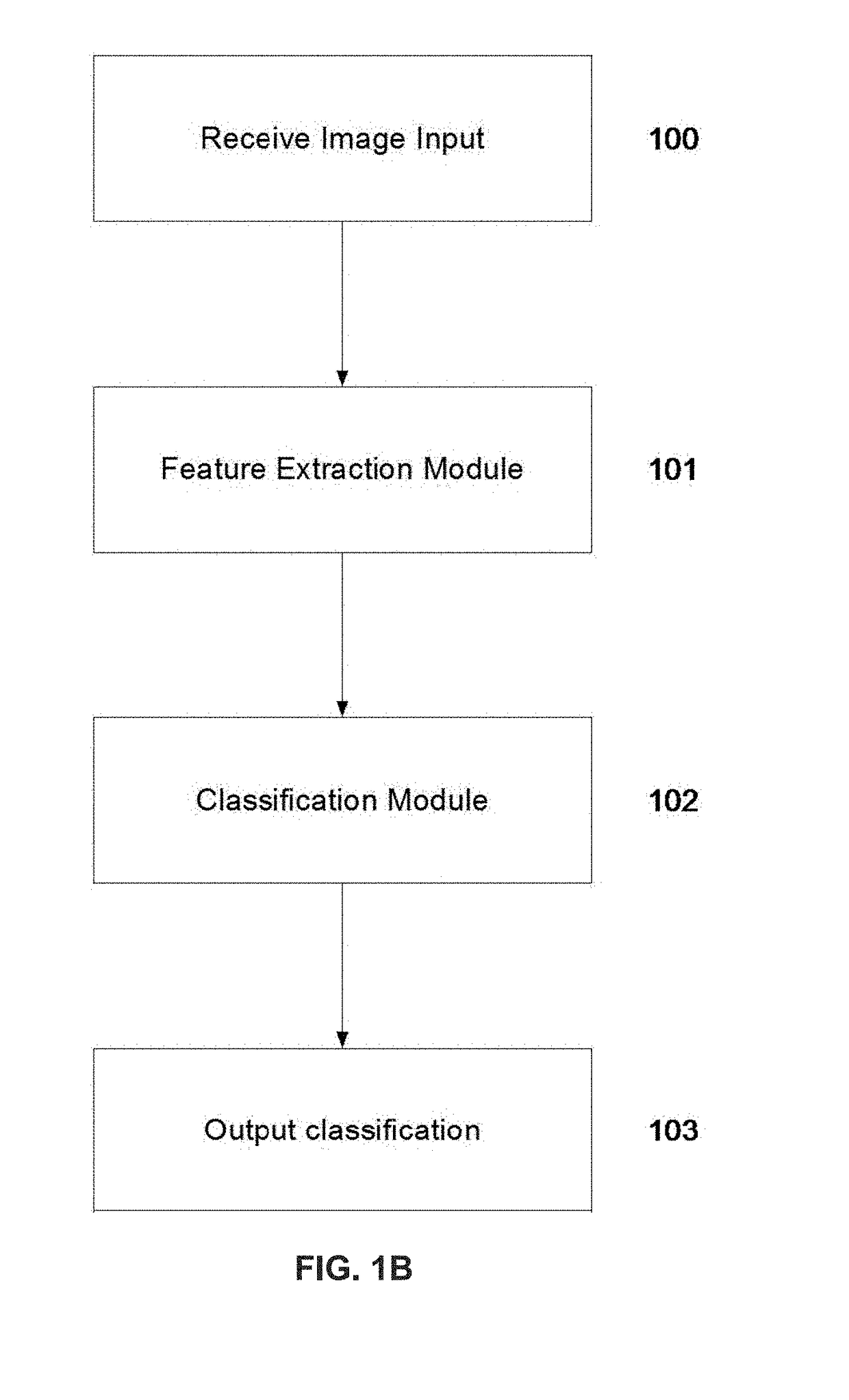
Patents
Literature
2255 results about "Cell nucleus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel or seed) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many.
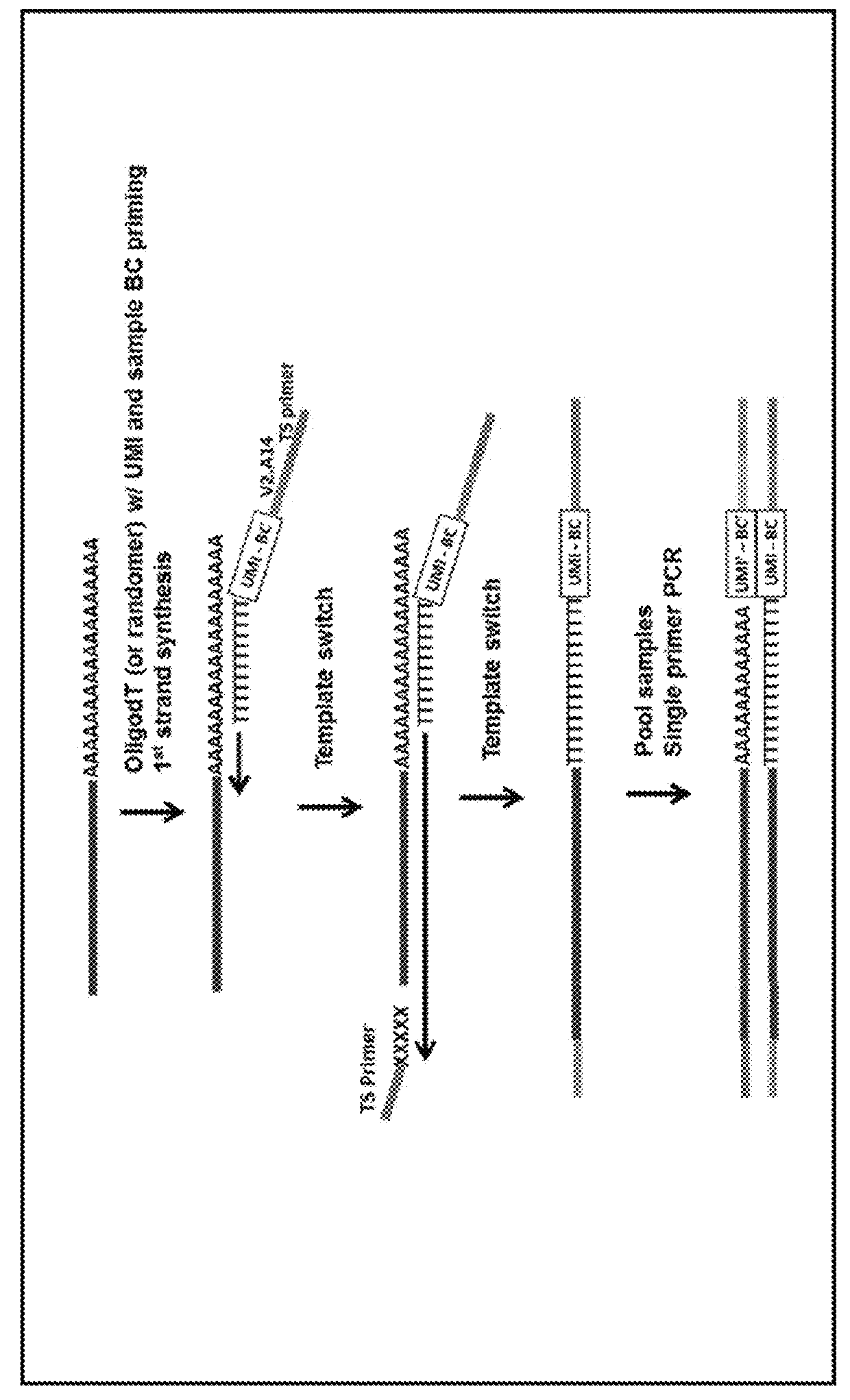
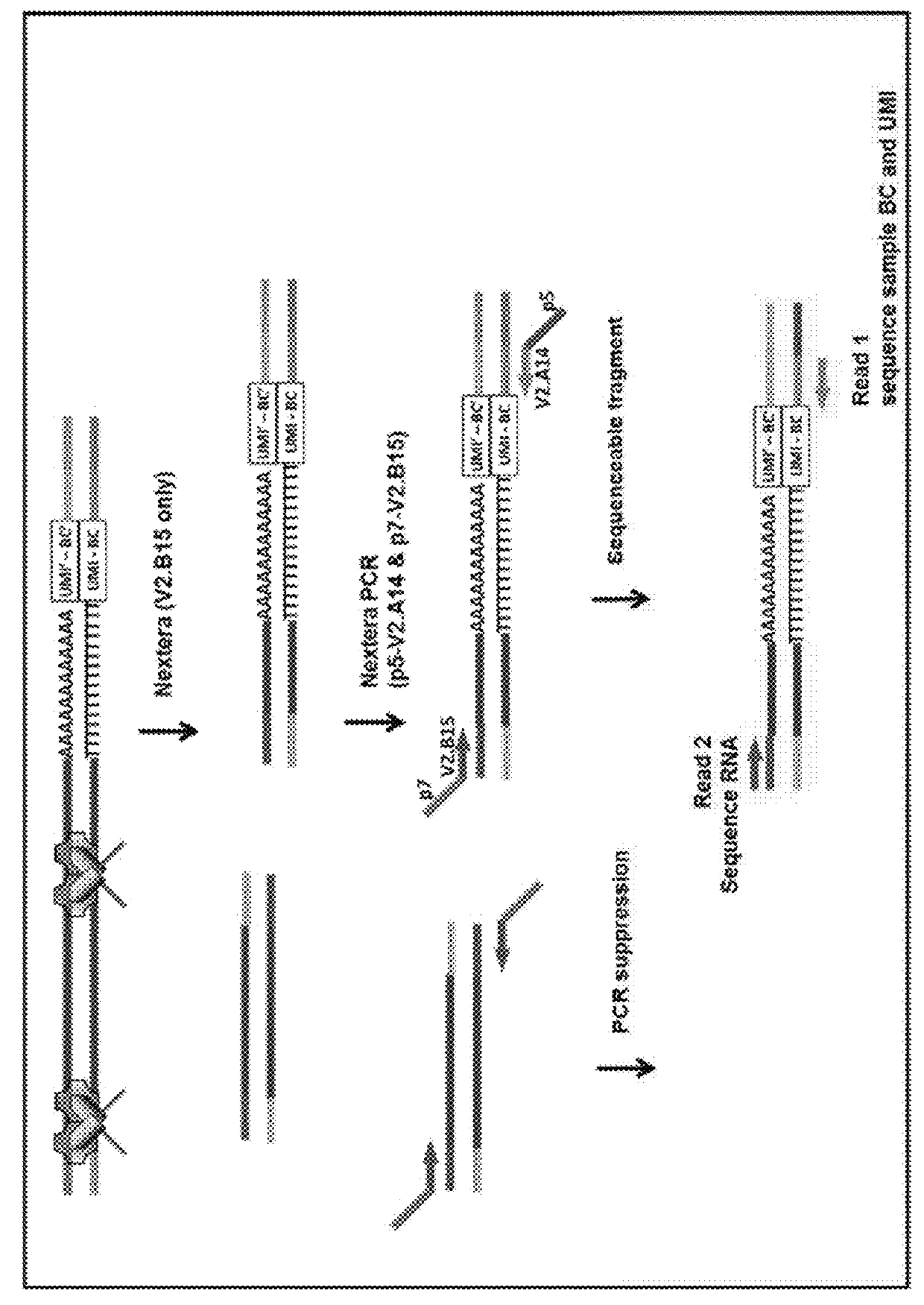
Safe sequencing system
ActiveUS20140227705A1Sensitively accurately determiningMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideInstrumentation
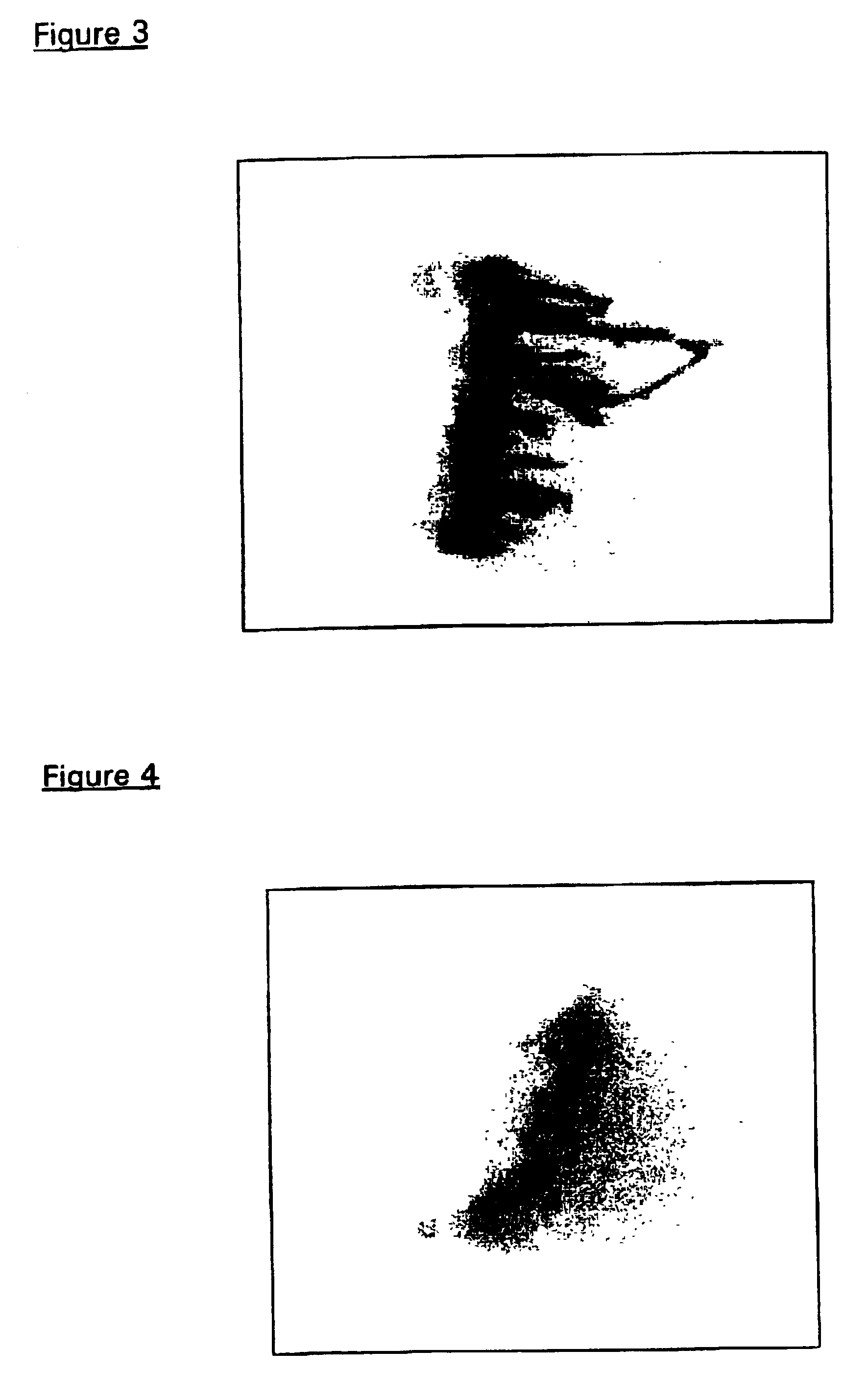
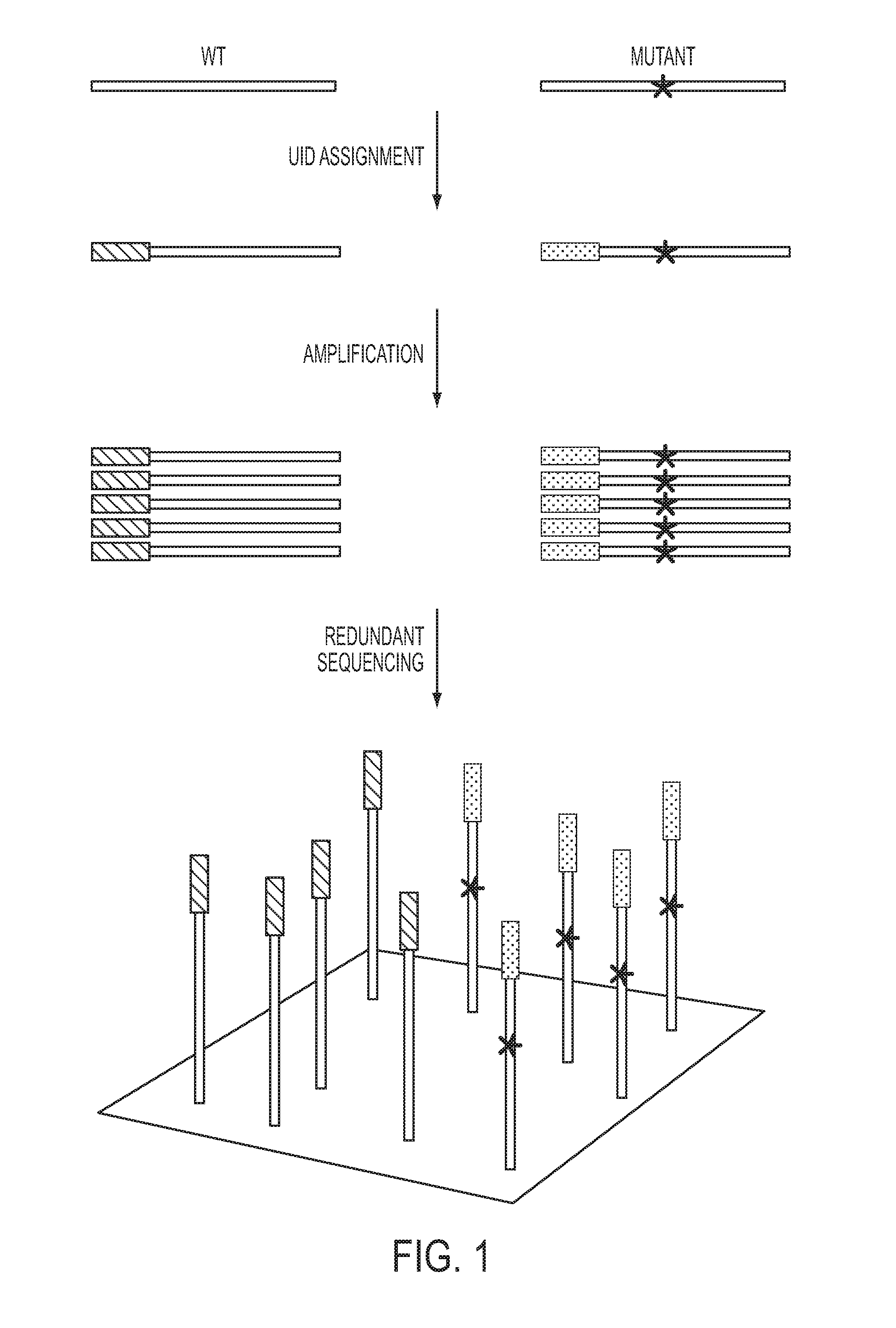
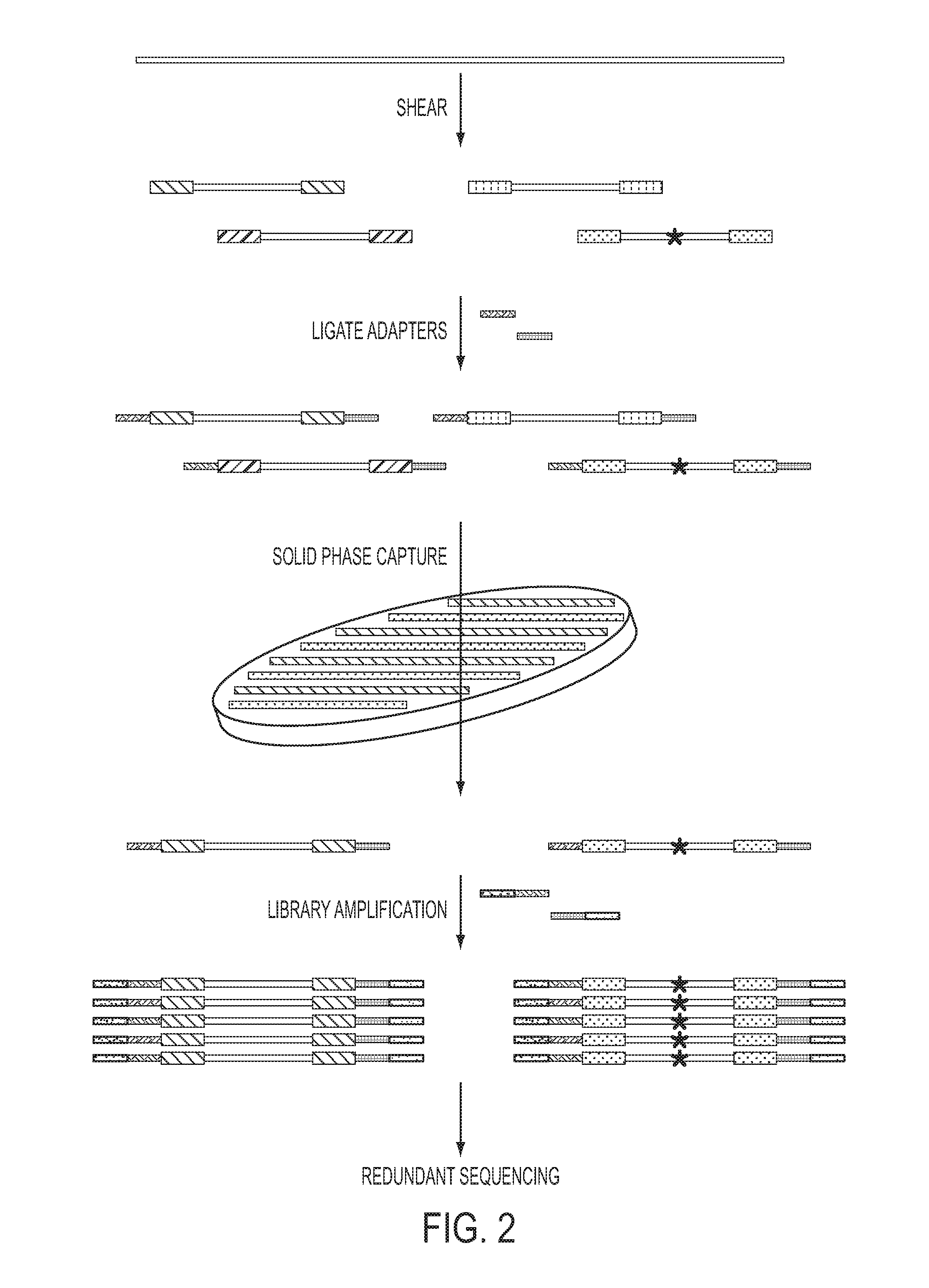
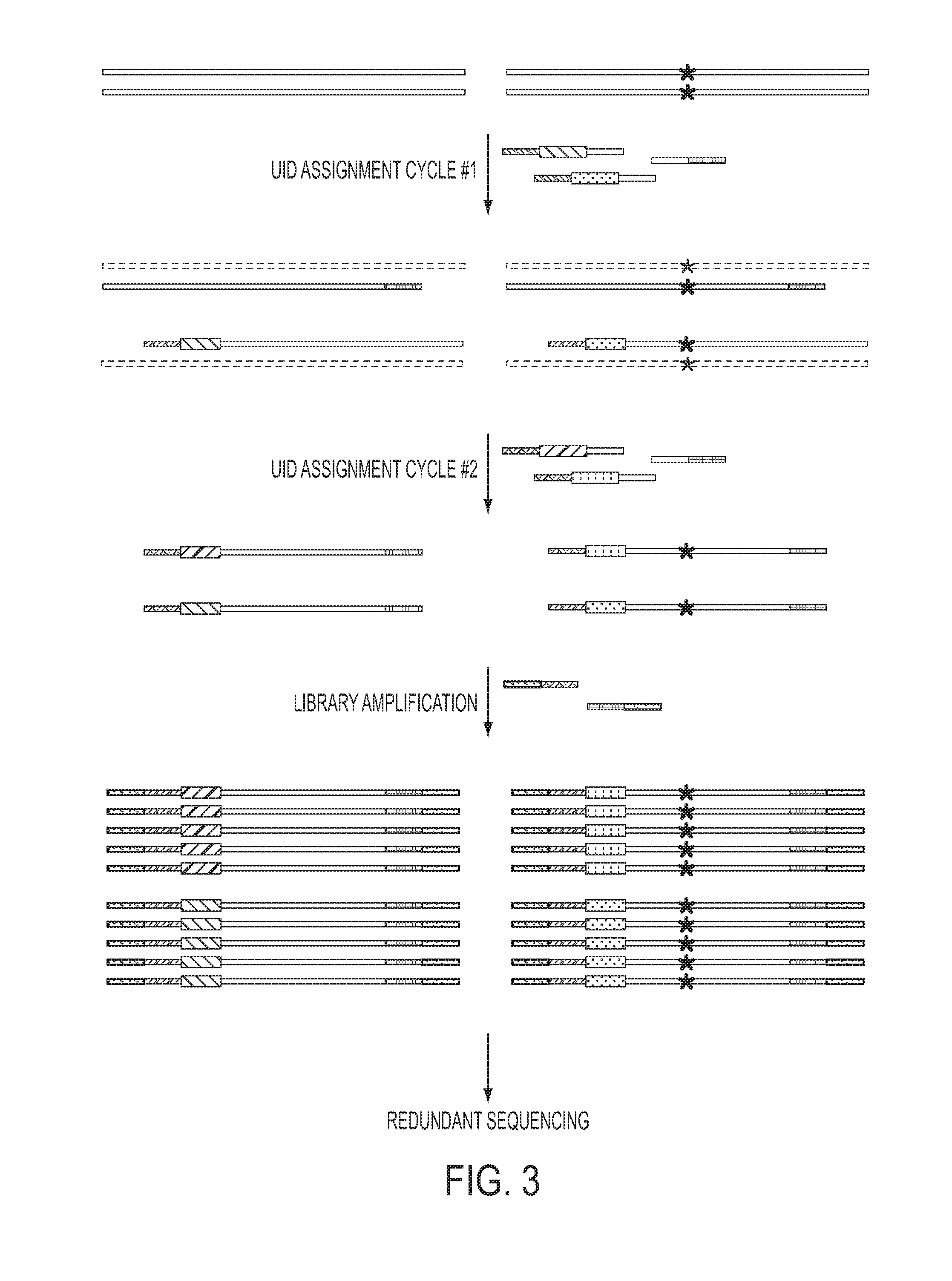
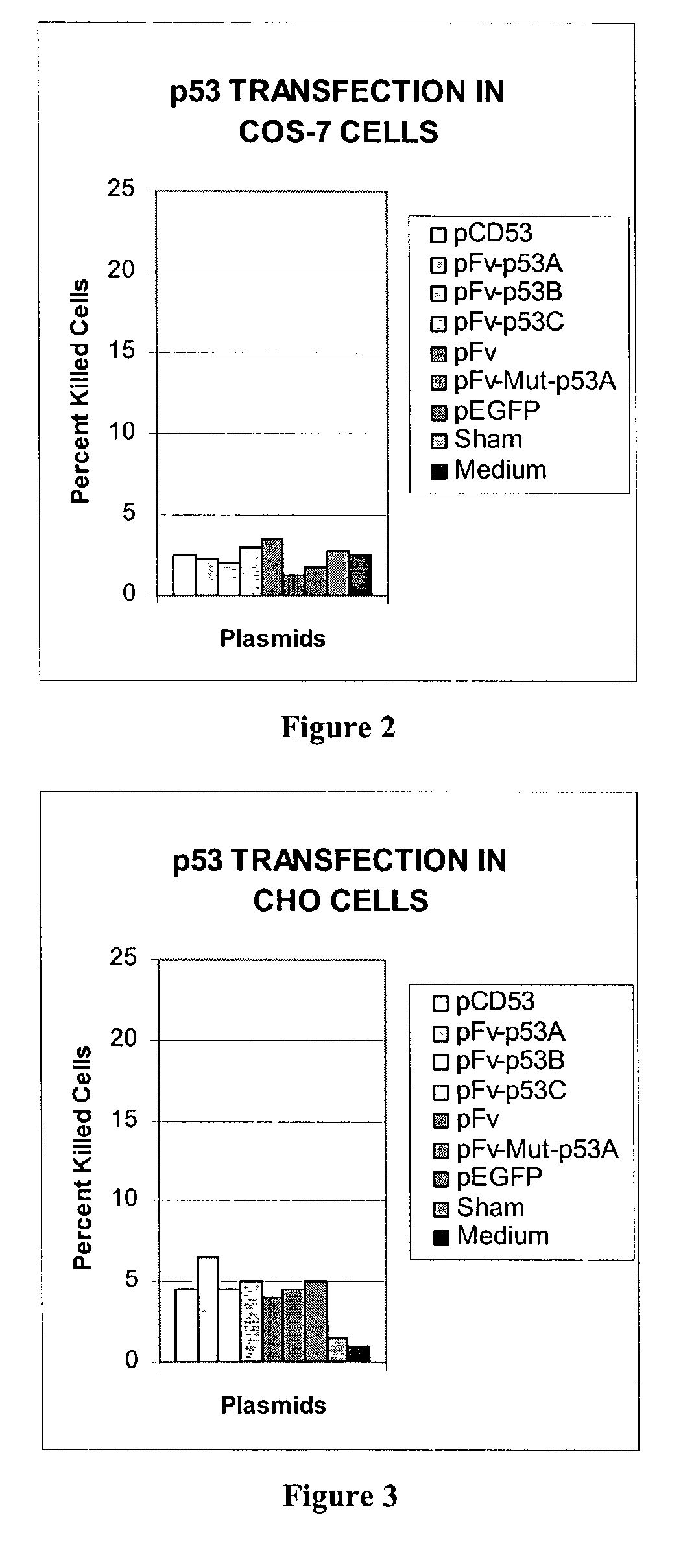
The identification of mutations that are present in a small fraction of DNA templates is essential for progress in several areas of biomedical research. Though massively parallel sequencing instruments are in principle well-suited to this task, the error rates in such instruments are generally too high to allow confident identification of rare variants. We here describe an approach that can substantially increase the sensitivity of massively parallel sequencing instruments for this purpose. One example of this approach, called “Safe-SeqS” for (Safe-Sequencing System) includes (i) assignment of a unique identifier (UID) to each template molecule; (ii) amplification of each uniquely tagged template molecule to create UID-families; and (iii) redundant sequencing of the amplification products. PCR fragments with the same UID are truly mutant (“super-mutants”) if ≧95% of them contain the identical mutation. We illustrate the utility of this approach for determining the fidelity of a polymerase, the accuracy of oligonucleotides synthesized in vitro, and the prevalence of mutations in the nuclear and mitochondrial genomes of normal cells.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
System and Methods for Massively Parallel Analysis of Nucleic Acids in Single Cells
InactiveUS20140057799A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenetic analysisPopulation
Methods and systems are provided for massively parallel genetic analysis of single cells in emulsion droplets or reaction containers. Genetic loci of interest are targeted in a single cell using a set of probes, and a fusion complex is formed by molecular linkage and amplification techniques. Methods are provided for high-throughput, massively parallel analysis of the fusion complex in a single cell in a population of at least 10,000 cells. Also provided are methods for tracing genetic information back to a cell using barcode sequences.
Owner:GIGAGEN
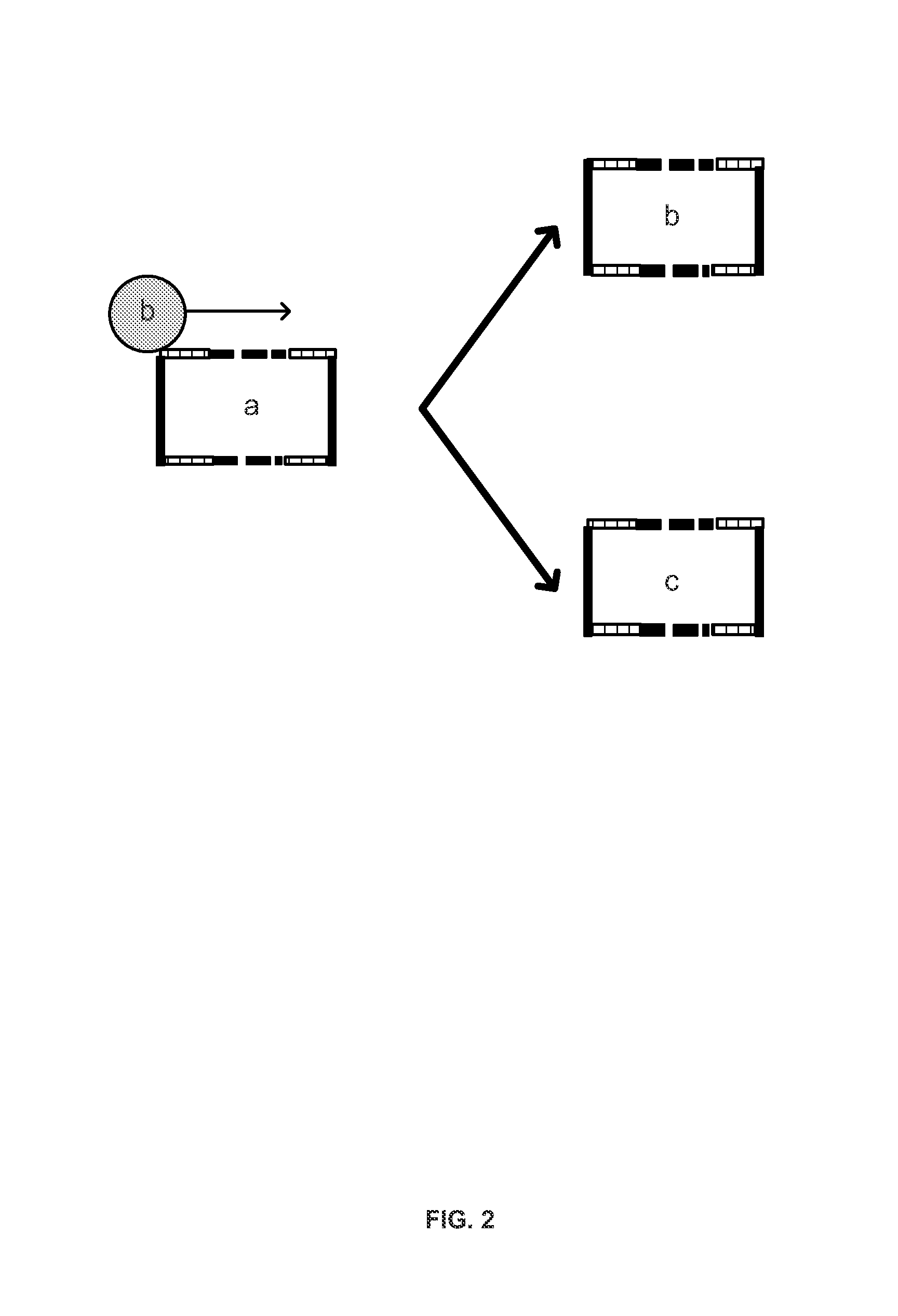
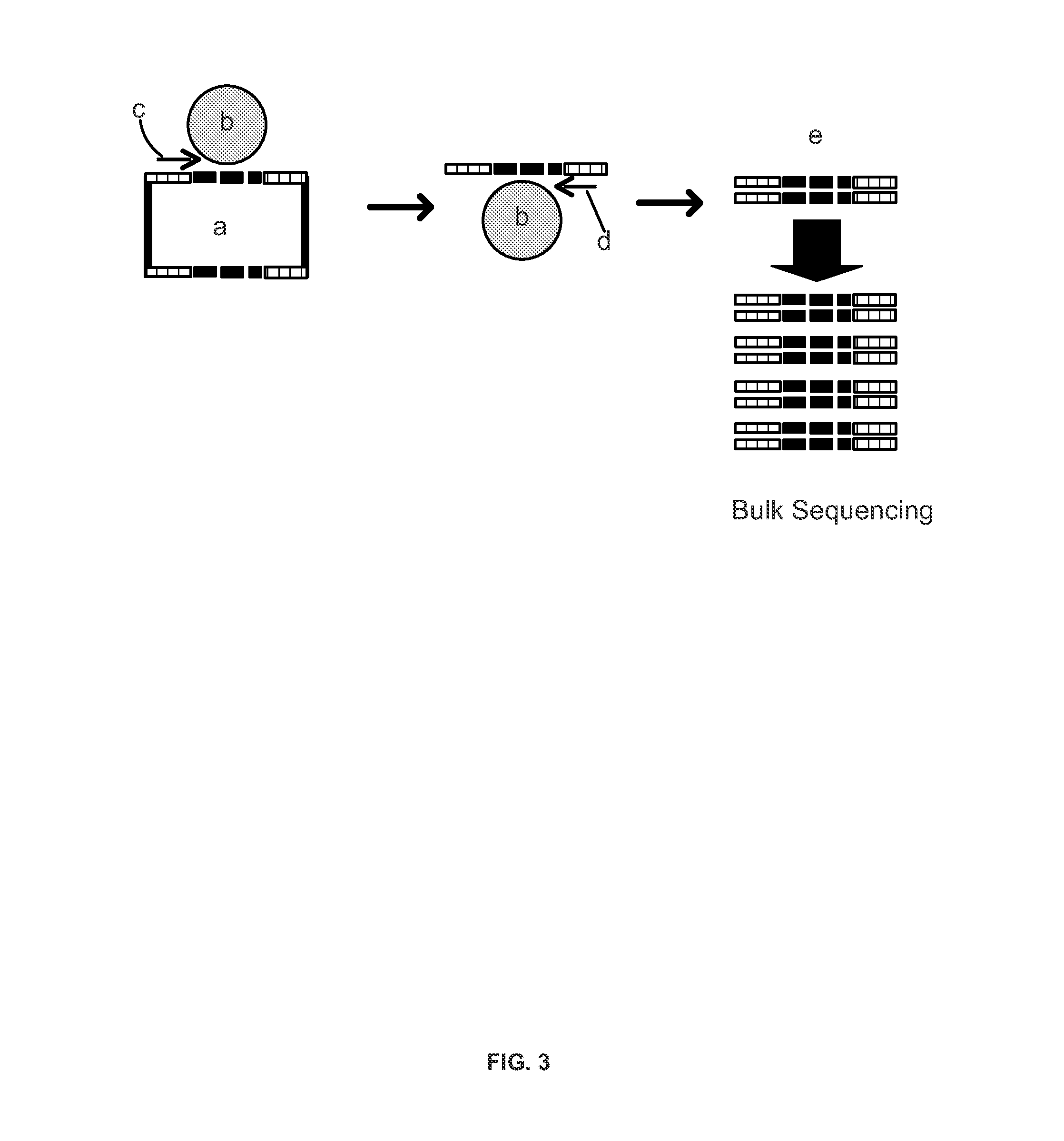
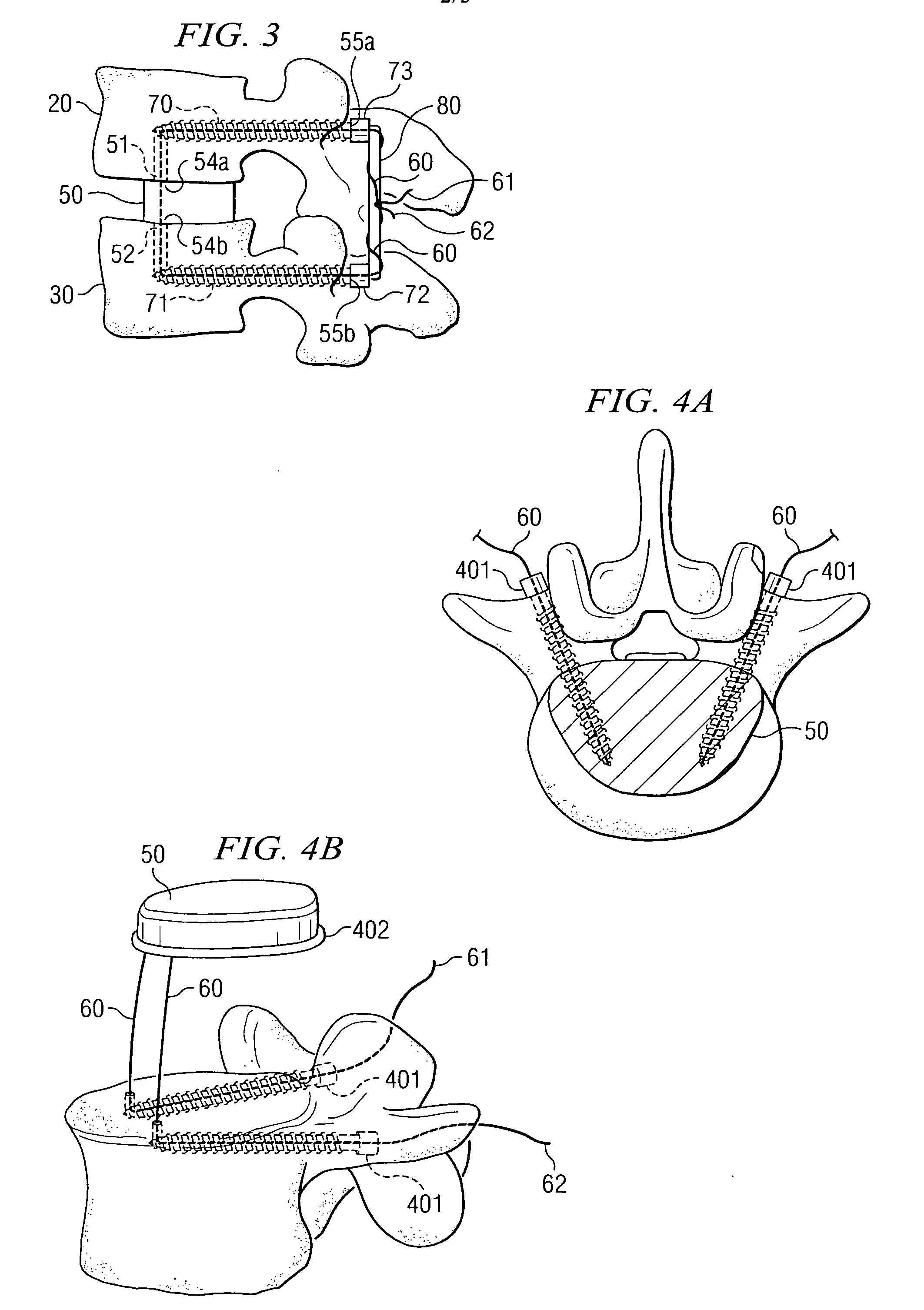
Nucleus replacement securing device and method
There is disclosed systems and methods for spinal nucleus replacement by constructing channels through vertebral segments on either side of an area into which the spinal nucleus is to be positioned, the channels running from a channel end outside of the area to a channel end abutting the area. One end of a suture is inserted into the outside channel end of a first one of the channels and passed through the first channel and into the area and out of the area through the second channel until it emerges from the second channel. The suture is then used to pull the nucleus into the area.
Owner:THEKEN SPINE
Devices and methods for enrichment and alteration of cells and other particles
ActiveUS20070026381A1Increase volumeReduced deformabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCellular componentLysis
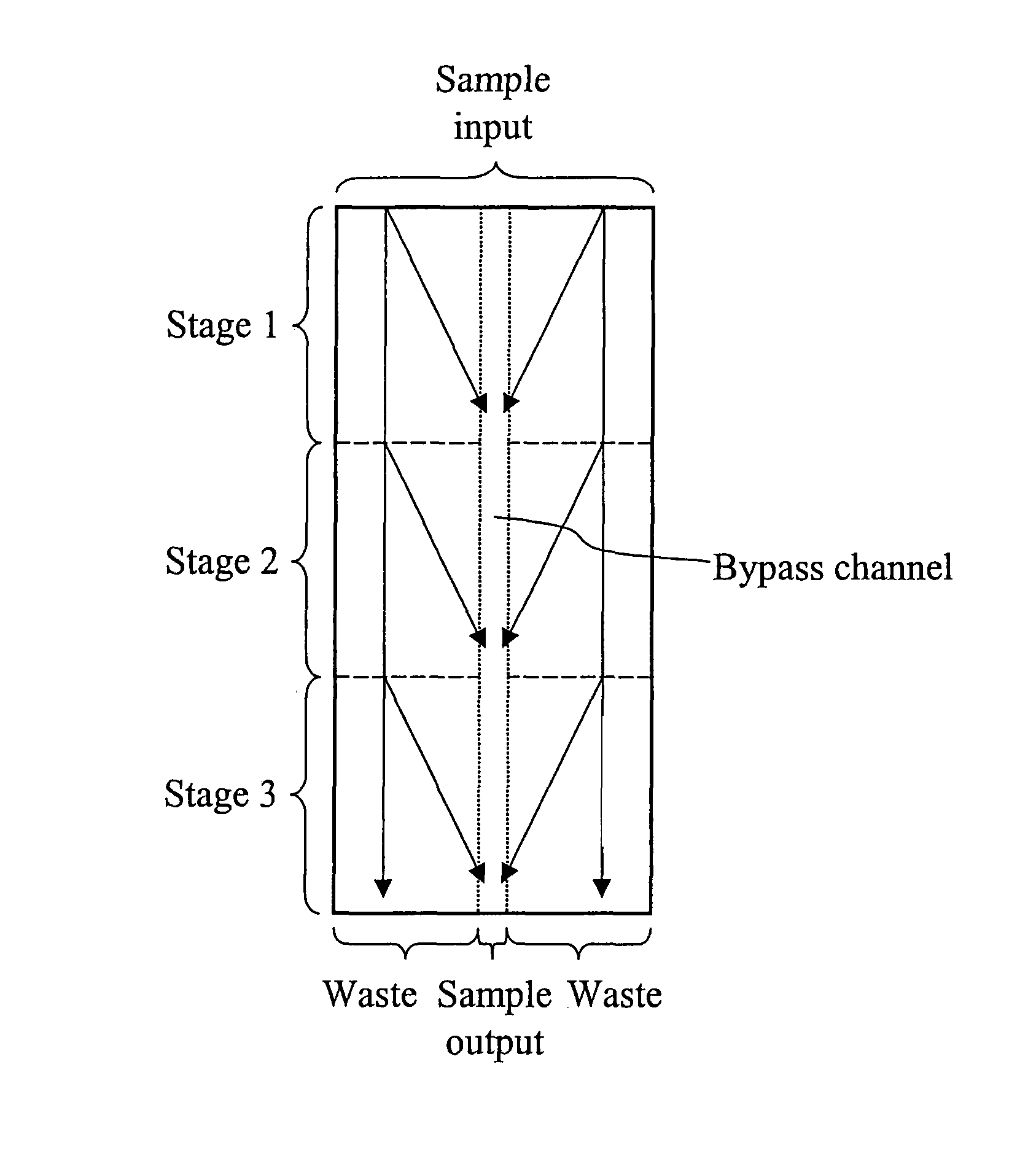
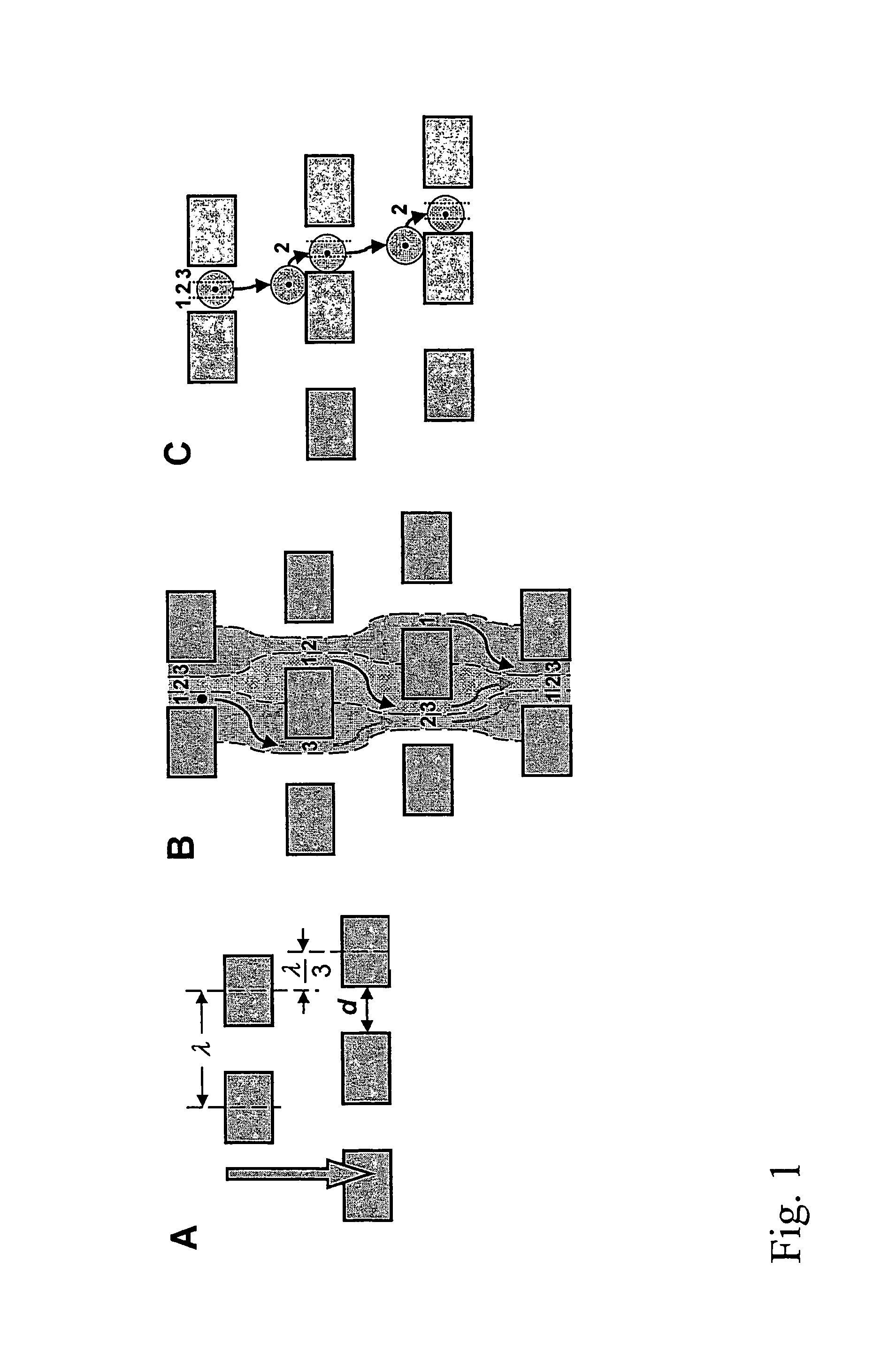
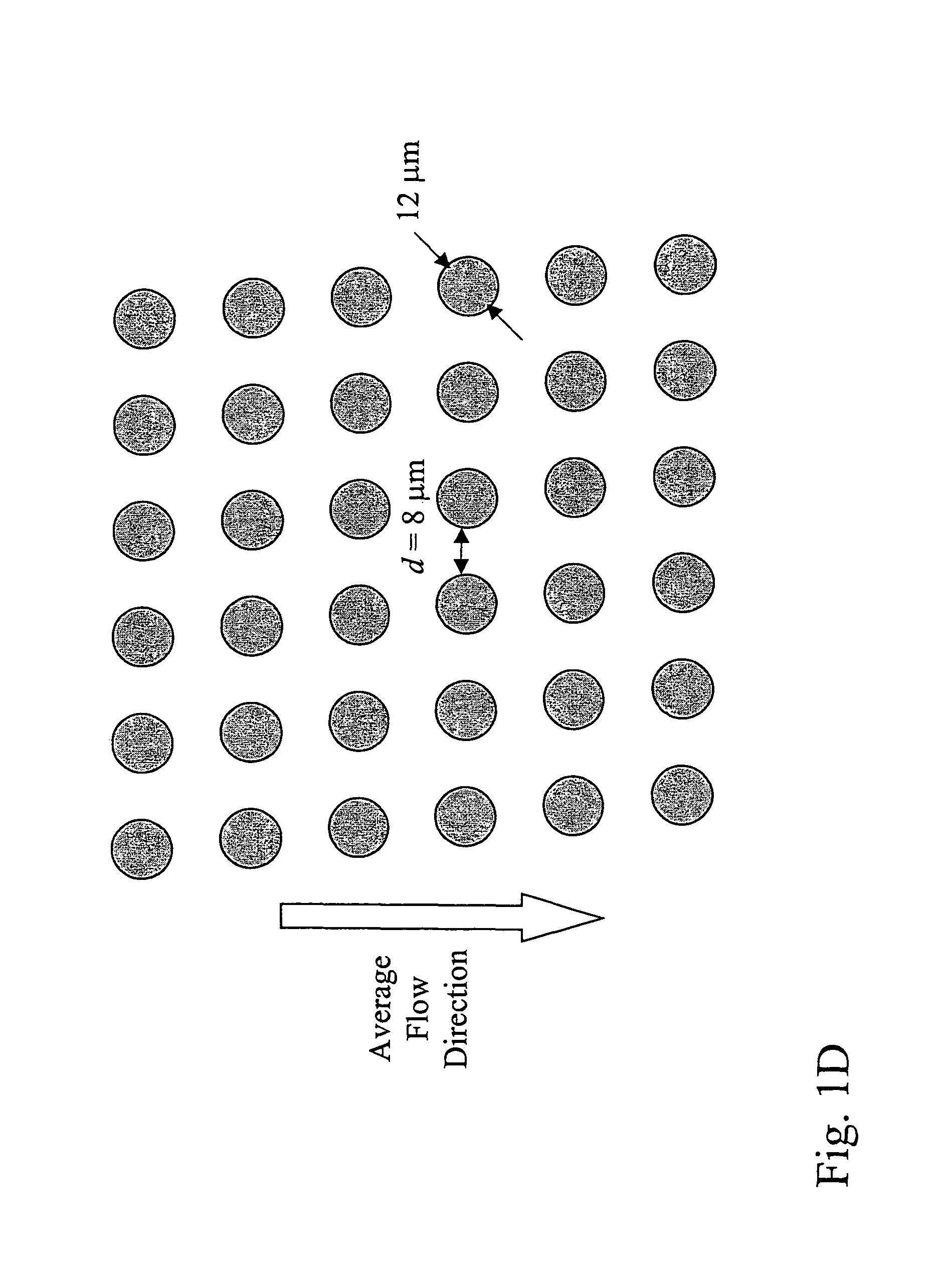
The invention features devices and methods for the deterministic separation of particles. Exemplary methods include the enrichment of a sample in a desired particle or the alteration of a desired particle in the device. The devices and methods are advantageously employed to enrich for rare cells, e.g., fetal cells, present in a sample, e.g., maternal blood and rare cell components, e.g., fetal cell nuclei. The invention further provides a method for preferentially lysing cells of interest in a sample, e.g., to extract clinical information from a cellular component, e.g., a nucleus, of the cells of interest. In general, the method employs differential lysis between the cells of interest and other cells (e.g., other nucleated cells) in the sample.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Neurostimulation for affecting sleep disorders
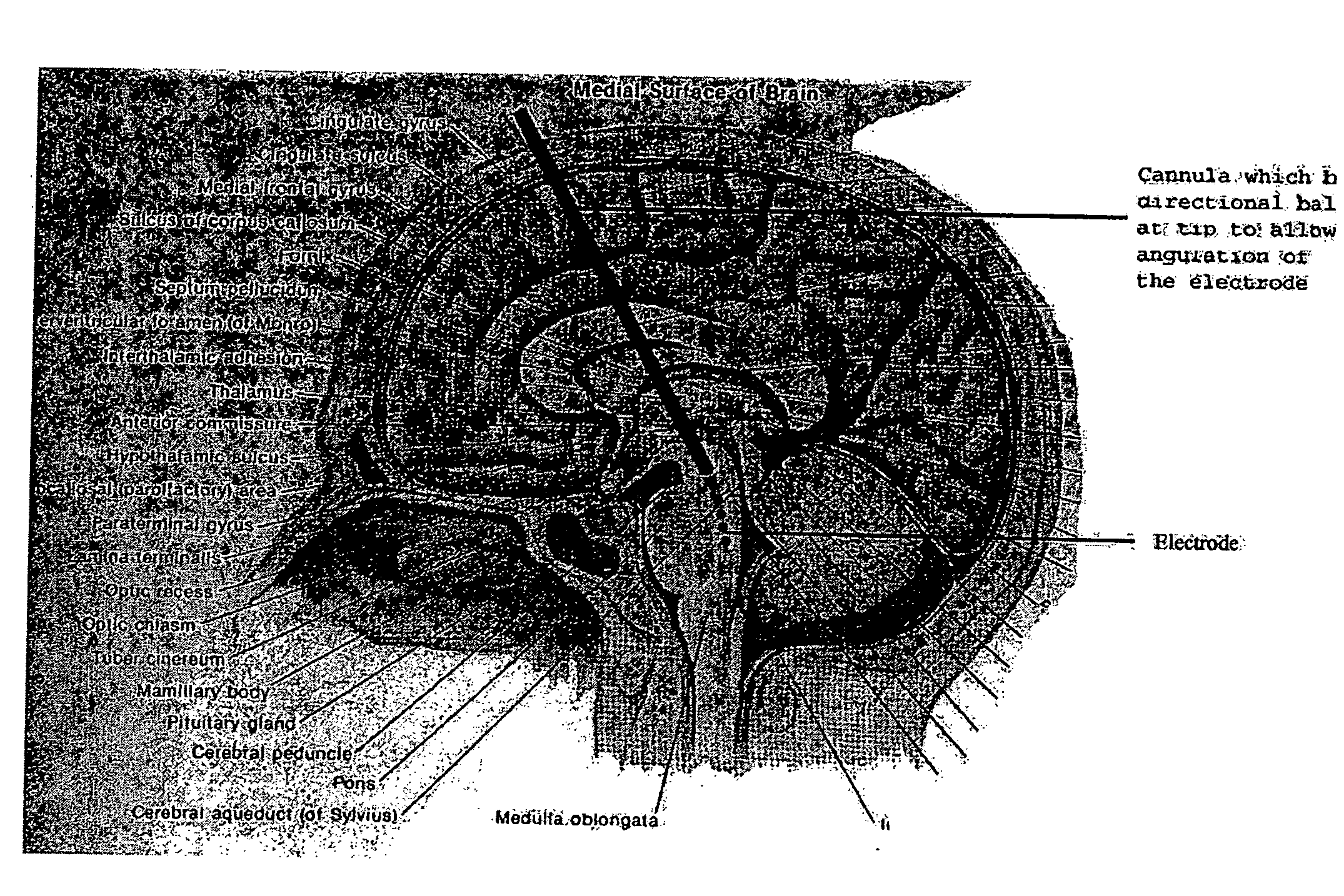
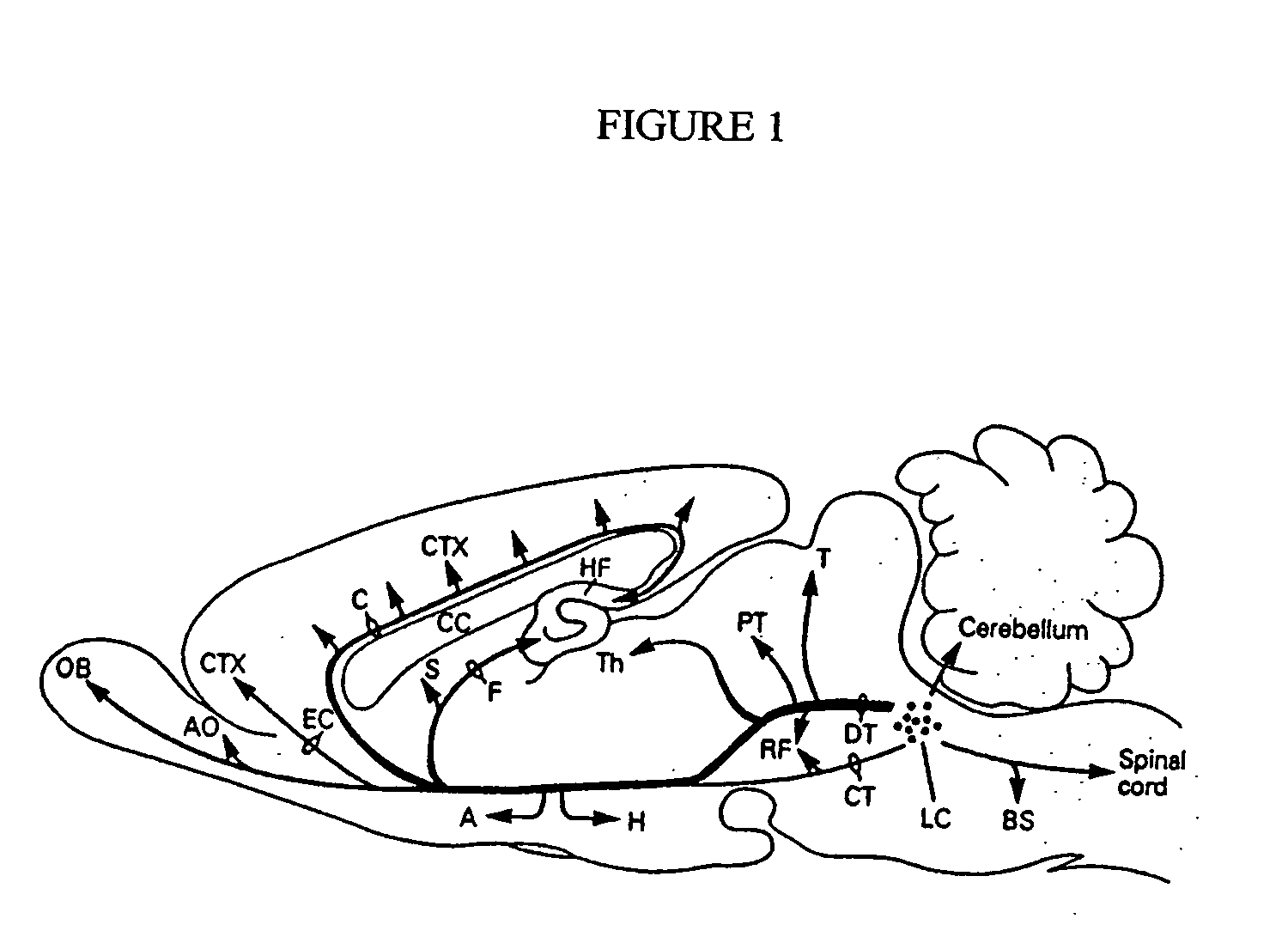
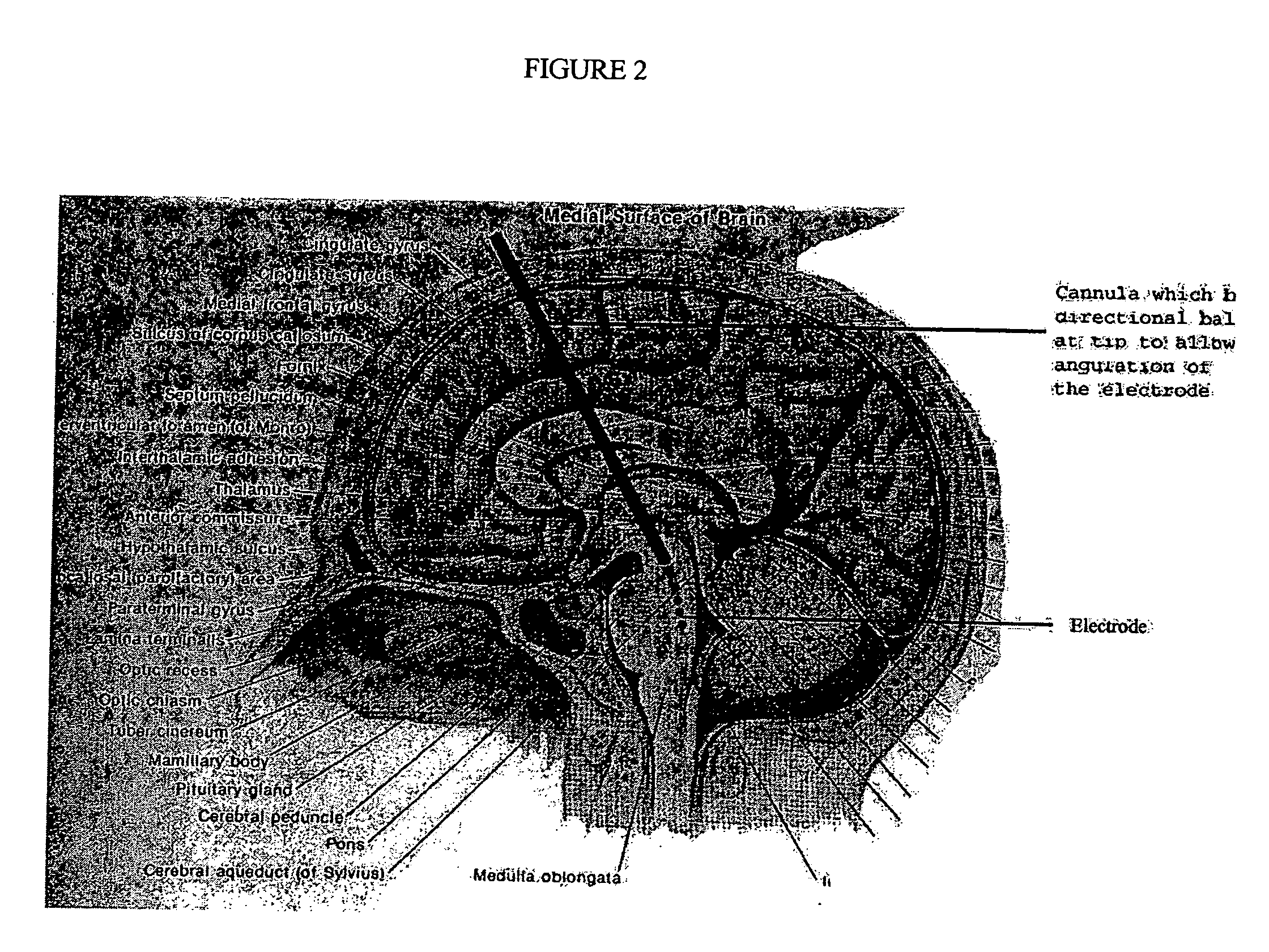
A method of affecting a sleep disorder in a subject having the sleep disorder and a method of affecting a normal awakeness-sleep cycle in a subject having an abnormal awakeness-sleep cycle, said methods comprising: a) identifying at least one nucleus in a brain of the subject, said nucleus being a nucleus of the sleep circuitry of the brain; and b) stimulating the at least one identified nucleus so as to modulate the nucleus, thereby affecting the sleep disorder.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Nucleic acid sequence analysis from single cells
ActiveUS20160053253A1Reduce cascadeNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBarcodeNucleic acid sequencing
Presented herein are methods and compositions for multiplexed single cell gene expression analysis. Some methods and compositions include the use of droplets and / or beads bearing unique barcodes such as unique molecular barcodes (UMI).
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Identication of peptides that facilitate uptake and cytoplasmic and/or nuclear transport of proteins, DNA and virues
InactiveUS6881825B1Reduce deliveryFacilitating uptakeCompound screeningApoptosis detectionIn vivoCell type
The present invention relates to internalizing peptides which facilitate the uptake and transport of cargo into the cytoplasm and nuclei of cells as well as methods for the identification of the peptides, and methods of use for the peptides. The internalizing peptides of the present invention are selected for their ability to efficiently internalize cargo into a wide variety of cell types both in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
CICM cells and non-human mammalian embryos prepared by nuclear transfer of a proliferating differentiated cell or its nucleus
InactiveUS6235970B1Simple procedureSimplifying and facilitating procedureNervous disorderMuscular disorderPresent methodNuclear transfer
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor differentiated cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of the same species as the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for multiplication of genotypes and transgenic genotypes by the production of fetuses and offspring, and for production of isogenic CICM cells, including human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. Production of genetically engineered or transgenic mammalian embryos, fetuses and offspring is facilitated by the present method since the differentiated cell source of the donor nuclei can be genetically modified and clonally propagated.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS AMHERST
Devices and methods for enrichment and alteration of cells and other particles
ActiveUS8021614B2Increases the hydrodynamic radius of a particleIncrease volumeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCellular componentClinical information
The invention features devices and methods for the deterministic separation of particles. Exemplary methods include the enrichment of a sample in a desired particle or the alteration of a desired particle in the device. The devices and methods are advantageously employed to enrich for rare cells, e.g., fetal cells, present in a sample, e.g., maternal blood and rare cell components, e.g., fetal cell nuclei. The invention further provides a method for preferentially lysing cells of interest in a sample, e.g., to extract clinical information from a cellular component, e.g., a nucleus, of the cells of interest. In general, the method employs differential lysis between the cells of interest and other cells (e.g., other nucleated cells) in the sample.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Identification of peptides that facilitate uptake and cytoplasmic and/or nuclear transport of proteins, DNA and viruses
The present invention relates to internalizing peptides which facilitate the uptake and transport of cargo into the cytoplasm and nuclei of cells as well as methods for the identification of such peptides. The internalizing peptides of the present invention are selected for their ability to efficiently internalize cargo into a wide variety of cell types both in vivo and in vitro. The method for identification of the internalizing peptides of the present invention comprises incubating a target cell with a peptide display library, isolating peptides with internalization characteristics and determining the ability of said peptide to internalize cargo into a cell.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Systems and methods for treating, diagnosing and predicting the occurrence of a medical condition
ActiveUS20100184093A1Reliable and accurate image segmentationMedical simulationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImmunofluorescenceClinical information
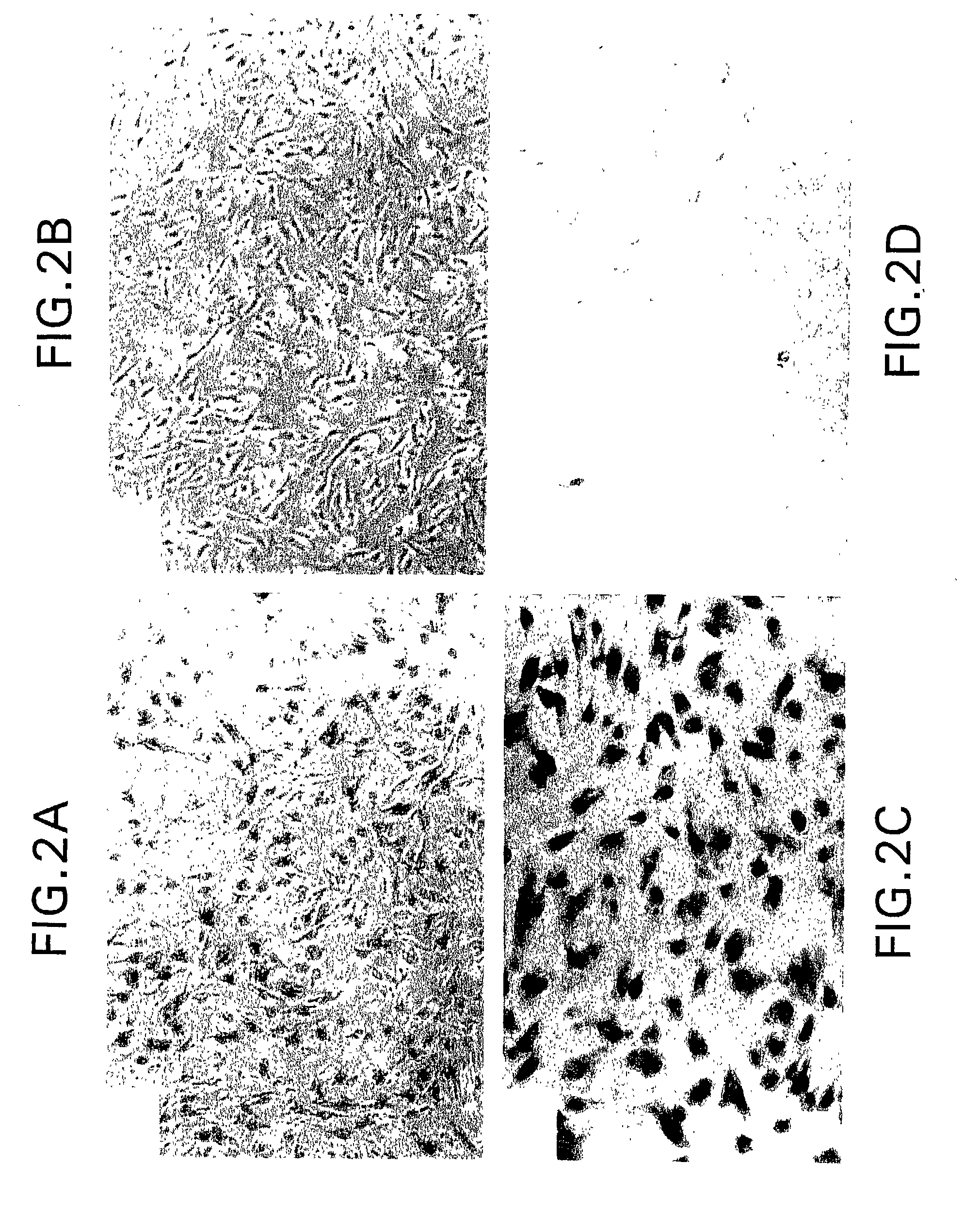
Clinical information, molecular information and / or computer-generated morphometric information is used in a predictive model for predicting the occurrence of a medical condition. In an embodiment, a model predicts whether a patient is likely to have a favorable pathological stage of prostate cancer, where the model is based on features including one or more (e.g., all) of preoperative PSA, Gleason Score, a measurement of expression of androgen receptor (AR) in epithelial and stromal nuclei and / or a measurement of expression of Ki67-positive epithelial nuclei, a morphometric measurement of a ratio of area of epithelial nuclei outside gland units to area of epithelial nuclei within gland units, and a morphometric measurement of area of epithelial nuclei distributed away from gland units. In some embodiments, quantitative measurements of protein expression in cell lines are utilized to objectively assess assay (e.g., multiplex immunofluorescence (IF)) performance and / or to normalize features for use within a predictive model.
Owner:AUREON LAB INC +1
Compounds acting at the centrosome
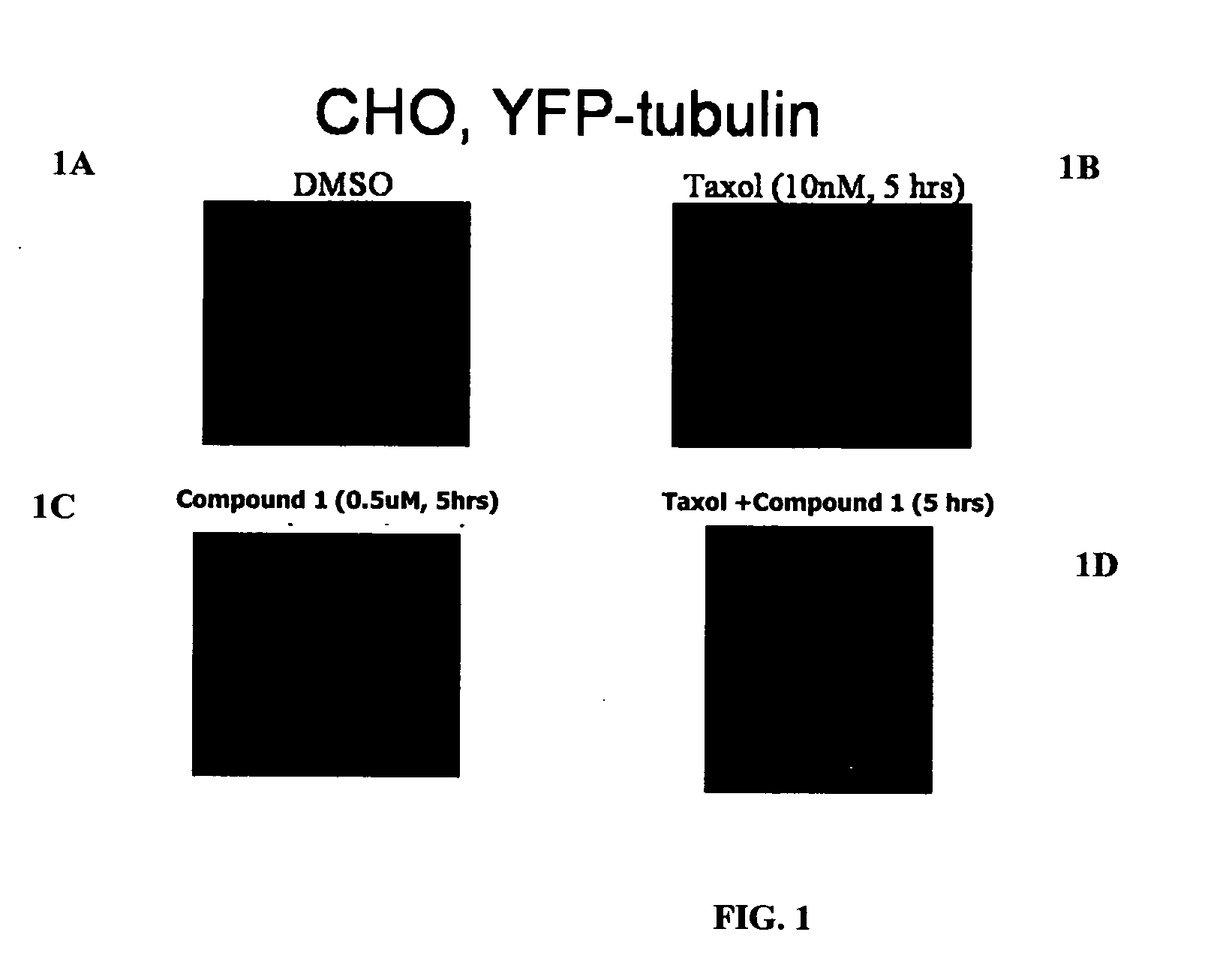
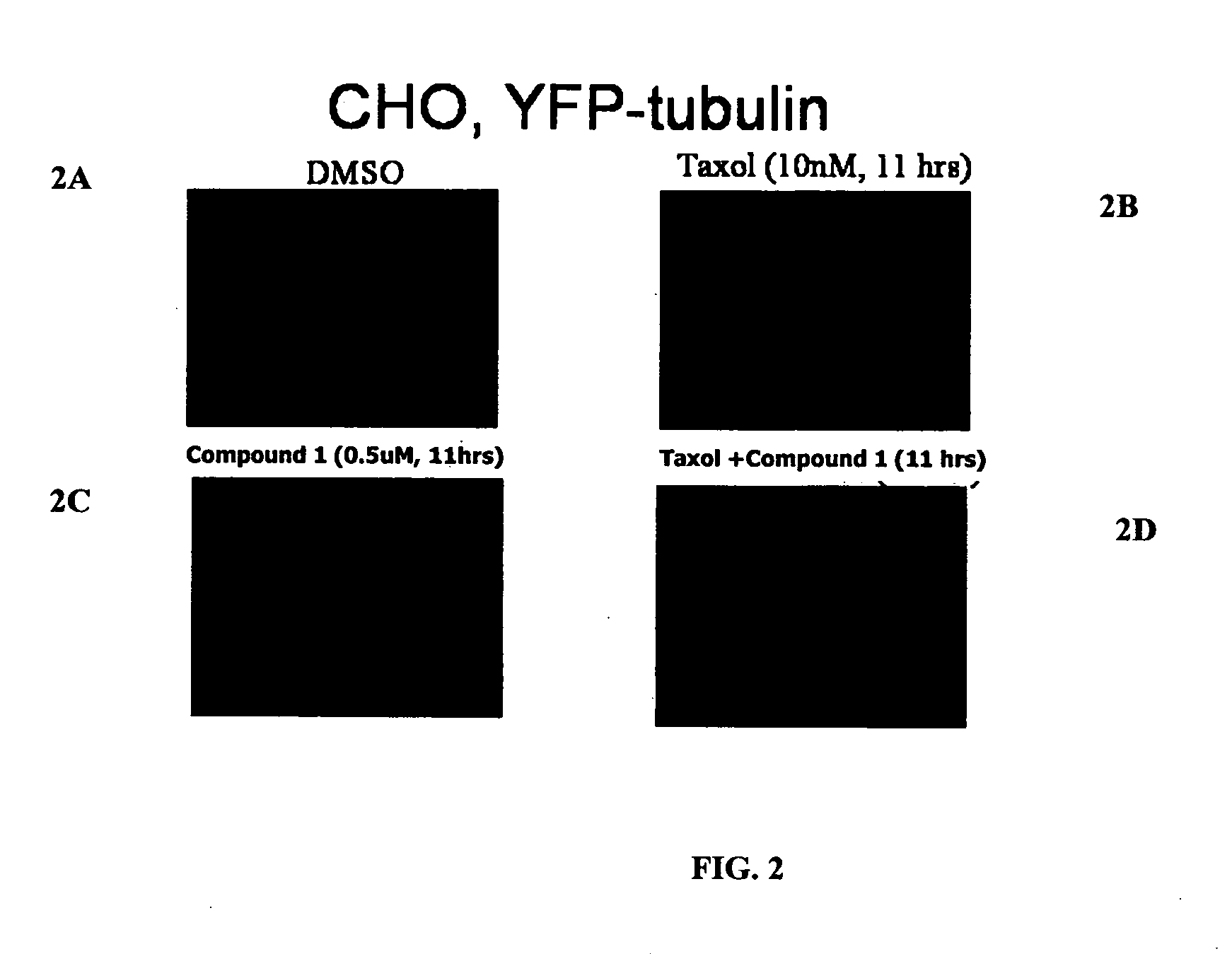
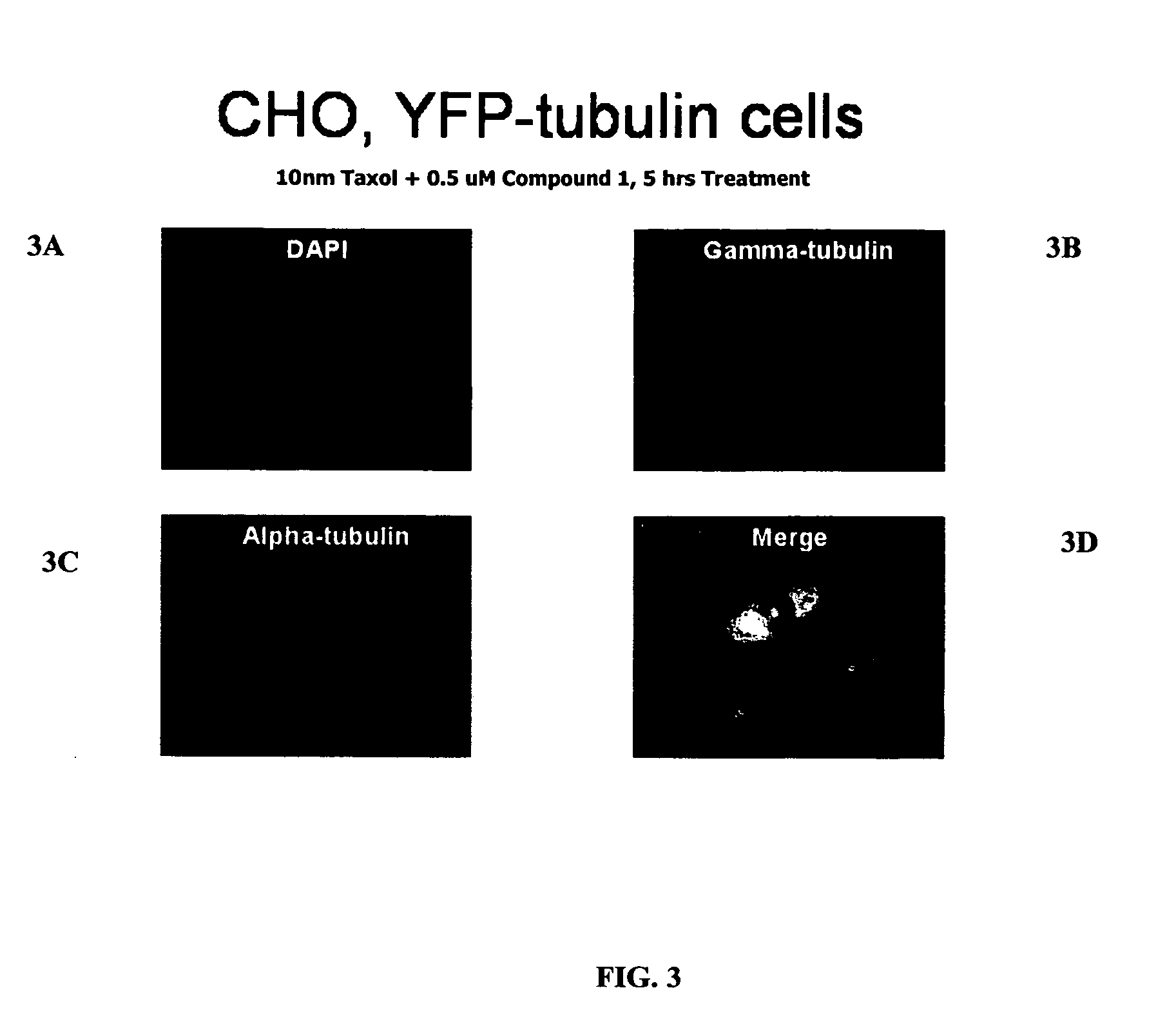
InactiveUS20060167106A1Network disruptionBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsActin cytoskeletonProteasome degradation
The present invention relates to compounds, and methods utilizing compounds, which exhibit one or more of the following properties: i) disrupts organization of an actin cytoskeleton of a cell; ii) disrupts organization of a microtubule network of a cell; iii) induces accumulation of tubulin at centrosomes but does not induce accumulation of tubulin in a nucleus of a cell; iv) induces accumulation of tubulin at centrosomes at a concentration of 500 nM or less within four hours; v) induces accumulation of Hsp70 and has weak-to-moderate proteasome inhibitory activity; and vi) does not have proteasome inhibitory activity when assayed on purified proteasomes.
Owner:SYNTA PHARMA CORP
DNA isolation method
InactiveUS6852851B1Not readyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNuclear membraneLysis
Owner:GYROS
Cell penetrating peptide
InactiveUS8044019B2High frequencyPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsCell nucleusProtein
Owner:MITSUBISHI TANABE PHARMA CORP
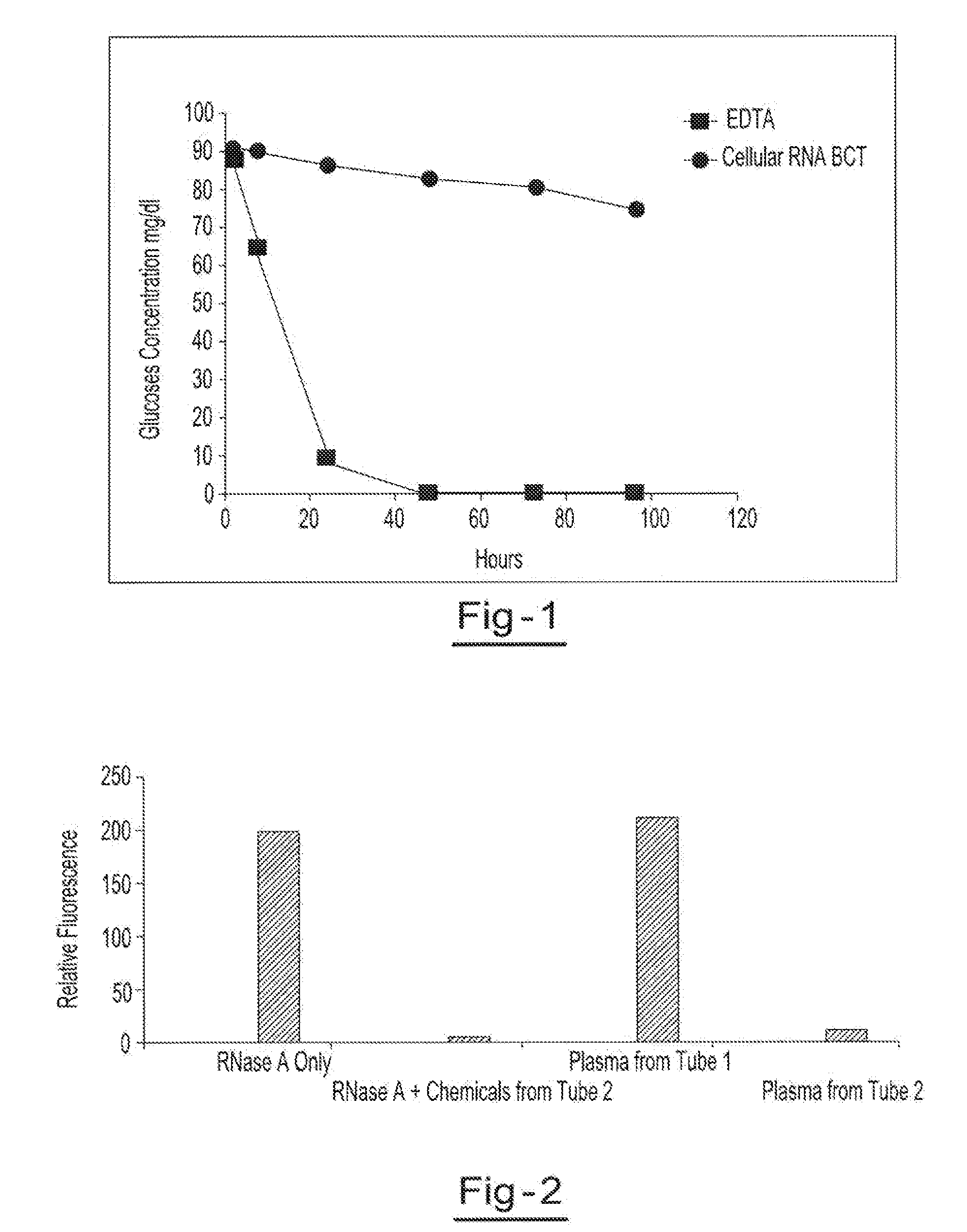
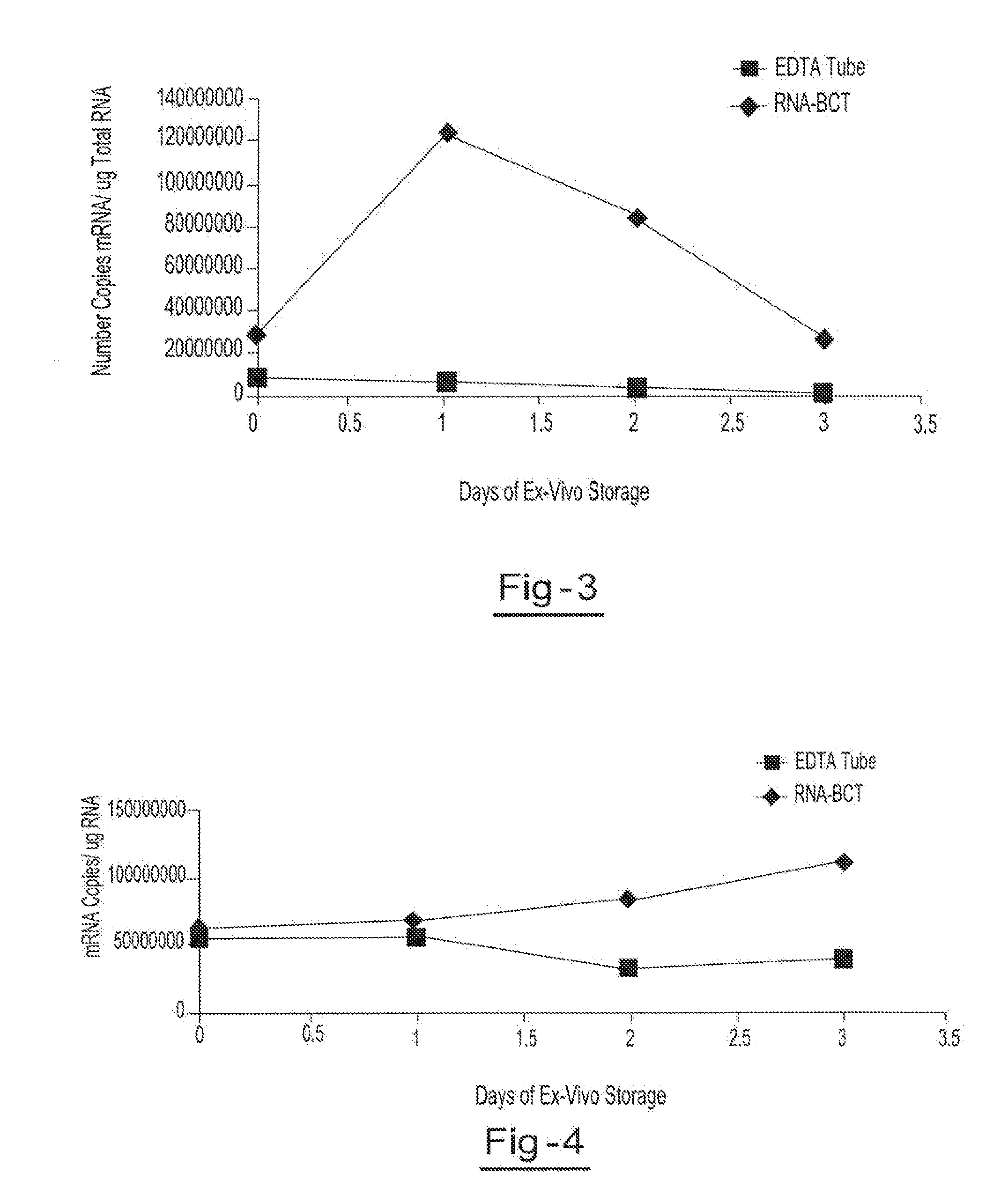
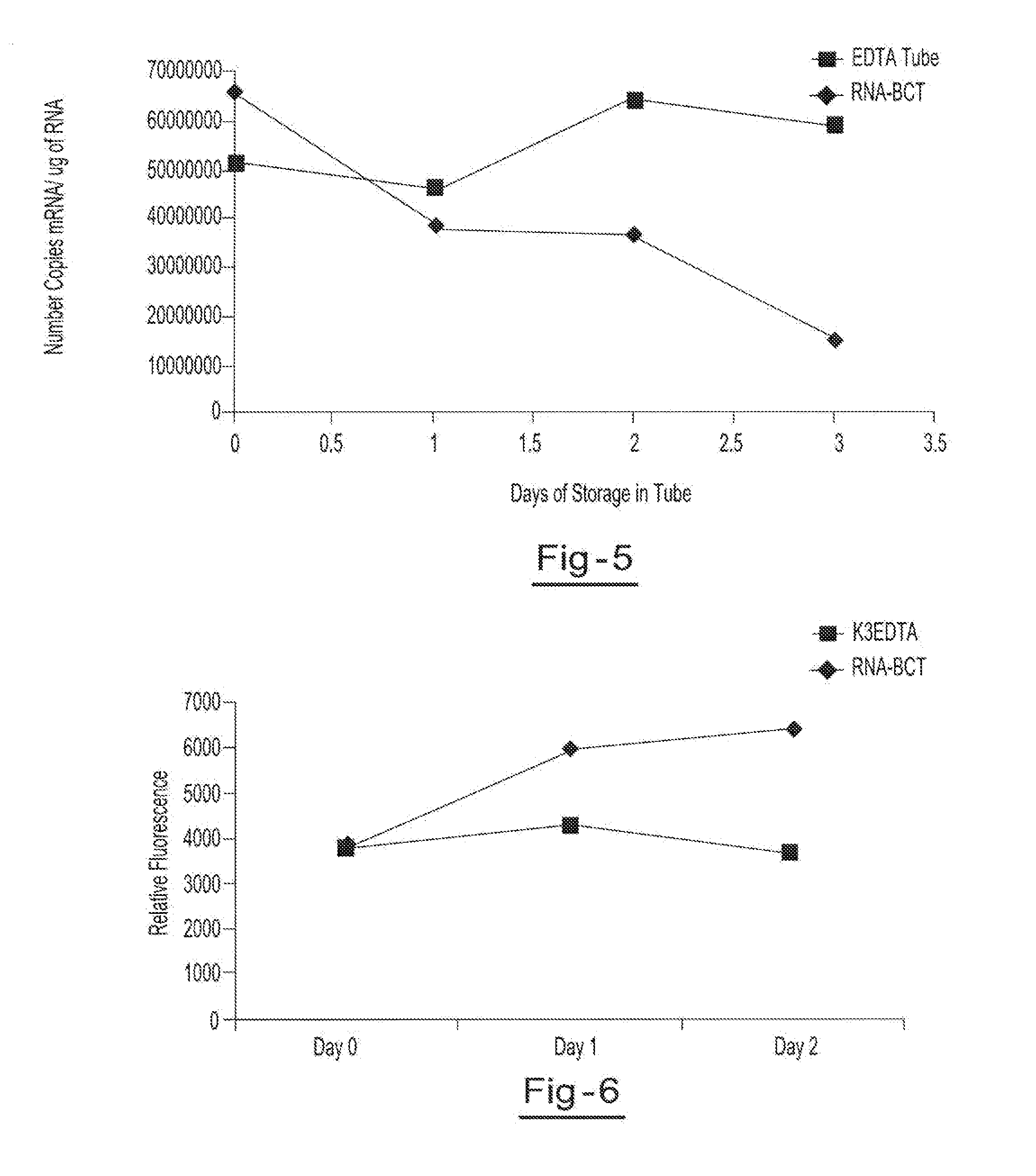
Stabilization of RNA in intact cells within a blood sample
InactiveUS20110111410A1Effective isolationEfficient testingMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureLysisNuclease
A method for preserving and processing nucleic acids located within a blood sample is disclosed, wherein a blood sample containing nucleic acids is treated to reduce both blood cell lysis and nuclease activity within the blood sample. The treatment of the sample aids in increasing the integrity and amount of cellular nucleic acids that can be identified and tested while avoiding contamination of the isolated nucleic acids with cell-free nucleic acids.
Owner:STRECK INC
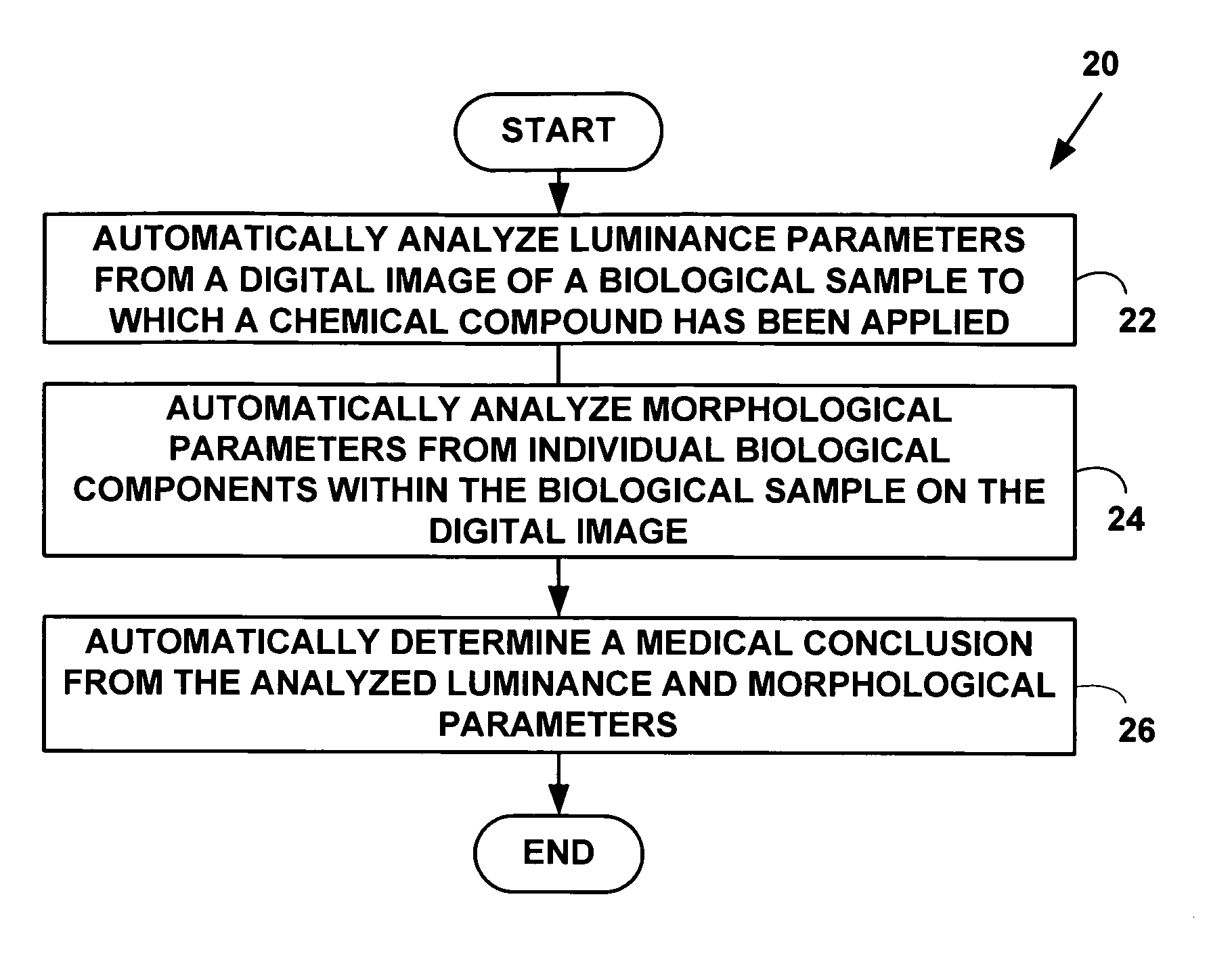
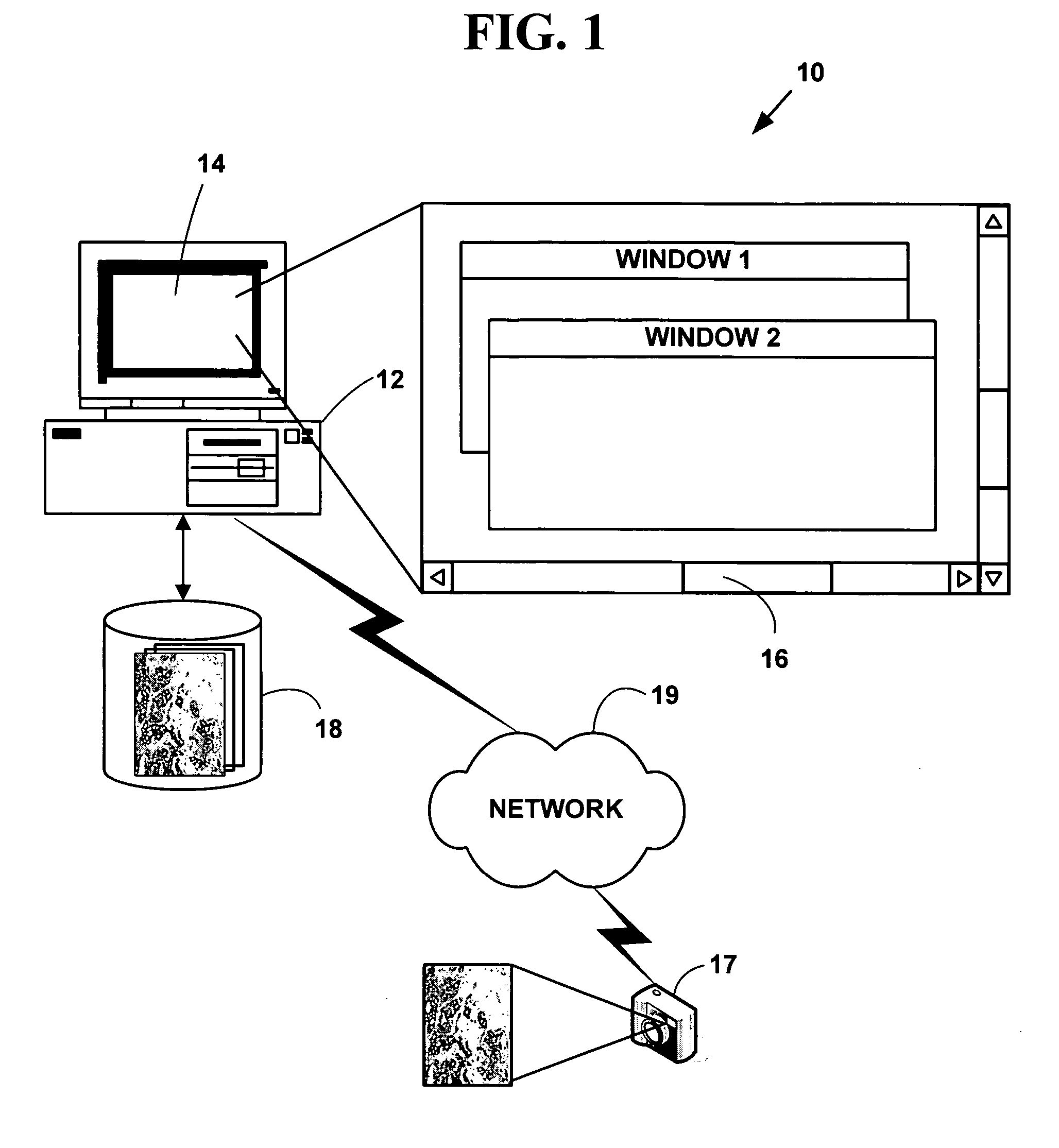
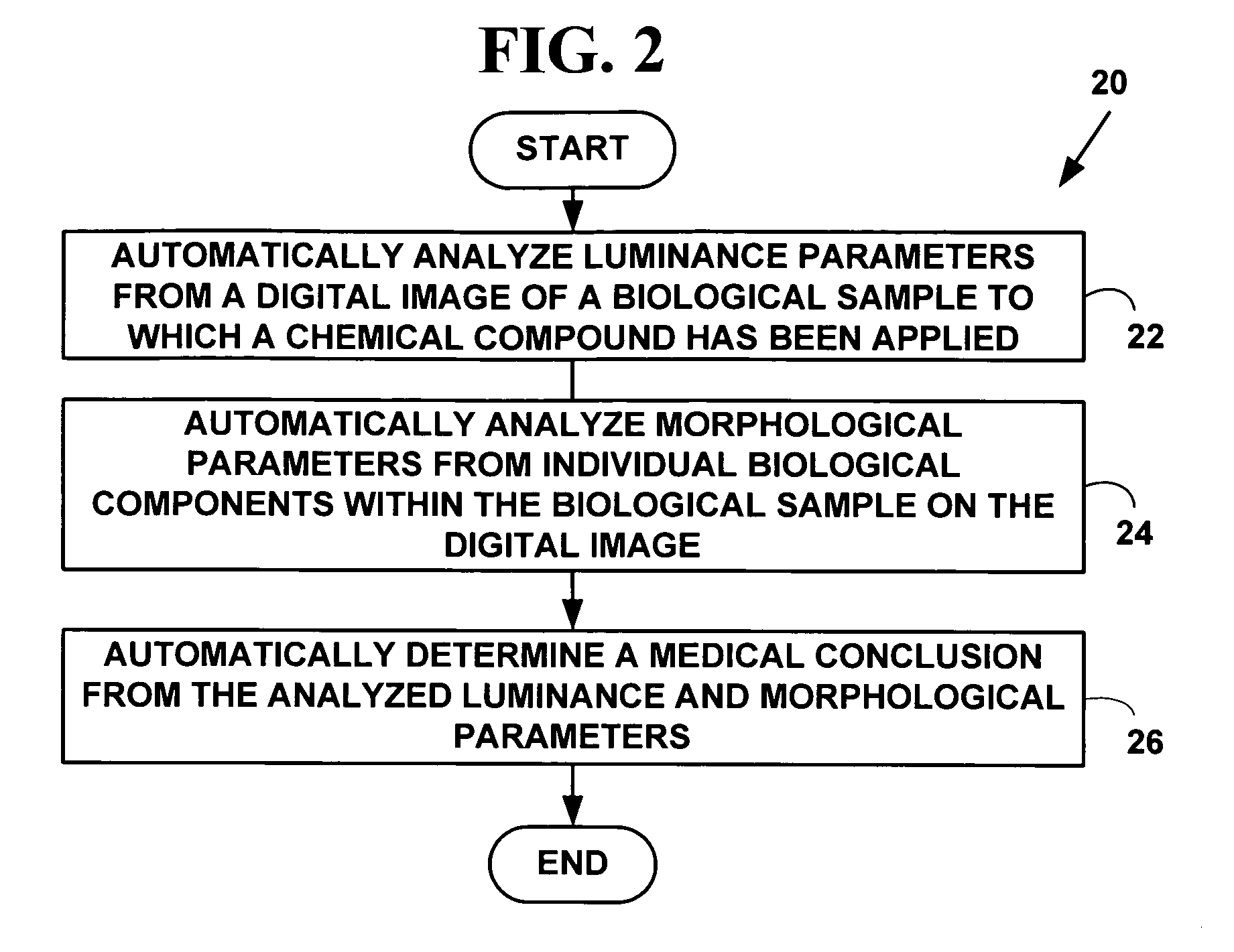
Method and system for automatically determining diagnostic saliency of digital images
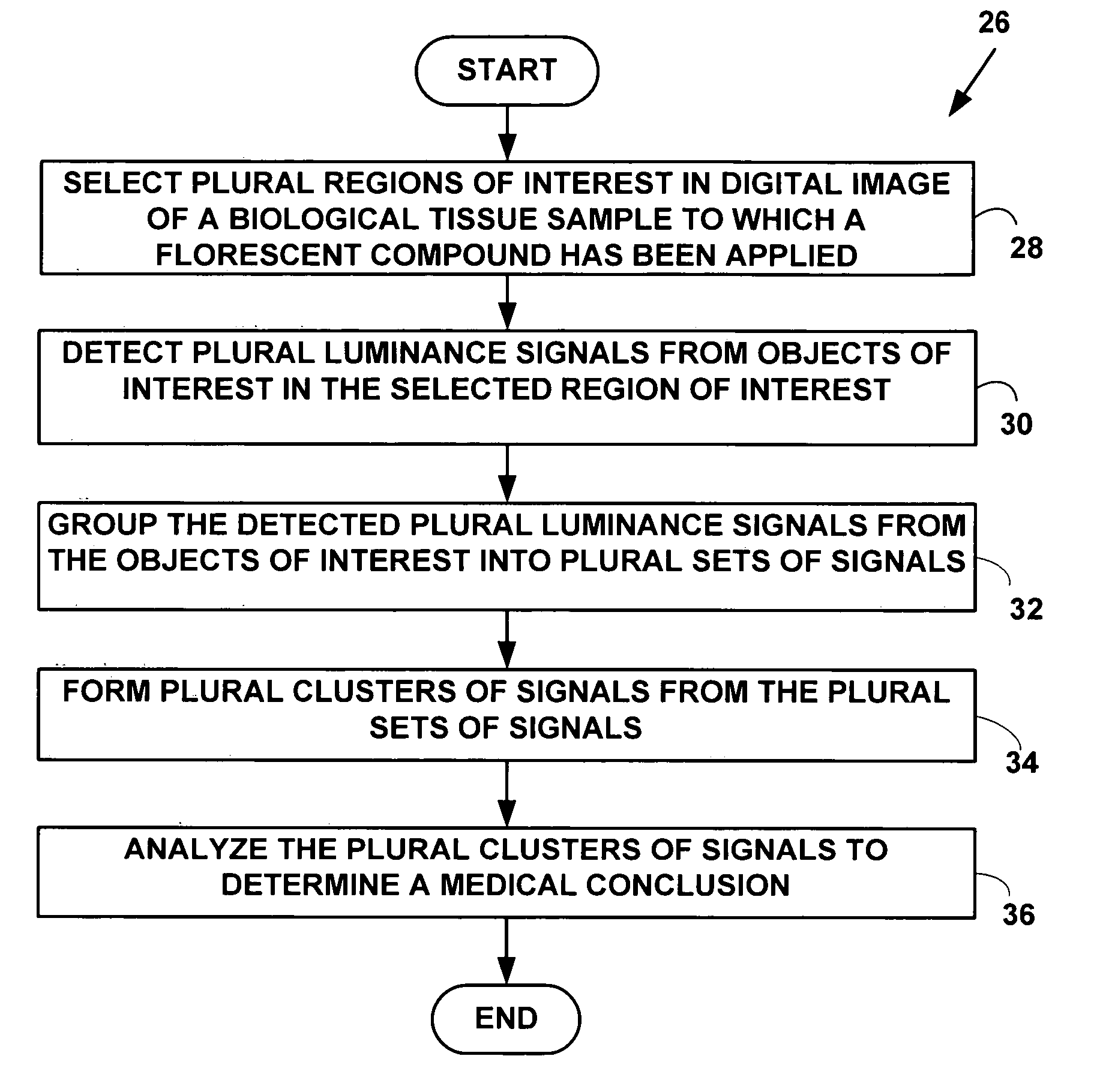
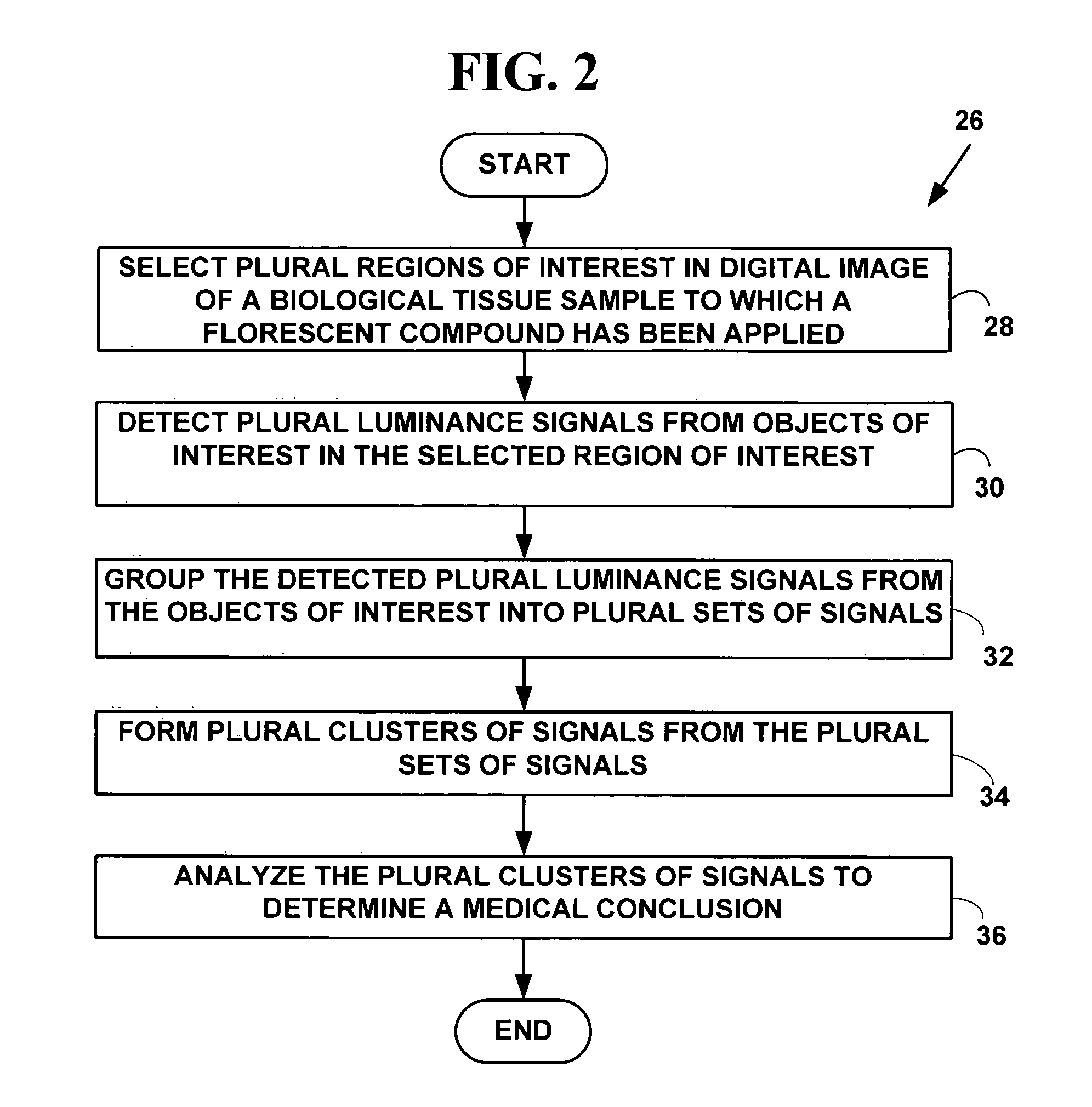
InactiveUS20050136549A1Facilitates automated analysisImage enhancementImage analysisChemical compoundCell membrane
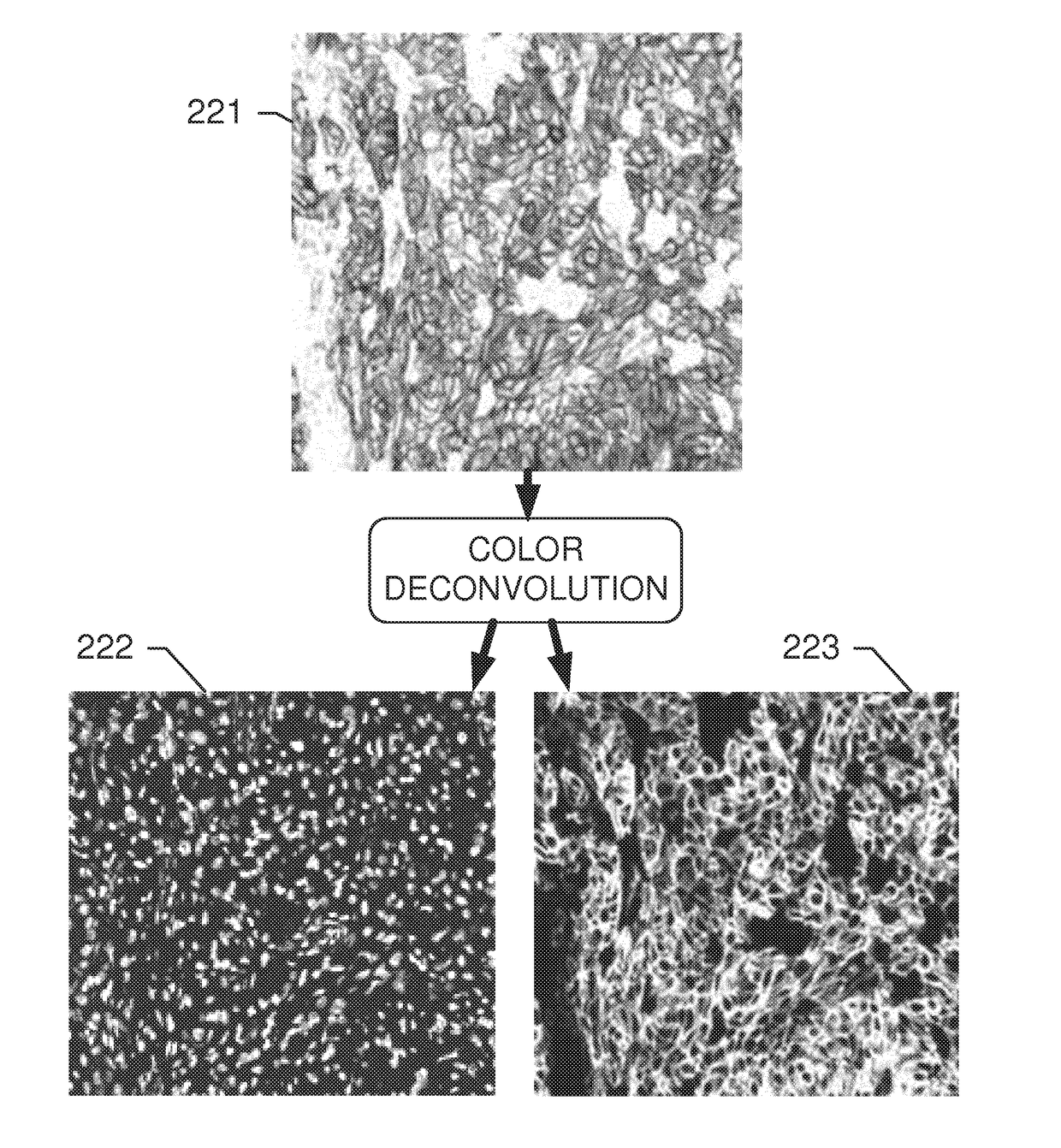
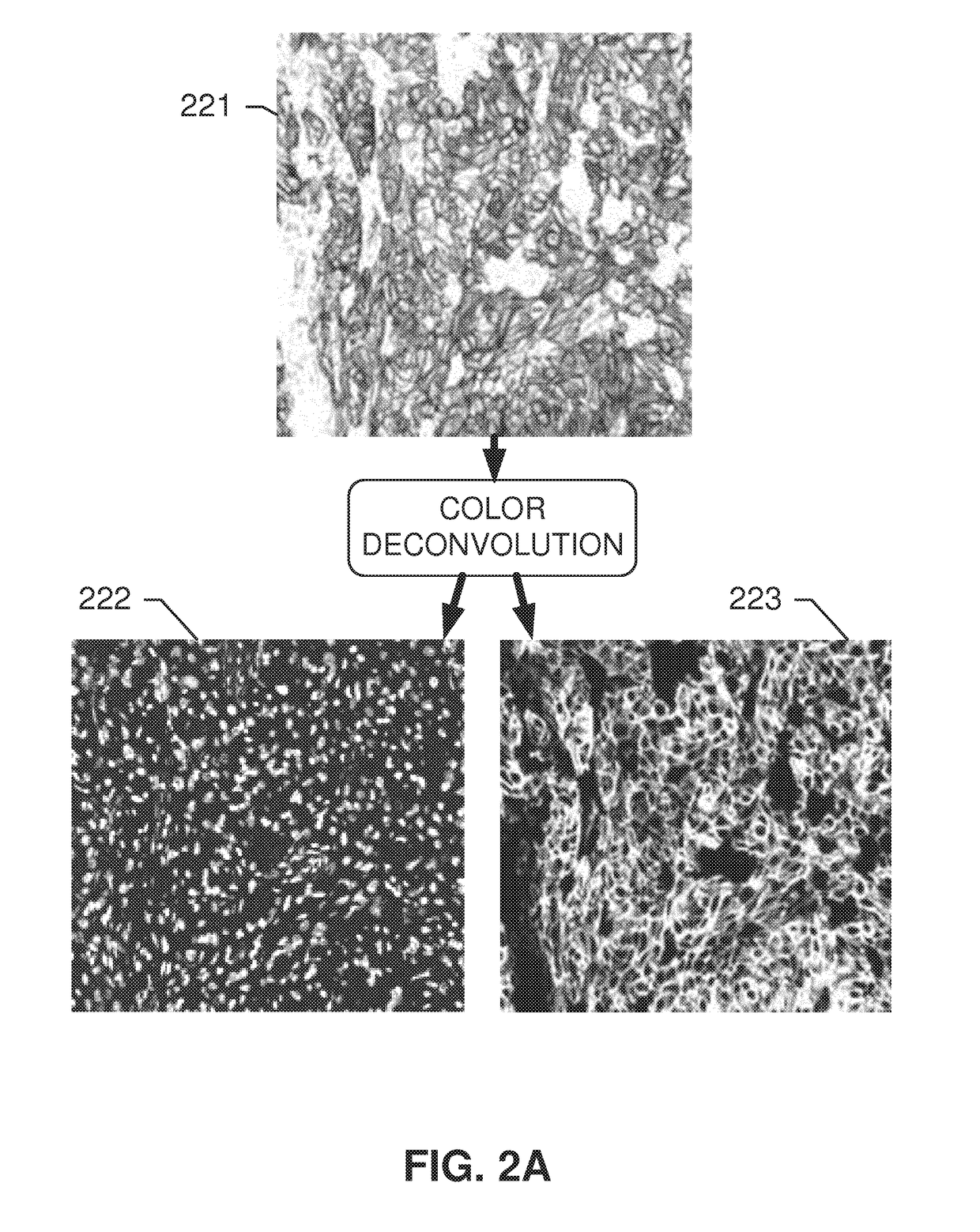
A method and system for automatically determining diagnostic saliency of digital images for medical and / or pathological purposes. Luminance parameters (e.g. intensity, etc.) from a digital image of a biological sample (e.g., tissue cells) to which a chemical compound (e.g., a marker dye) has been applied are automatically analyzed and automatically corrected if necessary. Morphological parameters (e.g., cell membrane, cell nucleus, mitotic cells, etc.) from individual components within the biological sample are automatically analyzed on the digital image. A medical conclusion (e.g., a medical diagnosis or prognosis) is automatically determined from the analyzed luminance and morphological parameters.
Owner:BIOIMAGENE
Cloning pigs using donor nuclei from non-quiescent differentiated cells
InactiveUS6235969B1Superior genotypes of pigsSpeed up genetic progressNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyPresent method
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor differentiated pig cell nuclei into enucleated pig oocytes is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for multiplication of genotypes and transgenic genotypes by the production of fetuses and offspring. Production of genetically engineered or transgenic pig embryos, fetuses and offspring is facilitated by the present method since the differentiated cell source of the donor nuclei can be genetically modified and clonally propagated.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF
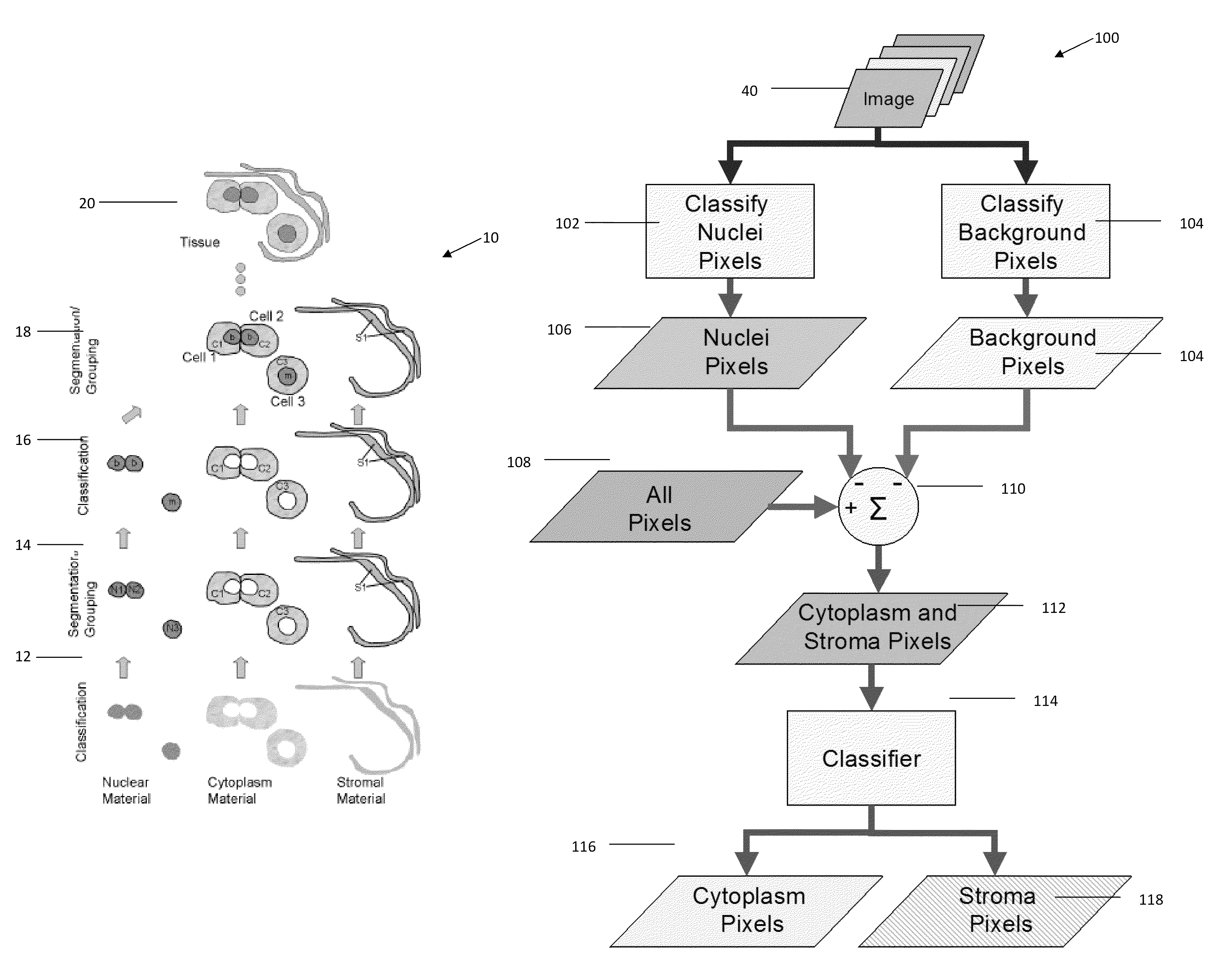
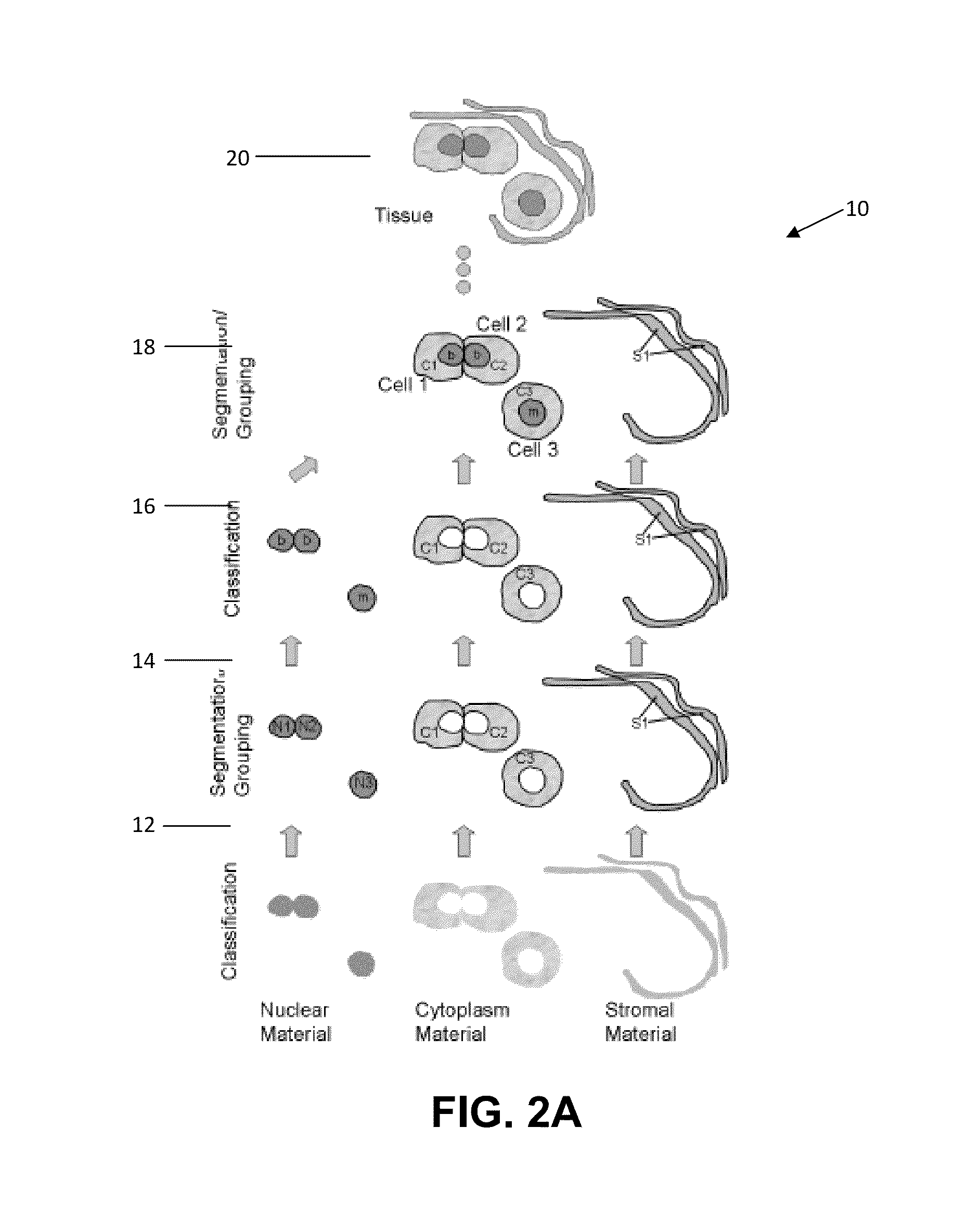
Combinational pixel-by-pixel and object-level classifying, segmenting, and agglomerating in performing quantitative image analysis that distinguishes between healthy non-cancerous and cancerous cell nuclei and delineates nuclear, cytoplasm, and stromal material objects from stained biological tissue materials
InactiveUS8488863B2Improve classification effectImprove classification performanceImage enhancementImage analysisStainingCytoplasm
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
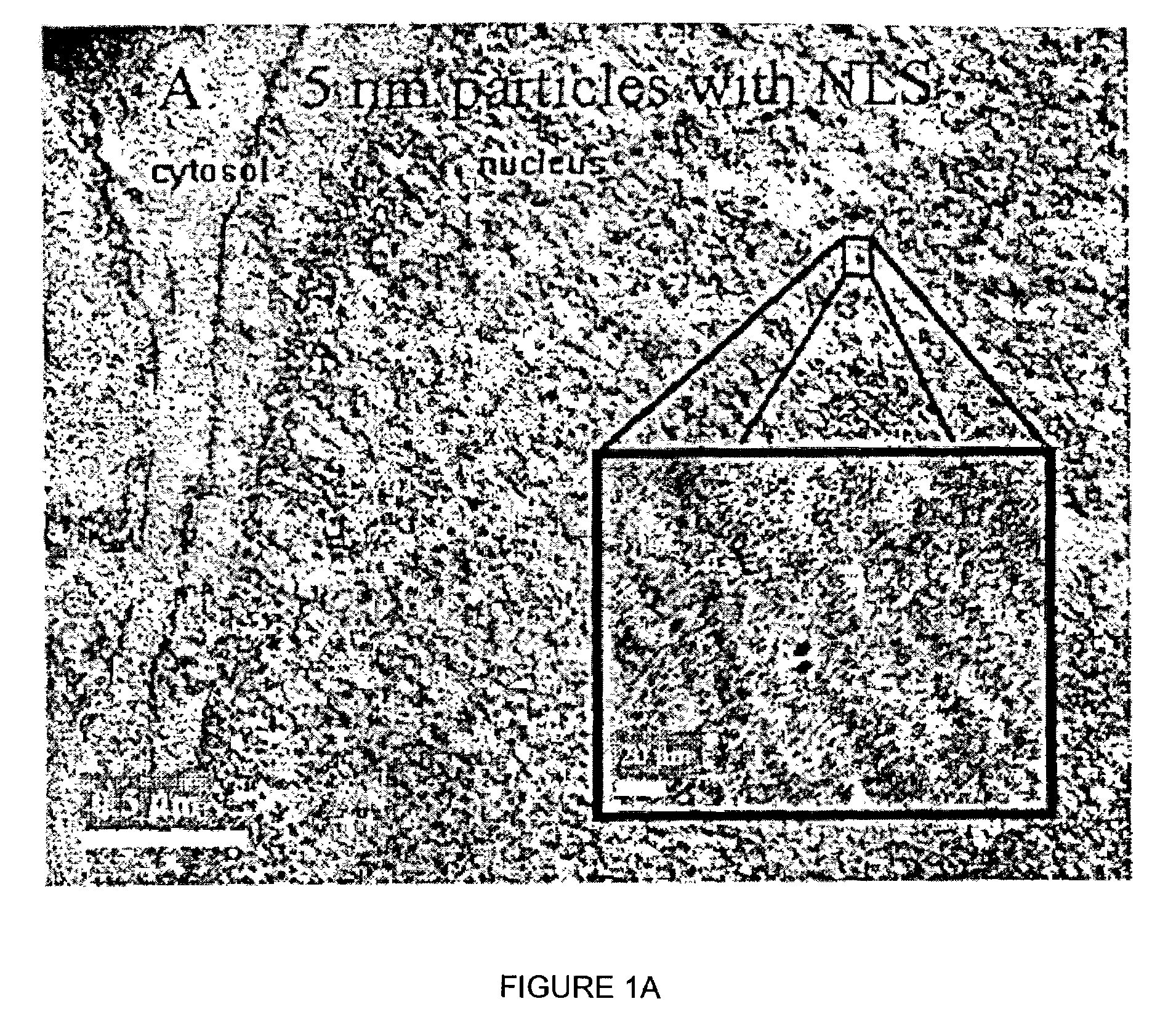
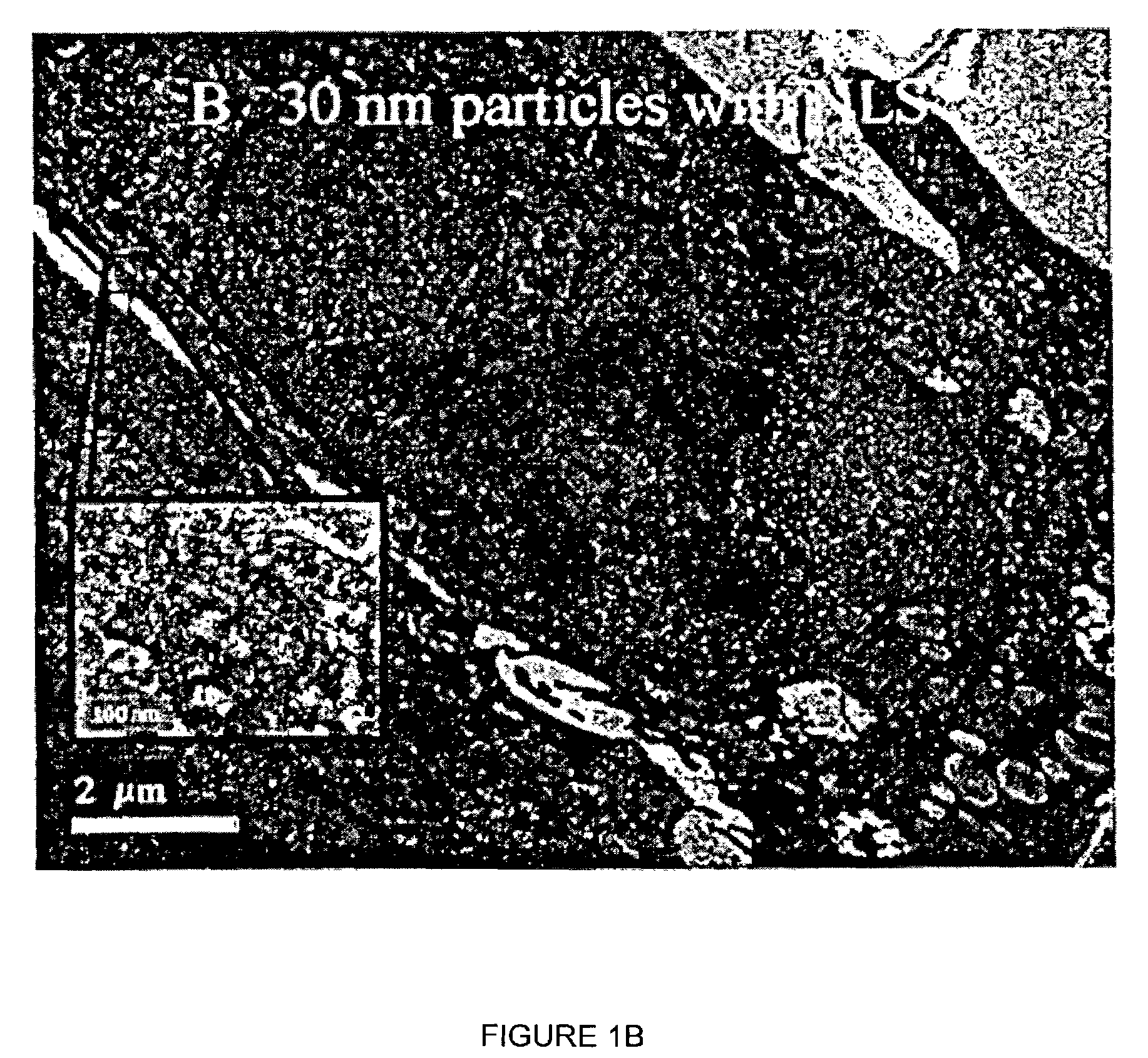
Nanoparticle delivery vehicle
A nanoparticle delivery vehicle, comprising a nanoparticle, an active agent and a nuclear localization signal and methods of modulating gene expression and protein expression employing the nanoparticle delivery vehicle. A representative method includes providing a nanoparticle delivery vehicle comprising a nanoparticle having a diameter of about 30 nm or less, an active agent and a nuclear localization signal; and contacting a target cell with the nanoparticle delivery vehicle, whereby an active agent is delivered to the nucleus of a target cell. Another representative method includes providing a nanoparticle delivery vehicle comprising a nanoparticle having a diameter greater than or equal to about 30 nm, an active agent and a nuclear localization signal; and contacting a target cell with the nanoparticle delivery vehicle, whereby an active agent is delivered to the cytoplasm of a cell.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Automated segmentation, classification, and tracking of cell nuclei in time-lapse microscopy
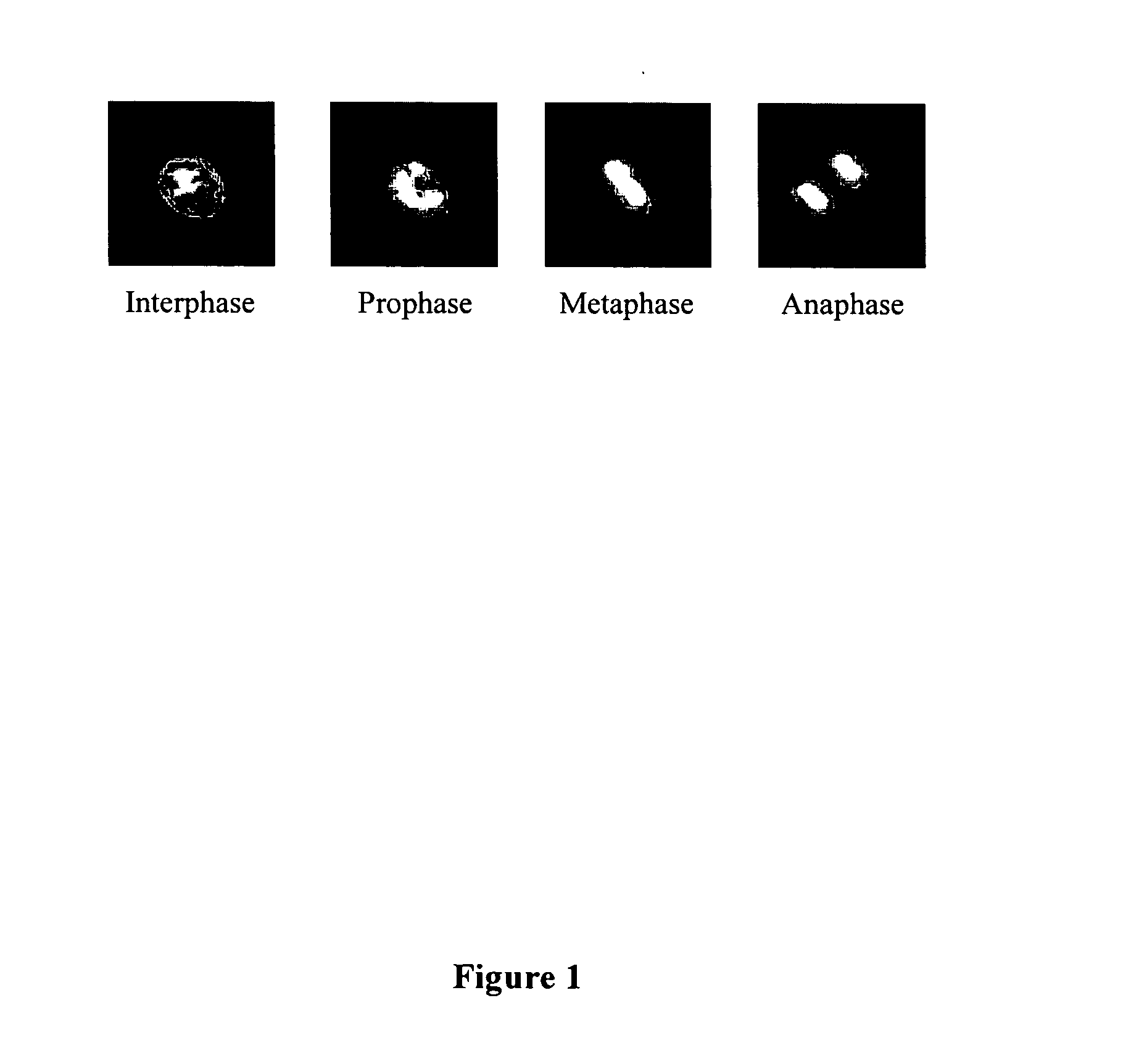
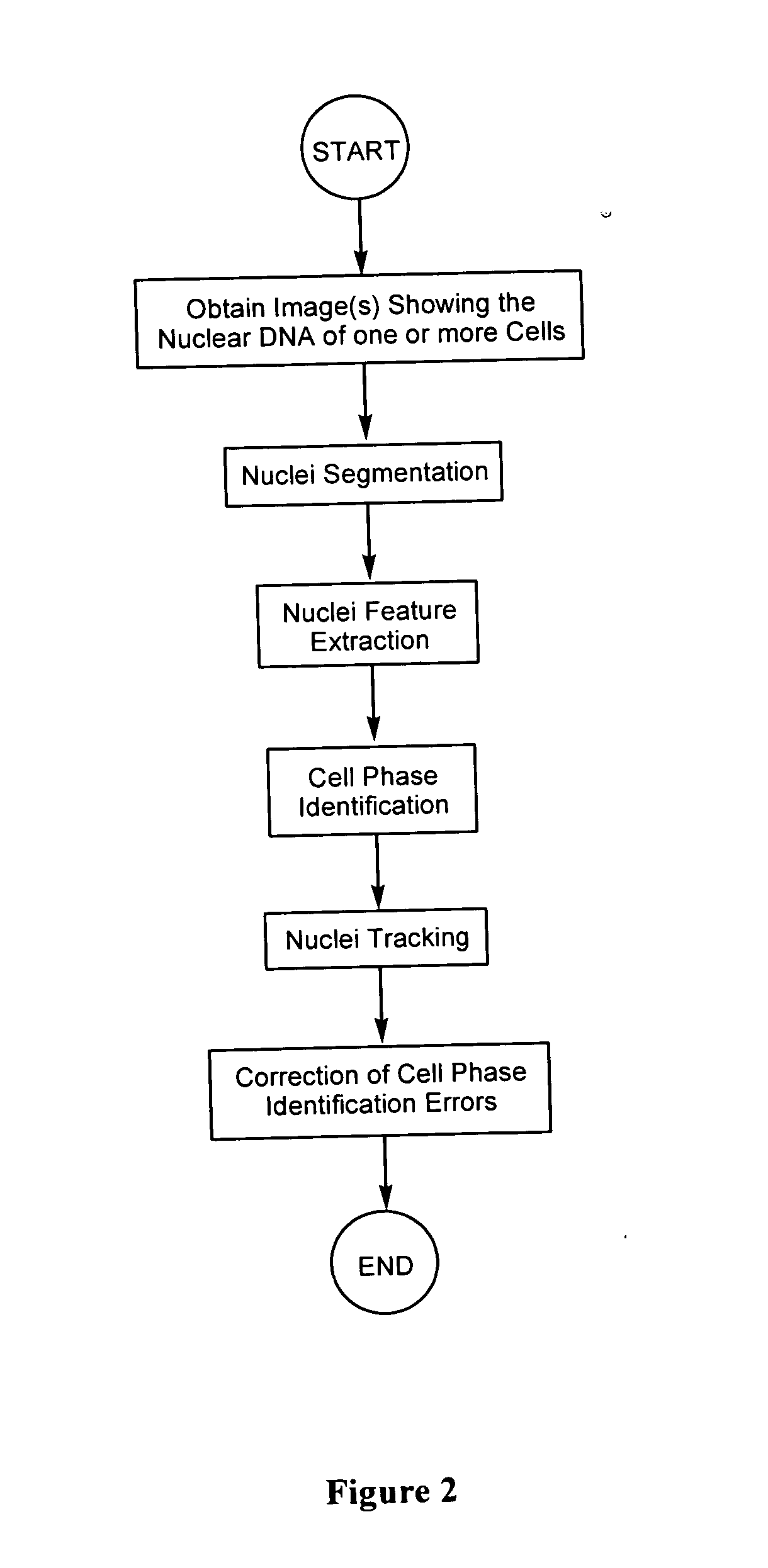
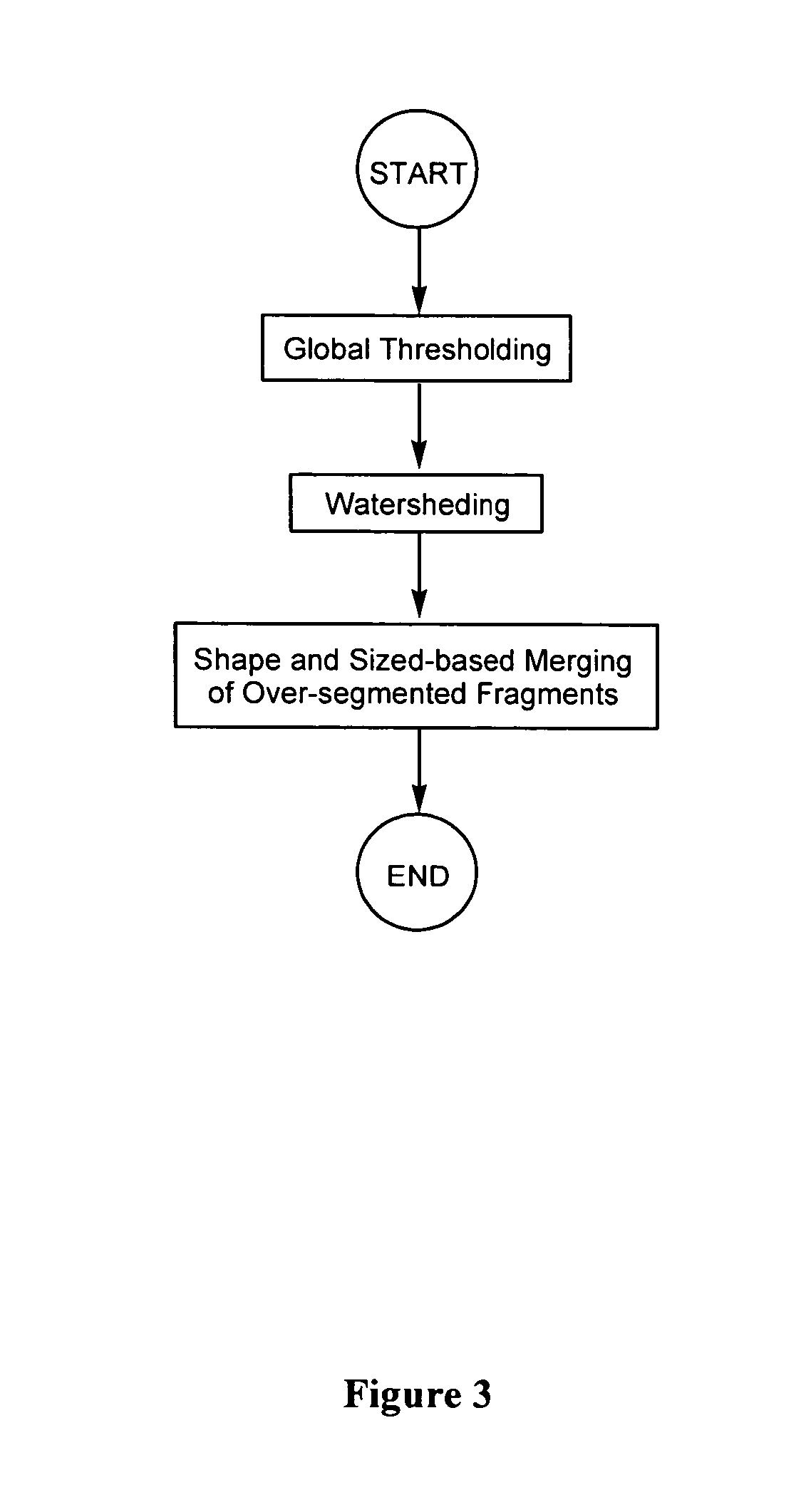
InactiveUS20060127881A1Efficient dynamic cell imaging studyIncrease capacityImage enhancementImage analysisAutomated segmentationInterphase Cell
Methods and apparatus are provided for the automated analysis of images of living cells acquired by time-lapse microscopy. The new methods and apparatus can be used for the segmentation, classification and tracking of individual cells in a cell population, and for the extraction of biologically significant features from the cell images. Based upon certain extracted features, the inventive image analysis methods can characterize a cell as mitotic or interphase and / or can classify a cell into one of the following mitotic phases: prophase, metaphase, arrested metaphase, and anaphase with high accuracy.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMENS HOSPITAL INC
Methods for determining spatial and temporal gene expression dynamics in single cells
PendingUS20190218276A1High throughput analysisHigh resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against virusesCell markerSingle cell transcriptome
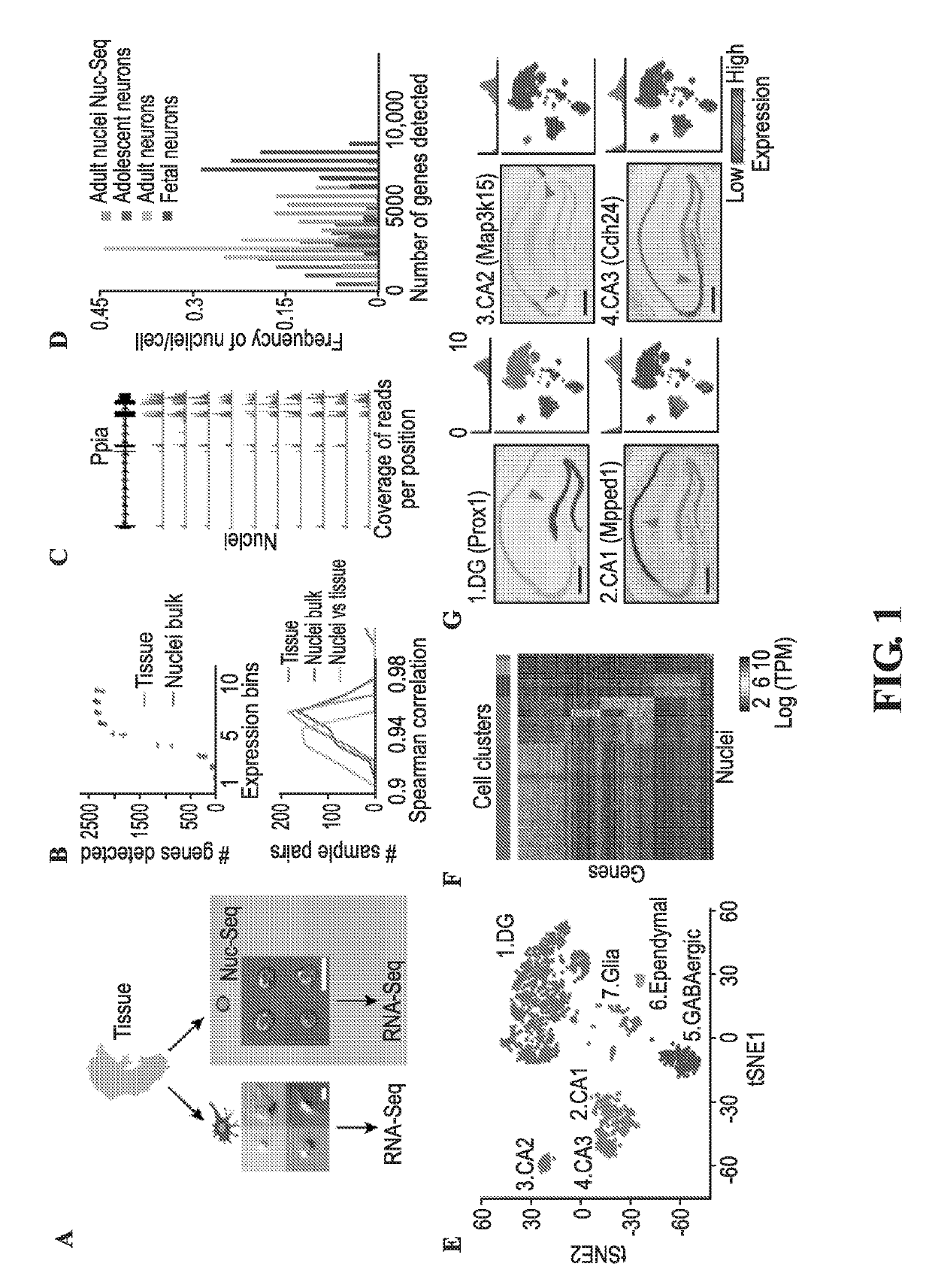
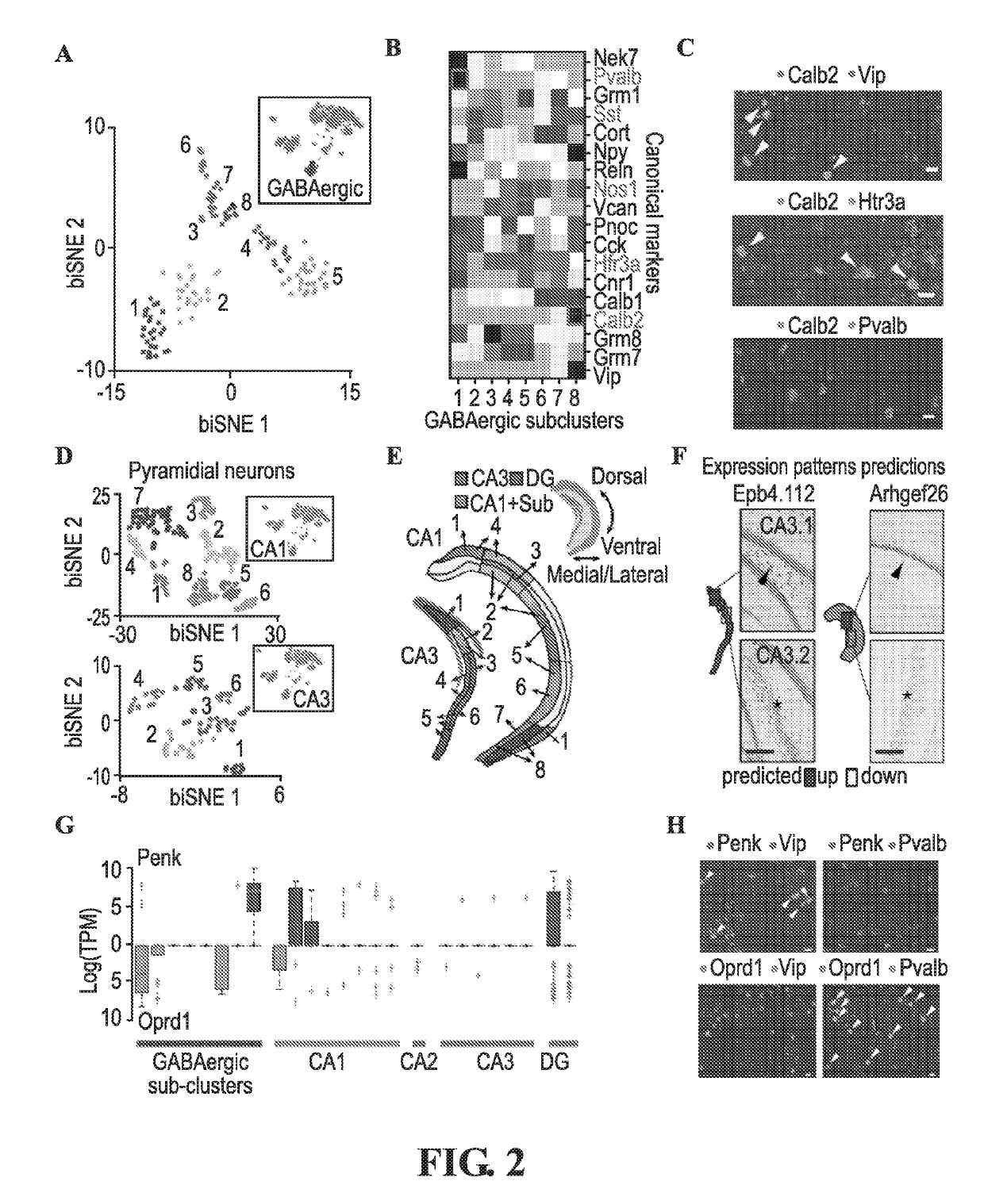
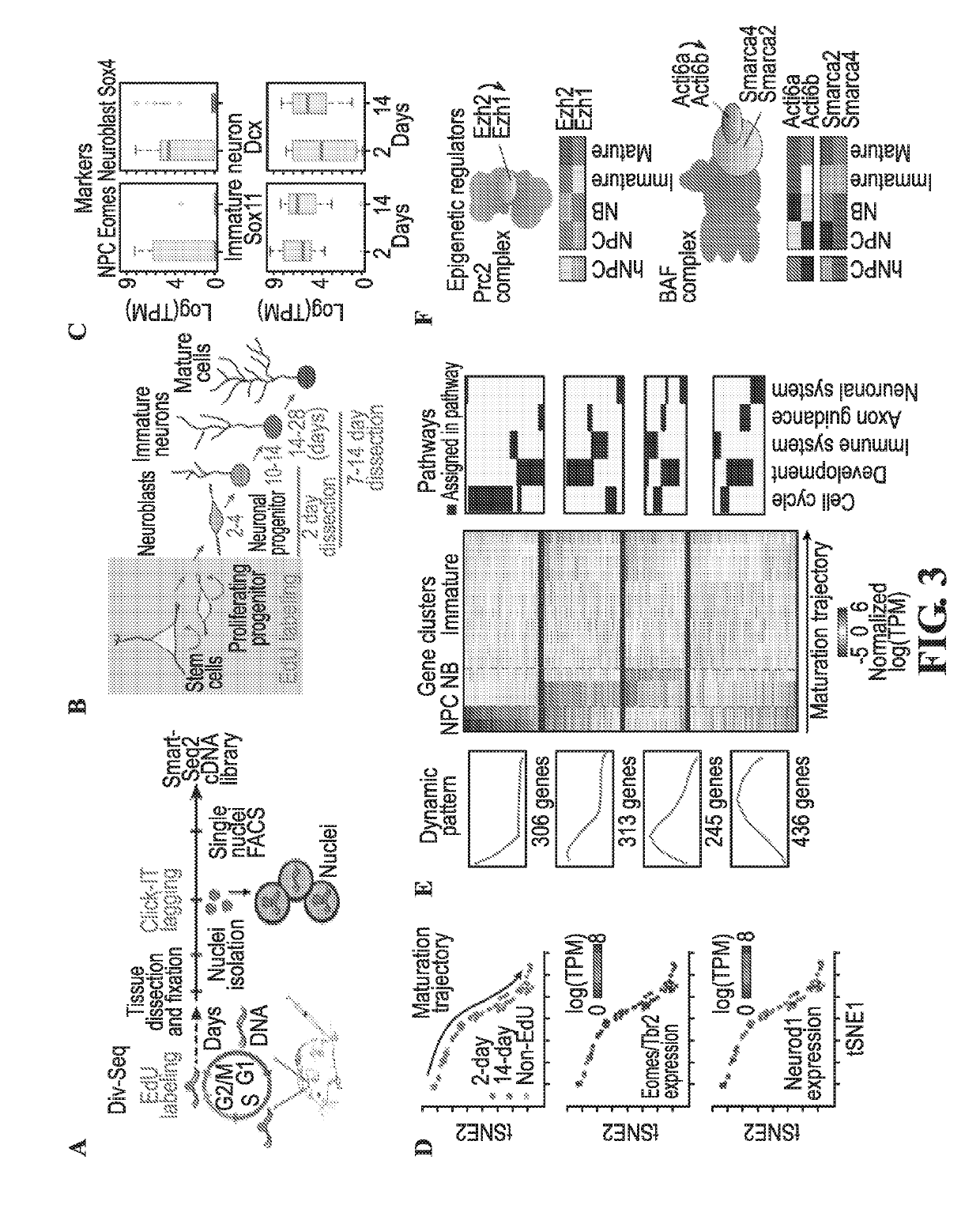
Transcriptomes of individual neurons provide rich information about cell types and dynamic states. However, it is difficult to capture rare dynamic processes, such as adult neurogenesis, because isolation from dense adult tissue is challenging, and markers for each phase are limited. Here, Applicants developed Nuc-seq, Div-Seq, and Dronc-Seq. Div-seq combines Nuc-Seq, a scalable single nucleus RNA-Seq method, with EdU-mediated labeling of proliferating cells. Nuc-Seq can sensitively identify closely related cell types within the adult hippocampus. Div-Seq can track transcriptional dynamics of newborn neurons in an adult neurogenic region in the hippocampus. Dronc-Seq uses a microfluidic device to co-encapsulate individual nuclei in reverse emulsion aqueous droplets in an oil medium together with one uniquely barcoded mRNA-capture bead. Finally, Applicants found rare adult newborn GABAergic neurons in the spinal cord, a non-canonical neurogenic region. Taken together, Nuc-Seq, Div-Seq and Dronc-Seq allow for unbiased analysis of any complex tissue.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
Medical image analysis for identifying biomarker-positive tumor cells
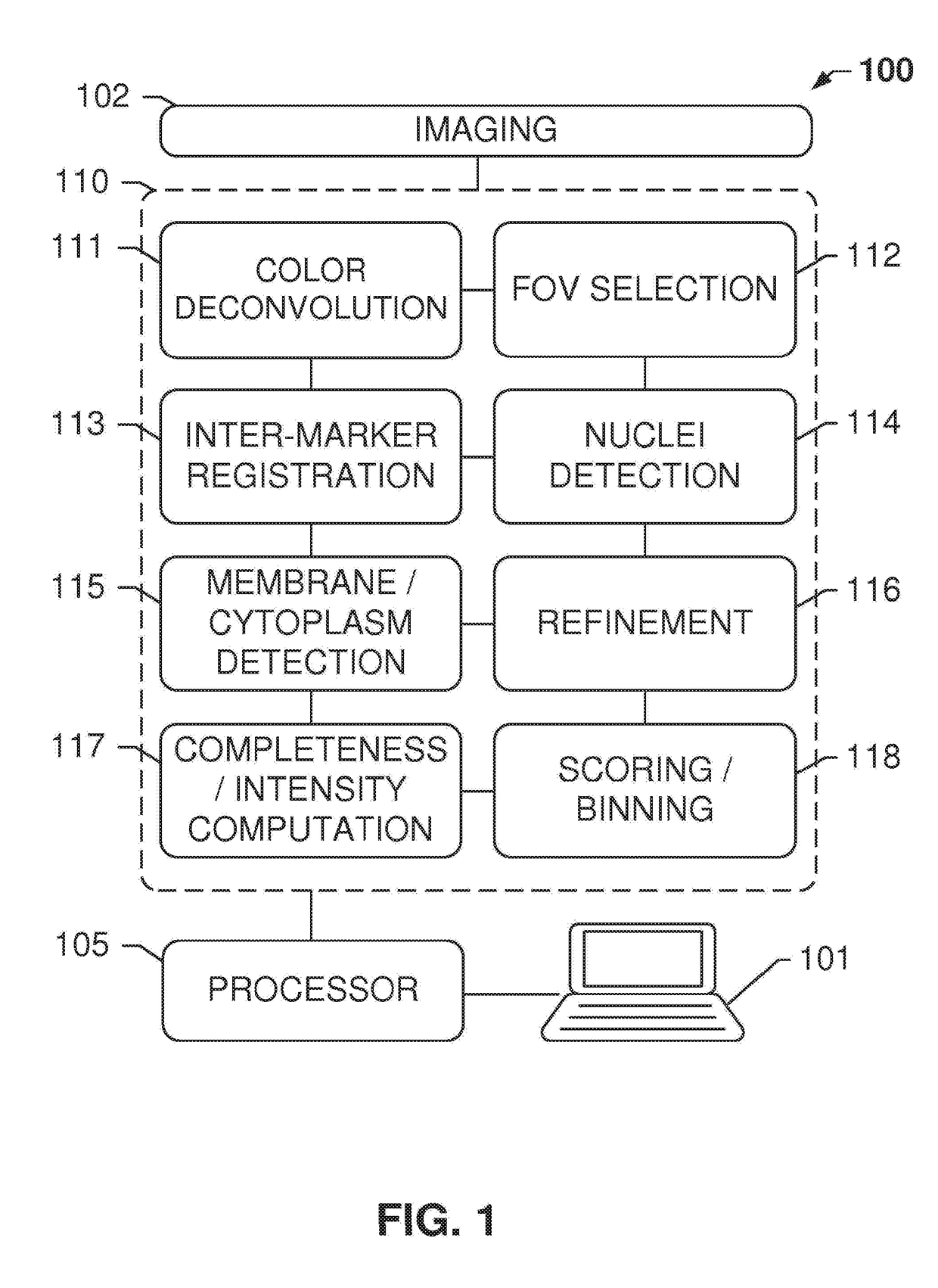
ActiveUS20170103521A1Accurate methodImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImaging analysisCell membrane
A method for identifying biomarker-positive tumor cells is disclosed. The method includes, for example, reading a first digital image and a second digital image into memory, the first and second digital image depicting the same area of a first slide; identifying a plurality of nuclei and positional information of said nuclei by analyzing the light intensities in the first digital image; identifying cell membranes which comprise the biomarker by analyzing the light intensities in the second digital image and by analyzing the positional information of the identified nuclei; and identifying biomarker-positive tumor cells in said area, wherein a biomarker-positive tumor cell is a combination of one identified nucleus and one identified cell membrane that surrounds the identified nucleus.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Delivery system using mAb 3E10 and mutants and/or functional fragments thereof
InactiveUS7189396B1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCancer cellCytotoxicity
A monoclonal antibody, 3E10, and active fragments thereof that selectively are transported in vivo to the nucleus of mammalian cells without cytotoxic effect are provided. The antibody and other molecules that bind to a variant of myosin IIb heavy chain found in the nucleus of skeletal muscle cells are useful as a non-viral delivery vector to target skeletal muscle in vivo. By contrast, in vitro the monoclonal antibody penetrates and is transported to the nucleus of multiple cell lines derived from different tissue types and can be used in screening tests to identify molecules that modulate growth of cells, such as cancer cells. Non-cytotoxic vectors for delivering a drug, polynucleotide or polypeptide selectively to skeletal muscle cells are also provided.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
Device for the production of capillary jets and micro-and nanometric particles
InactiveUS7341211B2High mechanical stiffnessGood effectFuel injection apparatusMachines/enginesMicrometerNanoparticle
The invention relates to a method and devices for the production of capillary microjets and microparticles that can have a size of between hundreds of micrometers and several nanometers. The inventive method makes use of the combined effects of electrohydrodynamic forces, fluid-dynamic forces and a specific geometry in order to produce micro- and nano-capsules or fluid jets, single- or multi-component, which, upon disintegrating or splitting, form a significantly monodispersed spray of drops which have a controlled micro- or nanometric size and which can also comprise a specific internal structure, such as, for example, a nucleus which is surrounded by a cortex of a different substance or several concentric or non-concentric nuclei or vesicles which are surrounded by a cortex.
Owner:UNIV DE SEVILLA
Process for modifying a cell by putting material into the cell
InactiveUS20160272961A1Maximize freedomPerformance maximizationOther foreign material introduction processesElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentDevice formNanoparticle
The present invention relates to a process for modifying a cell by putting material into the cell. More particularly, the present invention is directed to a process for modifying a cell by putting material, such as protein, DNA, RNA, ribozyme, various compounds, collagen, cell nucleus, mitochondria or nanoparticle into the cell, by using a sealing-less device formed within one solid and comprises a first passage on which the cell passes; a second passage on which said material passes and connected to the first passage at a position randomly selected between both ends of the first passage; and an apparatus which applies pressure difference or electric potential difference on the first passage and the second passage.
Owner:FEMTOBIOMED INC
Automatic screening system and automatic screening method using thin-prep cytology test
ActiveCN102682305AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionScreening method
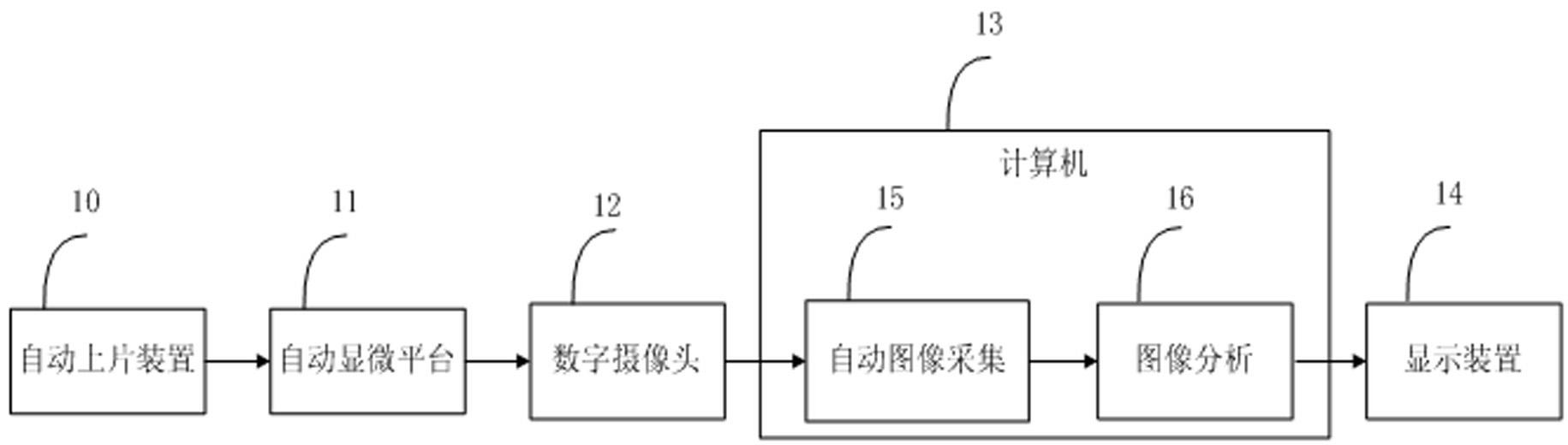
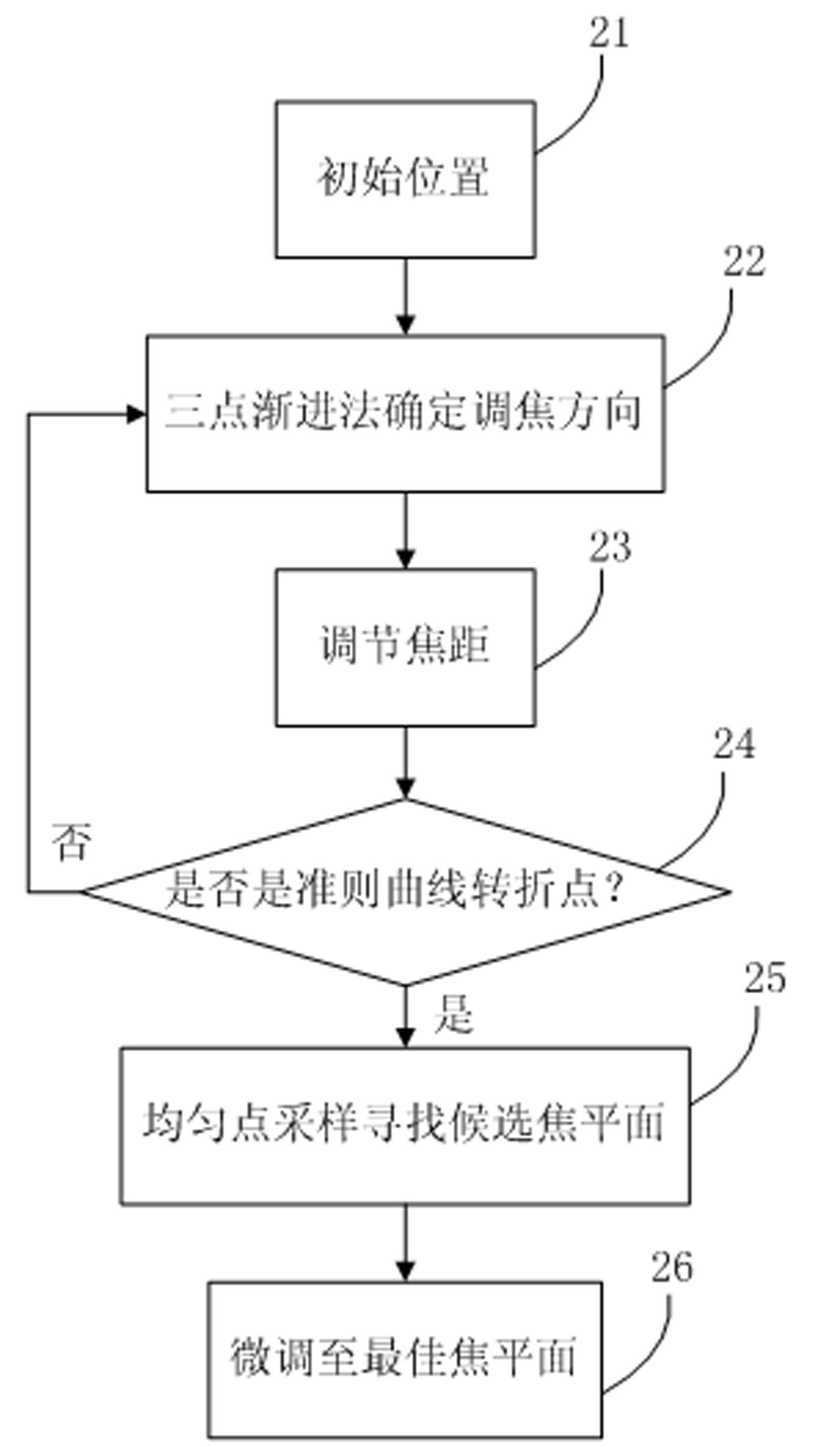
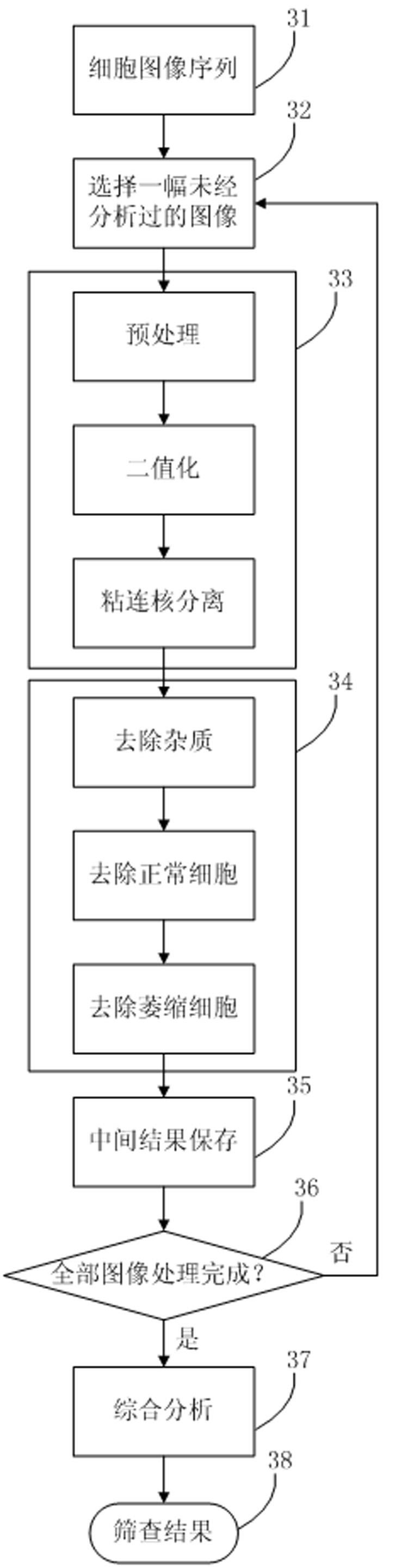
The invention discloses an automatic screening system and an automatic screening method using a thin-prep cytology test. The system comprises an image acquisition module, an image segmentation module, a target recognition module and a comprehensive analysis module. The method provided by the invention respectively adopts a three-point evolutionary uniform sampling method to guarantee the reliability of automatic focusing, the coarse-to-fine segmentation algorithm to improve the segmentation accuracy of pathological cell nucleuses, a series of filters to rapidly filter various impurities, and a cascade classifier training method to greatly reduce the false positive rate, and uses relative features to conduct comprehensive analysis. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity over pathological cells, high specificity over normal cells, high recognition speed and high automation degree, so that the diagnostic accuracy can be improved and the workload of a cytopathologist is reduced at the same time.
Owner:MAIKE SIBEI INTELLIGENT APP SHENZHEN
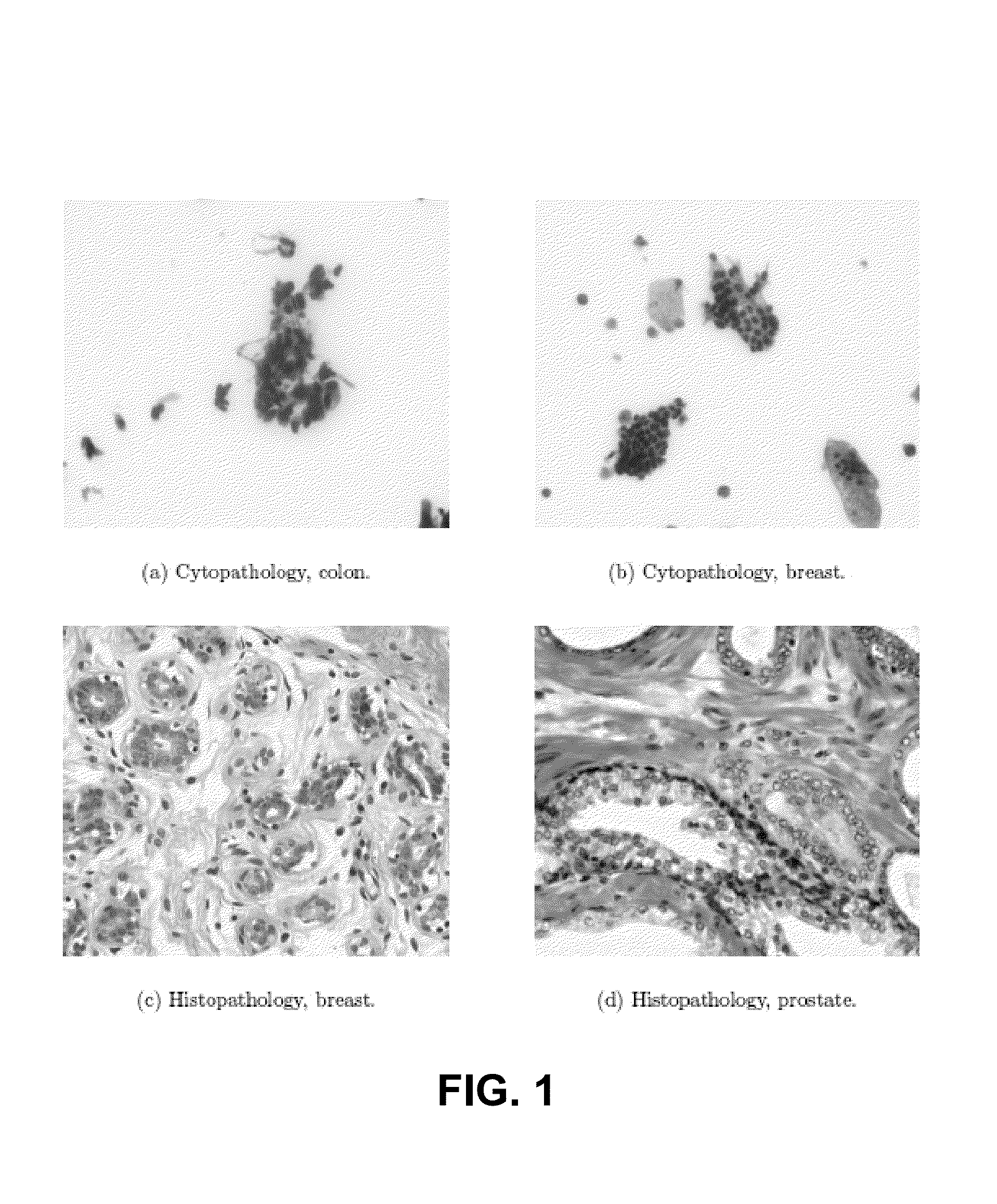
Method and device for segmentation of breast cancer pathologic image
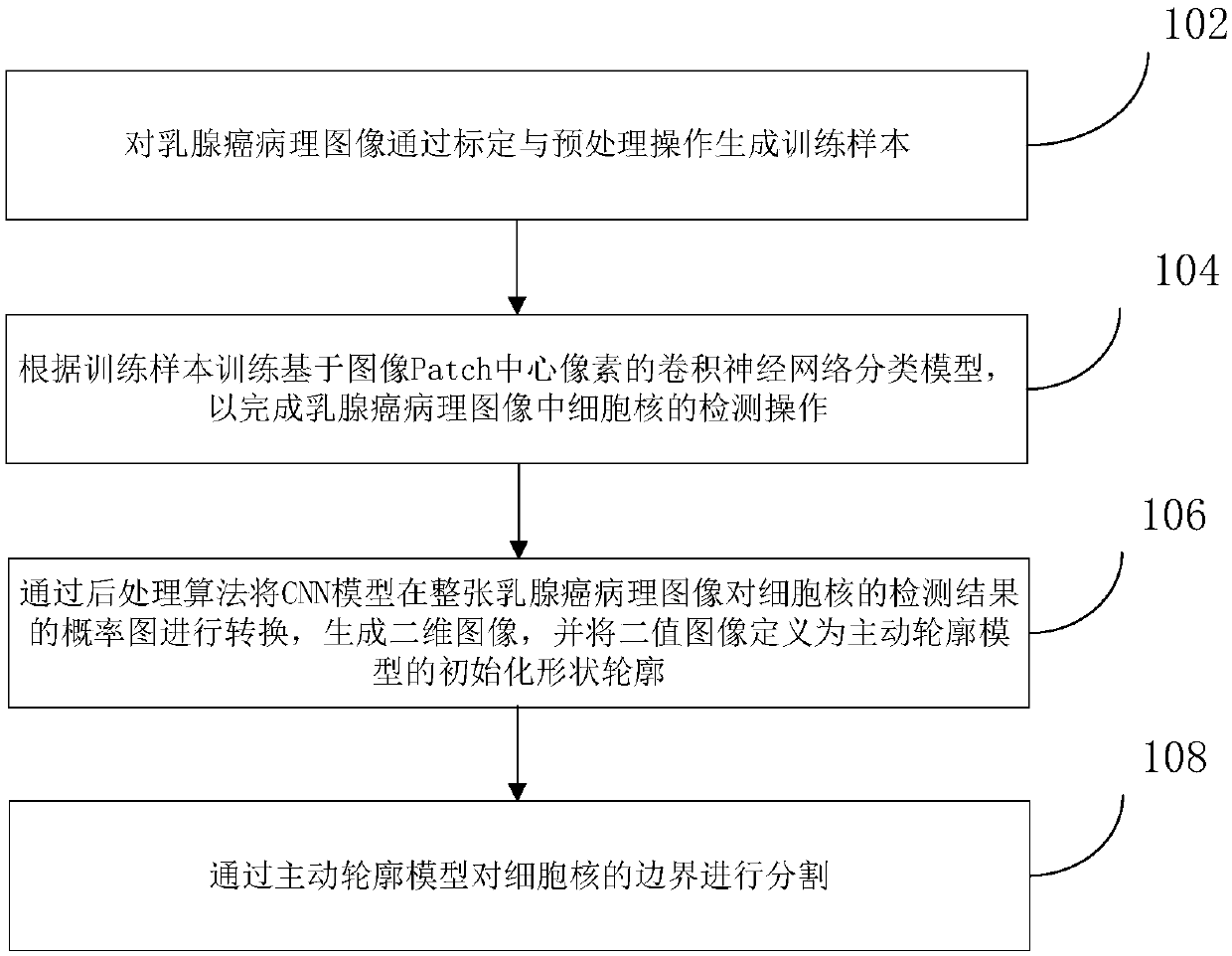
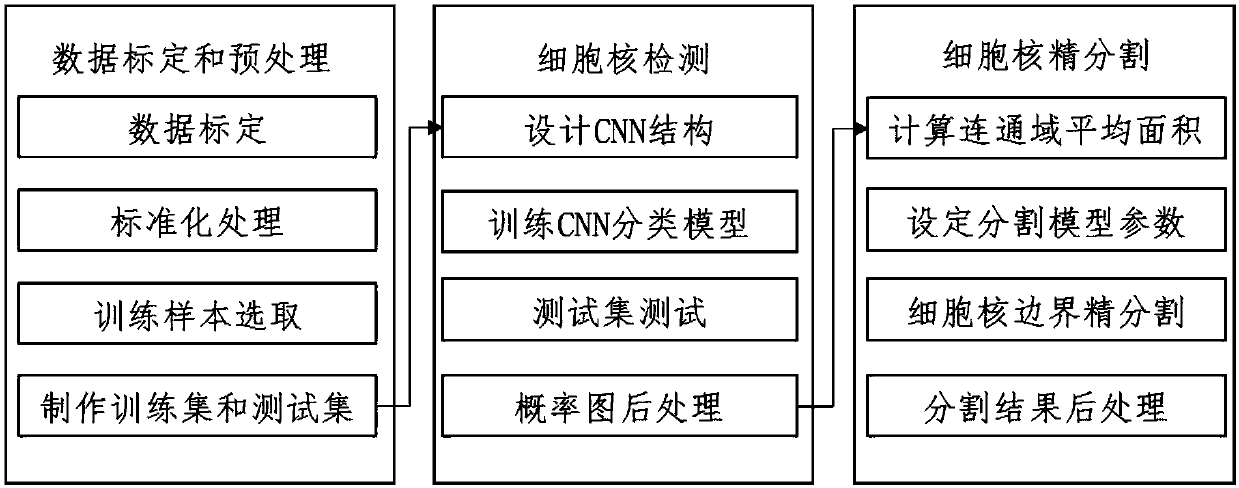
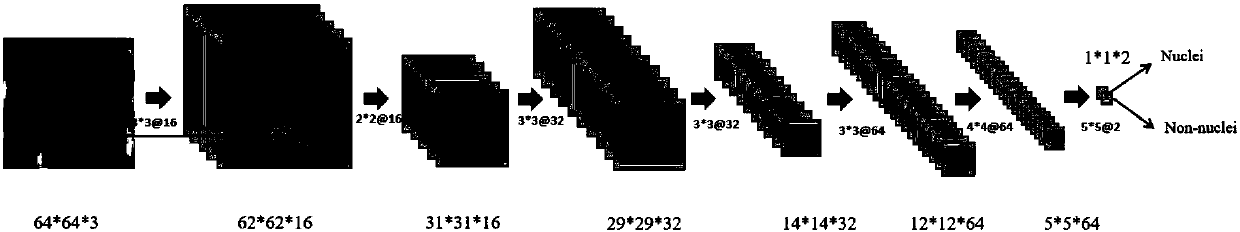
The present invention discloses a method for segmentation of a breast cancer pathologic image. There are three main modules consisting of data preprocessing, cell nucleus detection and cell nucleus boundary refinement segmentation. Pathology experts perform artificial calibration of a cell nucleus boundary, the pathologic image is subjected to standardization processing to eliminate dying difference, a training sample based on a cell nucleus pixel, and a cell nucleus boundary pixel and a background pixel is made to train a convolutional neural network classifier and achieve a classifier basedon a Patch image center pixel. A trained convolutional neural network model is detected on the whole pathologic image to output a probability graph, a postprocessing algorithm is employed to generatea binary image as an initialized shape outline of an active outline model, and the active outline model is employed to perform refinement segmentation of the cell nucleus boundary. The method and thedevice for segmentation of the breast cancer pathologic image are high in segmentation accuracy, and can achieve the algorithm for segmentation of overlapped cells in the breast cancer pathologic image. The present invention further discloses a device for segmentation of a breast cancer pathologic image.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Classifying nuclei in histology images
ActiveUS20170372117A1Reduced dimensionPromote resultsImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionRadiologyTissue sample
Disclosed, among other things, is a computer device and computer-implemented method of classifying cells within an image of a tissue sample comprising providing the image of the tissue sample as input; computing nuclear feature metrics from features of nuclei within the image; computing contextual information metrics based on nuclei of interest with the image; classifying the cells within the image using a combination of the nuclear feature metrics and contextual information metrics.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Method and system for digital image based flourescent in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis
A method and system for automated digital fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) image analysis. Luminance parameters from a digital image of a biological tissue sample to which a fluorescent compound (e.g., LSI-HER-2 / neu and CEP-17 dyes) have been applied are analyzed to determine plural regions of interest. Fluorescent color signals in the plural regions of interest including plural cell nuclei are identified, classified and grouped into plural groups. Each of the plural groups is validated based on pre-defined conditions. A medical diagnosis or prognosis or medical, life science or biotechnology experiment conclusion determined using a count of plural ratios of validated fluorescent color signals within each of the cell nuclei within the plural groups.
Owner:BIOIMAGENE
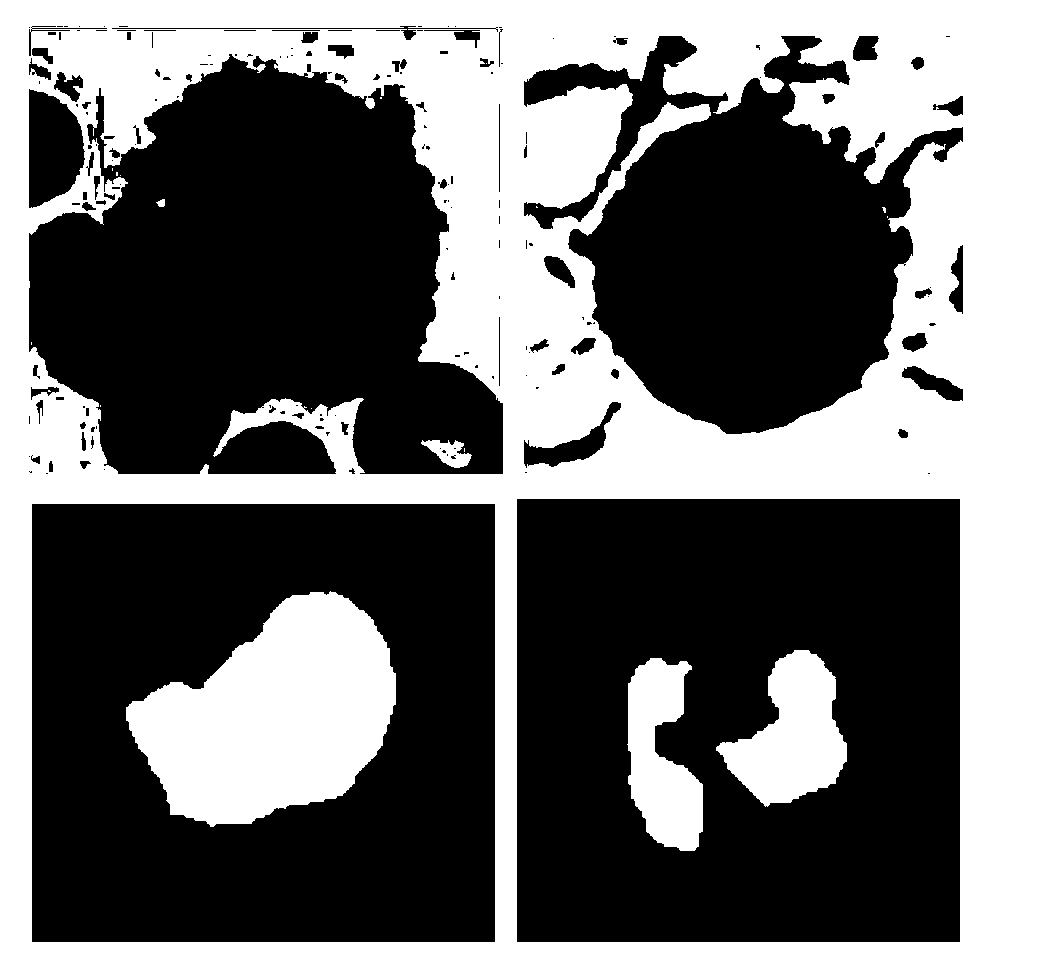
White blood cell image accurate segmentation method and system based on support vector machine
InactiveCN103473739AAccurate segmentationImprove stabilityImage enhancementImage analysisWhite blood cellVisual saliency
The invention discloses a white blood cell image accurate segmentation method and system based on a support vector machine. The method comprises performing nucleus initial positioning and segmenting, performing rough expansion so as to obtain a substantial area labeled graph of cells, and accurately segmenting the cells by using color characteristics and the classifier of the support vector machine. According to the method provided by the invention, on one hand, according to a mankind visual saliency attention mechanism, the sensitivity of human eyes to the change of image edges are simulated, and a nucleus area can be accurately and rapidly segmented by using the clustering of edge-color pairs; and on the other hand, the adopted classifier of the support vector machine has excellent stability and anti-interference performance, and at the same time the space relationship of color information and pixel points are fully utilized so that the training sample sampling mode of the classifier of the support vector machine is improved, thus the accurate segmentation of white blood cells in a cell small image can be realized.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com