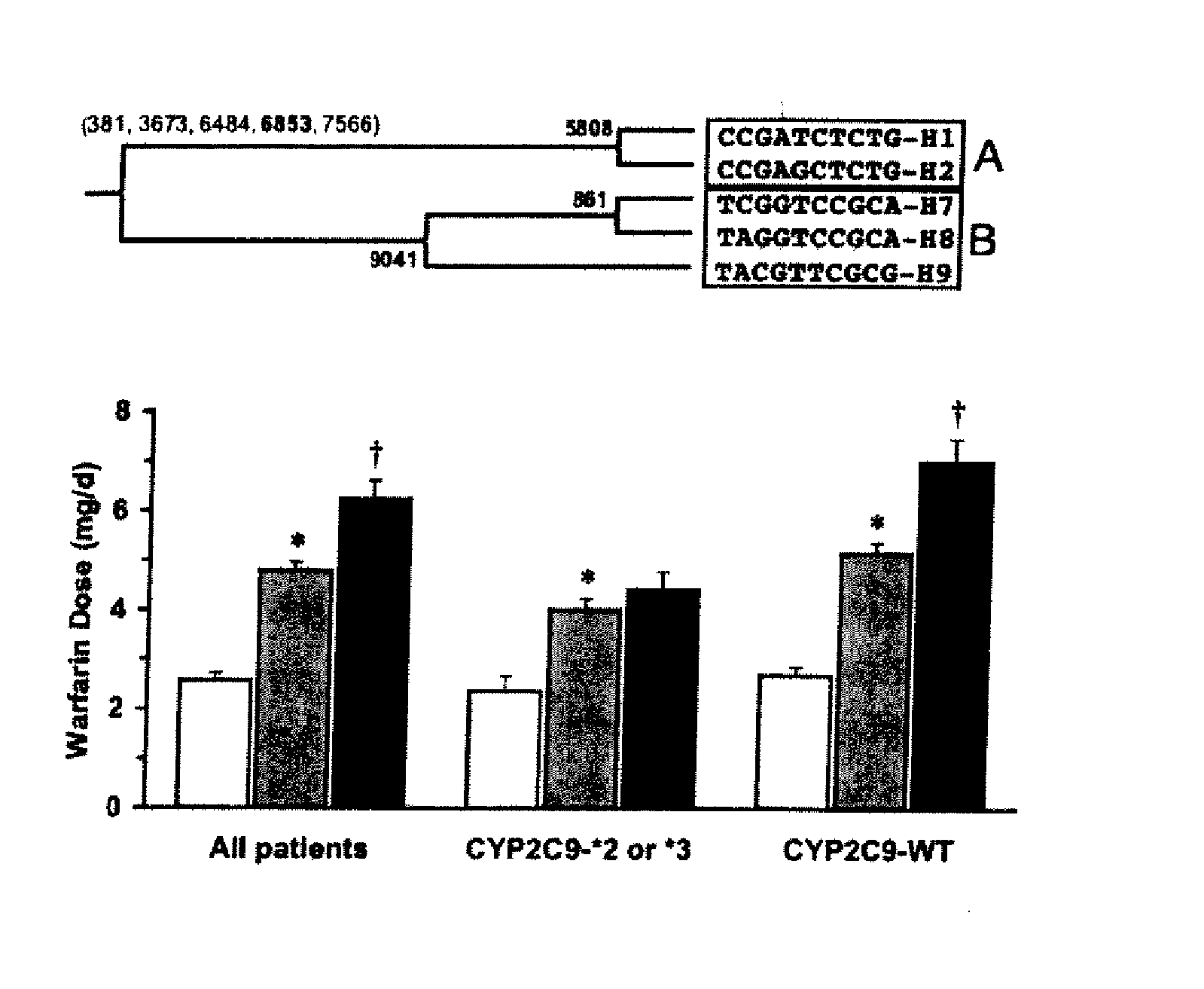
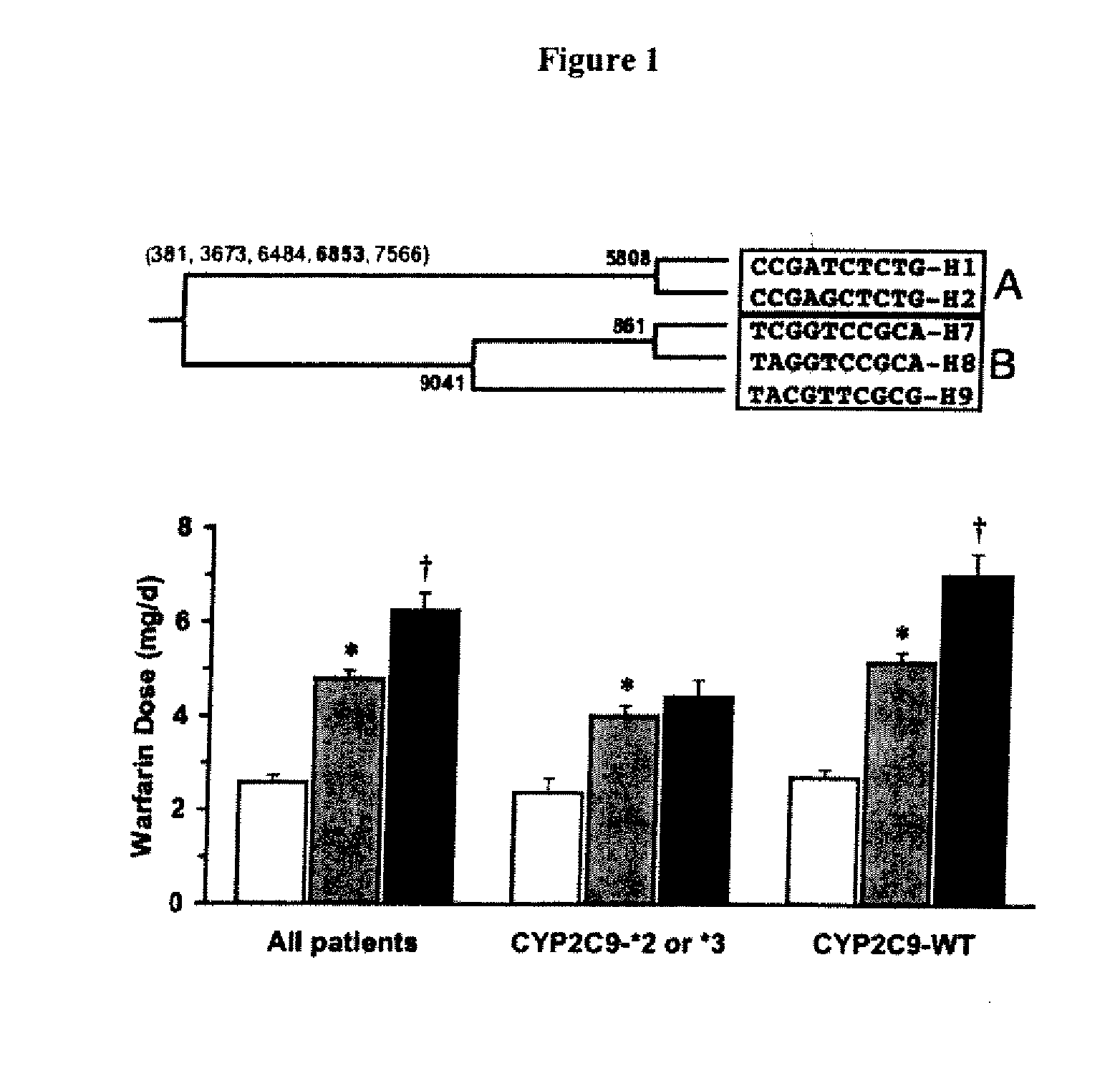
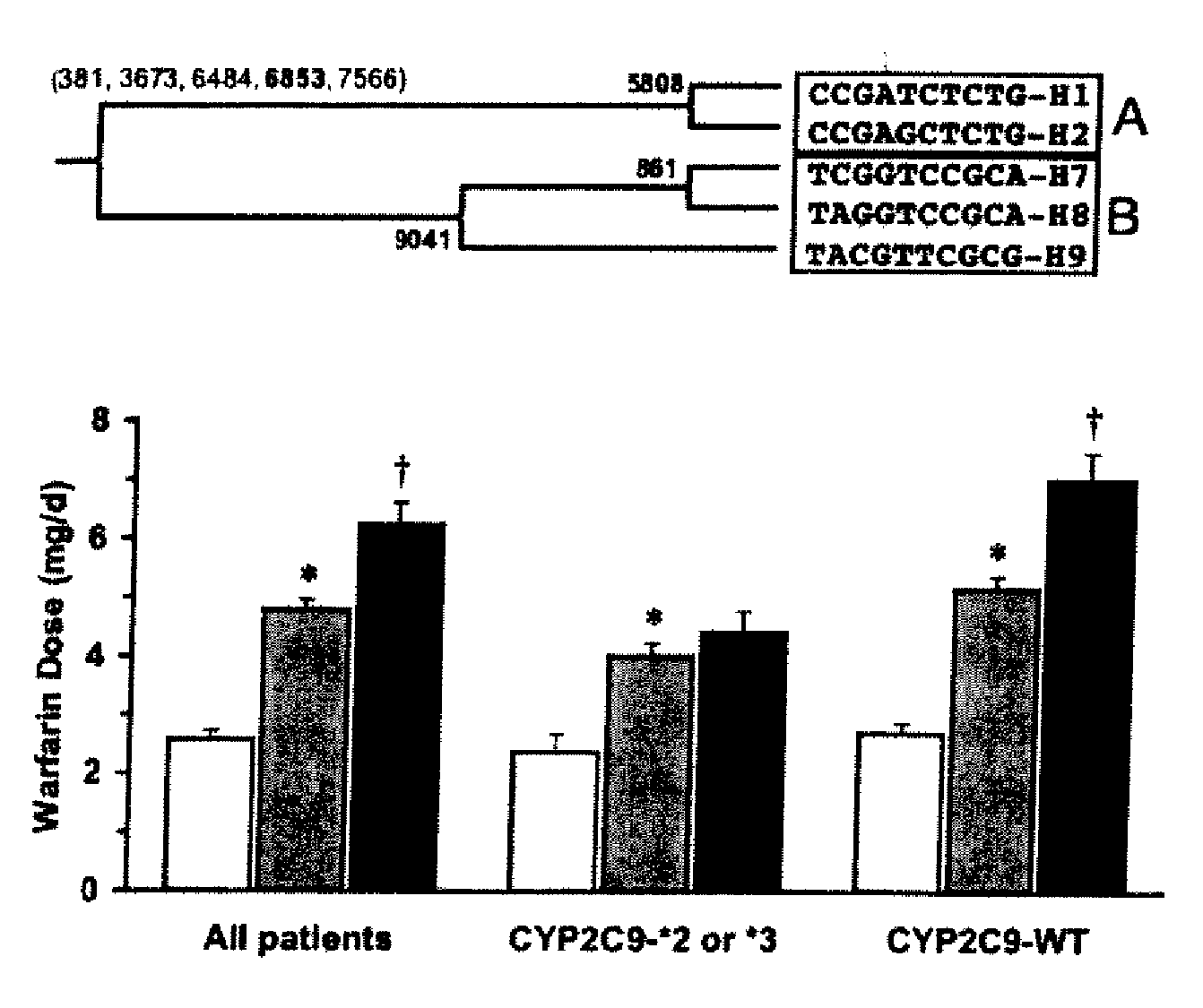
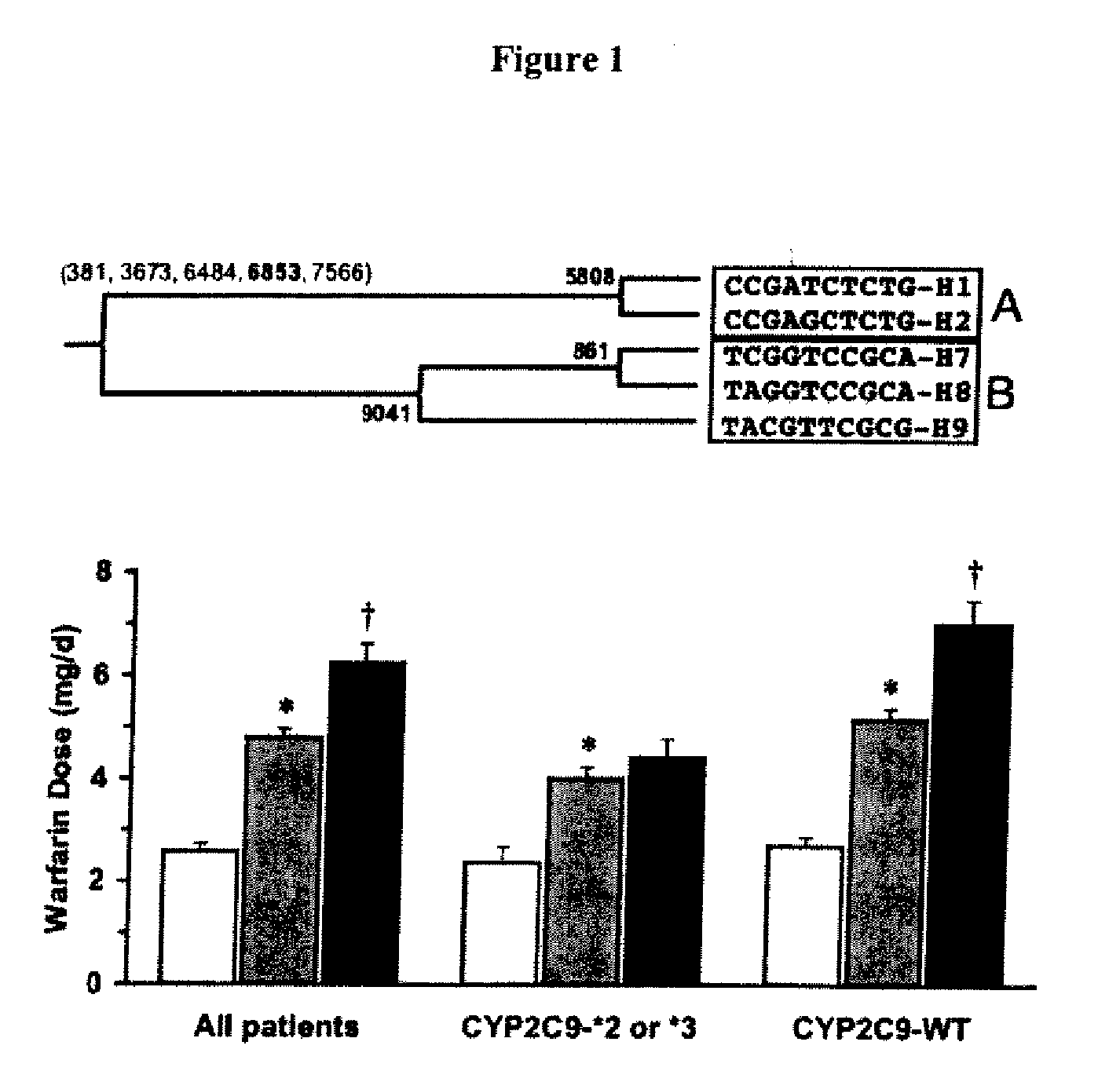
Patents
Literature
43 results about "Dna polymorphism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
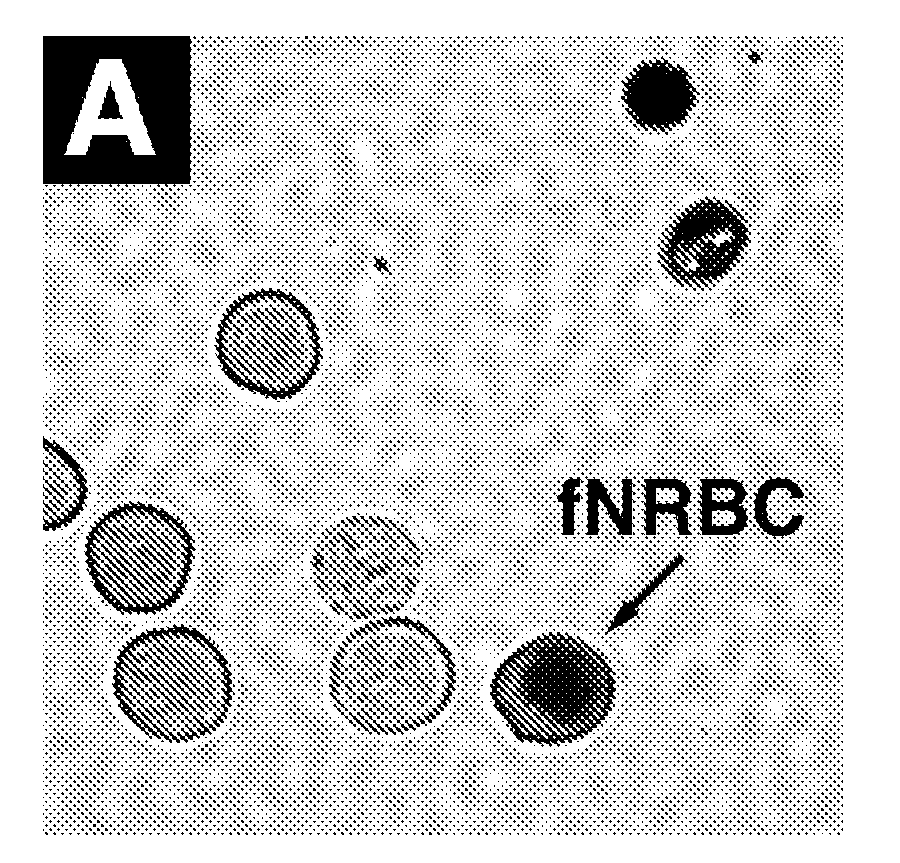
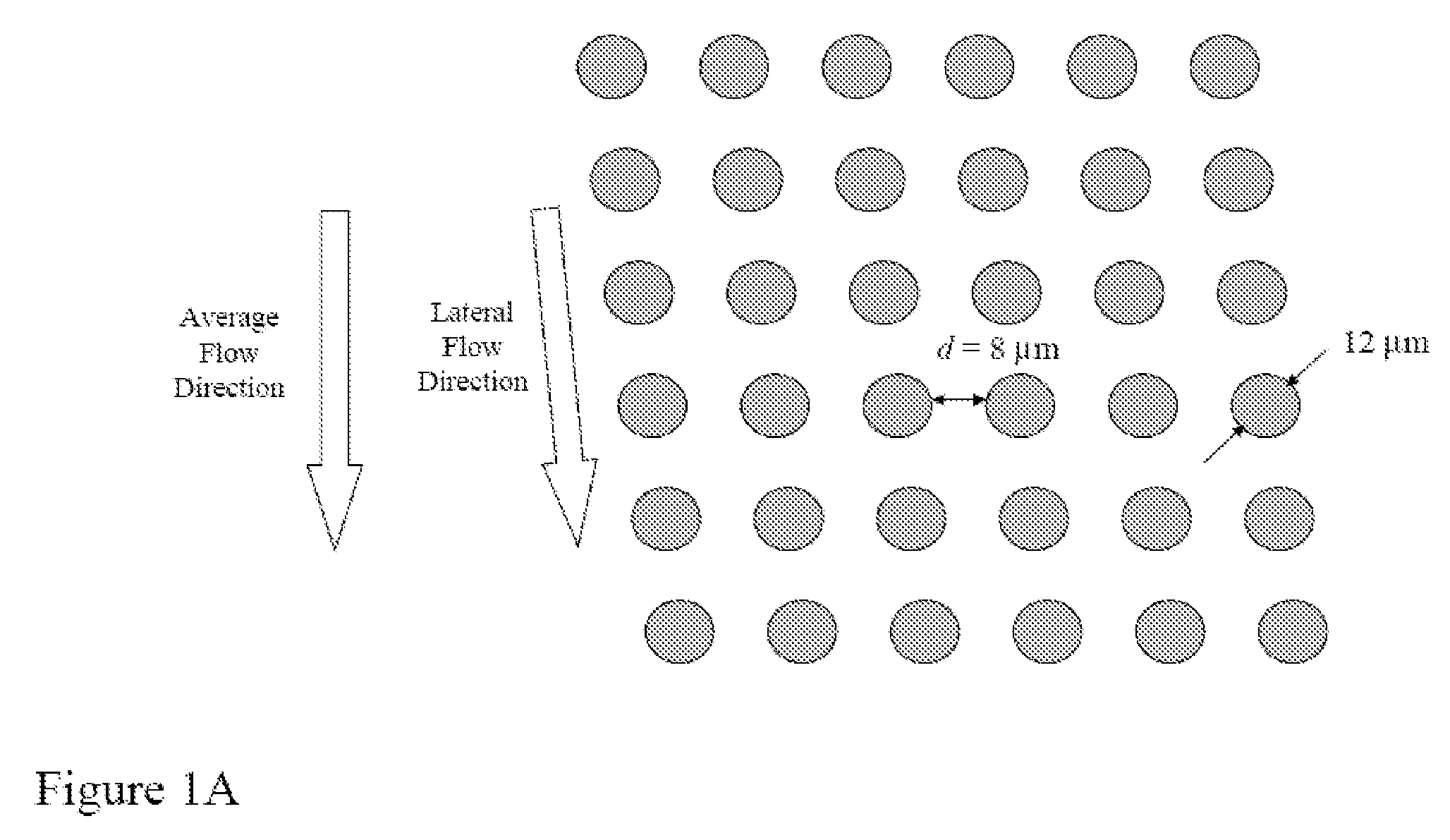
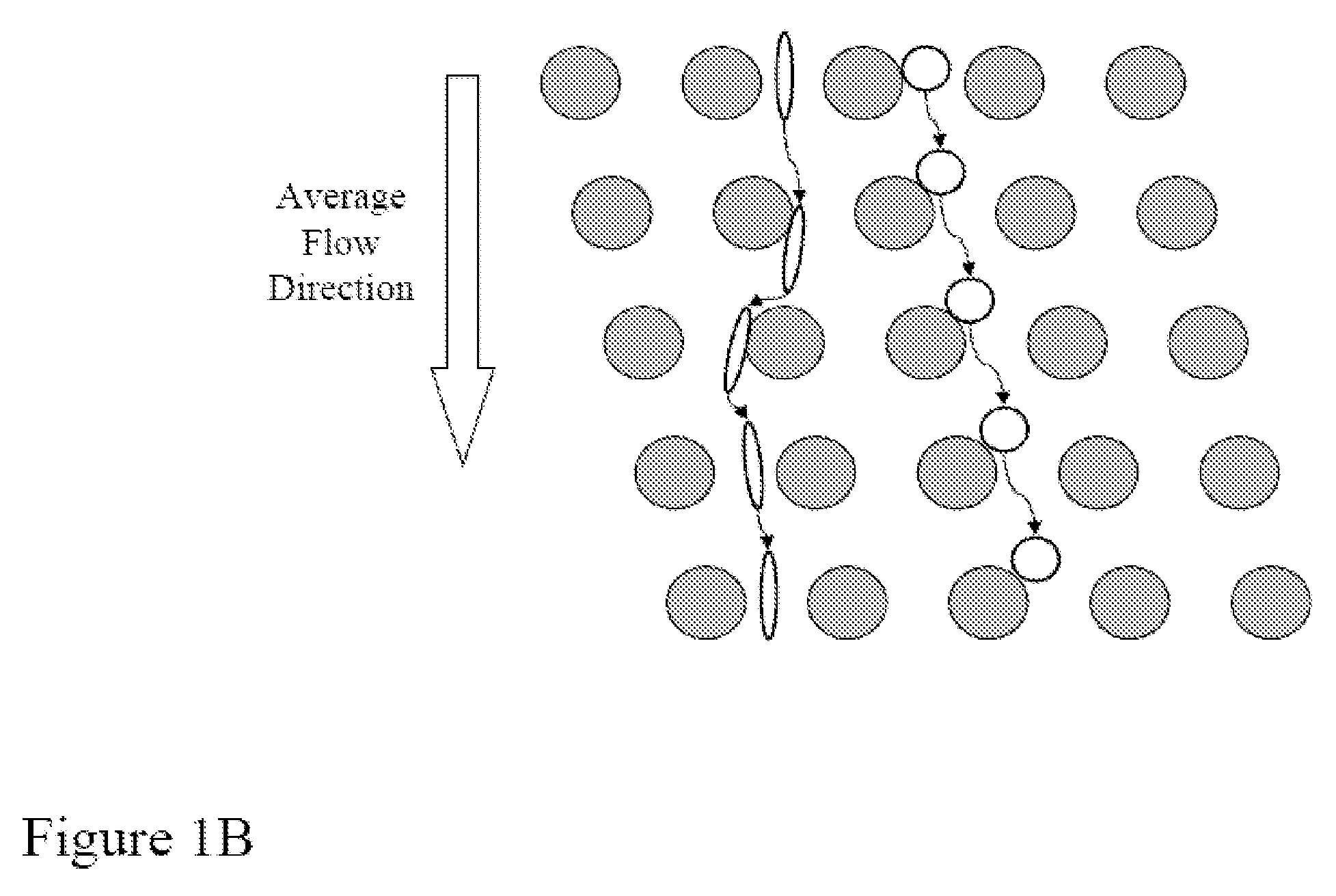
Rare cell analysis using sample splitting and DNA tags
ActiveUS20080220422A1Microbiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationFetal abnormalityRare cell
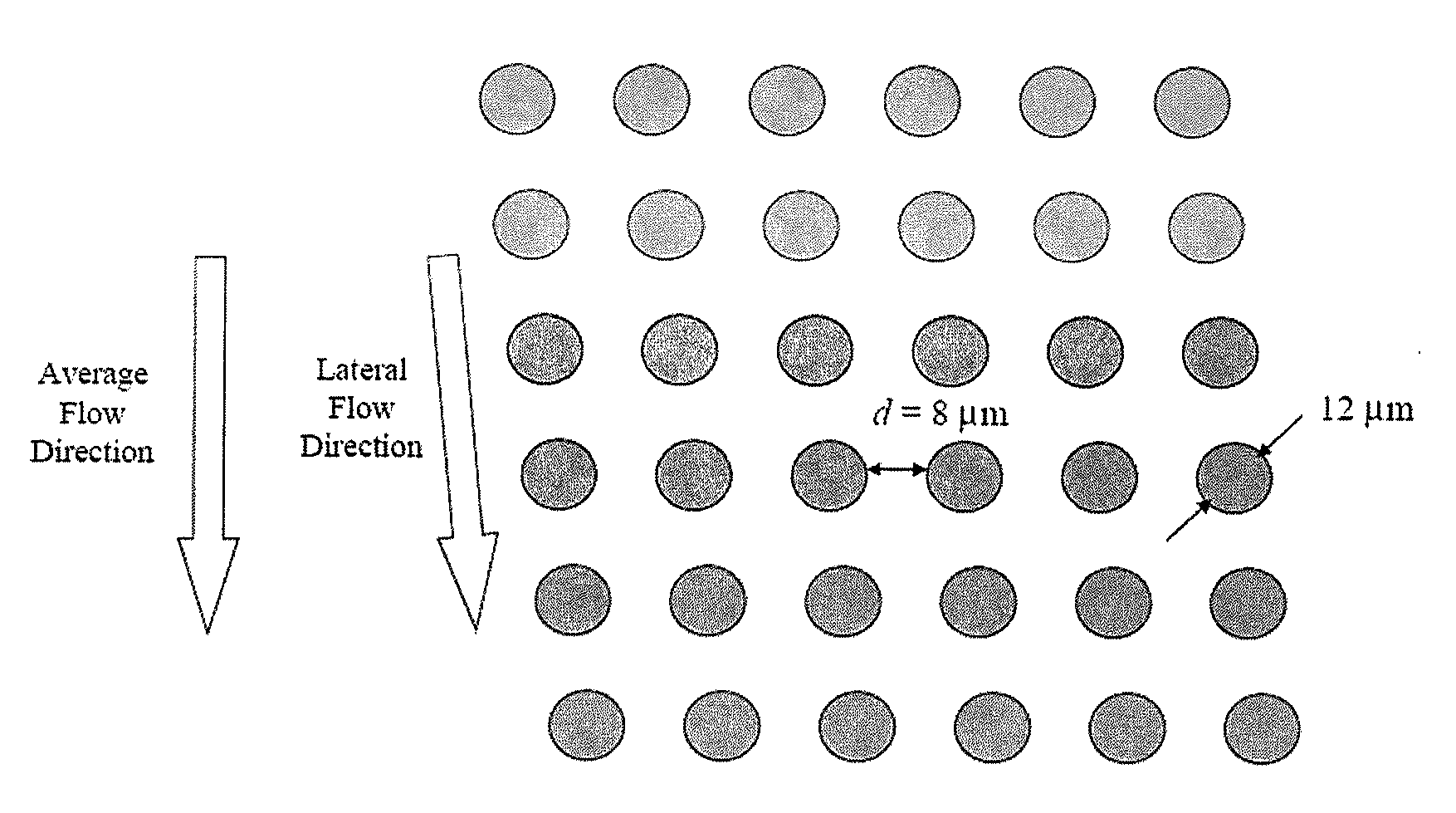
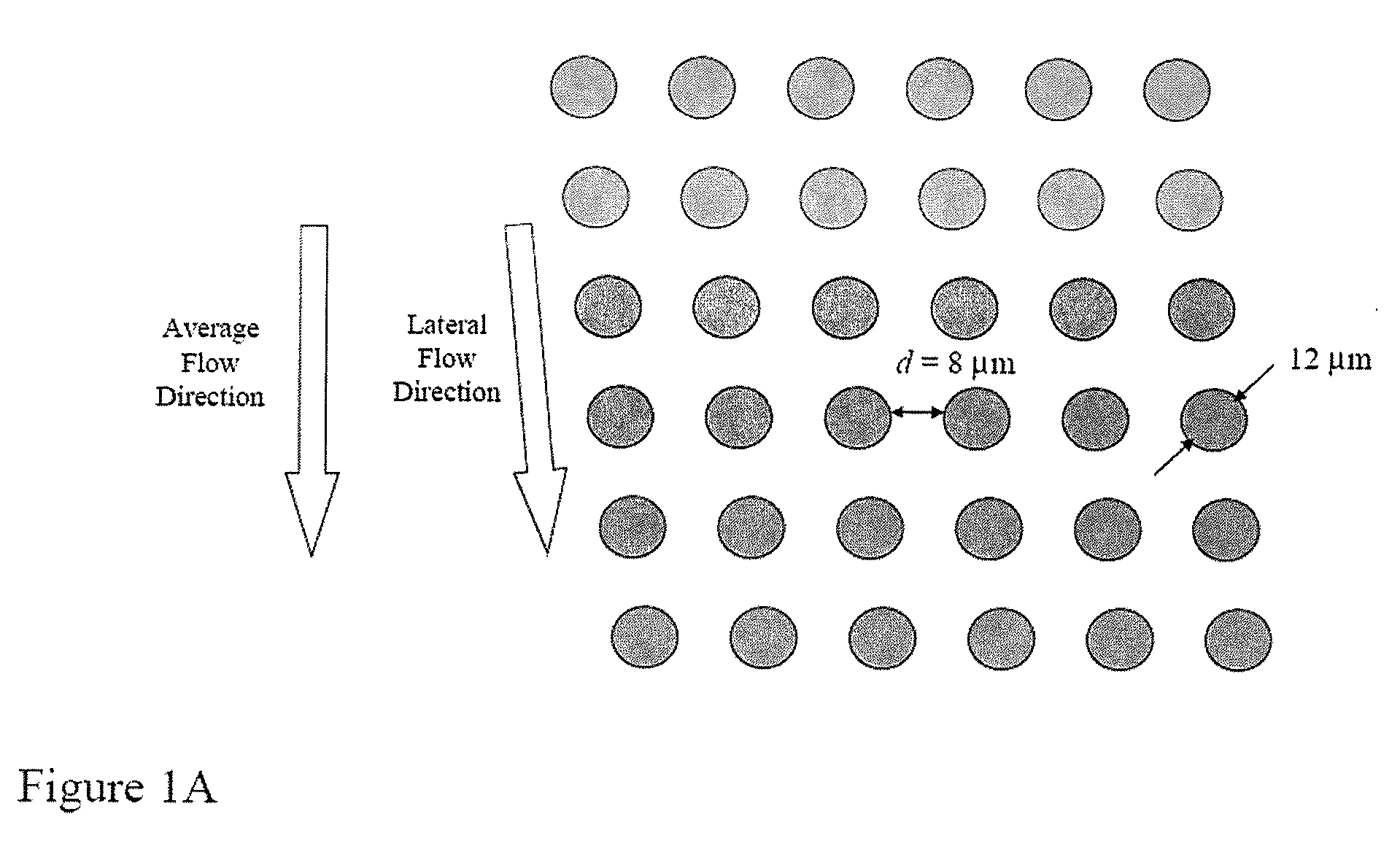
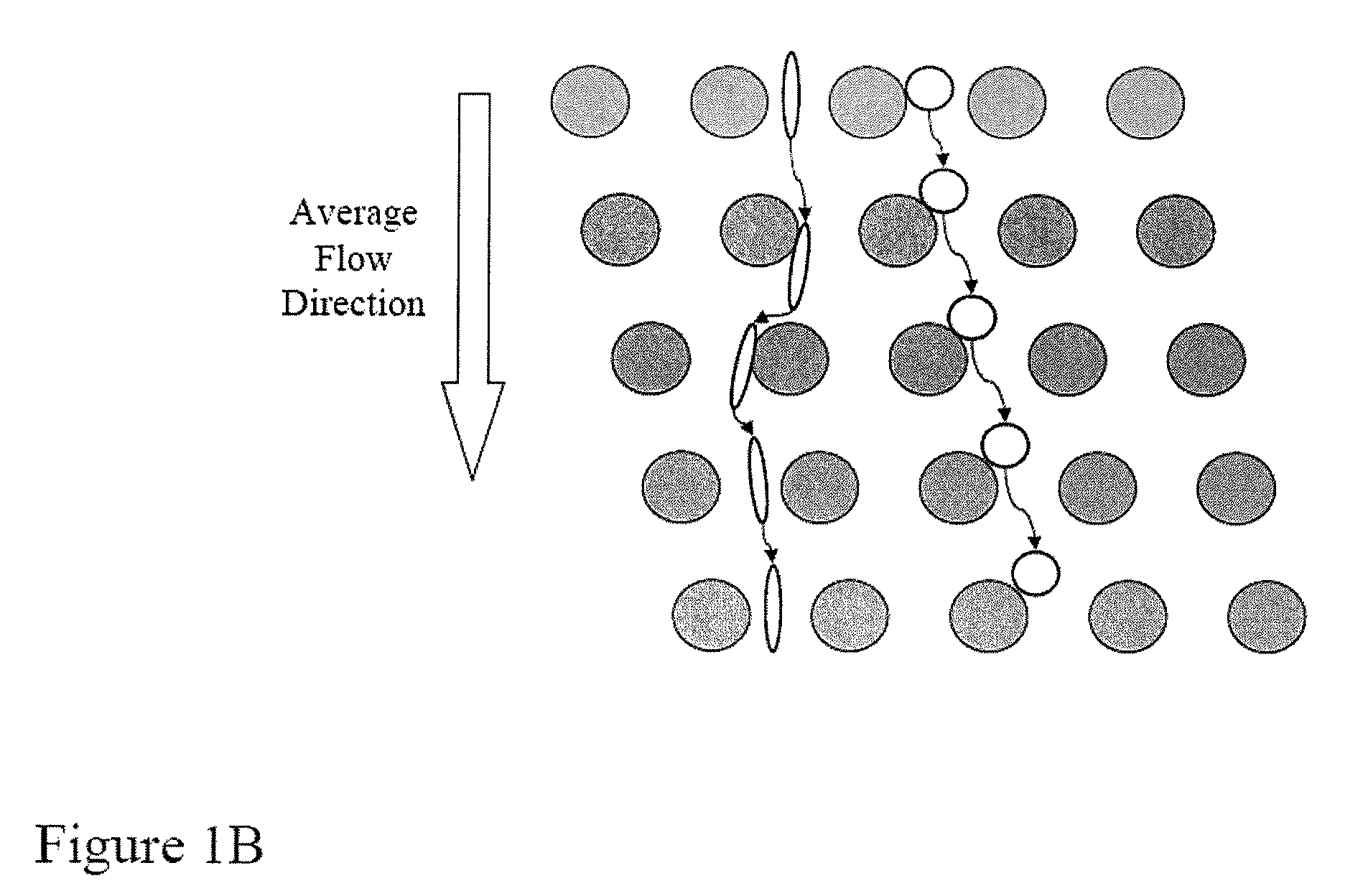
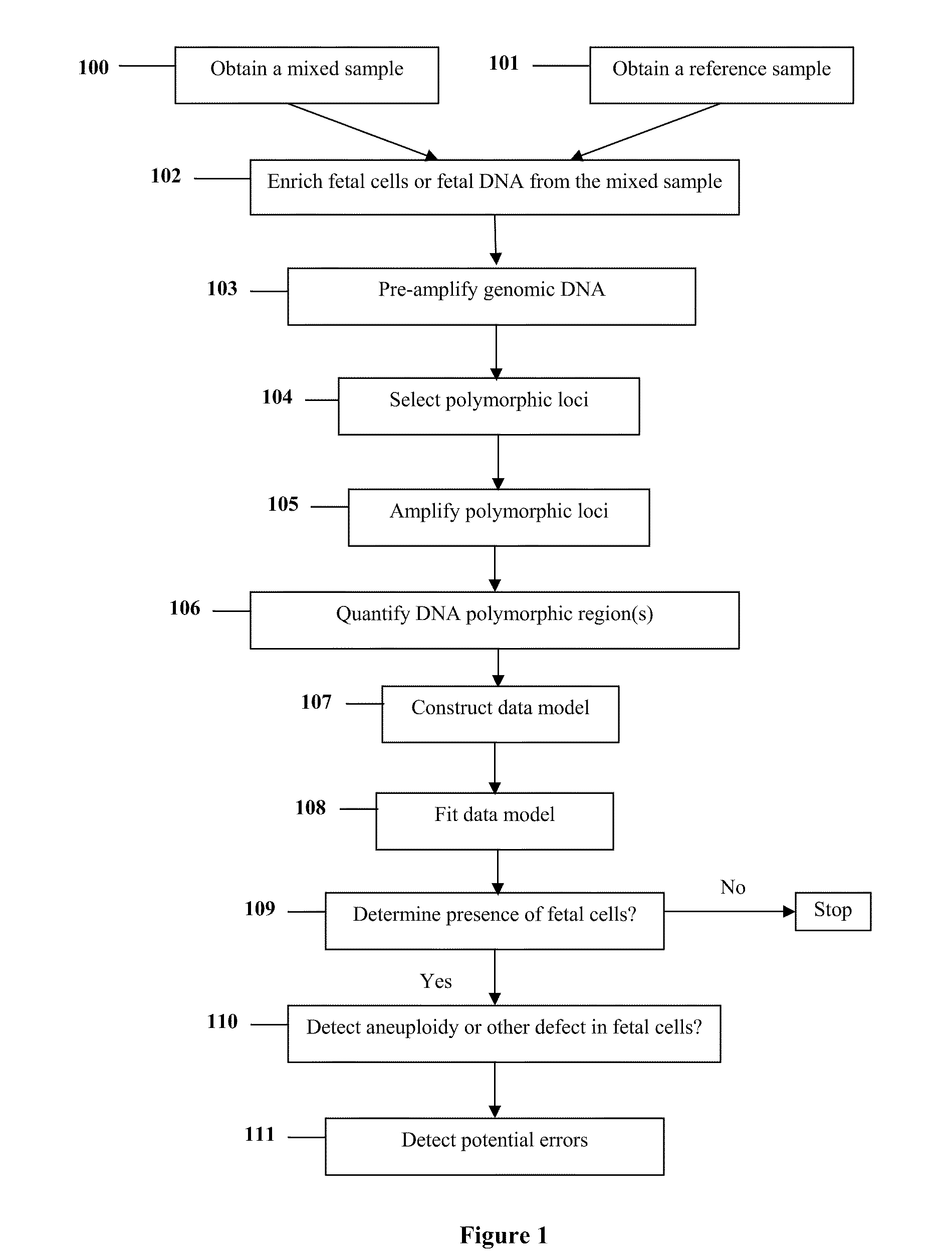
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to detect the presence of fetal cells when mixed with a population of maternal cells in a sample and to test fetal abnormalities, e.g. aneuploidy. The present invention involves labeling regions of genomic DNA in each cell in said mixed sample with different labels wherein each label is specific to each cell and quantifying the labeled regions of genomic DNA from each cell in the mixed sample. More particularly the invention involves quantifying labeled DNA polymorphisms from each cell in the mixed sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC +2
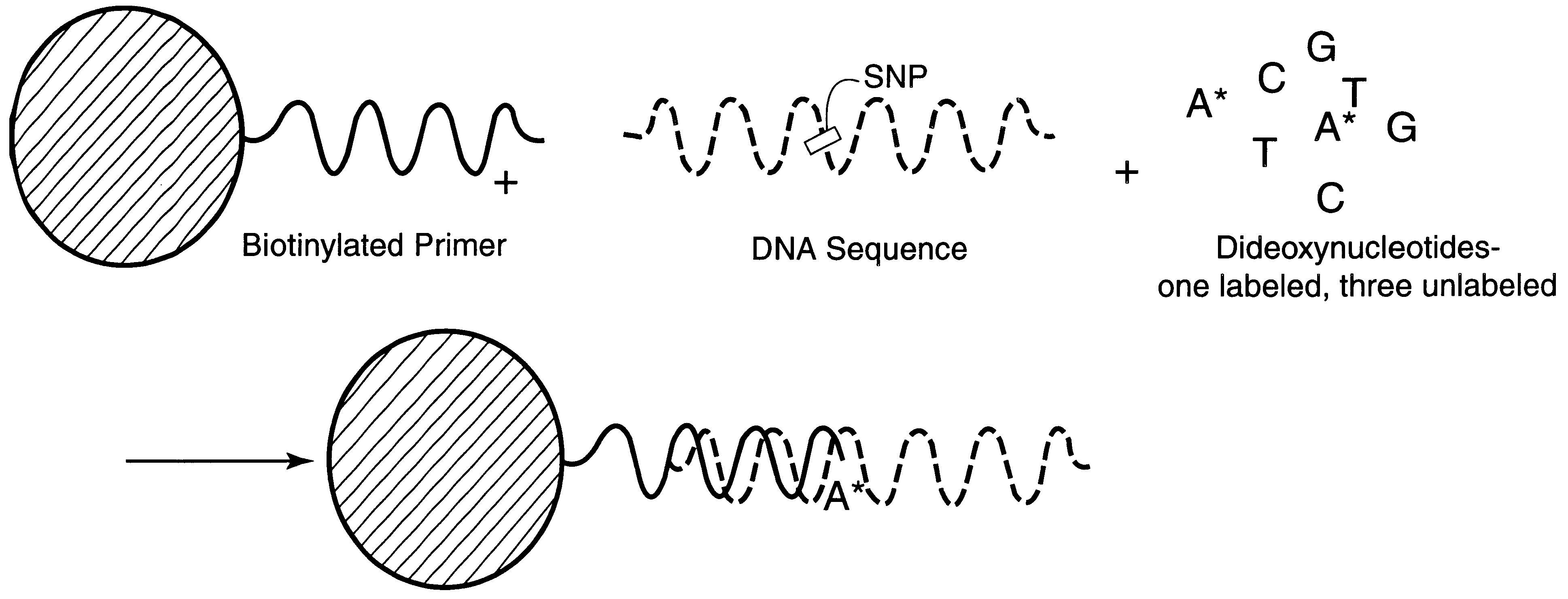
DNA polymorphism identity determination using flow cytometry
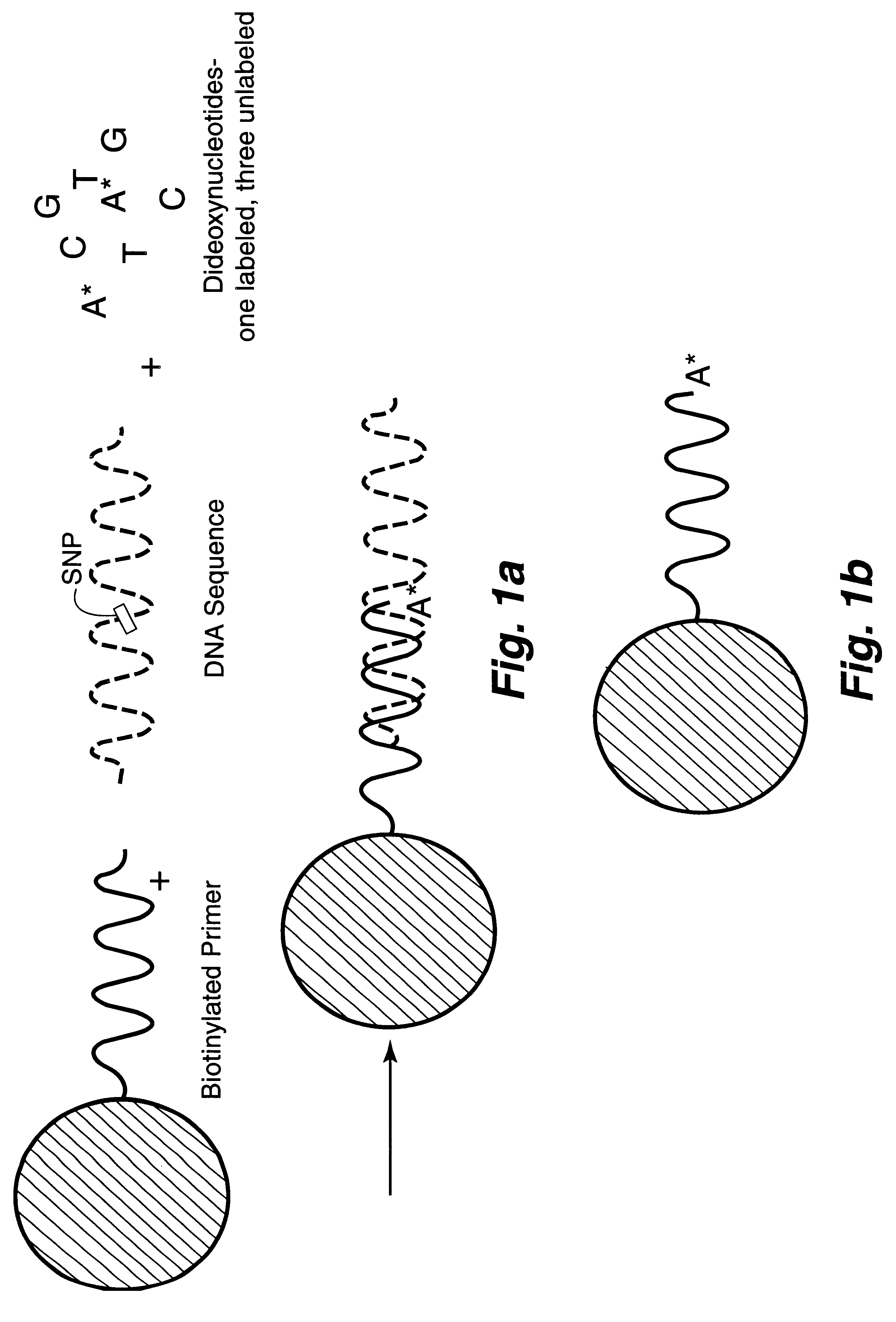
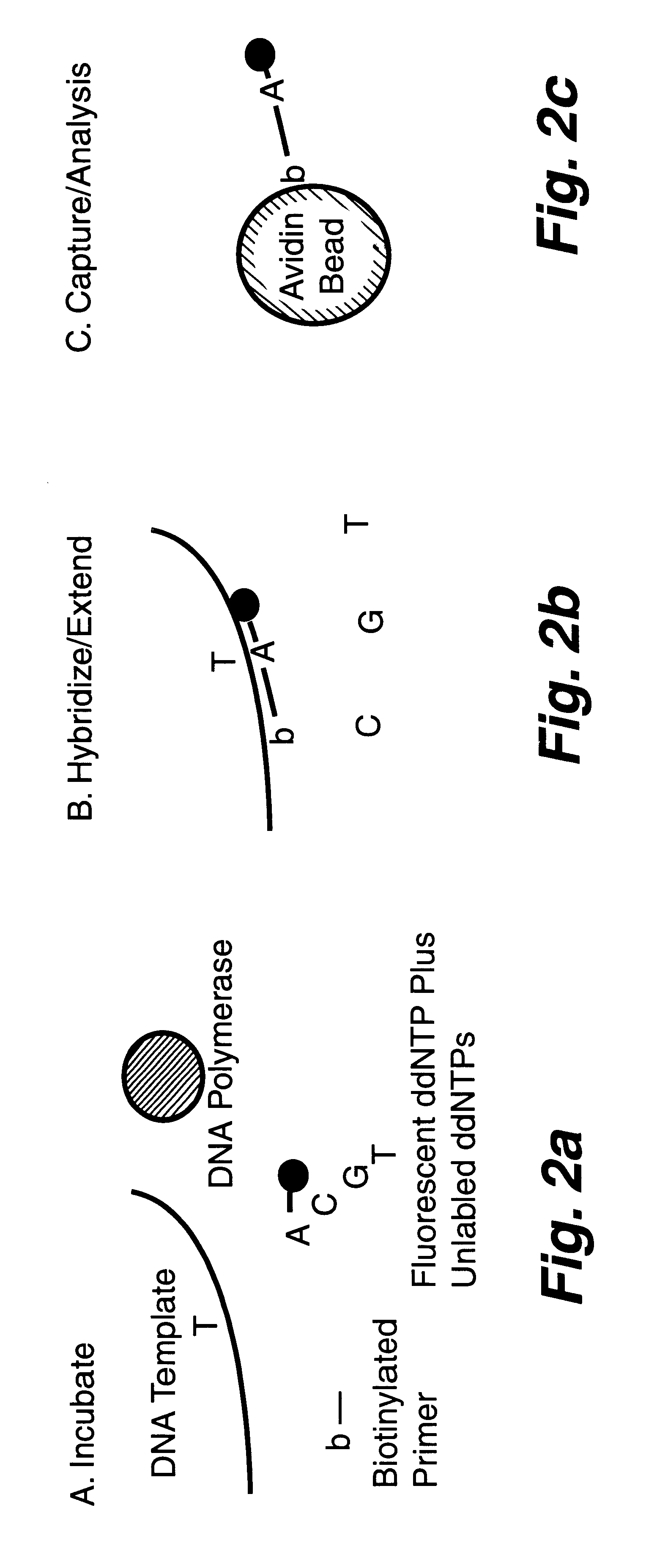
InactiveUS6287766B1Sensitive, homogenous, and flexibleSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosphereDideoxynucleotide Triphosphates
DNA polymorphism identity determination using flow cytometry. Primers designed to be immobilized on microspheres are allowed to anneal to the DNA strand under investigation, and are extended by either DNA polymerase using fluorescent dideoxynucleotides or ligated by DNA ligase to fluorescent reporter oligonucleotides. The fluorescence of either the dideoxynucleotide or the reporter oligonucleotide attached to the immobilized primer is measured by flow cytometry, thereby identifying the nucleotide polymorphism on the DNA strand.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Microdissection-based methods for determining genomic features of single chromosomes
InactiveUS20060211001A1Quick fixPromote associationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAChromosome regions
The present provides a microdissection-based method for identifying a genomic feature present within a visible chromosome region. The method includes steps of: (a) micro-dissecting a single copy of a chromosome to obtain a visible chromosome region; (b) amplifying the visible chromosome region to obtain amplified single chromosome DNA; and (c) subjecting the amplified single chromosome DNA to micro-array analysis whereby such analysis identifies at least one genomic feature present within the visible chromosome region. The method is applicable to determining genomic features including, but not limited to, genomic DNA size, gene content, DNA breakpoint, or DNA polymorphism (e.g., single nucleotide polymorphisms).
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Methods and compositions of molecular profiling for disease diagnostics
The present invention relates to compositions, kits, and methods for molecular profiling and cancer diagnostics, including but not limited to gene expression product markers, alternative exon usage markers, and DNA polymorphisms associated with cancer. In particular, the present invention provides molecular profiles associated with thyroid cancer, methods of determining molecular profiles, and methods of analyzing results to provide a diagnosis.
Owner:VERACYTE INC
Rare cell analysis using sample splitting and DNA tags
ActiveUS20100136529A1Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresFetal abnormalityRare cell
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to detect the presence of fetal cells when mixed with a population of maternal cells in a sample and to test fetal abnormalities, e.g. aneuploidy. The present invention involves labeling regions of genomic DNA in each cell in said mixed sample with different labels wherein each label is specific to each cell and quantifying the labeled regions of genomic DNA from each cell in the mixed sample. More particularly the invention involves quantifying labeled DNA polymorphisms from each cell in the mixed sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC +2
Diagnosis of fetal abnormalities using polymorphisms including short tandem repeats
InactiveUS20090280492A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationFetal abnormalityGenomic DNA
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to detect the presence of fetal cells when mixed with a population of maternal cells in a sample and to test fetal abnormalities, i.e. aneuploidy. In addition, the present invention provides methods to determine when there are insufficient fetal cells for a determination and report a non-informative case. The present invention involves quantifying regions of genomic DNA from a mixed sample. More particularly the invention involves quantifying DNA polymorphisms from the mixed sample.
Owner:STOUGHTON ROLAND +2
Methods and compositions of molecular profiling for disease diagnostics
The present invention relates to compositions, kits, and methods for molecular profiling and cancer diagnostics, including but not limited to gene expression product markers, alternative exon usage markers, and DNA polymorphisms associated with cancer. In particular, the present invention provides molecular profiles associated with thyroid cancer, methods of determining molecular profiles, and methods of analyzing results to provide a diagnosis.
Owner:VERACYTE INC
Genomic profiling: repid method for testing complex biological sample for presence of many types of organisms
InactiveCN1370242ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingFast methods
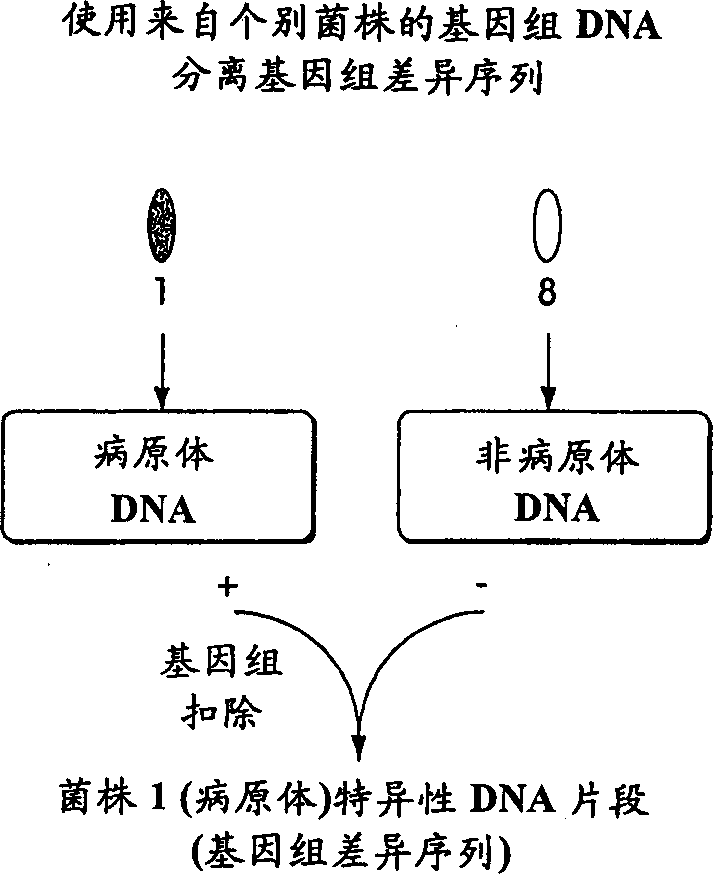
The present invention provides a method called genome distribution analysis, which simultaneously scans the nucleic acid sequences (including genome differential sequences, group-specific sequences, and DNA polymorphisms) of various types of biological characteristics in complex biological samples. exist. The invention also includes probes, detection assemblies and related molecules for use in the methods of the invention.
Owner:基因描绘系统有限公司
DNA polymorphism-based methods for identifying field resistance of rice to rice blast
InactiveUS6963020B1Conveniently and accurately selected indoorReduce laborPlant genotype modificationRice plantsOryza
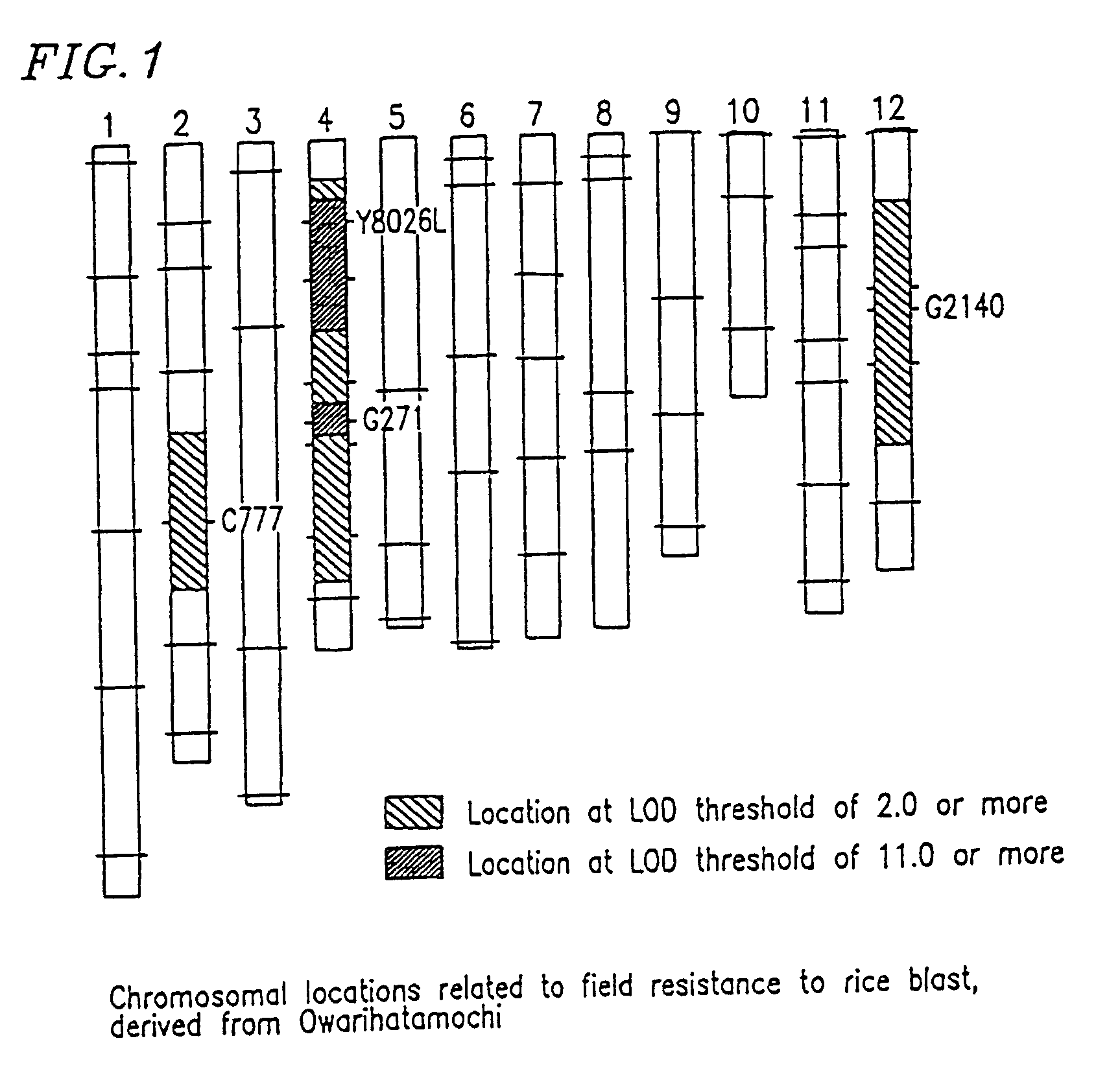
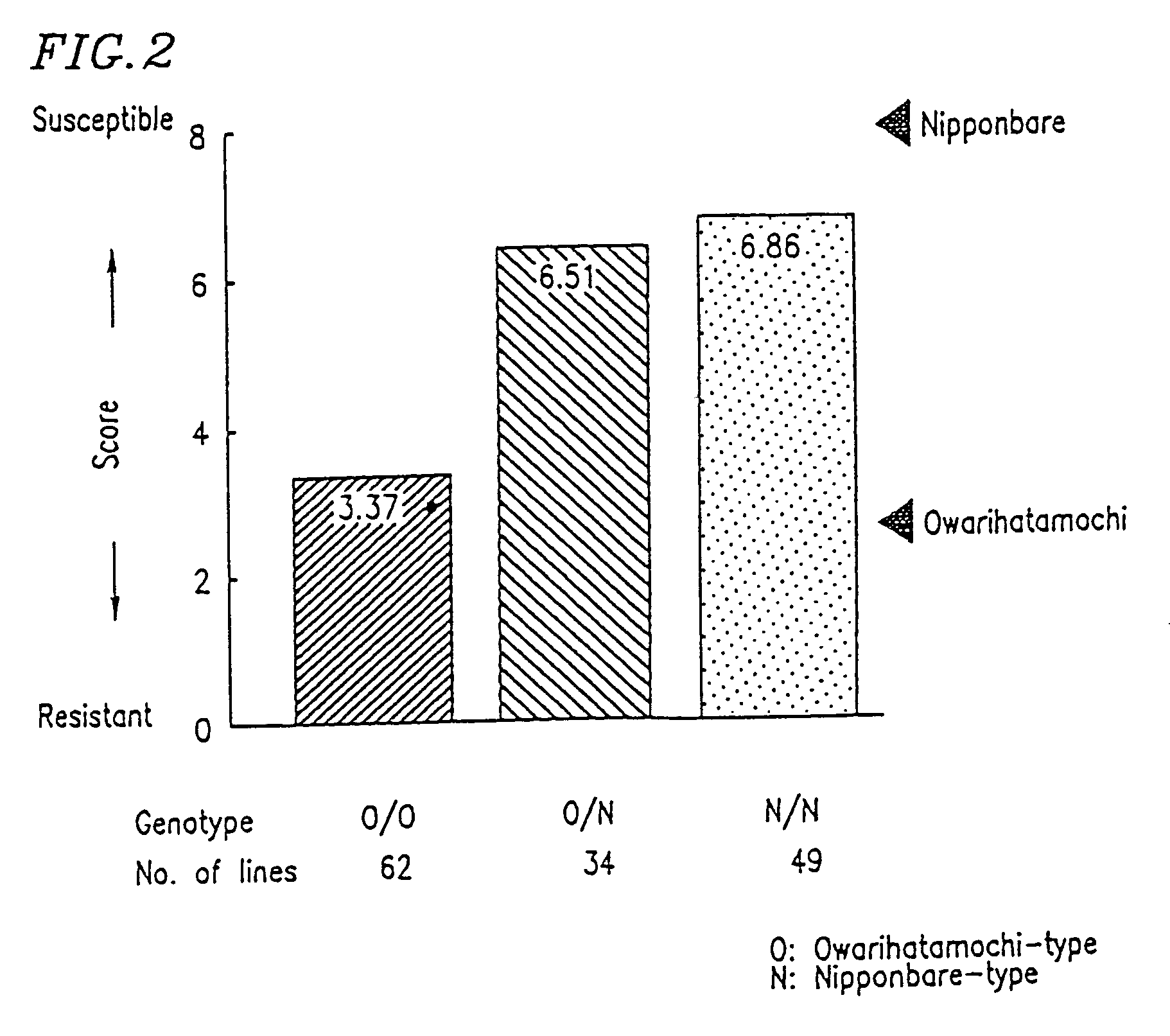
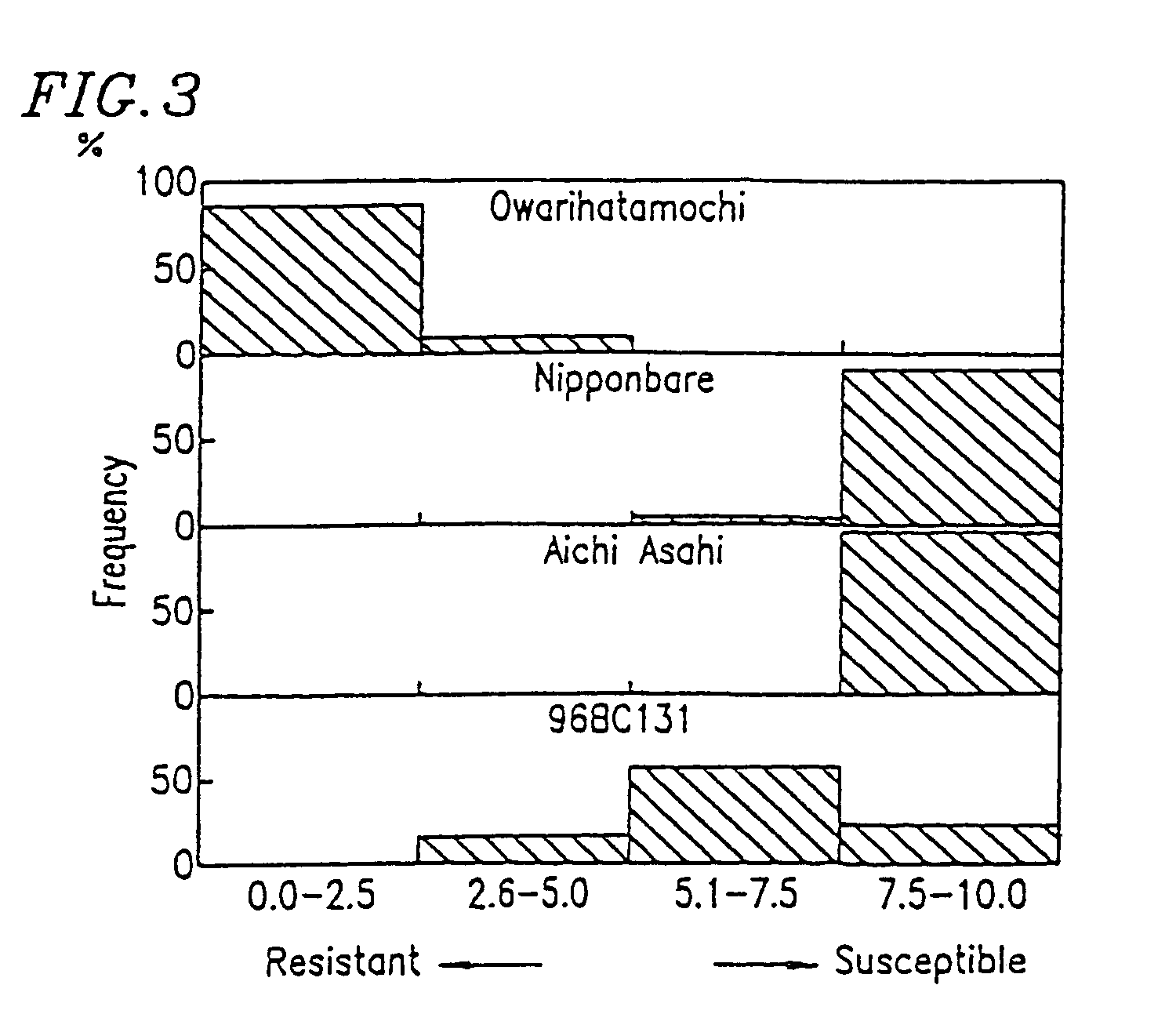
A method for identifying resistance of a rice plant to rice blast is provided. More particularly, a method for identifying resistance of a rice plant to rice blast by testing a genotype of the rice genome using a DNA marker (G271), which is closely linked to a gene controlling the field resistance to rice blast, is disclosed. The disclosed invention allows for evaluation of the field resistance of a rice plant to rice blast using a DNA marker, thereby allowing for a resistant variety to be conveniently and accurately selected. The disclosed invention contributes to reducing the time and labor that have conventionally been required for cross breeding, and is useful in developing novel rice varieties having a high degree of field resistance to rice blast.
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI
Multiple detection method for DNA polymorphism of genome and special probe thereof
InactiveCN102181443AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
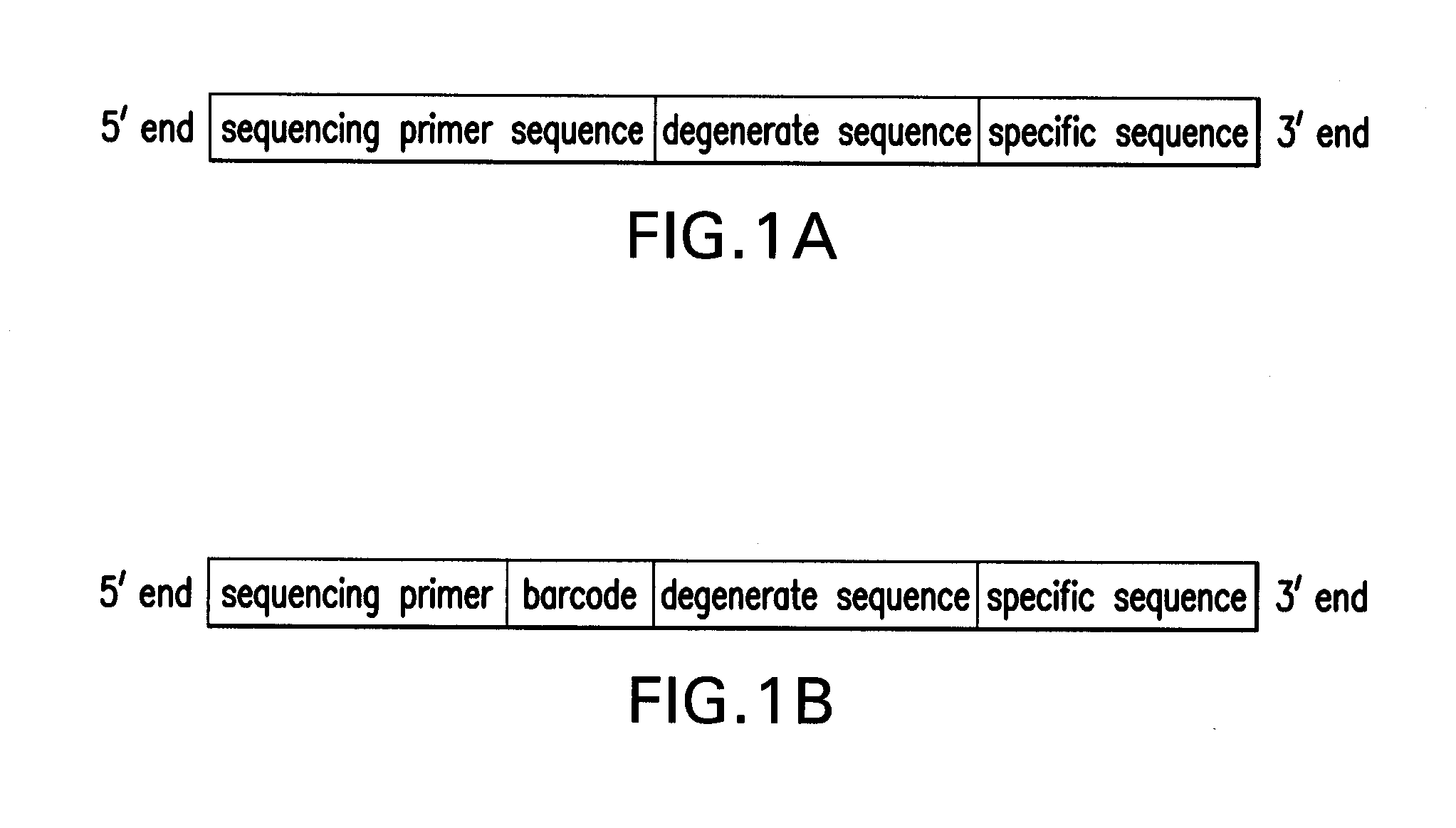
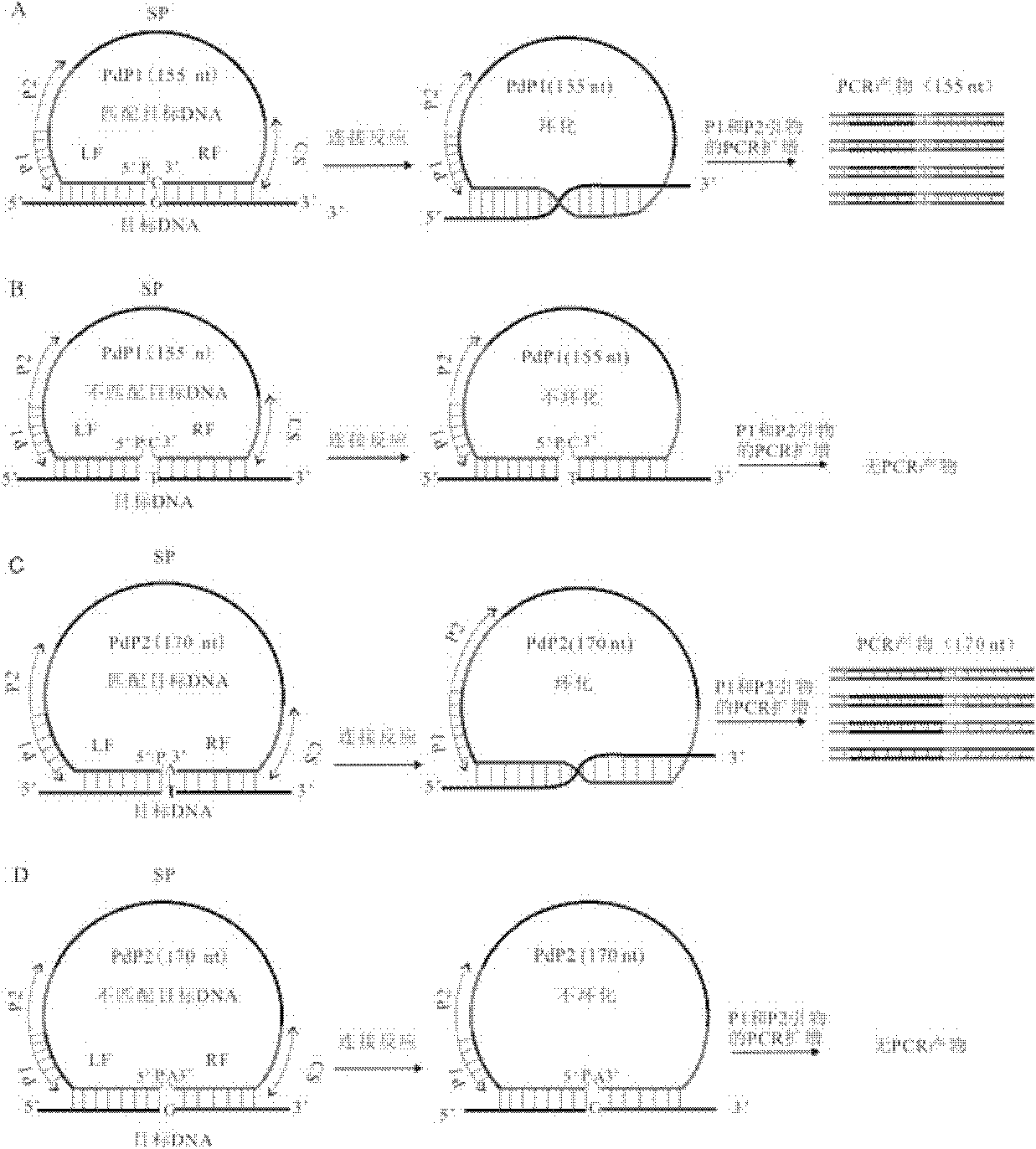
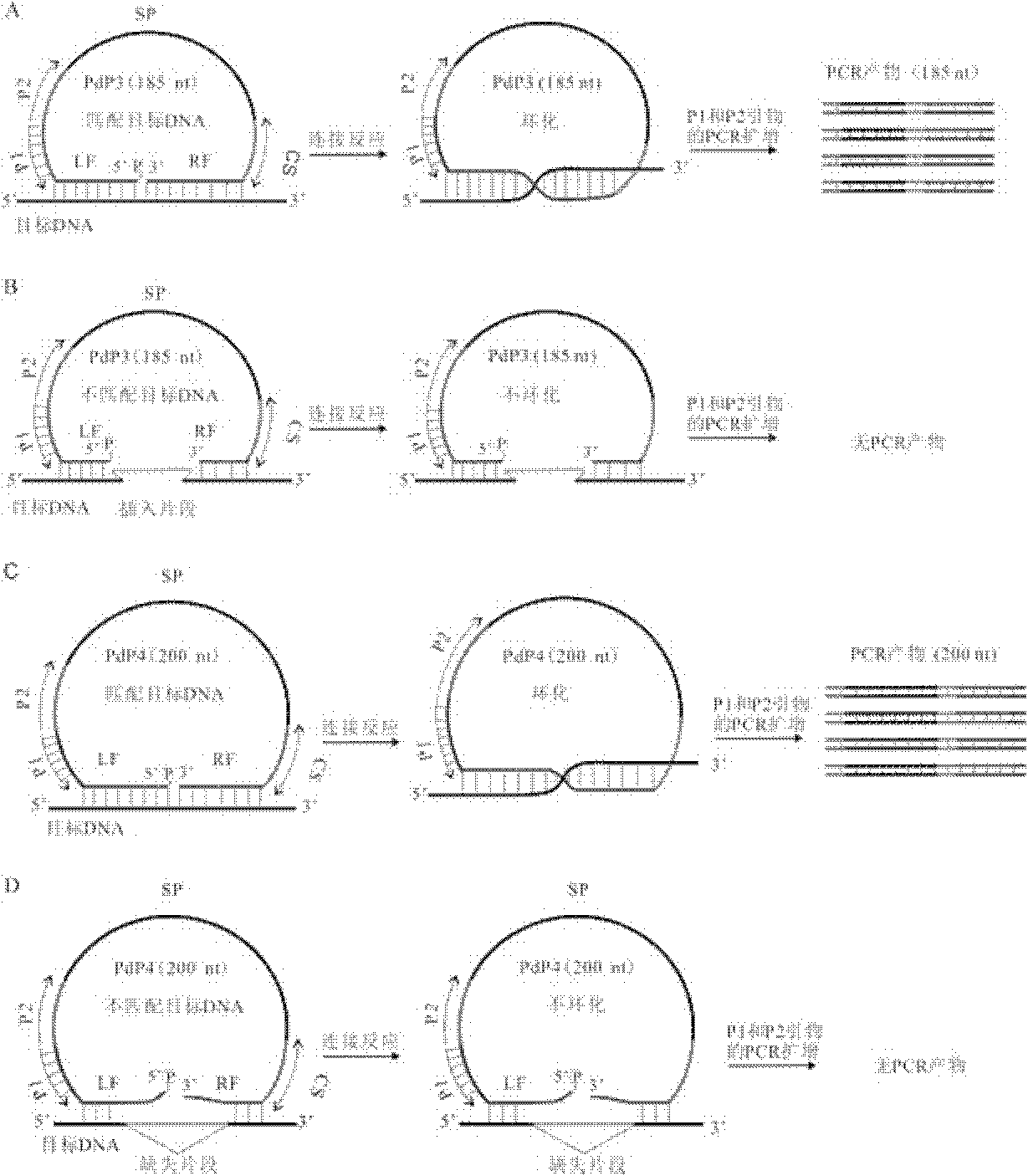
The invention discloses a multiple detection method for deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) of a genome and a special probe thereof, and provides a single chain DNA molecule. The single chain DNA molecule consists of the following segments sequentially from 5' tail end to 3' tail end: a left side oligonucleotide segment complementary with a 5' end of DNA to be detected, a main body segment and a rightside oligonucleotide segment complementary with a 3' end of the DNA to be detected. Experiments prove that: in the single chain DNA molecule provided by the invention, loci with different markers andalleles are distinguished from one another through a ligase reaction, buckled probes which have different lengths and are successfully connected through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification can simultaneously detect the polymorphism of a plurality of DNA markers through a gel or capillary electrophoretic separation and detection system, high sensitivity and accuracy can be realized, and the requirements of high throughout and low cost are met simultaneously.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
bPrimer batch PCR primer design method based on Primer 3
ActiveCN105718759AReduce amplification failureHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsCrowdsFailure causes
The invention provides a bPrimer batch PCR primer design method based on a Primer 3.The method includes the steps that an original sequence of a target DNA sequence is obtained; a high-frequency polymorphic locus in DNA polymorphic data is extracted; the high-frequency polymorphic locus is labeled; an annotated sequence of the labeled high-frequency polymorphic locus is output, and the annotated sequence and the original sequence are identical in basic group length; the annotated sequence is read to generate candidate primers; the candidate primers are screened.The bPrimer batch PCR primer design method based on the Primer 3 can avoid the high-frequency polymorphic locus, reduces amplification failure caused by genetic diversity of target population, can detect specificity of primers in batches, reduces amplification failure caused by nonspecific amplification, primer dimer and other reasons, can be used for evaluating specificity of existing primers, and can automatic segment long target segments.
Owner:HUNAN SHENGWEI GENE TECH
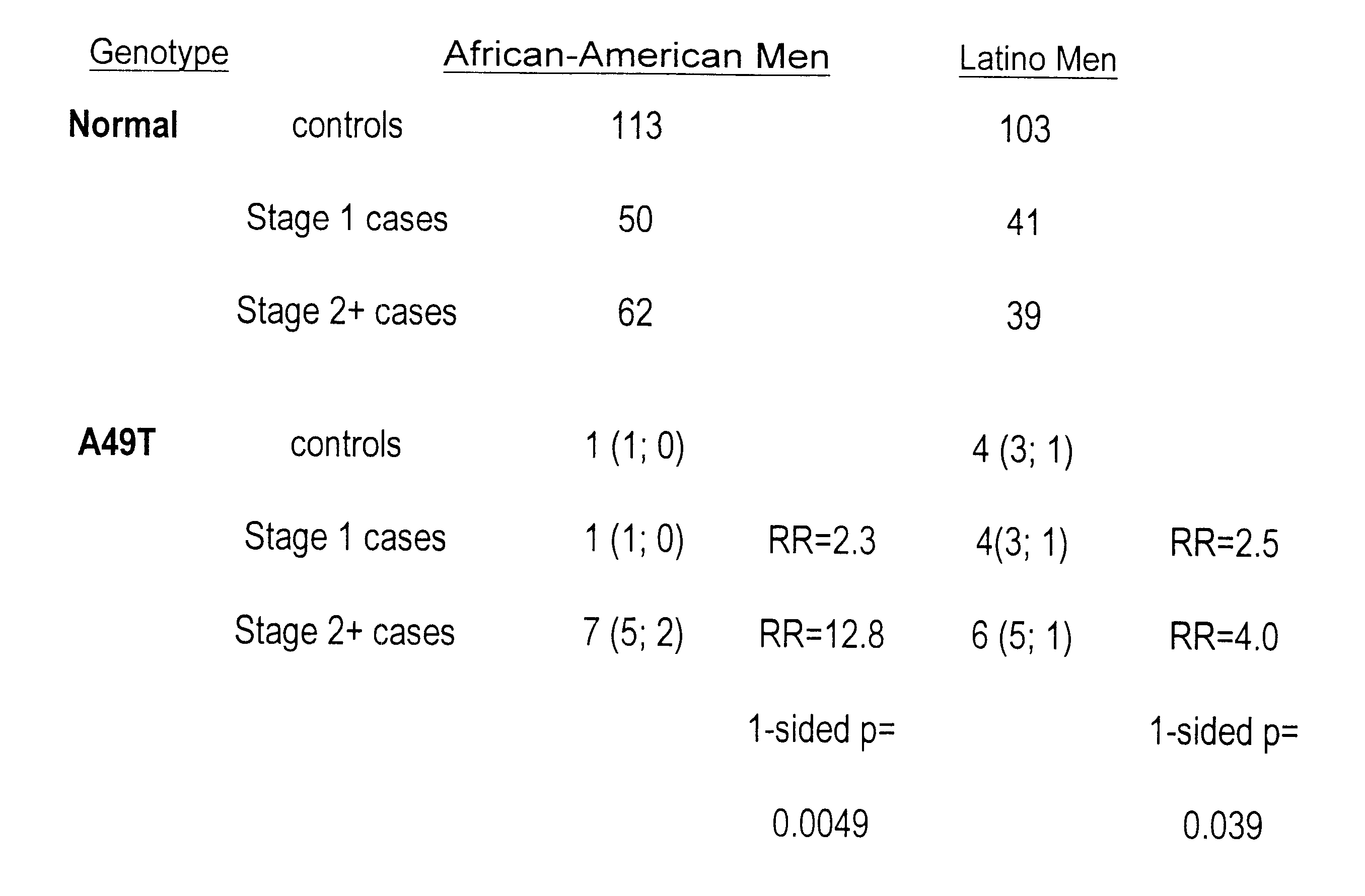
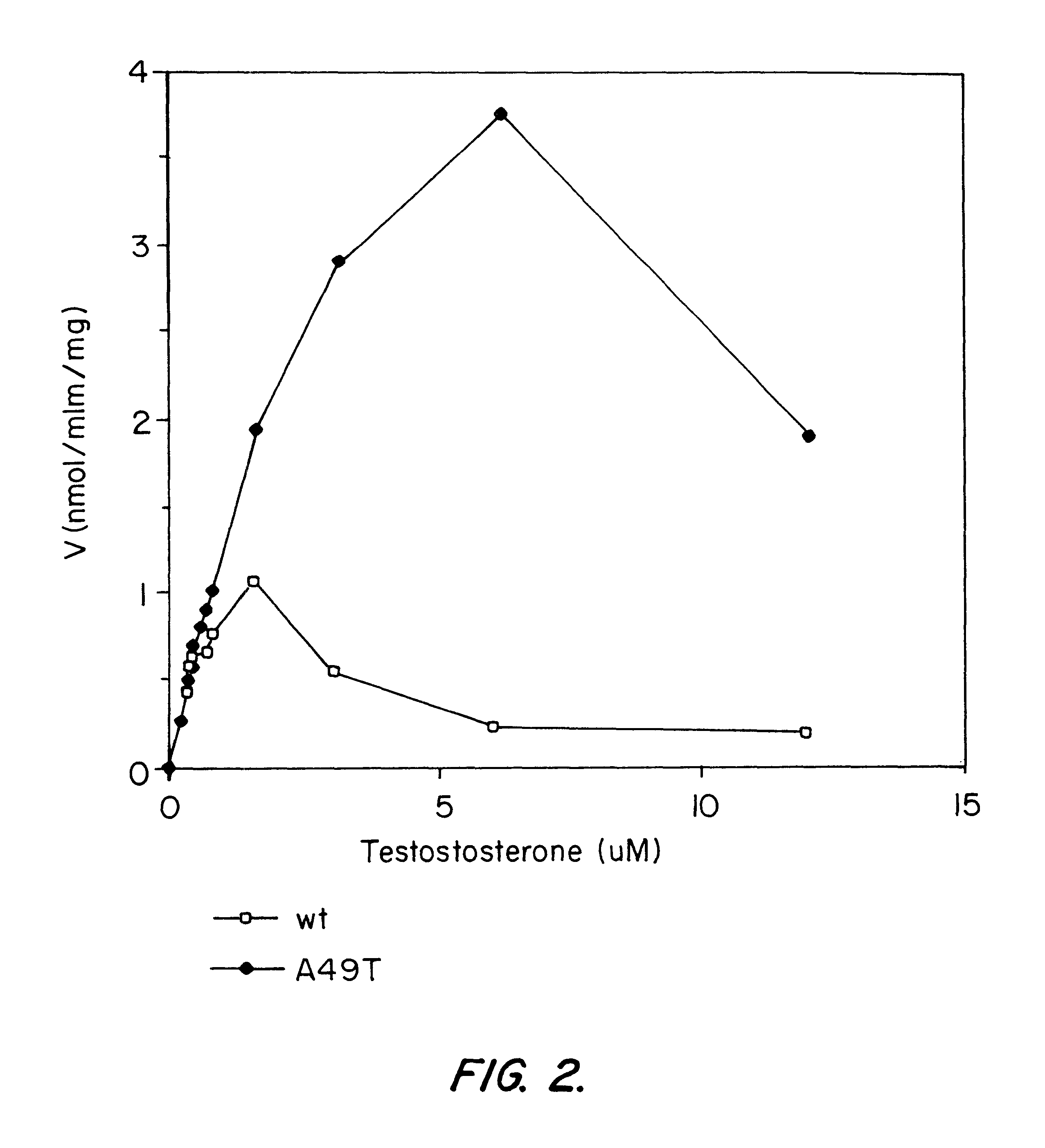
Androgen-metabolic gene mutations and prostate cancer risk
This present invention identifies mutations in several androgen-metabolic genes (SRD5A2, CYP17, HSD3B2, and HSD17B3) and methods of using such mutations in the diagnosis and treatment of inheritable prostate cancer susceptibility. Isolation of genomic DNA of various racial / ethnic populations followed by SSCP scanning and direct PCR sequencing of the aberrant SSCP (single-strand conformation dependent DNA polymorphism) patterns allows for identification of the disclosed polymorphisms. Screening for the disclosed mutations establishes a differential distribution among various racial / ethnic groups as well as altered in vivo enzyme activity that parallels prostate cancer risk.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Method for genome complexity reduction and polymorphism detection
The present invention provides methods to produce a reduced representation of a genome for sequencing and DNA polymorphism detection. In particular, the invention provides PCR-based methods, with normalization of the amplified products using a duplex-specific nuclease, in order to reduce over-representation of PCR products. Oligonucleotides for use in the disclosed method are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method for identifying meat production traits of sheep and special primer thereof
ActiveCN109234404AIncrease meat productionLong relief timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideTyping
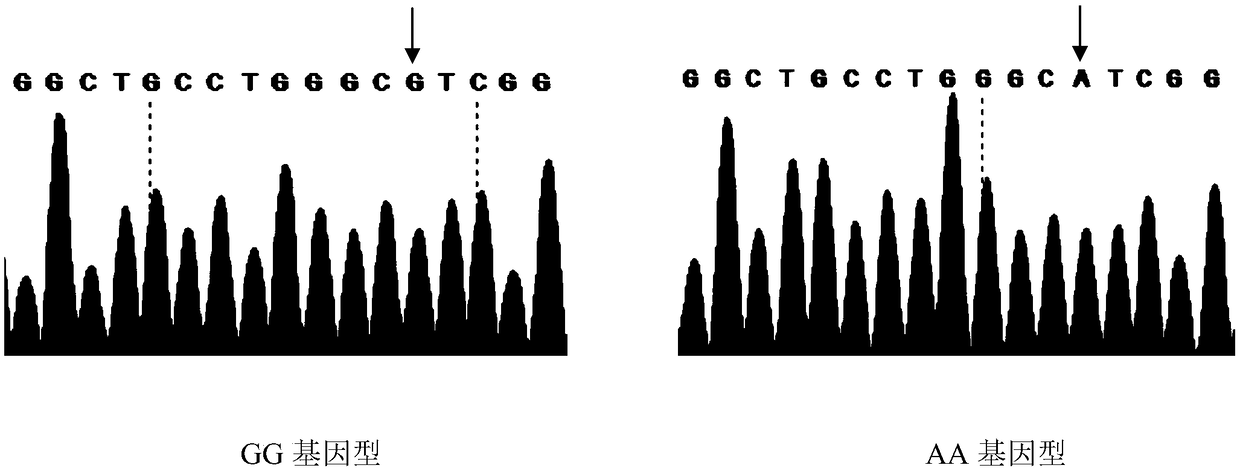
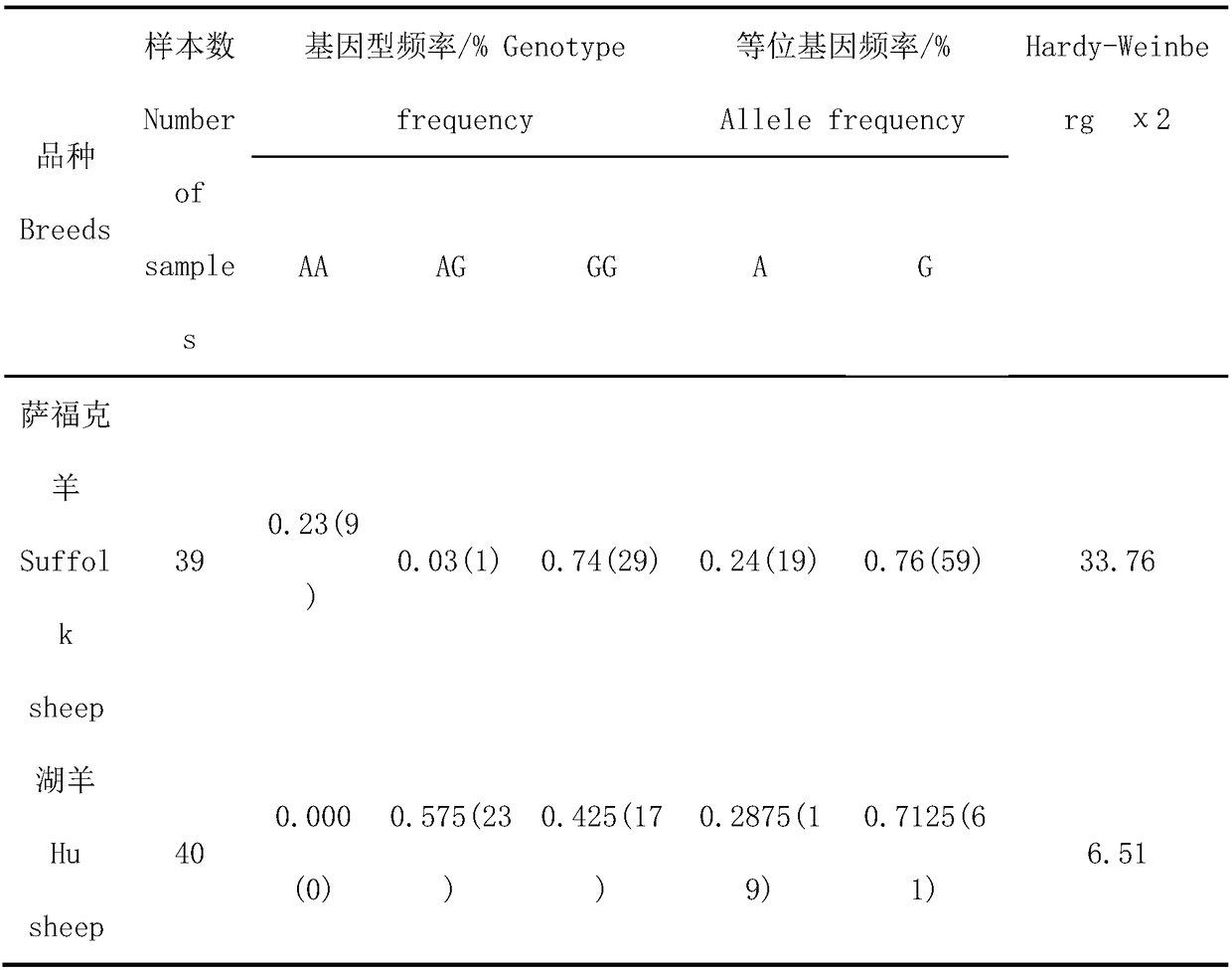
The invention discloses a method for assisting identification of meat production related traits of sheep and application thereof. The invention provides a method for assisting identification of meat-producing related traits of sheep, which comprises the following steps of: adopting specific primers to carry out PCR amplification on genomic DNA of sheep to be tested, utilizing DNA sequencing and asymmetric PCR; and using the specific primers to amplify the genomic DNA of sheep to be tested. DNA polymorphism detection and rapid typing by SSCP, The 209th nucleotide from 5 'end of PCR amplified product was A or G, and the genotype of sheep was GG or AA. There was a certain correlation between the SNP locus and the meat-producing traits of sheep. The meat-producing performance of sheep with GGgenotype was higher than that of sheep with AA genotype. The invention can be used for early screening of sheep meat production, effectively increasing the meat production of sheep breeding, reducingbreeding cost, and improving the economic benefit of sheep breeding. The method of the invention is simple in operation, low in cost and high in accuracy, and will have important significance for sheep breeding.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
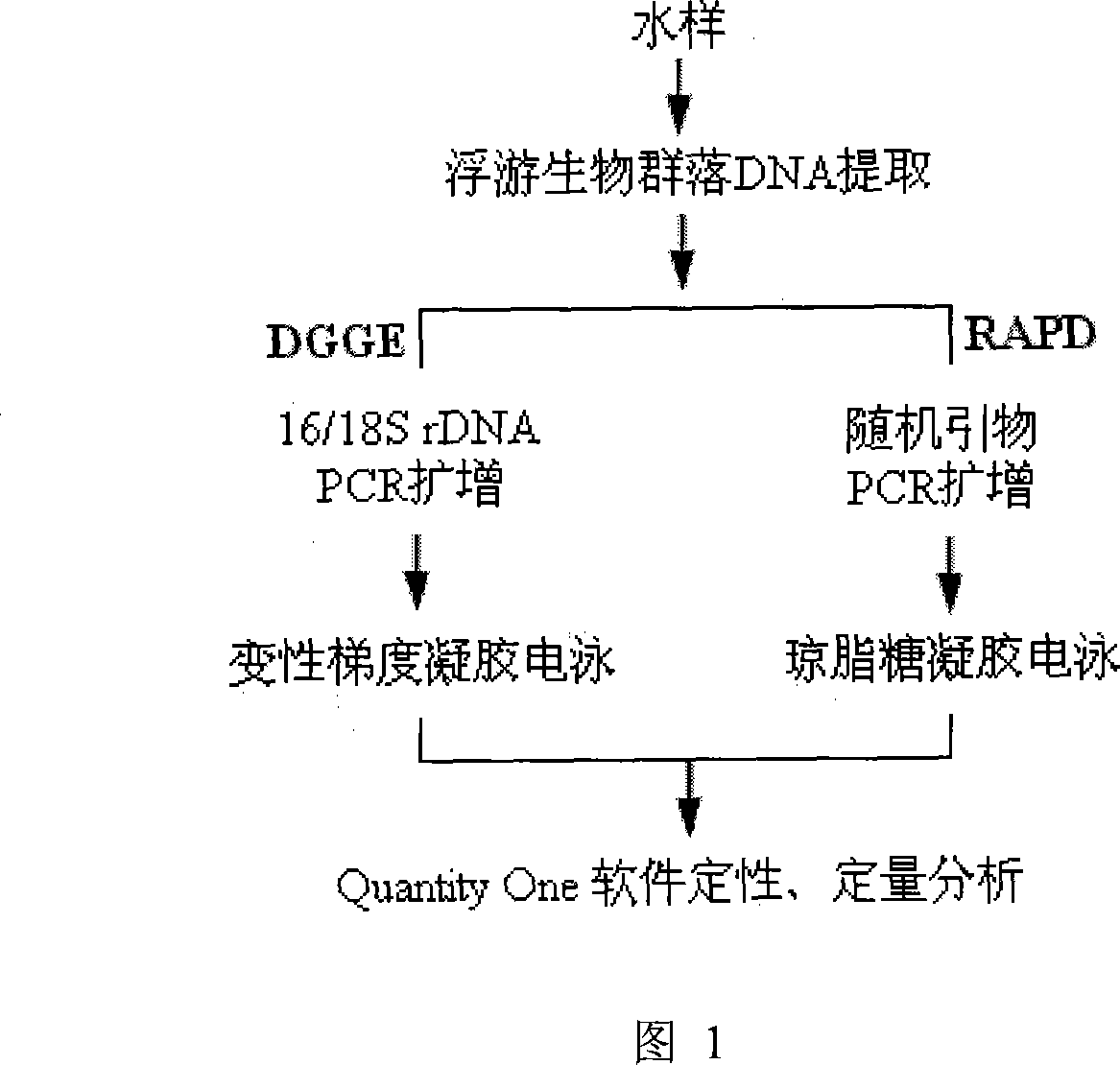
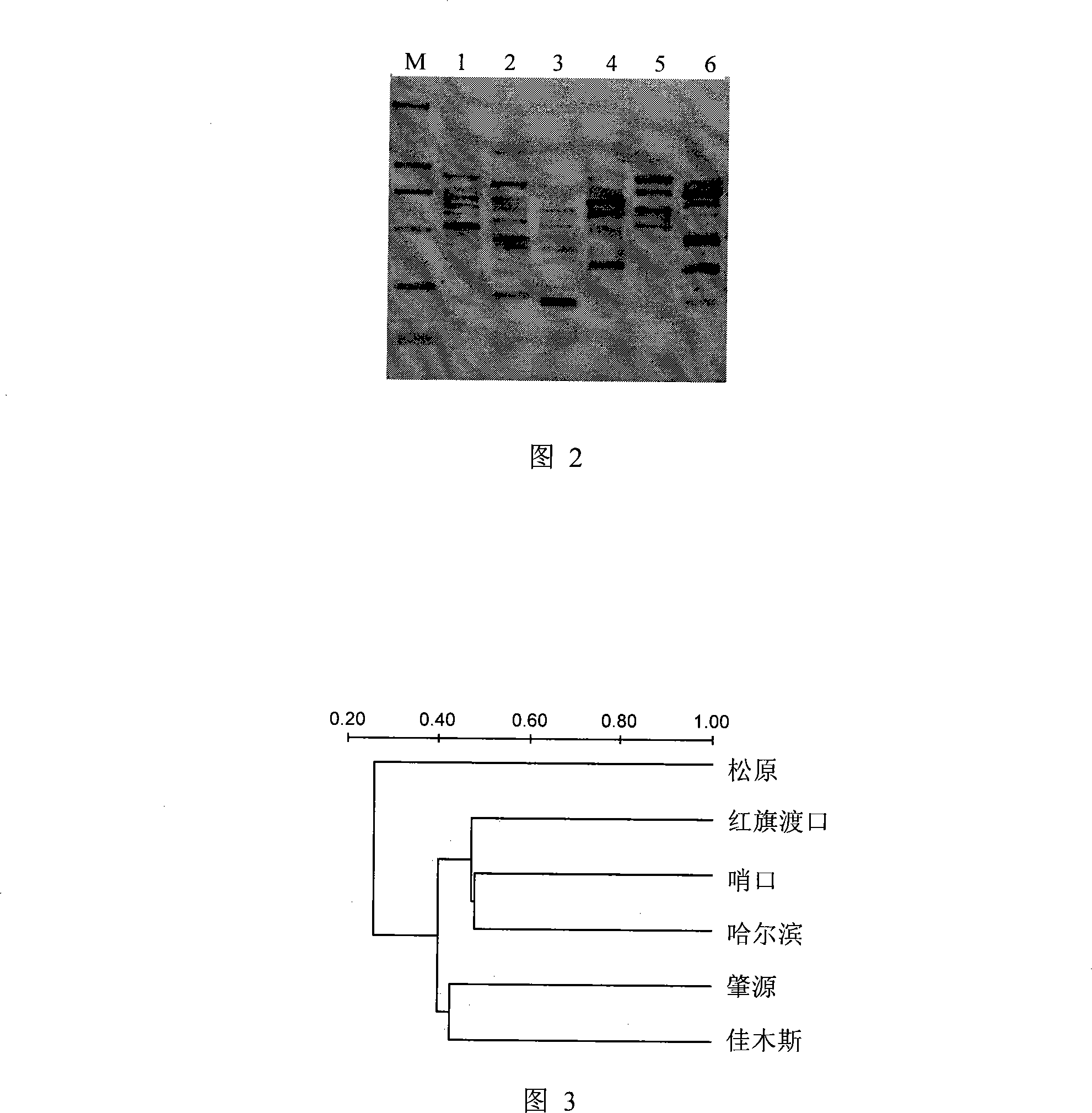
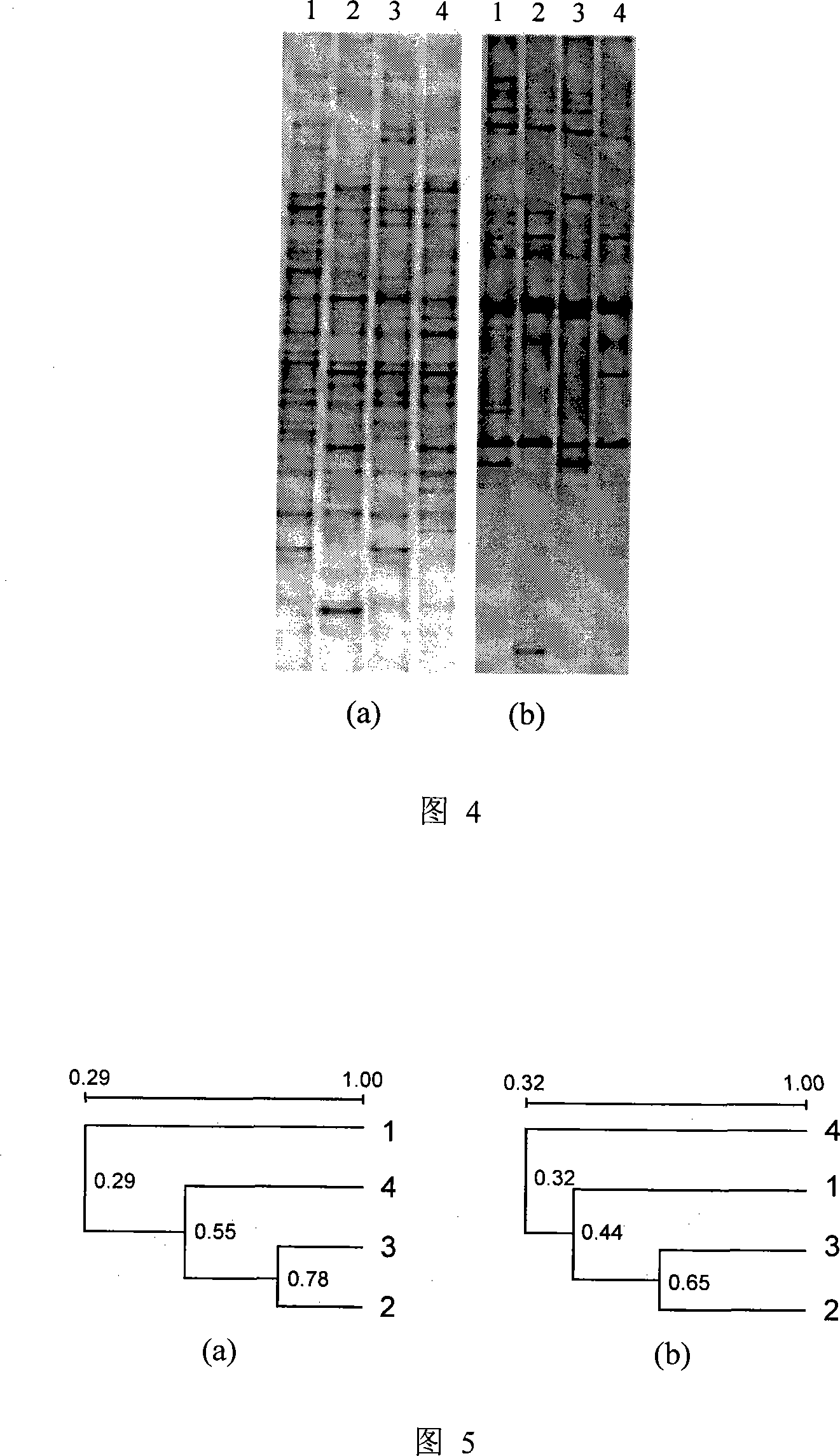
Method for analyzing plankton community DNA polymorphism
InactiveCN101215606AImprove comparabilitySimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementEcological studyGel electrophoresis
The invention discloses a process of analyzing DNA polymorphism of plankton coenosis, which comprises firstly collecting sample, secondly extracting plankton coenosis DNA, thirdly augmenting the analysis of DNA polymorphism randomly, fourthly carrying out PCR augmentation of ribosome RNA gene of plankton coenosis and degeneration gradient gel electrophoresis analysis, fifthly quantitatively analyzing atlas through utilizing Quantity One software to calculate the similarity of DNA polymorphism of plankton coenosis of each sample. The invention has the characteristics of technical route routinization and comparison and analysis standardization, also has simple operation, and can fast and effectively analyze in parallel a plurality of samples, which overcomes the affect by personal factors, increases comparability among different space-time researches, and provides reliable premise for searching for bio-ecology mechanism.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
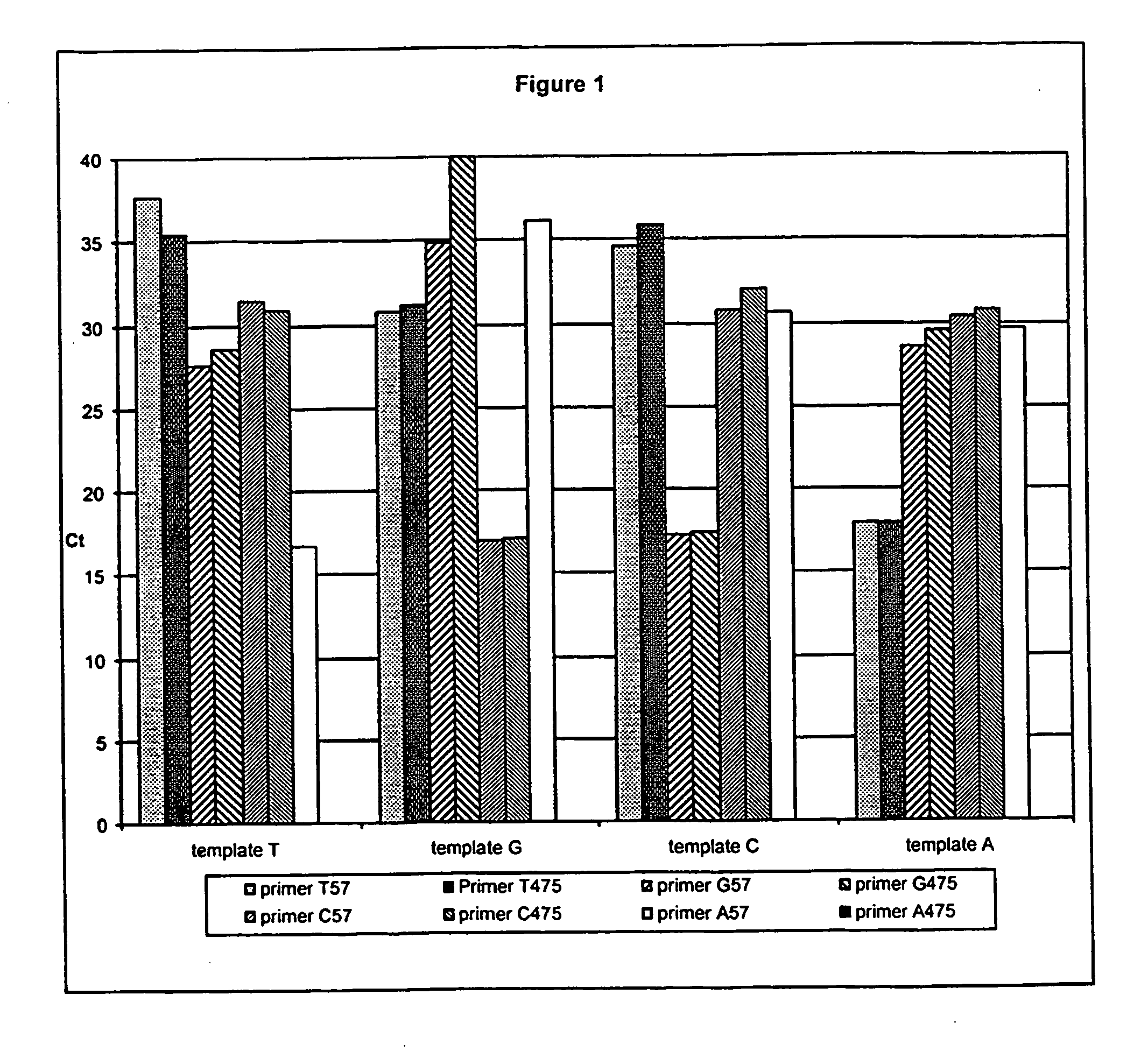
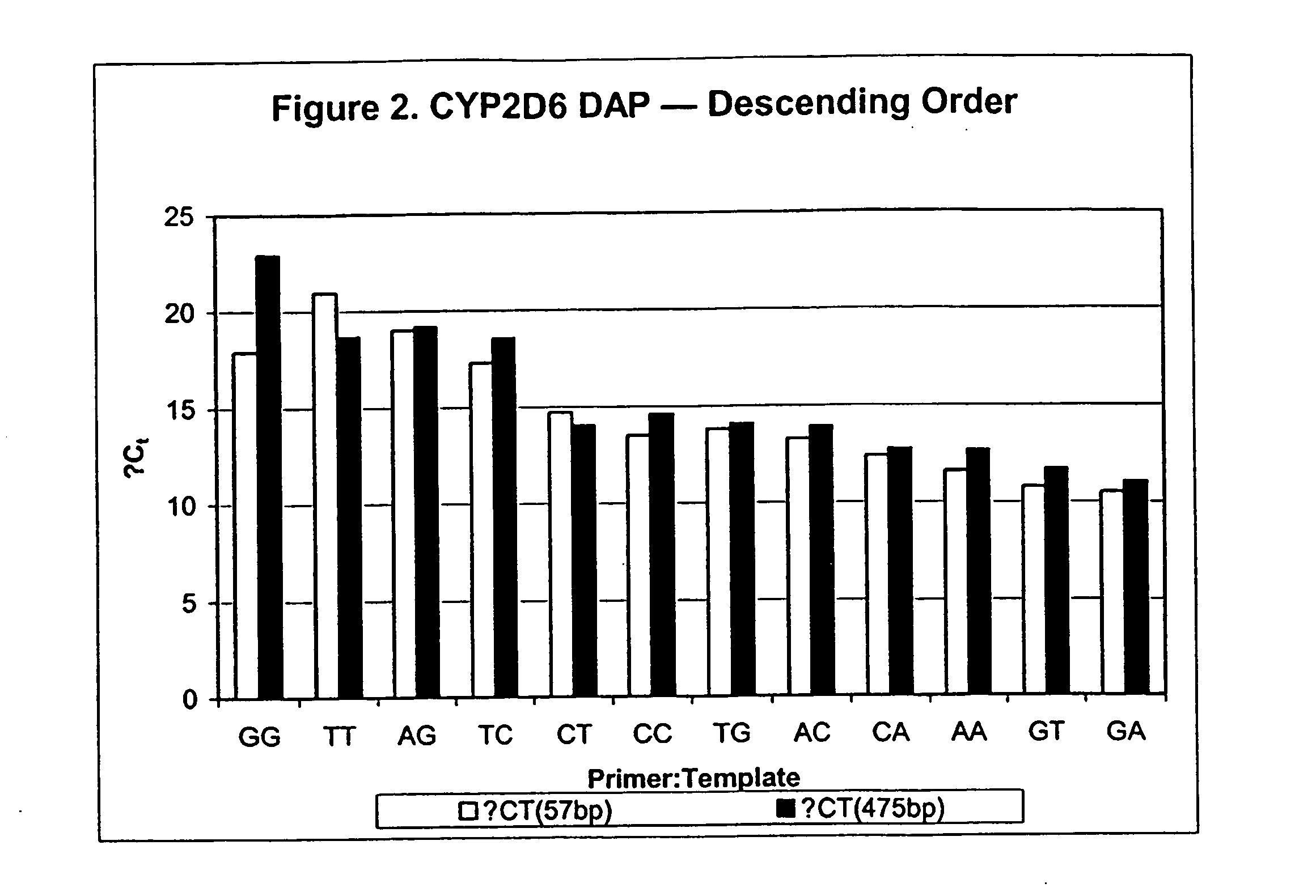
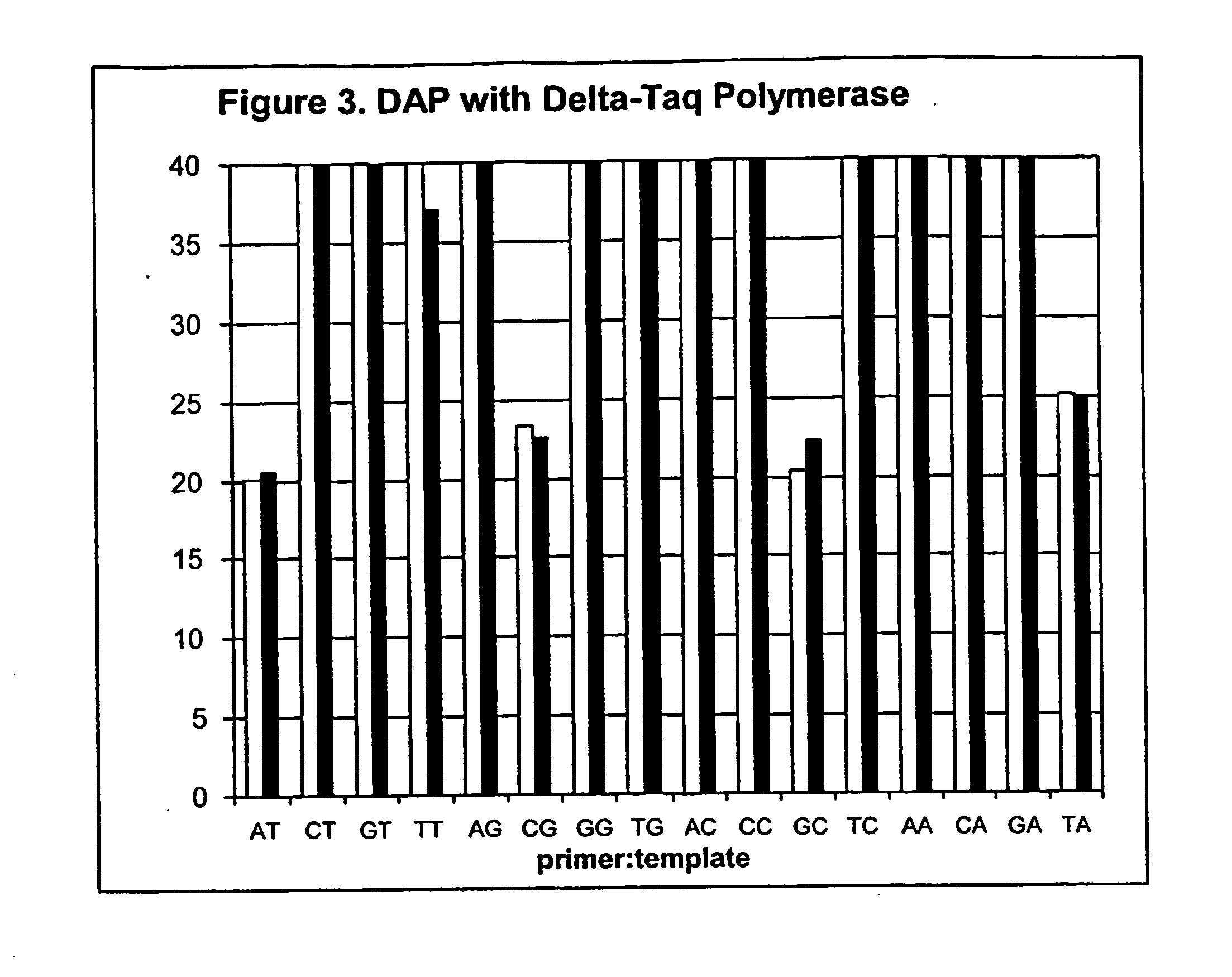
Polymorphism and haplotype scoring by differential amplification of polymorphisms
The current invention provides a method of performing DNA polymorphism assays. The assay combines allele-specific PCR with technology used for quantitative PCR. The method can be used to score the presence of absence of particular polymorphisms in a DNA sample. In a further aspect of the invention, the method is used to score the presence or absence of particular haplotypes in a DNA sample.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
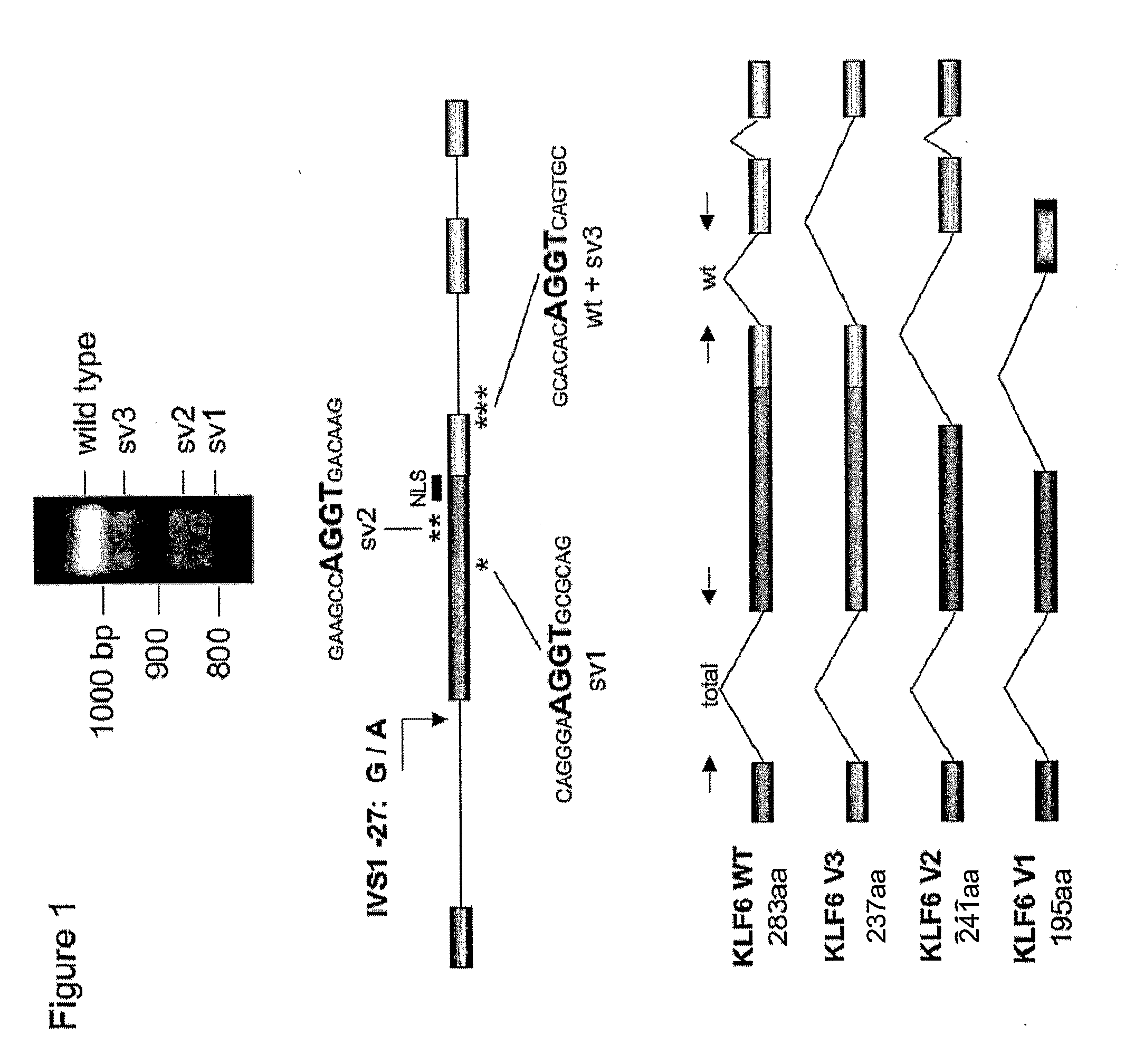
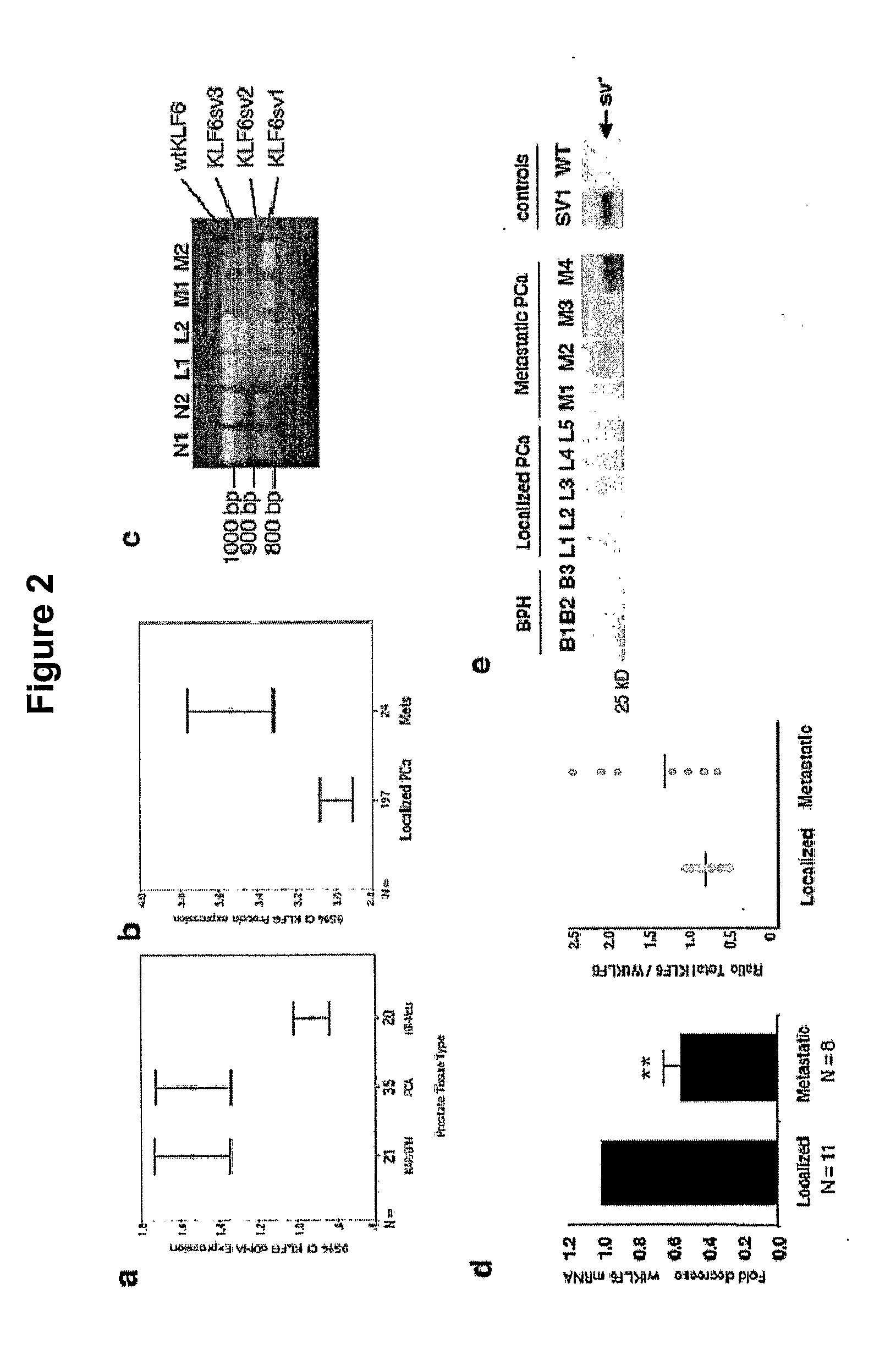
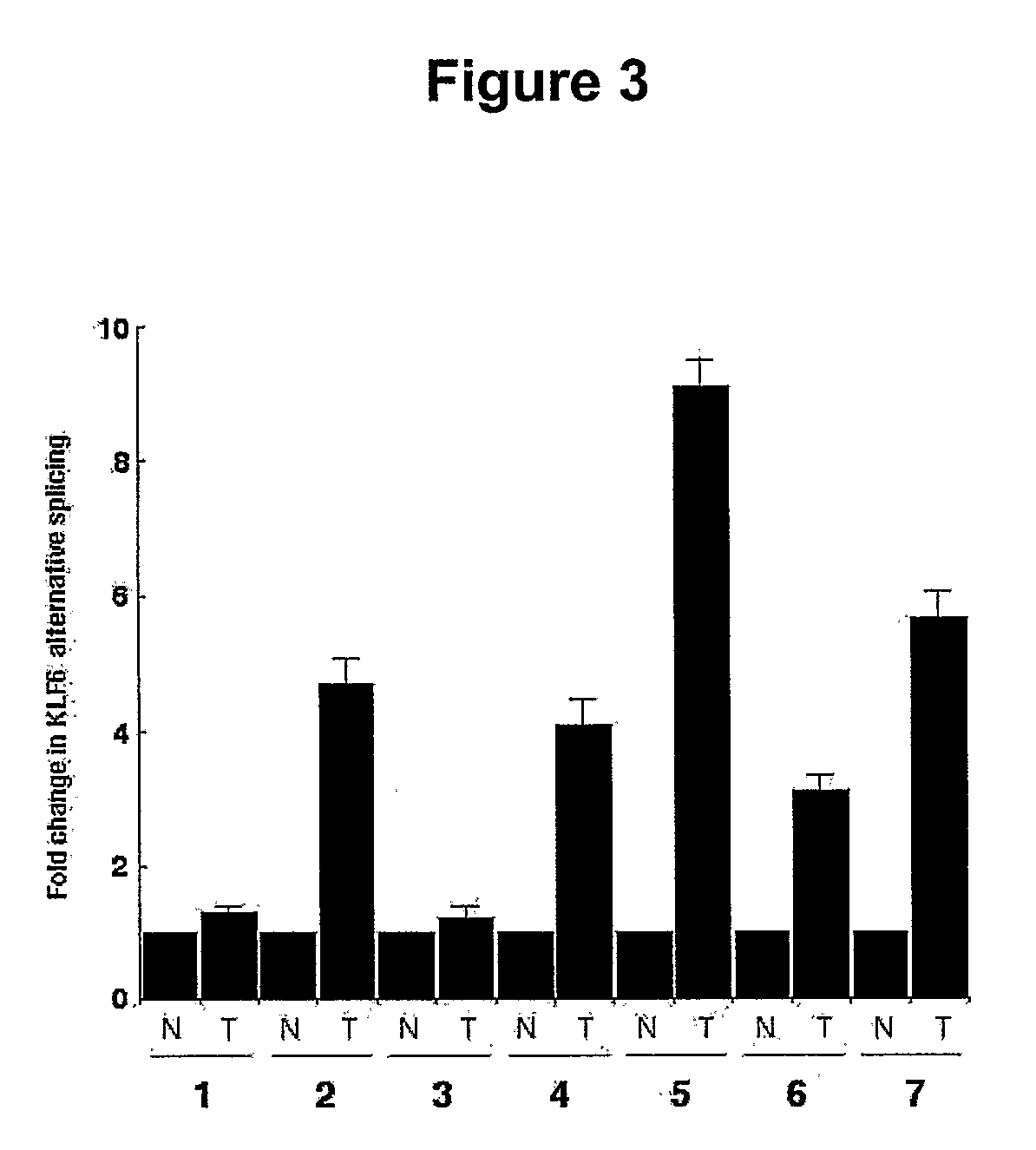
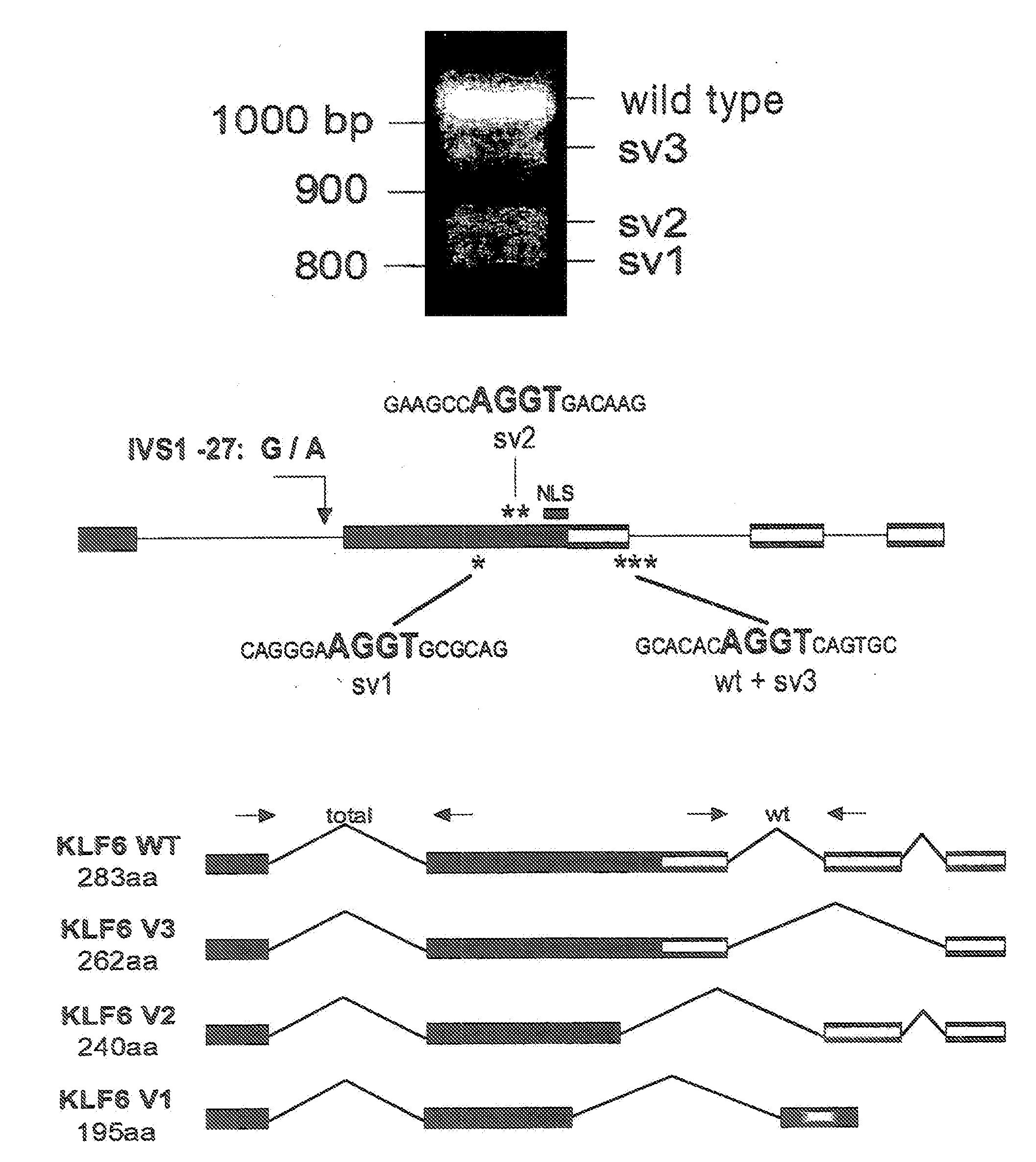
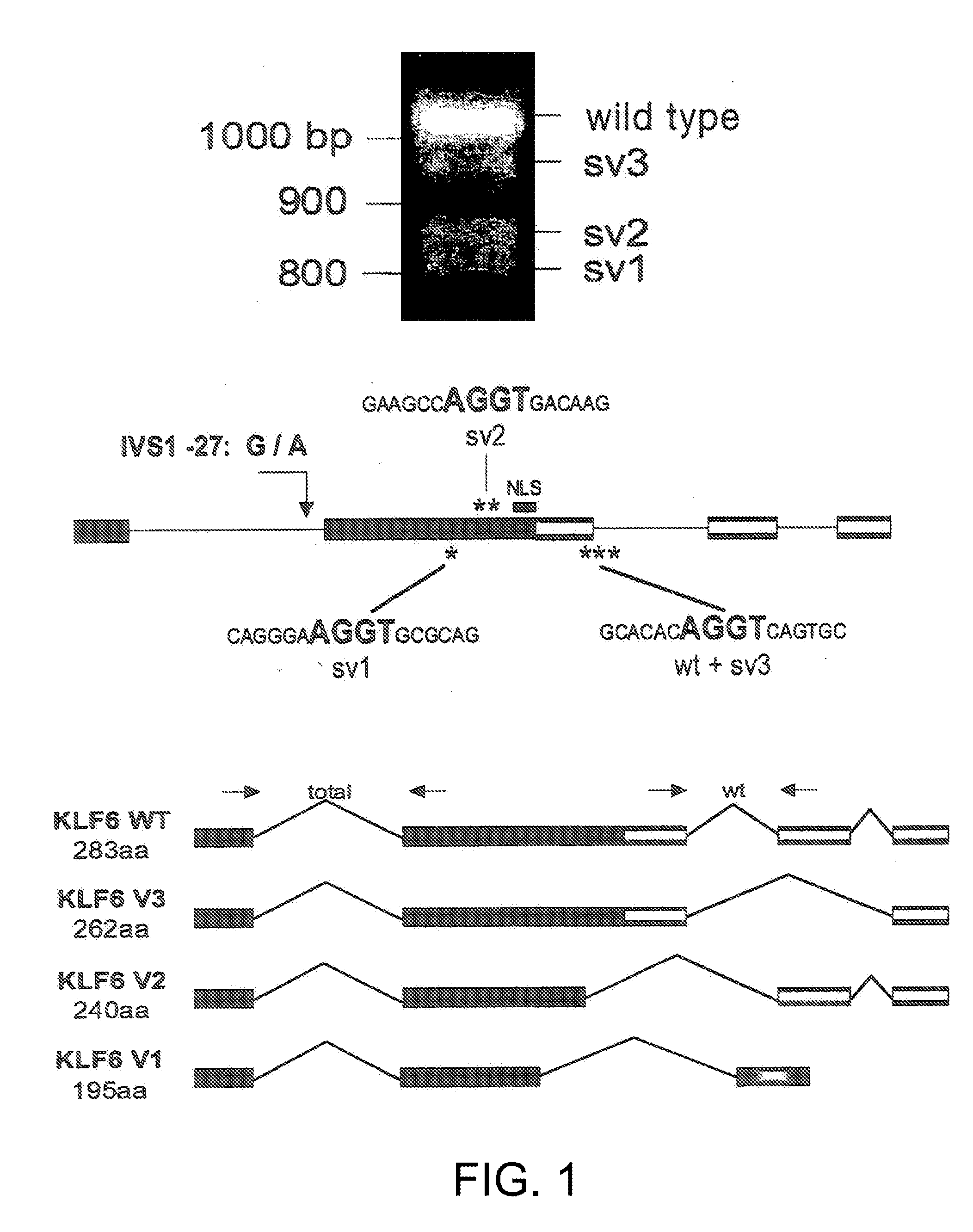
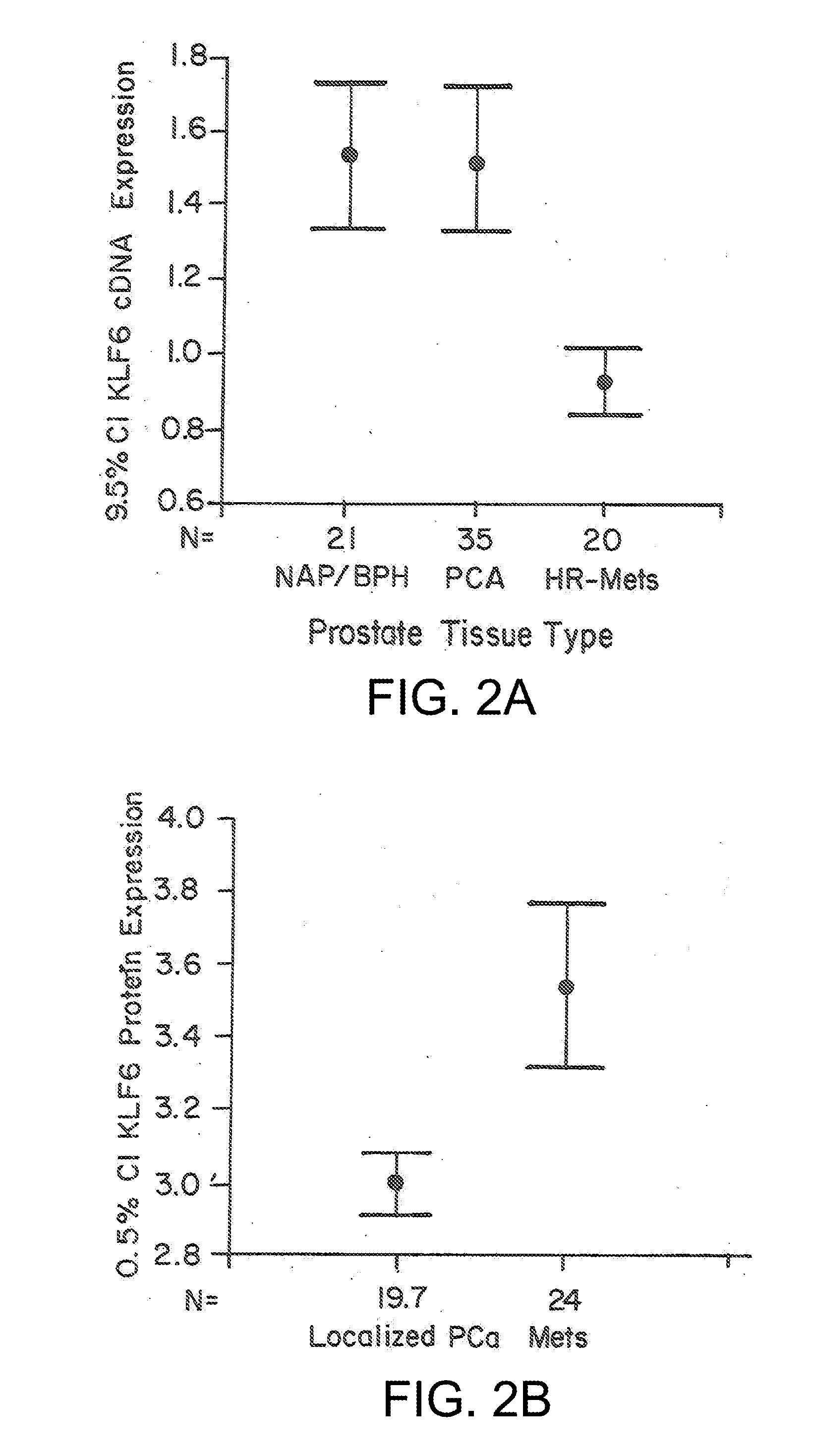
Klf6 alternative splice forms and a germline klf6 DNA polymorphism associated with increased cancer risk
InactiveUS20090325150A1Splicing alterationMicrobiological testing/measurementHeightened Cancer RiskNucleotide
Disclosed are methods of identifying and diagnosing certain types of cancers and pre-stages thereof in a patient by identifying alternatively spliced isoforms of wild type KLF6 (KLFwt), in particular anyone of the isoforms selected from the group consisting of: KLF6 splice variant-1 (KLF6SV1), KLF6 splice variant-2 (KLF6SV2), and KLF6 splice variant-3 (KLF6SV3). Also disclosed are methods diagnosing cancer using the polypeptides and polynucleotides identified herein, as well as methods of treating certain types of cancers by inhibiting polynucleotides and polypeptides identified herein.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods and compositions for identifying biomarkers useful in characterizing biological states
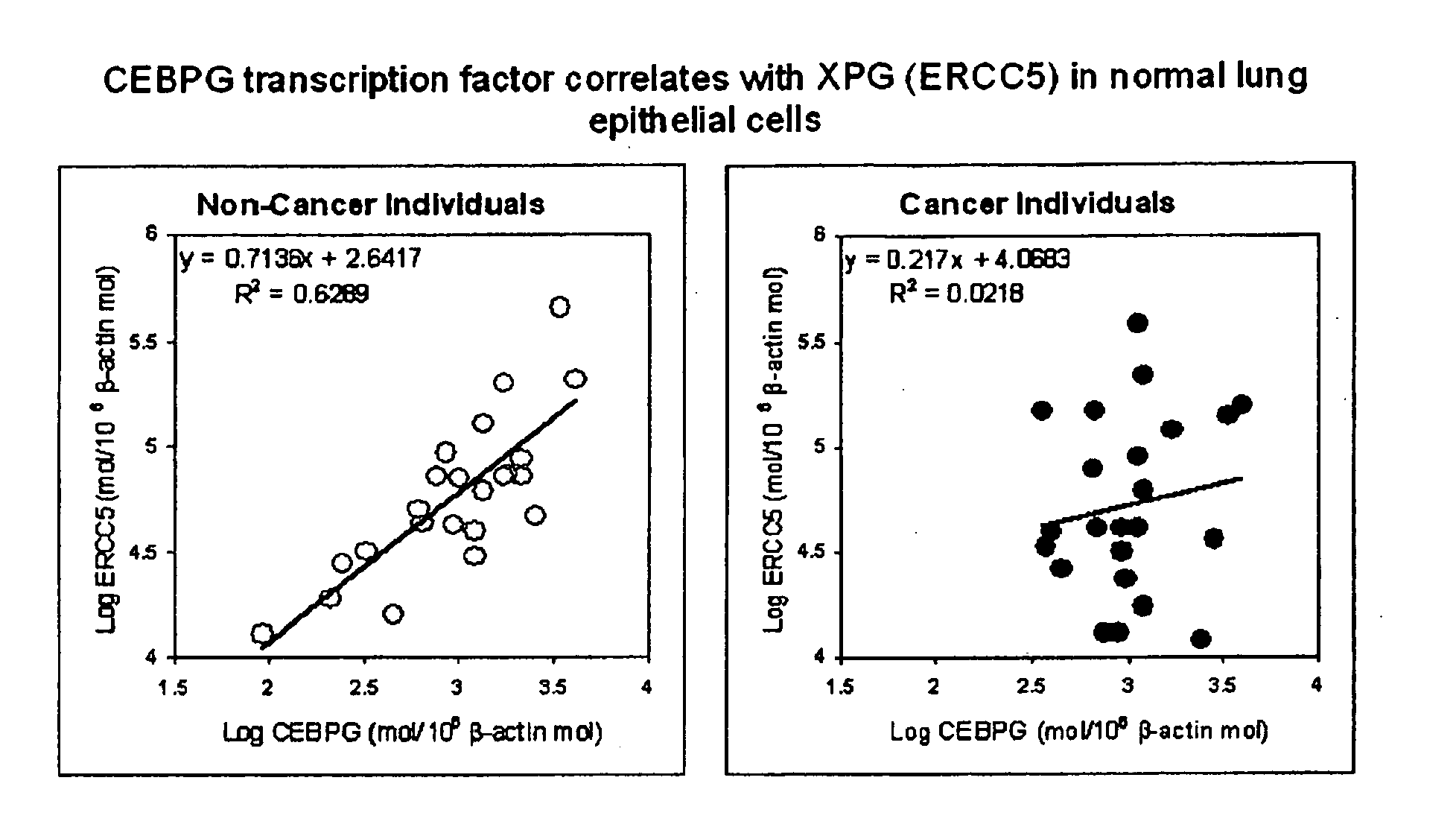
The present invention relates to methods, compositions, and kits for identifying biomarkers useful in characterizing biological states. In particular, the invention relates to methods and compositions for molecular characterization of biological states by gene expression profiling. The invention also relates to assessing effects of DNA polymorphisms on regulation of transcription. The biomarkers and polymorphisms identified find use in diagnostic and treatment approaches, e.g., some embodiments of the invention provide methods and kits for detecting bronchogenic carcinoma and risks thereof.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Codominant RFP molecular marker applicable for breeding citrus grandis with red-peel characteristic and application of codominant RFP molecular marker
ActiveCN105132537ANew colorHigh nutritional valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAnthocyanin synthesisDna polymorphism
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular breeding of citrus, and particularly relates to a codominant RFP molecular marker applicable for breeding citrus grandis with a red-peel characteristic and application of the codominant RFP molecular marker. Most varieties of citrus grandis are light yellow in peel and single in color in China; the citrus grandis with the red-peel characteristic is novel in color and variety, thereby being more attractive to consumers. The method includes: starting from a unique material, the red-peel citrus grandis, using a primer pair MYB2F / R to amplify the red-peel citrus grandis and common citrus grandis for regulating promoters of anthocyanin synthesis key transcription factor CgMYB2 genes so as to obtain two DNA fragments, then subjecting DNA polymorphic regions to PCR amplification, cloning and sequencing, and comparing two obtained nucleotide sequences to find that one segment of insertion mutation of 162bp is between the two sequences, resulting in polymorphism of the sequence-characterized amplified region; designing primer pairs RFP F / R1 and RFP F / R2 according to differences of the two nucleotide sequences prior to PCR amplification to obtain the codominant RFP molecular marker capable of distinguishing the red-peel citrus grandis from the common citrus grandis (being light yellow in peel). The invention further discloses a method for preparing the molecular marker.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Erigeron breviscapus DNA polymorphism detection method and application thereof
ActiveCN101914629AIncrease the amount of informationPromote planting industrializationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyResource protection
The invention provides an erigeron breviscapus DNA polymorphism detection method and application thereof. In the invention, an amplified fragment length polymorphism technology is used for erigeron breviscapus DNA polymorphism detection, an optimum primer combination is screened out, and reaction condition is optimized. The method can be effectively applied to the inheritance breeding, the resource protection, the introduction domestication, the breed optimization and the like of erigeron breviscapus.
Owner:YUNNAN SHIPURUI BIOLOGICAL ENG
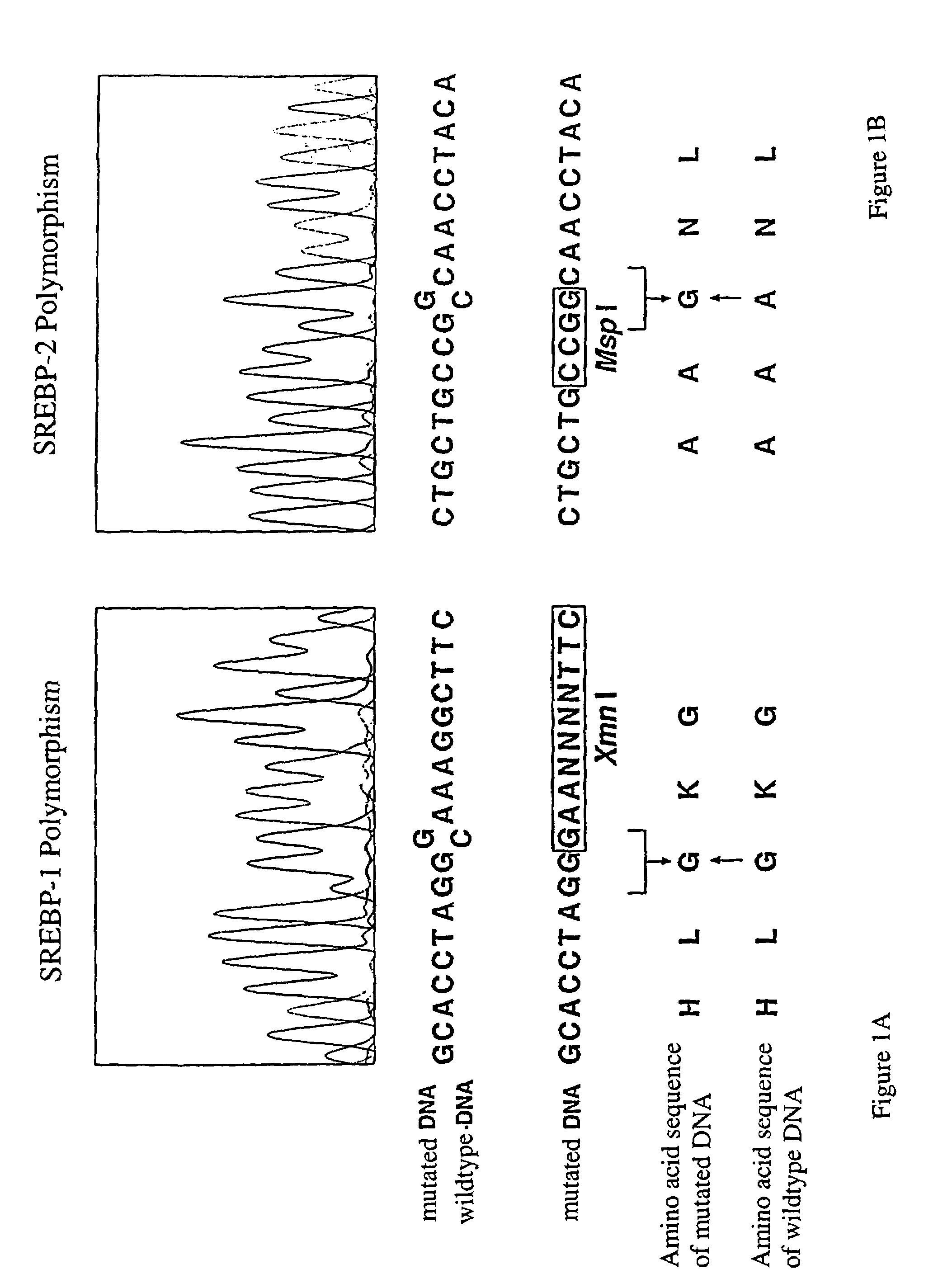
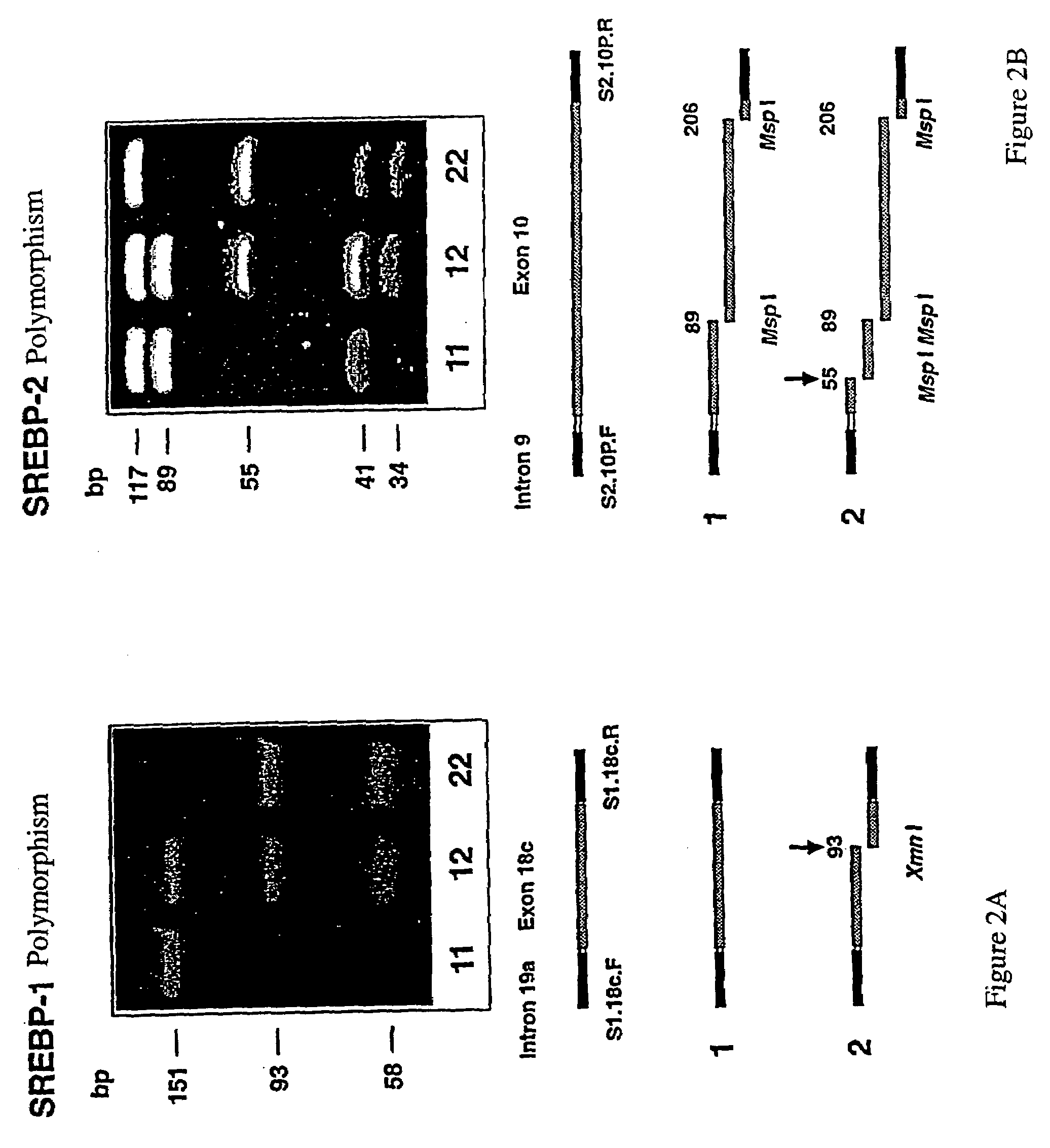
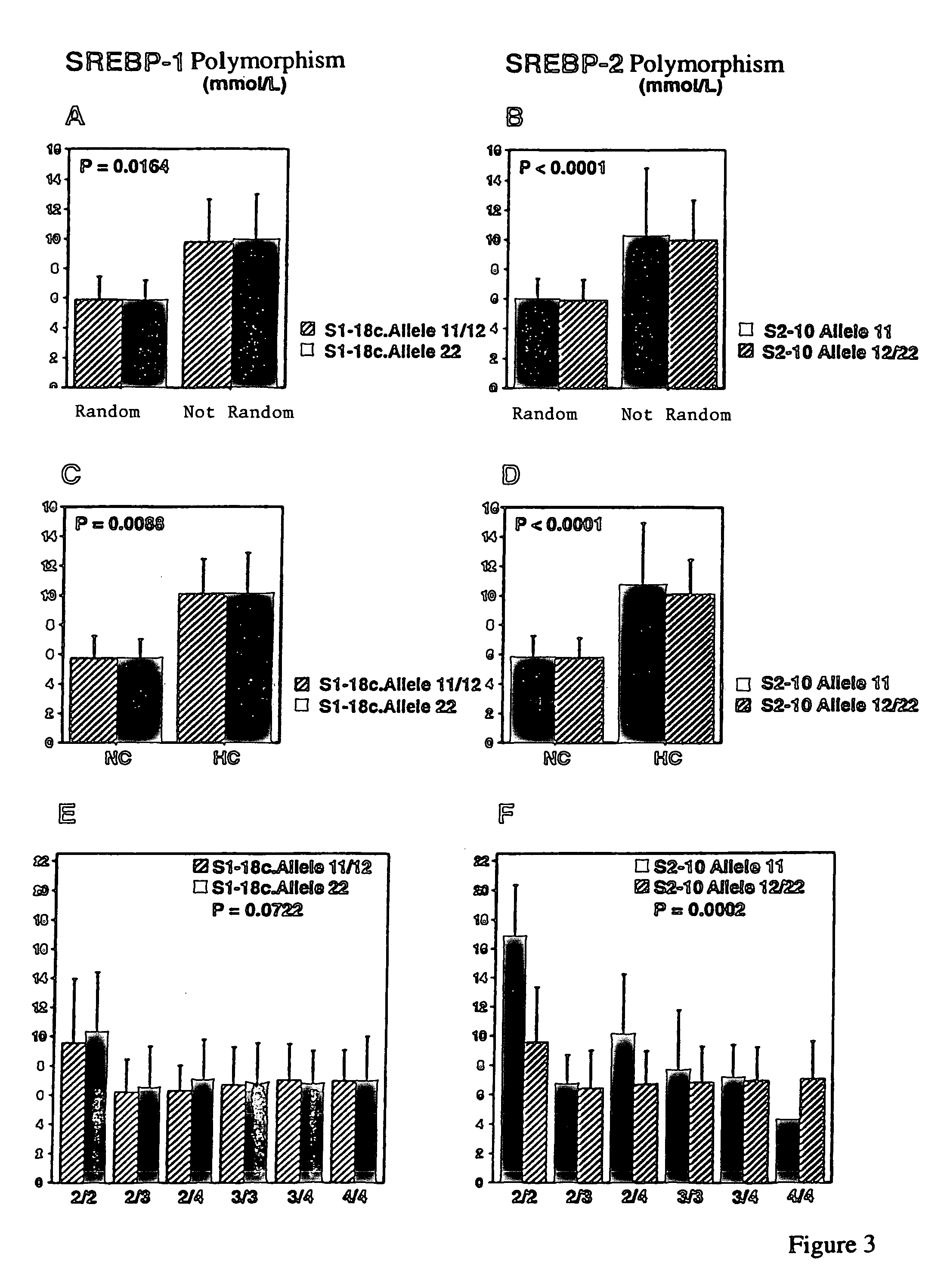
DNA polymorphisms in sterol regulator element binding proteins
InactiveUS7220846B1Increased and reduced disease risk and riskIncreased and reduced risk and mortality riskSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNADisease cause
The invention relates to DNA polymorphisms in sterol regulator element binding proteins (SREBP) that are characteristic of a higher risk of genetic diseases in humans such as hyperchlolesterolemia. The corresponding polymorphisms, especially the polymorphisms on SREBP-1 and SREBP-2 are frequently observed in Alzheimer patients (SREBP-2). They are also characterized by a specific behavior in the therapy of HIV patients with proteas inhibitors and appear to have an influence on the mortality.
Owner:MISEREZ ANDRE R
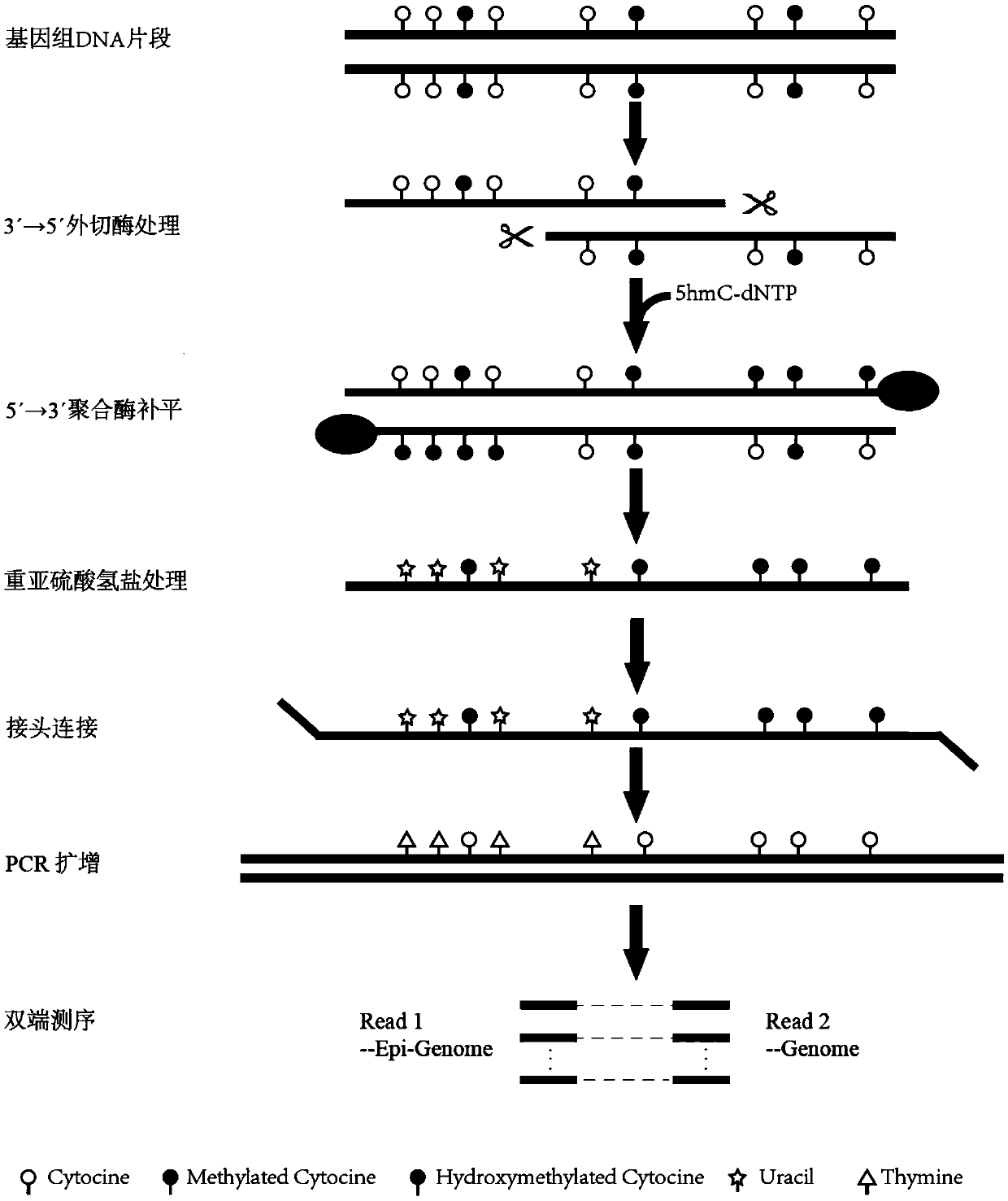
Method for simultaneously detecting genomic DNA polymorphism and methylation
PendingCN109554451ARealize synchronous detectionNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementModified dnaEpigenome
The invention provides a method for simultaneously detecting genomic DNA polymorphism and methylation. The method comprises the following steps: performing DNA fragmentation, and digesting the 3' endof the DNA fragment with DNA exonuclease; adding a dNTPs mixture containing 5-hydroxymethylcytosine deoxyribonucleotide, and performing completion the 3' end of the DNA fragment; performing bisulfiteconversion treatment on the modified DNA fragment and connecting an adaptor adapted to a high-throughput sequencing platform, and finally constructing a sequencing library by PCR amplification. By combining a double-end sequencing mode of the high-throughput sequencing platform, genomic DNA polymorphism and methylation detection can be performed simultaneously, and the goal of simultaneous detection of genome and epigenome is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI EPIPROBE BIOTECH CO LTD
Klf6 alternative splice forms and a germline klf6 DNA polymorphism associated with increased cancer risk
InactiveUS20130035243A1Splicing alterationMicrobiological testing/measurementHeightened Cancer RiskKLF6
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Rare cell analysis using sample splitting and DNA tags
ActiveCN108048549AMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresFetal abnormalityGenomic DNA
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to detect the presence of fetal cells when mixed with a population of maternal cells in a sample and to test fetal abnormalities, e.g.aneuploidy. The present invention involves labeling regions of genomic DNA in each cell in said mixed sample with different labels wherein each label is specific to each cell and quantifying the labeled regions of genomic DNA from each cell in the mixed sample. More particularly the invention involves quantifying labeled DNA polymorphisms from each cell in the mixed sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC +2
Method for genome complexity reduction and polymorphism detection
The present invention provides methods to produce a reduced representation of a genome for sequencing and DNA polymorphism detection. In particular, the invention provides PCR-based methods, with normalization of the amplified products using a duplex-specific nuclease, in order to reduce over-representation of PCR products. Oligonucleotides for use in the disclosed method are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Molecular label relevant with cotton fiber strength and arising from high-quality variety Xinluzao No.24
ActiveCN102181442BLarge additive effectImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGossypiumBiology
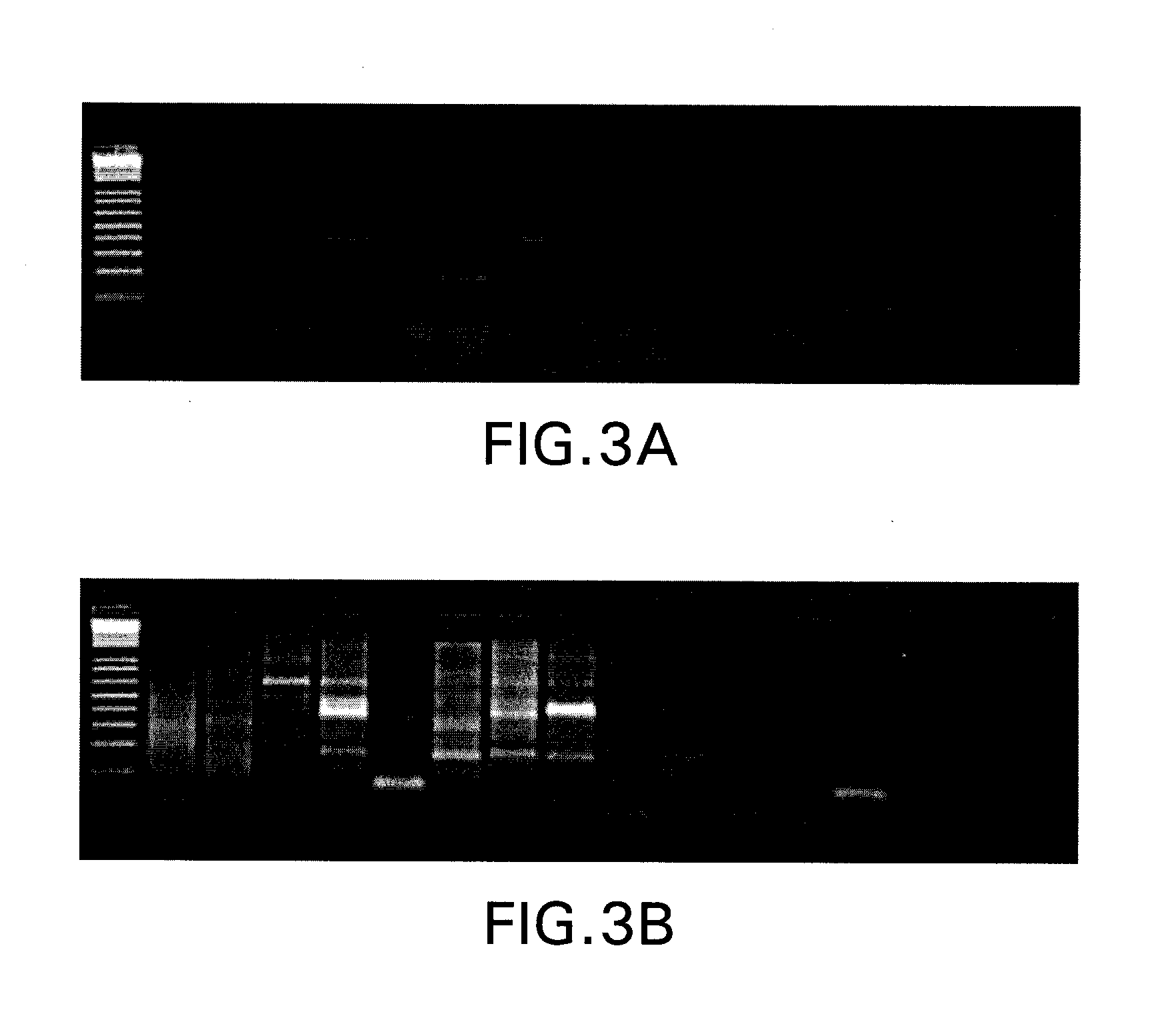
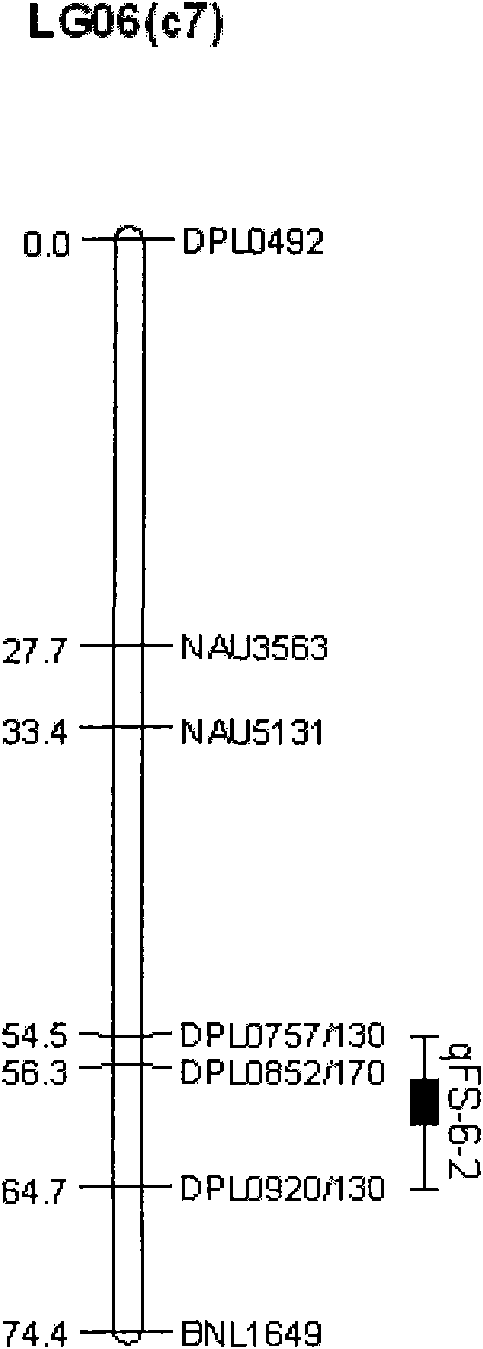
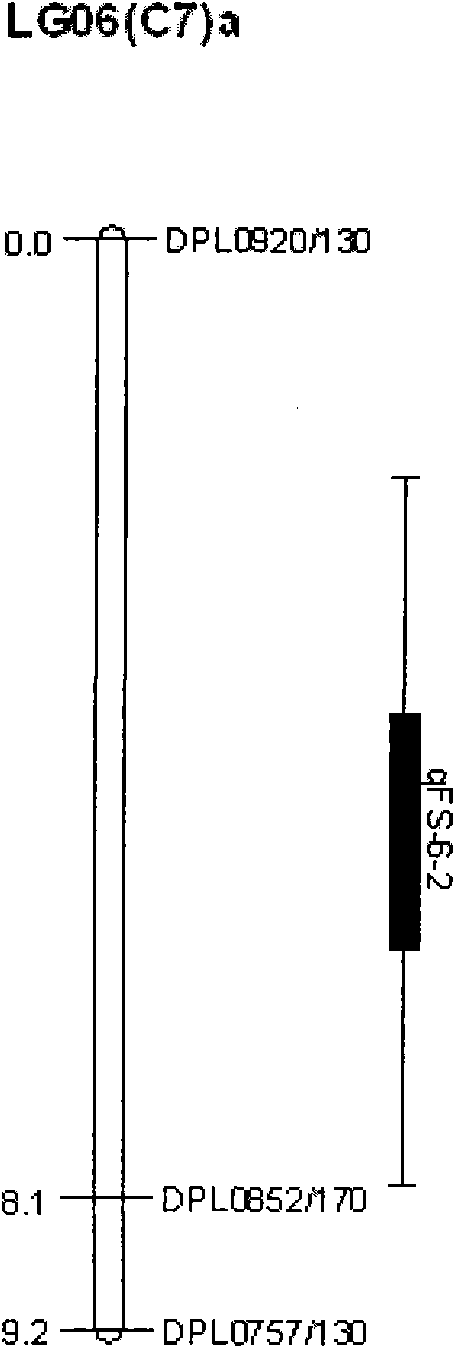
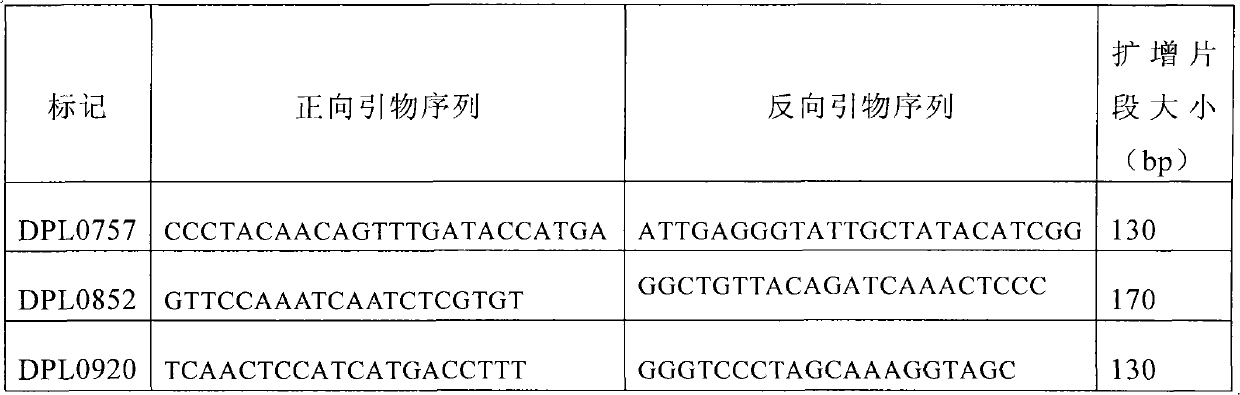
The invention discloses a molecular label linked with a major gene of a high-strength cotton fiber, which is obtained by the following method: taking the Xinluzao No.24 as a male parent, taking Lunianyan No.28 and Ji cotton 516 as female parents; respectively constructing two segregation populations of F2 and F2:3; carrying out polymorphism screening between parents (Lunianyan 28 and Xinluzao 24)by utilizing an SSR (simple sequence repeat) primer; constructing a genetic linkage map by utilizing F2; carrying out two generation quantitative trait locus (QTL); selecting an SSR label linked withthe high-strength cotton fiber to analyze the DNA polymorphism of the parent Xinluzao 24 and the Ji cotton 516; and constructing the genetic linkage map and positioning QTL; the fiber strength major QTL (qFS-62) can be stably detected in two populations and generations, and is positioned between the label interval of DPL0757-DPL0920 of chromosome c7; a synergtic gene is from the parent Xinluzao No.24; and the linking label of qFS-6-2 is DPL0757130, DPL0852170 and DPL0920130. By utilizing the label provided by the invention, molecule label assisted selection is carried out, thus improving the selection efficiency of the high-strength cotton fibre.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Multiple detection method for DNA polymorphism of genome and special probe thereof
InactiveCN102181443BMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCapillary electrophoresisDNA - Deoxyribonucleic acid
Provided are a method for multiplex detection of genomic DNA polymorphism and probes dedicated thereto. Also disclosed is a single-stranded DNA molecule comprising successively, from the 5' end to the 3' end, a left-side oligonucleotide fragment complementary to the 5' end of the DNA to be detected, a main fragment and a right-side oligonucleotide fragment complementary to the 3' end of the DNA to be detected. Through ligase reaction, different labels and different allelic sites are distinguished by the single-stranged DNA molecule. Hand-clasping probes of different lengths are successfully ligated by PCR amplification. Through gel or capillary electrophoresis separation and detection systems, simultaneous detection of the polymorphism of a multiple of deoxyribonucleic acids is achieved. High sensitivity and accuracy are attained, and the requirements for high-throughput and low cost are satisfied at the same time.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com