Patents
Literature
107 results about "Its region" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
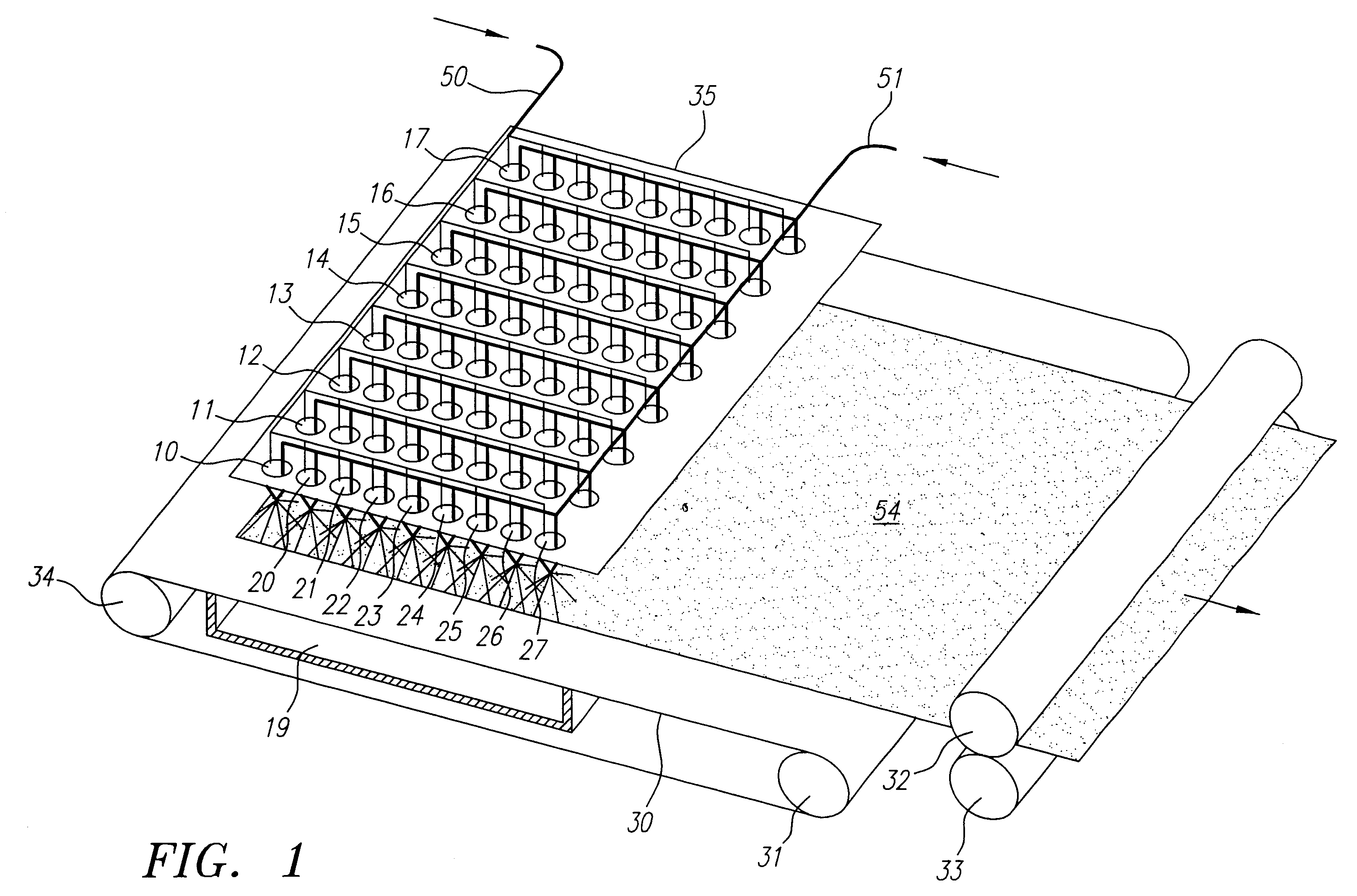
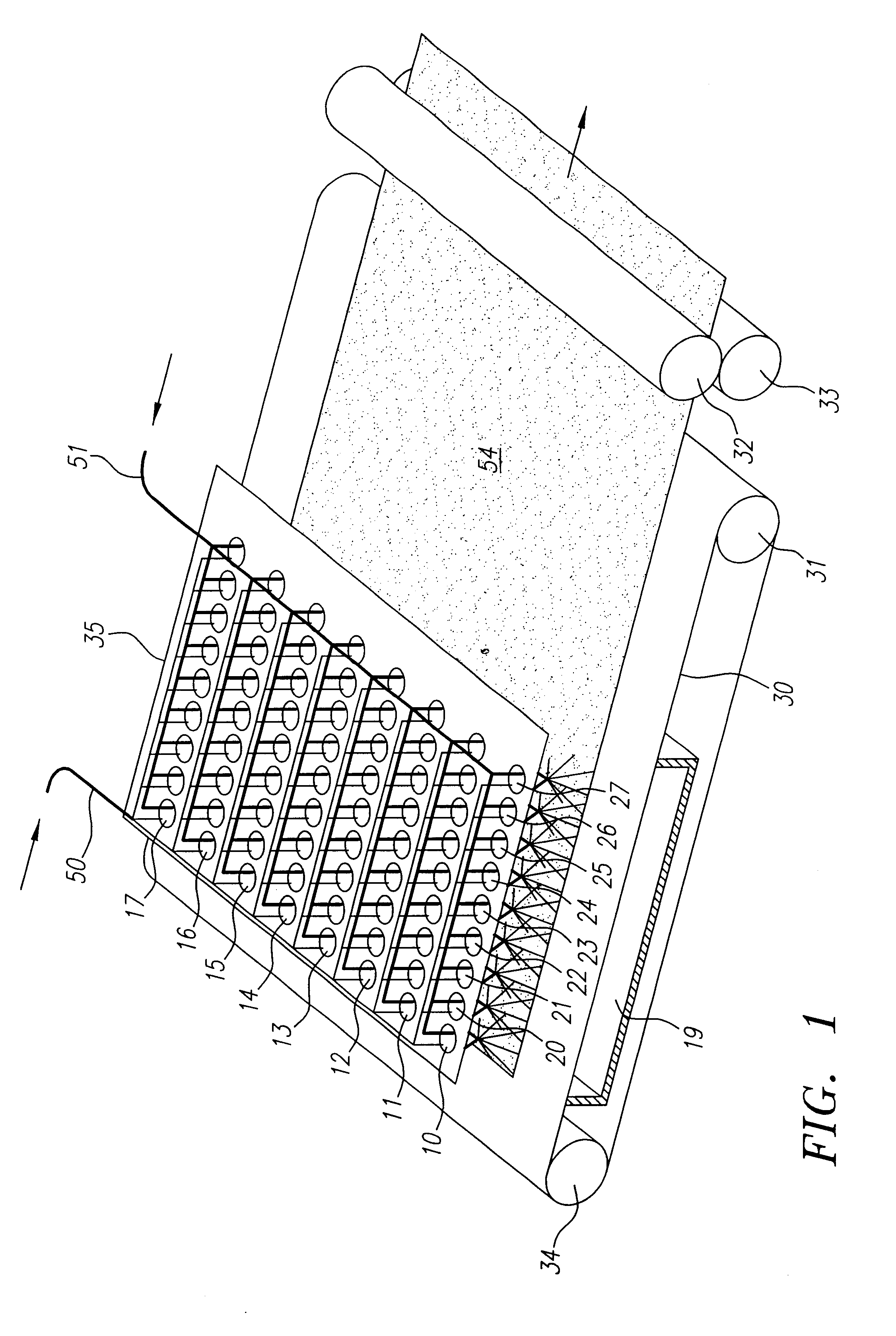
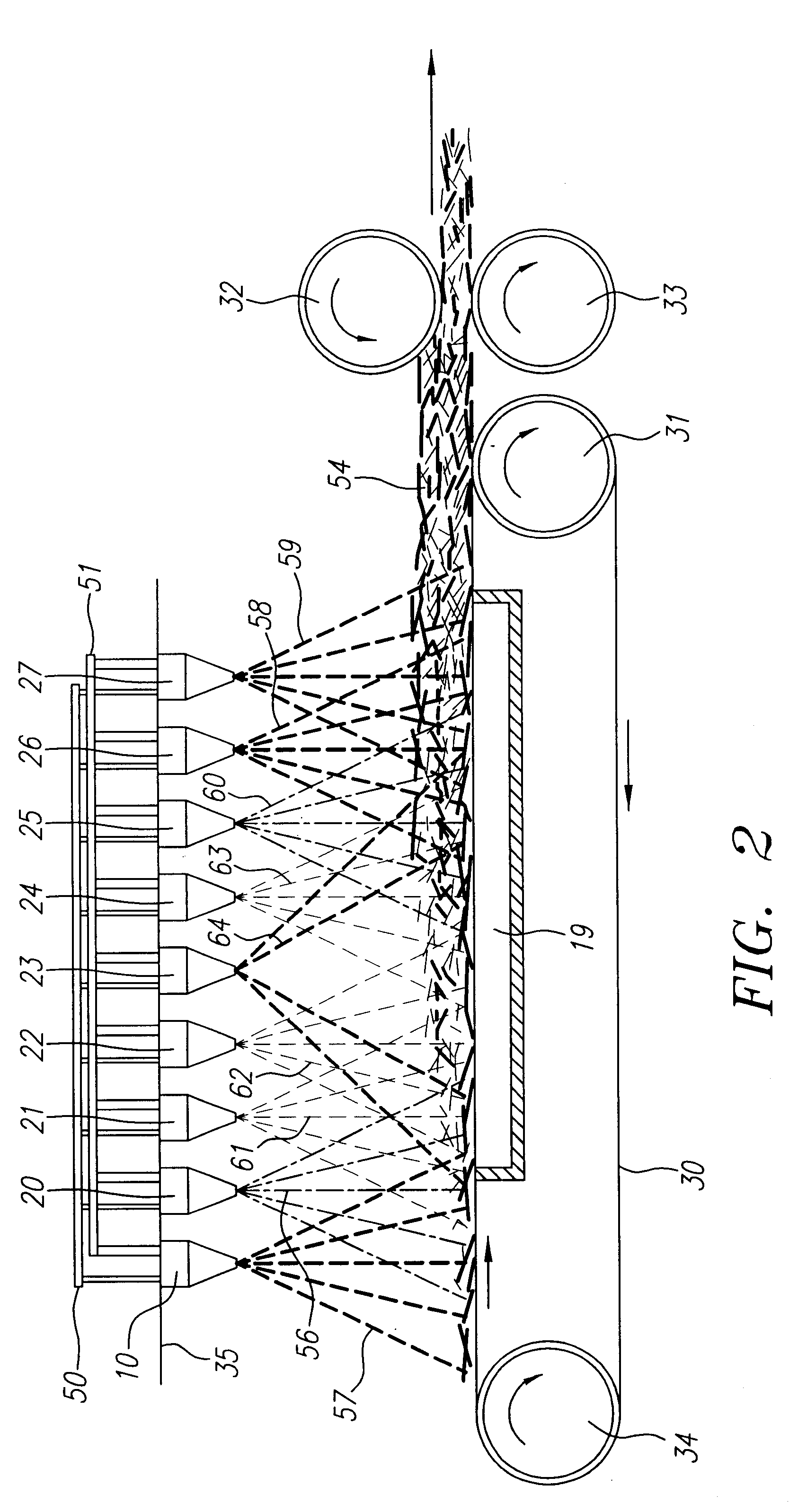
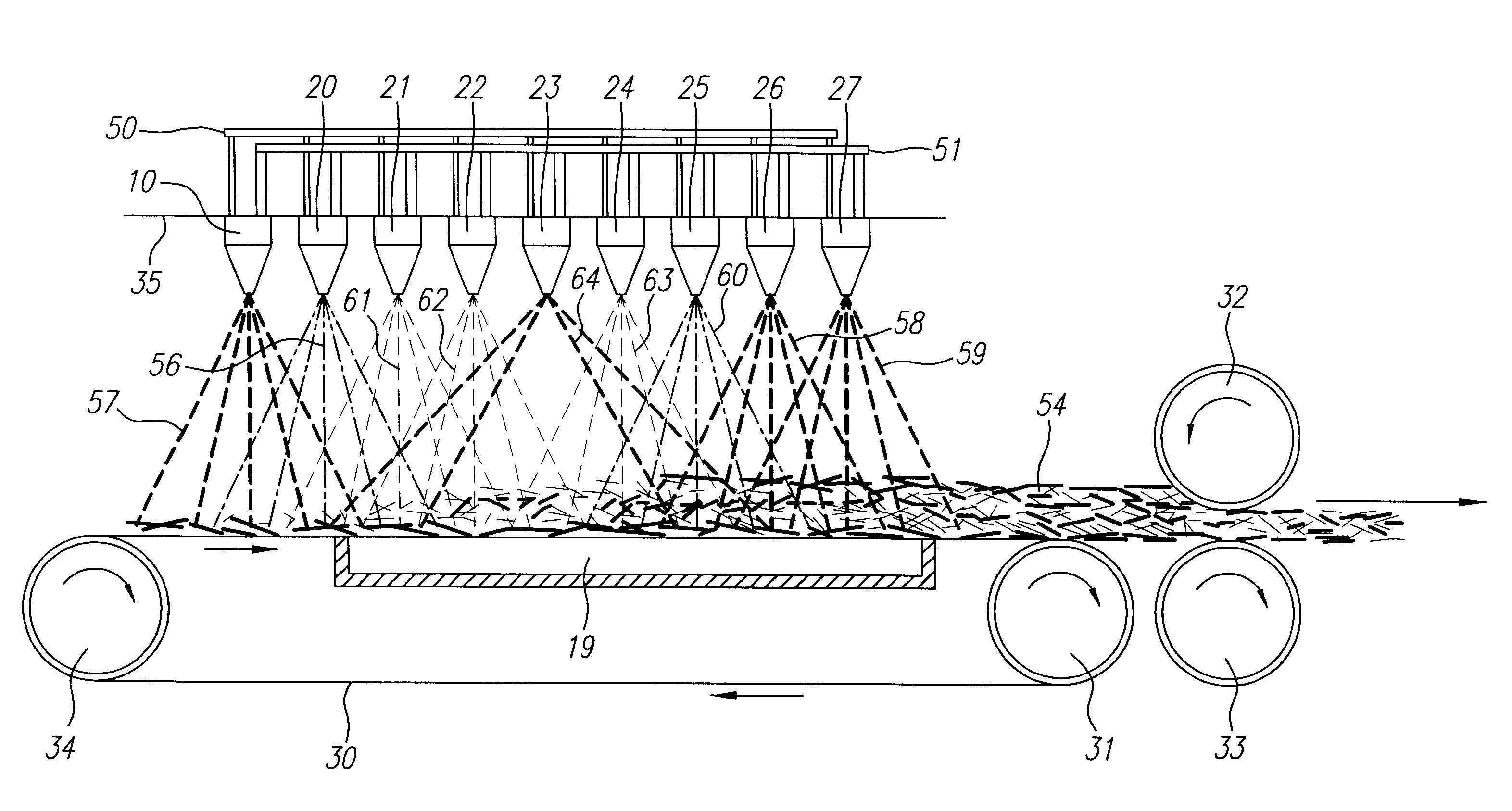
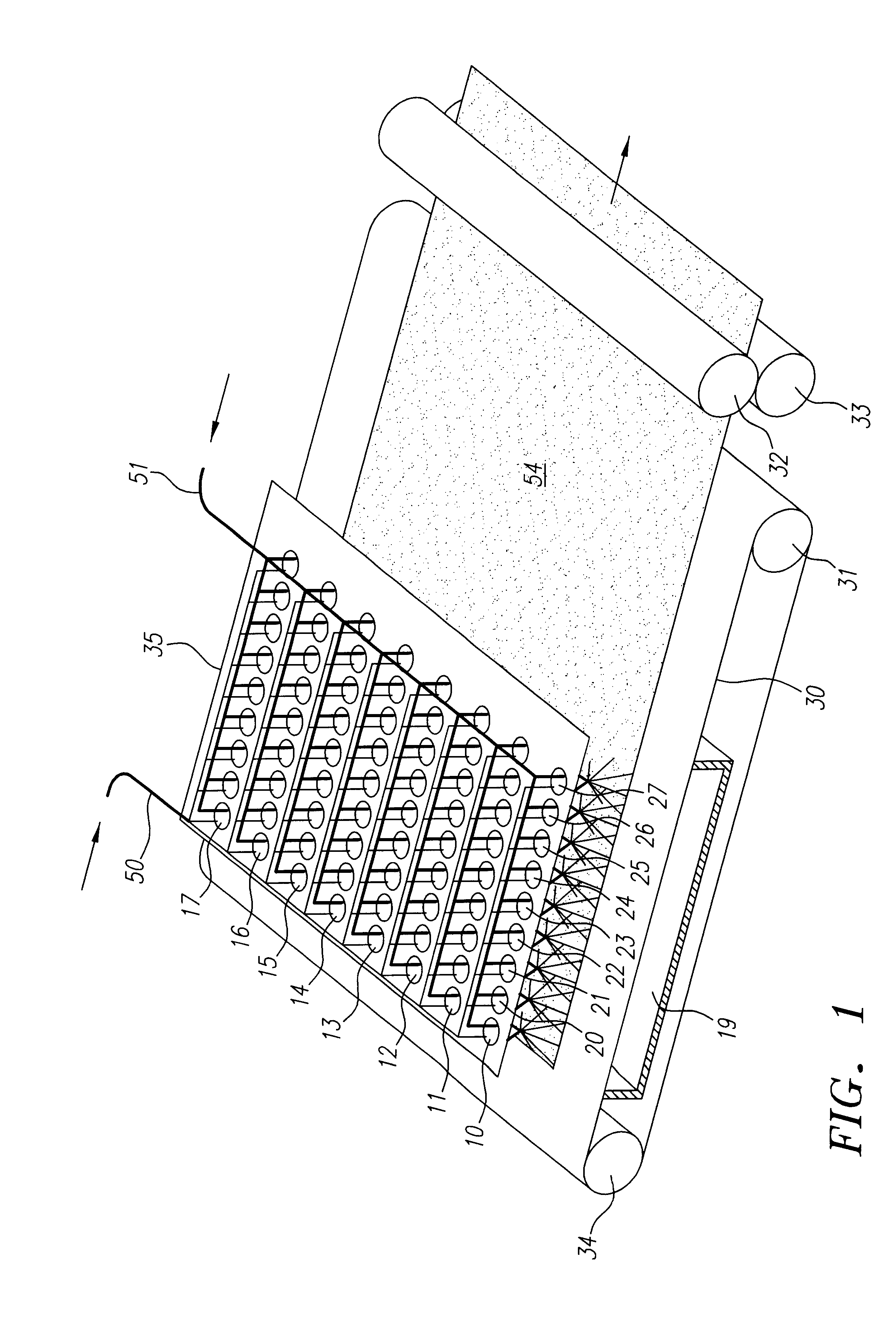
Method and apparatus for producing high efficiency fibrous media incorporating discontinuous sub-micron diameter fibers, and web media formed thereby
InactiveUS6315806B1Increase distanceReduce resistanceFilament/thread formingLoose filtering material filtersMean diameterFiber
A composite filtration medium web of fibers containing a controlled dispersion of a mixture of sub-micron and greater than sub-micron diameter polymeric fibers is described. The filtration medium is made by a two dimensional array of cells, each of which produces a single high velocity two-phase solids-gas jet of discontinuous fibers entrained in air. The cells are arranged so that the individual jets are induced to collide in flight with neighboring jets in their region of fiber formation, to cause the individual nascent fibers of adjacent jets to deform and become entangled with and partially wrap around each other at high velocity and in a localized fine scale manner before they have had an opportunity to cool to a relatively rigid state. The cells are individually adjusted to control the mean diameters, lengths and trajectories of the fibers they produce. Certain cells are adjusted to generate a significant percentage of fibers having diameters less than one micron diameter, and which are relatively shorter in length and certain other cells are adjusted to generate a significant percentage of structure-forming reinforcing fibers having diameters greater than one micron diameter which are relatively longer in length. By employing appropriate close positioning and orientation of the cells in the array, the sub-micron fibers are caused to promptly entangle with and partially wrap around the larger reinforcing fibers. The larger fibers thereby trap and immobilize the sub-micron diameter fibers in the region of formation, to minimize the tendency of sub-micron diameter fibers to clump, agglomerate, or rope together in flight. Also, the larger fibers in flight are made to form a protective curtain to prevent the sub-micron fibers from being carried off by stray air currents.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
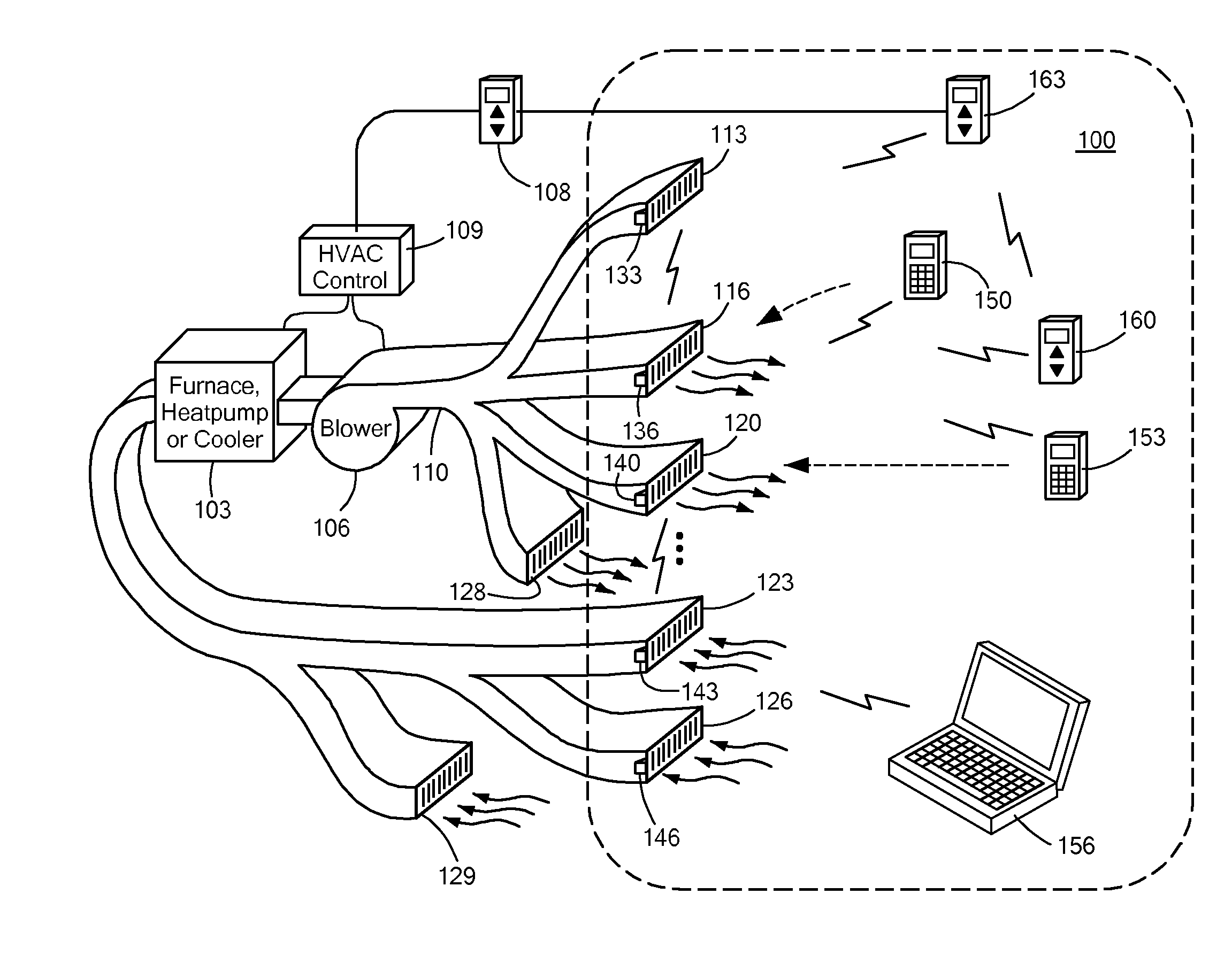
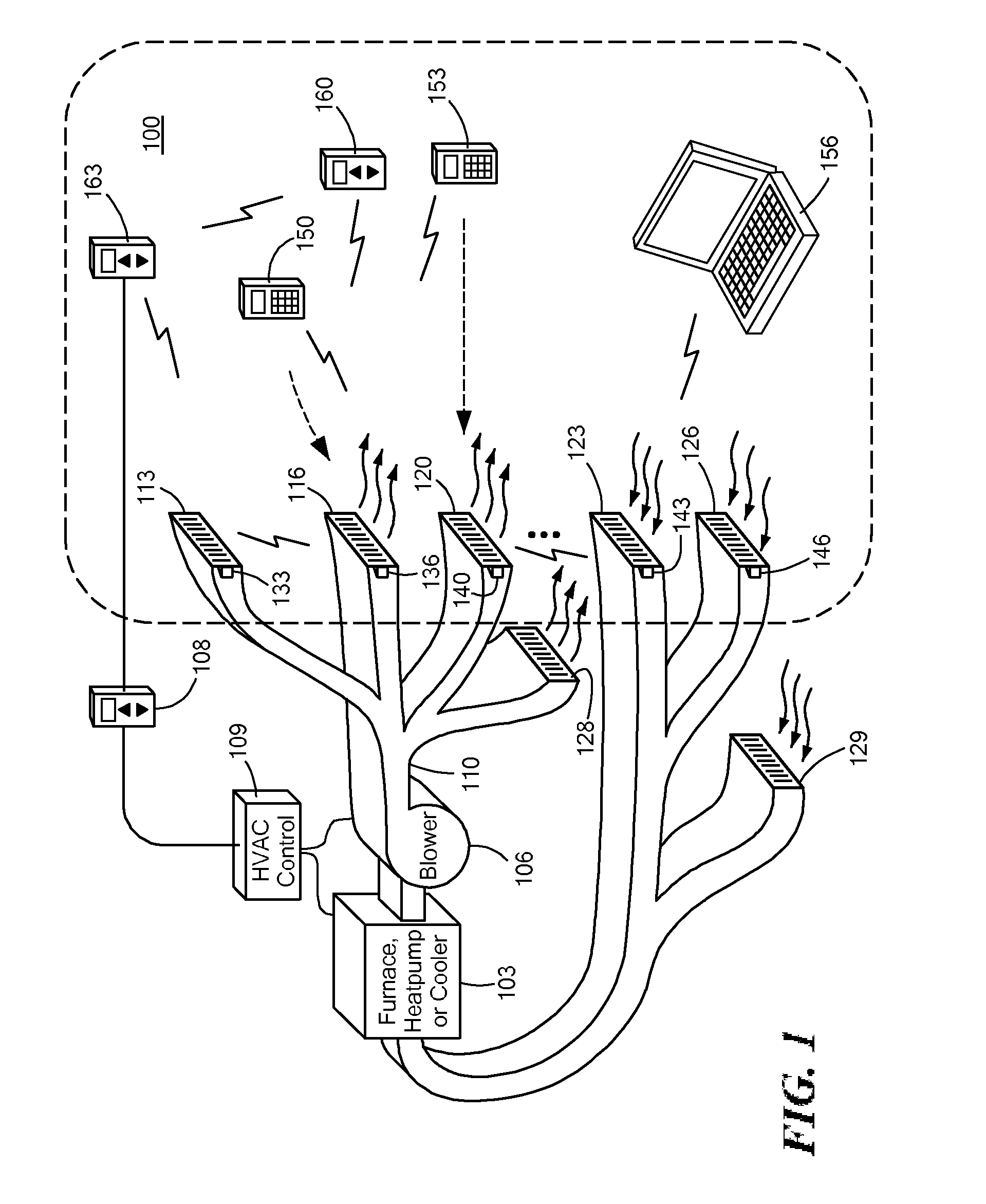
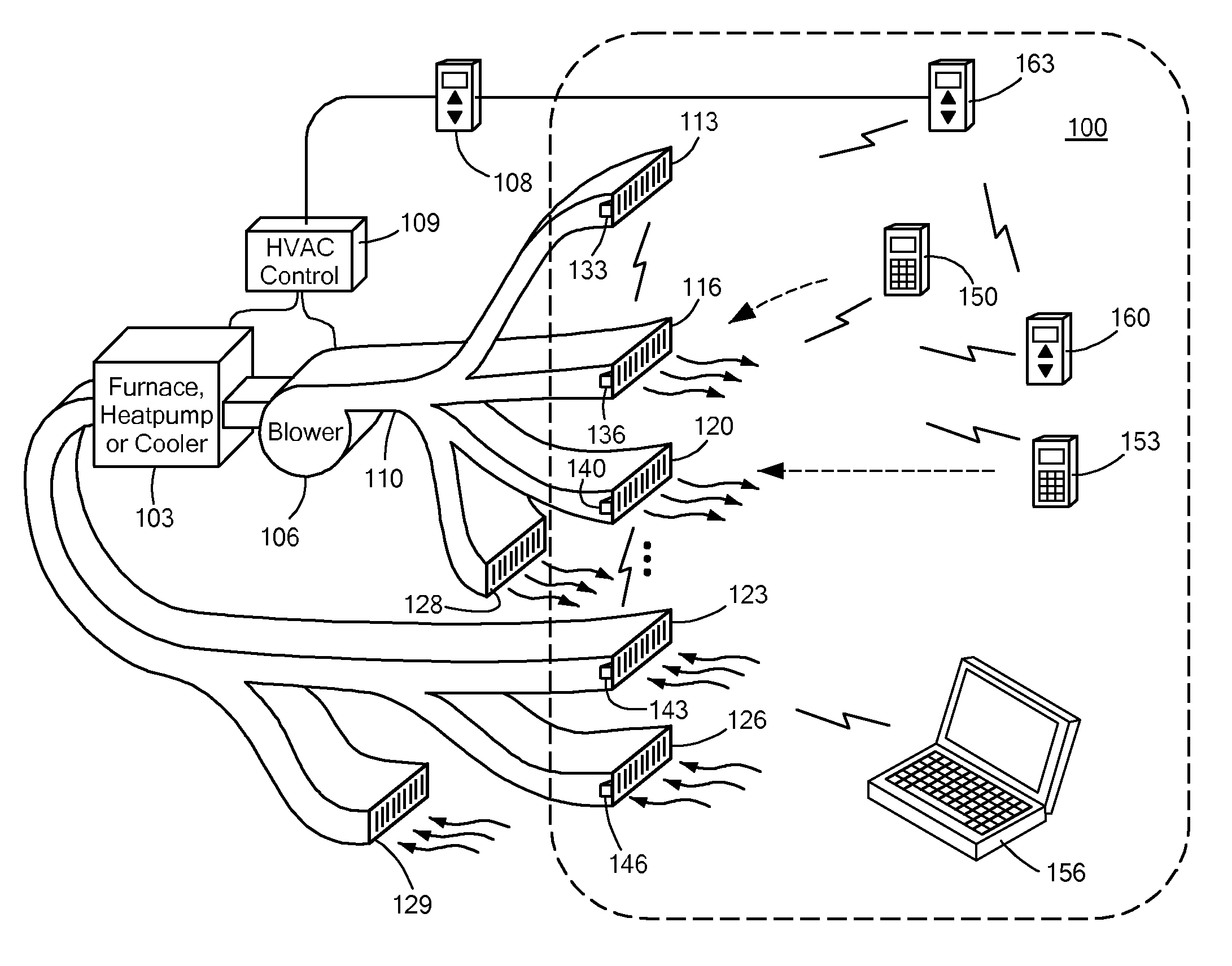
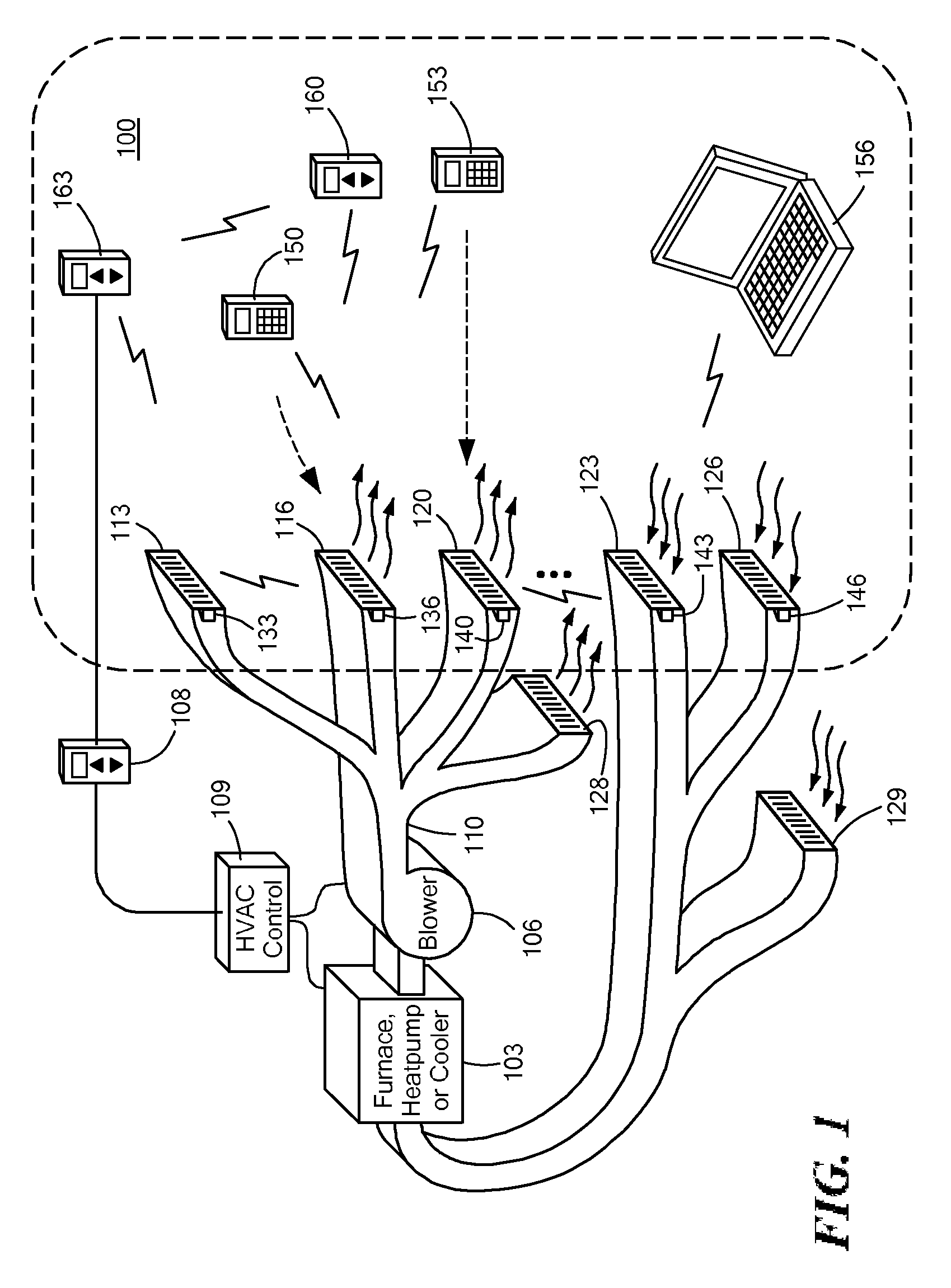
Automatically Balancing Register for HVAC Systems
Distributed nodes, such as intelligent register controllers, of a heating, ventilating and / or air conditioning (HVAC) system wirelessly communicate with each other on a peer-to-peer basis, forming a network, and collectively control the HVAC system, without a central controller. The intelligent register controllers collectively control the amount of conditioned air introduced into each region. Each node may base its operation at least in part on information about one or more (ideally all) of the other nodes. Each intelligent register controller automatically determines how much conditioned air to allow into its region, or how much return air to allow to be withdrawn from its region, based on information collected by the register controller, such as: current temperature of the region; desired temperature of the region; calculated amount of conditioned air required to change the region's temperature to the desired temperature; temperature of conditioned air begin supplied by a duct to the register; current time, day of week, vacation or other schedule data; temperatures of other regions and their respective desired temperatures; calculated amounts of air required to be supplied or withdrawn by the other controlled registers to change their respective regions' temperatures to their desired temperatures; or combinations thereof. Each register controller automatically determines when and to what extent to operate its respective controllable damper.
Owner:ZONER
Method and apparatus for producing high efficiency fibrous media incorporating discontinuous sub-micron diameter fibers, and web media formed thereby
InactiveUS6183670B1Increase collisionImprove compactionFilament/thread formingAuxillary shaping apparatusMean diameterFiber
A composite filtration medium web of fibers containing a controlled dispersion of a mixture of sub-micron and greater than sub-micron diameter polymeric fibers is described. The filtration medium is made by a two dimensional array of cells, each of which produces a single high velocity two-phase solids-gas jet of discontinuous fibers entrained in air. The cells are arranged so that the individual jets are induced to collide in flight with neighboring jets in their region of fiber formation, to cause the individual nascent fibers of adjacent jets to deform and become entangled with and partially wrap around each other at high velocity and in a localized fine scale manner before they have had an opportunity to cool to a relatively rigid state. The cells are individually adjusted to control the mean diameters, lengths and trajectories of the fibers they produce. Certain cells are adjusted to generate a significant percentage of fibers having diameters less than one micron diameter, and which are relatively shorter in length and certain other cells are adjusted to generate a significant percentage of structure-forming reinforcing fibers having diameters greater than one micron diameter which are relatively longer in length. By employing appropriate close positioning and orientation of the cells in the array, the sub-micron fibers are caused to promptly entangle with and partially wrap around the larger reinforcing fibers. The larger fibers thereby trap and immobilize the sub-micron diameter fibers in the region of formation, to minimize the tendency of sub-micron diameter fibers to clump, agglomerate, or rope together in flight. Also, the larger fibers in flight are made to form a protective curtain to prevent the sub-micron fibers from being carried off by stray air currents.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
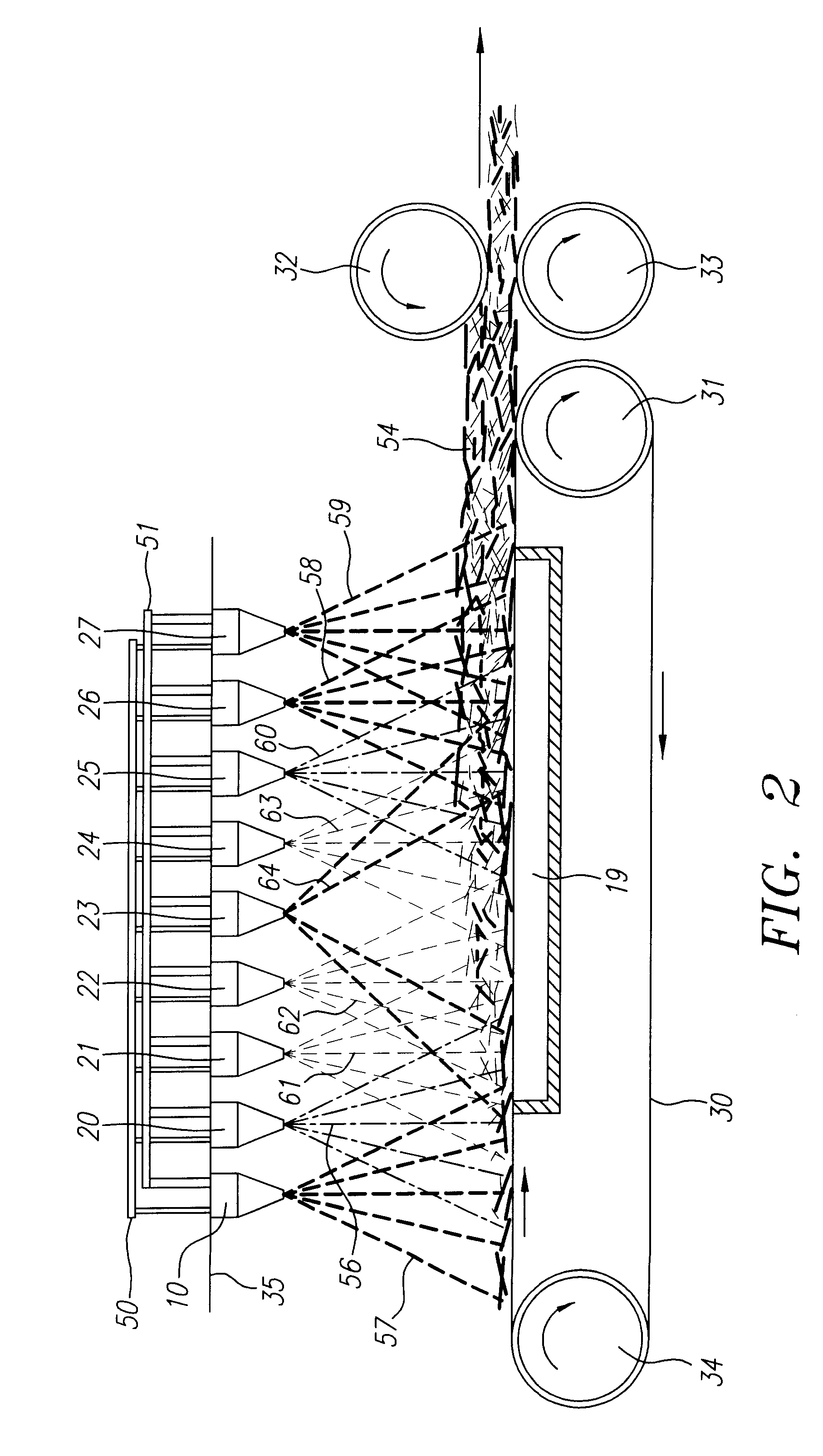
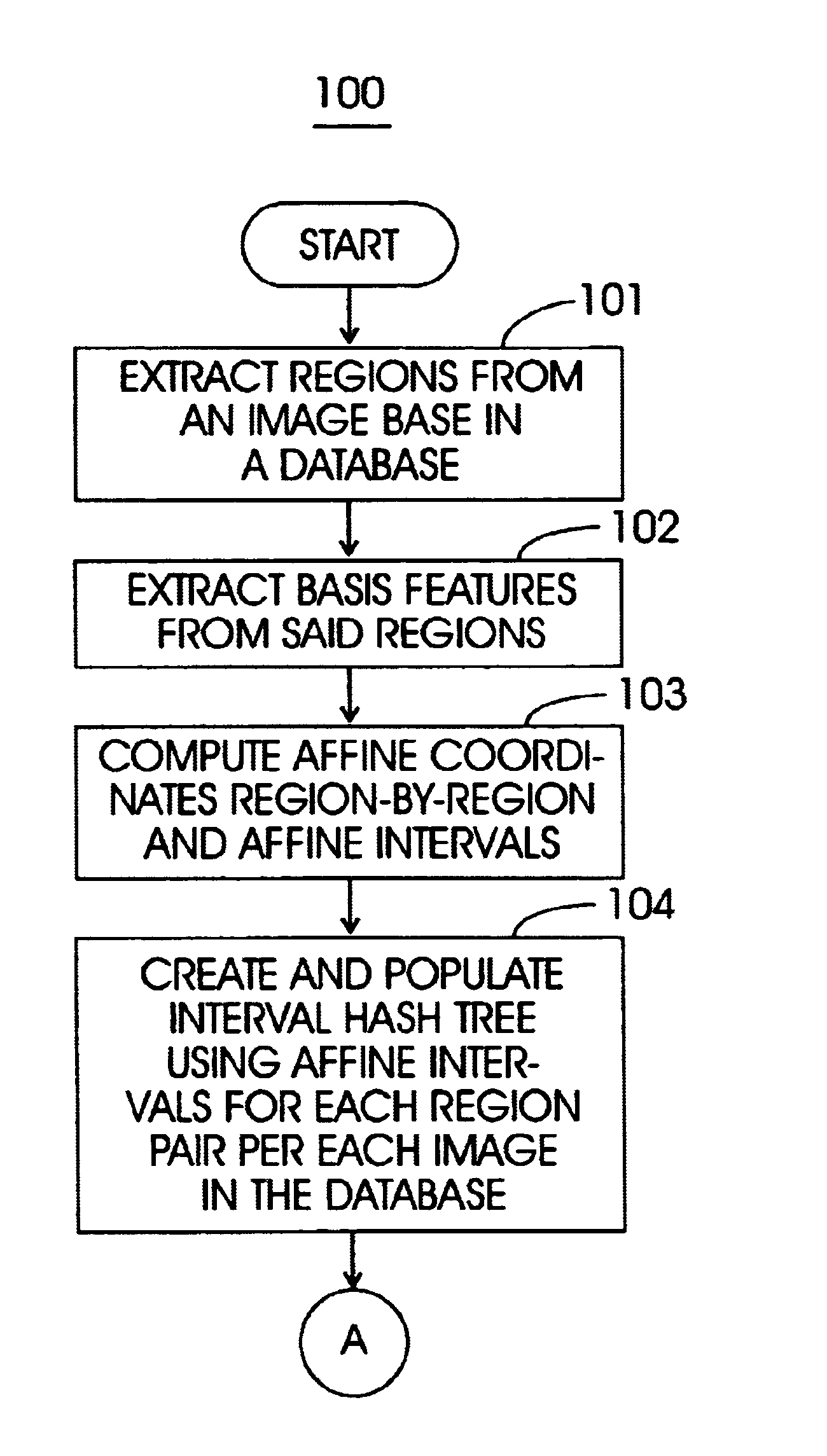
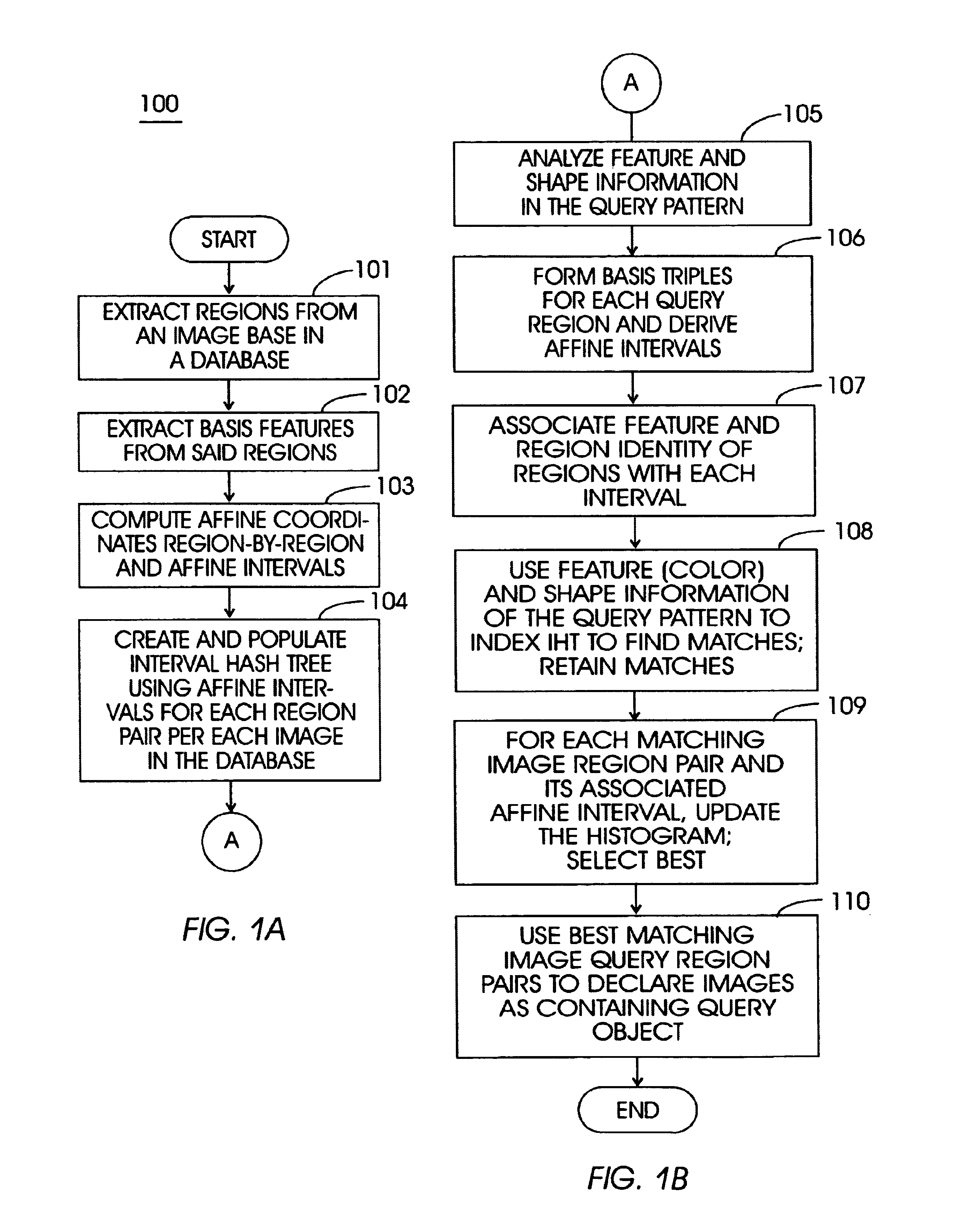
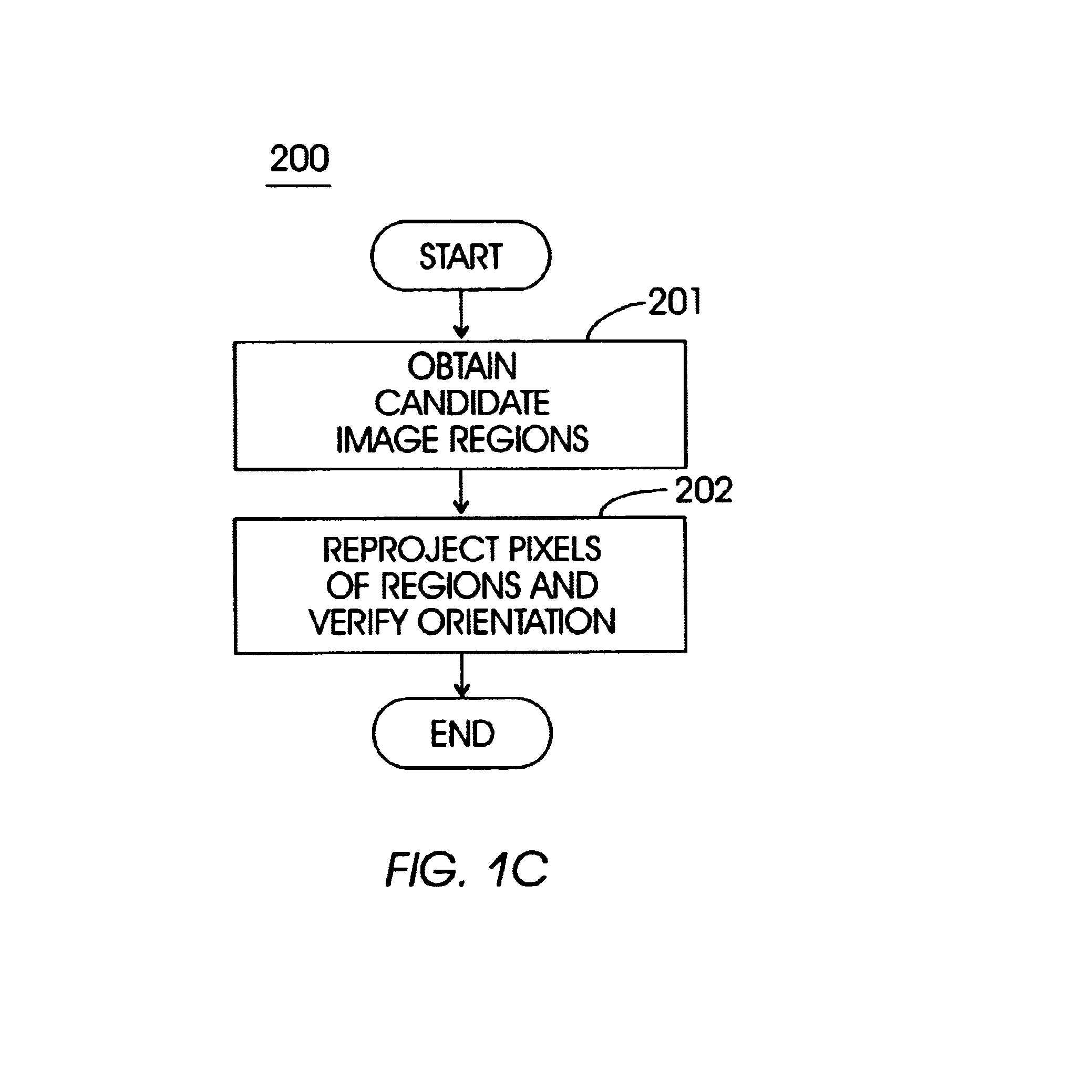
Method and apparatus for locating multi-region objects in an image or video database
InactiveUS6691126B1Robust methodDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsIts regionData mining
A method (and system) for specifying the region layout of objects in an affine invariant manner as a set of affine intervals between pairs of regions, includes representing database and query regions using affine intervals along with their region identity, matching query region layout to layout of database image regions using an index structure, and retrieving relevant images of the database by hashing for dominant hit regions in the index structure.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for supporting image creating and storing of the same
InactiveUS7139796B2Simple systemMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationIts regionMultimedia
At least a part of the three-dimensional community space is divided into regions and the right to use a region is sold at a particular price to a user who wants to obtain it. A user having the right to use a region is allowed to build an element such as a building or a signboard in the region via an avatar. If an attractive signboard with high originally is built, the region in which the signboard is built and also nearby regions become popular. As a result, the economic value of such a region becomes high. If desired, a user is allowed to resell his / her region via auction.
Owner:SONY CORP
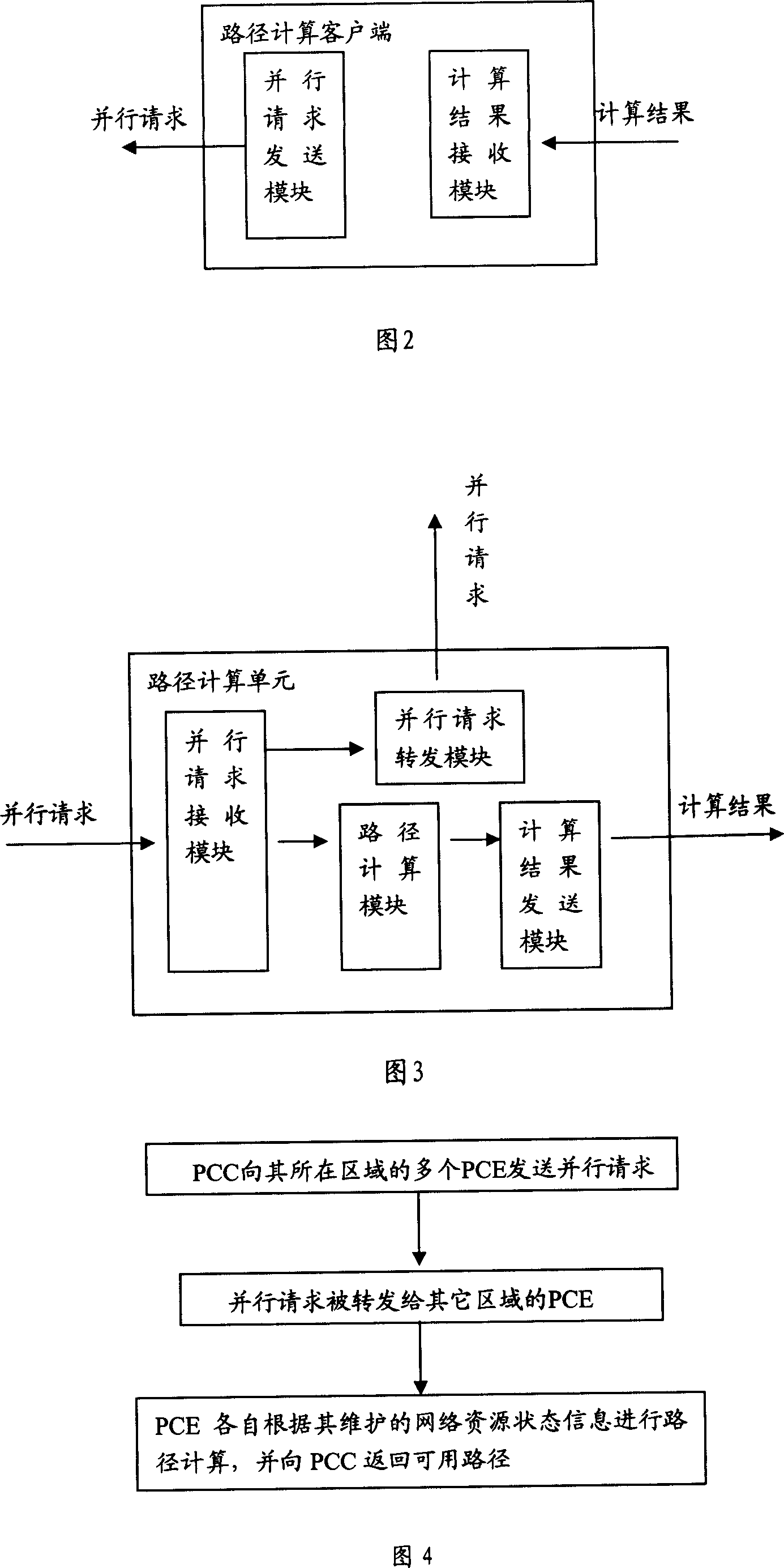
Flow engineering full network counting method and system between regions
This invention relates to a whole network computation method and a system for flow engineering among regions including the following steps: A, a computation client end of said route sends a parallel flow engineering route computing request to multiple route computation units in its region, B, said request is transferred to other route computation units of other regions, C, the uits receiving the request carries out route computation according to its maintained network resource state information and returns available routes to the route computation client end, besides, this invention also provides a whole net computing system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Automatically balancing register for HVAC systems
Distributed nodes, such as intelligent register controllers, of a heating, ventilating and / or air conditioning (HVAC) system wirelessly communicate with each other on a peer-to-peer basis, forming a network, and collectively control the HVAC system, without a central controller. The intelligent register controllers collectively control the amount of conditioned air introduced into each region. Each node may base its operation at least in part on information about one or more (ideally all) of the other nodes. Each intelligent register controller automatically determines how much conditioned air to allow into its region, or how much return air to allow to be withdrawn from its region, based on information collected by the register controller, such as: current temperature of the region; desired temperature of the region; calculated amount of conditioned air required to change the region's temperature to the desired temperature; temperature of conditioned air begin supplied by a duct to the register; current time, day of week, vacation or other schedule data; temperatures of other regions and their respective desired temperatures; calculated amounts of air required to be supplied or withdrawn by the other controlled registers to change their respective regions' temperatures to their desired temperatures; or combinations thereof. Each register controller automatically determines when and to what extent to operate its respective controllable damper.
Owner:ZONER
Trichoderma spore powder as well as preparation method and application thereof
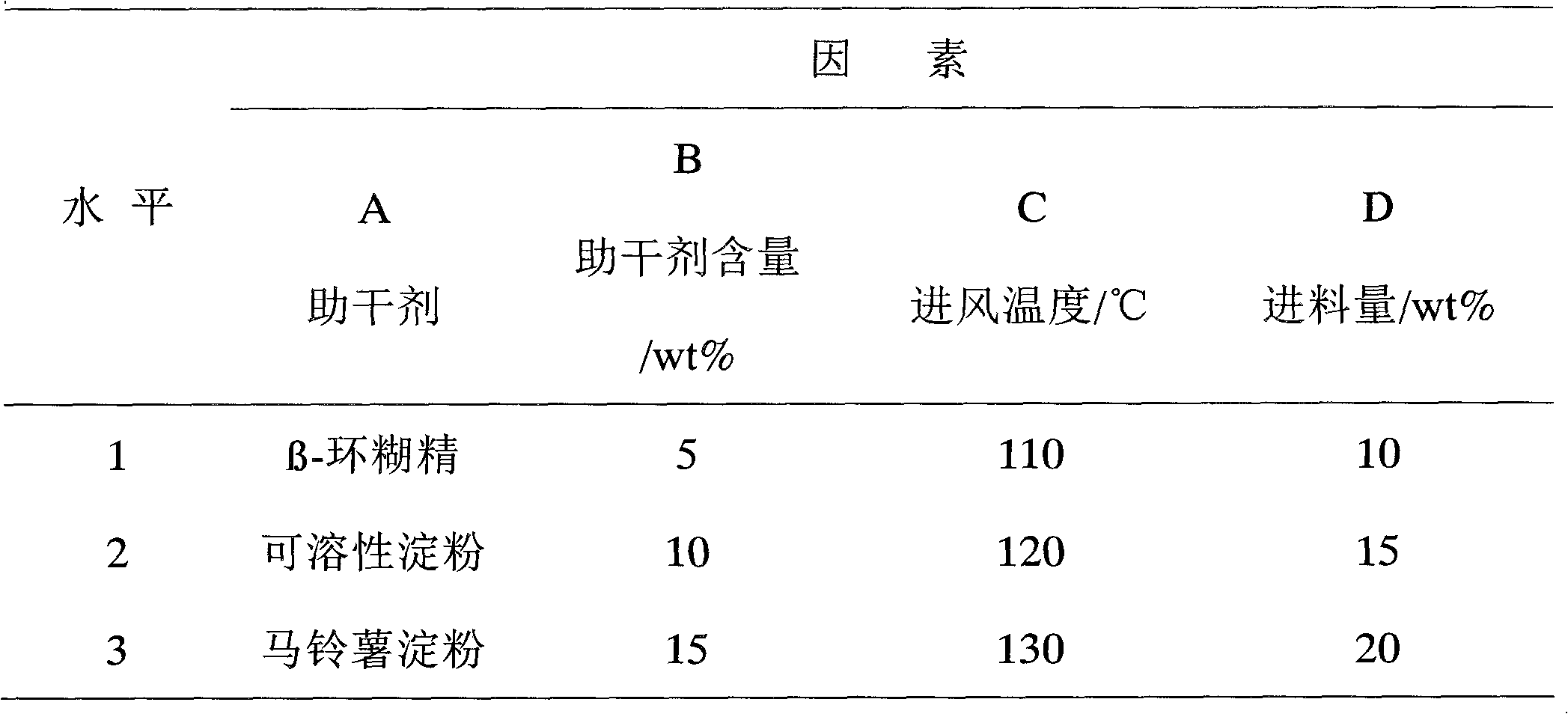
InactiveCN102067885AInhibitionTo achieve the effect of preventionBiocideFungicidesMicroorganismSpore
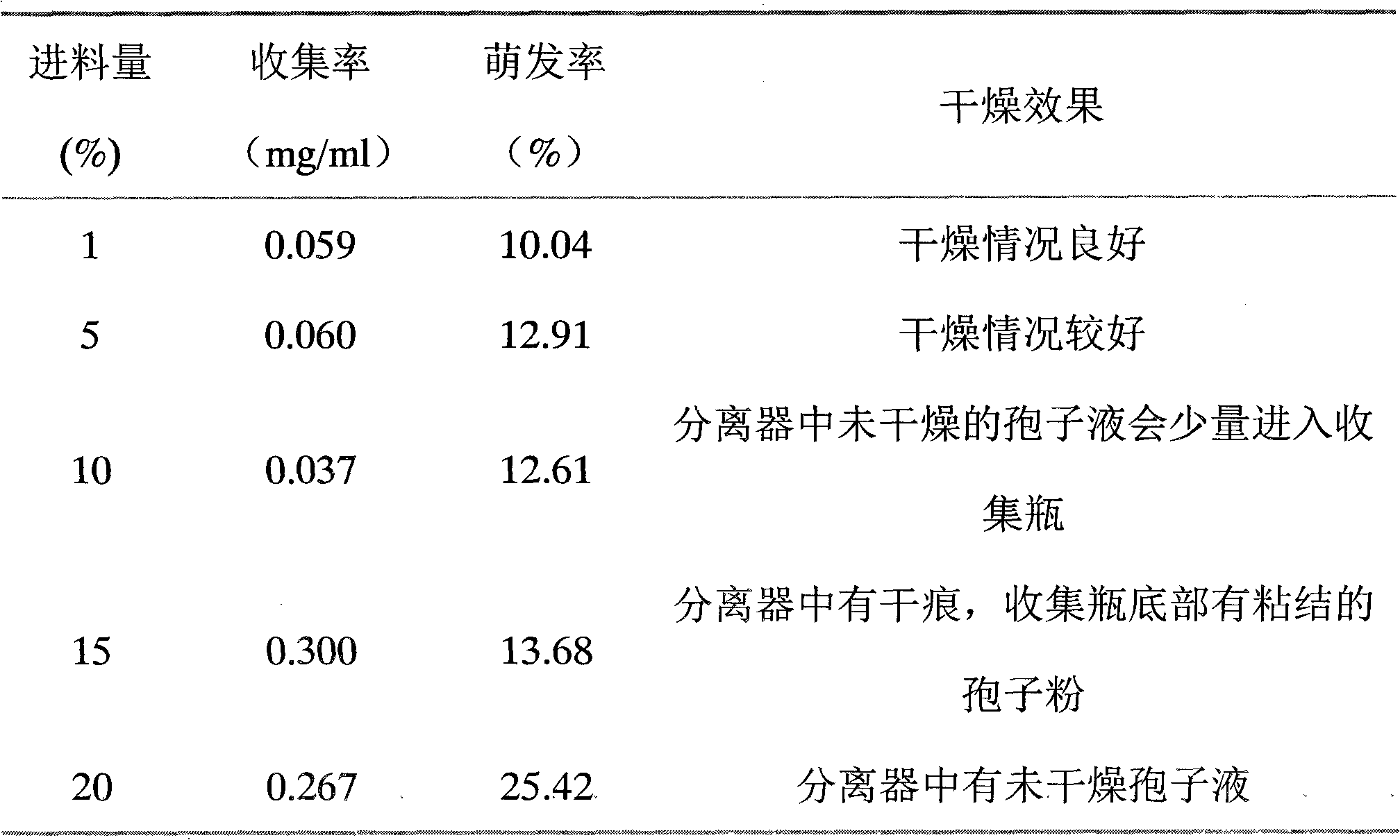
The invention discloses a trichoderma spore powder as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The trichoderma spore powder contains trichoderma spore powder and a drying aid, wherein the trichoderma spore powder is the spore powder of Trichoderma sperellum T1 which is preserved in the general microorganism center of CCCCM (China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms) and has the preservation number of CGMCC NO: 3531 and a rDNA ITS region segment sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1; the drying aid is one or more of beta-cyclodextrin, potato starch and soluble starch. The trichoderma spore powder has an effective prevention and control effect on banana vasicular wilt, and has a remarkable antagonism effect on various pathogenic funguses, especially on soil-borne funguses. The preparation time is saved with the preparation method of the trichoderma spore powder, which can be used for preparing the trichoderma spore powder which has high density, high germination rateand high drying efficiency and is easy to store, transport and use.
Owner:惠州市南天生物科技有限公司 +2
System and method for forming an image on a substrate
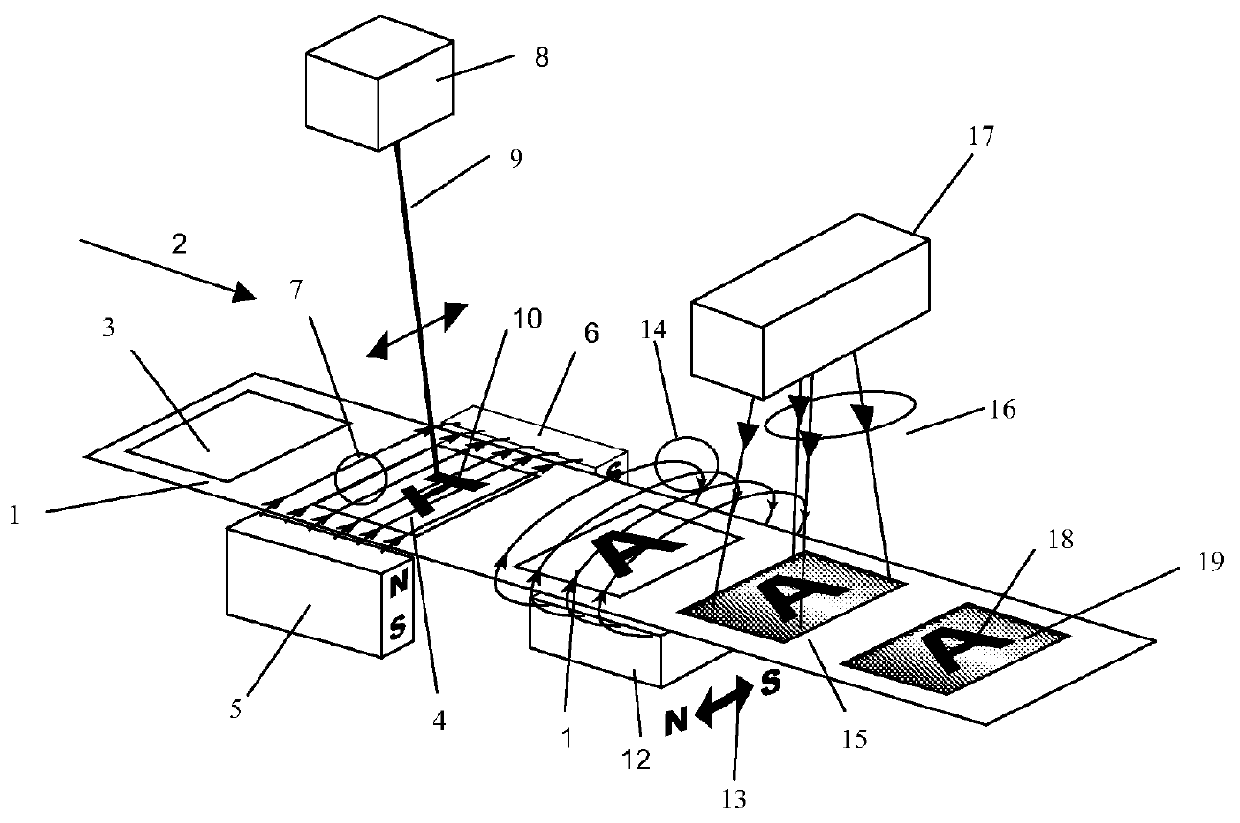
A scanning laser having a wavelength compatible with a coating binder so as to cure it as the laser scans and irradiates the coating on a moving web. A system and method for curing flakes by providing a scanning laser which scans across a moving coated substrate in a magnetic field allows images to be formed as magnetically aligned flakes are cured into a fixed position. The images have regions of cured aligned flakes. The scanning laser cures the magnetically aligned flakes within it region it irradiates. Alternatively an array of lasers can be used wherein individual lasers can be switched on and off to fix irradiated coating as a moving web is moved at a high speed.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
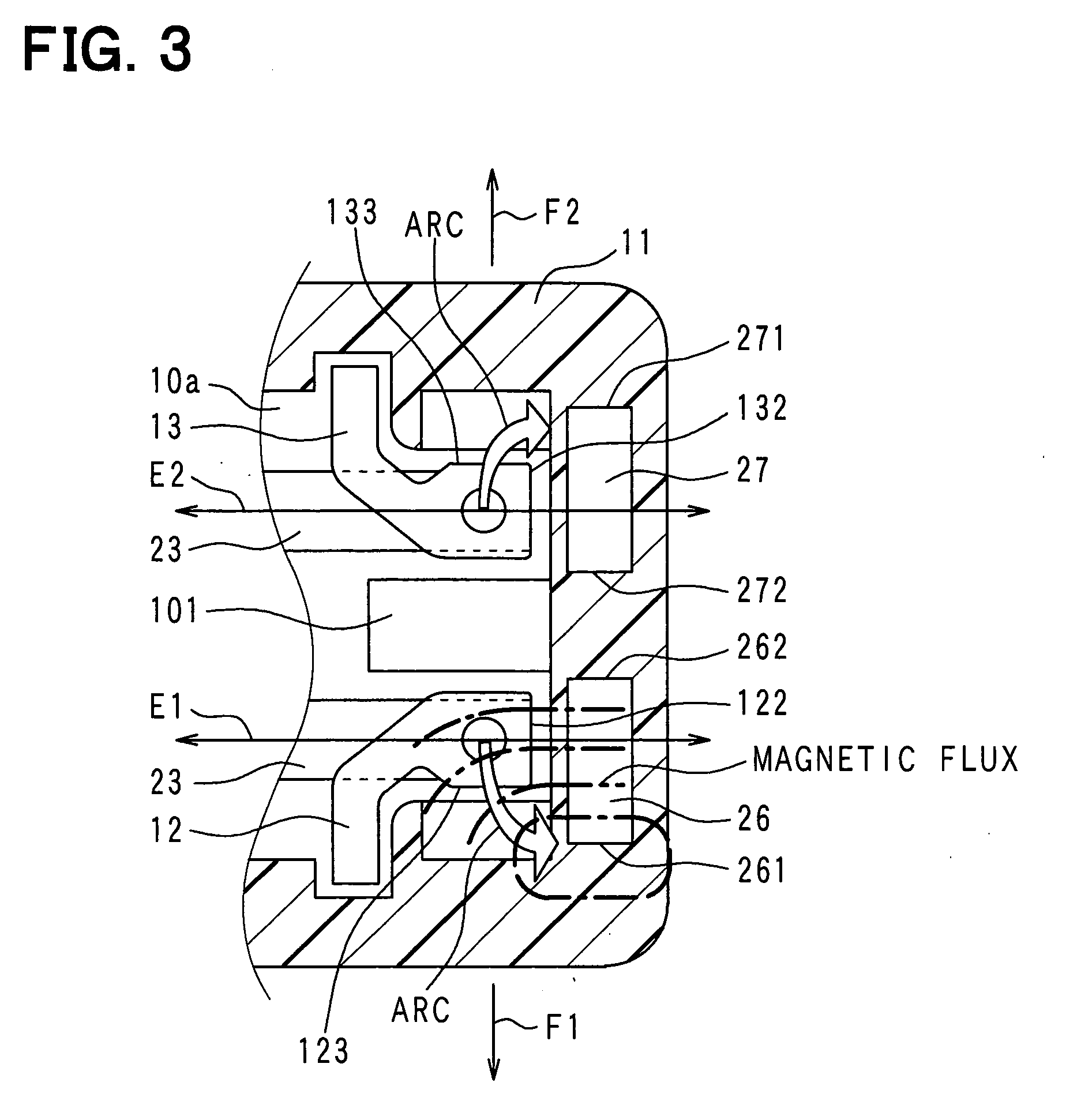
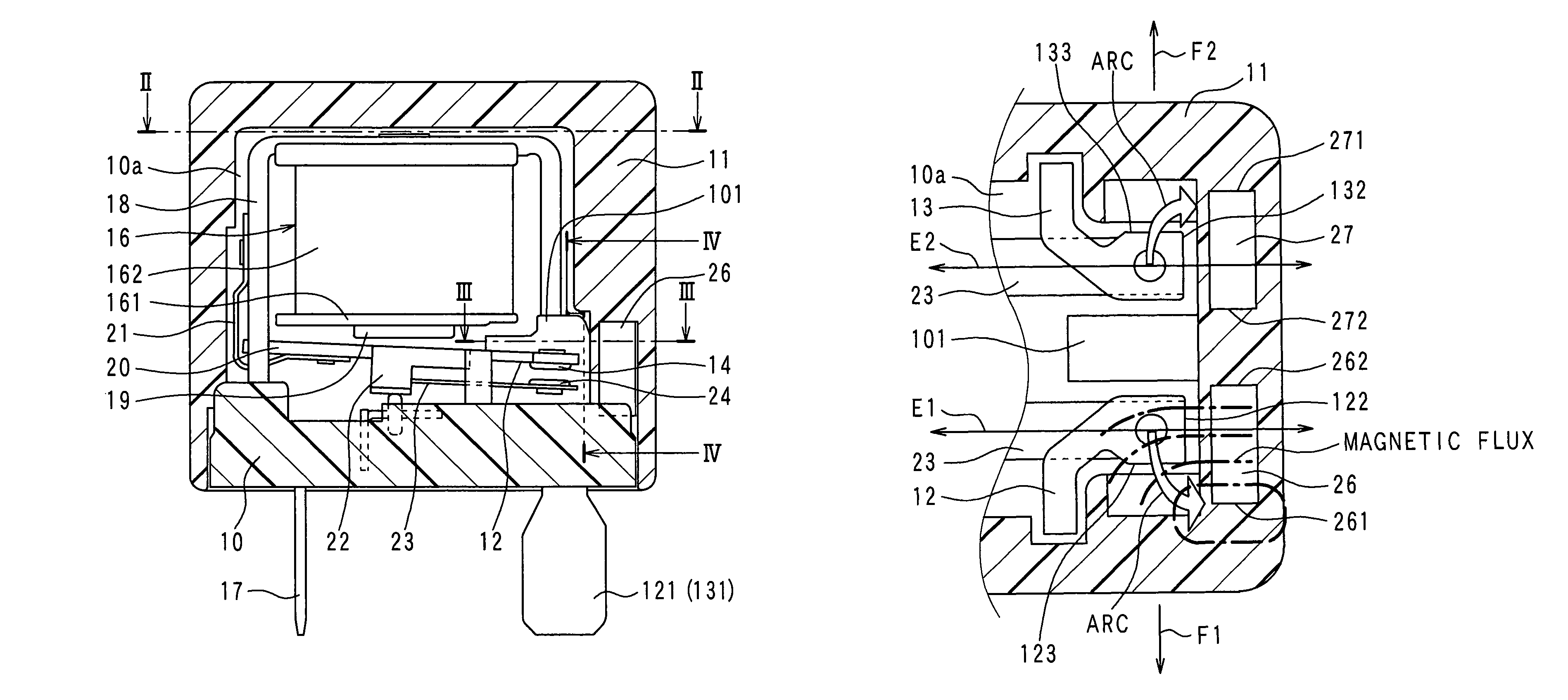
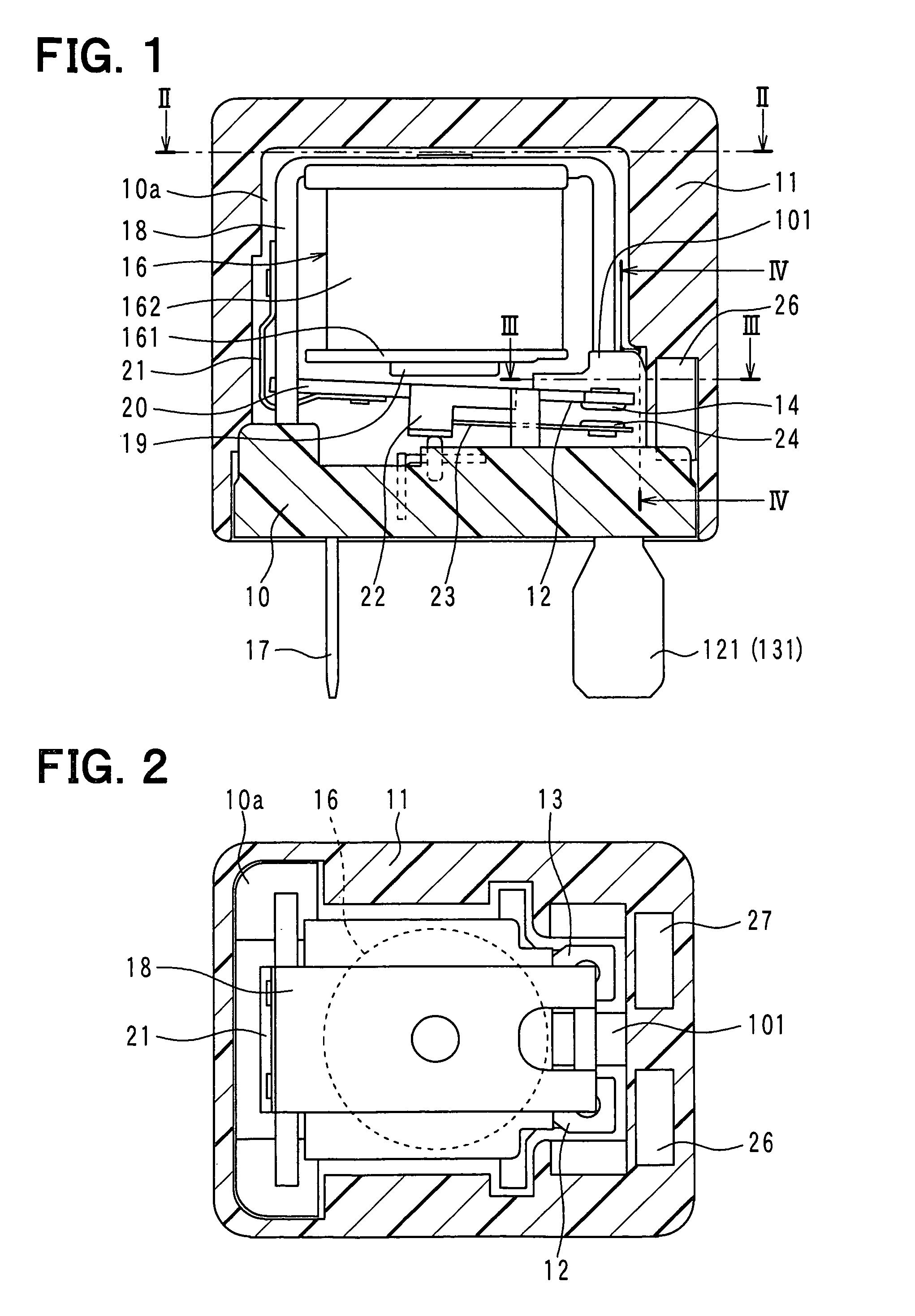
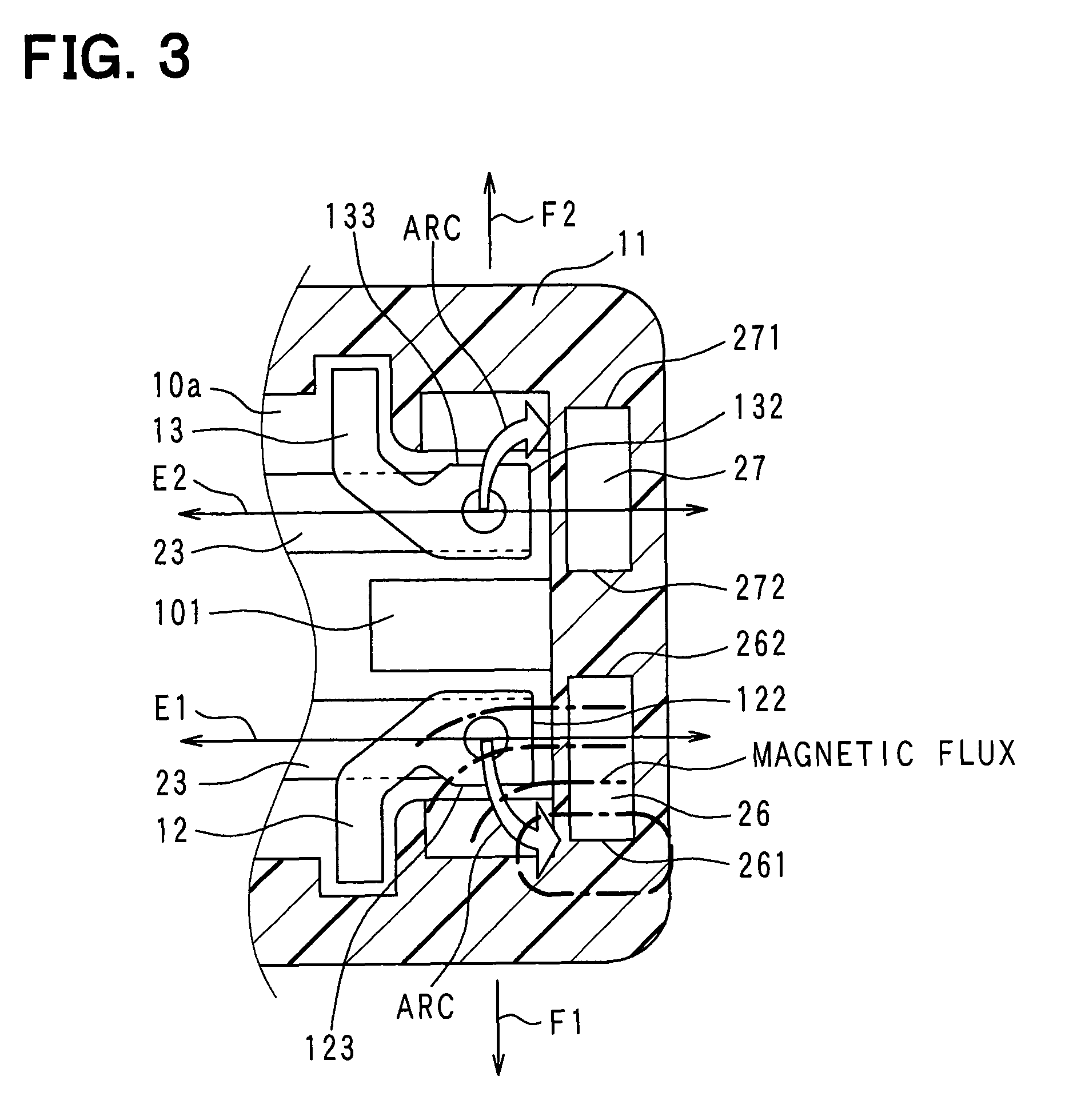
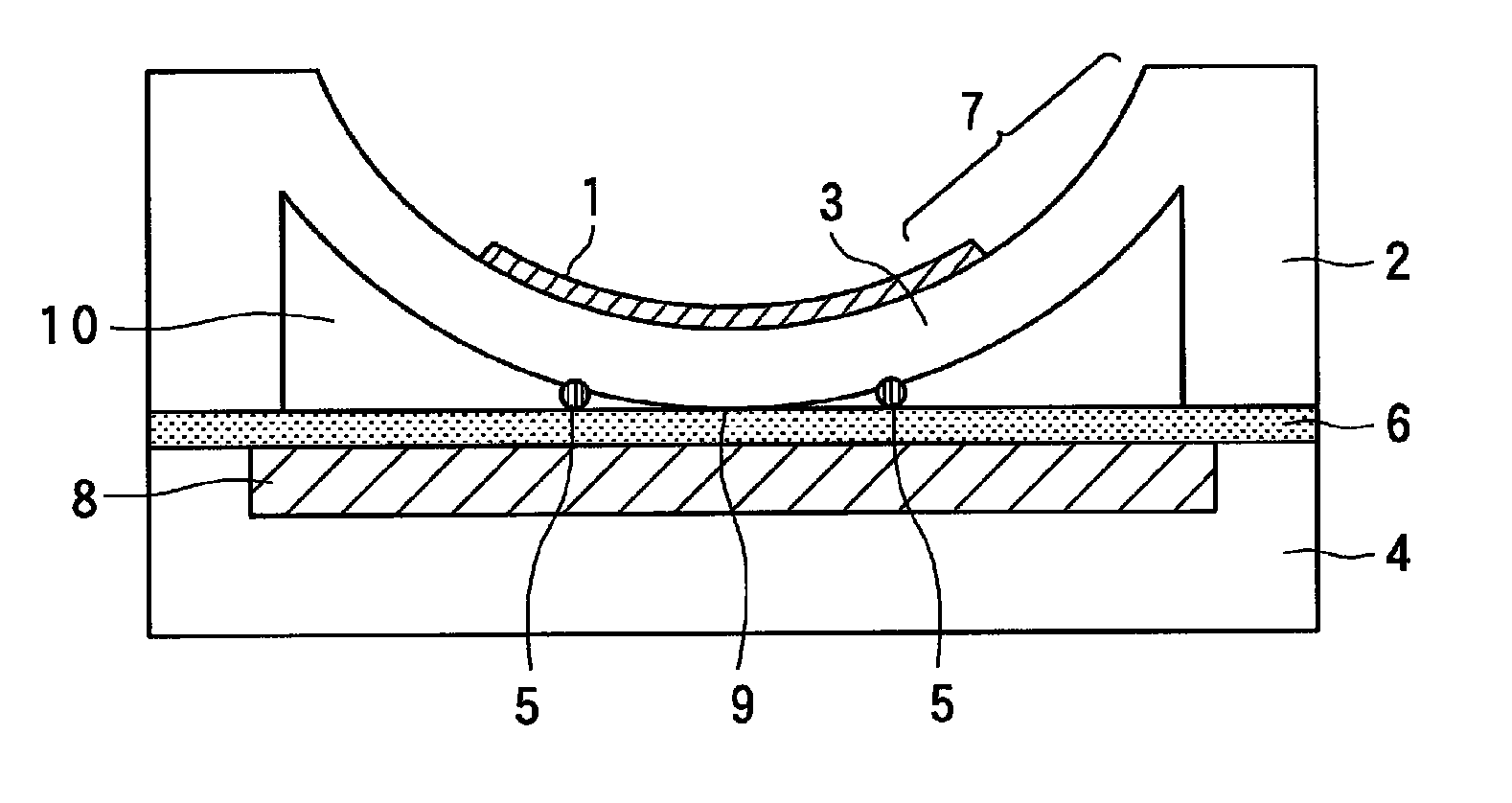
Electromagnetic relay
An electromagnetic relay includes a case, a base, a magnet coil, a movable member driven by electromagnetic force of the coil, a moving contact, a fixed contact engaged with or disengaged from the moving contact, a fixed contact holding member fixed to the base with the holding member passing therethrough and having a load circuit terminal, and a magnet applying Lorentz force to arc generated between the fixed contact and the moving contact. The case includes a guide part on its region with which arc extended in a Lorentz force application direction collides. The guide part guides arc after the collision to extend arc in a different direction from the application direction. The case includes a case partition wall between the guide part and the base. The holding member has a guide part opposing portion opposed to the guide part. The opposing portion is covered with the case partition wall.
Owner:ANDEN CORP
Microbial population analysis
ActiveUS20170159108A1Increase diversityMicrobiological testing/measurementICT adaptationMicroorganismIts region
The present invention relates to a method of typing a microbiome for having a desirable or undesirable signature, comprising analyzing the composition of the population of microorganisms in said microbiome based on taxonomic variation in the DNA sequence of the microbial 16S-23S rRNA internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions in the genomic DNA of said microorganisms, wherein the sequences of conserved DNA regions comprised in the 16S and 23S rRNA sequences flanking said ITS region in the genome of said microorganisms comprise primer binding sites for amplification of said ITS regions.
Owner:IS DIAGNOSTICS
Method and apparatus for utilizing magnetic field modulation to increase the operating frequency of sensors
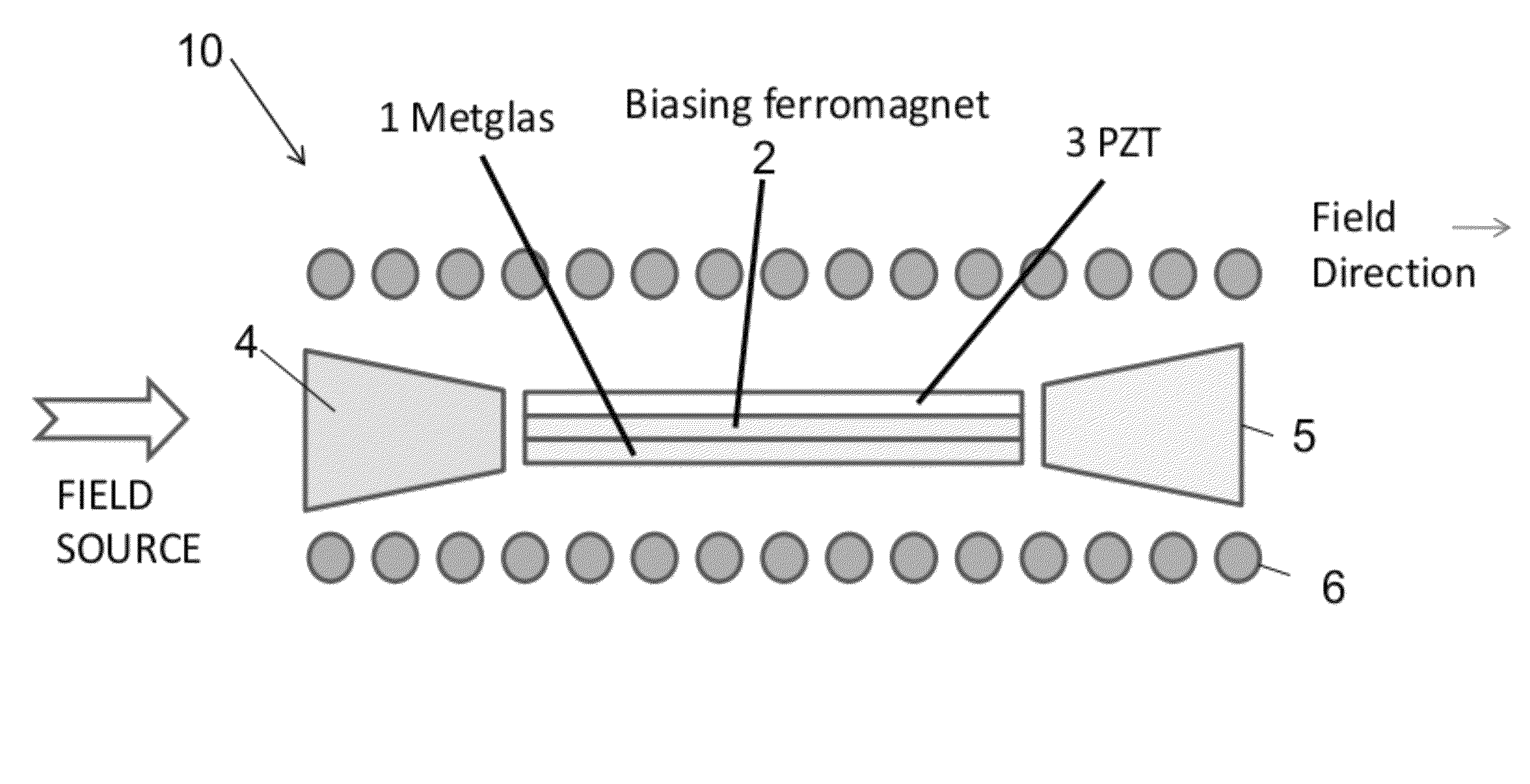
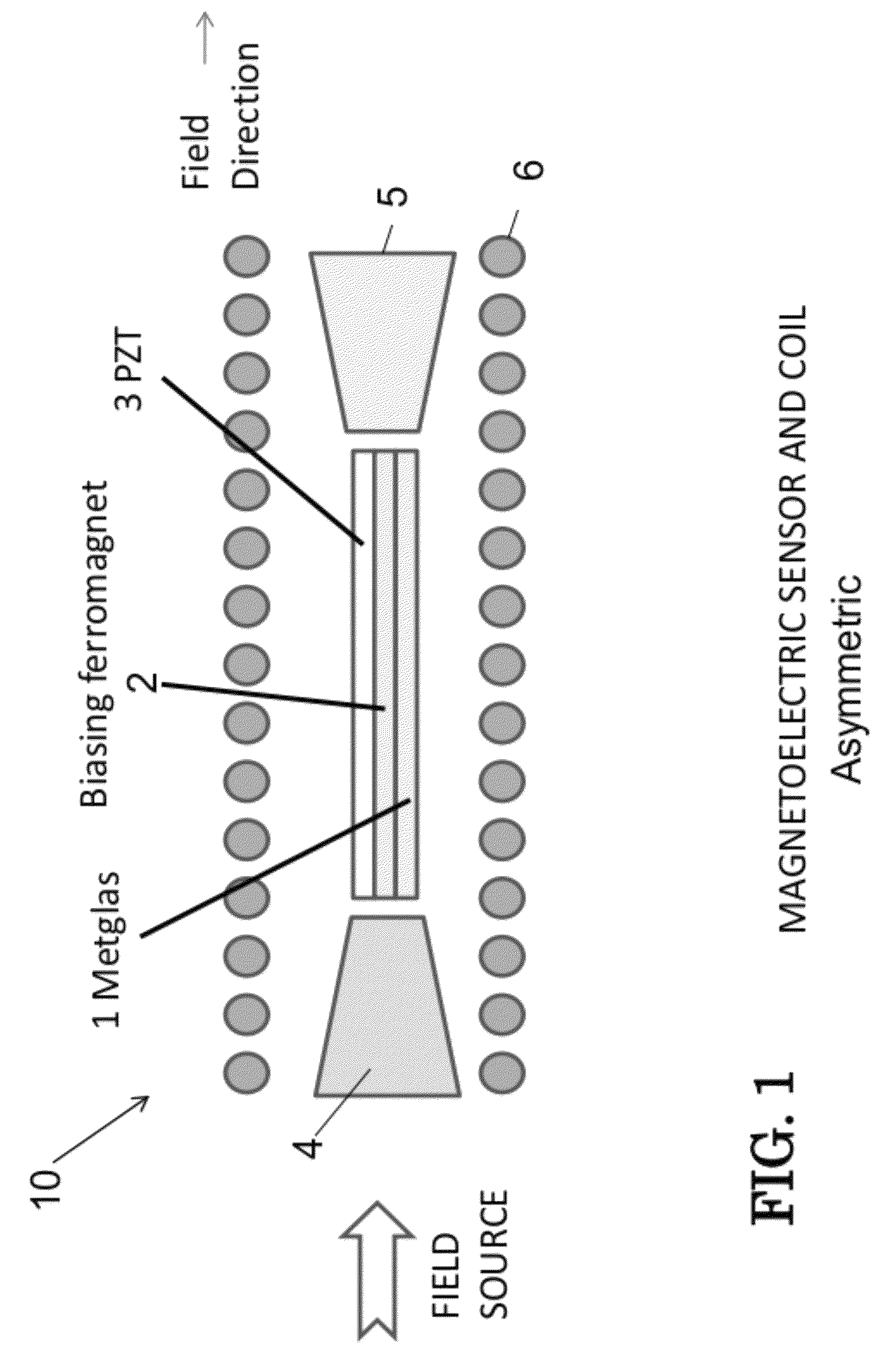
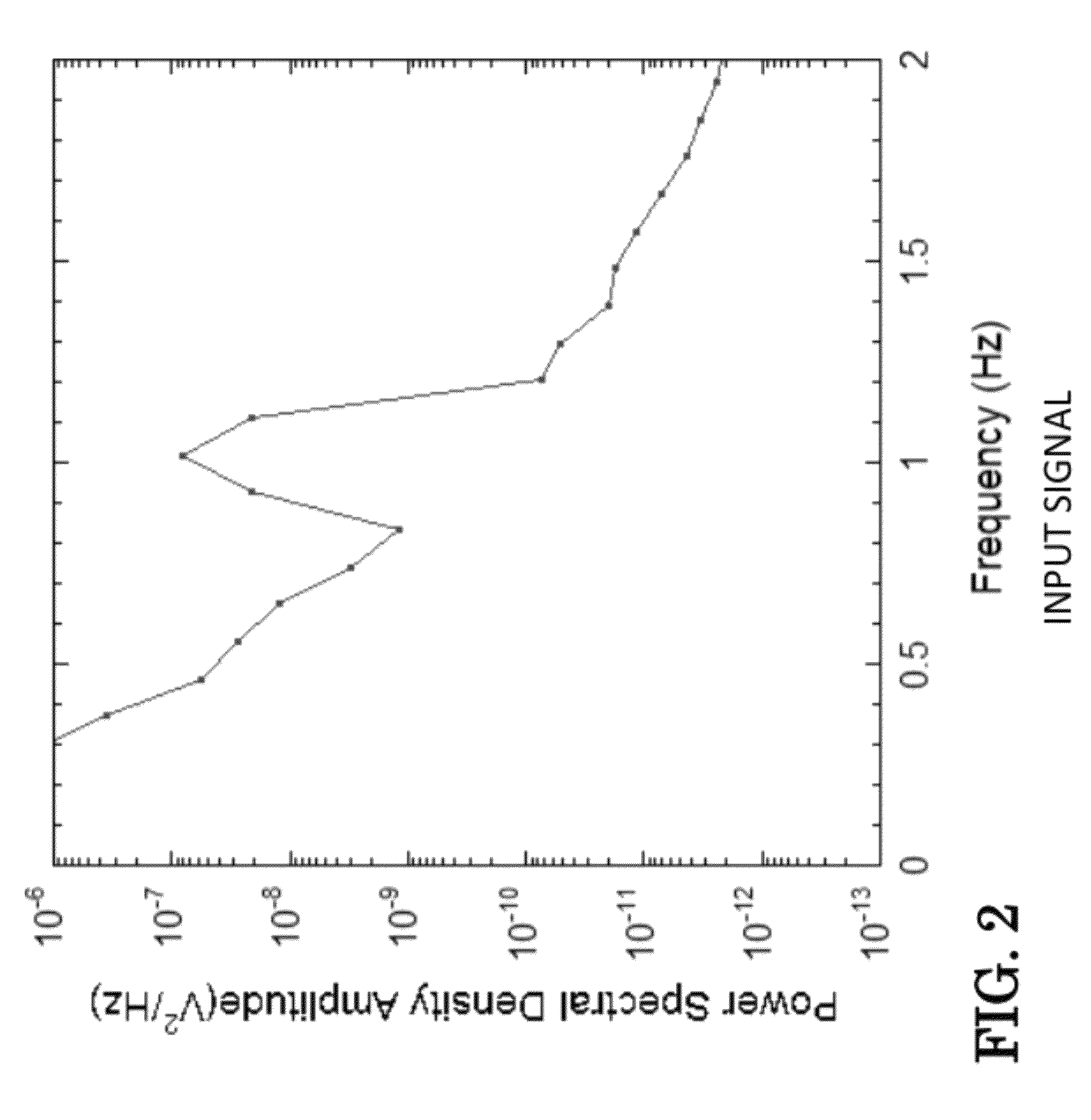
InactiveUS8222898B1Increase working frequencyReduce impactMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesIts regionAlternating current
A system for modulating a magnetic field sensor device comprising: a base; a magnetic sensor comprising a plurality of magnetic components; at least one coil for creating a magnetic field around the magnetic sensor; the at least one coil adapted to be connected to an alternating current source that passes through the coil to modulate the magnetic field at the magnetic sensor and drive at least one of the magnetic components of the magnetic sensor into and out of its region of increased magnetic response while shifting the frequency of the magnetic field that is sensed by the magnetic sensors a higher frequency to thereby minimize 1 / f-type noise, where f is the frequency of operation of the magnetic sensor. The method comprises forming at least one coil around the magnetic sensor; connecting the coil to an alternating current power source; and modulating the current from the power source.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
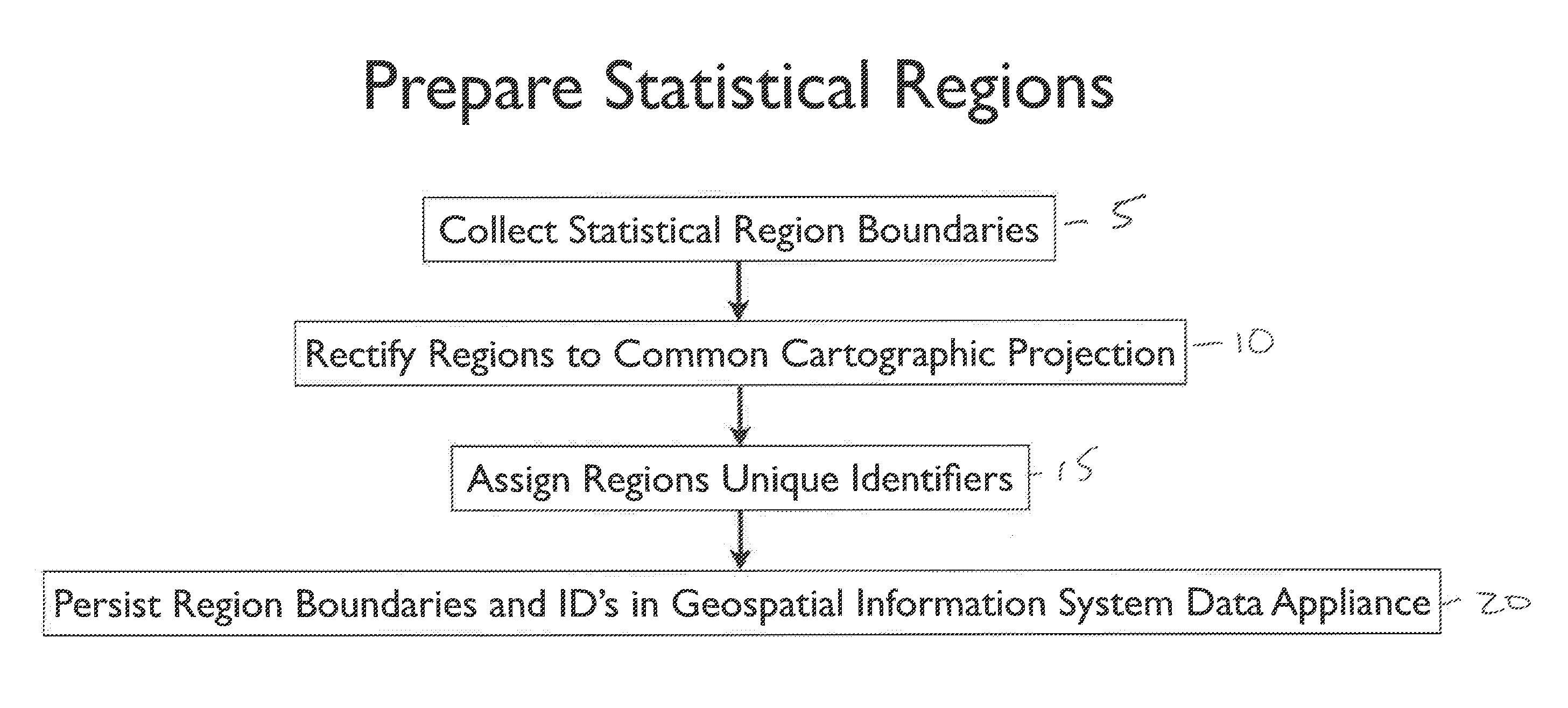
Geographic Information System For Researching, Identifying and Comparing Locations for Economic Development
ActiveUS20150186910A1Geographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsThird partyGeographic site
The invention includes systems and methods that permit users to research, identify and compare geographical regions for purposes of business formation, expansion or relocation decision making. The systems and methods include receiving, compiling and formatting data from a plurality of sources for use in the GIS system, populating a searchable database with the GIS data, and enabling the user to search the data using demographic, economic and other search parameters to identify and compare geographic locations of interest. The data further includes information provided by participating economic development organizations, enabling such data to be included in user search parameters, and permitting such third parties to provide commentary on regional data, and to market their regions and services to prospective businesses. The systems and methods also enable a user compare multiple regions of interest via an interface that displays different datasets selected by the user via tabs or buttons, and to generate reports using comparative data specifically selected by the user.
Owner:STATEBOOK INT INC
Semiconductor device and method of manufacture thereof, circuit board, and electronic instrument
InactiveUS7184276B2Easy to installSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIts regionSemiconductor chip
Owner:ADVANCED INTERCONNECT SYST LTD
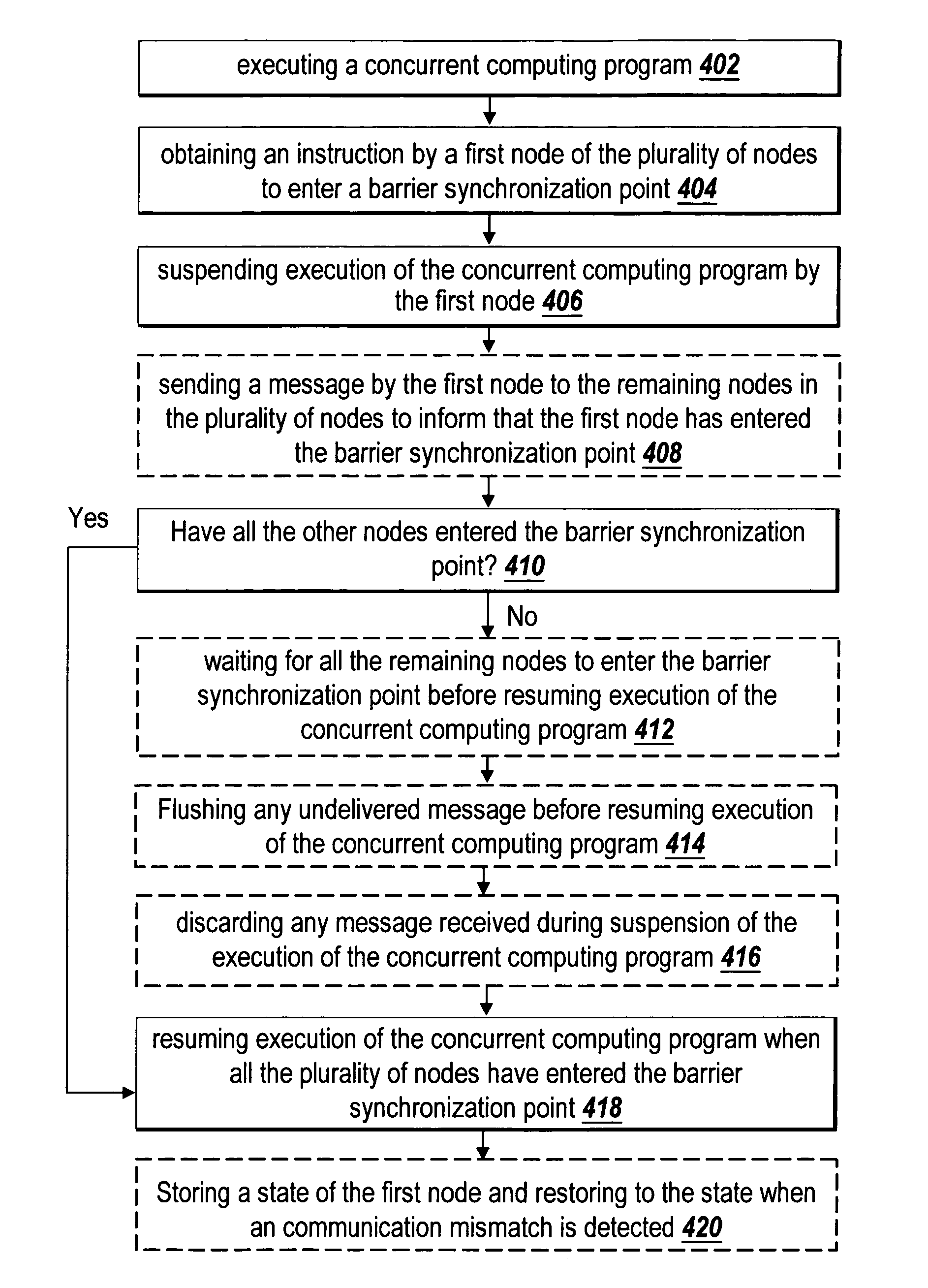
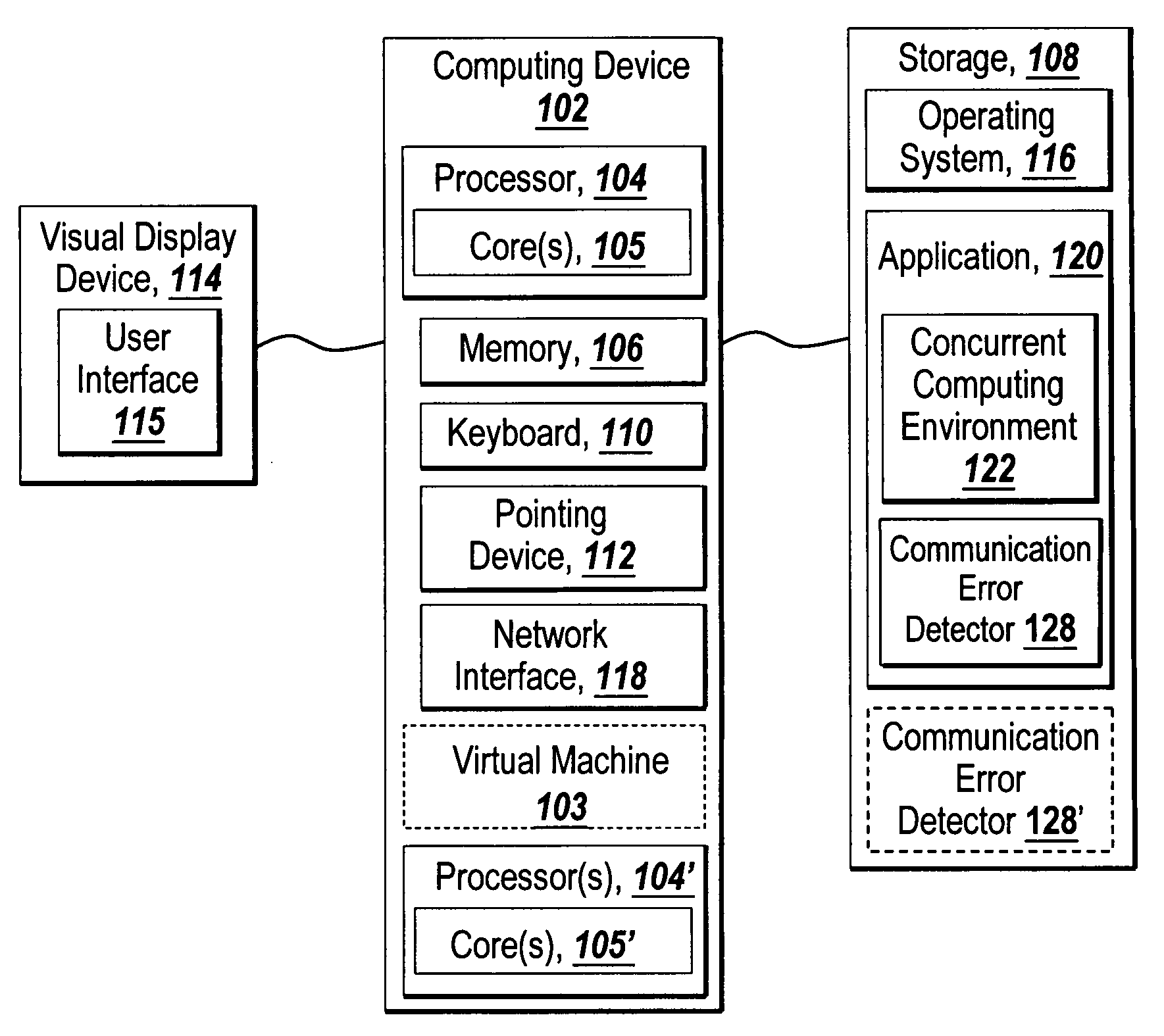
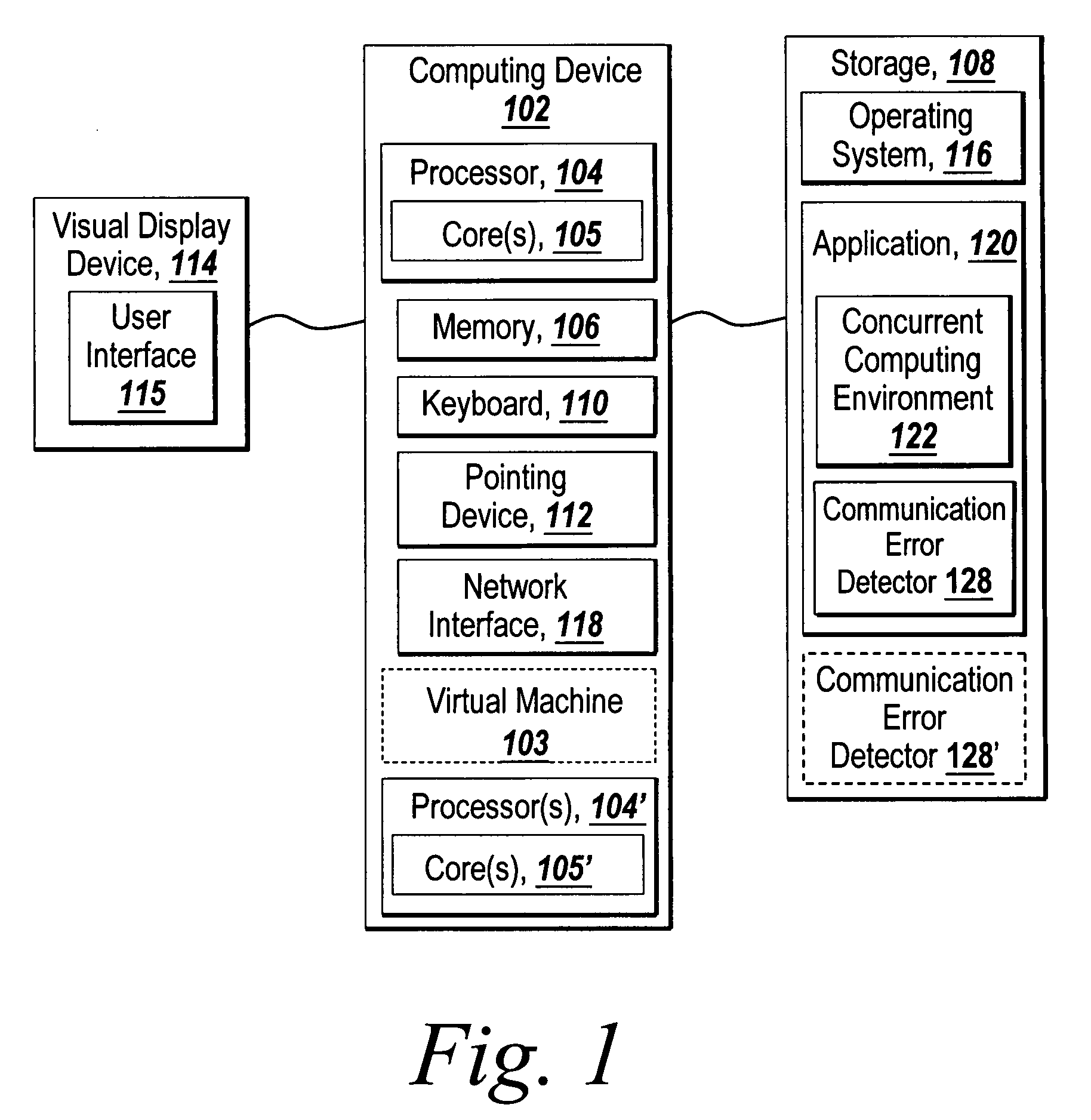
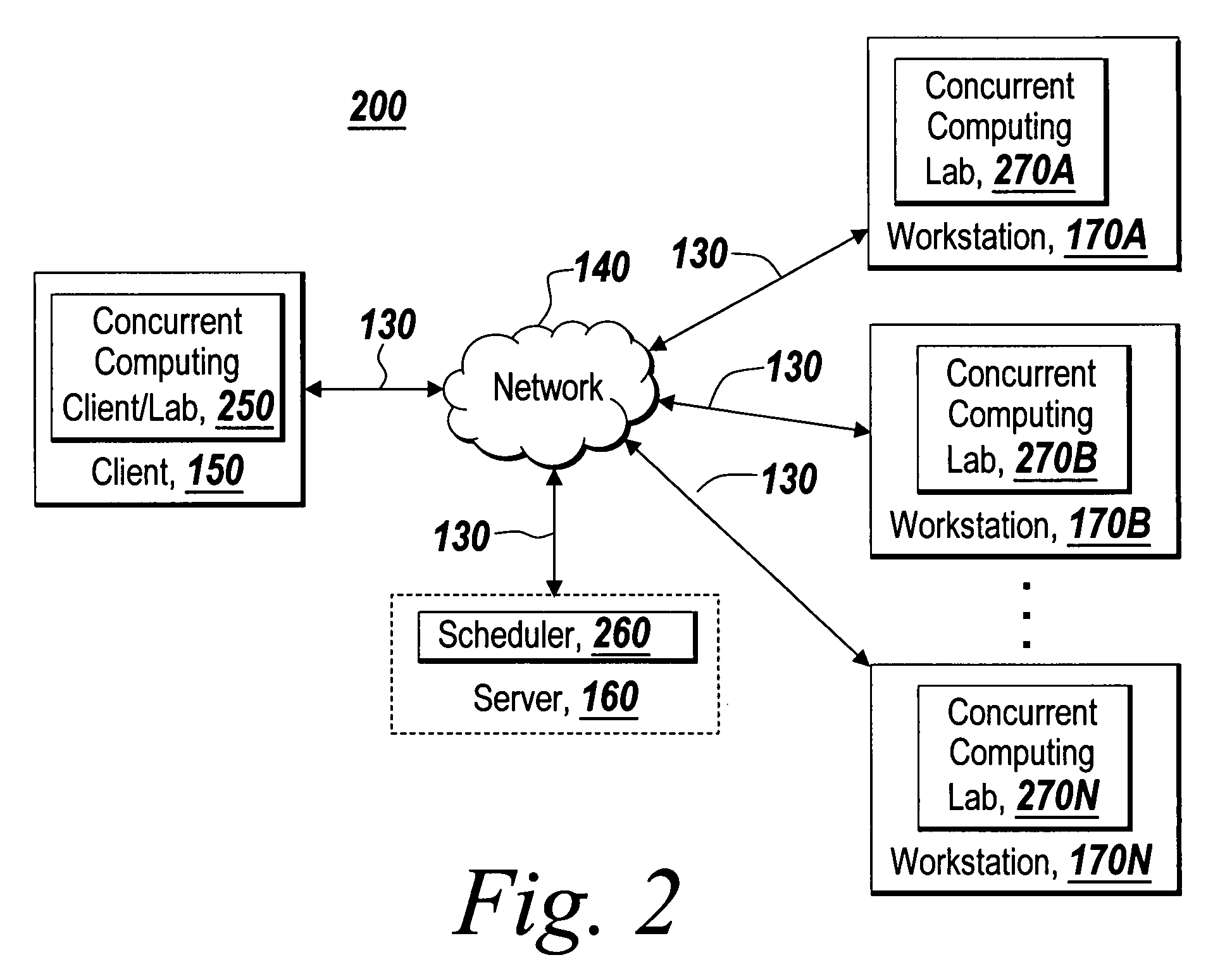
Recoverable error detection for concurrent computing programs
ActiveUS7925791B2Program synchronisationMultiple digital computer combinationsConcurrent computingIts region
The present invention provides a system and method for detecting communication error among multiple nodes in a concurrent computing environment. A barrier synchronization point or regions are used to check for communication mismatch. The barrier synchronization can be placed anywhere in a concurrent computing program. If a communication error occurred before the barrier synchronization point, it would at least be detected when a node enters the barrier synchronization point. Once a node has reached the barrier synchronization point, it is not allowed to communicate with another node regarding data that is needed to execute the concurrent computing program, even if the other node has not reached the barrier synchronization point. Regions can also be used to detect a communication mismatch instead of barrier synchronization points. A concurrent program on each node is separated into one or more regions. Two nodes can only communicate with each other when their regions are compatible. If their regions are not compatible, then there is a communication mismatch.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
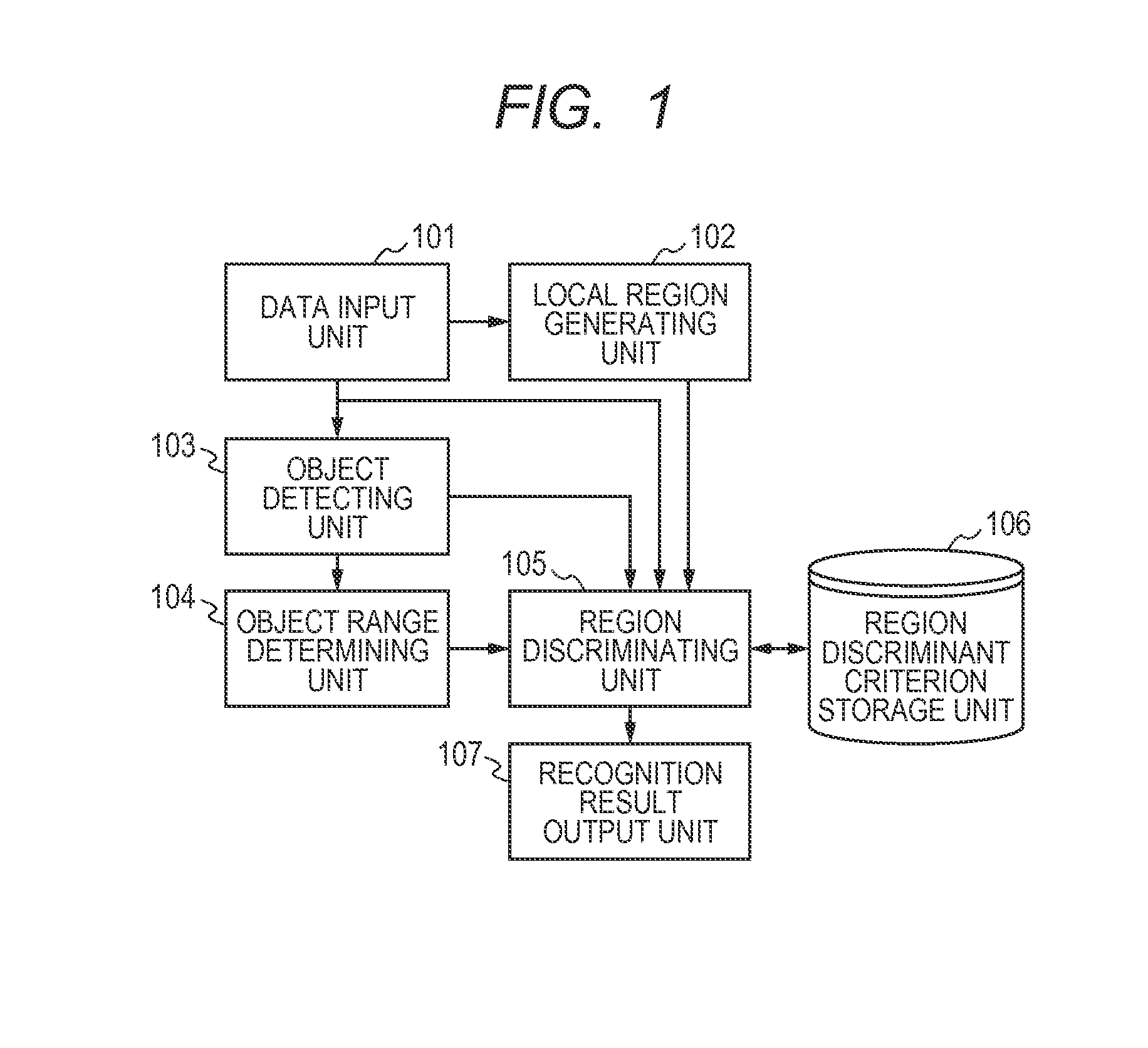
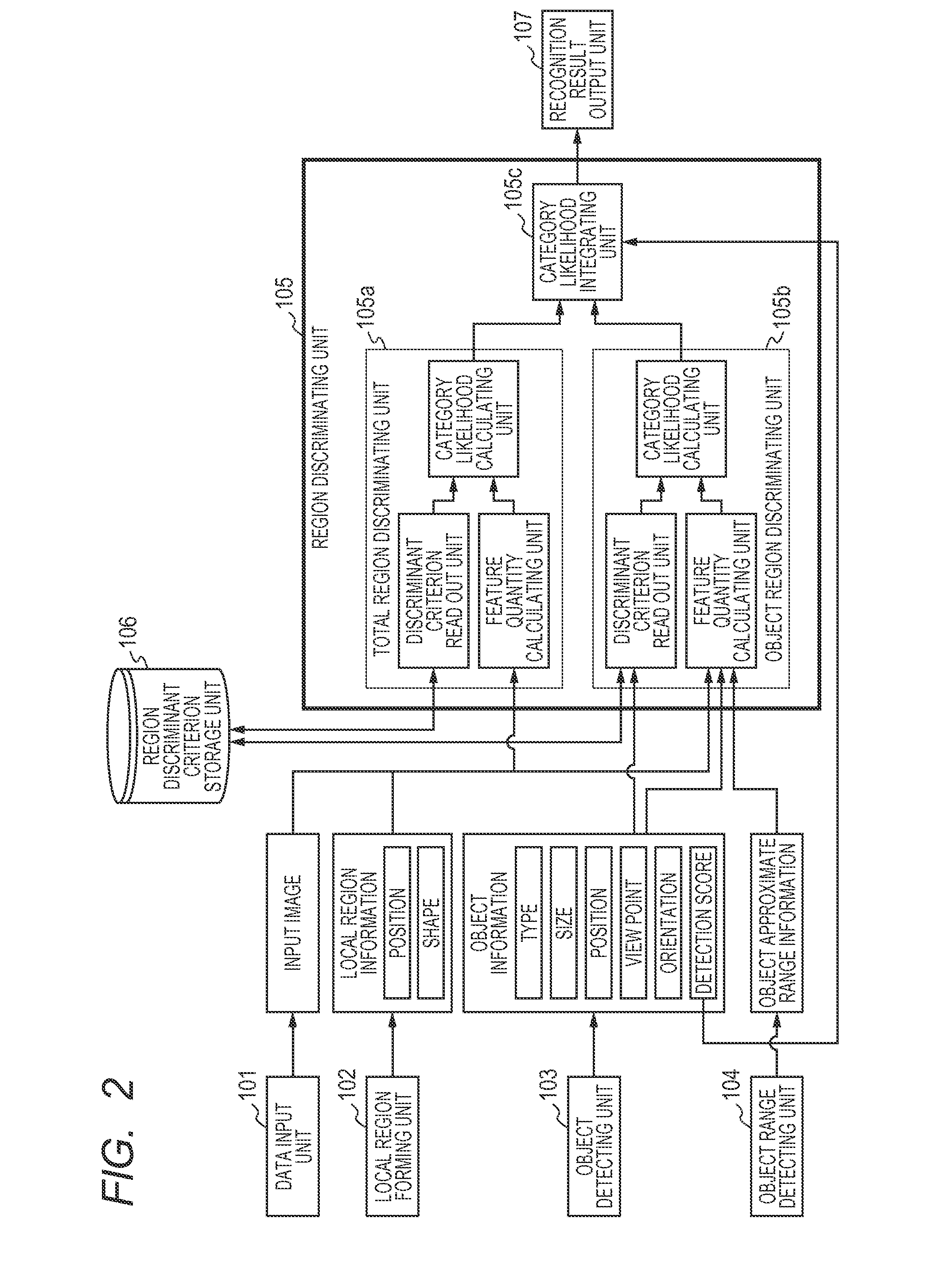
Image recognizing apparatus, image recognizing method, and storage medium
The accuracy of estimating the category of an object in an image and its region is improved. The present invention detects as to whether each of a plural types of objects is included in an object image, forms a plurality of local regions in a region including the object detected, and calculates a feature quantity of the plurality of local regions formed. Furthermore, the present invention selects a discriminant criterion adapted to the type of the object detected, from a plurality of discriminant criteria for discriminating the plural types of objects, and determines, based on the discriminant criterion selected and the feature quantity calculated, a region of the object detected from the plurality of local regions.
Owner:CANON KK
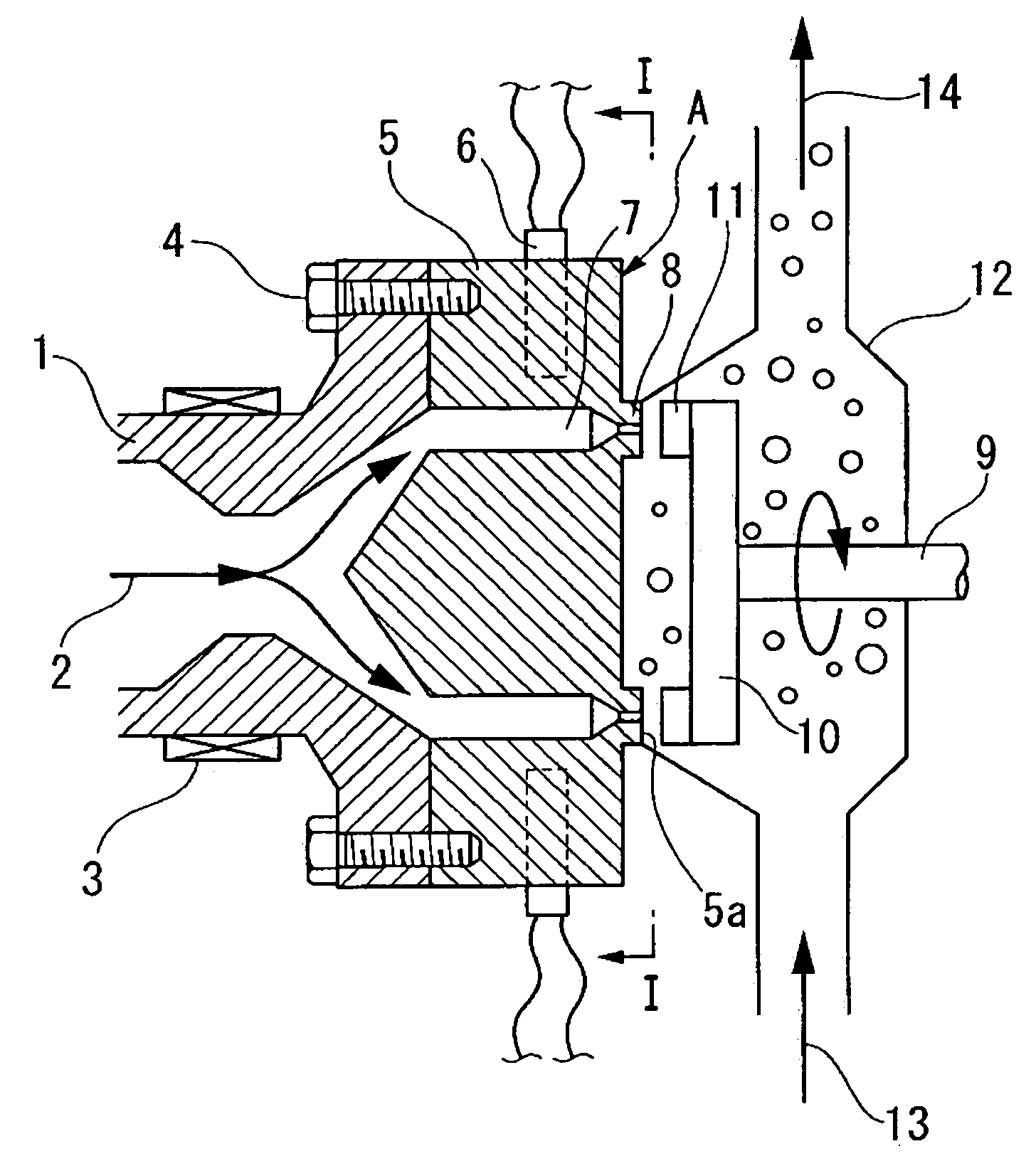
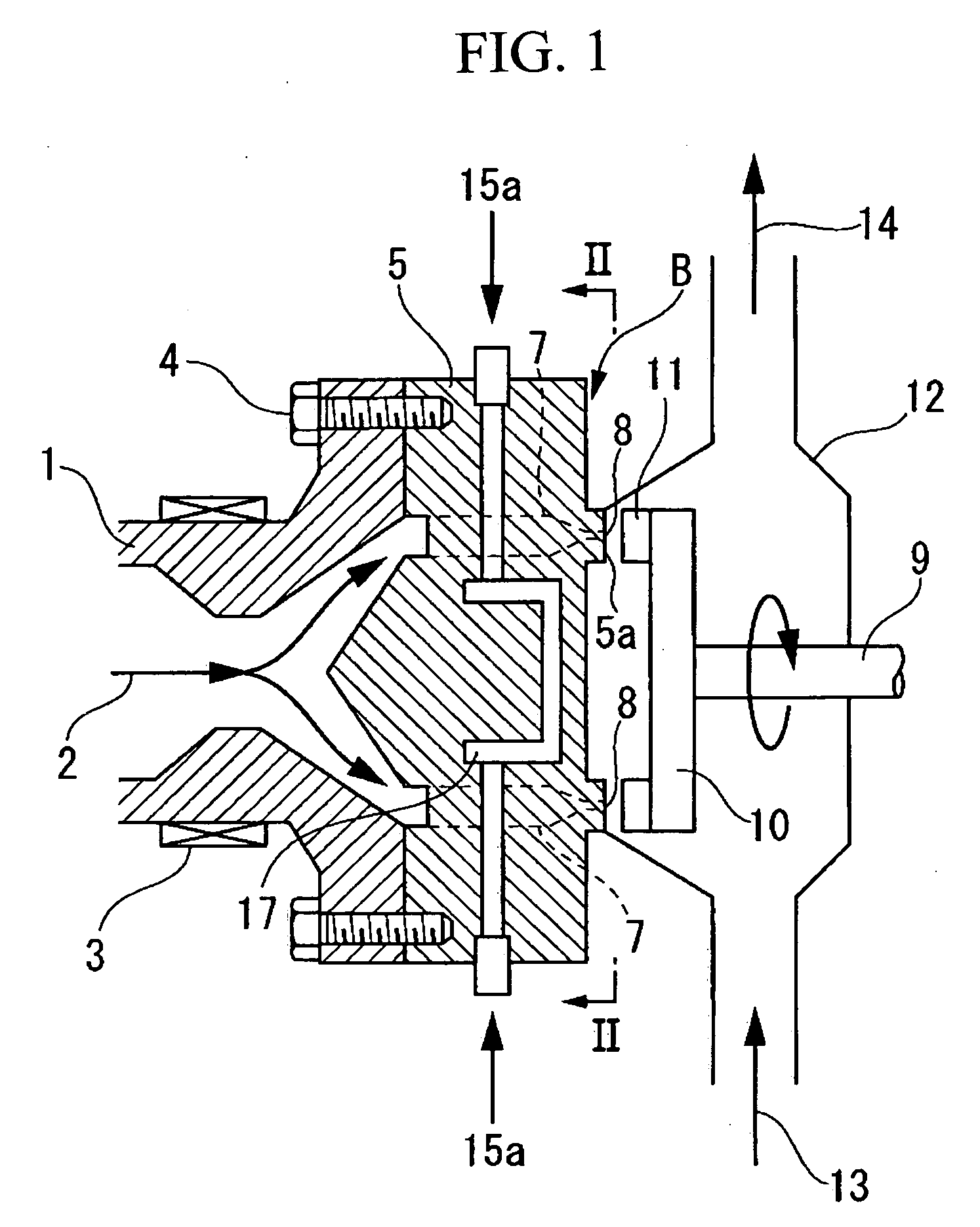
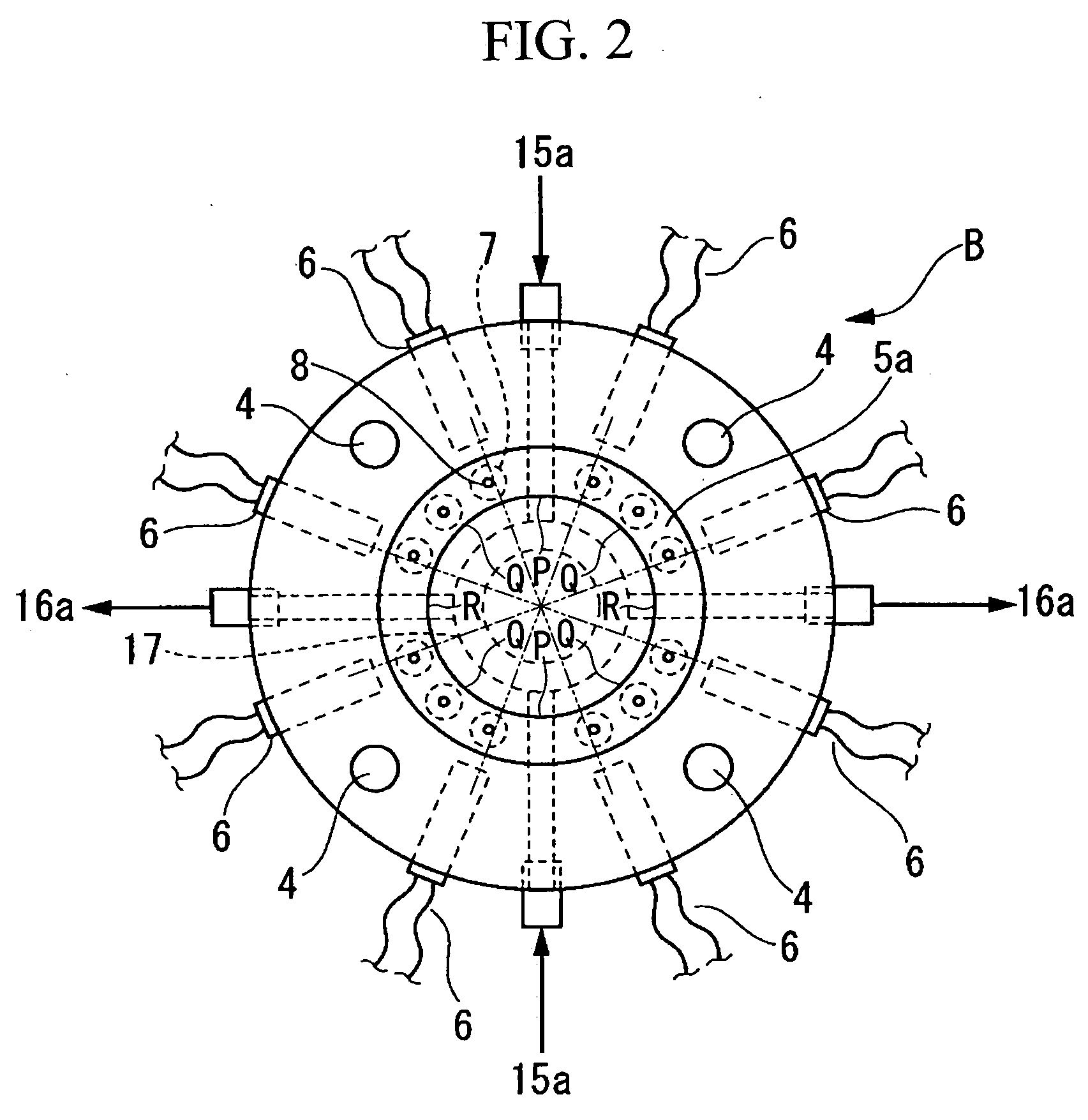
Granulation die, granulation apparatus, and process for producing expandable thermoplastic resin granule
A granulating die B is provided with a resin discharge surface 5a to which a flow of water is contacted; and a plurality of nozzles 8 which communicate to a cylinder of an extruder are provided in this resin discharge surface 5a. Upon the resin discharge surface 5a, these nozzles 8 are not formed in at least one of its regions P which are in the direction of inflow of the flow of water and in the direction of outflow of the flow of water, and its regions R which are in directions orthogonal to this direction of inflow of said flow of water and this direction of outflow of said flow of water, but are only formed in the other regions Q thereof.
Owner:SEKISUI PLASTICS CO LTD
PCR methods for the identification and detection of the soybean rust pathogen Phakopsora pachyrhizi
InactiveUS7097975B1Readily apparentSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhakopsora pachyrhiziIts region
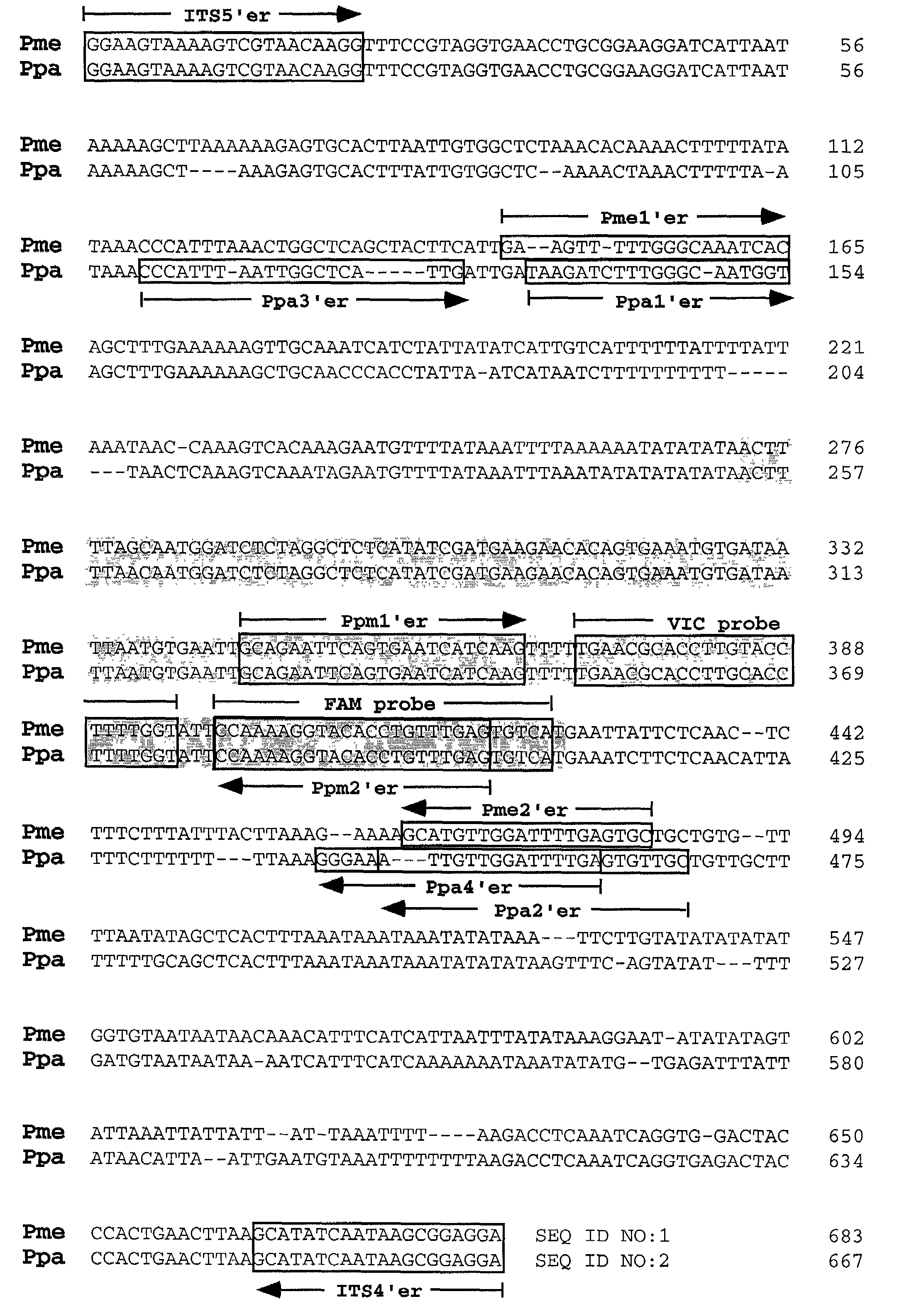
Soybean rust occurs in many countries throughout Asia, Australia, Africa, and South America. The causal agents of soybean rust are two closely related fungi, Phakopsora pachyrhizi and P. meibomiae, which are differentiated based upon morphological characteristics of the telia. Determination of the nucleotide sequence of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region revealed greater than 99% / 95% nucleotide sequence similarity among isolates of either P. pachyrhizi or P. meibomiae, but only 80% sequence similarity between the two species. Utilizing differences within the ITS region, four sets of PCR primers were designed specifically for P. pachyrhizi, and two sets of PCR primers were made specific to P. meibomiae. Classical and real-time fluorescent PCR assays were developed to identify and differentiate between P. pachyrhizi and P. meibomiae.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Trichoderma pill as well as preparation method and application thereof
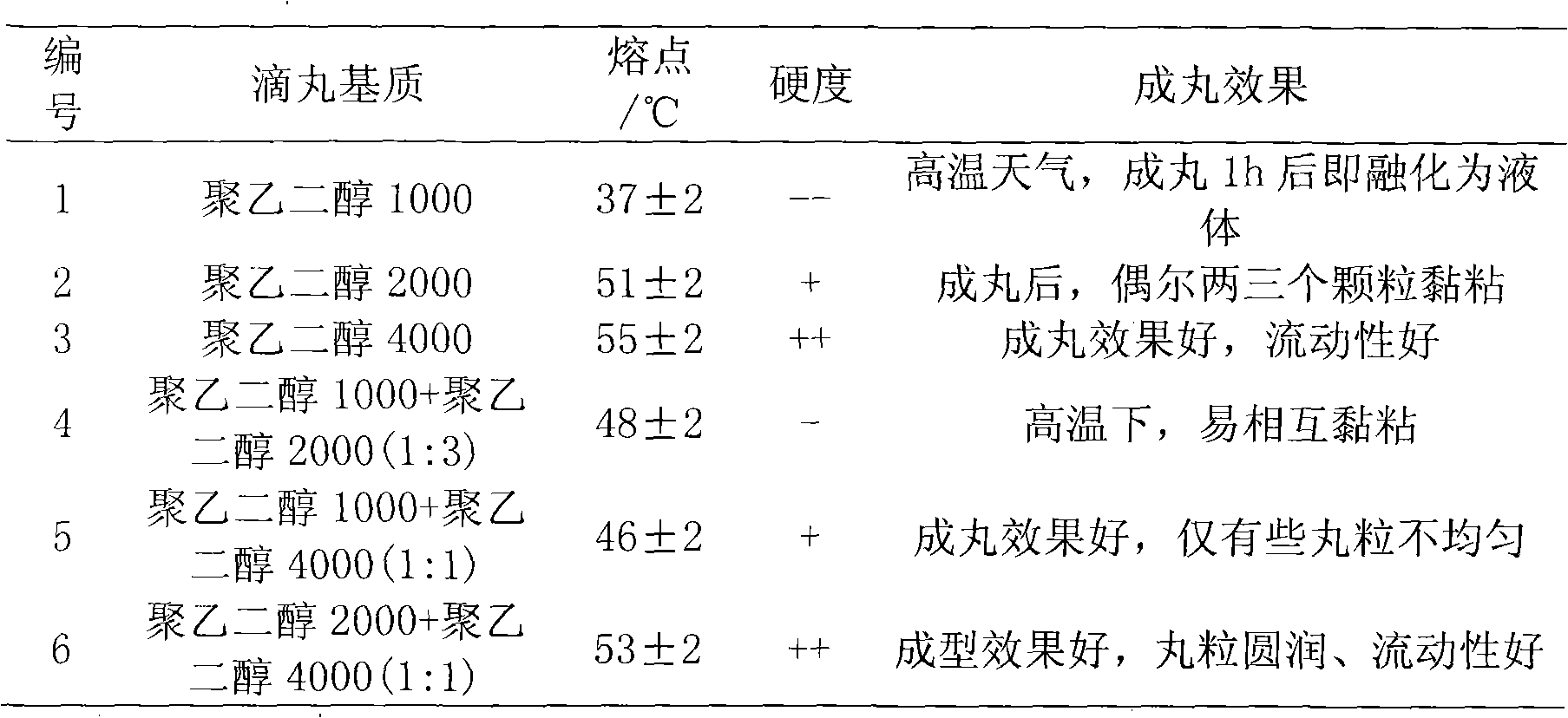
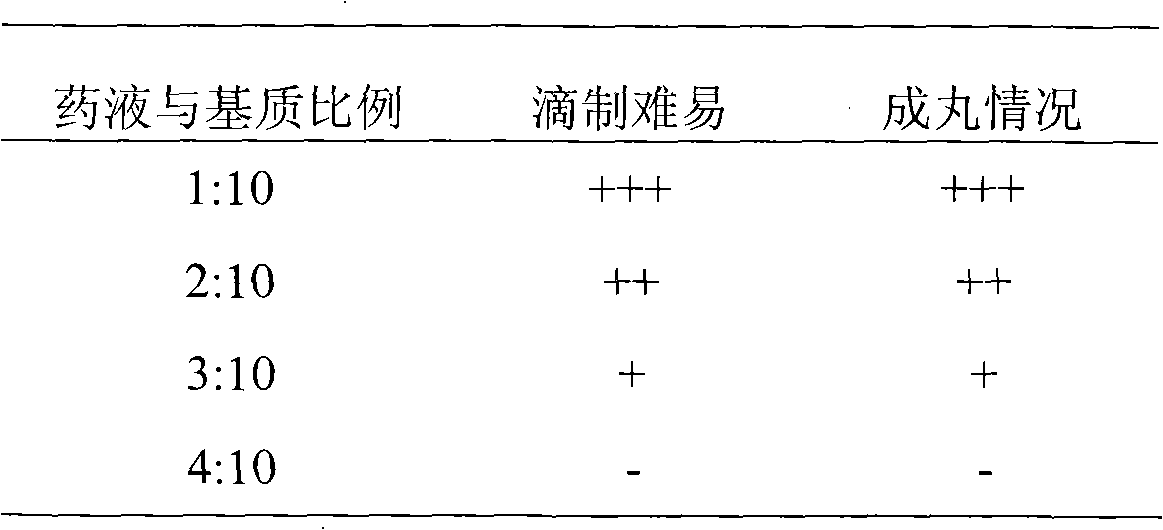
The invention belongs to the technical field of pesticides with microbial activity. A trichoderma pill provided by the invention comprises a trichoderma spore suspension and a pill matrix, wherein the trichoderma T1 bacterial strain spore suspension is prepared from spore powder of trichoderma asperellum T1 which is preserved in an ordinary microorganism center of the CCCCM (China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms), wherein the preservation number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection) NO: 3531 and the preservation date is December 17, 2009; the fragment sequence in DNA ITS region is shown as SEQ ID NO:1; a preservative agent of a spore suspension with the concentration of 0.5-1.5g / l is contained in the invention; and the pill matrix is a mixture of one or two or three of polyethylene glycol 1000, polyethylene glycol 2000 and polyethylene glycol 4000. The trichoderma pill provided by the invention has the advantages of high dose content, high biological activity and good molding effect, can be dissolved in the shortest time, and is convenient for storage, transportation and use.
Owner:惠州市南天生物科技有限公司 +2
Illuminating and panoramically viewing a macroscopically-sized specimen along a single viewing axis at a single time
InactiveUS20080055593A1Maximum effect extractionDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionSensorsMacroscopic scaleFluorescence
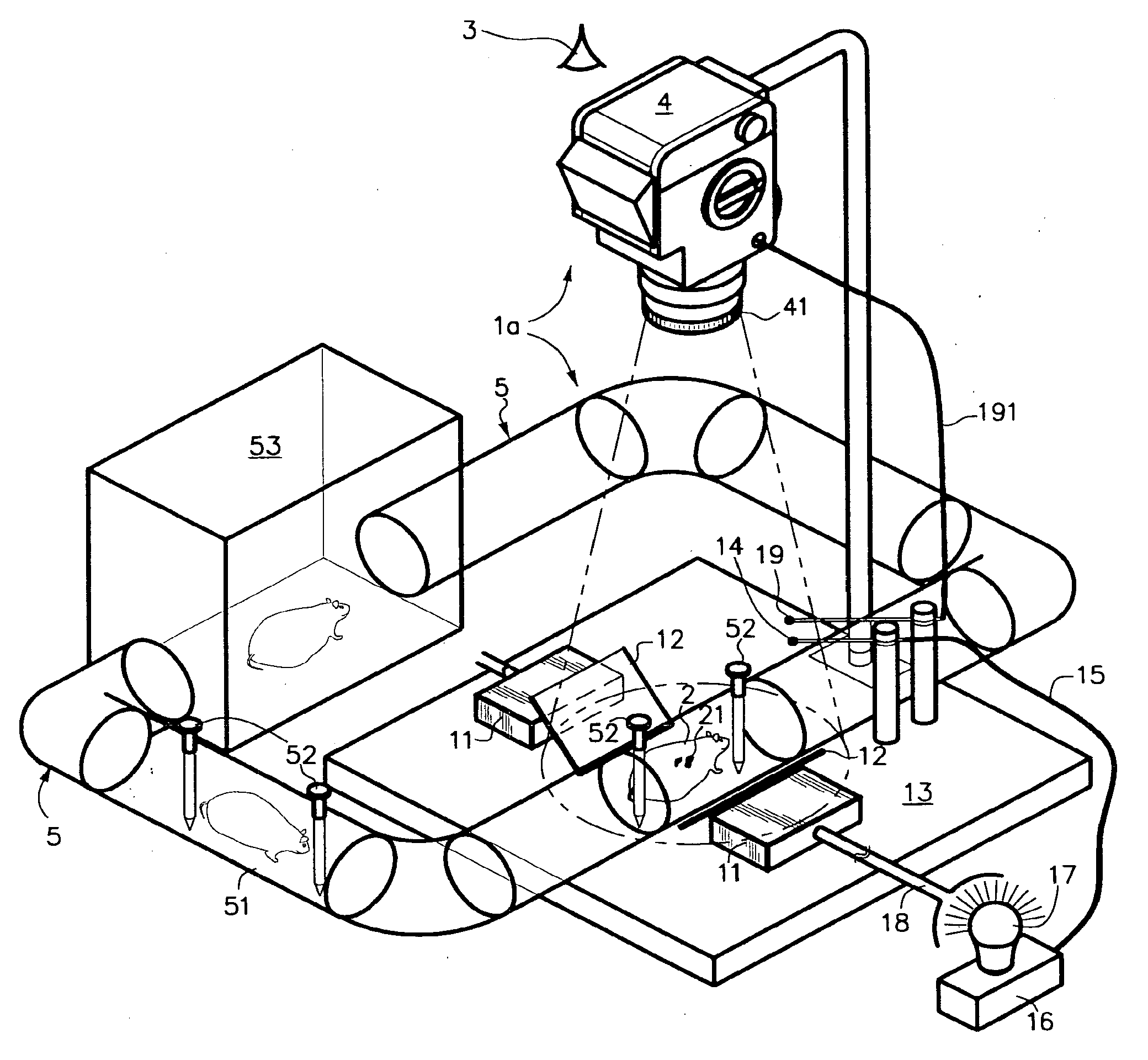
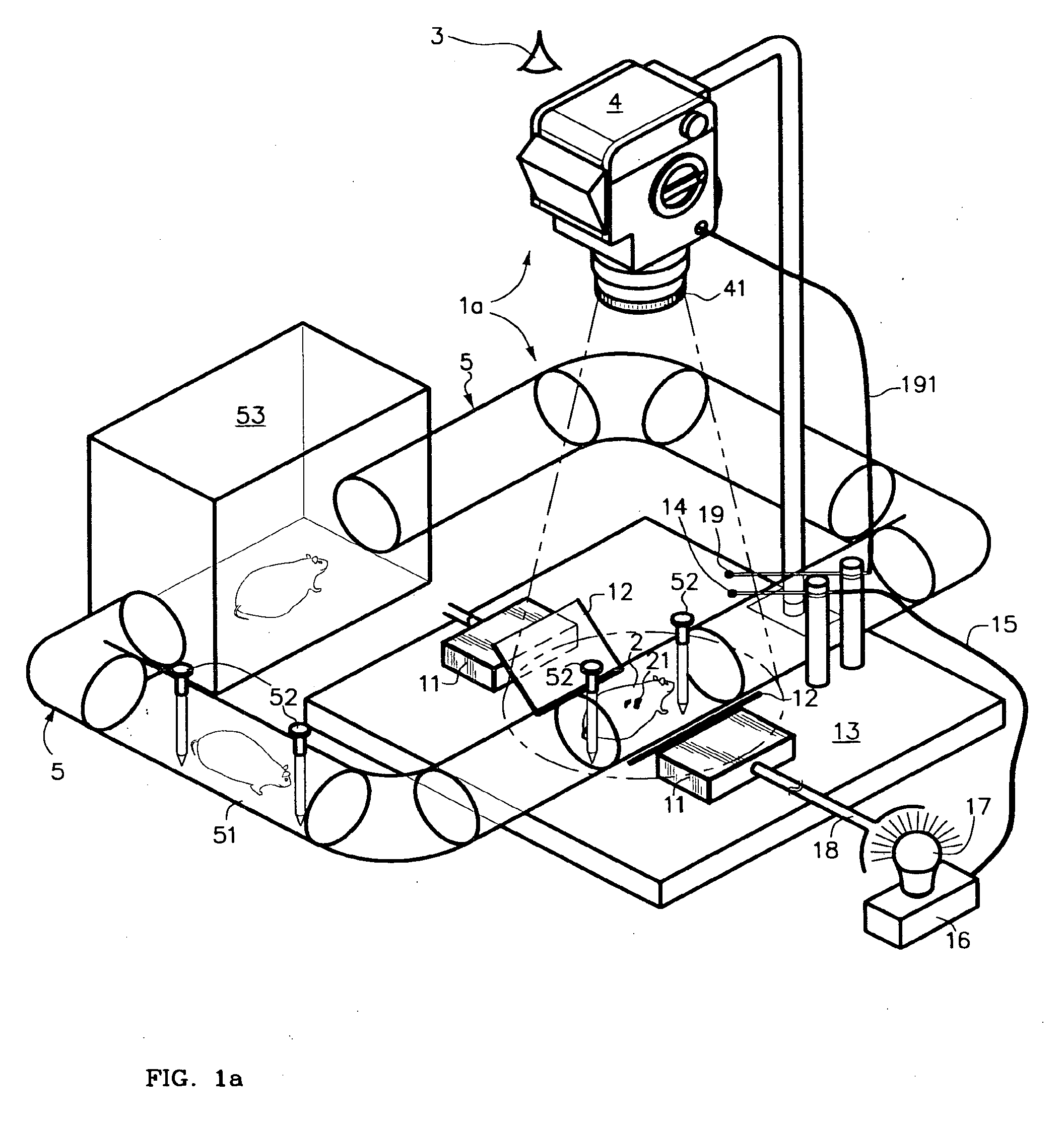
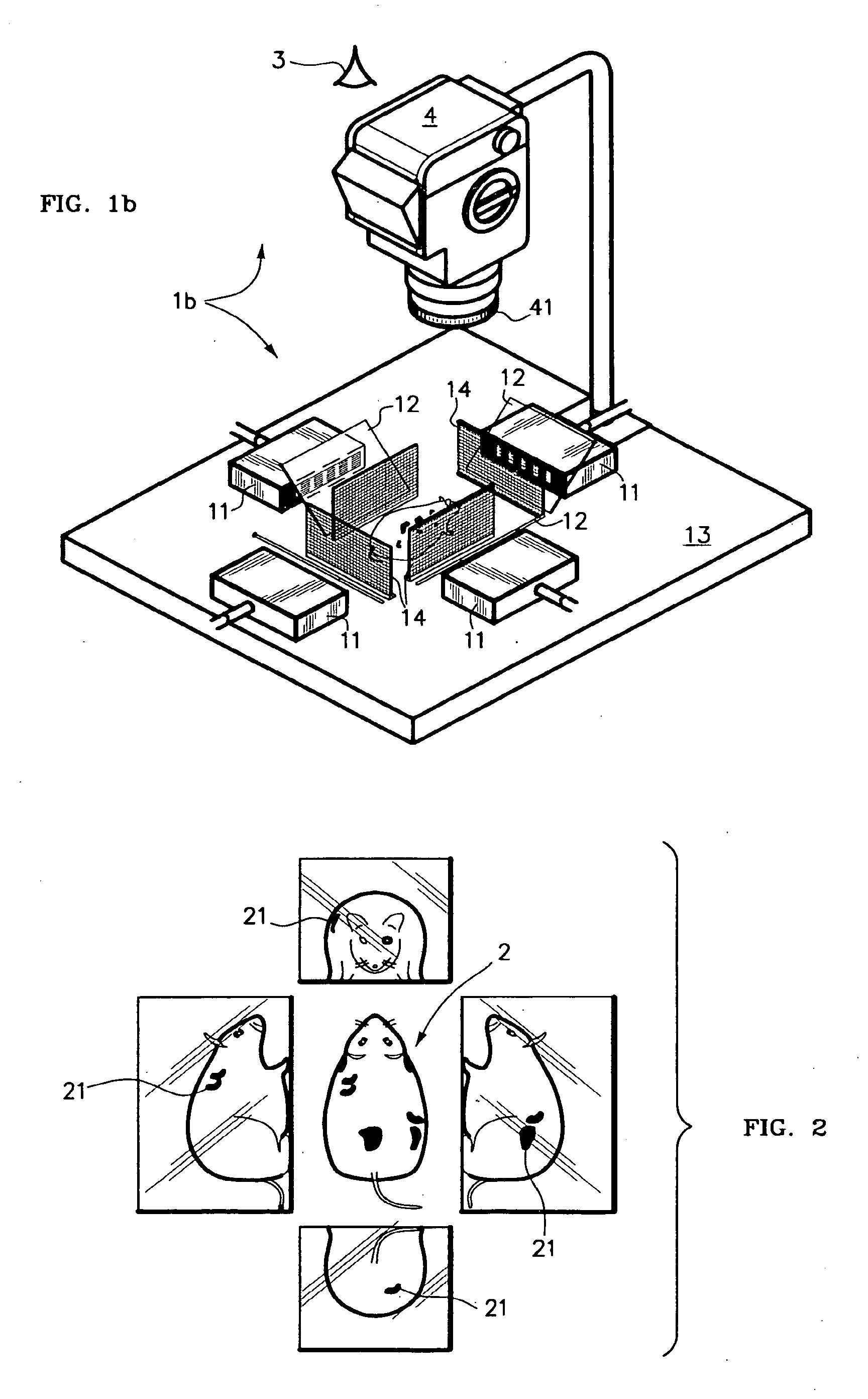
Simultaneous illumination along each of multiple axis for panoramic viewing of a macroscopically-sized specimen such as a mouse along a single viewing axis is realized by dichroic mirrors. Selective control of illumination intensity and / or color(s) of, permissively, each of multiple illuminating lights along each of multiple illumination axis permits that different regions and phenomena, such as tumors, of the specimen as are induced to fluoresce at corresponding different colors and intensities will all appear clearly visible, and well balanced, in a composite image nonetheless to intrinsically being of greatly differing brightness. Color and intensity calibration of the well-balanced composite image in all its colors and all its regions may optionally be realized by one or more fluorescent image calibration step wedges. A rule, or grid, scale may be imposed upon the image by use of one or more masks. The resulting panoramic composite image contains a great deal of quantitative information, being optionally calibrated in any of dimension, scale, overall brightness, color temperature and / or the separate intensities of, permissively, each of several separate differently-colored fluorescent emissions.
Owner:FOX JOHN S
Asymmetric valve for vehicle wheel
Owner:SCHREDER SA
Recoverable error detection for concurrent computing programs
A system and method detects communication error among multiple nodes in a concurrent computing environment. One or more barrier synchronization points / checkpoints or regions are used to check for a communication mismatch. The barrier synchronization point(s) / checkpoint(s) can be placed anywhere in the concurrent computing program. Once a node reaches a barrier synchronization point / checkpoint, it is not allowed to communicate with another node regarding data that is needed to execute the concurrent computing program, even if the other node has not reached the barrier synchronization point / checkpoint. Regions can also, or alternatively, be used to detect a communication mismatch instead of barrier synchronization points / checkpoints. A concurrent program on each node is separated into one or more regions. Two nodes communicate with each other when their regions are compatible. If their regions are not compatible, a communication mismatch occurs.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
Electromagnetic relay
An electromagnetic relay includes a case, a base, a magnet coil, a movable member driven by electromagnetic force of the coil, a moving contact, a fixed contact engaged with or disengaged from the moving contact, a fixed contact holding member fixed to the base with the holding member passing therethrough and having a load circuit terminal, and a magnet applying Lorentz force to arc generated between the fixed contact and the moving contact. The case includes a guide part on its region with which arc extended in a Lorentz force application direction collides. The guide part guides arc after the collision to extend arc in a different direction from the application direction. The case includes a case partition wall between the guide part and the base. The holding member has a guide part opposing portion opposed to the guide part. The opposing portion is covered with the case partition wall.
Owner:ANDEN CORP
Electromechanical transducer and manufacturing method therefor
In an electromechanical transducer which includes a vibration membrane provided with an upper electrode, a substrate provided with a lower electrode, and a support member adapted to support the vibration membrane in such a manner that a gap is formed between the vibration membrane and the substrate with these electrodes being arranged in opposition to each other, it is constructed such that a part of the vibration membrane and a region of the substrate are kept in contact with each other without application of an external force, and a remaining region of the vibration membrane other than its region in which the contact state is kept is able to vibrate.
Owner:CANON KK
Detection, identification and differentiation of eubacterial taxa using a hybridization assay
InactiveUS20060115819A1Rapid and reliable hybridization method for detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific detectionIts region
The present invention relates to a method for the specific detection and / or identification of Staphylococcus species, in particular Staphylococcus aureus, using new nucleic acid sequences derived from the ITS (Internal Transcribed Spacer) region. The present invention relates also to said new nucleic acid sequences derived from the ITS region, between the 16S and 23S ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) or rRNA genes, to be used for the specific detection and / or identification of Staphylococcus species, in particular of S. aureus, in a biological sample. It relates also to nucleic acid primers to be used for the amplification of said spacer region of Staphylococcus species in a sample.
Owner:INNOGENETICS NV +1
Method for positioning region of interest
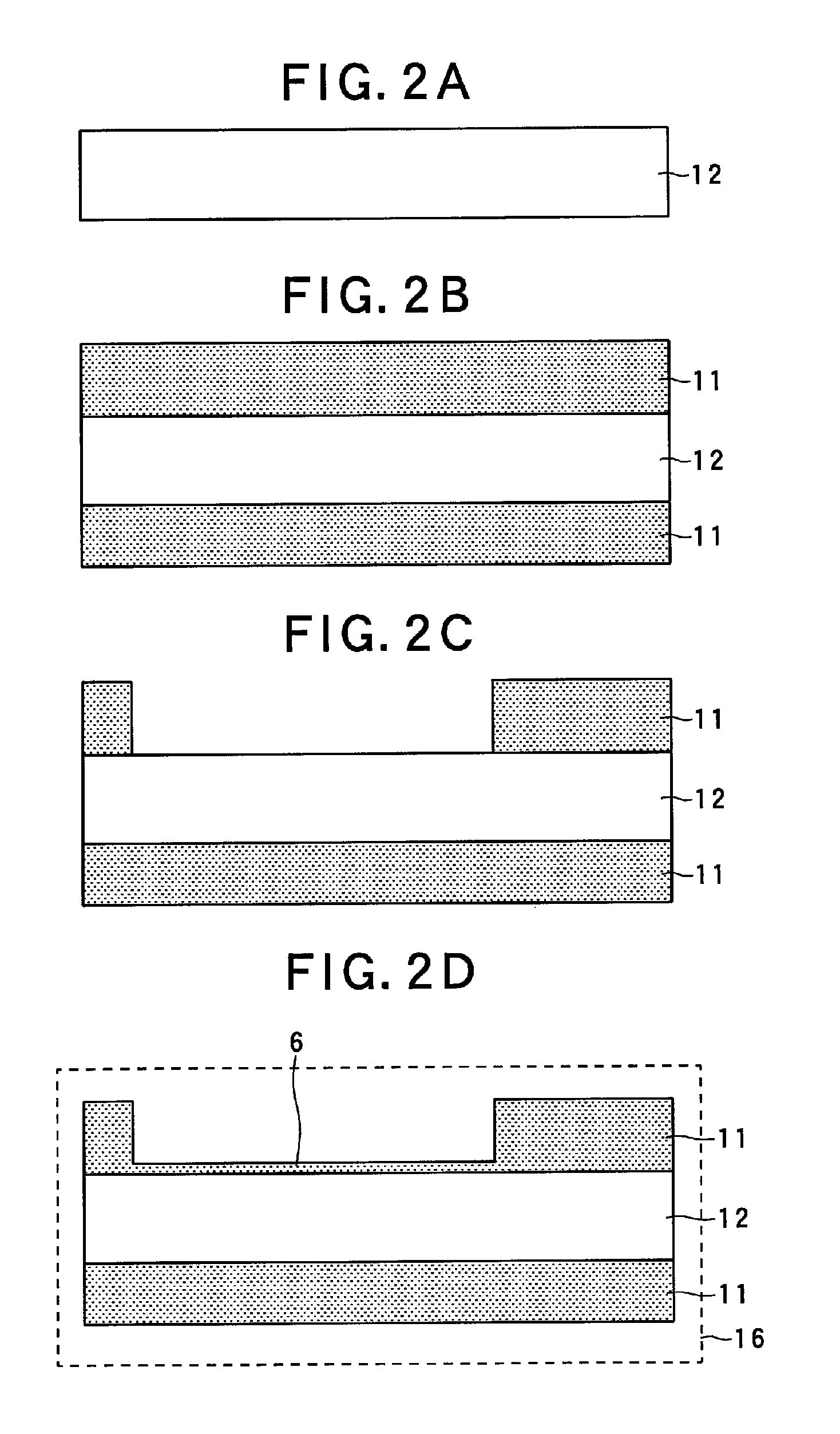
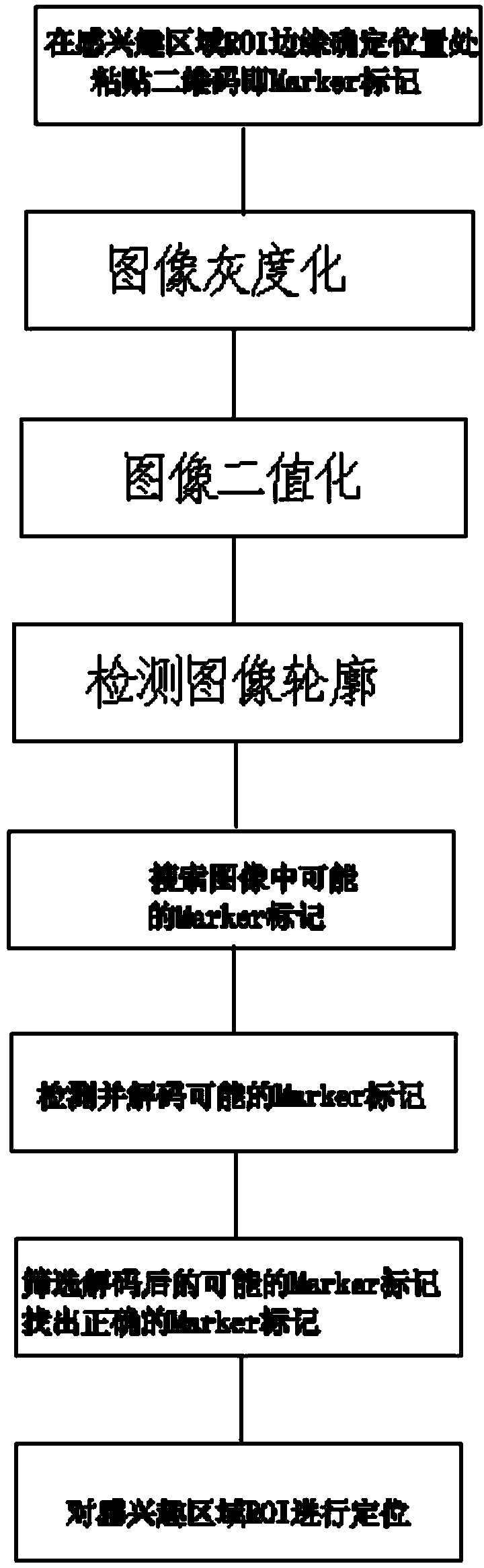
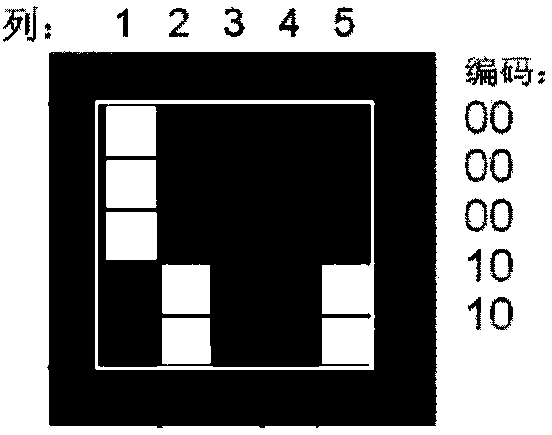
InactiveCN104331697AVersatilitySimplify preprocessing operationsCharacter and pattern recognitionIts regionPre treatment
The invention relates to a method for positioning a region of interest. The method comprises the specific steps of: A, sticking a two-dimensional code, namely, a Marker label, at a determined position of an edge, of the region of interest; B, detecting the Marker label and positioning the ROI region of interest, wherein the step B specifically comprises the sub-steps of: (1) performing image graying; (2) performing image binaryzation; (3) detecting image profile; (4) searching possible Marker labels in the image; (5) detecting and decoding the possible Marker labels; (6) sieving the decoded possible marker labels and finding a correct Marker label; (7) positioning he region of interest. The Marker label are only black and white in color, so that the image after binaryzation is obvious, and the region of interest can be positioned rapidly and exactly, the image pre-treatment operation is simplified, the condition of light change can be adapted to, and the robustness is very strong.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Medicine Storing And Dispensing Apparatus
InactiveUS20090289079A1Large capacityEvenly filledSmall article dispensingCoin-freed apparatus detailsIts regionDrug Storage
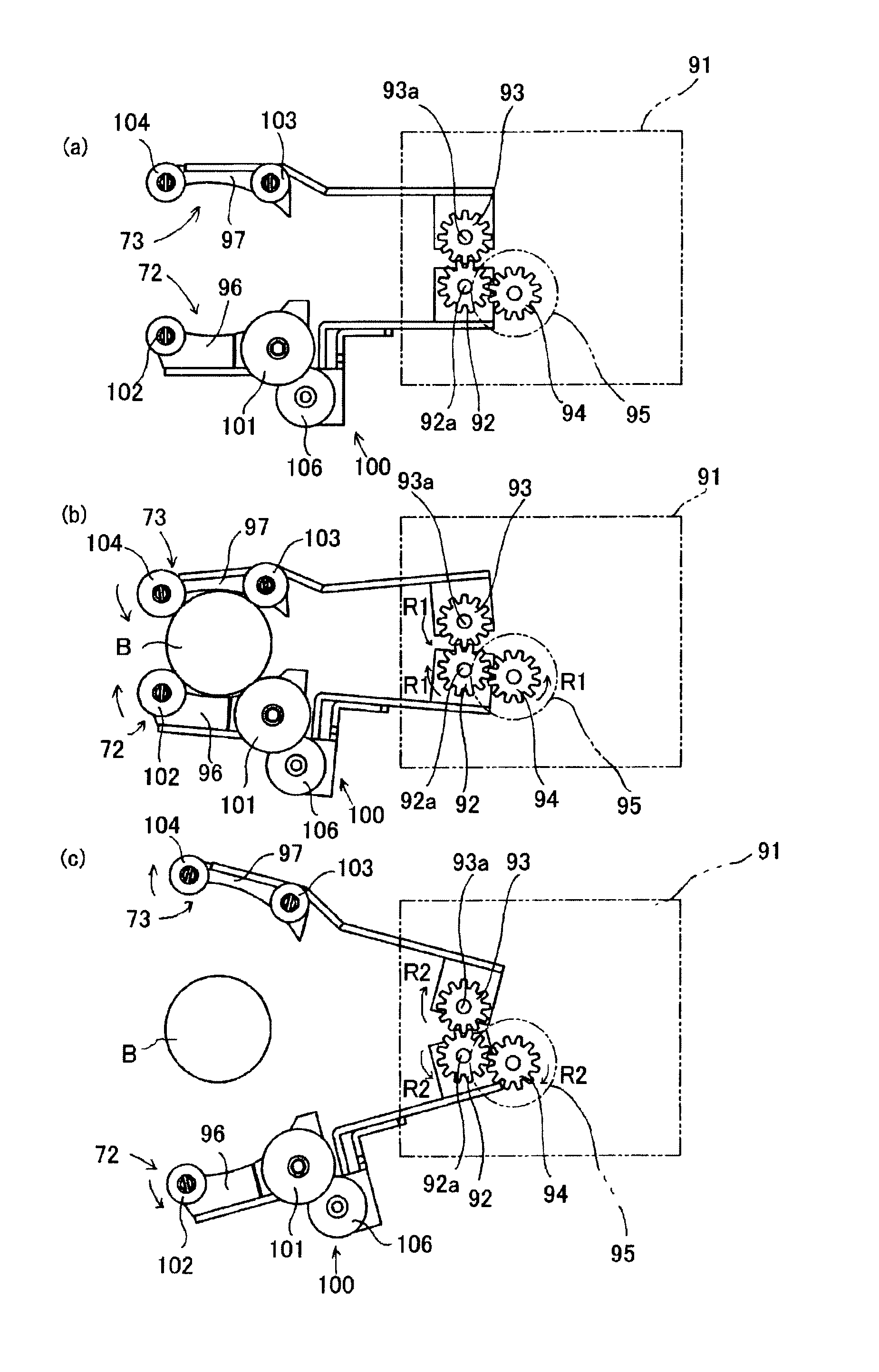
There is provided a medicine storing and dispensing apparatus, which is capable of filling medicines dispensed from a medicine feeding means into a container generally evenly without depending on its regions to thereby effectively utilize an internal space of the container. The medicine storing and dispensing apparatus has arms 72, 73 and is capable of filling tablets into a vial B held by the arms. A drive roller 101, which is rotated along with the operation of a motor, is provided at the arm 72. The medicine storing and dispensing apparatus can rotate the vial B by rotating the drive roller 101 when filling the tablets into the vial B held by the arms 72, 73.
Owner:YUYAMA MFG CO LTD
Pneumatic tire
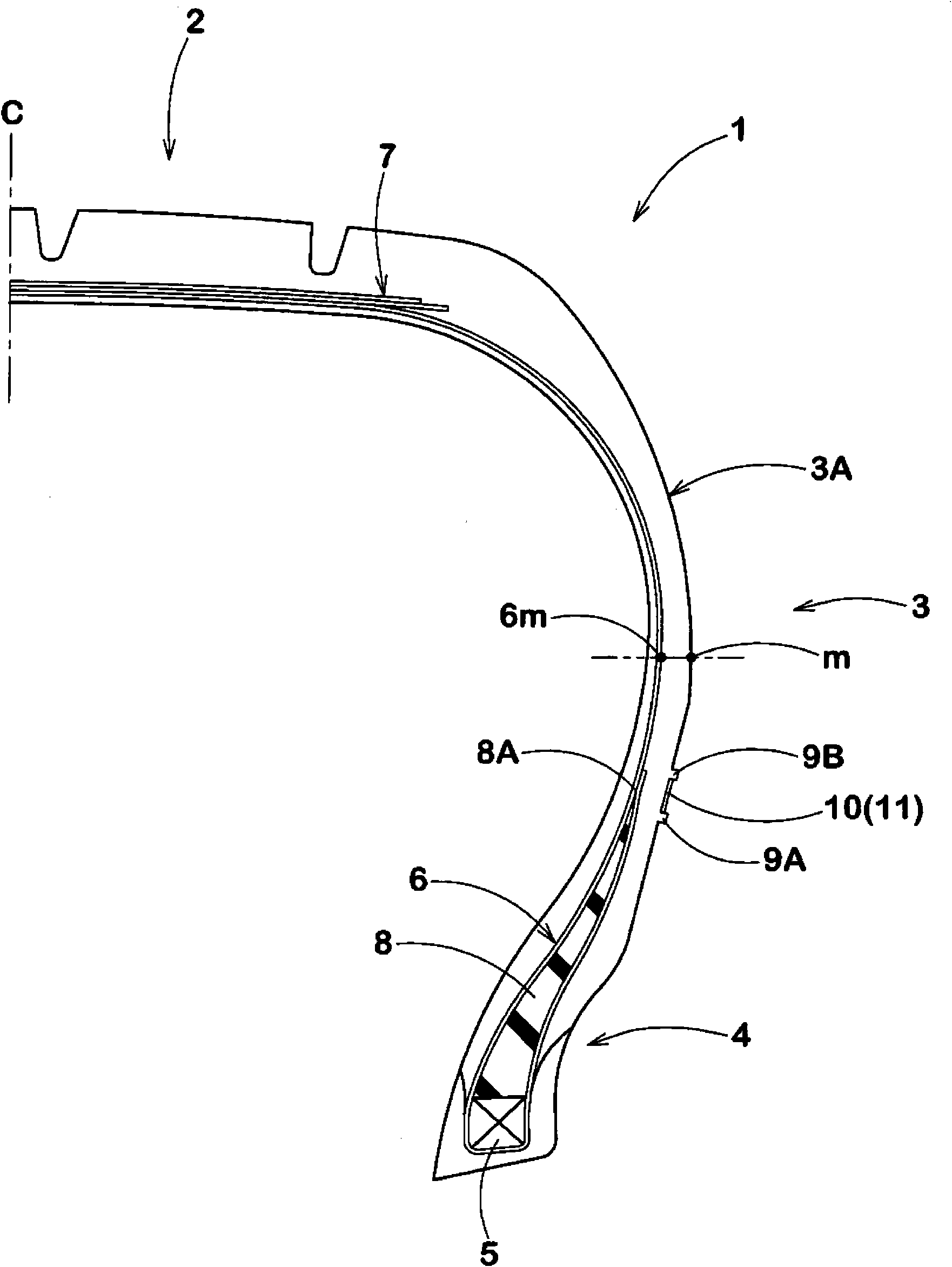
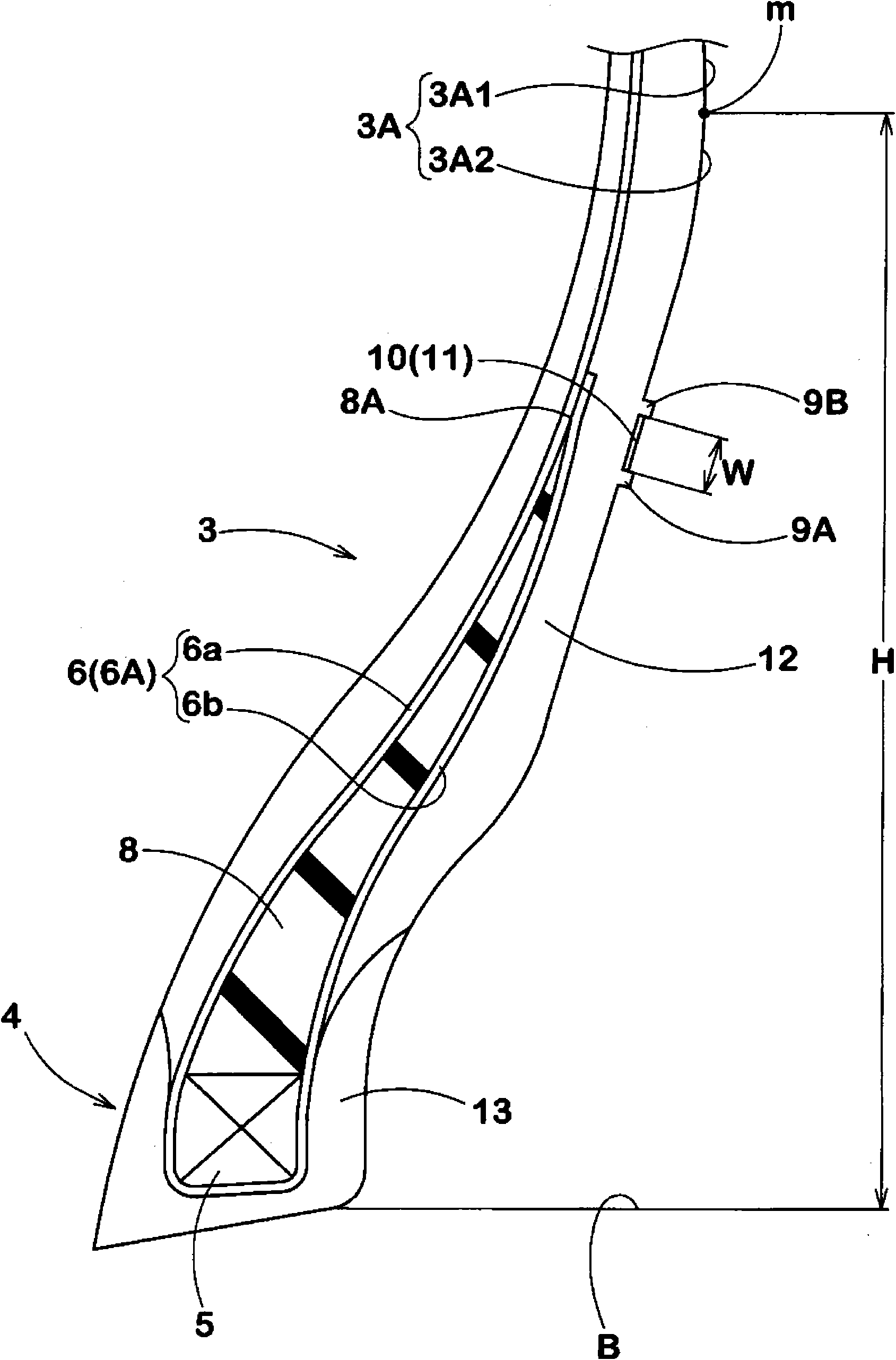
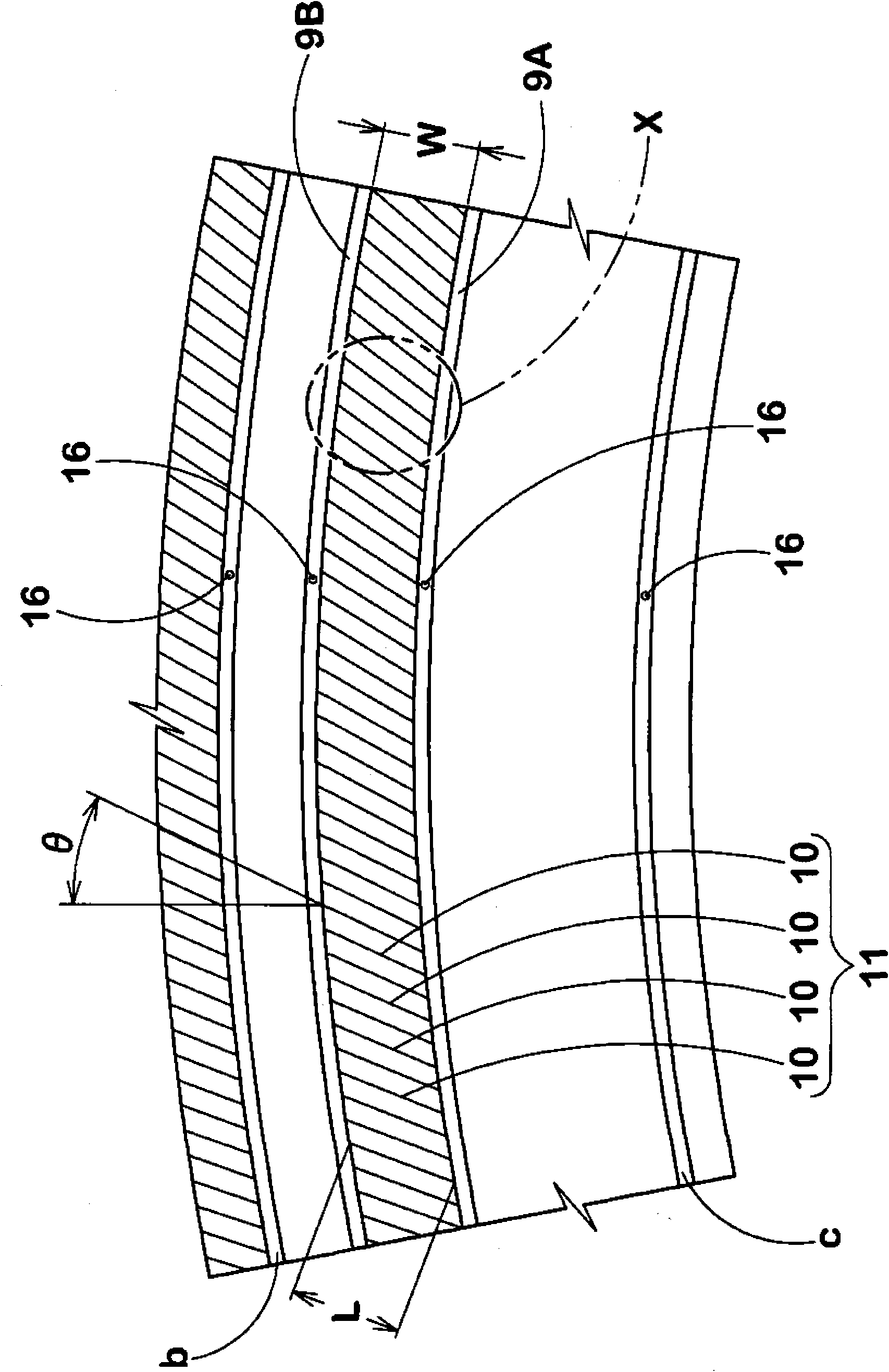
ActiveCN101898490AInhibition of encapsulationPrevent peelingTyre beadsTyre sidewallsIts regionEngineering
The invention provides a pneumatic tire in which bareness of rubber on the tire outer surface is effectively prevented. The outer surface of the tire is provided in its region radially inside a maximum width position of the carcass with vent lines (9) extending in a tire circumferential direction, wherein the vent lines (9) include a radially inner first vent line (9A) and a radially outer second vent line (9B). The area between the first vent line (9A) and second vent line (9B) is formed as a serrated area (11) comprising a plurality of circumferentially spaced small ribs (10) extending from the first vent line (9A) to the second vent line (9B). The serrated area (11) has deepest parts and shallowest parts. The shallowest parts are located inside the ridge of each of the vent lines, and the deepest parts are located at the same level as or outside a virtual tire outer surface.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Arrangement for connecting a drawer frame to the bottom of a drawer
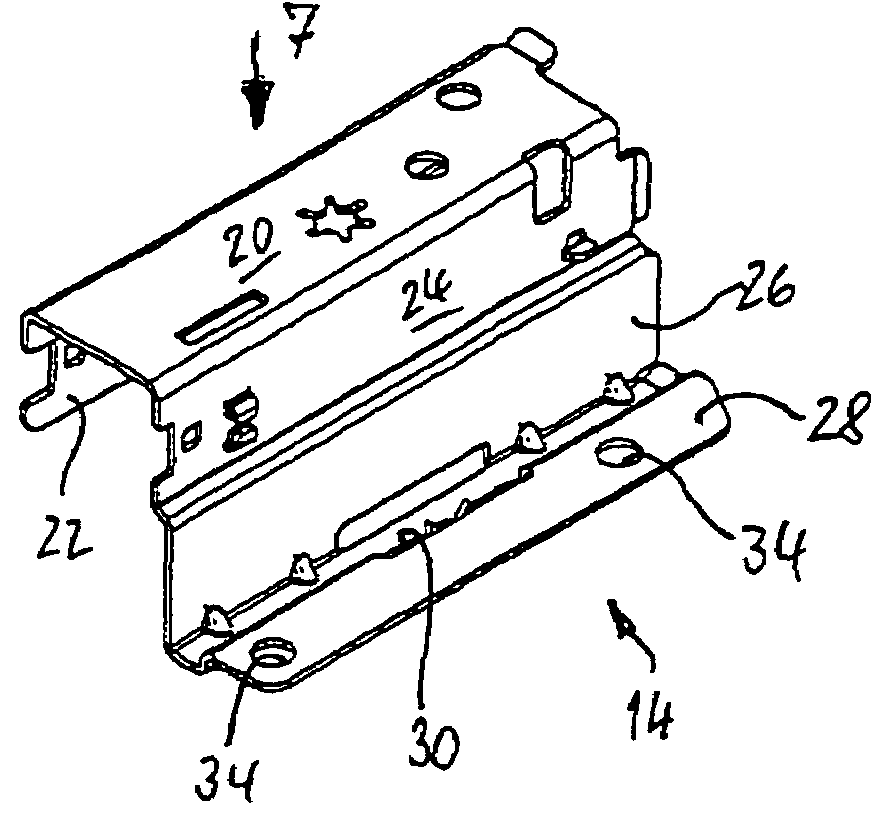
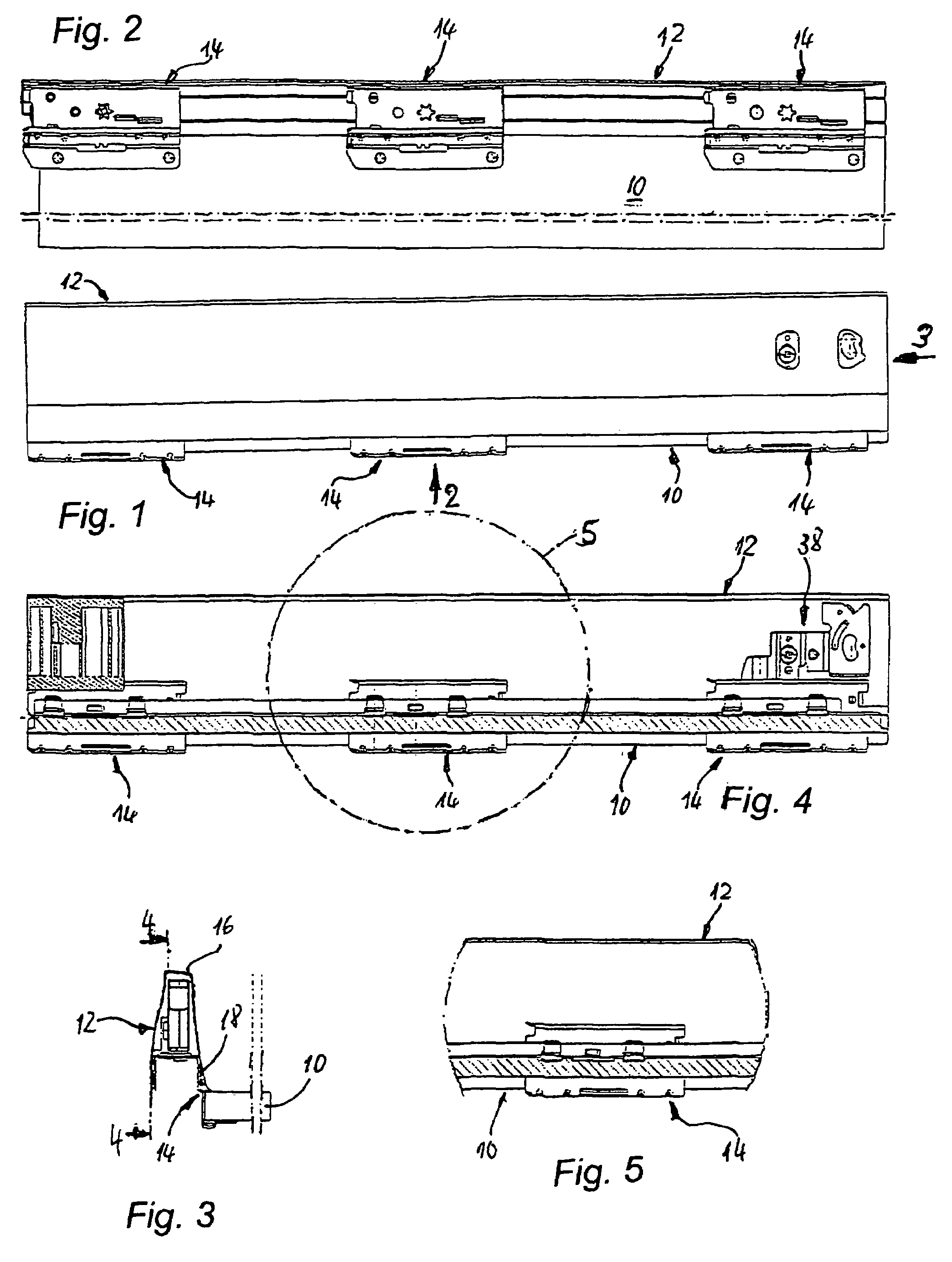
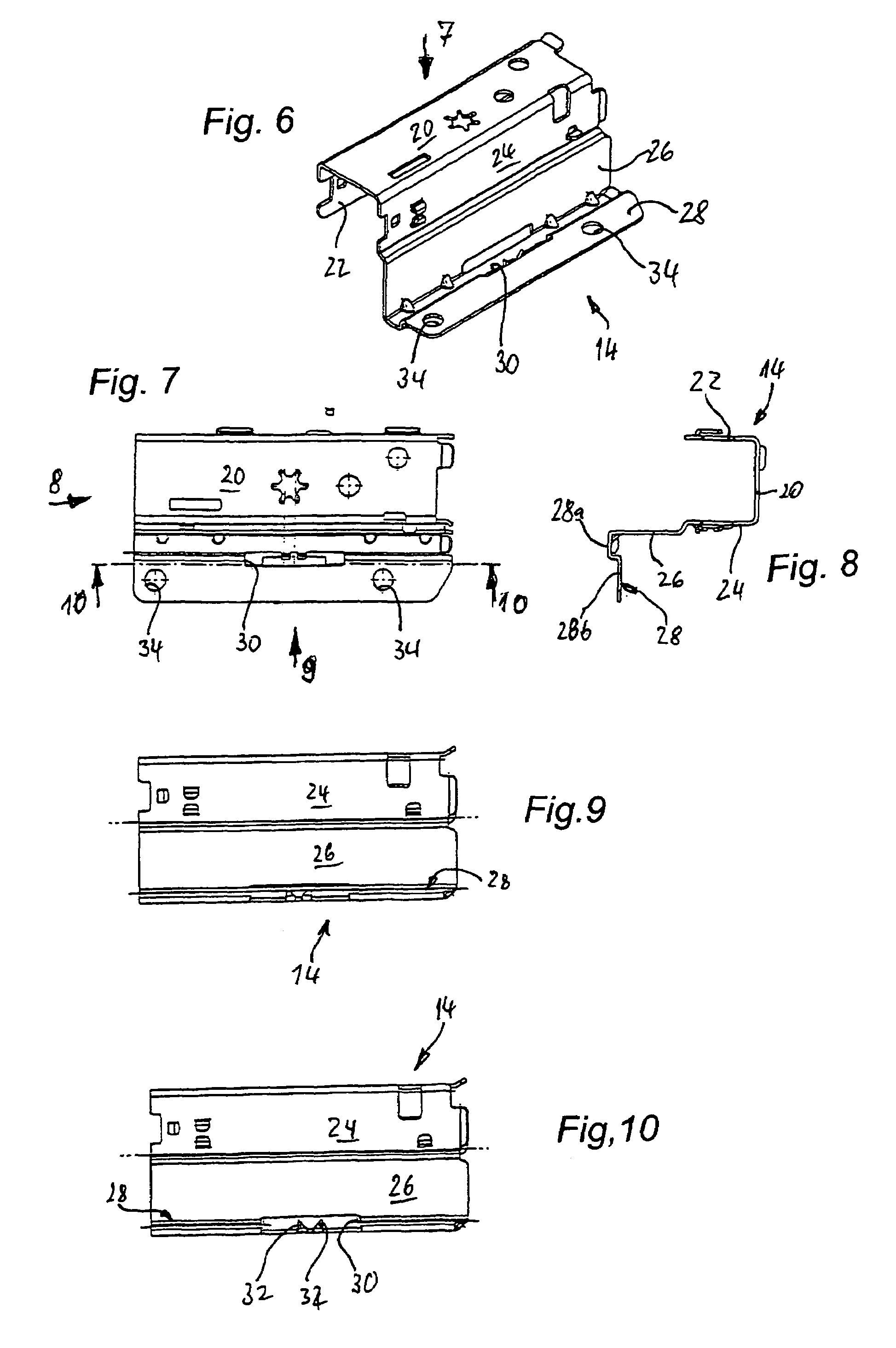
InactiveUS7455374B2Slows down retraction movementThe process is simple and fastDrawersIts regionEngineering
Arrangement for connecting a drawer frame (12) formed by a metal hallow chamber profile to the facing lateral edge of the associated plate-shaped drawer bottom (10), in which at least in part-regions of its lower end region opposite the end face of the edge of the drawer bottom (10) the drawer frame (12) has in each case a strip-shaped vertical contact web (26) for the lateral end face of the drawer bottom (10), and a supporting leg (28) which engages under the drawer bottom in the proper connection position is bent away from the lower end of the contact web. The supporting leg has integrally projecting from it fixing claws (32) which are pointed or sharpened at their free ends, project over the support surface of the supporting leg (28) and can be pressed into the material of a drawer bottom which is to be fixed. Each supporting leg (28) has at least one elongate punched-out slot (30) which is closed all round in its region between the strip-shaped contact web (26) and its free edge. The fixing claws (32) are attached integrally to one of the edges of the punched-out slot (30) and are extensions formed out of the material of the supporting leg (28) itself which are bent round substantially at right angles in the direction of the drawer bottom (10).
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA +1
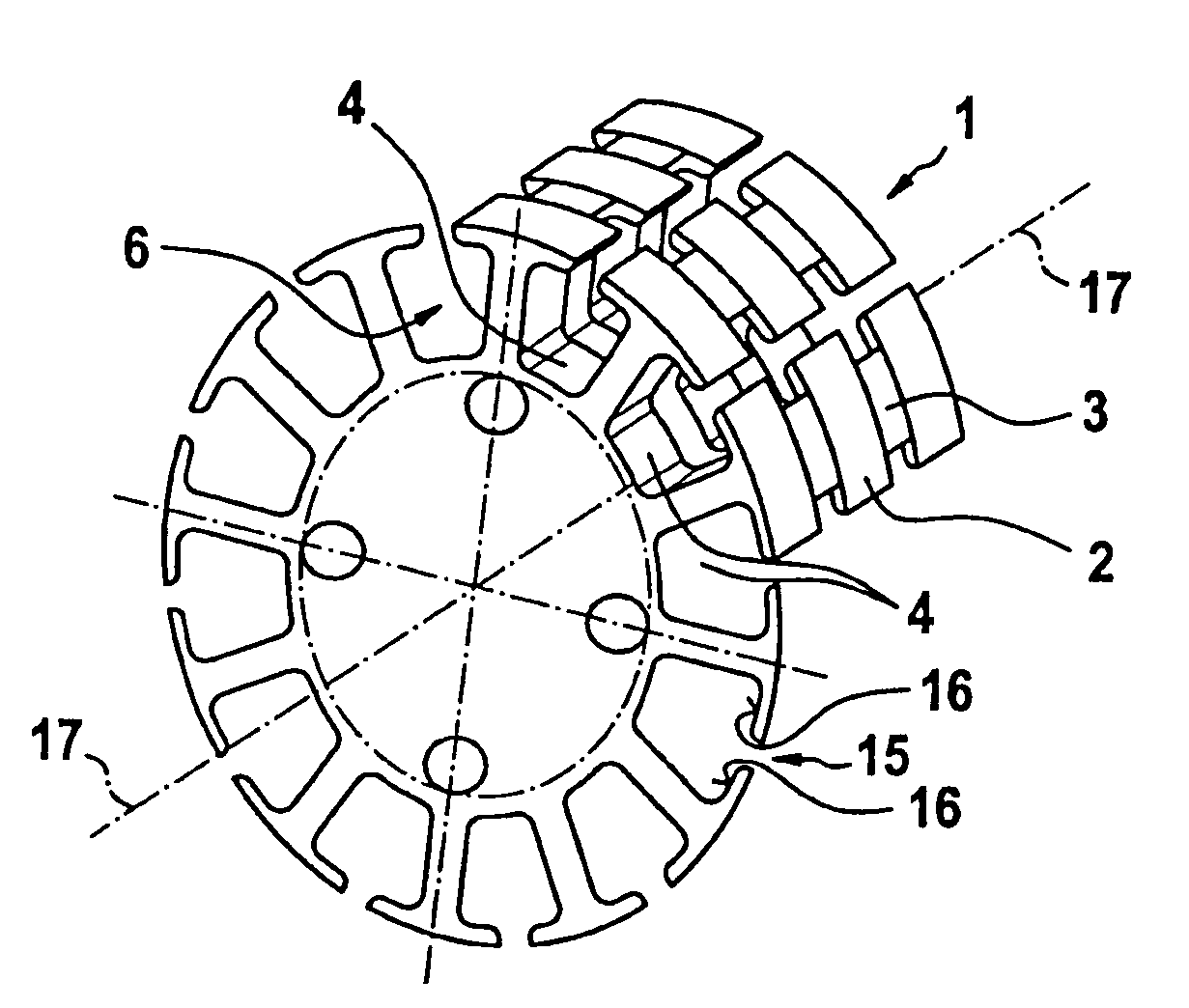
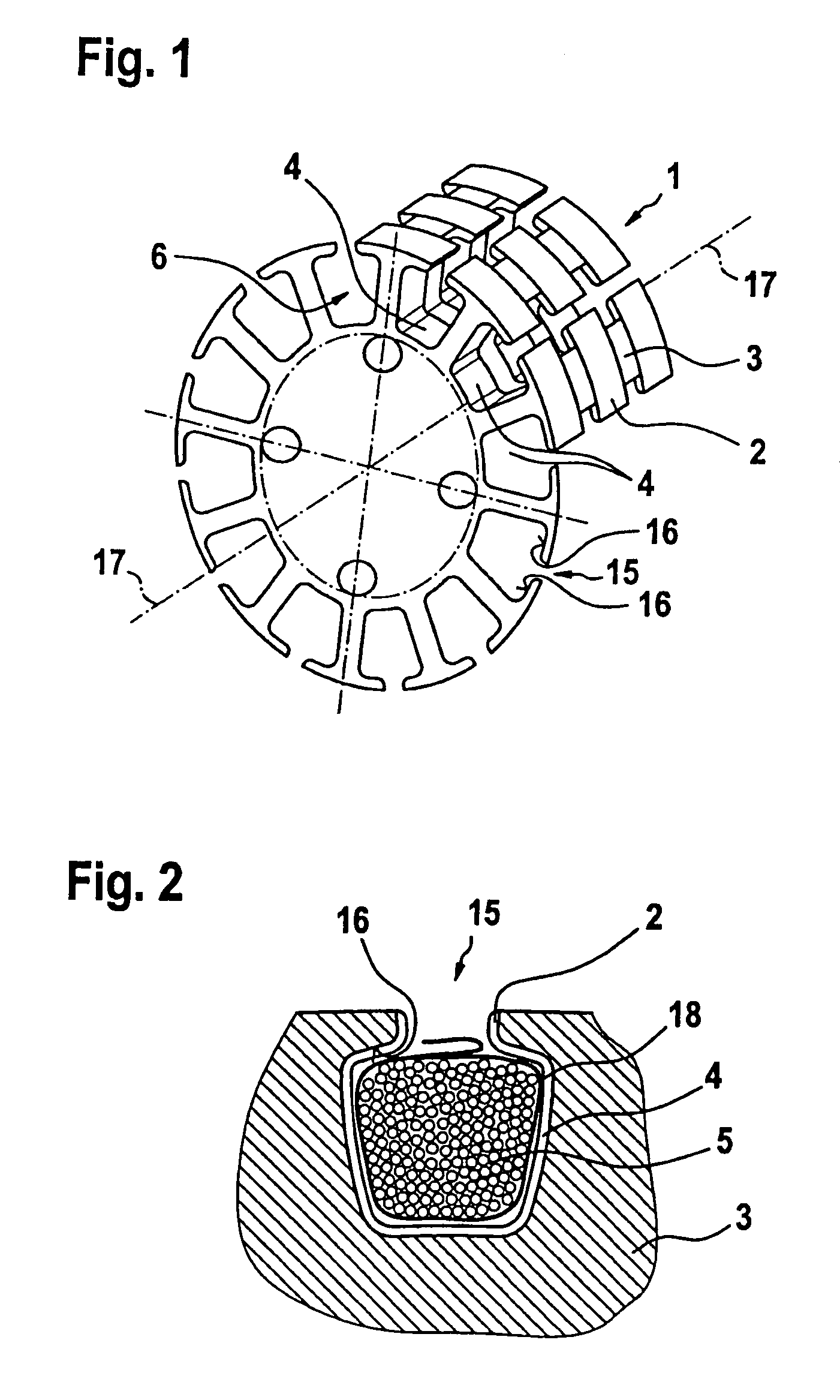
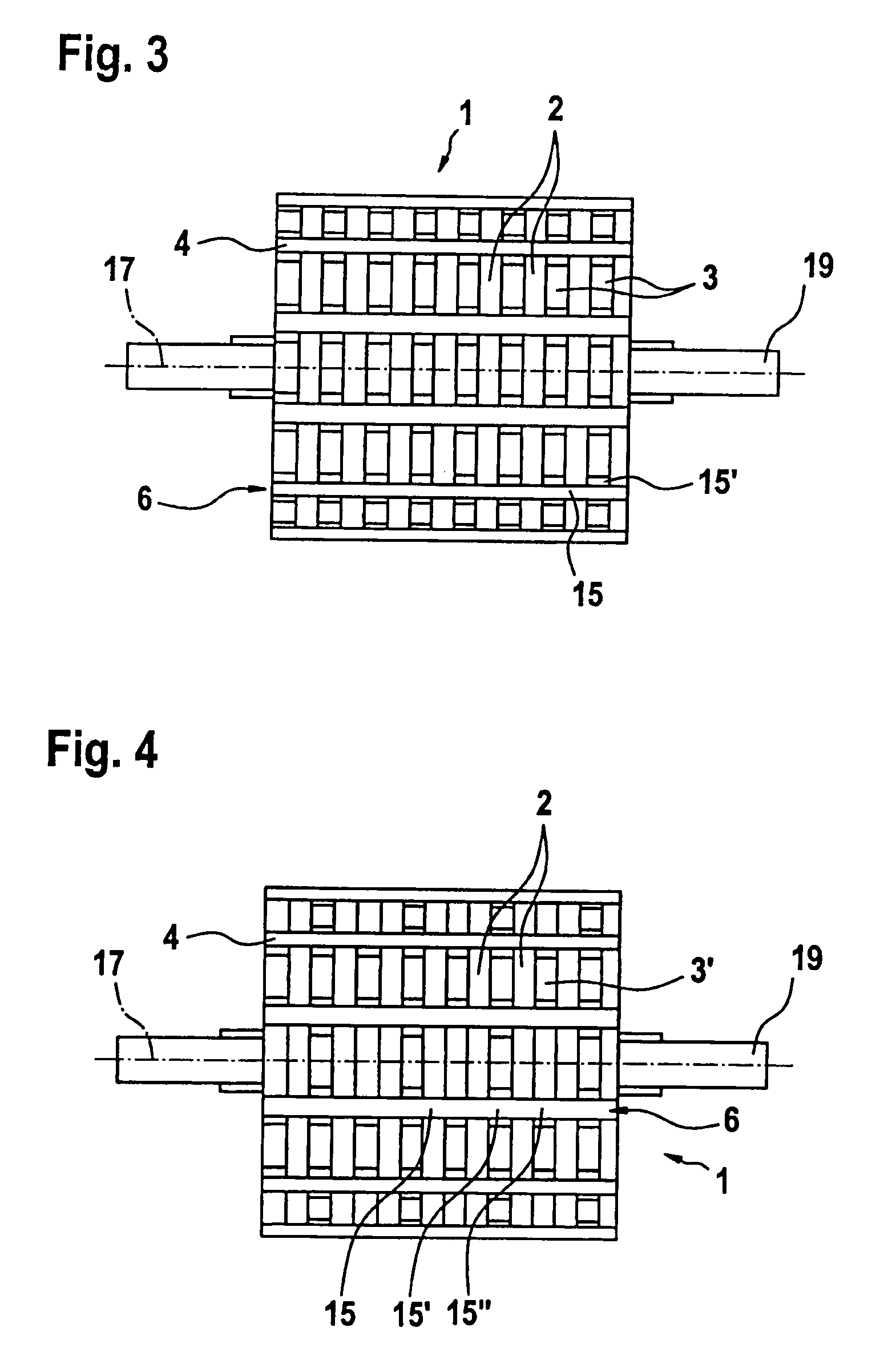
Laminated armature core for an electric motor
InactiveUS7365469B2Easy to fix and locateReduce vibrationWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuit rotating partsIts regionEngineering
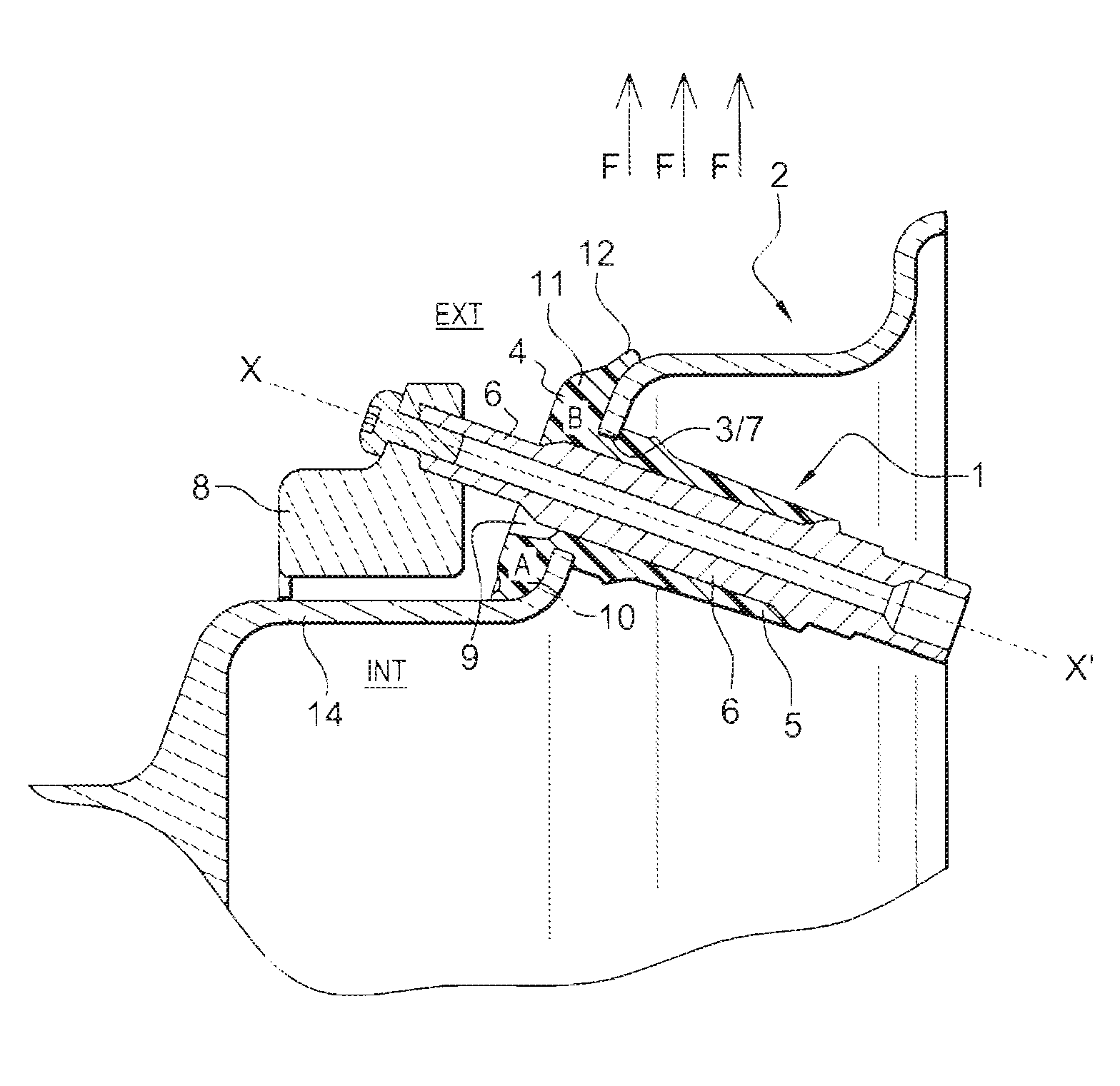
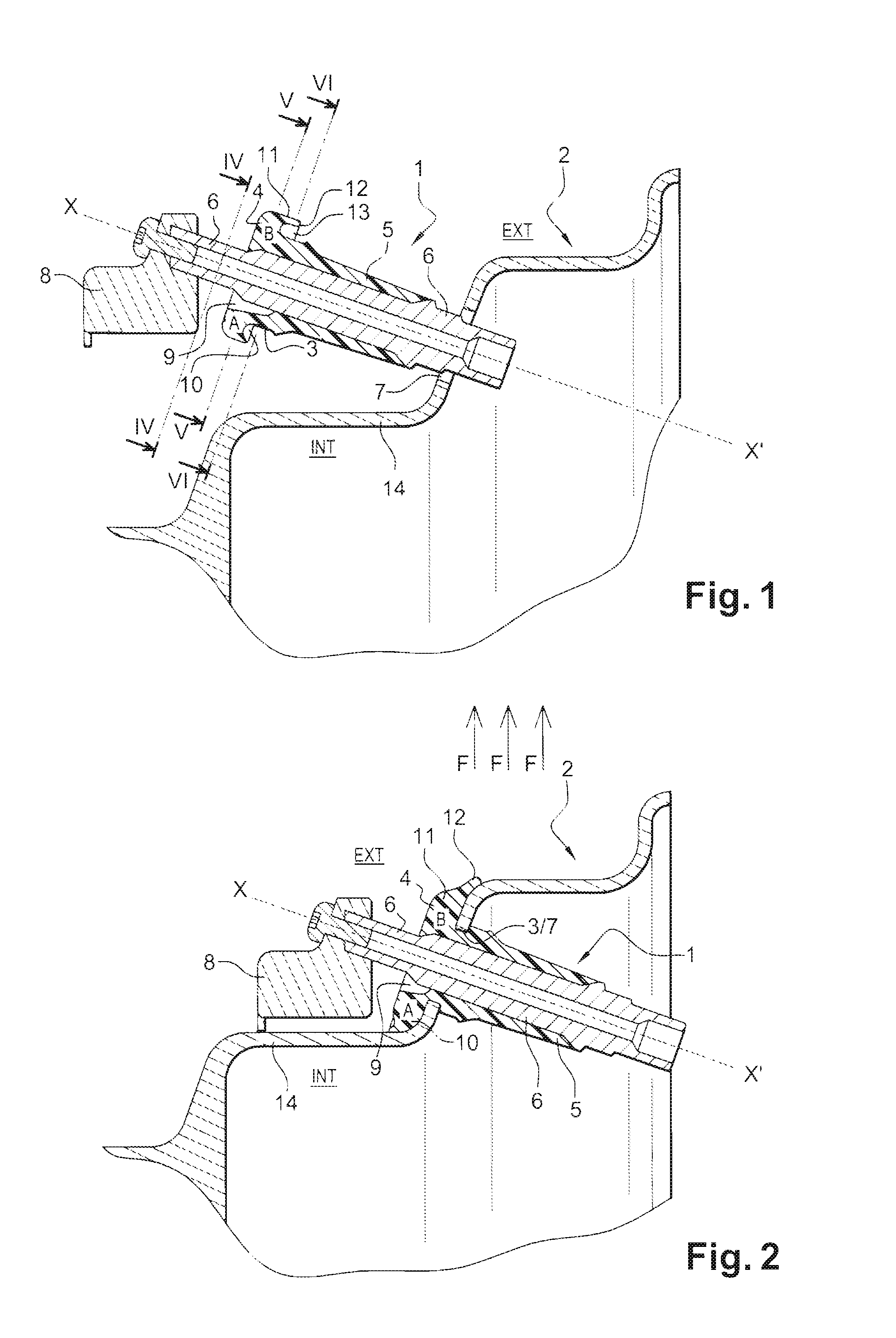
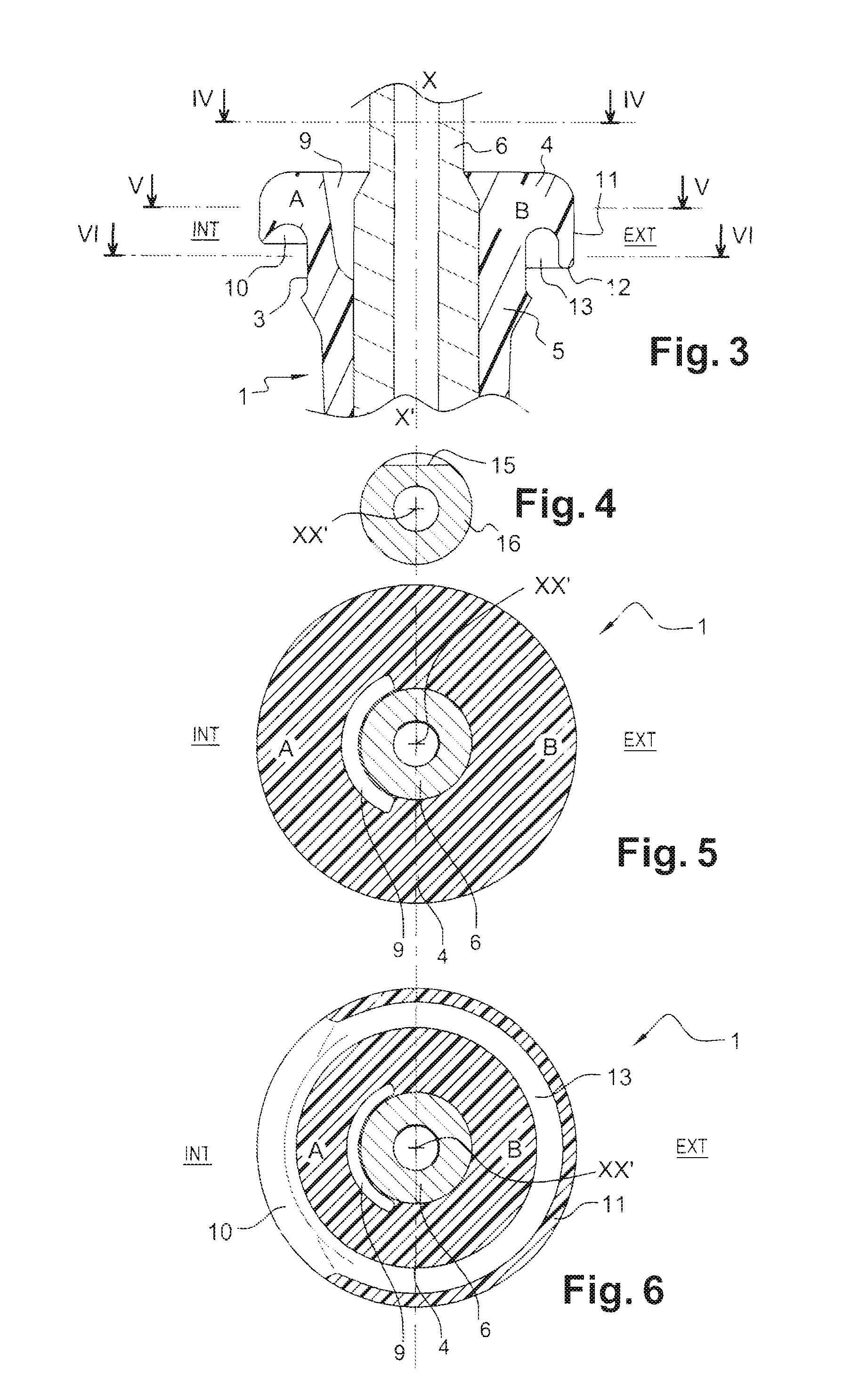
In an armature packet (1) for an electric motor, having a plurality of armature laminations (2, 3), in each of which a plurality of winding slots (4) for receiving an armature winding (5) are embodied, and the winding slots (4) of adjacent armature laminations (2, 3) are located in alignment with one another and form a conduit (6), a better positional fixation of the armature winding (5) is attained by providing that the winding slots (4), associated with one conduit (6), of different armature laminations (2, 3) have different geometries. The same is attained by providing that at least some of the winding slots (4) each have an influx conduit (11), each of which discharges into its region oriented toward the center of the armature packet (1).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com