Patents
Literature
49 results about "Vertebral segment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
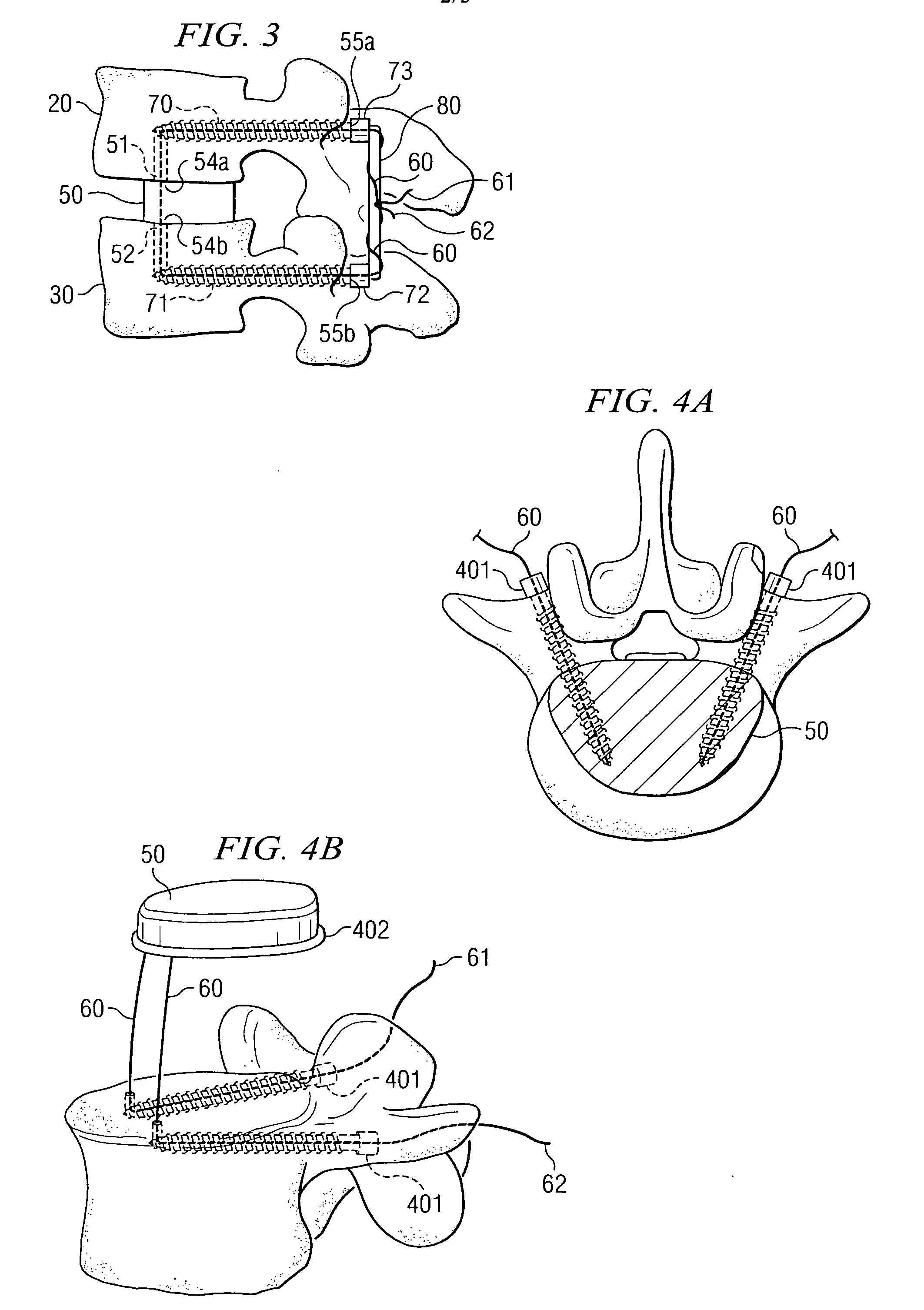
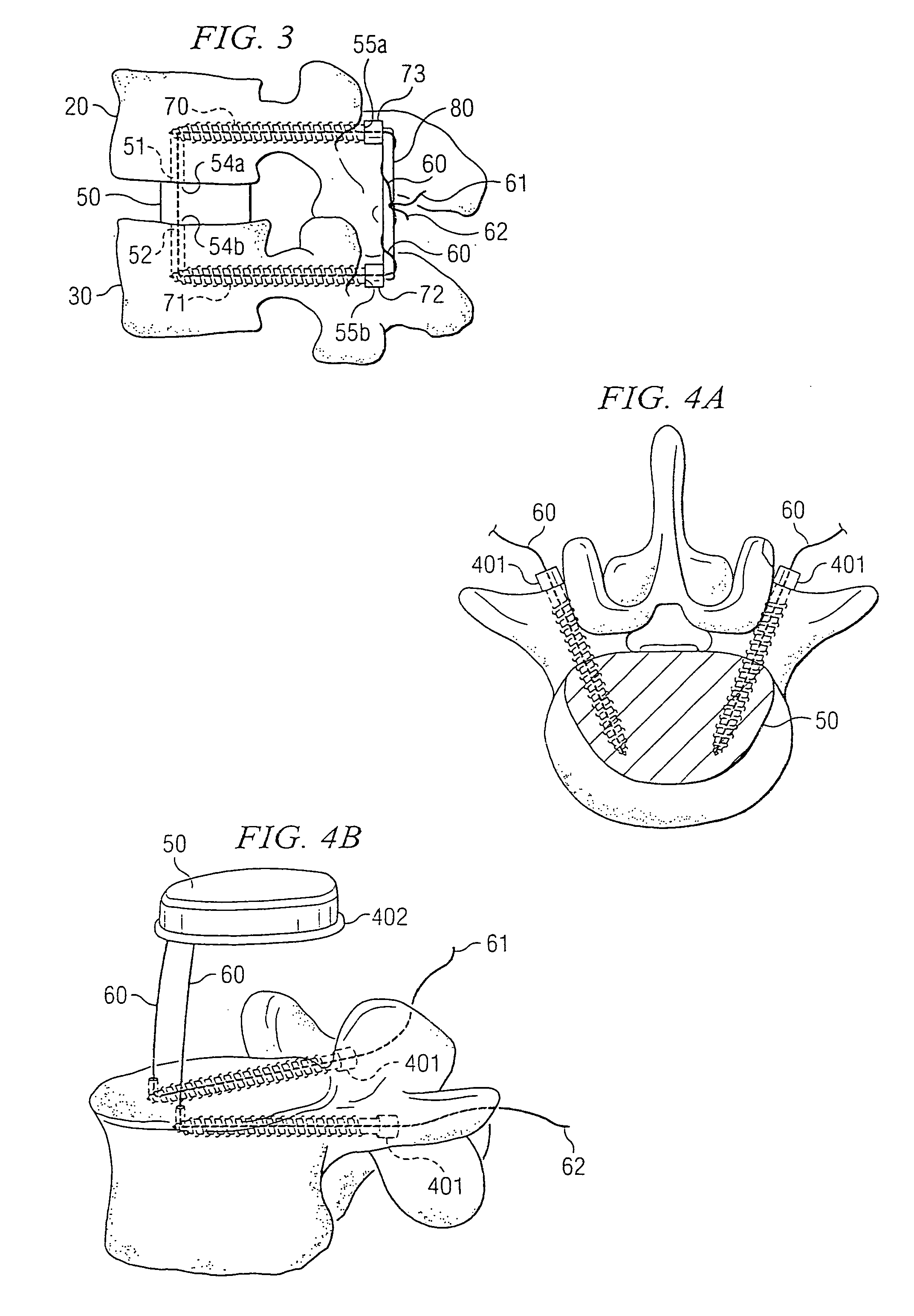
Stabilized interbody fusion system for vertebrae
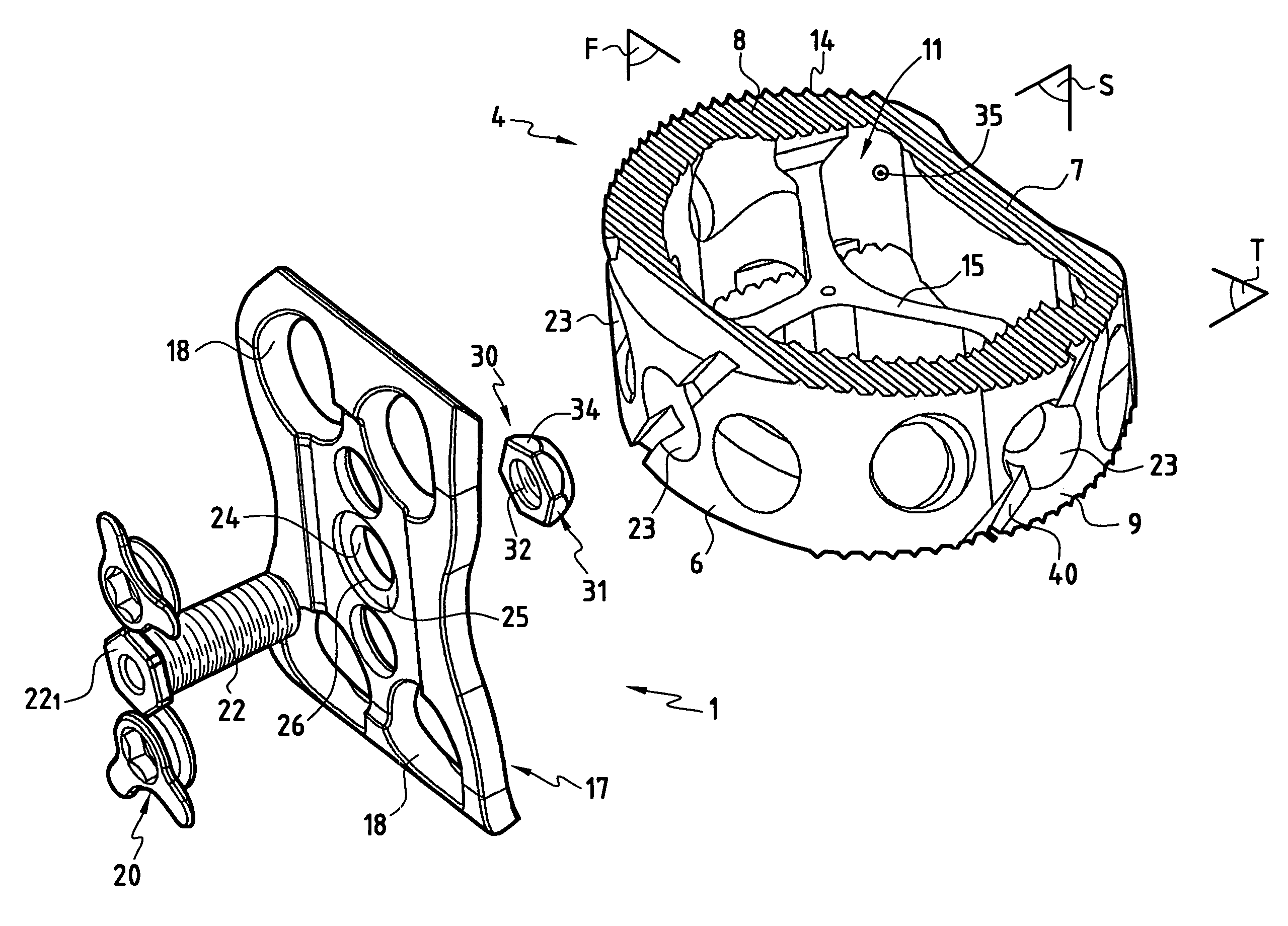
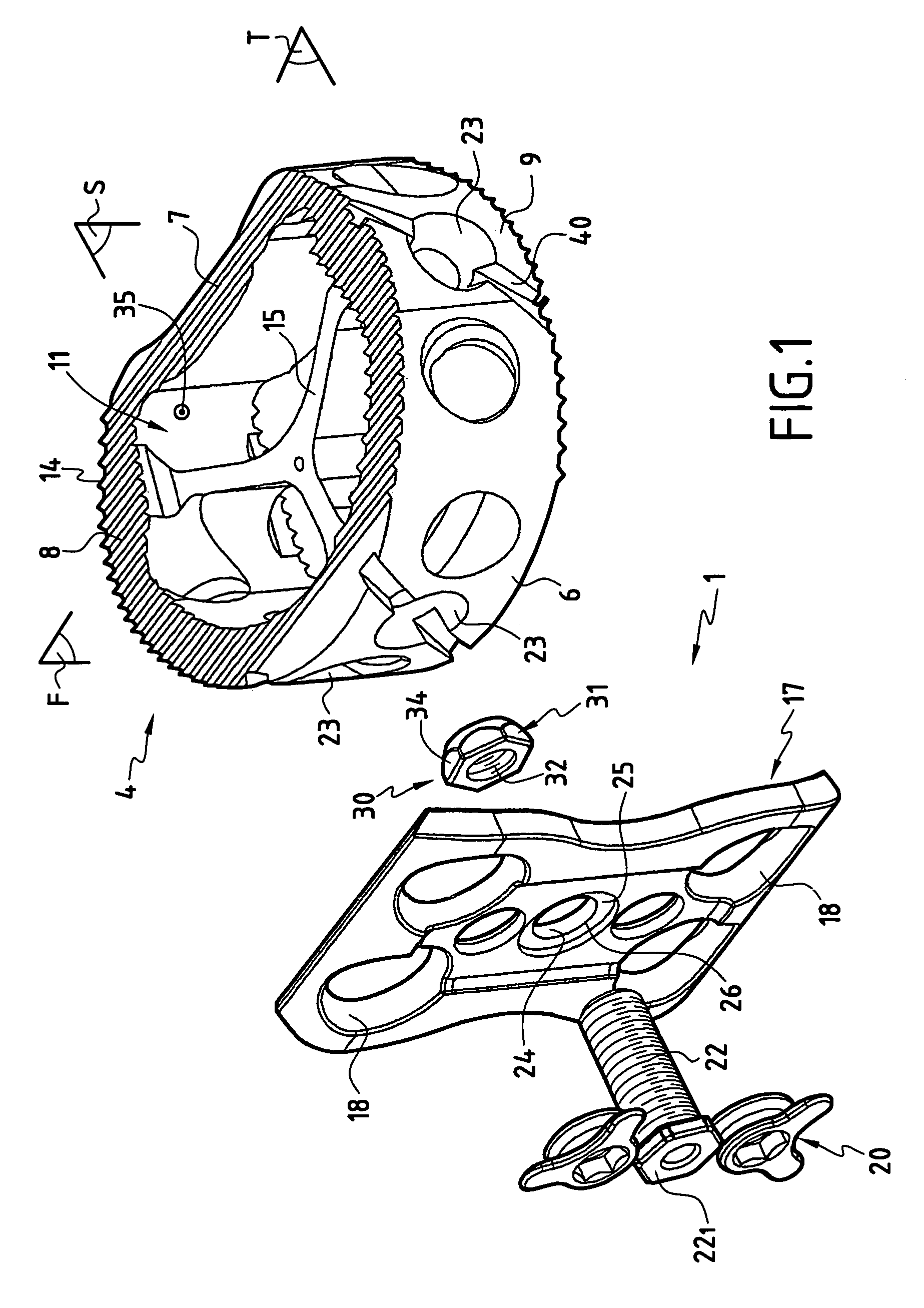
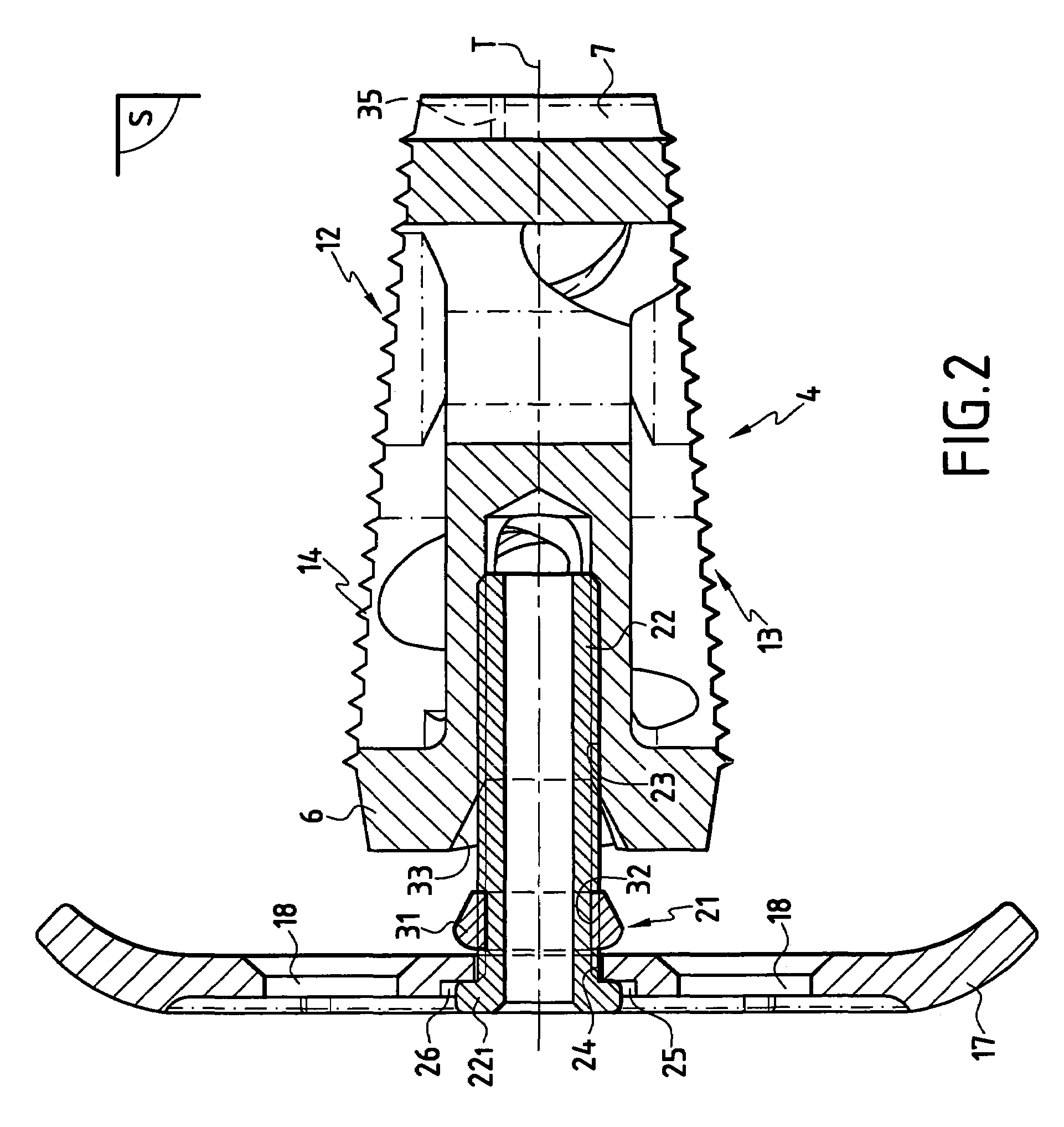
The invention concerns a stabilized interbody fusion system for vertebrae, of the type comprising an interbody implant (4) designed to be inserted in the intervertebral space defined between two neighboring vertebrae to be mutually secured, so as to restore the height and the angle of the lordosis of the vertebral segment defined by the two neighboring vertebrae and a stabilizing plate (17) provided, at each of its ends, with at least a passage hole (18) for an anchoring screw, the plate (17) and the implant (4) being provided with mutual assembly means, such that after assembly, the stabilizing plate (17) extends on each side of the implant to enable the stabilizing plate to be anchored on the neighboring vertebrae through the screws, characterized in that it comprises spacing means (30), interposed between the stabilizing plate (17) and the implant (4), to enable the stabilizing plate to be positioned at a specific distance relative to the implant.
Owner:SCIENTX
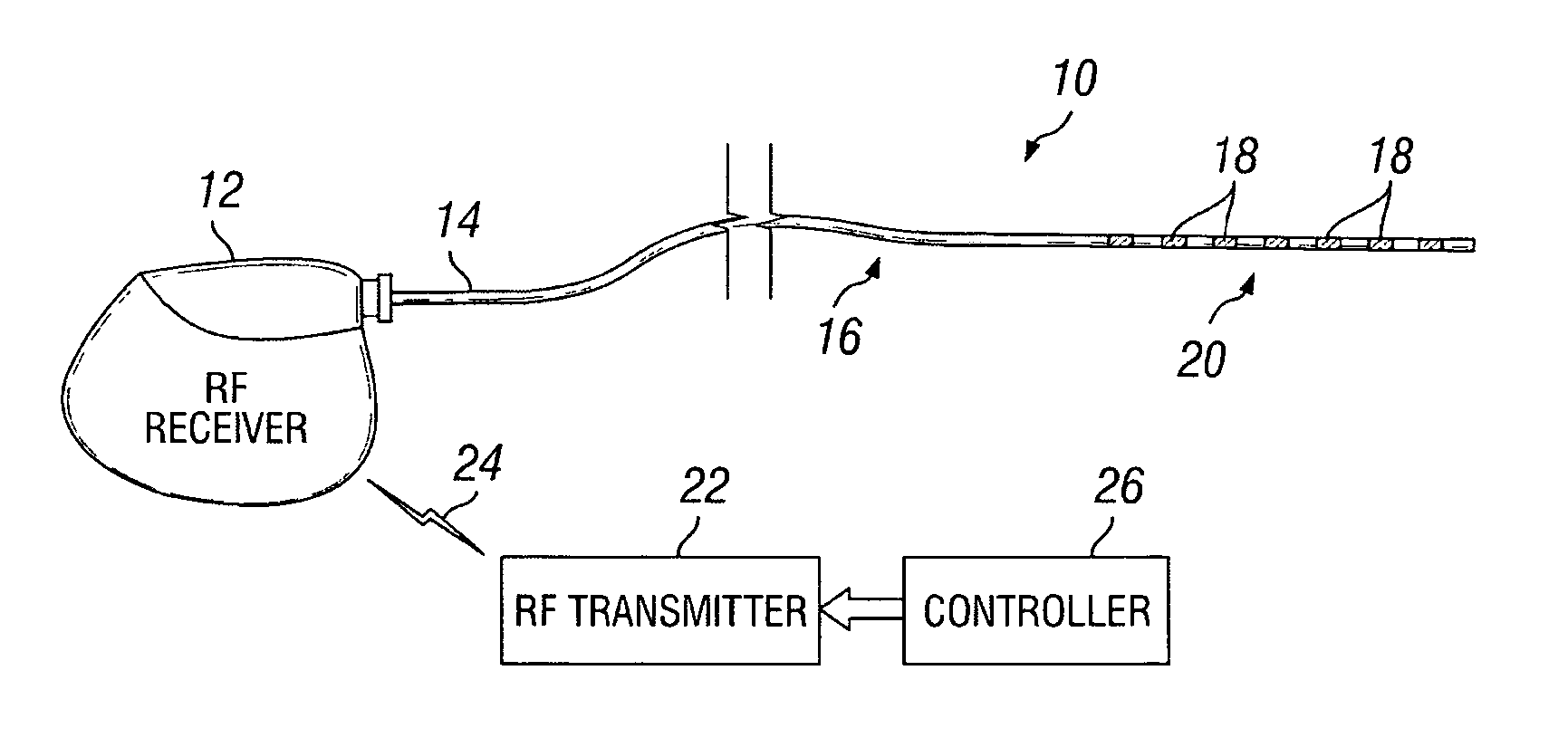
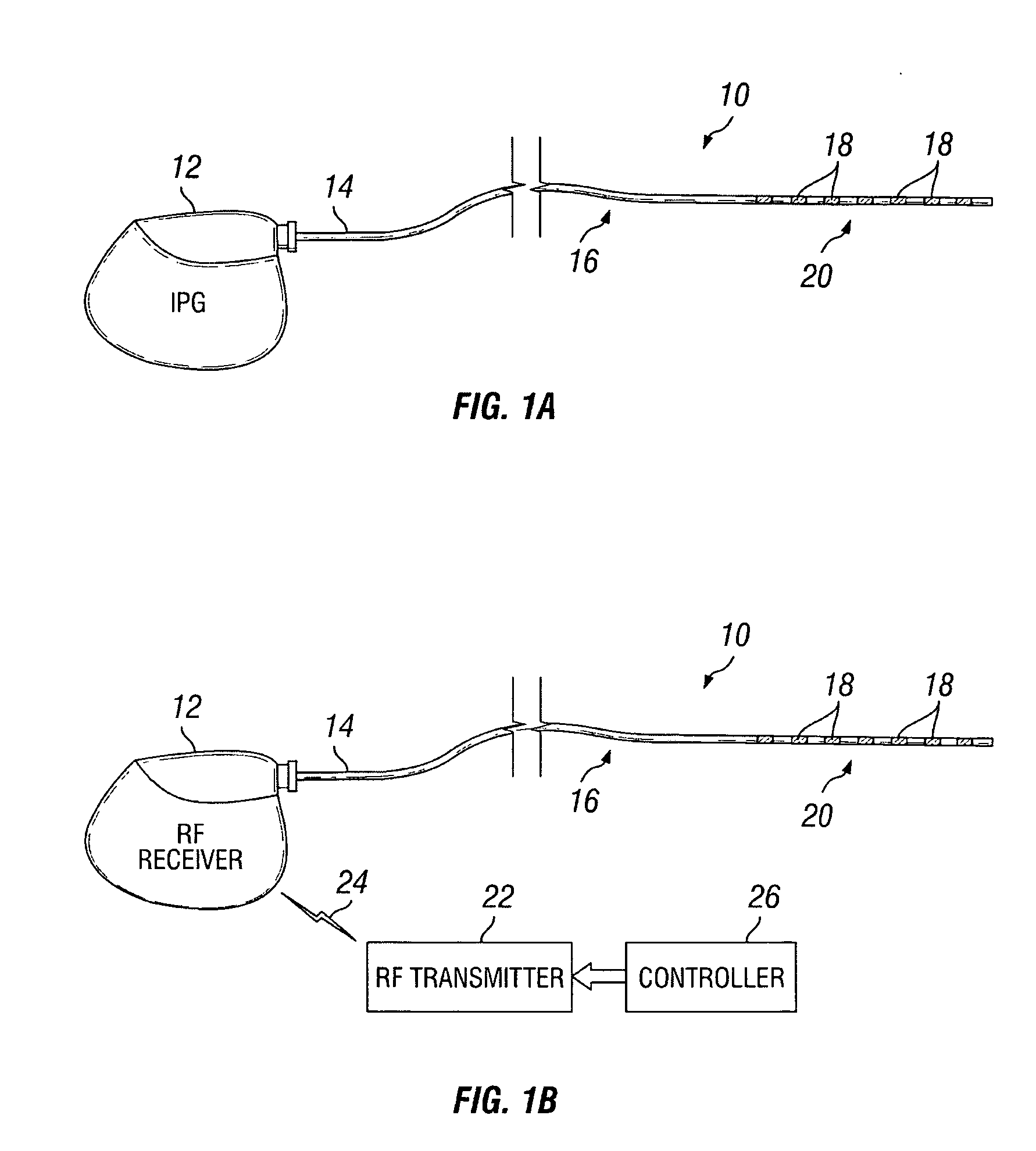
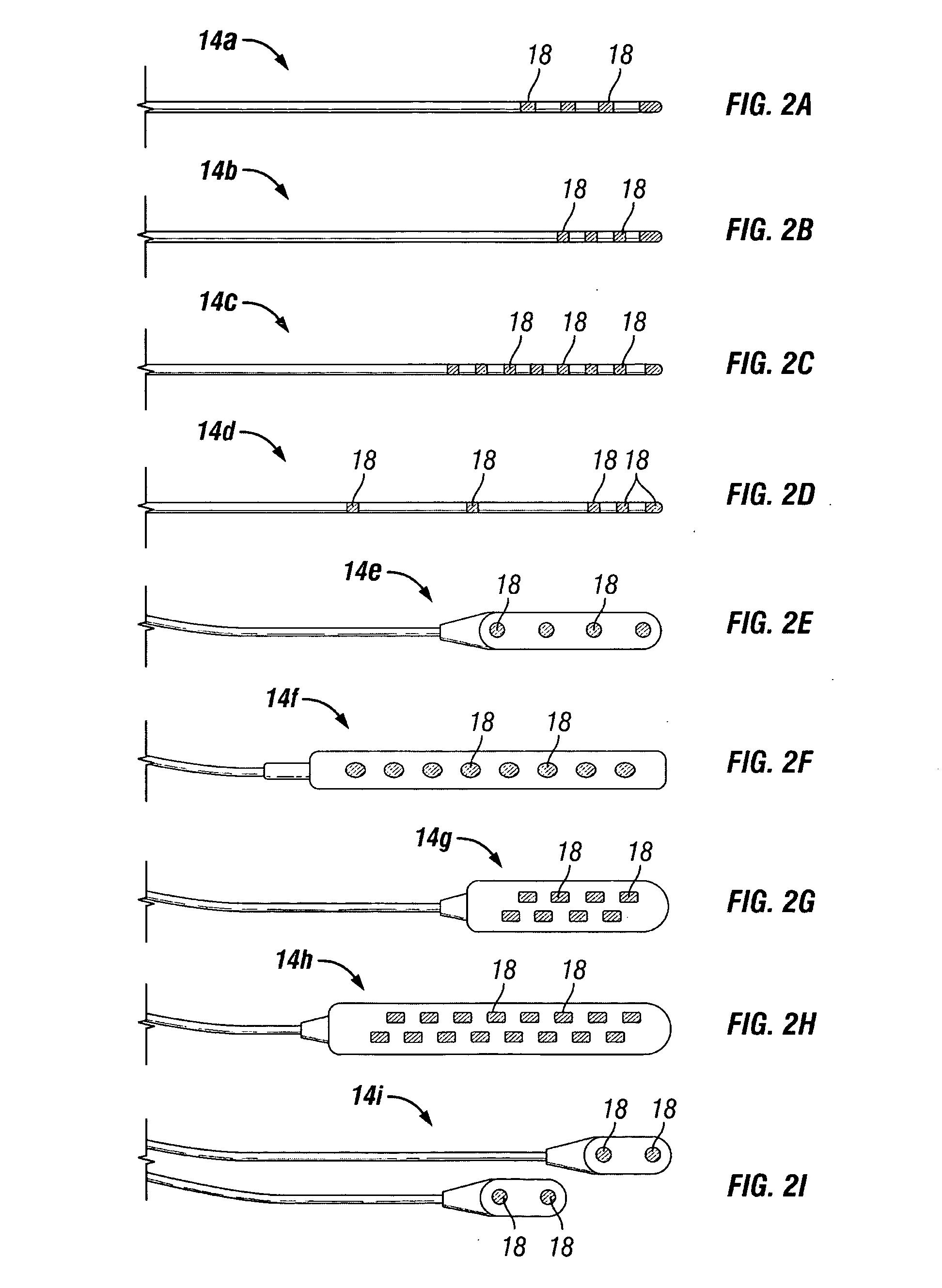
Method of using spinal cord stimulation to treat neurological disorders or conditions
InactiveUS20070060954A1Improve the quality of lifeEffectively treat lack of coordinationSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsMedicineElectrical stimulations
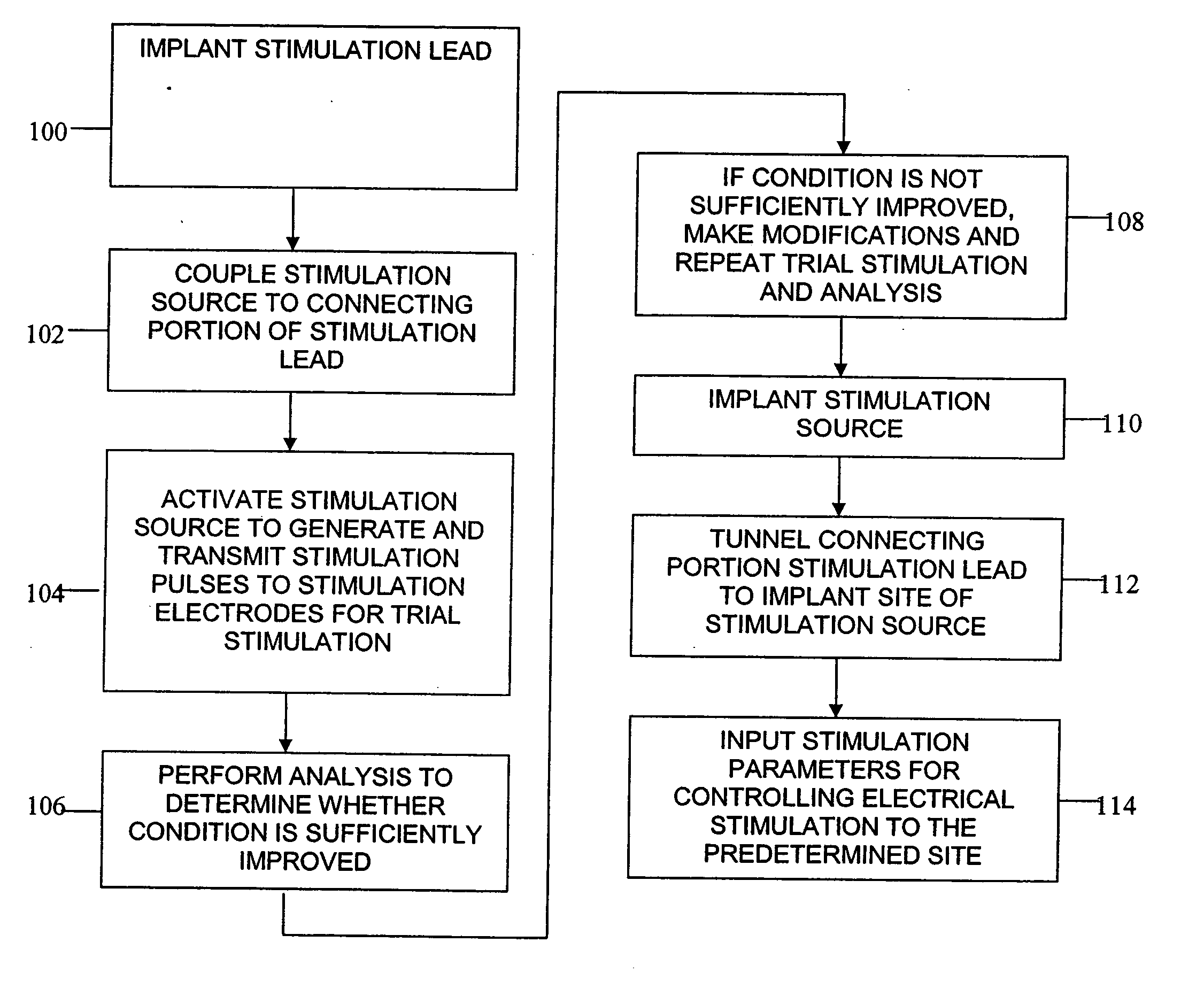
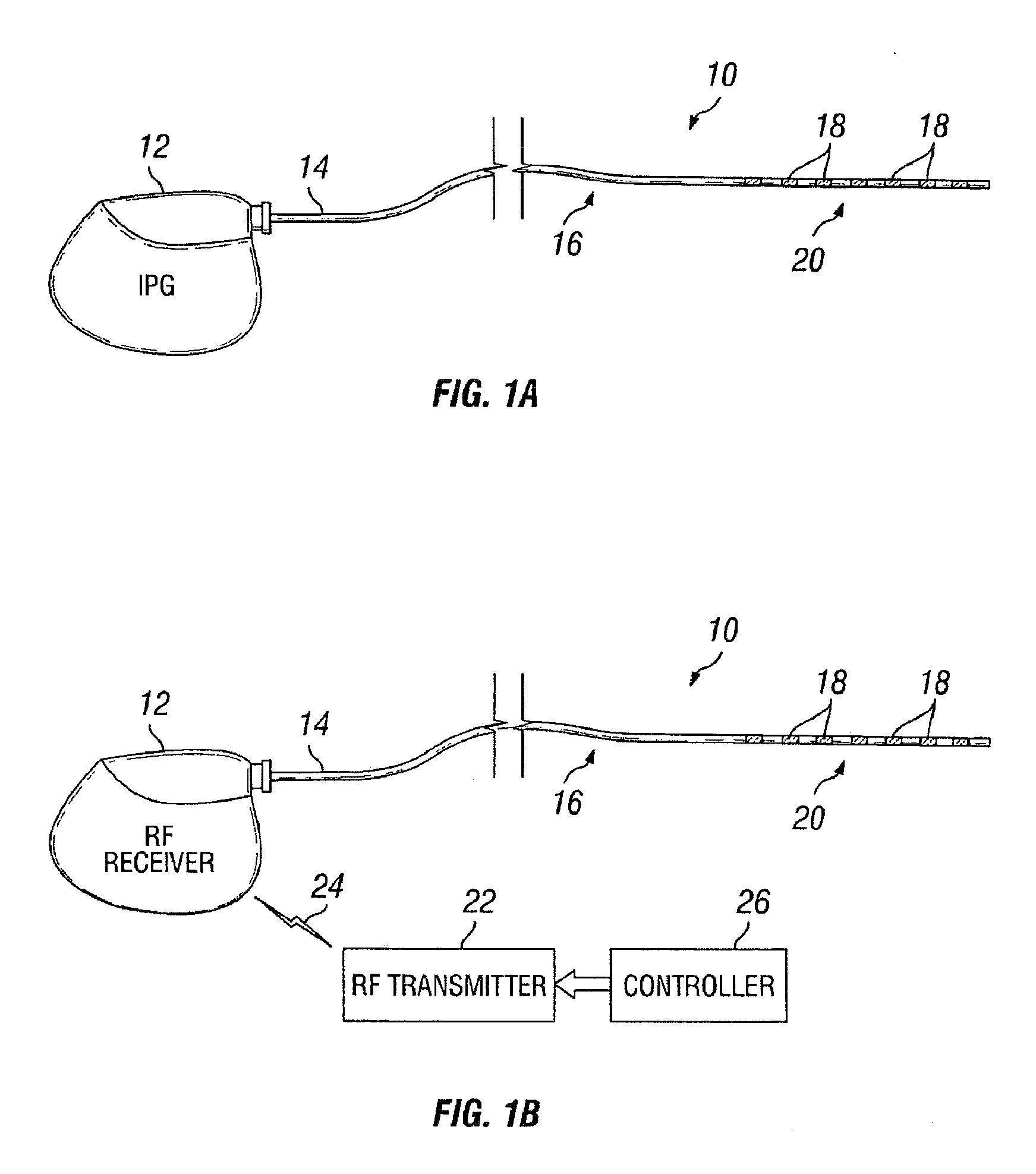
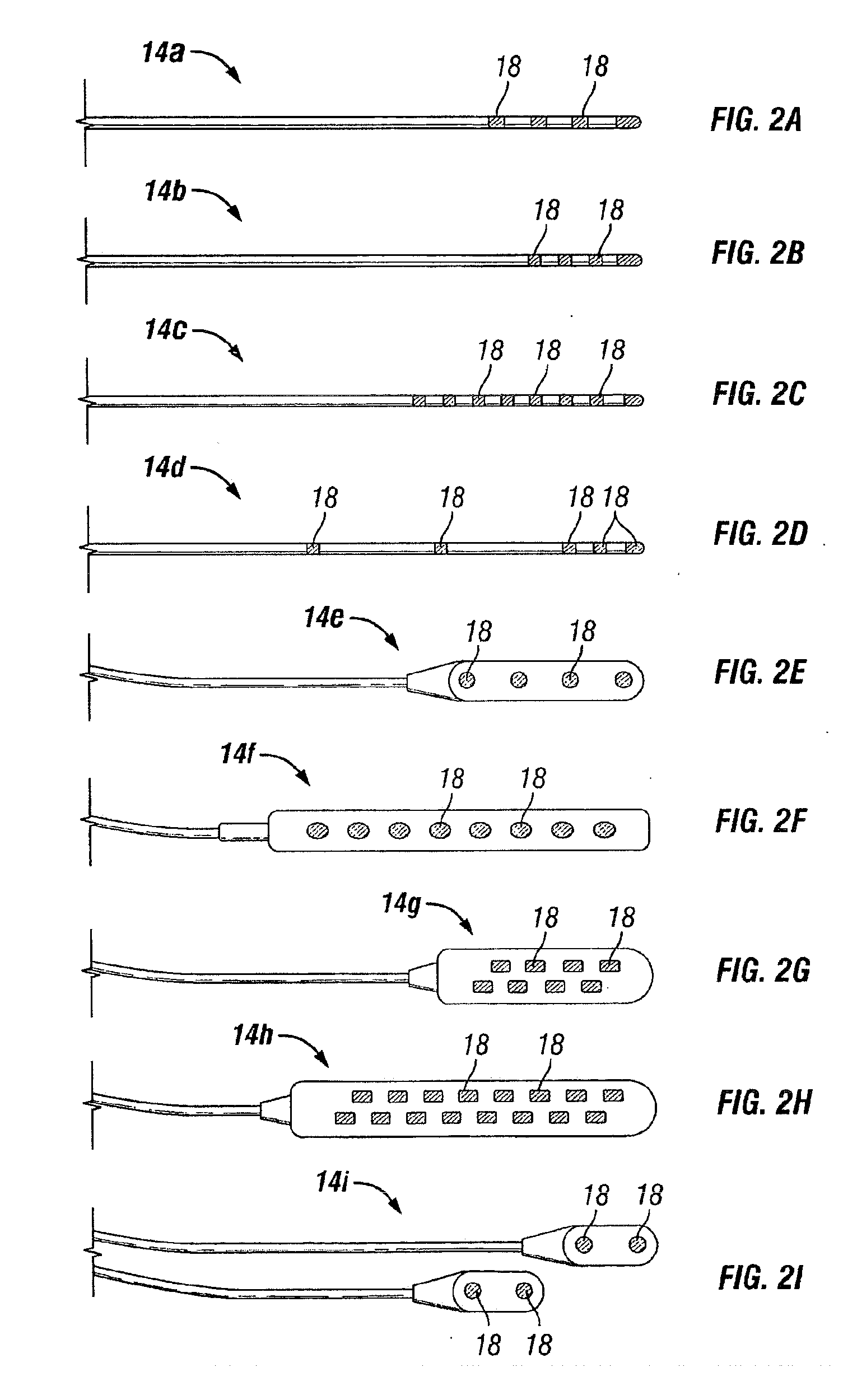
The present invention involves methods and systems for using electrical stimulation to treat neurological disorders. More particularly, the method comprises surgically implanting an electrical stimulation lead that is in communication with spinal nervous tissue associated with a first, second, or third cervical vertebral segment to result in spinal nervous tissue stimulation, thus treating a wide variety of neurological disorders.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Nucleus replacement securing device and method
There is disclosed systems and methods for spinal nucleus replacement by constructing channels through vertebral segments on either side of an area into which the spinal nucleus is to be positioned, the channels running from a channel end outside of the area to a channel end abutting the area. One end of a suture is inserted into the outside channel end of a first one of the channels and passed through the first channel and into the area and out of the area through the second channel until it emerges from the second channel. The suture is then used to pull the nucleus into the area.
Owner:THEKEN SPINE
Method of using spinal cord stimulation to treat gastrointestinal and/or eating disorders or conditions
ActiveUS20060074456A1Enhance gastric motilityIncreasing) gastric motilityElectrotherapyDiseaseMedicine
The present invention involves a method and a system for using electrical stimulation to treat gastrointestinal and / or eating disorders. More particularly, the method comprises surgically implanting an electrical stimulation lead that is in communication with predetermined thoracic vertebral segments to cause spinal nervous tissue stimulation, thus treating a wide variety of gastrointestinal disorders.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
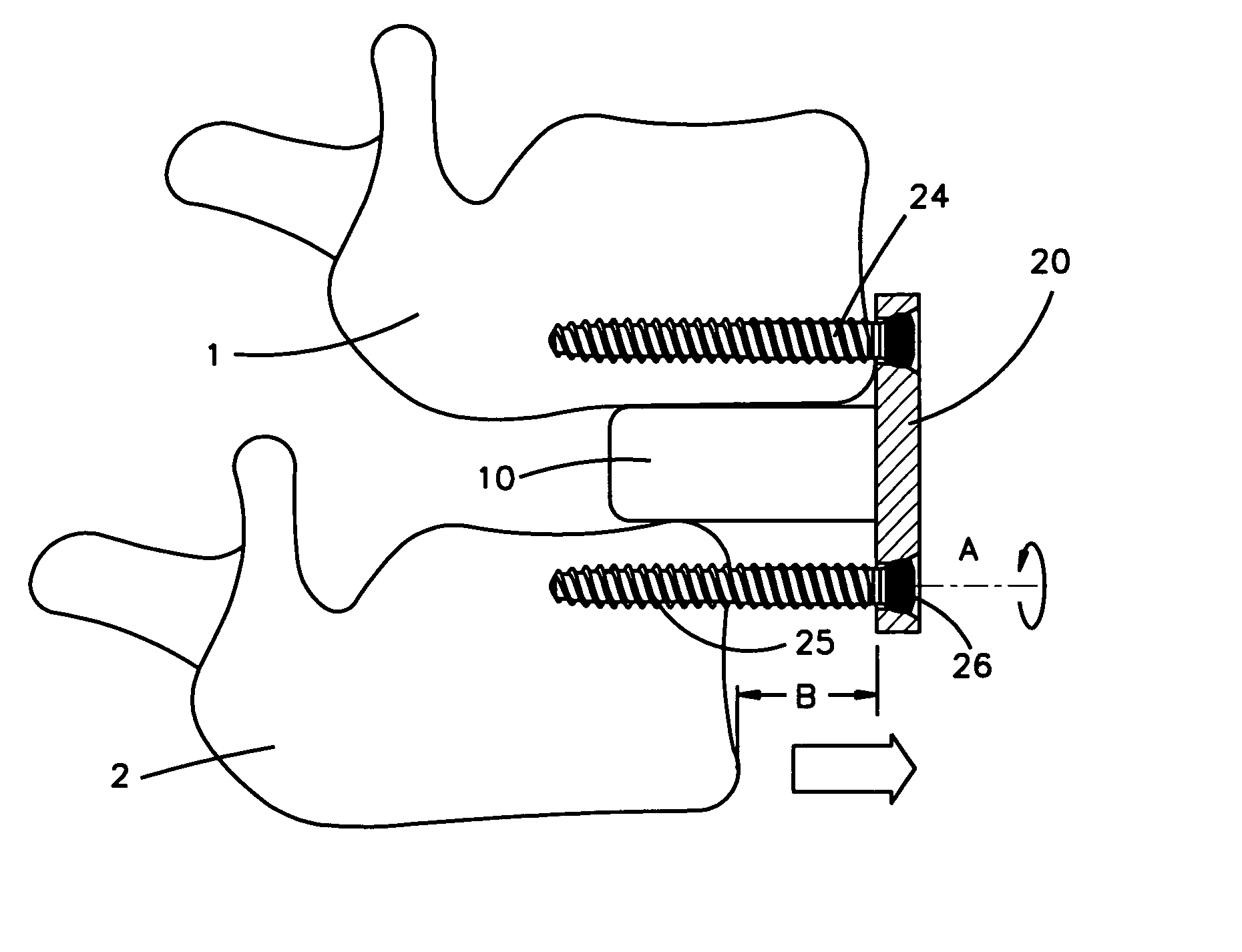
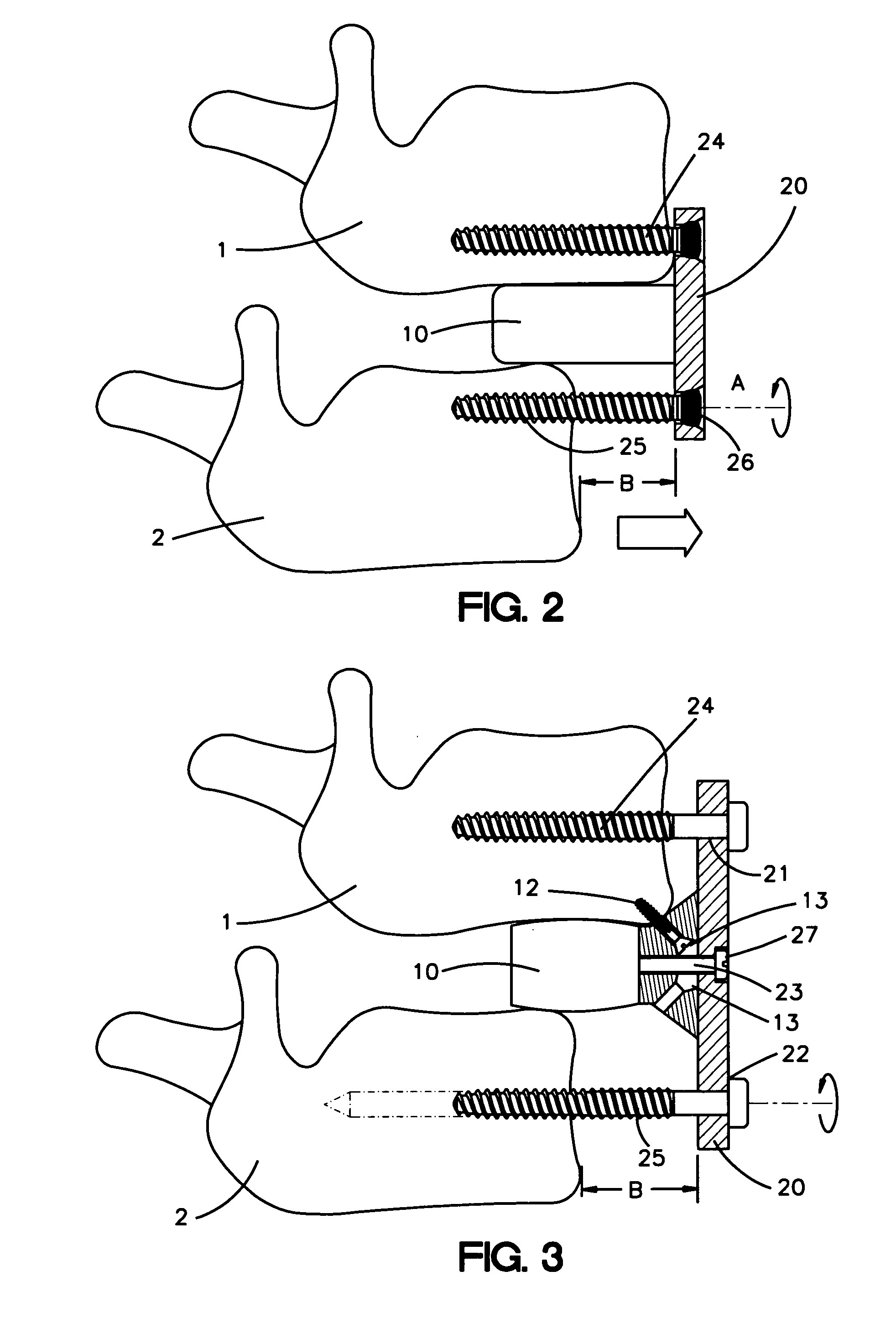
Apparatus and method for flexible spinal fixation
InactiveUS20070233064A1High tensile strengthReduce stretchInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsPlastic materialsUltimate tensile strength
Apparatus for connecting and stabilizing adjacent vertebral segments, comprising a flexible composite connecting rod extending between the segments, and connection devices for connecting the rod to the vertebral segments. The rod comprises a rod member formed of a flexible plastic material having a predetermined compression strength, and a high tensile strength, low stretch, flexible reinforcing element extending longitudinally through the entire length of the rod member and being bonded thereto. The reinforcing element may be in the form of a single cord, rope, braid or monofilament, a plurality of substantially parallel cords, ropes, braids or monofilaments, or a tubular cord, rope or braid extending through the rod member.
Owner:HOLT DEV
Spinal flexion and extension motion damper
ActiveUS20090149885A1Limited degreeSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisStretch exerciseEngineering
An orthopedic damper system and method to control the degree of flexion and / or extension motion of the mobile vertebral segment while providing additional stability to the spine. The damper system includes an anchor having a spring hitch, a spring coupled to the spring hitch, and a cap coupled to the spring. The anchor is adapted to connect to a spinous process. The spring includes an inner hollow area adapted to accommodate the spring hitch. The cap includes an opening connected to an inner cavity that is adapted to accommodate the spring and the spring hitch.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
Apparatus and method for flexible spinal fixation
InactiveUS20080269804A1High tensile strengthReduce stretchInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsPlastic materialsEngineering
Owner:HOLT DEV
Method and instruments to treat spondylolisthesis by an anterior minimally invasive approach of the spine
InactiveUS20070123989A1Reducing surgical morbidityReduce morbidityInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsSurgical treatmentLumbar vertebrae
A method for intra-operative surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis by an anterior minimally invasive approach of the lumbar spine includes inserting an interbody spacer between two vertebrae, attaching an anatomically designed reduction plate to at least one of the two vertebrae, and attaching the interbody spacer to the reduction plate by a fastening means through a central borehole of the reduction plate and the interbody spacer. The interbody spacer may be attached to the anteriorly positioned vertebra by at least bone screw. The upper and lower parts may be attached to the upper and lower vertebra by at least one bone screw to stabilize the displaced vertebral segment of the spine.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Apparatus and method for flexible spinal fixation
InactiveUS20080021469A1High tensile strengthReduce stretchInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsPlastic materialsUltimate tensile strength
Apparatus for connecting and stabilizing adjacent vertebral segments, comprising a flexible composite connecting rod extending between the segments, and connection devices for connecting the rod to the vertebral segments. The rod comprises a rod member formed of a flexible plastic material having a predetermined compression strength, and a high tensile strength, low stretch, flexible reinforcing element extending longitudinally through the entire length of the rod member. The reinforcing element may be in the form of a single cord, rope, braid or monofilament, a plurality of substantially parallel cords, ropes, braids or monofilaments, or a tubular cord, rope or braid extending through the rod member in slidable relation or bonded thereto.
Owner:HOLT RICHARD
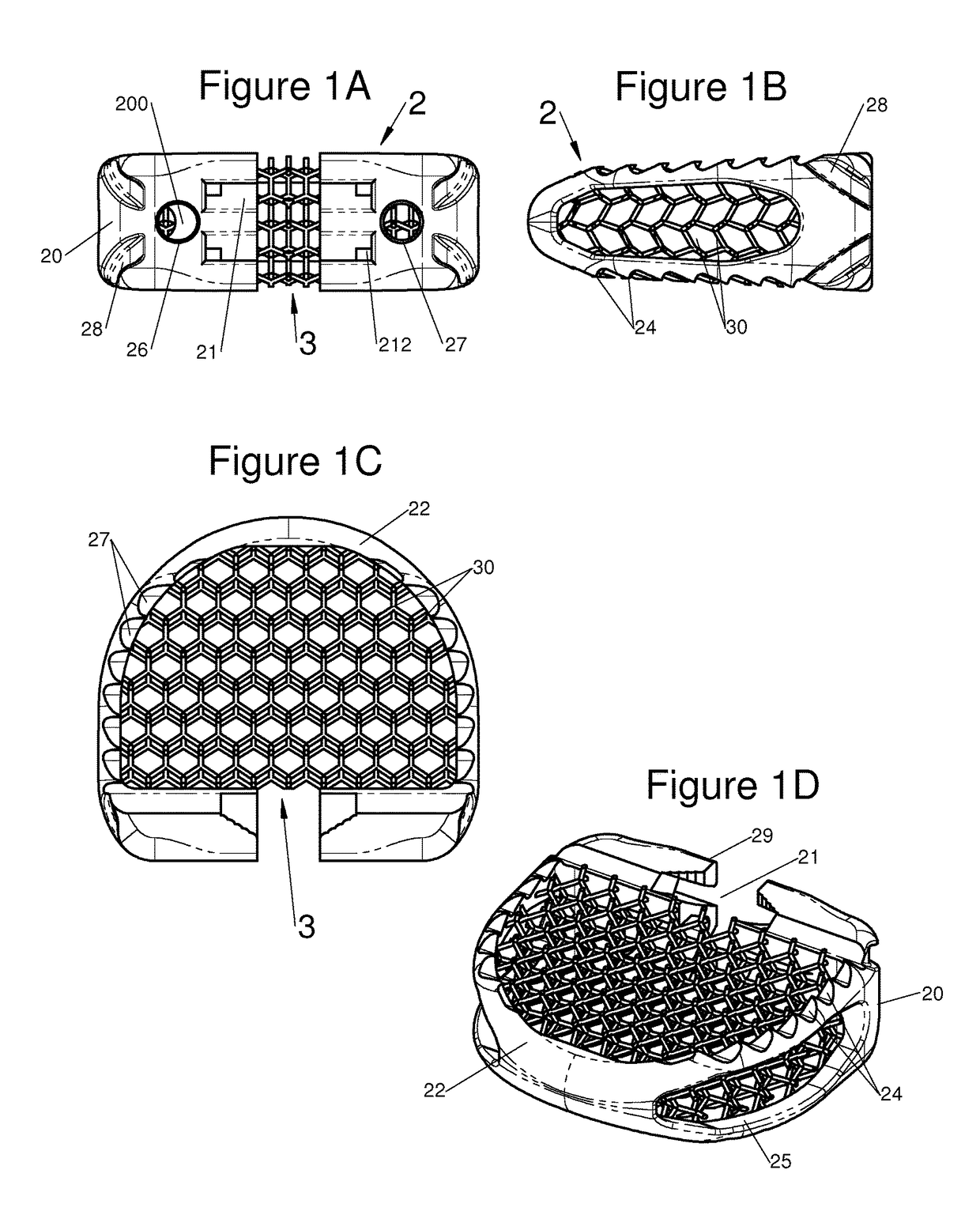
Vertebral System, Implant and Inserts for Vertebral System
InactiveUS20170333205A1Reliable and fast and usableLow costBone implantJoint implantsBone tissueBone anchor
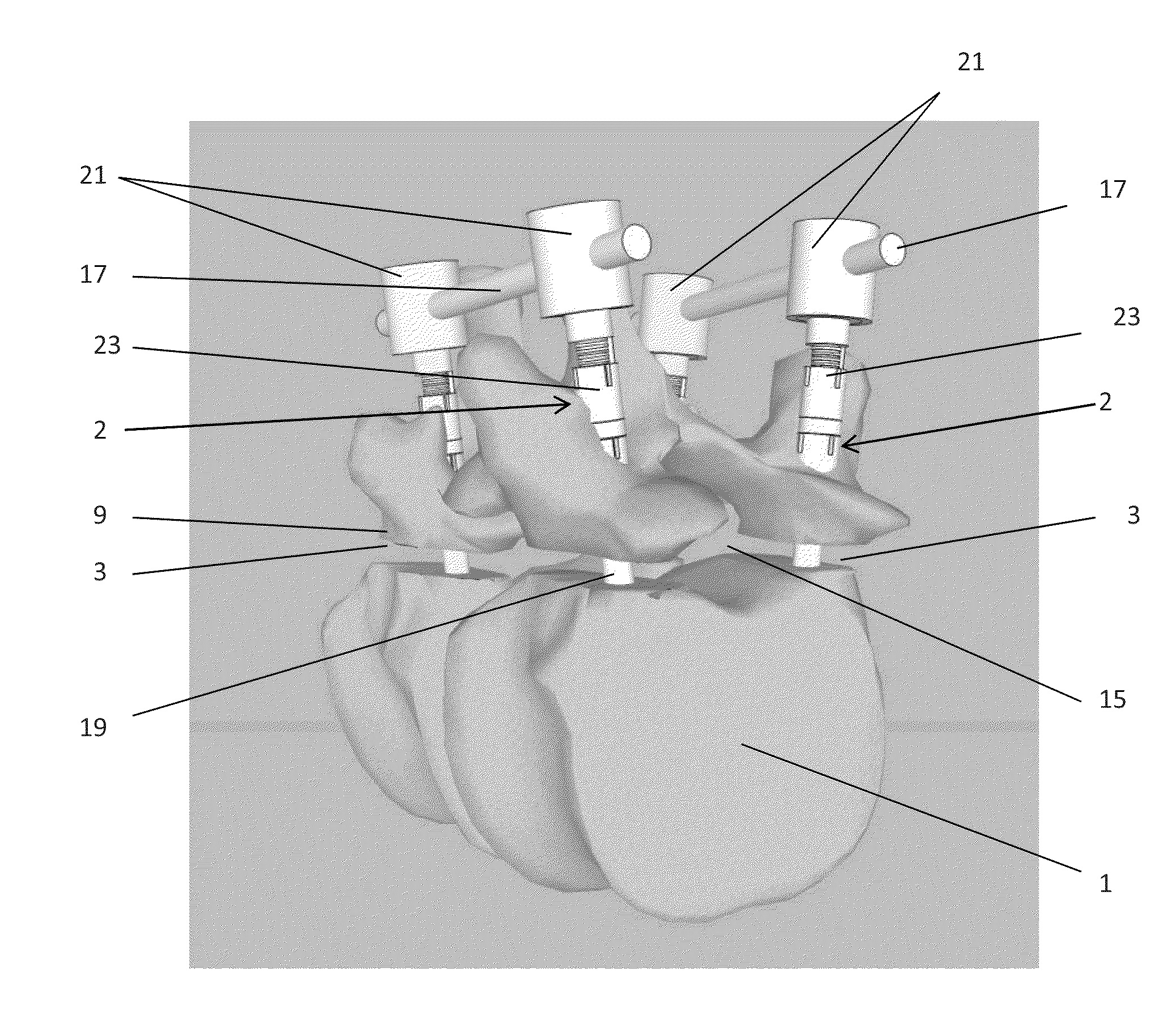
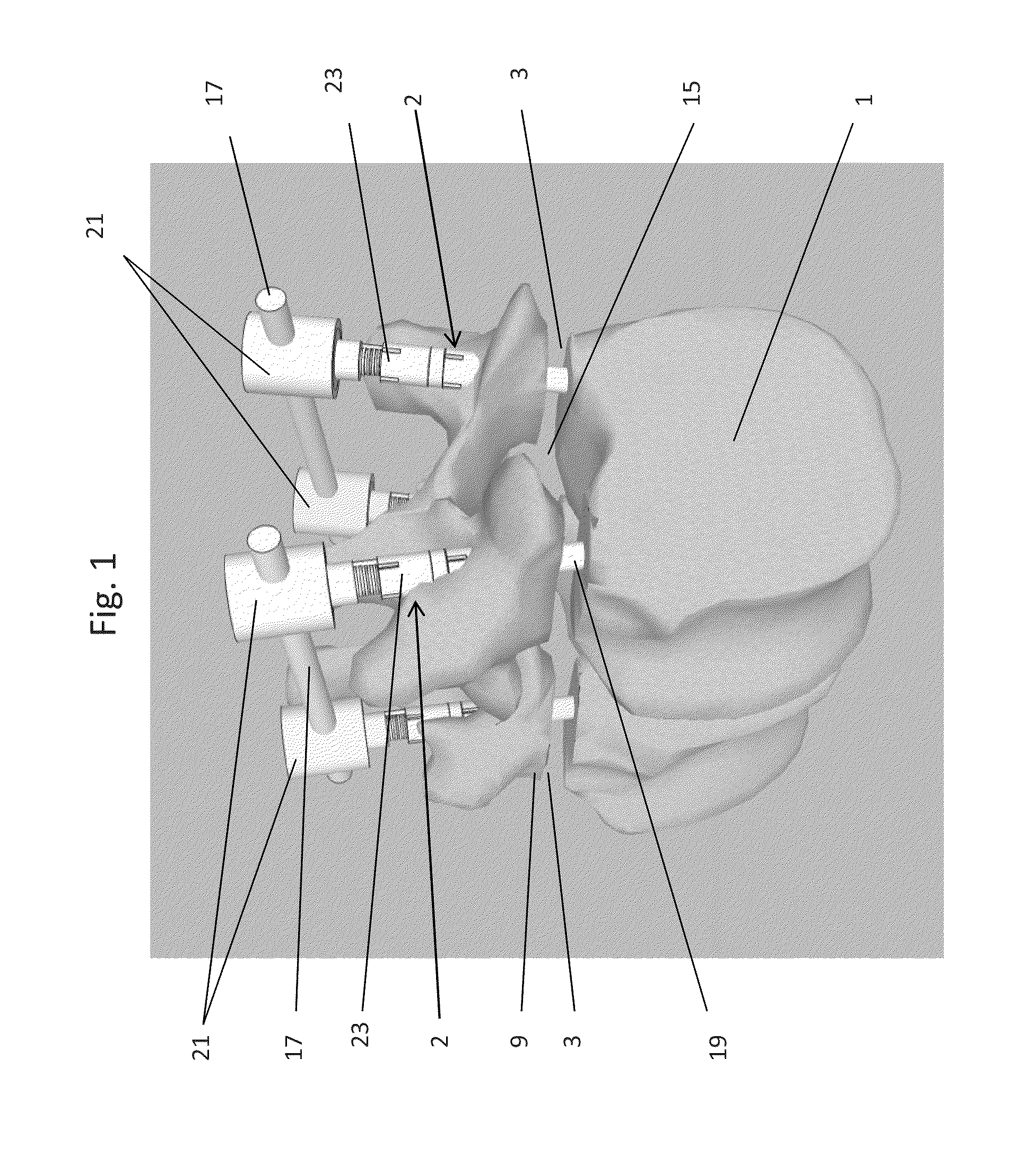
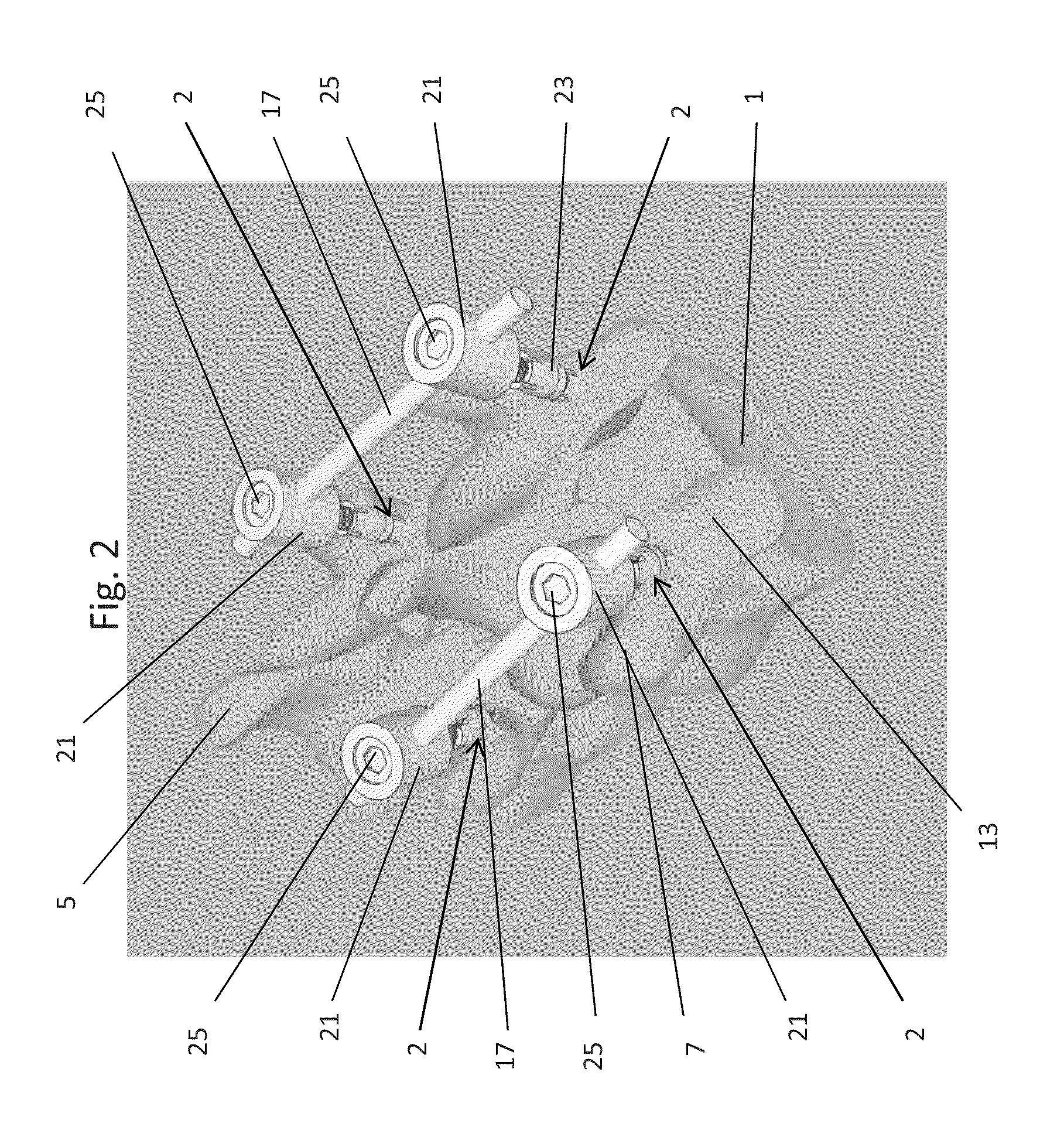
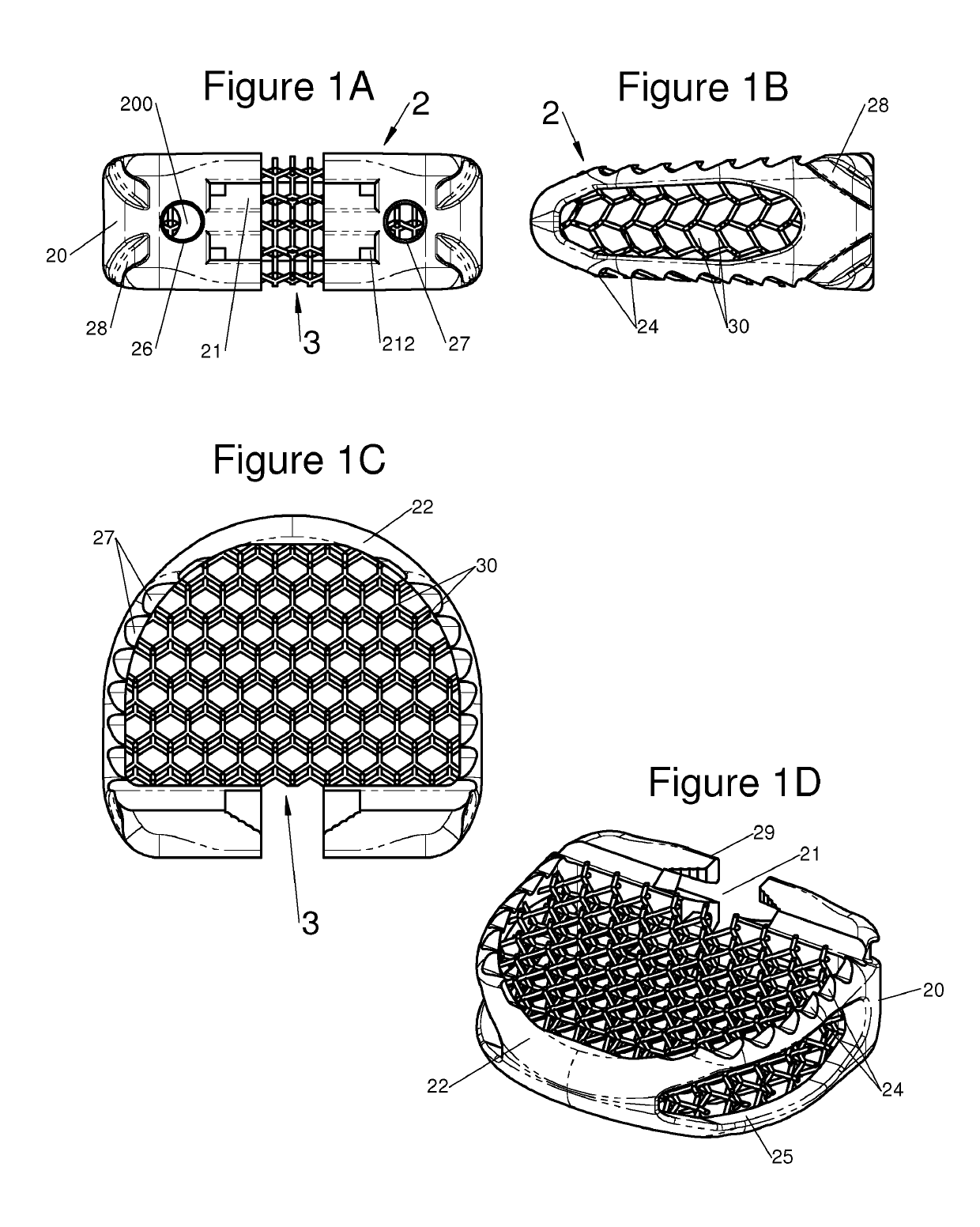
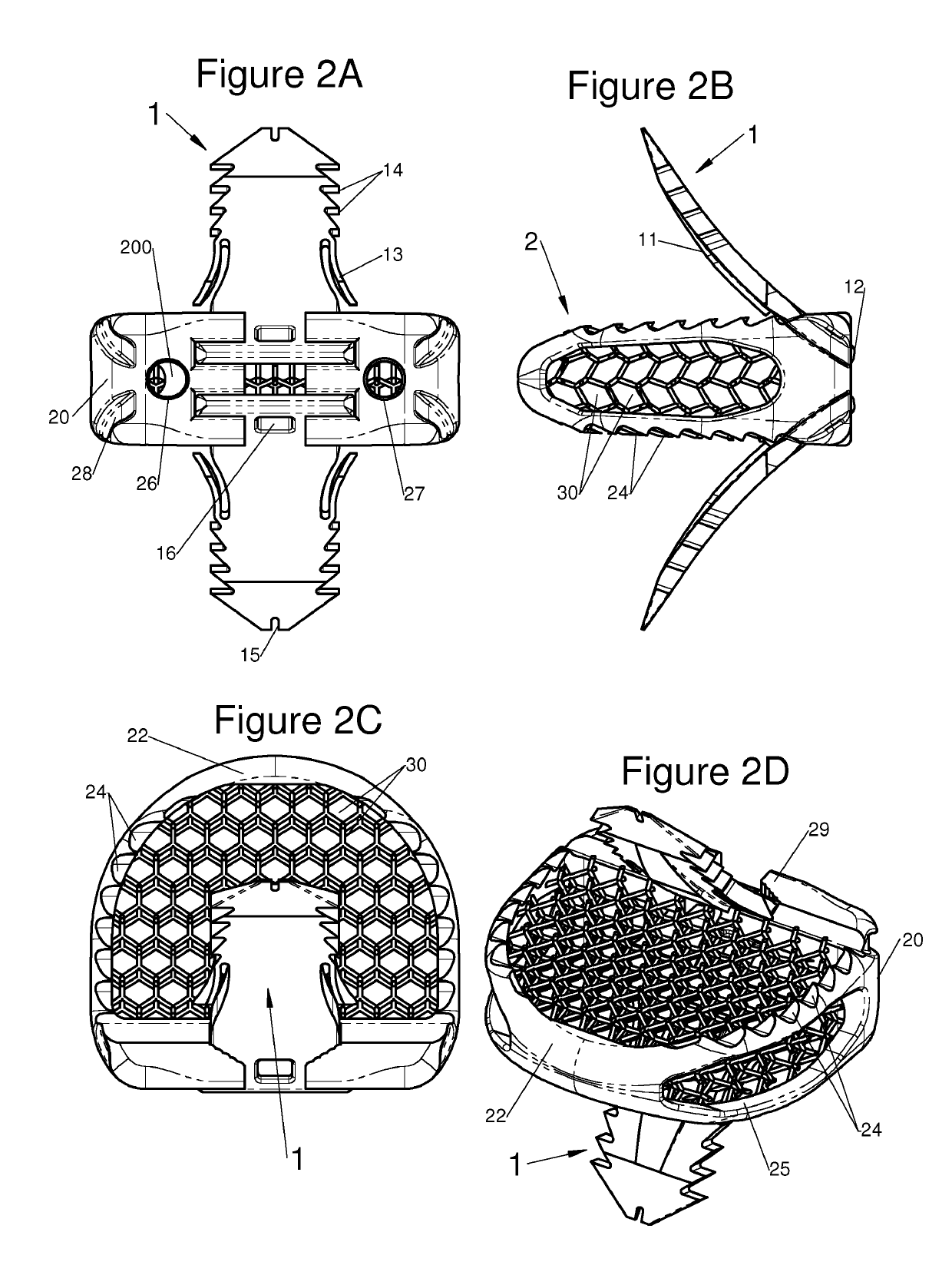
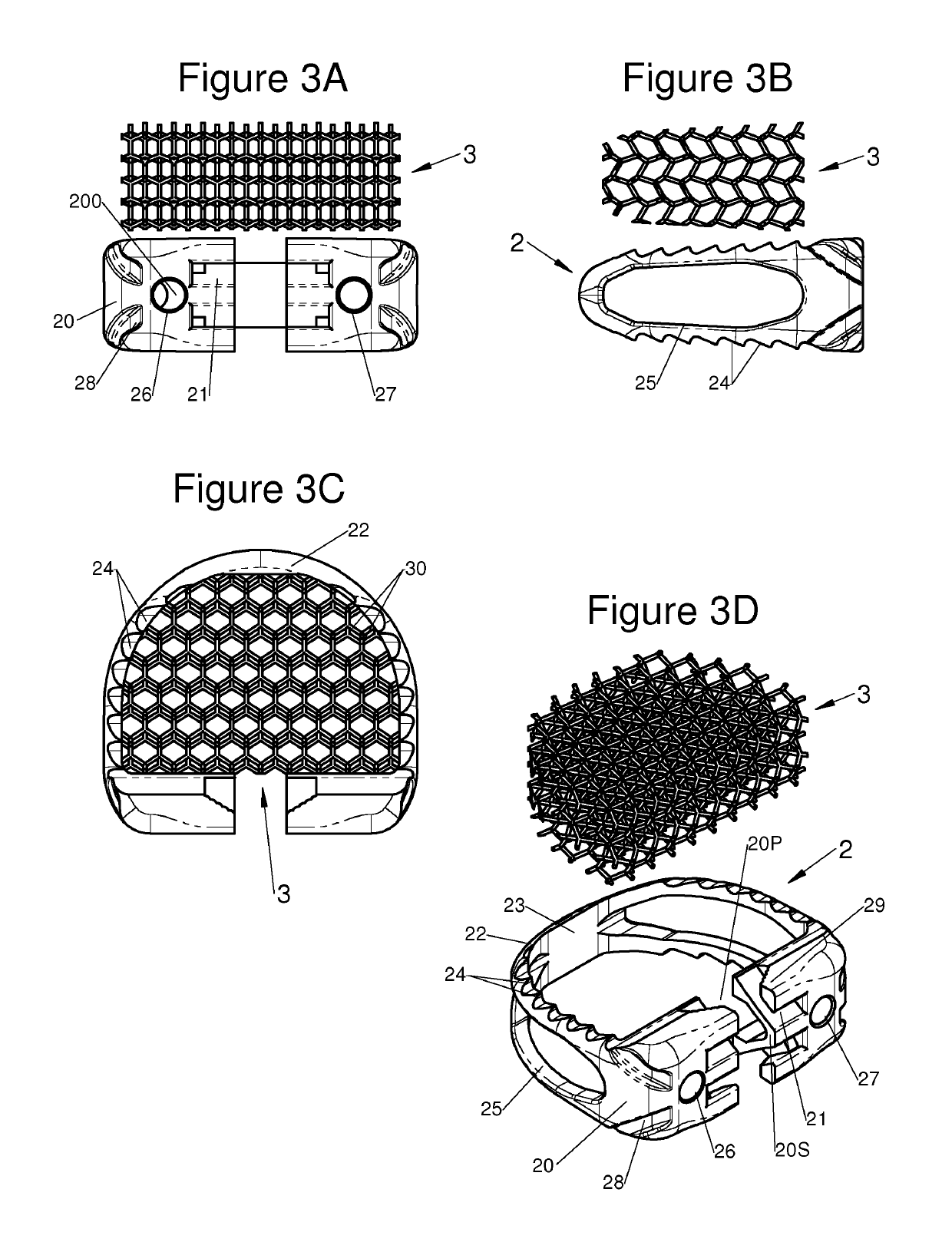
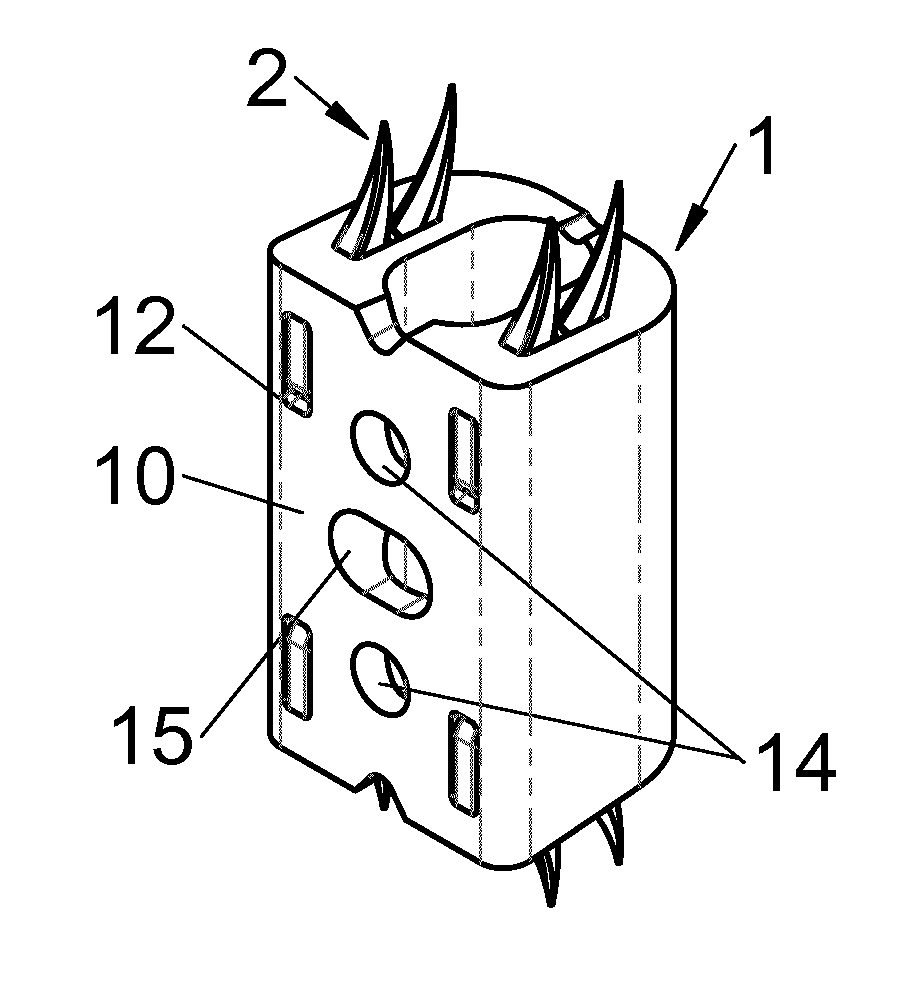
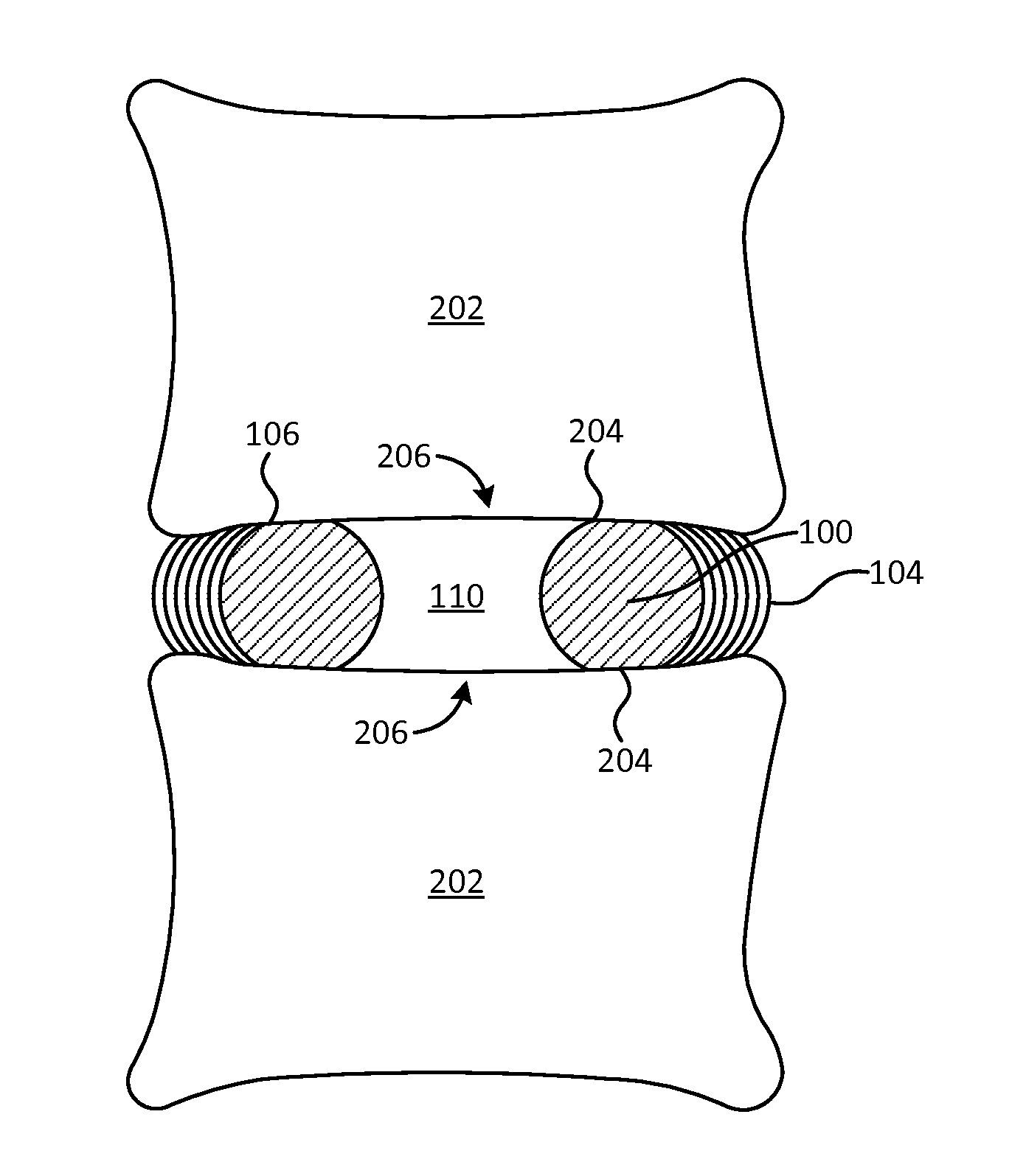
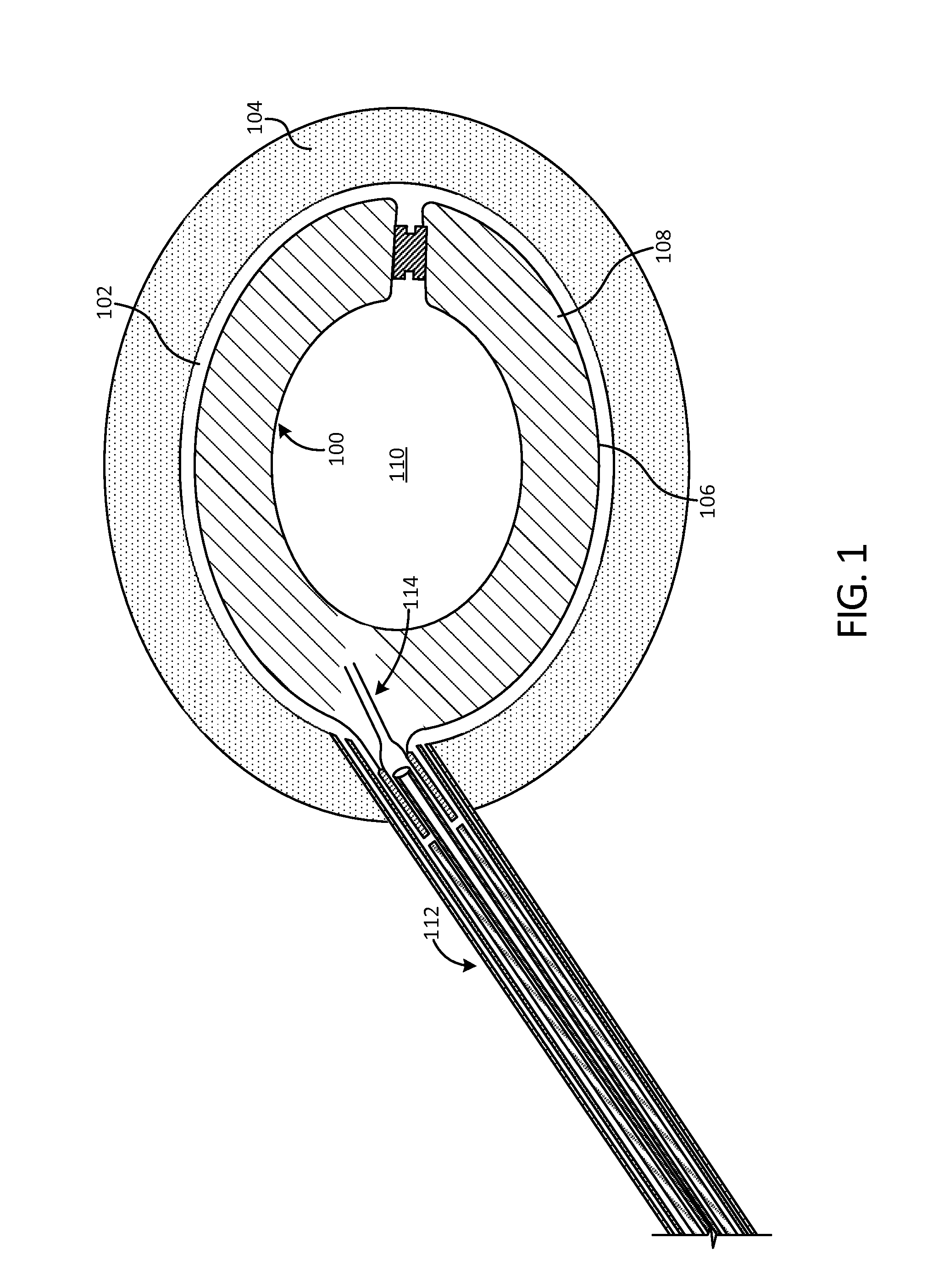
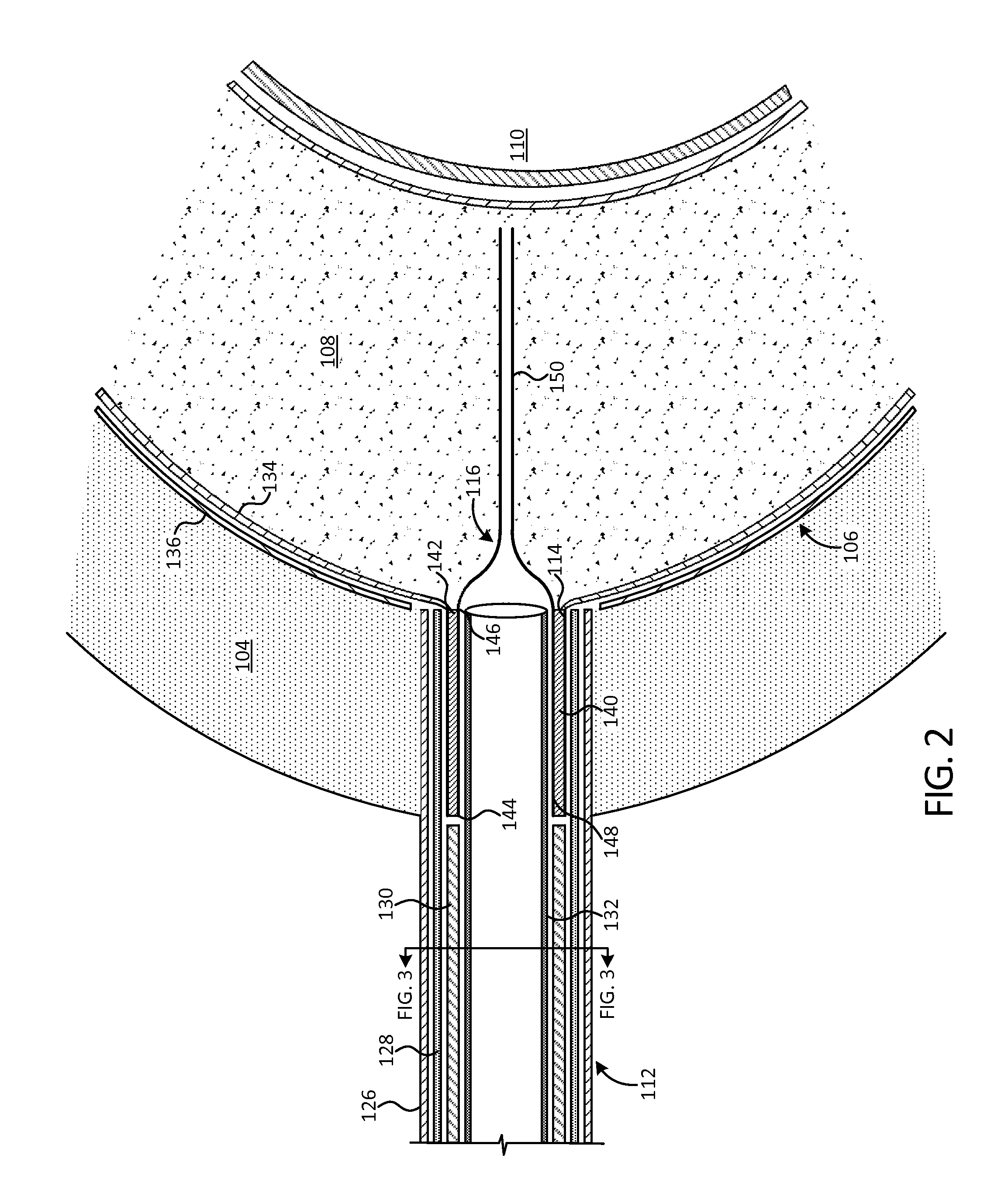
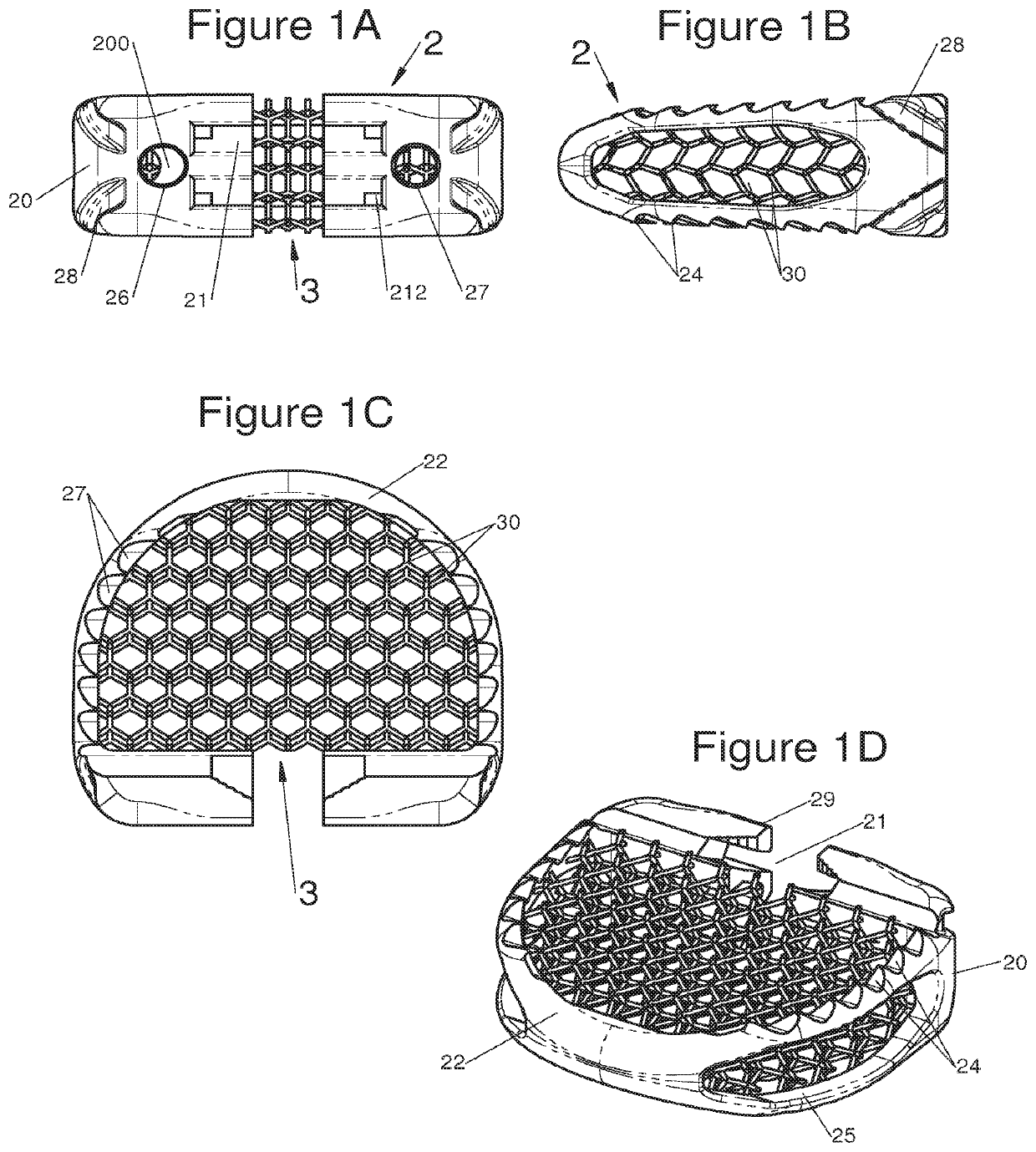
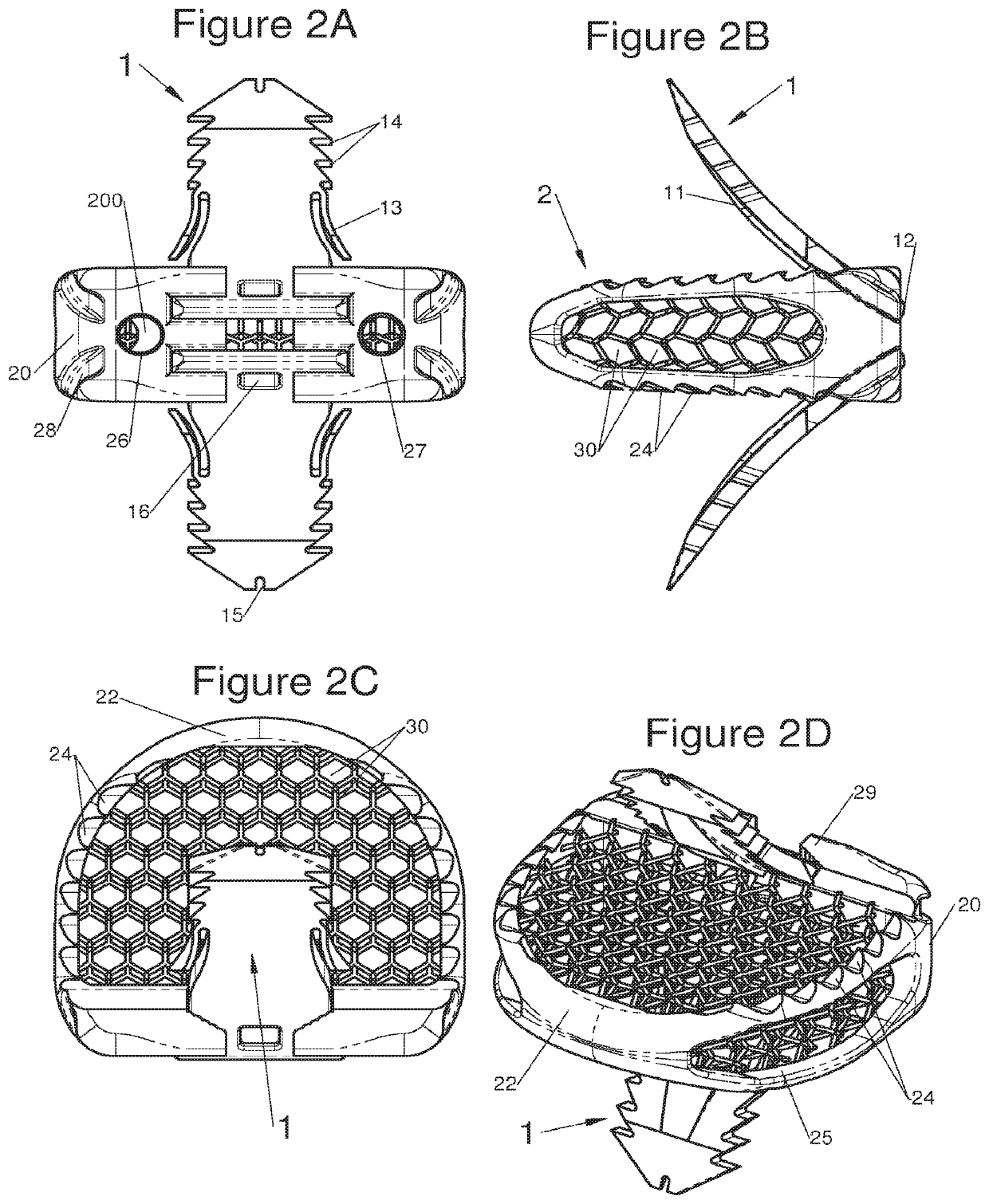
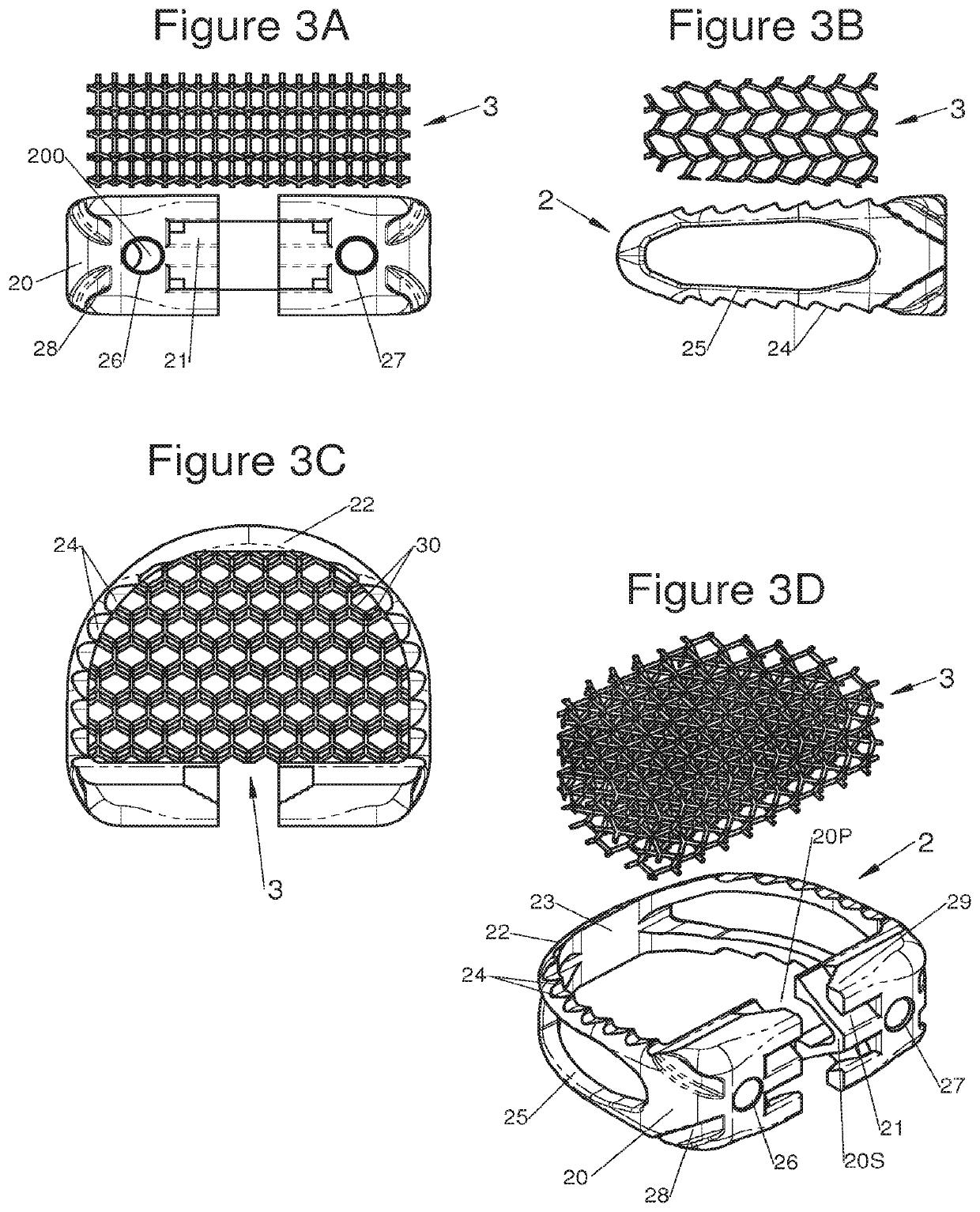
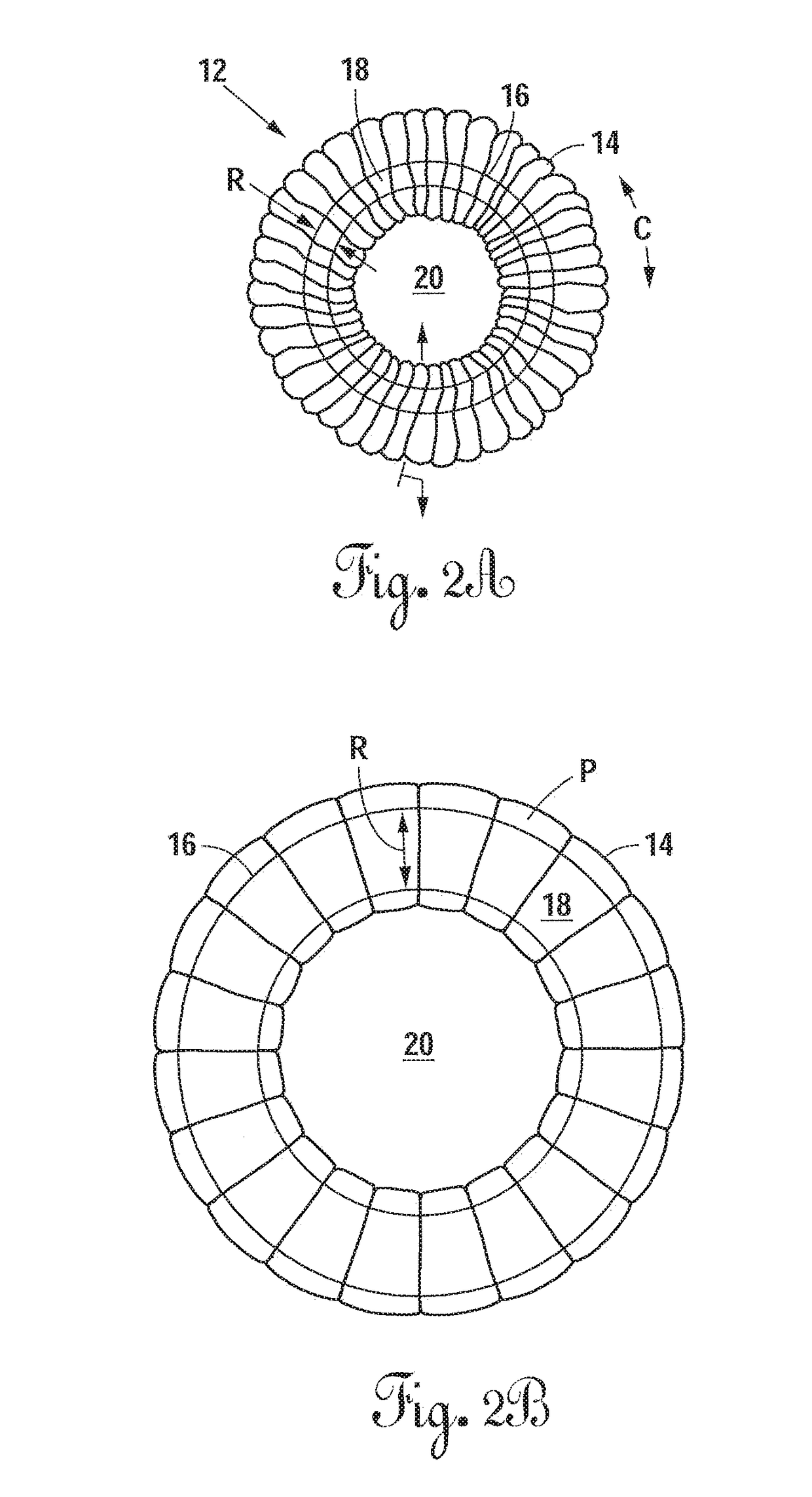
The present invention relates to a vertebral system comprising a vertebral implant (2) and a plurality of inserts, said implant being designed to be implanted in a vertebral segment composed of at least two vertebrae and including a body (20) the walls whereof delimit a cavity (23) leading to the outside of the body (20) through at least one opening in at least one of said walls, at least one passage (21) passing through the implant (2) from the periphery to an upper or lower surface to receive a bone-anchoring device (1) capable of anchoring the implant (2) in at least one of said vertebrae, the system being characterized in that it includes at least two inserts selected from among the following inserts:at least one graft insert (3, 3A, 3B, 4, 5A, 5B, 6A, 6B, 6C, 6D, 202, 250) capable of being colonized by bone tissue and / or receiving at least one bone tissue graft and / or at least one substitute;and / orat least one bone-anchoring insert (210) comprising said passage (21) capable of receiving said bone-anchoring device (1).
Owner:LDR MEDICAL
Nucleus replacement securing device and method
Owner:THEKEN SURGICAL LLC
Method of using spinal cord stimulation to treat neurological disorders or conditions
InactiveUS20100145428A1Improve the quality of lifeReduces, amelioratesSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsMedicineElectrical stimulations
The present invention involves methods and systems for using electrical stimulation to treat neurological disorders. More particularly, the method comprises surgically implanting an electrical stimulation lead that is in communication with spinal nervous tissue associated with a first, second, or third cervical vertebral segment to result in spinal nervous tissue stimulation, thus treating a wide variety of neurological disorders.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Device and Method for Expanding the Spinal Canal With Spinal Column Stabilization and Spinal Deformity Correction
ActiveUS20110230915A1LengtheningAchieve fixationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnSpinal deformity correction
Spinal canal expansion through pedicle lengthening in combination with spinal column stabilization, to treat spinal stenosis, spondylolisthesis, kyphosis, scoliosis or a major spinal rotational deformity, with or without a spinal fusion. A device or implant that includes a pedicle lengthening implant to decompress (expand) the spinal canal, and a bridge to connect two or more pedicle lengthening implants and / or pedicle screws or bone anchors to achieve simultaneous spinal stabilization across one or more vertebral segments. The bridge across the vertebral segments can include a longitudinal member, such as a plate or rod. The pedicle lengthening implant is originally made, or can be modified to, connect to the longitudinal member. Spinal deformity can be manipulated, through operation of one or more pedicle lengthening implants in respective vertebral segments, to improve a relative relationship between the respective vertebra segments, the longitudinal member then fixating the vertebral segments into a multi-level spinal construct.
Owner:INNOVATIVE SURGICAL DESIGNS
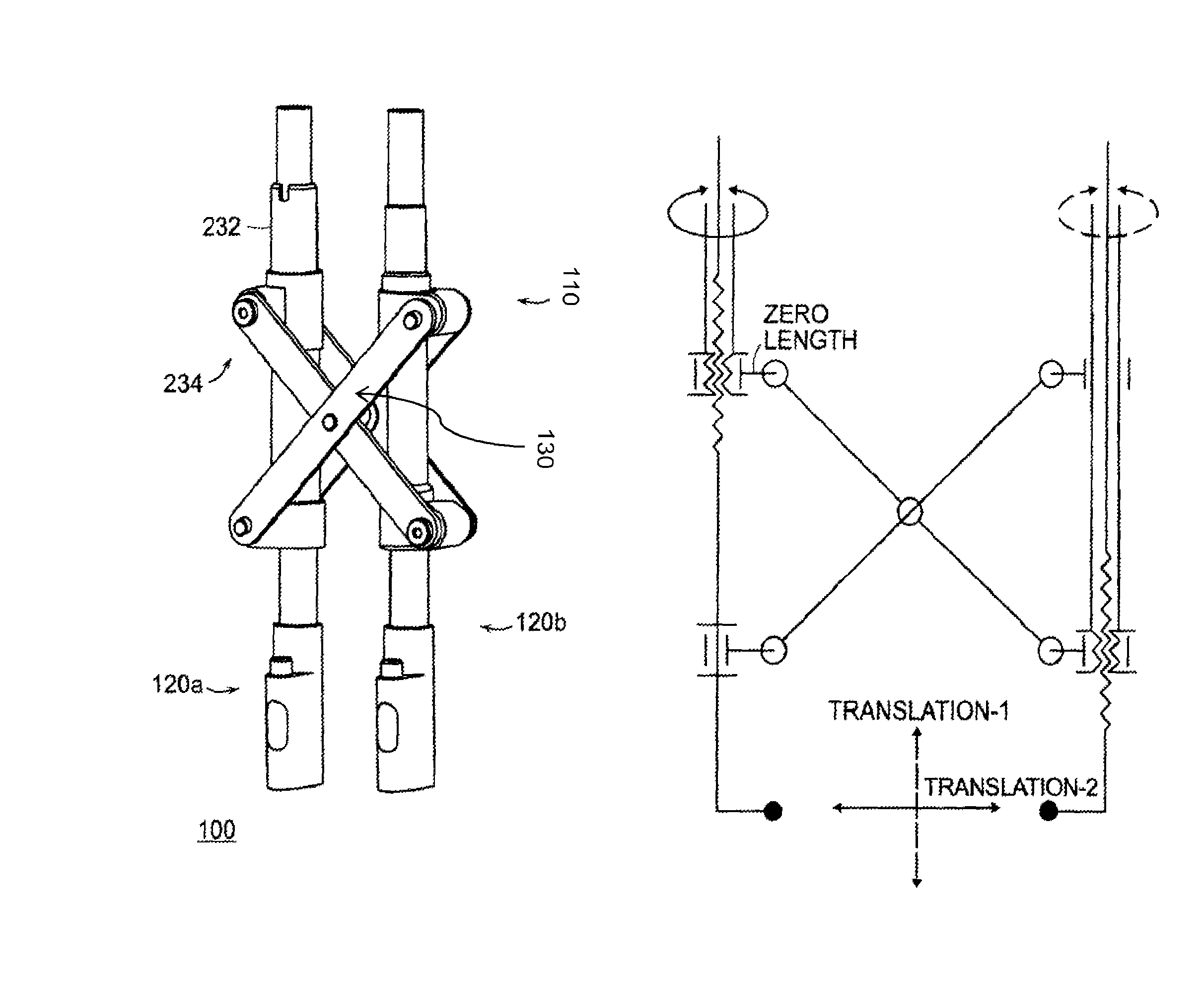
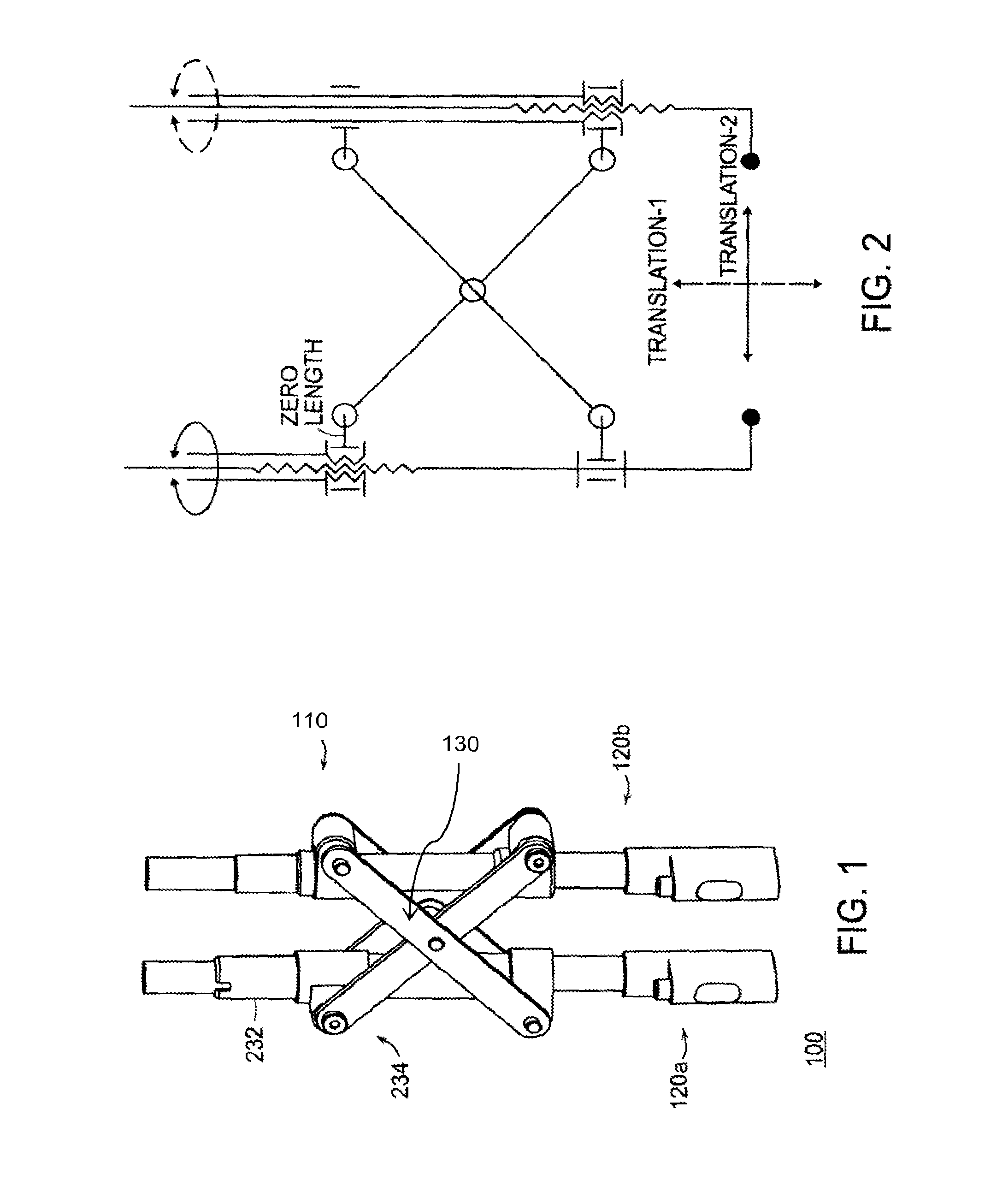
Vertebral body reduction instrument and methods related thereto
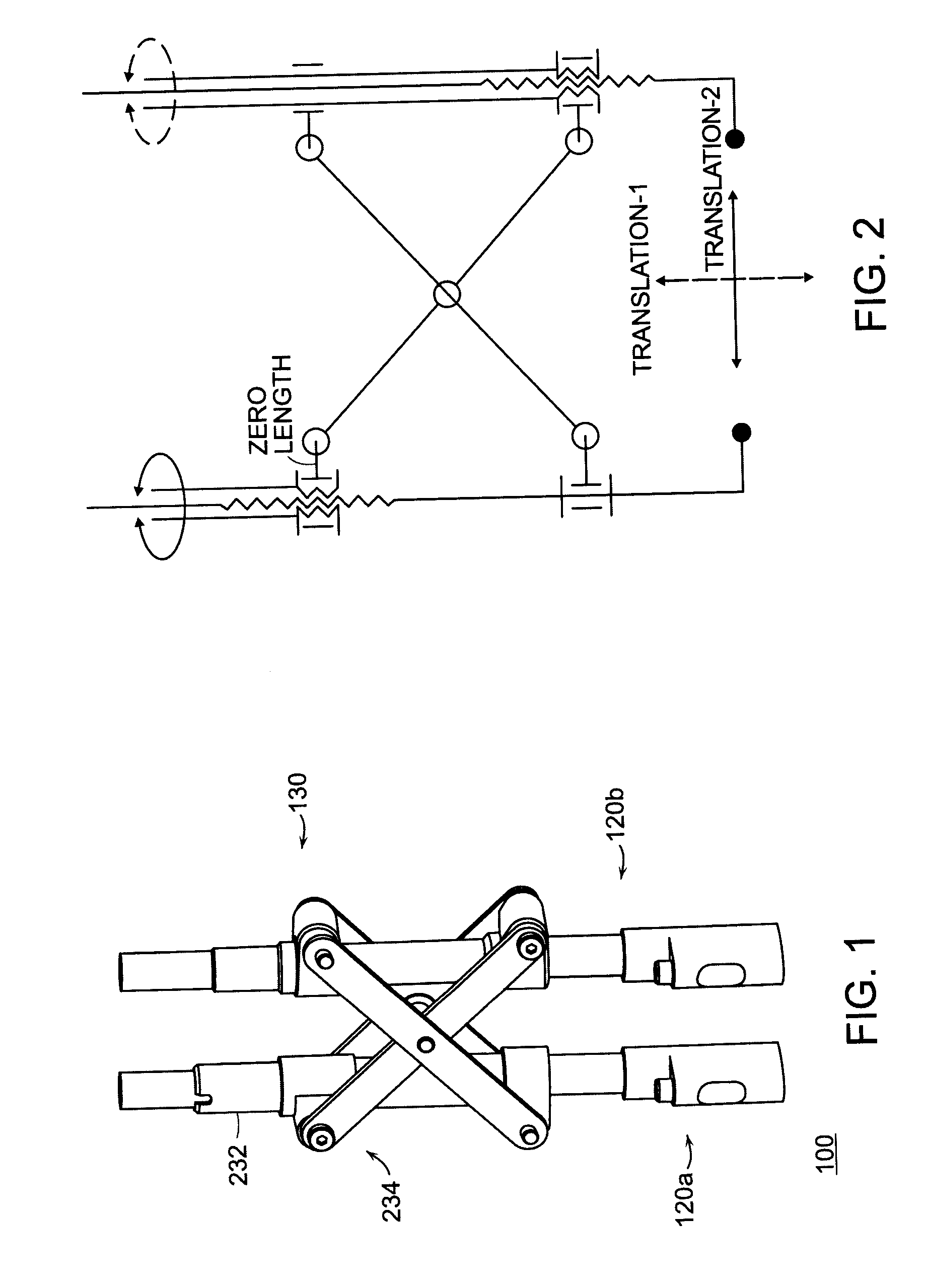
ActiveUS20100274252A1Reduce internal frictionStay rigidInternal osteosythesisProsthesisDistractionEngineering
Featured is a reduction instrument being configured and arranged to allow correction of vertebral translation and applying distraction across a segment in an independent fashion. Such a reduction instrument embodies one or more identical modules that are configured as needed for correcting the deformity. In more particular embodiments, each of the one or more modules has two degrees of freedom (DOF) with uncoupled orthogonal translations. Such a reduction instrument allows the reorientation of the vertebral segment as needed via uncoupled orthogonal translations. Such a reduction instrument also is usable in combination with a plurality of vertebral anchors, such vertebral anchors being any such vertebral anchors as are know to those skilled in the art (e.g., conventional spinal pedicle screw instrumentation) or hereinafter developed so as to form a spinal implant system. Also featured are treatment methods utilizing such a reduction instrument.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method making it possible to produce the ideal curvature of a rod of vertebral osteosynthesis material designed to support a patient vertebral column
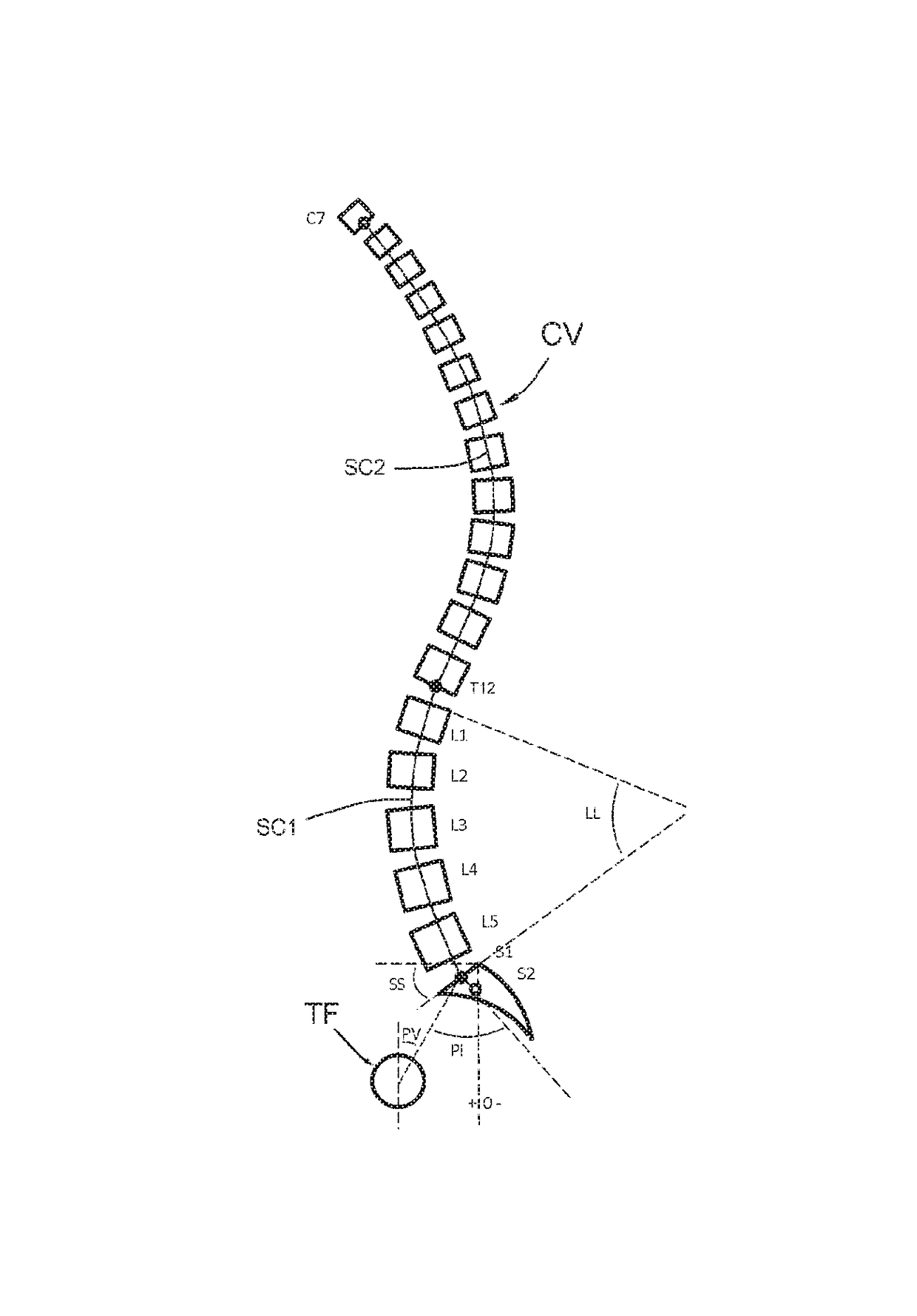
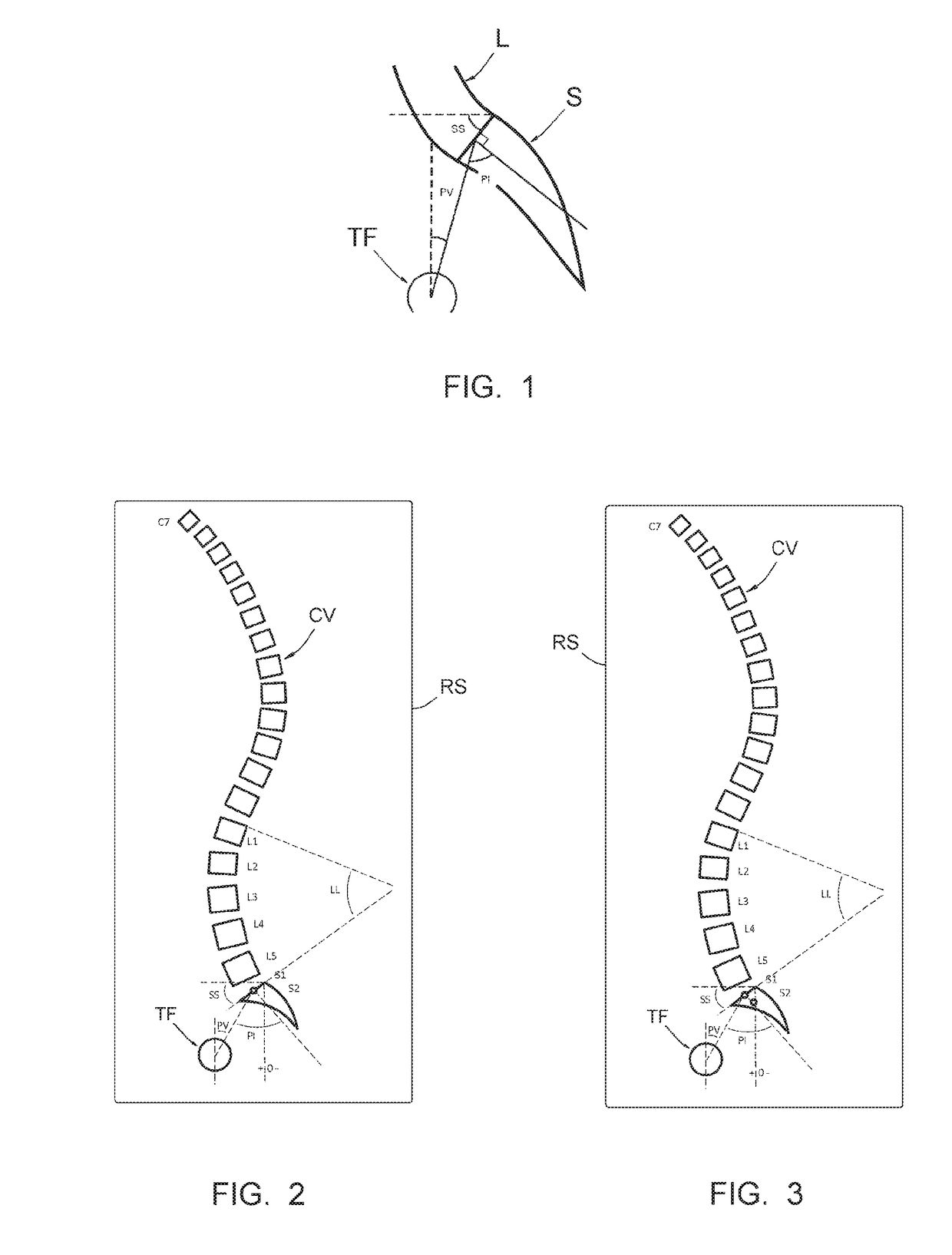
ActiveUS9693831B2Impart the appropriate curvature to a straight rod easilyEasily impartedImage enhancementImage analysisSpinal columnMedicine
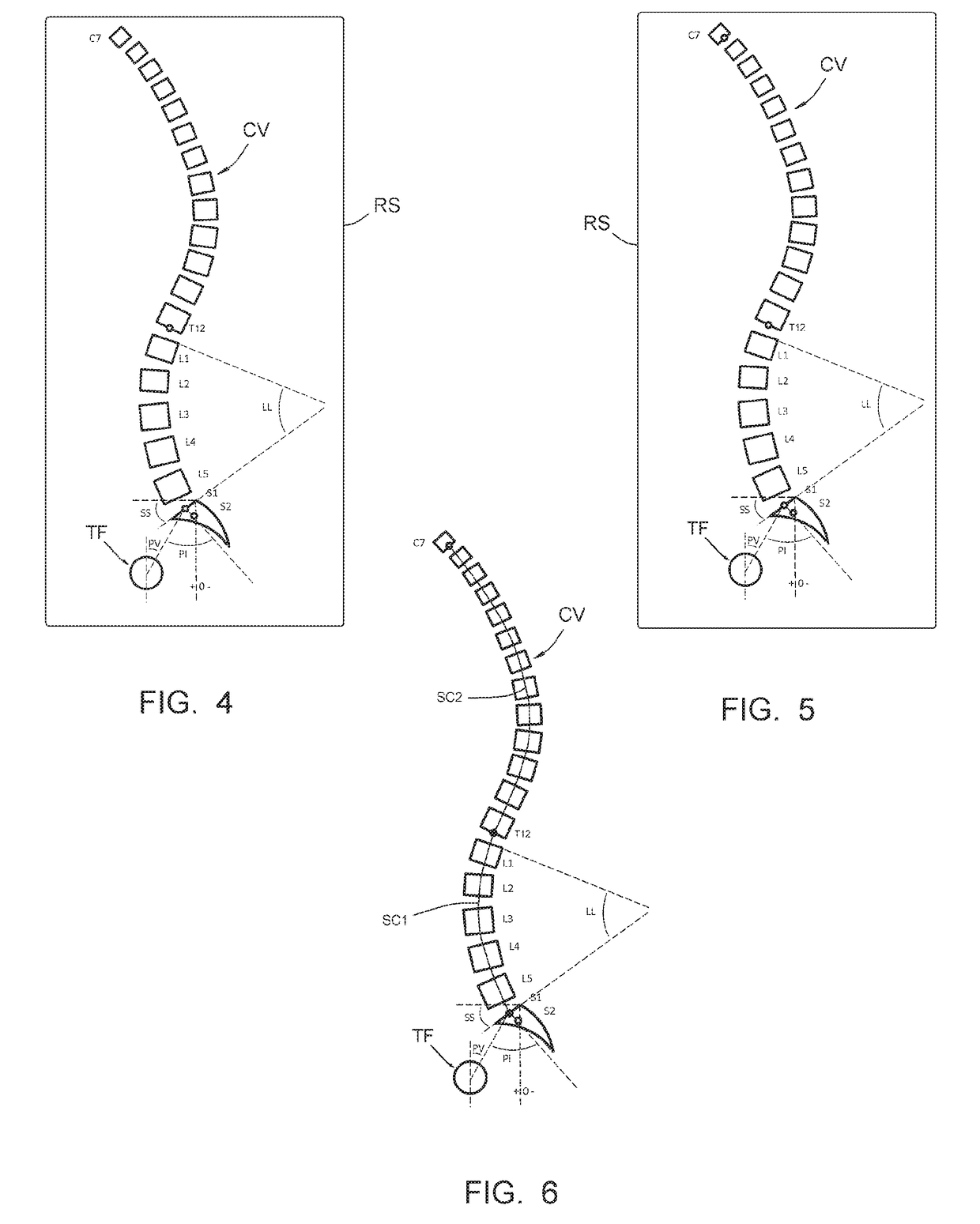
According to the invention, the process includes the steps of: a) taking a sagittal preoperative x-ray of the vertebral column of the patient to be treated, extending from the cervical vertebrae to the femoral heads; b) on that x-ray, identifying points on S1, S2, T12 et C7; c) depicting, on the said x-ray, curved segments beginning at the center of the plate of S1 et going to the center of the plate of C7; e) identifying, on that x-ray, the correction(s) to be made to the vertebral column, including the identification of posterior osteotomies to make; f) pivoting portions of said x-ray relative to other portions of that x-ray, according to osteotomies to be made; g) performing, on said x-ray, a displacement of the sagittal curvature segment extending over the vertebral segment to be corrected; h) from a straight vertebral rod (TV), producing the curvature of that rod according to the shape of said sagittal curvature segment in said displacement position.
Owner:MEDICREA INT SA
Method of using spinal cord stimulation to treat gastrointestinal and/or eating disorders or conditions
ActiveUS20080154329A1Enhance gastric motilityIncreasing) gastric motilityElectrotherapyArtificial respirationMedicineGastrointestinal disorder
The present invention involves a method and a system for using electrical stimulation to treat gastrointestinal and / or eating disorders. More particularly, the method comprises surgically implanting an electrical stimulation lead that is in communication with predetermined thoracic vertebral segments to cause spinal nervous tissue stimulation, thus treating a wide variety of gastrointestinal disorders.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Vertebral system, implant and inserts for vertebral system
InactiveUS10369009B2Reliable and fast and usableLow costBone implantJoint implantsBone tissueMedicine
The present invention relates to a vertebral system comprising a vertebral implant (2) and a plurality of inserts, said implant being designed to be implanted in a vertebral segment composed of at least two vertebrae and including a body (20) the walls whereof delimit a cavity (23) leading to the outside of the body (20) through at least one opening in at least one of said walls, at least one passage (21) passing through the implant (2) from the periphery to an upper or lower surface to receive a bone-anchoring device (1) capable of anchoring the implant (2) in at least one of said vertebrae, the system being characterized in that it includes at least two inserts selected from among the following inserts:at least one graft insert (3, 3A, 3B, 4, 5A, 5B, 6A, 6B, 6C, 6D, 202, 250) capable of being colonized by bone tissue and / or receiving at least one bone tissue graft and / or at least one substitute;and / orat least one bone-anchoring insert (210) comprising said passage (21) capable of receiving said bone-anchoring device (1).
Owner:LDR MEDICAL SAS
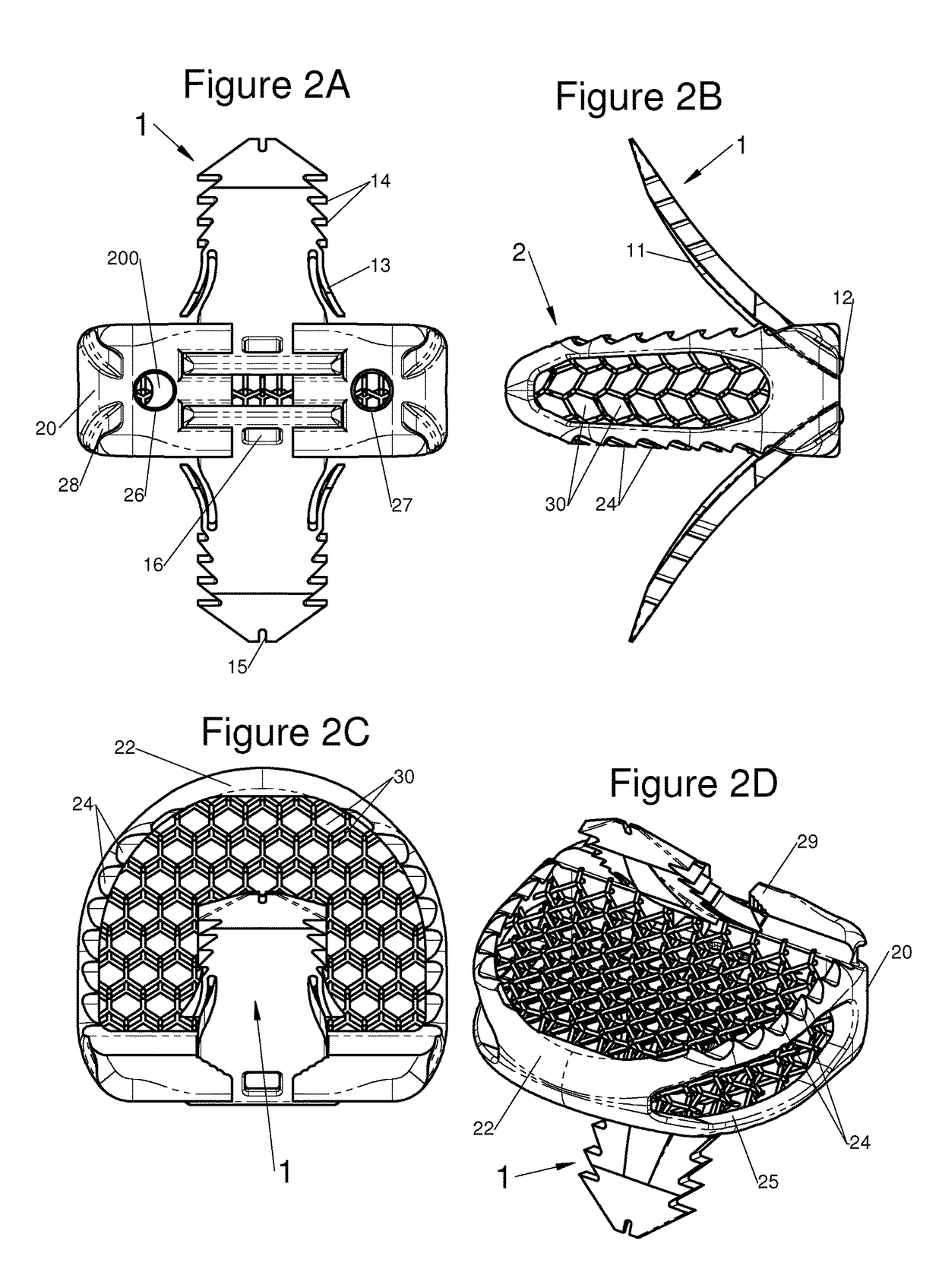
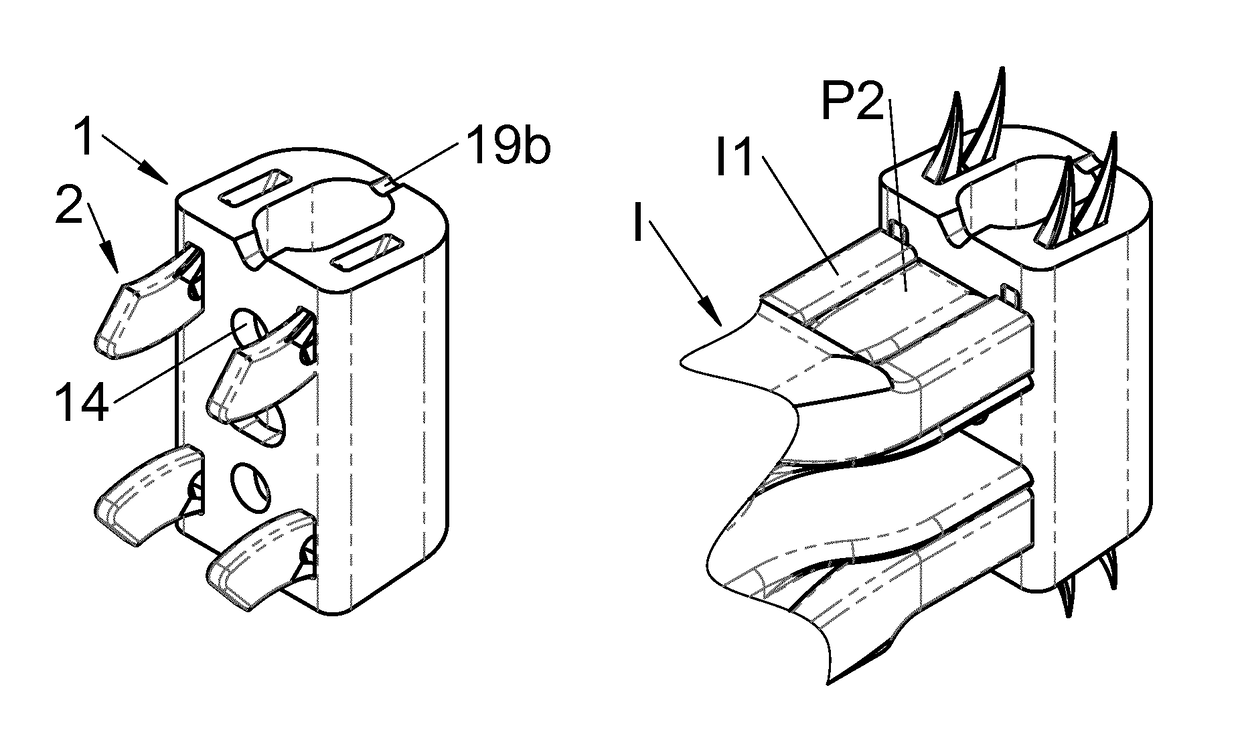
Vertebral implant, vertebral fastening device of the implant and implant instrumentation
ActiveUS20160100953A1Easy to implant and fix reliablyReliable and easy-to-use fasteningSpinal implantsLower upperVertical axis
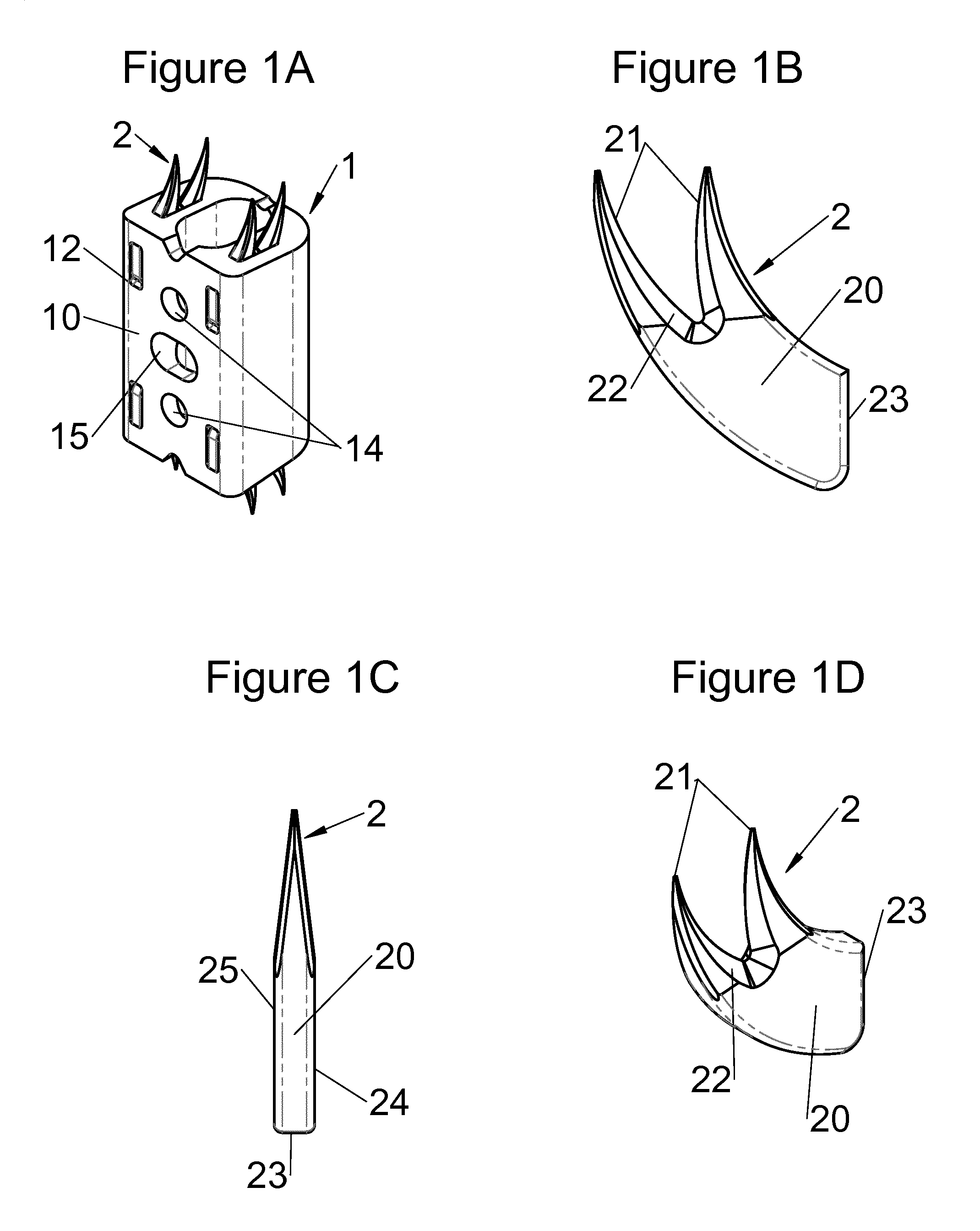
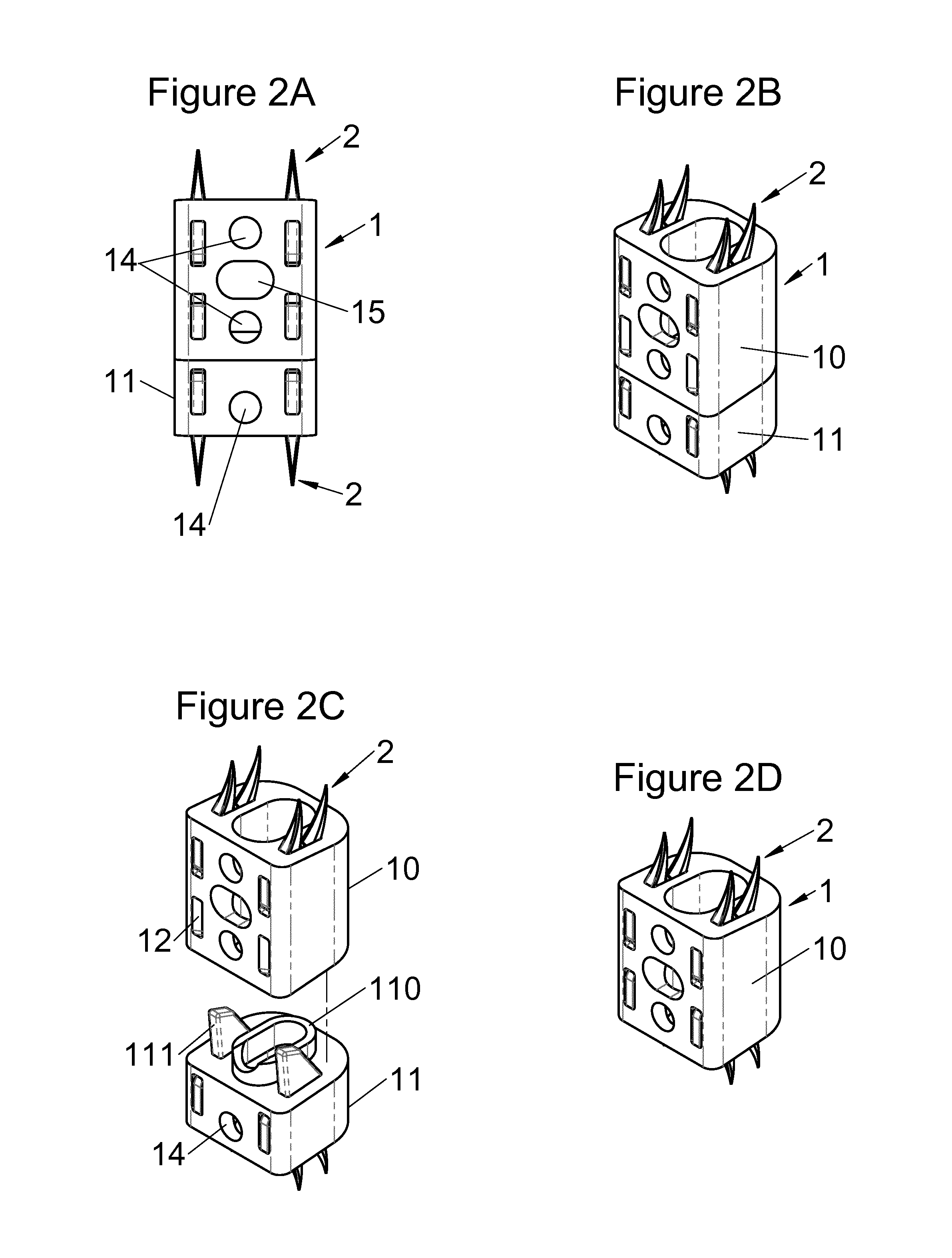
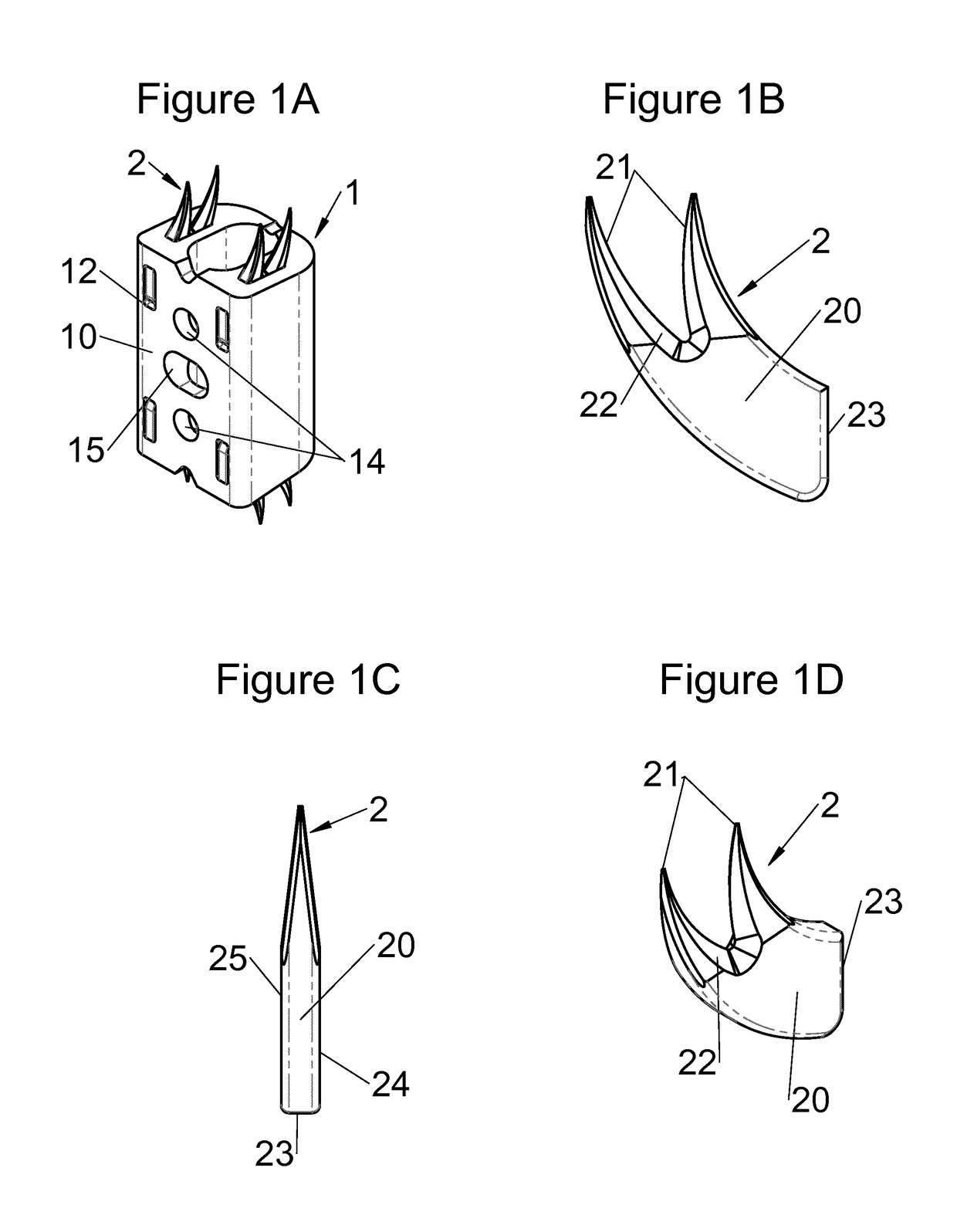
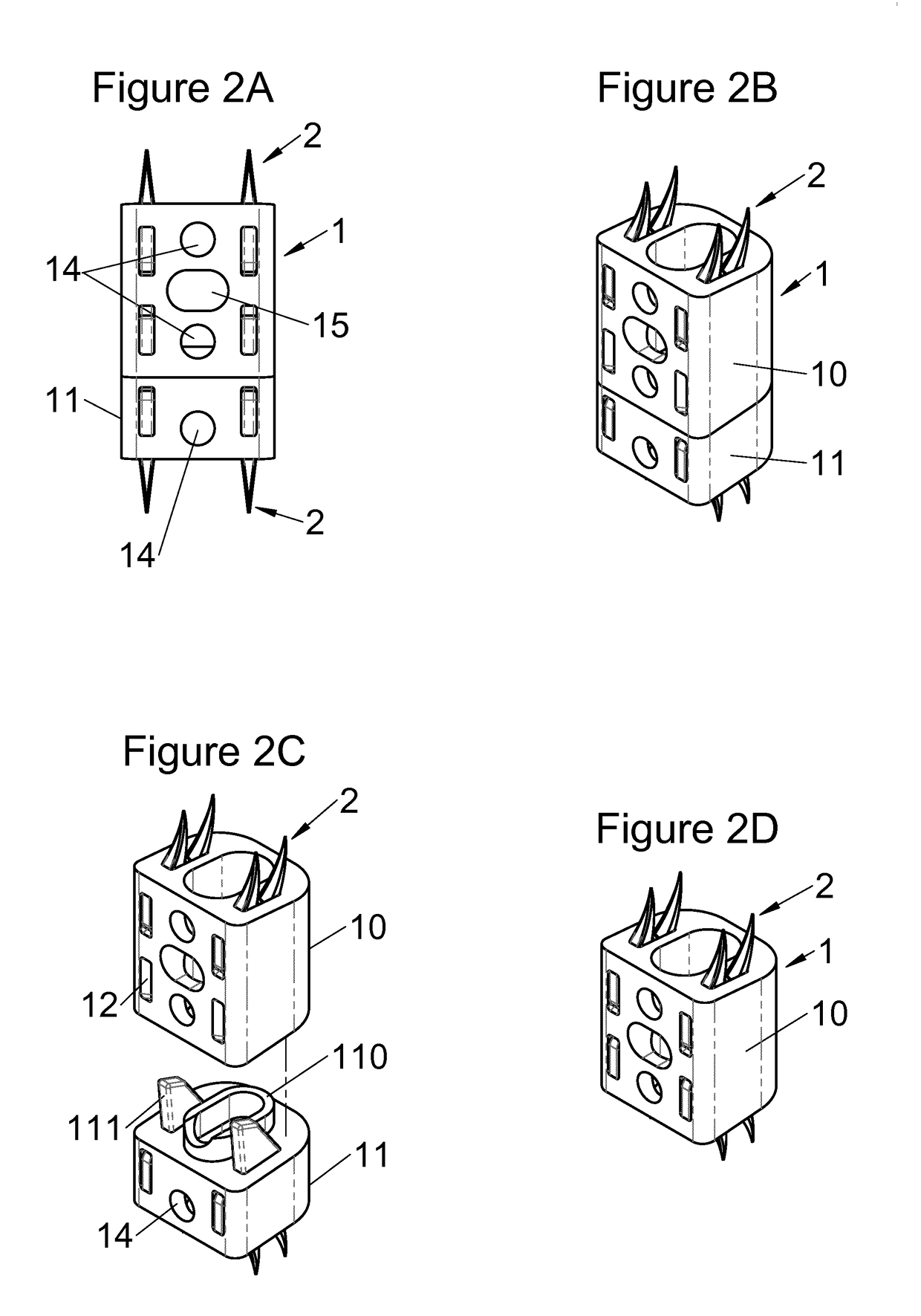
This disclosure provides vertebral implants, fastening devices for vertebral implants, and implant instrumentation, and various combinations thereof. In some embodiments, the implant comprises a peripheral wall extending according to a vertical axis between upper and lower surfaces of the implant, with each such surface configured to be placed in contact with a vertebral structure, respectively, at the top and the bottom of the vertebral segment replaced by the implant. Some embodiments comprise fastening means, deployment of which anchors the implant in the lower and upper vertebral structures. Some fastening means may be deployed by sliding parallel to the vertical axis of the implant, and may comprise a plate with at least one part remaining in contact with the peripheral wall of the implant when deployed and a pointed end projecting from one of the upper and lower surfaces of the implant to enter a vertebral structures on completion of deployment.
Owner:LDR MEDICAL
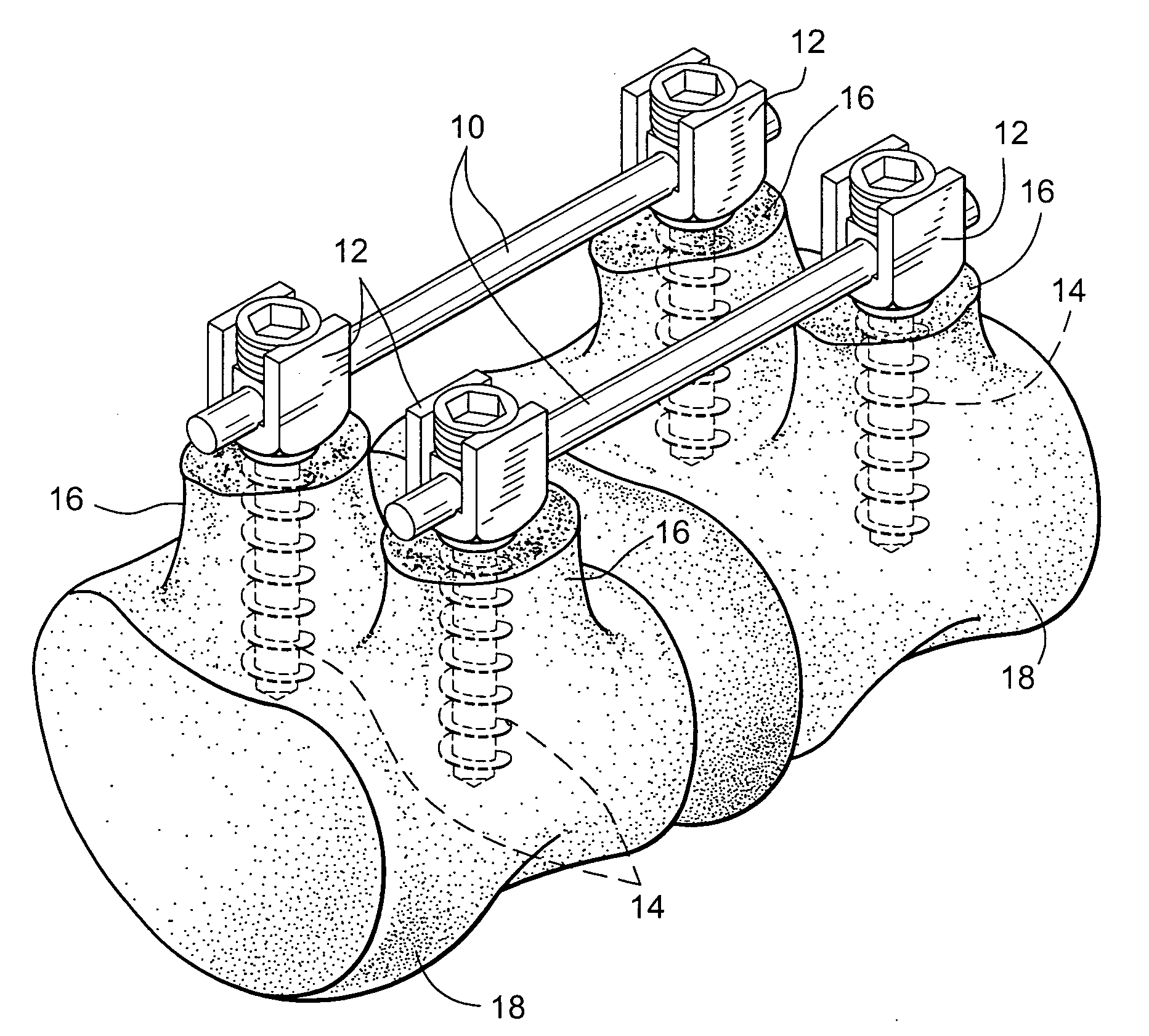
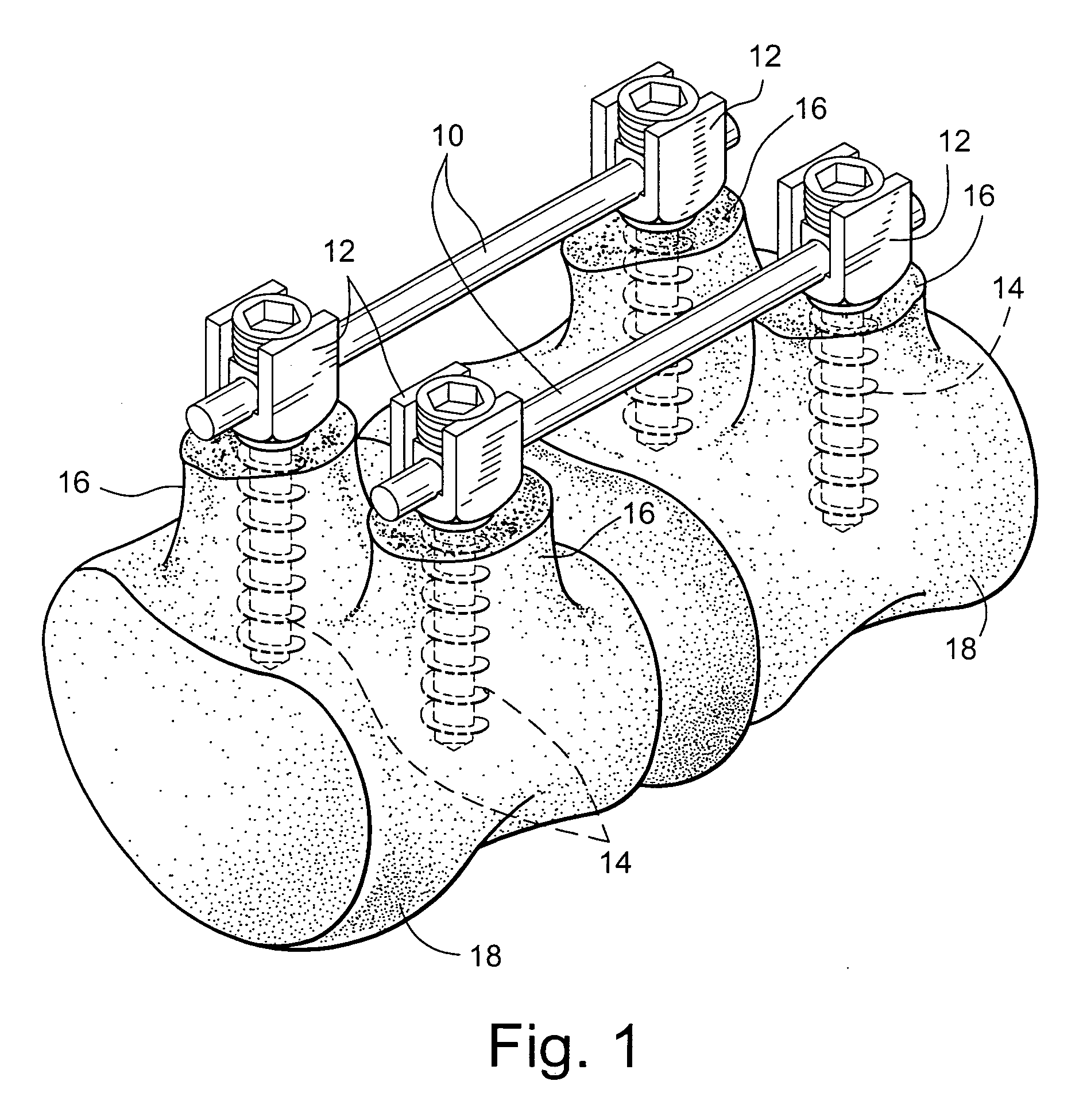
Multidirectional adaptable vertebral osteosyntsis device with reduced space requirement
InactiveUSRE42626E1Small spaceInternal osteosythesisNon-surgical orthopedic devicesVertebral boneSpace requirements
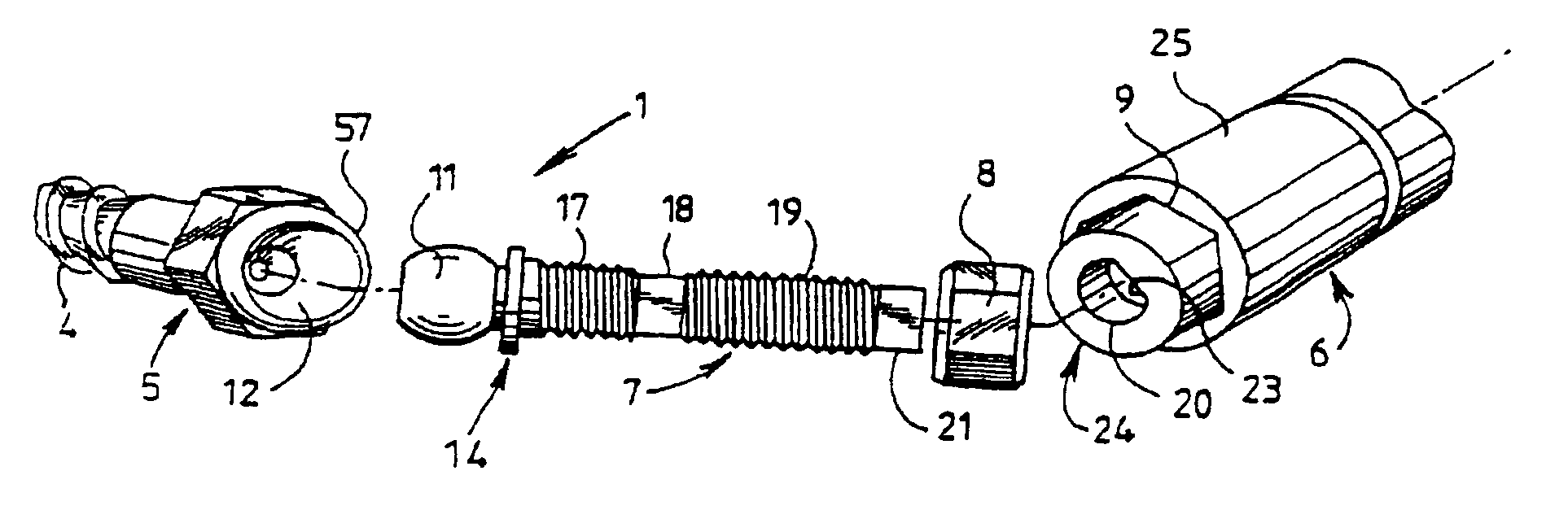
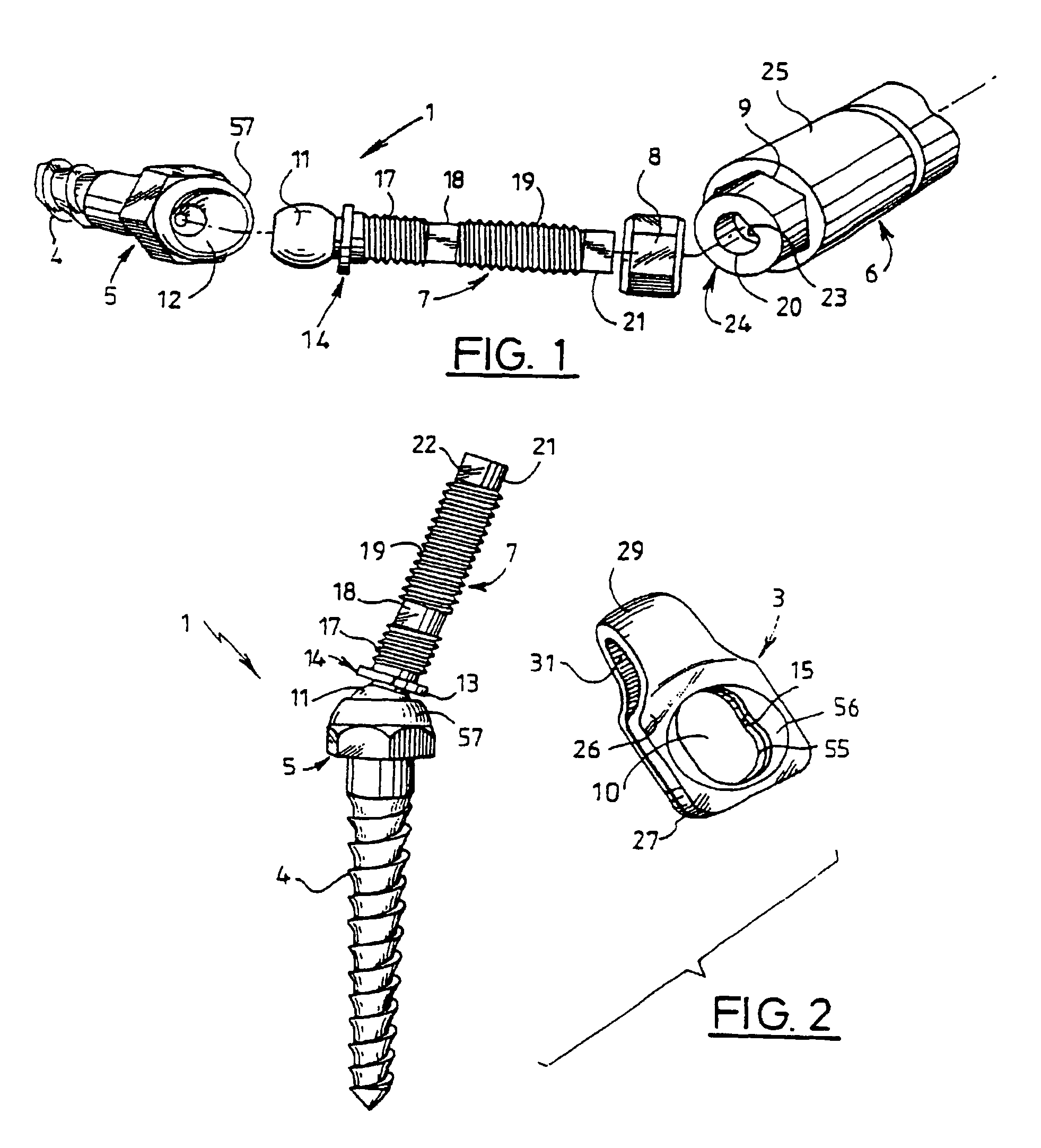
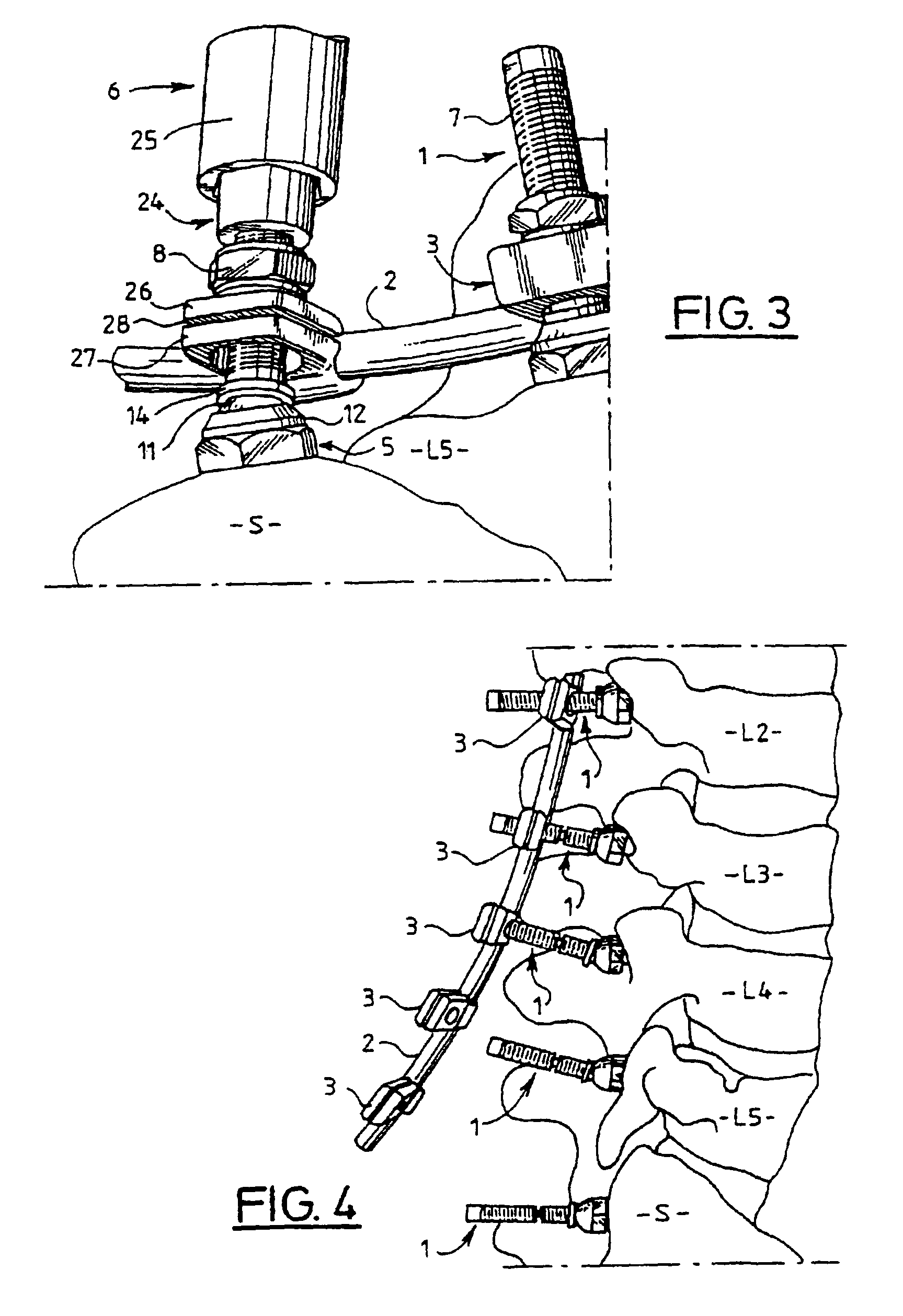
A vertebral osteosynthesis device includes at least two bone anchoring elements (1) in the vertebral bone structures respectively (S, L5.), a longitudinal linking member (2) between the bone anchoring elements, and connector links (3) between the bone anchoring elements and said linking members. Each bone anchoring element includes a bond fixing part (4), a head (5) to be gripped by a screwing device, a threaded shaft (7) extending the grip head, and a clamping element (8) to be screwed on said shaft to lock together the connector link, the longitudinal linking member and the corresponding bone anchoring element; the threaded shaft (7) is provided at its end with a hinge ball joint (11) in a housing (12) of the grip head (5), enabling a multidirectional adjustment of the shaft (7) and a positioning of the connector link (3) adapted to the vertebral segment configuration (S, L5, . . . Lw) receiving the bone anchoring elements.
Owner:MEDICREA TECH
Real-time in-vivo measuring method for right and left lateral flexion of thoracic and lumbar vertebrae
InactiveCN104856686AMotion posture obtained in real timeNo need to waitDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNODALSomatosensory system
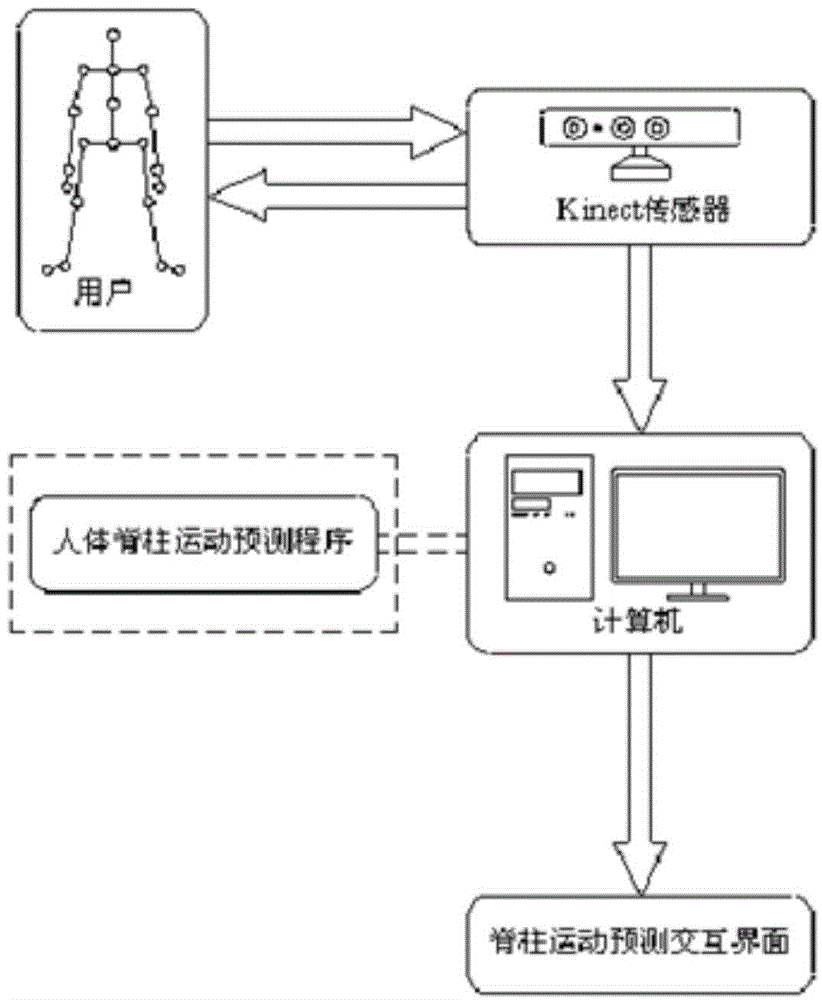
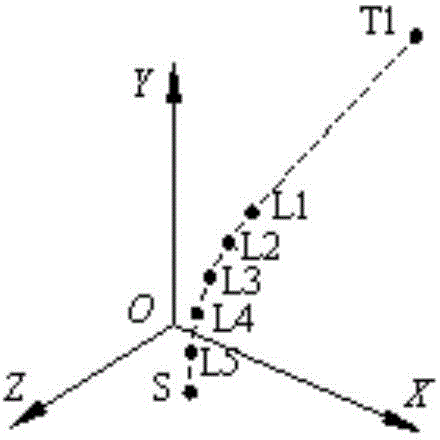
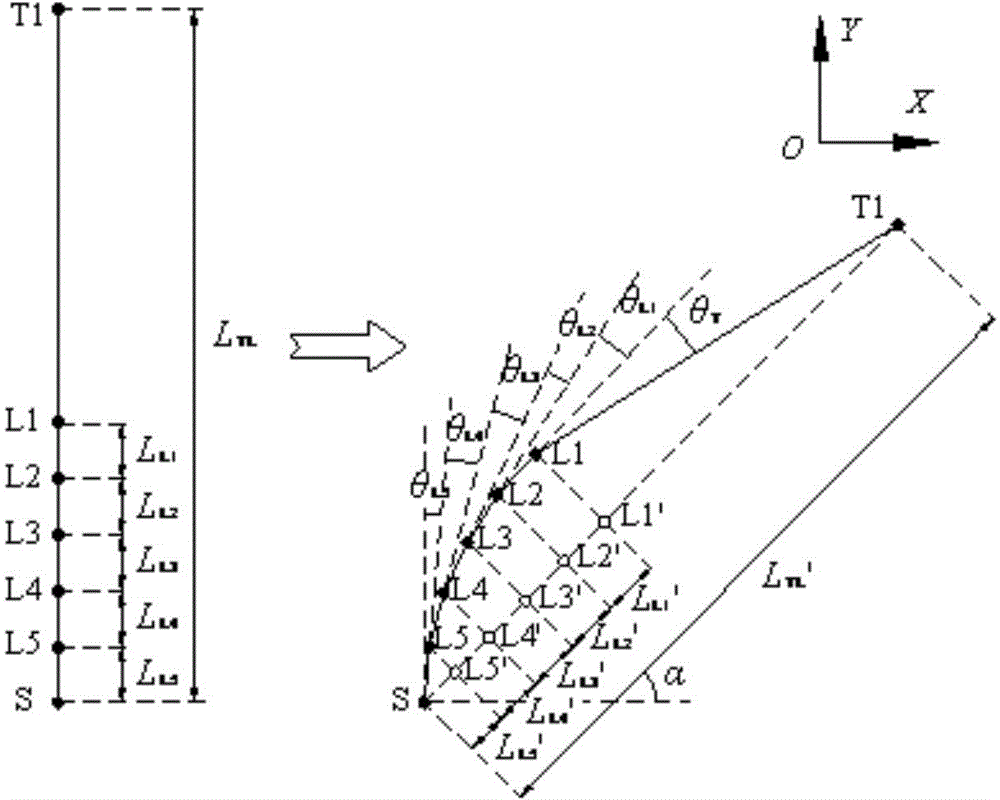
The invention discloses a real-time in-vivo measuring method for right and left lateral flexion of thoracic and lumbar vertebrae based on Kinect somatosensory interaction technology with the purpose of realizing posture determination and speculation during the motion process of lateral flexion of thoracic and lumbar vertebrae and outputting coordinates of center nodes of all centrums. During measurement, a somatosensory man-machine interaction mode is adopted and a Kinect sensor is utilized for real-time capture of postures and motion of a human torso. In combination with multi-body system kinemics, positions and postures of all centrums of a vertebral column are calculated in order to real-time acquisition of coordinates of center nodes of all centrums and posture angles. Operation is performed easily and conveniently. The postures of the vertebral column and the center nodes of all centrums are displayed on an interactive interface of a system in a real-time mode.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Percutaneous Implantable Nuclear Prosthesis
ActiveUS20160120654A1Extend working lifeReduce stressJoint implantsSpinal implantsFiberIntervertebral disc
A prosthesis for implantation in a de-nucleated intervertebral disc includes a fiber ring-like layer which encloses a polymeric layer to create an annular space. The annular space is inflatable with an in-situ curable liquid polymer and forms an interior cavity. The annular space may be expanded uniformly or differentially to be tailored to the needs of a particular vertebral segment and to achieve optimal disc space width and angle, thereby stabilizing the segment while preserving normal motion of the vertebral segment. The interior cavity provides a void that allows inward deformation of the implant during weight bearing activities and bending. The prosthesis can be elastically deformed through axial elongation to a reduced profile to load into a delivery cannula using pulling techniques.
Owner:SPINAL STABILIZATION TECH
Vertebral system, implant and inserts for vertebral system
ActiveUS20190336305A1Reliable and fast and usableLow costBone implantJoint implantsBone tissueVertebra
The present invention relates to a vertebral system comprising a vertebral implant (2) and a plurality of inserts, said implant being designed to be implanted in a vertebral segment composed of at least two vertebrae and including a body (20) the walls whereof delimit a cavity (23) leading to the outside of the body (20) through at least one opening in at least one of said walls, at least one passage (21) passing through the implant (2) from the to periphery to an upper or lower surface to receive a bone-anchoring device (1) capable of anchoring the implant (2) in at least one of said vertebrae, the system being characterized in that it includes at least two inserts selected from among the following inserts:at least one graft insert (3, 3A, 3B, 4, 5A, 5B, 6A, 6B, 6C, 6D, 202, 250) capable of being colonized by bone tissue and / or receiving at least one bone tissue graft and / or at least one substitute:and / orat least one bone-anchoring insert (210) comprising said passage (21) capable of receiving said bone-anchoring device (1).
Owner:LDR MEDICAL SAS
An automatic vertebral body recognition method based on coronal ultrasound images of spine
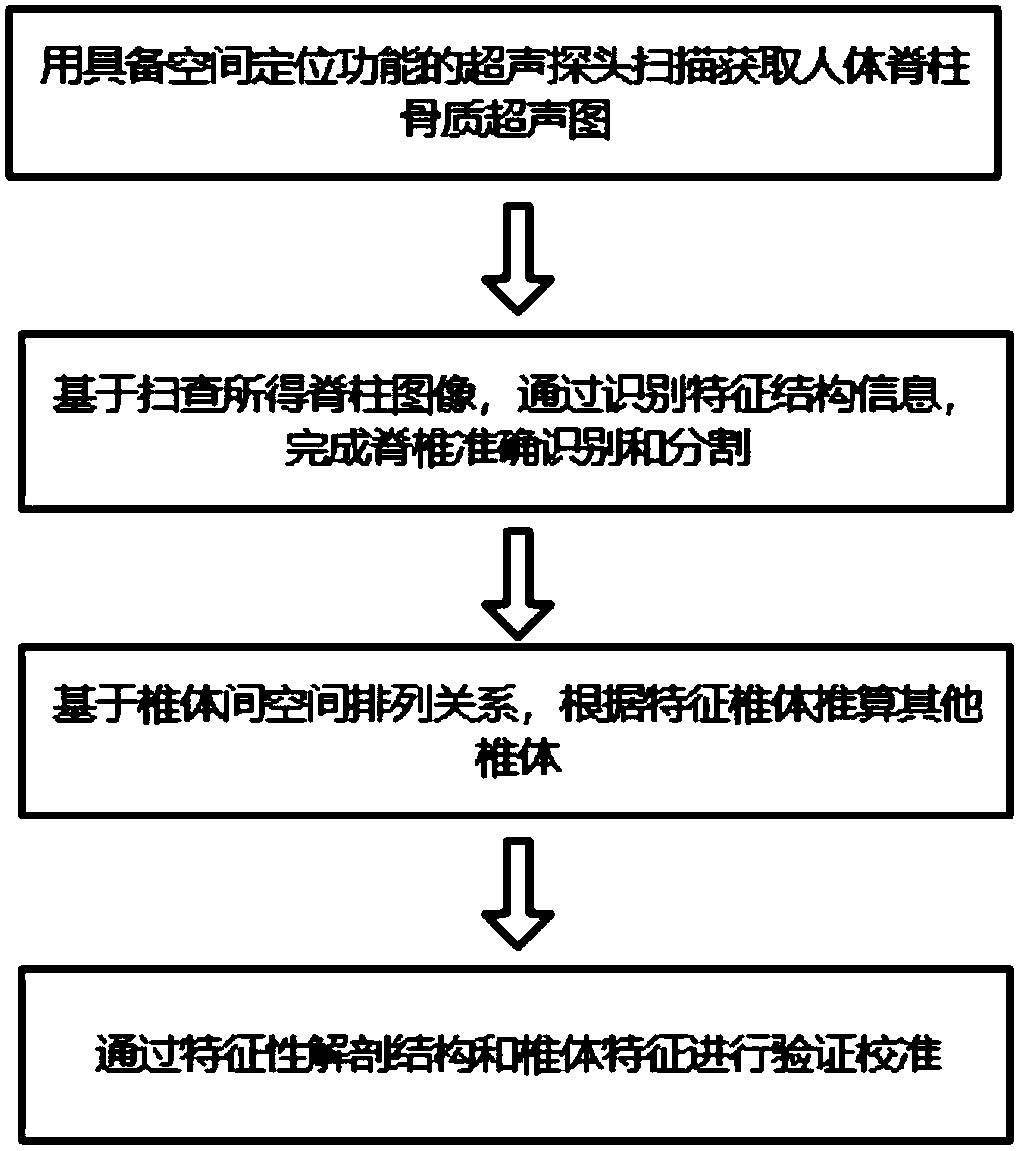
ActiveCN109360213AQuick identificationAvoid slow recognitionImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresSonification
An automatic vertebral recognition method based on ultrasonic coronal plane image of a spine comprises the following steps: 1) segmenting a vertebral body one by one in target spine segment ultrasonicimage by using the ultrasonic image segmentation technology; 2) performing identifying according to the characteristic anatomical structure, the characteristic vertebral body and the characteristic structure of the vertebral body, judging and identifying the characteristic vertebral body according to the characteristic anatomical structure, and calculating other vertebral body from the characteristic vertebral body; 3) performing verifying and calibrating by characteristic anatomy and vertebral body characteristics. The invention gives consideration to the accurate and efficient identification of ultrasonic bone image features, By using the original ultrasonic image segmentation method of spine, the characteristic anatomical structure of different vertebral segments of the spine is recognized, and the characteristic vertebral body is judged by the characteristic vertebral body. Then the other vertebral bodies are deduced from the count of the characteristic vertebral body according tothe long axis direction of the spine, until the target operative segment. Finally, the characteristic anatomical structure and the characteristic vertebral body are deduced by the bidirectional count, and the identification verification and calibration are completed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
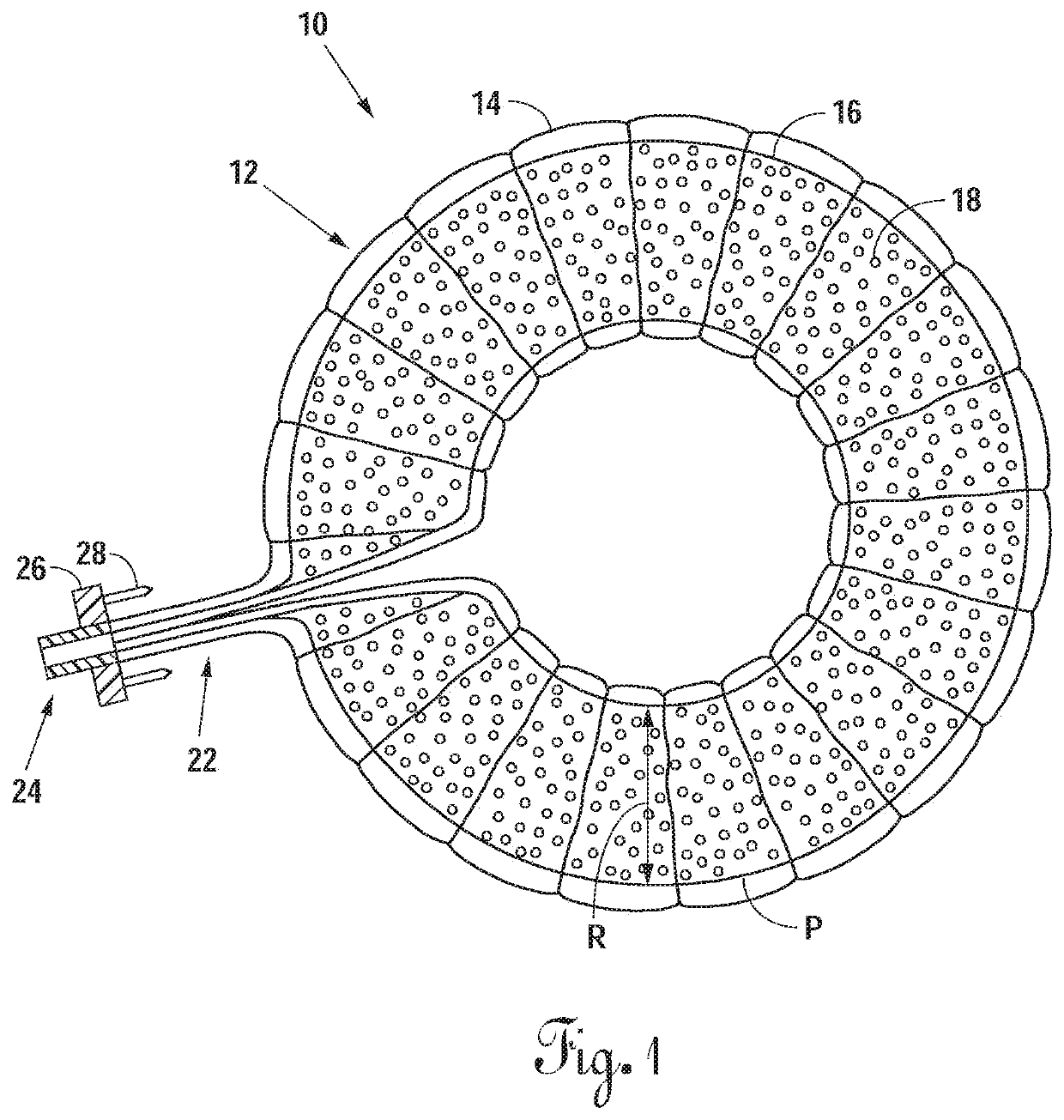
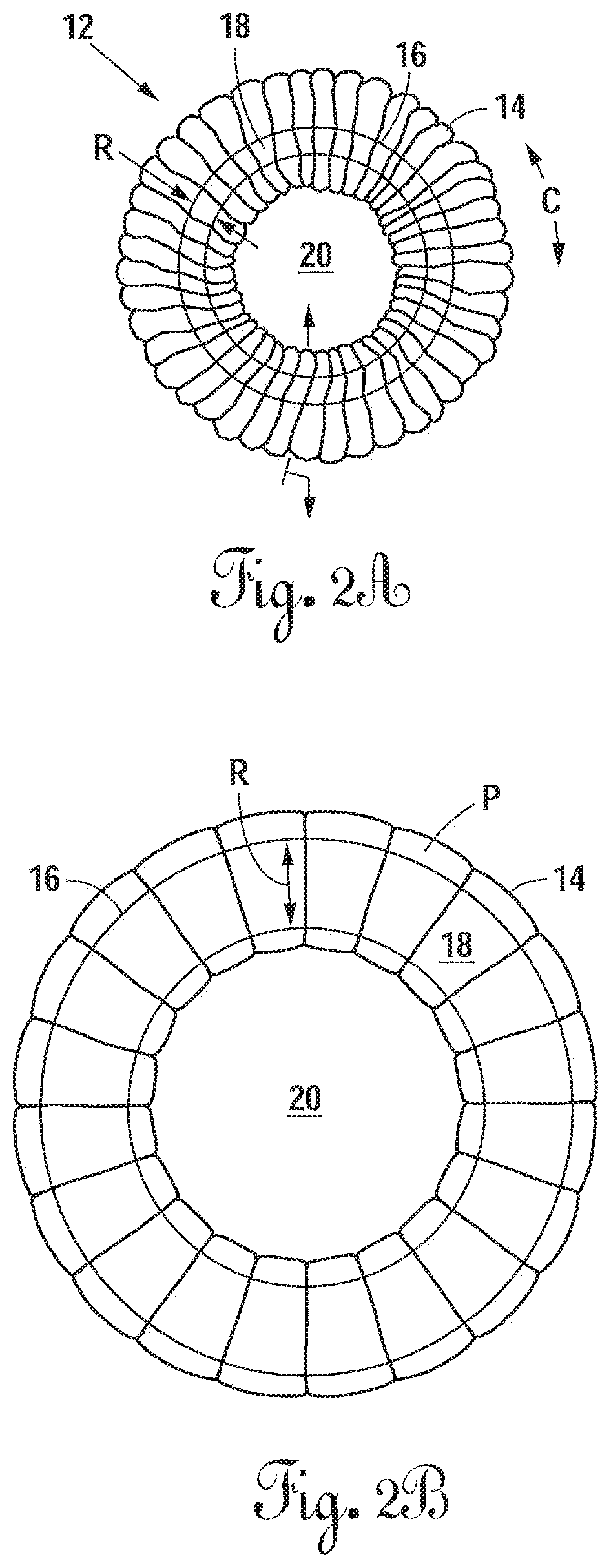
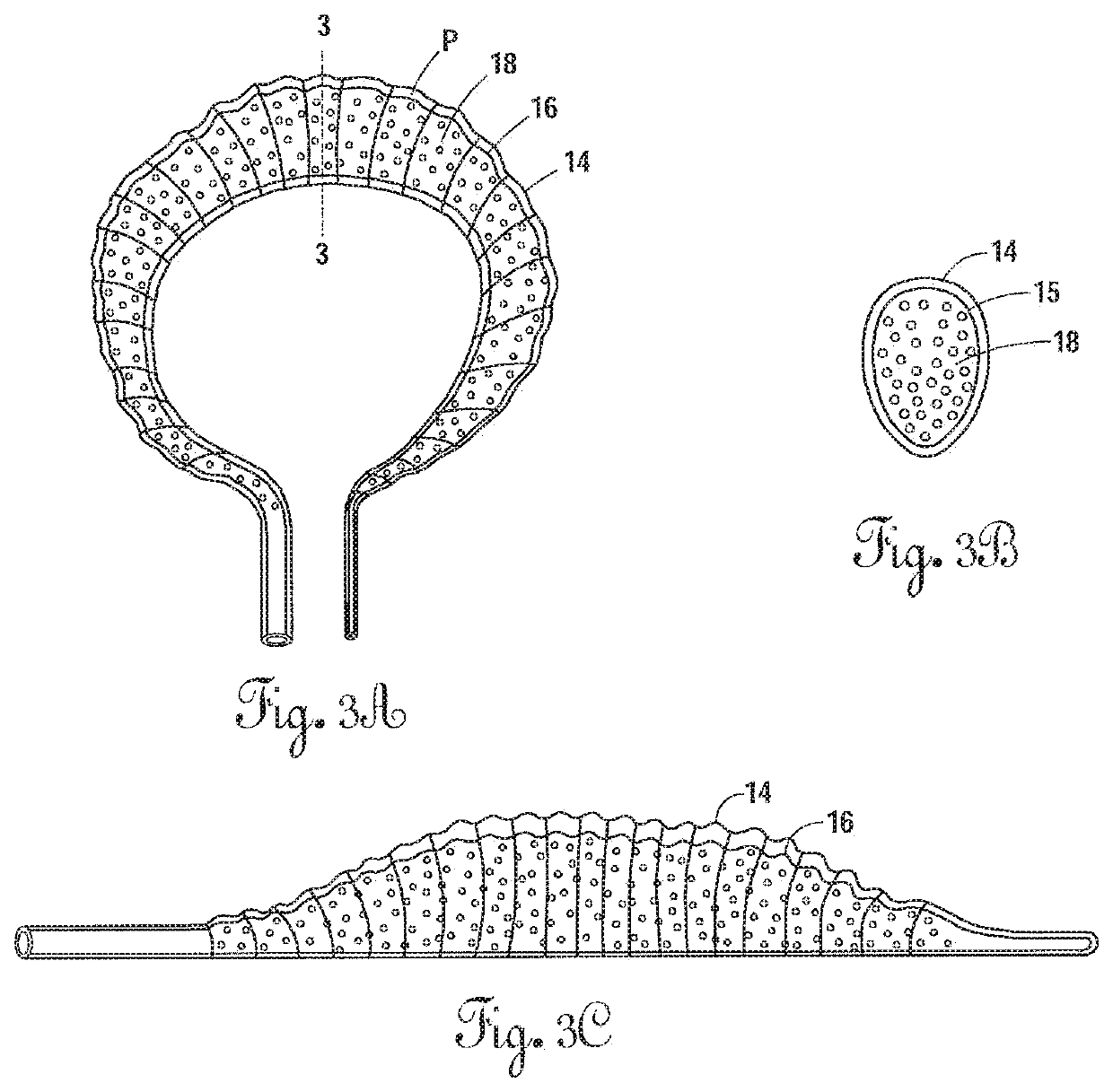
Radially expandable annulus reinforcement prosthesis
ActiveUS10881522B2Restore disc heightImprove mobilityJoint implantsSpinal implantsSurgical operationElastomer
An intervertebral implantation system for restoring disc height and vertebral alignment, while allowing dynamic mobility and stabilization of the vertebral segment, and minimally invasive methods of implanting the same. The implantation system includes an annular reinforcement implant, including an elastomeric balloon inserted into the hollow or interior of a tubular sleeve, and secured only at a first and second neck portions to a securement element coupled to an attachment fixture, forming an annular structure attached to the outer margin of the annulus fibrosus. When the prosthetic implant is in a contracted state the tubular sleeve is redundant and undulated, forming folds, gathered loosely around the circumference of the inner balloon. Upon pressurized inflation with in-situ curable polymer, the elastomeric balloon elongates and expands circumferentially, and the tubular sleeve stretches and unfolds, constraining further expansion and elongation of the elastomeric balloon. The attachment fixture is configured to provide secure attachment to the outer margin of the annulus fibrosus. A temporary, high pressure vertebral distraction balloon is utilized to aid in vertebral distraction during a surgical procedure to implant the annular reinforcement implant.
Owner:SPICA MEDICAL TECH LLC
Vertebral implant, vertebral fastening device of the implant and implant instrumentation
ActiveUS9937050B2Easy to implant and fix reliablyReliable and easy-to-use fasteningJoint implantsSpinal implantsVertical axisBiomedical engineering
This disclosure provides vertebral implants, fastening devices for vertebral implants, and implant instrumentation, and various combinations thereof. In some embodiments, the implant comprises a peripheral wall extending according to a vertical axis between upper and lower surfaces of the implant, with each such surface configured to be placed in contact with a vertebral structure, respectively, at the top and the bottom of the vertebral segment replaced by the implant. Some embodiments comprise fastening means, deployment of which anchors the implant in the lower and upper vertebral structures. Some fastening means may be deployed by sliding parallel to the vertical axis of the implant, and may comprise a plate with at least one part remaining in contact with the peripheral wall of the implant when deployed and a pointed end projecting from one of the upper and lower surfaces of the implant to enter a vertebral structures on completion of deployment.
Owner:LDR MEDICAL SAS
Radially Expandable Annulus Reinforcement Prosthesis
ActiveUS20180221163A1Restore disc heightImprove mobilityJoint implantsSpinal implantsDistractionProsthesis
An intervertebral implantation system for restoring disc height and vertebral alignment, while allowing dynamic mobility and stabilization of the vertebral segment, and minimally invasive methods of implanting the same. The implantation system includes an annular reinforcement implant, including an elastomeric balloon inserted into the hollow or interior of a tubular sleeve, and secured only at a first and second neck portions to a securement element coupled to an attachment fixture, forming an annular structure attached to the outer margin of the annulus fibrosus. When the prosthetic implant is in a contracted state the tubular sleeve is redundant and undulated, forming folds, gathered loosely around the circumference of the inner balloon. Upon pressurized inflation with in-situ curable polymer, the elastomeric balloon elongates and expands circumferentially, and the tubular sleeve stretches and unfolds, constraining further expansion and elongation of the elastomeric balloon. The attachment fixture is configured to provide secure attachment to the outer margin of the annulus fibrosus. A temporary, high pressure vertebral distraction balloon is utilized to aid in vertebral distraction during a surgical procedure to implant the annular reinforcement implant.
Owner:SPICA MEDICAL TECH LLC
Posterior functionally dynamic stabilization system
A functionally dynamic stabilization unit (10) and system for treatment of spinal instability are provided. Each unit, and collectively, the system, is configured to control flexion, extension and translation of the affected unstable vertebral area, thereby stabilizing the vertebral segments by restoring normal function. This is achieved by providing a unit and system that allow for lateral bending, axial compression, rotation, anterior segmental height adjustment, and posterior segmental height adjustment. The unit and system provide sufficient segmental stiffness, while also limiting, or controlling, the range of motion (i.e., sufficient stiffness in the neutral or active zone, while limiting or preventing motion outside of the active zone) to stabilize the vertebral segments. In use, the system mimics the natural movement of the normal spine. Furthermore, the system includes a rigid, fusion-promoting coupler (20) configured for use in an adjacent level, or as a substitute for the functionally dynamic unit. The modularity of the system allows adjustment over time and easier revision surgery, and is configured for minimally-invasive, delivery or implantation.
Owner:PARADIGM SPINE LLC
Animal spinal fixator
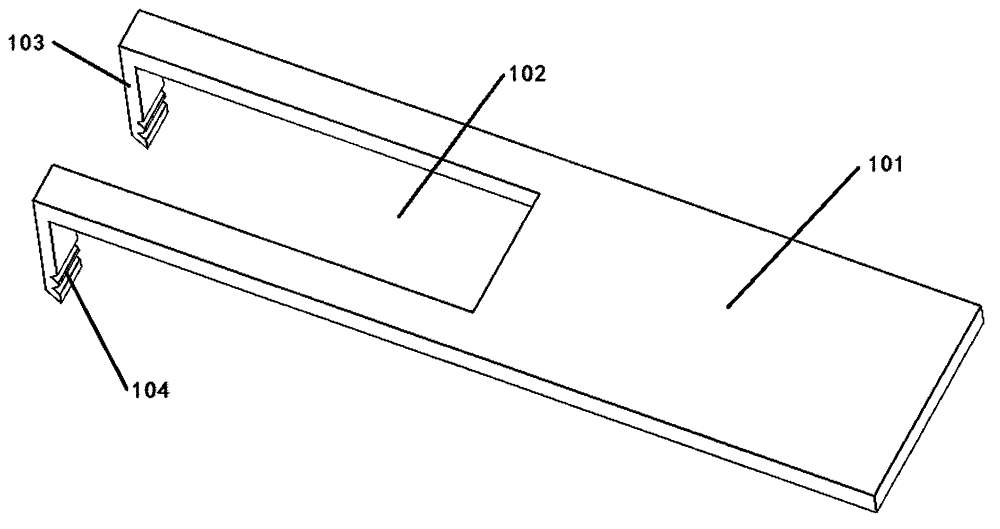
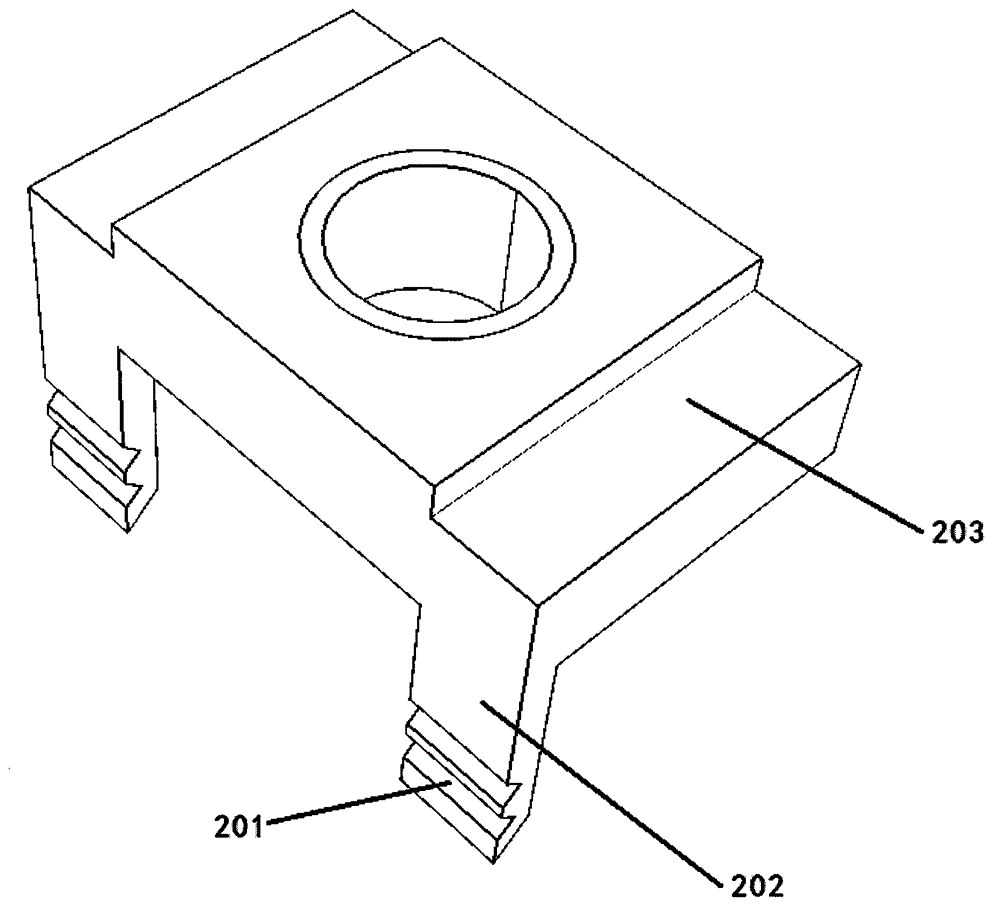
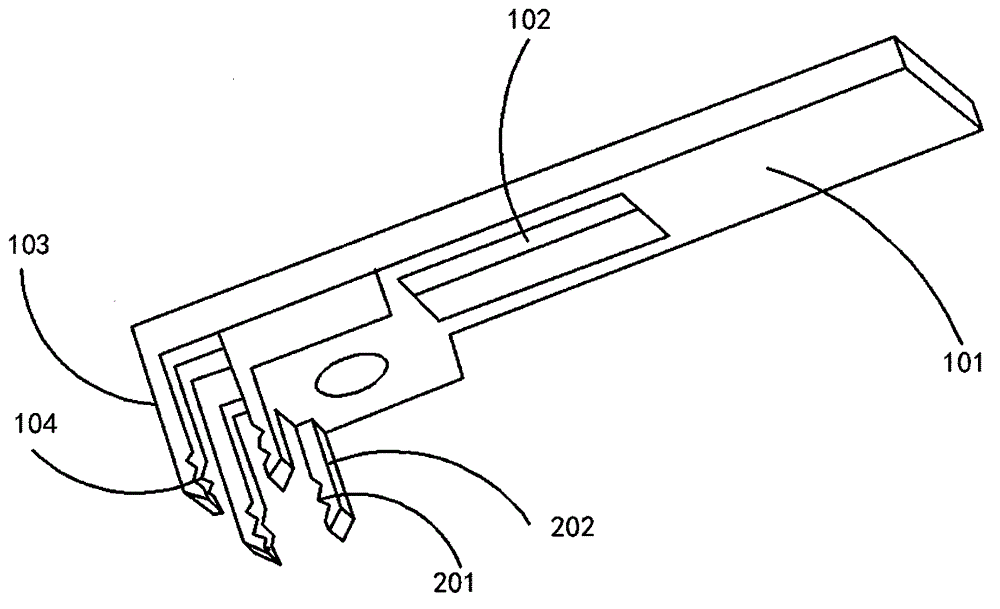
The invention relates to the field of fixators, in particular to an animal spinal fixator, comprising a first fixture, a second fixture and holding space. The first fixture is provided with a U-shaped channel; the front ends of the two sides of the U-shaped channel are bent, forming two first insert teeth; the second fixture fits the U-shaped channel and can slide in the same; the second fixture is provided with second insert teeth matching with the first insert teeth; the holding space fits the two first insert teeth and is communicated with clamping parts of the first and second fixtures. The animal spinal fixator allows an animal to be fixed and inspected after the animal wakens up; the animal can be fixed effectively; a ganglion and a spinal cord segment of a vertebral segment can be observed at the same time; in the research on spinal cord axon, the animal spinal fixator allows the spinal cord axon on the back of the animal to be observed.
Owner:张金辉 +4
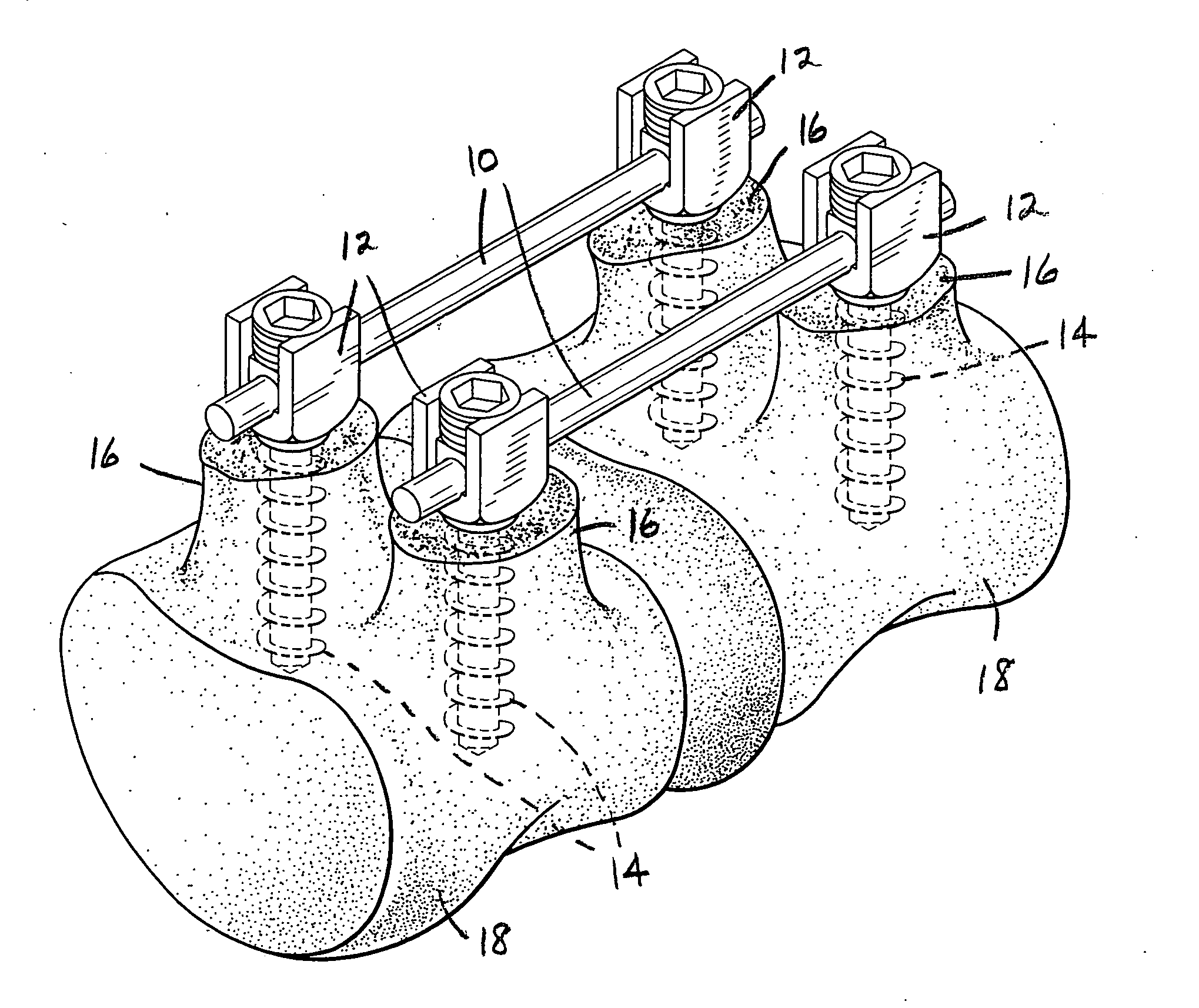
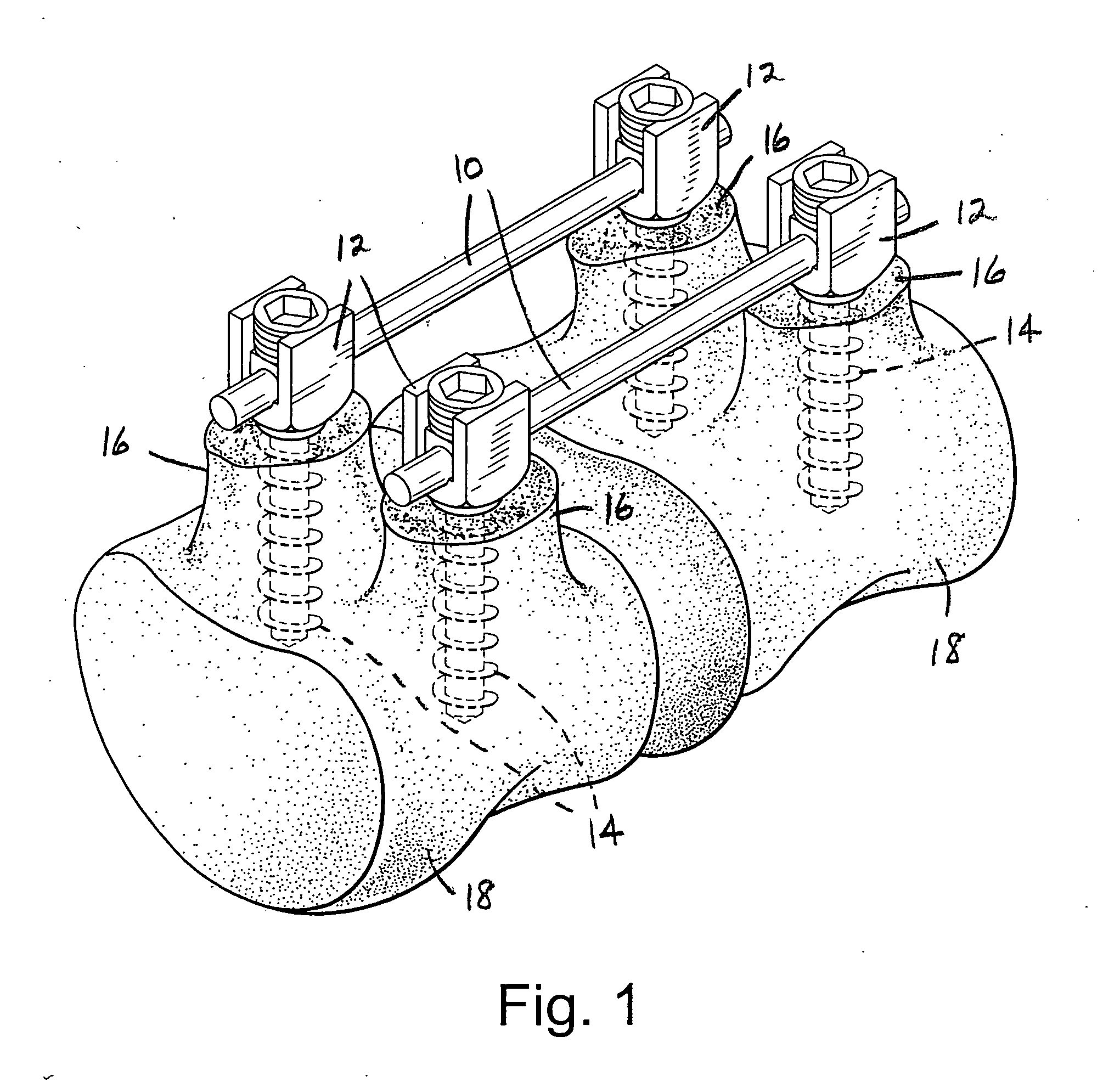
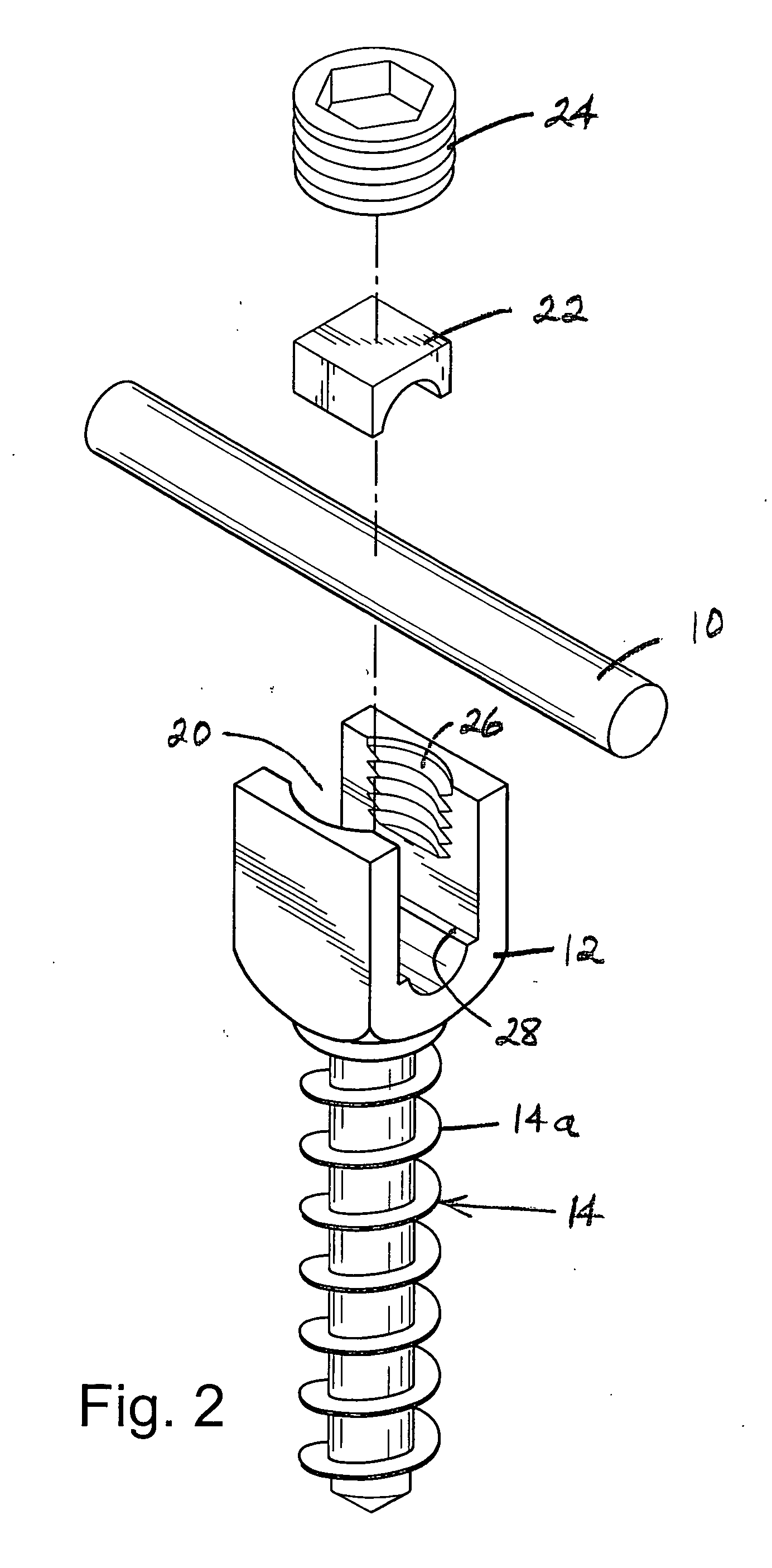
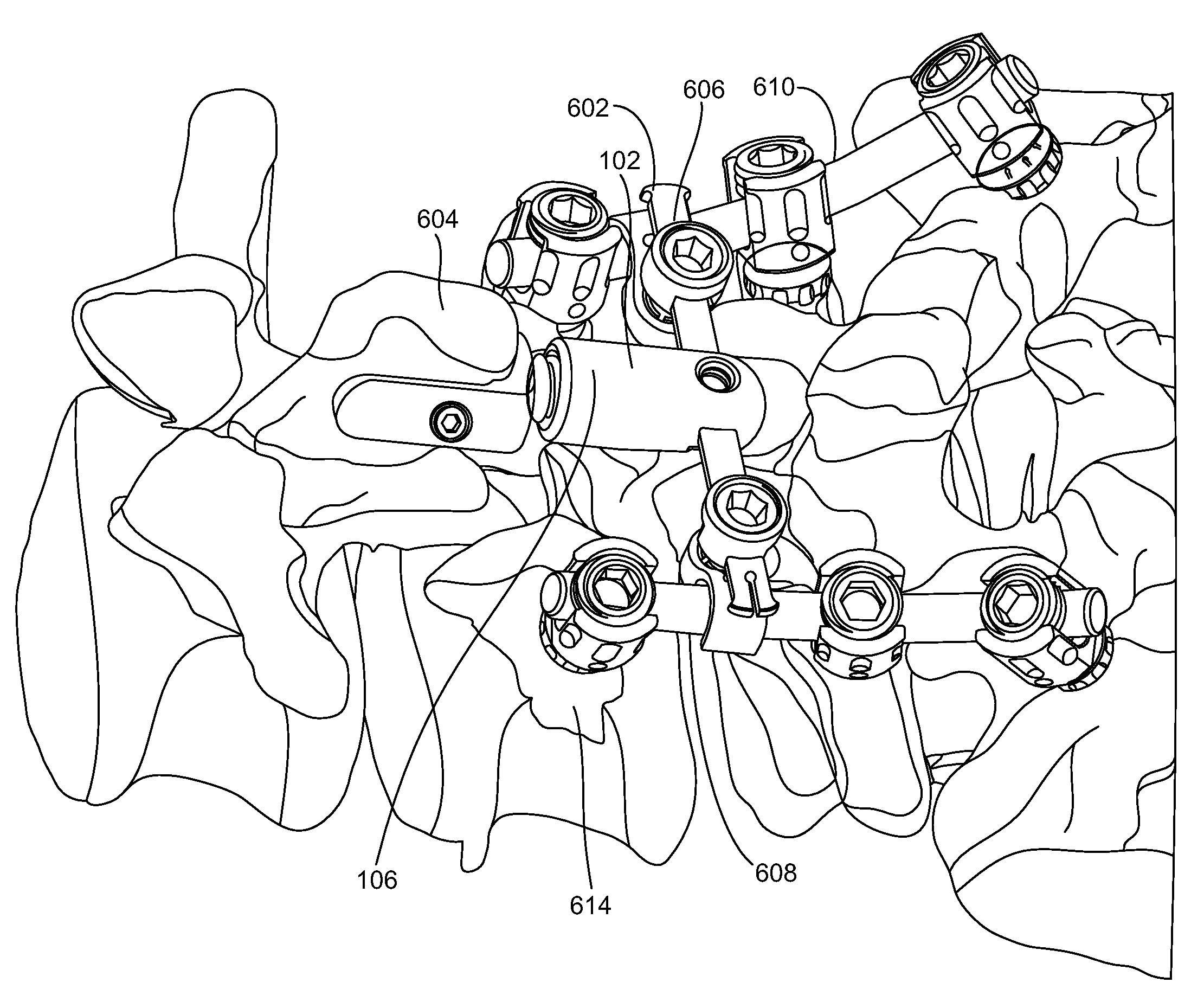
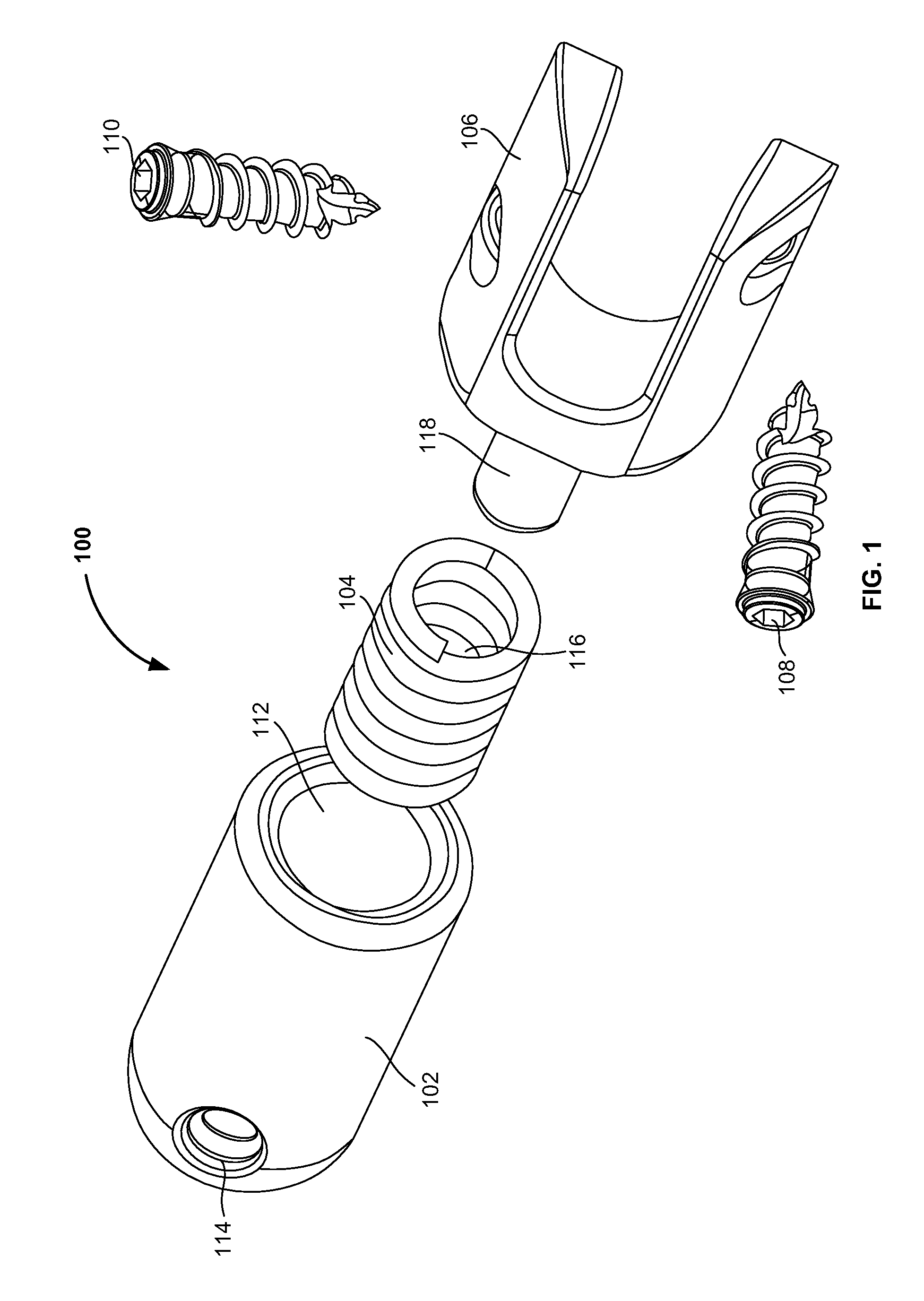
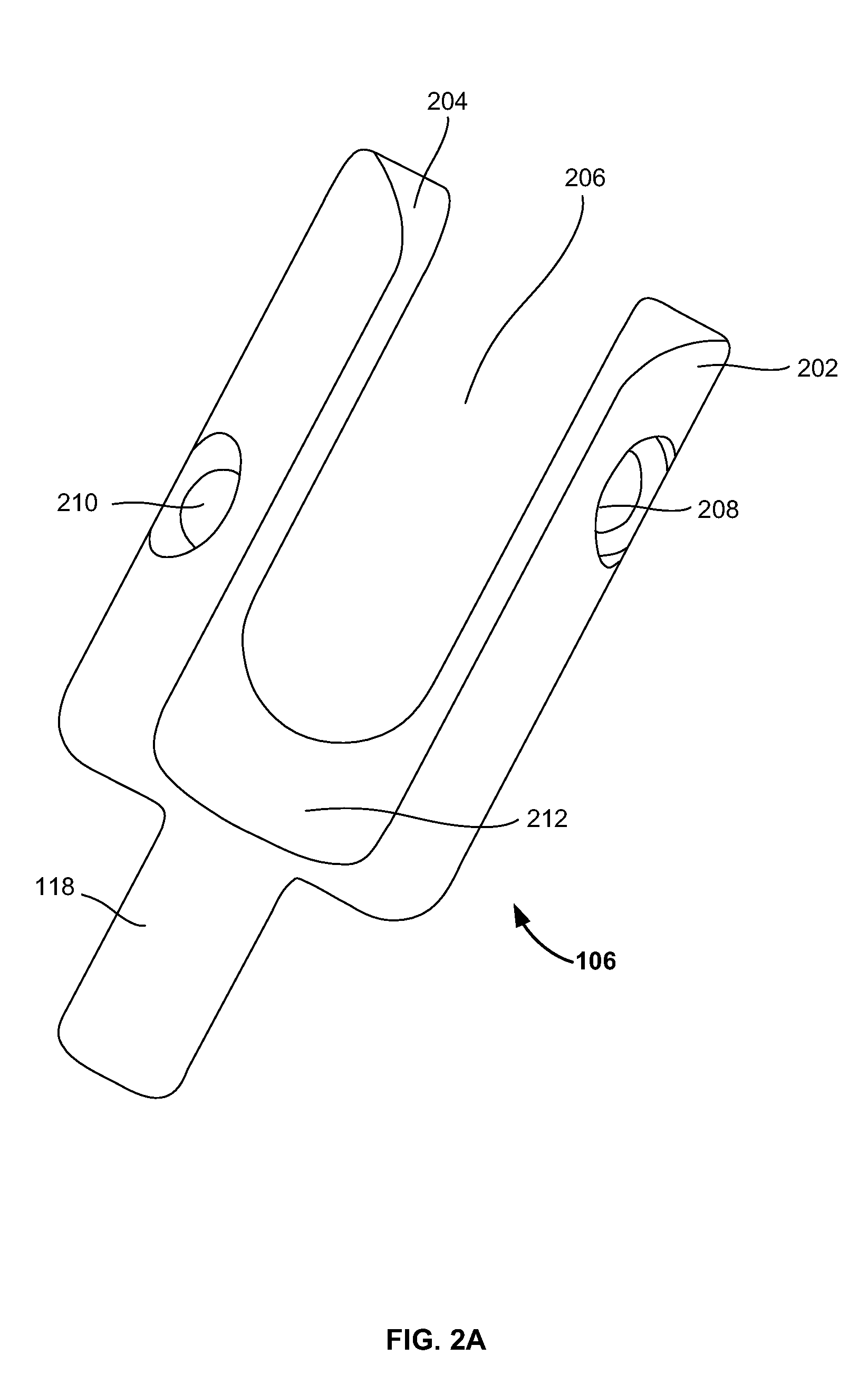
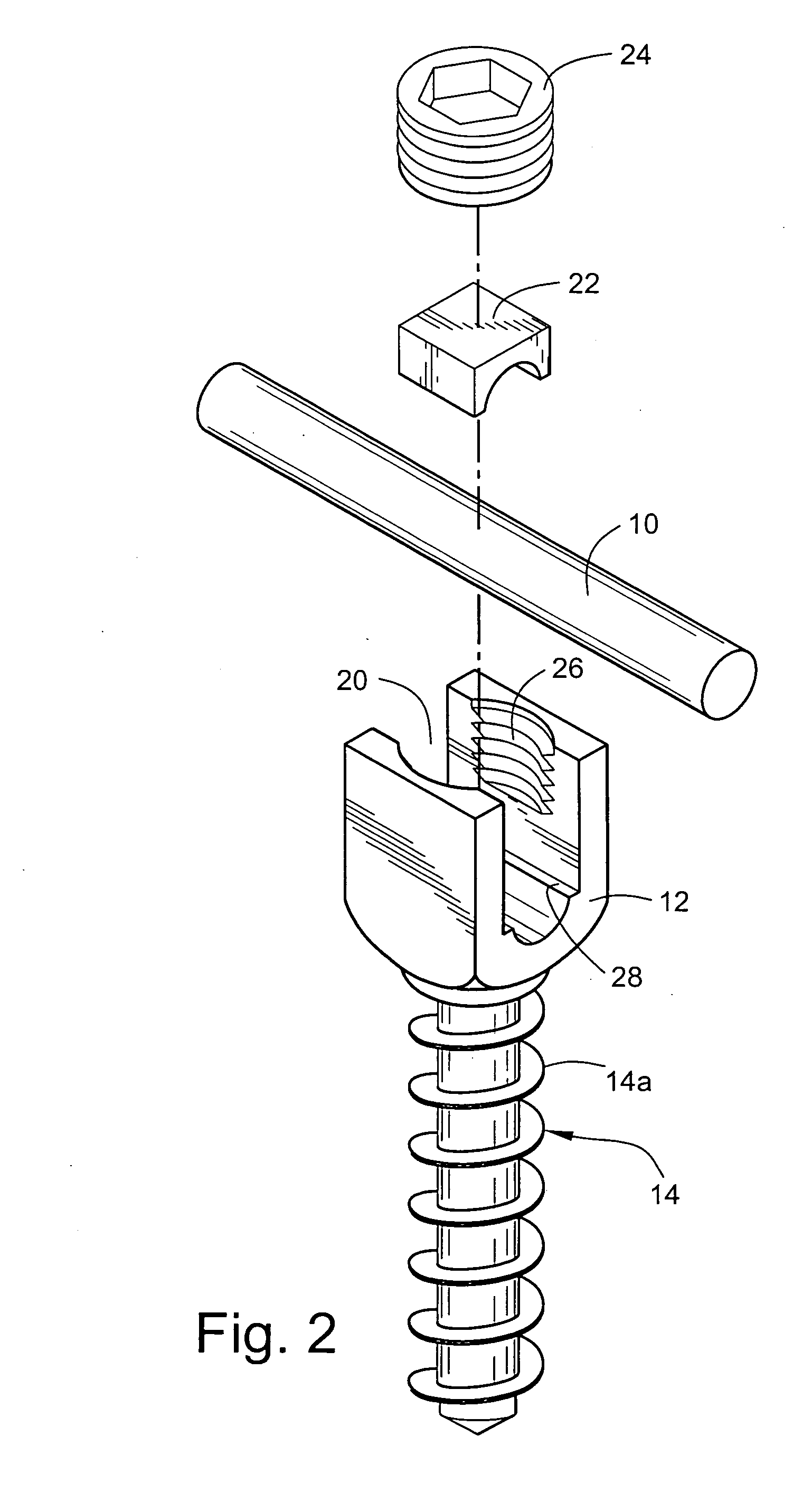
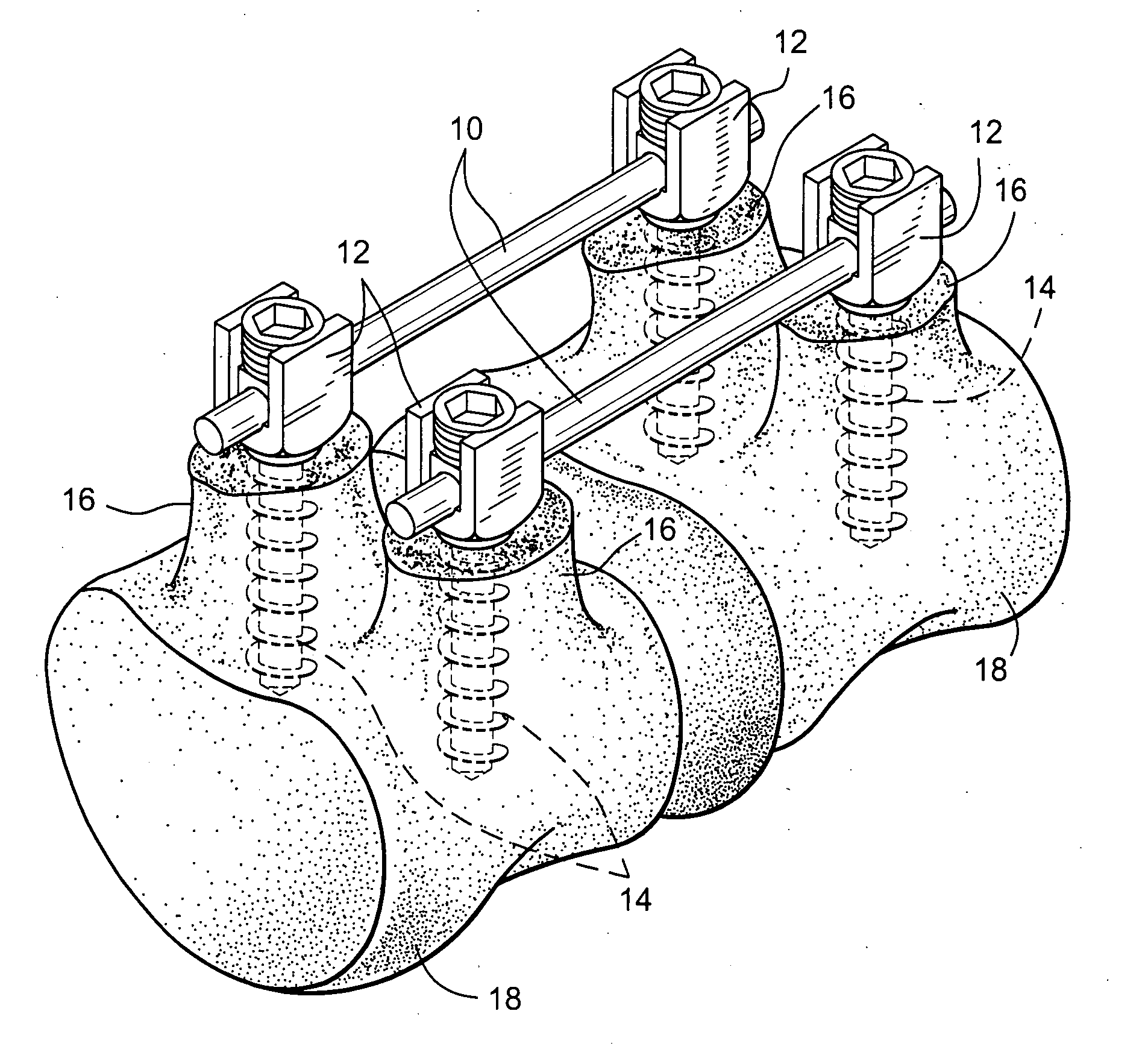
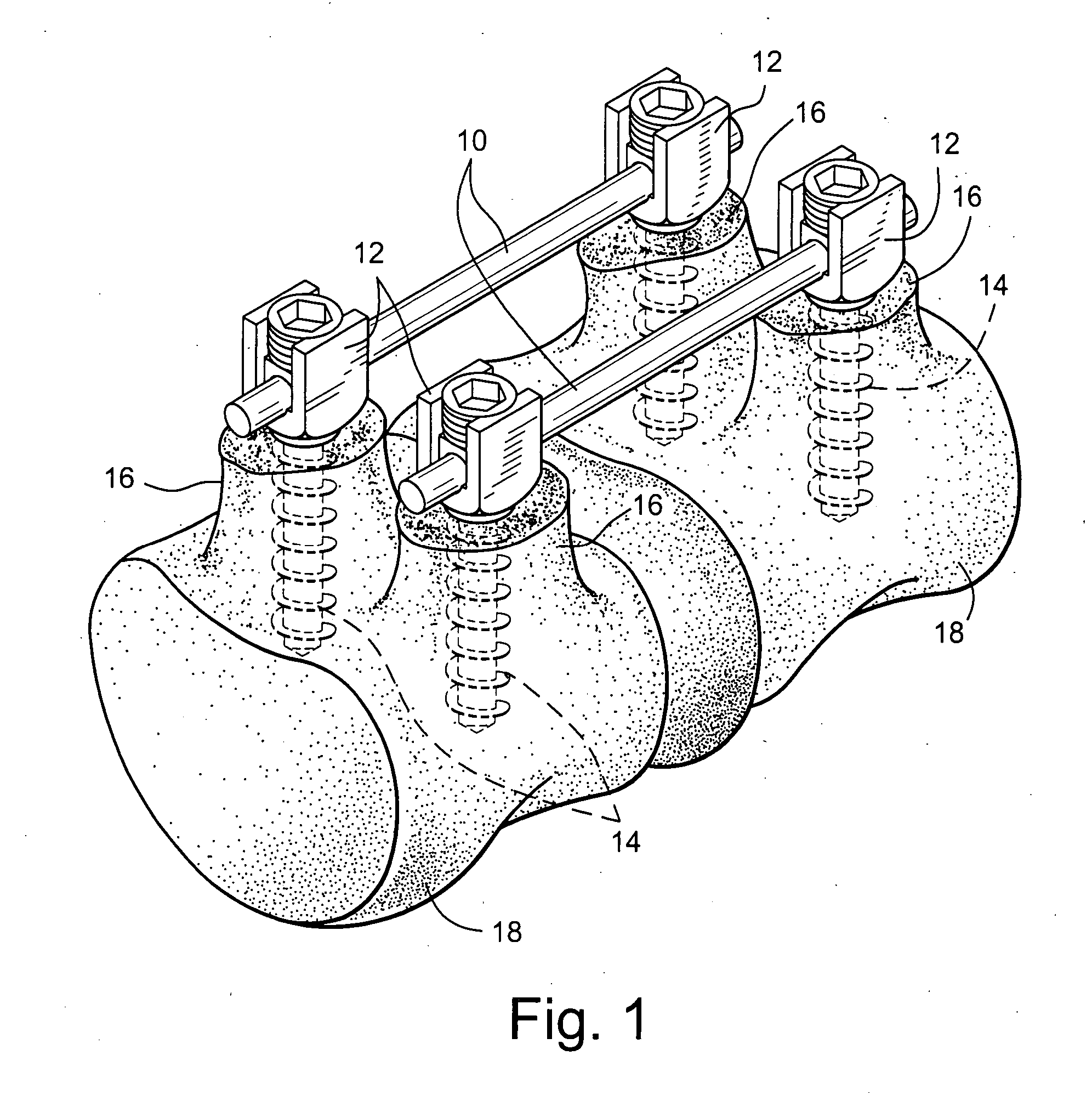
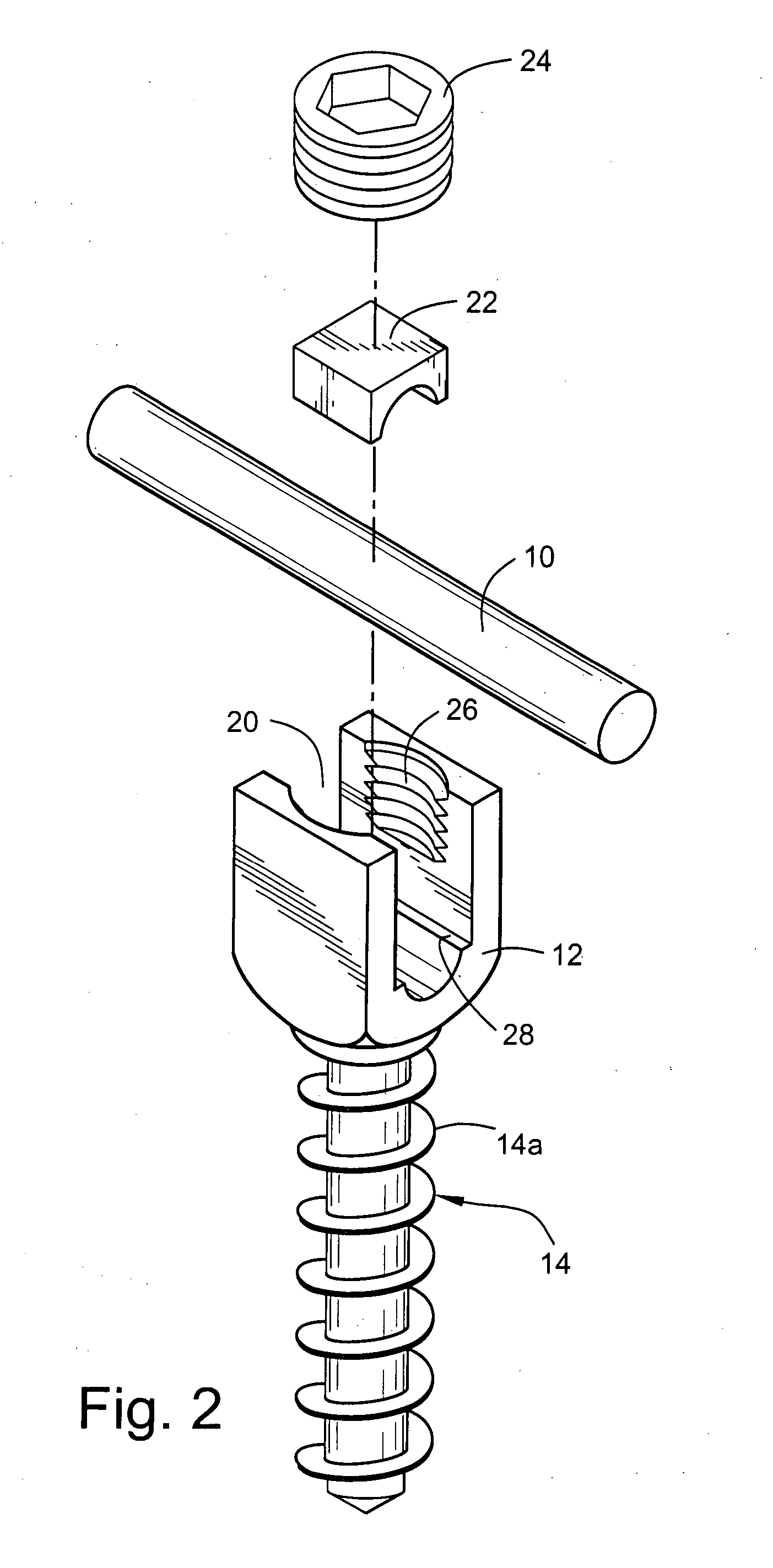
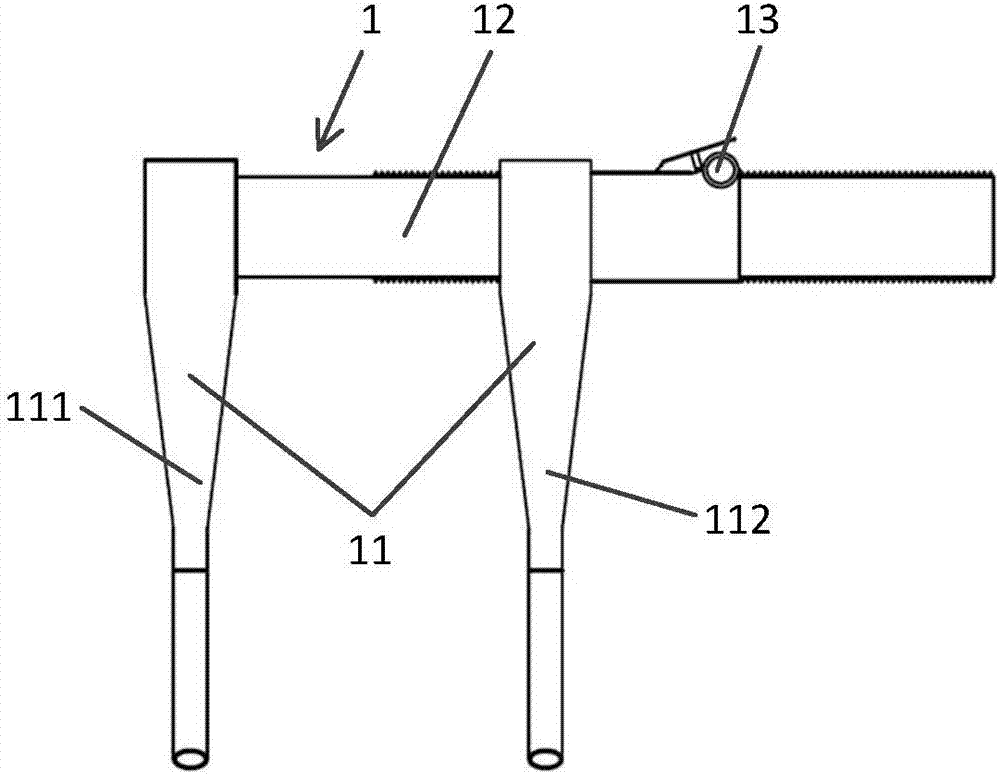
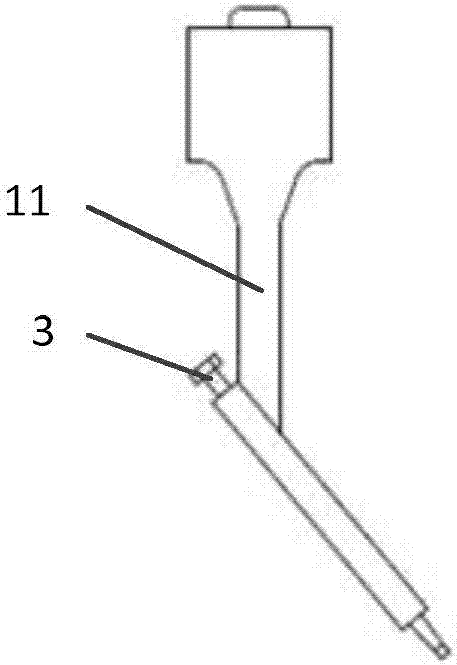
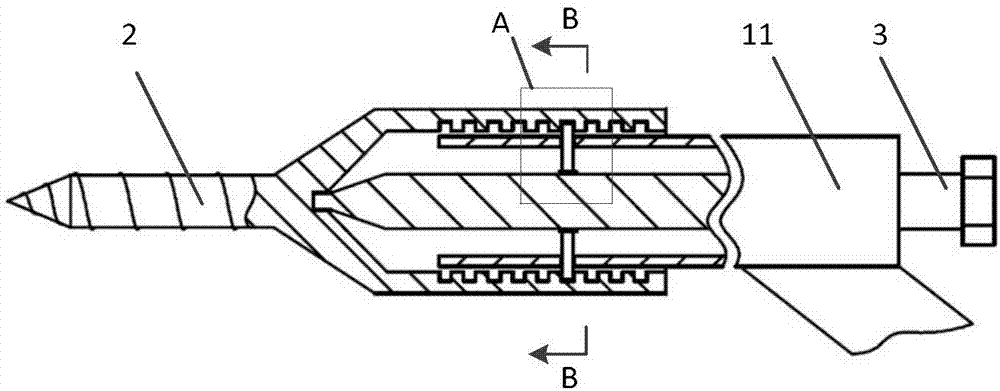
Vertebral segment distractor
The invention provides a vertebral segment distractor, which comprises distracting screws and a locating device, wherein the locating device comprises a plurality of supporting rods; a distance between the supporting rods is adjustable; the plurality of distracting screws correspond to the plurality of supporting rods one by one; and the distracting screws can be connected to the supporting rods in an embedded mode. According to the vertebral segment distractor provided by the invention, with the adoption of a structure that the tails of the screws are perforated and the supporting rods, which are matched with the screws, are inserted into the screws, peripheral nervous tissues are protected from getting hurt in the case that the supporting rods, which are relatively large in cross section, are inserted into a human body once again after the screws are rightly placed in a surgical process.
Owner:SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV
Vertebral body reduction instrument and methods related thereto
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com