Construct for epigenetic modification and its use in the silencing of genes
a technology of epigenetic modification and construct, applied in the field of gene silencing by epigenetics, can solve the problems of toxic adverse events, low efficiency of rnai especially for repressing highly expressed genes, and off-targeting of designer nucleases, so as to achieve the effect of effectively silencing a target gene and efficiently using a target gen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
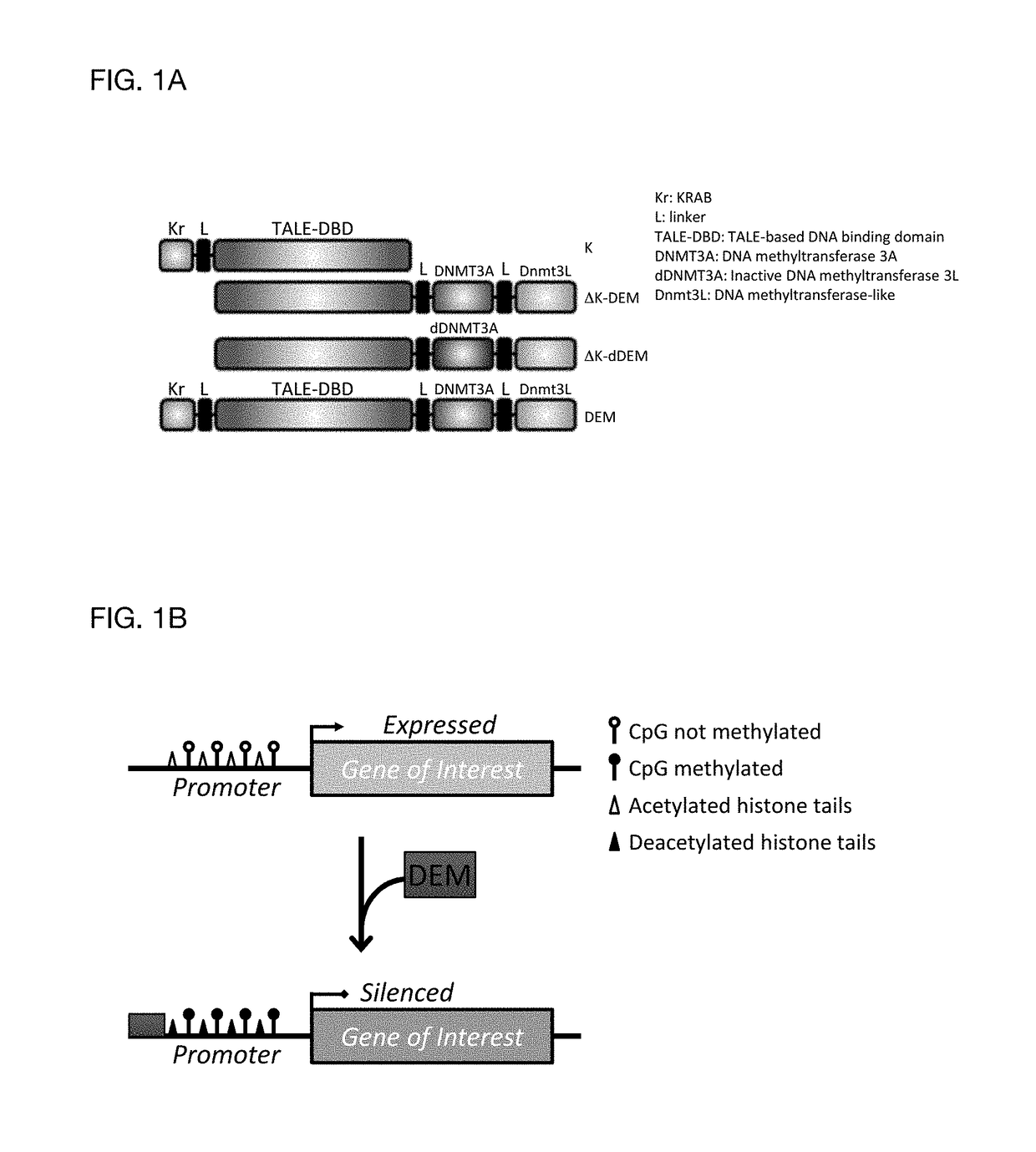
[0089]The ability to modulate the expression of target genes at will is a major need in the field of gene therapy. The present invention allows precise epigenome editing resulting in silencing of a target gene. The versatility of the platform concedes also that a silenced target gene can be transcriptionally reactivated by changing the combination of effector domains with transcription activator domains like herpes simplex virus-based transcriptional activator VP64 domain and DNA demethylase effectors from the TET family. The invention combines in a single molecule the highly specific DNA binding domain derived from transcription activator-like effectors (TALEs) identified in the plant pathogen Xanthomonas with the Krüppel-associated box (KRAB) domain, the human derived DNA methyltransferase 3a and the murine DNA methyltransferase 3L (FIG. 1A). The resulting construct also referred to as designer epigenome modifier or DEM, thereby combines the KRAB-induced recruitment of the scaffol...
example 2
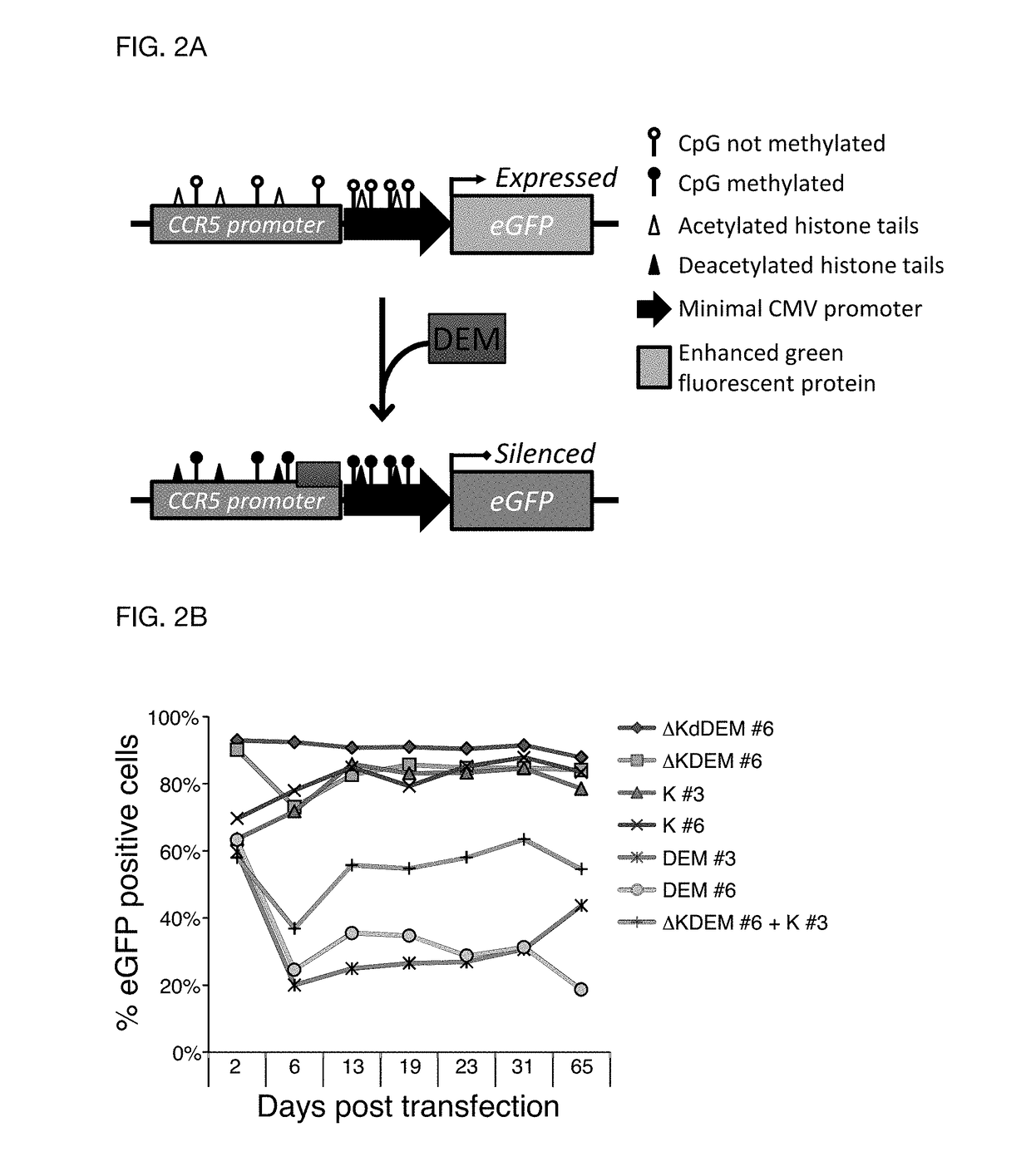
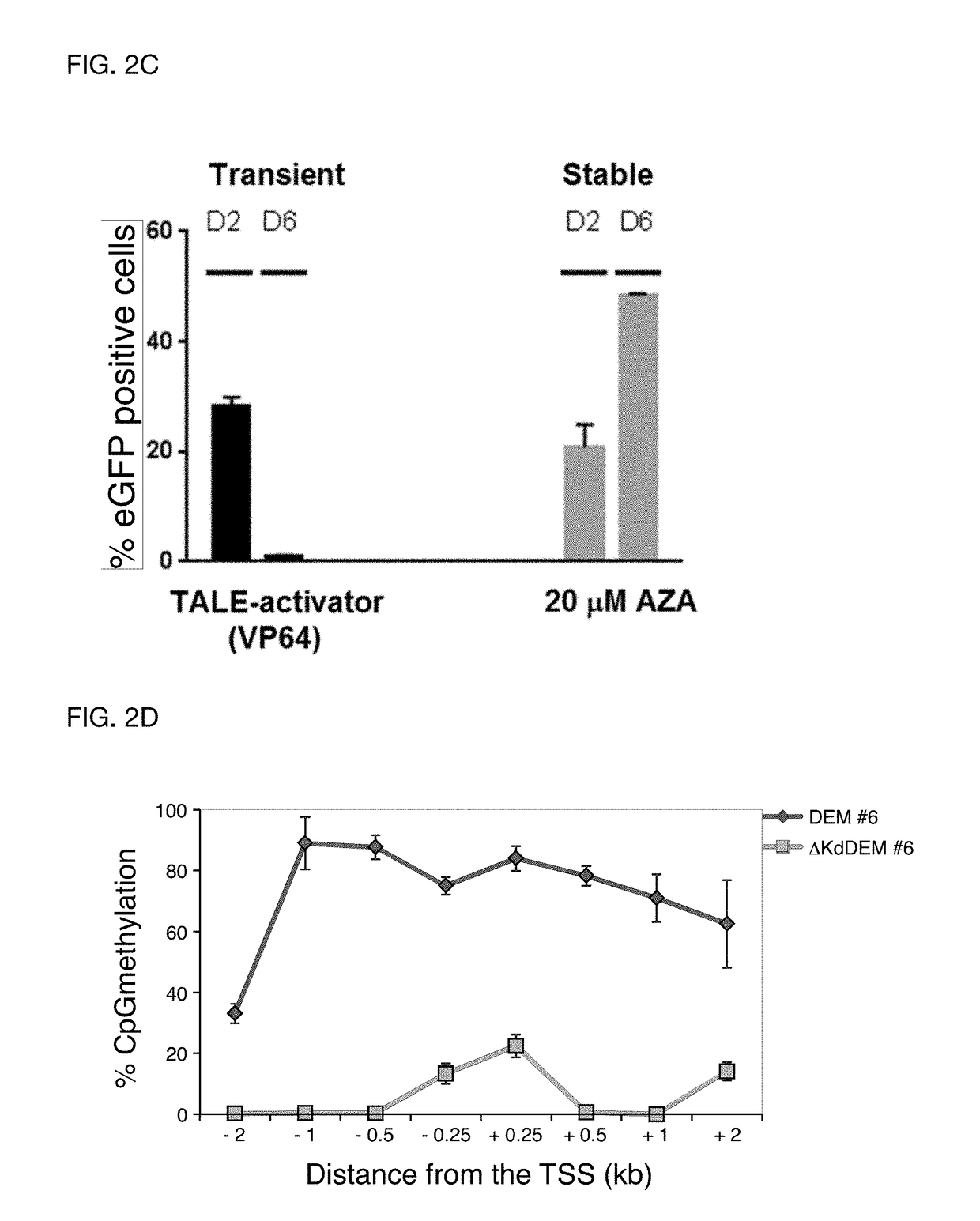
[0105]In order to prove the efficacy of the invention CCR5 was used as exemplary target gene which is known to be essential for infection of CD4+ T cells with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Individuals that harbor natural mutations inactivating the CCR5 gene are largely resistant to HIV infection. DEMs targeted to the CCR5 promoter were generated and to test their activity, a fluorescent reporter harboring an enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) gene driven by a minimal CMV (minCMV) promoter fused to a fragment of the CCR5 promoter containing the DEM target sites was prepared. The reporter was integrated in the genome of HEK293T cell line via lentiviral transduction resulting in a cell line expressing GFP (green fluorescent proteins) under the control of the CCR5-minCMV fusion promoter (FIG. 2A). Delivery of effectors having only the KRAB domain or only the DNA methyltransferase domains resulted in a transient silencing of the eGFP gene expression which came back to no...
example 3
[0107]To prove that the invention is easily scalable to different genes, four TALE-based DNA binding domains were constructed targeting the CXCR4 gene (FIG. 3A) with the aim to silence also the second co-receptor used by the HIV to infect the target CD4+ T cells. The CXCR4-specific TALE-DBDs were incorporated in the different construct depicted in FIG. 1A and delivered in form of mRNA into HEK293T cells. Three days after lipofection of the mRNA, the levels of CXCR4 transcripts were measured via qPCR. Interestingly, all four CXCR4-specific DEMs reduced 4- to 5-folds the CXCR4 transcripts levels with an average reduction of about 70% in gene expression (FIG. 3B). Similarly, protein levels measured via flow cytometry were also reduced to the same extent (FIG. 3C).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com