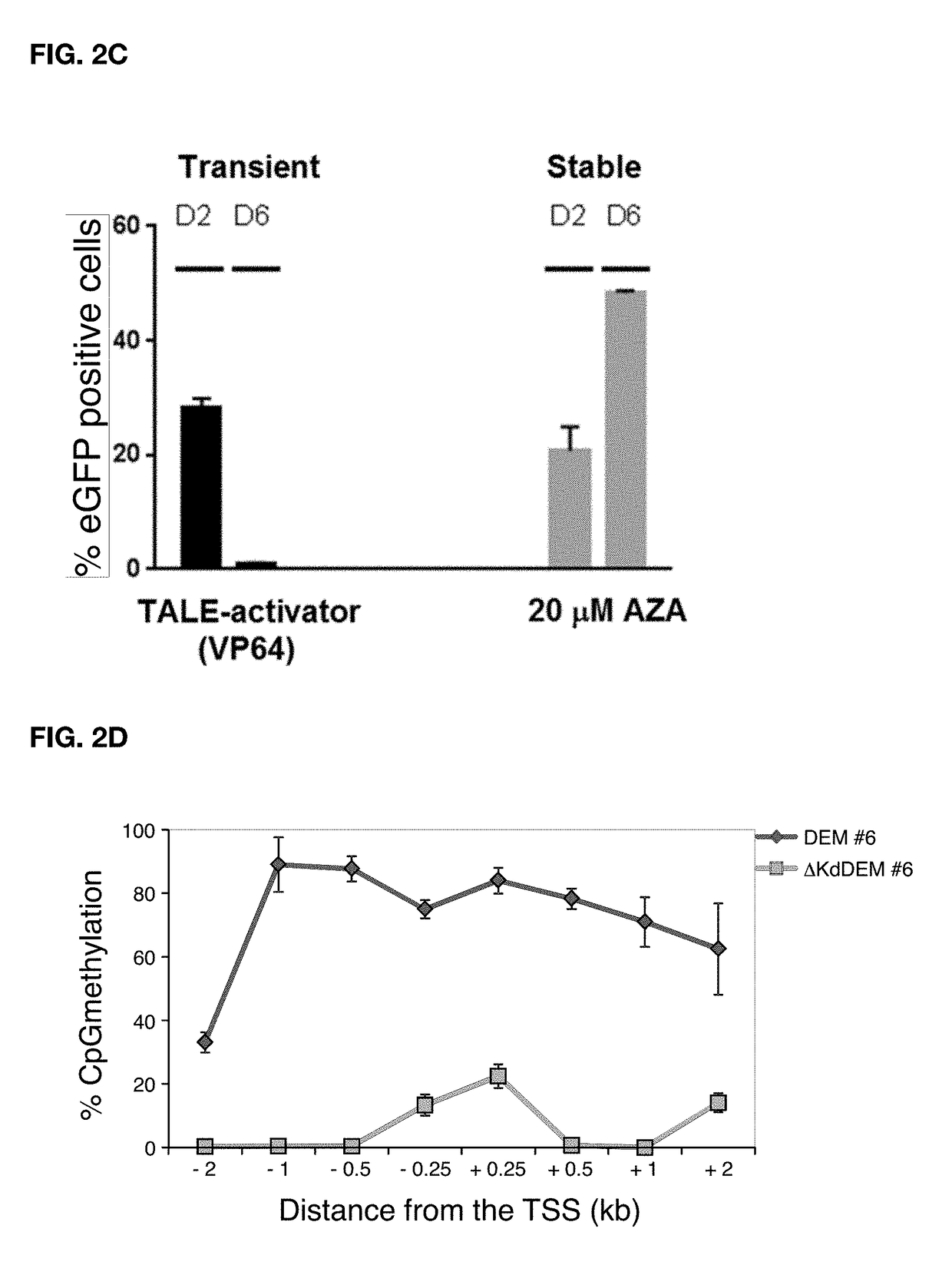
Patents
Literature
51 results about "Epigenome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An epigenome consists of a record of the chemical changes to the DNA and histone proteins of an organism; these changes can be passed down to an organism's offspring via transgenerational epigenetic inheritance. Changes to the epigenome can result in changes to the structure of chromatin and changes to the function of the genome.
Methods and compositions for differentiating tissues for cell types using epigenetic markers
InactiveUS20060183128A1Accurate and efficientMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenomic DNAEpigenetic Profile
The present invention provides, inter alia, a method for generating a genome-wide epigenomic map, comprising a correlation between methylation variable CpG positions (MVP) and genomic DNA sample types. MVP are those CpG positions that show a variable quantitative level of methylation between sample types. Particular genomic regions of interest (ROI) provide preferred marker sequences that comprise multiple, and preferably proximate MVP, and that have novel utility for distinguishing sample types. The epigenic maps have broad utility, for example, in identifying sample types, or for distinguishing between and among sample types. In a preferred embodiment the epigenomic map is based on methylation variable regions (MVP) within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), and has utility, for example, in identifying the cell or tissue source of a genomic DNA sample, or for distinguishing one or more particular cell or tissue types among other cell or tissue types. Analysis of epigenetic characteristics of one, or of a set of nucleic acid sequences, in the context of an inventive epigenomic map, allows for the determination of an origin of the nucleic acids.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
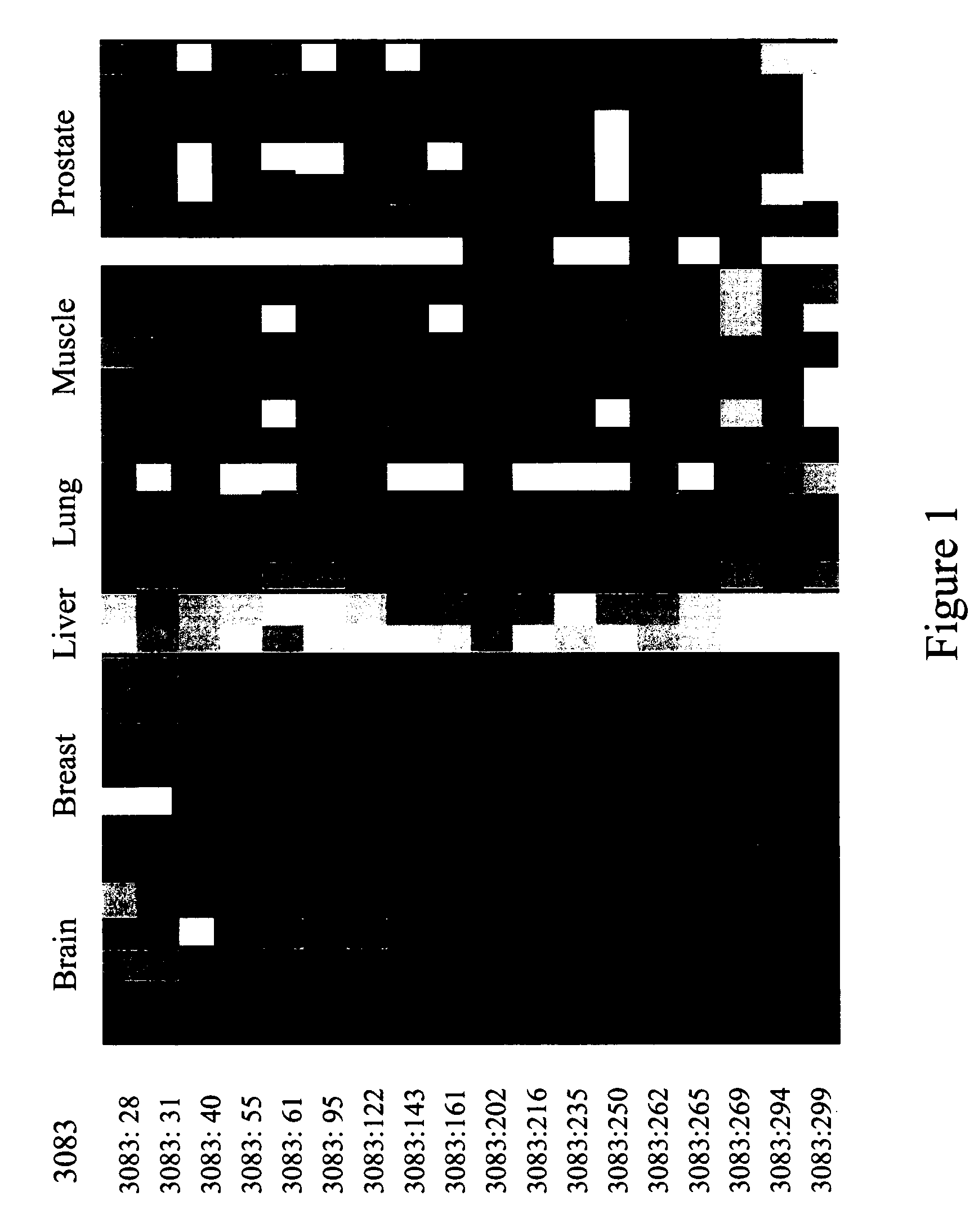
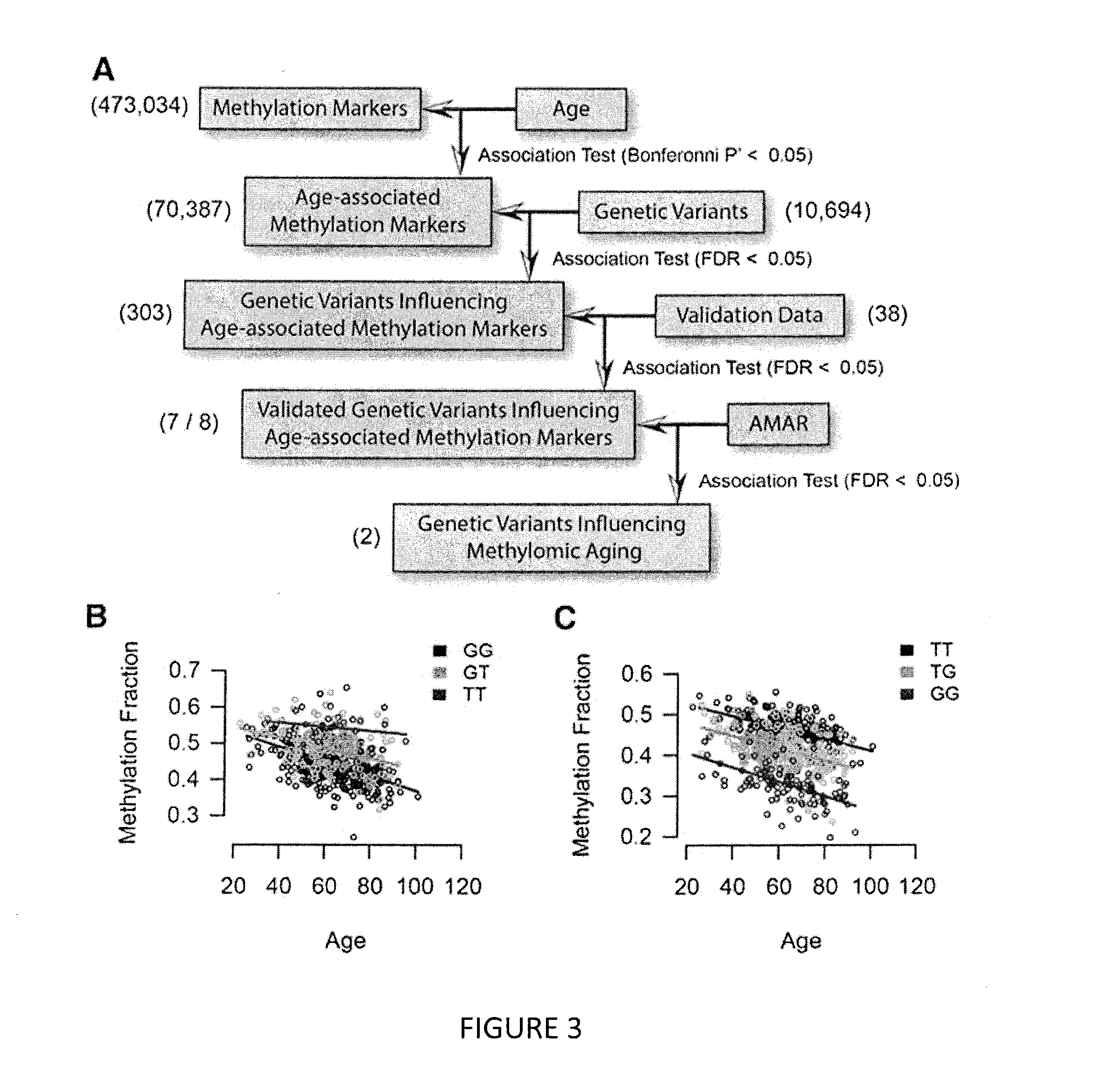
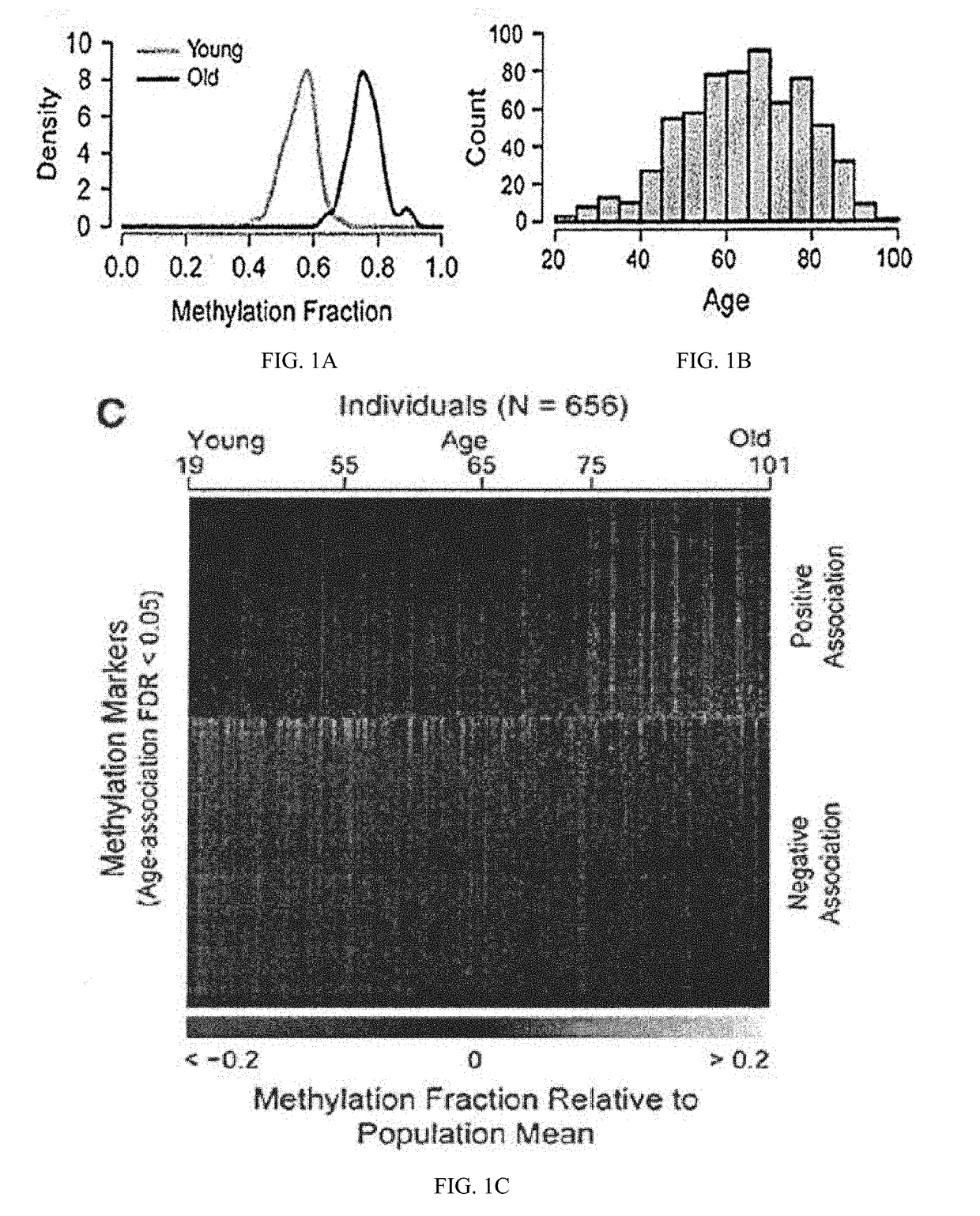
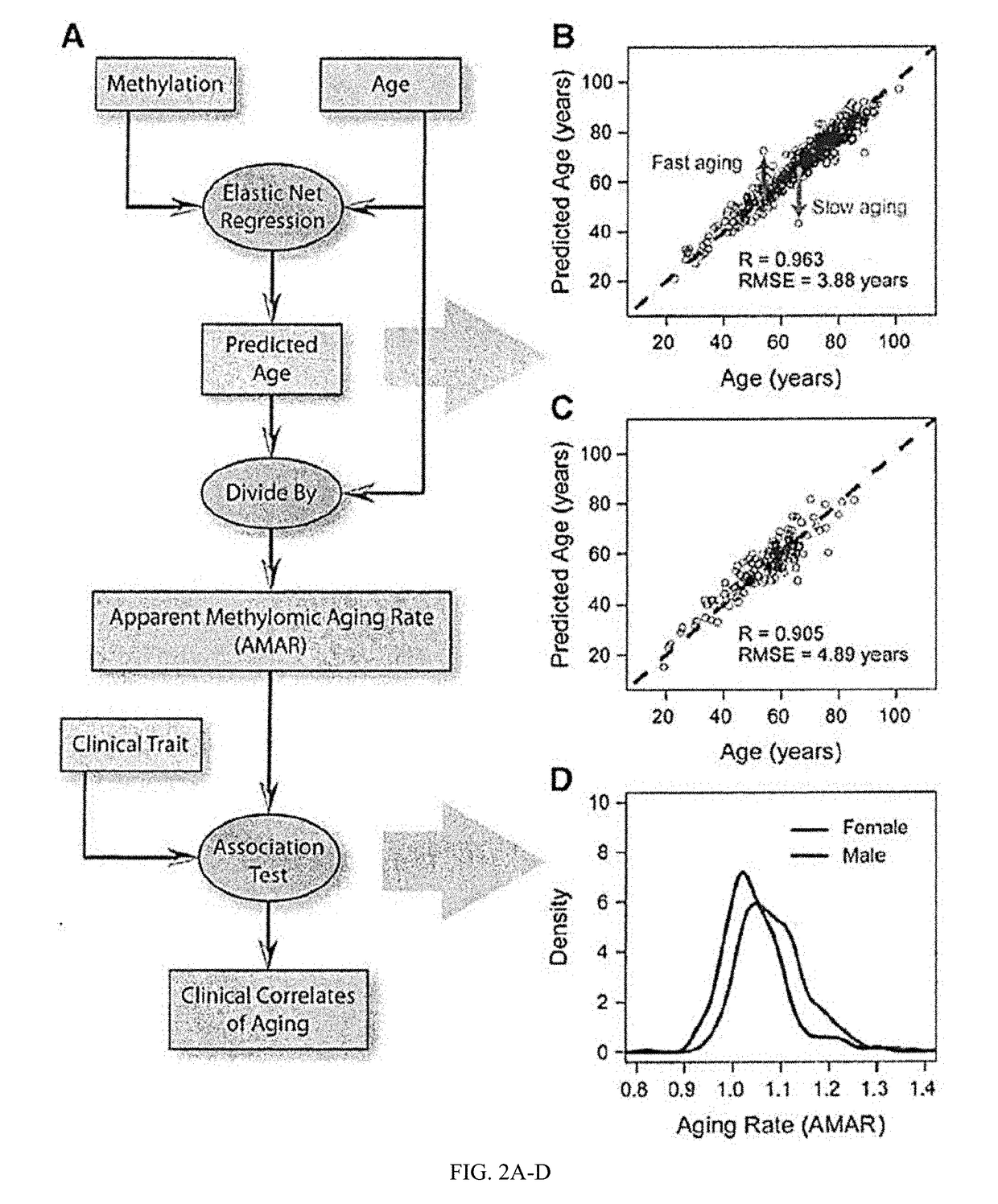
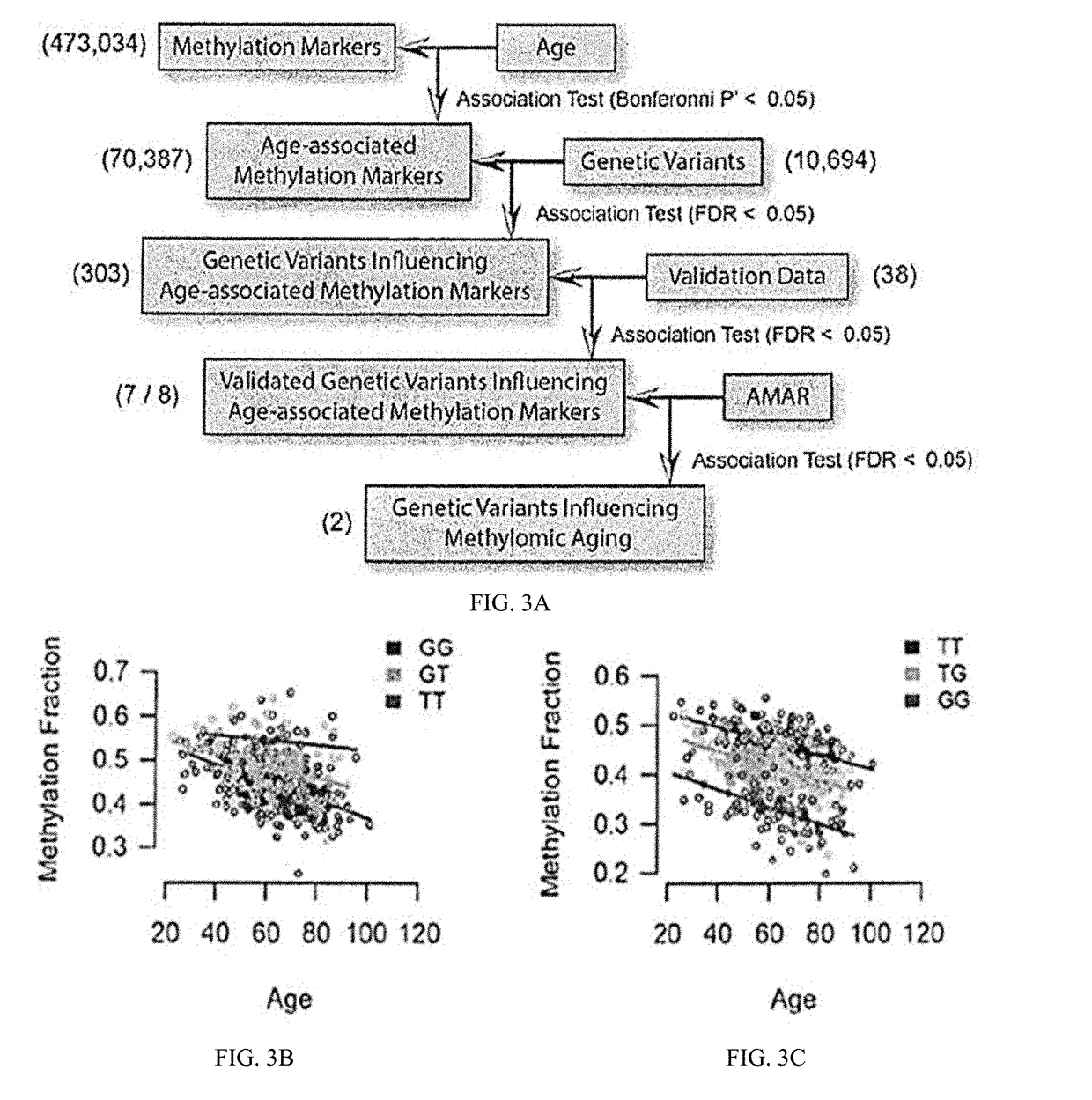
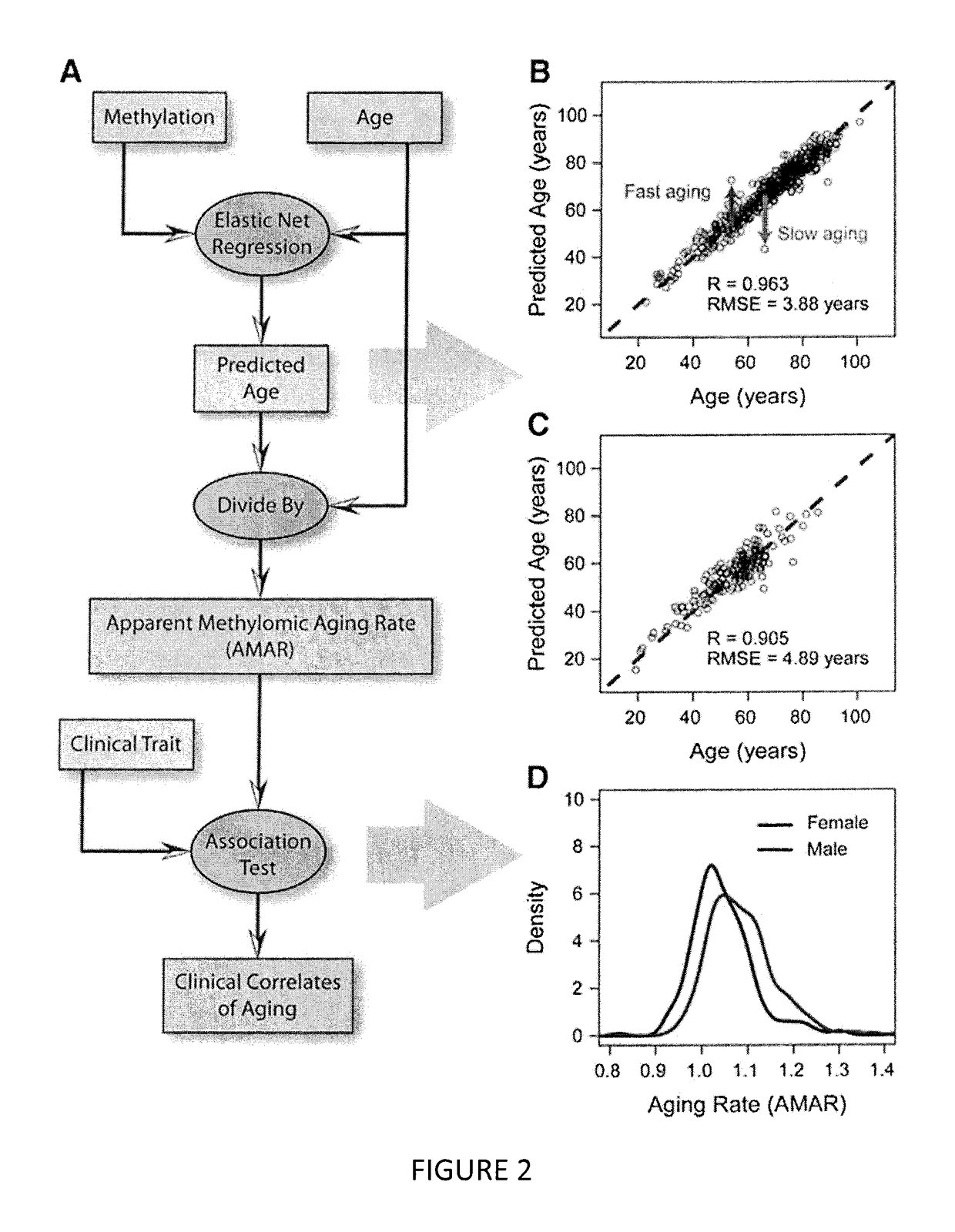
Methods for predicting age and identifying agents that induce or inhibit premature aging
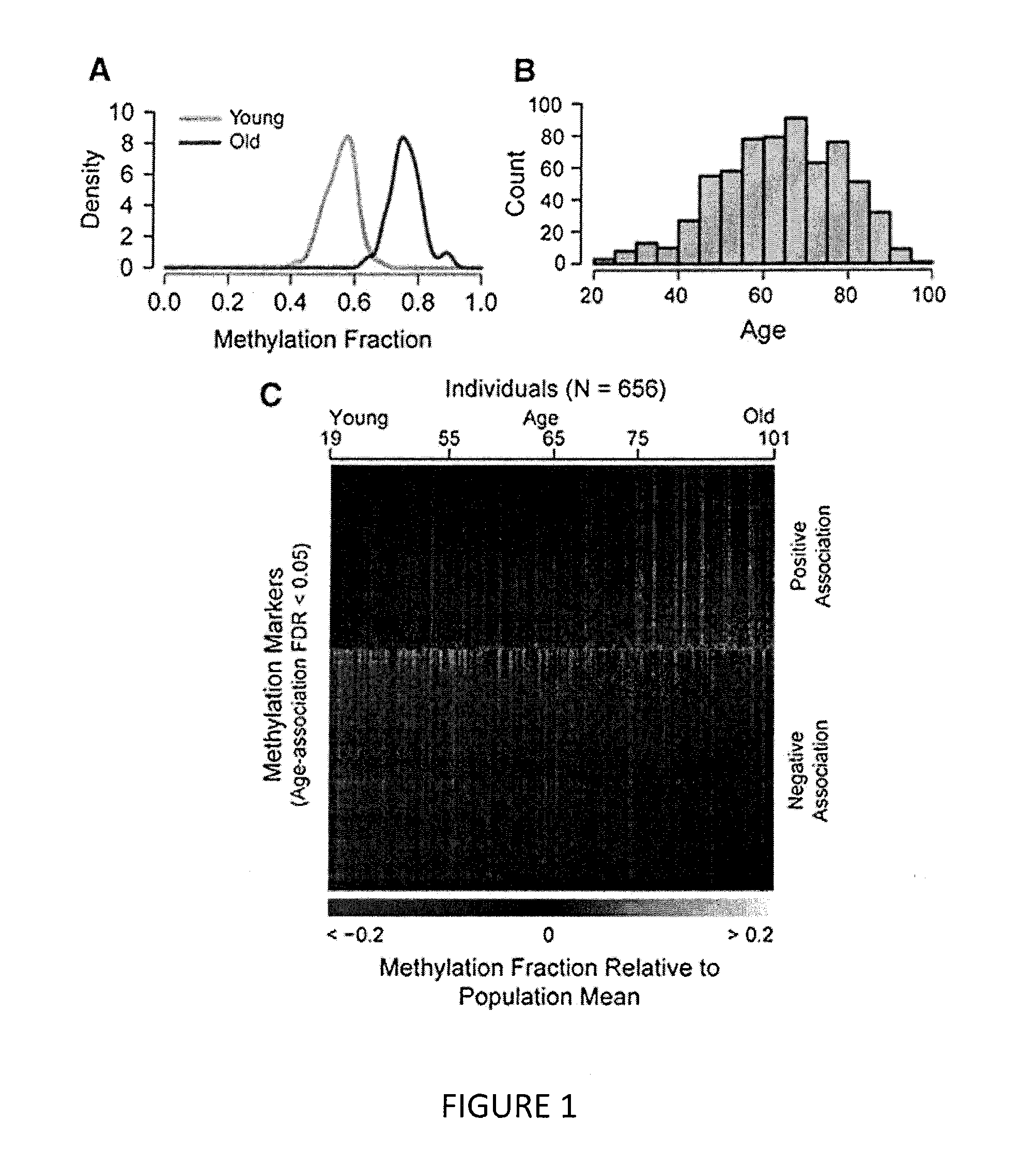
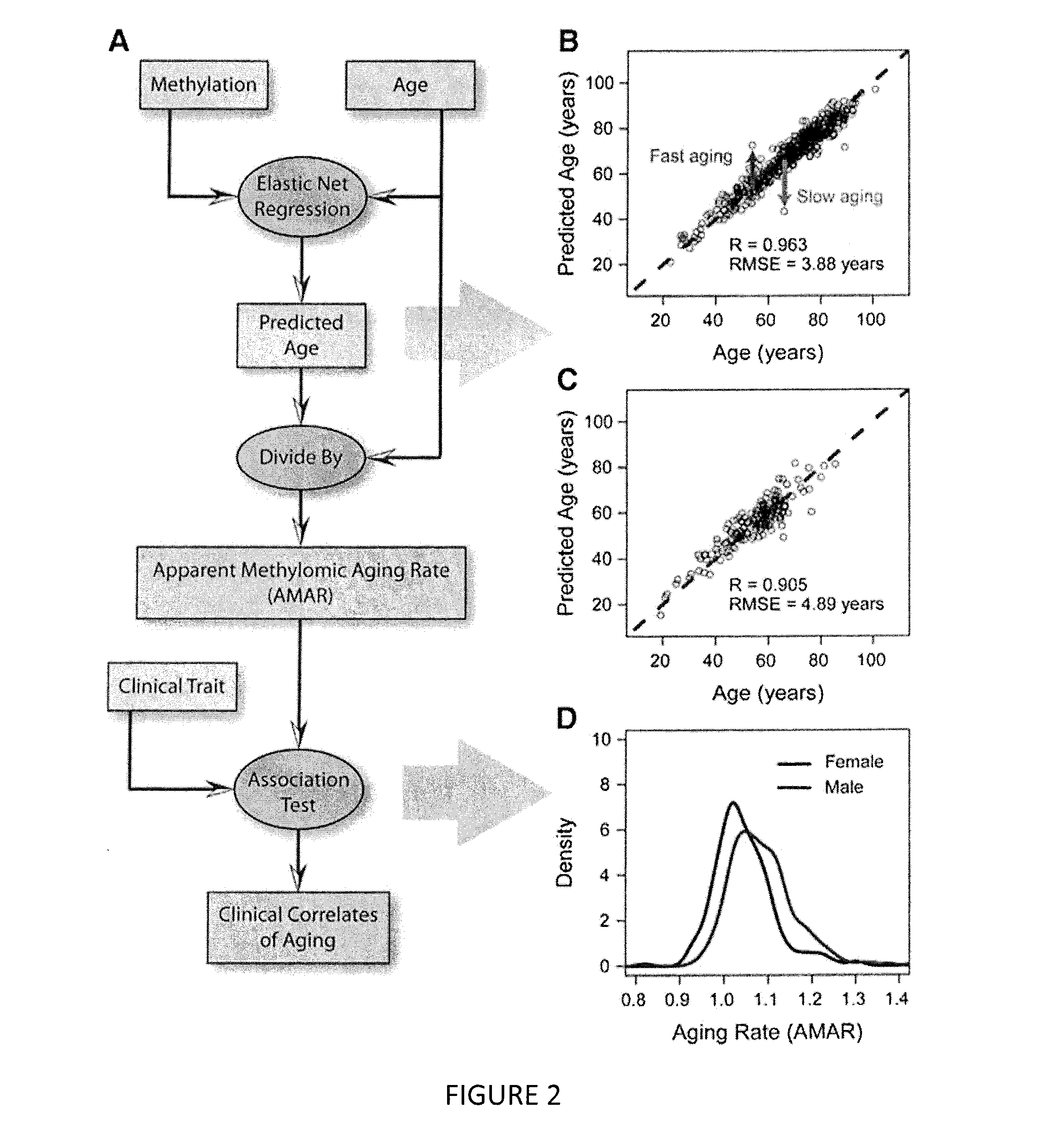
The invention provides for methods for predicting age of a subject based on the epigenome of the subject.
Owner:SAGE BIONETWORKS +1
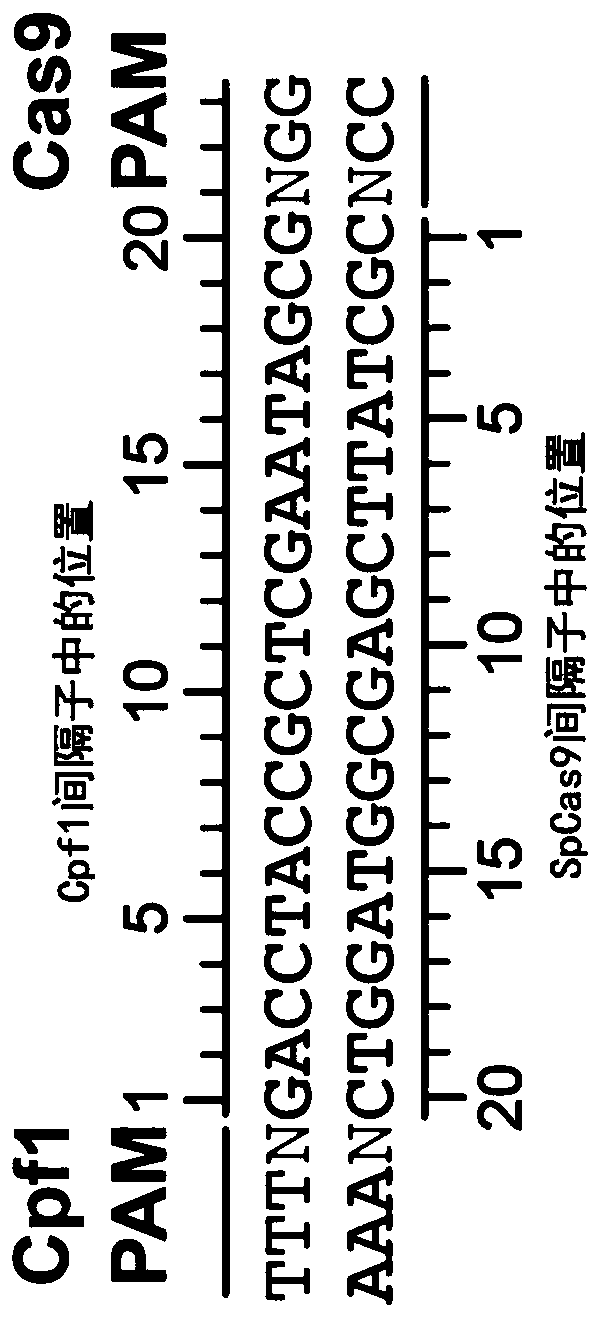
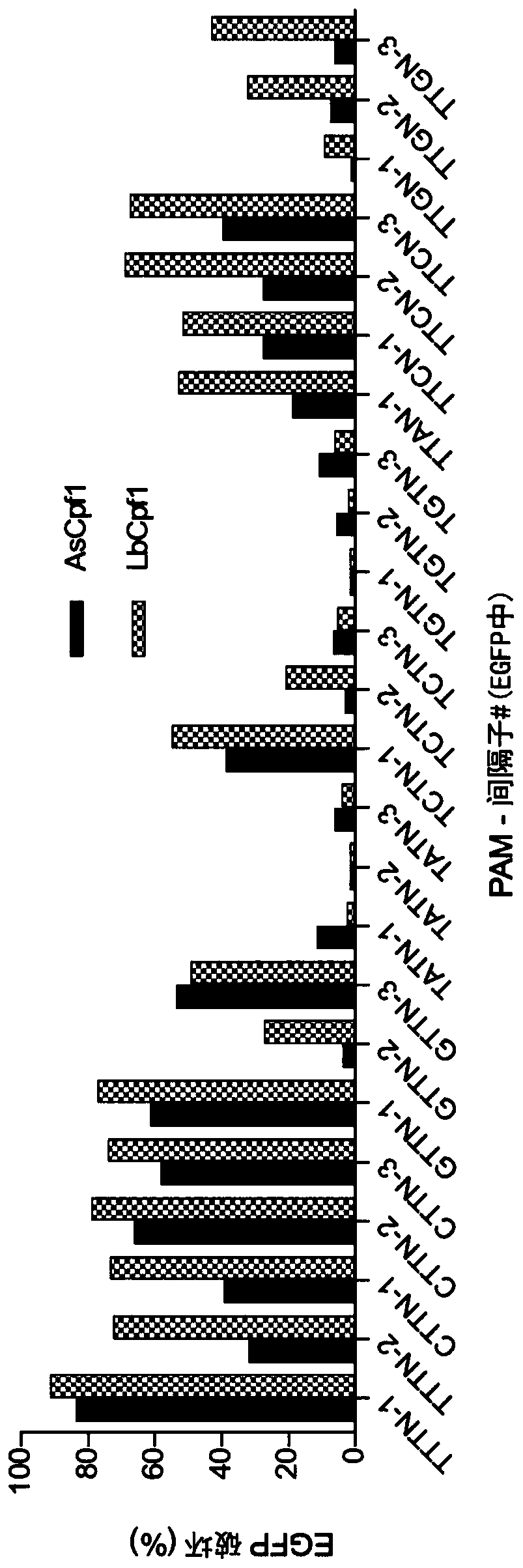
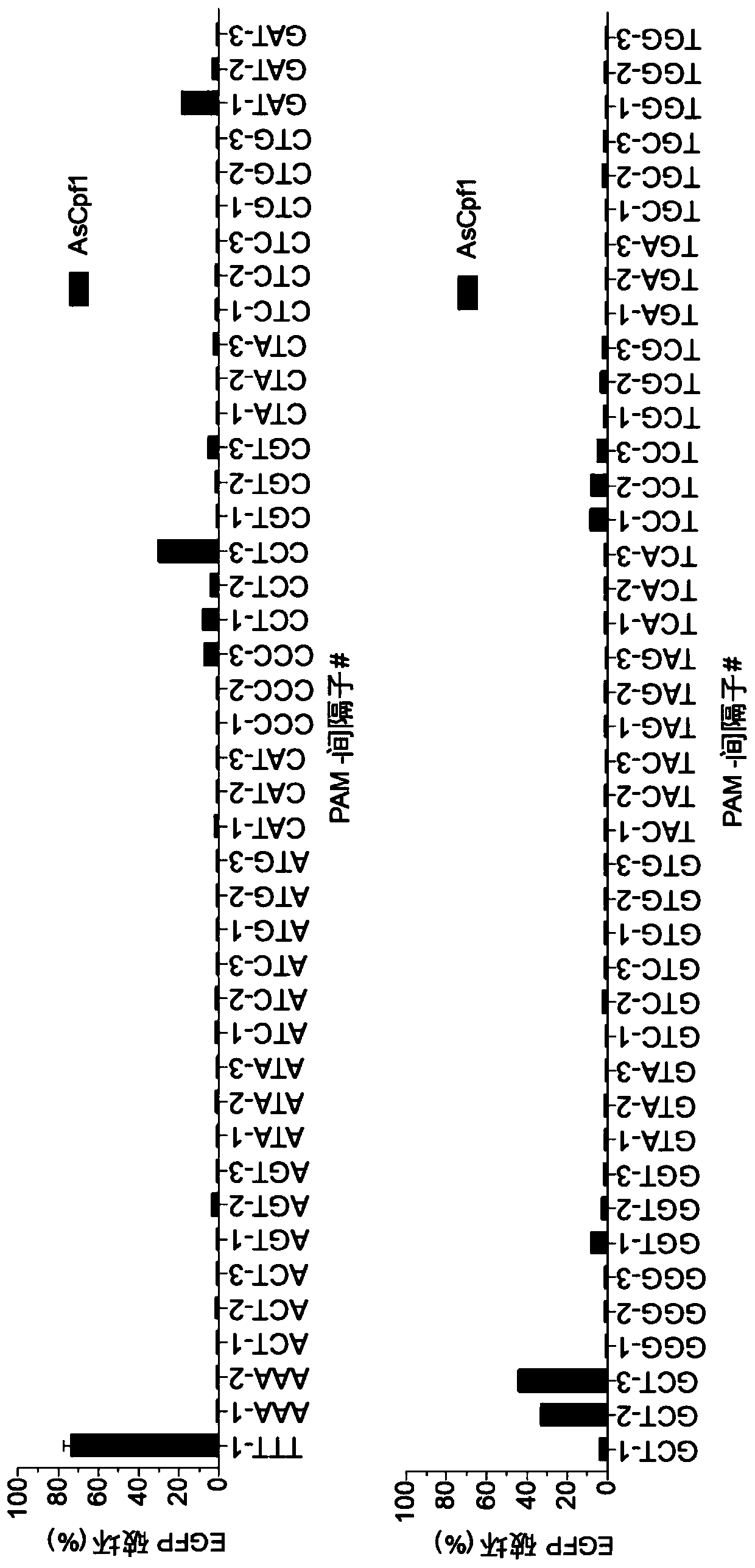
Variants of cpf1 (cas12a) with altered pam specificity
Engineered CRISPR from Prevotella and Francisella 1 (Cpf1) nucleases with improved targeting range and enhanced on-target activity, and their use in genomic engineering, epigenomic engineering, base editing, genome targeting, genome editing, and in vitro diagnostics.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
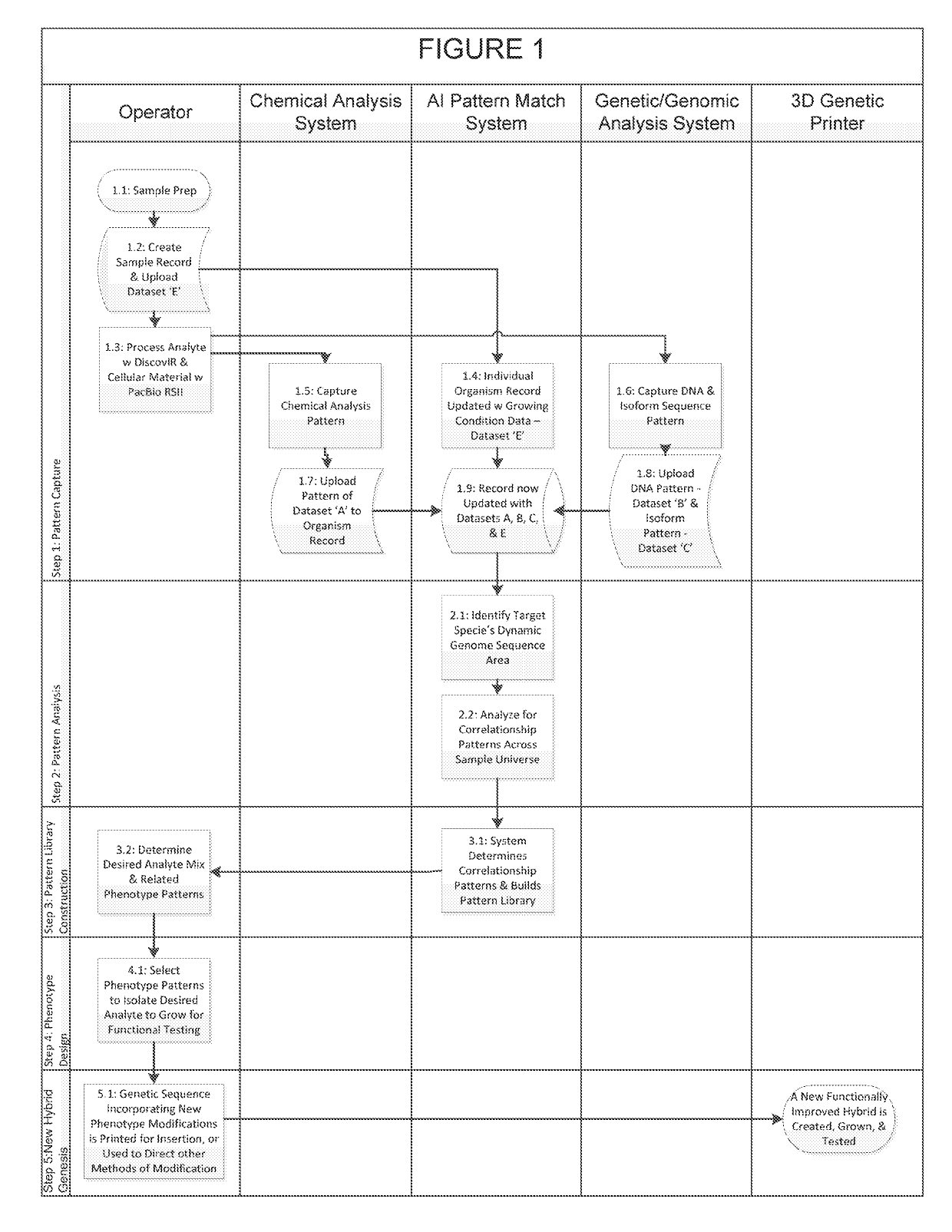
Biological organism development system
Owner:BUCHANAN CHARLES L
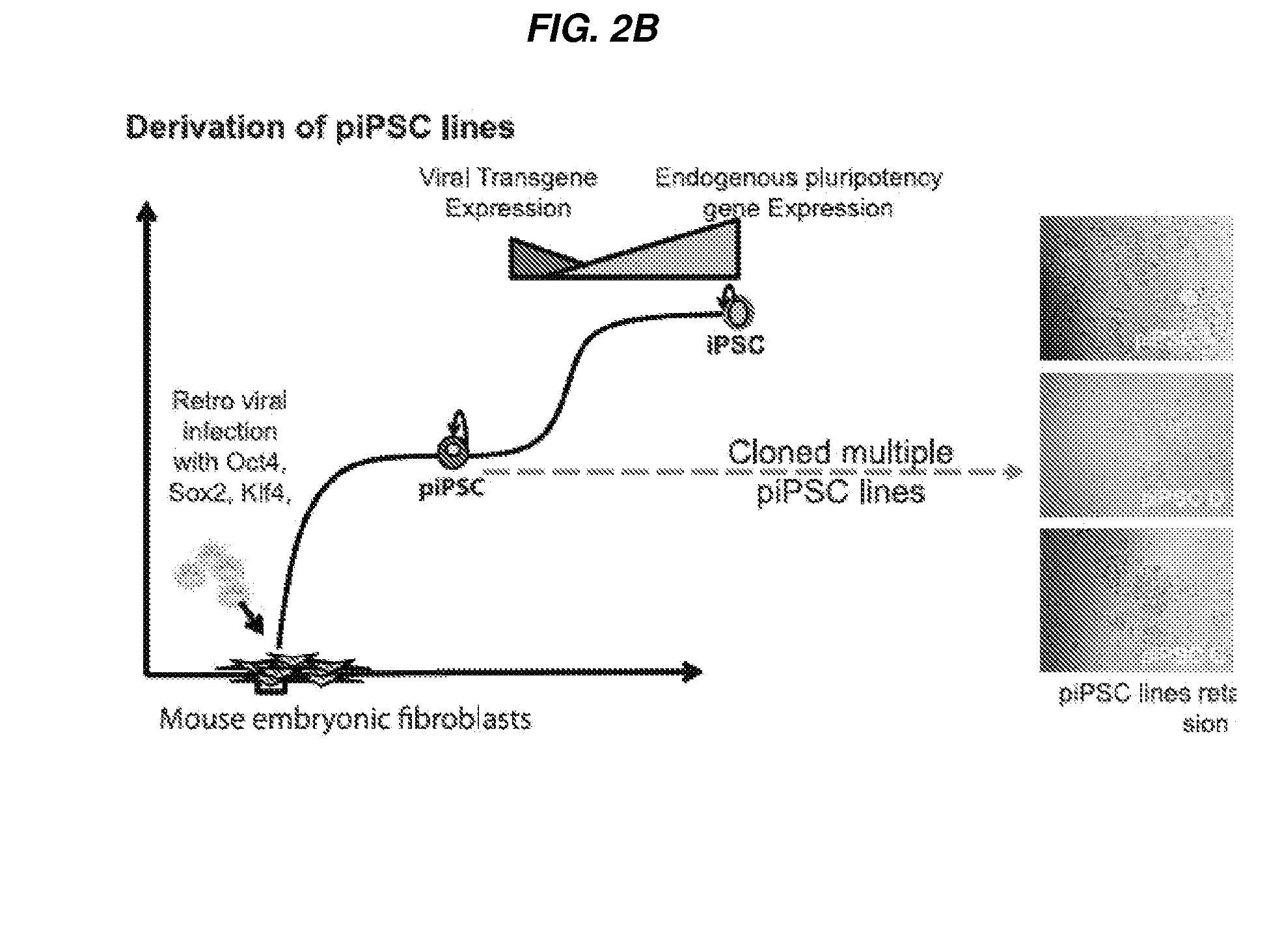
Stable reprogrammed cells
InactiveUS20130259842A1Rapidly and efficiently producedImprove efficiencyBiocideGenetic material ingredientsEpigenomeSOX2
The present invention relates to a stable pluripotent reprogrammed cells, and compositions and methods of isolation and uses thereof, wherein the stable pluripotent reprogrammed cells is derived from a somatic cell and has undergone incomplete remodeling of the epigenome. In some embodiments, the stable reprogrammed cell is a human stable reprogrammed cell. In some embodiments, the stable reprogrammed cell has a statistically significant lower level of expression of one or any combination of Nanog, Dnmt3b, Lefty2 as compared to an induced pluripotent stem cell. In some embodiments, the stable reprogrammed cell has a statistically significant higher level of expression of one or any combination of Tdgf1, Tert or endogenous Sox2 as compared to a somatic cell from which it was derived. In some embodiments, the stable reprogrammed cell has a statistically significant faster rate of doubling as compared to an induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) or an embryonic stem (ES) cell. Other aspects of the invention relate to compositions comprising the reprogrammed cell, method of isolation and method of use.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
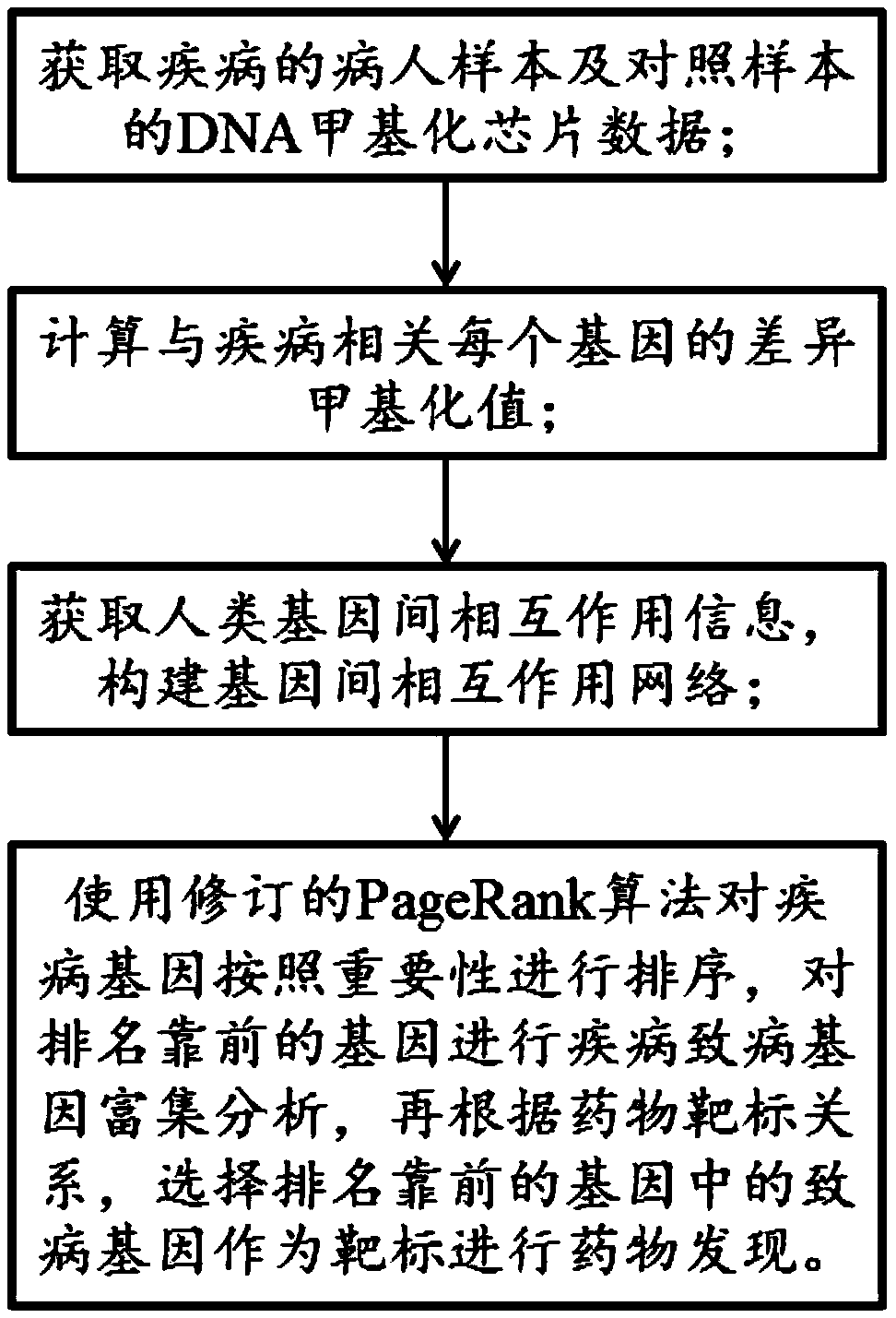
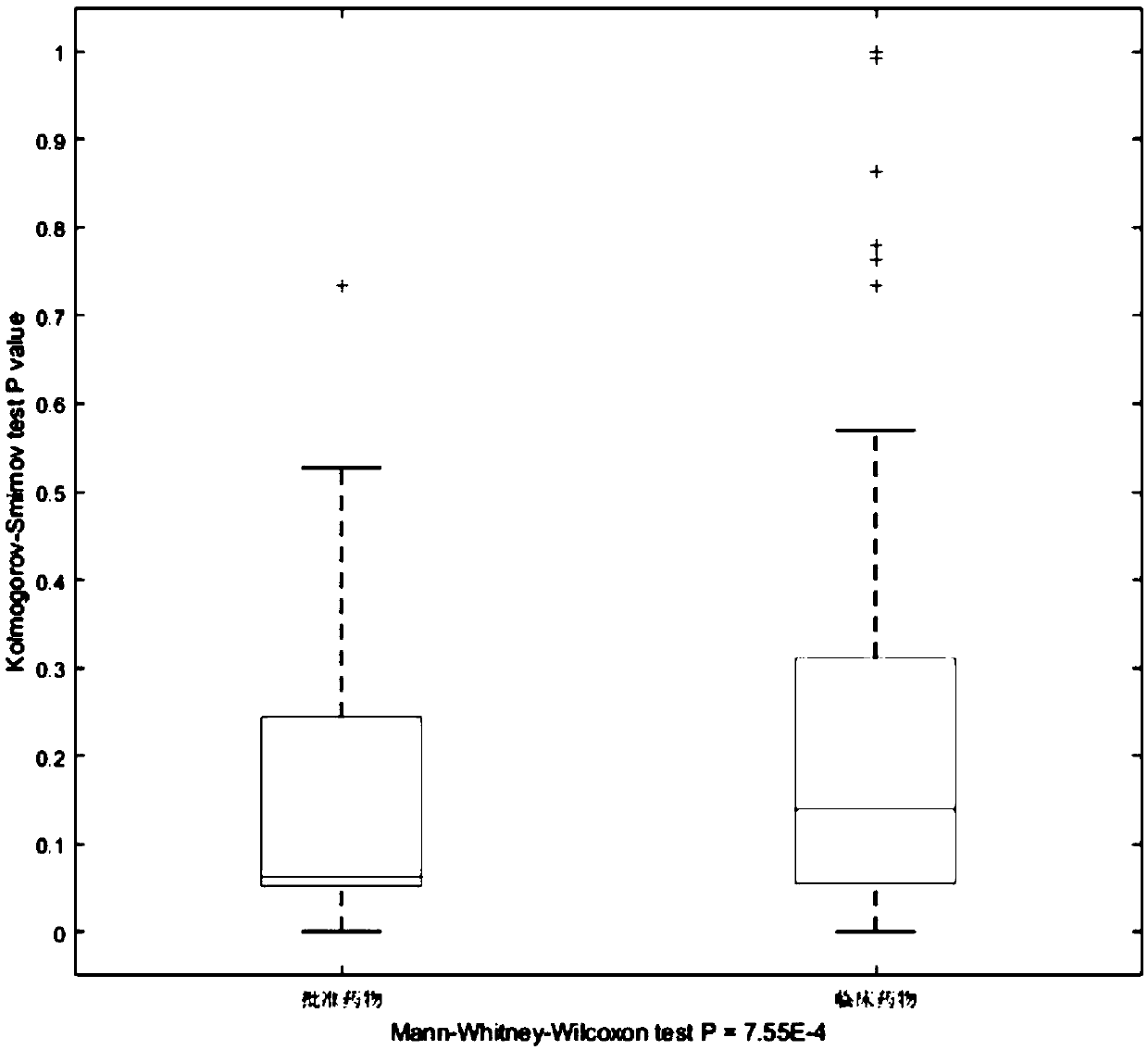
Drug discovering method based on epigenome and application of drug discovering method
ActiveCN109545276ASolid theoretical foundationEasy to implementMolecular designProteomicsDiseasePagerank algorithm
The invention relates to a drug discovering method based on epigenome and application of the drug discovering method, and belongs to the technical field of biological medicines. The invention starts from the basic principle of drug effects, DNA methylation chip data of a sample of a patient is combined to an intergenic interaction network, key pathogenic genes in a disease morbidity process is excavated by a revised PageRank algorithm, and therefore, potential drugs for treating diseases are found out according to a drug target corresponding relation. The method has the characteristics of solid theoretical basis, easiness in implementation and high efficiency, and has wide application prospect in drug discovery.
Owner:武汉百药联科科技有限公司 +1
Optimizing Successful Outcomes for Repurposing Existing Pharmaceutical Compounds
PendingUS20190243946A1Quicker and much less-expensiveReduced metabolismCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDiseaseGenomics
The present invention provides a process and method for preventing and / or treating protein based diseases, including, but not limited to: Alzheimer's and other amyloid based disease groups. This method recognizes correlative similarities across genomics, phenotypic and pharmacologic analytics and data to identify a list of existing compounds as high probability targets to act as inhibitors and / or stimulants close to a disease of interest. Pertinent genetic or epigenetic variances, or protein expression anomalies, are used to assemble a list of existing compounds through the use of artificial intelligence, machine learning and algorithmic relationships. This invention applies current genomic, phenotypic and pharmacological data to leverage data previously obtained in pursuit of other disease treatments. Accordingly, the current invention collapses cycle time to discovery and dramatically reduces costs. Through this system of active compounds created from tenuous relationships exhibits an elevated probability of success. Using a selection of algorithms that coordinate relationships including, but not limited to: genomic, epigenomic, phenotypic, protein dysregulation, cultural, pharmacological, etc., data, the present invention collapses cycle time of development and dramatically reduces costs by accessing data on target rich groups of previously tested abstractly related compounds.
Owner:POSTREL RICHARD
Pig tissue chromatin immunoprecipitation processing method
InactiveCN107254512AEasy to operatePromote resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyEpigenome
The invention belongs to the technical field of livestock immunology, and concretely relates to a pig tissue chromatin immunoprecipitation processing method. The method is named as ChIP for short. The method specially aims at pig tissue for optimization design, employs a tissue lysate and a Dounce grinder for combination, and develops the method, the processes and the flows of pig tissue homogenate, the tissue can be fully cracked, the obtained chromatin amount is large, the quality is high, and the quality of a peak graph of the subsequent ChIP-Seq experiments is high. The method has the advantages of simpleness and rapidity, can effectively prepare a tissue suspension, can satisfy the core requirement of the ChIP-Seq experiments, and provides the effective approach for developing the pig tissue epigenomics researches.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
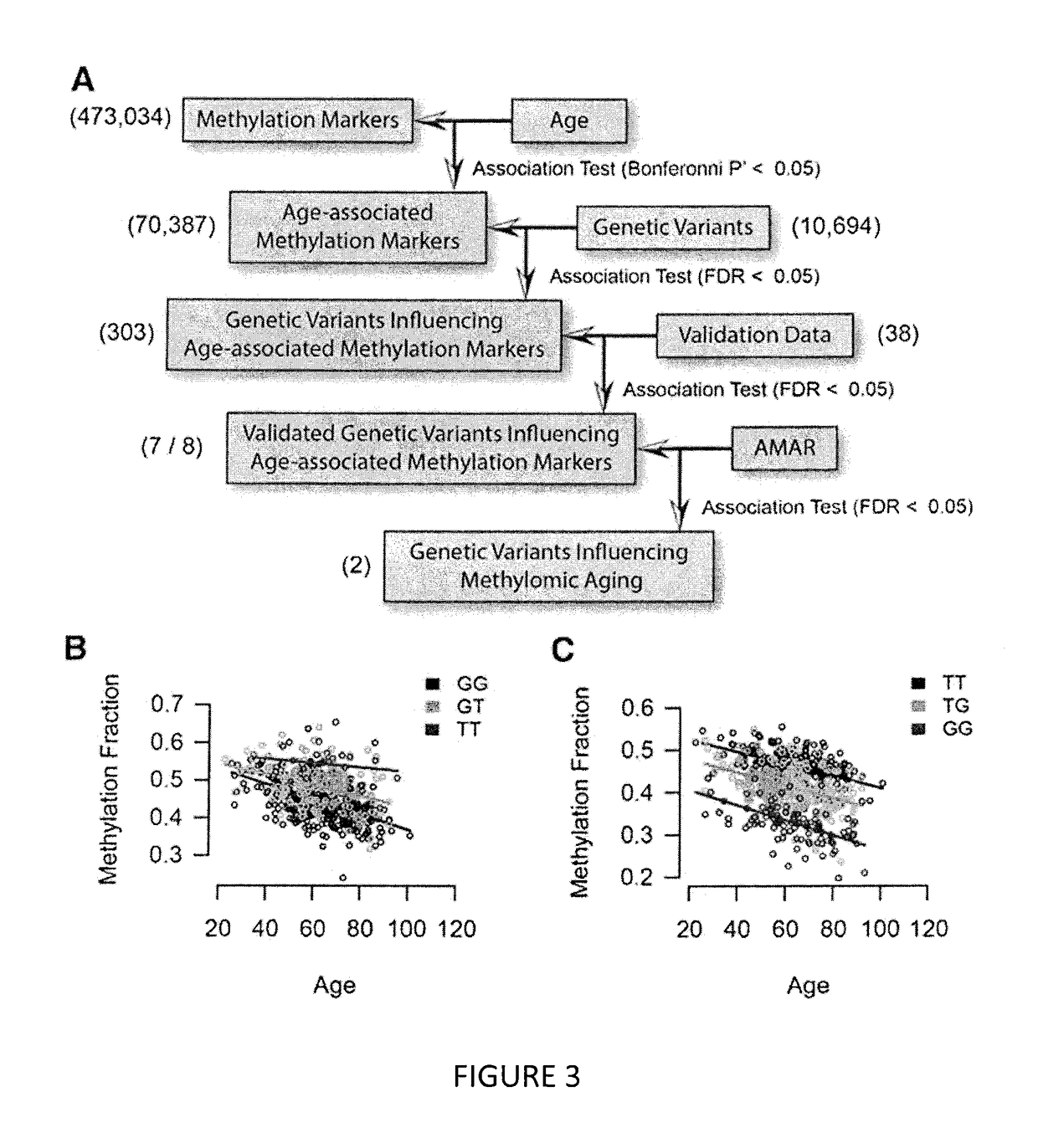
Methods for predicting age and identifying agents that induce or inhibit premature aging
The invention provides for methods for predicting age of a subject based on the epigenome of the subject.
Owner:SAGE BIONETWORKS +1
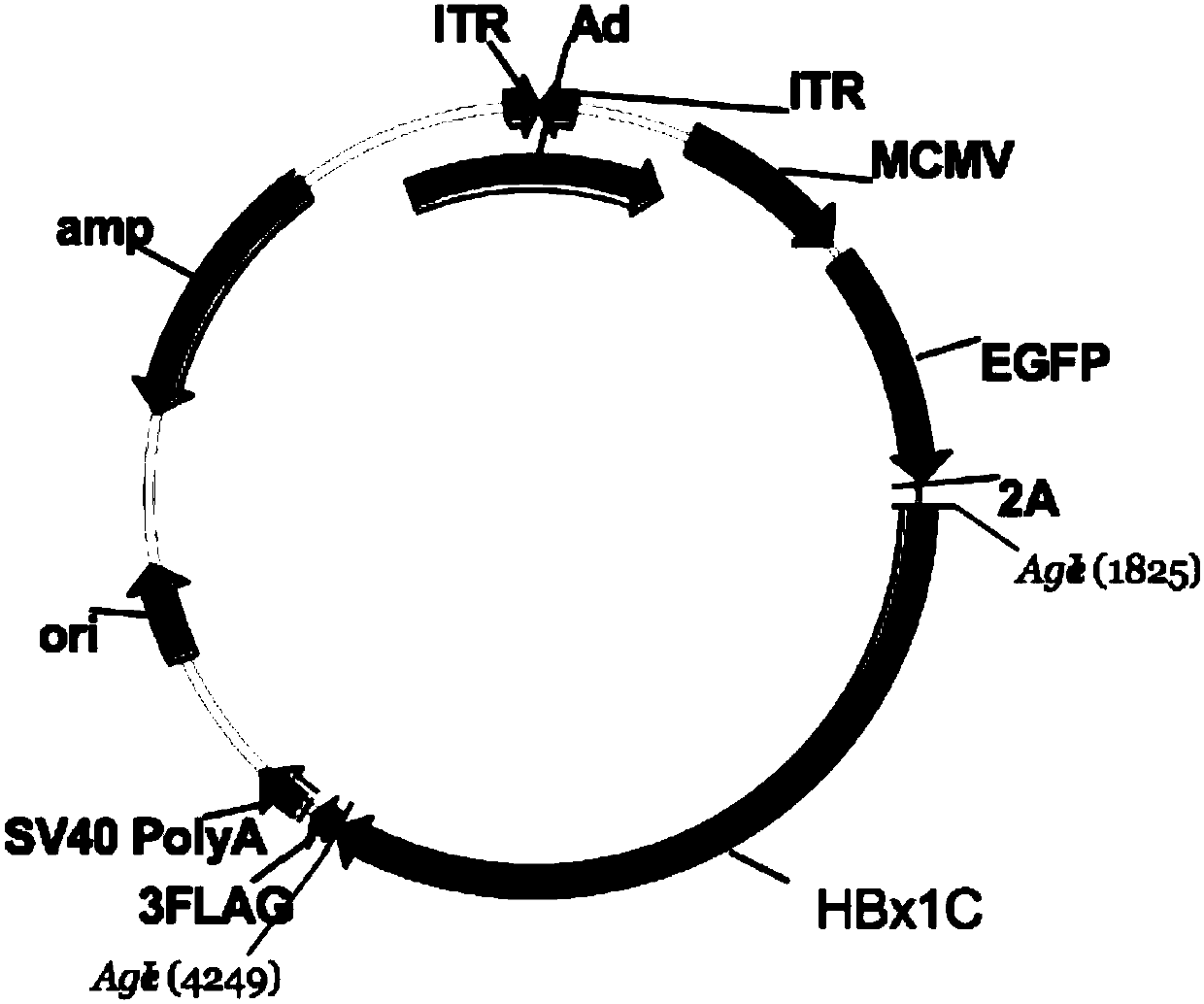
Targeted epigenome regulated and controlled hepatitis B virus (HBV)-resisting molecule HBx1C and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and in particular relates to a targeted epigenome regulated and controlled hepatitis B virus (HBV)-resisting molecule HBx1C and application thereof. A brand-new protein molecule HBx1C gene, which has a targeted specific affinity interaction effect on an HBV gene and can be used for carrying out epigenetic methylation modificationon DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of the HBV gene, is designed according to bioinformatics, epigenetic inheritance engineering and an immunology principle; an adenovirus vector is introduced into cells,and a targeted and specific protein molecule aiming at an HBV can be efficiently expressed; the methylation chemical modification on the virus gene also can be generated. In vivo and vitro experimentsprove that the targeted epigenome regulated and controlled HBV-resisting molecule HBx1C has a function of efficiently inhibiting HBV surface antigen expression and a treatment effect of resisting theHBV is realized; the targeted epigenome regulated and controlled HBV-resisting molecule HBx1C can be used for preparing a medicine for treating hepatitis B in epigenetic genetic engineering and has awide application prospect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
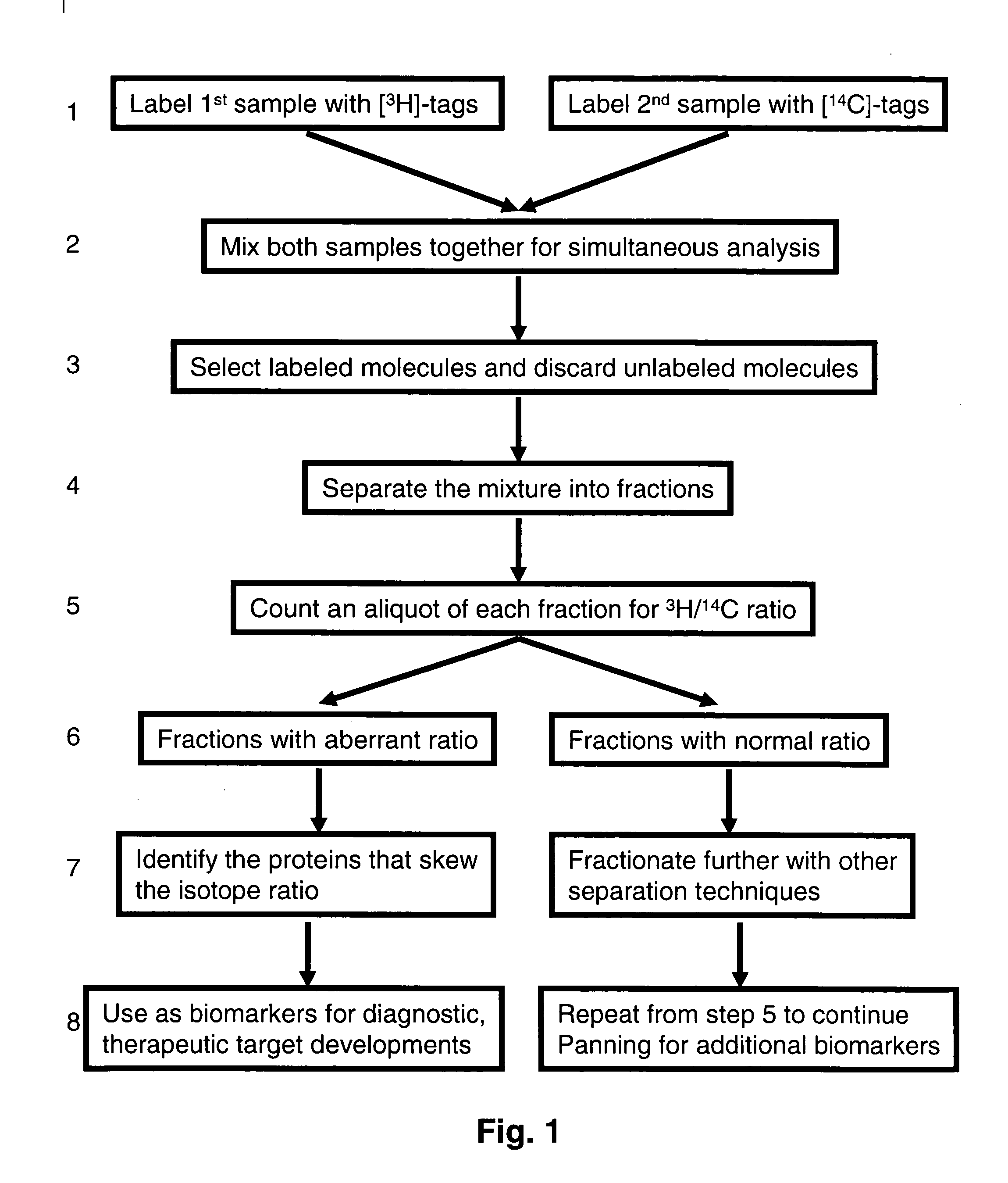
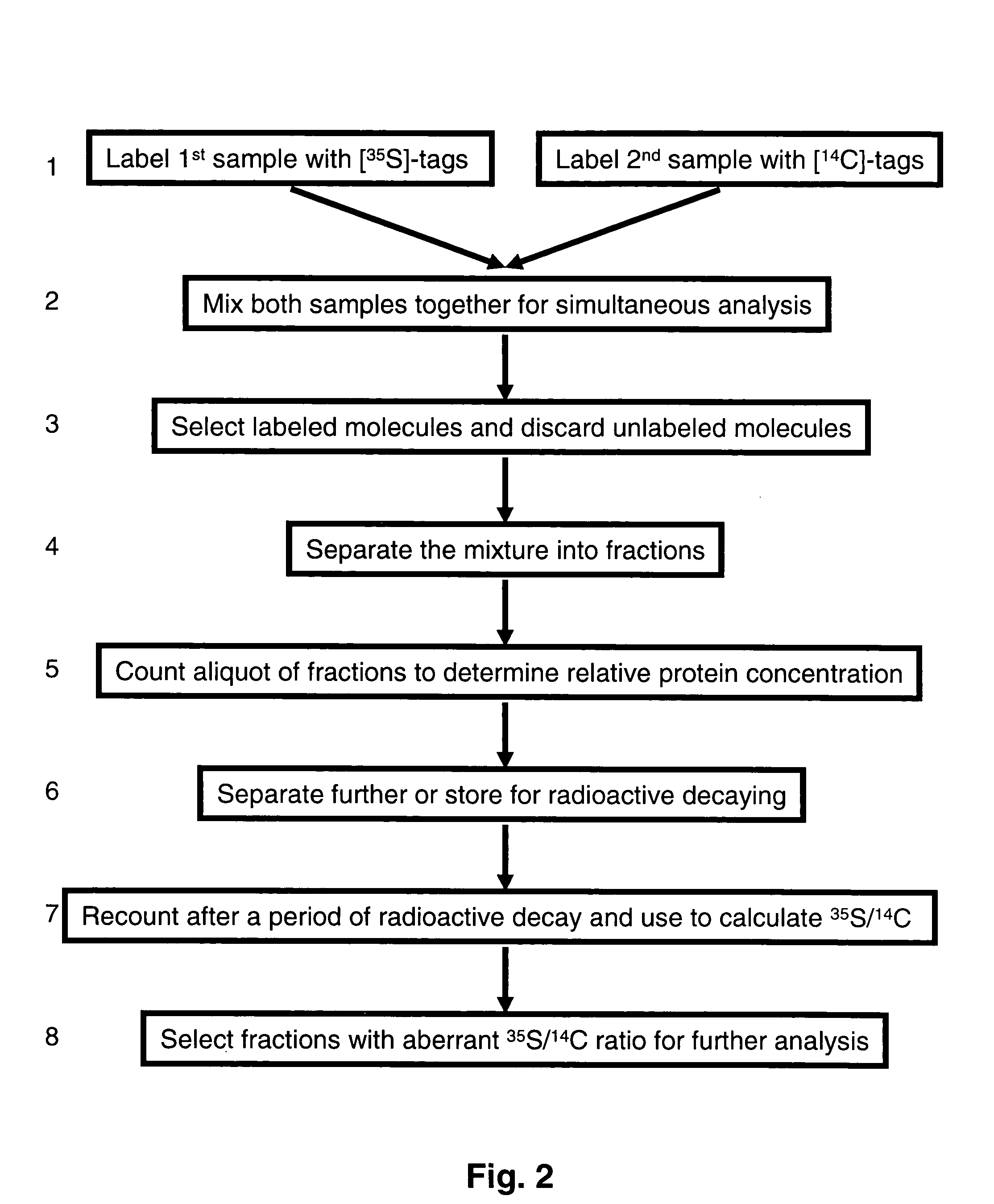
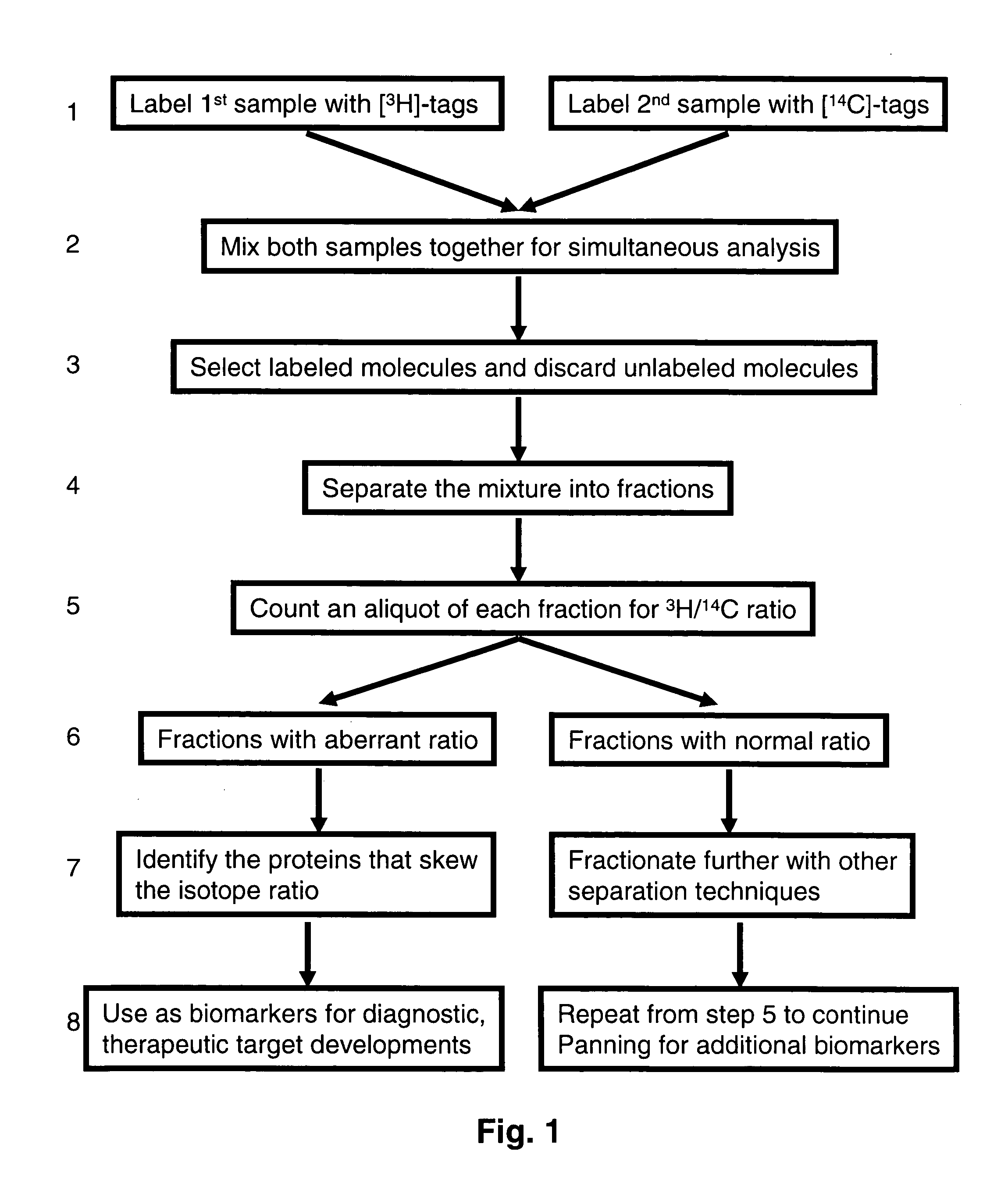
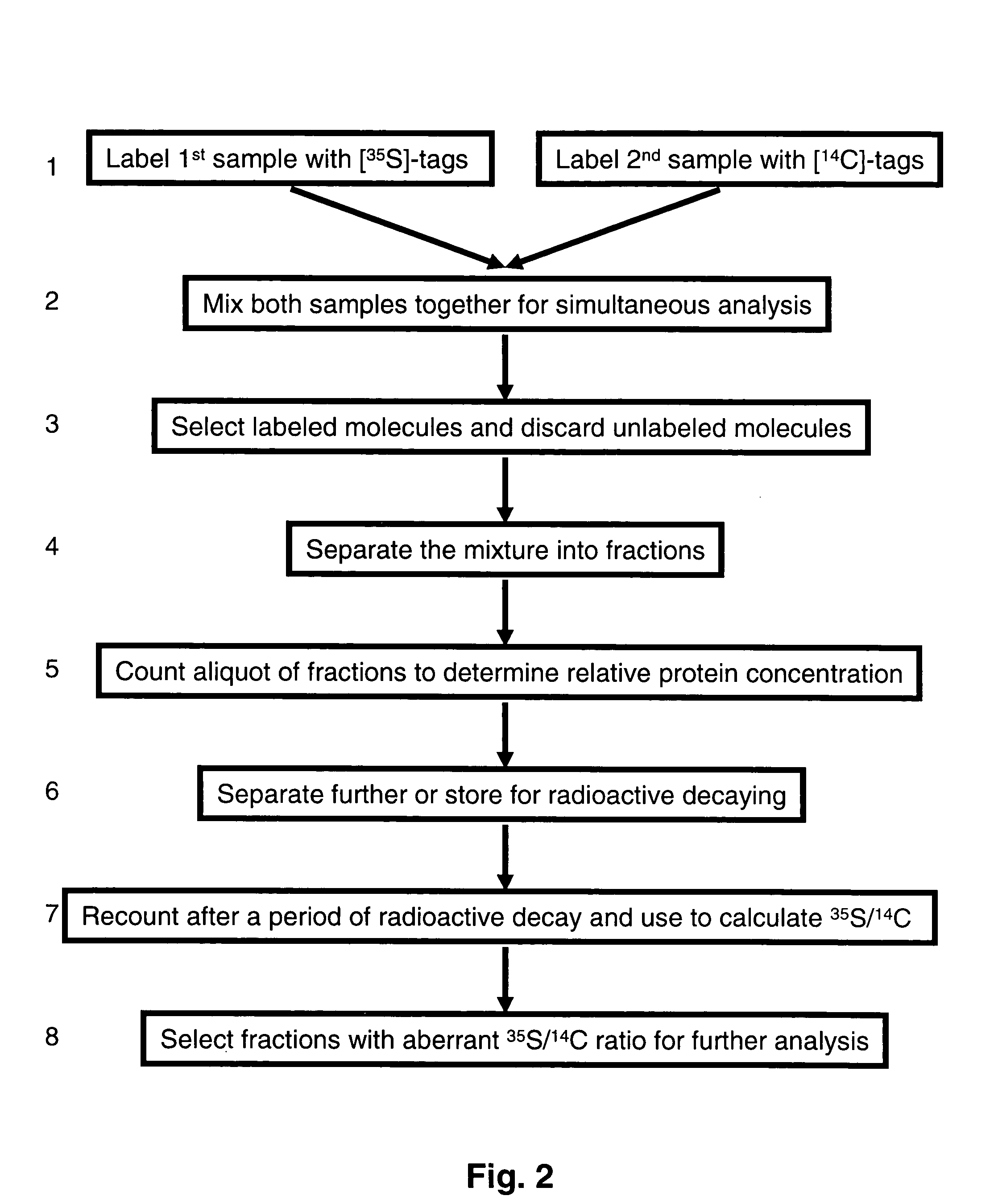
Methods and reagents for differential proteomic analysis
InactiveUS20050074794A1Easy to analyzeSimple methodSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsEpigenome
Methods and reagents for labeling molecules of interest in a plurality of samples, and then combining and selecting labeled molecules away from unlabeled molecules for use in simultaneous co-assaying analysis. The reagents comprise labeling means of distinguishable radioactive isotopes which remain with the labeled molecules. Additionally, the reagents also comprise selection means which can be affinity tags, beads, or immobilized surface which may remain or be cleaved off through cleavable linkers. A set of labeling reagent can be used to label a plurality of samples, combine them before or after selecting / enriching for labeled molecules and co-assay together for reliable comparison. This invention has many applications in comparing and panning for differentially abundant molecules or differential modification of molecules for proteomics, glycomics, phospho-proteomics, metabolomics, epi-genomics . . . studies.
Owner:PROTEOMYX
Genetic database system and method
InactiveUS20140236607A1High riskPayment schemes/modelsPathological referencesEpigenomeGenetic database
A system and method for performing an analysis of a subject's genome, transcriptome and / or epigenome is described. The identities of a predetermined number of, such as ten or more, characteristics in the subject's genome, transcriptome and / or epigenome which are associated with one or more particular phenotype(s) or an increased risk of a particular phenotype are determined by performing an analytical technique upon a biological sample obtained from the subject. The amounts of any royalties or fees required for determination of the identities of one or more of the ten or more characteristics in the subject's genome, transcriptome and / or epigenome are determined via a computer. The amount of a fee charged for a determination of the identities of the ten or more characteristics in the subject's genome, transcriptome and / or epigenome are adjusted via a computer to reflect the amount of the determined royalties or fees and / or the amount of a fee for a future treatment of the subject. A database accessed during the method is also described.
Owner:ALEXANDRE LAURENT
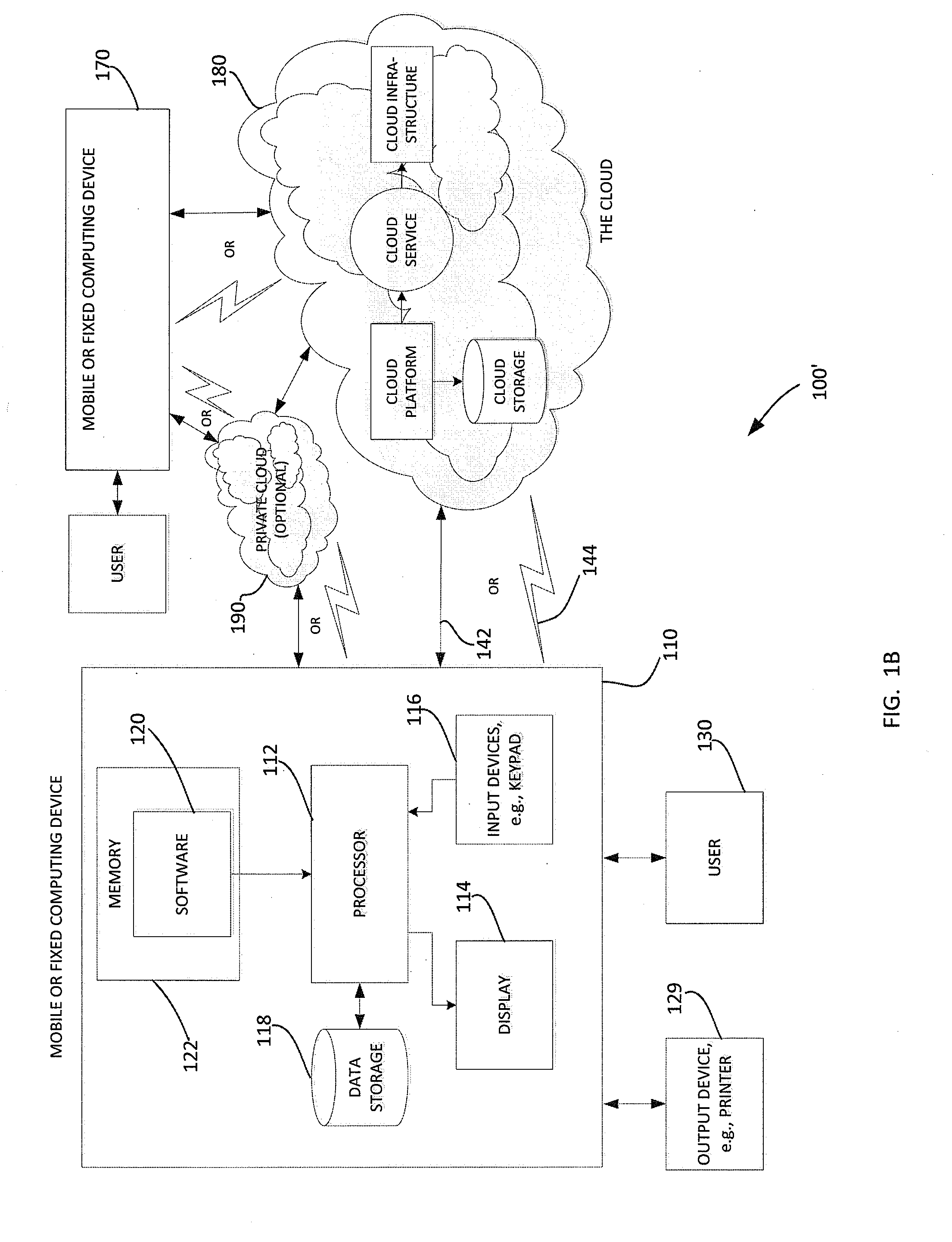
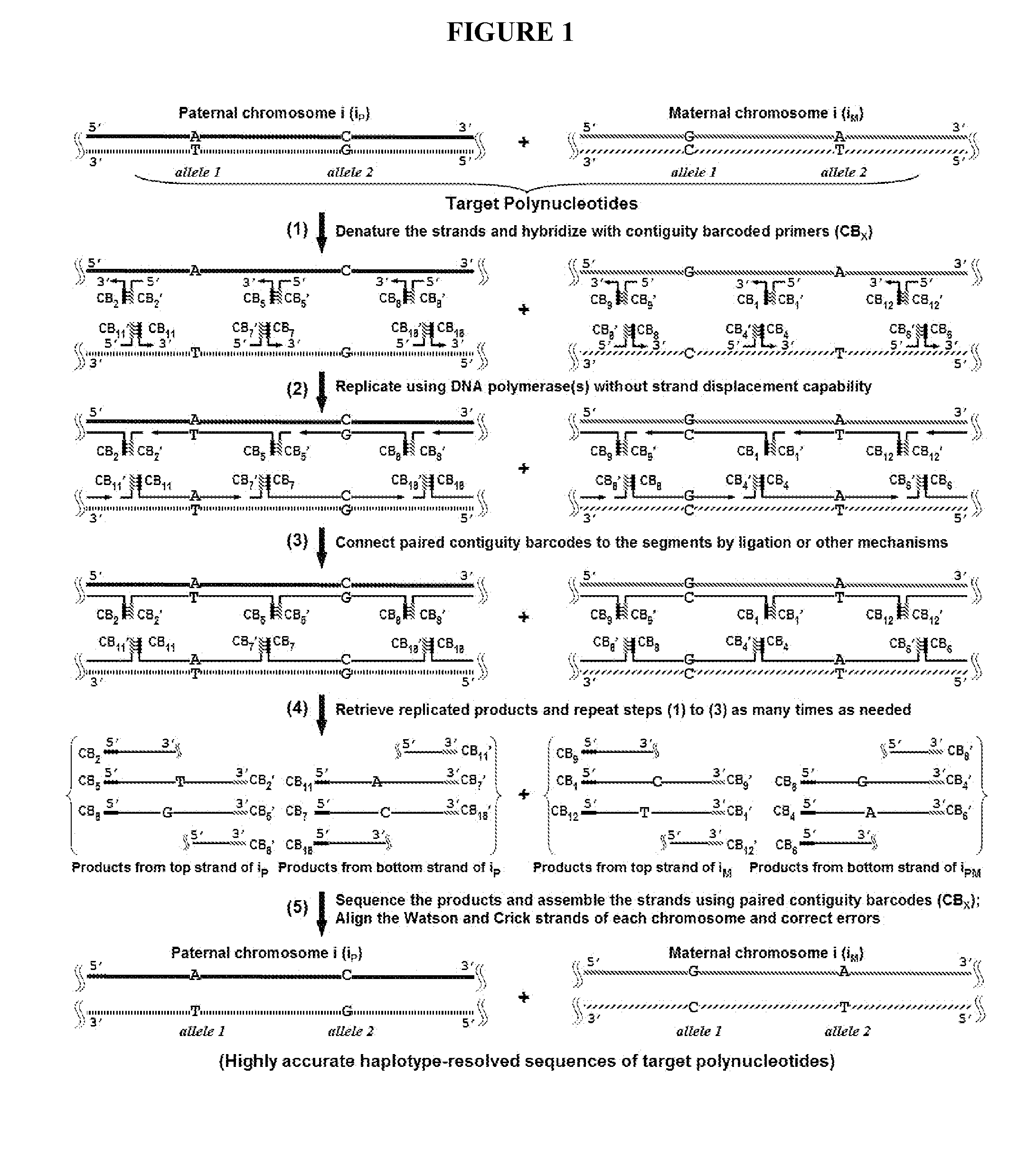
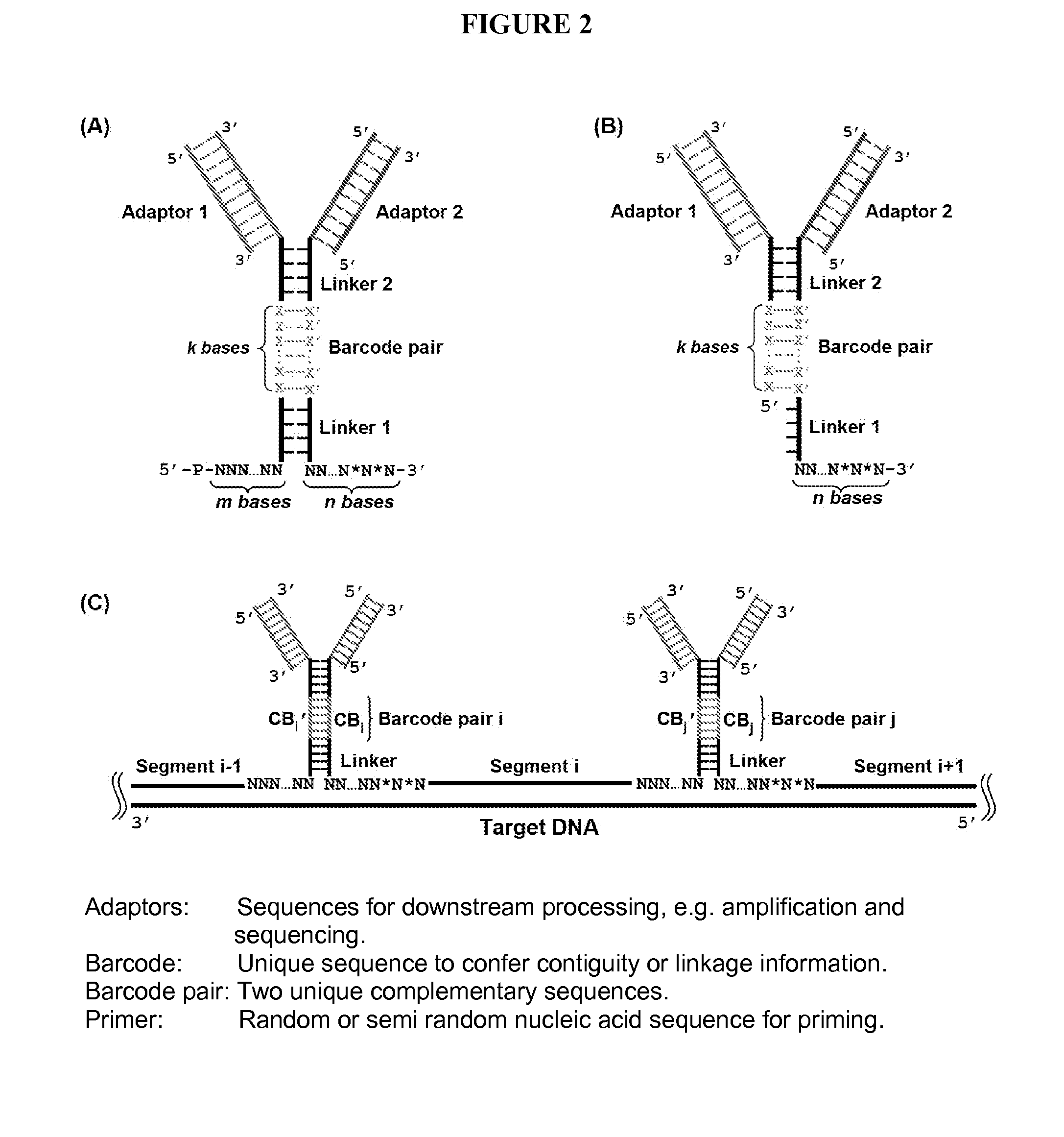
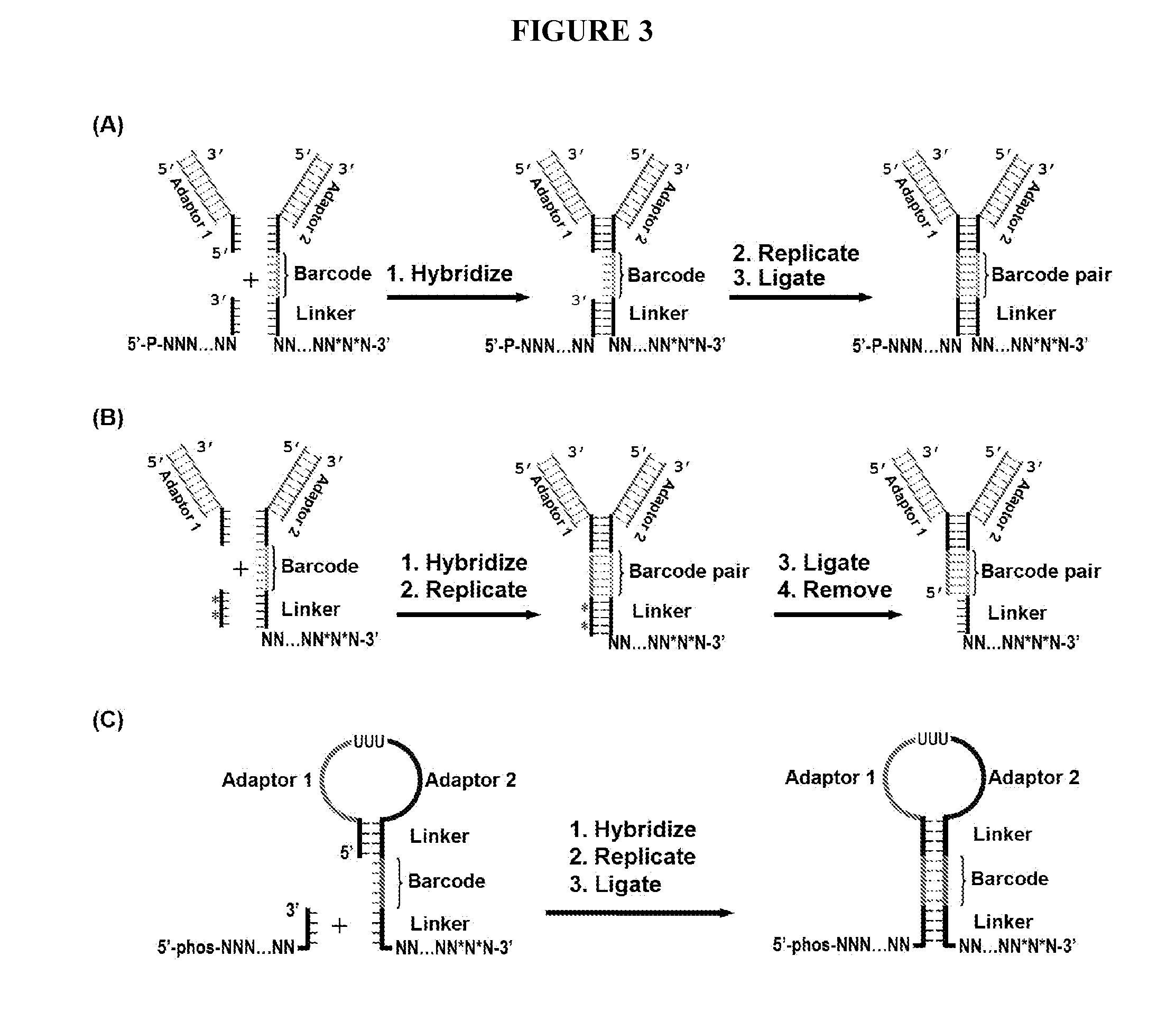
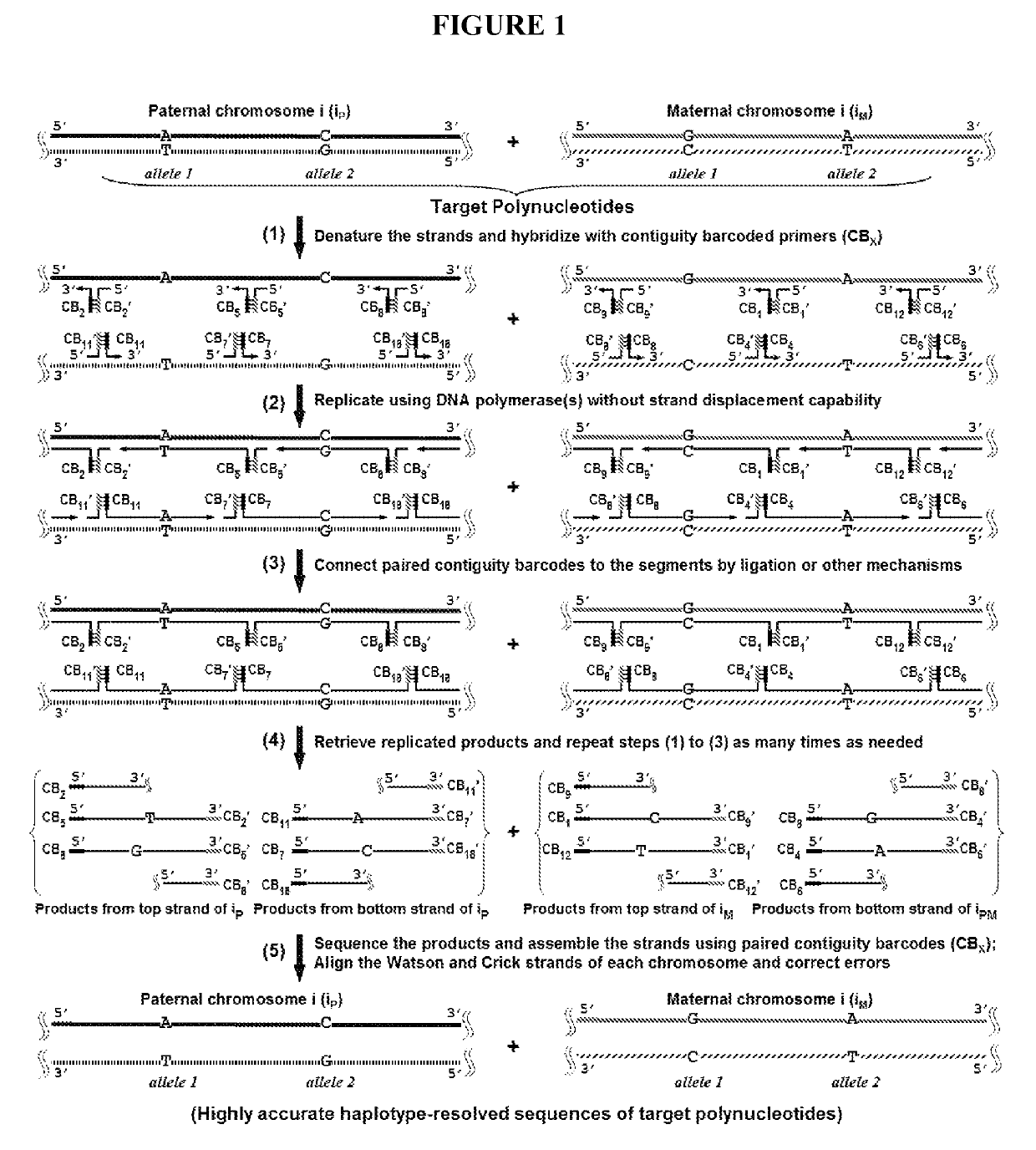
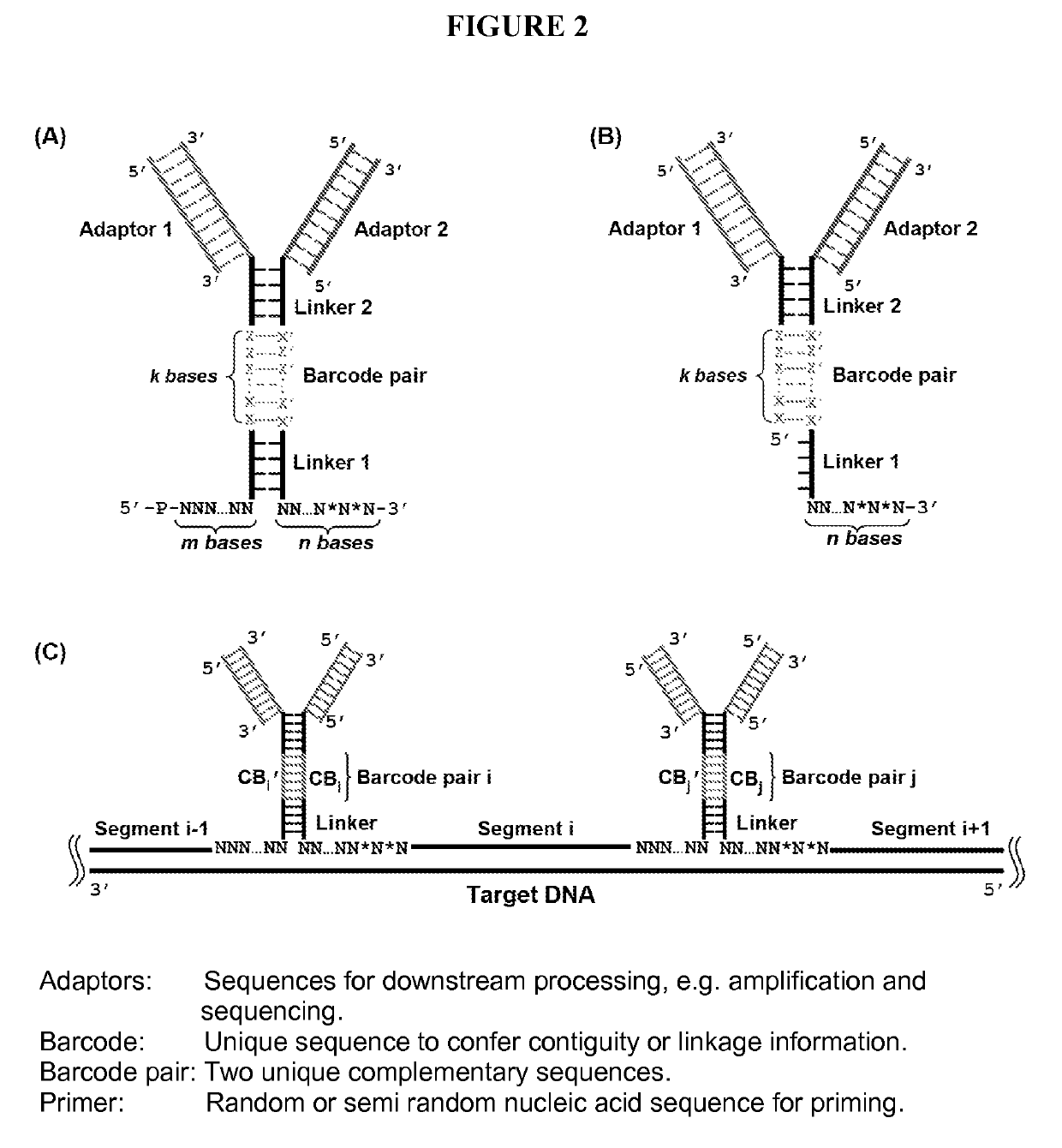
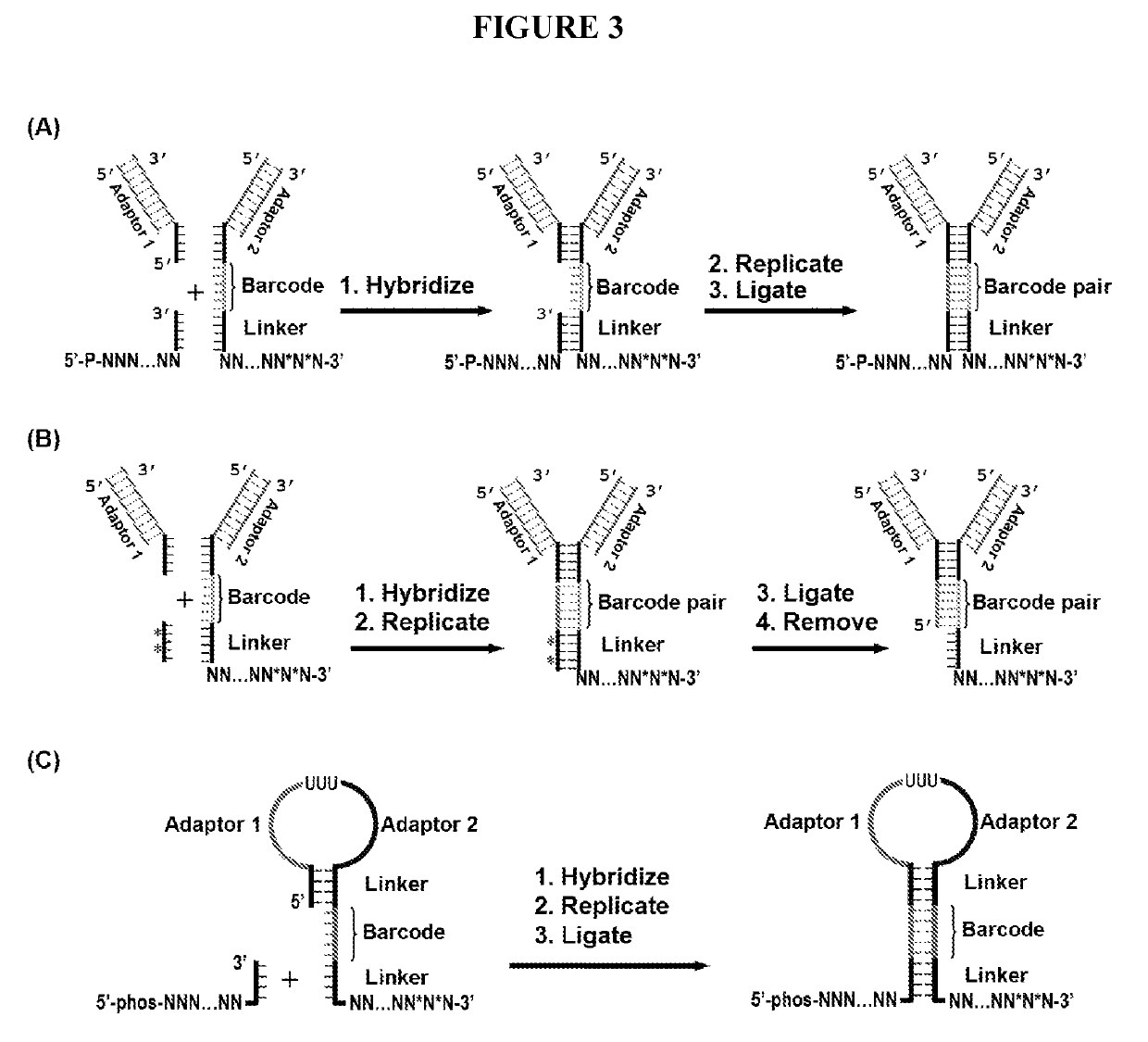
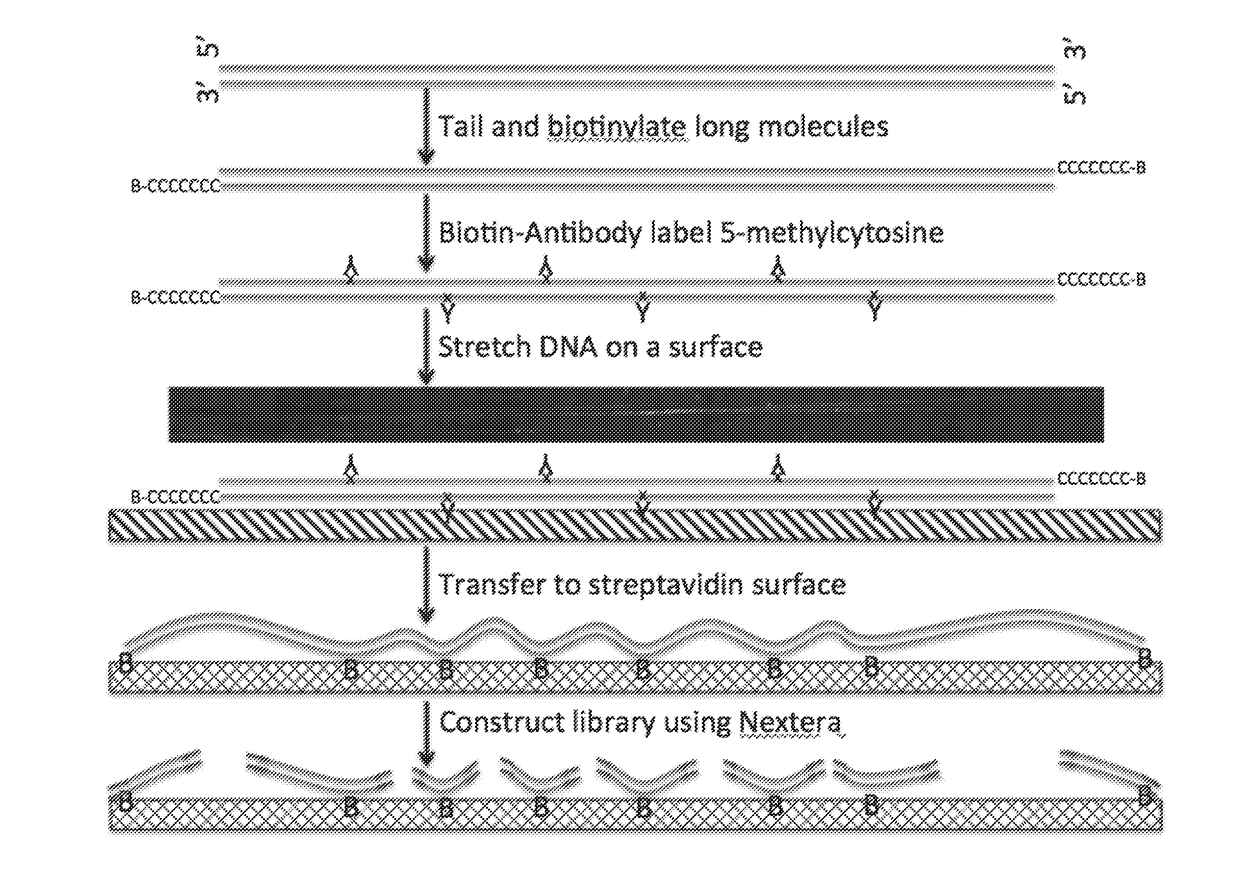
Duplicating DNA with contiguity barcodes for genome and epigenome sequencing
ActiveUS20160265039A1Improve Sequencing AccuracyQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresEpigenomeNucleotide
Provided herein are methods and devices for accurate sequencing and detection of epigenetic information from template polynucleotides. Also provided are methods for long-range strand displacement amplification of polynucleotides, microfluidic devices with selectively permeable barriers for multistep processing, and methods for polynucleotide amplification using the microfluidic devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods of preparing a re-usable single cell and methods for analyzing the epigenome, transcriptome, and genome of a single cell
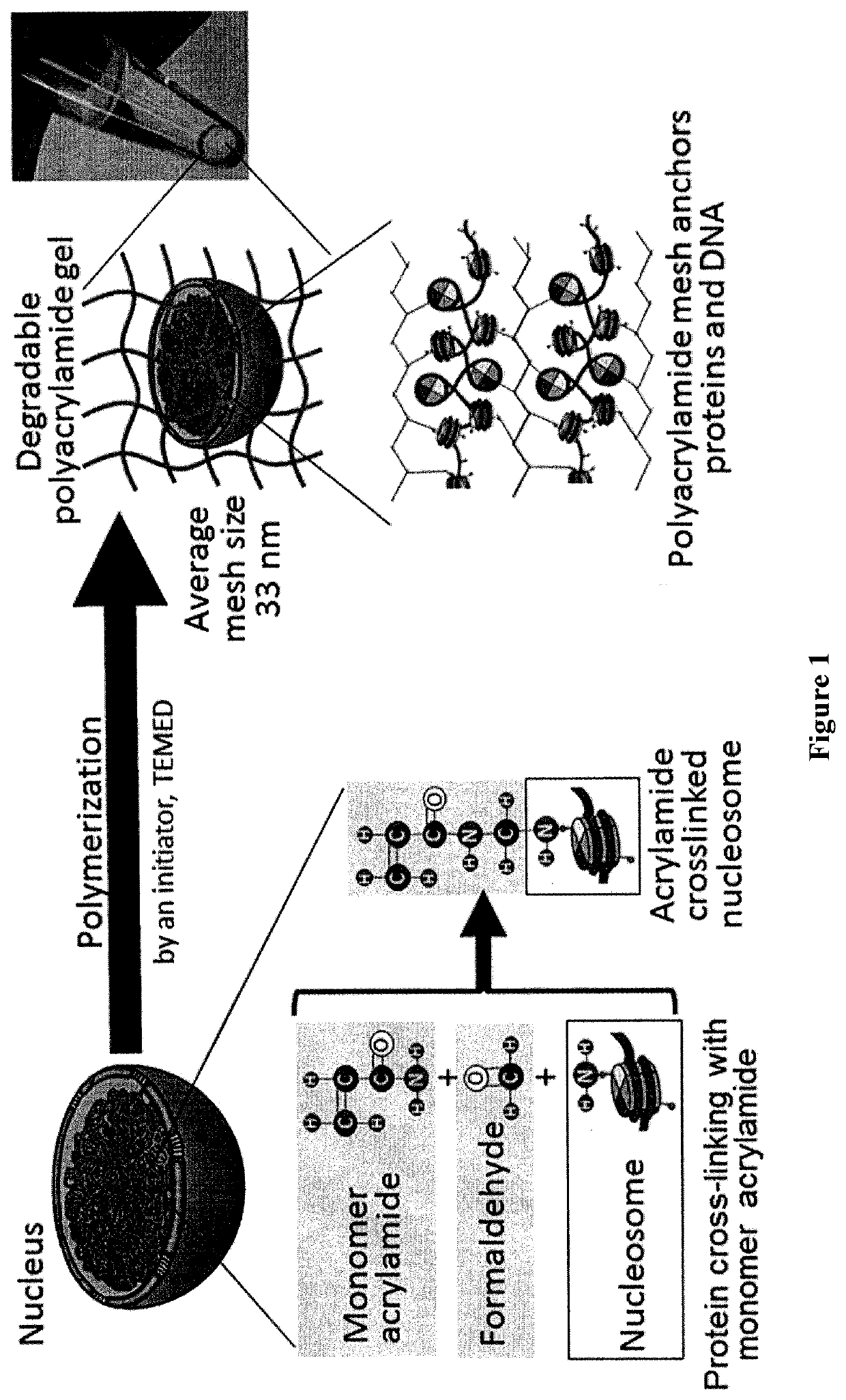
Methods and kits for preparing re-usable single cells are described. Cell components are anchored using a nano-scale scaffold to create a re-usable single cell. The nano-scale scaffold may be a polyacrylamide nano-scale scaffold. Methods to determine modifications of the genome, transcriptome, or epigenome are described.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Methods for predicting age and identifying agents that induce or inhibit premature aging
The invention provides for methods for predicting age of a subject based on the epigenome of the subject.
Owner:SAGE BIONETWORKS +1
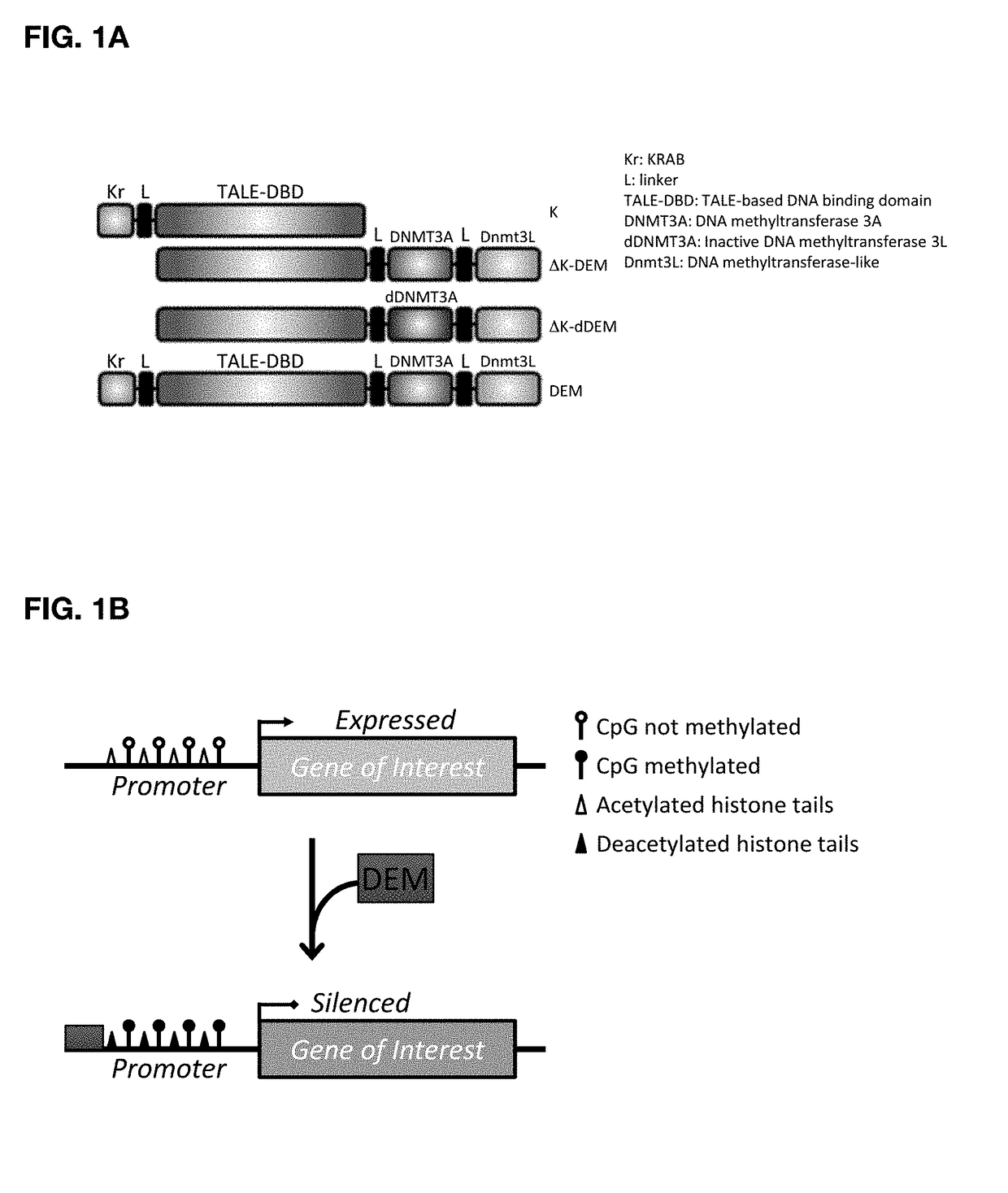
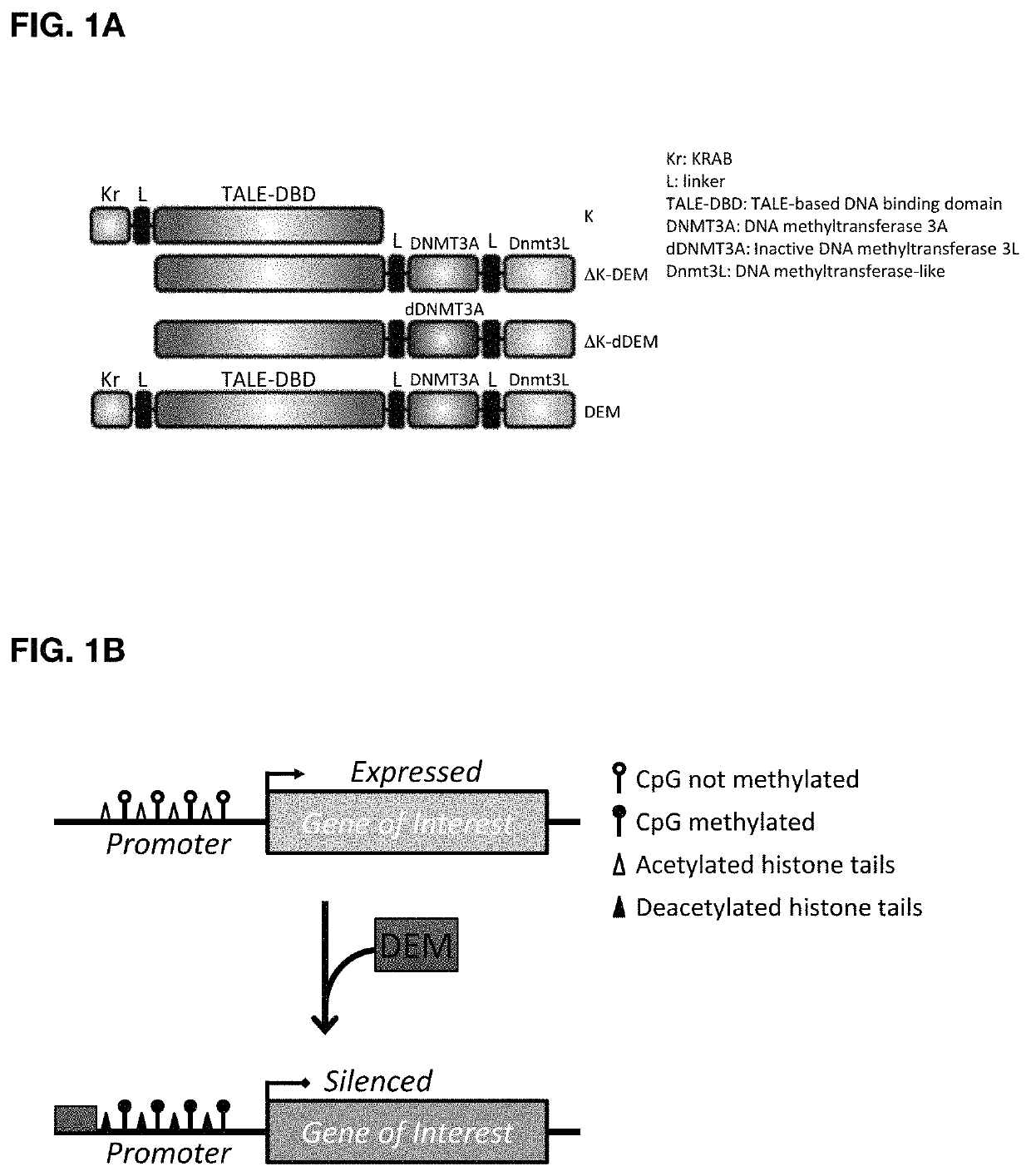
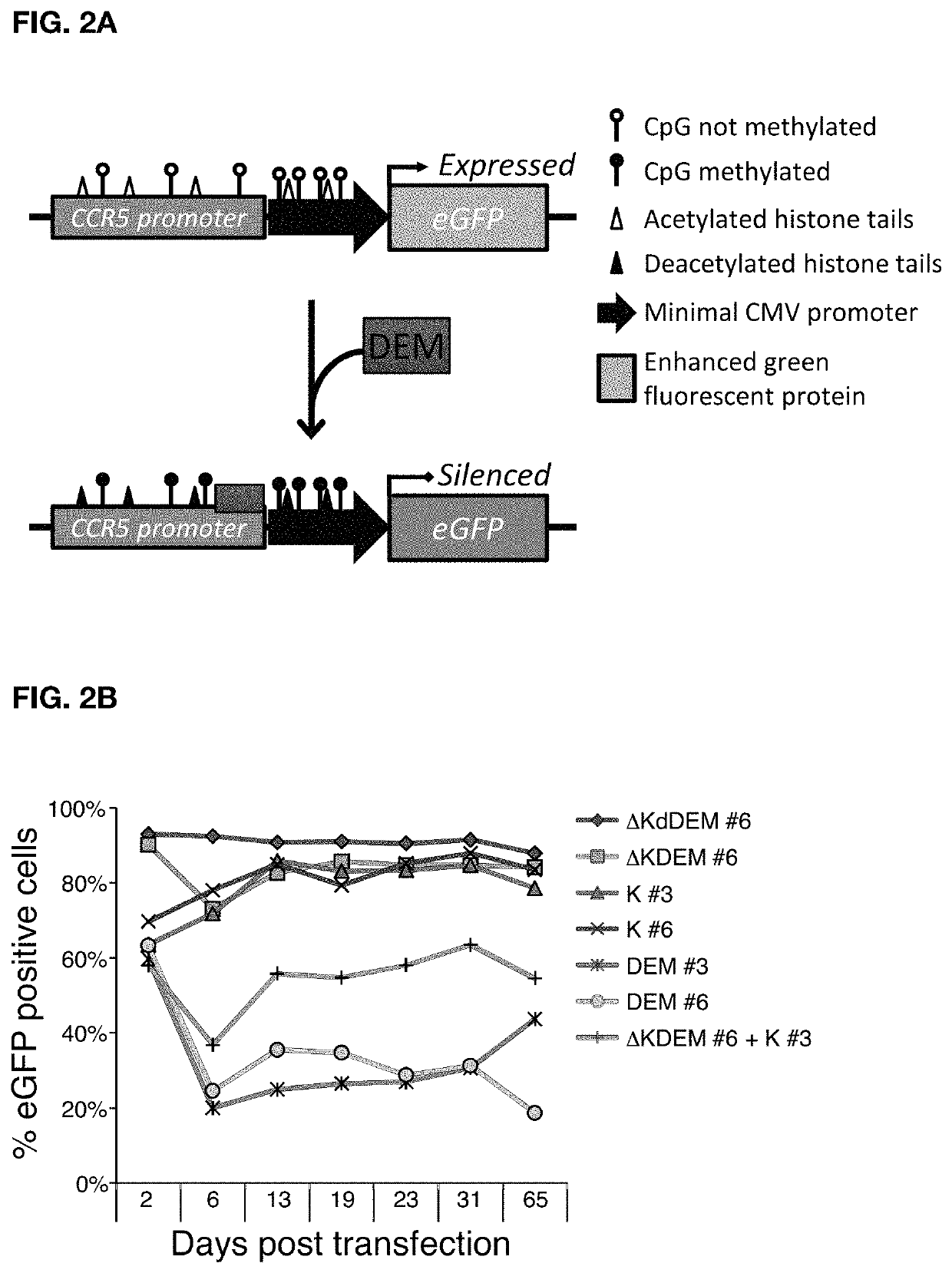
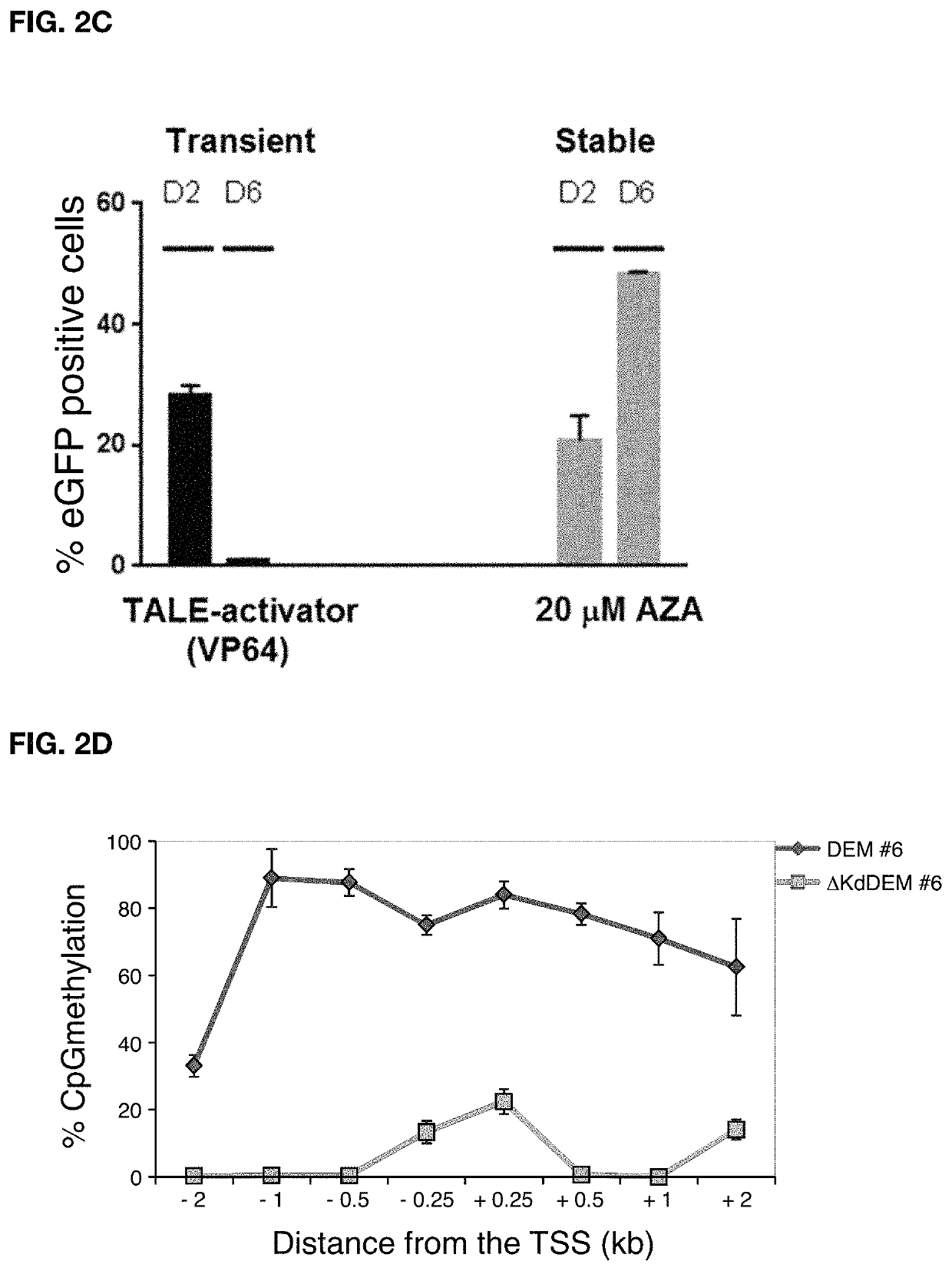
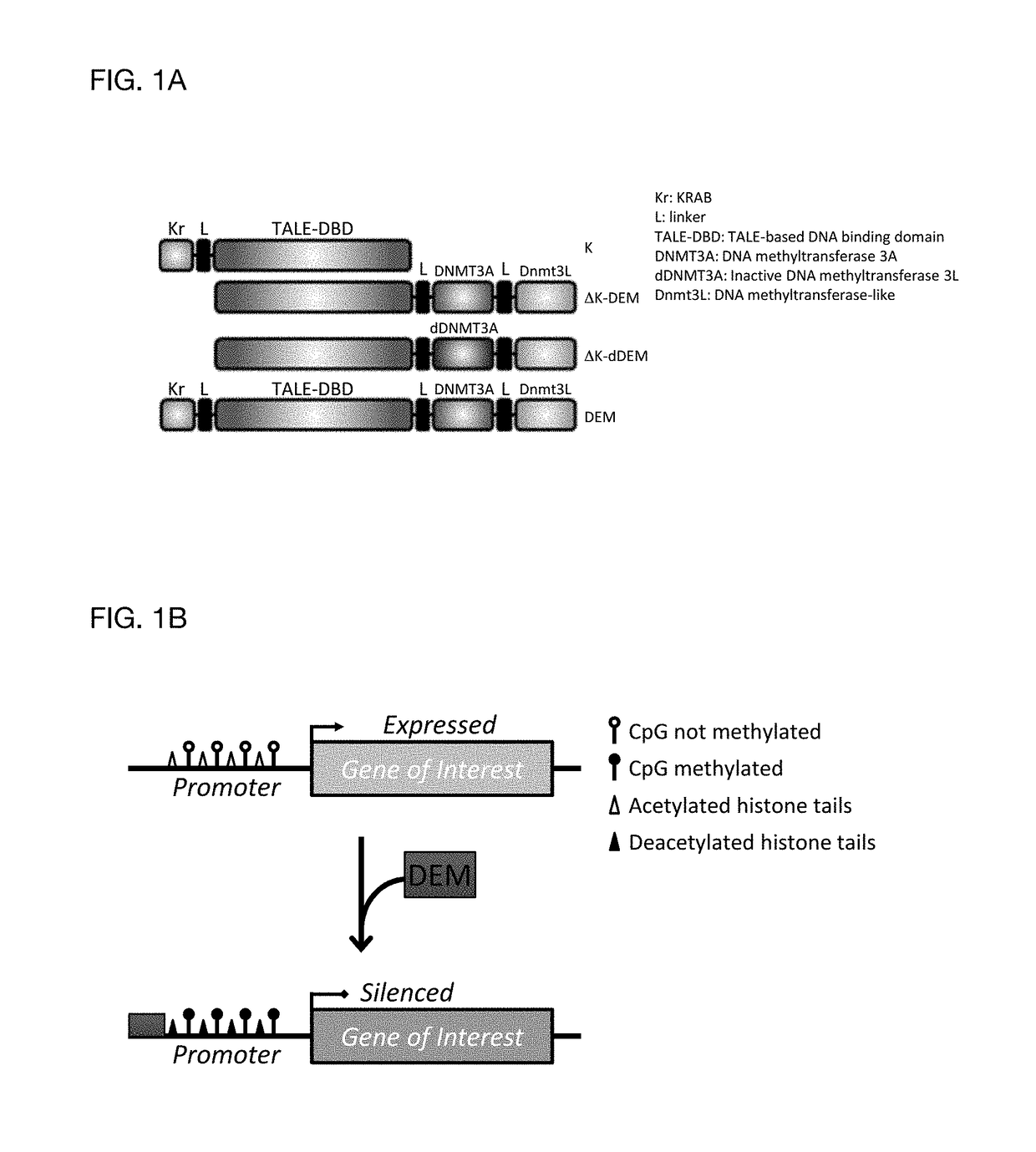
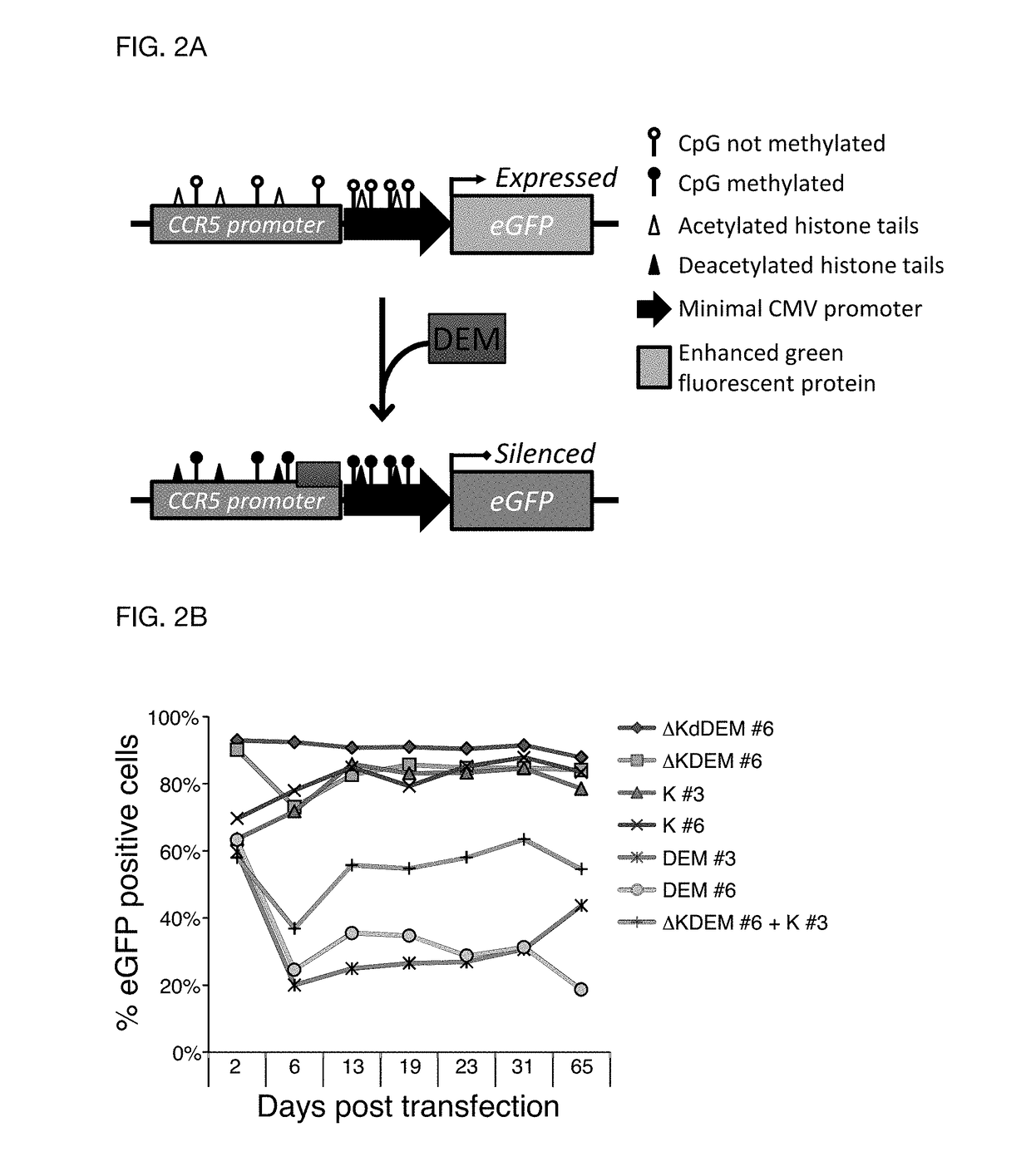
Construct for epigenetic modification and its use in the silencing of genes
ActiveUS20190024090A1Efficiently used to stably silence target geneSilencing of a target geneFusion with DNA-binding domainTransferasesWhite blood cellEpigenetic Profile
The present invention concerns a construct for epigenomic modification of genes comprising the following components:a) a Krüppel-associated box zinc finger protein or homologous,b) a DNA region capable of binding to the target gene or homologous,c) a human DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A or homologous andd) a murine DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3L or homologouswhereby components a), b), c) and d) are linked to each other either directly or via at least one linker. The construct is a designer epigenome modifier which can be used to silence genes coding for a protein in leukocytes which avoids the internalization of HI viruses in immune cells.
Owner:ALBERT LUDWIGS UNIV FREIBURG
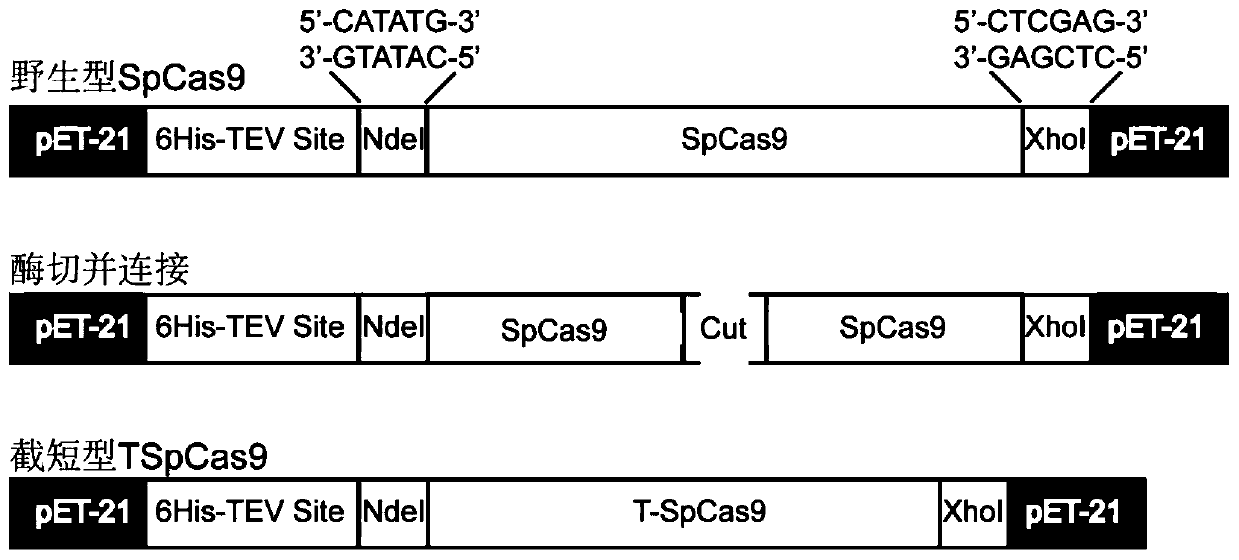
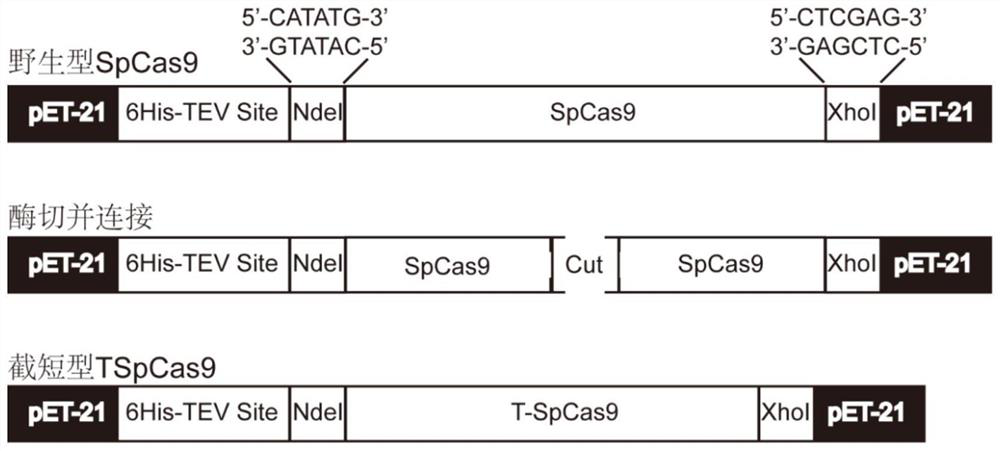
Truncated variant of CRISPR nuclease SpCas9 of streptococcus pyogenes and application of truncated variant
ActiveCN110241099AEasy to carryHas biomedical application valueHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAStreptococcus pyogenesWild type
The invention belongs to the technical field of protein engineering, and particularly relates to a truncated variant of CRISPR nuclease SpCas9 from streptococcus pyogenes and an application of the truncated variant. According to the truncated variant disclosed by the invention, CRISPR-Cas9(TSpCas9) nuclease belongs to a CRISPR-Cas9 system, has shearing activity equivalent to that of wild type CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease, and is obtained through the steps of cutting out 120 amino acids from the 180th to the 299th in an amino acid sequence of the wild type CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease and performing recombination; and the amino acid sequence of the wild type CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease is as shown in SEQID NO.7, or the CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease contains 90% of an amino acid sequence as shown in the SEQID NO.7, namely SEQID NO.15. The truncated variant can be used for genome editing, gene targeting, genome engineering, apparent genome engineering, gene therapy and in vitro diagnosis.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
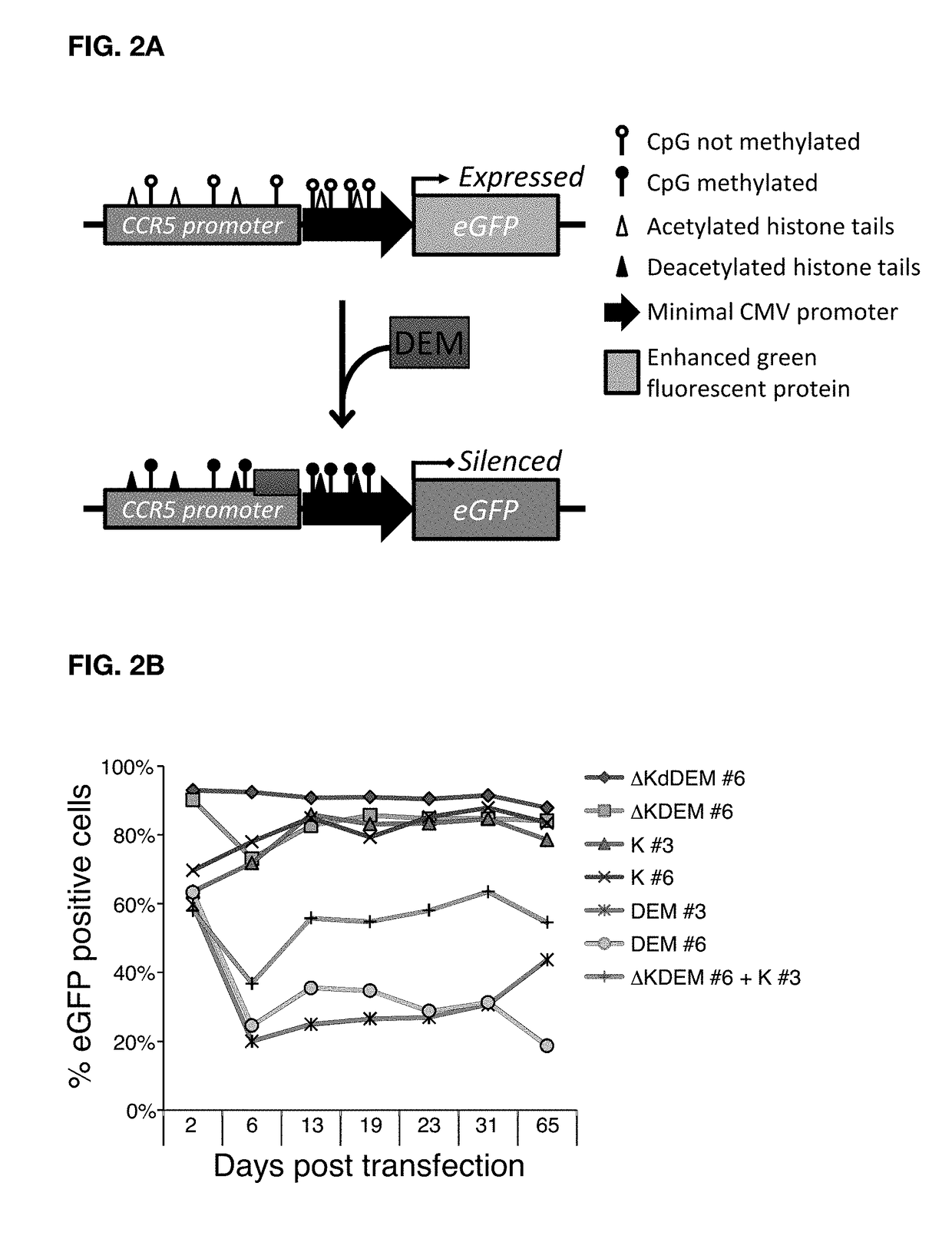
Construct for epigenetic modification and its use in the silencing of genes
ActiveUS11072782B2Efficiently used to stably silence target geneSilencing of a target geneFusion with DNA-binding domainTransferasesWhite blood cellEpigenetic Profile
Herein described is a construct for epigenomic modification of genes composed of: (a) a Krüppel-associated box zinc finger protein or homologous, (b) a DNA region capable of binding to the target gene or homologous, (c) a human DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A or homologous and (d) a murine DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3L or homologous, wherein components a), b), c) and d) are linked to each other either directly or via at least one linker. The construct is a designer epigenome modifier that can be used to silence genes coding for a protein in leukocytes that avoids the internalization of HI viruses in immune cells.
Owner:ALBERT LUDWIGS UNIV FREIBURG
Methods for phrasing epigenetic modifications of genomes
ActiveUS10538594B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHybrid immunoglobulinsEpigenomeEpigenetic Profile
Provided herein are methods and compositions for analyzing epigenetic modifications of genomes. The methods and compositions are suited for complete epigenome sequencing of any modification for which an antibody or an affinity binding agent has been developed. In one aspect, provided herein is a method for analyzing epigenetic modification of a genome. In some embodiments of aspects provided herein, the method further comprises sequencing a sequencing library to generate sequence reads, and assembling the sequence reads with aid of a positional barcode sequence information. In some embodiments of aspects provided herein, the method further comprises determining a location of at least two different epigenetic modifications of the nucleic acid. Another aspect of the present disclosure provides a kit for analyzing an epigenetic modification of a nucleic acid.
Owner:CENTRILLION TECH HLDG
Construct for epigenetic modification and its use in the silencing of genes
InactiveUS20190024072A1Efficiently used to stably silence target geneSilencing of a target geneTransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionWhite blood cellADAMTS Proteins
The present invention concerns a construct for epigenomic modification of genes that includes the following components:a) a Krüppel-associated box zinc finger protein or homologous,b) a DNA region capable of binding to the target gene or homologous,c) a human DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A or homologous andd) a murine DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3L or homologouswhereby components a), b), c) and d) are linked to each other either directly or via at least one linker. The construct is a designer epigenome modifier which can be used to silence genes coding for a protein in leukocytes which avoids the internalization of HI viruses in immune cells.
Owner:ALBERT LUDWIGS UNIV FREIBURG
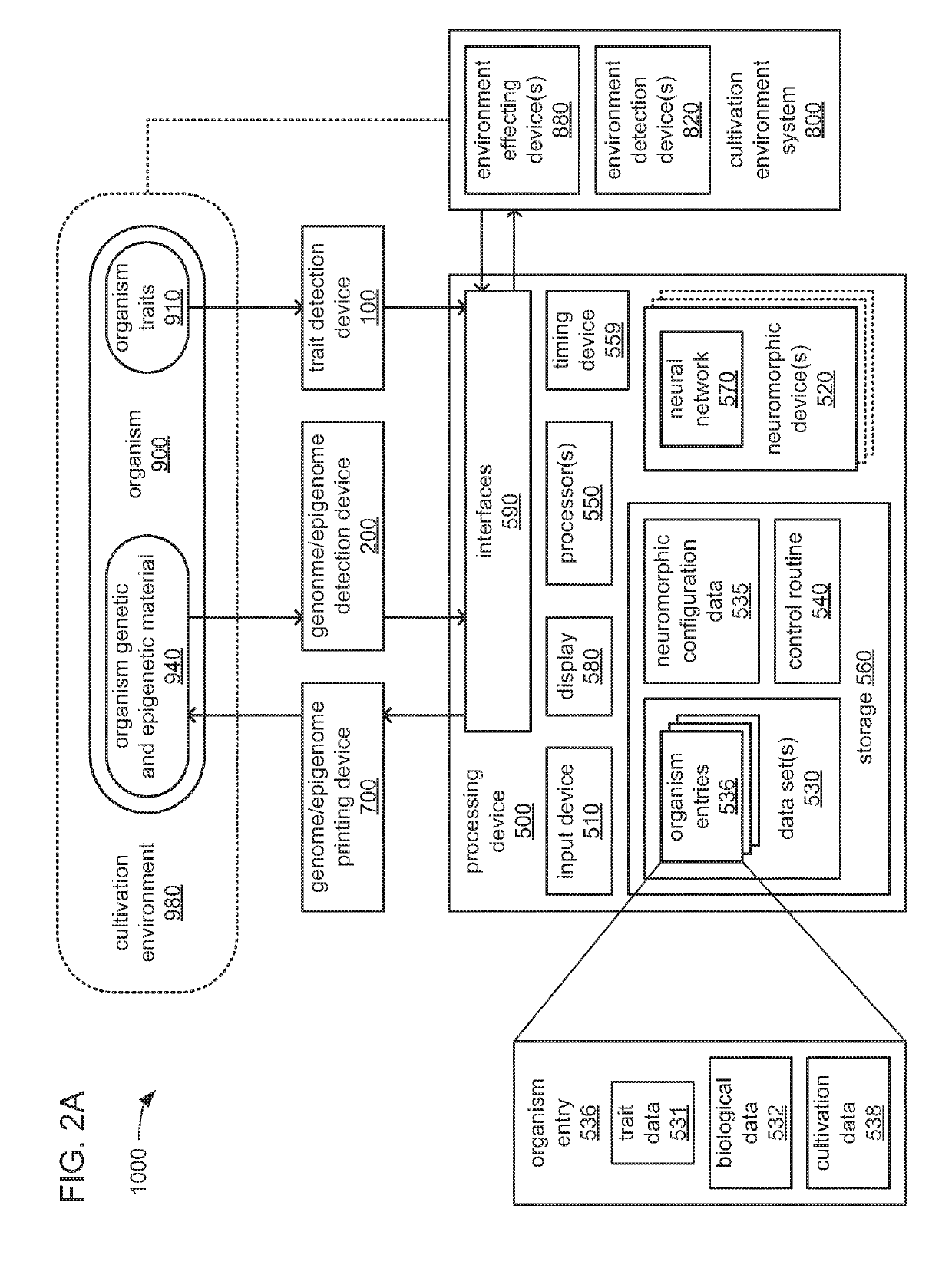
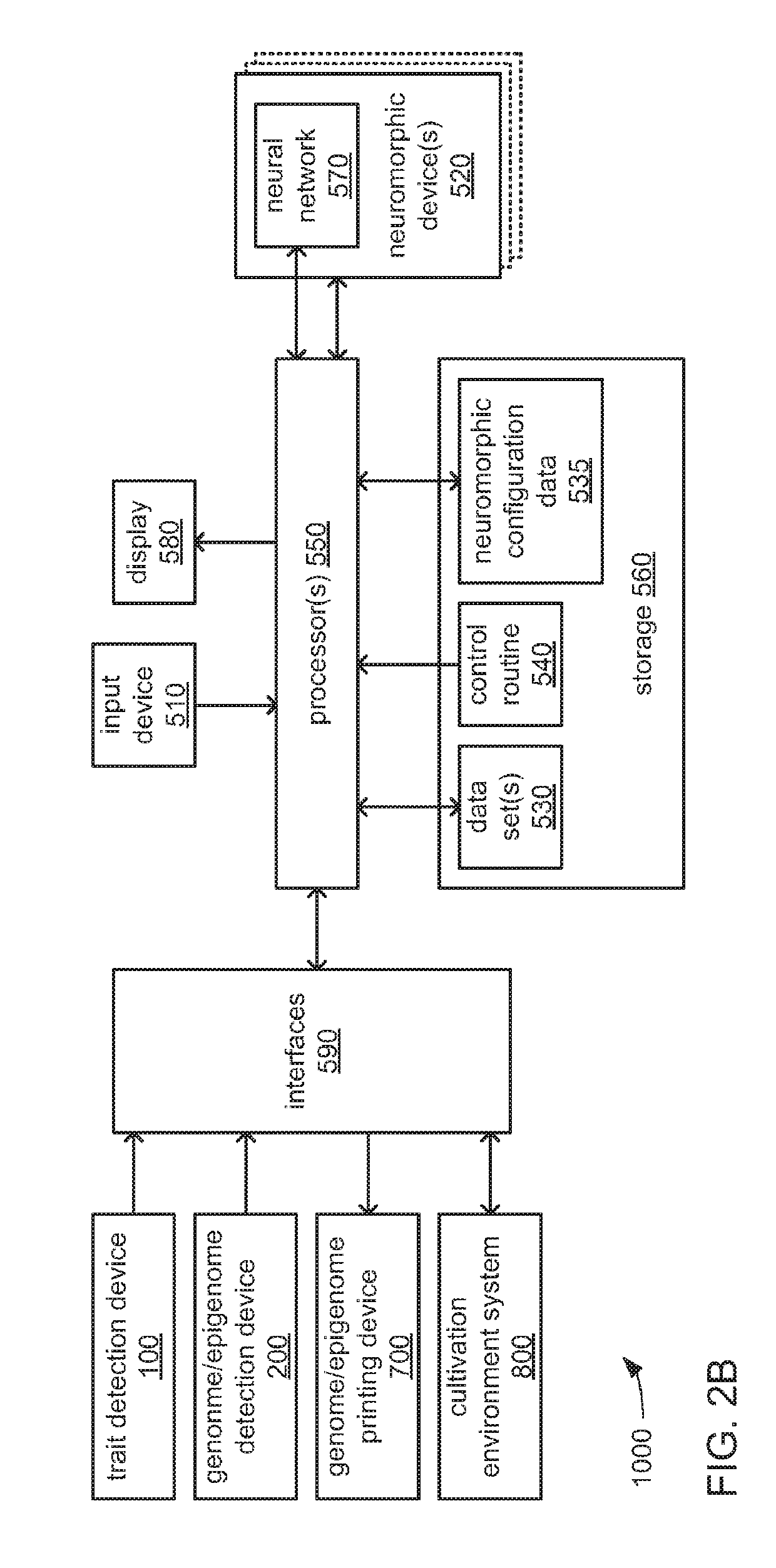
Biological organism development system
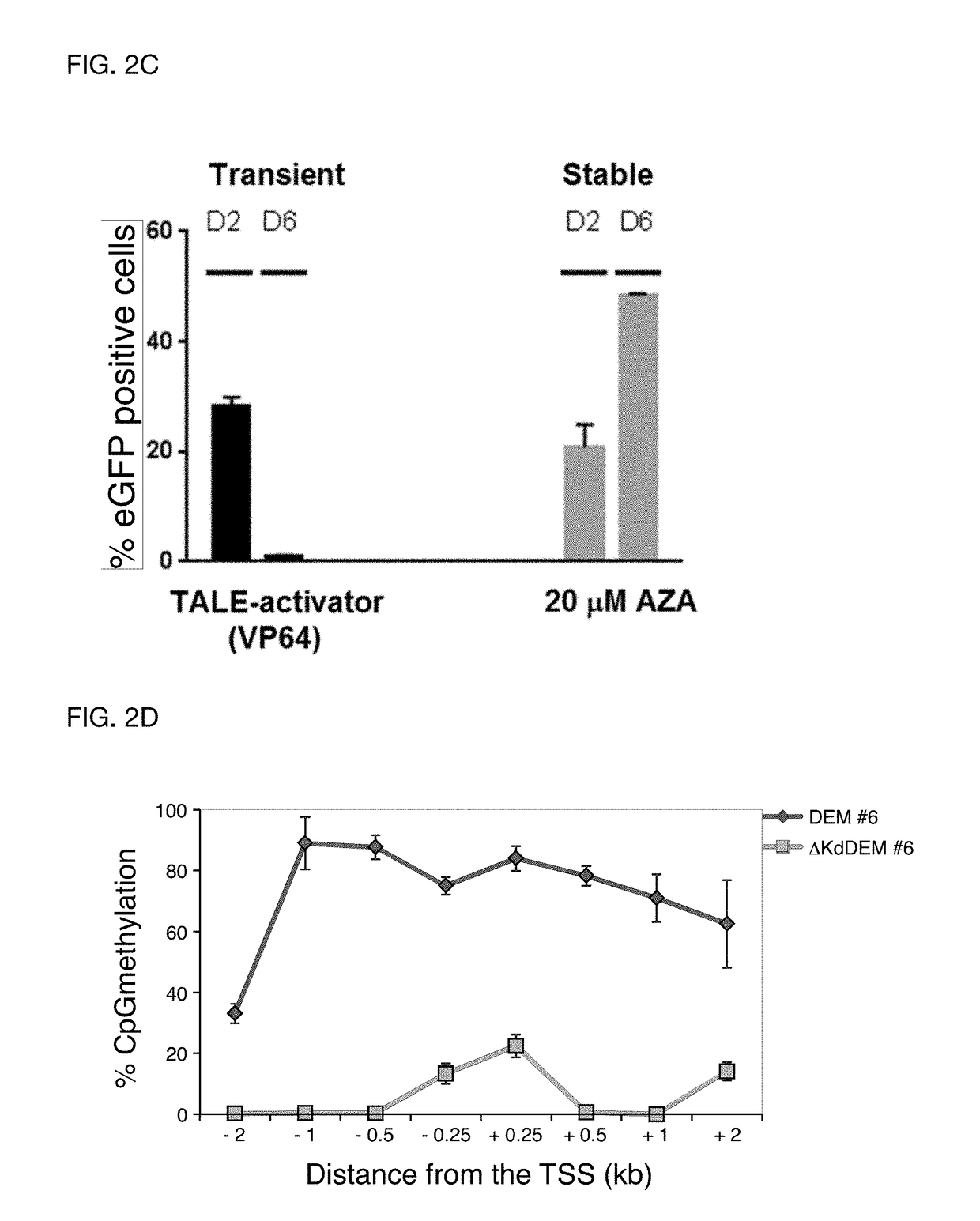
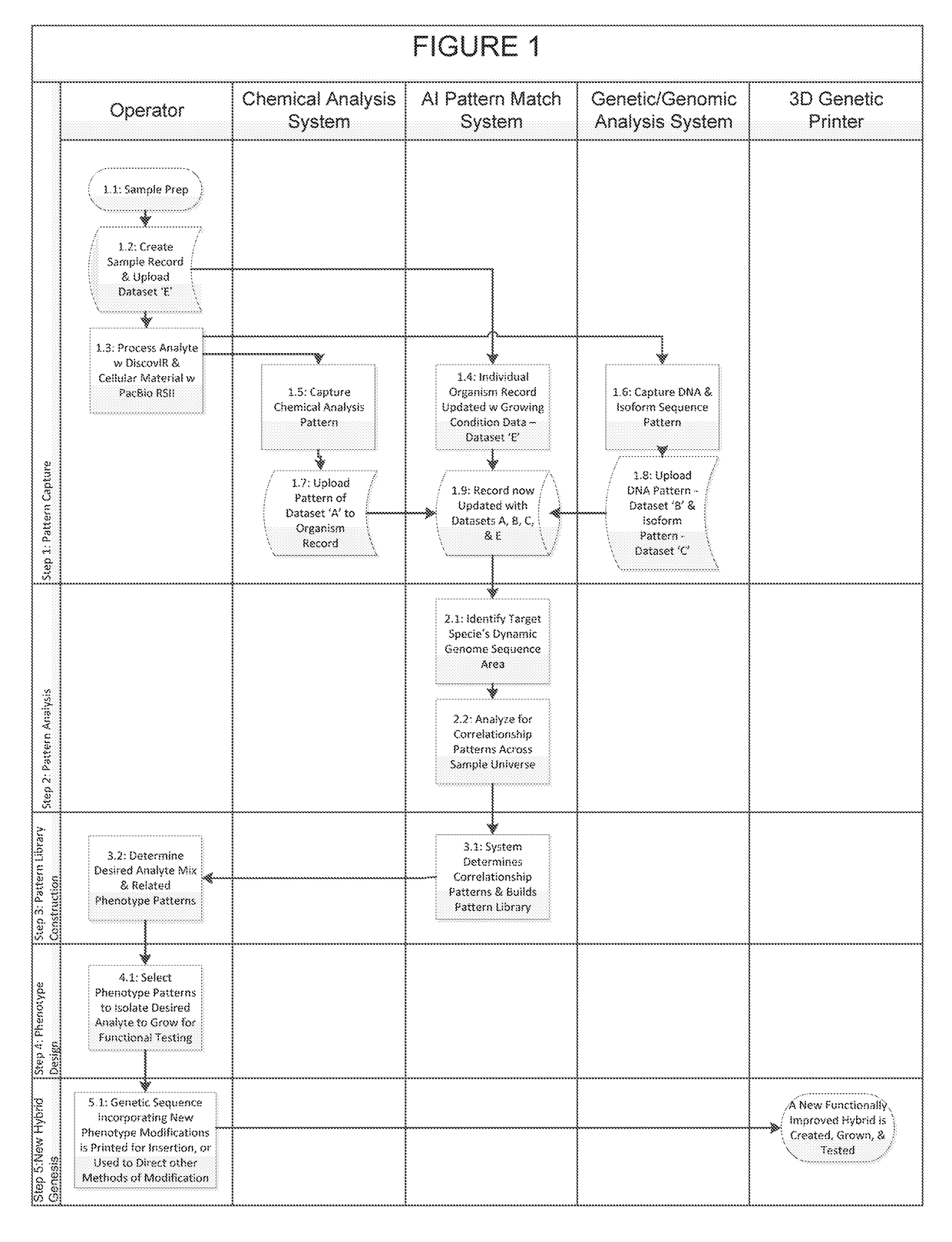
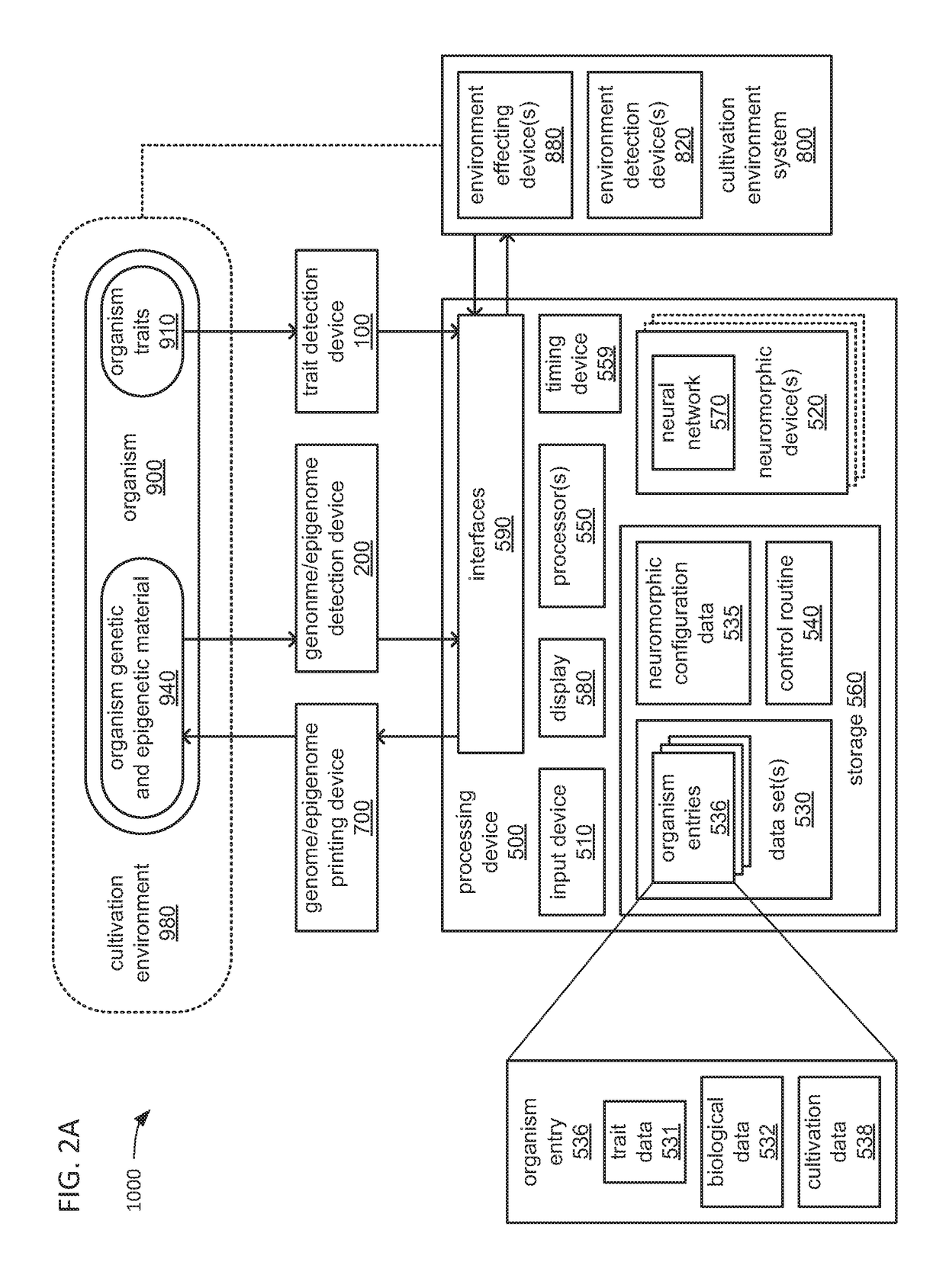
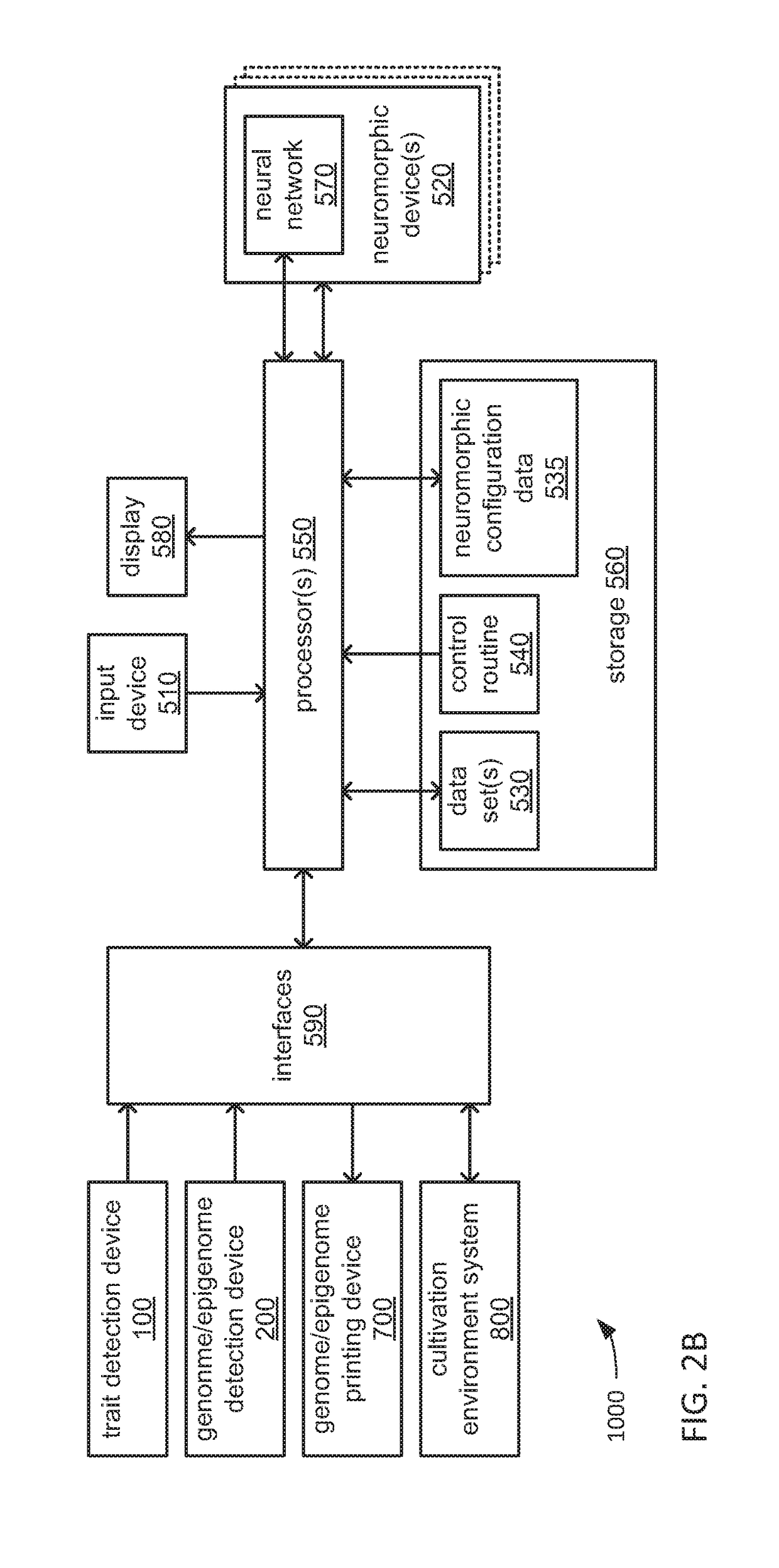
InactiveUS20180322241A1Easy to separatePrecision productionBiostatisticsCheminformatics programming languagesBiological bodyEpigenome
An organism development system includes: at least one neuromorphic device including multiple sets of hardware components that each store one or parameters of neuromorphic configuration data to implement a neuron of a neural network, wherein: the neural network is configured by neuromorphic configuration data to derive a proposed genome or epigenome of a new organism meant to have a sought-for trait, and the neuromorphic configuration data is generated by training the neural network with a usage data set that includes trait data indicative of a trait and biological data indicative of a genome for each of multiple organisms; a genome or epigenome printing device to print genetic / epigenetic material of the new organism based on the proposed genome or epigenome, respectively; and a trait detection device to detect an observed trait of the new organism following its at least its generation for incorporation back into the usage data set.
Owner:BUCHANAN CHARLES L
Methods and reagents for differential proteomic analysis
InactiveUS7175986B2Easy to analyzeSimple methodSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsEpigenome
Methods and reagents for labeling molecules of interest in a plurality of samples, and then combining and selecting labeled molecules away from unlabeled molecules for use in simultaneous co-assaying analysis. The reagents comprise labeling means of distinguishable radioactive isotopes which remain with the labeled molecules. Additionally, the reagents also comprise selection means which can be affinity tags, beads, or immobilized surface which may remain or be cleaved off through cleavable linkers. A set of labeling reagent can be used to label a plurality of samples, combine them before or after selecting / enriching for labeled molecules and co-assay together for reliable comparison. This invention has many applications in comparing and panning for differentially abundant molecules or differential modification of molecules for proteomics, glycomics, phospho-proteomics, metabolomics, epi-genomics . . . studies.
Owner:PROTEOMYX
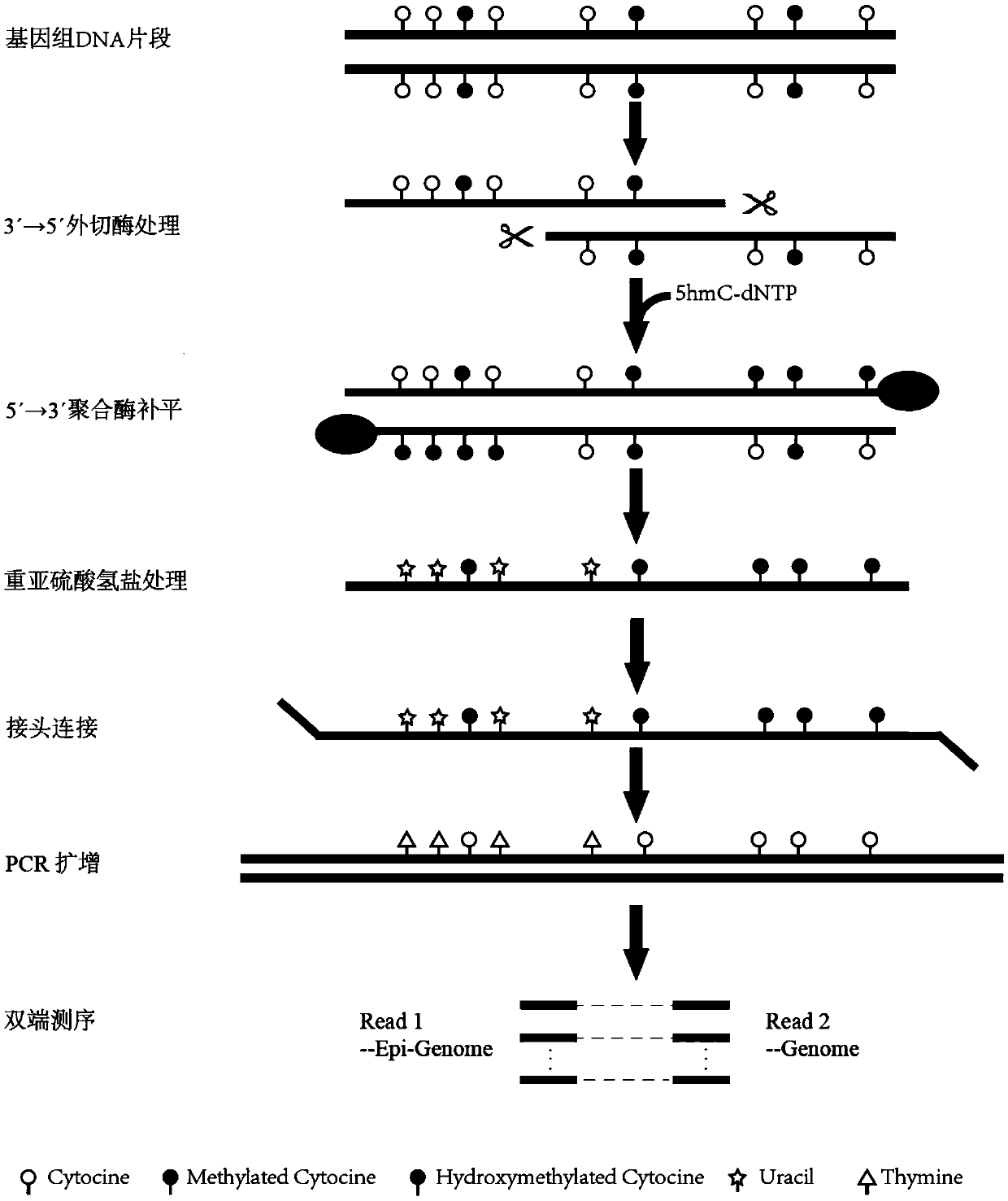
Method for simultaneously detecting genomic DNA polymorphism and methylation
PendingCN109554451ARealize synchronous detectionNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementModified dnaEpigenome
The invention provides a method for simultaneously detecting genomic DNA polymorphism and methylation. The method comprises the following steps: performing DNA fragmentation, and digesting the 3' endof the DNA fragment with DNA exonuclease; adding a dNTPs mixture containing 5-hydroxymethylcytosine deoxyribonucleotide, and performing completion the 3' end of the DNA fragment; performing bisulfiteconversion treatment on the modified DNA fragment and connecting an adaptor adapted to a high-throughput sequencing platform, and finally constructing a sequencing library by PCR amplification. By combining a double-end sequencing mode of the high-throughput sequencing platform, genomic DNA polymorphism and methylation detection can be performed simultaneously, and the goal of simultaneous detection of genome and epigenome is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI EPIPROBE BIOTECH CO LTD
A set of vector system for rice epigenome methylation/demethylation
The invention discloses a set of vector system for rice epigenome methylation / demethylation. The invention provides a set of vector system for rice epigenome demethylation. According to the system, DNA methylation variation is rapidly generated by randomly demethylating a rice genome. The system relates to the expression of rice OsALKBH DNA 6mA demethylase, resulting in a wide range of low methylation. The mutagenesis technique is of great significance to plants with important agricultural significance, which may result in differential expression of alleles that are generally silenced by DNA methylation, thereby revealing the application of previously hidden phenotypic variations.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Duplicating DNA with contiguity barcodes for genome and epigenome sequencing
ActiveUS10428373B2Quality improvementHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresEpigenomeEpigenetic Profile
Provided herein are methods and devices for accurate sequencing and detection of epigenetic information from template polynucleotides. Also provided are methods for long-range strand displacement amplification of polynucleotides, microfluidic devices with selectively permeable barriers for multistep processing, and methods for polynucleotide amplification using the microfluidic devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
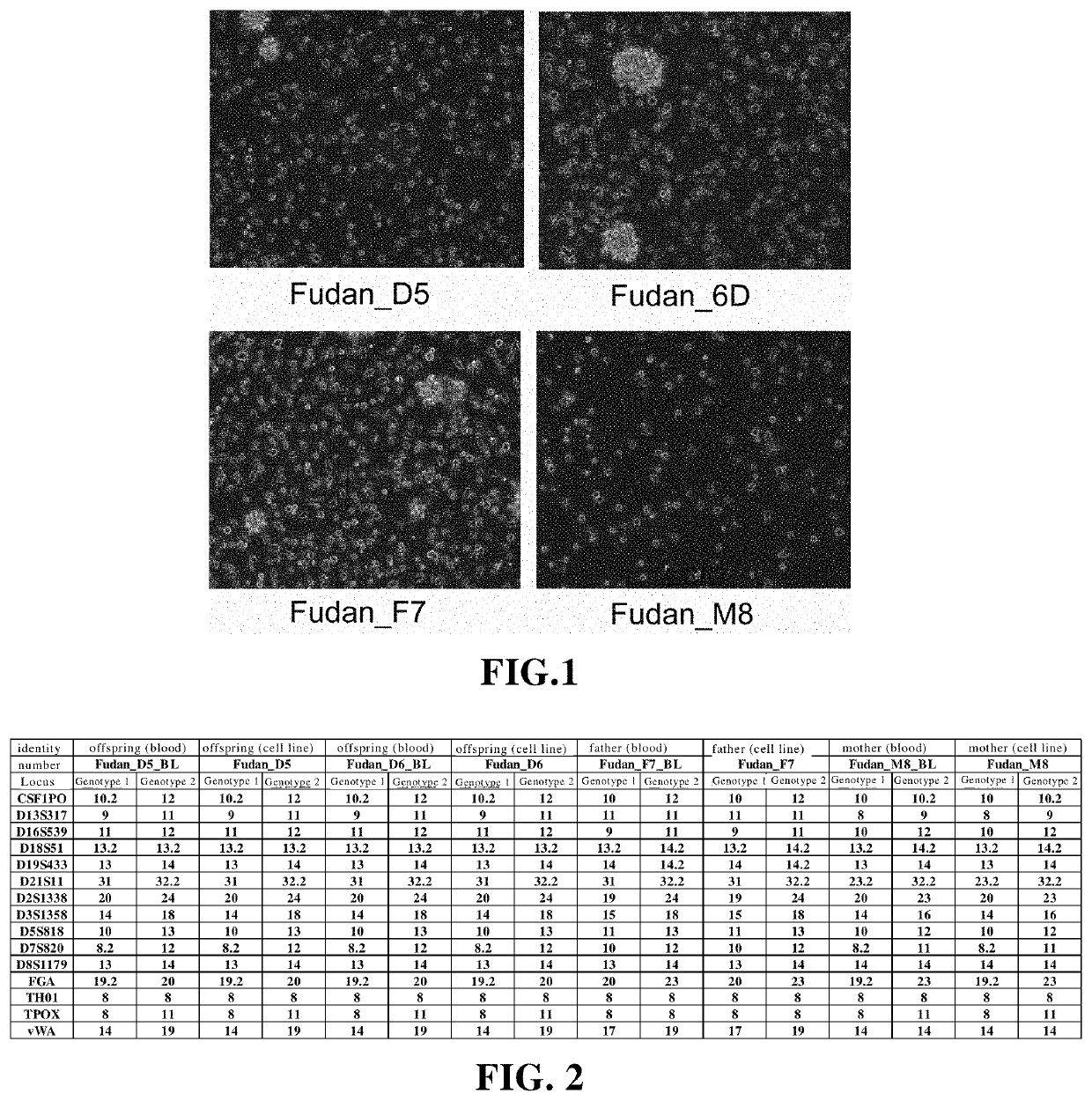
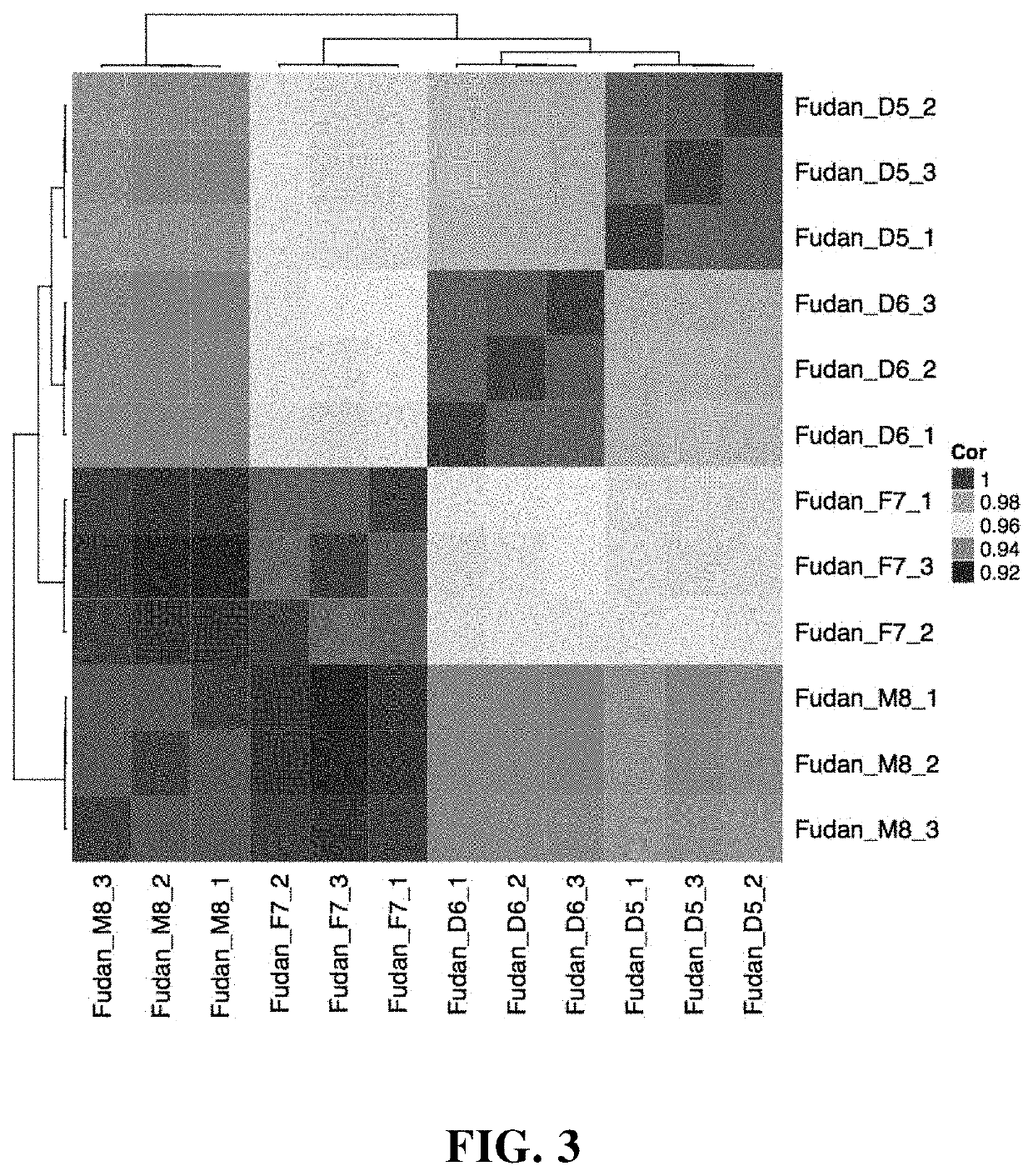
Establishment and application of human immortalized b lymphocyte cell line group
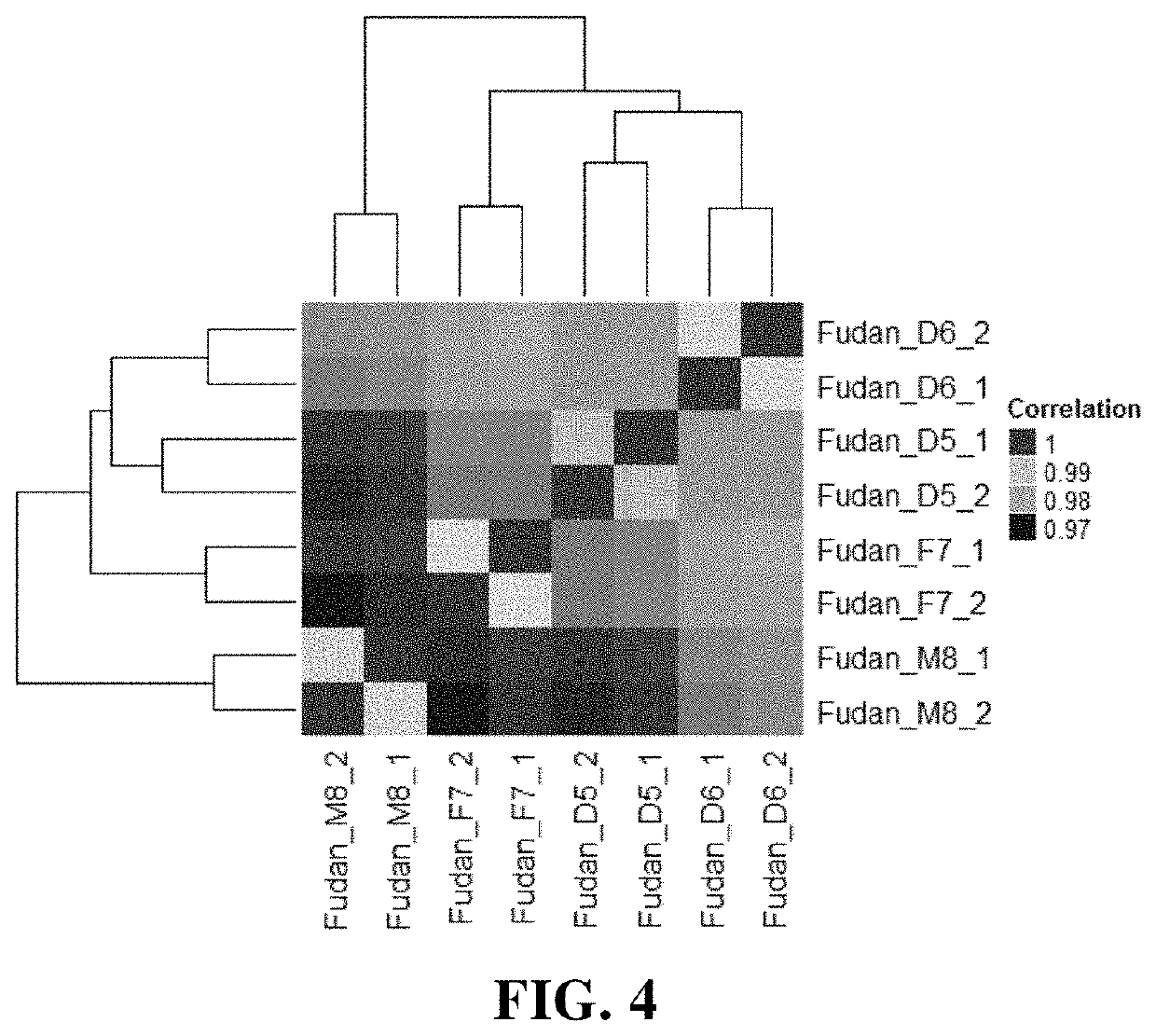
The present application provides a group of human immortalized B lymphocyte cell lines and use thereof, and specifically provides a combination of four closely related immortalized lymphocyte cell lines. The combination can be used as a standard product for accuracy evaluation of a detection platform. When the four closely related immortalized lymphocyte cell lines are used as standard products for epigenome, transcriptome, proteome, and metabolome, an intrinsic magnitude difference gradient can be formed to evaluate the sensitivity of histological detection.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Methods for phrasing epigenetic modifications of genomes
ActiveUS20180112010A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHybrid immunoglobulinsEpigenomeBarcode
Provided herein are methods and compositions for analyzing epigenetic modifications of genomes. The methods and compositions are suited for complete epigenome sequencing of any modification for which an antibody or an affinity binding agent has been developed. In one aspect, provided herein is a method for analyzing epigenetic modification of a genome. In some embodiments of aspects provided herein, the method further comprises sequencing a sequencing library to generate sequence reads, and assembling the sequence reads with aid of a positional barcode sequence information. In some embodiments of aspects provided herein, the method further comprises determining a location of at least two different epigenetic modifications of the nucleic acid. Another aspect of the present disclosure provides a kit for analyzing an epigenetic modification of a nucleic acid.
Owner:CENTRILLION TECH HLDG
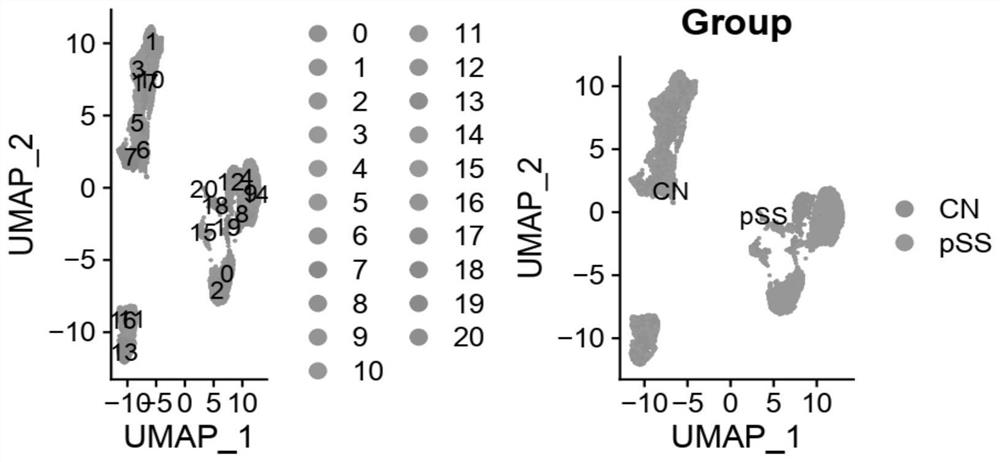
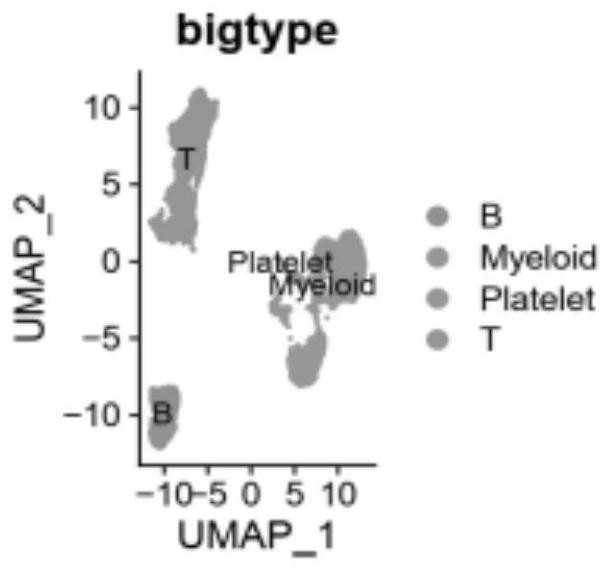
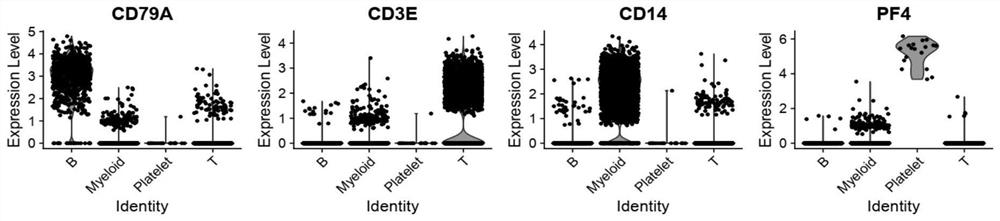
Application of single cell sequencing as marker in preparation of diagnostic primary sicca syndrome
PendingCN113564246ASequencing is easyLess traumaticMicrobiological testing/measurementPeripheral blood mononuclear cellCell layer
The invention provides application of single cell sequencing as a marker in preparation of a diagnostic primary sicca syndrome. The single cell sequencing is obtained by separating peripheral blood mononuclear cells through flow-type activated cells, and the primary sicca syndrome is mainly composed of NK cells, and then T cells and B cells. According to the single cell sequencing technology, a genome, a transcriptome, a proteome and an epigenome are sequenced on the single cell level, heterogeneity information among different cells can be obtained from a tissue sample, the advantages of being accurate, efficient, safe and reliable are achieved, and therefore the differential expression marker of the sicca syndrome is screened out on the cell level, and the defects of sicca syndrome diagnosis are overcome. The single cell sequencing is easy and convenient, special preparation and specific time are not needed, and a specimen can be collected anytime and anywhere. In addition, the advantages of being extremely small in trauma and high in sensitivity are achieved.
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ANHUI UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Truncated variants of the CRISPR nuclease spcas9 of Streptococcus pyogenes and their applications
ActiveCN110241099BEasy to carryHas biomedical application valueHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAStreptococcus pyogenesWild type
The invention belongs to the technical field of protein engineering, and specifically relates to a truncated variant of CRISPR nuclease SpCas9 derived from Streptococcus pyogenes and an application thereof. In the present invention, the CRISPR-Cas9 (TSpCas9) nuclease belongs to the CRISPR-Cas9 system and has the equivalent cutting activity of the wild-type CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease. The amino acid sequence of the wild-type CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease is shown in SEQ ID NO.7; or the CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease contains 90% of the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.7, namely SEQ ID NO.15. The truncated variant can be used for genome editing, gene targeting, genome engineering, epigenome engineering, gene therapy and in vitro diagnosis.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com