Patents
Literature
194 results about "Computer aided detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
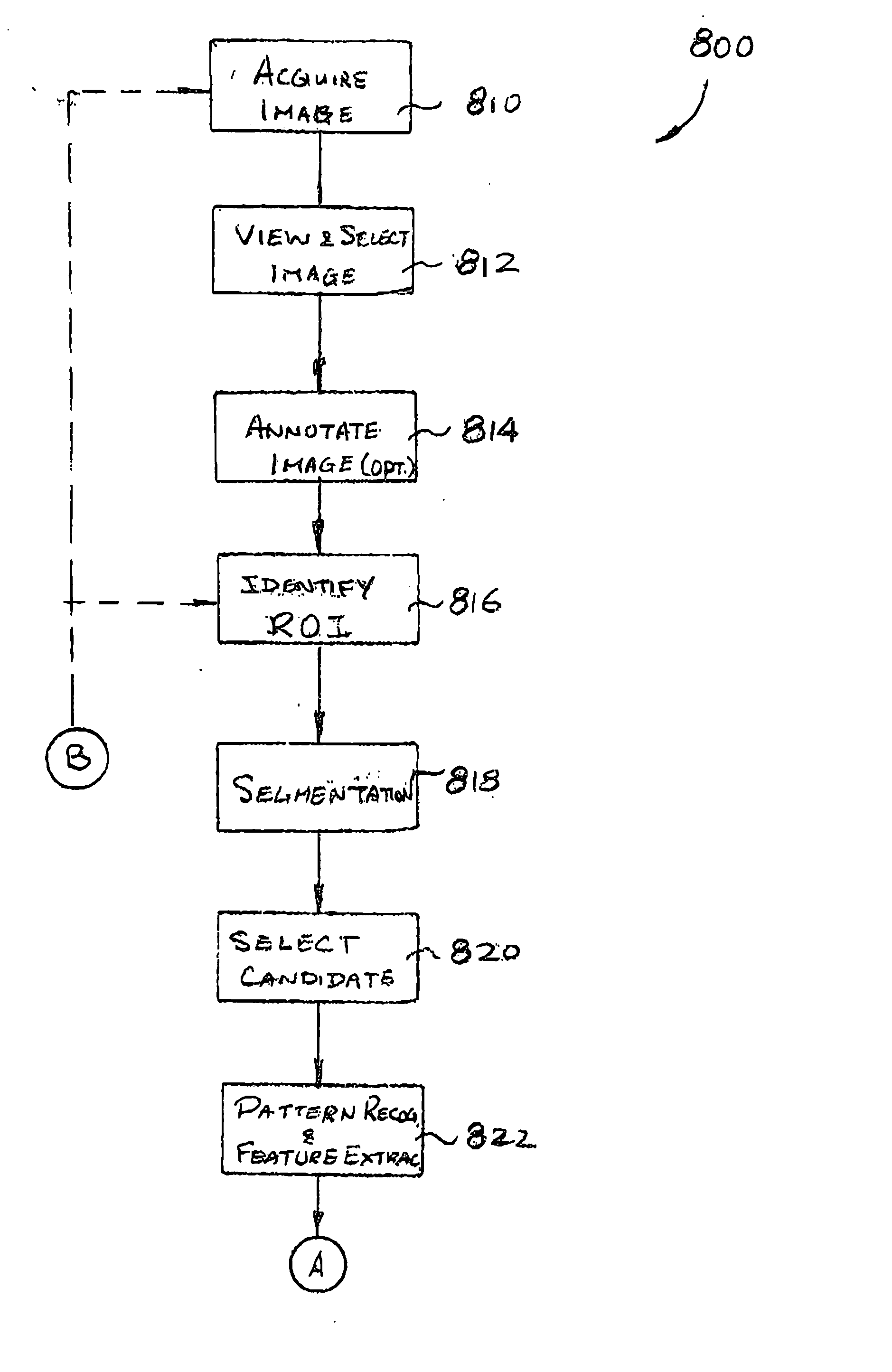
Computer-Aided Detection (CAD), which is becoming more widely used as an adjunct technology to conventional mammography, improves cancer detection by automatically locating and highlighting regions of concern through digital analysis of conventional mammograms.
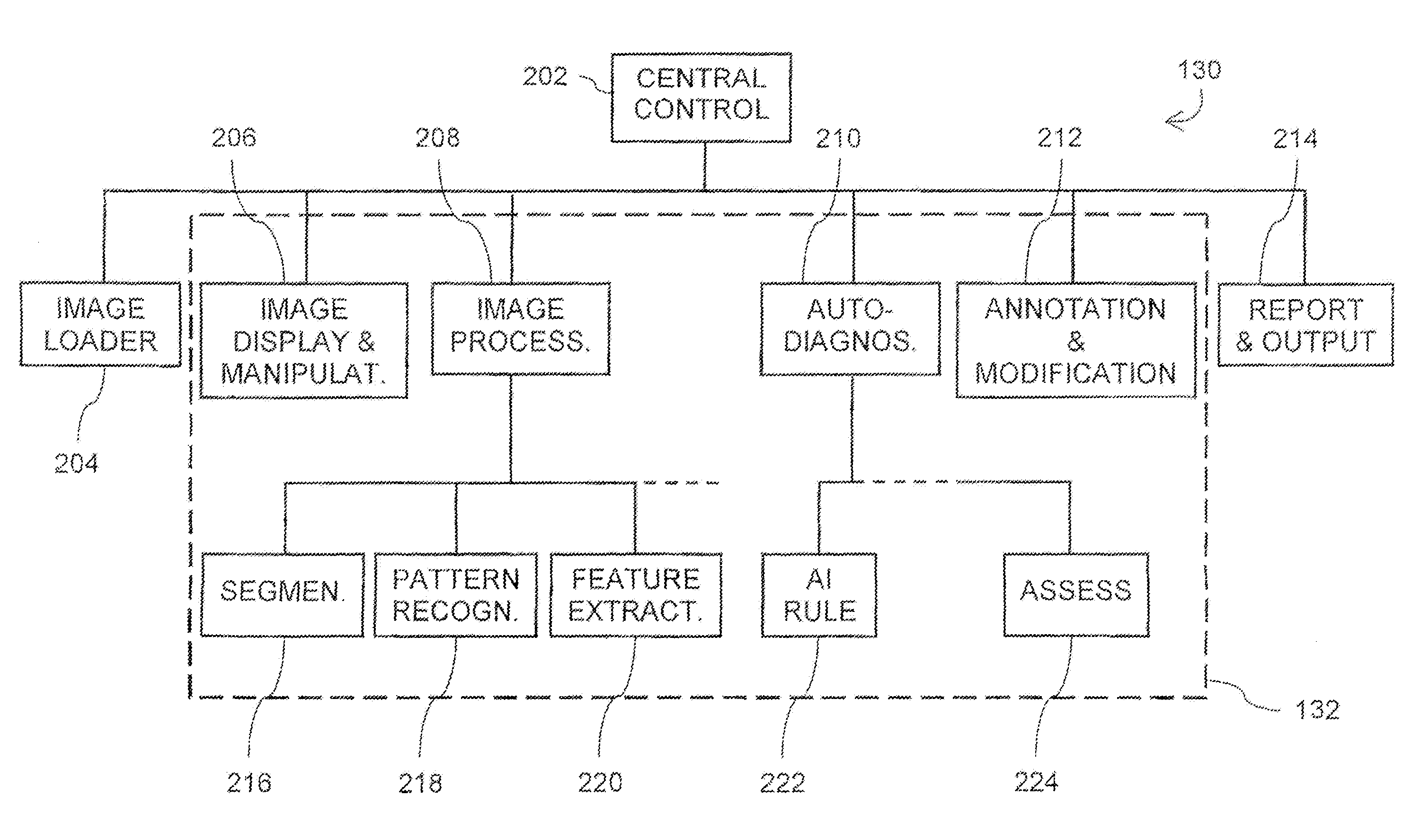
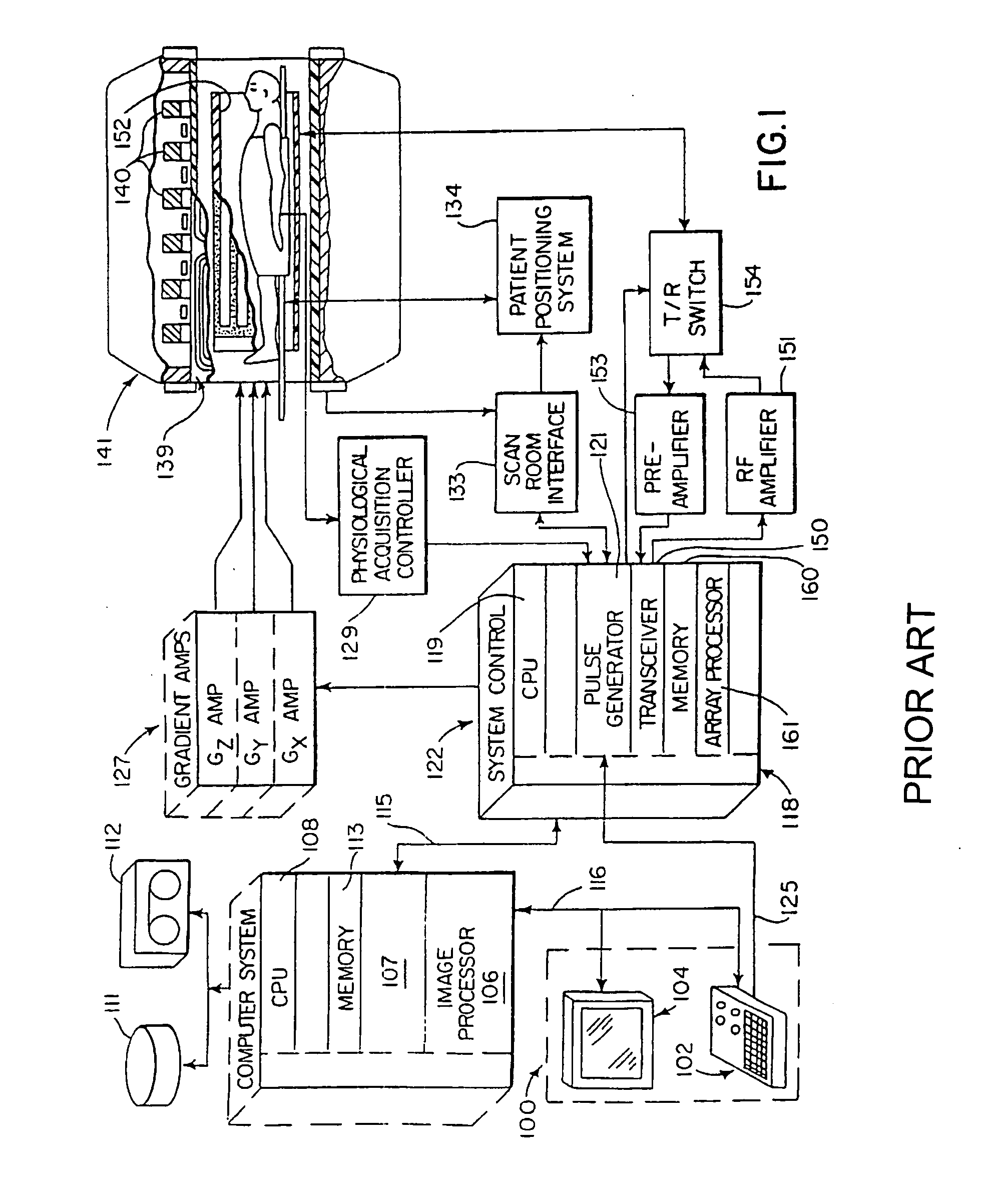
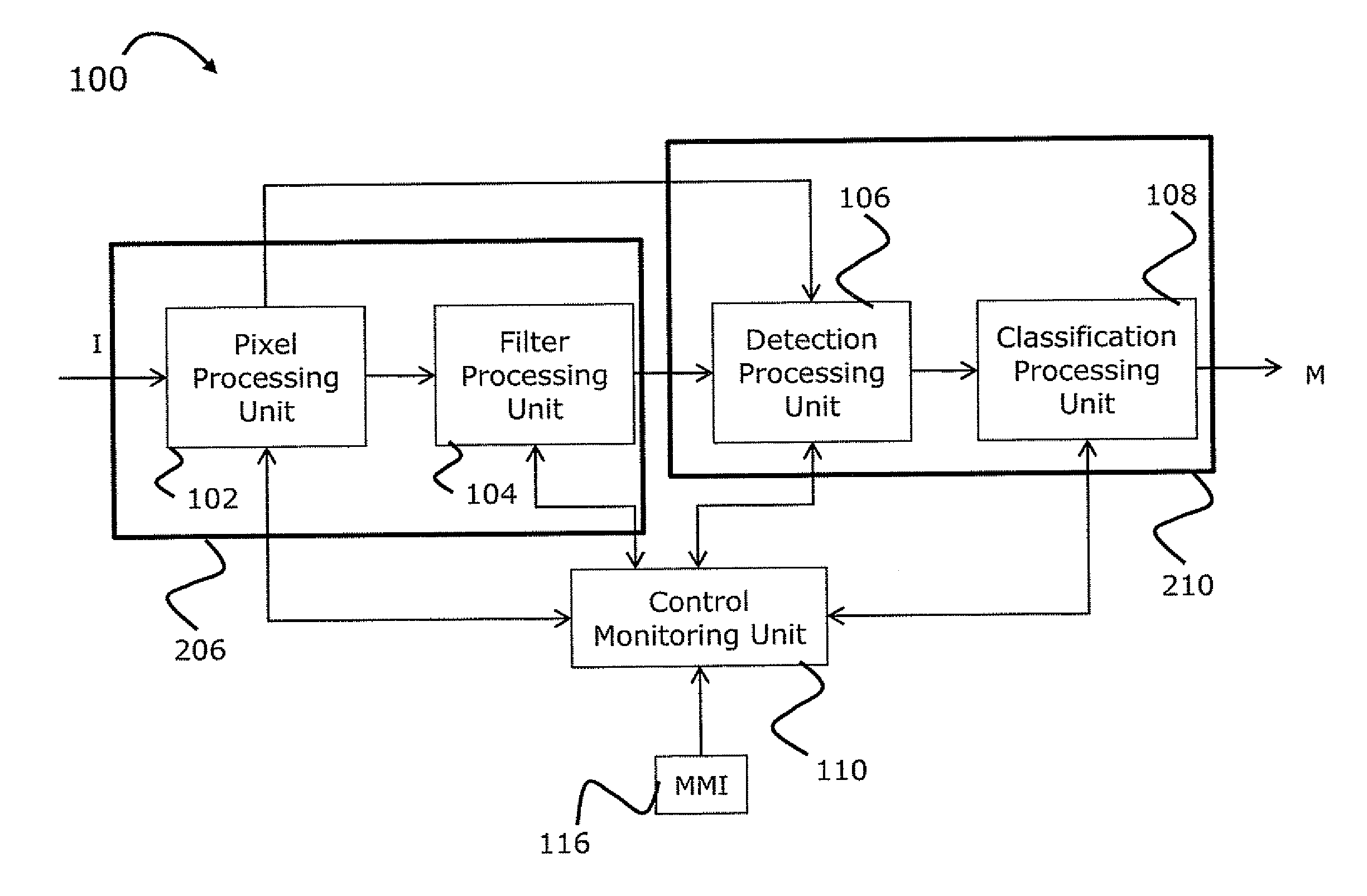
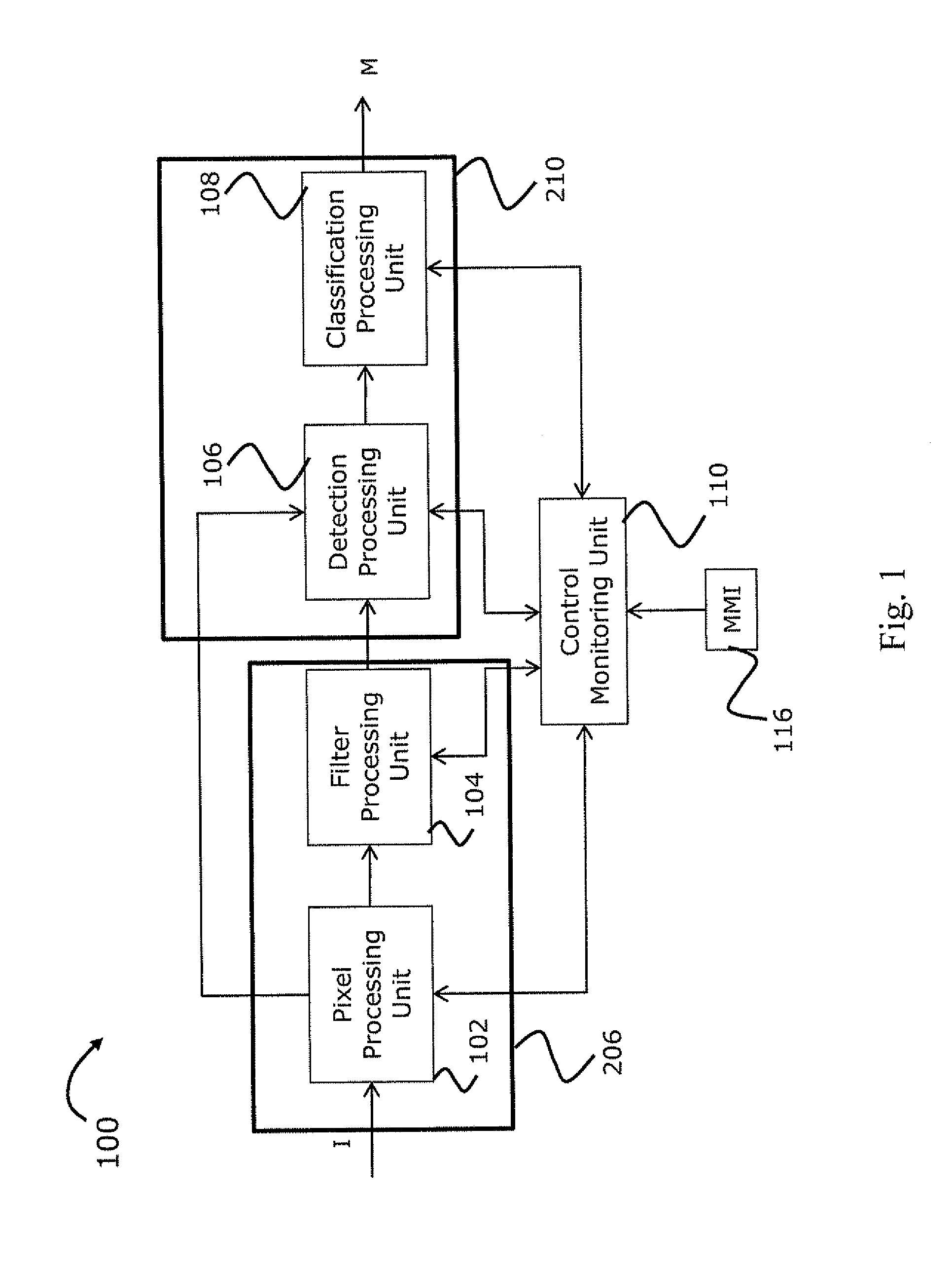
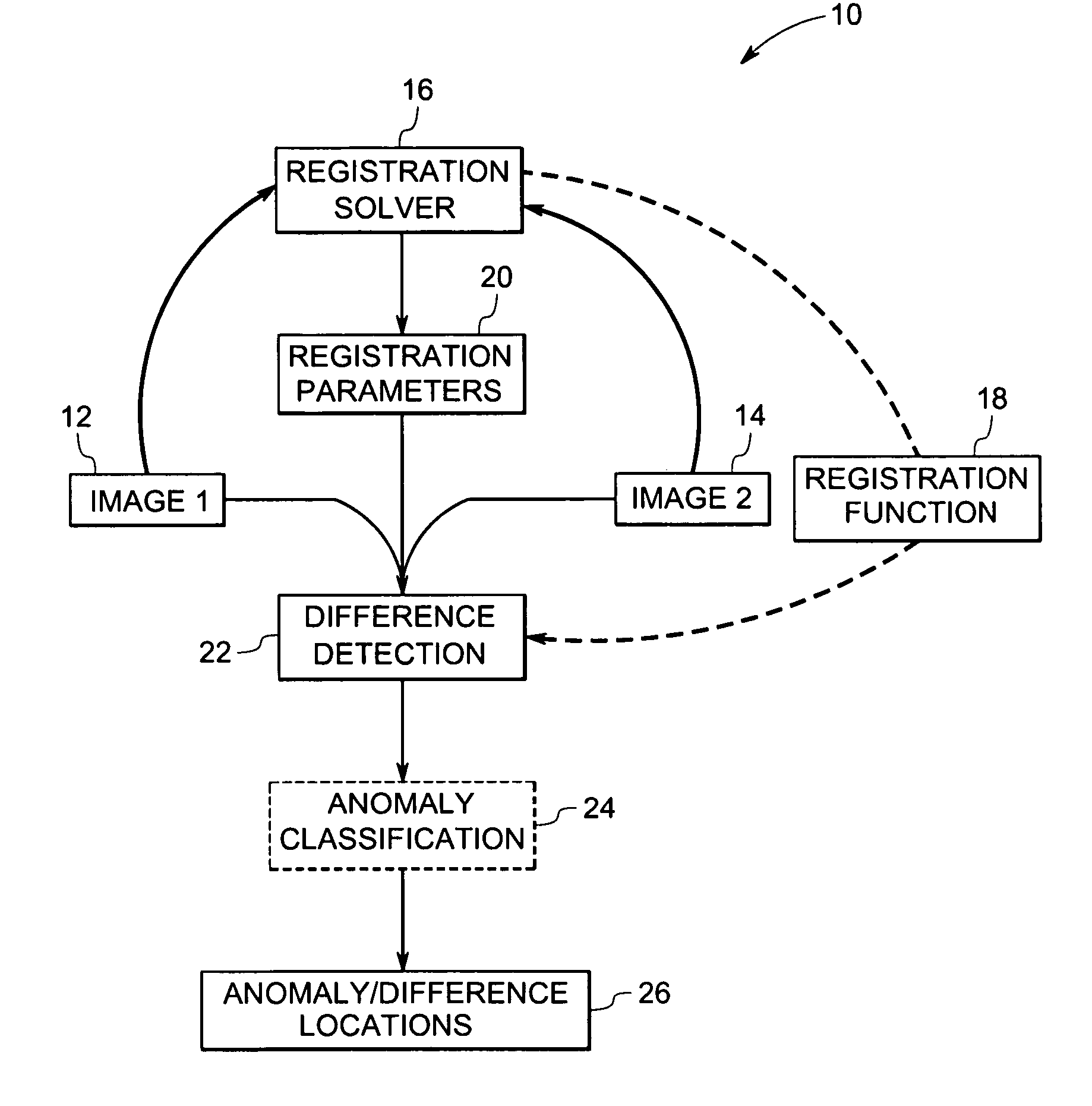
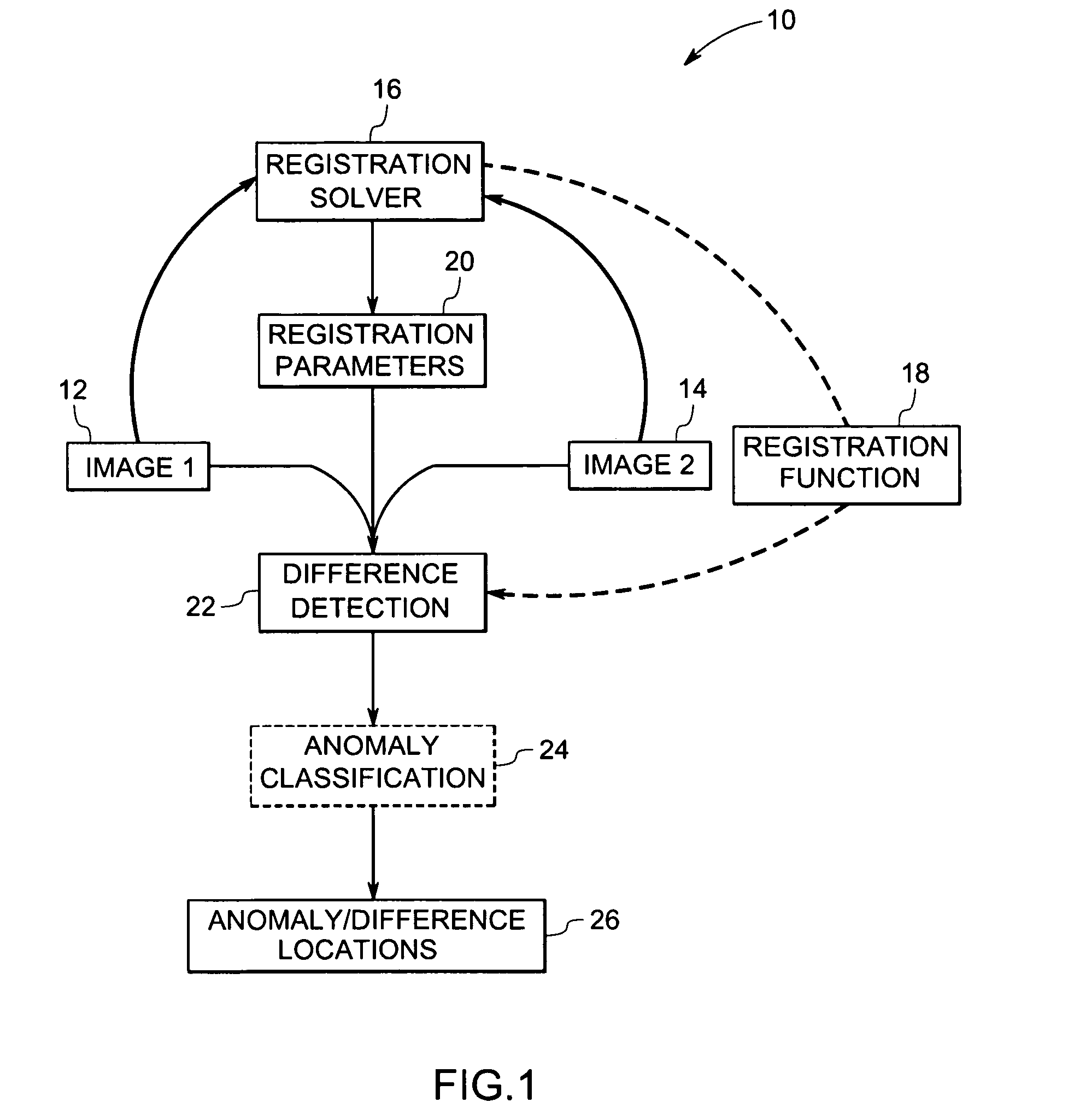
System and method of computer-aided detection
ActiveUS20060274928A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementPattern recognitionComputer-aided
The invention provides a system and method for computer-aided detection (“CAD”). The invention relates to computer-aided automatic detection of abnormalities in and analysis of medical images. Medical images are analyzed, to extract and identify a set of features in the image relevant to a diagnosis. The system computes an initial diagnosis based on the set of identified features and a diagnosis model, which are provided to a user for review and modification. A computed diagnosis is dynamically re-computed upon user modification of the set of identified features. Upon a user selecting a diagnosis based on system recommendation, a diagnosis report is generated reflecting features present in the medical image as validated by the user and the user selected diagnosis.
Owner:THE MEDIPATTERN CORP +1
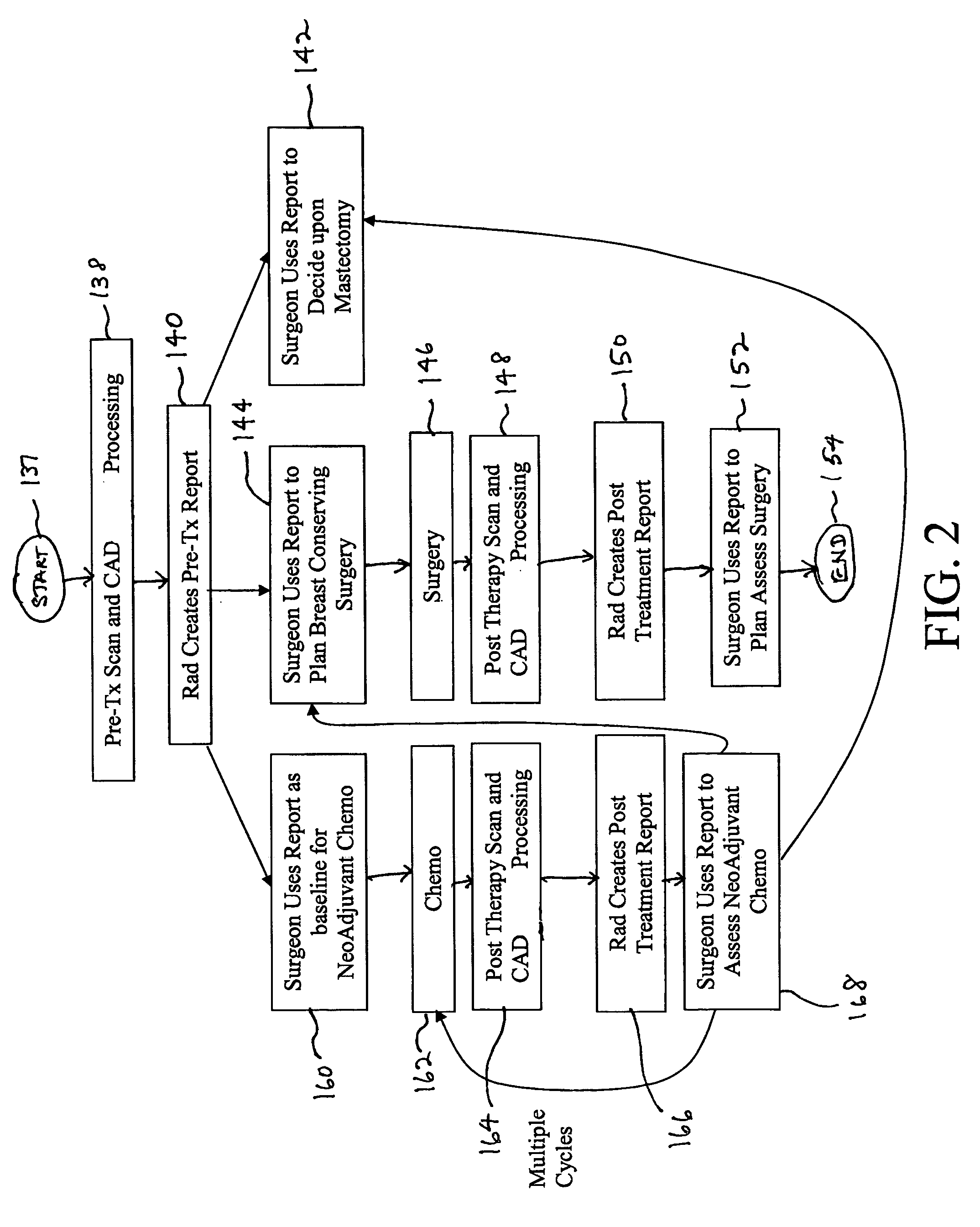
Apparatus and method for surgical planning and treatment monitoring
A system for surgical planning and therapeutic monitoring utilizes imaging data and computer-aided detection (CAD) technology to identify cancerous tumors. A pre-treatment report identifies all volumes of interest (VOIs) and provides data regarding the size and location of each VOI as well as volumetric data for use in surgical planning. The system can be used to monitor the progress of adjuvant chemotherapy or other non-surgical treatment and measures changes in tumor size and location. Post-treatment reports provide data regarding changes in tumor size and location as well as trend data to provide guidance to the physician.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP +1
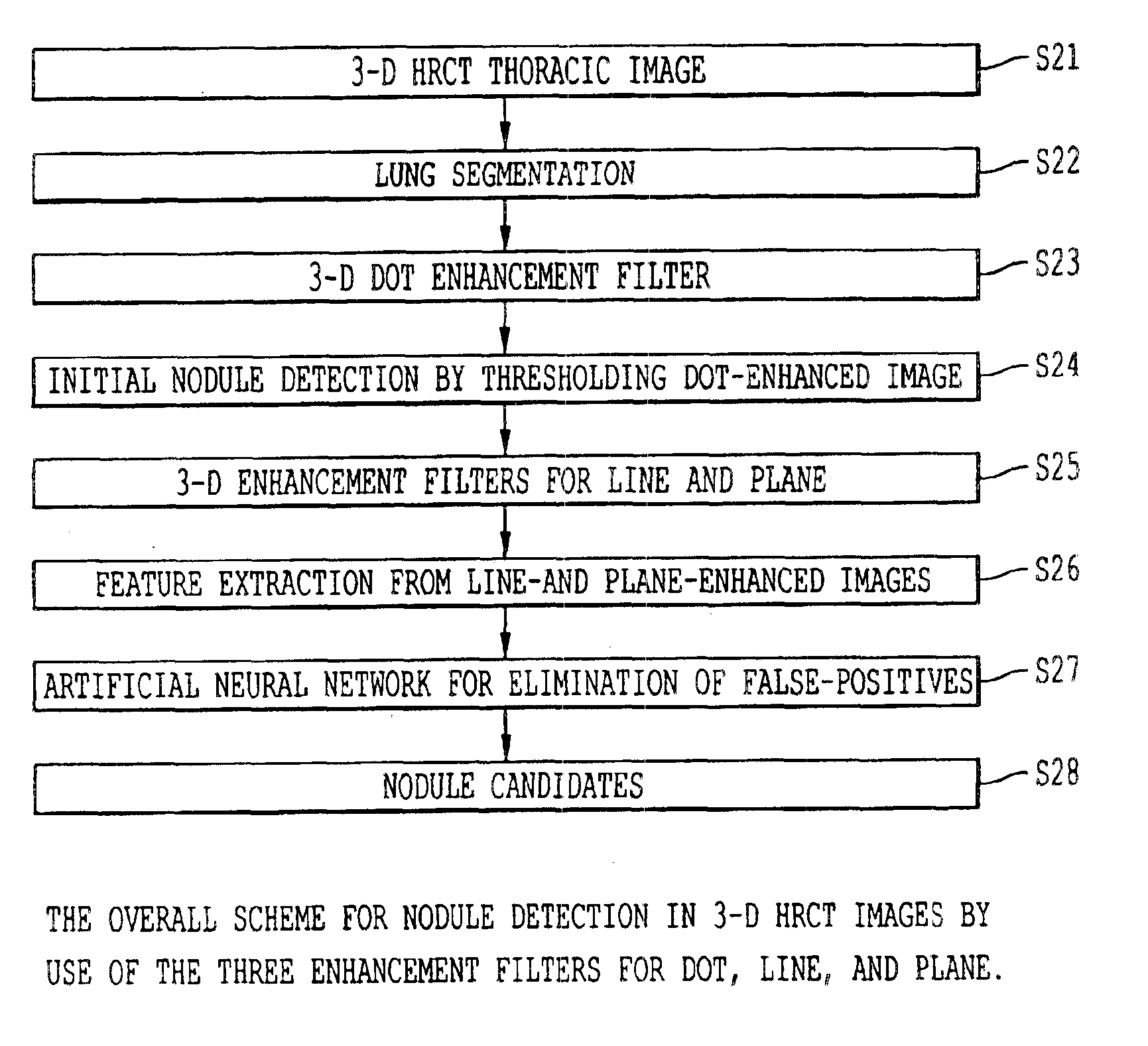
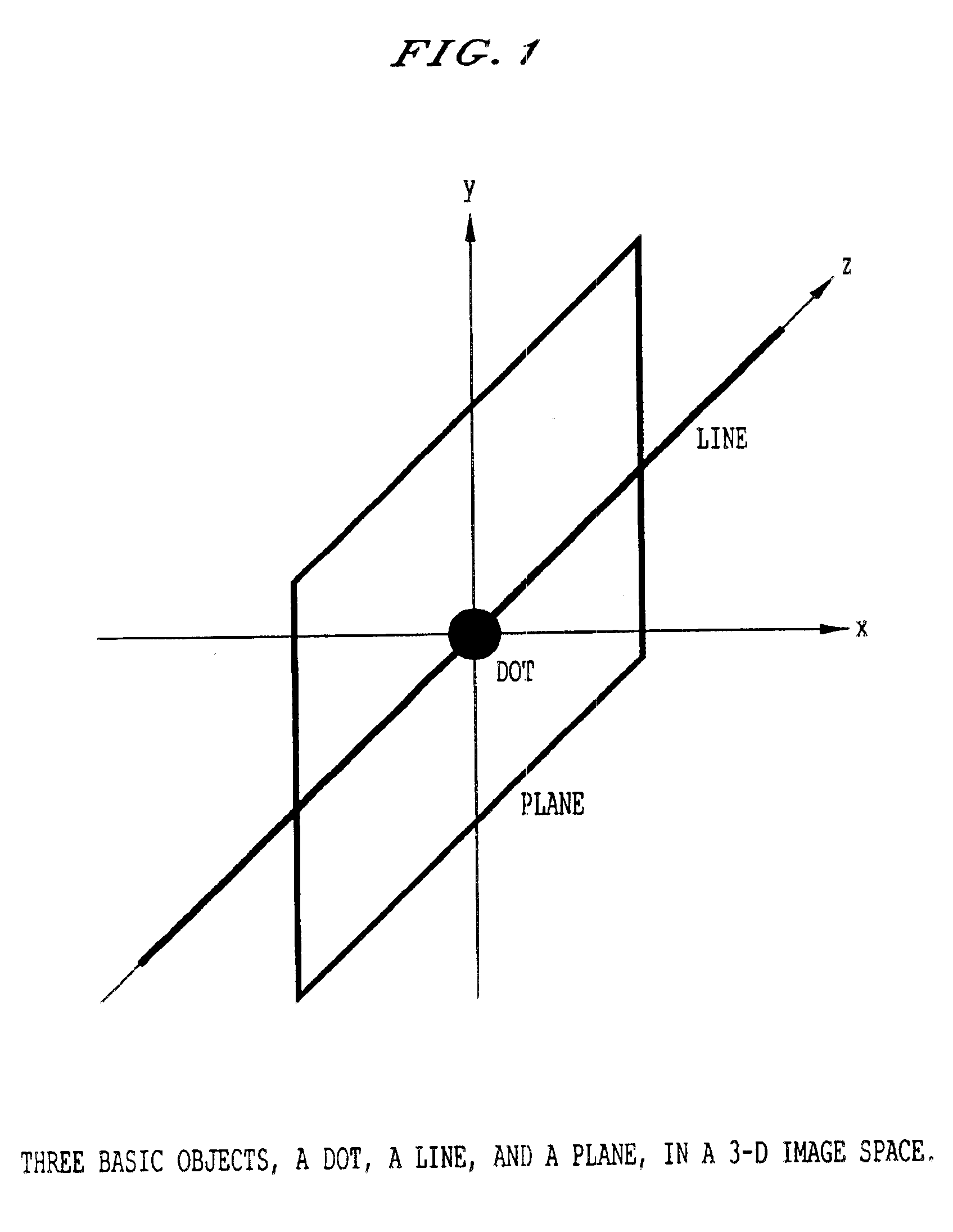
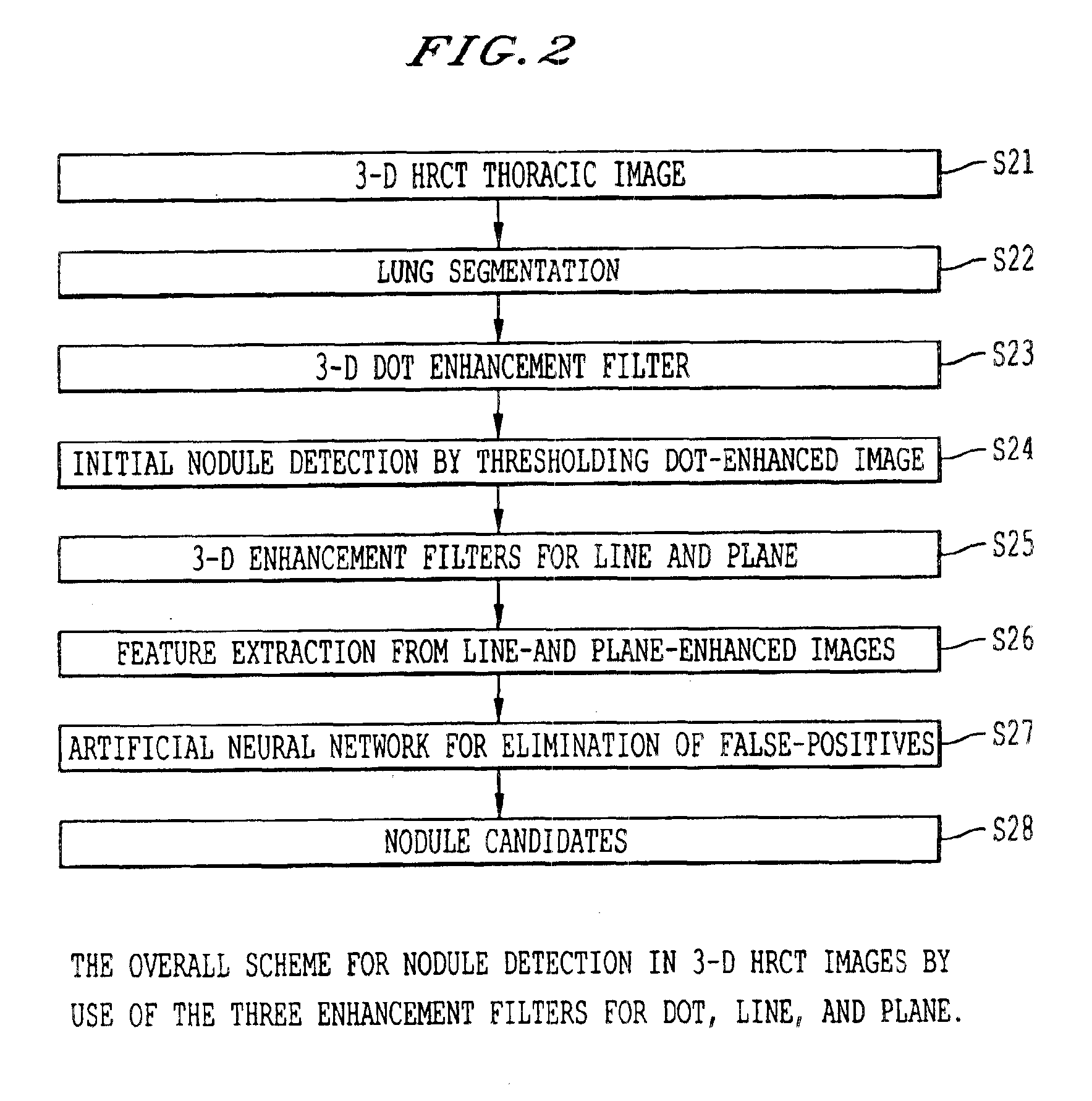
Method, system, and computer program product for computer-aided detection of nodules with three dimensional shape enhancement filters
InactiveUS6937776B2High sensitivityStrong specificityImage enhancementImage analysisThree dimensional shapeComputer science
A method, system, and computer program product for evaluating an image including an object, including filtering image data derived from the image with a first geometric enhancement filter having magnitude and likelihood filter components so as to produce first filtered image data in which a first geometric pattern is enhanced. Thereafter the filtered image data can be subjected to processing to derive a measure indicative of the presence of the object in the image, including determining a region of interest in the image, extracting at least one feature from the first filtered image data from within the region of interest, and applying the at least one extracted feature to a classifier configured to output the measure indicative of the presence of the object in the image. The image data can also be subjected to filtering with second and / or third geometric filters which enhance different geometric patterns, and which produce respective filtered data which are also processed to derive the measure indicative of the presence of the object.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
System and method of computer-aided detection
ActiveUS7783094B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementPattern recognitionComputer aid
The invention provides a system and method for computer-aided detection (“CAD”). The invention relates to computer-aided automatic detection of abnormalities in and analysis of medical images. Medical images are analyzed, to extract and identify a set of features in the image relevant to a diagnosis. The system computes an initial diagnosis based on the set of identified features and a diagnosis model, which are provided to a user for review and modification. A computed diagnosis is dynamically re-computed upon user modification of the set of identified features. Upon a user selecting a diagnosis based on system recommendation, a diagnosis report is generated reflecting features present in the medical image as validated by the user and the user selected diagnosis.
Owner:THE MEDIPATTERN CORP +1
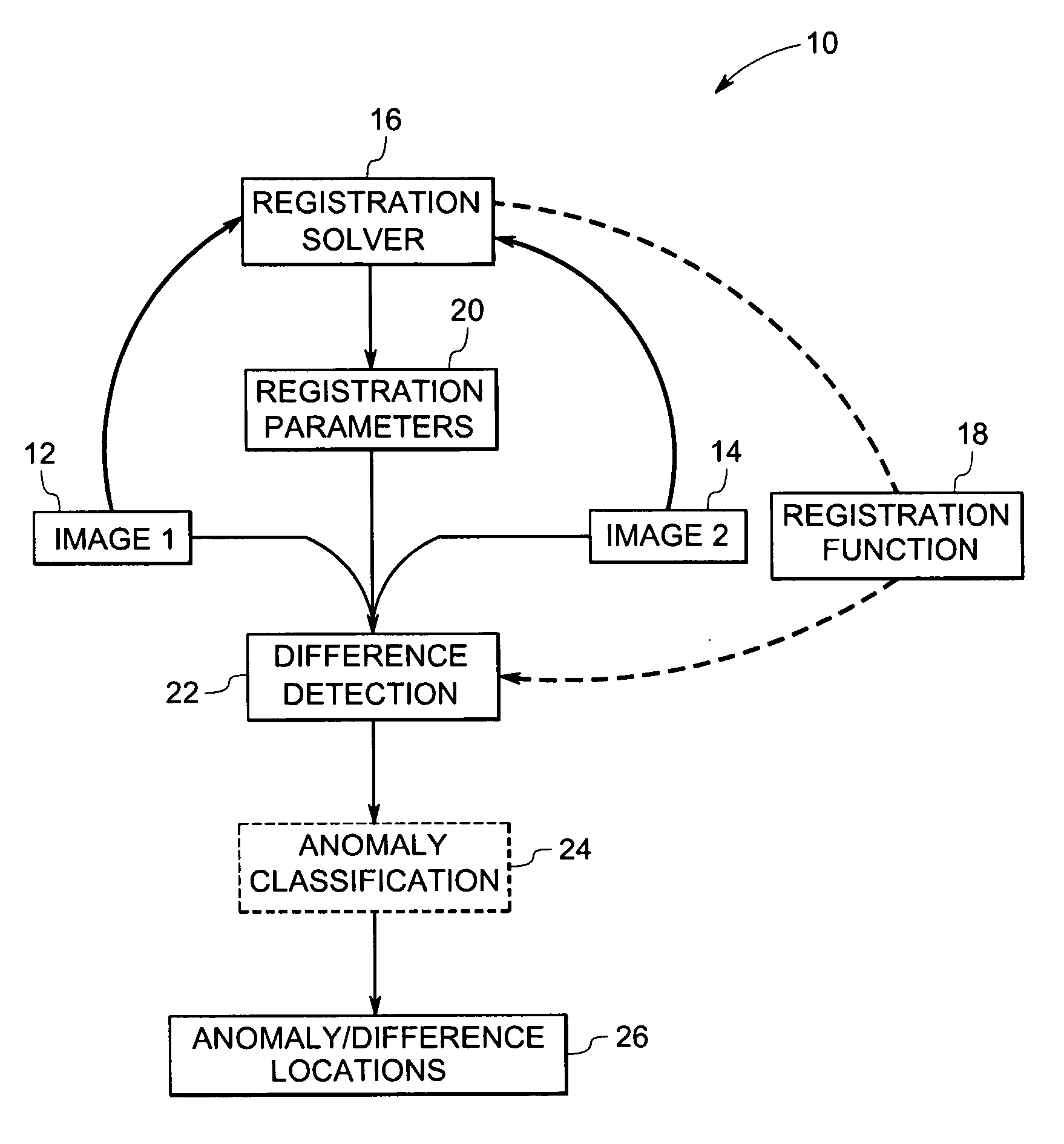
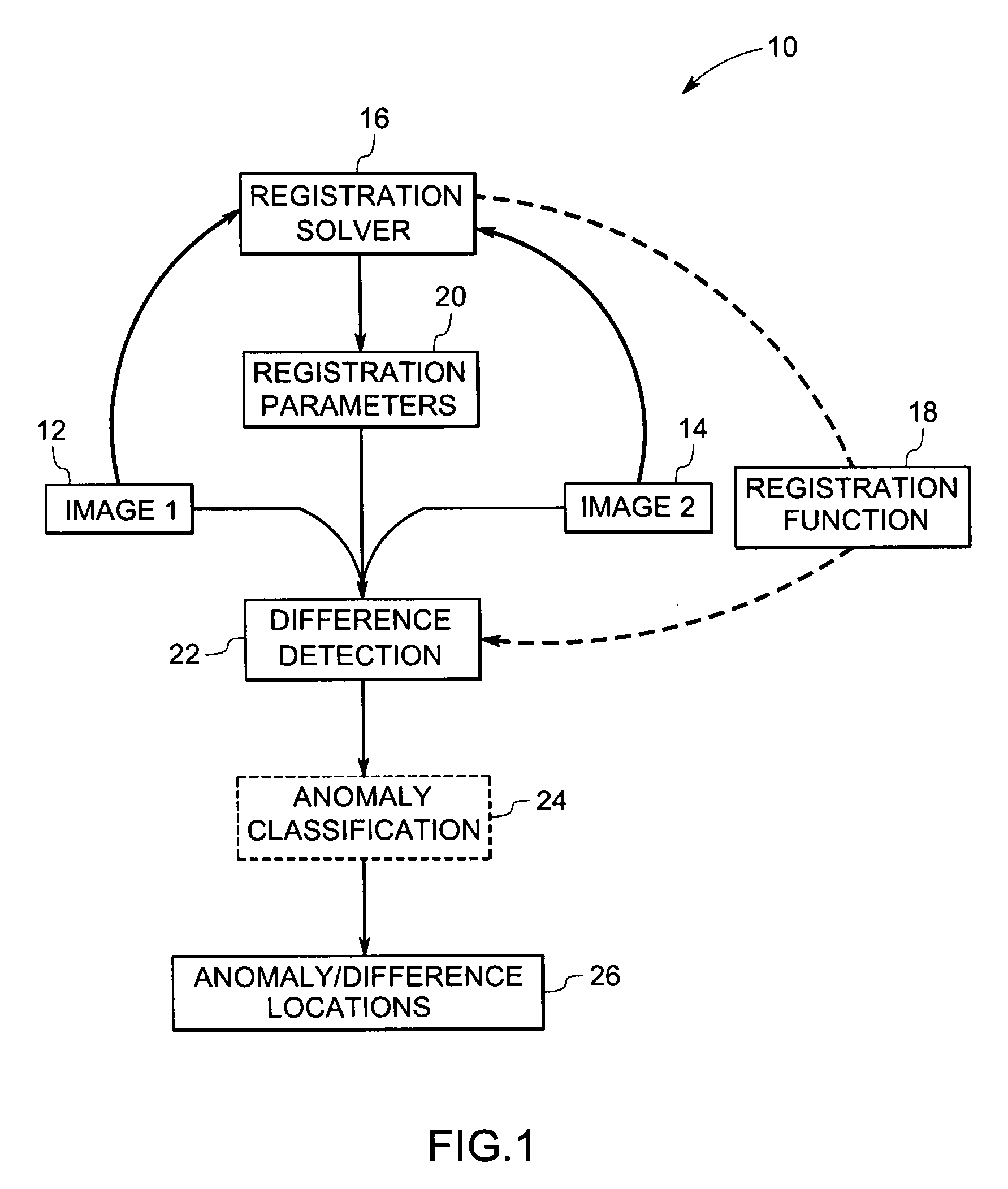
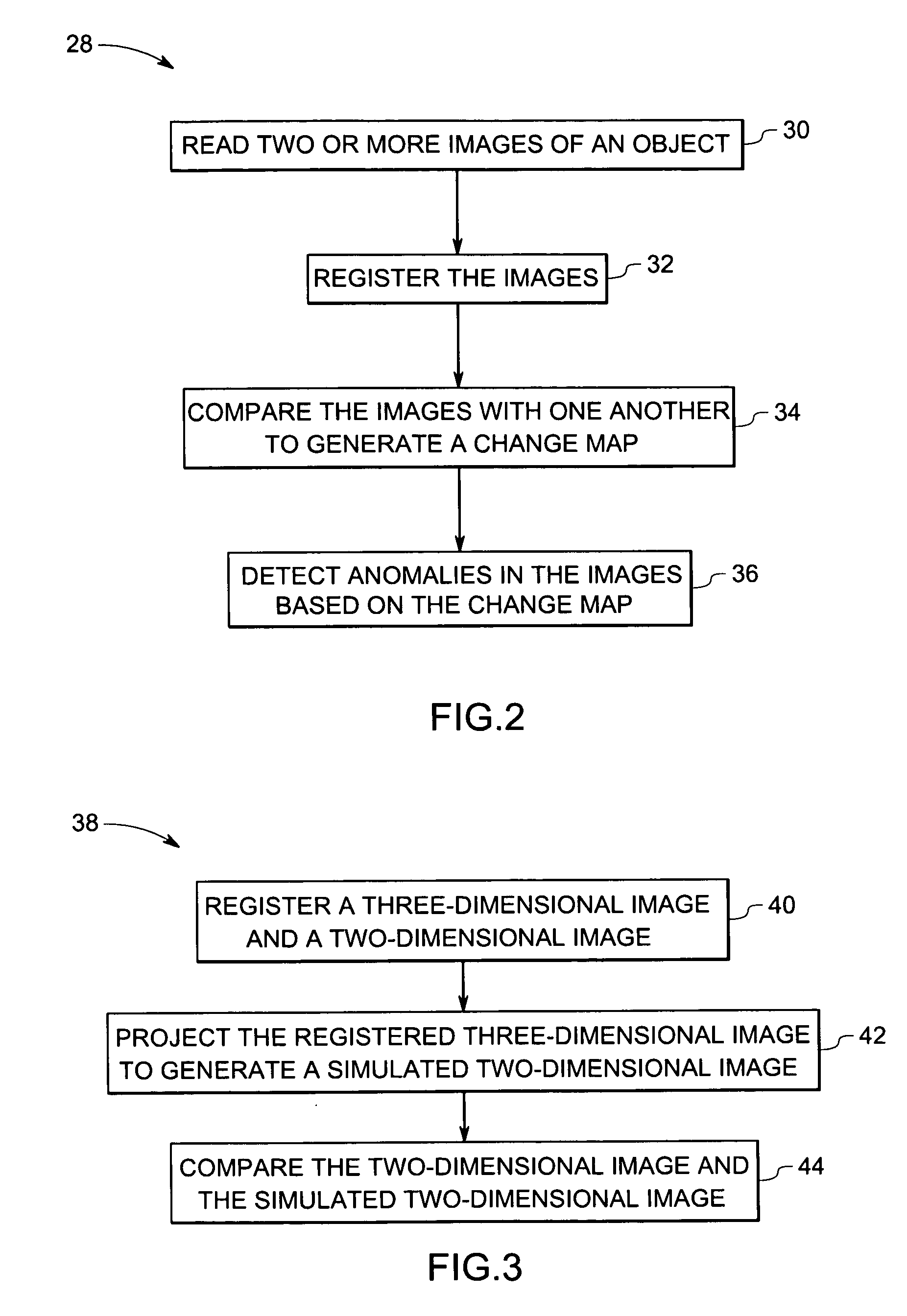
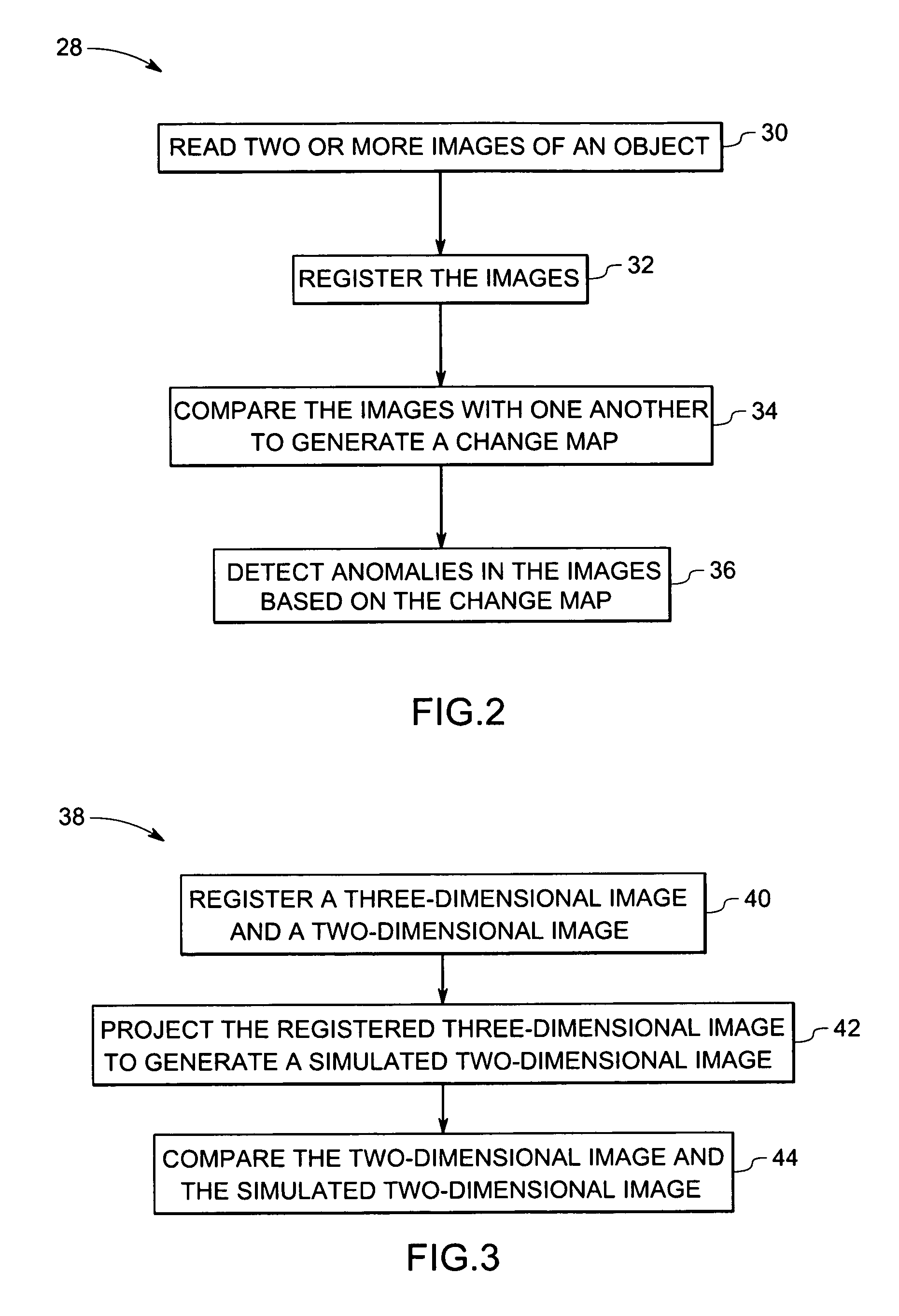
Method and system for volumetric comparative image analysis and diagnosis
ActiveUS20070003117A1Automatic detectionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging analysis
A technique is provided for comparative image analysis and / or change detection using computer assisted detection and / or diagnosis (CAD) algorithms. The technique includes registering two or more images, comparing the images with one another to generate a change map, and detecting anomalies in the images based on the change map.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
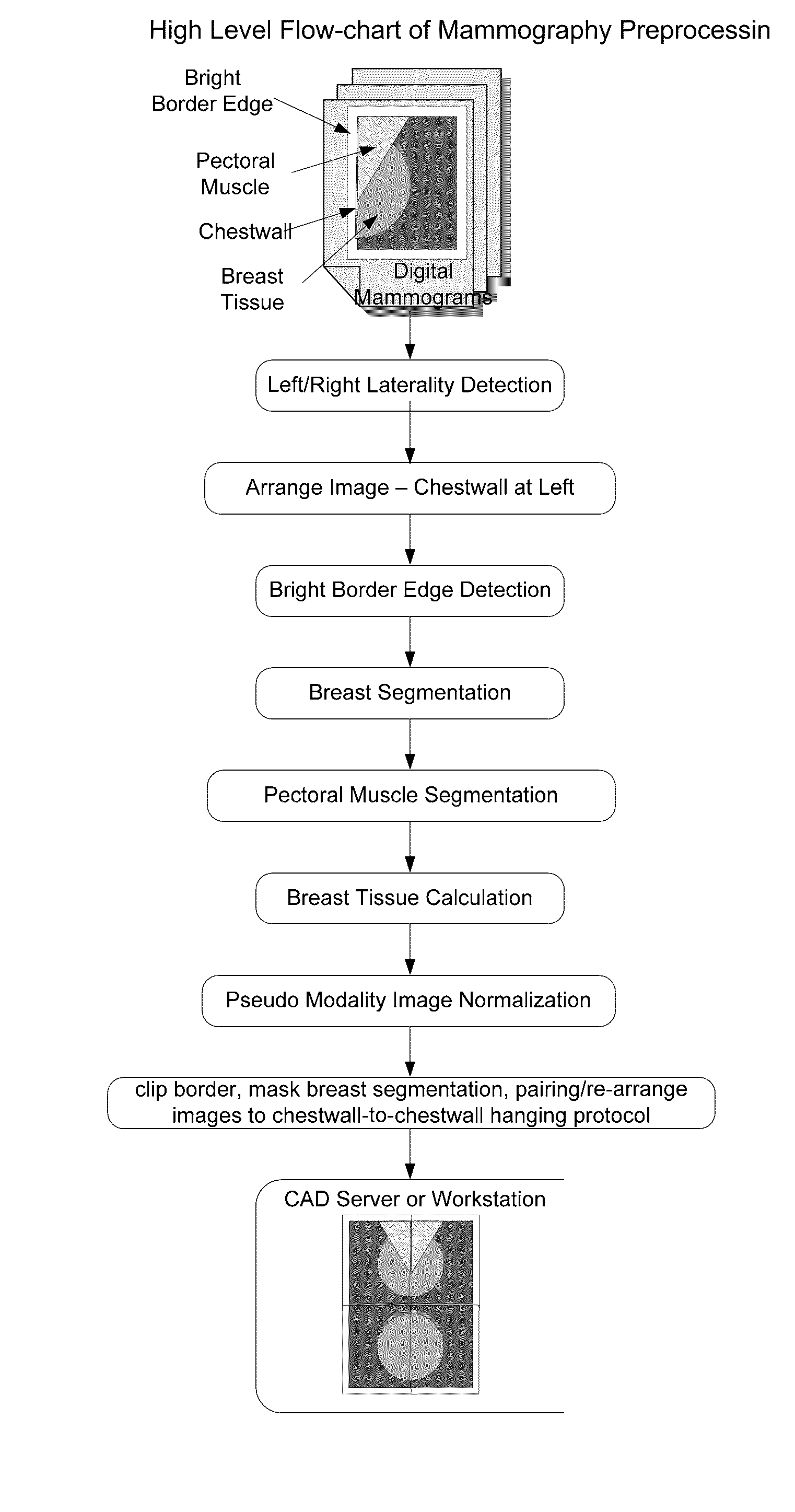
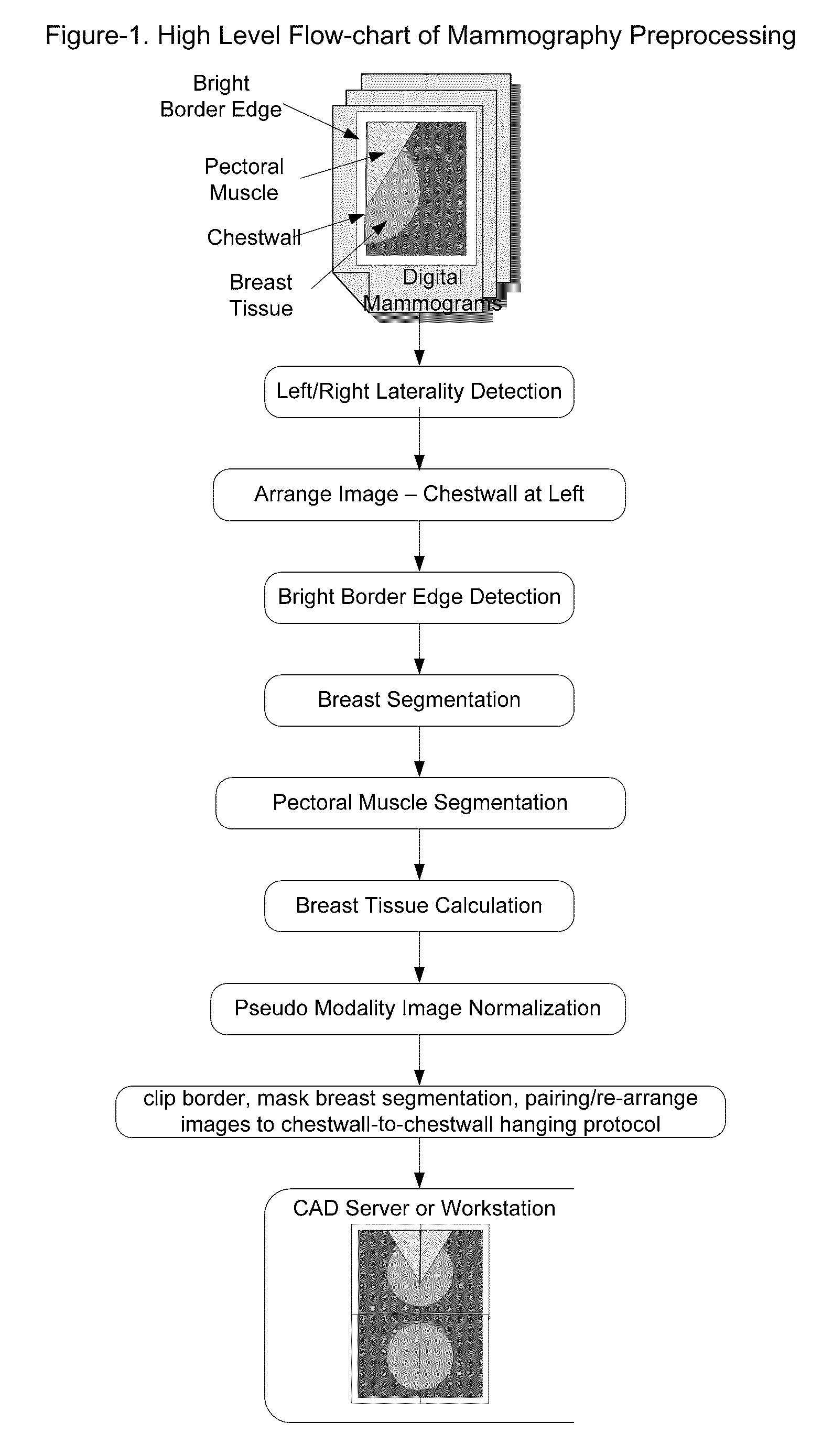
Fast preprocessing algorithms for digital mammography CAD and workstation
ActiveUS20090220138A1Faster and accurate segmentation algorithmAutomatic detectionImage enhancementImage analysisDigital mammographyImage contrast
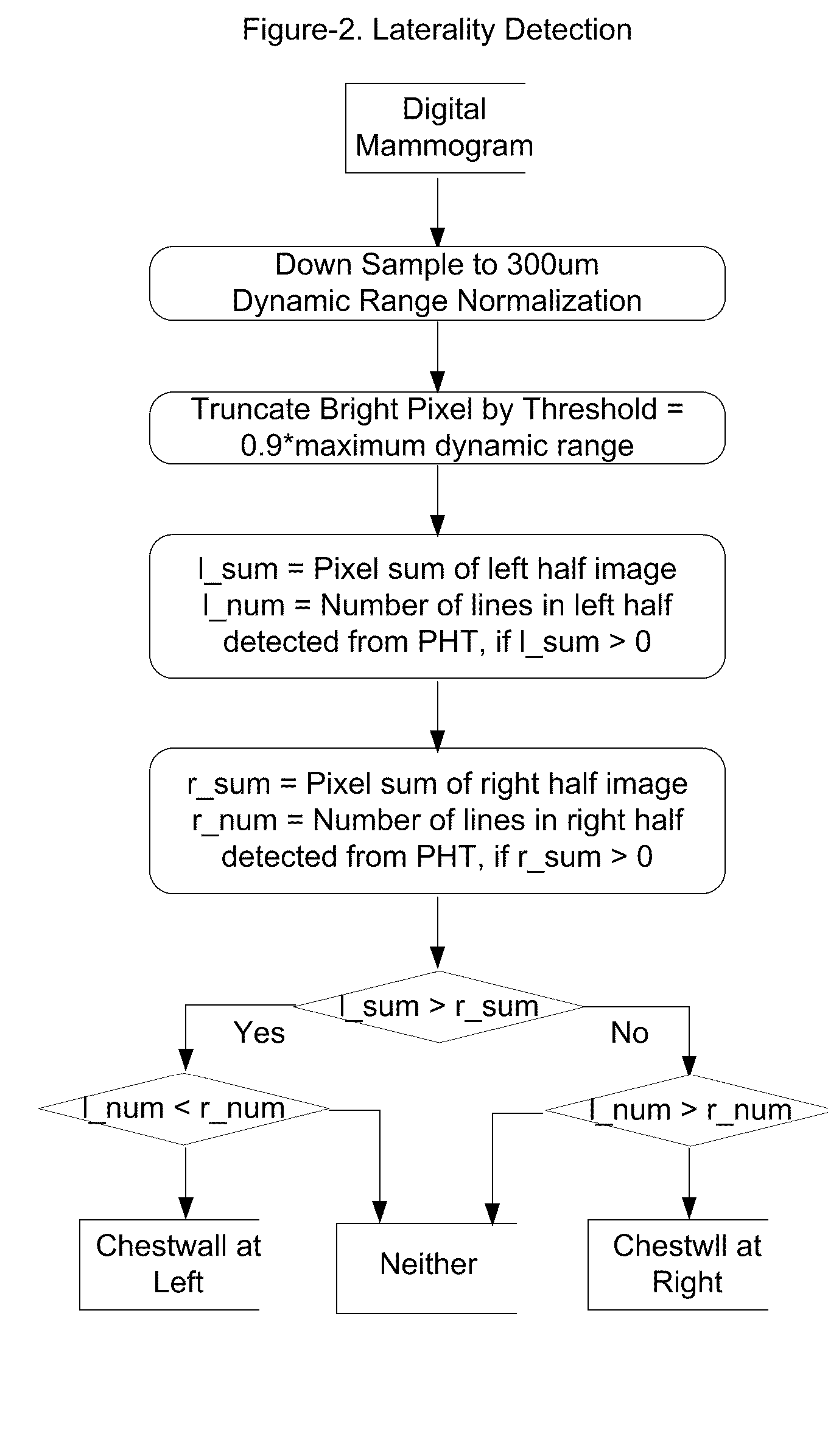
A method and apparatus are disclosed for an image preprocessing device that automatically detects chestwall laterality; removes border artifacts; and segments breast tissue and pectoral muscle from digital mammograms. The algorithms in the preprocessing device utilize the computer cache, a vertical Sobel filter and a probabilistic Hough transform to detect curved edges. The preprocessing result, along with a pseudo-modality normalized image, can be used as input to a CAD (computer-aided detection) server or to a mammography image review workstation. In the case of workstation input, the preprocessing results improve the protocol for chestwall-to-chestwall image hanging, and support optimal image contrast display of each segmented region.
Owner:THREE PALM SOFTWARE
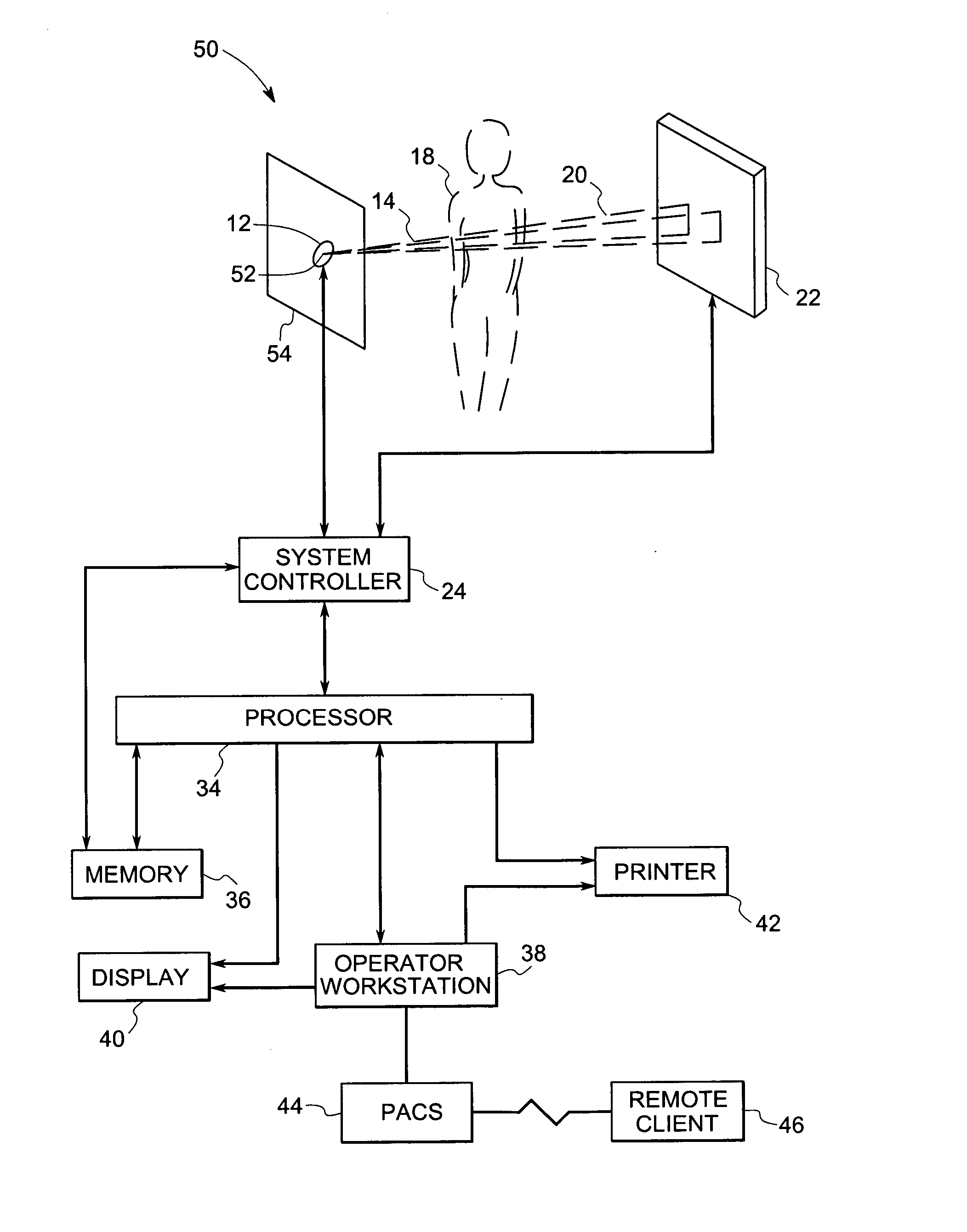
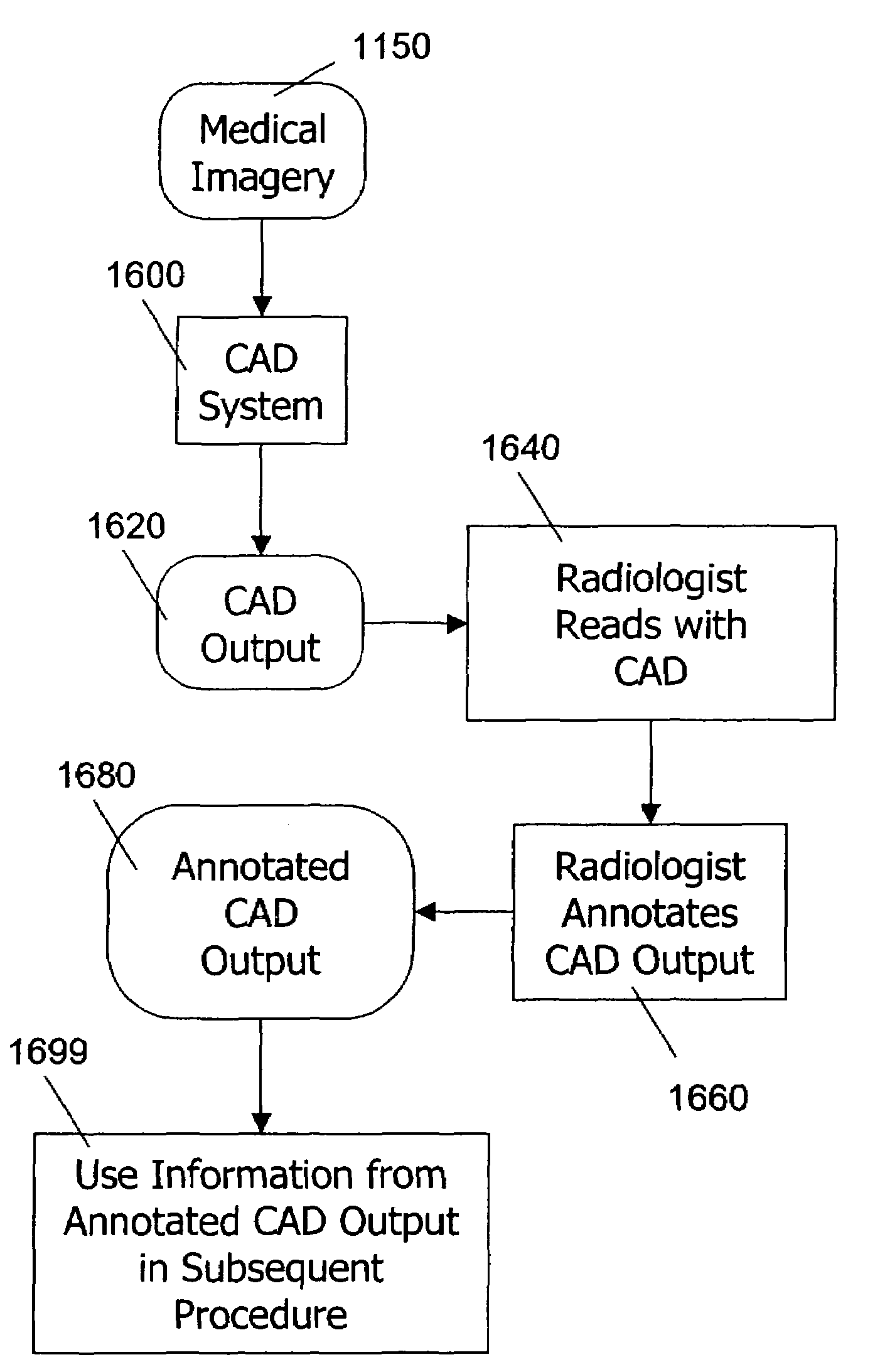
Use of computer-aided detection system outputs in clinical practice
InactiveUS6970587B1Accurate representationEfficient and precise positioningImage enhancementImage analysisDisplay deviceMinutiae
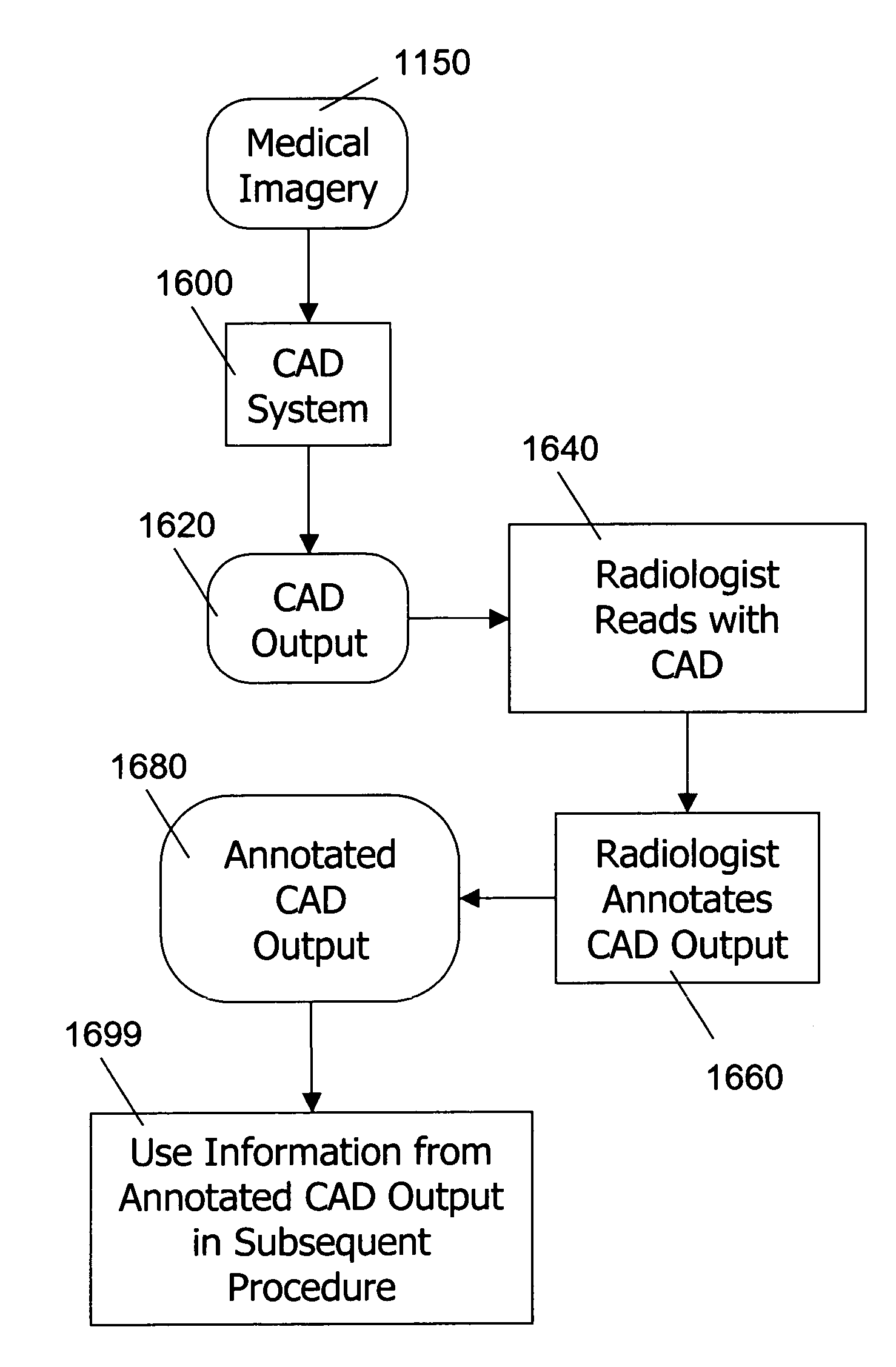
The present invention provides for the use of computer-aided detection (CAD) system output displays for providing accurate representations of areas for subsequent exams. Since the CAD output, unlike the original medical imagery, is not used during the initial reading, the radiologist does not mark it until a final determination is reached regarding subsequent procedures. Additionally, since the CAD output contains versions of the original imagery, the regions indicated by the radiologist are shown in the context of the particular anatomical detail for the given patient. This detail assists the technologist in more efficiently and accurately locating the exact area for subsequent exams.
Owner:ICAD INC
Computer Aided Detection Of Abnormalities In Volumetric Breast Ultrasound Scans And User Interface
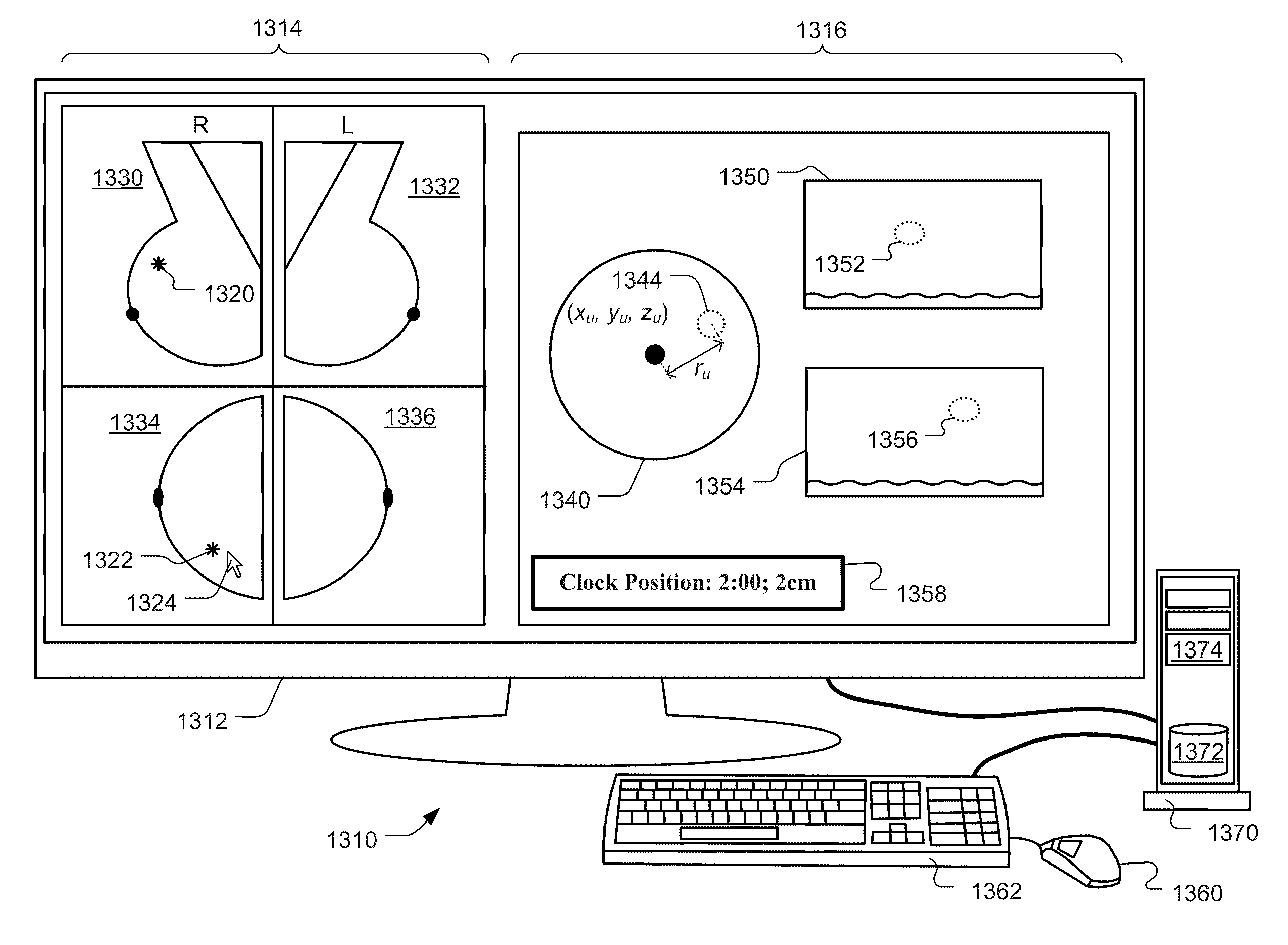
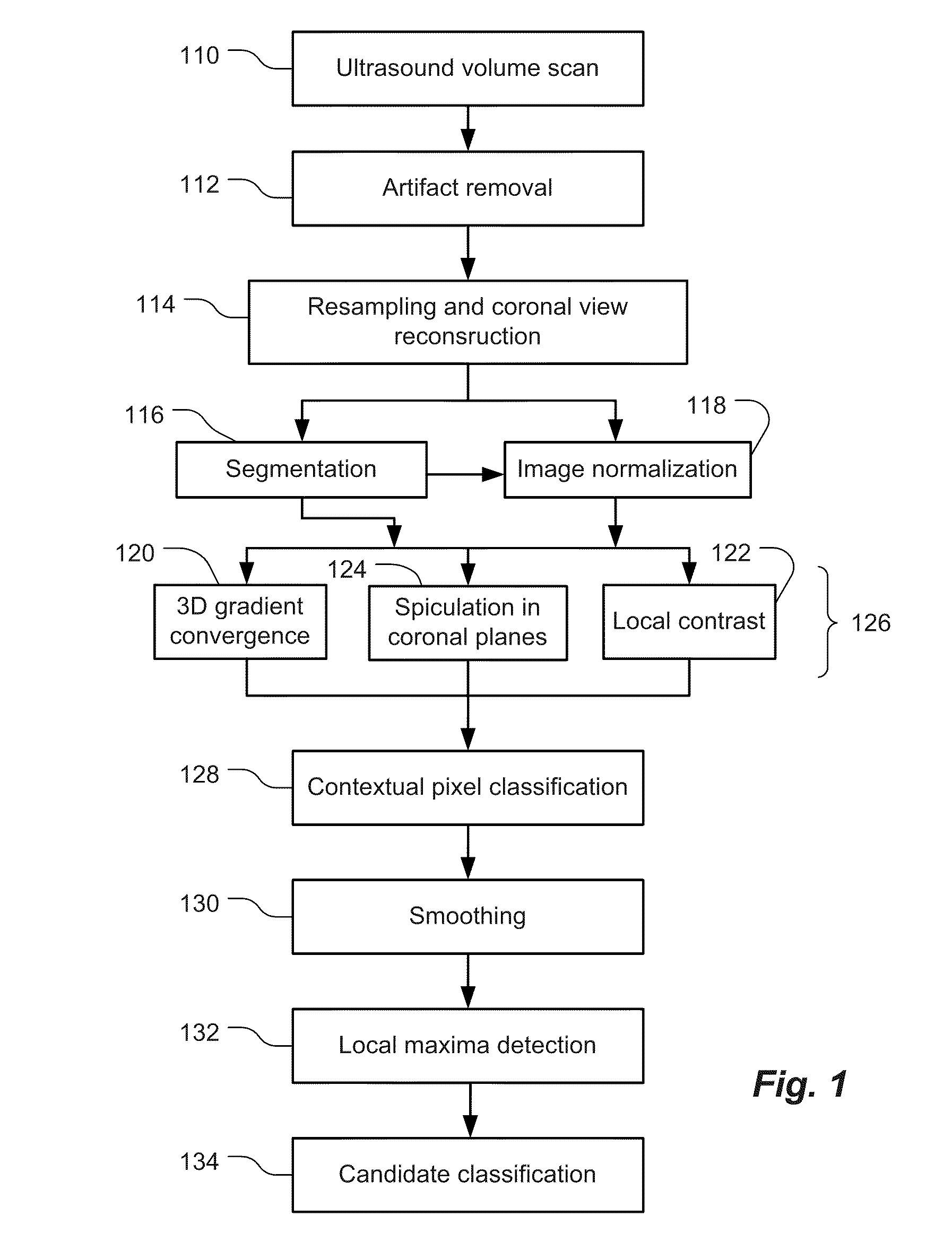
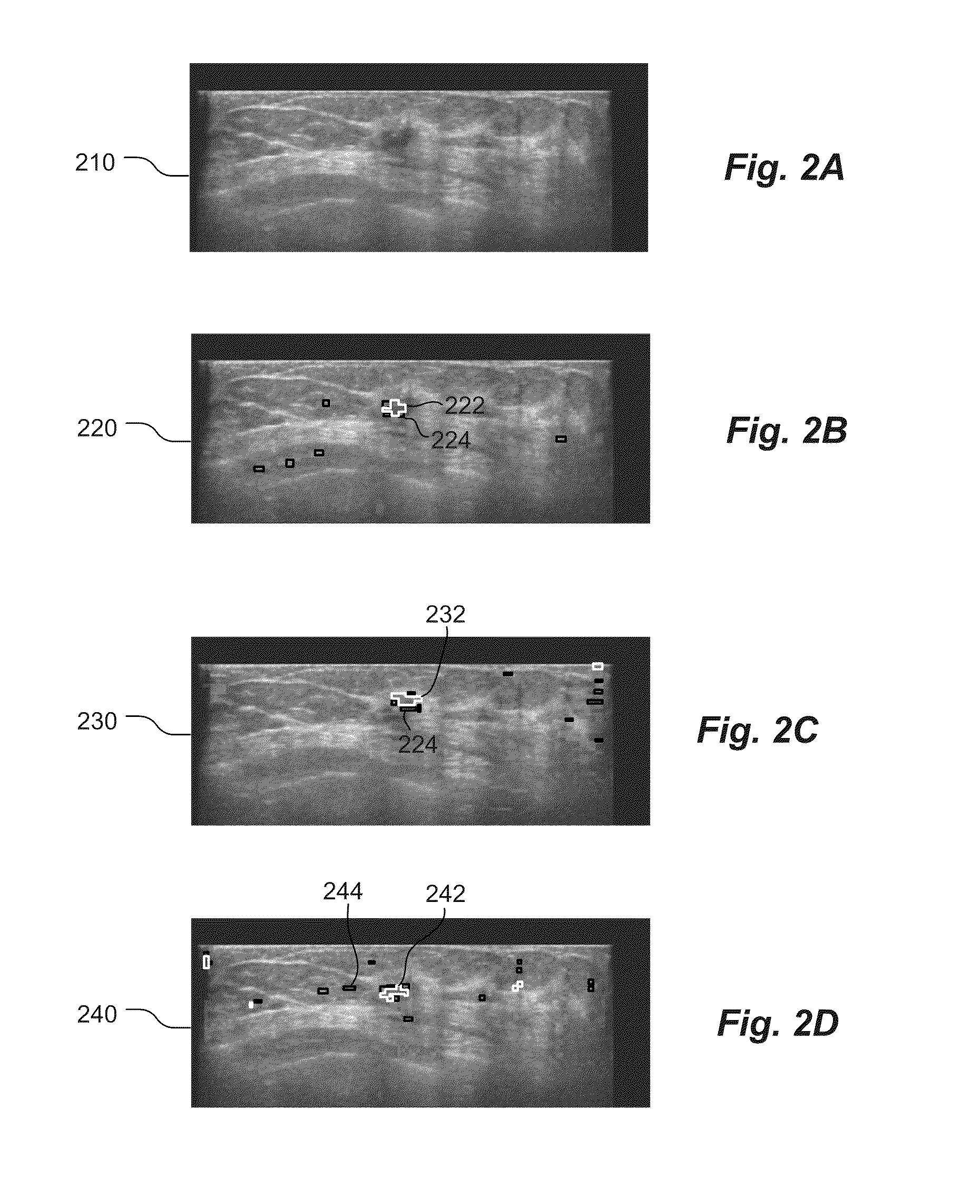
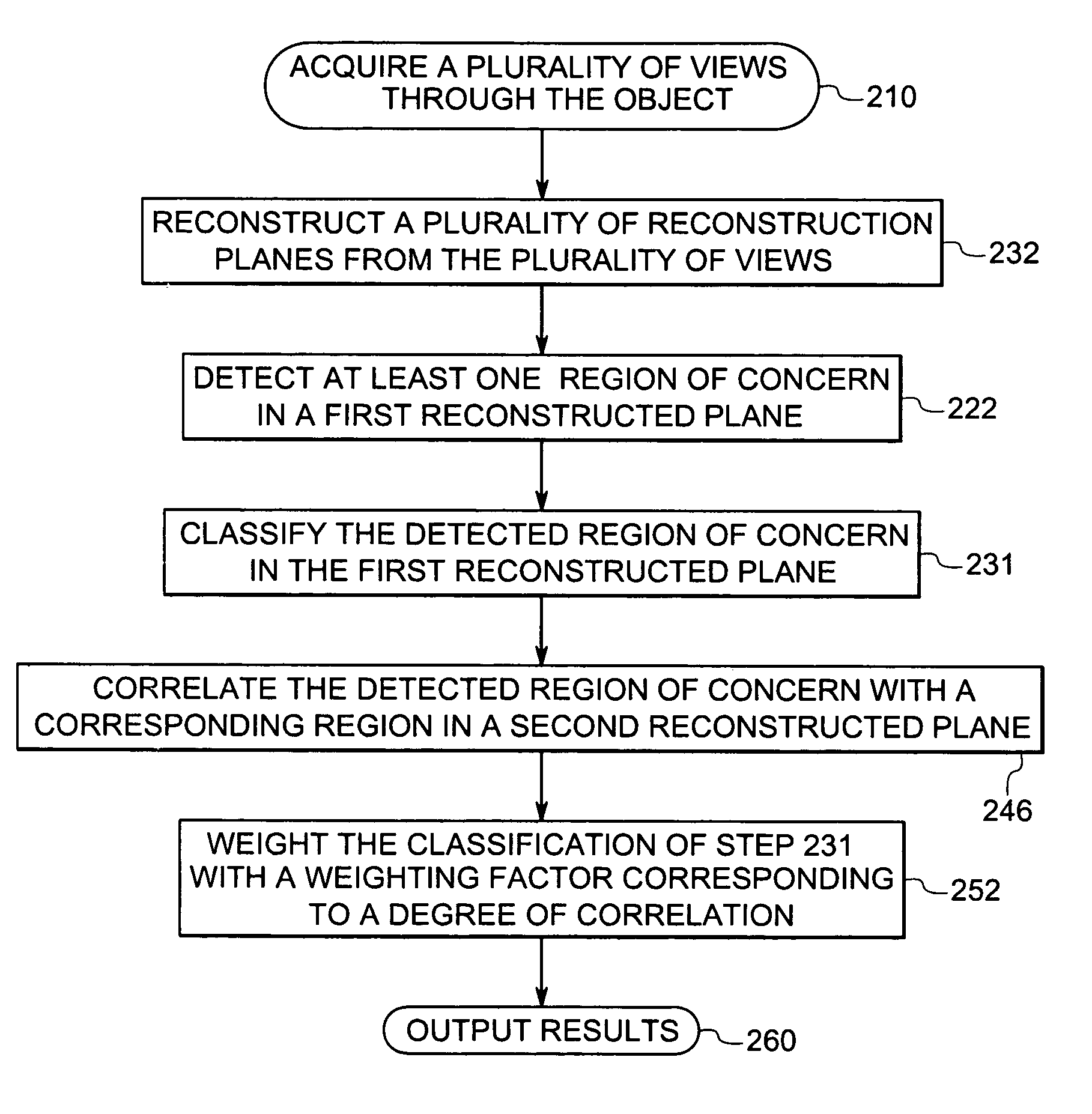
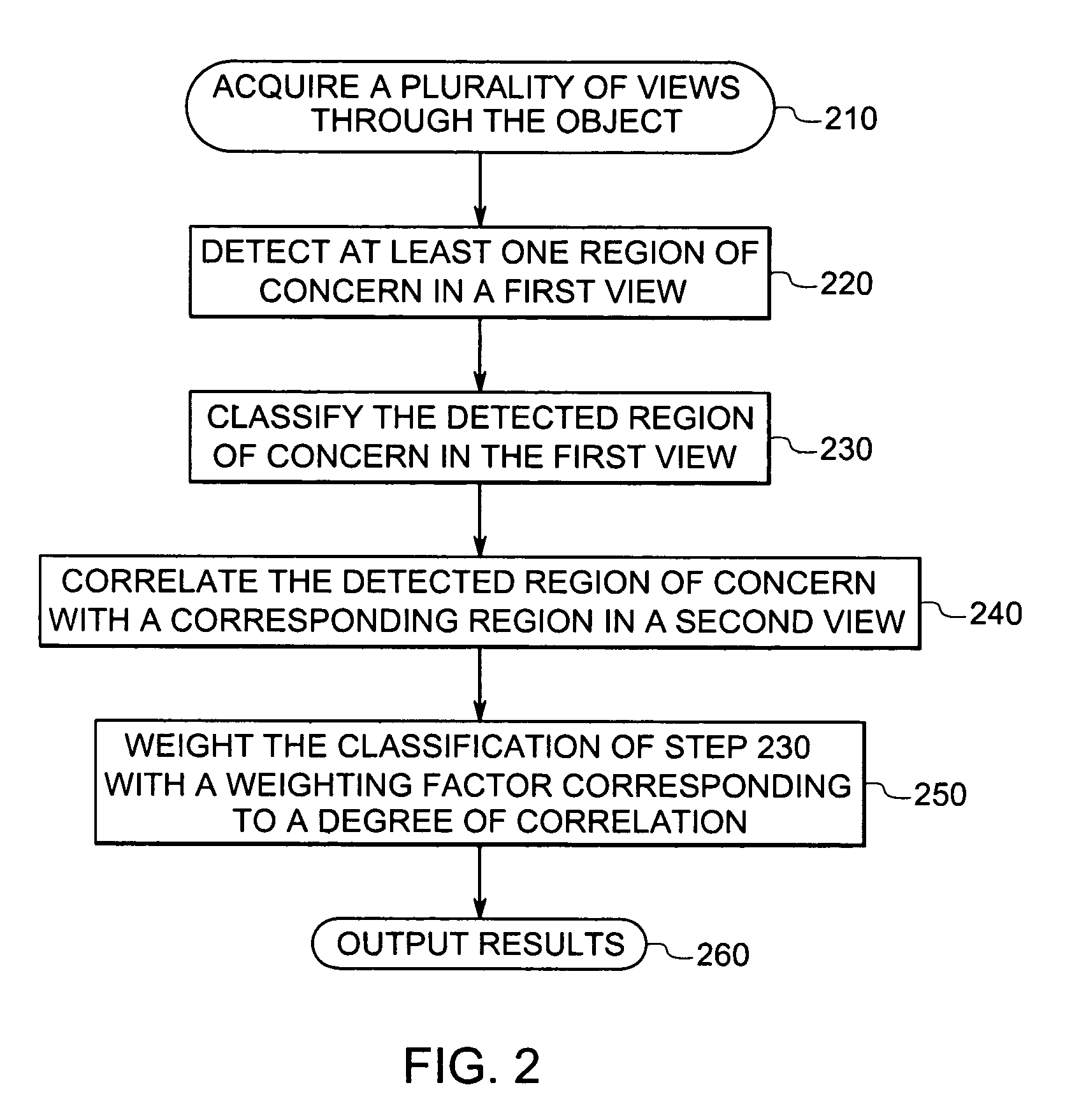
Methods and related systems are described for detection of breast cancer in 3D ultrasound imaging data. Volumetric ultrasound images are obtained by an automated breast ultrasound scanning (ABUS) device. In ABUS images breast cancers appear as dark lesions. When viewed in transversal and sagittal planes, lesions and normal tissue appear similar as in traditional 2D ultrasound. However, architectural distortion and spiculation are frequently seen in the coronal views, and these are strong indicators of the presence of cancer. The described computerized detection (CAD) system combines a dark lesion detector operating in 3D with a detector for spiculation and architectural distortion operating on 2D coronal slices. In this way a sensitive detection method is obtained. Techniques are also described for correlating regions of interest in ultrasound images from different scans such in different scans of the same breast, scans of a patient's right versus left breast, and scans taken at different times. Techniques are also described for correlating regions of interest in ultrasound images and mammography images. Interactive user interfaces are also described for displaying CAD results and for displaying corresponding locations on different images.
Owner:QVIEW MEDICAL
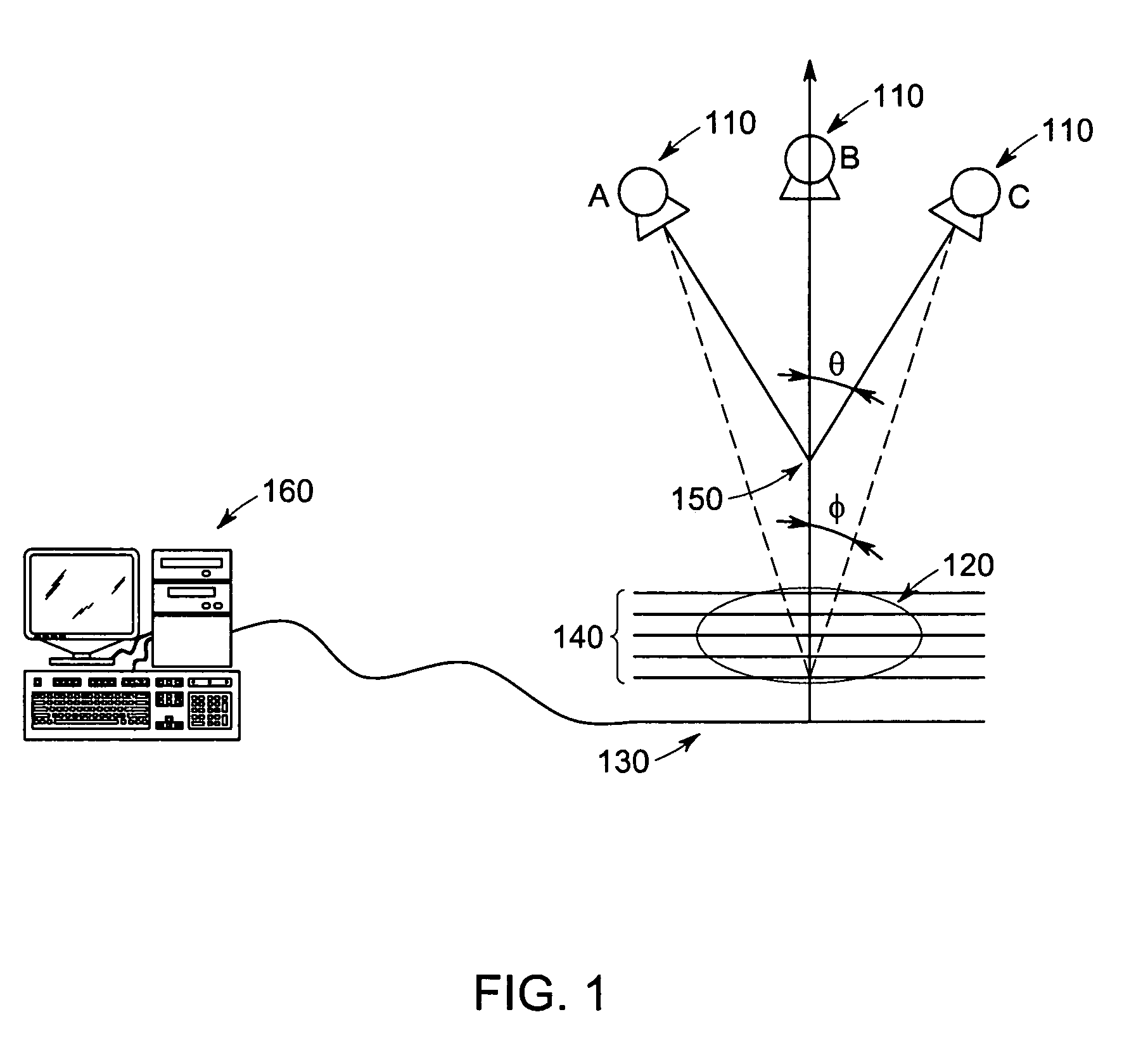
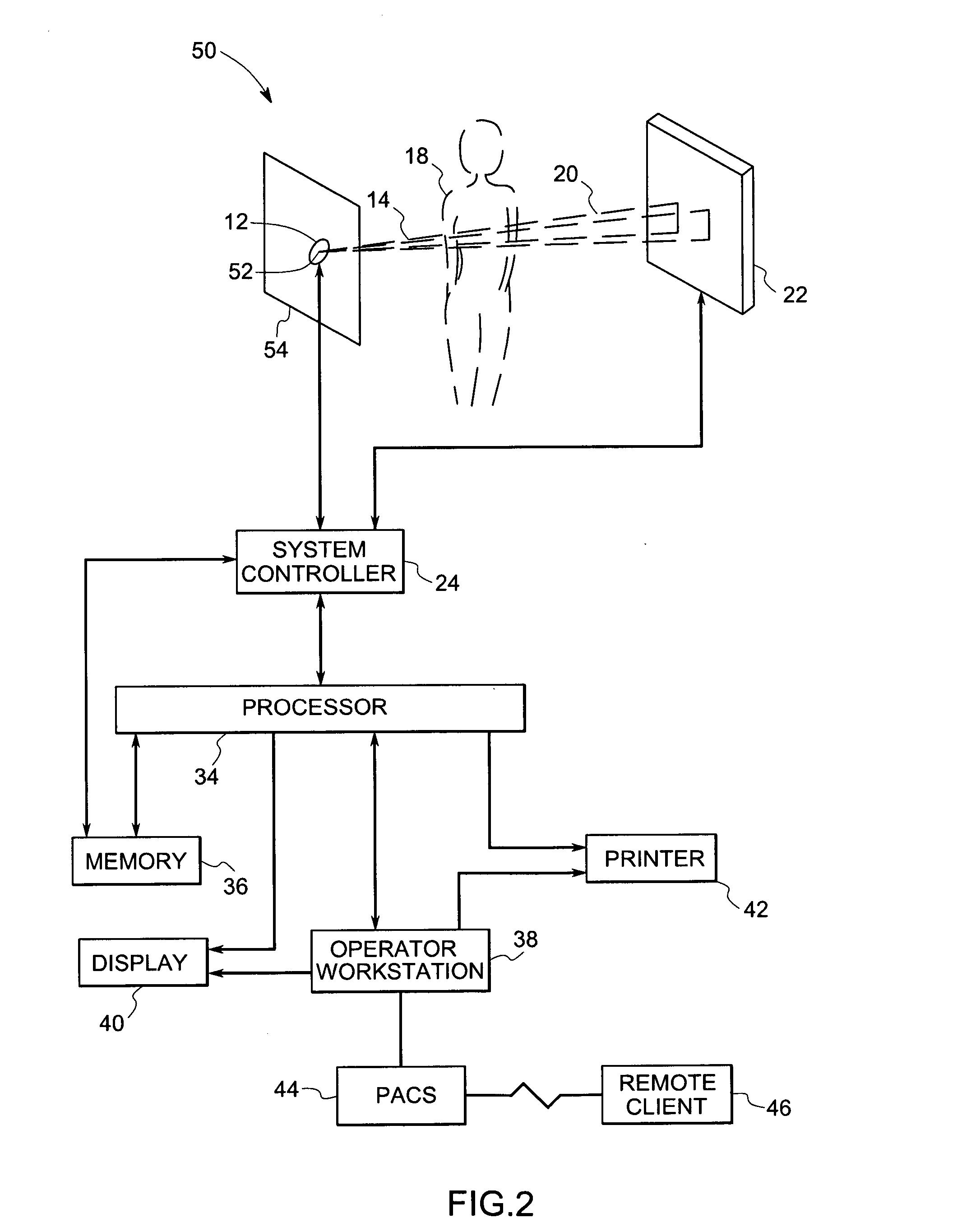
Computer aided detection (CAD) for 3D digital mammography
ActiveUS7218766B2Solve lack of contrastReduce contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementDigital mammographyComputer vision
There is provided a method of analyzing a plurality of views of an object, the object including an edge portion partially extending from a surface of the object into an internal volume of the object, comprising the step of analyzing each acquired view. The step of analyzing each acquired view includes analysis of the edge portion. Preferably, the object comprises breast tissue.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
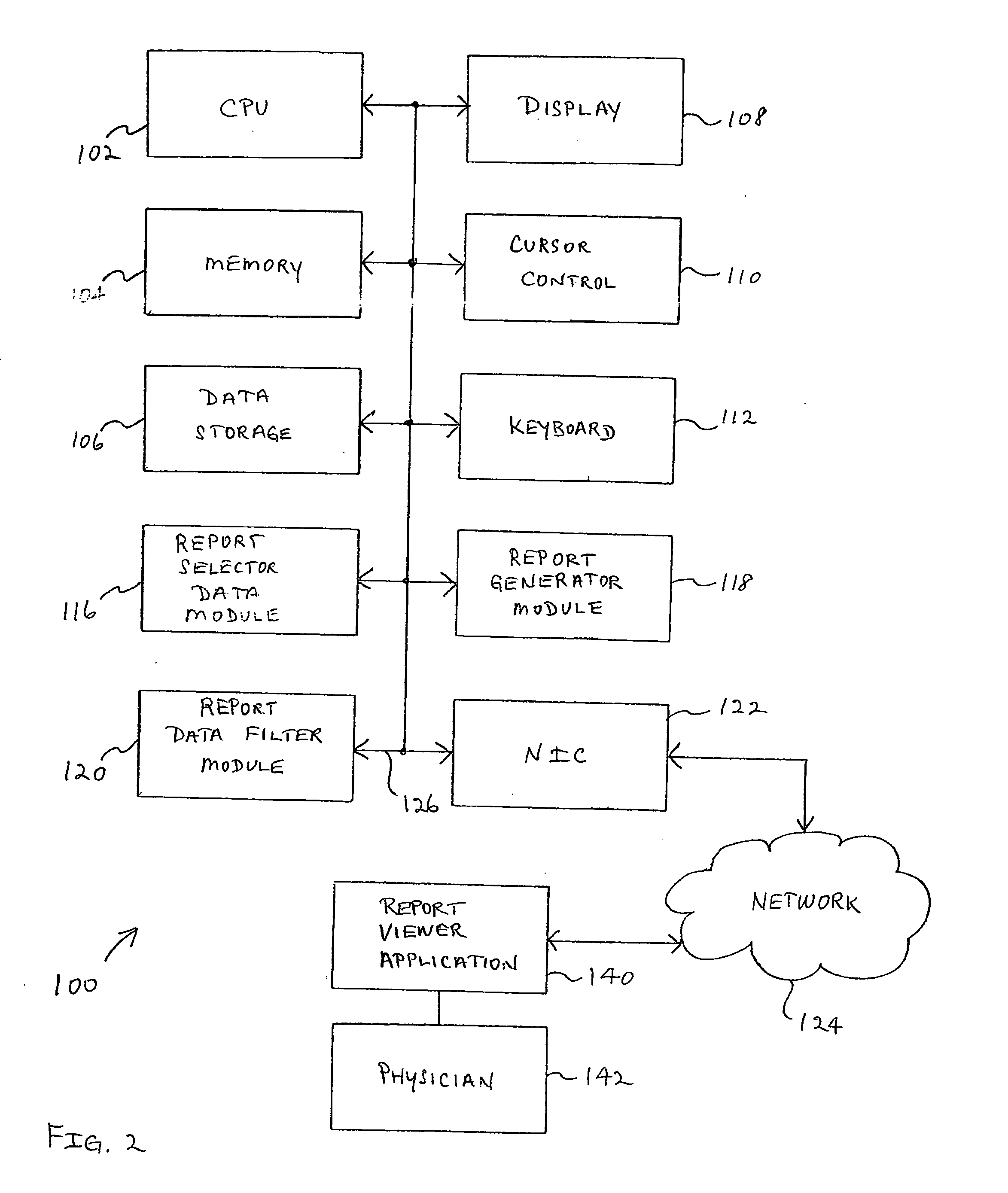
Apparatus and method for customized report viewer
InactiveUS20050096530A1Character and pattern recognitionMedical report generationAbnormal tissue growthBI-RADS
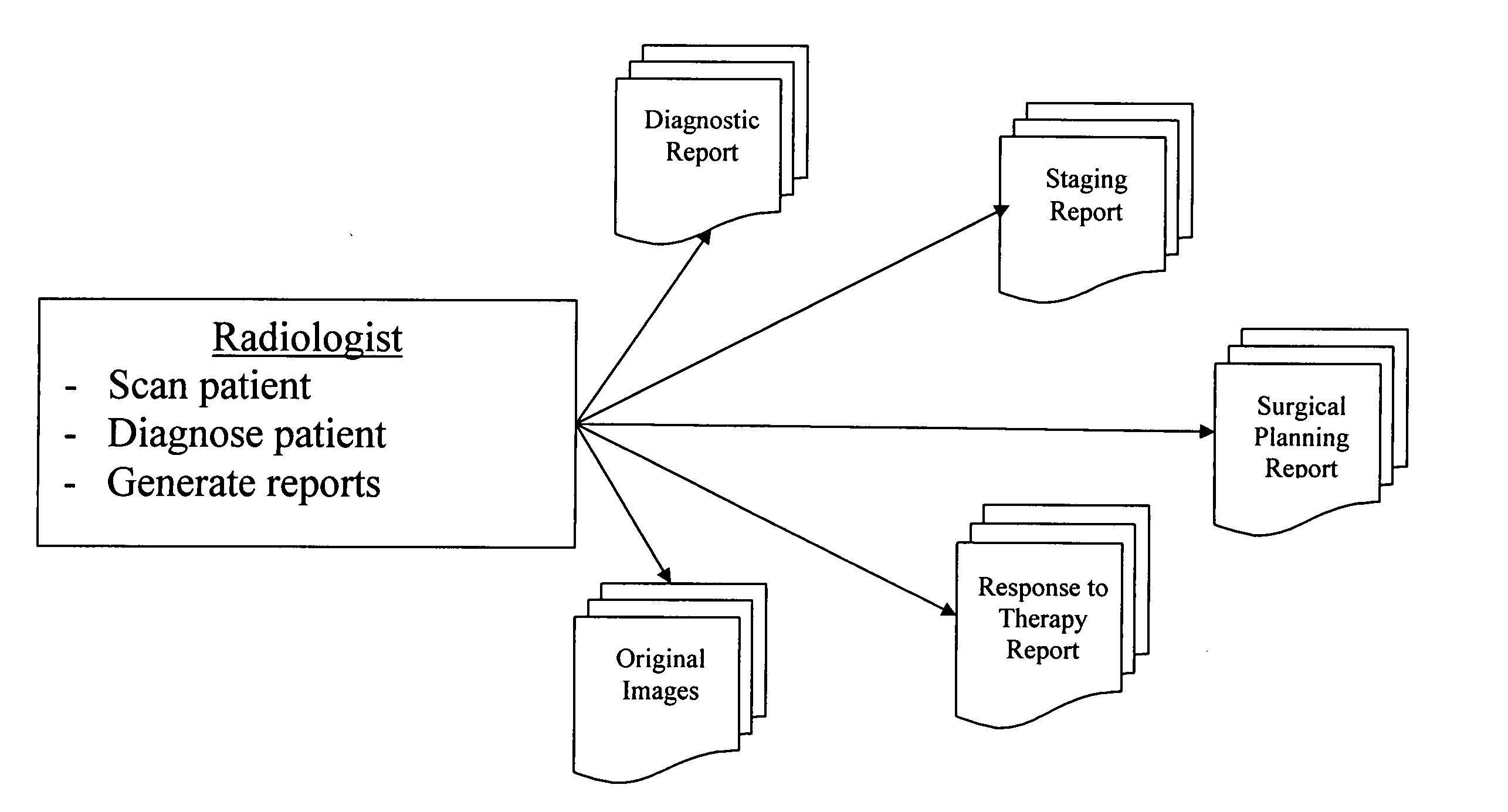
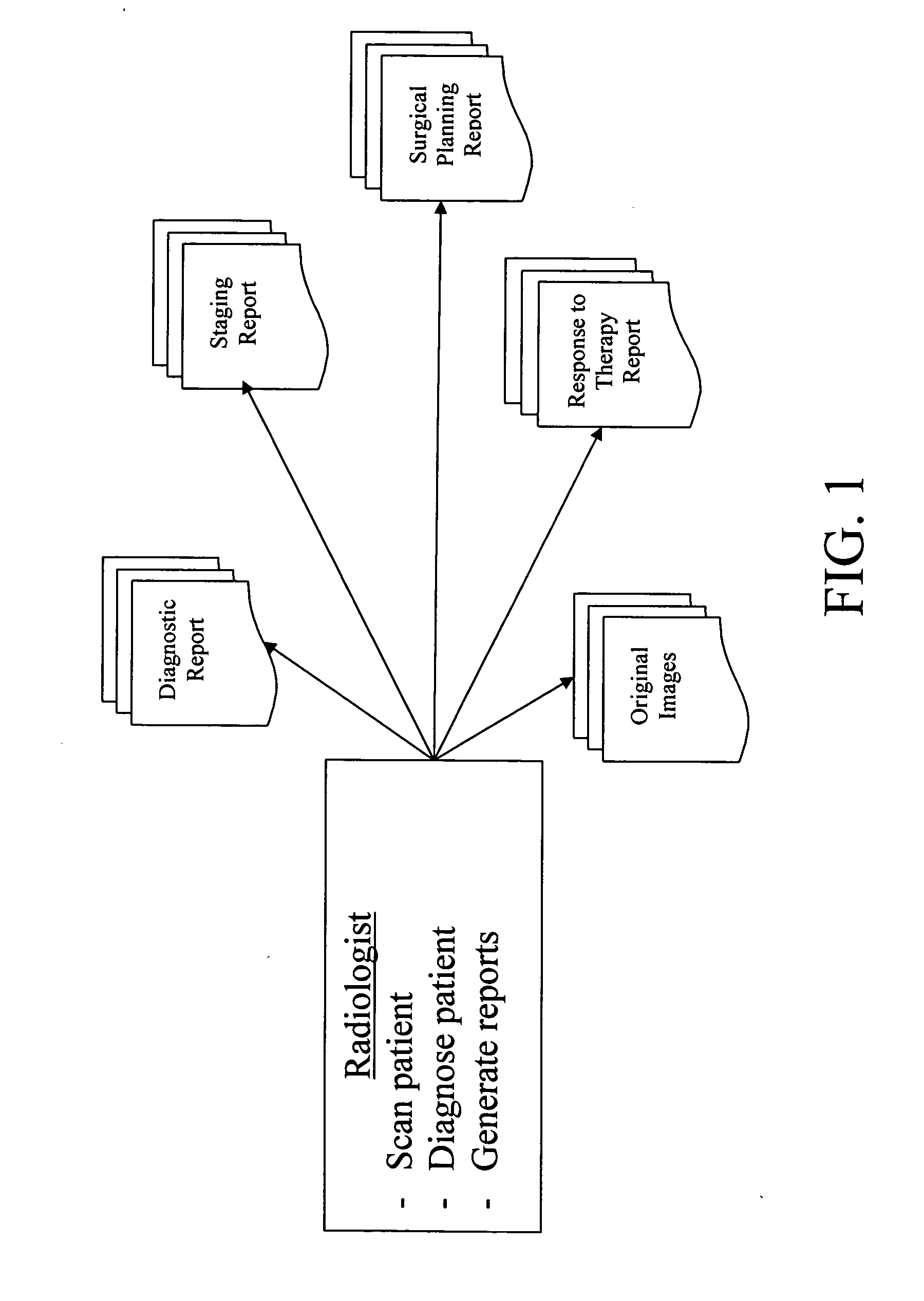
A system for the automatic generation of custom report viewing utilizes imaging data and computer-aided detection technology to identify cancerous tumors. A typical collection of data from a patent's scan may include hundreds of images and associated data. The custom report viewer allows one physician, such as a radiologist, to analyze the data and prepare a report. The generated report may contain images, computed measurements, classifications based on a standard (such as the ACR BI-RADS for Breast MR), and locations relative to landmarks. Different physicians, such as an oncologist or a surgeon, may have need of differing images and supporting data for their own purposes. Each physician may select, in advance, custom selection criteria that are stored in association with that physician. A report generator module uses the stored selection criteria and report filtering to extract the images and supporting data specified by the particular physician. The system allows a surgeon to alter the selection criteria and obtain further images if necessary and permits the generation of multiple selection criteria by one physician for different purposes, such as surgical planning, therapy reporting, and the like.
Owner:MERGE CAD
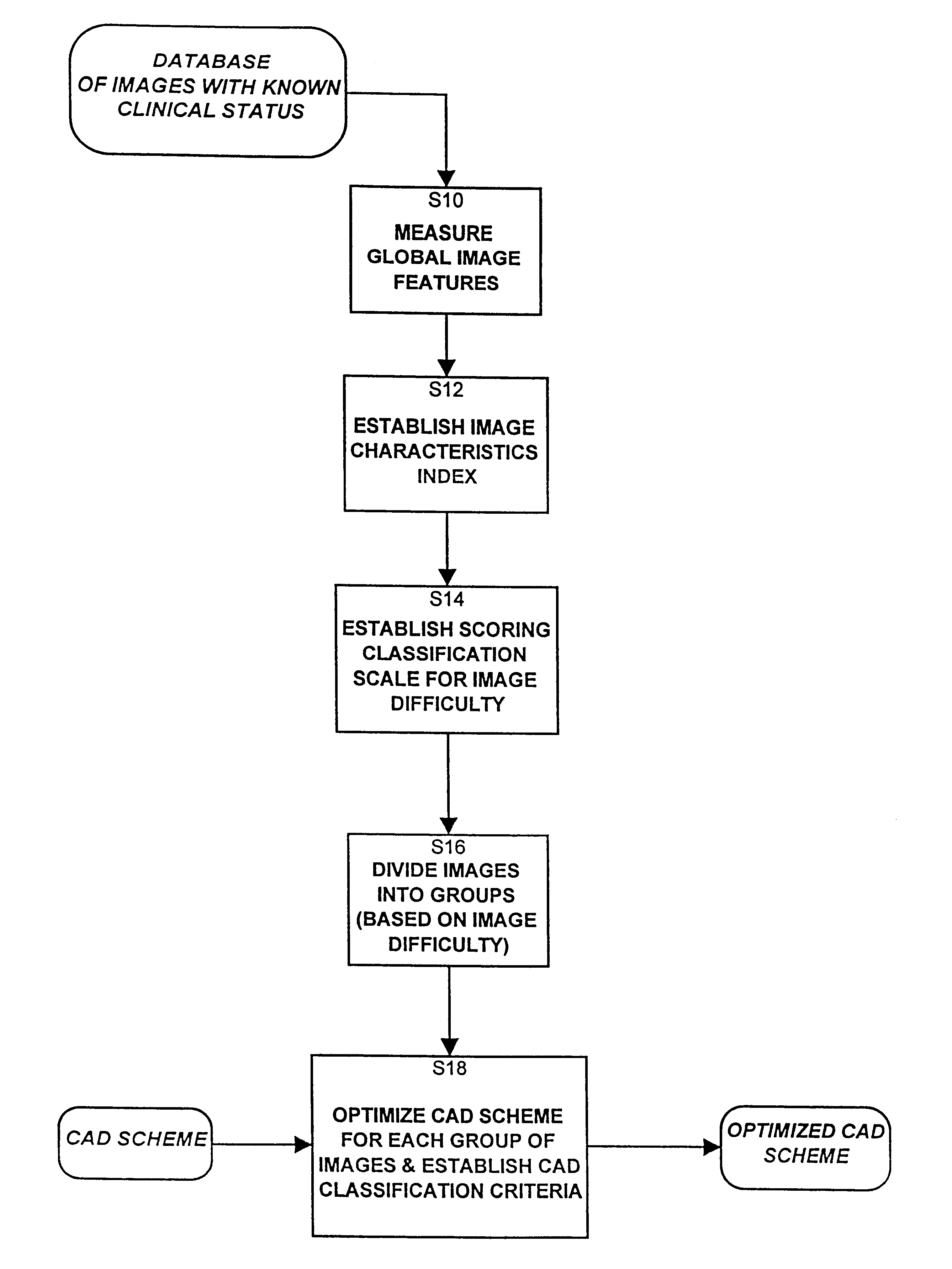
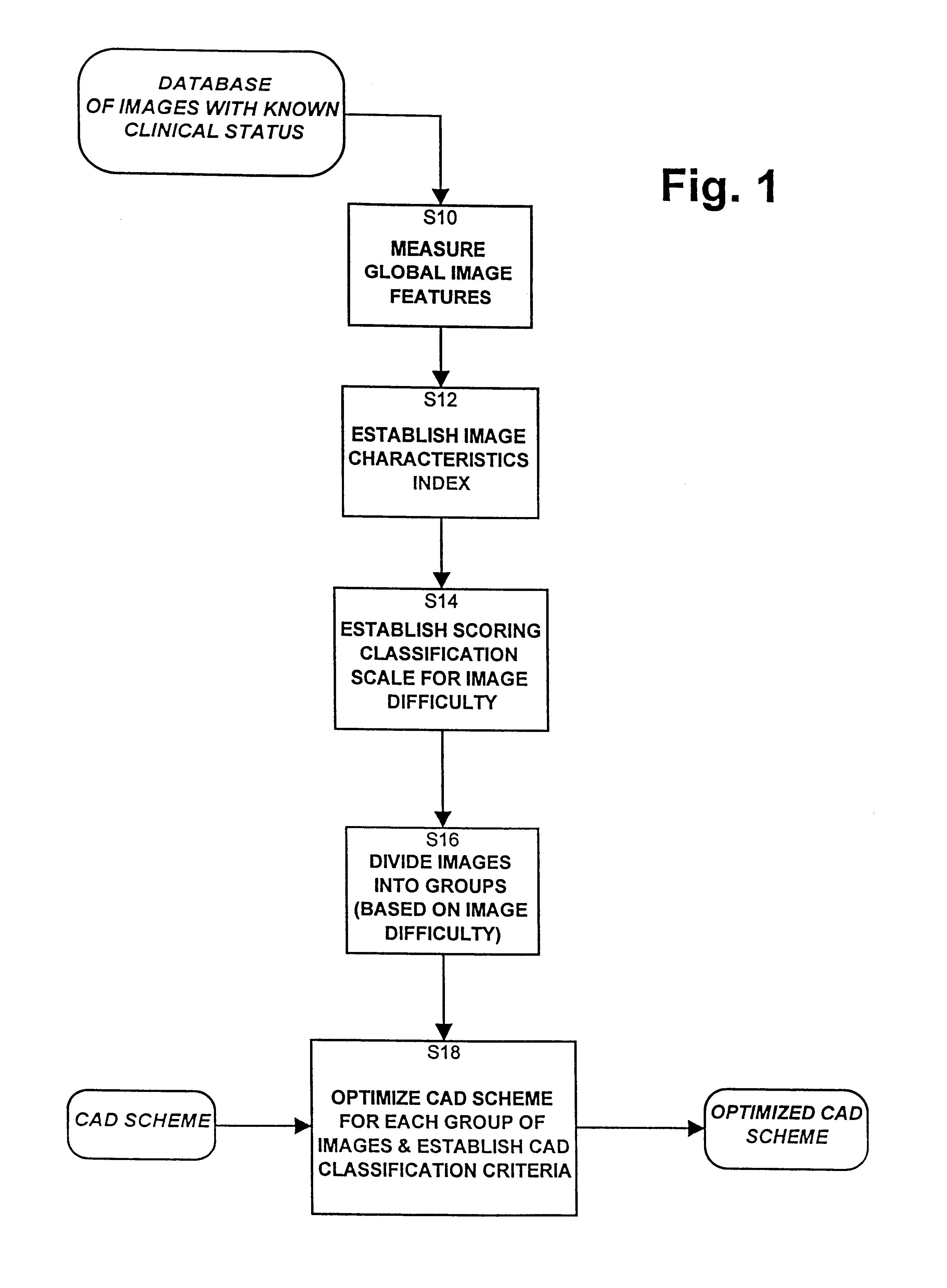
Image quality based adaptive optimization of computer aided detection schemes
A computerized method of detecting regions of interest in a digital image optimizes and adapts a computer aided scheme for detecting regions of interest in images. The optimization is based on global image characteristics. For each image in a database of images having known regions of interest, global image features are measured and an image characteristic index is established based on these global image features. All the images in the database are divided into a number of image groups based on the image characteristic index of each image in the database and the CAD scheme is optimized for each image group. Once the CAD scheme is optimized, to process a digital image, an image characteristics based classification criteria is established for that image, and then global image features of the digitized image are determined. The digitized image is then assigned an image characteristics rating based on the determined global image features, and the image is assigned to an image group based on the image rating. Then regions of interest depicted in the image are determined using a detection scheme adapted for the assigned image group.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
System and method for accurate and rapid identification of diseased regions on biological images with applications to disease diagnosis and prognosis
ActiveUS20110243417A1Easy to handleImprove abilitiesImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseImage resolution
The present invention relates to a method and system for detecting biologically relevant structures in a hierarchical fashion, beginning at a low-resolution and proceeding to higher levels of resolution. The present invention also provides probabilistic pairwise Markov models (PPMMs) to classify these relevant structures. The invention is directed to a novel classification approach which weighs the importance of these structures. The present invention also provides a fast, efficient computer-aided detection / diagnosis (CAD) system capable of rapidly processing medical images (i.e. high throughput). The computer-aided detection / diagnosis (CAD) system of the present invention allows for rapid analysis of medical images the improving the ability to effectively detect, diagnose, and treat certain diseases.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +1
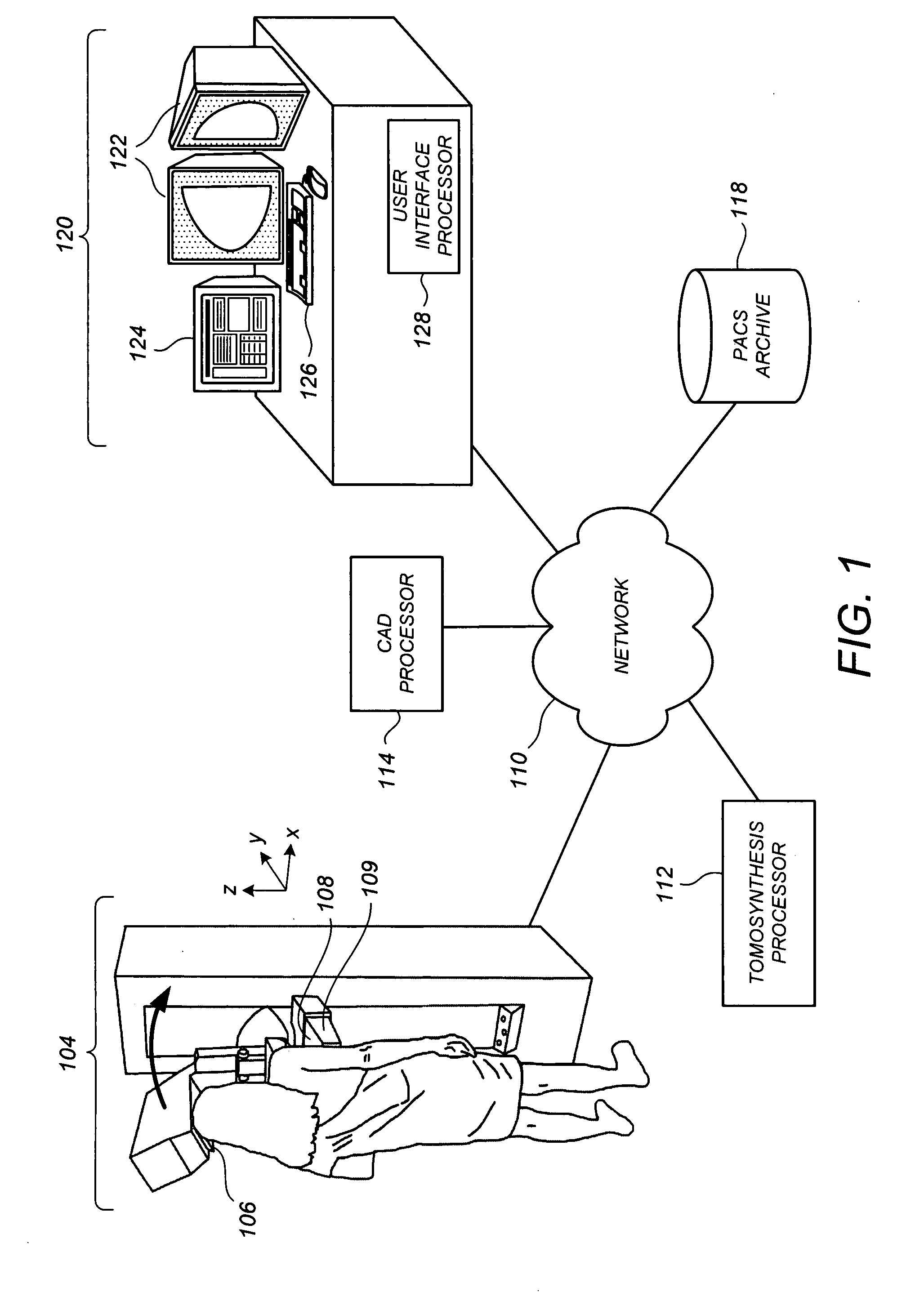
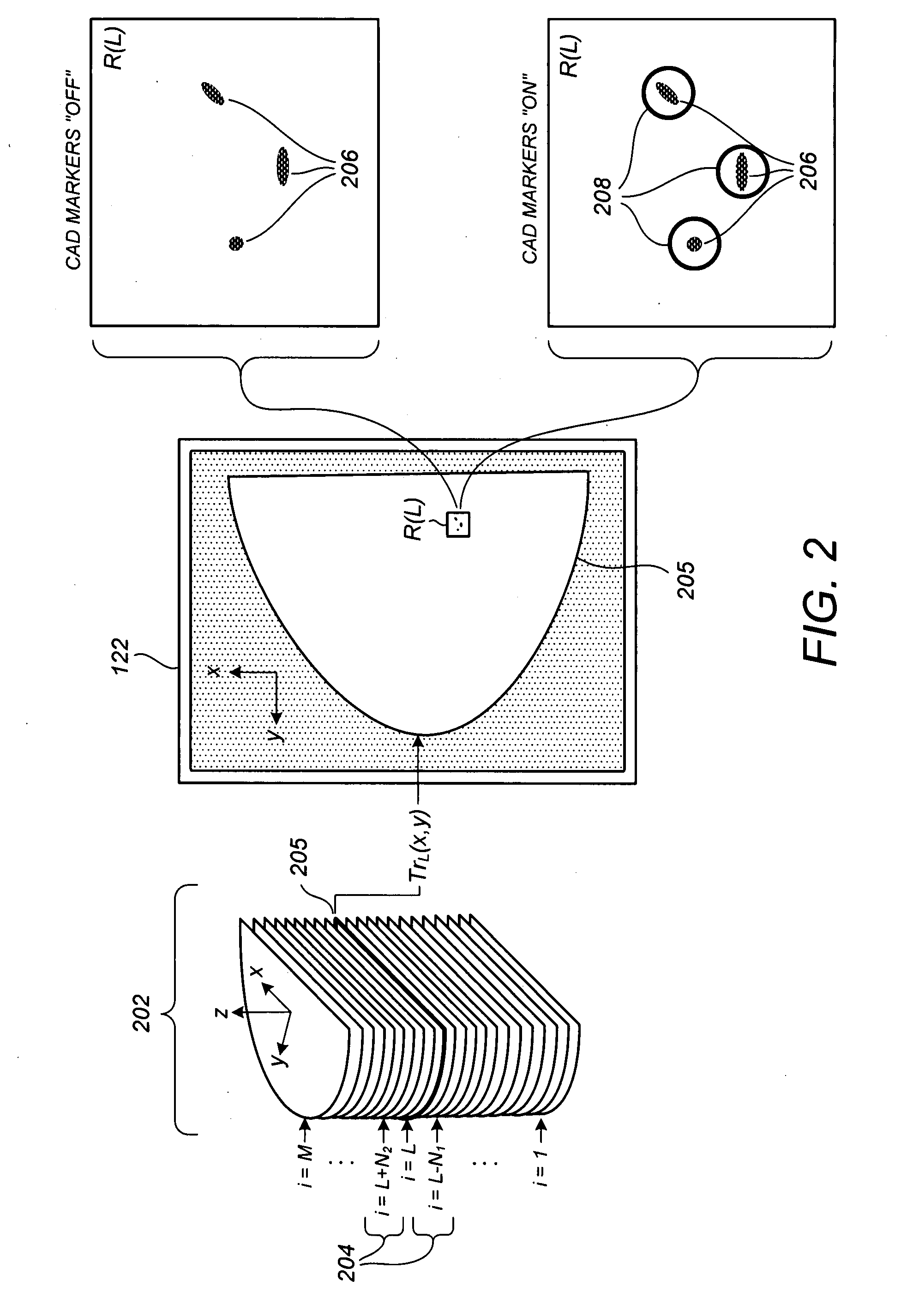
Displaying breast tomosynthesis computer-aided detection results
InactiveUS20090087067A1Raise the possibilityIncrease speedTomosynthesisPatient positioning for diagnosticsTomosynthesisX-ray
Methods, systems, and related computer program products for processing and displaying computer-aided detection (CAD) results in conjunction with breast x-ray tomosynthesis data are described. For one preferred embodiment, as a user pages through a notional stack of tomosynthesis reconstructed slice images (Tr images), including a detection-containing Tr image on which a CAD marker is to be displayed at an identified coordinate location, one or more CAD proximity markers is displayed at that coordinate location on one or more neighboring Tr images. While not themselves indicative of CAD findings on their respective Tr images, the CAD proximity markers encourage user attention toward the coordinate location of the CAD detection marker of the detection-containing Tr image. Preferably, the CAD proximity markers are of noticeably different size from each other and from the CAD detection marker to promote their perception in the peripheral vision of the user during the paging process.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
System and method for 3D CAD using projection images
InactiveUS20070052700A1Image analysisImage data processing detailsProjection imageComputer aided detection
A technique is provided for performing a computer aided detection (CAD) analysis of a three-dimensional volume using a computer assisted detection and / or diagnosis (CAD) algorithms. The technique includes selecting one or more three-dimensional points of interest in a three-dimensional volume, forward projecting the one or more three-dimensional points of interest to determine a corresponding set of projection points within one or more two-dimensional projection images, and computing output values at the one or more three-dimensional points of interest based on one or more feature values or a CAD output at the corresponding set of projection points.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
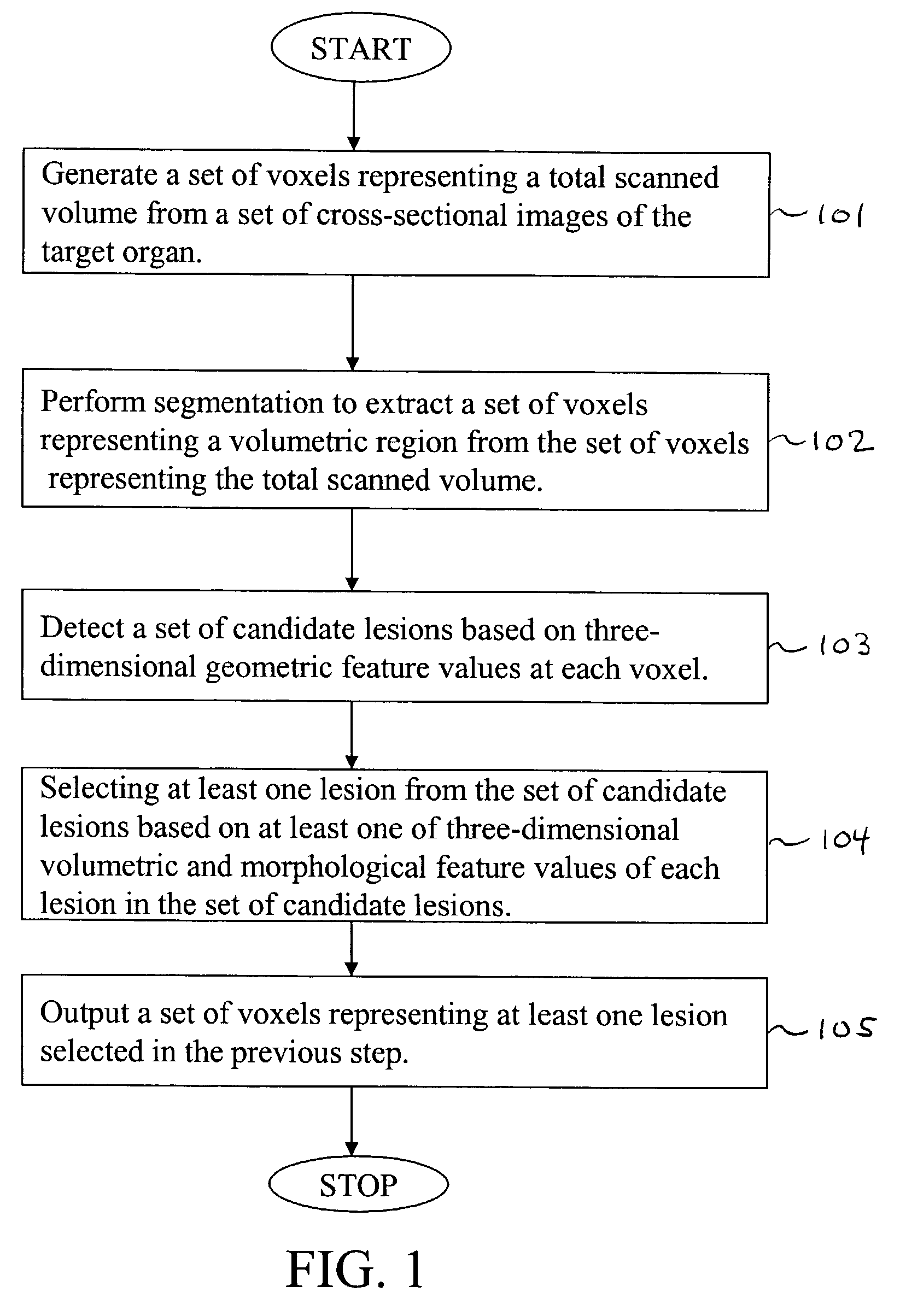
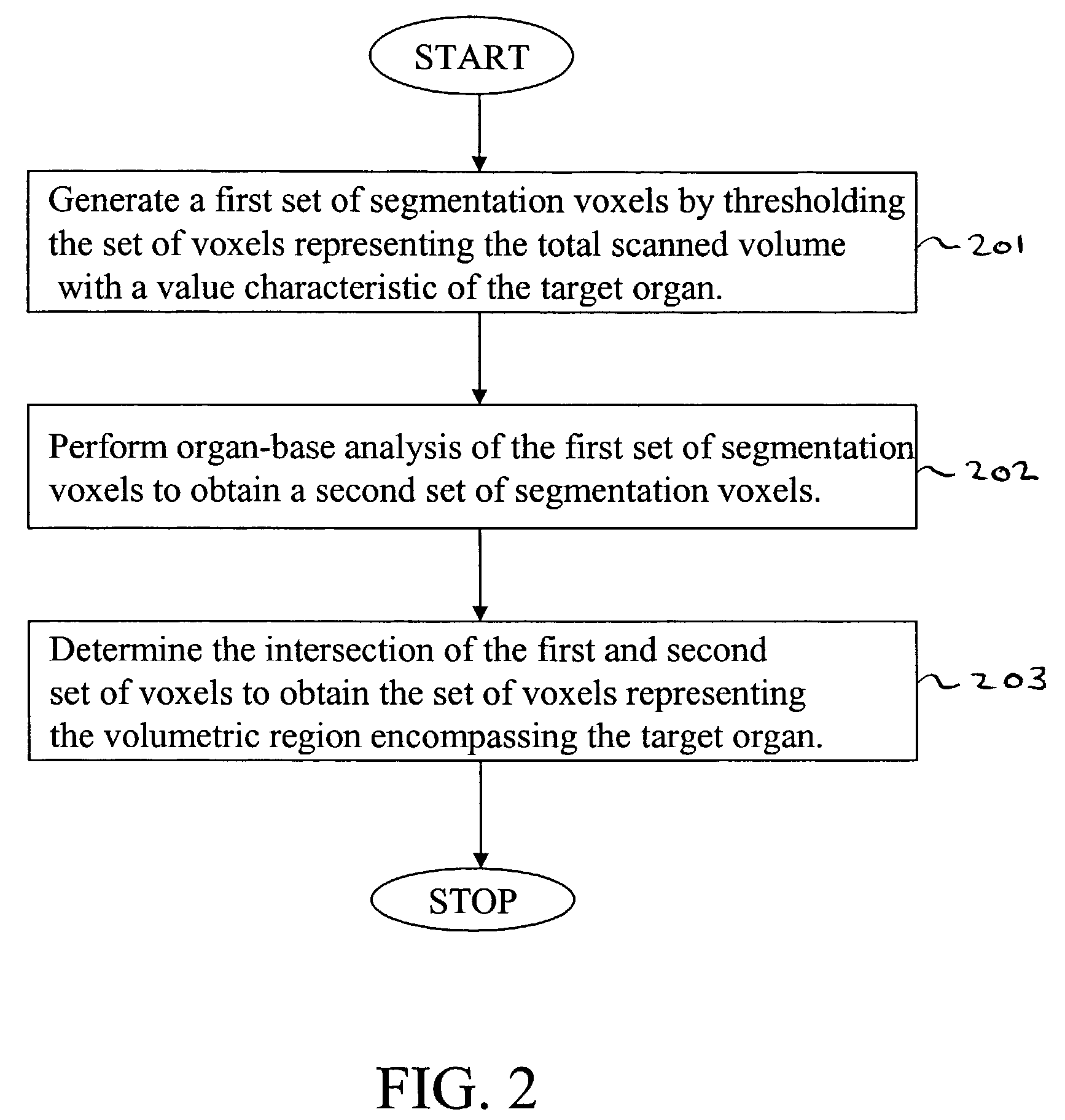
Method for computer-aided detection of three-dimensional lesions
ActiveUS7379572B2Maximize sensitivityReducing false positiveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementVoxelLesion
A method, system, and computer program product for identifying at least one three-dimensionally extended lesion within a volumetric region encompassing an inner surface, an outer surface, and intervening tissue of a target organ. The method includes: (1) generating a set of voxels representing a total scanned volume from a set of cross-sectional images of the target organ; (2) performing segmentation to extract a set of voxels representing the volumetric region from the set of voxels representing the total scanned volume; (3) detecting a set of candidate lesions based on geometric feature values of each voxel in the set of voxels representing the volumetric region; and (4) selecting the at least one three-dimensionally extended lesion from the set of candidate lesions based on at least one of volumetric, morphologic, and texture feature values of each lesion in the set of candidate lesions.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
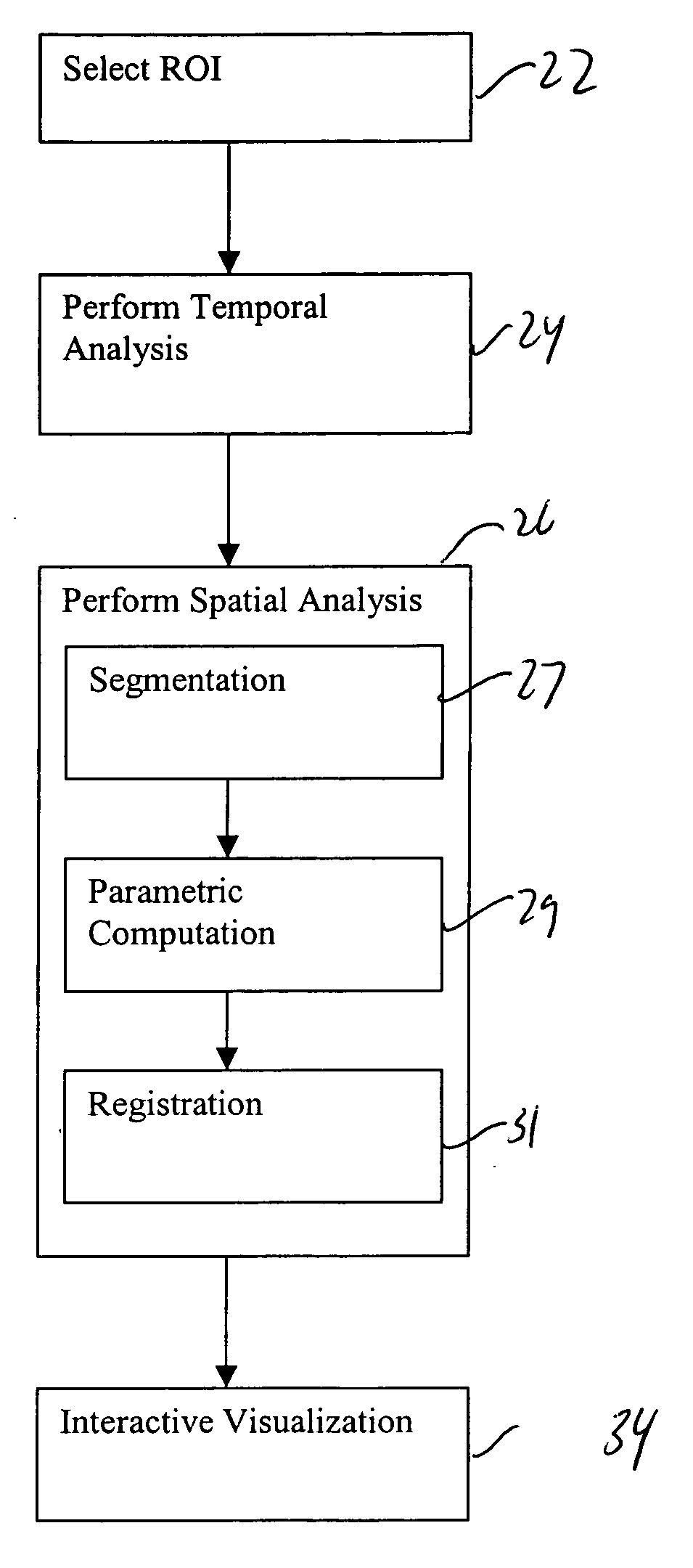
Computer-aided detection system utilizing temporal analysis as a precursor to spatial analysis
ActiveUS20070165920A1Improve analysisImprove interpretabilityImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsSpatial analysis
A computer-aided detection system for evaluating tissue based on a series of timed images acquired both before and after a contrast agent is administered performs a temporal analysis of the tissue and then a spatial analysis in which the tissue is categorized. After the temporal and spatial analysis is performed, the results can be displayed. The displayed results can include both tissue characterization results, underlying curves used to determine the characterization, and confidence data regarding how good the characterization is expected to be. The confidence data can be provided, for example, by using variations in color schemes, displaying numerical confidence levels, or providing graphical features such as piecewise linear models.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Use of computer-aided detection system outputs in clinical practice
InactiveUS20060171573A1Efficient and precise positioningAccurate representationImage enhancementImage analysisMedicineMinutiae
The present invention provides for the use of computer-aided detection (CAD) system output displays for providing accurate representations of areas for subsequent exams. Since the CAD output, unlike the original medical imagery, is not used during the initial reading, the radiologist does not mark it until a final determination is reached regarding subsequent procedures. Additionally, since the CAD output contains versions of the original imagery, the regions indicated by the radiologist are shown in the context of the particular anatomical detail for a given patient. This detail assists the technologist, other physicians and patients in more efficiently and accurately locating the exact area for subsequent exams.
Owner:ICAD INC
Inspection of region of interest
InactiveUS20130121546A1Improve abilitiesSpeed up the processImage enhancementImage analysisImaging dataImage system
An imaging system for inspection of a region of interest. The system includes a data processing and analyzing utility responsive to input data indicative of one or more images of a region of interest and identifying one or more objects therein. The data processing and analyzing utility includes a visualization processor utility and a computer aided detection processor connected to the visualization processor utility. The visualization processor utility is configured and operable for receiving the input image data, converting the received image data into a desired representation, and decomposing image data of said desired representation into different components. The computer aided detection processor is configured and operable for scoring said components according to one or more predetermined scoring schemes, and classifying the blobs and contours according to a degree of match with reference data indicative of one or more predetermined objects.
Owner:D V P TECH
Computer-assisted detection of systolic murmurs associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
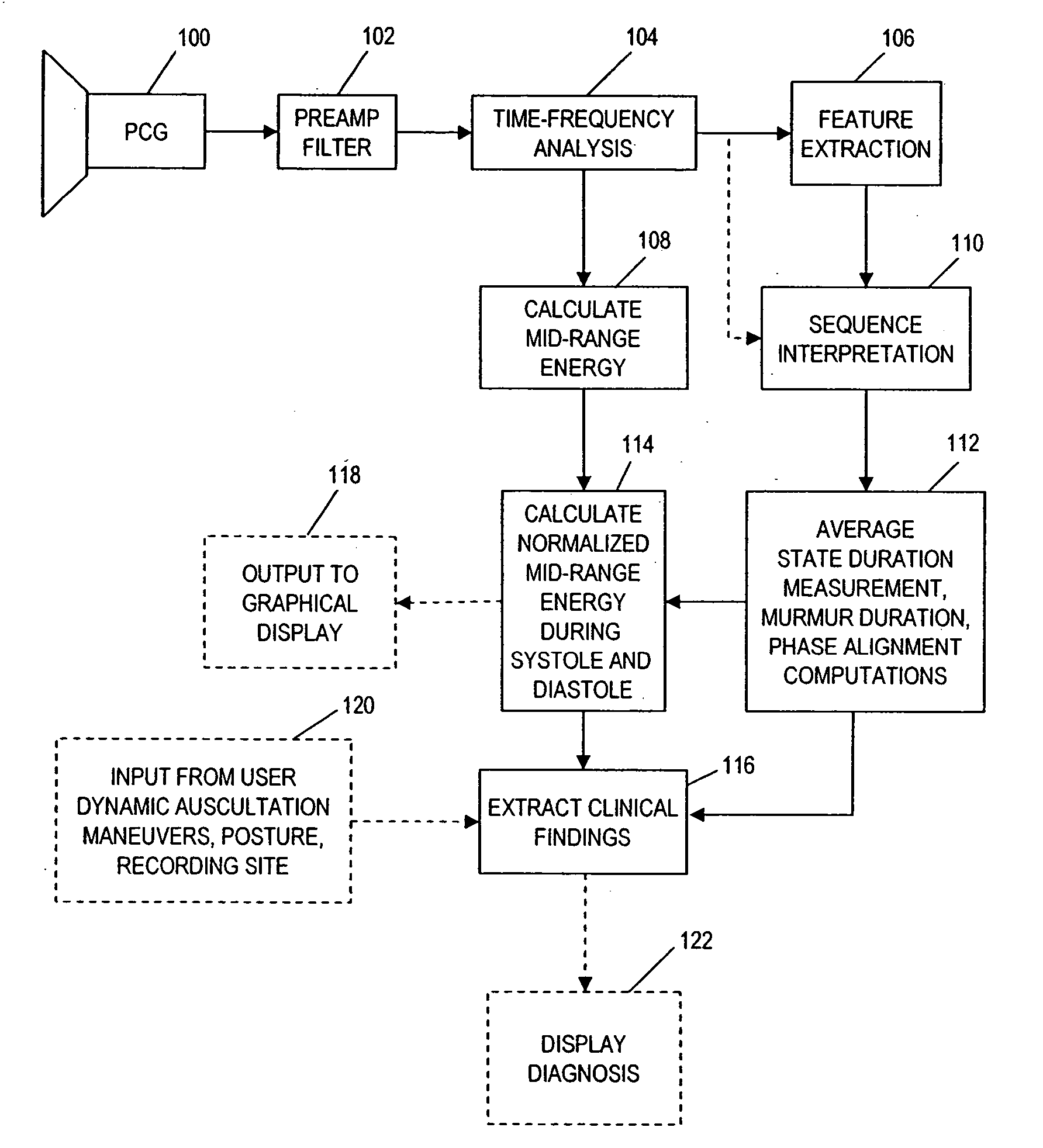
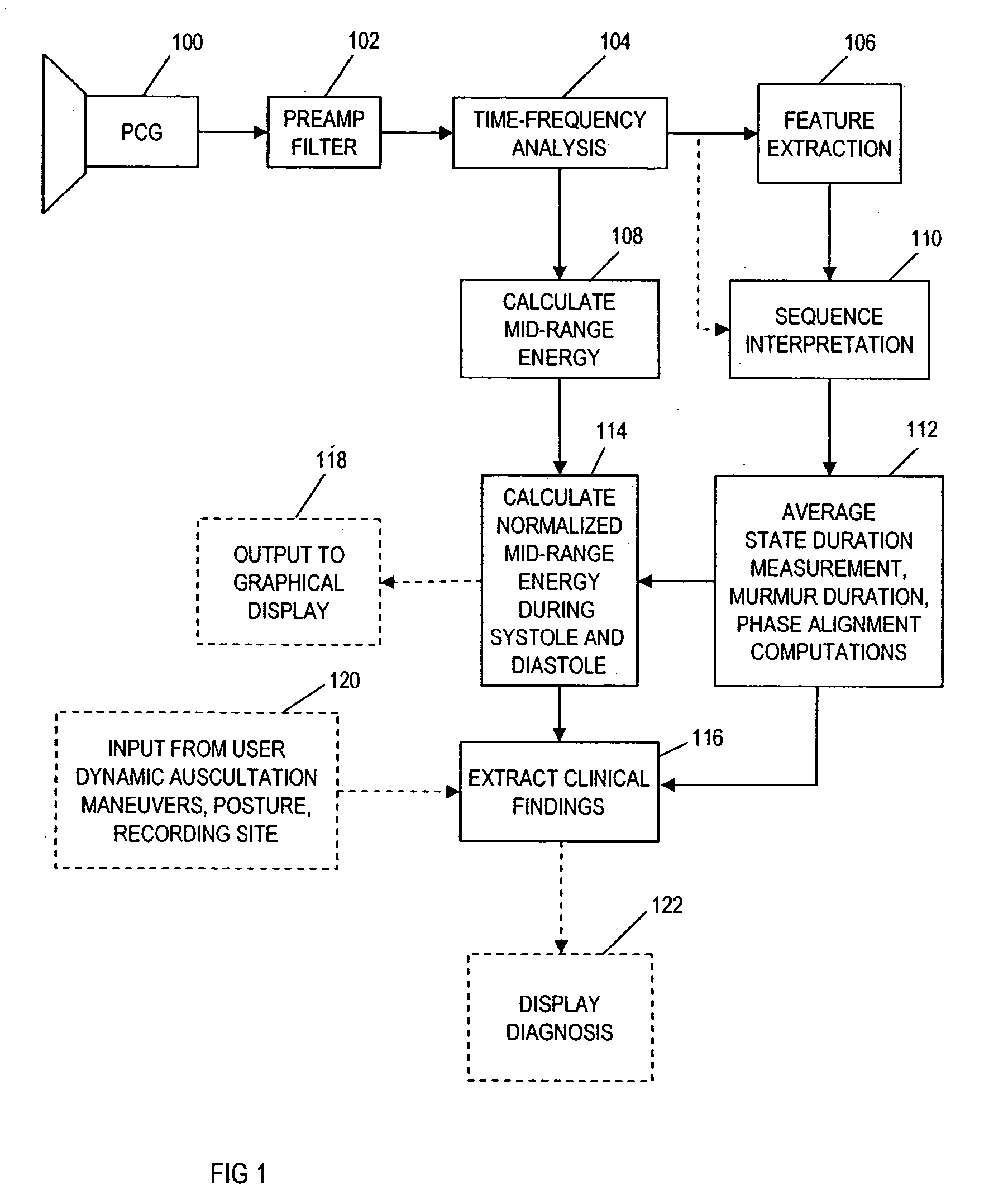
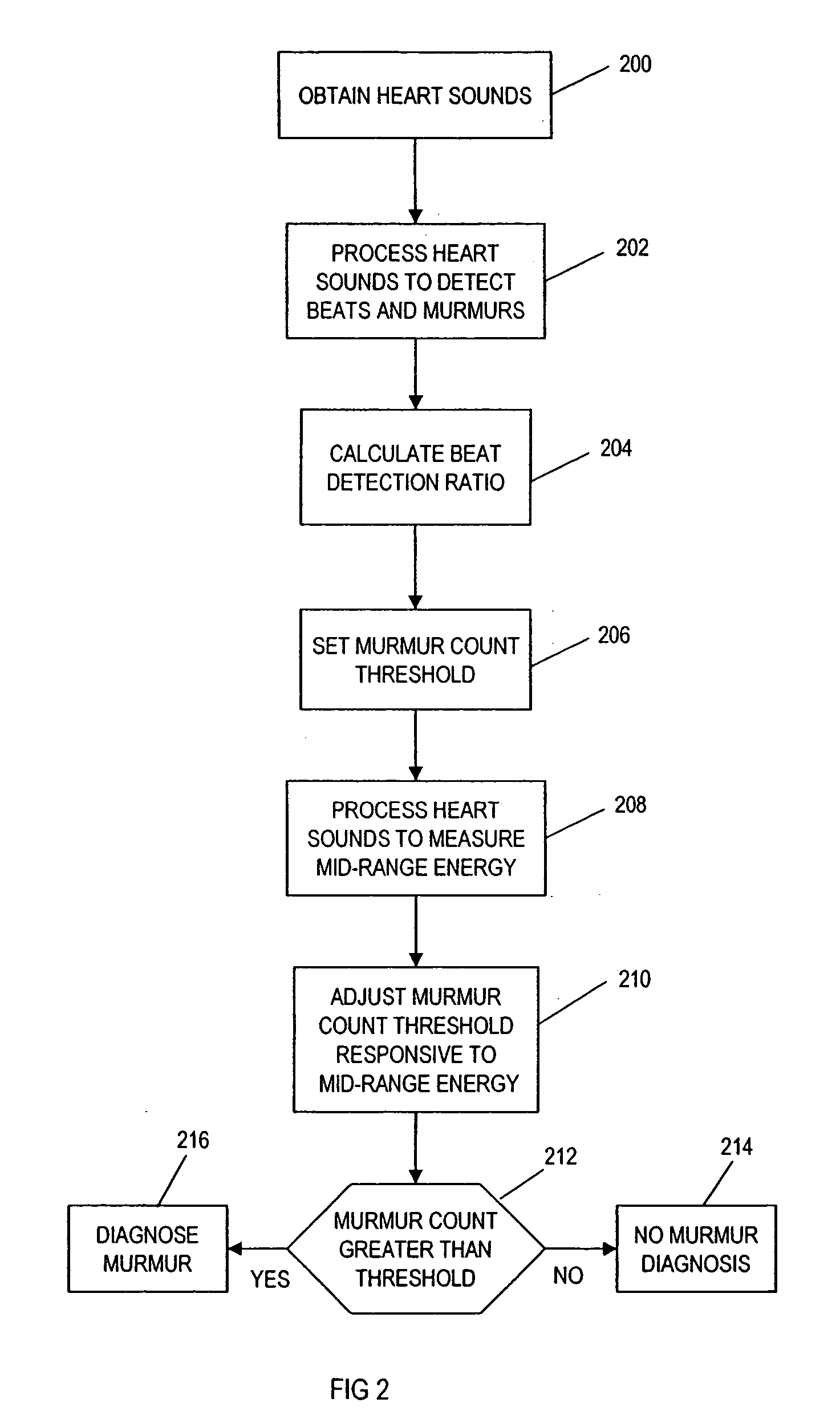
A method for assisting in the diagnosis of heart murmurs. The method calculates a normalized measure of mid-range energy for at least one systolic or diastolic interval in a sequence of heartbeats and displays the mid-range energy measure of the systolic and / or diastolic interval in a graphical form. The sequence of heartbeats is also processed to detect and diagnose heart murmurs by adjusting a murmur count threshold responsive to the mid-range energy. The method may be used to diagnose hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and to determine effective therapeutic drug dosage or therapeutic device setting.
Owner:ZARGIS MEDICAL
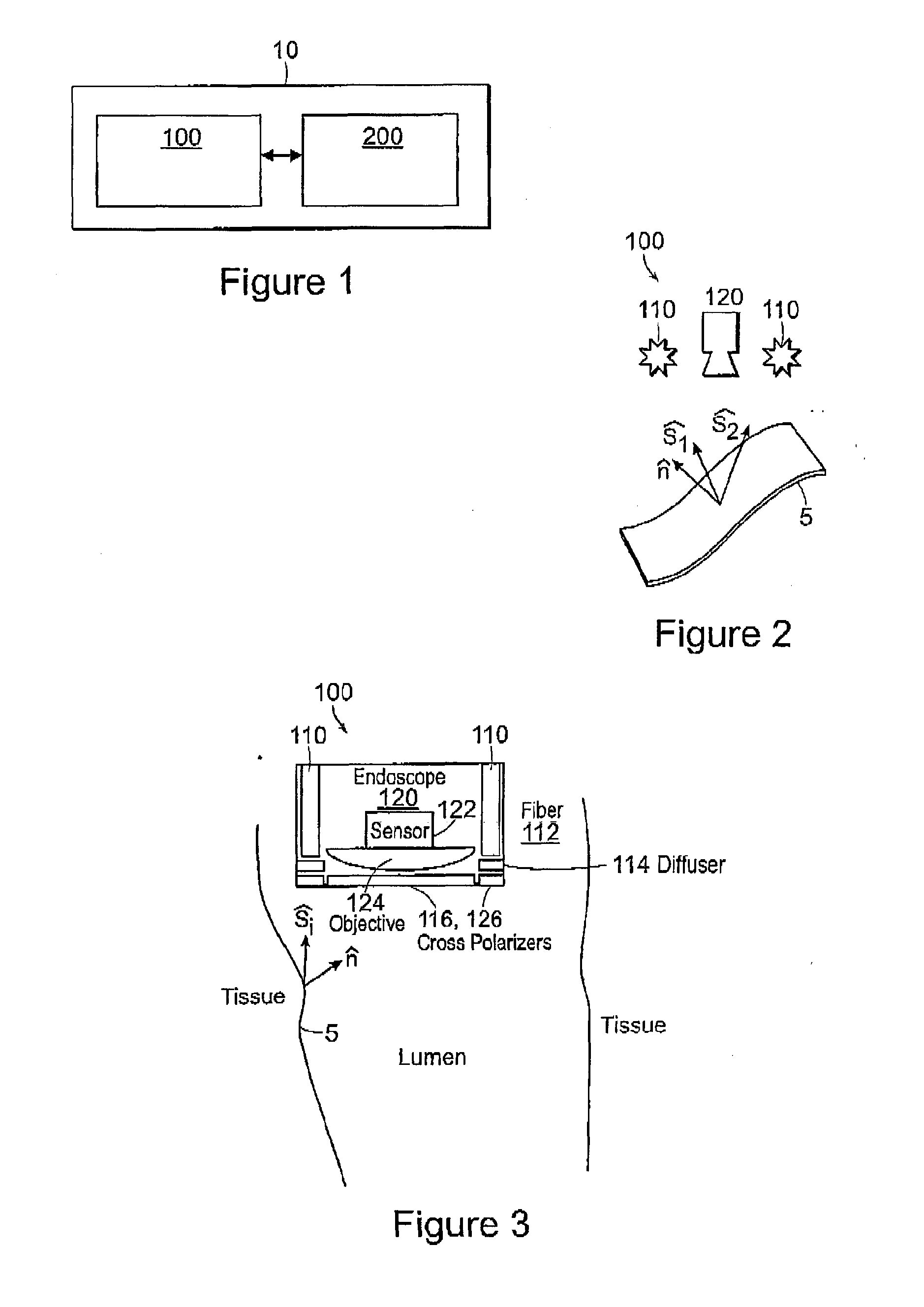
Photometric stereo endoscopy
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
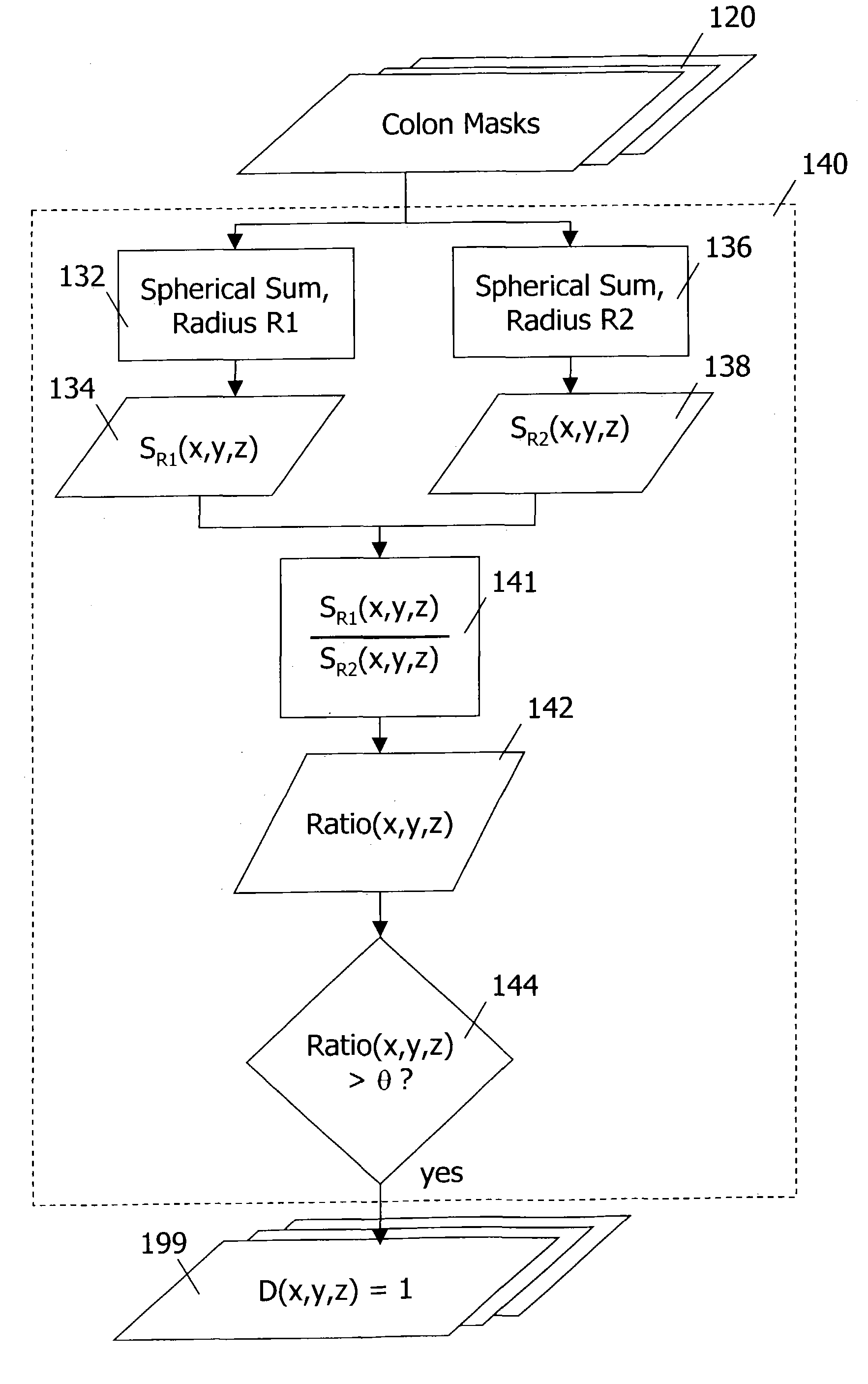
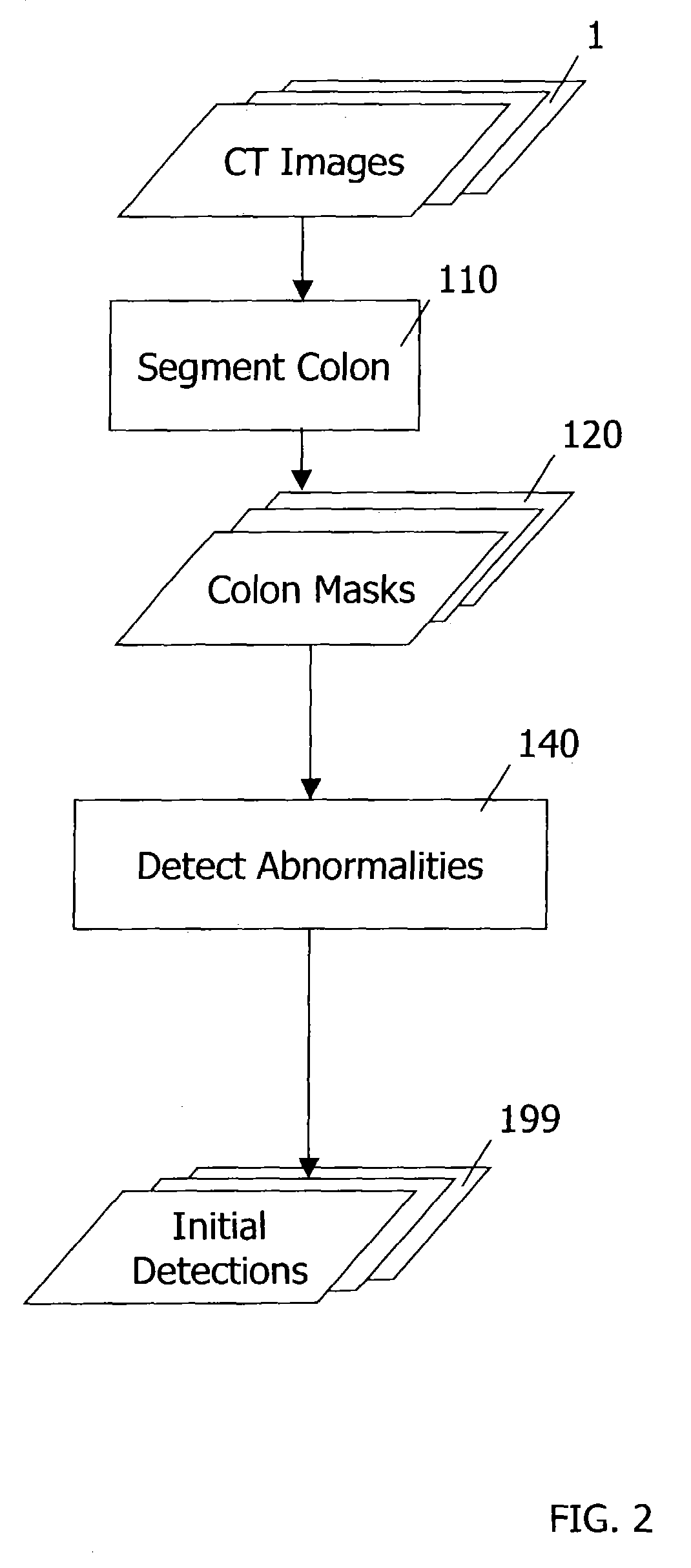
Computer-aided detection methods in volumetric imagery
This invention provides a method for detecting abnormalities in medical images, particularly for the detection of polyps in the colon from computed tomography imagery. Specifically a set of colon masks is input to a detector where summations over spherical volumes with two different radii are computed. Abnormalities are detected based on the ratio of spherical summation values computed for every pixel location.
Owner:ICAD INC
Use of computer-aided detection system outputs in clinical practice
InactiveUS7308126B2Efficient and precise positioningAccurate representationImage enhancementImage analysisMedicineDisplay device
The present invention provides for the use of computer-aided detection (CAD) system output displays for providing accurate representations of areas for subsequent exams. Since the CAD output, unlike the original medical imagery, is not used during the initial reading, the radiologist does not mark it until a final determination is reached regarding subsequent procedures. Additionally, since the CAD output contains versions of the original imagery, the regions indicated by the radiologist are shown in the context of the particular anatomical detail for a given patient. This detail assists the technologist, other physicians and patients in more efficiently and accurately locating the exact area for subsequent exams.
Owner:ICAD INC
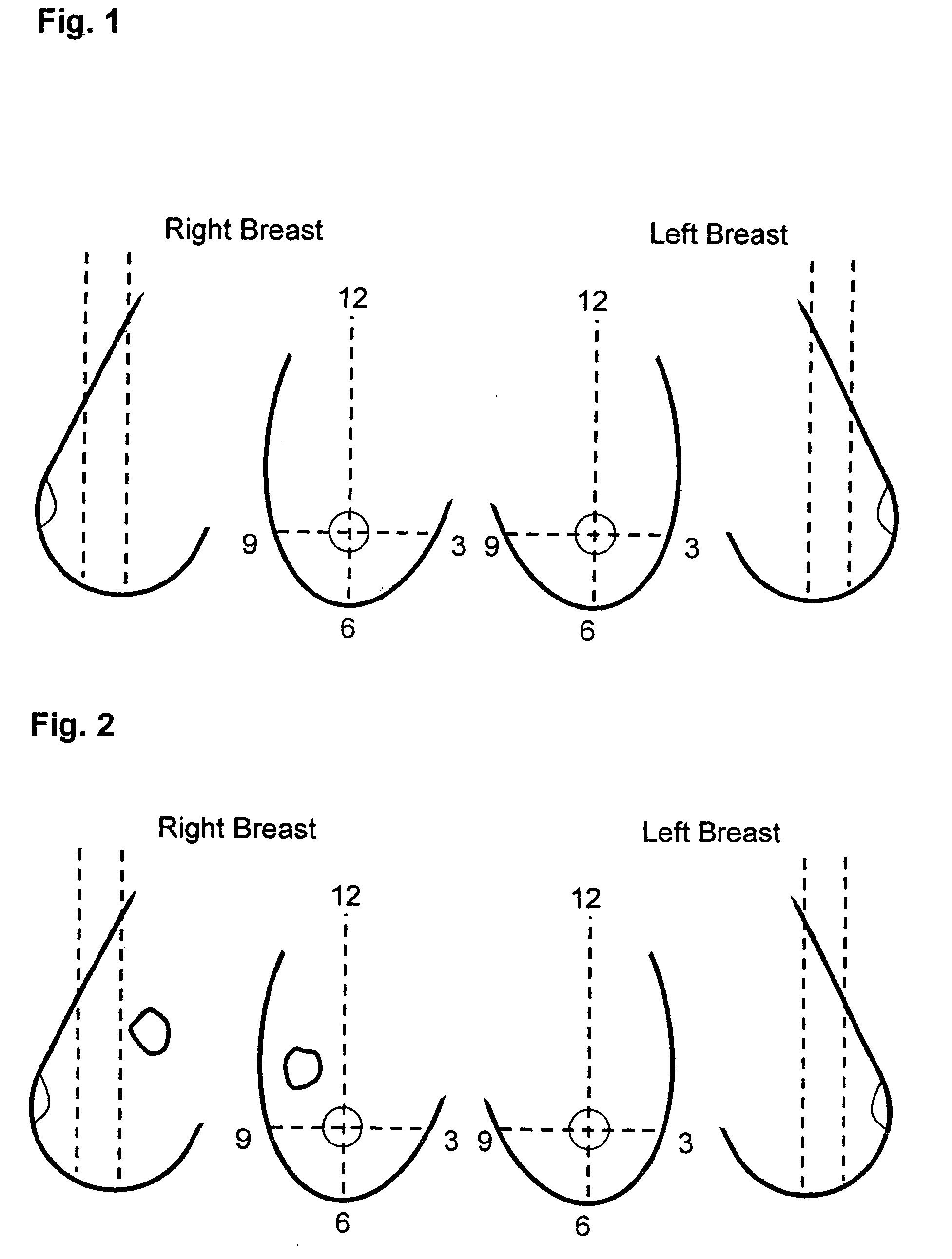
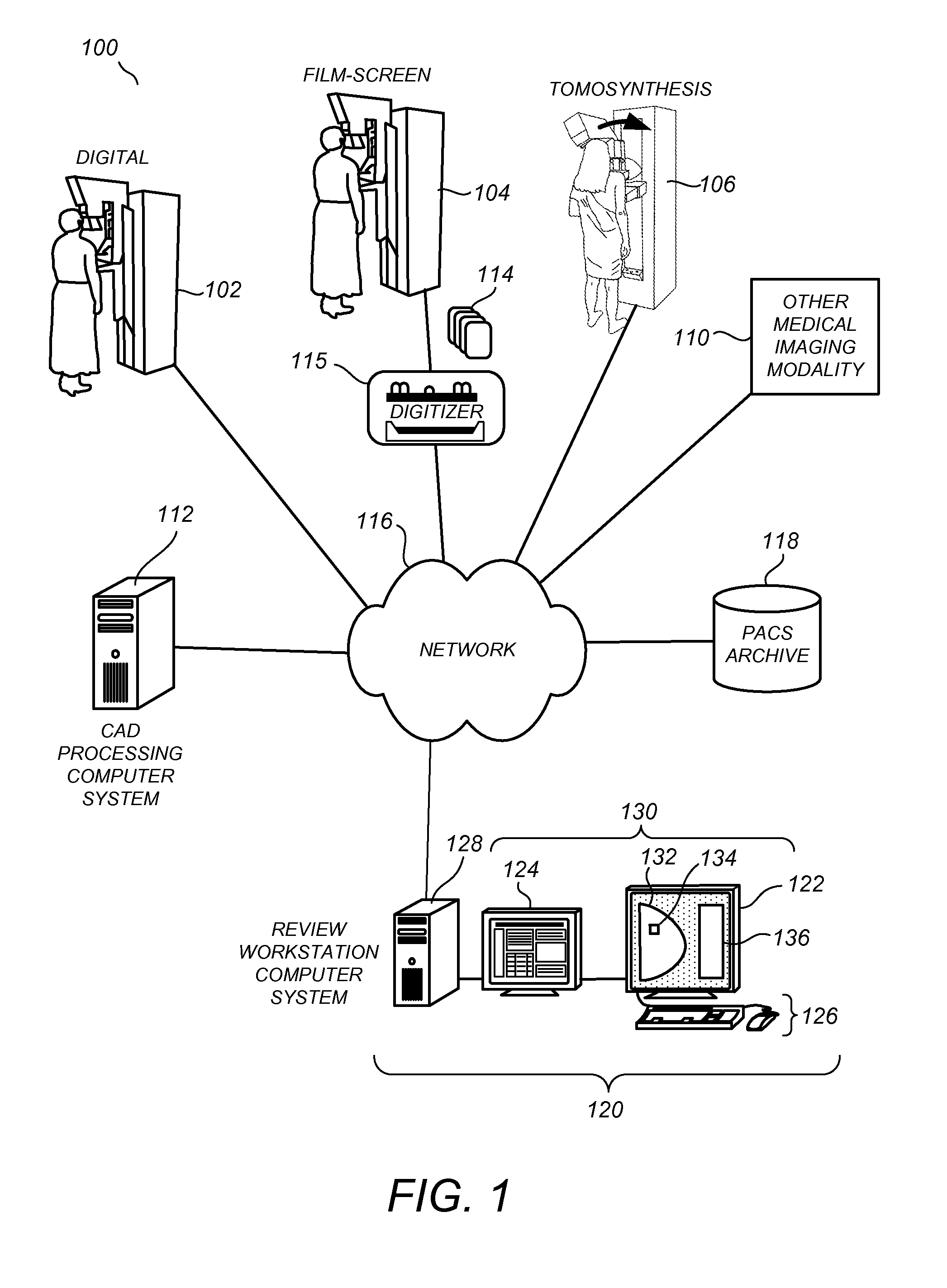
Method and system for automatic identification and orientation of medical images
InactiveUS7146031B1Reduce errorsShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisDigital mammogramDisplay device
A method and system for computer-aided detection of abnormal lesions in digital mammograms is described, wherein digital films are processed using an automated and computerized method of detecting the order and orientation of a set of films. In one embodiment, anatomic features are used to detect the order, orientation and identification of a film series. In another embodiment of the invention, a technologist feeds films into the system in any order and orientation. After processing, the system provides an output on a display device to a radiologist that is in an order and orientation preferred by the radiologist. In yet another embodiment of the invention, films from one case are distinguished from films of another case. In this manner and through the use of a bulk loader, a large number of films can be stacked together and fed into the system at one time.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
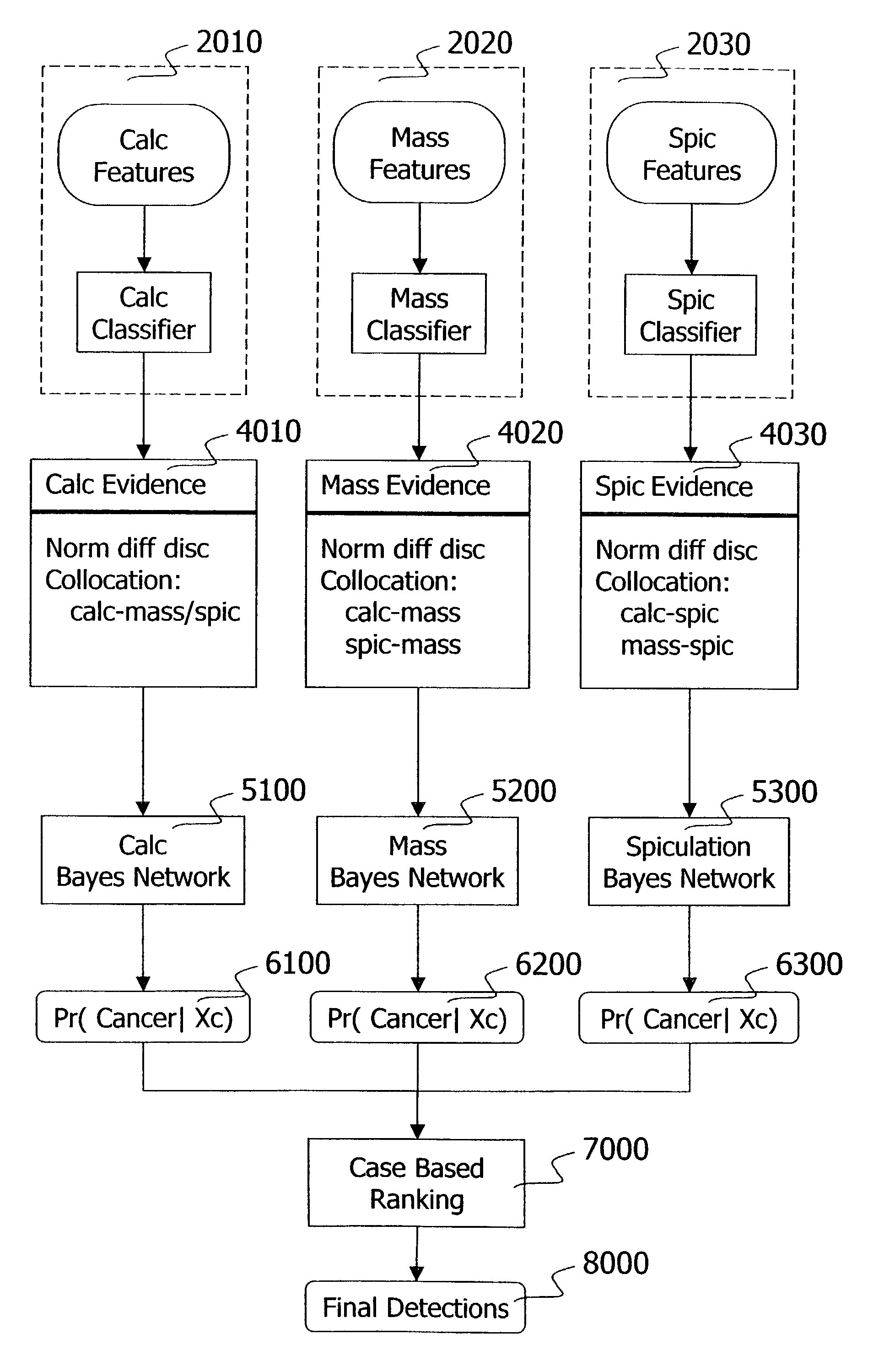
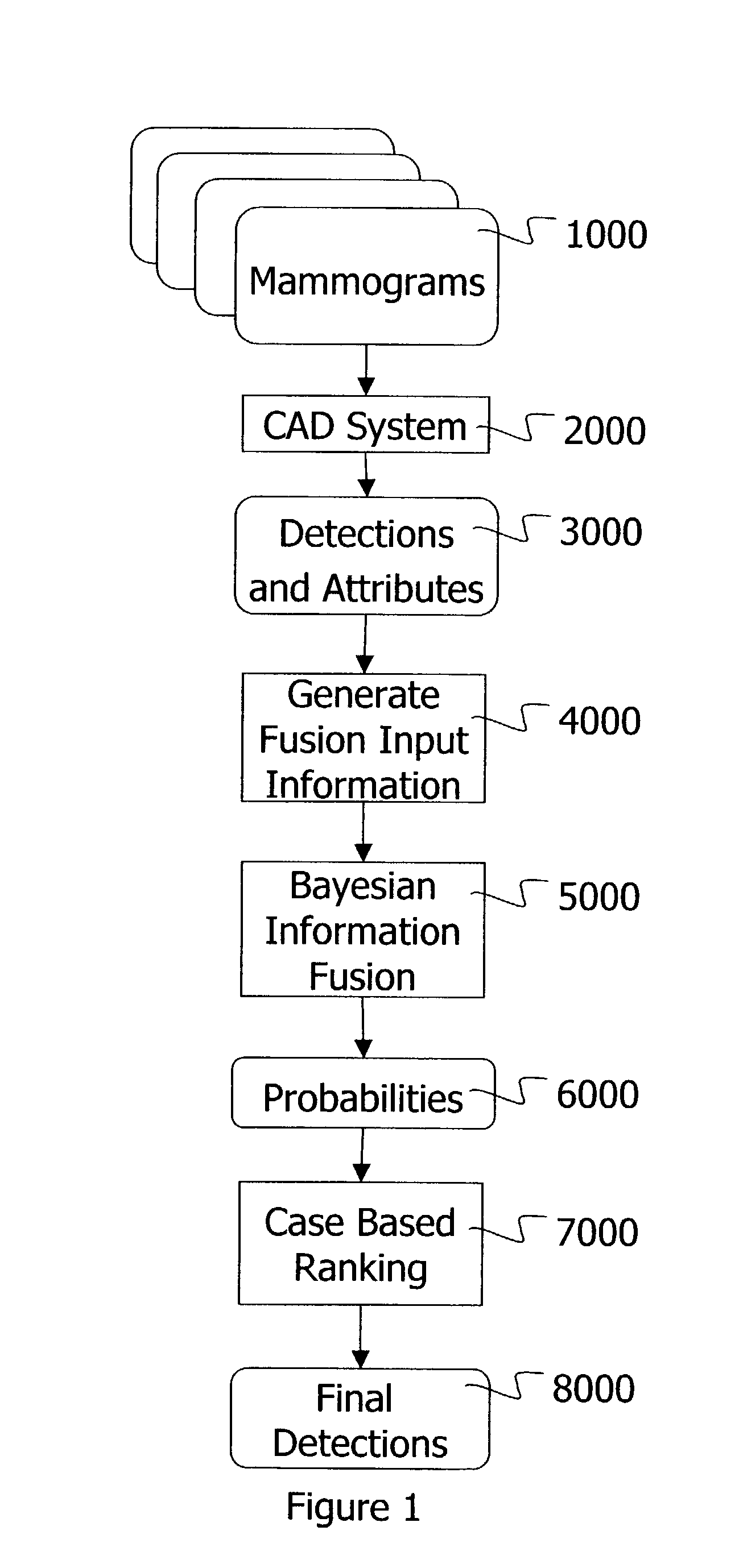
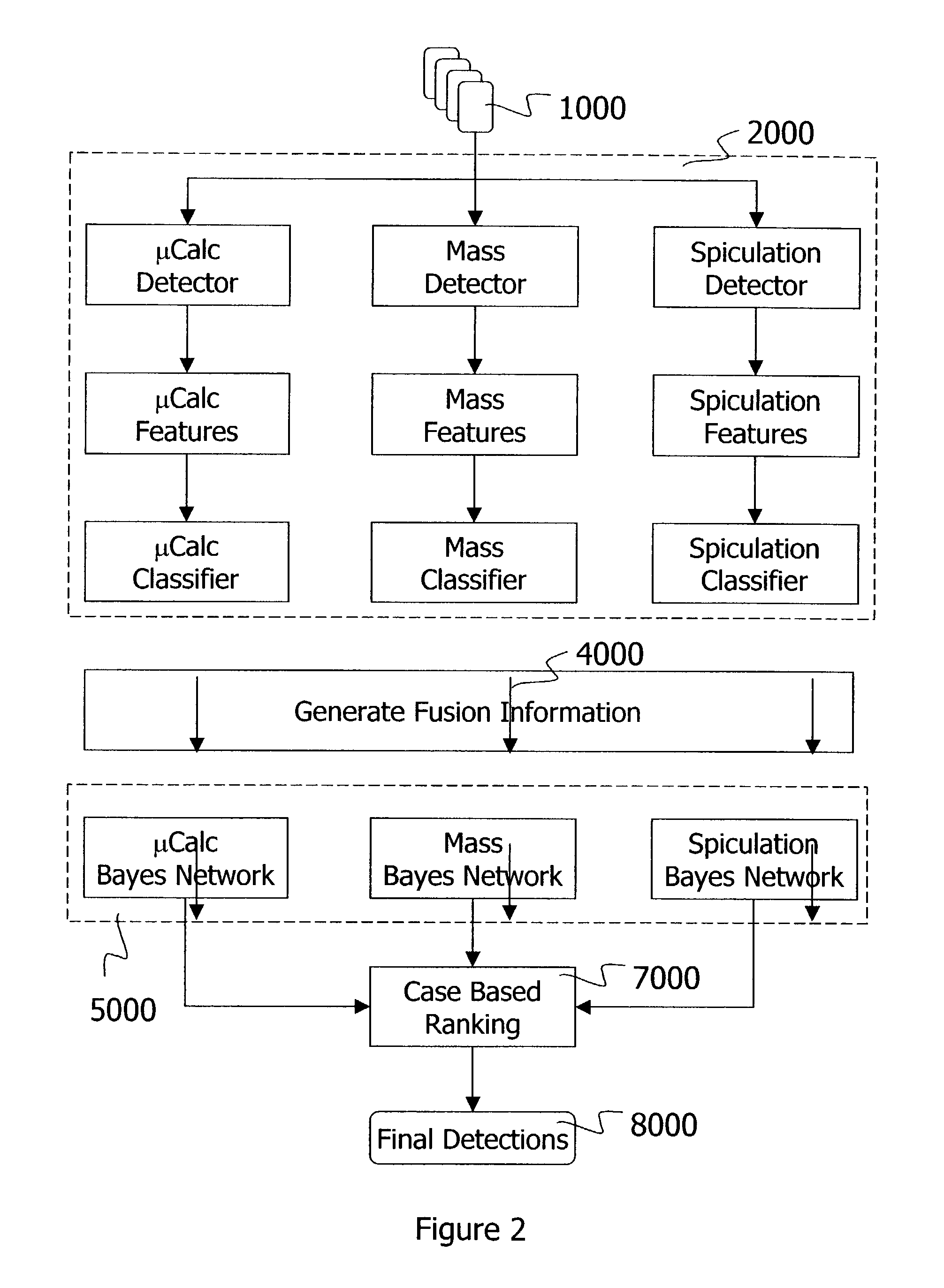
Information fusion with Bayes networks in computer-aided detection systems
This invention provides an information fusion method for multiple indicators of cancers detected with multiple channels. Each channel consists of specifically tuned detectors, features, classifiers and Bayes networks. The outputs of the Bayes networks are probabilities of malignancy for the detections passing the corresponding classifier.
Owner:ICAD INC
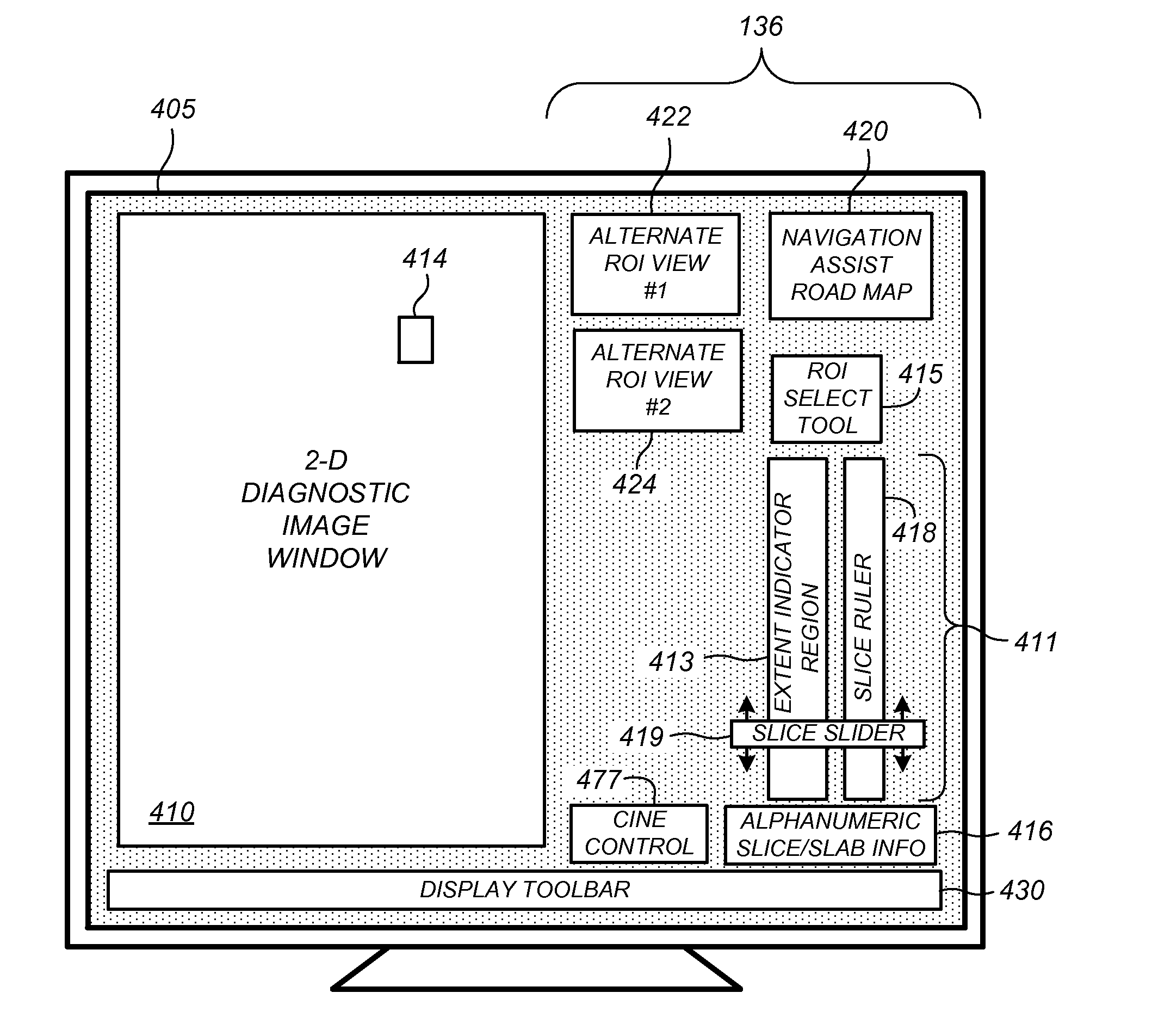
Displaying Computer-Aided Detection Information With Associated Breast Tomosynthesis Image Information
Methods, systems, and related computer program products for processing and displaying computer-aided detection (CAD) information associated with medical breast x-ray images, such as breast x-ray tomosynthesis volumes, are described. An interactive graphical user interface for displaying a tomosynthesis data volume is described that includes a display of a two-dimensional composited image having slabbed sub-images spatially localized to marked CAD findings. Also described is a graphical navigation tool for optimized CAD-assisted viewing of the data volume, comprising a plurality of CAD indicator icons running near and along a slice ruler, each CAD indicator icon spanning a contiguous segment of the slice ruler and corresponding in depthwise position and extent to a subset of image slices spanned by the associated CAD finding, each CAD indicator icon including at least one single-slice highlighting mark indicating a respective image slice containing viewable image information corresponding to the associated CAD finding.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
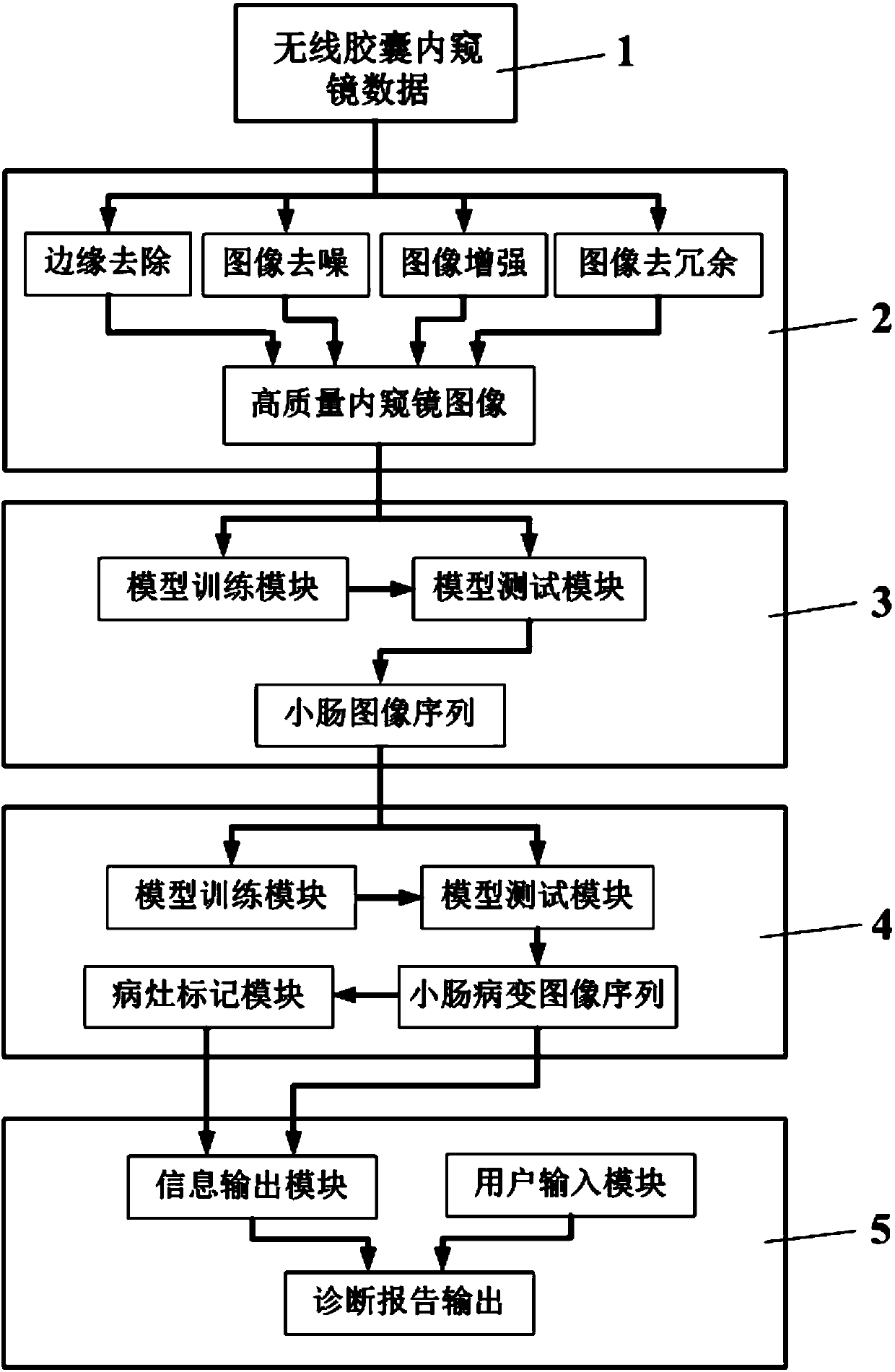
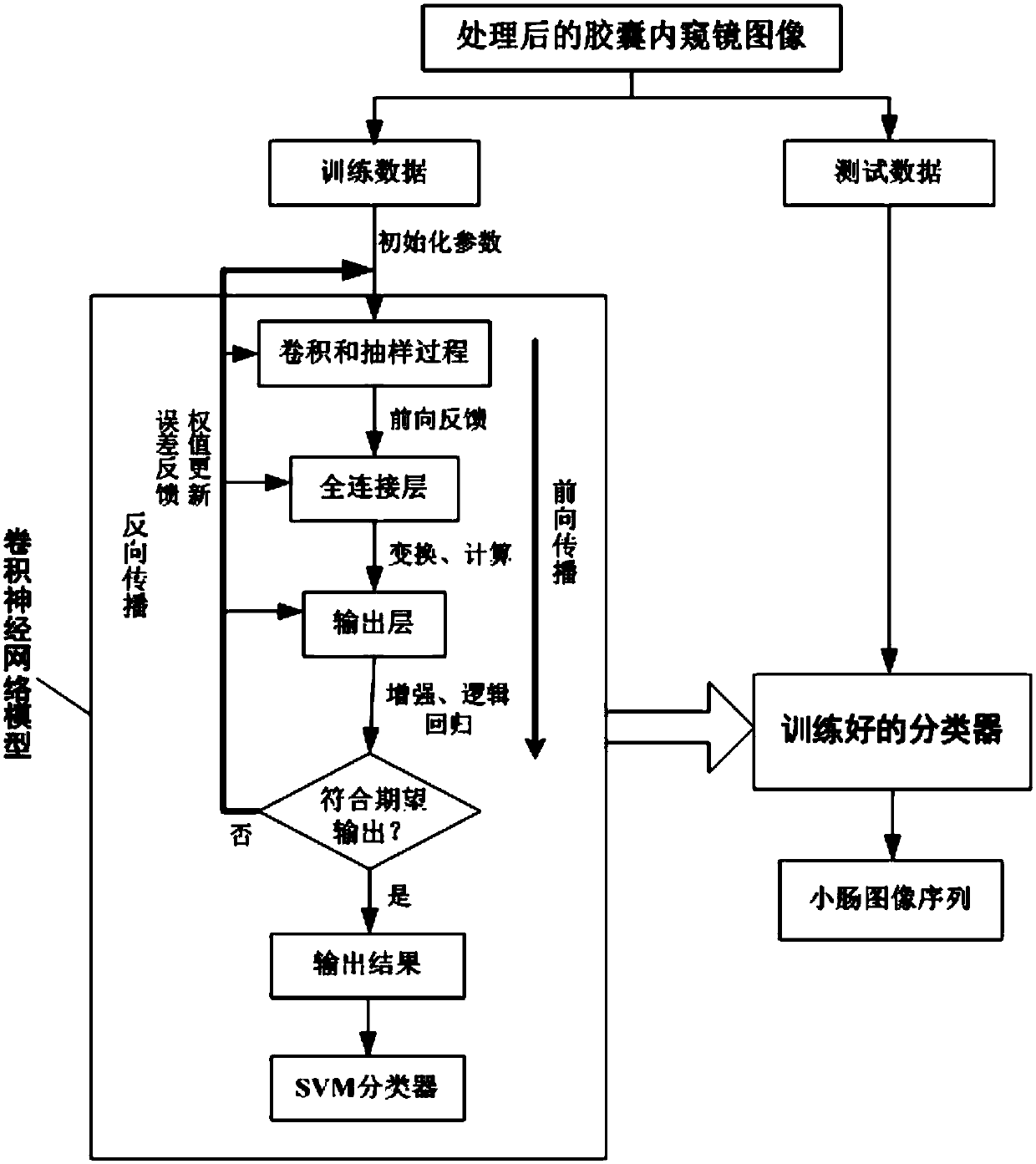
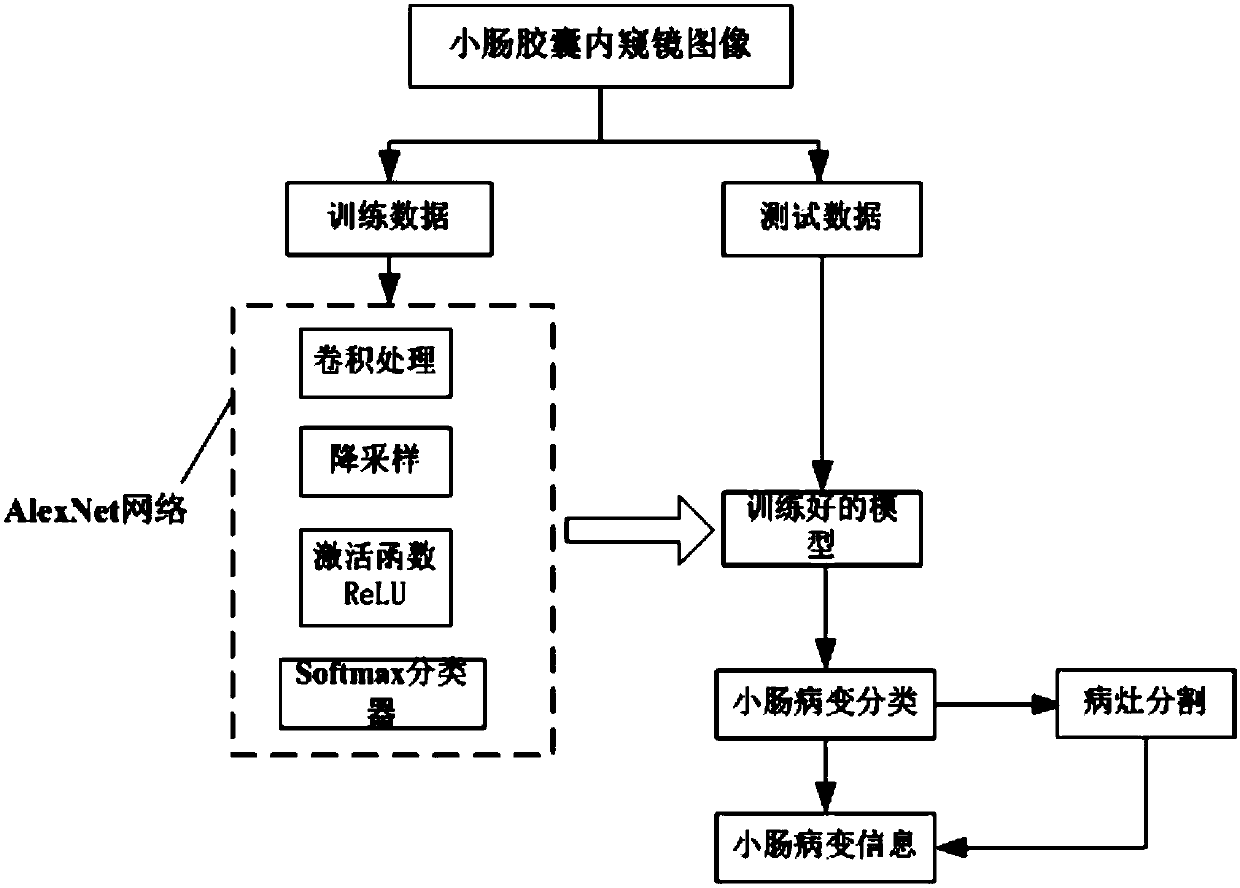
Wireless capsule endoscope-based computer-aided detection system and detection method for pathological changes in small intestine
InactiveCN107730489AHigh practical valueReduce work intensityImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic modalitiesCapsule Endoscopes
The invention discloses a wireless capsule endoscope small intestine lesion computer auxiliary detection system and method. At present, the technology of the capsule endoscope in the aspect of intelligent lesion identification and accurate positioning is very limited. The data input module is used for acquiring the video data of the wireless capsule endoscope of the patient, and an image of the capsule endoscope is obtained by extracting a video frame technology; the image preprocessing module is used for preprocessing the image of the wireless capsule endoscope, the small intestine image recognition module is used for recognizing and extracting a small intestine image and an image sequence in the preprocessed capsule endoscope image; the small intestine lesion analysis and positioning module is used for identifying and classifying the small intestine lesion and extracting the specific position of the focus; the user interaction module forms an auxiliary diagnosis result according to the small intestine lesion information and the analysis result of the positioning module, and the doctor can confirm, modify or input the medical advice so as to form a diagnosis report. According to the invention, the practical value of the capsule endoscope in clinic is promoted, so that a more efficient and more standard diagnosis mode is formed.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Method and system for projective comparative image analysis and diagnosis
A technique is provided for comparative image analysis and / or change detection using computer assisted detection and / or diagnosis (CAD) algorithms. The technique includes registering a three-dimensional image and a two-dimensional image, projecting the registered three-dimensional image to generate a reprojected two-dimensional image, and automatically comparing the two-dimensional image and the reprojected two-dimensional image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Automated optical metrology computer aided inspection station and method of operation
InactiveUS20170249729A1Quick testImprove throughputProgramme controlImage analysisGeometric consistencyRobotic arm
An automated 3D Optical Metrology Scanning and Computer Aided Inspection System for dimensional inspection of precision manufactured parts. The system example and implemented configuration is based within a relocatable cabinet providing ambient light and optional temperature control. The cabinet further includes a part placement area having an optical metrology scanner positioned over a multi-axis robotic arm positioned in the part placement area. The robotic arm is constructed and arranged to grip and manipulate parts within a field of view of the optical metrology scanner. The robotic arm provides adequate multi-axis control to rotate and tilt and translate tp manipulate the part to allow substantially every surface of the part to be scanned. Dimensional comparison and analysis software application provide geometric conformance / deviation plus extraction of the dimensions indicated in the part computer aided design (CAD) model.
Owner:LEVEL 3 INSPECTION
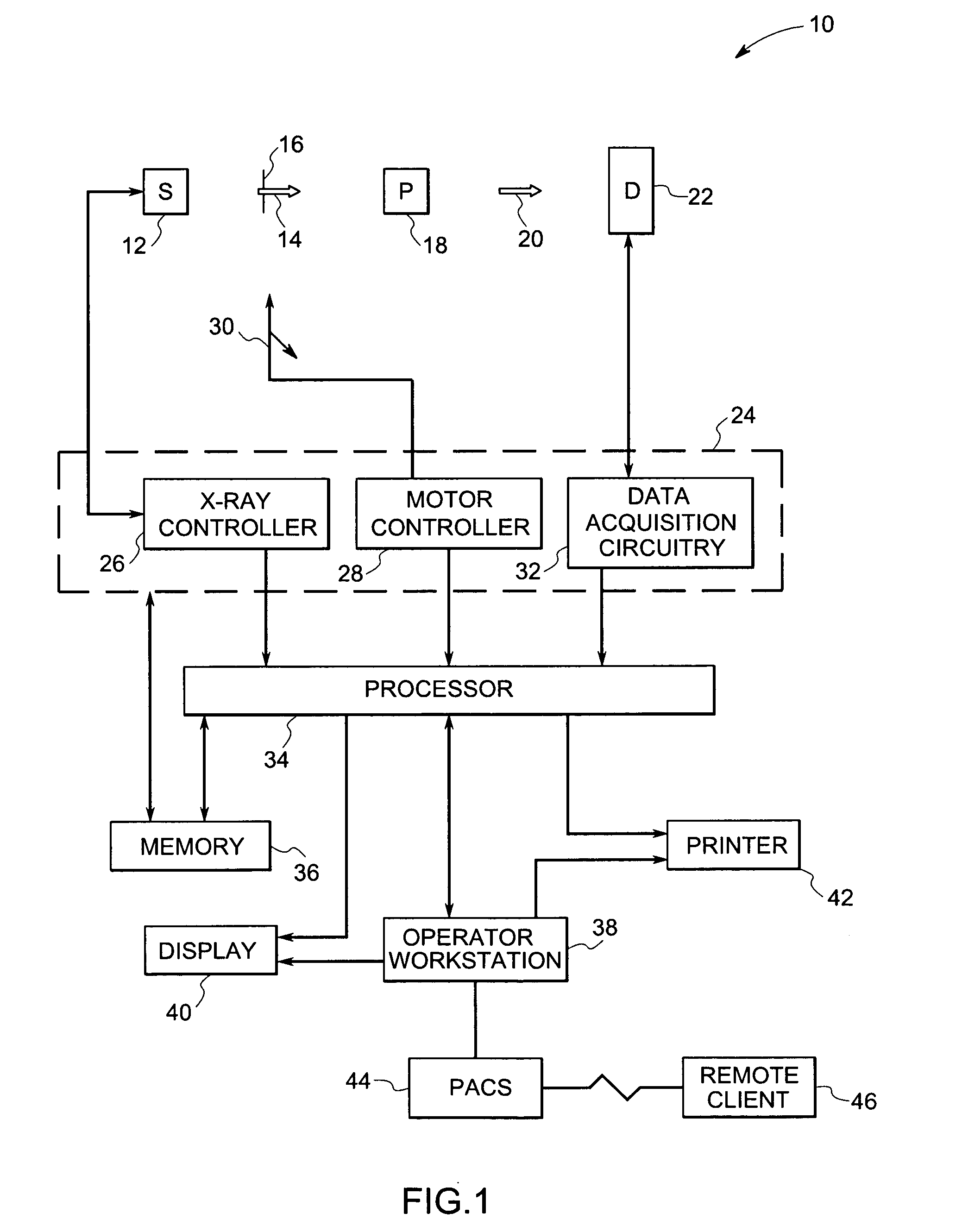
Methods and apparatus for anomaly detection
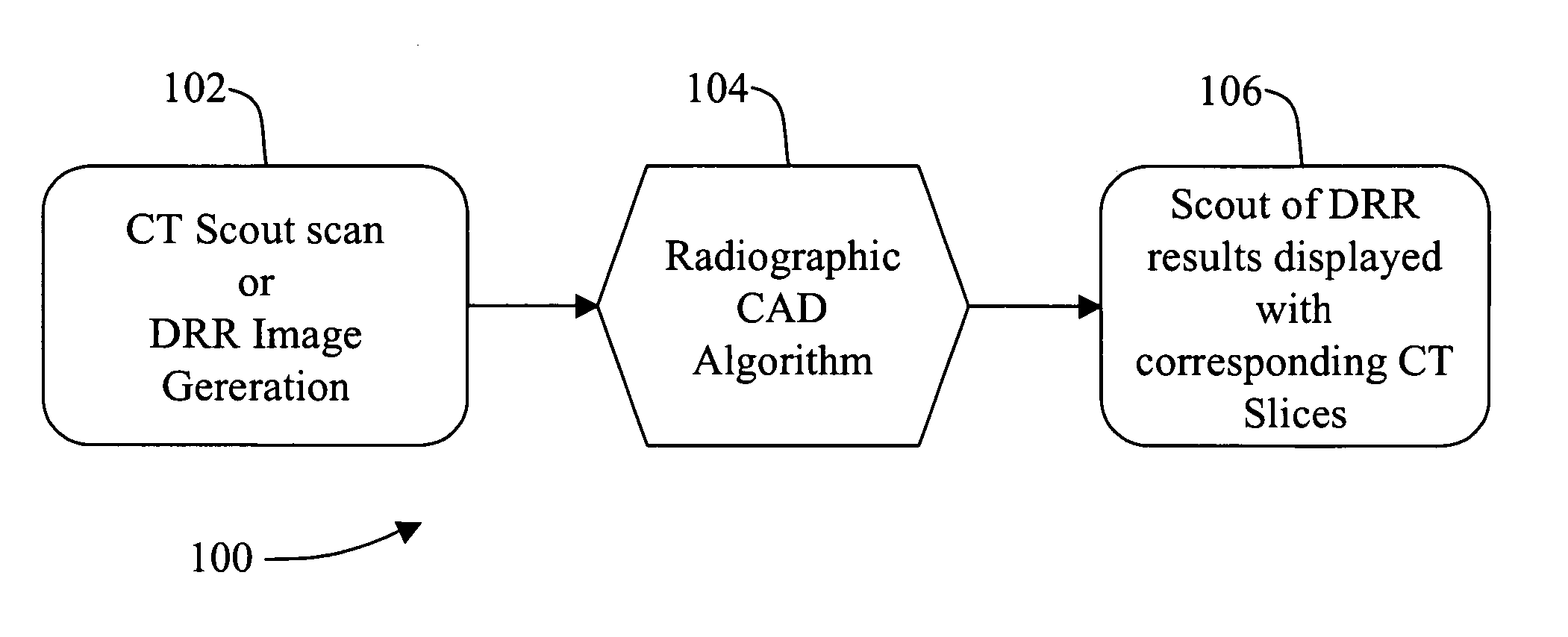
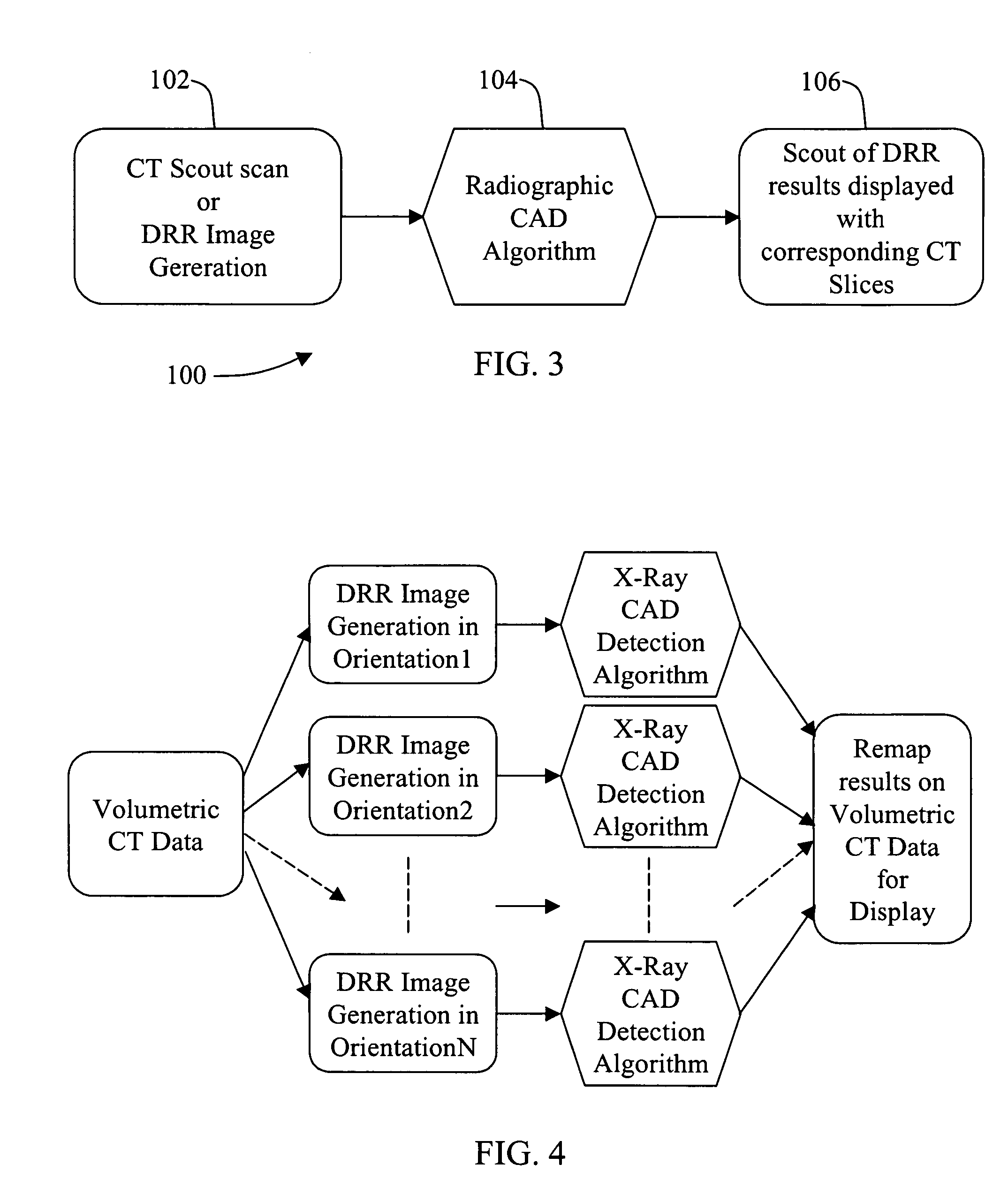
ActiveUS7072435B2Radiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsAnomaly detectionComputing tomography
A method for detecting an anomaly includes performing a computed tomography (CT) scout scan to obtain data, and supplying the obtained data to a radiographic computer aided detection (CAD) algorithm.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
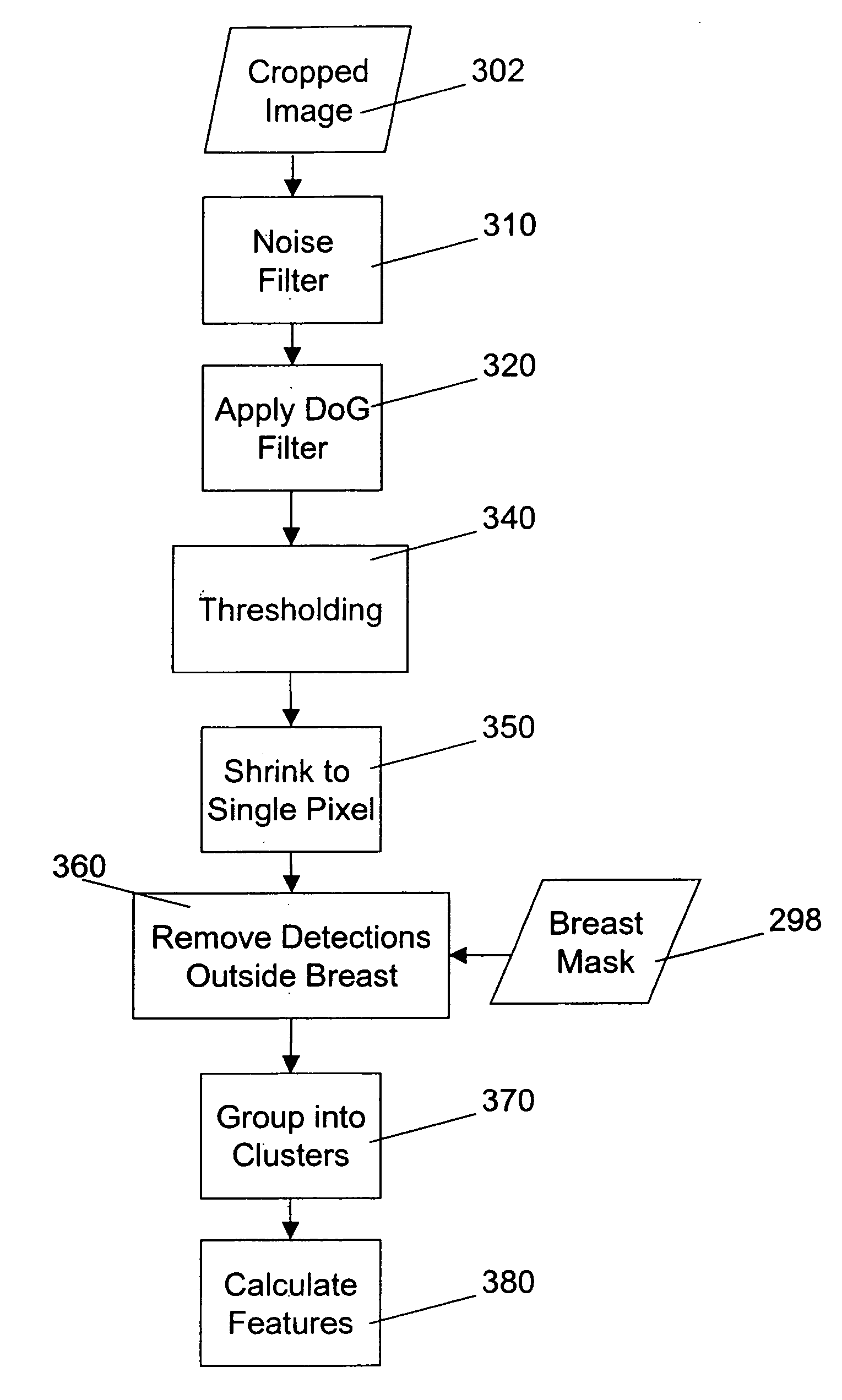
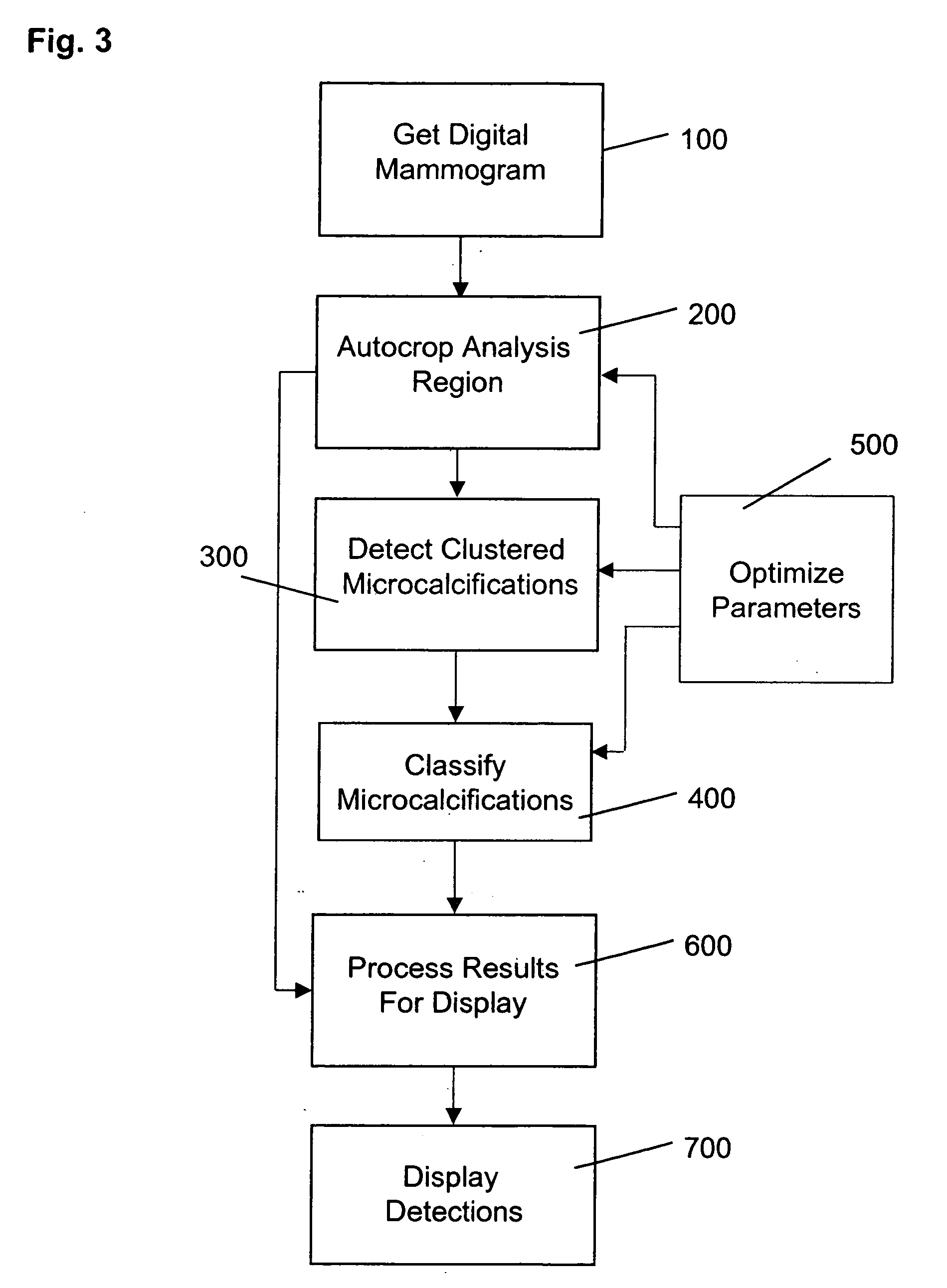
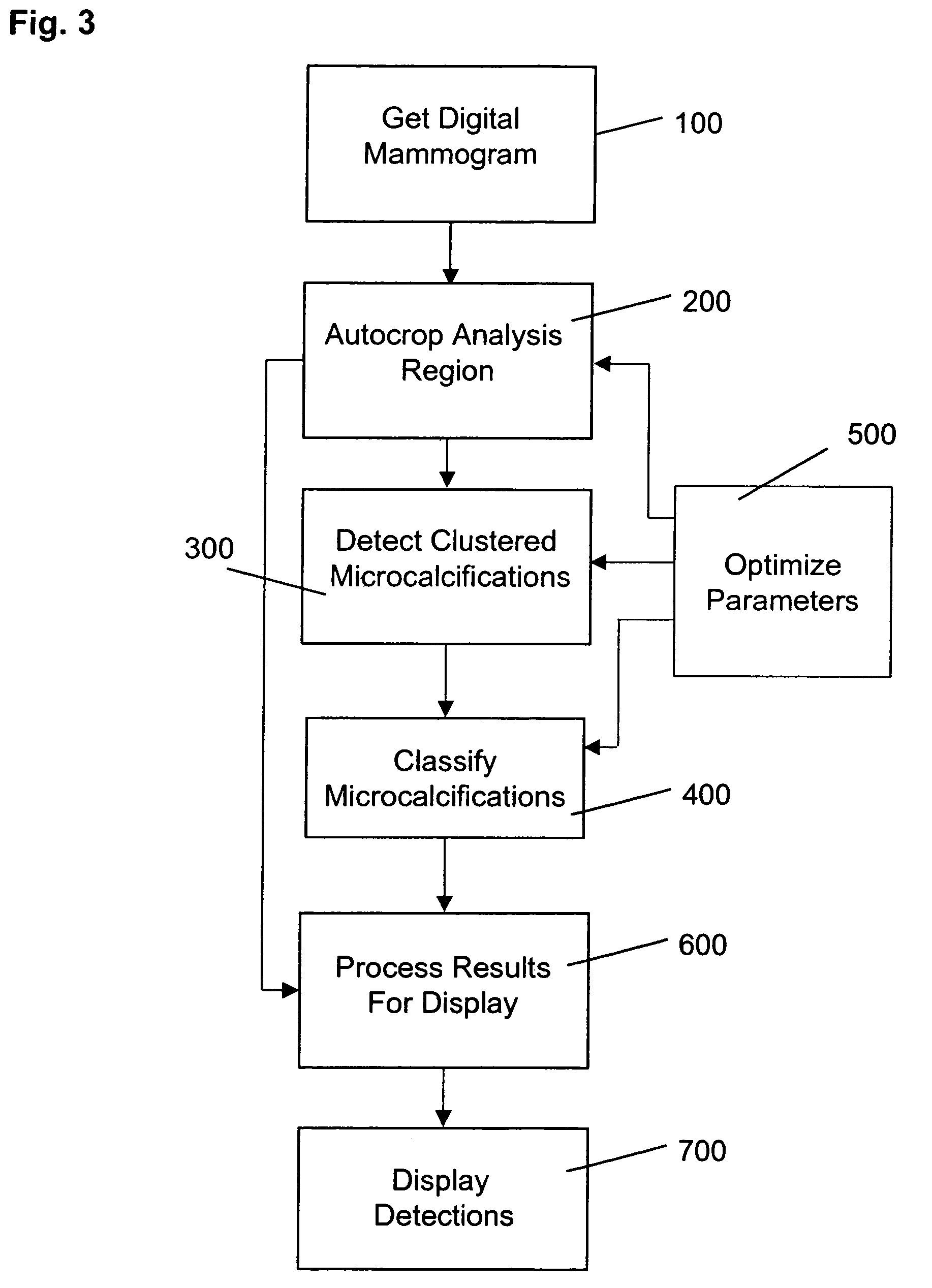
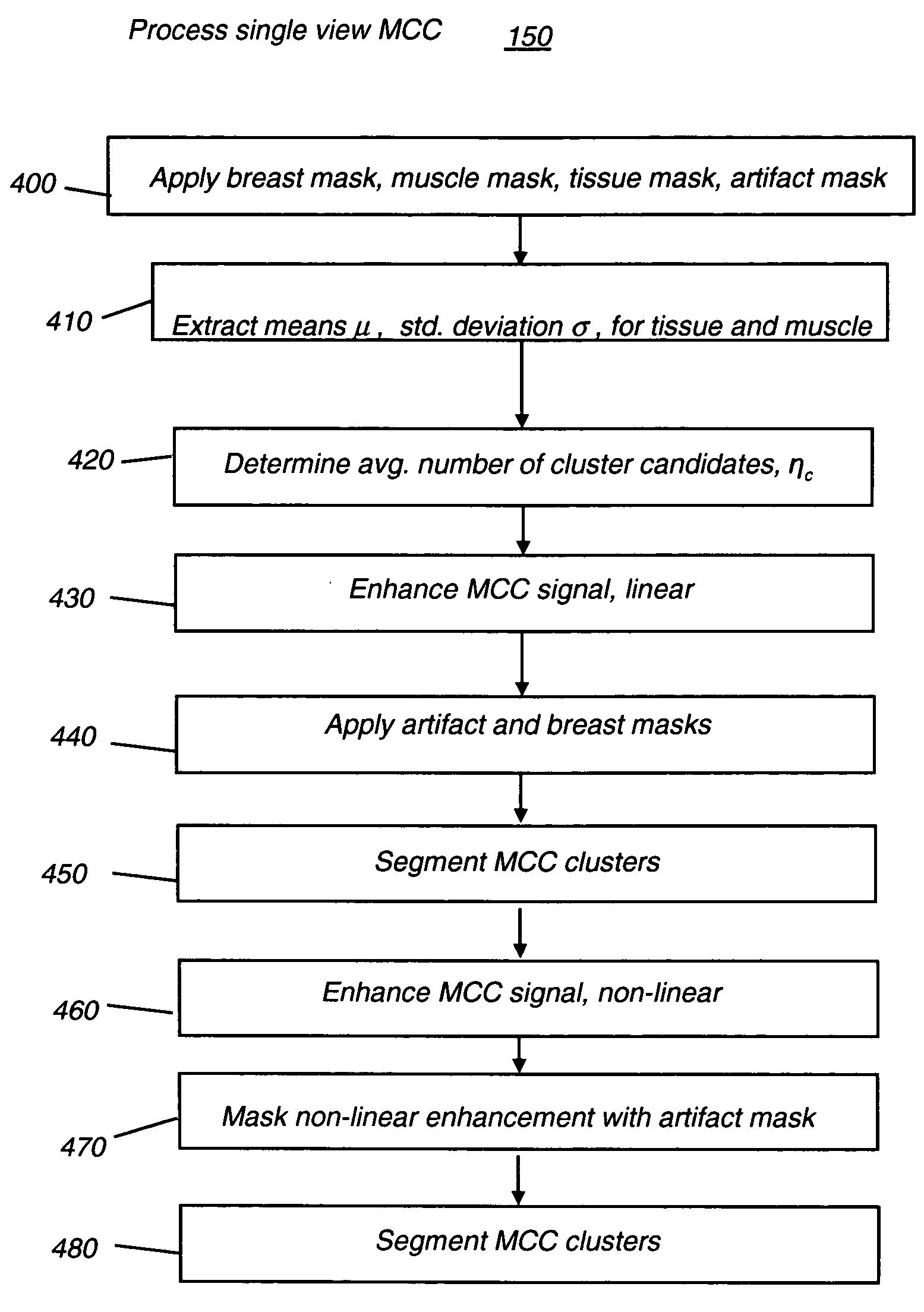
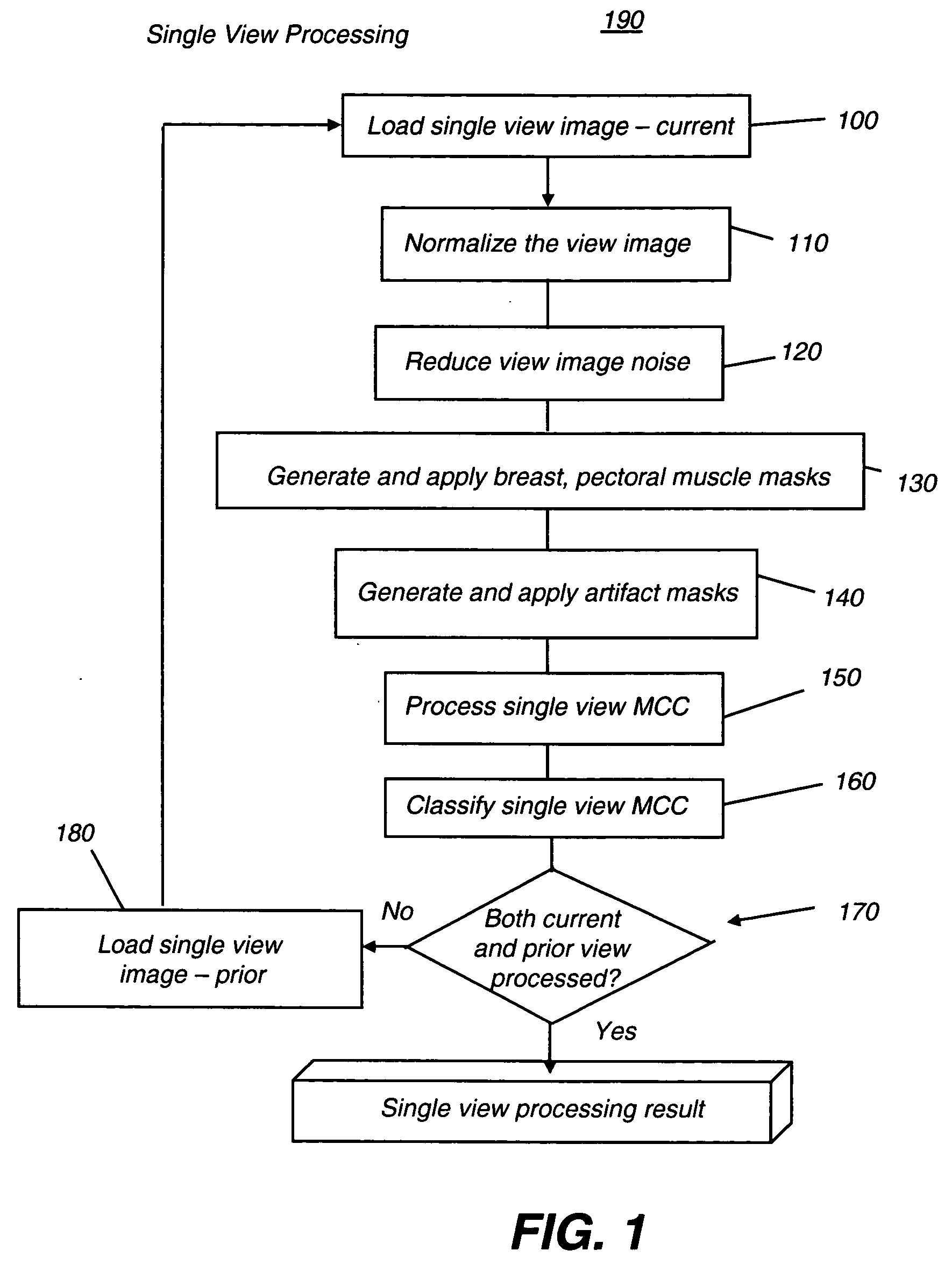
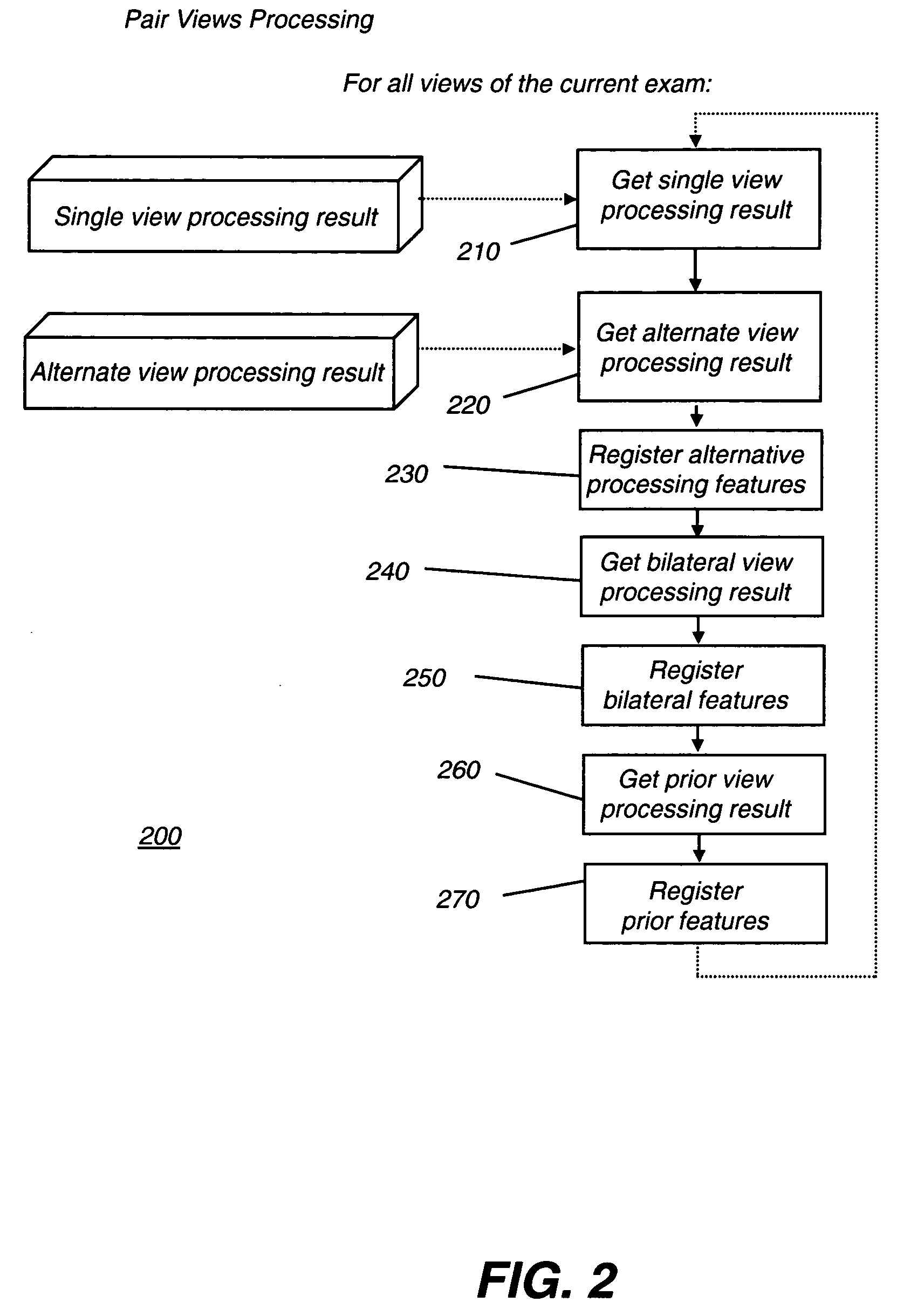
Computer aided detection of microcalcification clusters
InactiveUS20060147101A1Reduce edge effectsReduce image noiseImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
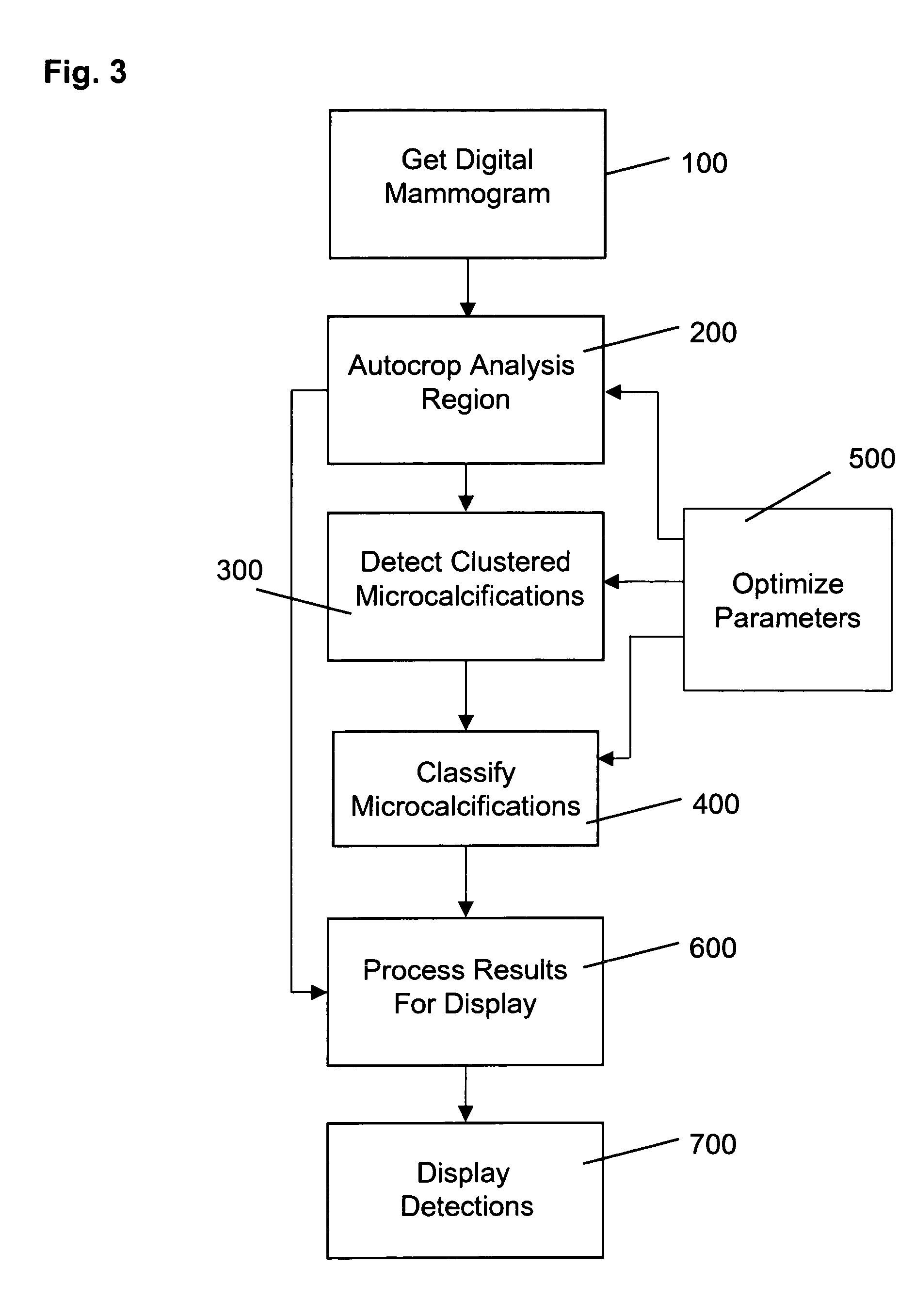
A method for computer-aided detection of microcalcification clusters obtains digital mammography data for a single view image and normalizes and filters the image data to reduce noise. A first mask is generated and applied to the image data for defining the breast structure, forming a first cropped image. A second mask is generated and applied to the image data for defining muscle structure, forming a second cropped image. An artifact mask corresponding to vascular calcifications and known imaging artifacts is generated and applied to the first and second cropped images, defining first and second artifact-masked cropped images. In a repeated sequence, portions of each artifact-masked cropped image are processed using an enhancement algorithm and reducing edge effects to obtain a set of microcalcification cluster candidates and suspected microcalcification clusters. Image processing algorithms remove false positives from the listing of microcalcification clusters and classify candidate microcalcification clusters to identify true positives.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com