Patents
Literature
150 results about "Lipid vesicle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
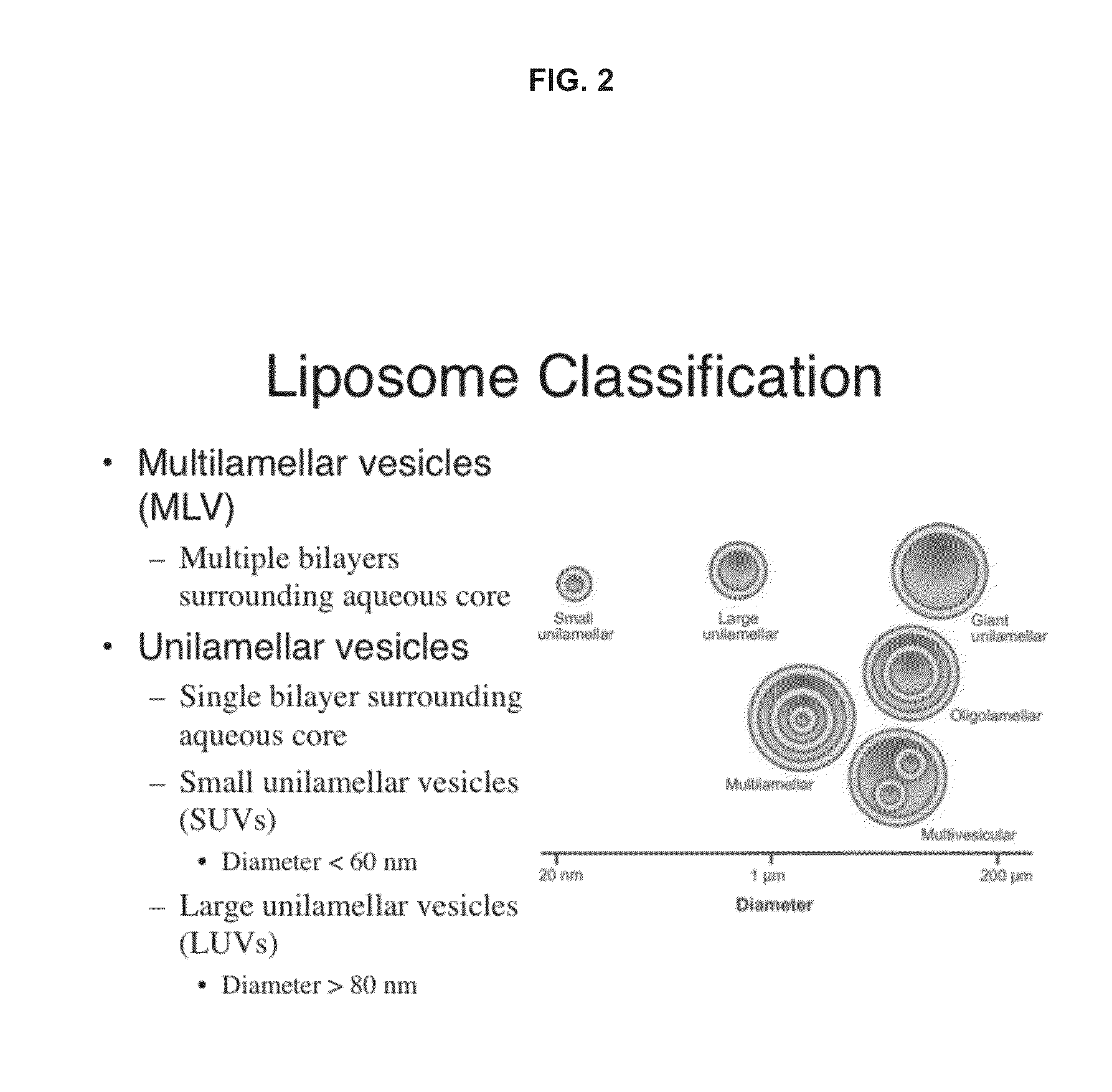
In cell biology, a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion ( exocytosis ), uptake ( endocytosis) and transport of materials within the plasma membrane.
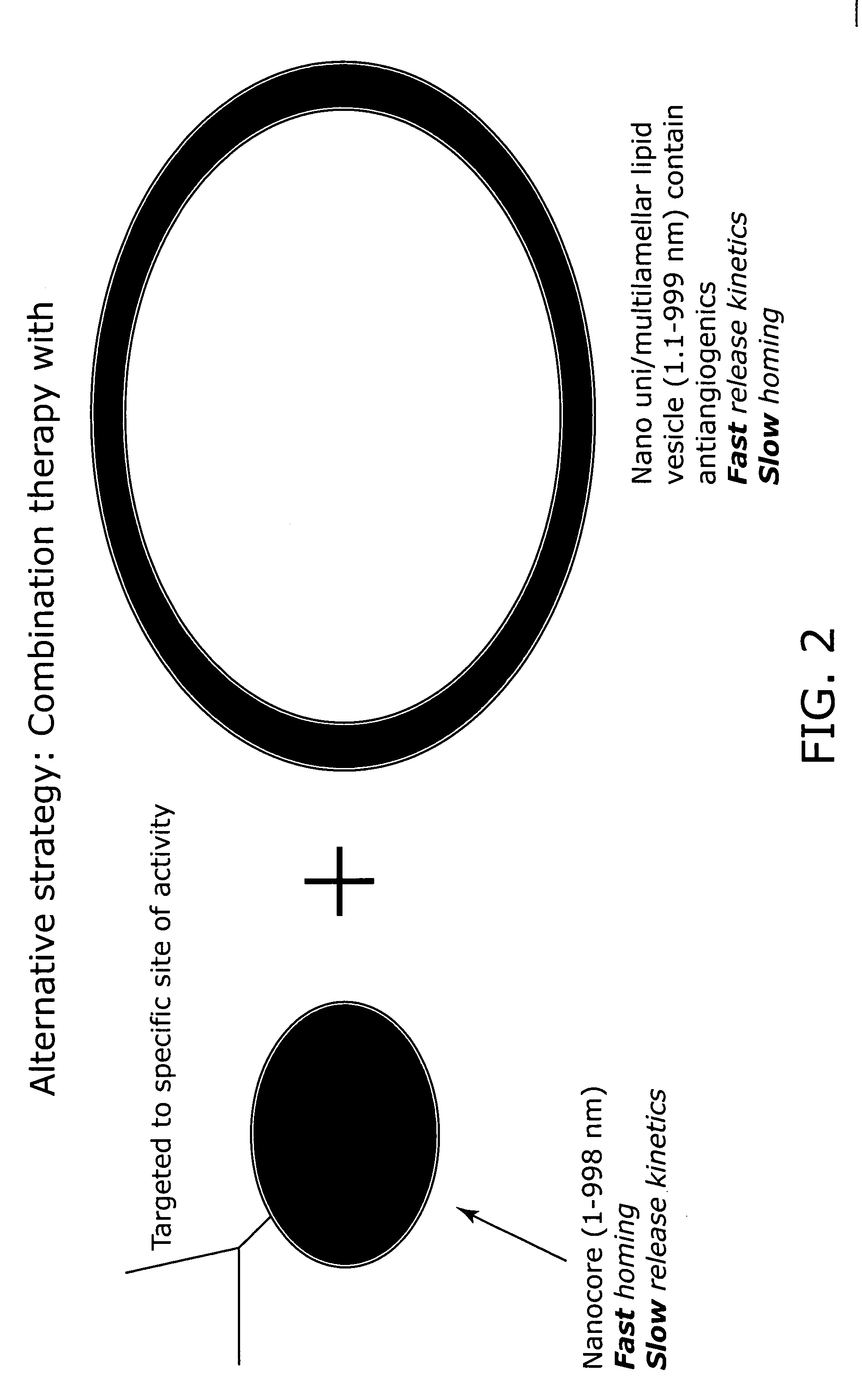
Nanocell drug delivery system
InactiveUS20050266067A1Avoid flowIncreased toxicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationAntigen
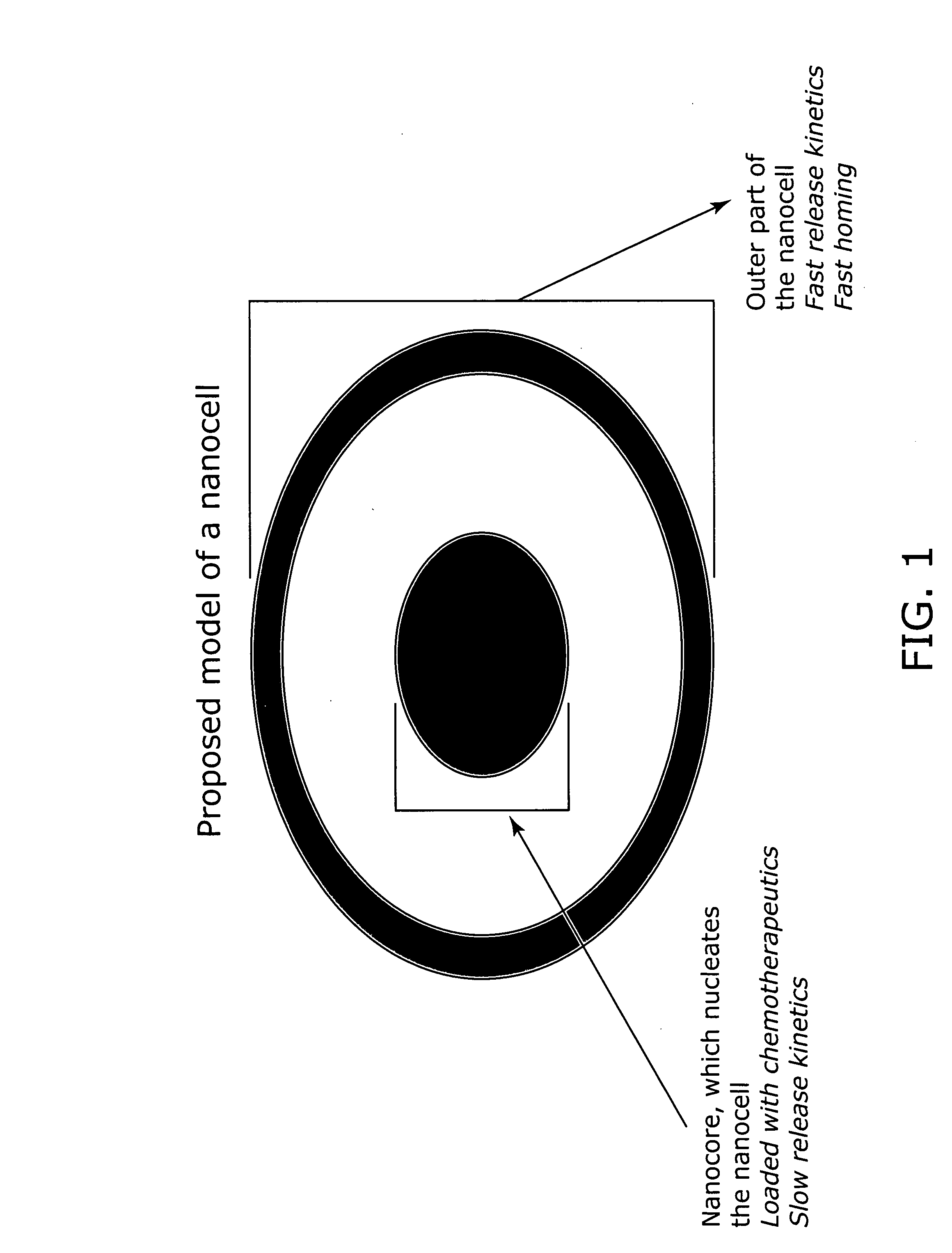
Nanocells allow the sequential delivery of two different therapeutic agents with different modes of action or different pharmacokinetics. A nanocell is formed by encapsulating a nanocore with a first agent inside a lipid vesicle containing a second agent. The agent in the outer lipid compartment is released first and may exert its effect before the agent in the nanocore is released. The nanocell delivery system may be formulated in pharmaceutical composition for delivery to patients suffering from diseases such as cancer, inflammatory diseases such as asthma, autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, infectious diseases, and neurological diseases such as epilepsy. In treating cancer, a traditional antineoplastic agent is contained in the outer lipid vesicle of the nanocell, and an antiangiogenic agent is loaded into the nanocore. This arrangement allows the antineoplastic agent to be released first and delivered to the tumor before the tumor's blood supply is cut off by the antianiogenic agent.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Compositions and methods for improved skin care
InactiveUS20070077292A1Safe and effective amount of collagenPrevent adverse side effectsOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsMedicineInstability
Compositions and methods for administering collagen to a human subject have been developed. The collagen-containing lipid vesicles of the invention provide a delivery system for human collagen which eliminates problems associated with chemical and physical instability of the collagen as well as immune responses to non-human collagen.
Owner:PINSKY MARK A
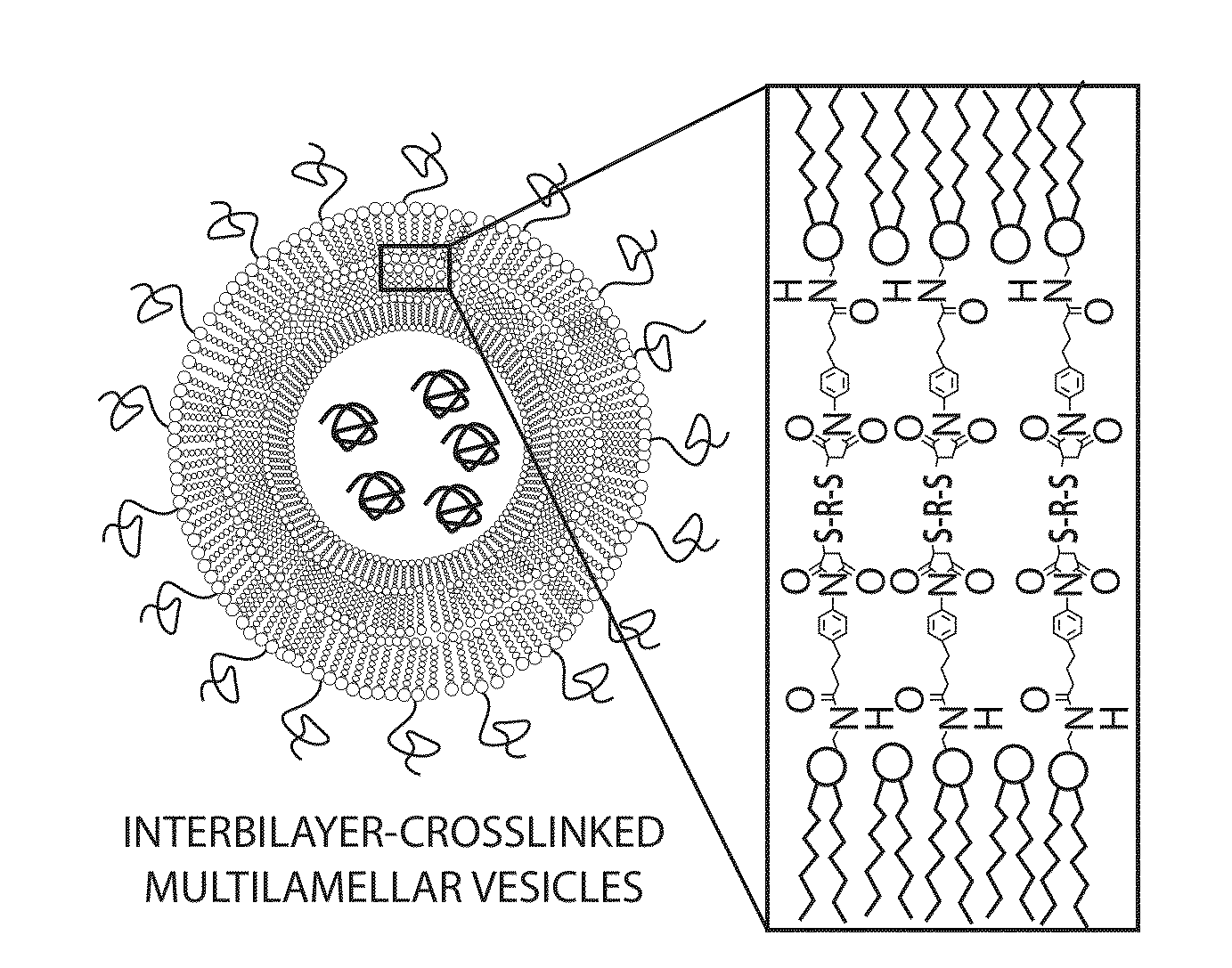
Lipid vesicle compositions and methods of use
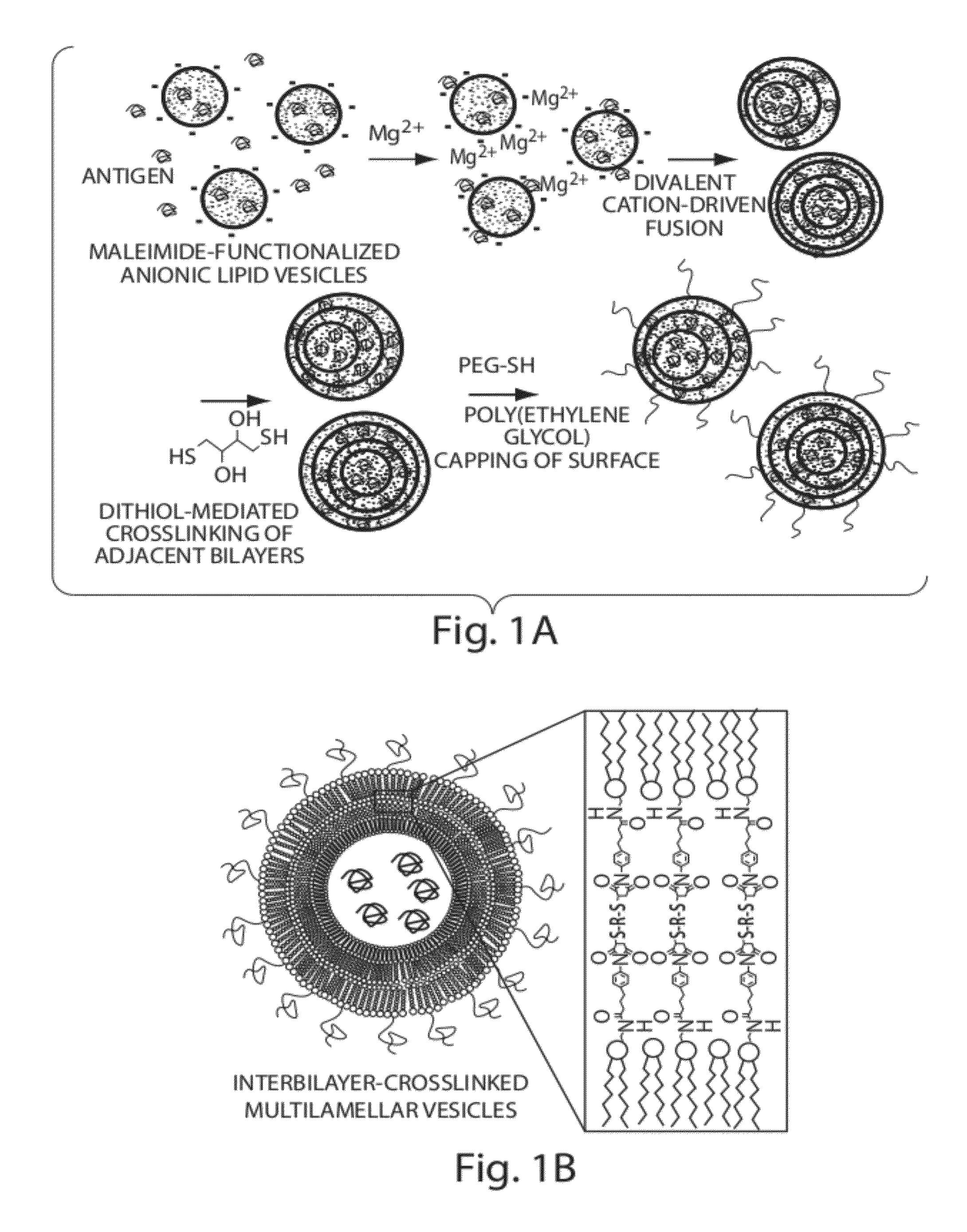
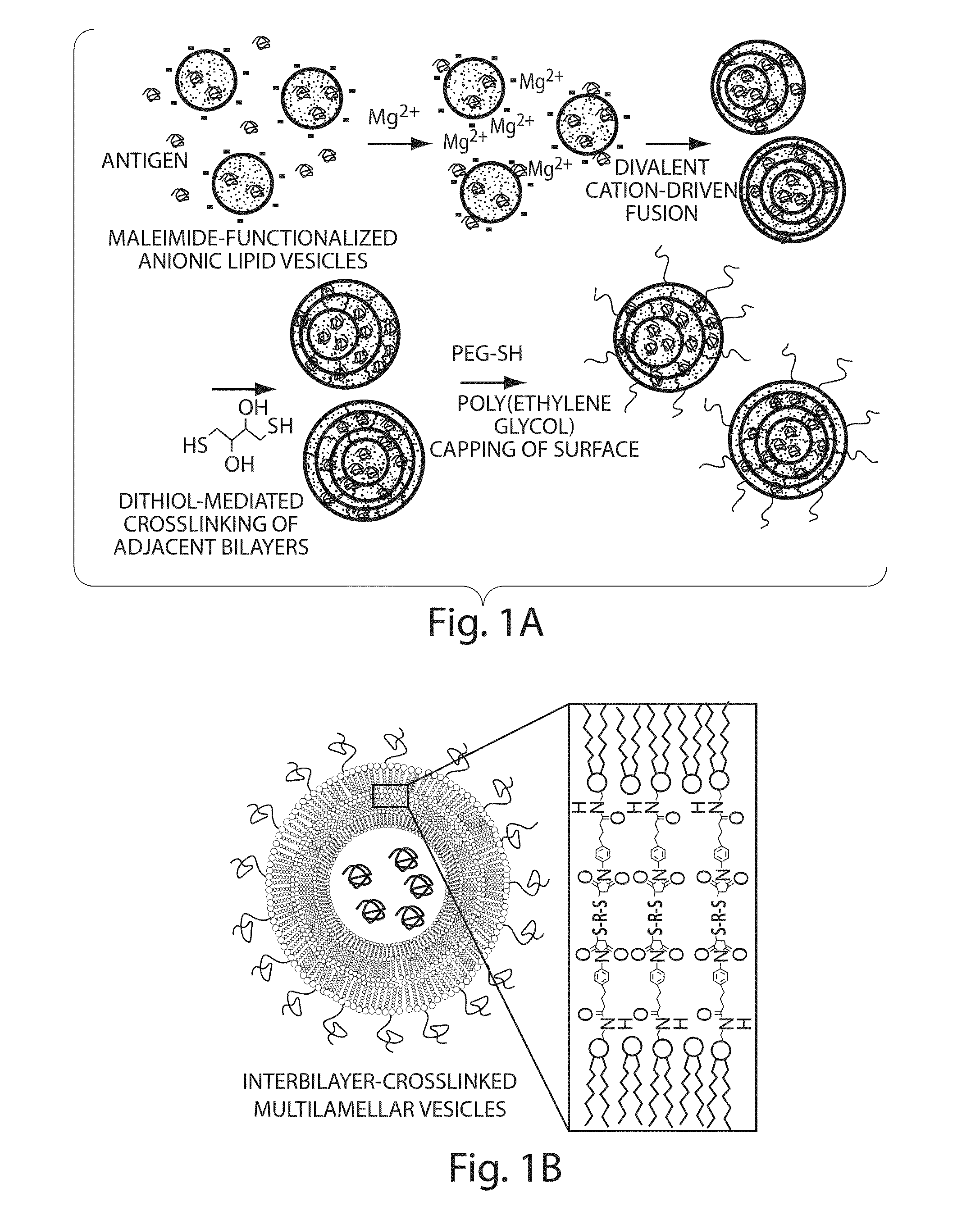
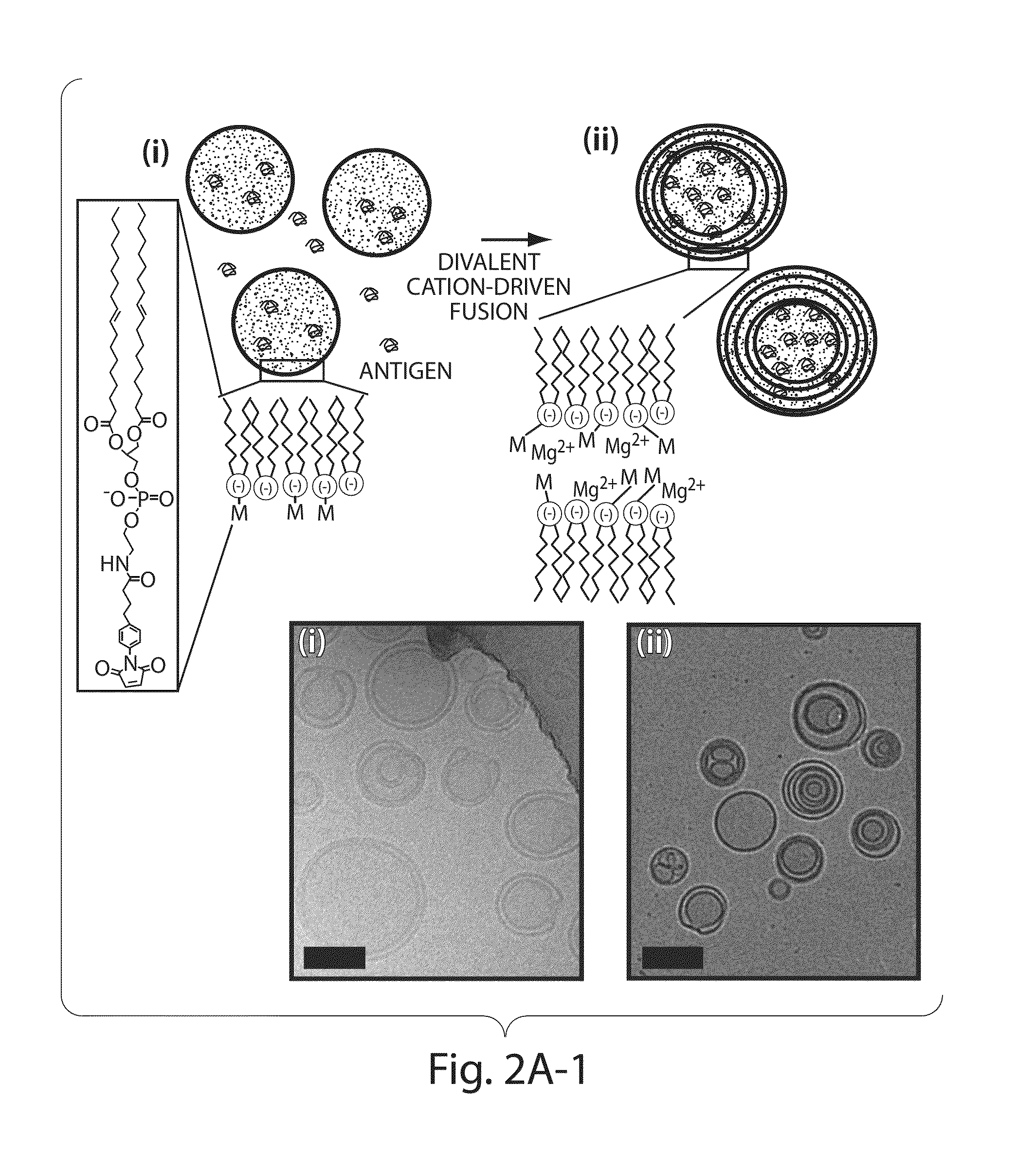
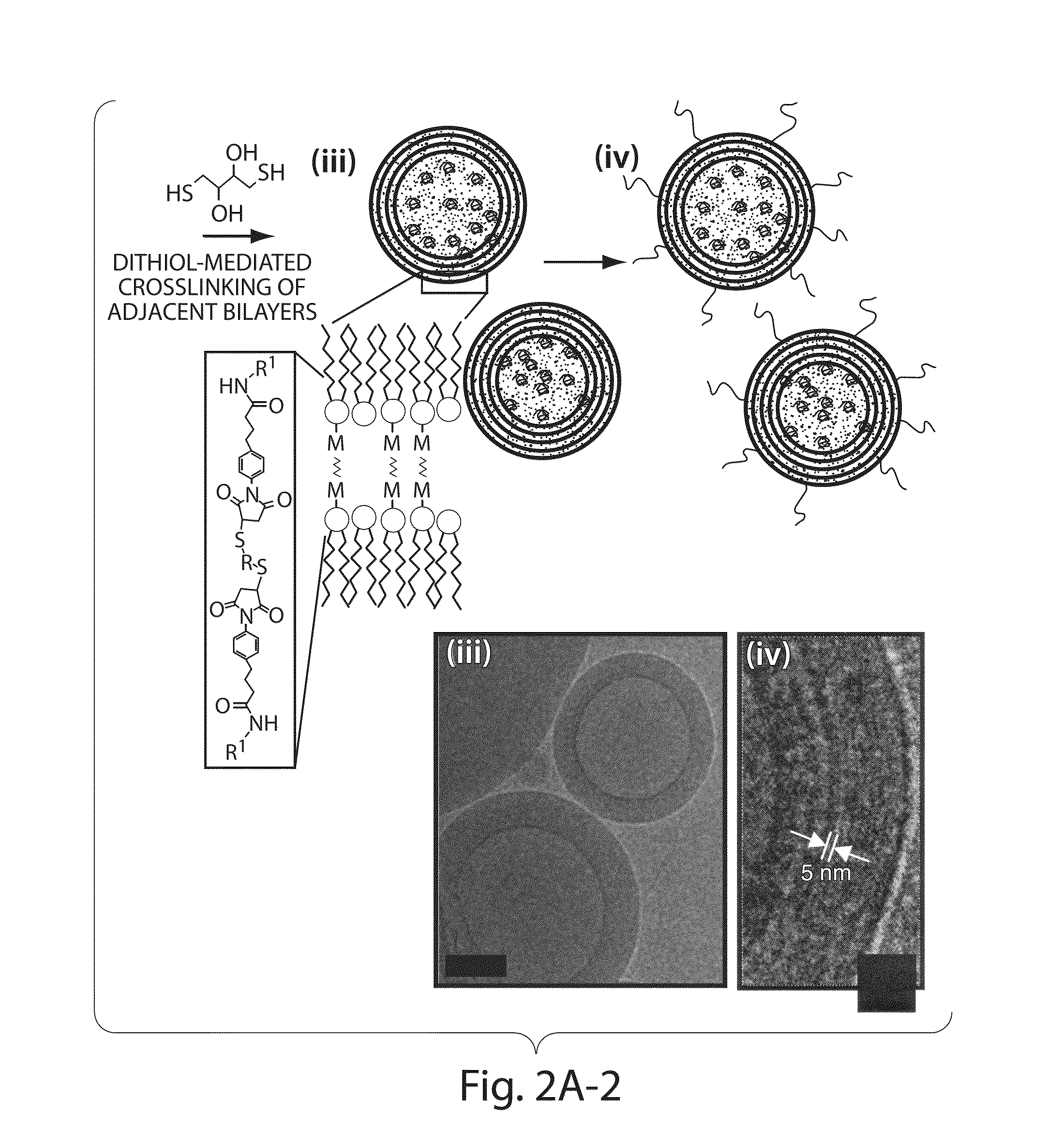
ActiveUS20120177724A1Increase load capacityImprove the level ofPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedAntigenVesicle/vacuole
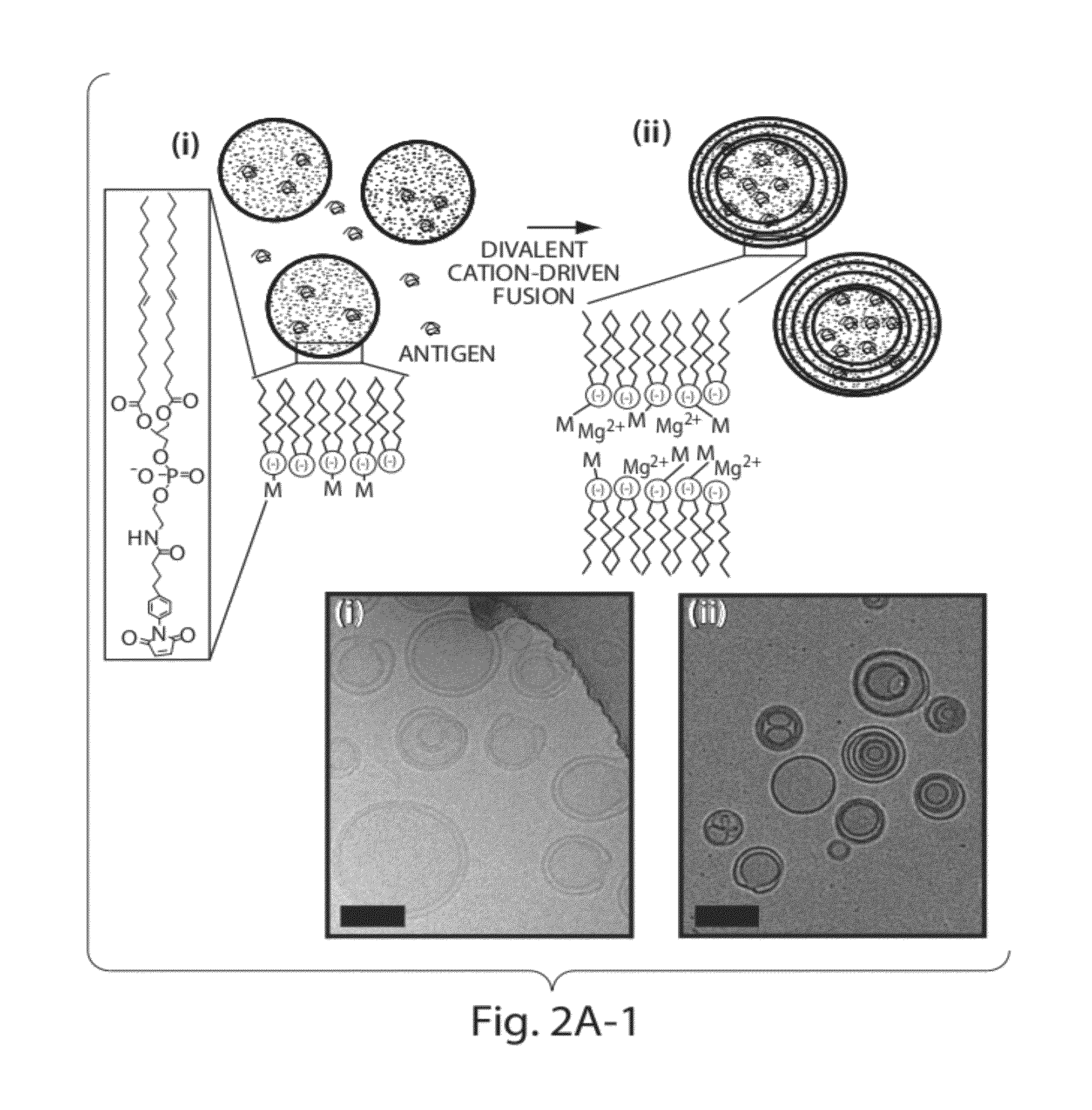
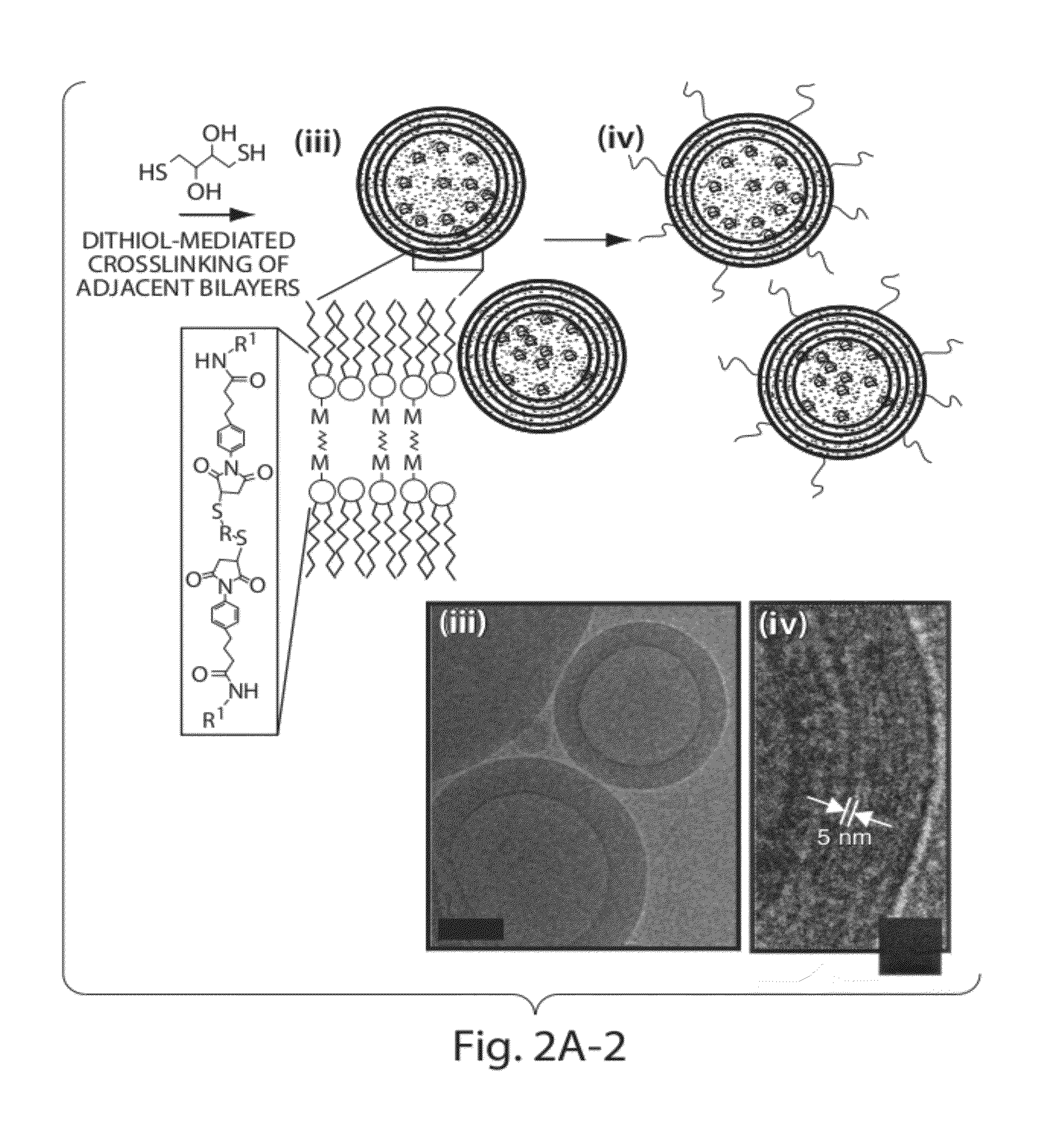
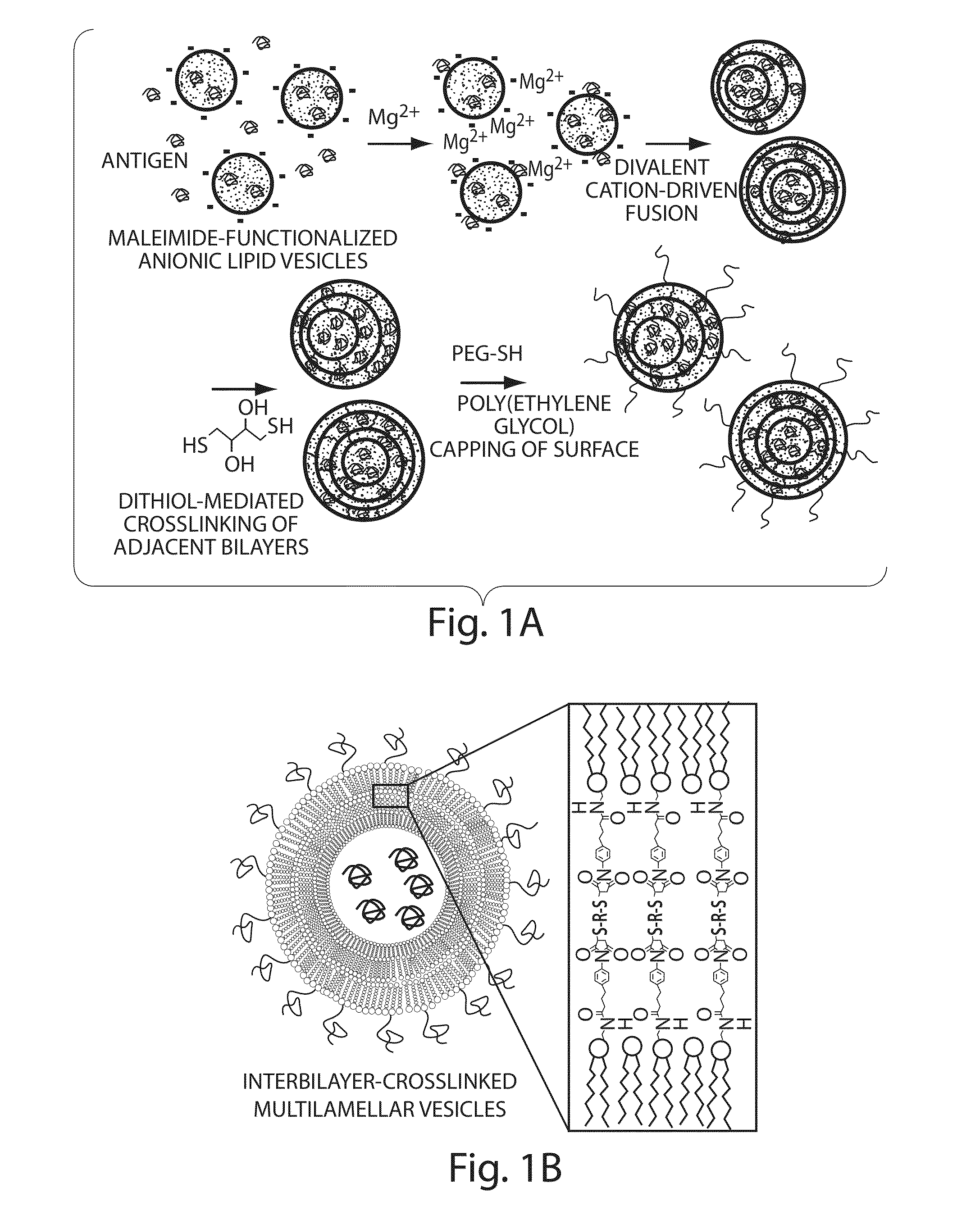
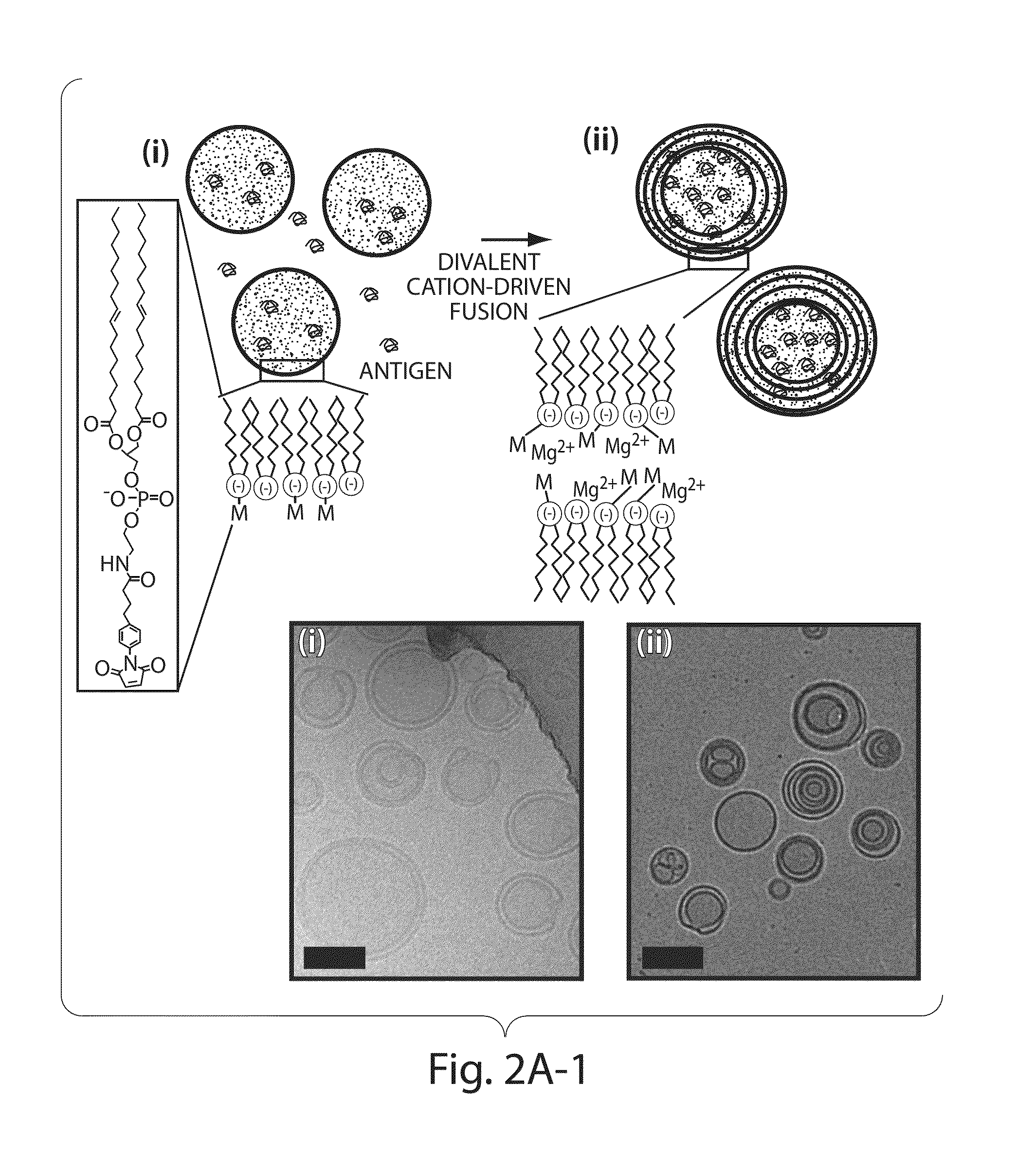
The invention provides delivery systems comprised of stabilized multilamellar vesicles, as well as compositions, methods of synthesis, and methods of use thereof. The stabilized multilamellar vesicles comprise terminal-cysteine-bearing antigens or cysteine-modified antigens, at their surface and / or internally.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Silk microspheres for encapsulation and controlled release
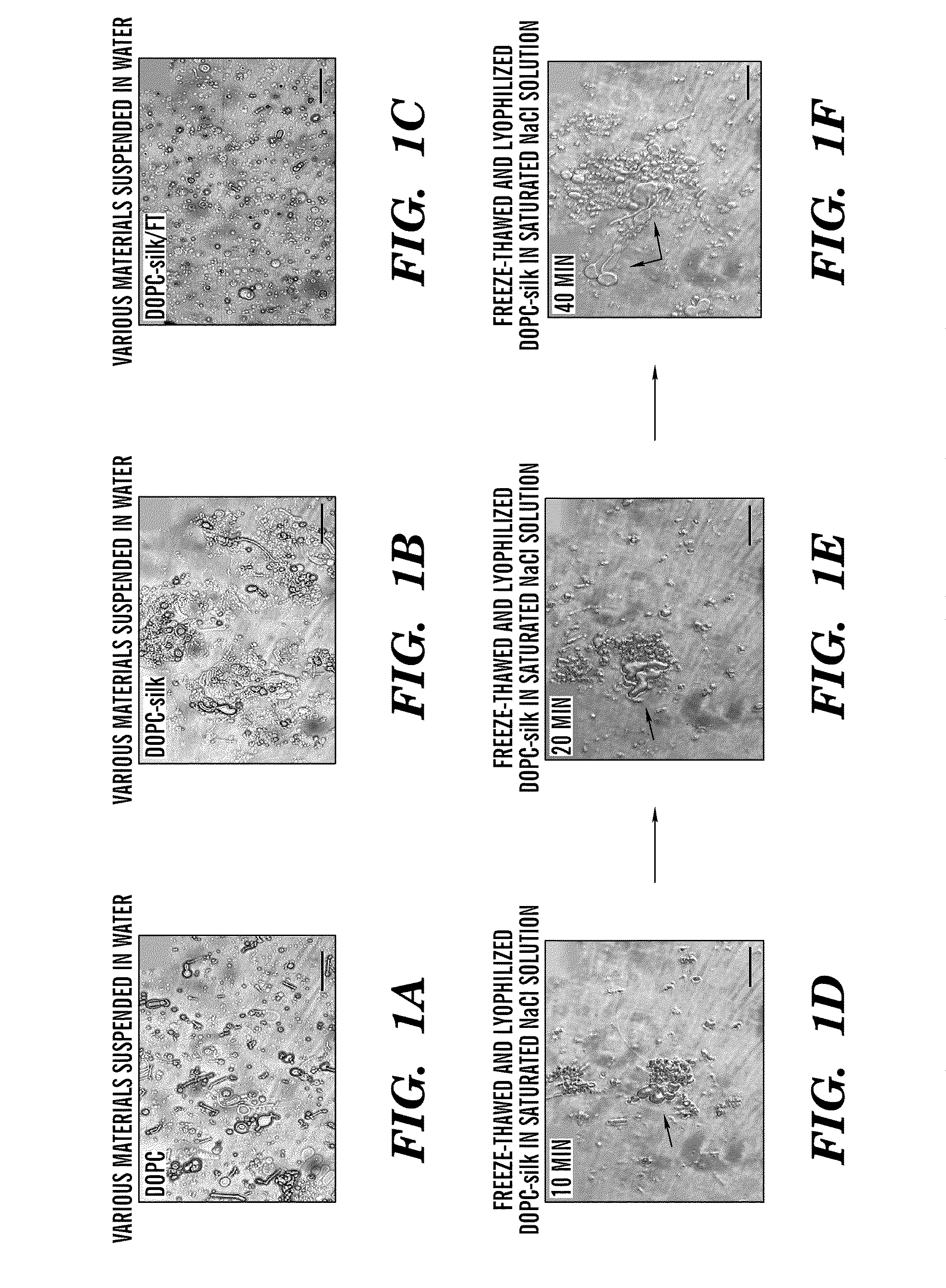
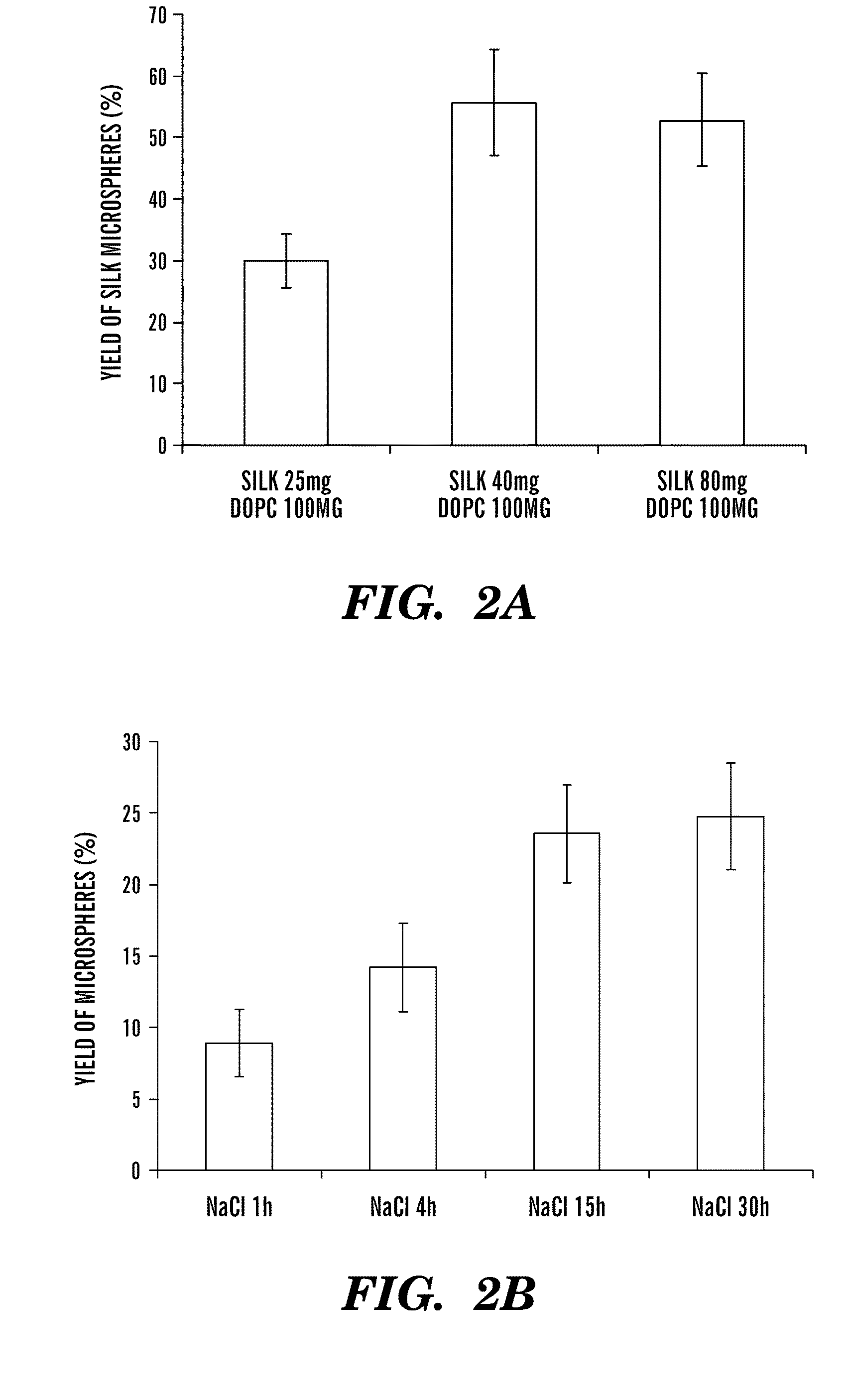
A method was developed to prepare silk fibroin microspheres using lipid vesicles as templates to efficiently load therapeutic agents in active form for controlled release. The lipids are subsequently removed through the use of a dehydration agent, such as methanol or sodium chloride, resulting in β-sheet structure dominant silk microsphere structures having about 2 μm in diameter. The therapeutic agent can be entrapped in the silk microspheres and used in pharmaceutical formulations for controlled-release treatments.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
Peptide/lipid complex formation by co-lyophilization
The invention relates to the formation of peptide / lipid vesicles and complexes through the co-lyophilization of peptides, preferably that are able to adopt an amphipathic alphahelical conformation, and one or more lipids. A single solution which solubilizes both the peptides and lipids or two separate solutions may be lyophilized.
Owner:ESPERION THERAPEUTICS
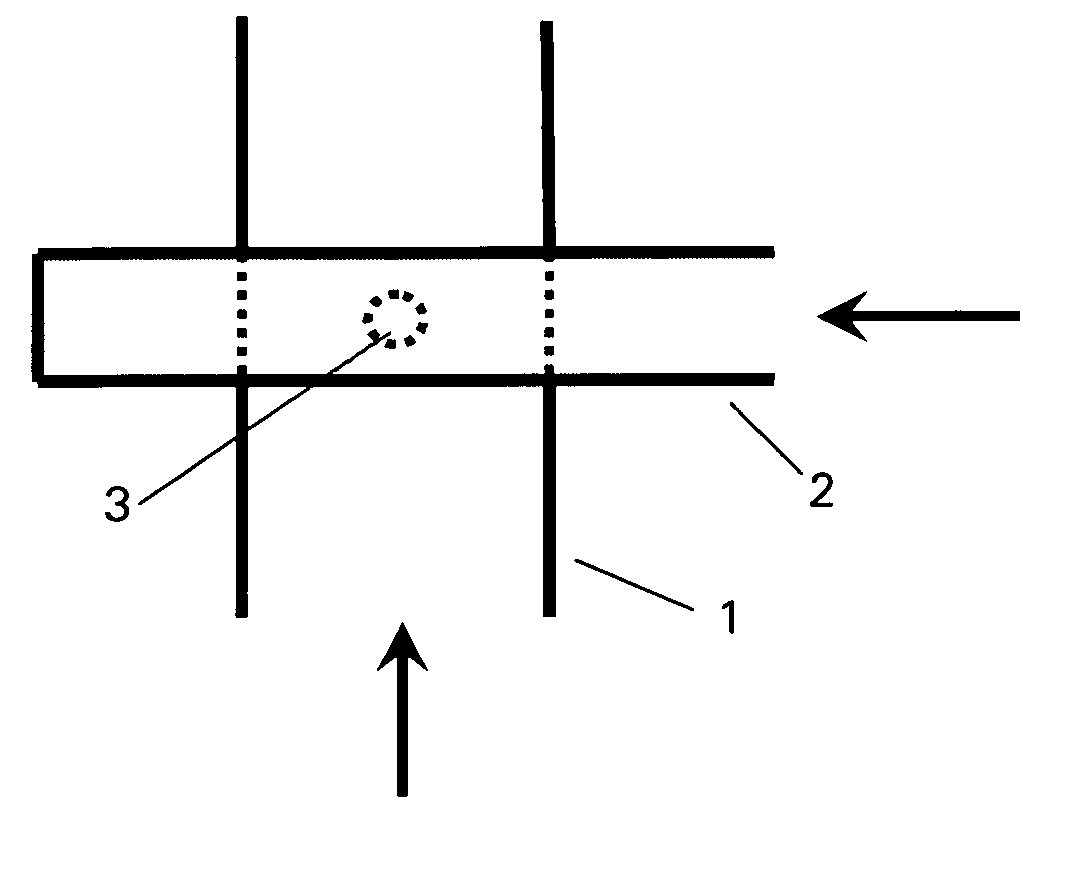
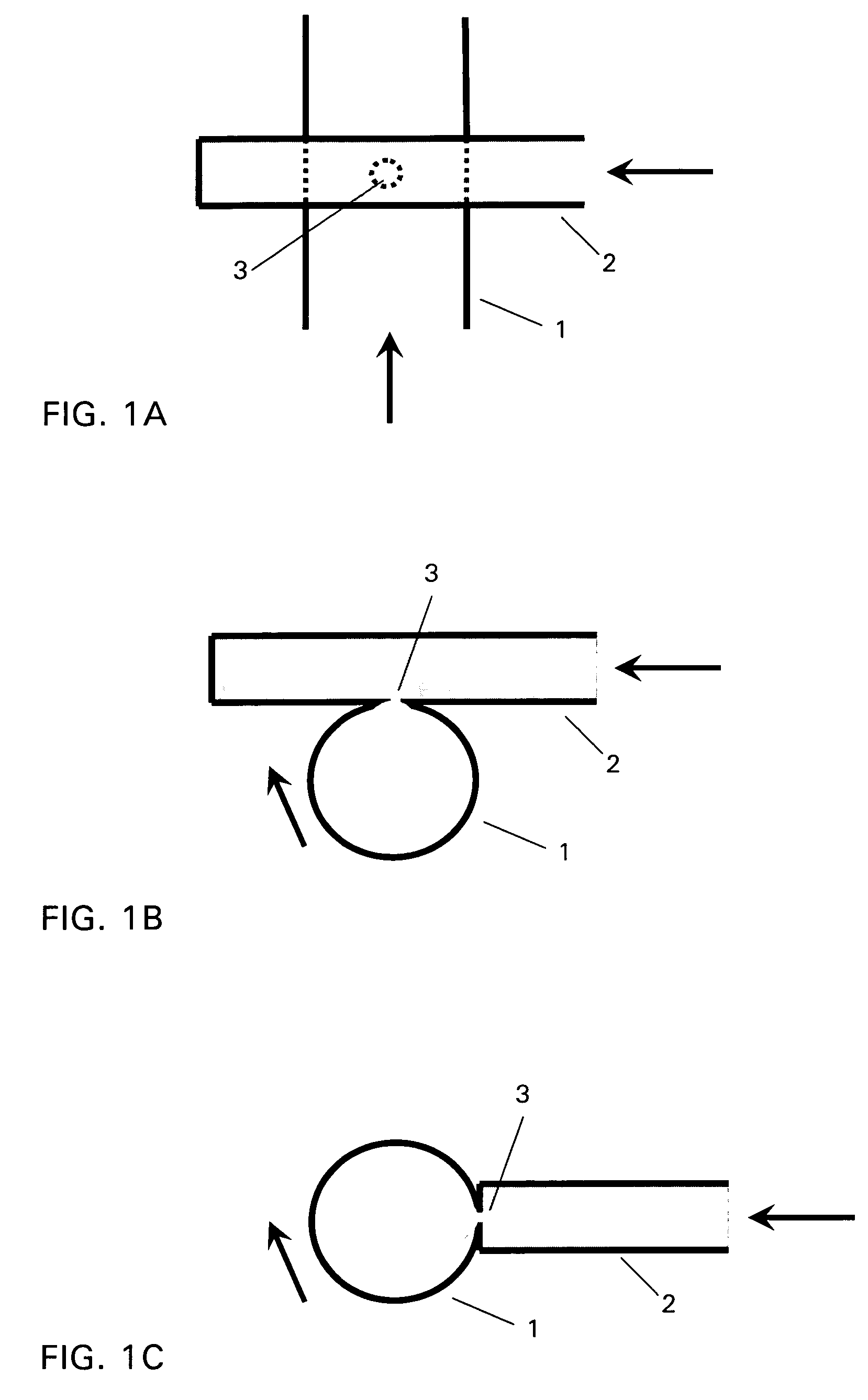
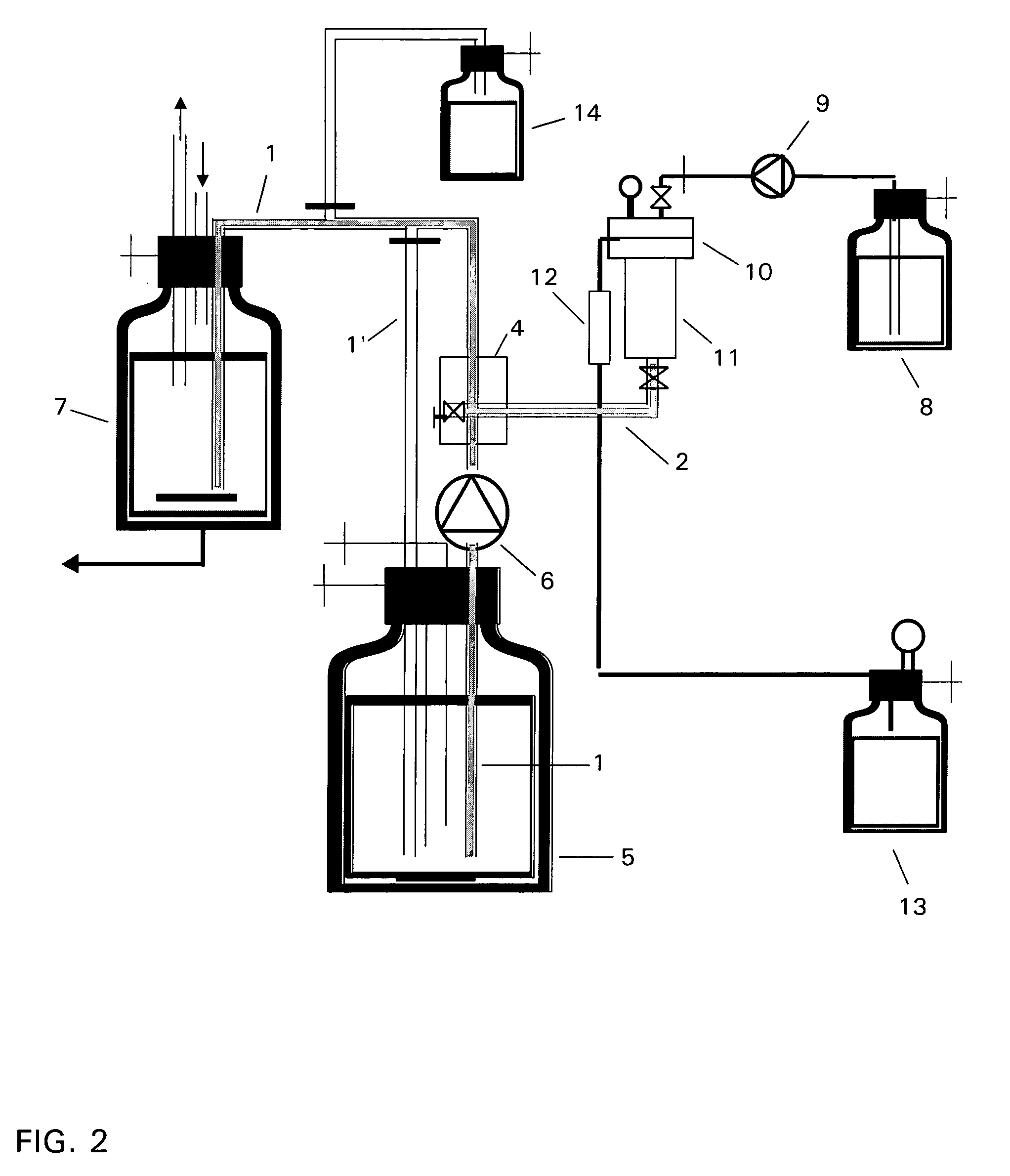
Method and device for producing lipid vesicles
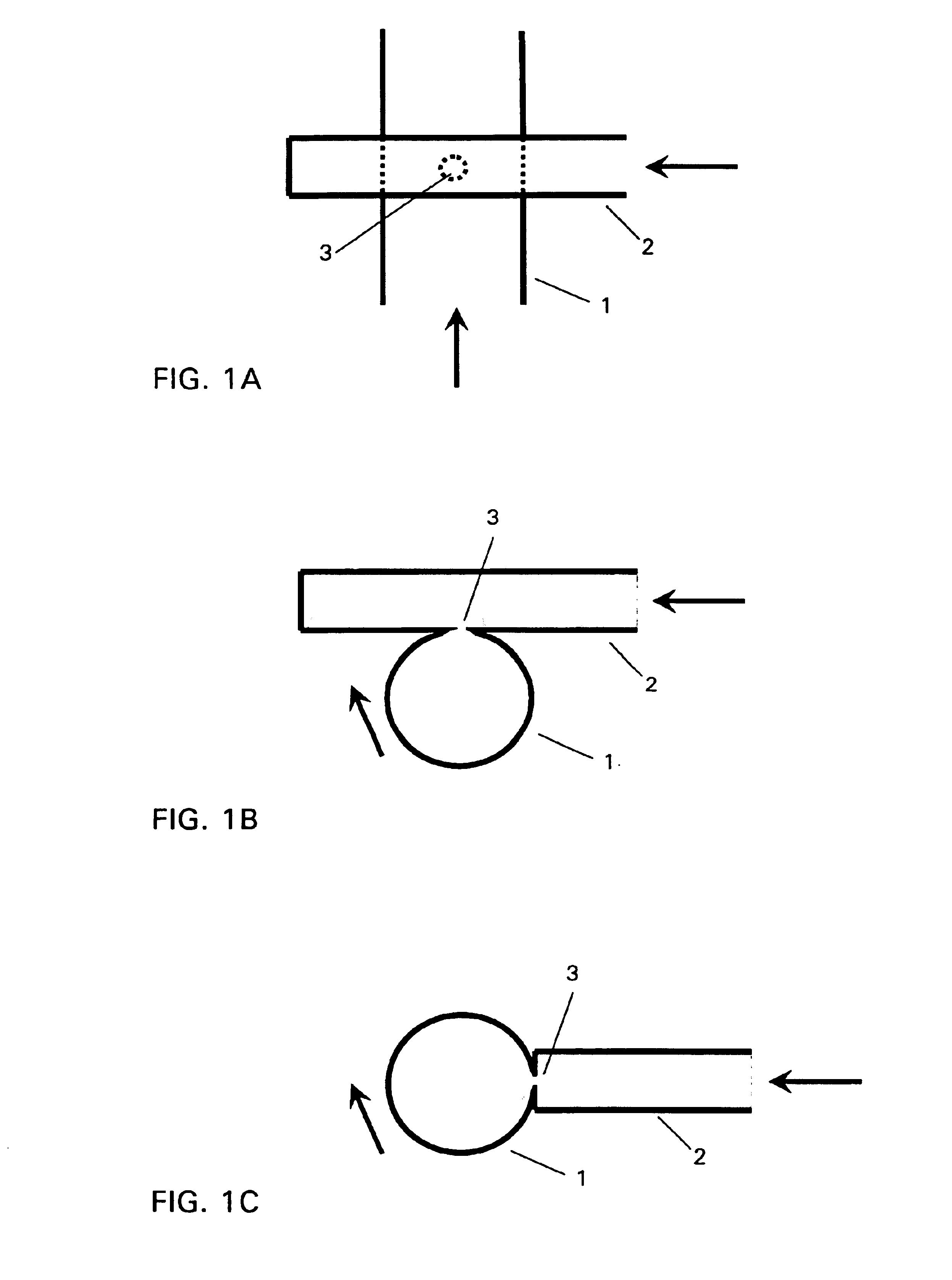
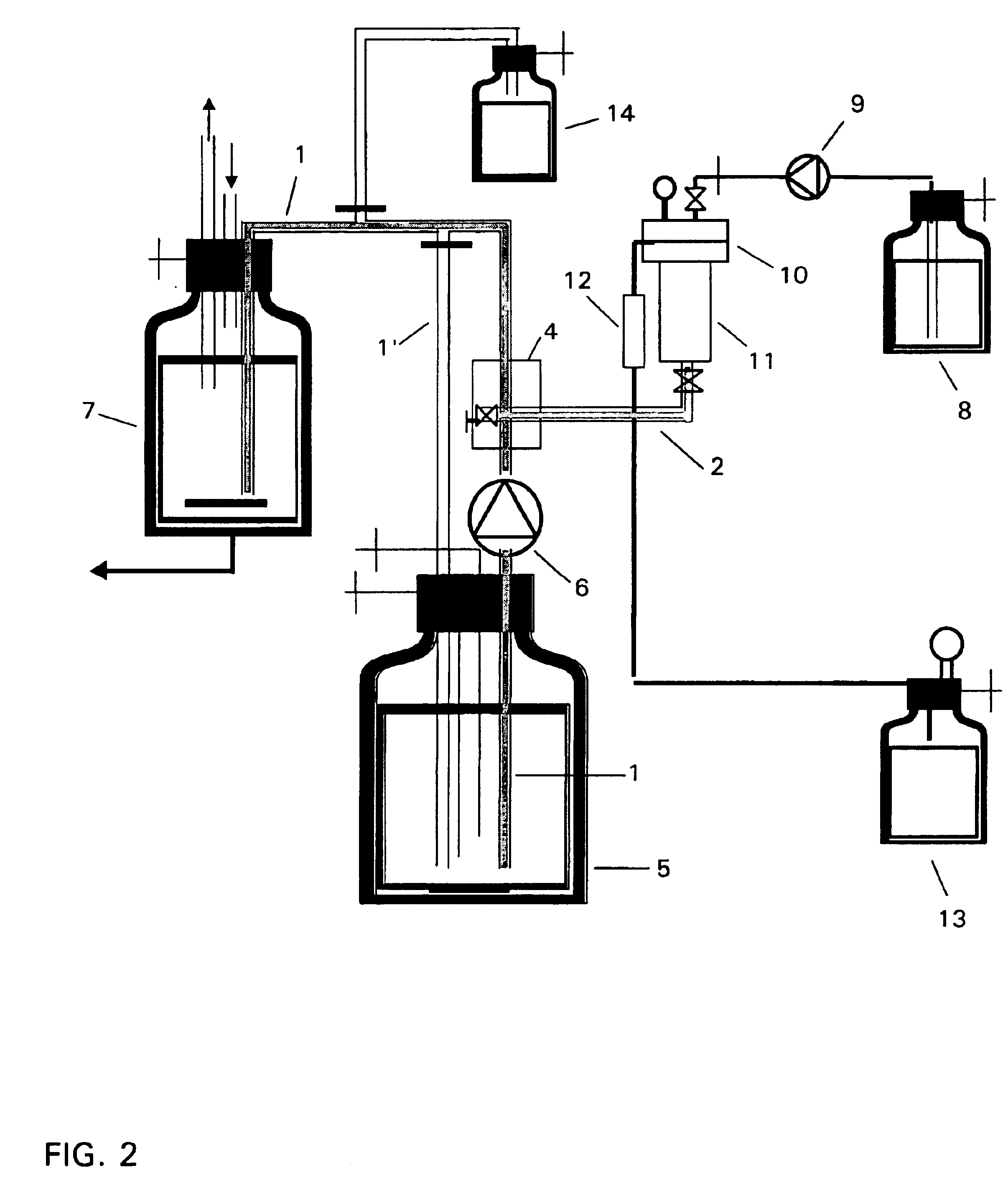
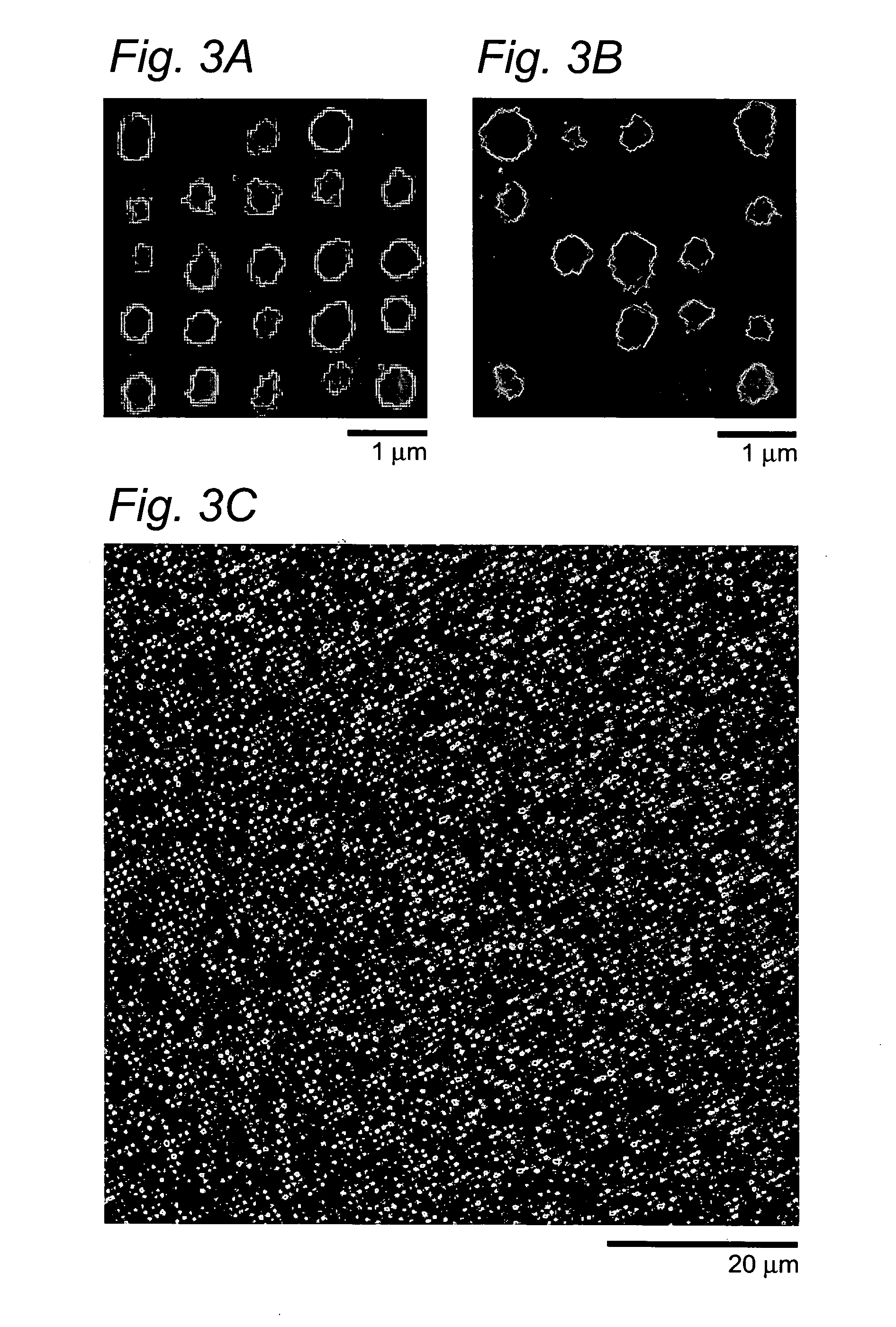
InactiveUS6843942B2Little eddy formationImprove stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsLipid formationEngineering
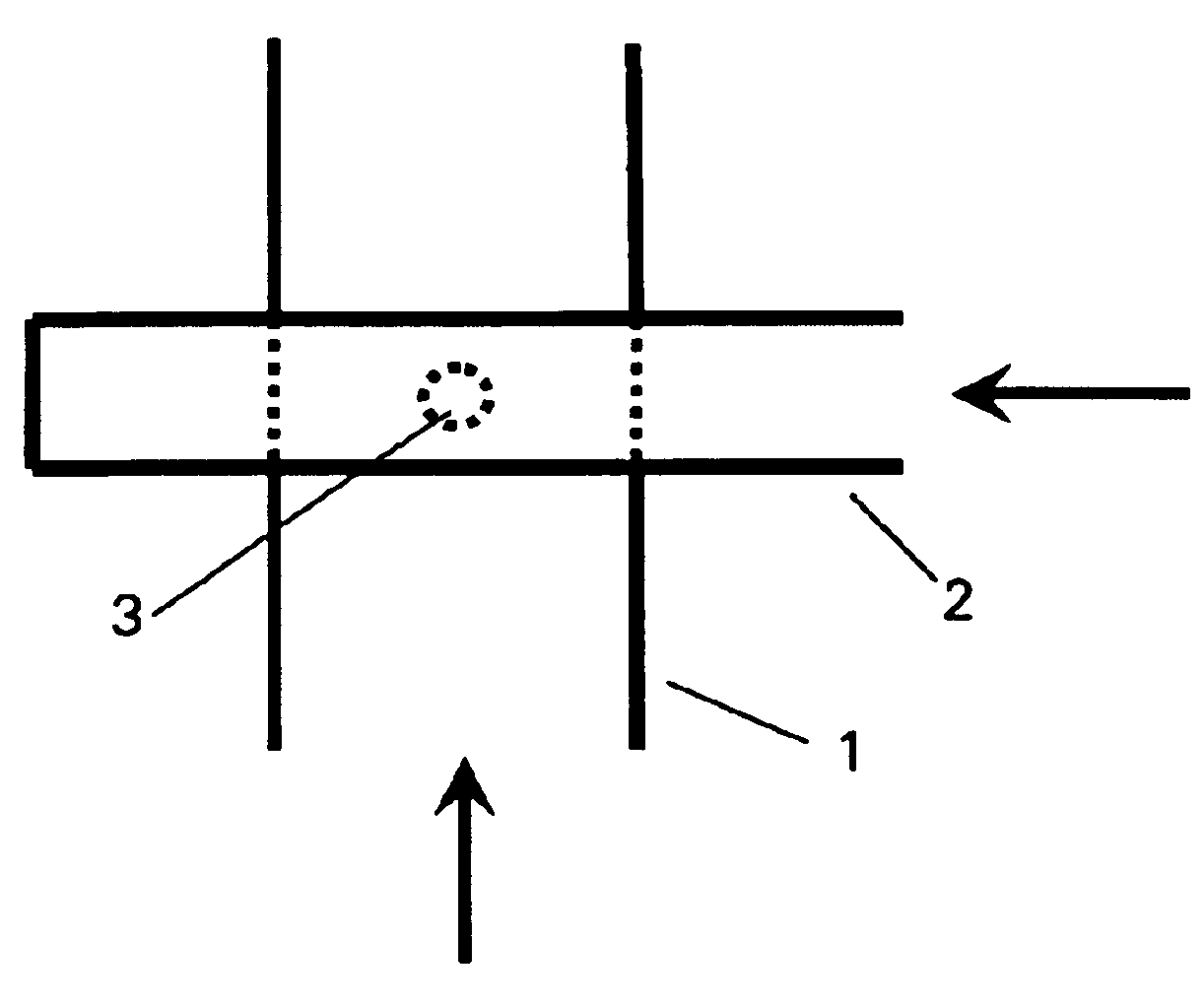
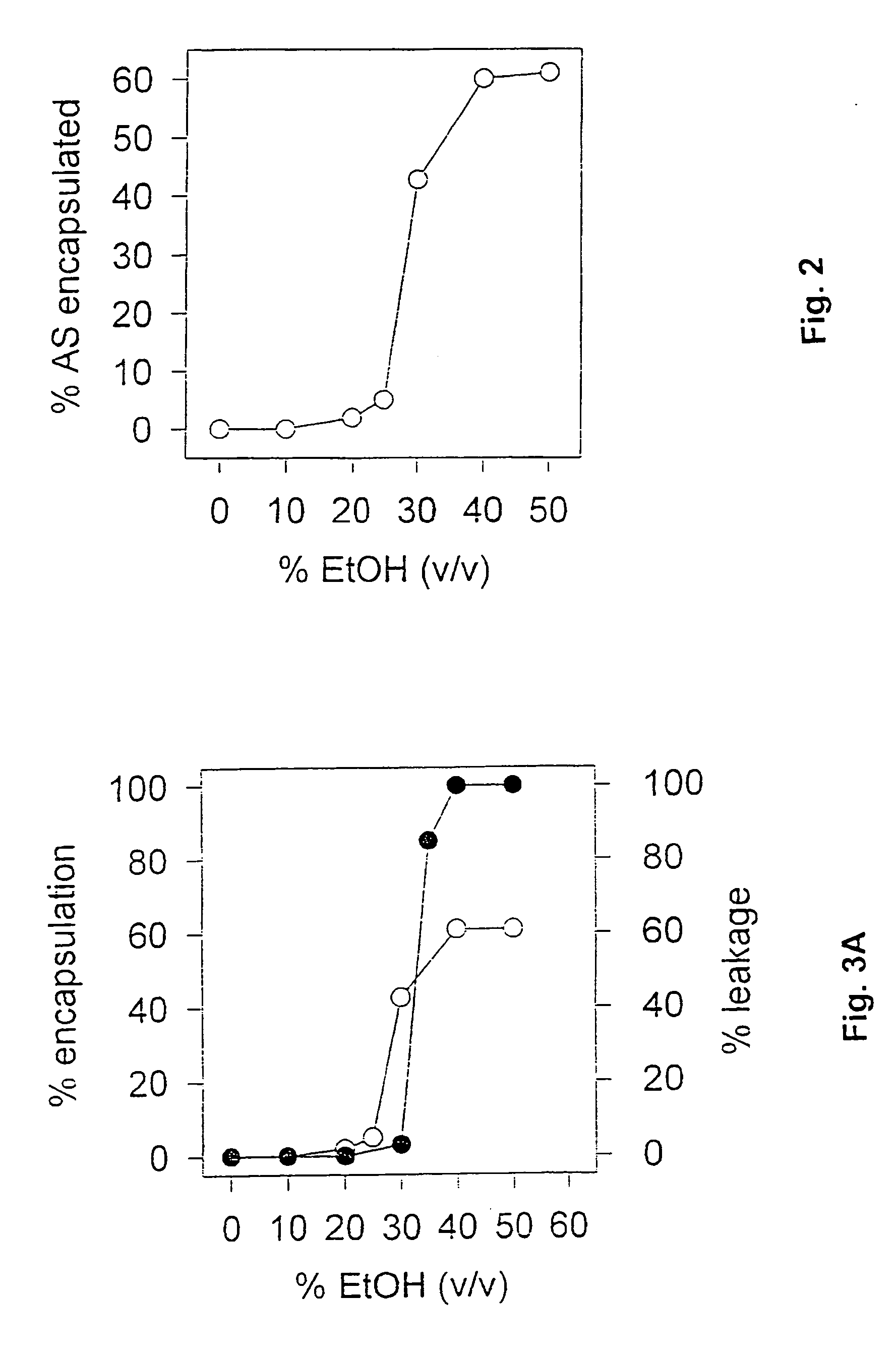
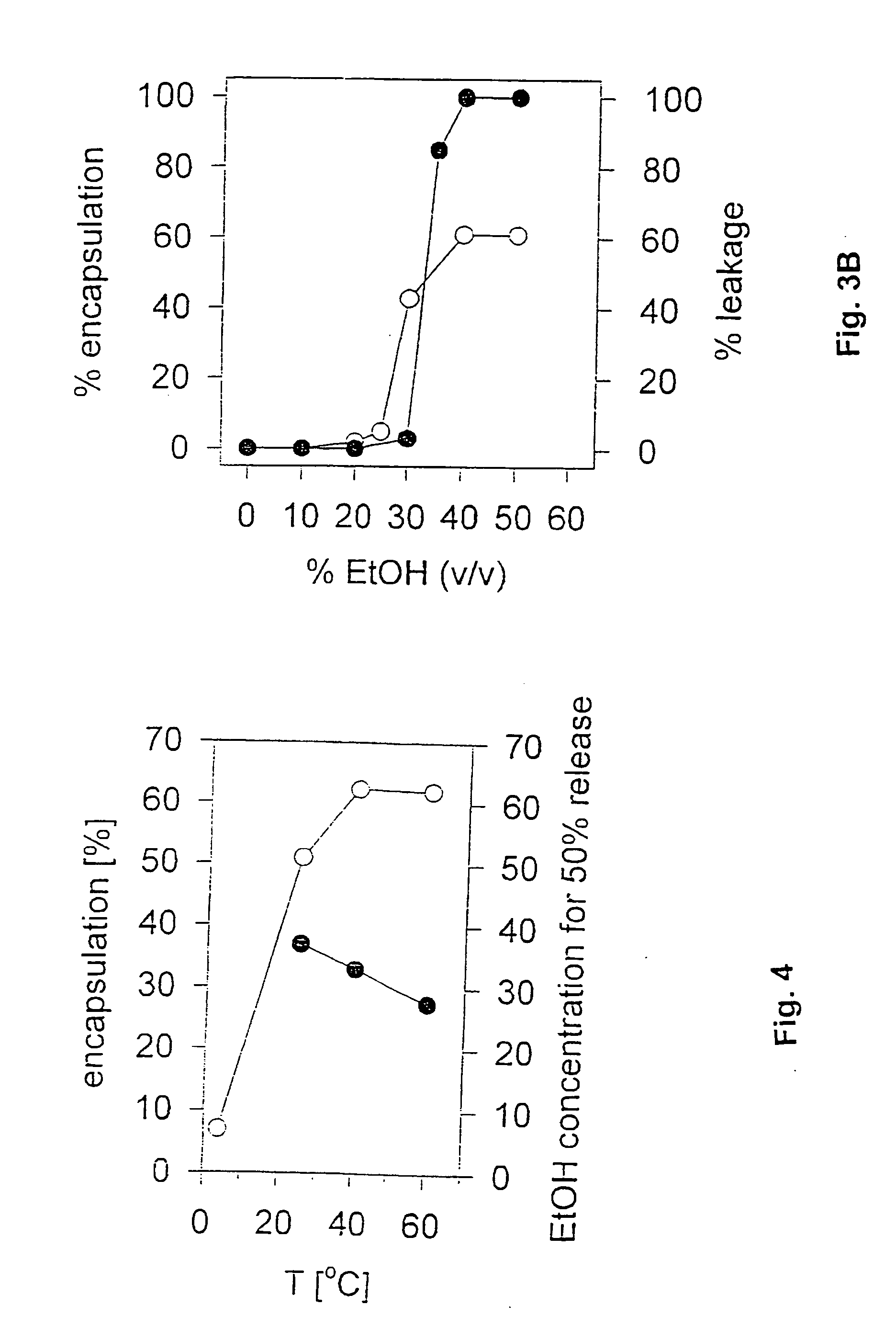
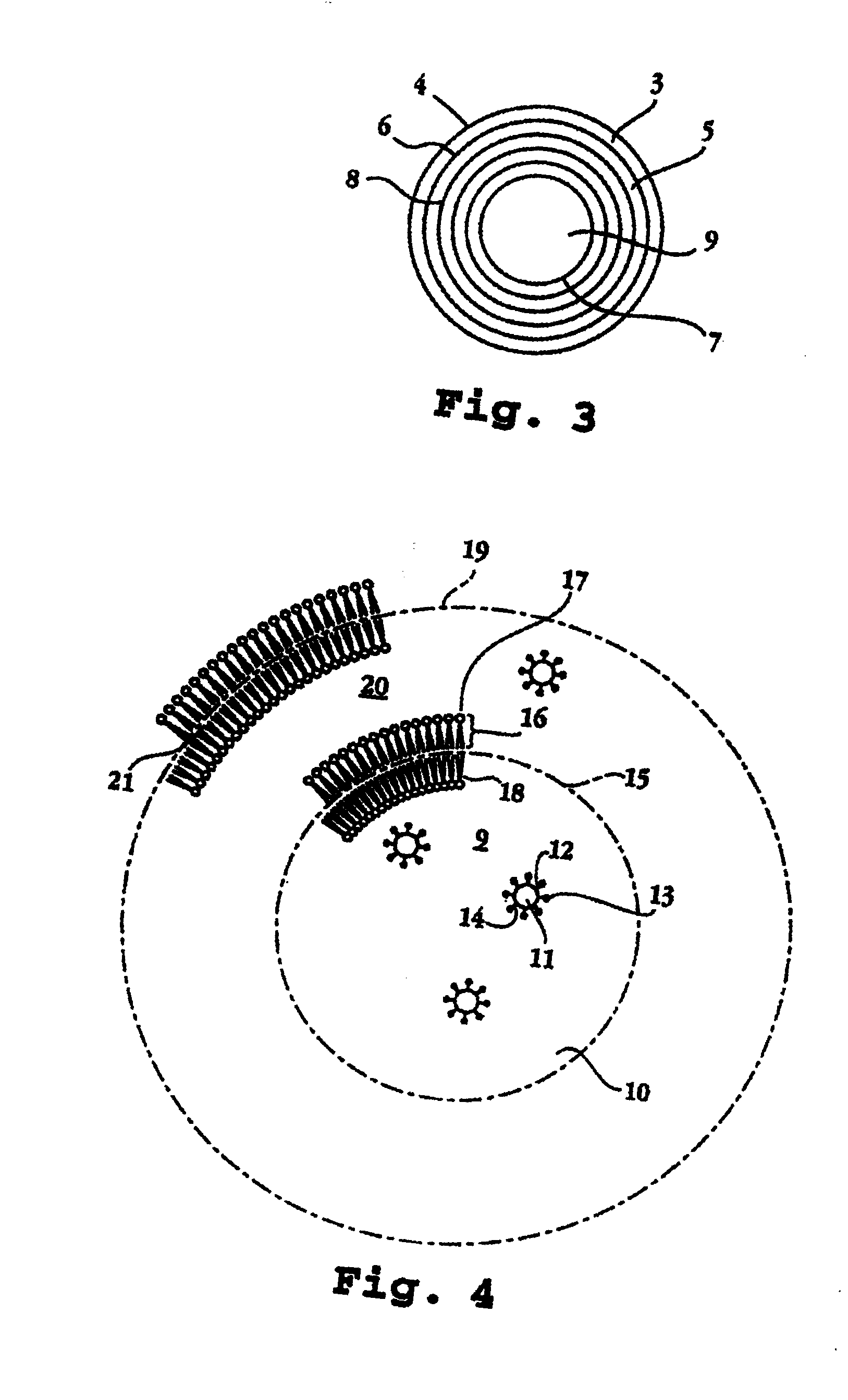
The invention relates to a device for producing lipid vesicles, which is equipped with a line (1) for transporting a polar liquid phase, with a line (2) for transporting an organic liquid phase containing lipids, with a collecting receptacle (7) for accommodating produced lipid vesicles, and with means for conveying the liquid phases through lines (1) and (2). At at least one location, the outer side of line (1) forms a common contact surface with line (2) inside of which a common opening (3) is provided that permits the flow of liquid and joins the inside of line (2) to the inside of line (1). Lines (1) and (2) do not contain agitating or dispersing aids in the area of the opening (3). The invention also relates to a method for the careful production of lipid vesicles, wherein the lipid phase is sprayed under pressure perpendicular to the direction of flow of the polar phase and into the same, whereupon lipid vesicles having a narrow size distribution form spontaneously and without the action of mechanical agitating or dispersing aids.
Owner:POLYMUN SCI IMMUNBIOLOGISCHE FORSCHUNG
Lipid-encapsulated polyanionic nucleic acid
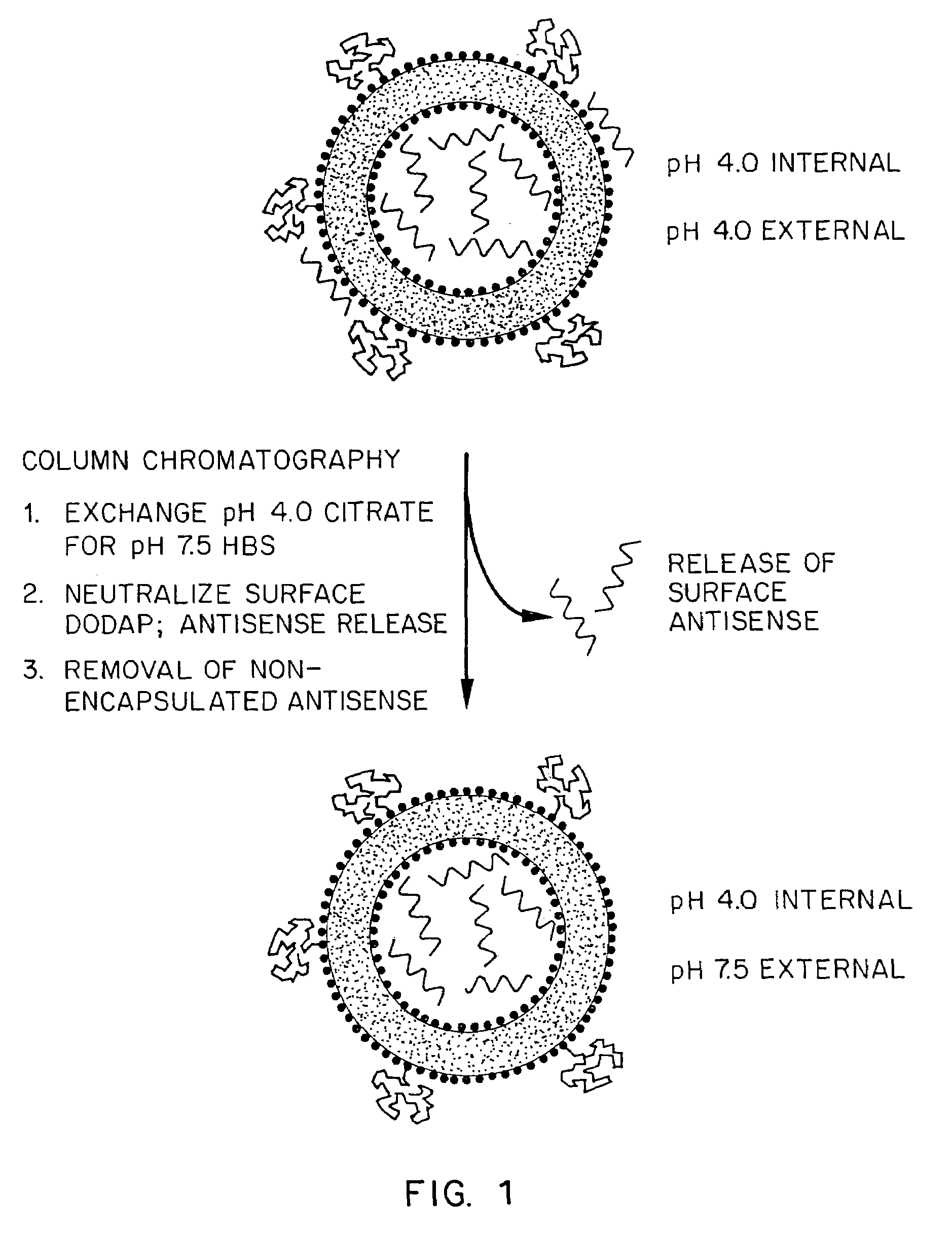
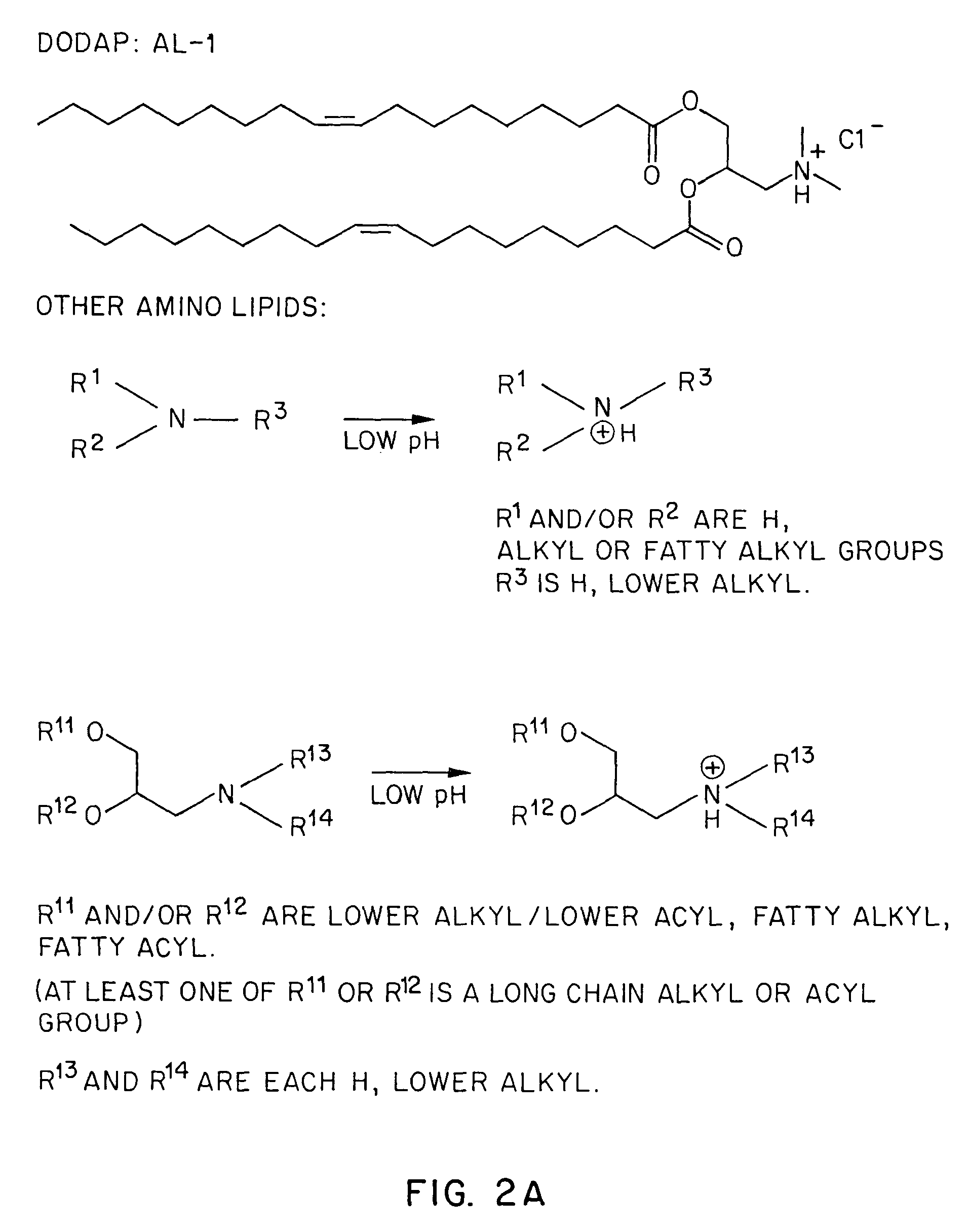
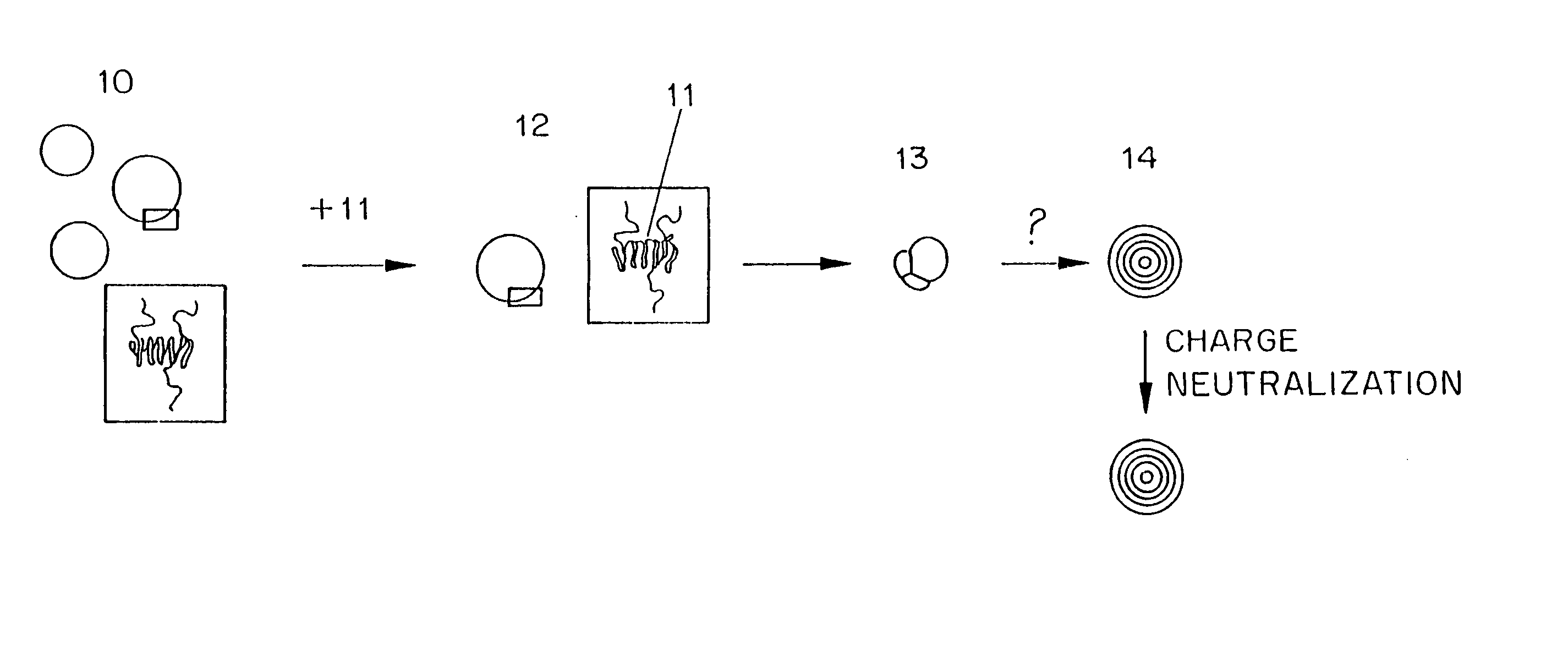
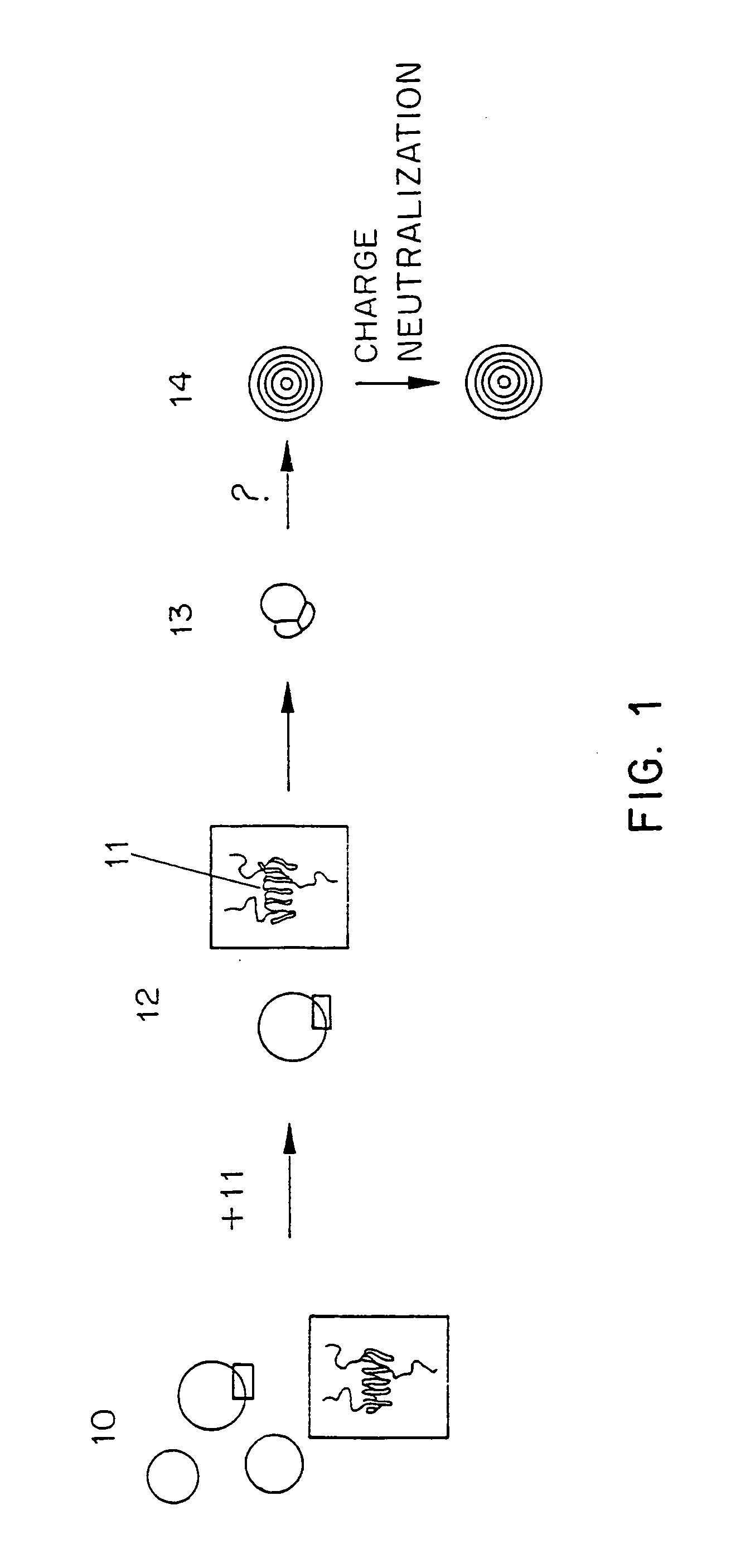
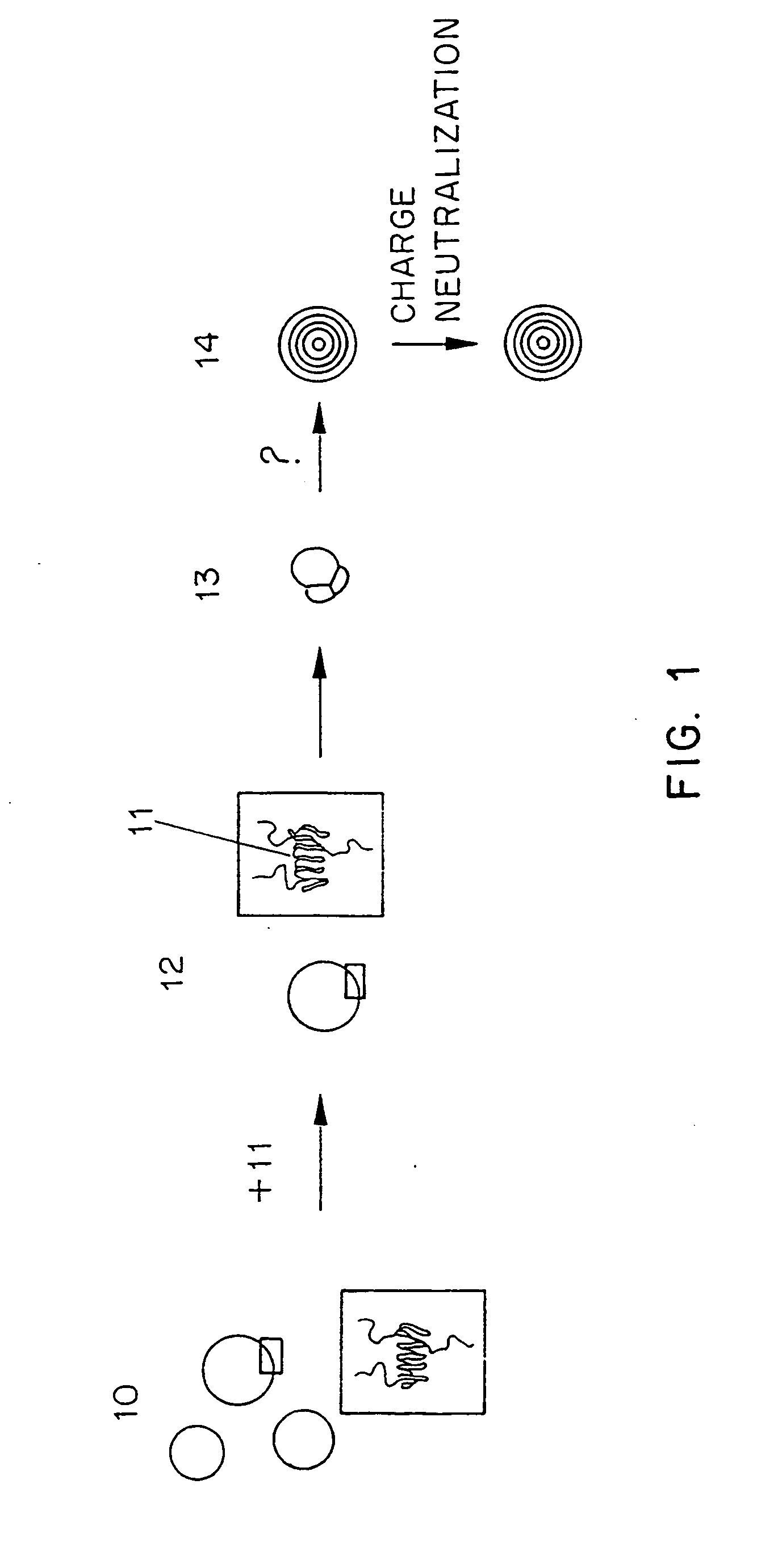
Methods for the preparation of a lipid-nucleic acid composition are provided. According to the methods, a mixture of lipids containing a protonatable or deprotonatable lipid, for example an amino lipid and a lipid such as a PEG- or Polyamide oligomer-modified lipid is combined with a buffered aqueous solution of a charged therapeutic agent, for example polyanionic nucleic acids, to produce particles in which the therapeutic agent is encapsulated in a lipid vesicle. Surface charges on the lipid particles are at least partially neutralized to provide surface-neutralized lipid-encapsulated compositions of the therapeutic agents. The method permits the preparation of compositions with high ratios of therapeutic agent to lipid and with encapsulation efficiencies in excess of 50%.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Collagen Formulations for Improved Skin Care
InactiveUS20090169615A1Optimized formulaGood for healthCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationMedicine
Compositions and methods for administering collagen to a human subject have been developed. The collagen-containing lipid vesicles of the invention provide a delivery system for human collagen which eliminates problems associated with chemical and physical instability of the collagen as well as immune responses to non-human collagen.
Owner:PINSKY MARK A
Peptide/lipid complex formation by co-lyophilization
The invention relates to the formation of peptide / lipid vesicles and complexes through the co-lyophilization of peptides, preferably that are able to adopt an amphipathic alphahelical conformation, and one or more lipids. A single solution which solubilizes both the peptides and lipids or two separate solutions may be lyophilized.
Owner:DASSEUX JEAN LOUIS
Method and device for producing lipid vesicles
InactiveUS20040032037A1Little eddy formationImprove stabilityLiposomal deliveryThin material handlingLipid formationLine tubing
The invention relates to a device for producing lipid vesicles, which is equipped with a line (1) for transporting a polar liquid phase, with a line (2) for transporting an organic liquid phase containing lipids, with a collecting receptacle (7) for accommodating produced lipid vesicles, and with means for conveying the liquid phases through lines (1) and (2). At at least one location, the outer side of line (1) forms a common contact surface with line (2) inside of which a common opening (3) is provided that permits the flow of liquid and joins the inside of line (2) to the inside of line (1). Lines (1) and (2) do not contain agitating or dispersing aids in the area of the opening (3). The invention also relates to a method for the careful production of lipid vesicles, wherein the lipid phase is sprayed under pressure perpendicular to the direction of flow of the polar phase and into the same, whereupon lipid vesicles having a narrow size distribution form spontaneously and without the action of mechanical agitating or dispersing aids.
Owner:POLYMUN SCI IMMUNBIOLOGISCHE FORSCHUNG
Lipid vesicle compositions and methods of use
ActiveUS20110229529A1Increase load capacityLong release profileOrganic active ingredientsVirusesDiagnostic agentVesicle/vacuole
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods for preparation of lipid-encapsulated therapeutic agents
InactiveUS7094423B1Efficient formationOrganic active ingredientsDrug compositionsLipid formationSolvent
Fully lipid-encapsulated therapeutic agent particles of a charged therapeutic agent are prepared by combining a lipid composition containing preformed lipid vesicles, a charged therapeutic agent, and a destabilizing agent to form a mixture of preformed vesicles and therapeutic agent in a destabilizing solvent. The destabilizing solvent is effective to destabilize the membrane of the preformed lipid vesicles without disrupting the vesicles. The resulting mixture is incubated for a period of time sufficient to allow the encapsulation of the therapeutic agent within the preformed lipid vesicles. The destabilizing agent is then removed to yield fully lipid-encapsulated therapeutic agent particles. The preformed lipid vesicles comprise a charged lipid which has a charge which is opposite to the charge of the charged therapeutic agent and a modified lipid having a steric barrier moiety for control of aggregation.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
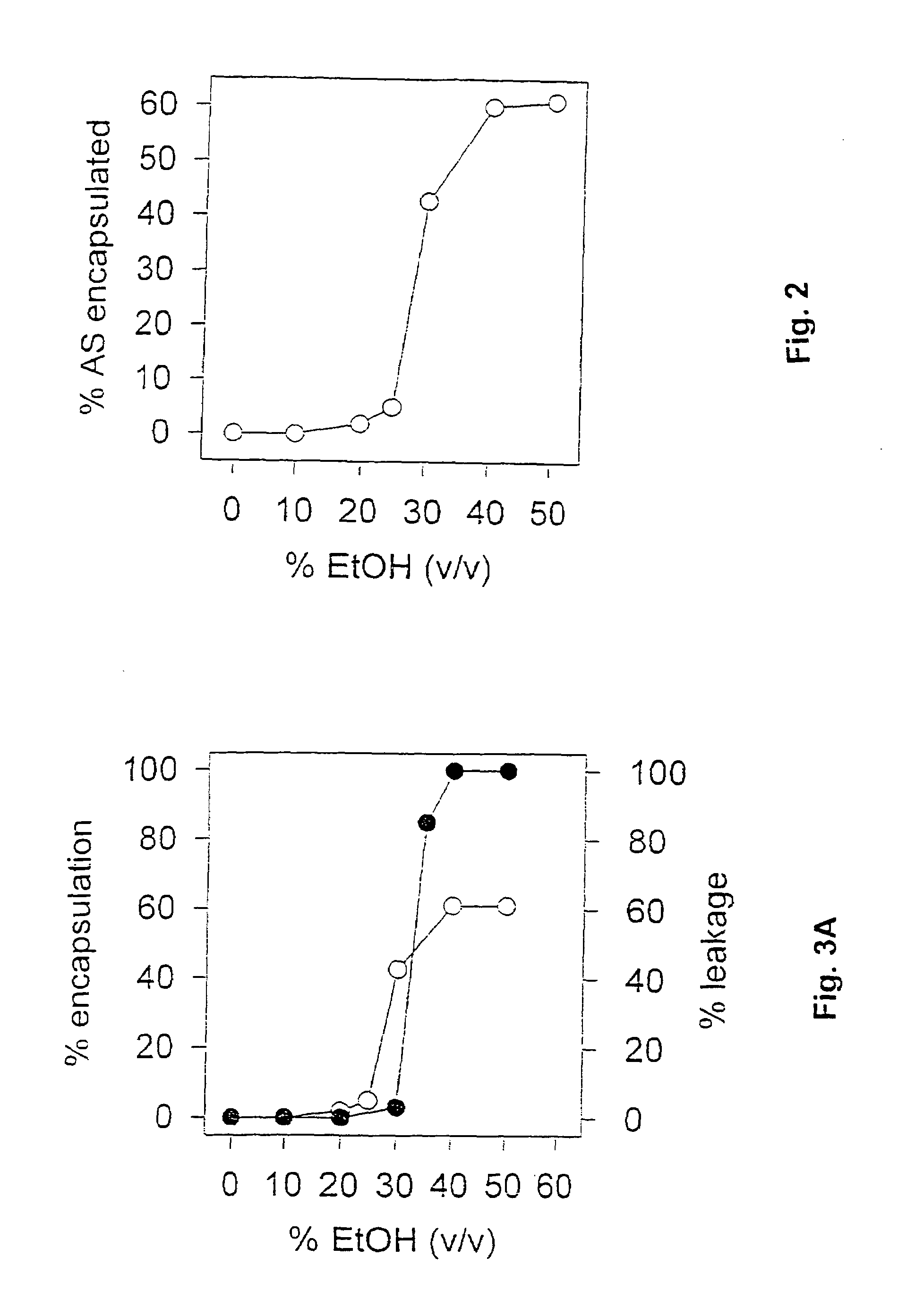
Transformation of drug cyclodextrin complex compositions into compositions of mixtures of lipid vesicle encapsulated drug and cyclodextrin drug complexes
InactiveUS20140220112A1Cost efficiencyReduce the amount requiredBiocideTetrapeptide ingredientsLipid formationMedication injection
Sparingly water-soluble agents can be formulated as cyclodextrin complexes, however, these water-soluble drug-cyclodextrin complexes dissociate when the complex is administered into patients. The dilution of the complex in the patient leads to the drug being released from the complex, so the drug is not effectively targeted. In contrast, drugs encapsulated in the aqueous core of a lipid vesicles are not released when the liposome is diluted in blood. This invention describes compositions and methods whereby cyclodextrin or polyanionic beta-cyclodextrin drug-complexes are mixed with a preformed liposome containing the amine salts of an acidic compound. This results in the drug cyclodextrin complex being transferred into the liposome where it is stably retained. The liposome-encapsulated drug can then be injected into a patient.
Owner:ZONEONE PHARMA
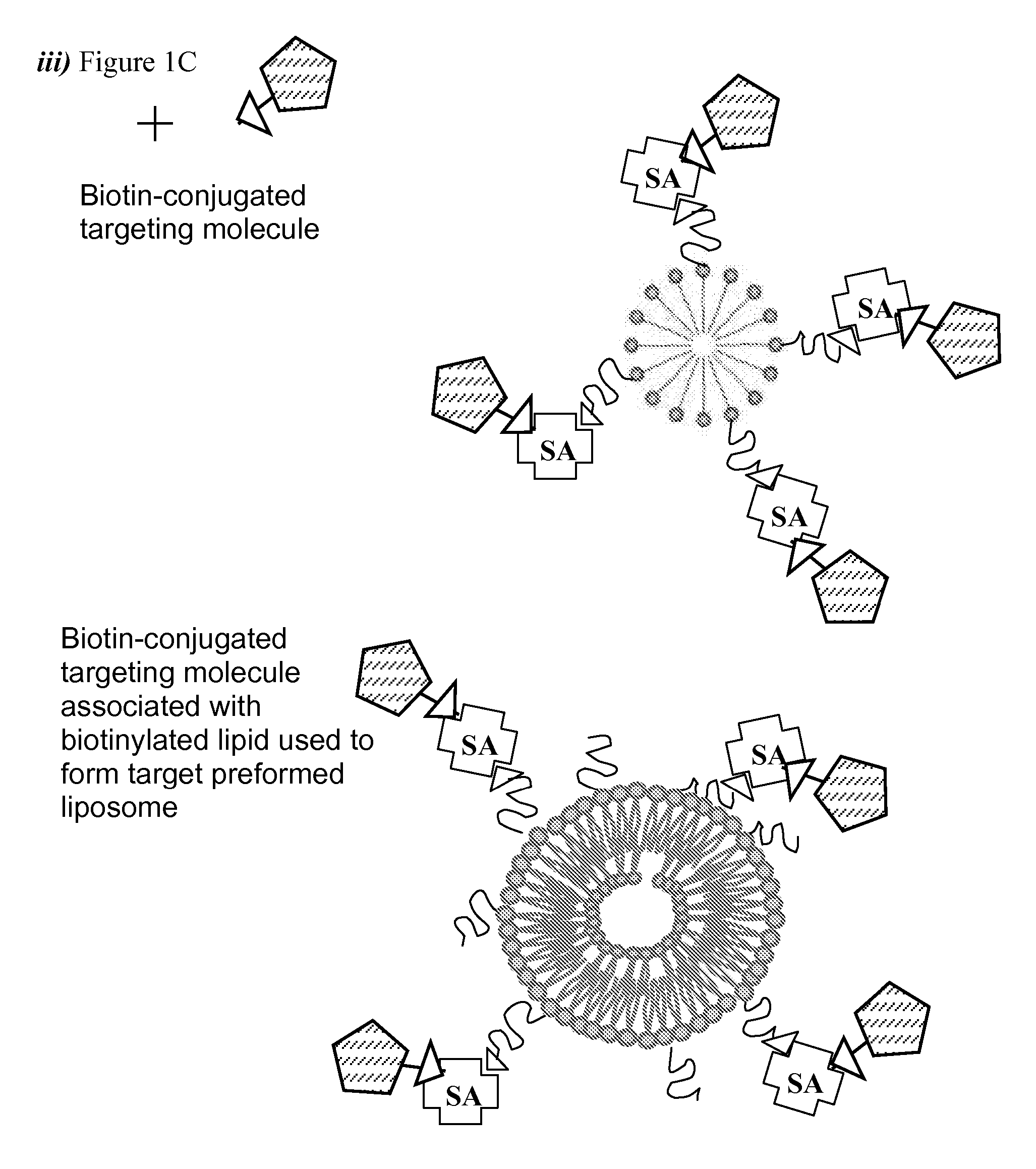
Methods of Preparing Targeted Immunoliposomes
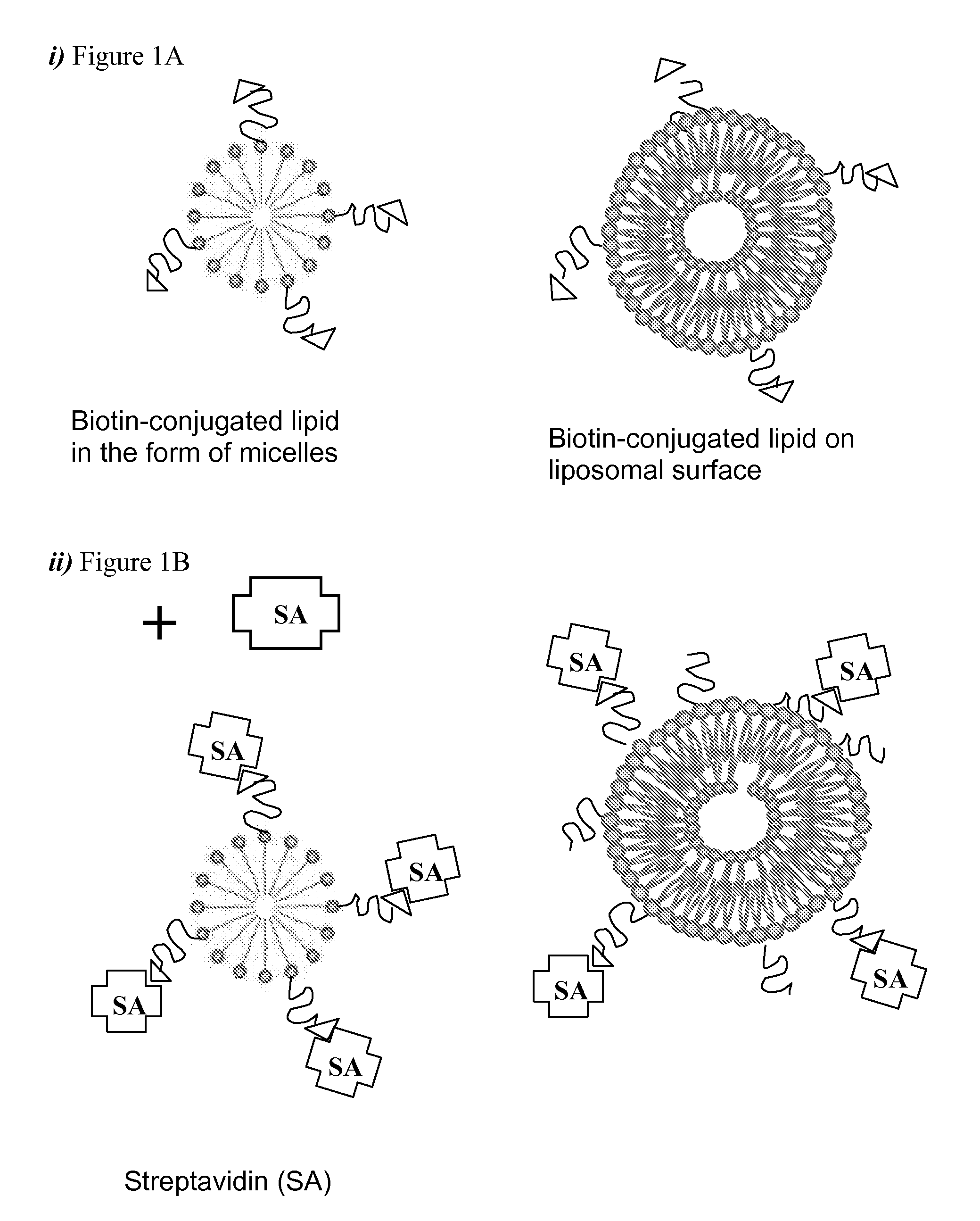
Methods of preparing targeting ligand bound avidin-lipid vesicles for use in preparing a targeted, therapeutic liposome composition are disclosed. Each vesicle comprises an avidin molecule coupled to the polymer-conjugated biotin which retains multiple free site biotin-binding sites such that the vesicle may be used to further couple a biotinylated-targeting ligand.
Owner:HEAVNER GEORGE +2
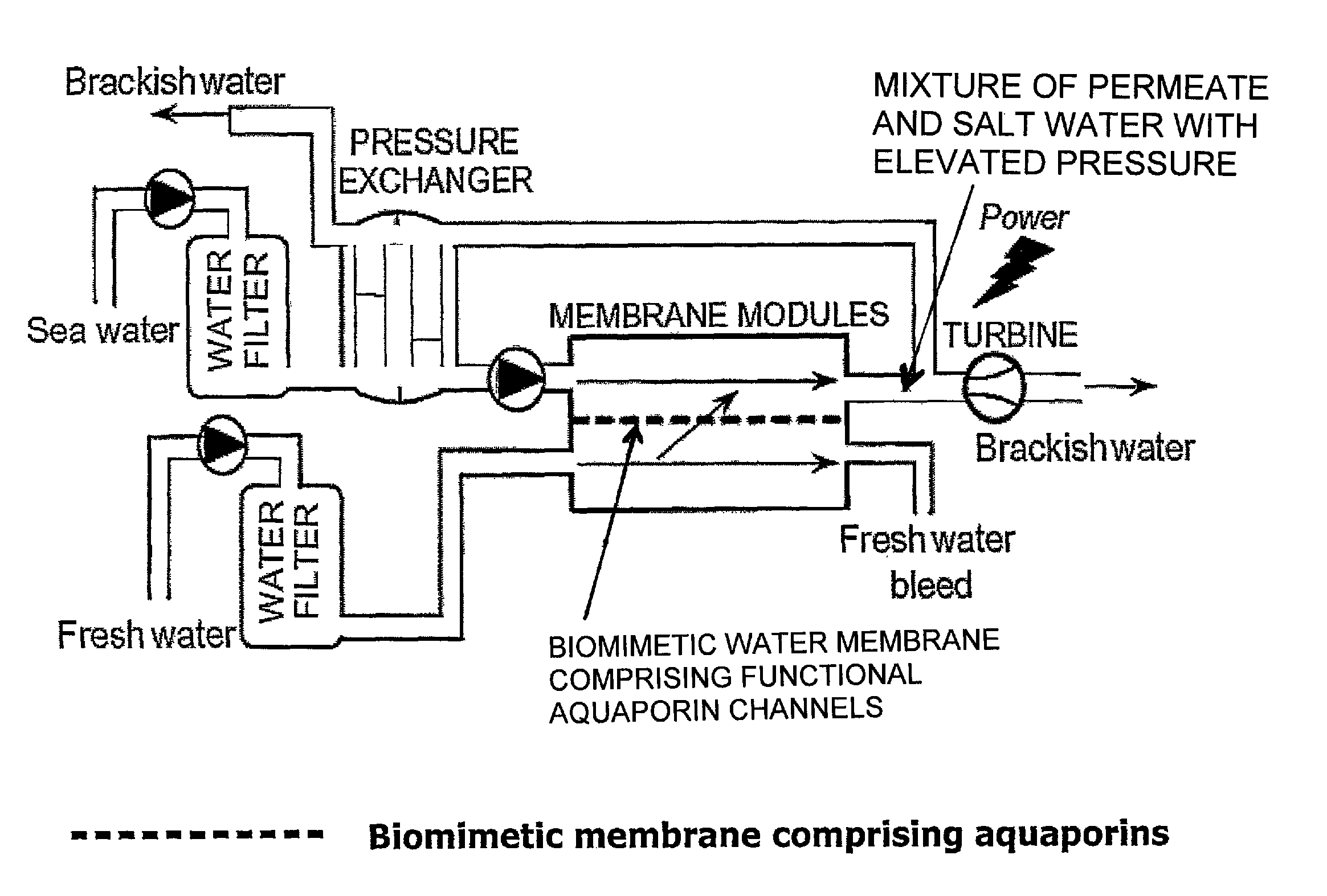
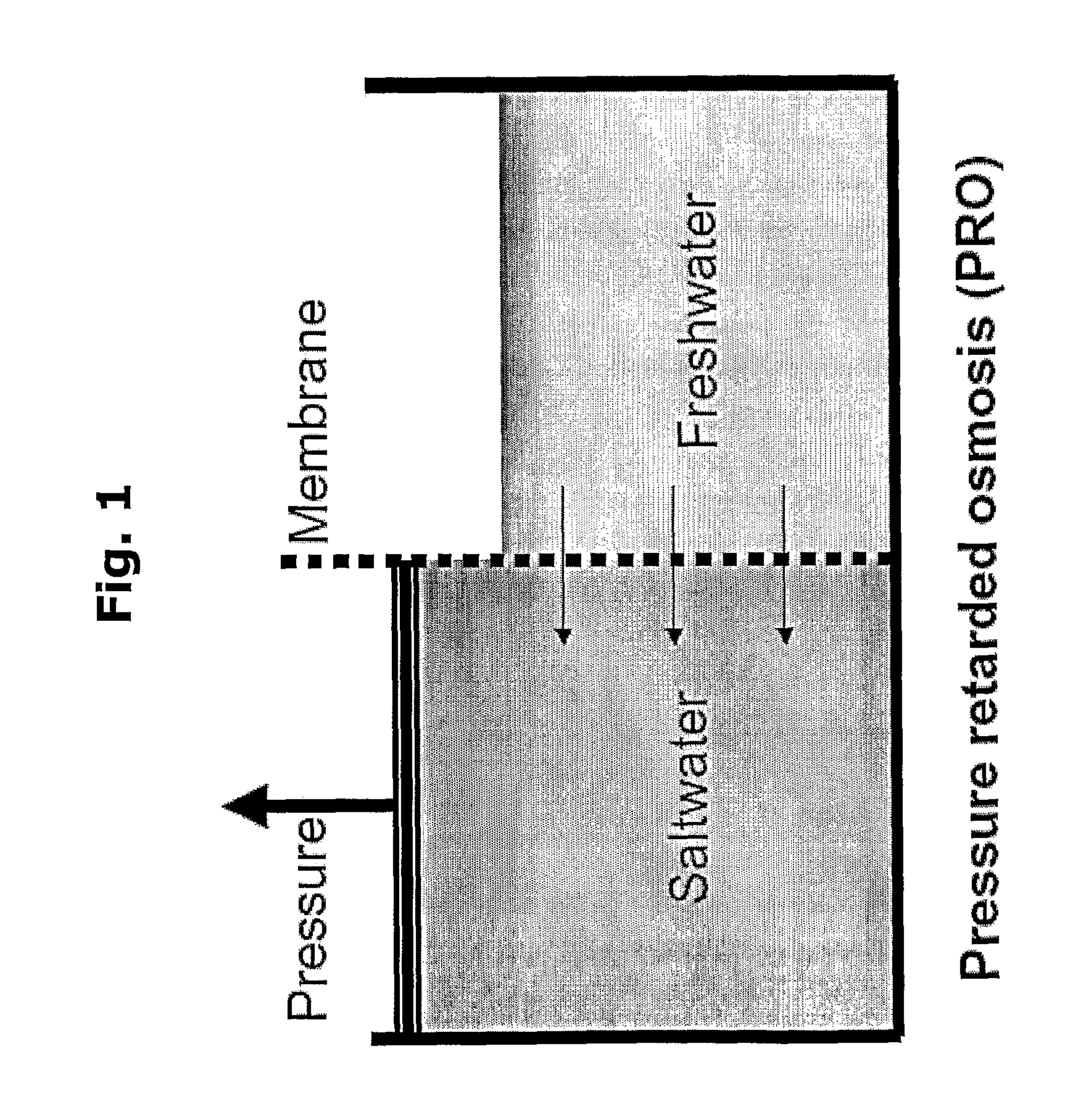
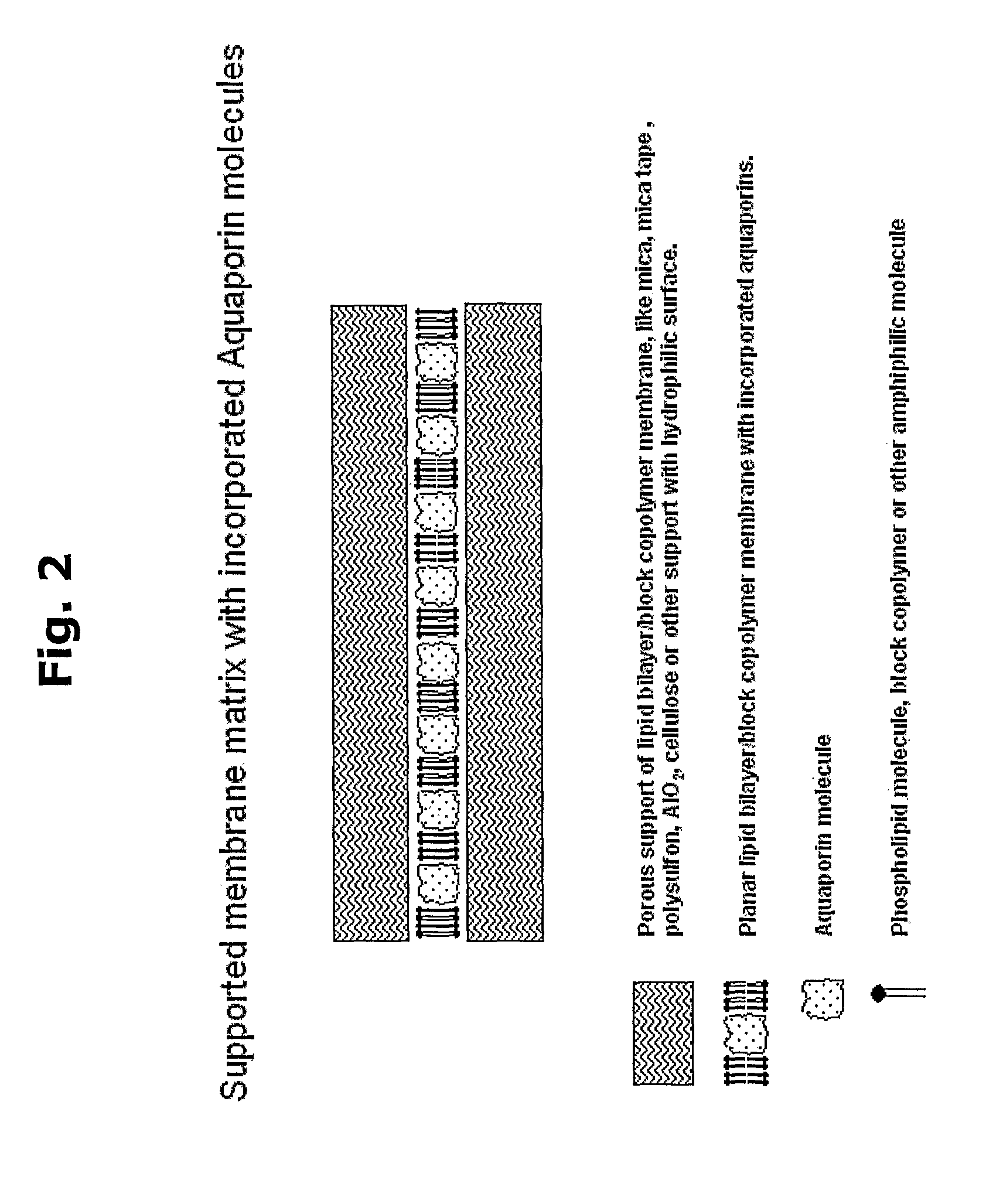
Biomimetic water membrane comprising aquaporins used in the production of salinity power
The present invention provides methods for producing salinity power using pressure retarded osmosis and a biometric membrane (e.g., a liquid bilayer membrane or a lipid membrane containing multiple bilayers of fused deposited lipid vesicles) containing aquaporin water channels. The invention also provides power plants for producing salinity energy using pressure retarded osmosis and a biometric water membrane containing functional aquaporin channels.
Owner:AQUAPORIN AS
Compositions and methods useful for the reduction of fine lines and wrinkles
InactiveUS7785623B2Reducing fine lineReduce wrinklesCosmetic preparationsElectrotherapyWrinkle skinLipid formation
A cosmetic treatment process is provided herein useful for reducing fine lines, wrinkles, or fine lines and wrinkles. The process comprises contacting a composition to an area of the skin or tissue of a subject, wherein the composition comprises a substance encapsulated within a lipid vesicle comprising a lipid having one or more polyethylene glycol (PEG) chains. The lipid vesicle has a charged surface, and an electric voltage is applied directly to the area of the skin that is contacted with the composition, whereby fine lines, wrinkles, or fine lines and wrinkles are reduced.
Owner:BIOZONE LAB
Lipid vesicle compositions and methods of use
ActiveUS8747869B2Increase load capacityImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsFatty acid chemical modificationLipid formationDiagnostic agent
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Anti-aging co-transport nanolipid vesicle and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109044921AIncrease loadStable vesicle structureCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCholesterolWater insoluble
The invention provides an anti-aging co-transport nano lipid vesicle and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of functional cosmetics. The anti-aging co-transport nano lipid vesicle comprises the following components in parts by weight: 0.02-32 parts of an anti-aging active component, 11.1-65 parts of a nano lipid vesicle, and 3-88 parts of water, wherein the nano lipid vesicle comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5.0-20.0 parts of a nonionic surfactant, 5.0-30.0 parts of water-soluble alcohol, 1.0-10.0 parts of compound phosphatide, and 0.1-5.0 parts of cholesterol; and the anti-aging active component includes a water insoluble anti-aging component and / or a water soluble anti-aging component. According to the preparation method, the anti-aging active components are loaded in the same nano lipid vesicle, so that transdermal co-transport of multi-target-point anti-aging active components of various anti-aging mechanisms can be realized; and synergistic interaction is realized, and thus the anti-aging effect is improved.
Owner:WUHAN BEST CARRIER NANO TECH
Novel formulation of dehydrated lipid vesicles for controlled release of active pharmaceutical ingredient via inhalation
InactiveUS20090047336A1Reduce systemic side effectsLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideLipid formationSide effect
A new formulation of dehydrated lipid vesicles employs a vesicle preserver and permits the control of release and delivery of active pharmaceutical ingredients into the respiratory system for treatment in particular of asthma. The typical formulation provides controlled release of the active pharmaceutical ingredient from 0% to 100% from 0 to 72 hours after inhalation, changes the systemic administration to topical administration, allows prolonged therapeutic period for one administration, increased stability, with reduced dose, reduced systemic side effects, reduced toxicity.
Owner:HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIV
Methods for Transmembrane Treatment and Prevention of Otitis Media
Methods for treating and preventing middle ear infections by transmembrane administration of medicament-containing transmembrane carrier compositions, such as liposomes and other lipid vesicles, to the tympanic membrane. Medicaments useful for treating pain, inflammation or infection in the outer ear may be co-administered. If utilized for transmembrane administration, the liposomes or other lipid vesicles will usually not be sterically stabilized. The medicaments delivered according to the methods of the invention include antibiotic, anti-viral, anti-fungal and anti-inflammatory agents that are useful in treatment and / or prophylaxis of middle ear infections and their sequelae.
Owner:PIEDMONT PHARMA LLC
Water-soluble cationic magnetic fine particles and method for separating or detecting lipid vesicle using the same
InactiveUS20070105094A1Substance reductionEasy to processMicrobiological testing/measurementRecovery/purificationPhysisorptionWater soluble
A phospholipid vesicle such as a virus is to be rapidly separated (concentrated, roughly purified) and good detection (diagnosis) results can be obtained with suppressing inhibition of virus-denature, PCR inhibition, latex-aggregation inhibition, and the like. Moreover, the above operations are to be automated. A phospholipid vesicle is separated using a water-soluble cationic magnetic fine particle by a composite formation through a covalent bond or physical adsorption of a substance having a cationic functional group, a substance having a hydroxyl group, and a substance having magnetism.
Owner:JNC CORP
Lipid Vesicle Composition
InactiveUS20090297592A1Excellent in stability in bloodEasy to usePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderLipid bilayerOptic vesicle
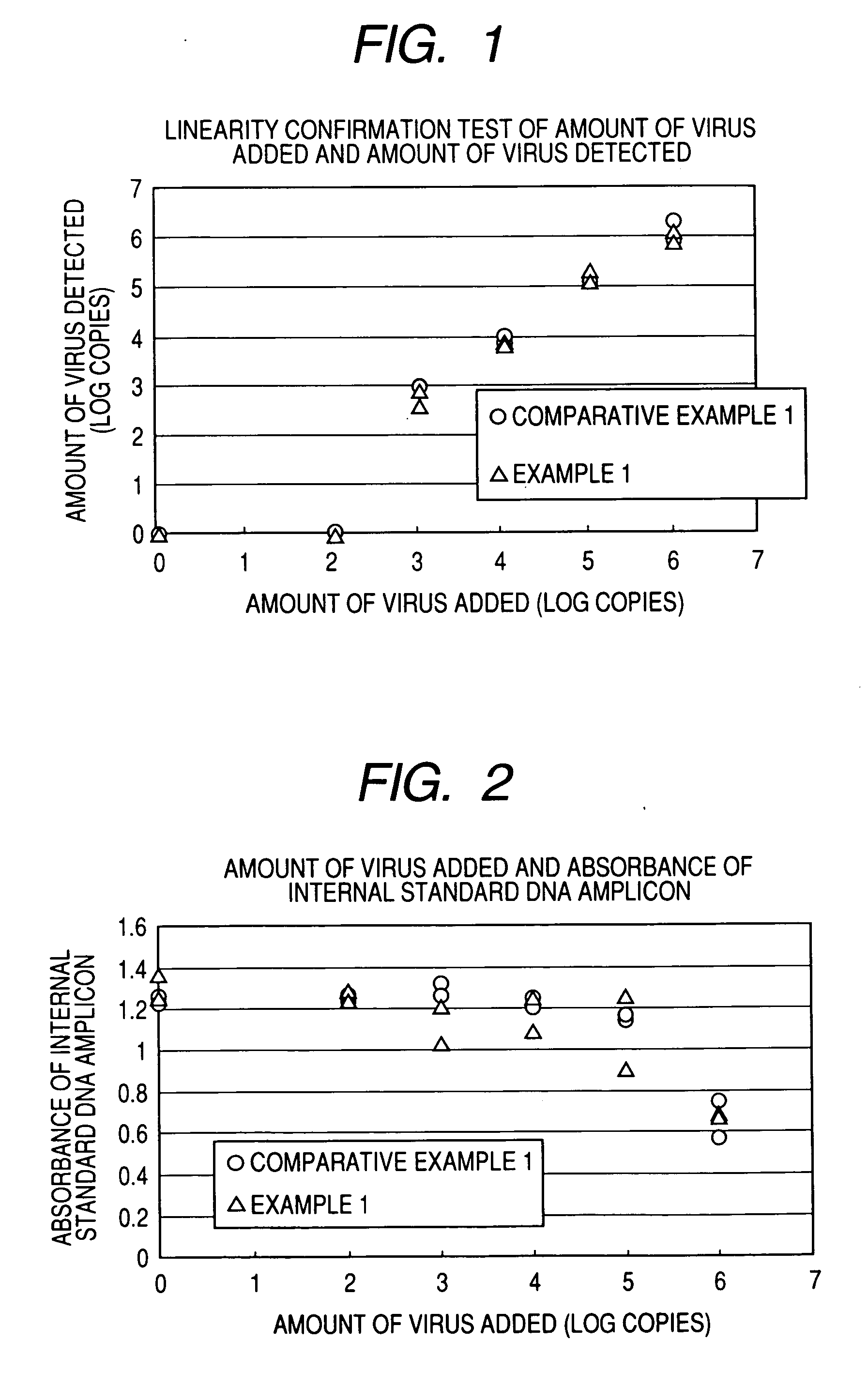
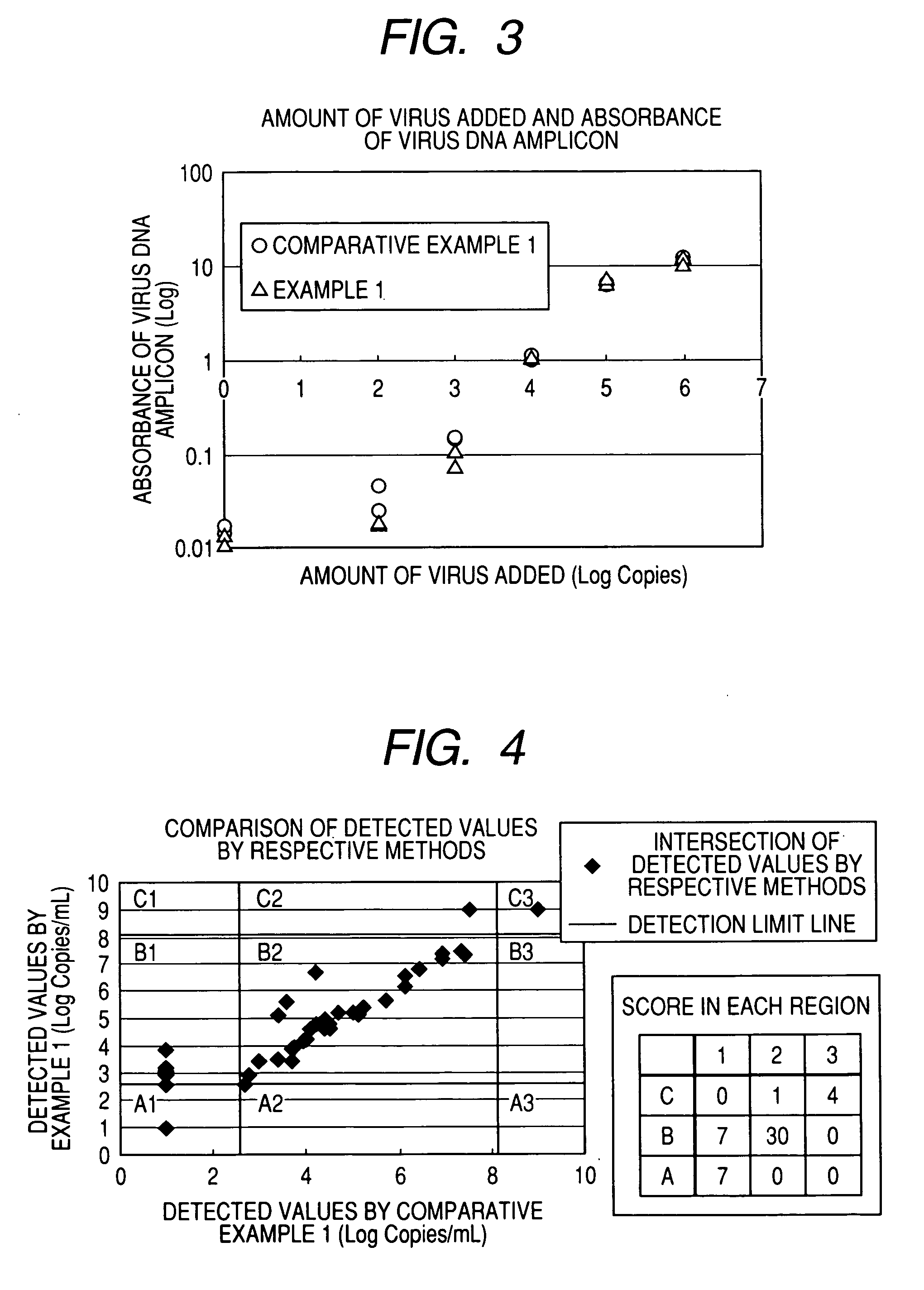
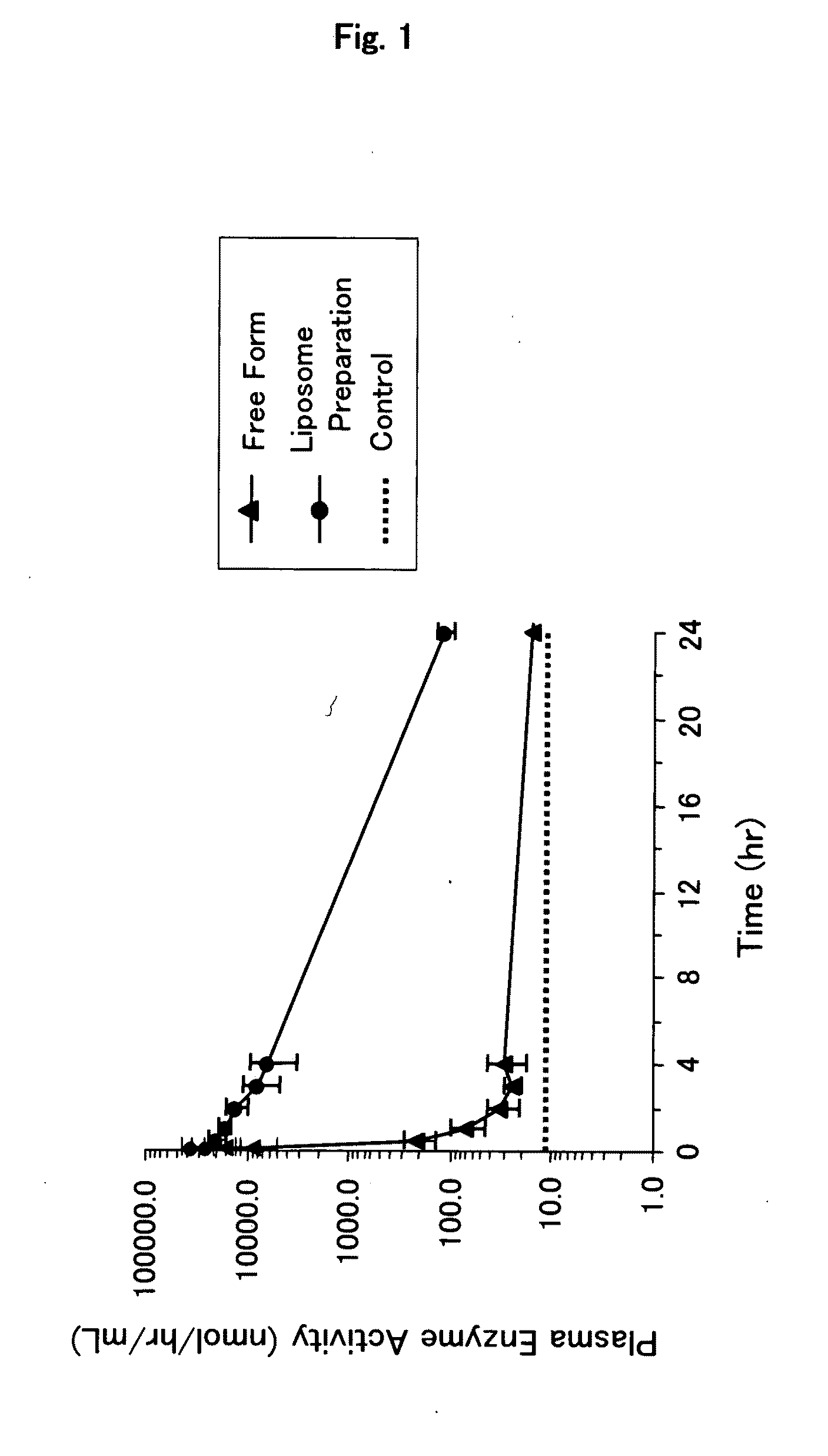
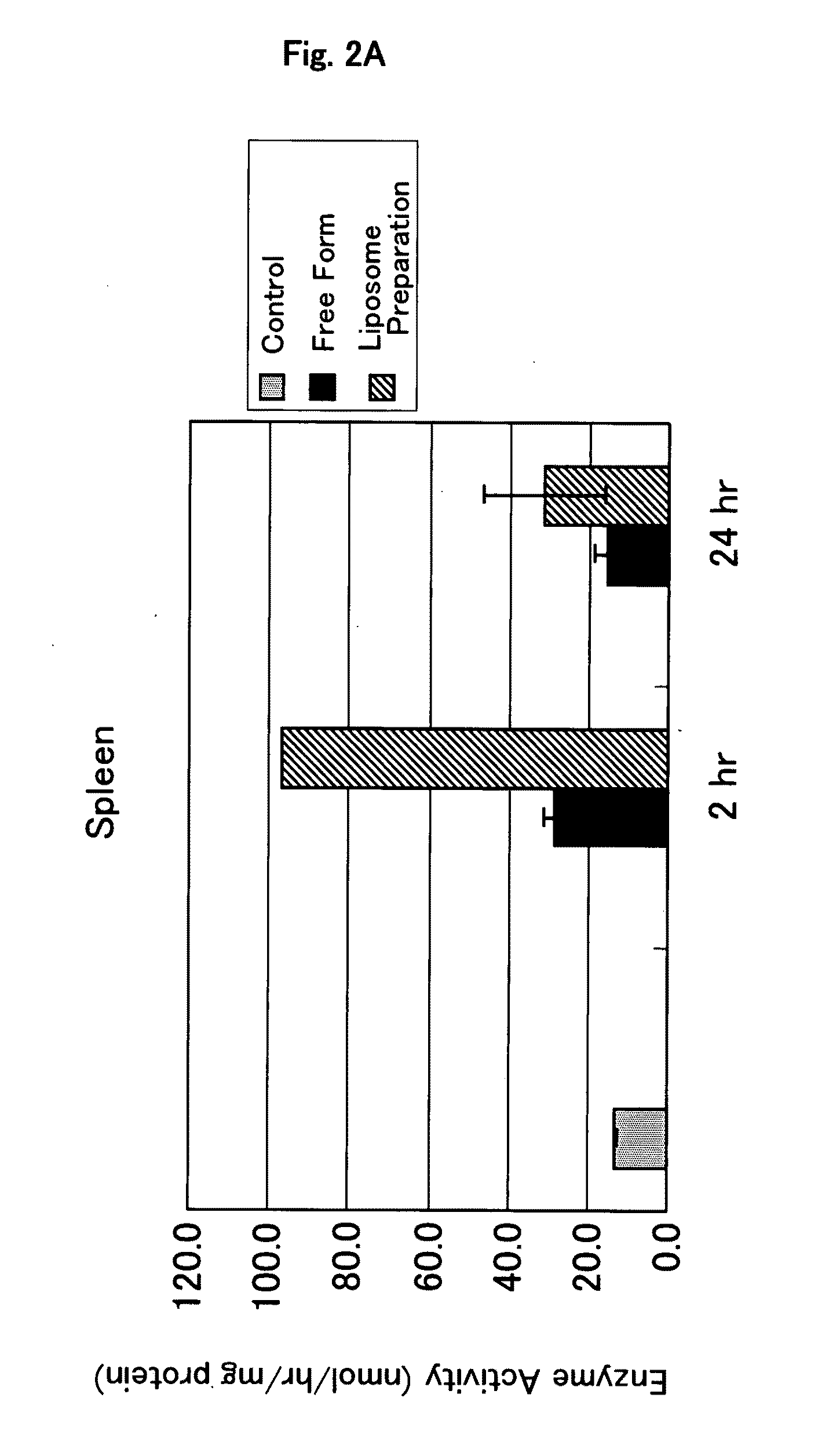
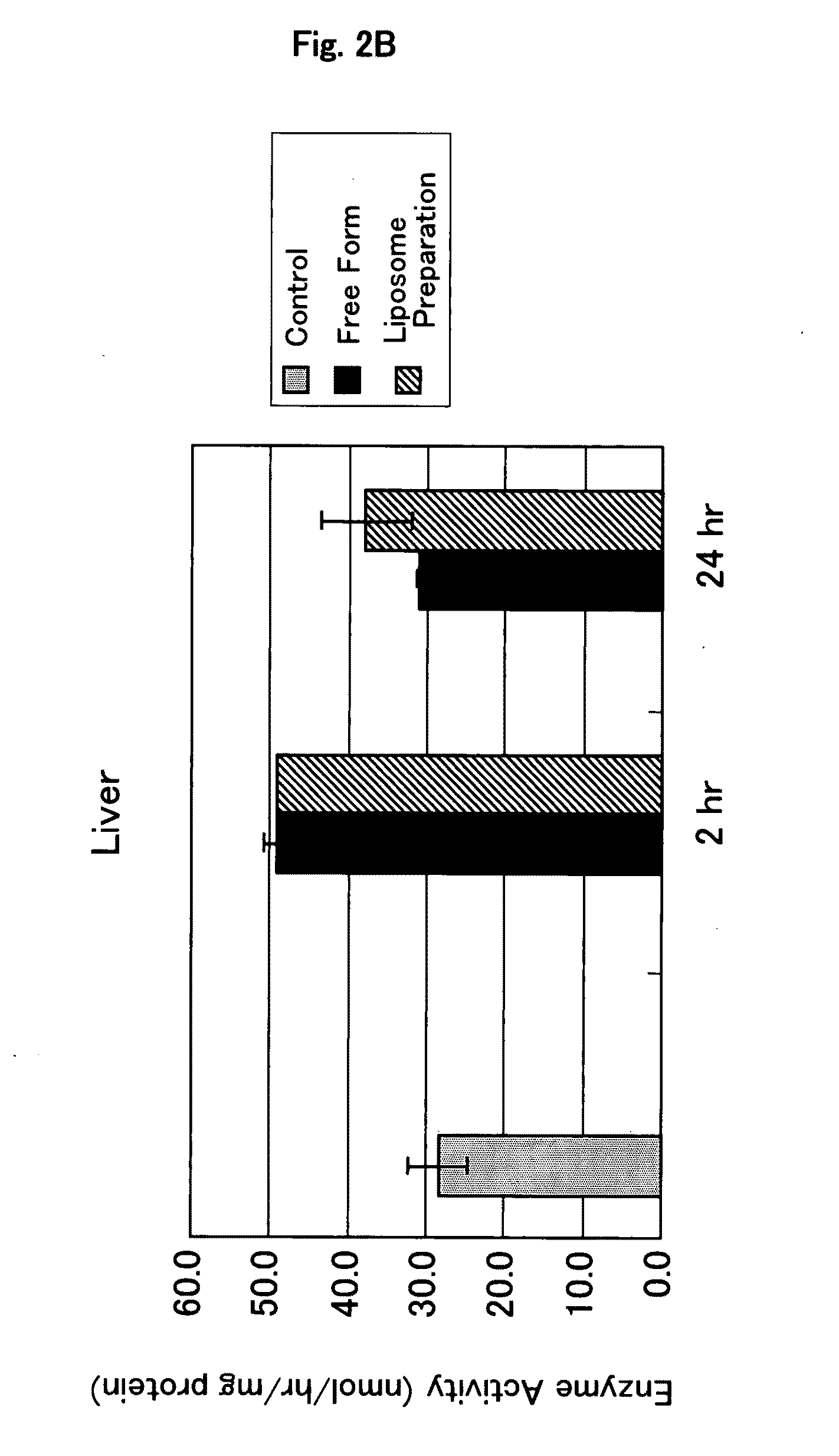
It is an object of the present invention to provide an enzyme preparation which is excellent in stability in blood (blood residence) and in transfer to a target organ (targeting property), and can be used effectively in enzyme replacement therapy or the like.This problem is solved by a lipid vesicle composition wherein vesicles composed of a lipid bilayer membrane are encapsulating an enzyme, the composition being capable of retaining stably the activity of the enzyme even outside the stable pH range of the enzyme.
Owner:JCR PHARMA +1
Methods for preparation of lipid-encapsulated therapeutic agents
InactiveUS20060257465A1Efficient formationOrganic active ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedLipid formationSolvent
Fully lipid-encapsulated therapeutic agent particles of a charged therapeutic agent are prepared by combining a lipid composition containing preformed lipid vesicles, a charged therapeutic agent, and a destabilizing agent to form a mixture of preformed vesicles and therapeutic agent in a destabilizing solvent. The destabilizing solvent is effective to destabilize the membrane of the preformed lipid vesicles without disrupting the vesicles. The resulting mixture is incubated for a period of time sufficient to allow the encapsulation of the therapeutic agent within the preformed lipid vesicles. The destabilizing agent is then removed to yield fully lipid-encapsulated therapeutic agent particles. The preformed lipid vesicles comprise a charged lipid which has a charge which is opposite to the charge of the charged therapeutic agent and a modified lipid having a steric barrier moiety for control of aggregation.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Materials and Methods for Delivering Antioxidants into the Skin
InactiveUS20100098752A1React SafeLarge cavity sizeBiocideCosmetic preparationsLipid formationAntioxidant
Compositions and methods for administering one or more antioxidants to a human subject have been developed. The antioxidant-containing lipid vesicles of the invention provide a delivery system for antioxidants which can be applied topically to the skin.
Owner:PINSKY MARK A
Novel formulation of dehydrated lipid vesicles for controlled release of active pharmaceutical ingredient via inhalation
A new formulation of dehydrated lipid vesicles employs a vesicle preserver and permits the control of release and delivery of active pharmaceutical ingredients into the respiratory system for treatment in particular of asthma. The typical formulation provides controlled release of the active pharmaceutical ingredient from 0% to 100% from 0 to 72 hours after inhalation, changes the systemic administration to topical administration, allows prolonged therapeutic period for one administration, increased stability, with reduced dose, reduced systemic side effects, reduced toxicity.
Owner:HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIV
Lecithin carrier vesicles and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20110318406A1Small sizeHigh shear mixingBiocideDough treatmentVesicle/vacuoleBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
A hydrated lecithin carrier vesicle composition includes a lecithin-derived membrane-forming lipid vesicle in conditioned water for incorporation of an active ingredient to form a dispersed composition. A method of making the hydrated lecithin carrier vesicle includes using lecithin having not more than about 80% w / w phosphatidylcholine in the presence of conditioned water.
Owner:BIO UP MIMETIC TECH INC
Antigen presenting vesicles
The present invention relates to an antigen presenting membrane vesicle comprising on its surface a composition of either relevant molecules for antigen-specific activation or deactivation of T lymphocytes and which is present in the form of an artificially induced lipid vesicle budded from a plasma membrane of a eukaryotic, preferably human, cell, and wherein the composition of said relevant molecules for activation or deactivation present on the vesicle surface is adjustable to a recipient's needs or requirements independently of any blood or tissue cells of said recipient. The invention further relates to a method of manufacture of the vesicles and to compositions containing the vesicles as well as to the use of the vesicles for various purposes including medical and diagnostic applications.
Owner:WINFRIED PICKL +1
Intracellular delivery of therapeutic agents
InactiveUS20050163832A1Easy to useGood curative effectVectorsGenetic material ingredientsLipid formationIn vivo
The preparation and use of a transducing polypeptide (TP)— lipid vesicle complex having a small proportion of positively charged (cationic) lipids in the make-up of the lipid vesicle, e.g., liposome, for safe and efficient intracellular delivery of therapeutic agents, such as proteins, DNA, small molecules and / or other drugs, into a cell of a higher organism, in vitro or in vivo is disclosed. The delivery system of the invention results in increased efficacy of intracellular delivery of such agents, bypassing the endocytotic pathway of intracellular delivery while at the same time minimizing the toxicity of the delivery system towards the recipient cells.
Owner:FLASHLIGHTILIN VLADIMIR +3
Self-assembled arrays of lipid-bilayer vesicles
InactiveUS20060094053A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLipid formationChemical reaction
High-density arrays of attoliter volume elements can be created within minutes in a parallel and effortless manner by using self-assembly of nanometer-sized components (e.g., lipid vesicles containing (bio)chemicals) based on biological recognition. The ultrasmall volumes allow localization to a predefined position of a few or single molecules, and then screening for their (bio)chemical properties or performing confined (bio)chemical reactions.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Biphasic lipid-vesicle composition and method for treating cervical dysplasia by intravaginal delivery
InactiveUS20130216610A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsInterferon alphaLipid vesicle
A biphasic lipid vesicle composition for treating cervical displasia by intravaginal delivery. The composition includes a suspension of lipid-bilayer vesicles having entrapped therein, an oil-in-water emulsion, human interferon alpha-2b and L-methionine, the composition having an interferon alpha-2b specific activity of between about 1-10 MIU (million international units) per gram composition, and between 0.01 to 0.5 weight percent L-methionine. In the treatment method, the composition is administered at a dose of between about 1-20 MIU interferon alpha-2b, and this dose is administered at least 3 days / week, for a period of at least 4 weeks.
Owner:HELIX BIOPHARMA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com