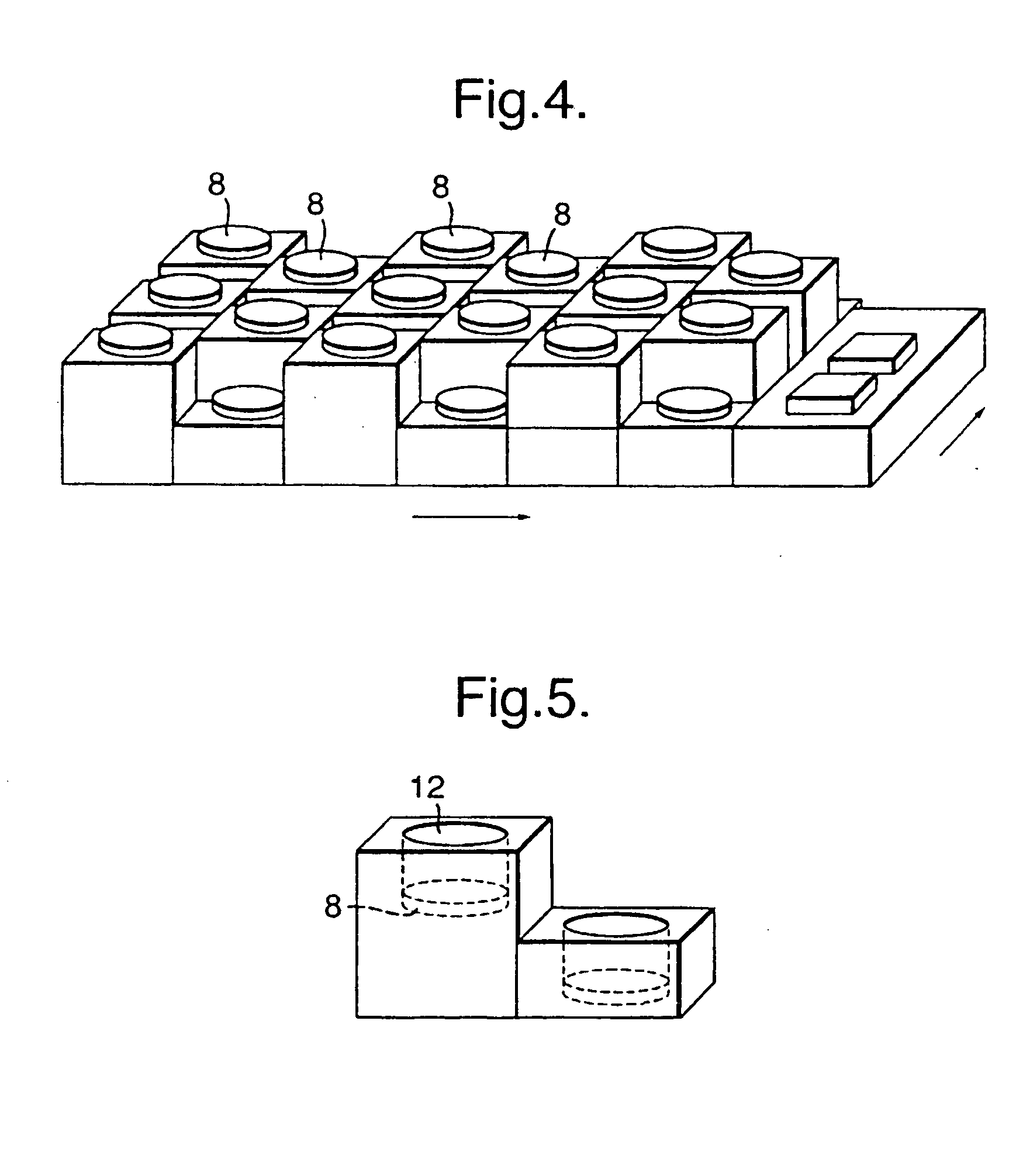
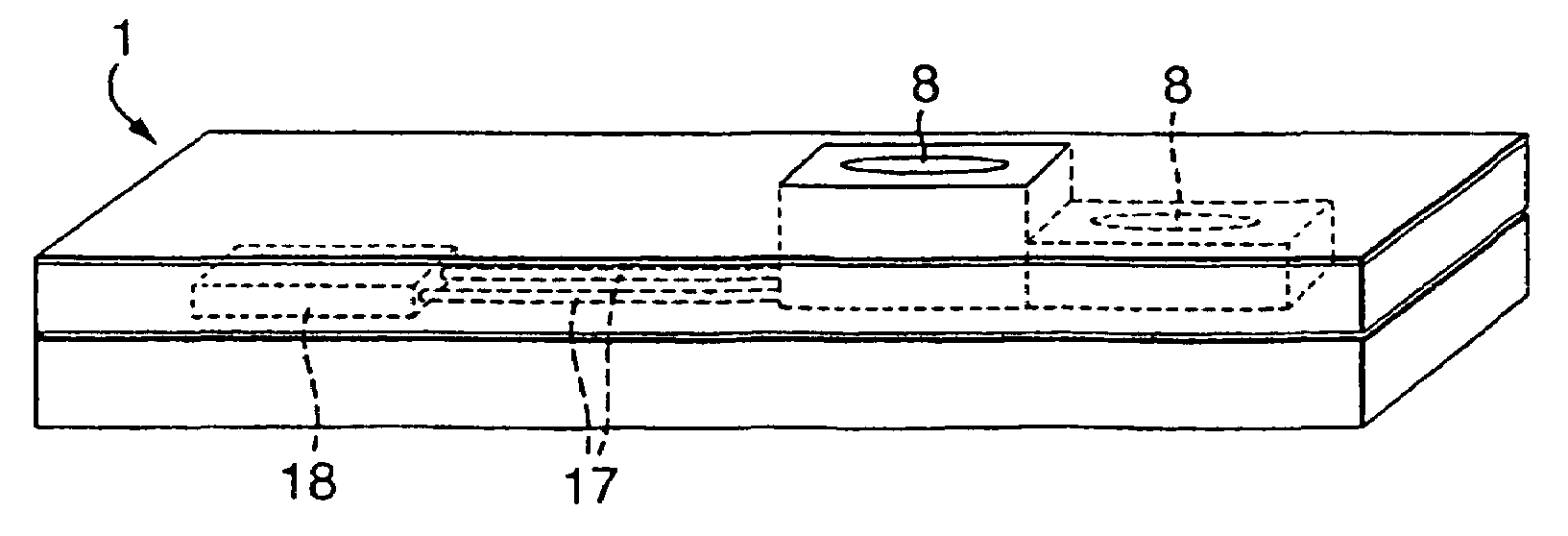
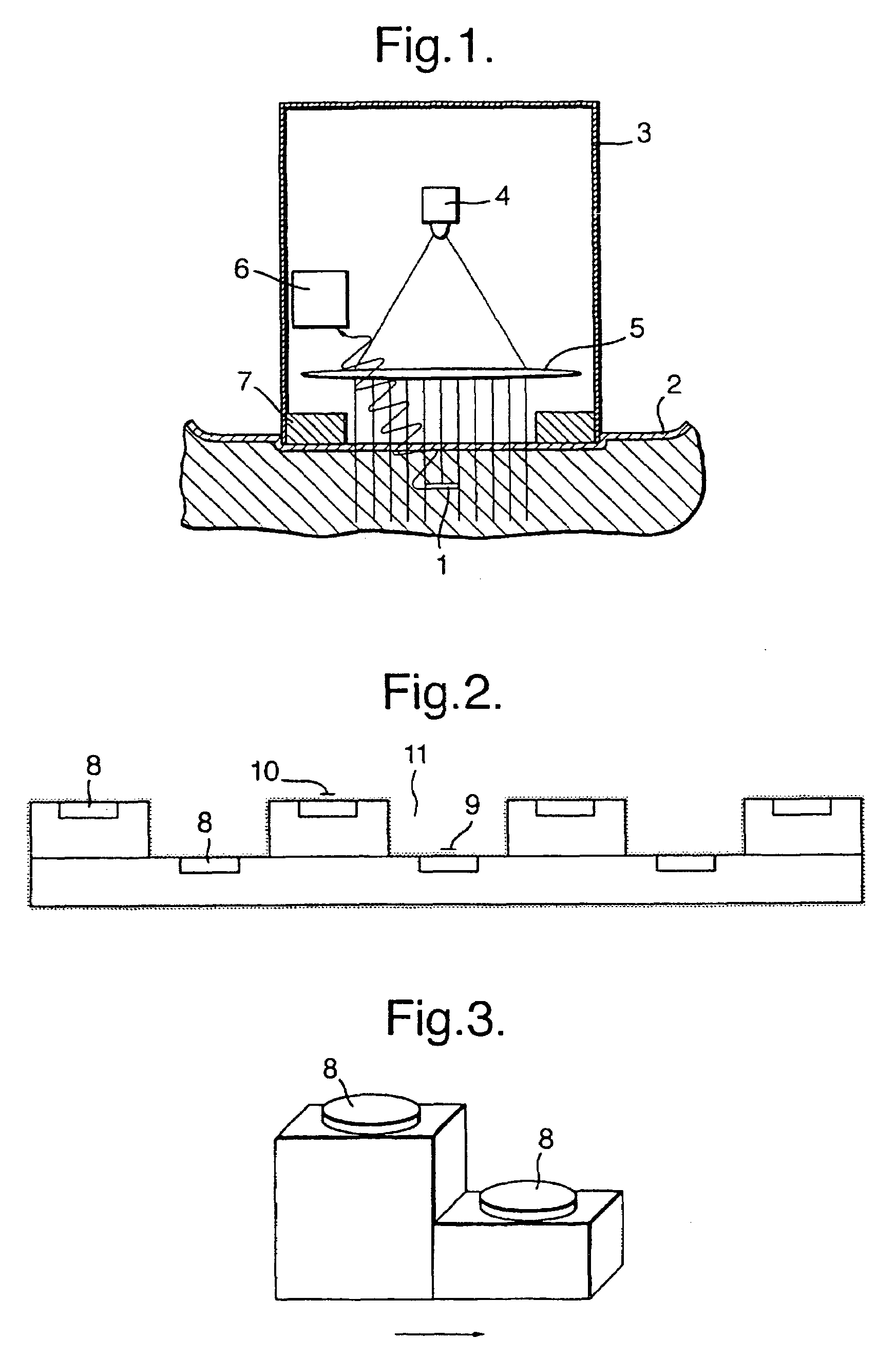
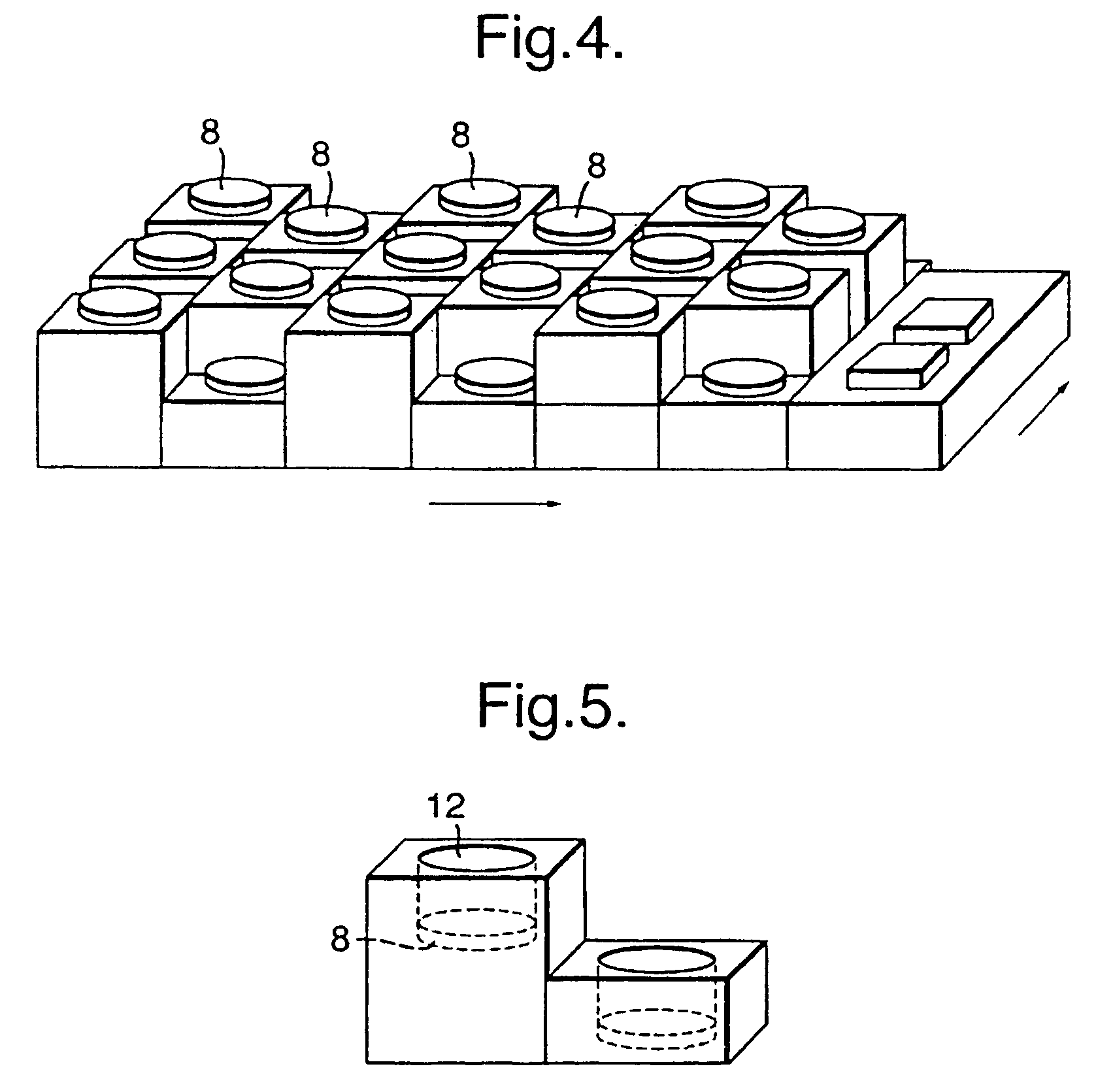
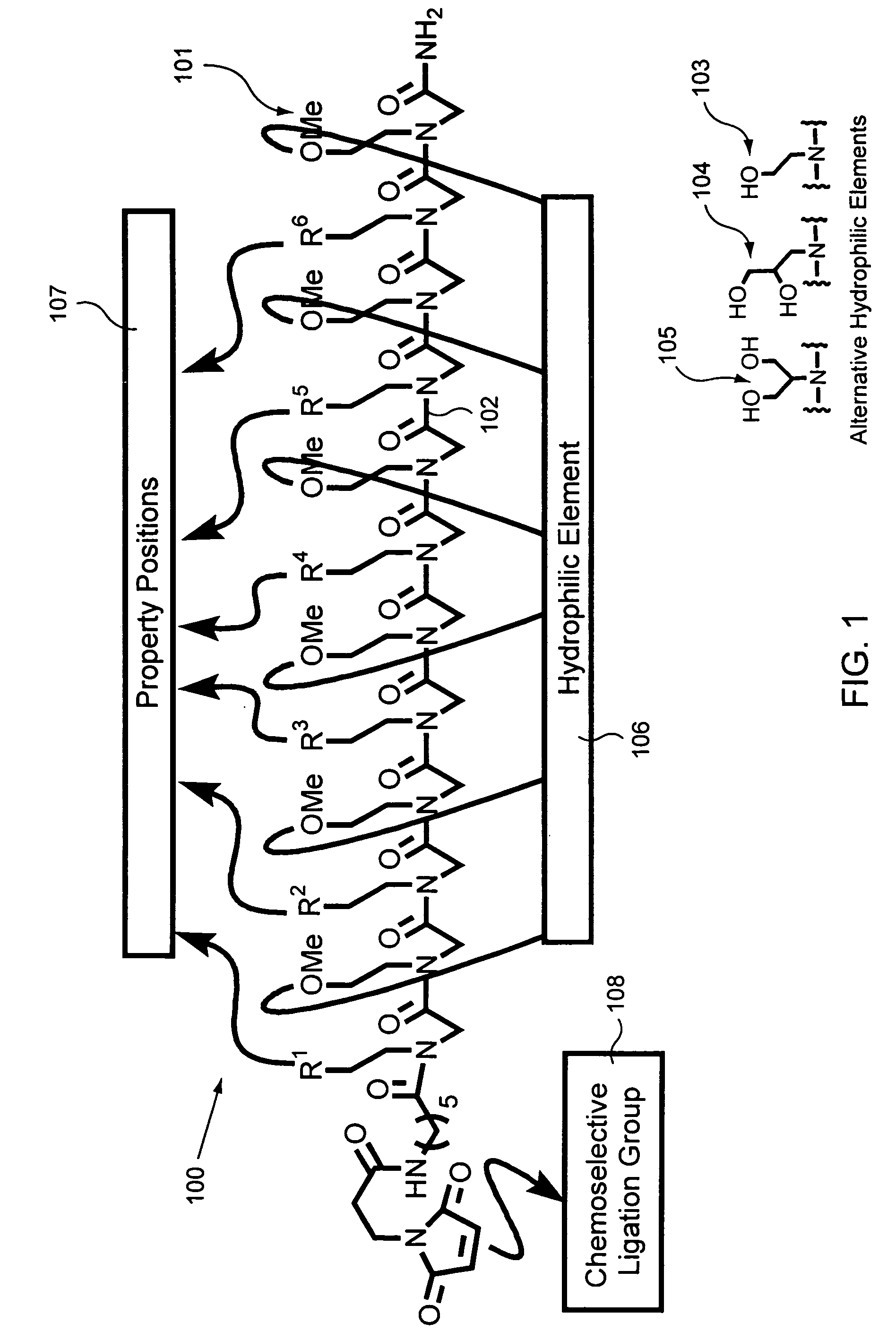
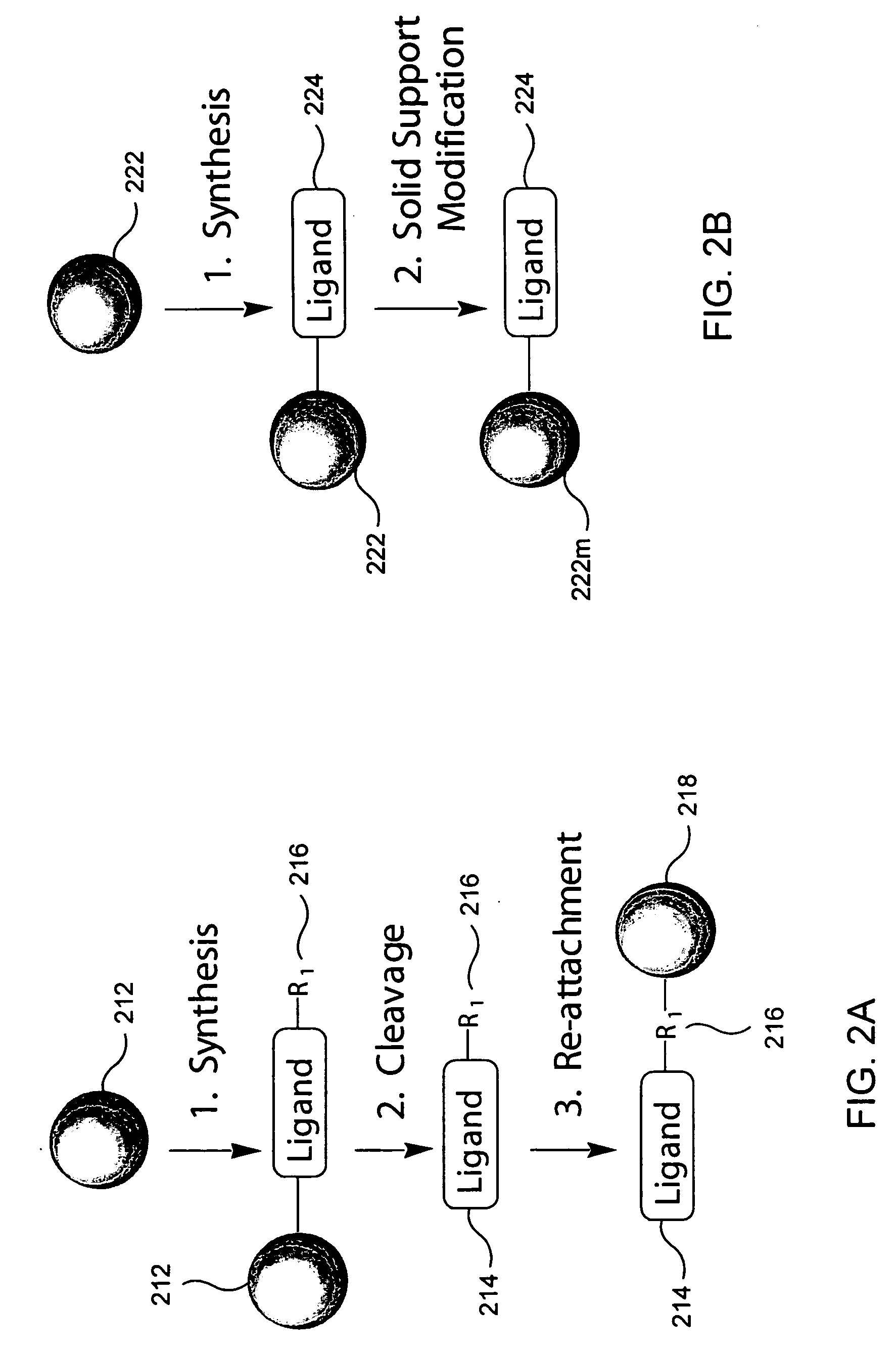
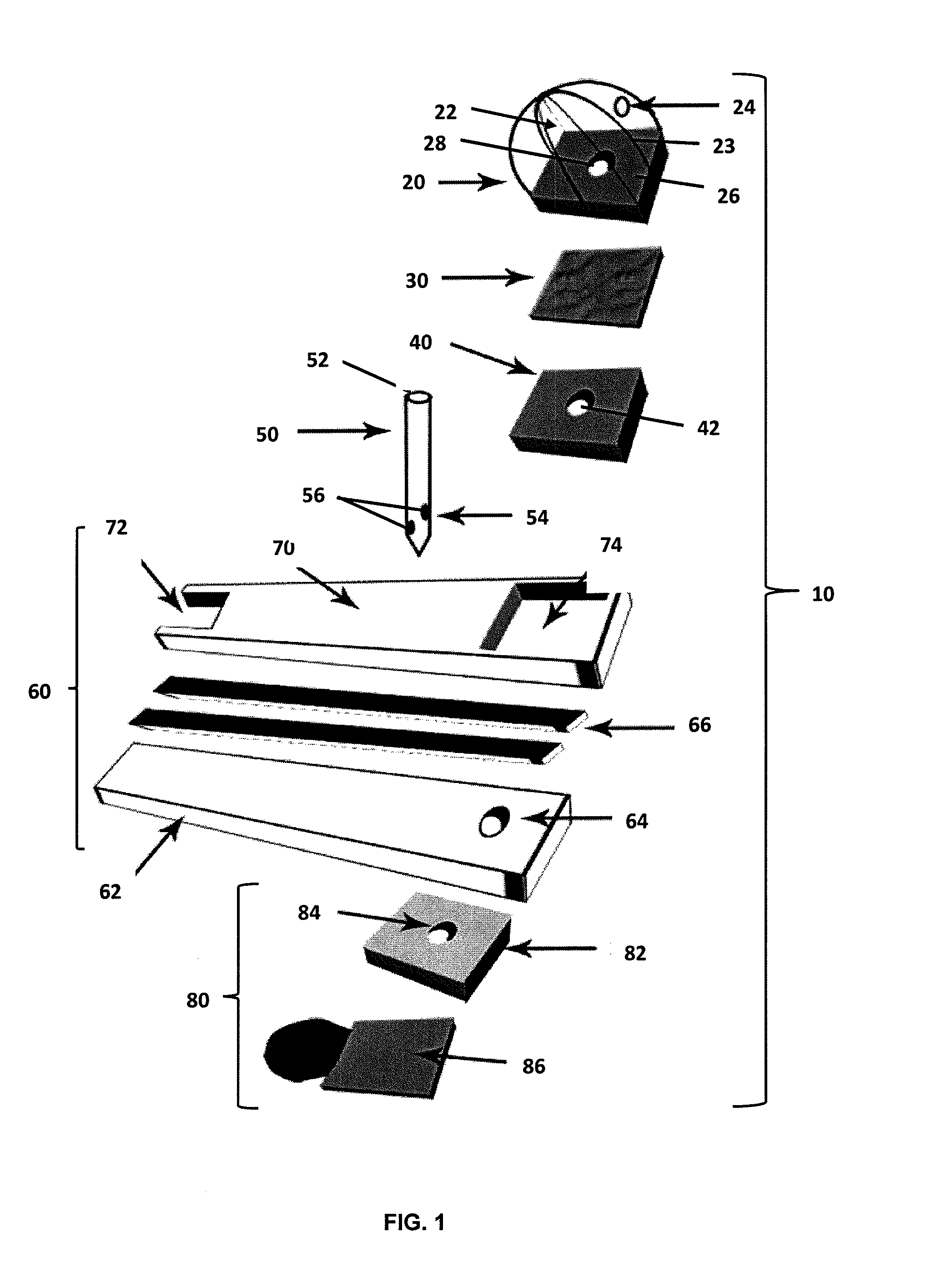
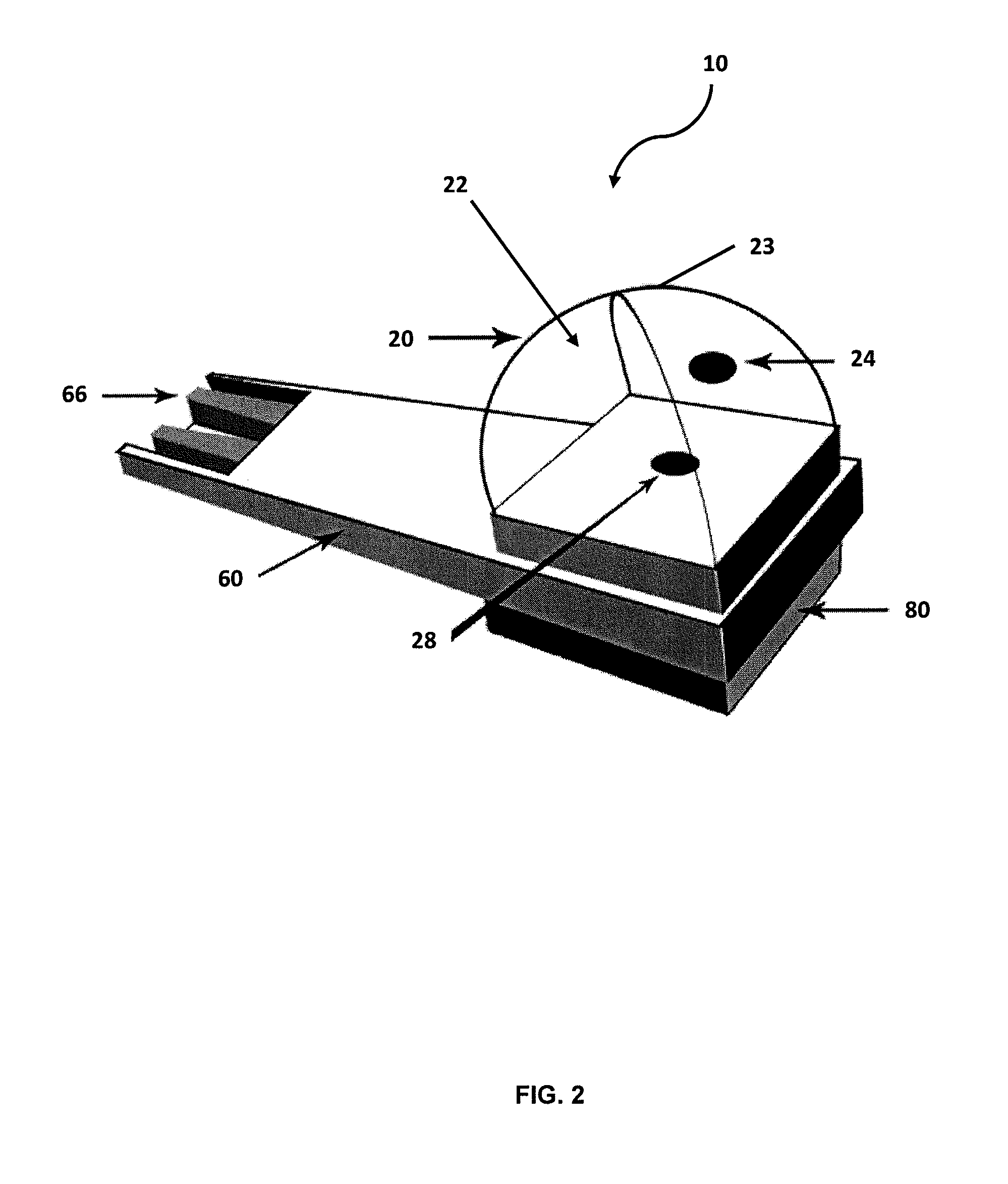
Patents
Literature
87 results about "Blood or Tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Blood is considered a connective tissue for two basic reasons: (1) embryologically, it has the same origin (mesodermal) as do the other connective tissue types and (2) blood connects the body systems together bringing the needed oxygen, nutrients, hormones and other signaling molecules, and removing the wastes.
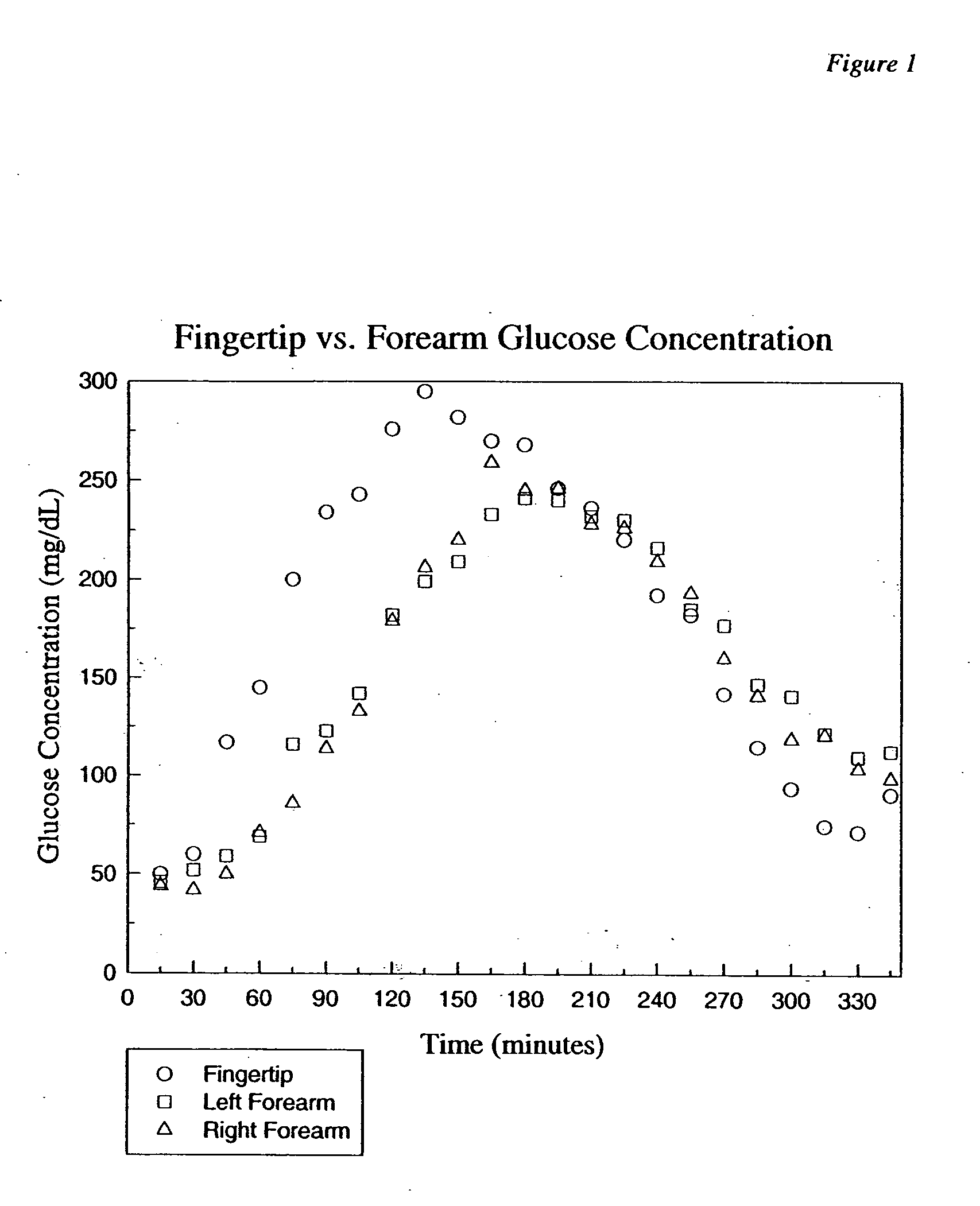
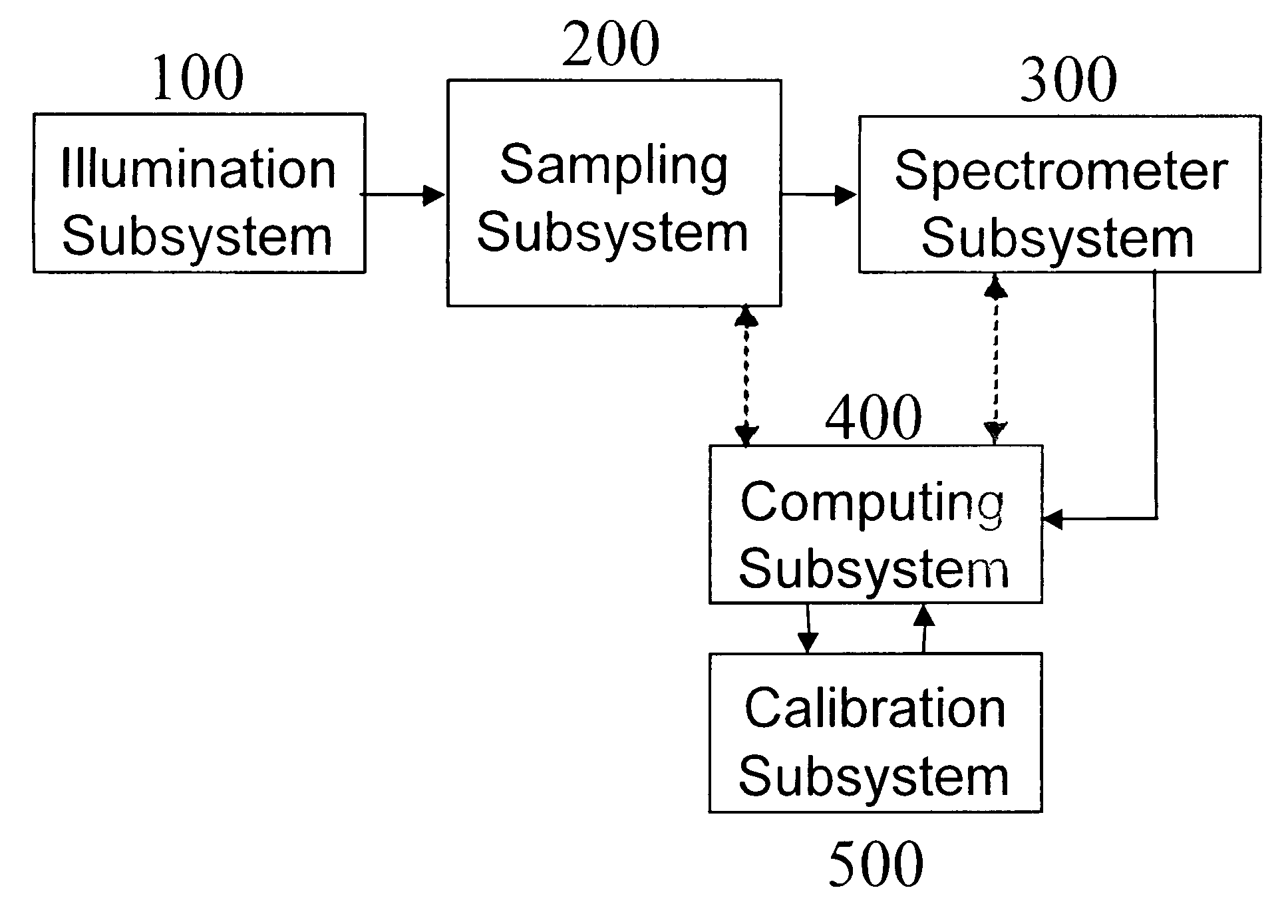
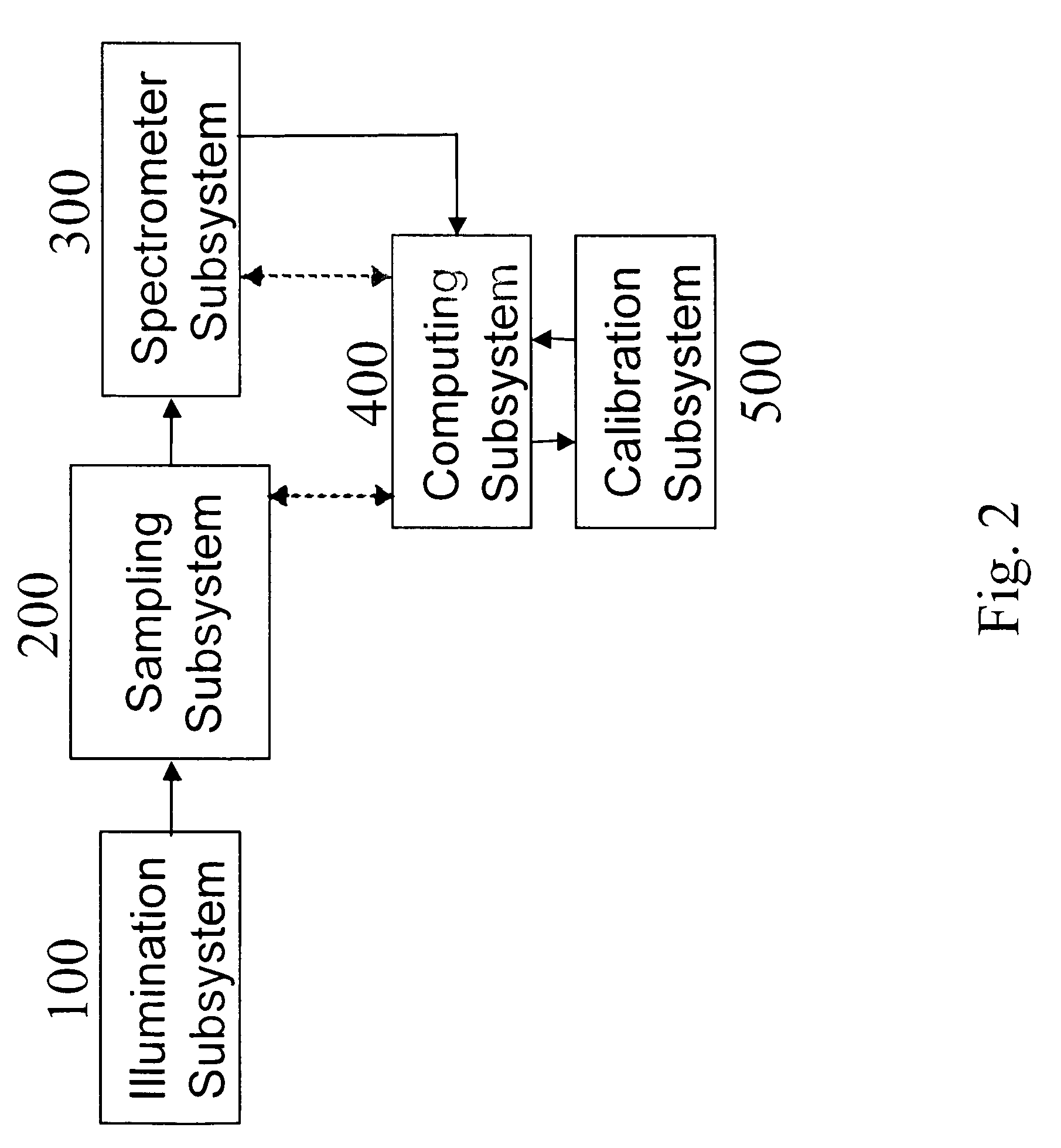
Non-invasive determination of direction and rate of change of an analyte
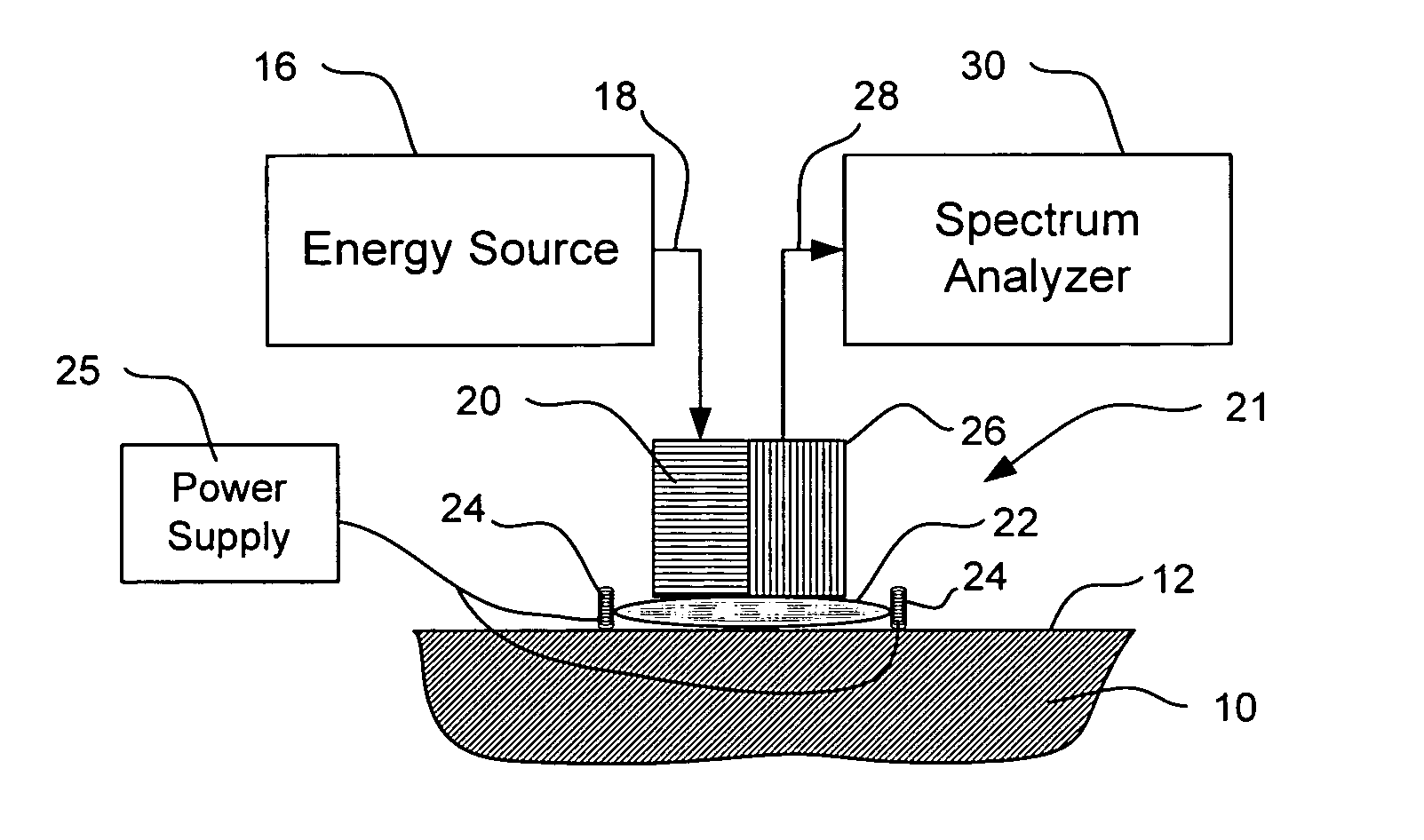
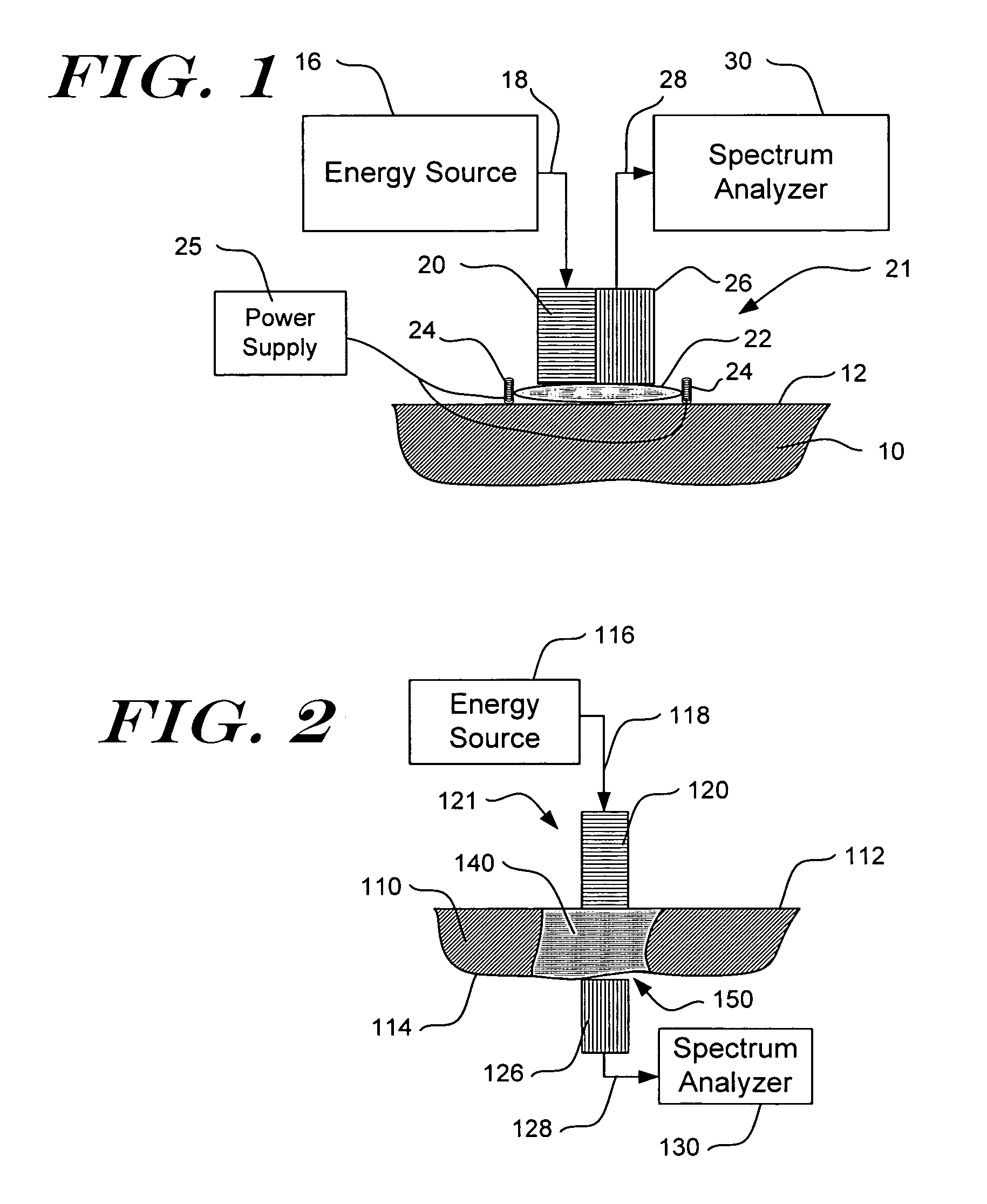
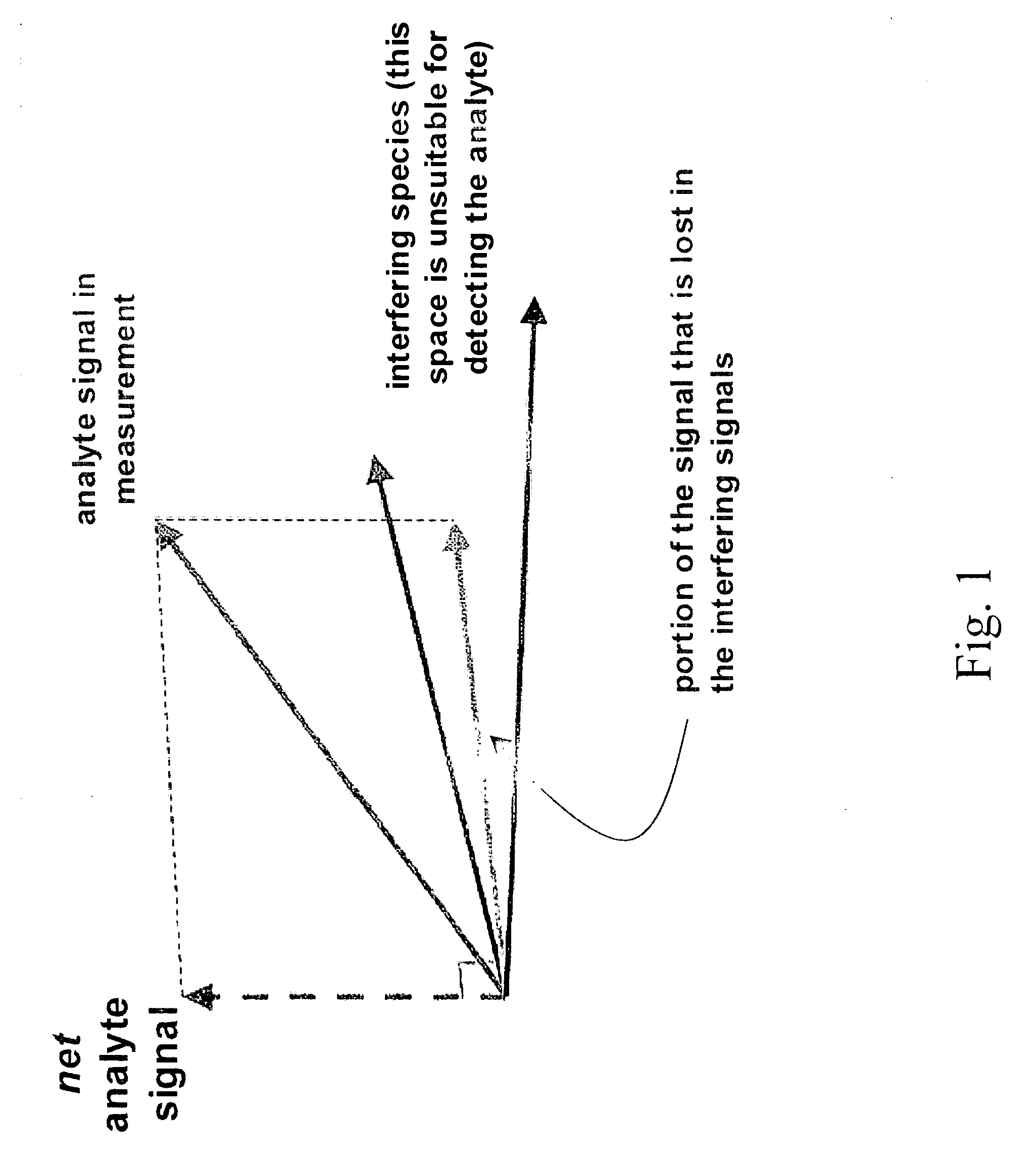
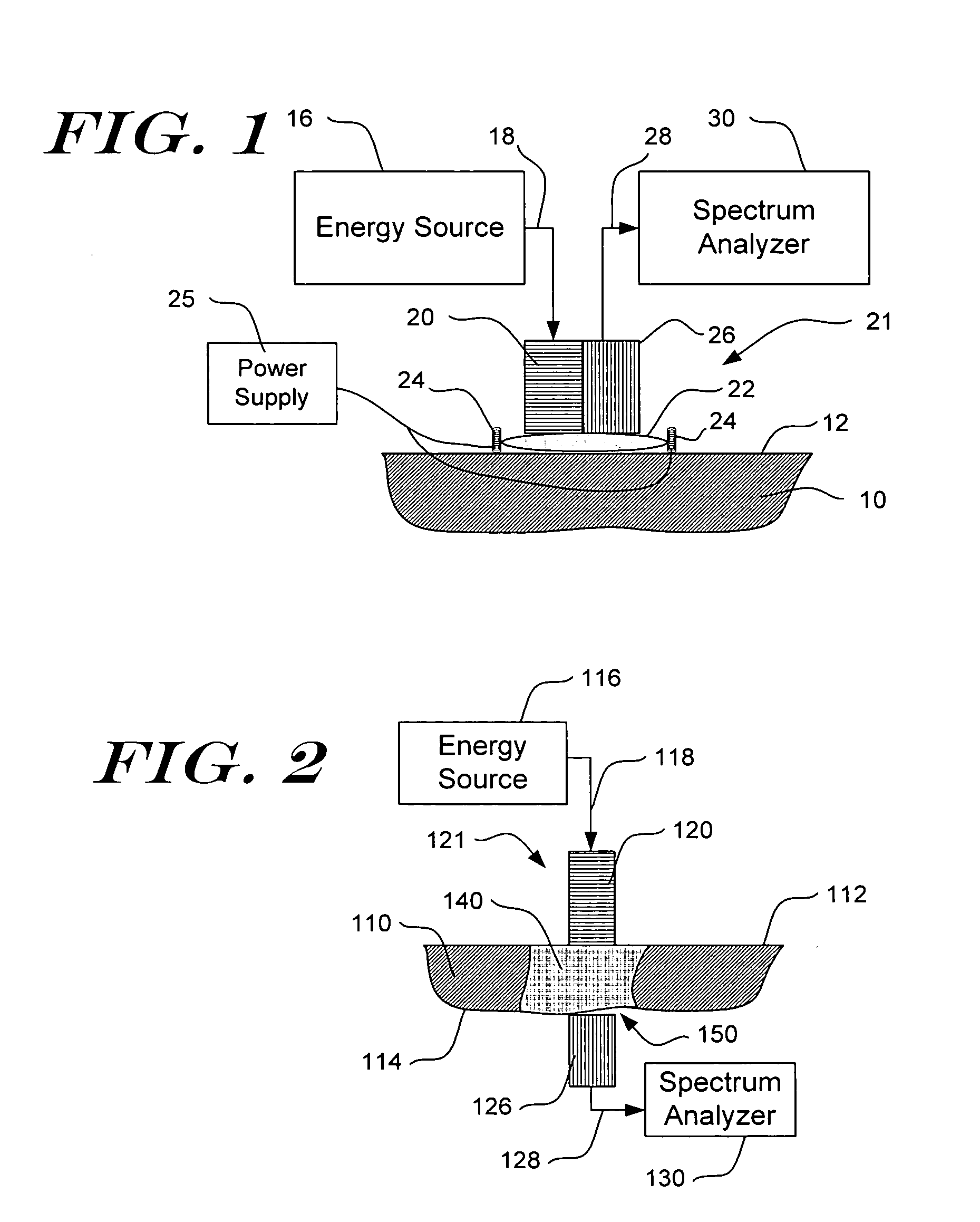
InactiveUS7016713B2Improve accuracyImprove stabilityDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyAlcoholAnalyte
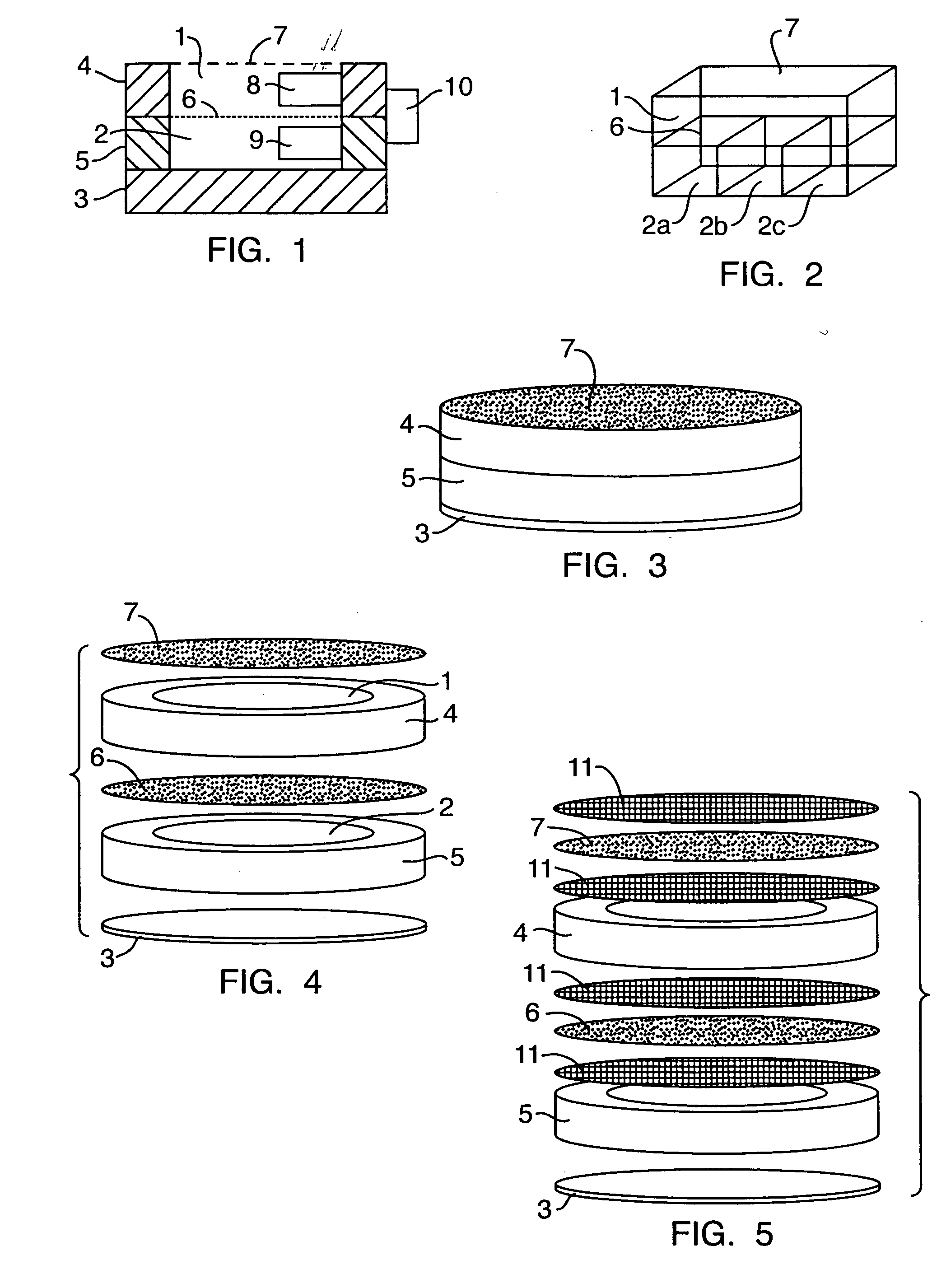
The present invention relates generally to a non-invasive method and apparatus for measuring a fluid analyte, particularly relating to glucose or alcohol contained in blood or tissue, utilizing spectroscopic methods. More particularly, the method and apparatus incorporate means for detecting and quantifying changes in the concentration of specific analytes in tissue fluid. Also, the method and apparatus can be used to predict future levels of analyte concentration either in the tissue fluid or in blood in an adjacent vascular system.
Owner:INLIGHT SOLUTIONS
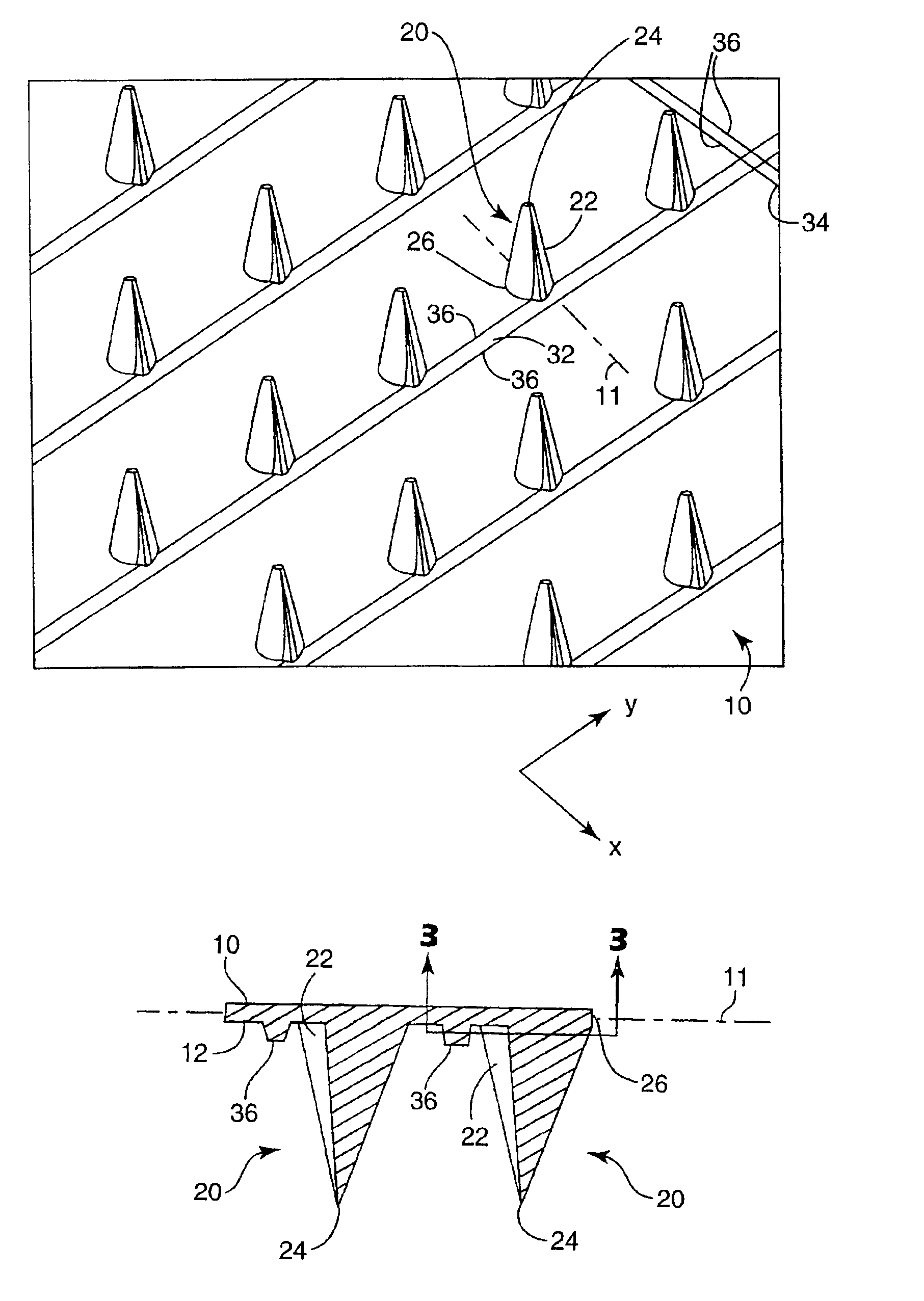
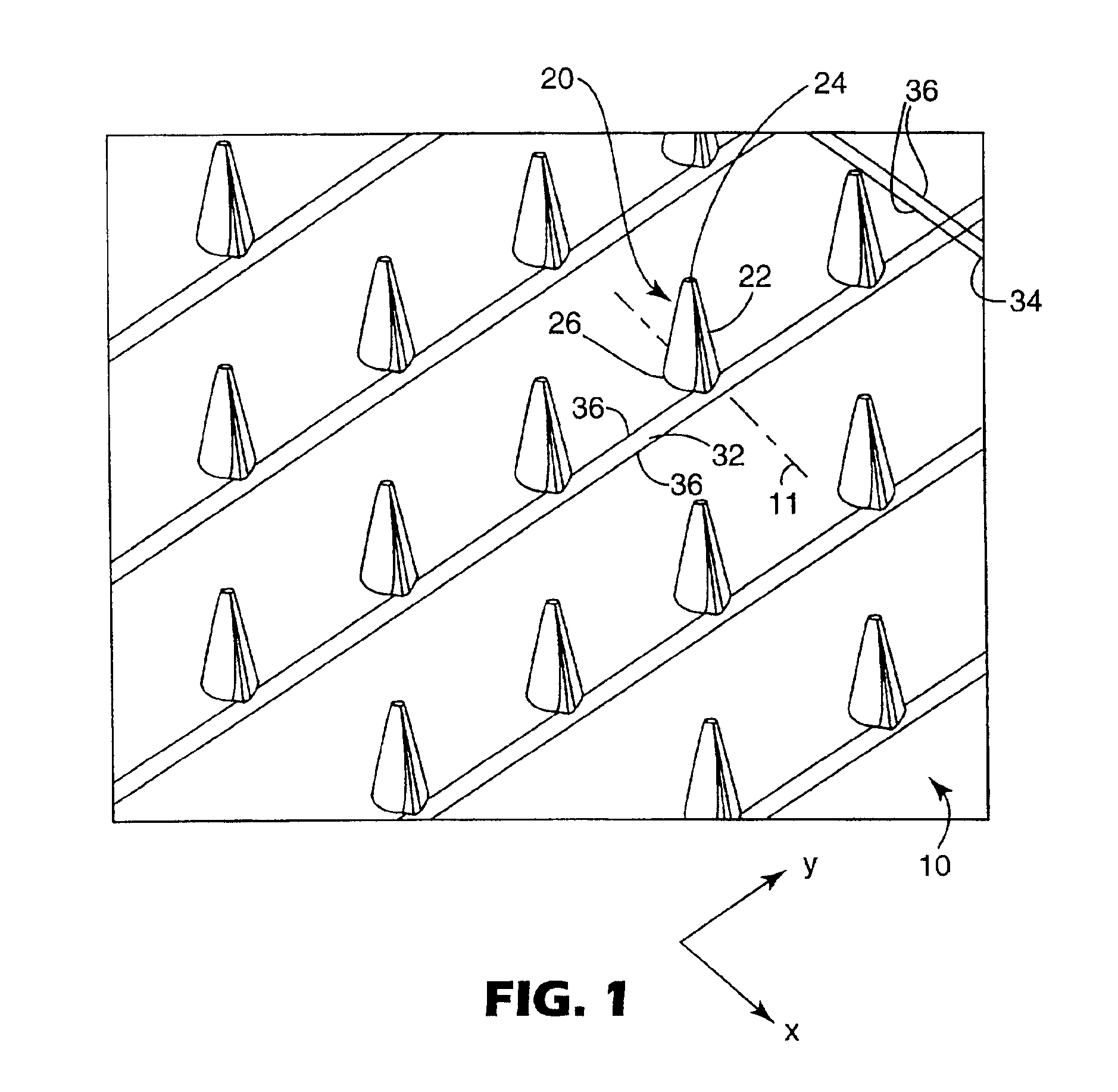
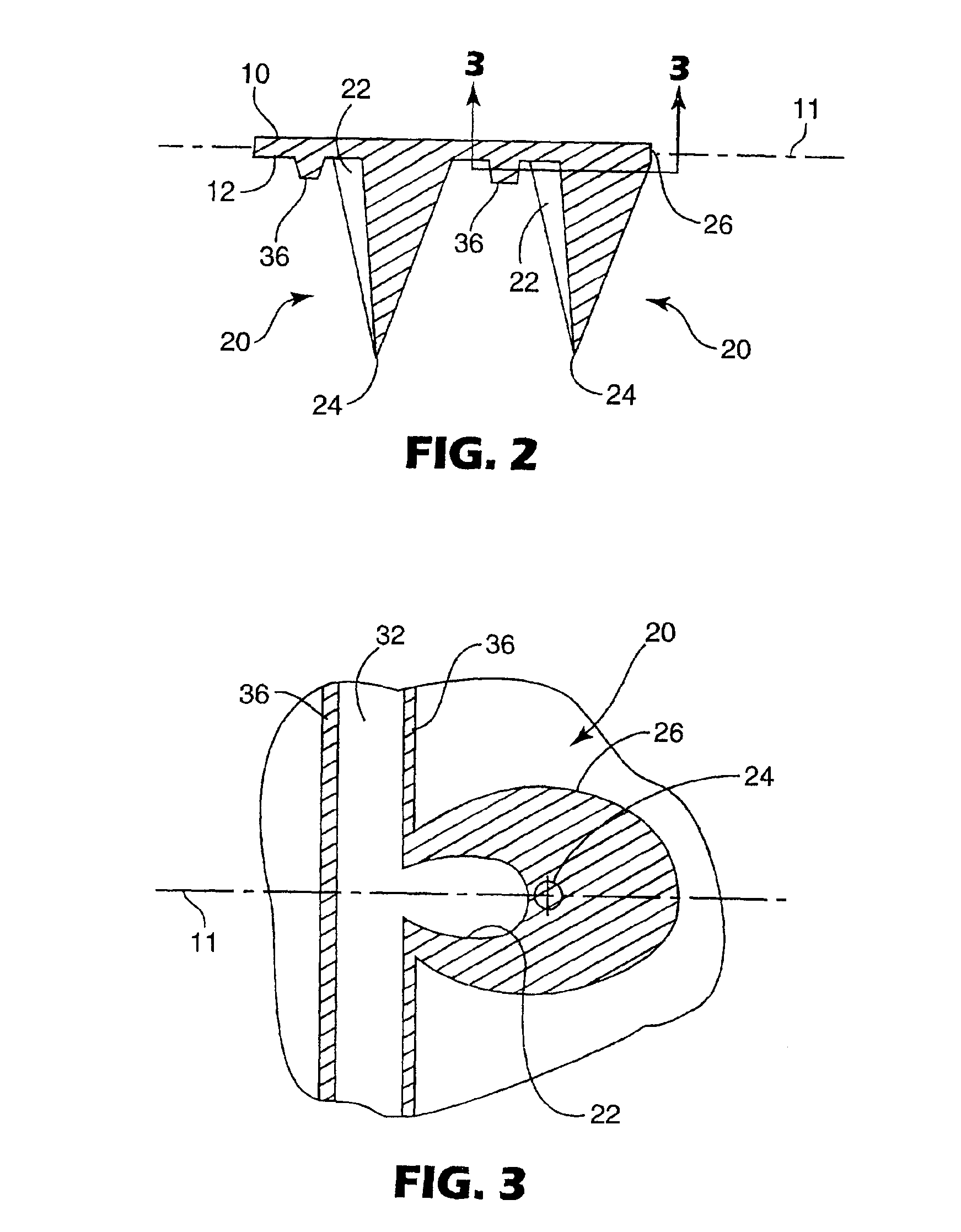
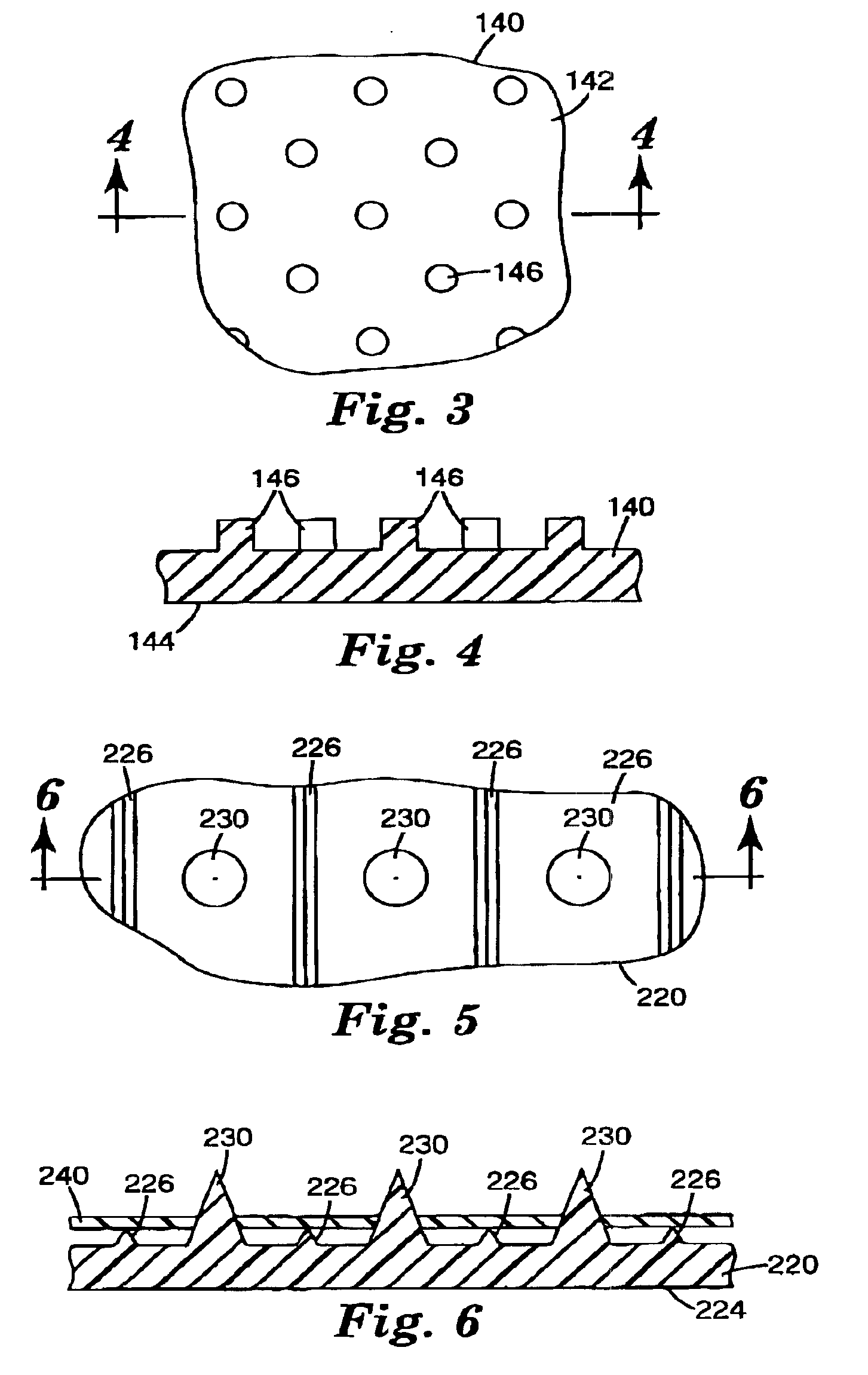
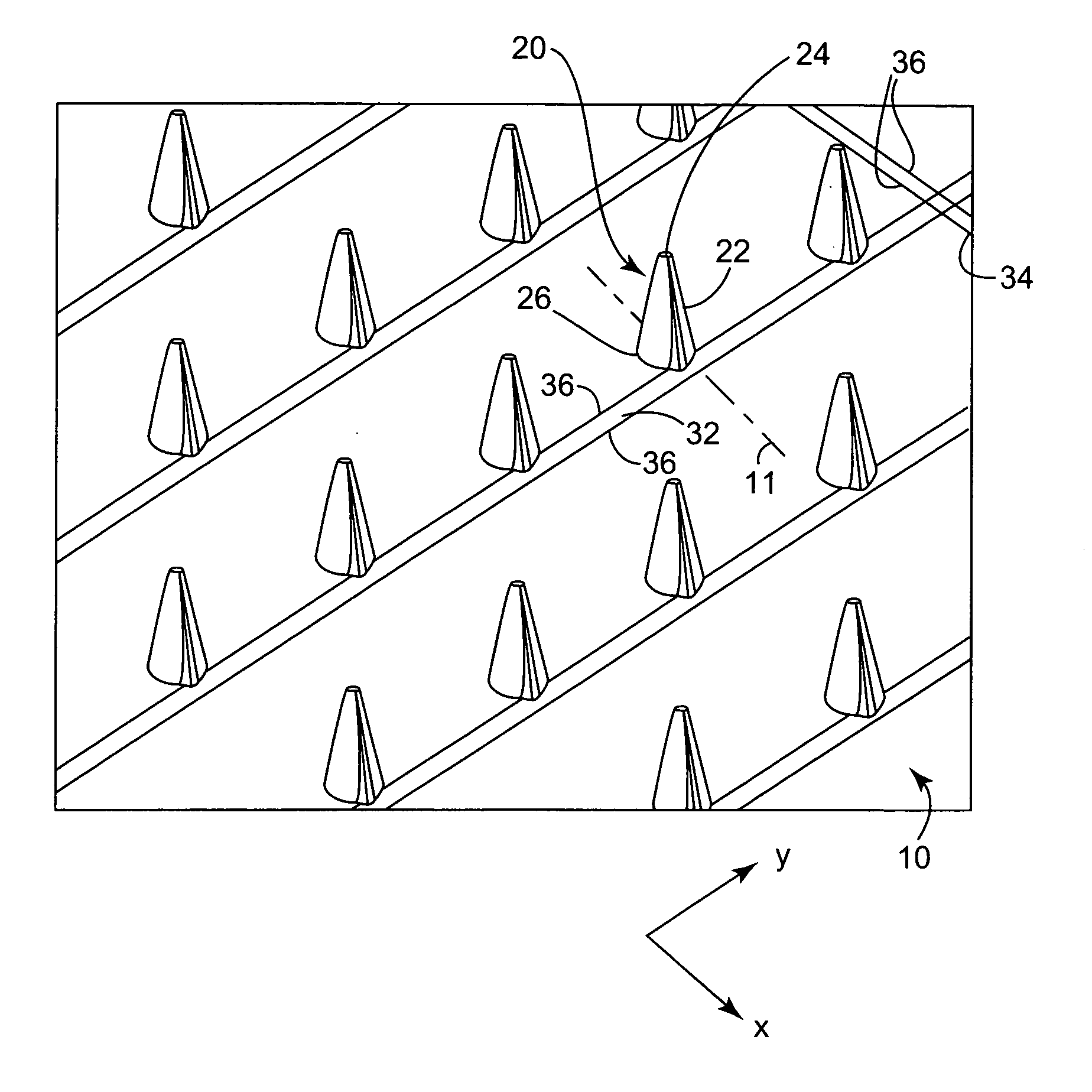
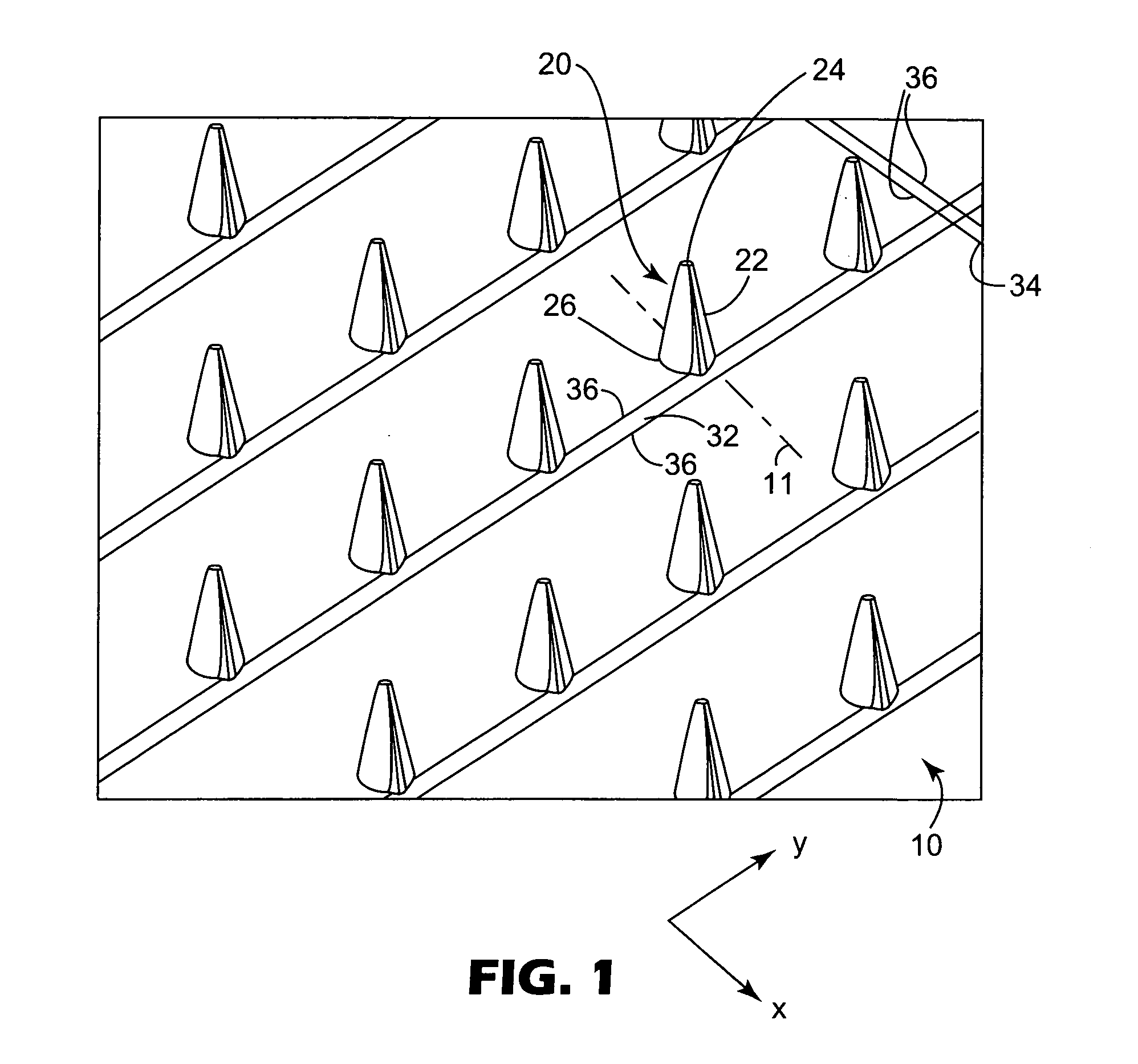
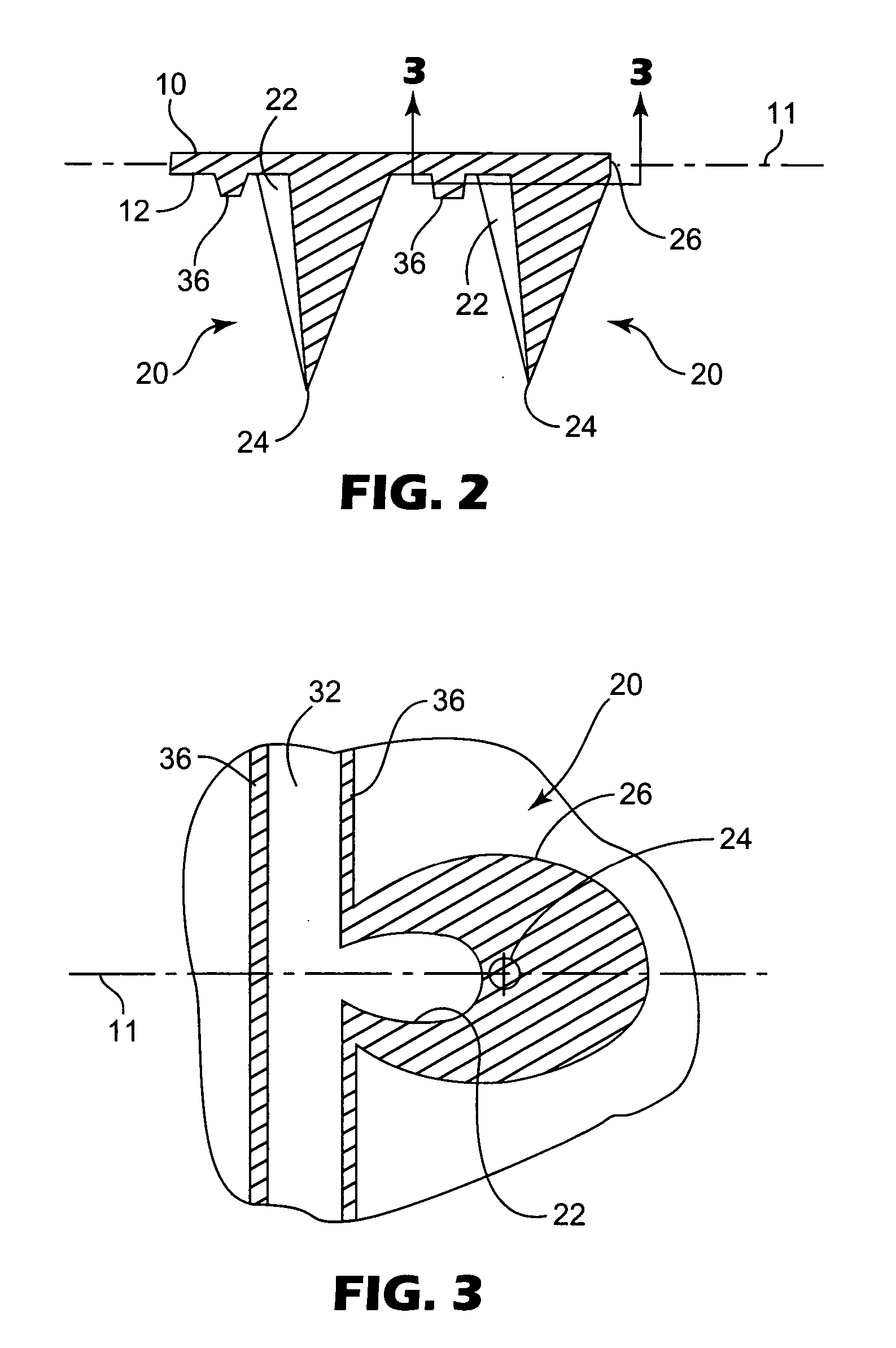
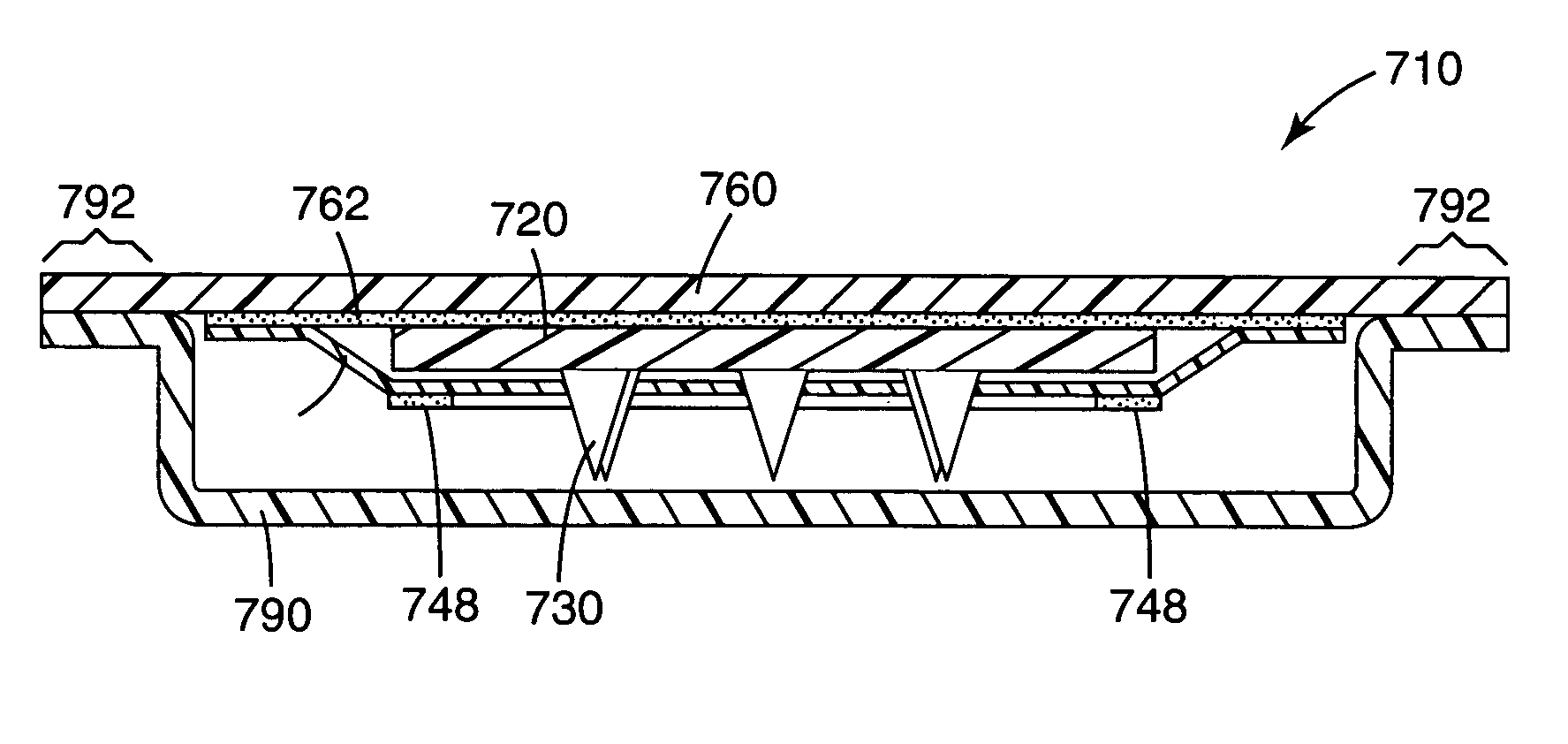
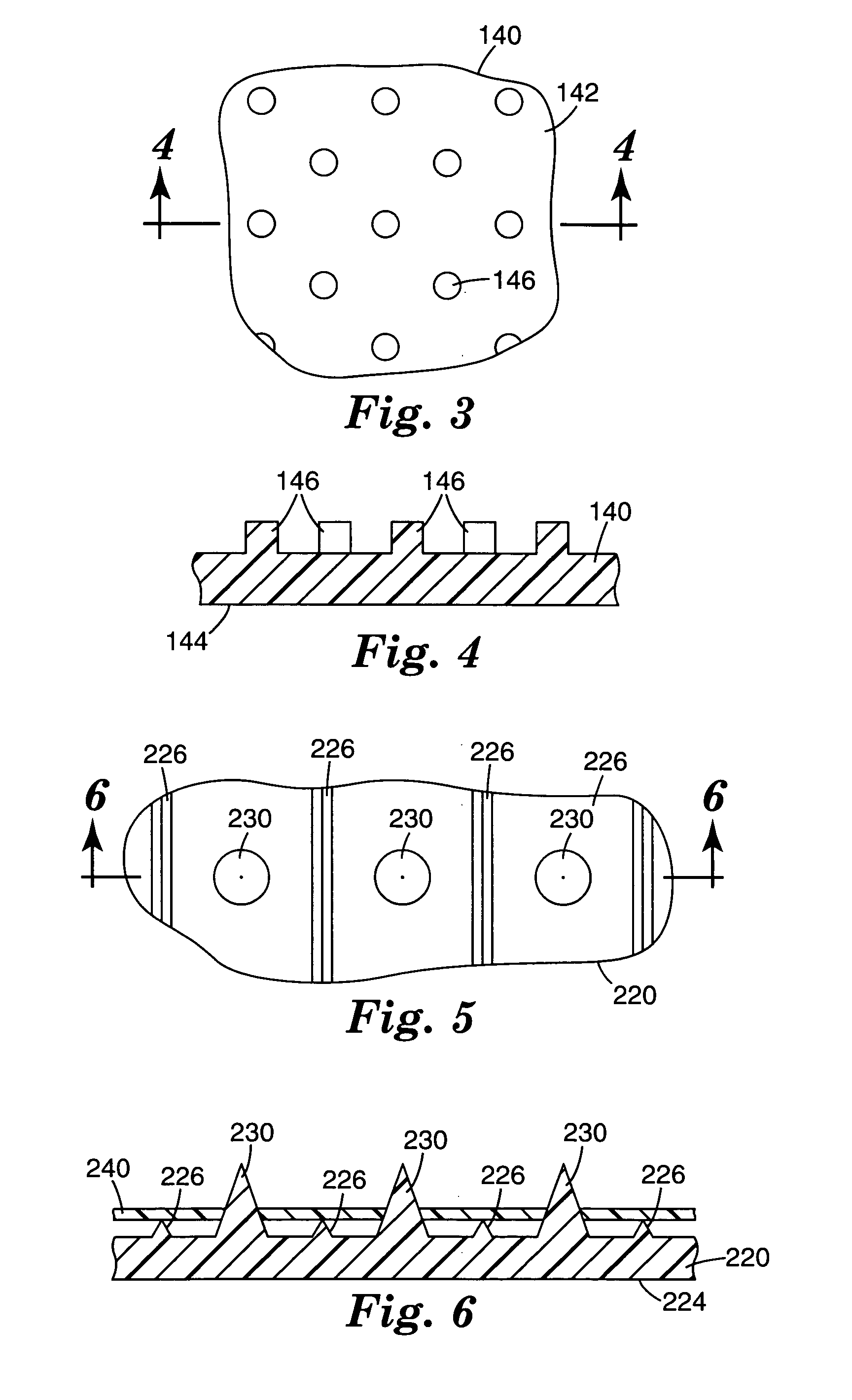
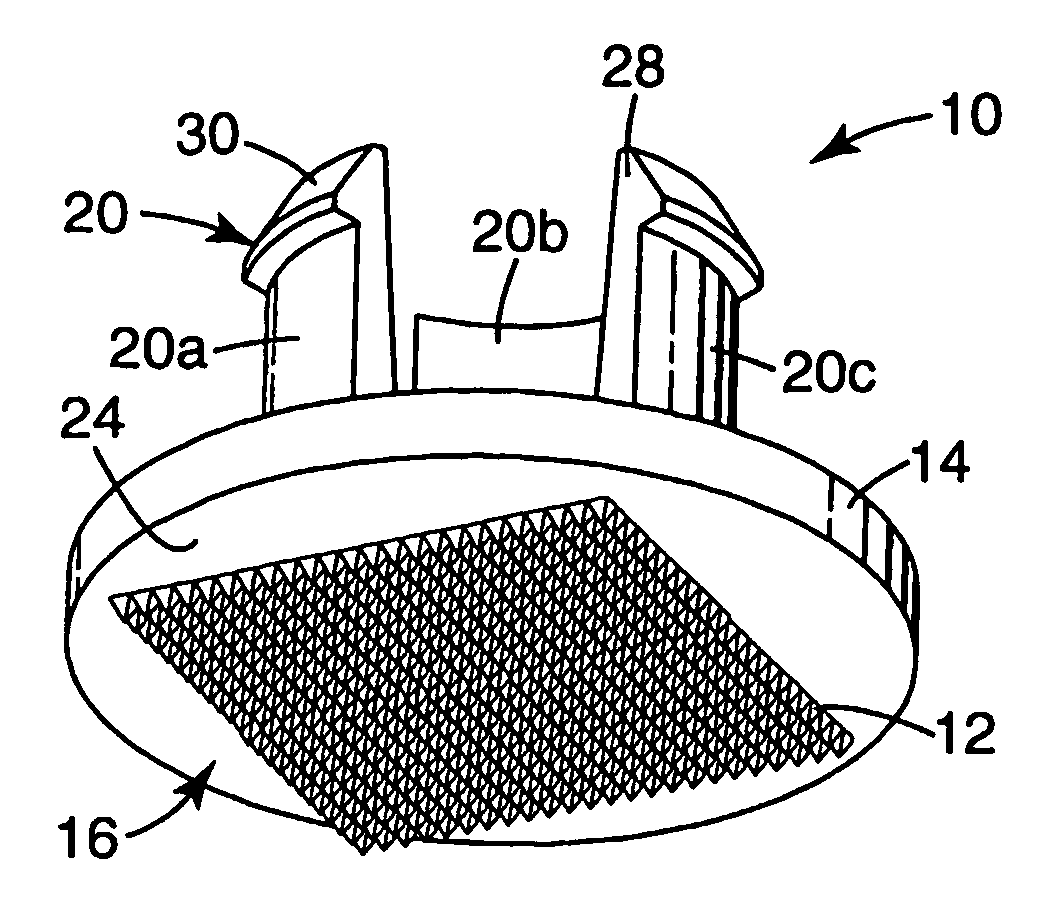
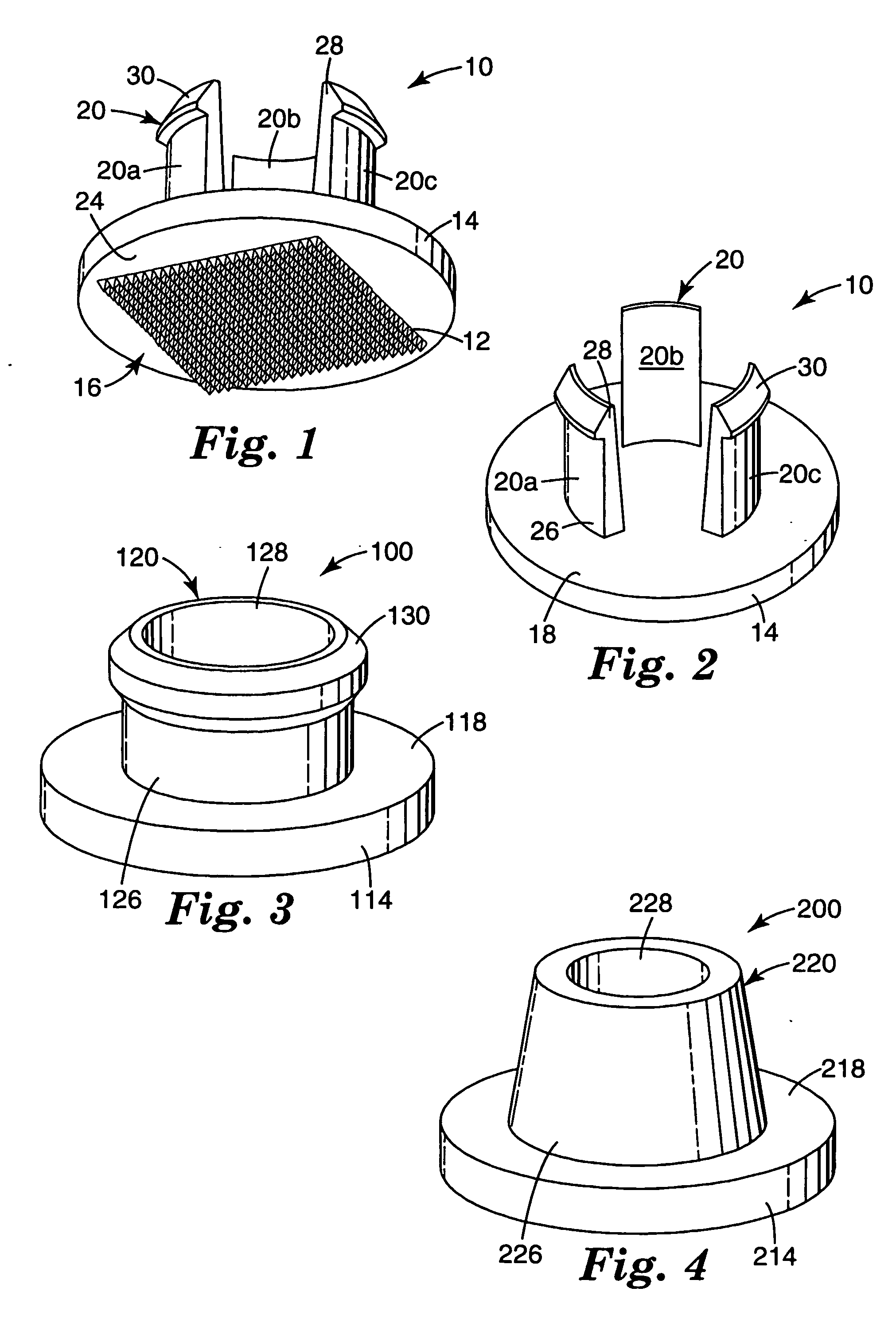
Microneedle arrays and methods of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6881203B2Additional rigidity and structural integrityImprove puncture abilitySurgeryMicroneedlesCatheterMicro-needle
Microneedle arrays, methods of manufacturing microneedles and methods of using microneedle arrays. The microneedles in the microneedle arrays may be in the form of tapered structures that include at least one channel formed in the outside surface of each microneedle. The microneedles may have bases that are elongated in one direction. The channels in microneedles with elongated bases may extend from one of the ends of the elongated bases towards the tips of the microneedles. The channels formed along the sides of the microneedles may optionally be terminated short of the tips of the microneedles. The microneedle arrays may also include conduit structures formed on the surface of the substrate on which the microneedle array is located. The channels in the microneedles may be in fluid communication with the conduit structures. One manner of using microneedle arrays of the present invention is in methods involving the penetration of skin to deliver medicaments or other substances and / or extract blood or tissue.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
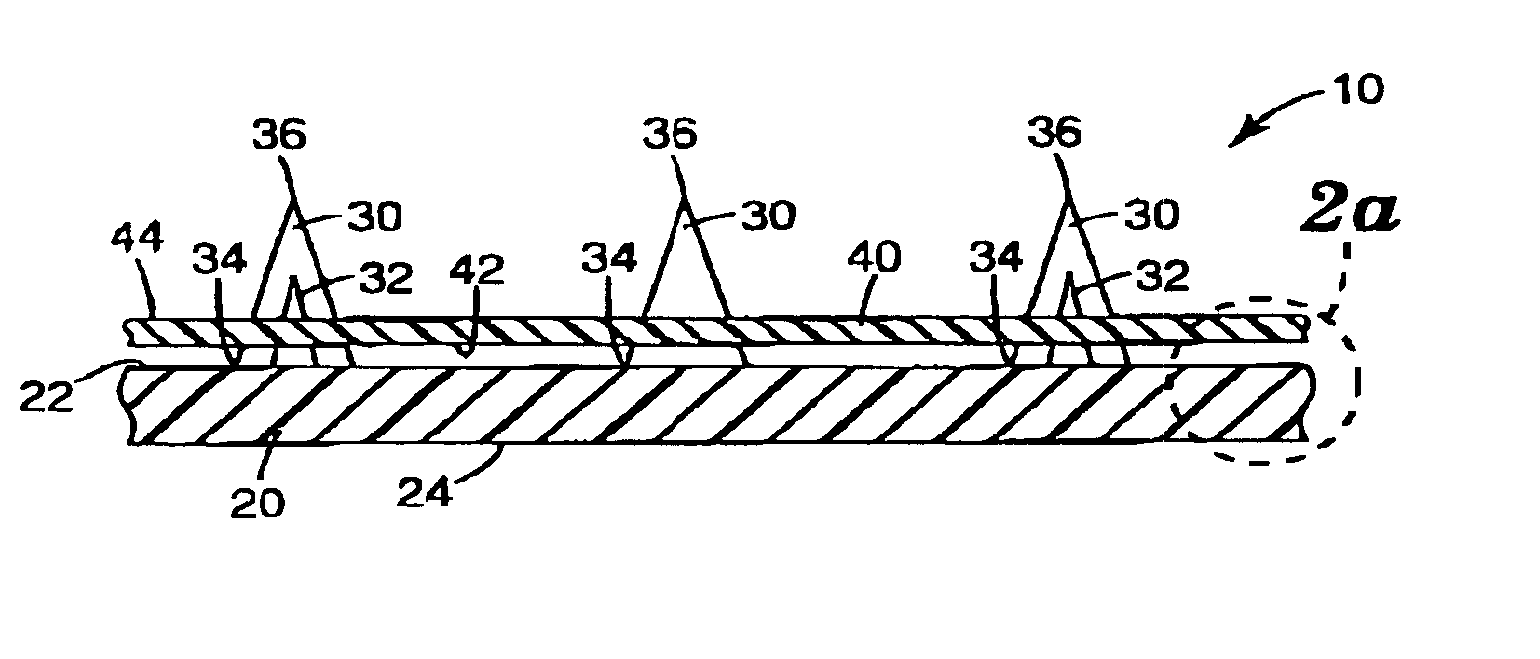
Microneedle devices and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS6908453B2Enhanced fluid movementImprove actionSurgical needlesMicroneedlesCapillary volumeSubstrate surface
Microneedle devices and methods of manufacturing the microneedle devices. The microneedle devices include microneedles protruding from a substrate, with the microneedles piercing a cover placed over the substrate surface from which the microneedles protrude. The cover and the microneedle substrate together define a capillary volume in fluid communication with the base of each microneedle. One manner of using microneedle arrays of the present invention is in methods involving the penetration of skin to deliver medicaments or other substances and / or extract blood or tissue. Manufacturing methods may include simultaneous application of pressure and ultrasonic energy when piercing the cover with the microneedles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
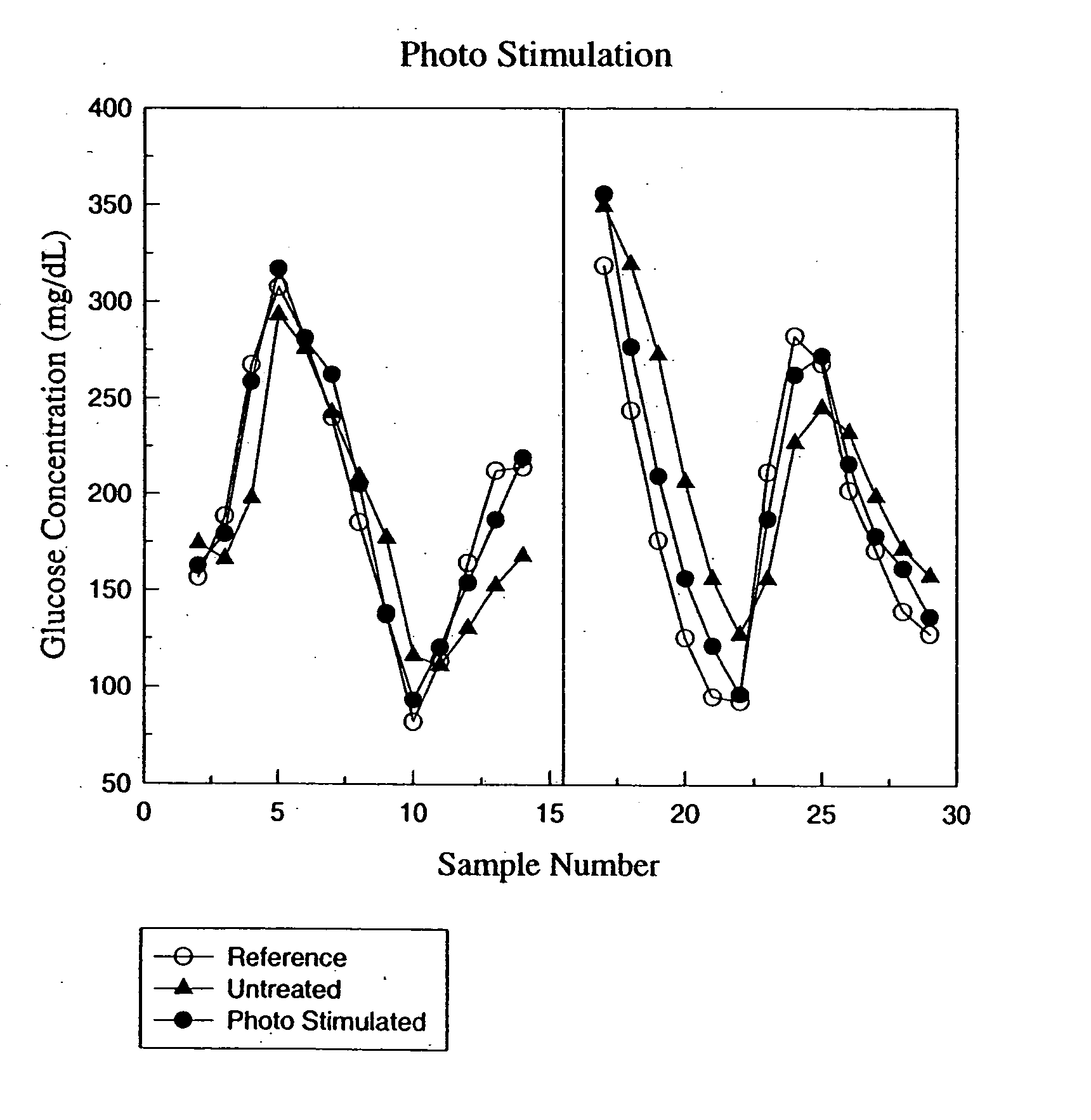
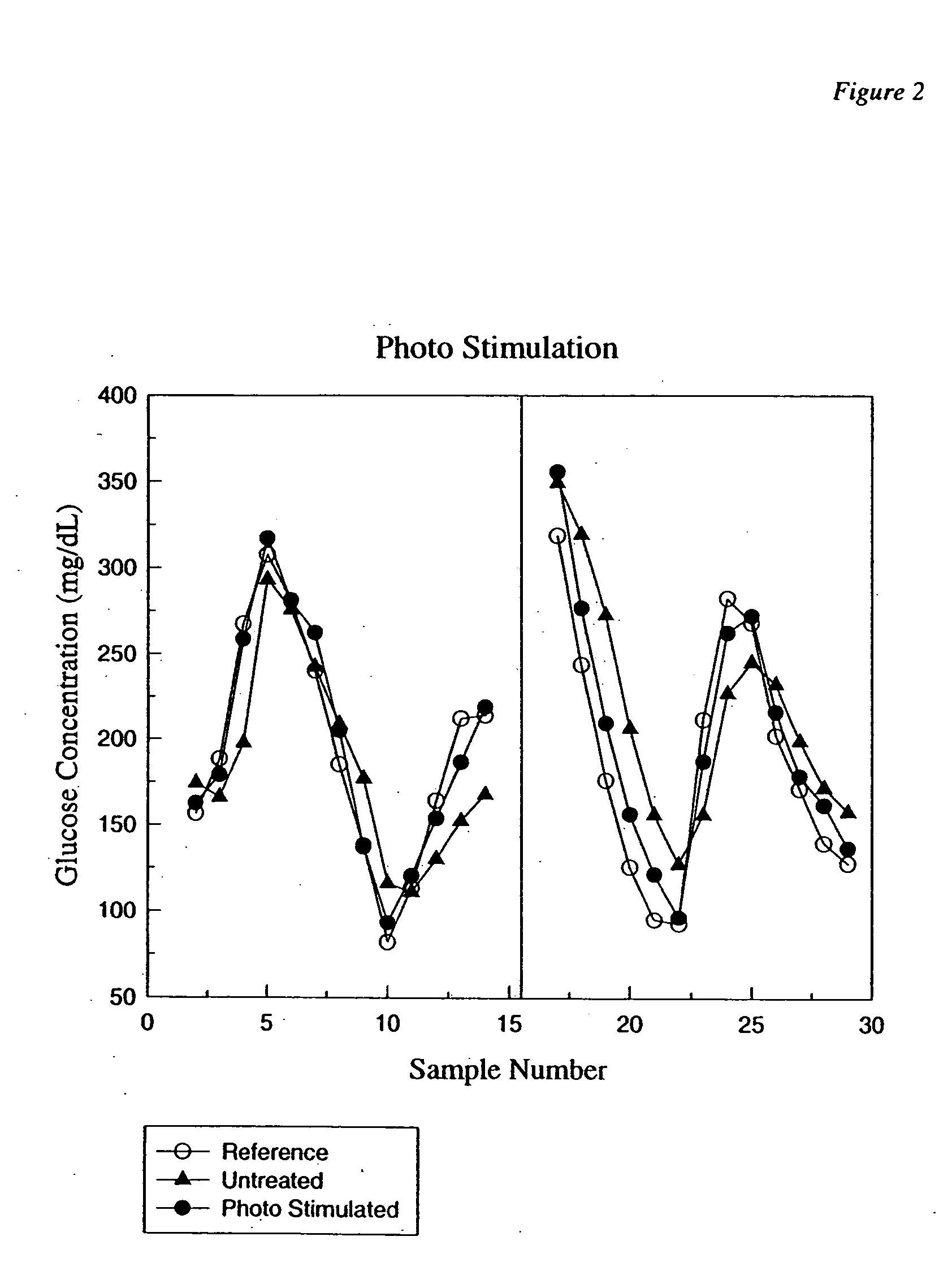
Photostimulation method and apparatus in combination with glucose determination
InactiveUS20050054908A1Increase perfusionReduce errorsDiagnostics using spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsBody compartmentPerfusion
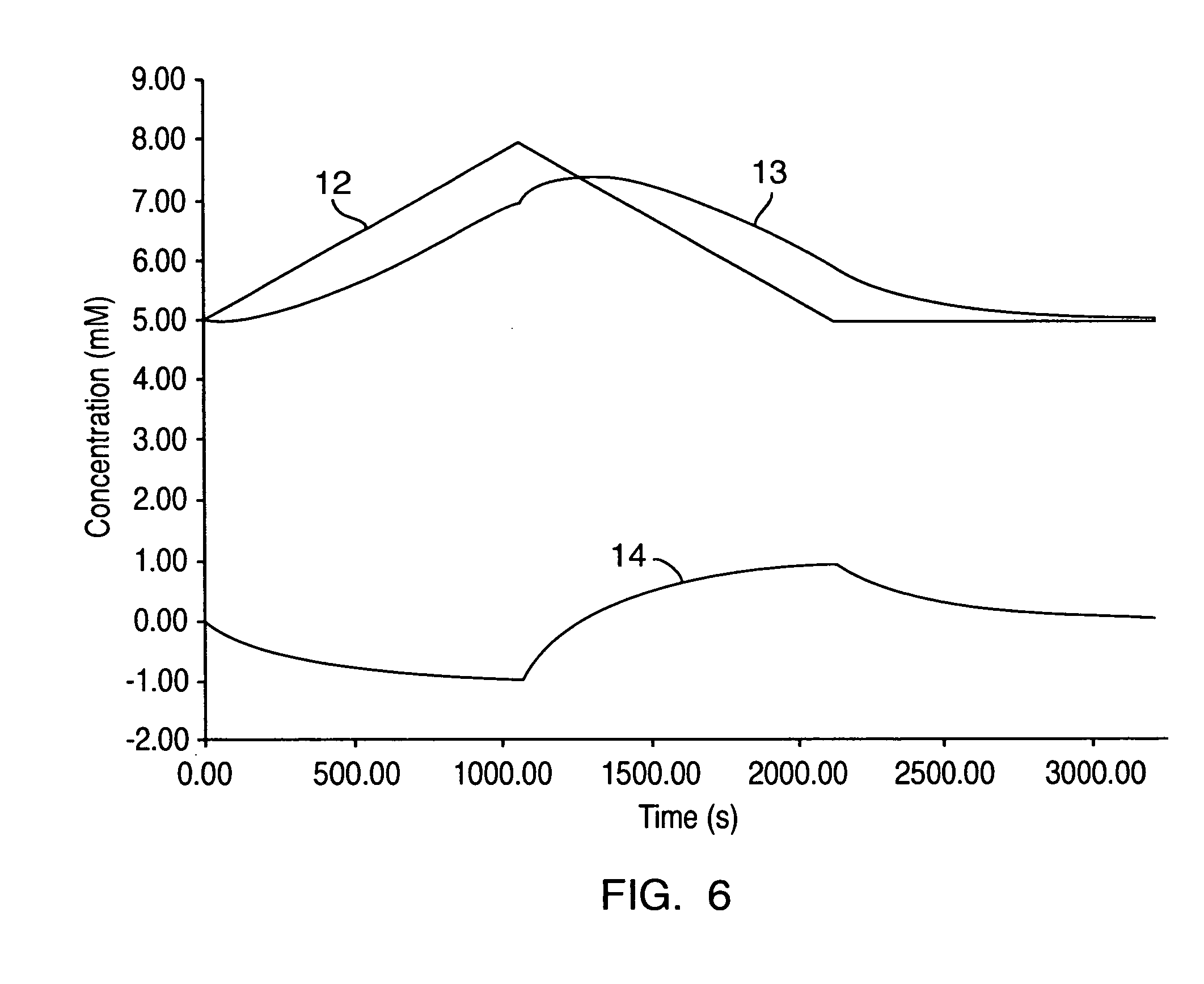
A method and apparatus using photo-stimulation to treat or pretreat a sample site prior to analyte concentration determination is presented. More particularly, photo-stimulation at or near at least one sample site is used to enhance perfusion of the sample site leading to reduced errors associated with sampling. Increased perfusion of the sample site leads to increased volume percentages of the target analyte and / or allows the blood or tissue constituent concentrations to more accurately and / or precisely track corresponding sample constituents in more well perfused body compartments or sites such as arteries, veins, or fingertips. In one embodiment, analysis of the photo-stimulated site is used in conjunction with glucose analyzers to determine the analyte concentration with greater ease, accuracy, or precision and may allow determination of the analyte concentration of another non-sampled body part or compartment.
Owner:GLENN PATENT GROUP
Microneedle arrays and methods of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050143713A1Additional rigidity and structural integrityImprove puncture abilityAutomatic syringesMicroneedlesCatheterTissue skin
Microneedle arrays, methods of manufacturing microneedles and methods of using microneedle arrays. The microneedles in the microneedle arrays may be in the form of tapered structures that include at least one channel formed in the outside surface of each microneedle. The microneedles may have bases that are elongated in one direction. The channels in microneedles with elongated bases may extend from one of the ends of the elongated bases towards the tips of the microneedles. The channels formed along the sides of the microneedles may optionally be terminated short of the tips of the microneedles. The microneedle arrays may also include conduit structures formed on the surface of the substrate on which the microneedle array is located. The channels in the microneedles may be in fluid communication with the conduit structures. One manner of using microneedle arrays of the present invention is in methods involving the penetration of skin to deliver medicaments or other substances and / or extract blood or tissue.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method and device for monitoring analyte concentration by use of differential osmotic pressure measurement
InactiveUS20050154272A1Reduce decreaseSurface/boundary effectEndoradiosondesConcentrations glucoseBlood or Tissue
A method is provided for the determination of the concentration of compounds in body tissue and fluids. The method utilises two compartments containing reference solutions, which are separated from the sample by two different semi-permeable membranes, in a serial manner, whereby a difference in osmotic pressure occurs in the two compartments due to compounds, which can permeate one of the membranes, but not the other. The difference in osmotic pressure reflects the concentration of these compounds. The method is especially suited for analysis of the concentration of glucose in blood or tissue of diabetic patients, where a device is implanted underneath the skin of the patient and where the method is carried out by using the implanted device.
Owner:DANFOSS AS
Method and device for monitoring analyte concentration by optical detection
InactiveUS20050070770A1Reduce the impactBad influenceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringPhotovoltaic detectorsAnalyte
A method and device are provided for the determination of the concentration of compounds in body tissue. The method utilises optical methods based on the interaction of light with compounds, whereby the concentration of the compound under analysis is determined. The method is especially suited for analysis for the concentration of glucose in blood or tissue of diabetic patients, a device being implanted underneath the skin of the patient and the method being carried out by using the implanted device. The device contains photo detectors at different levels connected by wires to an electronic circuit device. A differential analysis is performed on the signals from the detectors to reduce the effect of skin on the analysis.
Owner:P&V CONSULTING
Method and device for monitoring analyte concentration by optical detection
InactiveUS7248906B2Effect of skin can be reduced and avoidedReduce impactCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringPhotovoltaic detectorsAnalyte
A method and device are provided for the determination of the concentration of compounds in body tissue. The method utilises optical methods based on the interaction of light with compounds, whereby the concentration of the compound under analysis is determined. The method is especially suited for analysis for the concentration of glucose in blood or tissue of diabetic patients, a device being implanted underneath the skin of the patient and the method being carried out by using the implanted device. The device contains photo detectors at different levels connected by wires to an electronic circuit device. A differential analysis is performed on the signals from the detectors to reduce the effect of skin on the analysis.
Owner:P&V CONSULTING
Methods and devices for continuous and mobile measurement of various bio-parameters in the external auditory canal
InactiveUS20090088611A1High frequencyElectrocardiographyCatheterExternal Auditory CanalsPulse oximetry
A method and a device for the continuous, mobile non-invasive and aesthetically unobtrusive measurement of important vital parameters, in particular body(core)temperature, arterial oxygen saturation, heart rate, respiration rate (by pulse oximetry), blood pressure, ECG, and substance concentrations in blood or tissue. The measuring site and the position of the sensor components is the (proximal) auditory canal, whereby there results an unobtrusive sensor technology suitable for a stable monitoring in everyday life i.e. even unaffected by motion. The sensor system includes a small evaluation unit and electronics for signal processing and e.g. means for wireless transmission to a mobile phone. Thus physiological parameters become available for long term diagnostics, for outpatients, for monitoring during rehabilitation, or for monitoring the health status in everyday life, while doing sports and during training, for an increase of the safety of individuals or of people with dangerous occupations or risky hobbies.
Owner:BUSCHMANN JOHANNES
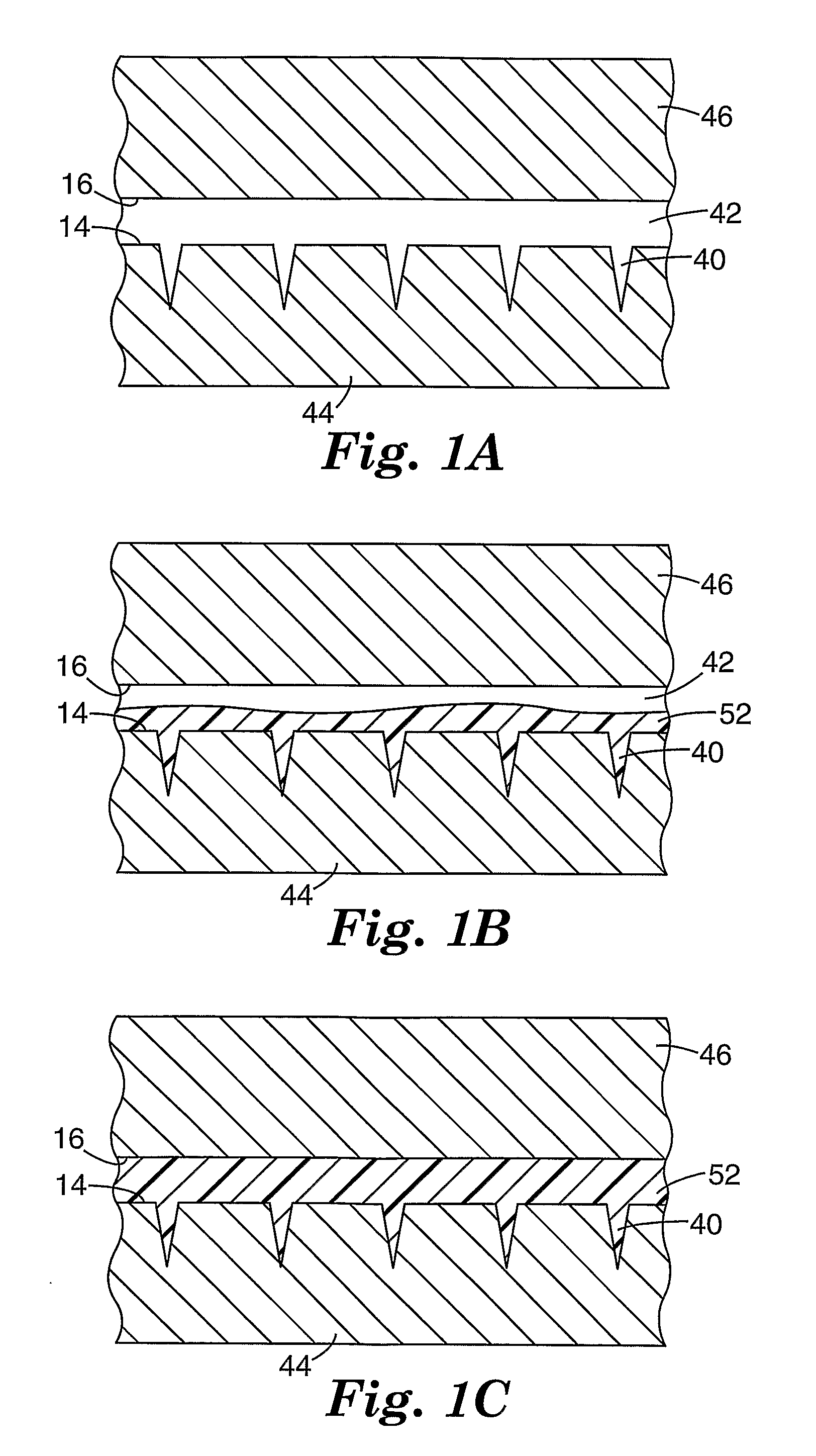
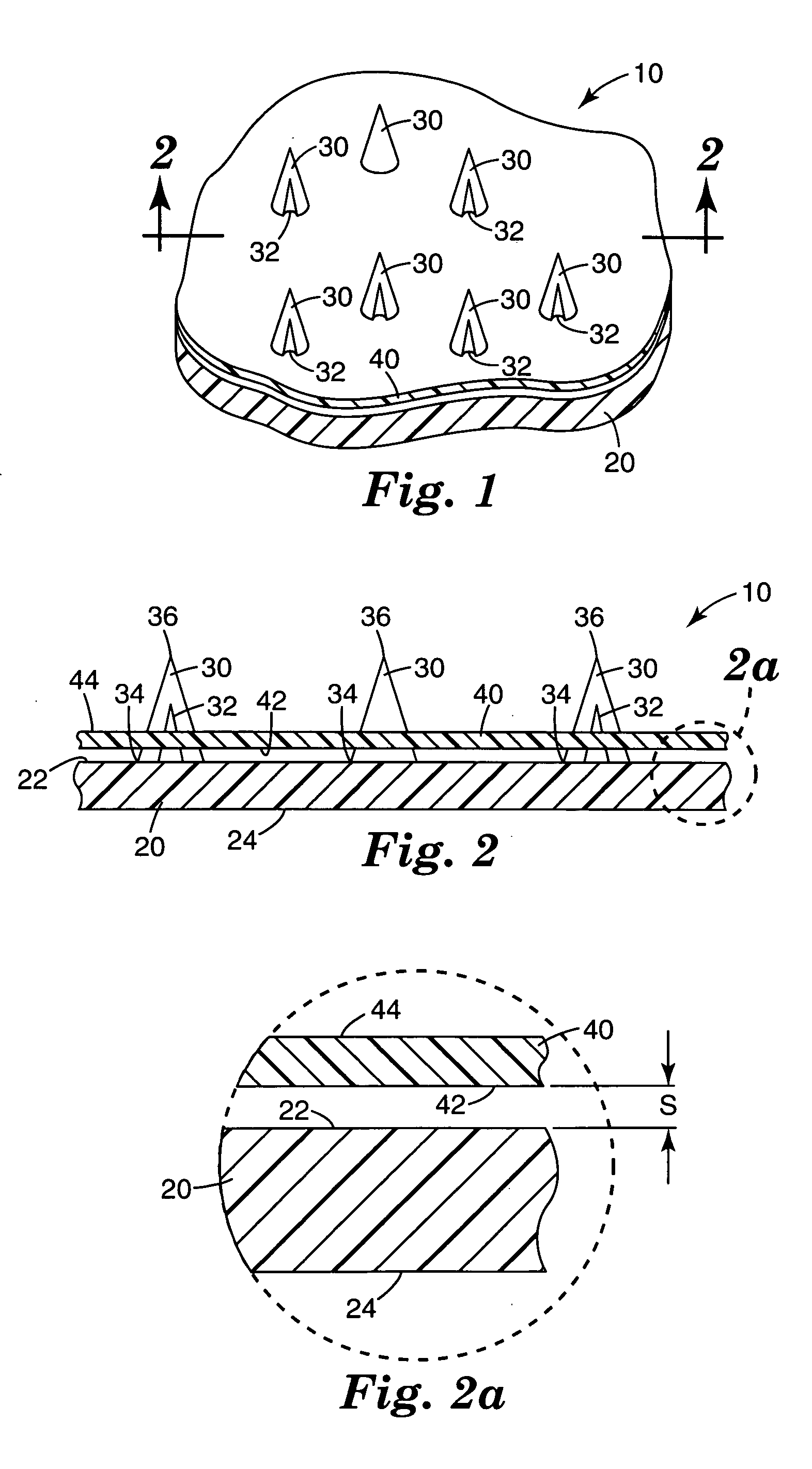
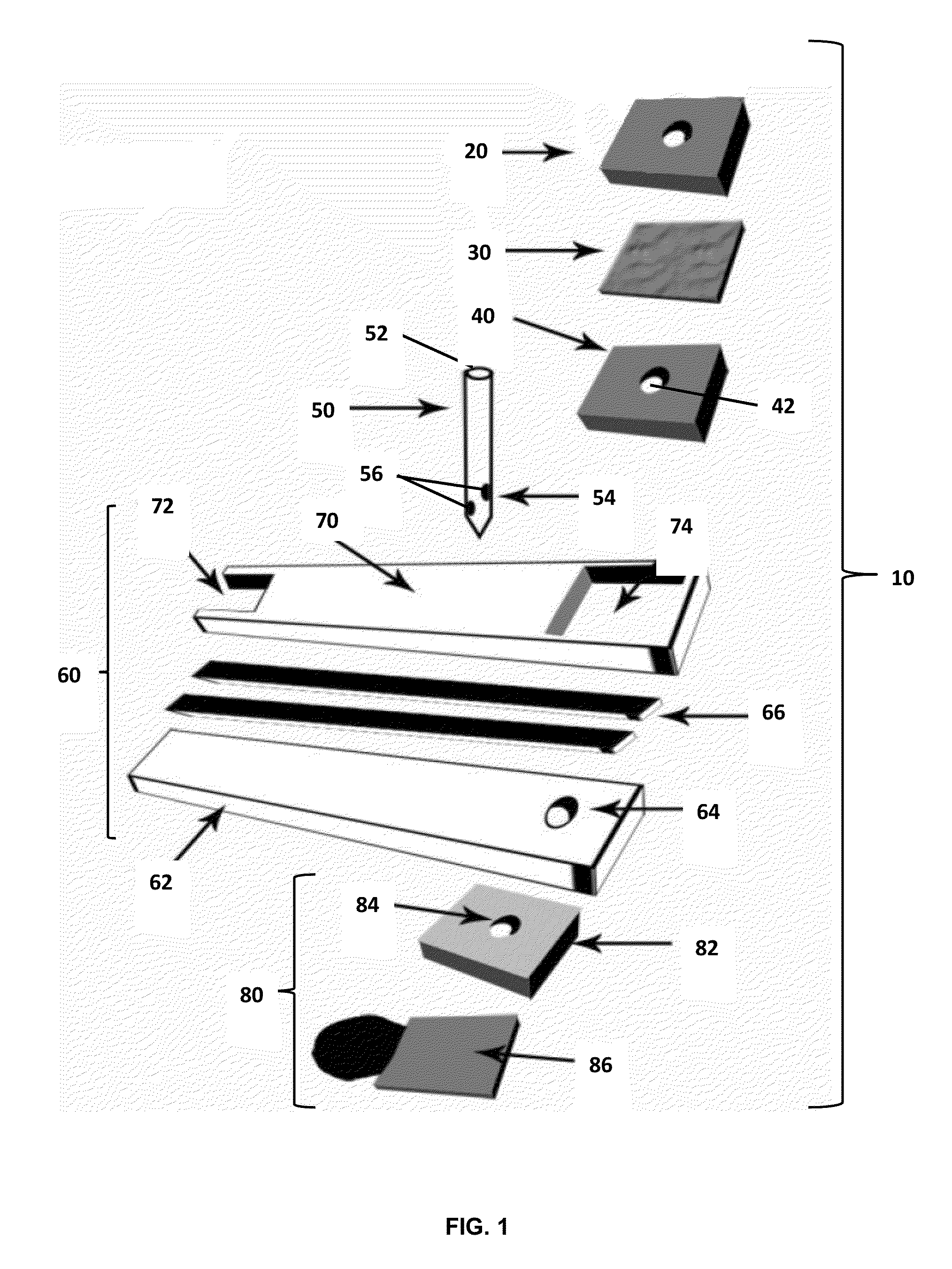
Method of molding for microneedle arrays
InactiveUS20070191761A1Meet needsDuplicating/marking methodsSurgical needlesMaterials scienceTissue skin
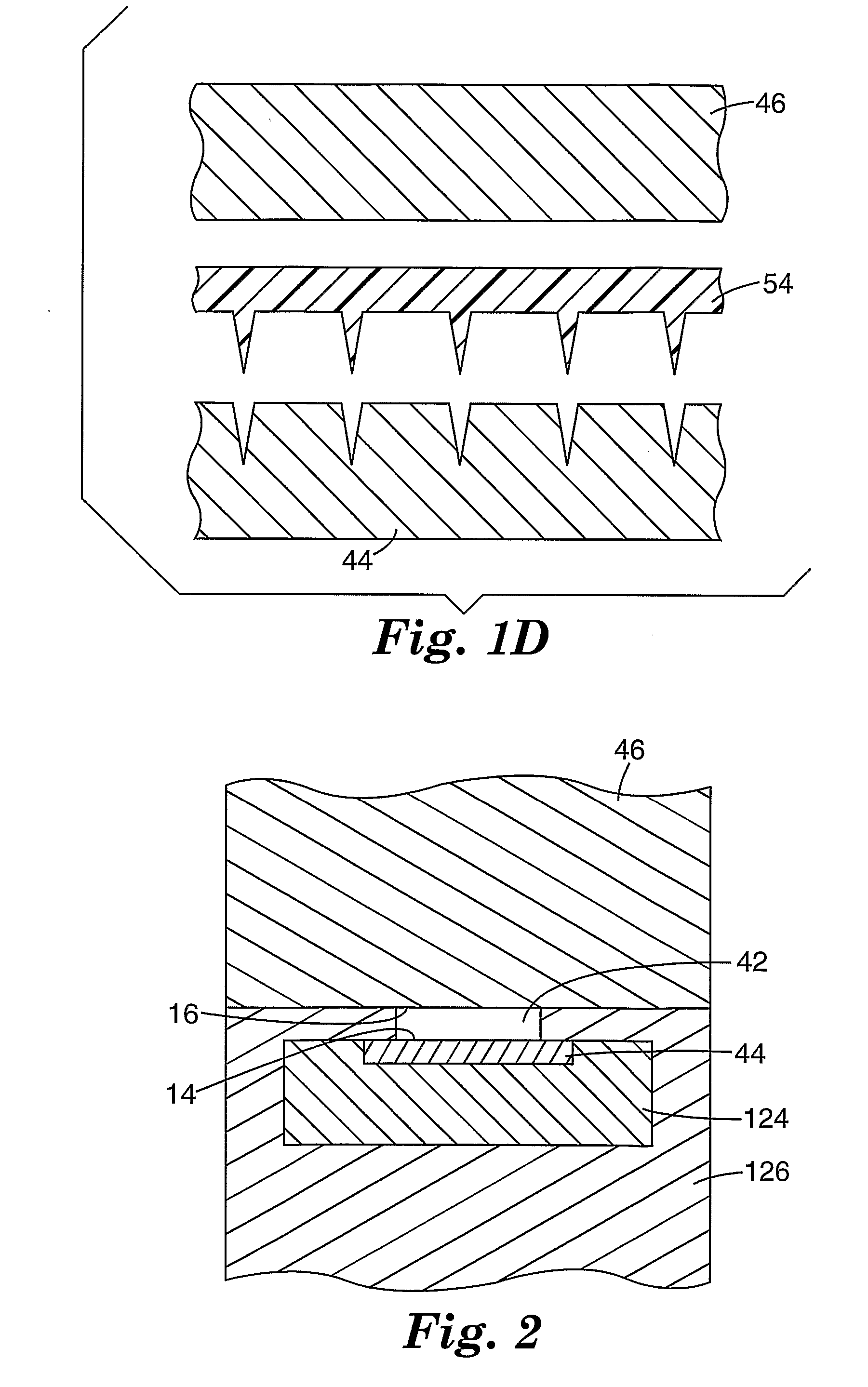
A method of manufacturing a moldable microneedle array (54) is described comprising providing a negative mold insert (44) characterized by a negative image of microneedle topography wherein at least one negative image of a microneedle is characterized by an aspect ratio of between about 2 to 1 and about 5 to 1. The negative mold insert (44) is used to define a structured surface of a negative mold cavity (42). Molten plastic material is injected into the heated negative mold cavity. The molten plastic material is subsequently cooled and detached from the mold insert to provide a molded microneedle array (54). One manner of using microneedle arrays of the present invention is in methods involving the penetration of skin to deliver medicaments or other substances and / or extract blood or tissue through the skin.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
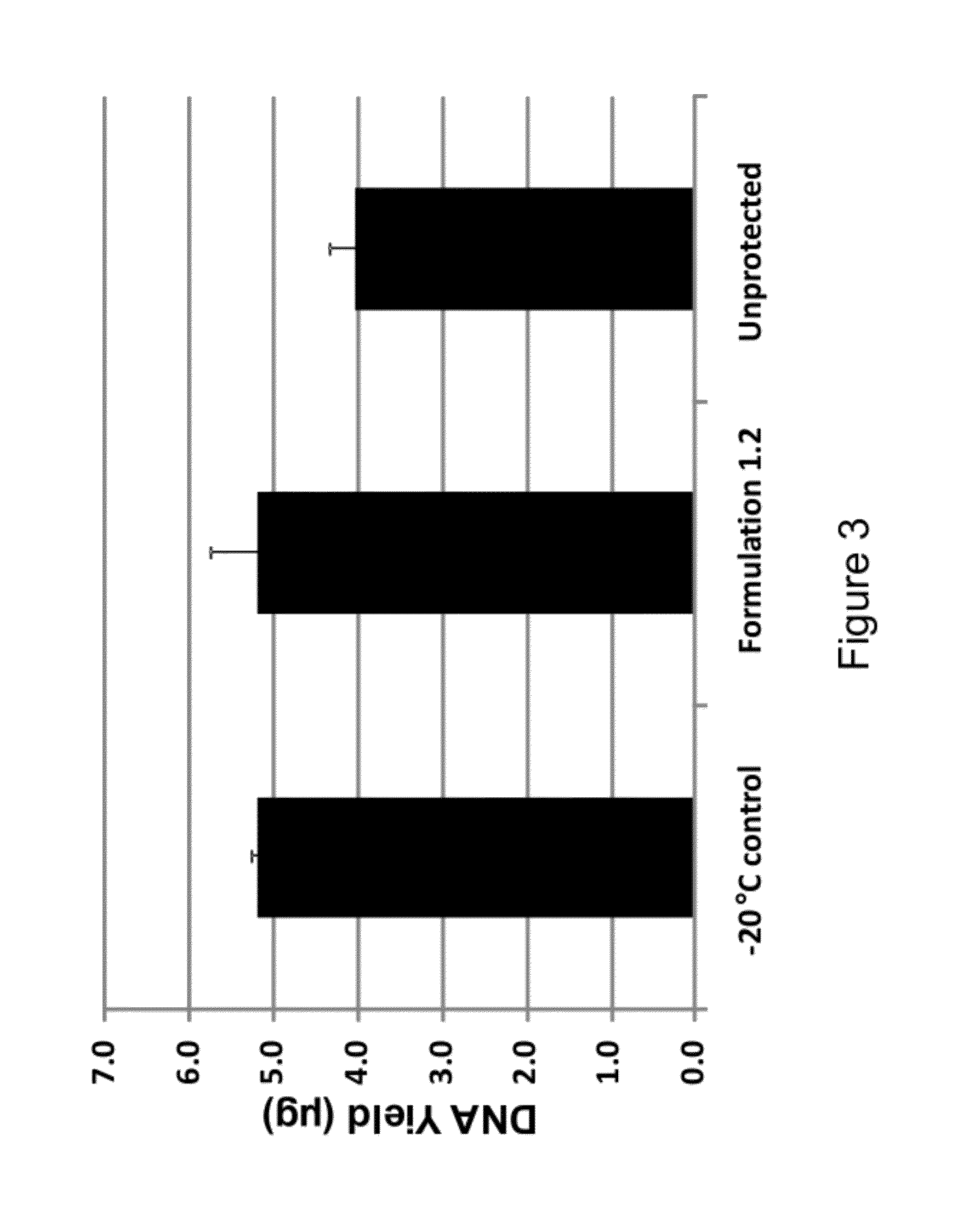
Compositions for stabilizing dna, RNA and proteins in blood and other biological samples during shipping and storage at ambient temperatures
ActiveUS20120052572A1Prevent degradationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSlurryColloid
Compositions and methods are disclosed for substantially liquid, gel, suspension, slurry, semisolid and / or colloid storage of biological samples following admixture with the herein disclosed storage composition, permitting substantial recovery of biological activity following storage without refrigeration. In certain embodiments, unfractionated blood or tissue samples may be stored without refrigeration for weeks, months or years in a form that permits recovery of intact DNA, RNA or protein components following the storage period.
Owner:BIOMATRICA INC
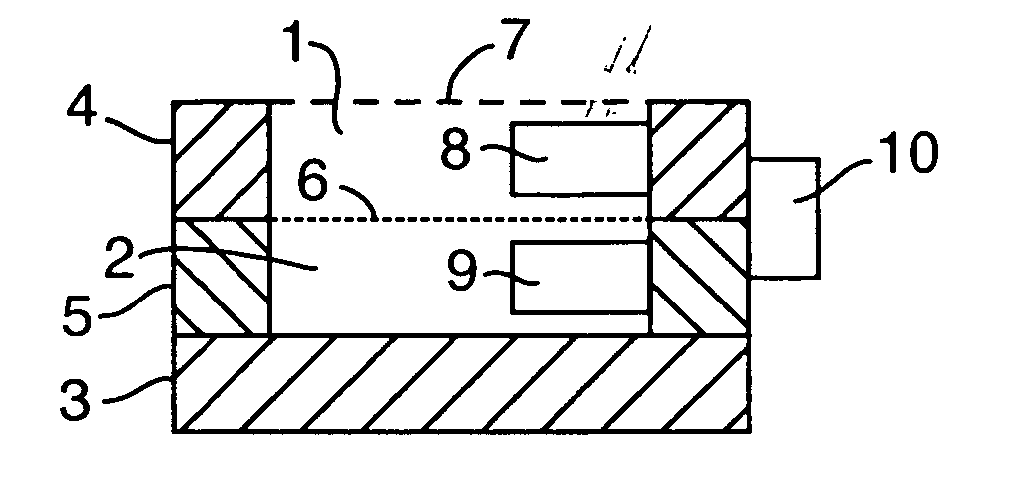
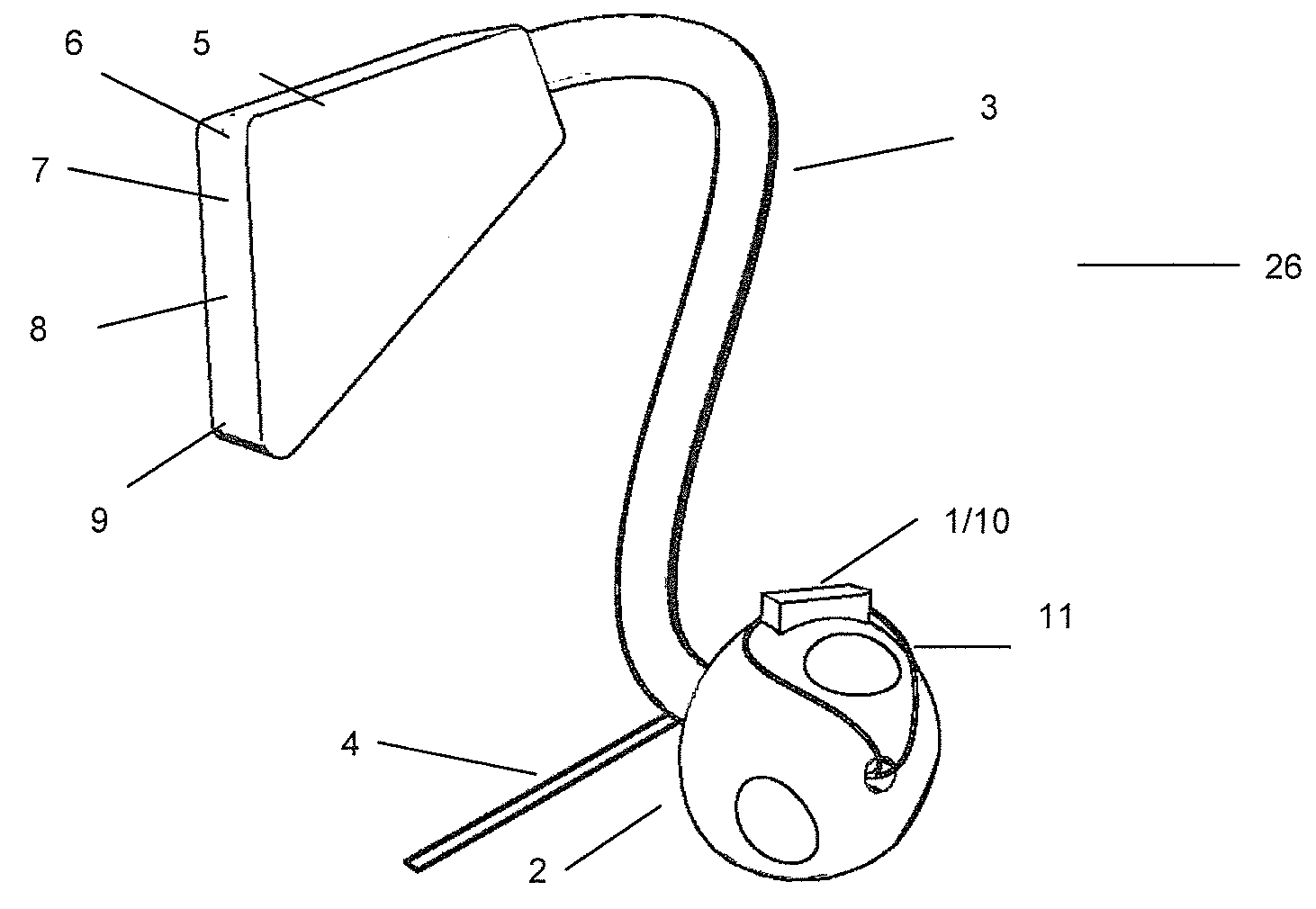
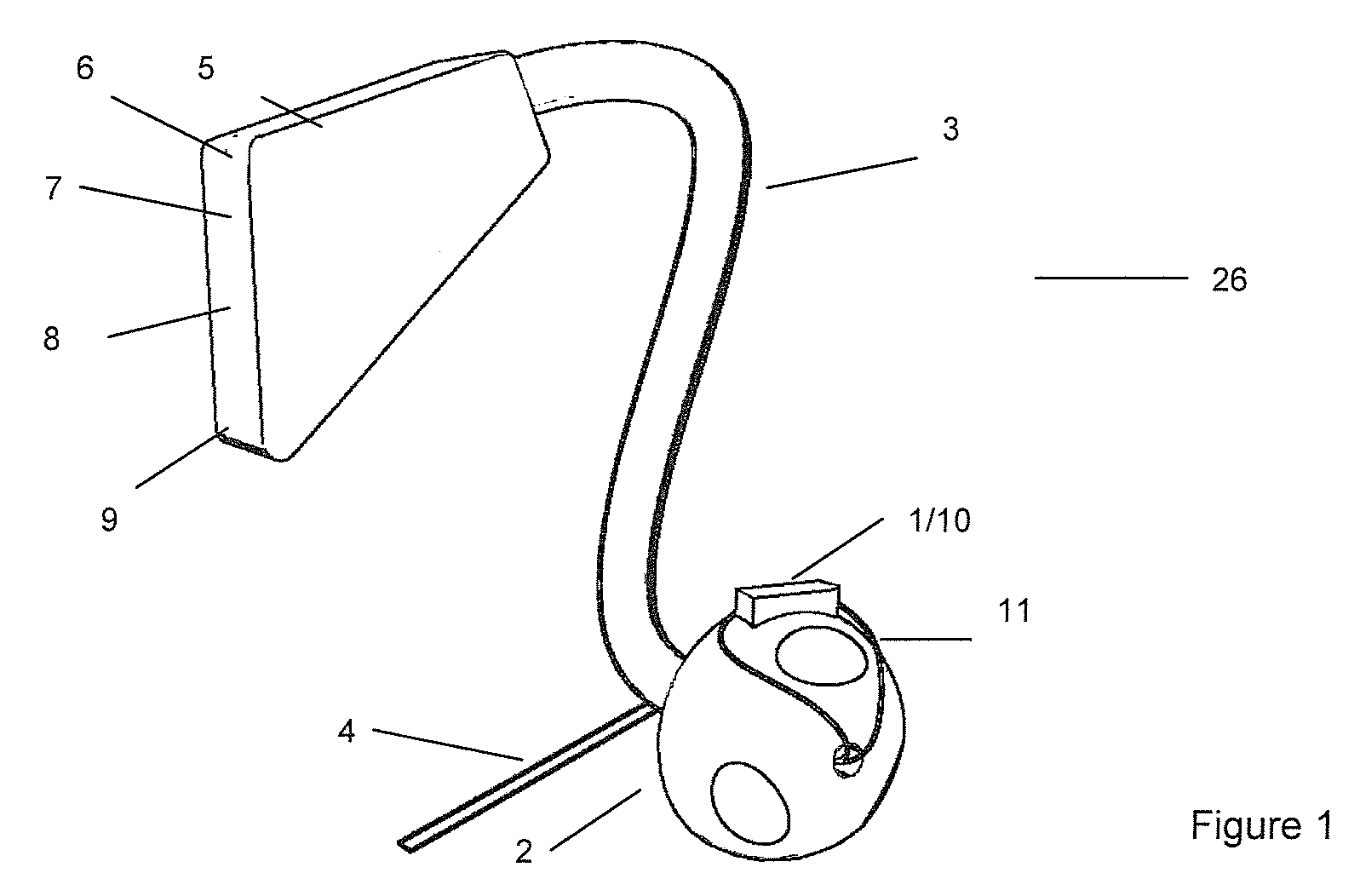
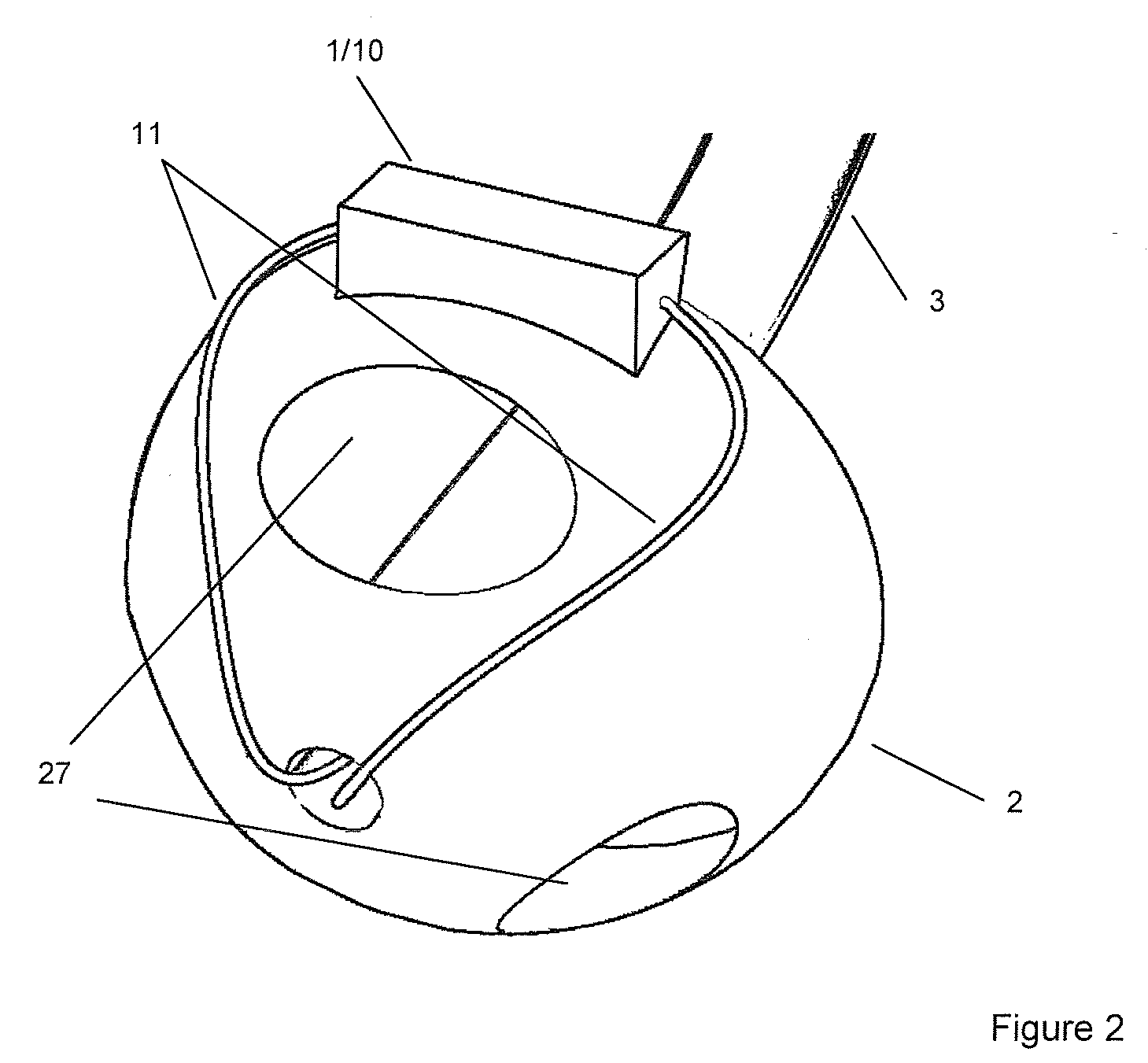
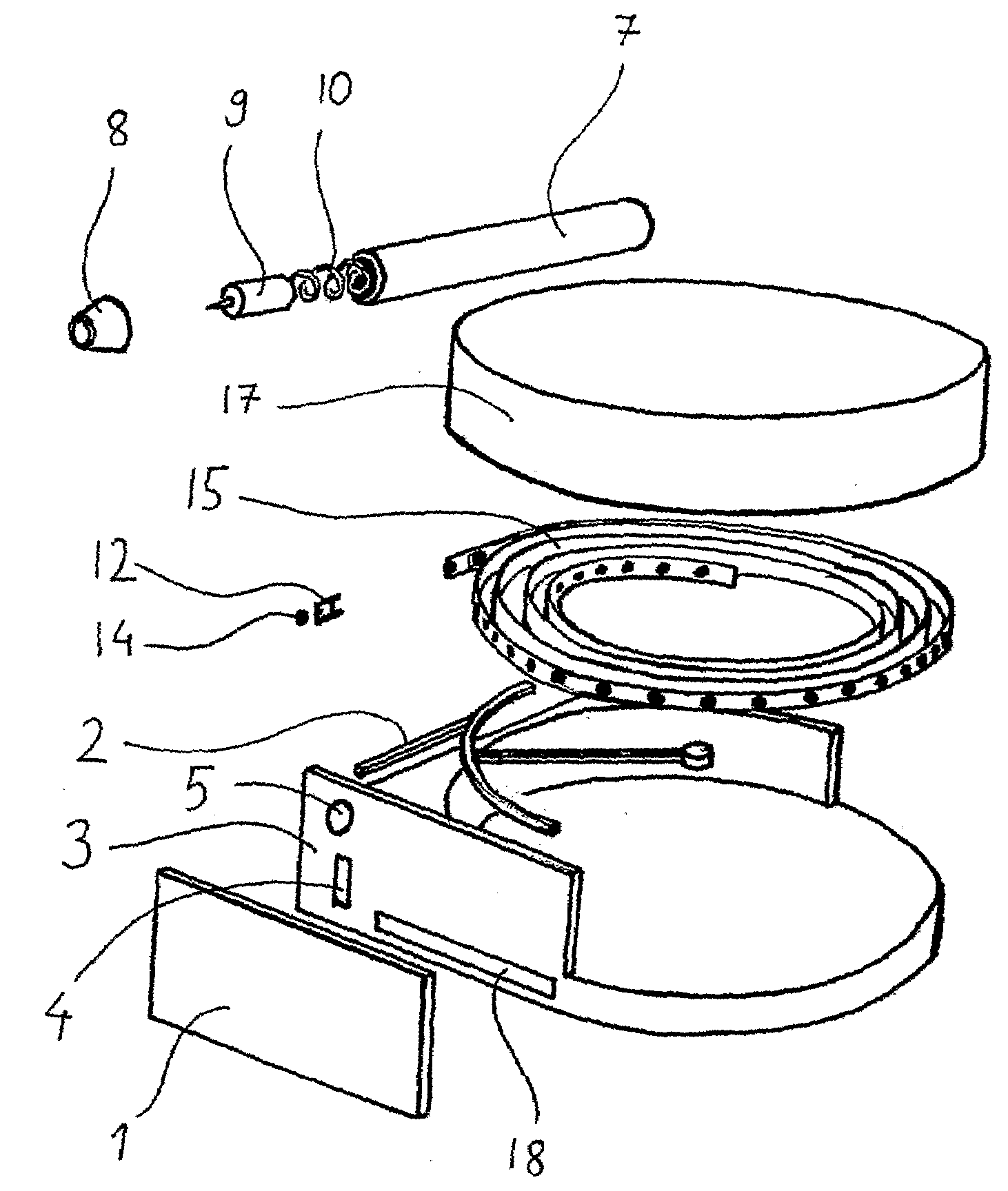
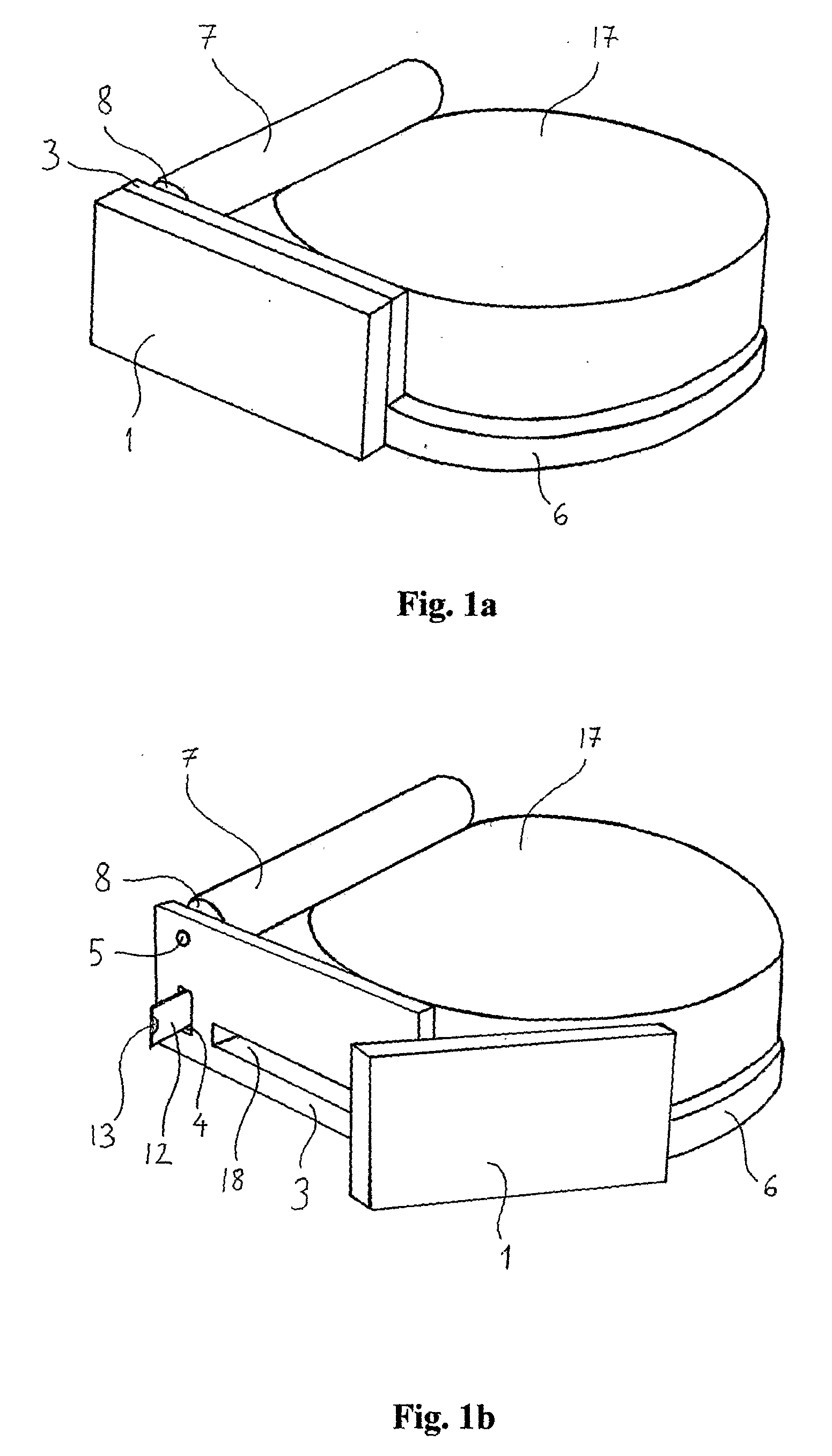
Health Monitoring Device, Device Modules and Method
ActiveUS20080200782A1Simple and less conspicuousEasy to disassembleSurgical needlesCatheterComputer moduleBiomedical engineering
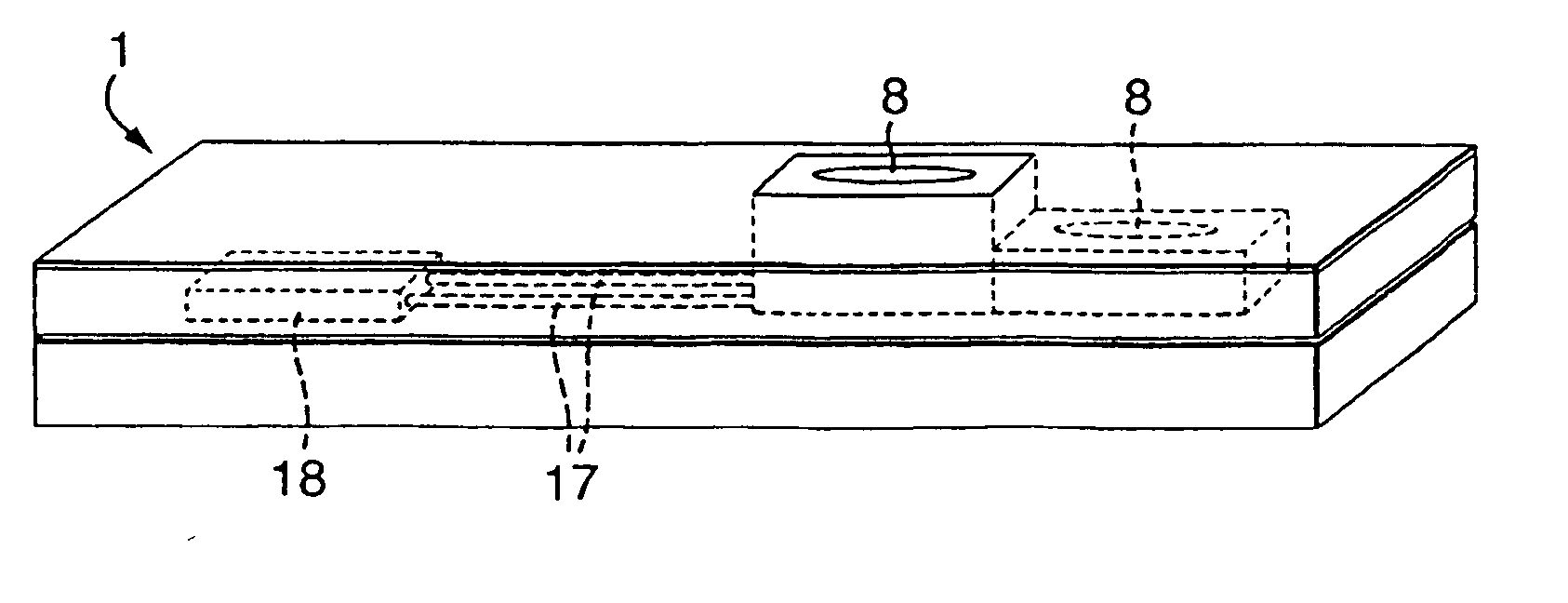
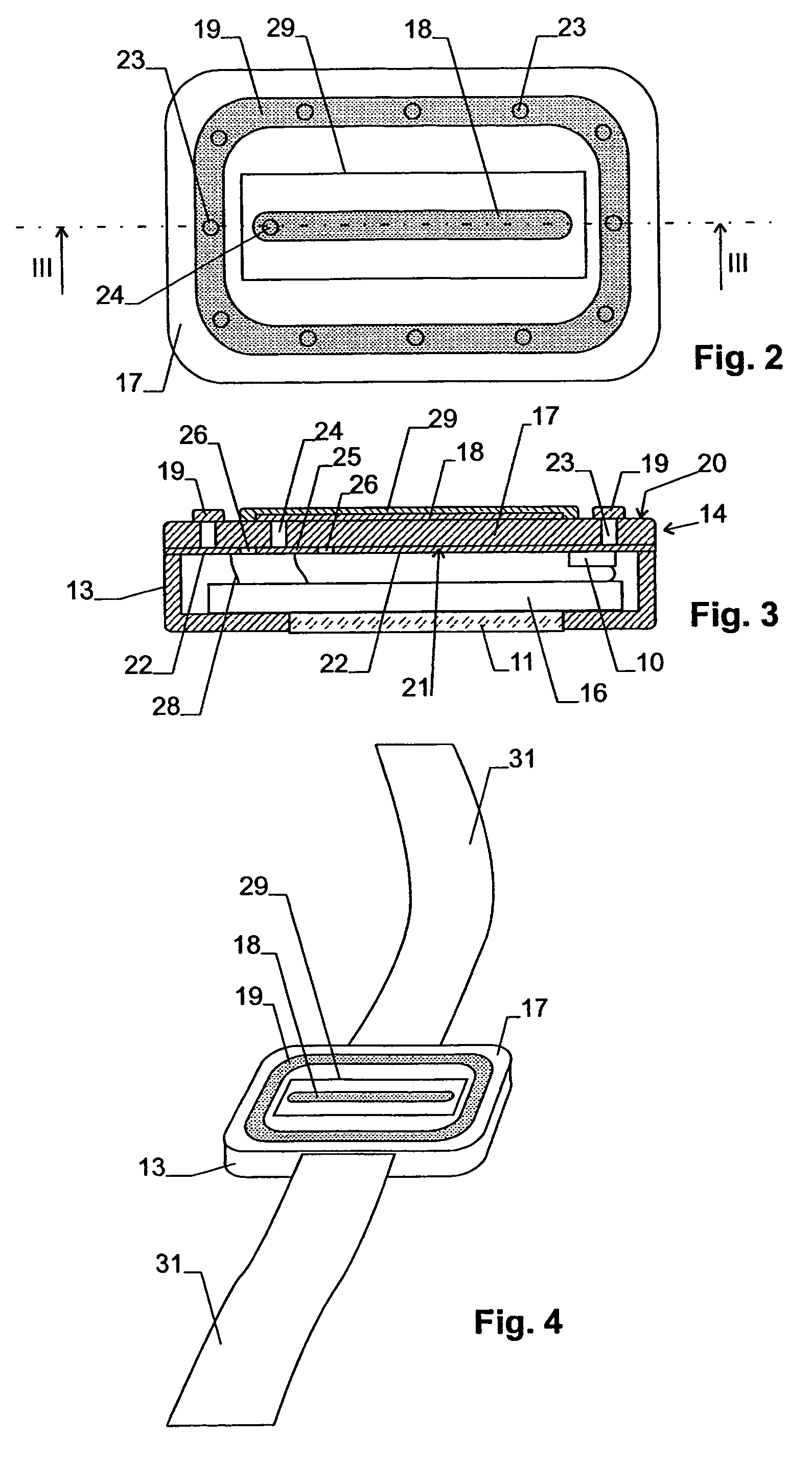
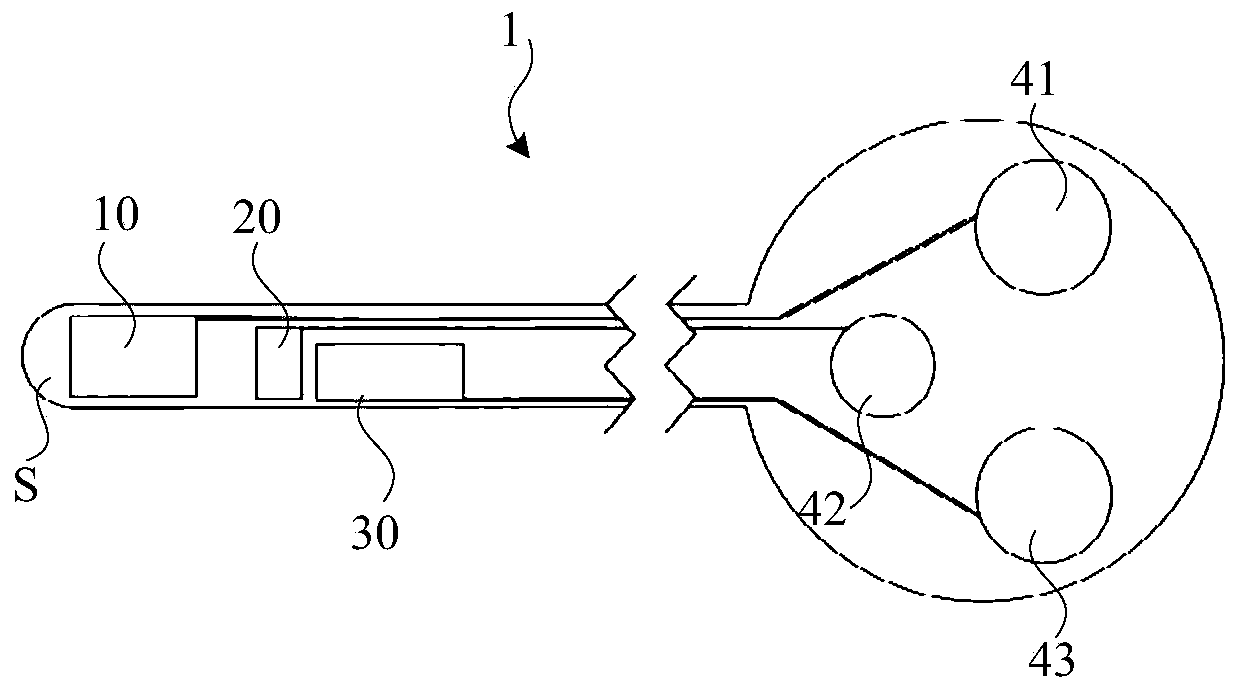
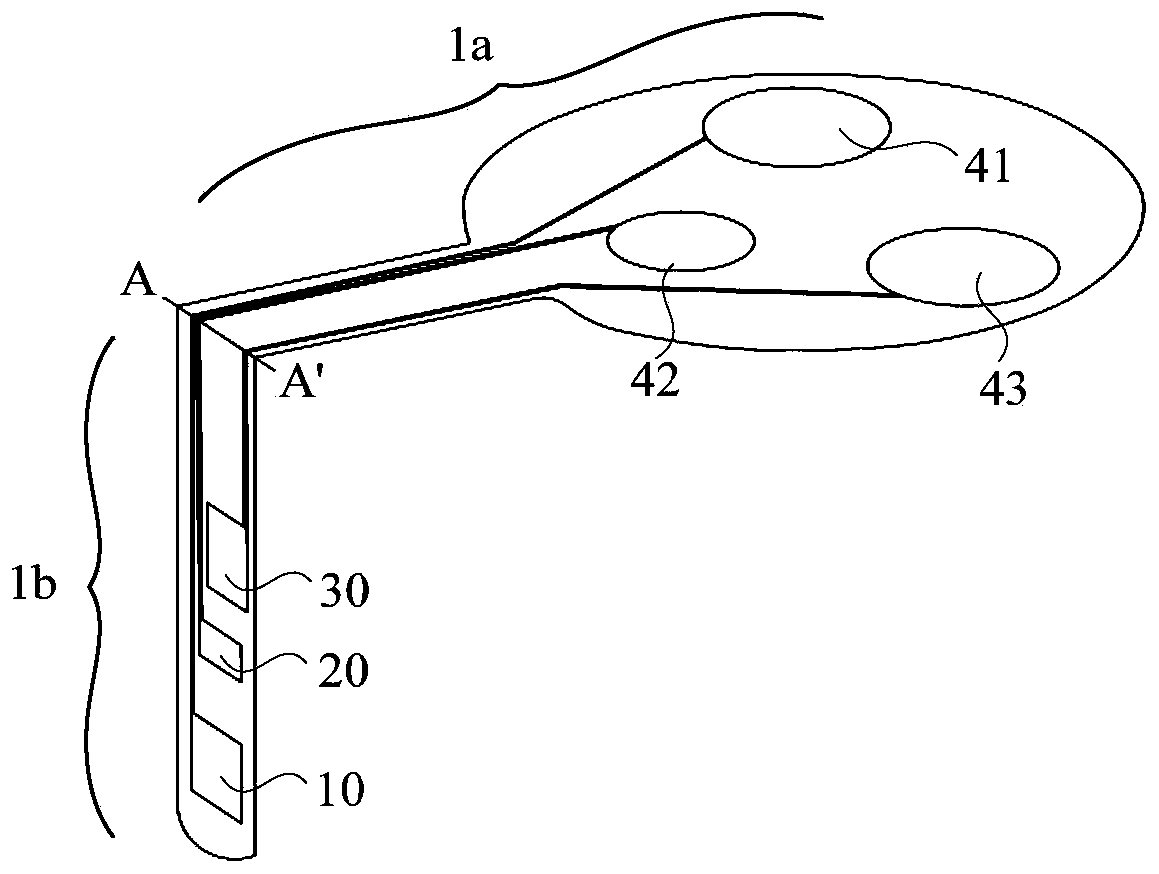
The present invention relates to a health monitoring device for measuring blood or tissue indicators and a strip cassette suitable for use in connection with the device. The device comprises a body (6) having a first opening (5) and a second opening (4), a piercing means (7) having a piercing head and connected to the body, the piercing means being arranged to extend from the first opening of the body and being cockable and further releasable for piercing the skin with the piercing head, and a space (17) arranged in connection with the body, into which space a number of sensor strips (12) can be arranged so that the strips can be brought out from the body one at a time. According to the invention the device comprises a shutter (1) functionally connected to the body, the shutter being arranged to tightly close the first and second openings of the body in its first position and which can be moved to the second position for allowing one sensor strip to be pushed from the first opening of the body into sampling position and for exposing the first and second openings of the body. With the invention an easy to use, easily portable and small device for repeated measurement of blood indicators can be produced.
Owner:I SENS INC
Method and apparatus for computer controlled cell based diagnosis
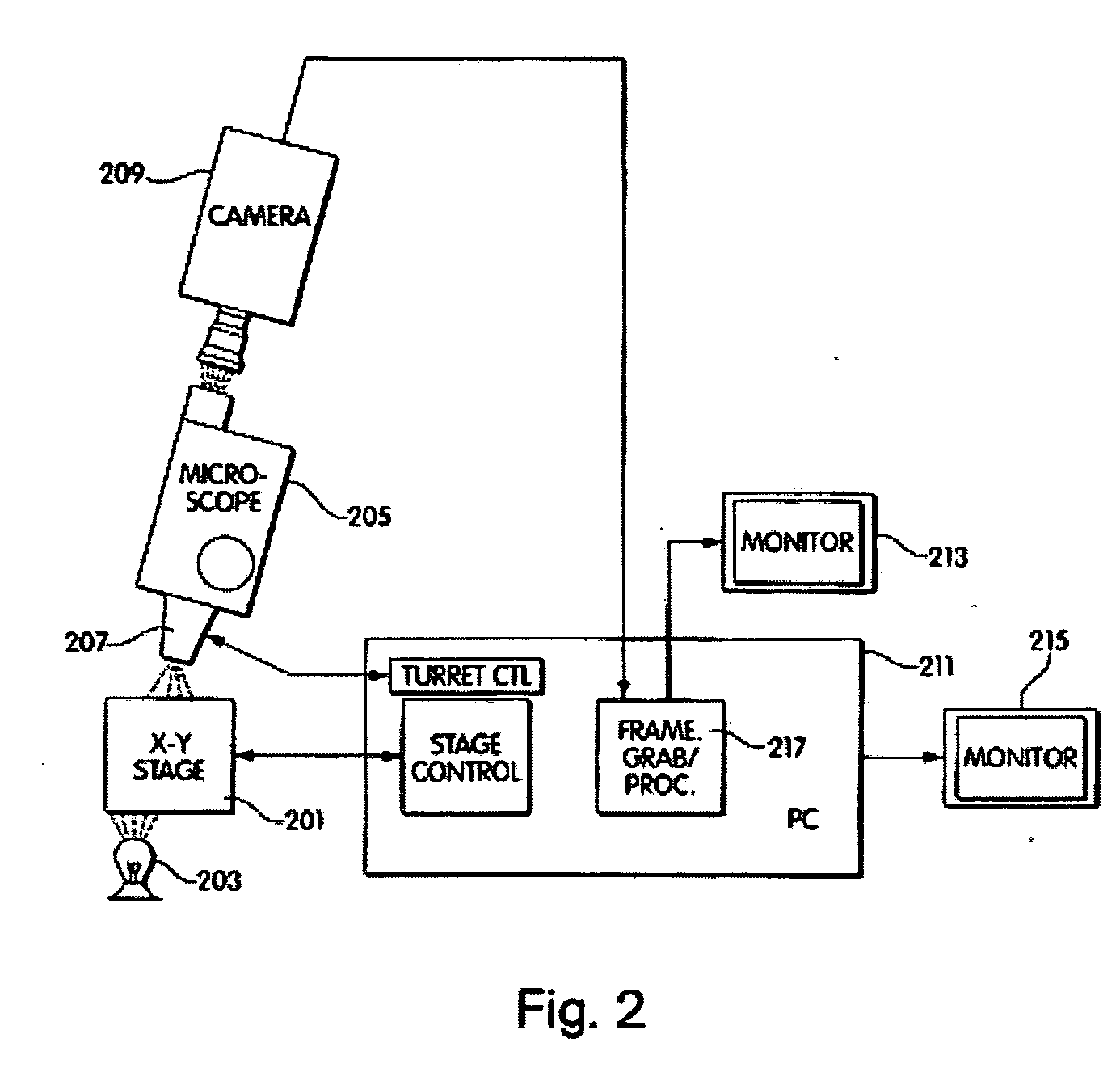
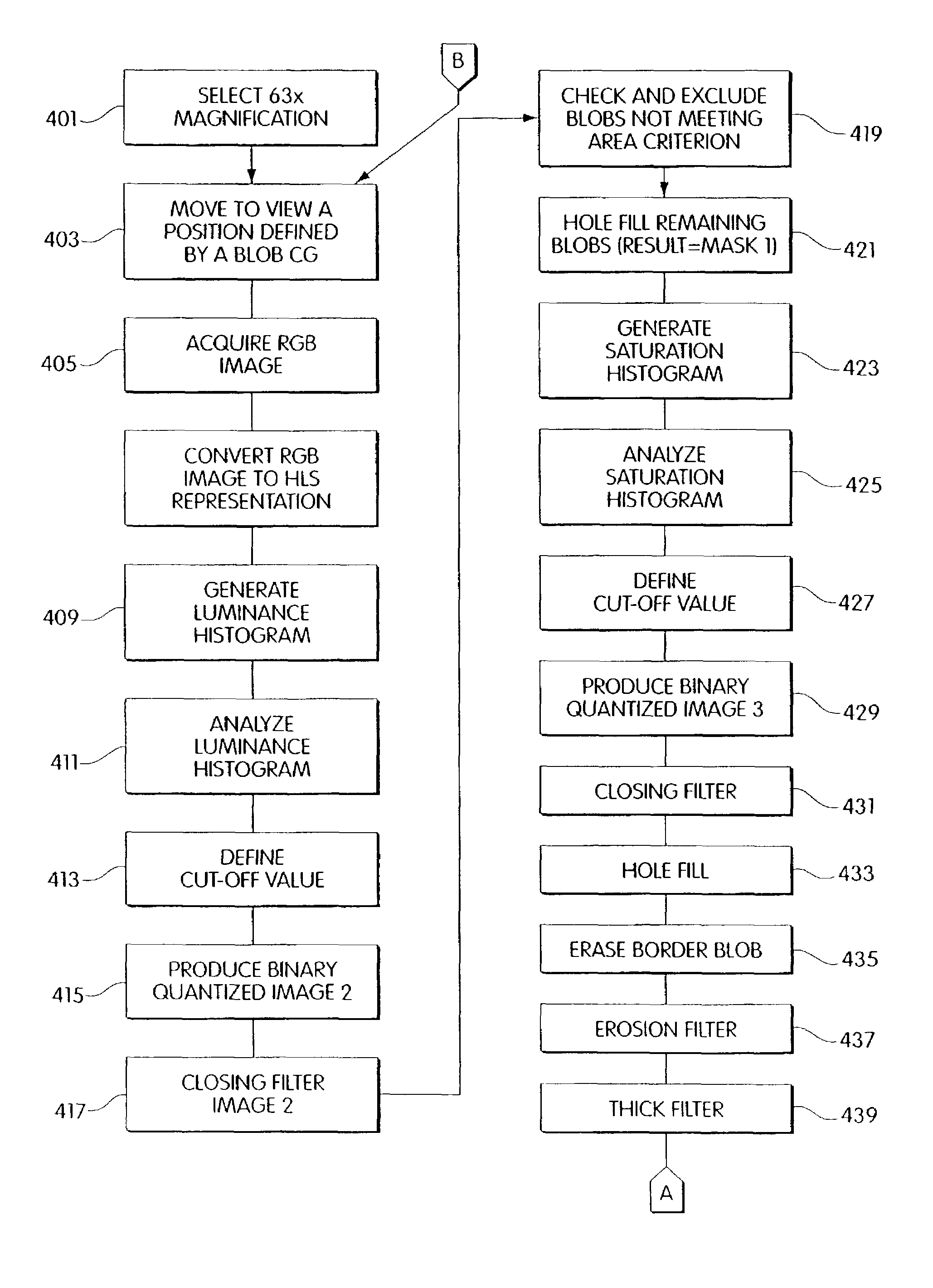
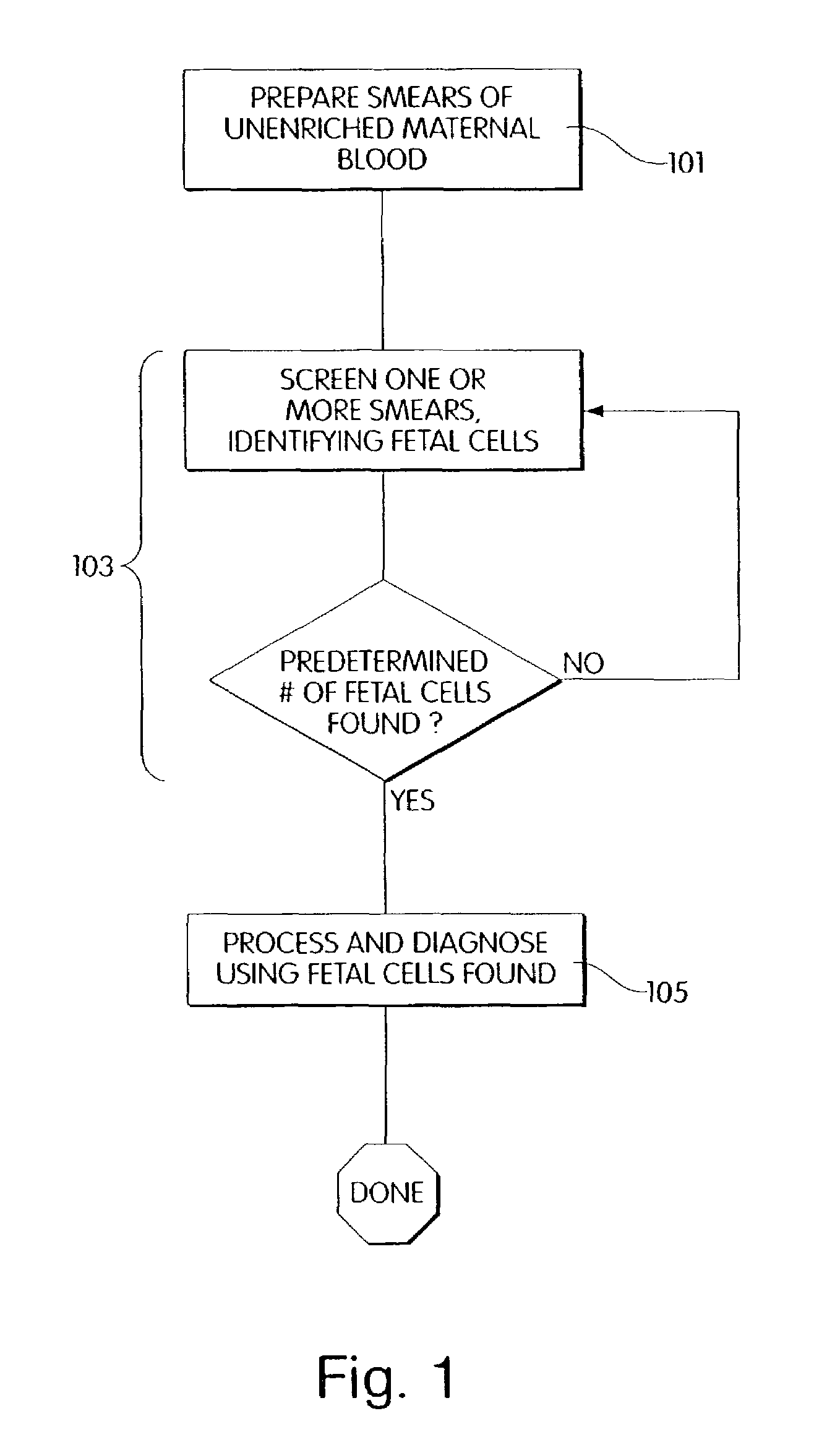
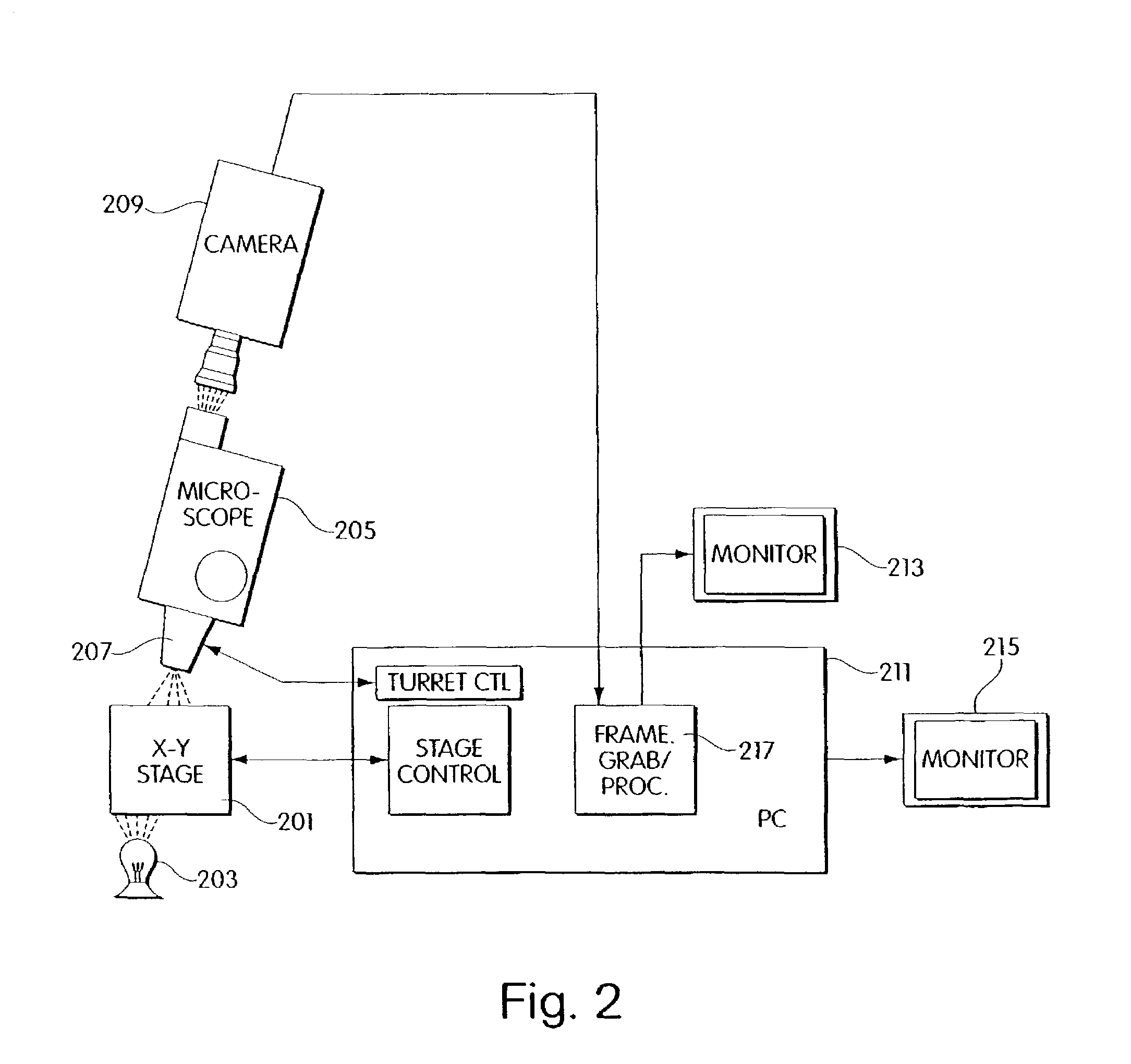
InactiveUS20060072805A1Minimize timePossible amount of timePreparing sample for investigationDisease diagnosisCancer cellRare cell
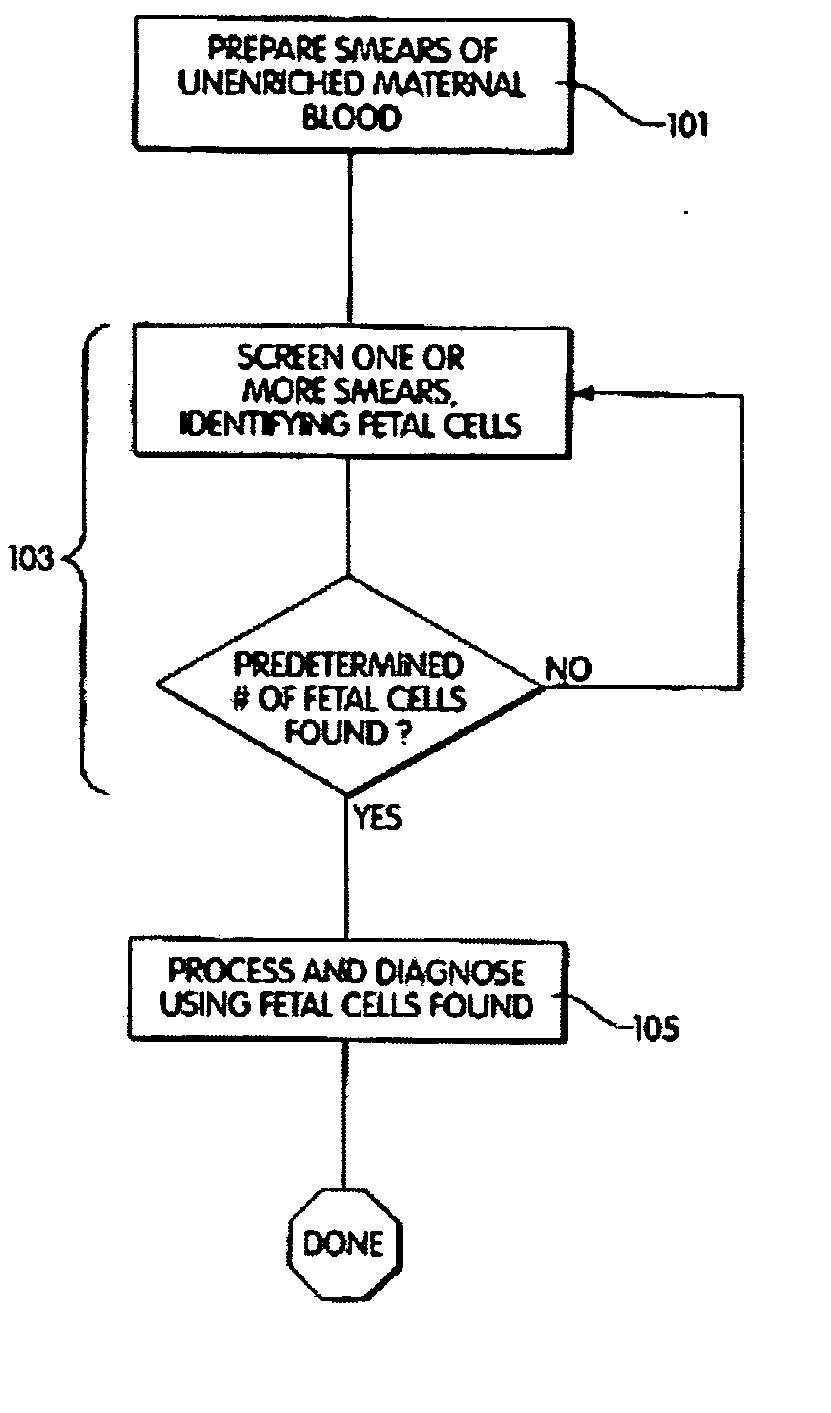
A computer controlled method for detecting and diagnosing a rare cell type in a tissue sample is provided, said method comprising treating the tissue sample such that it generates a first signal indicative of the presence at a location of a rare cell, detecting the first signal, treating the location at which the first signal is detected to generate a second signal indicative of a diagnostically useful cellular characteristic and detecting the second signal. The first signal can be morphological or a color present in a sought cell either before or after staining. The second signal can be generated by in situ PCR or PCR in situ hybridization. In one preferred embodiment, the rare cell type is a fetal cell in a maternal blood tissue sample, said sample consisting of a smear of unenriched maternal blood. In another embodiment, the method is used to diagnose or genotype cancer cells in a blood or tissue biopsy sample.
Owner:IKONISYS INC
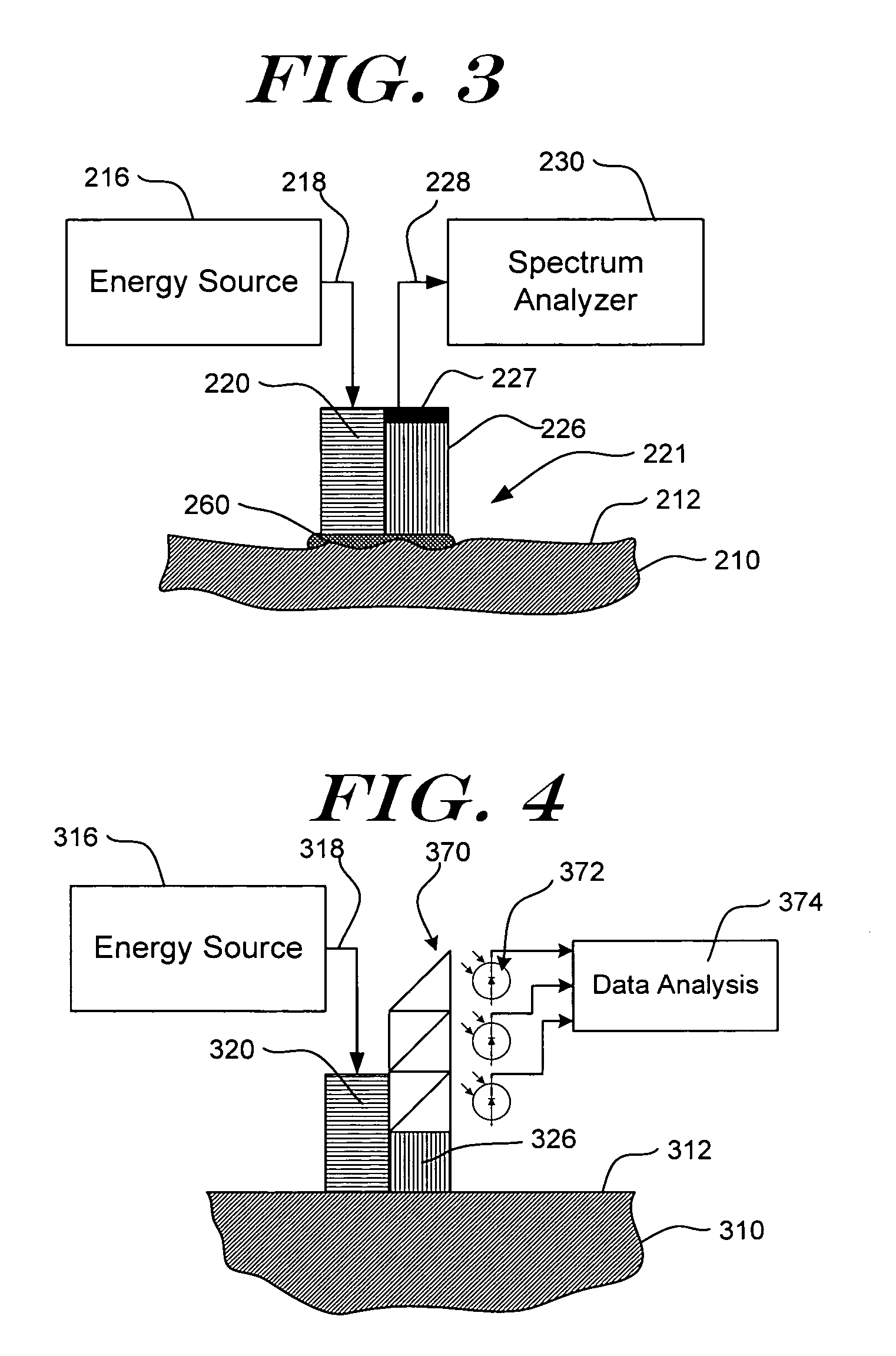
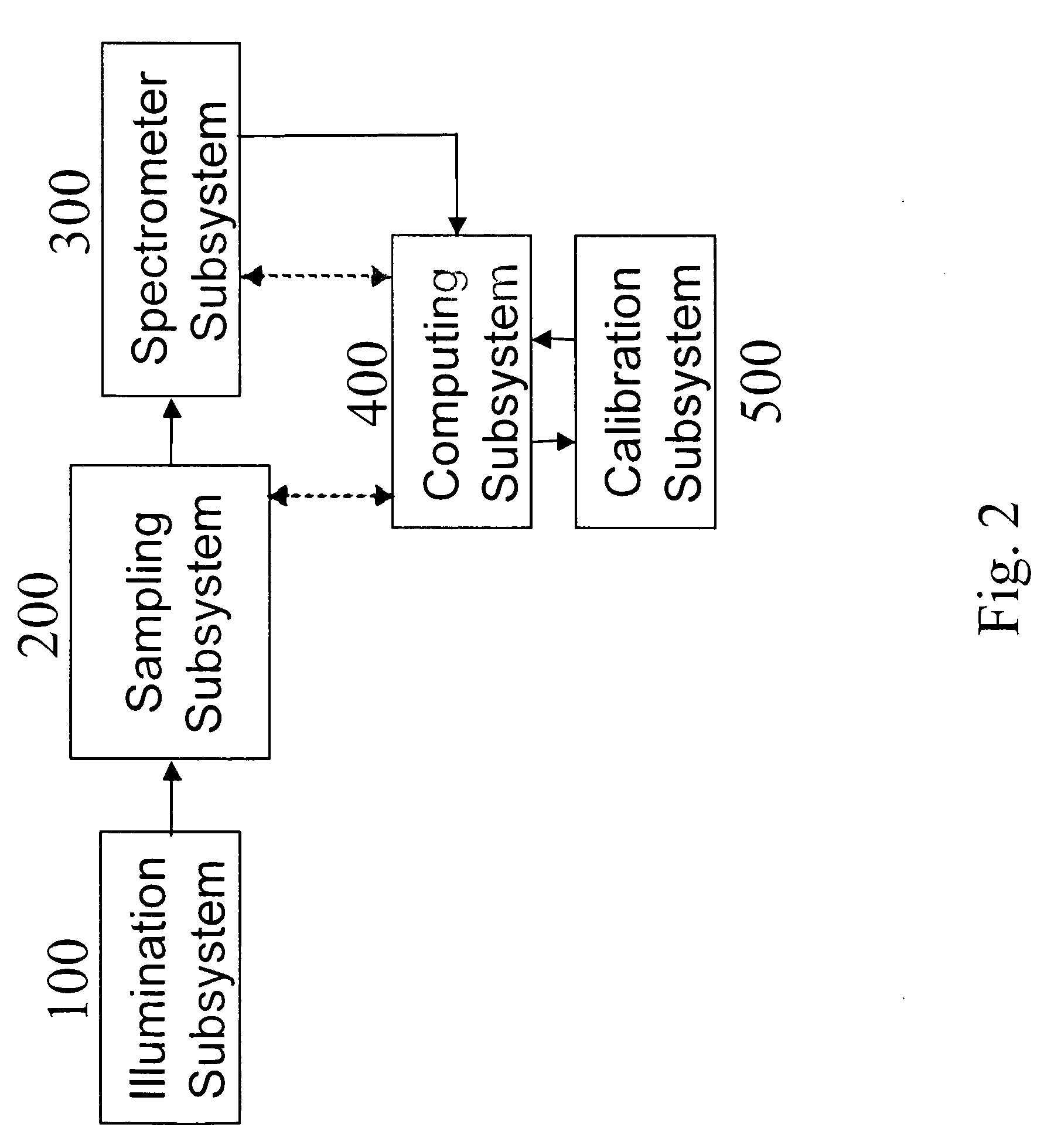
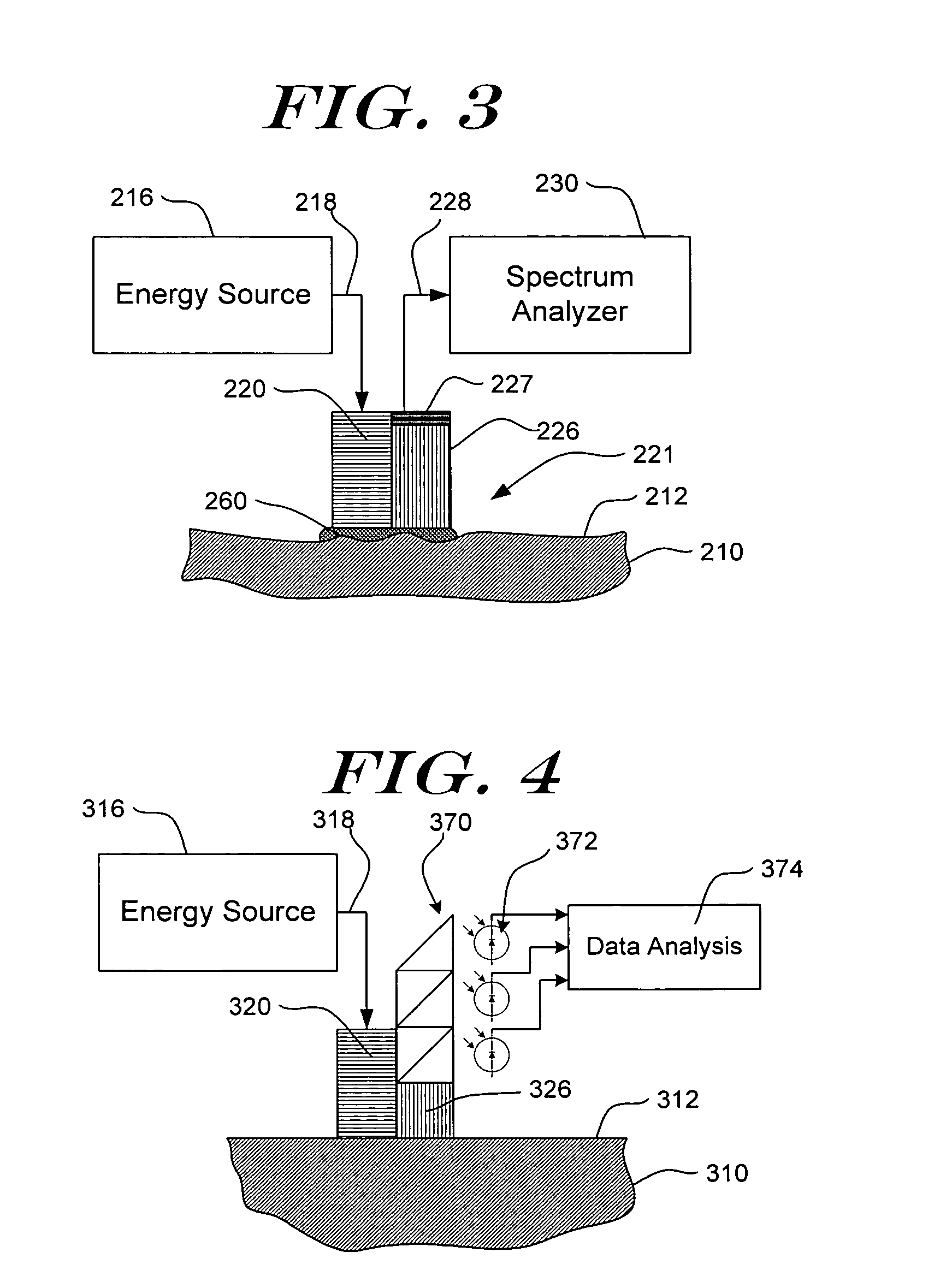
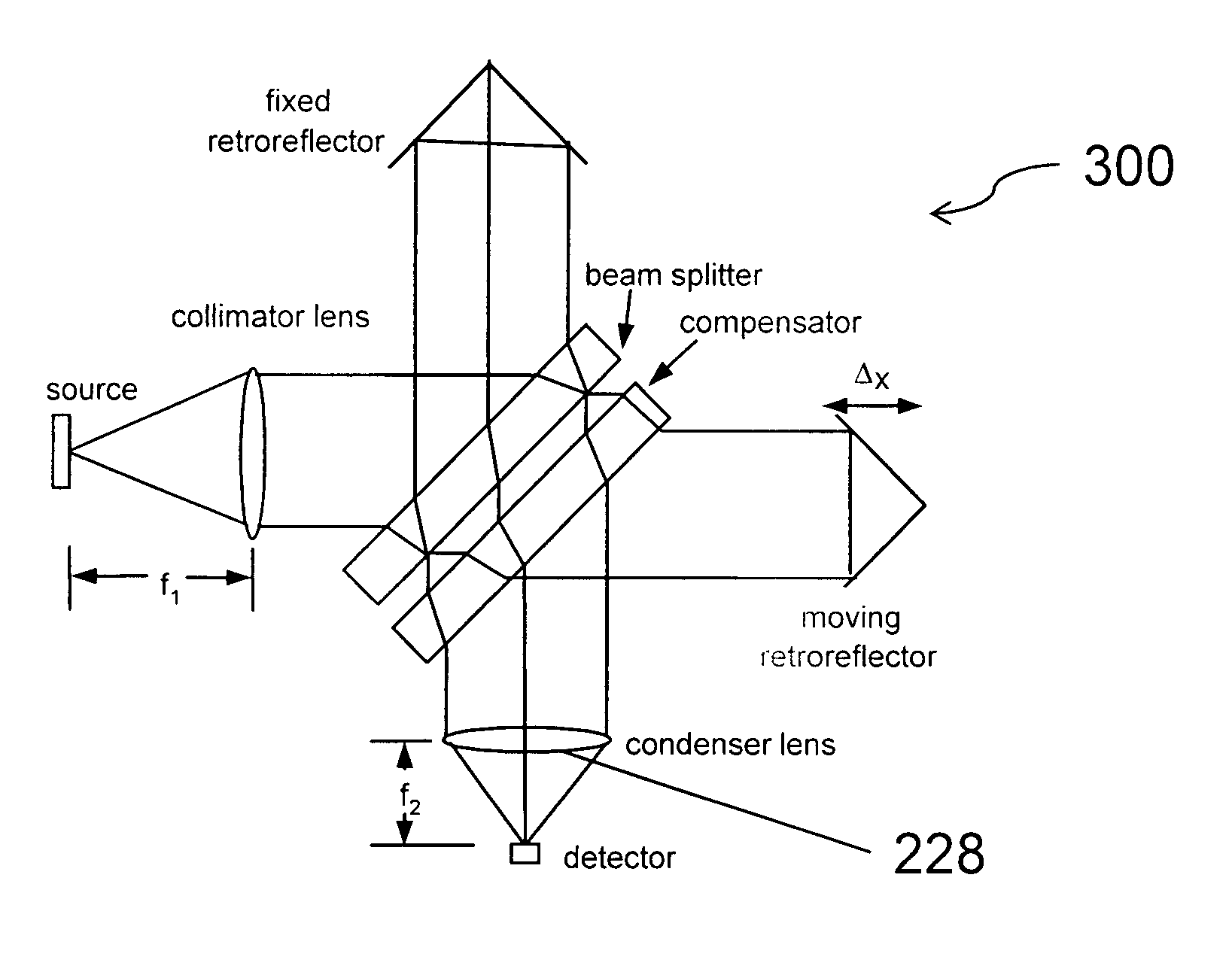
Apparatuses for Noninvasive Determination of in vivo Alcohol Concentration using Raman Spectroscopy
ActiveUS20080208018A1Efficient collectionIncrease luminous fluxProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsNon invasiveIn vivo
Methods and apparatuses for the determination of an attribute of the tissue of an individual use non-invasive Raman spectroscopy. For example, the alcohol concentration in the blood or tissue of an individual can be determined non-invasively. A portion of the tissue is illuminated with light, the light propagates into the tissue where it is Raman scattered within the tissue. The Raman scattered light is then detected and can be combined with a model relating Raman spectra to alcohol concentration in order to determine the alcohol concentration in the blood or tissue of the individual. Correction techniques can be used to reduce determination errors due to detection of light other than that from Raman scattering from the alcohol in the tissue. Other biologic information can be used in combination with the Raman spectral properties to aid in the determination of alcohol concentration, for example age of the individual, height of the individual, weight of the individual, medical history of the individual and his / her family, ethnicity, skin melanin content, or a combination thereof. The method and apparatus can be highly optimized to provide reproducible and, preferably, uniform radiance of the tissue, low tissue sampling error, depth targeting of the tissue layers or sample locations that contain the attribute of interest, efficient collection of Raman spectra from the tissue, high optical throughput, high photometric accuracy, large dynamic range, excellent thermal stability, effective calibration maintenance, effective calibration transfer, built-in quality control, and ease-of-use.
Owner:ROCKLEY PHOTONICS LTD
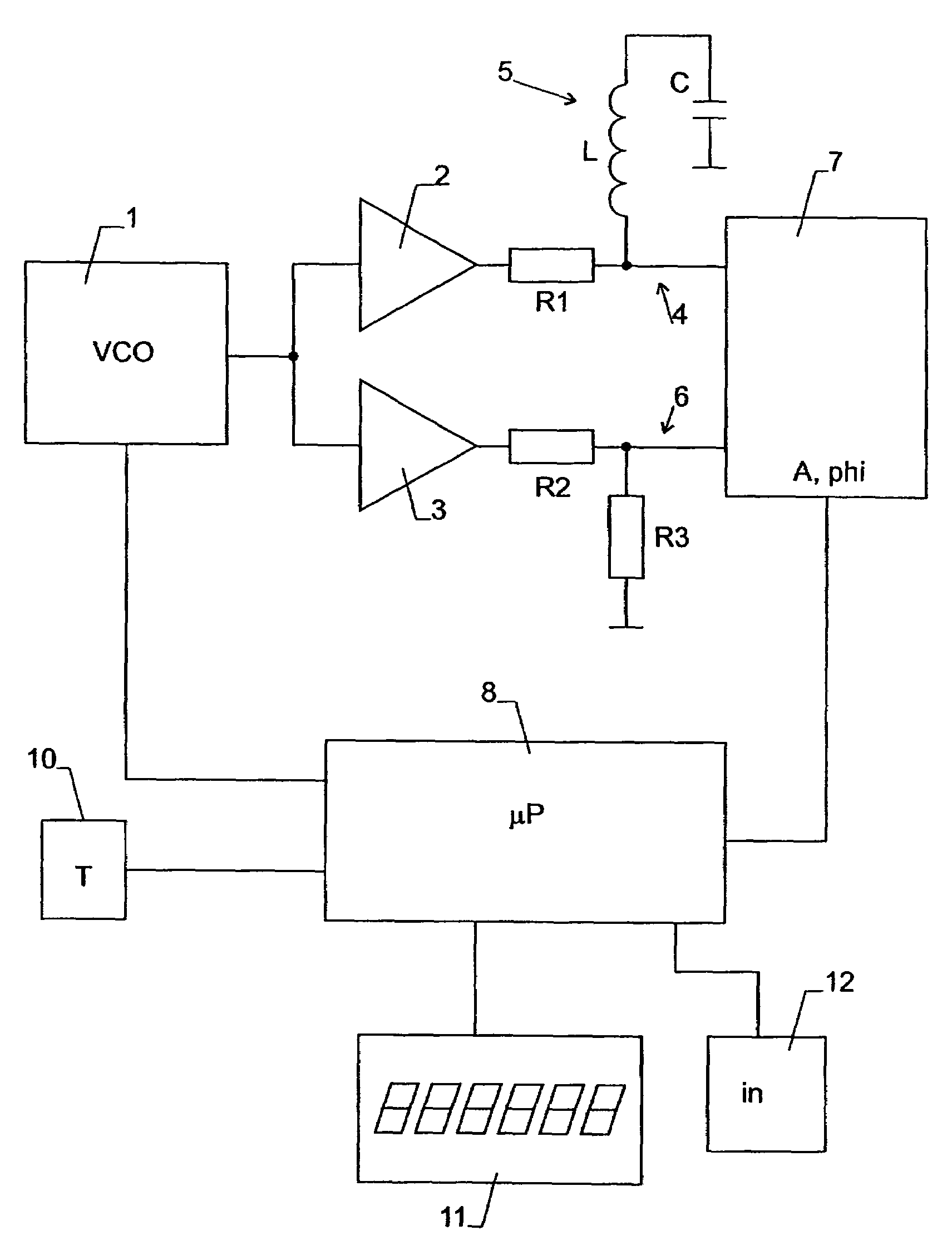
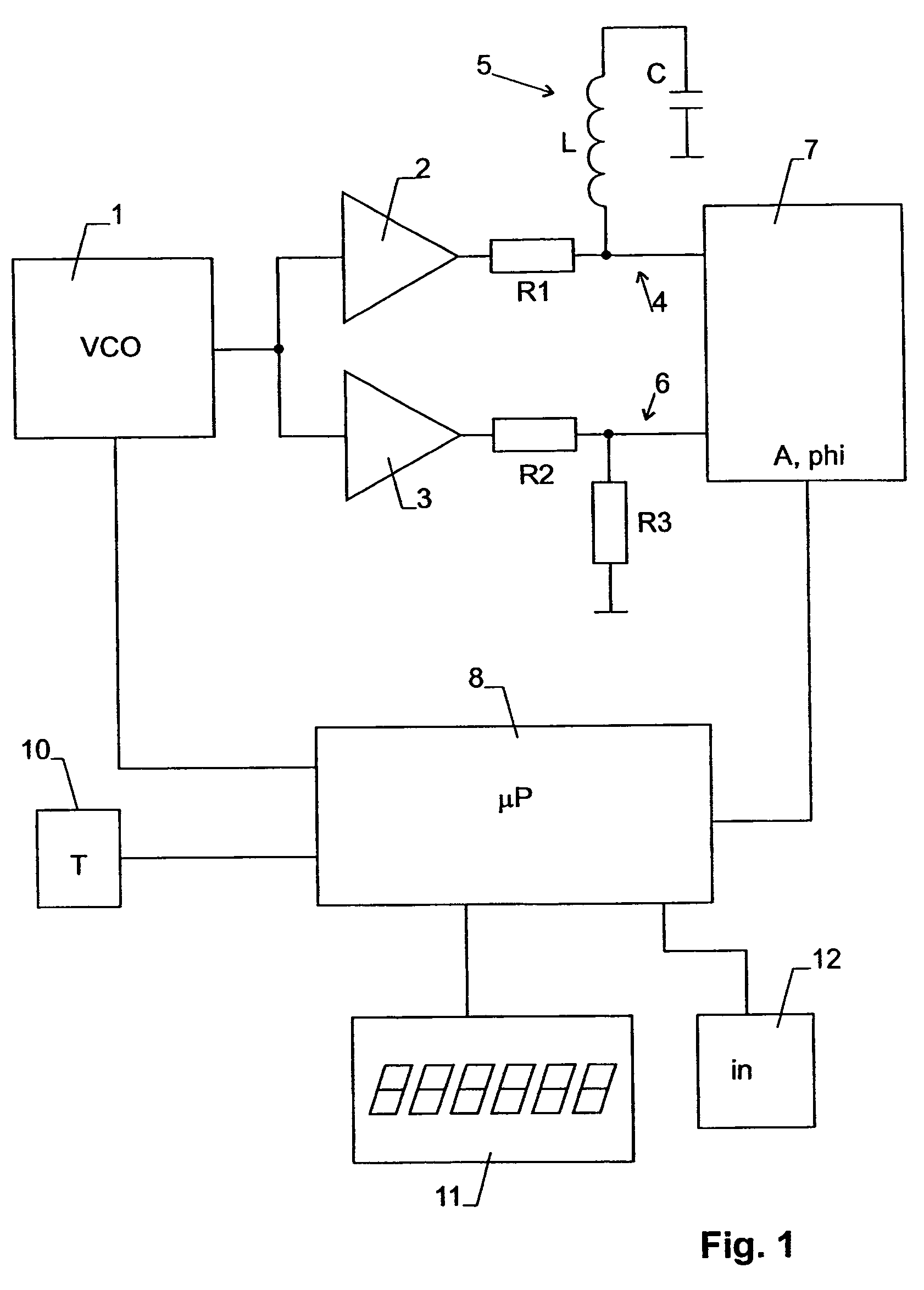
Method and device for determining the concentration of a substance in body liquid
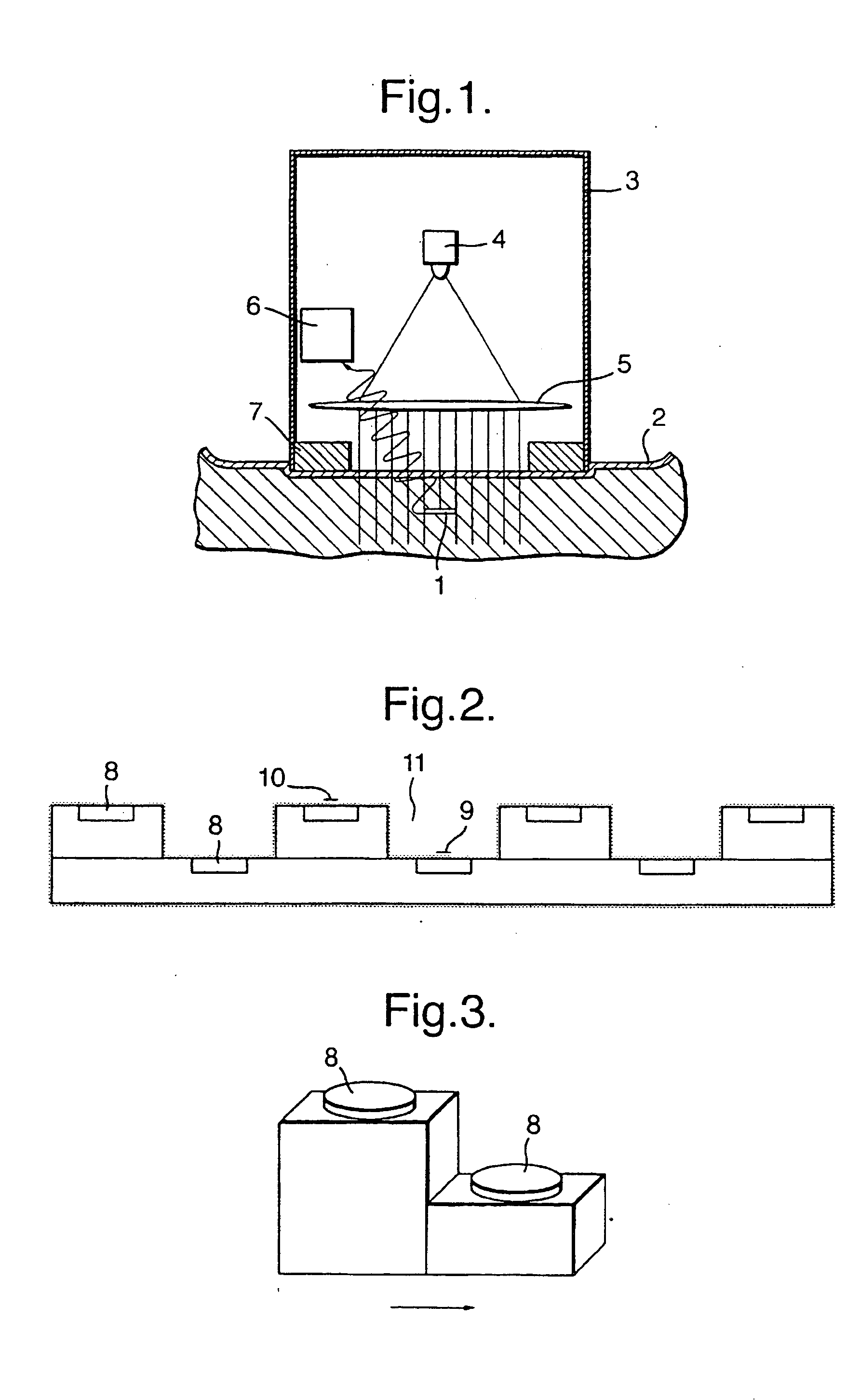
For measuring the concentration of a substance in body fluid, such as the glucose level in blood or tissue, a strip electrode (18) and a ring electrode (19) are arranged at the specimen. The ring electrode (19) is in direct electrical contact with the specimen while the strip electrode (18) is electrically insulated therefrom. The strip electrode (18) is arranged parallel to an arm or a leg for obtaining a large interaction length. The electrodes (18, 19) form a capacitor in a resonant circuit. A modulated voltage in the MHz range close to or at the resonance frequency is applied to the electrodes and the response of the body fluid is measured. This design allows a measurement of high accuracy.
Owner:BIOSIGNS PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for computer controlled cell based diagnosis
InactiveUS7346200B1Suitable for control and processingMinimize timePreparing sample for investigationDisease diagnosisCancer cellRare cell
A computer controlled method for detecting and diagnosing a rare cell type in a tissue sample is provided, said method comprising treating the tissue sample such that it generates a first signal indicative of the presence at a location of a rare cell, detecting the first signal, treating the location at which the first signal is detected to generate a second signal indicative of a diagnostically useful cellular characteristic and detecting the second signal. The first signal can be morphological or a color present in a sought cell either before or after staining. The second signal can be generated by in situ PCR or PCR in situ hybridization. In one preferred embodiment, the rare cell type is fetal cell in a maternal blood tissue sample, said sample consisting of a smear of unenriched maternal blood. In another embodiment, the method is used to diagnose or genotype cancer cells in a blood or tissue biopsy sample.
Owner:IKONISYS INC
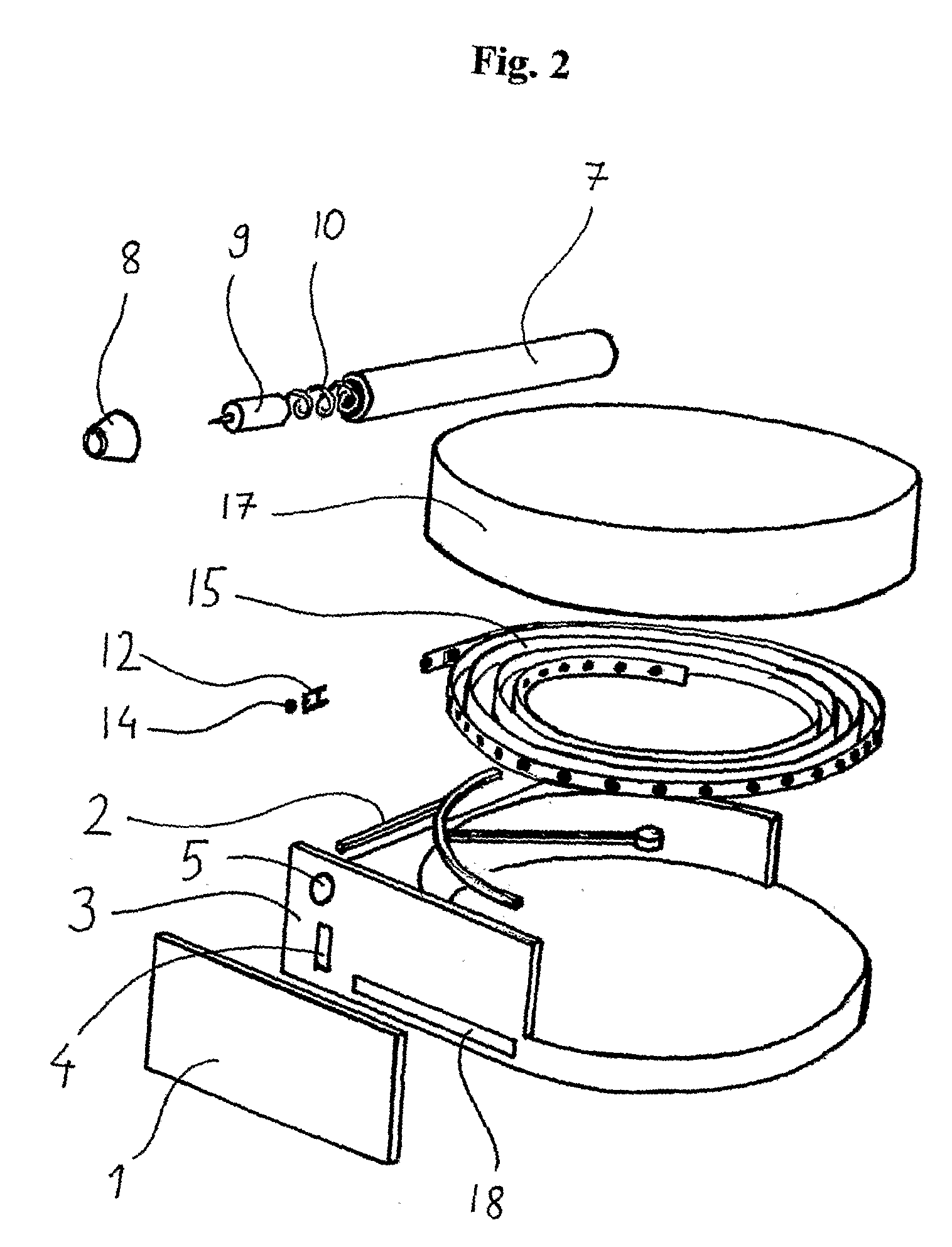
Health monitoring device, device modules and method
InactiveUS8062235B2Simple and less conspicuousCover tightlyCatheterSensorsComputer moduleBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates to a health monitoring device for measuring blood or tissue indicators and a strip cassette. The device comprises a body having first and second openings, a piercing means being connected to the body and having a piercing head, the piercing means being arranged to extend from the first opening and cockable and releasable for piercing the skin with the piercing head, and a space, into which a number of sensor strips can be arranged so that the strips can be brought out from the body one at a time. The device further comprises a shutter that is functionally connected to the body and has a first position arranged to tightly close the first and second openings, and a second position for allowing one sensor strip to be pushed from the first opening into sampling position and for exposing the first and second openings.
Owner:I SENS INC
Apparatus for non-invasive determination of direction and rate of change of an analyte
InactiveUS20060167349A1Amplifying the ability to monitor changesPrevent reflection and absorptionDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyAnalyteAlcohol
The present invention relates generally to a non-invasive method and apparatus for measuring a fluid analyte, particularly relating to glucose or alcohol contained in blood or tissue, utilizing spectroscopic methods. More particularly, the method and apparatus incorporate means for detecting and quantifying changes in the concentration of specific analytes in tissue fluid. Also, the method and apparatus can be used to predict future levels of analyte concentration either in the tissue fluid or in blood in an adjacent vascular system.
Owner:INLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Microneedle devices and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20050187521A1Easy to moveEnhance capillary wicking actionMicroneedlesMedical devicesCapillary volumeSubstrate surface
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Integrated Needle and Test Strip Assembly and Method of Use
InactiveUS20130172780A1Relieve painLess manual dexterityCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalytePositive pressure
Methods and systems to collect a sample of bodily fluid from a patient using an integrated needle and test strip assembly are provided. The test strip and needle form one unit that captures the sample of blood or interstitial fluid from the patient once the apparatus is pressed to the skin. The hollow needle includes more than one opening at a distal end, each opening coming into contact with the bodily fluid when disposed within a cutaneous or subcutaneous layer of the patient's skin. The sample may flow through the needle onto a test region by capillary action and / or the positive pressure of the bodily fluid (e.g. blood or interstitial fluid) relative to the external environment. The disclosed test strip includes at least one reaction site for testing analyte concentrations and a means for interfacing with many commercially available test strip meters to provide readout of the analyte concentration.
Owner:CHARLESTON AREA MEDICAL CENT
Methods for noninvasive determination of in vivo alcohol concentration using Raman spectroscopy
ActiveUS8515506B2Efficient collectionIncrease luminous fluxProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsCorrection techniqueNon invasive
Methods and apparatuses for the determination of an attribute of the tissue of an individual use non-invasive Raman spectroscopy. For example, the alcohol concentration in the blood or tissue of an individual can be determined non-invasively. A portion of the tissue is illuminated with light, the light propagates into the tissue where it is Raman scattered within the tissue. The Raman scattered light is then detected and can be combined with a model relating Raman spectra to alcohol concentration in order to determine the alcohol concentration in the blood or tissue of the individual. Correction techniques can be used to reduce determination errors due to detection of light other than that from Raman scattering from the alcohol in the tissue. Other biologic information can be used in combination with the Raman spectral properties to aid in the determination of alcohol concentration, for example age of the individual, height of the individual, weight of the individual, medical history of the individual and his / her family, ethnicity, skin melanin content, or a combination thereof. The method and apparatus can be highly optimized to provide reproducible and, preferably, uniform radiance of the tissue, low tissue sampling error, depth targeting of the tissue layers or sample locations that contain the attribute of interest, efficient collection of Raman spectra from the tissue, high optical throughput, high photometric accuracy, large dynamic range, excellent thermal stability, effective calibration maintenance, effective calibration transfer, built-in quality control, and ease-of-use.
Owner:ROCKLEY PHOTONICS LTD
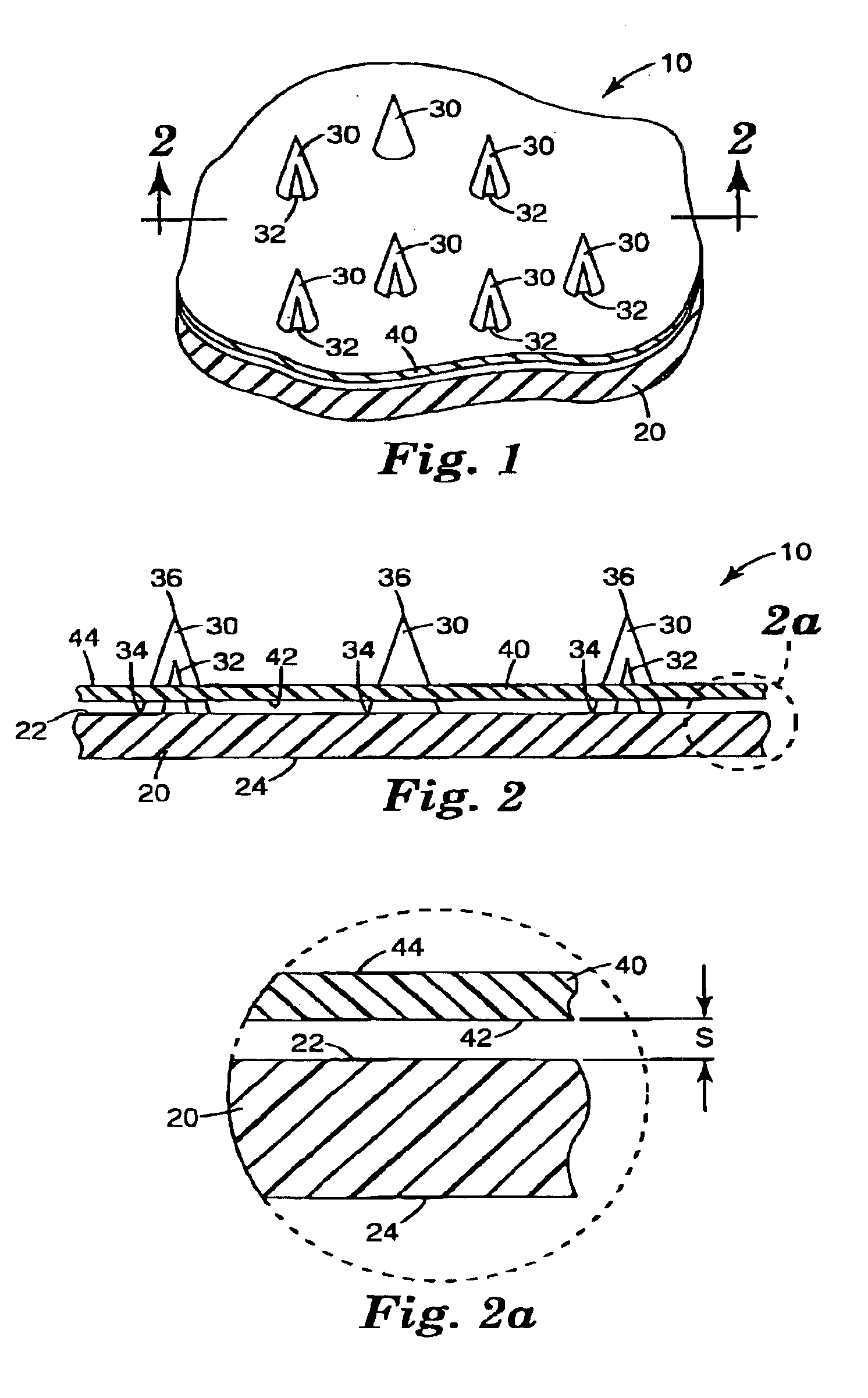
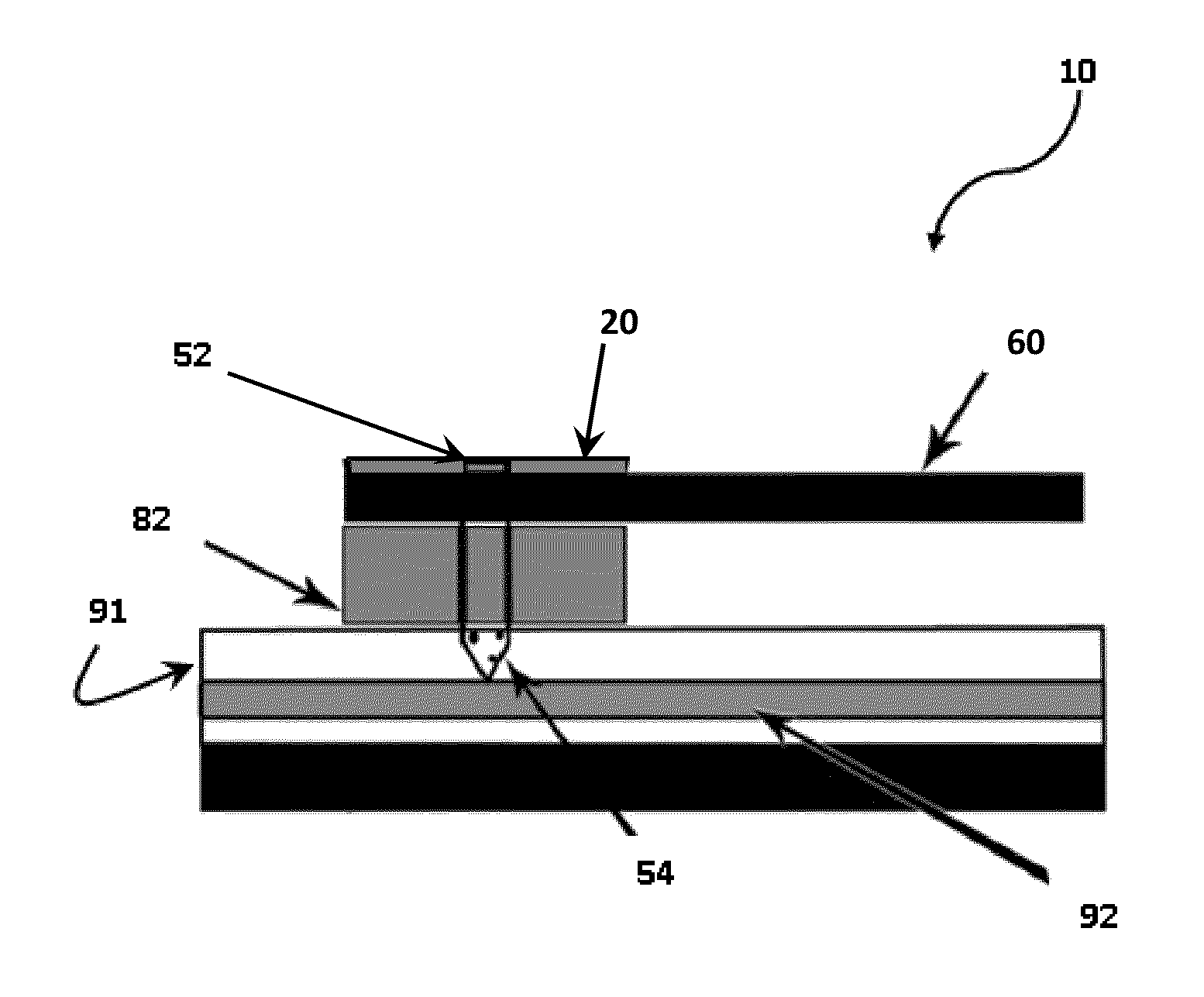
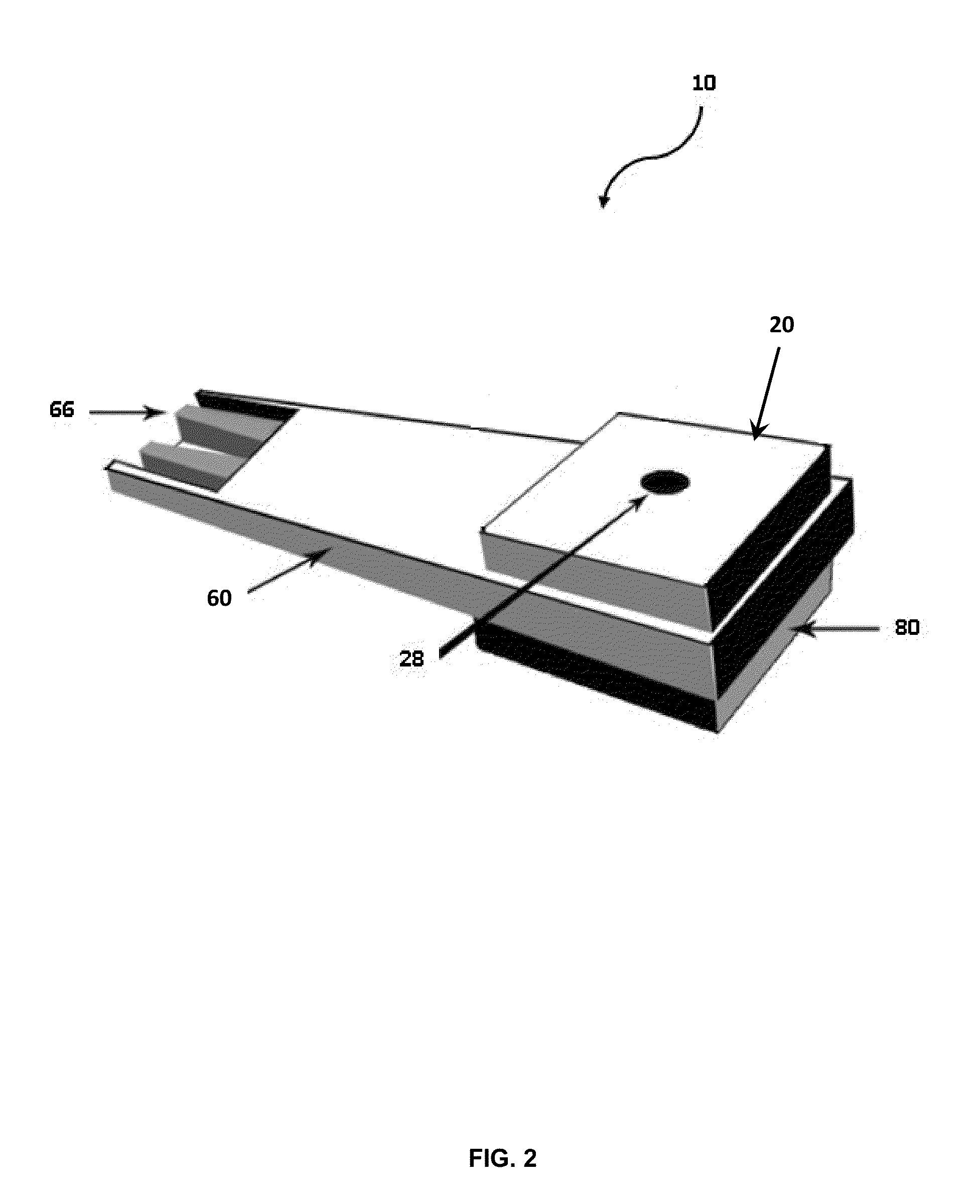
Medical devices and kits including same
A medical device is described, comprising an array (10) comprising microstructures (12) configured to penetrate the stratum corneum upon impact, and a connection member (20) affixed to the array in a one piece construction, the connection member configured to reversibly connect the medical device to an applicator. The medical devices of the invention may be used in methods requiring the penetration of skin to deliver medicaments or other substances and / or extract blood or tissue through the skin. In use, it is generally desirable to provide the microstructures at a height sufficient to penetrate the stratum corneum. A medical kit is also described, comprising the foregoing medical device and a tray (34) configured to hold the medical device.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
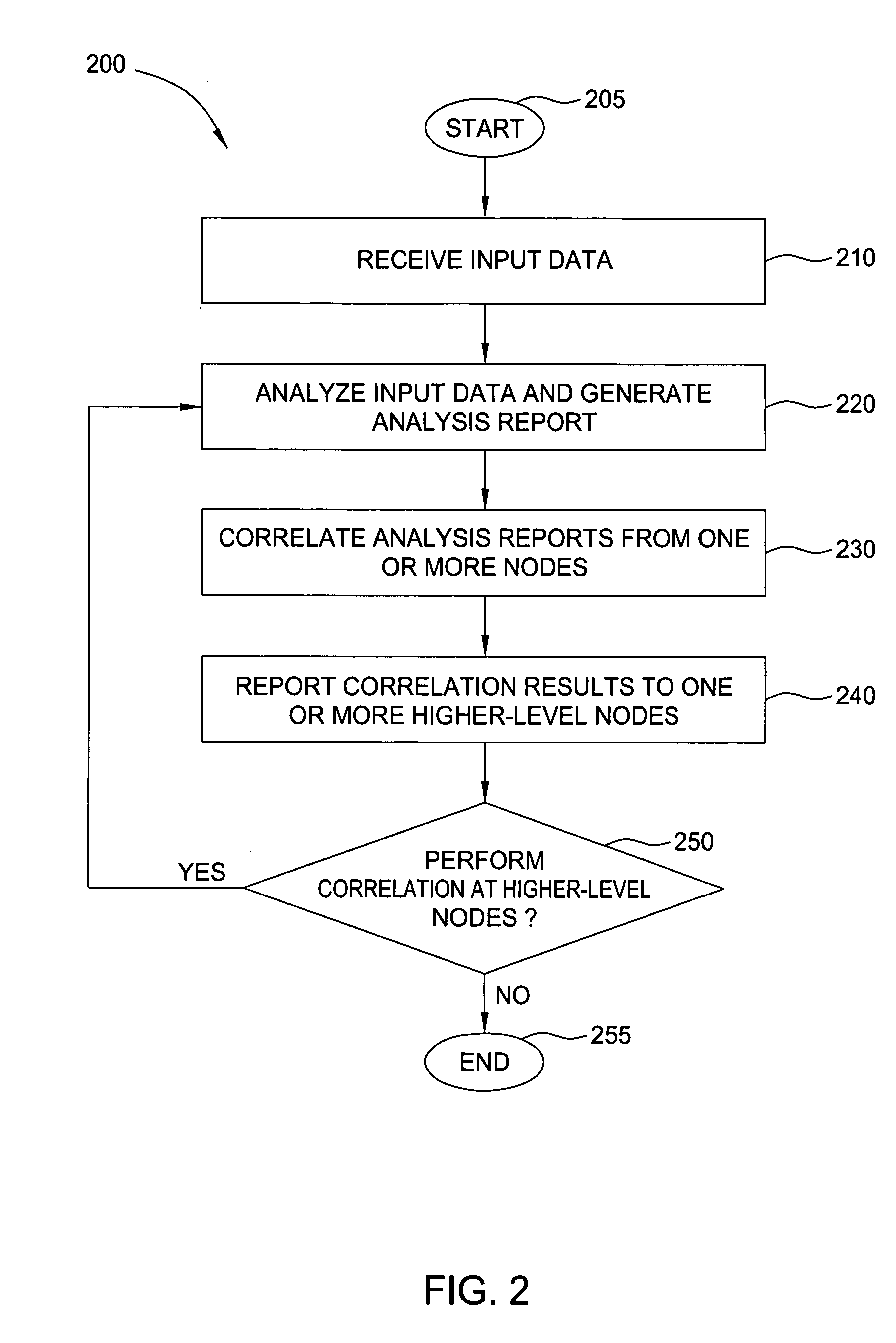
Method and apparatus for real-time correlation of data collected from biological sensors
InactiveUS20070005256A1Quick identificationHigh sensitivityEpidemiological alert systemsBiological testingTime correlationRapid identification
A method and apparatus are provided for performing real-time correlation of data collected from biological sensors, including, but not limited to, sensors adapted to analyze biological material (e.g., blood or tissue samples) and environmental material (e.g., air or water samples). In one embodiment, a method for correlating biological data over a broad (geographic or demographic) domain includes receiving data relating to at least two samples of biological material, where the samples originate at two different regions of the broad domain. This data is then correlated to produce a domain-wide view of the biological data, thereby enabling the rapid identification of domain-wide medical emergencies. Moreover, this correlated information may be provided to lower-level correlation sources or to the biological sensors in order to increase the sensitivities of the correlation sources or biological sensors to emerging threats.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Antigen presenting vesicles
The present invention relates to an antigen presenting membrane vesicle comprising on its surface a composition of either relevant molecules for antigen-specific activation or deactivation of T lymphocytes and which is present in the form of an artificially induced lipid vesicle budded from a plasma membrane of a eukaryotic, preferably human, cell, and wherein the composition of said relevant molecules for activation or deactivation present on the vesicle surface is adjustable to a recipient's needs or requirements independently of any blood or tissue cells of said recipient. The invention further relates to a method of manufacture of the vesicles and to compositions containing the vesicles as well as to the use of the vesicles for various purposes including medical and diagnostic applications.
Owner:WINFRIED PICKL +1
Working electrode of glucose monitoring probe and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN111248924AExtended service lifeHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCatheterCarbon nanotubeCross linker
The present disclosure relates to a working electrode for a glucose monitoring probe, the working electrode comprising: a base layer provided on a flexible substrate; a sensing layer formed on the base layer by coating a sensing layer reagent, the sensing layer being capable of chemically reacting with glucose in blood or tissue fluid, the sensing layer reagent comprising a metal polymer, a glucolase, a carbon nanotube, and a cross-linking agent, the carbon nanotube adsorbing the metal polymer and the glucolase, amino modification is added to the carbon nano tube, so that the metal polymer andthe carbon nano tube tightly form covalent bond combination and are combined with glucolase; a semipermeable membrane is formed on the sensing layer and is used for controlling the passing rate of glucose molecules; and a biocompatible membrane formed on the semipermeable membrane. According to the invention, the working voltage of the working electrode can be reduced, the interference is reduced, the service life of the glucose monitoring probe is prolonged, and the reaction sensitivity to glucose is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN SISENSING TECH CO LTD
Biological sample component purification and differential display
InactiveUS20050003558A1Reduce complexityEasy to separateOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationDifferential displayFractionation
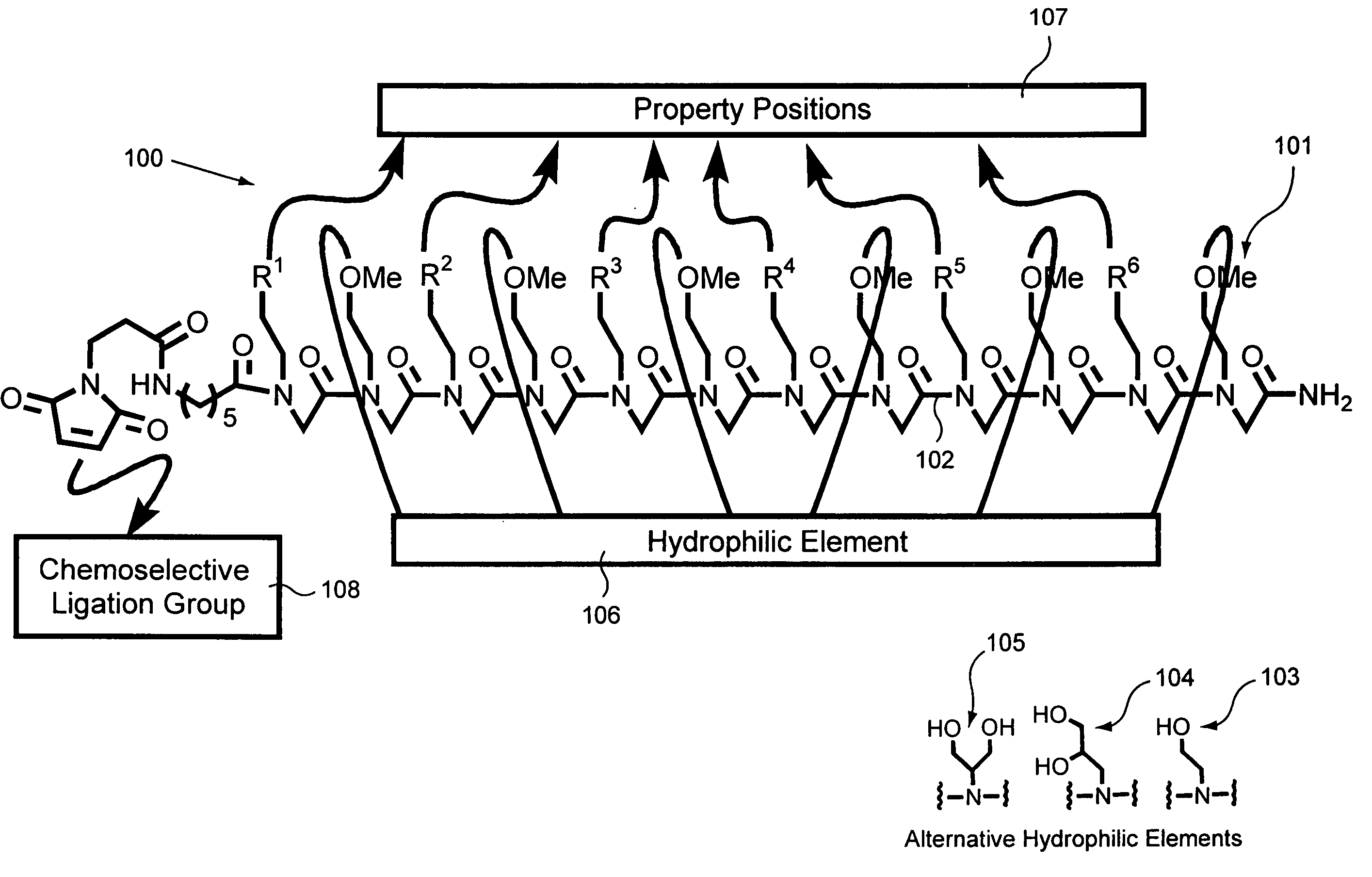
Provided are affinity support materials having intermediate binding affinity for biological samples. Among the materials provided by the present invention are hydrophilic solid supports composed of hydrophilic ligands coupled to hydrophilic matrixes which are compatible with biological samples, for example, a cell line, a biological fluid such as blood, or a tissue cell lysate. The ligands may include affinity property groups and hydrophilic groups pendent from a backbone, and be configured to at least partially resolve components of a biological sample. Affinity supports in accordance with the present invention may be used in a variety of techniques and apparatuses to achieve improved separations of complex biological samples and thereby enhance the results of biological sample component fractionations, enrichments, purifications, expression product determinations and comparisons, and other biological sample processing techniques. In addition, the affinity supports may be included in kits useful in processing biological samples.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
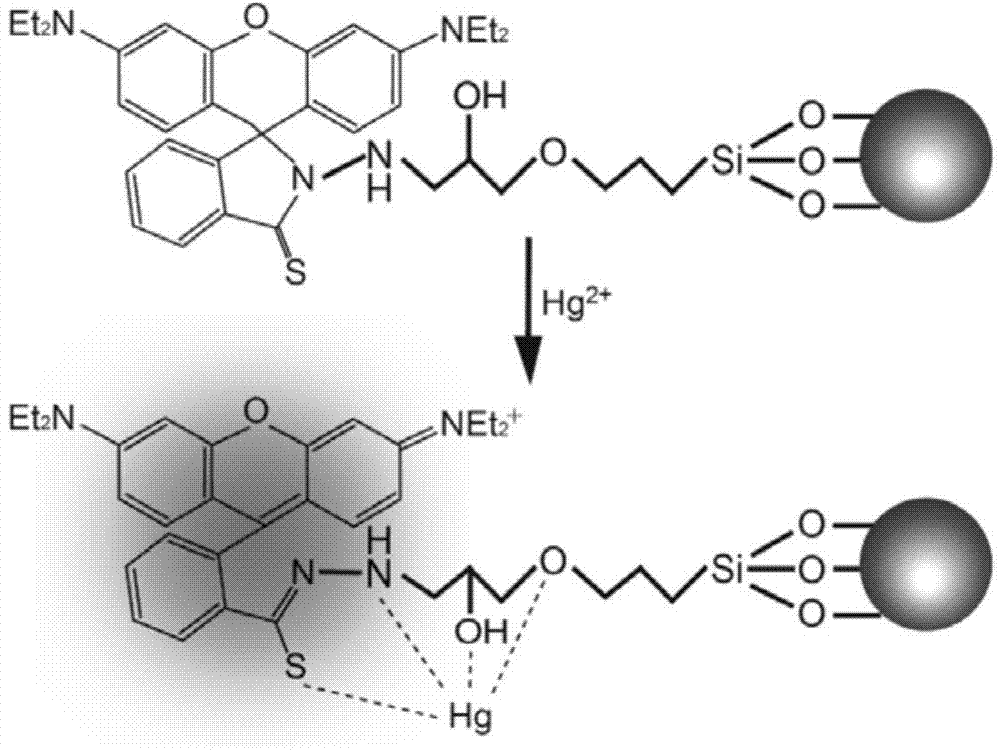
Modified SBA-15 mesoporous material as well as preparation method and application thereof
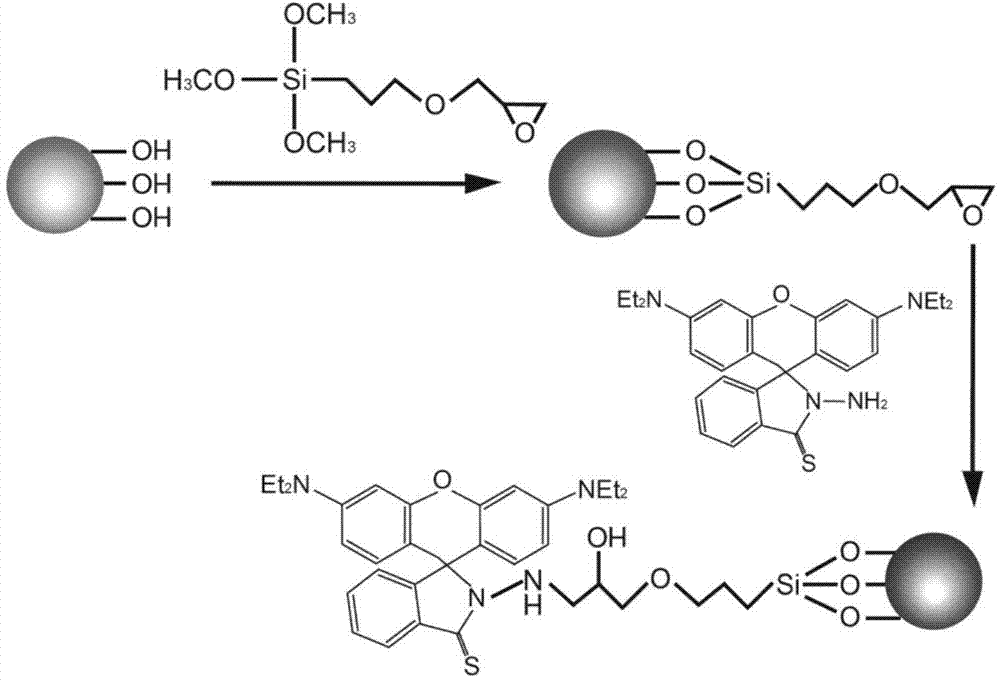
InactiveCN104741085AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionChemical structureMercuric ion
The invention belongs to the technical field of a functional material, and in particular relates to a modified SBA-15 mesoporous material as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The mesoporous material is an SBA-15 mesoporous material modified by trimethoxy-[(3-ethylene oxide methox)yl propyl] silane and rhodamine B derivative, and the modified mesoporous material is prepared by the following steps: firstly, substituting silicon hydroxyl of an SBA-15 mesoporous material which is prepared in advance with a substitute (as shown in Specification), and then, carrying out a cycloaddition reaction with thio rhodamine B hydrazide (as shown in Specification), so as to obtain the modified SBA-15 mesoporous material with chemical structural formula as shown in Specification. The modified SBA-15 mesoporous material, as a hybridized mesoporous fluorescent adsorbent showing efficient detection and a capacity of removing mercury ions in a water body and integrating multiple functions, can simultaneously carry out detection and recovery processes on dangerous chemical substances in a water solution, an air system, and in particular in body blood or tissue.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE +1
Apparatuses for noninvasive determination of in vivo alcohol concentration using raman spectroscopy
ActiveUS8581697B2Efficient collectionIncrease luminous fluxProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsNon invasiveIn vivo
Methods and apparatuses for the determination of an attribute of the tissue of an individual use non-invasive Raman spectroscopy. For example, the alcohol concentration in the blood or tissue of an individual can be determined non-invasively. A portion of the tissue is illuminated with light, the light propagates into the tissue where it is Raman scattered within the tissue. The Raman scattered light is then detected and can be combined with a model relating Raman spectra to alcohol concentration in order to determine the alcohol concentration in the blood or tissue of the individual. Correction techniques can be used to reduce determination errors due to detection of light other than that from Raman scattering from the alcohol in the tissue. Other biologic information can be used in combination with the Raman spectral properties to aid in the determination of alcohol concentration, for example age of the individual, height of the individual, weight of the individual, medical history of the individual and his / her family, ethnicity, skin melanin content, or a combination thereof. The method and apparatus can be highly optimized to provide reproducible and, preferably, uniform radiance of the tissue, low tissue sampling error, depth targeting of the tissue layers or sample locations that contain the attribute of interest, efficient collection of Raman spectra from the tissue, high optical throughput, high photometric accuracy, large dynamic range, excellent thermal stability, effective calibration maintenance, effective calibration transfer, built-in quality control, and ease-of-use.
Owner:ROCKLEY PHOTONICS LTD
Methods and Apparatuses for Noninvasive Determination of in vivo Alcohol Concentration using Raman Spectroscopy
InactiveUS20130317328A1Efficient collectionIncrease luminous fluxDiagnostics using spectroscopyOptical sensorsNon invasiveIn vivo
Methods and apparatuses for the determination of an attribute of the tissue of an individual use non-invasive Raman spectroscopy. For example, the alcohol concentration in the blood or tissue of an individual can be determined. A portion of the tissue is illuminated with light, which propagates into the tissue where it is Raman scattered. The Raman scattered light is detected and can be combined with a model relating Raman spectra to alcohol concentration to determine the alcohol concentration in the blood or tissue. Correction techniques can reduce determination errors due to detection of light other than that from Raman scattering from the alcohol in the tissue. Other biologic information can be used with the Raman spectral properties to aid in the determination of alcohol concentration, for example age, height, weight, medical history and his / her family, ethnicity, skin melanin content, or a combination thereof. The method and apparatus can be optimized to provide reproducible and uniform radiance of the tissue, low tissue sampling error, depth targeting of the tissue layers or sample locations that contain the attribute of interest, efficient collection of Raman spectra, optical throughput, photometric accuracy, large dynamic range, thermal stability, calibration maintenance, calibration transfer, built-in quality control, and ease-of-use.
Owner:TRUTOUCH TECH
Integrated needle and test strip with aspiration apparatus and method of use
Methods and systems to collect a sample of bodily fluid from a patient using an integrated needle and test strip assembly are provided. In this novel assembly, the test strip and needle form one unit that captures the sample of blood or interstitial fluid from the patient once the apparatus is pressed to the skin. The hollow aspiration needle includes more than one opening at a distal end, each opening coming into contact with the bodily fluid when disposed within a cutaneous or subcutaneous layer of the patient's skin. The disclosed test strip includes at least one reaction site for testing analyte concentrations and a means for linking to many commercially available test strip meters to provide readout of the analyte concentration. The sample may be captured by capillary flow, by an integrated aspirator, or by a differential vacuum device resident on the test strip meter.
Owner:CHARLESTON AREA MEDICAL CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com