Methods for preparation of lipid-encapsulated therapeutic agents
a technology lipid-encapsulated nucleic acids, which is applied in the field of making particles can solve the problems of limiting the actual application of lipid-encapsulated therapeutic agents, low levels of therapeutic agent incorporation on a drug/lipid basis, and low efficiency of capture of therapeutic agents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
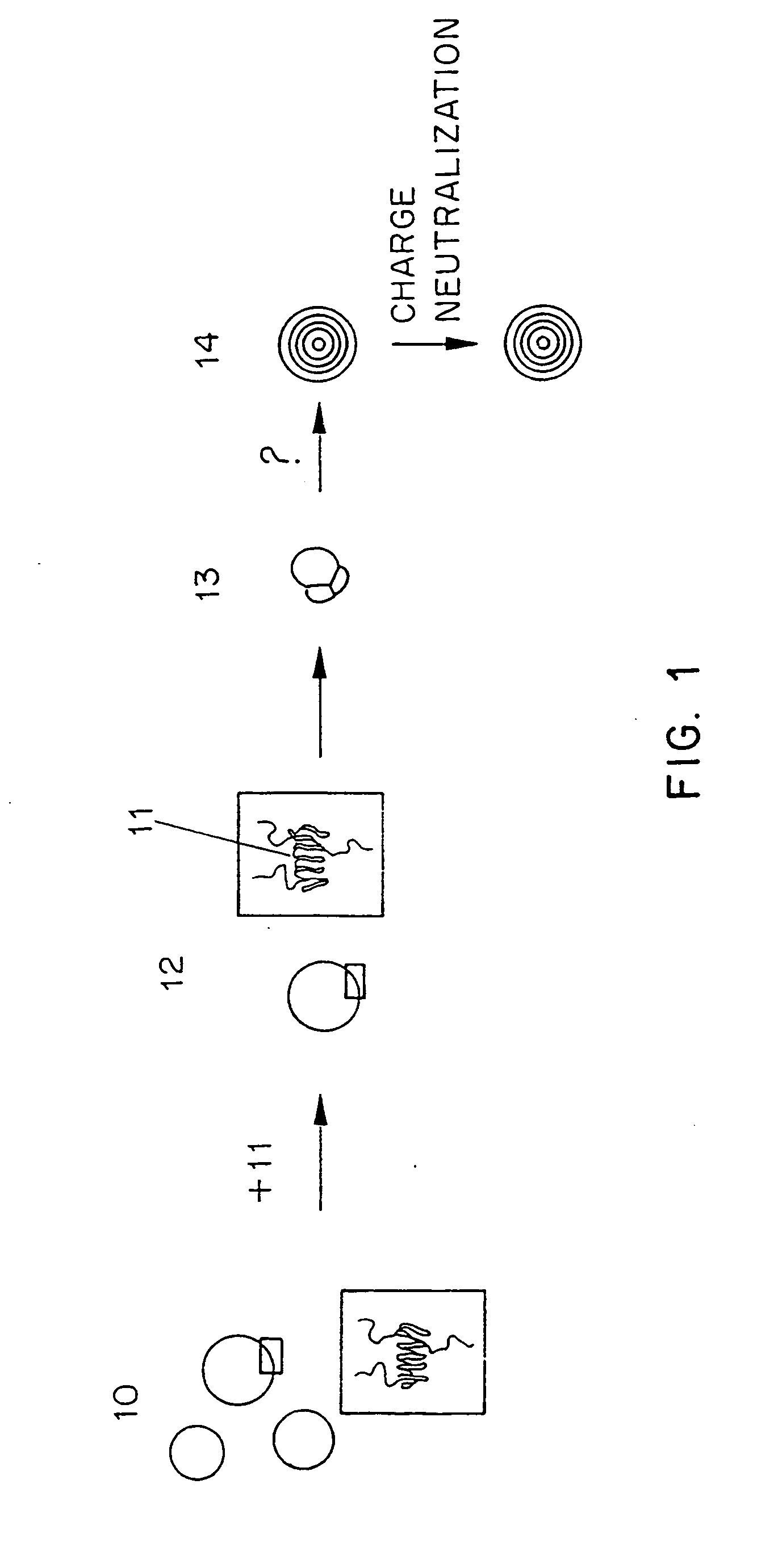
[0083] Empty preformed vesicles were prepared from a lipid mixture containing PEG-CerC14, DODAP, DPSC and CHOL in a molar ratio of 5:25:25:45. The four lipids were dissolved in a 100% ethanol to a total lipid concentration of 25 mg / ml (33 mM). The ethanolic lipid was then introduced through an injection port with an orifice diameter of 0.25 mm into a reservoir containing 300 mM citrate buffer, pH 4.0. The reservoir and all solutions were at room temperature. The total volume of ethanolic lipid was 6 liters, and the flow rate for lipid introduction was 200-300 ml / min. The total volume of citrate buffer was 9 liters. The resulting 15 liter mixture had an ethanol concentration of 40% and 180 mM citrate. Vesicles of 170±20 nm median diameter were generated. The empty preformed vesicles were sized to 90-120 nm median diameter by 1-3 passes through the extrusion circuit (65° C.) at low pressure (100 p.s.i., reduced from classical 500-1000 p.s.i.) using two stacked 80 nm membranes. The emp...
example 2
[0084] Preformed vesicles of example 1 were used to make fully lipid-encapsulated therapeutic agent particles using oligonucleotide INX-6295 (Seq. ID No. 1) as the therapeutic agent. Oligonucleotide INX-6295 in distilled water was diluted by the addition of 100% ethanol to form a various solutions of 10, 20, 30 40 or 50 mg / ml oligonucleotide in 40% ethanol. The ethanolic oligonucleotide was added to the preformed vesicles in reservoir 20 at 40° C. with gentle mixing. The amount and volume of ethanolic oligonucleotide was calculated to provide a final drug:lipid ratio of 0.1 to 0.25 by weight. The mixture was then incubated at 40° C. with gentle and periodic mixing for 1 hour. After incubation, the solution was processed by diafiltration to strip free or excess associated oligonucleotide, remove ethanol and exchange the buffer system to phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4. Concentration, sterile filtration and packaging complete the preparation of a commercial product.
example 3
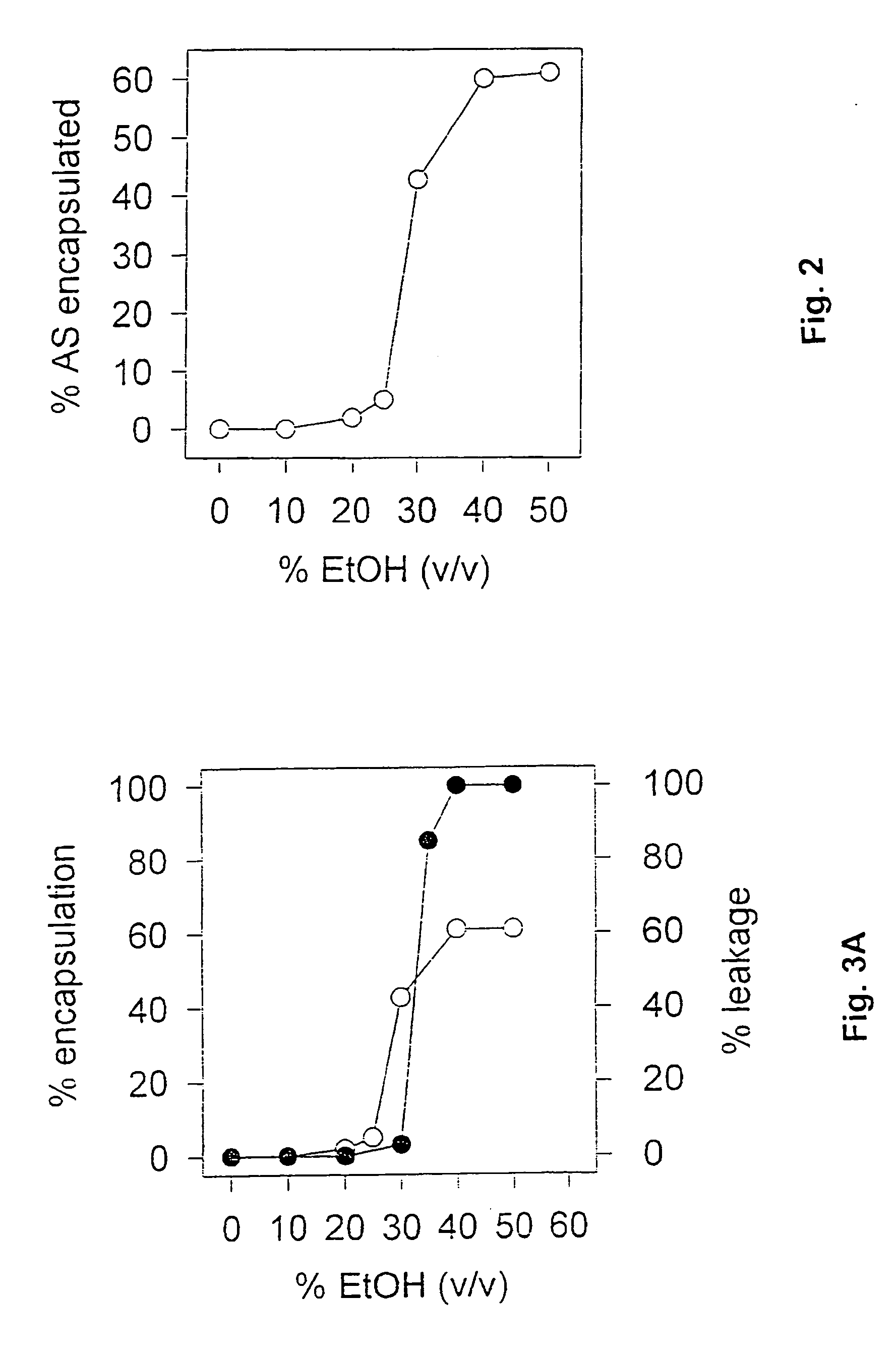
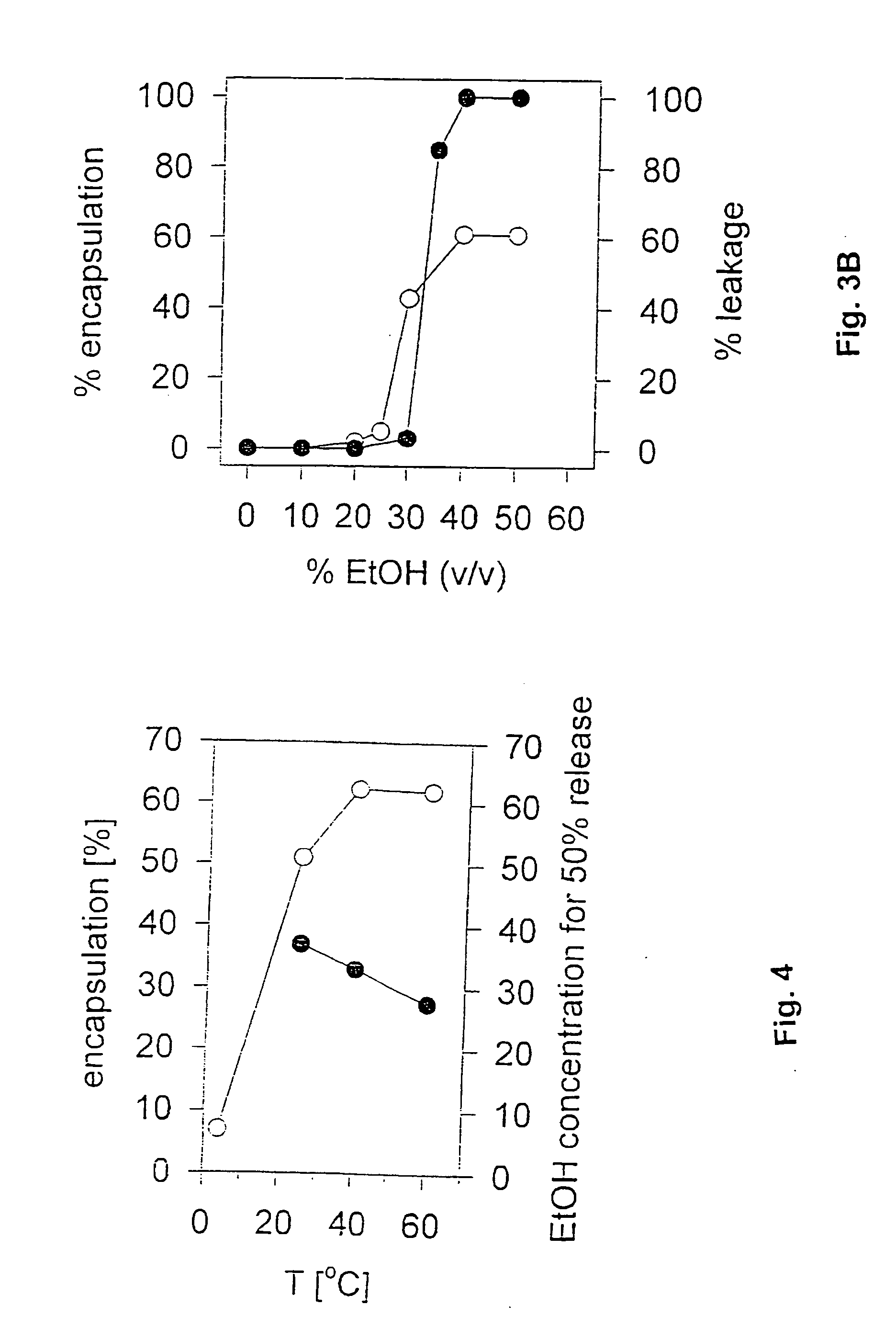
[0085] The procedure of Example 2 was repeated with changes to various parameters to determine which might be critical to the preparation of fully lipid-encapsulated therapeutic agent particles in accordance with the invention. In these experiments, the total oligonucleotide recovery (yield), the total lipid recovery (yield) and the encapsulation efficiency were considered as indications of the quality of the product and the process. Total oligonucleotide recovery was calculated using the formula: final oligo concentration (mg / ml)×final volume (ml) initial oligo concentration (mg / ml)×initial volume (ml)×100%
Total lipid recovery was calculated using the formula: final lipid concentration (mg / ml)×final volume (ml) initial lipid concentration (mg / ml)×initial volume (ml)×100%
Encapsulation Efficiency (E.E.) was calculated using the formula: initial oligo (mg / ml) / initial lipid (mg / ml)final oligo (mg / ml)×final li...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| mol % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mol % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com