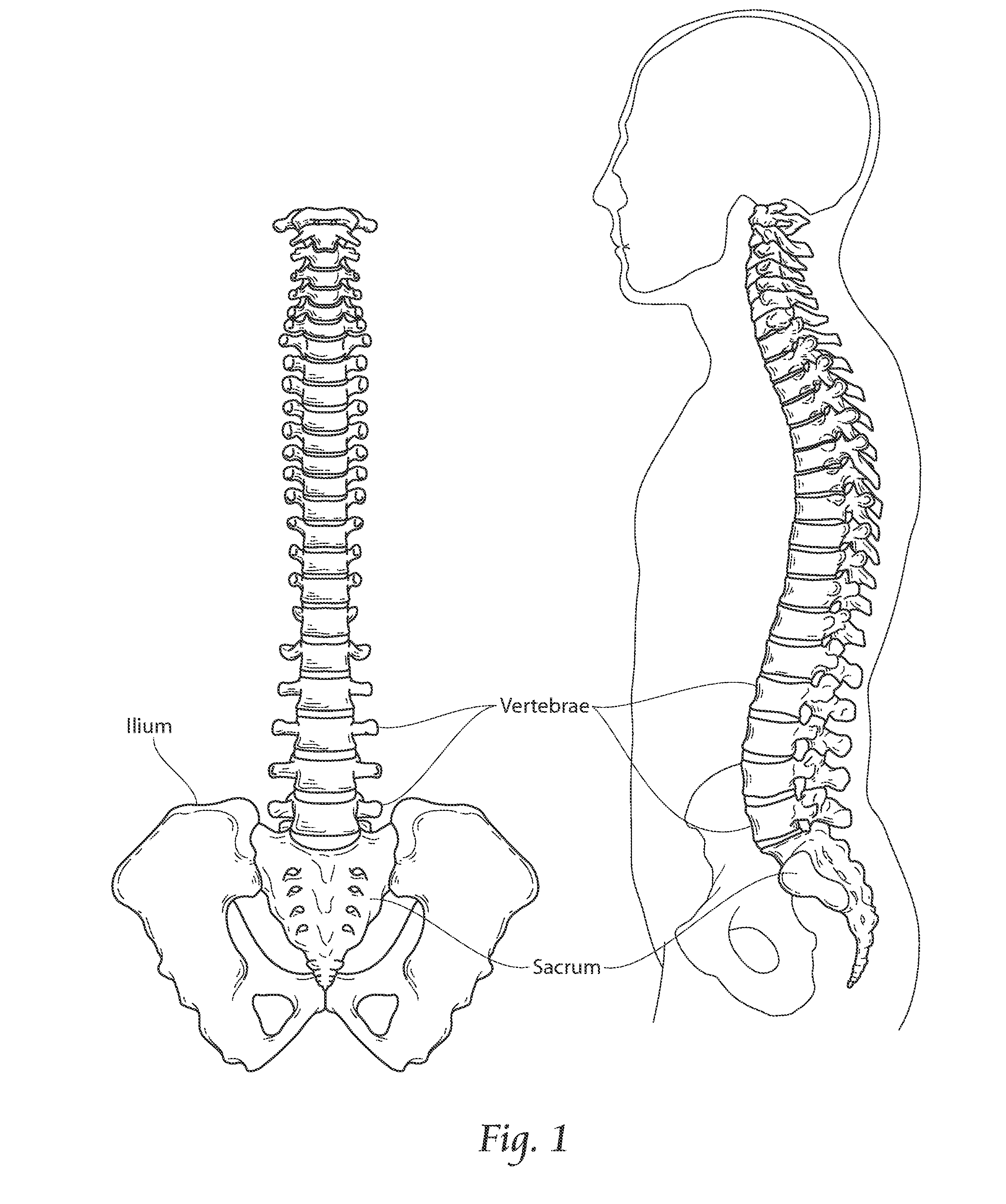
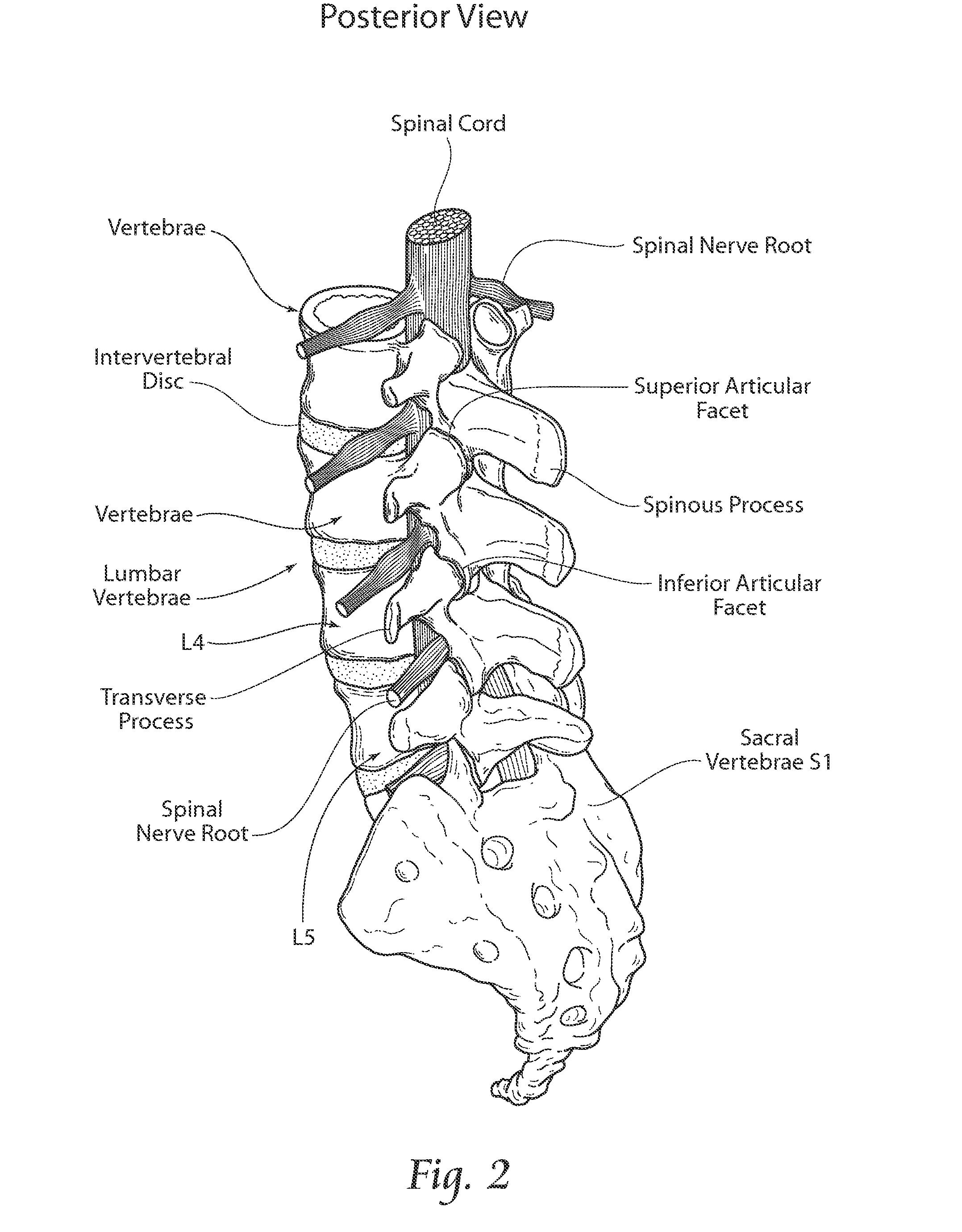
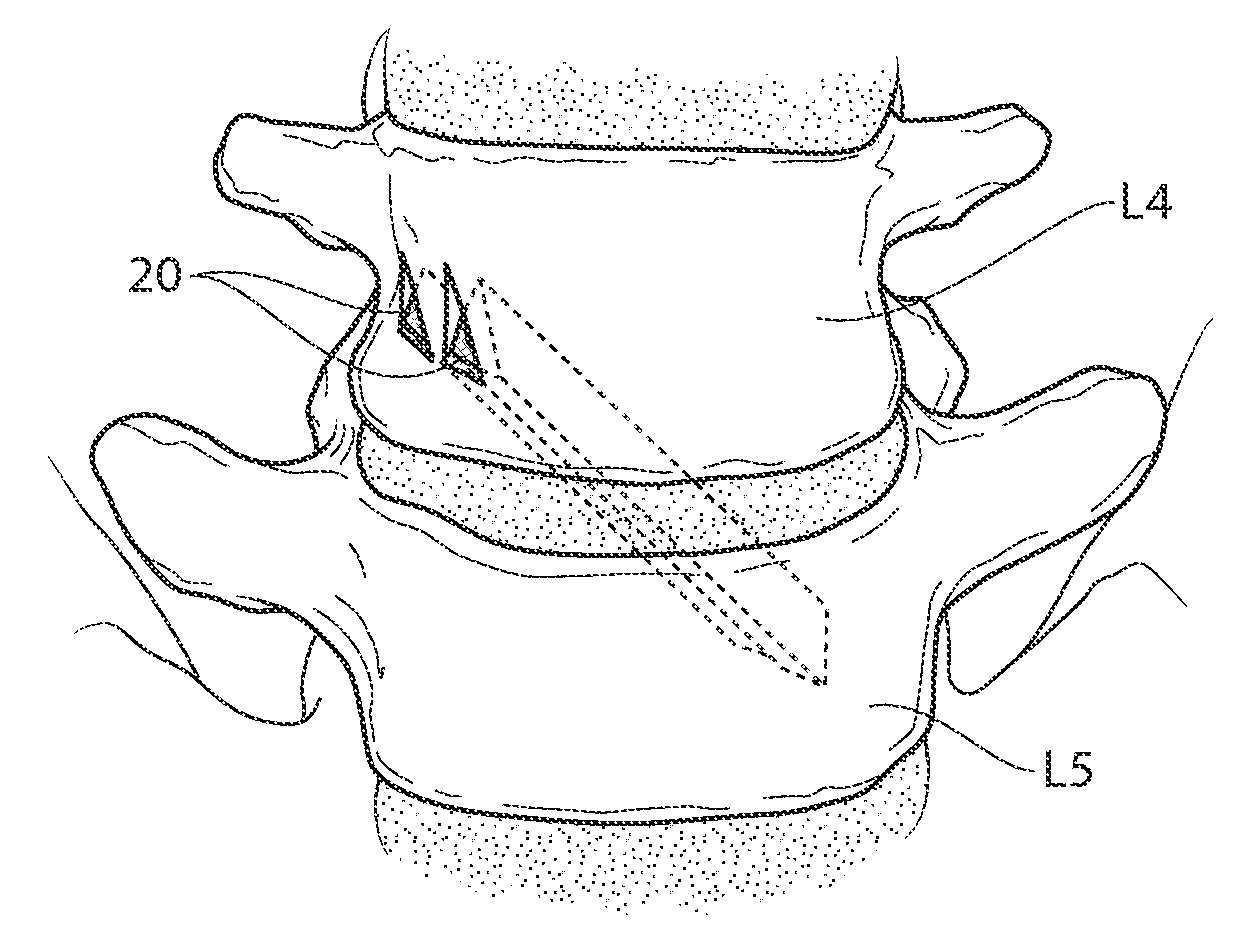
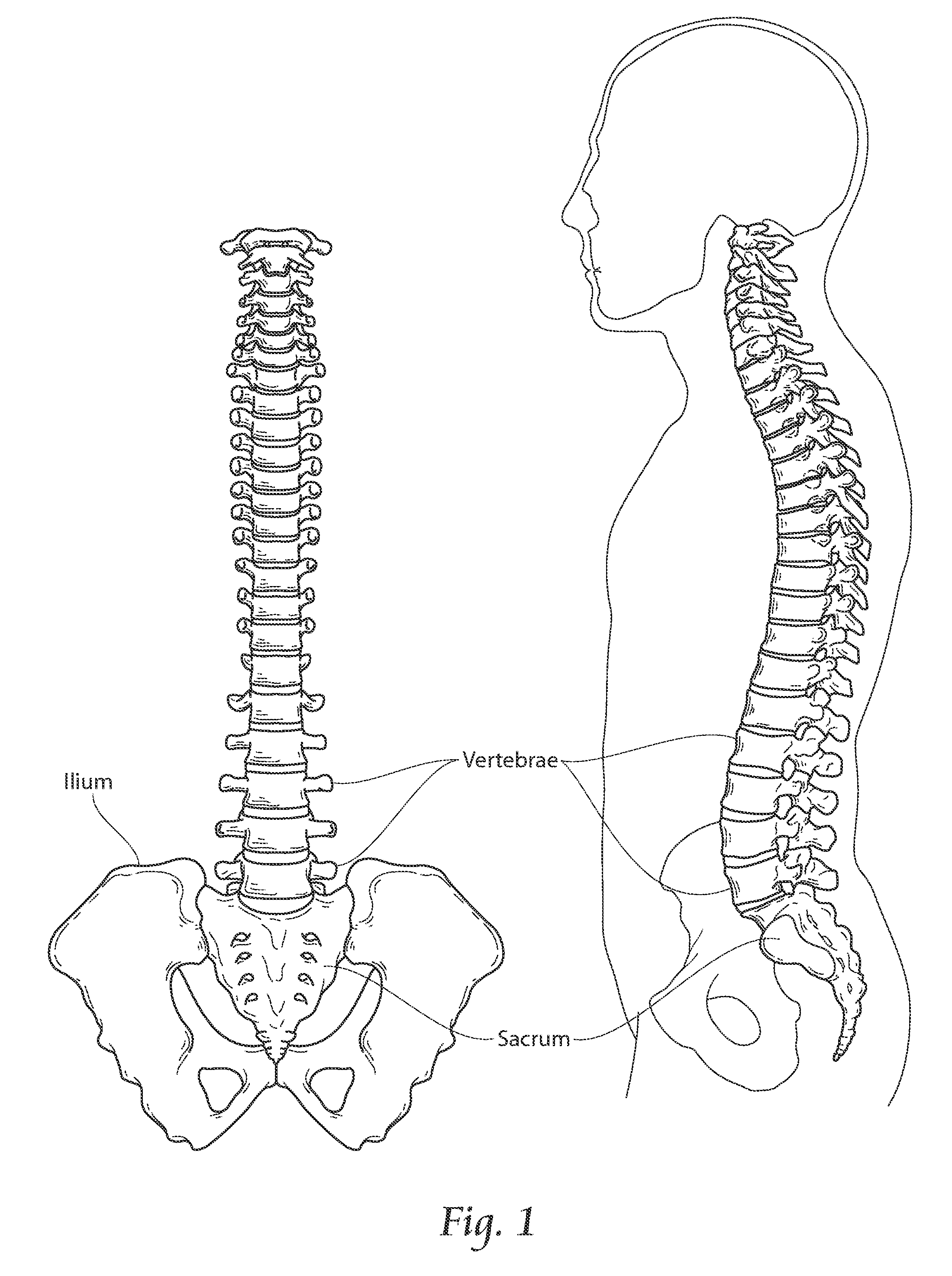
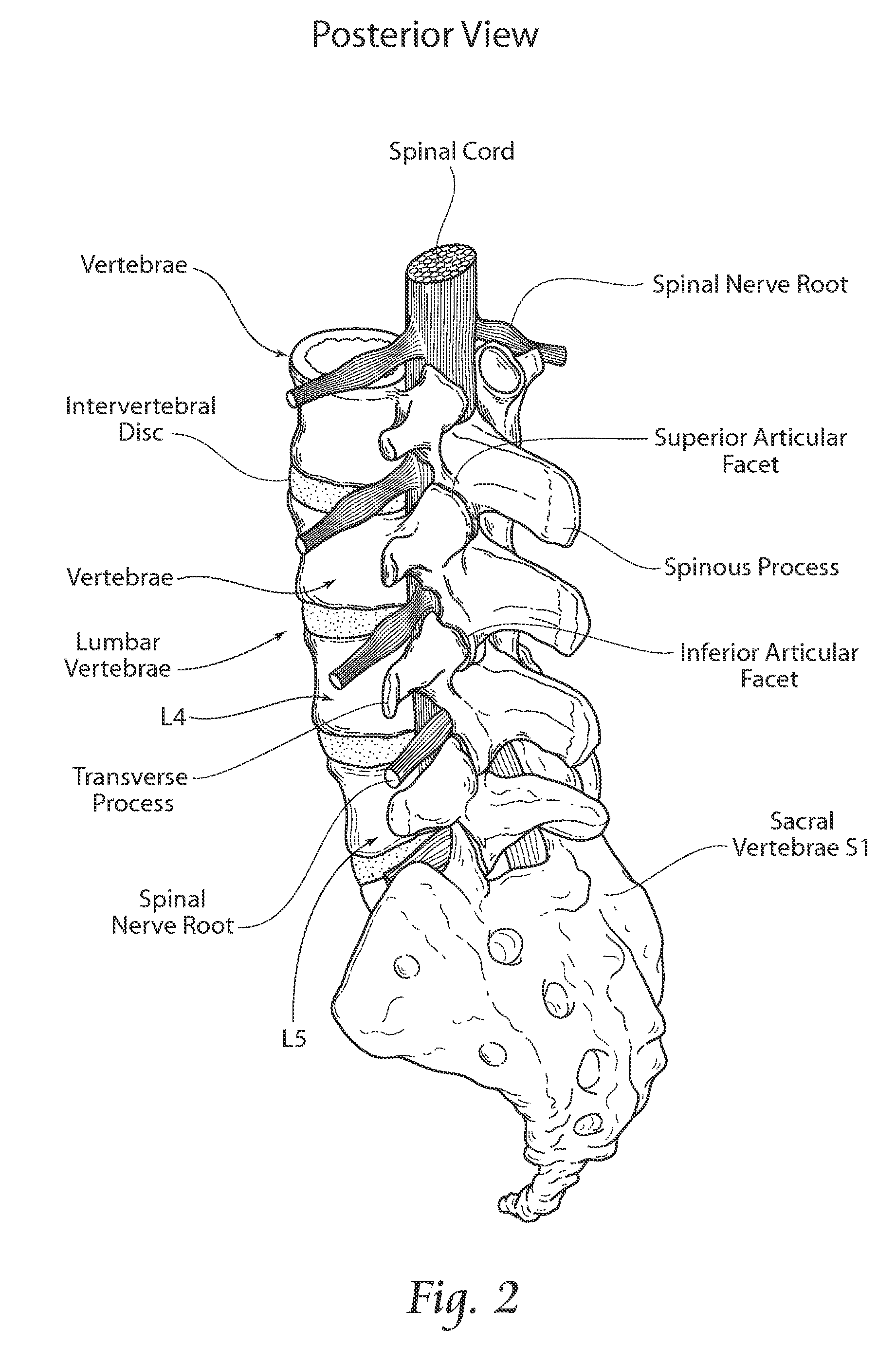
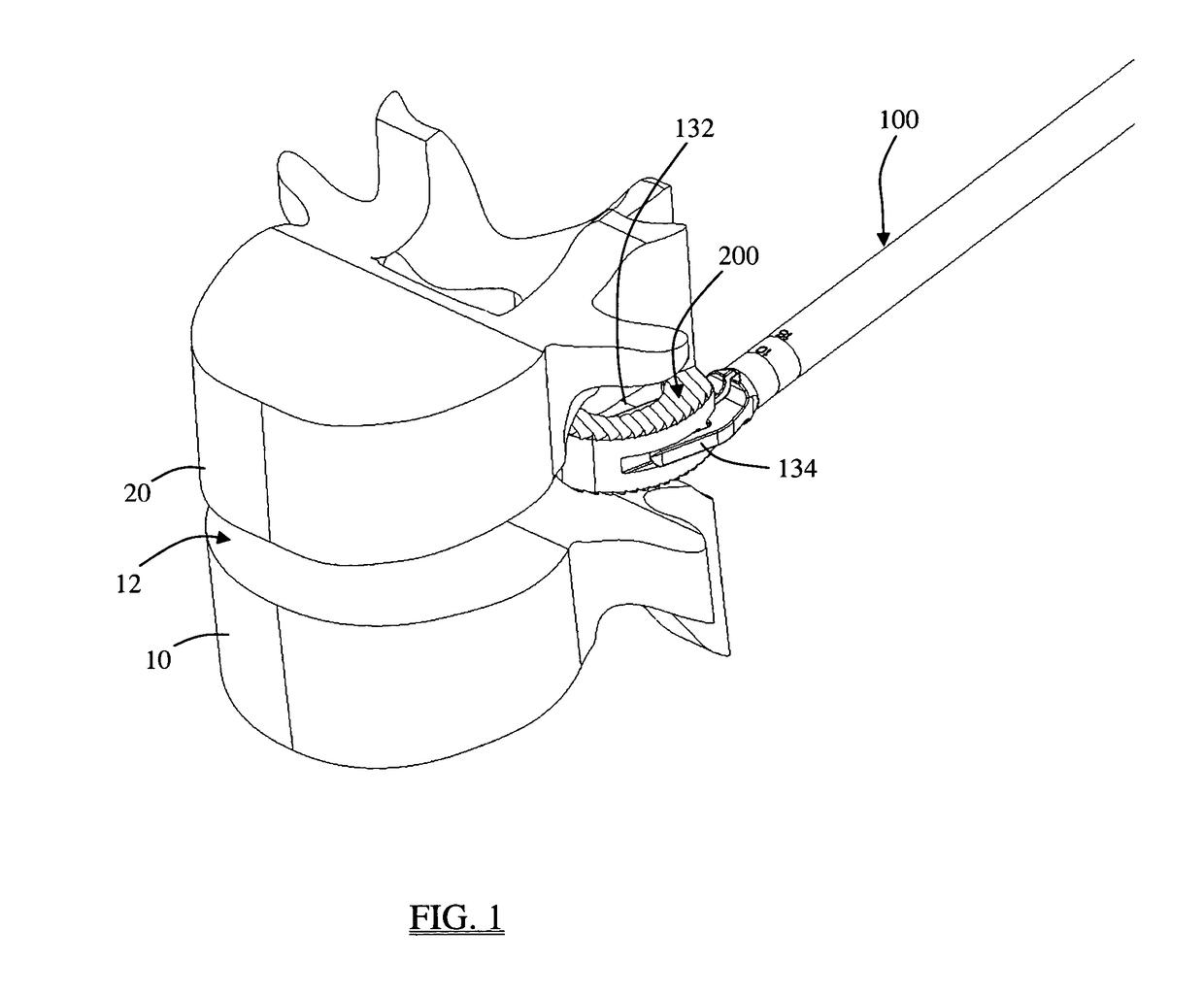
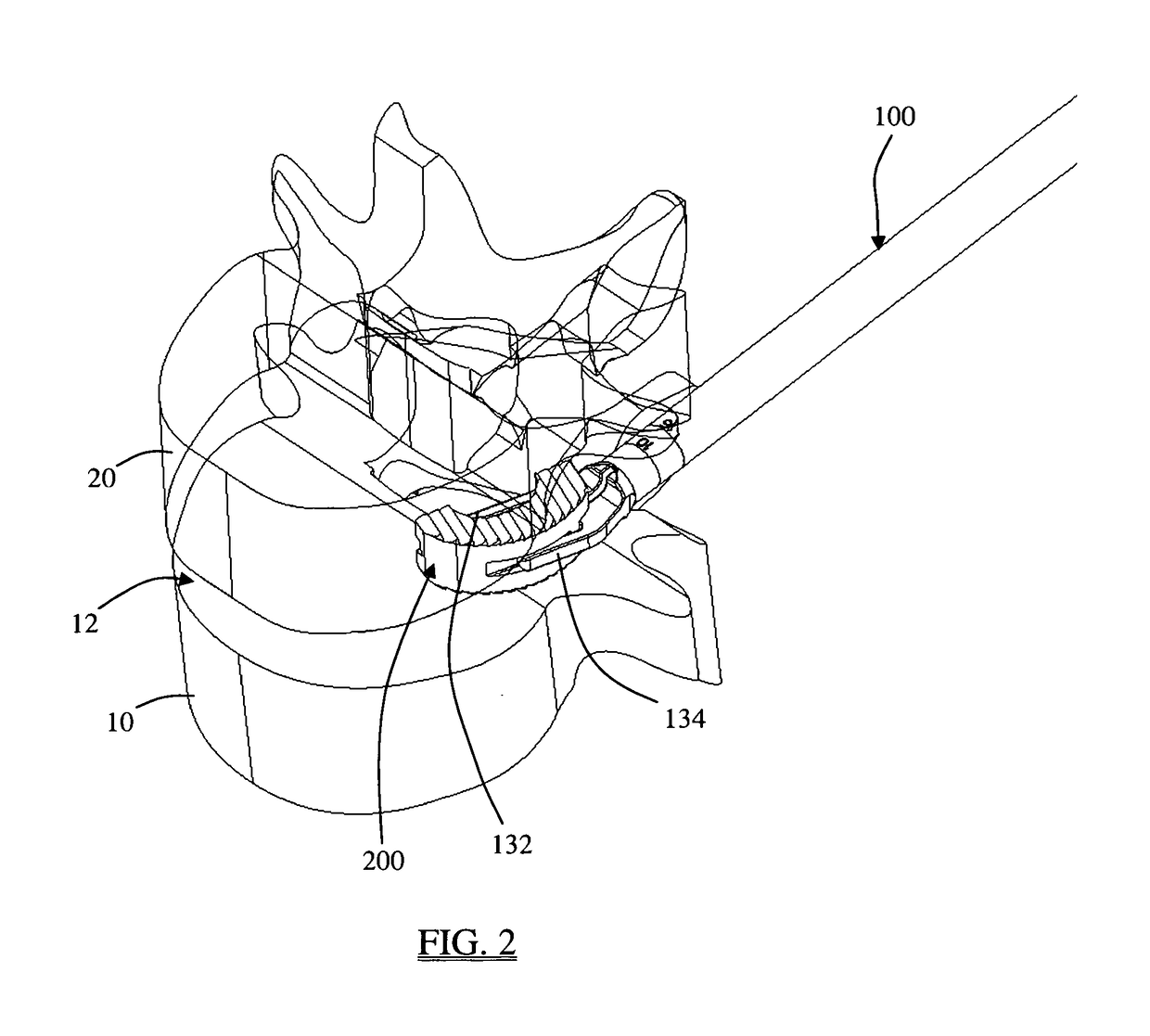
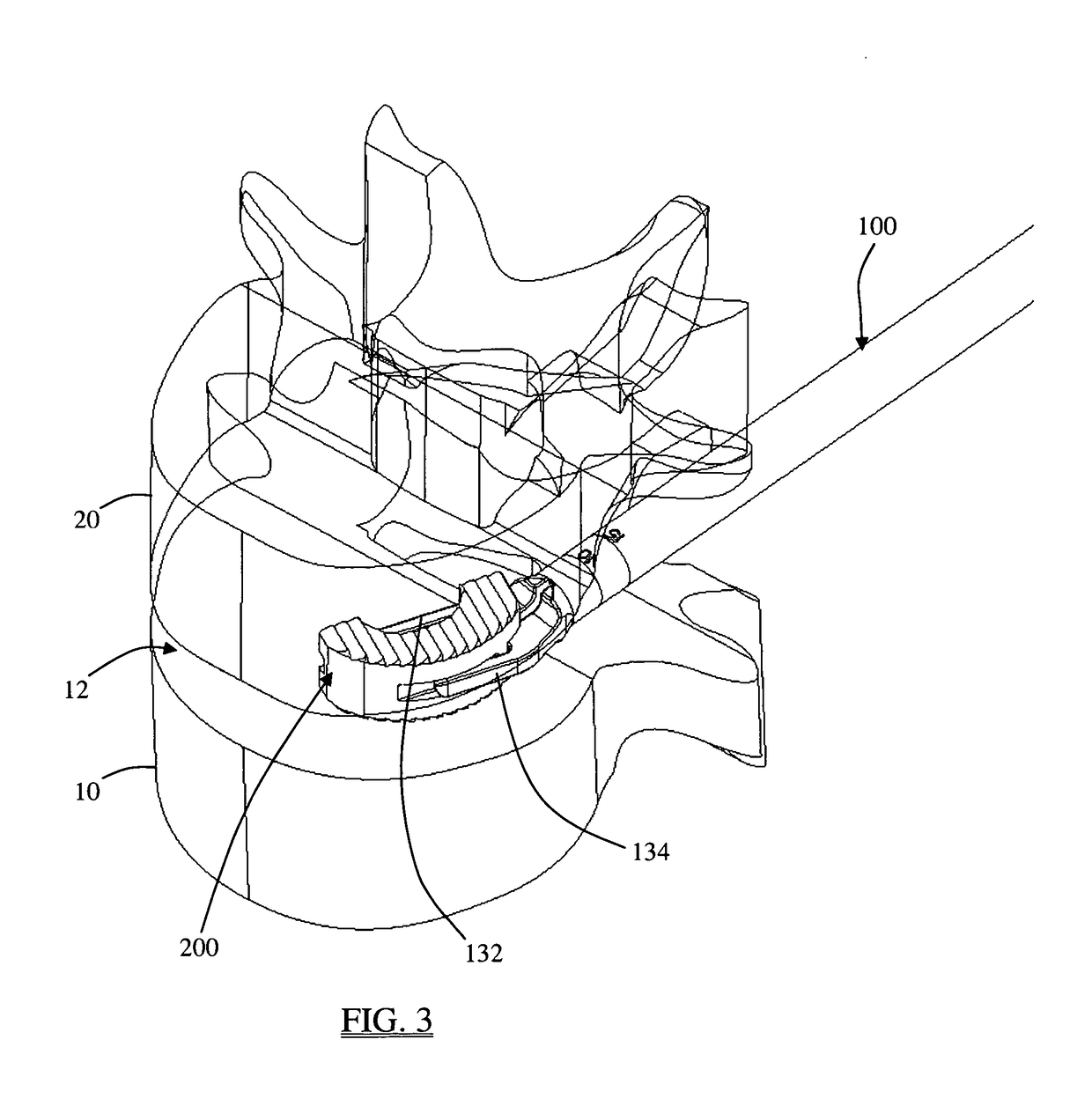
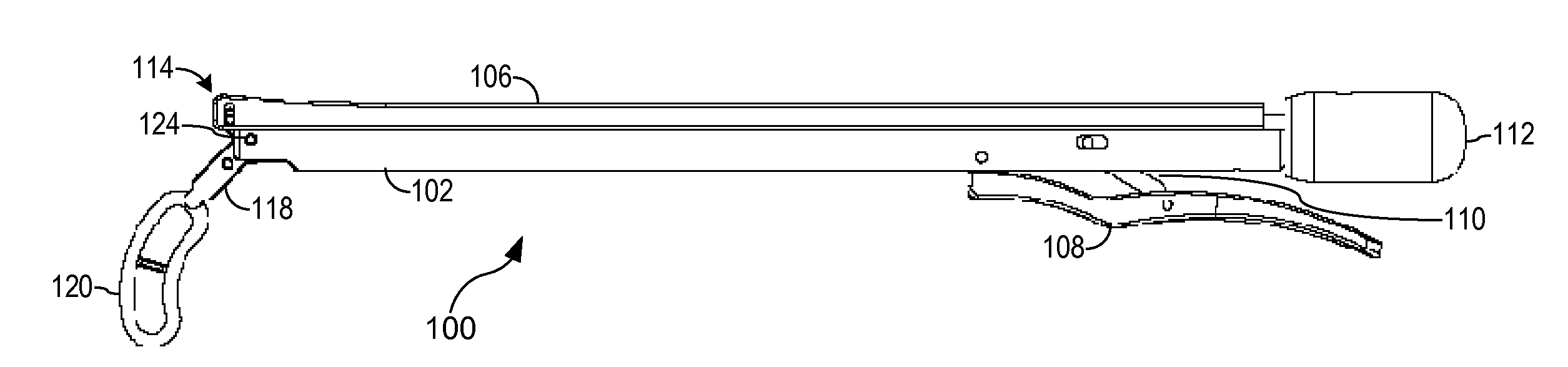Patents
Literature
152 results about "Lumbar interbody fusion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
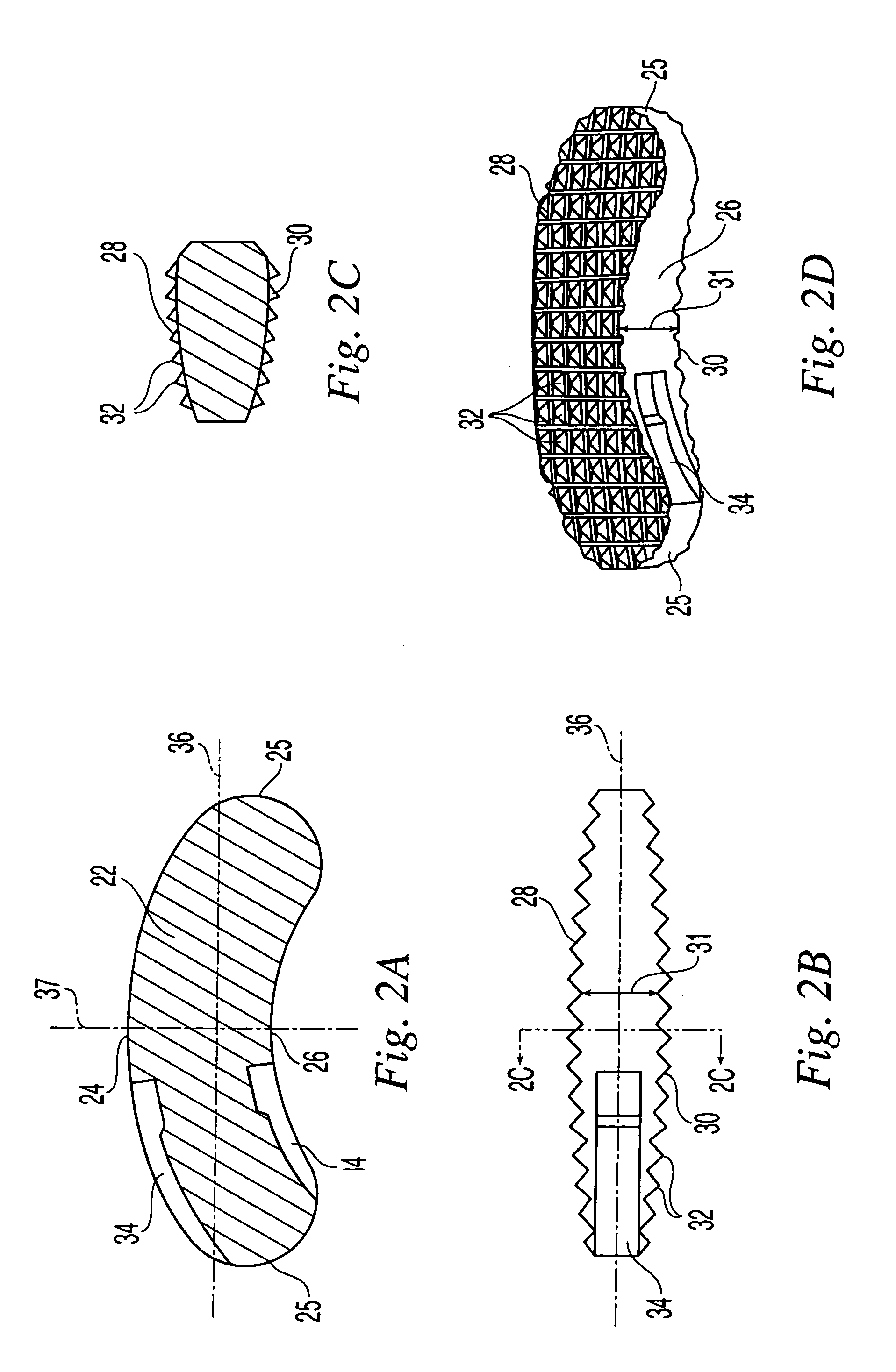
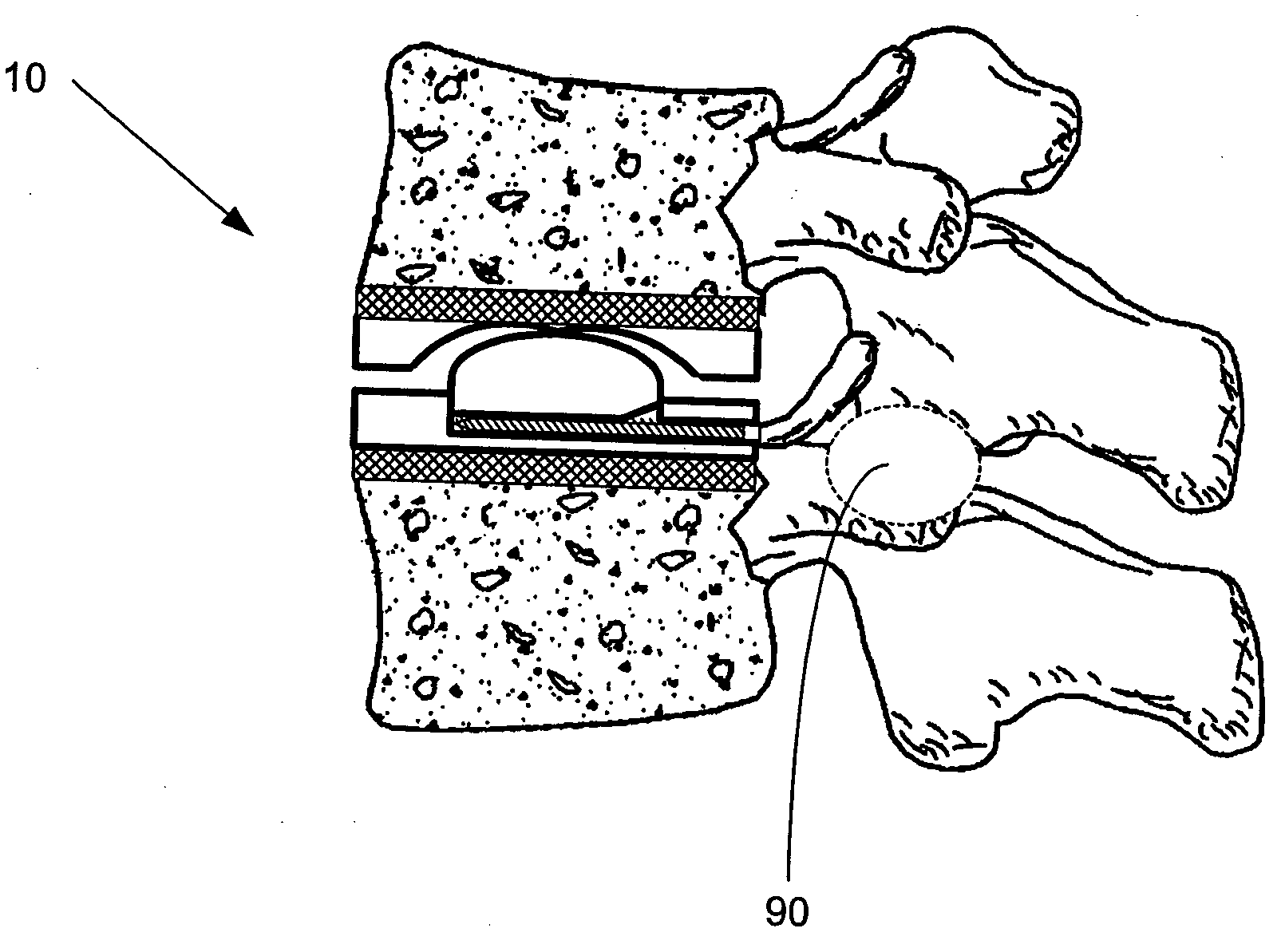
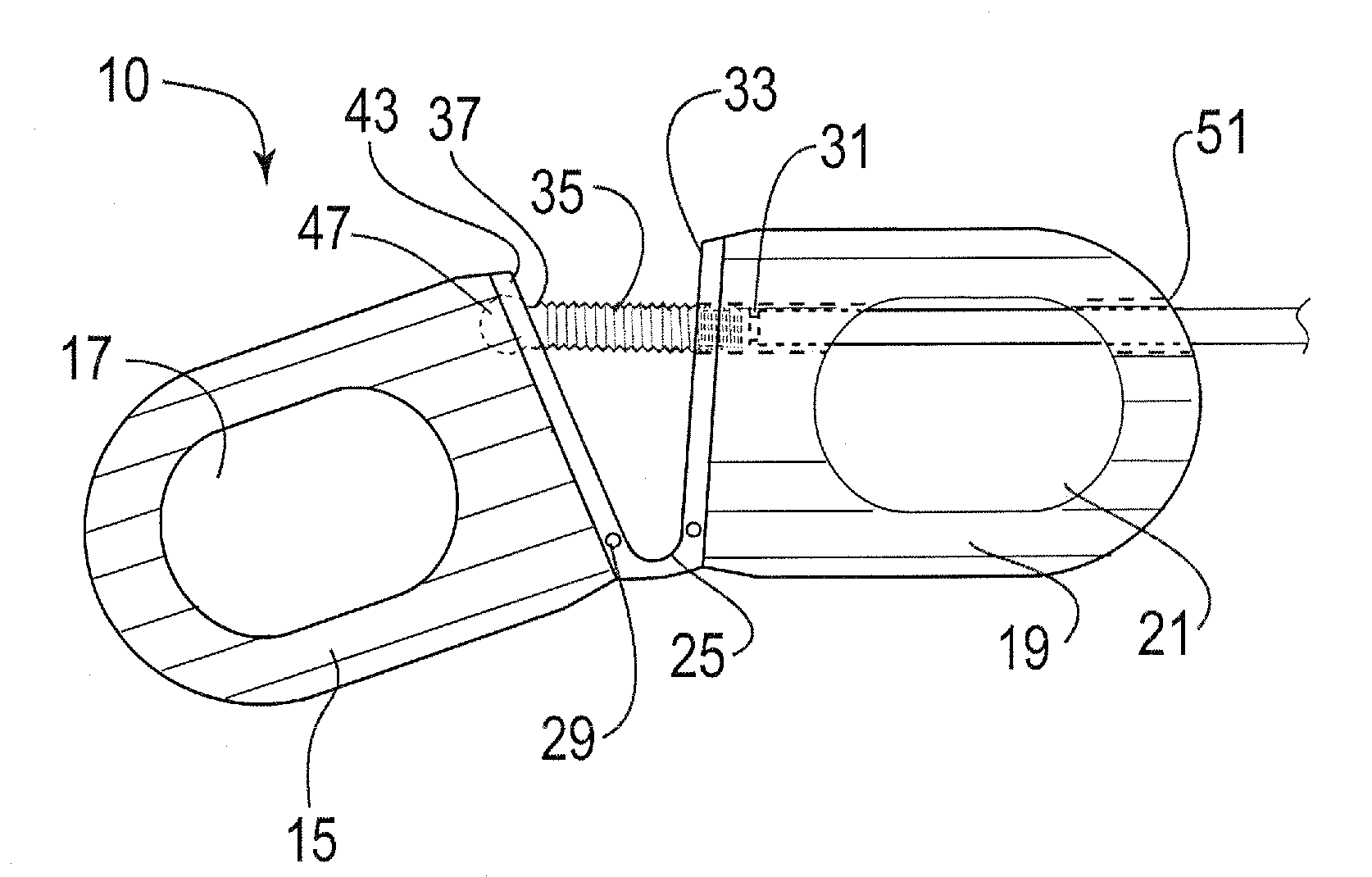
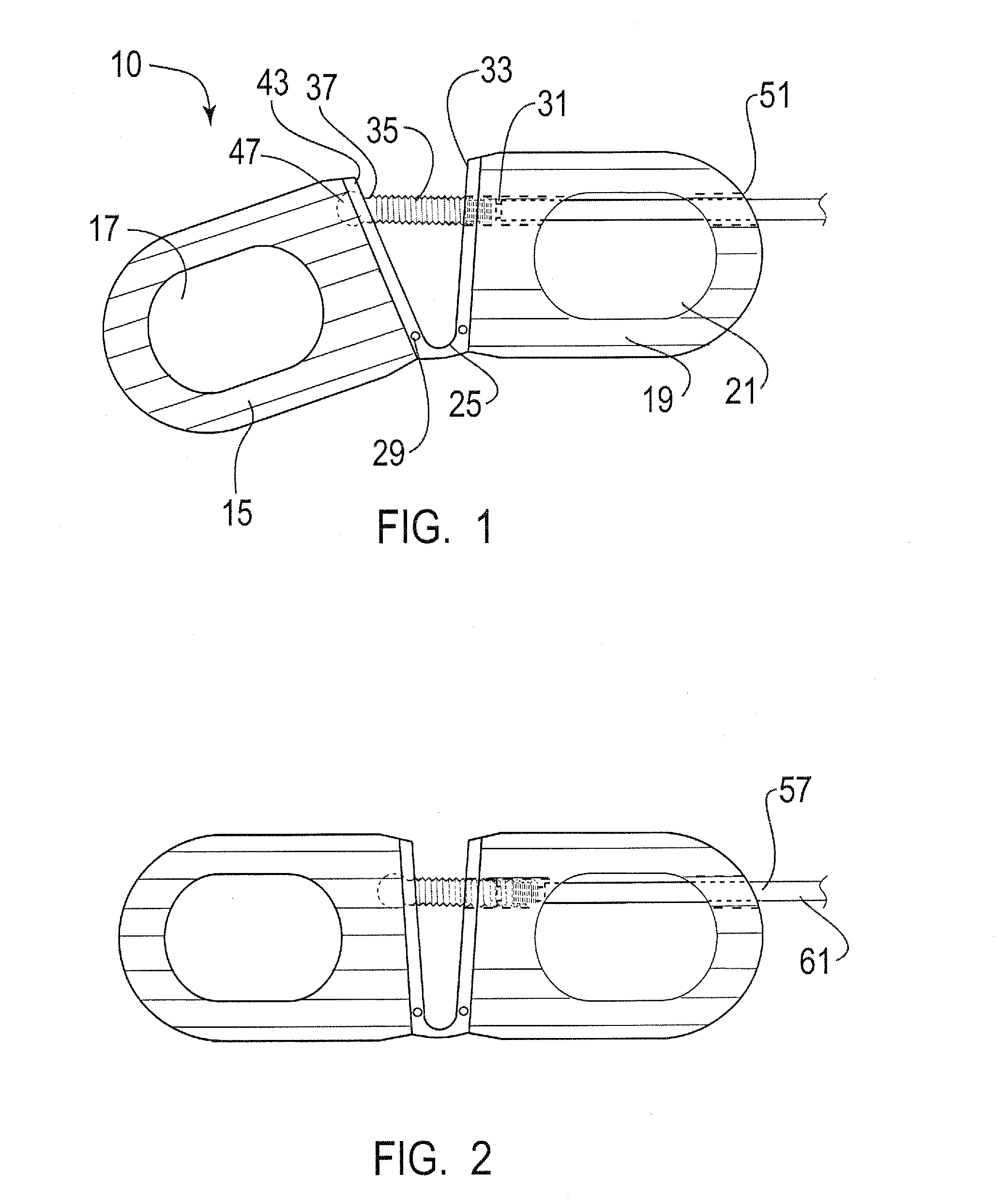
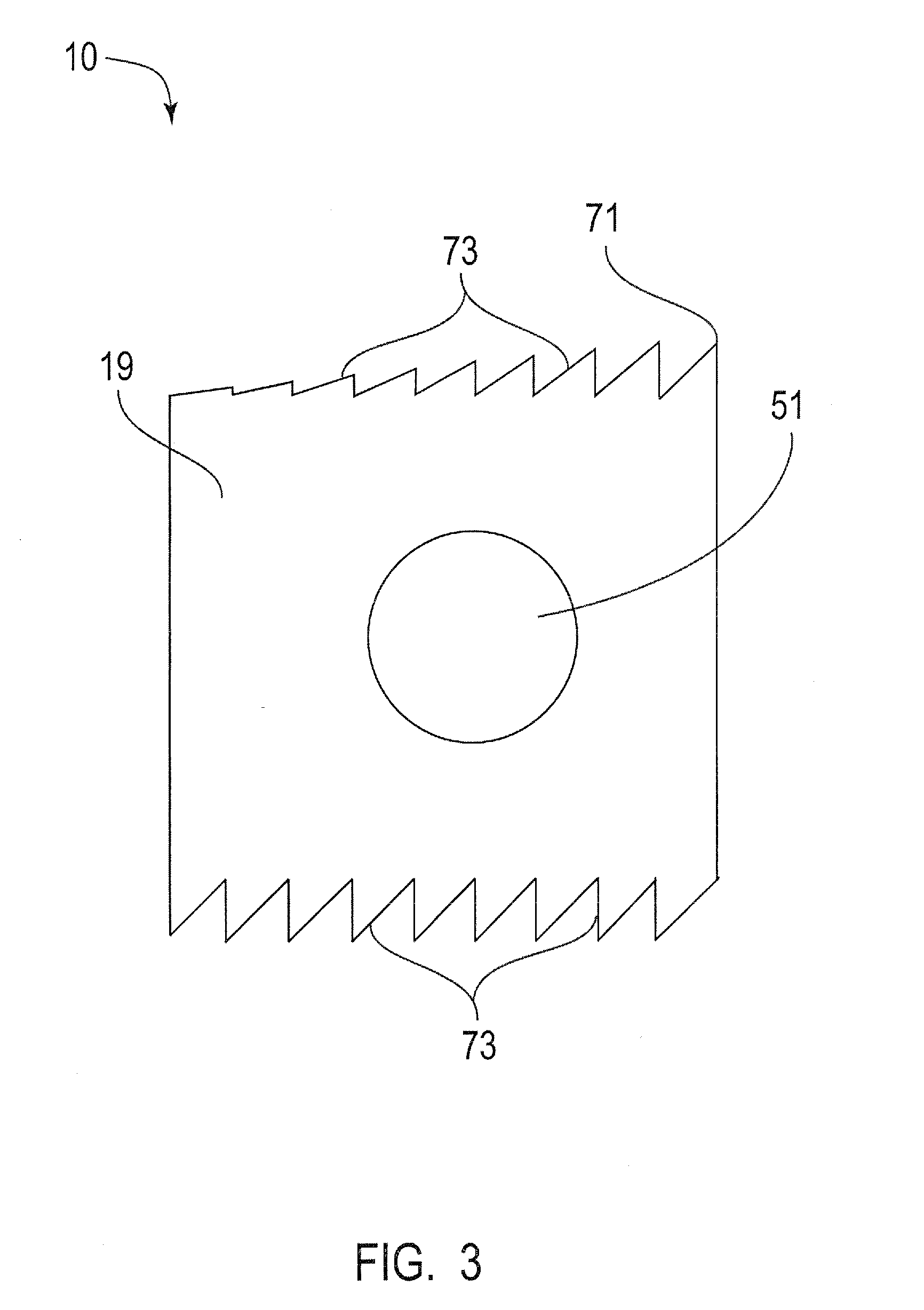
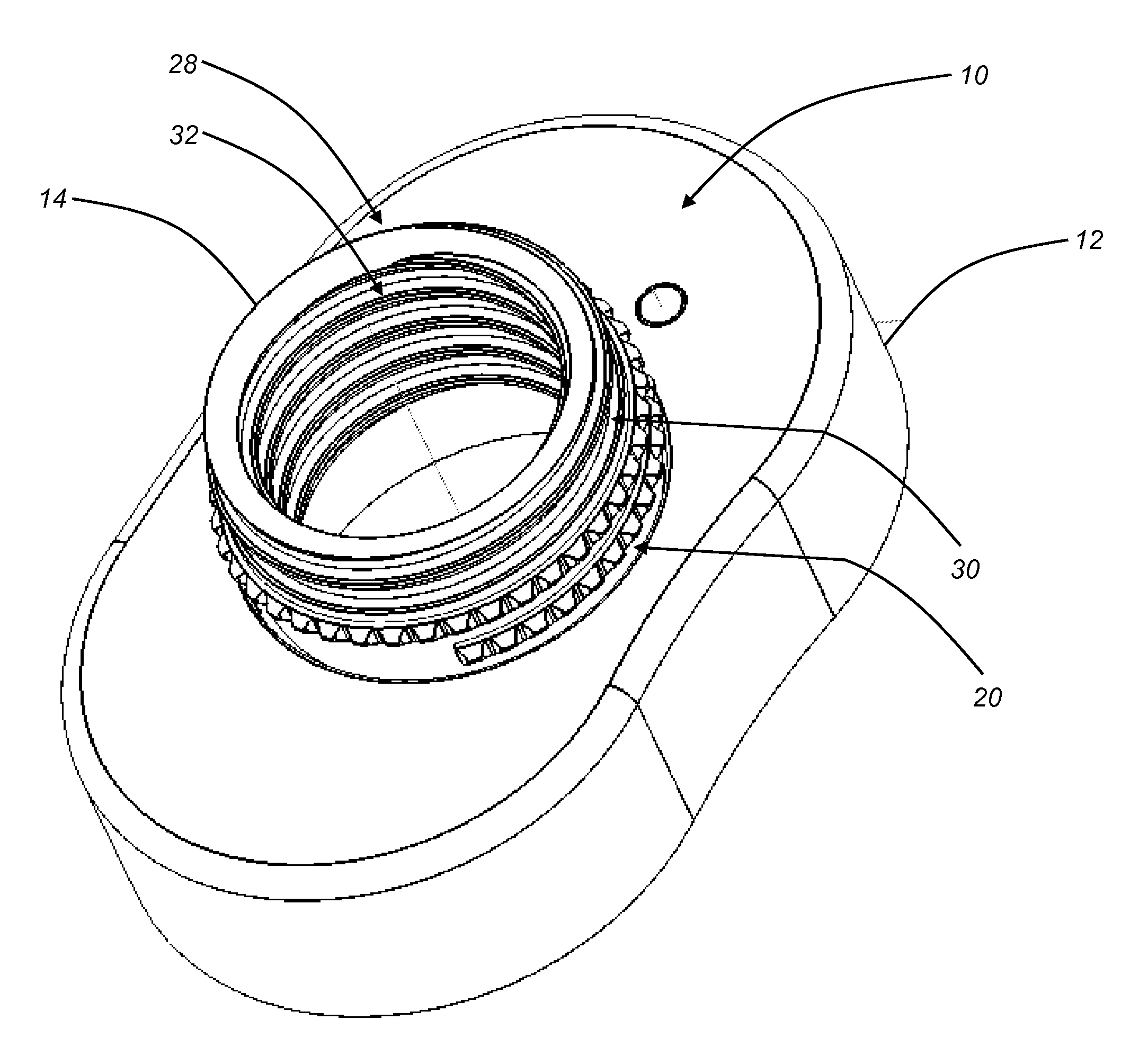
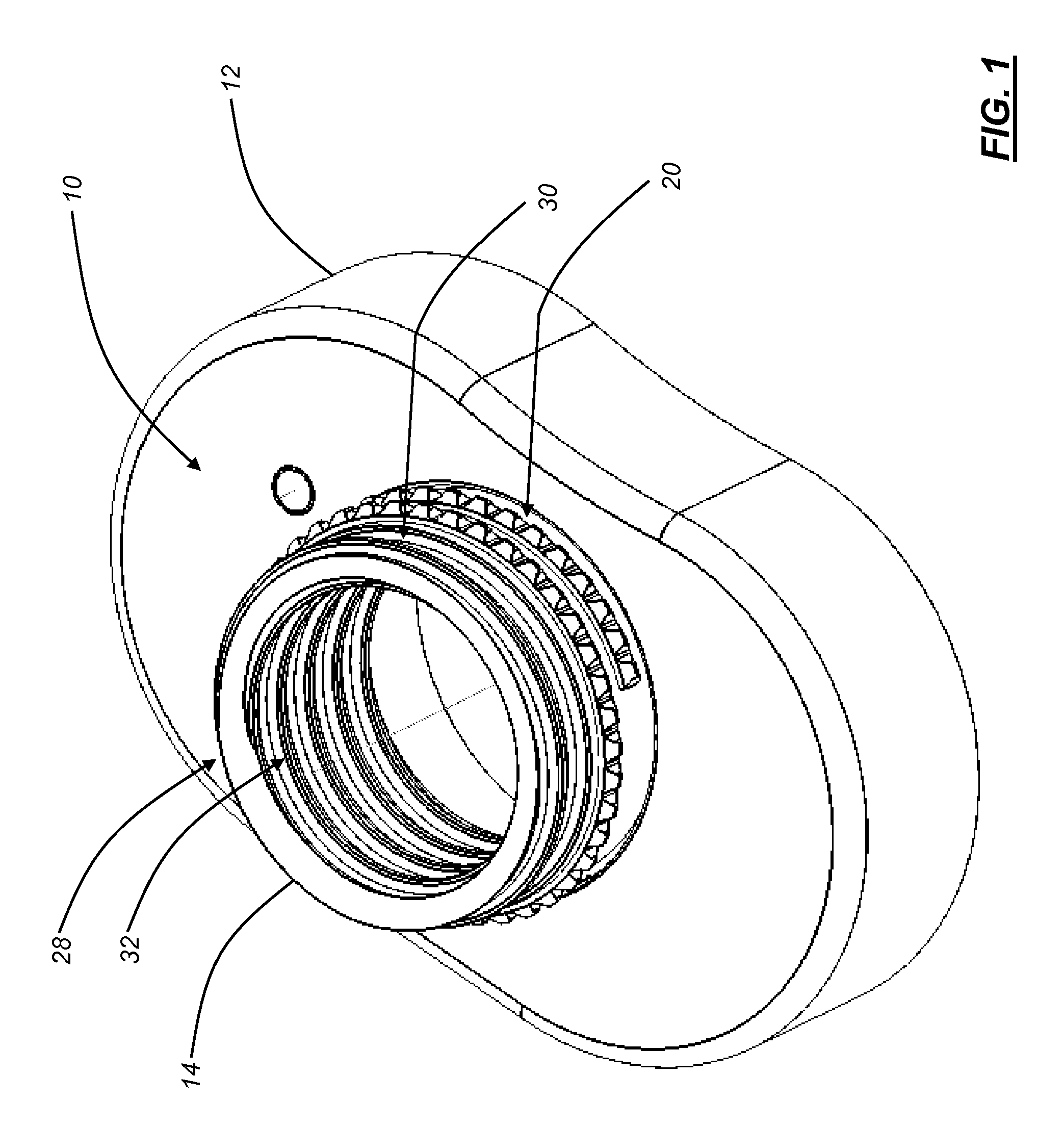
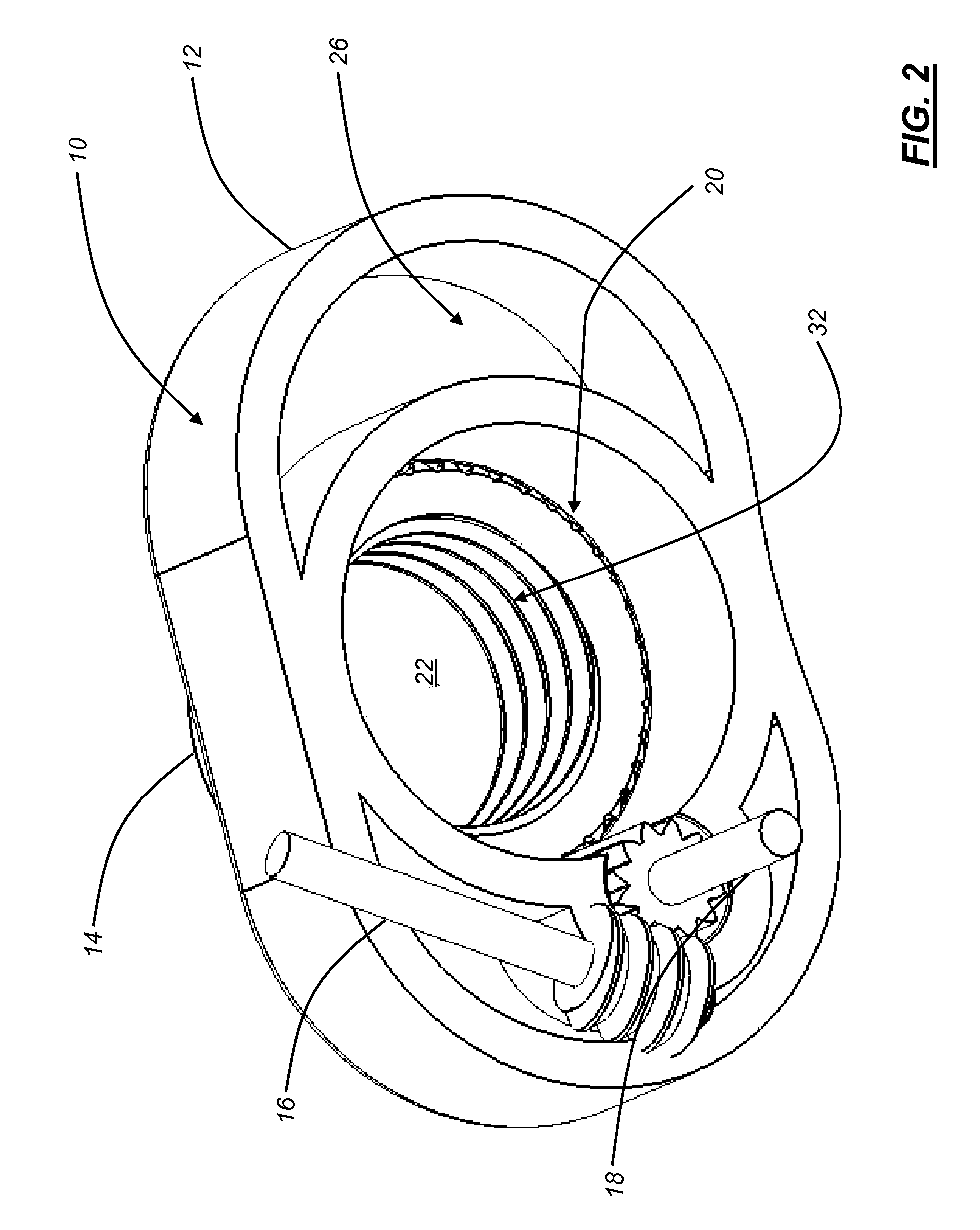
Interbody fusion grafts and instrumentation
InactiveUS7479160B2Maintain disc heightMaintain distractionInternal osteosythesisBone implantMedicineDonor bone
This invention relates to implants formed from donor bone for use in lumbar interbody fusion procedures and instruments for performing such procedures. The implants are formed to include a concave surface formed from a portion of the medullary canal of a long bone. The concaved surface defines a recess in the implant that serves as a depot for osteogenic material. Specific instruments for inserting the implants prepared according to this invention and for preparing the intervertebral space to receive the implants are also provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Posterior lumbar interbody fusion expandable cage with lordosis and method of deploying the same
A spinal fusion cage comprises an upper half-cage, a lower half-cage, and a plunger with a cam. The upper half-cage and lower half-cage have a first collapsed configuration which has a thin, flat, rectangular envelope and a second expanded configuration. The half-cages have at least one ramped surface on which the cam of the plunger rides. The cam bears against the ramped surface and spreading the two half-cages apart. A method of deploying a spinal fusion cage comprises the steps of disposing in a spinal space an upper half-cage and lower half-cage in a first collapsed configuration which has a thin, flat, rectangular envelope and a second expanded configuration. The method continues with the step of distally advancing a plunger between the upper half-cage and lower half-cage and spreading the two half-cages apart.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Bioactive spinal implants and method of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS7238203B2Facilitating radiographic assessmentEnhance bone contact and stability and fusionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsLumbar vertebraeCervical fusions
A bioactive spinal implant used in cervical fusion, Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF), Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF), and Transforaminal Interbody Fusion (TLIF), having properties and geometries that enhance bone contact, stability, and fusion between adjacent vertebral bodies.
Owner:VIA SPECIAL PURPOSE CORP +1
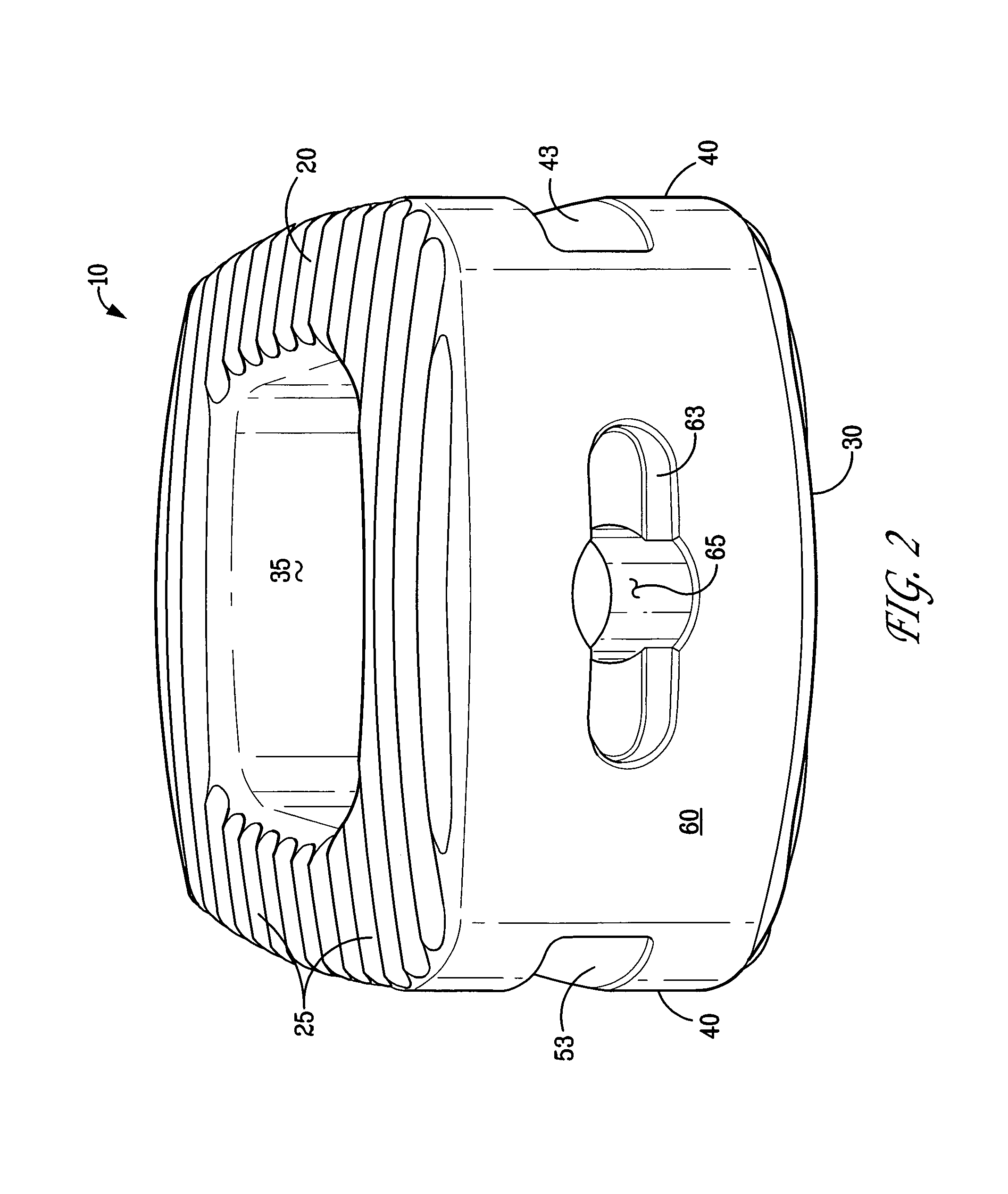
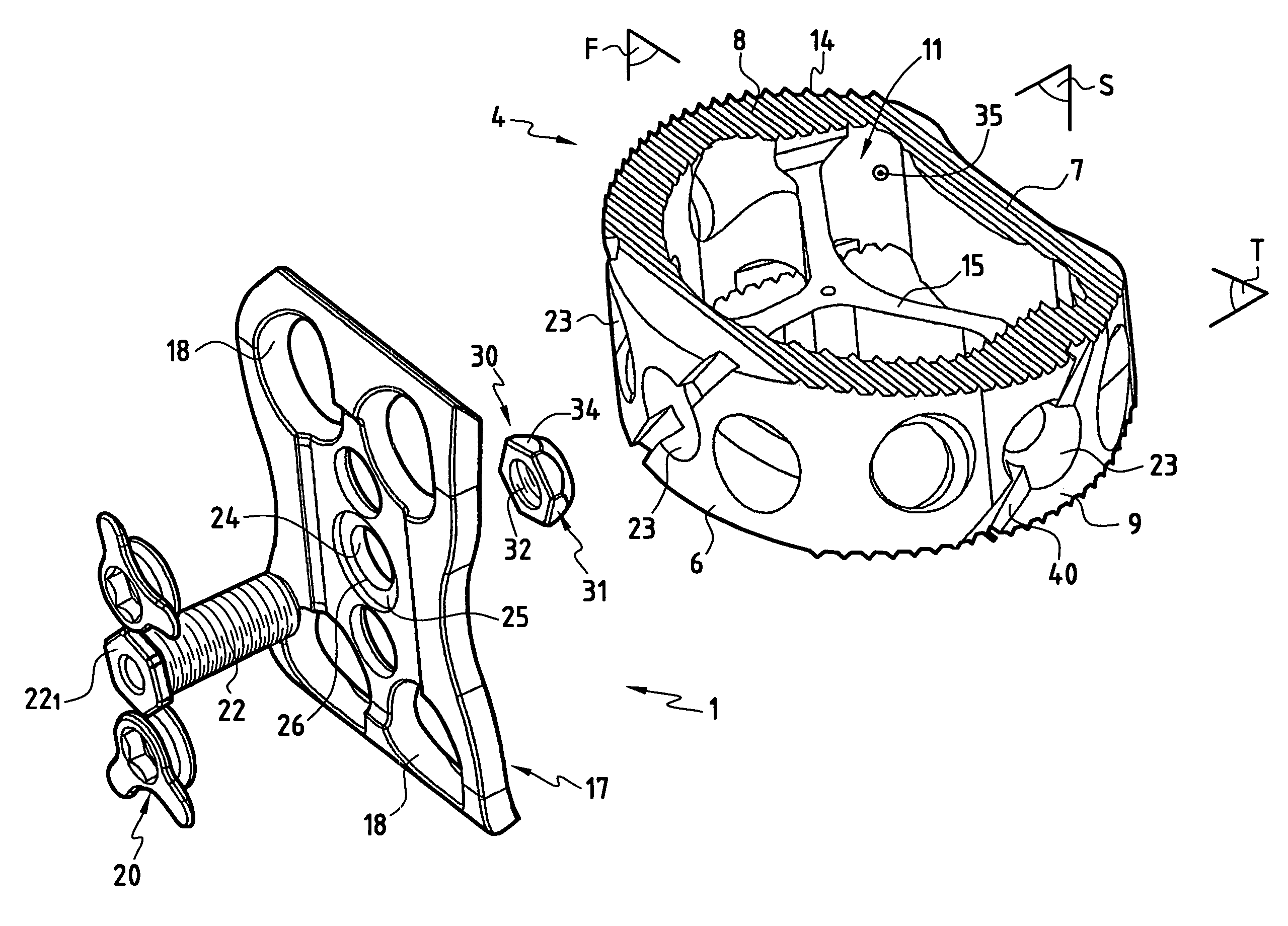
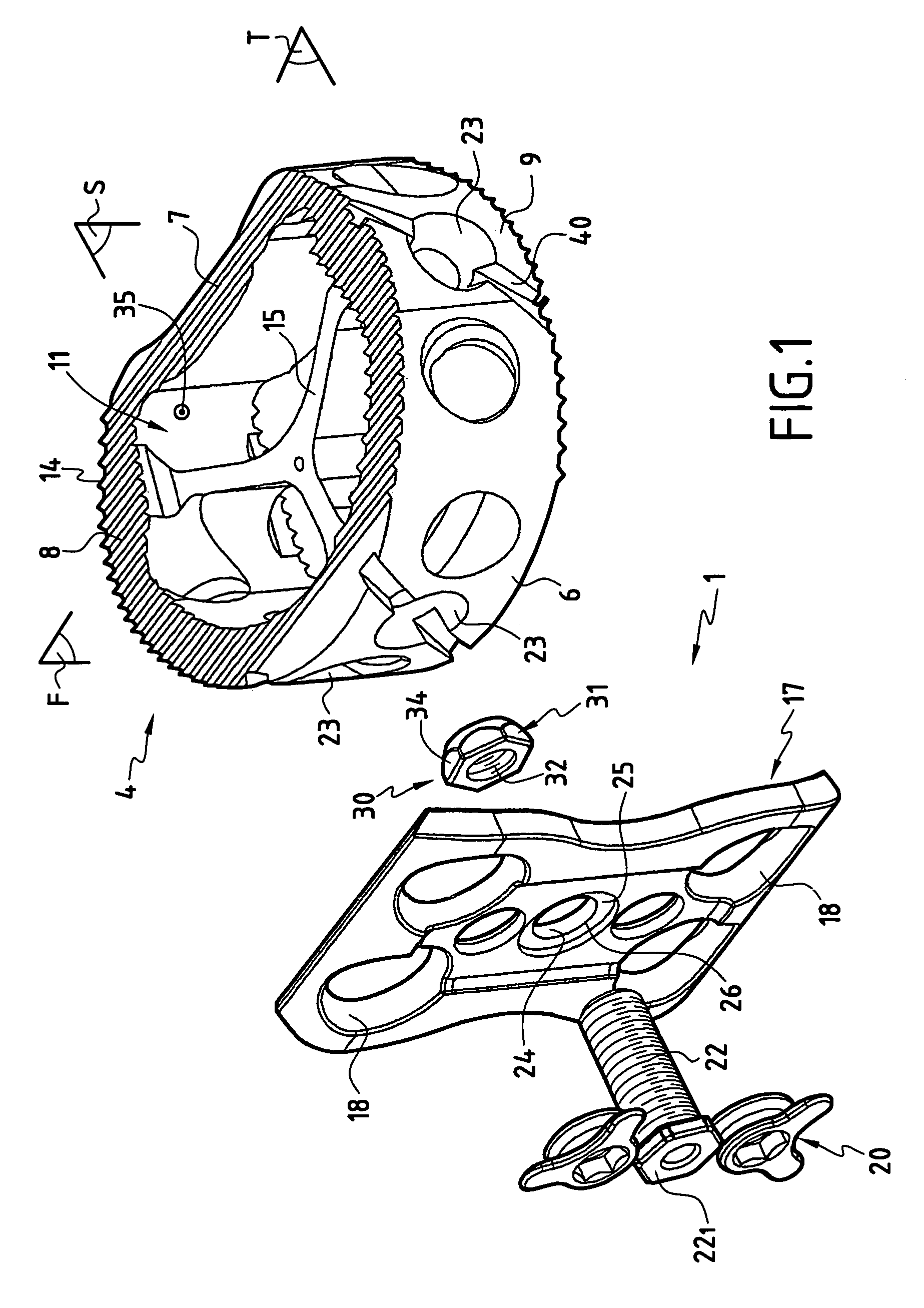
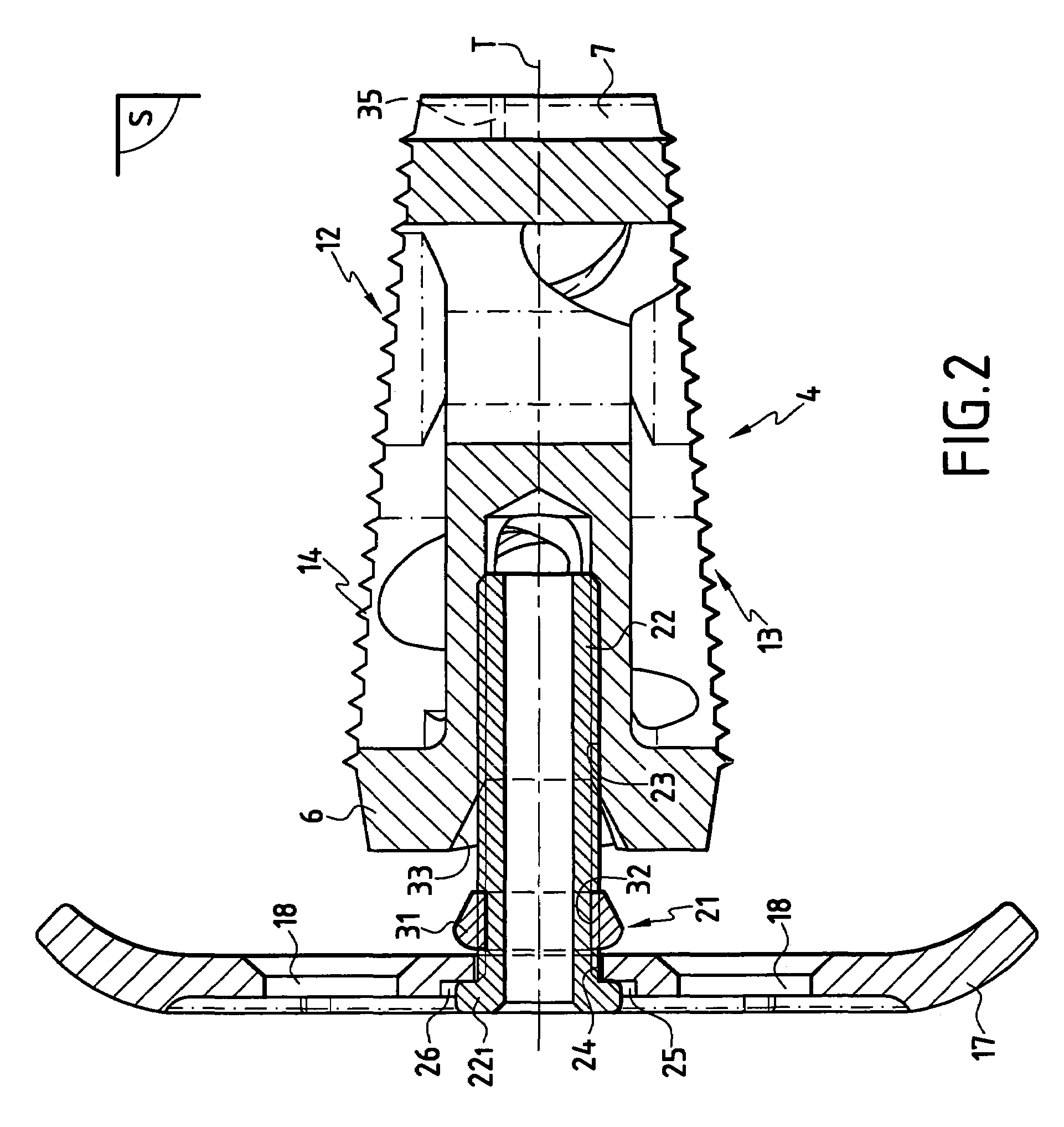
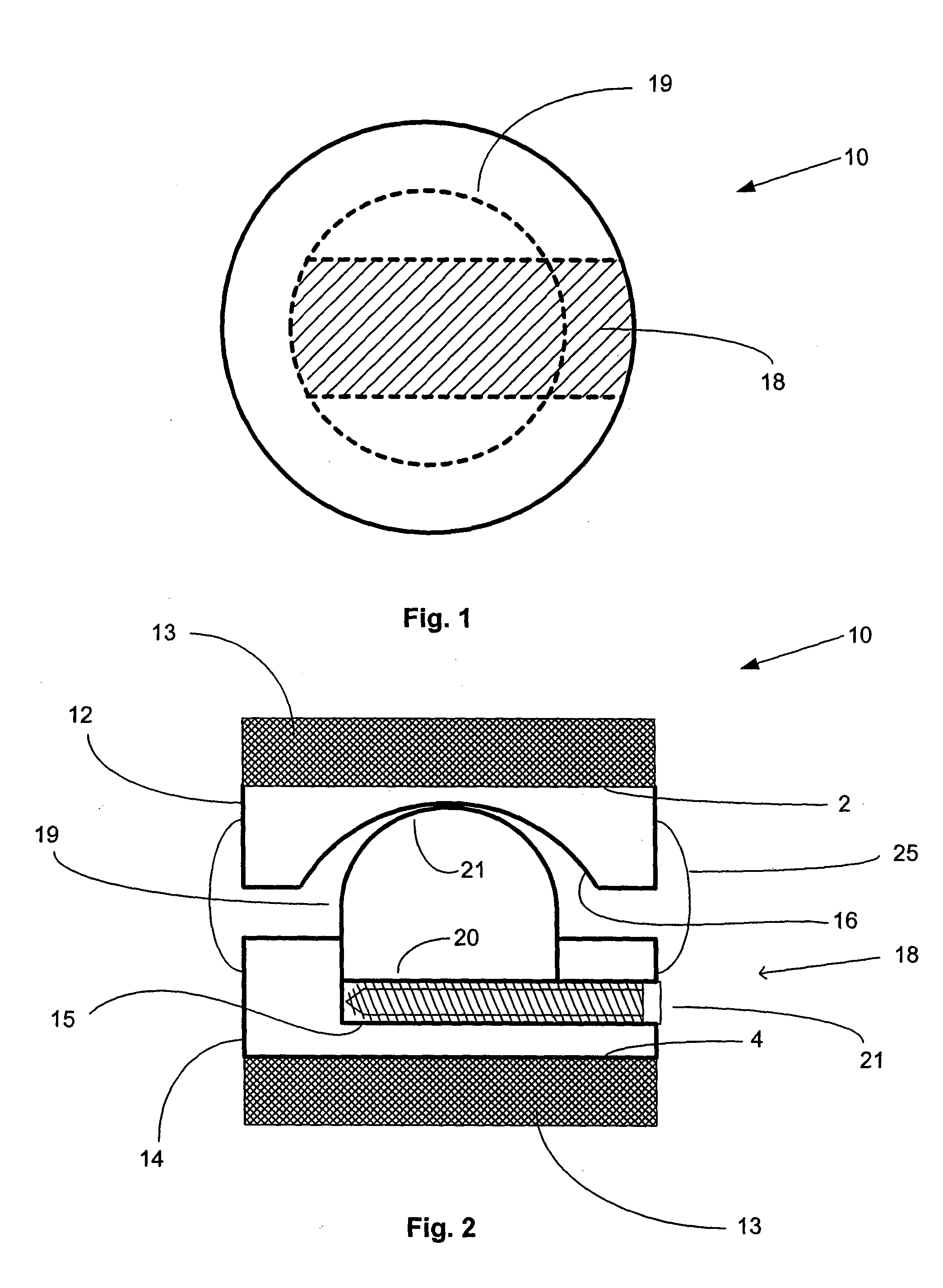
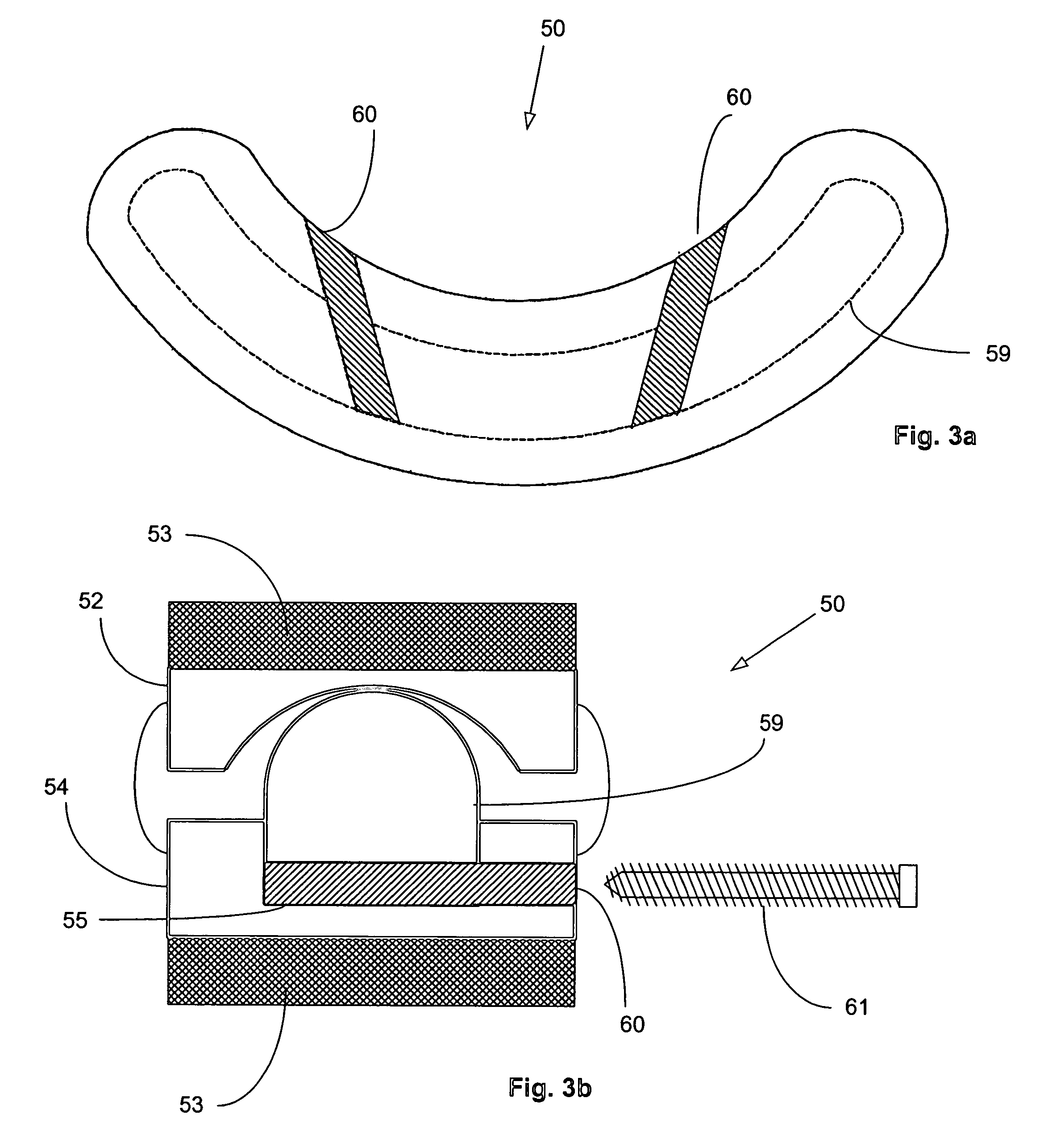
Stabilized interbody fusion system for vertebrae
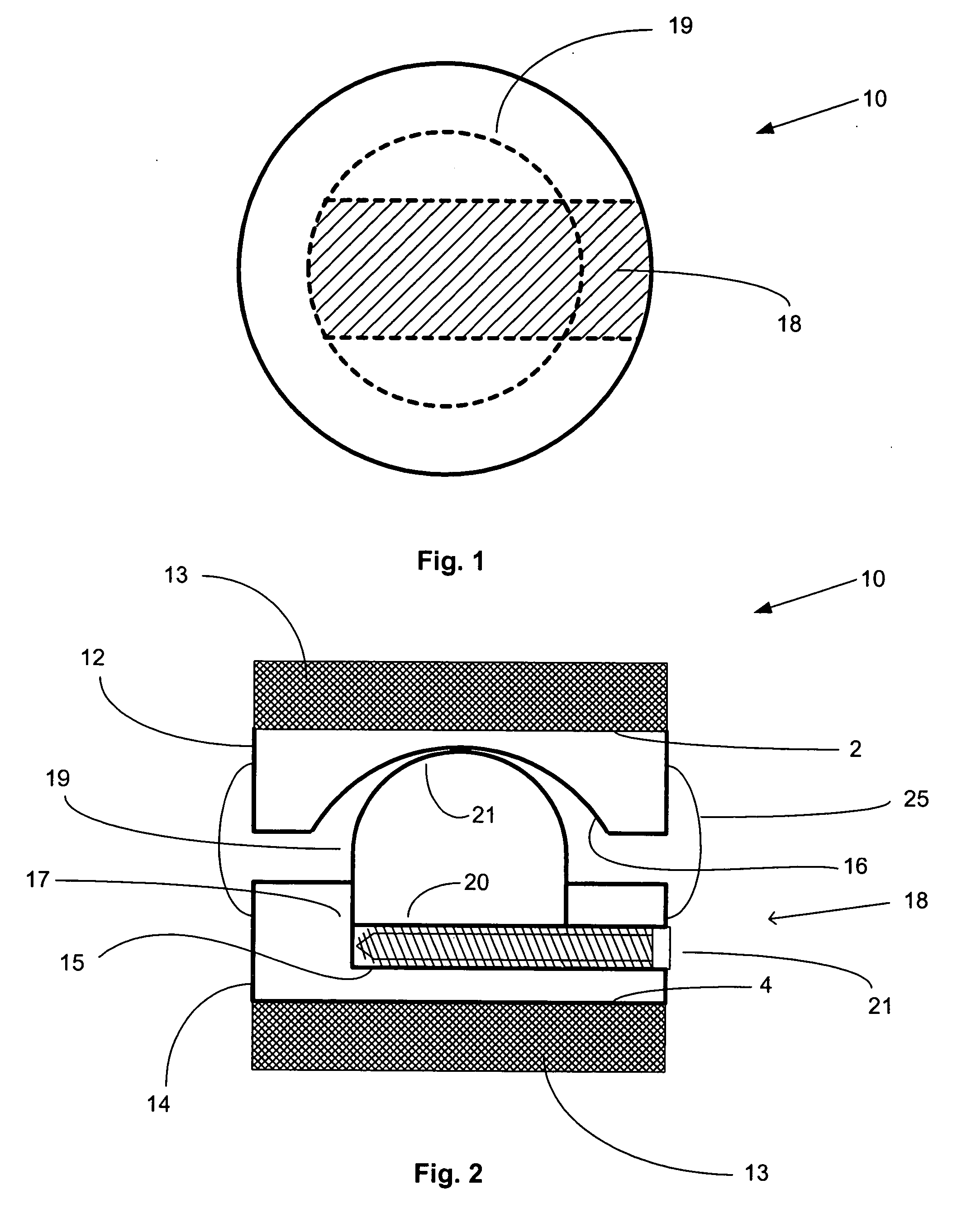
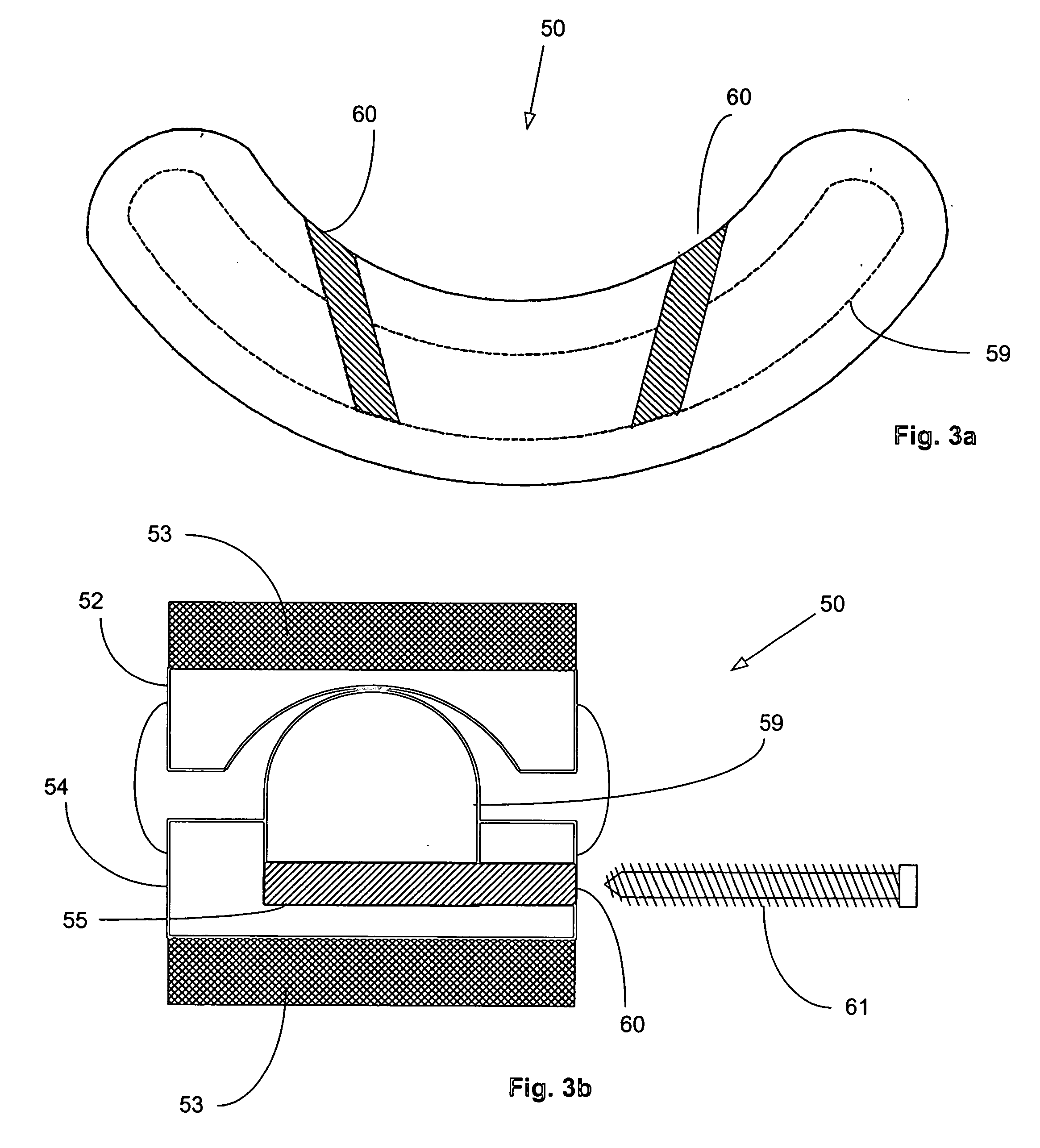
The invention concerns a stabilized interbody fusion system for vertebrae, of the type comprising an interbody implant (4) designed to be inserted in the intervertebral space defined between two neighboring vertebrae to be mutually secured, so as to restore the height and the angle of the lordosis of the vertebral segment defined by the two neighboring vertebrae and a stabilizing plate (17) provided, at each of its ends, with at least a passage hole (18) for an anchoring screw, the plate (17) and the implant (4) being provided with mutual assembly means, such that after assembly, the stabilizing plate (17) extends on each side of the implant to enable the stabilizing plate to be anchored on the neighboring vertebrae through the screws, characterized in that it comprises spacing means (30), interposed between the stabilizing plate (17) and the implant (4), to enable the stabilizing plate to be positioned at a specific distance relative to the implant.
Owner:SCIENTX
Artificial functional spinal unit assemblies
InactiveUS7316714B2Promote growthPromoting bony end growthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical operationSurgical approach
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
Artificial spinal unit assemblies
ActiveUS20050033432A1Prohibit some movementPrevent movementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnSurgical approach
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE
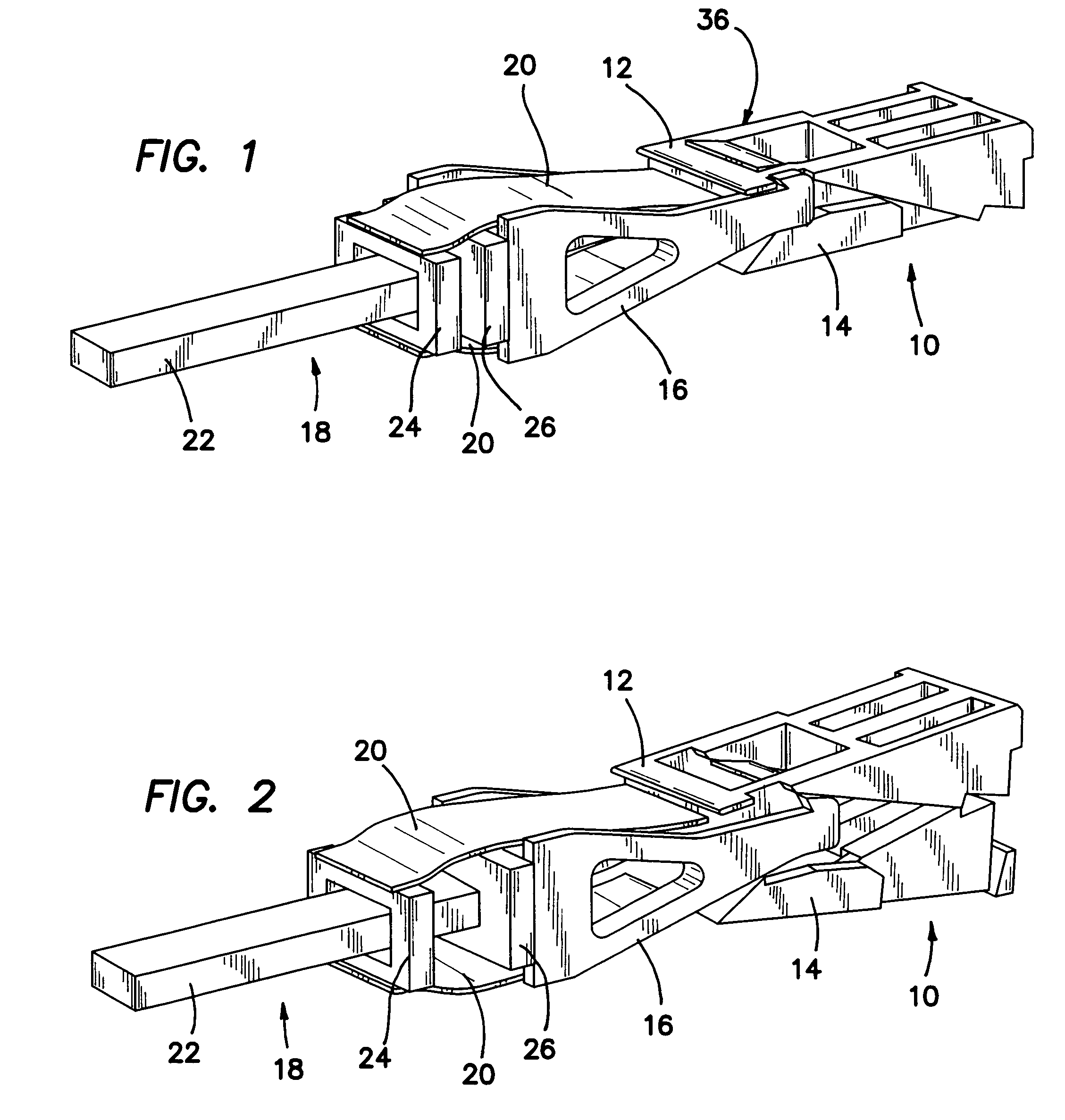
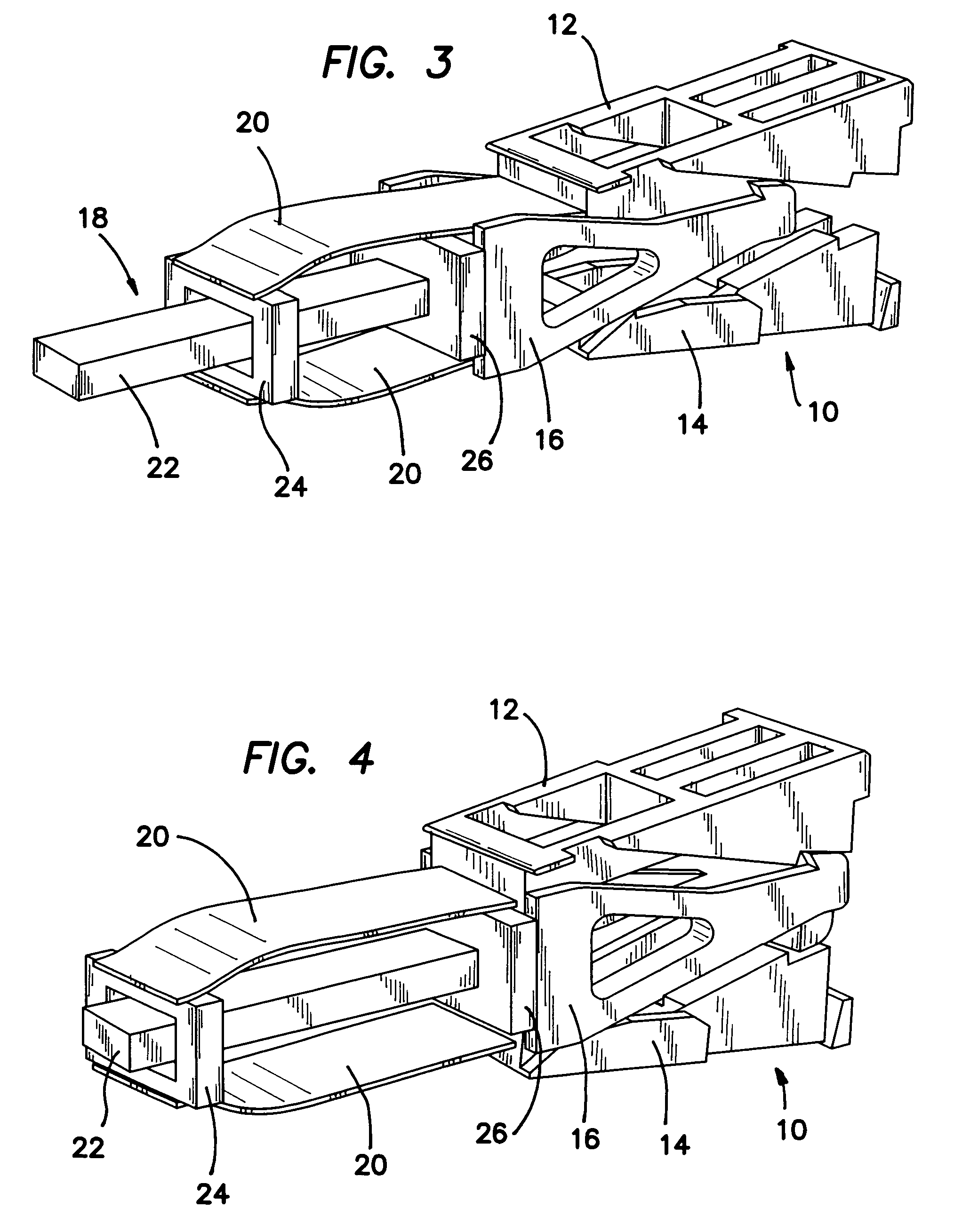
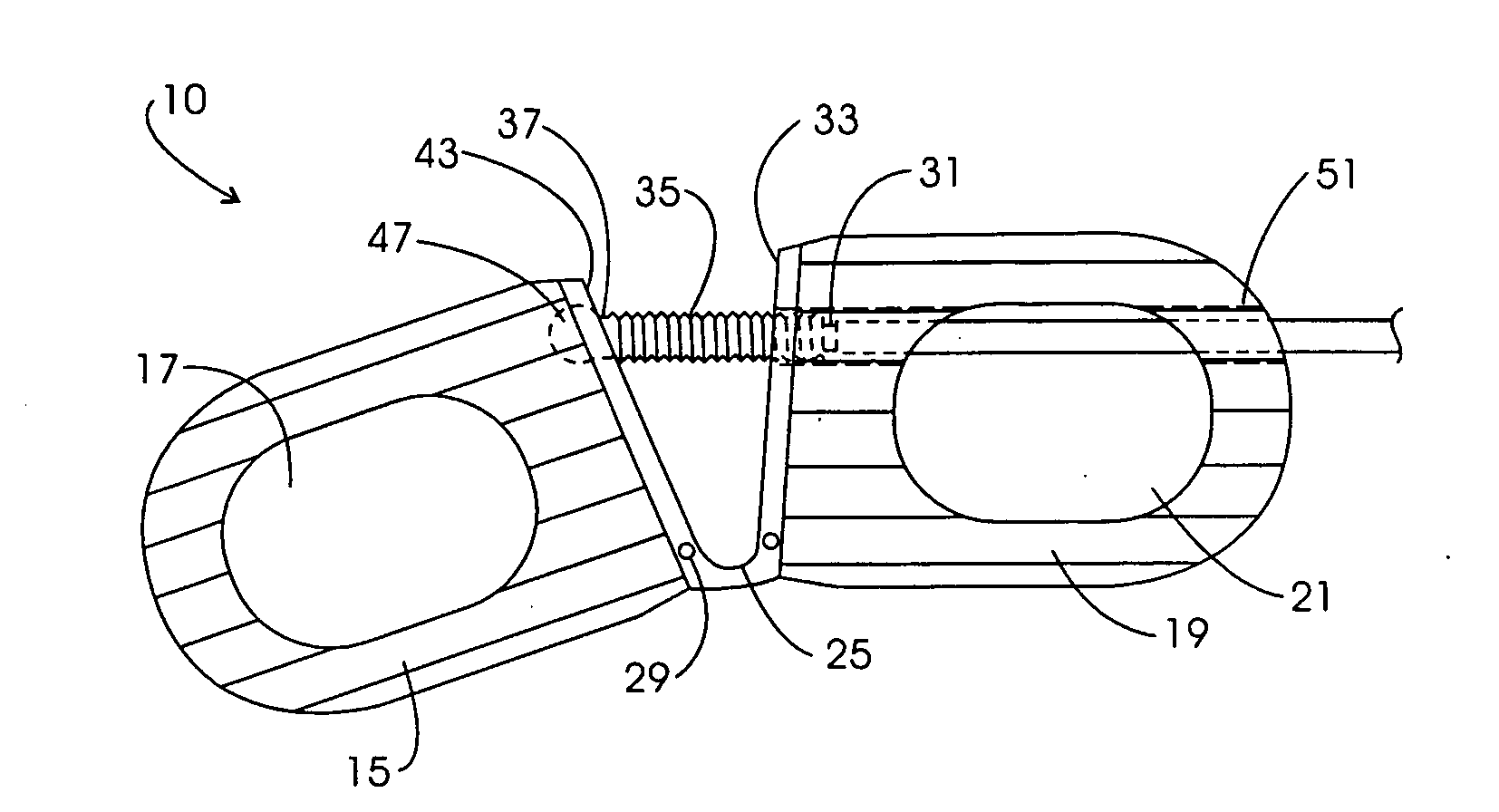
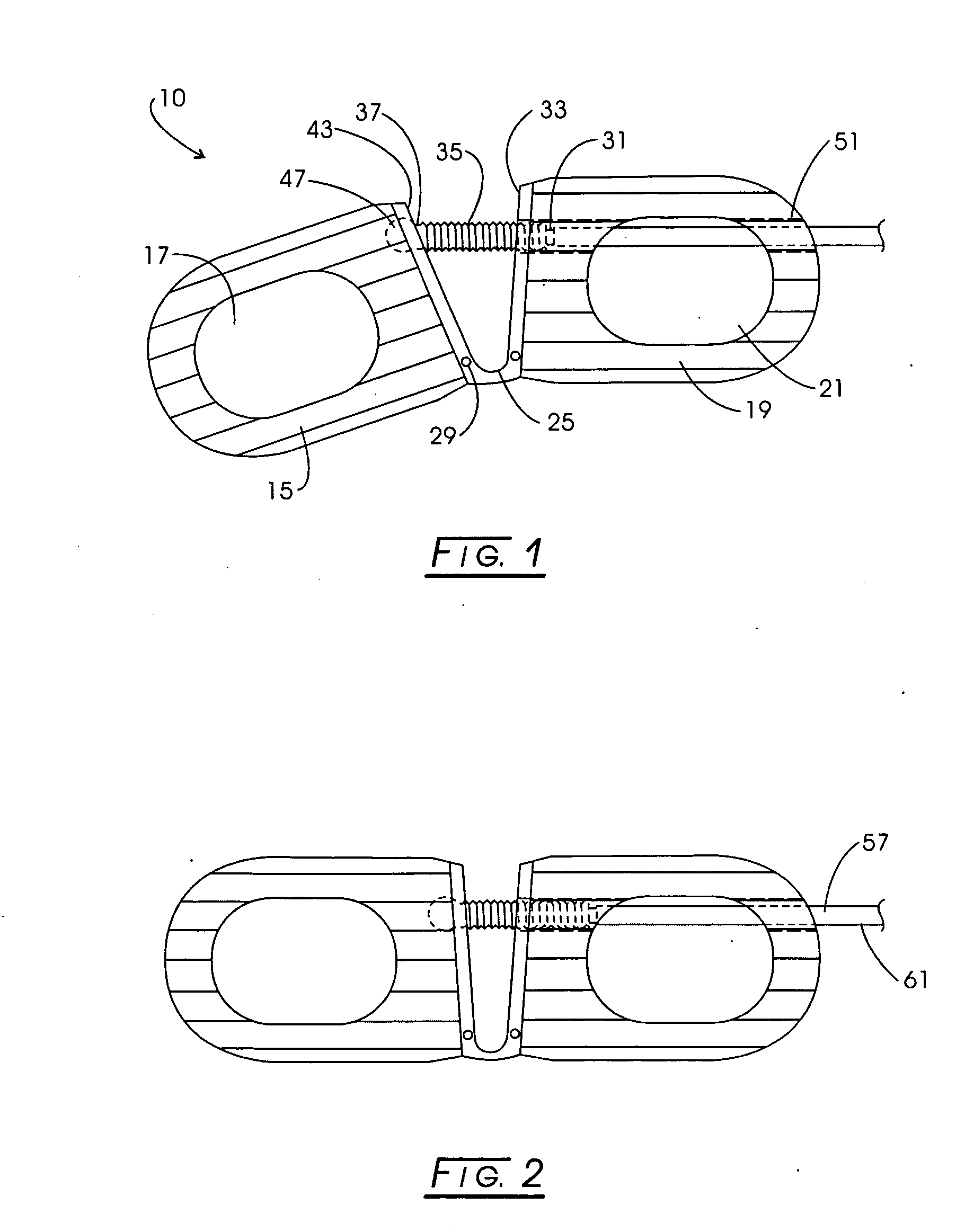
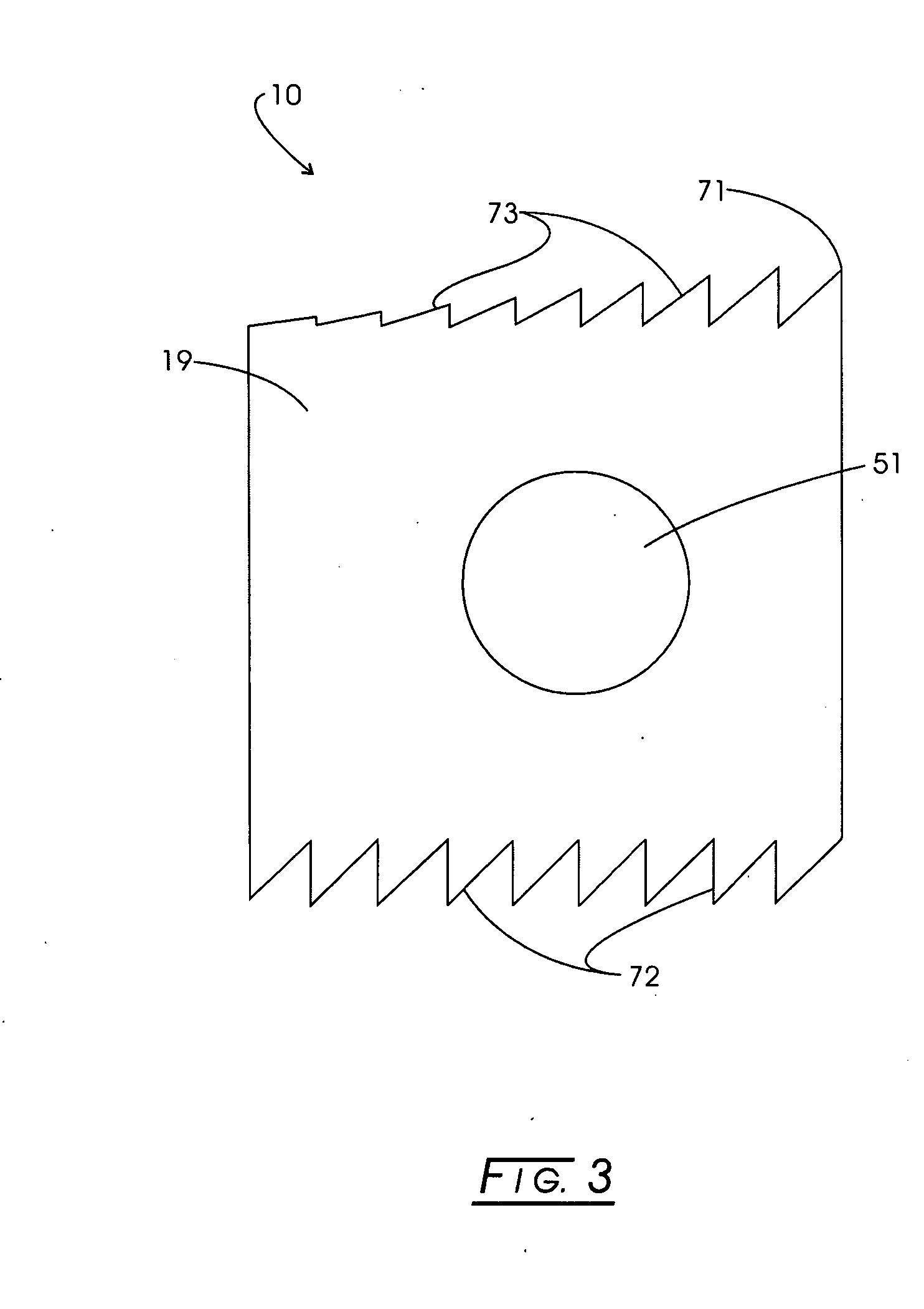
Intervertebral implant for transforaminal posterior lumbar interbody fusion procedure
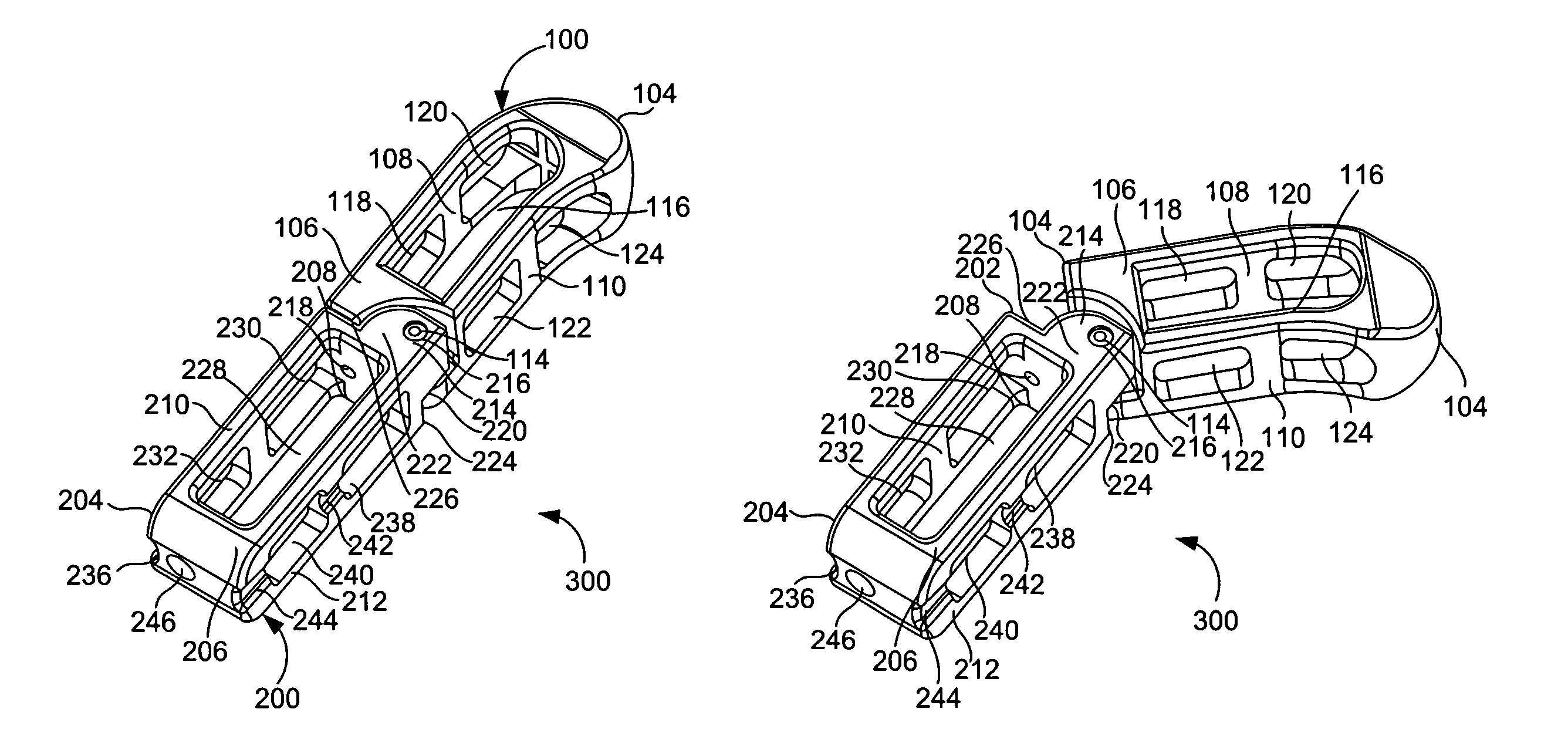
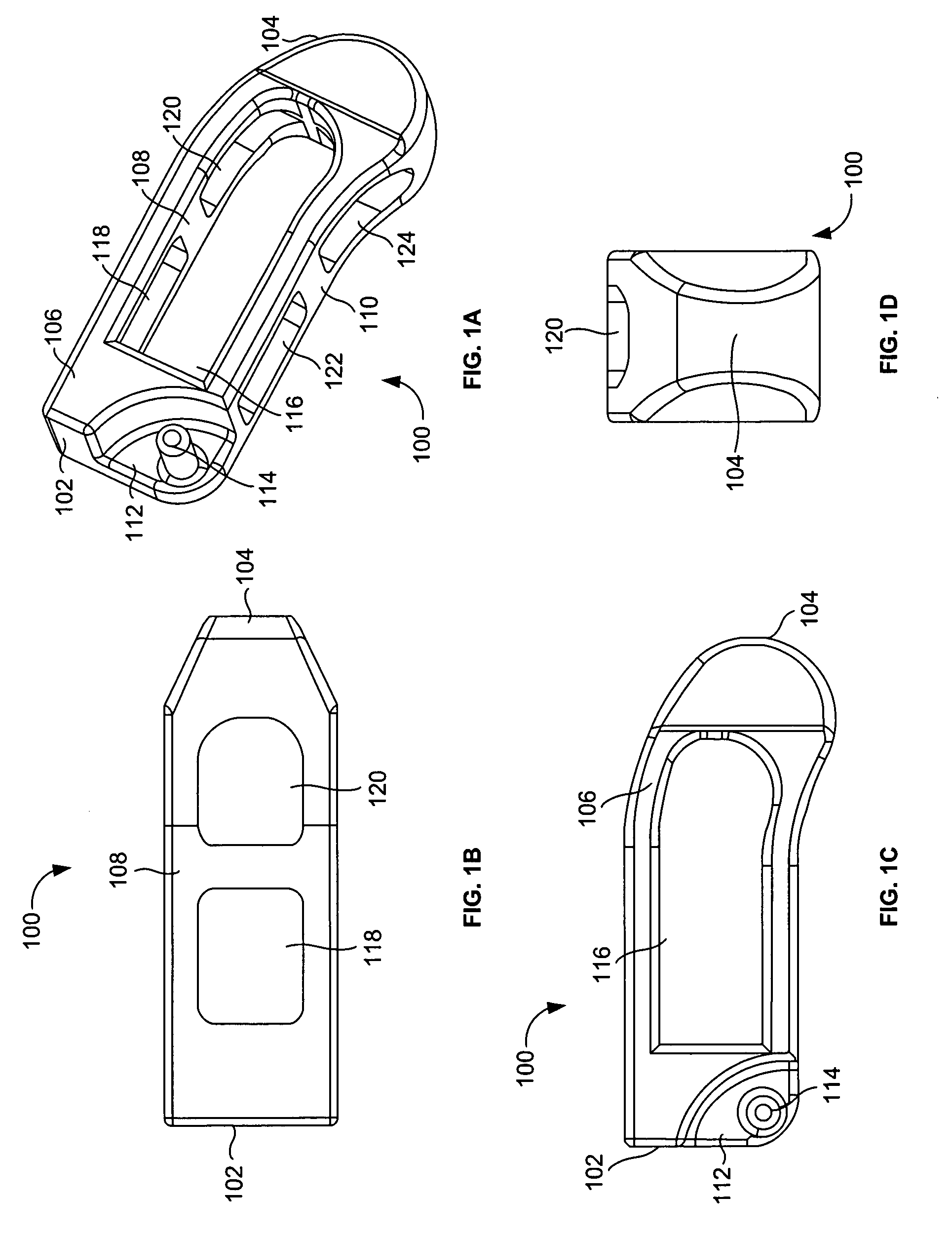
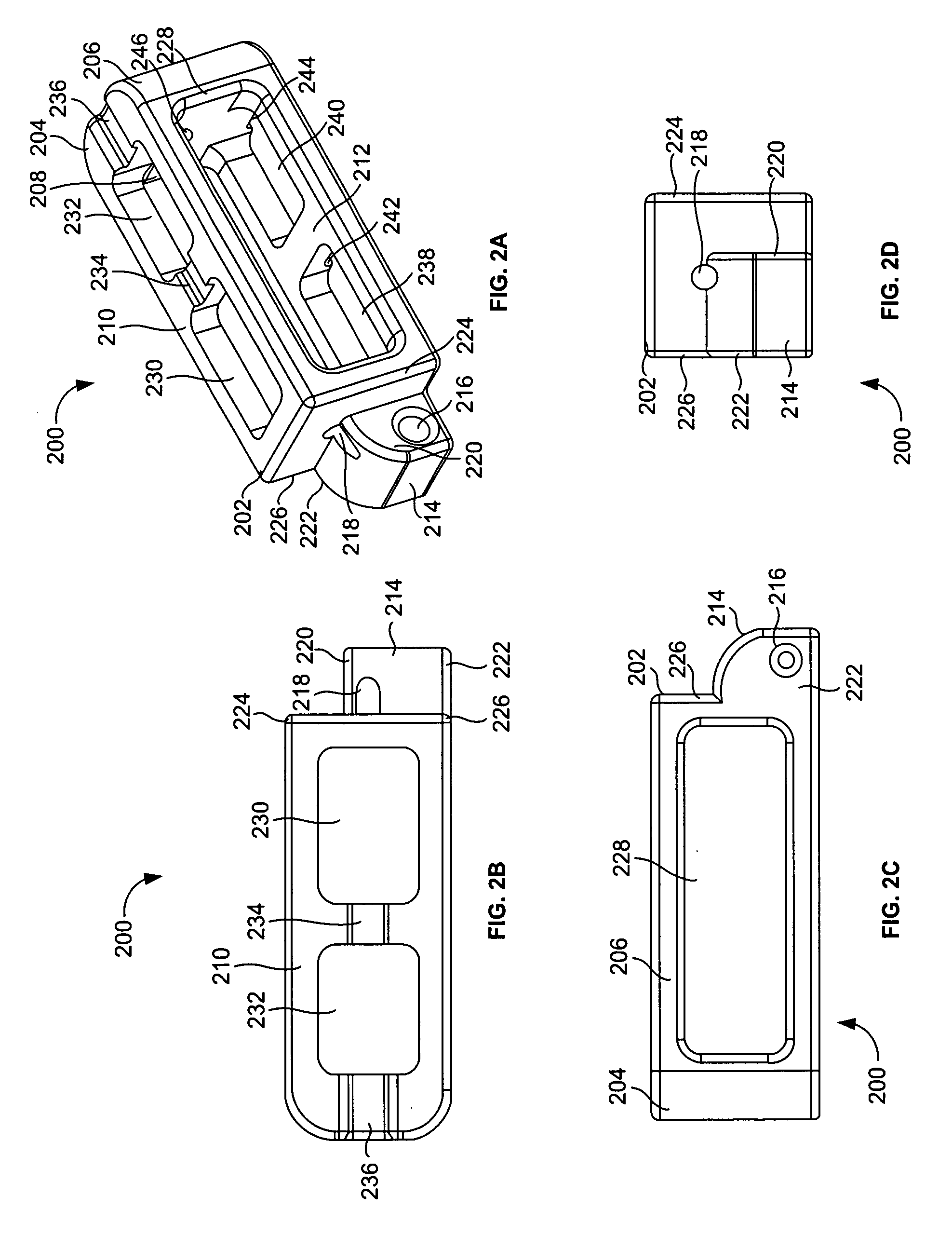
InactiveUS6974480B2Easy to insertPrevent slippingBone implantSurgeryTransforaminal approachSpinal column
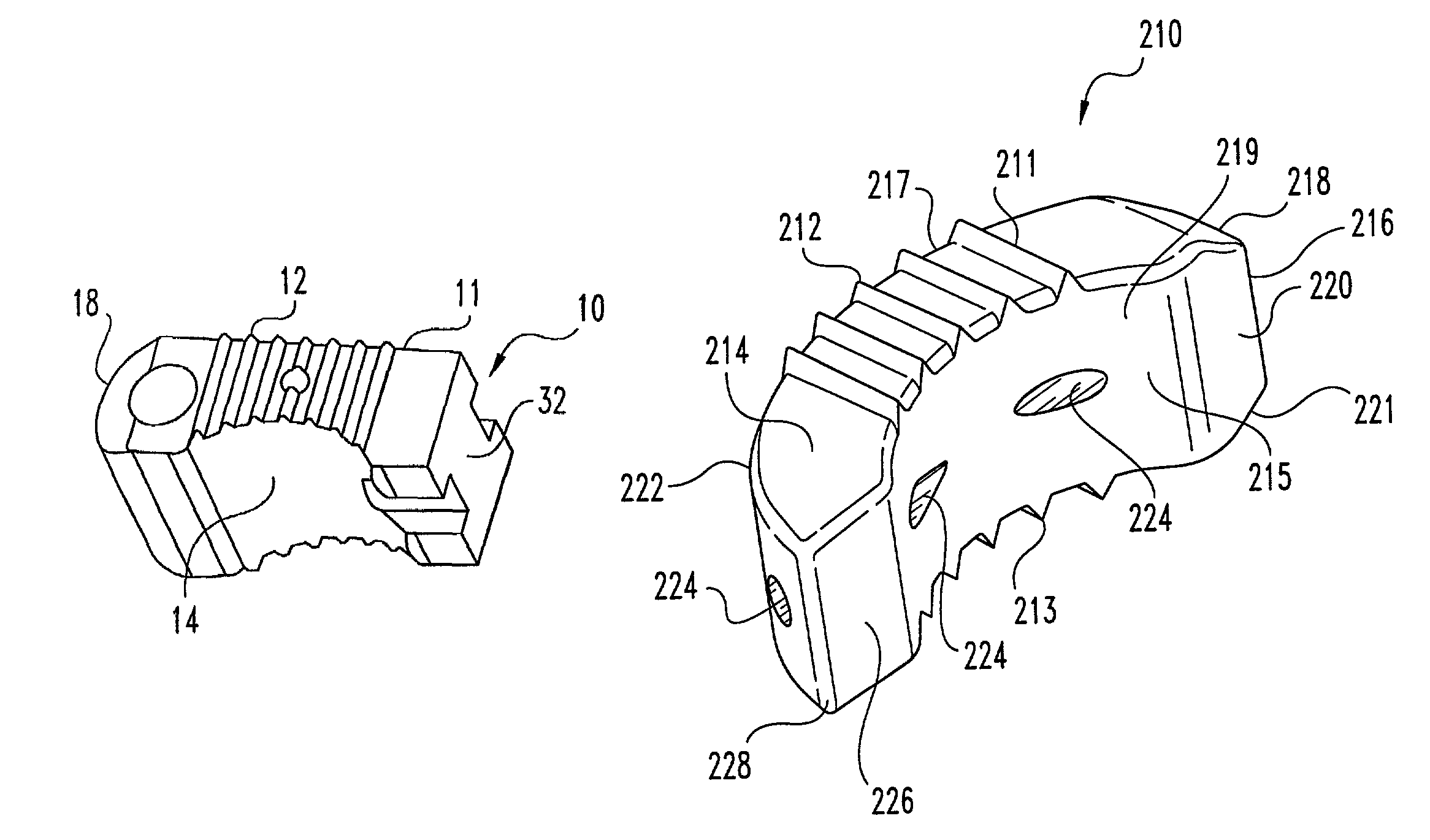
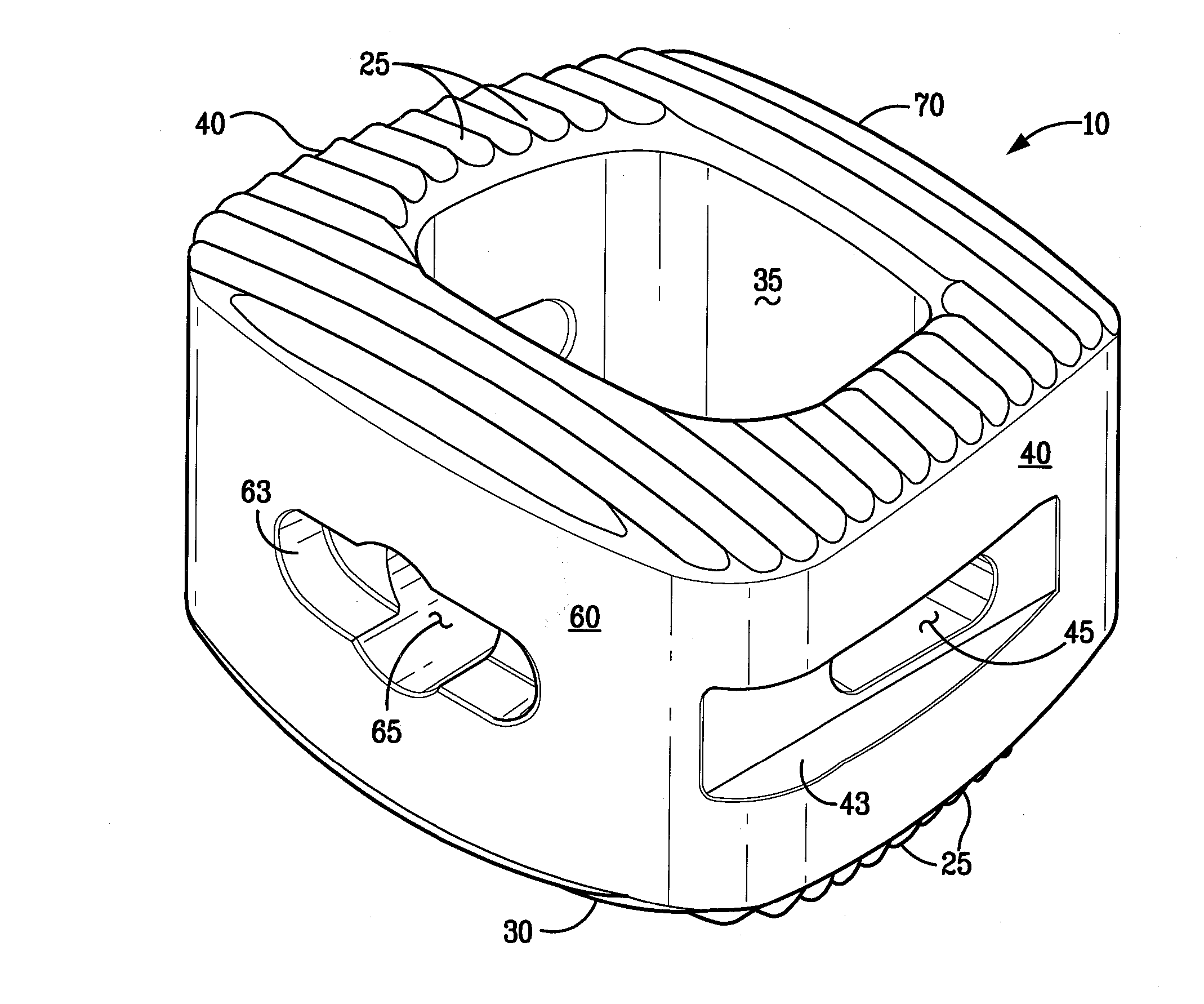
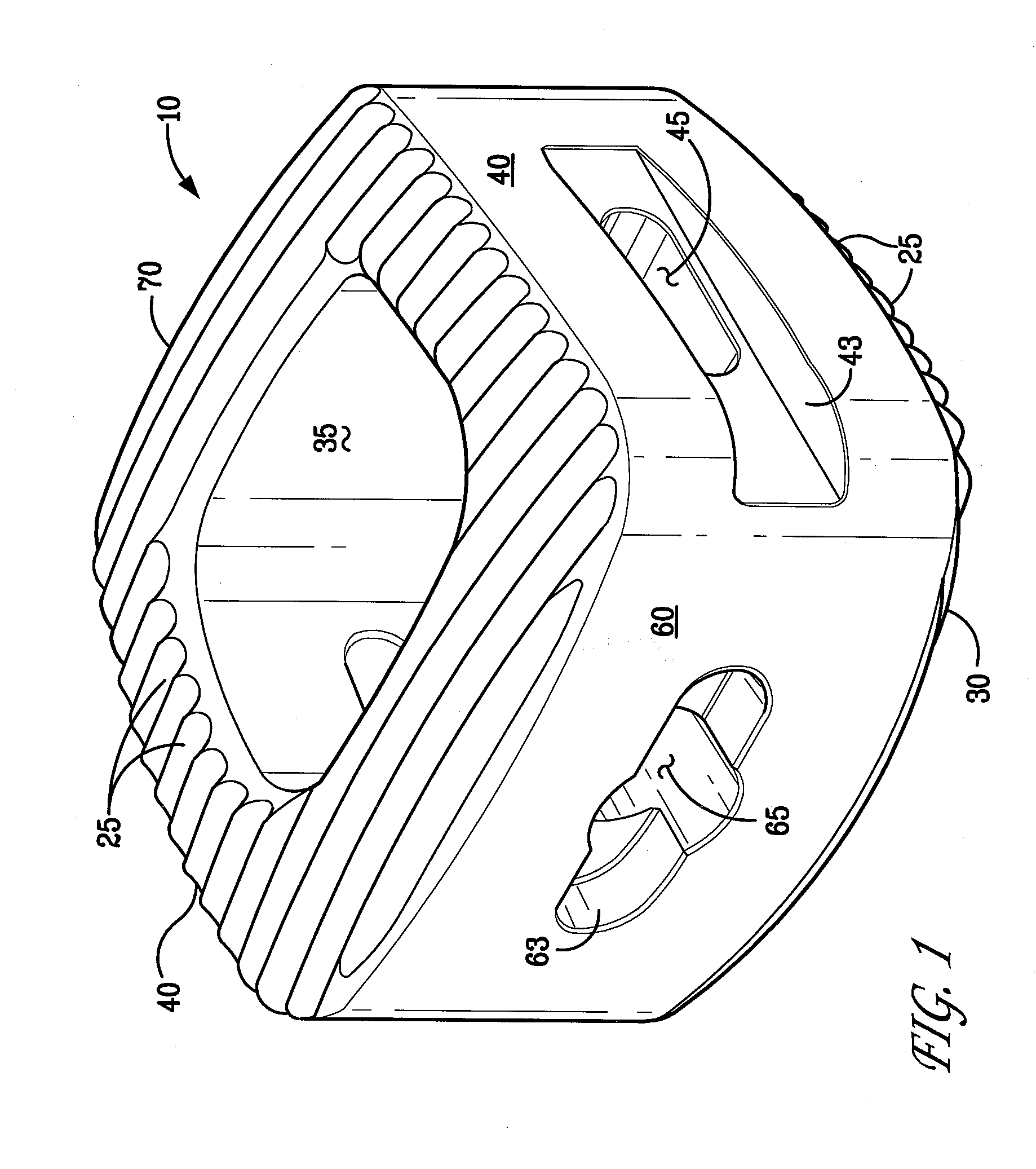
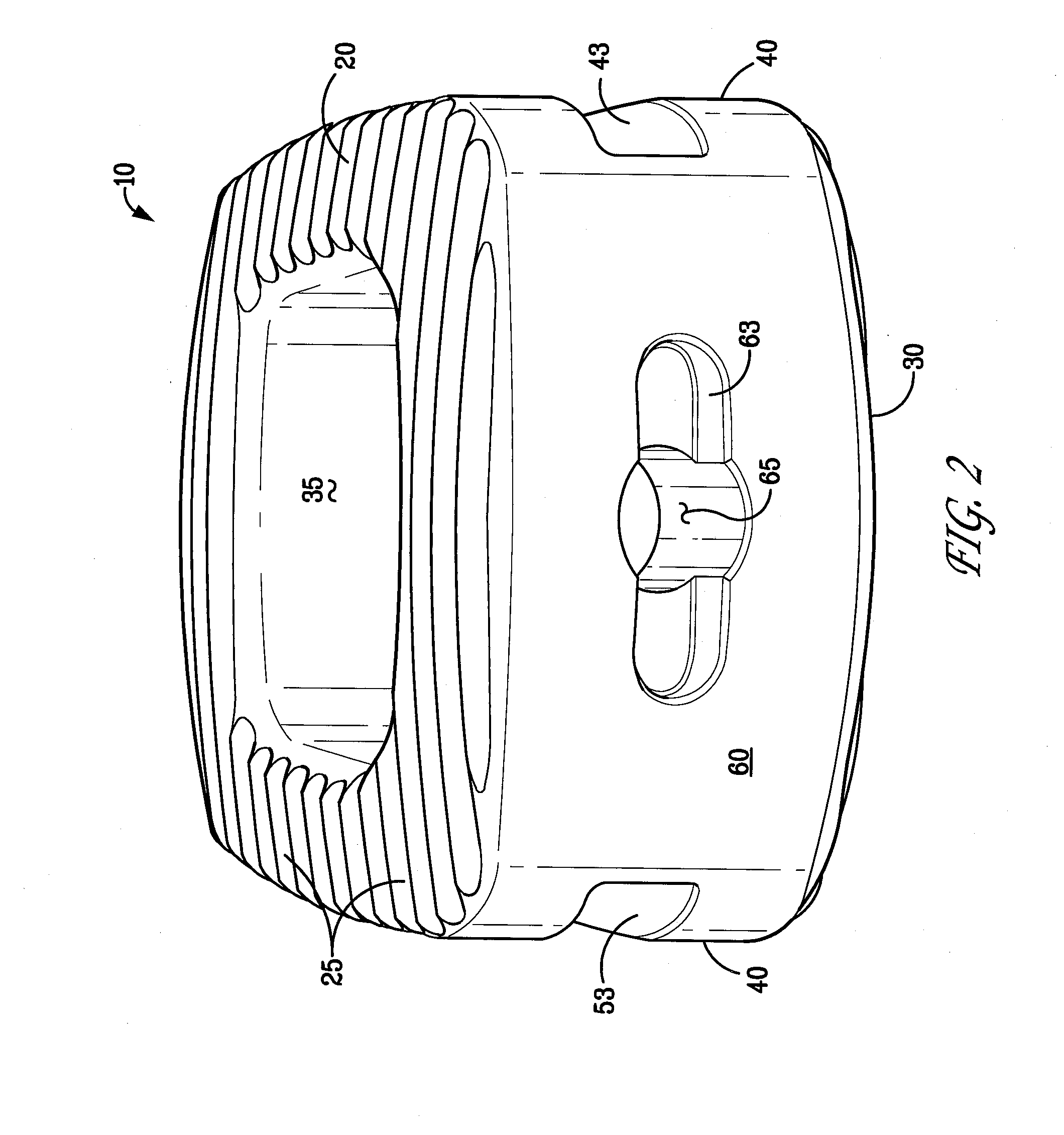
An intervertebral implant for fusing vertebrae is disclosed. The implant has a body with curved, substantially parallel posterior and anterior faces separated by two narrow implant ends, superior and inferior faces having a plurality of undulating surfaces for contacting upper and lower vertebral endplates, and at least one depression in the anterior or posterior face for engagement by an insertion tool, at least two vertical through-channels extending through the implant from the superior face to the inferior face, a chamfer on the superior and inferior surfaces at one of the narrow implant ends, and a beveled edge along a perimeter of the superior and inferior faces. The arcuate implant configuration and the chamfers on the superior and inferior faces at the narrow end facilitate insertion of the implant from a transforaminal approach into a symmetric position about the midline of the spine so that a single implant provides balanced support to the spinal column. The implant may include radiopaque markers extending through the thickness of the implant to indicate the location and size of the implant. The implant may be formed of a plurality of interconnecting bodies assembled to form a single unit. An implantation kit and method are also disclosed.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC +1
Artificial functional spinal unit assemblies
ActiveUS20050033439A1Promote growthPromoting bony end growthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical approachFunctional spinal unit
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
Artificial functional spinal unit assemblies
InactiveUS20050033431A1Promote growthPromoting bony end growthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical approachFunctional spinal unit
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
Artificial functional spinal unit assemblies
InactiveUS20060195192A1Promote growthPromoting bony end growthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical approachFunctional spinal unit
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
Artificial spinal unit assemblies
ActiveUS7909869B2Promote growthPromoting bony end growthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnSurgical operation
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion cage
InactiveUS20090054991A1Easy to insertShrink the necessary spaceSpinal implantsSpinal cageBiomedical engineering
A spinal cage system for inserting a spinal cage assembly into a spine to separate and support adjacent spinal vertebrae, includes a first cage member; a second cage member; and an articulating mechanism adapted to connect the first cage member to the second cage member and to permit the first and second cage members to move relate to each other. An insertion instrument is adapted to capture the spinal cage assembly for insertion of the spinal cage assembly into a spine and to rotate the first and second cage members relative to each other to achieve a desired orientation in the spine.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Bioactive Spinal Implants and Method of Manufacture Thereof
InactiveUS20070293948A1Facilitating radiographic assessmentEnhance bone contact and stability and fusionJoint implantsSpinal implantsLumbar vertebraeCervical fusions
A bioactive spinal implant used in cervical fusion, Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF), Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF), and Transforaminal Interbody Fusion (TLIF), having properties and geometries that enhance bone contact, stability, and fusion between adjacent vertebral bodies.
Owner:ORTHOVITA INC
Maximum support tlif implant
A transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) implant to be placed in an intervertebral space includes a front member and a back member. The front member includes a first end having a hinge, a second end, a pair of lateral portions, a top wall and a bottom wall, an opening configured through the pair of lateral portions and a plurality of openings in each of the top wall and the bottom wall. The back member includes a first end having an arcuately-shaped attachment head comprising a receptor dimensioned and configured to accommodate the hinge of the front member, a second end, a pair of lateral portions, a top wall, a bottom wall and an opening configured through the pair of lateral portions. The top wall and the bottom wall of the back member further comprise a plurality of openings.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
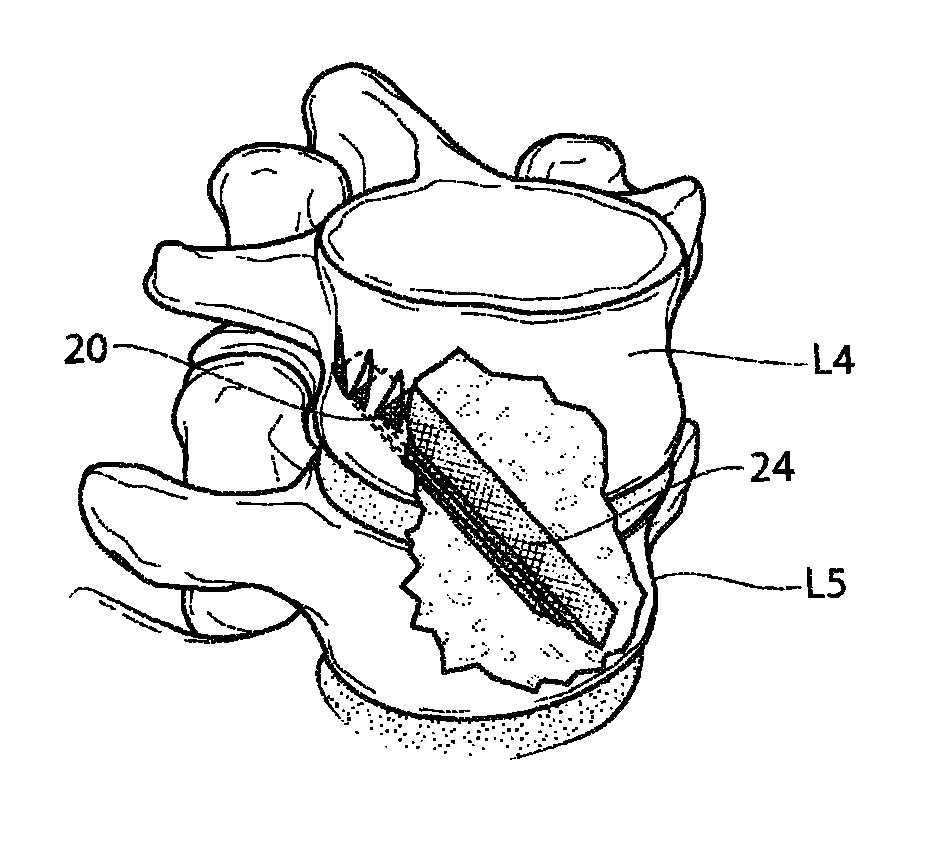
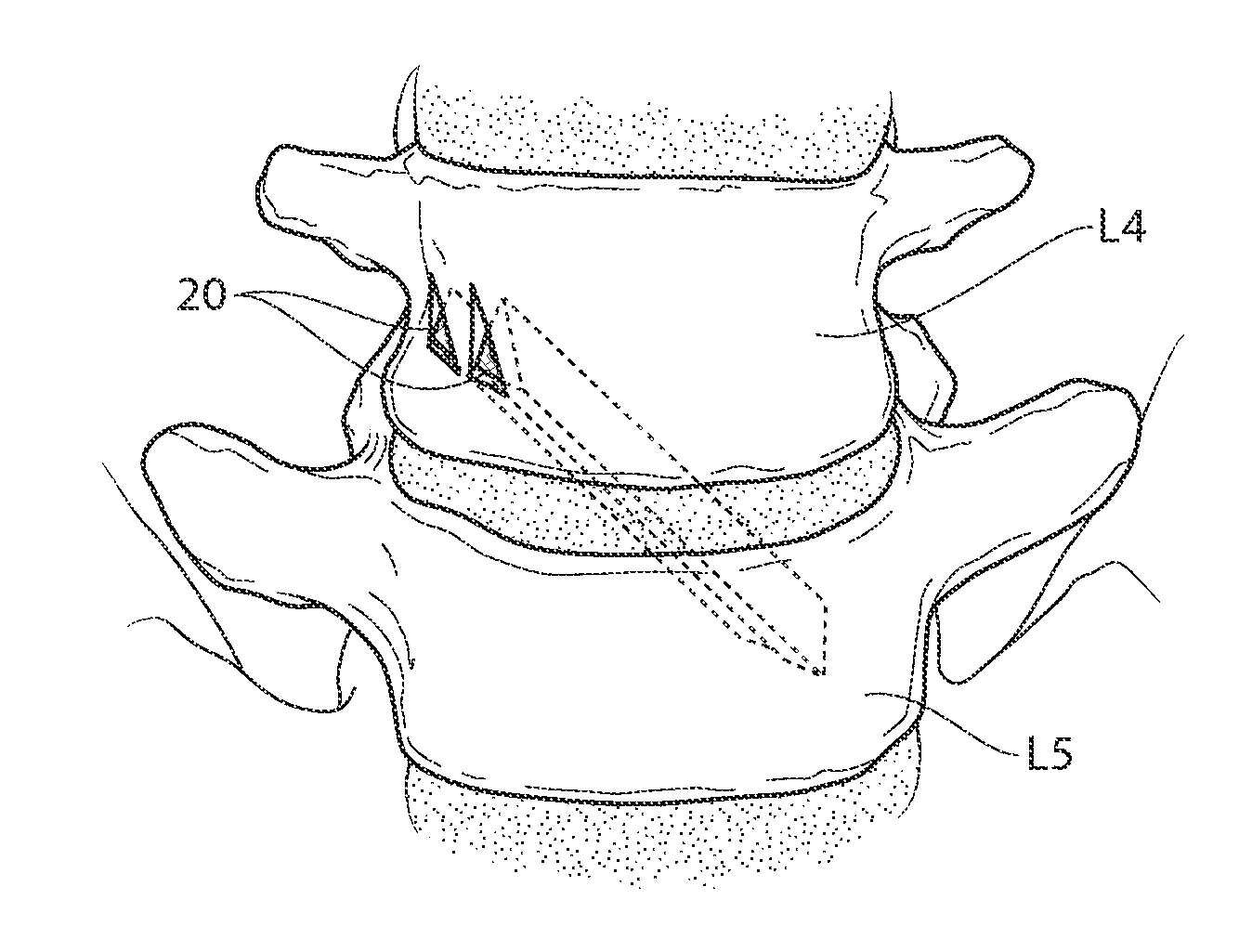
Oblique lumbar interbody fusion
A method fuses an inferior vertebra and a superior vertebra together. The method includes the steps of: extending a screw obliquely, both anteriorly and superiorly, through the inferior vertebra; and further extending the screw across an interbody space and into the superior vertebra both anteriorly and superiorly.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion cage
InactiveUS20070260314A1Easy to insertShrink the necessary spaceSpinal implantsSpinal cordEngineering
A cage to separate and support adjacent vertebrae in the spine that have undergone orthopedic spinal fusion procedures. The cage has first and second spacer members for insertion between adjacent vertebrae with a hinge located between the spacers. An advancing mechanism is located between the first and second spacer members that pivotally moves the first and second spacer members relative to each other at an angle which facilitates the insertion of the cage around the spinal cord. After insertion, the advancing mechanism is operable to position the first and second spacer members in the desired position between the two adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:BIYANI ASHOK
Anterior lumbar interbody fusion cage device and associated method
The disclosure relates to a cage device for performing spinal fusion, including, in some embodiments: a housing defining one or more ports that is selectively disposed in an intervertebral space between adjacent vertebrae; one or more extensible retention structures that are selectively advanced out of the housing through the one or more ports and into one or more endplates of the adjacent vertebrae; and one or more actuation mechanisms for selectively advancing the one or more extensible retention structures out of the housing through the one or more ports and into the one or more endplates of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:CTL MEDICAL CORP
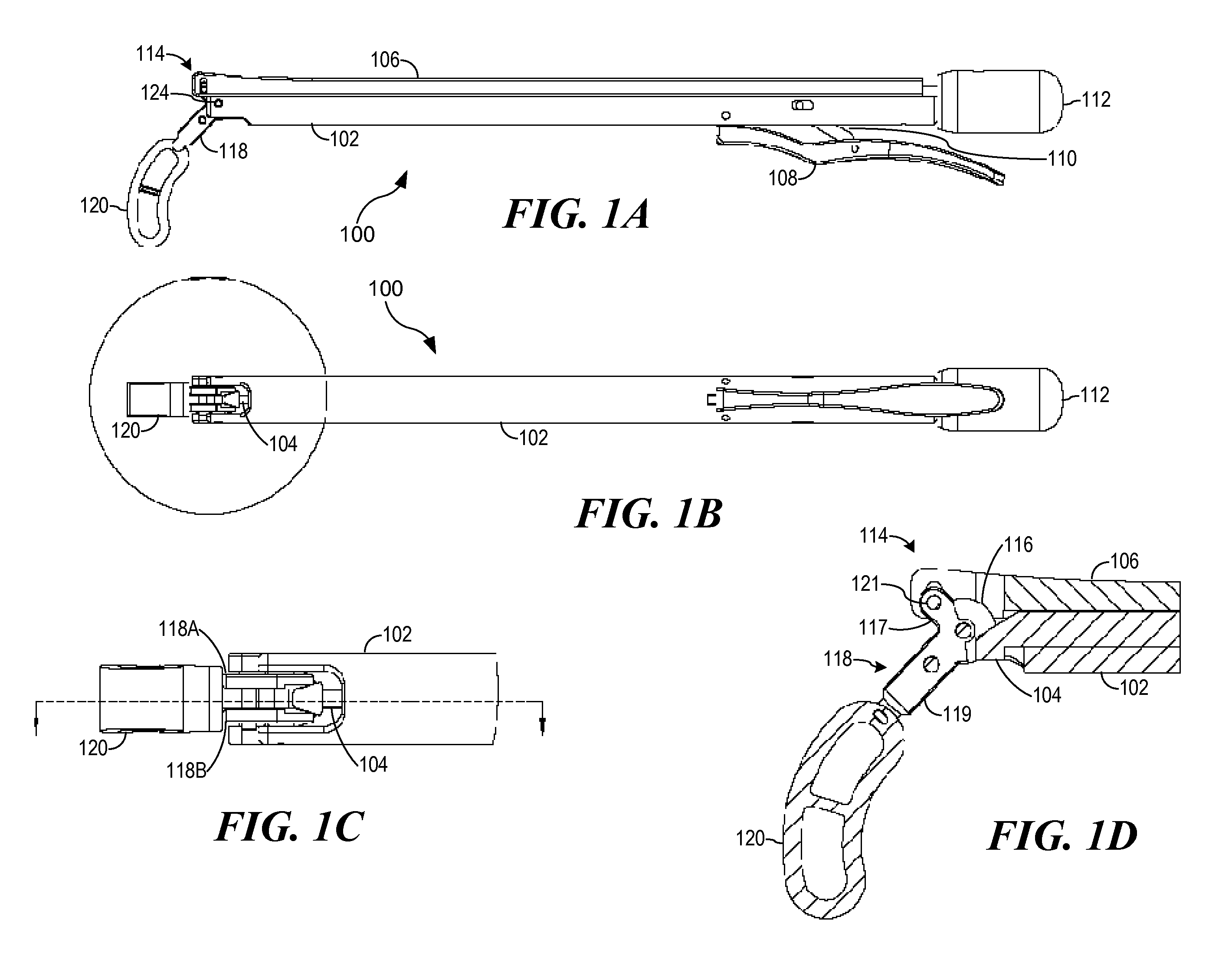
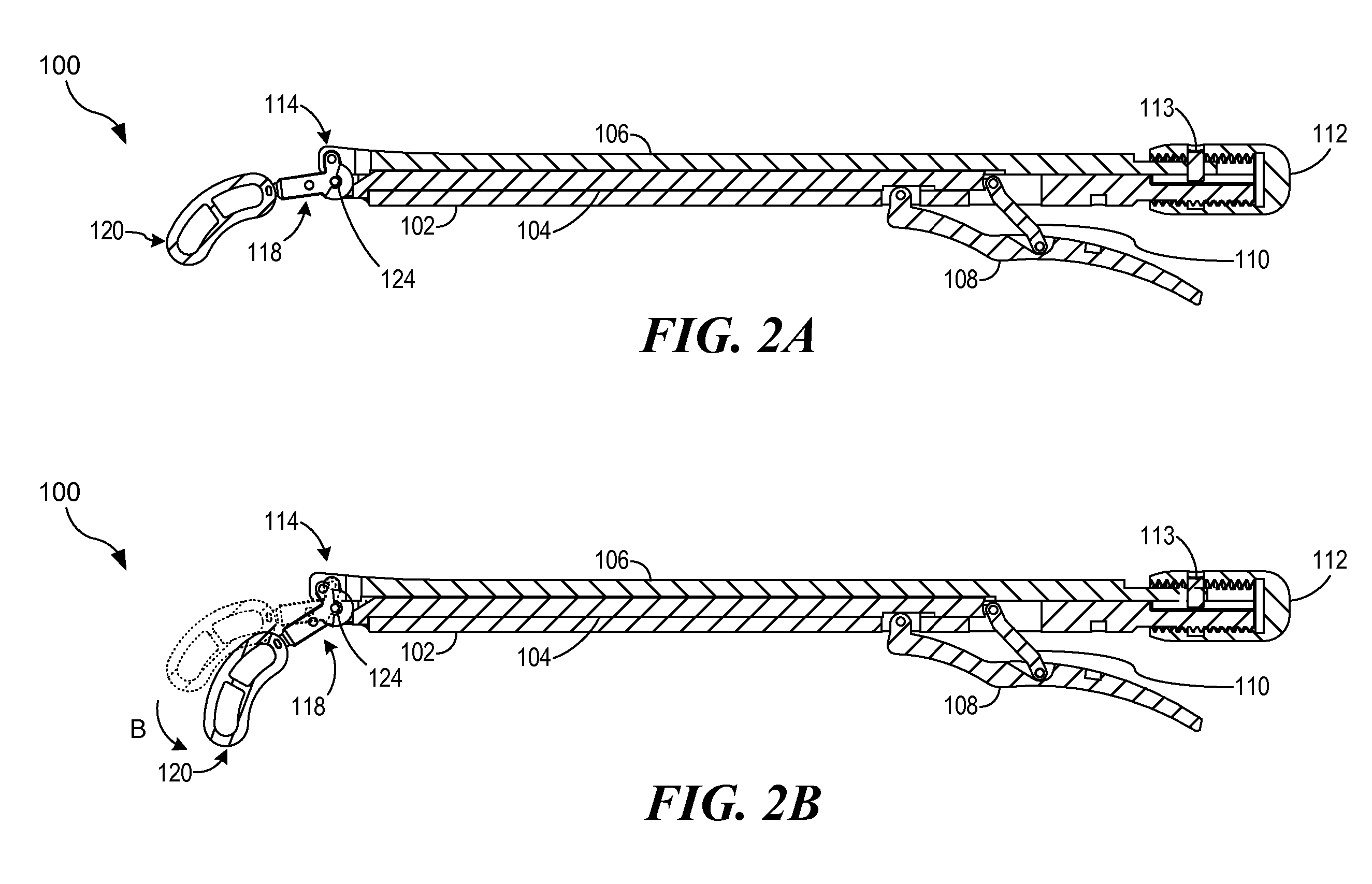
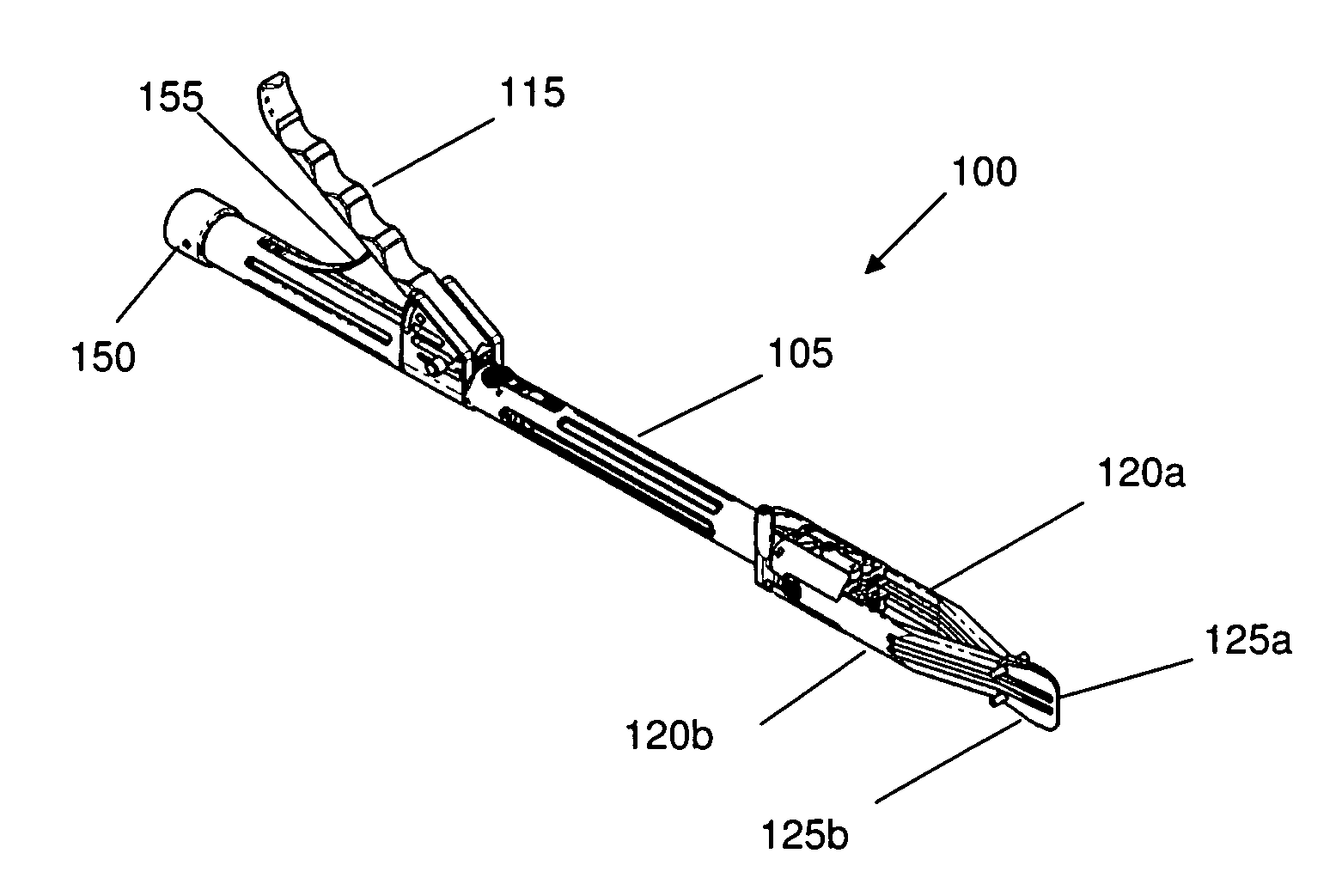
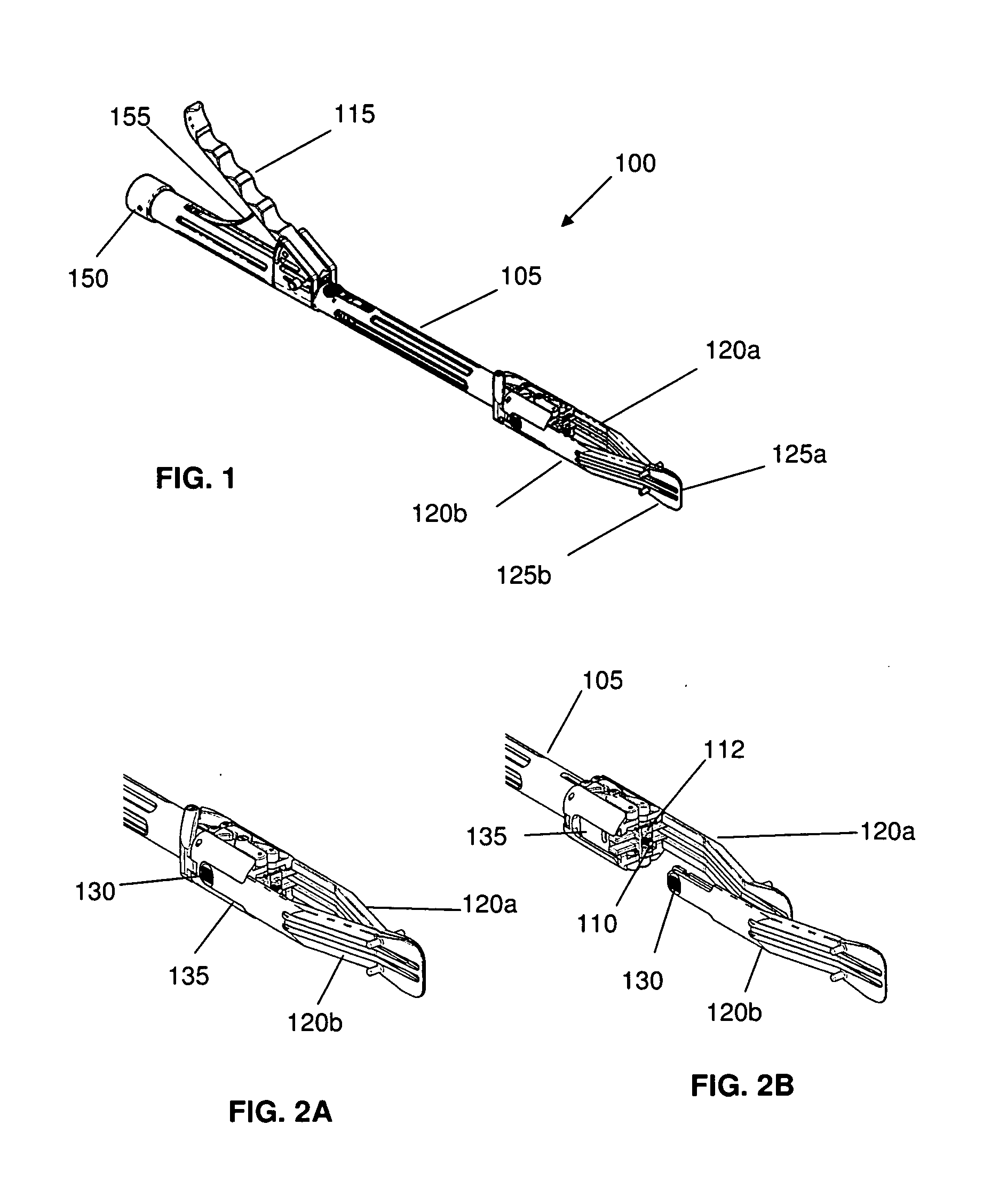
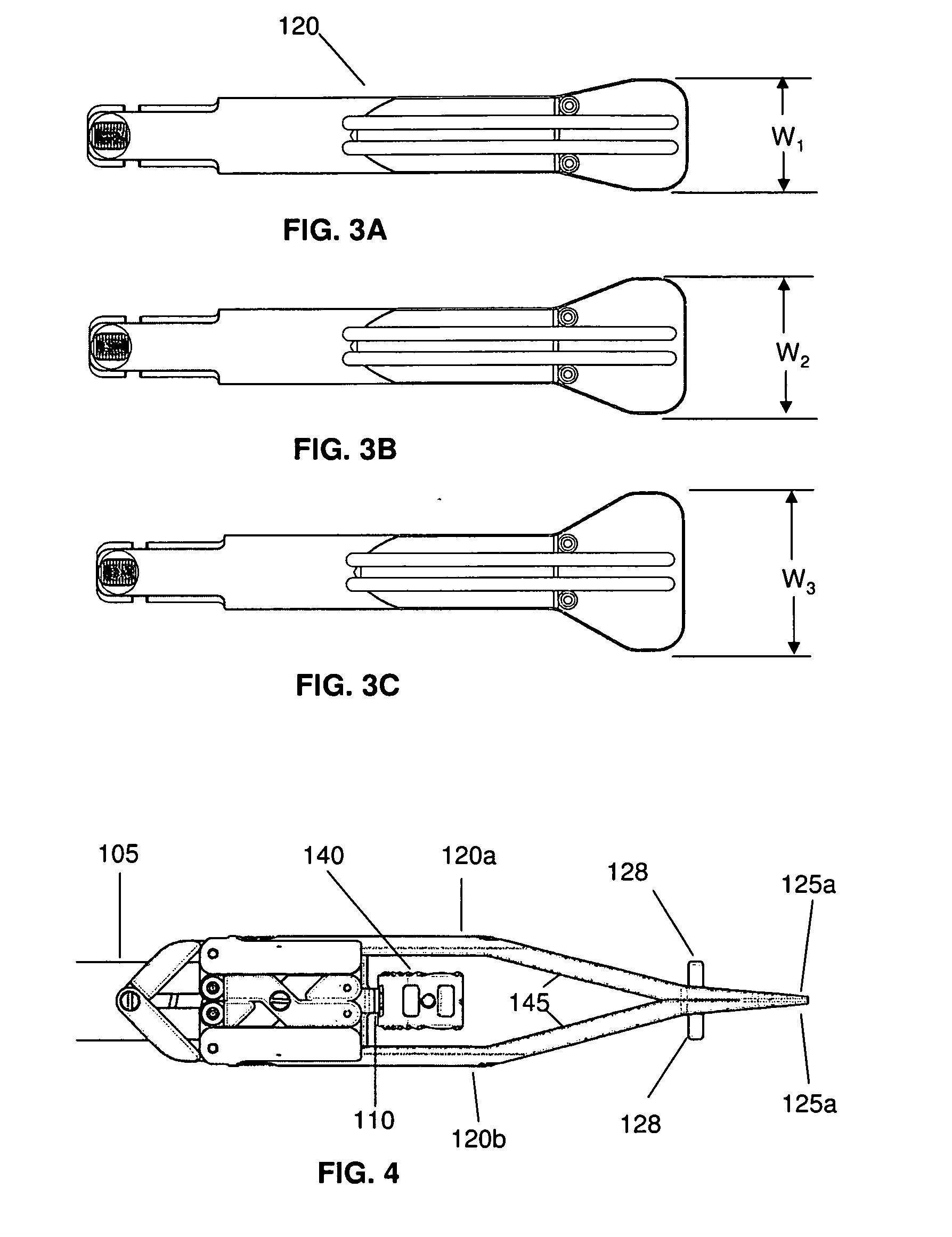
Articulated delivery instrument
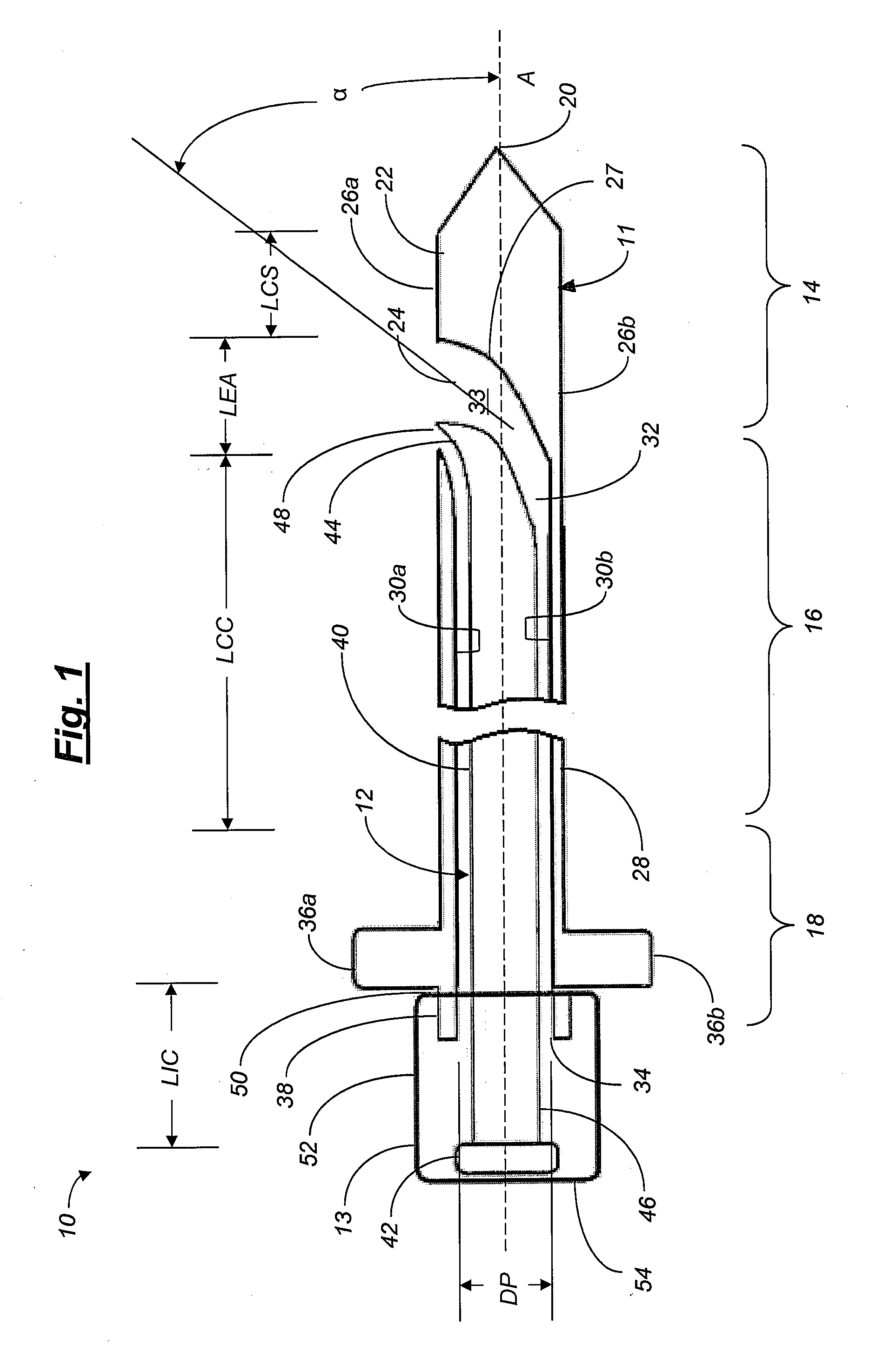
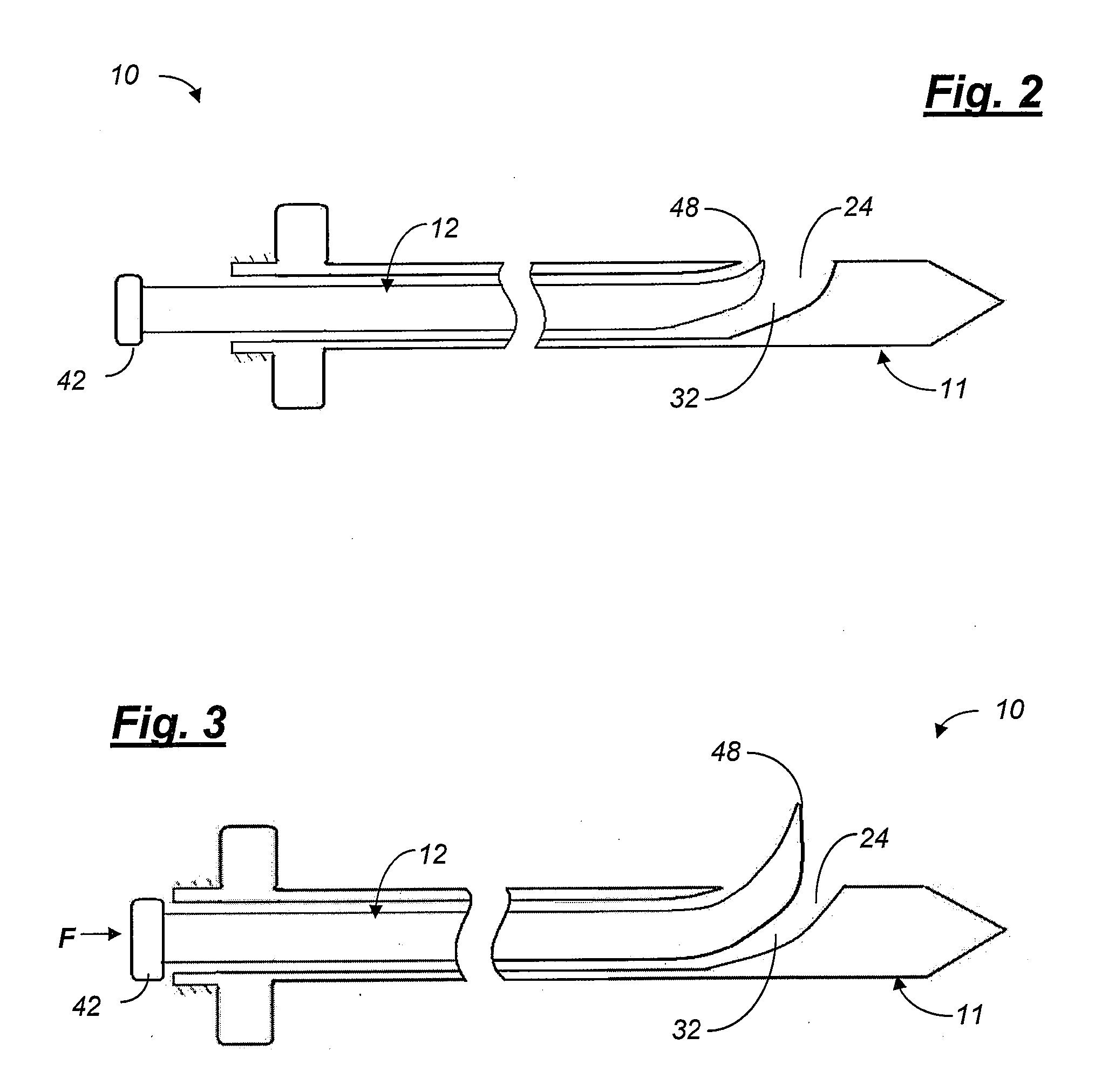
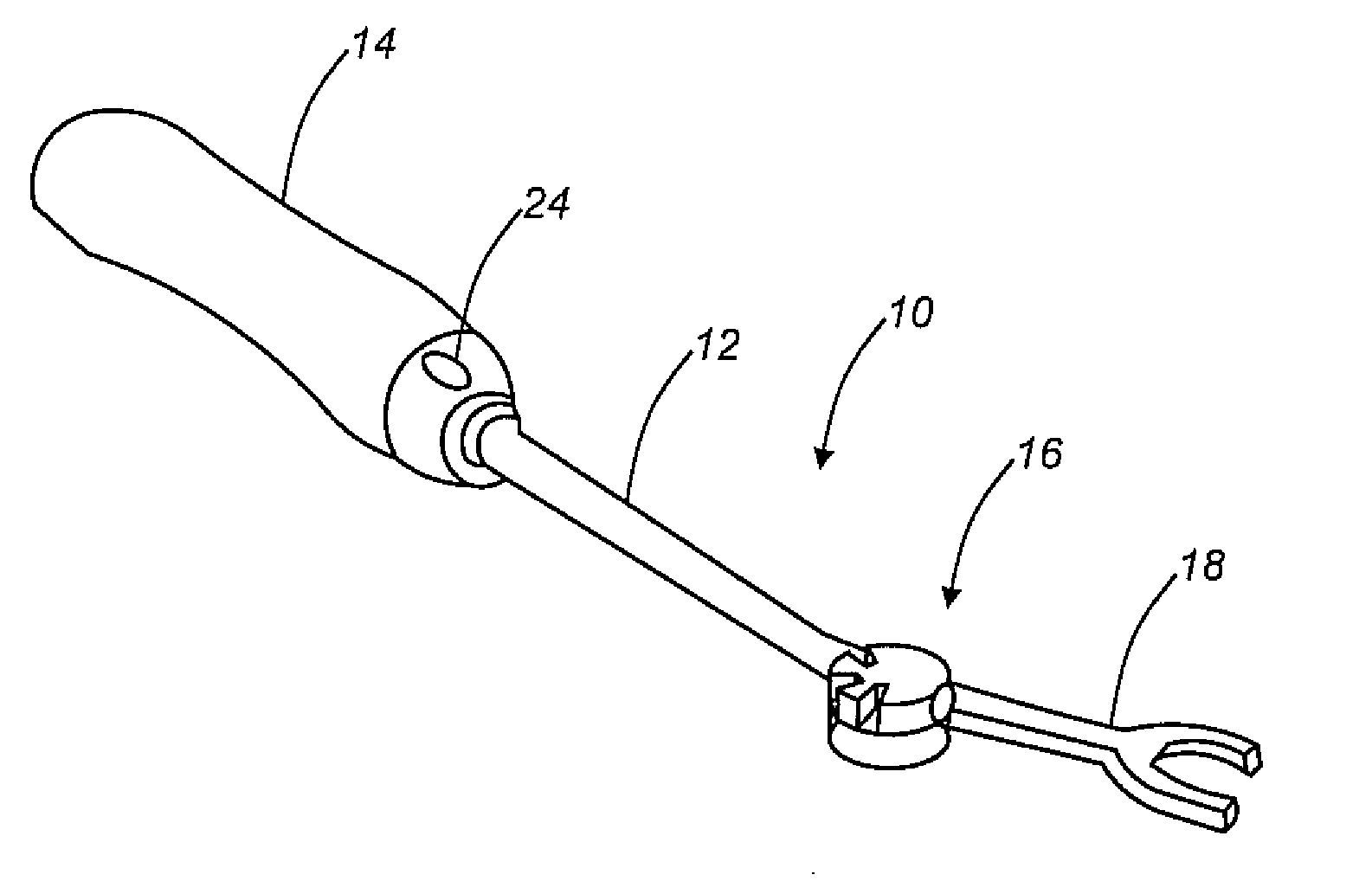
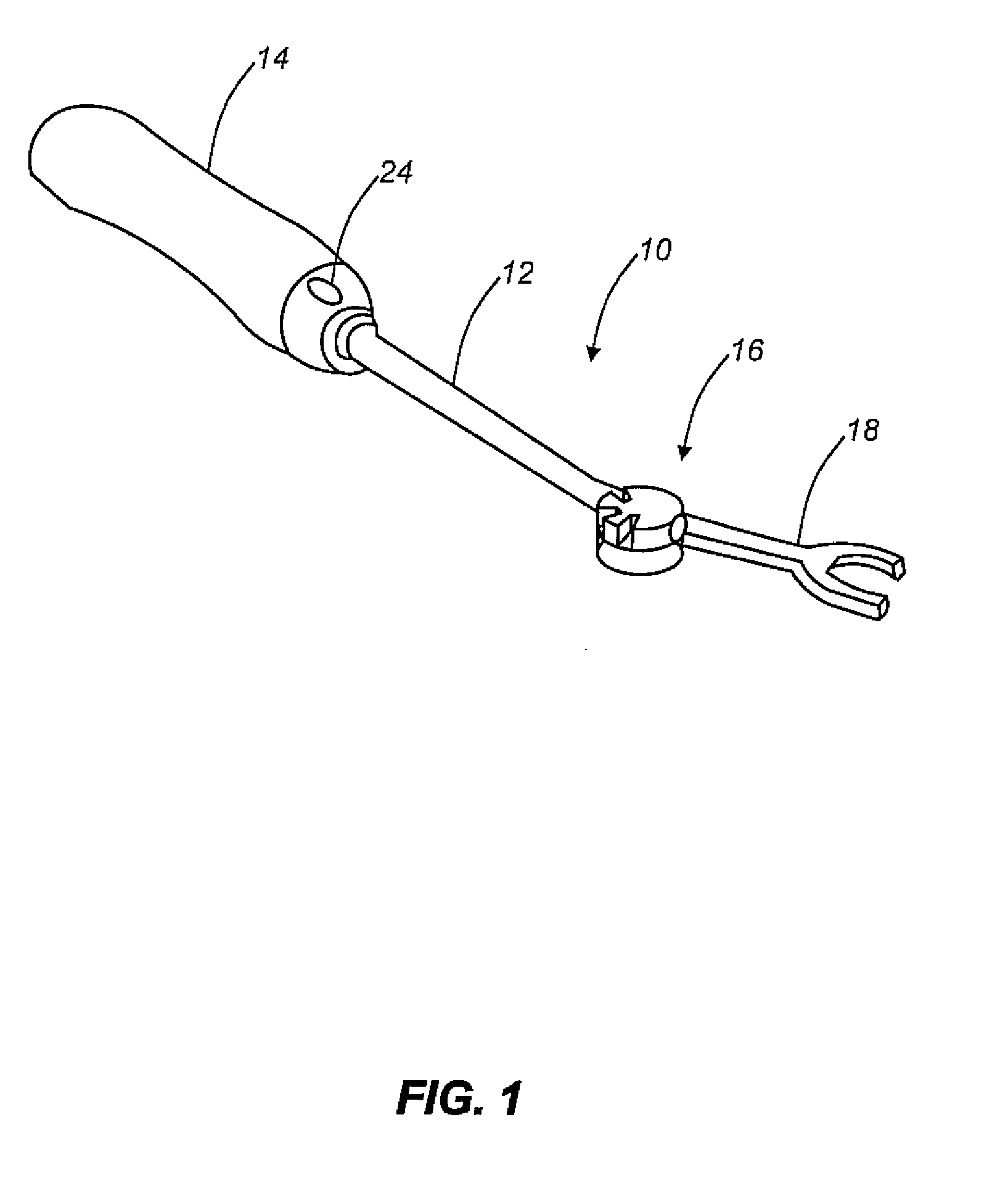
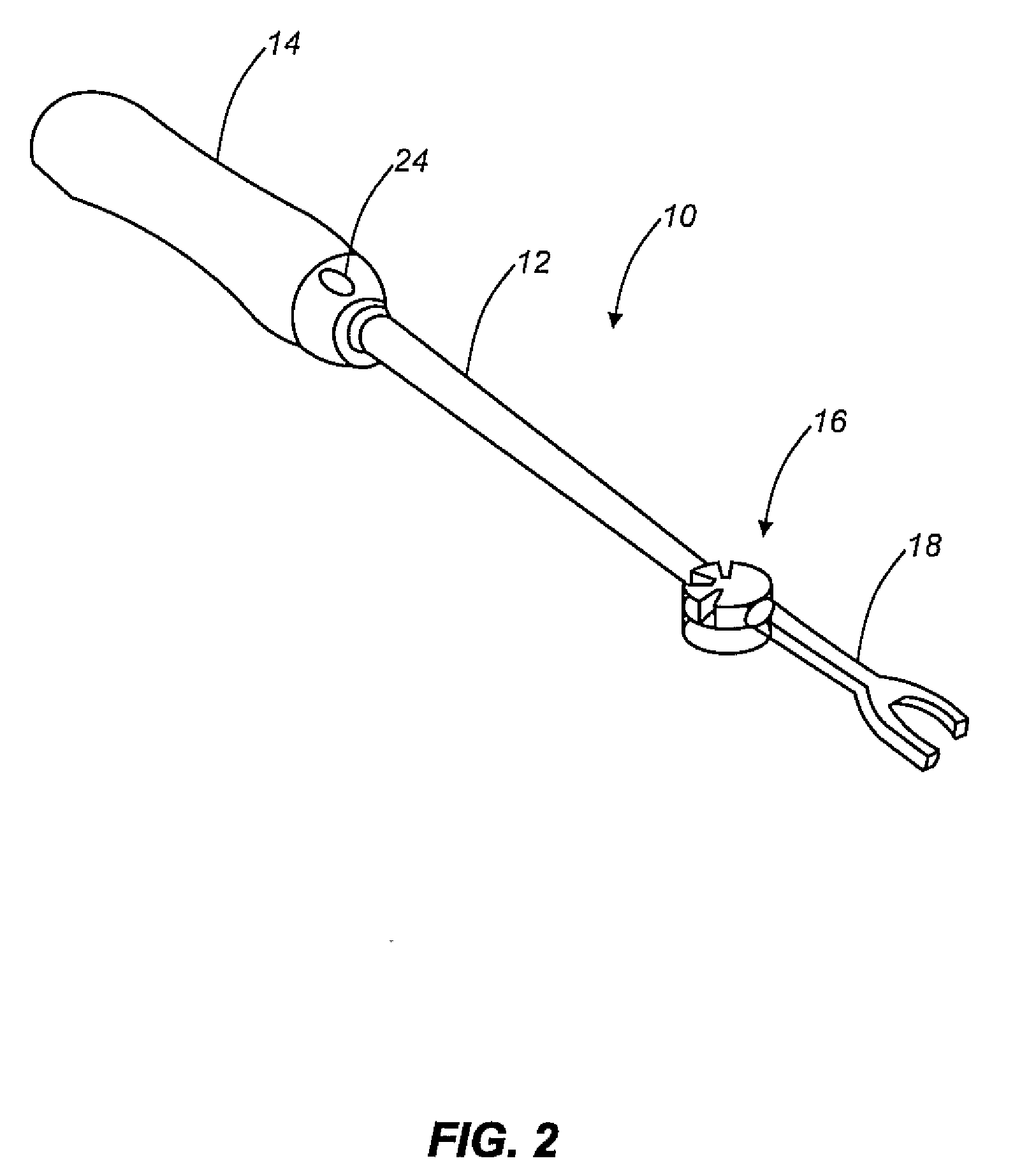
An articulated delivery instrument for the proper positioning and placements of inserts, for example, an insert such as a lumbar interbody fusion device (“LIF”). The instrument may comprise a body and a first member slidingly coupled to the body. A rotating member for releasably retaining an insert may be pivotally coupled to a distal end of the body and the first member. A first actuator may function to translate the first member relative to the body. Translation of the first member relative to the body may rotate the rotating member relative to the instrument. A second actuator may function to transition the rotating member between release and retention of the insert.
Owner:THEKEN SPINE
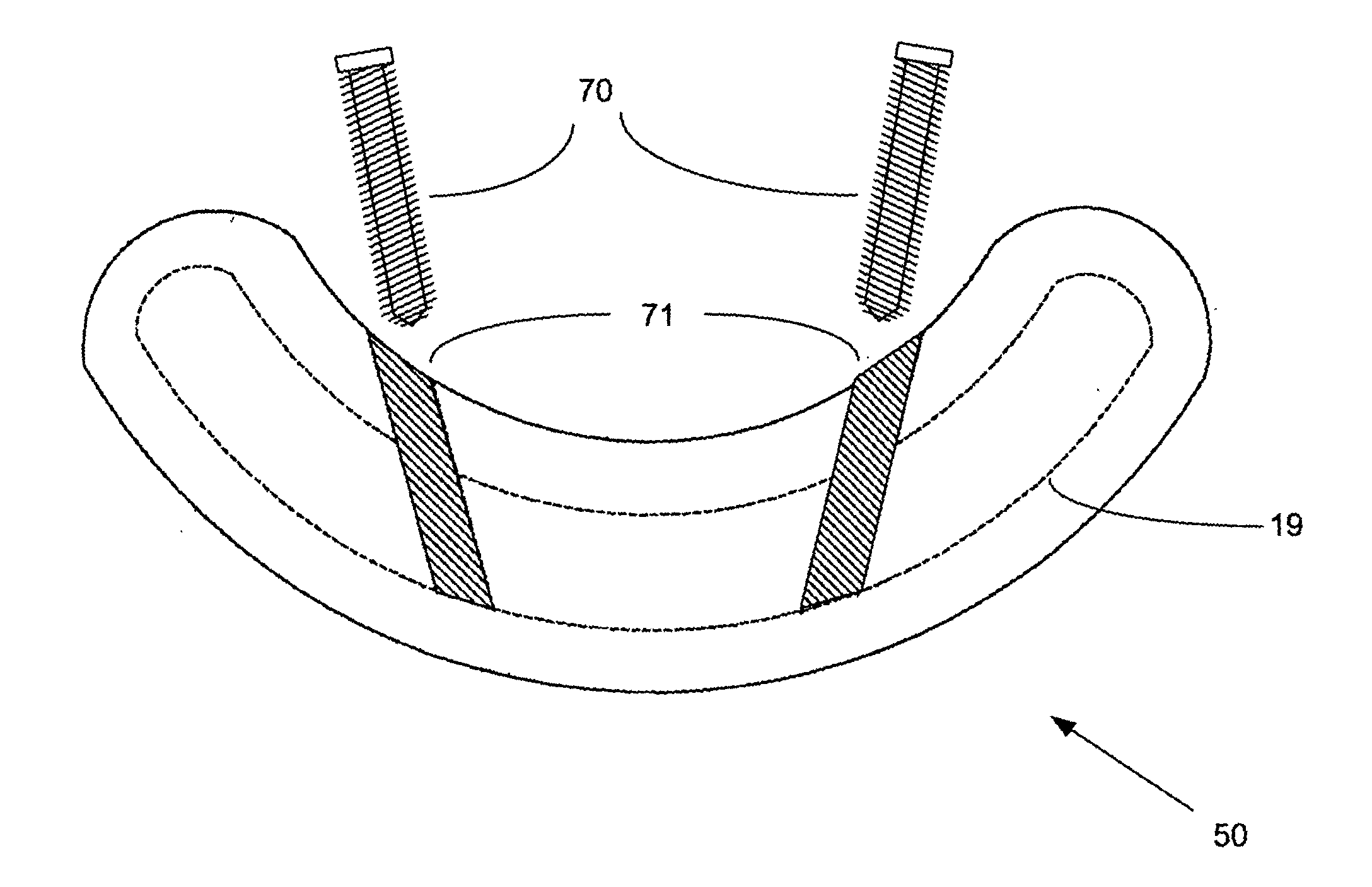
Apparatus, systems, and methods for stabilizing a spondylolisthesis
ActiveUS8470004B2Speed up fusion and stabilization processFusion and/or stabilization of the lumbar spineInternal osteosythesisToe jointsLumbar facet jointIntervertebral disc
Assemblies of one or more implant structures make possible the achievement of diverse interventions involving the fusion and / or stabilization of lumbar and sacral vertebra in a non-invasive manner, with minimal incision, and without the necessitating the removing the intervertebral disc. The representative lumbar spine interventions, which can be performed on adults or children, include, but are not limited to, lumbar interbody fusion; translaminar lumbar fusion; lumbar facet fusion; trans-iliac lumbar fusion; and the stabilization of a spondylolisthesis.
Owner:SI BONE INC
Apparatus, systems, and methods for achieving lumbar facet fusion
ActiveUS8444693B2Speed up fusion and stabilization processFusion and/or stabilization of the lumbar spineInternal osteosythesisBone implantLumbar facet jointIntervertebral disc
Assemblies of one or more implant structures make possible the achievement of diverse interventions involving the fusion and / or stabilization of lumbar and sacral vertebra in a non-invasive manner, with minimal incision, and without the necessitating the removing the intervertebral disc. The representative lumbar spine interventions, which can be performed on adults or children, include, but are not limited to, lumbar interbody fusion; translaminar lumbar fusion; lumbar facet fusion; trans-iliac lumbar fusion; and the stabilization of a spondylolisthesis.
Owner:SI BONE INC
Apparatus, systems, and methods for achieving trans-iliac lumbar fusion
ActiveUS8414648B2Speed up fusion and stabilization processFusion and/or stabilization of the lumbar spineInternal osteosythesisBone implantLumbar facet jointIntervertebral disc
Assemblies of one or more implant structures make possible the achievement of diverse interventions involving the fusion and / or stabilization of lumbar and sacral vertebra in a non-invasive manner, with minimal incision, and without the necessitating the removing the intervertebral disc. The representative lumbar spine interventions, which can be performed on adults or children, include, but are not limited to, lumbar interbody fusion; translaminar lumbar fusion; lumbar facet fusion; trans-iliac lumbar fusion; and the stabilization of a spondylolisthesis.
Owner:SI BONE INC
Apparatus, systems, and methods for achieving anterior lumbar interbody fusion
ActiveUS8425570B2Speed up fusion and stabilization processFusion and/or stabilization of the lumbar spineInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsLumbar facet jointIntervertebral disc
Assemblies of one or more implant structures make possible the achievement of diverse interventions involving the fusion and / or stabilization of lumbar and sacral vertebra in a non-invasive manner, with minimal incision, and without the necessitating the removing the intervertebral disc. The representative lumbar spine interventions, which can be performed on adults or children, include, but are not limited to, lumbar interbody fusion; translaminar lumbar fusion; lumbar facet fusion; trans-iliac lumbar fusion; and the stabilization of a spondylolisthesis.
Owner:SI BONE INC
Maximum support TLIF implant
A transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) implant to be placed in an intervertebral space includes a front member and a back member. The front member includes a first end having a hinge, a second end, a pair of lateral portions, a top wall and a bottom wall, an opening configured through the pair of lateral portions and a plurality of openings in each of the top wall and the bottom wall. The back member includes a first end having an arcuately-shaped attachment head comprising a receptor dimensioned and configured to accommodate the hinge of the front member, a second end, a pair of lateral portions, a top wall, a bottom wall and an opening configured through the pair of lateral portions. The top wall and the bottom wall of the back member further comprise a plurality of openings.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
Transpedicular access to the intervertebral disc space for discectomy, end plate preparation, and interbody fusion
An insertion device is configured to access a disc positioned between adjacent vertebrae. The insertion device includes a cannula having a passage formed therein. The cannula has an exit aperture. An obturator is substantially positioned within the passage formed in the cannula. One end of the obturator has a probe and the other end of the obturator has a head. An impaction cap is in contact with the cannula and is positioned to cover the head of the obturator. The impaction cap is configured to allow at least a portion of the cannula to be inserted through a portion of one vertebra without deployment of the probe of the obturator through the exit aperture of the cannula.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Articulating Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Inserter Device and Associated Method of Use
InactiveUS20090043312A1Minimal disruptionBig impactSpinal implantsOsteosynthesis devicesSpinal columnIntervertebral space
The present invention provides an articulating TLIF inserter device operable for placing, positioning, and inserting a spinal implant into an intervertebral space with minimum tissue disruption and maximum inline impaction forces, including: an elongate shaft having a proximal end, a distal end, and an axis; an ergonomic handle disposed at the proximal end of the elongate shaft; an articulating joint mechanism disposed at the distal end of the elongate shaft; and an inserter piece coupled to the articulating joint mechanism, wherein the inserter piece is operable for selectively retaining the spinal implant, and wherein the articulating joint mechanism is operable for selectively actuating the inserter piece between one or more substantially off-axis configurations and a substantially on-axis configuration with respect to the elongate shaft. The articulating TLIF inserter device also includes a release mechanism disposed one of at and near the ergonomic handle, wherein the release mechanism is coupled to and operable for selectively actuating the articulating joint mechanism.
Owner:CTL MEDICAL CORP
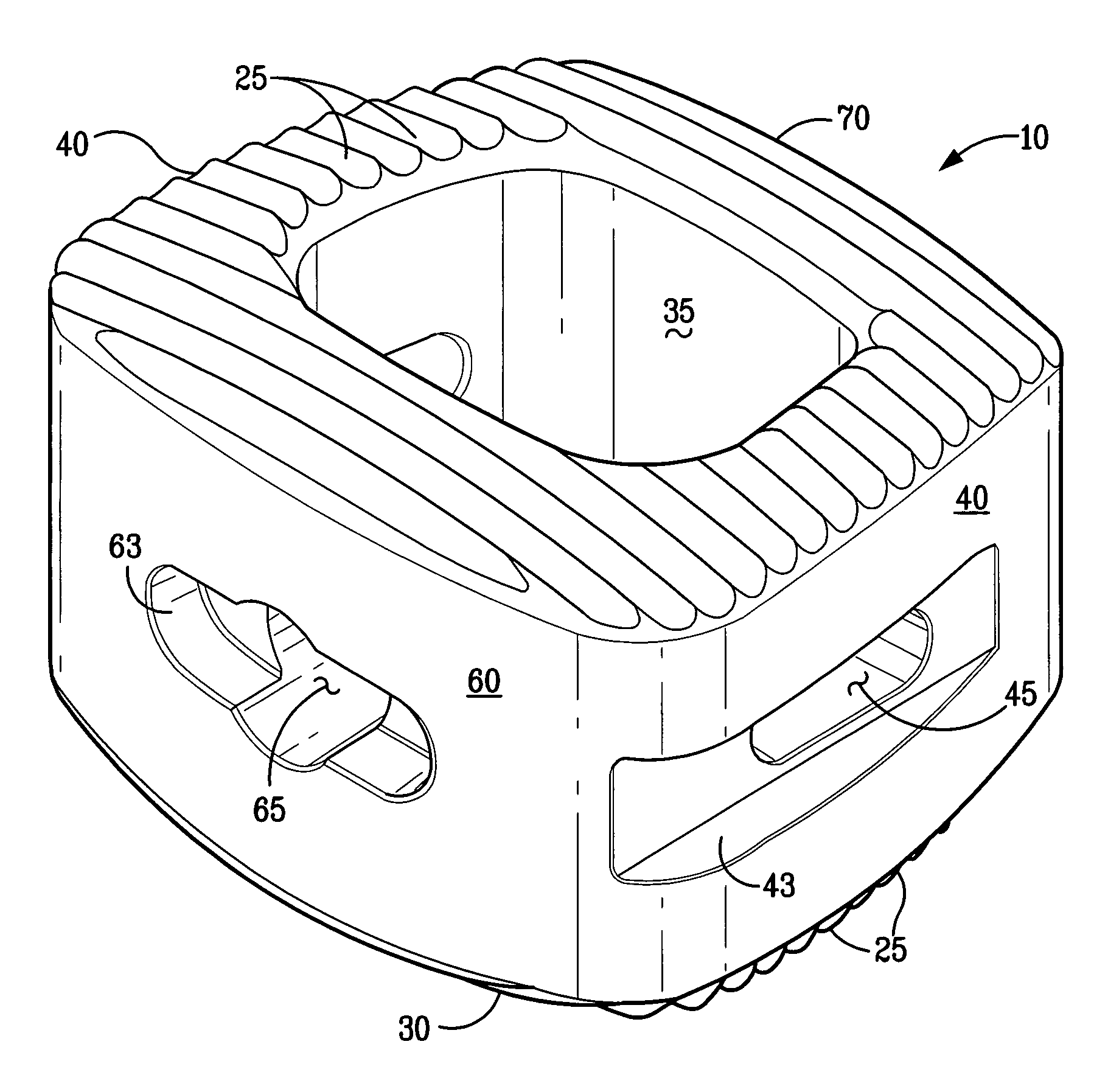
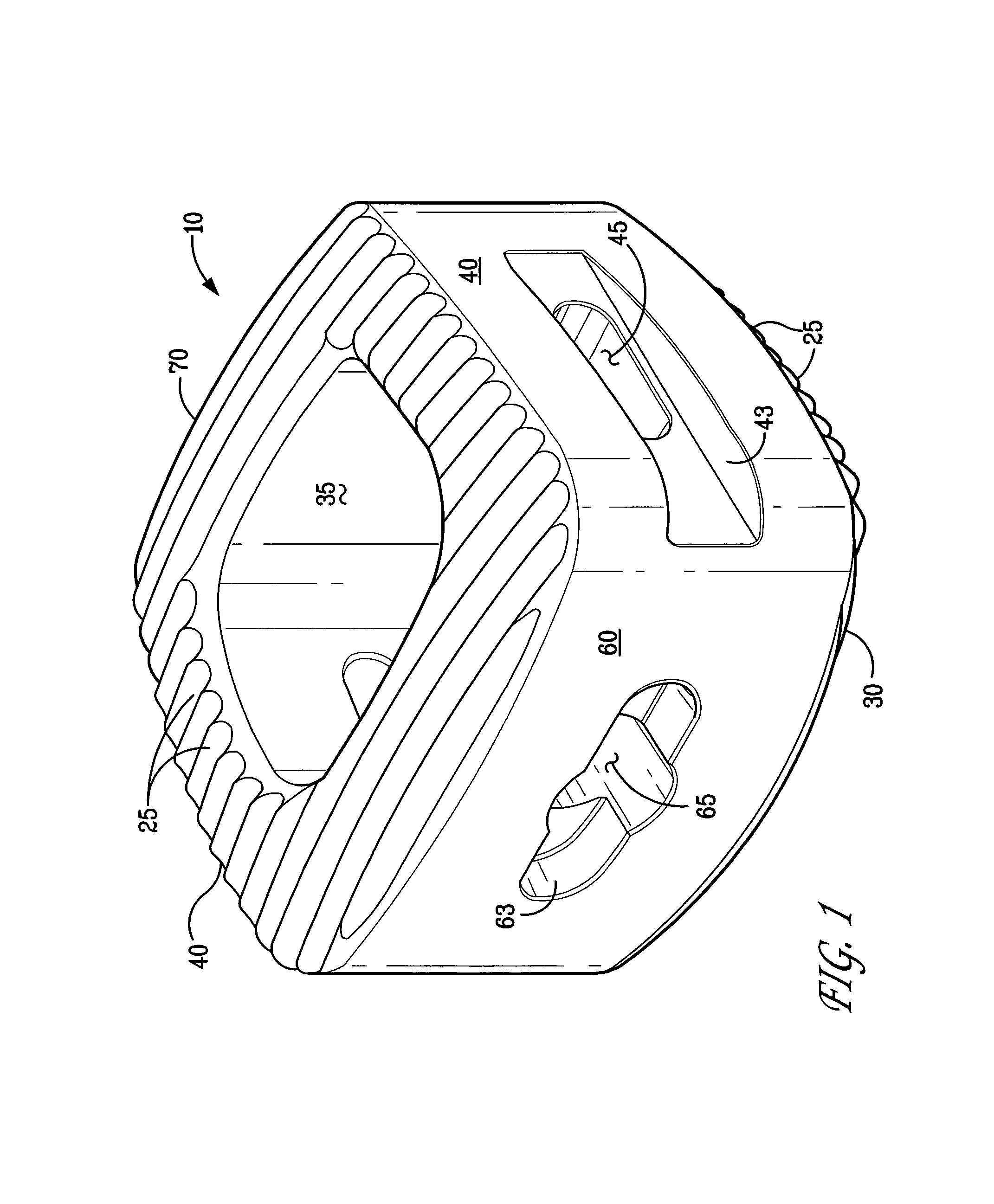
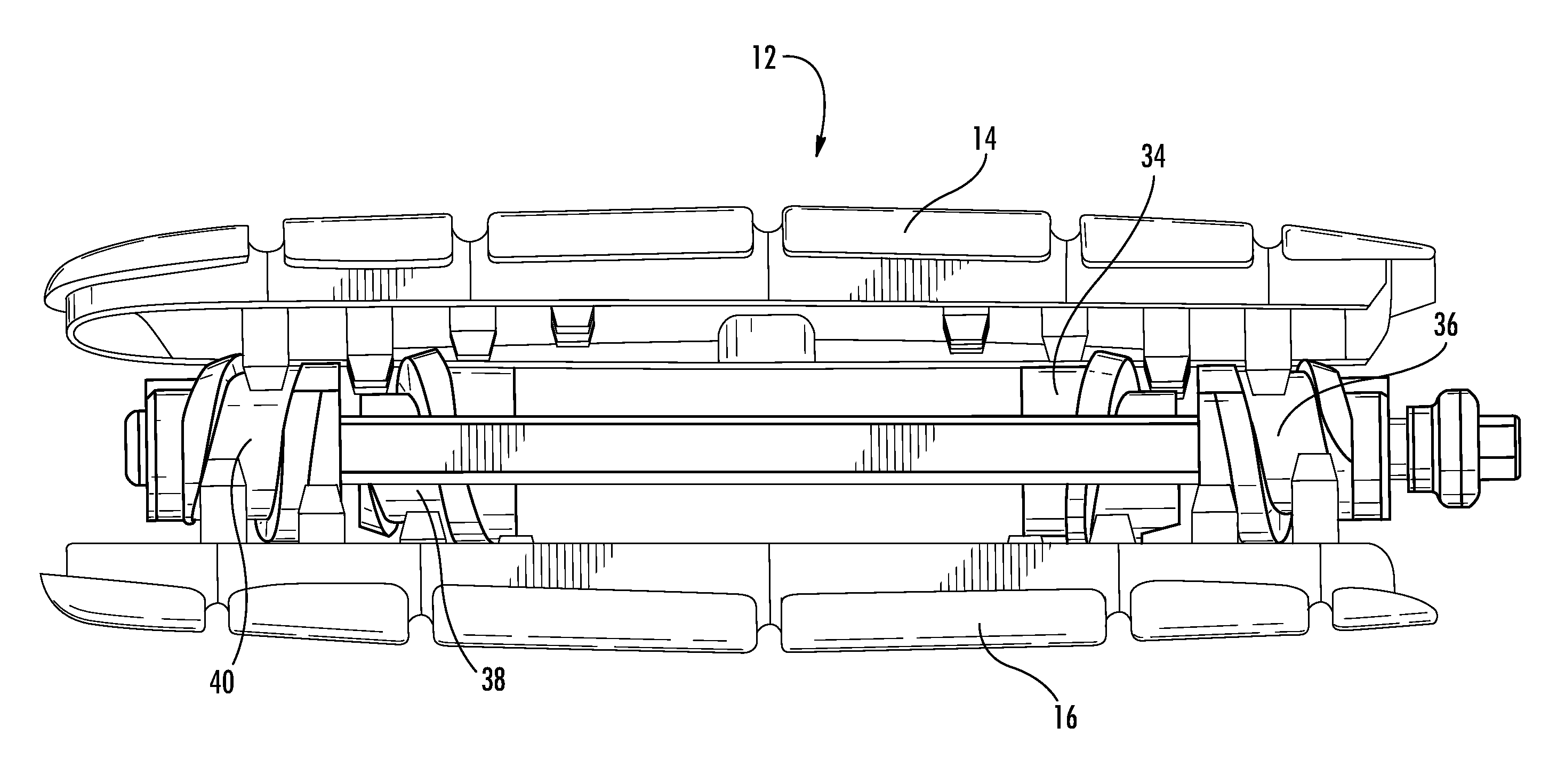
Expandable and adjustable lordosis interbody fusion system
ActiveUS20150066145A1Assists lordotic adjustmentEffective tool for in situ adjustmentJoint implantsSpinal implantsVertebraLumbar interbody fusion
An expandable housing for an interbody fusion system has movable tapered external helical threaded members that travel along tracking to operably engage against the top and bottom shell members, urging them apart to cause expansion in the height of the housing. In an embodiment, the tapered members are disposed in a dual arrangement such that independent engagement of the tapered members along lateral portions of the top and bottom shells cause an angular tilt to the exterior surface of the housing when the tapered members are moved to different degrees. This function permits adjustment in the angular relationship between adjacent vertebrae and assists the lordotic adjustment of the patient's spine. When the functions of the device are used in combination by the surgeon, the device provides an effective tool for in situ adjustment when performing lateral lumbar interbody fusion.
Owner:ADCURA INC
Alif inserter/distractor
Apparatus and method for an instrument for use in an anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) procedure for distraction of adjacent vertebrae and insertion of a vertebral body replacement (VBR) implant. The instrument includes a hollow body having a proximal end and a distal end, an inserter shaft positioned within the body configured to removably engage a VBR implant near the distal end of the body, an actuatable handle coupled to the body, the handle being configured to engage the inserter shaft to advance the VBR implant in a distal direction during handle actuation, and a pair of opposed distraction arms removably coupled to the distal end of the body, the distraction arms having paddle tips configured to fit between adjacent vertebrae, the distraction arms being movable from a closed position to an open position during distal advancement of the VBR implant between the distraction arms.
Owner:ALPHATEC SPINE INC
Intervertebral implant for transforaminal posterior lumbar interbody fusion procedure
InactiveUS20060106460A1Easy to insertPrevent slippingBone implantSurgeryTransforaminal approachSpinal column
An intervertebral implant for fusing vertebrae is disclosed. The implant has a body with curved, substantially parallel posterior and anterior faces separated by two narrow implant ends, superior and inferior faces having a plurality of undulating surfaces for contacting upper and lower vertebral endplates, and at least one depression in the anterior or posterior face for engagement by an insertion tool, at least two vertical through-channels extending through the implant from the superior face to the inferior face, a chamfer on the superior and inferior surfaces at one of the narrow implant ends, and a beveled edge along a perimeter of the superior and inferior faces. The arcuate implant configuration and the chamfers on the superior and inferior faces at the narrow end facilitate insertion of the implant from a transforaminal approach into a symmetric position about the midline of the spine so that a single implant provides balanced support to the spinal column. The implant may include radiopaque markers extending through the thickness of the implant to indicate the location and size of the implant. The implant may be formed of a plurality of interconnecting bodies assembled to form a single unit. An implantation kit and method are also disclosed.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Systems, devices and methods for posterior lumbar interbody fusion
InactiveUS20090292323A1Easy to cutEasy to shapeJoint implantsSpinal implantsSurgical operationIntervertebral disc
Described herein are stabilization devices, systems and methods to aid in posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) surgeries. The stabilization devices (“devices”) described herein are typically self-expanding devices that may be implanted into an intervertebral disc and packed with a bone graft or biologic or synthetic material to promote anchoring of the stabilization device and fusion of the vertebrae adjacent to the intervertebral disc.
Owner:SPINEALIGN MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com