Biological sample component purification and differential display
a biological sample and component technology, applied in the field of biological sample component purification and differential display, can solve problems such as affecting their ability, and achieve the effect of reducing the complexity of biological samples
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
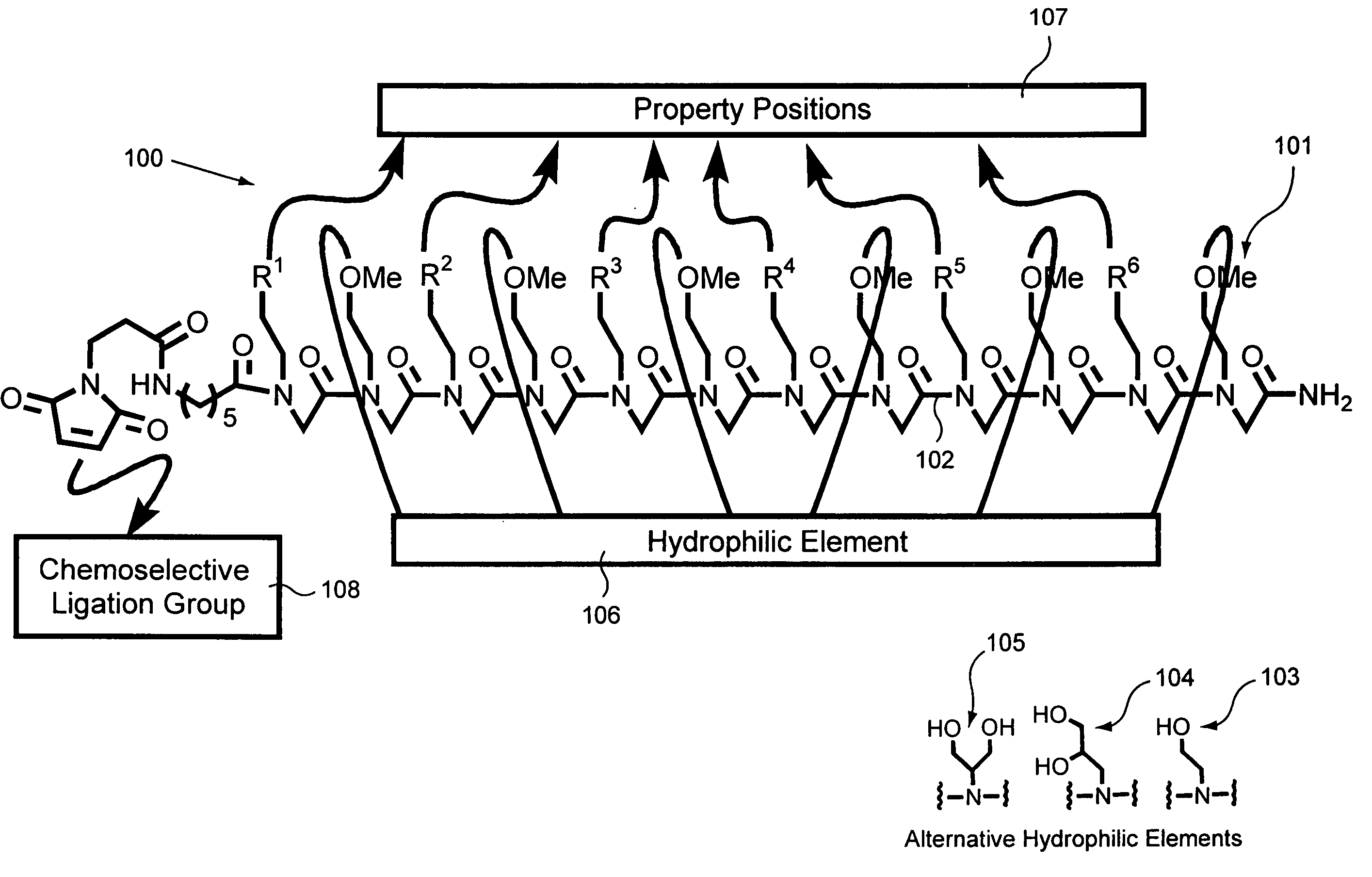
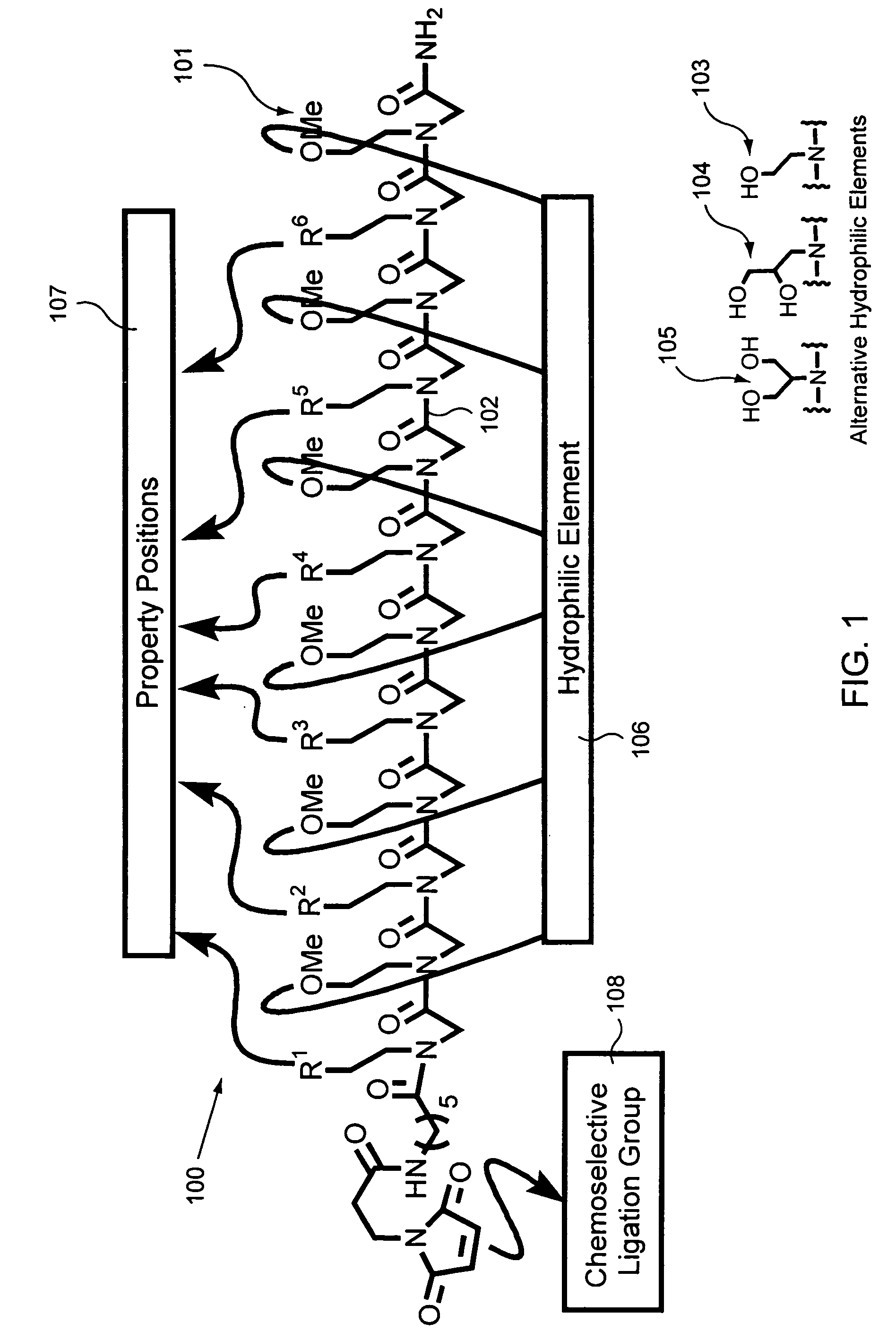
Preparation of a Peptoid on a Hydrophilic Support
Peptoids were prepared on Rink amide polystyrene resin as illustrated and described in FIG. 6, part A, Peptoid Synthesis. The synthesis procedure is also reported in Figliozzi, G. M., Goldsmith, R., Ng, S. C., Banville, S. C., Zuckermann, R. N. Methods Enzymol. 1996, 267, 437-447, the disclosure of which is incorporated by reference herein for all purposes.
Before cleavage, the peptoids on Rink resin were treated with N-FMOC-aminohexanoic acid (0.4M), HOBT (0.4M), DIC (0.44M) at 35° C. for 2 hr. Double coupling was performed when the ninhydrin test exhibit blue colored beads. After piperidine treatment to remove the FMOC protecting group, the beads were treated with 3-maleimido propionic acid (0.4M), HOBT (0.4M), DIC (0.44M) for 1 hr. at 35° C. After cleavage from the resin using 95% TFA [v / v] in H2O the resulting solution was filtered, mixed with H2O, frozen and lyophilized. The resulting product was dissolved in 100% AcOH, frozen...
example 2
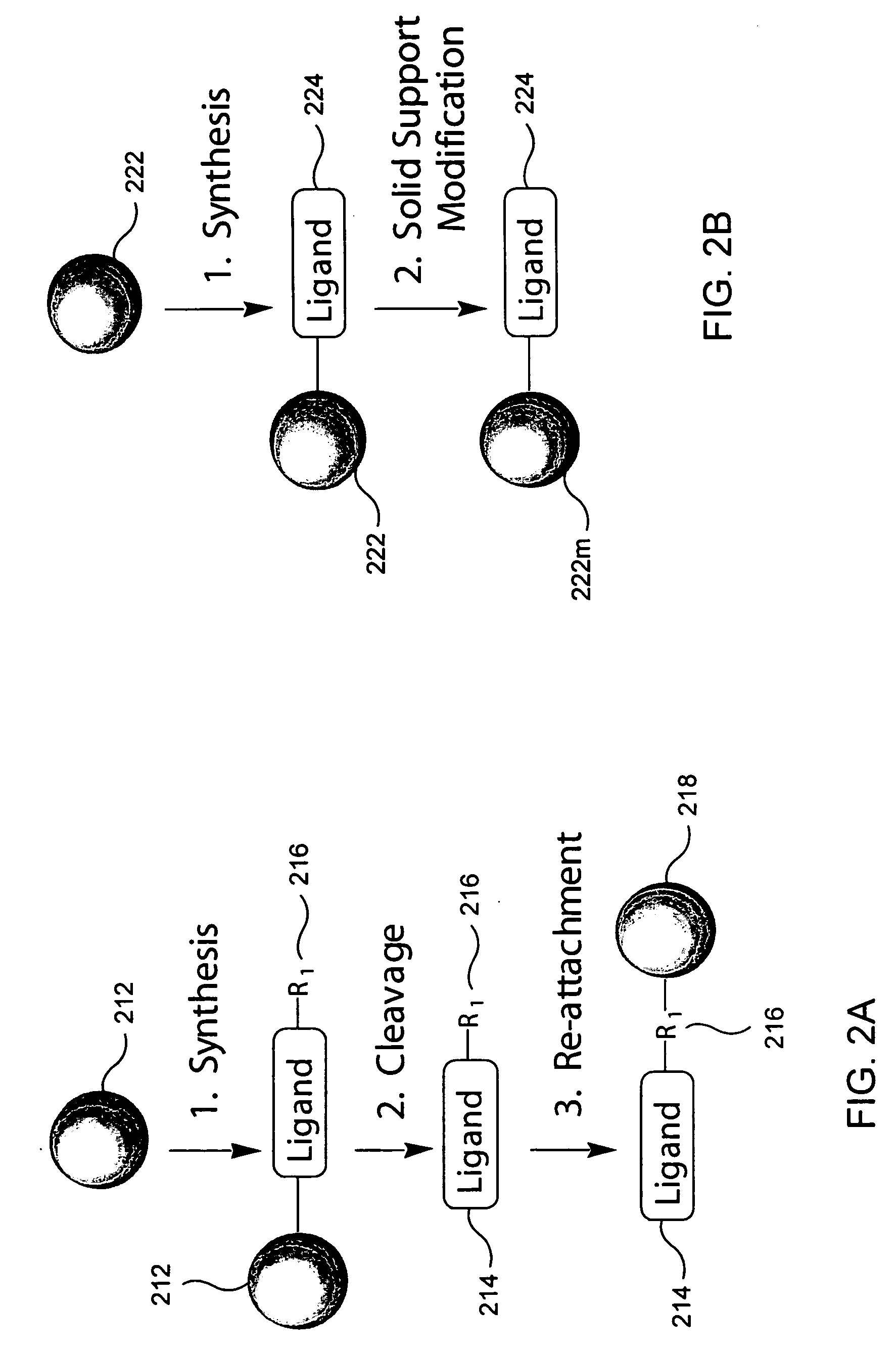
Evaluation of Fabricated Hydrophilic Affinity Supports
Each solid phase attached peptoid was packed in a column and loaded with a cell lysate. After a certain period, the column was washed with the loading buffer. The resin bound proteins were eluted using a variety of elution buffers. The fractions collected were analyzed using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
The versatility of these materials was evaluated using four criteria: reproducibility, binding capacity, enrichment and specificity. The structures of the various peptoids used in these evaluation are found in FIGS. 3A-C.
FIG. 7, shows the elution product reproducibility of peptoid / sepharose column after three loadings, washings and elutions of the HeLa cell lysate. The gel shows a high degree of reproducibility.
FIG. 8 shows the binding capacity of peptoid sepharose columns EB8224 and EB8225 toward protein sets of a HeLa cell lysate. EB8224 bound 7% of the cell lysate, while EB8225 bound 11% of the cell lysate. This dem...
example 3
Identification of a Support Ligand that Selectively Binds
Four peptoid-based affinity supports prepared in accordance with the present invention were used to purify a protein from a crude cell lysate. The four columns used in this example, identified as 01, 02, 03 and 04 in FIG. 10, were the columns identified as EB8201, EB8202, EB8203 and EB8204, respectively, in FIGS. 3A and 3C. A peptoid that binds selectively to the protein FGF (Fibroblast Growth Factor) was located. Each different column was loaded with a FGF-containing cell lysate and run using the cationic conditions described above in Table 1. The flow through fraction (FT) from the column and the initially bound and then eluted fraction (Eluate) were subjected to gel electrophoresis together with a FGF standard. The peptoid ligand (FIG. 4b, lane 6; bFGF) that bound selectively to FGF (FIG. 4b, lane 10) was determined, as shown in FIG. 10.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hydrophilic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| binding affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com