Patents
Literature
102 results about "Elongation factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Elongation factors are a set of proteins that function at the ribosome, during protein synthesis, to facilitate translational elongation from formation of the first to the last peptide bond of a growing polypeptide. Bacteria and eukaryotes use elongation factors that are largely homologous to each other, but with distinct structures (and different research nomenclatures).
Method and system for rapid biomolecular recognition of amino acids and protein sequencing
InactiveUS6846638B2Low costHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein Sequence DeterminationDigestion
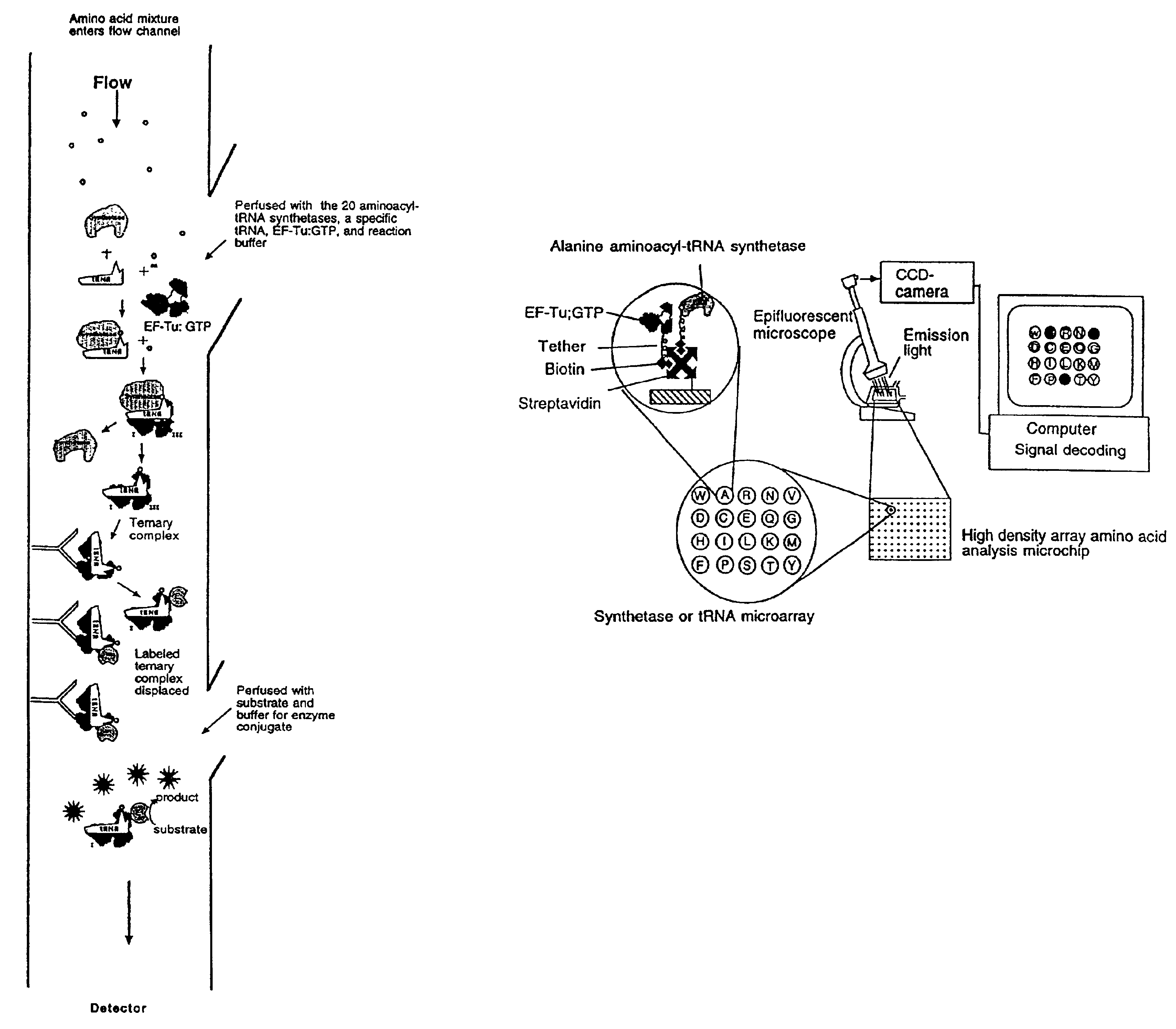
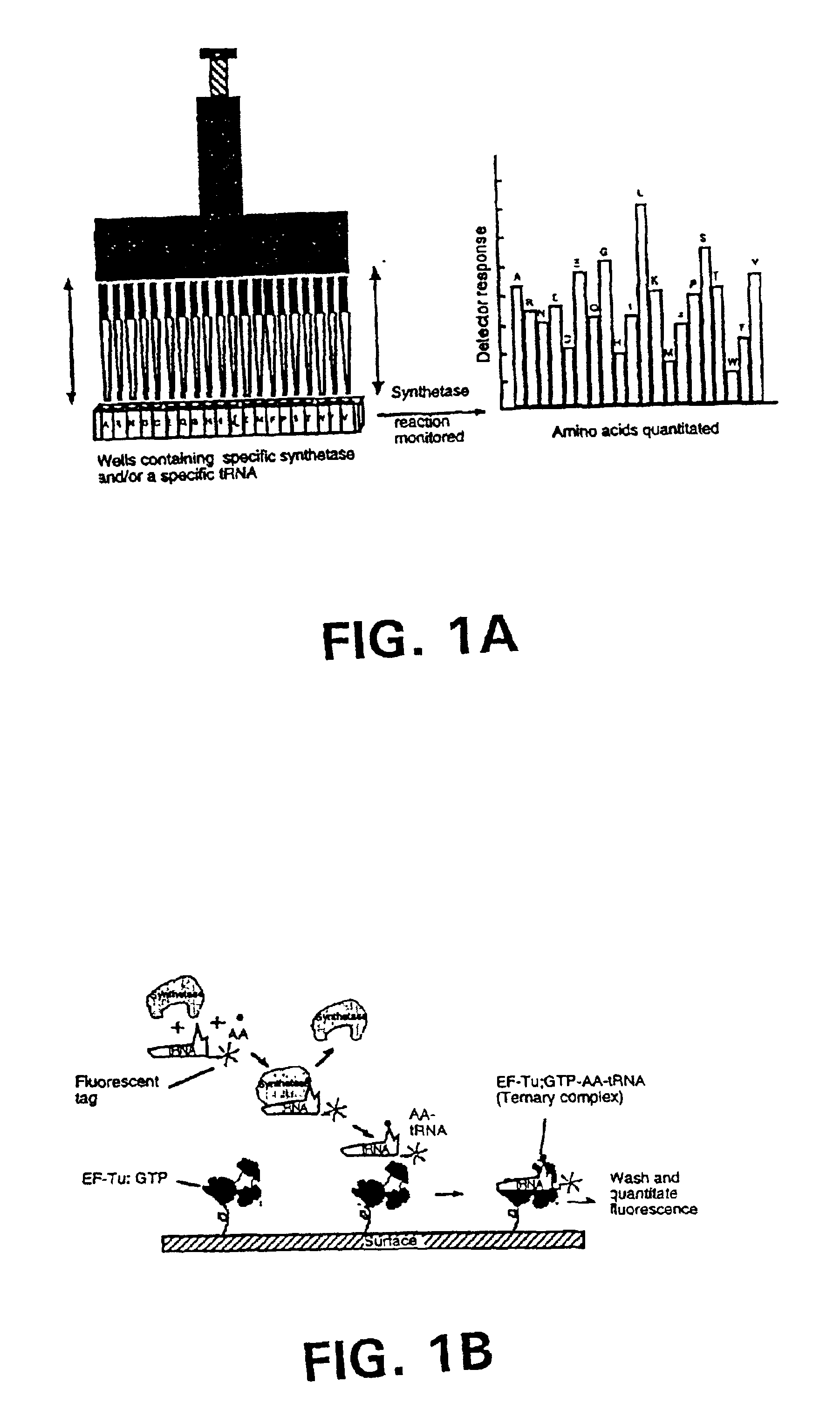
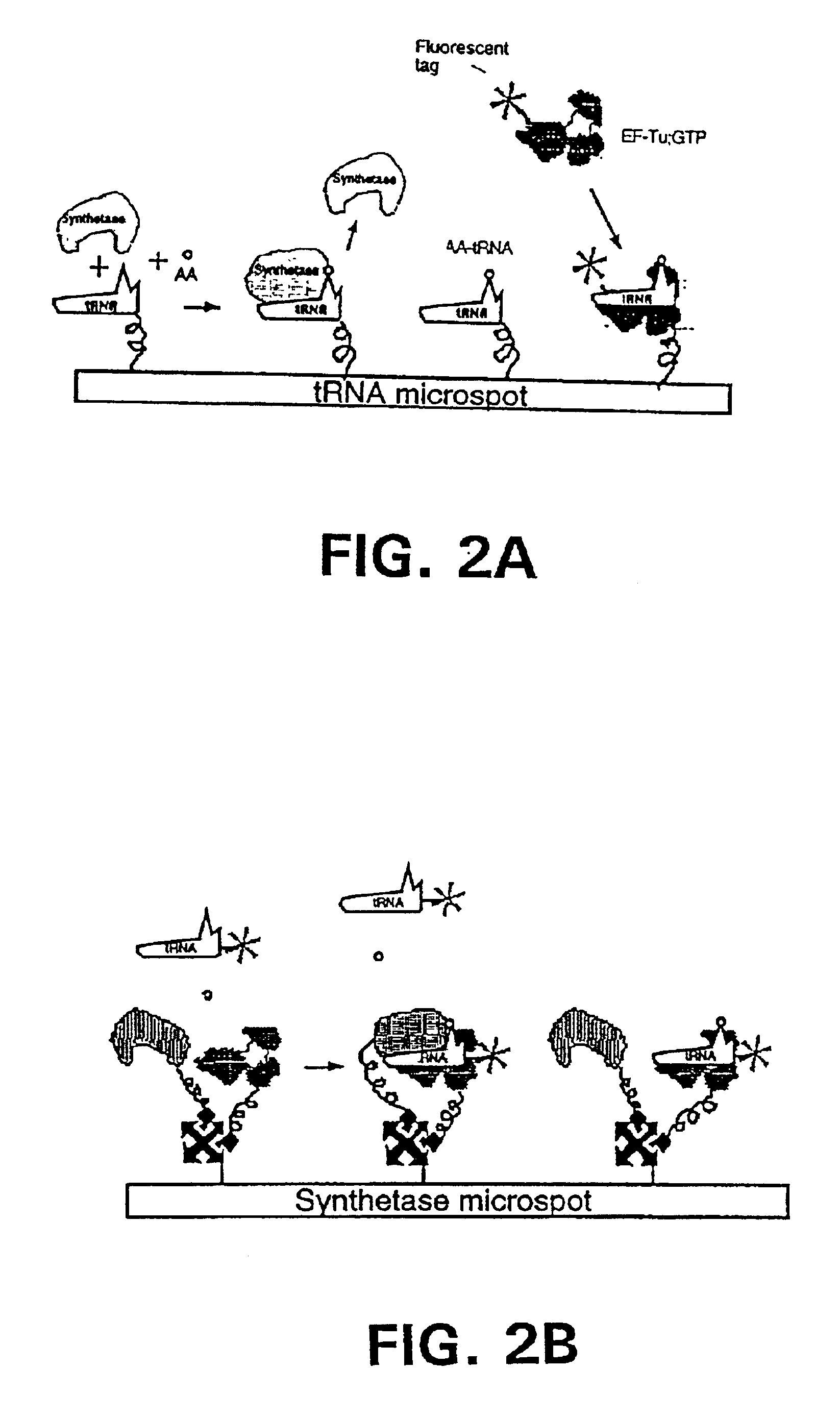
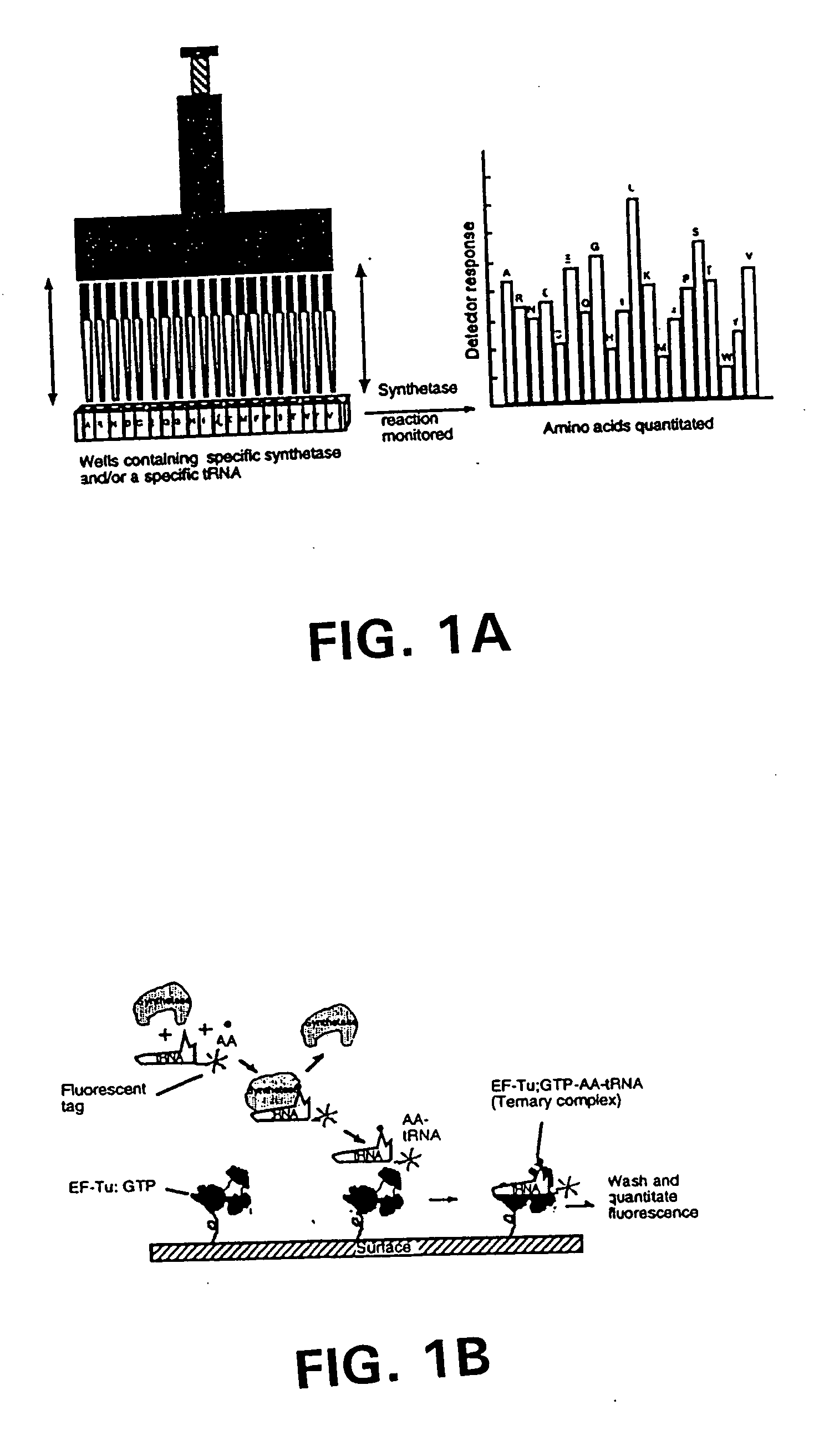
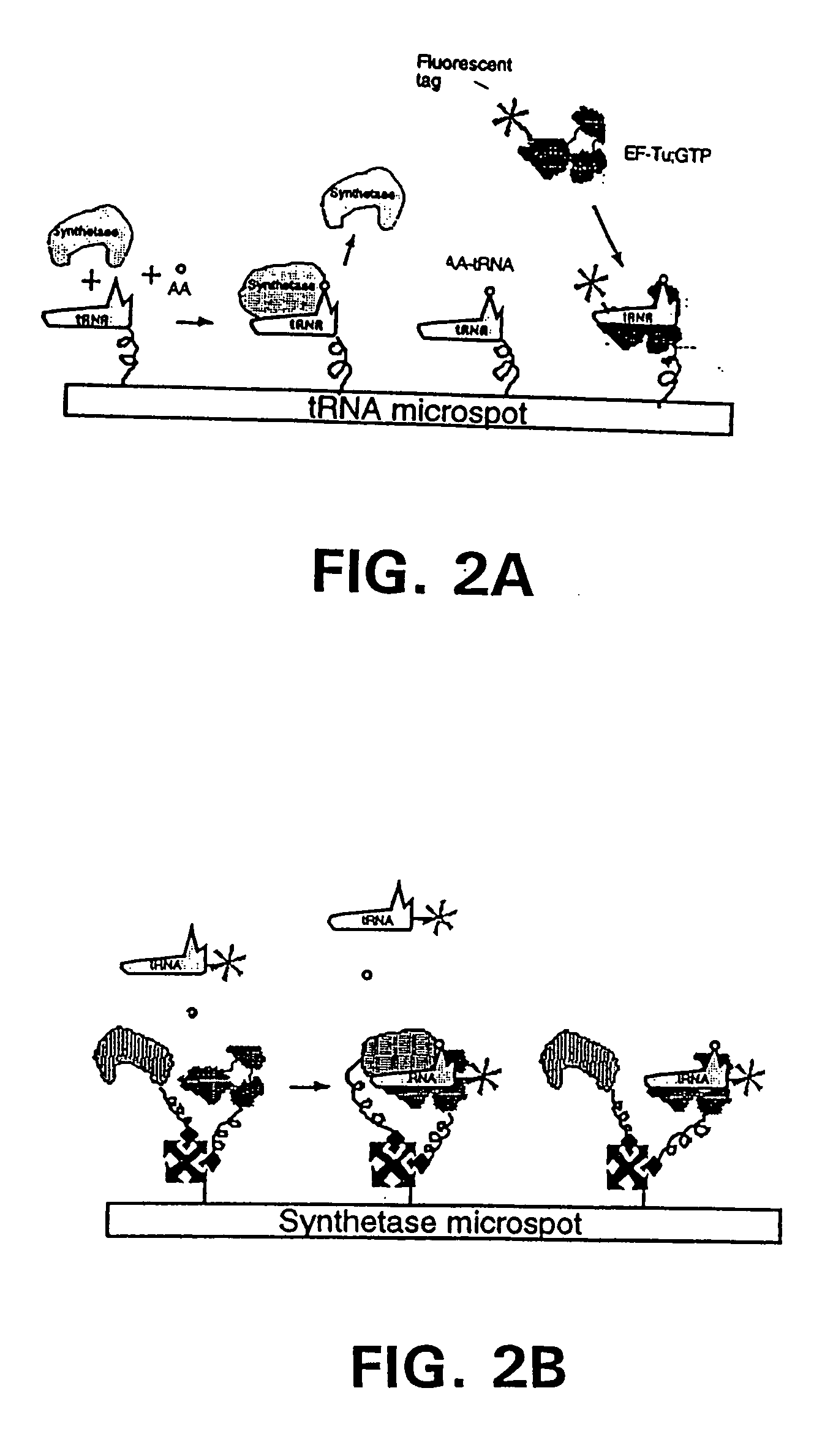
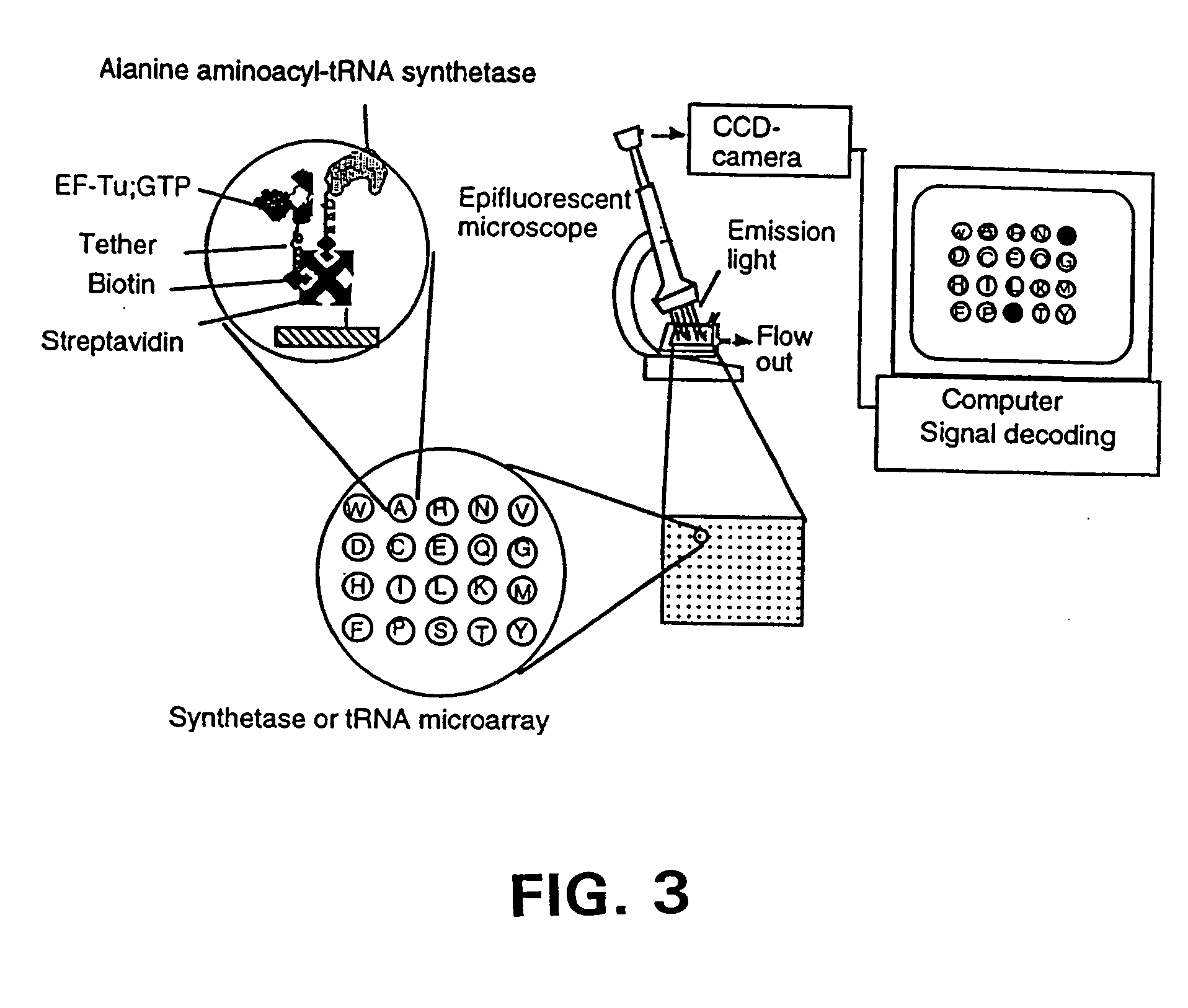
Methods, compositions, kits, and apparatus are provided wherein the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase system is used to analyze amino acids. The method allows very small devices for quantitative or semi-quantitative analysis of the amino acids in samples or in sequential or complete proteolytic digestions. The methods can be readily applied to the detection and / or quantitation of one or more primary amino acids by using cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and cognate tRNA. The basis of the method is that each of the 20 synthetases and / or a tRNA specific for a different amino acid is separated spatially or differentially labeled. The reactions catalyzed by all 20 synthetases may be monitored simultaneously, or nearly simultaneously, or in parallel. Each separately positioned synthetase or tRNA will signal its cognate amino acid. The synthetase reactions can be monitored using continuous spectroscopic assays. Alternatively, since elongation factor Tu:GTP (EF-Tu:GTP) specifically binds all AA-tRNAs, the aminoacylation reactions catalyzed by the synthetases can be monitored using ligand assays. Microarrays and microsensors for amino acid analysis are provided. Additionally, amino acid analysis devices are integrated with protease digestions to produce miniaturized enzymatic sequenators capable of generating either N- or C-terminal sequence and composition data for a protein or peptide. The possibility of parallel processing of many samples in an automated manner is discussed.
Owner:NANOBIODYNAMICS
Water-dispersible patch containing an active agent for dermal delivery
A dermal patch having comprising at least two layers wherein at least one layer is a polymer matrix system having an active agent admixed therein. At least one of the layers includes a water-dispersible or water-dissipatable polymer. The dermal patch has an elongation factor of at least 50%.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Method and system for rapid biomolecular recognition of amino acids and protein sequencing
InactiveUS20050164264A1Quick analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein Sequence DeterminationDigestion
Methods, compositions, kits, and apparatus are provided wherein the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase system is used to analyze amino acids. The method allows very small devices for quantitative or semi-quantitative analysis of the amino acids in samples or in sequential or complete proteolytic digestions. The methods can be readily applied to the detection and / or quantitation of one or more primary amino acids by using cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and cognate tRNA. The basis of the method is that each of the 20 synthetases and / or a tRNA specific for a different amino acid is separated spatially or differentially labeled. The reactions catalyzed by all 20 synthetases may be monitored simultaneously, or nearly simultaneously, or in parallel. Each separately positioned synthetase or tRNA will signal its cognate amino acid. The synthetase reactions can be monitored using continuous spectroscopic assays. Alternatively, since elongation factor Tu:GTP (EF-Tu:GTP) specifically binds all AA−tRNAs, the aminoacylation reactions catalyzed by the synthetases can be monitored using ligand assays. Microarrays and microsensors for amino acid analysis are provided. Additionally, amino acid analysis devices are integrated with protease digestions to produce miniaturized enzymatic sequenators capable of generating either N- or C-terminal sequence and composition data for a protein or peptide. The possibility of parallel processing of many samples in an automated manner is discussed.
Owner:NANOBIODYNAMICS
Lonidamine analogues and their use in male contraception and cancer treatment
InactiveUS20060047126A1Synergistic effectOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHeat shockElongation factor
Novel compounds useful for inhibiting spermatogenesis and cancer treatment, and in particular as inhibitors of heat shock proteins and / or elongation factor 1 alpha.
Owner:KANSAS UNIV OF +1
Non-invasive detection of fish viruses by real-time PCR
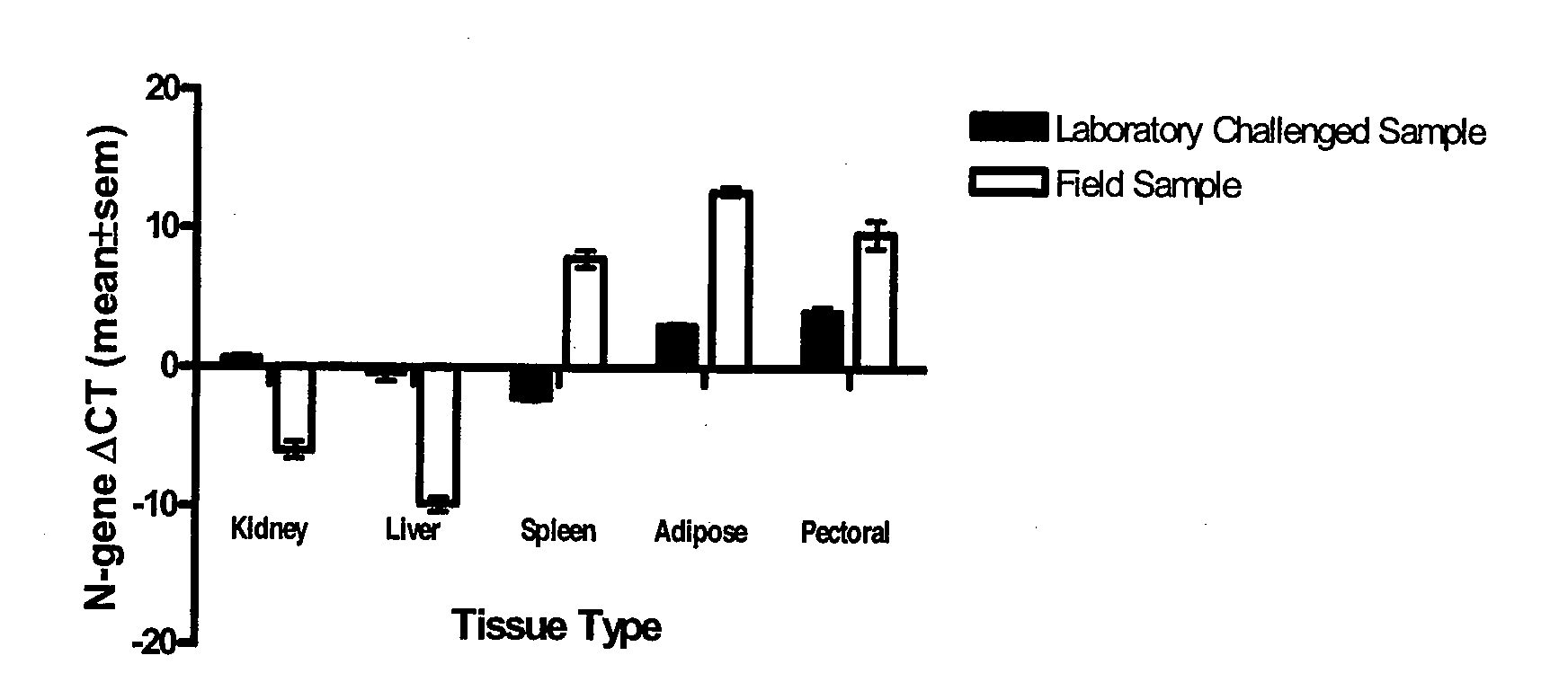
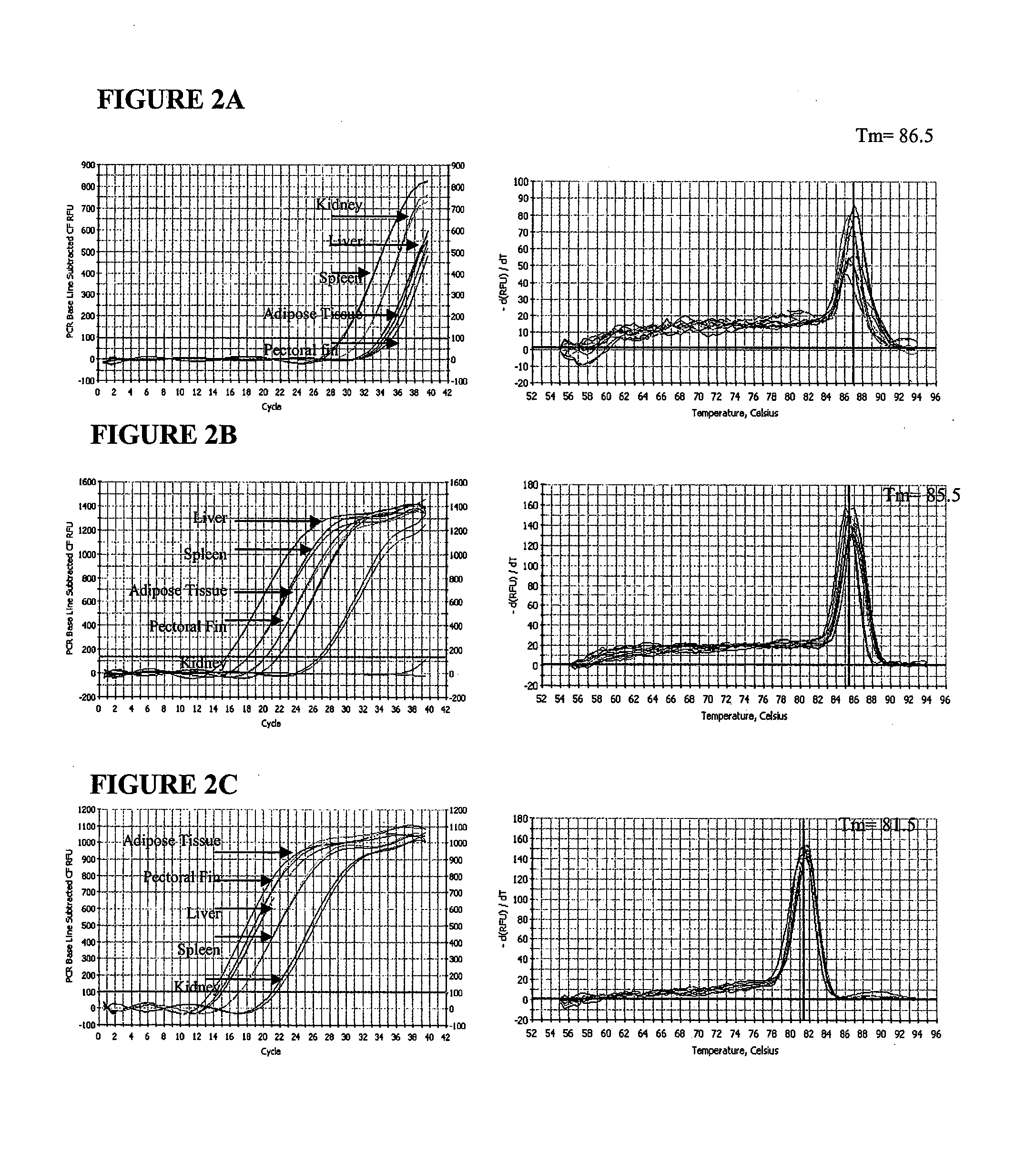
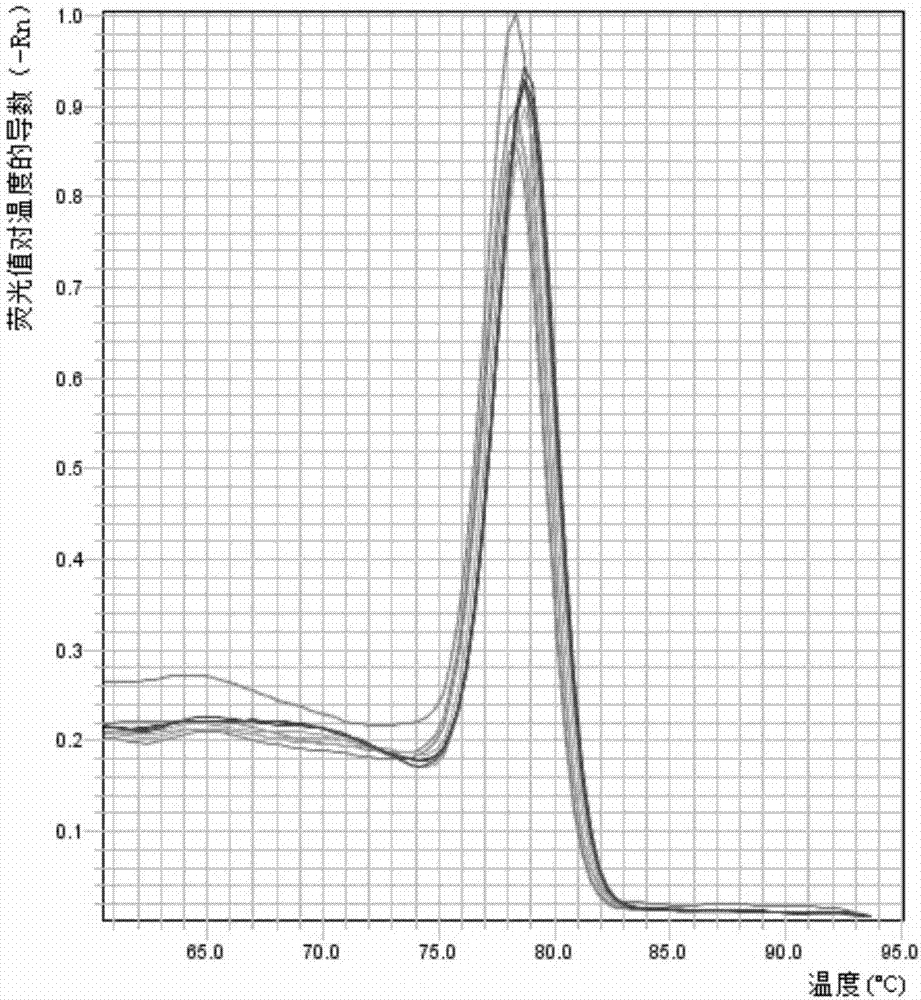
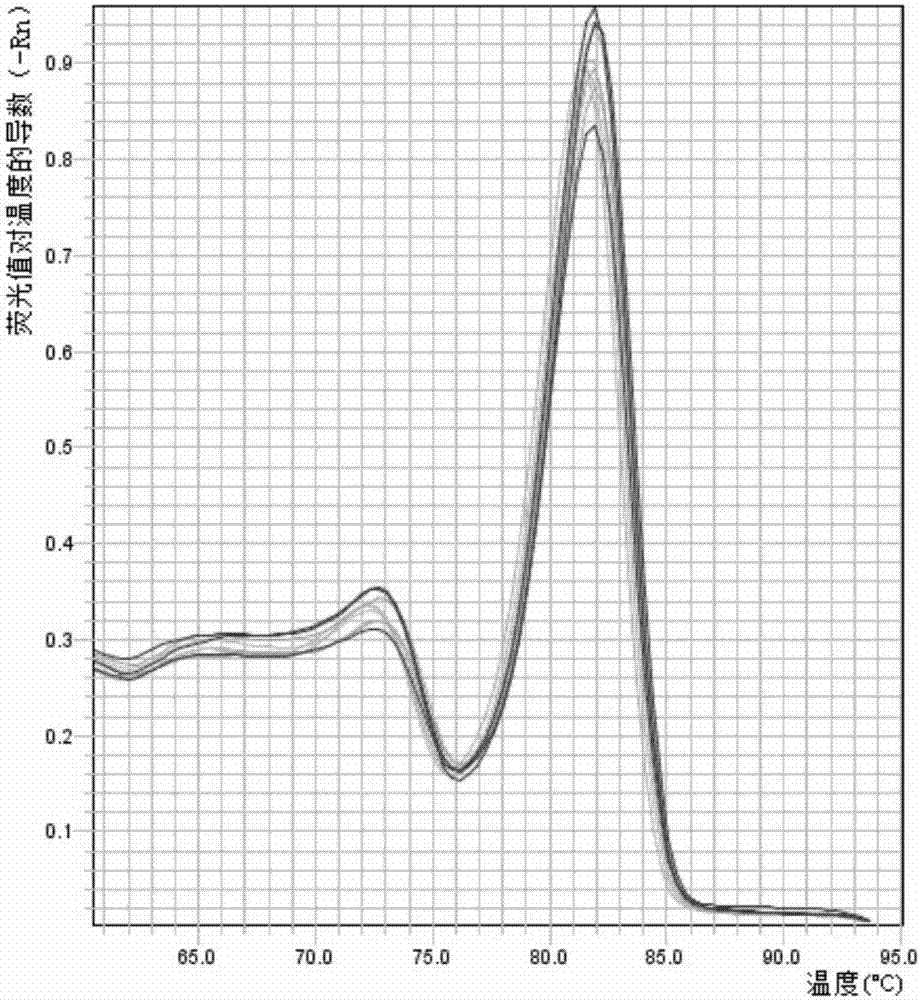
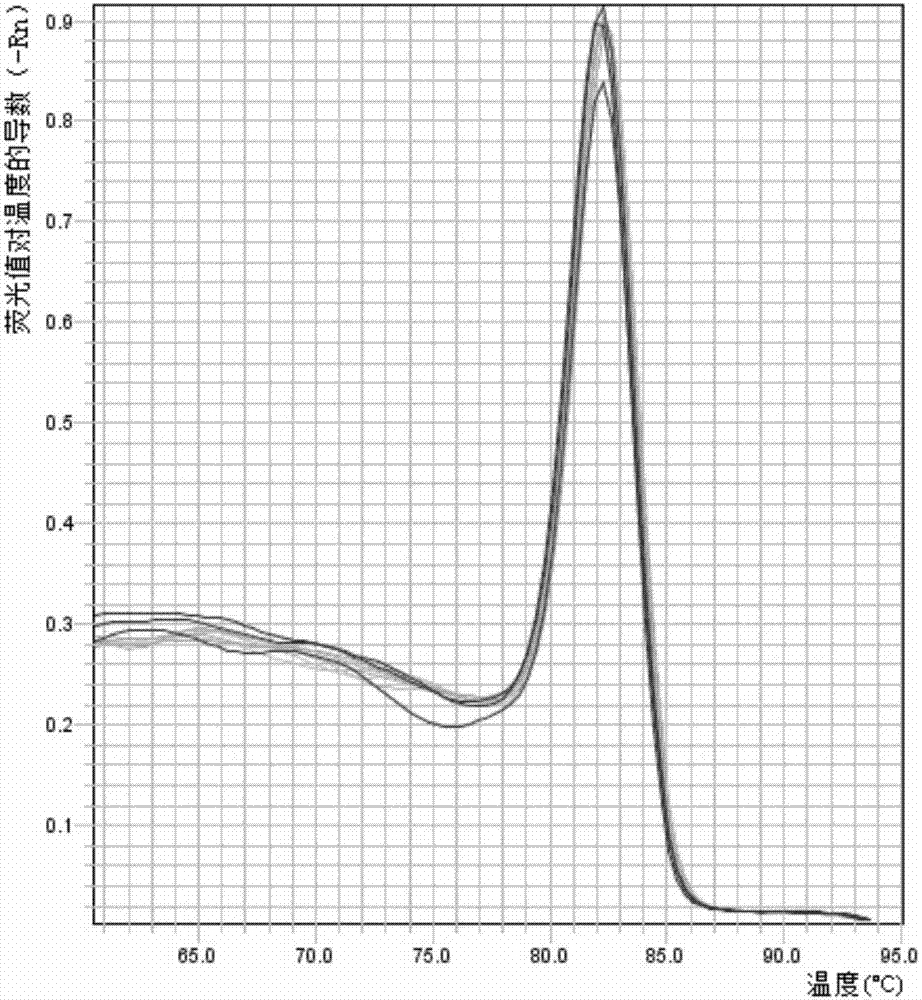
A real-time assay coupled with a non-invasive tissue sampling was developed for the detection and quantification of fish viruses. As a proof of principles, data were presented for the detection and quantification of infectious hypodermal necrosis virus (IHNV) in trout. The primers were designed for IHNV nucleocapsid (N), and surface glycoprotein (G) genes, and trout &bgr;-actin and elongation factor-l&agr; (EF-I &agr;) were used as internal control for the assay. The reaction conditions for the real-time RT-PCR were optimized using cDNA derived from IHNV-infected Epithelioma papulosum cyprinid (EPC) cells. Using both N- and G-gene primers, IHNV was successfully detected in liver, kidney, spleen, adipose tissue and pectoral fin samples of laboratory-challenged and wild samples. The dissociation curves with a single melting peak at expected temperature (85° C. for the N-gene and 86.5° C. for the G-gene) confirmed the specificity of the N- and G-gene amplicons. The IHNV N- and the G-gene expression levels in different tissues of laboratory challenged samples were in the order of spleen, liver, kidney, adipose tissue and pectoral fin, however in the field-collected samples the order of gene expression was liver, kidney, pectoral fin, adipose tissue, and spleen. The N- and G-gene expressions in spleen were found to be dramatically lower in the field-collected samples compared to the laboratory-challenged samples indicating a potential difference in the IHNV replication in the laboratory as opposed to field conditions. The real-time PCR assay was found to be rapid, highly sensitive, and reproducible. Based upon the ability to detect the virus in pectoral fins a non-invasive detection method for IHNV and other fish viruses is developed. Such a non-invasive tissue sampling coupled with real-time PCR assay is very valuable for large-scale virus screening of fish in aquaculture facilities as well as for epidemiological studies.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONUTRITION CORP
Lonidamine analogues and their use in male contraception and cancer treatment
Owner:KANSAS UNIV OF +1
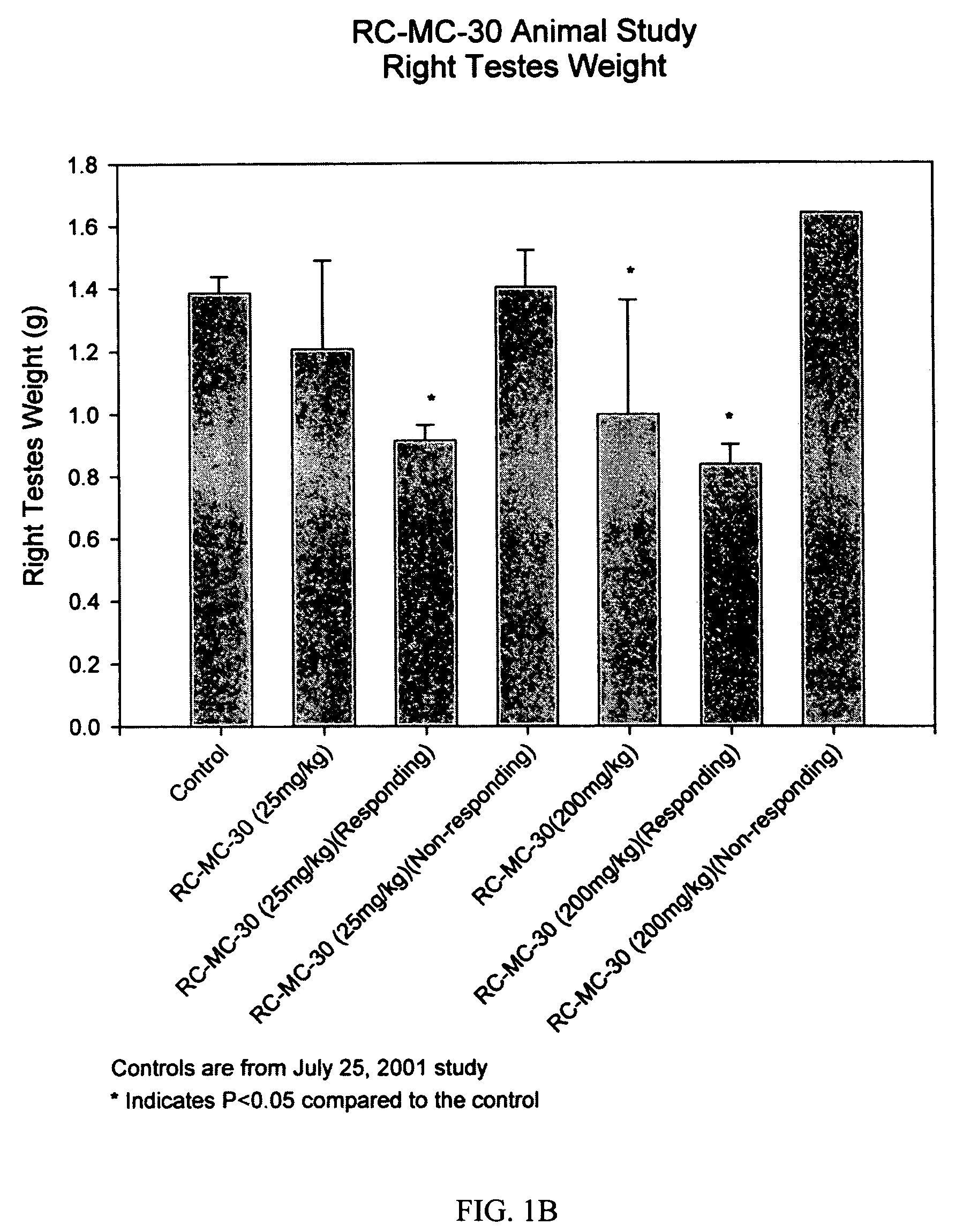
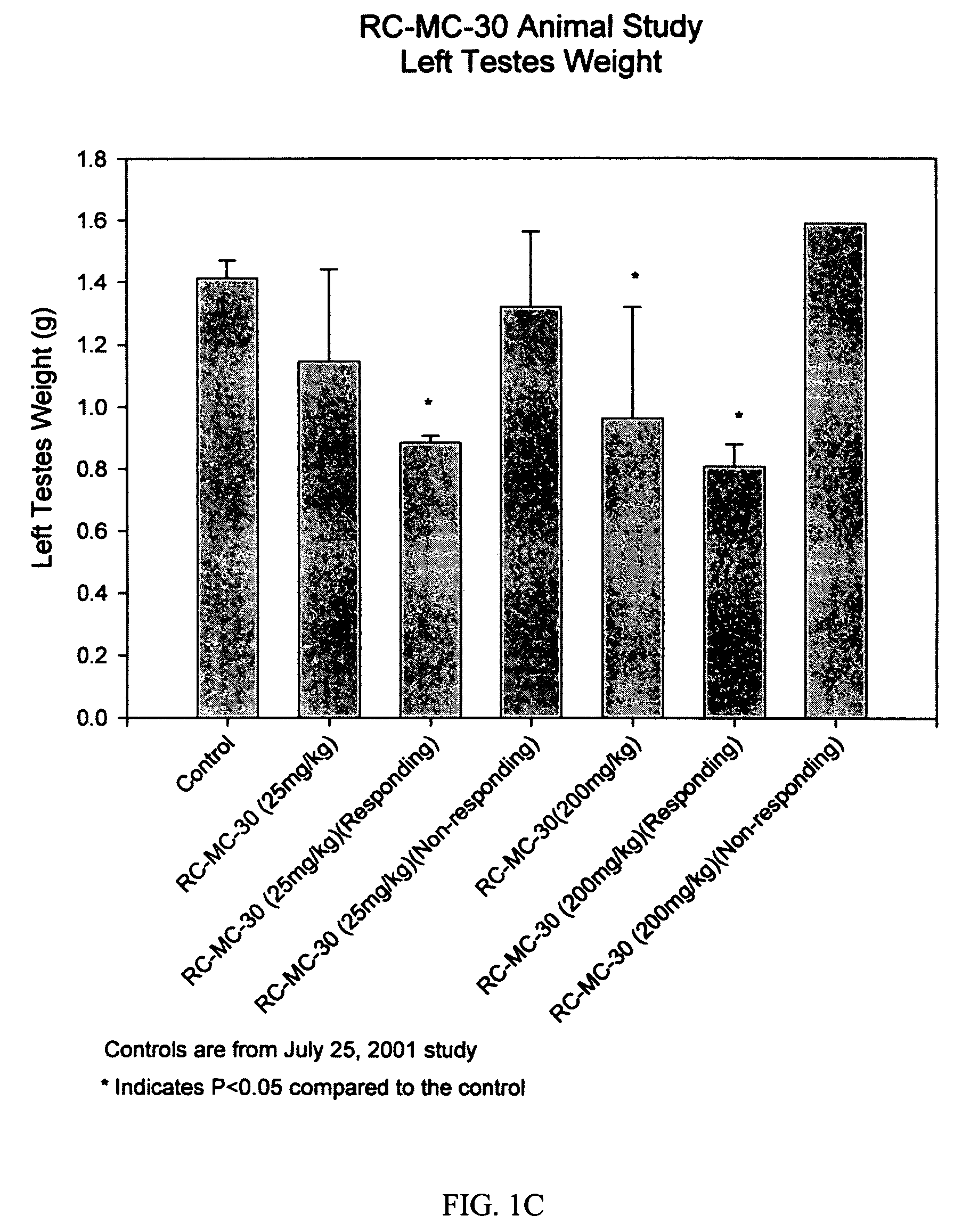
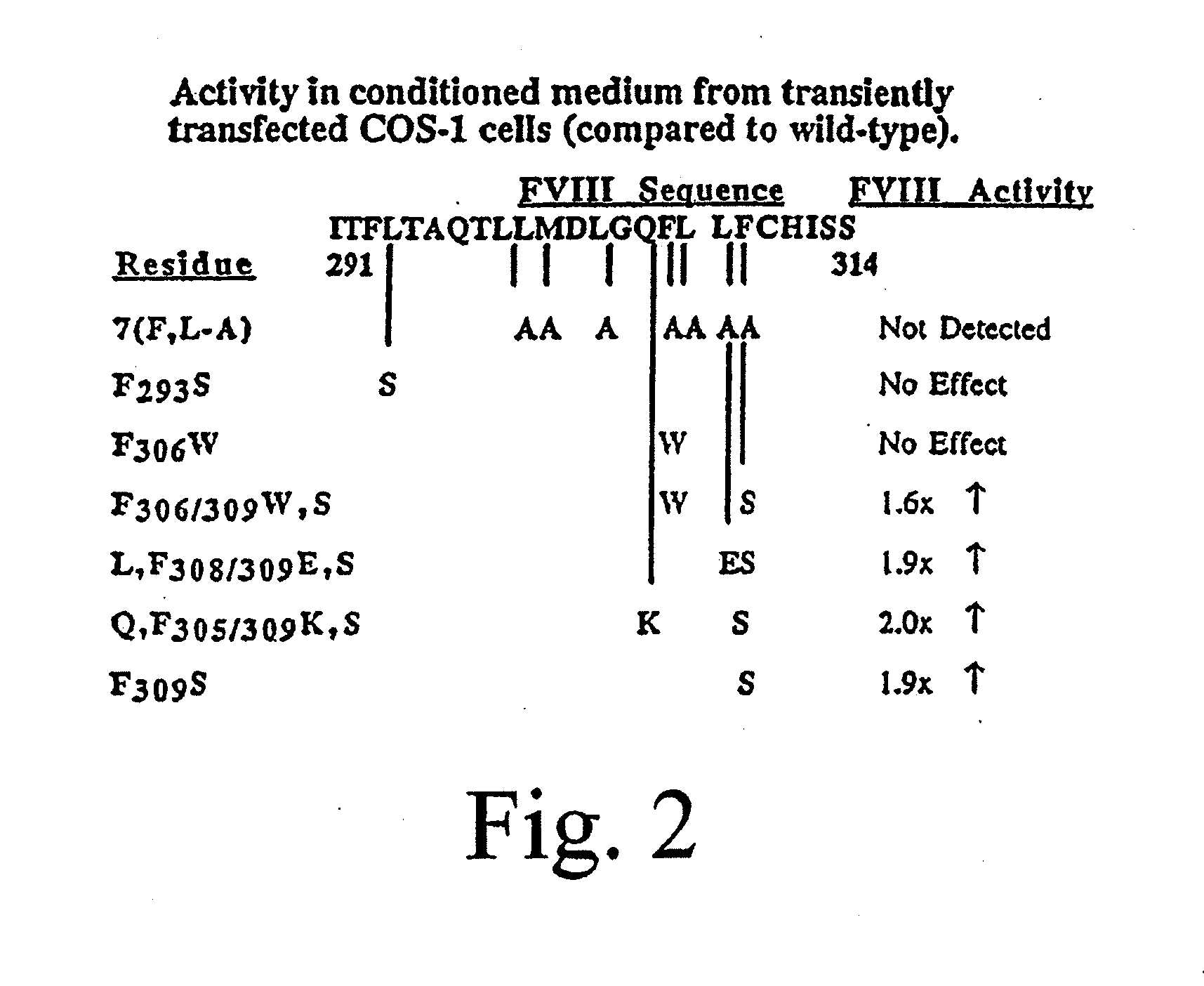
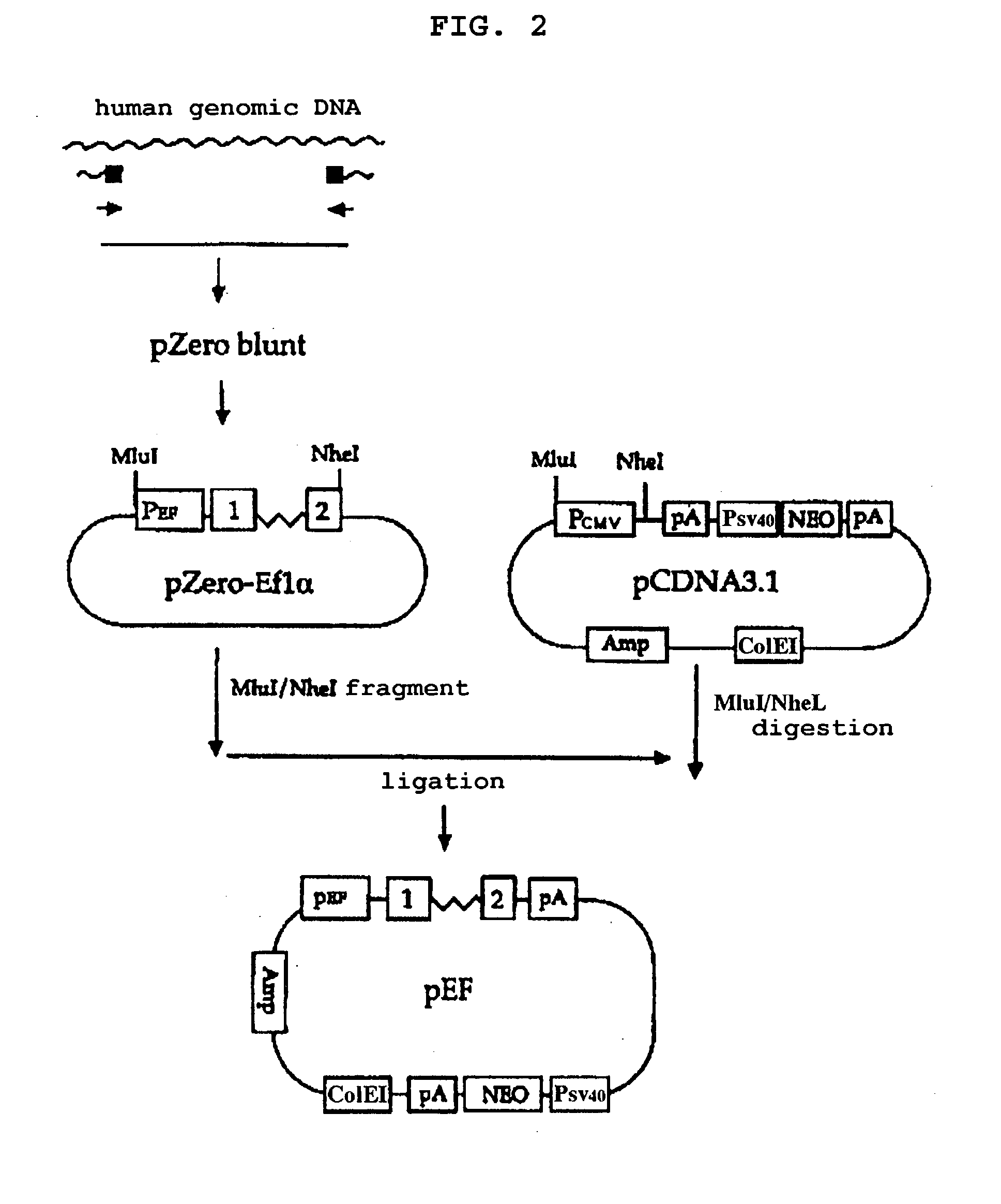
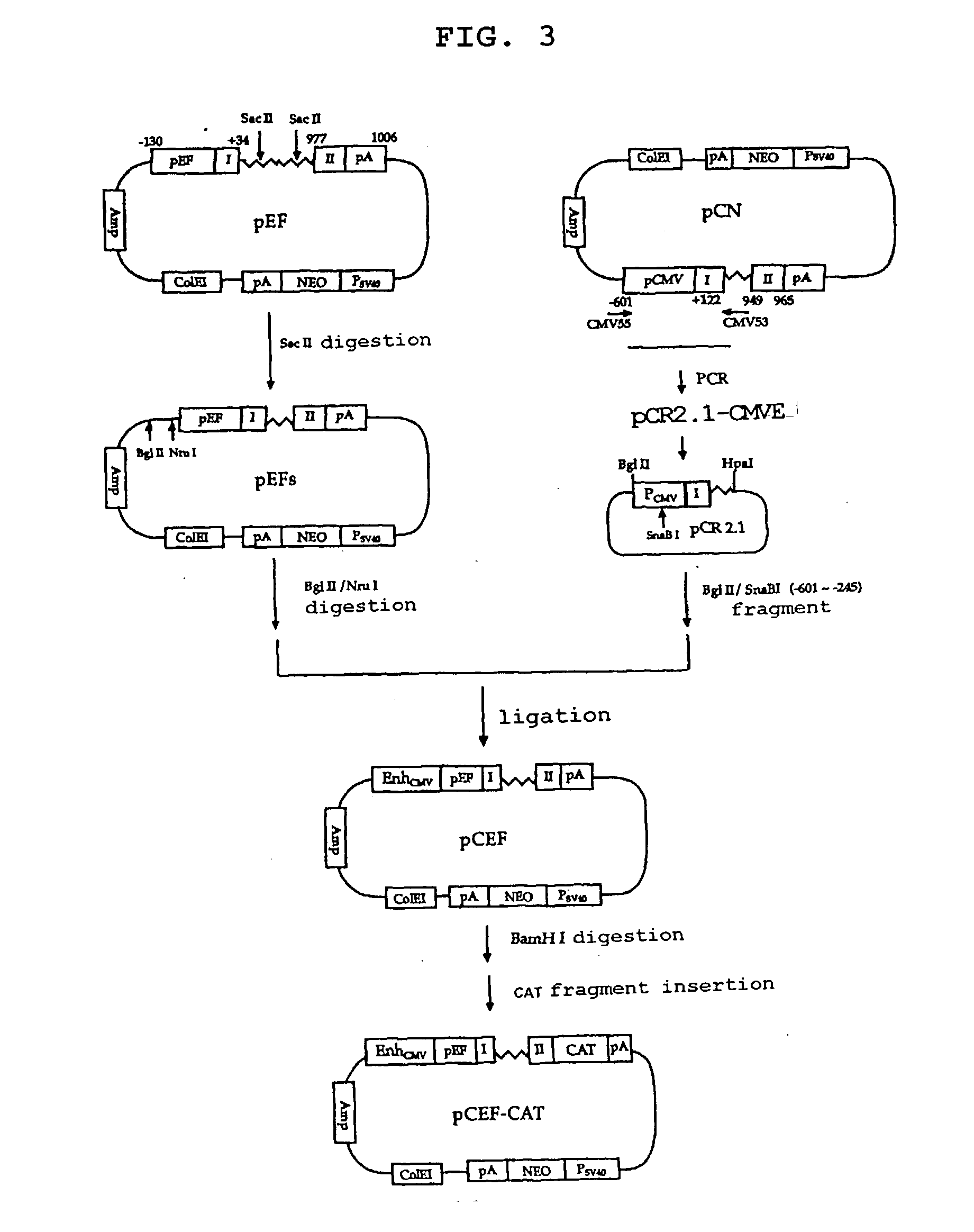
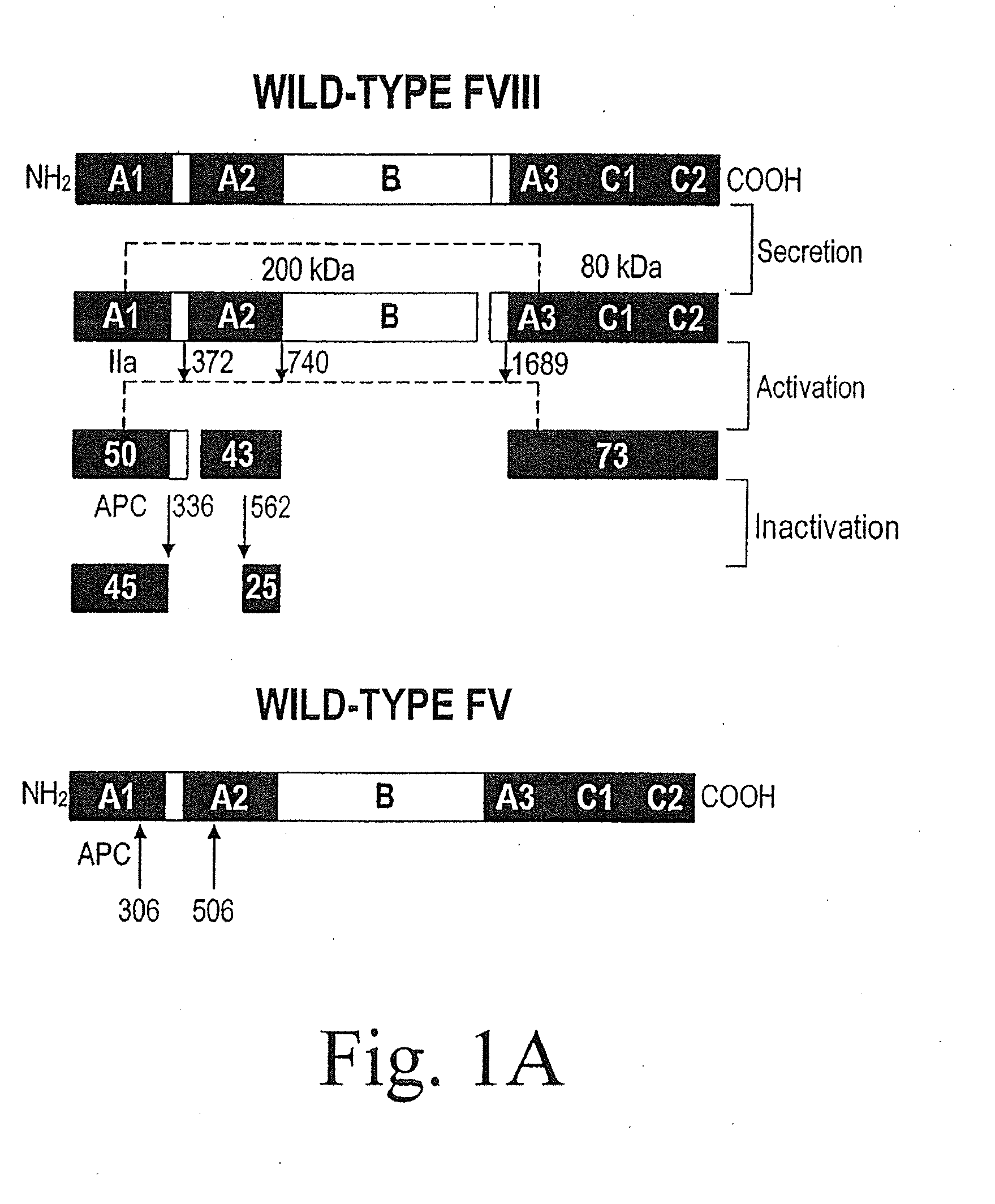
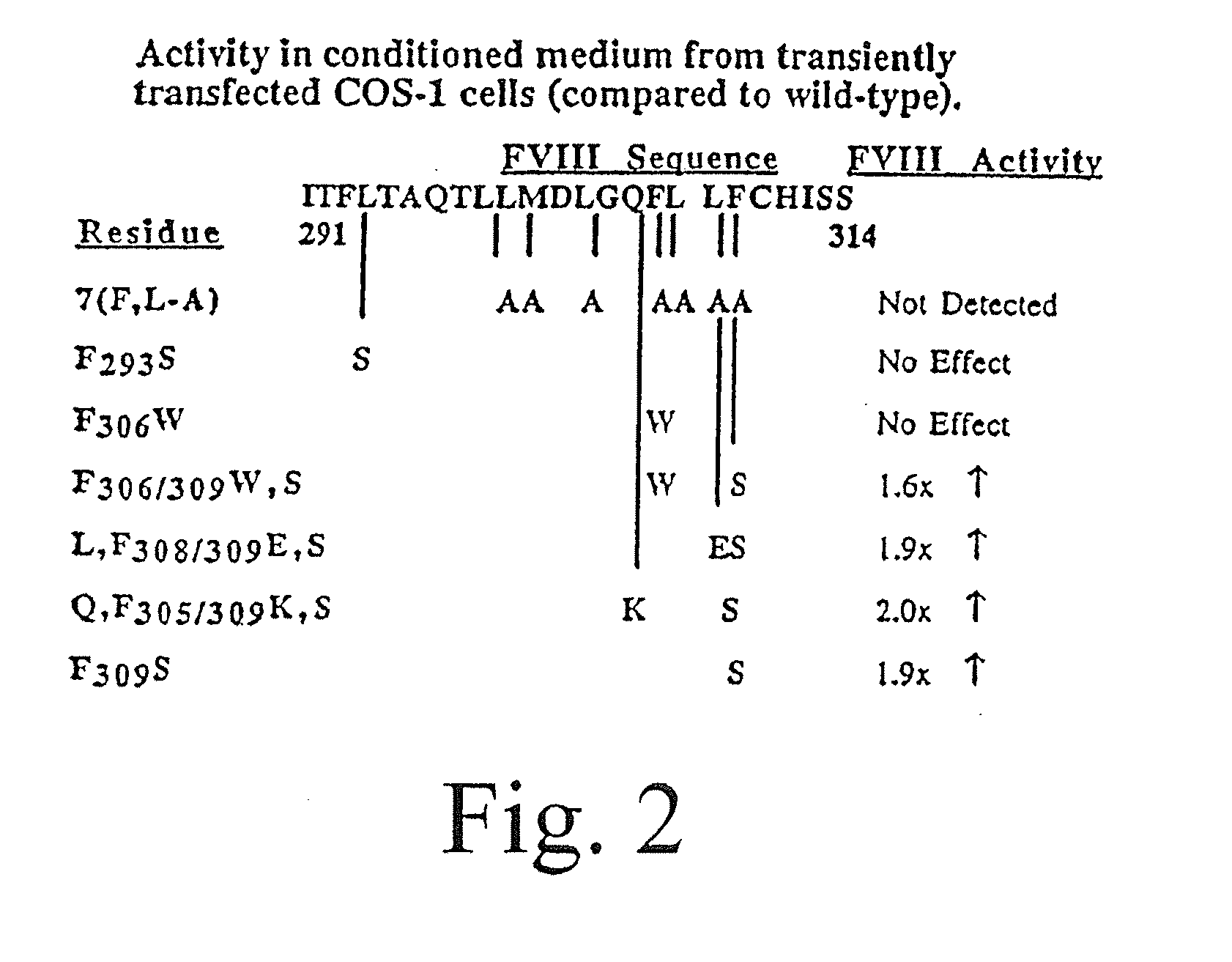
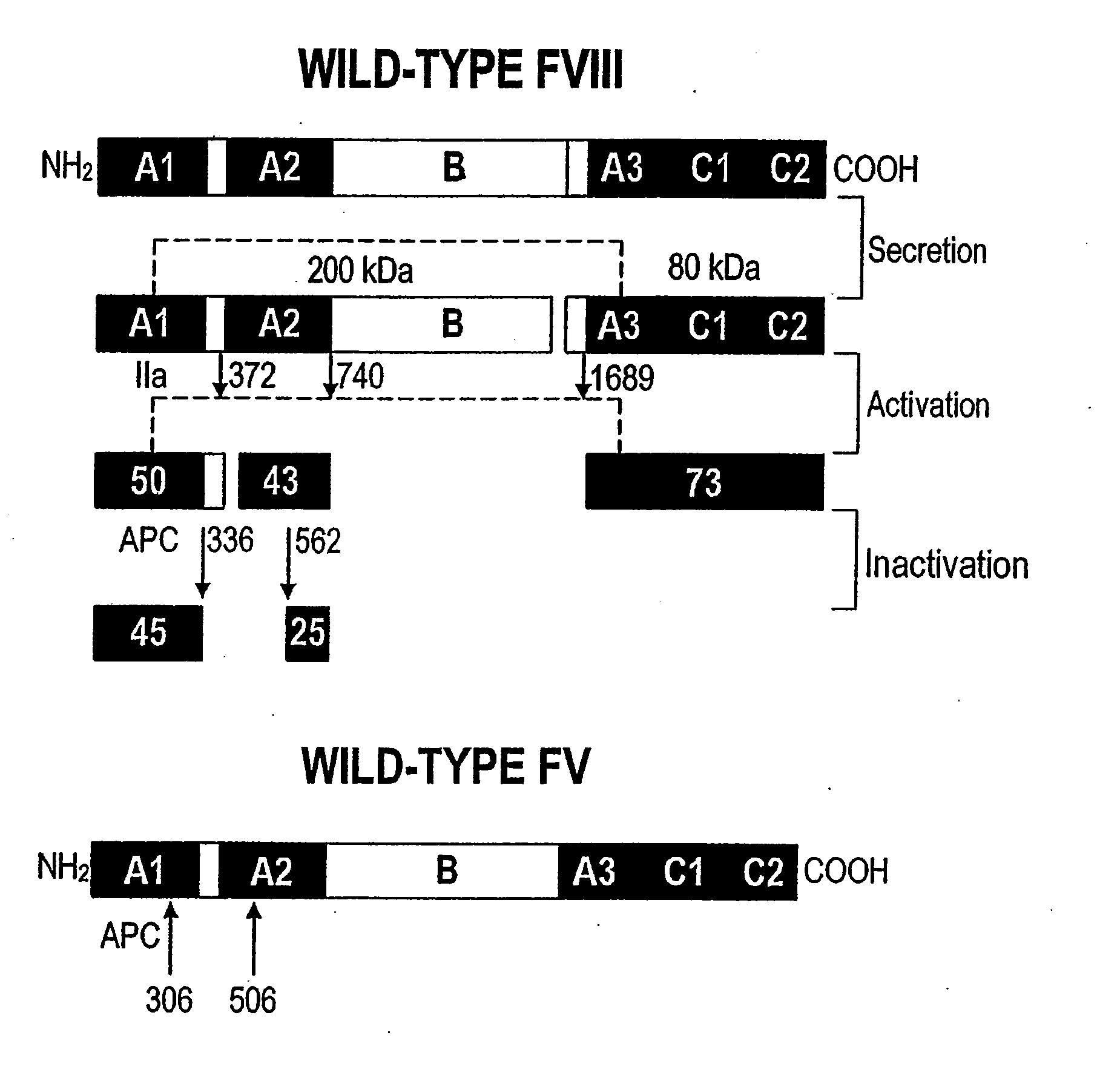
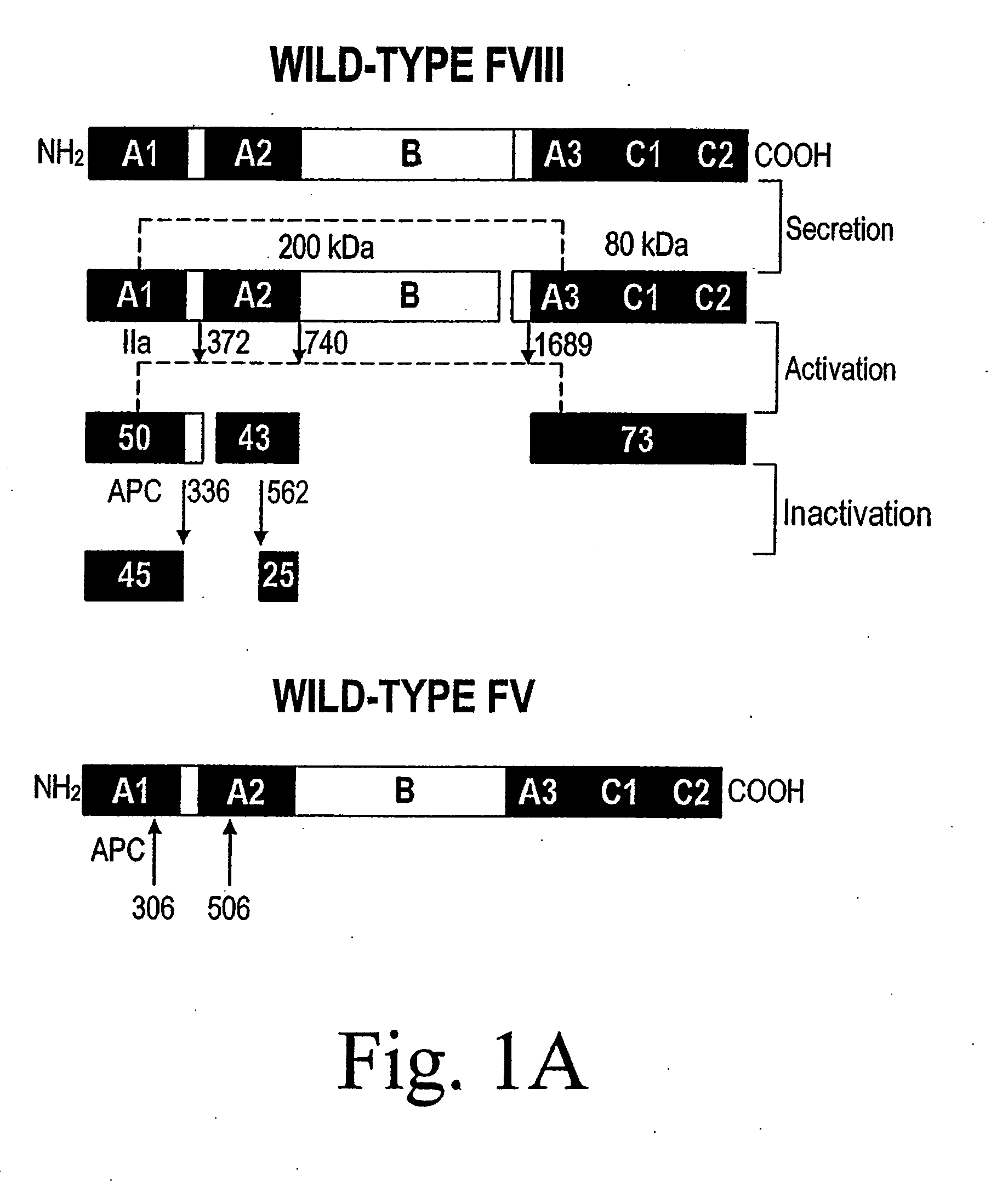
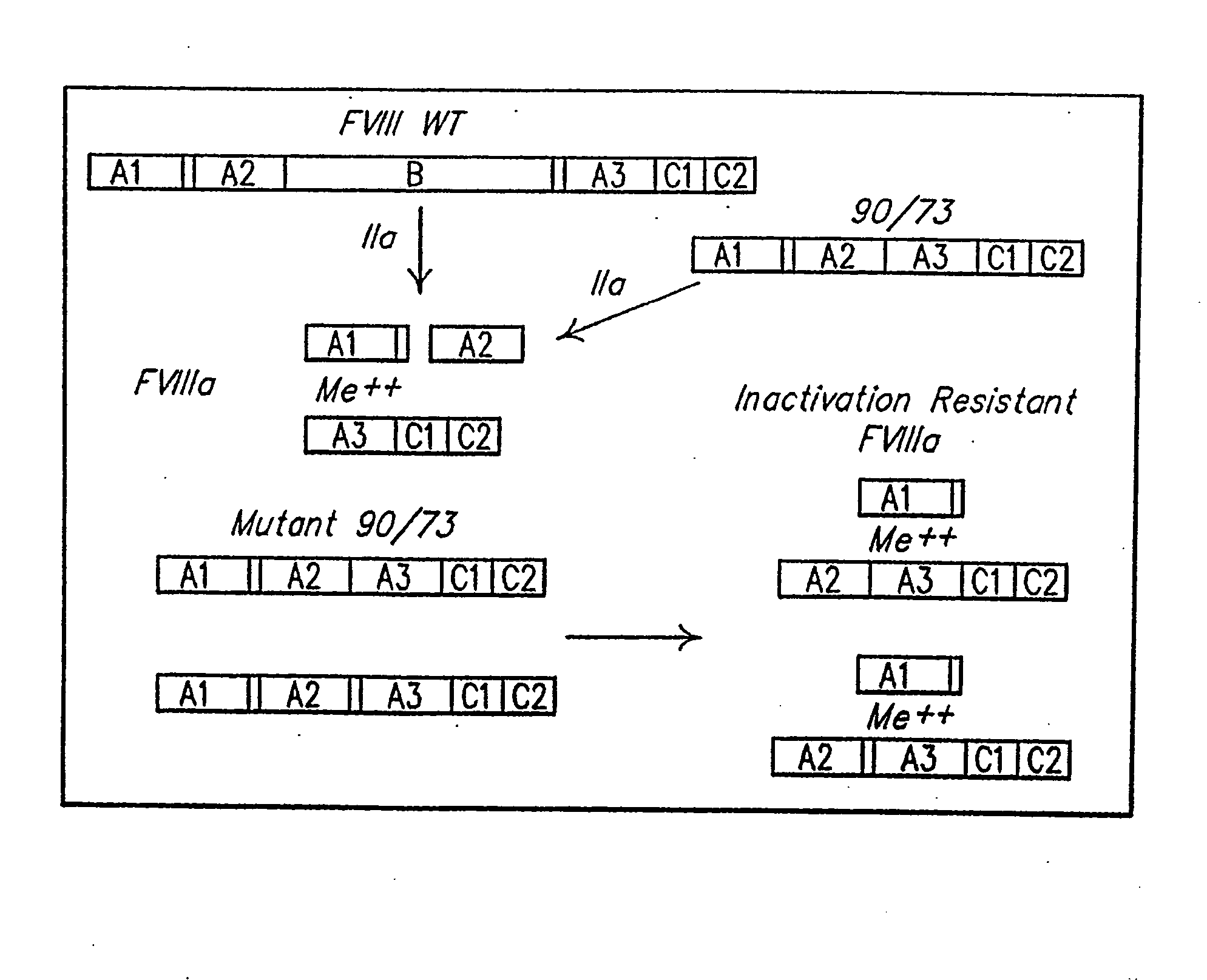
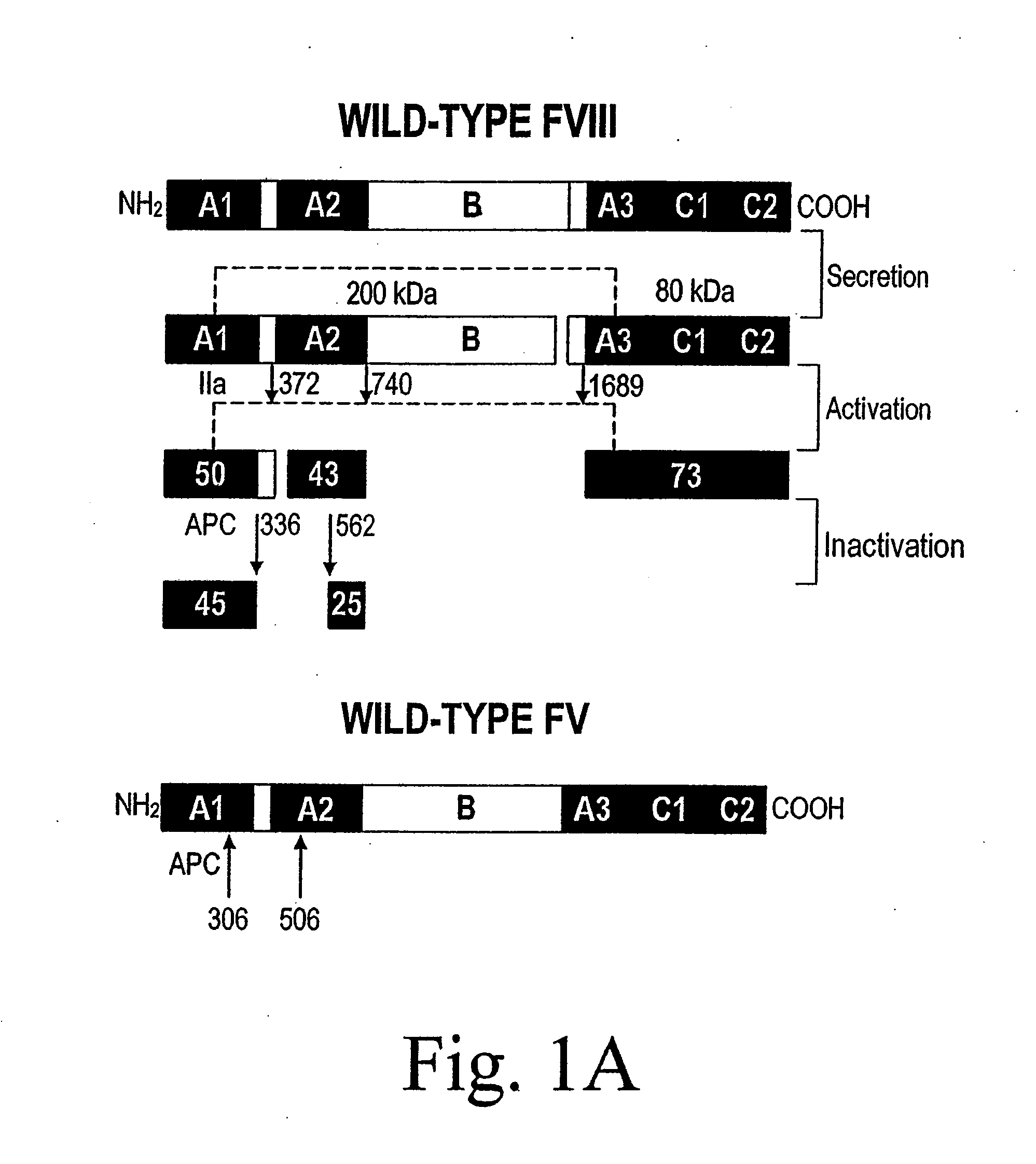
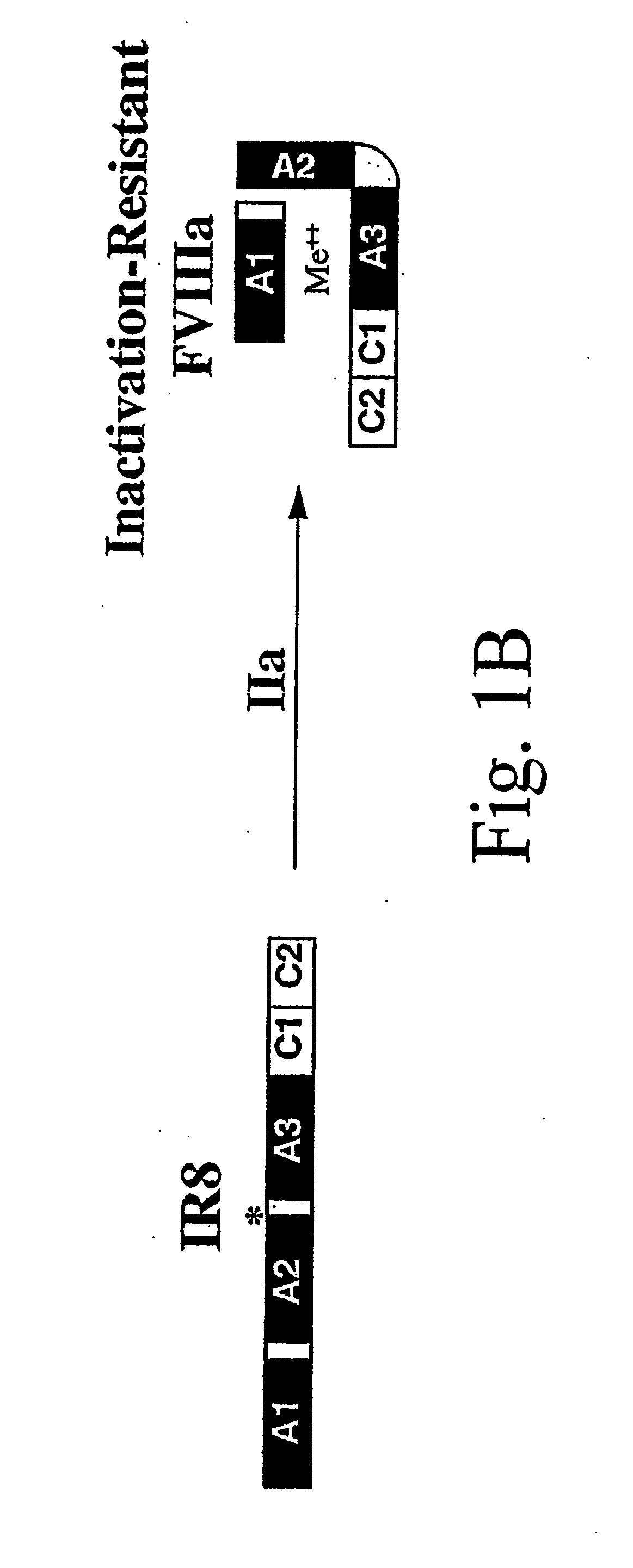
Method of producing factor viii proteins by recombinant methods
InactiveUS20120028900A1High expressionFacilitates secretionOrganic active ingredientsFungiElongation factorChinese hamster
Provided herein are methods and compositions for producing Factor VIII proteins. Such methods include introducing into a cell a nucleic acid molecule encoding a Factor VIII protein operably linked to a promoter, wherein the promoter is characterized by the ability to produce commercially viable Factor VIII protein; and incubating the cell under conditions for producing commercially viable Factor VIII protein. Also provided are nucleic acid molecules which encode a Factor VIII protein operably linked to a Chinese hamster elongation factor 1-α (CHEF1) promoter, which may be used in the methods provided herein.
Owner:CNJ HLDG +1
Methods of diagnosing and treating autism
The present invention provides diagnostic methods for determining the risk of developing an autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in a fetus or child by detecting in a biological sample from the mother antibodies that bind to one or more biomarkers selected from the group consisting of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), guanine deaminase (GDA), collapsin response mediator protein 1 (CRMP1), stress-induced phosphoprotein 1 (STIP1), alpha subunit of the barbed-end actin binding protein Cap Z (CAPZA2), Y Box Binding Protein 1 (YBX1), eukaryotic translation and elongation factor 1A1 (EEF1A1), microtubule-associated protein Tau (MAPT), dihydropyrimidinase-like protein 2 (DPYSL2), dynamin 1-like protein (DNM1L), radixin (RDX), moesin (MSN), and ezrin (EZR). The invention further provides methods of preventing or reducing the risk of a fetus or child developing an ASD by administering to the mother an agent that blocks the binding of maternal antibodies to the one or more fetal biomarkers listed above or by removing from the mother antibodies that bind to the one or more fetal biomarkers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Maize chloroplast protein synthesis elongation factors and methods of use for same
InactiveUS7388125B2Improve stabilityImprove toleranceSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyBreeding program
Owner:THE UNIV OF SOUTH DAKOTA +2
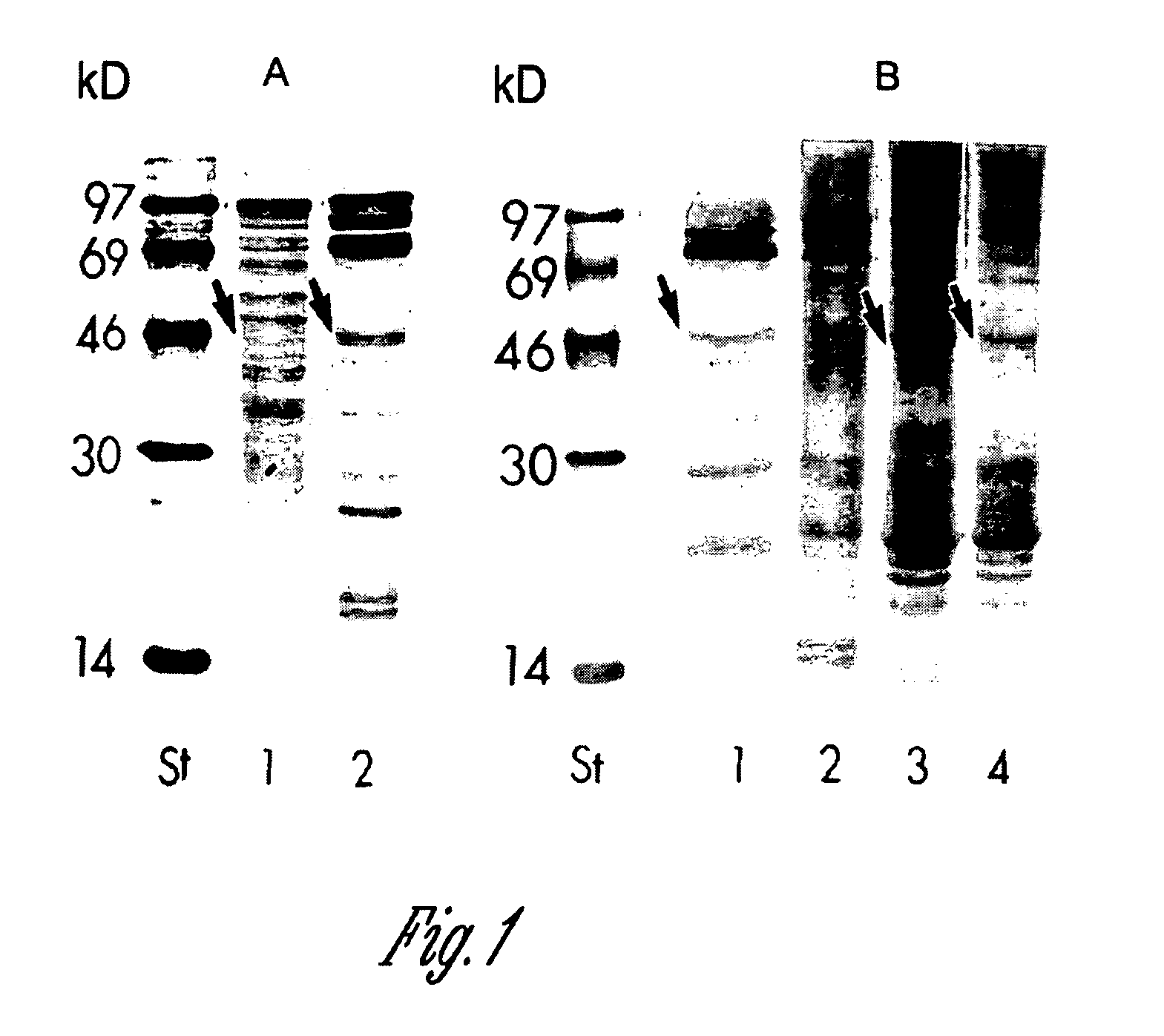
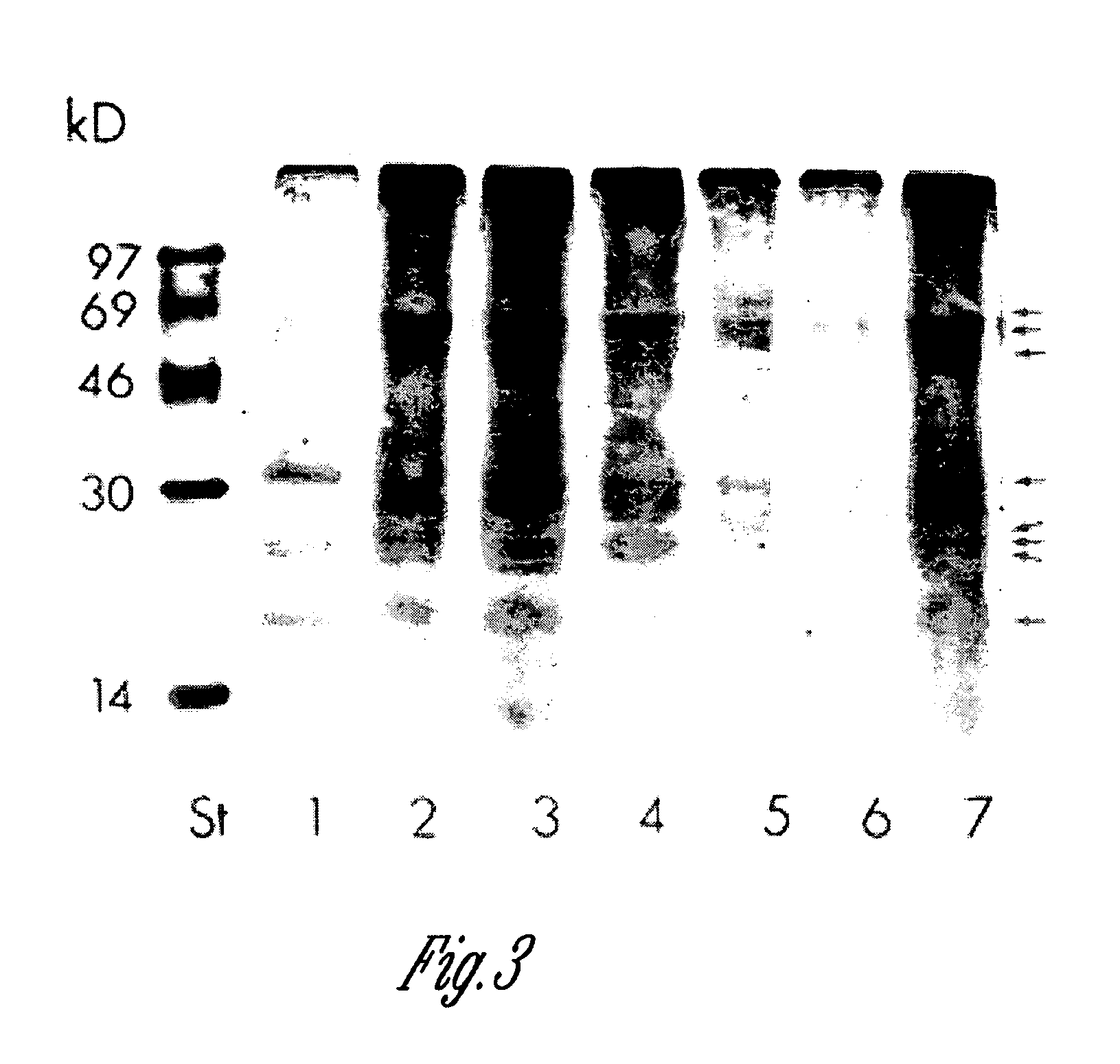
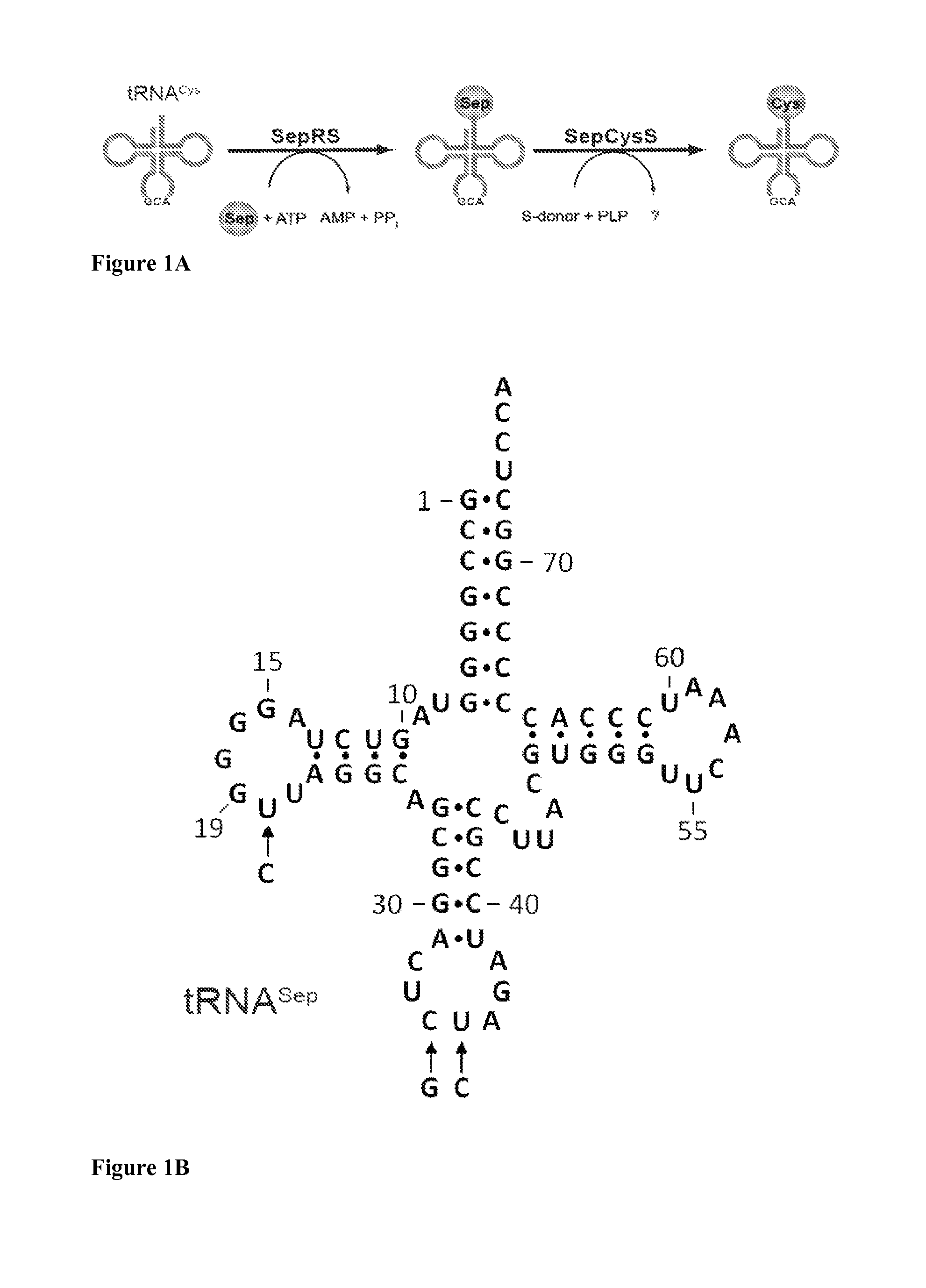
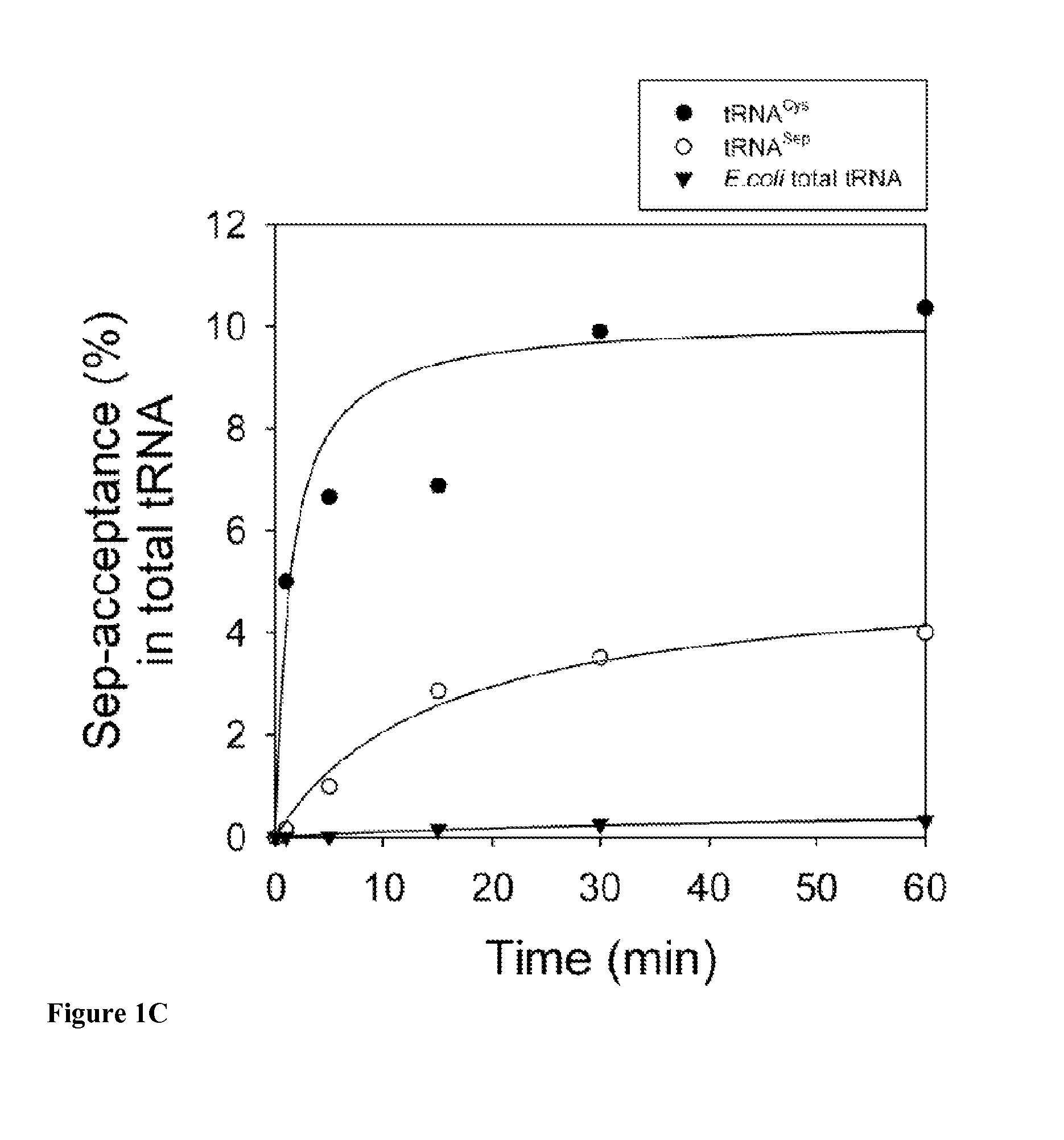
Site-specific incorporation of phosphoserine into proteins in Escherichia coli
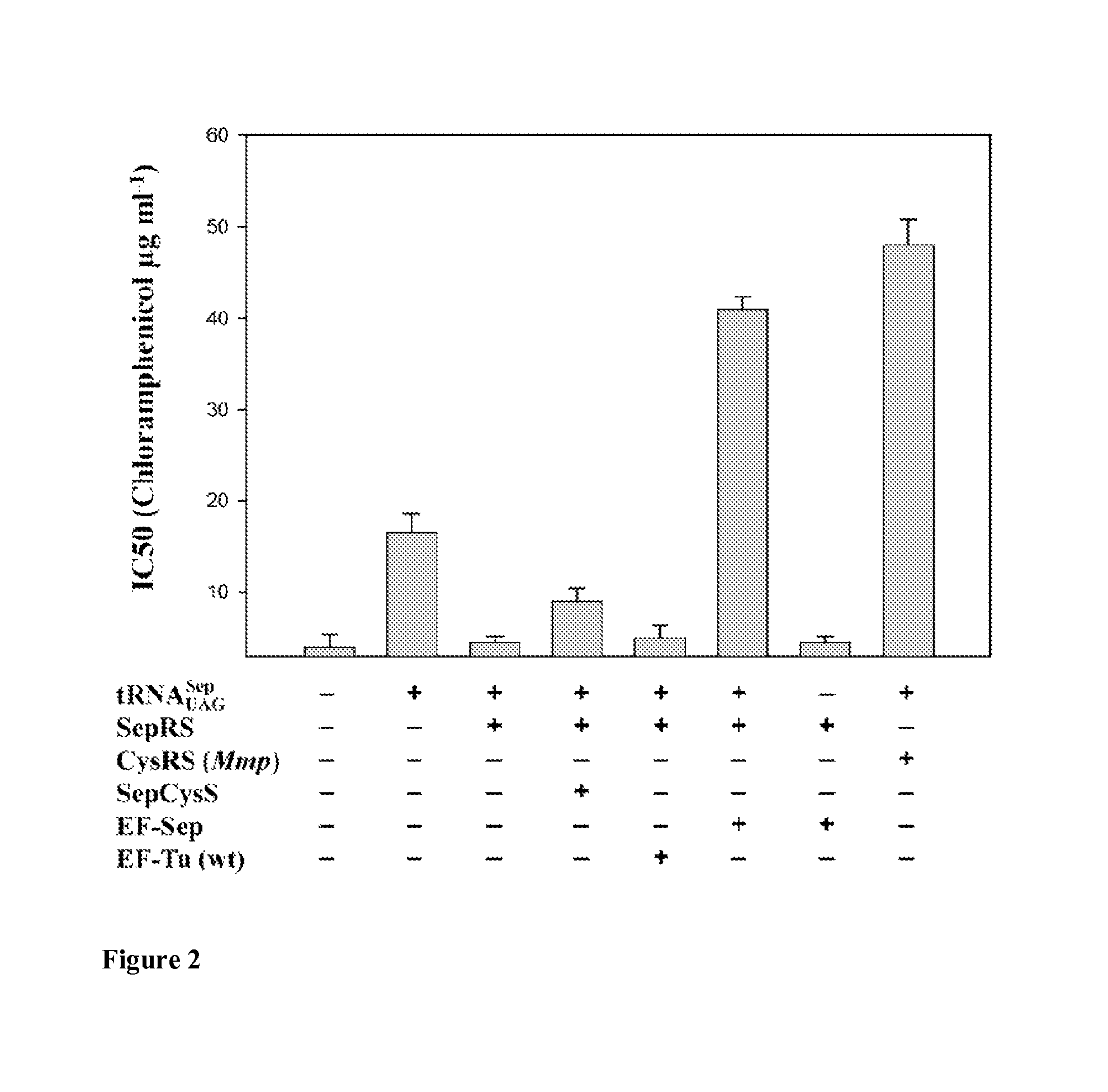
Nucleic acids encoding mutant elongation factor proteins (EF-Sep), phosphoseryl-tRNA synthetase (SepRS), and phosphoseryl-tRNA (tRNASep) and methods of use in site specific incorporation of phosphoserine into a protein or polypeptide are described. Typically, SepRS preferentially aminoacylates tRNASep with O-phosphoserine and the tRNASep recognizes at least one codon such as a stop codon. Due to the negative charge of the phosphoserine, Sept-tRNASep does not bind elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu). However, mutant EF-Sep proteins are disclosed that bind Sep-tRNASep and protect Sep-tRNASep from deacylation. In a preferred embodiment the nucleic acids are on vectors and are expressed in cells such as bacterial cells, archeaebacterial cells, and eukaryotic cells. Proteins or polypeptides containing phosphoserine produced by the methods described herein can be used for a variety of applications such as research, antibody production, protein array manufacture and development of cell-based screens for new drug discovery.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Transposable element carrier expressing pig telomerase reverse transcriptase, building method thereof and application in building pig immortalization cell line
ActiveCN103923942AVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsBiotechnology researchVaccine Production
The invention provides a building method of a transposable element carrier expressing pig telomerase reverse transcriptase, and application in building a pig immortalization cell line, and belongs to the field of biotechnology research. The building method includes the steps of cloning of a promoter of a pig protein translation elongation factor 1a and detection of transcriptional activity, building of an SB transposable element expression vector and exogenous gene integration, pig telomerase reverse transcriptase cDNA cloning, activity detection and building of the pig fibroblast immortalization cell line. Compared with other methods, the pig immortalization cell line built through the transposable element carrier comprises non-transformed normal cells, does not contain resistance genes, virogenes or oncogenes, and is suitable for cell physiological function researching, pig virus separation cultivation and vaccine production.
Owner:ZHONGCHONG XINNUO BIOTECH TAIZHOU CO LTD
Highly efficient eukaryotic expression vector comprising an exogenous transcription regulatory element
ActiveUS20030229046A1Increased gene expression levelsIncrease gene expressionVectorsSugar derivativesElongation factorNucleotide
The present invention relates to a highly efficient eukaryotic expression vector containing an exogenous transcription regulatory element which comprises a promoter / enhancer and the nucleotide sequence upstream of the translation initiation codon derived from human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) immediately early (IE) gene or human elongation factor 1alpha (EF1alpha) gene.
Owner:HELIXMITH CO LTD
Method of producing factor viii proteins by recombinant methods
InactiveUS20090203077A1Increase secretionHigh expressionFactor VIISugar derivativesElongation factorFactor ii
Provided herein are methods and compositions for producing Factor VIII proteins. Such methods include introducing into a cell a nucleic acid molecule encoding a Factor VIII protein operably linked to a promoter, wherein the promoter is characterized by the ability to produce commercially viable Factor VIII protein; and incubating the cell under conditions for producing commercially viable Factor VIII protein. Also provided are nucleic acid molecules which encode a Factor VIII protein operably linked to a Chinese hamster elongation factor 1-α (CHEF1) promoter, which may be used in the methods provided herein.
Owner:CNJ HLDG +1
Method of Producing Factor VIII Proteins by Recombinant Methods
Provided herein are methods and compositions for producing Factor VIII proteins. Such methods include introducing into a cell a nucleic acid molecule encoding a Factor VIII protein operably linked to a promoter, wherein the promoter is characterized by the ability to produce commercially viable Factor VIII protein; and incubating the cell under conditions for producing commercially viable Factor VIII protein. Also provided are nucleic acid molecules which encode a Factor VIII protein operably linked to a Chinese hamster elongation factor 1-α (CHEF1) promoter, which may be used in the methods provided herein.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
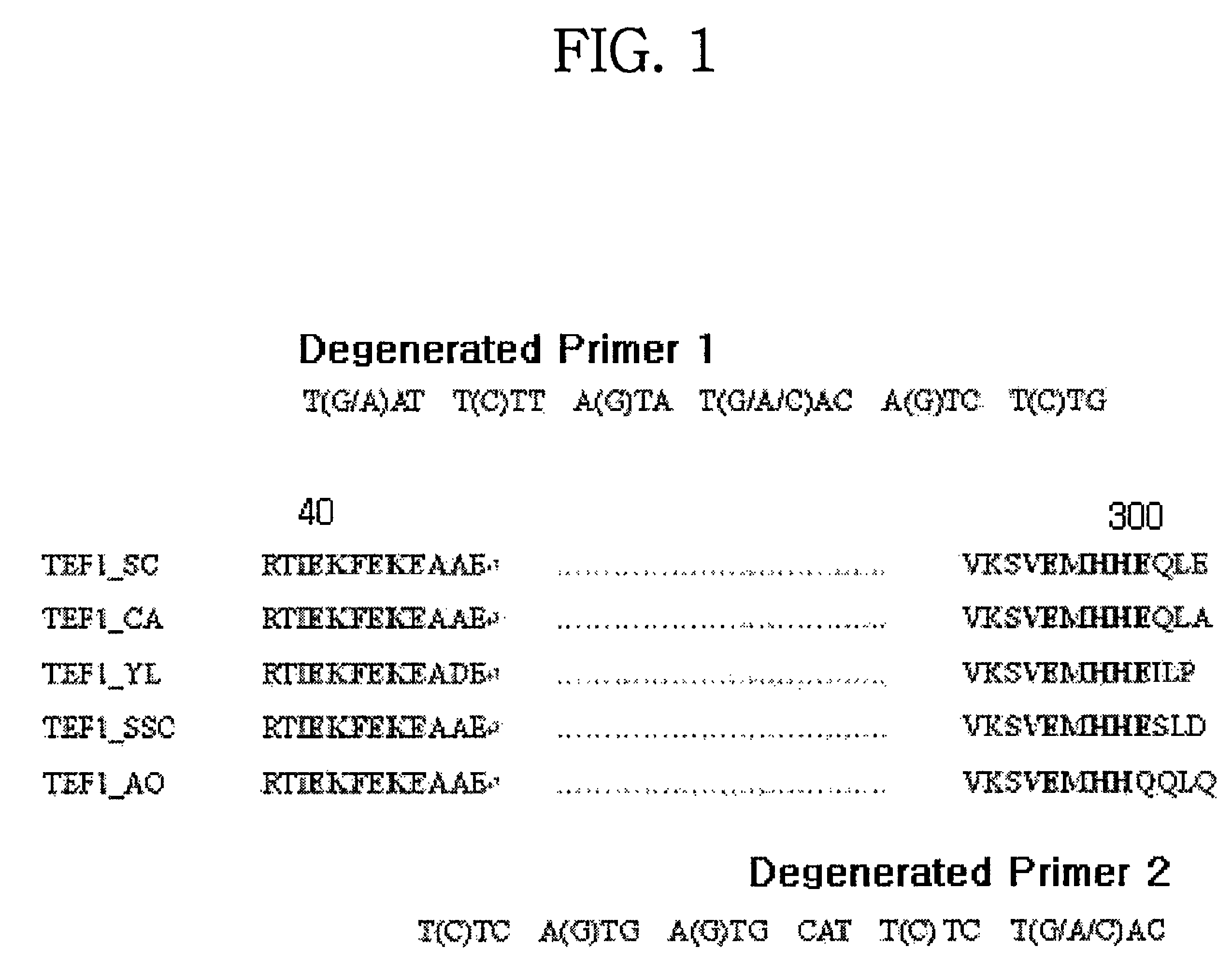
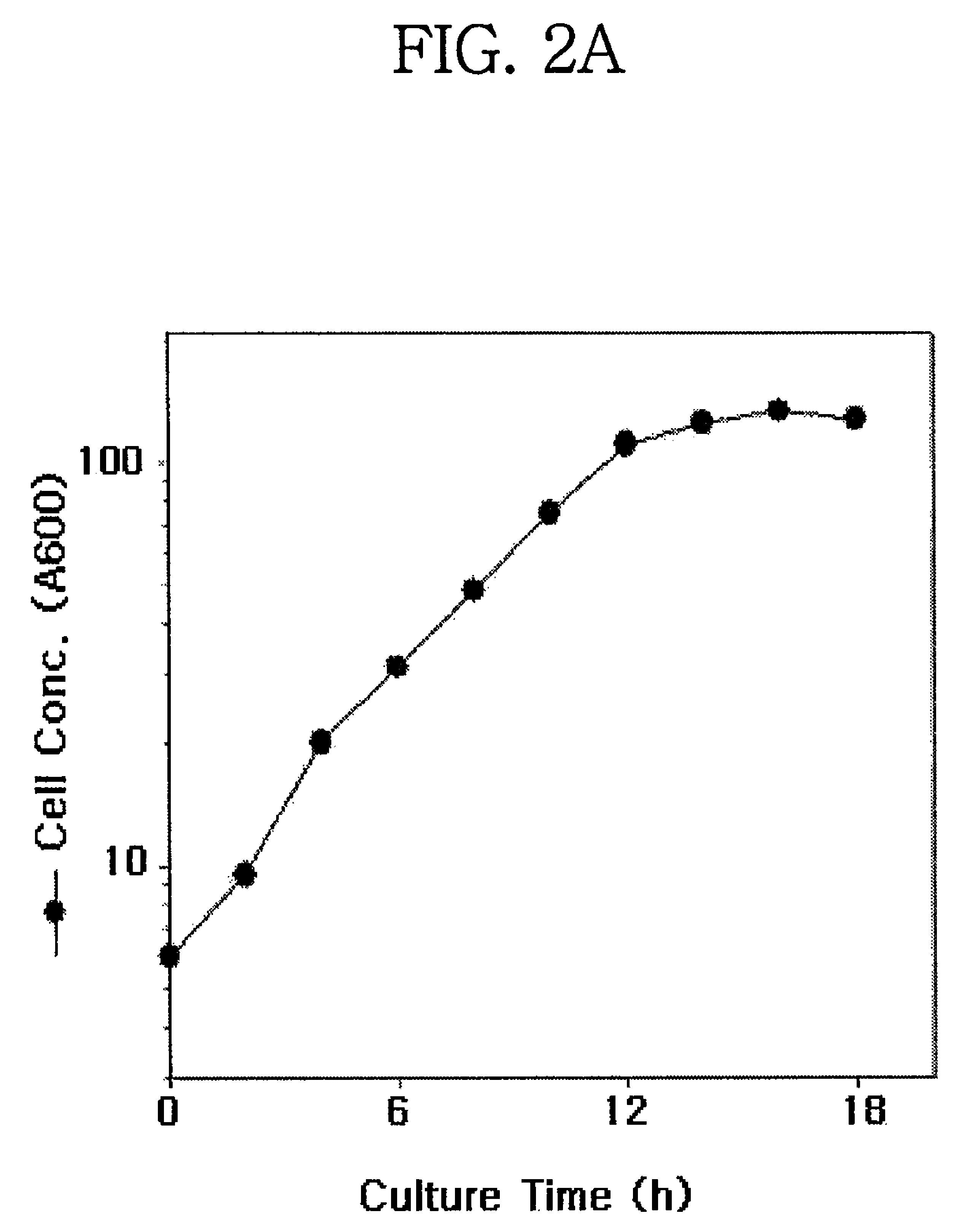
Translational elongation factor promoter from Pichia pastoris and method for producing recombinant protein using the same
Disclosed are a Pichia pastoris-derived translation elongation factor (TEF) promoter, a recombinant expression vector carrying the promoter and a heterologous protein encoding base sequence operably linked to the promoter, and a host cell transfected or transformed with the recombinant expression vector. Also, a method is provided for producing a heterologous protein. The method comprises culturing the host cell to express the Pichia pastoris-derived TEF promoter and isolating the promoter from the culture. The TEF promoter can be utilized for the mass production of heterologous proteins without the need for inducers.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
Method of Producing Factor VIII Proteins by Recombinant Methods
InactiveUS20080070251A1Increase secretionHigh expressionFactor VIISugar derivativesElongation factorChinese hamster
Provided herein are methods and compositions for producing Factor VIII proteins. Such methods include introducing into a cell a nucleic acid molecule encoding a Factor VIII protein operably linked to a promoter, wherein the promoter is characterized by the ability to produce commercially viable Factor VIII protein; and incubating the cell under conditions for producing commercially viable Factor VIII protein. Also provided are nucleic acid molecules which encode a Factor VIII protein operably linked to a Chinese hamster elongation factor 1-α (CHEF1) promoter, which may be used in the methods provided herein.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
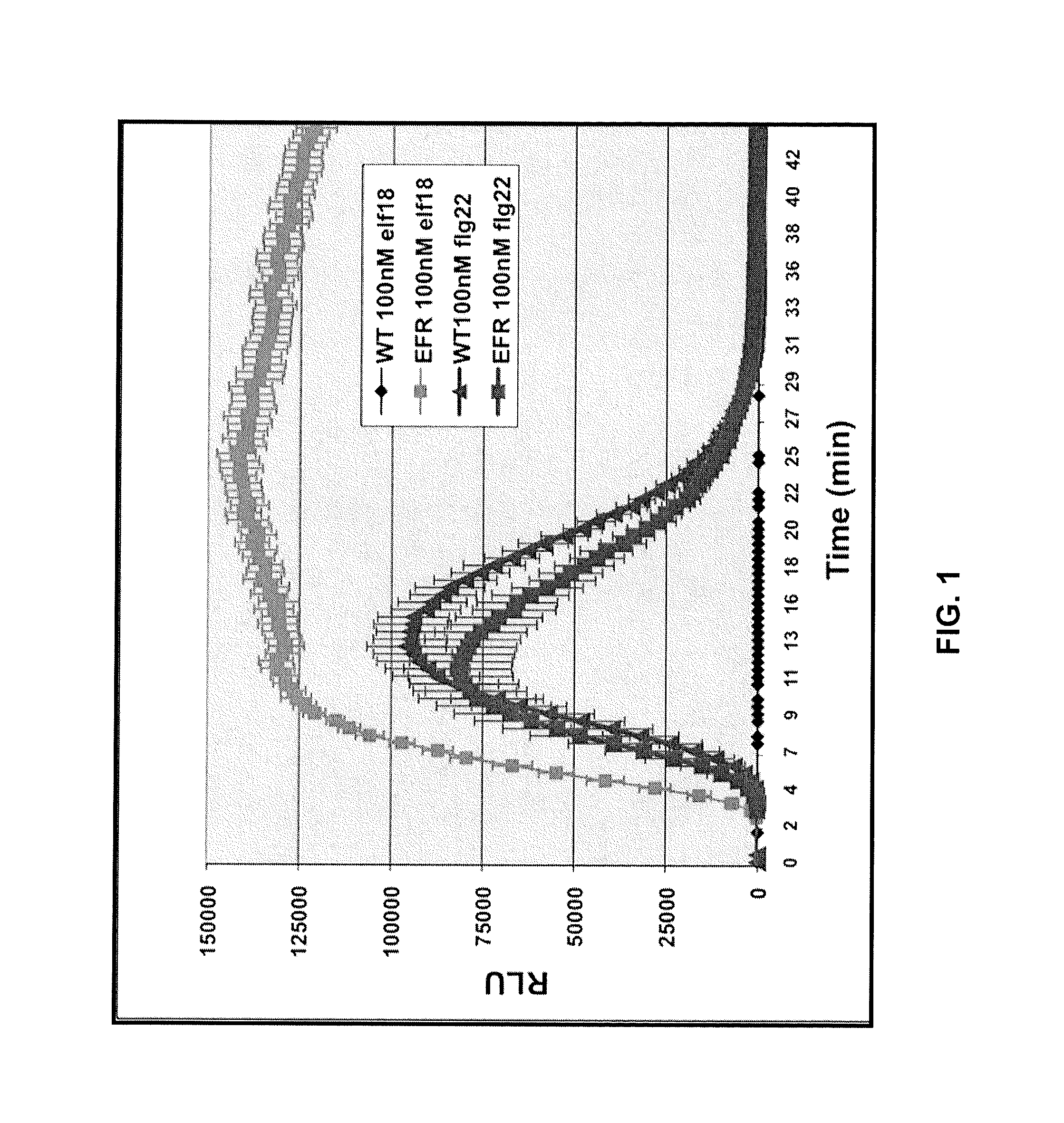
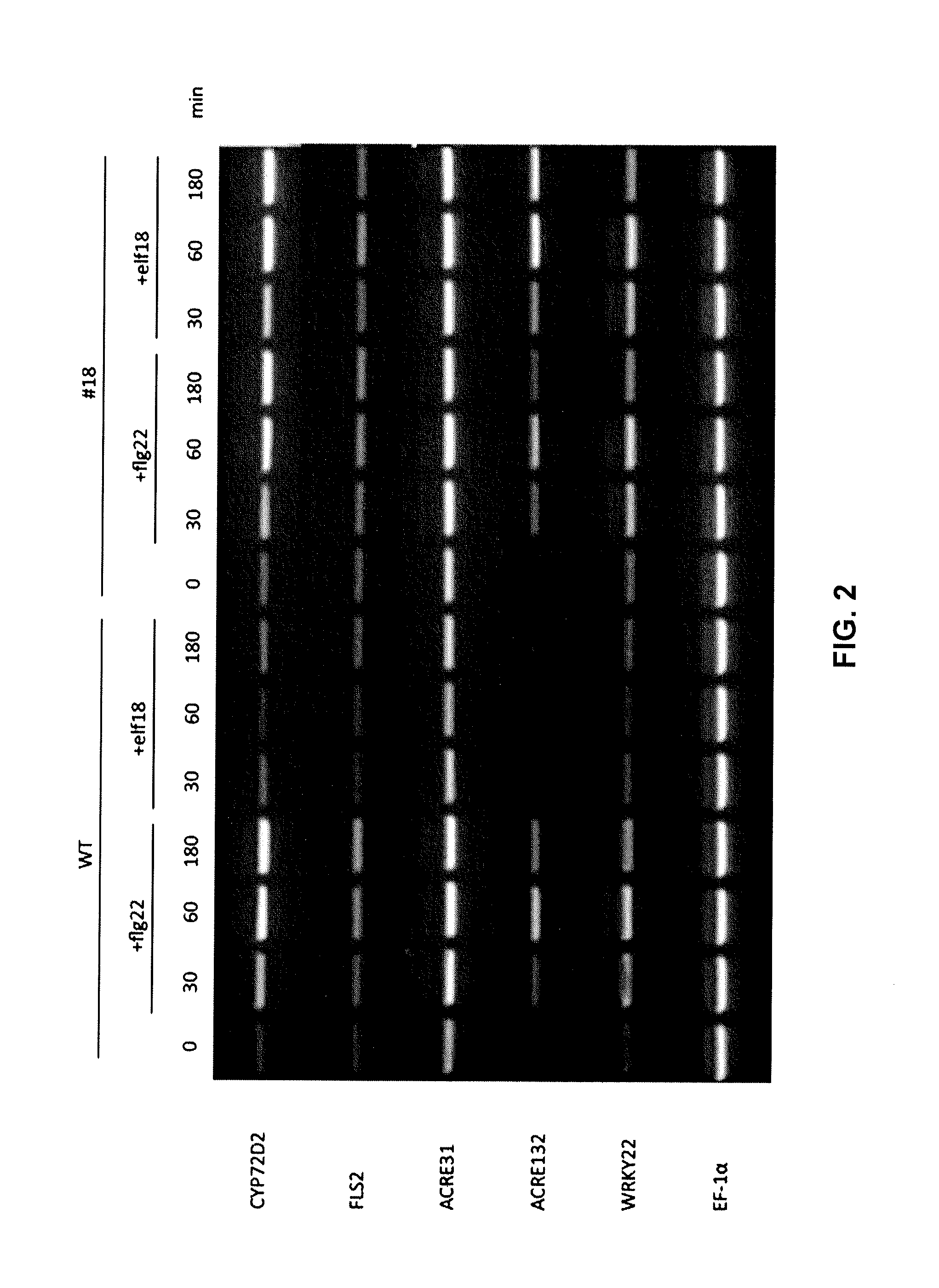
Methods of enhancing the resistance of plants to bacterial pathogens
ActiveUS9222103B2Improve the immunityBacteriaOther foreign material introduction processesElongation factorPlant cell
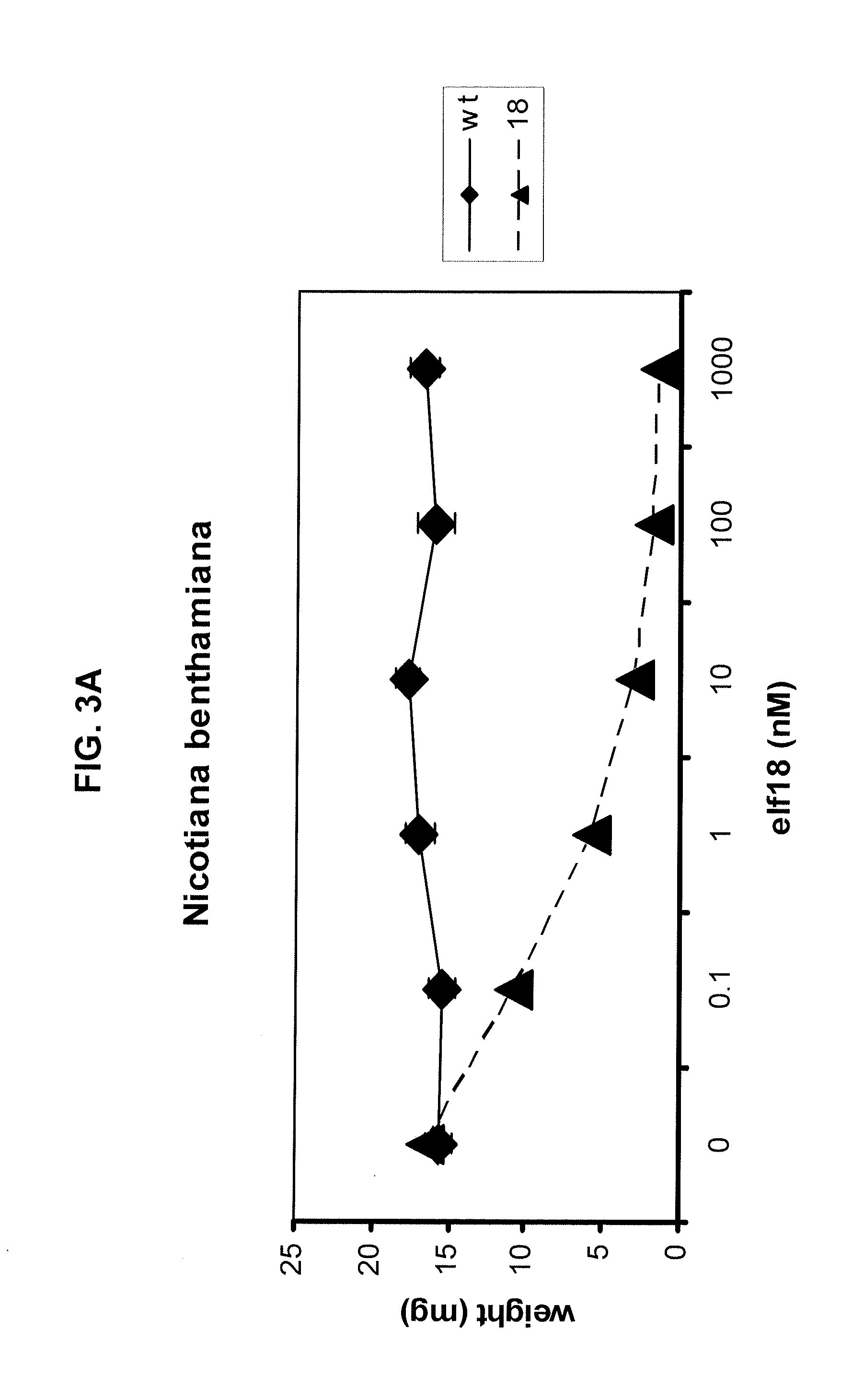
Methods are provided for enhancing the resistance of plants to bacterial pathogens. The methods involve transforming a plant with a polynucleotide molecule comprising a plant promoter operably linked to a nucleotide sequence that encodes a plant receptor that binds specifically with bacterial elongation factor-Tu. Further provided are expression cassettes, transformed plants, seeds, and plant cells that are produced by such methods.
Owner:TWO BLADES FOUND
Photosensitizer binding protein/polypeptide and application thereof to photodynamic gene therapy
InactiveCN102174478APhotodynamic therapy works wellPeptide/protein ingredientsEnergy modified materialsProtein moleculesComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
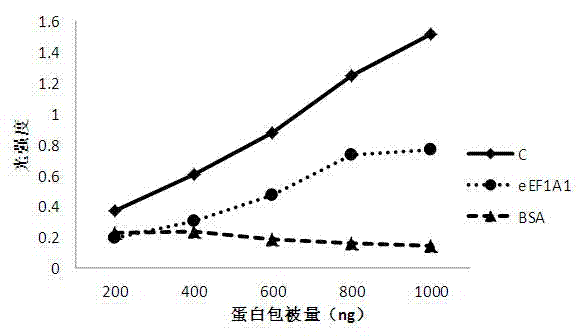
The invention belongs to the technical field of photodynamic gene therapy, particularly relating to a photosensitizer binding protein and polypeptide and application thereof. In the invention, the photosensitizer binding protein is screened from a human liver cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) phage display library. The binding protein is a human eukaryotic translation elongation factor (eEF1A1) protein and a protein molecule which is 70 to 80 percent similar to the protein in protein structure; the photosensitizer binding polypeptide is eEF1A1 C terminal 25aa and polypeptide which is70 to 80 percent similar to the 25aa in amino acid sequence. The photosensitizer binding protein can be bound with a porphyrin type photosensitizer in vitro and has an effect of enriching the porphyrin type photosensitizer in vivo; photosensitizer binding protein genes are transfected to various mammalian cells through adenoviruses, slow viruses or other modes; and a better photodynamic therapy effect is produced after artificial adjustment and control over inducible expression. In addition, the photosensitizer binding protein and polypeptide (PSP) provide a valuable reference for developing a photosensitizer prodrug and designing the specifically targeted photosensitizer.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Leishmania antigens suitable for a diagnostic kit of Leishmania
A purified Leishmania infantum polypeptide comprising at least 10 consecutive amino acids of a protein is provided. The protein is mitochondrial integral ADP / ATP carrier protein, NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase, mitochondrial carrier protein, guanine nucleotide binding protein beta subunit (LACK), aldehyde reductase, ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase Rieske iron-sulfur protein, truncated elongation factor 1-alpha having a molecular weight as determined by SDS-PAGE of 36.4 kDa, truncated elongation factor 1-alpha having a molecular weight as determined by SDS-PAGE of 34.5 kDa, or truncated elongation factor 1-alpha having a molecular weight as determined by SDS-PAGE of 30.6 kDa. Methods for using the polypeptides for diagnosing MVL are disclosed.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
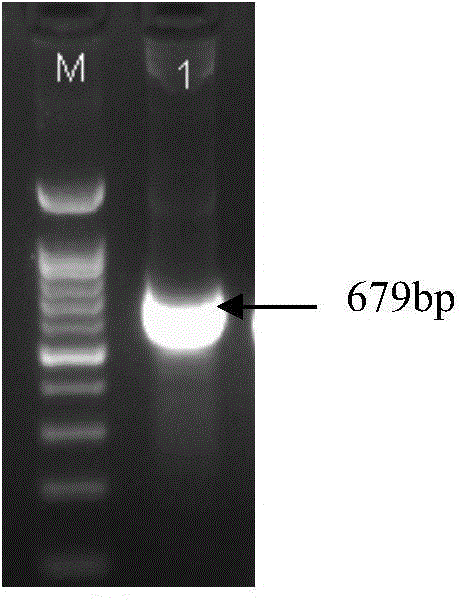
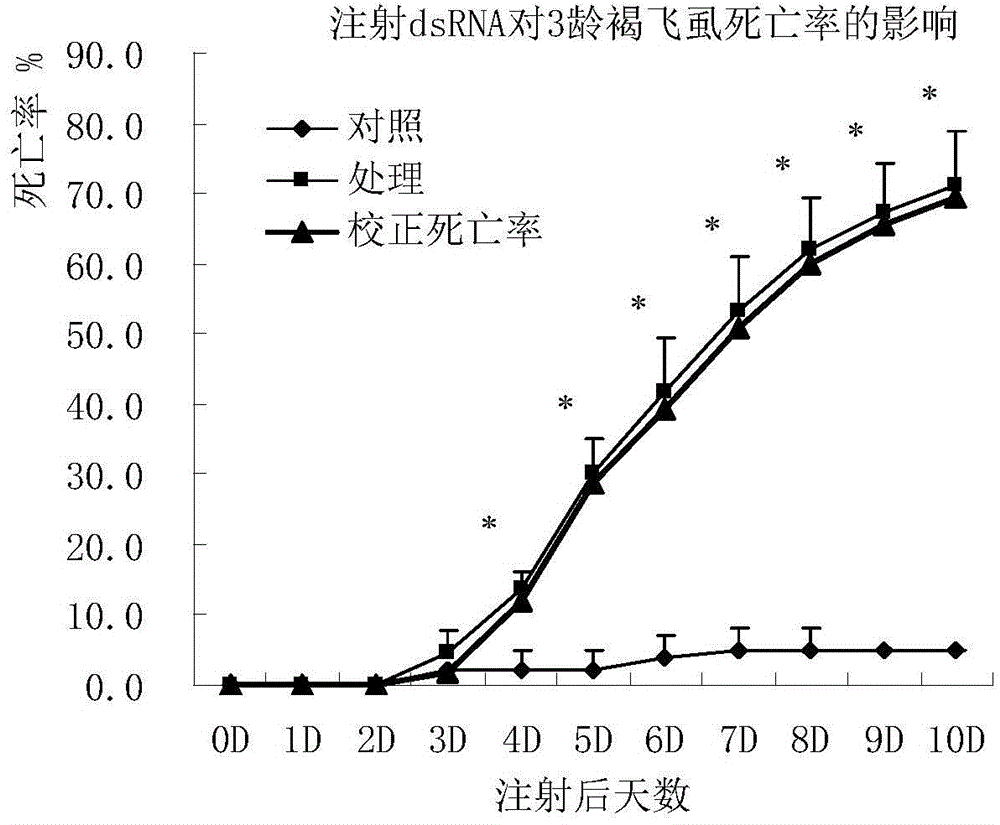
Brown planthopper protein translation elongation factor NlEF1gamma, and encoded protein and application thereof
The invention discloses a brown planthopper protein translation elongation factor NlEF1gamma, an encoded protein, synthesized dsRNA, and an application thereof in controlling brown planthopper pest diseases. The gene performs an important function in maintaining the normal growth and development processes of brown planthoppers. When the function is inhibited, brown planthopper nymph growth is slower, brown planthopper nymph size is smaller, and brown planthopper nymph dies because it couldn't develop into adult. When the function of the gene in a brown planthopper female adult is inhibited, its ovaries stop developing and it couldn't spawn normally. According to the invention, brown planthoppers are injected and fed with the dsRNA of the gene fragment. With both means the brown planthopper death rates reach 70% and brown planthopper spawning amounts are 0. Sequence and data bases are provided for establishing novel strategies for controlling pests with an RNA interference technology. The application has significant lethal and ovarian development inhibition effects against brown planthoppers. Therefore, the gene can be sued as an effective target for controlling the pest with an RNAi technology.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Three reference genes suitable for qPCR of octopuses and universal primer thereof
InactiveCN107586860AImprove stabilityImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesElongation factor
The invention discloses three reference genes suitable for qPCR of octopuses and the application of the genes in real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR. The beneficial effect is that the genes can bestably expressed under different environments and experimental conditions without being affected by any internal and external factors; by using elongation factor-1 alpha, 18s and ubiquitin elongationfactor-1 alpha as the reference genes to be applied to real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR, the requirement for real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection of the genetic transcription expression level of the octopuses can be met, and the stability and reliability of gene expression analysis and study of the octopuses are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
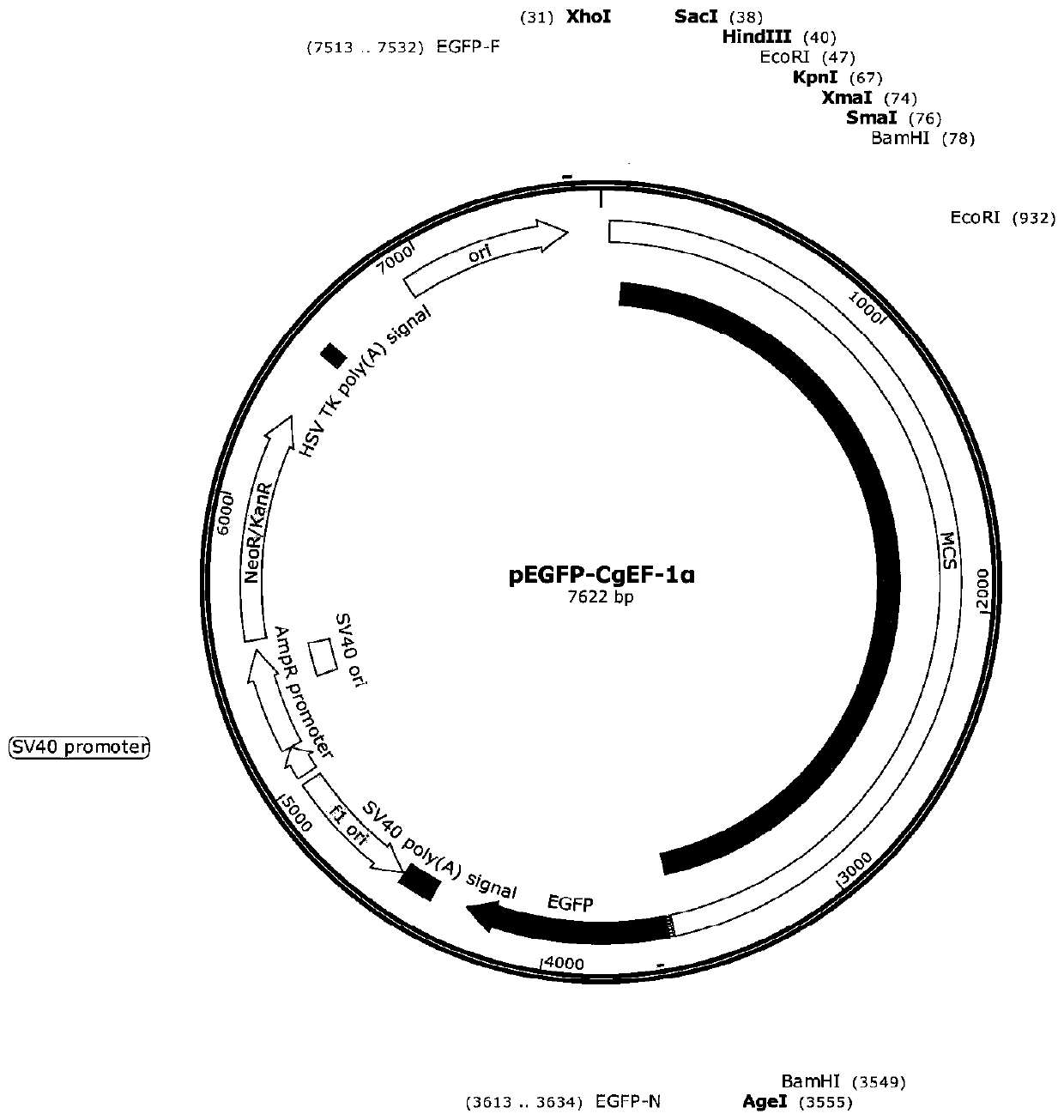
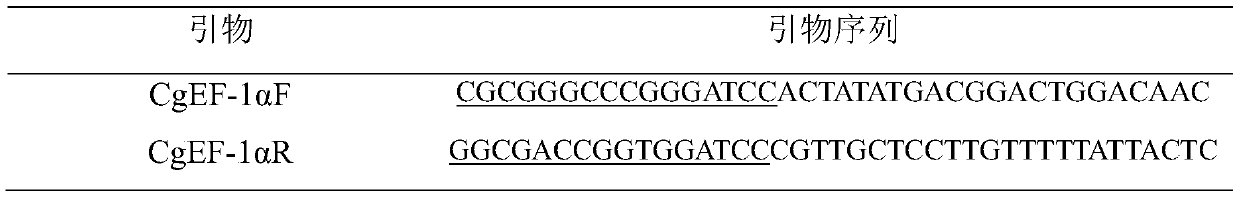
Crassostrea gigas elongation factor-1-alpha (EF-1-alpha) promoter, and recombinant vector and application thereof
The invention discloses a crassostrea gigas elongation factor-1-alpha (EF-1-alpha) promoter as well as a recombinant vector and application thereof. The invention provides an EF-1-alpha promoter. TheEF-1-alpha promoter is a high-expression housekeeping gene promoter which can be expressed in early stage of embryo development of crassostrea gigas. The EF-1-alpha promoter is specifically expressedas follows: designing a specific primer; amplifying a fragment of the crassostrea gigas EF-1-alpha promoter; inserting the crassostrea gigas EF-1-alpha promoter into a vector containing a GFP reportergene by utilizing In-fusion connection so as to obtain a recombinant vector; and then, introducing the recombinant vector into fertilized eggs of crassostrea gigas, thereby efficiently driving expression of the GFP reporter gene in embryos and larvae of crassostrea gigas. A universal-type efficient promoter sequence for crassostrea gigas is prepared according to the invention; and thus, importanttechnical basis is provided for development of CRISPR / cas9 targeted gene editing technology.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Multiplex RT-PCR method for simultaneously detecting four corn viruses
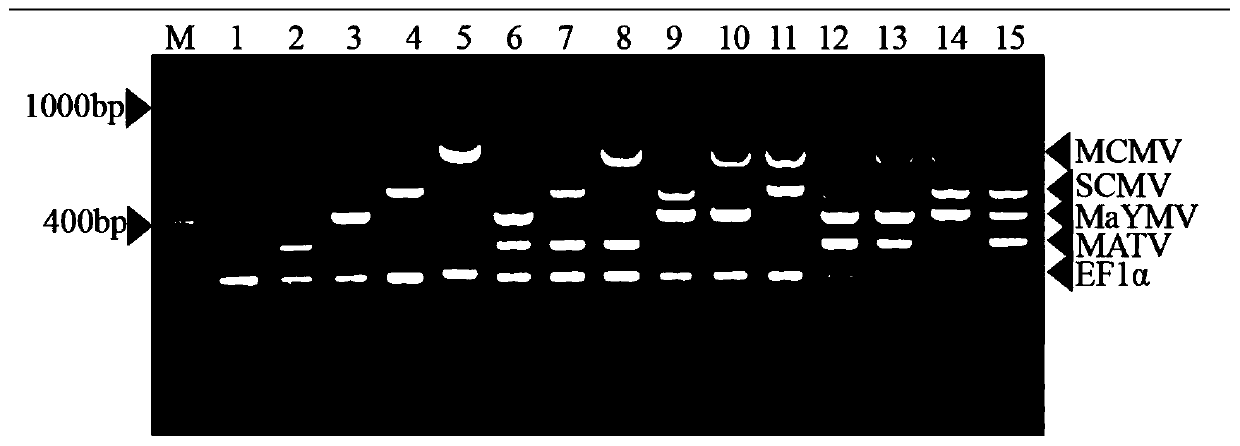
ActiveCN110904273AStable detectionEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMultiplex
The invention discloses a multiplex RT-PCR method for simultaneously detecting four corn viruses, and belongs to the technical field of plant virus detection. According to the method disclosed by theinvention, corn elongation factor 1 alpha (Elongation factor 1 alpha, EF 1 alpha) gene is used as a reference gene; on the basis of optimizing the annealing temperature and the primer concentration ofa multiplex PCR detection system, a multiplex RT-PCR detection method for simultaneously detecting four kinds of maize viruses MCMV, SCMV, MaYMV and MATV is established. The multiplex PCR detection system disclosed by the invention is a detection method which is simple, rapid, economical and low in time consumption, and can be used for simultaneously detecting four viruses (MCMV, SCMV, MaYMV andMATV) of corn; the method can be widely applied to agriculture to diagnose the four viruses on the corn in advance, and has very important significance in controlling the occurrence of diseases and increasing economic benefits.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Hybridized tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) and application thereof to glutathione peroxidase preparation
ActiveCN105018482AEasy to prepareIncrease vitalityEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses hybridized tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) and application thereof to glutathione peroxidase preparation and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The hybridized tRNA relates to sequences SEQ ID No: 1-16, consists of 90 basic groups, and not only can serve as substrate tRNA for selenocysteine synthesis, but also can be recognized by autologous elongation factor EF-Tu of escherichia coli. A hybridized tRNA gene is obtained by a gene synthesis method, then a GPX (glutathione peroxidase) gene is synthetized or amplified, the hybridized tRNA gene and the GPX gene are assembled on a secretory prokaryotic expression vector capable of expressing the hybridized tRNA, a TAG engineering strain is transformed and subjected to induced expression in presence of sodium selenite, and a catalytic group Sec of the GPX is introduced into a substrate binding site of protein in a way that conventional amino acids enter a peptide chain, so that the protein is given with high GPX activity. The hybridized tRNA and application thereof to glutathione peroxidase preparation have the advantages that the method is simple, and zymoprotein is high in activity, yield and stability, so that the problems that natural GPX is limited in source and instable in property are solved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
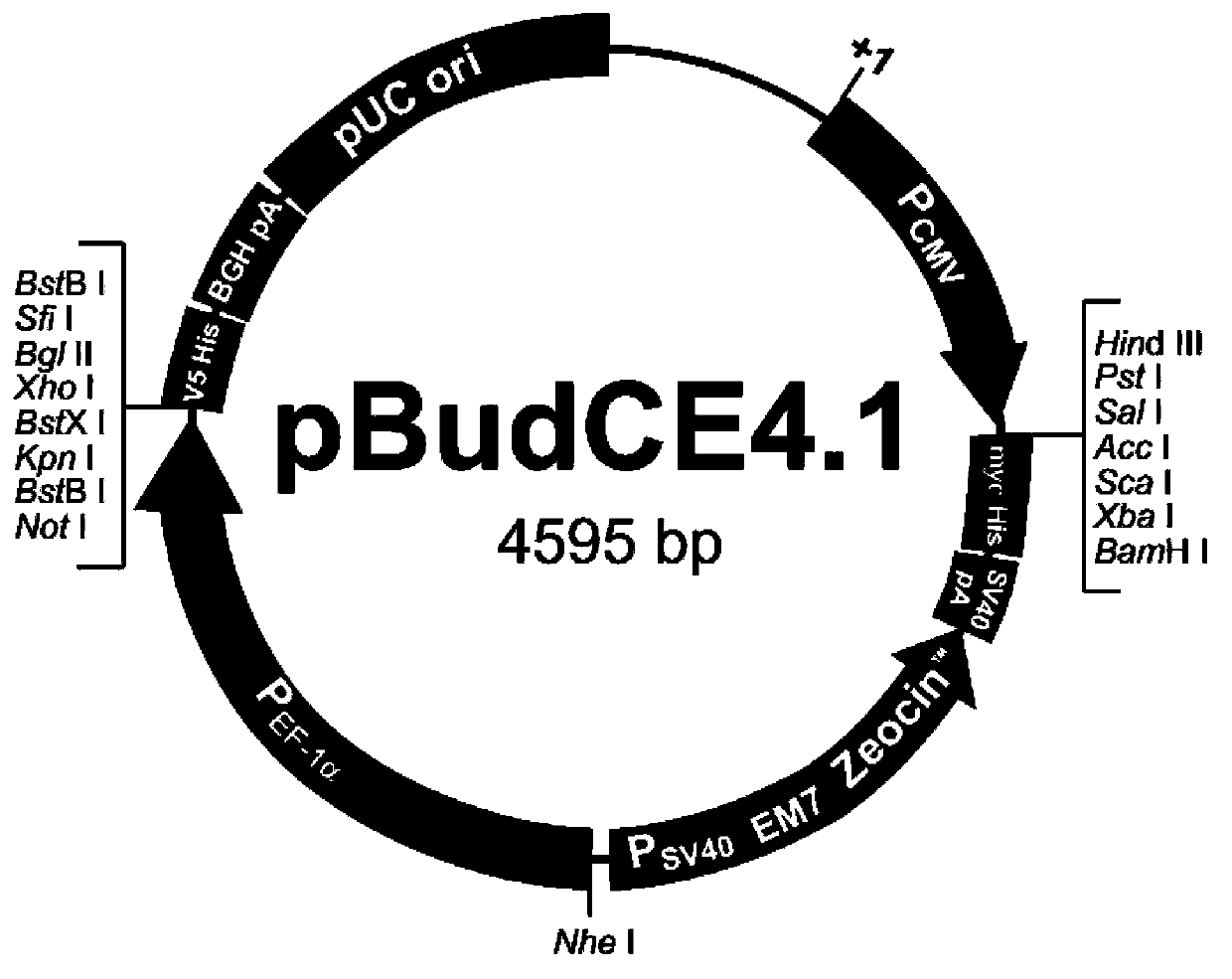
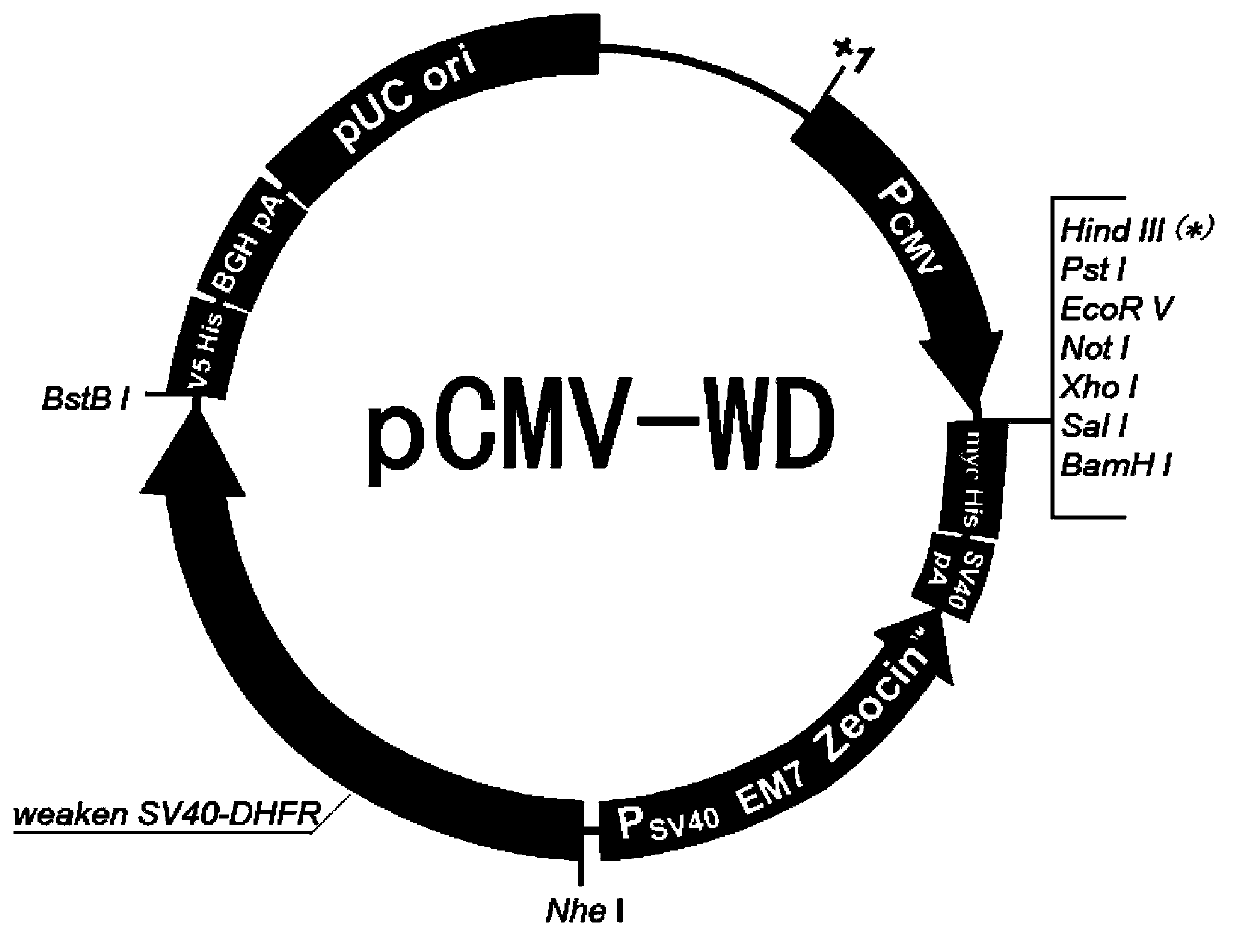
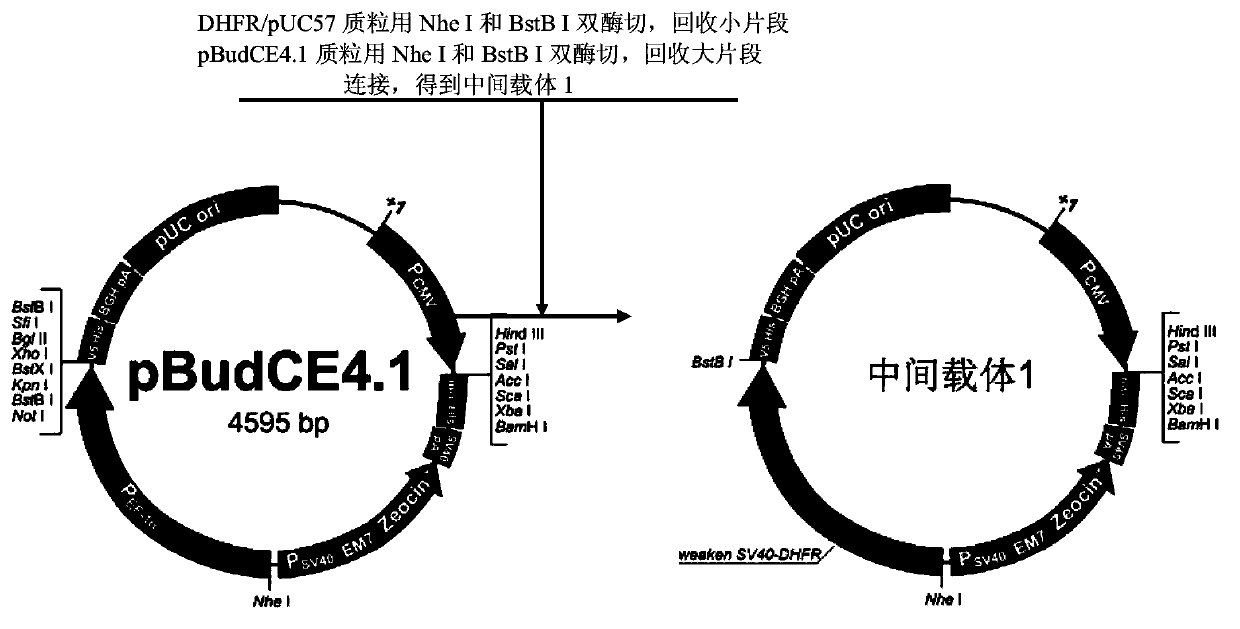
Eukaryotic expression vector containing attenuated SV40 promoter/dihydrofolate reductase expression element, and construction method thereof
InactiveCN103865947AGuaranteed universalityRecombination operations are easy to implementVector-based foreign material introductionElongation factorMultiple cloning site
The invention provides a eukaryotic expression vector capable of selecting high expression clones conveniently and high efficiently. The eukaryotic expression vector is obtained via structure modification by taking pBudCE4.1 carrier as a basic carrier; peptide chain elongation factor gene promoter (P) on the basic carrier, and multiple cloning sites on the downstream of the peptide chain elongation factor gene promoter (P) are replaced by an expression element composed of attenuated SV40 promoter and dihydrofolate reductase gene on the downstream of the attenuated SV40 promoter; multiple cloning sites on the downstream of cytomegalovirus early promoter (P) of the basic carrier are replaced by new multiple cloning sites.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF BIOLOGICAL PROD
Antifungal combination use
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
Reference gene for barley gene expression researches as well as application of reference gene
ActiveCN107058539AImprove accuracyReduce dosageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReference genesElongation factor
The invention discloses a reference gene for barley gene expression researches as well as application of the reference gene. The reference gene is a gene segment of a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2, an elongation factor EF2 and / or a tubulin beta-tubulin 6, wherein a nucleotide sequence of the gene segment of the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, a nucleotide sequence of the gene segment of the elongation factor EF2 is shown as SEQ ID NO.2, and a nucleotide sequence of the gene segment of the tubulin beta-tubulin 6 is shown as SEQ ID NO.3. According to the reference gene, the detection accuracy of a barley related gene (such as low nitrogen stress and drought stress) expression can be improved, and the reference gene is large in expression quantity and stable in expression, and has a Ct value of 20 to 30.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Translational Elongation Factor Promoter From Pichia Pastoris And Method For Producing Recombinant Protein Using The Same
Disclosed are a Pichia pastoris-derived translation elongation factor (TEF) promoter, a recombinant expression vector carrying the promoter and a heterologous protein encoding base sequence operably linked to the promoter, and a host cell transfected or transformed with the recombinant expression vector. Also, a method is provided for producing a heterologous protein. The method comprises culturing the host cell to express the Pichia pastoris-derived TEF promoter and isolating the promoter from the culture. The TEF promoter can be utilized for the mass production of heterologous proteins without the need for inducers.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
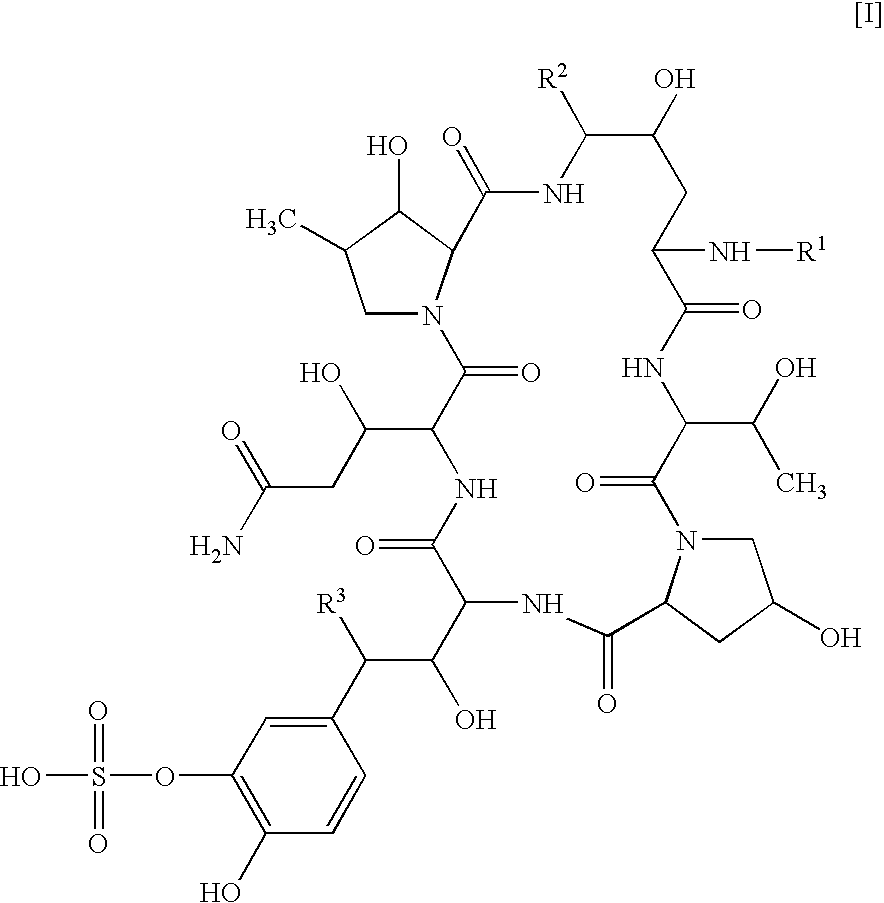
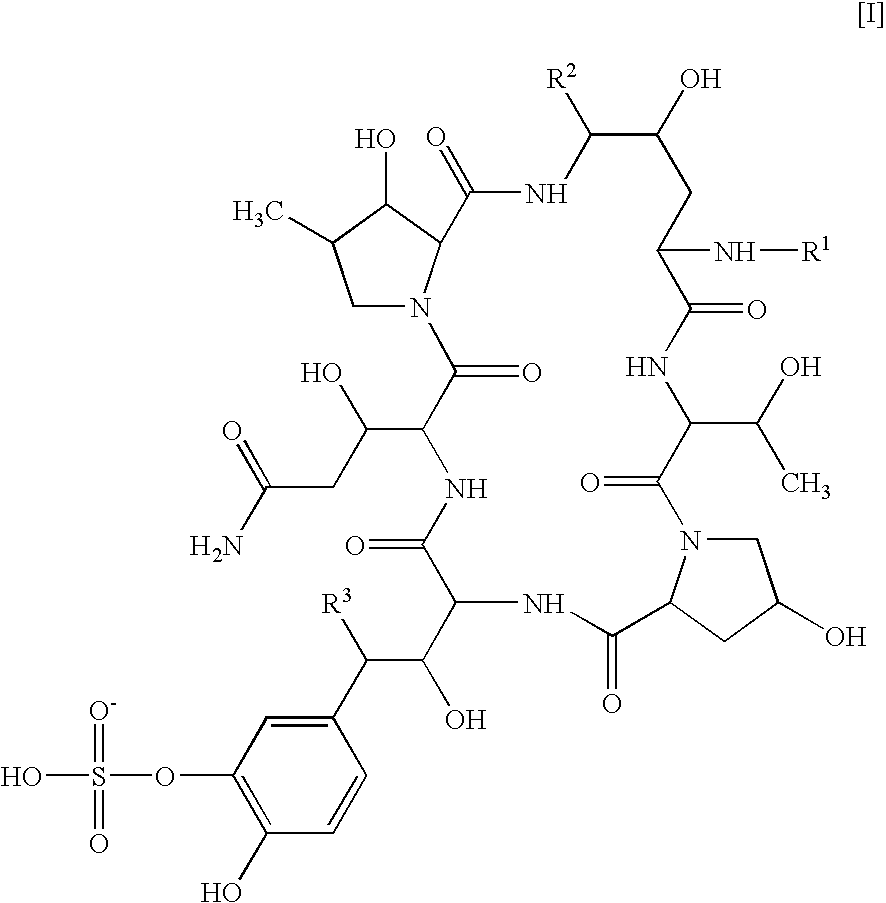
Combination of a cyclic hexapeptide with antifungal drugs for treatment of fungal pathogens
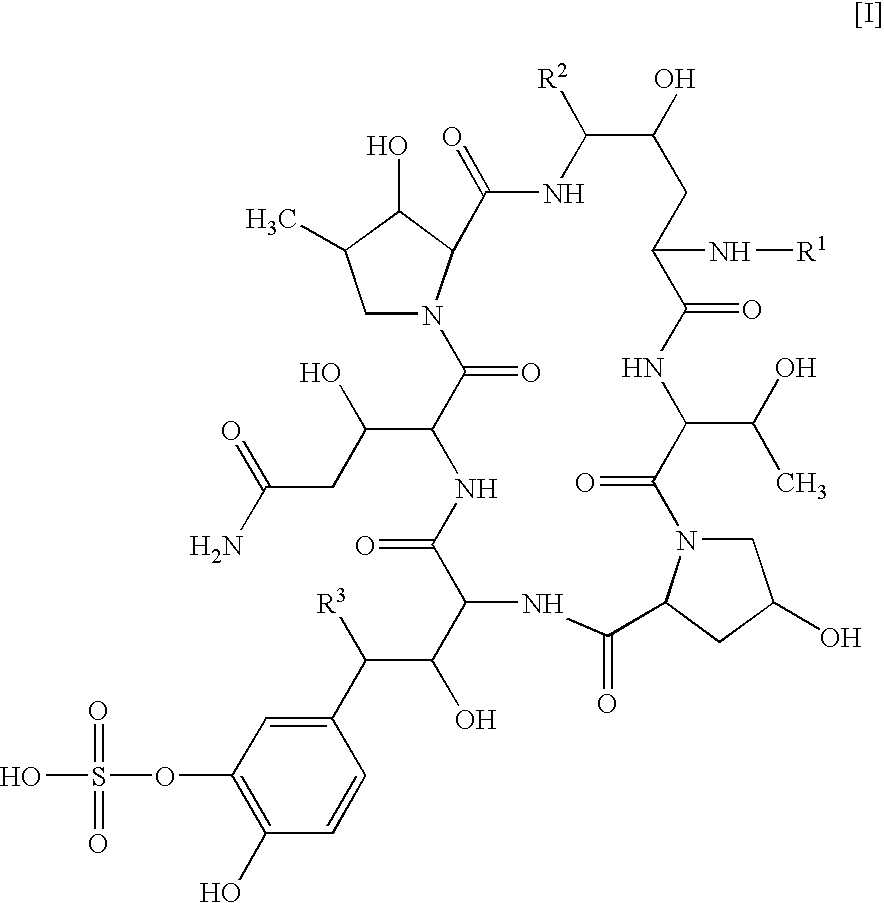
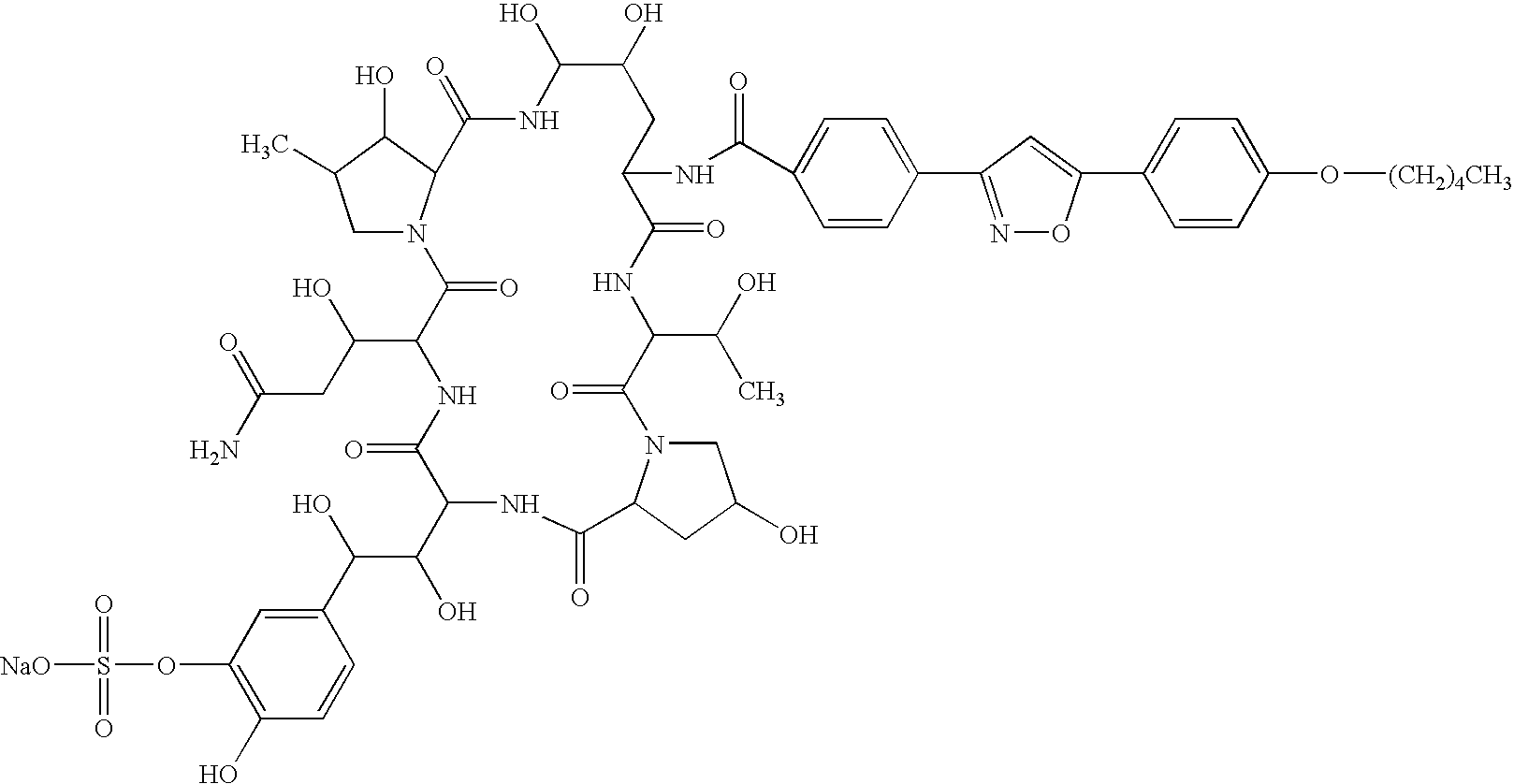
There is described antifungal combination use of known antifungal agents such as the azoles or polyenes in combination with a lipopeptide compound antifungal agent. More particularly, the invention relates to antifungal combination use of azols such as fluconazole voriconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole, miconazole, ER 30346 and SCH 56592; polyenes such as amphotericin B, nystatin, liposomal and lipid forms thereof such as Abelcet, AmBisome and Amphocil; purine or pyrimidine nucleotide inhibitors such as flucytosine; or polyoxins such as nikkomycins, in particular nikkomycin Z or nikkomycin X; other chitin inhibitors; elongation factor inhibitors such as sordarin and analogs thereof; mannan inhibitors such as predamycin, bactericidal / permeability-inducing (BPI) protein products such as XMP.97 or XMP.127; or complex carbohydrate antifungal agents such as CAN-296; with a lipopeptide compound (I) as described herein.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
Method for producing polyisoprenoid, transformed plant, method for producing pneumatic tire and method for producing rubber product
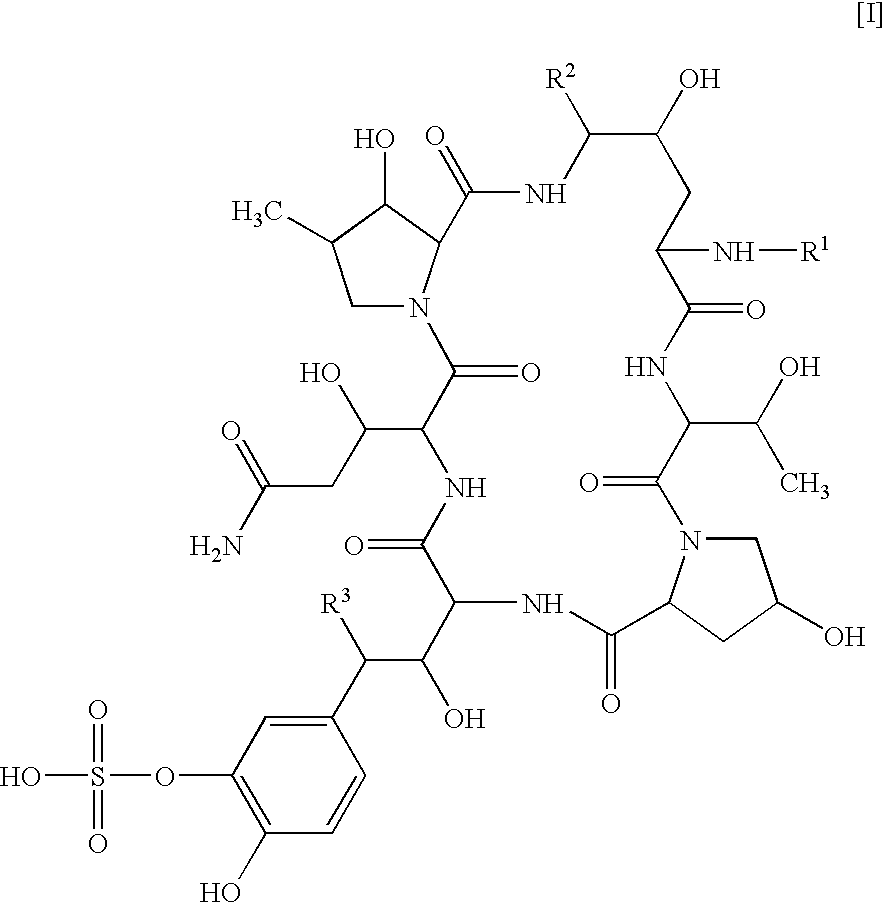
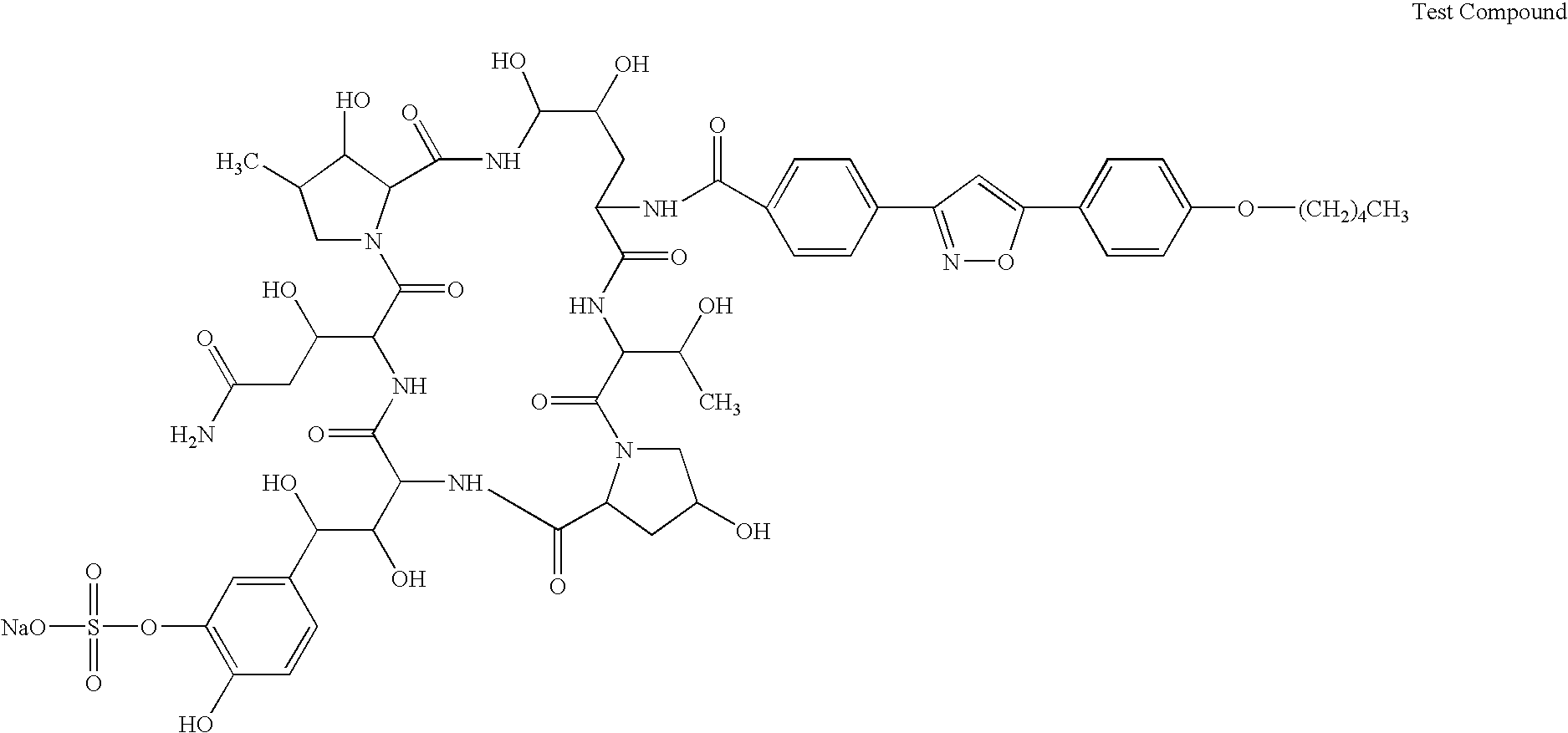
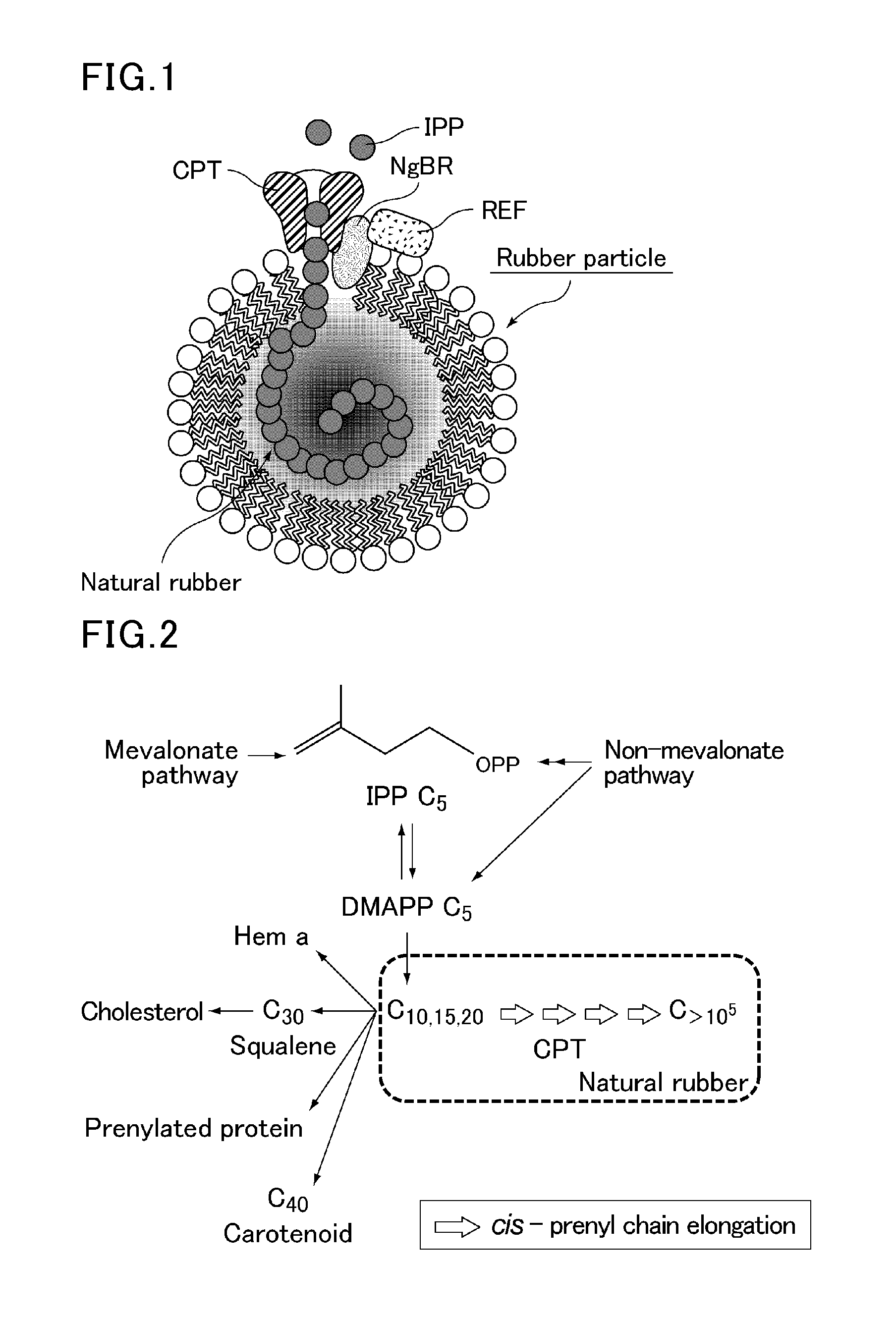
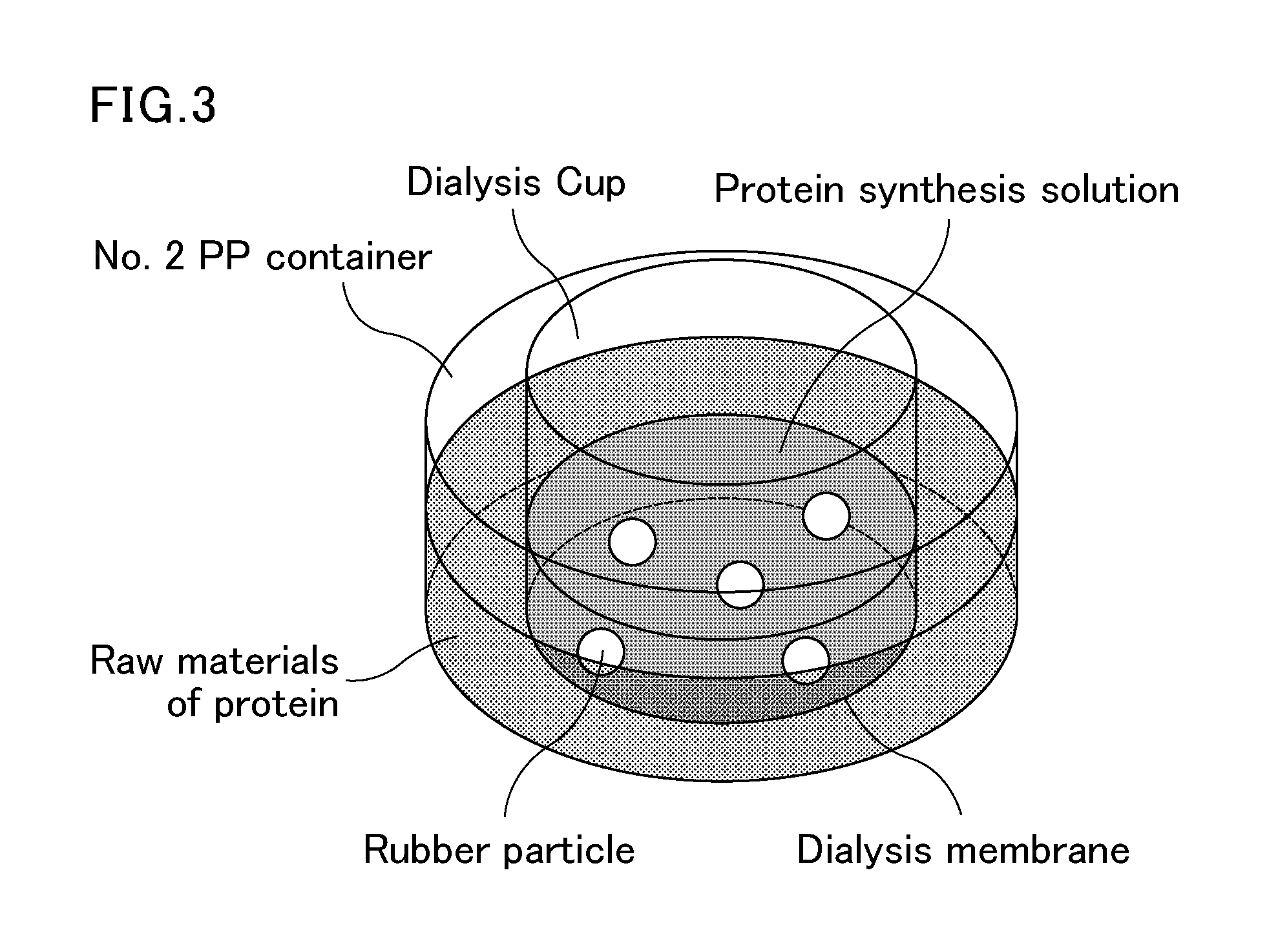
ActiveUS20170051313A1Enhanced rubber synthesis activityEfficient productionTransferasesTyresBiological bodyElongation factor
Provided is a method for producing a polyisoprenoid, which can increase natural rubber production by enhancing the rubber synthesis activity of rubber particles. The present invention provides methods for producing a polyisoprenoid using a gene coding for a cis-prenyltransferase (CPT) family protein, a gene coding for a Nogo-B receptor (NgBR) family protein and a gene coding for a rubber elongation factor (REF) family protein, specifically a method for producing a polyisoprenoid in vitro using rubber particles bound to proteins coded for by these genes, and a method for producing a polyisoprenoid in vivo using a recombinant organism (plant) having these genes introduced therein.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com