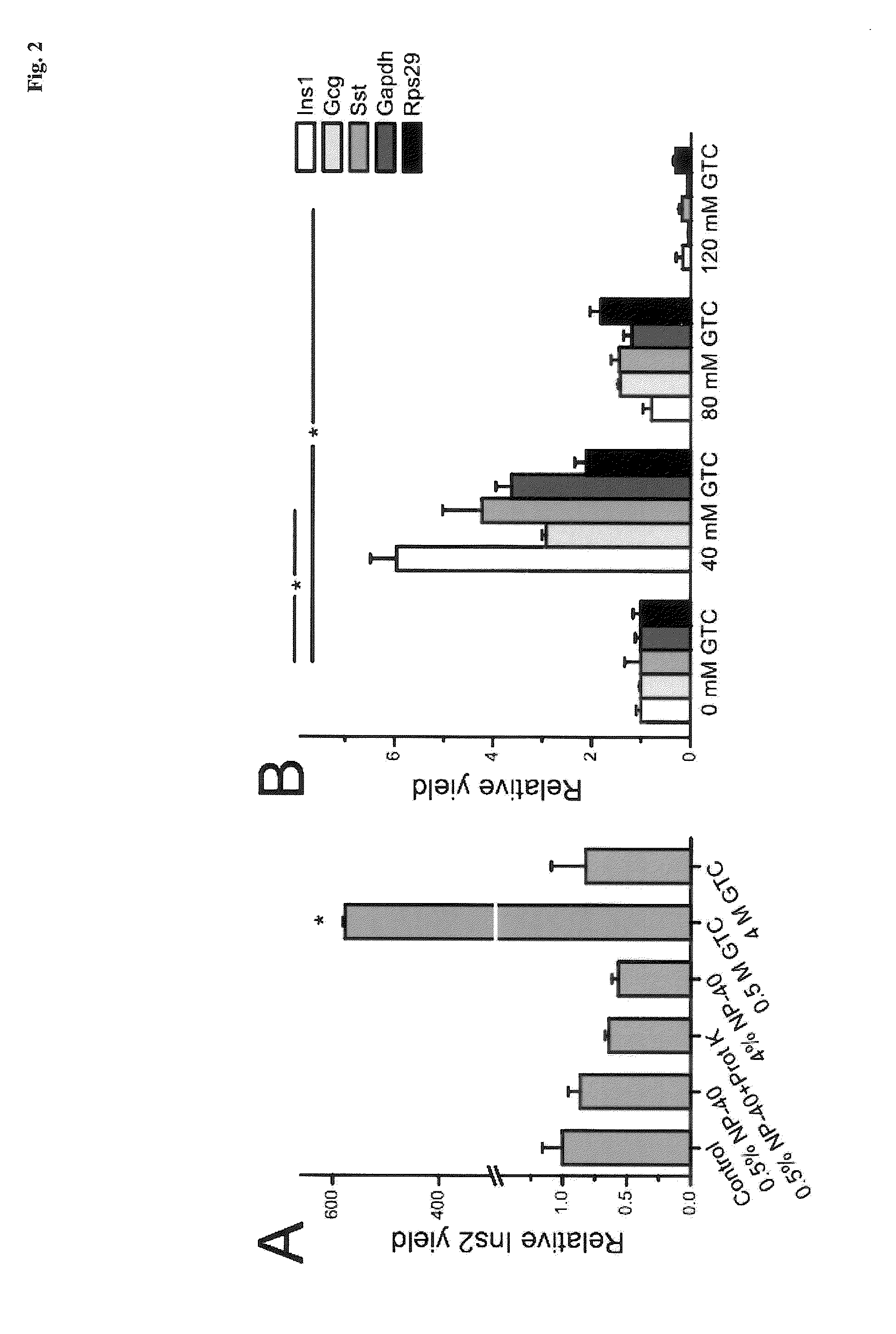
The present invention is directed to a method for performing an RT-PCR for amplifying a target RNA comprising the steps of a) lysis of a cellular sample which is supposed to contain the target RNA with a lysis buffer comprising between 0.2 M and 1 M guanidine thiocyanate, b) diluting the sample to an extend such that guanidine thiocyanate is present in a concentration of about 30 to 50 mM, c) reverse transcribing in the presence of a mixture of first strand cDNA synthesis primers, the mixture consisting of oligo dT primers and random primers, and d) subjecting the sample to multiple cycles of a thermocycling protocol and monitoring amplification of the first strand cDNA in real time.
Owner:TATAA BIOCENT +1
Primer and probe of west nile virus and real time RT-PCR detection reagent kit with one-step method
ActiveCN101245394AQuick checkReduce false positive resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReference genesReal-Time PCRs
The invention relates to a group of primers and probes and a corresponding kit, including a pair of primers which can simultaneously detect West Nile virus and the reference gene and two TaqMan probes against the West Nile virus and the reference gene, so as to reduce the number of the primers and the probes in a PCR reaction system from the usual 6 to 4, further to realize the high efficient amplification of the West Nile virus and the reference gene in the same tube, thus realizing the detection of the target genes of the different species, having strong universality, reducing the number of the primers and the probes, the cost of the reagents and the operation steps, and reducing the pollution chances which need to be avoided generally in a PCR experiment. The kit of the invention is applicable to the detection of the West Nile virus in the scientific research or the clinical aspect, especially the monitoring of the West Nile virus in the prevention and the control works of viral diseases.
Owner:谢鹏 +1
Real-time fluorescent RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection reagent and detection method for lupulus masking virus
InactiveCN102382903AQuick checkSensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesReal-Time PCRsFluorescence
The invention discloses a real-time fluorescent RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection reagent and a detection method for lupulus masking virus. The real-time RT-PCR detection reagent comprises a pair of special primers and a special fluorescent probe. An amplification target fragment is 61bp in length, and the primers have the HLV-F sequence as follows: CGTGGAACGGCTCCTTCTT; the primers have the HLV-R sequence as follows: AGAGTTGTATCCACCGGGTAGTTT; and the probe has the HLV-P sequence as follows: CACCAGCCGGAGTT, 5' of the probe contains FAM report fluorescent dye, and the nucleotide sequence of the amplification target fragment is shown as SEQIDNO:4. The detection method comprises the steps of total RNA extraction and real-time fluorescent PCR reaction, in the RT-PCR reaction, the amplification of the primers and the detection of the probe are conducted simultaneously, a pipe is closed completely in the whole detection process, the PCR aftertreatment is not needed, the pollution caused by a PCR product is eliminated, the detection steps are reduced, the time is saved, and the detection method is special and sensitive for the lupulus masking virus. The detection reagent and the detection method can rapidly and accurately detect the lupulus masking virus, and has flexible operation.
Owner:中华人民共和国北仑出入境检验检疫局 +1
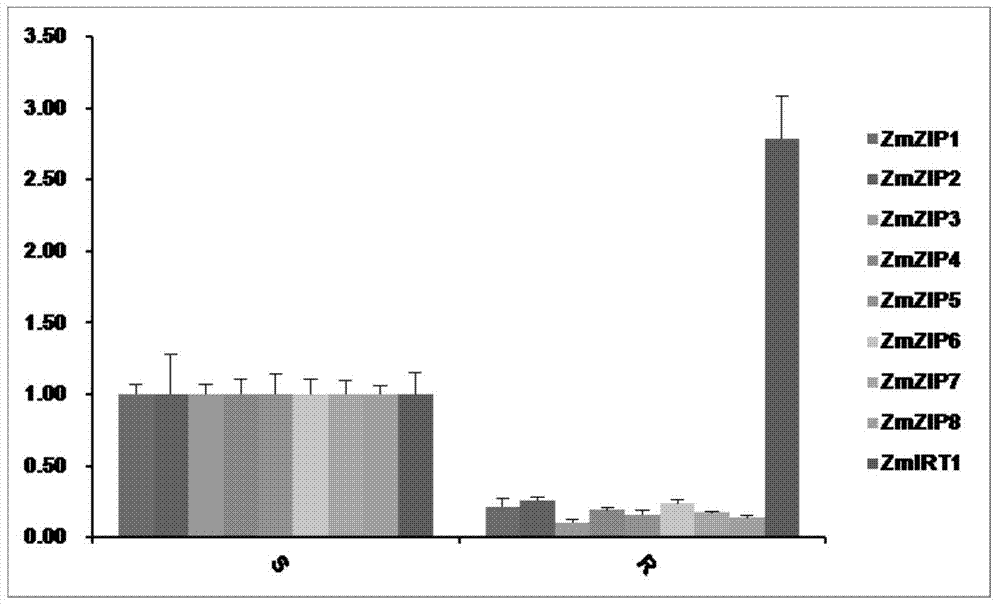
Zea mays zinc iron-regulated transporter ZmZIP4 and ZmZIP6 genes and applications thereof
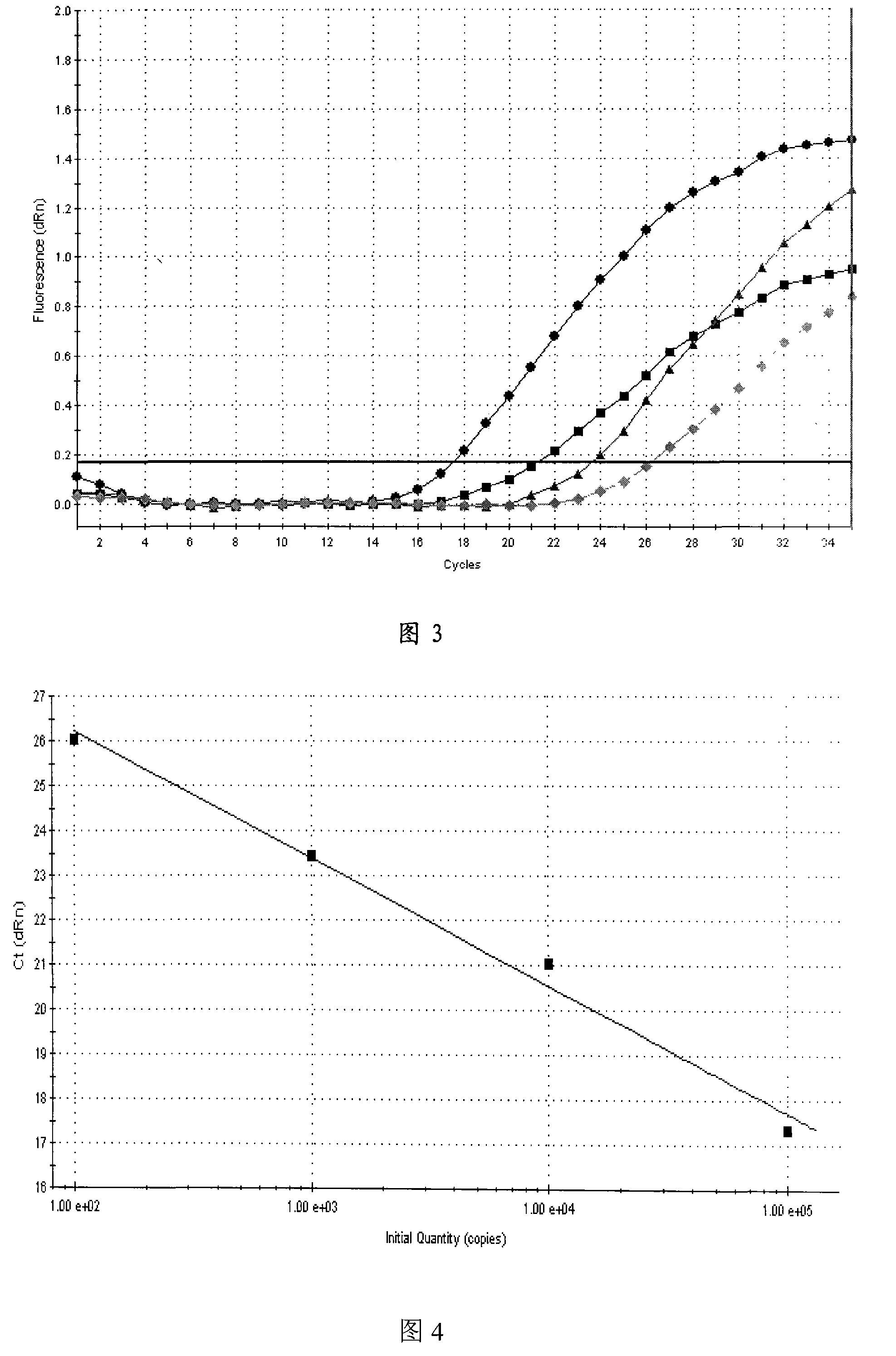
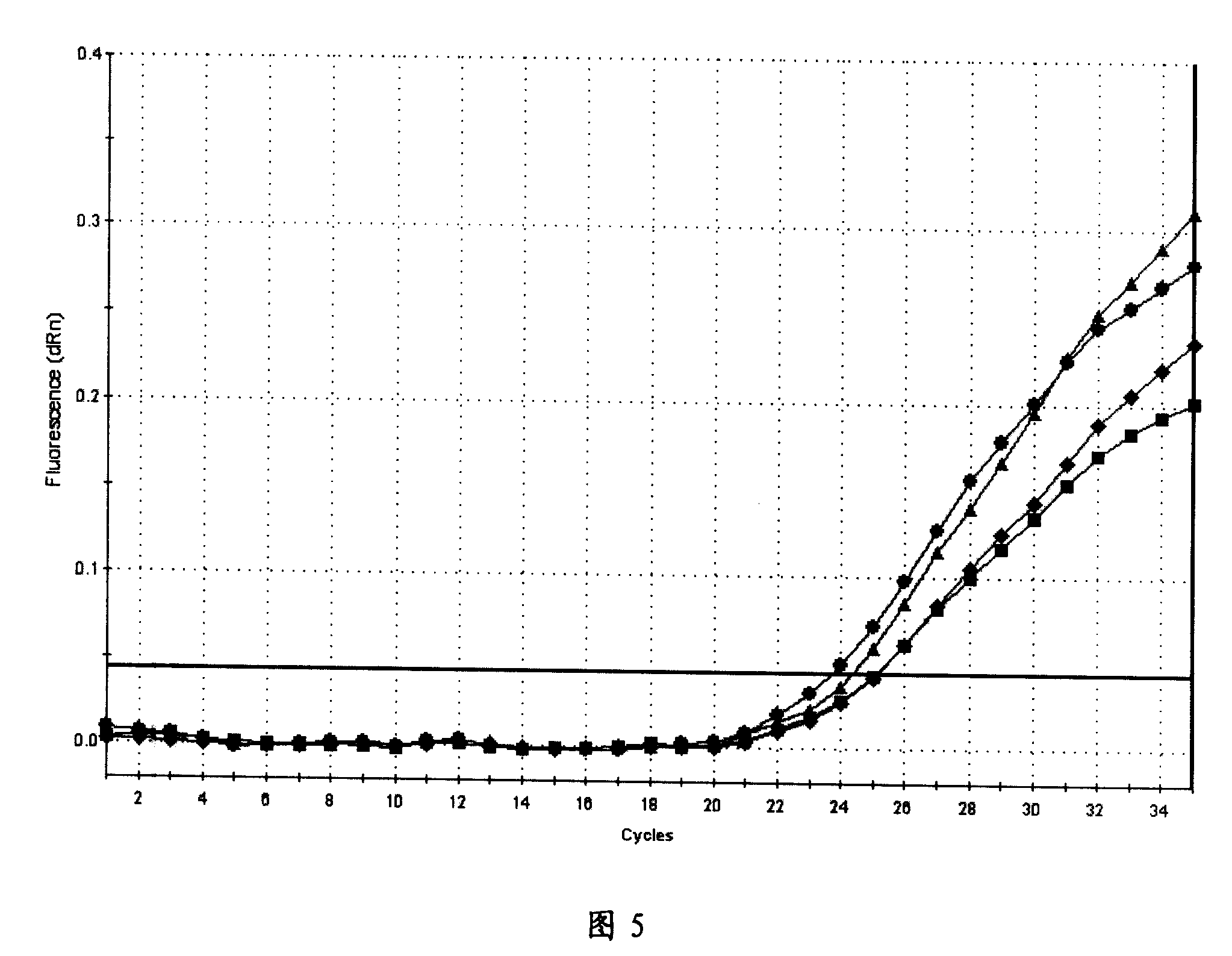
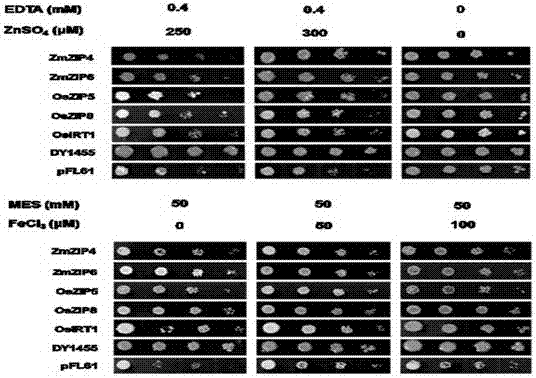
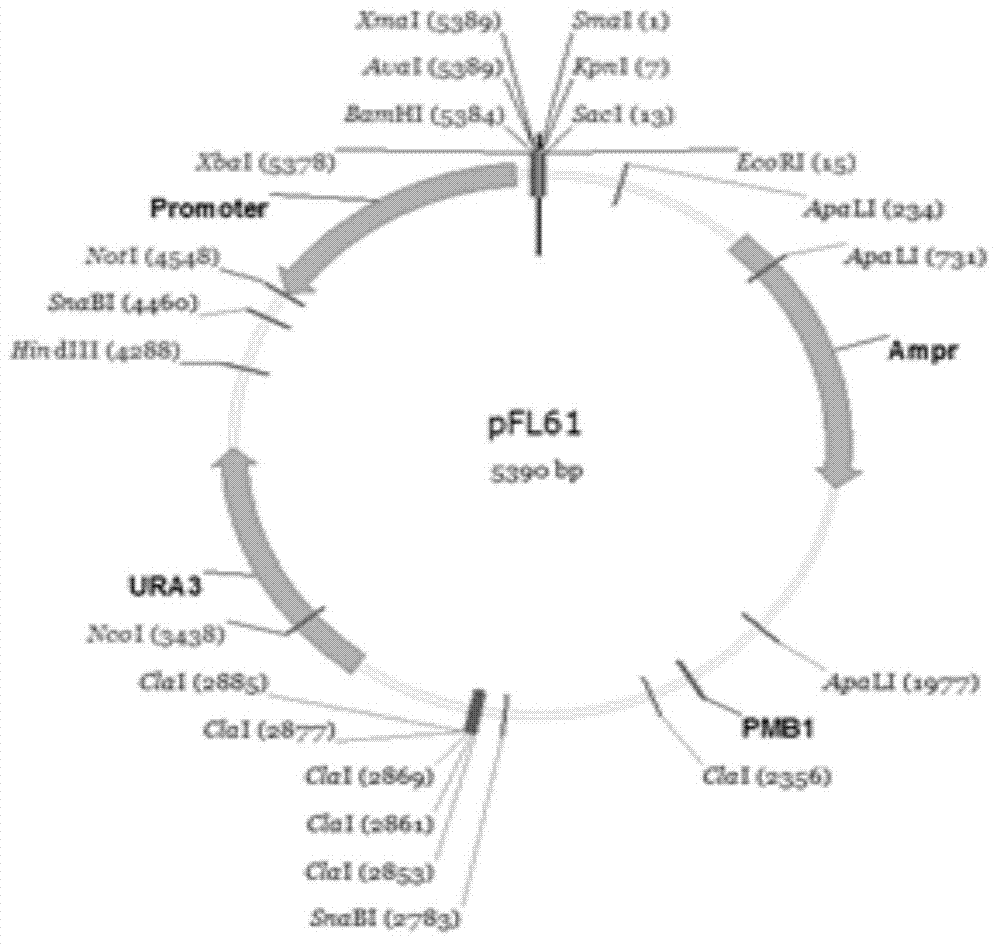
The invention discloses Zea mays zinc iron-regulated transporter ZmZIP4 and ZmZIP6 genes and applications thereof. The Zea mays zinc iron-regulated transporter ZmZIP4 and ZmZIP6 genes are separated from Zea mays, and the cDNA sequences of the genes are represented by SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.3 respectively. Subcellular localization shows that a zinc iron-regulated transporter encoded by the two genes is localized in the plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum of a cell. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR expression analysis shows that the ZmZIP4 plays a role in the embryo growth process, and the ZmZIP6 is related to embryo maturation. Yeast complementation experiments show that each of the ZmZIP4 and the ZmZIP6 has a zinc and iron transportation function. The separated ZmZIP4 and ZmZIP6 genes have important application prospects in the regulation of zinc and iron absorption, transportation and storage of plants, and promotion of the embryo maturation, and radicle and germ growth.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Method for detecting magnaporthe grisea genes for enhancing magnaporthe grisea strain pathogenicity
InactiveCN105177145AIncrease infectivityOvercoming the disadvantages of understanding the infectivity of germsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyReal-Time PCRs
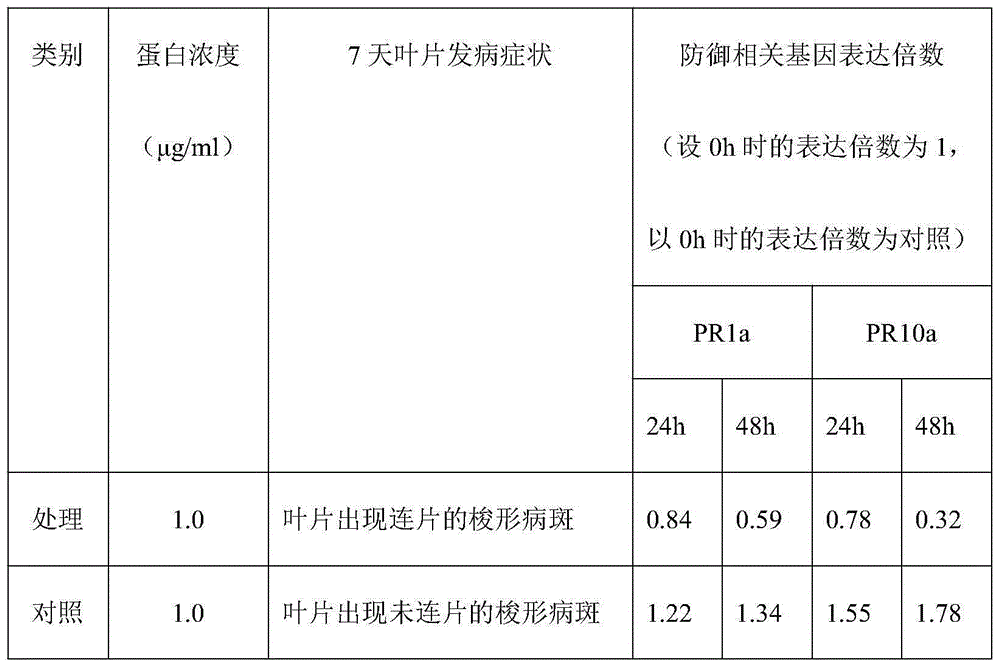
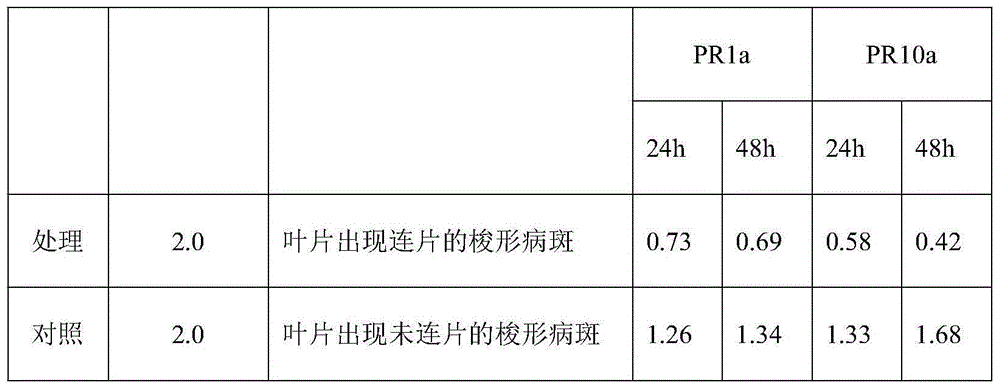
The invention discloses a method for detecting magnaporthe grisea genes for enhancing magnaporthe grisea strain pathogenicity, and relates to the field of plant protection and biological technology. The method comprises the steps that a reaction of resistance or susceptibility and a real-time RT-PCR are inspected for analyzing defense related gene expression of rice early stage response and a qPCR is adopted for detecting the relative fungus growth amount of disease spots; a prokaryotic expression product of the genes is sprayed to leaves for 24 h on the basis of the concentration being 1.0 microgram / ml-6.0 microgram / ml, and then strong / weak pathogenic strains are inoculated; the reaction of resistance or susceptibility and the real-time RT-PCR are inspected for analyzing rice defense related gene expression; overexpression strains of the genes are utilized for being inoculated on rice blades in an in-vitro mode, and the reaction of resistance or susceptibility and the real-time RT-PCR are inspected for analyzing the rice defense related gene expression and the qPCR is inspected for analyzing relative fungus growth amount on disease spots. The method can comprehensively and accurately clear pathogen effect protein genes and improve the pathogen infective ability, and the accurate and comprehensive method is provided for determining the pathogen effect protein for improving the pathogen infective ability in the future.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Standard article and method for detecting carry quantity of leucovirus
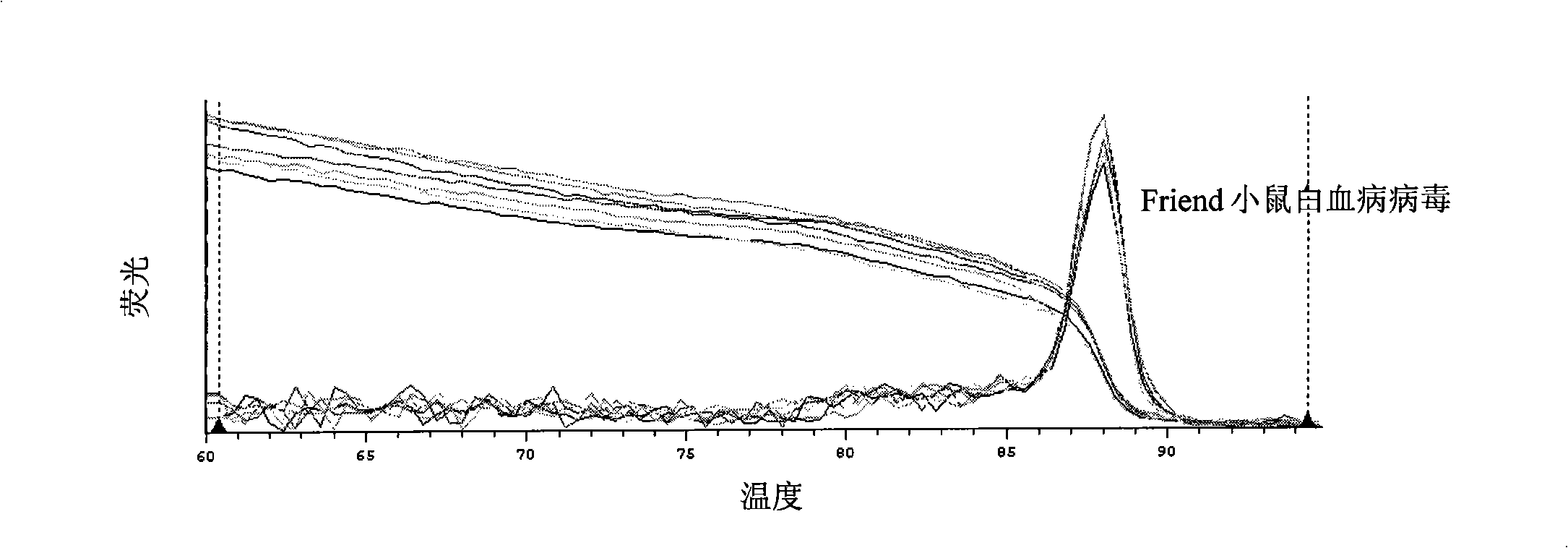
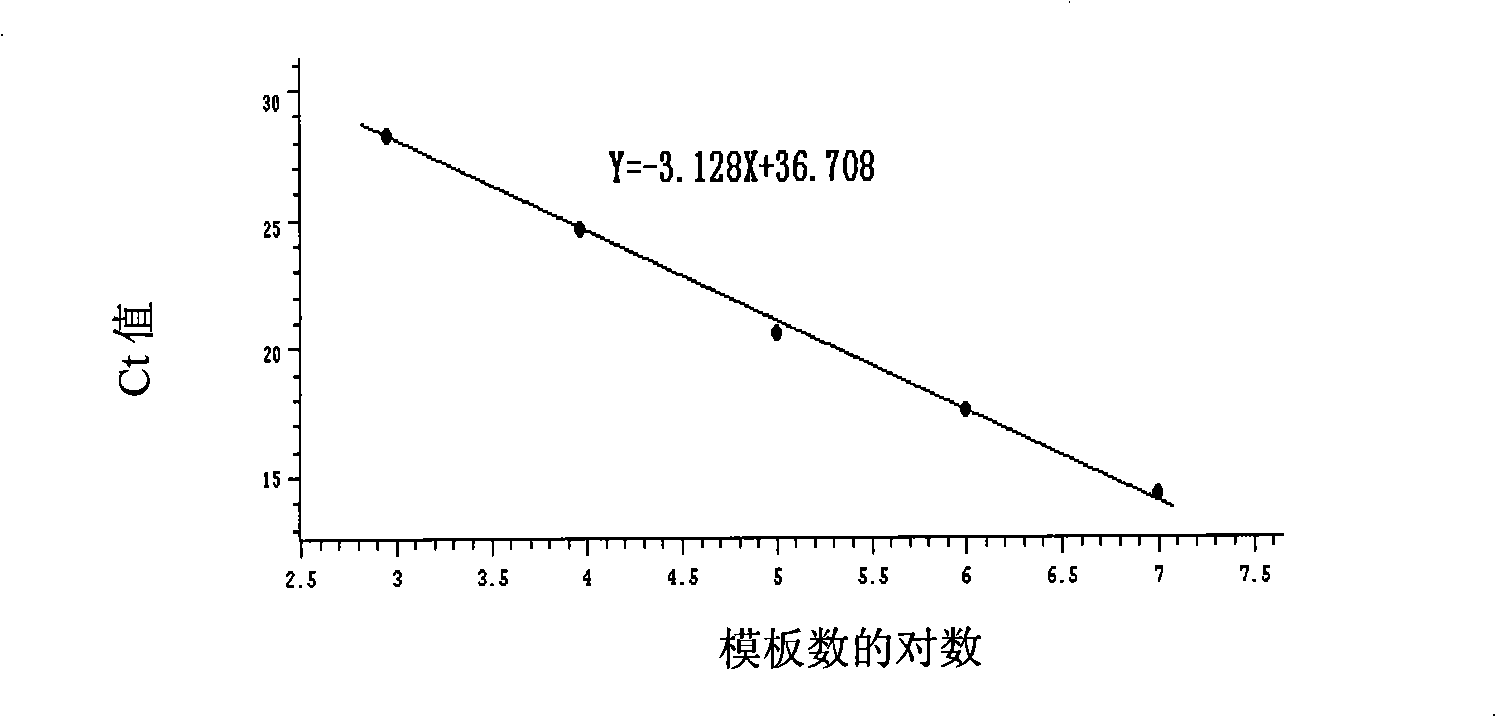
The invention discloses a standard product which is used for detecting the viral load of Friend murine leukemia, and a method which detects the viral load of the Friend murine leukemia by a real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction method (Real-Time RT-PCR method) by using the standard product. The detection process includes the steps of the extraction and content measurement of leukovirus nucleic acid (RNA), the obtaining of the nucleic acid segment by amplifying reverse transcription by using a primer, the detection of the real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (Real-time PCR), and the like. Compared with conventional PCR detection methods, the method of the invention, which detects the viral load of the Friend murine leukemia, has better specificity. The detected genetic amplified products are target genetic products to be detected. The method has a better linear relationship and is suitable for being applied to the detection of the viral load of the Friend murine leukemia (Fr. MuLV).
Owner:崔晓兰
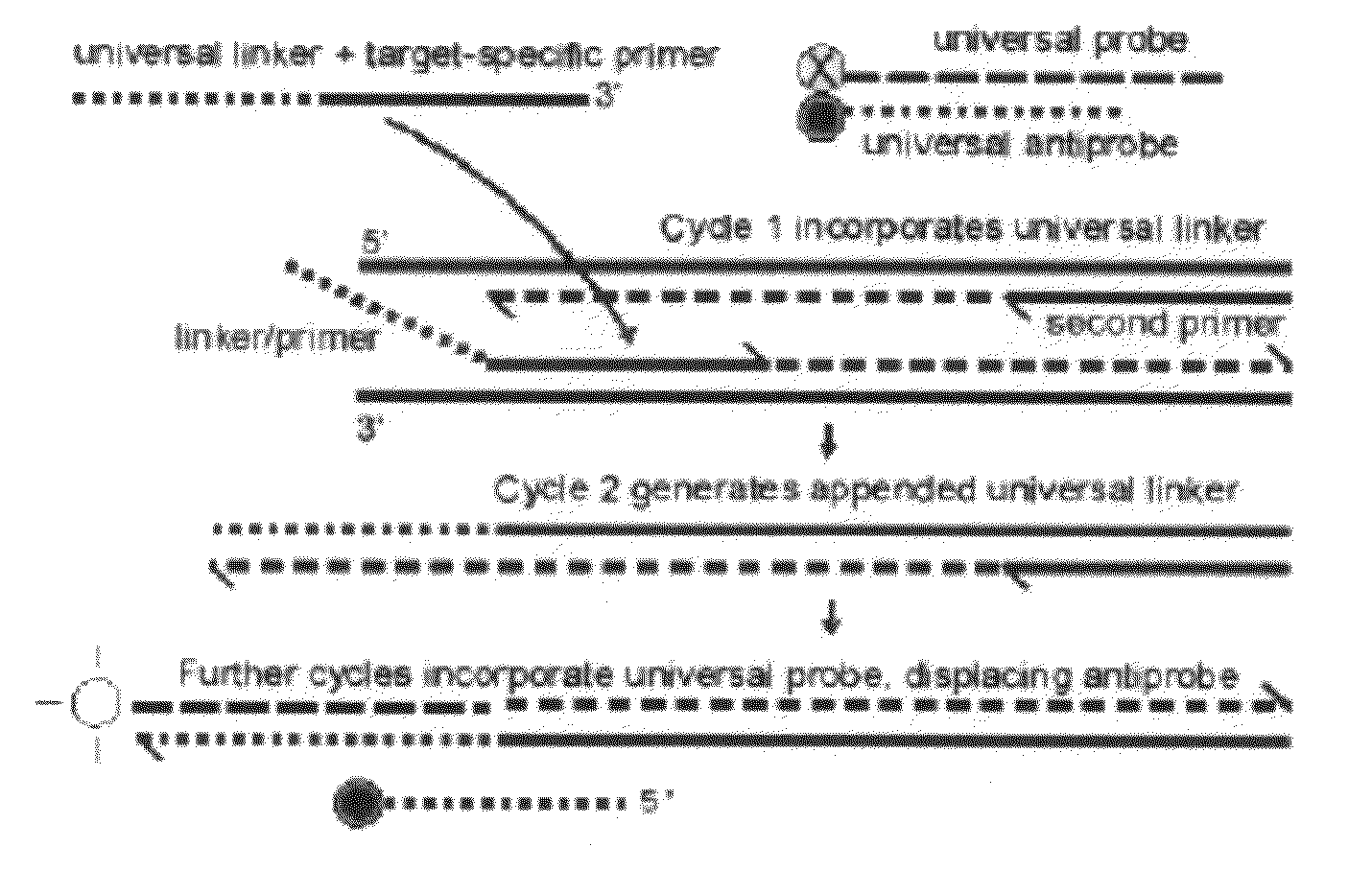
One step real-time rt pcr kits for the universal detection of organisms in industrial products
This invention is related to a novel sample preparation, probes, couple primer sets for one step real time reverse transcriptase polymerise chain reaction (RT-PCR), methods and kits for the universal detection of alive bacteria and / or fungus-yeast in pharmaceutical, cosmetic and non clinical samples.
Owner:GENOLIFE
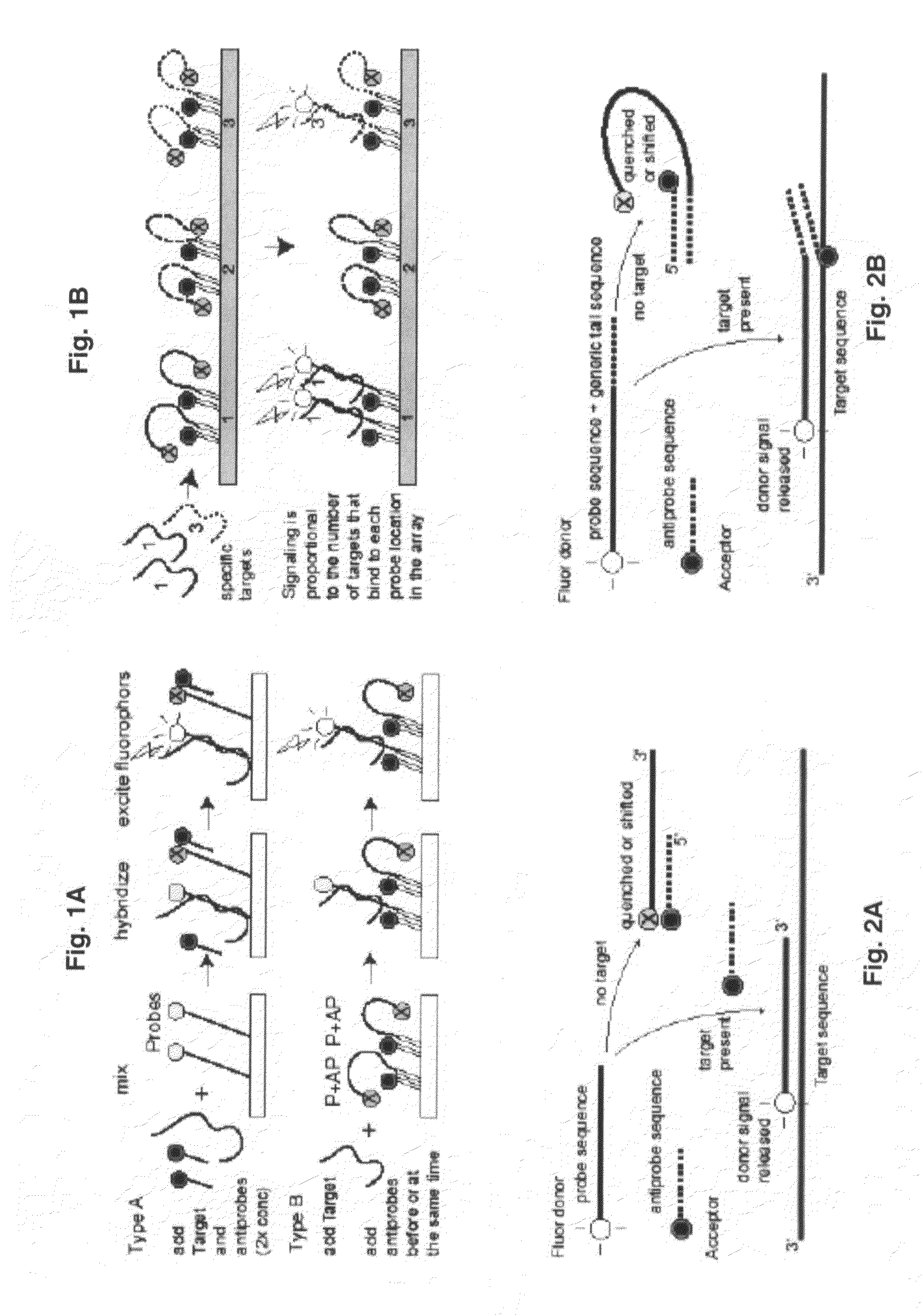
Probe-antiprobe compositions and methods for DNA or RNA detection
ActiveUS8076067B2Avoiding preventing detectionImprove bindingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementReal-Time PCRsMicroorganism
The invention provides novel compositions and methods for detecting unlabeled nucleic acid targets using labeled polynucleotide probes and partially complementary antiprobes. The interaction of probes, antiprobes and targets result in signaling changes that indicate target frequency. This novel detection mechanism is called a DNA detection switch, and it enable end-point detection, microarray detection and real-time PCR detection of a variety of nucleic acid targets including microbial species and subspecies, drug resistant mutants, and pathogenic strains.
Owner:GENETAG TECH
Method for providing information for diagnosing cancer using quantitative real-time PCR and kit for diagnosing cancer for the same
InactiveUS20120244531A1Strong specificityEasy to findMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantitative Real Time PCRReal-Time PCRs
Owner:M&D
Double stranded linear nucleic acid probe
ActiveUS20140087381A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementReal-Time PCRsHybridization probe
A double-stranded nucleic acid hybridization probe and methods of using the same are described. The probe described is particularly suited for real-time RT-PCR reactions and has high tolerance to mismatches.
Owner:ABBOTT MOLECULAR INC
Diagnostic method for detecting acute kidney injury using heat shock protein 72 as a sensitive biomarker
InactiveUS20130065239A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisReal-Time PCRsWestern blot
The invention relates to a reliable, easy-to-implement non-invasive diagnostic method for detecting early acute kidney injury by measuring the concentration of a biomarker in urine samples, said biomarker being selected from heat shock proteins of the 70 KDa family. More specifically, the invention relates to the identification of heat shock protein 72, whereby said biomarker is identified by means of ELISA and Western blot or by means of the level of RNAm using real-time RT-PCR. The invention helps to solve the current problem that exists in medicine whereby it is not possible to detect acute renal failure in the early stages or the severity of the renal damage in order to treat the patient in a timely manner with an effective therapy.
Owner:UNIV NAT AUTONOMA DE MEXICO
Systems and methods for monitoring the amplification of DNA
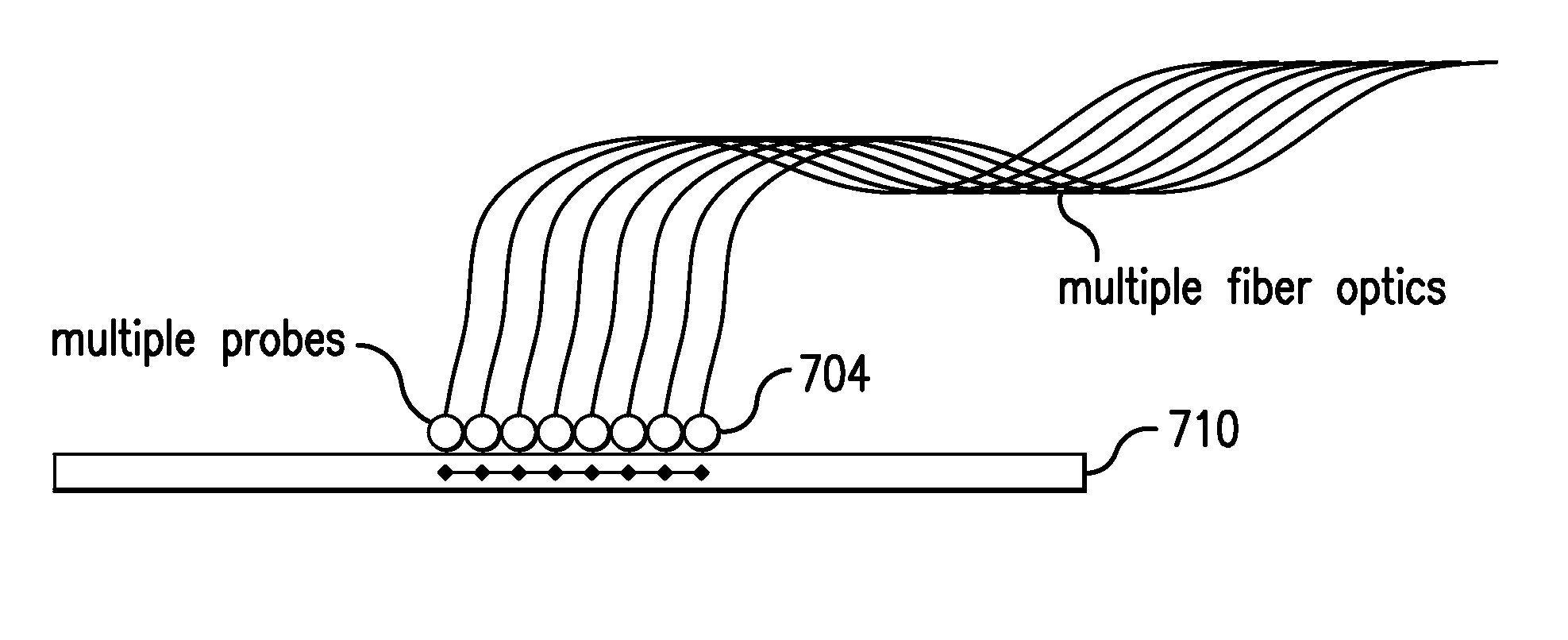
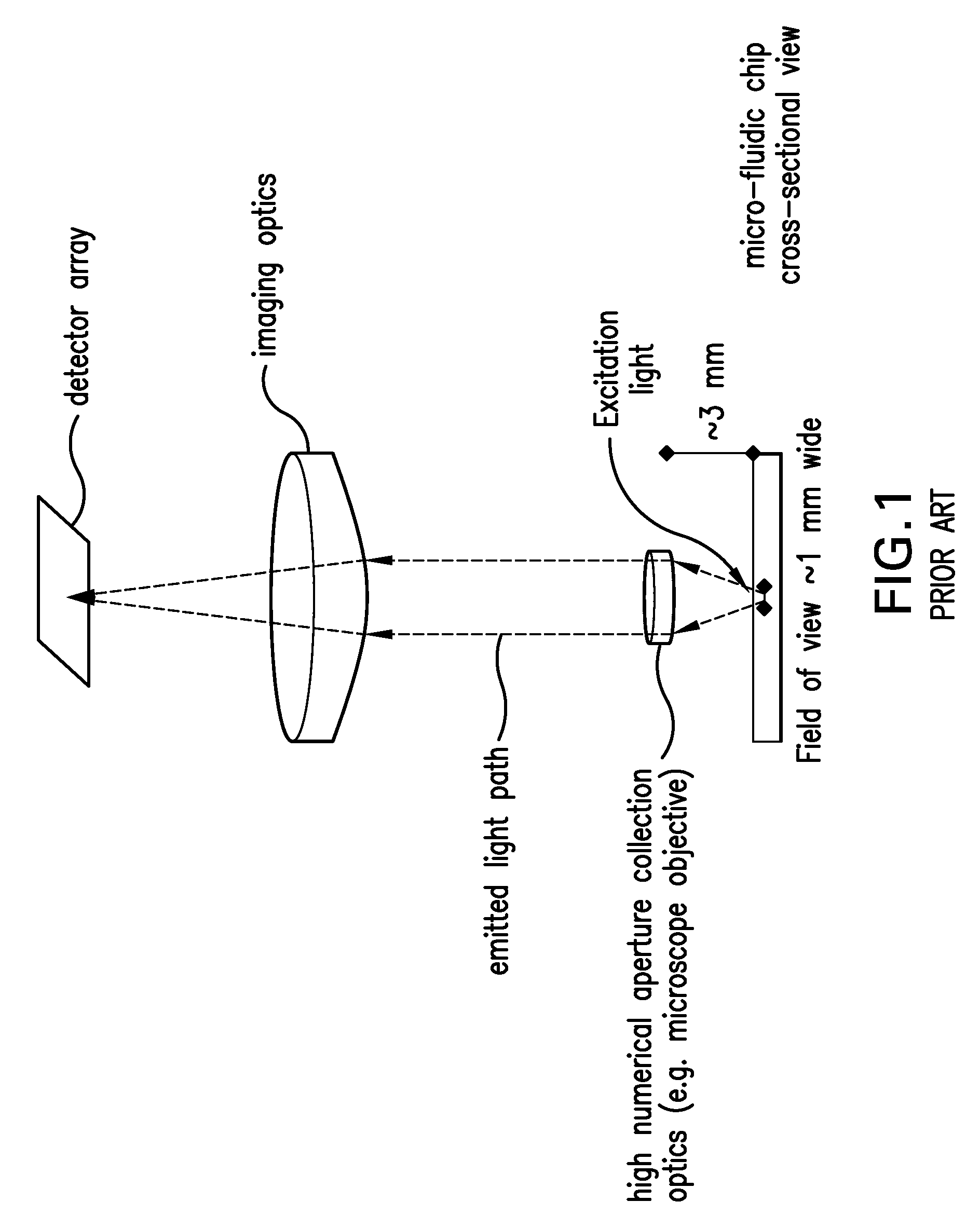
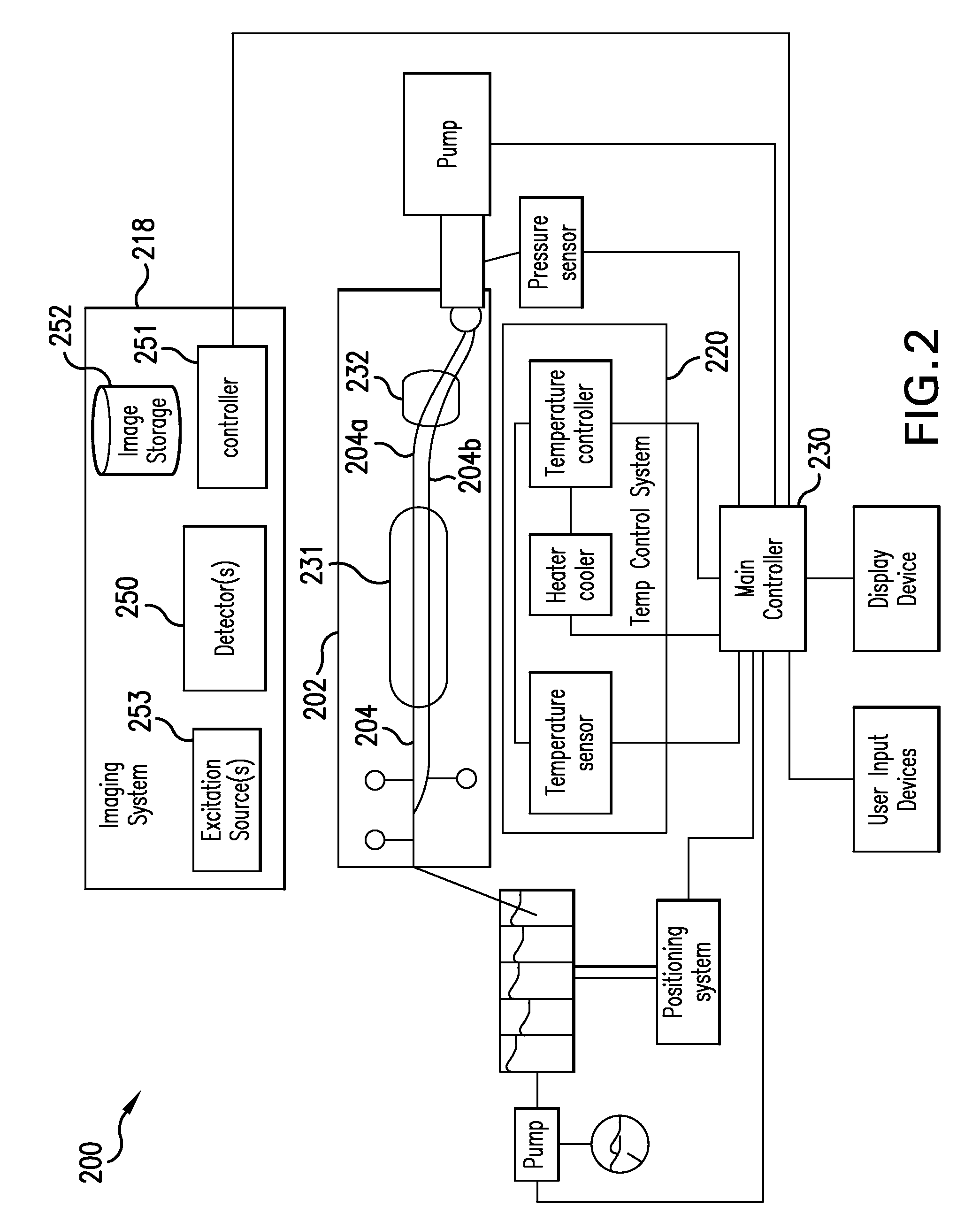
InactiveUS9017946B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiberTemperature control
A system and method for amplifying and detecting nucleic acids are disclosed. In one embodiment, the system includes: a microfluidic device comprising a channel for receiving a sample of solution containing real-time PCR reagents; a temperature control system configured to cycle the temperature of the sample; an excitation source for illuminating the sample; a fiber optic probe comprising (i) an optical fiber having a distal end and a proximal end and (ii) a probe head connected to the distal end of the optical fiber and positioned between the distal end of the optical fiber and the channel; and a detector configured to detect emissions exiting the proximal end of the optical fiber.
Owner:CANON USA
Real-time fluorescent RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection reagent and detection method for lupulus masking virus
InactiveCN102382903BQuick checkSensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesReal-Time PCRsFluorescence
The invention discloses a real-time fluorescent RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection reagent and a detection method for lupulus masking virus. The real-time RT-PCR detection reagent comprises a pair of special primers and a special fluorescent probe. An amplification target fragment is 61bp in length, and the primers have the HLV-F sequence as follows: CGTGGAACGGCTCCTTCTT; the primers have the HLV-R sequence as follows: AGAGTTGTATCCACCGGGTAGTTT; and the probe has the HLV-P sequence as follows: CACCAGCCGGAGTT, 5' of the probe contains FAM report fluorescent dye, and the nucleotide sequence of the amplification target fragment is shown as SEQIDNO:4. The detection method comprises the steps of total RNA extraction and real-time fluorescent PCR reaction, in the RT-PCR reaction, the amplification of the primers and the detection of the probe are conducted simultaneously, a pipe is closed completely in the whole detection process, the PCR aftertreatment is not needed, the pollution caused by a PCR product is eliminated, the detection steps are reduced, the time is saved, and the detection method is special and sensitive for the lupulus masking virus. The detection reagent and the detection method can rapidly and accurately detect the lupulus masking virus, and has flexible operation.
Owner:中华人民共和国北仑出入境检验检疫局 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com