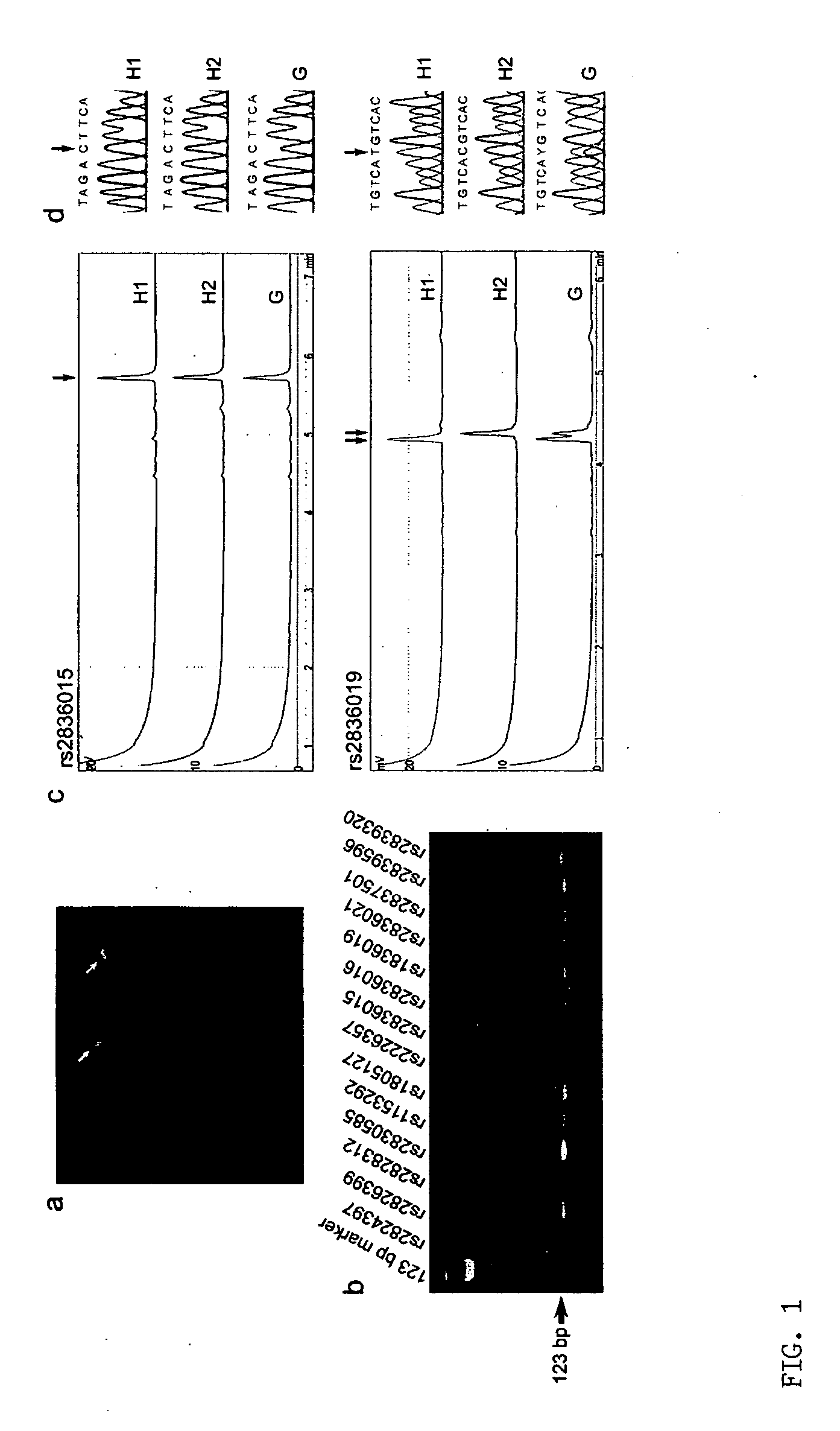
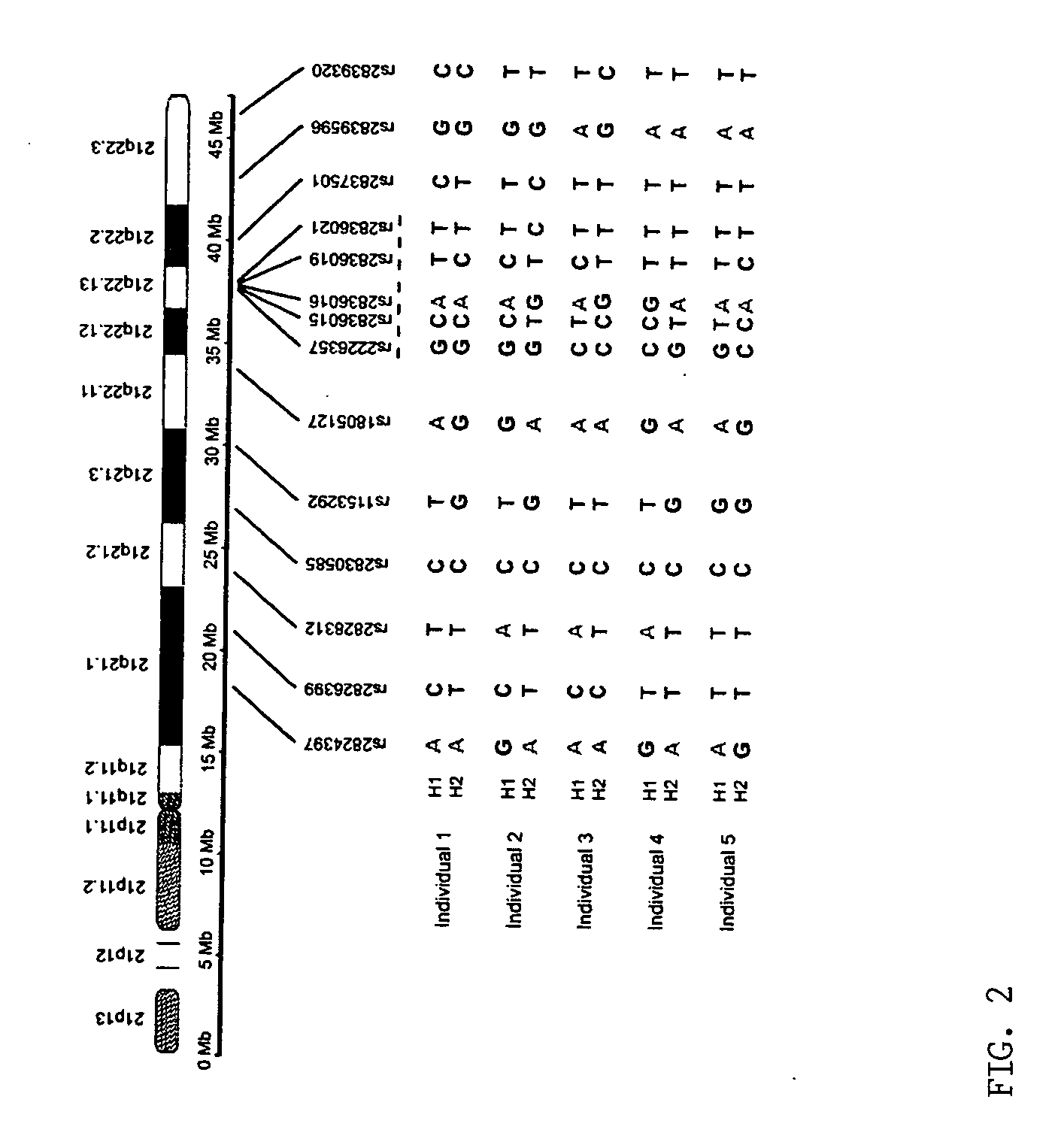
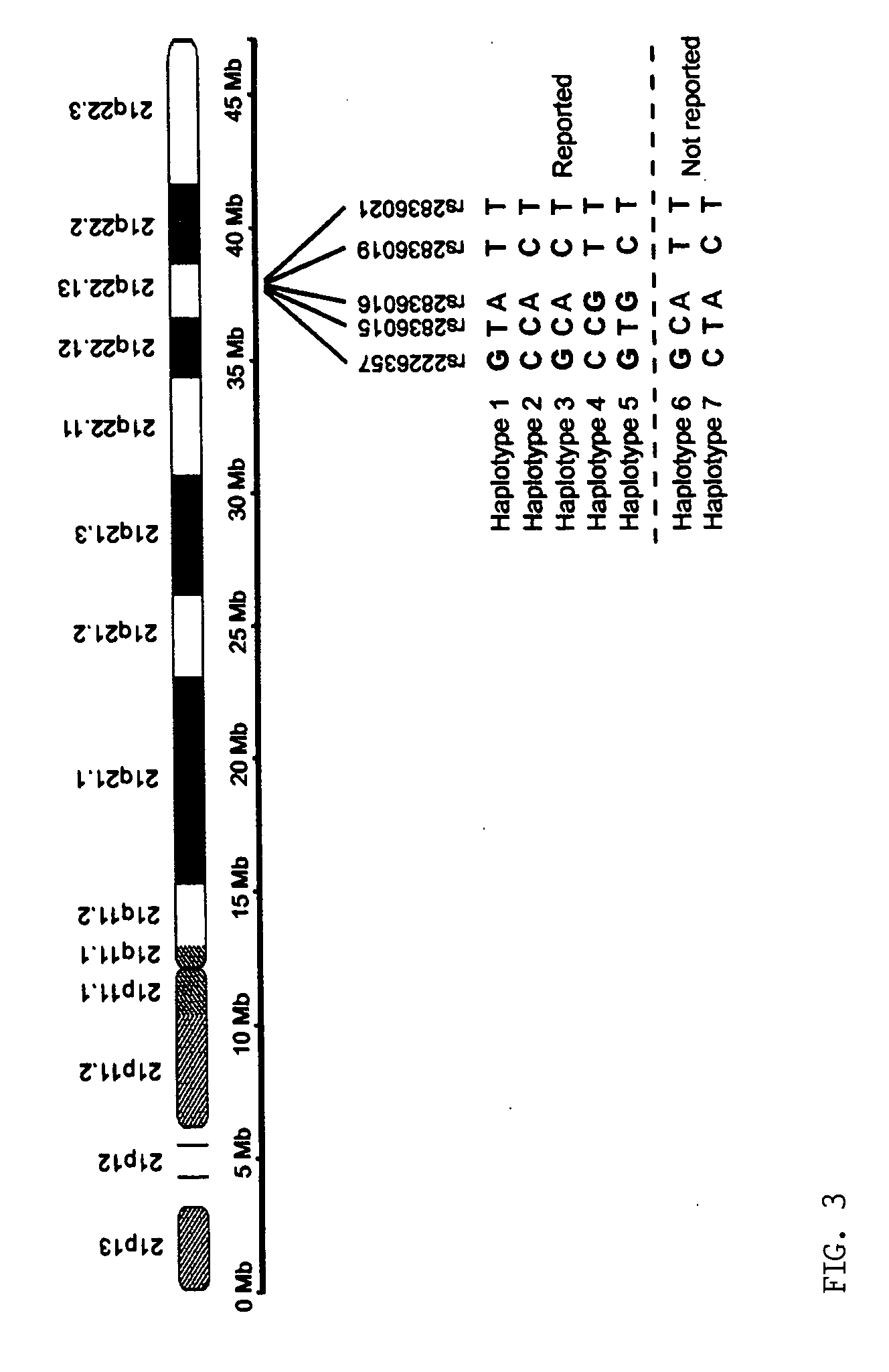
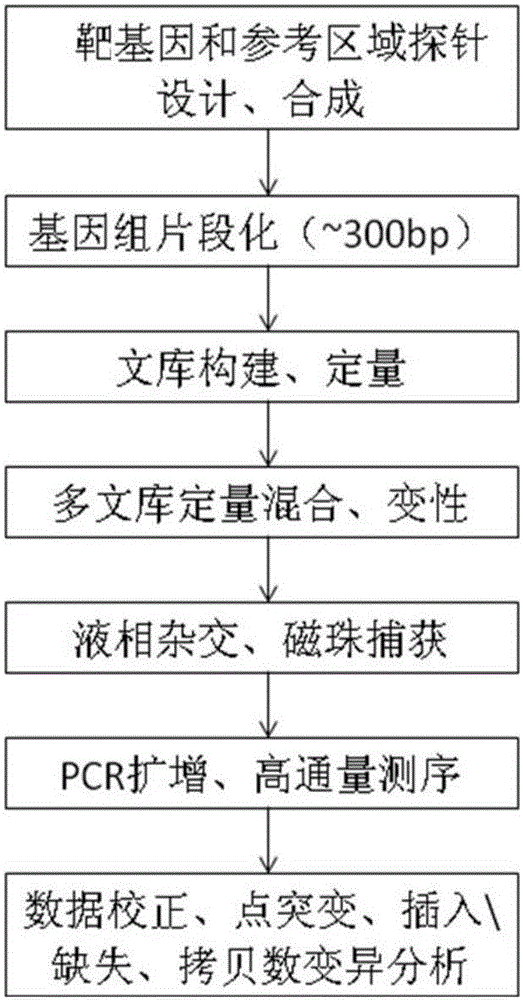
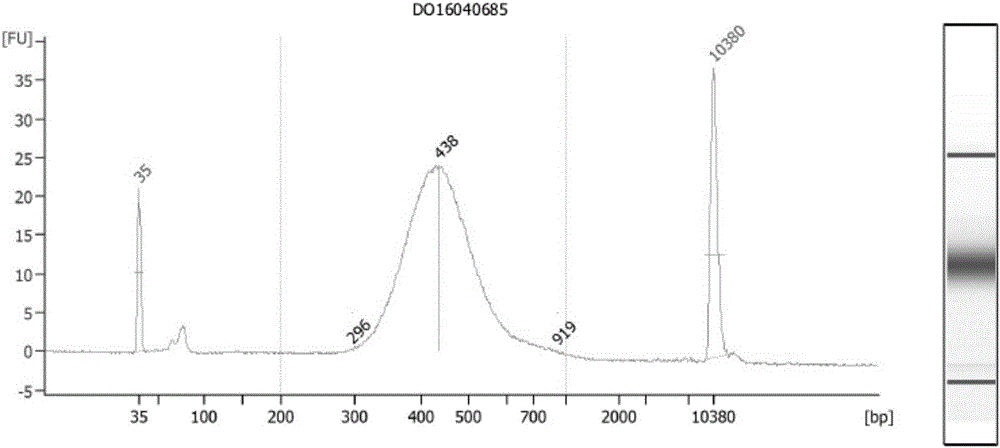
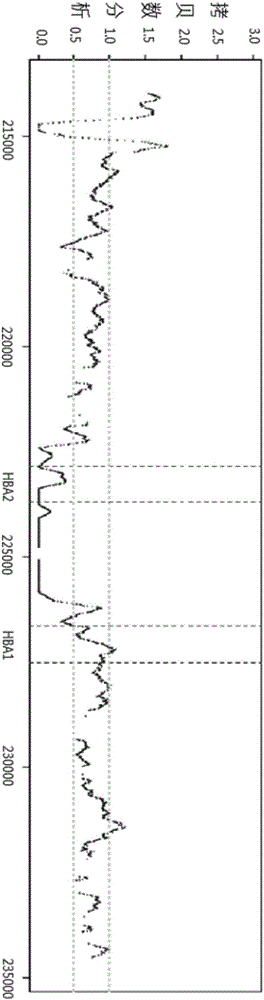
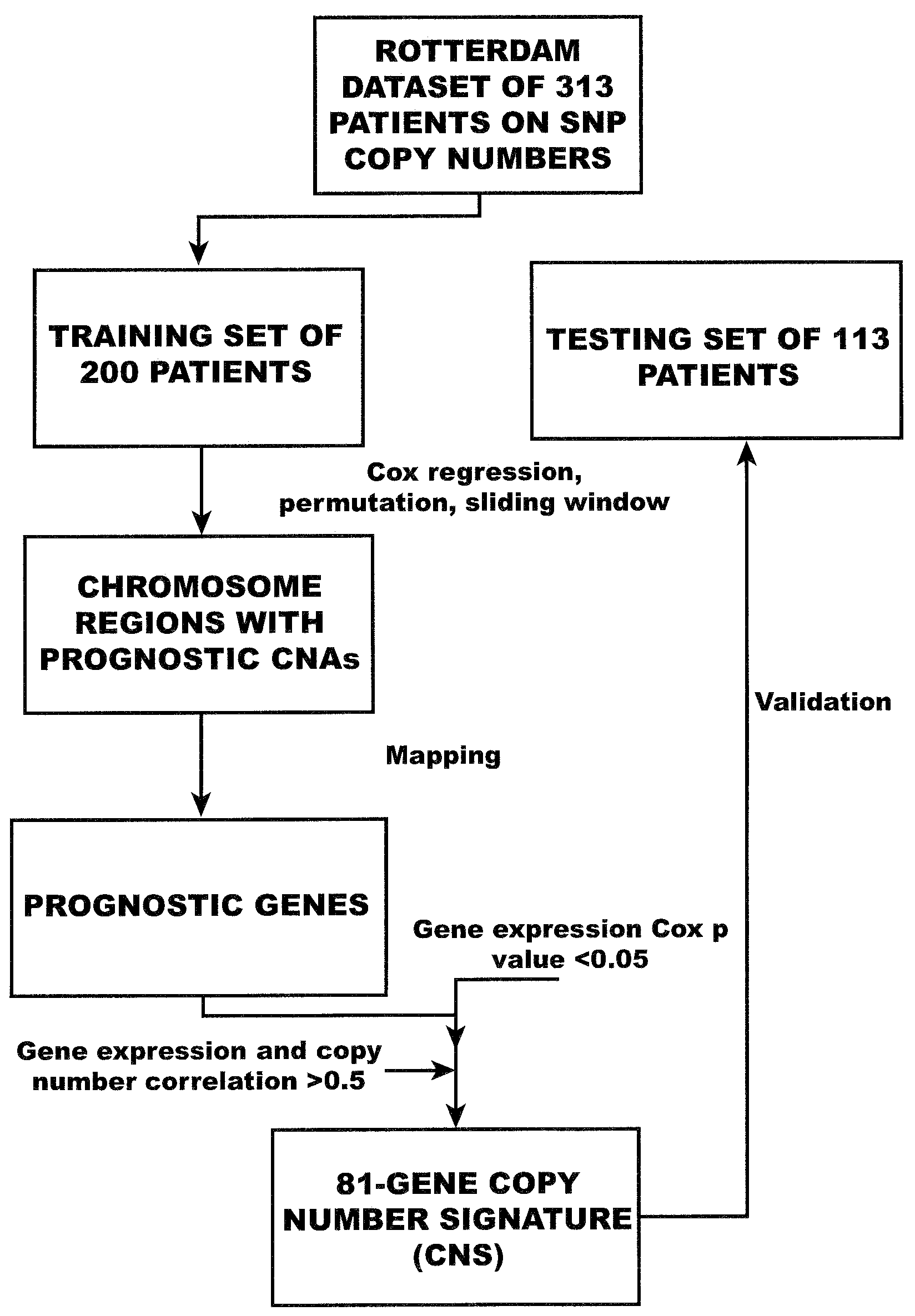
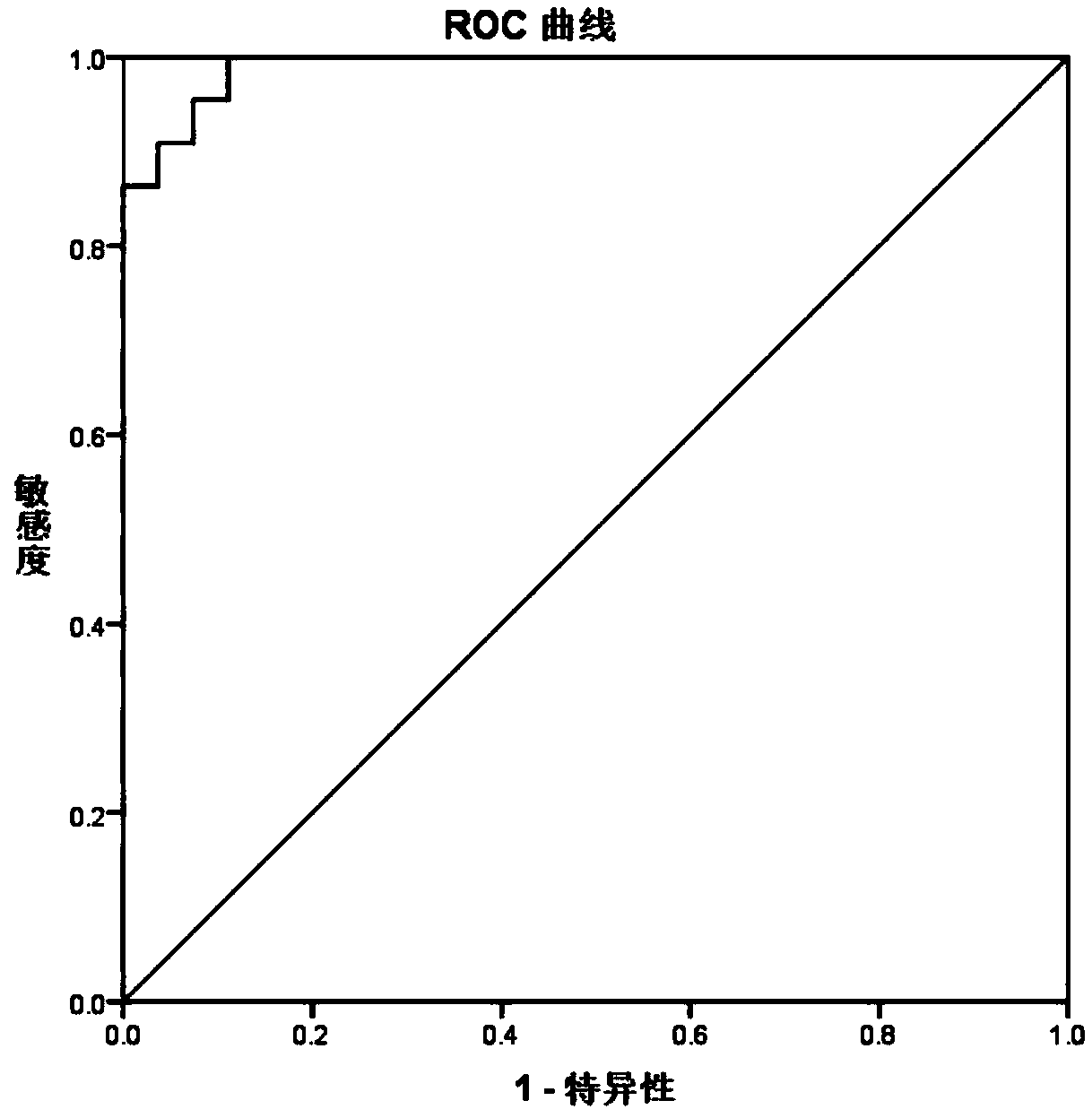
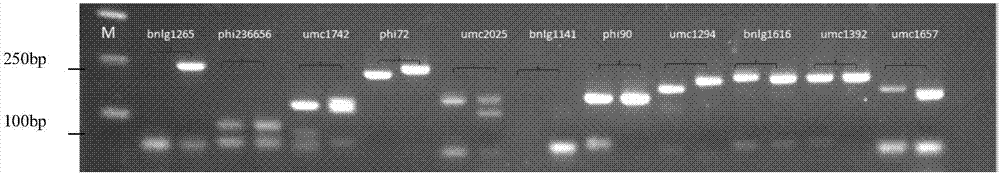
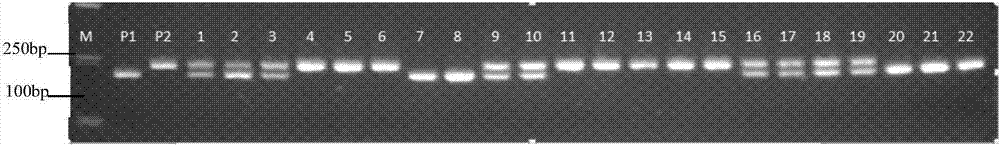
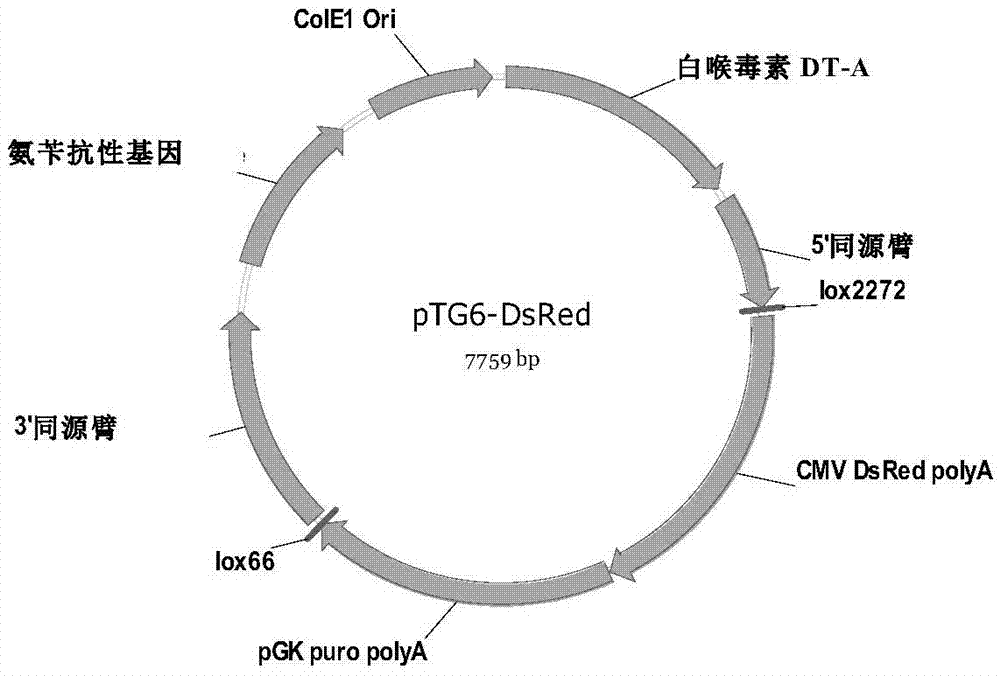
Patents
Literature
67 results about "Chromosome regions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Several chromosome regions have been defined by convenience in order to talk about gene loci. Most important is the distinction between chromosome region p and chromosome region q. These are virtual regions that exist in all chromosomes.
Microdissection-based methods for determining genomic features of single chromosomes
InactiveUS20060211001A1Quick fixPromote associationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAChromosome regions
The present provides a microdissection-based method for identifying a genomic feature present within a visible chromosome region. The method includes steps of: (a) micro-dissecting a single copy of a chromosome to obtain a visible chromosome region; (b) amplifying the visible chromosome region to obtain amplified single chromosome DNA; and (c) subjecting the amplified single chromosome DNA to micro-array analysis whereby such analysis identifies at least one genomic feature present within the visible chromosome region. The method is applicable to determining genomic features including, but not limited to, genomic DNA size, gene content, DNA breakpoint, or DNA polymorphism (e.g., single nucleotide polymorphisms).
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Probes, method and chip for detecting alpha and/or beta-thalassemia mutation based on whole-gene capture sequencing and application of such probes, such method and such chip
ActiveCN106591441AEnables detection of deletions in large regionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBeta thalassemiaNew mutation
The invention provides primers, a method and a chip for detecting alpha and / or beta-thalassemia point mutation and deletion mutation based on whole-gene capture sequencing and application of such primers, such method and such chip. The primers, the method, the chip and application thereof have the advantages that through designing of capture probes, relevant genes involved in alpha-thalassemia and beta-thalassemia are enriched and all mutation information including SNP and indel in full-length sequences of genes is detected; through addition of autosome, X-chromosome and Y-chromosome regions as well as upstream and downstream regions of coded genes as references, structure variations such as SNV and CNV are detected; compared with existing various hotspot mutation site detection technologies, the method is capable of detecting hotspot mutation information as well as some rare mutations and undiscovered new mutation types to detect and analyze full-length sequence specificity of target genes, fully covers the mutation types and makes up the defect that a conventional detection method easily causes missing detection of low-frequency mutations and rare mutations greatly.
Owner:SHENZHEN E GENE TECH
Oligonucleotide probe and acquisition method thereof
ActiveCN106566876ASimple designLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationRepetitive SequencesIn situ hybridisation
The invention relates to a method for acquisition of an oligonucleotide probe. The method comprises the following steps: downloading genomic sequence of crop species from a public database, filtering and finding out tandem repeat sequences, screening preliminarily found repetitive sequences, comparing residual tandem repeat sequence and known probe sequence, removing already used probe sequence, comparing residual screened tandem repeat sequences, carrying out probe design and synthesizing and verifying the designed probe sequence so as to obtain effective oligonucleotide sequence. According to the invention, cost is low and efficiency is high. The probe can be used for non-degenerated fluorescence in situ hybridization (ND-FISH) analysis of crop chromosome, determination of distribution of tandem repeat sequences represented by the probe on chromosome, understanding of the structure characteristics of chromosome and establishment of specific landmark of chromosome. Thus, specific chromosome or chromosome region of crops is identified, and the developed new oligonucleotide probe has specificity of chromosome or chromosome region.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
G-banded adherent chromosome segmentation method based on geometrical features and region fusion is proposed
InactiveCN109146838AImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionChromosome regionsMonosomal karyotype
The invention discloses a G-banded adherent chromosome segmentation method based on geometrical feature and region fusion, At first, that concave point of the region outline of the adherent chromosomeare extracted, then the image of the adherent chromosome is cut by a cutting line for by two concave points, and finally, the local region aft the cutting is fused, and the most suitable region is selected as the final single chromosome region. The invention realizes automatic division of adherent chromosomes and improves the efficiency of chromosome karyotype analysis.
Owner:HUNAN ZIXING INTELLIGENT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
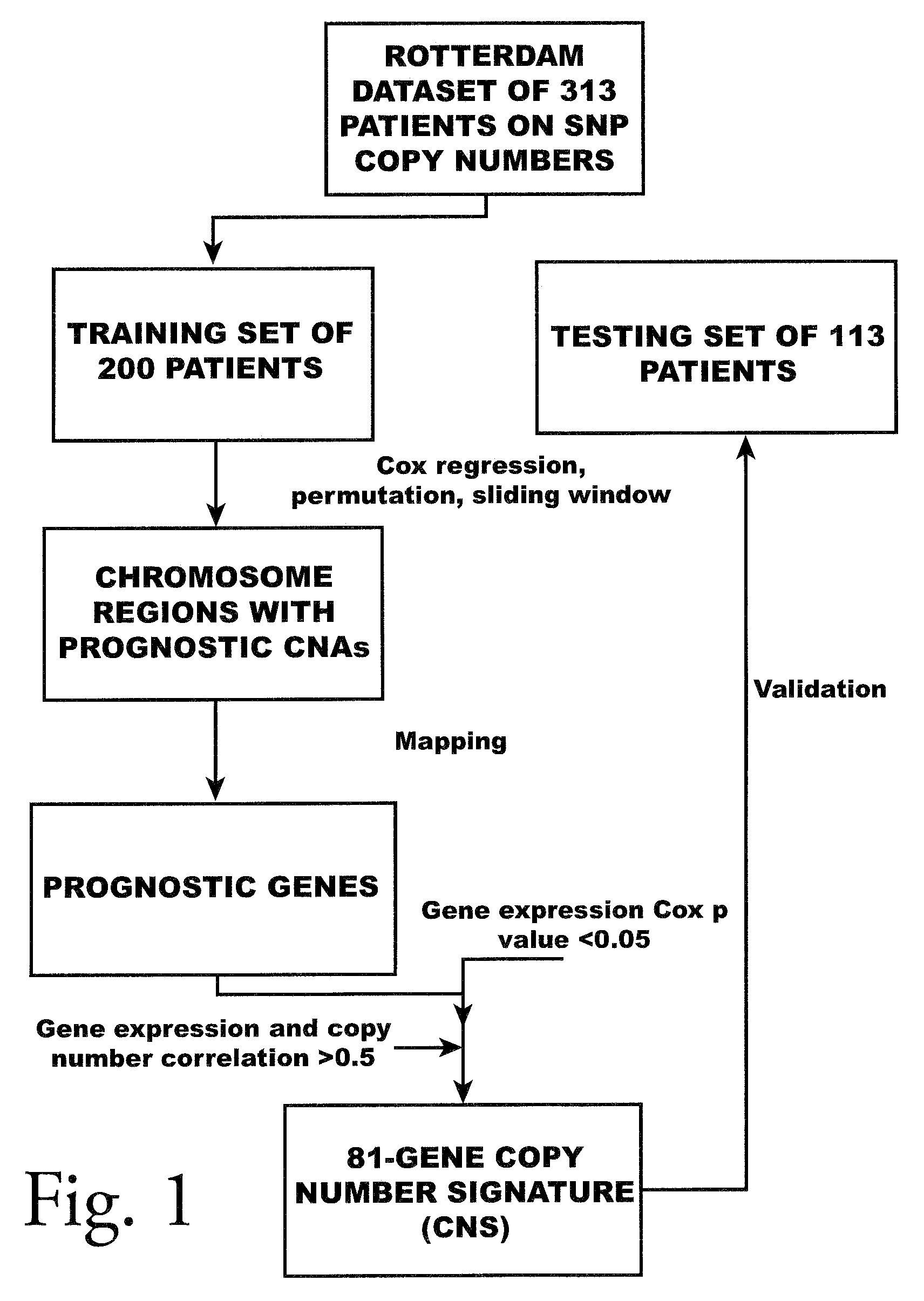
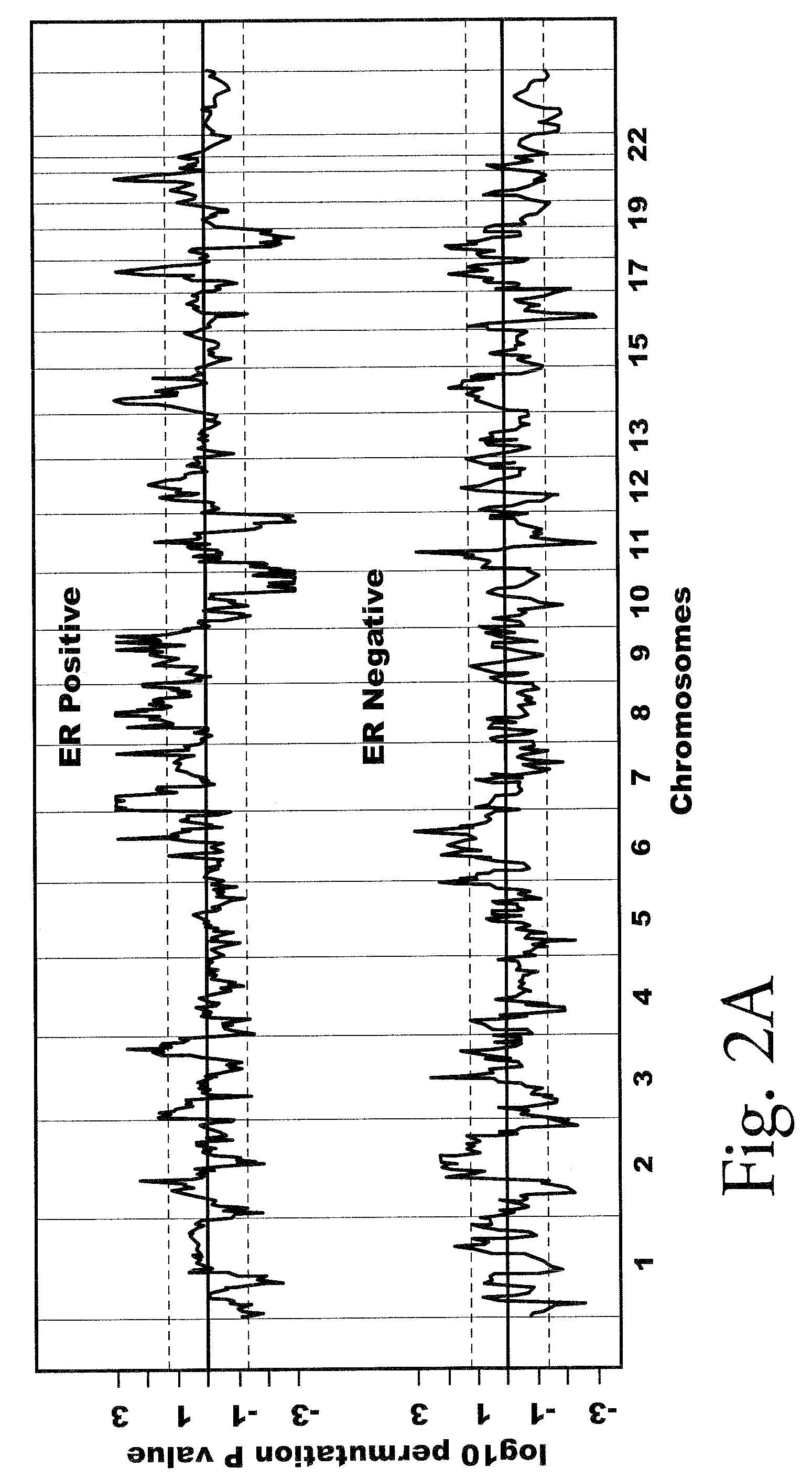
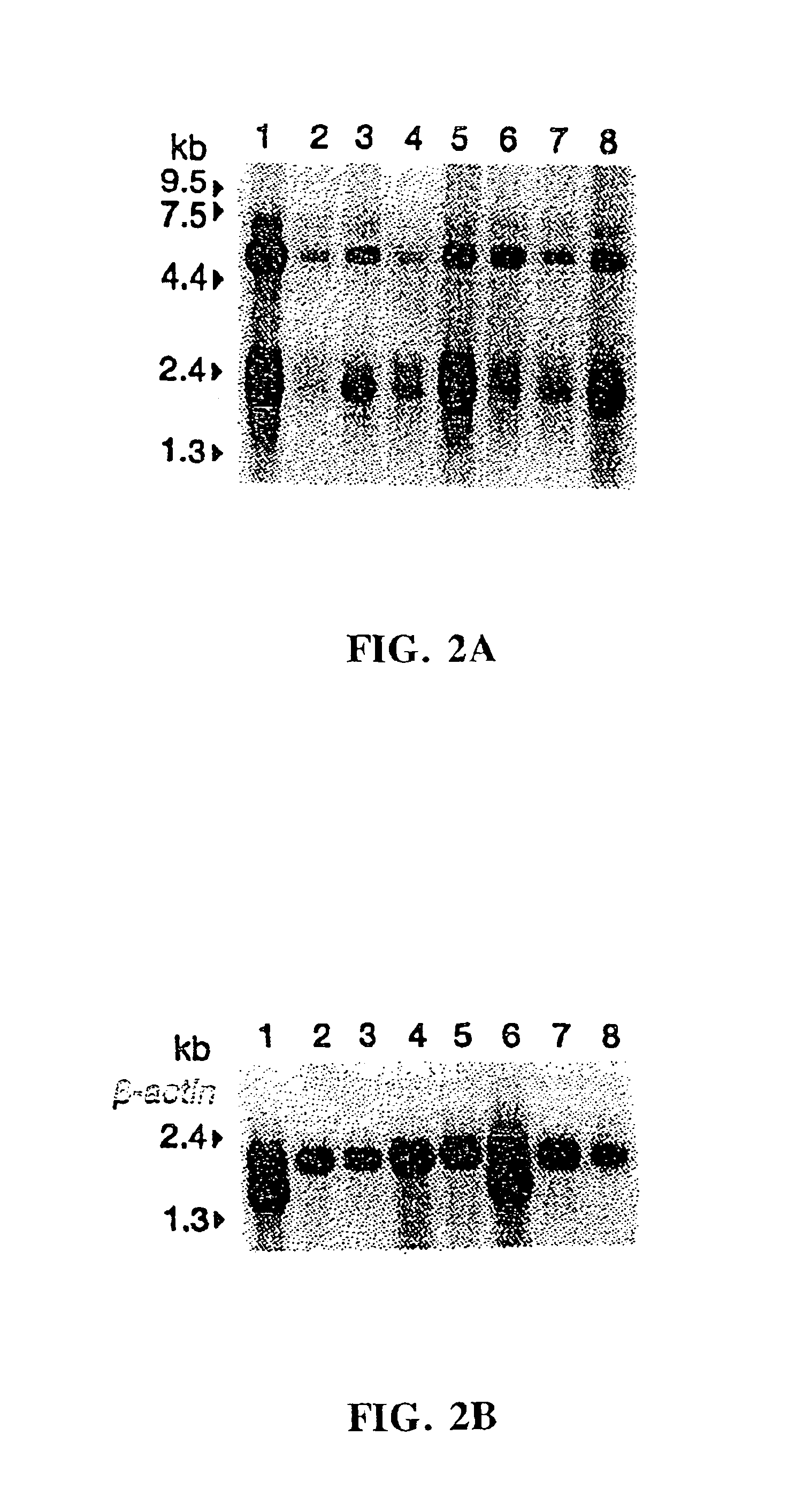
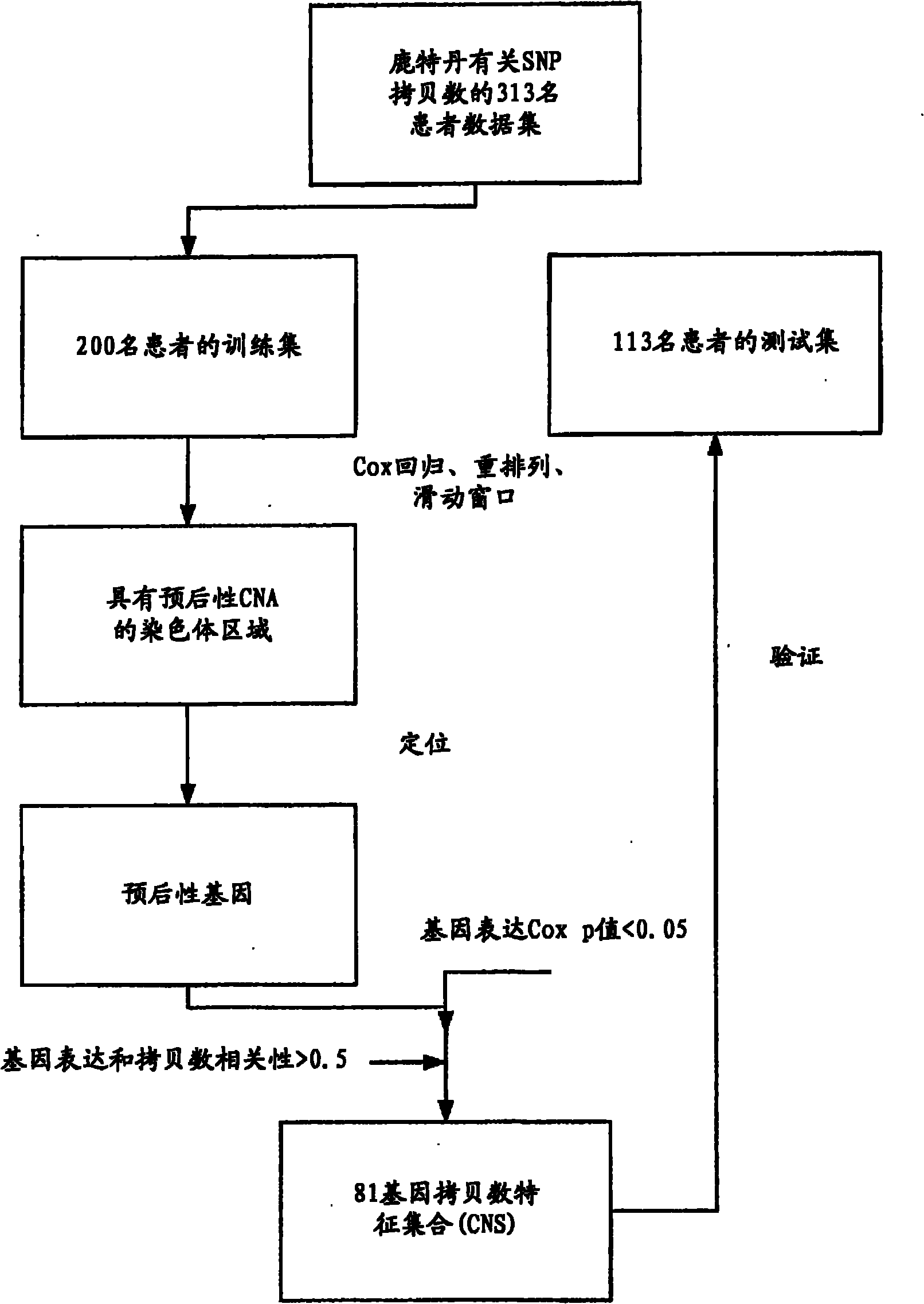
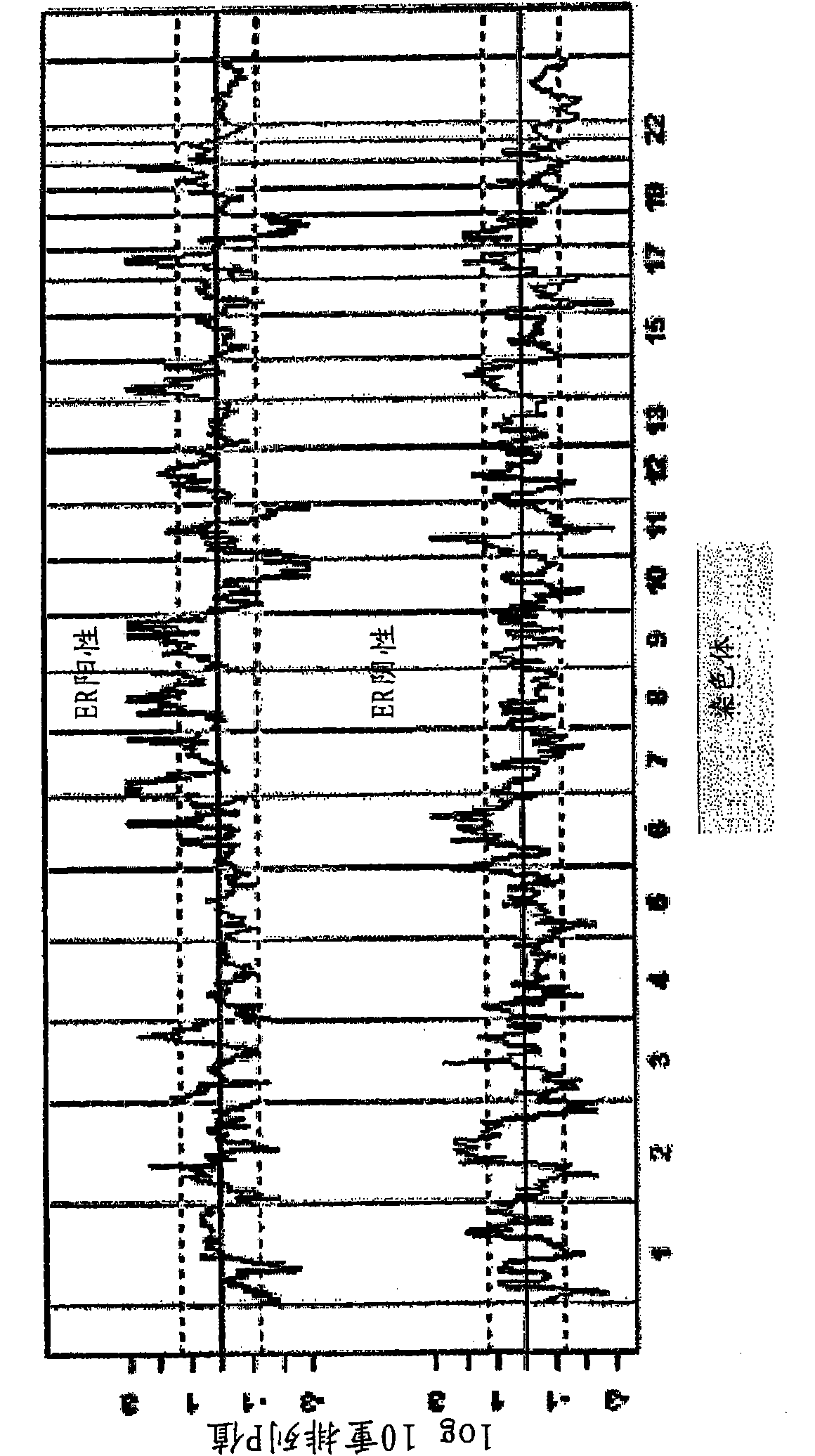
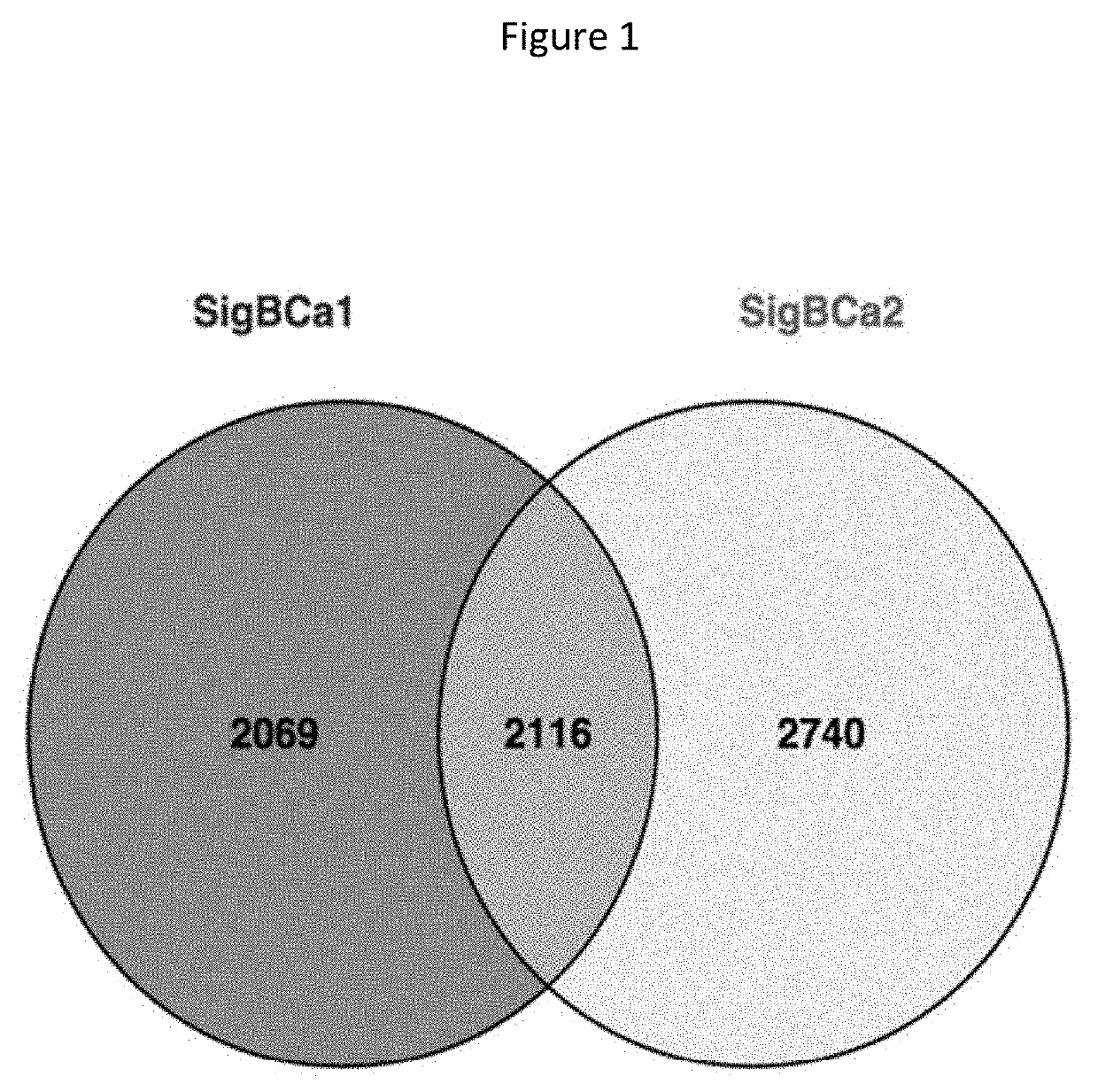
Copy number alterations that predict metastatic capability of human breast cancer
InactiveUS20090155805A1Poor prognosisMicrobiological testing/measurementBreast cancer metastasisChromosome regions
Disclosed in this specification is a method of defining chromosome regions of prognostic value by summarizing the significance of all SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphism) in a predetermined section of a chromosome to define chromosome regions of prognostic value. Based on the SNPs in specified genes, a more accurate prognosis for breast cancer may be provided.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
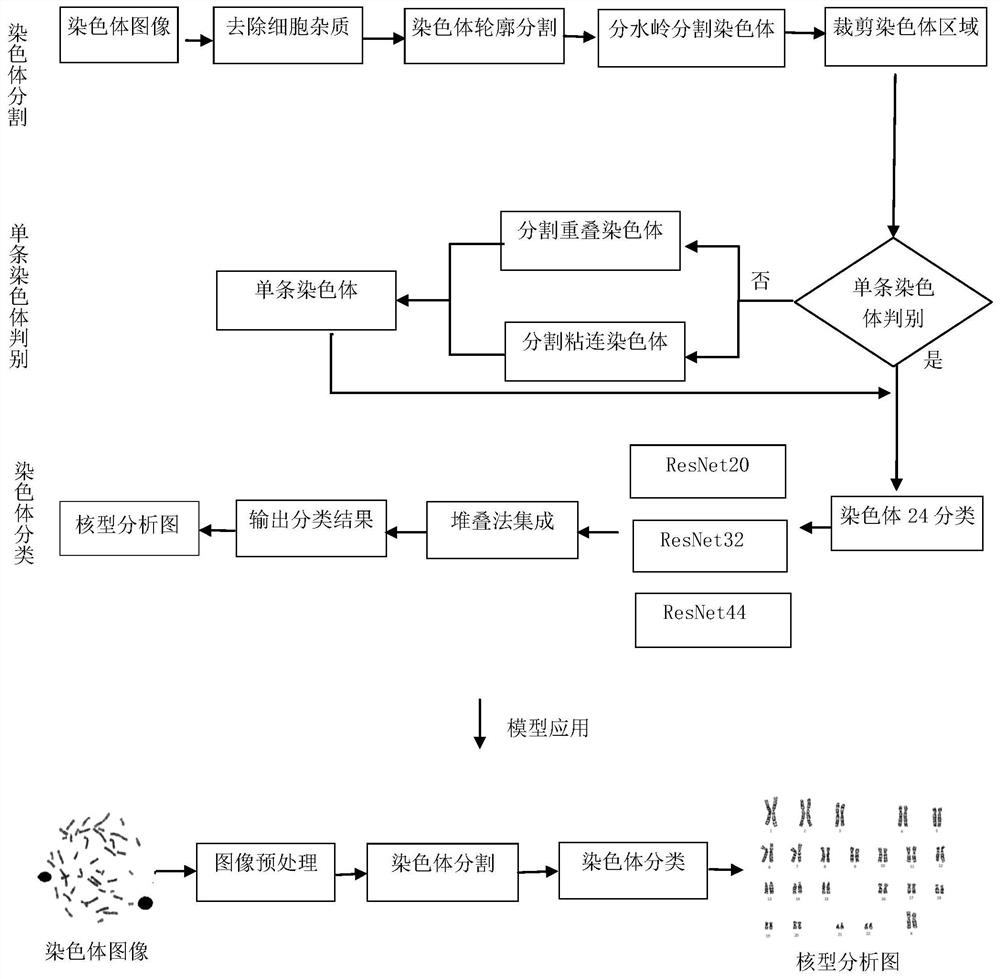
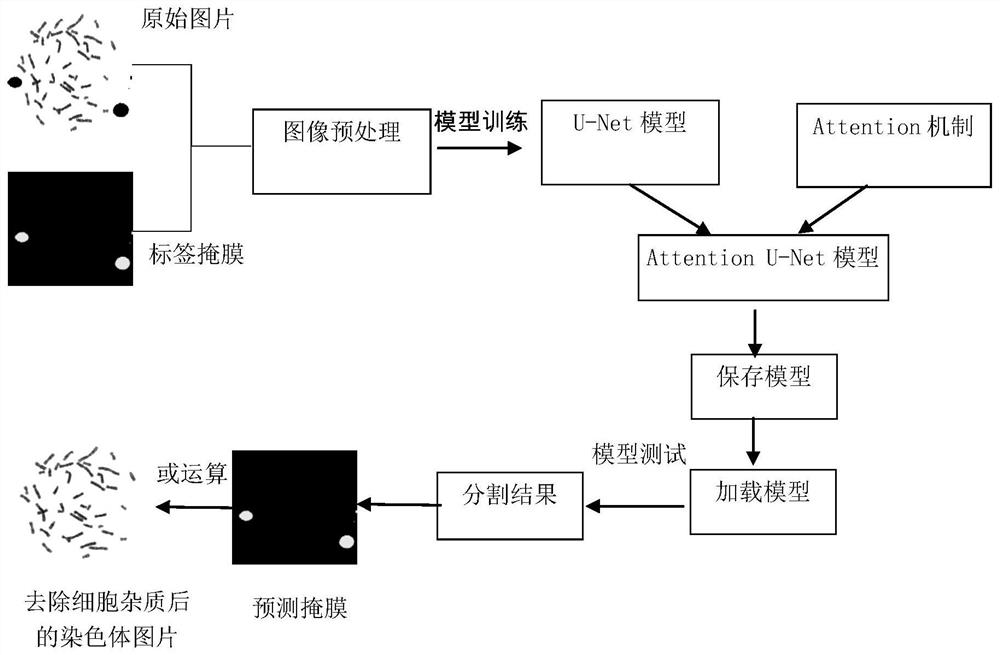
Automatic chromosome segmentation and classification method based on deep learning
ActiveCN113658150AFully automatedRealize intelligenceImage enhancementImage analysisSupport vector machineClassification methods
The invention discloses an automatic chromosome segmentation and classification method based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a chromosome image and filtering cell impurities by using an Attention U-Net model; segmenting chromosomes and cutting out each chromosome region image; extracting features from the obtained chromosome region, training a support vector machine, a random forest and a logistic regression classifier, and carrying out model integration by adopting a voting method so as to identify overlapped adhesion chromosomes or single chromosomes; respectively designing independent segmentation modules for the overlapped adhesion chromosomes, segmenting the overlapped chromosomes by utilizing a method of separating and then splicing, and segmenting the adhesion chromosomes by utilizing a convex defect point detection method; and respectively inputting the chromosome training data with marked types into 24 classification models ResNet20, ResNet32 and ResNet44 for training, then carrying out model integration by using a stacking method, and outputting a final chromosome classification result and a chromosome karyotype analysis chart so as to carry out chromosome anomaly identification.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Method for detecting abortion tissue DNA copy number variation and chimera
The invention discloses a method for detecting abortion tissue DNA copy number variation and a chimera. The method comprises the steps of data quality control, data correction, copy number variation determination, result display and reference range determination. Copy number variation determination comprises the steps that (1) a copy number variation value of corrected data is determined according to a Circular Binary Segmentation algorithm; (2) a copy number variation value is determined according to a Hidden Markov Model algorithm; and (3) statistics is further performed on significance of copy number variation in an interval according to a Z-score. According to reference range determination, the reference range of an R value is [-0.2,0.2], the reference range of a Z value is [-3,3], and the situation that copy number repetition or deletion exists in a chromosome region is indicated for an interval where the R value is greater than 0.2 or smaller than -0.2 and an interval where the Z value is greater than or smaller than 3. The method can be used for analyzing abortion causes and further elaborating the important role of genetic factors in abortion generation specifically.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for randomly knocking out streptomyces genome DNA large fragment in vivo
InactiveCN104109688AEfficient removalReduced Genome SizeVector-based foreign material introductionChromosome regionsIn vivo
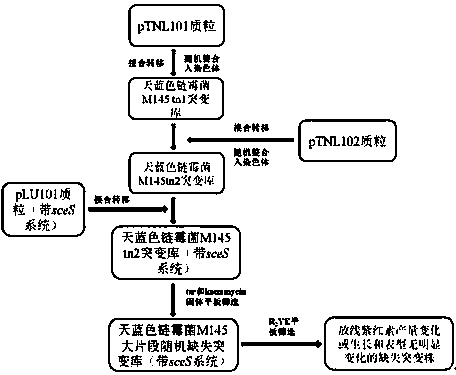
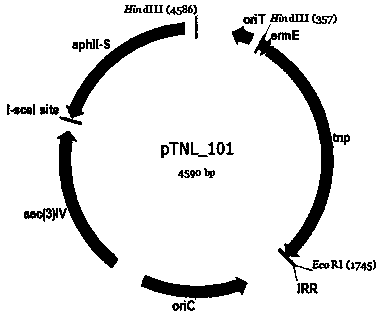
The invention discloses a method for randomly knocking out a streptomyces genome DNA large fragment in vivo. The method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing series of recombinant plasmids pTNL_101, pTNL_103, pTNL_104 and pTNL_105 as a first sceS enzyme cutting site random introduced plasmid; (2) introducing the constructed recombinant plasmids pTNL_101, pTNL_103, pTNL_104 and pTNL_105 into streptomyces coelicolor M145, and constructing a mutant sub-library 1 without random chromosome large fragment; (3) constructing the series of recombinant plasmids pTNL_102 as a second sceS enzyme cutting site random introduced plasmid, and introducing into the mutant sub-library 1 to obtain a mutant sub-library 2; (4) screening out large fragment knockout muton by using an R2YE flat panel, precisely positioning a chromosome deletion region segment, and performing positioning knockout in an original strain to perform verification. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for removing removable parts of a chromosome region effectively and randomly; at present, a positioning result shows that the lengths of the knockout fragments are between 2kb and 100kb, thus an evidence for transforming streptomyces into antibiotic heterologous expression hosts and chassis organisms can be provided.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
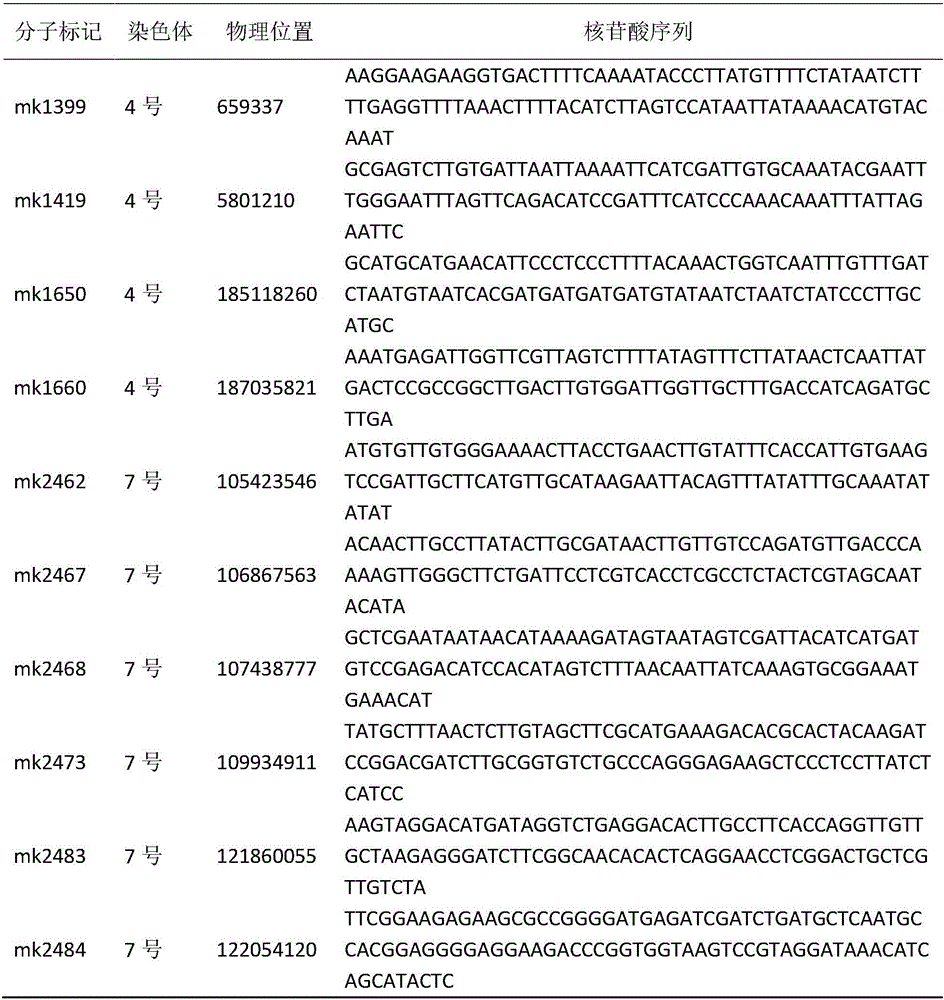
Maize single panicle weight main effect QTL, as well as acquisition method and application thereof
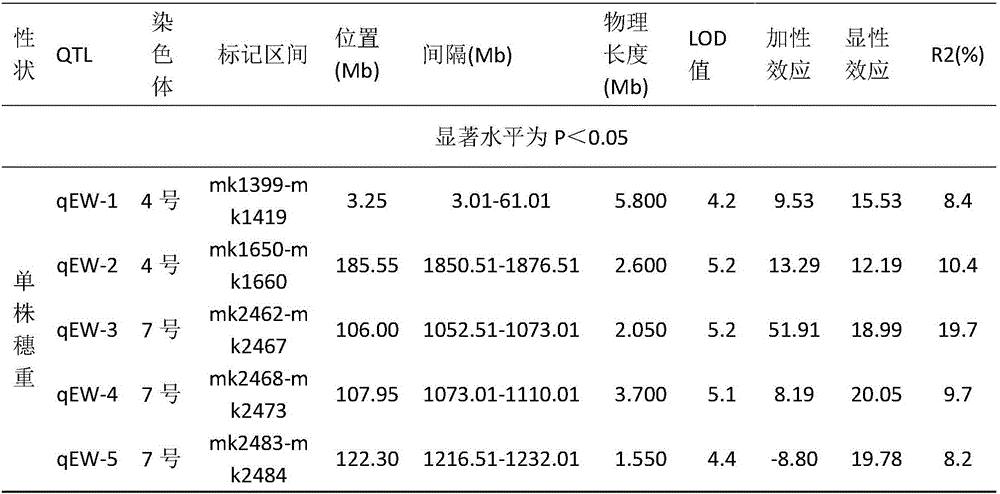
The invention provides a maize single panicle weight main effect QTL, as well as an acquisition method and application thereof. The QTL comprises qEW-1, qEW-2, qEW-3, qEW-4 and qEW-5. The method comprises the following steps: configuring cross combination by taking a high-yield early-maturity maize inbred line SG5 as a female parent and a maize inbred line SG7 with relatively poor yield trait as a male parent, and constructing an F2 genetic group of the cross combination; performing GBS sequencing-basing typing on the F2 genetic group, and performing genotyping by combining differential SNP validated based on SG5 and SG7 parents; investigating the yield trait of single F2 panicle, performing QTL analysis on the F2 single panicle yield trait by utilizing a winQTLcart2.5 software composite interval mapping method, and analyzing the chromosome region of the main effect QTL and the genetic effect. According to the method, a theoretic base is provided to excavating and controlling the maize single panicle weight main effect QTL and linked marker, a molecular marker closely linked with the target QTL is acquired, and foundation is laid to maize single panicle yield trait QTL candidate gene prediction, cloning and molecular mark assisted breeding.
Owner:LIUPANSHUI NORMAL UNIV
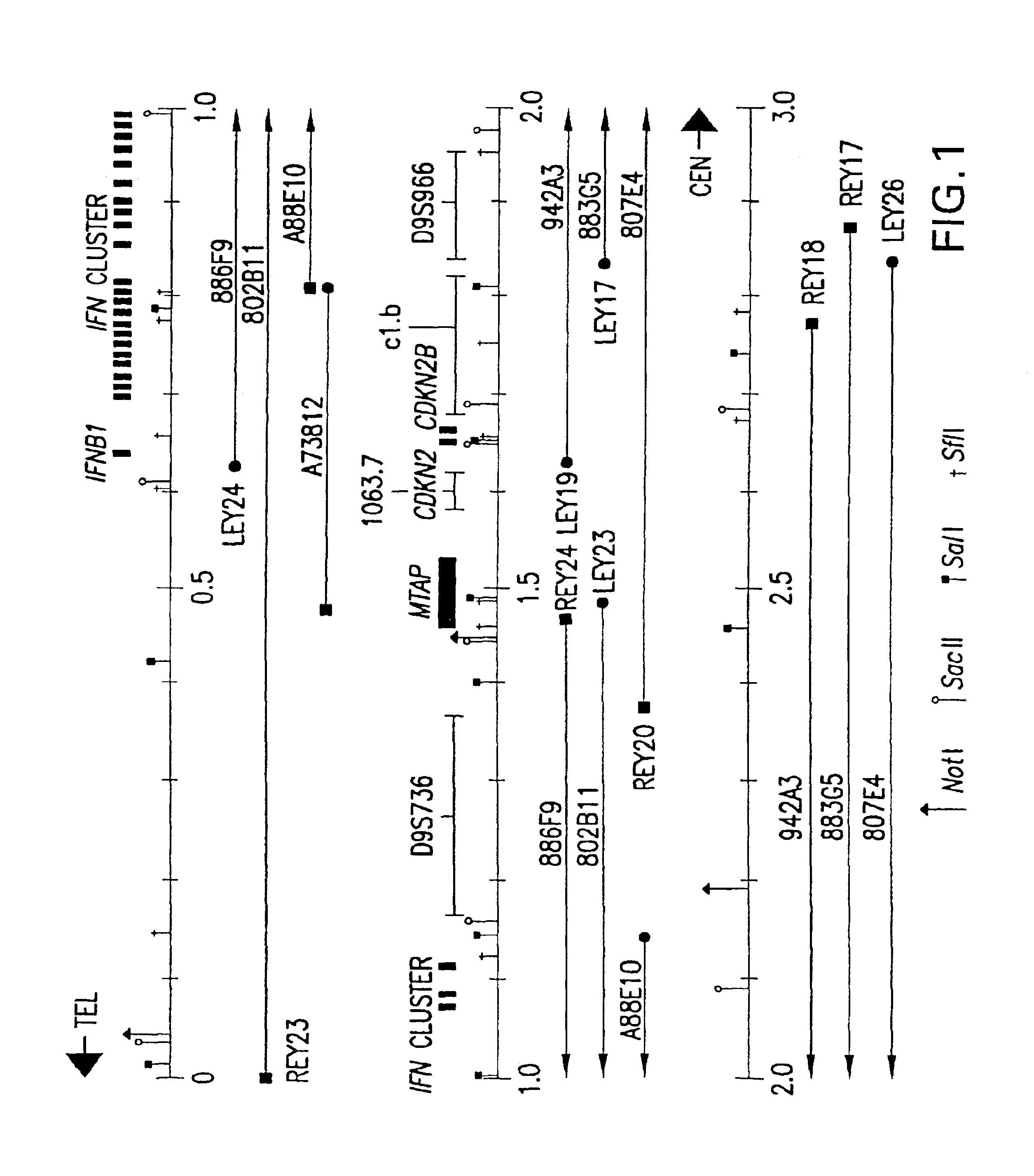
Methylthioadenosine phosphorylase compositions and methods of use in the diagnosis and treatment of proliferative disorders
InactiveUS6870037B1Overcomes drawbackIncrease ratingsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChromosome regionsWilms' tumor
Disclosed are novel nucleic acid and peptide compositions comprising methythioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) and methods of use for MTAP amino acid sequences and DNA segments comprising MTAP in the diagnosis of human cancers and development of MTAP-specific antibodies. Also disclosed are methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumors and other proliferative cell disorders, and idenification tumor suppressor genes and gene products from the human 9p21-p22 chromosome region. Such methods are useful in the diagnosis of multiple tumor types such as bladder cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, brain tumors, lymphomas, gliomas, melanomas, and leukemias.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
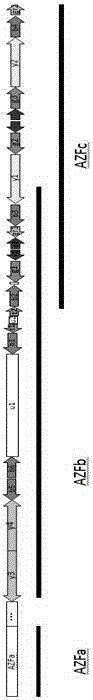
AZF region microdeletion detection kit for Y chromosome
The invention provides a detection reagent for AZF (azoospermia factor) region microdeletion of a Y chromosome. The detection reagent comprises a primer composition, wherein primer sequences are designed for such primer sites aiming at the AZF region of the Y chromosome and other specificity regions serving as internal references; the characteristics of the primer sequences comprises: (1) in each group of primers, three continuous primers are designed by taking the previous sequence of a genome as a template, and form a PCR template after being connected; (2) a primer site sequence has a known and unchanged copy number in the target region of the chromosome of a normal person, and the sequence does not exist in other chromosome regions except the target region; (3) the sequence primers have close annealing temperatures, and the fluctuation range is lower than 5 DEG C; (4) the primer sequences do not have complementarity to a general amplification primer sequence; (5) an internal reference site only appears in the target region, and does not exist in other regions of the genome. The invention further provides a kit for detecting the AZF region microdeletion of the Y chromosome and a method for detecting the AZF region microdeletion of the Y chromosome.
Owner:PEKING JABREHOO MED TECH CO LTD +1
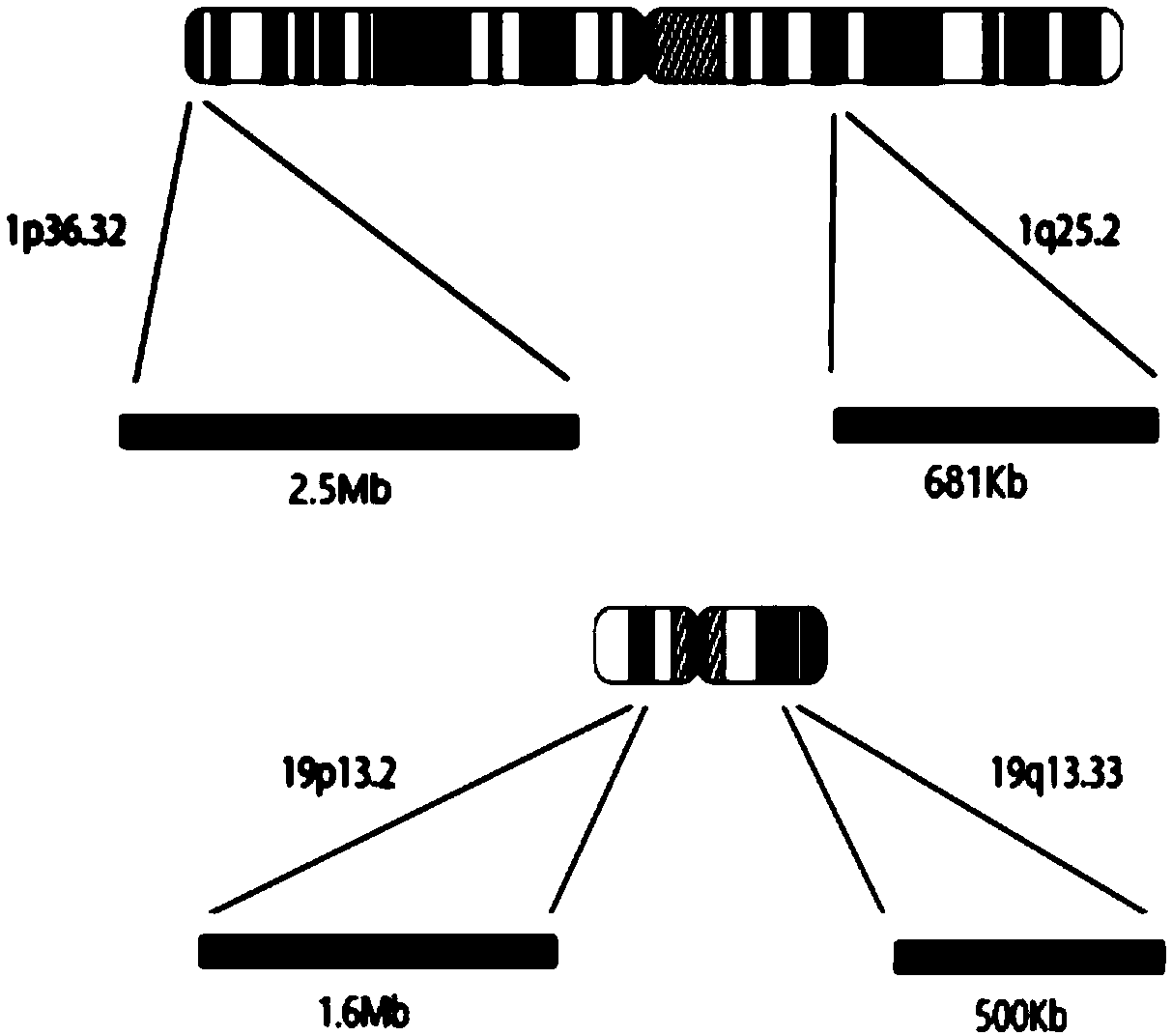
Kit and method for detecting chromosome heterozygosity loss on basis of amplicon sequencing
ActiveCN109504770AComprehensive, true and accurate responseReduce the amount of solutionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleic acid detectionChromosome regions
The invention discloses a kit and method for detecting chromosome heterozygosity loss on the basis of amplicon sequencing, belongs to the field of molecular biology nucleic acid detection, and relatesto the kit and method for detecting chromosome heterozygosity loss by means of amplicon sequencing. The kit contains a mixture of 14 groups of primer pairs used for detecting a 1p36.32 region of a human chromosome 1, 6 groups of primer pairs used for detecting a 1q25.2 region of the human chromosome 1, 14 groups of primer pairs used for detecting a 19p13.2 region of a human chromosome 19 and 7 groups of primer pairs used for detecting a 19q13.33 region of the human chromosome 19, 20 kinds of tag primers used for distinguishing samples, a GC stabilizer, a PCR enzyme mixture, purifying magneticbeads, a quality control standard substance and ddH2O. Through two-time PCR amplification and two-time product purification and sequencing, through a ratio of READS(1p) / READS(1q) to READS(19q) / READS(19p), the heterozygosity loss state of 1p19q in the samples is analyzed. By adopting the method, the variation situation of the 1p19q can be reflected comprehensively, truly and accurately, and gene variation of the 96 samples can be subjected to high-throughput detection and analysis simultaneously, so that the detection cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:艾普拜生物科技(苏州)有限公司
Molecular marker interlinked with major QTL qFSW-2 and qFSW-5 for storage capability of corn seeds and application
ActiveCN107400703AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMolecular breeding
The invention relates to a molecular marker interlinked with major QTL qFSW-2 and qFSW-5 for storage capability of corn seeds and application. The major QTL for the storage capability of the corn seeds is qFSW-2 in a Bin2.06 region of No.2 chromosome of corns and qFSW-5 in a Bin5.03 region of No.5 chromosome of the corns, wherein the molecular marker closely interlinked with qFSW-2 includes umc1079 and umc1028; and the molecular marker closely interlinked with qFSW-5 includes umc2063 and umc2400. According to the molecular marker, by positioning two major QTL sites, namely qFSW-2 and qFSW-5, for the storage capability of the corn seeds, four SSR molecular markers closely interlinked with the two major QTL are found, so that a feasible technological approach is provided for the molecular breeding for storable character of the corn seeds.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Gene mapping integration and expression system and application thereof
ActiveCN106978416AMicroencapsulation basedMicroinjection basedGene mappingSite-specific recombination
The invention relates to a gene mapping integration and expression system and application thereof. Particularly, the invention relates to integration and high-efficiency expression of a nucleic acid constructor at a specific site in a transgenic sheep genome, wherein the nucleic acid constructor contains a homologous arm sequence combined with a chromosome region, a site-specific recombination sequence, an exogenous gene expression cassette and a selection marker gene expression cassette. By delivering the constructor into a host cell, mapping integration and expression of a target gene in a host cell genome can be achieved, a transgenic cell can be obtained, and transgenic sheep expressing the target gene can be obtained with the transgenic cell as a donor cell. By means of the site-specific recombination technique, expression of other specific exogenous genes and genetic modification of a transgene can be achieved in somatic cells of the transgenic sheep.
Owner:SHANGHAI TRANSGENIC RES CENT
Molecular marker interlinked with major QTL qSVI-7-2 and qSVI-10 for storage capability of corn seeds and application
ActiveCN107400702AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMolecular breeding
The invention relates to a molecular marker interlinked with major QTL qSVI-7-2 and qSVI-10 for storage capability of corn seeds and application. The major QTL for the storage capability of the corn seeds is qSVI-7-2 in a Bin7.05 region of No.7 chromosome of corns and qSVI-10 in a Bin10.04 region of No.10 chromosome of the corns, wherein the molecular marker closely interlinked with qSVI-7-2 includes umc1545 and umc2333; and the molecular marker closely interlinked with qSVI-10 includes umc1367 and umc2043. According to the molecular marker, by positioning two major QTL sites, namely qSVI-7-2 and qSVI-10, for the storage capability of the corn seeds, four SSR molecular markers closely interlinked with the two major QTL are found, so that a feasible technological approach is provided for the molecular breeding for storable character of the corn seeds.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Copy number alterations that predict metastatic capability of human breast cancer
Disclosed in this specification is a method of defining chromosome regions of prognostic value by summarizing the significance of all SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphism) in a predetermined section of a chromosome to define chromosome regions of prognostic value. Based on the SNPs in specified genes, a more accurate prognosis for breast cancer may be provided.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
Preparation method and application of Cucumis sativus. L chromosome-6 probe
InactiveCN104593508ASimplicity guaranteedAvoid interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationFluorescenceGenome database
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a Cucumis sativus. L chromosome-6 probe. According to the method, on the basis of a Cucumis sativus. L genomic sequence, a DNA sequence containing no repetitive sequence is selected through RepeatMasker and Cucumis sativus. L genome database BLAST analysis, and primer design is performed through Primer Premier 5.0. A PCT product covering single chromosomes is obtained through PCR amplification, the PCT product is purified in agarose gel electrophoresis, the concentration is measured with a nucleic acid concentration measurement instrument, then equal amounts of products of all pairs of primers are mixed, and a probe is marked by a nick translation method and is hybridized to a chromosome flake by a FISH (Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization) technology so as to complete the preparation, detection and application of the single-chromosome probe. Through the application of the method, Cucumis sativus. L single chromosomes and a probe of any chromosome region can be obtained quickly, and precise analysis and research on a single chromosome and the morphological structure of any chromosome can be performed.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Detection of chromosome interaction relevant to breast cancer
ActiveUS20190241964A1Resource optimizationMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsChromosome regionsOncology
Owner:OXFORD BIODYNAMICS PLC
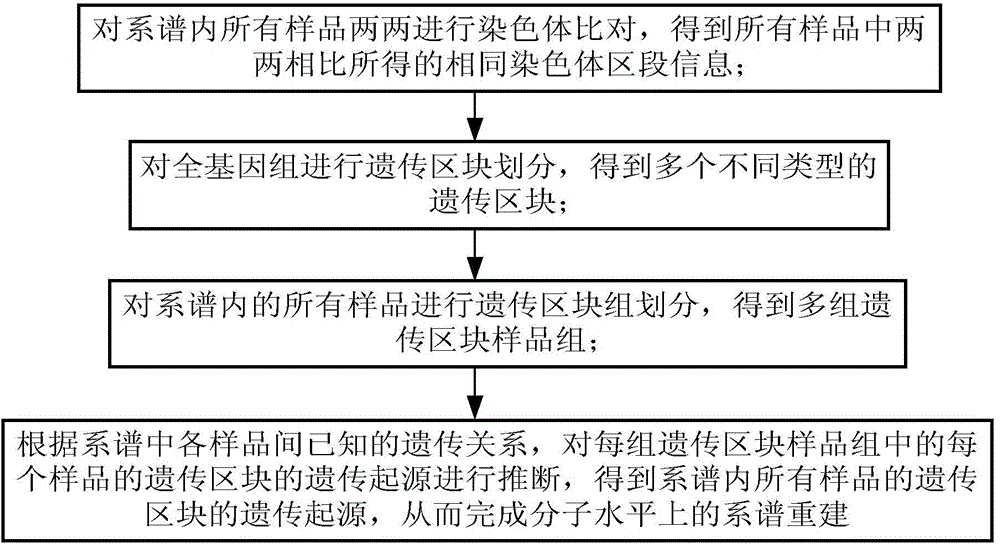
Device and method for genealogy reestablishing on molecular level
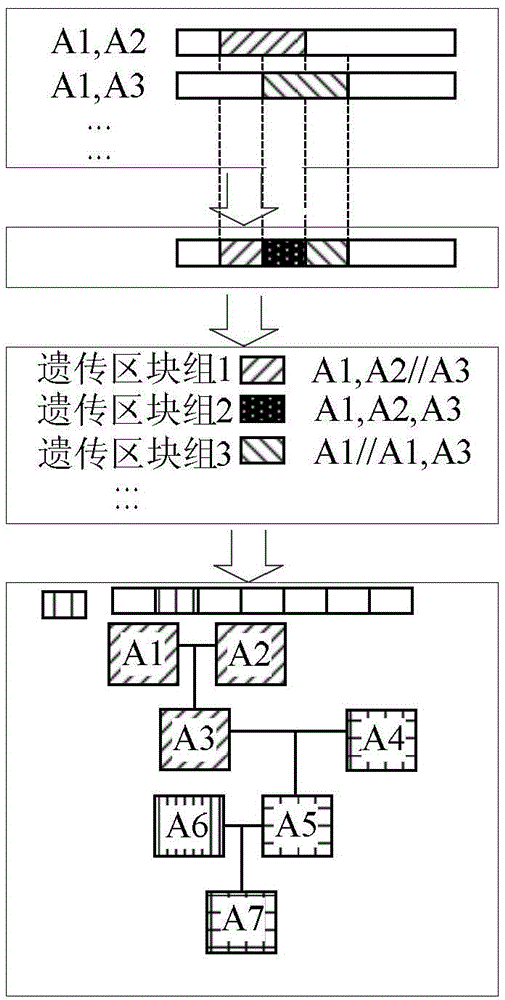
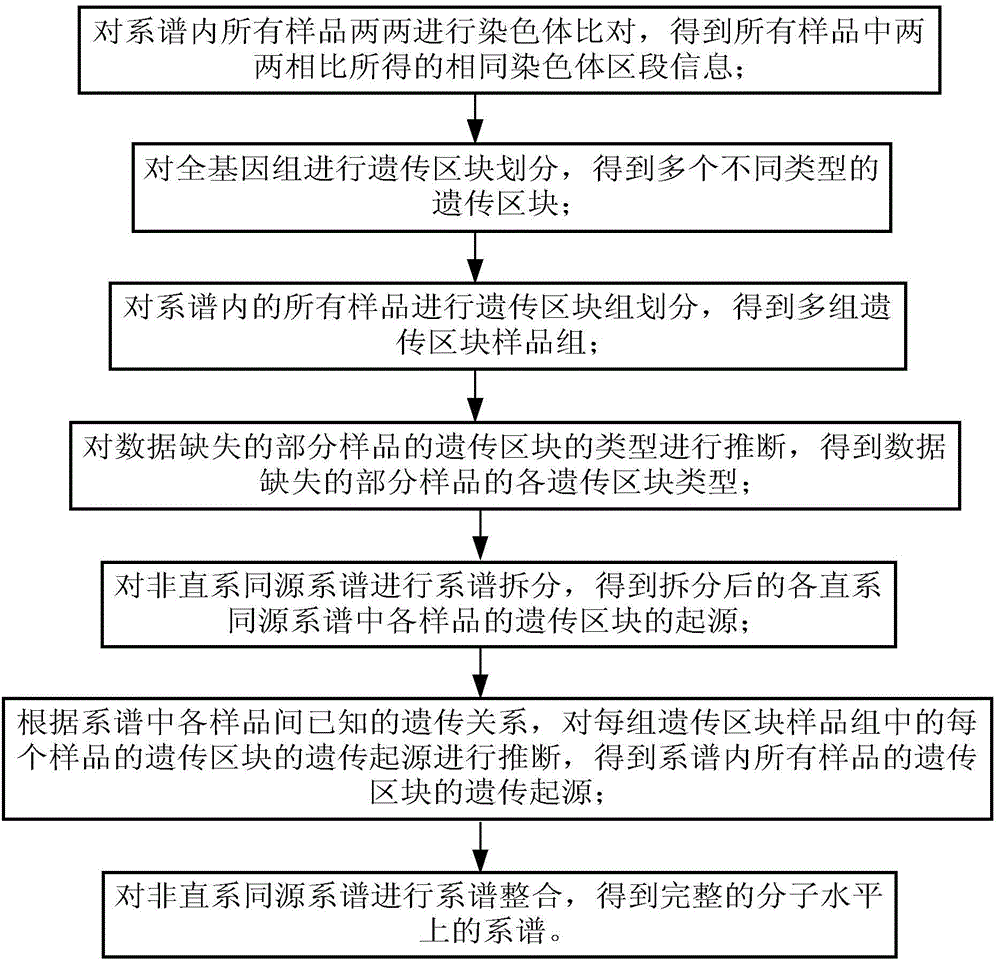
ActiveCN104134016AEasy to operateSpecial data processing applicationsMolecular levelChromosome regions
The invention discloses a device and method for genealogy reestablishing on the molecular level. The method comprises the following steps that all samples in genealogy are subjected to chromosome comparison in a pairing mode, and identical chromosome region information obtained by pairing comparison in all the samples is obtained; according to the identical chromosome region information obtained by pairing comparison in all the samples, a whole genome is subjected to heredity region division, and a plurality of heredity regions of different types are obtained; according to the different types of the heredity regions, all the samples in the genealogy are subjected to heredity region group division, and a plurality of heredity region sample groups are obtained; according to the known genetic relationship between the samples in the genealogy, the heredity sources of the heredity regions of each sample in each heredity region sample group are subjected to inference, and the heredity sources of the heredity regions of all the samples in the genealogy are obtained; and accordingly genealogy reestablishing on the molecular level is completed. The method has the obvious advantages of being precise, complete in function, easy to operate and good in compatibility.
Owner:BEIJING NOVOGENE TECH CO LTD
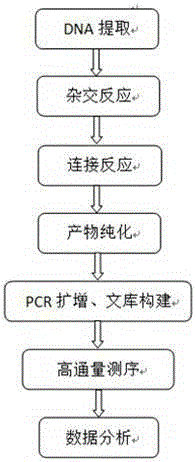
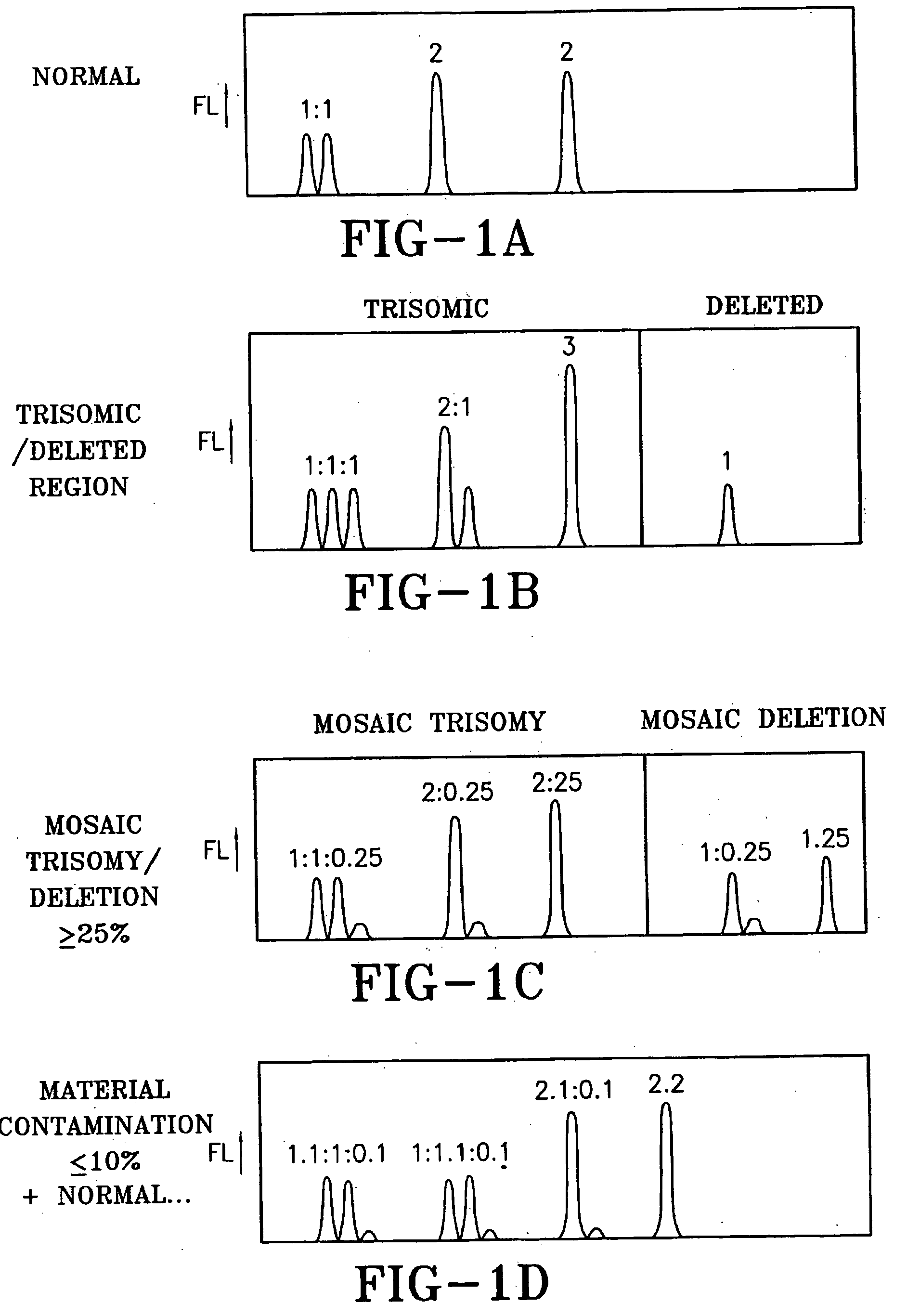
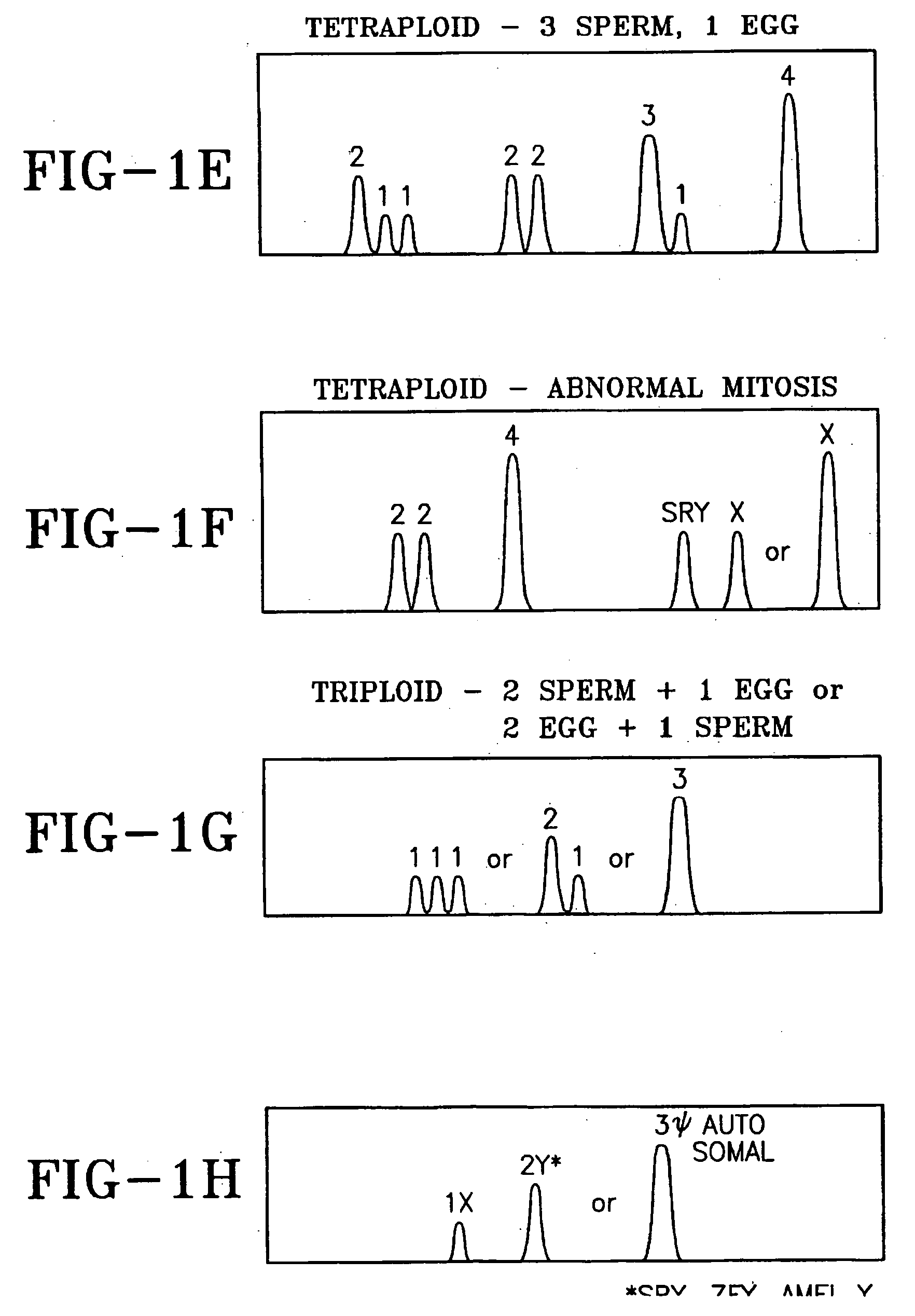
Method of detecting genomic aberrations for prenatal diagnosis
InactiveUS20100015619A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementChorionic villiGenetics
This invention relates to assays used to detect and confirm genomic aberrations, such as chromosomes 13, 18, 21, X and Y aneuploidy as well as 22q11.2 deletions, for prenatal diagnosis. For the detection, combined STR markers (all tetra-nucleotide repeats) are employed to cover different chromosome regions. For the confirmation step, individual chromosome specific STR markers (tetra-nucleotide repeats) are utilized. This invention particularly relates to multiplex analysis for the presence or absence of STR markers in genomic DNA isolated from peripheral blood, amniotic fluid, cultured amniocytes, chorionic villi, or fetal cells existing in maternal blood. This invention offers an efficient approach to identify chromosomal abnormalities by using STR markers.
Owner:BEIJING GP MEDICAL TECH
Optimizing genome-wide mutation analysis of chromosomes and genes
InactiveUS20060031052A1Raise the ratioReliable analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesCrowdsChromosome regions
A method of genome-wide testing of gene copy number at the genetically most important loci to determine whether the gene and / or its selected larger surrounding chromosome region is rearranged to result in an unbalanced abnormality in one or more subjects, said method including selecting multiple gene loci of said DNAs to be examined in said test, conducting said test, and comparing the number of copies at each locus tested by quantification of total gene target number to determine the relative, number of each polymorphic sequence detected to assure that each important tested sequence is distinguished from the other alleles at the same locus. A method of detecting the highest number of abnormal patients possible based upon the number of test sites available in a protocol including selecting the most common genetic disease-causing mutations in a population by frequency, selecting and identifying the most common mutations in each by frequencies, multiplying the two frequencies together to get a frequency product which is the frequency of each mutation in the population, and ordering the frequency products beginning with the most common to prioritize which are the most common to detect the largest number of genetic abnormalities possible per test. Depending upon the stage of the life cycle, both of the methods can be done together or in sequence.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT OF AKRON
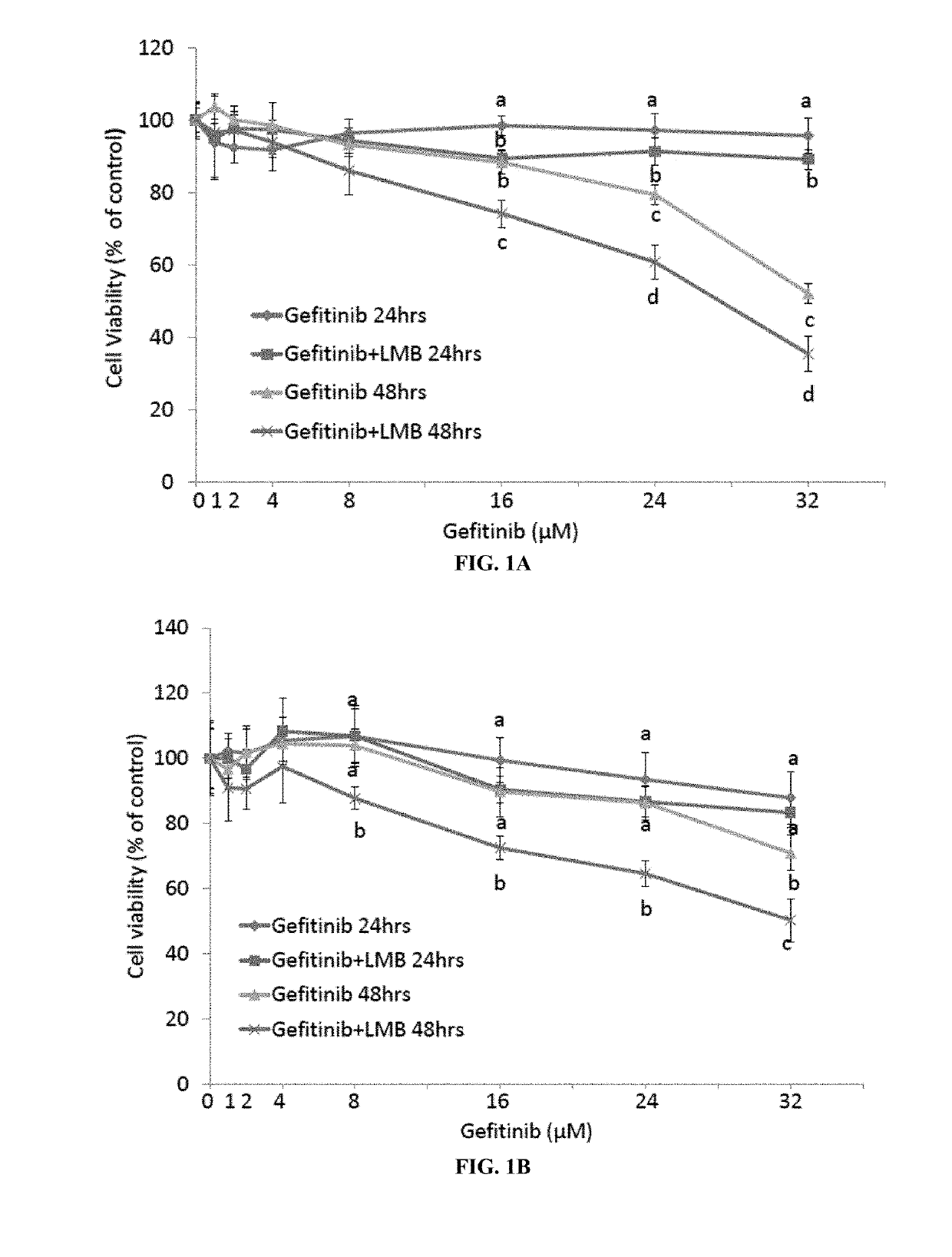
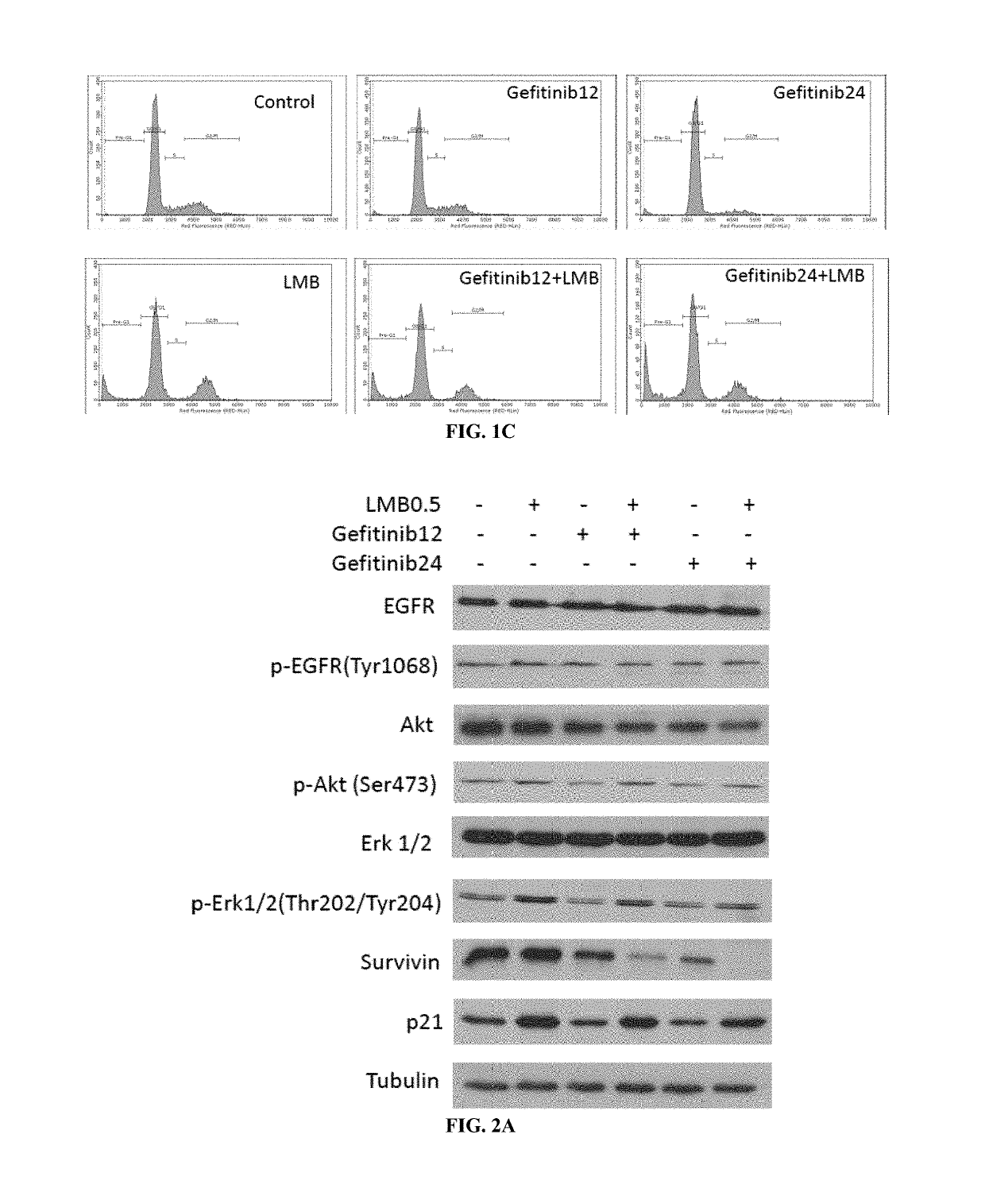
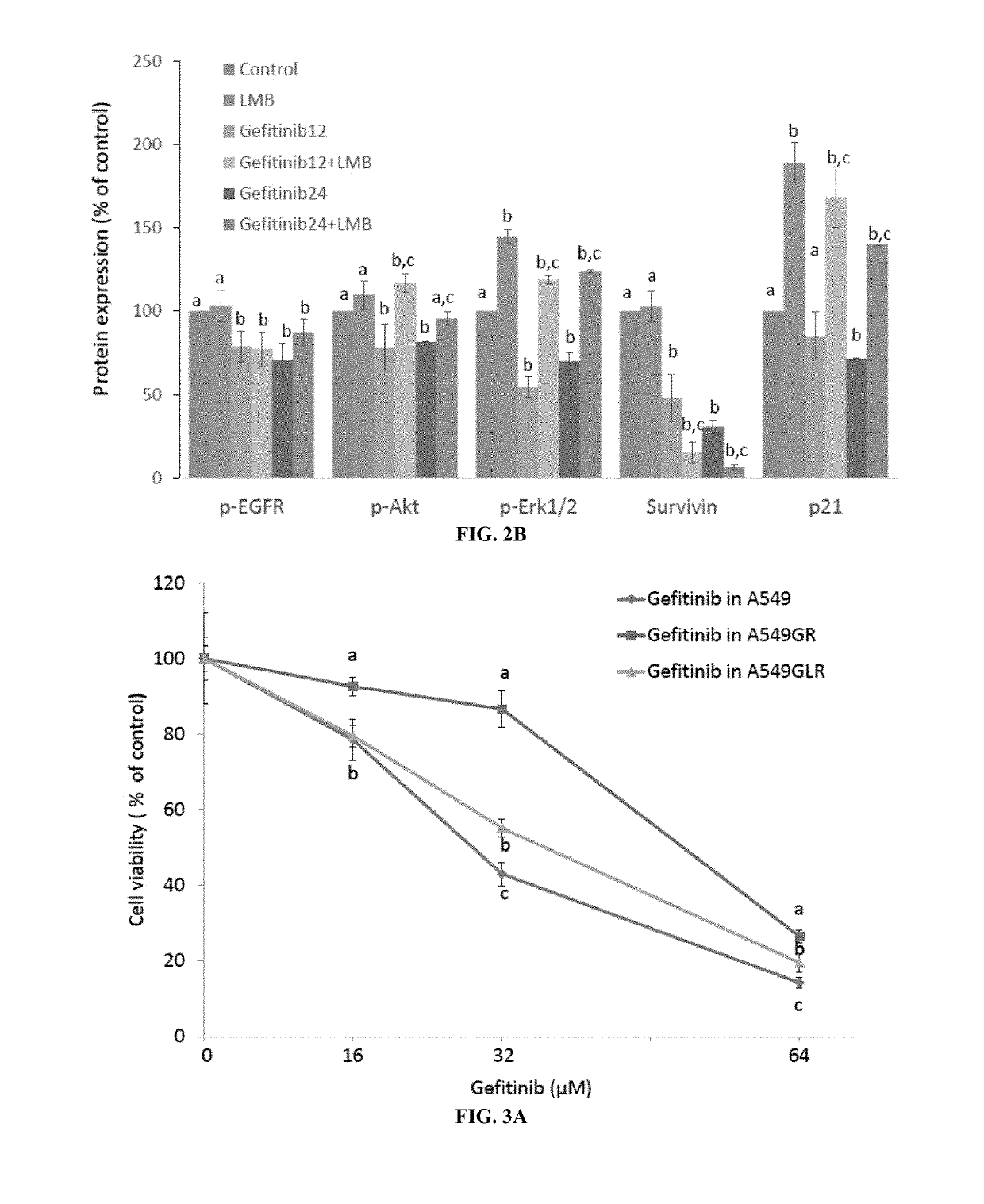
Crm1 inhibitors reduce primary and acquired resistance of EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer cells
The present invention includes a method and compositions for preventing primary or acquired resistance of epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR) inhibitors in a cancer with deregulated EGFR comprising: identifying a subject suspected of needing treatment for primary or acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors of the cancer with deregulated EGFR; and providing the subject with a therapeutically effective amount of a chromosome region maintenance 1 (CRM1) inhibitor and an inhibitor of EGFR in an amount sufficient to reduce or eliminate the cancer.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST
Primers, probes, identification method and kit for identifying fetal chromosome sex in early pregnancy
ActiveCN110607358AQuick checkThe detection method is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPhysiologyChromosome regions
The present invention relates to the technical field of gene identification and specifically discloses primers, probes, an identification method and a kit for identifying fetal chromosome sex. The primers and probes for identifying the fetal sex are primers and probes designed according to a male sex determining gene SRY, and three pairs of the primers and probes designed according to gene sequences of a, b, and c regions in an AZF region of Y chromosome, respectively. The plurality of pairs of the primers and corresponding probes are designed and a four-channel fluorescence detection method is used to determine existence of the SRYgene and the Y chromosome in a detection process, and the method has characteristics of high accuracy, high detection flux and high sensitivity.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF HEBEI MEDICAL UNIV
Indel molecular marker closely linked with capsicum annuum clustered inflorescence genes, primers and application
ActiveCN110592255AResolution cycleSolve efficiency problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceCandidate Gene Association Study
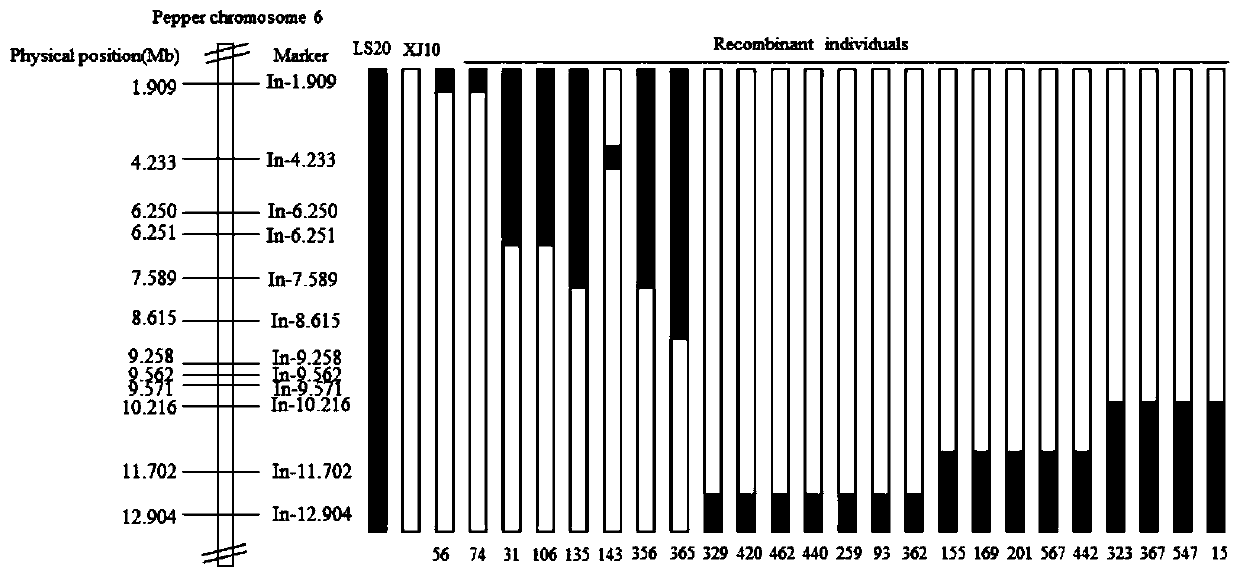
The invention discloses an Indel molecular marker closely linked with capsicum annuum clustered inflorescence genes, primers and application. An F2 population is constructed by utilizing two highly-homozygous inbred lines. A chromosome region closely linked with capsicum annuum clustered inflorescences is acquired by using a BSR and linkage positioning method, and an InDel marker is developed in acandidate interval for verification. Finally, InDel closely linked with the vicinity of a candidate gene is obtained, a molecular marker In-9258 is designed according to the InDel, genotype identification is conducted on 100 randomly-sampled single plants of the F2 population by using the marker, and the coincidence rate reaches 100%. The research result not only can be used for capsicum annuum inflorescence type identification and molecular assisted breeding, but also provides a basis for controlling map-based cloning of capsicum annuum clustered inflorescence genes and for analyzing the forming molecular mechanism of clustered inflorescences.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV +1
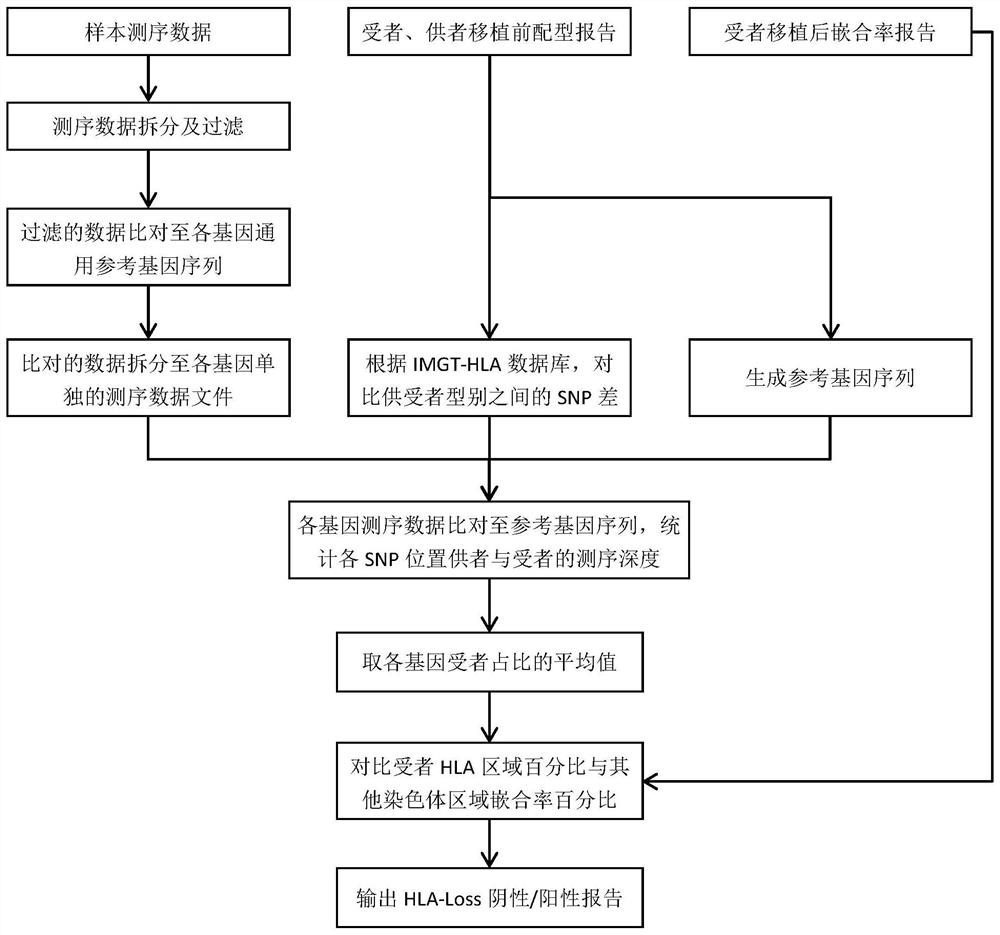
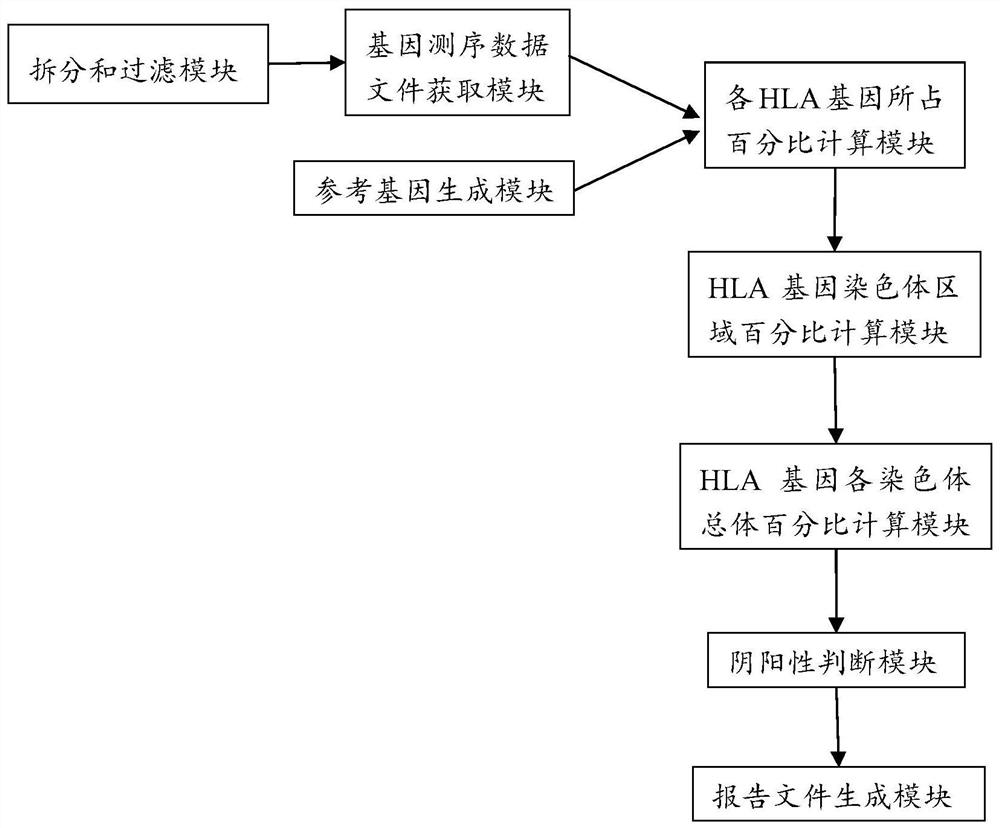
Analysis method and analysis processing device for heterozygous deletion of human HLA chromosome region
The invention belongs to the field of biological information analysis, and discloses an analysis method and an analysis processing device for heterozygous deletion of a human HLA chromosome region. Aiming at the detection requirement of post-transplantation recurrence caused by HLA Loss, the invention provides the analysis method and the analysis processing device for human HLA chromosome region heterozygous deletion based on the second-generation sequencing data, so that the process and batch operation can be conveniently carried out, the workload of manual interpretation is small, whether HLA chromosome region heterozygous deletion occurs in a sample or not can be accurately detected, and the method has important significance in detecting recurrence after transplantation caused by HLA Loss.
Owner:SHENZHEN TISSUEBANK PRECISION MEDICINE CO LTD +3
Molecular marker linked with pepper fruit cuticle deficiency genes and application thereof
ActiveCN111560459ASolve the problem of long conventional breeding cycle and easy to be affected by the environmentReduce planting sizeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyCapsicum annuum
The invention discloses a molecular marker linked with a pepper fruit cuticle synthesis gene and an application thereof. The F2 population is constructed by using wild type and mutant type chili materials. A chromosome region closely linked with a pepper fruit cuticle synthesis gene is obtained by using a BSA group positioning method, and a molecular marker is developed in a candidate interval. AnAKASP molecular marker is designed according to single base mutation, the marker is utilized to perform genotype identification on 182 single plants in the F2 population, and the coincidence rate reaches 100%. The research results not only are beneficial to identification and assisted breeding of the fruit cuticle deficiency type pepper, but also provide a basis for map-based cloning of fruit cuticle synthesis genes and analysis of a molecular mechanism of cuticle synthesis, and have a wide popularization value.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Assessment of risk of aneuploidy
ActiveUS20150337381A1Reduce in quantityLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningChromosome regionsWhole chromosome
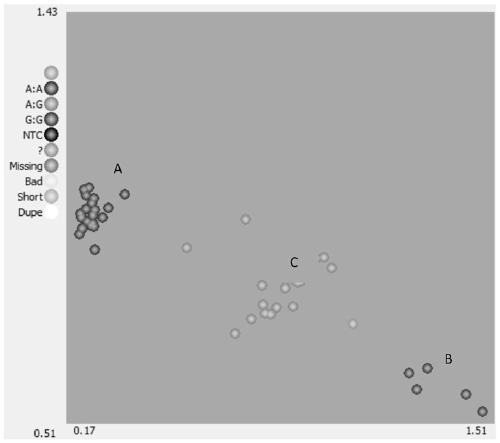
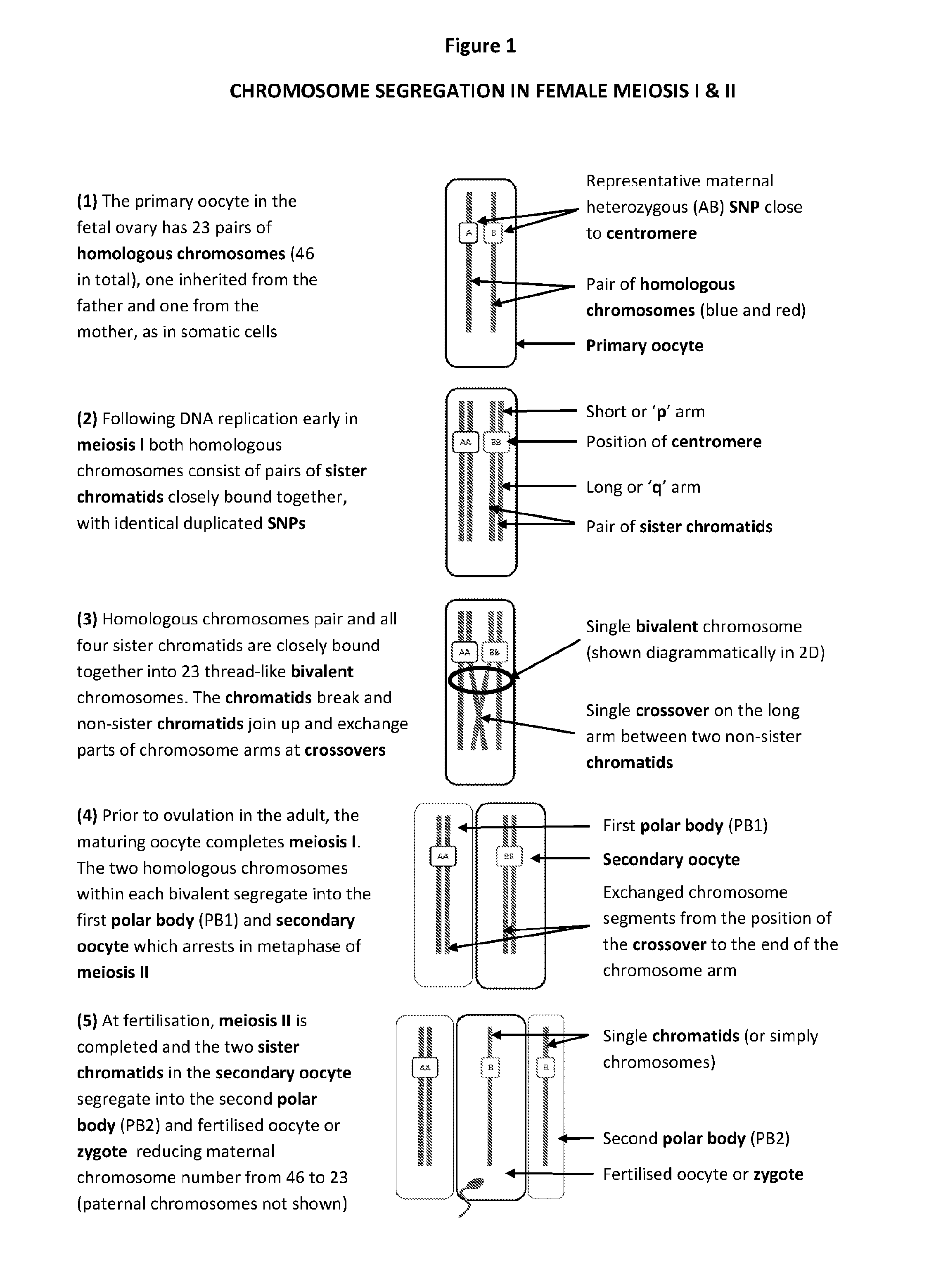
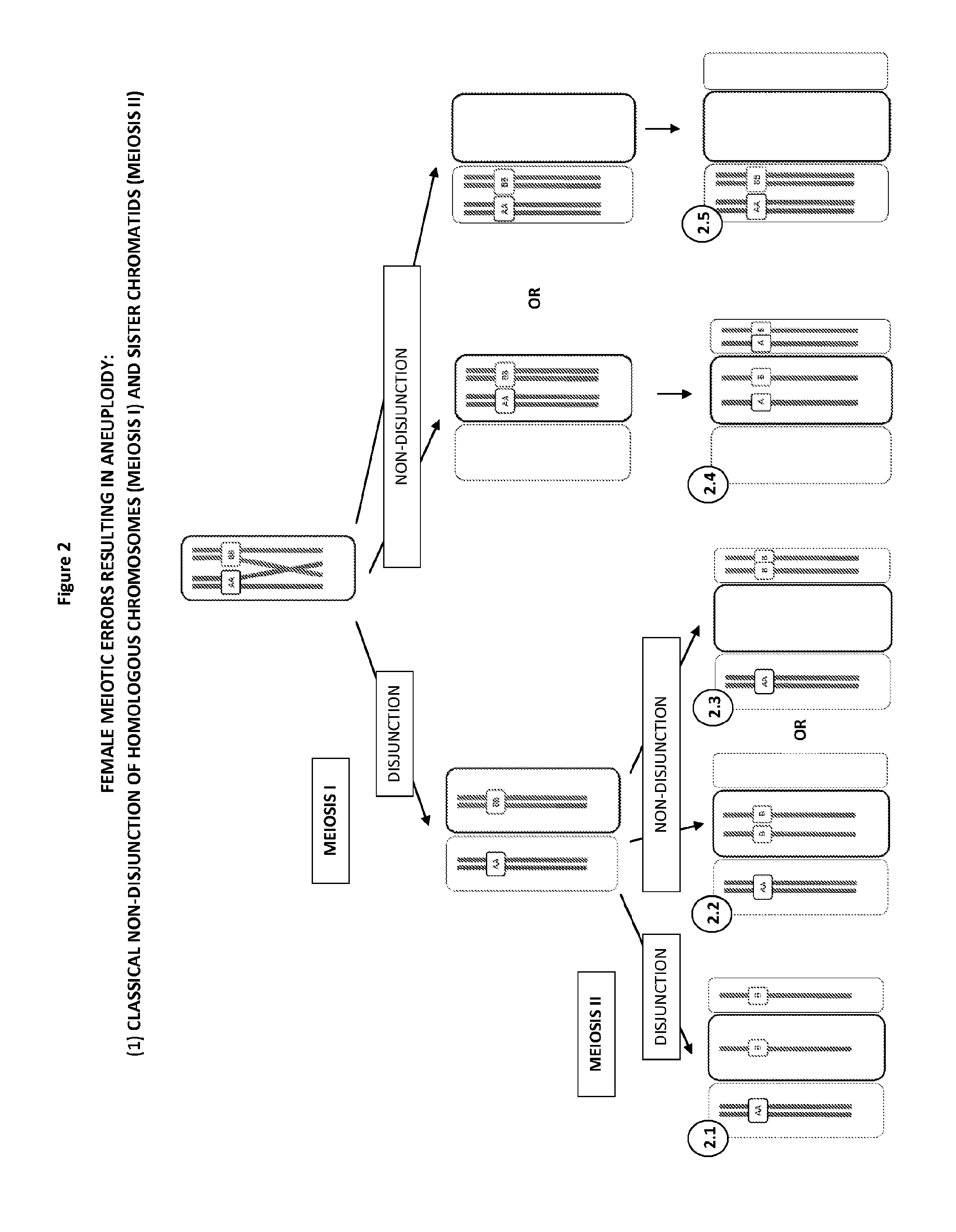
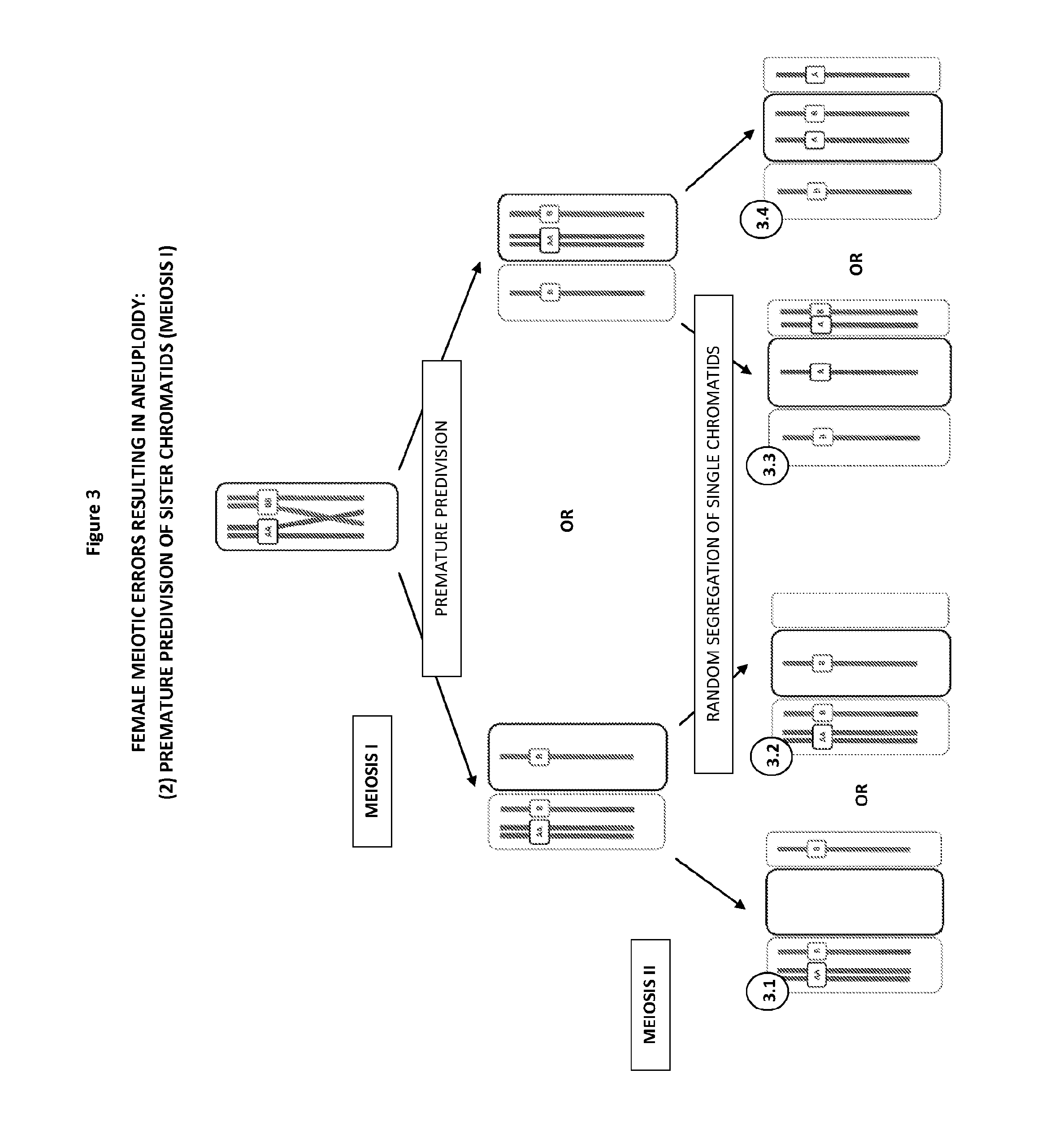
The present disclosure relates generally to methods and materials for use in detecting abnormalities of the number of whole chromosomes or chromosome regions (aneuploidy). It has particular utility for assessing the risk of aneuploidy of eggs (i.e., oocytes), fertilised eggs or embryos developed therefrom in the context of in vitro fertilisation.
Owner:HANDYSIDE ALAN
DNA sequence processing method and apparatus
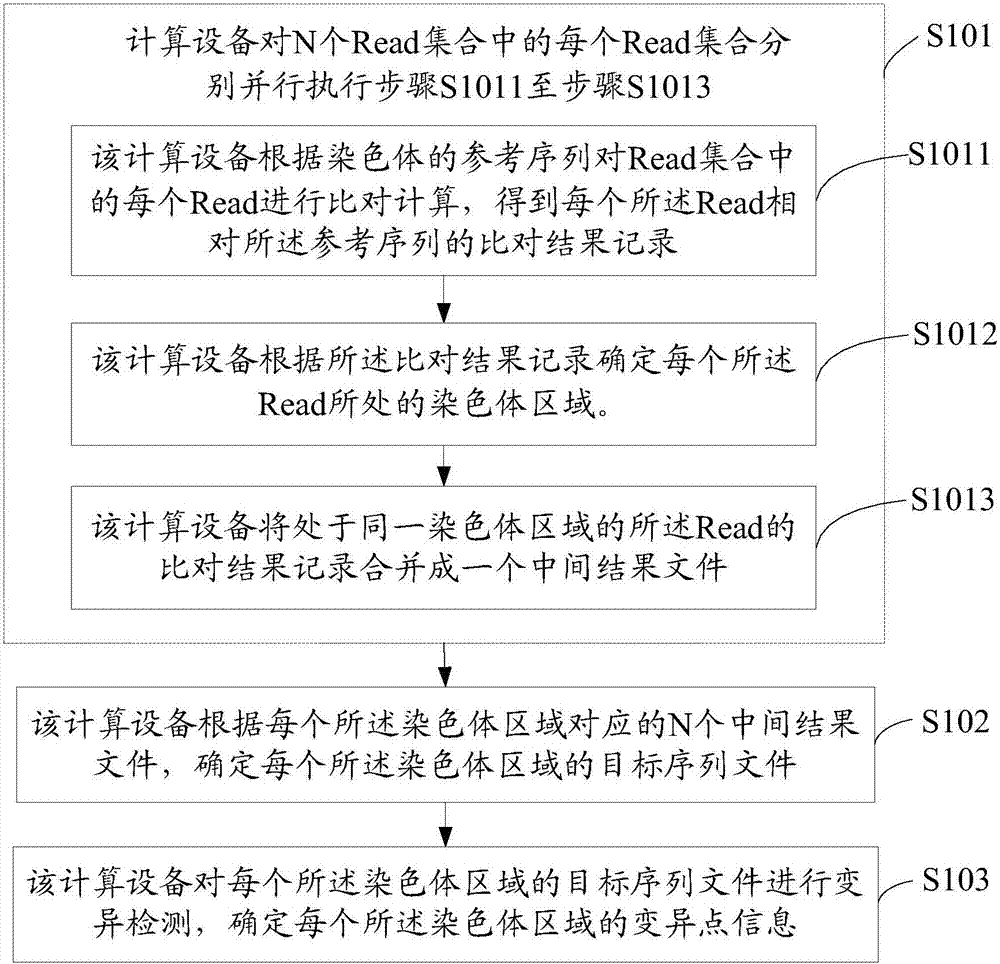
ActiveCN107403076AImprove processing efficiencyShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsSequence processingMutation detection
A DNA sequence processing method and apparatus are to resolve the problem of inefficiency in performing mutation detection on DNA samples in the prior art. The DNA sequence processing method comprises the following steps for conducting parallel operations on each Read set respectively: obtaining a record of an intercomparison result of each Read relative to the reference sequence, wherein each Read in the Read set is compared and calculated according to a chromosome reference sequence; determining the chromosome regions in which each Read is located according to the intercomparison result record; merging the intercomparison result records of Reads in the same chromosome region to form an intermediate result file, wherein each chromosome region respectively corresponds to N intermediate result files after performing the above operations on the N Read sets; determining mutation point information of each chromosome region according to the target sequence file of each chromosome region, wherein the target sequence file of each chromosome region is determined according to the N intermediate result files which correspond to each chromosome region respectively.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
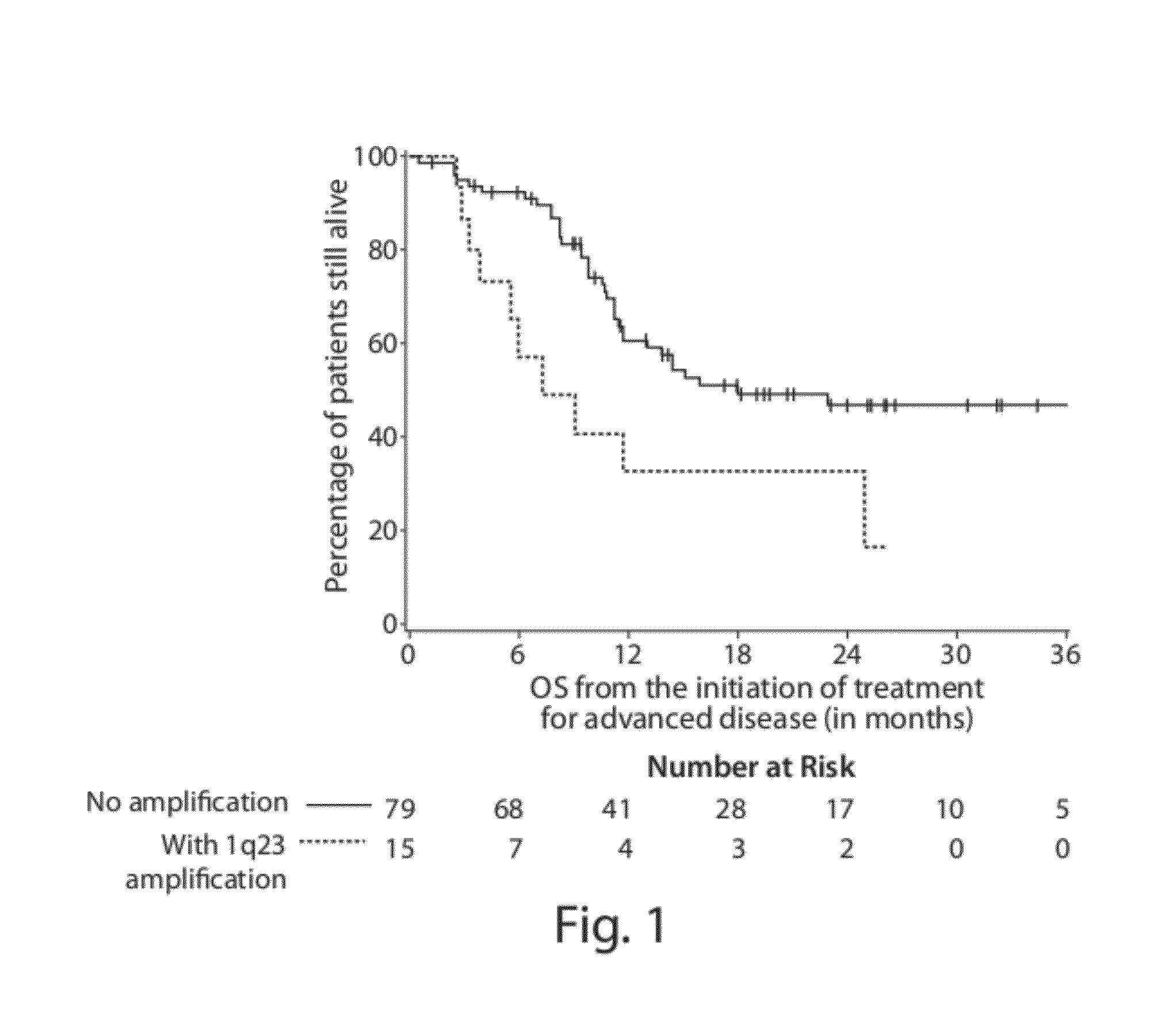
Chromosome copy number gain as a biomarker of urothelial carcinoma lethality
ActiveUS20120295807A1Improved prognosisHigh risk of developingMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningFavorable prognosisTissue sample
Diagnostic assays for medically classifying cancer patients are provided. The method comprises assessing a tissue sample of the patient for the presence of a copy number gain of chromosome regions 1q23.3 and / or 1q21.2. Copy number gain of chromosome regions 1q23.3 and / or 1q21.2 is indicative of a less favorable prognosis as compared to the prognosis if there was no copy number gain in the same regions.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Optimizing genome-wide mutation analysis of chromosomes and genes
InactiveUS20060031051A1Raise the ratioOptimal lifelong careMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesCrowdsChromosome regions
A method of genome-wide testing of gene copy number at the genetically most important loci to determine whether the gene and / or its selected larger surrounding chromosome region is rearranged to result in an unbalanced abnormality in one or more subjects, said method including selecting multiple gene loci of said DNAs to be examined in said test, conducting said test, and comparing the number of copies at each locus tested. by quantification of total gene target number to determine the relative number of each polymorphic sequence detected to assure that each important tested sequence is distinguished from the other alleles at the same locus. A method of detecting the highest number of abnormal patients possible based upon the number of test sites available in a protocol including selecting the most common genetic disease-causing mutations in a population by frequency, selecting and identifying the most common mutations in each by frequencies, multiplying the two frequencies together to get a frequency product which is the frequency of each mutation in the population, and ordering the frequency products beginning with the most common to prioritize which are the most common to detect the largest number of genetic abnormalities possible per test. Depending upon the stage of the life cycle, both of the methods can be done together or in sequence.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT OF AKRON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com