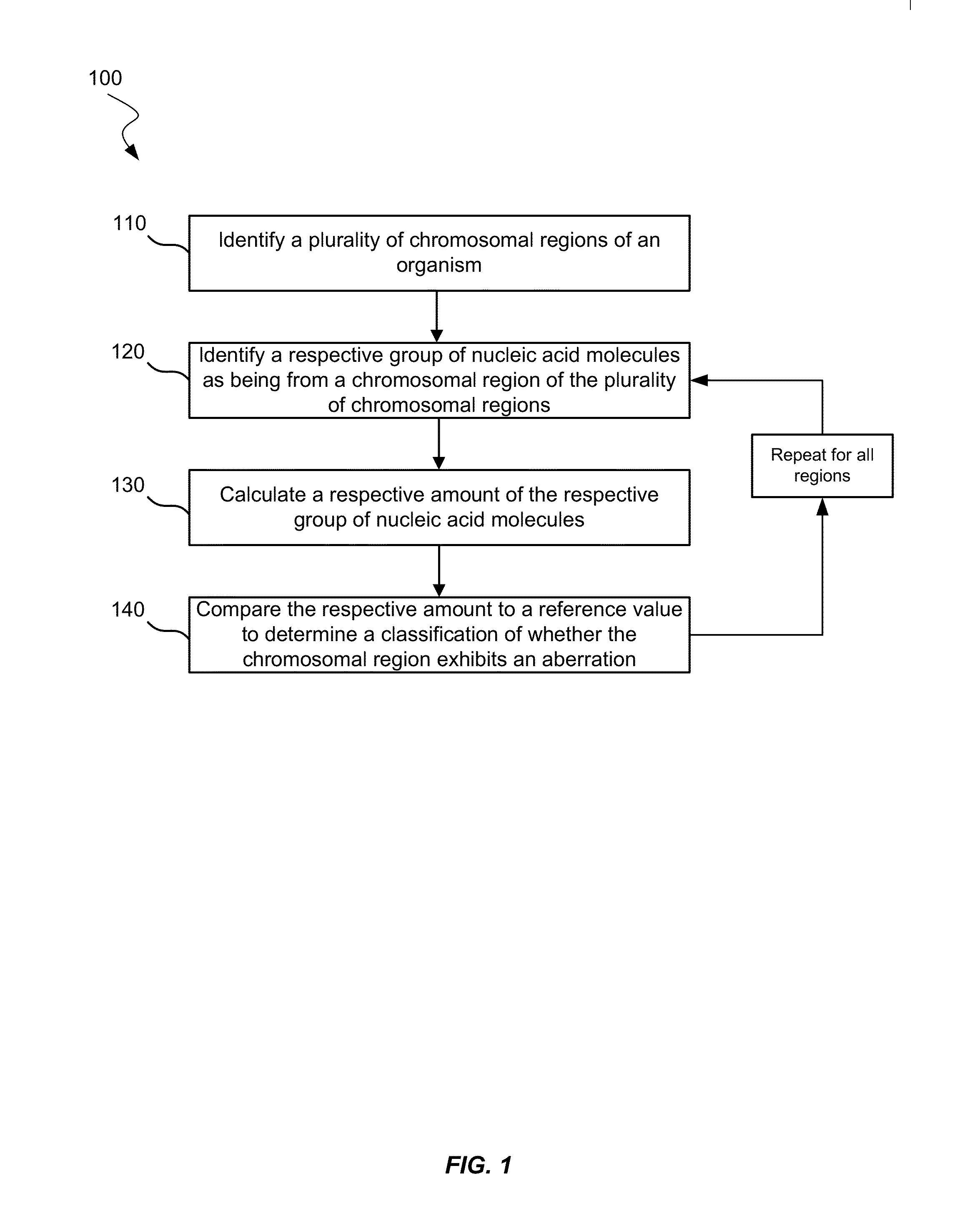
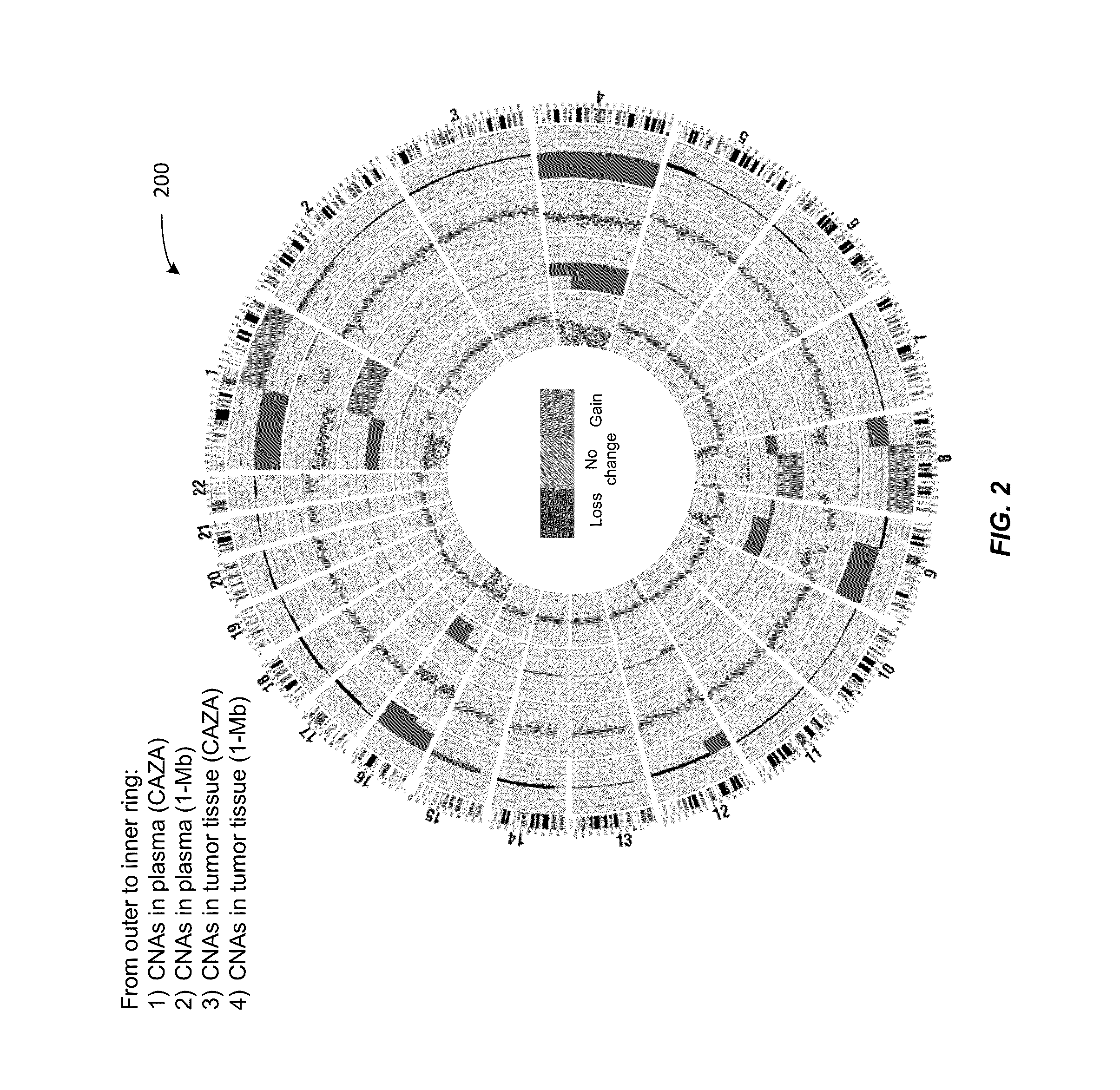
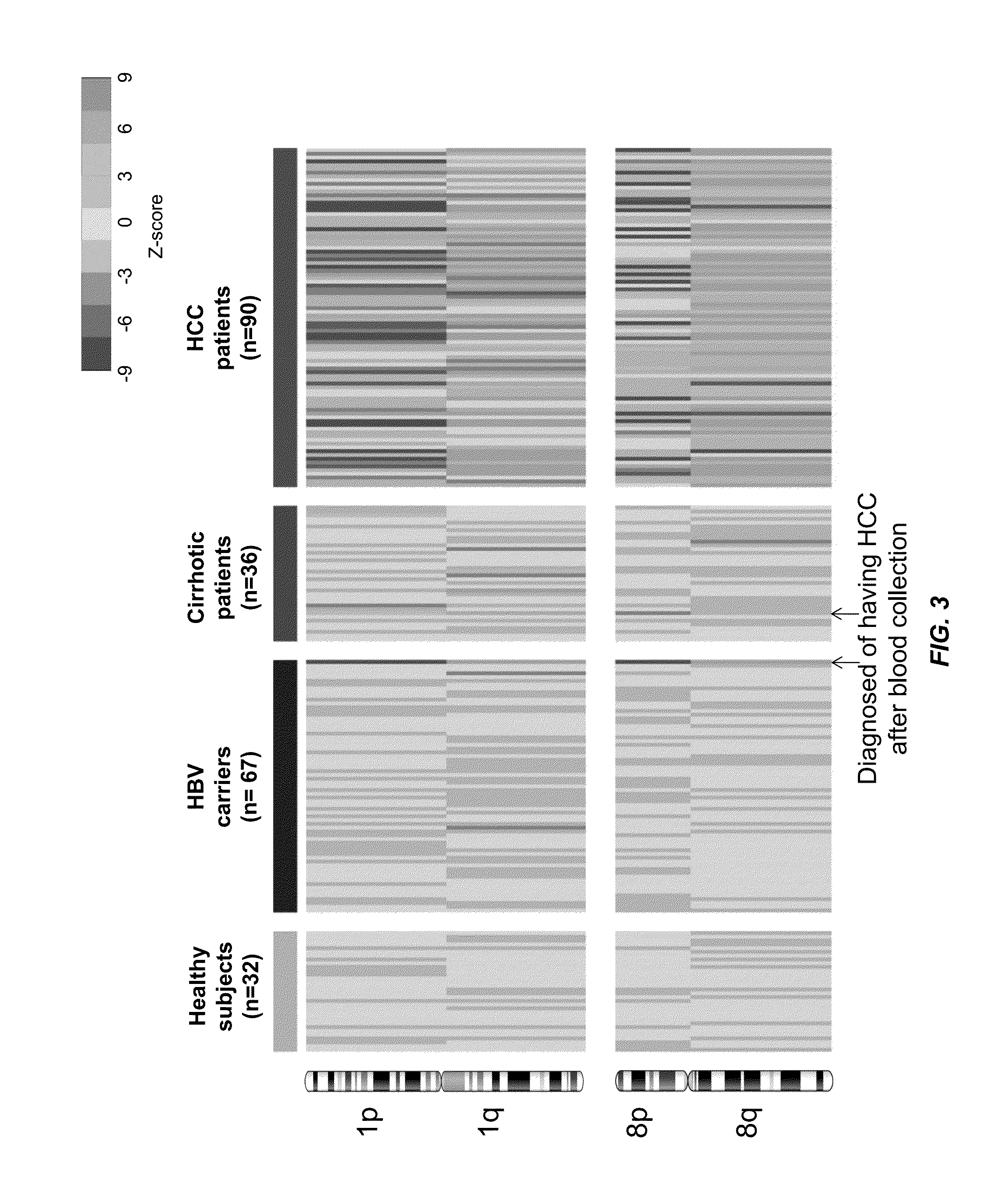
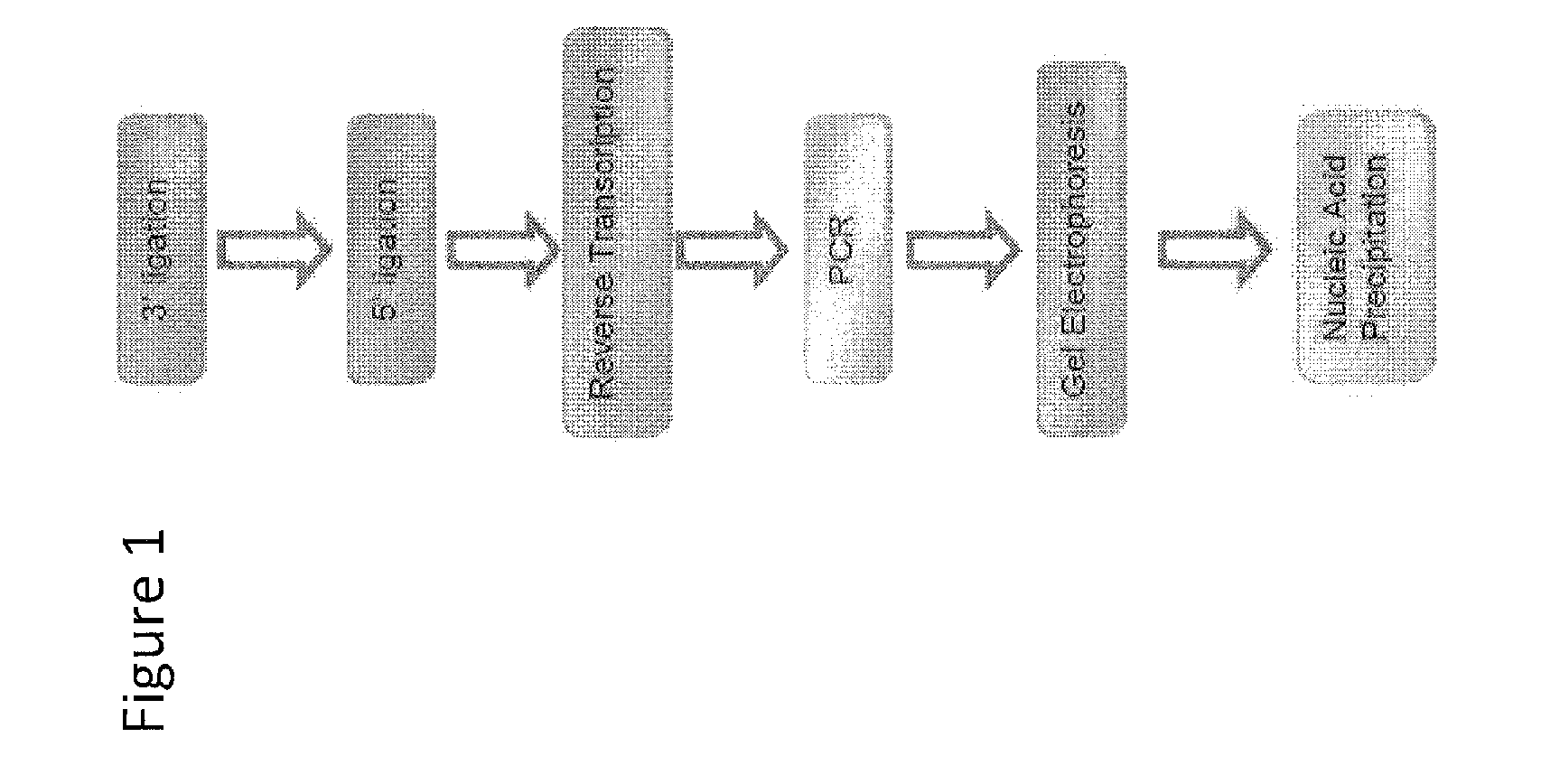
Patents
Literature
48 results about "Massive parallel sequencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
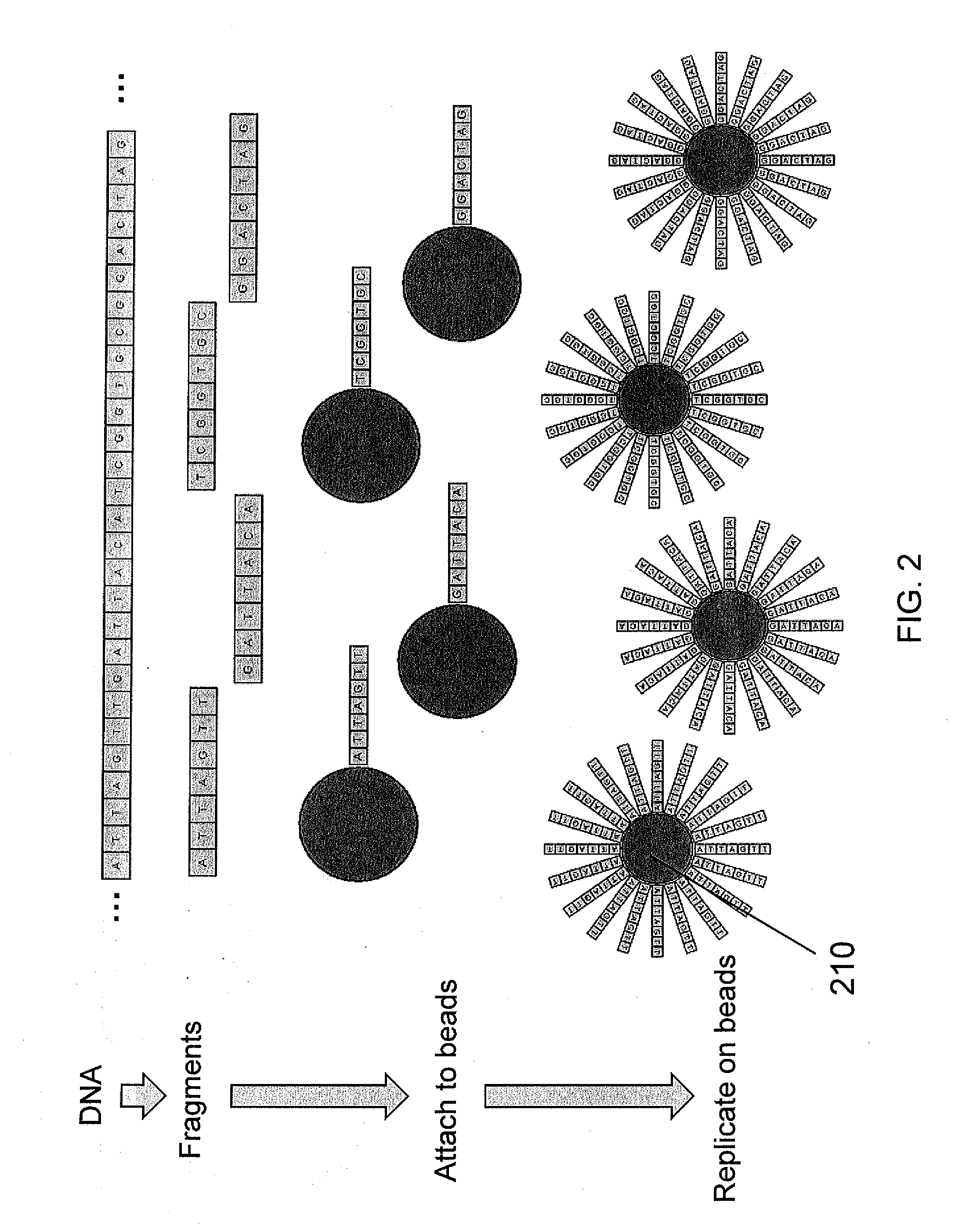
Massive parallel sequencing or massively parallel sequencing is any of several high-throughput approaches to DNA sequencing using the concept of massively parallel processing; it is also called next-generation sequencing (NGS) or second-generation sequencing. Some of these technologies emerged in 1994-1998 and have been commercially available since 2005. These technologies use miniaturized and parallelized platforms for sequencing of 1 million to 43 billion short reads (50-400 bases each) per instrument run.
Noninvasive Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy by Sequencing
InactiveUS20100112575A1Maximum resultMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMassive parallel sequencingFetal aneuploidy
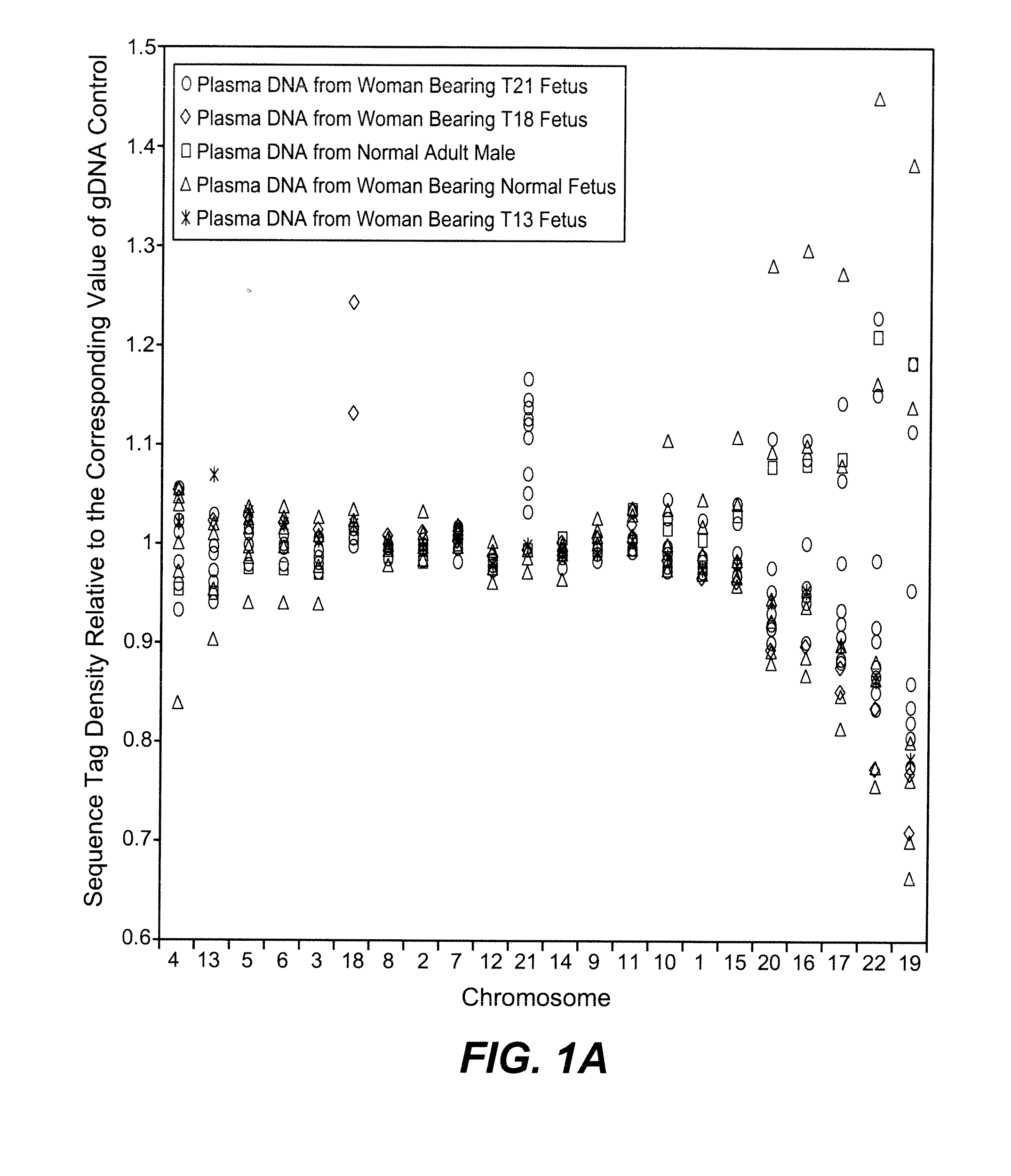
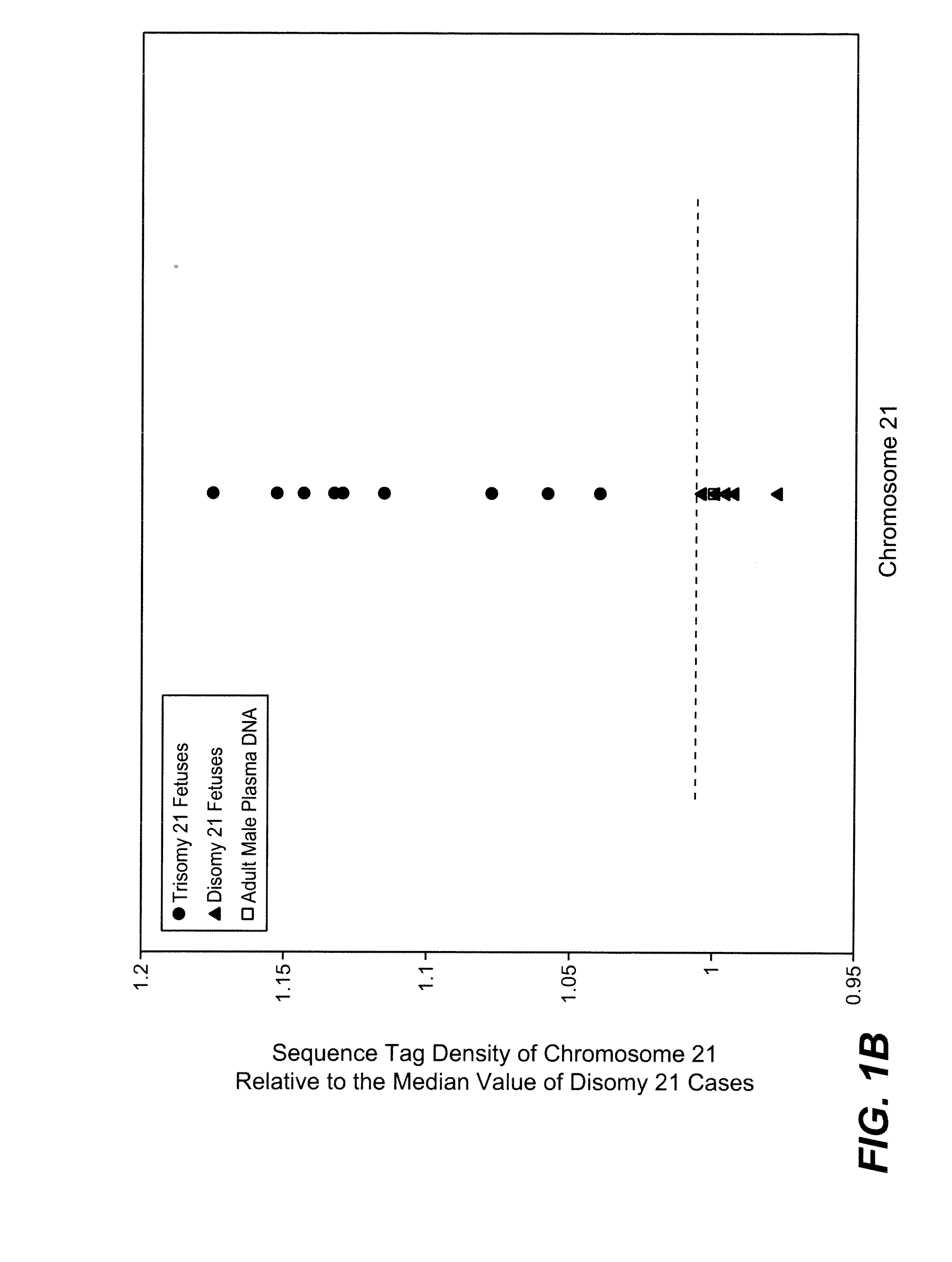
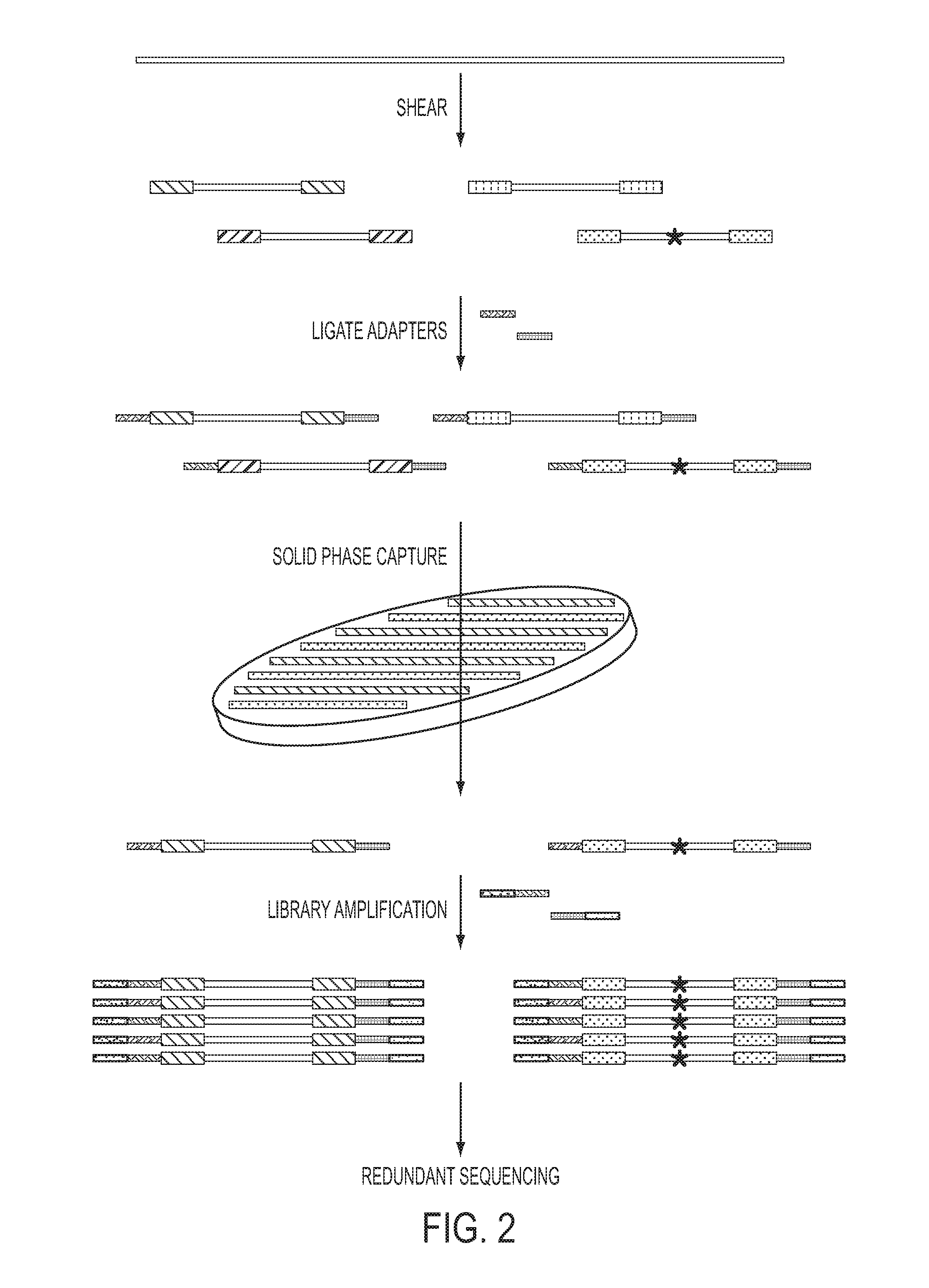
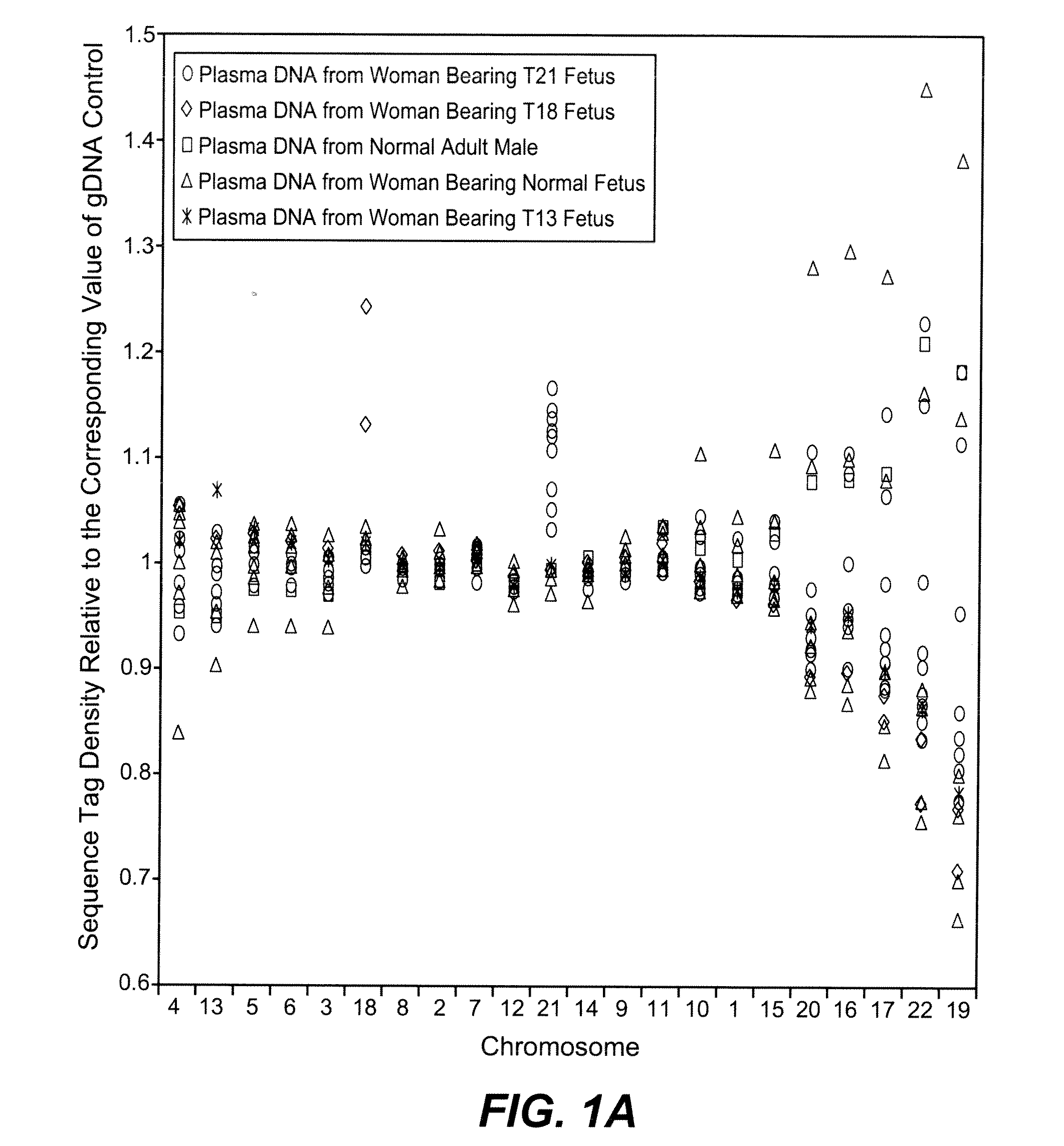
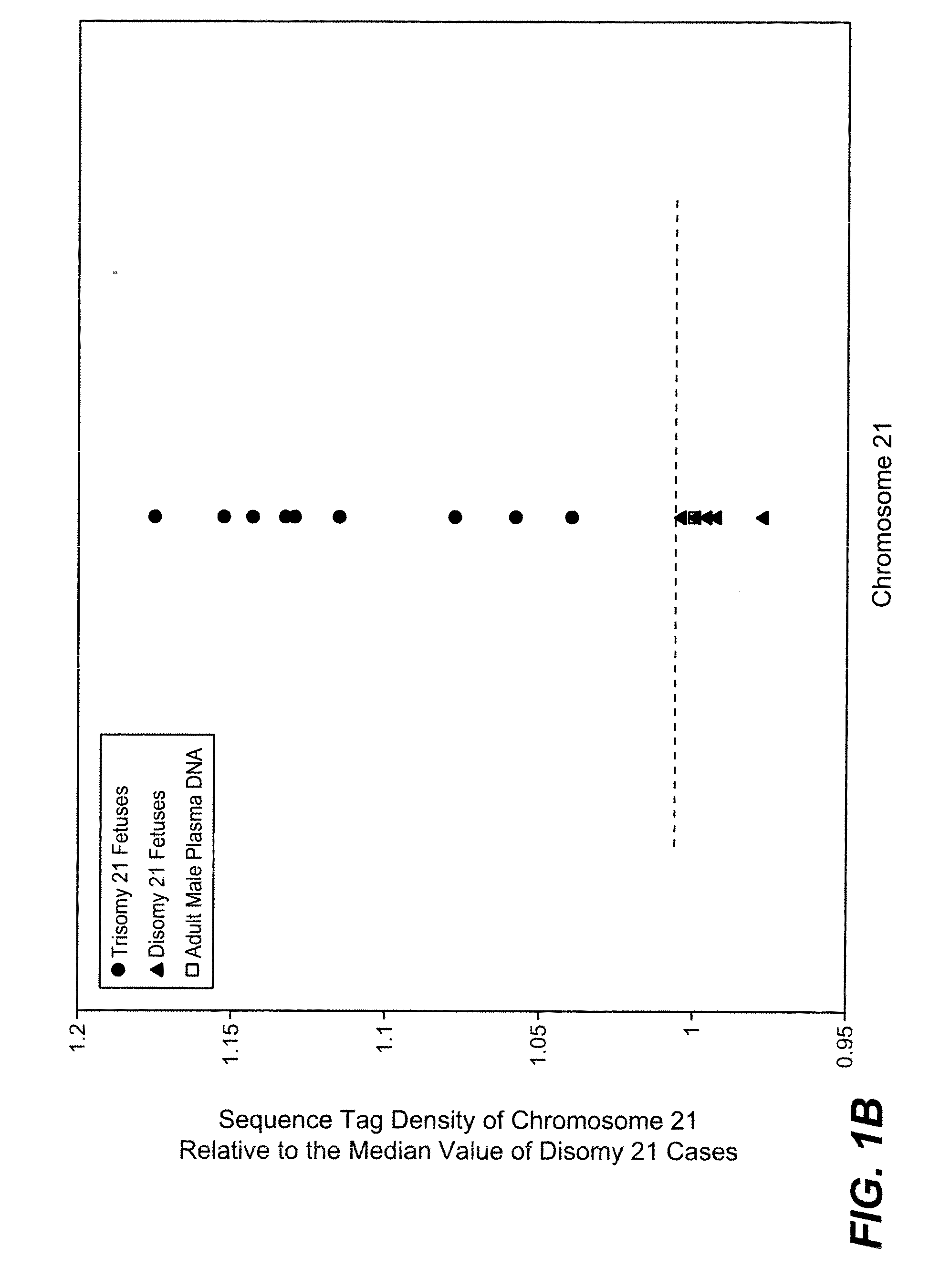
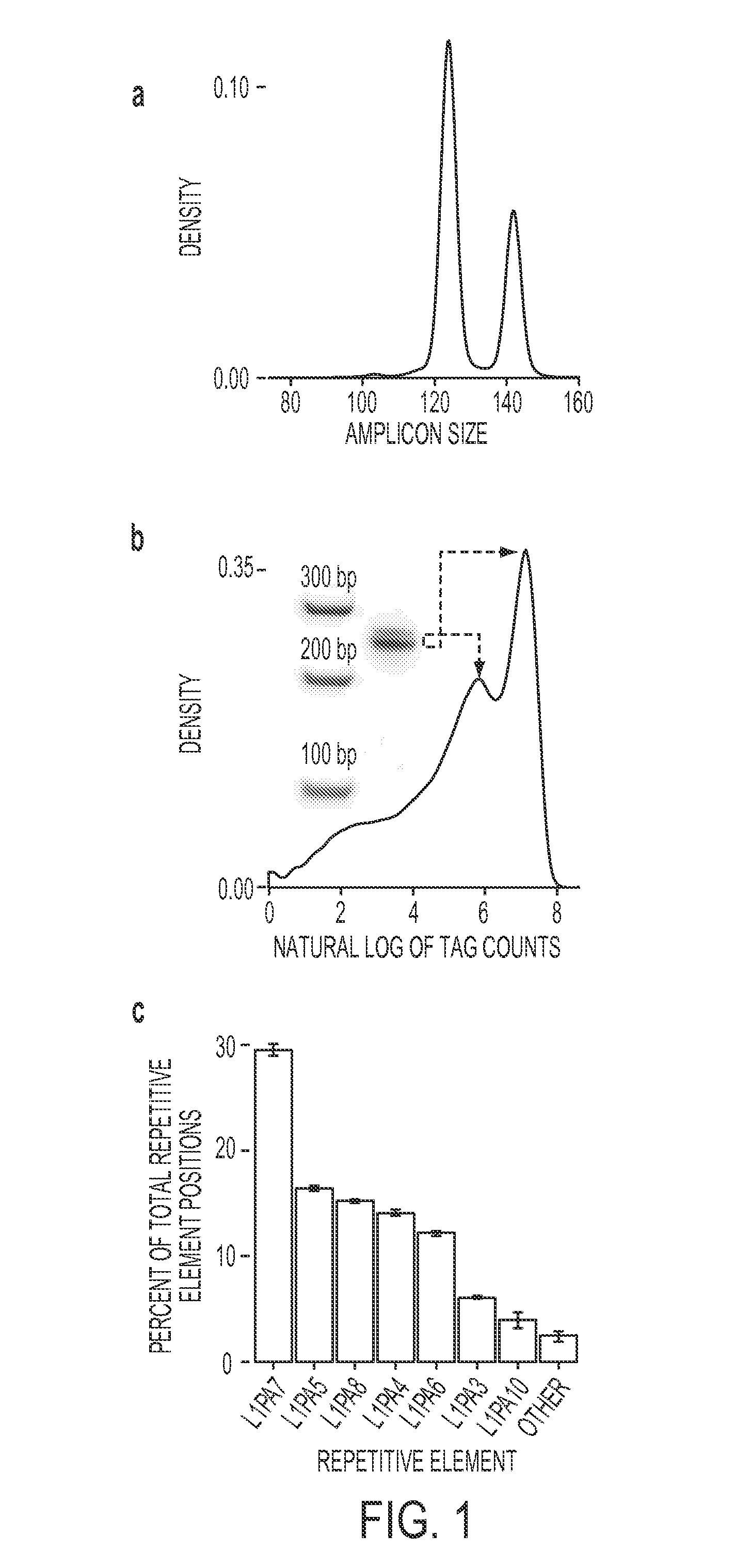
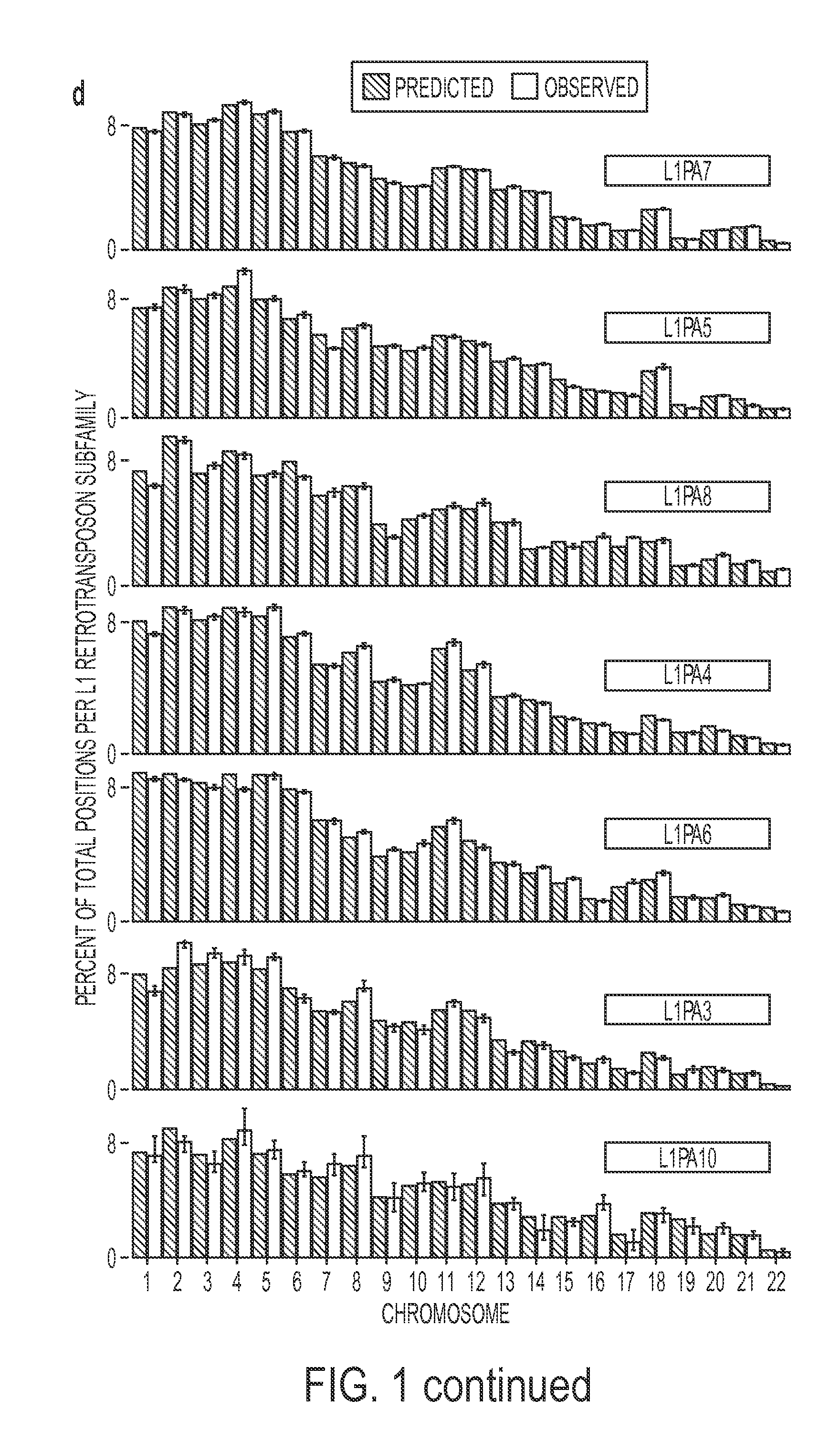
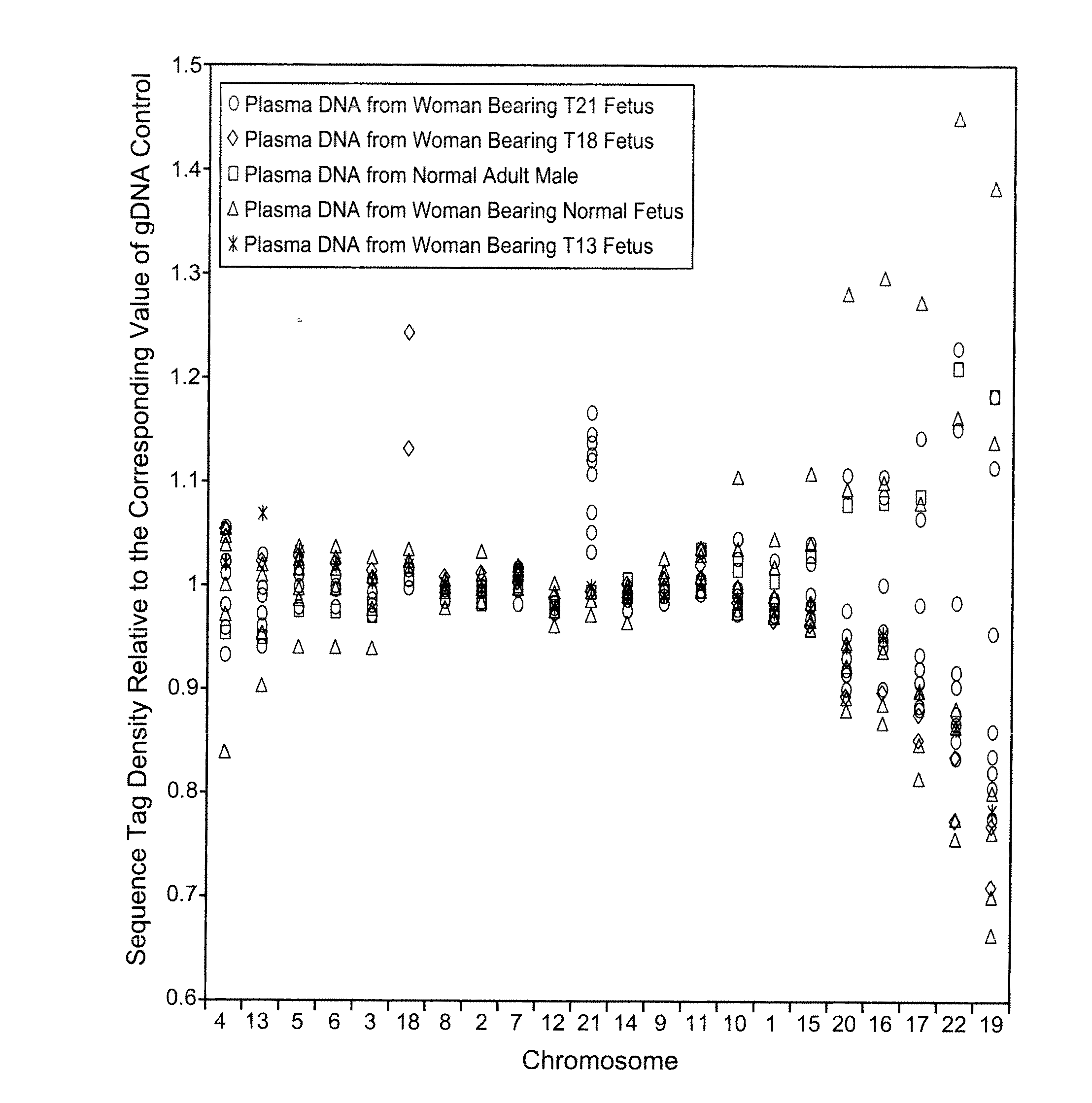
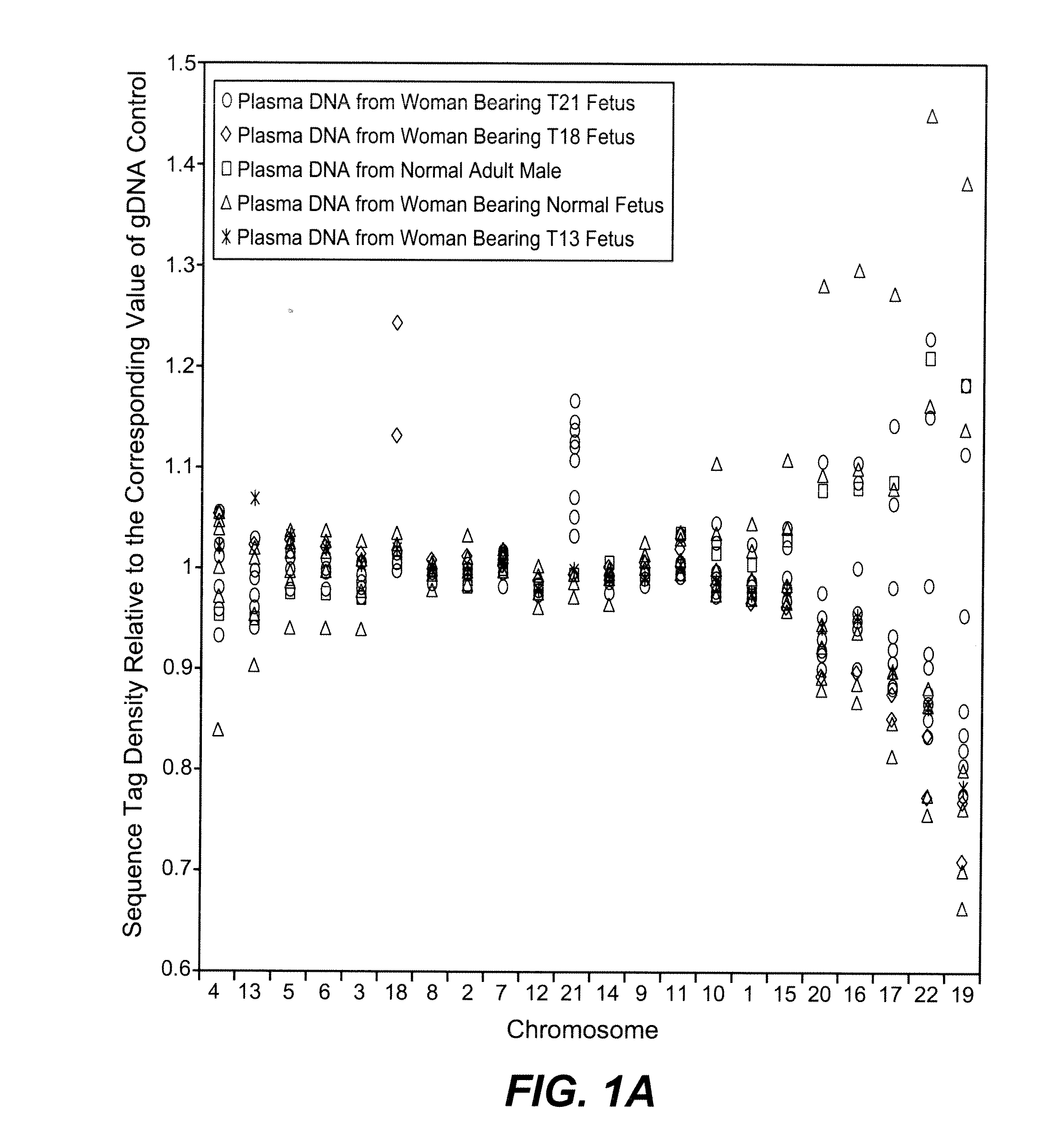
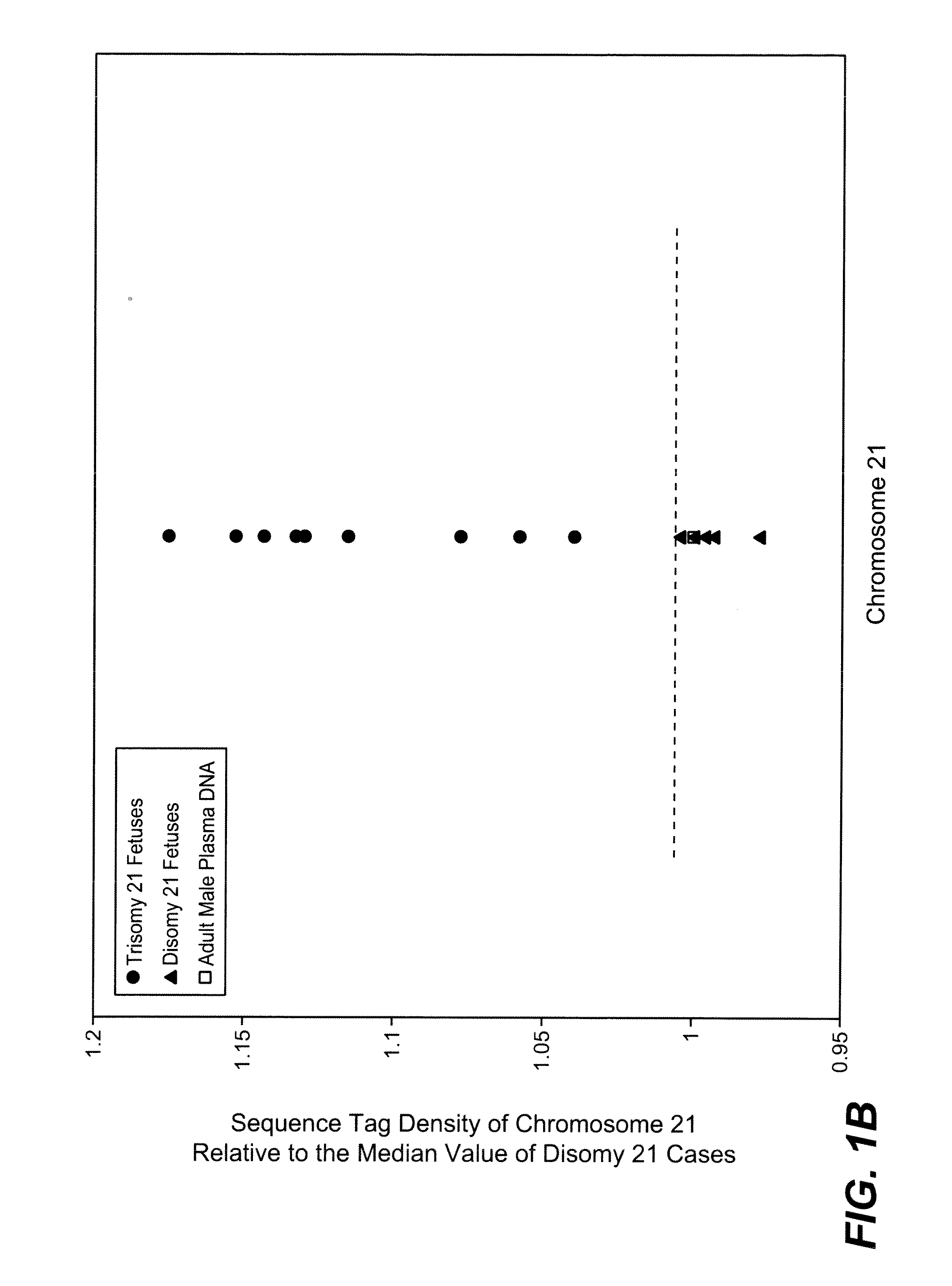
Disclosed is a method to achieve digital quantification of DNA (i.e., counting differences between identical sequences) using direct shotgun sequencing followed by mapping to the chromosome of origin and enumeration of fragments per chromosome. The preferred method uses massively parallel sequencing, which can produce tens of millions of short sequence tags in a single run and enabling a sampling that can be statistically evaluated. By counting the number of sequence tags mapped to a predefined window in each chromosome, the over- or under-representation of any chromosome in maternal plasma DNA contributed by an aneuploid fetus can be detected. This method does not require the differentiation of fetal versus maternal DNA. The median count of autosomal values is used as a normalization constant to account for differences in total number of sequence tags is used for comparison between samples and between chromosomes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
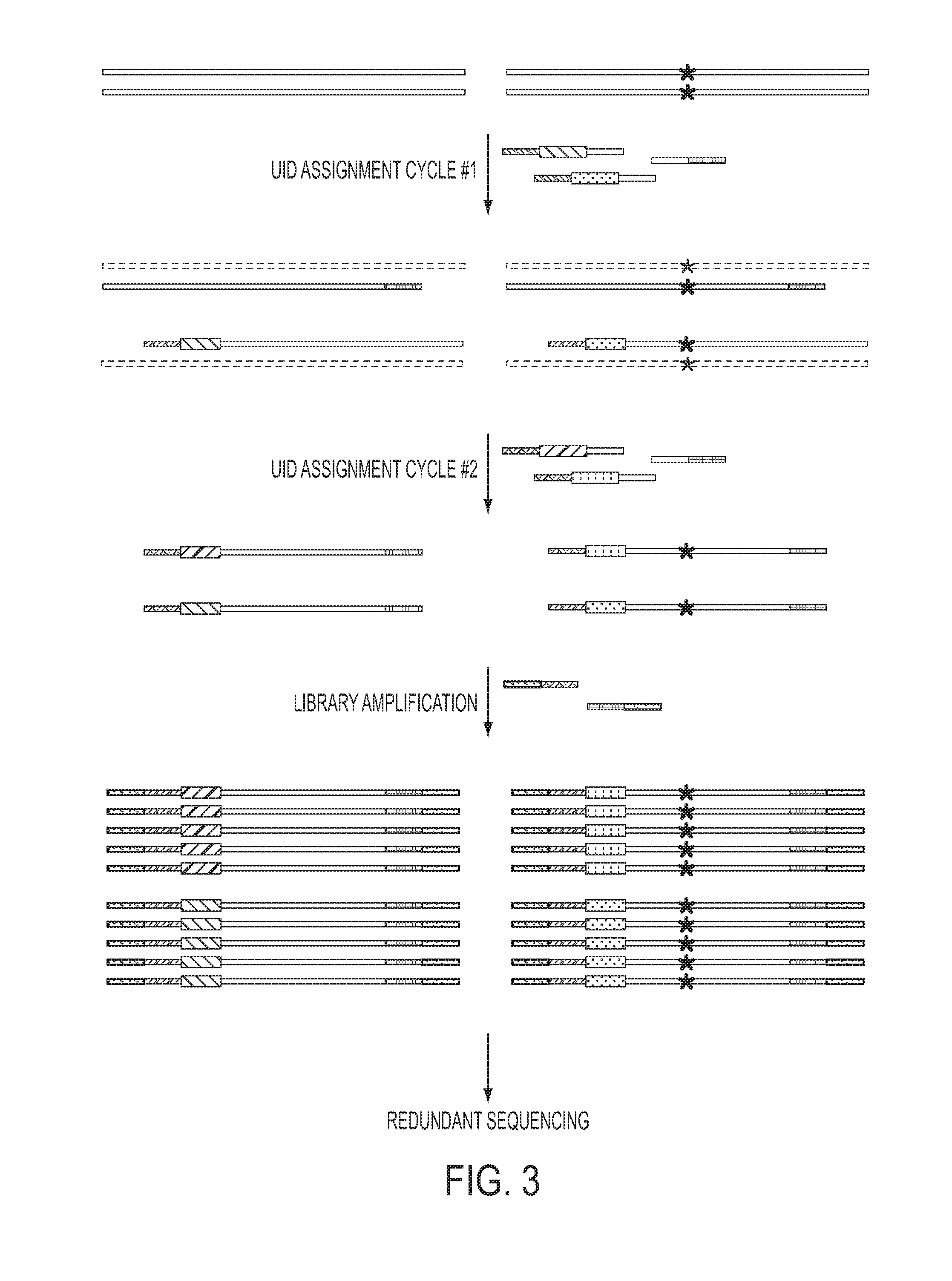
Safe sequencing system
ActiveUS20140227705A1Sensitively accurately determiningMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideInstrumentation
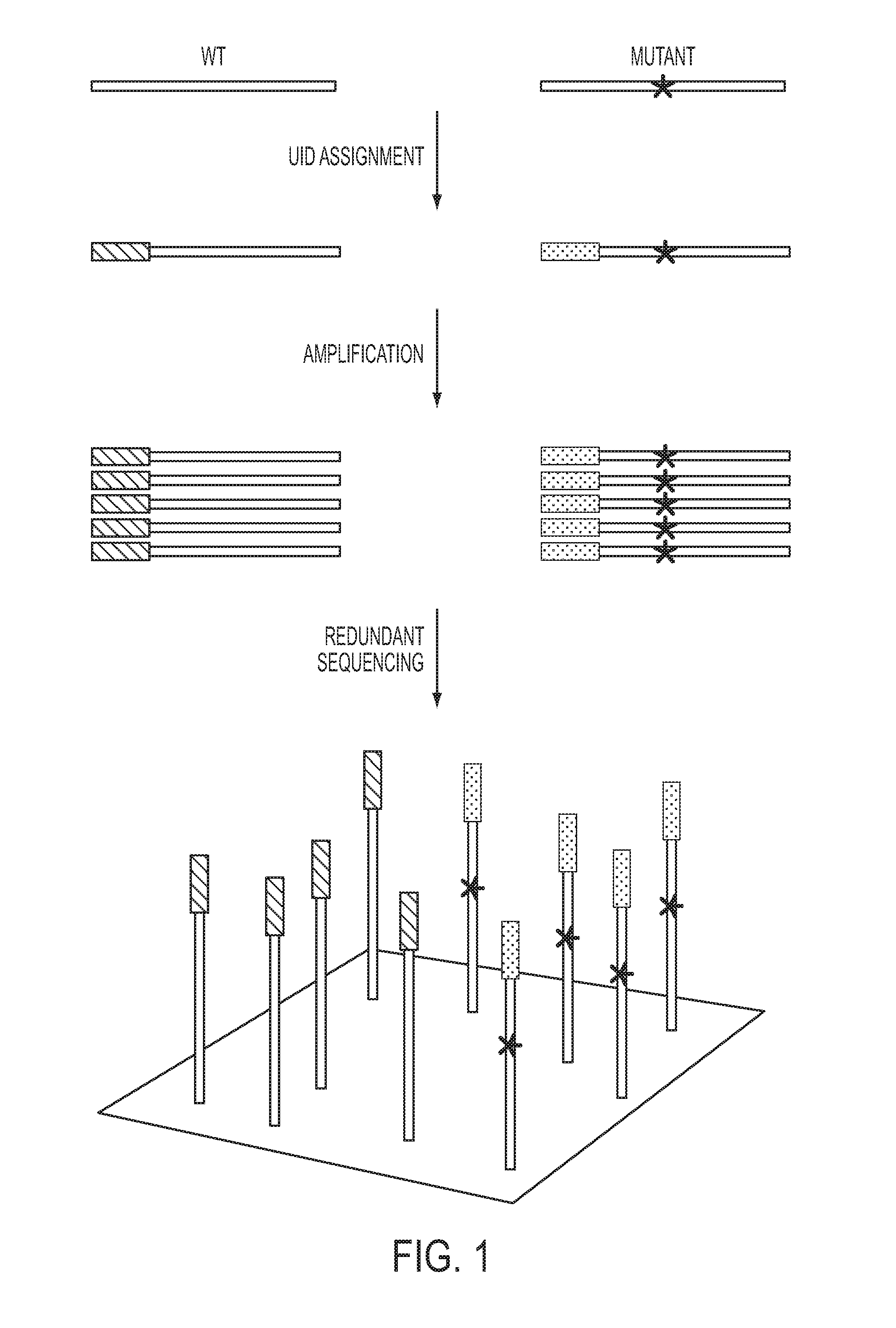
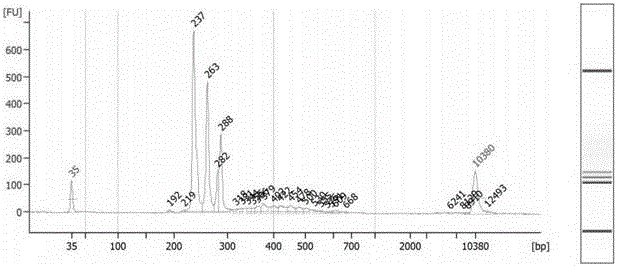
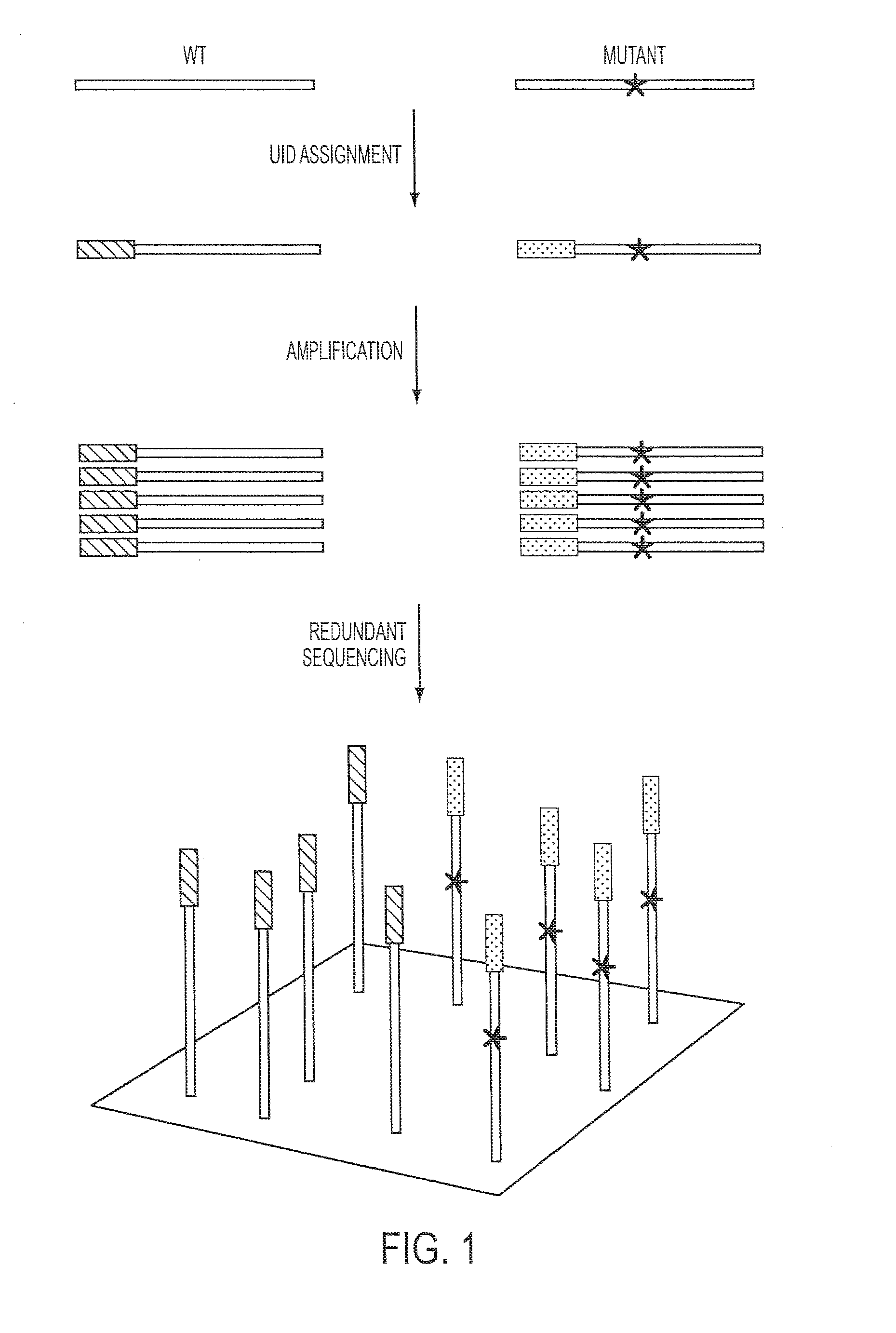
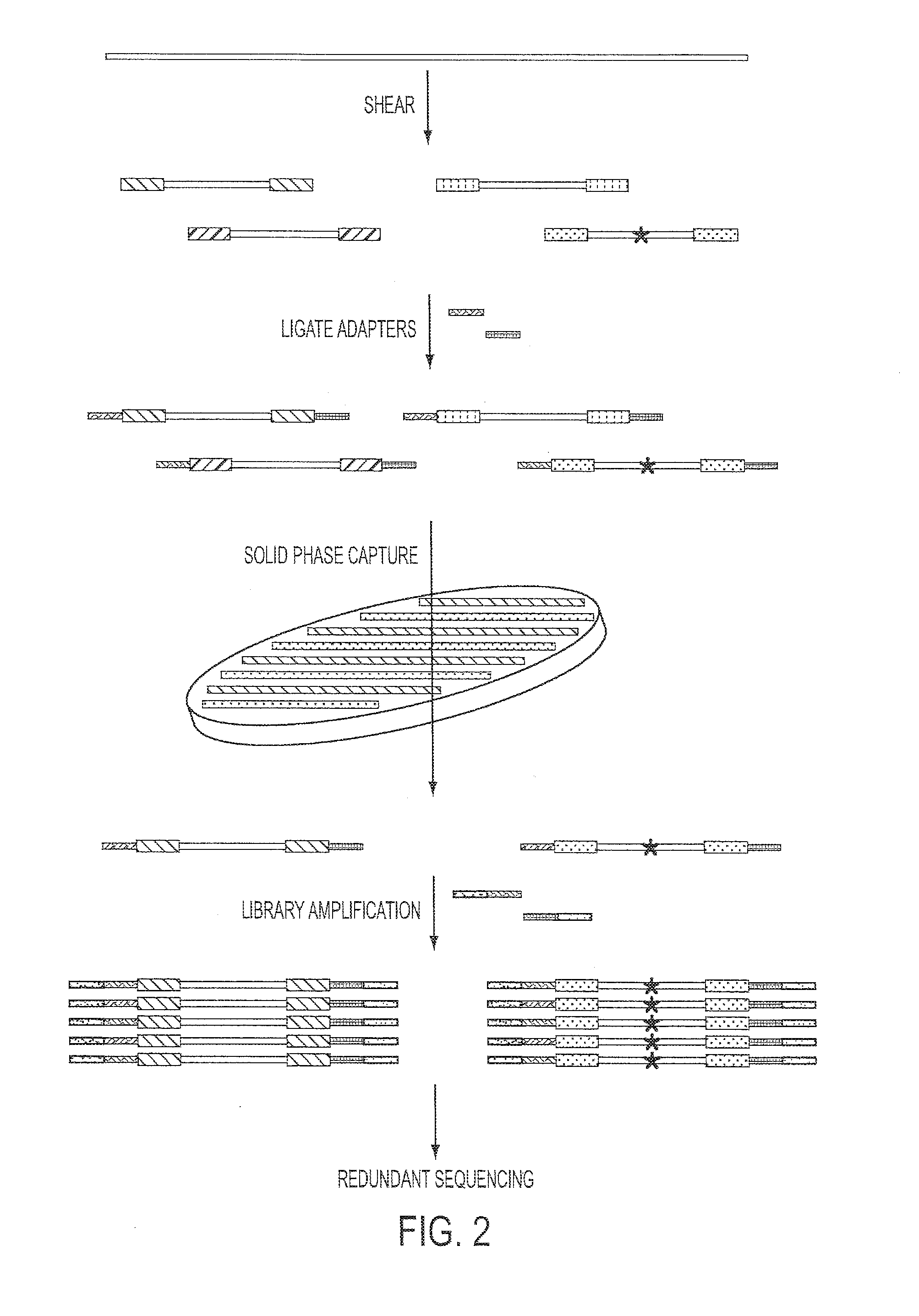
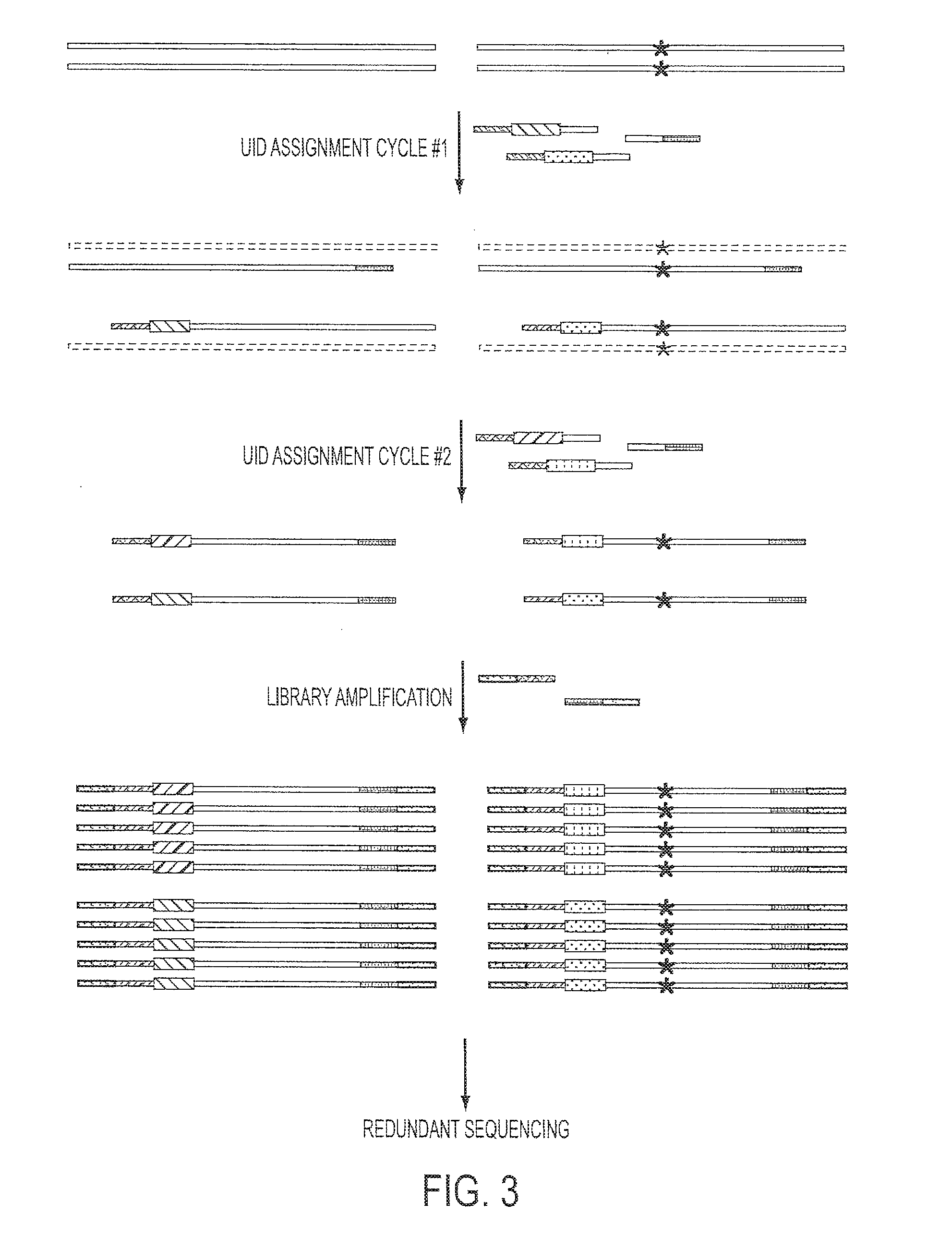
The identification of mutations that are present in a small fraction of DNA templates is essential for progress in several areas of biomedical research. Though massively parallel sequencing instruments are in principle well-suited to this task, the error rates in such instruments are generally too high to allow confident identification of rare variants. We here describe an approach that can substantially increase the sensitivity of massively parallel sequencing instruments for this purpose. One example of this approach, called “Safe-SeqS” for (Safe-Sequencing System) includes (i) assignment of a unique identifier (UID) to each template molecule; (ii) amplification of each uniquely tagged template molecule to create UID-families; and (iii) redundant sequencing of the amplification products. PCR fragments with the same UID are truly mutant (“super-mutants”) if ≧95% of them contain the identical mutation. We illustrate the utility of this approach for determining the fidelity of a polymerase, the accuracy of oligonucleotides synthesized in vitro, and the prevalence of mutations in the nuclear and mitochondrial genomes of normal cells.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Noninvasive Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy by Sequencing
ActiveUS20100138165A1Maximum resultMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMassive parallel sequencingFetal aneuploidy
Disclosed is a method to achieve digital quantification of DNA (i.e., counting differences between identical sequences) using direct shotgun sequencing followed by mapping to the chromosome of origin and enumeration of fragments per chromosome. The preferred method uses massively parallel sequencing, which can produce tens of millions of short sequence tags in a single run and enabling a sampling that can be statistically evaluated. By counting the number of sequence tags mapped to a predefined window in each chromosome, the over- or under-representation of any chromosome in maternal plasma DNA contributed by an aneuploid fetus can be detected. This method does not require the differentiation of fetal versus maternal DNA. The median count of autosomal values is used as a normalization constant to account for differences in total number of sequence tags is used for comparison between samples and between chromosomes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
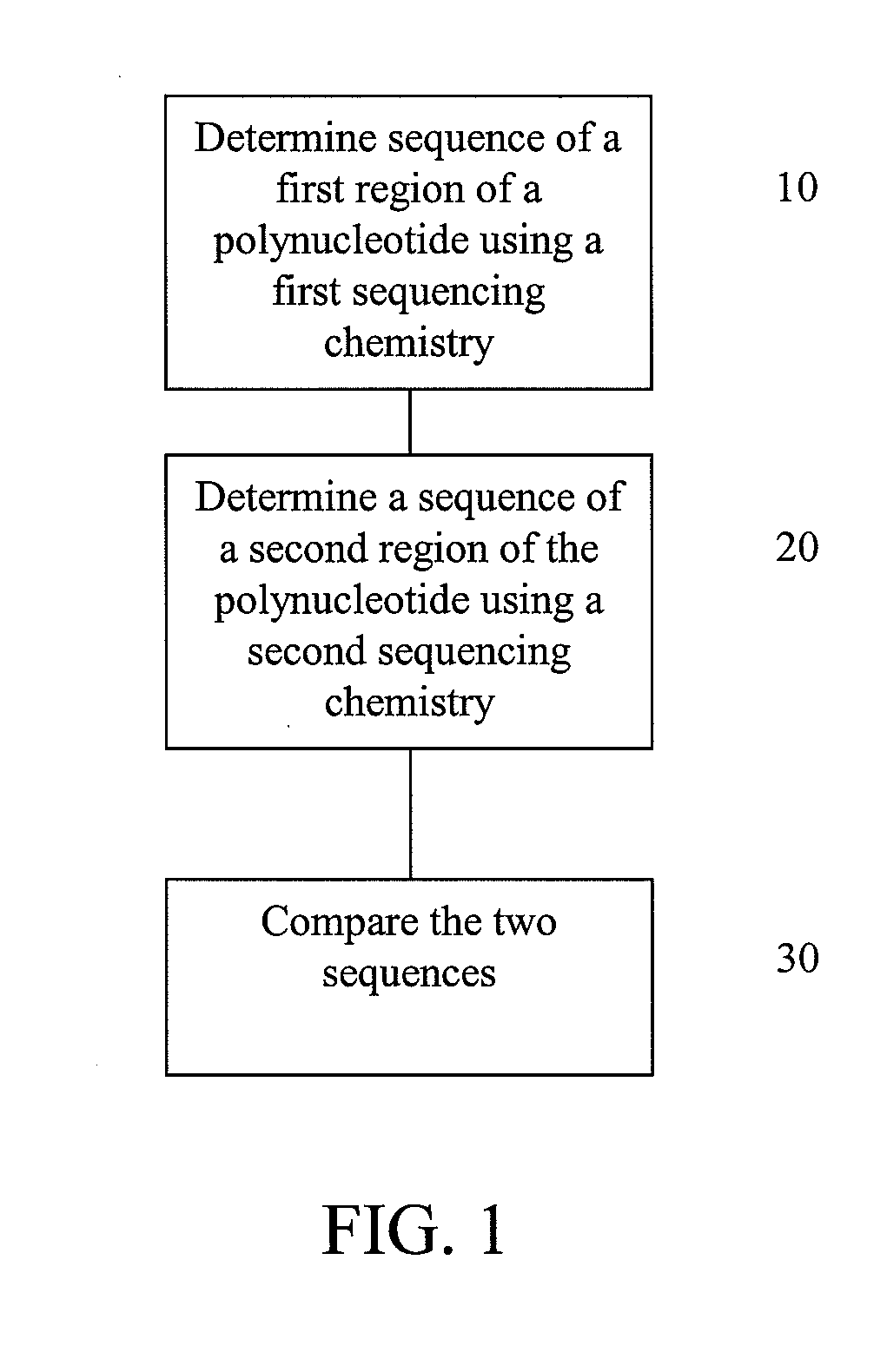
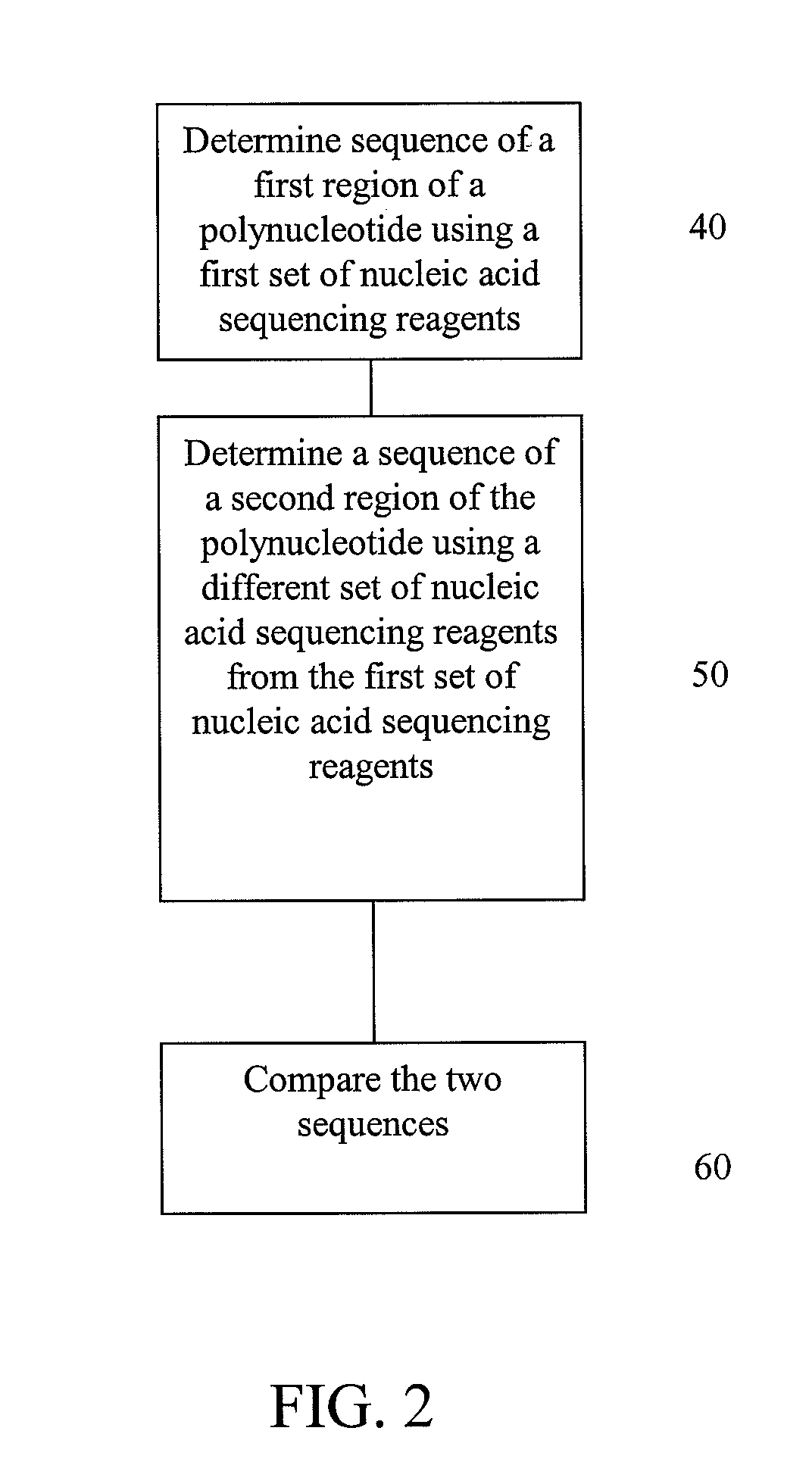
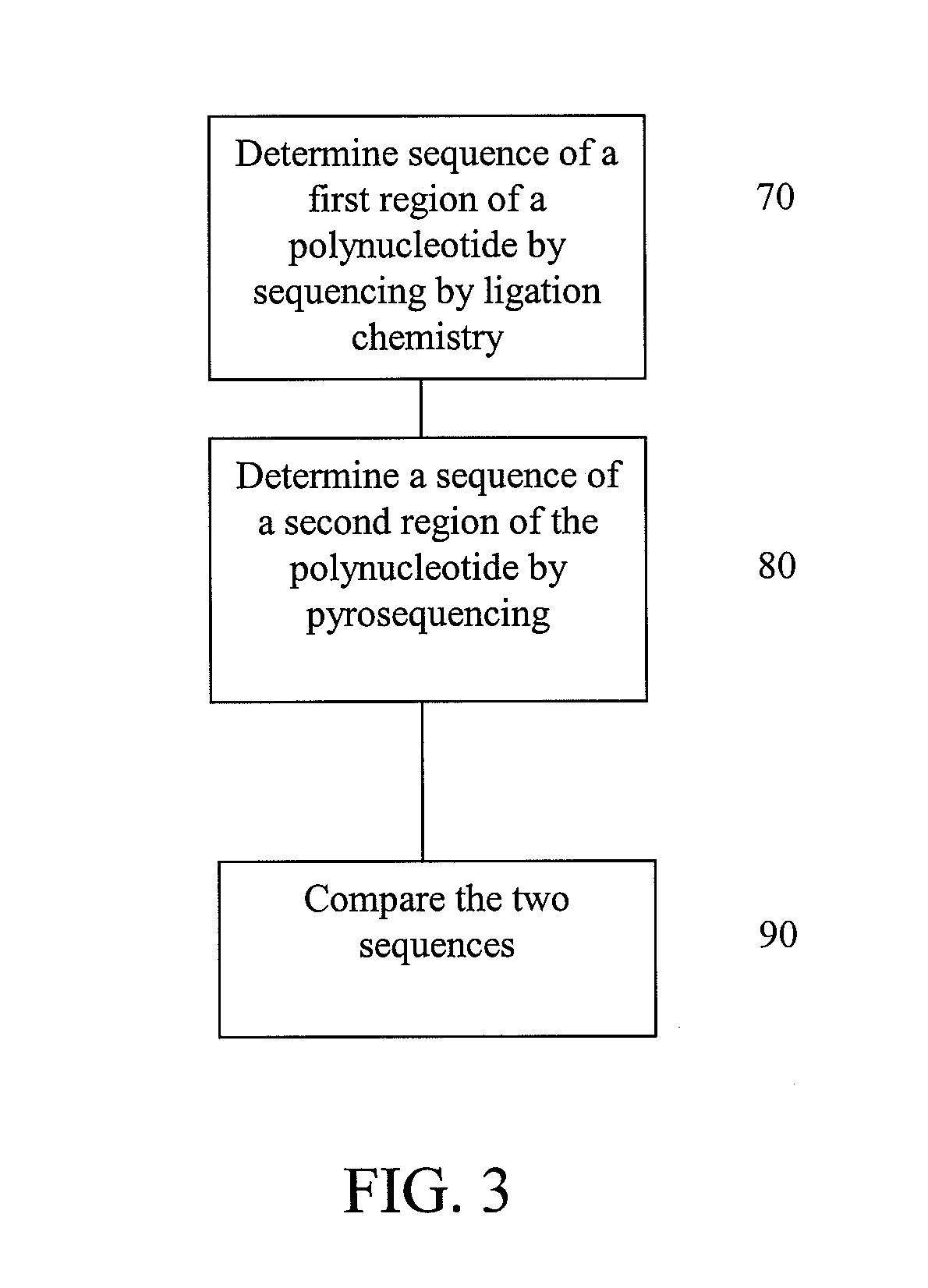
Alternative nucleic acid sequencing methods
InactiveUS20090062132A1Efficient sortingAccurate sortingNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingMassive parallel sequencing
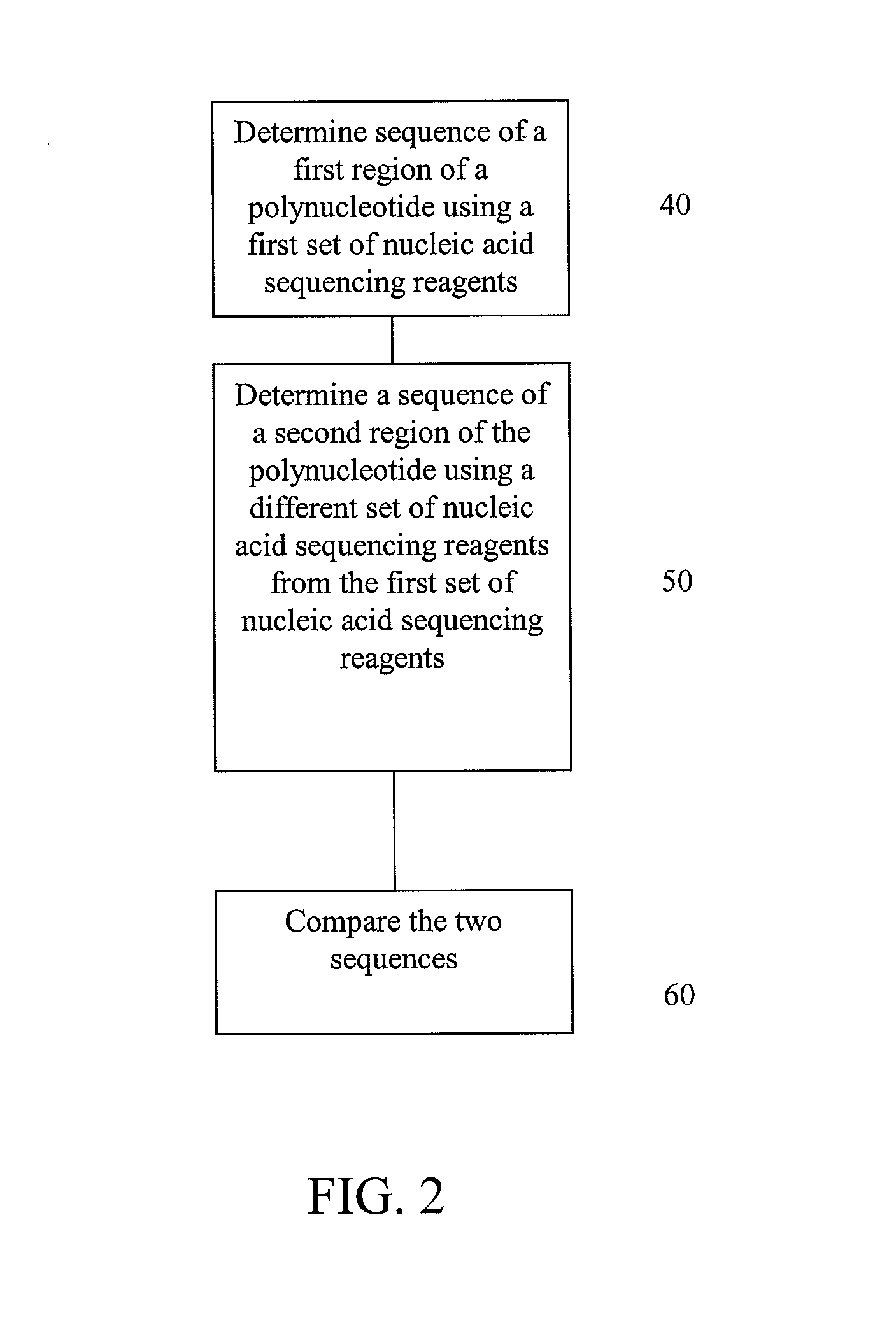
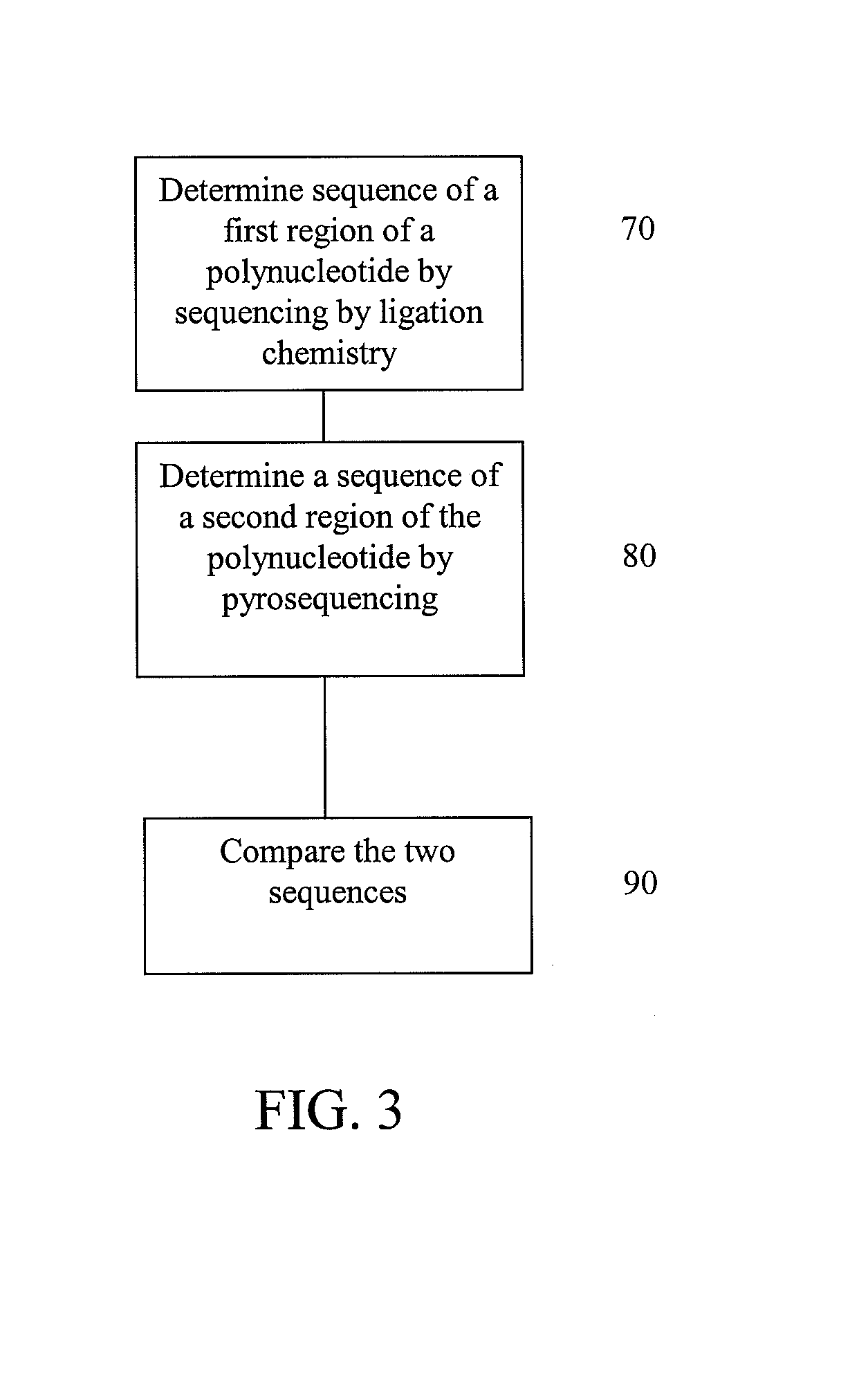
Embodiments are provided that provide for parallel sequencing of nucleic acid segments. In some embodiments, a single sequence is sequenced by at least two different sequencing techniques and the results compared, allowing for deficiencies or strengths of one technique to be complemented by the second technique.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Rapid aneuploidy detection
ActiveUS20150051085A1Assessing genomic copy number sensitively and rapidlyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCell freeTrisomy
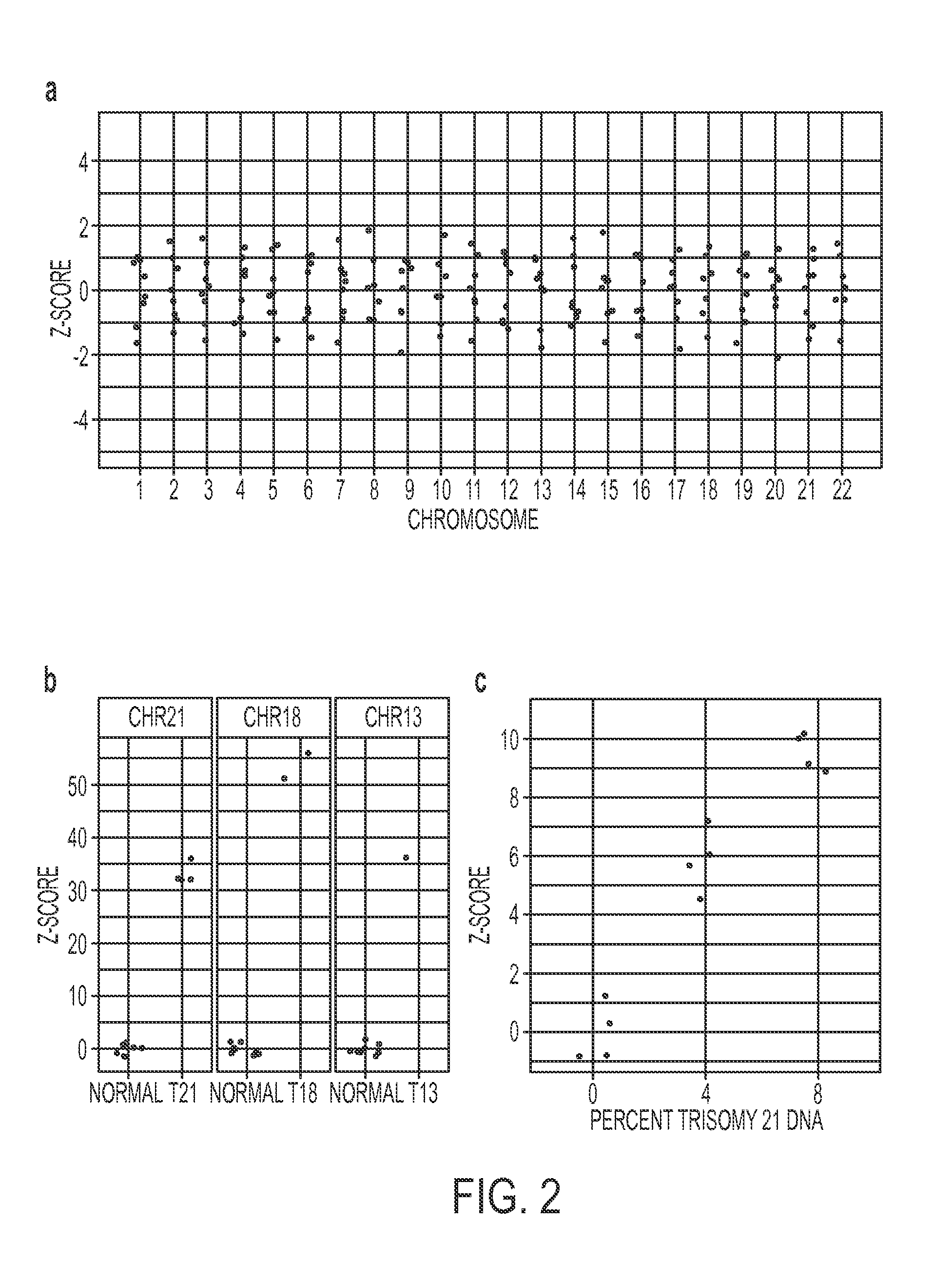
Massively parallel sequencing of cell-free, maternal plasma DNA was recently demonstrated to be a safe and effective screening method for fetal chromosomal aneuploidies. Here, we report an improved sequencing method achieving significantly increased throughput and decreased cost by replacing laborious sequencing library preparation steps with PCR employing a single primer pair. Using this approach, samples containing as little as 4% trisomy 21 DNA could be readily distinguished from euploid samples.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
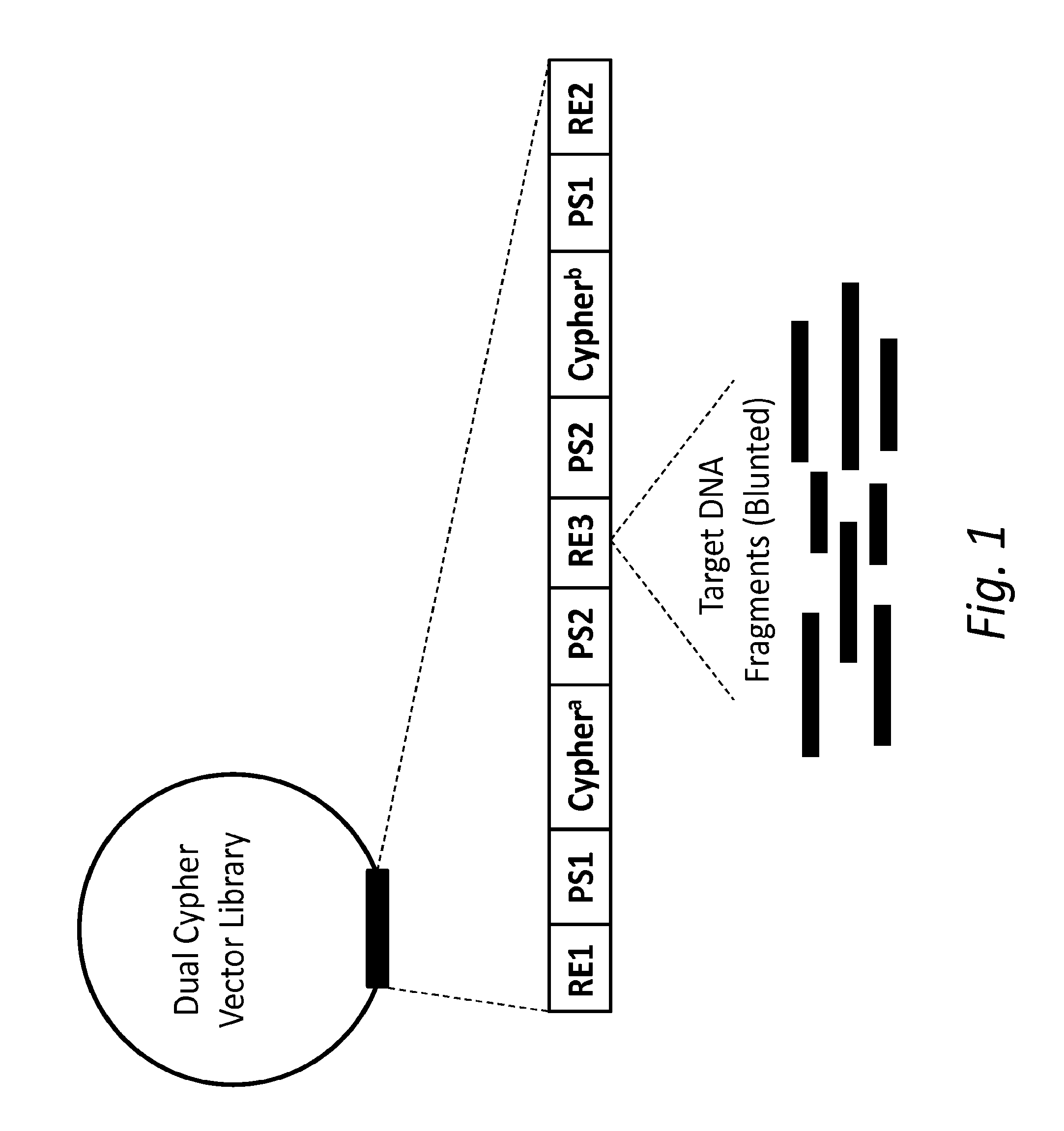
Compositions and methods for accurately identifying mutations
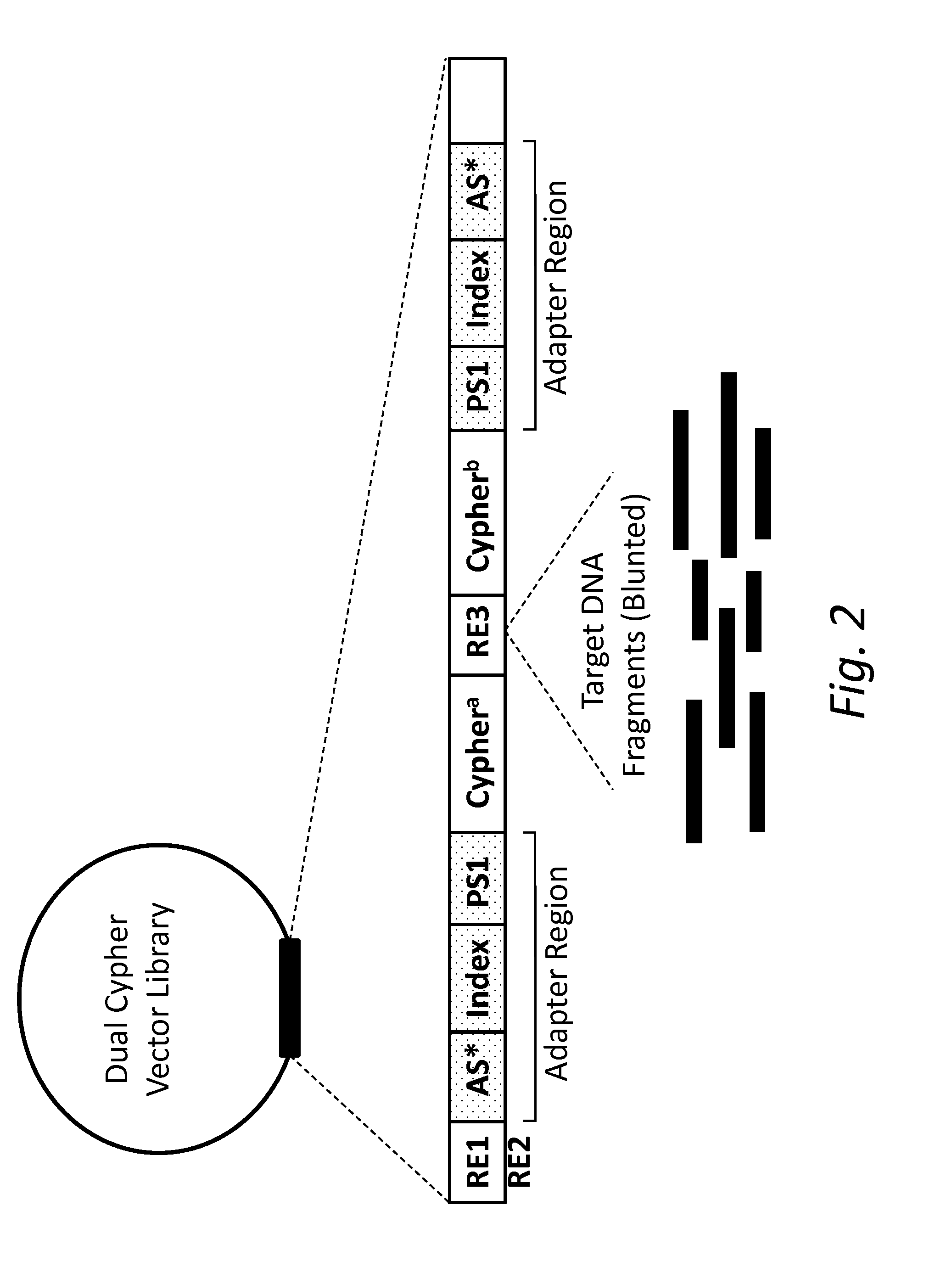
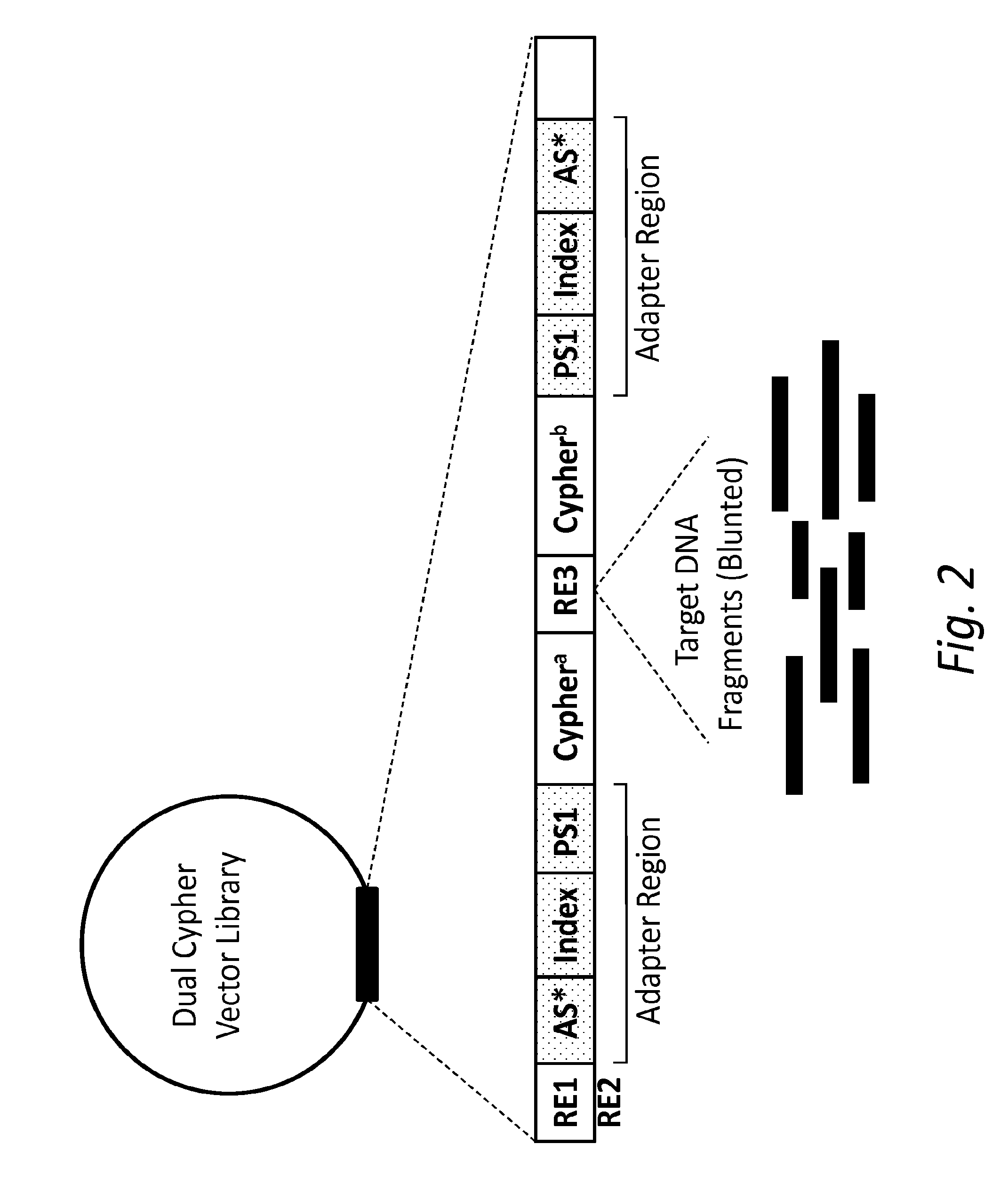
ActiveUS20150024950A1Accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism librariesSense strandMassive parallel sequencing
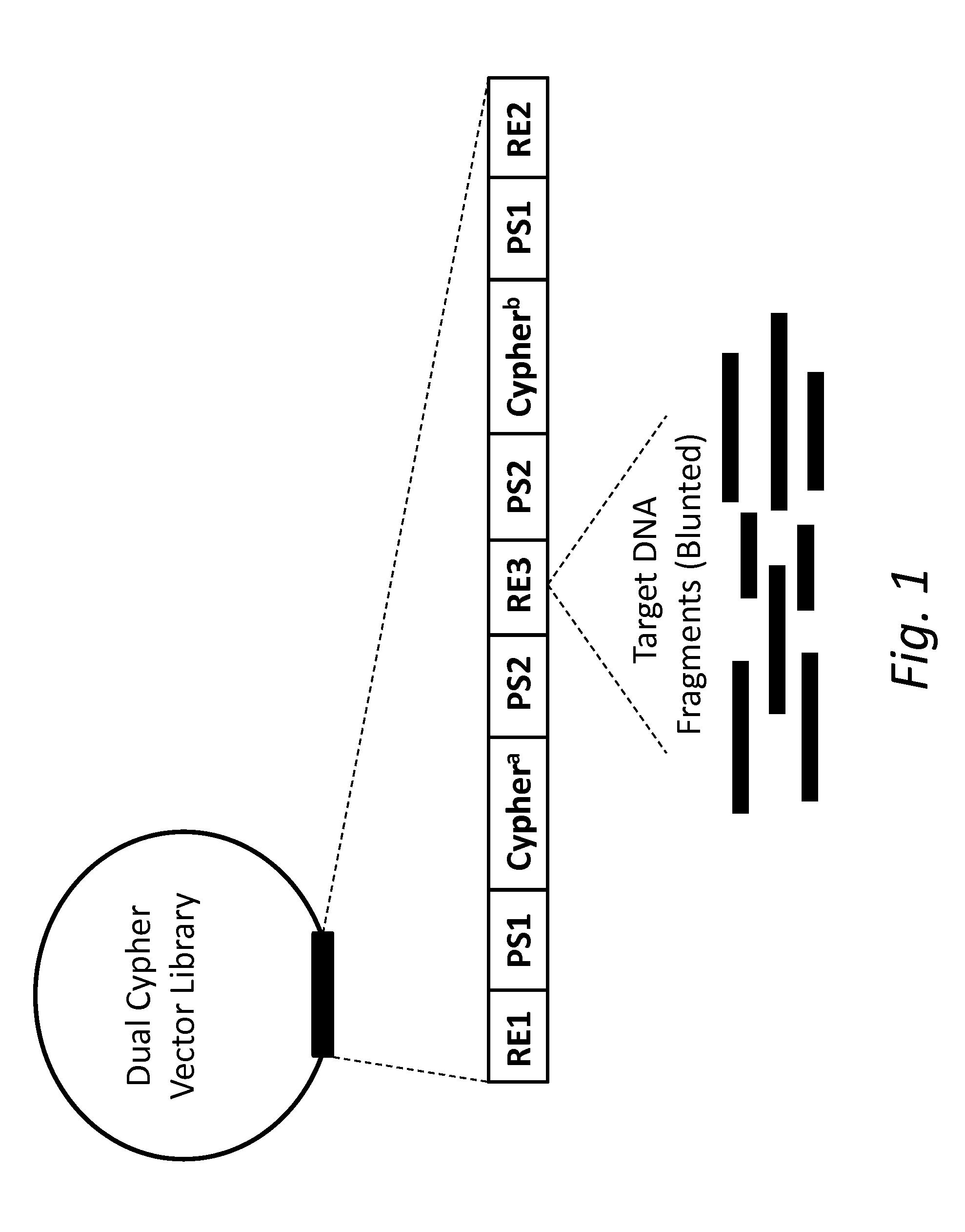
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for accurately detecting mutations by uniquely tagging double stranded nucleic acid molecules with dual cyphers such that sequence data obtained from a sense strand can be linked to sequence data obtained from an anti-sense strand when sequenced, for example, by massively parallel sequencing methods.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER CENT
Noninvasive Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy by Sequencing
ActiveUS20110246083A1Maximum resultMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMassive parallel sequencingFetal aneuploidy
Disclosed is a method to achieve digital quantification of DNA (i.e., counting differences between identical sequences) using direct shotgun sequencing followed by mapping to the chromosome of origin and enumeration of fragments per chromosome. The preferred method uses massively parallel sequencing, which can produce tens of millions of short sequence tags in a single run and enabling a sampling that can be statistically evaluated. By counting the number of sequence tags mapped to a predefined window in each chromosome, the over- or under-representation of any chromosome in maternal plasma DNA contributed by an aneuploid fetus can be detected. This method does not require the differentiation of fetal versus maternal DNA. The median count of autosomal values is used as a normalization constant to account for differences in total number of sequence tags is used for comparison between samples and between chromosomes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
High throughput oligonucleotide sequencing method
The present invention relates to the field of gene engineering, provides a high throughout oligonucleotides sequencing method. Said sequencing method includes following steps: the generation of a short DNA tag, single-molecule PCR amplification benefit-marking sequence, enrichment of high-density DNA tags and large-scale cycle parallel sequencing, etc. By using a molecular scale for parallel sequencing in a sequencing method which takes complexation as the base or expanded synthesis as the base, the scale or an expanded anchor primer is used for expanding the base points which are read out on a template. By using the primer, longer sequence on the template can be read out, and the only identification can be obtained from the genome sequence of various organisms with the range from microorganisms, plants, and animals to human, thereby having greater practical value.
Owner:SHENGZHEN CHINA GENE TECH COMPANY
Using size and number aberrations in plasma DNA for detecting cancer
Analysis of tumor-derived circulating cell-free DNA opens up new possibilities for performing liquid biopsies for solid tumor assessment or cancer screening. However, many aspects of the biological characteristics of tumor-derived cell-free DNA remain unclear. Regarding the size profile of plasma DNA molecules, some studies reported increased integrity of tumor-derived plasma DNA while others reported shorter tumor-derived plasma DNA molecules. We performed an analysis of the size profiles of plasma DNA in patients with cancer using massively parallel sequencing at single base resolution and in a genomewide manner. Tumor-derived plasma DNA molecules were further identified using chromosome arm-level z-score analysis (CAZA). We showed that populations of aberrantly short and long DNA molecules co-existed in the plasma of patients with cancer. The short ones preferentially carried the tumor-associated copy number aberrations. These results show the ability to use plasma DNA as a molecular diagnostic tool.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
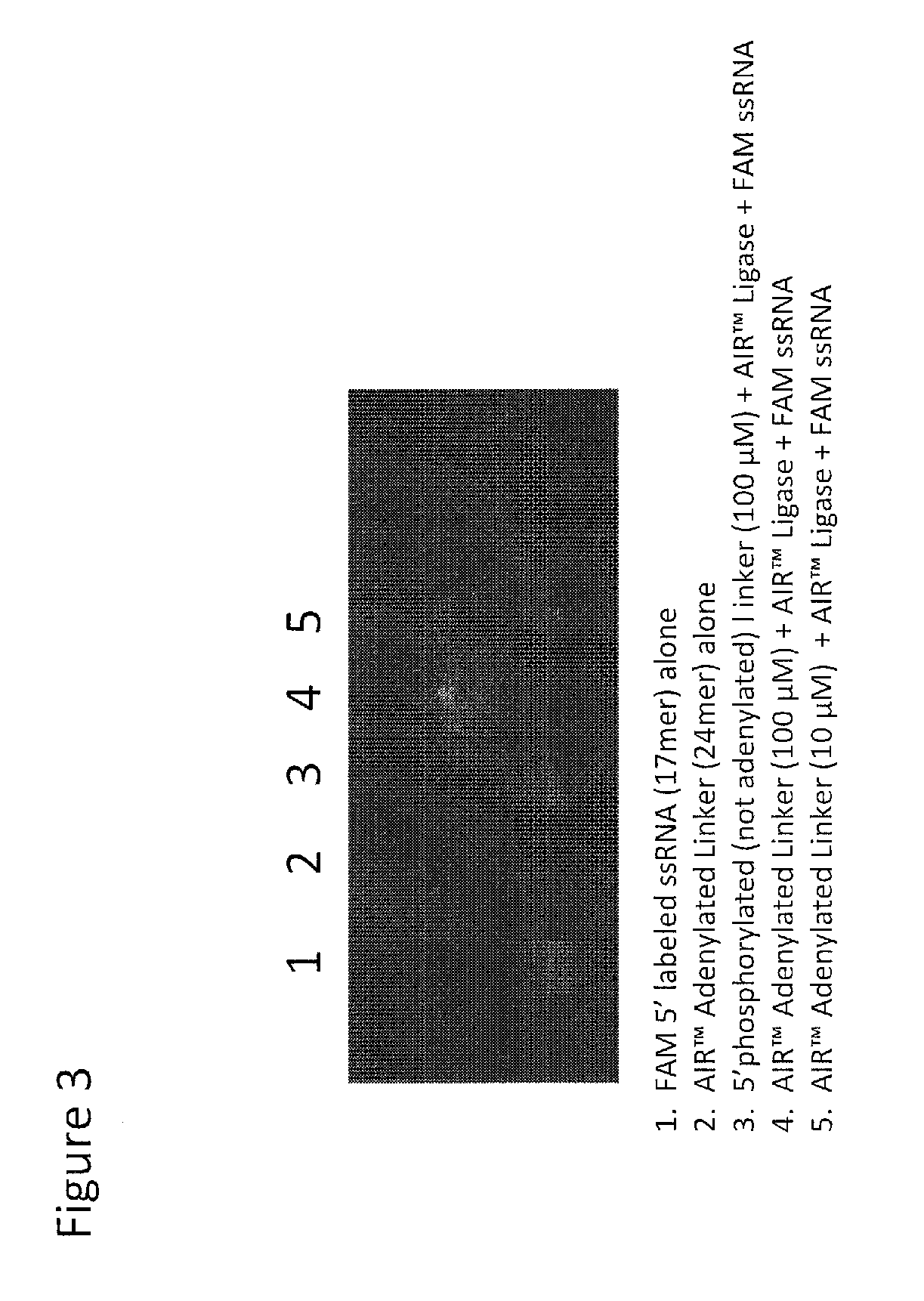
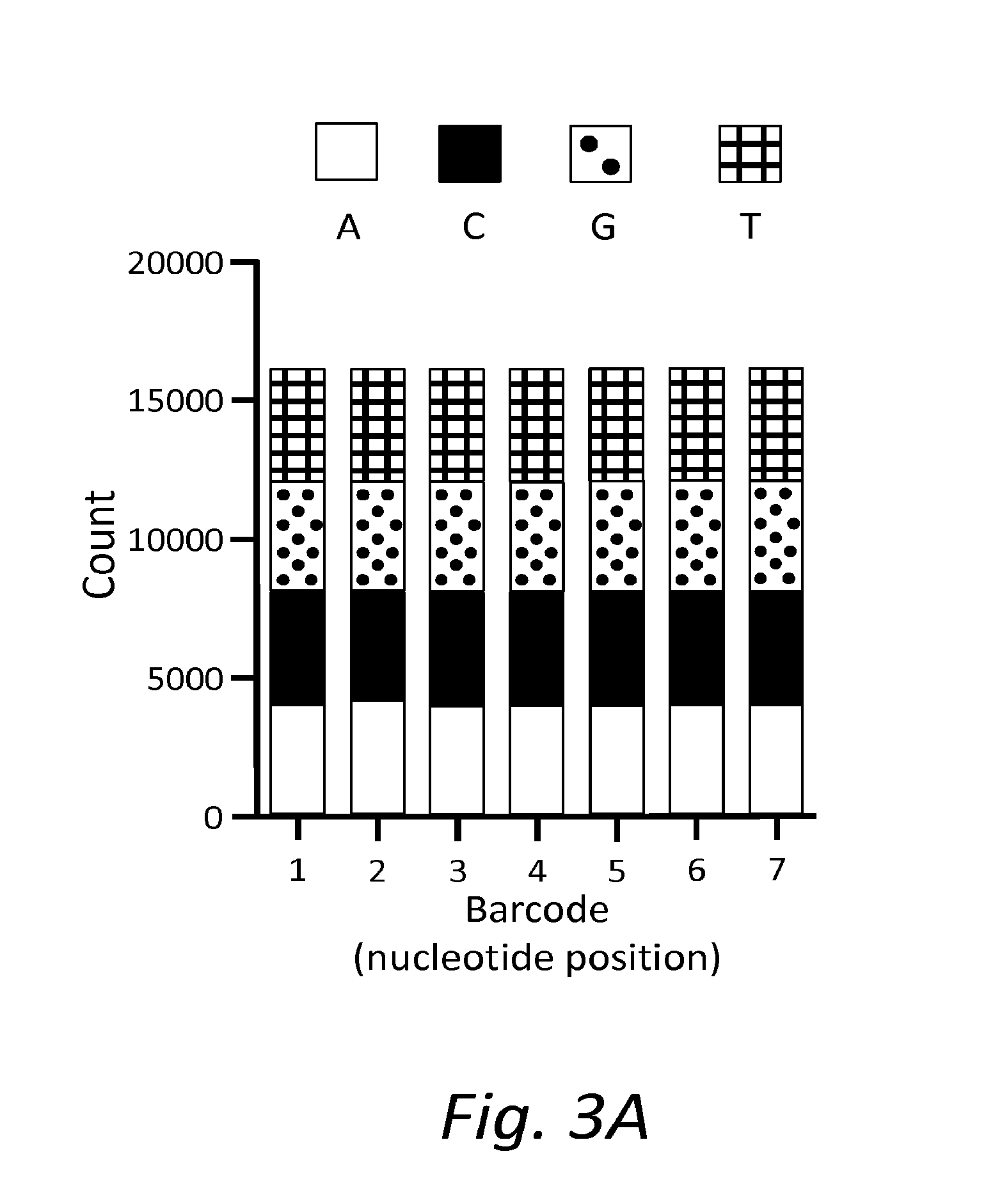
Oligonucleotide ligation, barcoding and methods and compositions for improving data quality and throughput using massively parallel sequencing
ActiveUS20120028814A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationRe sequencingBarcode
Described herein is a buffer concentration for highly efficient ligation of two oligonucleotides. The embodiments herein have led to the development of an optimized ligation step used in the sample preparation for sequencing reactions. Further, embodiments herein describe a high-throughput method for sequencing using barcodes or the purpose of multiplexing several samples simultaneously and novel methods for making targeted DNA libraries for re-sequencing on massively parallel next-generation sequencing platforms and for alternatives to gel-purification for recovering the desired templates from small RNA libraries for next generation sequencing.
Owner:BICO SCI CORP
Establishment method of gene library of fecal flora based on high-throughput gene sequencing
InactiveCN105937053AFast database buildingImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSequence databaseGenomic library
An establishment method of a gene library of fecal flora based on high-throughput gene sequencing employs a ''nested PCR'' method for enrichment amplification on 16S rDNA, so as to reduce the host and food residue genome pollution by the maximum; and V3 and V6 are combined for specific amplification and massive parallel sequencing, so as to obtain the a target gene sequence database of the flora. The library can increase the identification of the bacterial flora from Genus level to Species level. The method can maximally avoid the interference of host cell nucleic acid, and completely and efficiently detect 16SrDNA tag sequence of all bacteria varieties, so as to accurately determine the ecological structure of the intestinal flora.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SAGENE BIOTECH
Safe sequencing system
The identification of mutations that are present in a small fraction of DNA templates is essential for progress in several areas of biomedical research. Though massively parallel sequencing instruments are in principle well-suited to this task, the error rates in such instruments are generally too high to allow confident identification of rare variants. We here describe an approach that can substantially increase the sensitivity of massively parallel sequencing instruments for this purpose. One example of this approach, called “Safe-SeqS” for (Safe-Sequencing System) includes (i) assignment of a unique identifier (UID) to each template molecule; (ii) amplification of each uniquely tagged template molecule to create UID-families; and (iii) redundant sequencing of the amplification products. PCR fragments with the same UID are truly mutant (“super-mutants”) if ≧95% of them contain the identical mutation. We illustrate the utility of this approach for determining the fidelity of a polymerase, the accuracy of oligonucleotides synthesized in vitro, and the prevalence of mutations in the nuclear and mitochondrial genomes of normal cells.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
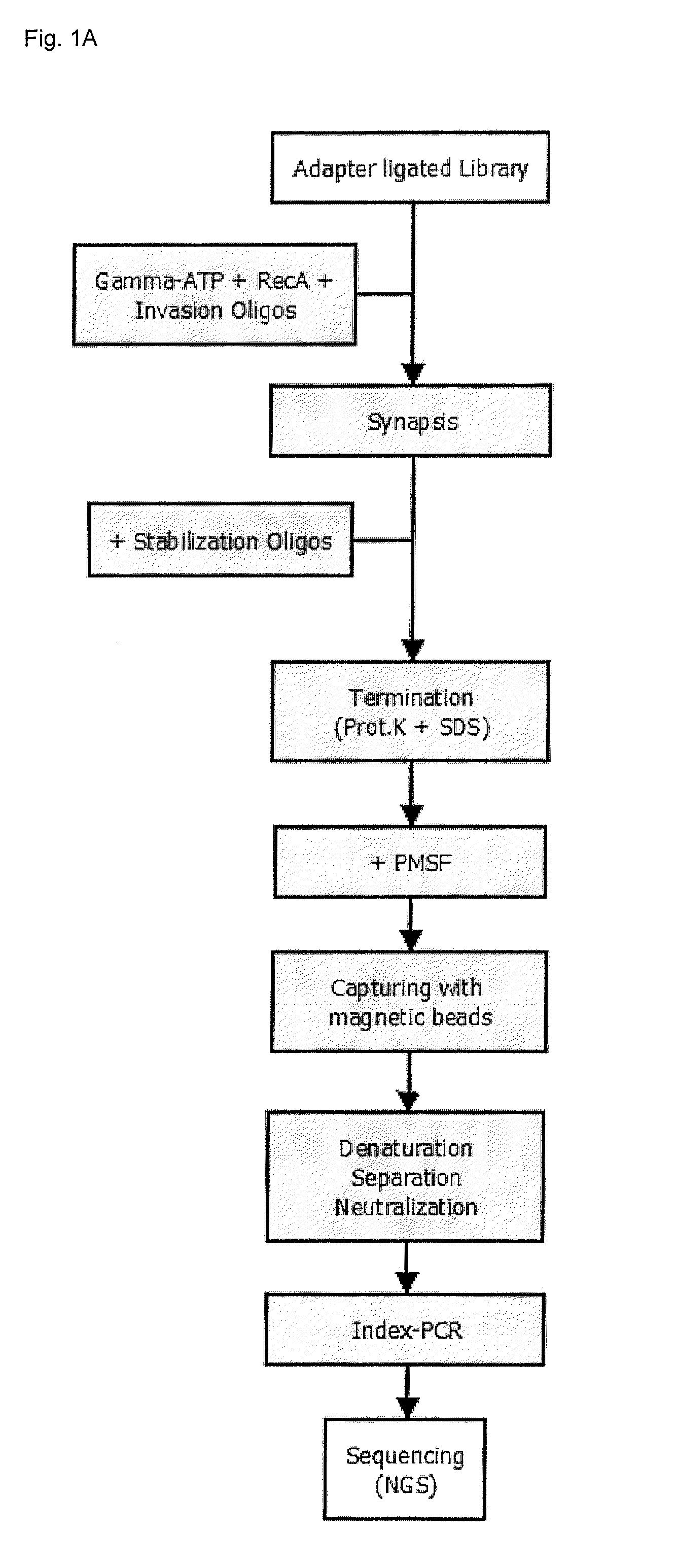
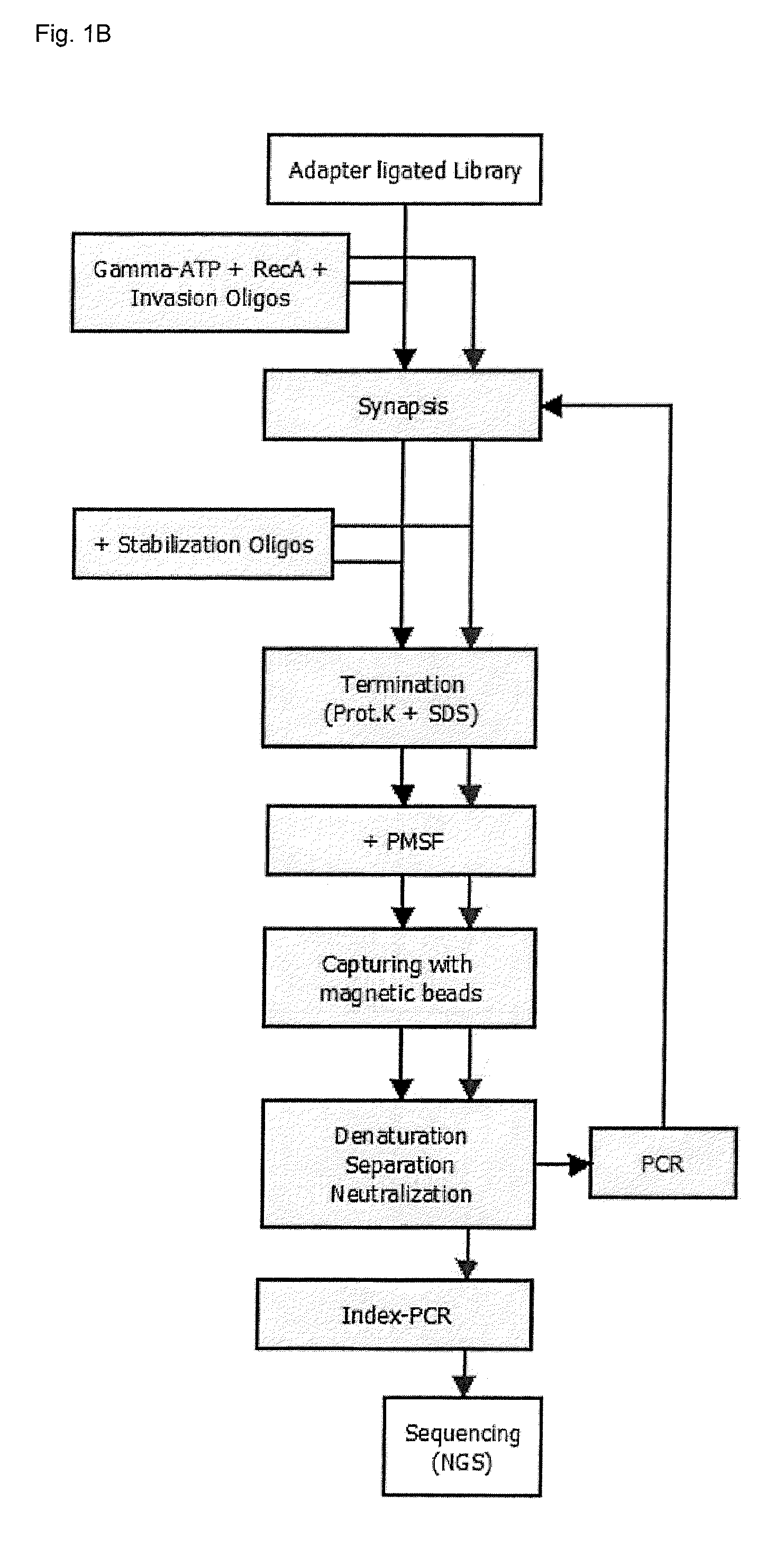
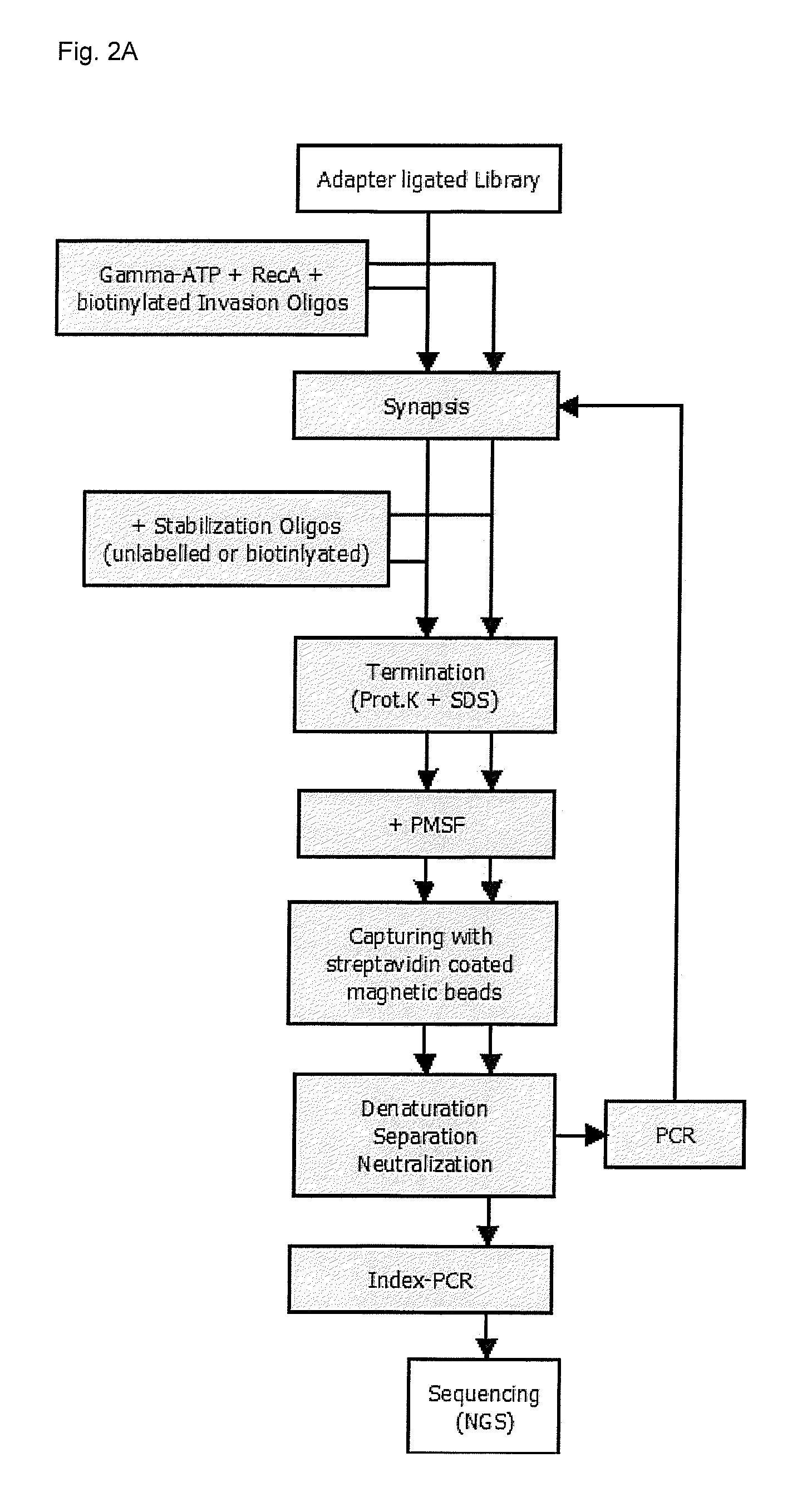
Recombinase mediated targeted DNA enrichment for next generation sequencing
InactiveUS20150197787A1Simple and quick to carry-outNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMassive parallel sequencingDouble stranded
The present invention provides methods, kits and compositions for enriching target sequences from a sequencing library to provide a target enriched sequencing library, wherein the sequencing library is suitable for massive parallel sequencing and comprises a plurality of double-stranded nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Compositions and methods for accurately identifying mutations
ActiveUS20160326578A1Accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiofuelsGeneticsSense strand
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for accurately detecting mutations by uniquely tagging double stranded nucleic acid molecules with dual cyphers such that sequence data obtained from a sense strand can be linked to sequence data obtained from an anti-sense strand when sequenced, for example, by massively parallel sequencing methods.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER CENT
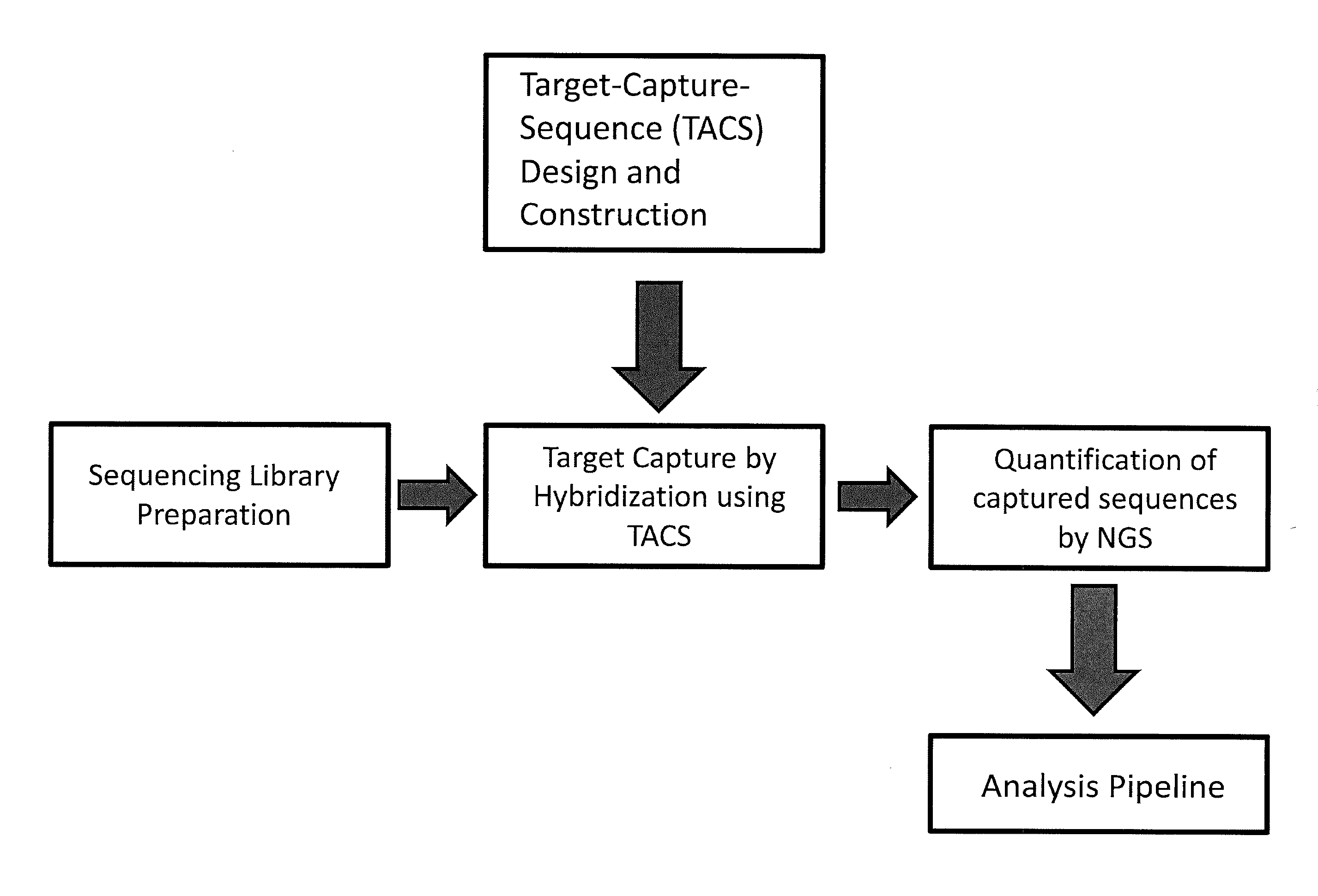
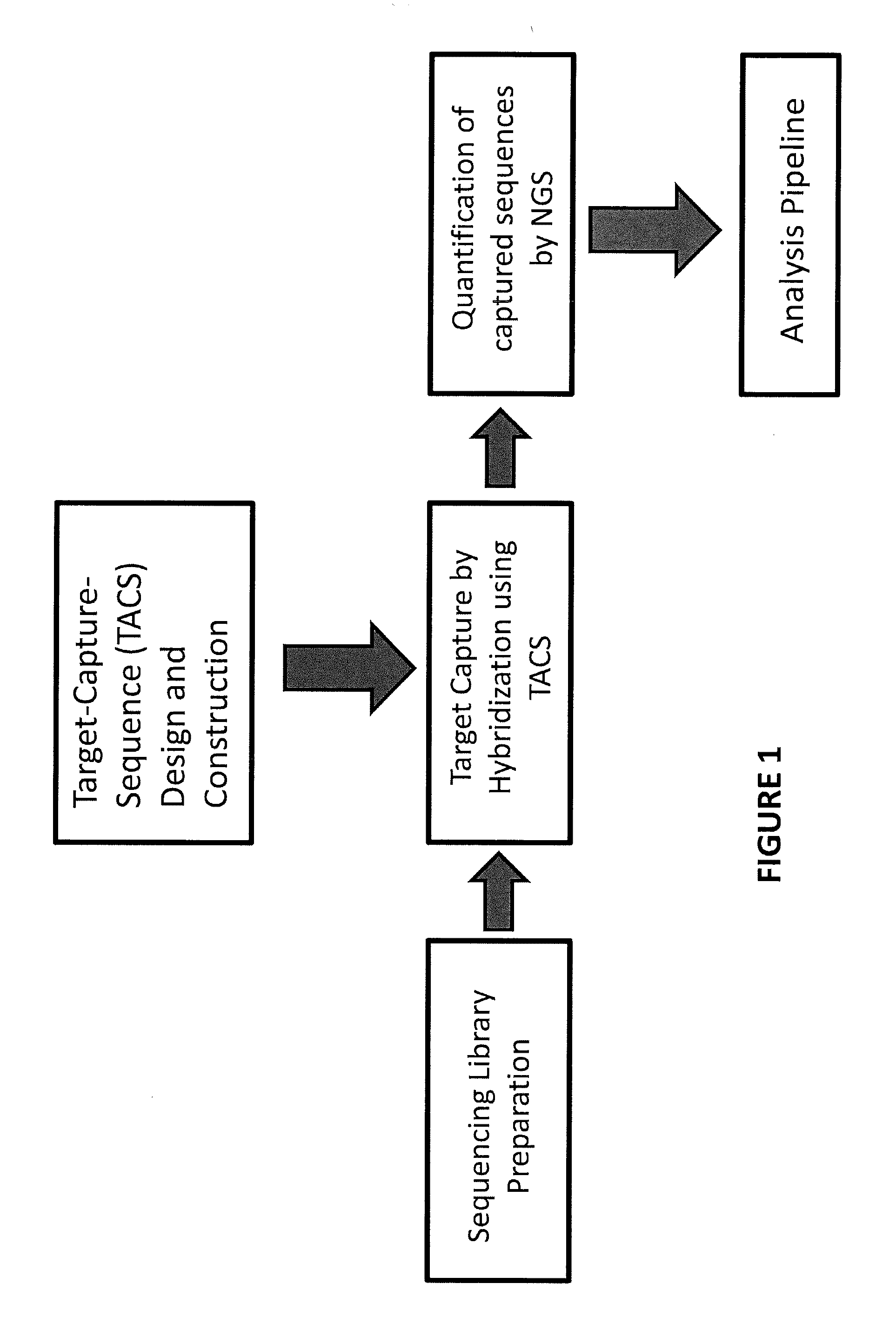
Multiplexed parallel analysis of targeted genomic regions for non-invasive prenatal testing
ActiveUS20160340733A1Highly accurate countingHighly accurate assessmentMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisTarget captureStatistical analysis
The invention provides methods for non-invasive prenatal testing that allow for detecting risk of chromosomal and subchromosomal abnormalities, including but not limited to aneuploidies, microdeletions and microduplications, insertions, translocations, inversions and small-size mutations including point mutations and mutational signatures. The methods of the invention utilize a pool of TArget Capture Sequences (TACS) to enrich for sequences of interest in a mixed sample containing both maternal and fetal DNA, followed by massive parallel sequencing and statistical analysis of the enriched population to thereby detect the risk of a genetic abnormality in the fetal DNA. Kits for carrying out the methods of the invention are also provided.
Owner:NIPD GENETICS PUBLIC CO LTD
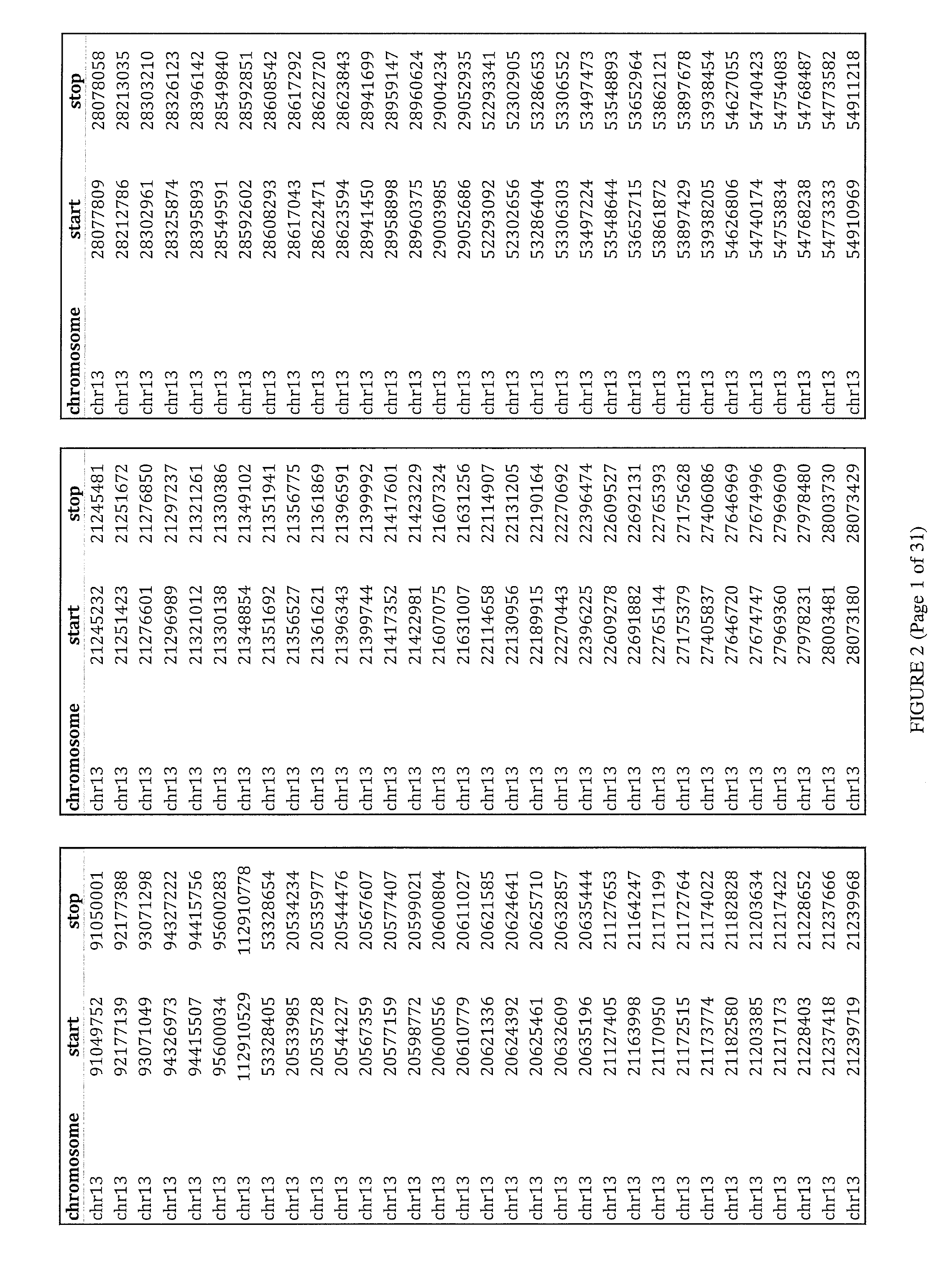
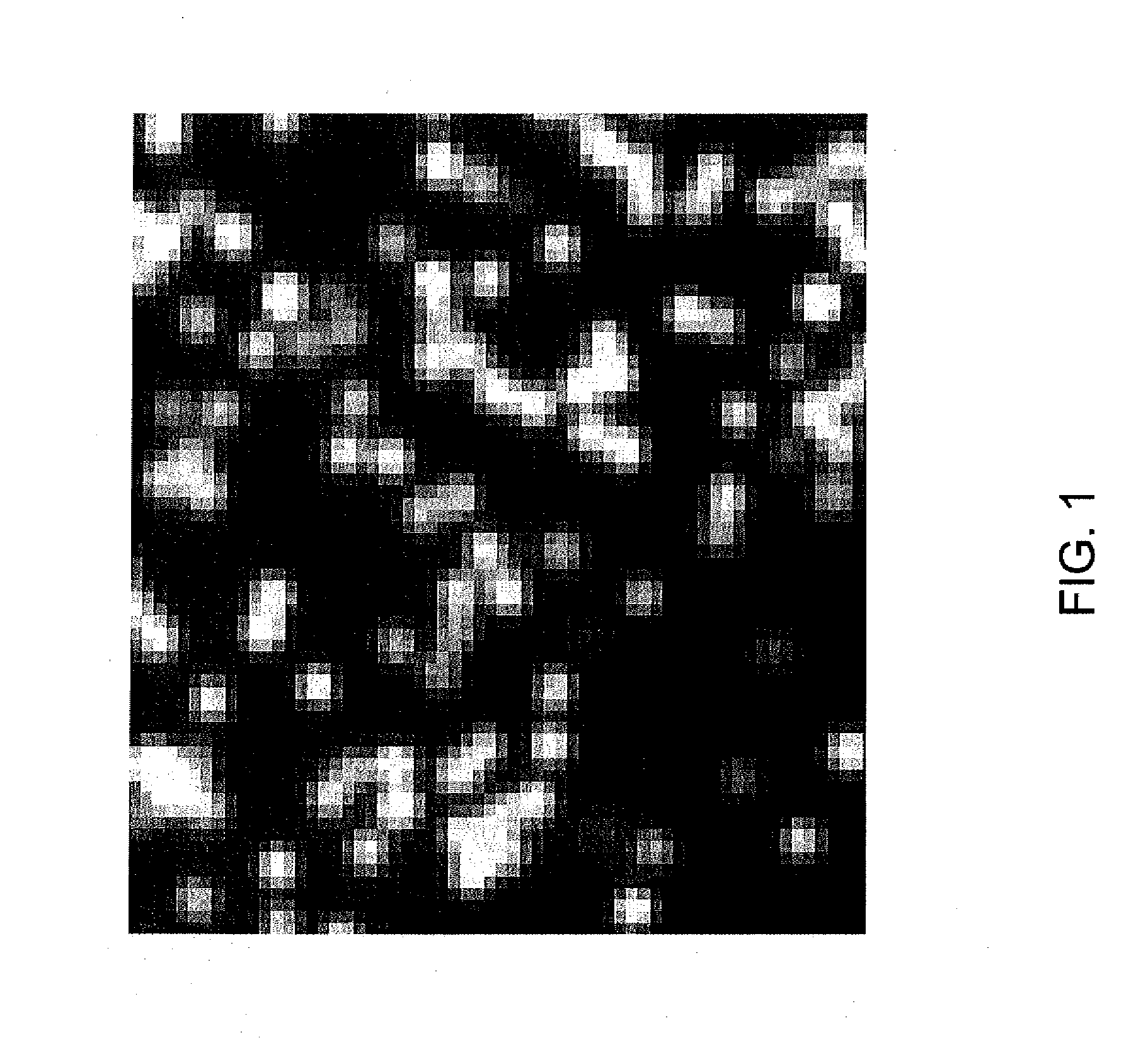
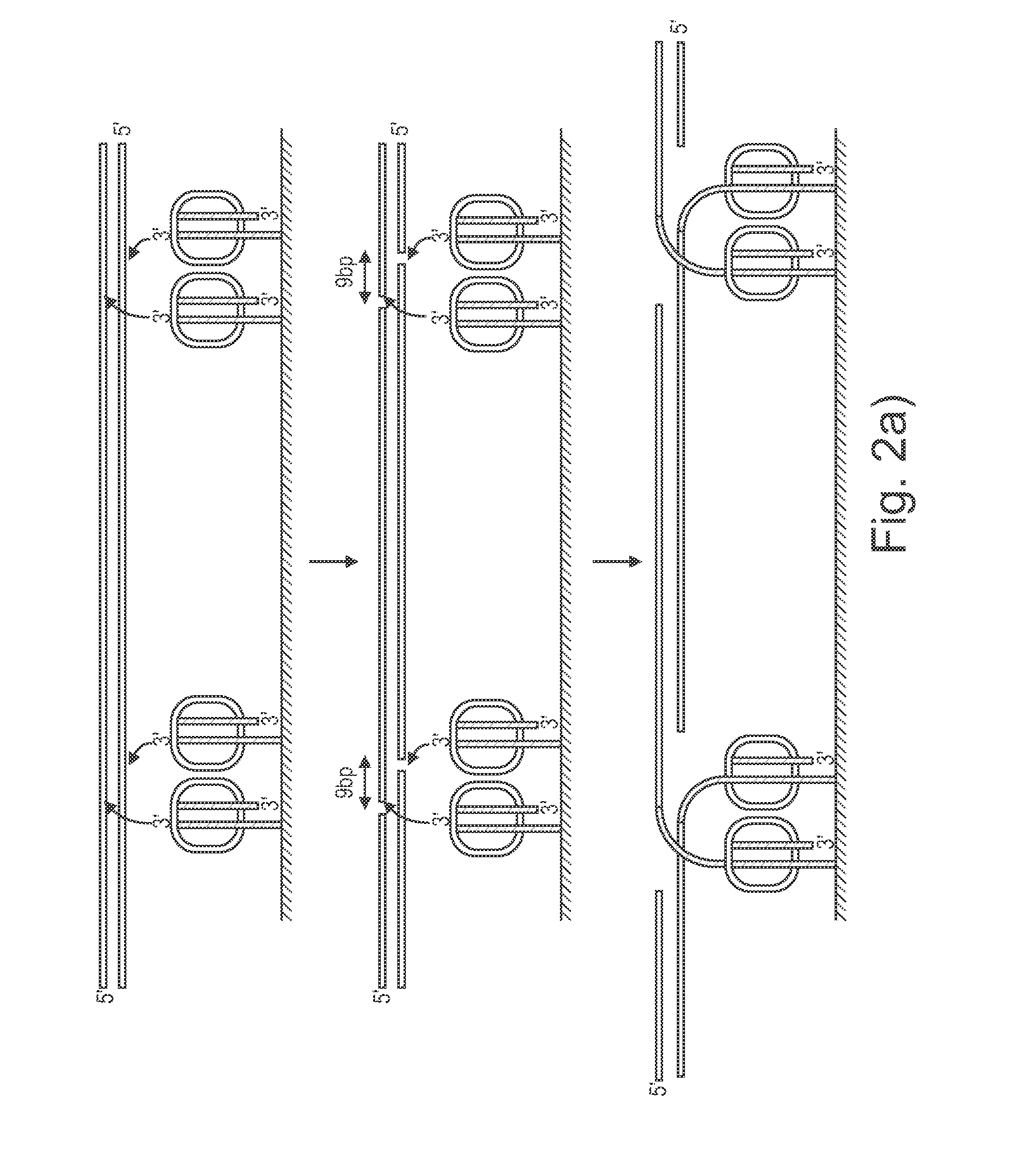
Method and apparatus for image processing for massive parallel DNA sequencing
InactiveUS20110007981A1Increase speedImprove accuracyImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersPattern recognitionPoint spread
Owner:LEVEL SET SYST
29 micro-haplotype sites, screening method, multiplex amplification system and application
ActiveCN108504749AReduce dosageReduce difficultyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTypingAllele frequency
The invention discloses 29 micro-haplotype sites, a screening method, a multiplex amplification system and an application. The screening method comprises the following steps: acquiring population data, acquiring micro-haplotype genotypes and allele frequencies from the population data, calculating forensic related parameters of candidate sites in different populations and excluding sites affectingsubsequent sequencing typing to obtain the 29 micro-haplotype sites; designing primers and amplification conditions according to the 29 micro-haplotype sites, and establishing the multiplex amplification system based on three-round PCR amplification systems. According to the multiplex amplification system, DNA templates extracted from mixed biological samples are amplified, amplification resultsare subjected to large-scale parallel sequencing, value of the sequencing depth of each micro-haplotype site in the DNA templates is obtained, and finally, the purpose of typing the mixed biological samples is achieved. The multiplex amplification system is suitable for large-scale parallel sequencing technology and has the advantages of high detection flux, high detection speed, large quantity ofobtained data, more accurate detection results and the like.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
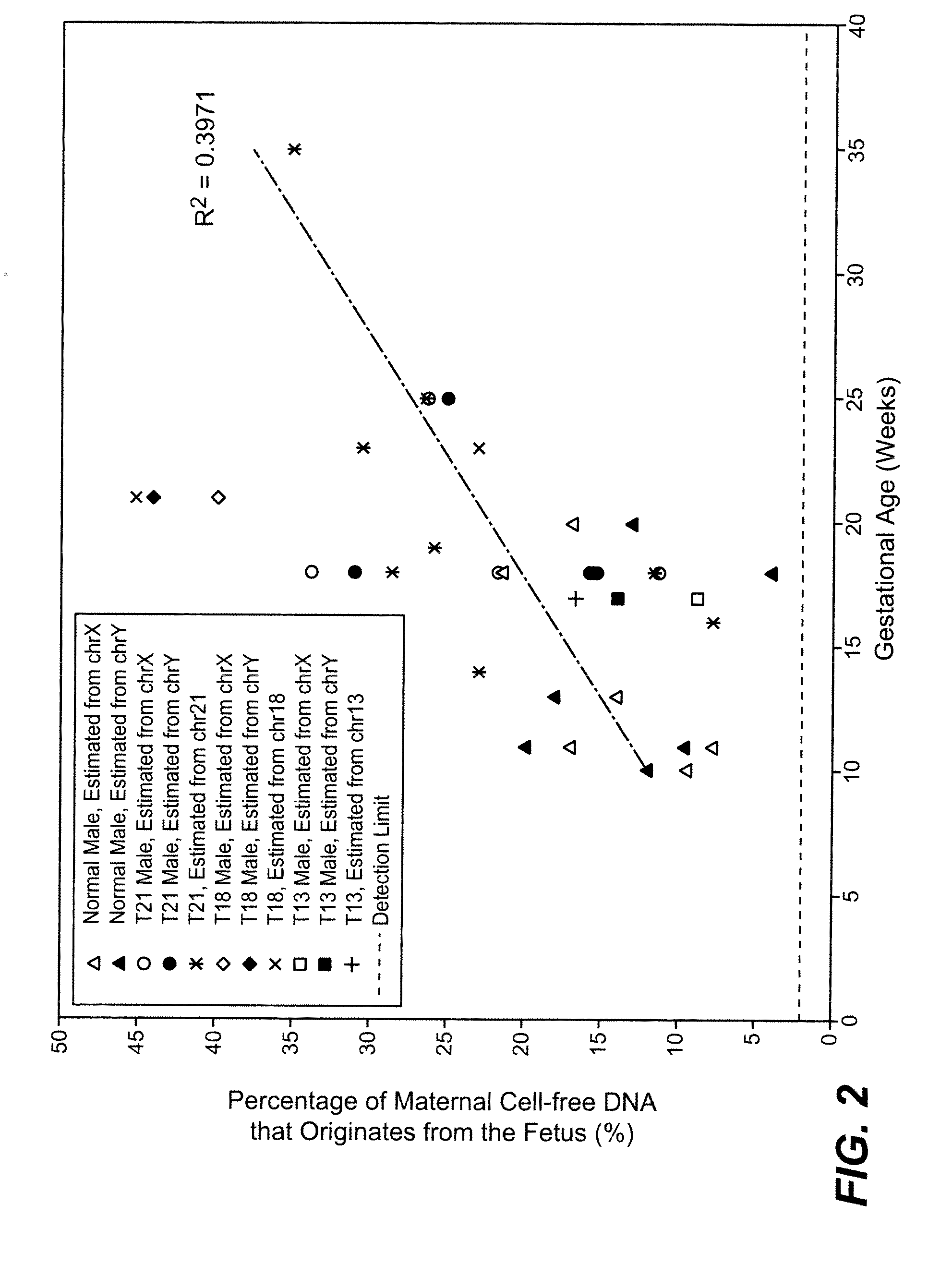
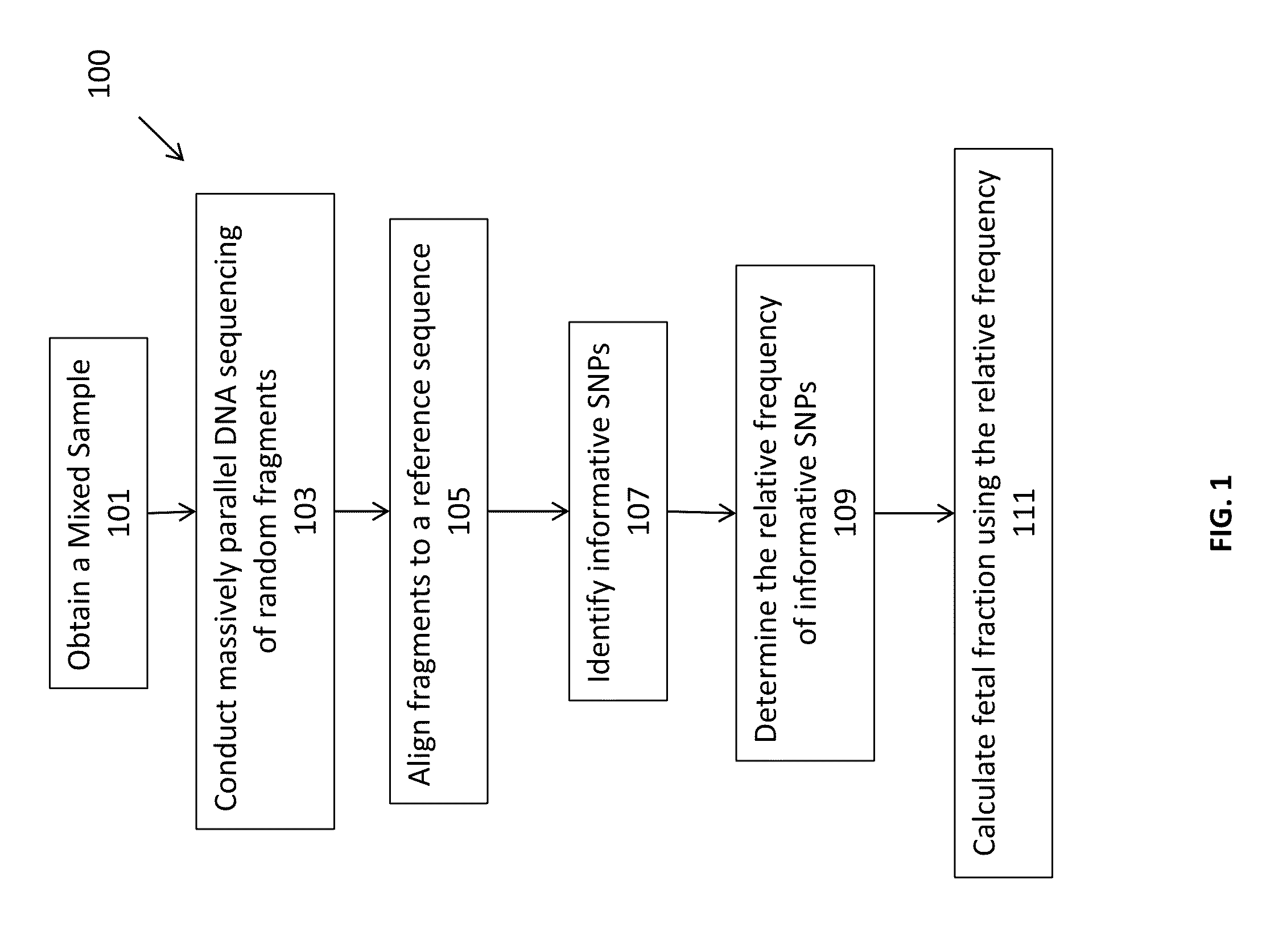
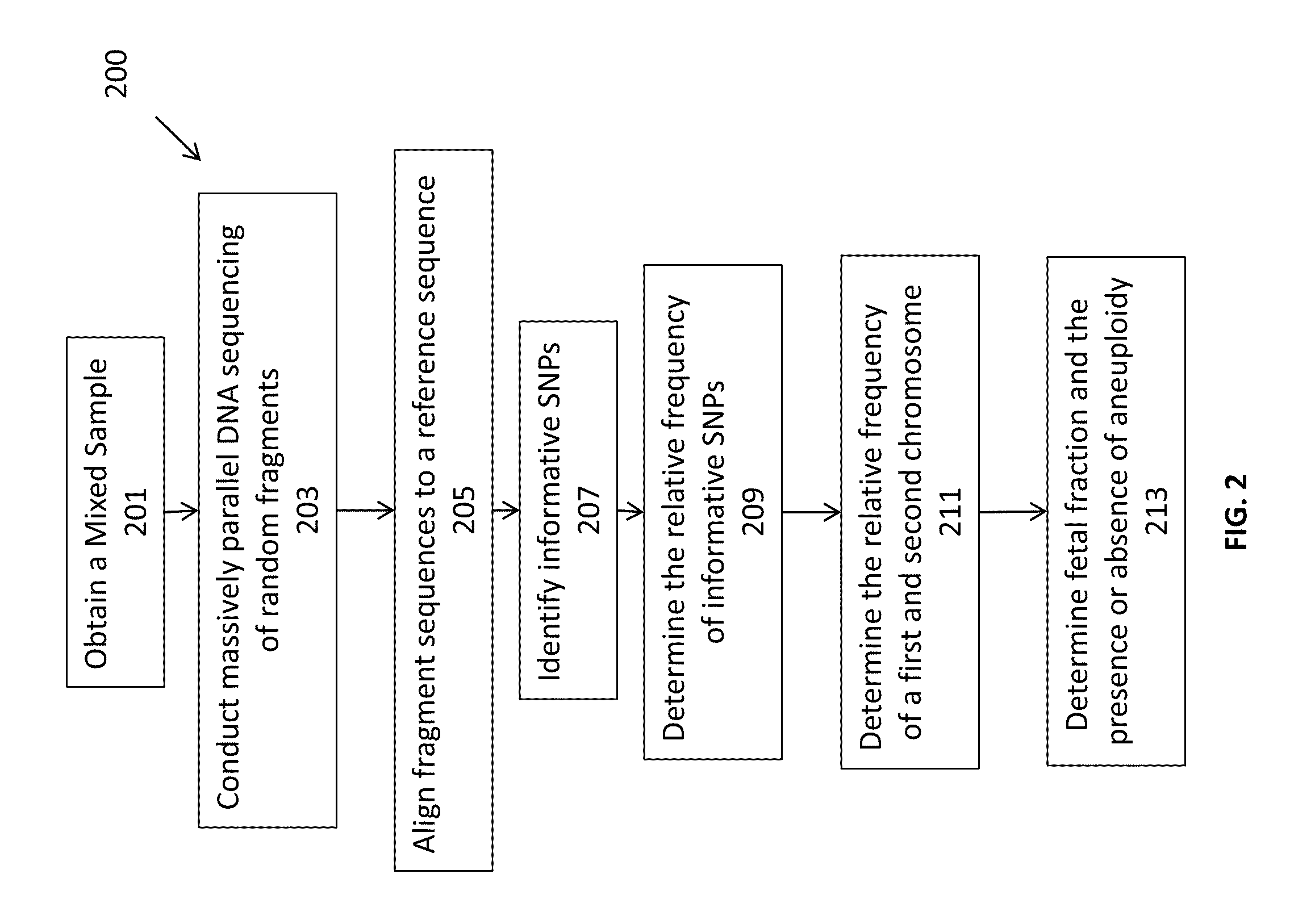
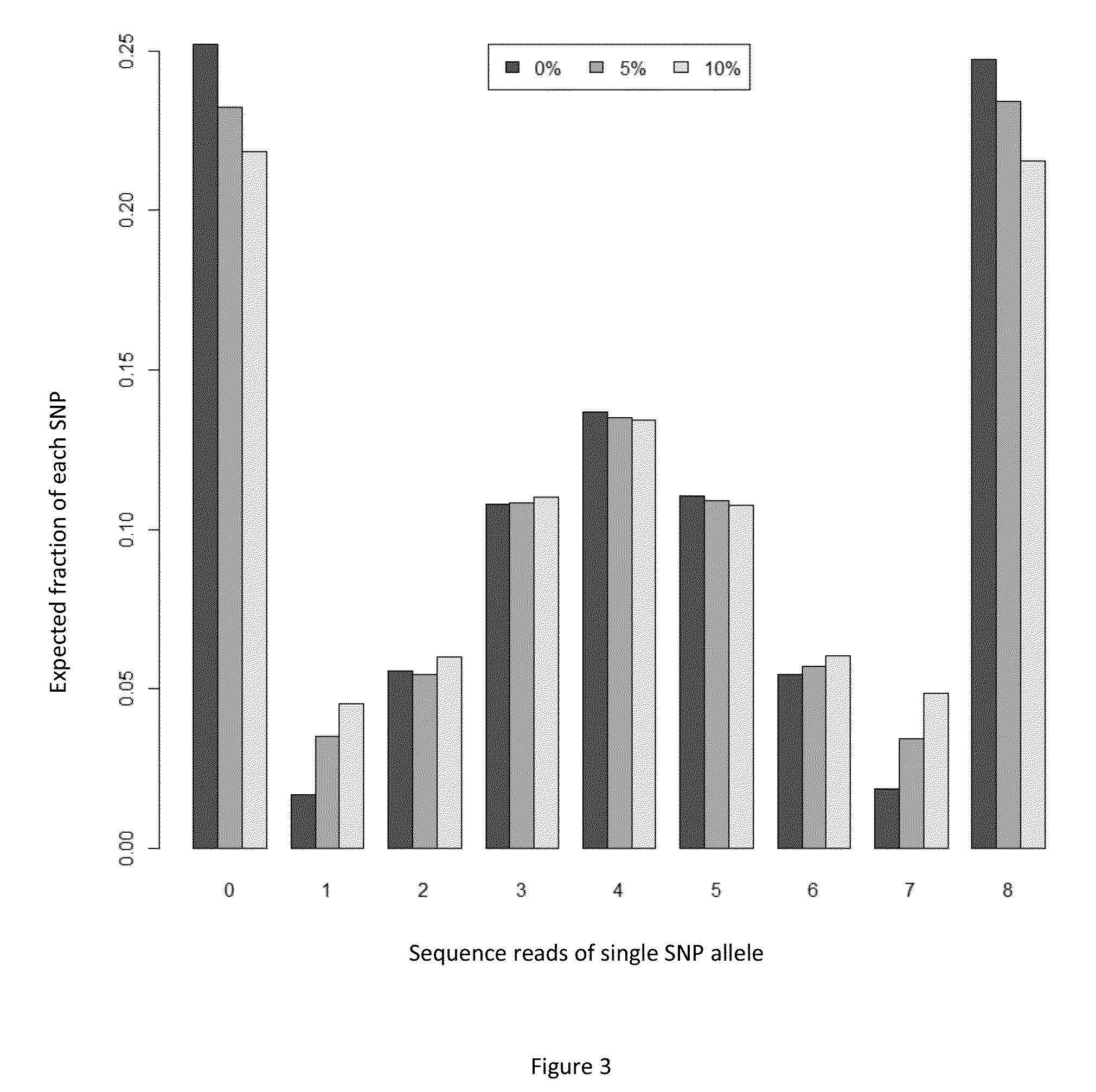
Massively parallel sequencing of random DNA fragments for determination of fetal fraction
InactiveUS20150004601A1Microbiological testing/measurementProteomicsDNA fragmentationMassive parallel sequencing
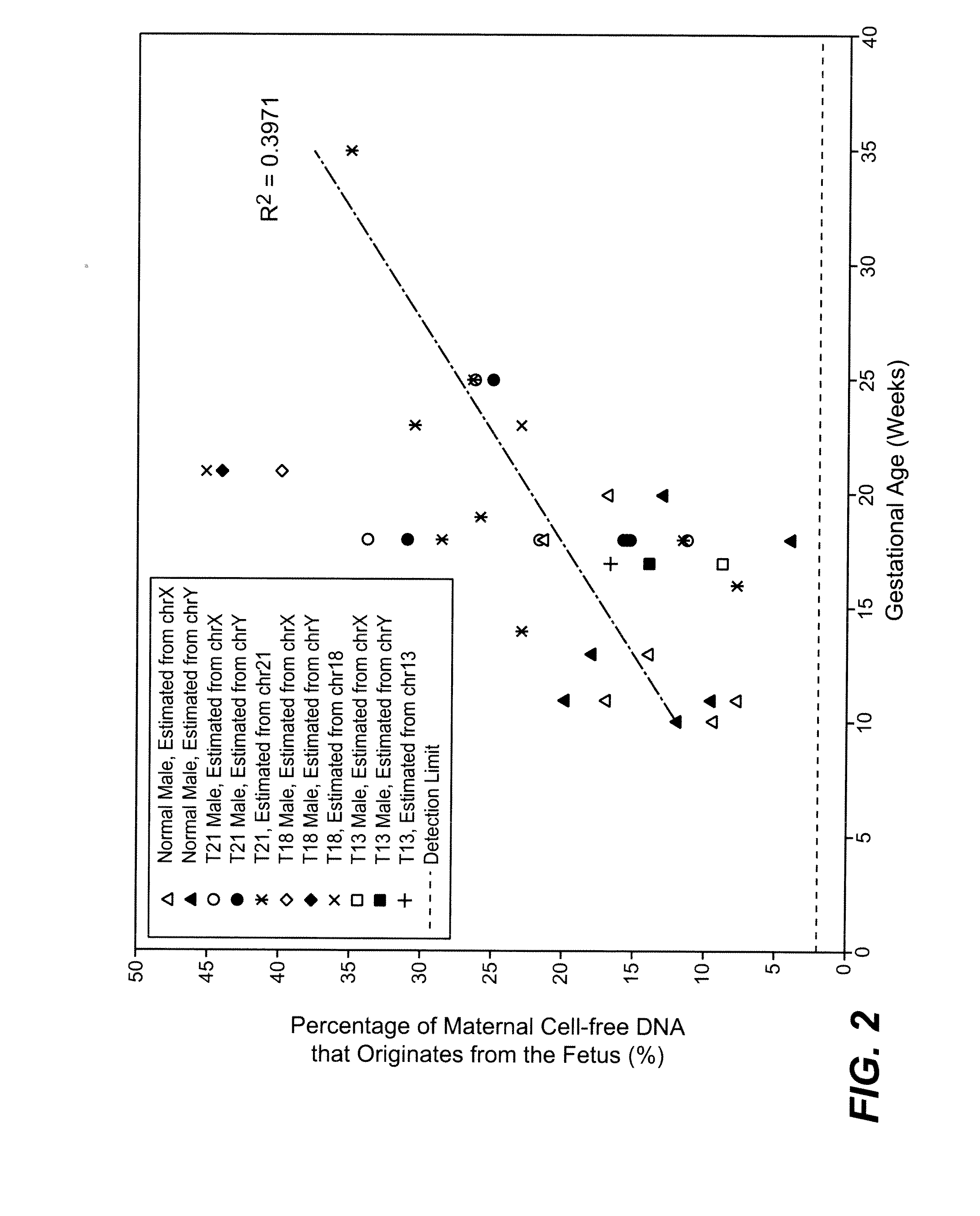
The present invention provides methods for determining the fraction of fetal DNA in a maternal sample using massively parallel shotgun sequencing techniques and statistical probability calculations. The invention utilizes a novel method of identifying polymorphisms through the sequencing process that align to designated regions in the genome. By identifying a statistically significant number of such polymorphisms in multiple designated regions across the genome the fetal fraction, or estimation thereof, can be determined. In certain aspects, the observed distribution of polymorphisms in the genome of a maternal sample can be compared to a fetal proportion reference to estimate the fetal fraction in the sample.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Sample preparation on a solid support
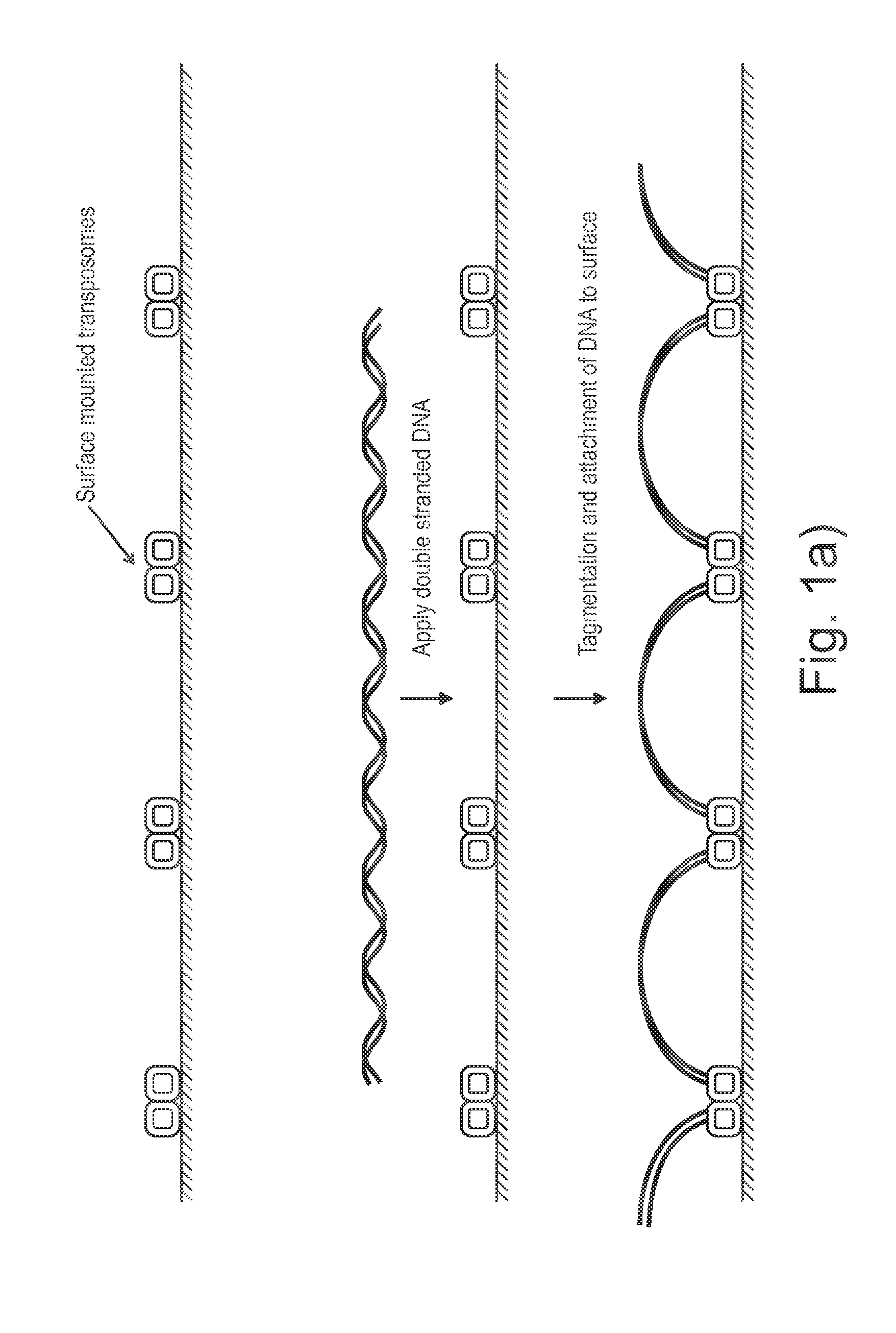
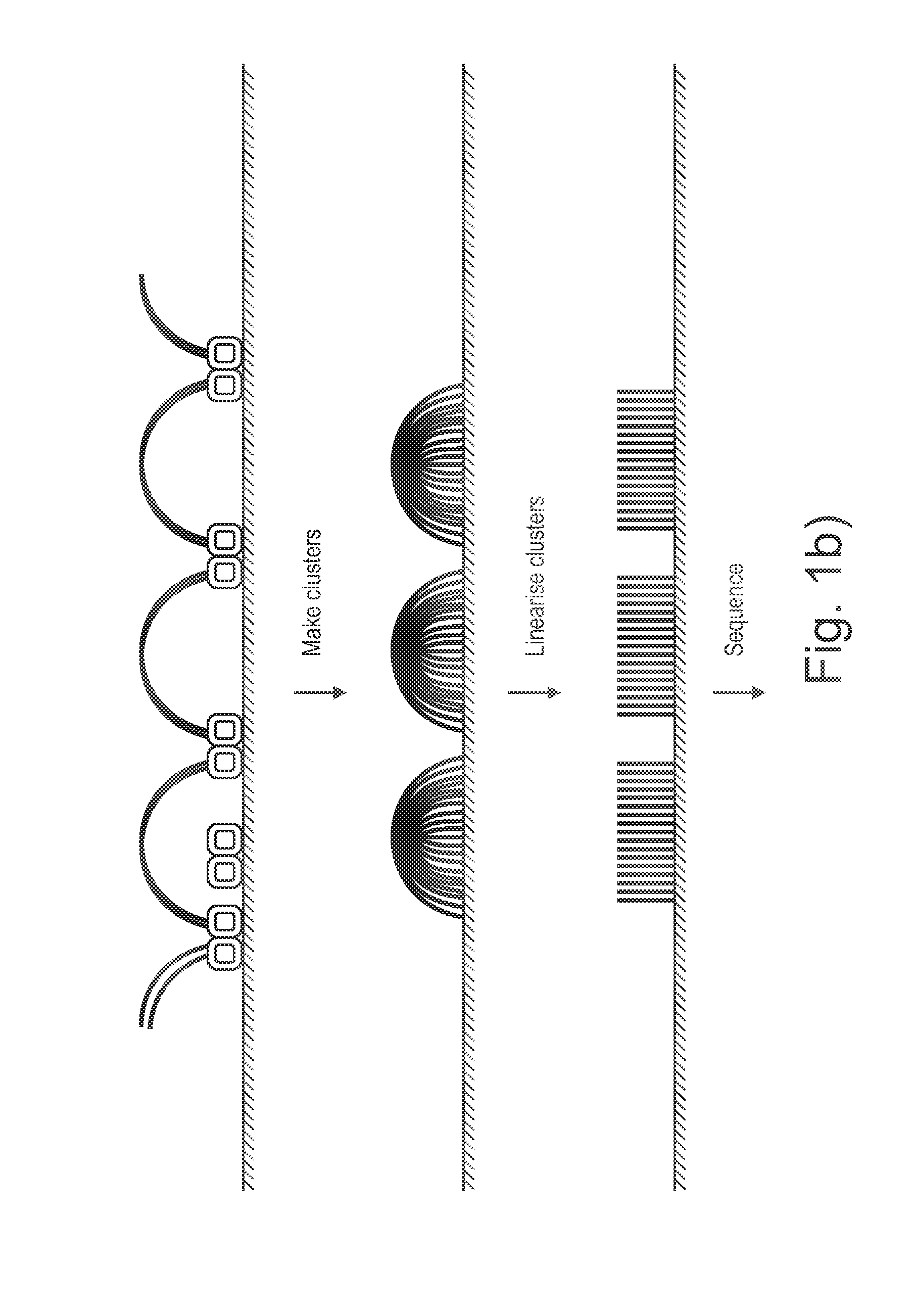
ActiveUS20150284714A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementSolid massDNA fragmentation
Presented are methods and compositions for using immobilized transposase and a transposon end for generating an immobilized library of 5′-tagged double-stranded target DNA on a surface. The methods are useful for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged DNA fragments for use in a variety of processes, including massively parallel DNA sequencing.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Method and apparatus for parallel sequencing of messages between disparate information systems
ActiveUS8015256B2Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksTelecommunicationsUnique identifier
A system and method are provided for coordinating concurrent processing of messages communicated over a network. The messages include a pair of related messages having a common first unique identifier and an unrelated message having a second unique identifier different from the first unique identifier. A sequencer module determines which of the plurality of messages are the pair of related messages and which of the plurality of messages are the unrelated message. The sequencer module identifies a sequence order for the pair of related messages by determining a first position in the sequence order for a first message of the pair of related messages and a second position in the sequence order for a second message of the pair of related messages. The sequencer module inhibits the progression of processing of the second message until the first message is no longer pending while facilitating concurrent processing of the unrelated message.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal trisomy by allelic ratio analysis using targeted massively parallel sequencing
InactiveUS20130267425A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationMassive parallel sequencingTrisomy 22
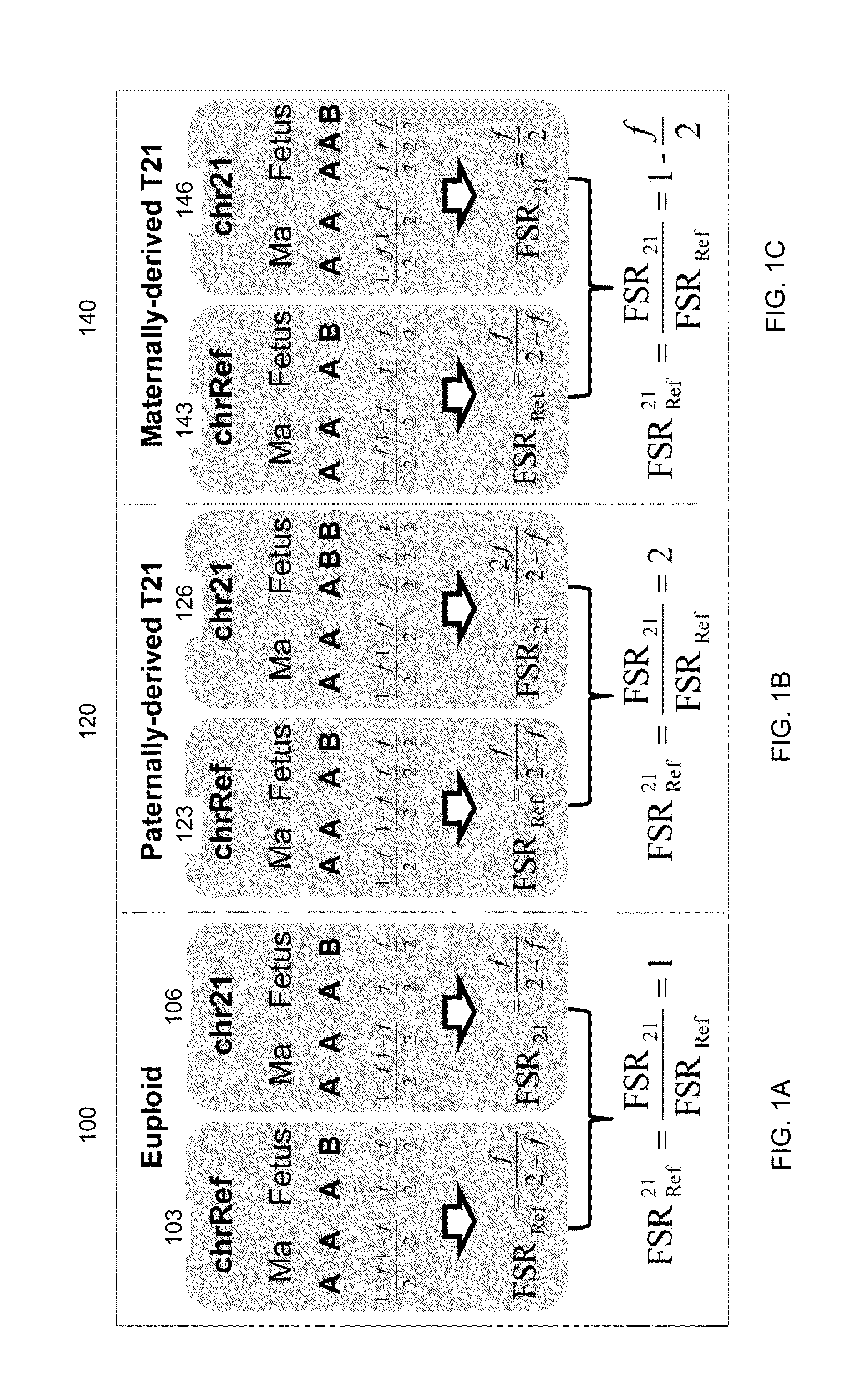
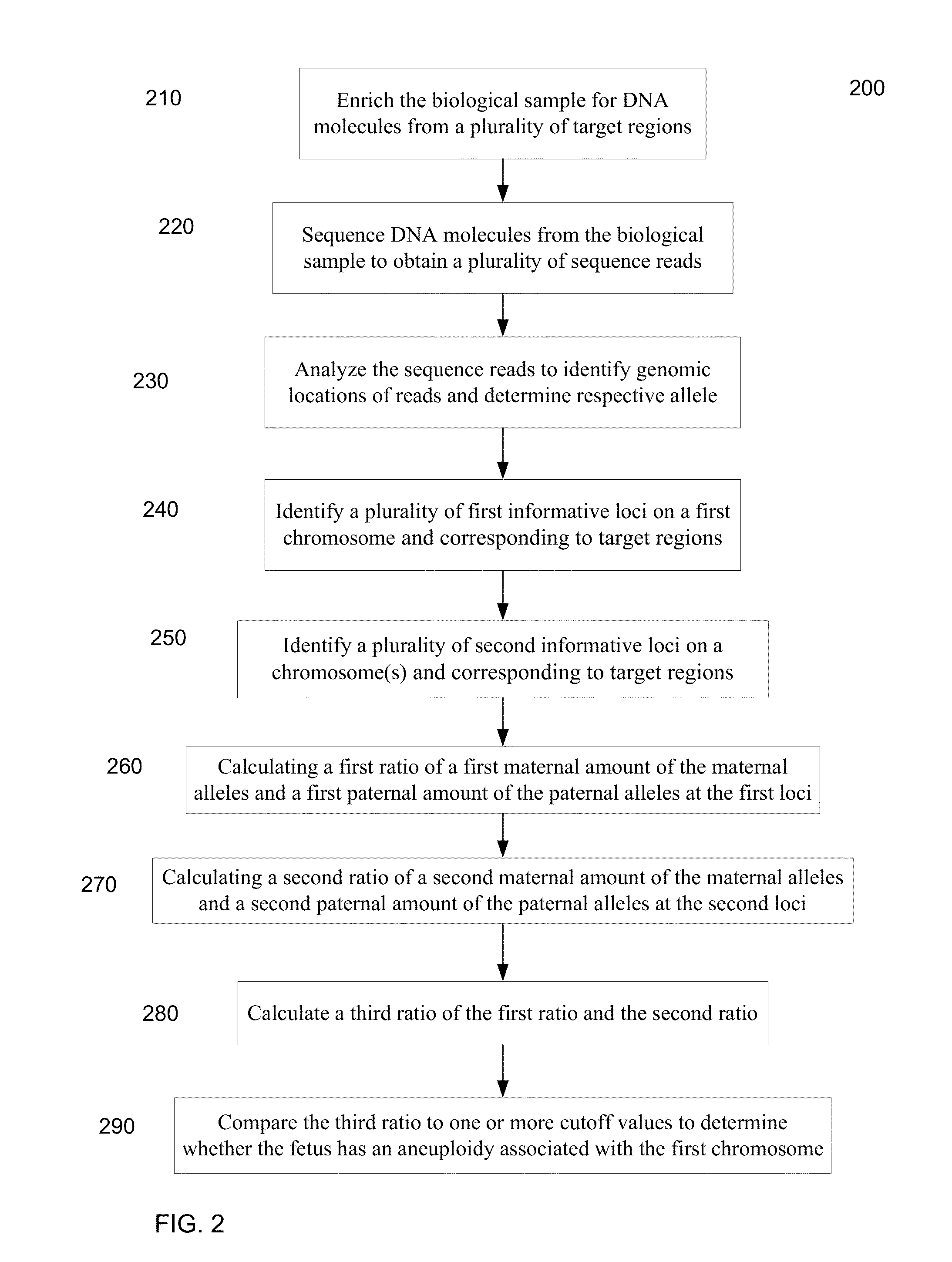
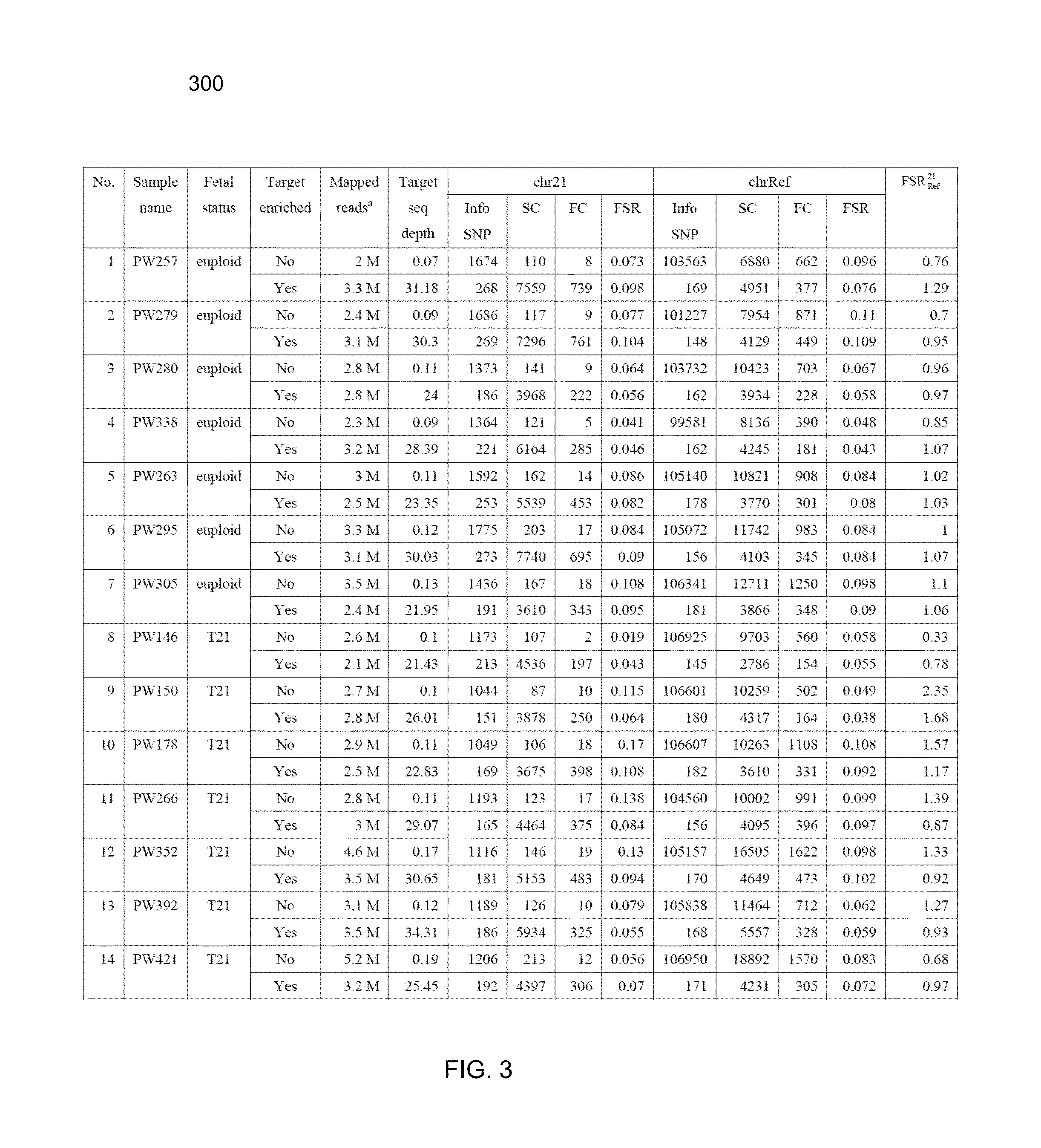
Whether a fetus has an aneuploidy associated with a first chromosome is detected using ratios of alleles detected in a maternal sample having a mixture of maternal and fetal DNA. DNA from the sample is enriched for target regions associated with polymorphic loci and then sequenced. Polymorphic loci (e.g., single nucleotide polymorphisms) in the target regions with fetal-specific alleles are identified on a first chromosome and on one or more reference chromosomes. A first ratio of the fetal-specific alleles and shared alleles is determined for the loci on the first chromosome. A second ratio of the fetal-specific alleles and shared alleles is determined for the loci on the reference chromosome(s). A third ratio of the first and second ratio can be compared to a cutoff to determine whether an aneuploidy is present, and whether the aneuploidy is maternally-derived or paternally-derived.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Target preparation for parallel sequencing of complex genomes
InactiveUS20100204050A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAMassive parallel sequencing
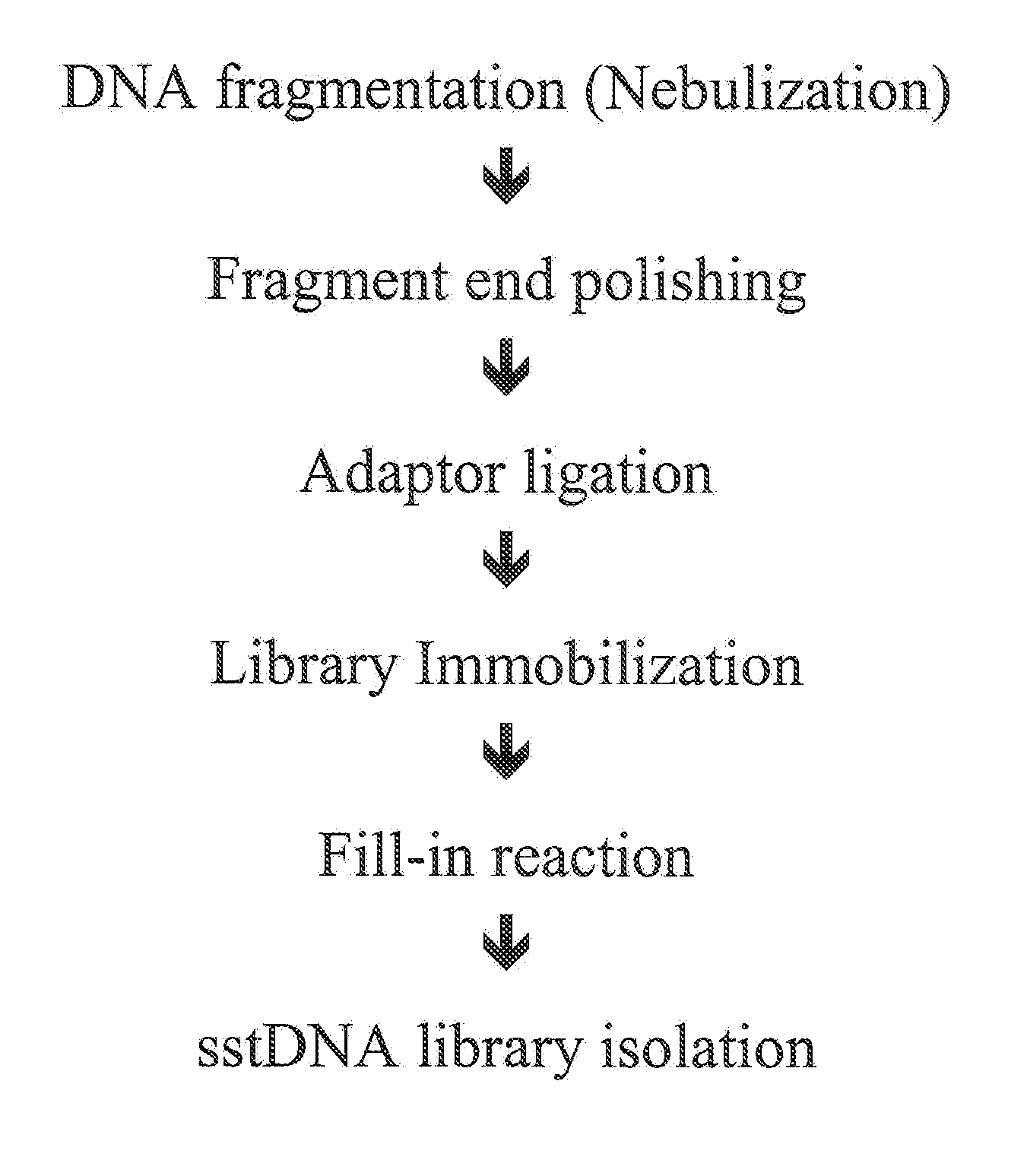
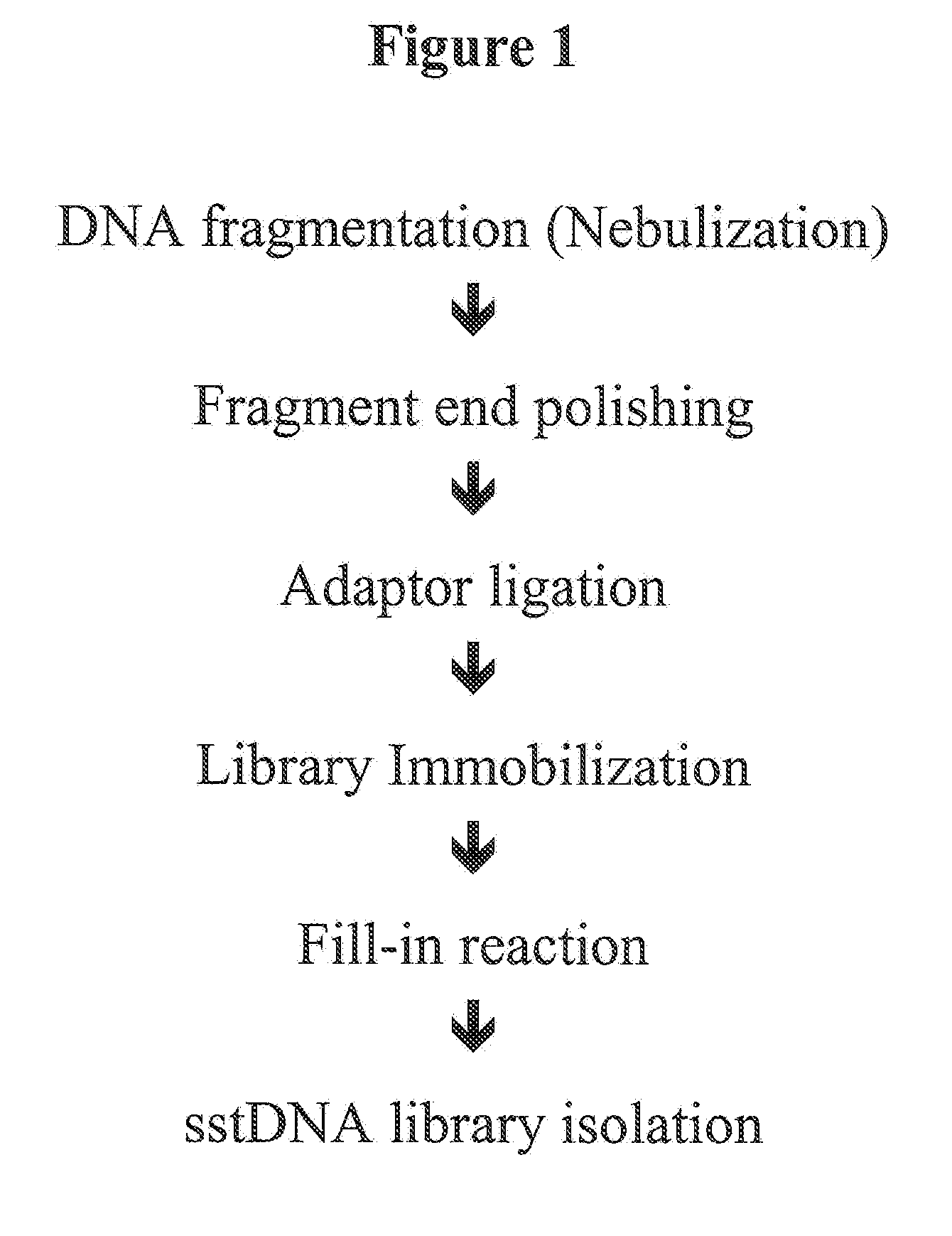
The present invention provides a method for the isolation and analysis of a target nucleic acid, the target nucleic acid being present in a sample of genomic DNA, comprising the steps of a) fragmentation of the genomic DNA, b) hybridization of the genomic DNA on a nucleic acid solid support, the solid support comprising a plurality of oligonucleotide probes, the probes being characterized in that each probe is at least partially complementary to the sequence of the target nucleic acid or its complement, under hybridization conditions, characterized in that the plurality of probes hybridizes to fragments of the target nucleic acid but does not hybridize to other nucleic acids which are present in the sample, c) stripping off the target molecules hybridized to the nucleic acid array, d) overlap extension synthesis in order to generate double stranded overlap extension synthesis product, e) fragment polishing, and f) adaptor ligation.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Paired end bead amplification and high throughput sequencing
ActiveUS20140031241A1Quick sortingQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationEmulsionEmulsion polymerization
The present invention is related to genomic nucleotide sequencing. In particular, the invention describes a paired end sequencing method that enables the sequencing of unique read pairs by co-localizing both 5′ ends on a single emulsion polymerase chain reaction bead. The method may use a customized forked adaptor primer pair that is compatible with massively parallel sequencing techniques. The compositions and methods disclosed herein contemplate sequencing complex genomes, amplified genomic regions, as well as detecting chromosomal structural rearrangements.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC
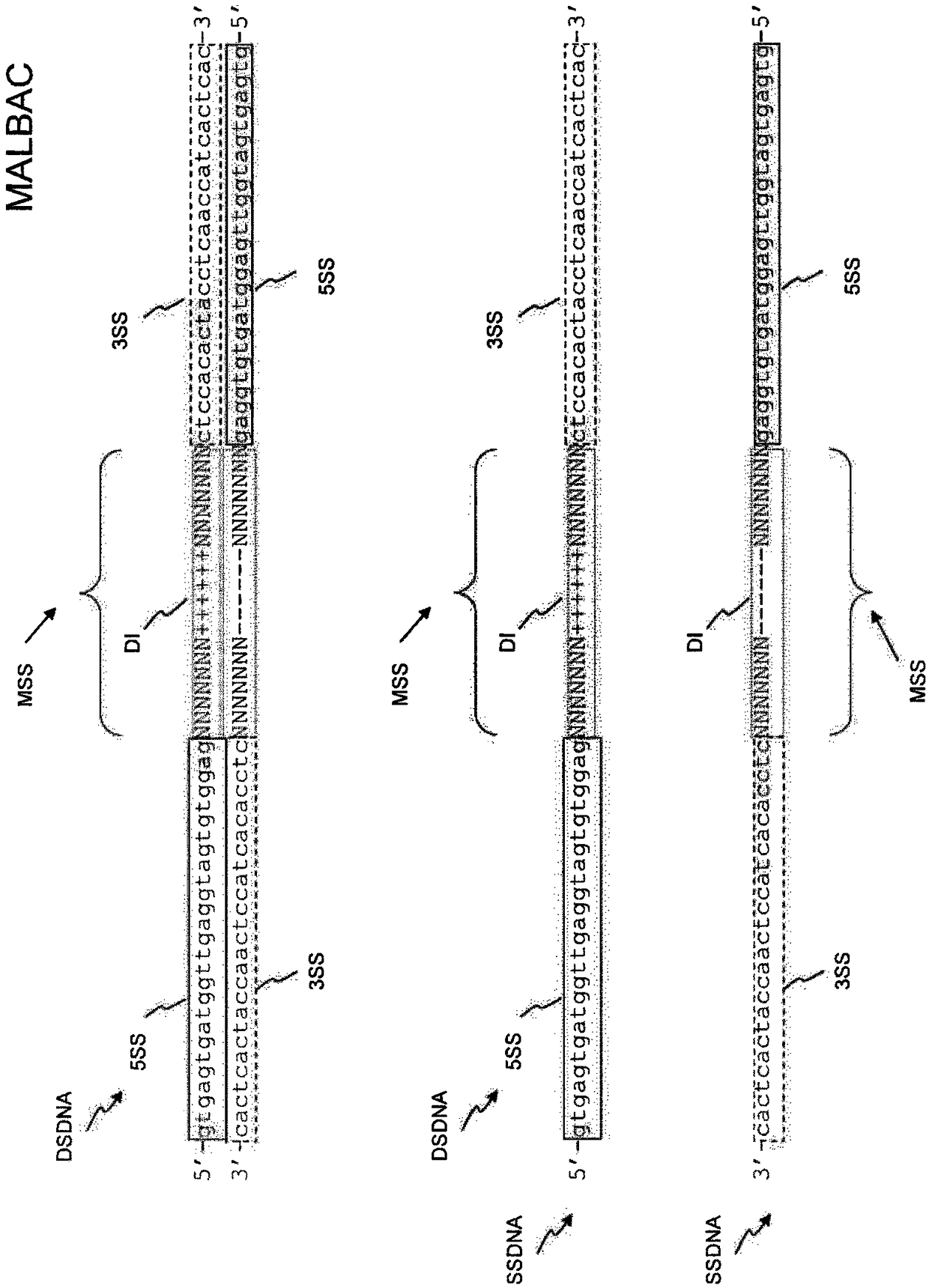
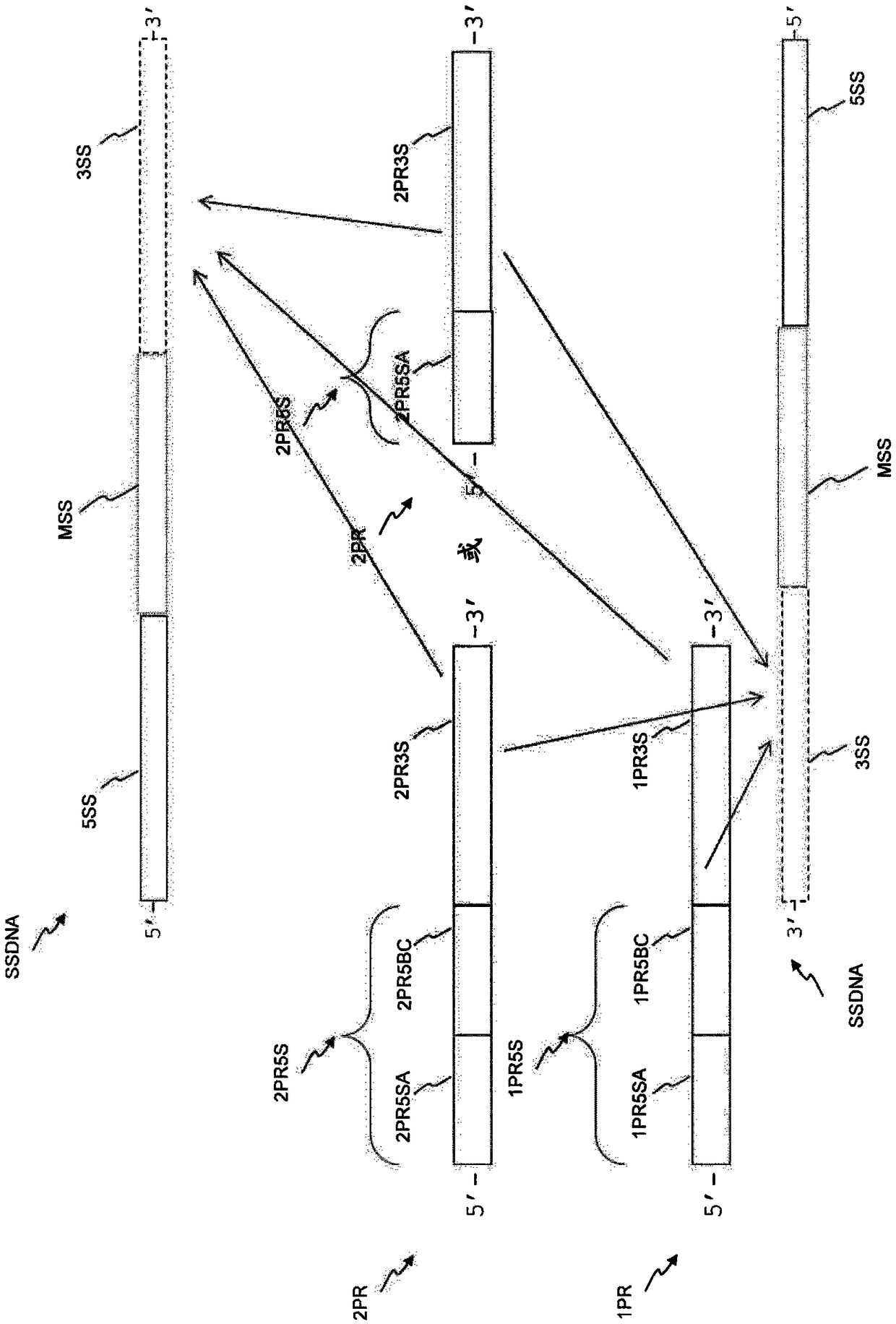
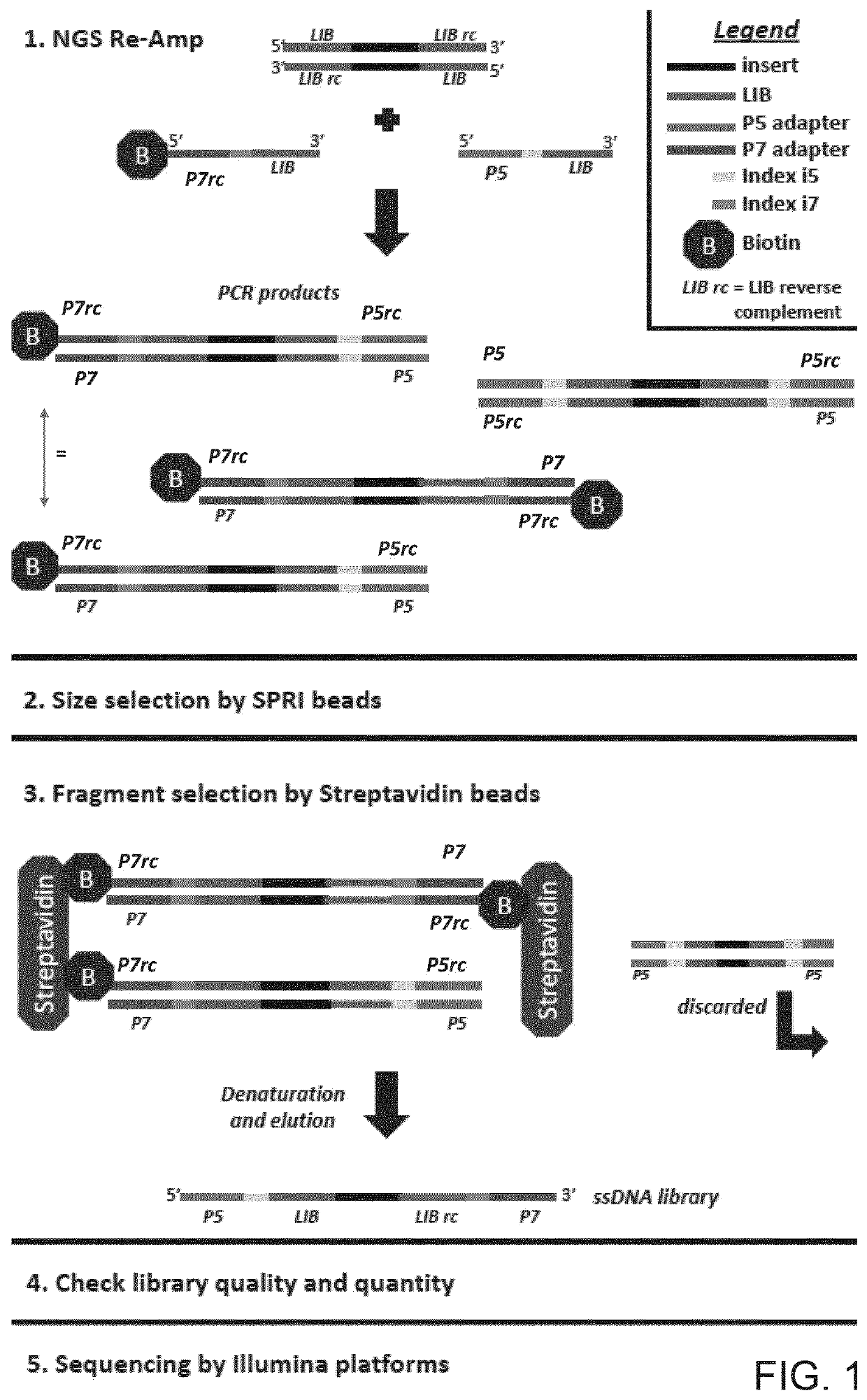
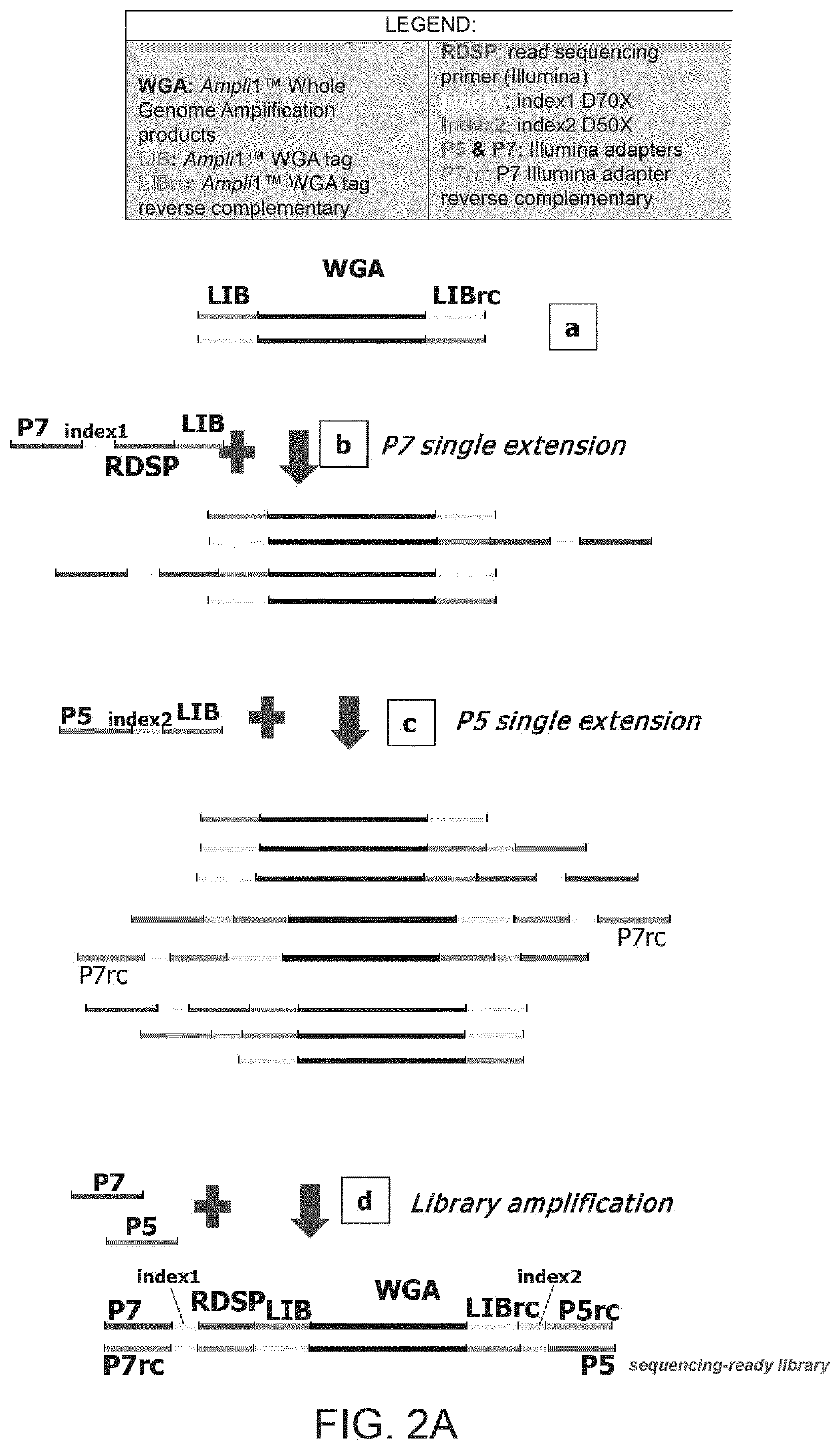
Method and kit for the generation of DNA libraries for massively parallel sequencing
PendingCN109477245ALess enzymatic reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationCDNA libraryBarcode
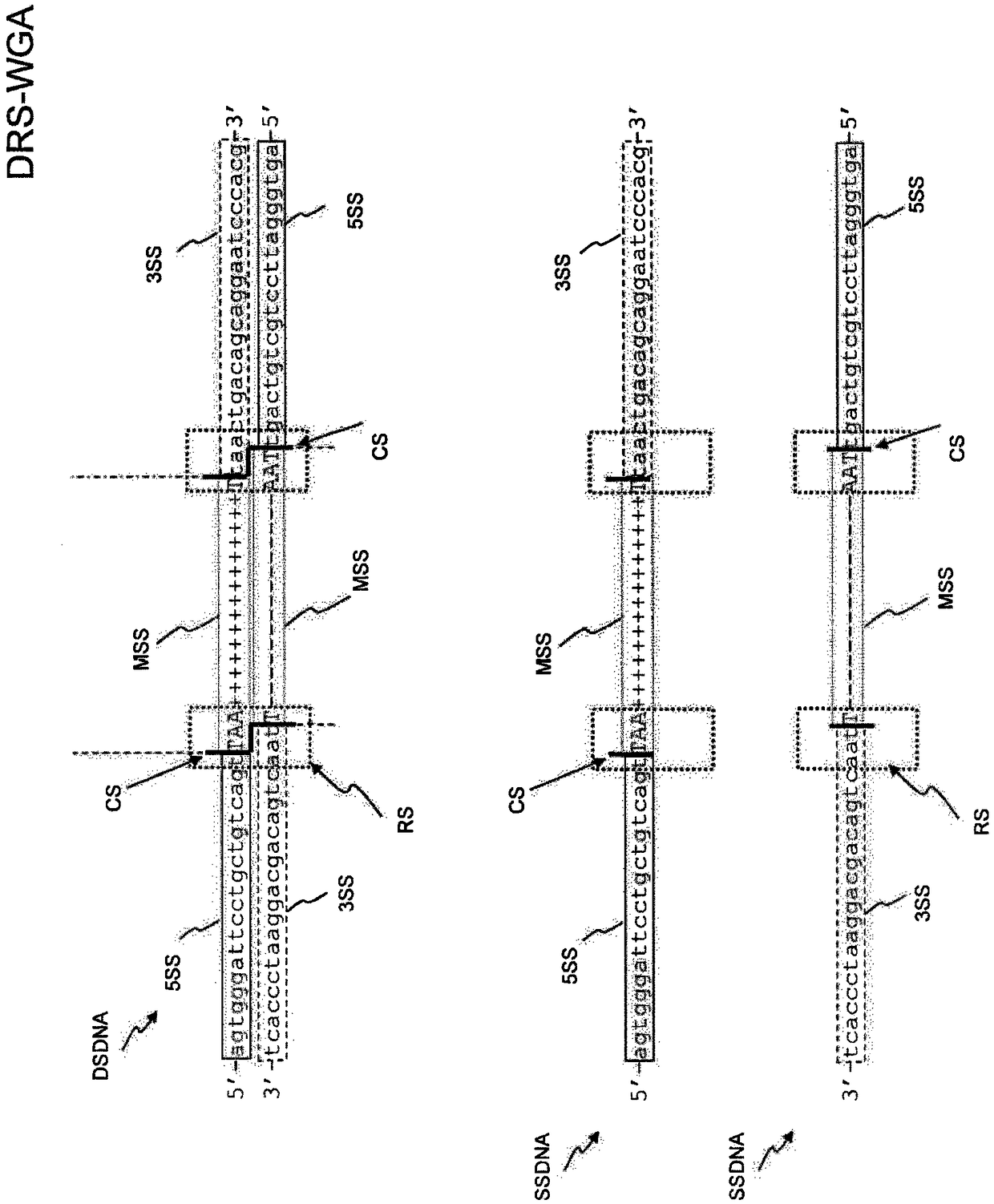
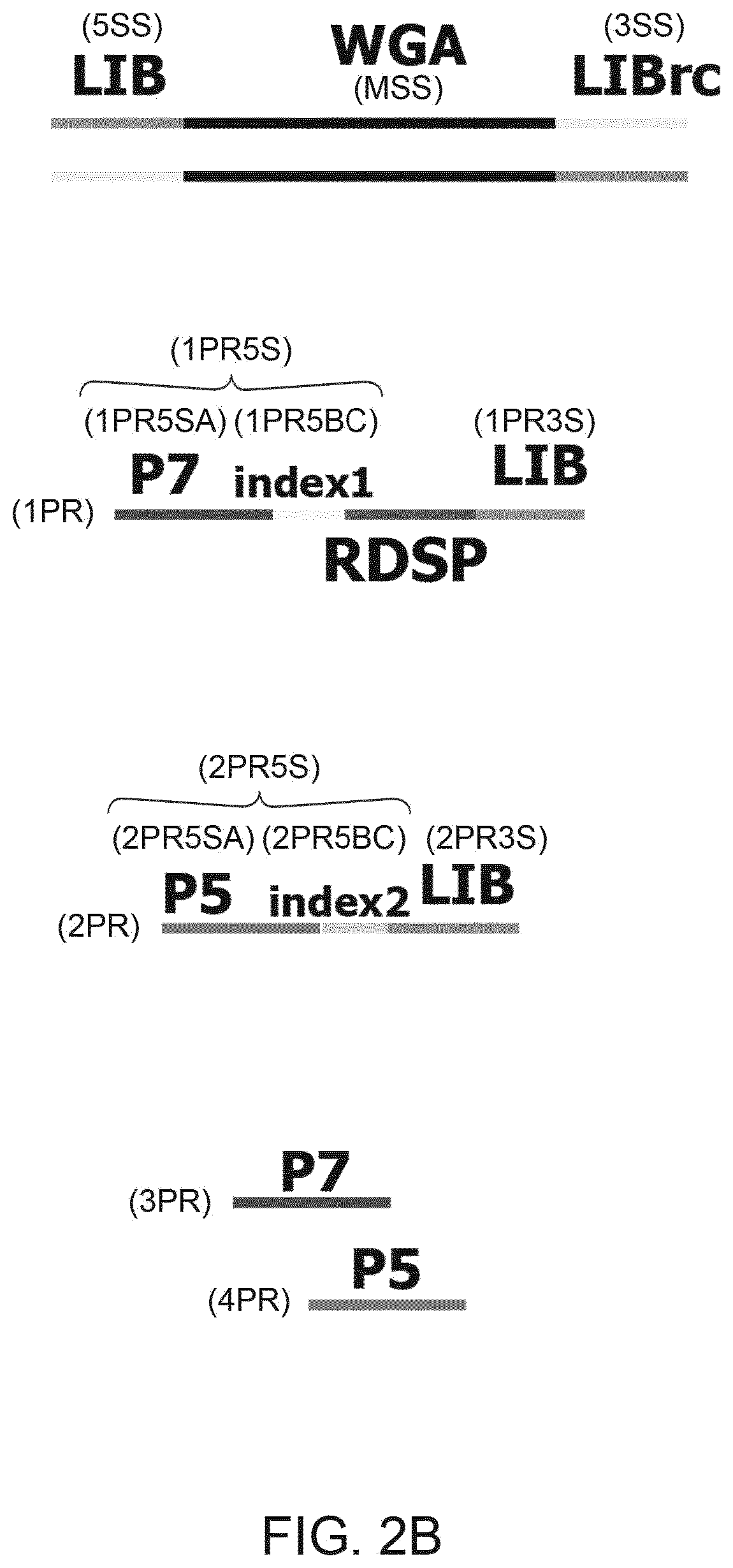
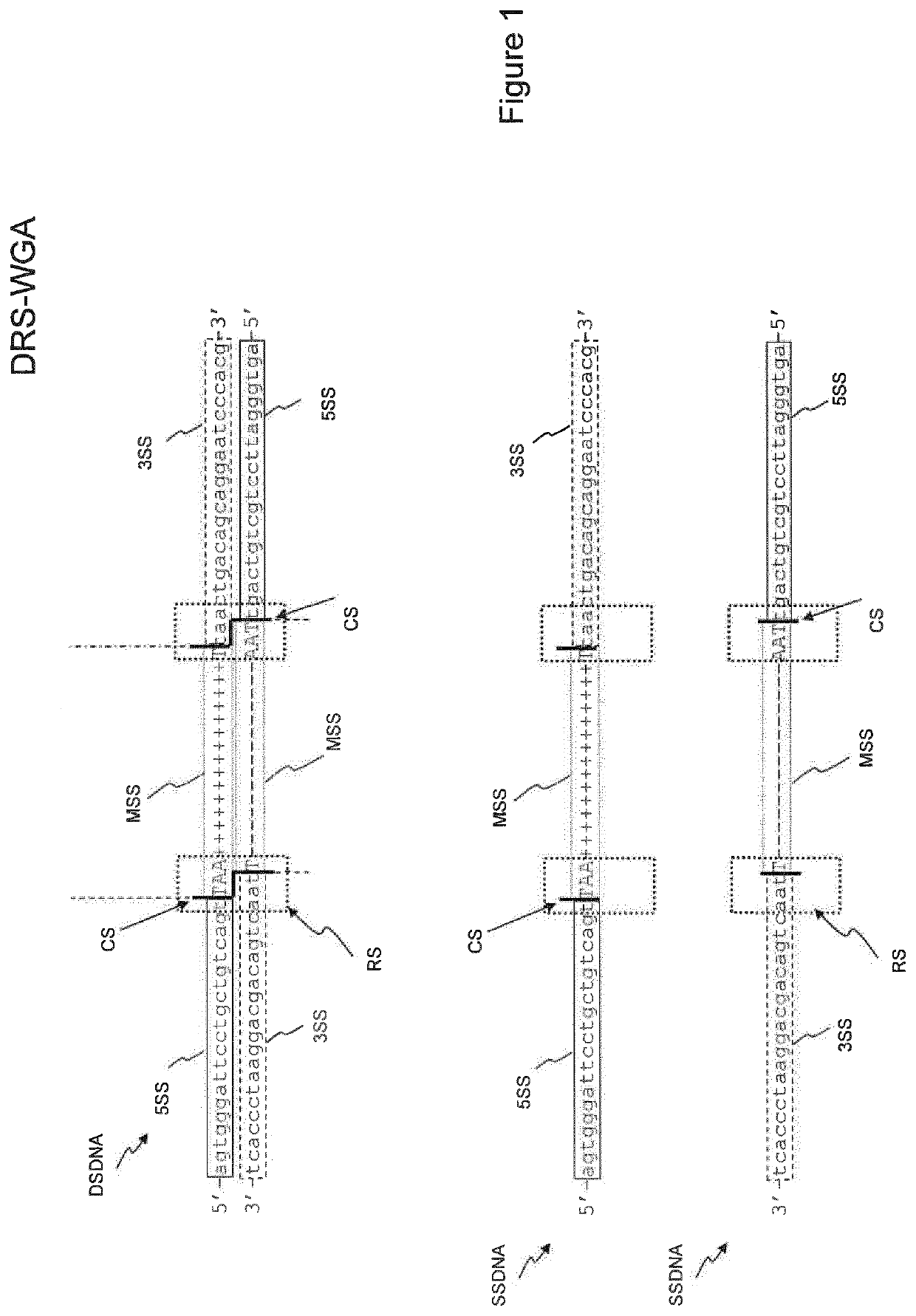
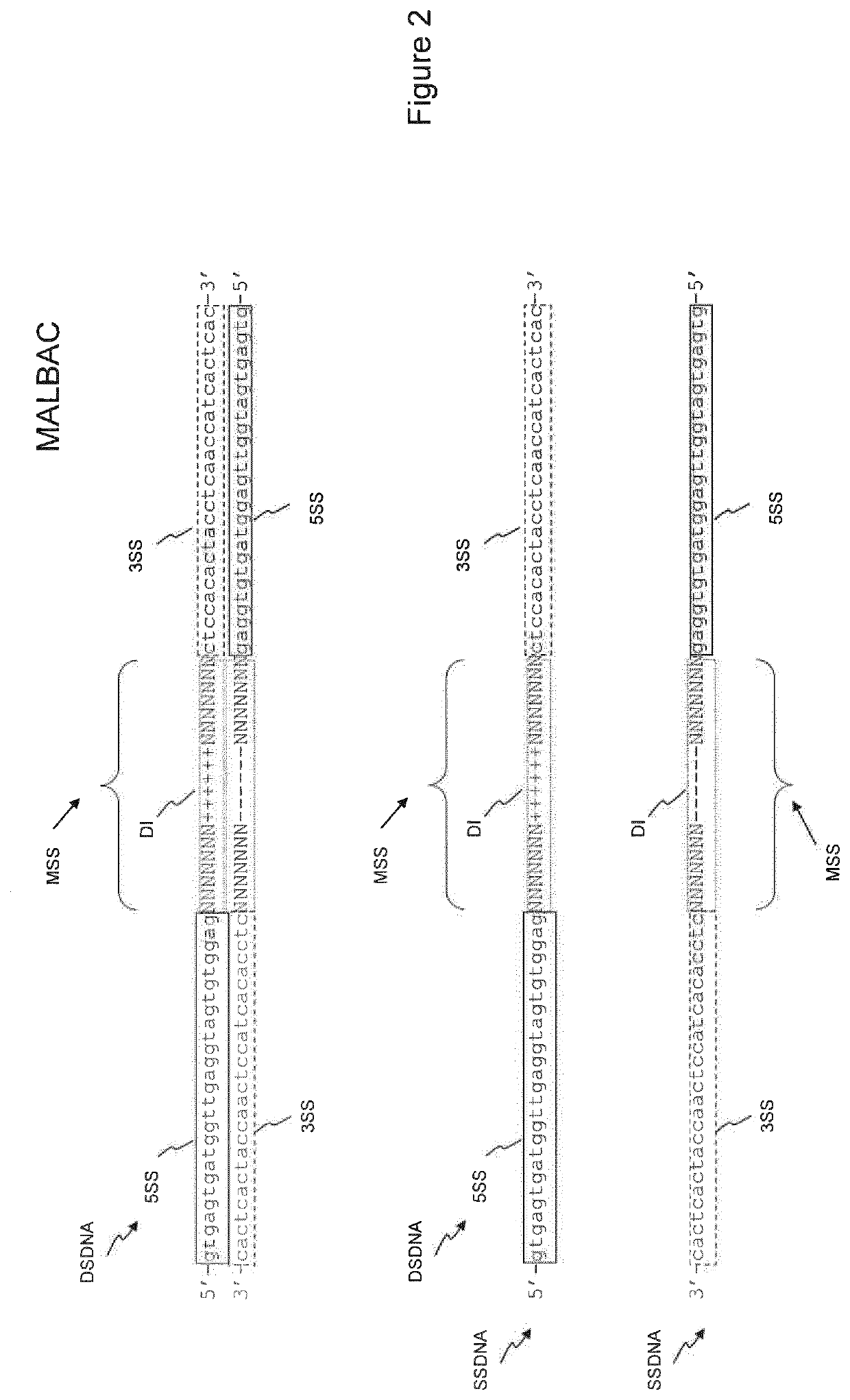
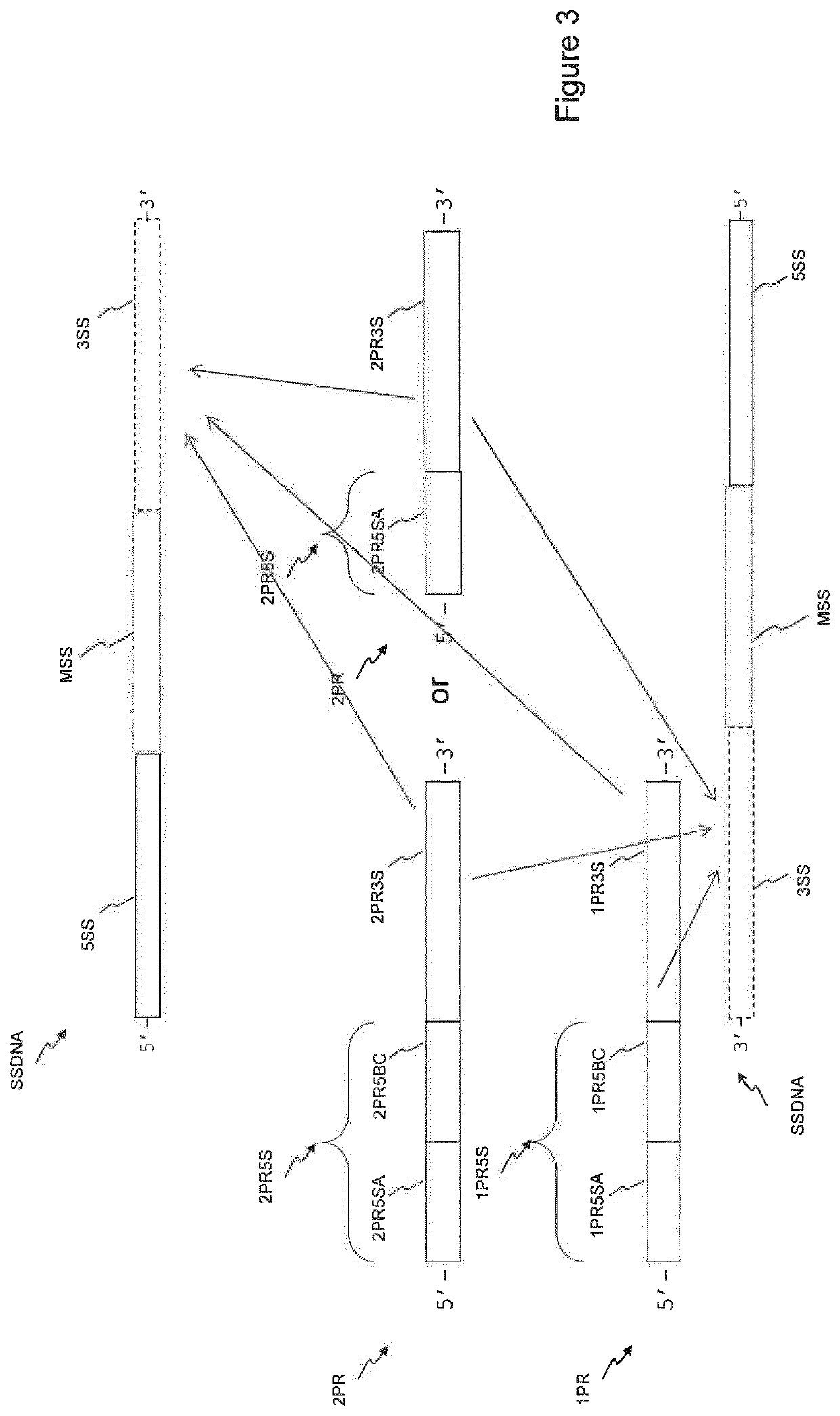
There is disclosed a method of generating a massively parallel sequencing library comprising the steps of :a) providing a primary WGA DNA library (pWGAlib), including fragments comprising a WGA library universal sequence adaptor; b)re-amplifying the primary WGA DNA library using at least one first primer (1PR) and at least one second primer (2PR); the at least one first primer (1PR) comprising from 5' to 3' at least one first sequencing adaptor (1PR5SA), at least one first sequencing barcode (1PR5BC) and a first primer 3' section (1PR3S) hybridizing to either the WGA library universal sequenceadaptor or its reverse complementary; the at least one second primer (2PR) comprising from 5' to 3' at least one second sequencing adaptor (2PR5SA) different from the at least one first sequencing adaptor (1PR5SA), and a second primer 3' section (2PR3S) hybridizing to either the WGA library universal sequence adaptor or its reverse complementary.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Improved method and kit for the generation of DNA libraries for massively parallel sequencing
PendingUS20200362406A1Microbiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMassively parallelMassive parallel sequencing
There is disclosed a method of generating a massively parallel sequencing library comprising the steps of: a) providing a primary WGA DNA library (pWGAlib), including fragments comprising a WGA library universal sequence adapter; b) performing a single PCR cycle on the pWGAlib using a first primer (1PR) comprising from 5′ to 3′ a first sequencing adapter (1PR5SA) and a first primer 3′ section (1PR3S) hybridizing to the reverse complementary of the WGA library universal sequence adapter; c) performing a single PCR cycle on the on the product of step b) using a second primer (2PR) comprising from 5′ to 3′ a second sequencing adapter (2PR5SA) different from the 1PR5SA, and a second primer 3′ section (2PR3S) hybridizing to the WGA library universal sequence adapter reverse complementary; d) amplifying by PCR the product of step c) using a third primer comprising the 1PR5SA and a fourth primer comprising 2PR5SA.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Method and kit for the generation of DNA libraries for massively parallel sequencing
InactiveUS20200299680A1Less enzymatic reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMassively parallelMassive parallel sequencing
There is disclosed a method of generating a massively parallel sequencing library comprising the steps of: a) providing a primary WGA DNA library (pWGAlib), including fragments comprising a WGA library universal sequence adaptor; b) re-amplifying the primary WGA DNA library using at least one first primer (1PR) and at least one second primer (2PR); the at least one first primer (1PR) comprising from 5′ to 3′ at least one first sequencing adaptor (1PR5SA), at least one first sequencing barcode (1PR5BC) and a first primer 3′ section (1PR3S) hybridizing to either the WGA library universal sequence adaptor or its reverse complementary; the at least one second primer (2PR) comprising from 5′ to 3′ at least one second sequencing adaptor (2PR5SA) different from the at least one first sequencing adaptor (1PR5SA), and a second primer 3′ section (2PR3S) hybridizing to either the WGA library universal sequence adaptor or its reverse complementary.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Oligonucleotide ligation methods for improving data quality and throughput using massively parallel sequencing
Described herein is a buffer concentration for highly efficient ligation of two oligonucleotides. The embodiments herein have led to the development of an optimized ligation step used in the sample preparation for sequencing reactions. Further, embodiments herein describe a high-throughput method for sequencing using barcodes or the purpose of multiplexing several samples simultaneously and novel methods for making targeted DNA libraries for re-sequencing on massively parallel next-generation sequencing platforms and for alternatives to gel-purification for recovering the desired templates from small RNA libraries for next generation sequencing.
Owner:BICO SCI CORP
Alternative nucleic acid sequencing methods
ActiveUS20130303381A1Efficient sortingAccurate sortingMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationNucleic acid sequencingSingle sequence
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
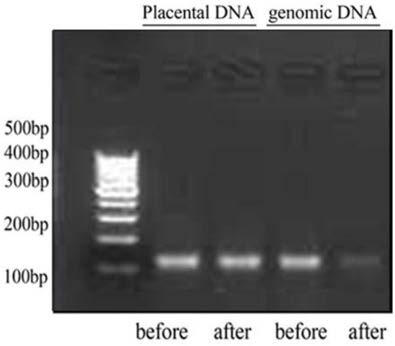
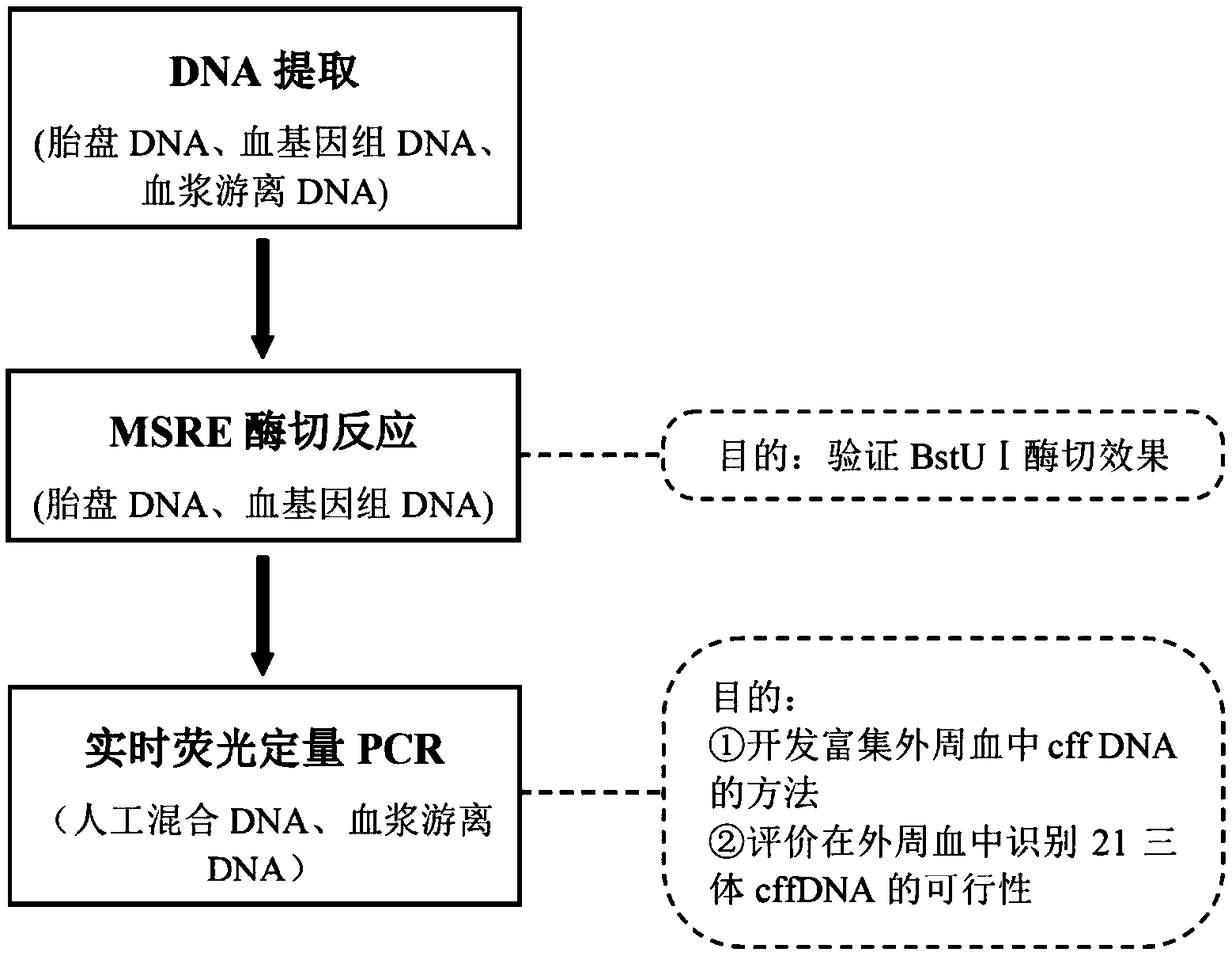
Kit and method for concentrating fetal free DNA, and application of kit
InactiveCN109022541AHigh sensitivitySimple trisomy syndromeMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionTrisomy
The invention relates to a kit and a method for concentrating fetal free DNA, and an application of the kit. DNA extracted from pregnant women peripheral blood or a mixture of placental tissues and the pregnant women peripheral blood is used as a DNA template, MSRE enzyme digestion is carried out, and an amplification primer is adopted to carry out RT-qPCR amplification in order to obtain a PCR product. Compared with kits in the prior art, the kit in the invention has the advantages of detection of the cffDNA of fetal specific trisomy 21st chromosome, being as low as 0.1%, and high sensitivity. The kit is simpler and cheaper than massive parallel sequencing detection of the trisomy 21 syndrome. The kit uses MSRE to process a gene, so the gene loss is less than that of sulfite gene treatment, and the diagnosis accuracy is improved.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SUZHOU UNIV
Methods, Compositions, and Kits for Preparing Nucleic Acid Libraries
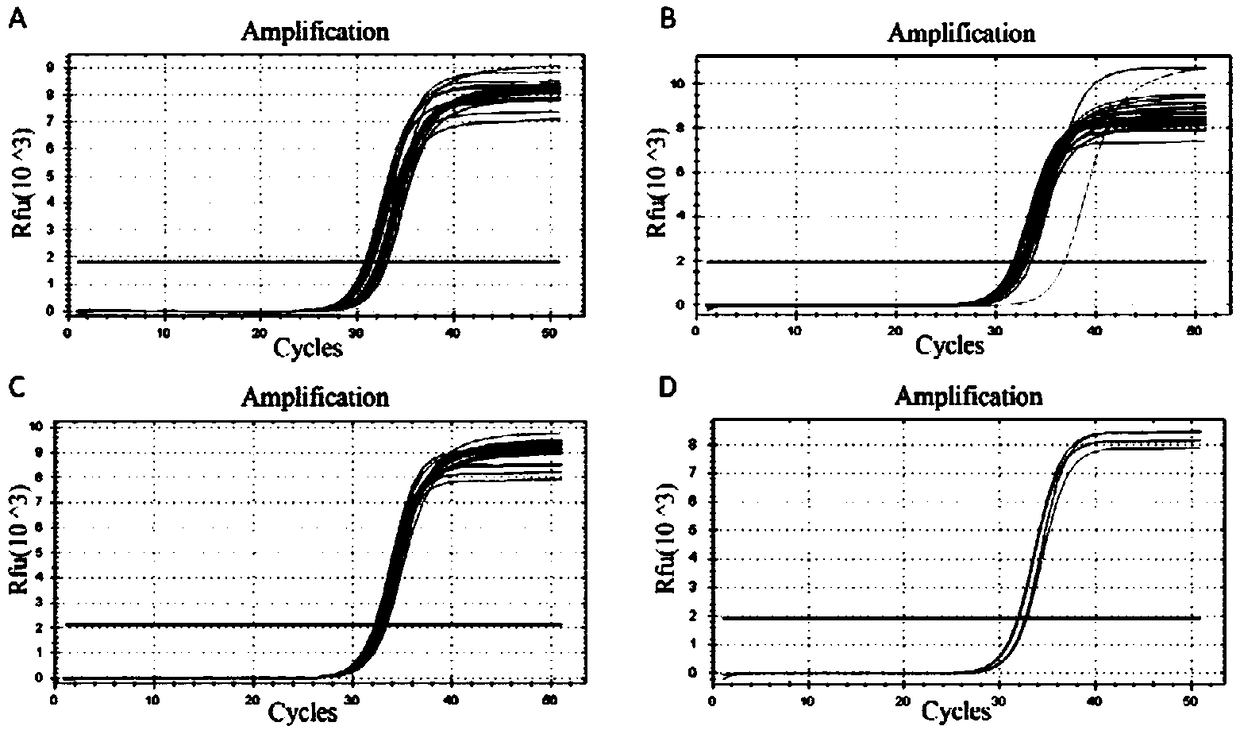
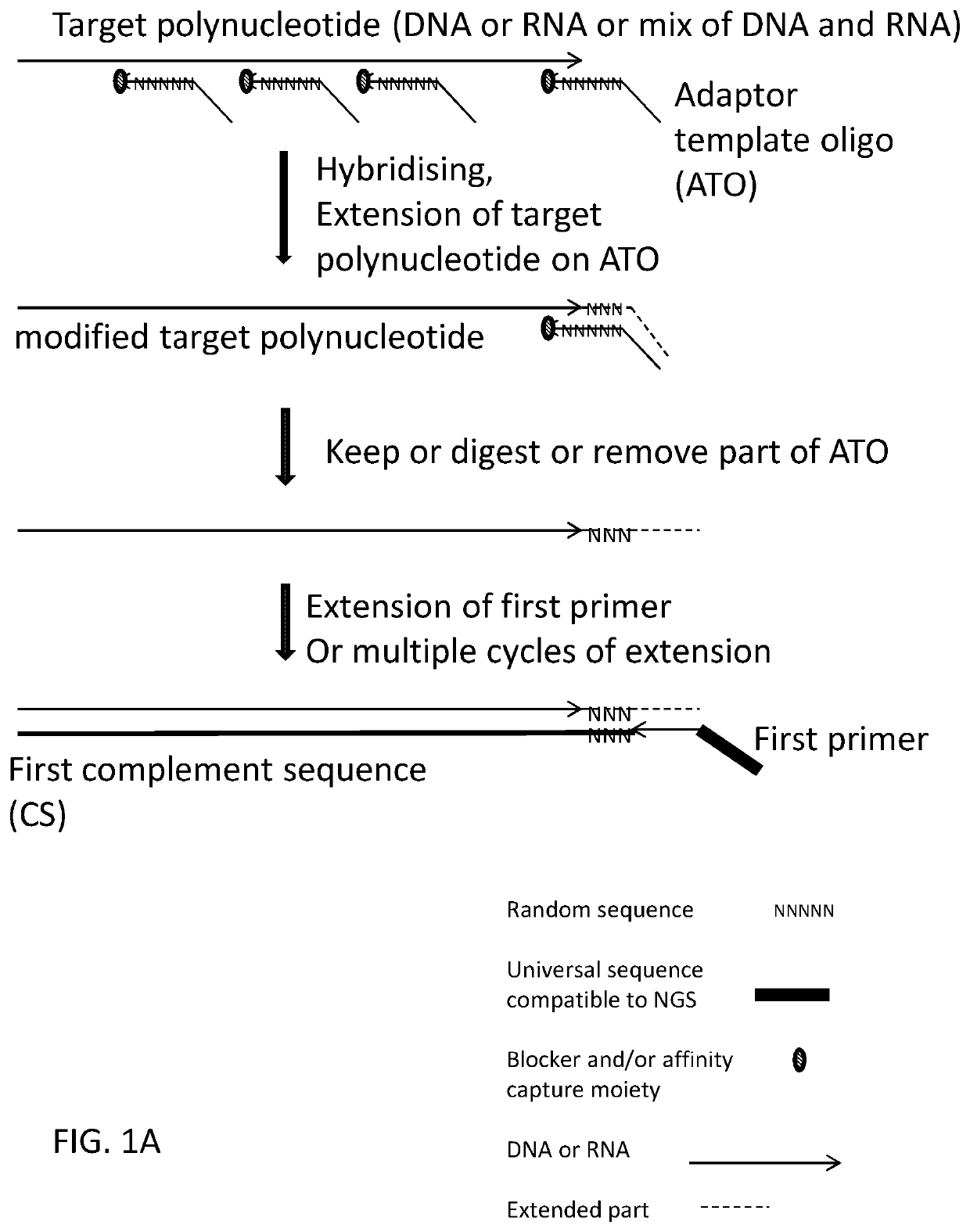
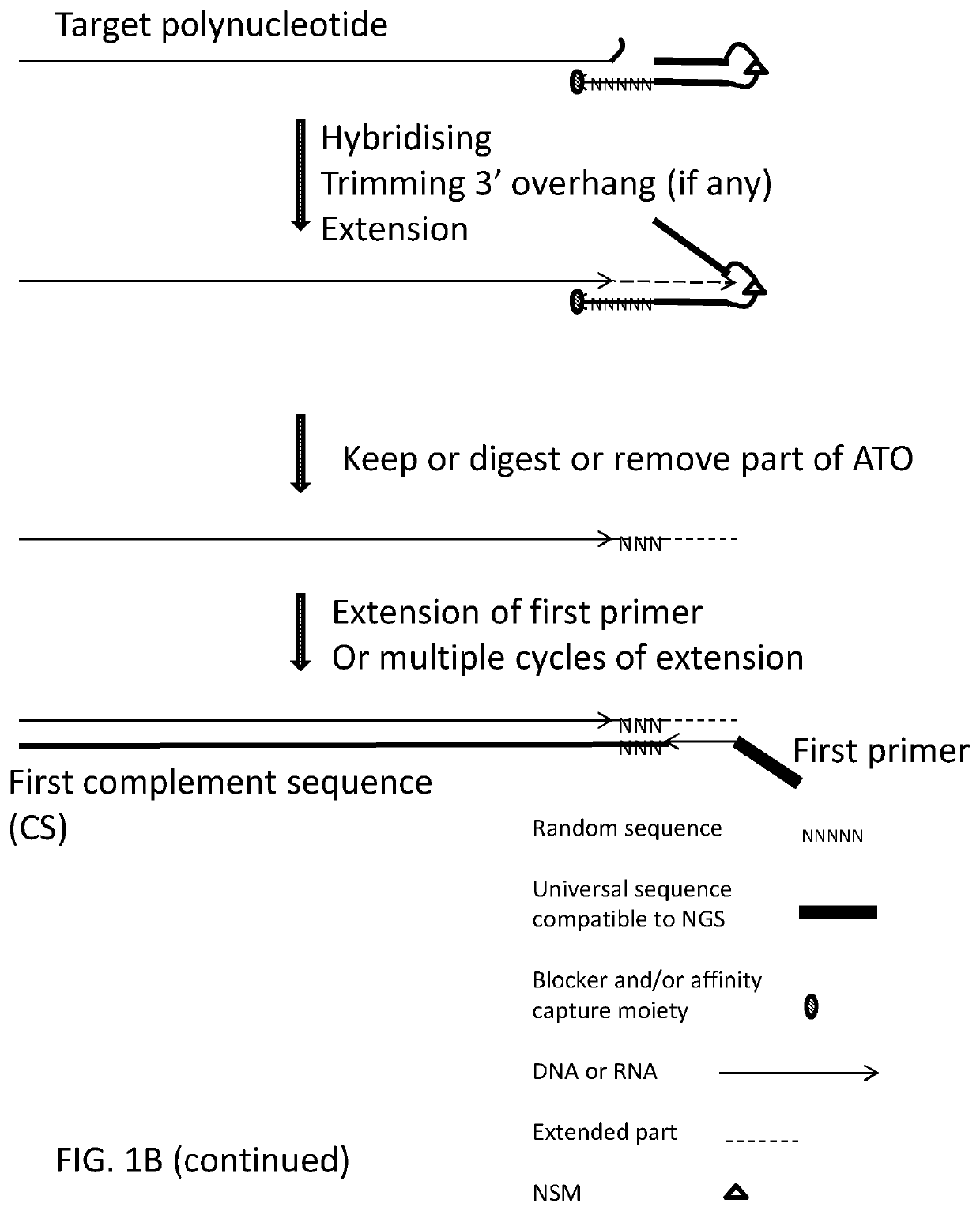
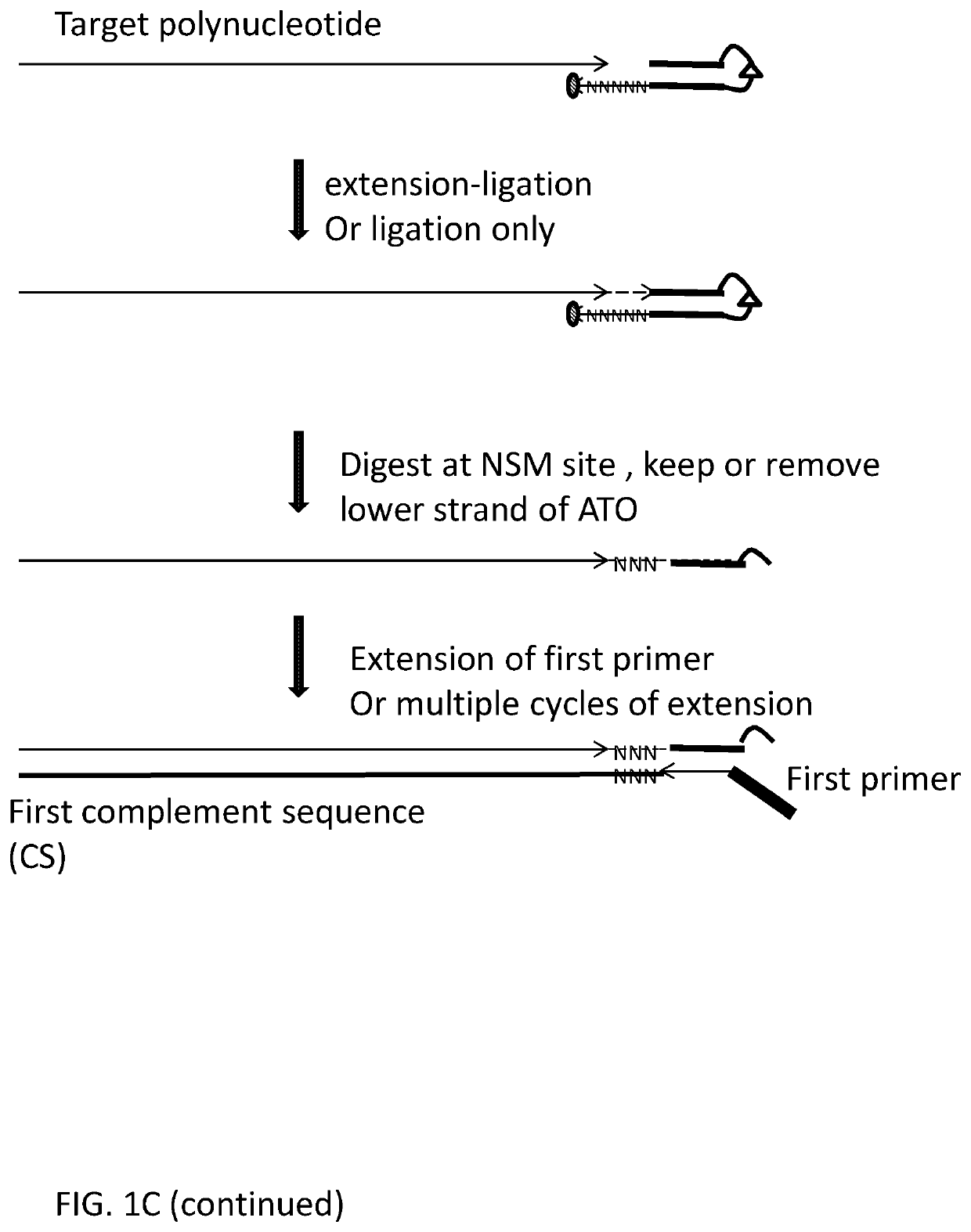
ActiveUS20200115736A1Facilitates digestion/removalReduce errorsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGeneticsBiochemistry
This invention relates to methods, compositions and kits for extending a polynucleotide and for preparing sequencing library of polynucleotides involving generating modified target polynucleotide on an adaptor template oligonucleotide and tagging one or two strands of a target sequence. The sequencing library is suitable for massive parallel sequencing and comprises a plurality of double-stranded nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:GENEFIRST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com