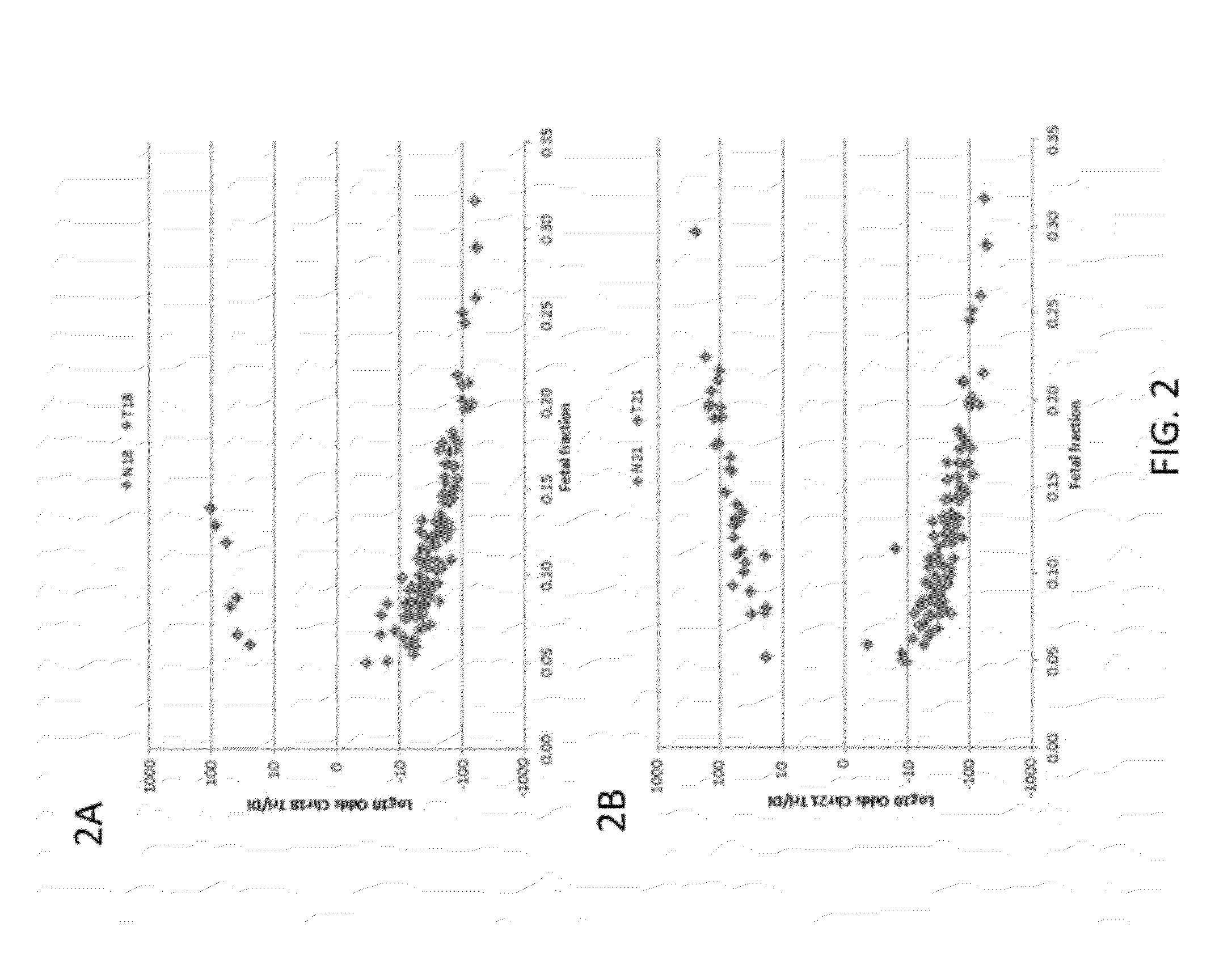
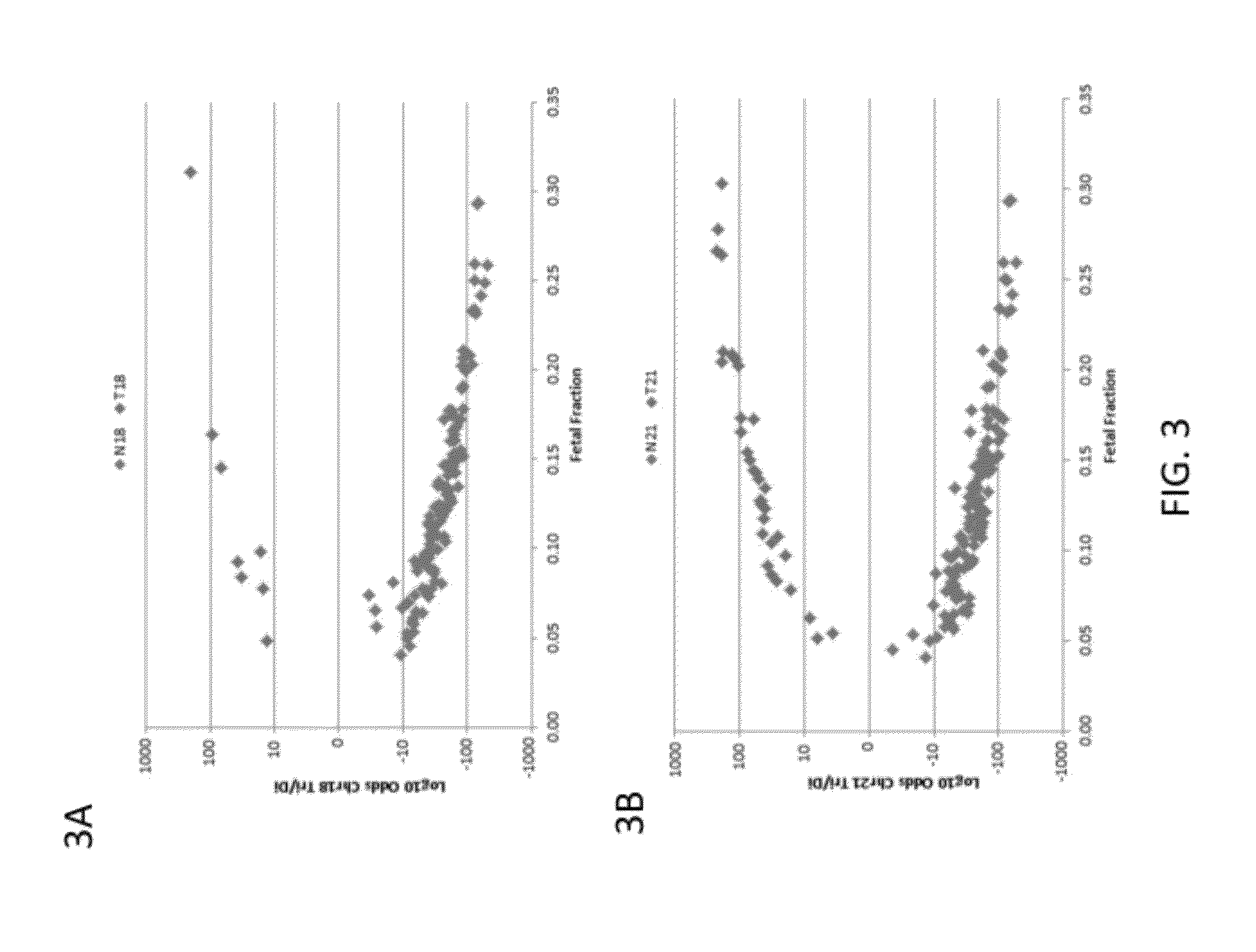
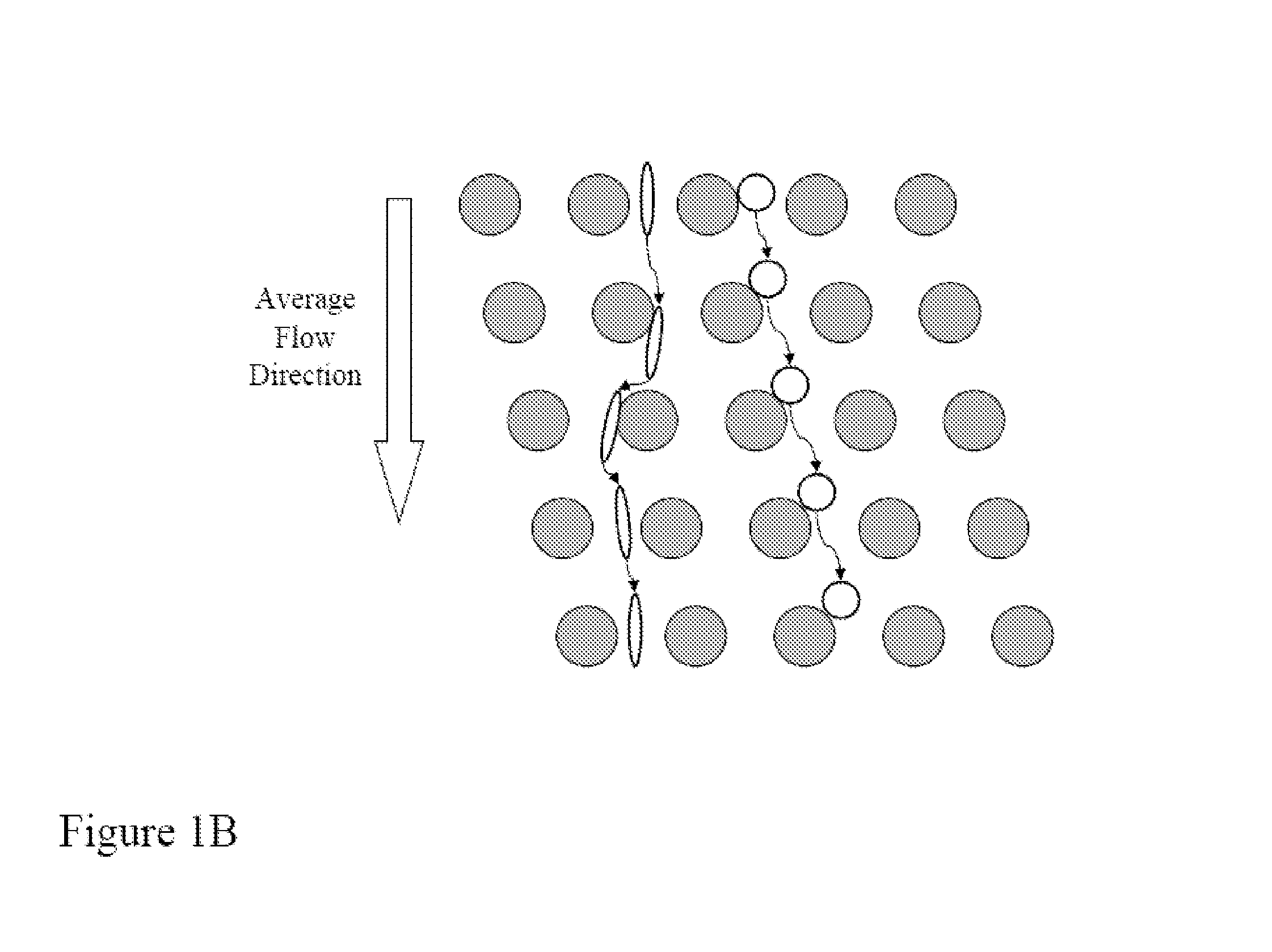
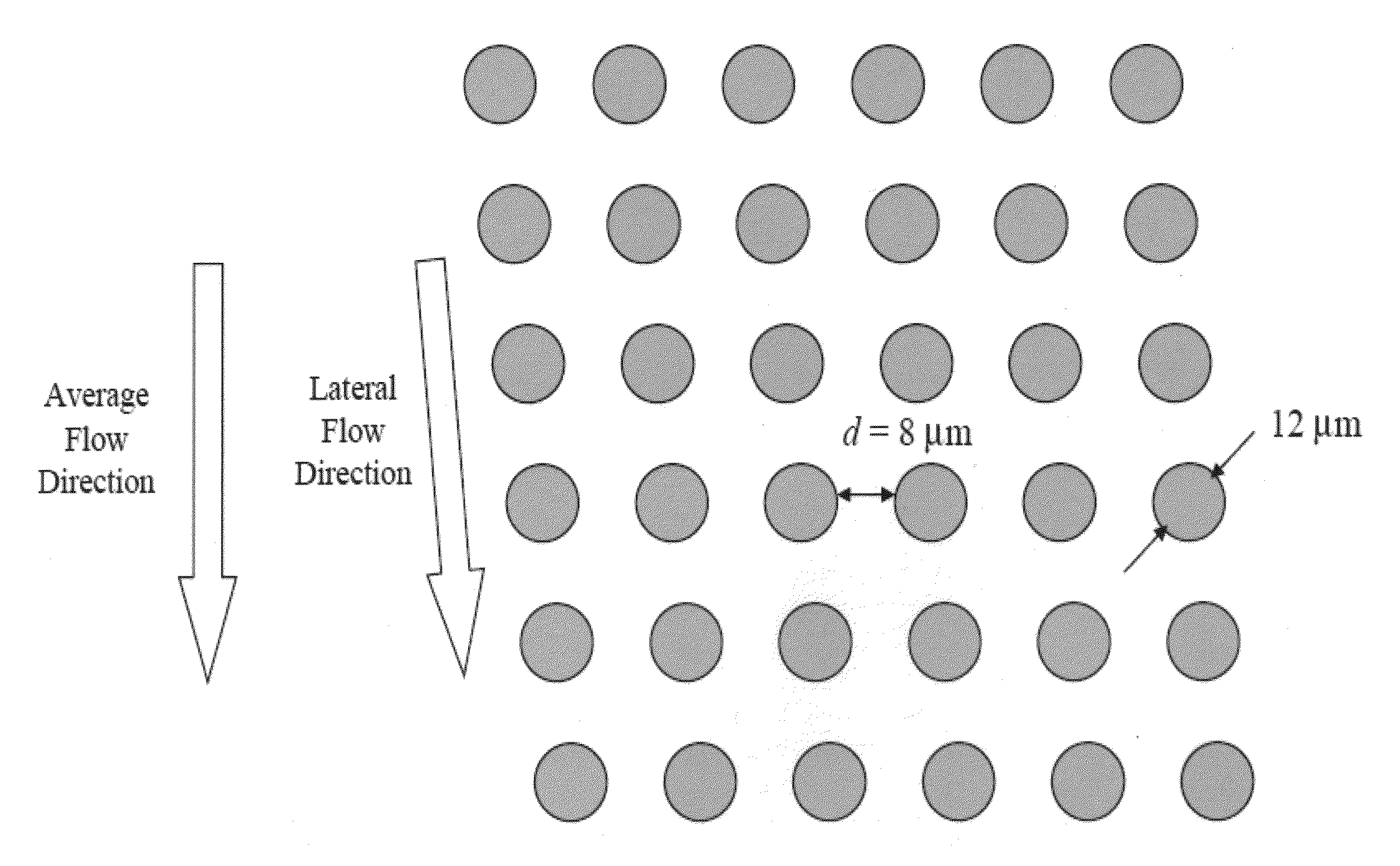
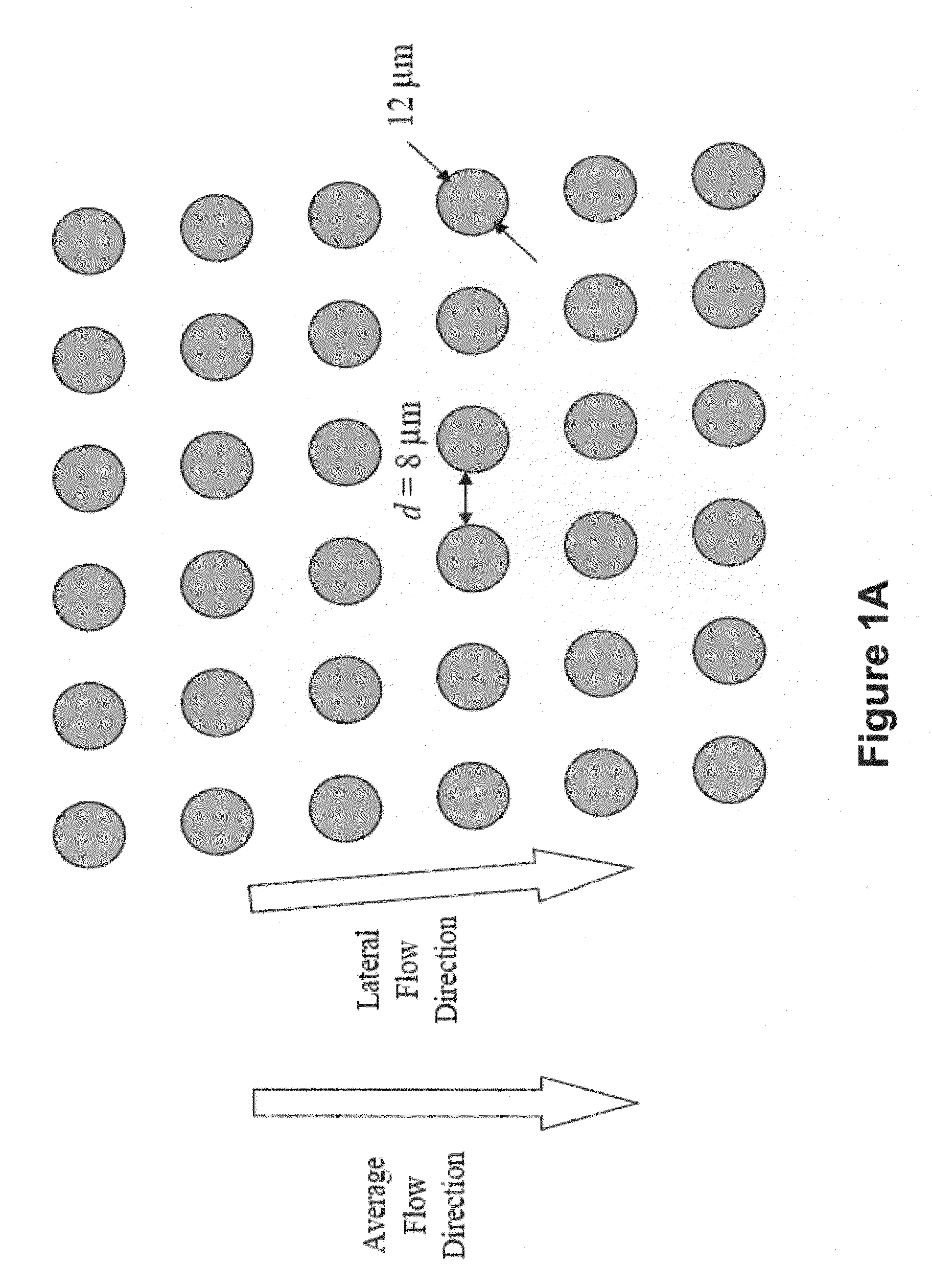
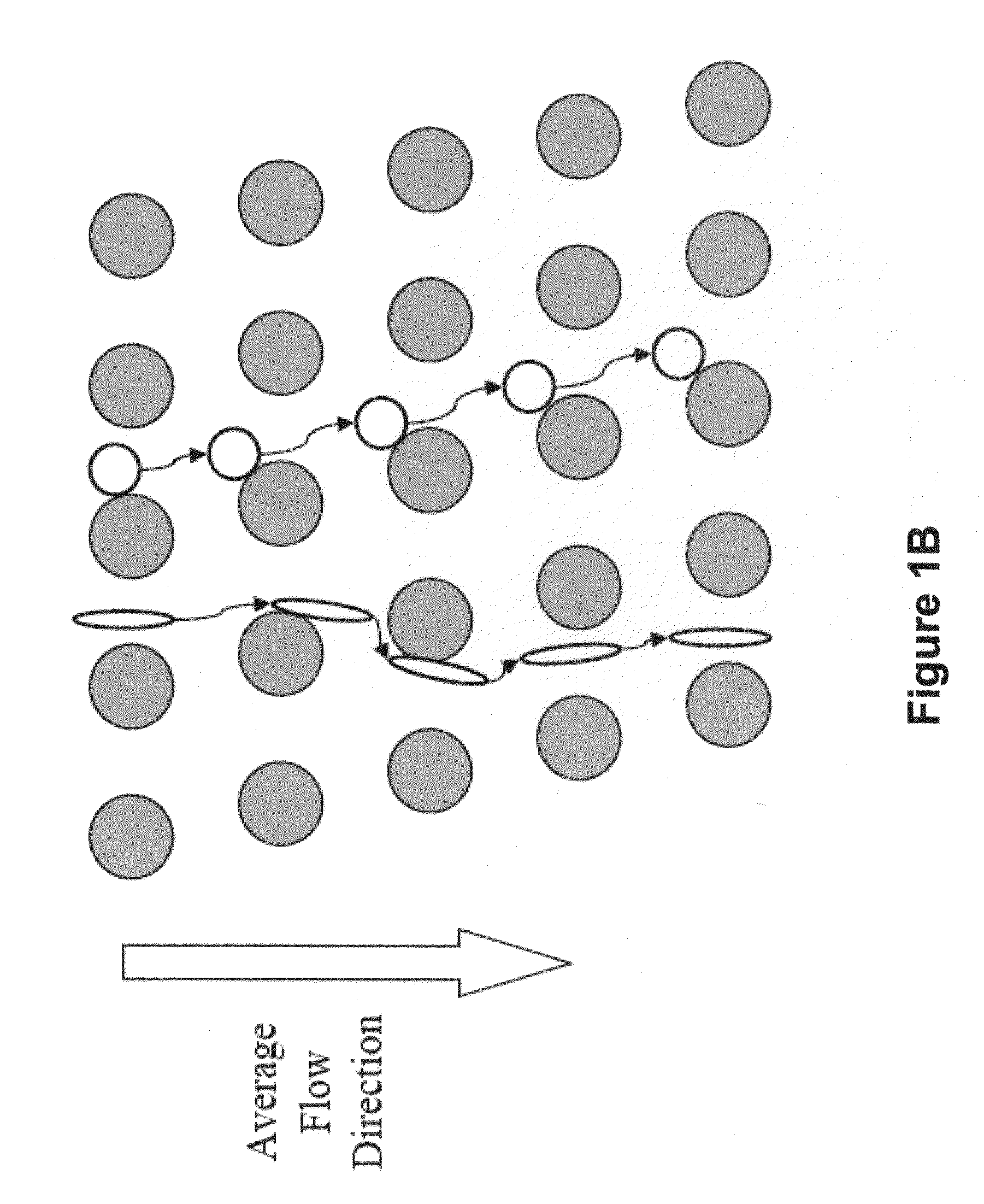
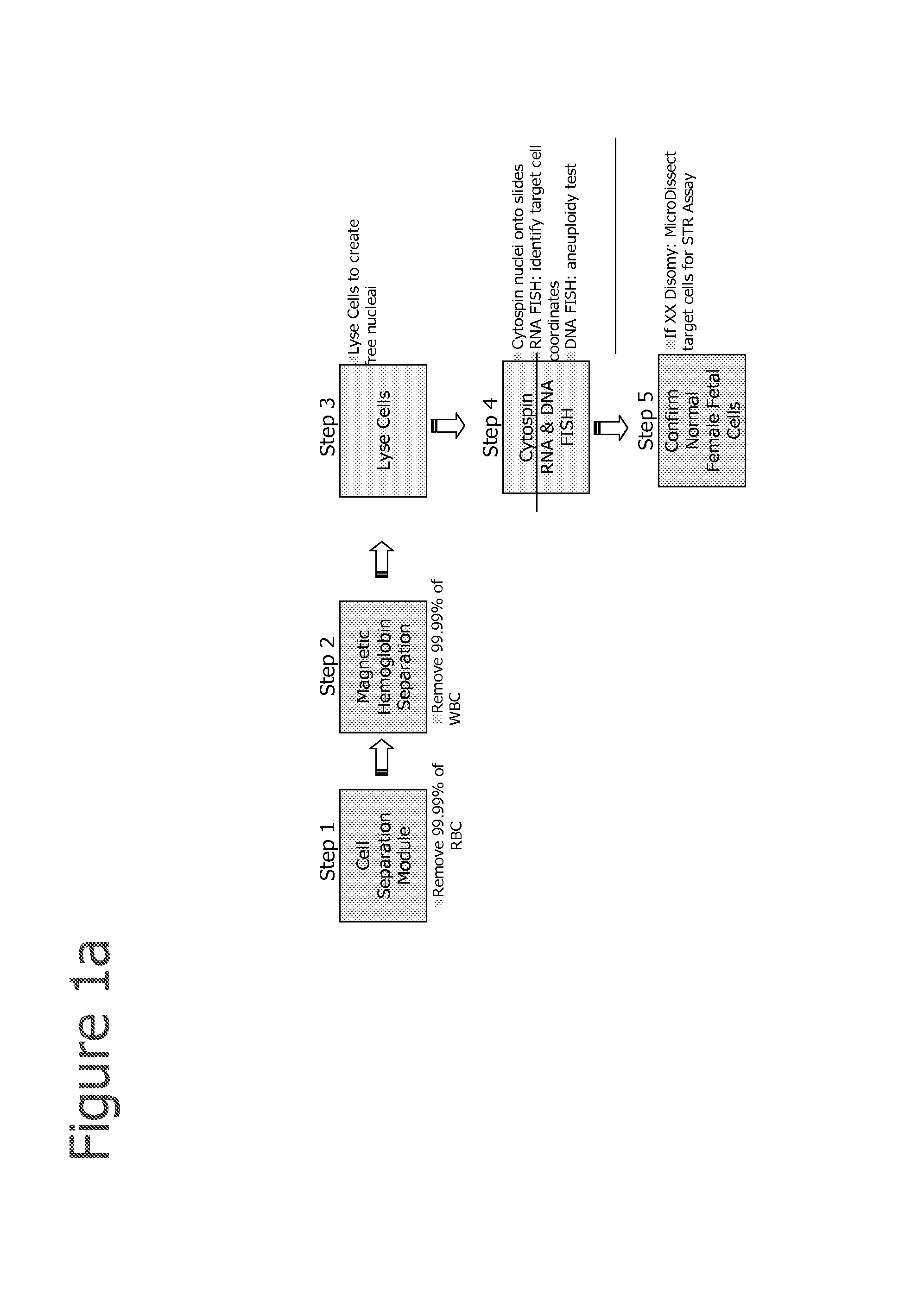
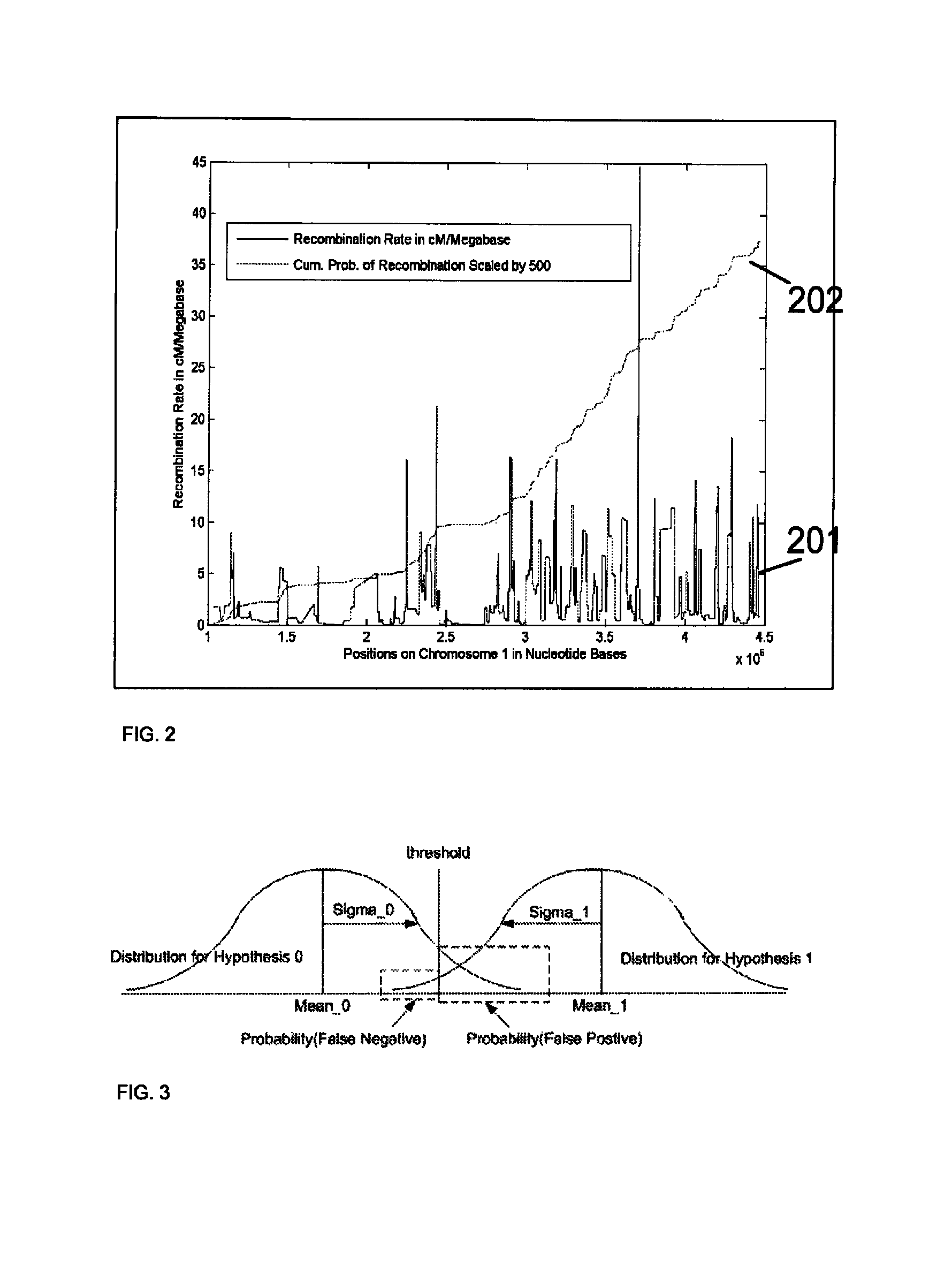
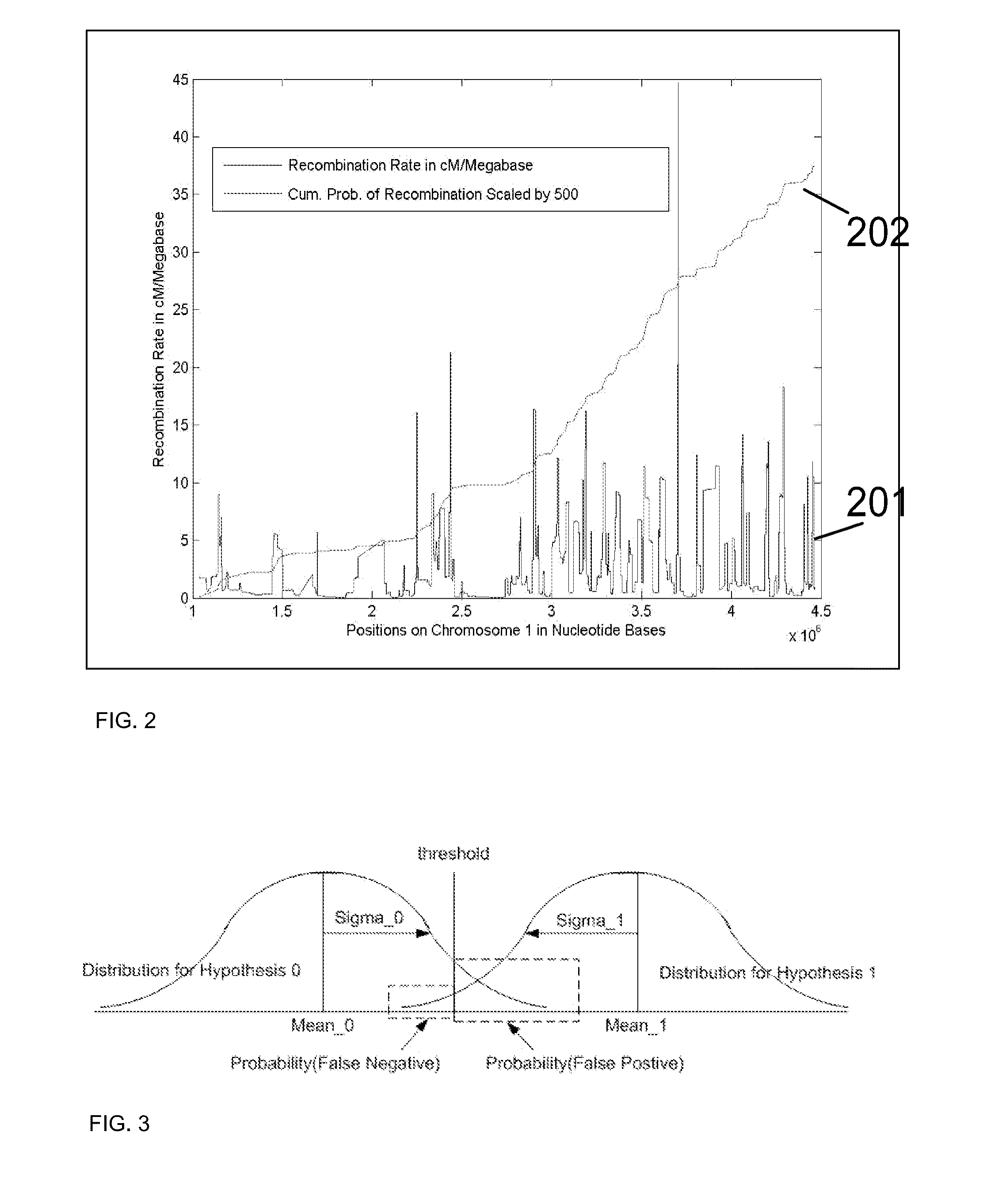
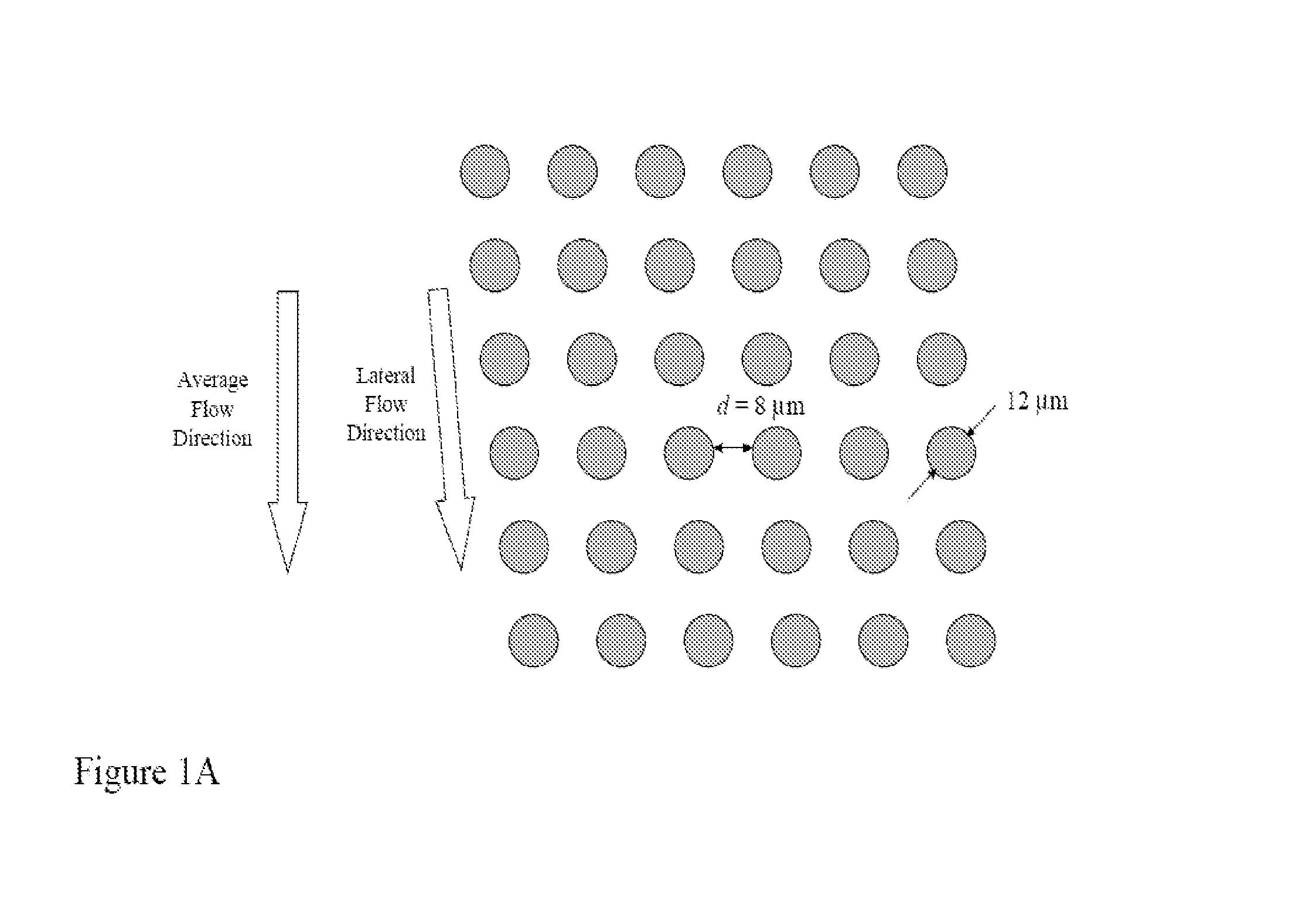Patents
Literature
121 results about "Fetal cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
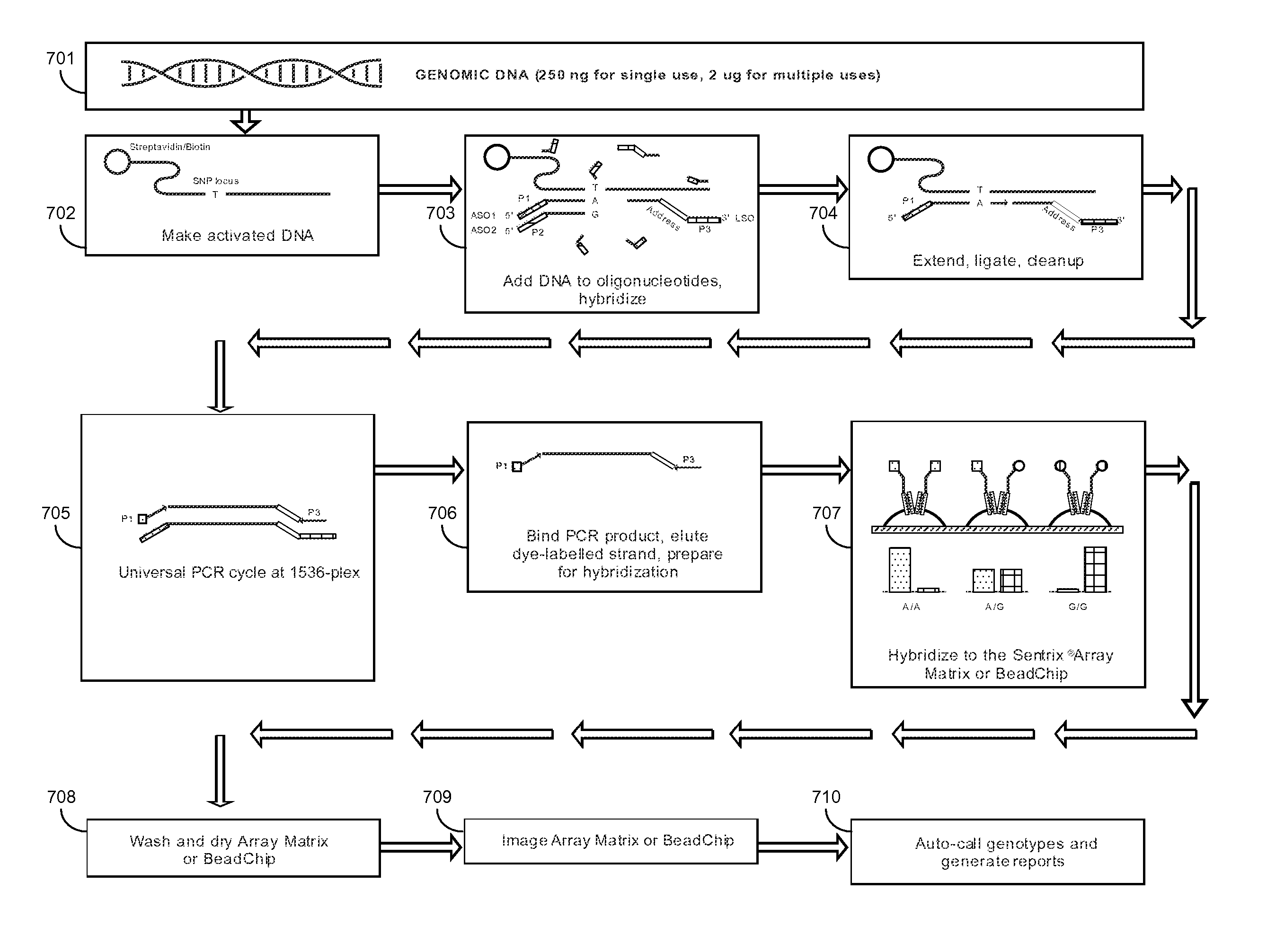
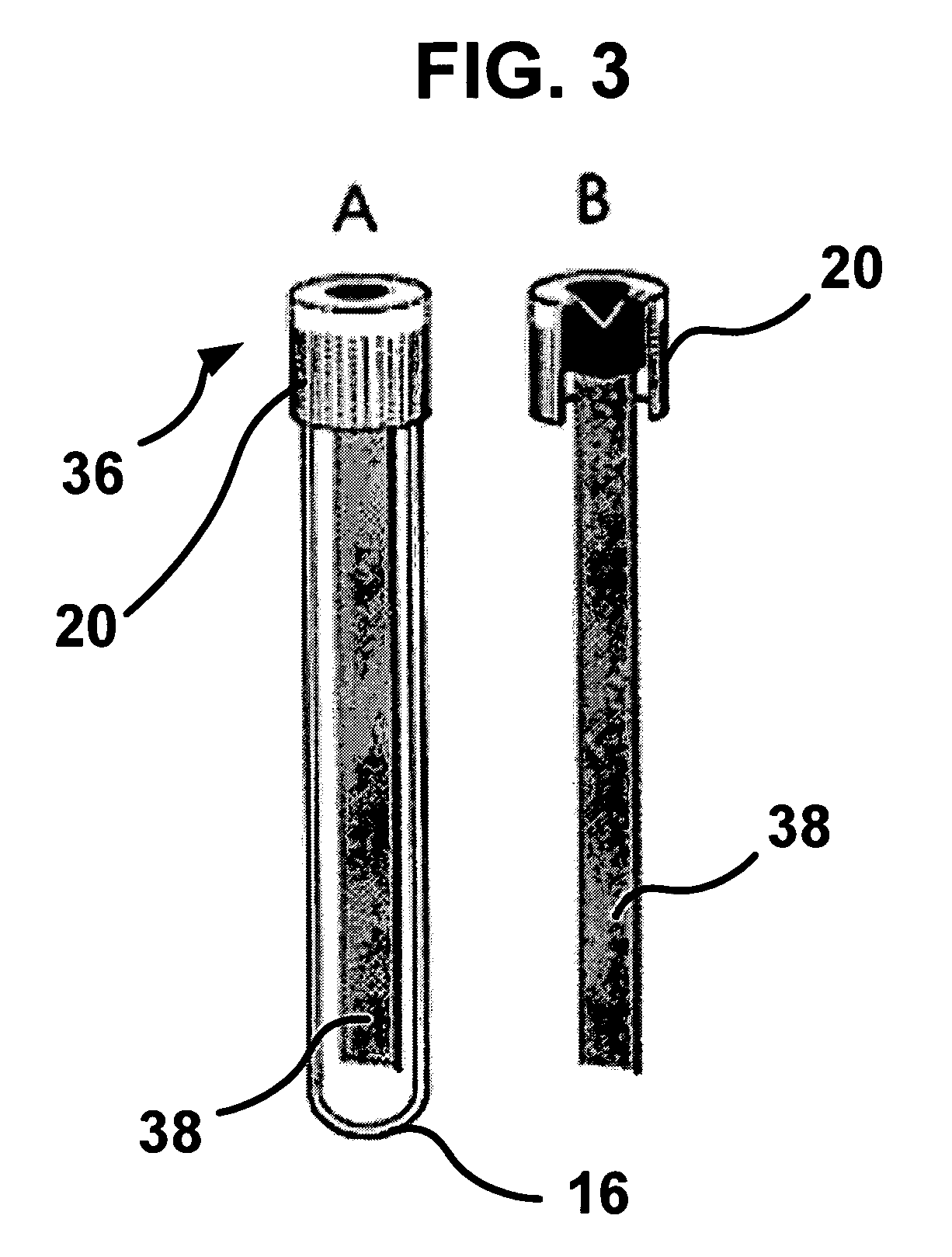
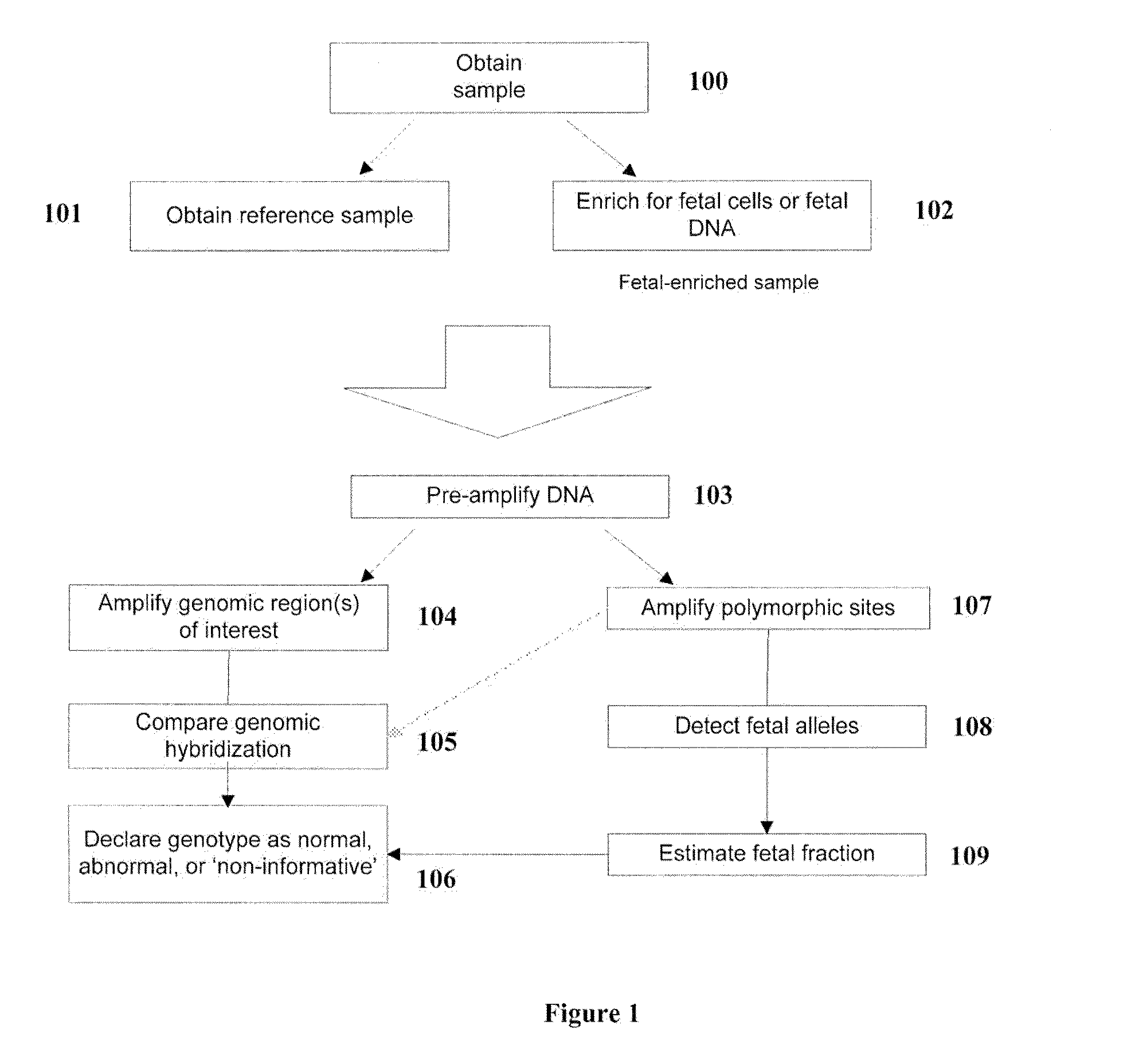
Methods for the Diagnosis of Fetal Abnormalities
ActiveUS20080138809A1Reliable and accurate clinical diagnosisAccurate and reliable diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationFetal abnormalityRare cell
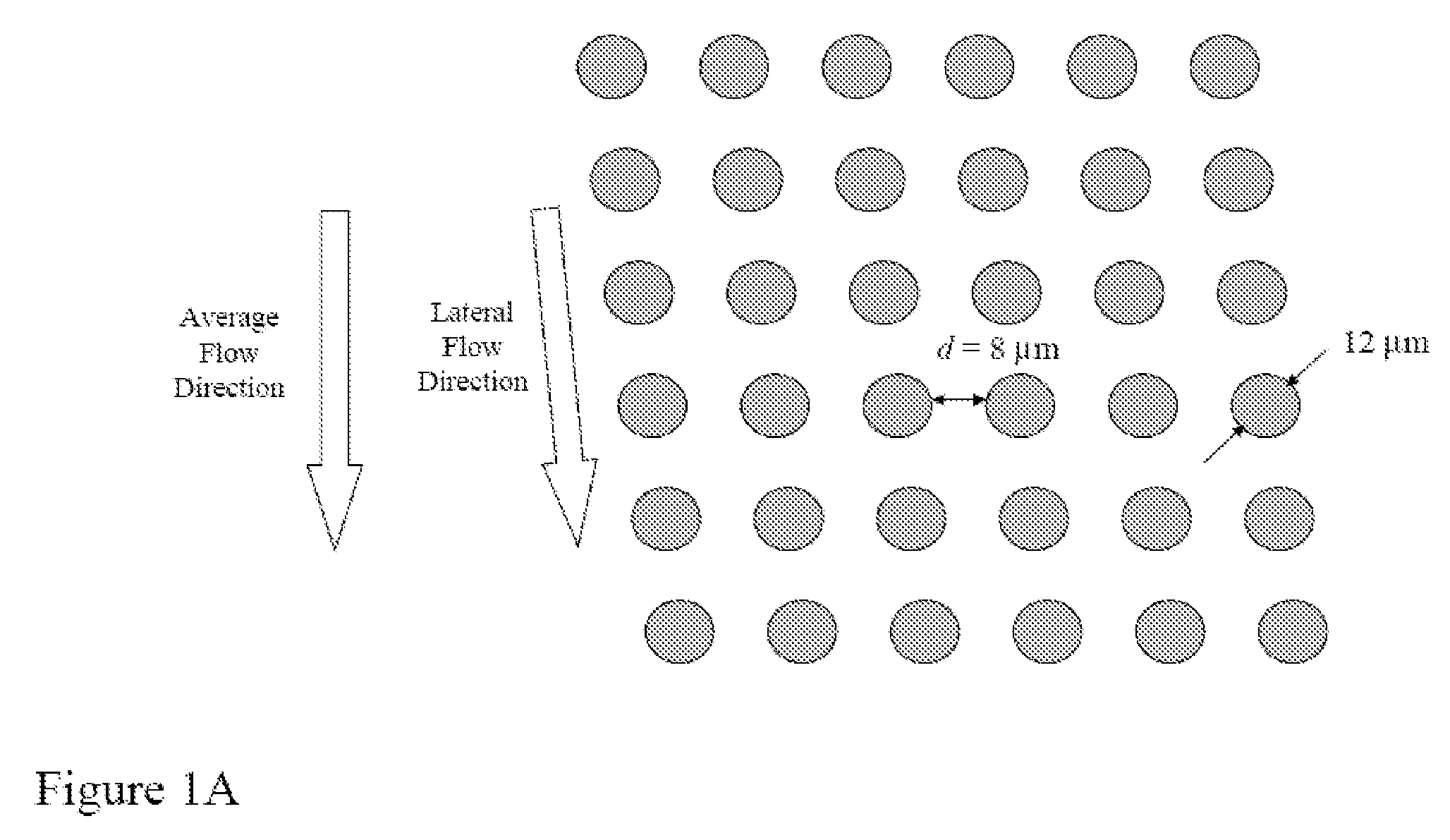
The present invention relates to methods for detecting, enriching, and analyzing rare cells that are present in the blood, e.g. fetal cells. The invention further features methods of analyzing rare cell(s) to determine the presence of an abnormality, disease or condition in a subject, e.g. a fetus by analyzing a cellular sample from the subject.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC +2
Rare cell analysis using sample splitting and DNA tags
ActiveUS20080220422A1Microbiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationFetal abnormalityRare cell
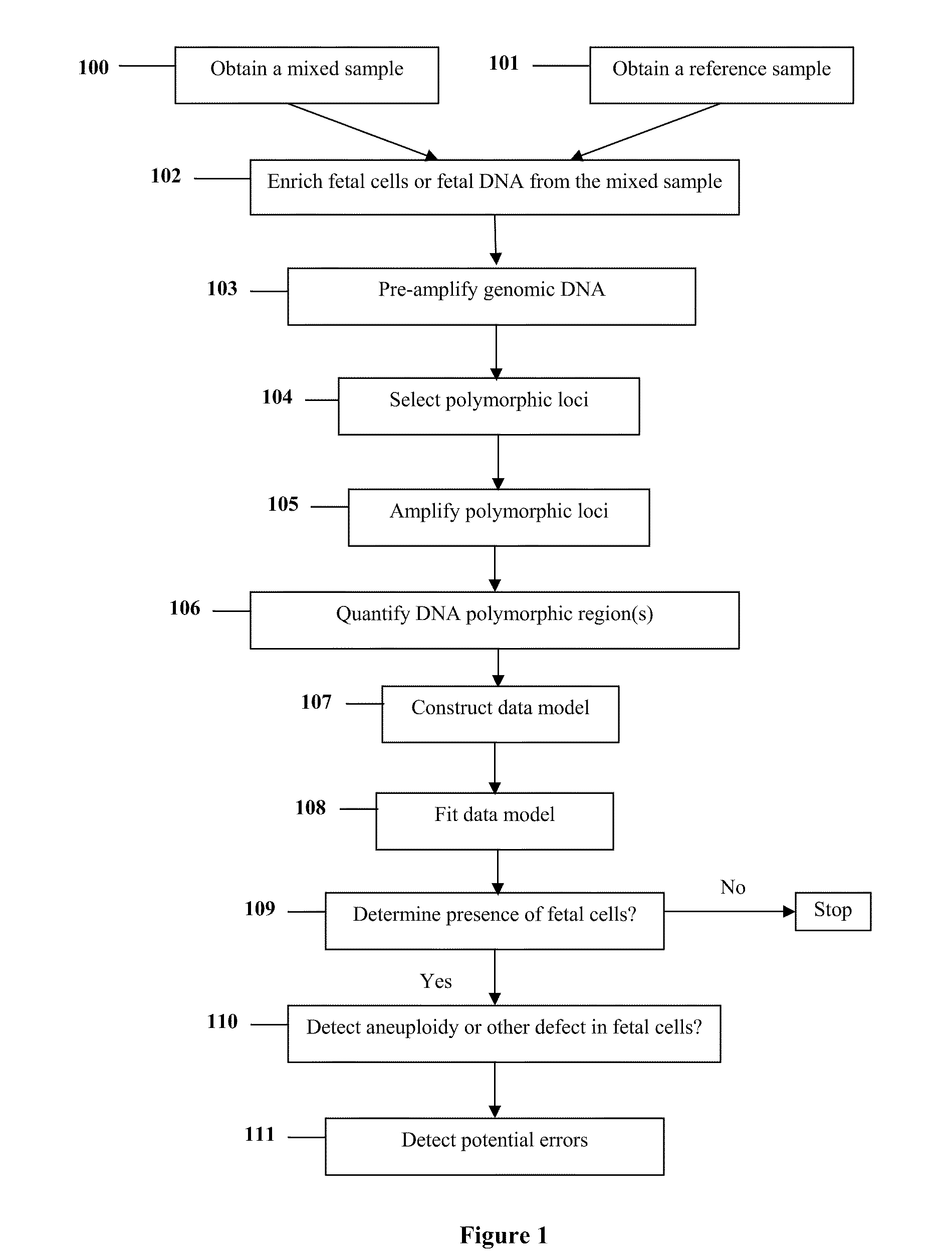
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to detect the presence of fetal cells when mixed with a population of maternal cells in a sample and to test fetal abnormalities, e.g. aneuploidy. The present invention involves labeling regions of genomic DNA in each cell in said mixed sample with different labels wherein each label is specific to each cell and quantifying the labeled regions of genomic DNA from each cell in the mixed sample. More particularly the invention involves quantifying labeled DNA polymorphisms from each cell in the mixed sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC +2
Devices and methods for magnetic enrichment of cells and other particles
InactiveUS20060223178A1Small particle sizeLower the volumeArtificial cell constructsLaboratory glasswaresAnalyteMedicine
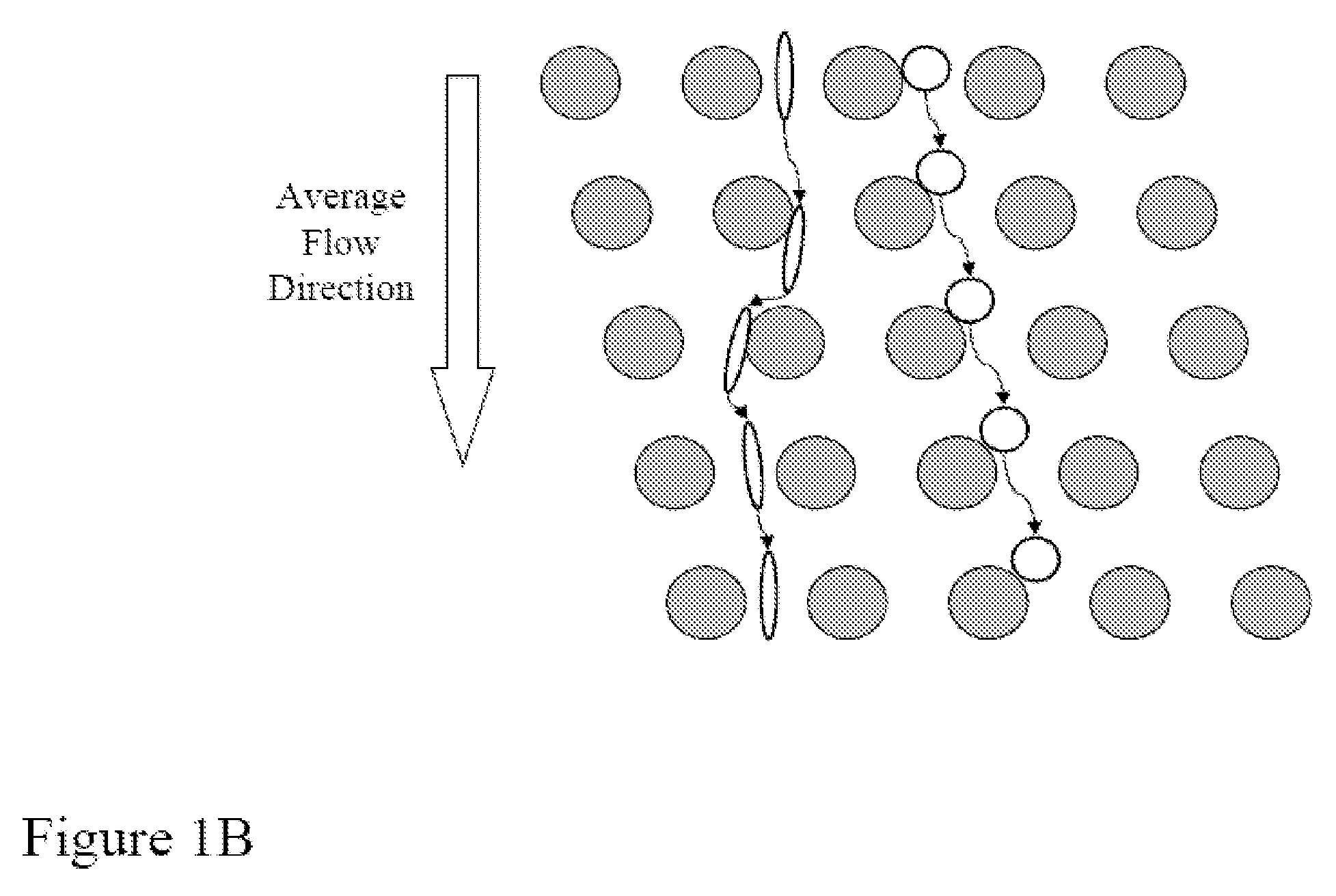
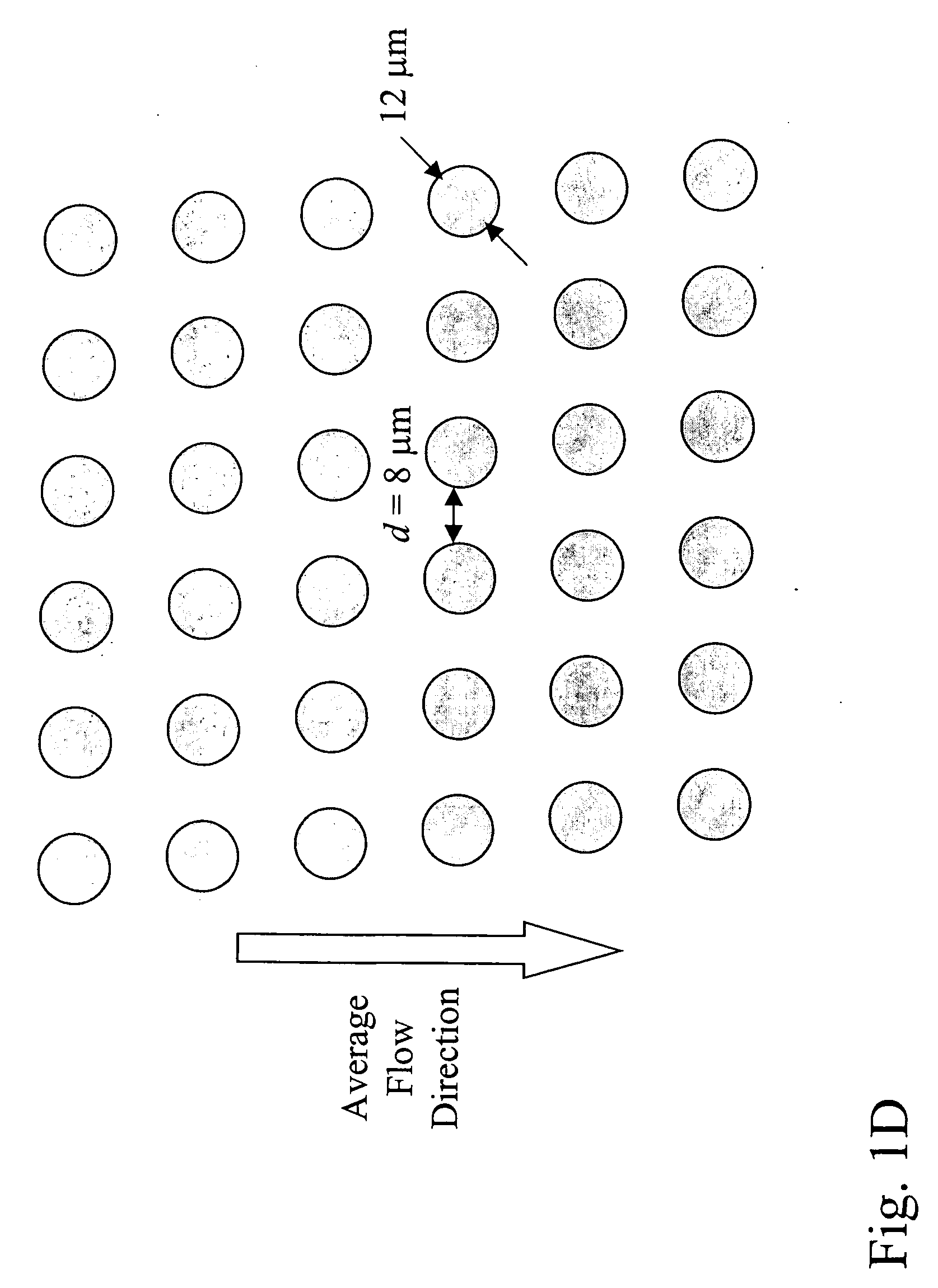
The invention features devices and methods for the enrichment of cells and other desired analytes by employing a magnetic field, alone or in conjunction with size-based separation. The devices and methods may be advantageously employed to enrich for rare cells, e.g., fetal cells or epithelial cells, present in a sample, e.g., maternal blood.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Devices and methods for enrichment and alteration of cells and other particles
ActiveUS20070026381A1Increase volumeReduced deformabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCellular componentLysis
The invention features devices and methods for the deterministic separation of particles. Exemplary methods include the enrichment of a sample in a desired particle or the alteration of a desired particle in the device. The devices and methods are advantageously employed to enrich for rare cells, e.g., fetal cells, present in a sample, e.g., maternal blood and rare cell components, e.g., fetal cell nuclei. The invention further provides a method for preferentially lysing cells of interest in a sample, e.g., to extract clinical information from a cellular component, e.g., a nucleus, of the cells of interest. In general, the method employs differential lysis between the cells of interest and other cells (e.g., other nucleated cells) in the sample.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data from target individuals using genetic data from genetically related individuals
ActiveUS20070184467A1Significant resultMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsUniparental disomyEmbryo
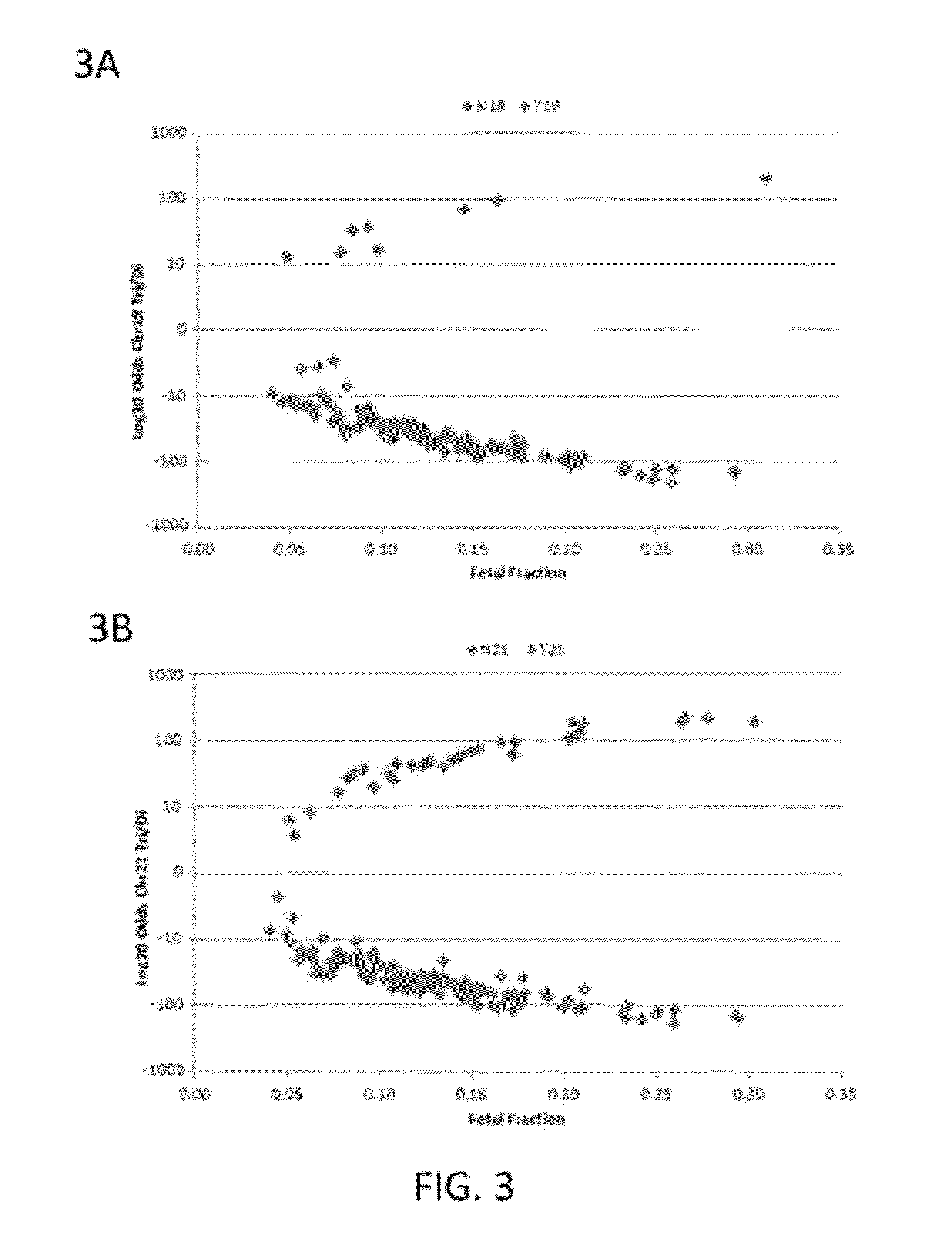
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In accordance with another embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from a fetus is acquired from fetal cells, or cell-free fetal DNA isolated from the mother's blood, and the incomplete genetic data is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In one embodiment, the genetic data can be reconstructed for the purposes of making phenotypic predictions. In another embodiment, the genetic data can be used to detect for aneuploides and uniparental disomy.
Owner:NATERA
Detection of genetic abnormalities
InactiveUS20120190020A1Quick sortingEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellNormal cell
The present invention provides assay systems and related methods for determining genetic abnormalities in mixed samples comprising cell free DNA from both normal and putative genetically atypical cells. Exemplary mixed samples for analysis using the assay systems of the invention include samples comprising both maternal and fetal cell free DNA and samples that contain DNA from normal cells and circulating cancerous cells.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Methods for the diagnosis of fetal abnormalities
ActiveUS8137912B2Accurate and reliable diagnosisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseFetal abnormality
The present invention relates to methods for detecting, enriching, and analyzing rare cells that are present in the blood, e.g. fetal cells. The invention further features methods of analyzing rare cell(s) to determine the presence of an abnormality, disease or condition in a subject, e.g. a fetus by analyzing a cellular sample from the subject.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC +2
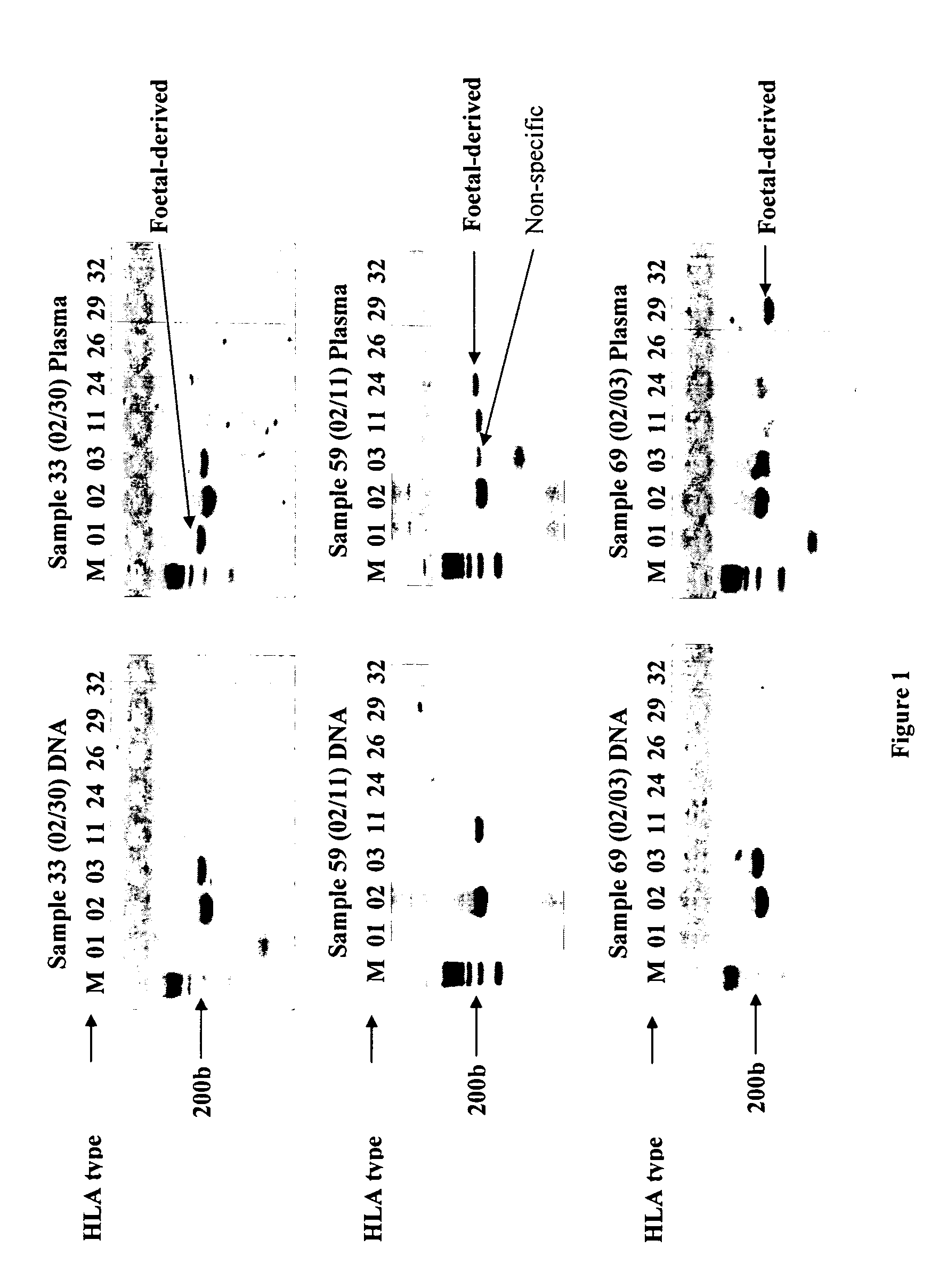
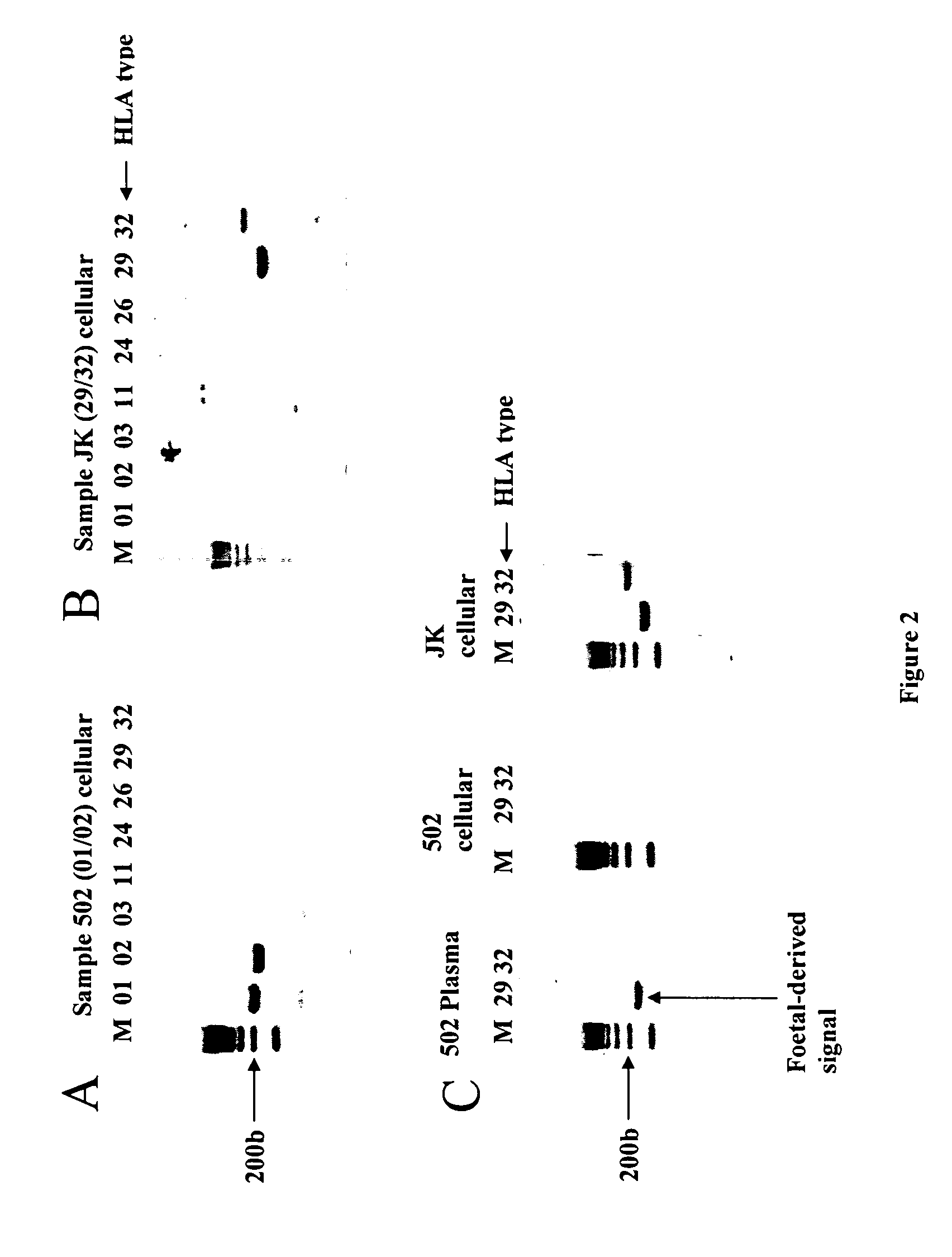
Identification of fetal dna and fetal cell markers in maternal plasma or serum
InactiveUS20070134658A1Reduce in quantityMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureAntigenAllele
The present invention relates to the identification of fetal specific nucleic acids and fetal cell markers in maternal plasma or serum. In particular, the present invention relates to methods which rely on the analysis of polymorphic alleles of a population to determine an allele which is possessed by the fetus but absent from the mother. Fetal specific alleles identified using the methods of the invention can be used to quantify fetal DNA from maternal plasma or serum. In addition, antigens encoded by alleles identified using the methods of the invention can be targeted in methods of isolating or detecting fetal cells.
Owner:GENETIC TECHNOLOGIES LIMTIED
Devices and methods for enrichment and alteration of cells and other particles
InactiveUS20070196820A1High magnetic responsivenessSmall particle sizeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteRare cell
The invention features a device for the deterministic separation of analytes coupled to a reservoir containing a reagent that alters a magnetic propert of the analyte. Exemplary methods include the enrichment of a sample in a desired analyte (e.g., using deterministic separation) or the alteration of a desired analyte in the device. The devices and methods may be advantageously employed to enrich for rare cells, e.g., fetal cells or epithelial cells, present in a sample, e.g., maternal blood.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Methods, compositions, and automated systems for separating rare cells from fluid samples
InactiveUS6949355B2Aid in diagnosis and prognosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCancer cellRed blood cell
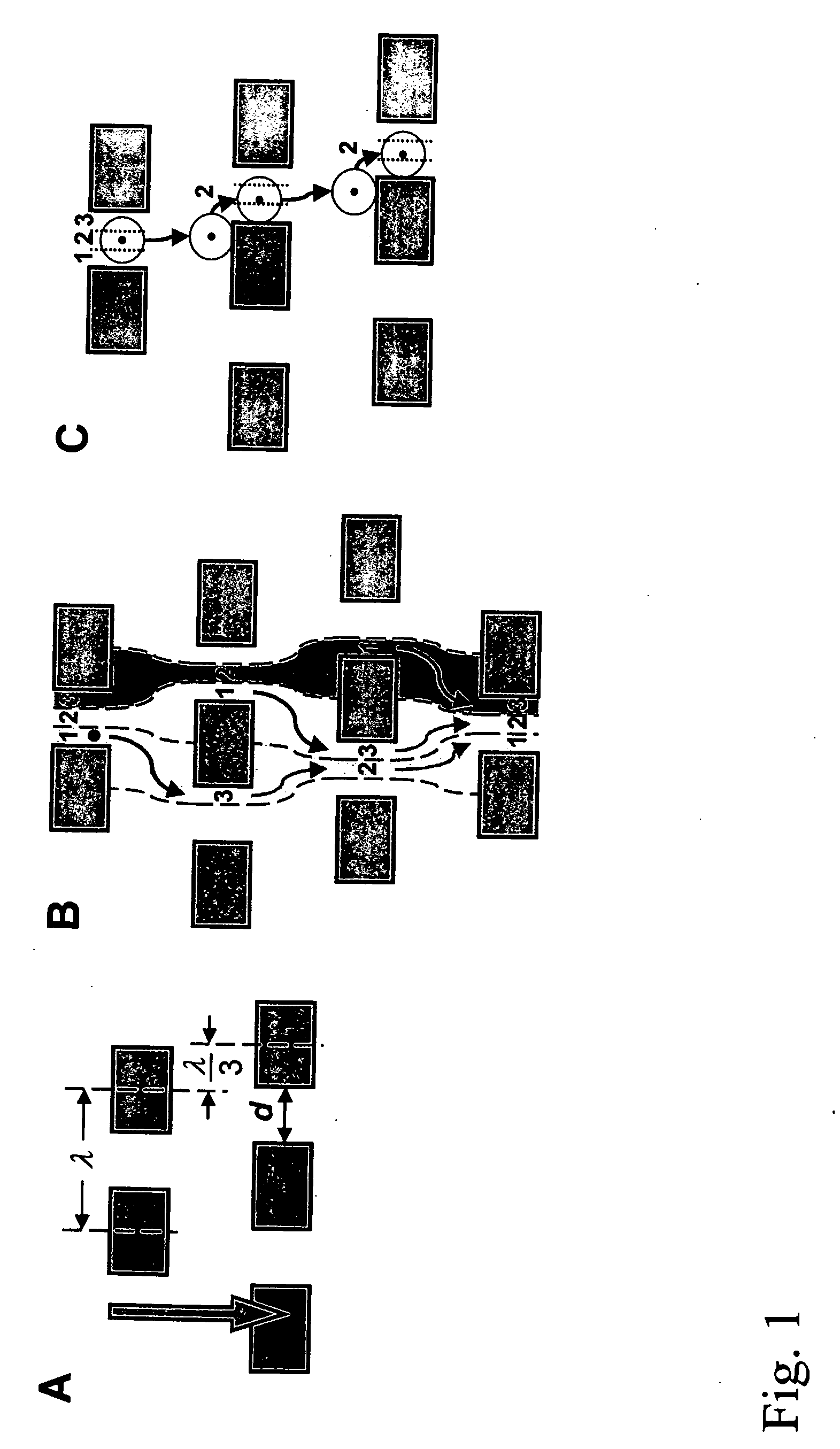
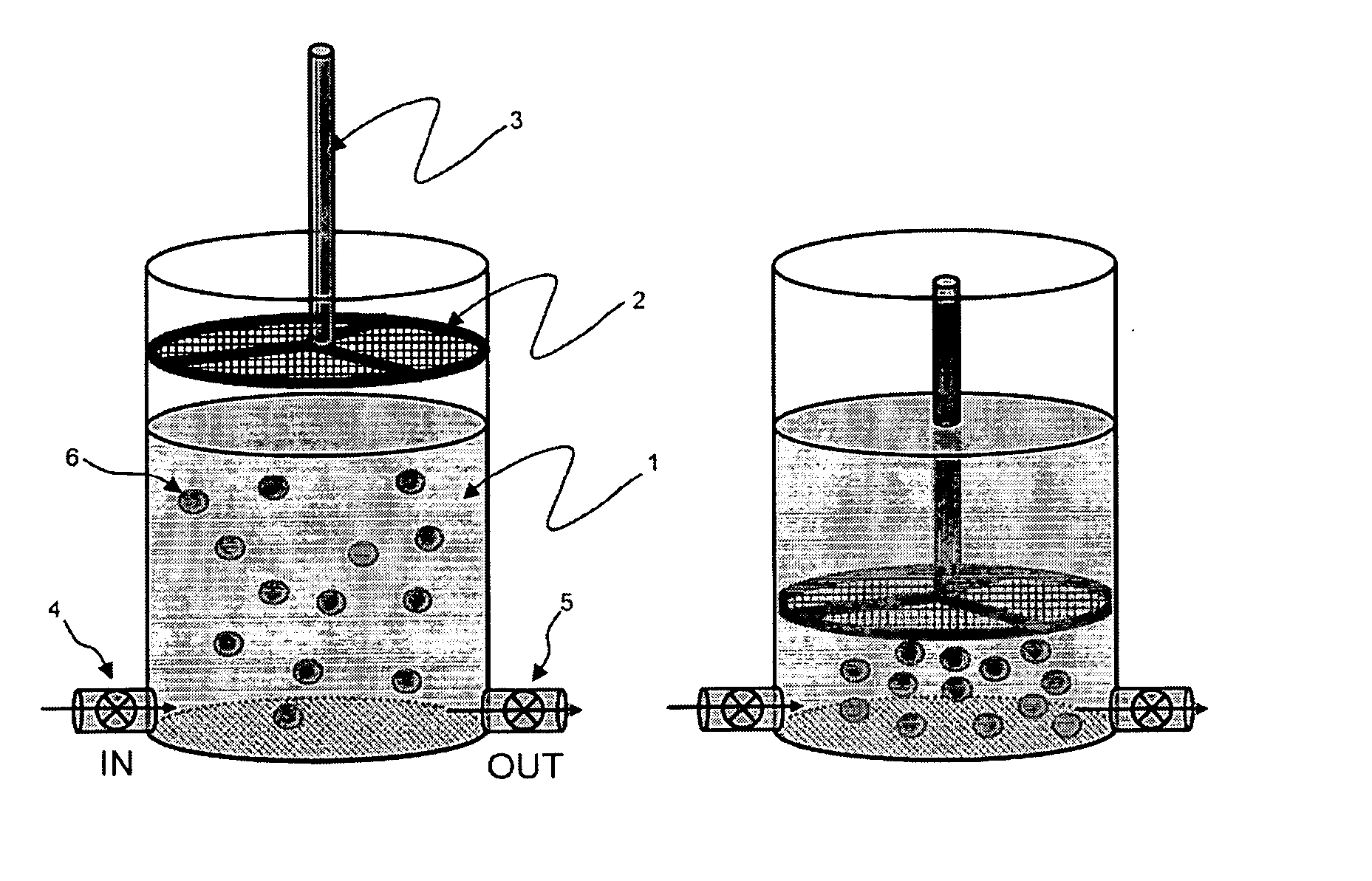
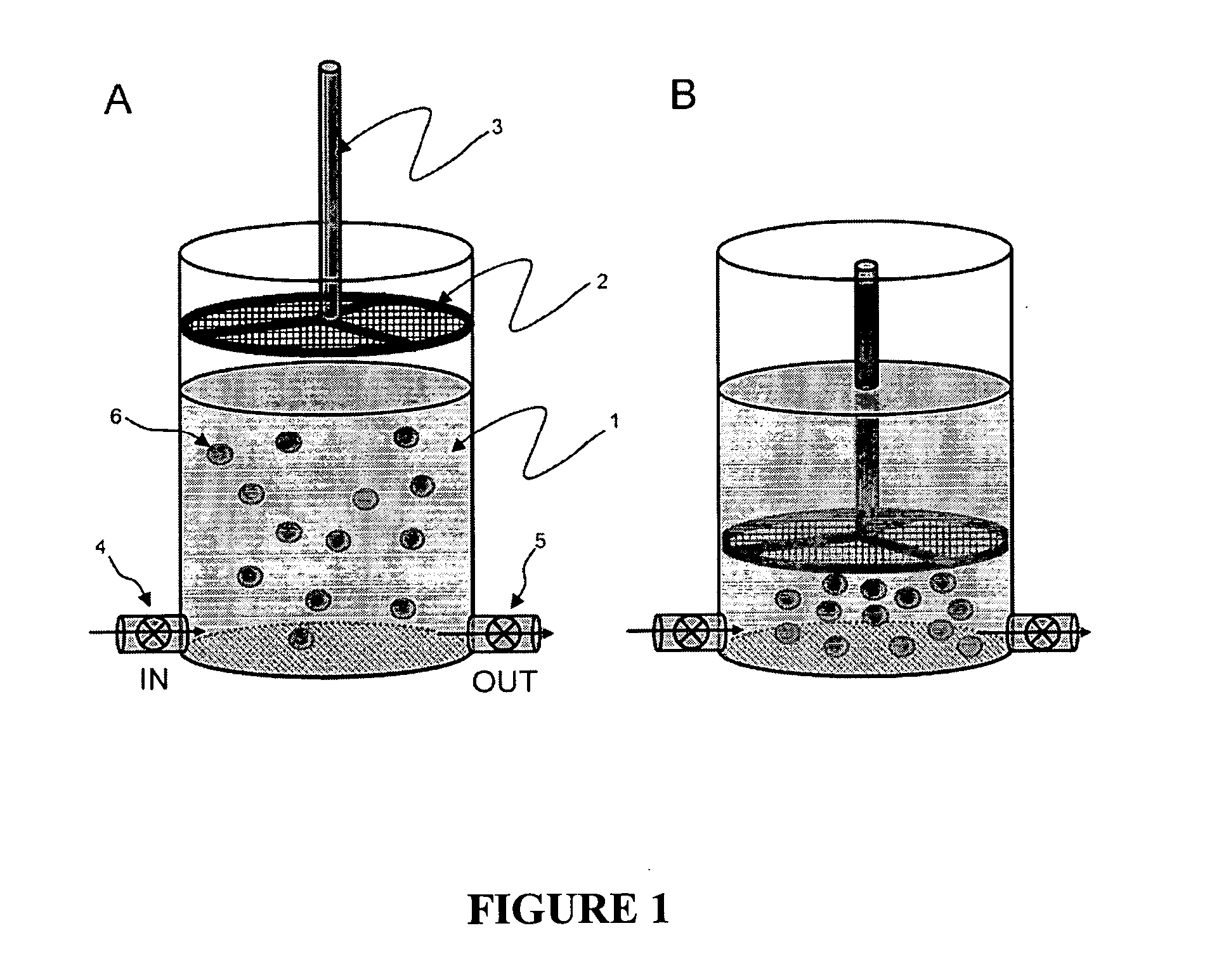
The present invention recognizes that diagnosis and prognosis of many conditions can depend on the enrichment of rare cells from a complex fluid sample. In particular, the enrichment of fetal cells from maternal samples, such as maternal blood samples, can greatly aid in the detection of fetal abnormalities or a variety of genetic conditions. In addition, the present invention recognizes that the enrichment of rare malignant cells from patient samples, can aid in diagnosis, prognosis, and development of therapeutic modalities for patients.A first aspect of the present invention is a microfabricated filter for filtering a fluid sample. A microfabricated filter of the present invention comprises at least one tapered pore, and preferably comprises at least two tapered pores whose variation in size is 20% or less. The present invention also includes a method of enriching rare cells of a fluid sample using a microfabricated filter of the present invention.Another aspect of the invention is solutions for the selective sedimentation of red blood cells (RBCs) from a blood sample comprising a red blood cell aggregating agent and at least one specific binding member that selectively binds RBCs. Solutions of the present invention include a combined solution for rare cell enrichment that comprise RBC aggregating agents, at least one specific binding member that selectively binds RBCs, and at least one additional specific binding member for the removal of undesirable sample components other than RBCs. The invention also includes methods of using selective RBC sedimentation solutions and combined solutions for enriching rare cells of a fluid sample.Yet another aspect of the invention is an automated system for processing a fluid sample that includes: at least one filtration chamber that comprises or engages one or more microfabricated filters of the present invention; automated means for directing fluid flow through the one or more filtration chambers of the automated system, and means for collecting enriched rare cells. The present invention also includes methods of using an automated system for separating rare cells from a fluid sample. Preferred fluid samples are effusion, blood, or urine samples, and rare cells that can be enriched from such sample include nucleated red blood cells and cancer cells.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Methods and compositions for identifying a fetal cell
InactiveUS20100304978A1High expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCandidate Gene Association StudyTrophoblast
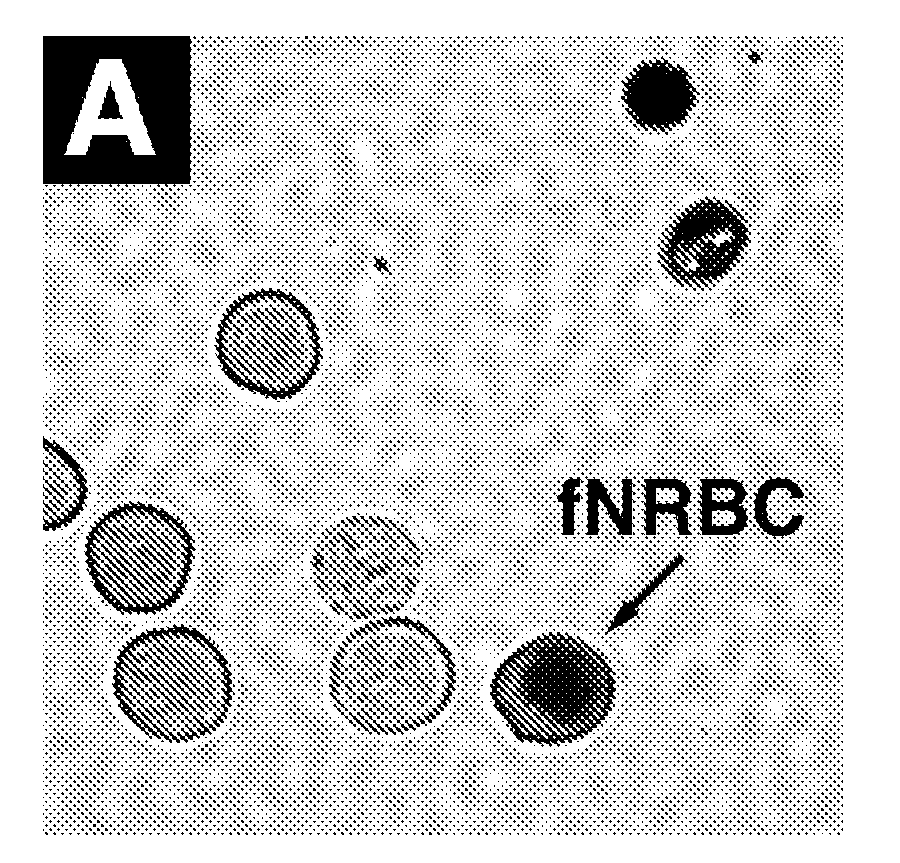
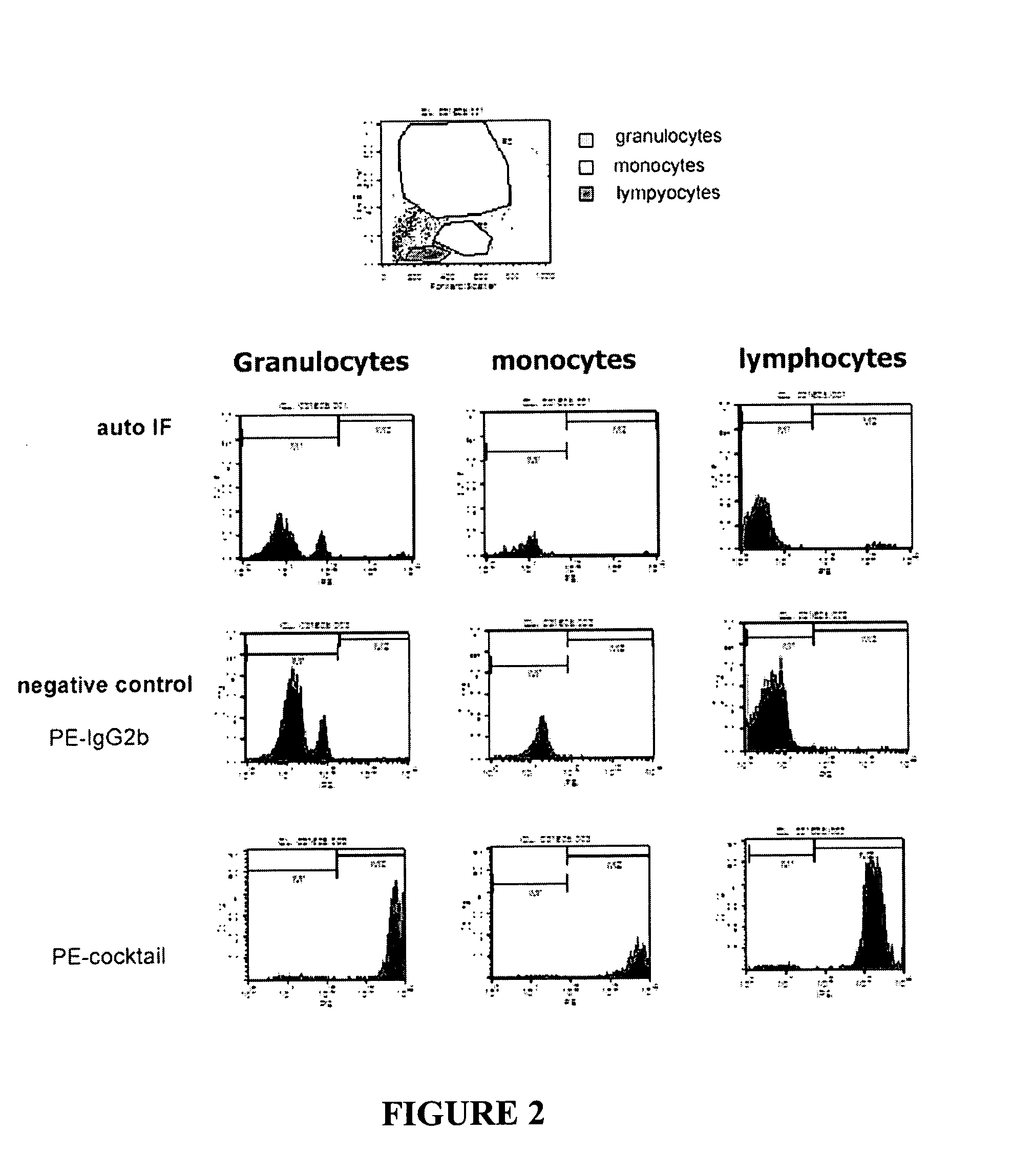
The present invention provides methods and compositions for specifically identifying a fetal cell. An initial screening of approximately 400 candidate genes by digital PCR in different fetal and adult tissues identified a subset of 24 gene markers specific for fetal nucleated RBC and trophoblasts. The specific expression of those genes was further evaluated and verified in more defined tissues and isolated cells through quantitative RT-PCR using custom Taqman probes specific for each gene. A subset of fetal cell specific markers (FCM) was tested and validated by RNA fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) in blood samples from non-pregnant women, and pre-termination and post-termination pregnant women. Applications of these gene markers include, but are not limited to, distinguishing a fetal cell from a maternal cell for fetal cell identification and genetic diagnosis, identifying circulating fetal cell types in maternal blood, purifying or enriching one or more fetal cells, and enumerating one or more fetal cells during fetal cell enrichment.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Selection of cells using biomarkers
InactiveUS20080113358A1Easy to separateIncrease the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisFetal abnormalityFetal cell
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to isolate, select or detect the presence of a target cell (e.g., fetal cells) in a sample comprising mixed populations of cells that vastly outnumber the target cells. Target cells include fetal cells, such as nucleated red blood cells, and methods of selecting such cells include diagnosis of fetal abnormalities, i.e., aneuploidy. Furthermore, methods comprise utilizing fetal biomarkers to select fetal cells in a sample comprising fetal and adult cells.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
Detection of genetic abnormalities
InactiveUS20120190021A1Quick sortingEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellNormal cell
The present invention provides assay systems and related methods for determining genetic abnormalities in mixed samples comprising cell free DNA from both normal and putative genetically atypical cells. Exemplary mixed samples for analysis using the assay systems of the invention include samples comprising both maternal and fetal cell free DNA and samples that contain DNA from normal cells and circulating cancerous cells.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Method of isolating cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050123914A1Rapid and non-invasive diagnosticHigh yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsTrophoblastNon invasive
The present invention relates to a non-invasive method of retrieving and identifying cells particularly fetal cells and trophoblastic cells. The invention includes methods for use of the cells for identifying chromosomal abnormalities and mutations particularly for prenatal diagnosis by performing genetic diagnosis for chromosomal and single gene disorders. The invention also includes methods of confirming cells of fetal origin.
Owner:MONASH UNIV +1
Method for determining the number of copies of a chromosome in the genome of a target individual using genetic data from genetically related individuals
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In accordance with another embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from a fetus is acquired from fetal cells, or cell-free fetal DNA isolated from the mother's blood, and the incomplete genetic data is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In one embodiment, the genetic data can be reconstructed for the purposes of making phenotypic predictions. In another embodiment, the genetic data can be used to detect for aneuploides and uniparental disomy.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data from target individuals using genetic data from genetically related individuals
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available, are disclosed. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention incomplete genetic data is acquired from embryonic cells, fetal cells, or cell-free fetal DNA isolated from the mother's blood, and the incomplete genetic data is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data from target individuals using genetic data from genetically related individuals
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available, are disclosed. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data is acquired from embryonic cells, fetal cells, or cell-free fetal DNA isolated from the mother's blood, and the incomplete genetic data is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals.
Owner:NATERA
Methods and reagents for identifying rare fetal cells in the maternal circulation
Owner:SCHUELER PAULA A +6
Business methods for prenatal Diagnosis
The present invention relates to business methods in which screening services and diagnostics for the condition of a fetus are provided. Fetal abnormalities, include chromosomal and other genetic ies, are detected through the analysis of fetal cells obtained from maternal blood samples.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
Methods and compositions for detecting rare cells from a biological sample
InactiveUS20080057505A1Strong specificityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomass after-treatmentHematopoietic cellWhite blood cell
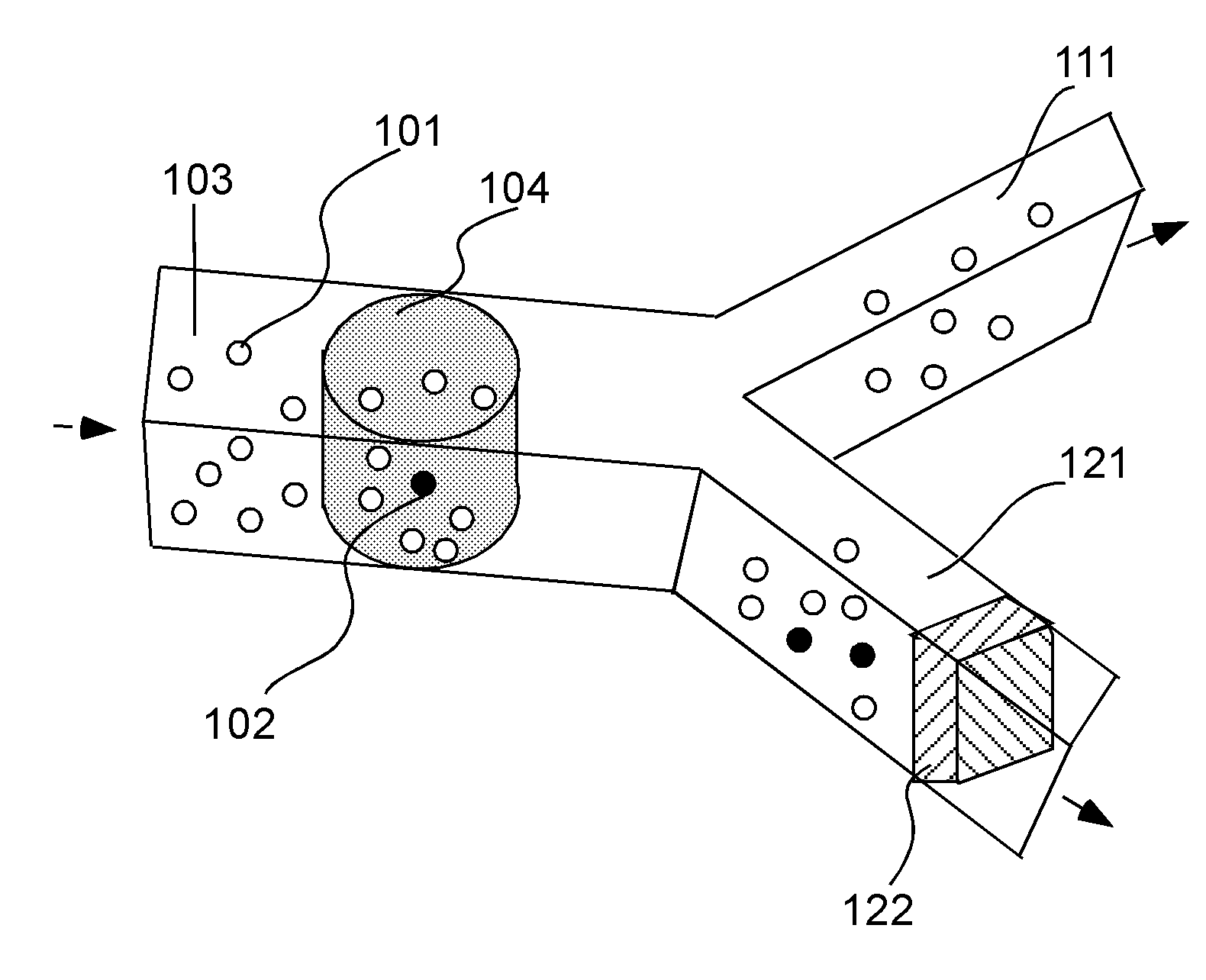
The present invention provides methods and compositions for isolating and detecting rare cells from a biological sample containing other types of cells. In particular, the present invention includes a debulking step that uses a microfabricated filters for filtering fluid samples and the enriched rare cells can be used in a downstream process such as identifies, characterizes or even grown in culture or used in other ways. The invention also include a method of determining the aggressiveness of the tumor or of the number or proportion of cancer cells in the enriched sample by detecting the presence or amount of telomerase activity or telomerase nucleic acid or telomerase expression after enrichment of rare cells. This invention further provides an efficient and rapid method to specifically remove red blood cells as well as white blood cells from a biological sample containing at least one of each of red blood cells and white blood cells, resulting in the enrichment of rare target cells including circulating tumor cells (CTC), stromal cells, mesenchymal cells, endothelial cells, fetal cells, stem cells, non-hematopoietic cells etc from a blood sample. The method is based upon combination of immuno-microparticles (antibody coated microparticles) and density-based separation. The final enriched target cells can be subjected to a variety of analysis and manipulations, such as flowcytometry, PCR, immunofluorescence, immunocytochemistry, image analysis, enzymatic assays, gene expression profiling analysis, efficacy tests of therapeutics, culturing of enriched rare cells, and therapeutic use of enriched rare cells. In addition, depleted plasma protein and white blood cells can be optionally recovered, and subjected to other analysis such as inflammation studies, gene expression profiling, etc.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Ensemble-decision aliquot ranking
InactiveUS20120129190A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRare cellCirculating cancer cell
Provided herein, among other aspects, are methods and apparatuses for ranking aliquots from a suspension containing bioparticles. In certain embodiments, the bioparticles may be cells, organelles, proteins, DNAs, debris of biological origin, microbeads coated with biological compounds, or viral particles. As such, the methods and apparatuses provided herein may be used to quantify rare cells such as circulating cancer cells, fetal cells and other rare cells present in bodily fluids for disease diagnosis, prognosis, or treatment.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Blood test prototypes and methods for the detection of circulating tumor and endothelial cells
InactiveUS20050244843A1Enhance anti-tumor immune responseDramatic utilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAbnormal tissue growthProgenitor
Methods and devices for isolating and diagnosing disease with a cell adhesion matrix system, mimicking a metastatic, cardiovascular or placental environment, are disclosed. The cell adhesion matrix facilitates the enrichment of target cells such as metastatic tumor cells, fetal cells and endothelial progenitor cells from a fluid sample such as blood for diagnostic and therapeutic applications in treating patients afflicted with disease, such as cancerous, cardiovascular and fetal diseases, as well as for research applications in molecular analysis of metastatic, and cardiovascular and fetal diseases. Blood test prototypes and methods for the cell enrichment and detection of circulating tumor and endothelial cells using multiplex molecular analysis are described herein. In addition, methods and compositions for determining host immunity to tumor in subjects with risk of cancer progression and methods for isolating an enriched fraction of fetal cells from pregnant females for prenatal diagnosis are also described herein.
Owner:CHEN WEN TIEN +2
Rare cell analysis using sample splitting and DNA tags
ActiveUS20100136529A1Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresFetal abnormalityRare cell
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to detect the presence of fetal cells when mixed with a population of maternal cells in a sample and to test fetal abnormalities, e.g. aneuploidy. The present invention involves labeling regions of genomic DNA in each cell in said mixed sample with different labels wherein each label is specific to each cell and quantifying the labeled regions of genomic DNA from each cell in the mixed sample. More particularly the invention involves quantifying labeled DNA polymorphisms from each cell in the mixed sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC +2
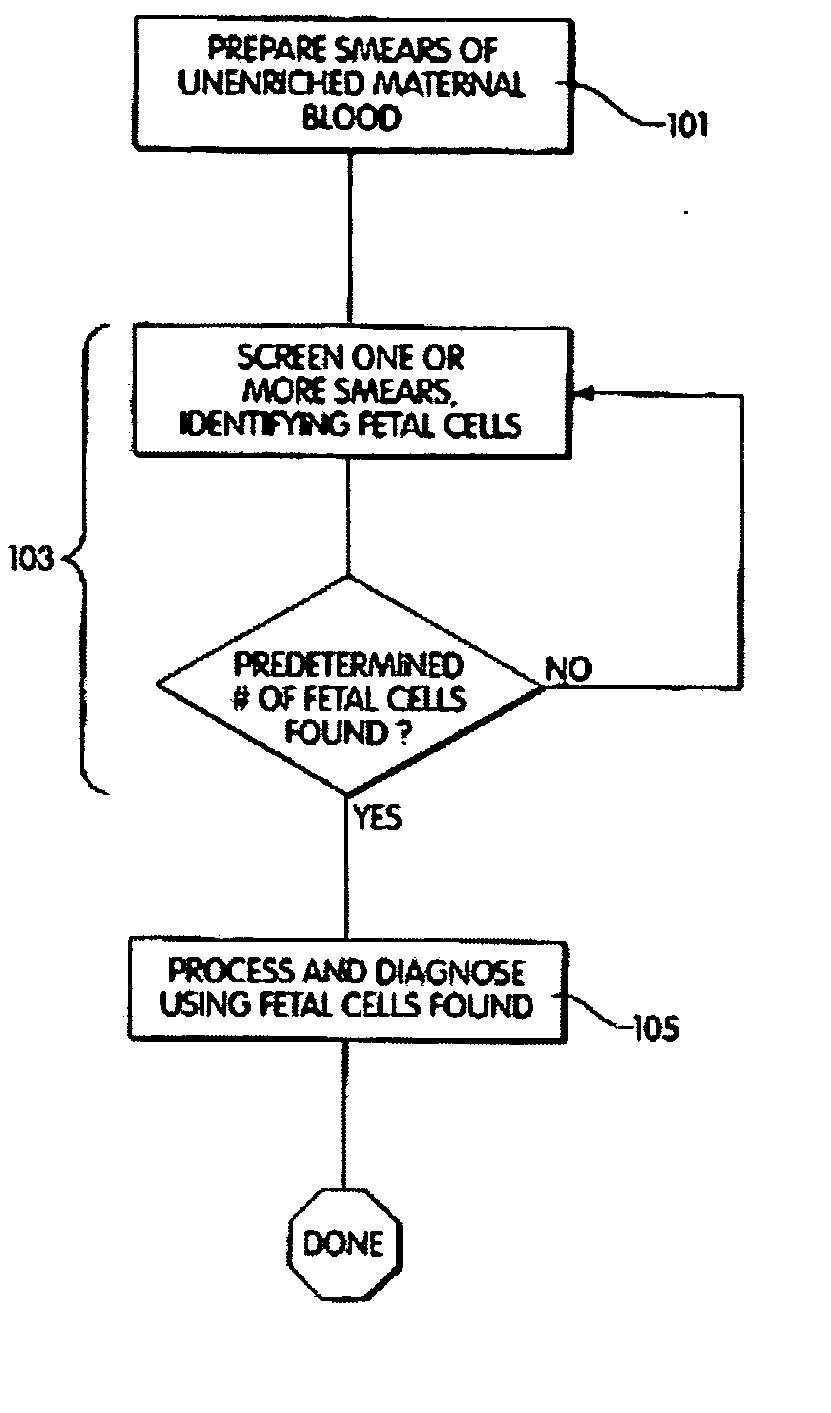
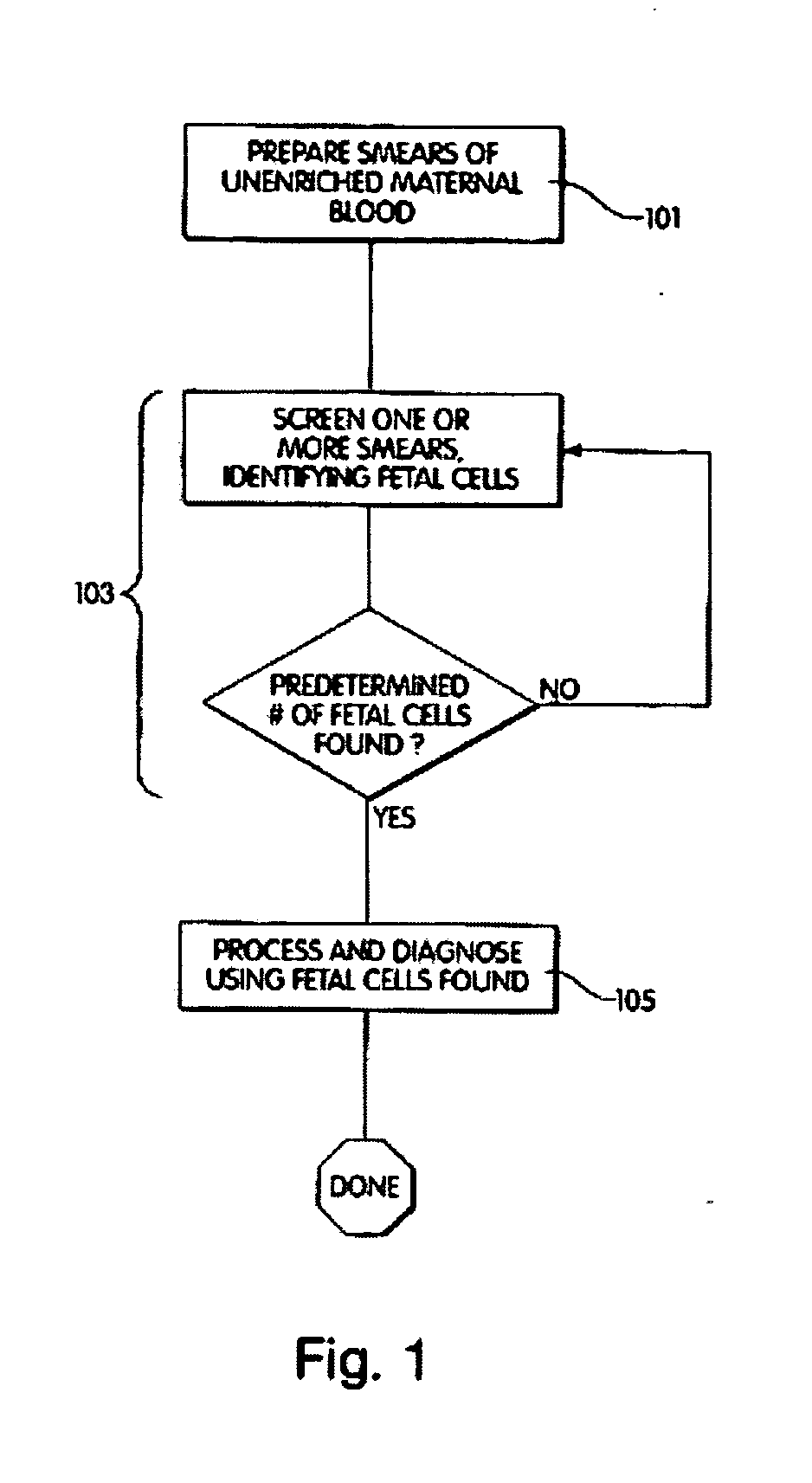
Diagnosis of fetal abnormalities using polymorphisms including short tandem repeats
InactiveUS20090280492A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationFetal abnormalityGenomic DNA
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to detect the presence of fetal cells when mixed with a population of maternal cells in a sample and to test fetal abnormalities, i.e. aneuploidy. In addition, the present invention provides methods to determine when there are insufficient fetal cells for a determination and report a non-informative case. The present invention involves quantifying regions of genomic DNA from a mixed sample. More particularly the invention involves quantifying DNA polymorphisms from the mixed sample.
Owner:STOUGHTON ROLAND +2
Method for genotype determination
InactiveUS20040115684A1Enabling detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationReference genesMedicine
The present invention is directed to a new method for genotype determination at a specific gene locus of an individual or a fetus comprising (i) amplifying a first sequence of said gene locus and a second sequence of a second reference gene locus from DNA originating from a sample containing biological material of said individual or fetus (ii) Monitoring both amplifications preferably in real time and determining the amount of amplification products after each cycle, and (iii) Calculating the ratio between the amount of DNA from the first gene locus and the amount of DNA from the second gene locus. The new method is useful for a variety of applications, especially for detection of chromosomal abnormalities in fetal cells.
Owner:COSTA JEAN MARC
Diagnosis of fetal abnormalities by comparative genomic hybridization analysis
InactiveUS20100112586A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisFetal abnormalityComparative genomic hybridization
Owner:STOUGHTON ROLAND +1
Devices and methods for magnetic enrichment of cells and other particles
InactiveCN101305087ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRare cellAnalyte
The present invention relates to devices and methods for the enrichment of cells and other desired analytes by employing a magnetic field, alone or in conjunction with size-based separation. The devices and methods may be advantageously employed to enrich for rare cells, e.g., fetal cells or epithelial cells, present in a sample, e.g., maternal blood.
Owner:ARTEMIS HEALTH INC +1
Method and apparatus for computer controlled cell based diagnosis
InactiveUS20060072805A1Minimize timePossible amount of timePreparing sample for investigationDisease diagnosisCancer cellRare cell
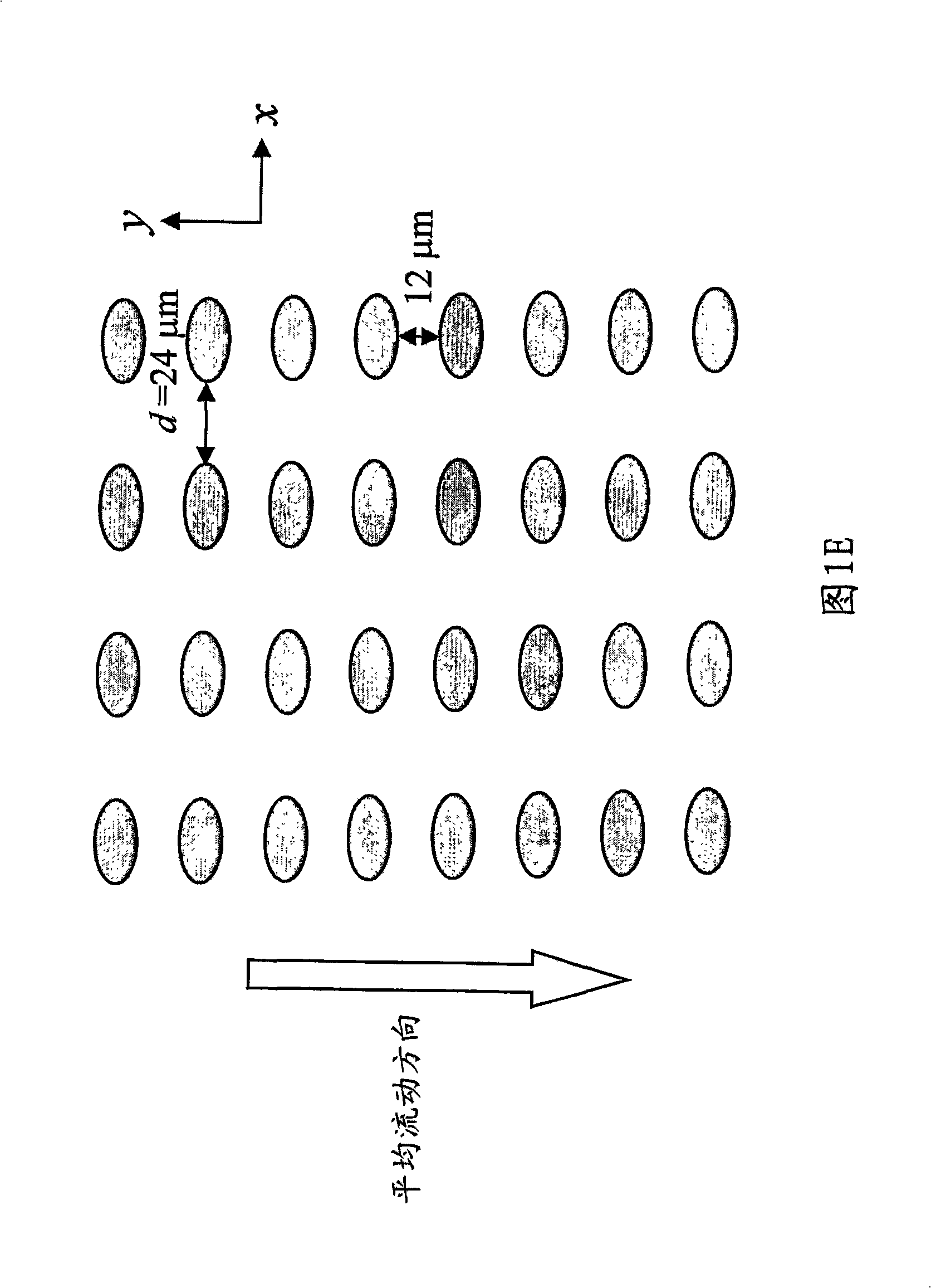
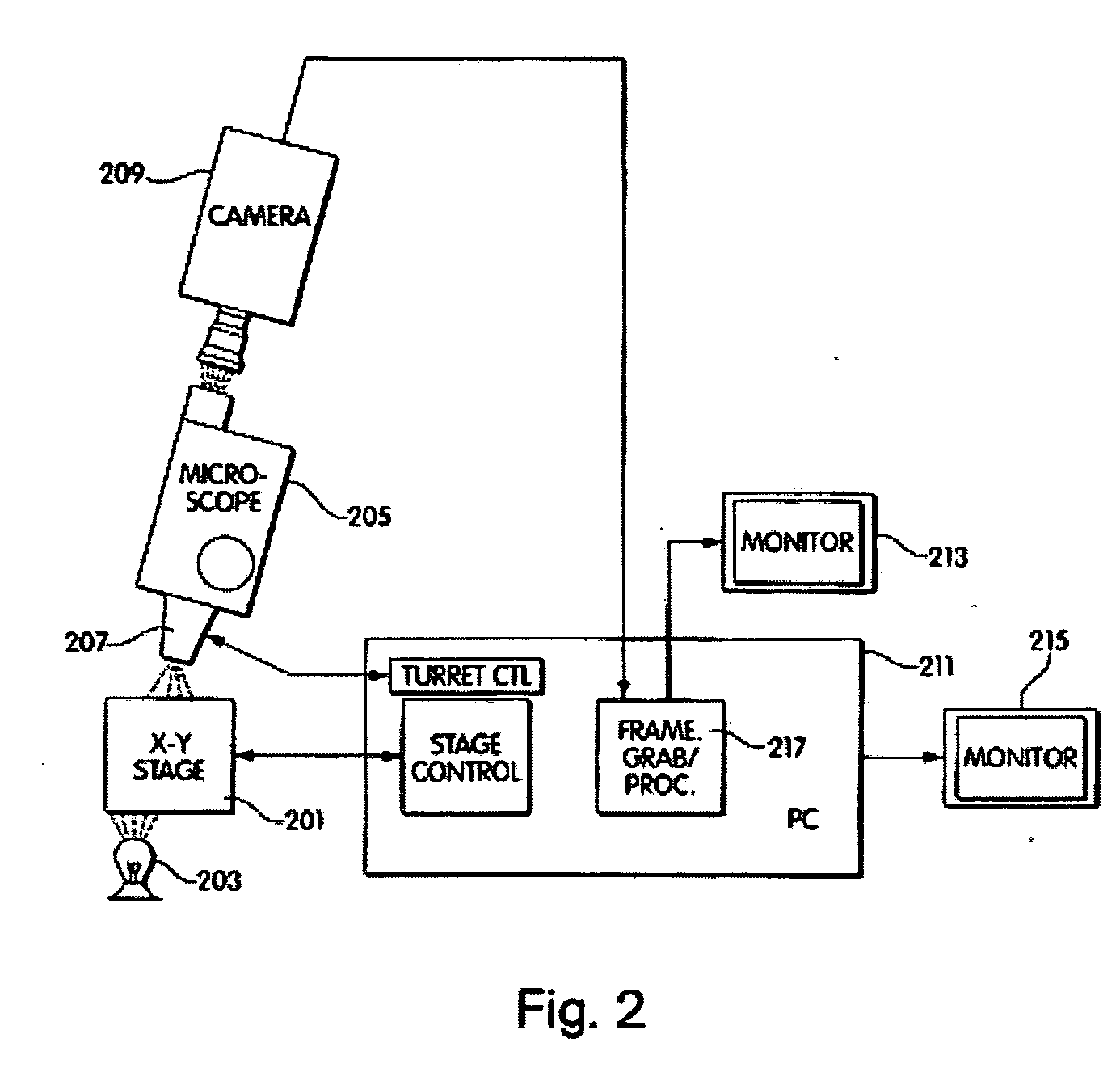
A computer controlled method for detecting and diagnosing a rare cell type in a tissue sample is provided, said method comprising treating the tissue sample such that it generates a first signal indicative of the presence at a location of a rare cell, detecting the first signal, treating the location at which the first signal is detected to generate a second signal indicative of a diagnostically useful cellular characteristic and detecting the second signal. The first signal can be morphological or a color present in a sought cell either before or after staining. The second signal can be generated by in situ PCR or PCR in situ hybridization. In one preferred embodiment, the rare cell type is a fetal cell in a maternal blood tissue sample, said sample consisting of a smear of unenriched maternal blood. In another embodiment, the method is used to diagnose or genotype cancer cells in a blood or tissue biopsy sample.
Owner:IKONISYS INC
Identification and isolation of fetal cells and nucleic acid
The present invention provides methods, antibodies and kits useful for detecting the presence of a fetal cell and / or fetal nucleic acids in a biological sample obtained from a maternal host. It also provides methods and kits for isolating fetal nucleic acid from maternal cervical mucus samples, and for testing or screening the isolated fetal nucleic acid for genetic abnormalities in fetuses.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com