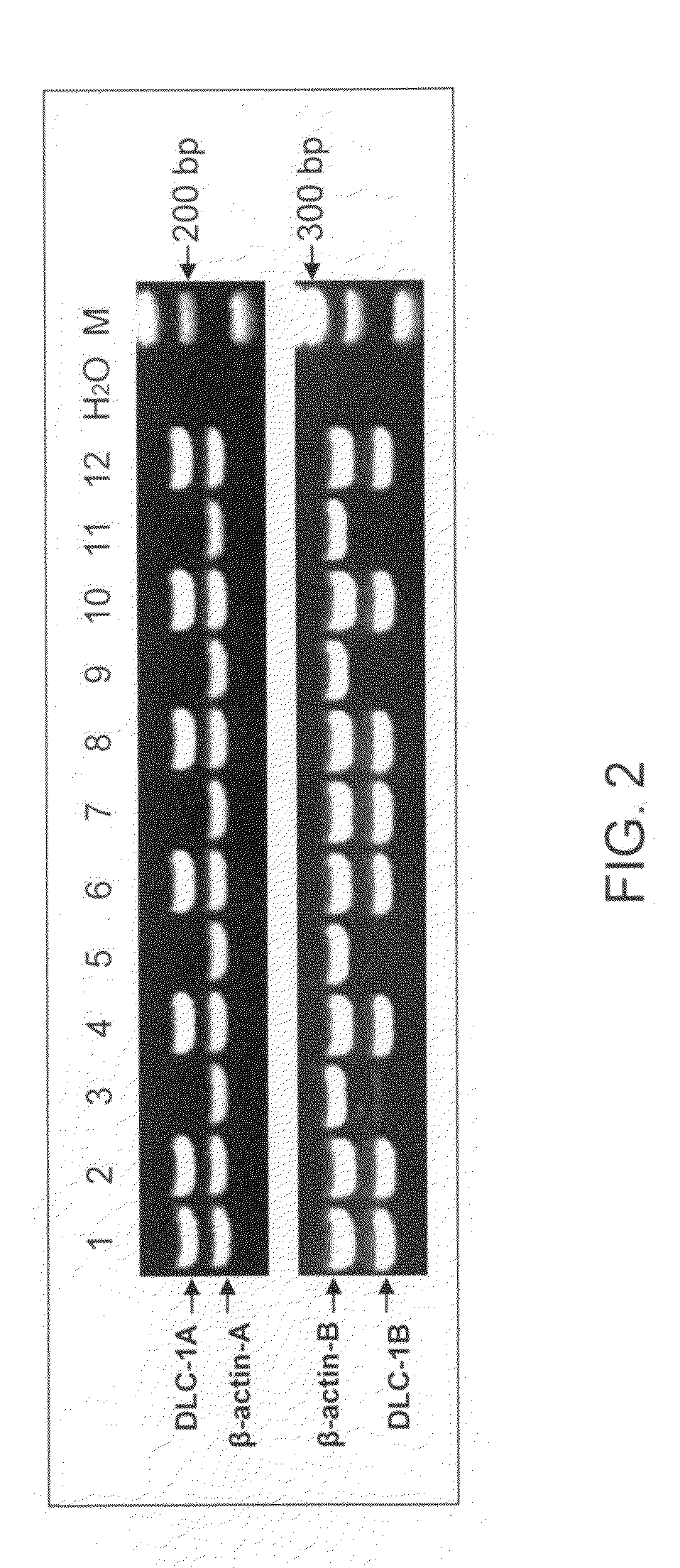
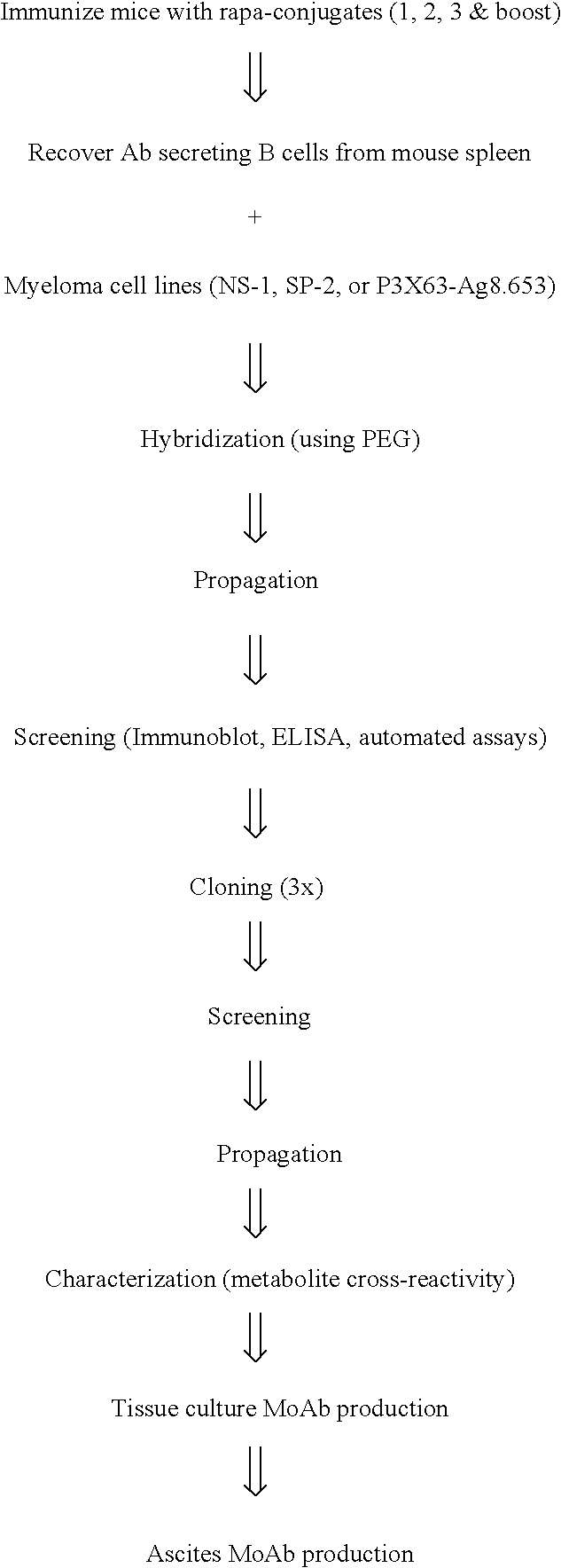
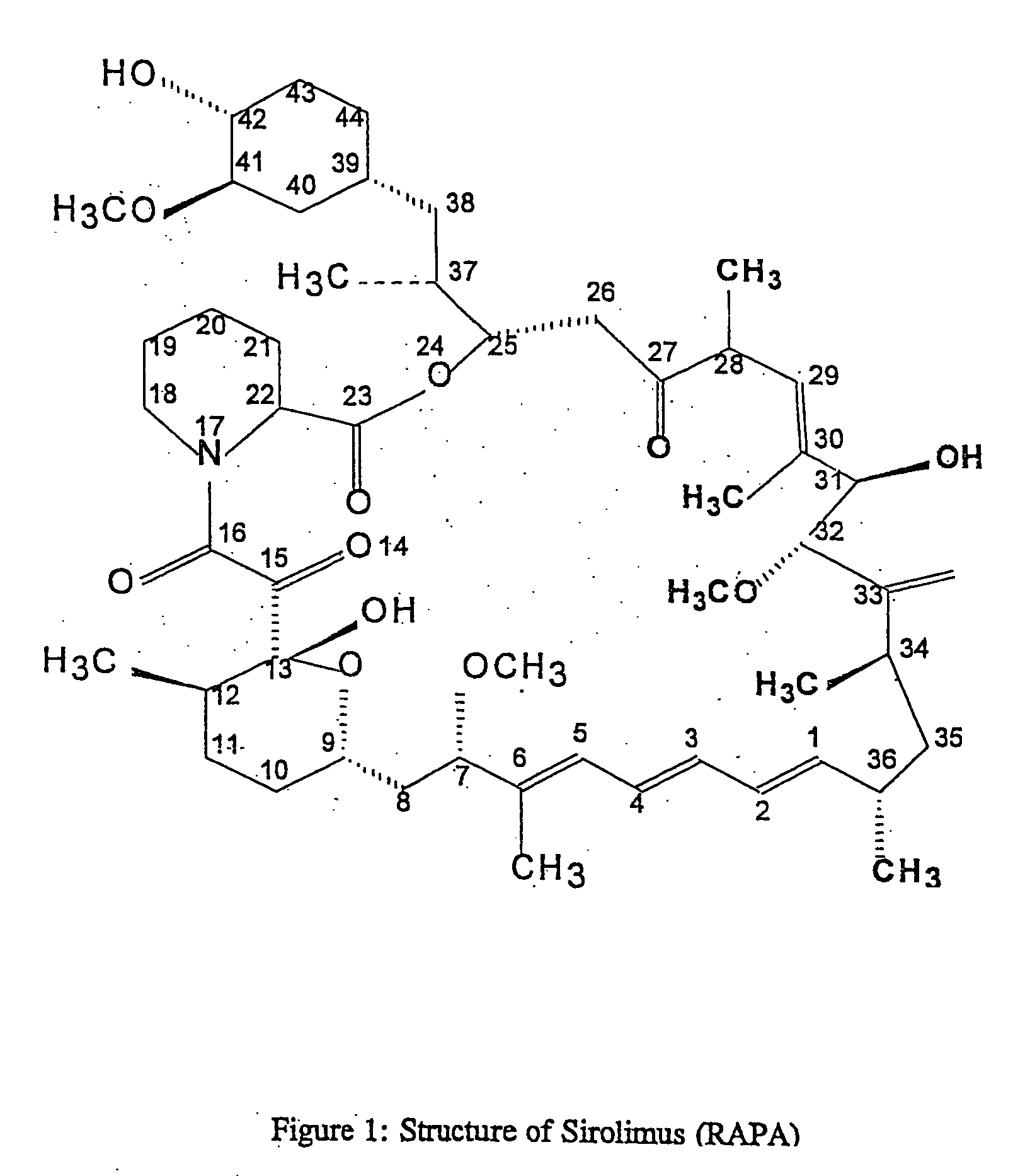
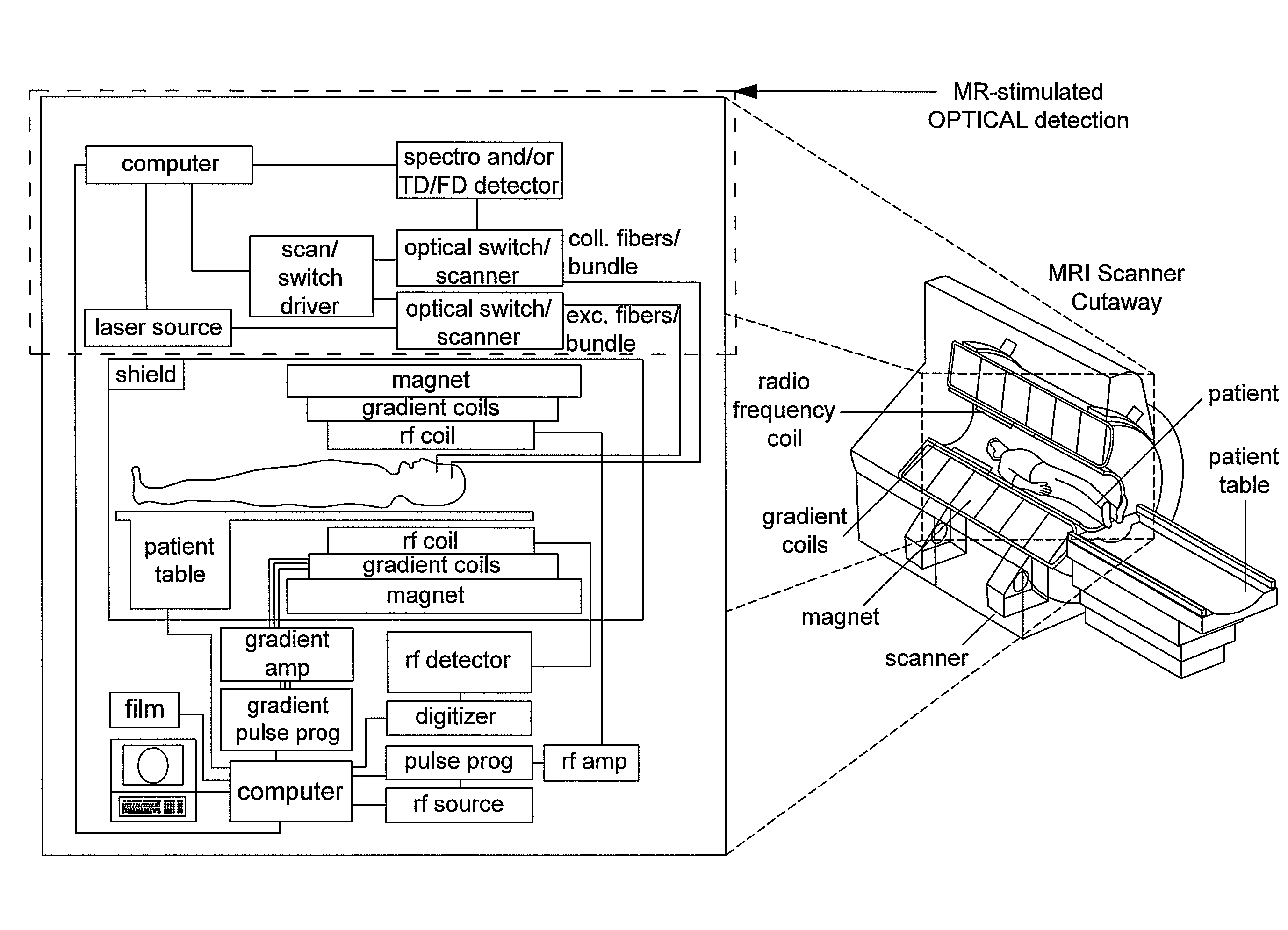
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Therapeutic monitoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is commonly used to help physicians monitor and maintain drug levels within the therapeutic window. The therapeutic window is the concentration range in which a drug exerts its clinical effect with minimal adverse effects for most patients.
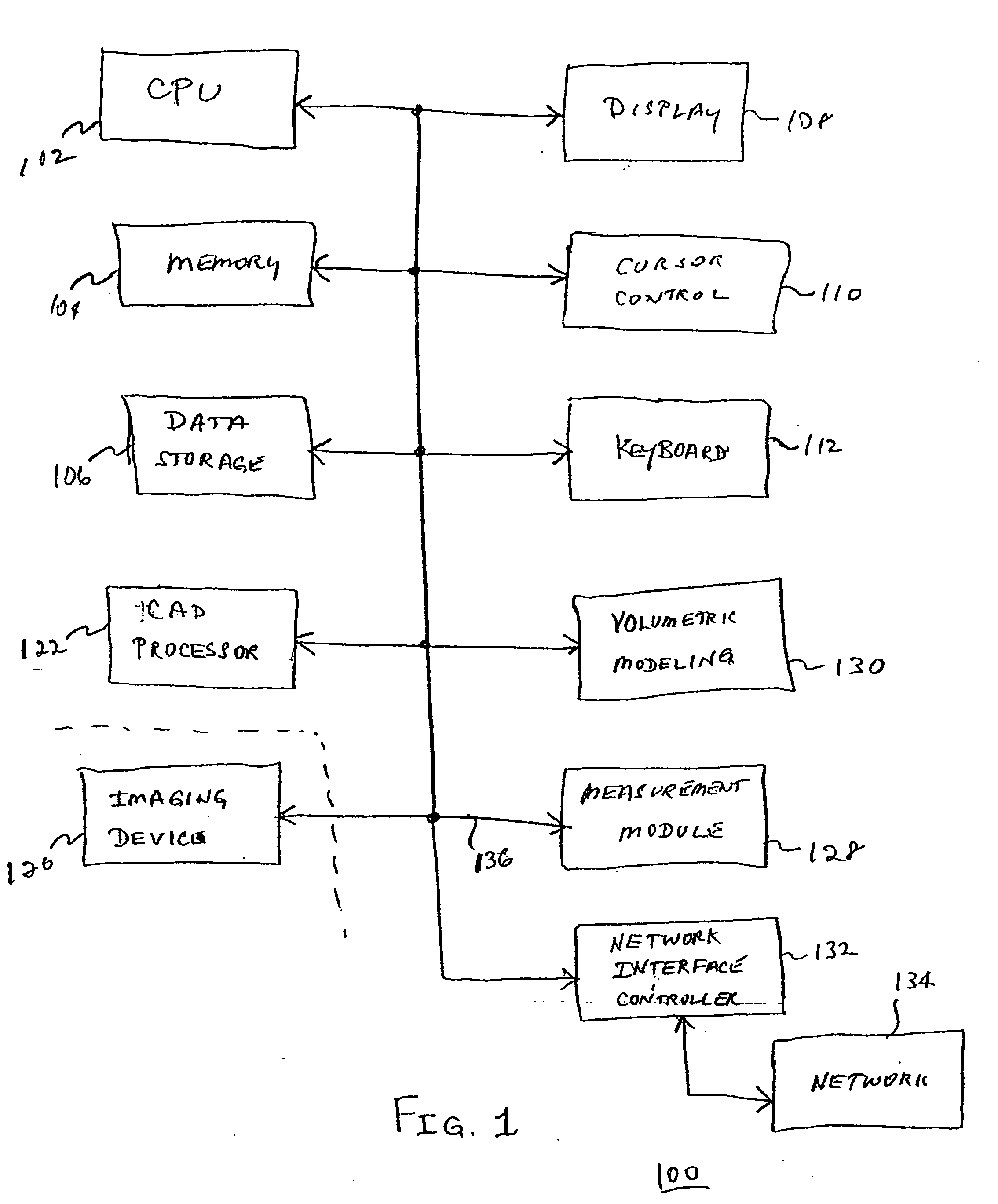
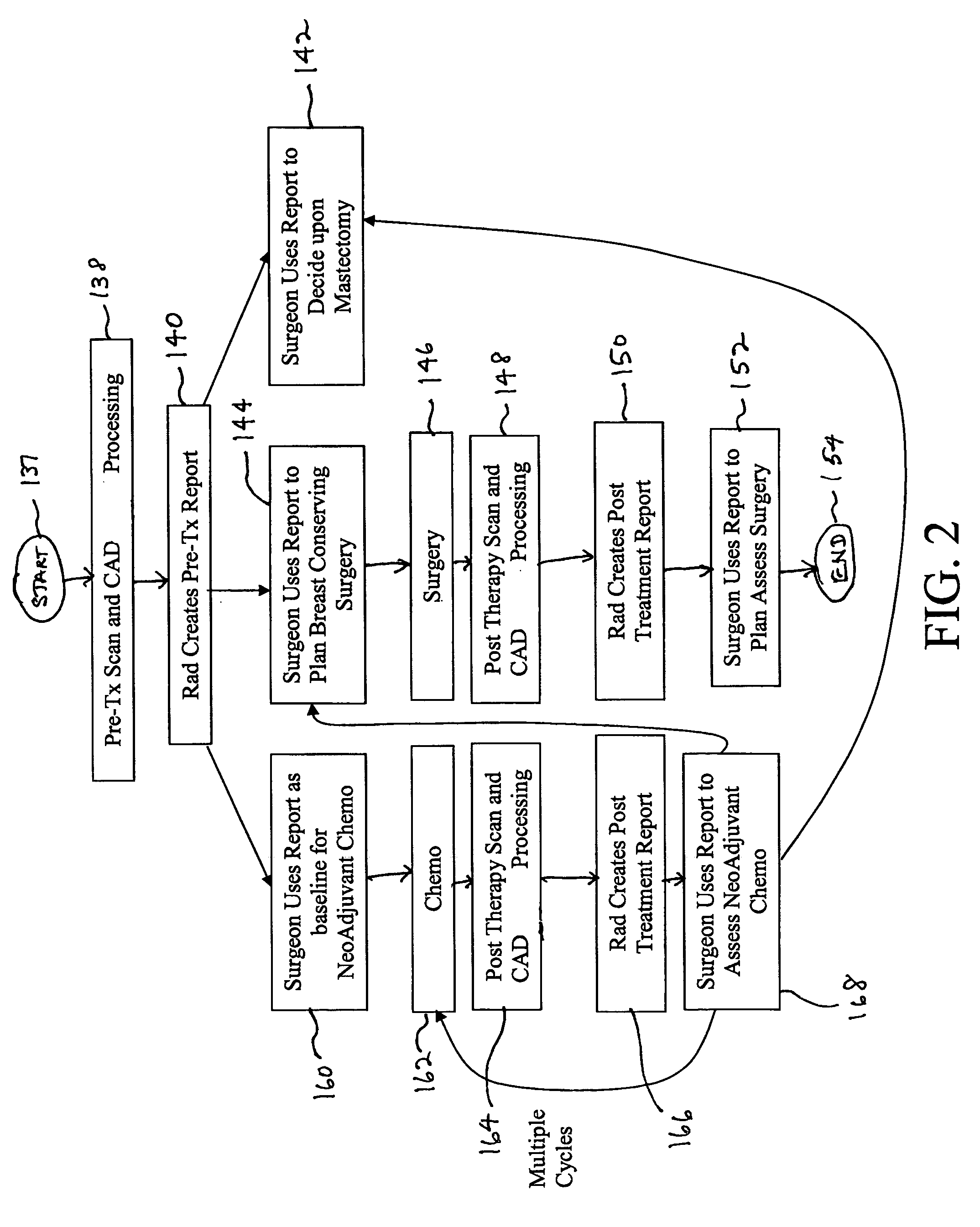
Apparatus and method for surgical planning and treatment monitoring
A system for surgical planning and therapeutic monitoring utilizes imaging data and computer-aided detection (CAD) technology to identify cancerous tumors. A pre-treatment report identifies all volumes of interest (VOIs) and provides data regarding the size and location of each VOI as well as volumetric data for use in surgical planning. The system can be used to monitor the progress of adjuvant chemotherapy or other non-surgical treatment and measures changes in tumor size and location. Post-treatment reports provide data regarding changes in tumor size and location as well as trend data to provide guidance to the physician.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP +1
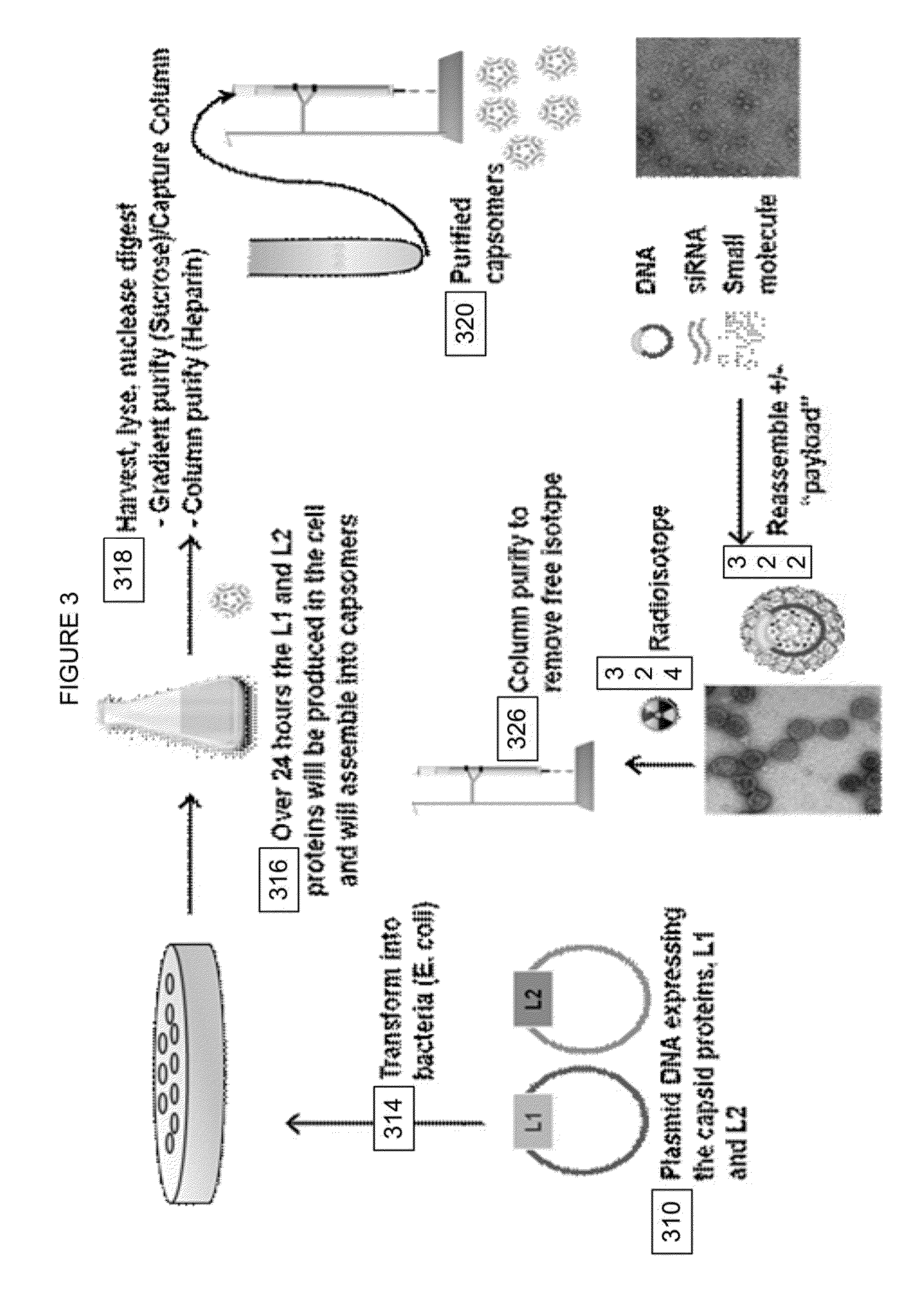
Virion Derived Protein Nanoparticles For Delivering Radioisotopes For The Diagnosis And Treatment Of Malignant And Systemic Disease And The Monitoring Of Therapy
InactiveUS20130115247A1Precise deliveryIncrease differentiationOrganic active ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsWhole bodyNanoparticle
The invention is directed to novel compositions and methods utilizing virion derived protein nanoparticles for delivery of medical imaging agents and therapeutic agents for the diagnosis and treatment of malignant and systemic diseases.
Owner:AURA BIOSCI
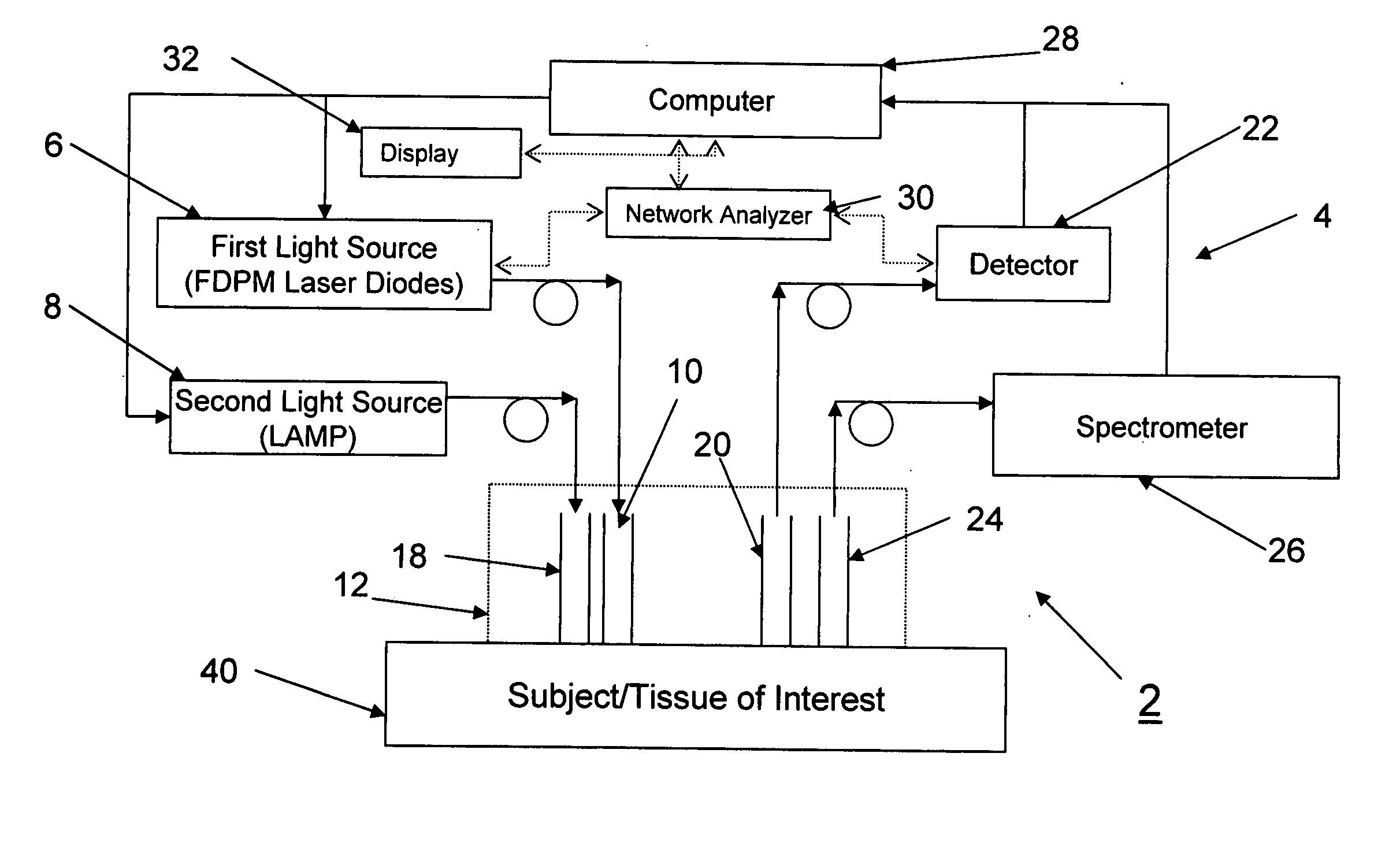
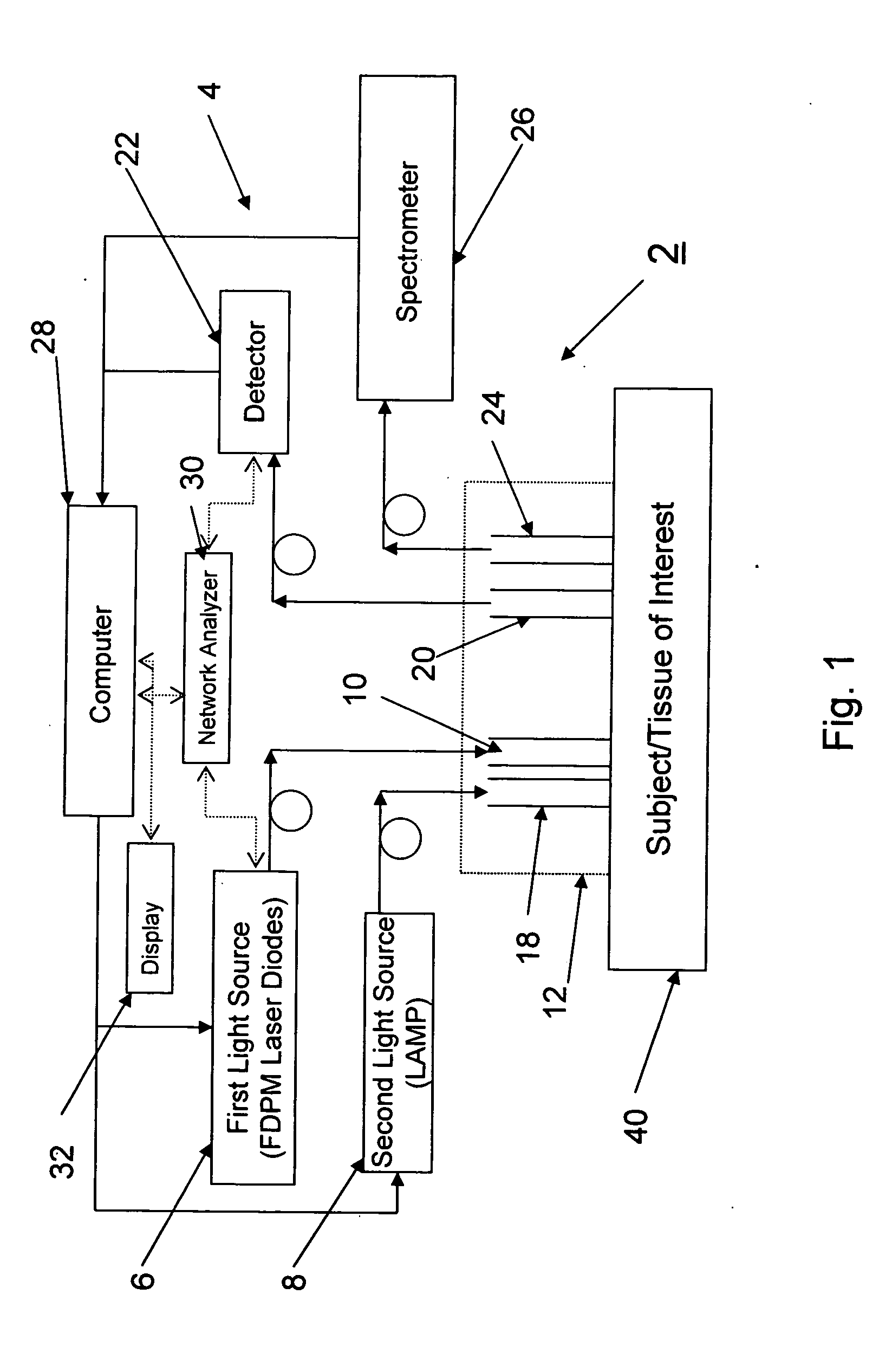
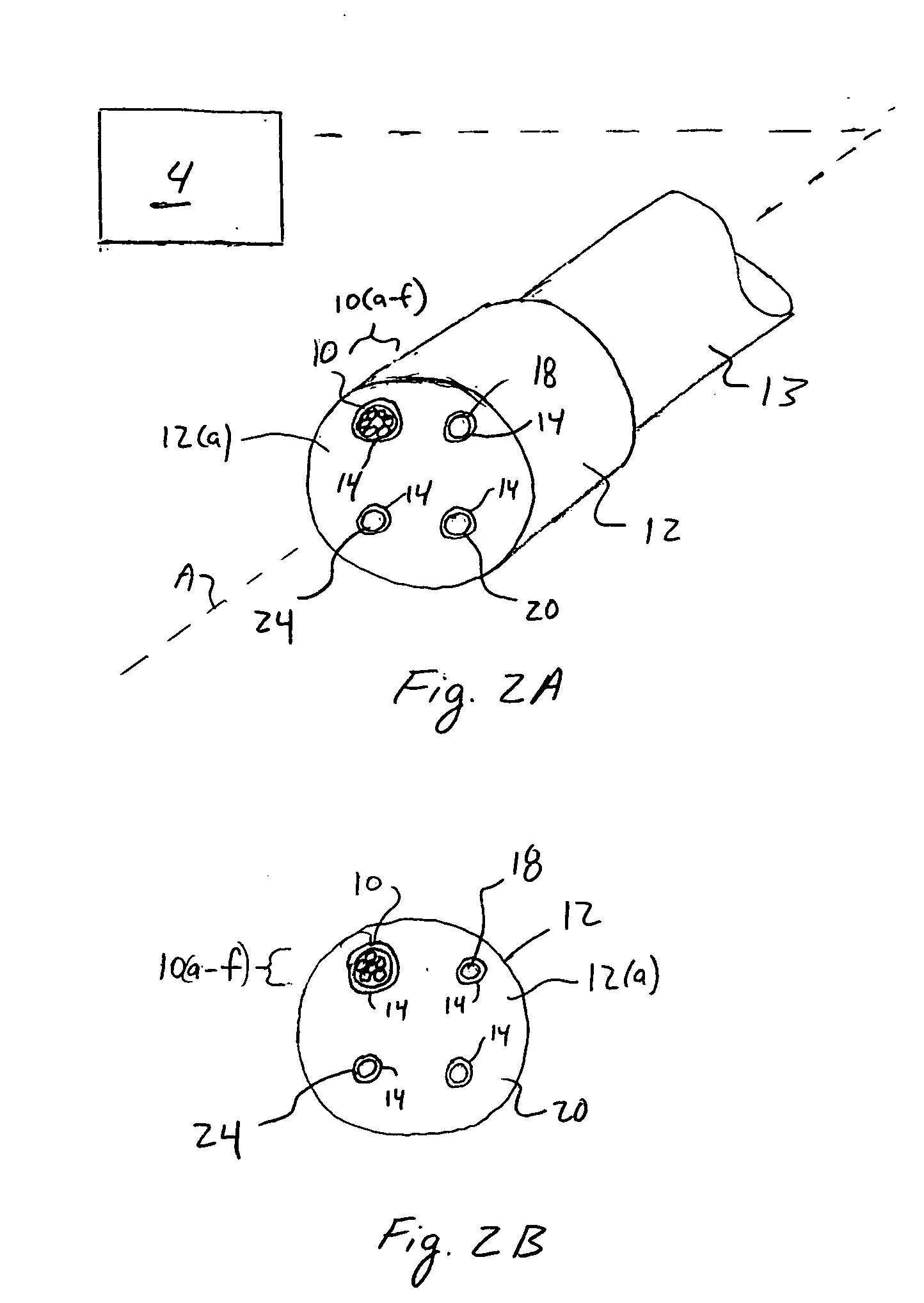
Method and apparatus for dynamically monitoring multiple in vivo tissue chromophores
InactiveUS20050228246A1Spectrum investigationScattering properties measurementsDynamic monitoringSpectroscopy
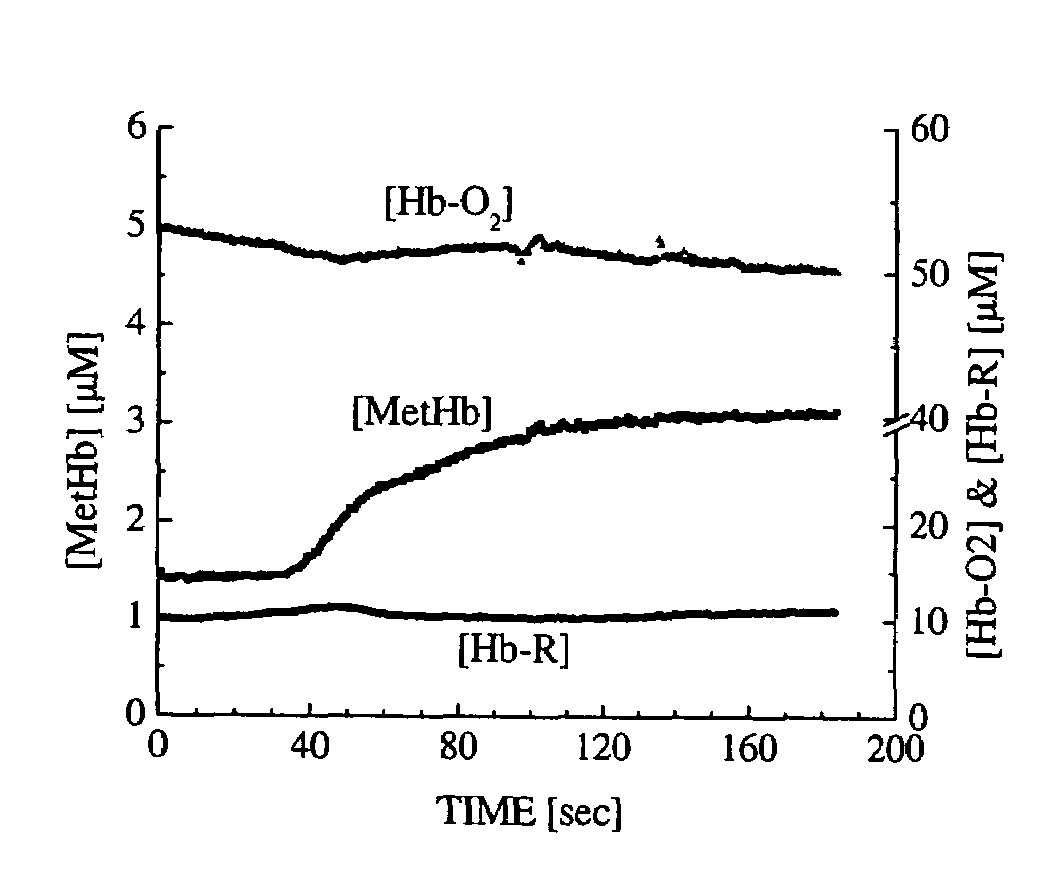
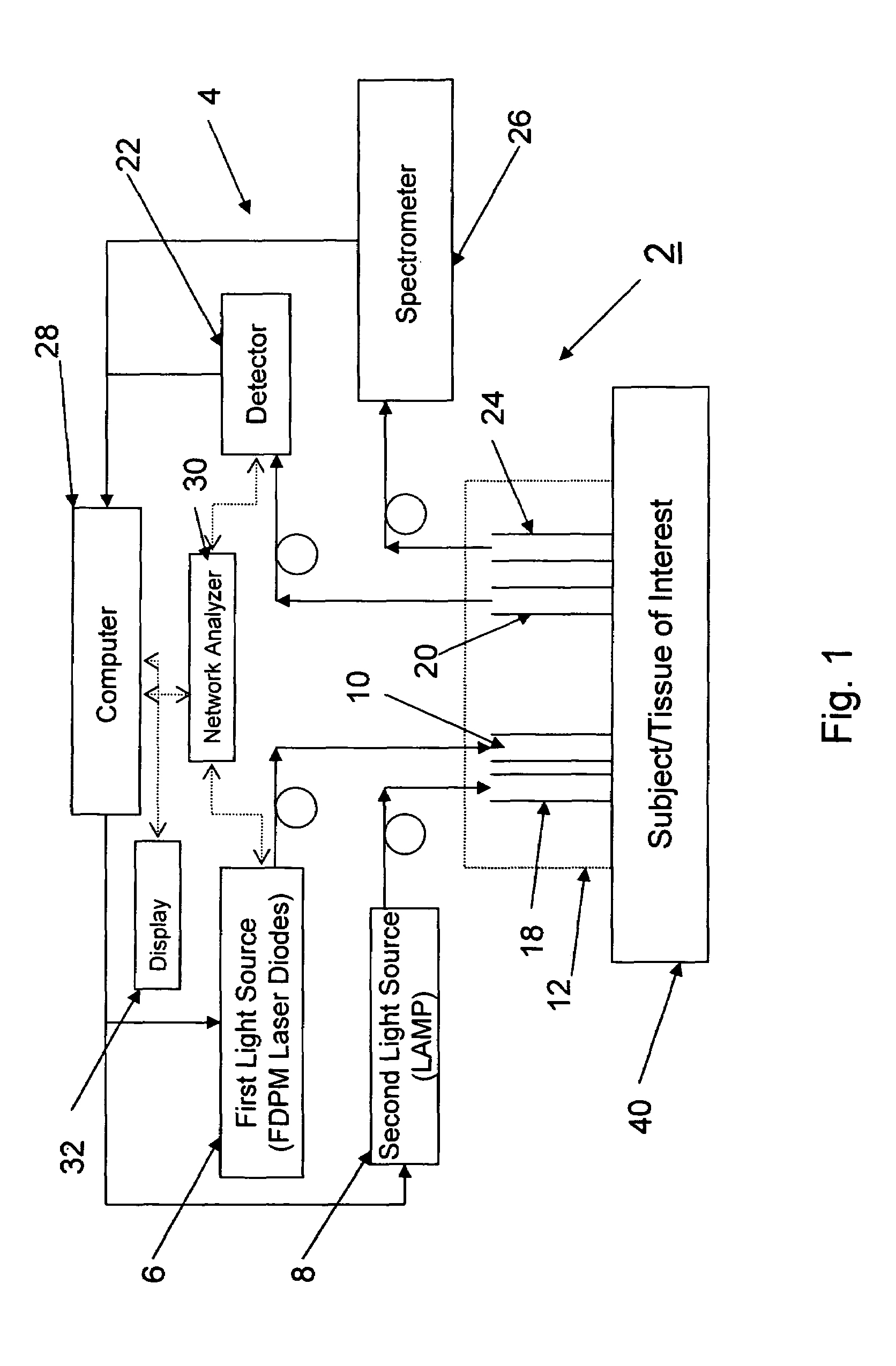
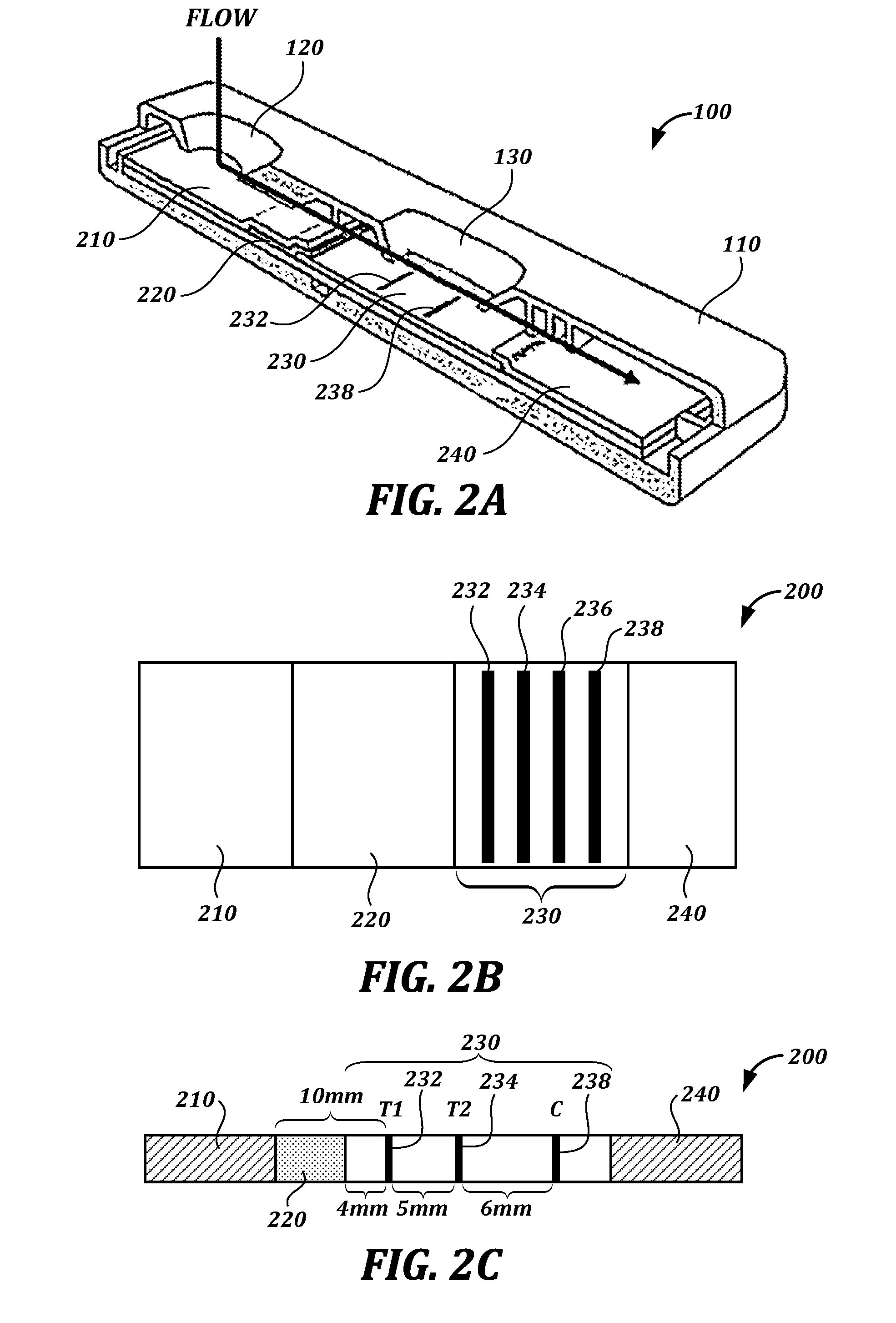
A device and method utilizes a broadband diffuse optical spectroscopy (DOS) system to dynamically calculate the concentrations of multiple chromophores in vivo using a non-invasive probe. The device and method permit dynamic monitoring of multiple in vivo tissue chromophores non-invasively with sensitivities necessary for effective therapeutic monitoring. The device includes a probe containing first and second source optical fibers as well as first and second detector optical fibers. The probe is placed adjacent to a sample of interest and detects reflected light which is passed to a proximally located detector and spectrometer. The concentrations of multiple chromophores are determined in real time. In a preferred embodiment, the multiple tissue chromophores include at least two of methemoglobin (MetHb), deoxyhemoglobin (Hb-R), oxyhemoglobin (Hb-O2), water (H2O), and methylene blue (MB). The device and method can be used quantify and monitor methemoglobin formation in subjects suffering from methemoglobinemia.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Systems and methods to quantify and amplify both signaling probes for cdna chips and genes expression microarrays
InactiveUS20040053275A1Excessive signalingGood signalSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCDNA MicroarraysGene Expression Array
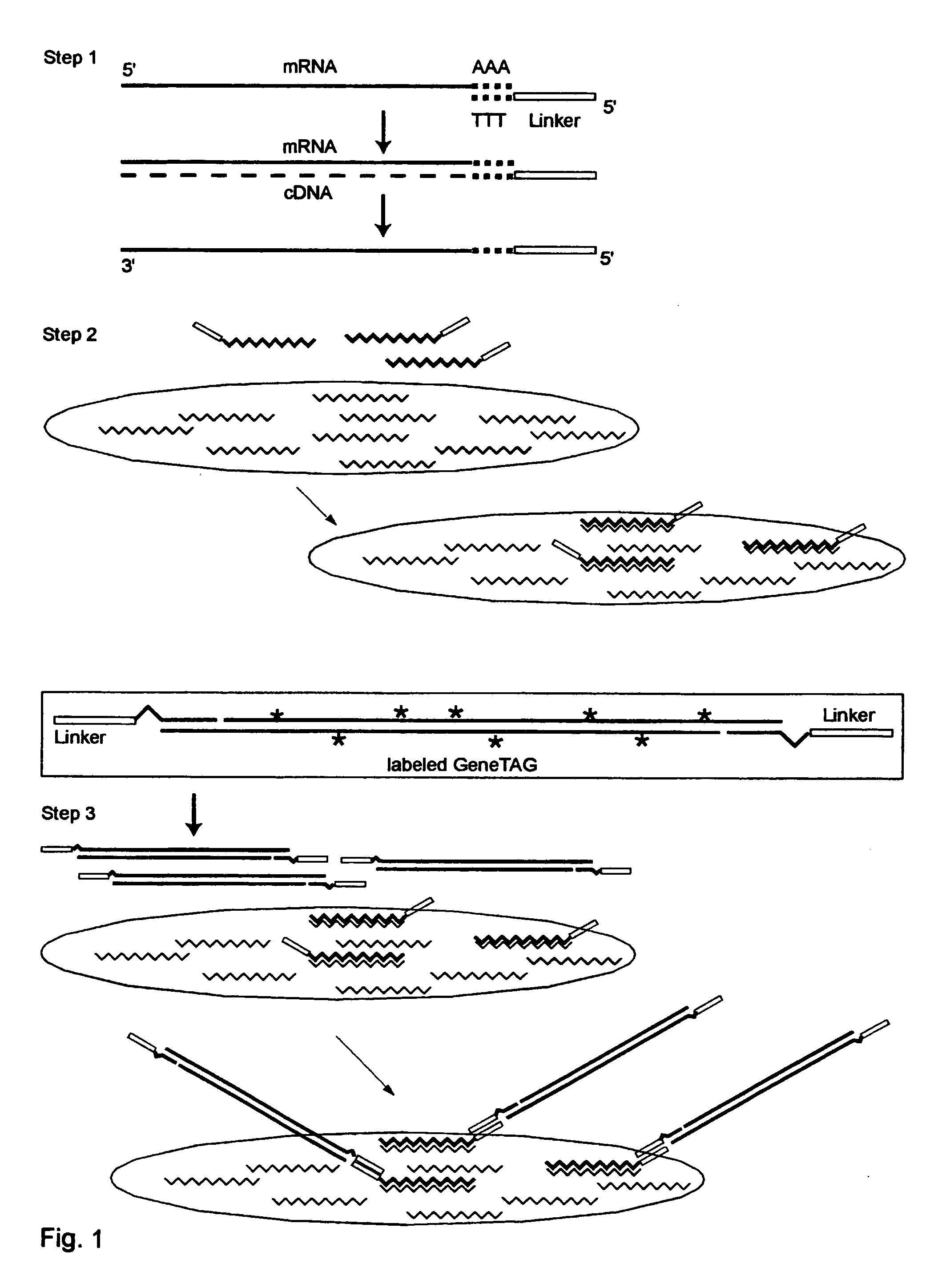
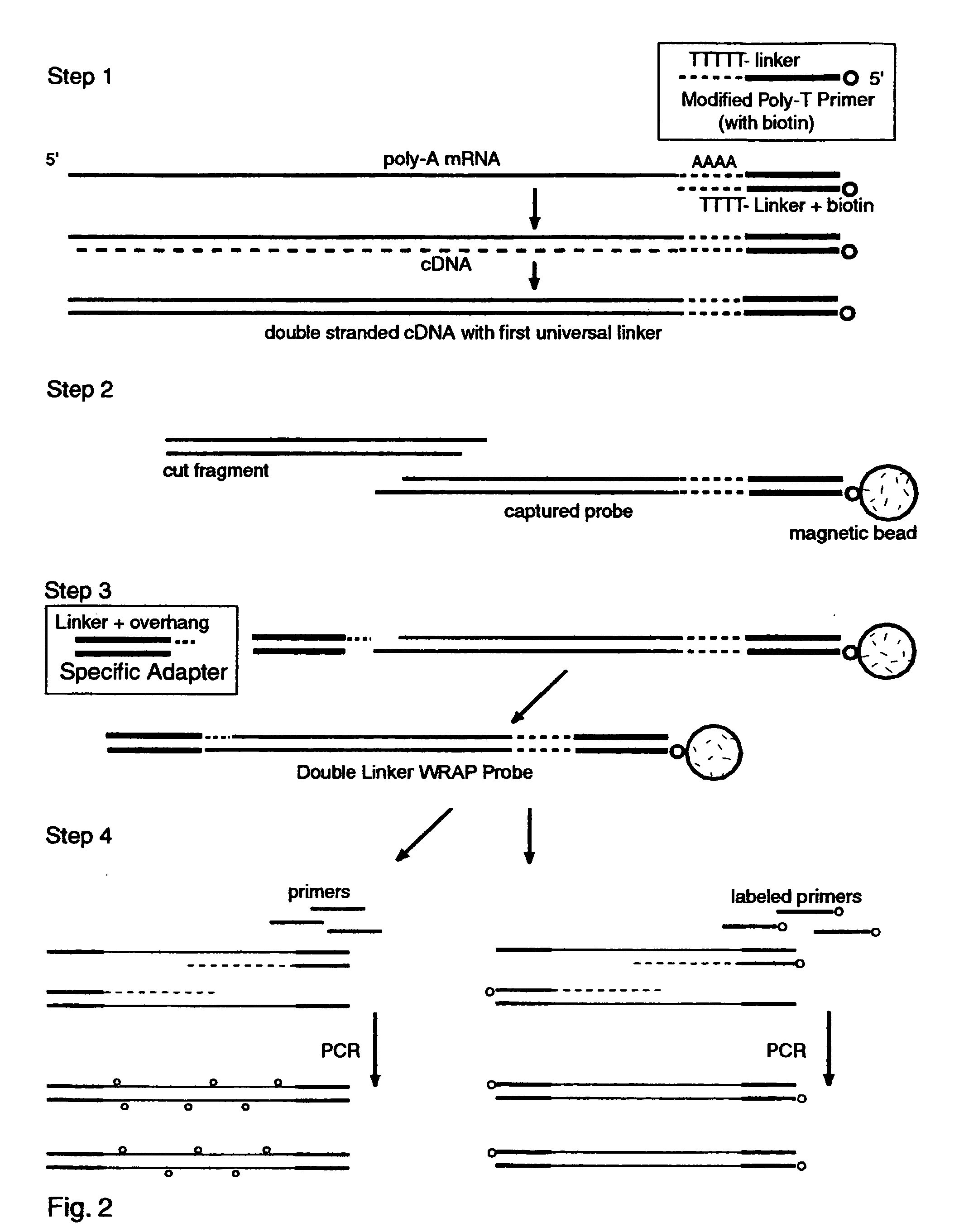
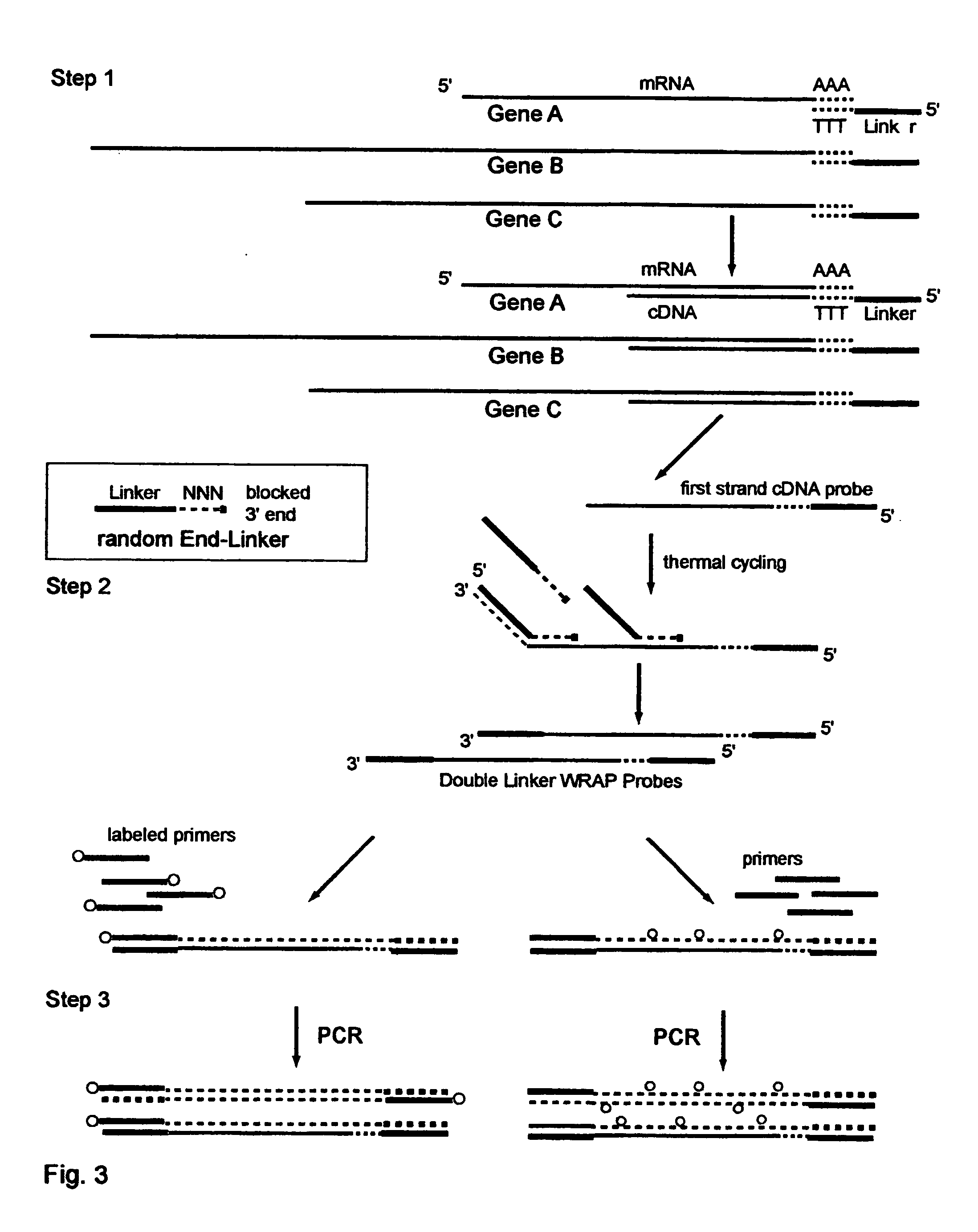
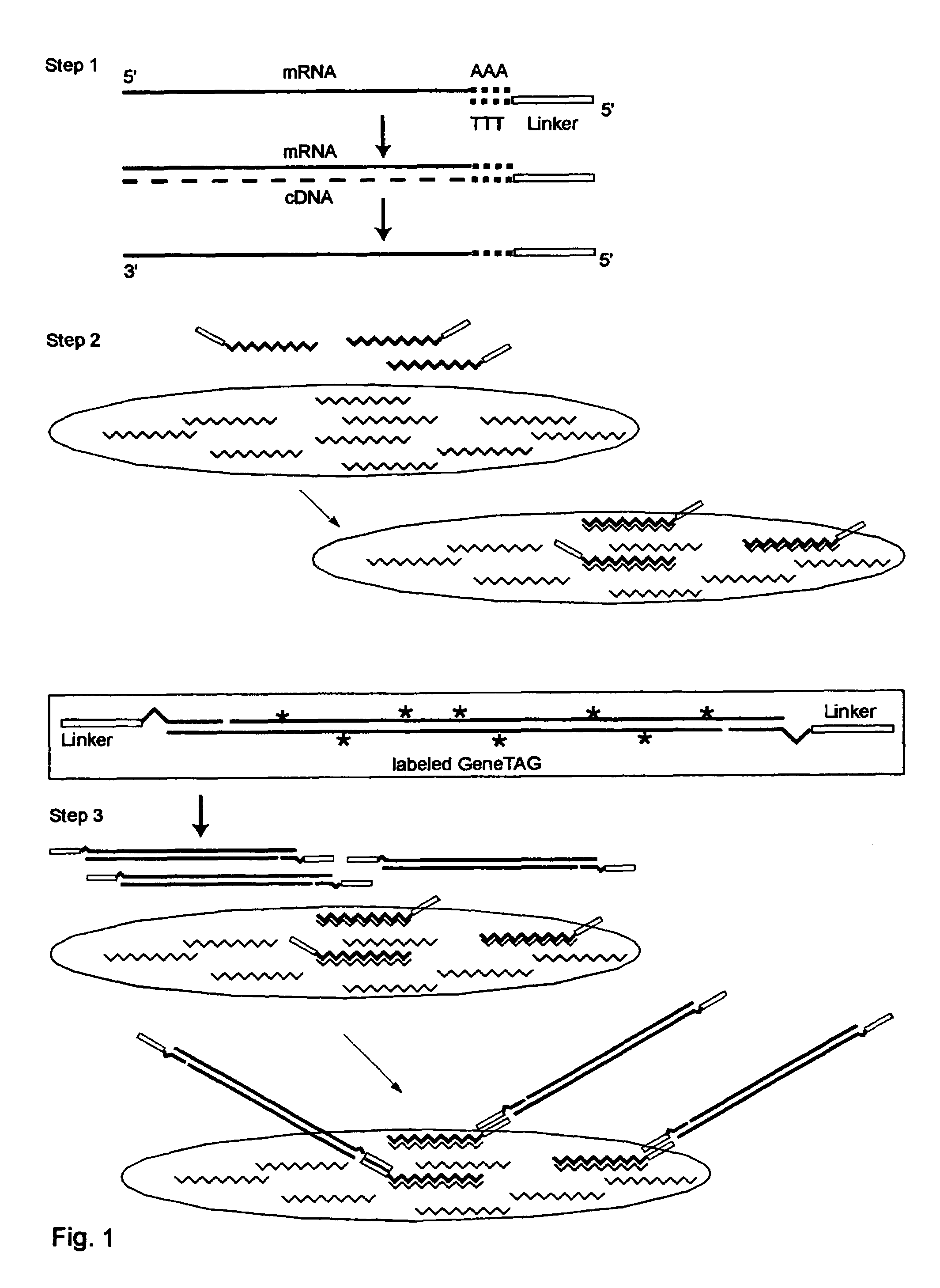
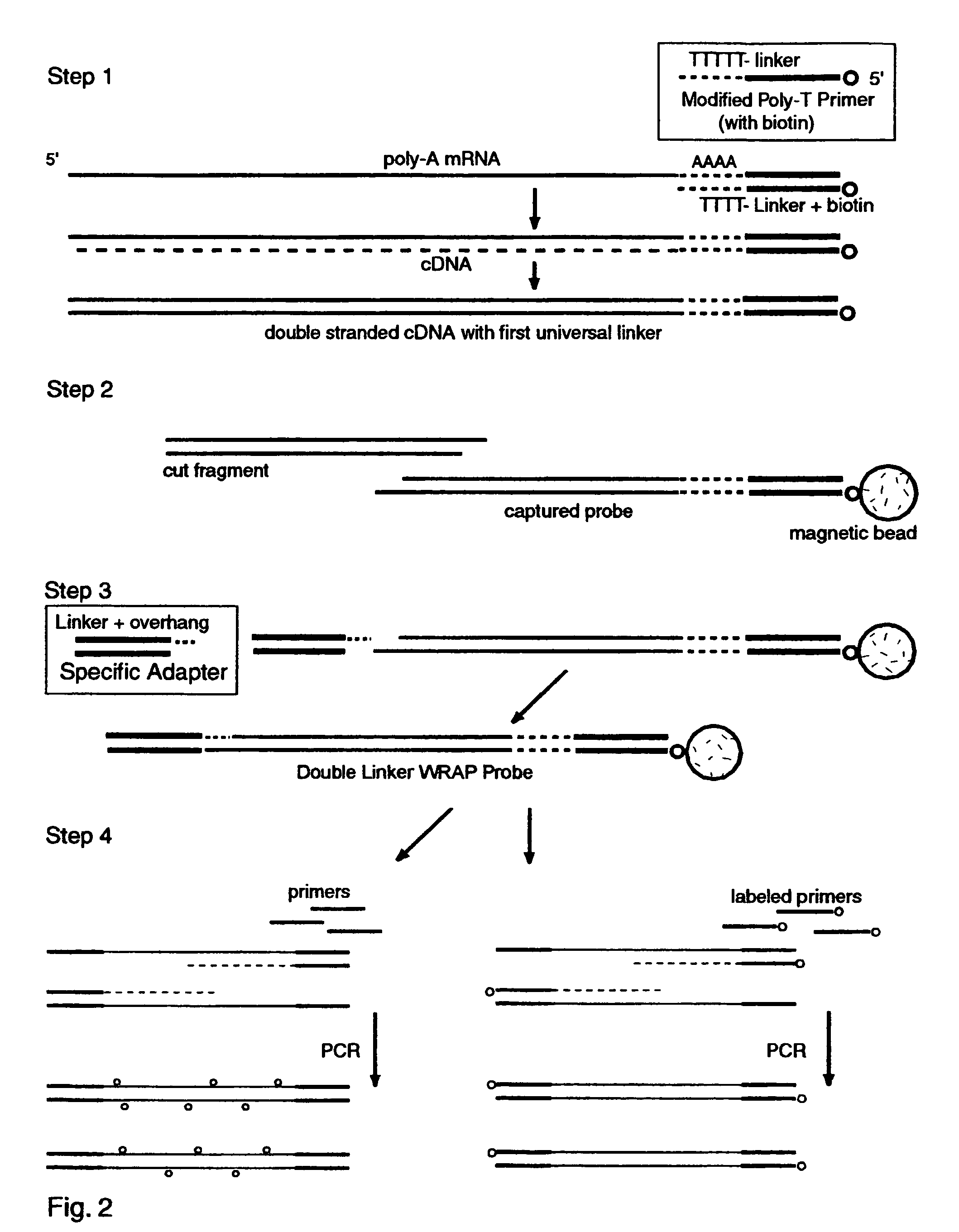
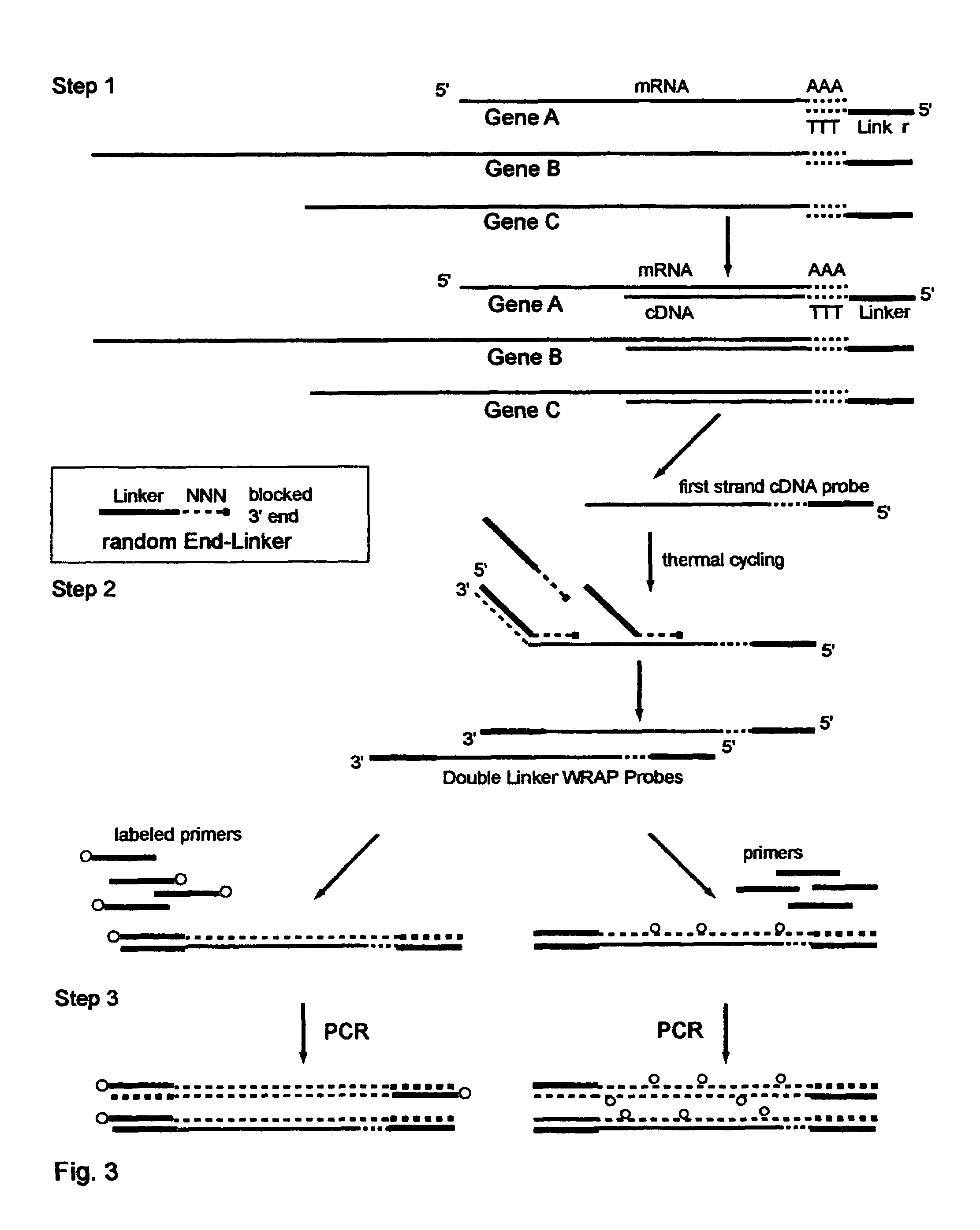
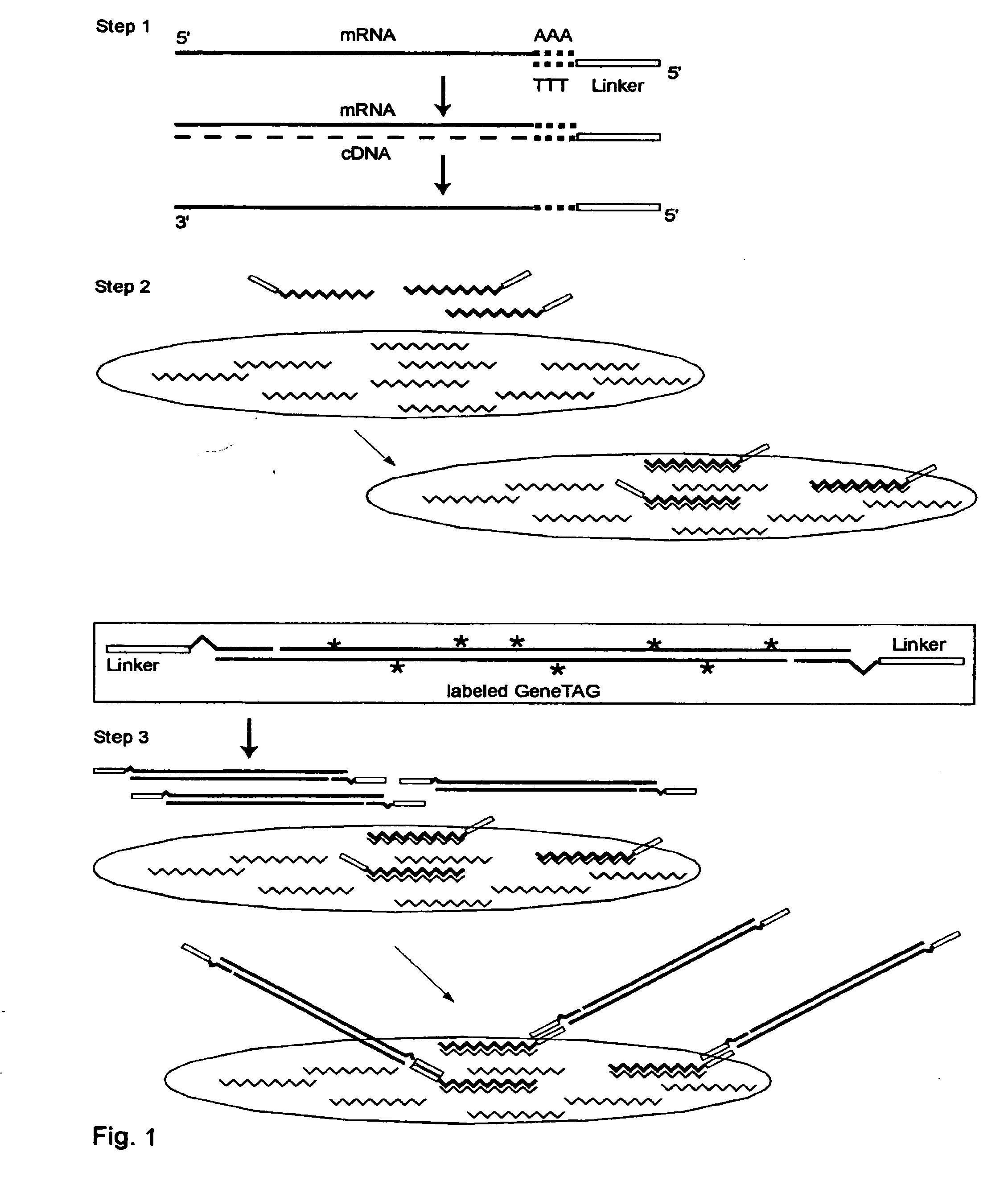
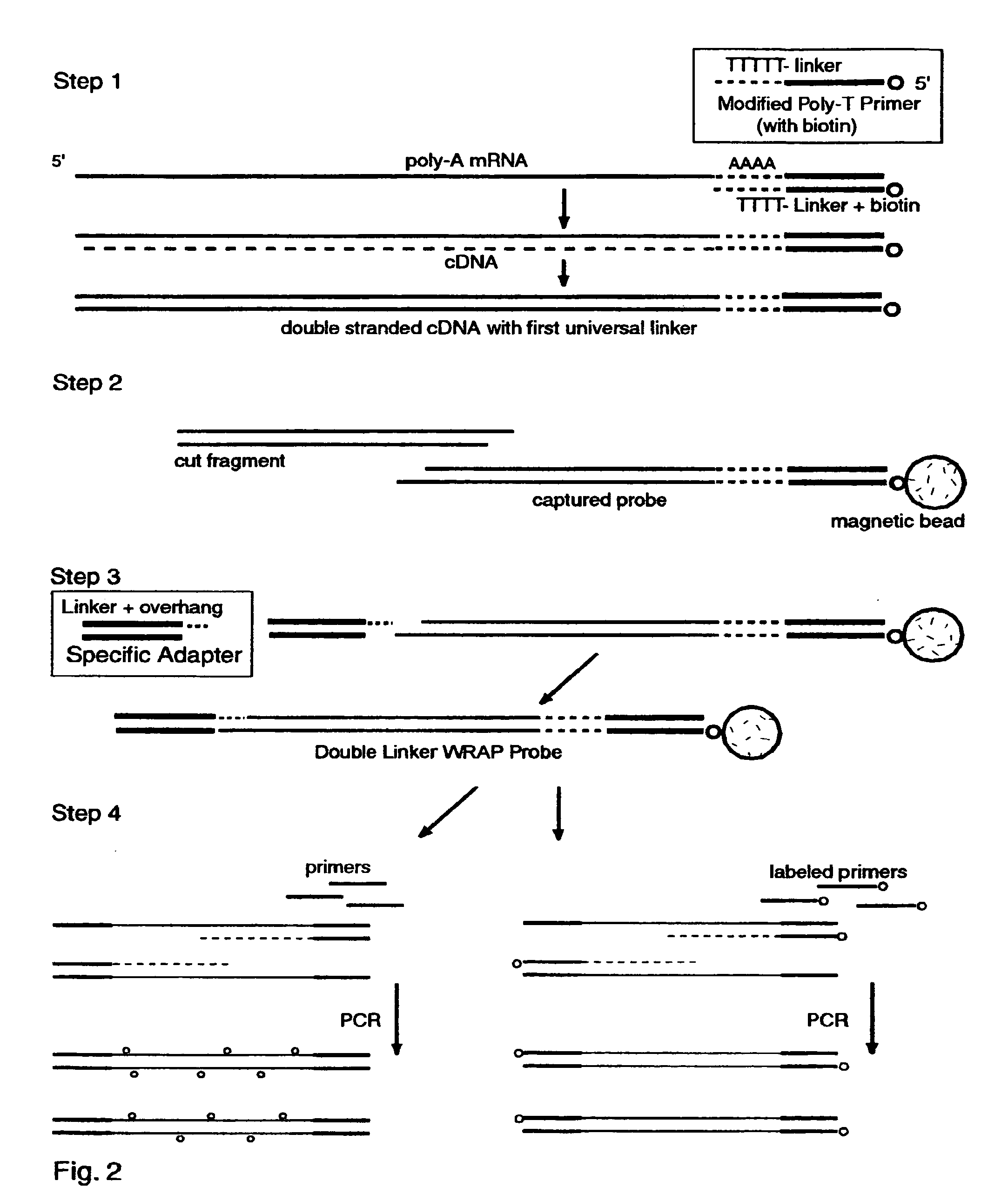
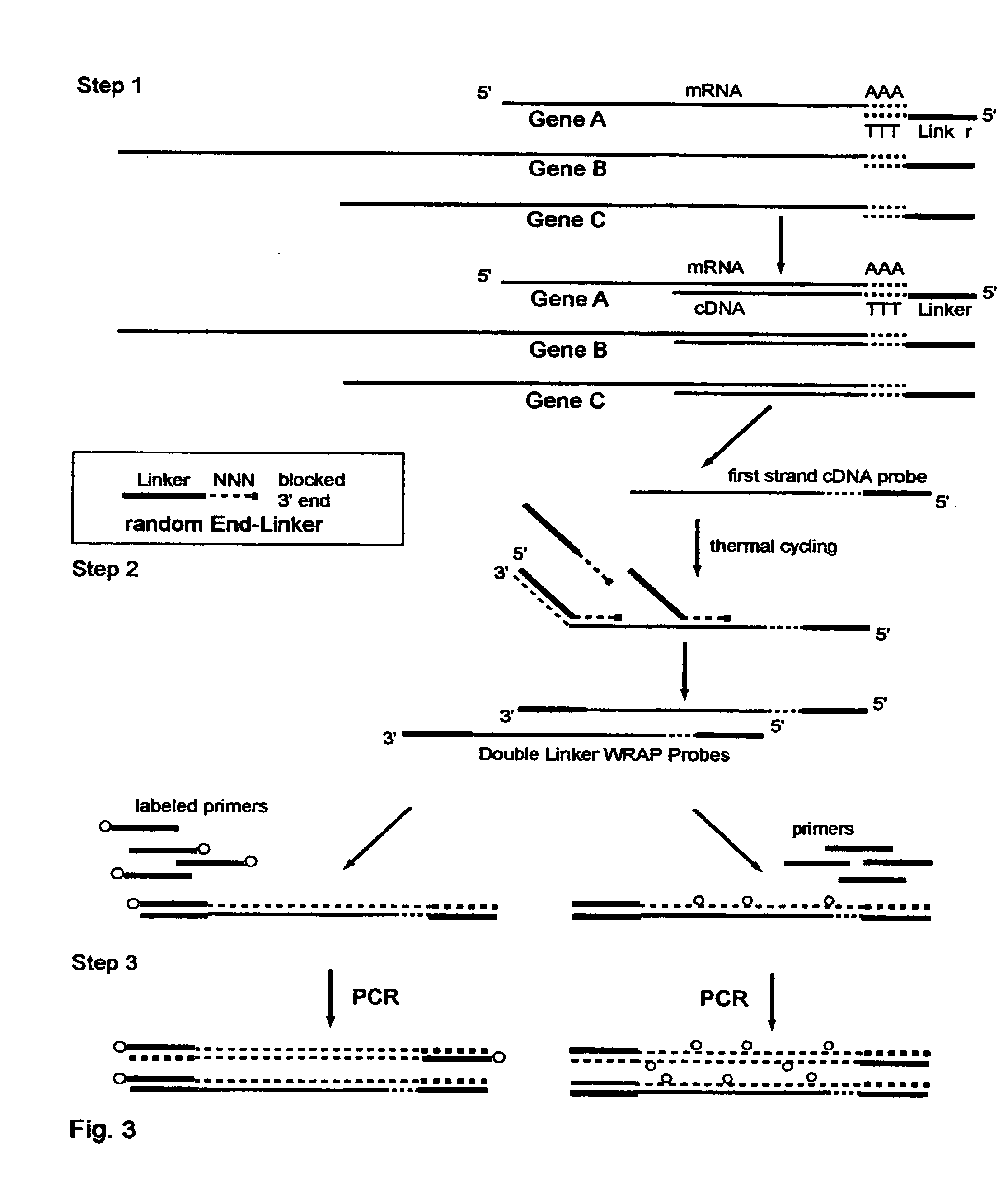
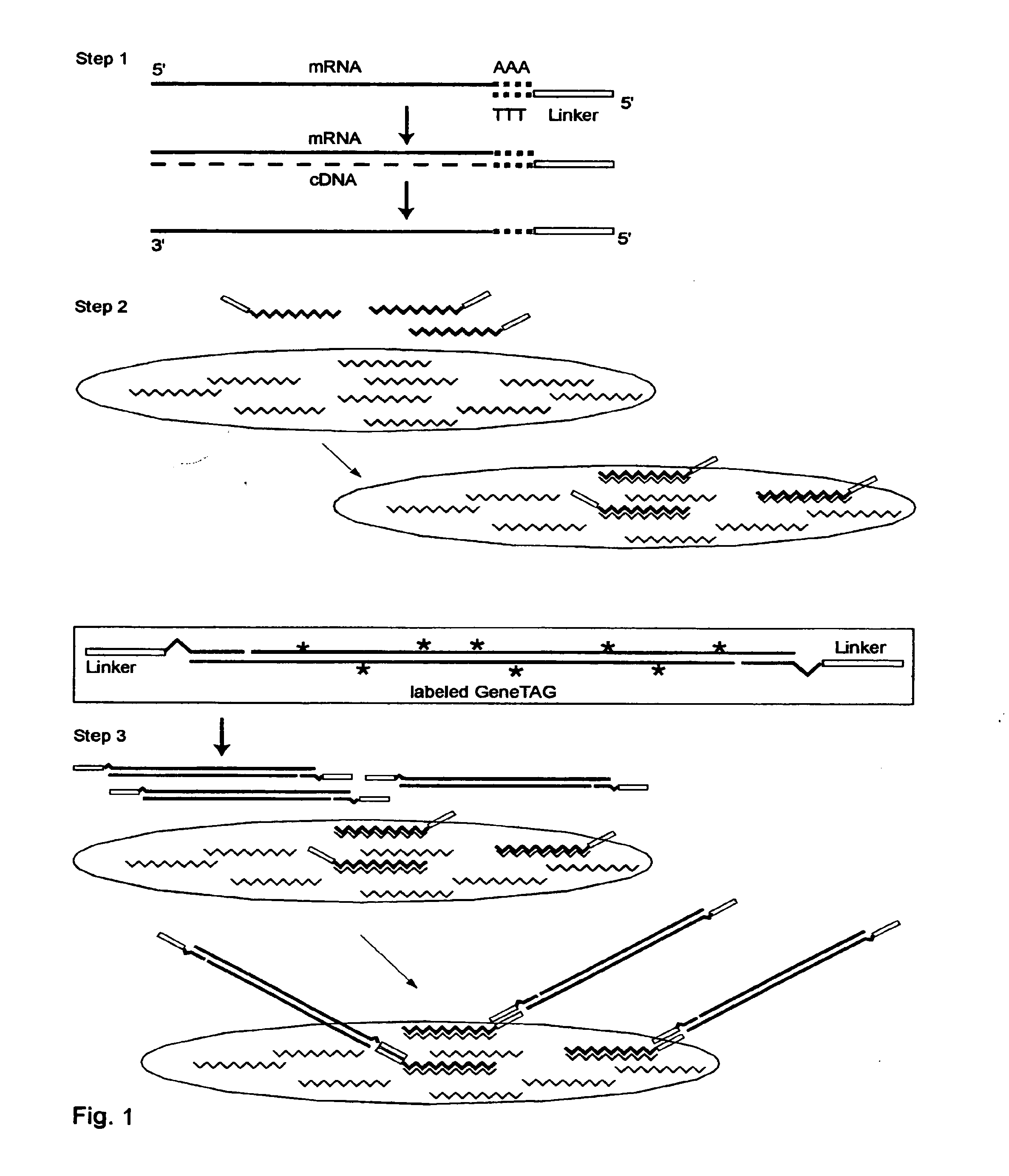
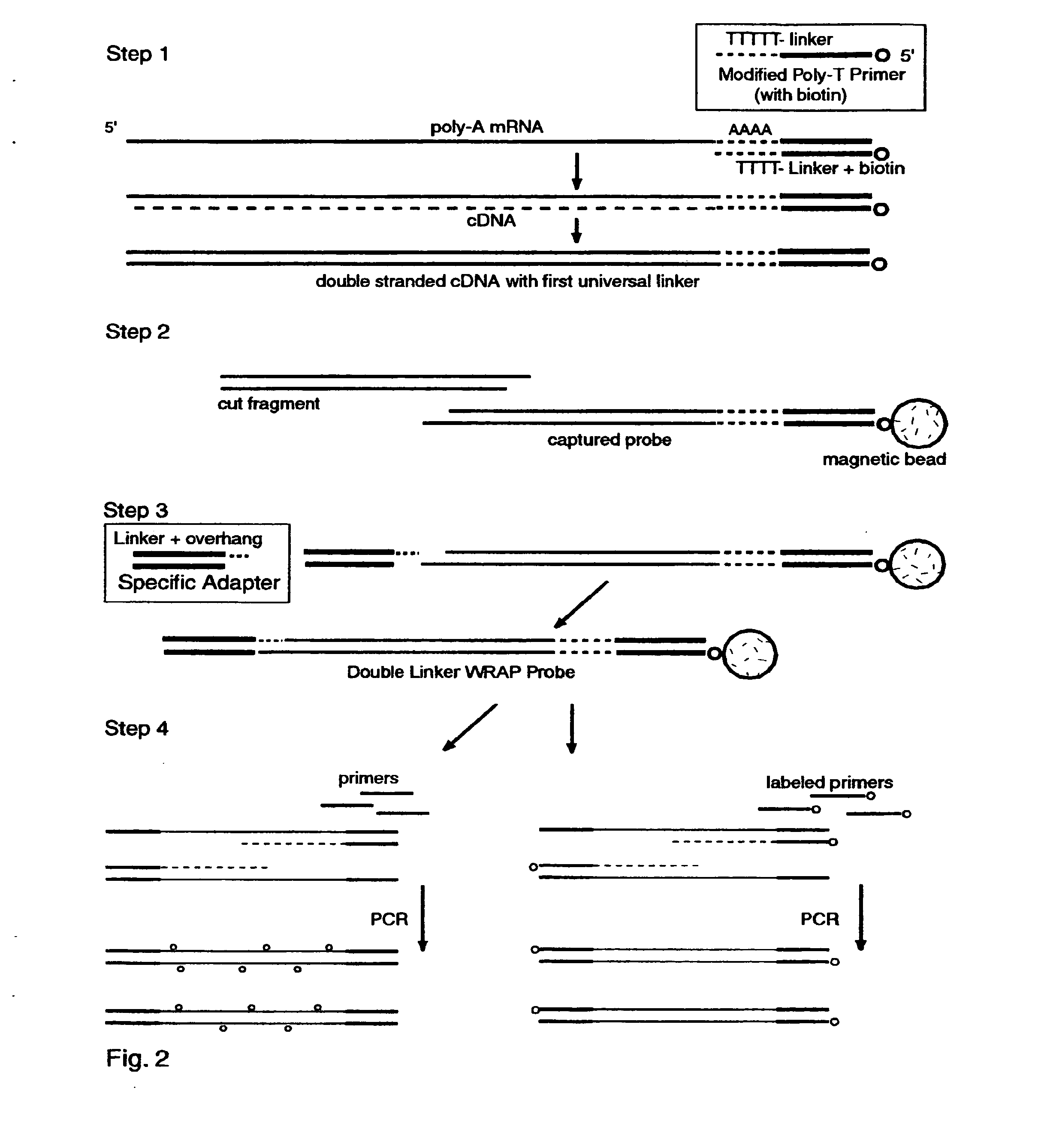
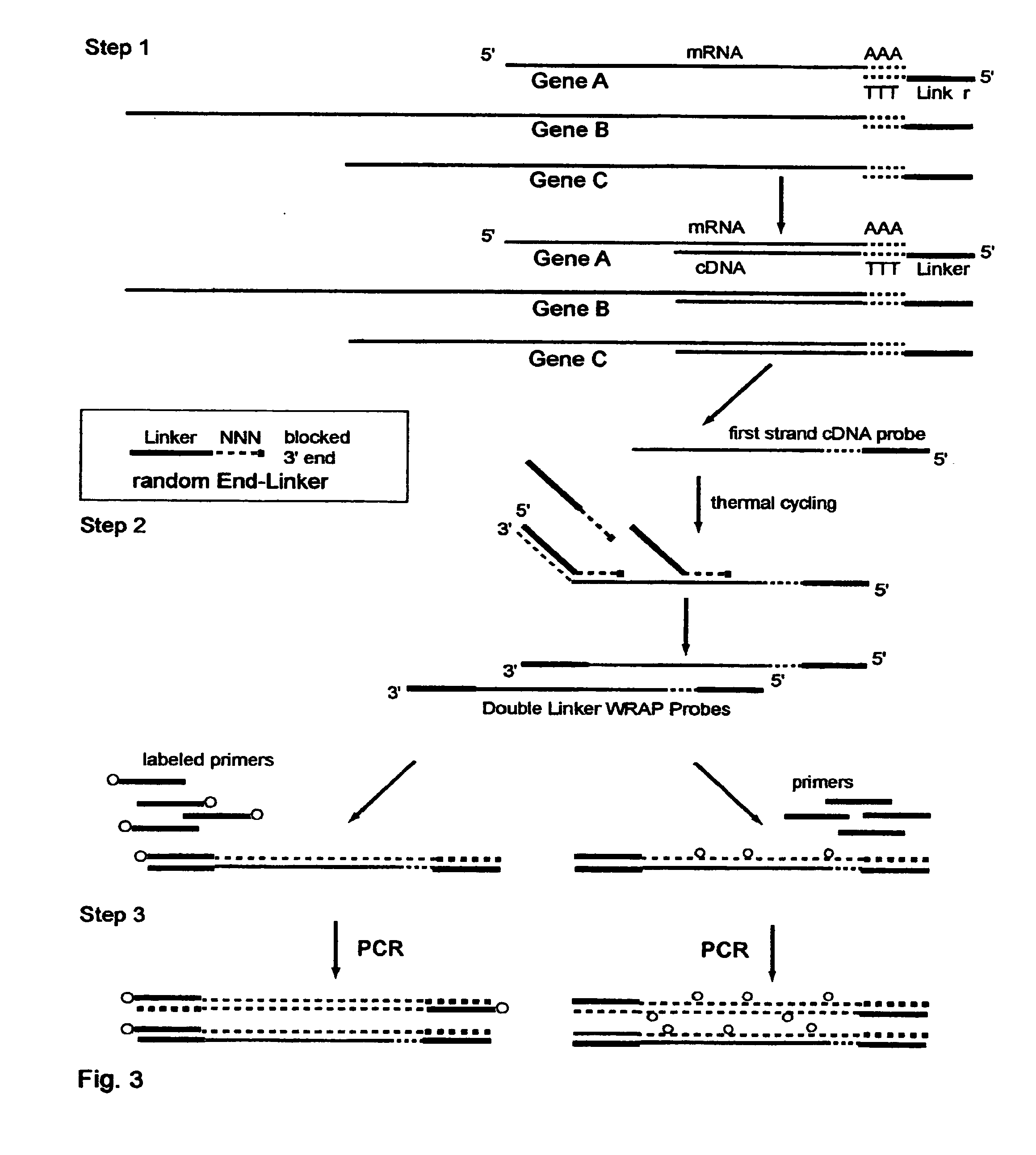
The invention provides a series of reagent compositions and methods for making and amplifying novel cDNA based probe sets from RNA samples to improve analysis with gene expression arrays. The methods globally produce probe sets with common universal linkers at one or both ends, called WRAP-Probes, wherein the linkers do not bind to the target sequences and they can efficiently bind added reporters to the probes. The universal linkers are also designed as primer binding sites for copying and amplifying the probes, either linearly with one linker, or exponentially with double linkers. The capacity to globally and exponentially amplify the probe set by PCR is a primary advantage. Adding reporters by terminal linkers also improves quantification since each probe gets equivalent signaling. The invention allows expression analysis of small research, clinical and forensic samples to enable improved diagnostics, drug discovery, therapeutic monitoring, and medical, agricultural and general research.
Owner:GENETAG TECH
Anti-LFL2 antibodies for the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20050260212A1Useful in therapyAnimal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAbnormal tissue growthCancer targeting
Particular anti-LFL2 antibody compositions are provided herein. These antibodies may be used for diagnosis, prognosis, therapeutic monitoring and treatment of cancer, especially breast cancer, head / neck cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, stomach cancer and pancreatic cancer. Furthermore, anti-LFL2 antibodies are provided herein which target the LFL2 stump remaining after proteolytic cleavage of the extracellular domain of LFL2. Additionally, anti-LFL2 antibodies are provided herein which target the stroma surrounding cancer tumors, wherein said stroma-targeting anti-LFL2 antibodies disrupt the integrity of the stroma surrounding the cancer tumor, and also make the stroma more permeable to chemotherapeutic agents and other molecular drug agents that target tumor cells.
Owner:ABBVIE BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Formulation and Methods for Enhanced Interventional Image-Guided Therapy of Cancer
InactiveUS20120277517A1Reducing field inhomogenitiesImprove permeabilityBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsMagnetite NanoparticlesTherapeutic effect
An embodiment in accordance with the present invention provides a thermo-chemoembolization formulation and method for enhanced interventional image-guided therapy for cancer. The T-C formulation includes magnetic iron oxide nano-particles (MIONs) that heat when exposed to an alternating magnetic field (AMF), a liquid tumorphilic drug carrier that enhances tumor retention of the T-C formulation, and a chemotherapeutic or radiotherapeutic agent. The T-C formulation enhances delivery of heat and chemo- or radio-therapeutic agents with hyperthermia produced by magnetic nanoparticles to improve therapeutic outcomes. The magnetic nanoparticles and tumorphilic drug carrier also allow for multimodal image-guided monitoring of treatment and patient follow-up. The method for enhanced interventional image-guided therapy for cancer includes using an AMF to heat the T-C formulation and activate the thermotherapy.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Pharmacodiagnostic test targeting oncology and neurodegeneration
ActiveUS20090311681A1Increase in cytoplasmic fractionInduce tumor suppressor gene silencingSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsProstate cancerOncology
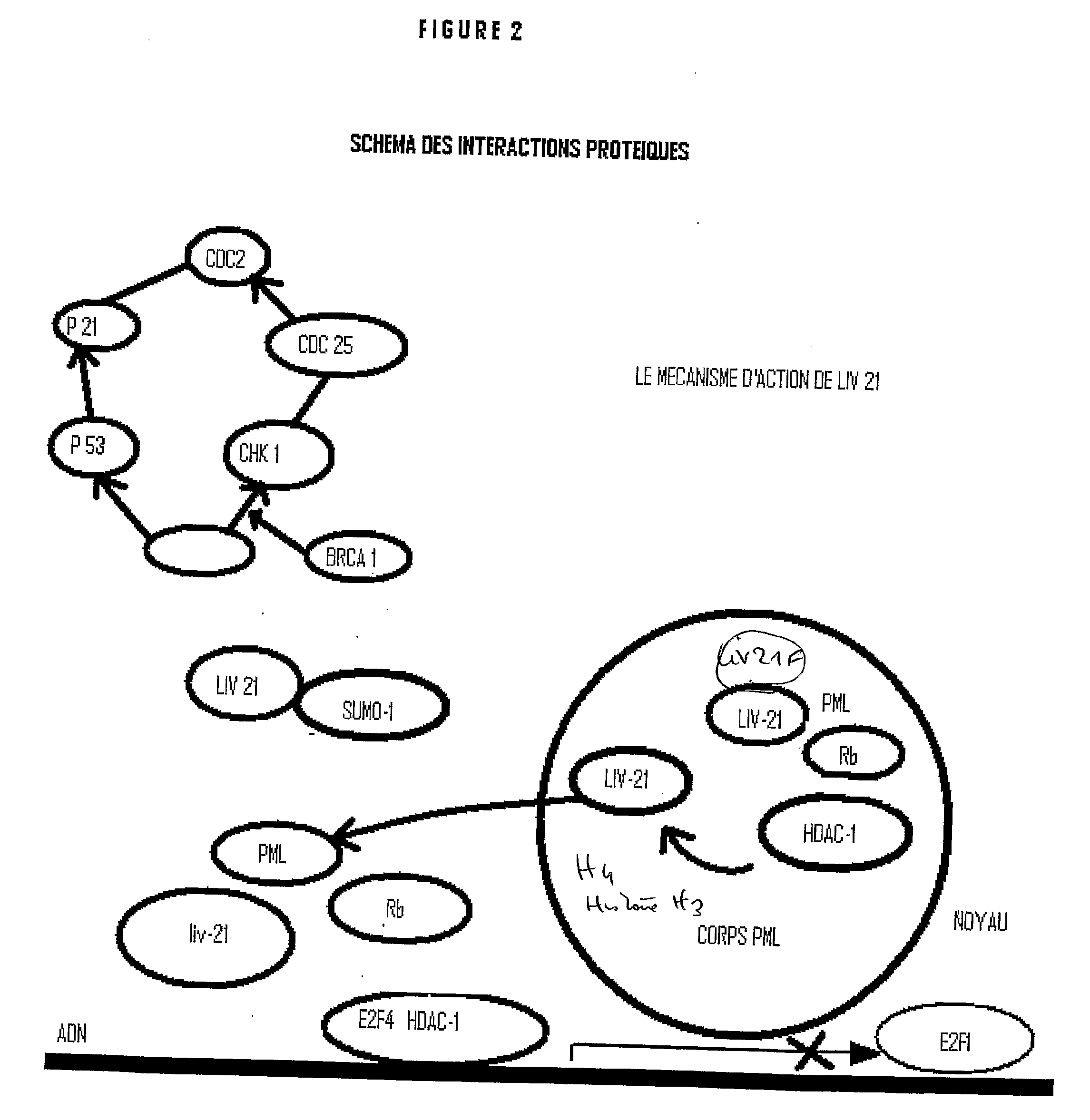
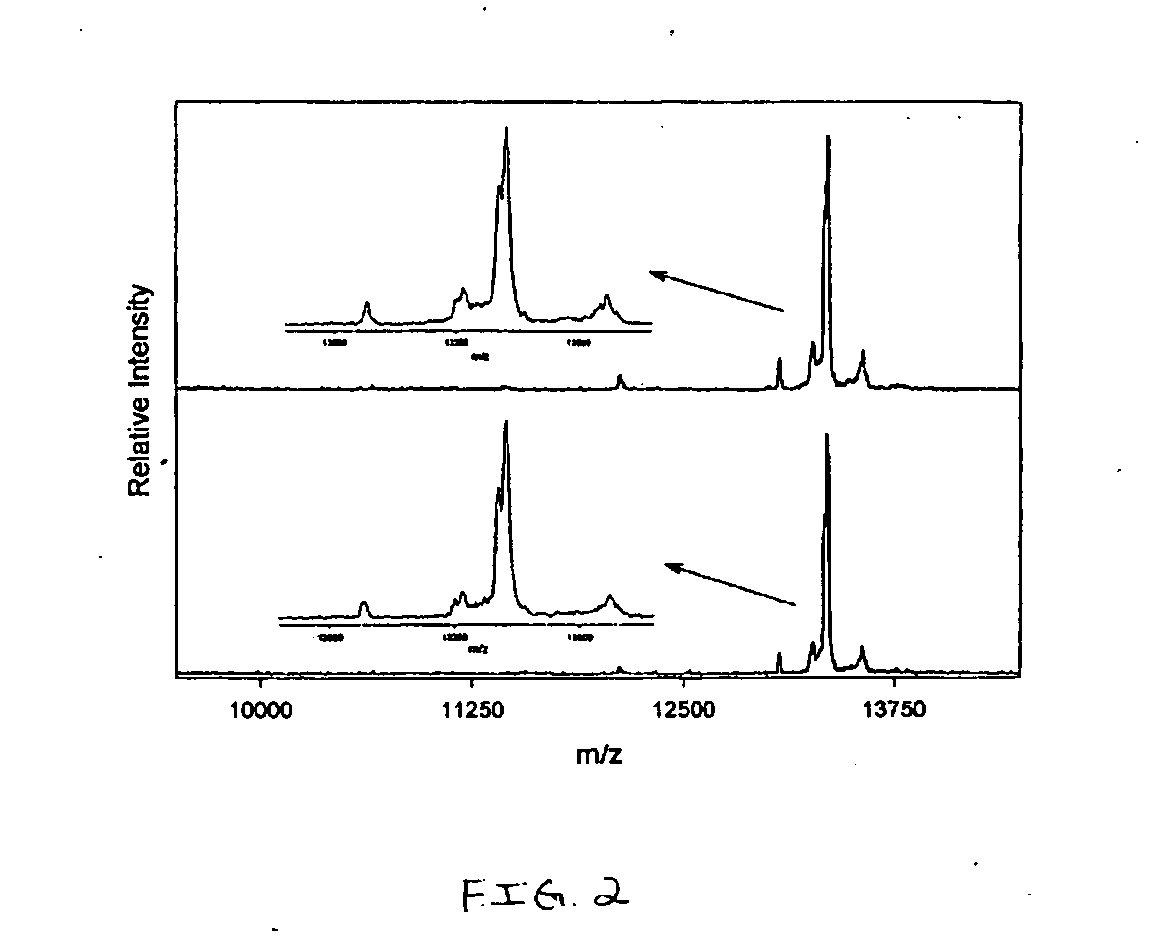
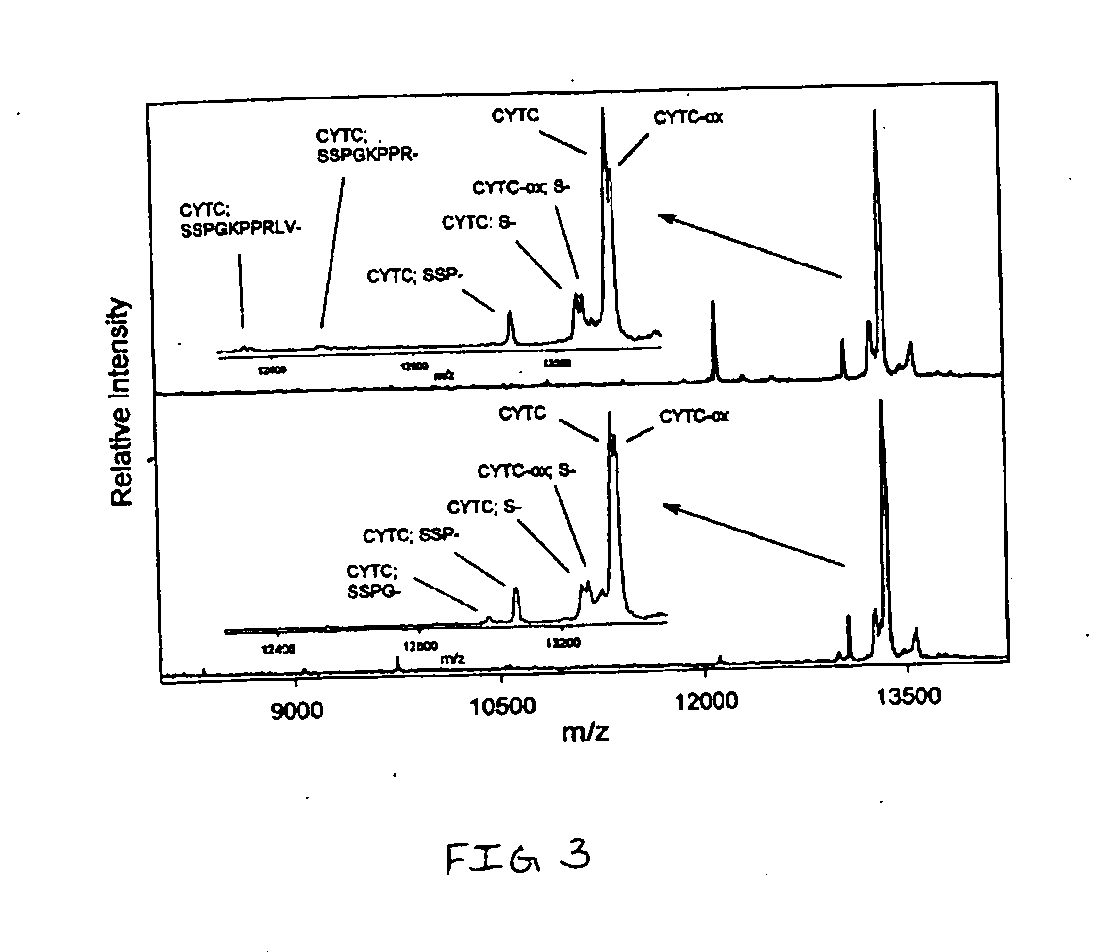
A first objective of the present invention is to demonstrate a method for the detection and prognosis of cancer and of its metastatic potential. Preferably, the cancer is selected from breast cancer, bladder cancer, ovarian cancer, lung cancer, skin cancer, prostate cancer, colon cancer, liver cancer, a sarcoma and a leukaemia, without being limited thereto. One aspect of the present invention consists of the use of the LIV21 complex as a prognostic indicator for cancer and in the therapeutic monitoring thereof. The LIV21 complex is defined in terms of the extract of proteins and peptides studied by Maldi and ESI MS / MS or Maldi Tof / Tof mass spectrometry. Said extract was obtained by attachment of the LIV21 complex to one of these LIV21 polyclonal antibodies. The LIV21 complex is also defined in terms of its overall mass spectrometry profile (FIG. 5) and the number and the molecular weight of the bands of protein extracts obtained as a function of the temperature to which the sample is subjected and the migration conditions described. Another aspect is the use of biochips for the pharmacodiagnosis of oncological pathologies and of neurodegeneration.
Owner:FAURE LAURENCE CLAUDE
Method and apparatus for dynamically monitoring multiple in vivo tissue chromophores
InactiveUS7248909B2Spectrum investigationScattering properties measurementsDynamic monitoringSpectroscopy
A device and method utilizes a broadband diffuse optical spectroscopy (DOS) system to dynamically calculate the concentrations of multiple chromophores in vivo using a non-invasive probe. The device and method permit dynamic monitoring of multiple in vivo tissue chromophores non-invasively with sensitivities necessary for effective therapeutic monitoring. The device includes a probe containing first and second source optical fibers as well as first and second detector optical fibers. The probe is placed adjacent to a sample of interest and detects reflected light which is passed to a proximally located detector and spectrometer. The concentrations of multiple chromophores are determined in real time. In a preferred embodiment, the multiple tissue chromophores include at least two of methemoglobin (MetHb), deoxyhemoglobin (Hb-R), oxyhemoglobin (Hb-O2), water (H2O), and methylene blue (MB). The device and method can be used quantify and monitor methemoglobin formation in subjects suffering from methemoglobinemia.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Anti-LFL2 antibodies for the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of cancer
ActiveUS7399469B2Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsOncologyWilms' tumor
Particular anti-LFL2 antibody compositions are provided herein. These antibodies may be used for diagnosis, prognosis, therapeutic monitoring and treatment of cancer, especially breast cancer, head / neck cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, stomach cancer and pancreatic cancer. Furthermore, anti-LFL2 antibodies are provided herein which target the LFL2 stump remaining after proteolytic cleavage of the extracellular domain of LFL2. Additionally, anti-LFL2 antibodies are provided herein which target the stroma surrounding cancer tumors, wherein said stroma-targeting anti-LFL2 antibodies disrupt the integrity of the stroma surrounding the cancer tumor, and also make the stroma more permeable to chemotherapeutic agents and other molecular drug agents that target tumor cells.
Owner:ABBVIE BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Systems and methods to quantify and amplify both signaling probes for cDNA chips and genes expression microarrays
InactiveUS7482443B2Increase valueEnhanced signalSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGene Expression ArrayTherapeutic monitoring
The invention provides a series of reagent compositions and methods for making and amplifying novel cDNA based probe sets from RNA samples to improve analysis with gene expression arrays. The methods globally produce probe sets with common universal linkers at one or both ends, called WRAP-Probes, wherein the linkers do not bind to the target sequences and they can efficiently bind added reporters to the probes. The universal linkers are also designed as primer binding sites for copying and amplifying the probes, either linearly with one linker, or exponentially with double linkers. The capacity to globally and exponentially amplify the probe set by PCR is a primary advantage. Adding reporters by terminal linkers also improves quantification since each probe gets equivalent signaling. The invention allows expression analysis of small research, clinical and forensic samples to enable improved diagnostics, drug discovery, therapeutic monitoring, and medical, agricultural and general research.
Owner:GENETAG TECH
ddPCR detection optimization method of lung cancer EGFR T790M sites and application thereof
PendingCN107058528AReal-time reflection of mutationsReflect mutationMicrobiological testing/measurementEGFR T790MFluorescence
The invention discloses a ddPCR detection optimization method of lung cancer EGFR T790M sites and application thereof. The detection optimization method comprises the following steps: optimizing the extraction of cfDNA, and performing PCR amplification and probe detection on the cfDNA by use of the mutant type and wild type fluorescence detection probe designed for the T790M gene sites and a specific primer pair for performing specific amplification on a target region; performing data analysis of a detected fluorescence signal value to acquire the accurate EGFR gene T790M sites information. The noninvasive detection can be really realized by only needing a small amount of peripheral blood. The detection optimization method disclosed by the invention performs detection analysis of the important sites related to the lung cancer target medication in the ctDNA, and provides the medication related gene sites mutant information for the lung cancer patient in the late treatment process of the lung cancer, thereby providing the important reference evidence for the personalized accurate medication guidance, the drug efficacy evaluation and therapeutic monitoring.
Owner:深圳海普洛斯医学检验实验室
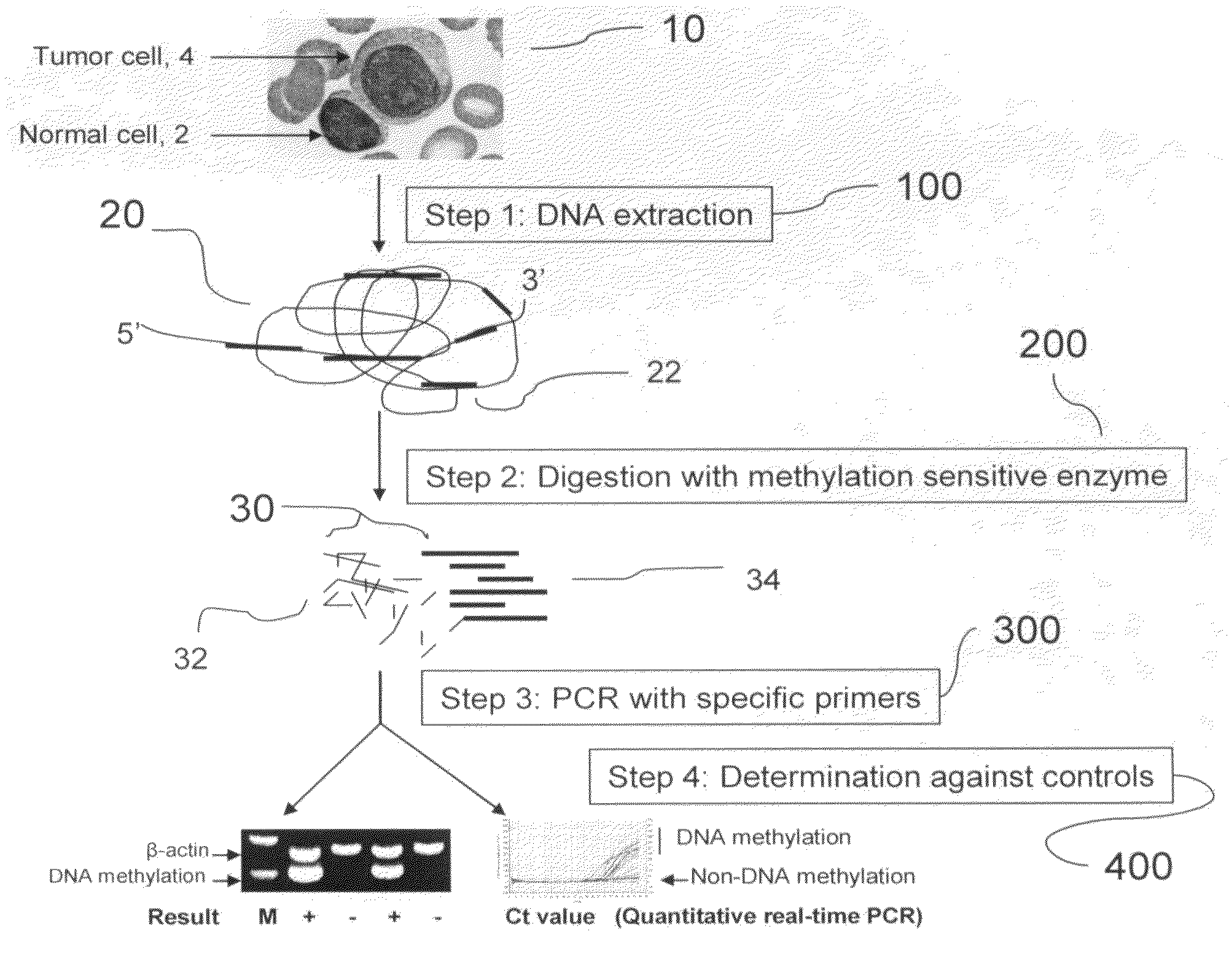
Method for detecting DNA methylation in cancer cells
The present invention provides a detecting method of detecting malignant cells in a patient's specimen or a biological sample. Specifically, the inventive method includes the steps of extracting a genomic DNA, digesting said genomic DNA with one or multiple methylation sensitive restriction enzymes, and amplifying by PCR with one or multiple selected primers. The PCR can be performed in a conventional or a real-time platform. The inventive method can detect leukemia cells in 90% ALL patients at a sensitivity of up to 10−6. The inventive method also provides broad clinical applications in cancer (including hematopoietic and solid tumors) screening and risk assessment, early detection and diagnosis confirmation, and therapeutic monitoring, minimal residual disease detection and prognostic prediction.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Method for producing rapamycin-specific antibodies
This invention relates to the production of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies to specific sites of rapamycin (Sirolimus). The reactivity of these poly and monoclonal antibodies make them particularly useful for immunoassays for therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM). These immunoassays or TDM kits may include polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies to specific sites of rapamycin. These kits may also include various combinations of polyclonal antibodies, polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies or a panel of monoclonal antibodies. Rapamycin conjugate immunogens are prepared for the immunization of a host animal to produce antibodies directed against specific regions of the rapamycin molecule. By determining the specific binding region of particular antibody, immunoassays which are capable of distinguishing between the parent molecule, active metabolites, inactive metabolites and other structurally similar immunosuppressant compounds are developed. The use of divinyl sulfone (DVS) as the linker arm molecule for forming rapamycin-protein conjugate immunogens is described. DVS-linked rapamycin-protein conjugates were found to elicit antibodies with greater specificity to the rapamycin molecule than succinate linked conjugates.
Owner:YATSCOFF RANDALL W +2
Hybridized optical-MRI method and device for molecular dynamic monitoring of in vivo response to disease treatment
An apparatus for providing physiological information from an organism in disease diagnosis and treatment monitoring, for use in an MRI instrument. The apparatus operates on the concept of hybridized magneto-optical sensitivity. The MRI includes an MRI scanner and a controller for controlling the MRI scanner. The MRI scanner provides a magnetic field of at least 0.5T. The apparatus further includes a front end built of non-magnetic components, comprising light guides for illuminating a region of interest (ROI) and for collecting light emitted at said ROI; and a back-end comprising a light source for injecting light into said light guides; a light detector for receiving light collected at said ROI; and a processing and control unit for processing said light collected at said ROI.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Methods, devices, and reagents for monitoring paclitaxel concentration in plasma for pharmacokinetic-guided dosing of paclitaxel
InactiveUS20150285827A1High sensitivityImprove dynamic rangeDisease diagnosisBiological testingPharmaceutical drugBlood plasma
Methods, devices, and compositions for assaying therapeutic agents. In one aspect, methods, devices, and compositions for assaying paclitaxel to provide therapeutic drug monitoring guided therapy of paclitaxel.
Owner:AUTOTELIC
Systems and Methods to Quantify and Amplify Both Signaling and Probes for CDNA Chips and Gene Expression Microarrays
InactiveUS20090275029A1Increase valueEnhanced signalSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCDNA MicroarraysGene Expression Array
The invention provides a series of reagent compositions and methods for making and amplifying novel cDNA based probe sets from RNA samples to improve analysis with gene expression arrays. The methods globally produce probe sets with common universal linkers at one or both ends, called WRAP-Probes, wherein the linkers do not bind to the target sequences and they can efficiently bind added reporters to the probes. The universal linkers are also designed as primer binding sites for copying and amplifying the probes, either linearly with one linker, or exponentially with double linkers. The capacity to globally and exponentially amplify the probe set by PCR is a primary advantage. Adding reporters by terminal linkers also improves quantification since each probe gets equivalent signaling. The invention allows expression analysis of small research, clinical and forensic samples to enable improved diagnostics, drug discovery, therapeutic monitoring, and medical, agricultural and general research.
Owner:GENETAG TECH
Methods for identifying therapeutic targets and treating monitoring cancers
ActiveUS20160289686A1Well formedHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsTumour suppressor geneAbnormal tissue growth
The present invention provides methods for treating cancers having a mutation in one or more tumor suppressor genes, comprising providing to a subject in need thereof an inhibitor of a kinase, as well as related methods and compositions.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER CENT
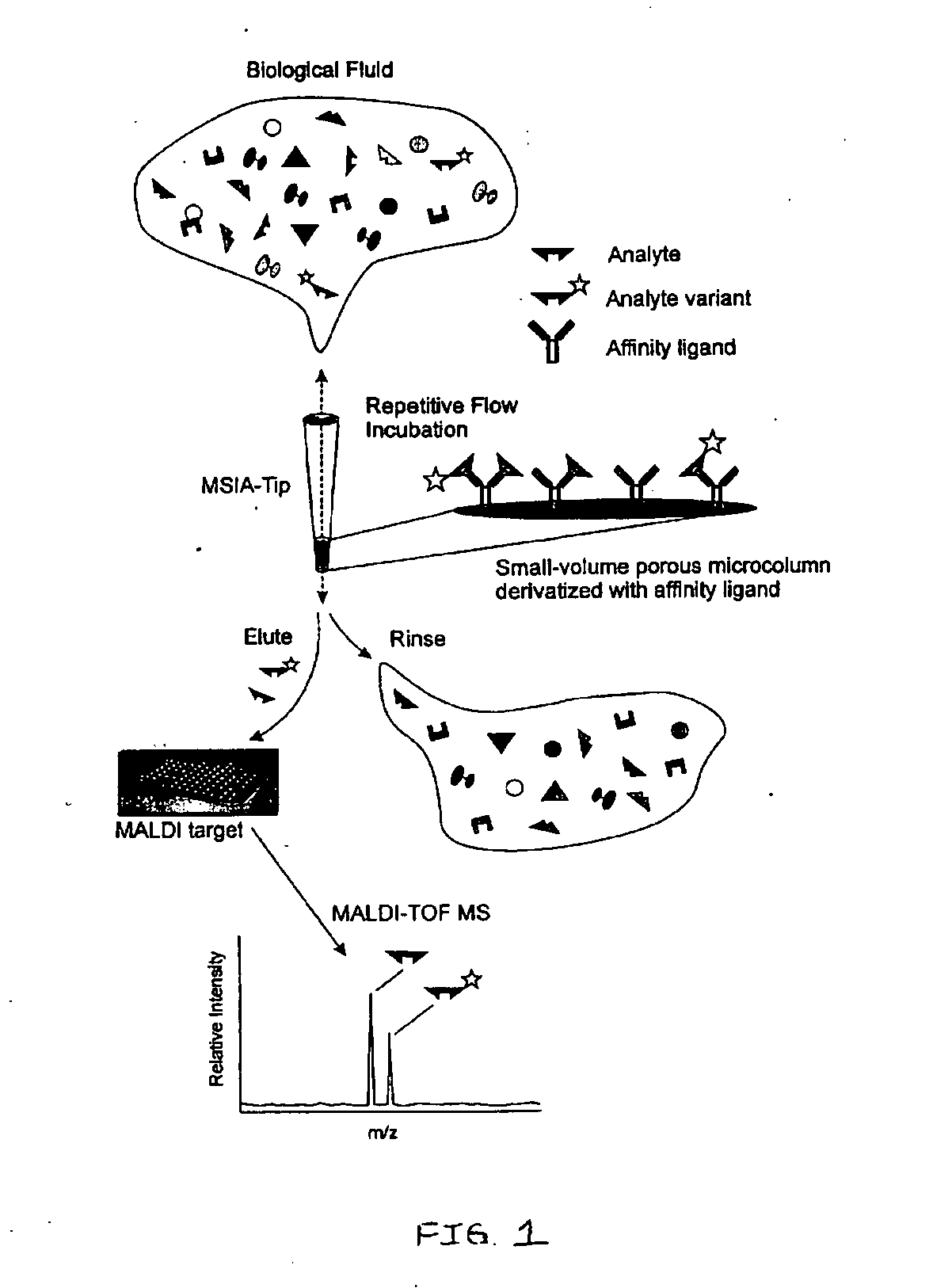
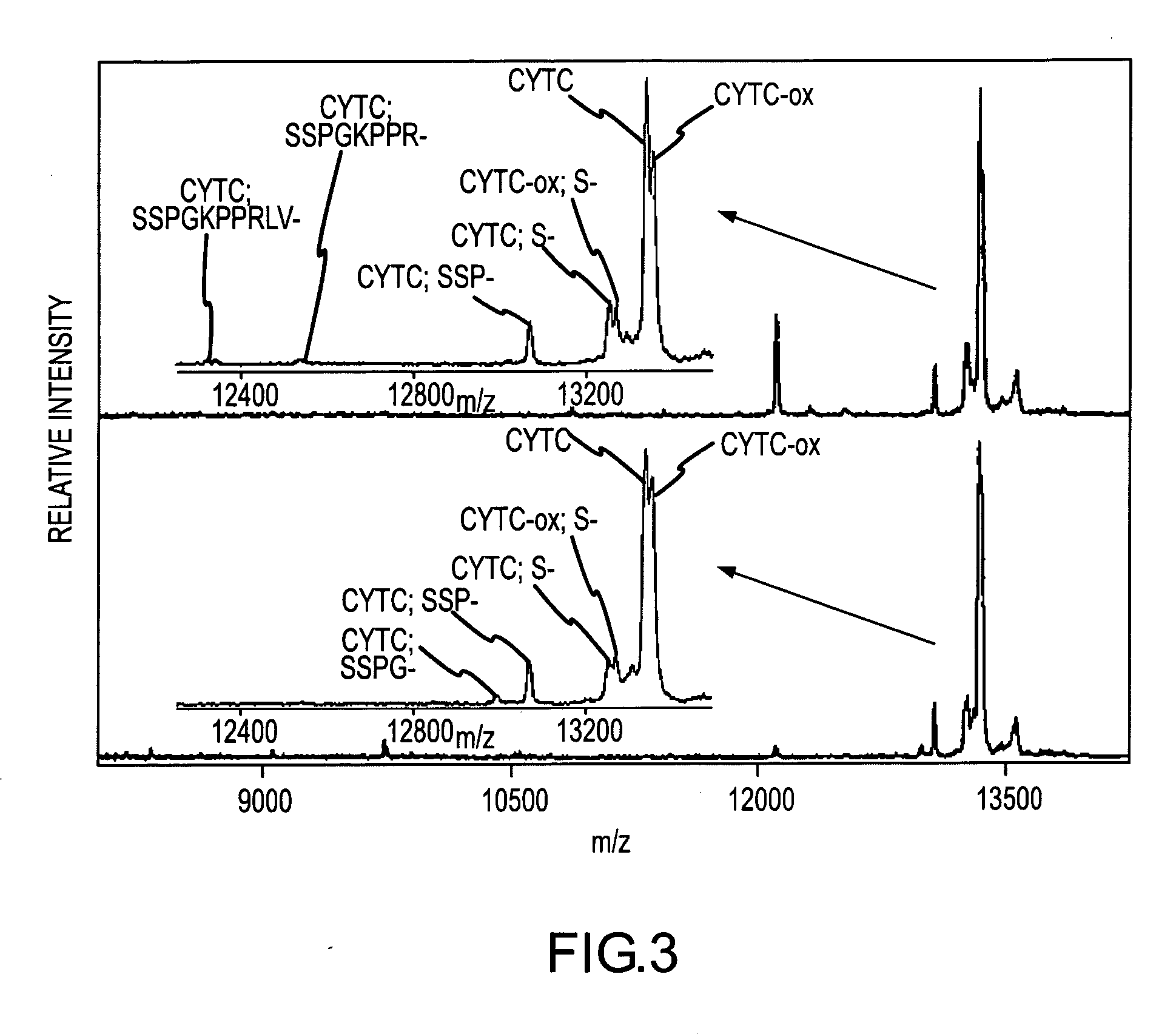
Analysis of proteins from biological fluids using mass spectrometric immunoassay
InactiveUS20060127948A1Sufficient dynamic rangeBiological testingImmunoassaysDrug targetMass spectrometric immunoassay
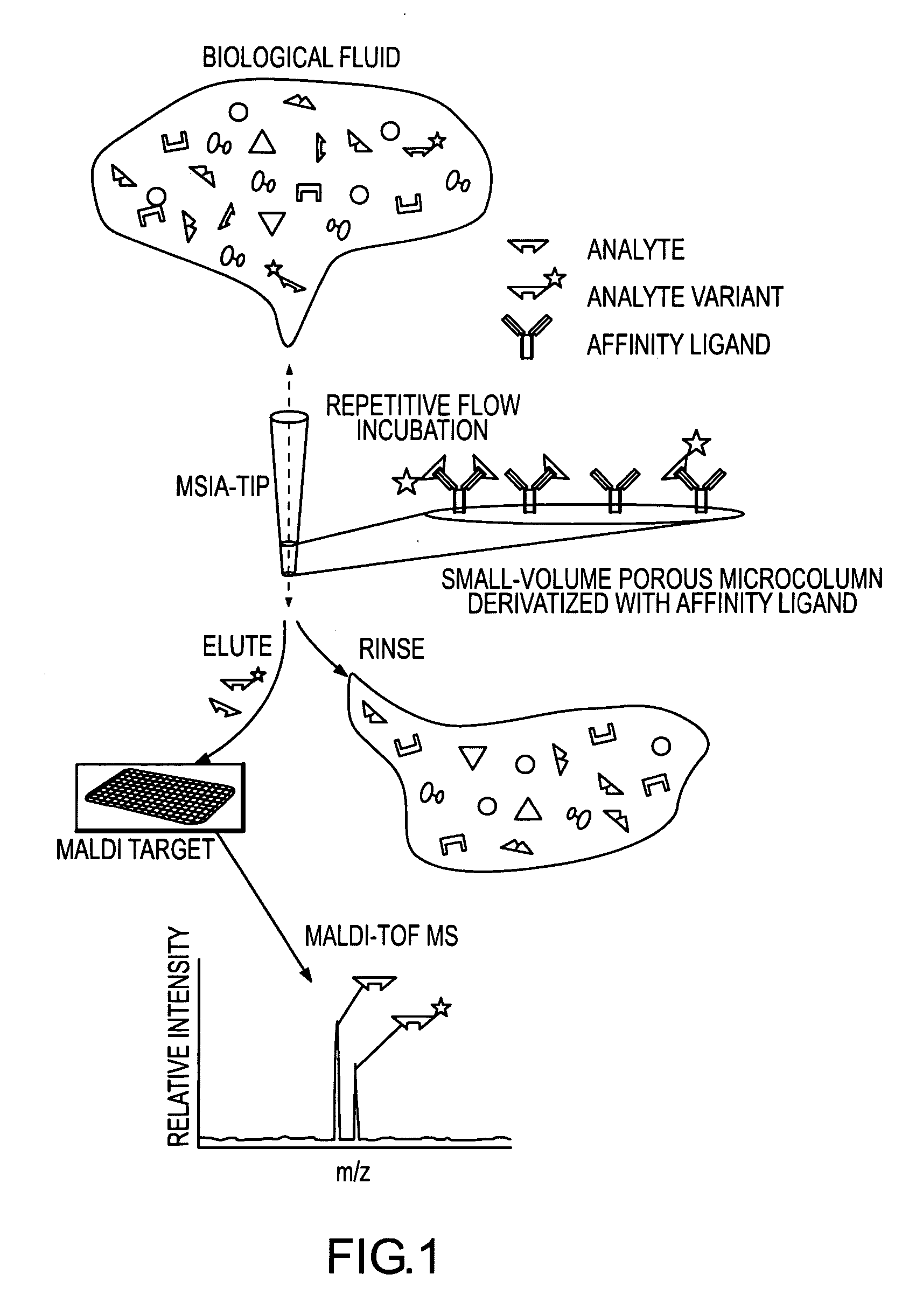
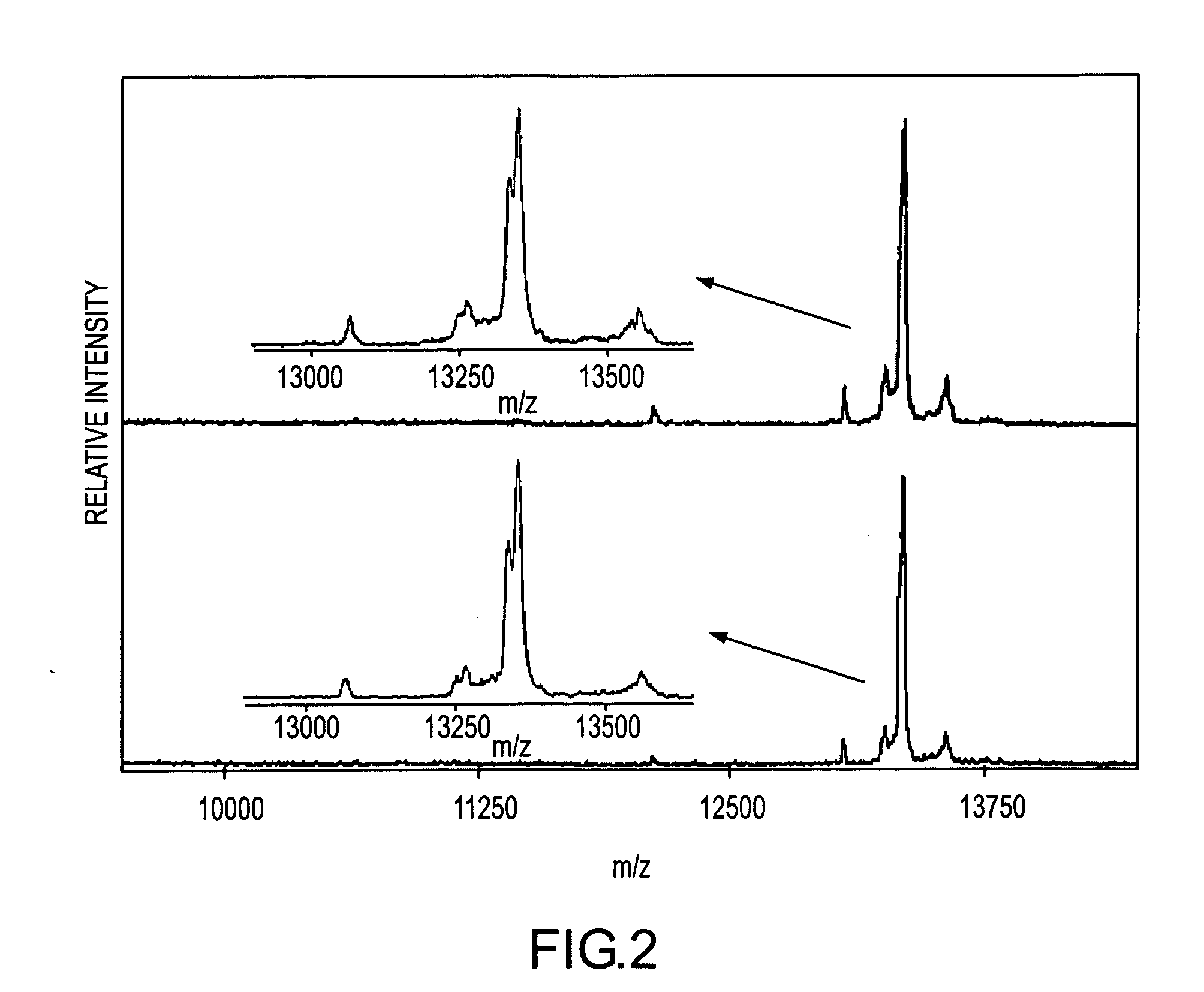
Presented herein are methods, devices and kits for the mass spectrometric immunoassay (MSIA) of proteins present in complex biological fluids or extracts. Pipettor tips containing porous solid supports that are covalently derivatized with affinity ligand and used to extract specific proteins and their variants from various biological fluids. Nonspecifically bound compounds are rinsed from the extraction devices using a series of buffer and water rinses, after which the wild type protein (and / or its variants) are eluted directly onto a target in preparation for analysis such as matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). Mass spectrometry of the eluted sample then follows with the retained proteins identified via accurate molecular mass determination. Protein and variant levels can be determined using quantitative methods in which the protein / variant signals are normalized to signals of internal reference standard species (either doped into the samples prior to the MSIA analysis, or other endogenous protein co-extracted with the target proteins) and the values compared to a working curves constructed from samples containing known concentrations of the protein or variants. Such MSIA devices, kits and methods have significant application in the fields of; basic research and development, proteomics, protein structural characterization, drug discovery, drug-target discovery, therapeutic monitoring, clinical monitoring and diagnostics, as well as in the high throughput screening of large populations to establish and recognize protein / variant patterns that are able to differentiate healthy from diseased states.
Owner:INTRINSIC BIOPROBES
System and Methods to Quantify and Amplify Both Signaling and Probes for cDNA Chips and Gene Expression Microarrays
InactiveUS20120157343A1Increase valueEnhanced signalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCDNA MicroarraysGene Expression Array
The invention provides a series of reagent compositions and methods for making and amplifying novel cDNA based probe sets from RNA samples to improve analysis with gene expression arrays. The methods globally produce probe sets with common universal linkers at one or both ends, called WRAP-Probes, wherein the linkers do not bind to the target sequences and they can efficiently bind added reporters to the probes. The universal linkers are also designed as primer binding sites for copying and amplifying the probes, either linearly with one linker, or exponentially with double linkers. The capacity to globally and exponentially amplify the probe set by PCR is a primary advantage. Adding reporters by terminal linkers also improves quantification since each probe gets equivalent signaling. The invention allows expression analysis of small research, clinical and forensic samples to enable improved diagnostics, drug discovery, therapeutic monitoring, and medical, agricultural and general research.
Owner:GENETAG TECH
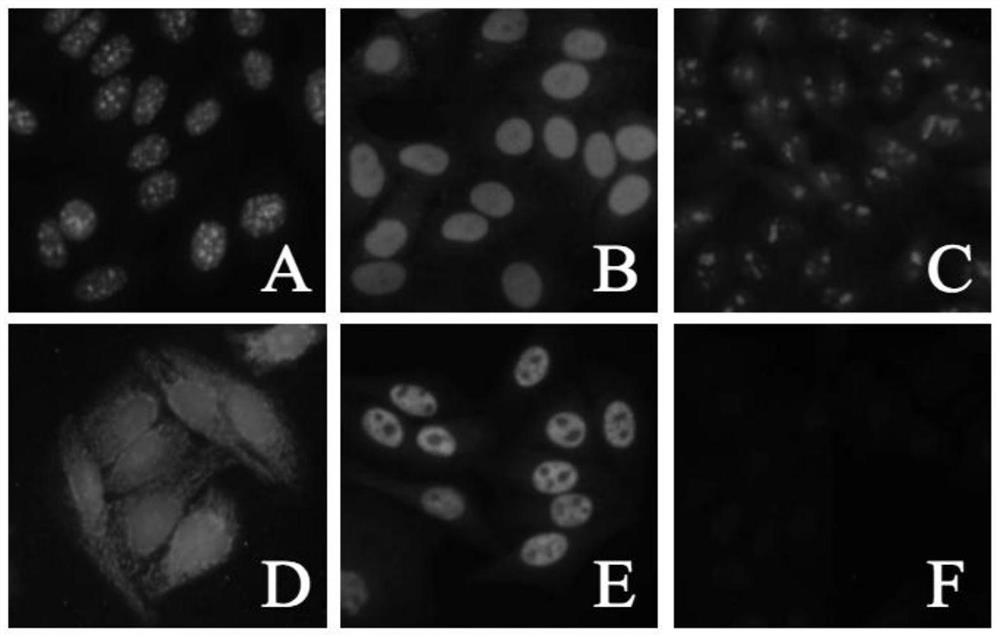
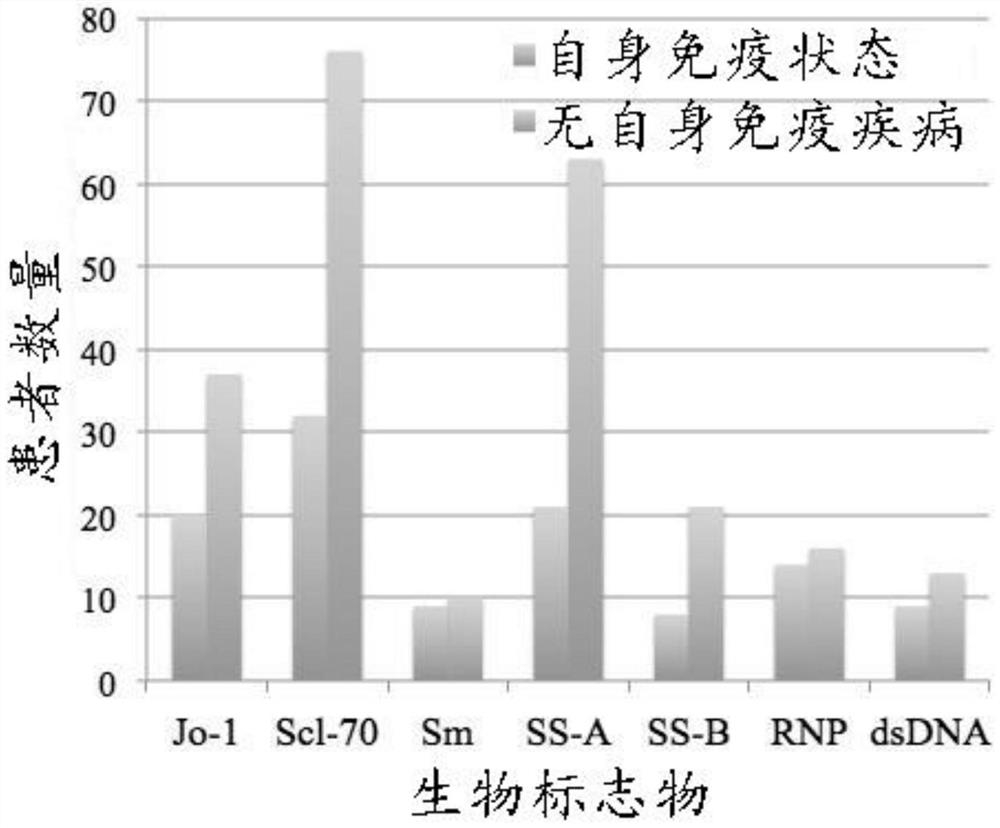
Reagents and methods for cancer detection, prognosis, and therapeutic monitoring
Methods and related reagents are disclosed for diagnosing cancer, prognosing cancer occurrence or recurrence, and / or monitoring cancer therapy, involving contacting a bodily fluid sample from a subject at risk of having cancer or cancer recurrence, or from a subject that has been treated for cancer wl fit (a)one or more first antibody detection marker molecules that hind to human autoantibodies against at least one tumor associated antigen (TAA); and (fa) one or more second antibody detection marker molecules that bind to human autoantibodies against at least one extractable nuclear antigen (ENA).
Owner:SANFORD HEALTH +1
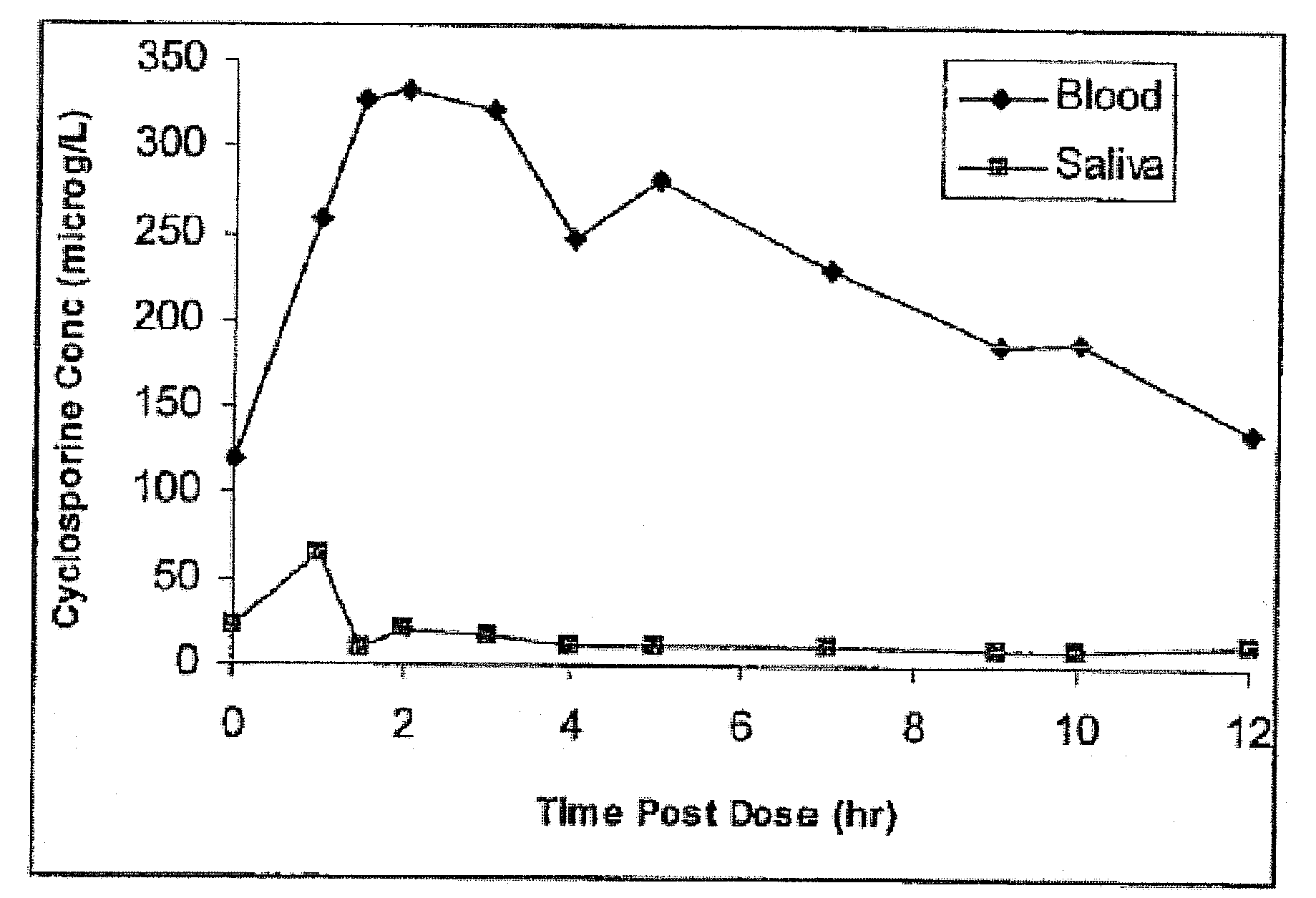
Monitoring cyclosporine in saliva
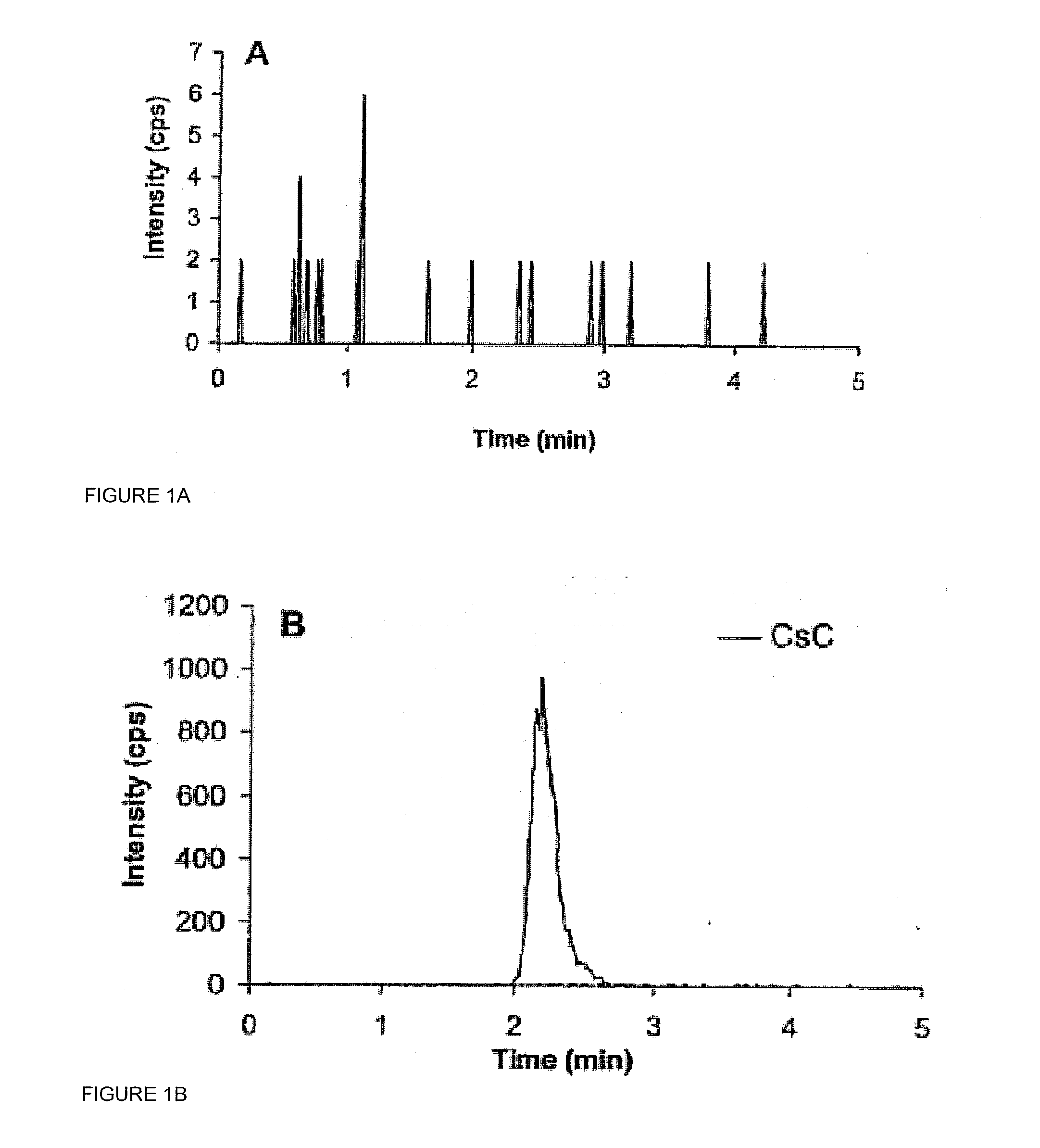
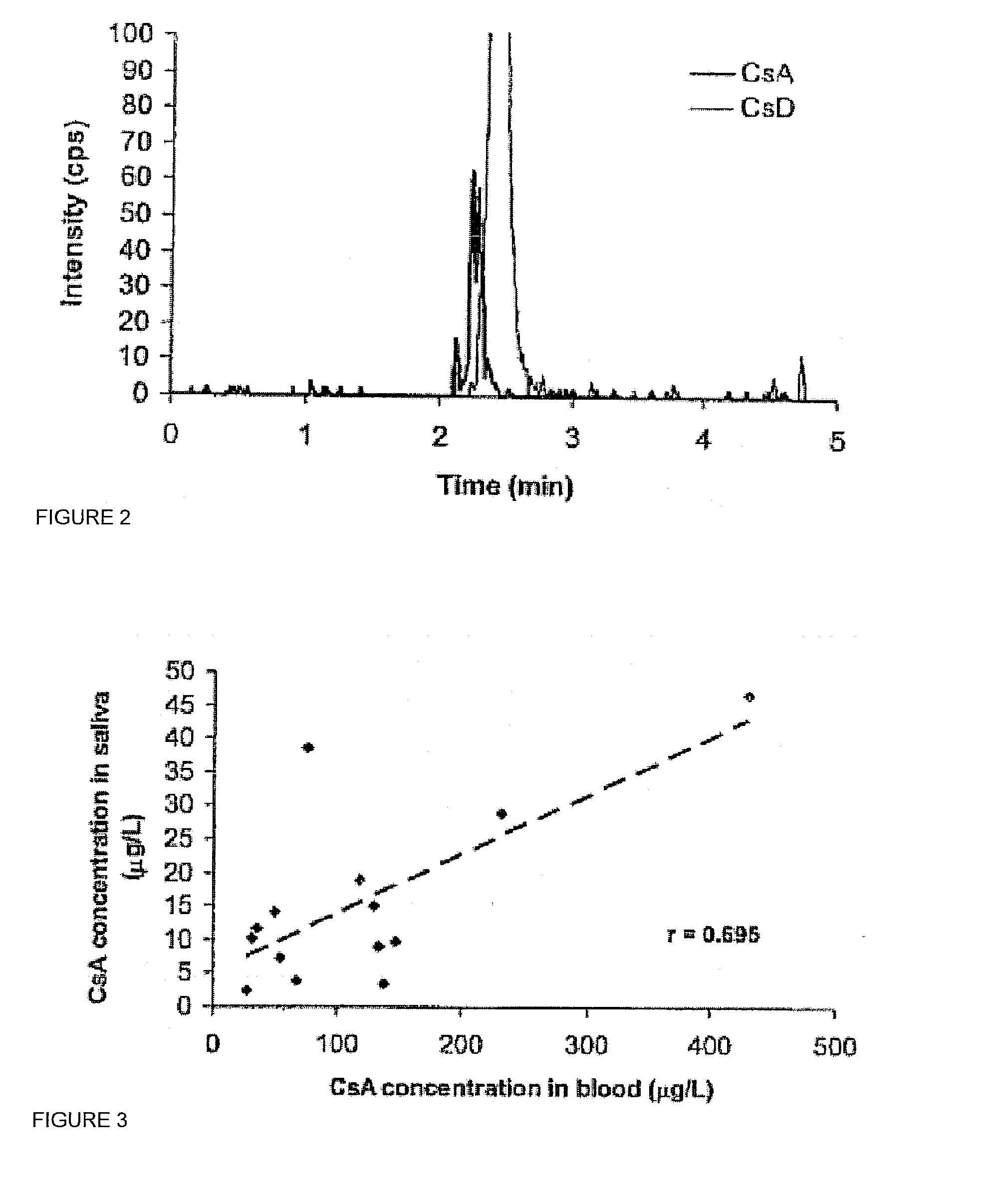
InactiveUS20080255765A1Promote recoveryImprove consistencyPreparing sample for investigationCyclic peptide ingredientsVenous accessBound drug
Saliva offers an alternative specimen for the therapeutic monitoring of cyclosporine (CsA) in children and patients with difficult venous access. For a highly protein-bound drug such as CsA, saliva provides a practical approach for measuring the unbound concentration. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS / MS) is ideally suited for the measurement of drugs in saliva. A solid-phase extraction technique, analytic liquid chromatography over an Aqua Perfect column, maintained at 65° C., and electrospray tandem mass spectrometry were used to quantify CsA in saliva. The method used cyclosporine C (CsC) as the internal standard. Mobile phase comprised of a 97:3 voL mixture of methanol and 30 mmol / L ammonium acetate at a flow rate of 0.5 mL / min. Chromatograms using mass transitions of m / z 1219.9→m / z 1202.9 for CsA and m / z 1235.9→m / z 1218.9 for CsC were obtained. The calibration curve was linear from 1 to 300 μg / L with correlation coefficient values ranging from 0.9732 to 0.9968). The lower limit of quantification was 1 μg / L and limit of detection was 0.6 μg / L with an average extraction recovery of 84.7±2.6% for CsA and 93.7±4.4% for CsC from the saliva matrix. The accuracy of the method ranged from 92% to 104.7%, and the intra- and interim coefficients of variation were 6.9-12.2% and 8.3-12.1%, respectively. The correlation coefficient value between the CsA concentration measurements in 15 paired blood-saliva samples from kidney transplant recipients was 0.695 (P=0.006). The noninvasive and simple method of saliva collection coupled with the LC-MS / MS quantification technique for CsA analysis would generate novel data that could benefit patients undergoing CsA therapy.
Owner:BOARD OF GOVERNORS FOR HIGHER EDUCATION STATE OF RHODE ISLAND & PROVIDENCE PLANTATIONS
Analysis of proteins from biological fluids using mass spectrometric immunoassay
InactiveUS20060121533A1Solve the lack of dynamic rangeSufficient dynamic rangeBiological testingImmunoassaysDrug targetMass spectrometric immunoassay
Presented herein are methods, devices and kits for the mass spectrometric immunoassay (MSIA) of proteins present in complex biological fluids or extracts. Pipettor tips containing porous solid supports that are covalently derivatized with affinity ligand and used to extract specific proteins and their variants from various biological fluids. Nonspecifically bound compounds are rinsed from the extraction devices using a series of buffer and water rinses, after which the wild type protein (and / or its variants) are eluted directly onto a target in preparation for analysis such as matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). Mass spectrometry of the eluted sample then follows with the retained proteins identified via accurate molecular mass determination. Protein and variant levels can be determined using quantitative methods in which the protein / variant signals are normalized to signals of internal reference standard species (either doped into the samples prior to the MSIA analysis, or other endogenous protein co-extracted with the target proteins) and the values compared to a working curves constructed from samples containing known concentrations of the protein or variants. Such MSIA devices, kits and methods have significant application in the fields of; basic research and development, proteomics, protein structural characterization, drug discovery, drug-target discovery, therapeutic monitoring, clinical monitoring and diagnostics, as well as in the high throughput screening of large populations to establish and recognize protein / variant patterns that are able to differentiate healthy from diseased states.
Owner:INTRINSIC BIOPROBES
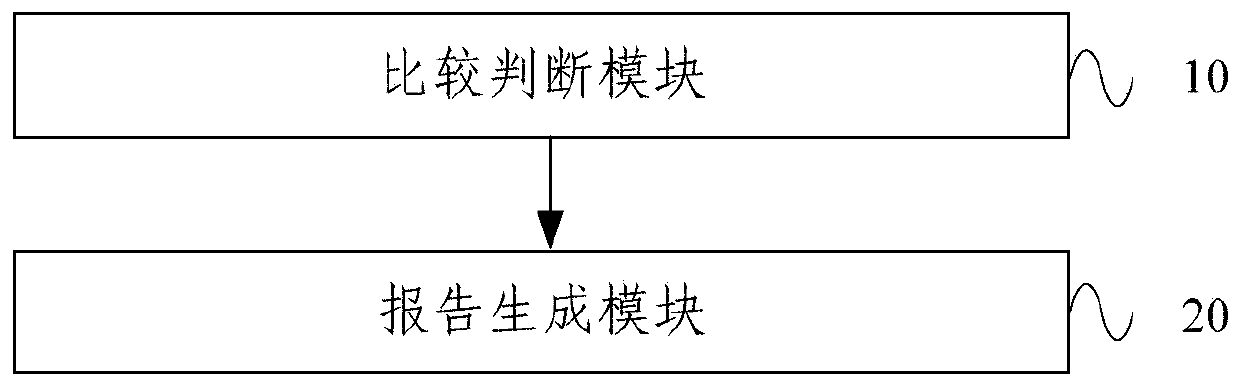
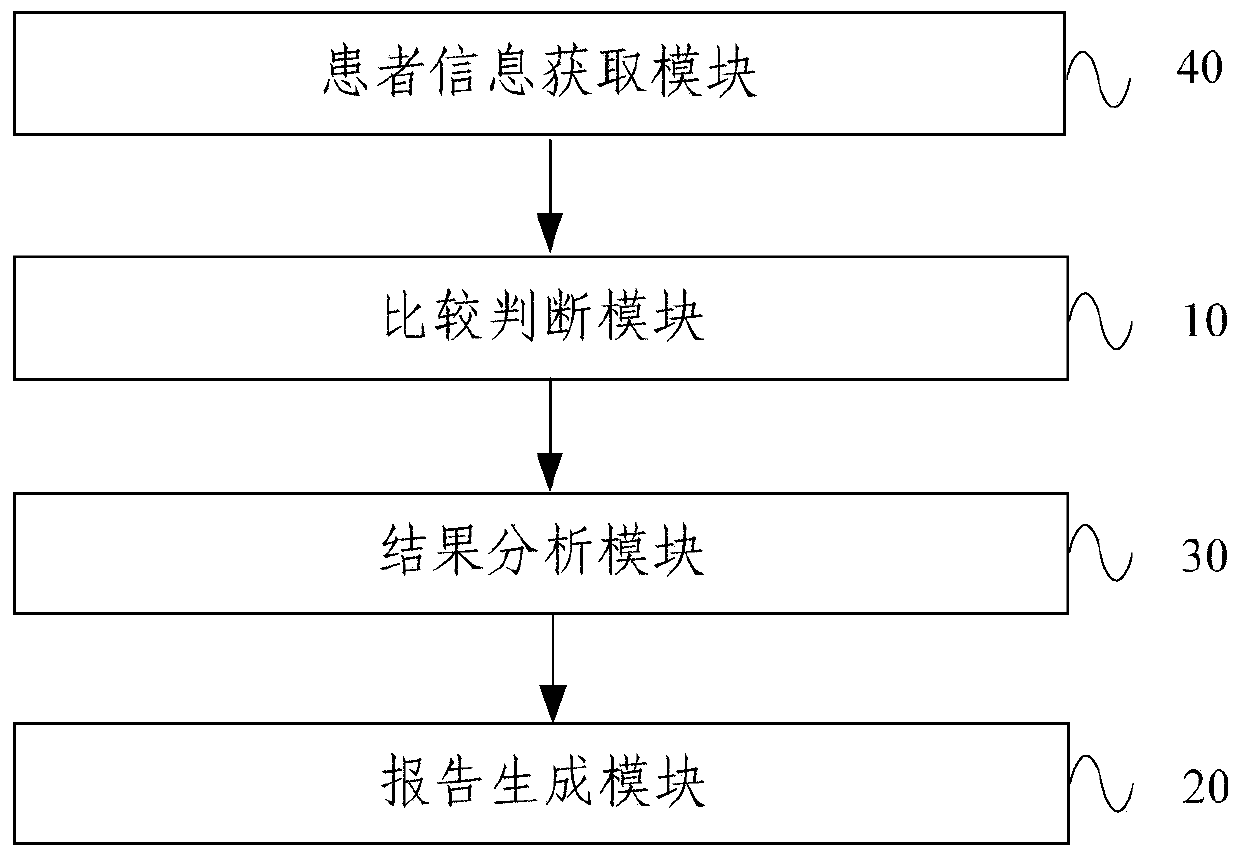
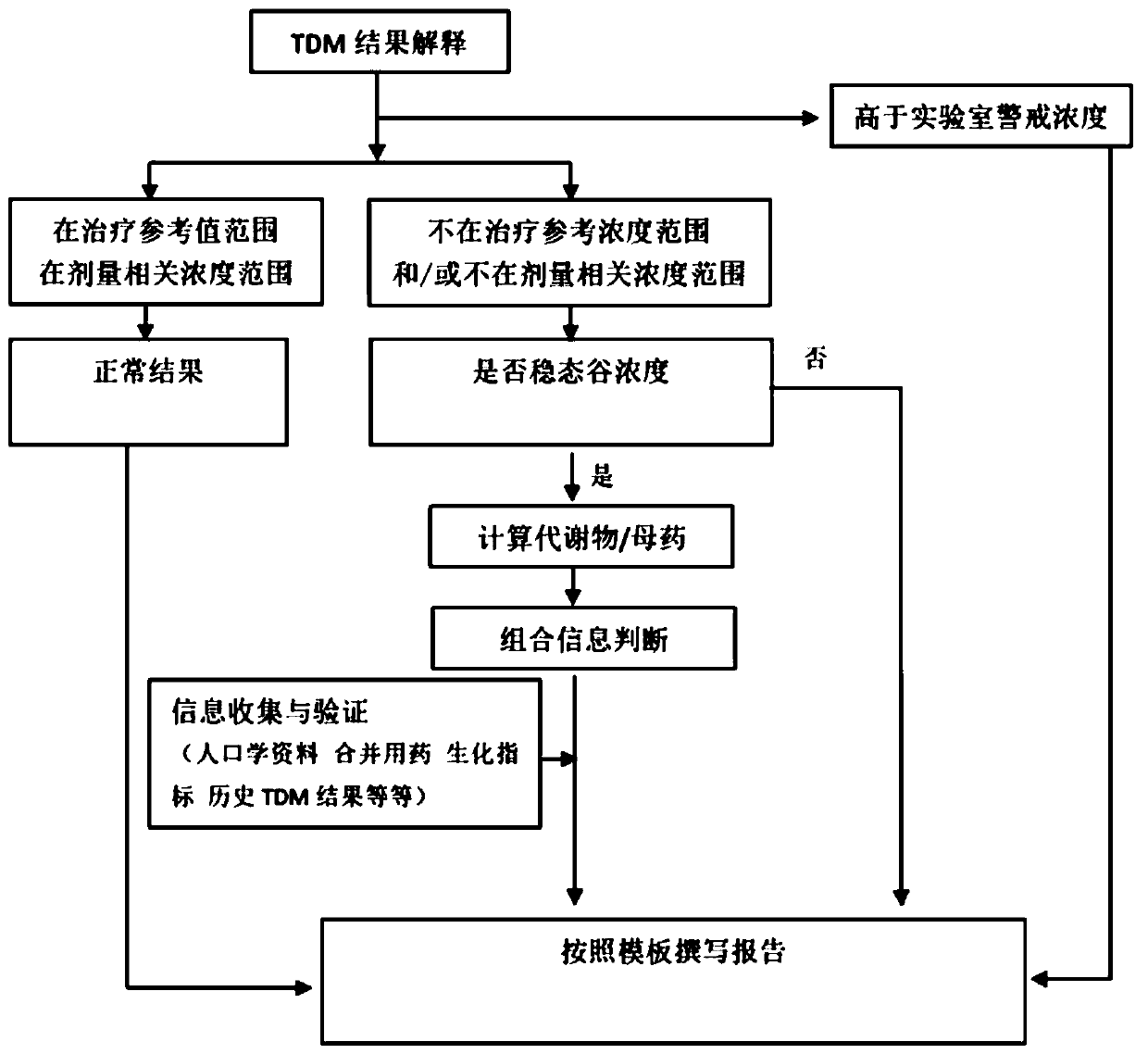
A therapeutic drug monitoring result interpretation system
PendingCN111489822AAchieve standardizationFully automatedMedical automated diagnosisMedical reportsMedication monitoringPharmaceutical drug
The embodiment of the invention provides a therapeutic drug monitoring result interpretation system, which comprises a comparison and judgment module used for comparing a therapeutic drug monitoring result with at least one preset first reference concentration range; and / or obtaining at least one preset statistical result according to the therapeutic drug monitoring result, and comparing the preset statistical result with a corresponding preset second reference concentration range to obtain a therapeutic drug monitoring comparison result; and a report generation module used for generating a therapeutic drug monitoring result interpretation report according to the therapeutic drug monitoring comparison result and a corresponding preset report template. The embodiment of the invention provides a therapeutic drug monitoring result interpretation system. A therapeutic drug monitoring comparison result is obtained through preset comparison, and a therapeutic drug monitoring result interpretation report is generated according to the therapeutic drug monitoring comparison result and the corresponding preset report template, so that standardization and automation of generation of the therapeutic drug monitoring result interpretation report are realized, and the generation efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIJING ANDING HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Pharmacodiagnostic test targeting oncology and neurodegeneration
ActiveUS8314221B2Increase in cytoplasmic fractionInduce tumor suppressor gene silencingOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesProstate cancerOncology
A first objective is to demonstrate a method for the detection and prognosis of cancer and of its metastatic potential. Preferably, the cancer is selected from breast cancer, bladder cancer, ovarian cancer, lung cancer, skin cancer, prostate cancer, colon cancer, liver cancer, a sarcoma and a leukaemia, without being limited thereto. One aspect consists of the use of the LIV21 complex as a prognostic indicator for cancer and in the therapeutic monitoring thereof. The LIV21 complex is defined in terms of the extract of proteins and peptides studied by Maldi and ESI MS / MS or Maldi Tof / Tof mass spectrometry. The extract was obtained by attachment of the LIV21 complex to one of these LIV21 polyclonal antibodies. The LIV21 complex is also defined in terms of its overall mass spectrometry profile and the number and the molecular weight of the bands of protein extracts obtained as a function of the temperature to which the sample is subjected and the migration conditions described. Another aspect is the use of biochips for the pharmacodiagnosis of oncological pathologies and of neurodegeneration.
Owner:FAURE LAURENCE CLAUDE
Methods, devices, and reagents for monitoring paclitaxel concentration in plasma for pharmacokinetic-guided dosing of paclitaxel
Methods, devices, and compositions for assaying therapeutic agents. In one aspect, methods, devices, and compositions for assaying paclitaxel to provide therapeutic drug monitoring guided therapy of paclitaxel.
Owner:AUTOTELIC
Preparation method of stable isotope labeled alprazolam and estazolam internal standard reagent
InactiveCN113549078AHigh chemical purityRaw materials are easy to obtainIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsStable Isotope LabelingIsotopic labeling
The invention relates to a preparation method of a stable isotope labeled alprazolam and estazolam internal standard reagent for monitoring the blood concentration of a clinical treatment drug, and belongs to a standard substance for monitoring the clinical treatment drug. The stable isotope labeled alprazolam or stable isotope labeled estazolam is obtained by taking stable isotope labeled phenylboronic acid as a raw material, performing catalytic addition, acylation, cyclization, sulfur-oxygen exchange and cyclization and finally conducting separating and purifying. The process has the advantages that raw materials needed for synthesis are simple and easy to obtain, reaction conditions are mild, the chemical purity of the target product stable isotope labeled alprazolam and stable isotope labeled estazolam can reach 98% or above, and the isotope abundance can reach 98% or above. The preparation method can meet the technical requirements of a stable isotope labeling internal standard reagent required by a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for monitoring the blood concentration of a clinical treatment drug.
Owner:谱同生物医药科技常州有限公司
Method for simultaneously determining concentrations of anticoagulant drugs and active metabolite in plasma
ActiveCN113030312AHigh sensitivityMeet analysis requirementsComponent separationPharmaceutical drugEdoxaban
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously determining the concentrations of anticoagulant drugs and an active metabolite in plasma. The anticoagulant drugs are dabigatran etexilate, rivaroxaban, edoxaban and apixaban respectively, and the active metabolite is dabigatran. The specificity, precision, accuracy, linearity, stability and the like of the method all meet the analysis requirements of biological samples, the sensitivity is high, and the method can be used for clinical monitoring of therapeutic drugs of dabigatran etexilate, dabigatran, rivaroxaban, edoxaban and apixaban.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
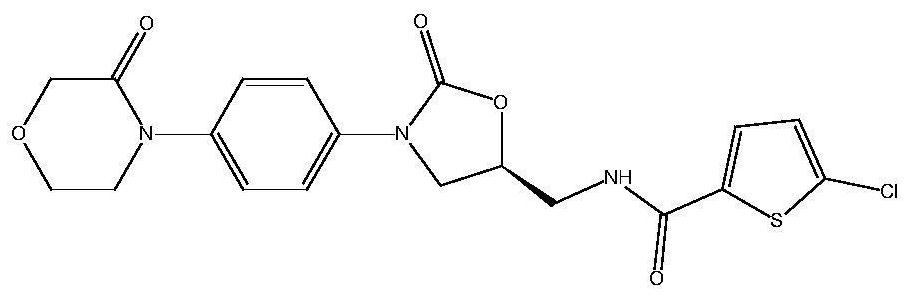
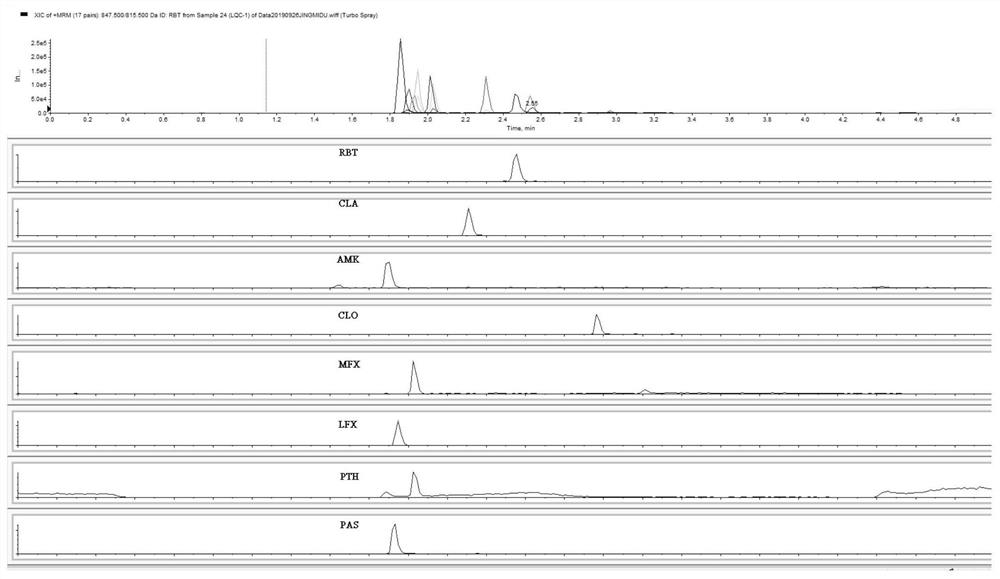
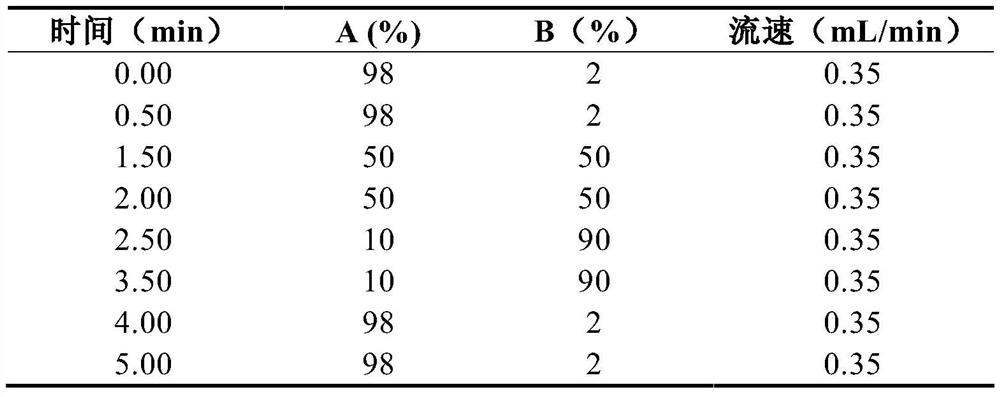
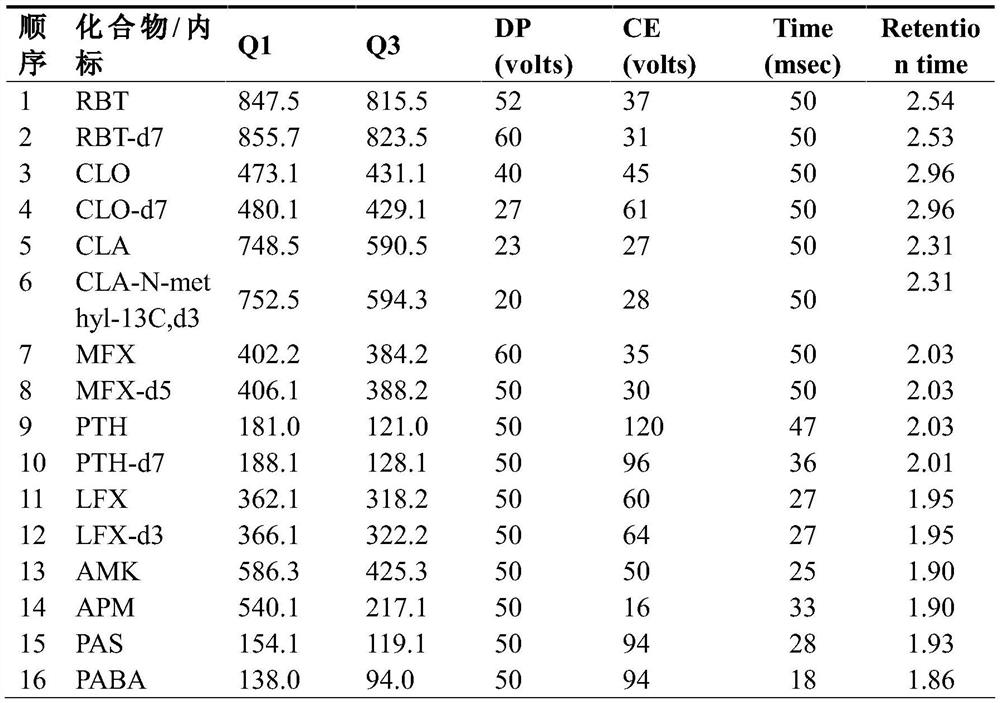
Method for simultaneously determining eight antituberculous drugs in human plasma based on LC-MS
InactiveCN112782322AMeet the needs of actual testingHigh sensitivityComponent separationChlorobenzeneLiquid chromatography mass spectroscopy
The invention belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry, and particularly relates to a method for simultaneously determining the concentrations of eight antituberculous drugs in plasma by adopting a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method, wherein the eight antituberculous drugs comprise rifudine, chlorphenazine, levofloxacin, clarithromycin, sulfimide, p-aminosalicylic acid, moxifloxacin and amikacin. According to the method, the characteristics of hydrophilic and hydrophobic compounds are considered, protein precipitation is carried out by utilizing ACN:MEOH:45%TCA, the extraction rate of the hydrophilic compound AMK is improved, 20% of ACN, 0.2% of FA and 1% of HFBA are used as diluents, and the retention time of the hydrophilic compound AMK is prolonged by adding the HFBA. The method is high in sensitivity, strong in specificity and wide in linear range, can be used for qualitative and quantitative analysis of to-be-detected substances with unknown concentrations in plasma of tuberculosis patients, is simple and rapid to operate, does not need an extraction and volatilization process, and can meet the characteristics of urgent clinical treatment drug monitoring tasks and high requirements on detection time. The detection system provided by the invention provides a new technical platform for tuberculosis patient treatment drug monitoring, and is easy to popularize and apply.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUBLIC HEALTH CLINICAL CENT
Therapeutic drug monitoring
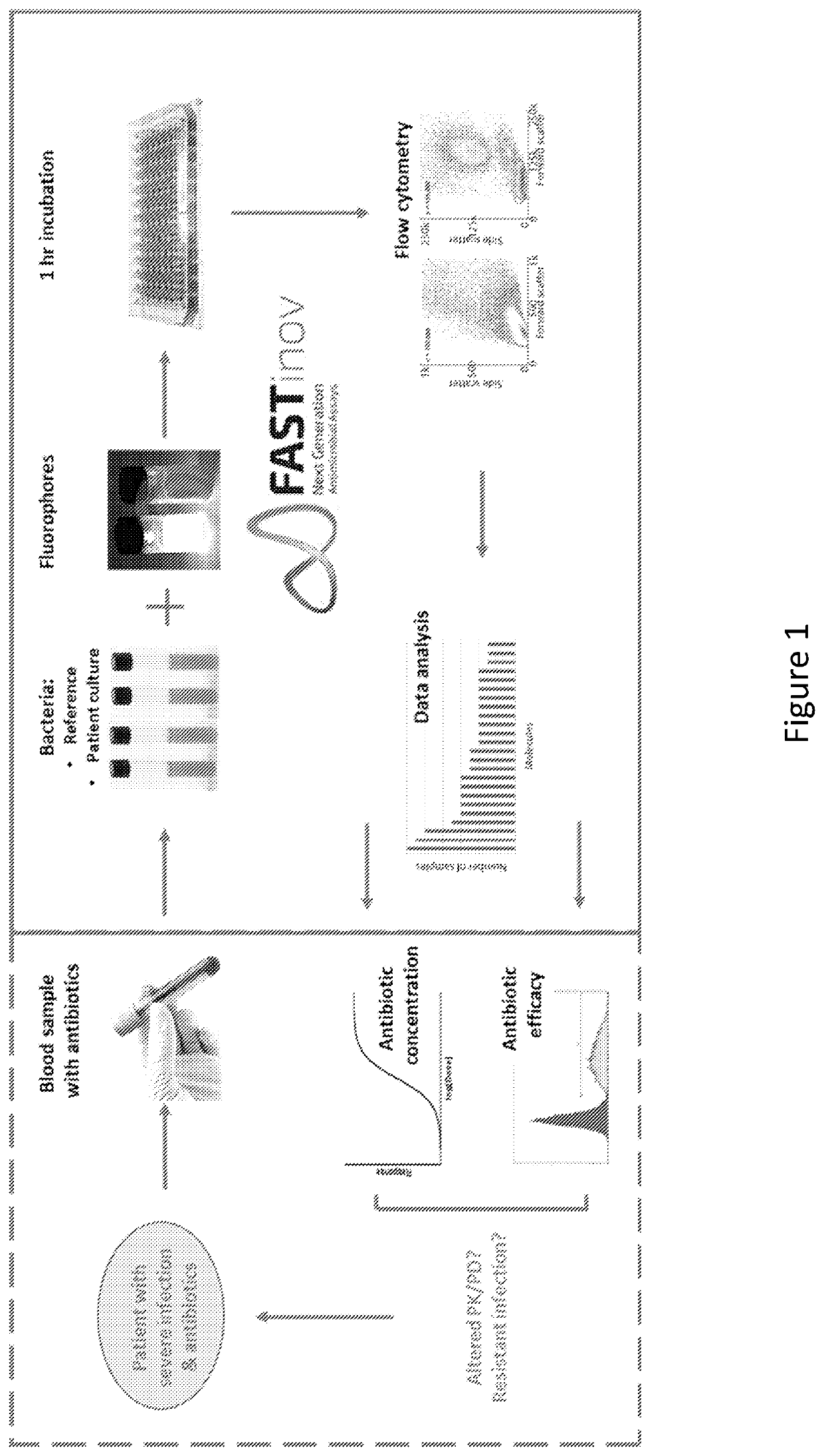
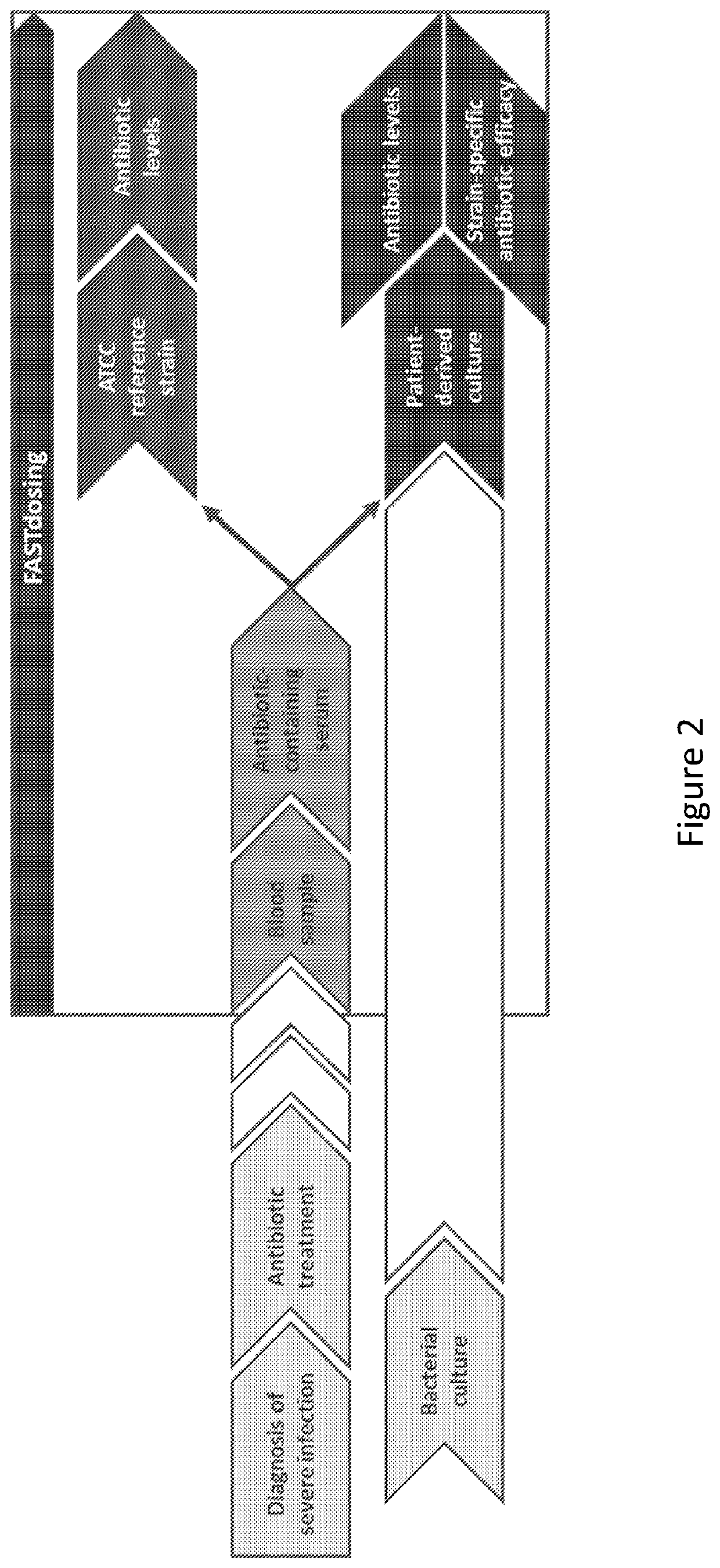
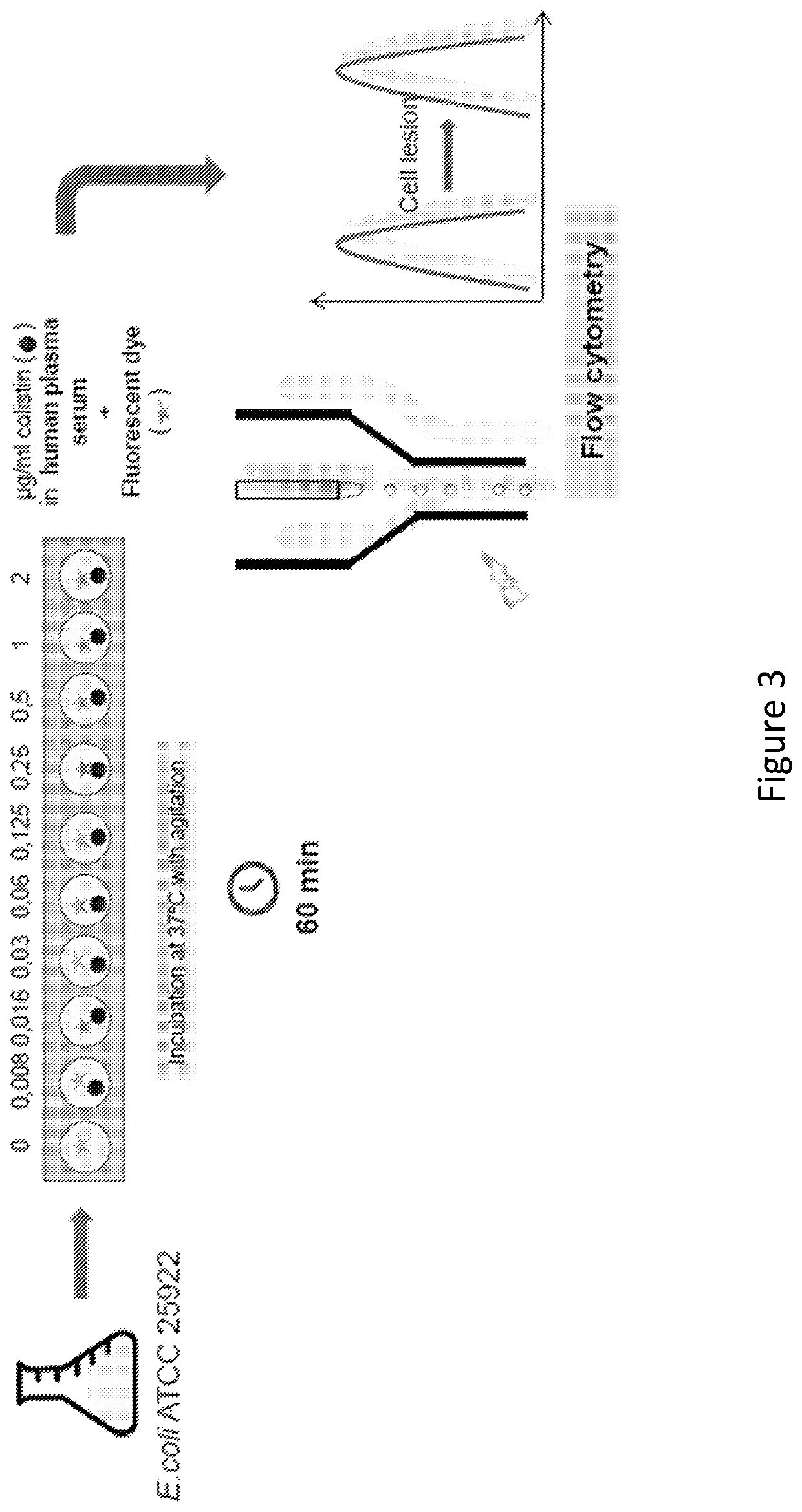
ActiveUS11485993B2Microbiological testing/measurementIndividual particle analysisMicrobial agentFluorophore
Disclosed herein are methods and compositions for antimicrobial quantification and functional measurement. In one aspect, a method for quantifying antimicrobial comprises: obtaining a biological sample from a patient receiving an antimicrobial; incubating the biological sample with a reference microbial strain and a fluorophore for detecting cell lesion; measuring a first signal of fluorescent intensity in the incubated biological sample using flow cytometry; and comparing the first signal to a calibrating curve previously generated for the antimicrobial, thereby quantifying the antimicrobial present in the biological sample.
Owner:FASTINOV SA
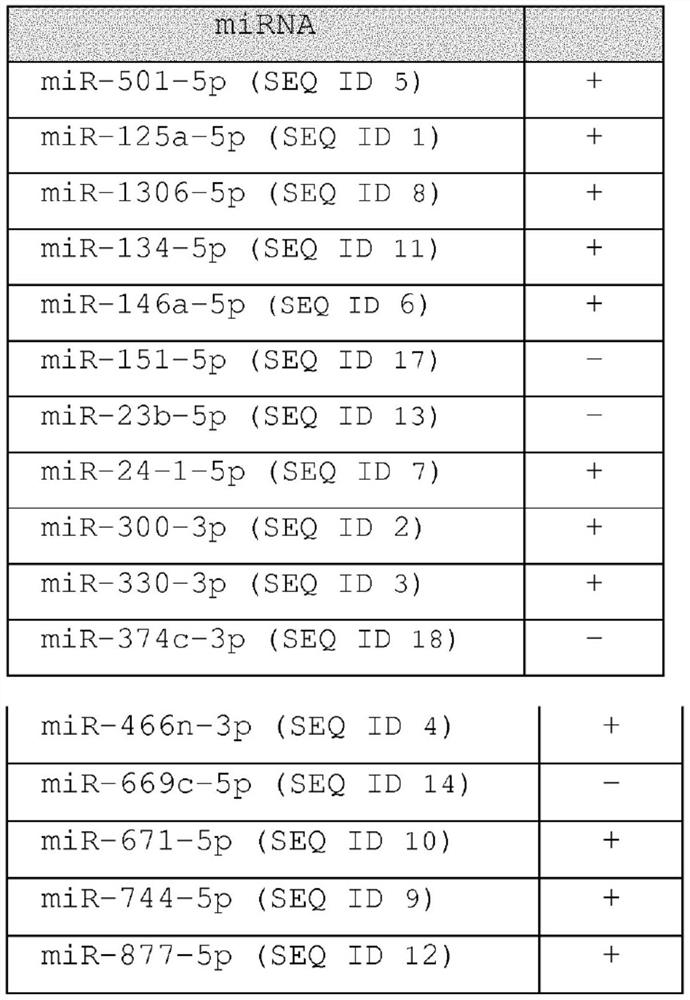
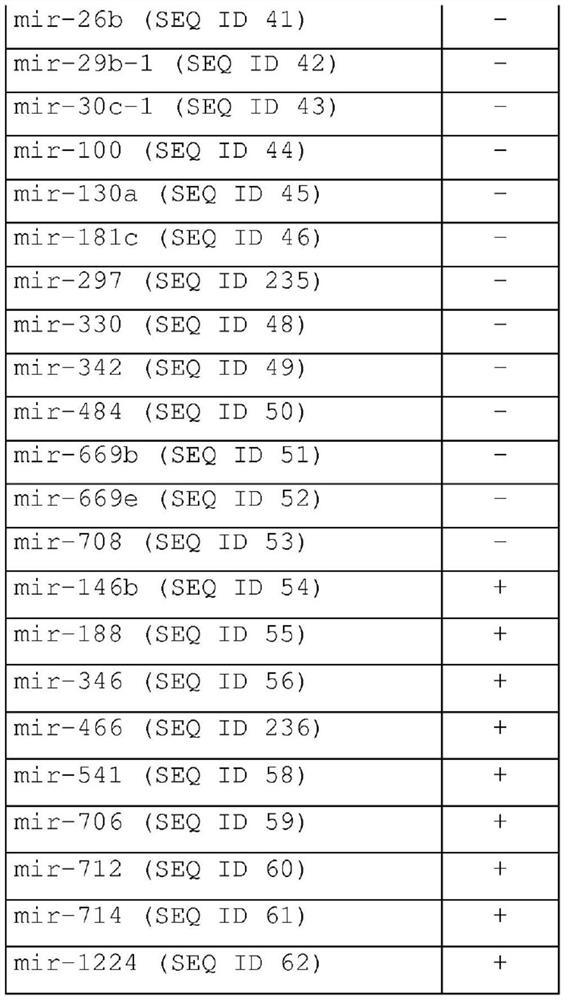
Methods for diagnosing, prognosing and therapeutically monitoring neurological, neurodegenerative and inflammatory based diseases comprising microRNA-based microglia microvesicles
ActiveCN108463561BMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNeuro-degenerative diseaseMicroRNA
Owner:BRAINDTECH SRL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com