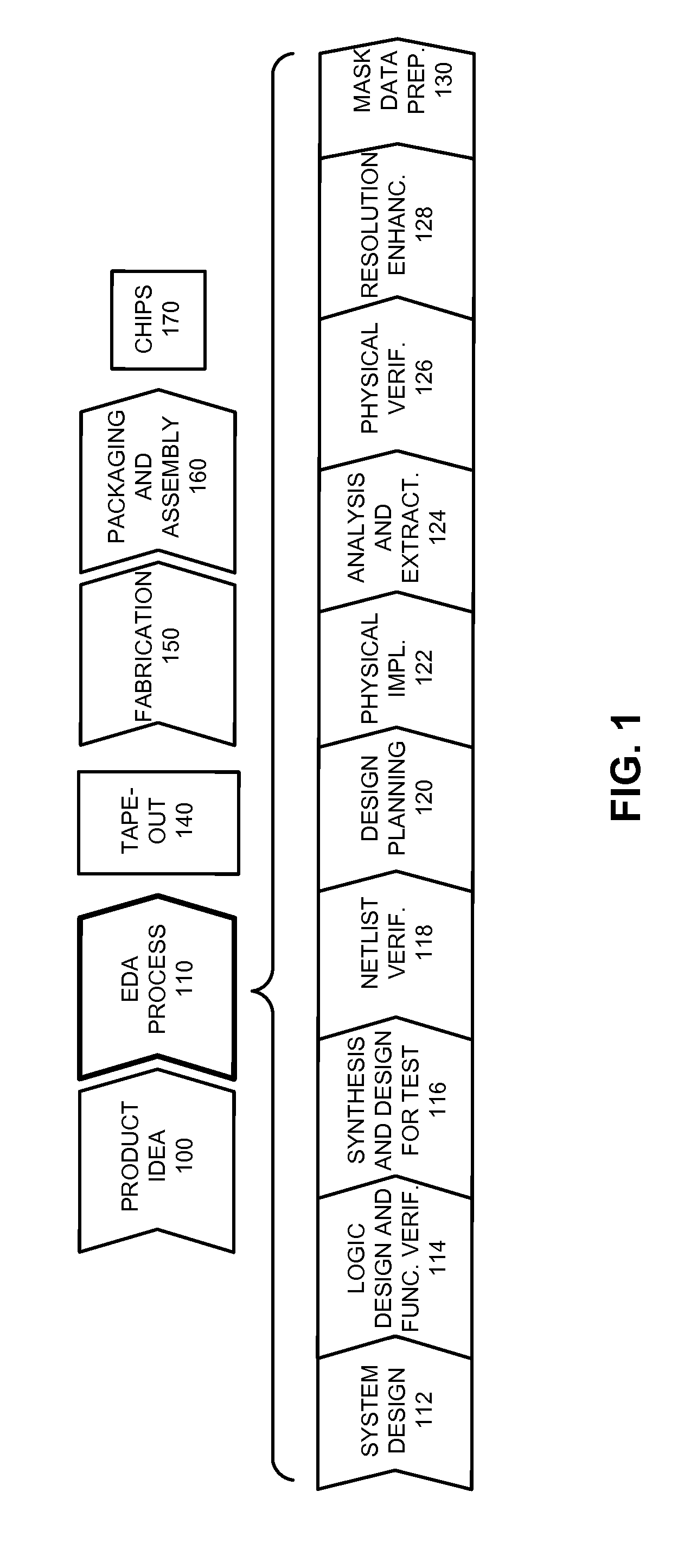
Patents
Literature
111 results about "Concurrent computing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
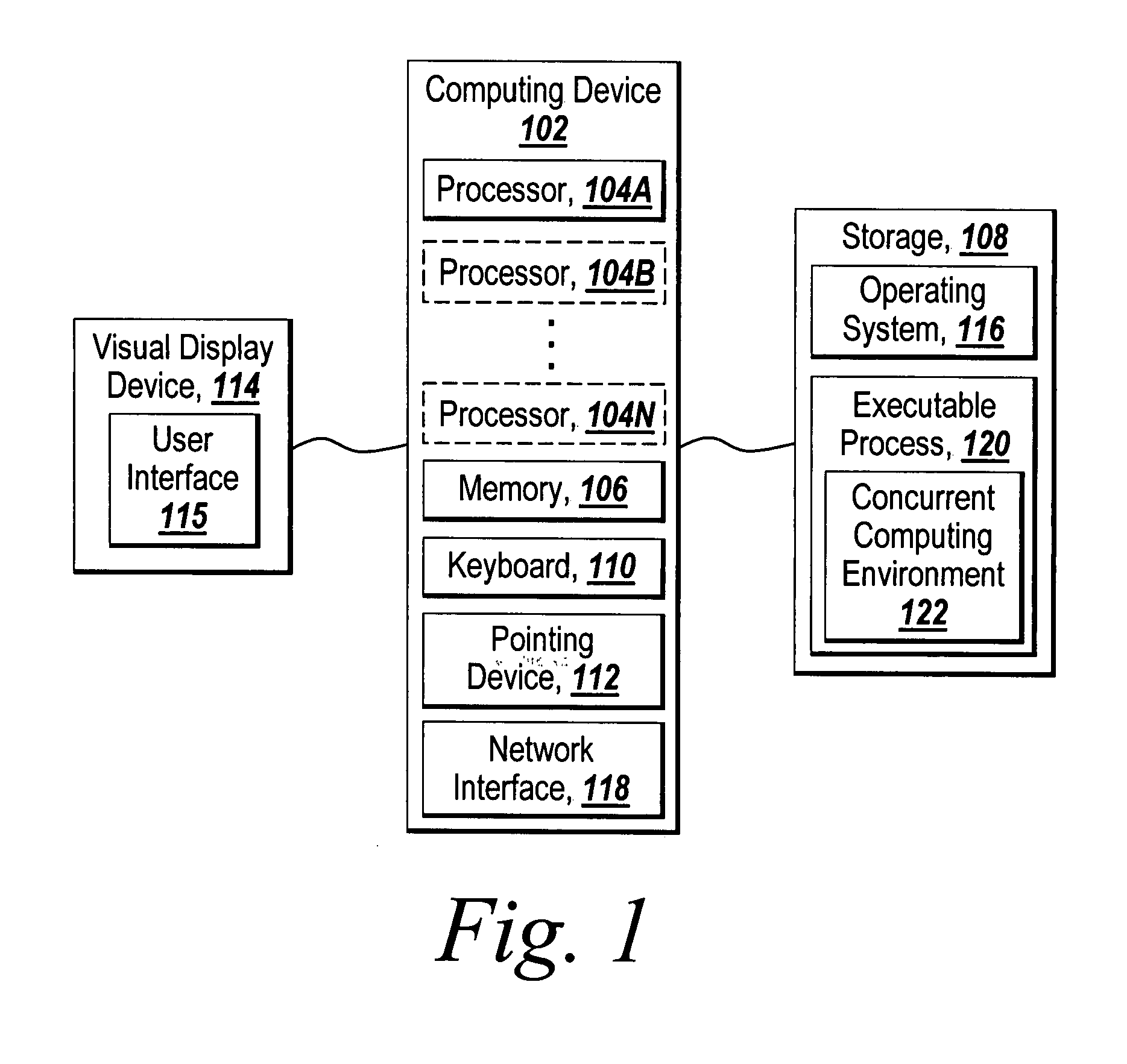
Concurrent computing is a form of computing in which several computations are executed during overlapping time periods—concurrently—instead of sequentially (one completing before the next starts). This is a property of a system—this may be an individual program, a computer, or a network—and there is a separate execution point or "thread of control" for each computation ("process"). A concurrent system is one where a computation can advance without waiting for all other computations to complete.
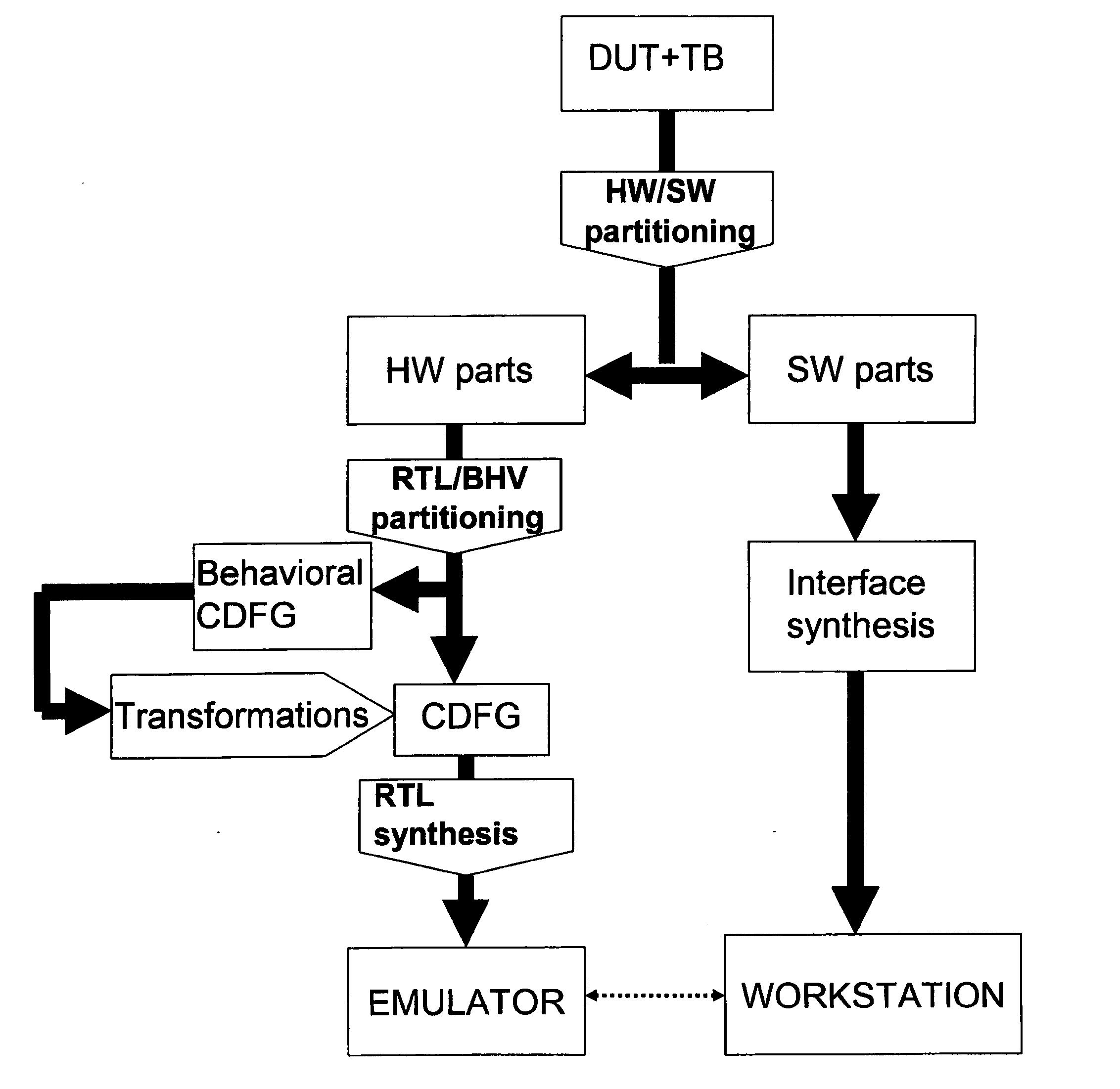
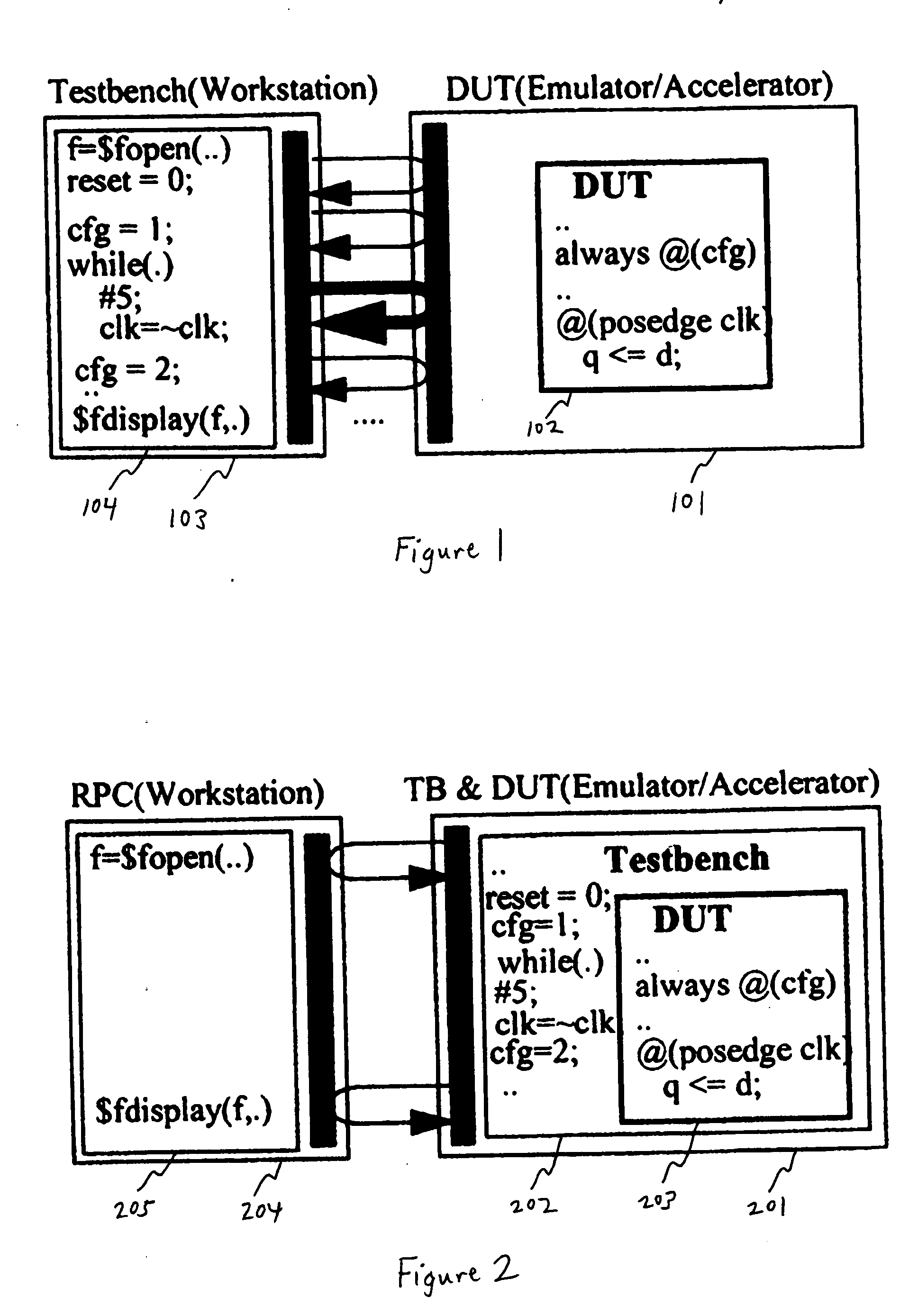
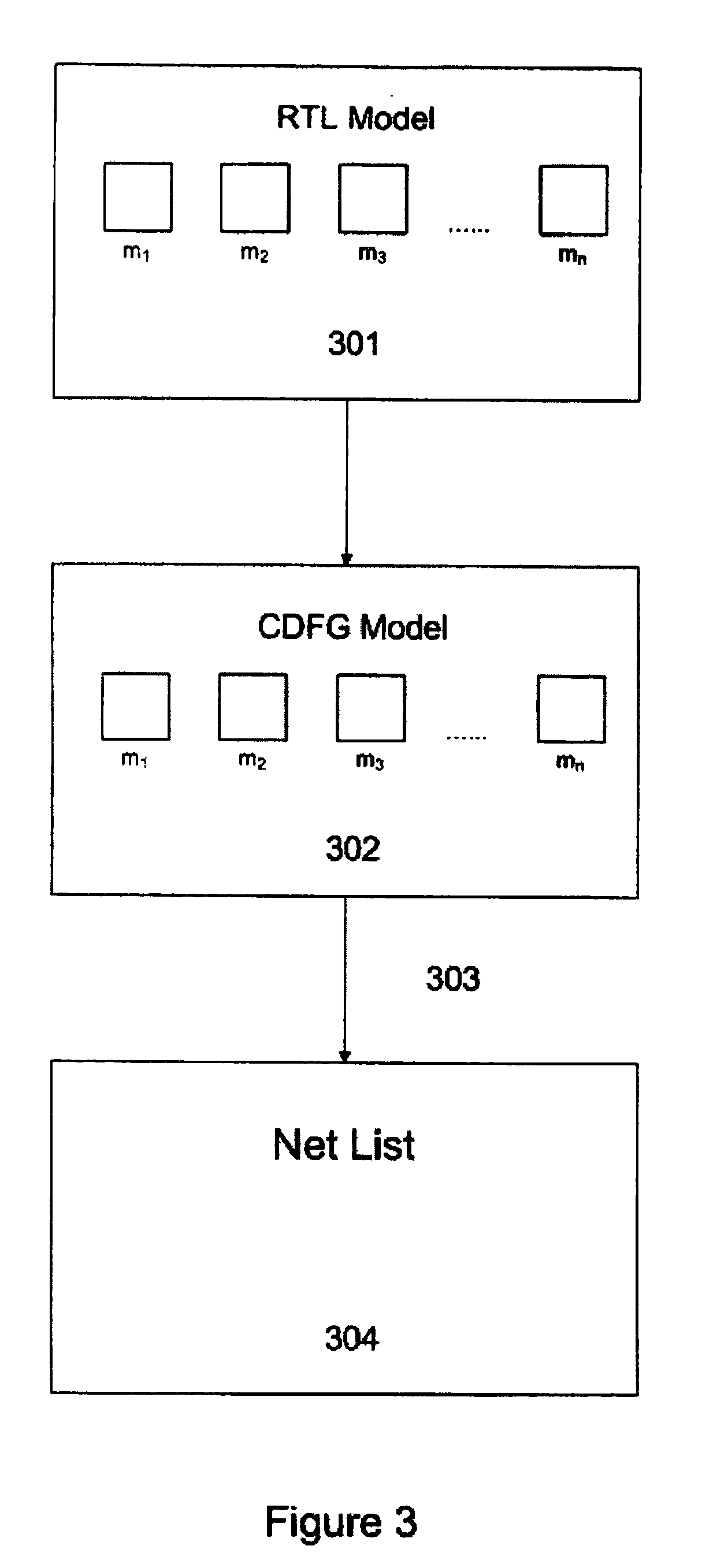
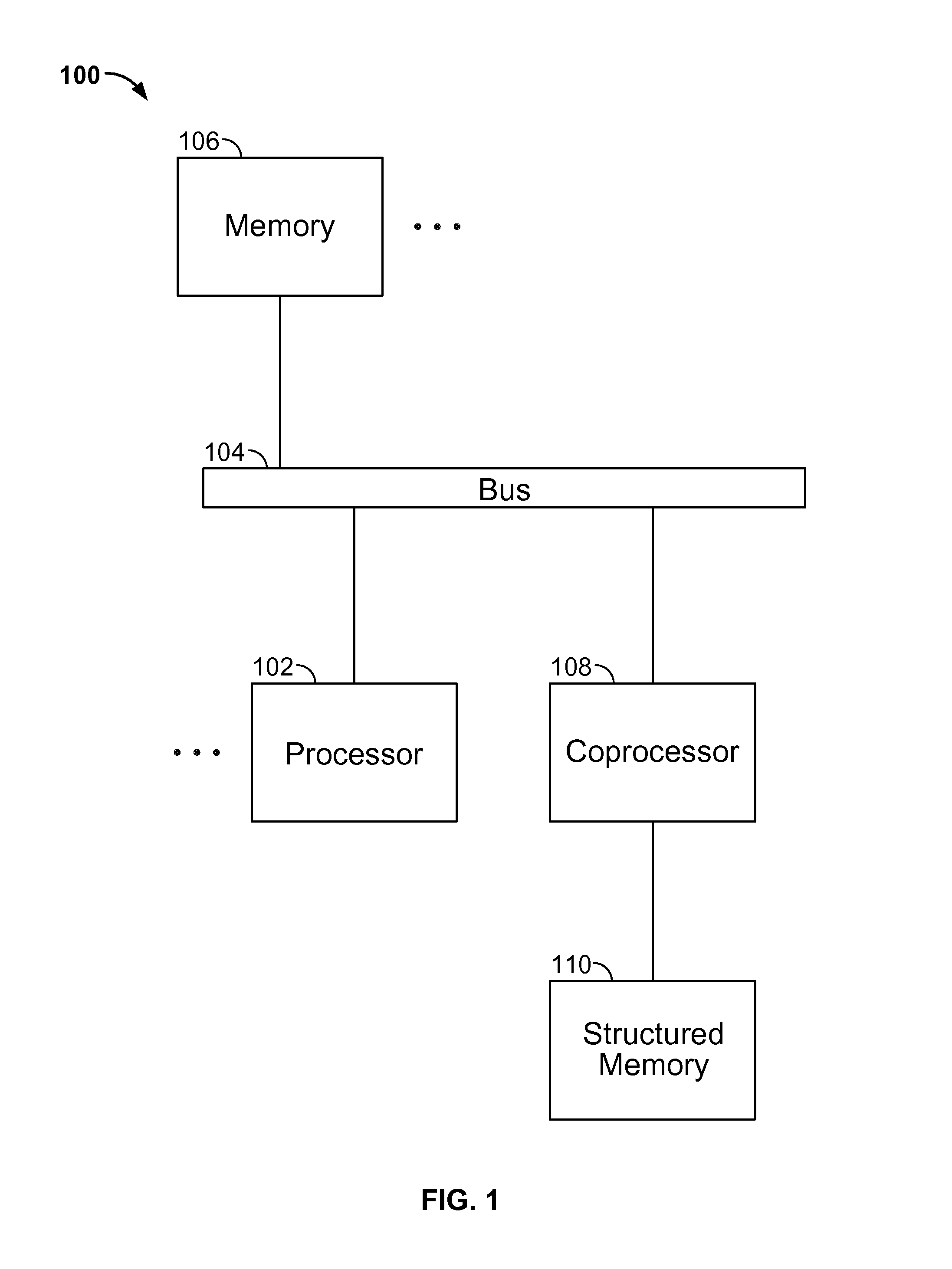
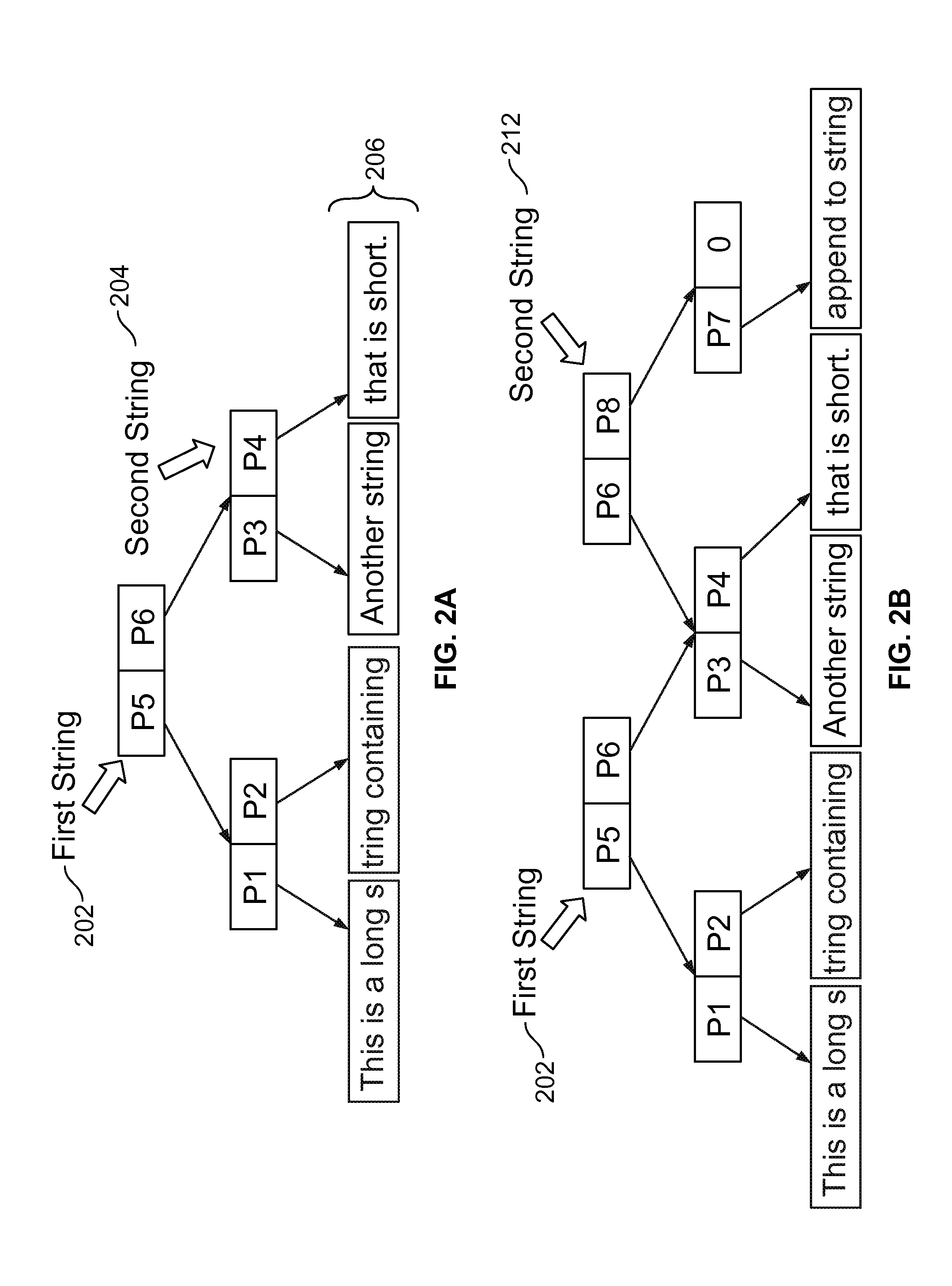
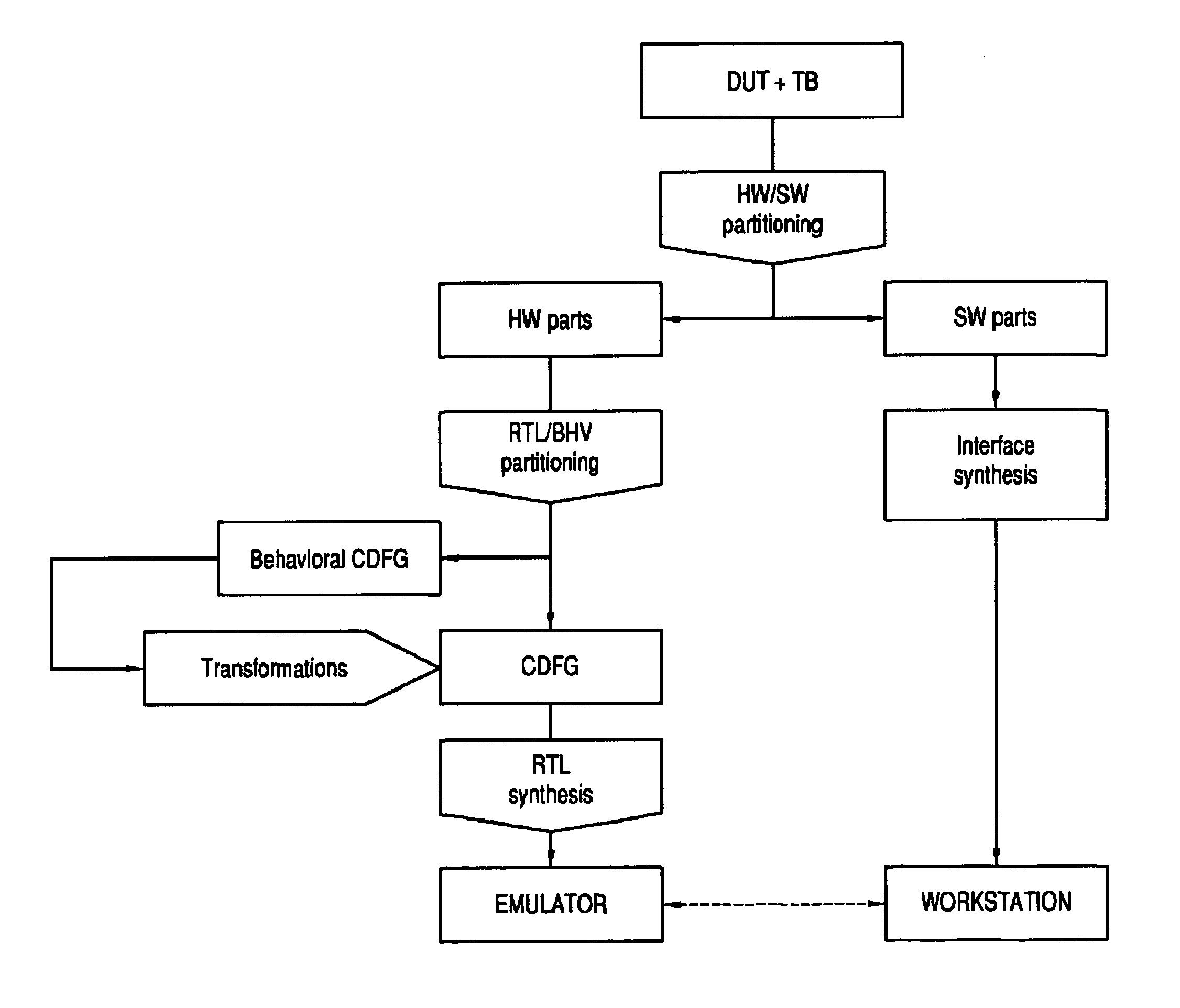
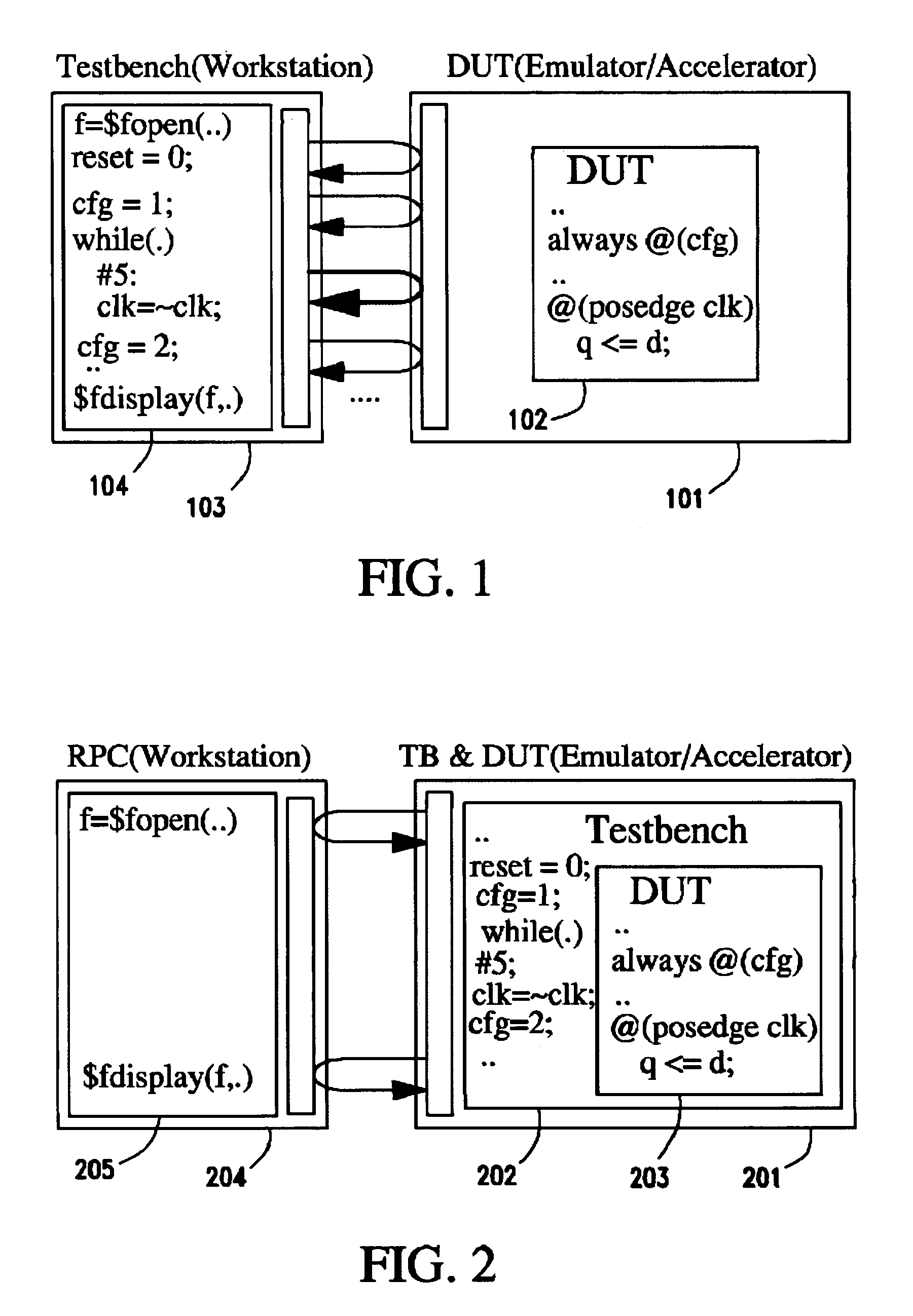
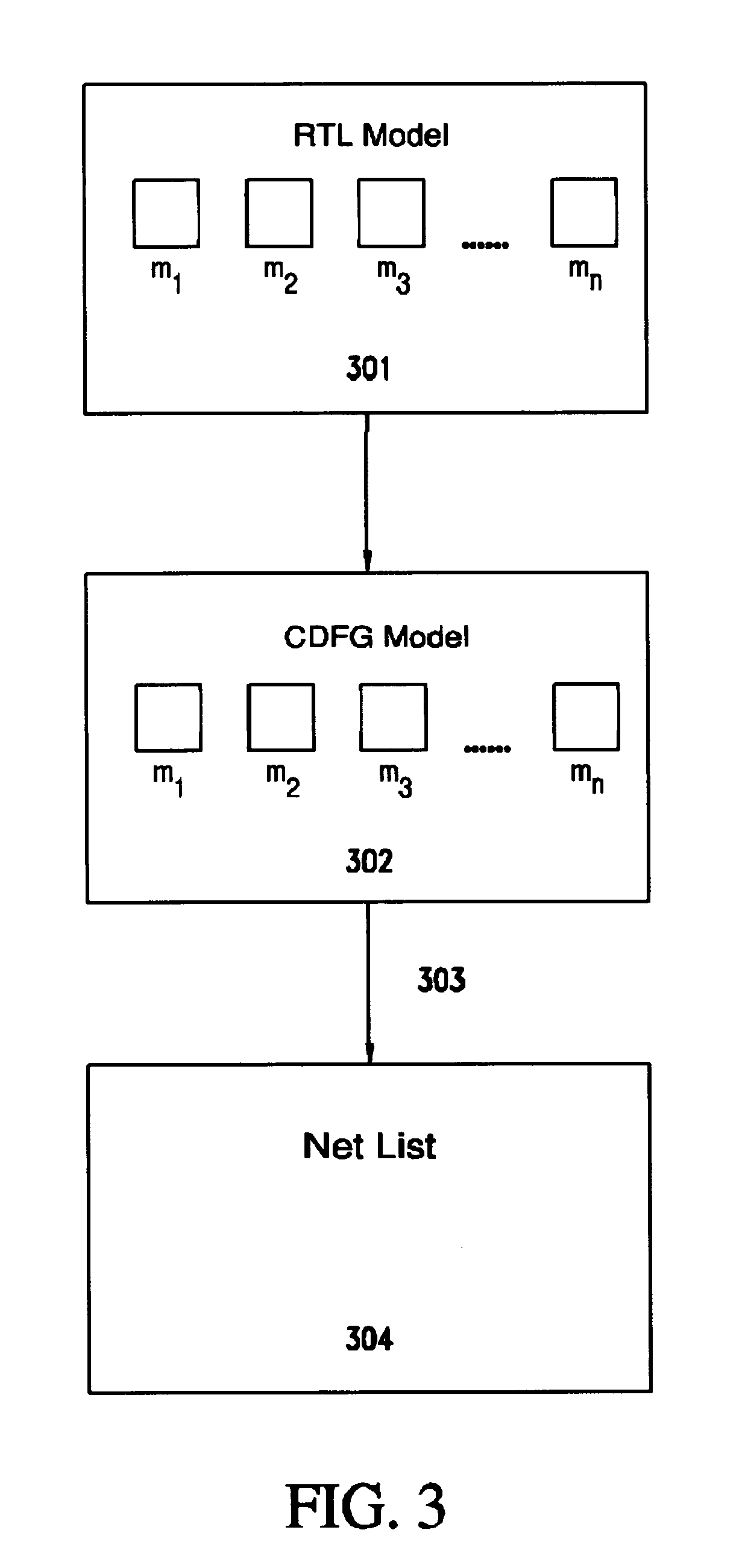
Method and system for hardware accelerated verification of digital circuit design and its testbench
ActiveUS20050144585A1Quick verificationOvercomes drawbackElectrical testingComputer aided designConcurrent computingValidation methods
A system and method is presented for synthesizing both a design under test (DUT) and its test environment (i.e., the testbench for the DUT), into an equivalent structural model suitable for execution on a reconfigurable hardware platform. This may be achieved without any change in the existing verification methodology. Behavioral HDL may be translated into a form that can be executed on a reconfigurable hardware platform. A set of compilation transforms are provided that convert behavioral constructs into RTL constructs that can be directly mapped onto an emulator. Such transforms are provided by introducing the concepts of a behavioral clock and a time advance finite state machine (FSM) that determines simulation time and sequences concurrent computing blocks in the DUT and the testbench.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
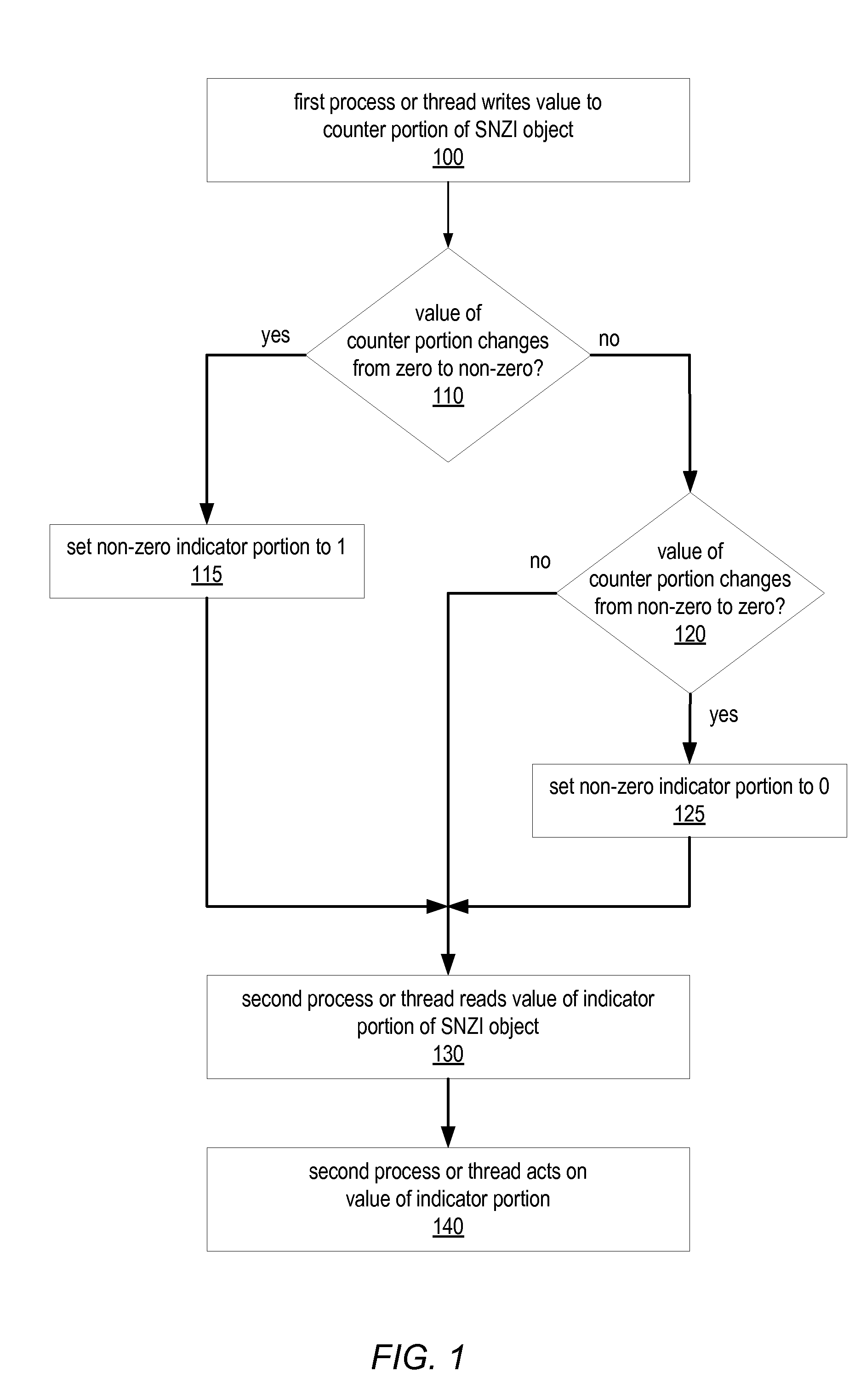
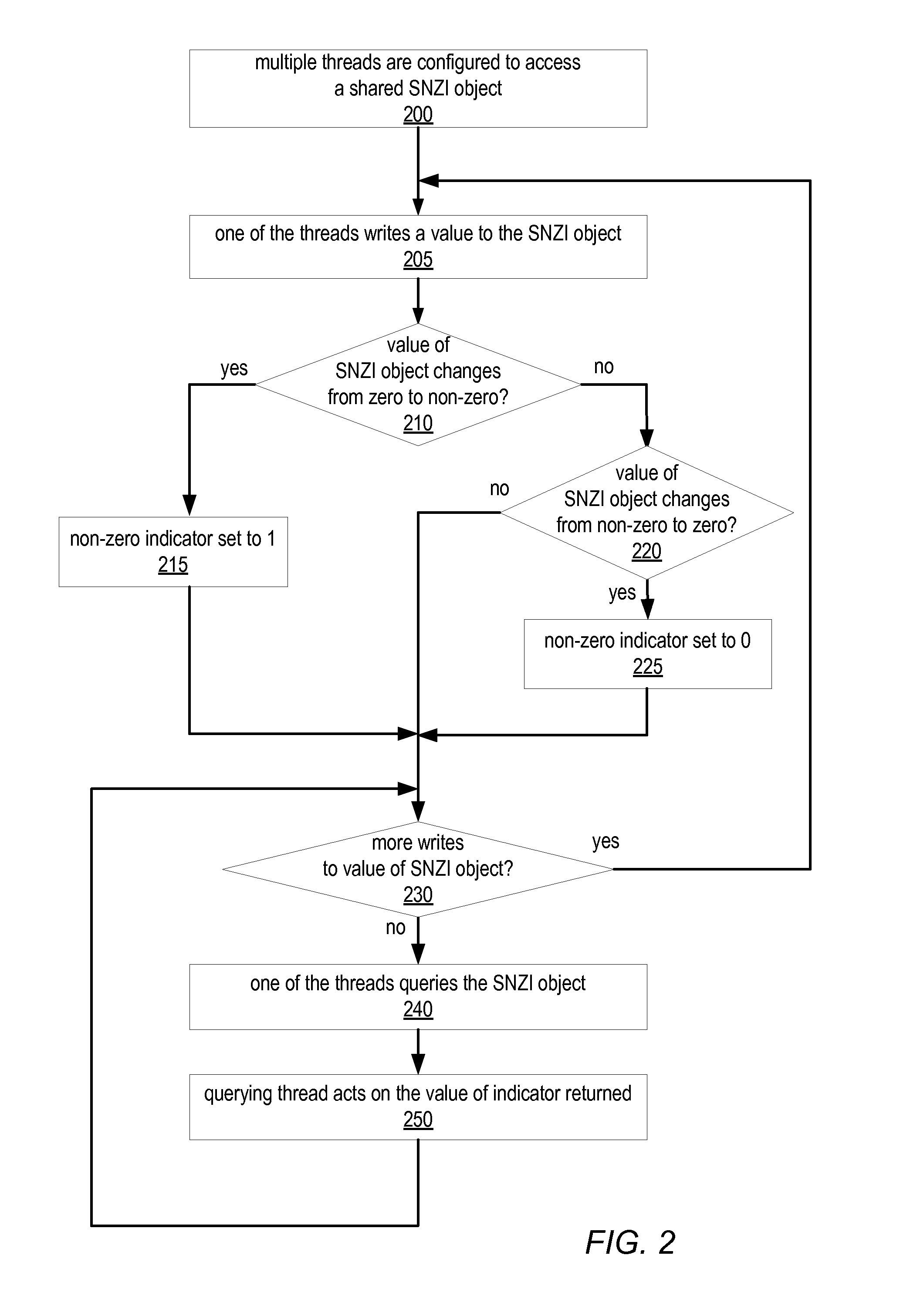
System and Method for Implementing Shared Scalable Nonzero Indicators
ActiveUS20090125548A1Program synchronisationSpecial data processing applicationsConcurrent computingConcurrent computation
A Scalable NonZero Indicator (SNZI) object in a concurrent computing application may include a shared data portion (e.g., a counter portion) and a shared nonzero indicator portion, and / or may be an element in a hierarchy of SNZI objects that filters changes in non-root nodes to a root node. SNZI objects may be accessed by software applications through an API that includes a query operation to return the value of the nonzero indicator, and arrive (increment) and depart (decrement) operations. Modifications of the data portion and / or the indicator portion may be performed using atomic read-modify-write type operations. Some SNZI objects may support a reset operation. A shared data object may be set to an intermediate value, or an announce bit may be set, to indicate that a modification is in progress that affects its corresponding indicator value. Another process or thread seeing this indication may “help” complete the modification before proceeding.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
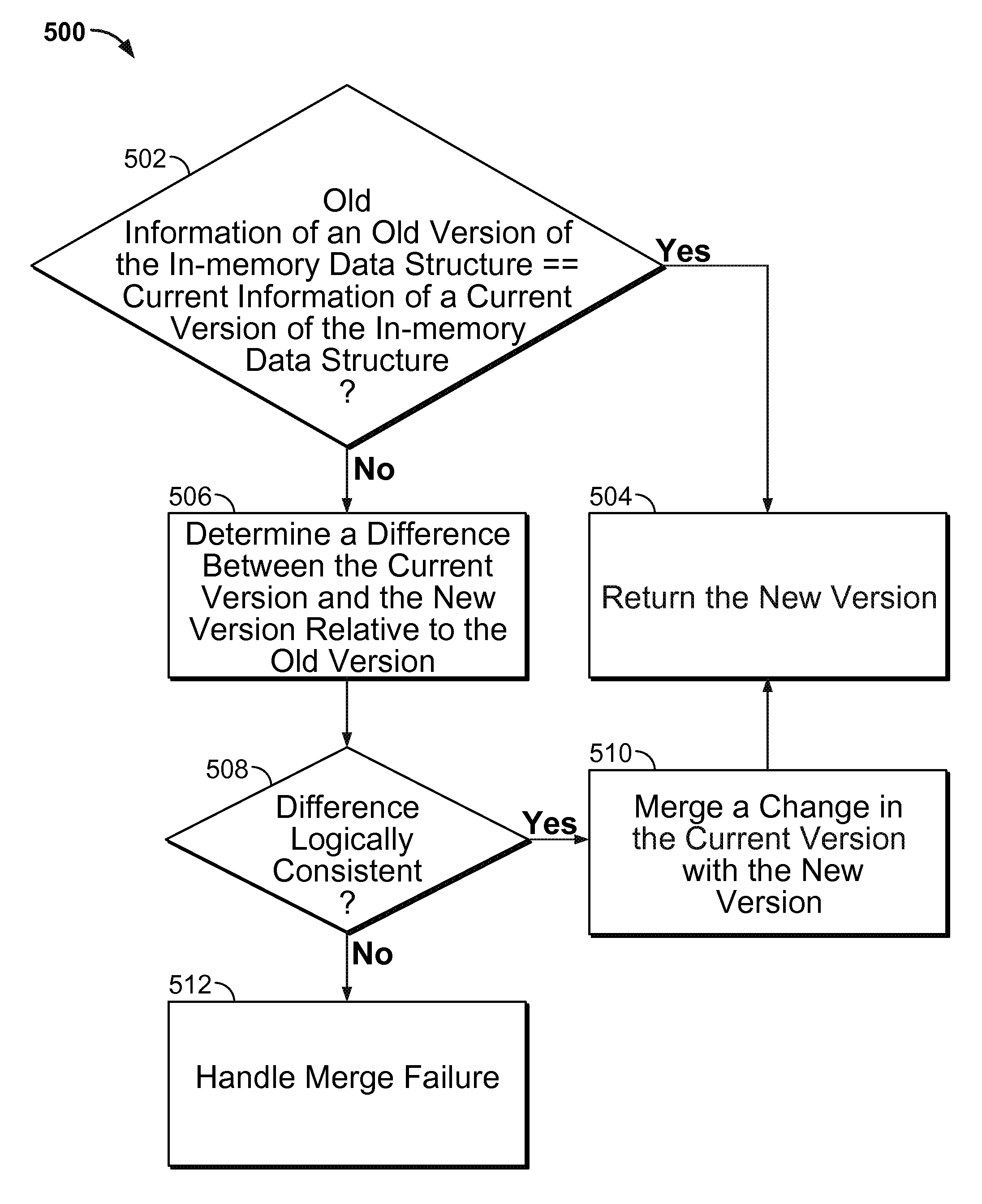
Merge-update for efficient atomic memory modification in concurrent computer systems
ActiveUS9047334B1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsConcurrent computingTheoretical computer science
Atomically updating an in-memory data structure that is directly accessible by a processor includes comparing old information associated with an old version of the in-memory data structure with current information associated with a current version of the in-memory data structure; in the event that the old information and the current information are the same, replacing the old version with a new version of the in-memory data structure; in the event that the old information and the current information are not the same, determining a difference between the current version of the in-memory data structure and the new version of the in-memory data structure, and determining whether the difference is logically consistent; and in the event that the difference is logically consistent, merging a change in the current version with the new version.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method for automatically extracting kernel keyword based on B2B platform
ActiveCN104408173AImprove performanceImprove availabilityWeb data indexingCommerceIndex termConcurrent computing
The invention discloses a method for automatically extracting a kernel keyword based on a B2B platform. The method is used for extracting the kernel keyword based on English grammar and semanteme according to the name of an English product. The method for automatically extracting the kernel keyword based on the B2B platform, disclosed by the invention, has obvious advantages in word treatment and self-learning according to a group of rules when various tenses of English words are changed into the original modes during big data concurrence compution.
Owner:FOCUS TECH
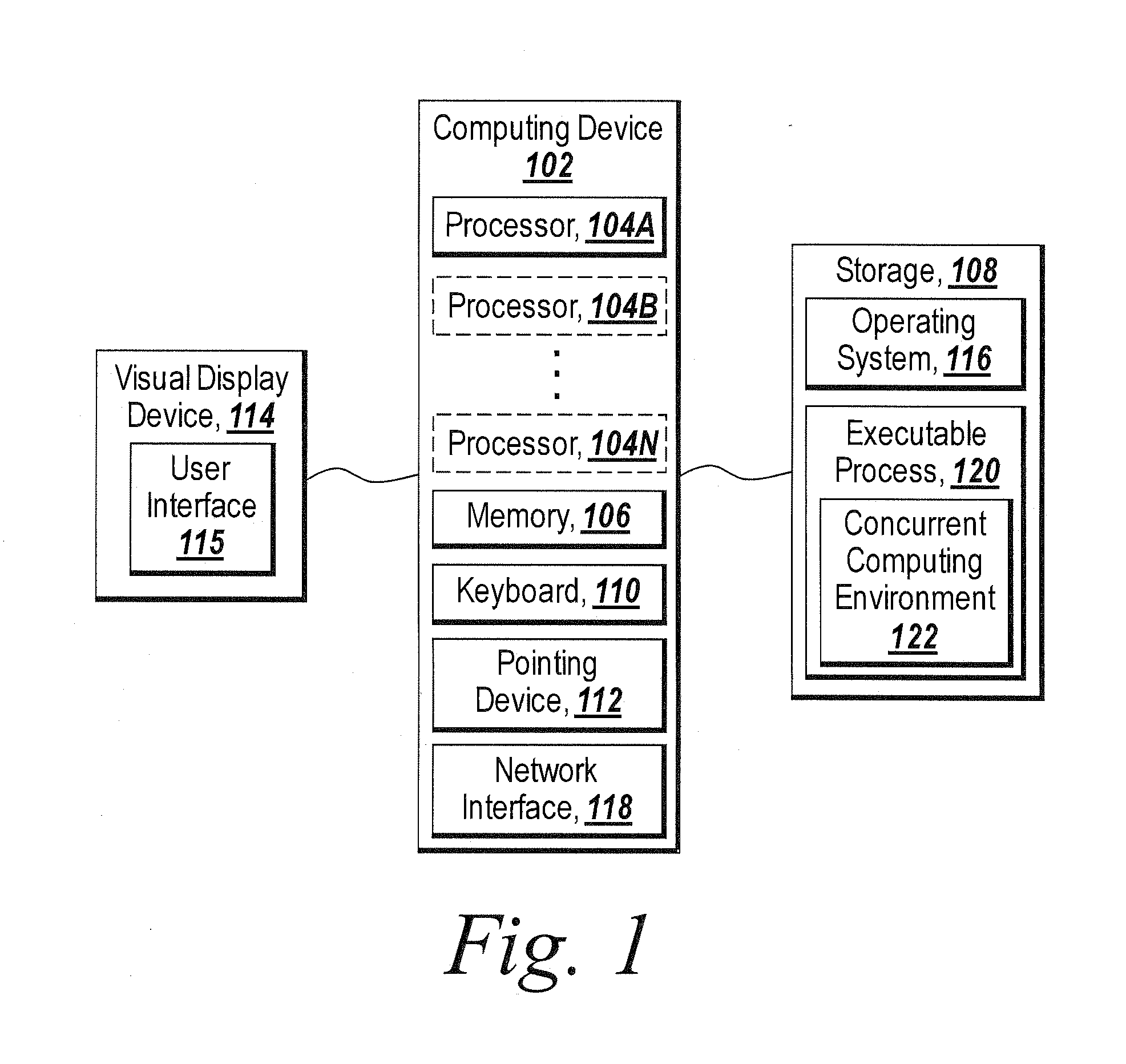
Dynamic definition for concurrent computing environments
ActiveUS20100333092A1Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsConcurrent computingDistributed Computing Environment
Exemplary embodiments allow a user to create configurations for use in distributed computing environments. Configurations can be arranged in hierarchies in which elements of the hierarchy can inherit characteristics from elements in other layers of the hierarchy. Embodiments also allow a user to flatten a hierarchical configuration to remove hierarchical dependencies and / or inheriting capabilities of elements in the hierarchy. Exemplary embodiments further allow users to deploy a distributed computing configuration on their desktop to evaluate performance of the configuration and then deploy the configuration in a distributed computing environment without having to change programming code run on the desktop / distributed computing environment.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
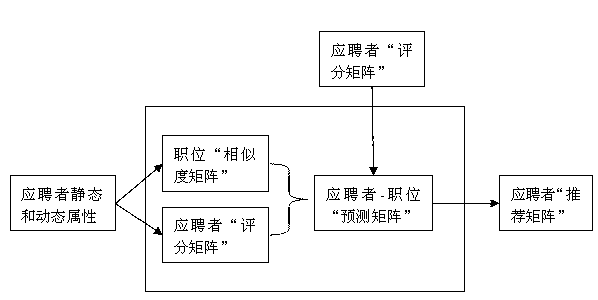
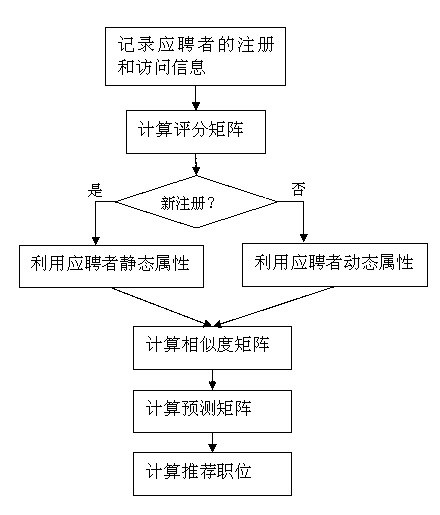
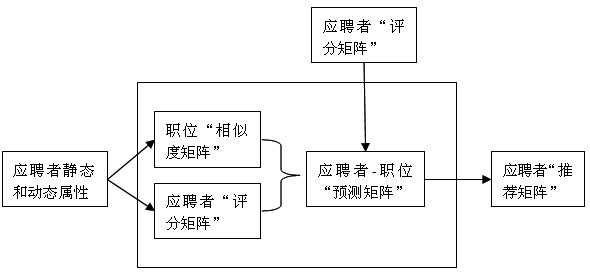
Vacant position intelligent recommendation method based on GPU (graphics processing unit) acceleration
InactiveCN102708525AReduce computing timeImprove performanceData processing applicationsEnergy efficient computingConcurrent computingComputer cluster
The invention provides a vacant position intelligent recommendation method based on GPU (graphics processing unit) acceleration. The vacant position intelligent recommendation method is applied in a recommendation engine on a recruitment website. With the adoption of the vacant position intelligent recommendation method, registration information and visit information of an applicant are expressed into matrix form suitable for being processed by the GPU; and with the adoption of strong processing ability of the GPU and a computing mode of remedying shortage of the GPU property by high bandwidth, thousands of GPU threads are subjected to concurrent computing. With the adoption of the vacant position intelligent recommendation method, the level of similarity between two applicants is calculated based on an Euclidean distance formula, then the appropriate level of all vacant positions corresponding to the applicant is predicated intelligently according to the attribute information of the applicant, and finally the most suitable vacant position is recommended to the applicant. The expensive traditional computer cluster technology is not used when mass data are processed but a GPU technique with high cost performance is used, so that the ultimate aims of high performance, low energy consumption and low cost are realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method and system for hardware accelerated verification of digital circuit design and its testbench
ActiveUS7257802B2Quick verificationOvercomes drawbackElectrical testingComputer aided designConcurrent computingValidation methods
A system and method is presented for synthesizing both a design under test (DUT) and its test environment (i.e., the testbench for the DUT), into an equivalent structural model suitable for execution on a reconfigurable hardware platform. This may be achieved without any change in the existing verification methodology. Behavioral HDL may be translated into a form that can be executed on a reconfigurable hardware platform. A set of compilation transforms are provided that convert behavioral constructs into RTL constructs that can be directly mapped onto an emulator. Such transforms are provided by introducing the concepts of a behavioral clock and a time advance finite state machine (FSM) that determines simulation time and sequences concurrent computing blocks in the DUT and the testbench.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
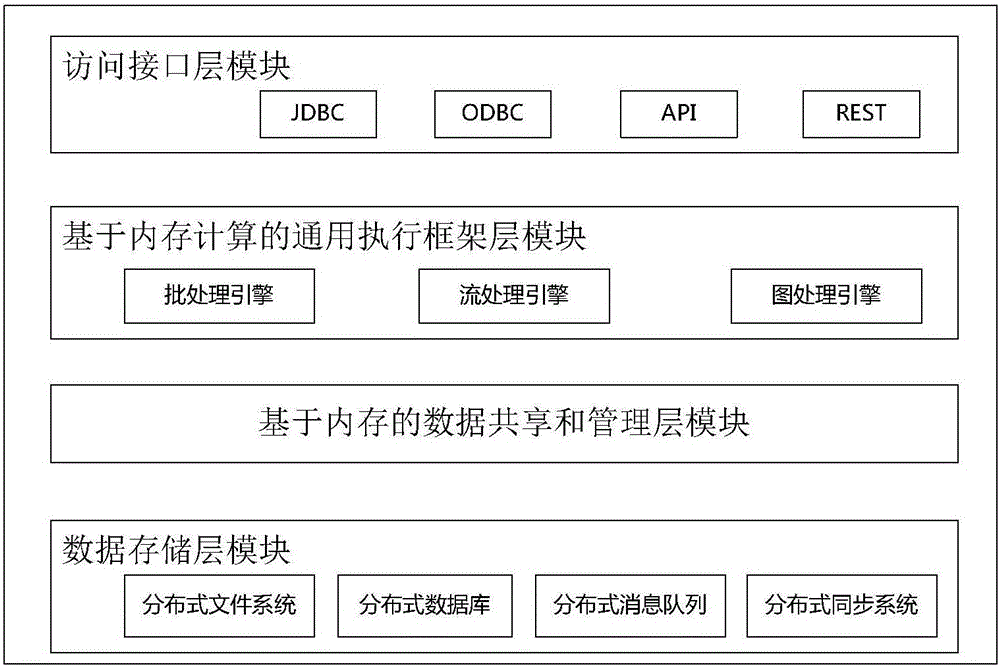
Memory computing-based customizable multimode big data processing system
InactiveCN106021484ATransparent hierarchical storageEfficient hierarchical storageDatabase management systemsSpecial data processing applicationsConcurrent computingData stream
The invention provides a memory computing-based customizable multimode big data processing system. The system comprises a data storage layer module, a memory-based data sharing and management layer module, a memory computing-based universal execution framework layer module and an access interface layer module, wherein a distributed memory abstraction mechanism, a position-sensing scheduling mechanism and a distributed hybrid column storage mechanism of data are adopted. According to the system, massive data storage is constructed; a cluster concurrent computing-oriented memory data management and sharing framework is provided, and an efficient and customized big data multimode universal processing framework is provided; batch processing and real-time data stream computing are supported; and the support is provided for flexible analysis and deep utilization of the data.
Owner:NO 32 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
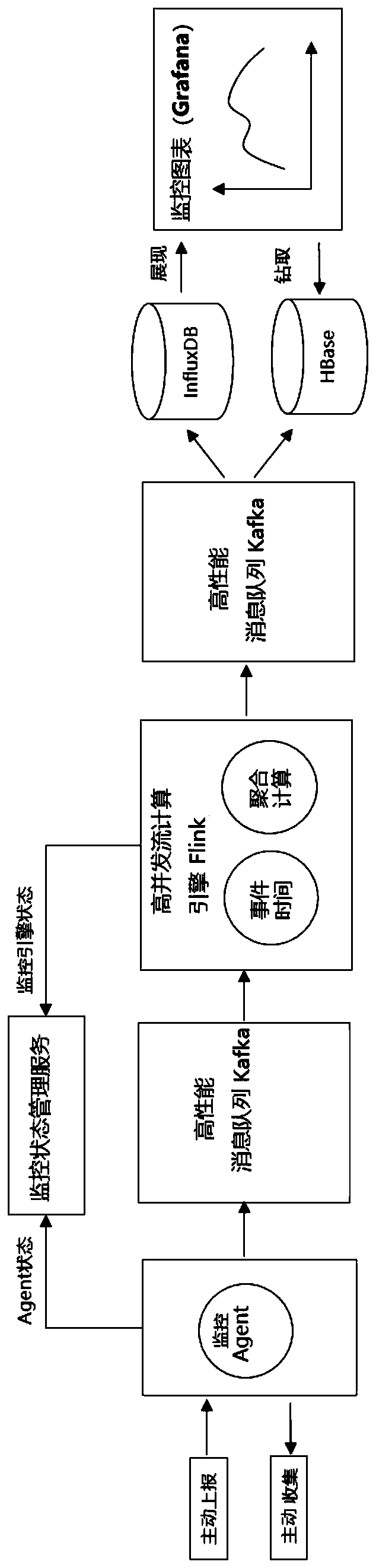
Real-time flow calculation monitoring system and method for processing monitoring big data
PendingCN109800129ASolve the poor performance of collecting dResolve accuracyHardware monitoringConcurrent computingOriginal data
The invention discloses a real-time stream computing monitoring system and method for processing monitoring big data, and the system comprises a data collection unit which employs a monitoring Agent,and obtains monitoring original data on a corresponding machine through an active reporting or active collection mode; The data caching unit comprises a high-performance message queue Kafka for storing the monitoring original data collected by the monitoring Agent and storing the monitoring data subjected to aggregation calculation; The data calculation unit is used for carrying out aggregation calculation on the original monitoring data based on a high concurrent flow calculation engine Flink, and the monitoring data subjected to aggregation calculation is sent to a high-performance message queue Kafka for temporary caching; The monitoring state management service unit is used for monitoring the operation states of the data acquisition unit and the data calculation unit; According to thesystem and the method disclosed by the invention, the accuracy of high-concurrency calculation is ensured, and the display speed is increased.
Owner:QINGDAO TELD NEW ENERGY TECH CO LTD
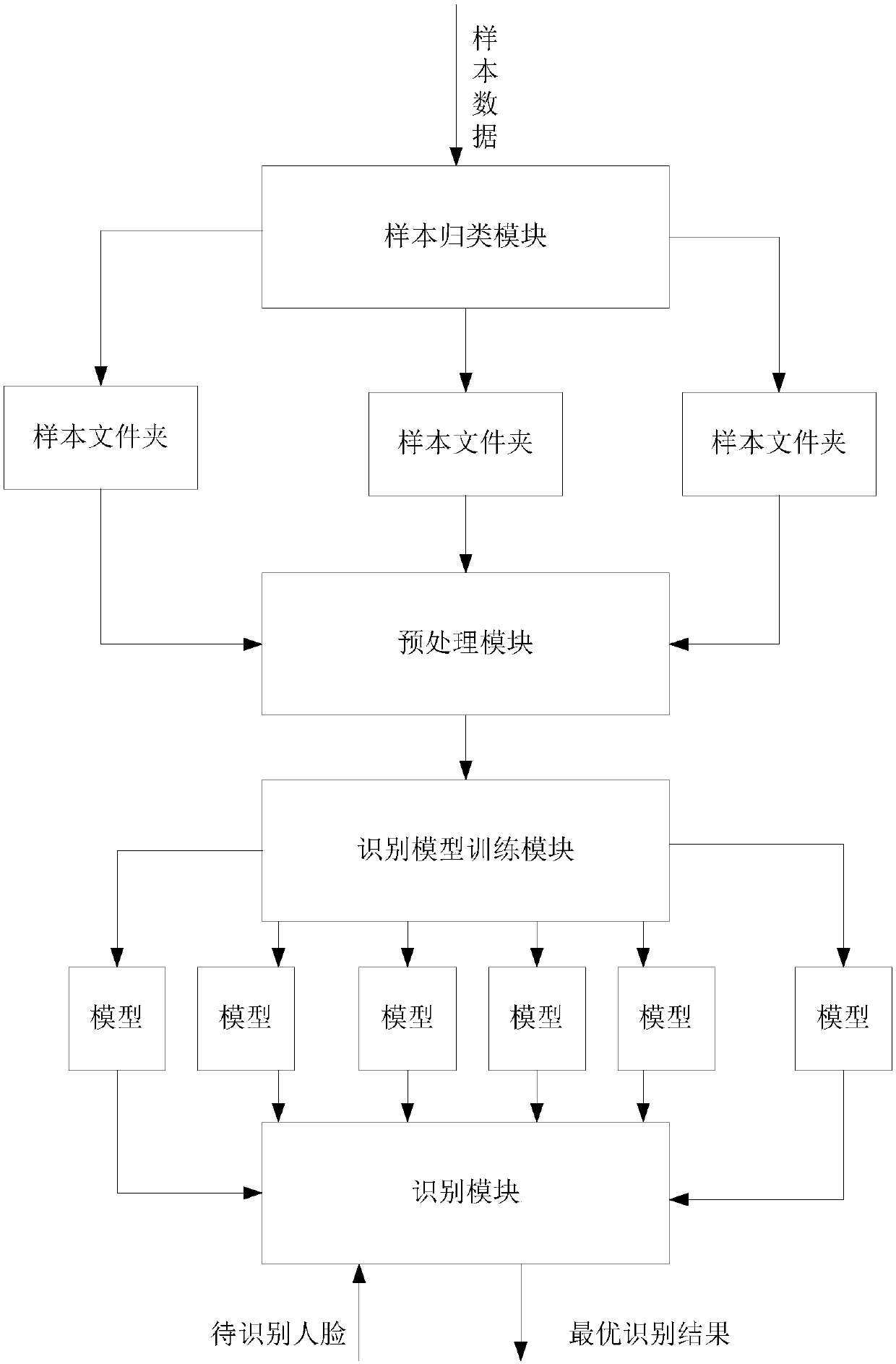
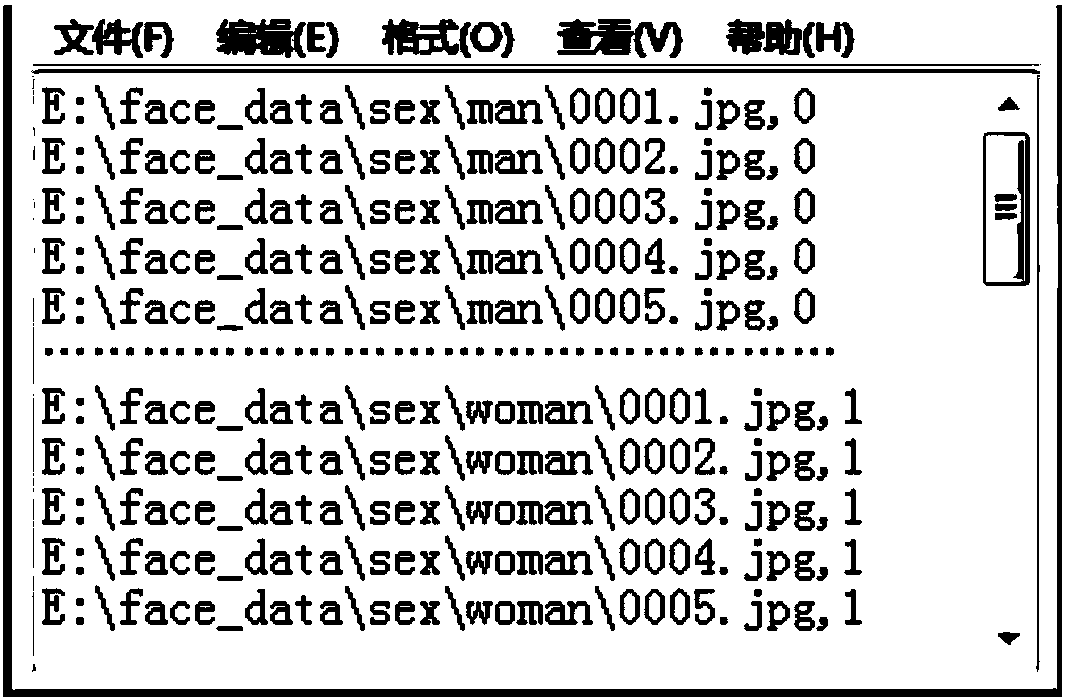
Face identification method and device based on multiple models
InactiveCN107563280AImprove the correct recognition rateThe correct recognition rate is lowCharacter and pattern recognitionConcurrent computingSample image
The invention discloses a face identification method and device based on multiple models. The face identification method comprises the steps of firstly dividing the sample data according to the defined classification, and generating a plurality of sample files, each of which includes a kind of sample data; secondly conducting preprocessing on the data samples of all the sample files, and detectingfaces in the sample images and conducting normalization; thirdly obtaining different models from the data sample of each sample file after preprocessing by using different training methods like different face identification algorithms or the same face identification algorithm, wherein the data sample of the same sample file corresponds to multiple models; finally adopting multiple models to conduct identification on faces to be identified, and obtaining multiple face identification results and selecting the final face identification result. The invention is advantageous in that the face identification accuracy can be increased; model training time can be reduced; with the adoption of multiple models for concurrent computing, time of searching and contrasting can be reduced.
Owner:南京道熵信息技术有限公司
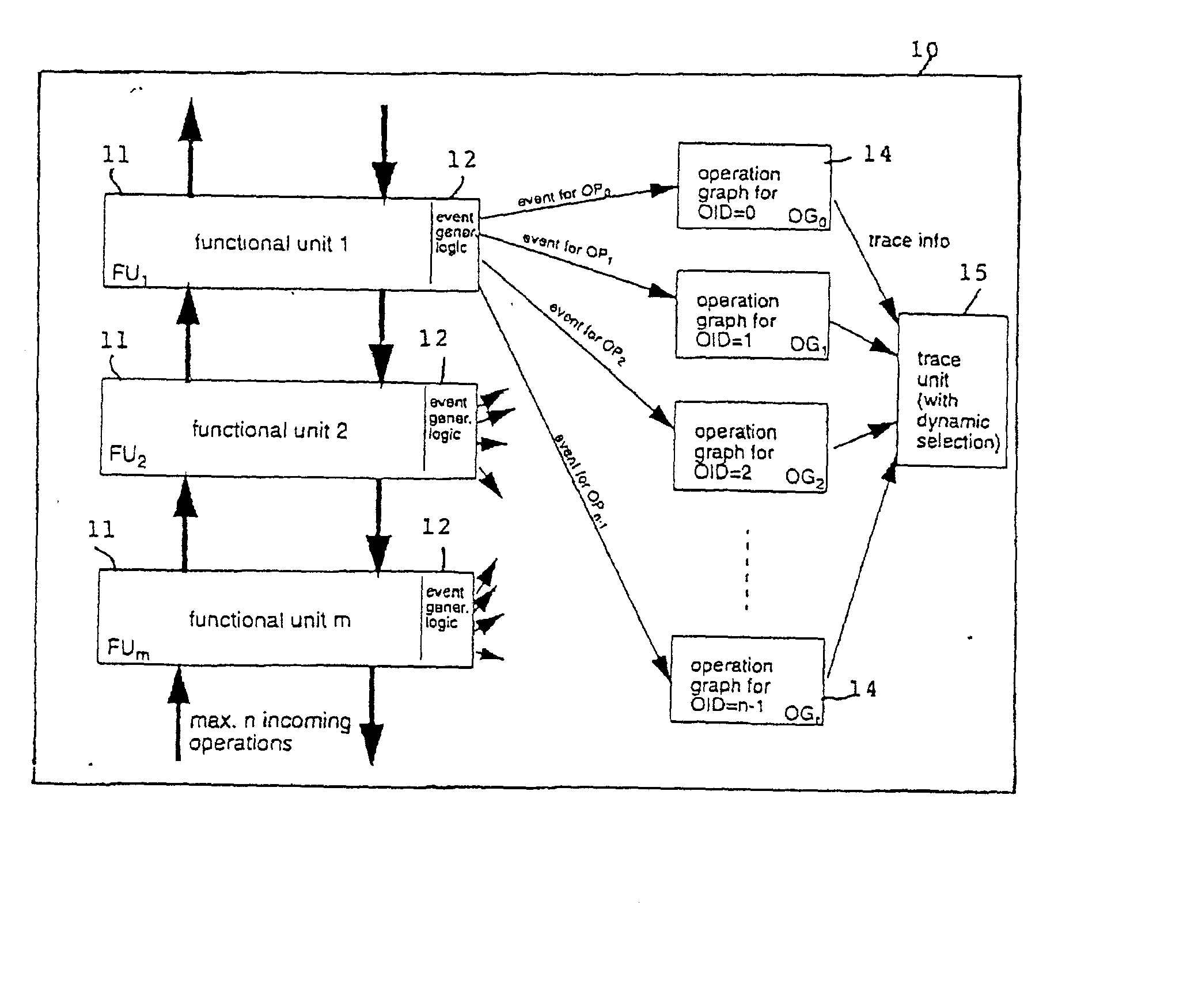
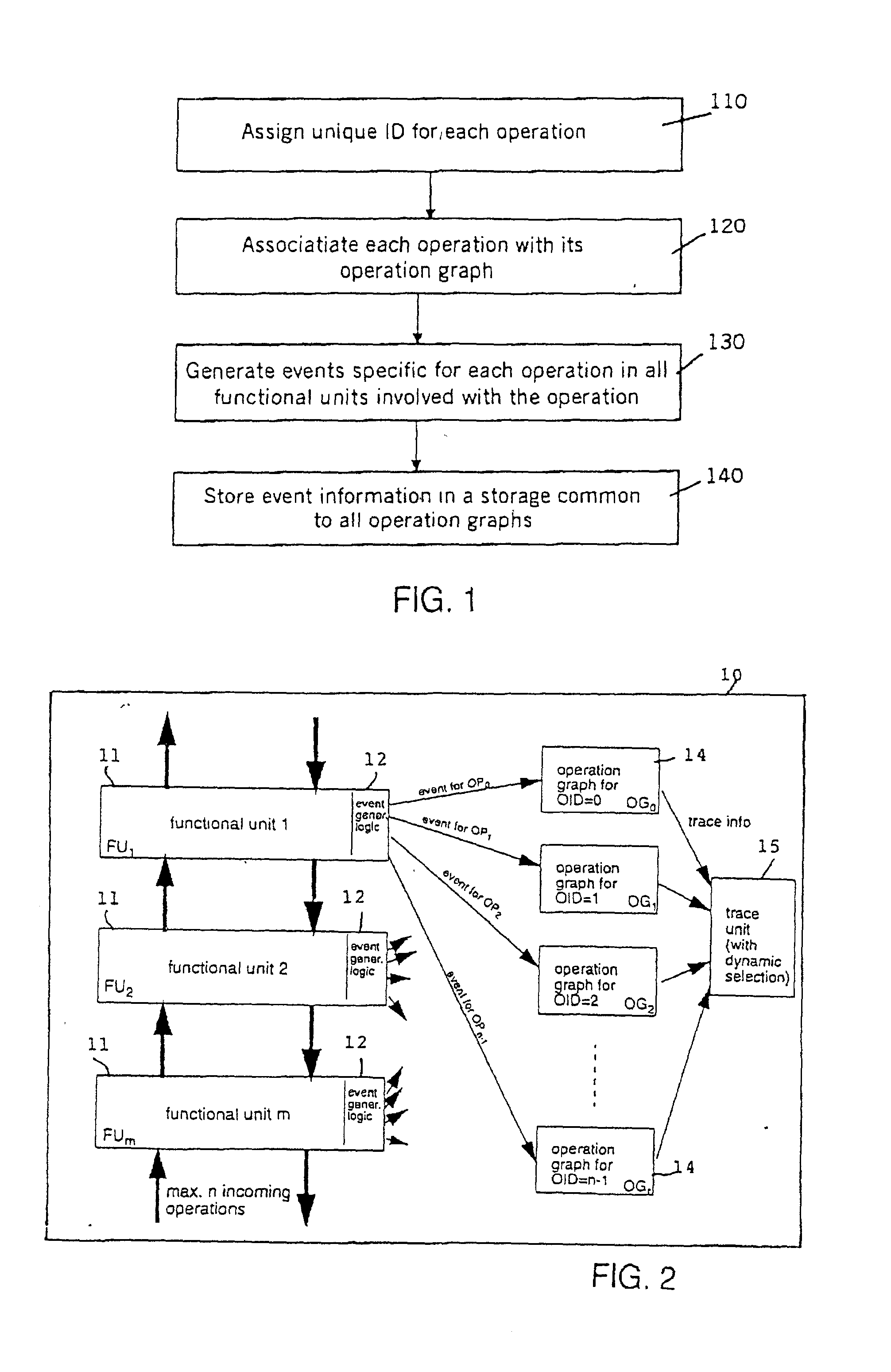
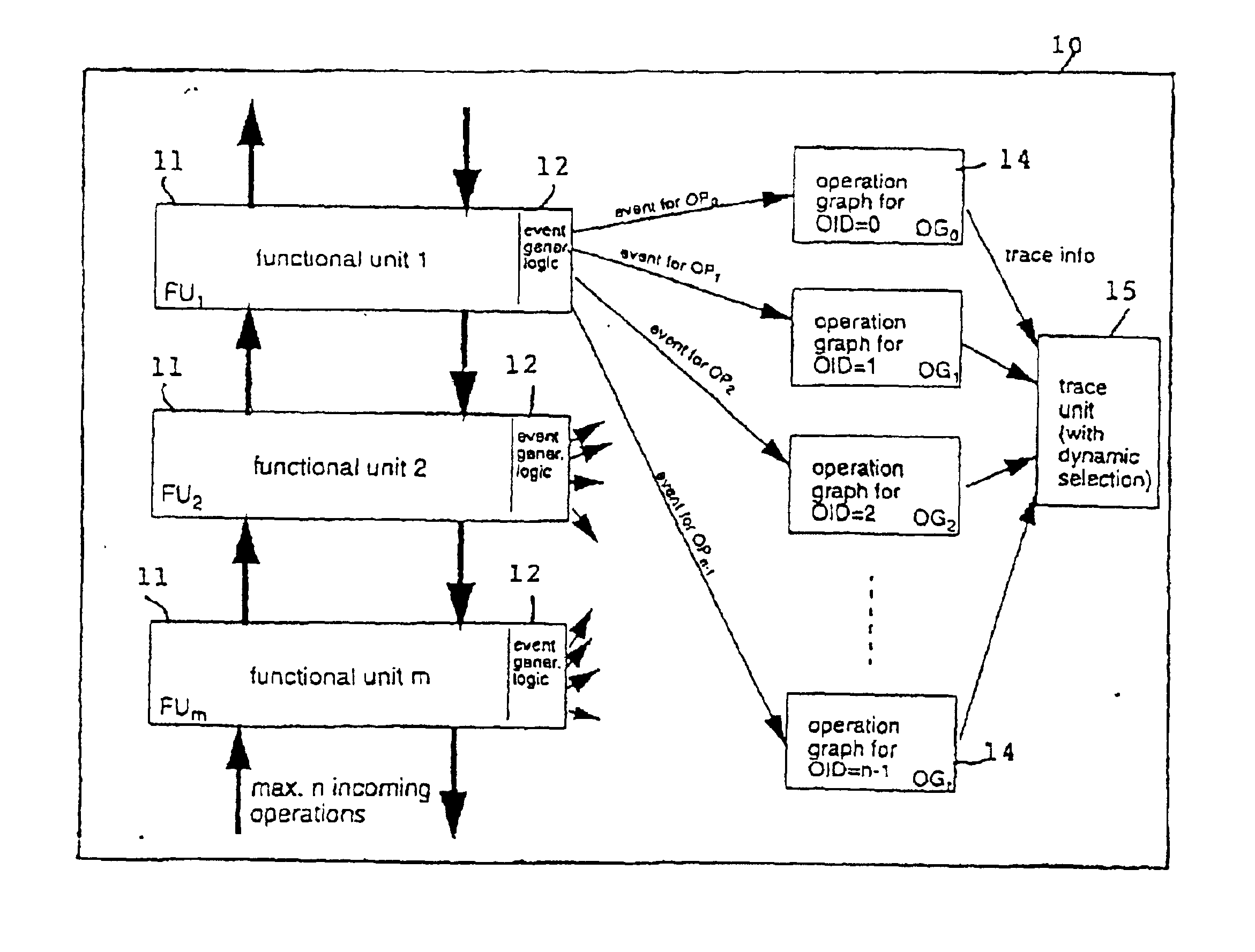
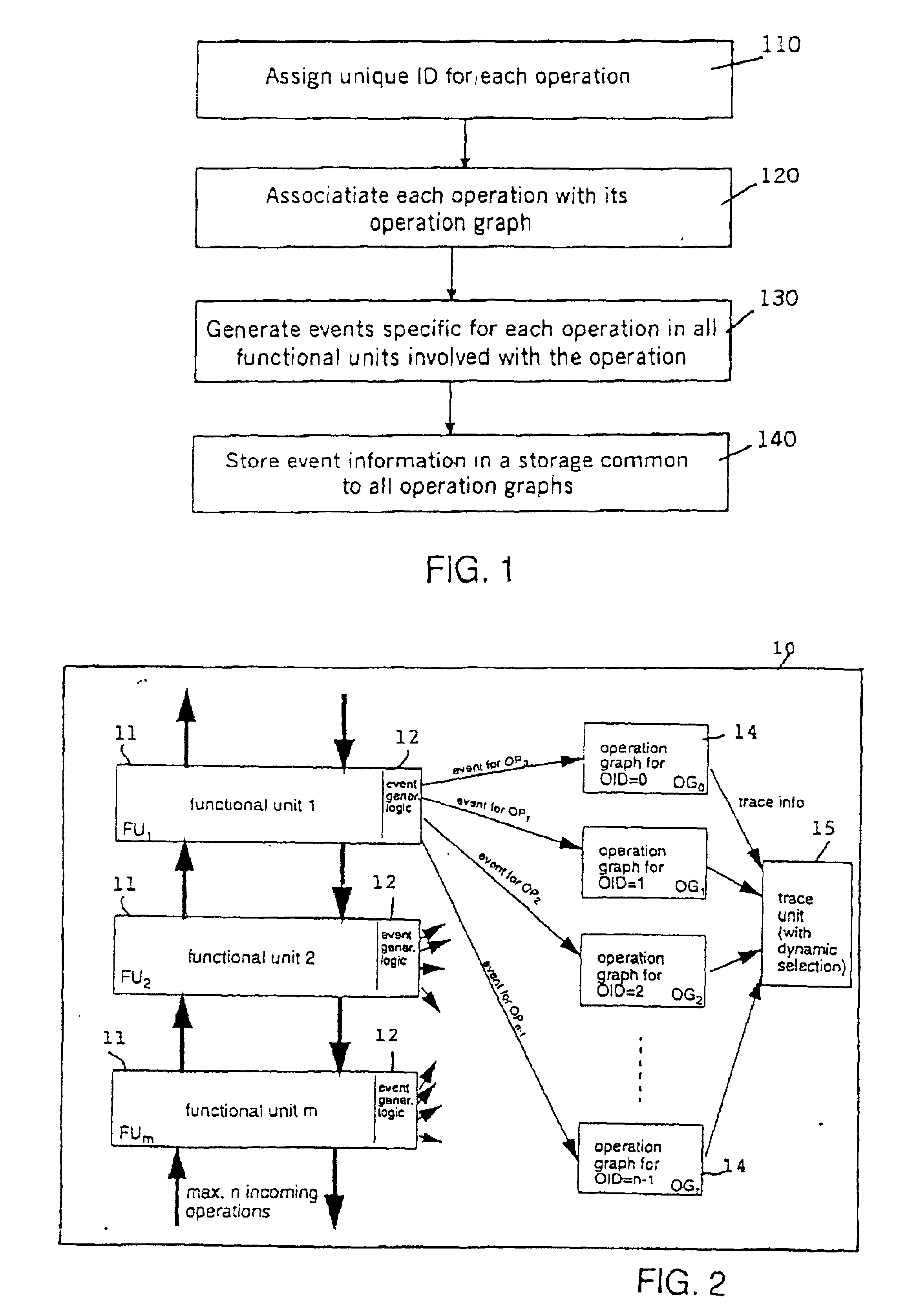
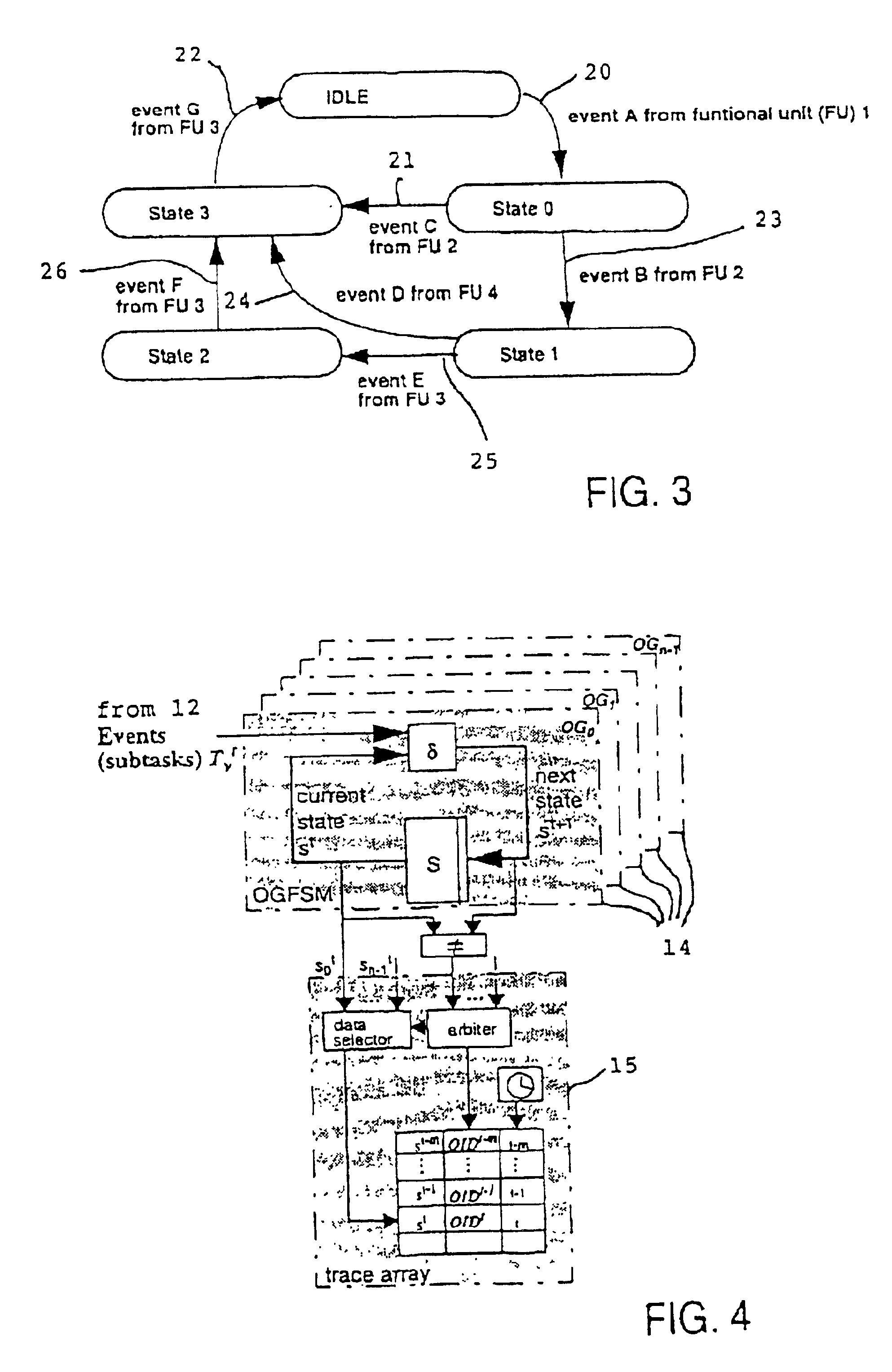
Operation graph based event monitoring system
InactiveUS20020100025A1Reduce in quantityPossible to monitorError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsConcurrent computingConcurrent computation
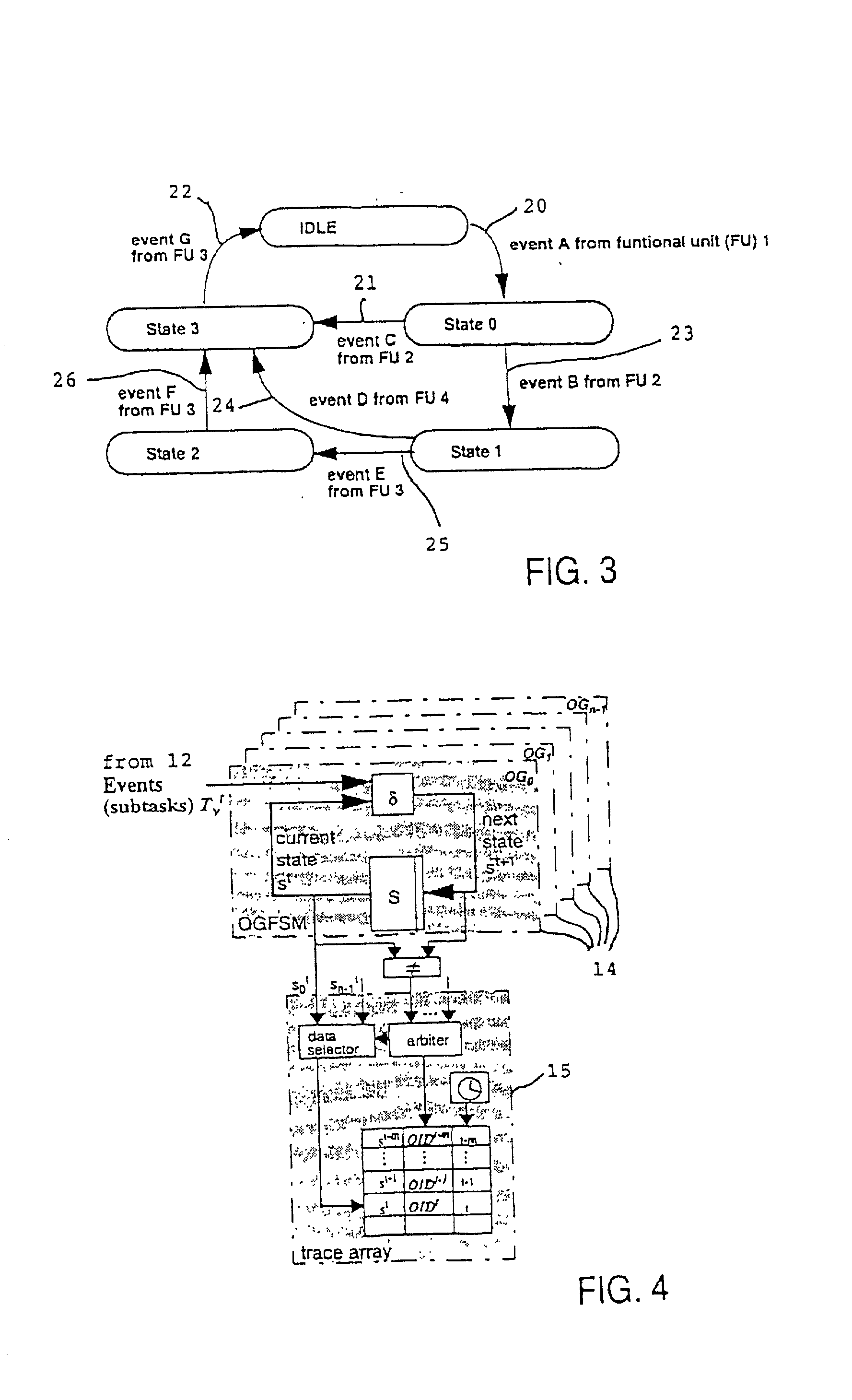
A non-obtrusive activity monitor is proposed for advantageously monitoring and tracing disjunct, concurrent computer system operations in heavily queued computer systems. For each traced and pending computer system operation, the monitor uses a hardware implementation of an event triggered operation graph to trace the path of the computer system operation through the computer system. For each followed path, a unique signature is generated that significantly reduces the amount of trace data to be stored. In a preferred embodiment, the trace information is stored together with a time stamp for debugging and measuring queuing effects and timing behavior in a computer system.
Owner:IBM CORP
Channel-based runtime engine for stream processing
InactiveUS20100318768A1Designing can be facilitatedDigital computer detailsResourcesConcurrent computingData source
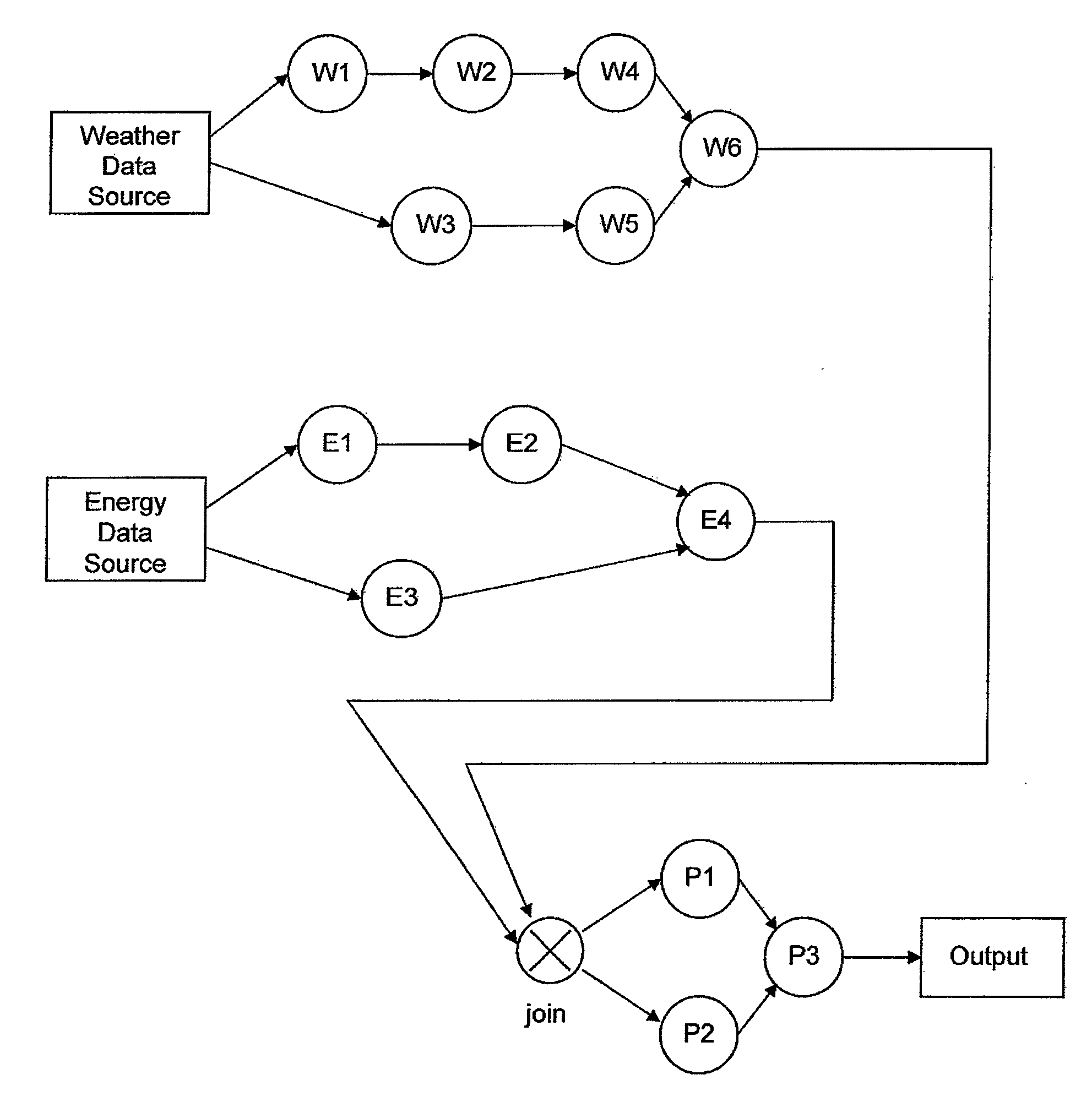
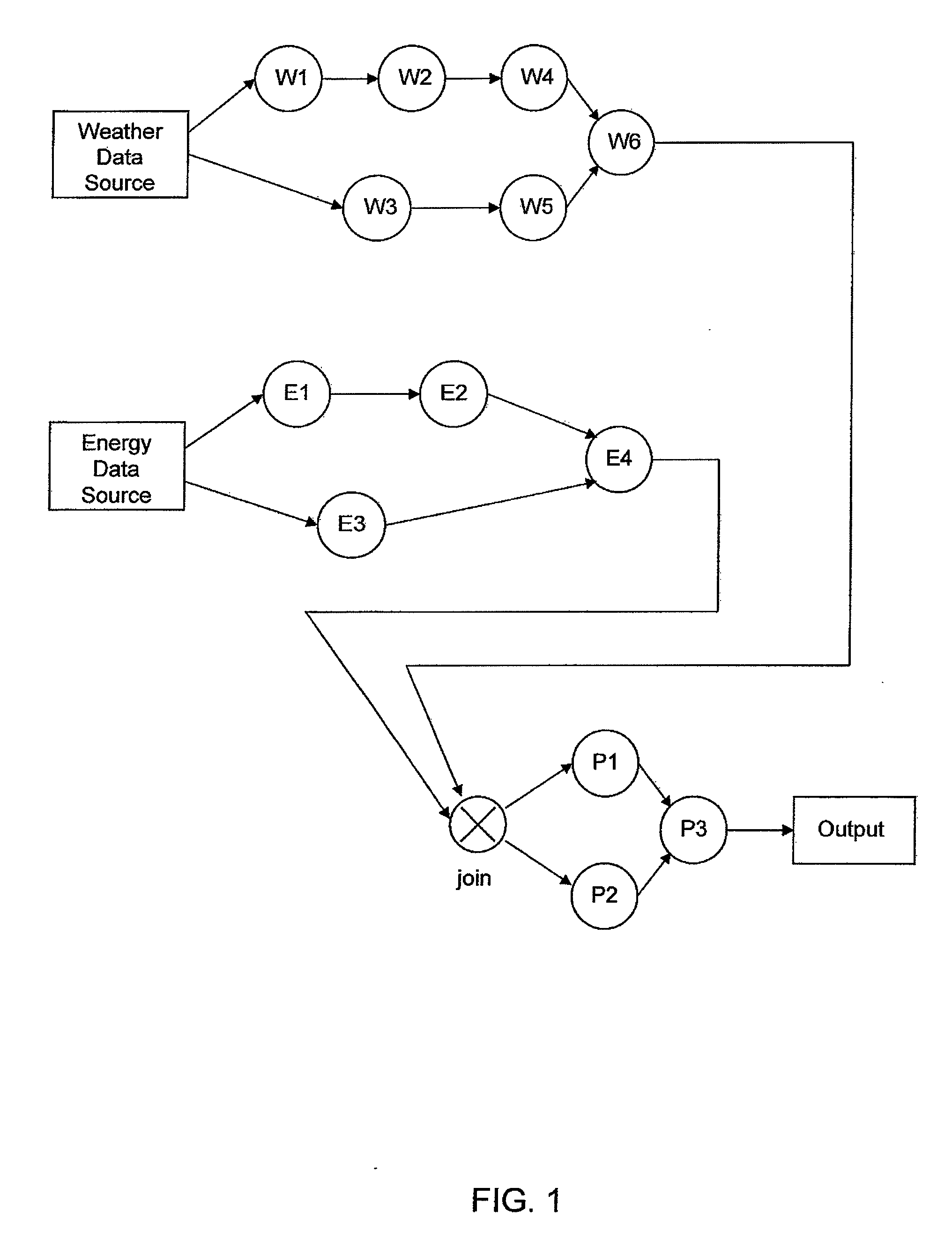
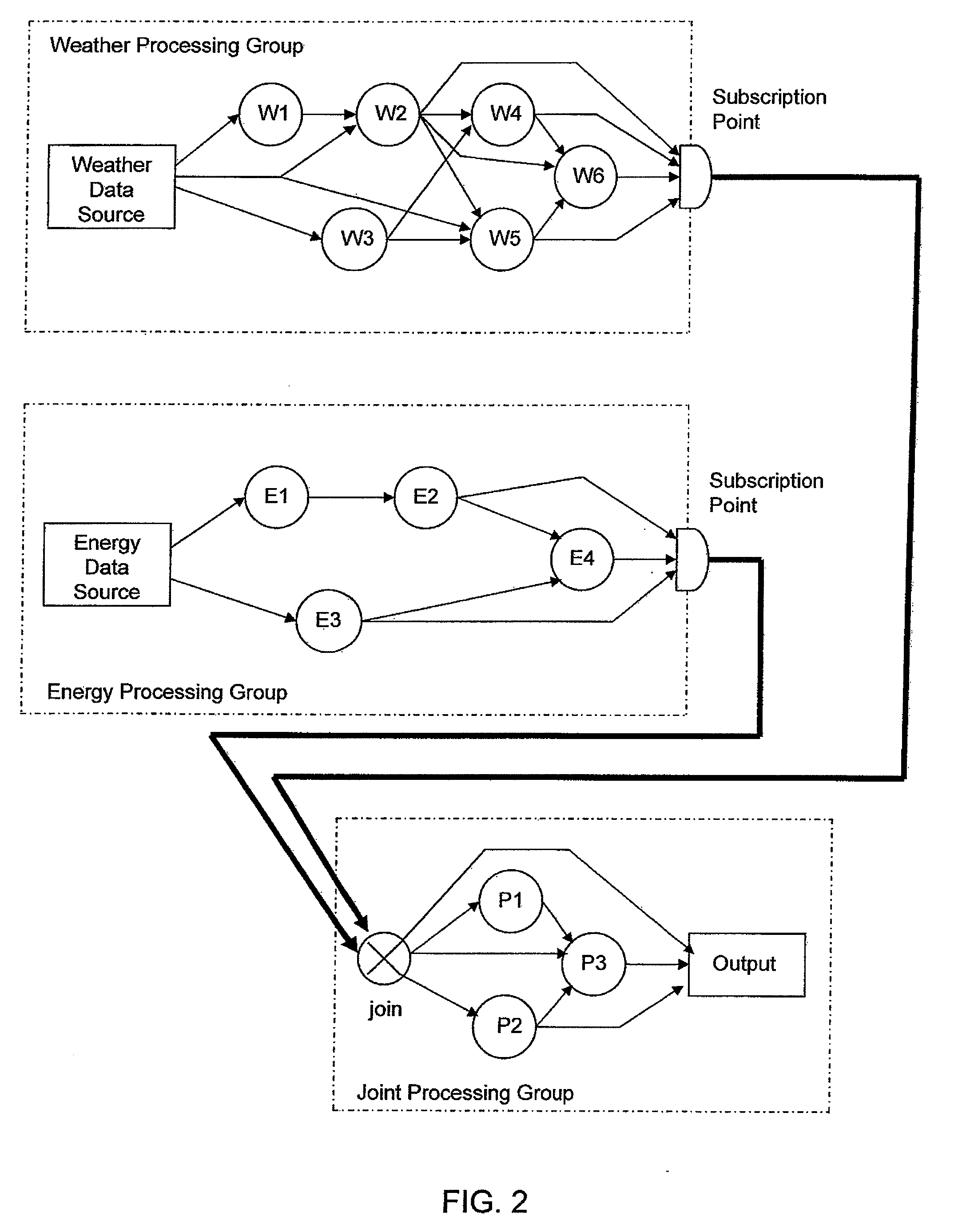
An apparatus, including a memory device for storing a program, and a processor in communication with the memory device, the processor operative with the program to facilitate design of a stream processing flow that satisfies an objective, wherein the stream processing flow includes at least three processing groups, wherein a first processing group includes a data source and an operator, a second processing group includes a data source and an operator and a third processing group includes a join operator at its input and another operator, wherein data inside each group is organized by channels and each channel is a sequence of data, wherein an operator producing a data channel does not generate new data for the channel until old data of the channel is received by all other operators in the same group, and wherein data that flows from the first and second groups to the third group is done asynchronously and is stored in a queue if not ready for processing by an operator of the third group, and deploy the stream processing flow in a concurrent computing system to produce an output.
Owner:AIRBNB
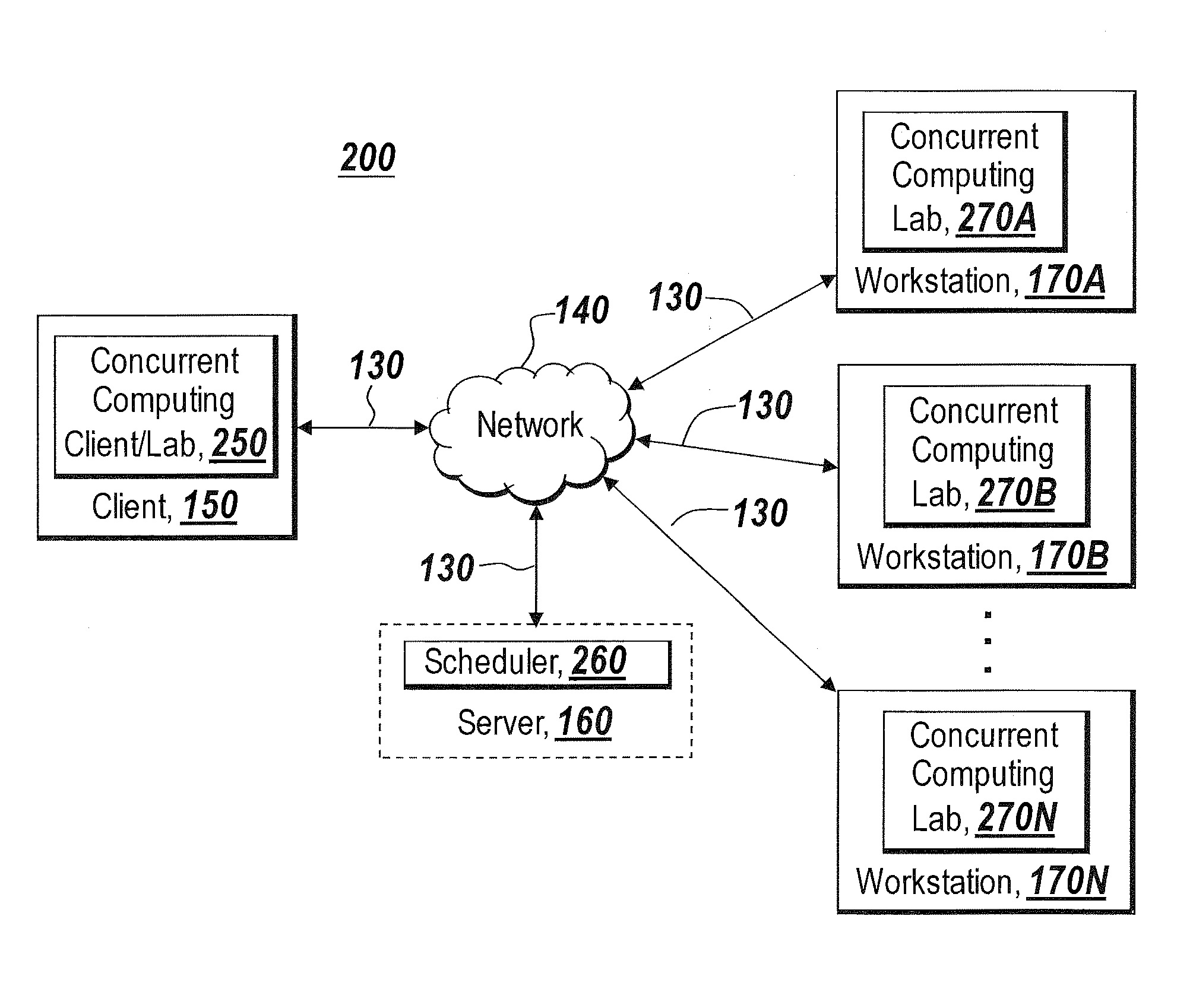
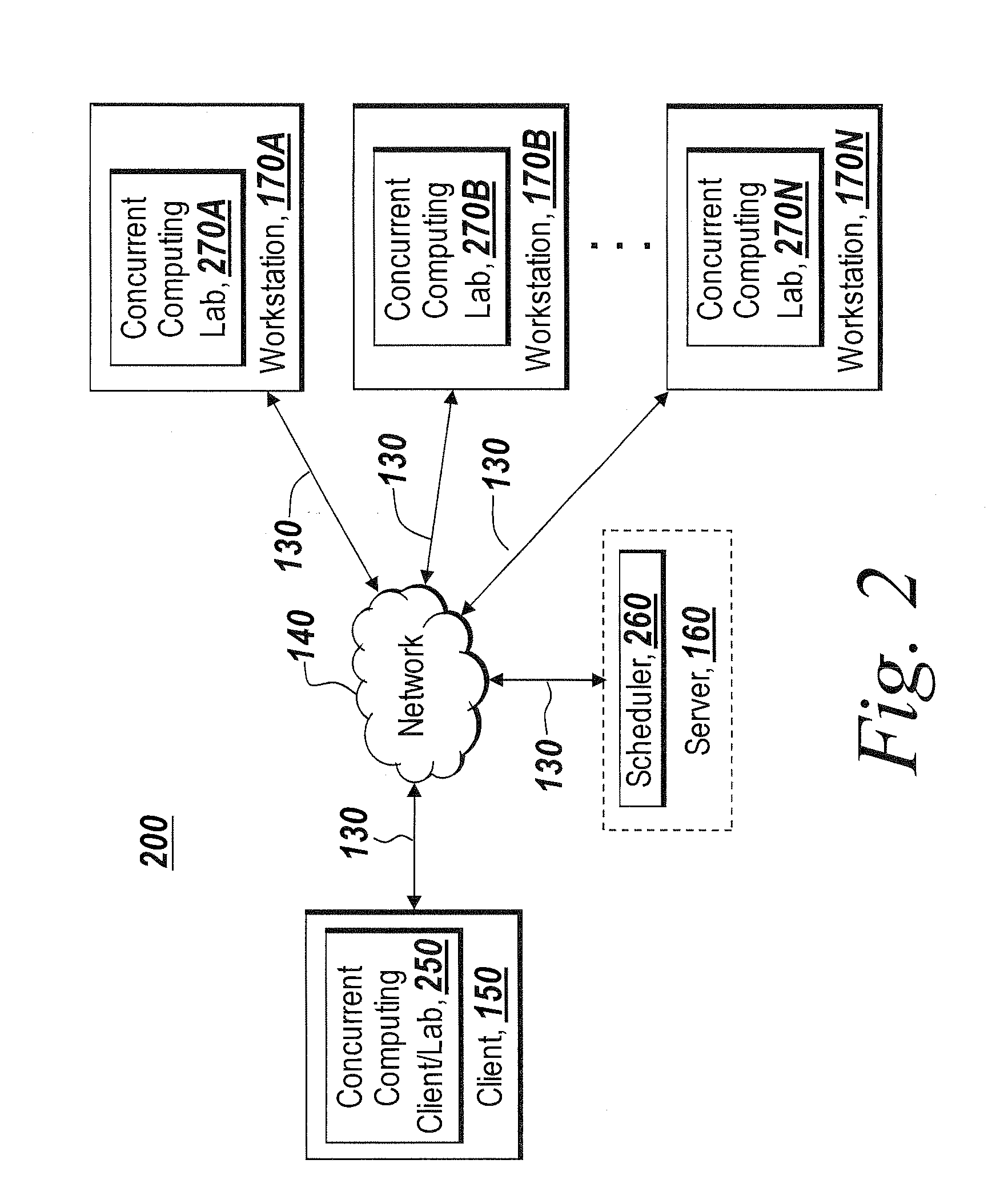
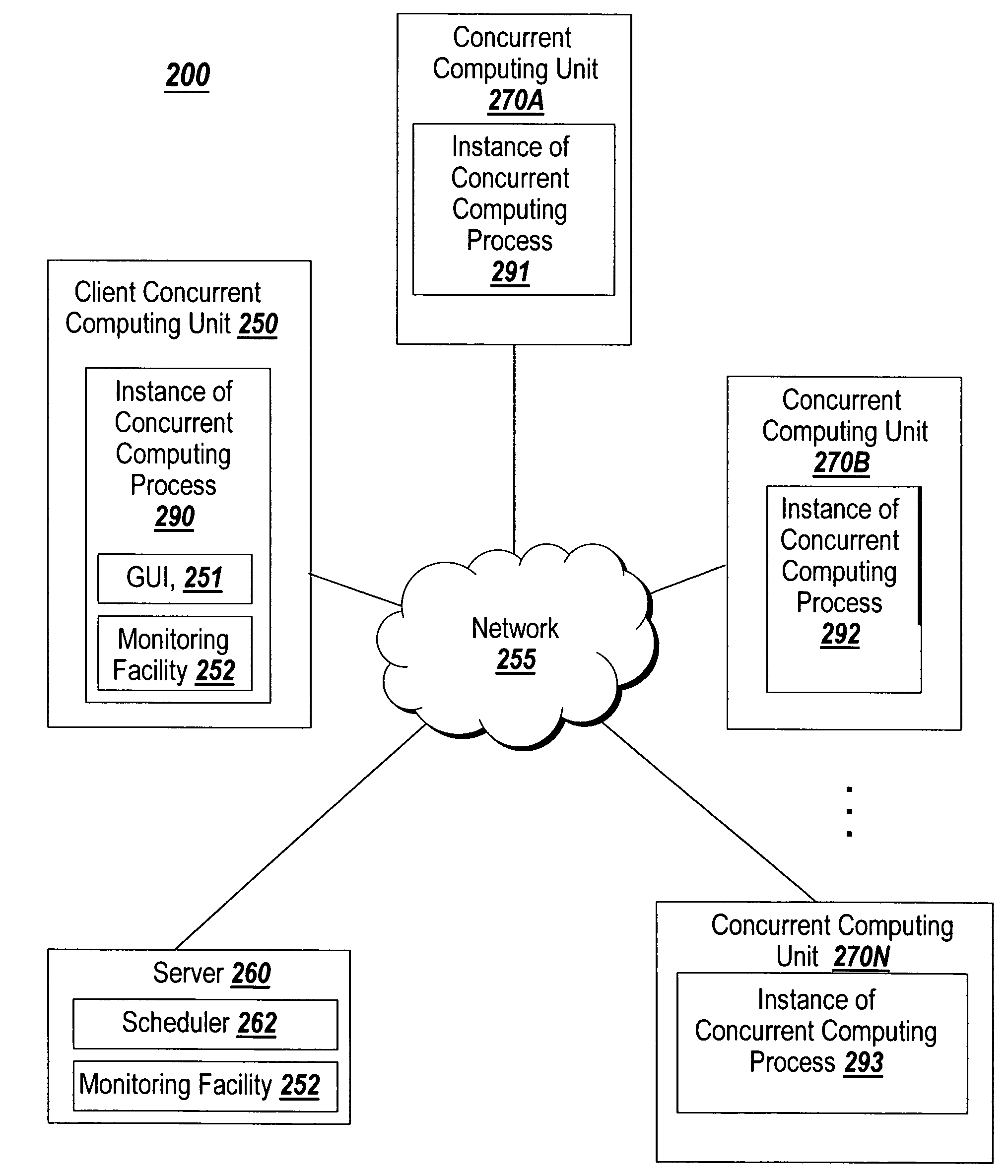
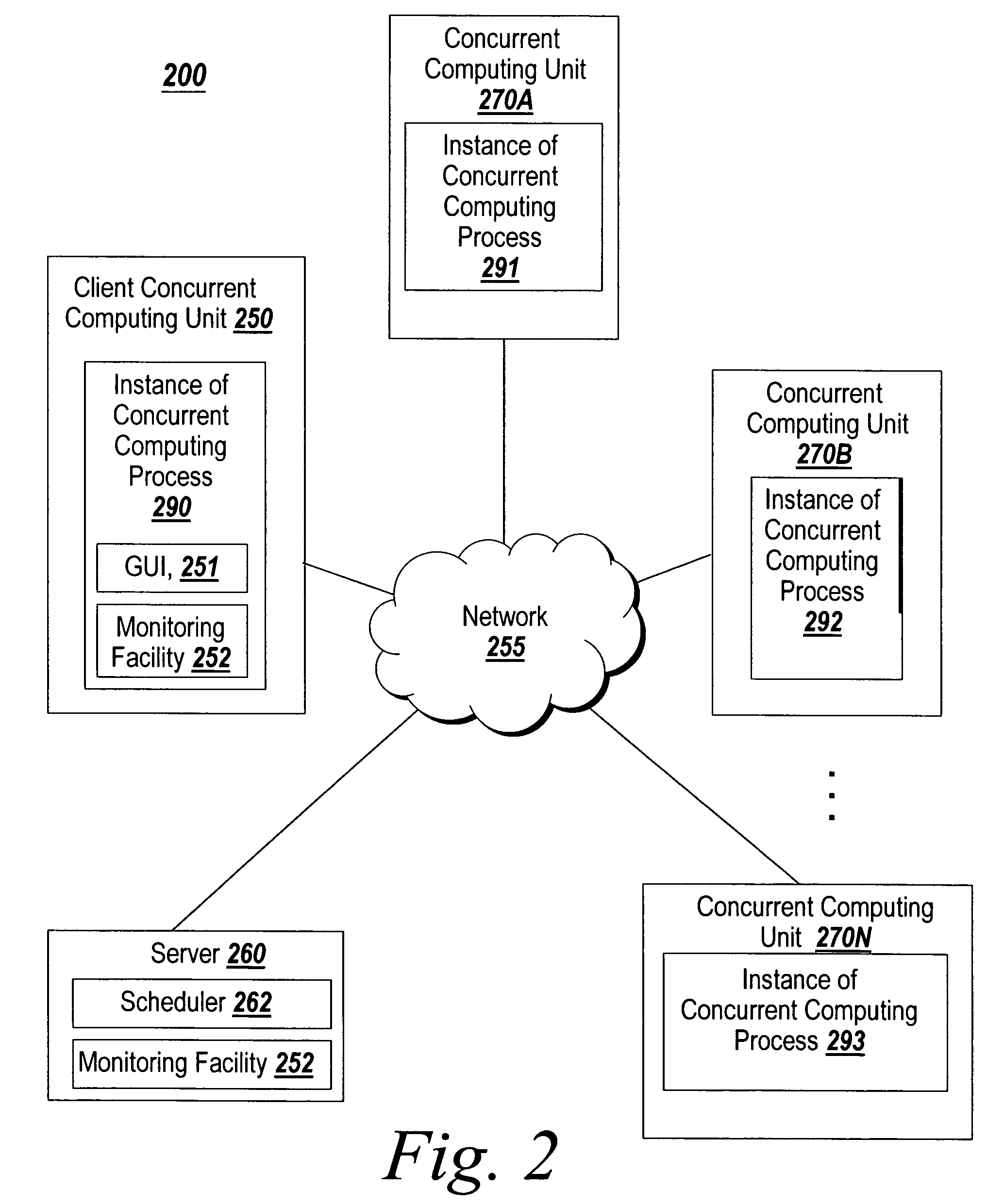
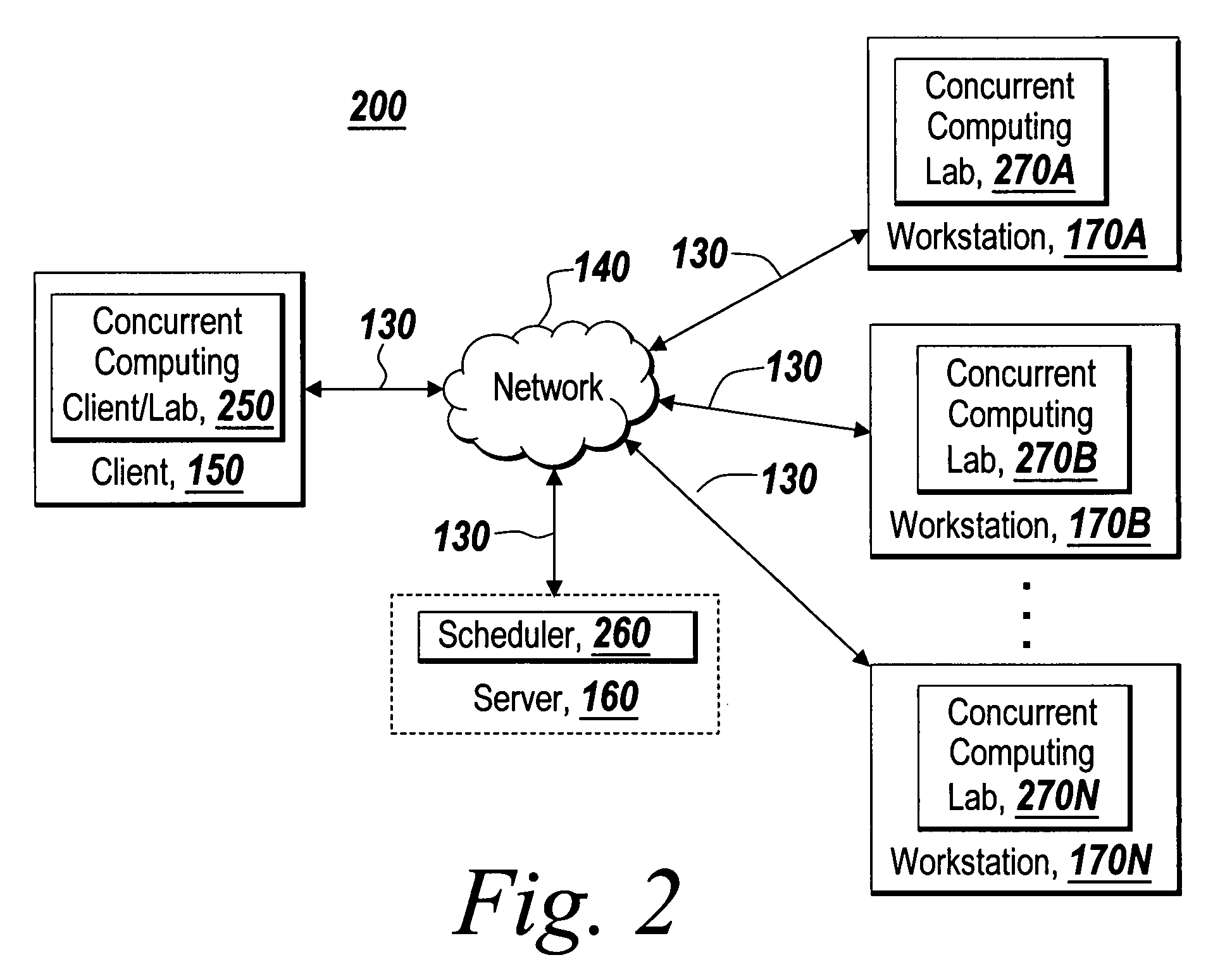
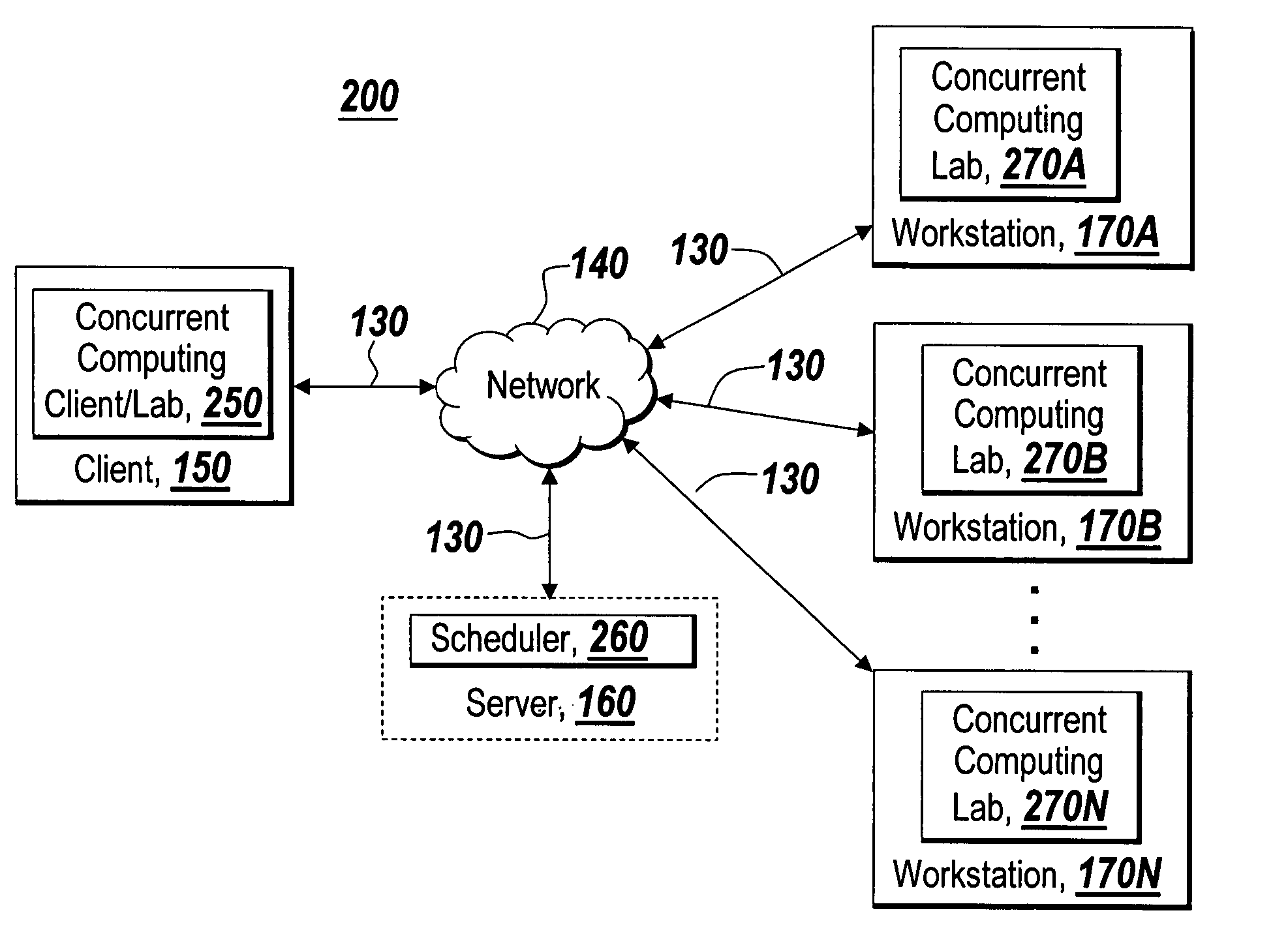
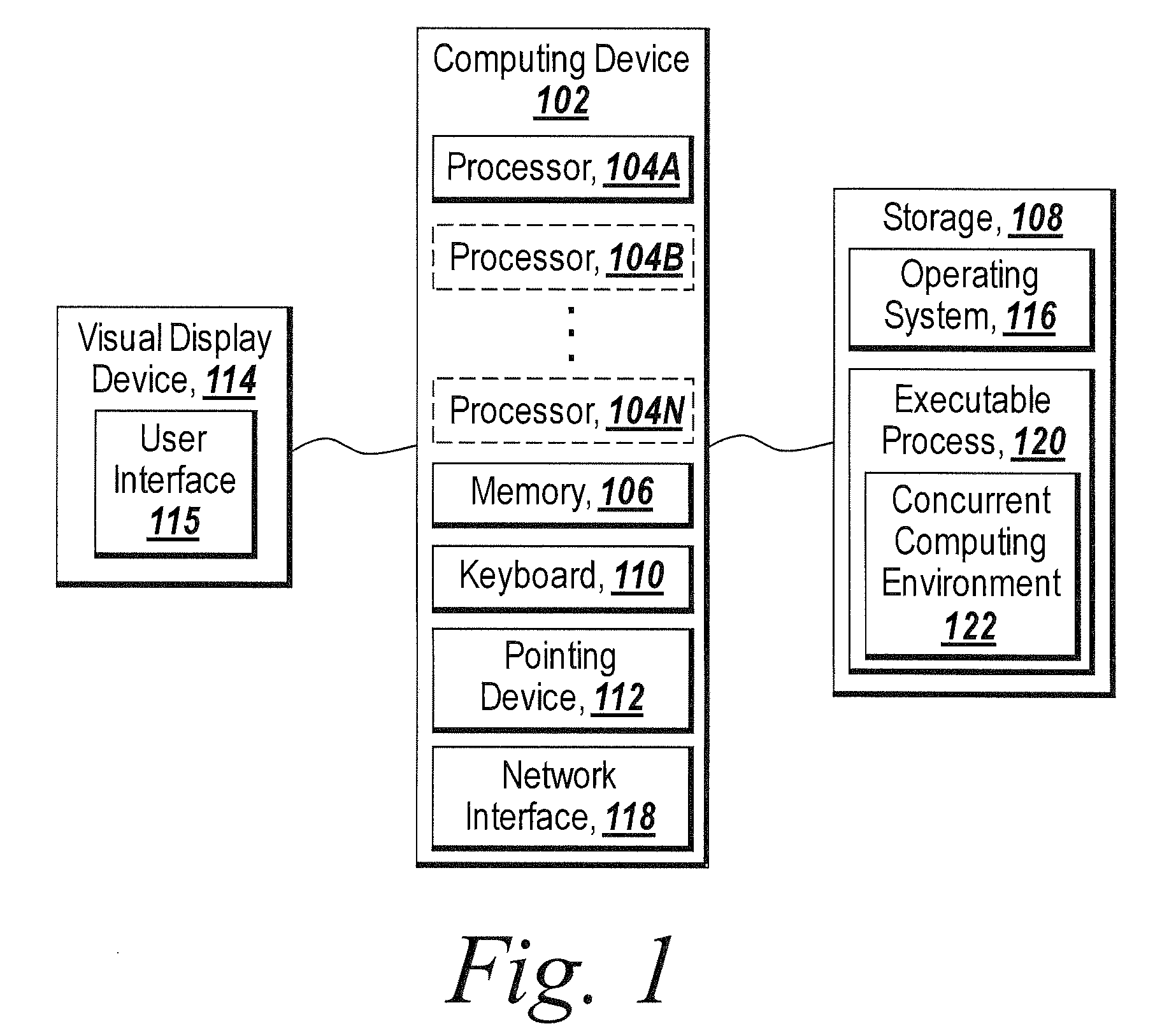
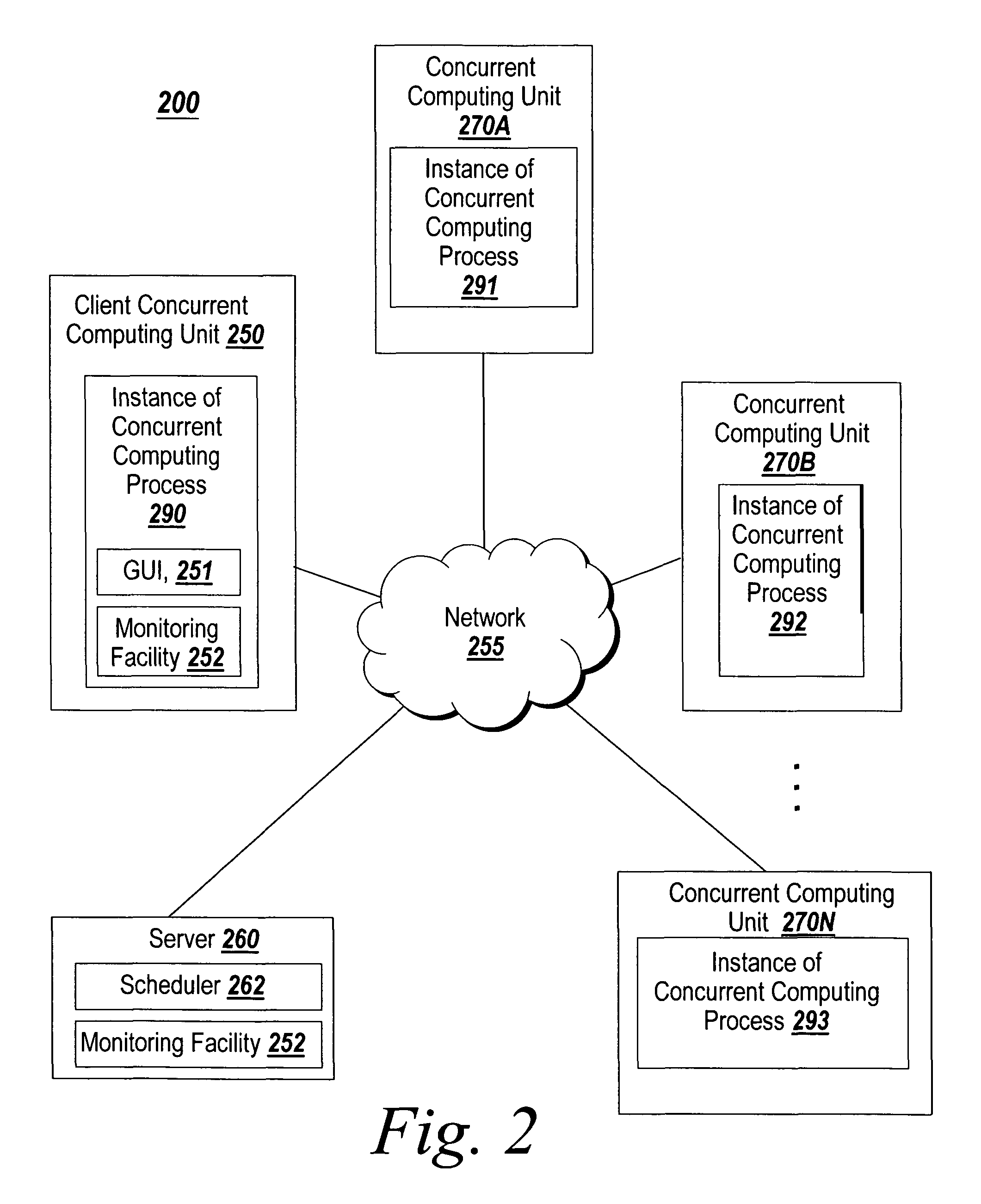
Graphical interface for grouping concurrent computing units executing a concurrent computing process
A graphical user interface for an interactive concurrent computing environment that conveys the concurrent nature of the computing environment and allows a user to monitor the status of a concurrent process being executed on multiple concurrent computing units is discussed. The graphical user interface indicates the status of groups of instances of the concurrent computing process including whether the instances of the concurrent process are idle, busy or stopped.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
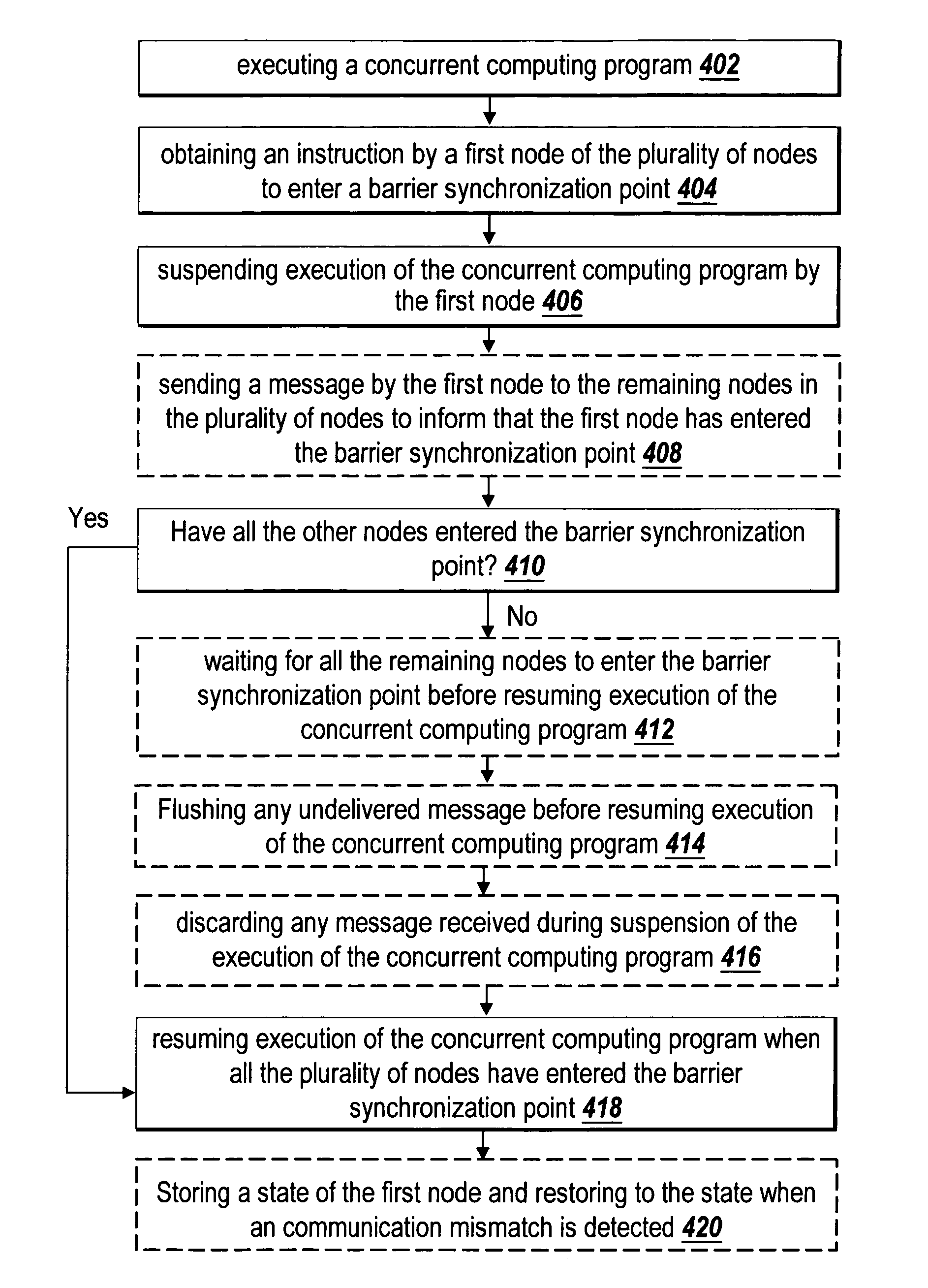
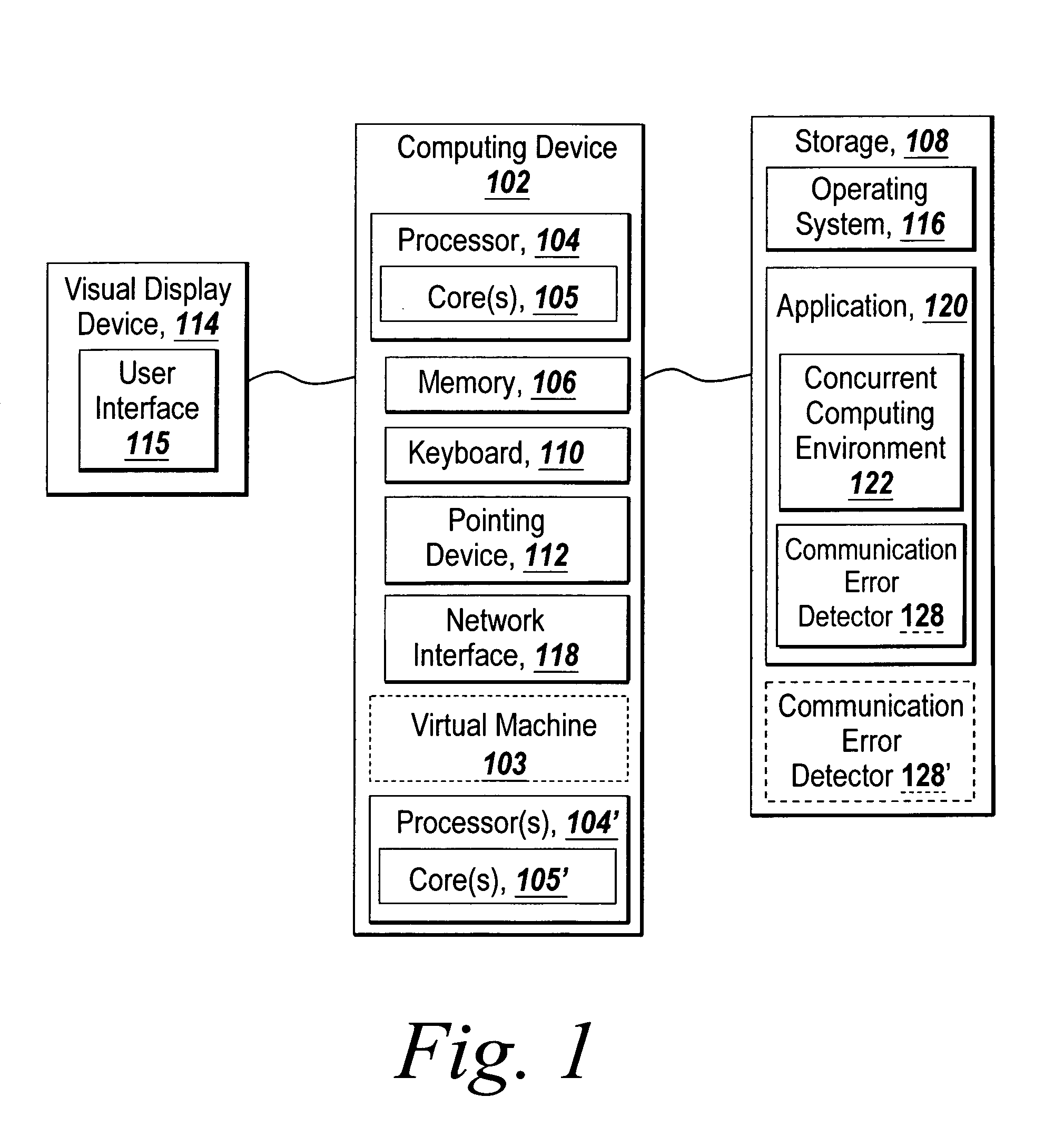
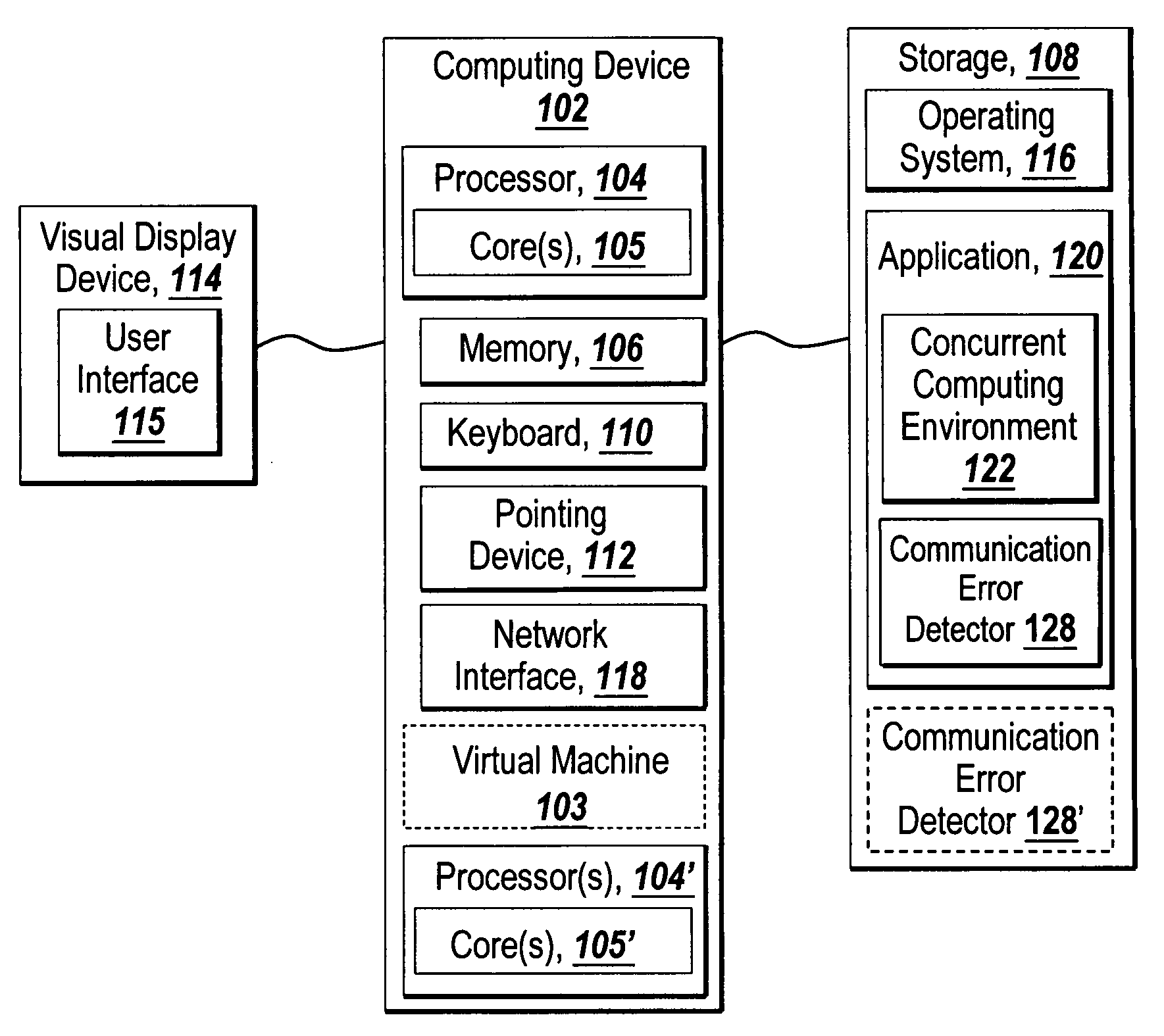
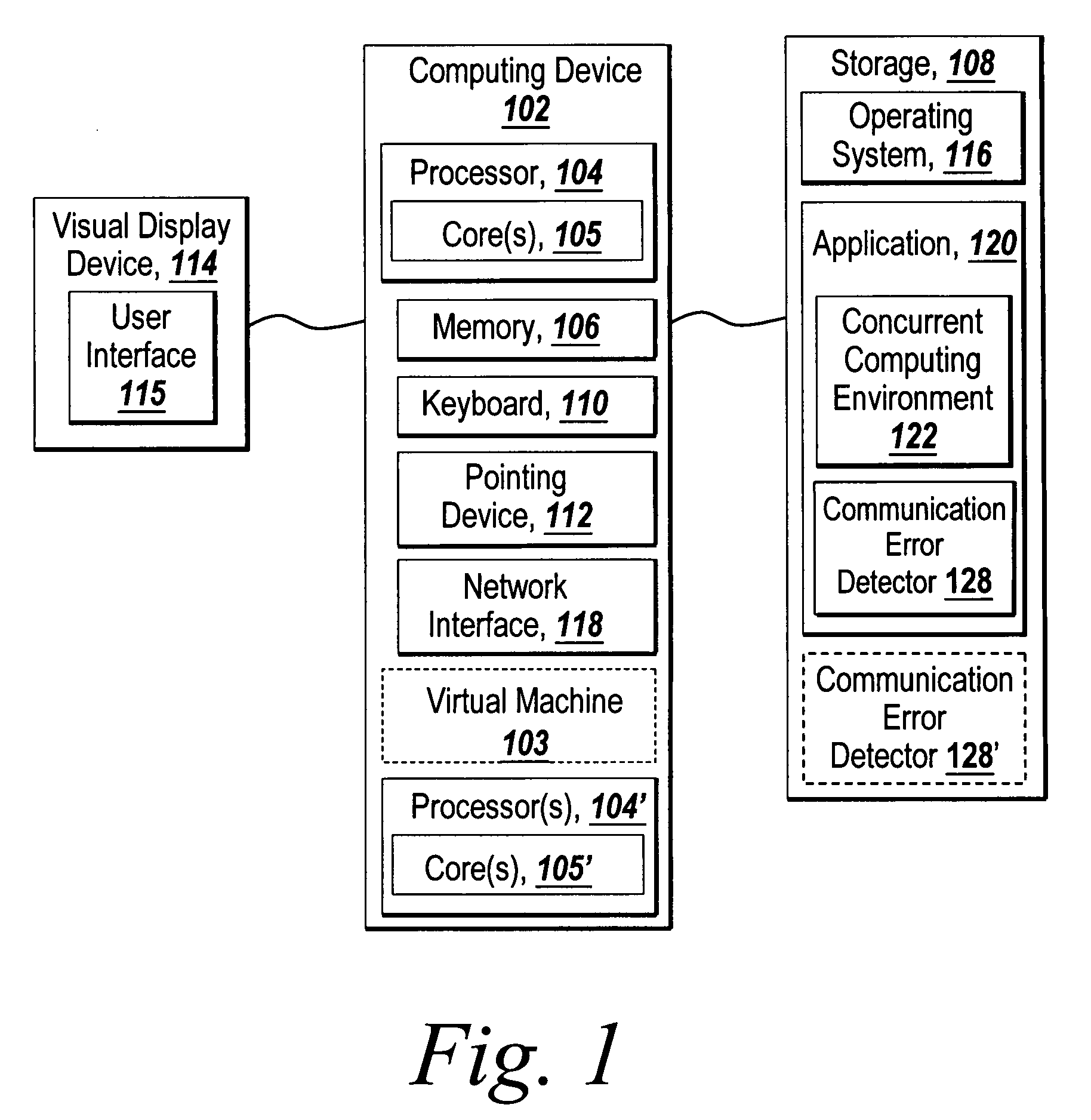
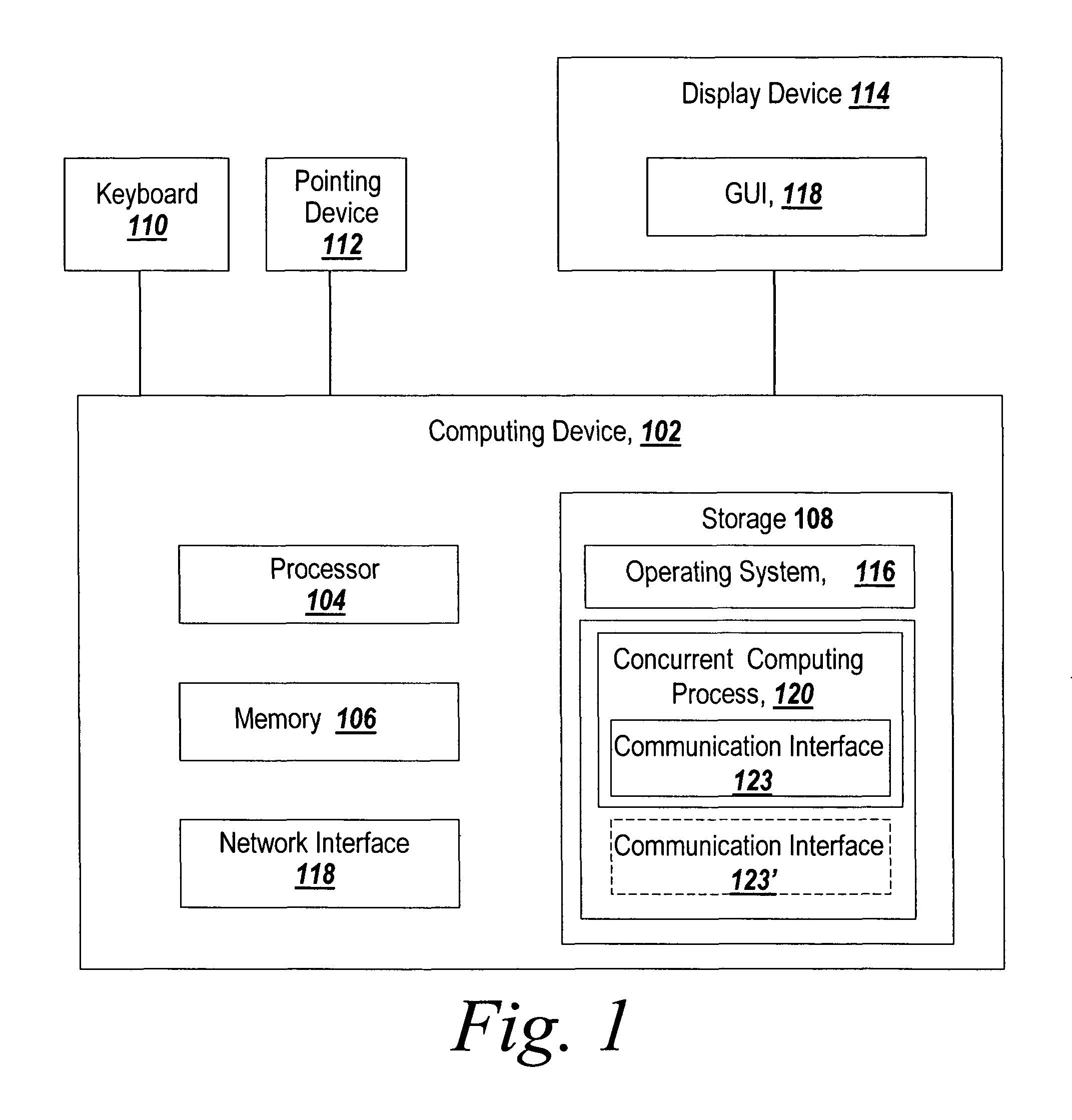
Recoverable error detection for concurrent computing programs
ActiveUS7925791B2Program synchronisationMultiple digital computer combinationsConcurrent computingIts region
The present invention provides a system and method for detecting communication error among multiple nodes in a concurrent computing environment. A barrier synchronization point or regions are used to check for communication mismatch. The barrier synchronization can be placed anywhere in a concurrent computing program. If a communication error occurred before the barrier synchronization point, it would at least be detected when a node enters the barrier synchronization point. Once a node has reached the barrier synchronization point, it is not allowed to communicate with another node regarding data that is needed to execute the concurrent computing program, even if the other node has not reached the barrier synchronization point. Regions can also be used to detect a communication mismatch instead of barrier synchronization points. A concurrent program on each node is separated into one or more regions. Two nodes can only communicate with each other when their regions are compatible. If their regions are not compatible, then there is a communication mismatch.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
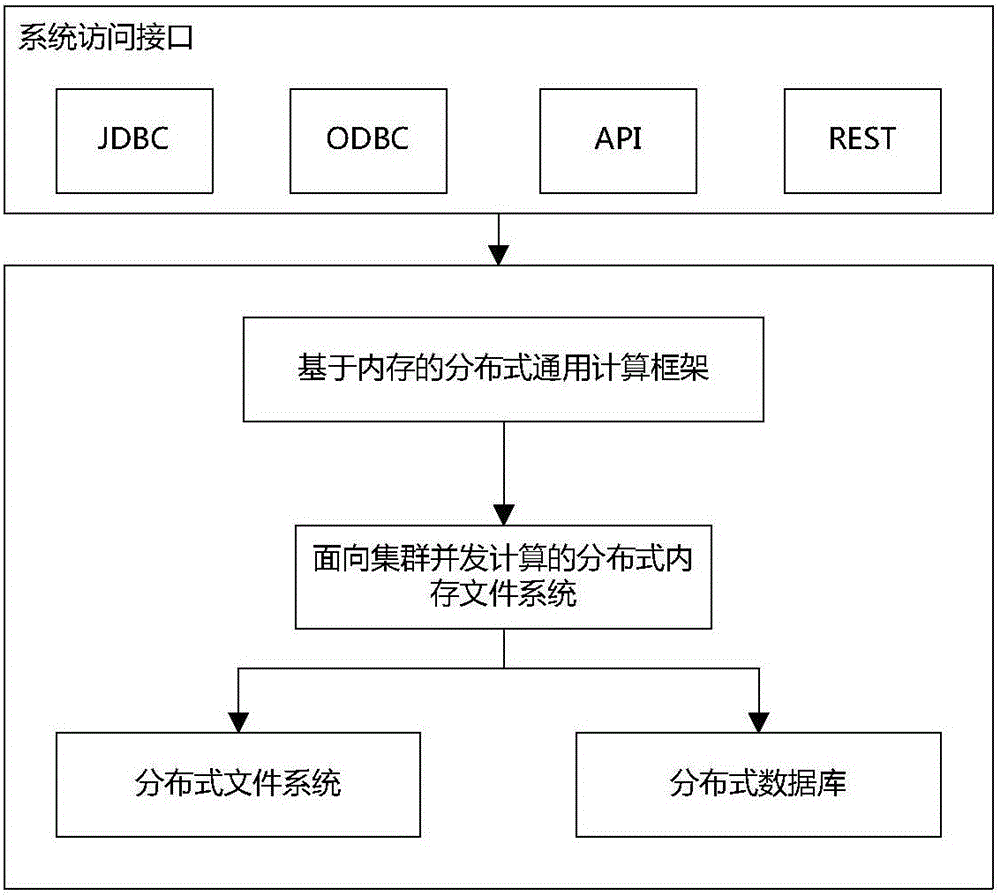
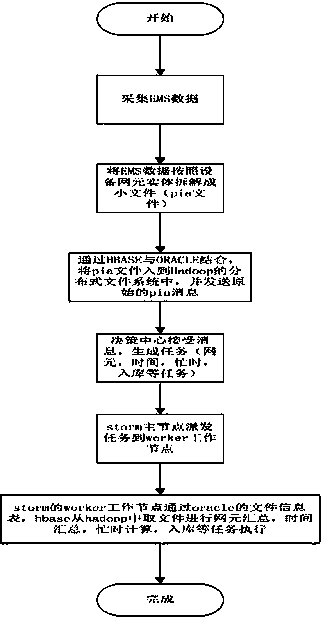
Distributed type performance data processing method
ActiveCN103853826AImprove access performanceImprove efficiencyMultiprogramming arrangementsFile access structuresConcurrent computingConcurrent computation
The invention provides a distributed type performance data processing method based on computing processing of distribution type stored data, and relates to storage and computing processing of network performance large data. A performance data file is stored and managed in a distributed manner through an HBASE and an HADOOP; meanwhile, missions are distributed to a plurality of worker nodes by using a STORM scheduling framework; concurrent computing and storage can be carried out; the entire treatment time is shortened by improving concurrence, so that the dependence on ORACLE is reduced, and the software cost is reduced.
Owner:INSPUR TIANYUAN COMM INFORMATION SYST CO LTD
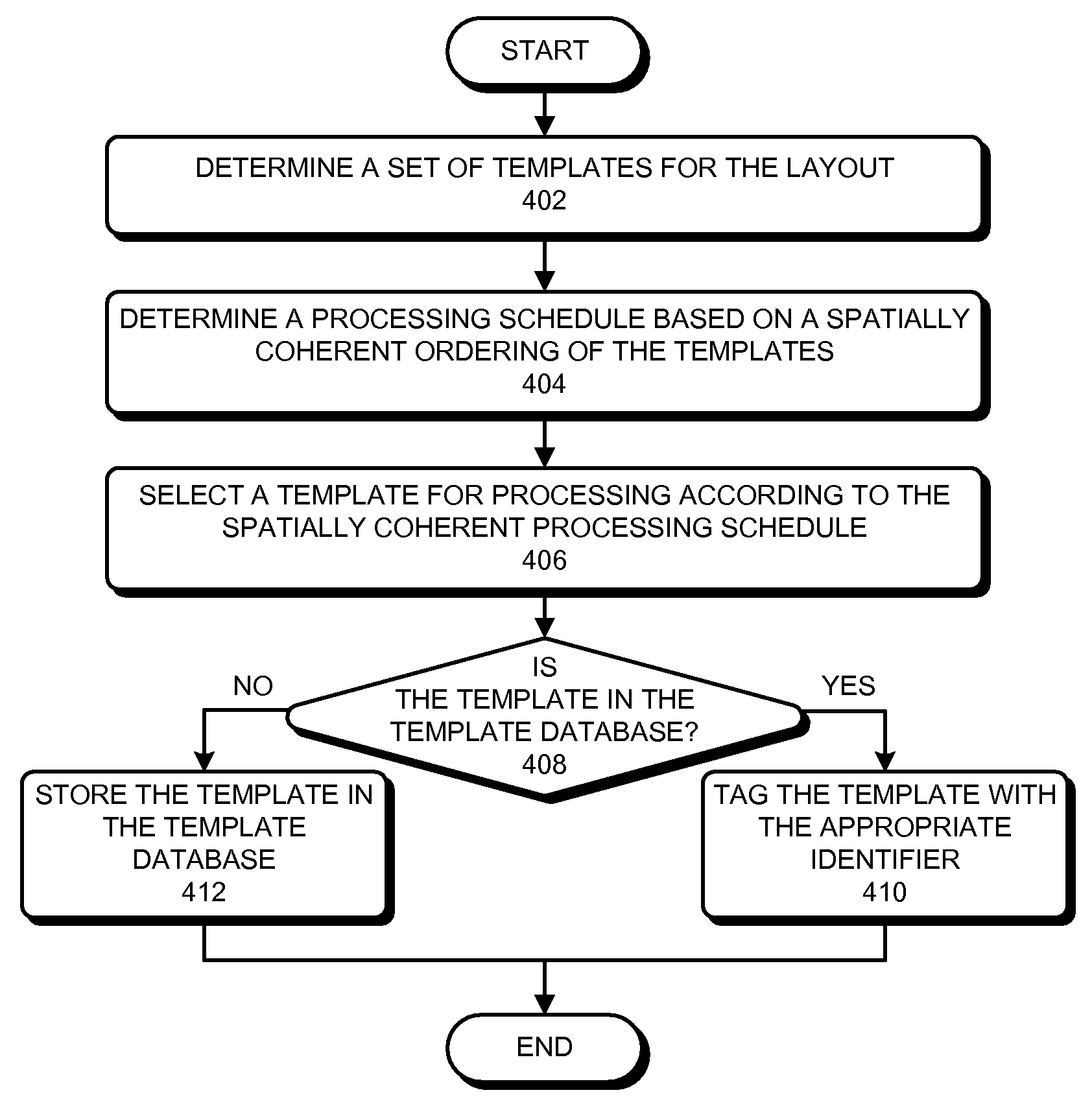
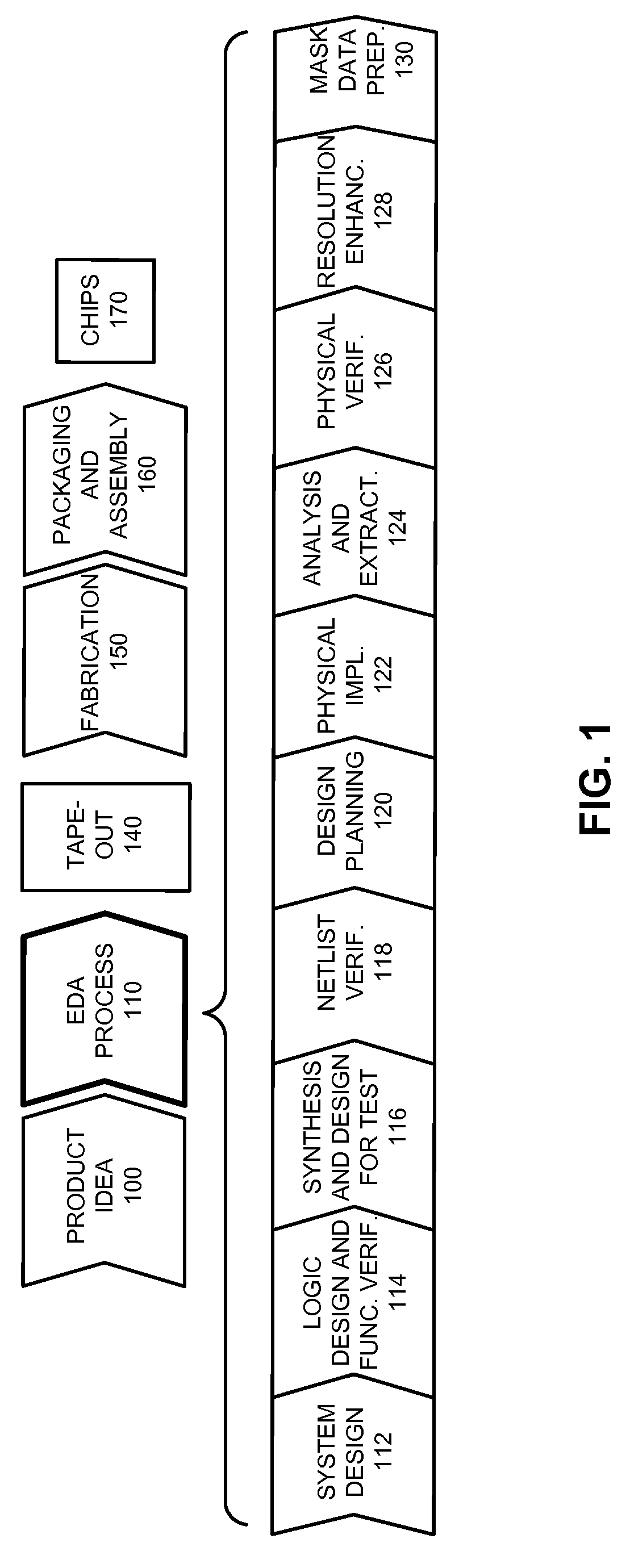
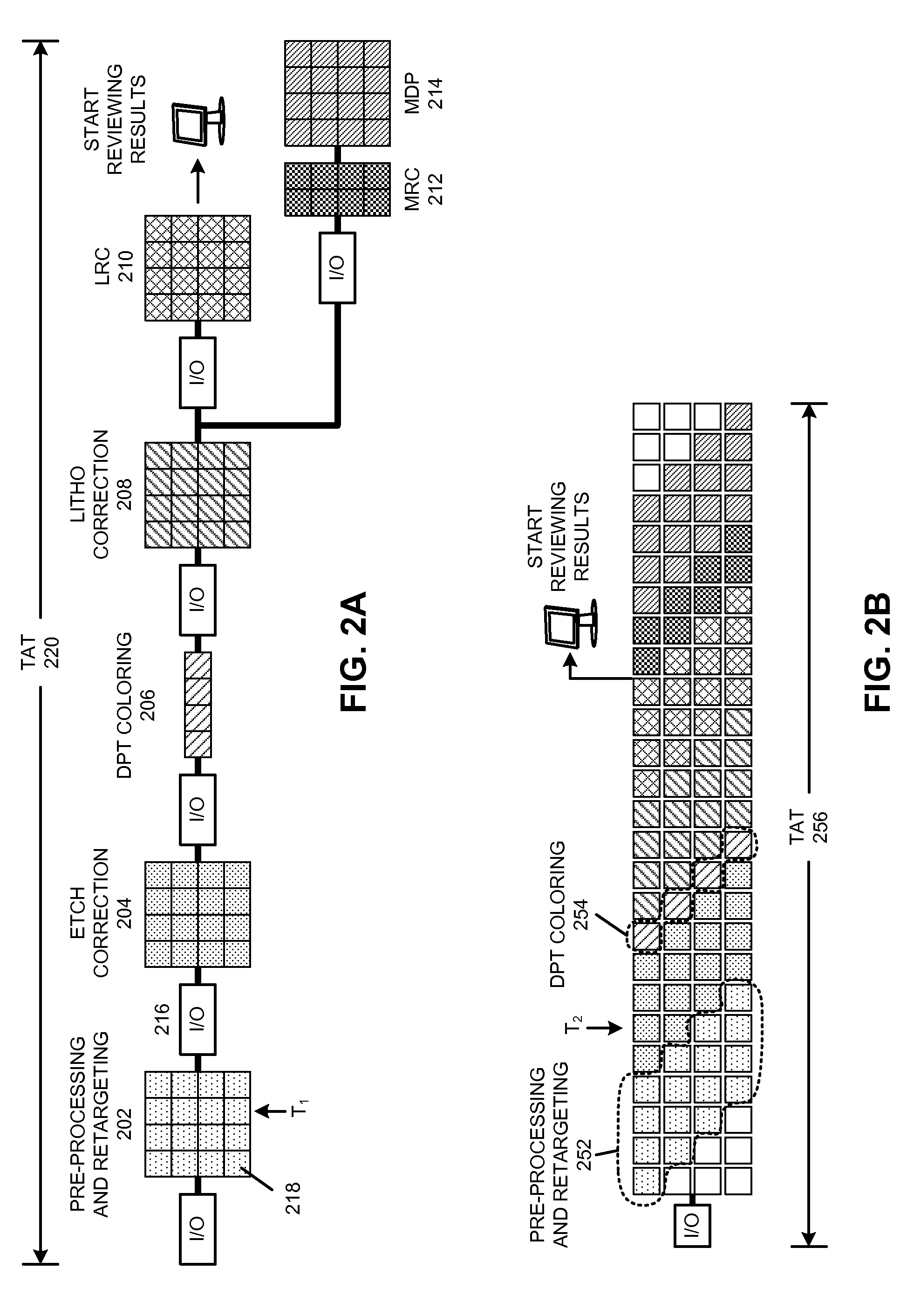
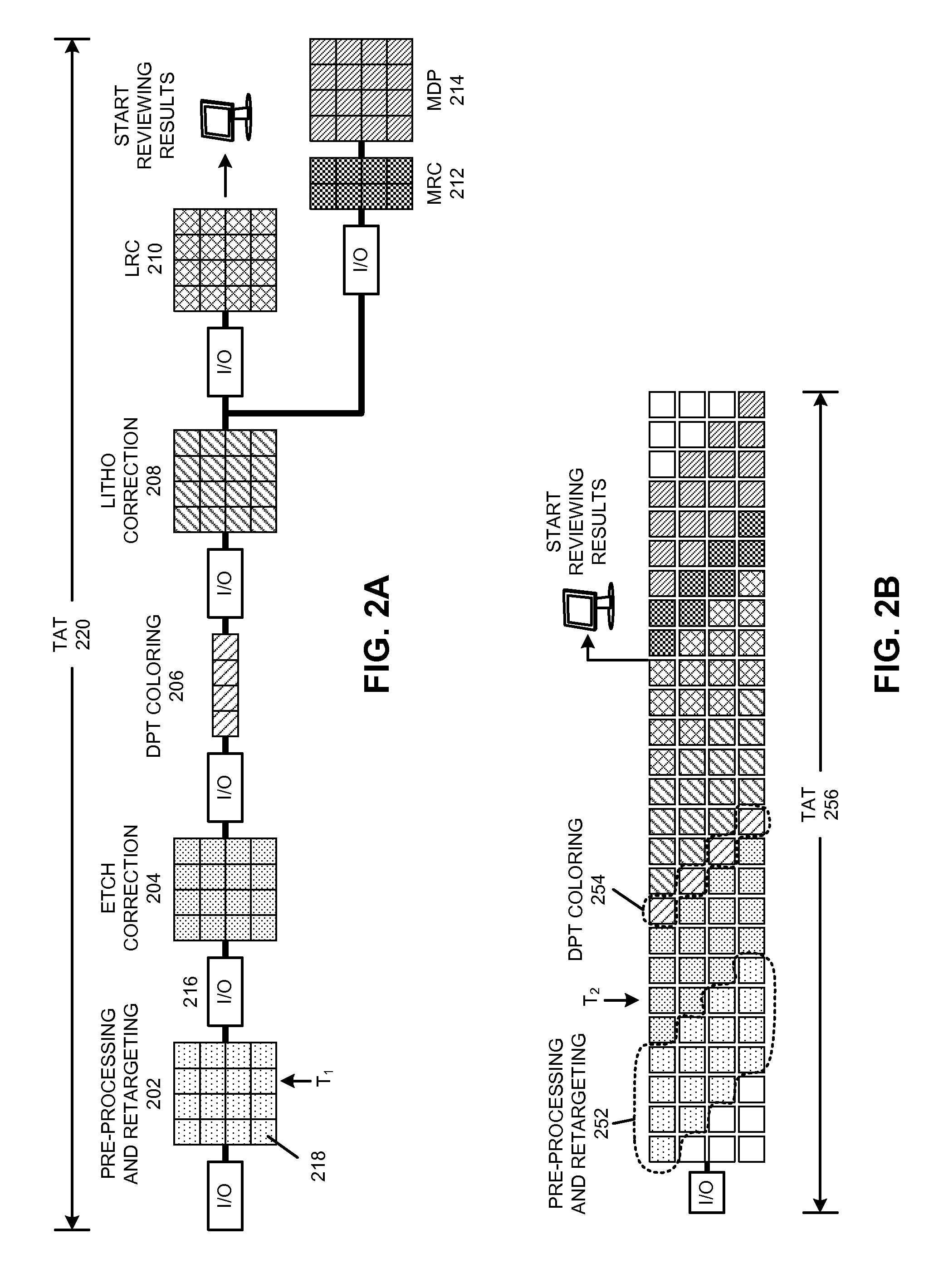
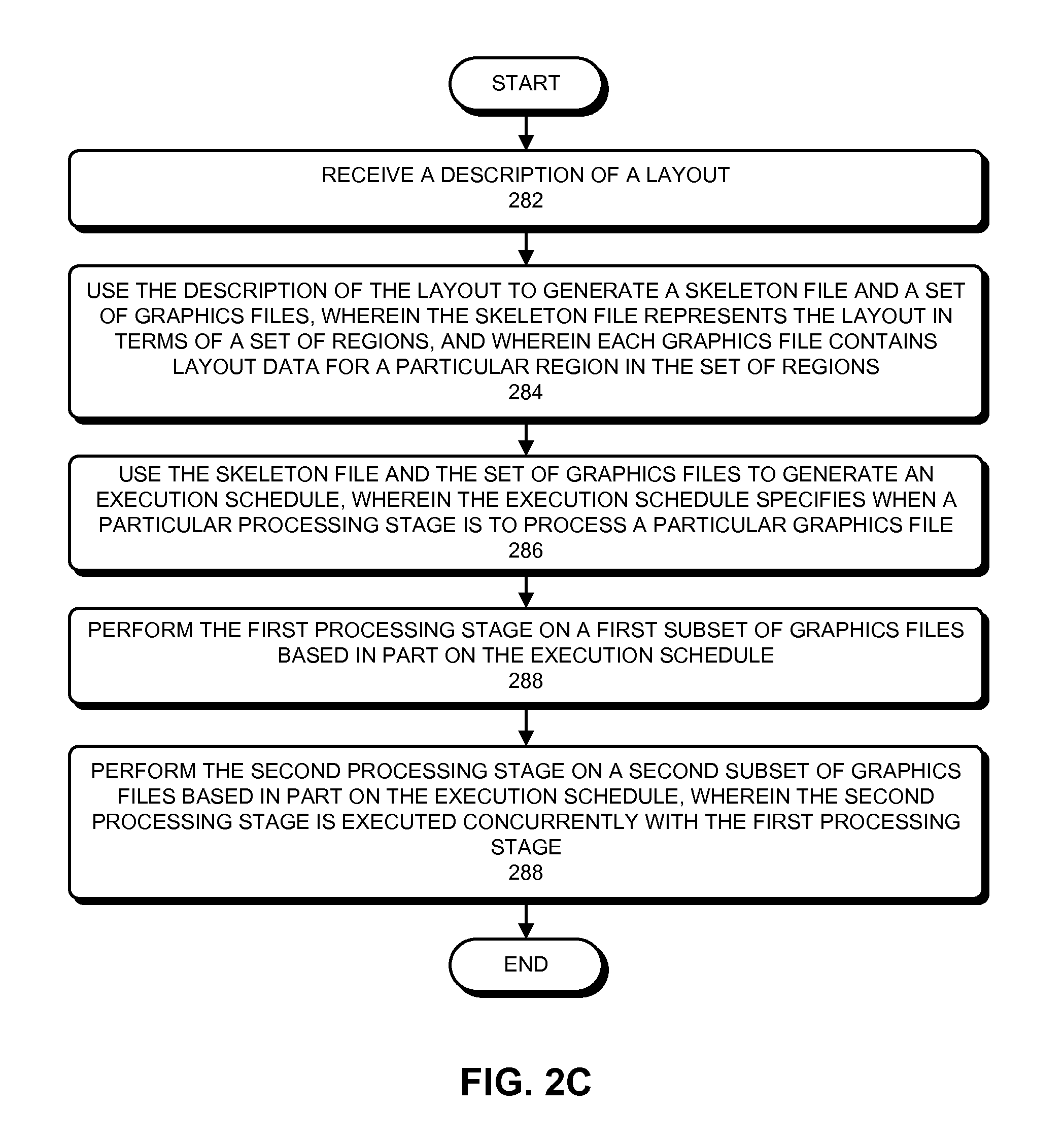
Incremental concurrent processing for efficient computation of high-volume layout data
ActiveUS20100198875A1Improve performanceDigital data processing detailsCAD circuit designConcurrent computingConcurrent computation
Some embodiments of the present invention overcome I / O bottlenecks of an EDA work flow by keeping layout data distributed during handoffs among different processing stages. Specifically, some embodiments leverage a concurrent computation paradigm where data is propagated incrementally between stages, and where data processing among consecutive stages and the I / O between stages are executed concurrently. Specifically, some embodiments can generate a template database which contains the unique templates in a set of templates. During operation, an embodiment can determine a set of templates for a layout. Next, the system can determine a processing schedule based on a spatially coherent ordering of the set of templates. Next, the system can process the templates according to the spatially coherent processing schedule. Processing templates in a spatially coherent order can ensure that the downstream processes in the concurrent work flow will be able to maximize concurrency, thereby improving overall performance of the system.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Recoverable error detection for concurrent computing programs
A system and method detects communication error among multiple nodes in a concurrent computing environment. One or more barrier synchronization points / checkpoints or regions are used to check for a communication mismatch. The barrier synchronization point(s) / checkpoint(s) can be placed anywhere in the concurrent computing program. Once a node reaches a barrier synchronization point / checkpoint, it is not allowed to communicate with another node regarding data that is needed to execute the concurrent computing program, even if the other node has not reached the barrier synchronization point / checkpoint. Regions can also, or alternatively, be used to detect a communication mismatch instead of barrier synchronization points / checkpoints. A concurrent program on each node is separated into one or more regions. Two nodes communicate with each other when their regions are compatible. If their regions are not compatible, a communication mismatch occurs.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
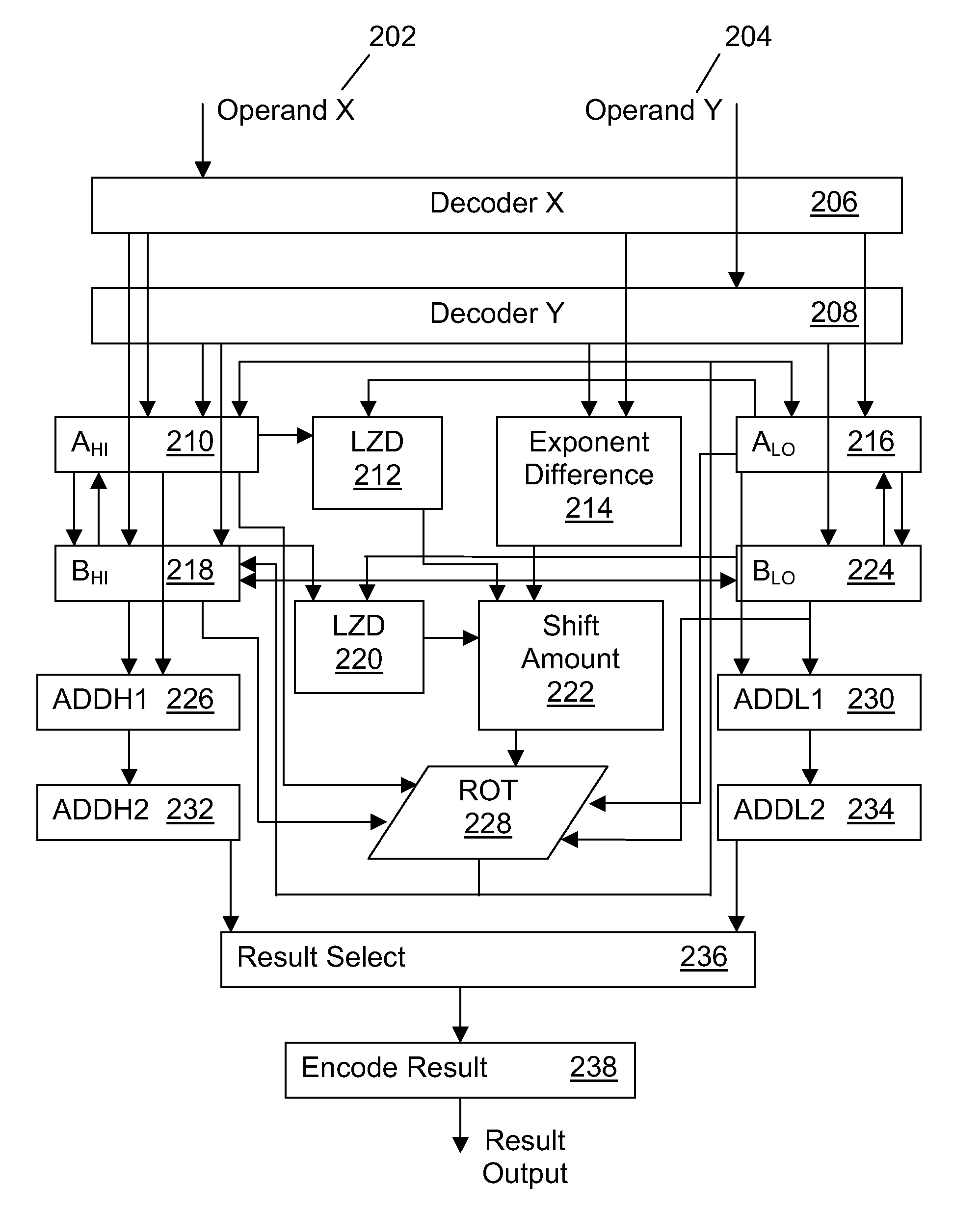
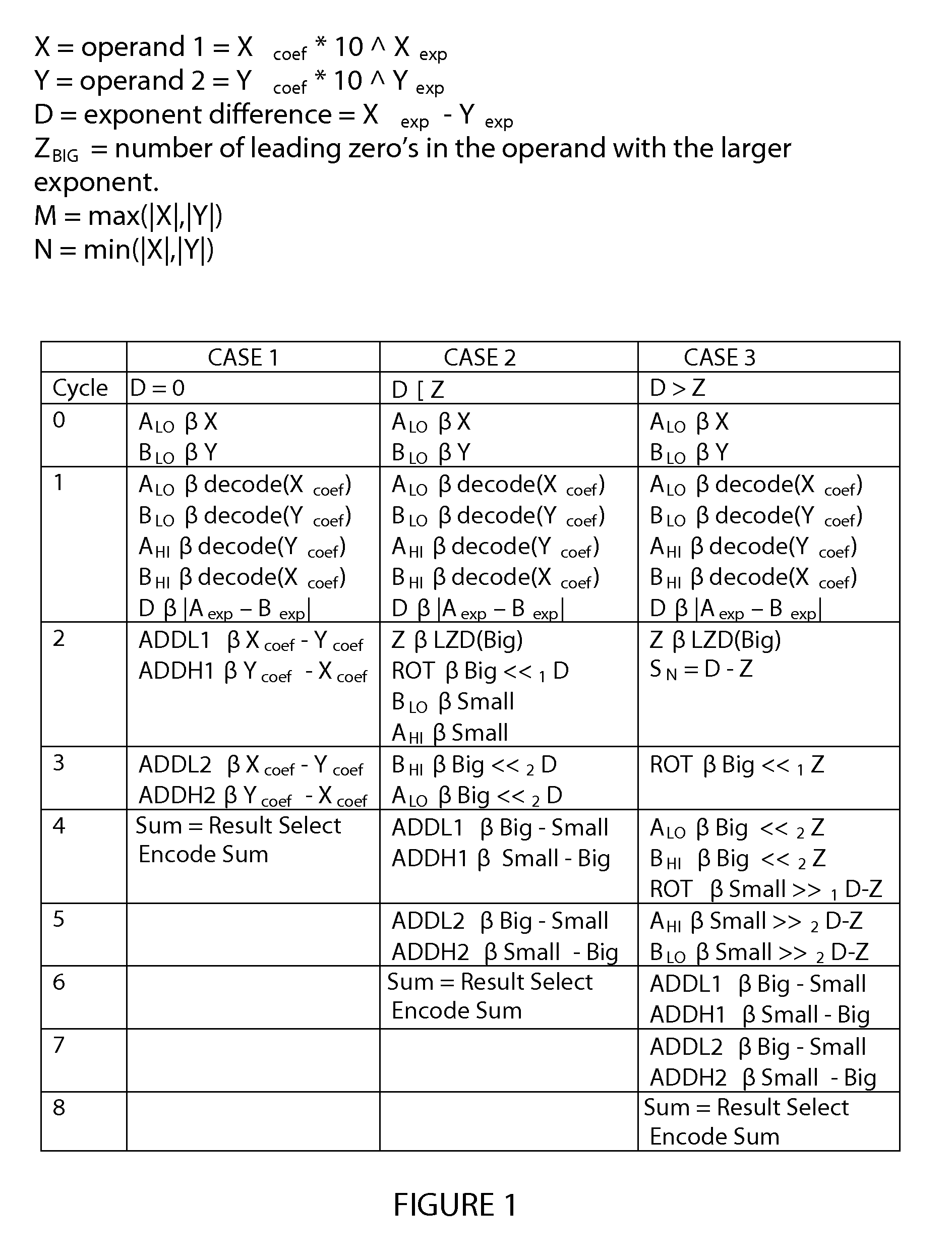
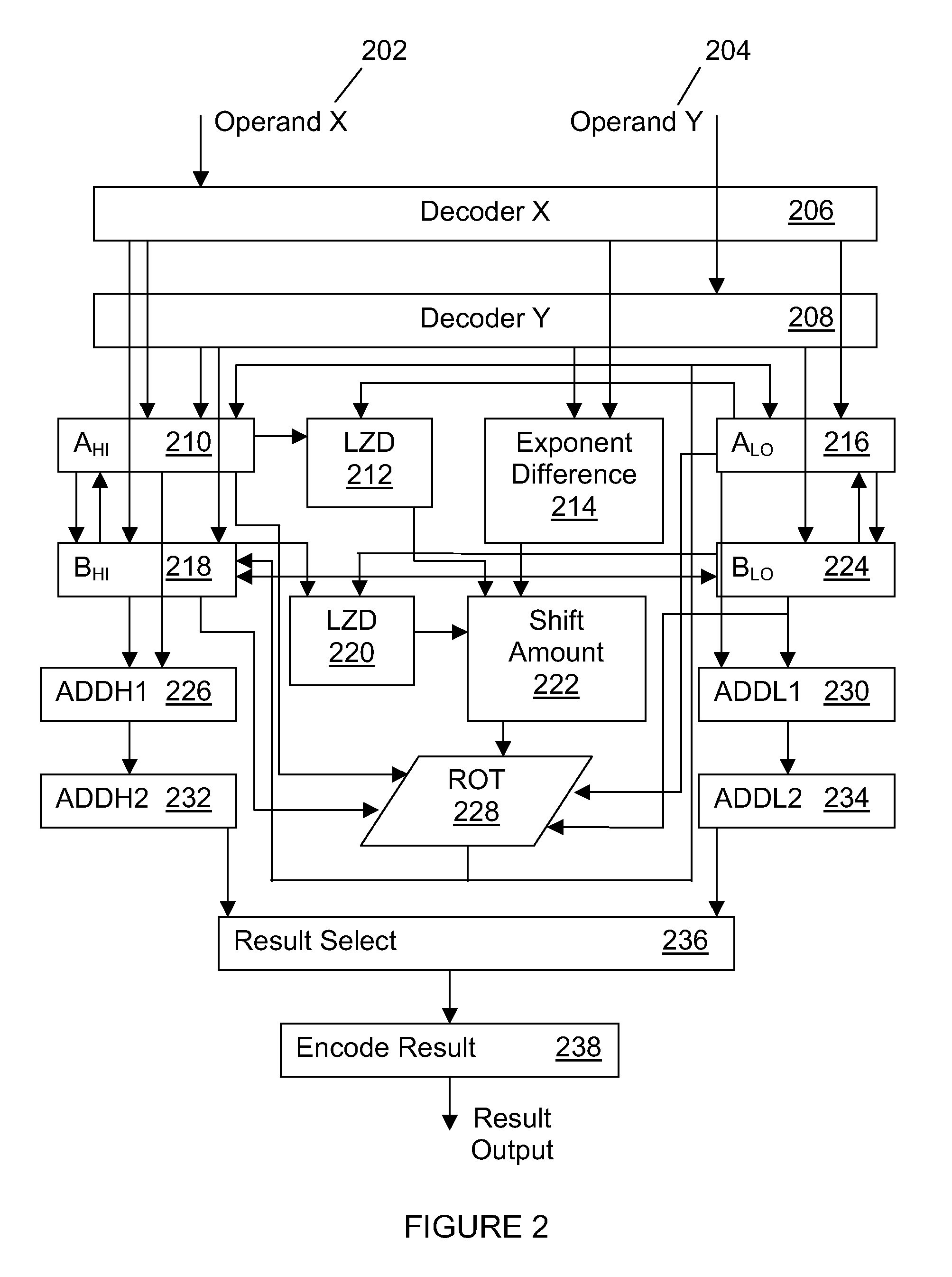
System and method for performing decimal floating point addition
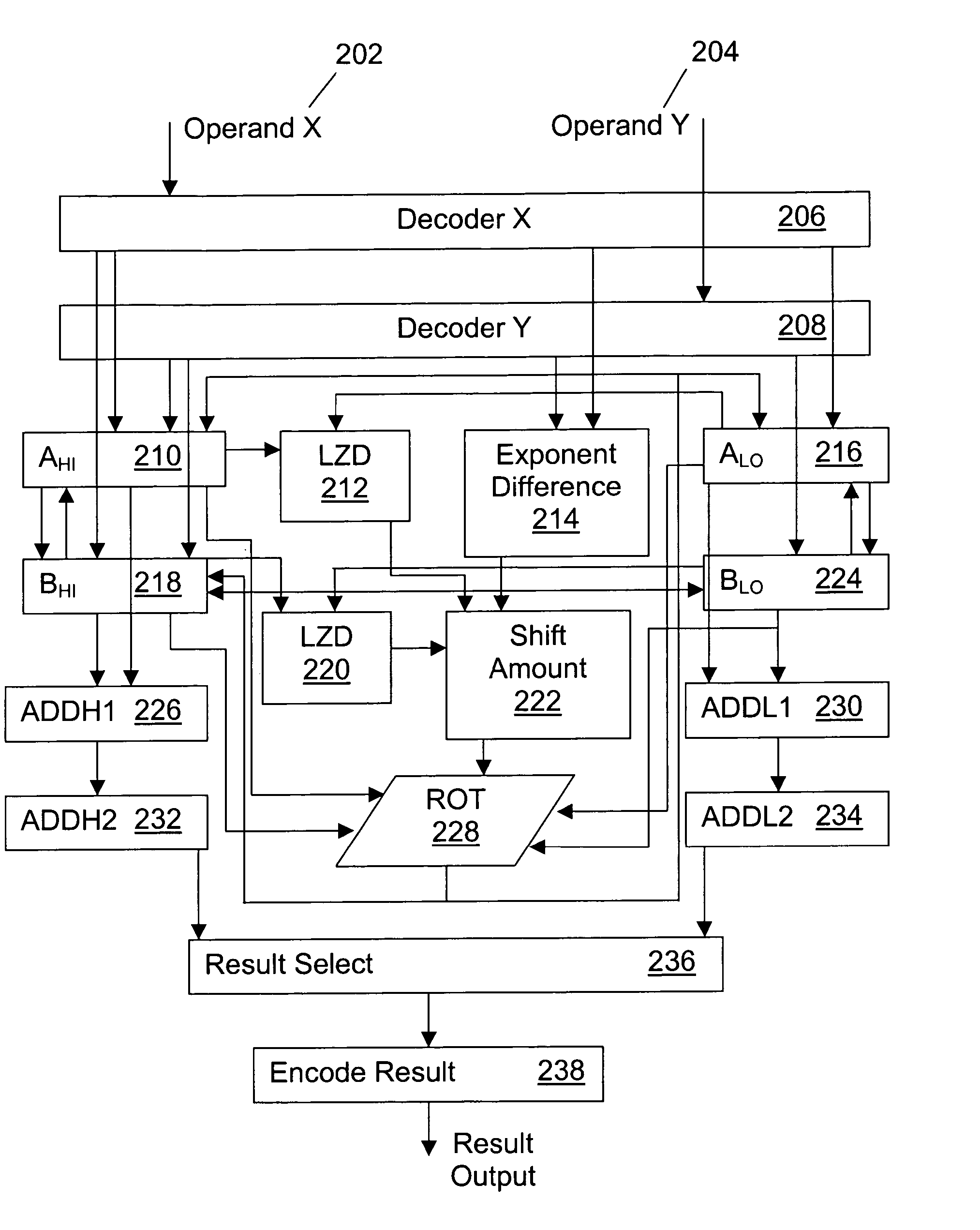
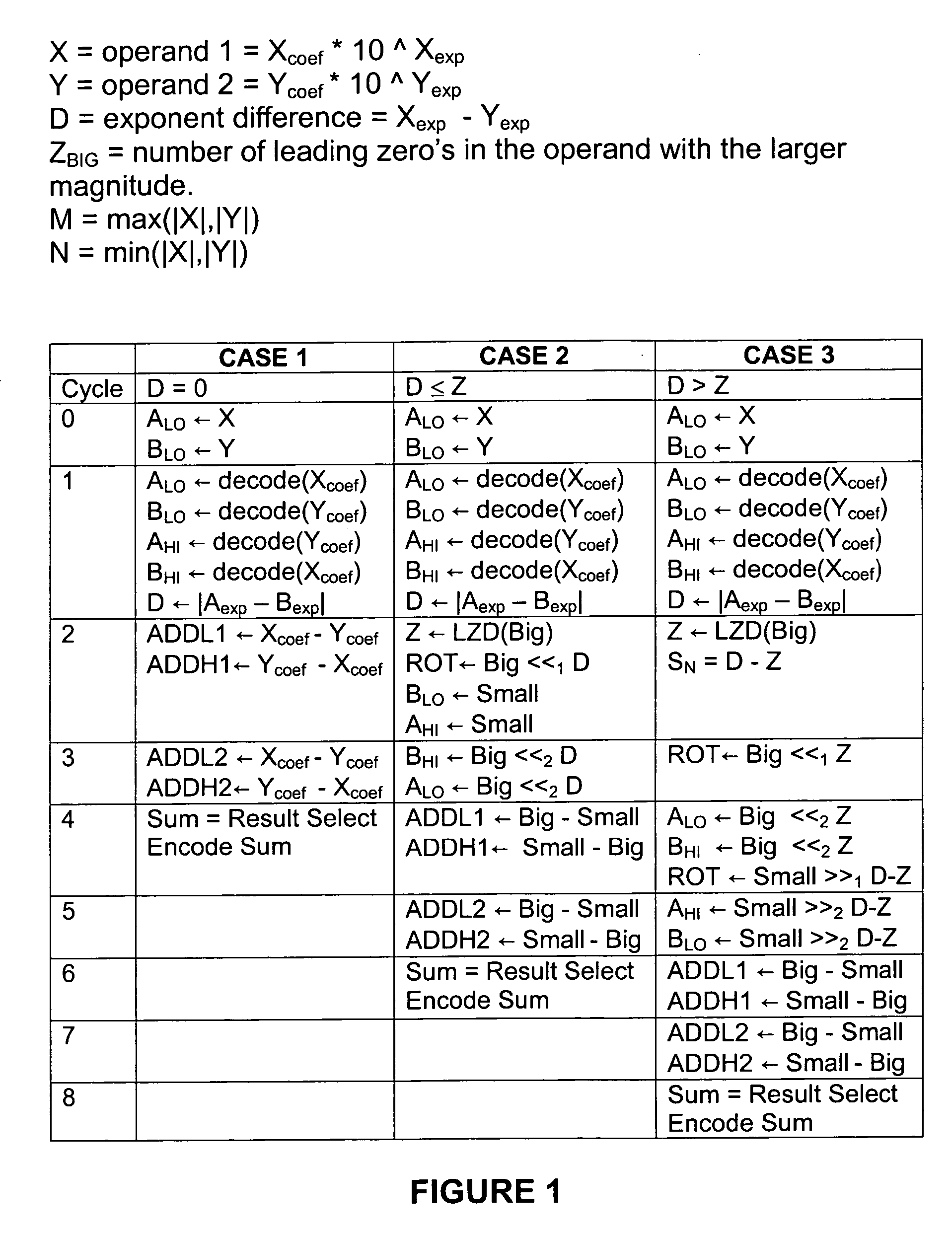
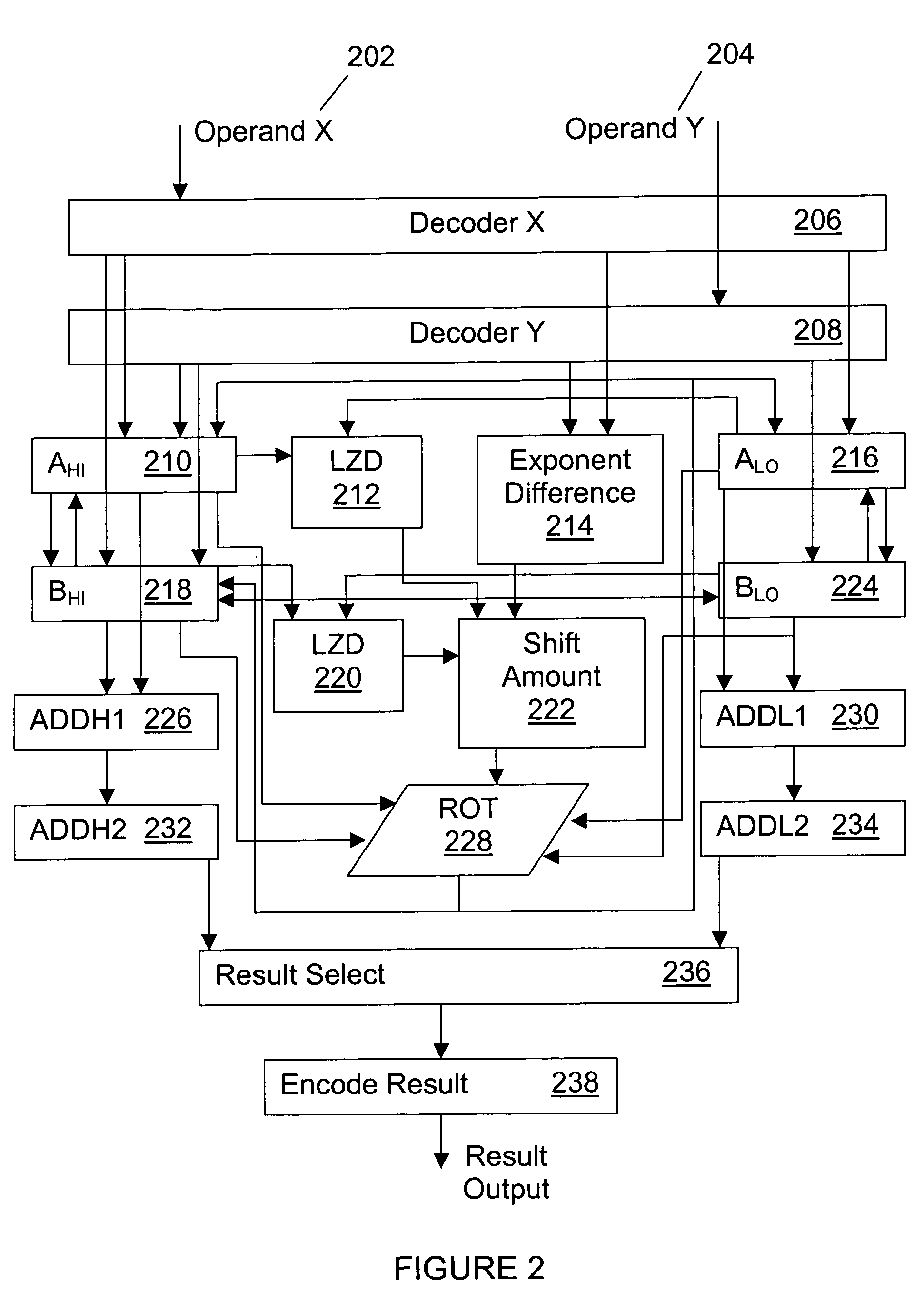
A method for performing a decimal floating point operation. A first operand including a first coefficient and a first exponent is received. The method also includes receiving a second operand that includes a second coefficient and a second exponent. An operation associated with the first operand and the second operand is received. The operation is an addition or a subtraction. Three concurrent calculations are performed on the first operand and the second operand. The first concurrent calculation includes applying the operation to the first operand and the second operand based on a first assumption that the first exponent is equal to the second exponent. The applying the operation based on the first assumption results in a first result and includes utilizing a two cycle adder. The second concurrent calculation includes applying the operation to the first operand and the second operand based on a second assumption that an absolute difference between the first exponent and the second exponent is less than or equal to a number of leading zeros in the coefficient of the operand with the larger exponent. The applying the operation based on the second assumption results in a second result and includes utilizing the two cycle adder. The third concurrent calculation includes applying the operation to the first operand and the second operand based on a third assumption that the absolute difference between the first exponent and the second exponent is greater than the number of leading zeros in the coefficient of the operand with the larger exponent. The applying the operation based on the third assumption results in a third result and includes utilizing the two cycle adder. A final result is selected from the first result, the second result and the third result.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Operation graph based event monitoring system
InactiveUS6874105B2Effective trackingMinimizing amount of dataError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsConcurrent computingConcurrent computation
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
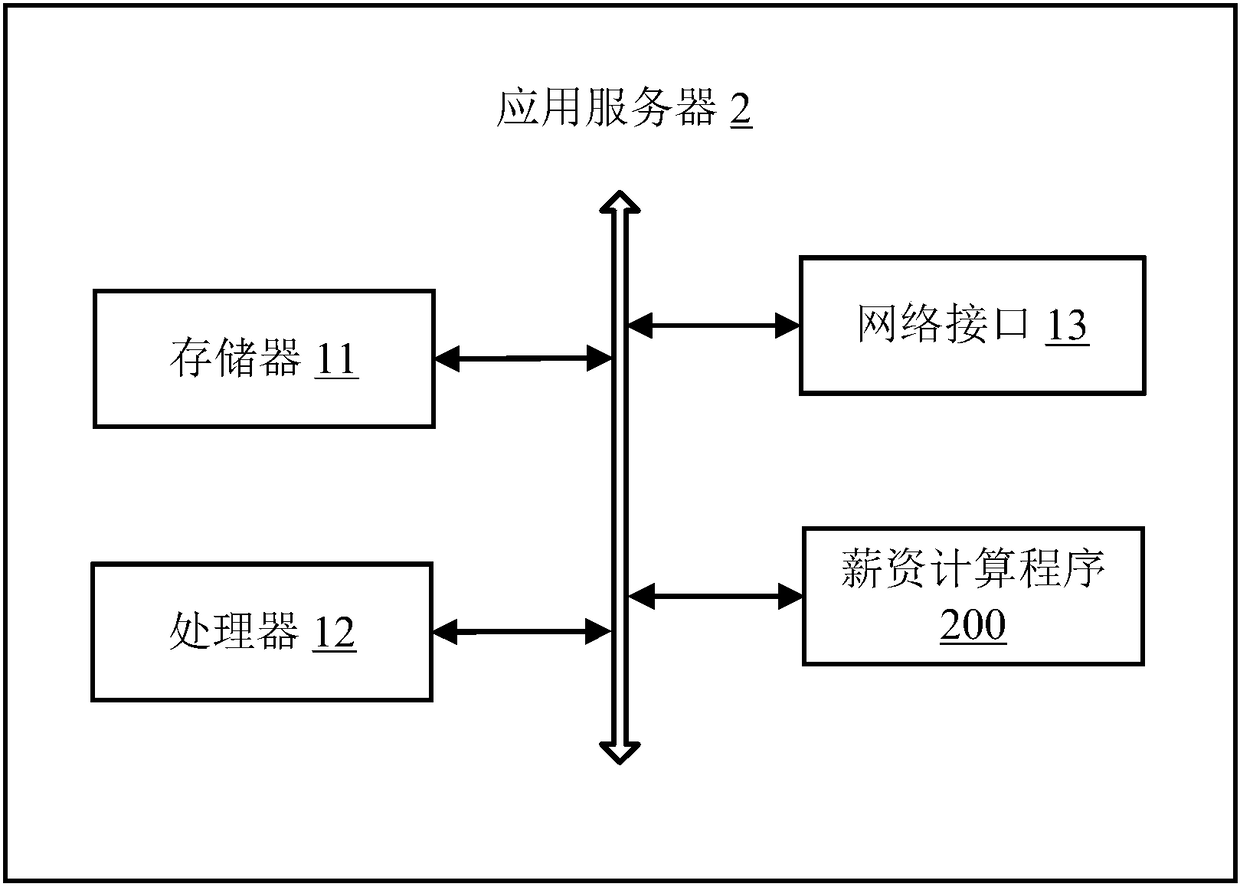
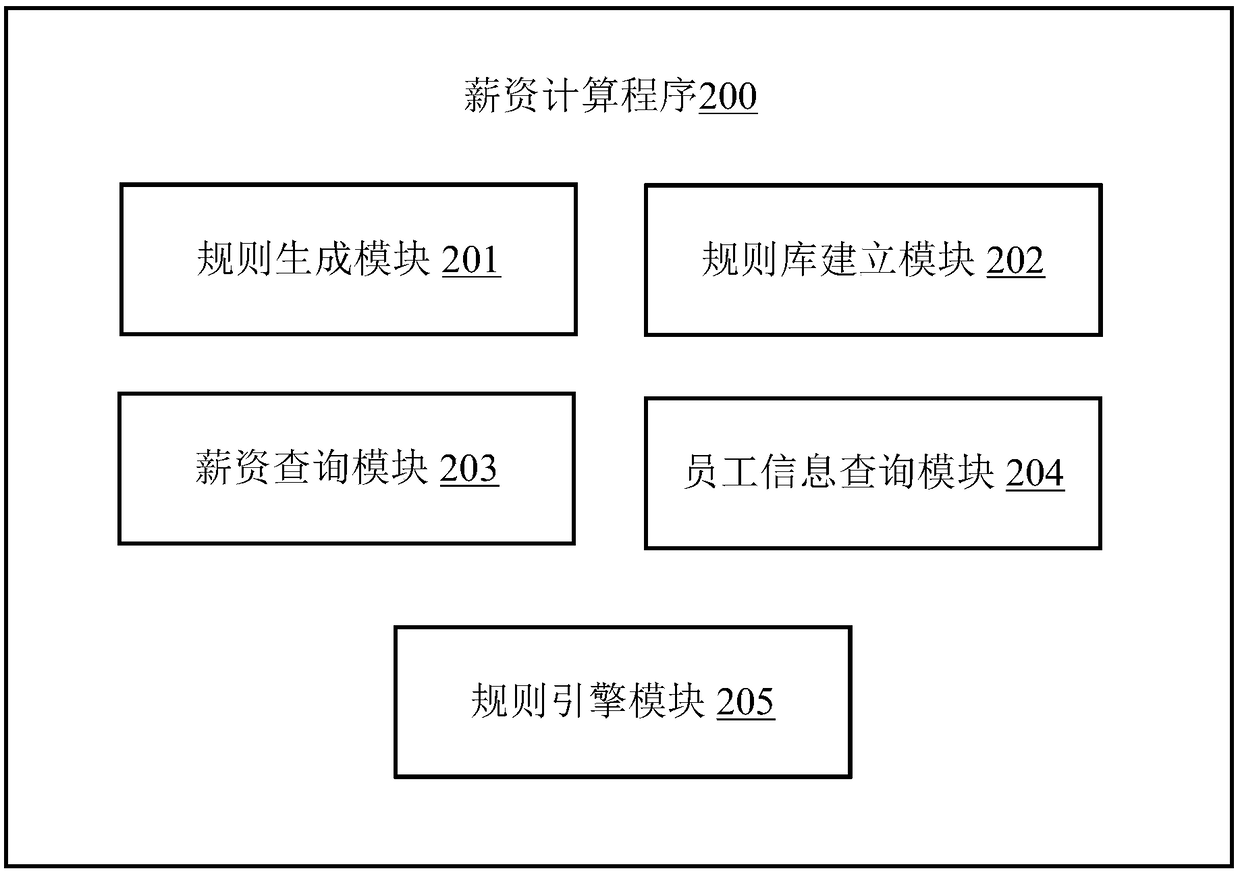
Salary calculation method, application server and computer readable storage medium
InactiveCN108428104ARealize hot deploymentAvoid the disadvantages of being very complex, not very readable, and difficult to maintainOffice automationConcurrent computingConcurrent computation
The invention discloses a salary calculation method, which comprises the following steps that: according to user input information, generating a business rule; storing the generated business rule, andconstructing a rule library; receiving an employee ID (Identity) input by a user; according to the employee ID, inquiring a database, and obtaining employee information corresponding to the employeeID; utilizing a rule engine to call the business rule from the rule library, and matching the business rule on the basis of the employee information; and after the employee information is matched withthe business rule, executing the business rule, and obtaining a salary calculation result. The invention also provides an application server and a computer readable storage medium. Through the implementation of the scheme of the invention, a great quantity of rule calculation is extracted from the database and is maintained in the rule engine, calculation can be more efficiently finished, concurrent calculation can be favorably supported, calculation efficiency is improved, and the hot deployment of the rule engine is realized.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Dynamic definition for concurrent computing environments
A system generates an executable process for execution by a concurrent computing environment, generates a configuration that specifies configurable properties of the concurrent computing environment, and initiates execution of the executable process, with the concurrent computing environment, to initiate configuration of the concurrent computing environment based on the configurable properties of the configuration.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
System and method for performing decimal floating point addition
InactiveUS20060179099A1Computations using contact-making devicesConcurrent computingAbsolute difference
A method for performing a decimal floating point operation. A first operand including a first coefficient and a first exponent is received. The method also includes receiving a second operand that includes a second coefficient and a second exponent. An operation associated with the first operand and the second operand is received. The operation is an addition or a subtraction. Three concurrent calculations are performed on the first operand and the second operand. The first concurrent calculation includes applying the operation to the first operand and the second operand based on a first assumption that the first exponent is equal to the second exponent. The applying the operation based on the first assumption results in a first result and includes utilizing a two cycle adder. The second concurrent calculation includes applying the operation to the first operand and the second operand based on a second assumption that an absolute difference between the first exponent and the second exponent is less than or equal to a number of leading zeros in the coefficient of the operand with the larger exponent. The applying the operation based on the second assumption results in a second result and includes utilizing the two cycle adder. The third concurrent calculation includes applying the operation to the first operand and the second operand based on a third assumption that the absolute difference between the first exponent and the second exponent is greater than the number of leading zeros in the coefficient of the operand with the larger exponent. The applying the operation based on the third assumption results in a third result and includes utilizing the two cycle adder. A final result is selected from the first result, the second result and the third result.
Owner:IBM CORP
Streaming graph calculation method and system based on state update propagation
ActiveCN109033234AReduce the numberControl area of influenceSpecial data processing applicationsConcurrent computingConcurrent computation
The invention relates to a streaming graph calculation method and system based on state update propagation. The streaming graph calculation model based on state update propagation can concurrently calculate the influence of incremental information on the basis of the original graph state without recalculating on the whole graph. At the same time, through the fine-grained distributed locking, the concurrent updating of the state is realized, and the correctness of the calculation results is ensured. The real-time performance and the accuracy of the invention are tested through a real data set,and the results show that the algorithm constructed by the flow chart calculation model based on the state update propagation can obtain more accurate calculation results, and the calculation deviation is less than 1%; 90% of the graph data update requests can be responded within 12 ms, which meets the real-time requirements; the collision probability of any two compute nodes is less than 3%, which can meet the requirement of high concurrency.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
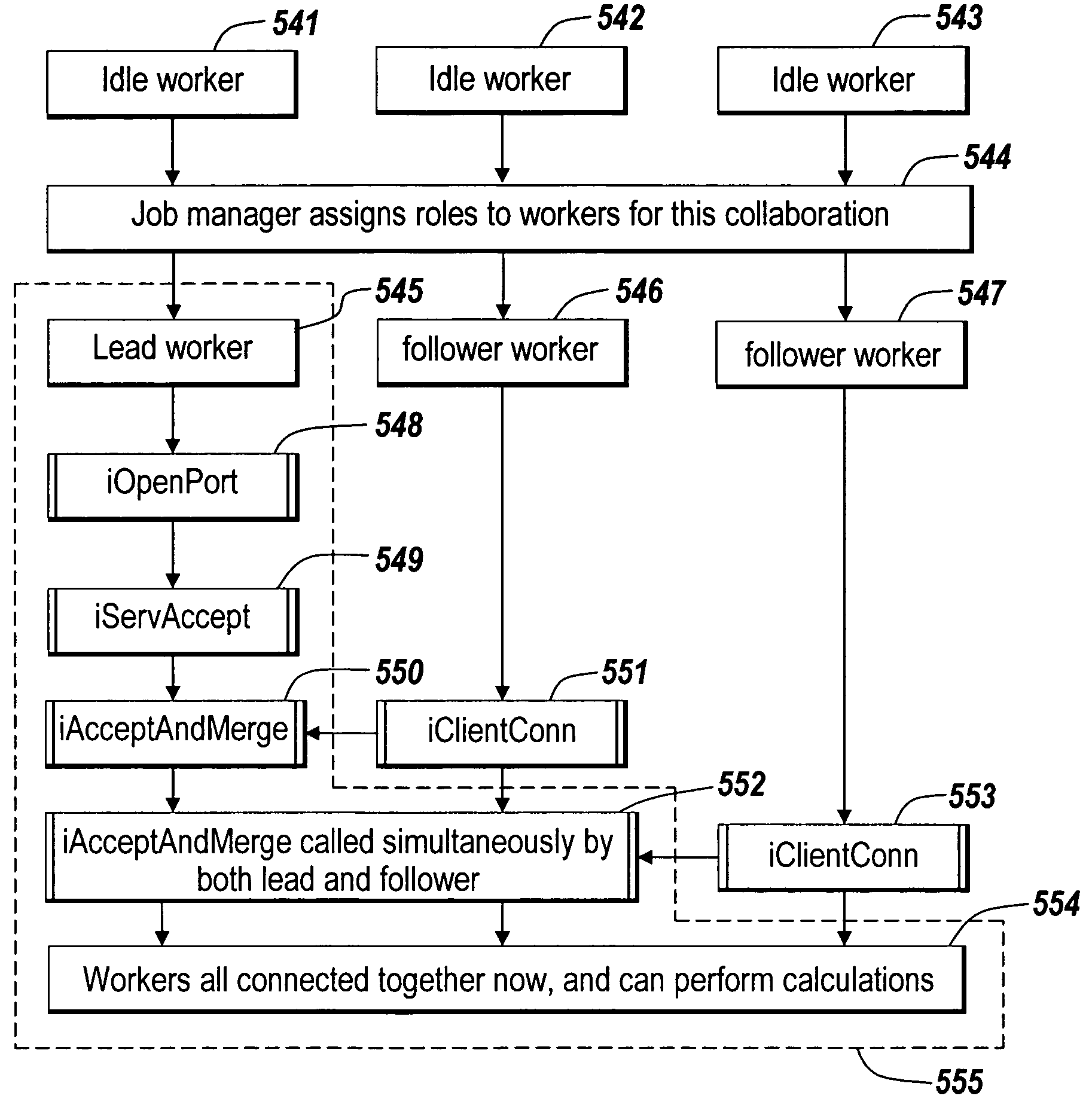
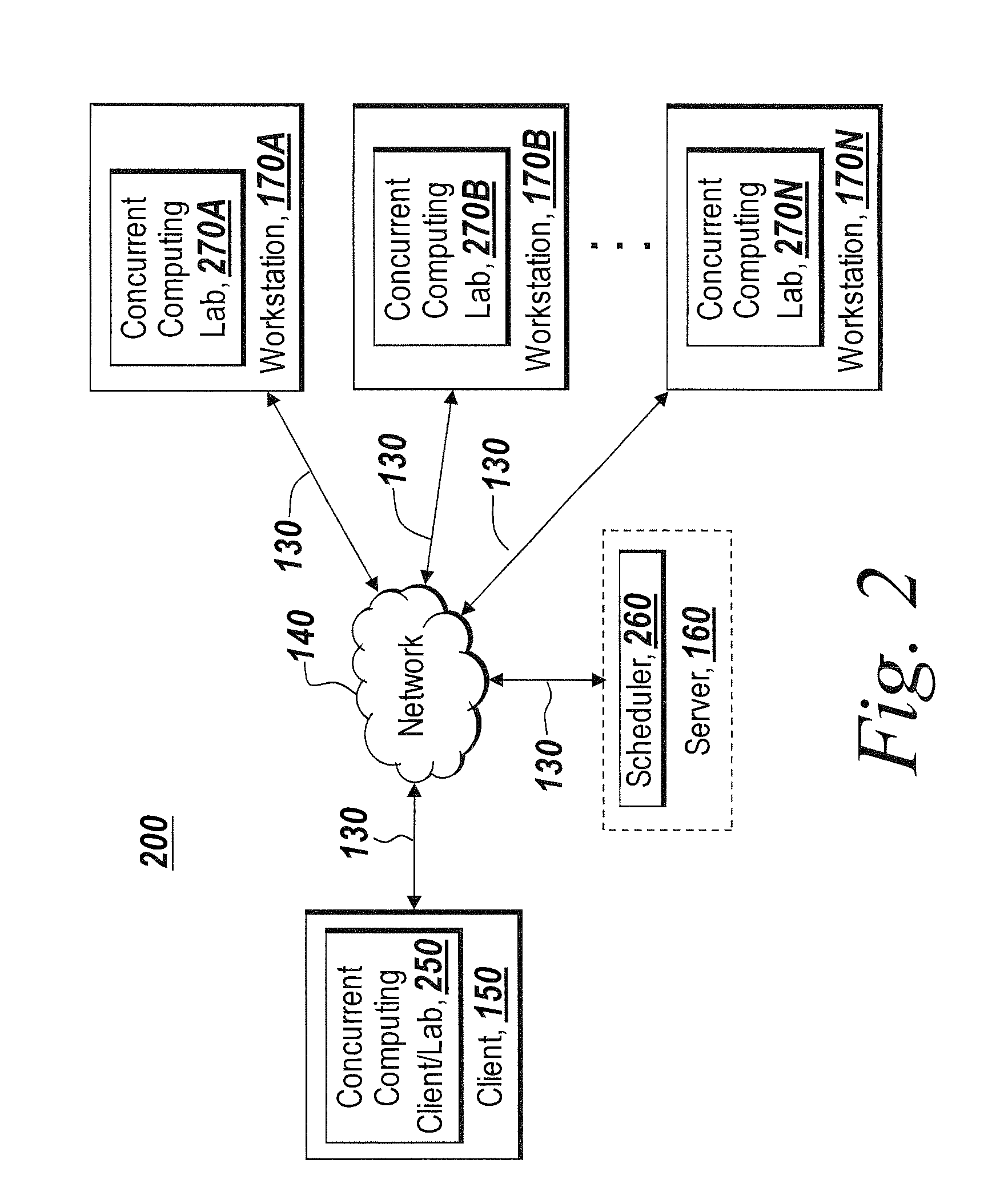
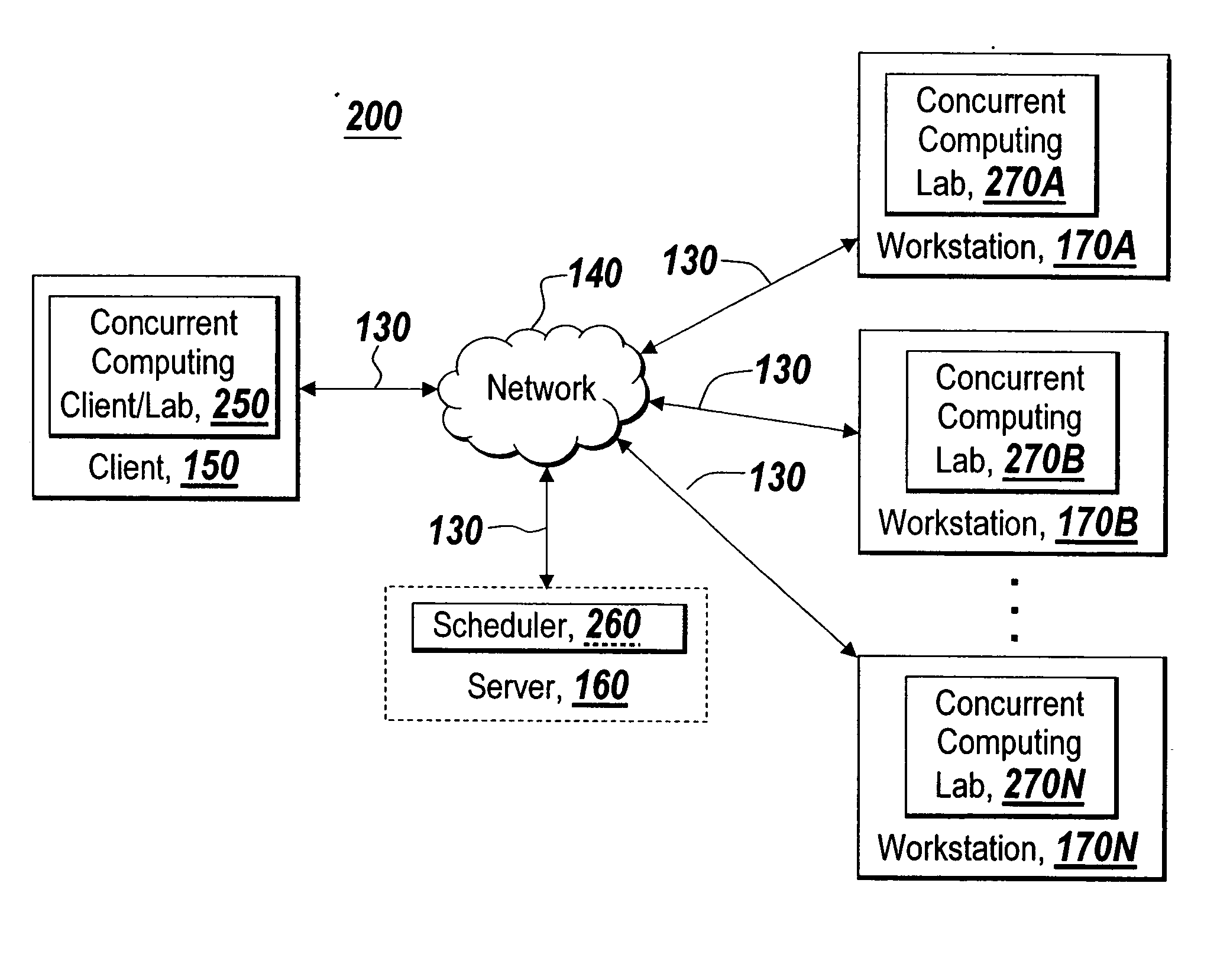
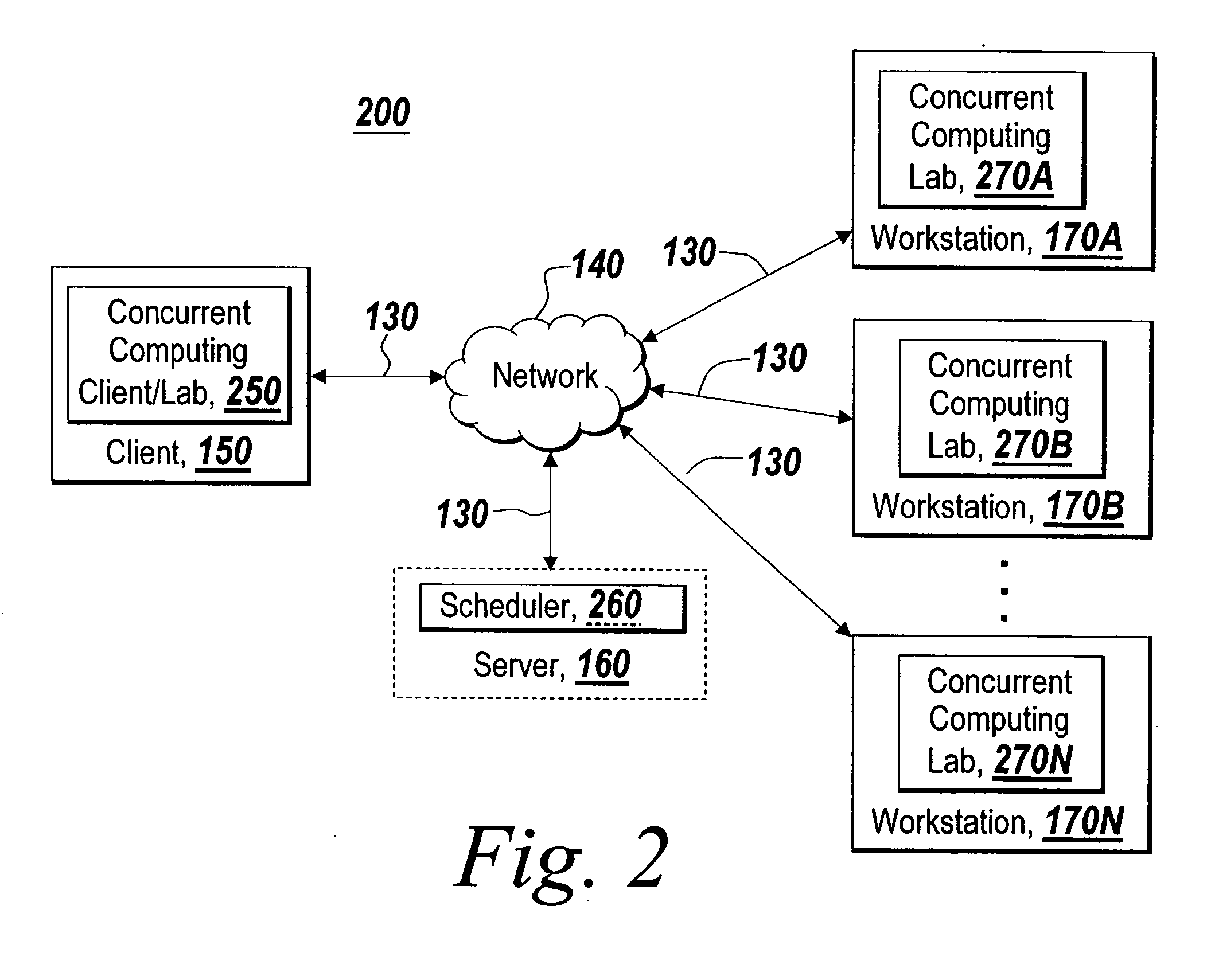
Dynamically sizing a collaboration of concurrent computing workers based on user inputs
ActiveUS7765561B1Reduces initial delayModified dynamicallyInterprogram communicationConcurrent instruction executionConcurrent computingUser input
A dynamic collaboration of processes in a concurrent computing environment is disclosed. A user can modify the size of collaboration or the number of processes that execute a computational job after the processes have been launched on the concurrent computing environment. A launched or running process can establish a communication channel with other processes in the collaboration so that the launched or running process can join the collaboration to execute the job. The user can also release a process from the collaboration so the released process can join a new collaboration to execute a different job. Once a job is completed, the processes can leave the collaboration, and the processes are then free to join a new collaboration subsequently.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
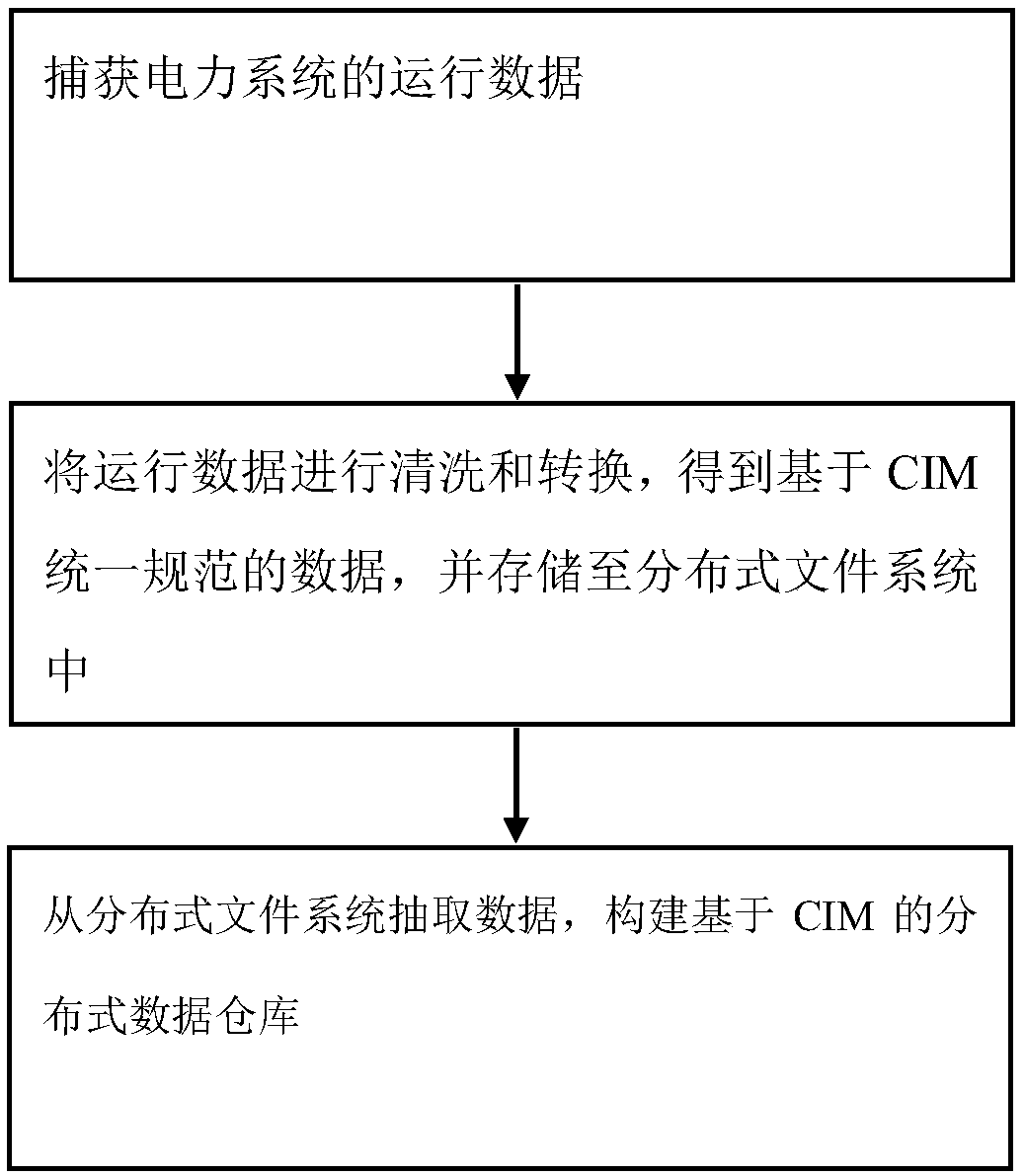
A data cleaning conversion method based on CIM
InactiveCN109213752ARealize unified standard data outputGuarantee data qualityData processing applicationsDatabase management systemsConcurrent computingData warehouse
The invention provides a data cleaning conversion method based on CIM. Cleaning and converting the captured power system operation data to obtain CIM-based uniform specification data, and storing thedata in the distributed file system; data are extracted from distributed file system and distributed data warehouse based on CIM is constructed. The invention provides a data cleaning conversion method based on CIM, supported by the improved grid operation data model and distributed data platform, extracting, cleaning, integrating the source data, ensuring the quality and reliability of the data,realizing the unified standard data output based on the database, has the wide applicability of supporting cluster deployment and concurrent computing, and can provide reliable support for the automated integration and analysis of power grid data.
Owner:STATE GRID FUJIAN ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD +3
Incremental concurrent processing for efficient computation of high-volume layout data
ActiveUS8893061B2Improve performanceCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsConcurrent computingConcurrent computation
Some embodiments of the present invention overcome I / O bottlenecks of an EDA work flow by keeping layout data distributed during handoffs among different processing stages. Specifically, some embodiments leverage a concurrent computation paradigm where data is propagated incrementally between stages, and where data processing among consecutive stages and the I / O between stages are executed concurrently. Specifically, different data processing stages can partition the layout data differently, and portions of the layout data that are not required by a data processing stage can be either passed-through or passed-around the data processing stage.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Dynamic definition for concurrent computing environments
Exemplary embodiments allow a user to create configurations for use in distributed computing environments. Configurations can be arranged in hierarchies in which elements of the hierarchy can inherit characteristics from elements in other layers of the hierarchy. Embodiments also allow a user to flatten a hierarchical configuration to remove hierarchical dependencies and / or inheriting capabilities of elements in the hierarchy. Exemplary embodiments further allow users to deploy a distributed computing configuration on their desktop to evaluate performance of the configuration and then deploy the configuration in a distributed computing environment without having to change programming code run on the desktop / distributed computing environment.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
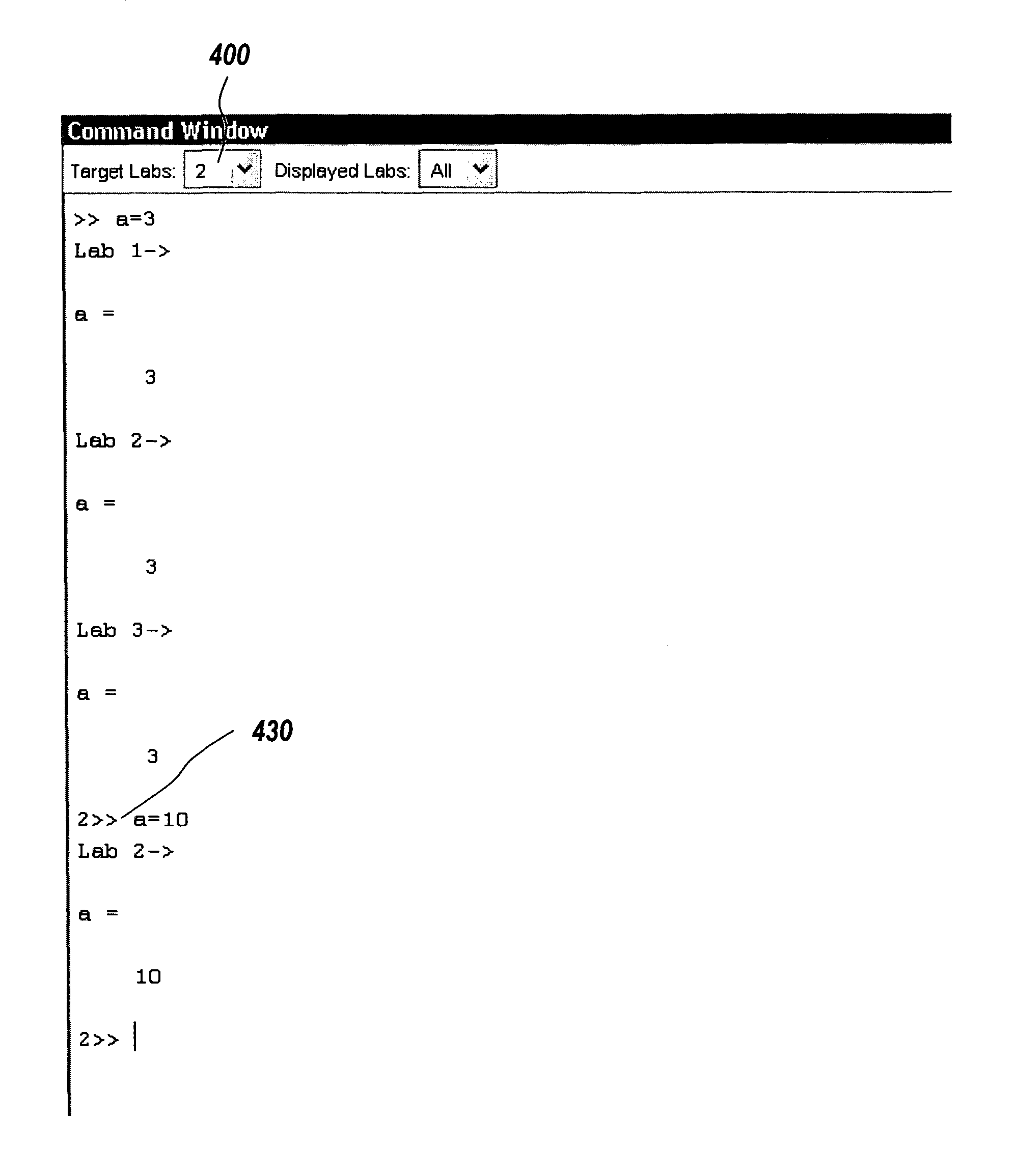
System and method for targeting commands to concurrent computing units executing a concurrent computing process
A graphical user interface for a concurrent computing environment that conveys the concurrent nature of a computing environment and allows a user to monitor the status of a concurrent process being executed on multiple concurrent computing units is discussed. The graphical user interface allows the user to target specific concurrent computer units to receive commands. The graphical user interface also alters the command prompt to reflect the currently targeted concurrent computing units.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
Dynamic definition for concurrent computing environments
InactiveUS20070130299A1Multiple digital computer combinationsMemory systemsConcurrent computingOperating system
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
Incremental concurrent processing for efficient computation of high-volume layout data
ActiveUS20140189616A1Improve performanceCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsConcurrent computingConcurrent computation
Some embodiments of the present invention overcome I / O bottlenecks of an EDA work flow by keeping layout data distributed during handoffs among different processing stages. Specifically, some embodiments leverage a concurrent computation paradigm where data is propagated incrementally between stages, and where data processing among consecutive stages and the I / O between stages are executed concurrently. Specifically, different data processing stages can partition the layout data differently, and portions of the layout data that are not required by a data processing stage can be either passed-through or passed-around the data processing stage.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com