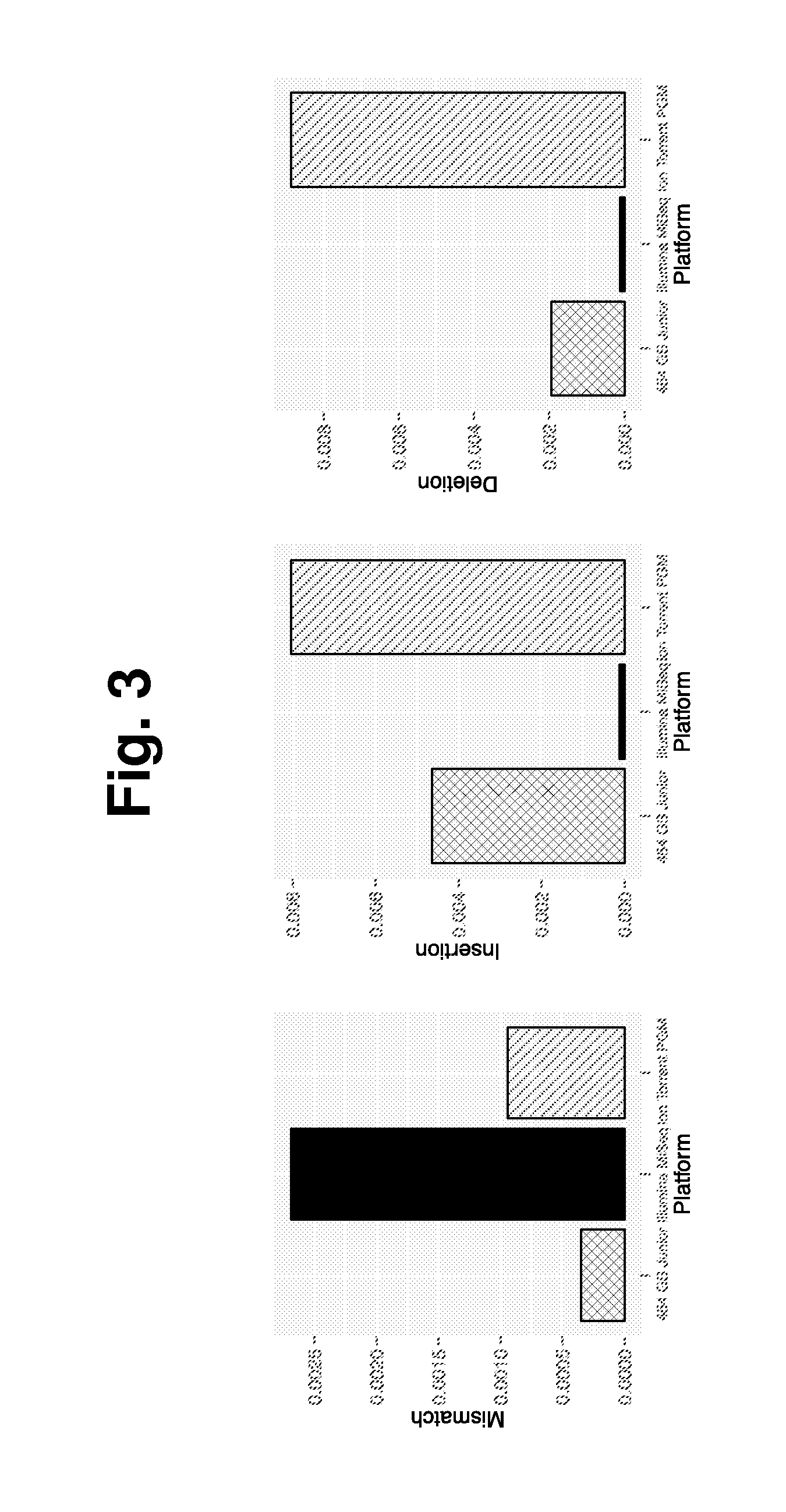
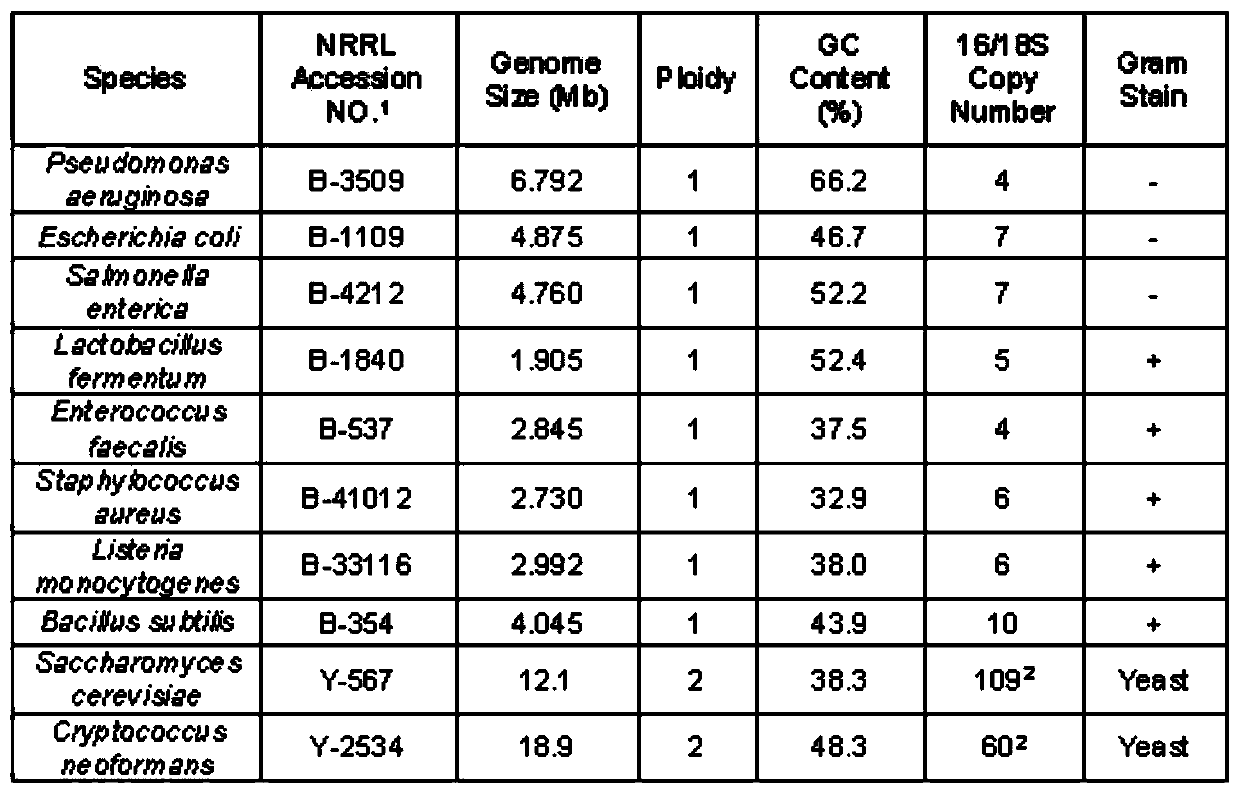
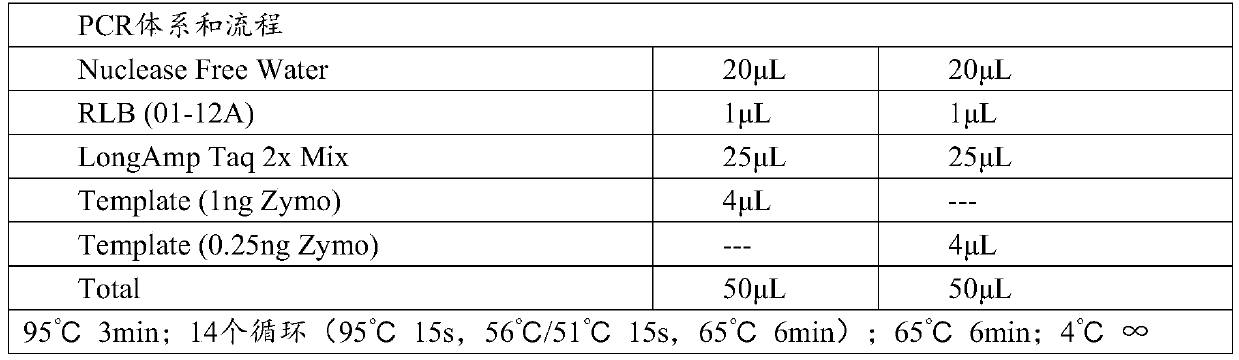
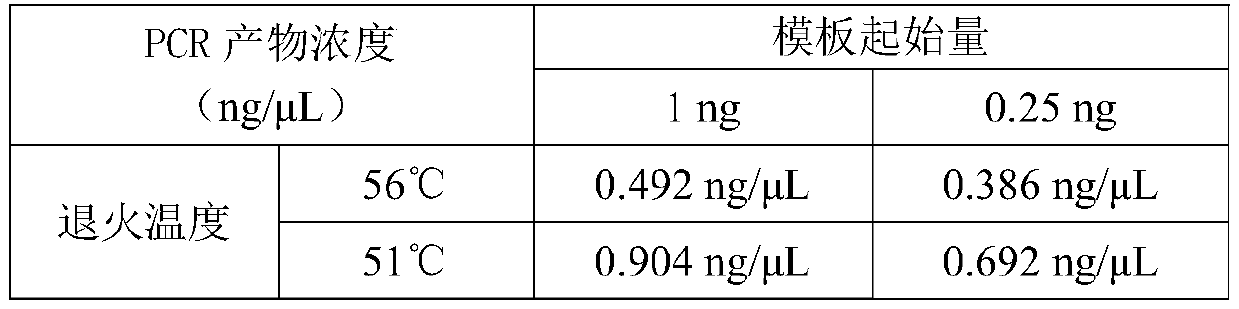
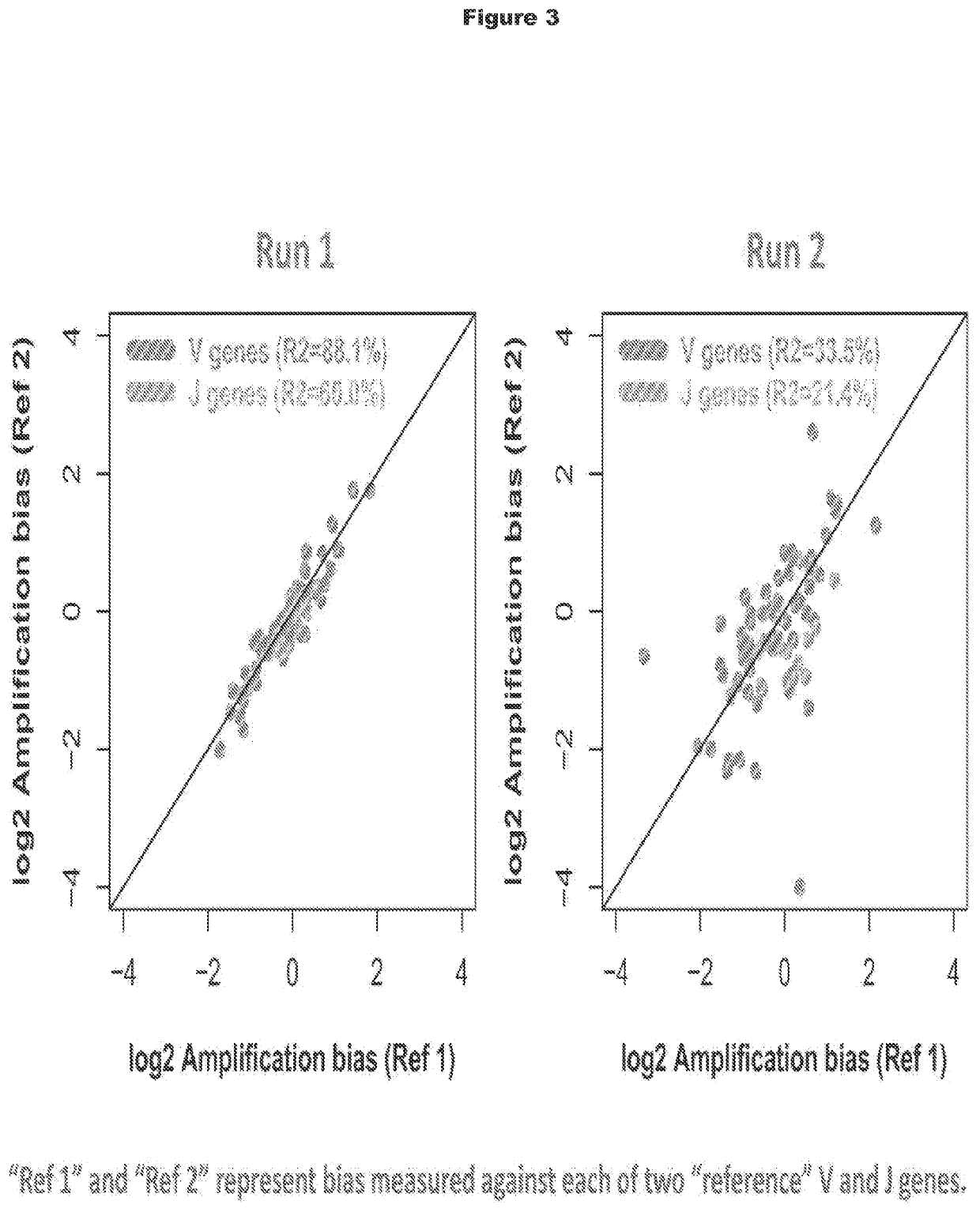
Patents
Literature
46 results about "Amplification bias" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
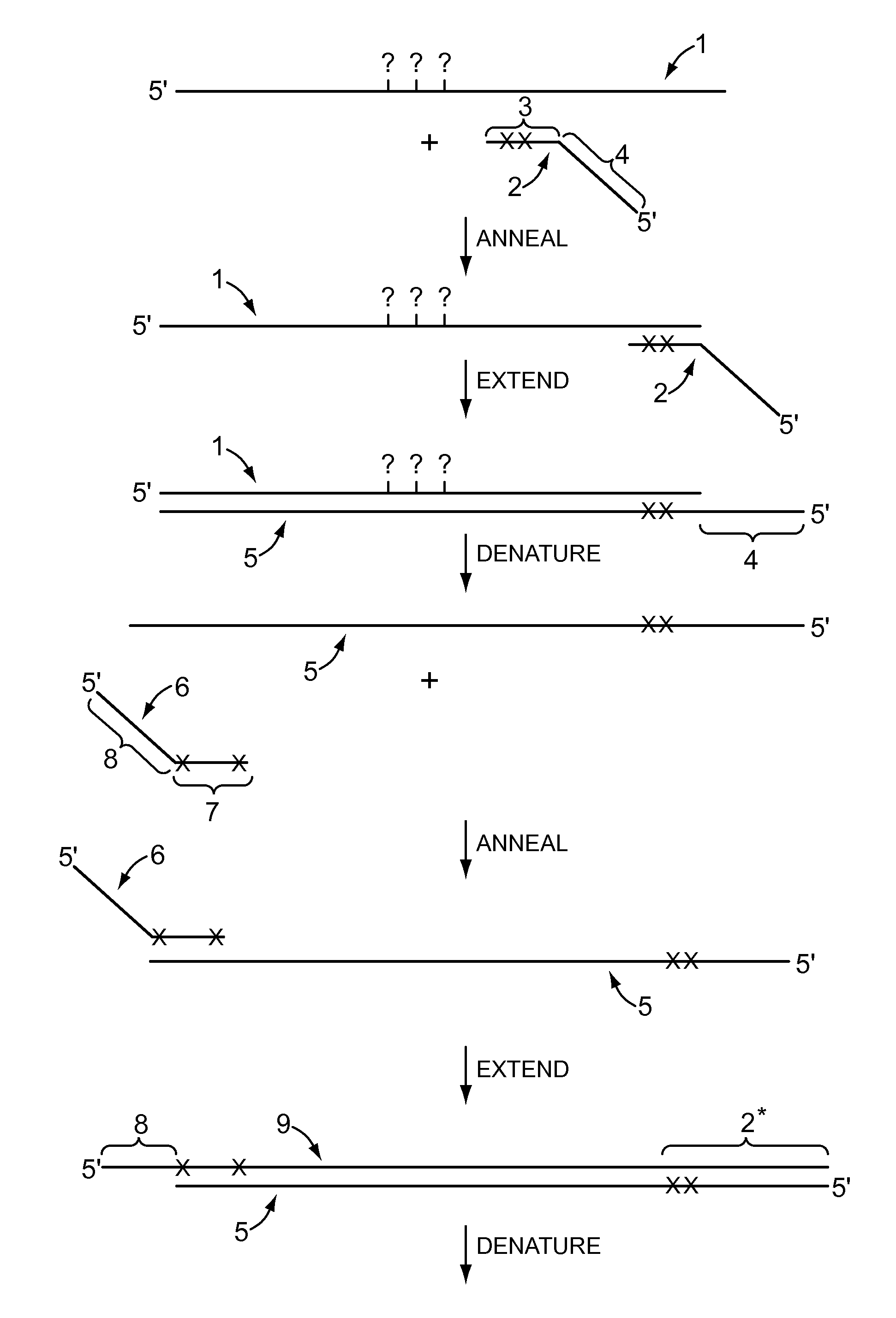
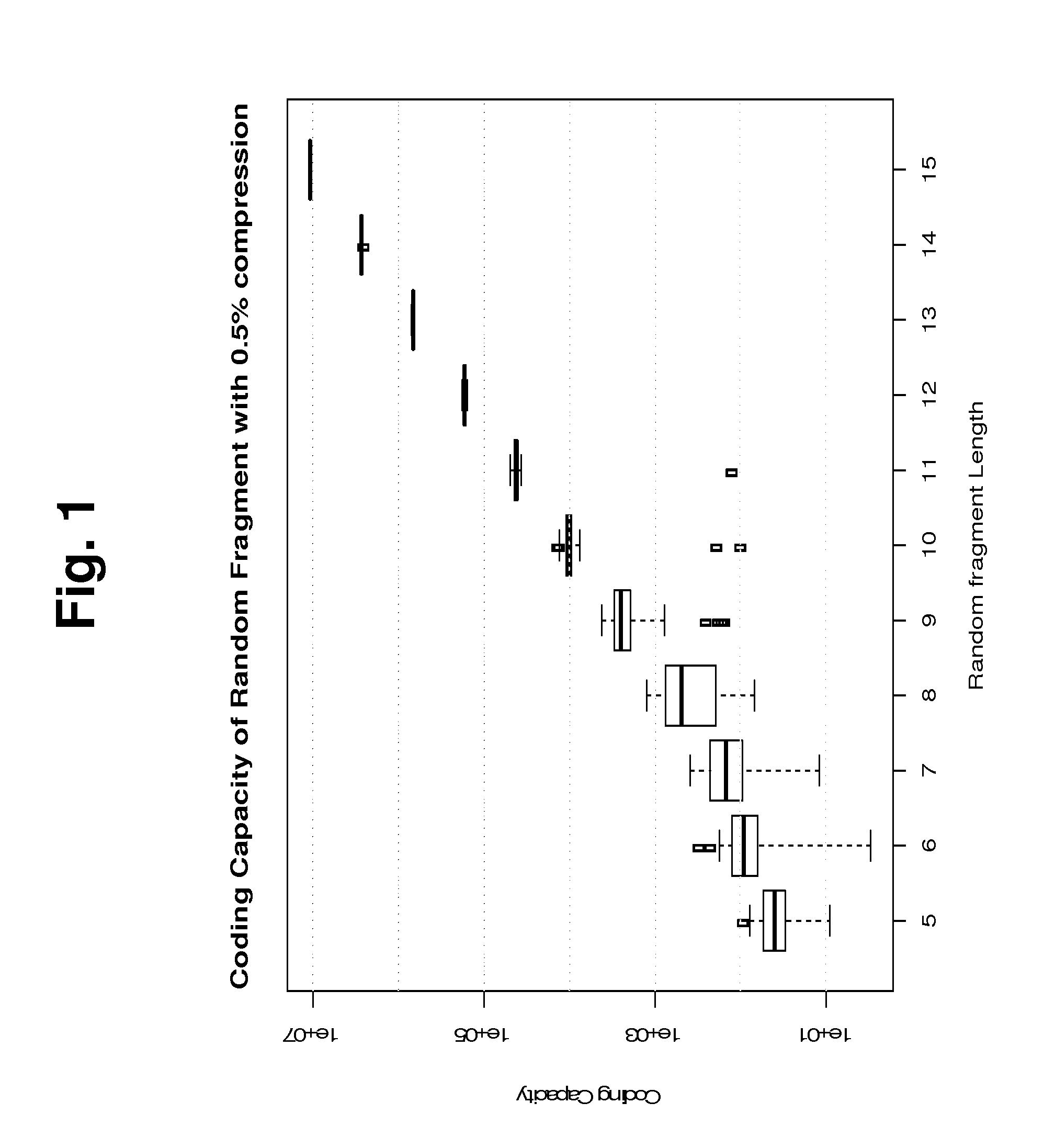
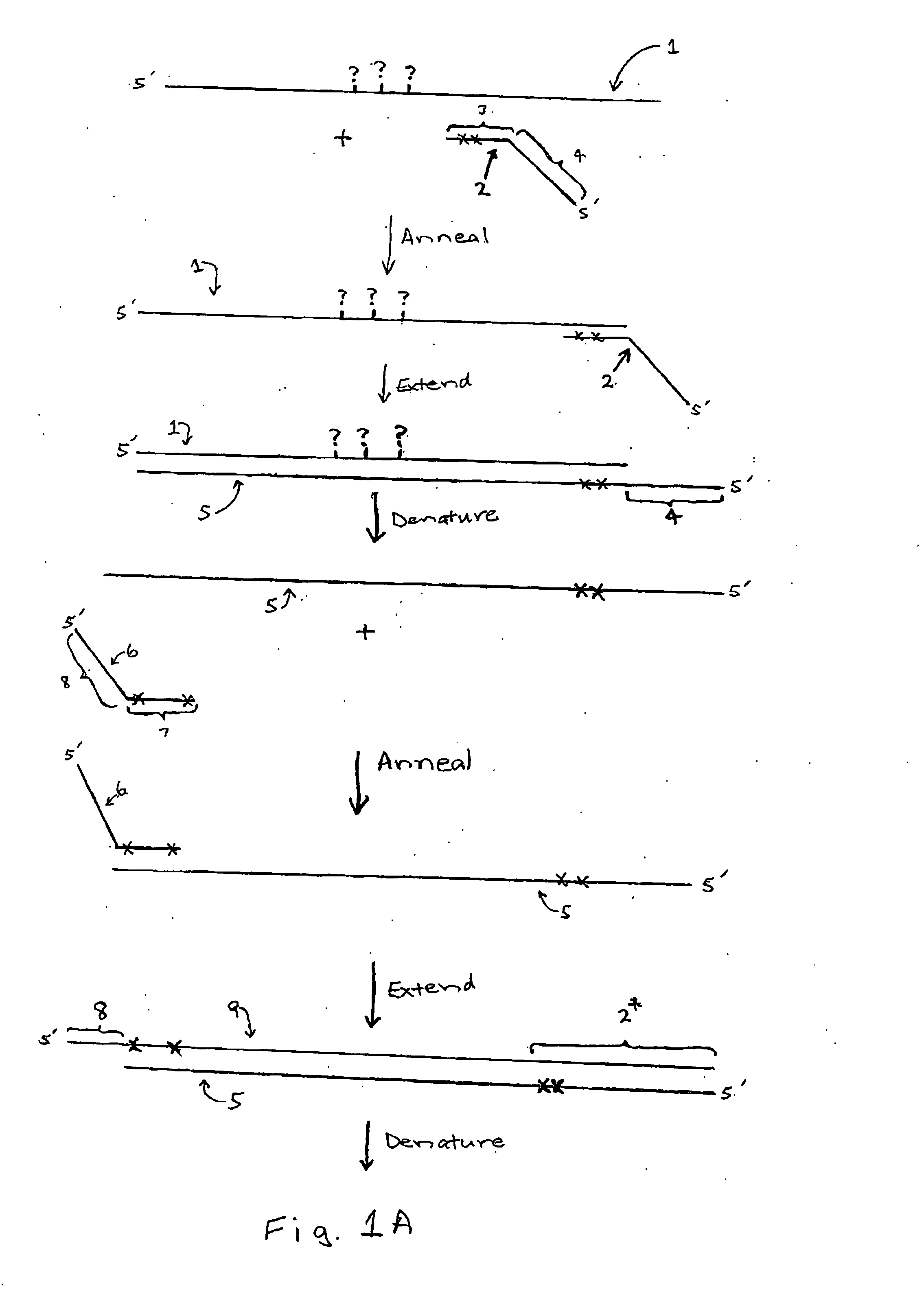
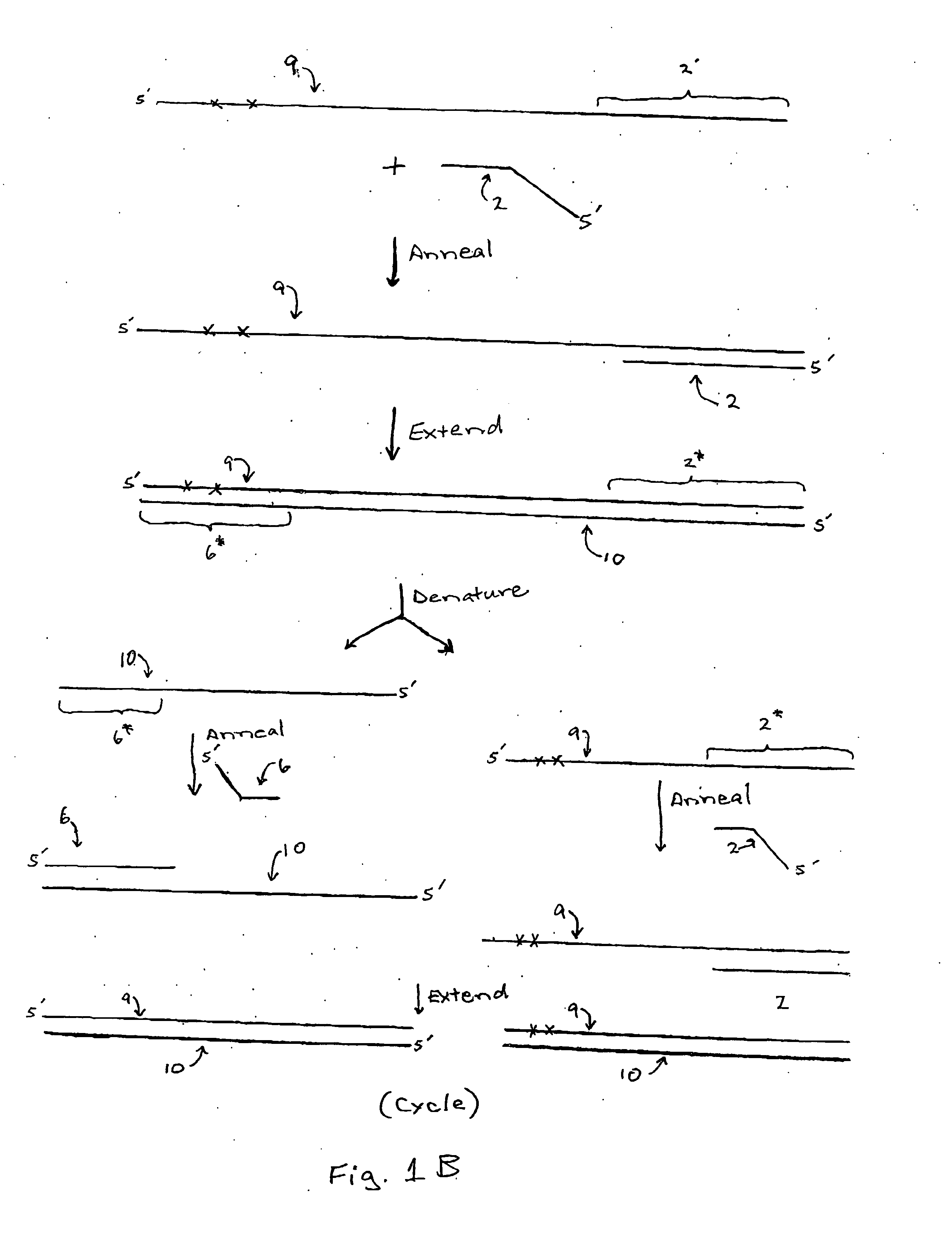
Amplification bias is a type of artifact common with Whole Genome Amplification (WGA). First described in 1992 (1, 2), WGA is a nucleic acid amplification approach (3, 4, 5) that increases the starting DNA quantity when it’s extremely limited, which is often the case in forensics, archaeological remains, fossils and the like.
Method for nucleic acid amplification that results in low amplification bias
InactiveUS7297485B2Consistent outputQuick buildMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid sequencingAmplification bias
Disclosed are compositions and methods for amplification of nucleic acid sequences of interest. It has been discovered that amplification reactions can produce amplification products of high quality, such as low amplification bias, if performed on an amount of nucleic acid at or over a threshold amount and / or on nucleic acids at or below a threshold concentration. The threshold amount and concentration can vary depending on the nature and source of the nucleic acids to be amplified and the type of amplification reaction employed. Disclosed is a method of determining the threshold amount and / or threshold concentration of nucleic acids that can be used with nucleic acid samples of interest in amplification reactions of interest. Because amplification reactions can produce high quality amplification products, such as low bias amplification products, below the threshold amount and / or concentration of nucleic acid, such below-threshold amounts and / or concentrations can be used in amplification reactions.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Nucleic acid amplification
InactiveUS20080128298A1Quality improvementLow amplification biasMicrobiological testing/measurementContainer/bottle contructionNucleic acid sequencingAmplification bias
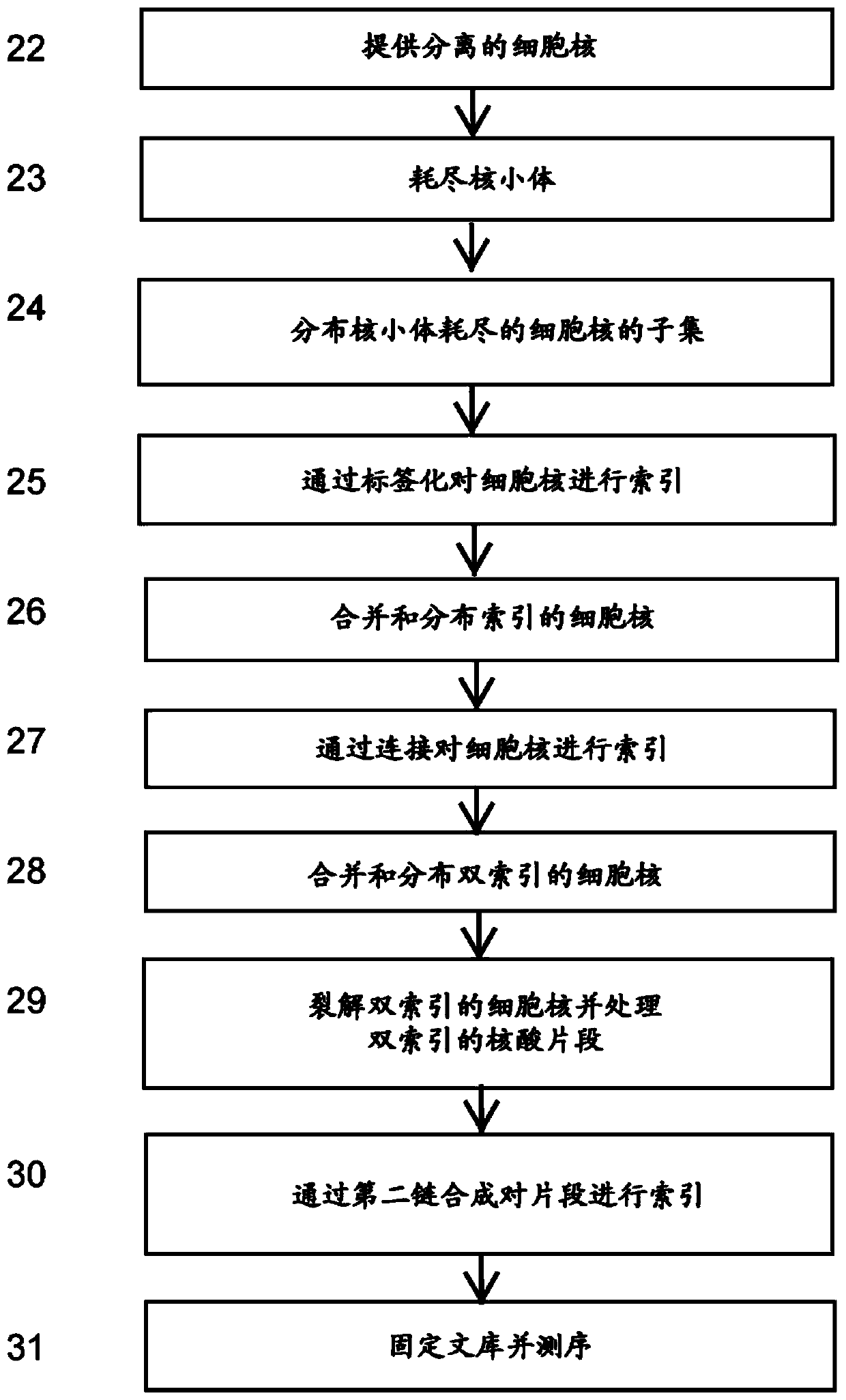
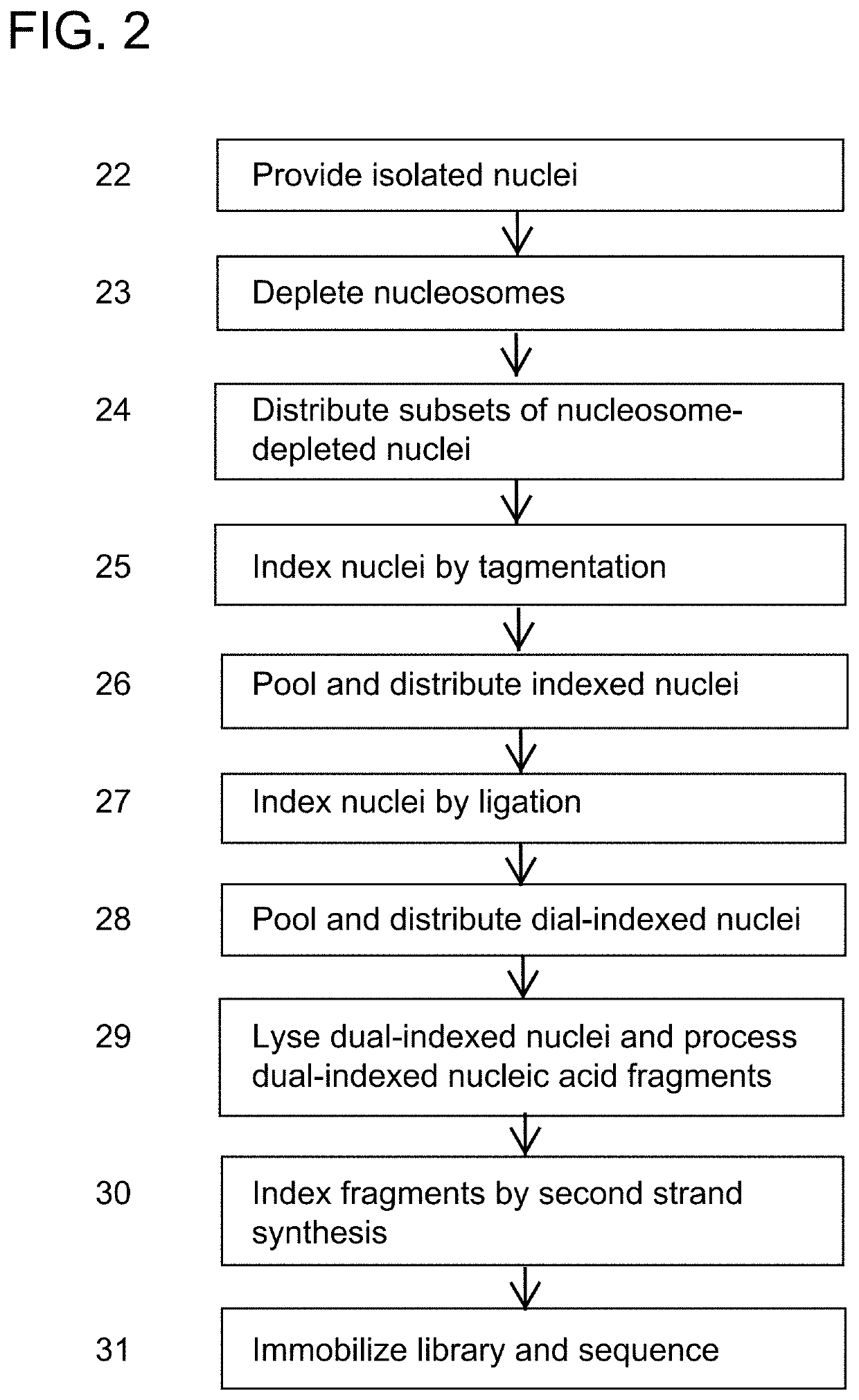
Disclosed are compositions and methods for amplification of nucleic acid sequences of interest. It has been discovered that amplification reactions can produce amplification products of high quality, such as low amplification bias, if performed on an amount of nucleic acid at or over a threshold amount and / or on nucleic acids at or below a threshold concentration. The threshold amount and concentration can vary depending on the nature and source of the nucleic acids to be amplified and the type of amplification reaction employed. Disclosed is a method of determining the threshold amount and / or threshold concentration of nucleic acids that can be used with nucleic acid samples of interest in amplification reactions of interest. Because amplification reactions can produce high quality amplification products, such as low bias amplification products, below the threshold amount and / or concentration of nucleic acid, such below-threshold amounts and / or concentrations can be used in amplification reactions.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Method of whole genome amplification with reduced artifact production
ActiveUS7955795B2Reduced and undetectable levelQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolymerase LNucleic acid sequencing
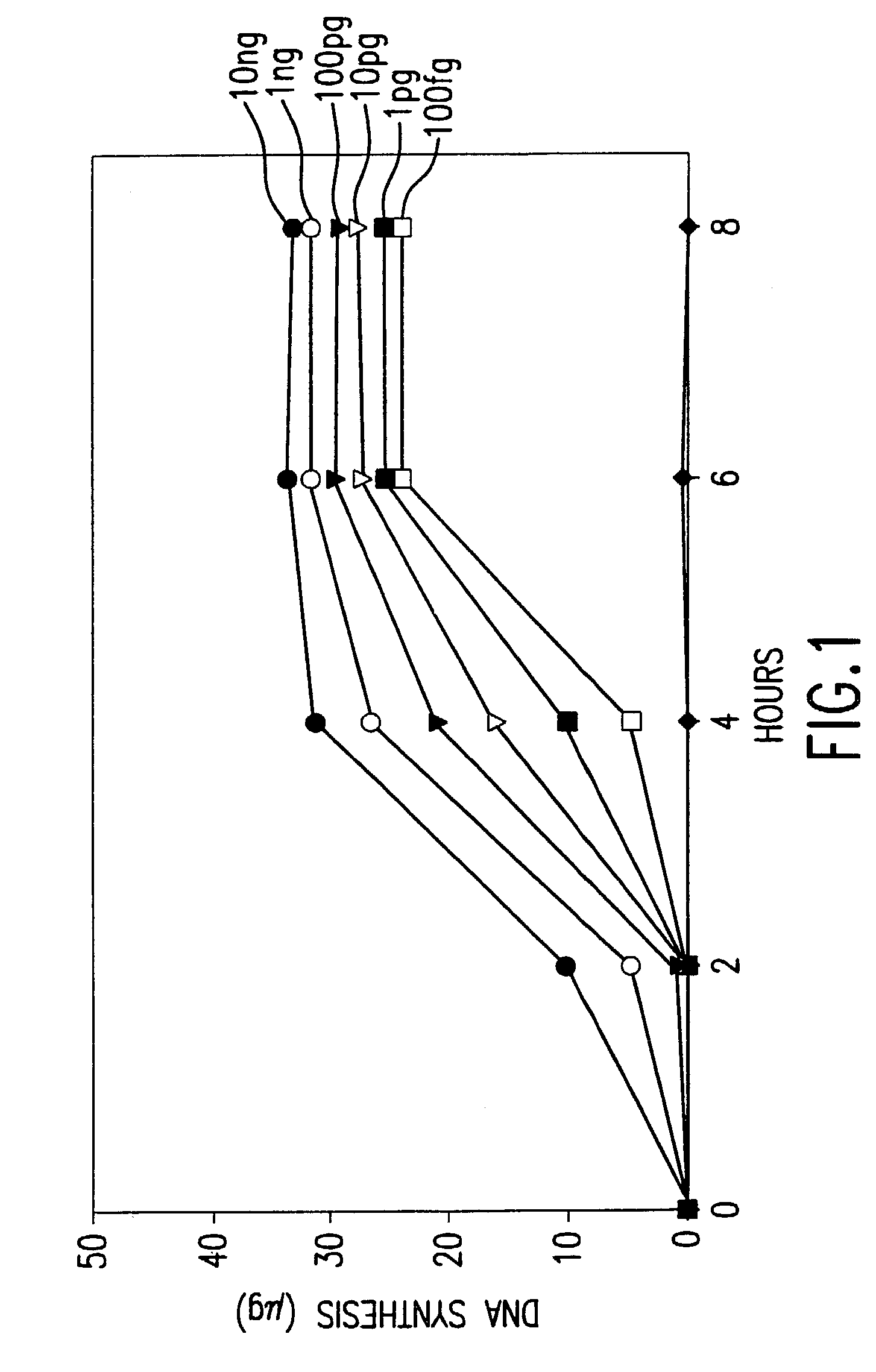
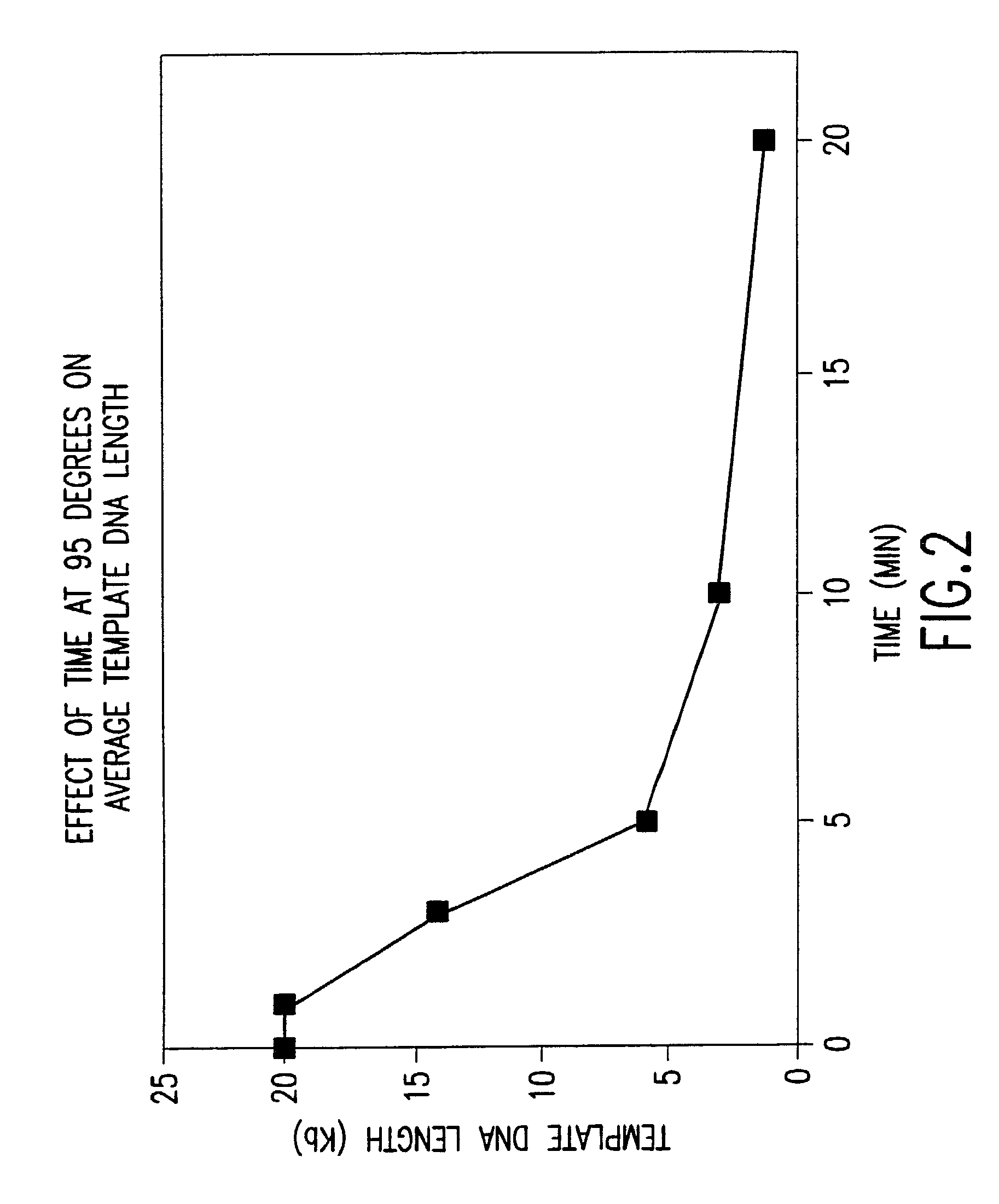
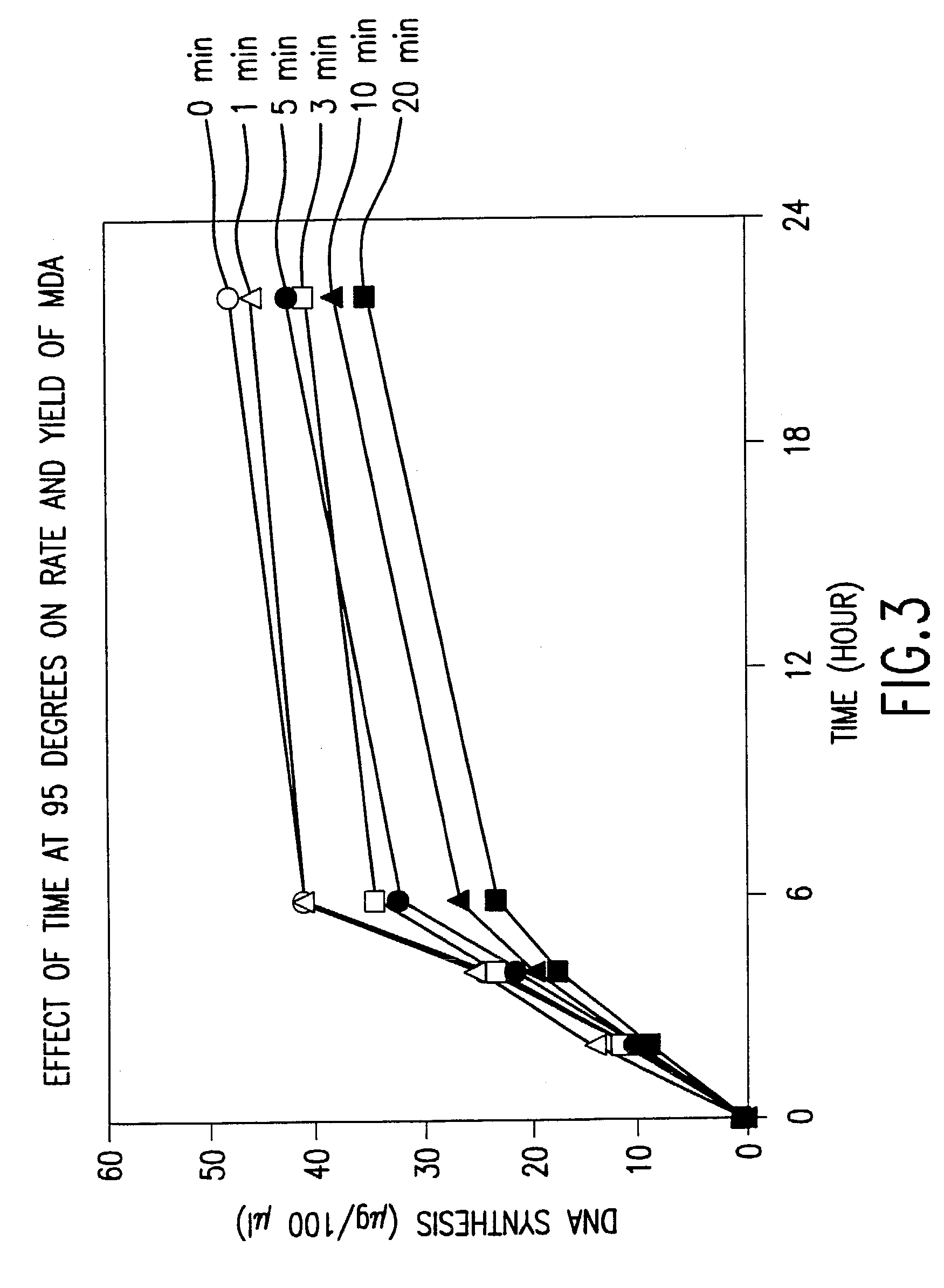
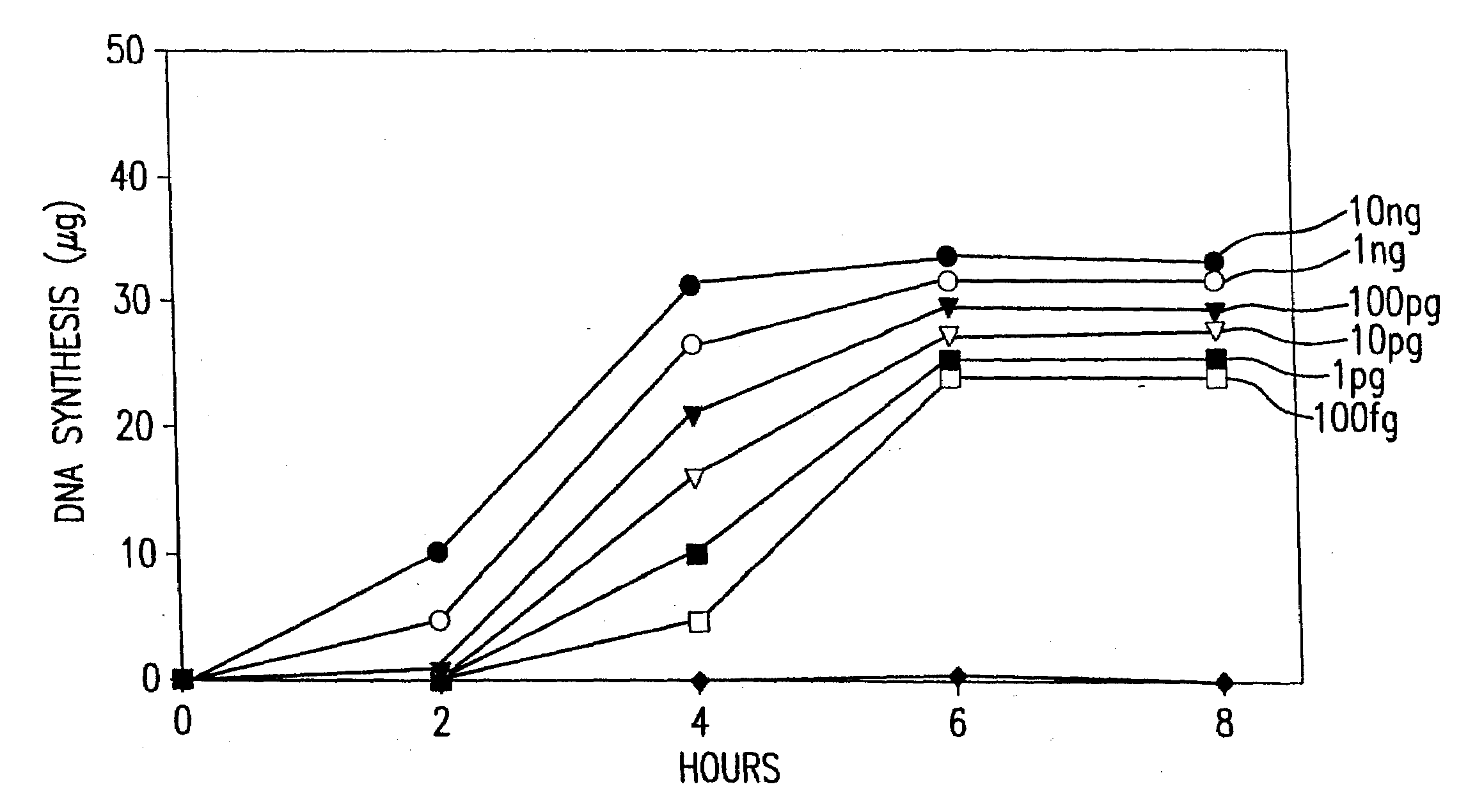
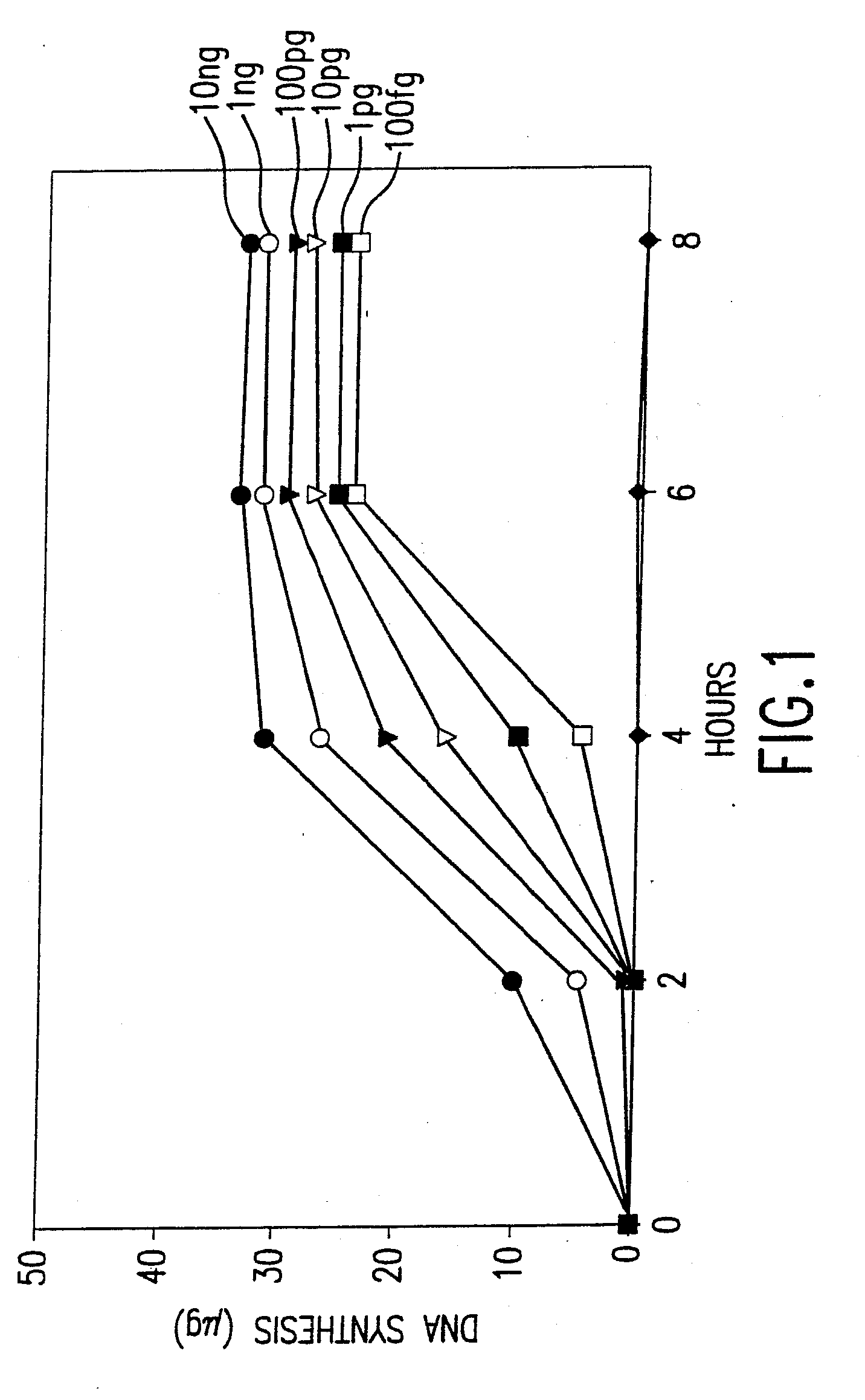
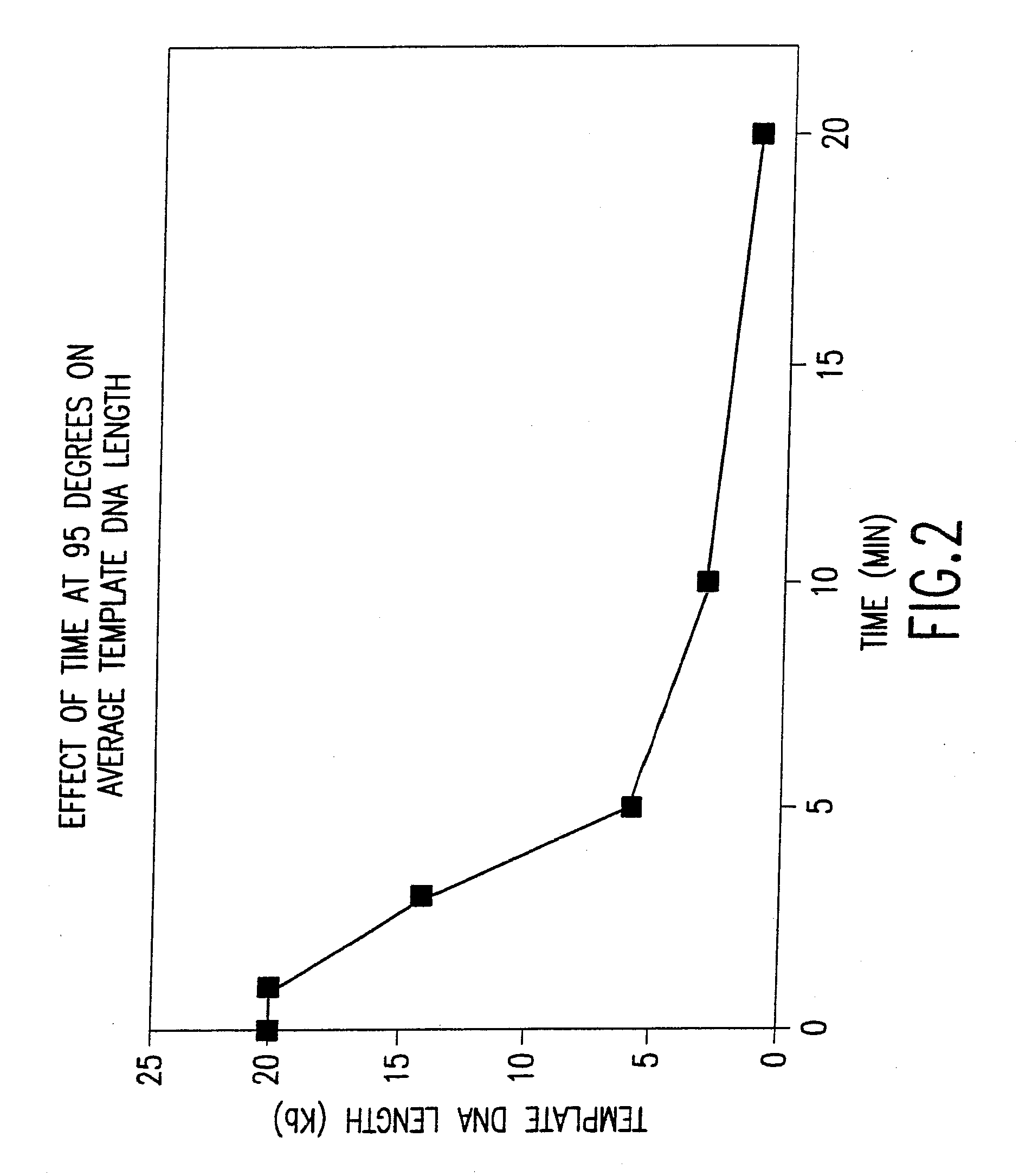
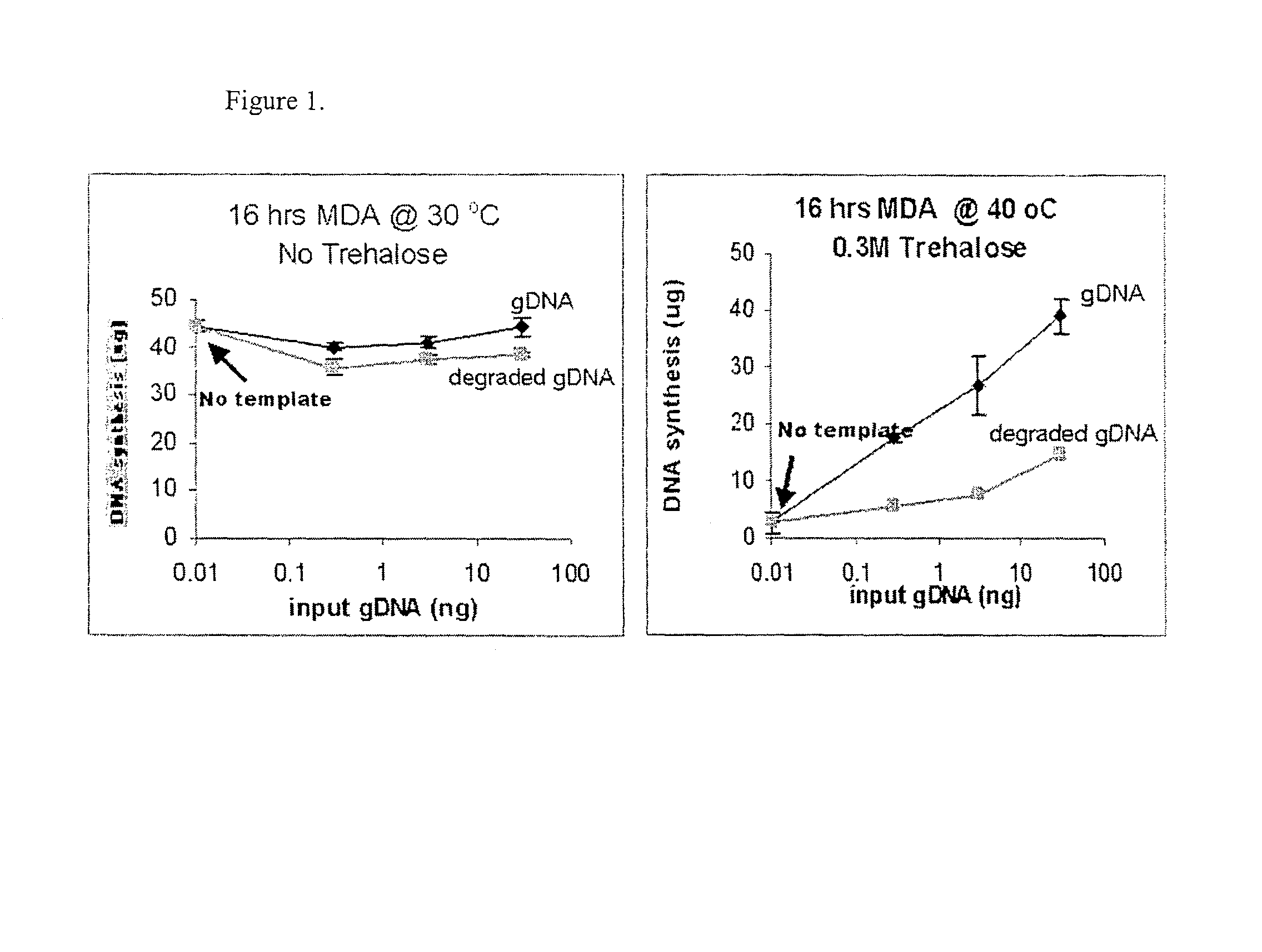
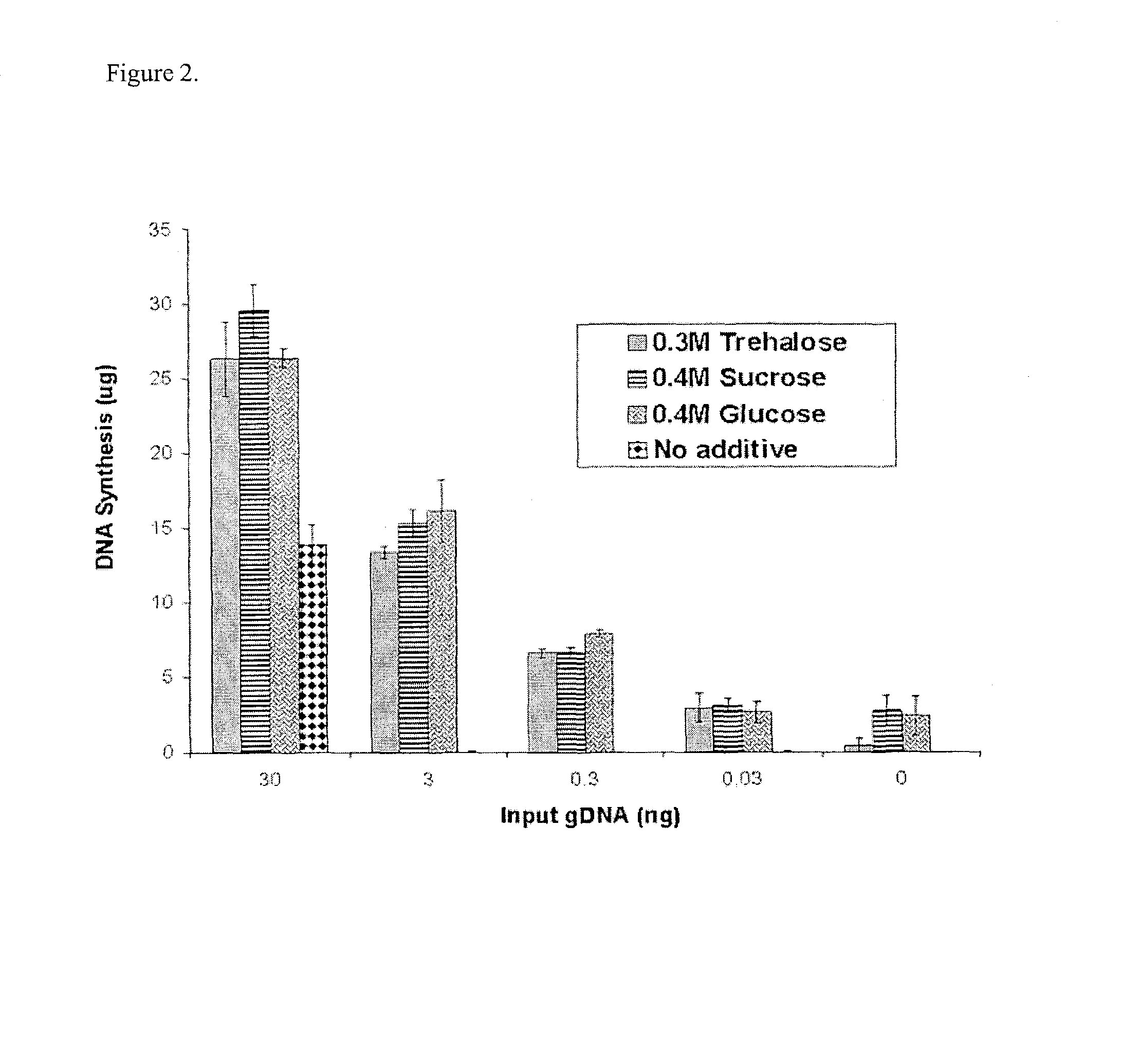
Disclosed are compositions and methods for amplification of nucleic acid sequences of interest with greater efficiency and fidelity. The disclosed method relates to isothermal amplification techniques, such as Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA), where the generation of DNA artifacts is decreased or eliminated. Generally, this can be accomplished by carrying out the reaction at elevated temperature. In particularly useful embodiments of the method, sugars and / or other additives can be used to stabilized the polymerase at high temperature. It has been discovered that generation of high molecular weight artifacts, in an isothermal amplification procedure, is substantially reduced or eliminated while still allowing the desired amplification of input DNA by carrying out the reaction at a higher temperature and, optionally, in the presence of one or more additives. It also has been discovered that isothermal amplification reactions can produce amplification products of high quality, such as low amplification bias, if performed at a higher temperature and, optionally, in the presence of one or more additives.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
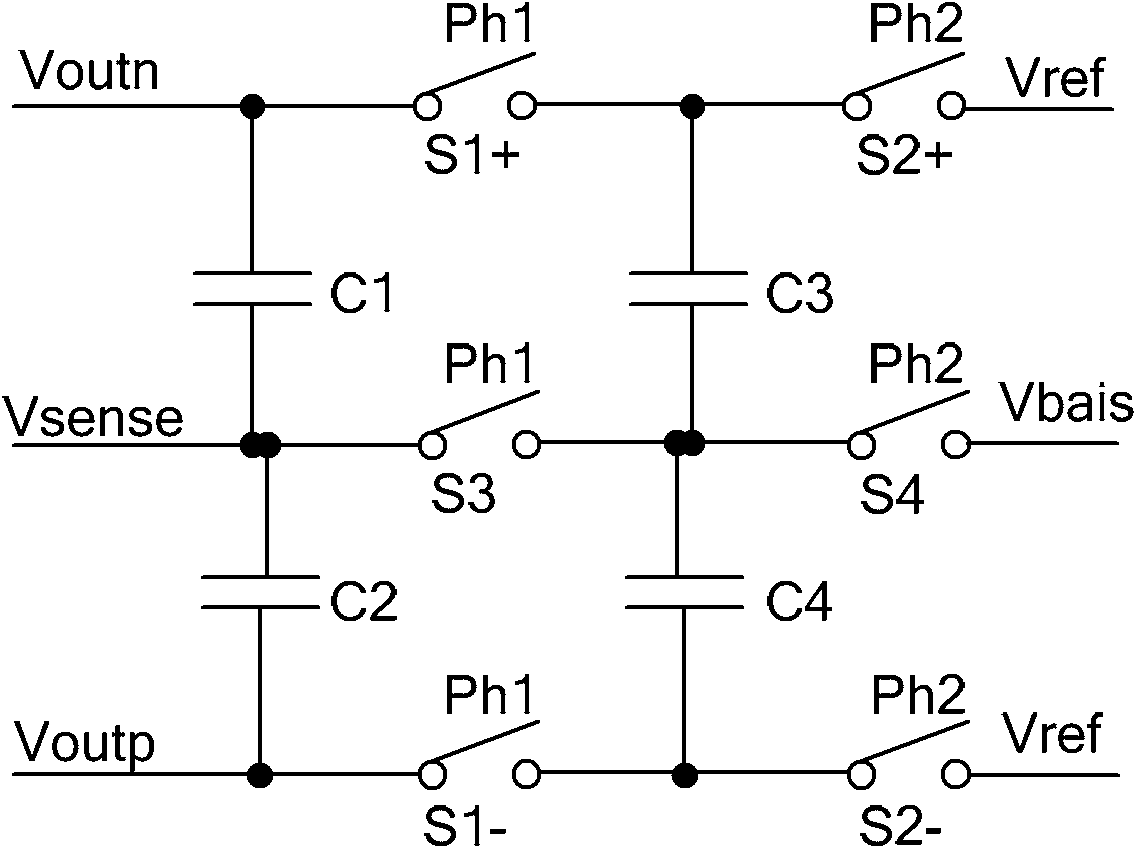
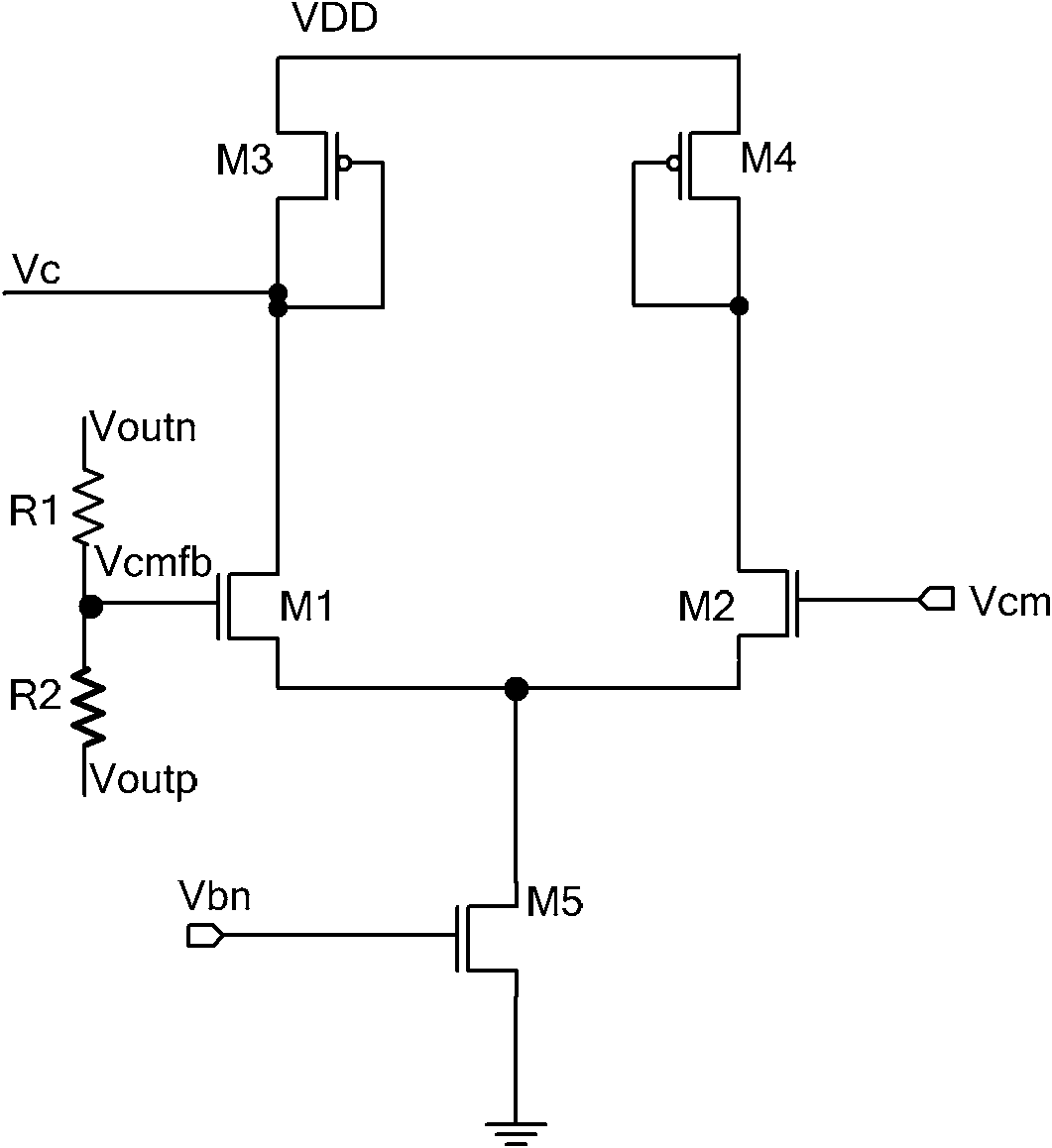
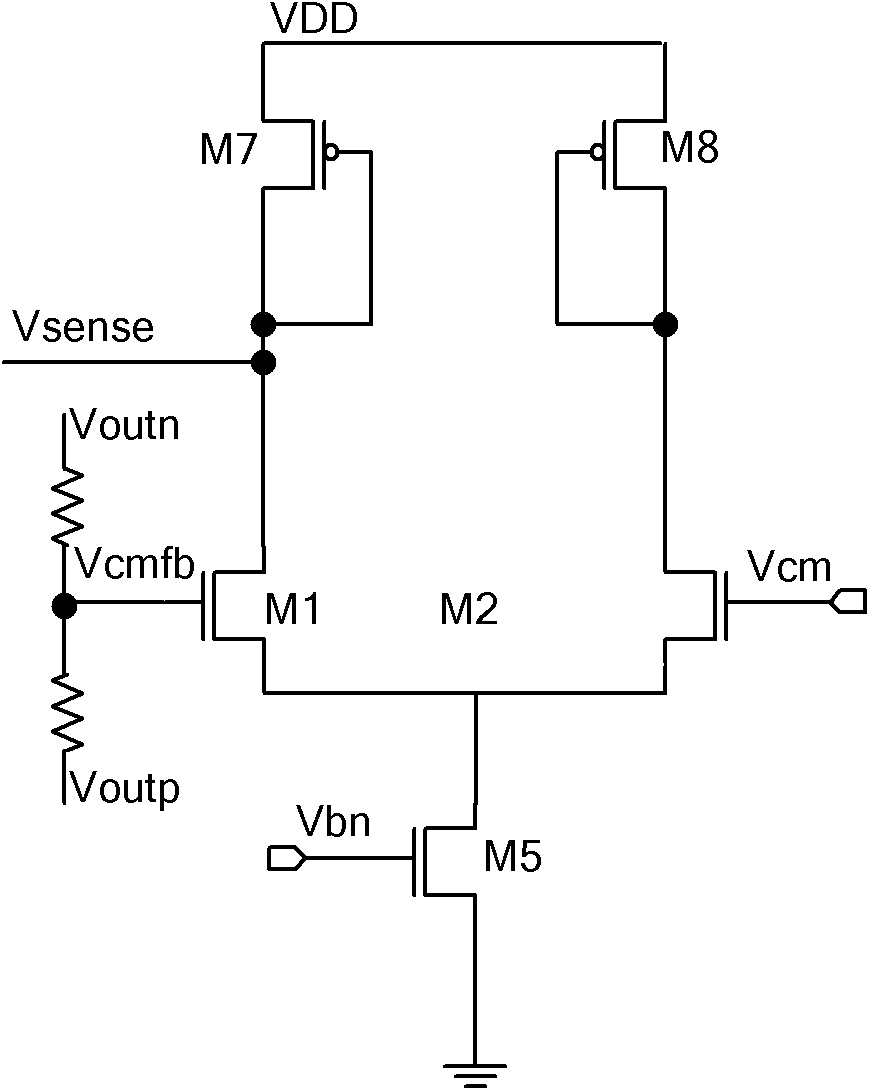
Large-bandwidth continuous time common-mode feedback circuit and design method thereof
InactiveCN101807893AImprove stabilityNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsDifferential amplifiersControl signalCascode
The invention relates to a large-bandwidth continuous-time common-mode feedback circuit and a design method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: designing an ideal common-mode signal; detecting the common-mode value of an operational amplification output signal through a common-mode detection circuit; comparing the detected common-mode value of the operational amplification output signal with that of the ideal common-mode signal; after amplifying an error signal through the common-mode feedback circuit, outputting two common-mode feedback control signals fed back to the drain electrode of a biasing tube of an operational amplification biasing circuit so that the whole common-mode feedback circuit forms a single-stage amplifier to ensure that the common-mode feedback circuit has enough phase margin; and finally stabilizing the operational-amplified output common-mode point on the ideal common-mode value according to the negative feedback function of common-mode feedback. The invention overcomes the defects that the traditional continuous-time common-mode feedback circuit is a multi-stage amplifier and has poor stability, and ensures that the common-mode feedback circuit is a one-stage common-source cathode-input amplifier through adjusting the feedback point of the common-mode feedback; and the common-mode feedback circuit has favorable stability and is suitable for large-bandwidth ultrahigh-speed full-differential analog circuits.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Compositions, methods, and kits for analyzing DNA methylation
InactiveUS20100028890A1Reducing strand amplification biasMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCytosineAnalysis dna
Compositions, methods, and kits for reducing strand amplification bias using bisulfite treated gDNA are provided. Methods for detecting and for quantitating the amplified bisulfite treated gDNA and inferring the presence, absence, and / or degree of methylation of target cytosine(s) in the gDNA are also provided. Such methods typically employ tailed first primer pairs, which can, but need not comprise nucleotide analogs, and optionally second primer pairs.
Owner:APPLERA
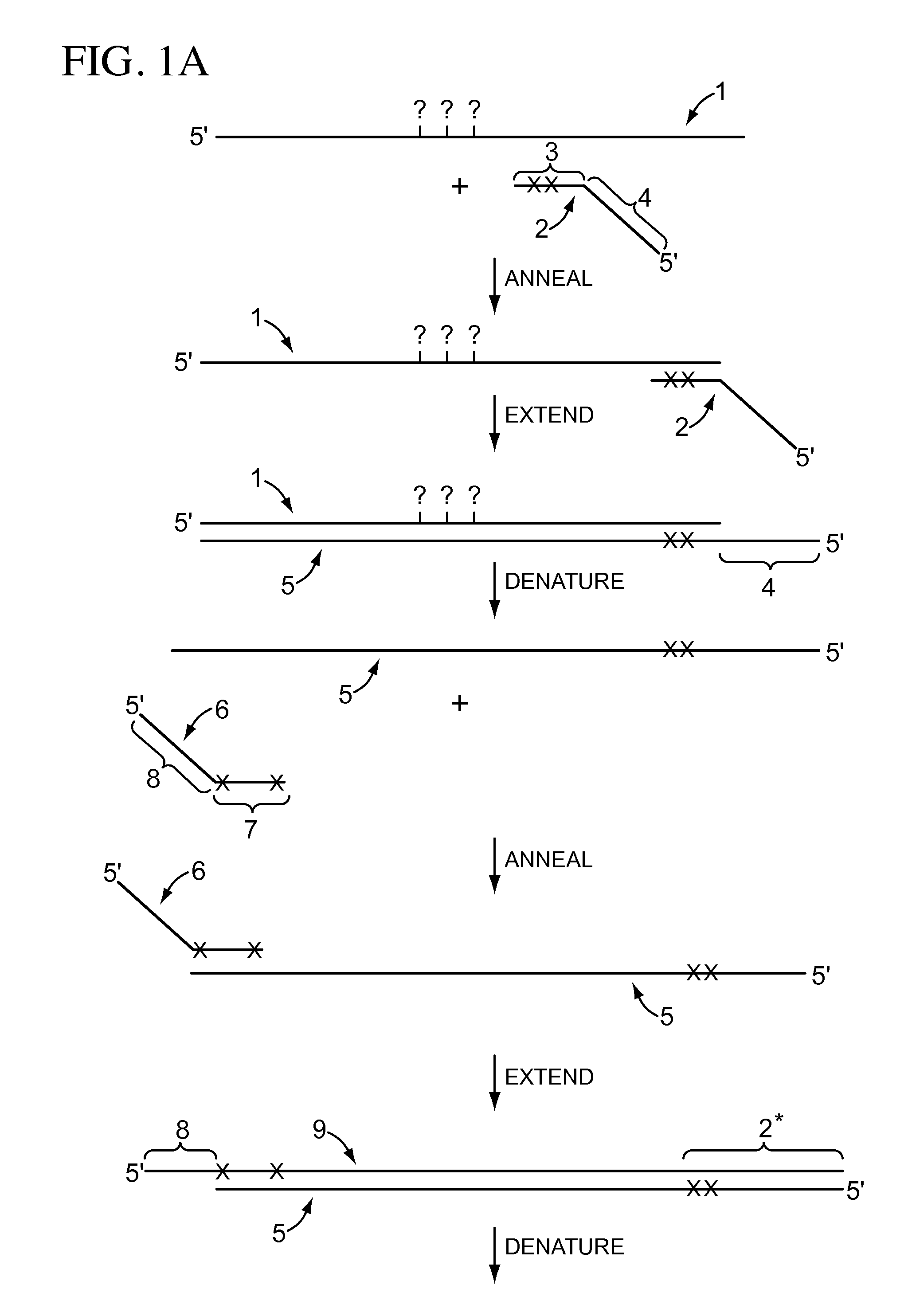
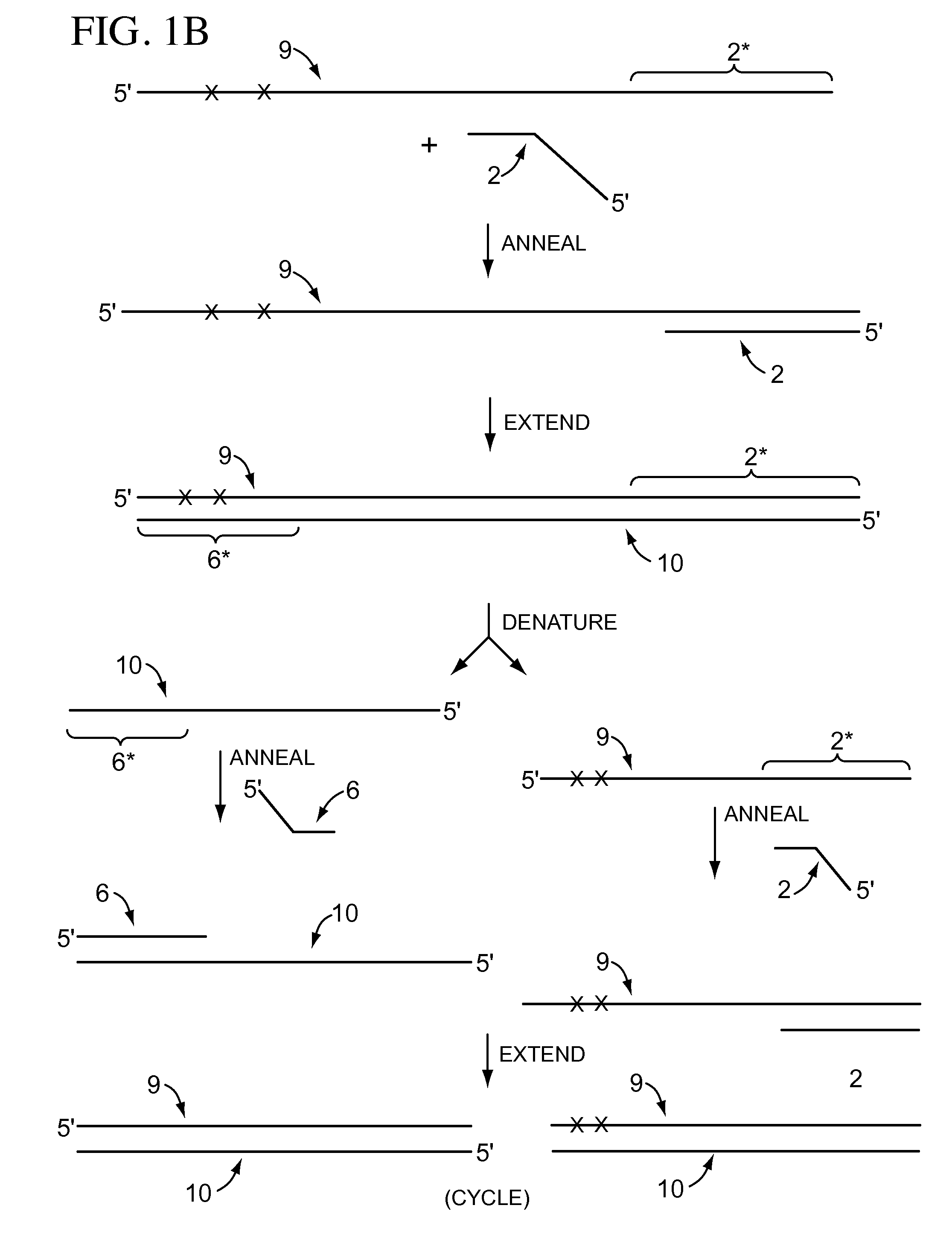
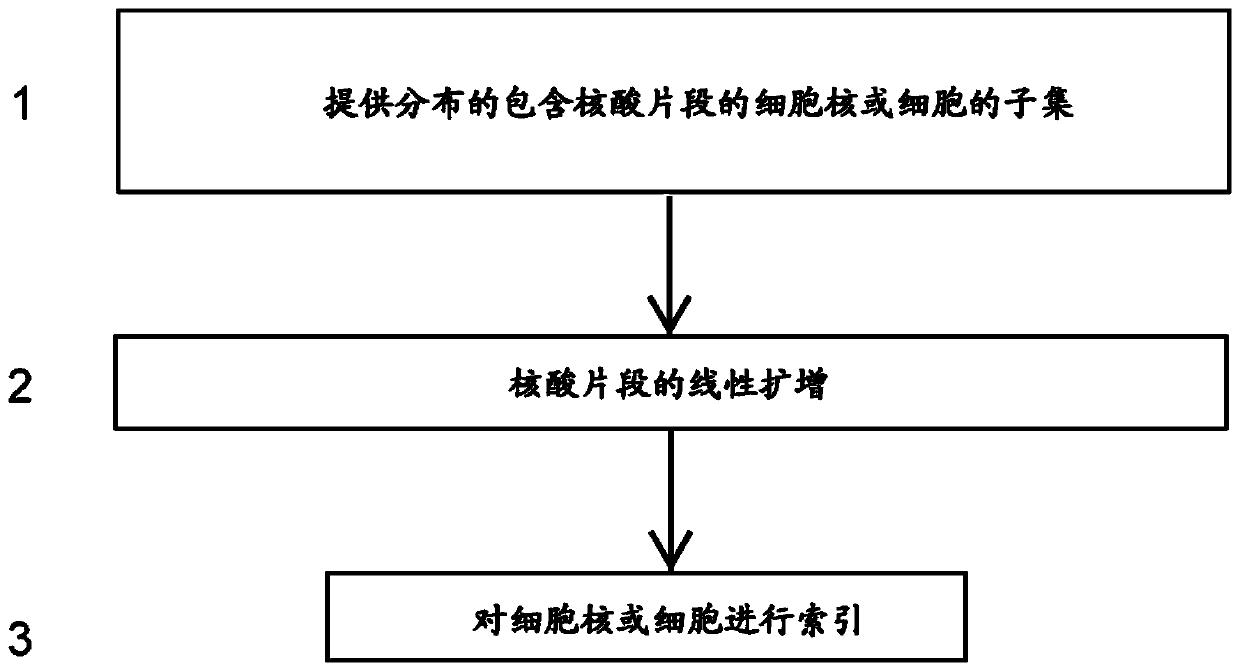
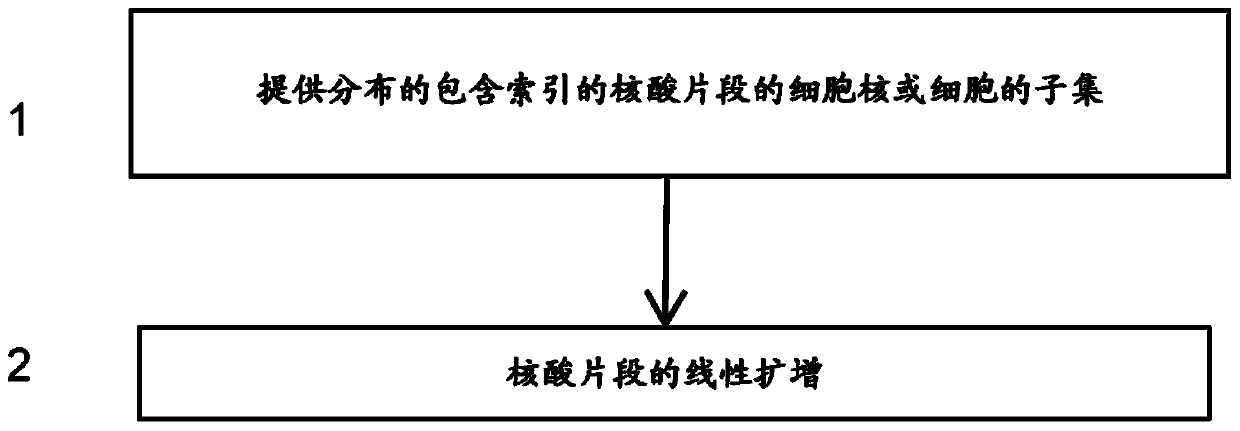
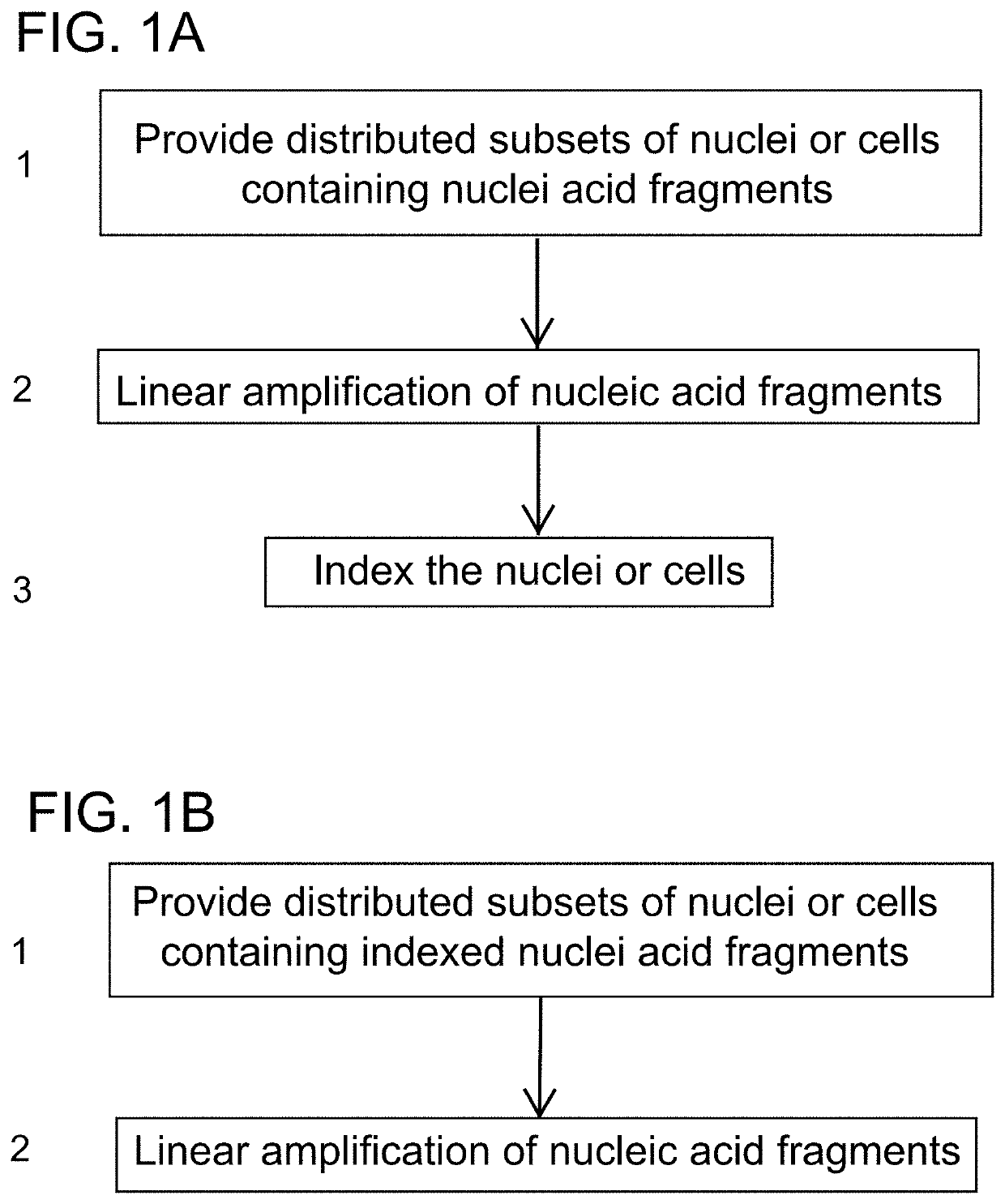
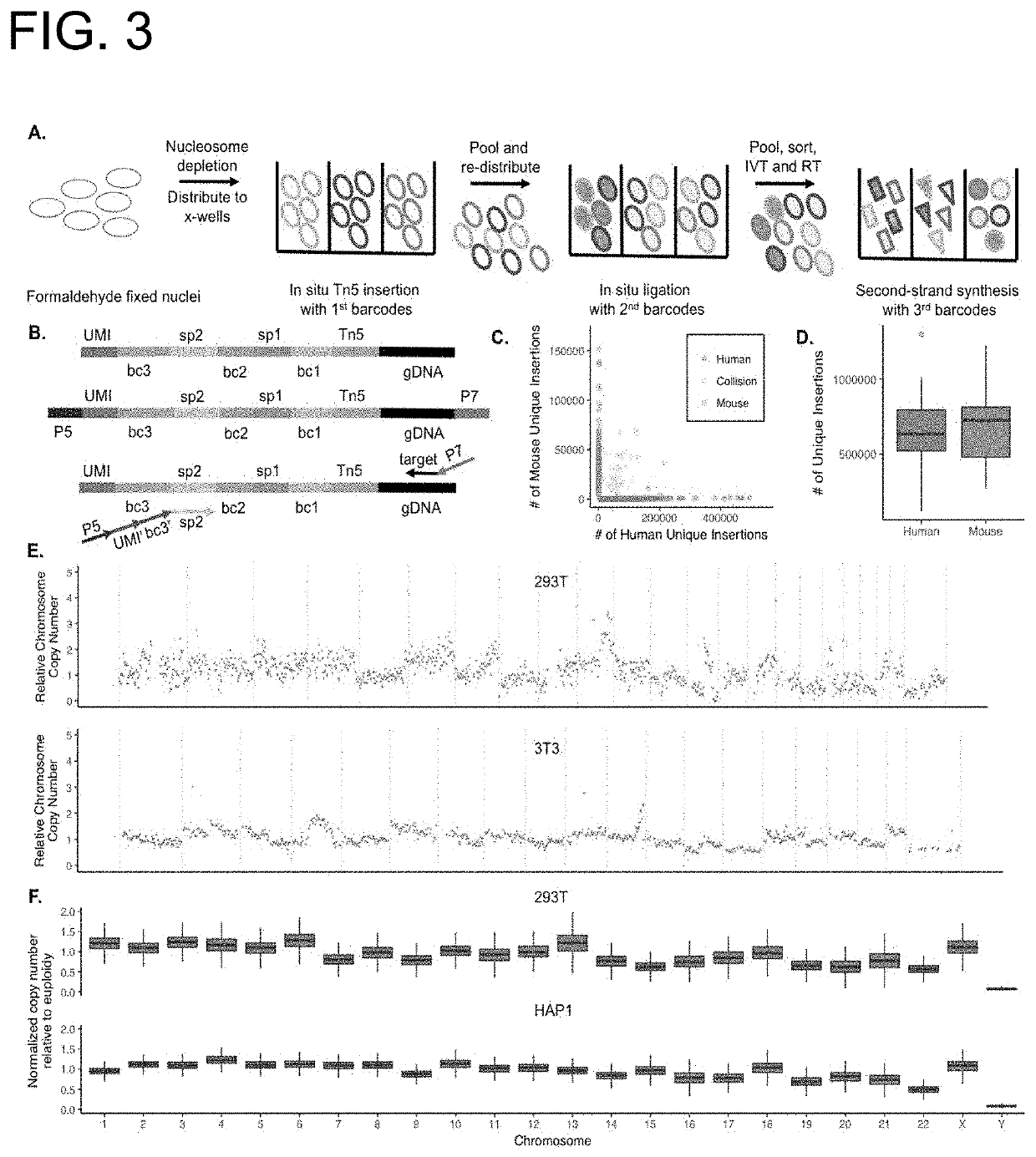
High-throughput single-cell sequencing with reduced amplification bias
Provided herein are methods for preparing a sequencing library that includes nucleic acids from a plurality of single cells. In one embodiment, the methods include linear amplification of the nucleicacids. In one embodiment, the sequencing library includes whole genome nucleic acids from the plurality of single cells. In one embodiment, the nucleic acids include three index sequences. Also provided herein are compositions, such as compositions that include the nucleic acids having three index sequences
Owner:ILLUMINA INC +1
High-throughput single-cell sequencing with reduced amplification bias
PendingUS20190382753A1Minimize amplification biasImprove throughputNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementLinear amplificationAmplification bias
Provided herein are methods for preparing a sequencing library that includes nucleic acids from a plurality of single cells. In one embodiment, the methods include linear amplification of the nucleic acids. In one embodiment, the sequencing library includes whole genome nucleic acids from the plurality of single cells. In one embodiment, the nucleic acids include three index sequences. Also provided herein are compositions, such as compositions that include the nucleic acids having three index sequences
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
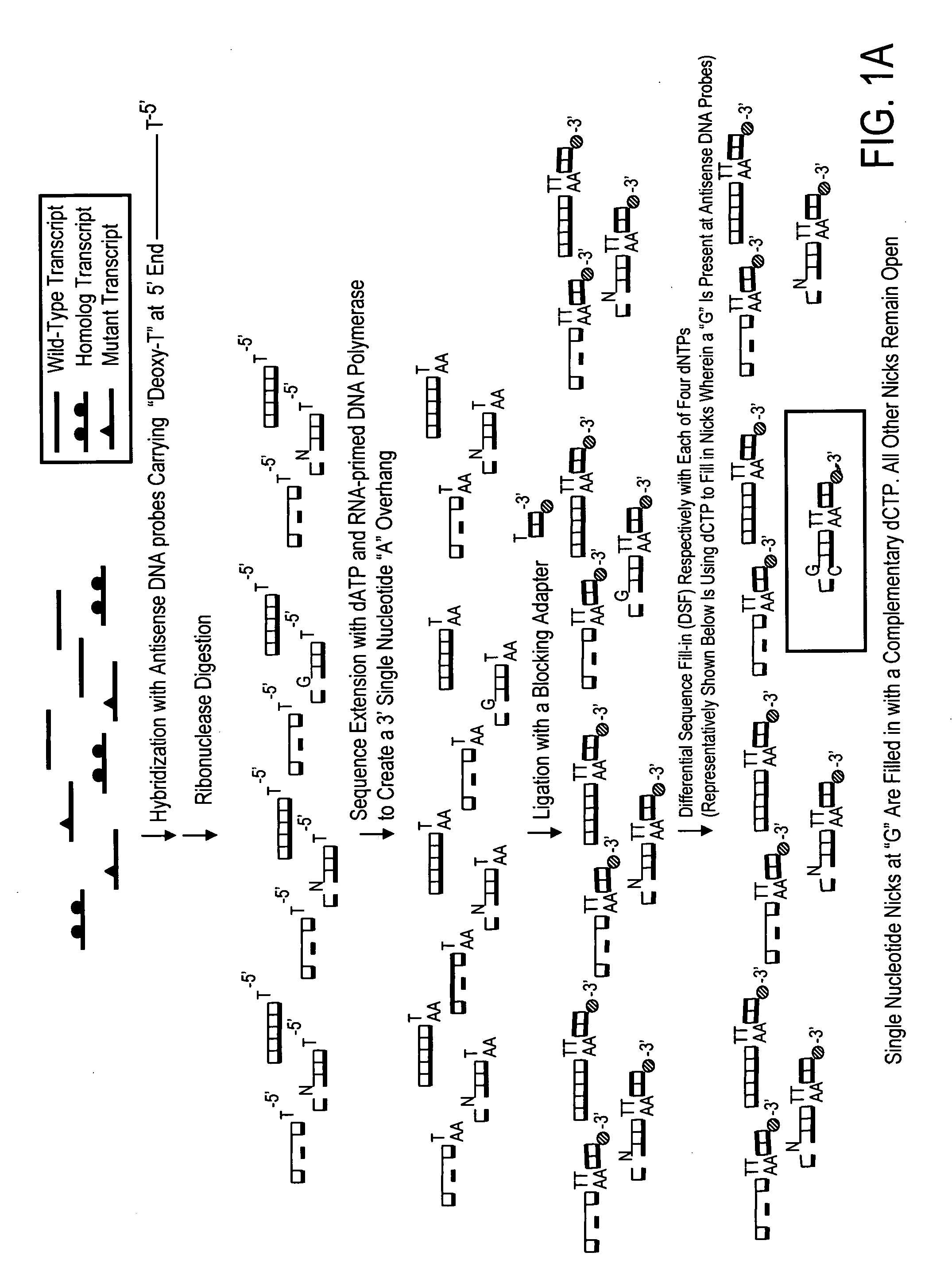
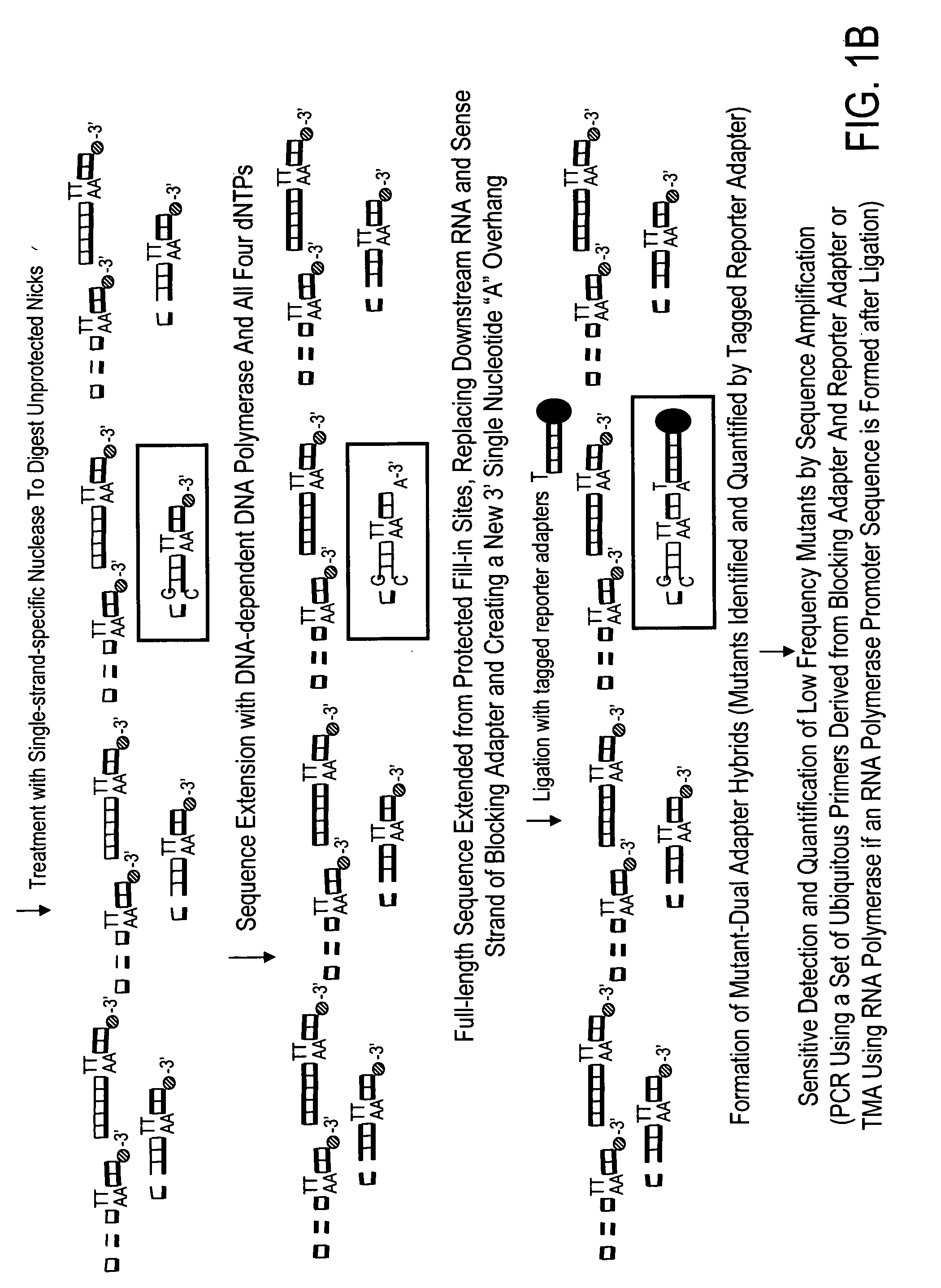
High throughput mutation screening methods and kits using a universalized approach - differential sequence fill-in (dsf)-enabled sequential adapter ligation and amplification
InactiveUS20090075276A1Facilitate simultaneous detectionProhibiting further ligationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationScreening methodSingle strand
This disclosure teaches high throughput mutation screening methods allowing simultaneous analysis of multiple genetic regions of interest and sensitive detection of very low frequency mutation(s) by the use of a universalized approach. Methods comprise treating RNA:DNA heteroduplexes of interest with a ribonuclease, sequence extension by an RNA-primed DNA polymerase, ligation with a blocking adapter, and differential sequence fill-in followed by single-strand-specific nuclease digestion to permit full-length sequence extension and subsequent ligation with a tagged reporter adapter solely in mutants filled in with a complementary deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate. By forming tagged mutant-dual adapter hybrids or mutant-triple adapter hybrids, the detection and / or quantification of mutants may be directed to the commonly shared tag(s) or flanking adapter sequences for signal detection / enhancement or sequence amplification in all different mutants regardless of the source or the number of mutations involved, thereby avoiding the tremendous effort of multiple target-specific sequence amplifications. Methods may be performed wholly or partially in solution, on solid phase media, in large scale, adapted for automated or semi-automated analysis, and any combinations thereof.
Owner:LEE MING SHENG +2
Method for increasing accuracy in quantitative detection of polynucleotides
InactiveUS20150132754A1Improve accuracyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification biasPolynucleotide
Disclosed is a method for improving the sensitivity and accuracy of quantitative detection of polynucleotides in a sample, such a clinical specimen, by a method that utilizes a two- or three-step process of tagging / labeling target molecules and adding an adapter sequence for adding a universal primer for efficient amplification of targets while decreasing target amplification bias. When combined with the step of statistically correcting for sequencing errors, the method can significantly increase the accuracy of quantitative detection of polynucleotides in a sample.
Owner:CB BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
Library establishment method for metagenome sequencing, kit and sequencing method
ActiveCN109778321AOptimizing the conditions for building a databaseReduce the initial amount of library constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGenomic sequencingA-DNA
Owner:BEIJING SIMCERE MEDICAL LAB CO LTD +2
Comparative genomic hybridization assays using immobilized oligonucleotide targets with initially small sample sizes and compositions for practicing the same
ActiveUS7211384B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSmall sampleComparative genomic hybridization
Comparative genomic hybridization assays and compositions for use in practicing the same are provided. In the subject methods, at least first and second genomic templates are prepared from first and second genomic sources using an amplification reaction that employs a highly processive polymerase, where the amplification reaction produces amplification products having an average molecular size of at least about 10 kb with substantially no amplification bias. The resultant templates are then employed to produce at least first and second probe nucleic acid populations. The resultant probe nucleic acid populations are then contacted with a plurality of oligonucleotide target elements immobilized on a solid support surface and the binding of at least first and second populations is then evaluated. Also provided are kits for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
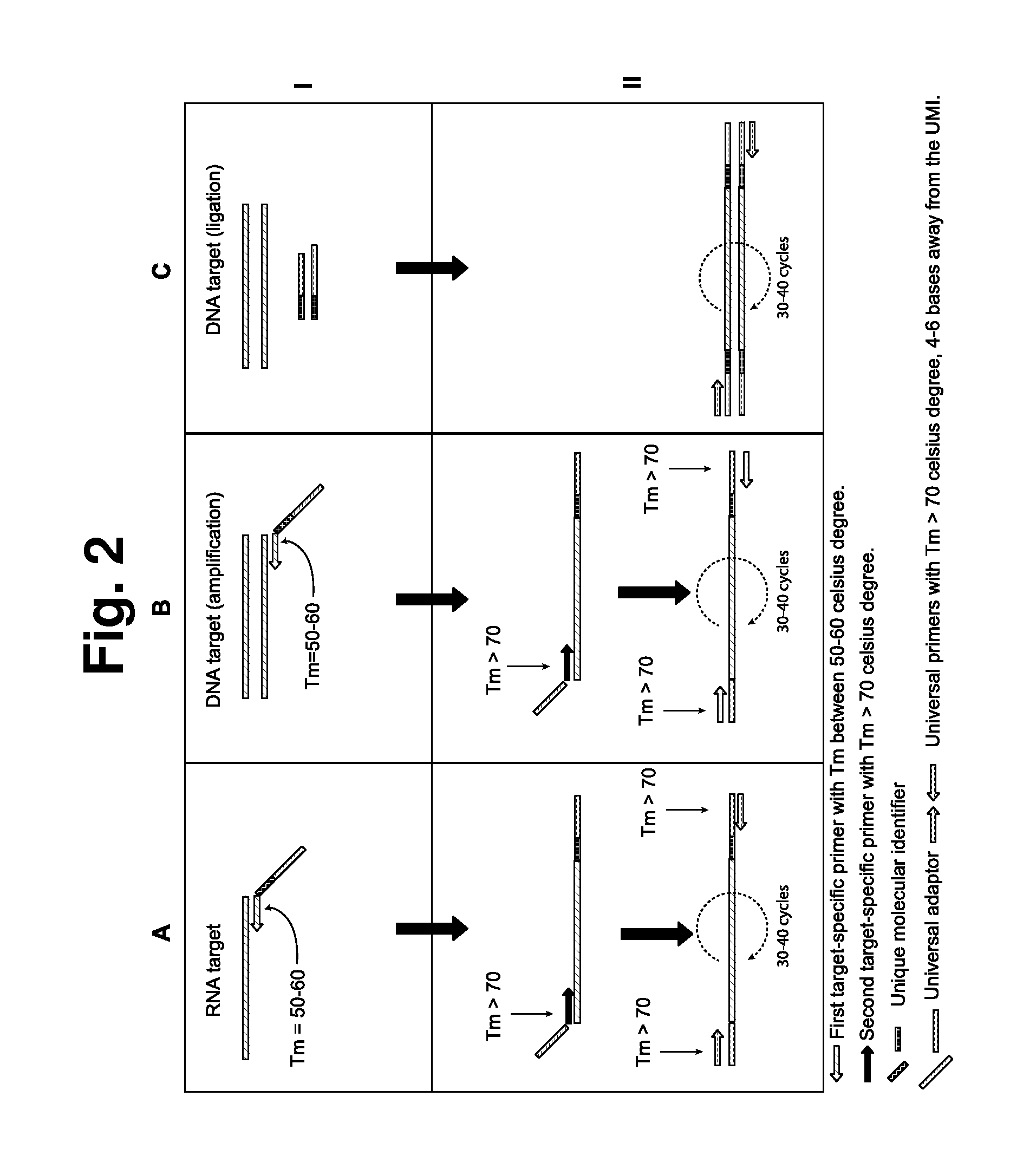
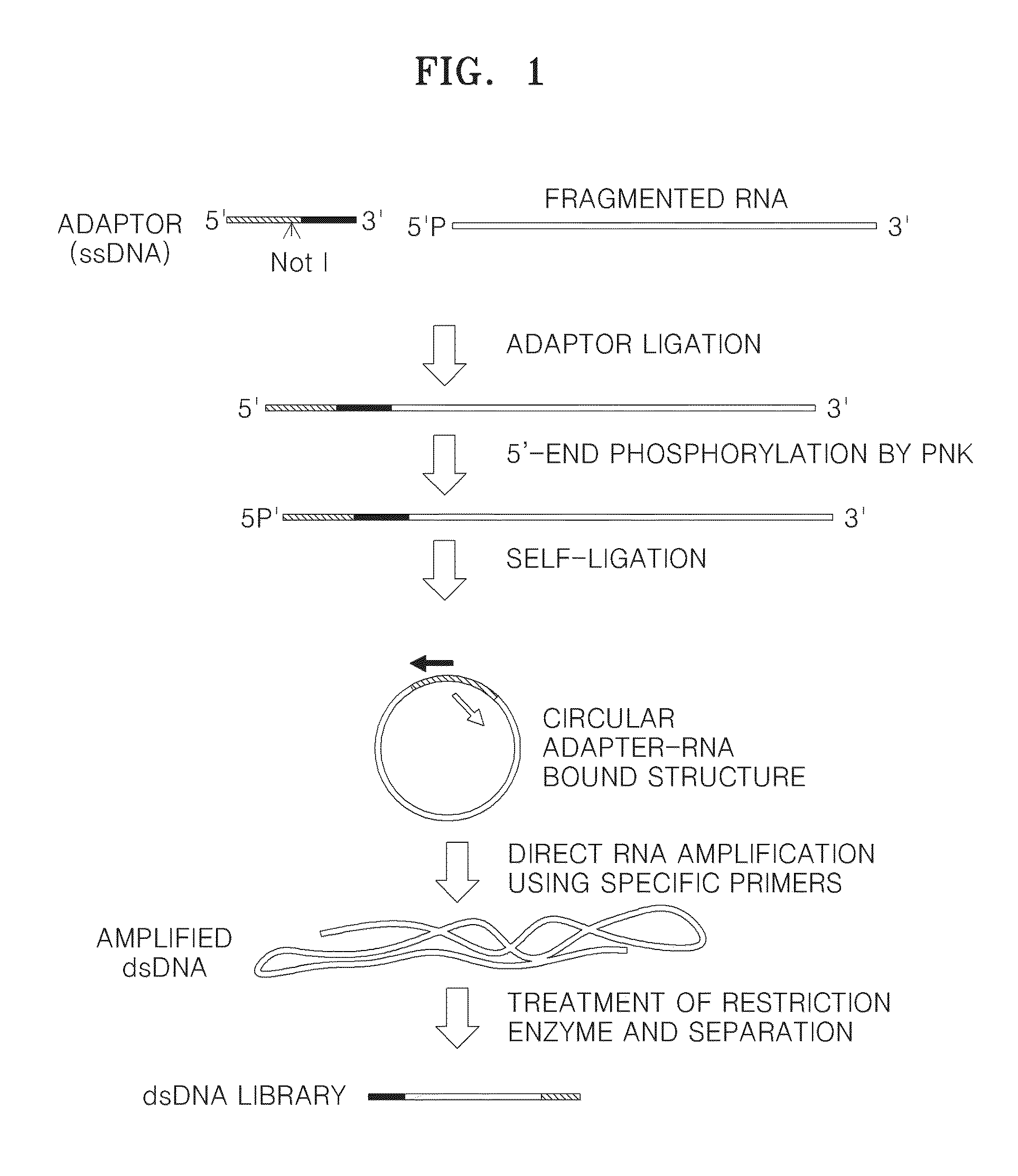
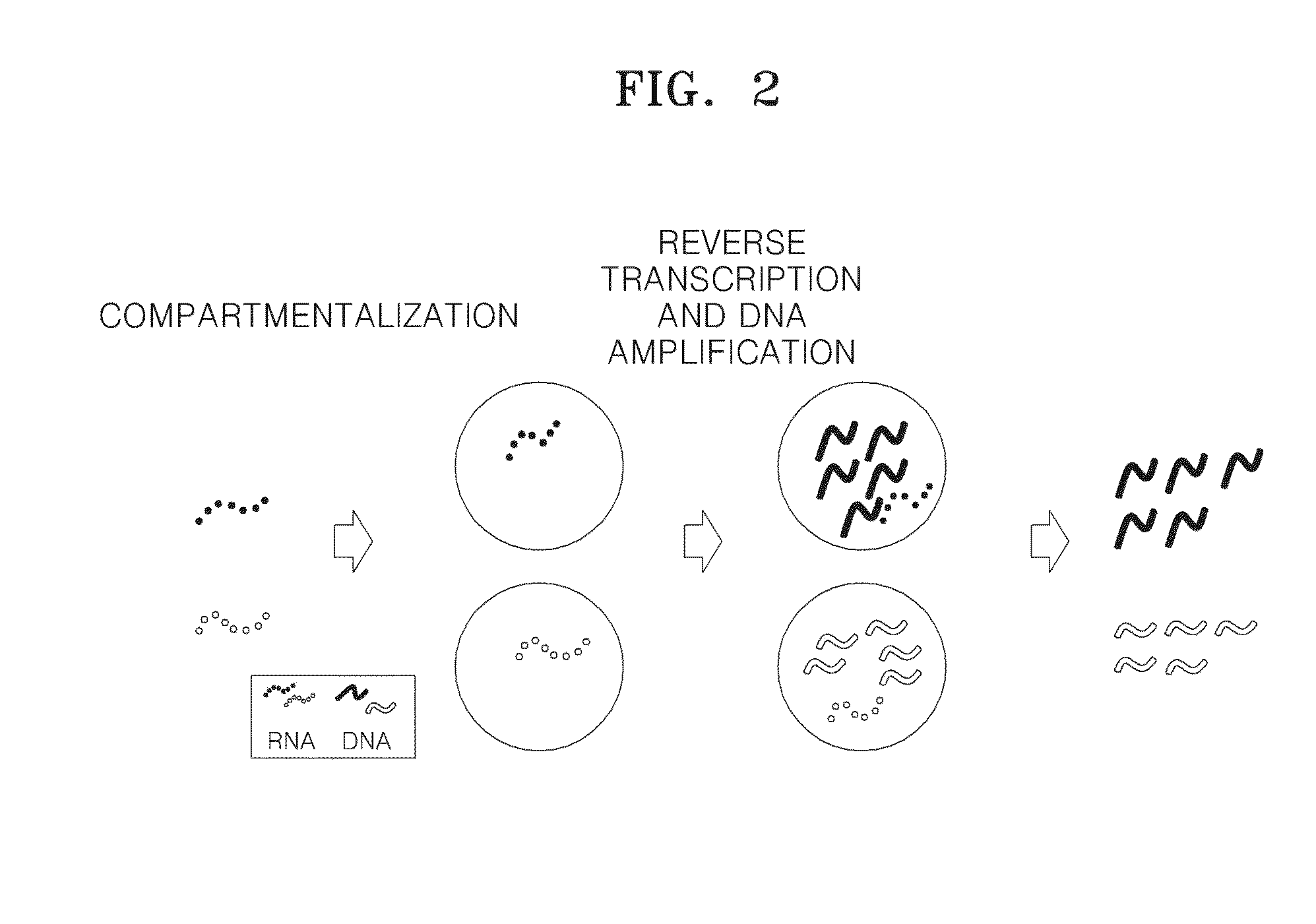
Method of amplifying DNA from RNA in a sample
A method of amplifying RNA in a sample and a method of amplifying a pool of RNA is provided. Gene loss and amplification bias may be reduced using the methods. Also, directionality may be preserved in the amplified RNA. The methods may be applied in sequence analysis as well as in general molecular diagnostic areas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Construction method of immune repertoire sequencing library and test kit
PendingCN111575343AEffectively eliminate amplification biasRule out amplification biasMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationAmplification biasImmune repertoire
The invention discloses a construction method of an immune repertoire sequencing library and a test kit, belongs to the field of biological medicines, and relates to a detection method of immune repertoire diversity. One of the purposes of the invention is to provide the construction method of the immune repertoire sequencing library; the construction method comprises the following steps of (a) extracting sample RNA, (b) carrying out reverse transcription by using a reverse transcription primer to synthesize cDNA, and adding a specific linker containing a molecular tag sequence at the tail end; (c) by taking the product obtained in the step b as a template, carrying out amplification through a specific linker primer and a gene specific primer containing a molecular tag sequence; and (d) finally, adding a sequencing library linker to an amplification product, so as to complete library construction. When sequencing data is analyzed, original RNA molecules are identified through moleculartag sequences, and amplification bias is excluded. By using the method, all CDR regions of TCR and BCR can be covered, PCR amplification bias interference is effectively eliminated, the specificity is higher, and the analysis result is more accurate. The other purpose of the invention is to provide the test kit for immune repertoire sequencing.
Owner:北京全谱医学检验实验室有限公司
Method for nucleic acid amplification
ActiveUS20170275685A1Easy to operateEliminate riskNucleotide librariesHydrolasesReverse transcriptaseWorking environment
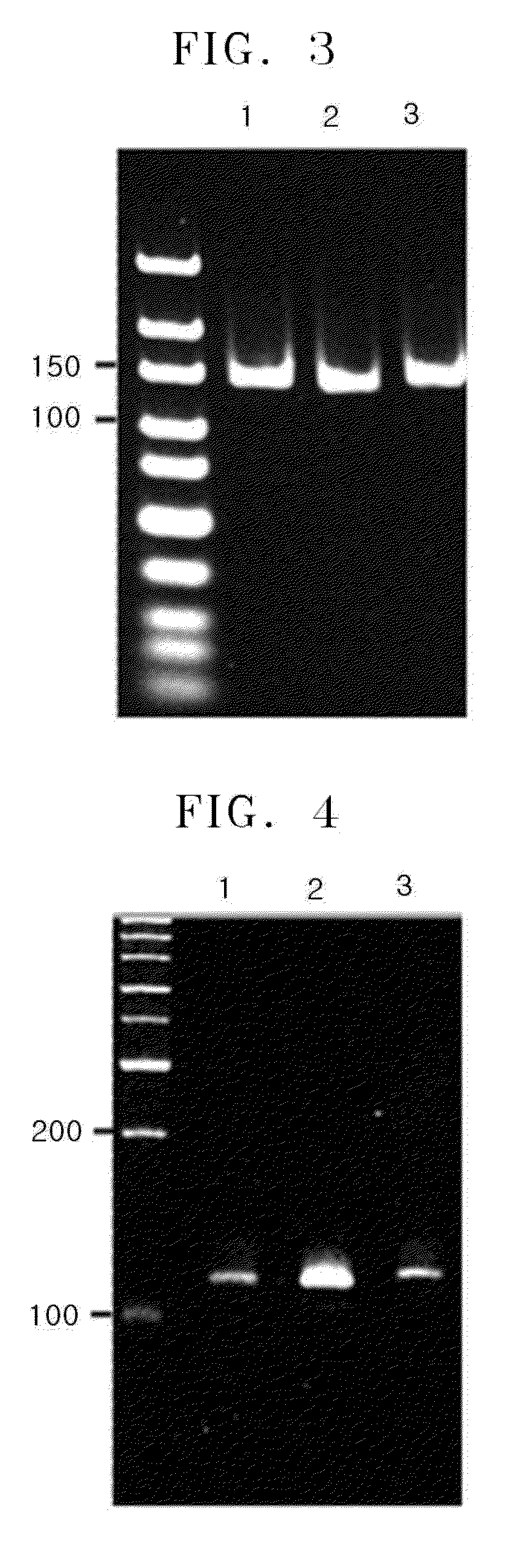
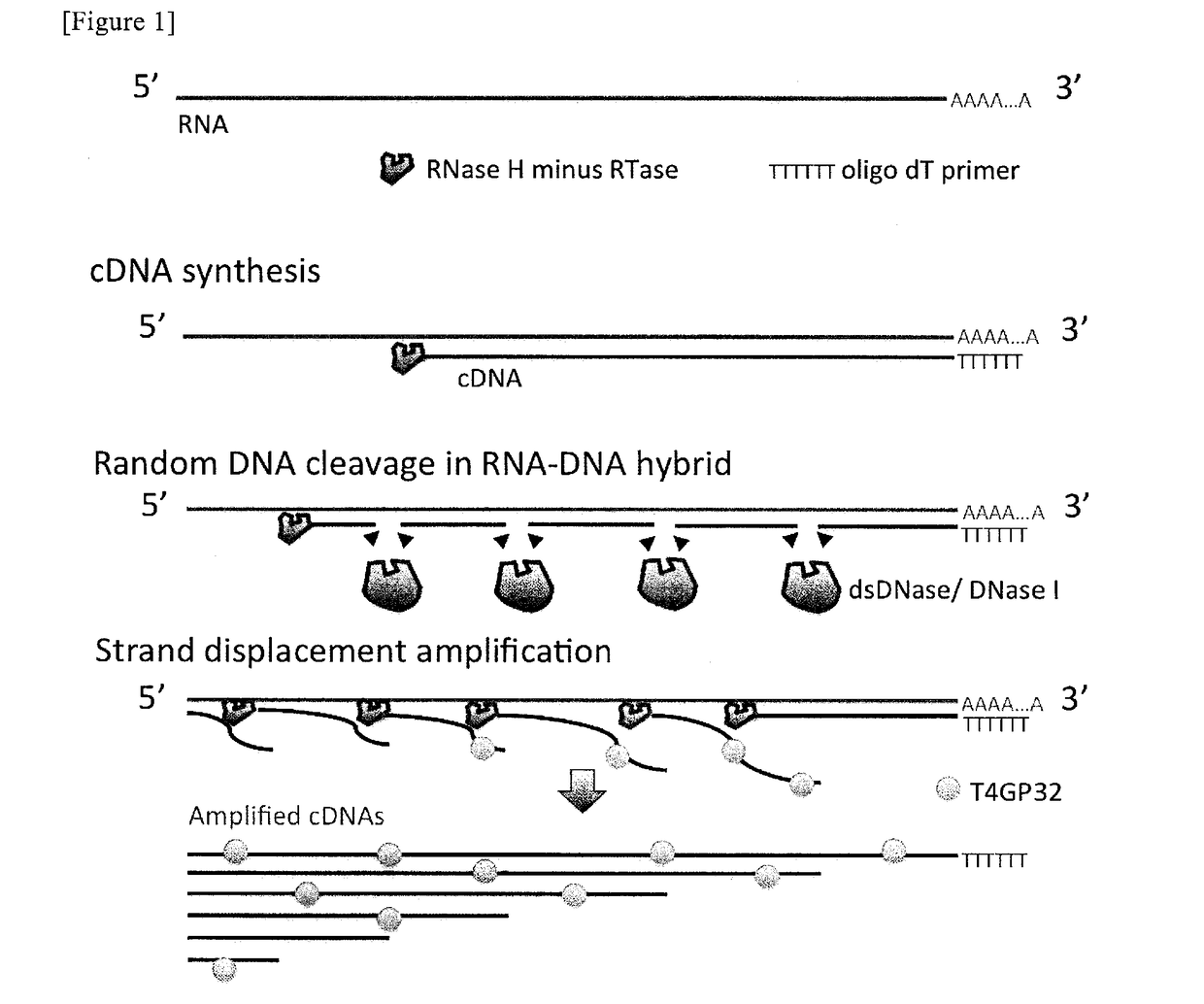
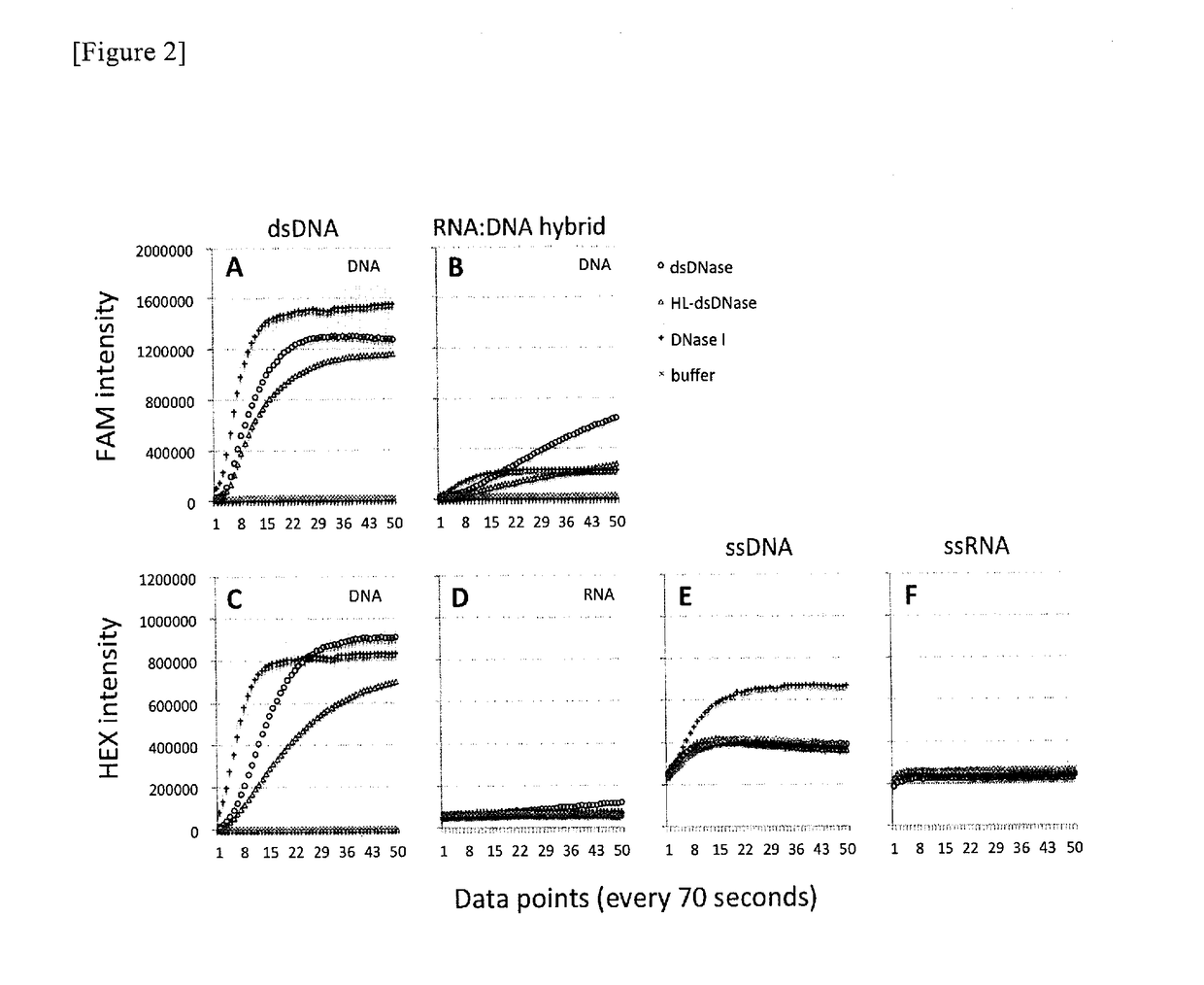
It is an object of the present invention to provide a method for amplifying a nucleic acid, using RNA as a template, which can realize elimination of the risk of non-specific amplification caused by DNA mixed from reagents and / or working environment, an increase in the detection sensitivity of trace RNA, and a reduction in amplification bias. According to the present invention, there is provided a method for amplifying a nucleic acid, which comprises a step of incubating a mixture comprising template RNA, a primer, a degrading enzyme specific to DNA in RNA-DNA hybrid, an RNase H minus reverse transcriptase, and a substrate.
Owner:RIKEN
Envelope tracking amplifier digital predistortion method based on improved model
ActiveCN106169985AImprove linearityImprove energy efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersConventional memoryAudio power amplifier
The invention provides an envelope tracking amplifier digital predistortion method based on an improved model. The method comprises the steps of: utilizing an improved memory polynomial model to dynamically adjust a predistortion parameter, and increasing a single baseband signal controlling the input data of a predistortion device to the baseband signal and an envelope signal for common control. According to the method, the method overcomes the defect that a conventional memory polynomial model predistortion method for a fixed bias voltage power amplifier is not suitable for an envelope tracking amplifier dynamically changing the power amplification bias voltage, a better linear effect can be achieved under the same complex condition, and the linearity of the envelope tracking amplifier is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Gene chip for integrated detection and on-substrate amplification method
InactiveCN103966320AImprove efficiencyLow costNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementSignal onPolymerase L
The invention discloses a gene chip for integrated detection and an on-substrate amplification method. The on-substrate amplification method comprises the following steps: (1) fixing specific nucleic acid primers on the substrate; (2) placing the substrate, on which the specific nucleic acid primers are fixed, in an amplification tube; (3) adding prepared a gene extract to be detected and an amplification system to the amplification tube; (4) placing the amplification tube in a gene amplification instrument for amplification; (5) after completion of the gene amplification, detecting fluorescent signals on the substrate so as to acquire genetic information. In the on-substrate amplification method, the general step of nucleic acid hybridization is removed, the benefits are greatly increased, and the cost is reduced; the specific nucleic acid primers are fixed on the substrate, and then the specific nucleic acid primers and the substrate are placed in the amplification tube for on-substrate PCRs (Polymerase Chain Reactions), so that the PCR reactions can be realized separately and the problem that primers interfere with one another during multiple PCRs can be solved; multiple pieces of genetic information can be detected integrally at the same time, and contamination, which can be generated in the amplification process and the product transfer process, is avoided; the used instrument is simple and universal, so that a common PCR instrument and a fluorescence microscope can complete the detection.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
In-vitro tissue cell nucleus separation method for reducing unicellular amplification bias
PendingCN112280828AImprove integrityDiscreteness of protectionMicrobiological testing/measurementGradient centrifugationTissue sample
The invention discloses a single cell sequencing cell nucleus separation method capable of reducing amplification bias and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out cracking treatment on a sample to be extracted in a buffer solution II; carrying out primary centrifugal treatment on the cracking product to obtain a cell nucleus precipitate; and washing the cell nucleus precipitate, re-suspending the cell nucleus precipitate in a buffer solution I, carrying out secondary centrifugal treatment, and finally re-suspending and uniformly mixing the cell nucleus precipitate in a buffer solution III to obtain the finally required cell nucleus. According to the method, only conventional and simple reagent consumables are needed, expensive separation equipment, long-time gradient centrifugation and other operations are not needed, and enough and complete single cell nucleuses can be obtained from few tissue samples or cells to be used for single-cell whole-genomeexperimental research. Compared with a method that usesnucleuses processed by a commercial kit, the amplification homogeneity of subsequent whole genome amplification product is better, the amplification effect is similar to that of a complete single cell, and meanwhile time and cost are saved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
A system and method for identifying balanced translocation carrier status of embryos
ActiveCN106929595BReduce Amplification BiasHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementCarrier statusCopy number analysis
The invention relates to a system and method for identifying the balanced translocation carrier state of an embryo. The system includes the following units: (1) a sampling unit; (2) a sequencing unit; (3) a copy number analysis unit; (4) an SNP analysis unit and (5) a comparison unit. The system and method provided by the invention adopt a single sperm amplification mode and a targeted PCR way to look for a break site, the operation is relatively simple, the PCR amplification bias can be effectively reduced, the sensitivity is high, embryo aneuploid screening and balanced translocation carrier state information can also be provided, and the system and method have relatively simple and practicable operation, are low in cost, and are easy for popularization and application.
Owner:YIKON GENOMICS SHANGHAI CO LTD +1
Multiple specific/nonspecific primers for PCR of a complex gene pool
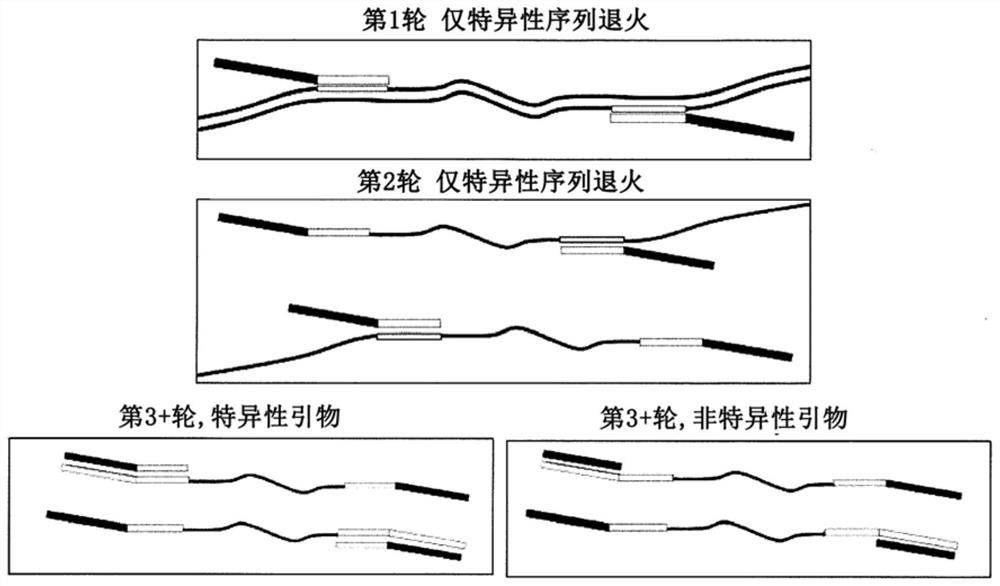
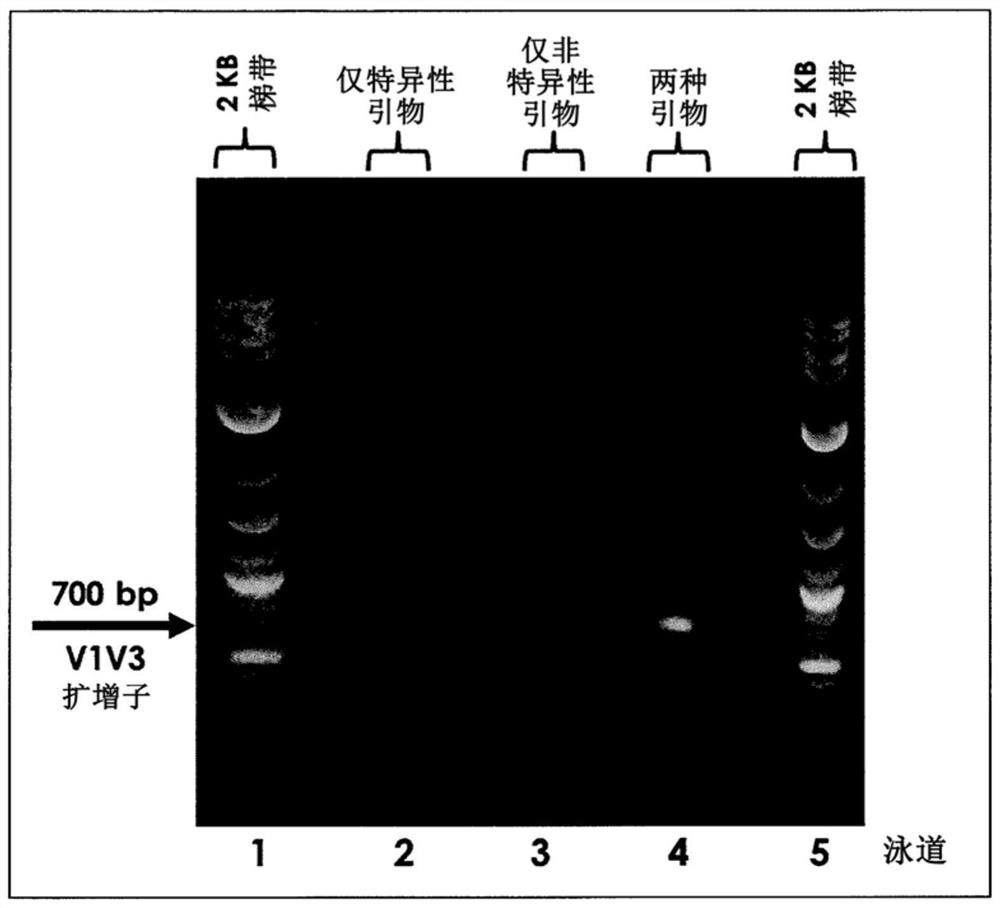
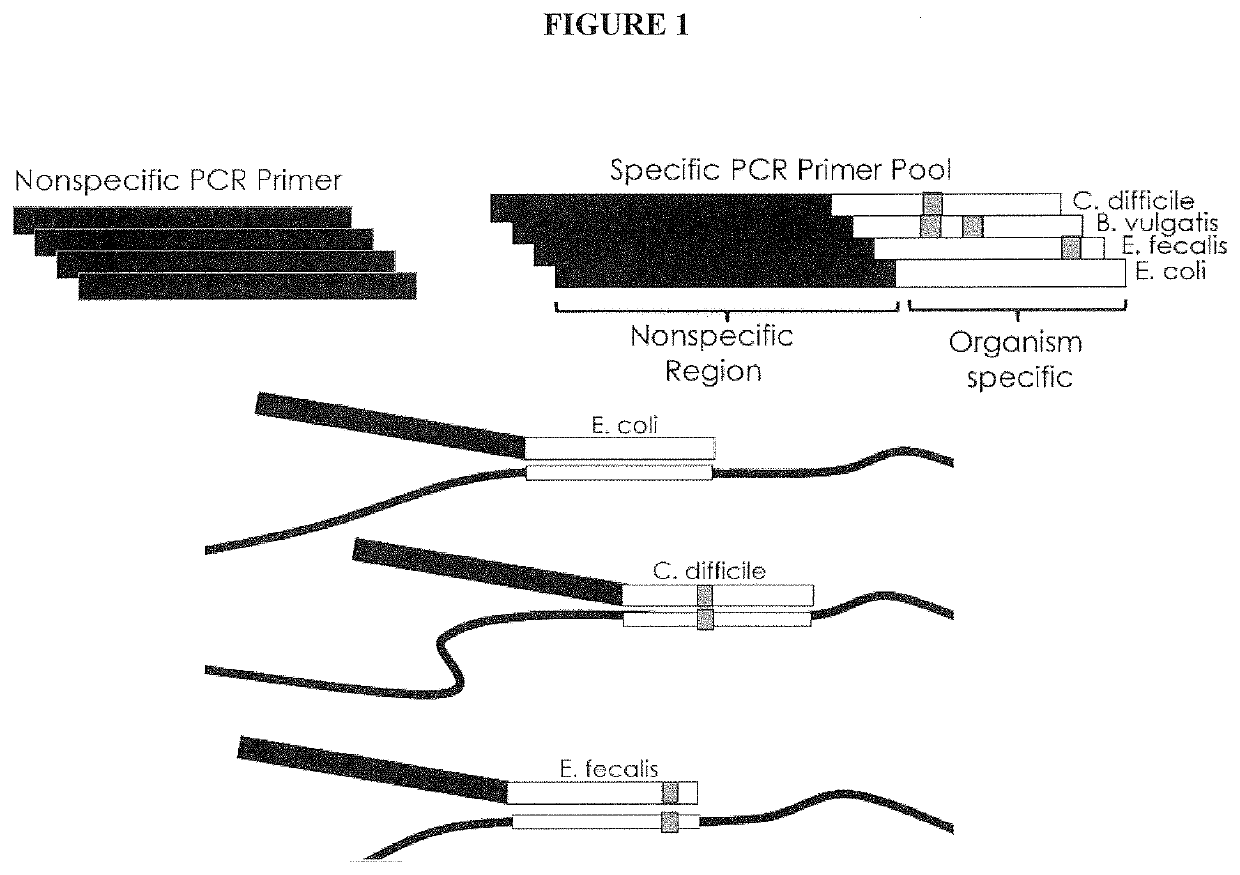
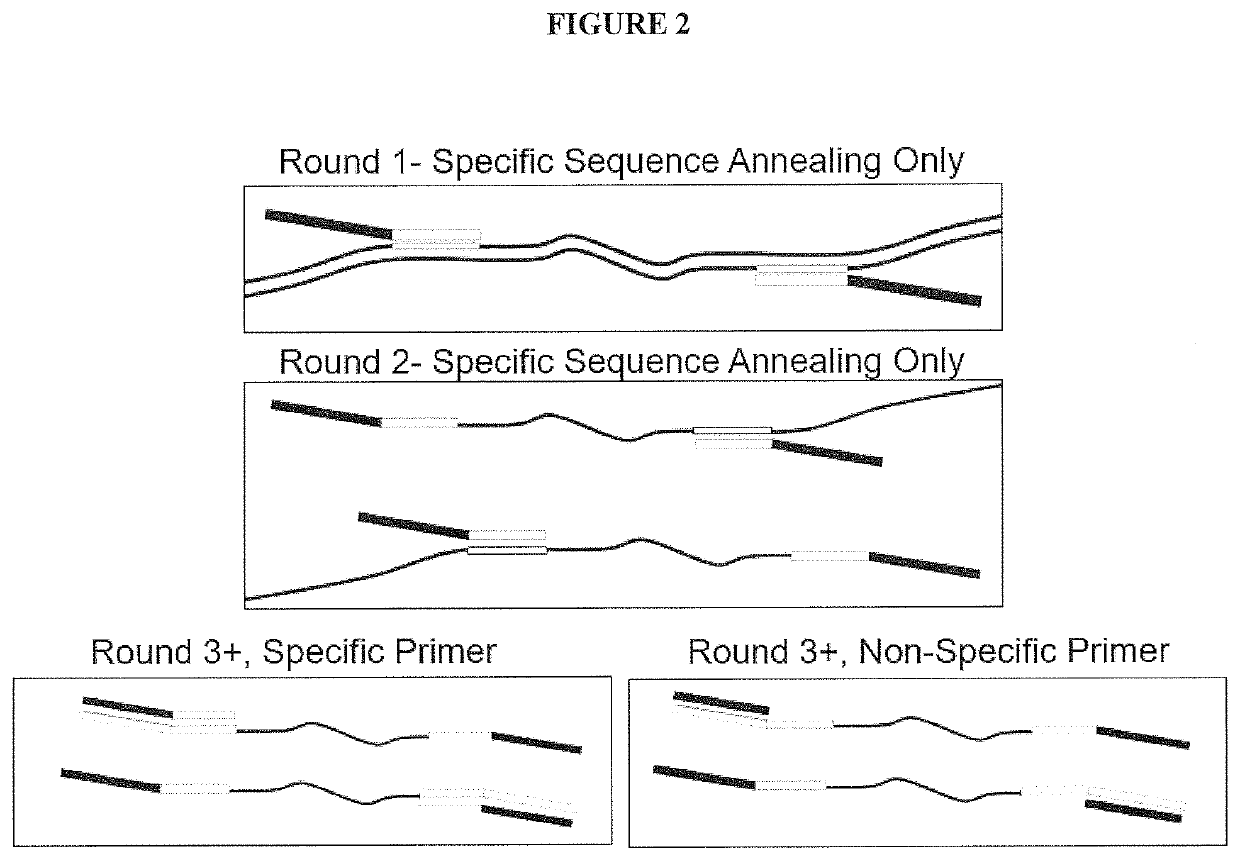
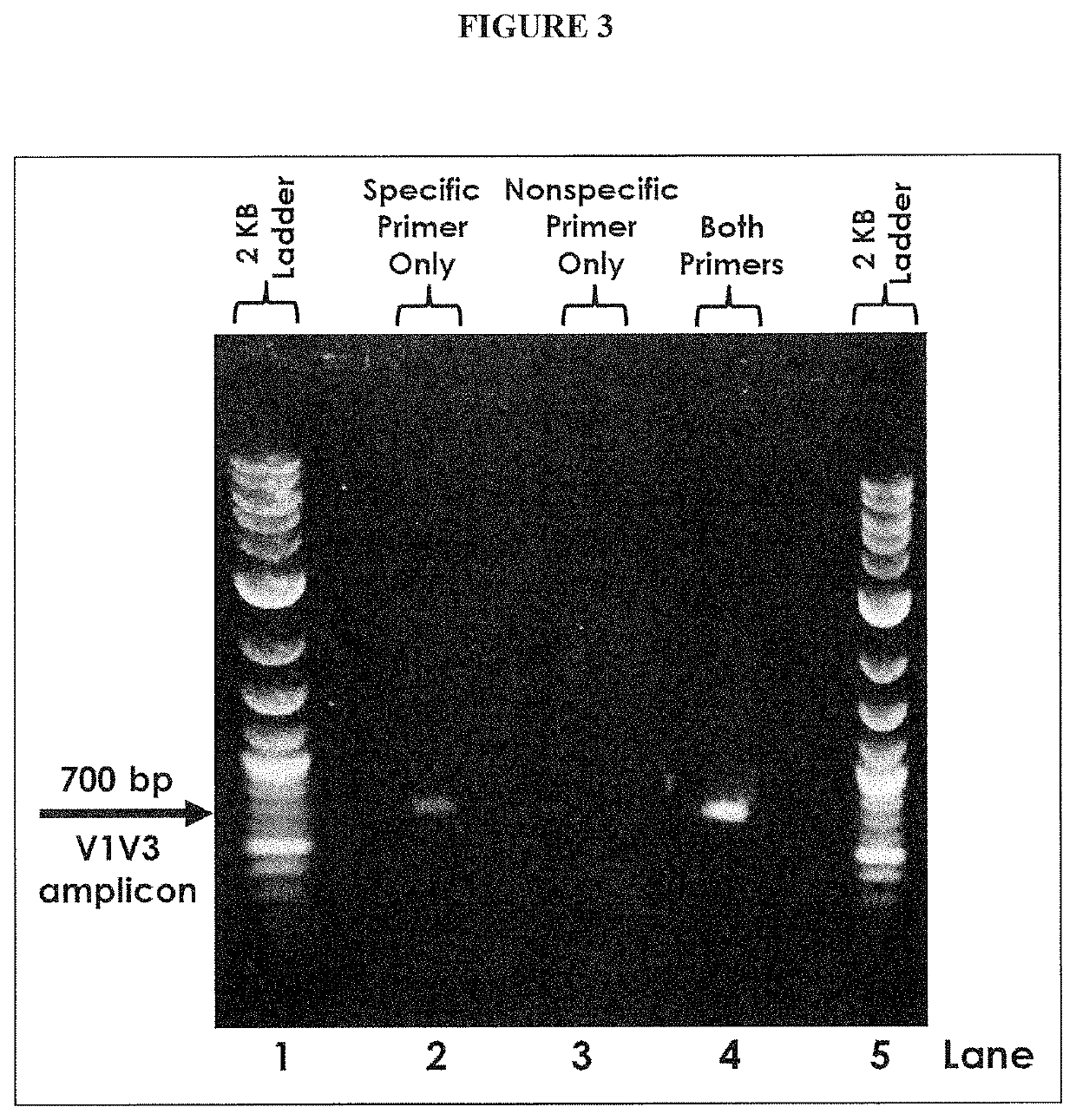
PendingCN112074613AEliminate amplification biasEliminate biasMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification biasVariome
Disclosed are compositions and methods for single-step PCR of a sample containing a complex target gene pool that can simultaneously amplify a wide variety of variant target gene sequences common to the sample while maintaining the original ratios of gene variants. The compositions and methods described herein utilize (1) a gene-specific primer pool that contains multiple variants that occur in asample containing a complex mixture of target sequences that are both required for amplification of variants in the mixture which may introduce amplification bias, with (2) a non-specific PCR primer that is designed to target multiple gene-specific primer variants and eliminate amplification bias.
Owner:SHORELINE BIOME LLC
Methods Using Randomer-Containing Synthetic Molecules
ActiveUS20200325526A1Good informationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification biasOligonucleotide
Methods are provided for correction of amplification bias and quantitation of adaptive immune cells in a sample using synthetic templates that include random oligonucleotide sequences.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
System and method for identifying balanced translocation carrier state of embryo
ActiveCN106929595AReduce Amplification BiasHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementCopy number analysisEmbryo
The invention relates to a system and method for identifying the balanced translocation carrier state of an embryo. The system includes the following units: (1) a sampling unit; (2) a sequencing unit; (3) a copy number analysis unit; (4) an SNP analysis unit and (5) a comparison unit. The system and method provided by the invention adopt a single sperm amplification mode and a targeted PCR way to look for a break site, the operation is relatively simple, the PCR amplification bias can be effectively reduced, the sensitivity is high, embryo aneuploid screening and balanced translocation carrier state information can also be provided, and the system and method have relatively simple and practicable operation, are low in cost, and are easy for popularization and application.
Owner:YIKON GENOMICS SHANGHAI CO LTD +1
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification kit for detecting metacercaria of Cs (clonorchis sinensis) on basis of ribosomal DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) ITS2 (internal transcribed spacer 2) and amplification primer
InactiveCN105154535AEasy to judgeHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerClonorchis sinensis
The invention discloses a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification kit for detecting metacercaria of Cs (clonorchis sinensis) on the basis of ribosomal DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) ITS2 (internal transcribed spacer 2) and an amplification primer. The PCR amplification kit comprises a PCR amplification reaction liquid, wherein the PCR amplification reaction liquid comprises 10 mmol / L of Tris-HCl , 50 mmol / L of KCl, 1.5 mmol / L of MgCl2, 0.8 mmol / L of dNTPs (deoxyribonucleoside-5'-triphosphate), 0.4 mu mol / L of a forward primer, 0.4 mu mol / L of a reverse primer, 20 ng / mu L of a DNA template and 0.075 U / mu L of a Taq enzyme. The PCR amplification kit is high in sensitivity and high in specificity, can detect metacercaria of Cs quickly and accurately and provides an effective technical means for diagnosis and prevention of Cs infection.
Owner:舟山出入境检验检疫局综合技术服务中心
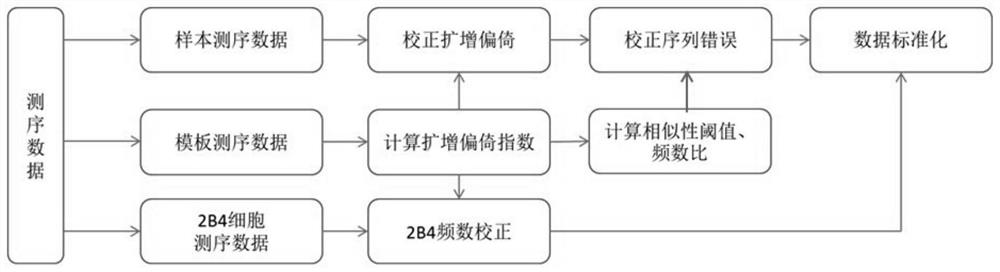
Method for correcting and standardizing TCR beta high-throughput sequencing data based on template sequence and reference cell
PendingCN114596915AAccurate and true distributionBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionSequence analysisMutation bias
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly discloses a TCR beta high-throughput sequencing data correction and standardization method based on a template sequence and a reference cell, which comprises the following steps: doping a fixed number of external reference cells and a fixed number of synthetic templates into a sample to construct a TCR beta high-throughput sequencing library, a high-throughput sequencing platform is used for sequencing; analyzing an amplification bias rule by using the added template sequence; a sequencing error caused by base mutation bias is corrected; standardizing the sample sequencing data by using the external reference cells; the T cell receptors in the sample are accurately quantified. According to the method, TCR beta high-throughput sequencing data can be corrected and standardized through amplification bias correction, sequencing error correction and sample standardization in a high-throughput sequencing mode by adopting a standardized process, and finally, accurate and real TCR beta library distribution is obtained.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
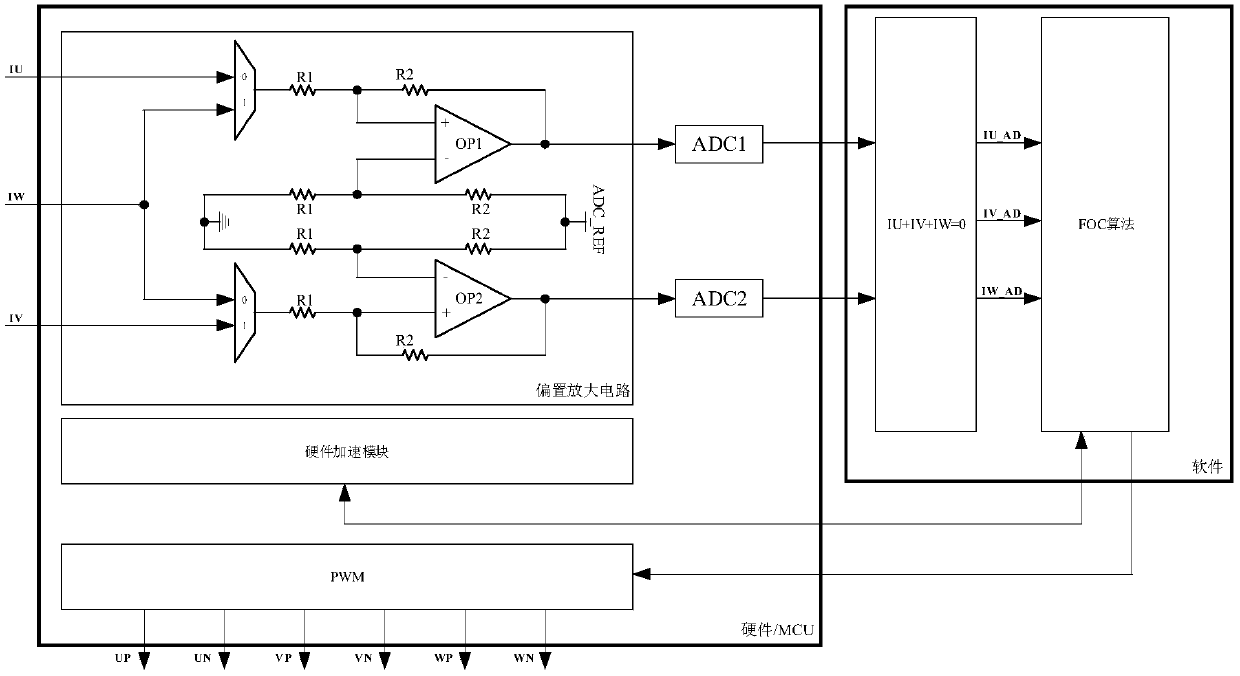
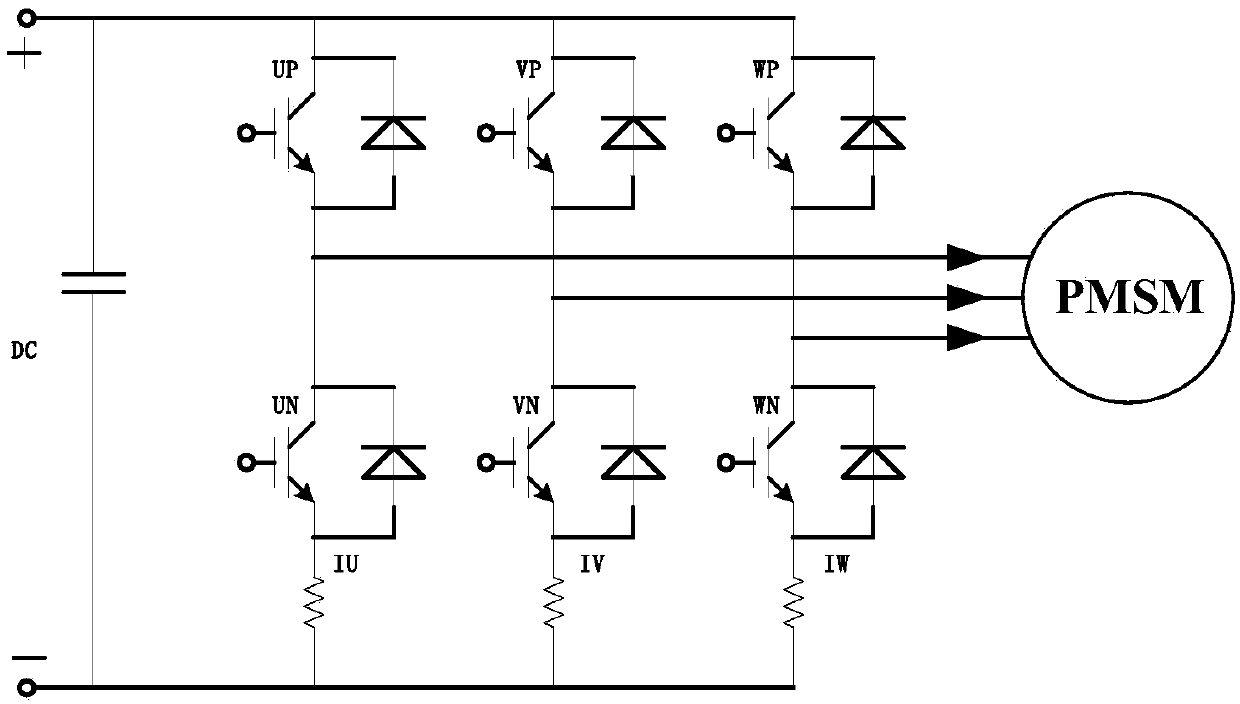
MCU chip provided built-in operational amplifier and application of MCU chip on variable frequency refrigerator
ActiveCN107678334AReduce Design ComplexityReduce design costProgramme controlComputer controlComputer moduleEngineering
The invention discloses an MCU chip provided with a built-in operational amplifier. An amplification biasing circuit module composed of the operational amplifier, a resistor and an either-or selectoris integrated in the MCU chip and voltage of two ends of a small resistor connected to a lower bridge arm of a three-phase inverter in series is sent to the MCU chip for processing and subsequent coordinate conversion calculation. At the same time, a hardware acceleration module is integrated in the MCU chip. The invention also provides the application of the MCU chip provided with the built-in operational amplifier on the variable frequency refrigerator. According to the invention, by adopting the MCU chip provided with the built-in operational amplifier for constructing the biasing amplification circuit, the design flexibility of a printed circuit and the BOM cost are reduced distinctively. By adopting hardware acceleration module for hardware driving of a CORDIC algorithm and FOC coordinate conversion calculation in the MCU chip, algorithm executing time is reduced distinctively and calculation precision is improved, so that the operation performance of a compressor is improved.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method of amplifying DNA from RNA in a sample
ActiveUS20140057322A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationSequence analysisAmplification bias
A method of amplifying RNA in a sample and a method of amplifying a pool of RNA is provided. Gene loss and amplification bias may be reduced using the methods. Also, directionality may be preserved in the amplified RNA. The methods may be applied in sequence analysis as well as in general molecular diagnostic areas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Primer group and kit for single-tube detection of human spinal muscular atrophy
PendingCN110885878AMultiple analysis informationReduce Amplification BiasMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPhysiologyNucleotide
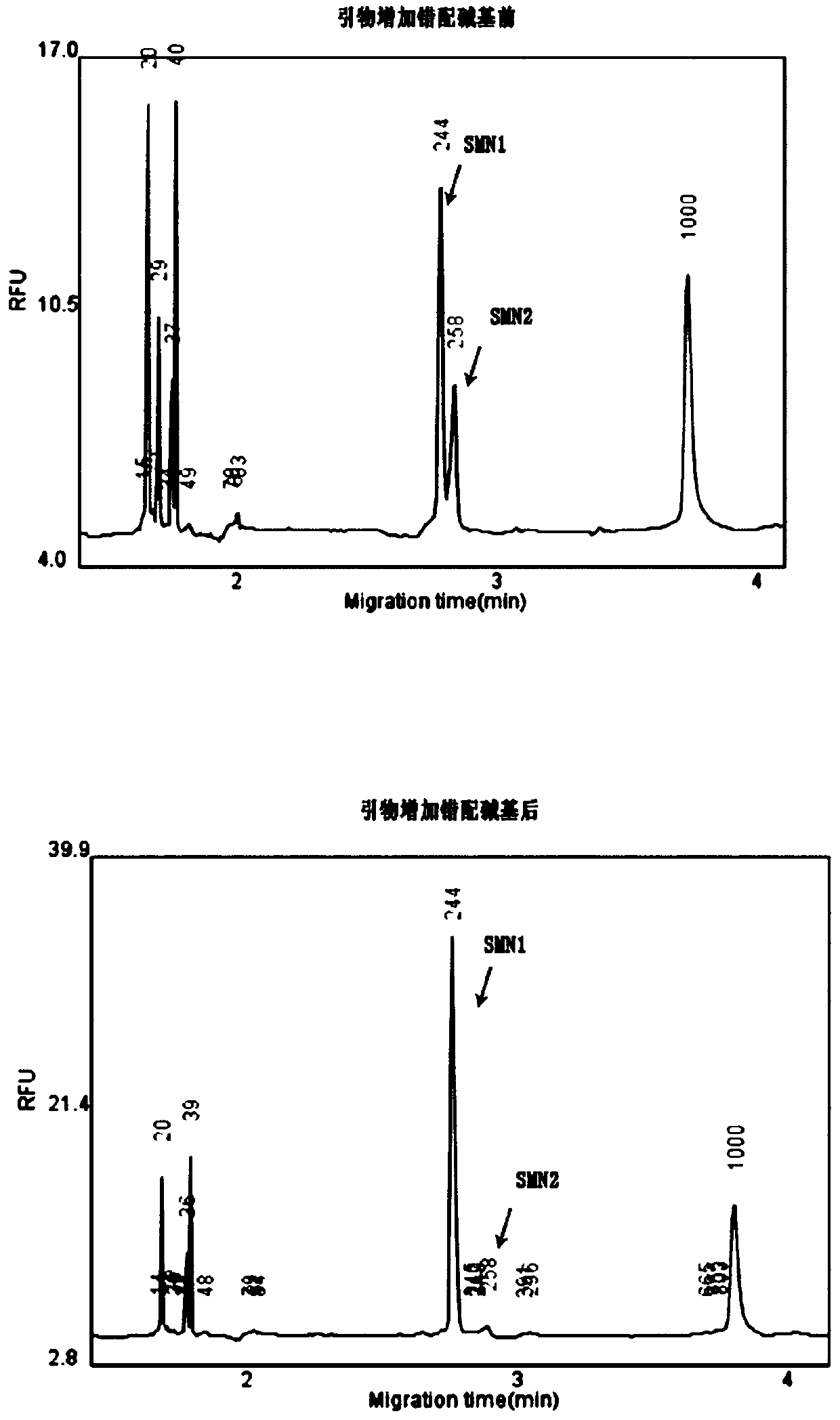
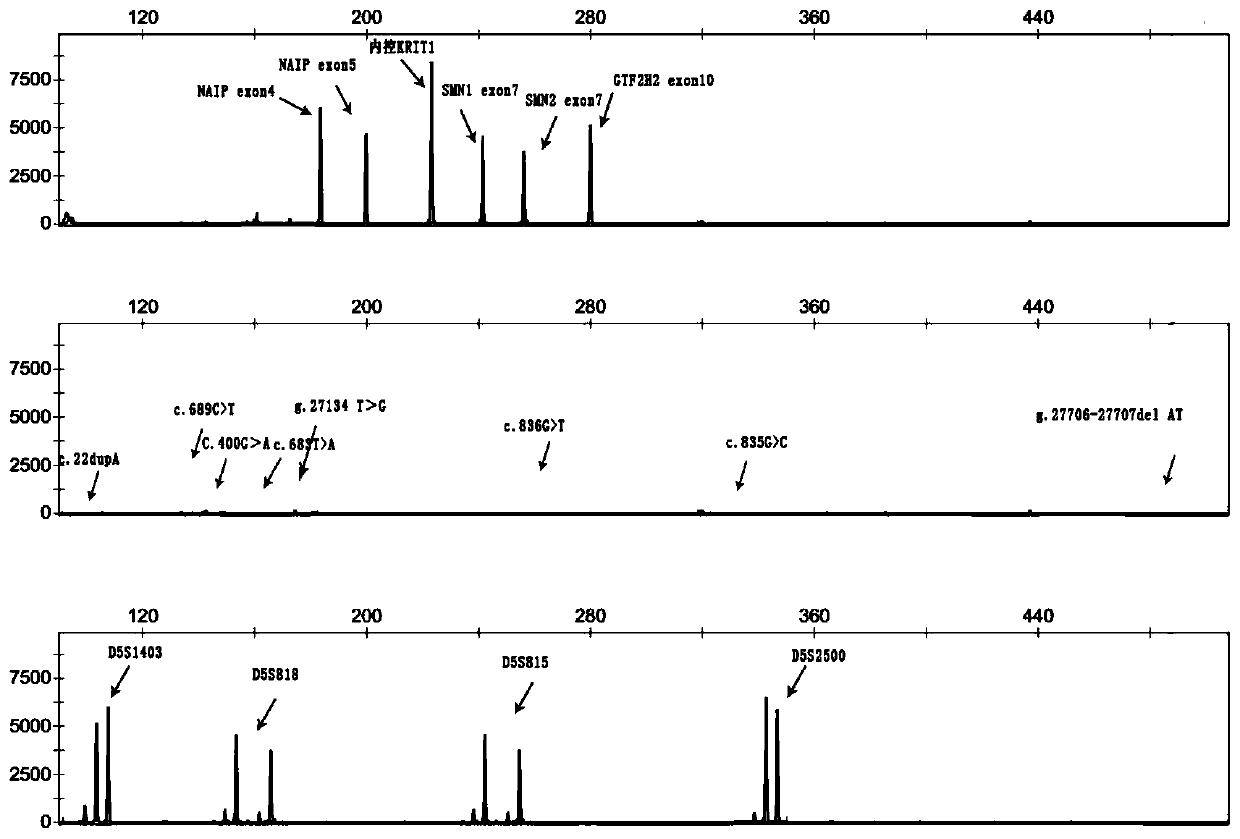
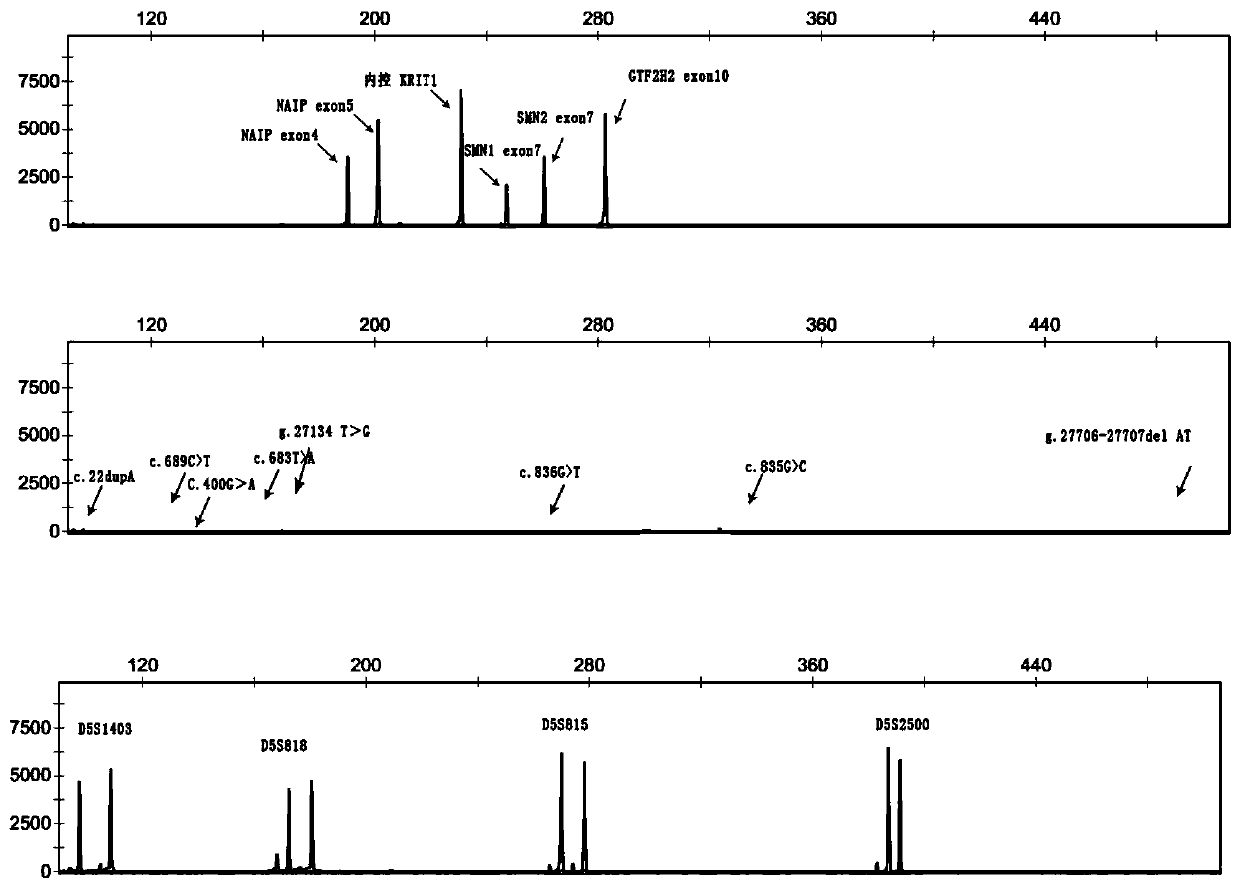
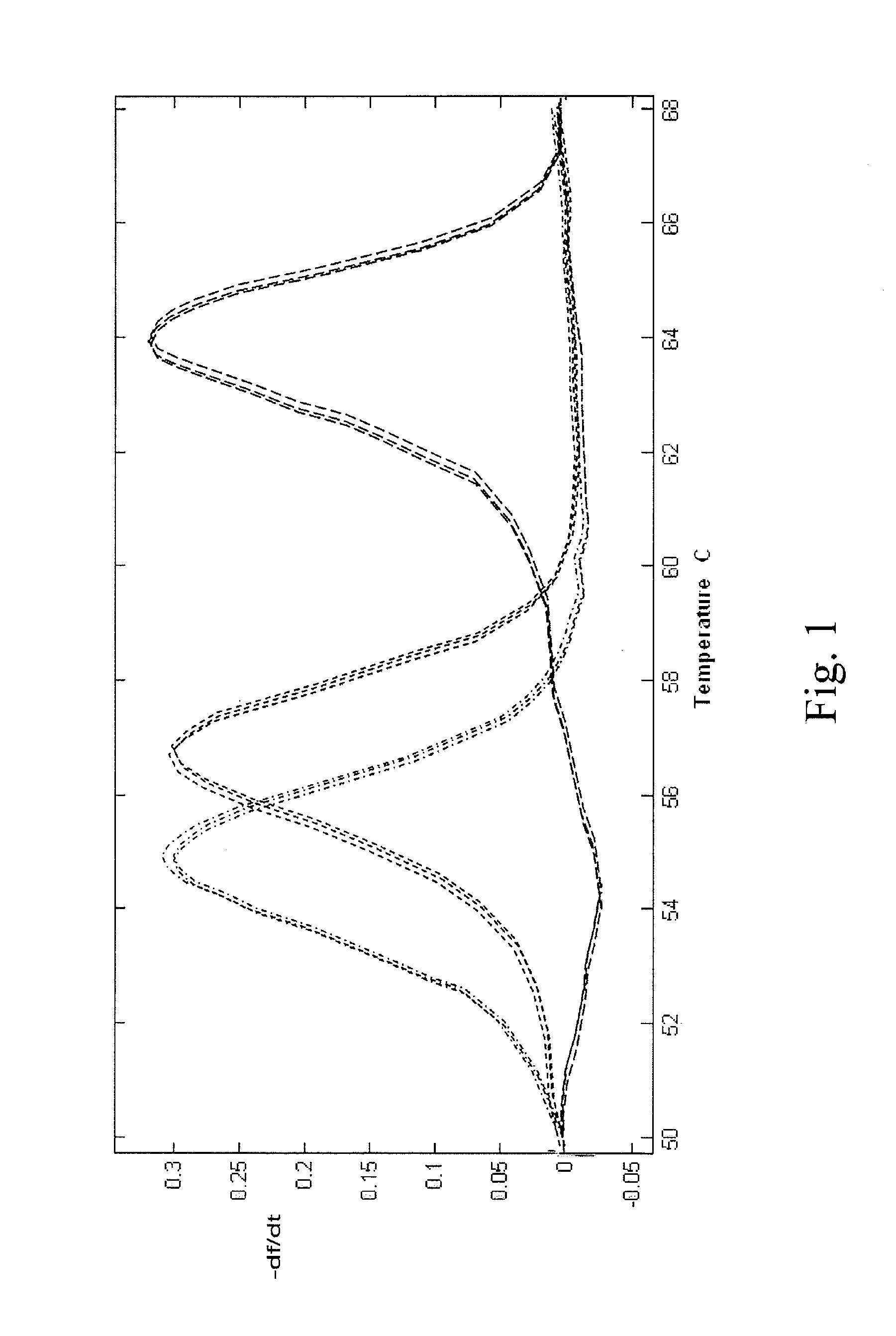
The invention discloses a primer group and a kit for detecting copy number and point mutation of a single-tube human spinal muscular atrophy related gene and typing a carrier. The nucleotide sequencesof the primer group are shown as SEQ ID NO. 1 to 38. The primer group is reasonable in design and high in specificity. The amplification bias is reduced, and the quantification accuracy is ensured. An identification sequence is introduced to realize identification of the conversion condition of the seventh exon of the SMN1 and the SMN2. UDG enzyme is introduced, and amplification products are cut, so as to avoid pollution. Clinical applications such as SMN1 / 2 gene copy number detection of human amyotrophy, SNP site detection of SMN1 / 2 Chinese population, NAIP and GTF2H2 gene copy number detection, typing of patients (I- VI types) and carriers ('1 + 0' and '2 + 0') and the like are simultaneously realized by the single tube. The method and the kit are rapid in detection, accurate in result, appropriate in cost, high in clinical occupancy of applicable instruments and suitable for clinical application.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
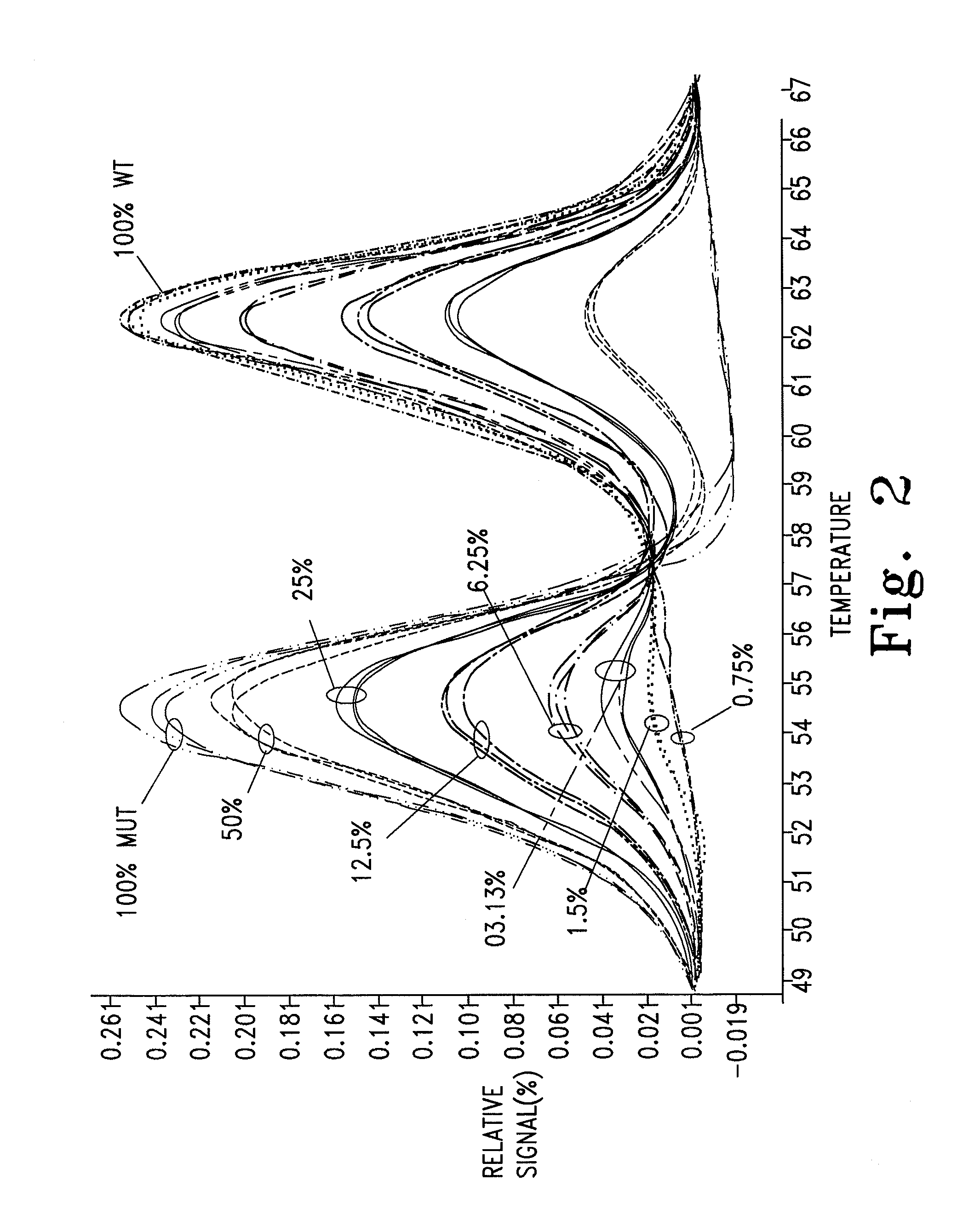
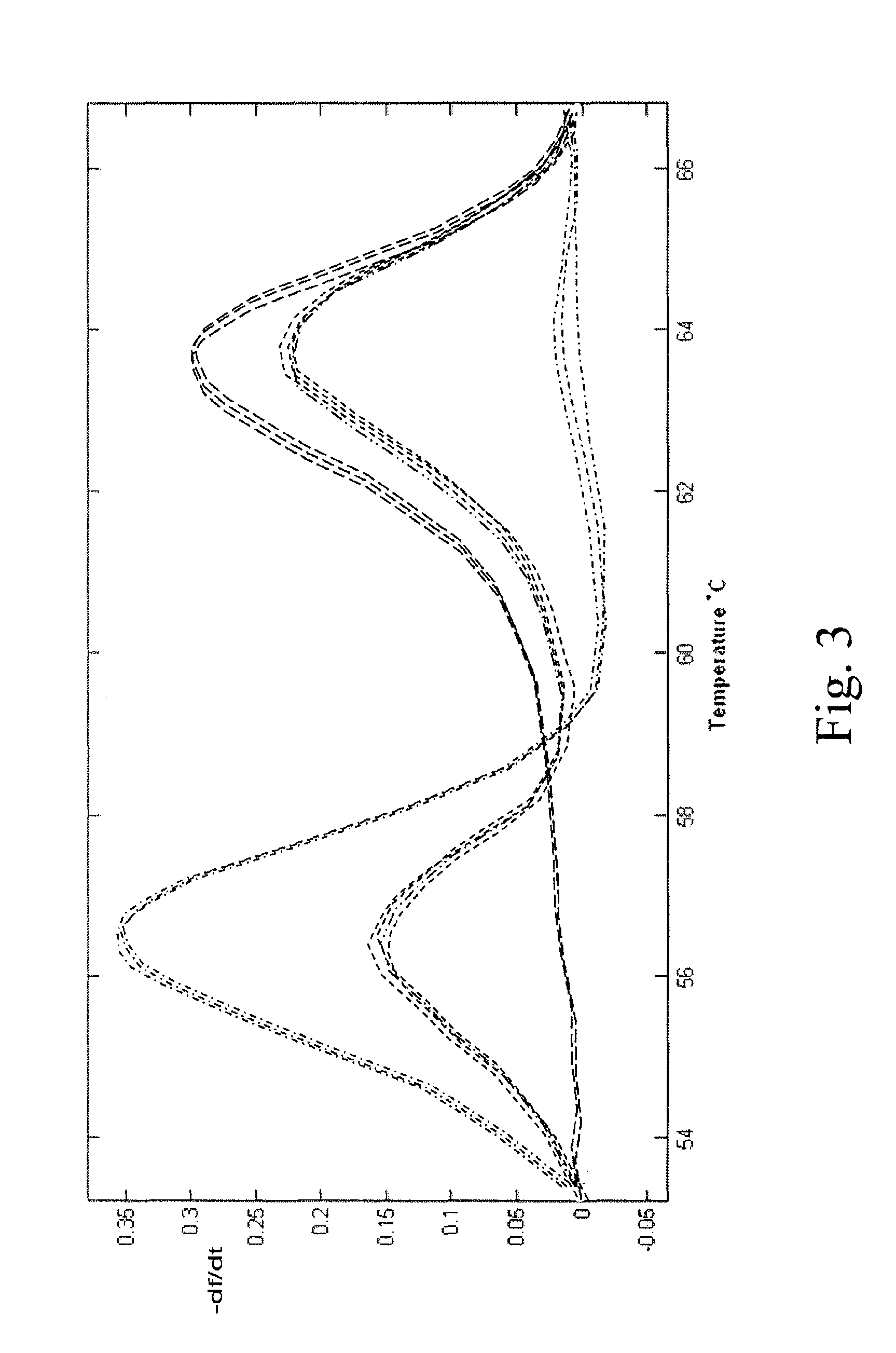
Allele amplification bias
Methods are provided for nucleic acid analysis. In an illustrative method, allele amplification bias is used to amplify preferentially a target nucleic acid that is present in a low allele fraction.
Owner:BIOFIRE DEFENSE +1
Multiple Specific/Nonspecific Primers for PCR of a Complex Gene Pool
PendingUS20190352712A1Accurate representationEliminate amplification biasMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification biasGene pool
Disclosed are compositions and methods for single-step PCR of a sample containing a complex target gene pool that can simultaneously amplify a wide variety of variant target gene sequences common to the sample while maintaining the original ratios of gene variants. The compositions and methods described herein utilize (1) a gene-specific primer pool that contains multiple variants that occur in a sample containing a complex mixture of target sequences that are both required for amplification of variants in the mixture which may introduce amplification bias, with (2) a non-specific PCR primer that is designed to target multiple gene-specific primer variants and eliminate amplification bias.
Owner:SHORELINE BIOME LLC
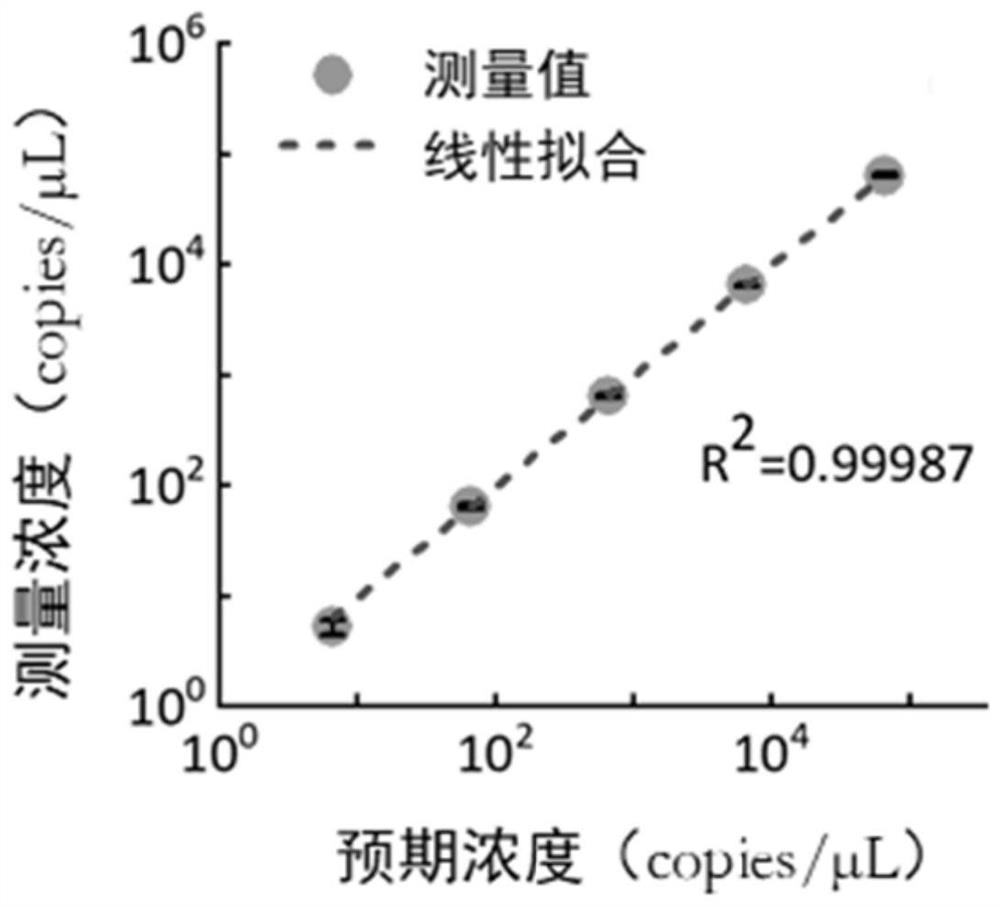
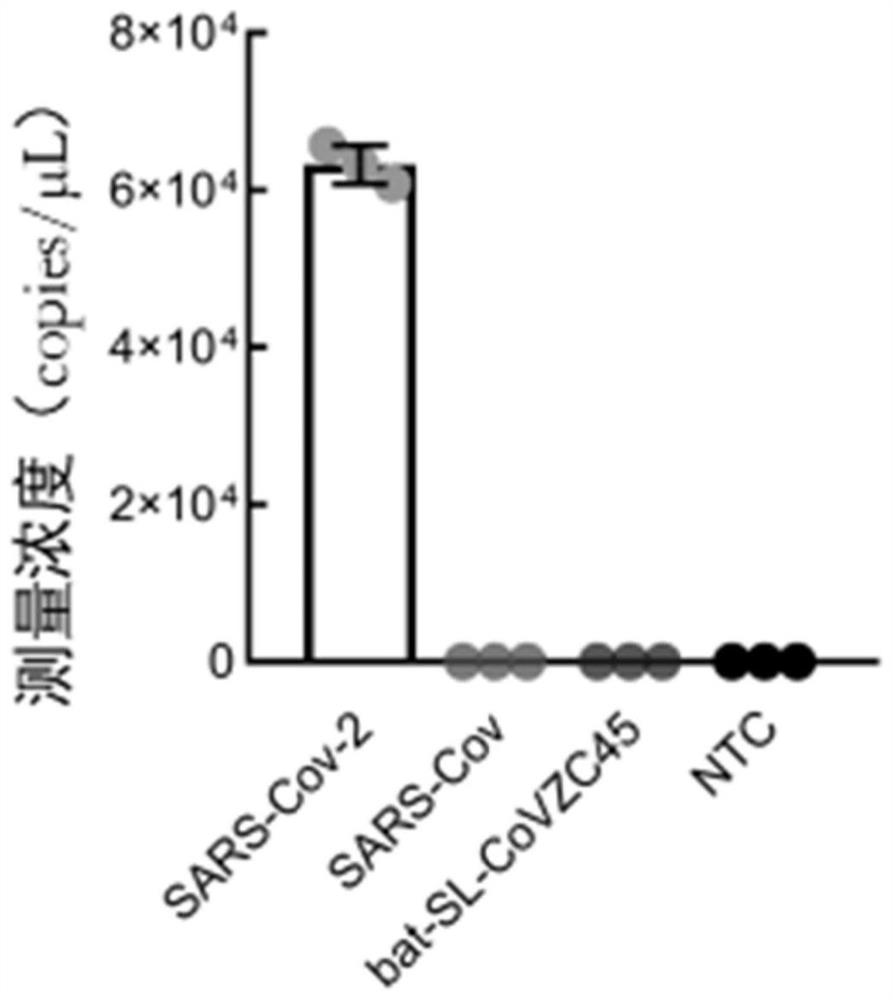
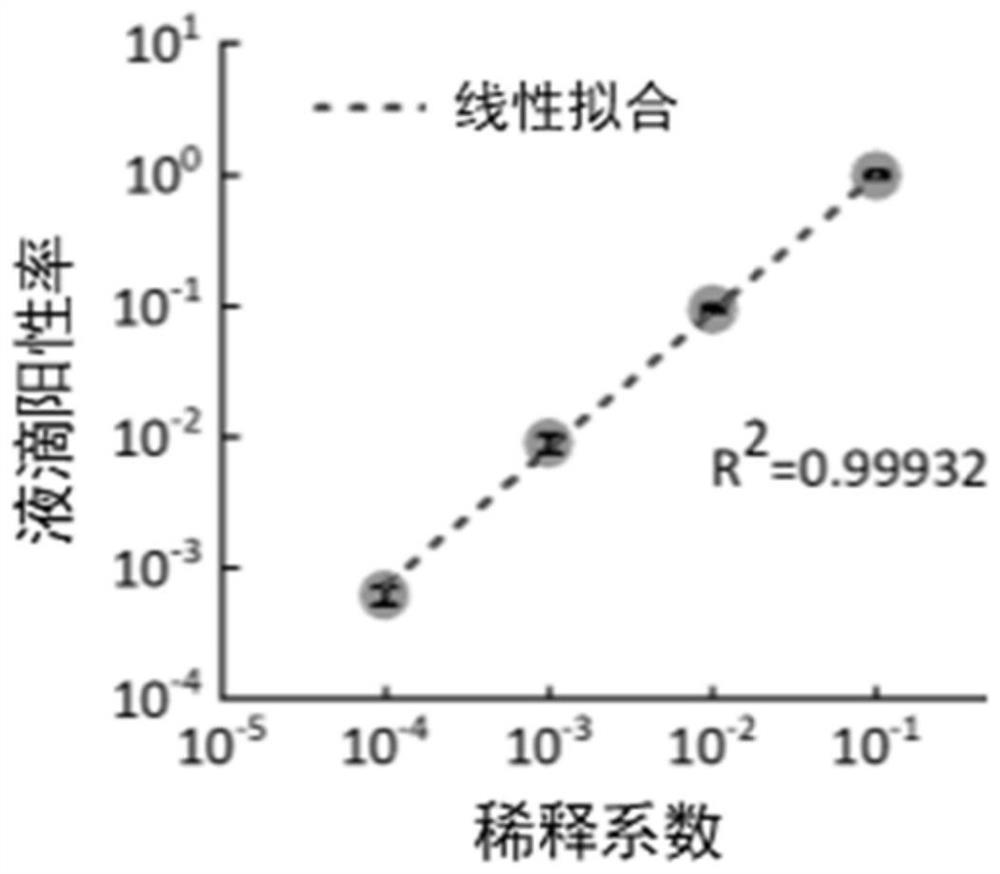
Novel coronavirus nucleic acid quantitative detection kit based on micro-droplet digital analysis
ActiveCN112813195AAvoid lostAvoid contamination riskMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesDigital analysisThermal cycler
The invention discloses a novel coronavirus nucleic acid quantitative detection kit based on micro-droplet digital analysis. The novel coronavirus nucleic acid quantitative detection kit is characterized by comprising O-crRNA targeting the ORF1ab gene 6513-6537nt of targeted SARS-CoV-2 RNA, N-crRNA targeting the N gene 29214-29238nt of targeted SARS-CoV-2 RNA, Cas13a protein, a single-chain RNA report probe and a reaction buffer solution. The detection method does not need the steps of reverse transcription or nucleic acid sequence amplification, so that the pollution risk possibly caused by sample loss, amplification deviation and nucleic acid replication products can be avoided; the operation steps are simple, expensive thermal cyclers are not needed, and the detection time is not more than 1 hour; SARS-CoV-2 RNA single copy level detection and absolute quantification can be realized, and internal reference correction and a standard curve establishment are not needed.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL (GUANGZHOU DIGESTIVE DISEASE CENT GUANGZHOU FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH) +1
Compositions, methods, and kits for analyzing DNA methylation
InactiveUS20060188910A1Reducing strand amplification biasMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCytosineNucleotide
Compositions, methods, and kits for reducing strand amplification bias using bisulfite treated gDNA are provided. Methods for detecting and for quantitating the amplified bisulfite treated gDNA and inferring the presence, absence, and / or degree of methylation of target cytosine(s) in the gDNA are also provided. Such methods typically employ tailed first primer pairs, which can, but need not comprise nucleotide analogs, and optionally second primer pairs.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com