Patents
Literature
57 results about "2d ultrasound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
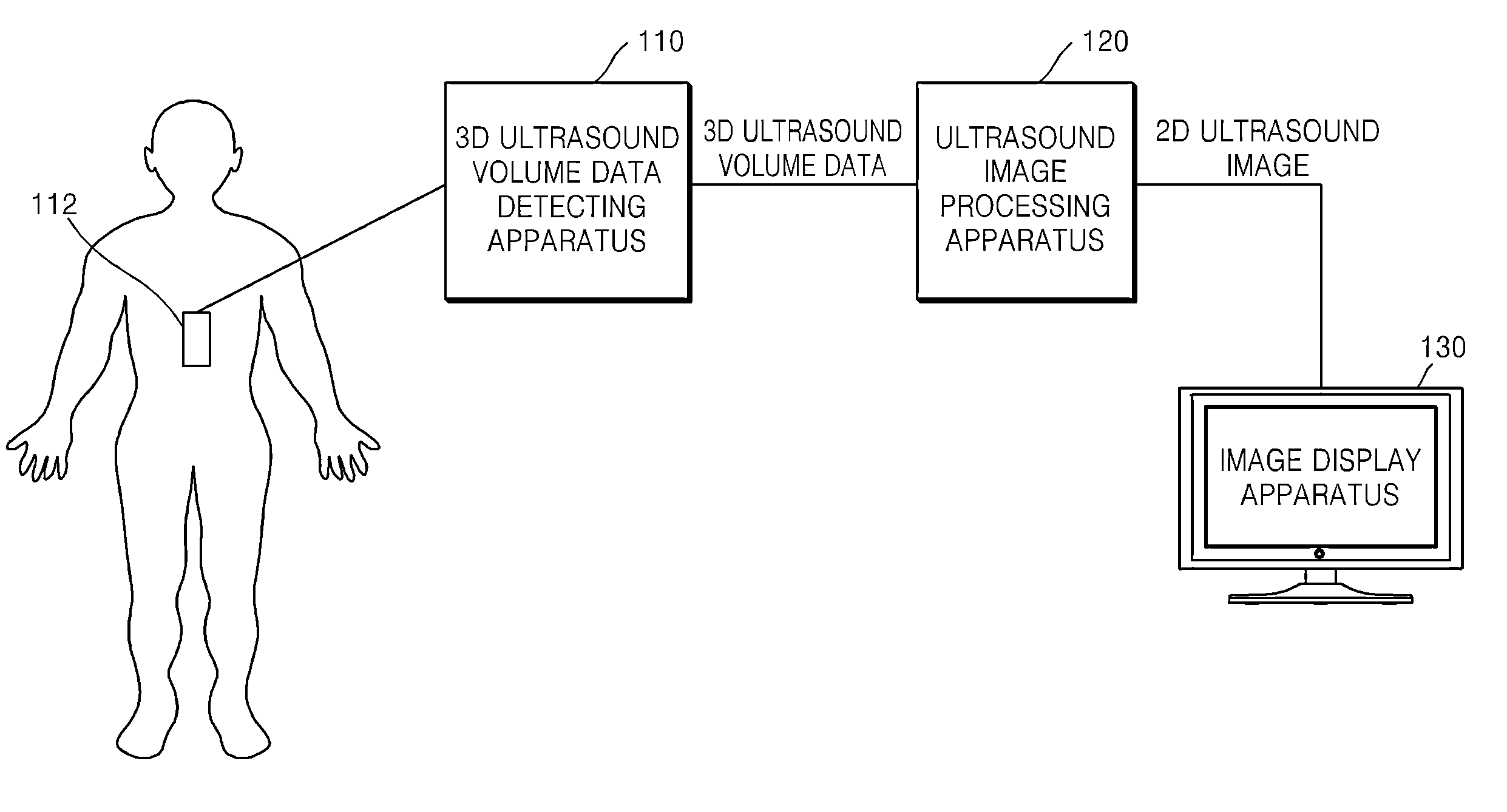
2D Ultrasound. It is the traditional ultrasound scanning. It means the probe sends and receives ultrasound frequency waves in one plane. Waves which are reflected back are black-and-white images of the fetus in a flat plane.
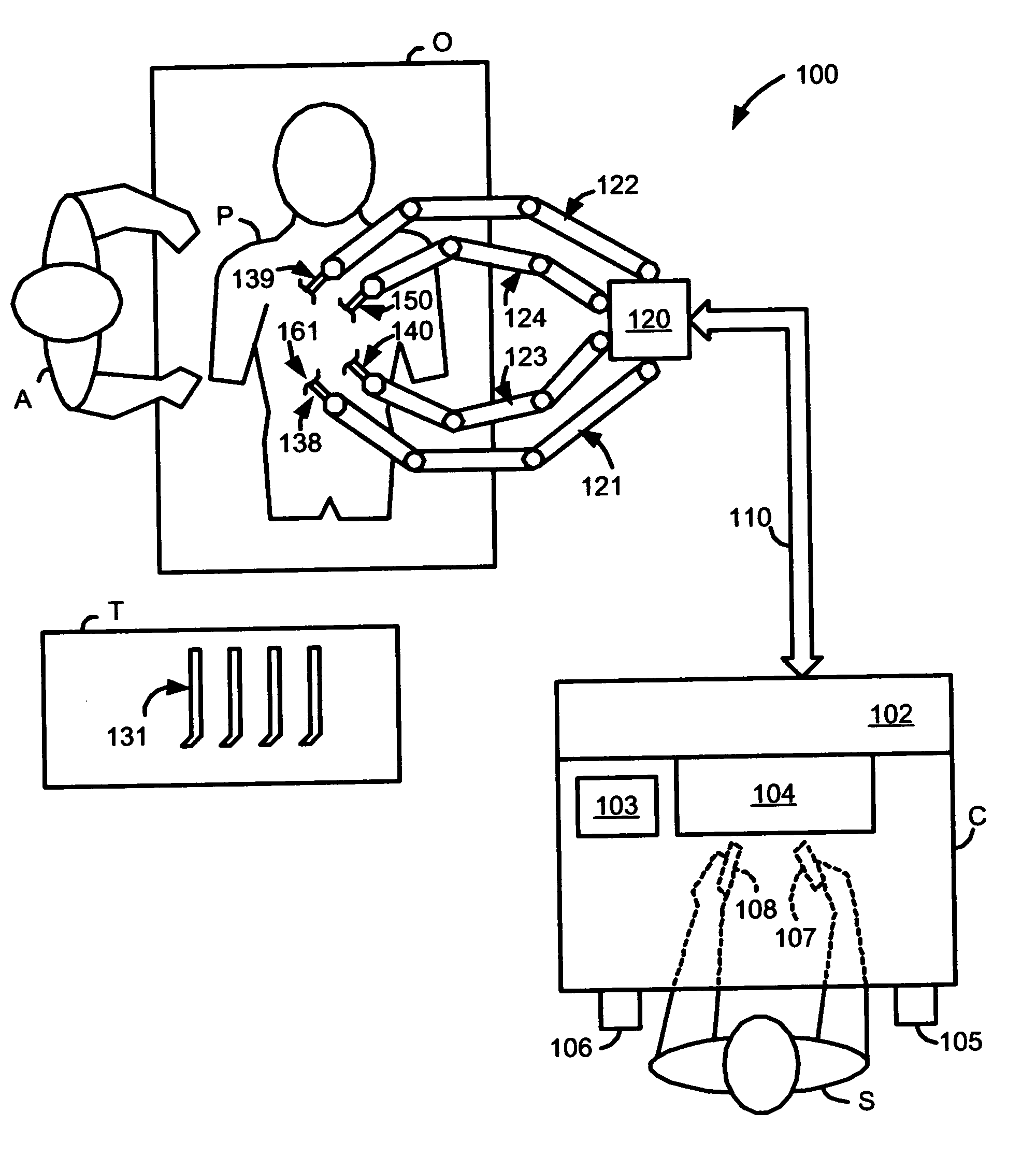
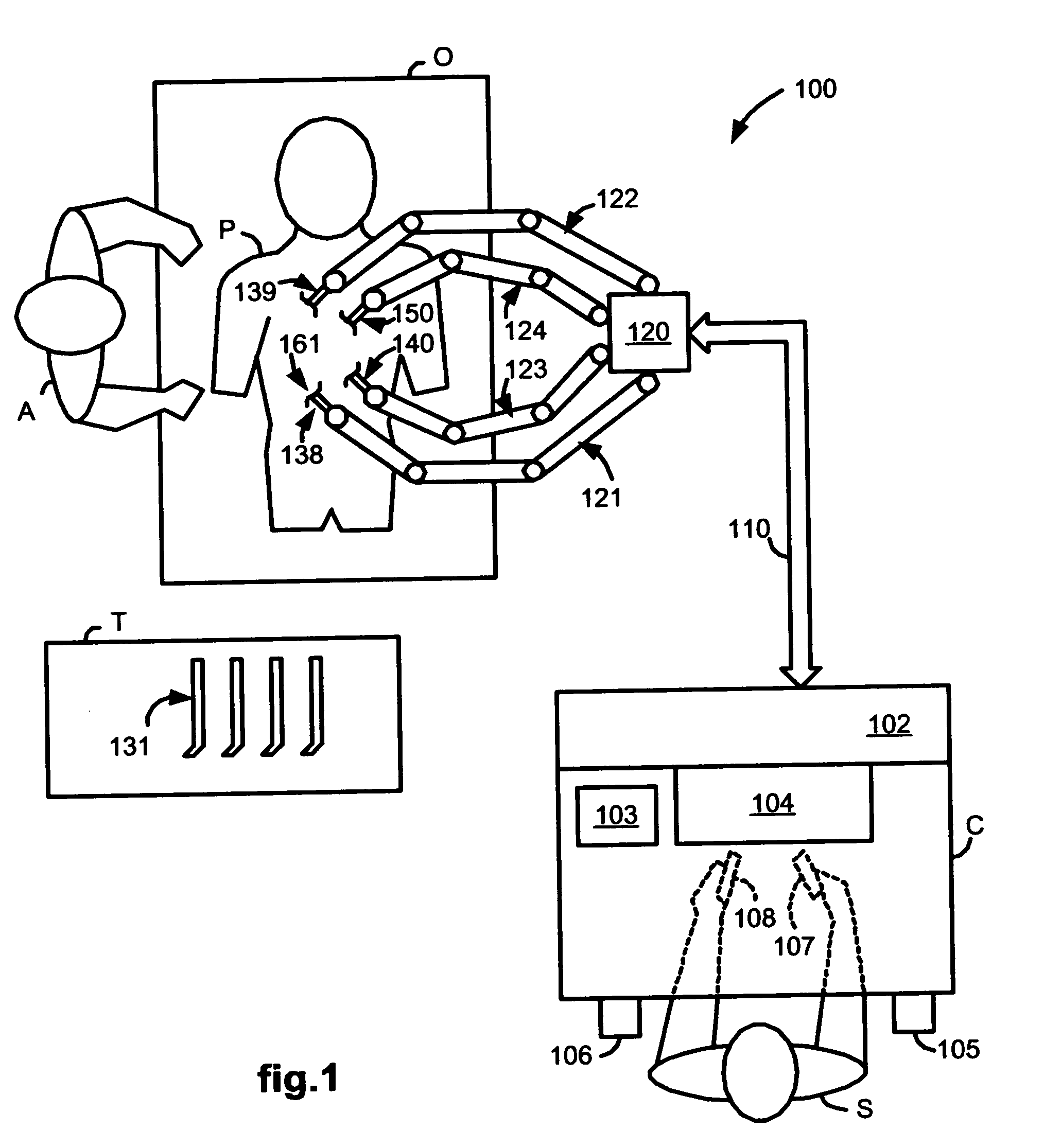
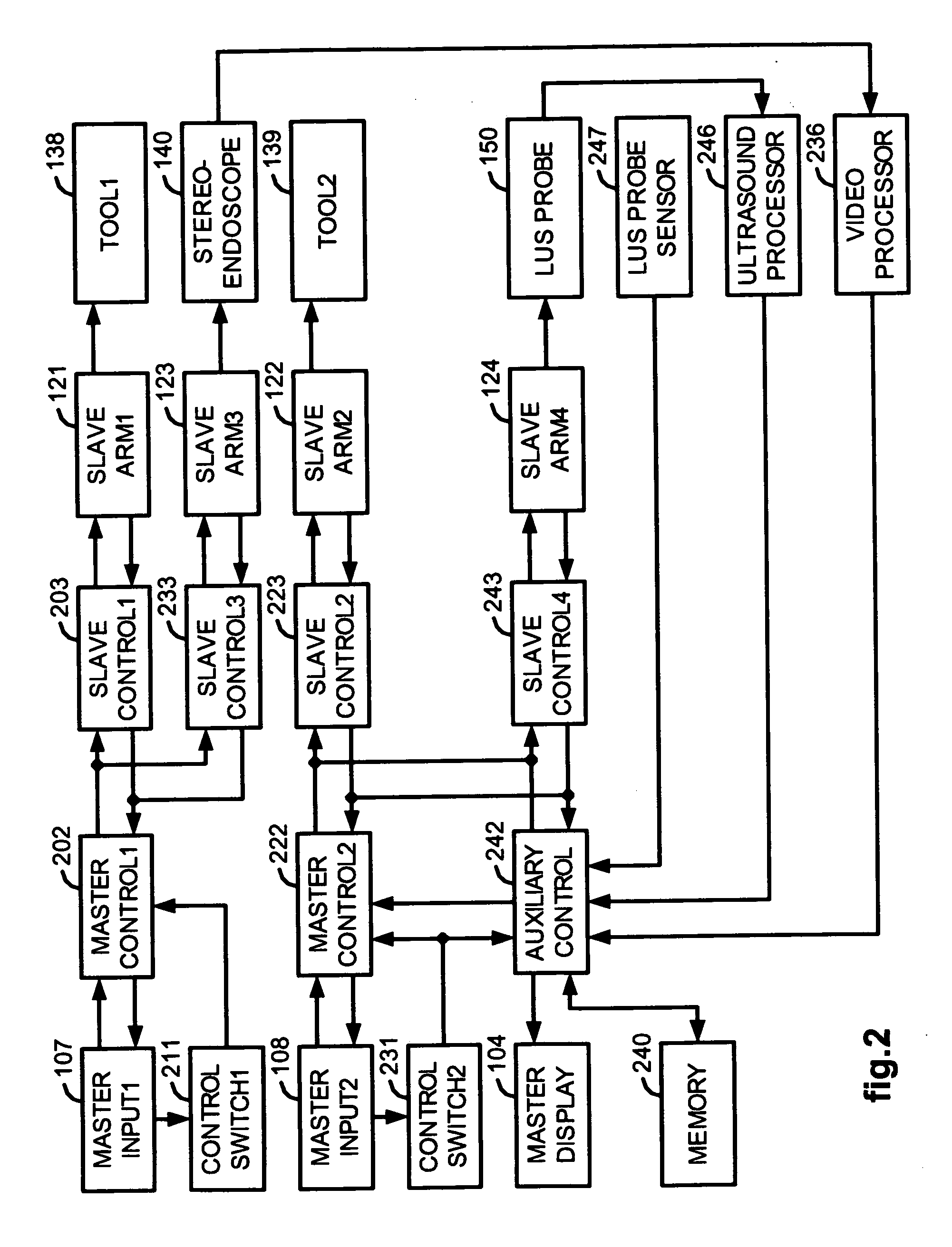
Laparoscopic ultrasound robotic surgical system
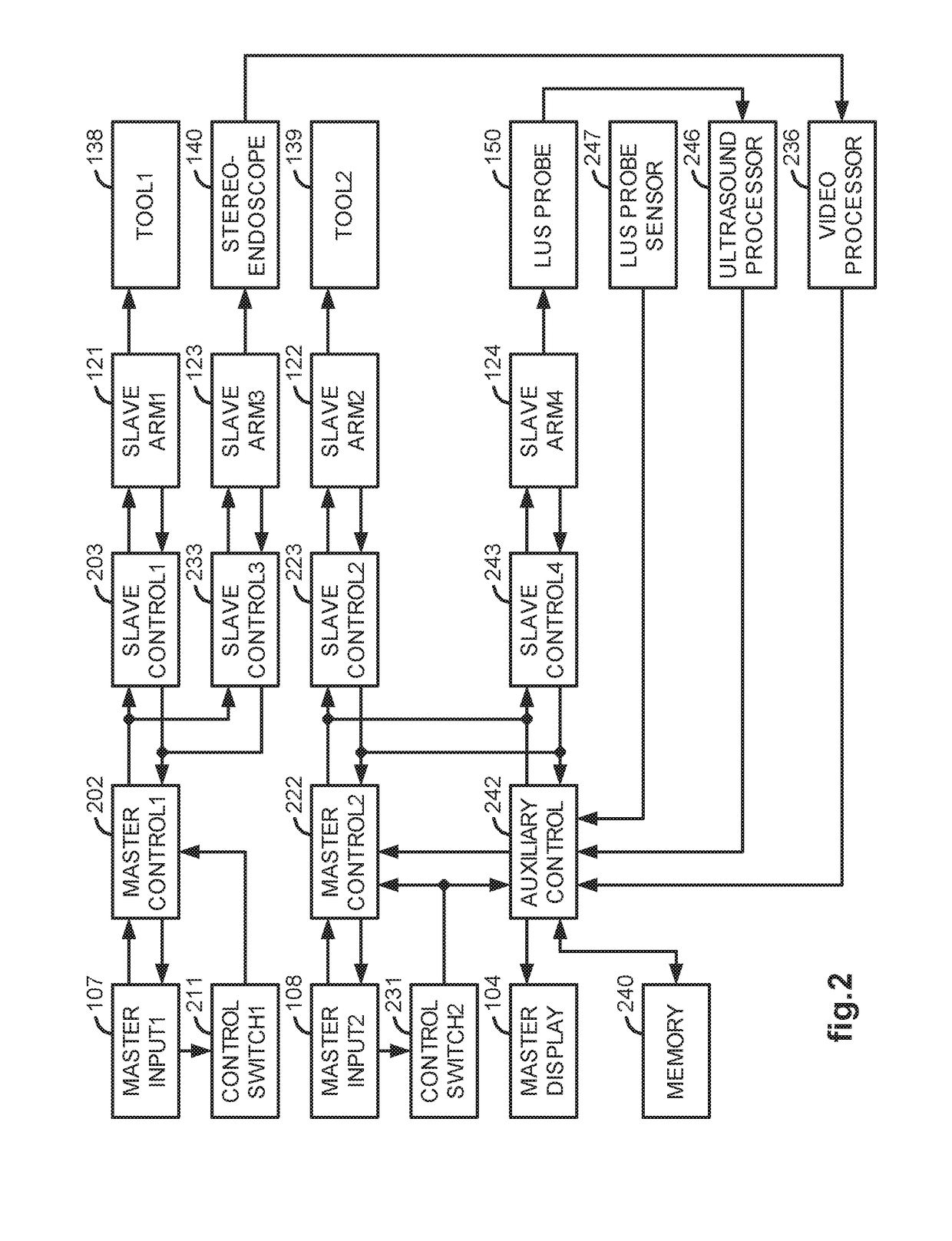
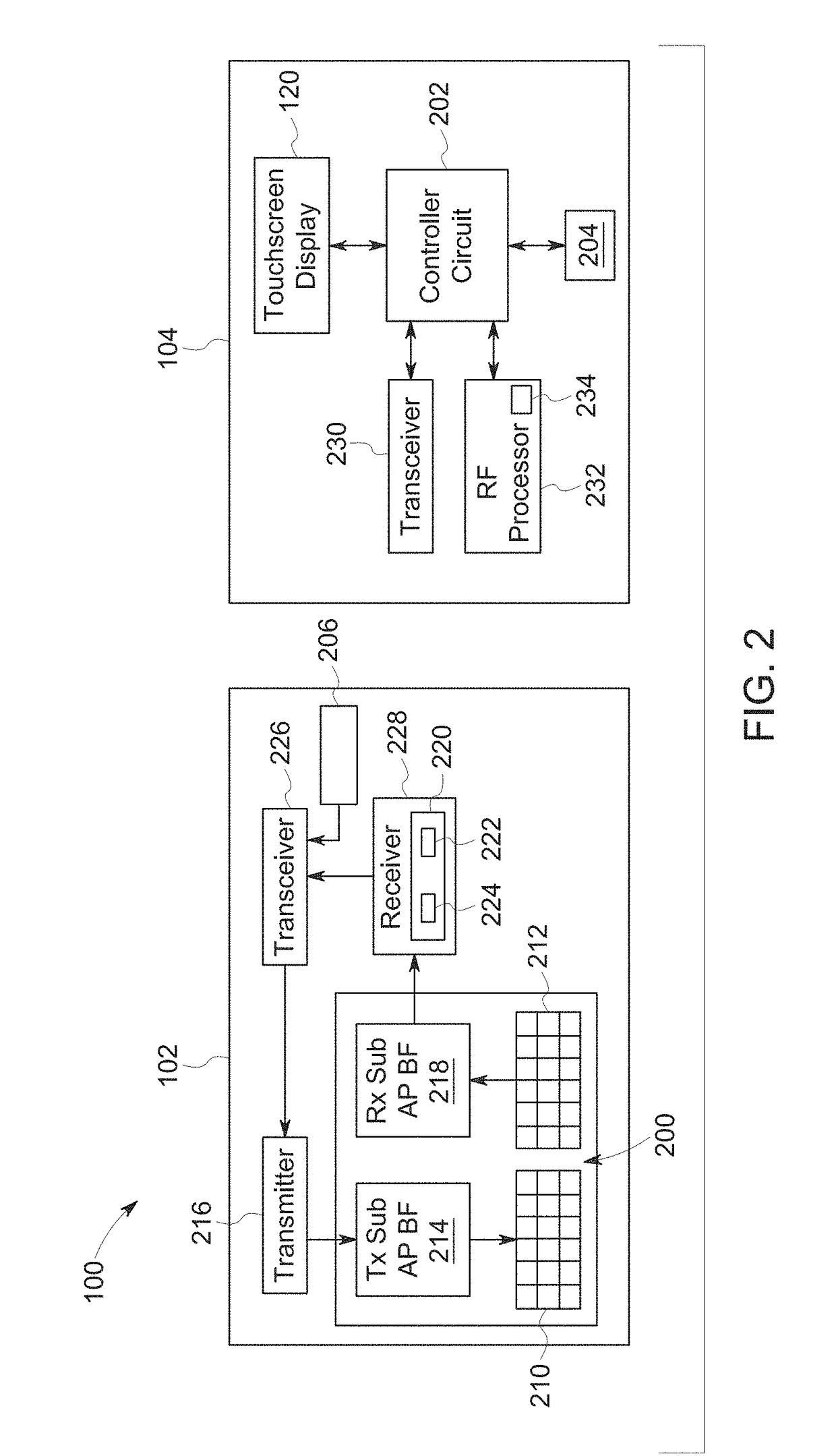
InactiveUS20070021738A1Easy to usePromote surgeon efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapies2d ultrasoundVirtual fixture
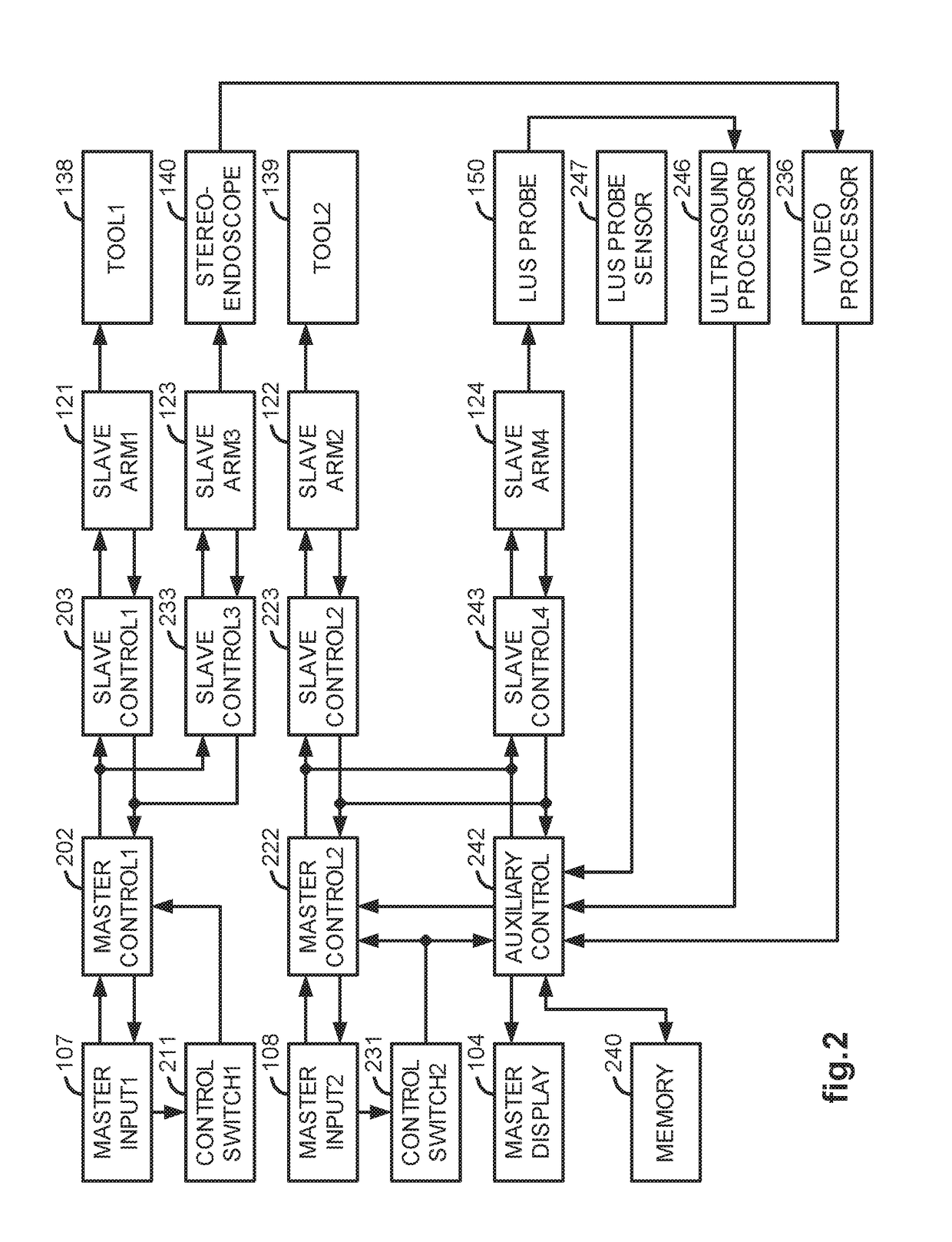
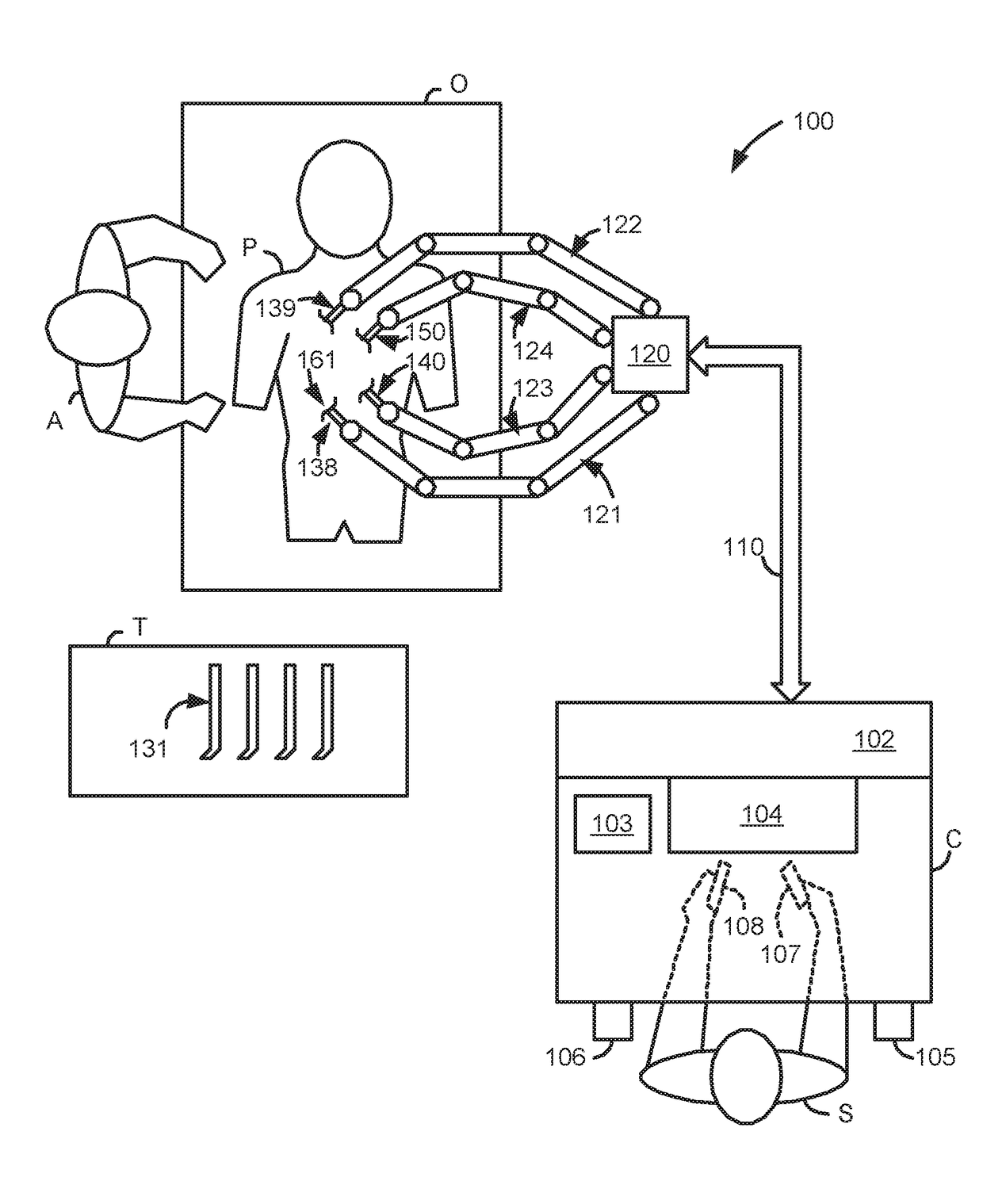
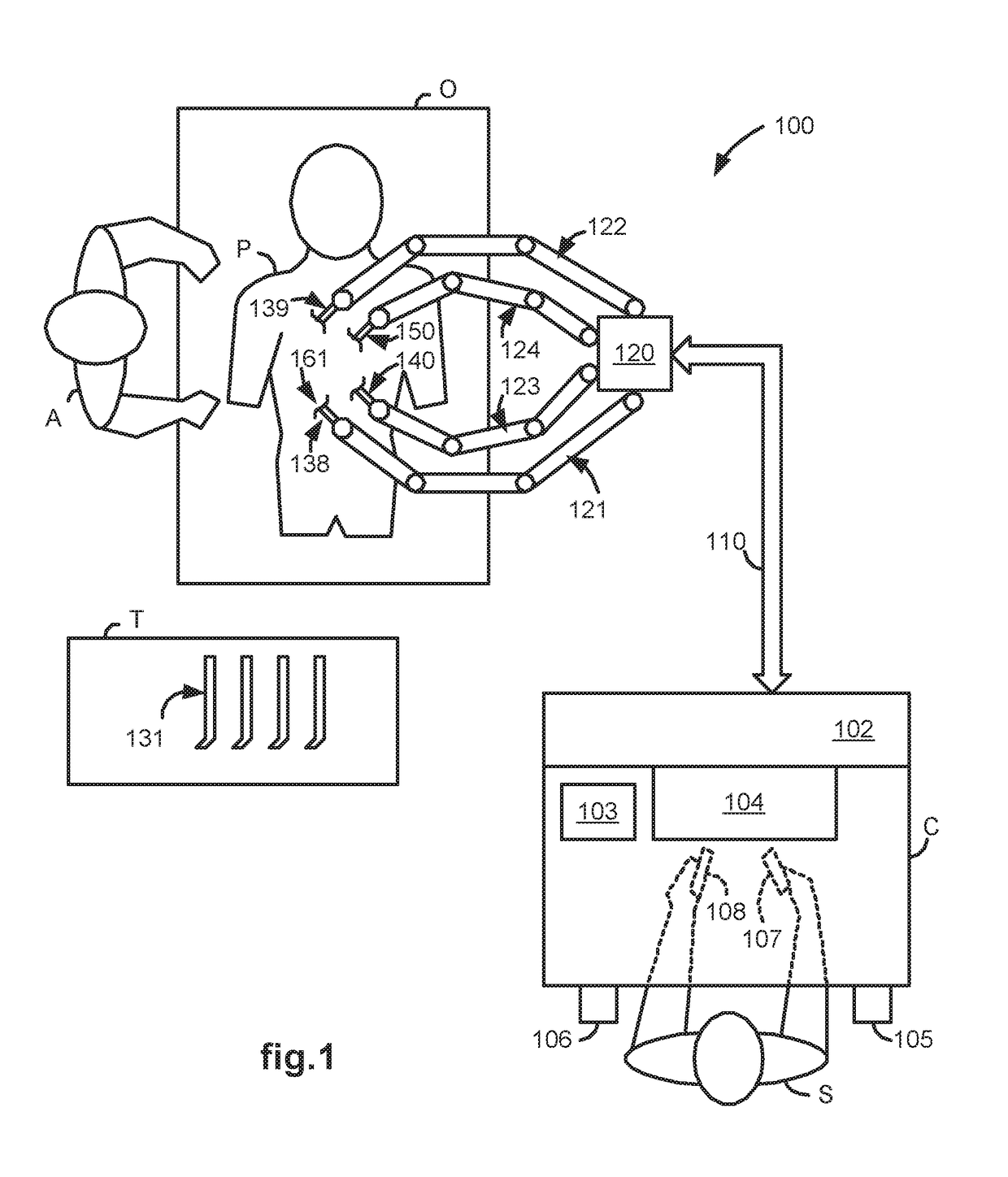
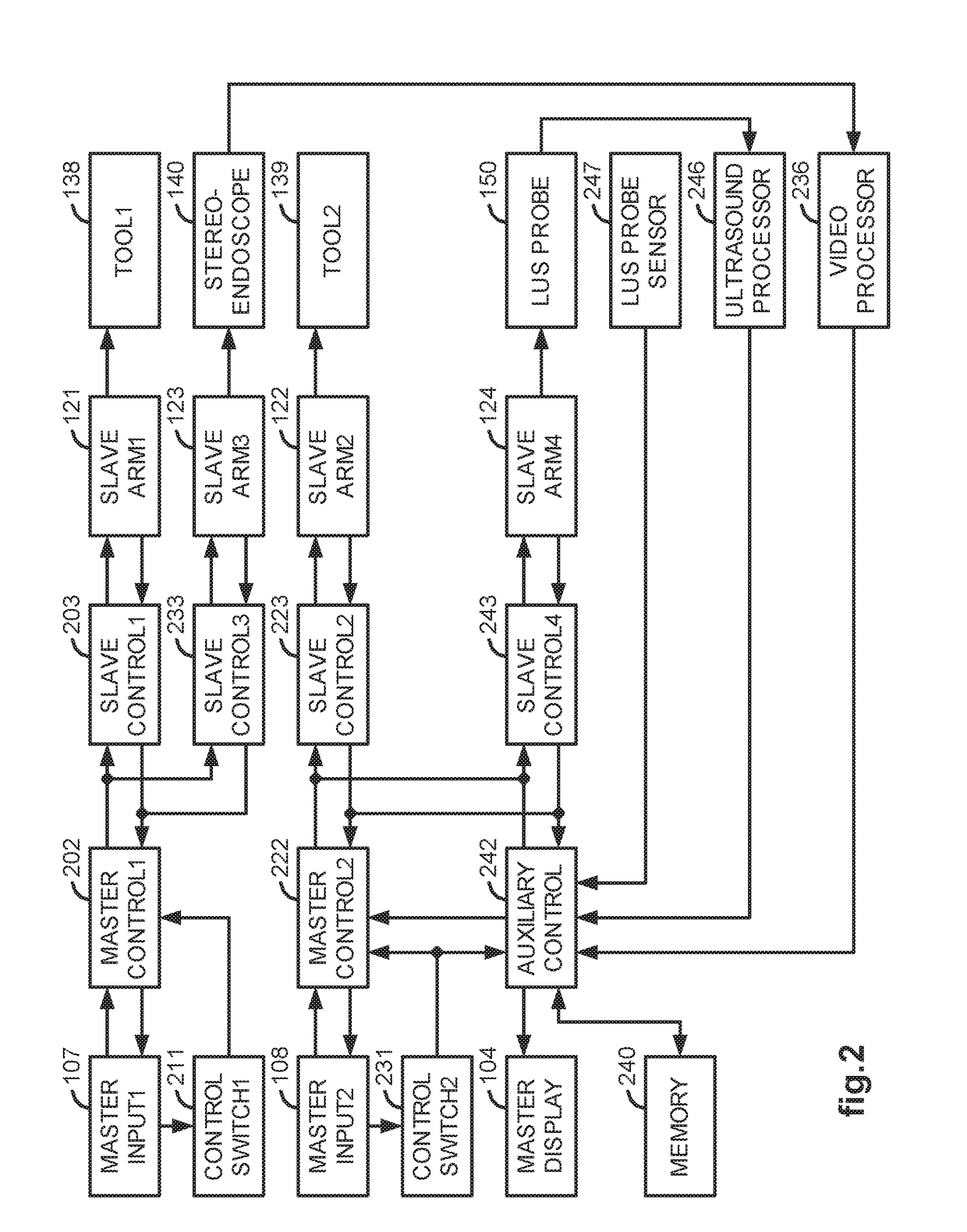
A LUS robotic surgical system is trainable by a surgeon to automatically move a LUS probe in a desired fashion upon command so that the surgeon does not have to do so manually during a minimally invasive surgical procedure. A sequence of 2D ultrasound image slices captured by the LUS probe according to stored instructions are processable into a 3D ultrasound computer model of an anatomic structure, which may be displayed as a 3D or 2D overlay to a camera view or in a PIP as selected by the surgeon or programmed to assist the surgeon in inspecting an anatomic structure for abnormalities. Virtual fixtures are definable so as to assist the surgeon in accurately guiding a tool to a target on the displayed ultrasound image.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
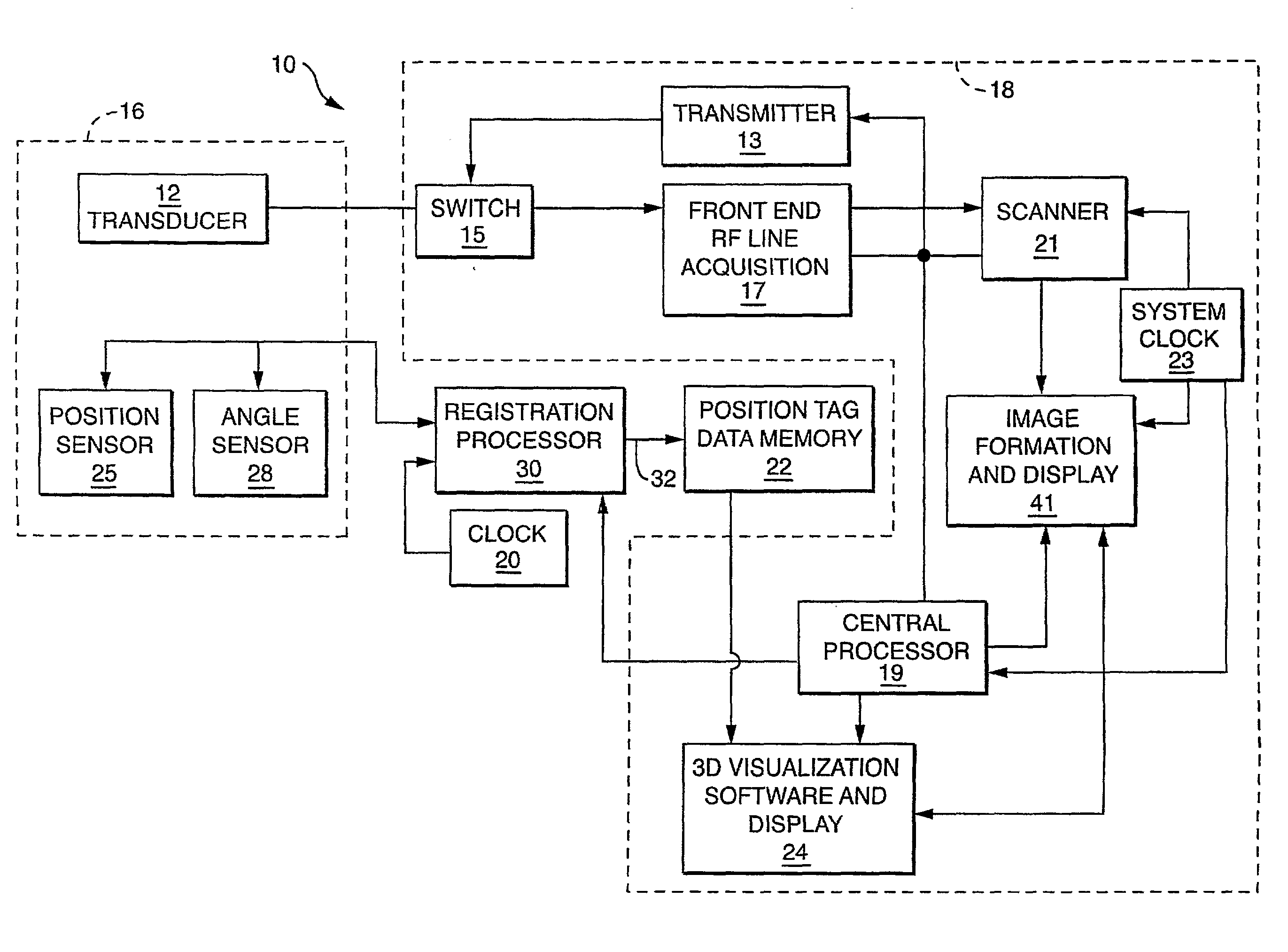
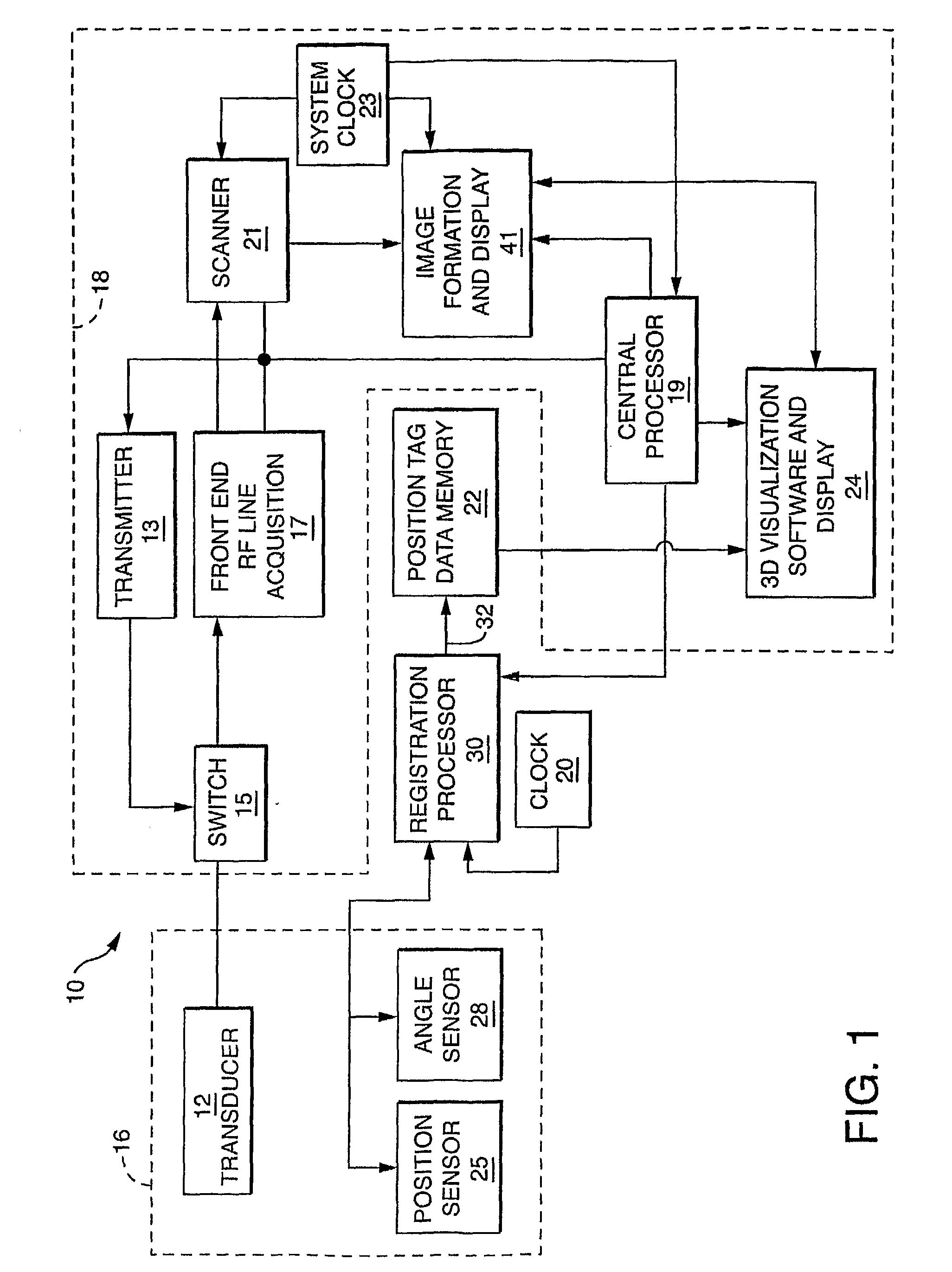
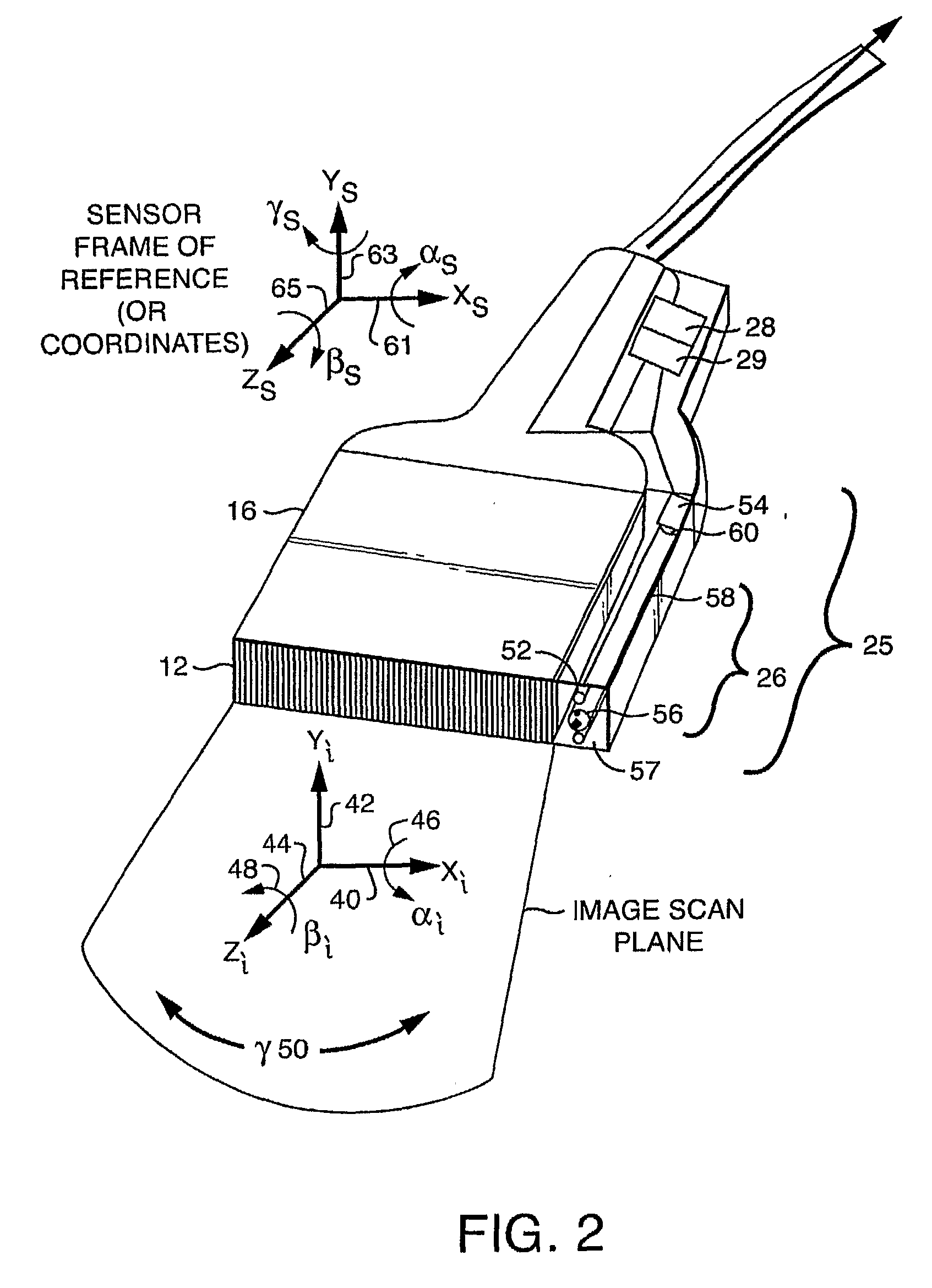
Free-hand three-dimensional ultrasound diagnostic imaging with position and angle determination sensors
InactiveUS20090306509A1Low costImprove scanning accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsUltrasonic sensor2d ultrasound
A freehand 3-D imaging system includes an integrated sensor configuration that provides position and orientation of each 2D imaging plane used for 3-D reconstruction without the need for external references. The position sensors communicate with the imaging system using either wired and wireless means. At least one translational and one angular sensor or three translational sensors acquire data utilized to compute position tags associated with 2D ultrasound image scan frames. The sensors can be built into the ultrasound transducer or can be reversibly connected and therefore retrofitted to existing imaging probes for freehand 3D imaging.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV +1
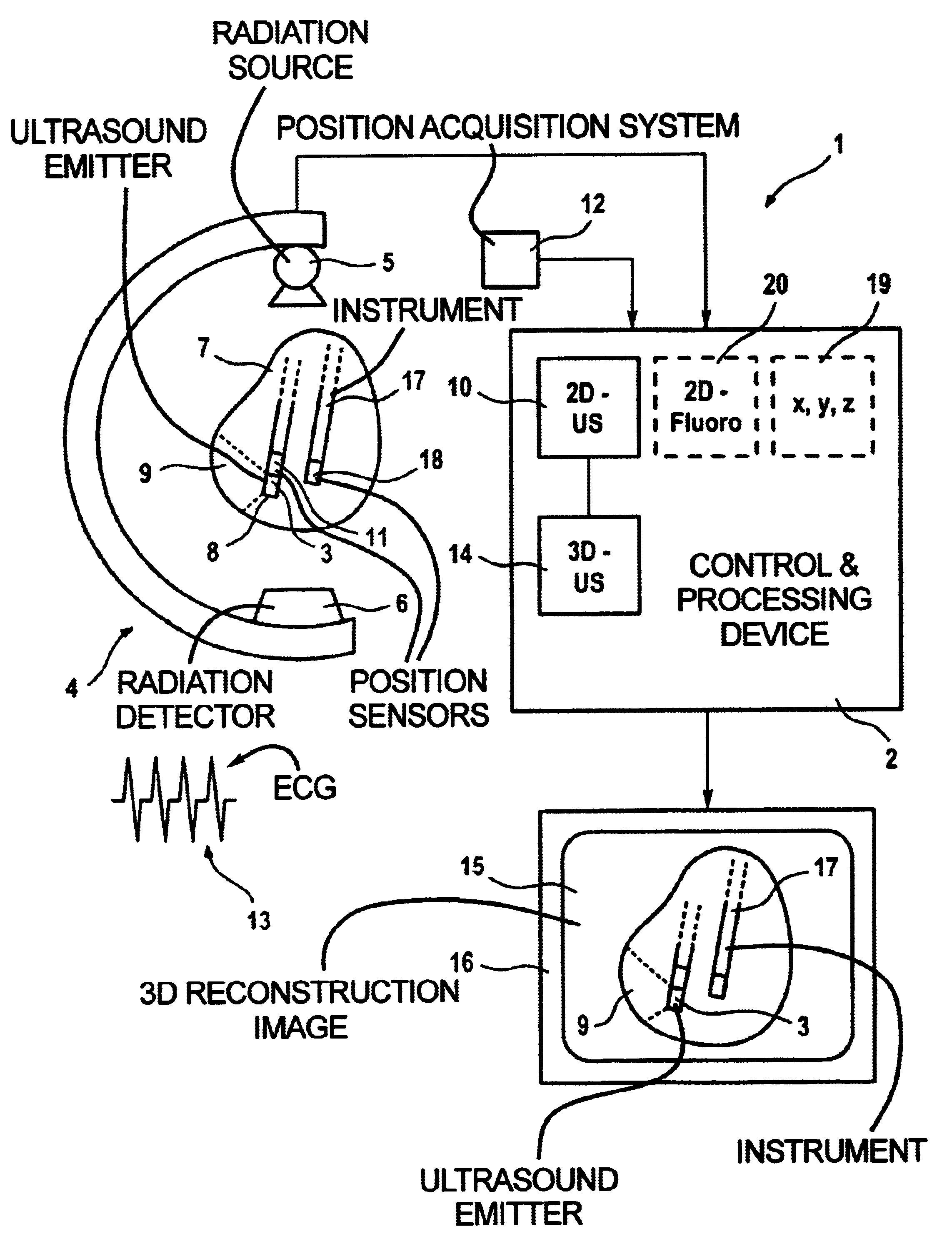
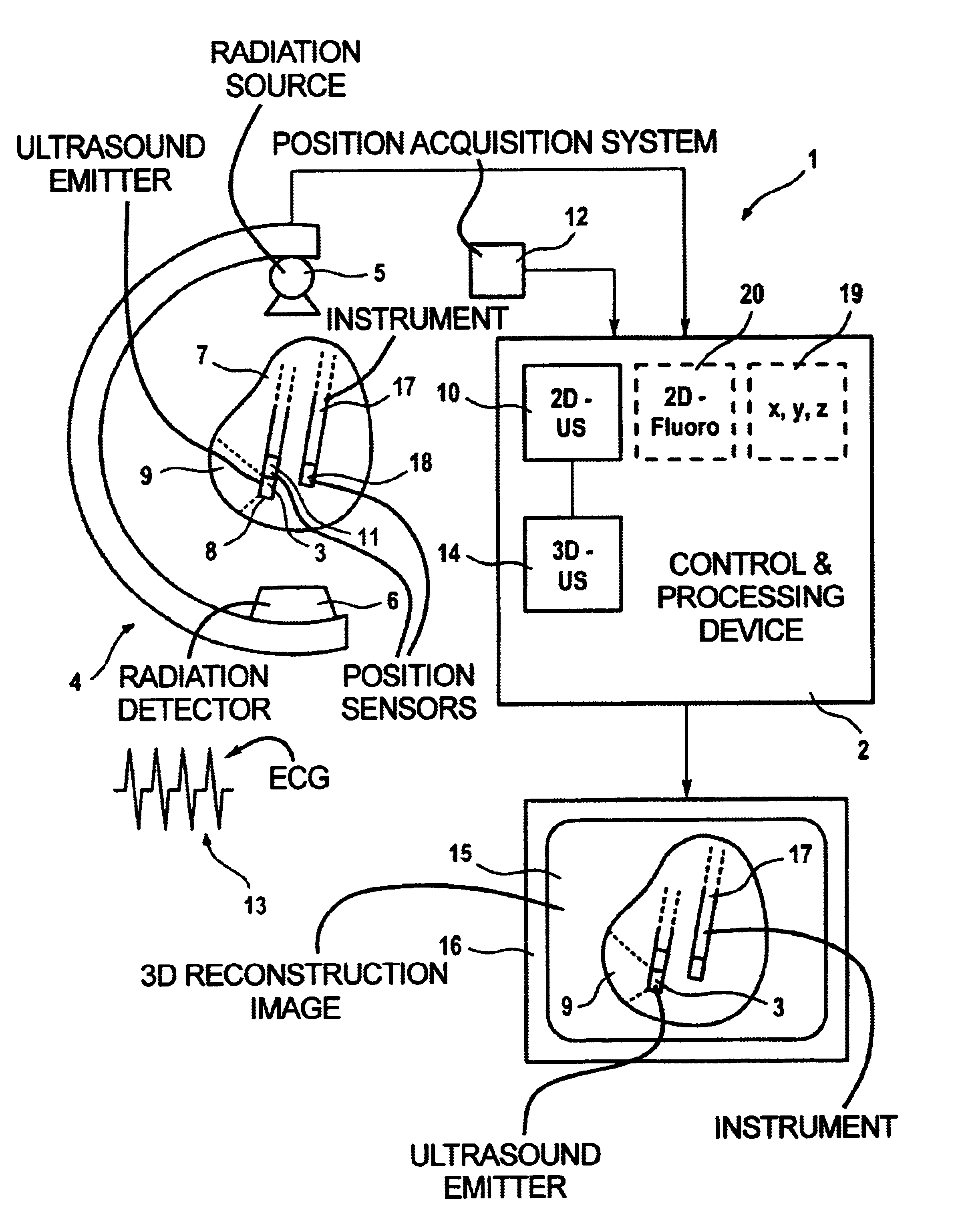
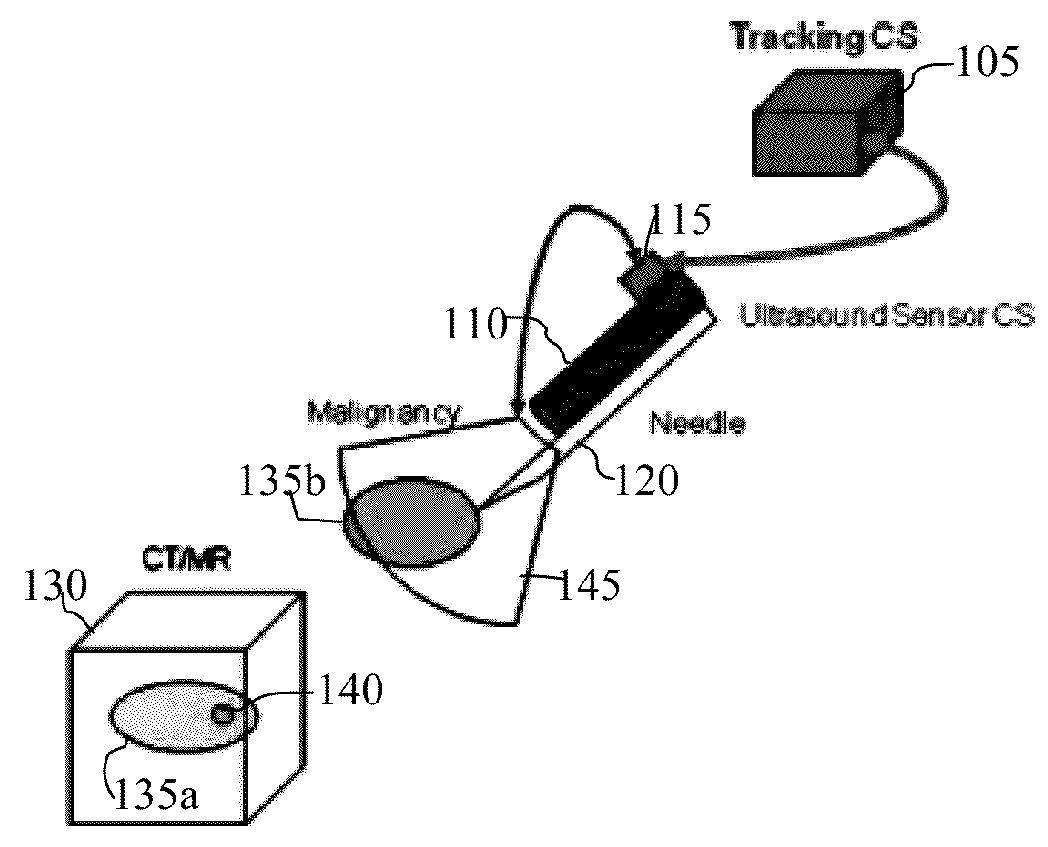
Method and apparatus for acquiring and displaying a medical instrument introduced into a cavity organ of a patient to be examined or treated
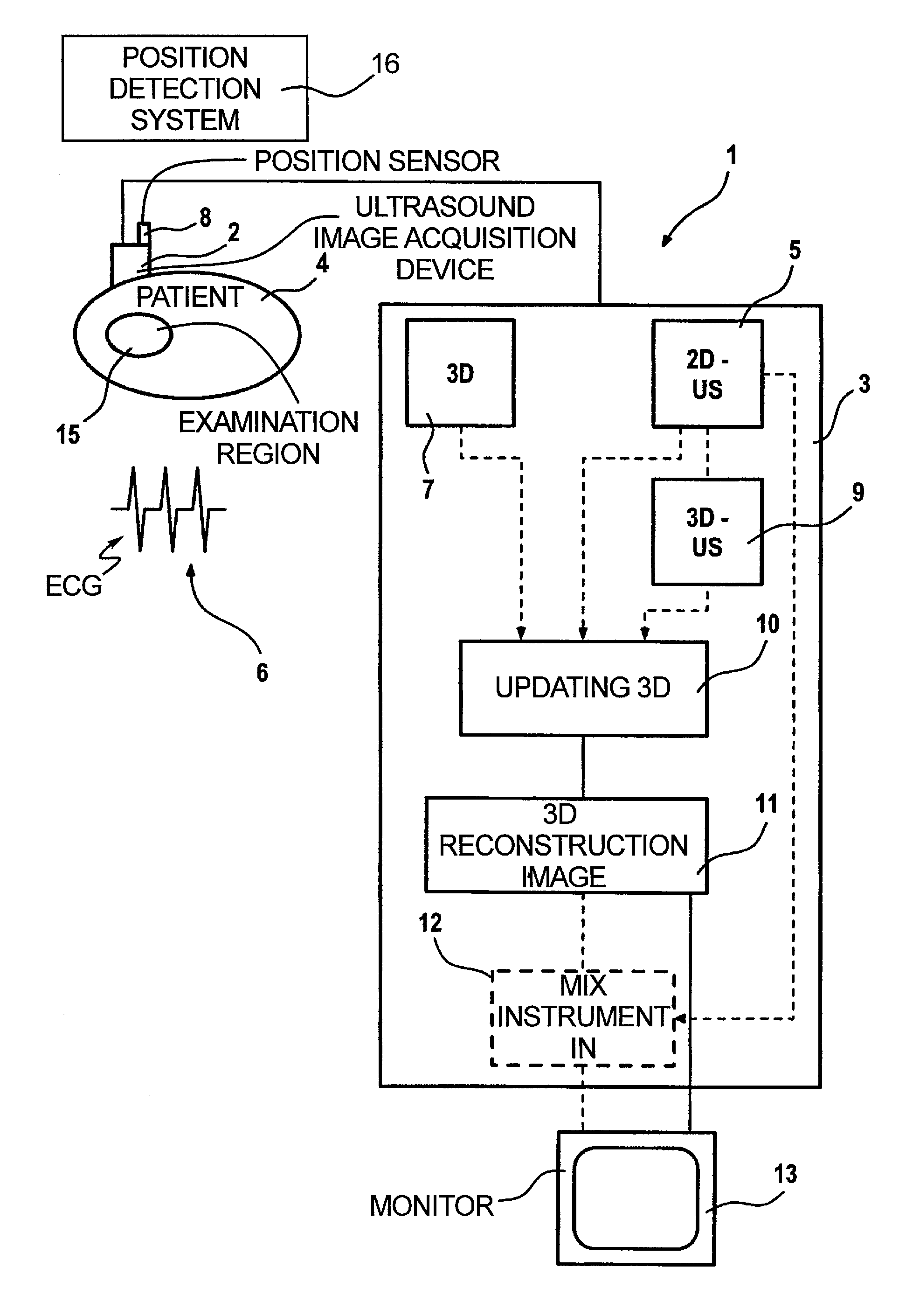
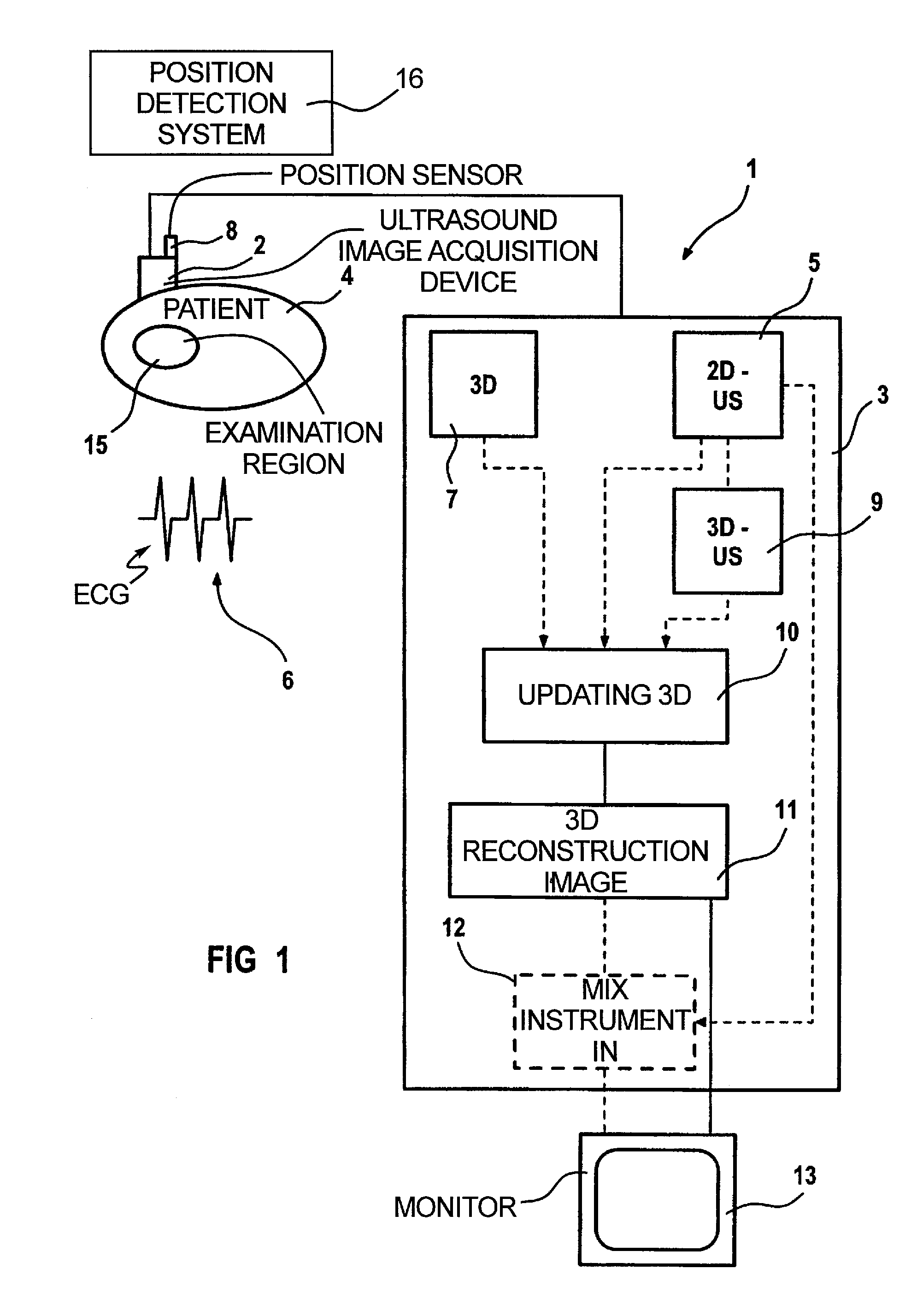
ActiveUS6923768B2Easy to identifyPrecise positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgerySonification2d ultrasound
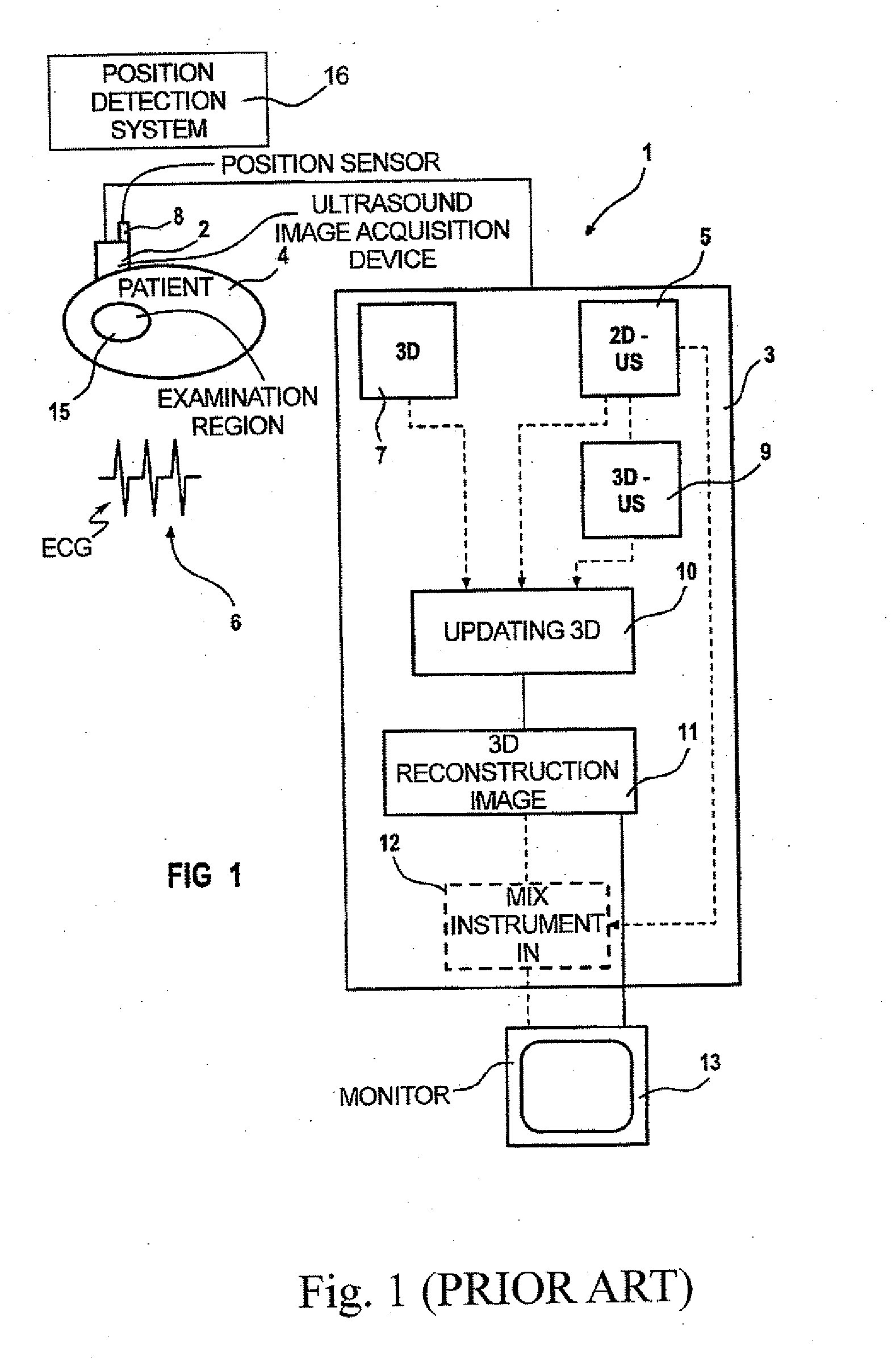
In a medical treatment / examination device and method for the acquisition and presentation of a medical instrument introduced into a cavity organ of a patient to be examined or treated, particularly in the framework of a cardial examination or treatment with a catheter, intracorporeal registration of 2D ultrasound images of the cavity organ is undertaken using a catheter-like ultrasound acquisition device guided into the cavity organ with simultaneous acquisition of the spatial position and orientation of a 2D ultrasound image by a position acquisition system, a 3D ultrasound image dataset is generated from the 2D ultrasound image, following introduction of the instrument, the instrument is acquired in a coordinate system registered with the 3D ultrasound image dataset, and a 3D reconstruction image is generated on the basis of the 3D image dataset and is presented at a monitor, containing a positionally exact presentation of the instrument in the 3D reconstruction image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
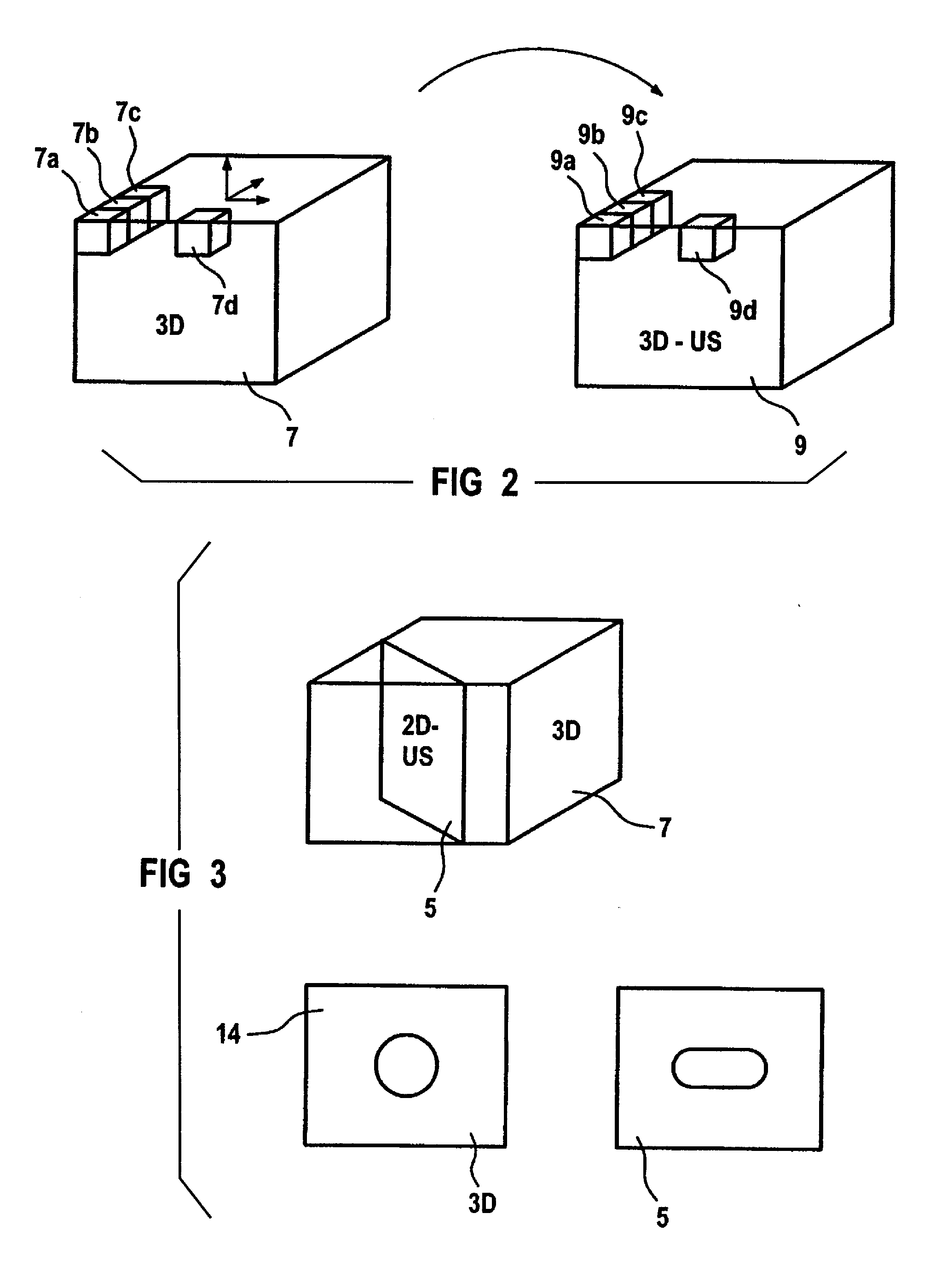
Method and apparatus for the three-dimensional presentation of an examination region of a patient in the form of a 3D reconstruction image
ActiveUS7302286B2Reduce disadvantagesKeep for a long timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryData set3d image
In a method and apparatus for the three-dimensional presentation of an examination region of a patient in the form of a 3D reconstruction image, a preoperatively acquired 3D image dataset of the examination region is employed in a medical procedure, datasets representing a number of 2D ultrasound images of the examination region are acquired, the preoperative 3D image dataset is updated using the datasets representing 2D ultrasound images, and the 3D reconstruction image is generated on the basis of the updated 3D image dataset.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
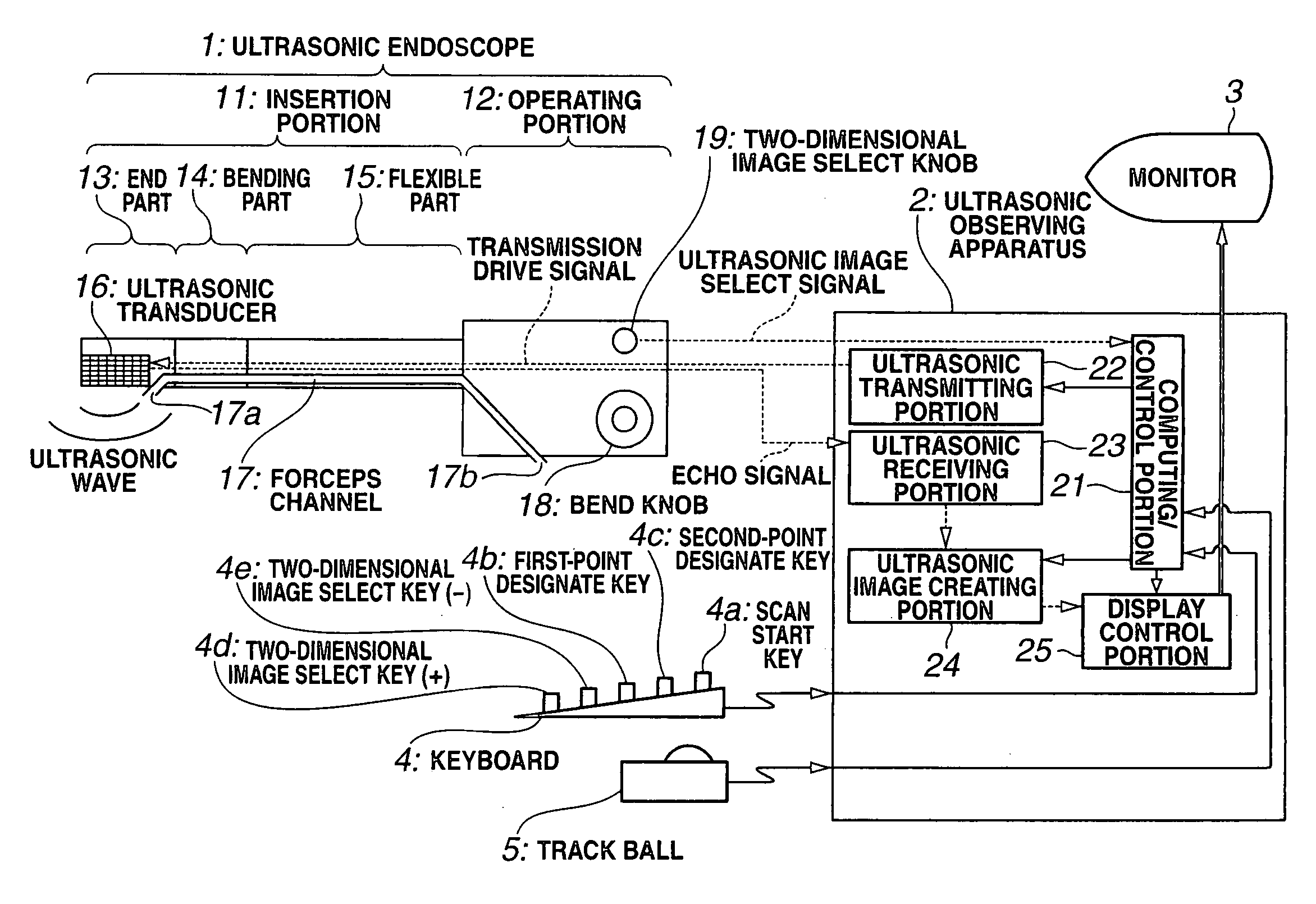
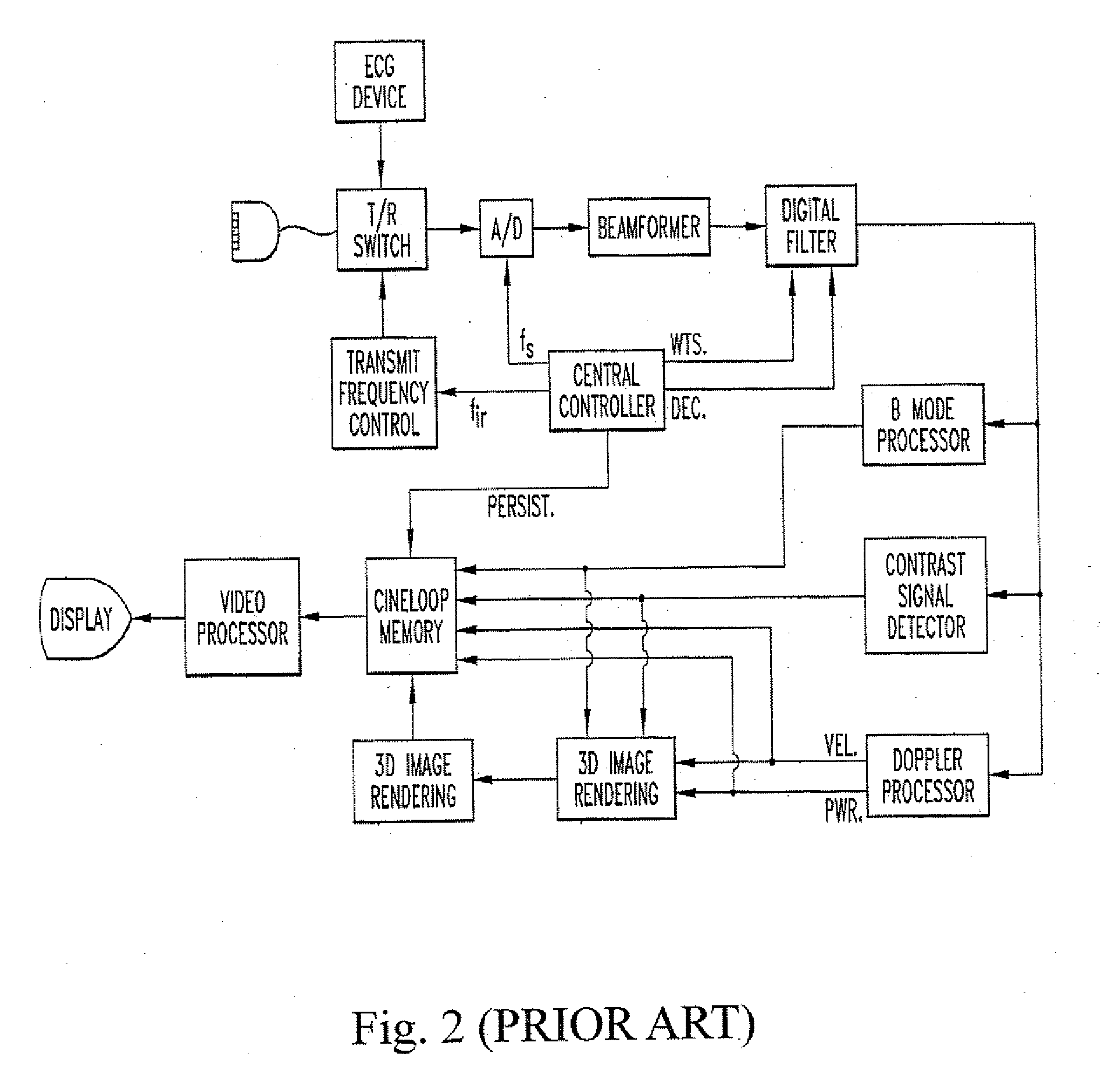
Ultrasonic diagnosis apparatus
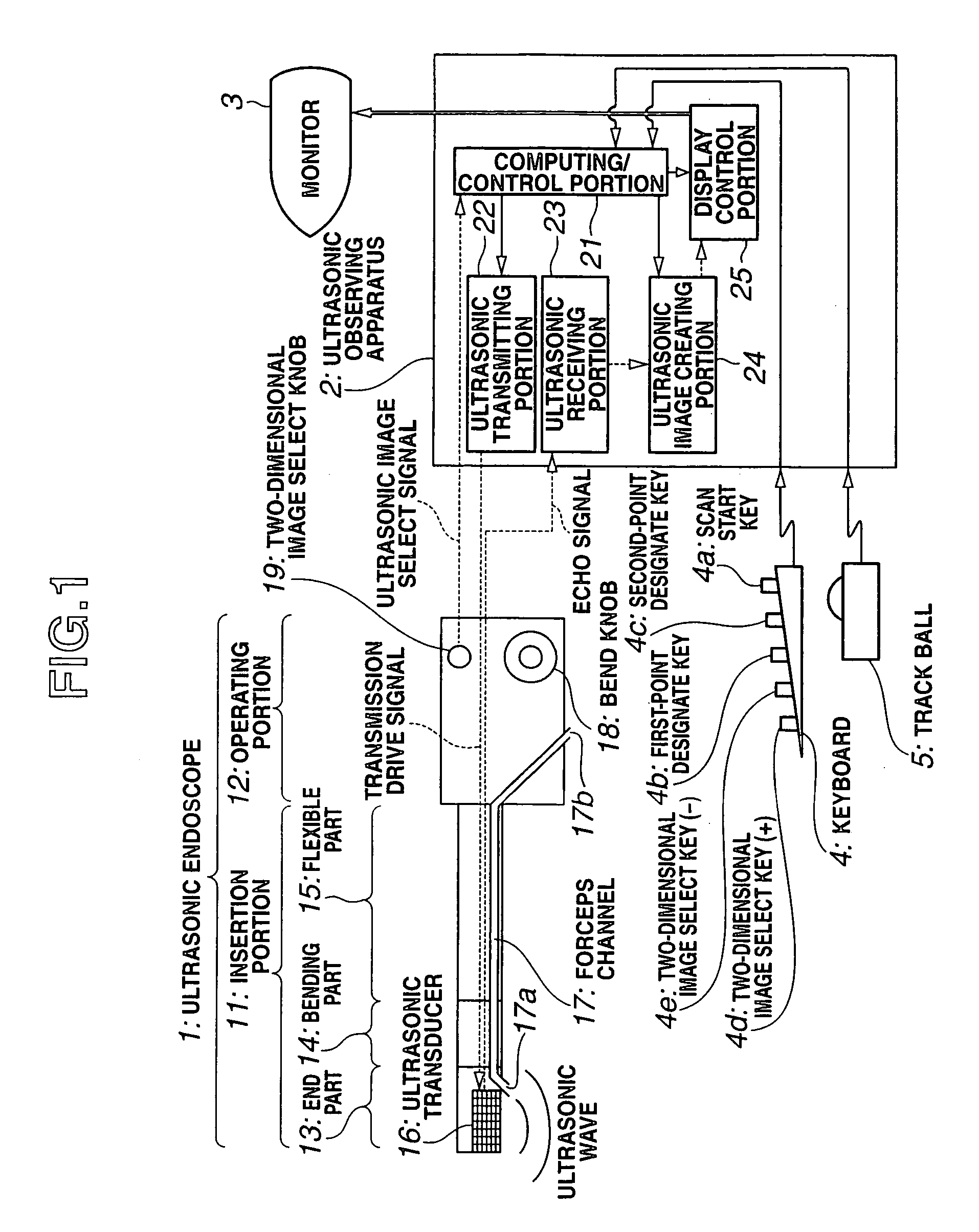
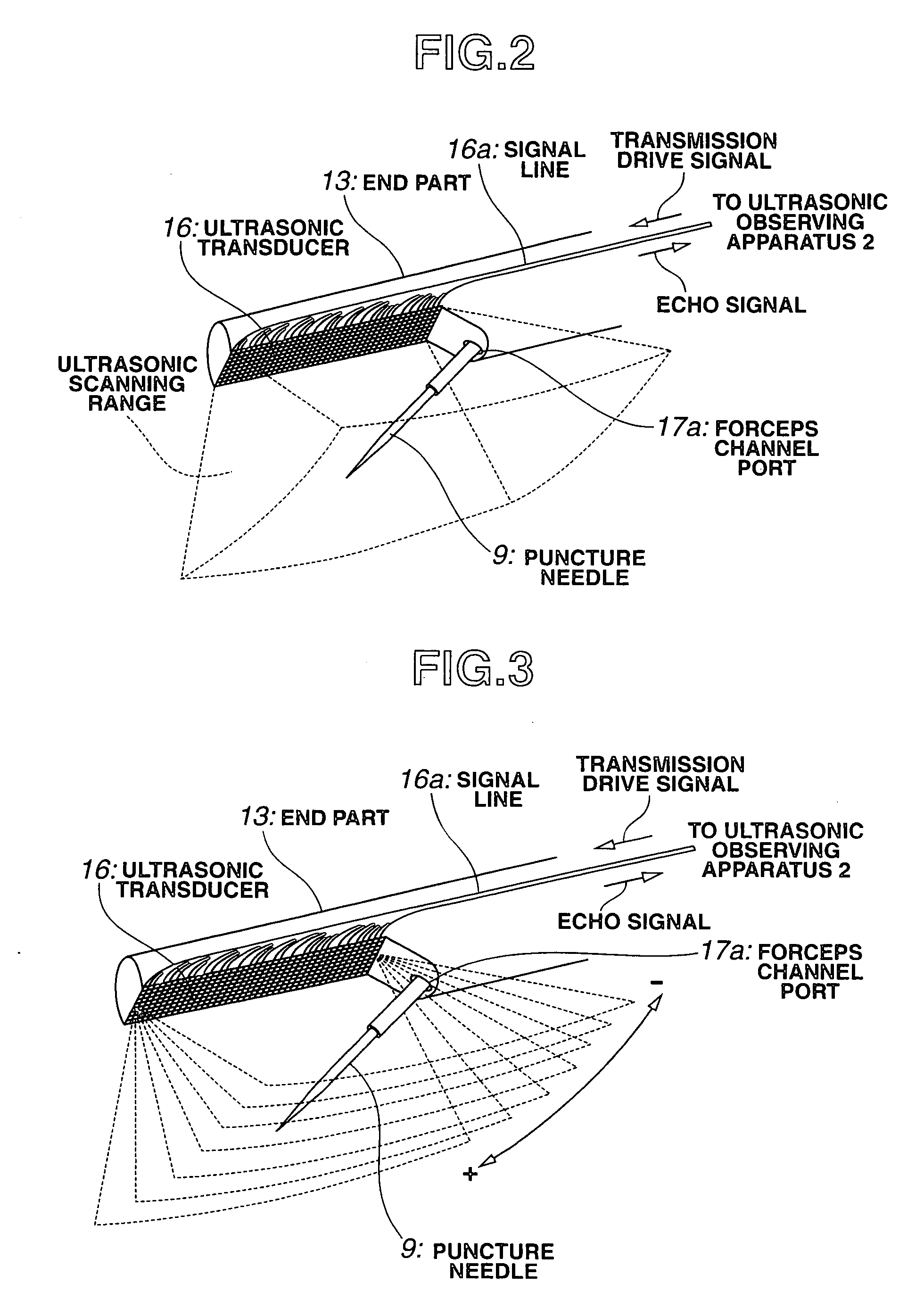
An ultrasonic diagnosis apparatus according to the present invention includes an ultrasonic endoscope having ultrasonic transducers for scanning ultrasonic wave in a living body three-dimensionally, an ultrasonic image creating portion of an ultrasonic observing apparatus for creating ultrasonic volume data based on an ultrasonic signal captured by the ultrasonic endoscope, a two-dimensional image select knob, keyboard, trackball, computing / control portion and display control portion for selecting a tomographic plane from the ultrasonic volume data by designating the angle of rotation about the straight line through two points designated on the ultrasonic volume data as the axis of rotation, and a monitor for displaying the tomographic plane selected during a scanning operation as a two-dimensional ultrasonic image.
Owner:OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYST CORP
System and Method for Real-Time Ultrasound Guided Prostate Needle Biopsy Based on Biomechanical Model of the Prostate from Magnetic Resonance Imaging Data
A method and system for real-time ultrasound guided prostate needle biopsy based on a biomechanical model of the prostate from 3D planning image data, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data, is disclosed. The prostate is segmented in the 3D ultrasound image. A reference patient-specific biomechanical model of the prostate extracted from planning image data is fused to a boundary of the segmented prostate in the 3D ultrasound image, resulting in a fused 3D biomechanical prostate model. In response to movement of an ultrasound probe to a new location, a current 2D ultrasound image is received. The fused 3D biomechanical prostate model is deformed based on the current 2D ultrasound image to match a current deformation of the prostate due to the movement of the ultrasound probe to the new location.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Computer Aided Detection Of Abnormalities In Volumetric Breast Ultrasound Scans And User Interface
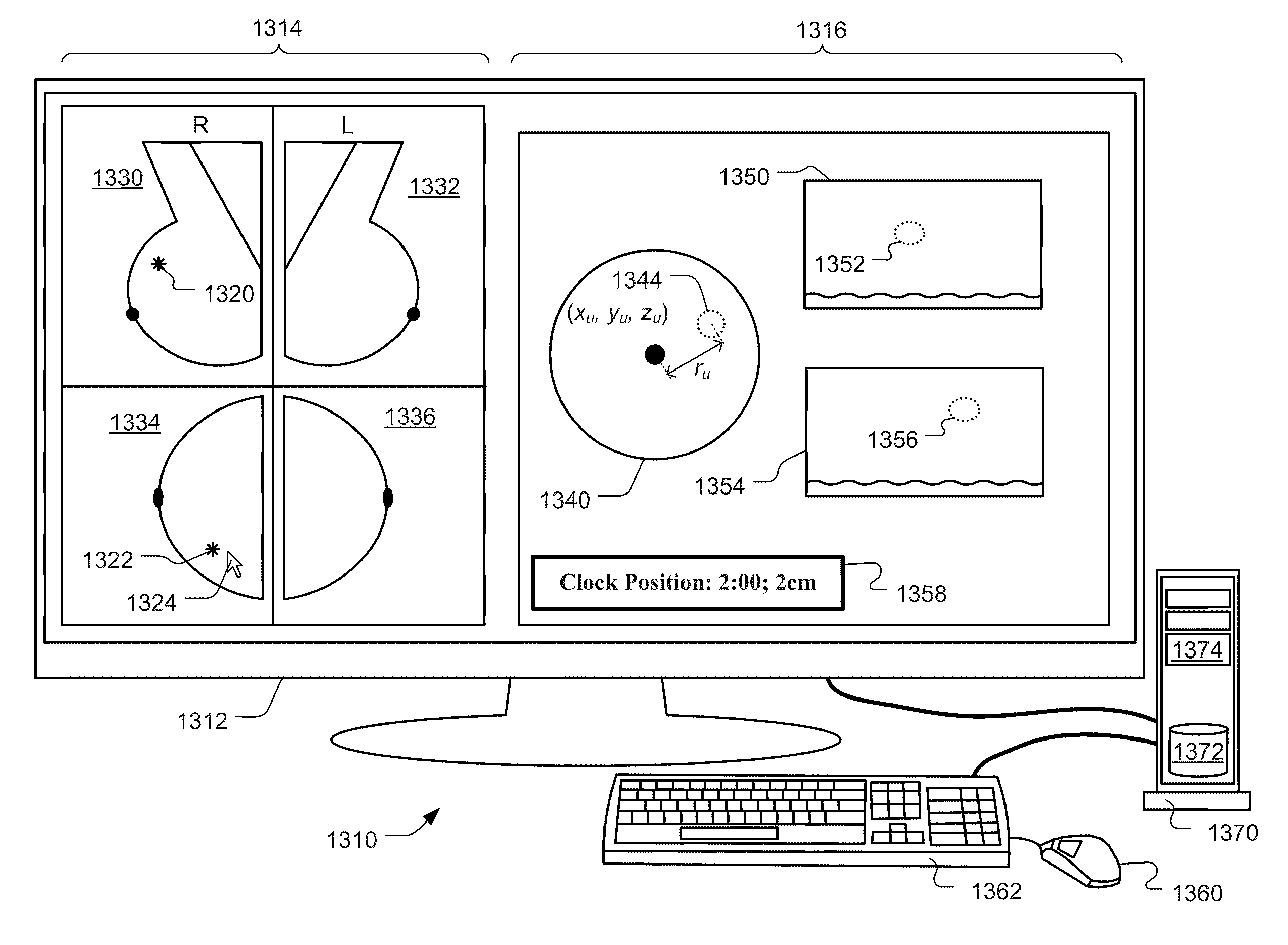
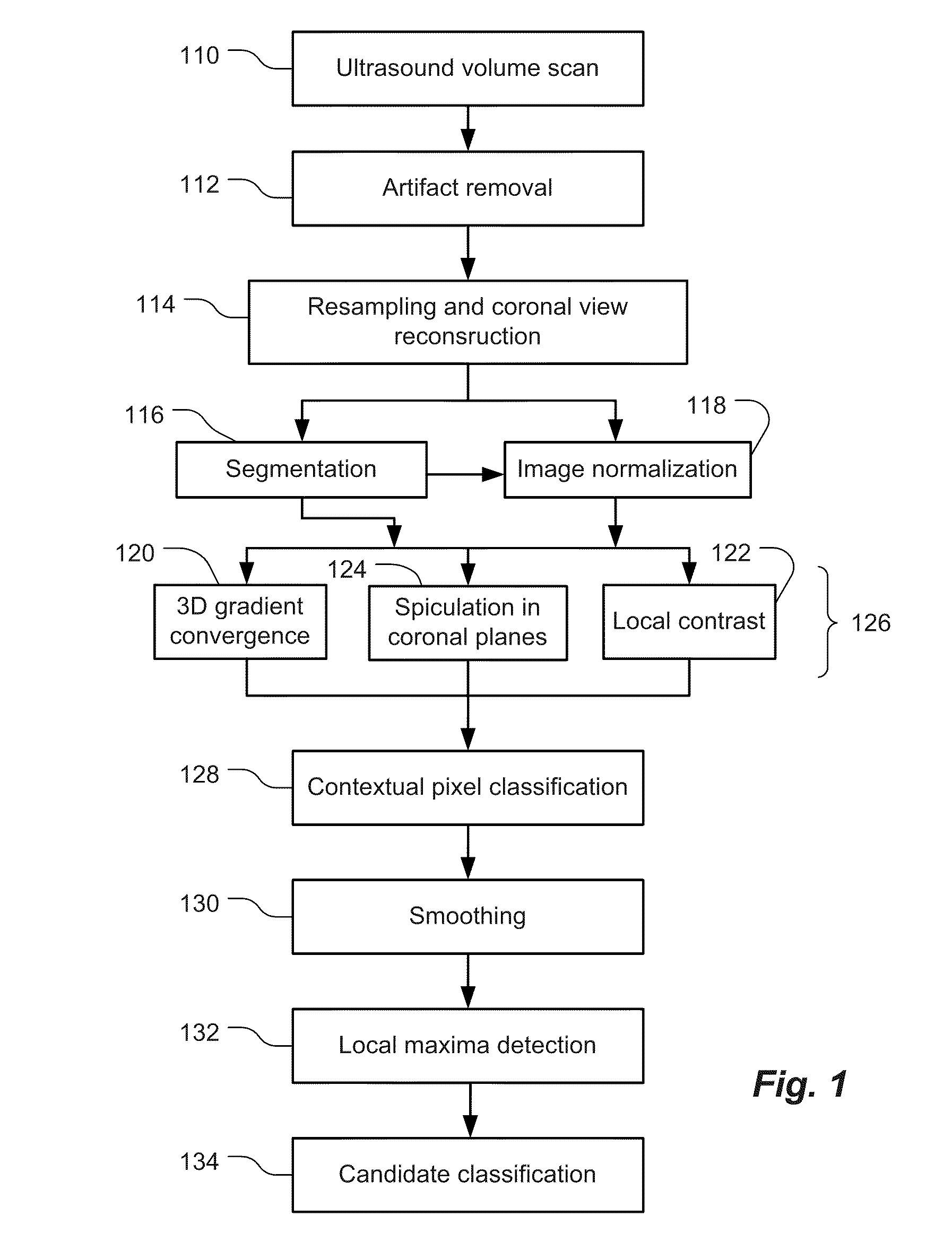
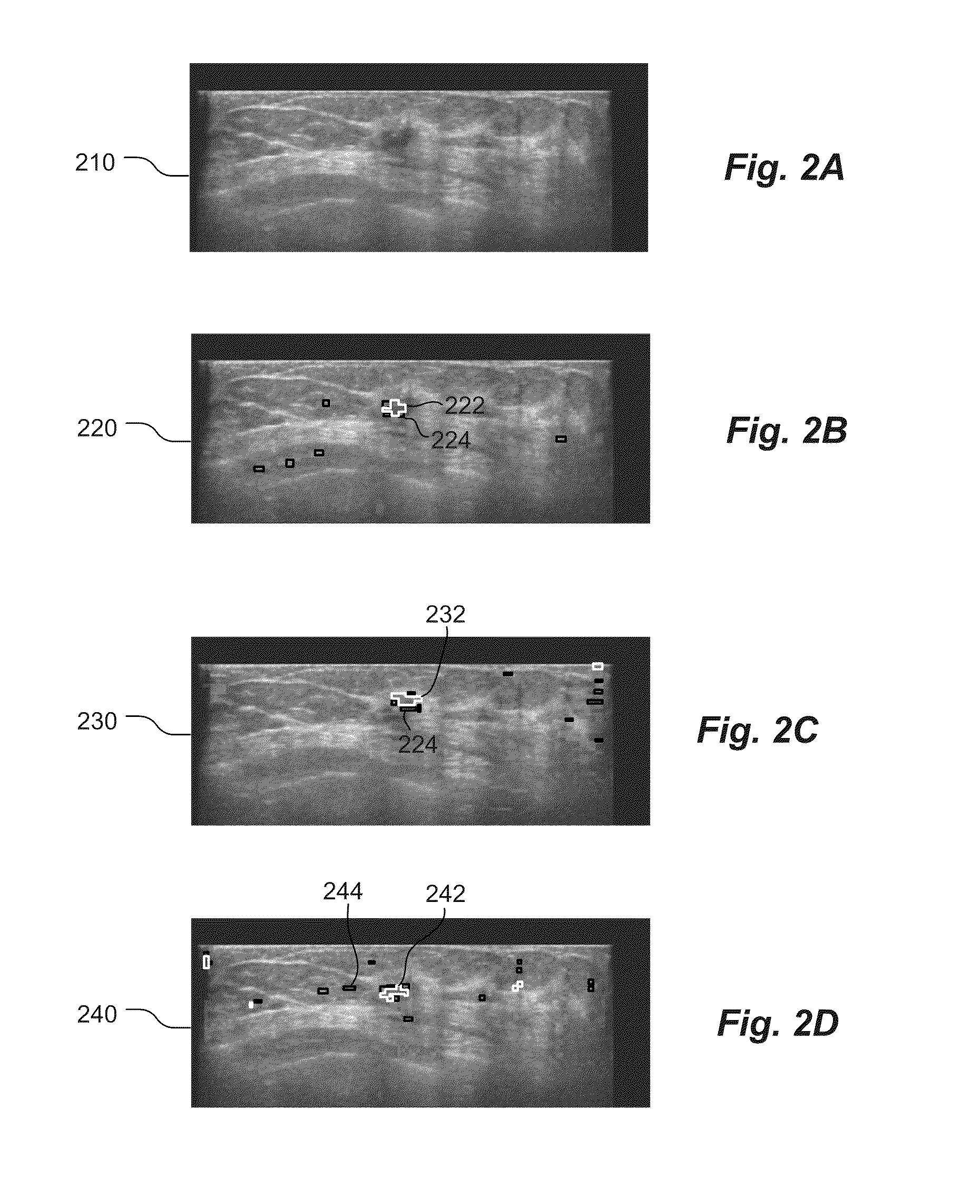
Methods and related systems are described for detection of breast cancer in 3D ultrasound imaging data. Volumetric ultrasound images are obtained by an automated breast ultrasound scanning (ABUS) device. In ABUS images breast cancers appear as dark lesions. When viewed in transversal and sagittal planes, lesions and normal tissue appear similar as in traditional 2D ultrasound. However, architectural distortion and spiculation are frequently seen in the coronal views, and these are strong indicators of the presence of cancer. The described computerized detection (CAD) system combines a dark lesion detector operating in 3D with a detector for spiculation and architectural distortion operating on 2D coronal slices. In this way a sensitive detection method is obtained. Techniques are also described for correlating regions of interest in ultrasound images from different scans such in different scans of the same breast, scans of a patient's right versus left breast, and scans taken at different times. Techniques are also described for correlating regions of interest in ultrasound images and mammography images. Interactive user interfaces are also described for displaying CAD results and for displaying corresponding locations on different images.
Owner:QVIEW MEDICAL
Apparatus and method for forming 3D ultrasound image
ActiveUS20050240104A1Reduce errorsReduce time consumptionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgerySonification2d ultrasound
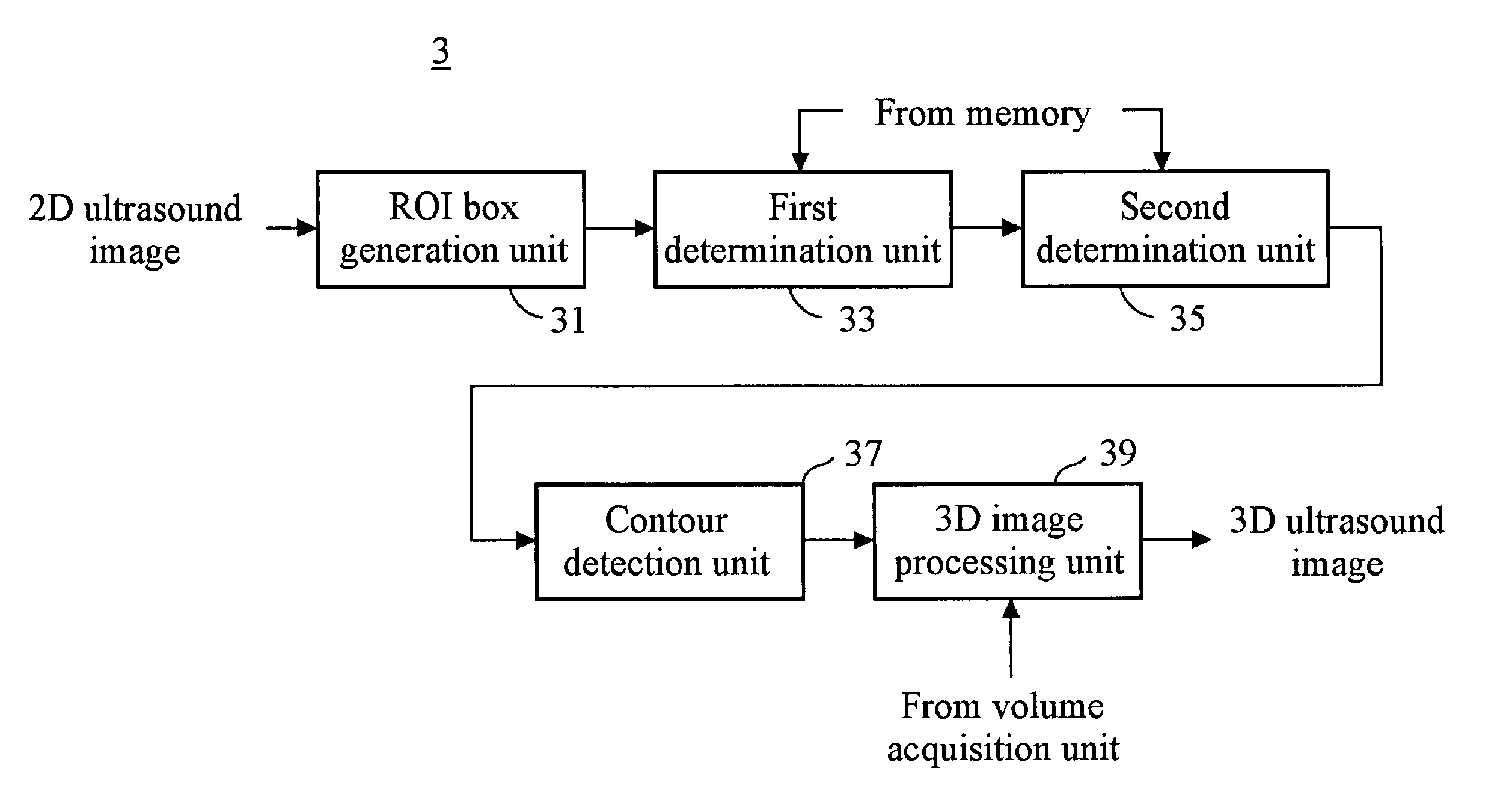
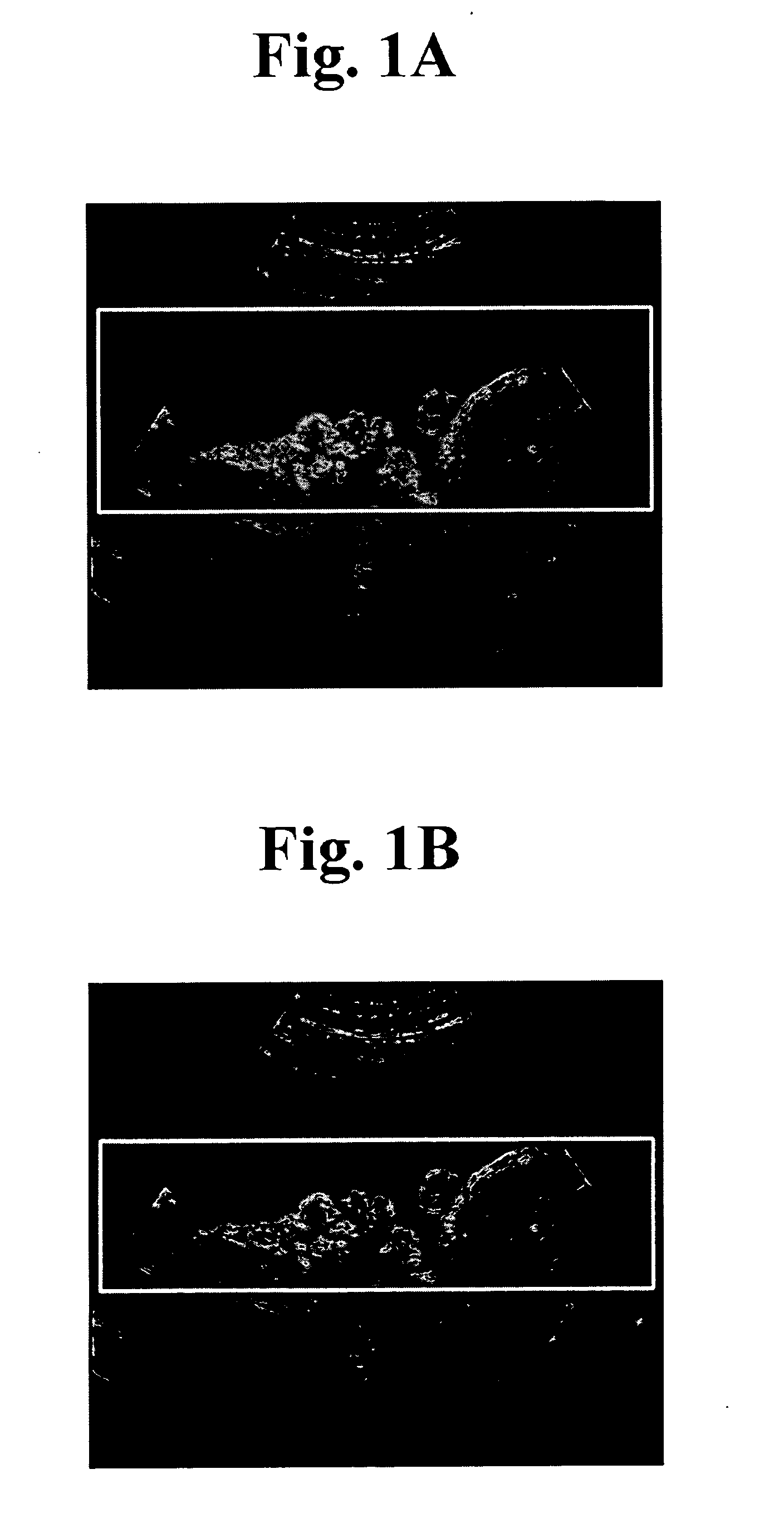
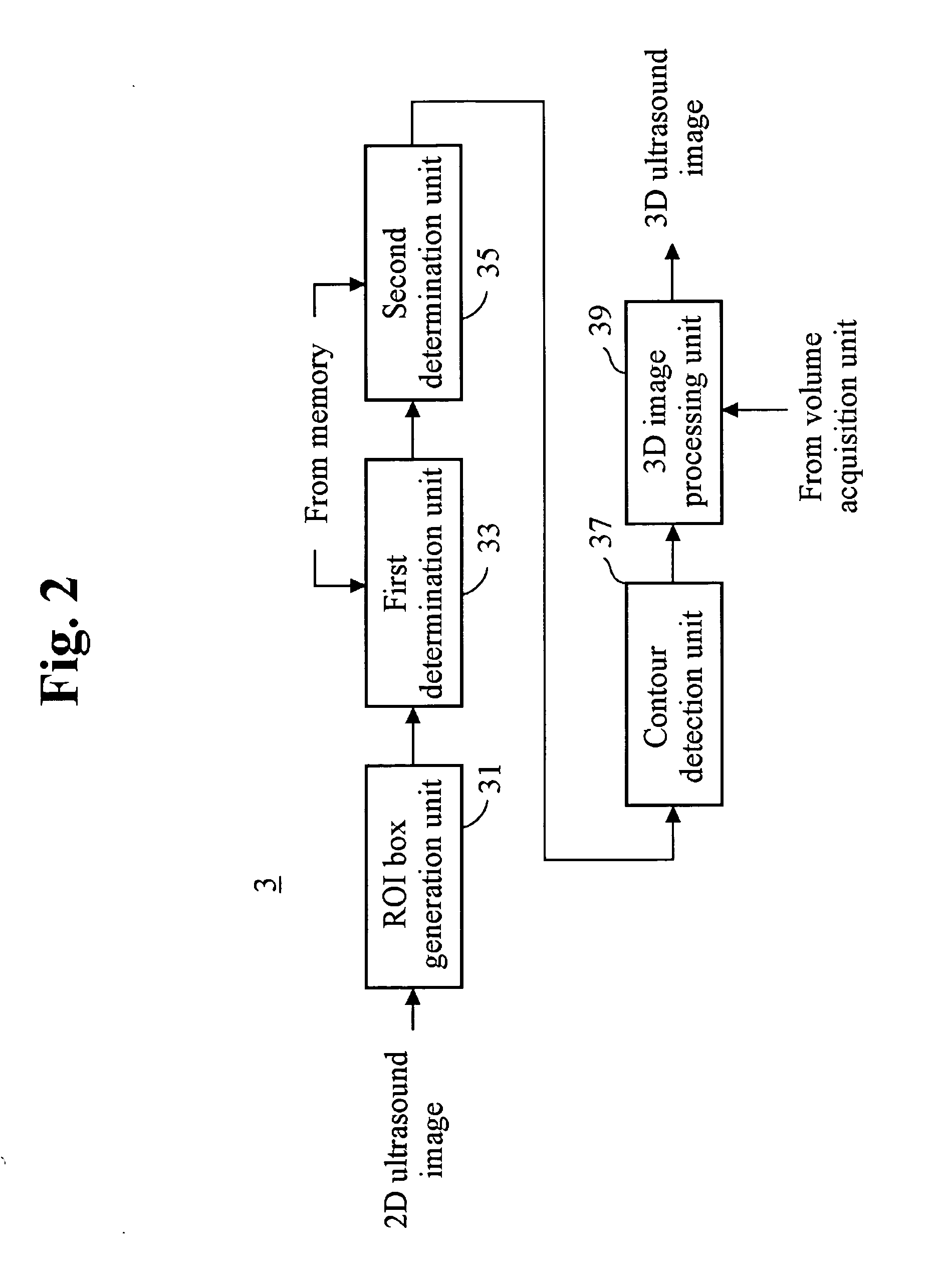
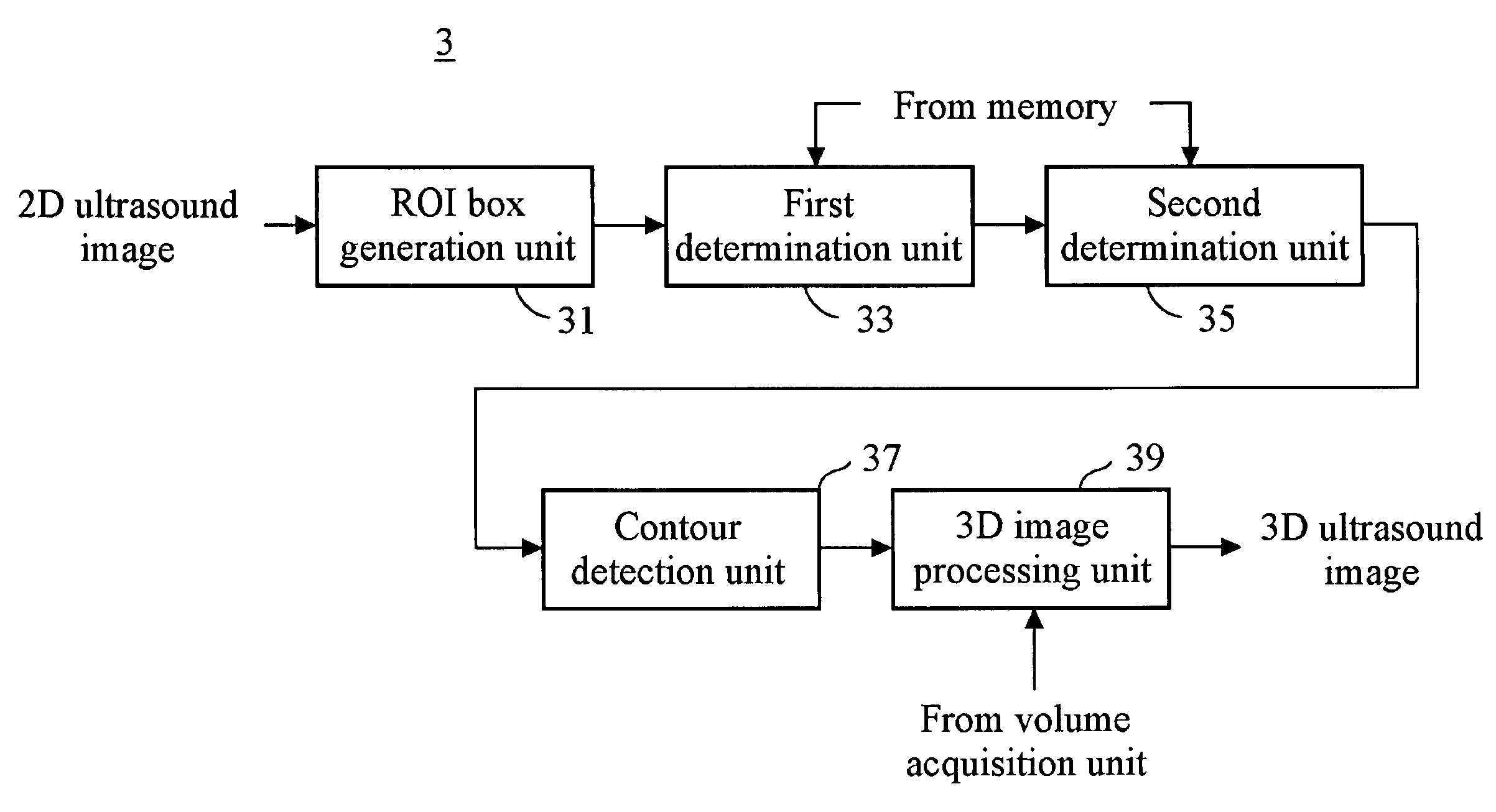
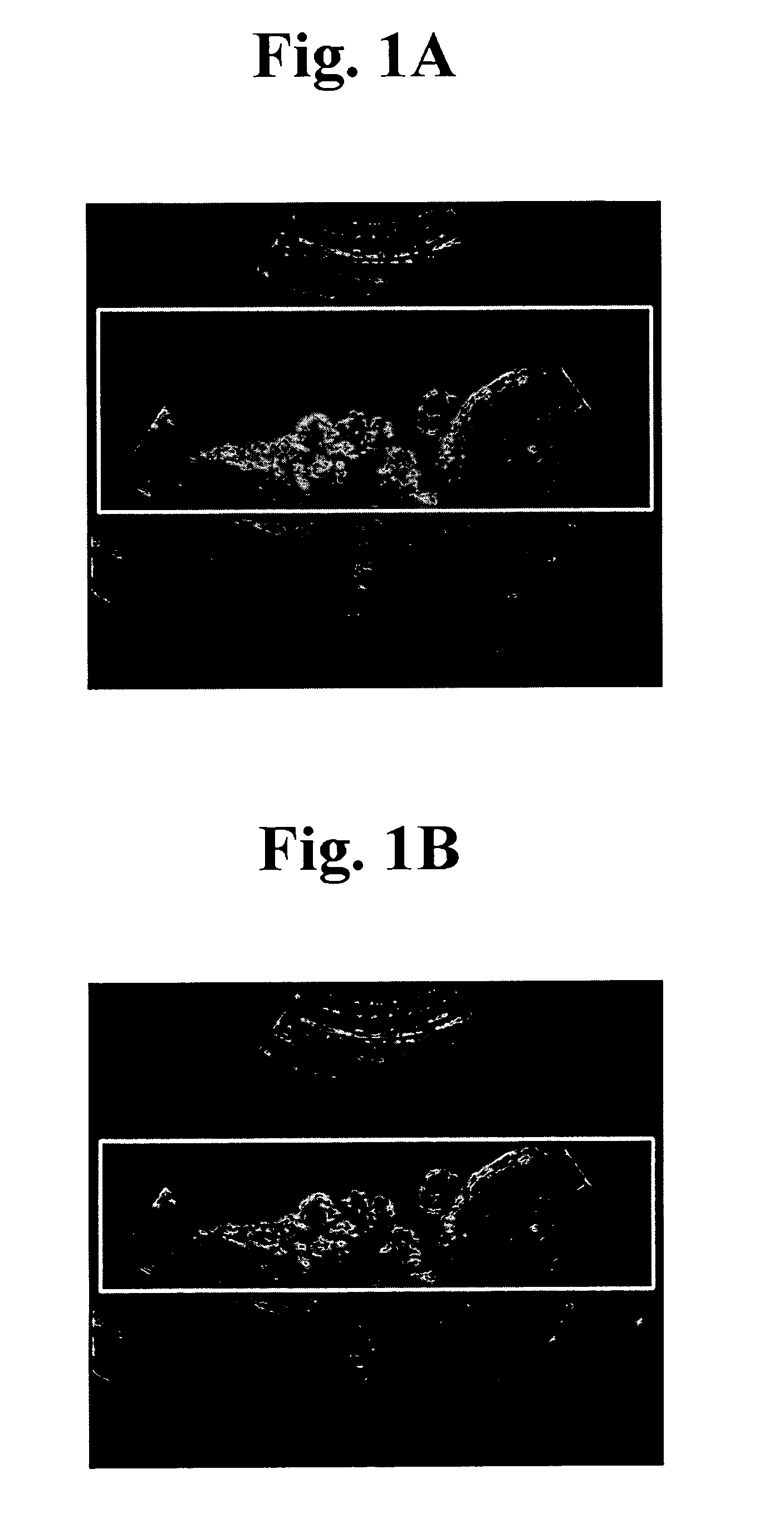
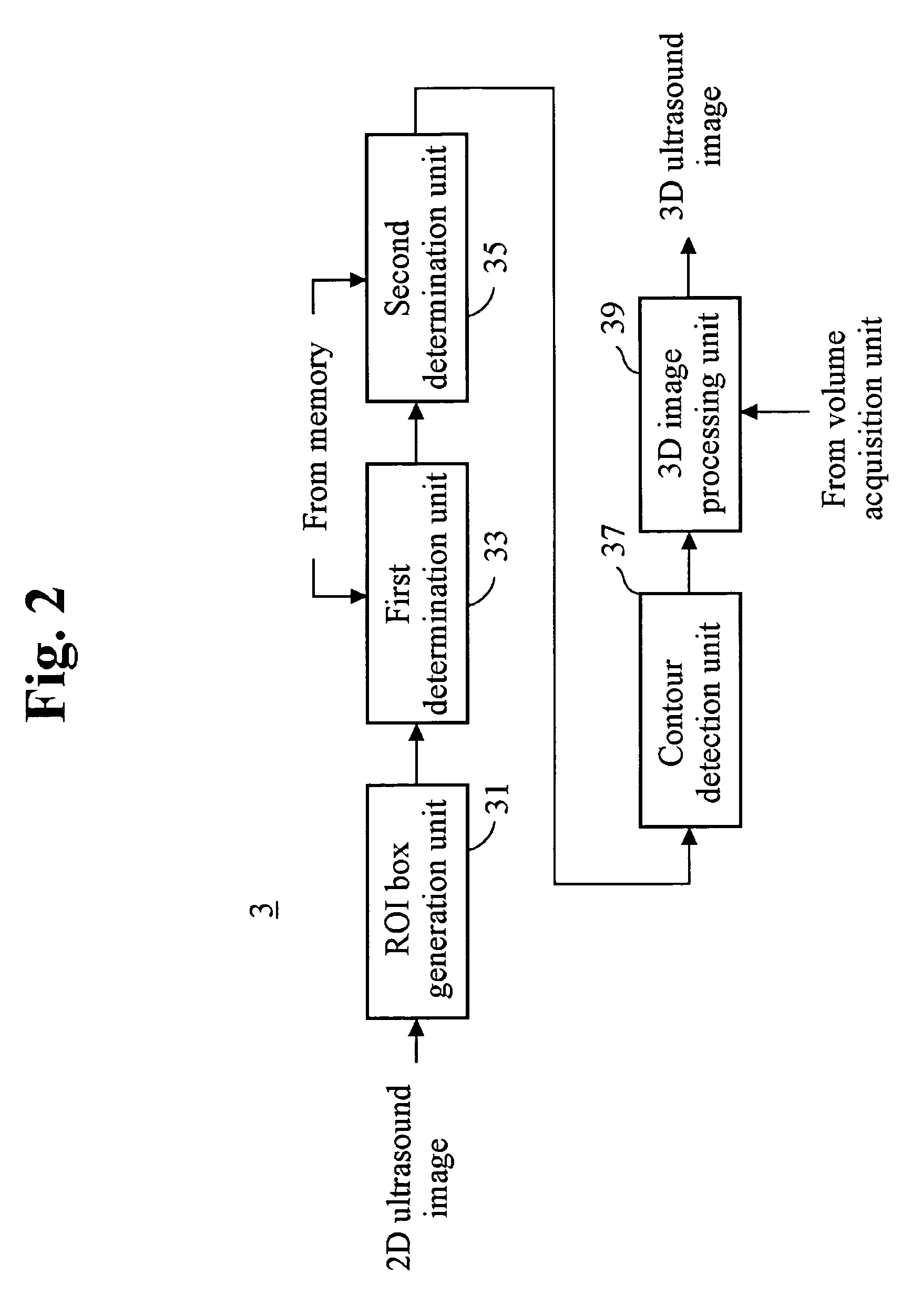
The present invention relates to a 3D ultrasound diagnostic forming a 3D ultrasound image only with volume data exiting within contour by automatically detecting the contour of a target object, comprising: a first unit for generating a region of interest (ROI) box on a 2D ultrasound image; a second unit for detecting a contour of a target object in the ROI box; and a third unit for forming a 3D ultrasound image by rendering volume data existing in the detected contour.
Owner:MEDISON CO LTD
Ultrasound image processing system
InactiveUS6108439AEasy to operateSimplify and accelerate signal processing operationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic sensorImaging processing
An ultrasound image processing system, having an ultrasound image capture device such as a B-mode ultrasound probe capable of making 2D scans over a predetermined range, and a drive for moving an ultrasound transducer in a direction different from the direction of 2D scans by the transducer to capture 2D ultrasound images sequentially in a predetermined pitch in the direction of movement of the ultrasound transducer. The ultrasound image processing system is provided with a marker for inserting a marker sign on field images selected from a large number of 2D ultrasound images sequentially captured by the image capture device, for use in three-dimensional image processing in a subsequent stage.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
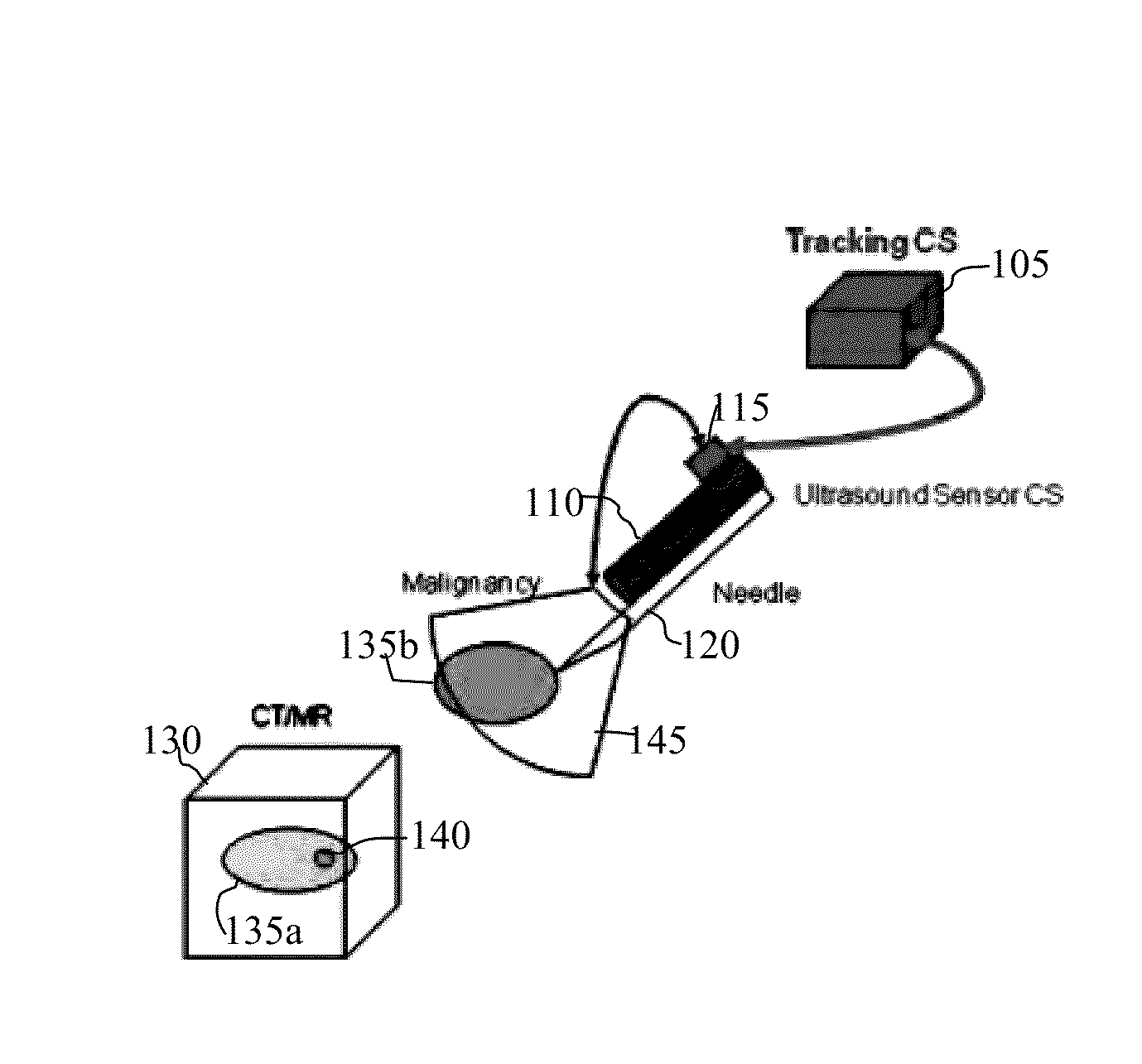
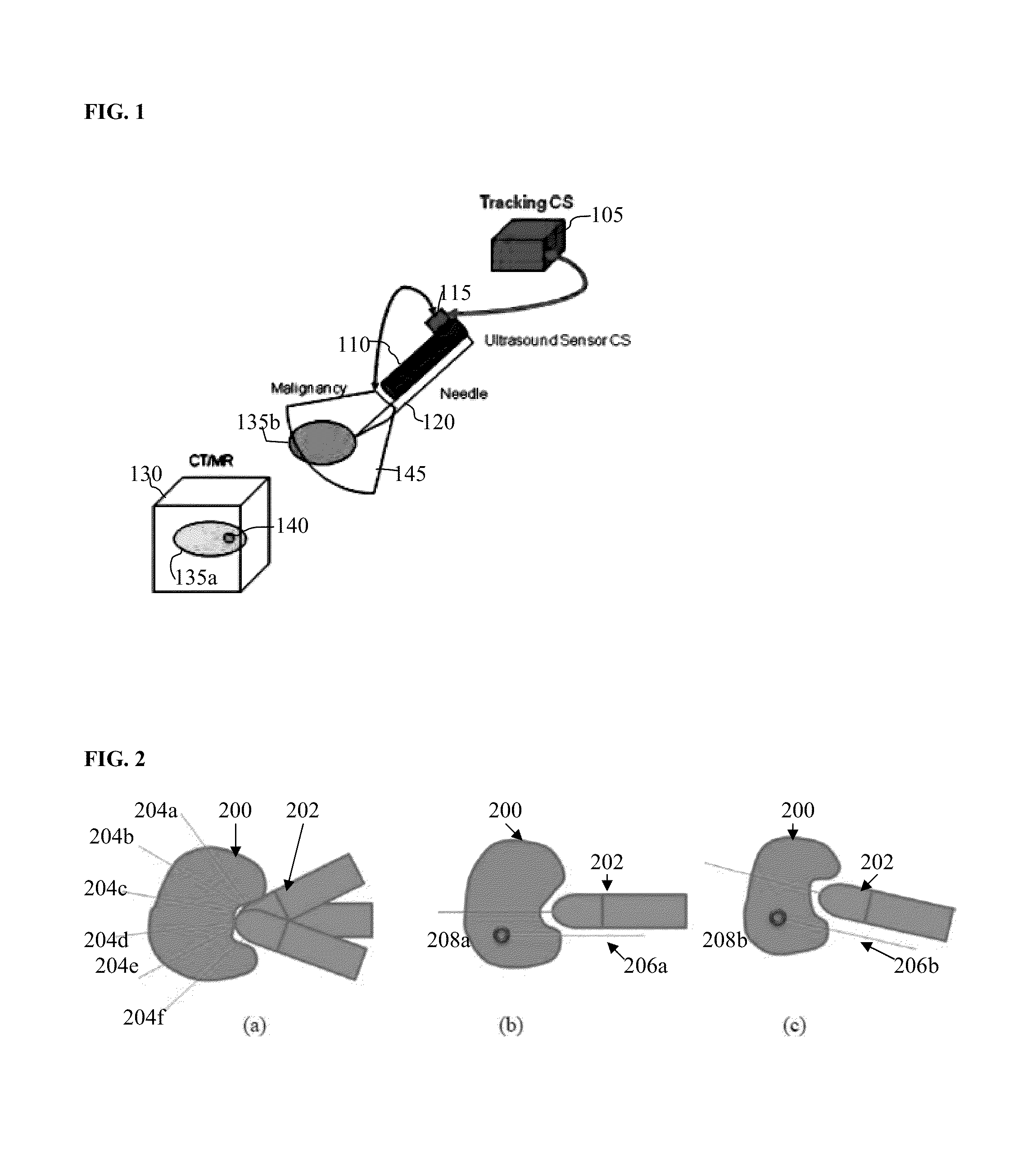
Ultrasound tracking adapter
InactiveUS20130178745A1Repeatable, rigid, and tool-lessReduce weightUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsGuidance system2d ultrasound
An ultrasound tracking adapter assembly that attaches to an ultrasound transducer in a repeatable, rigid, and tool-less manner. When used with a tracked body, the position of the tracking technology devices and the ultrasound transducer is fixed, so intraoperative calibration is not necessary. This permits a 3D guidance system and 2D ultrasound to be used together. The adapter provides a secure, rigid hold between the ultrasound transducer body and the clamping body. The ultrasound probe clamp assembly is attached to specific probe instruments used in the operating room that are to be tracked using 3D positioning technology.
Owner:PATHFINDER THERAPEUTICS
Methods and systems for generating an ultrasound image
InactiveUS20170238907A1Health-index calculationOrgan movement/changes detectionSonification2d ultrasound
Systems and methods are provided for generating an ultrasound image. The systems and methods acquire three dimensional (3D) ultrasound data of a volumetric region of interest (ROI) from an ultrasound probe. The systems and methods further identify a select set of the 3D ultrasound data that includes a plurality of anatomical markers. The one or more anatomical markers may correspond to an anatomy of interest within the volumetric ROI. The systems and methods further generate a two dimensional (2D) ultrasound image based on the select set of the 3D ultrasound data, and display the 2D ultrasound image on a display.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for implanting a cardiac implant with real-time ultrasound imaging guidance
InactiveUS20080146919A1Reduce disadvantagesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterUltrasound imaging2d ultrasound
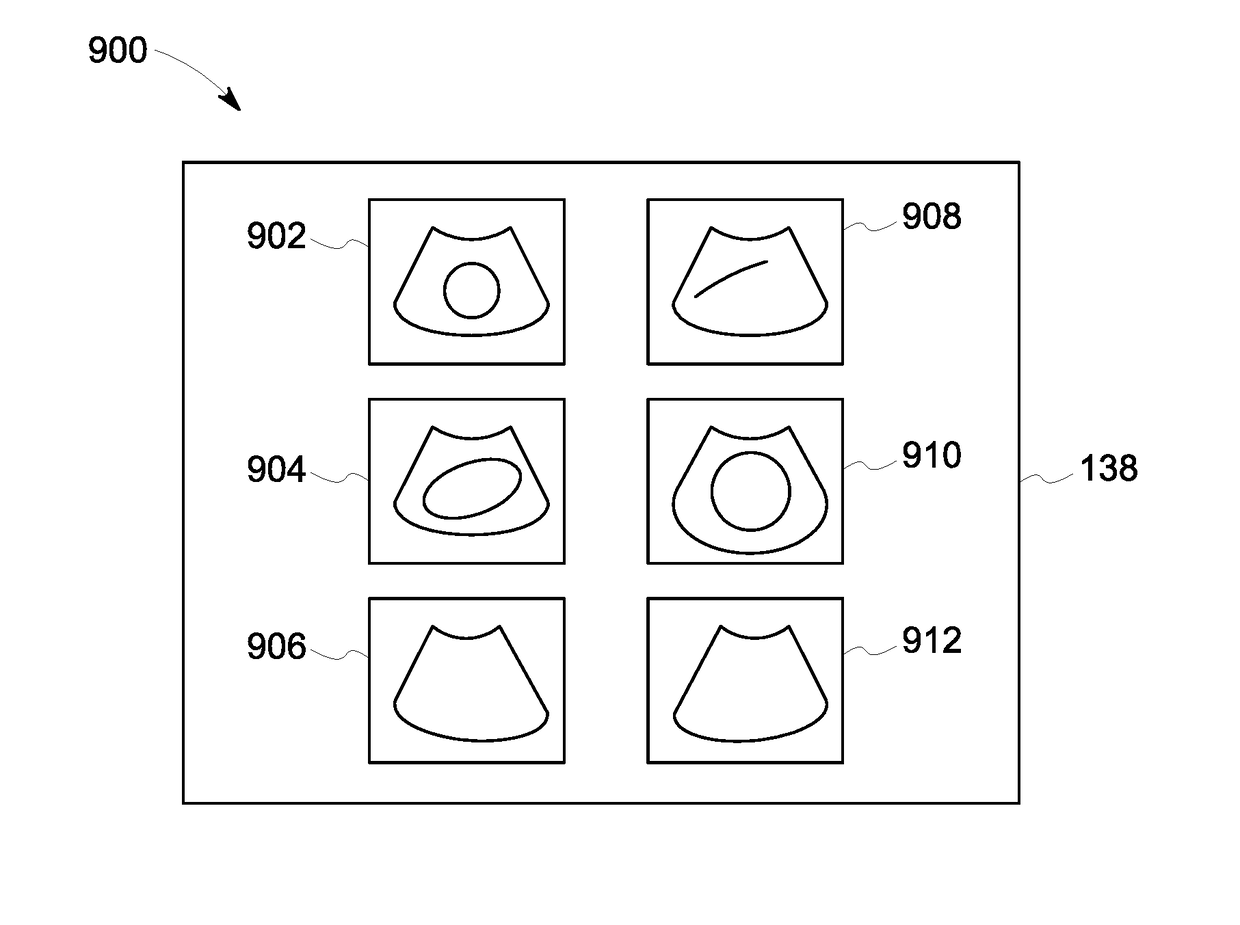
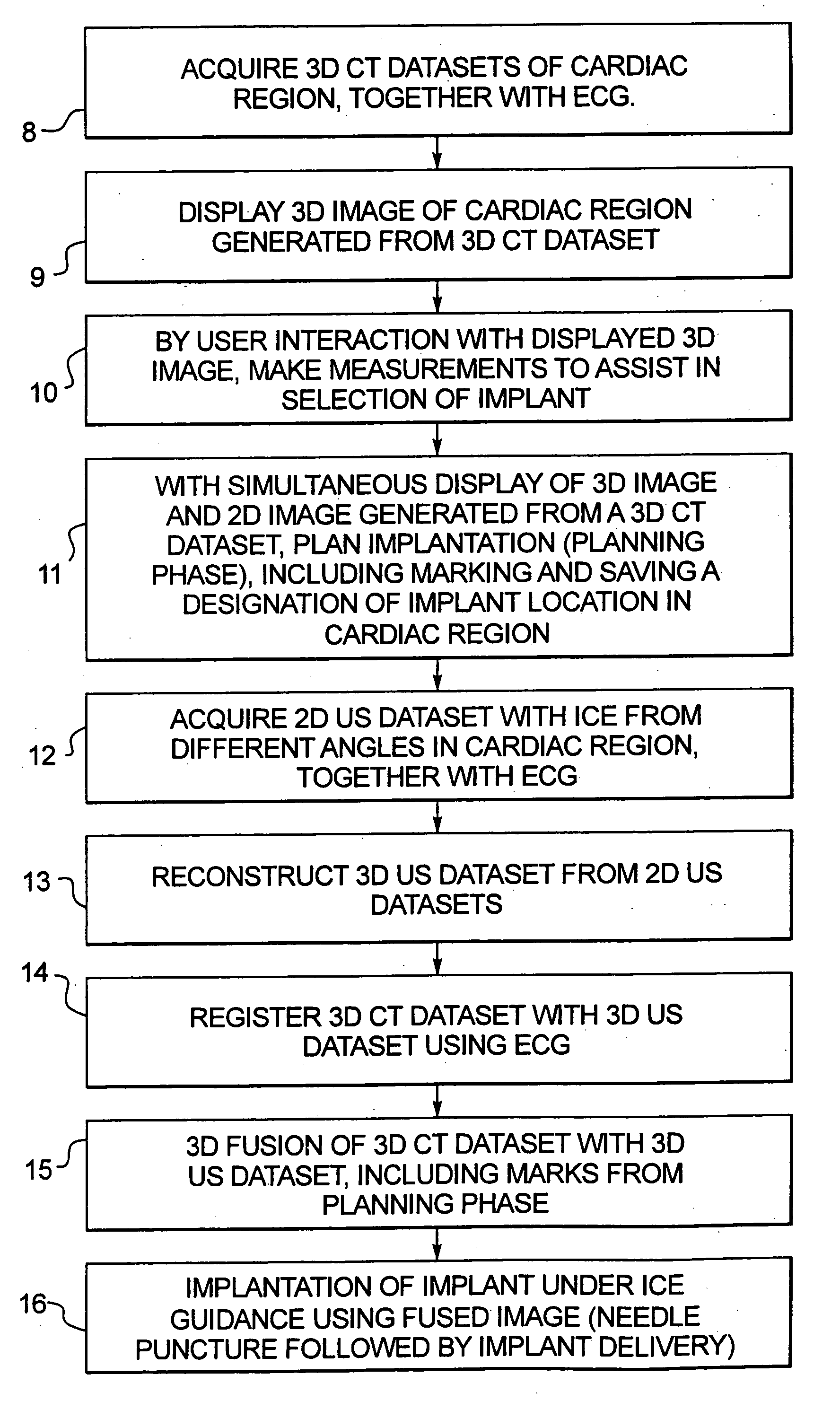
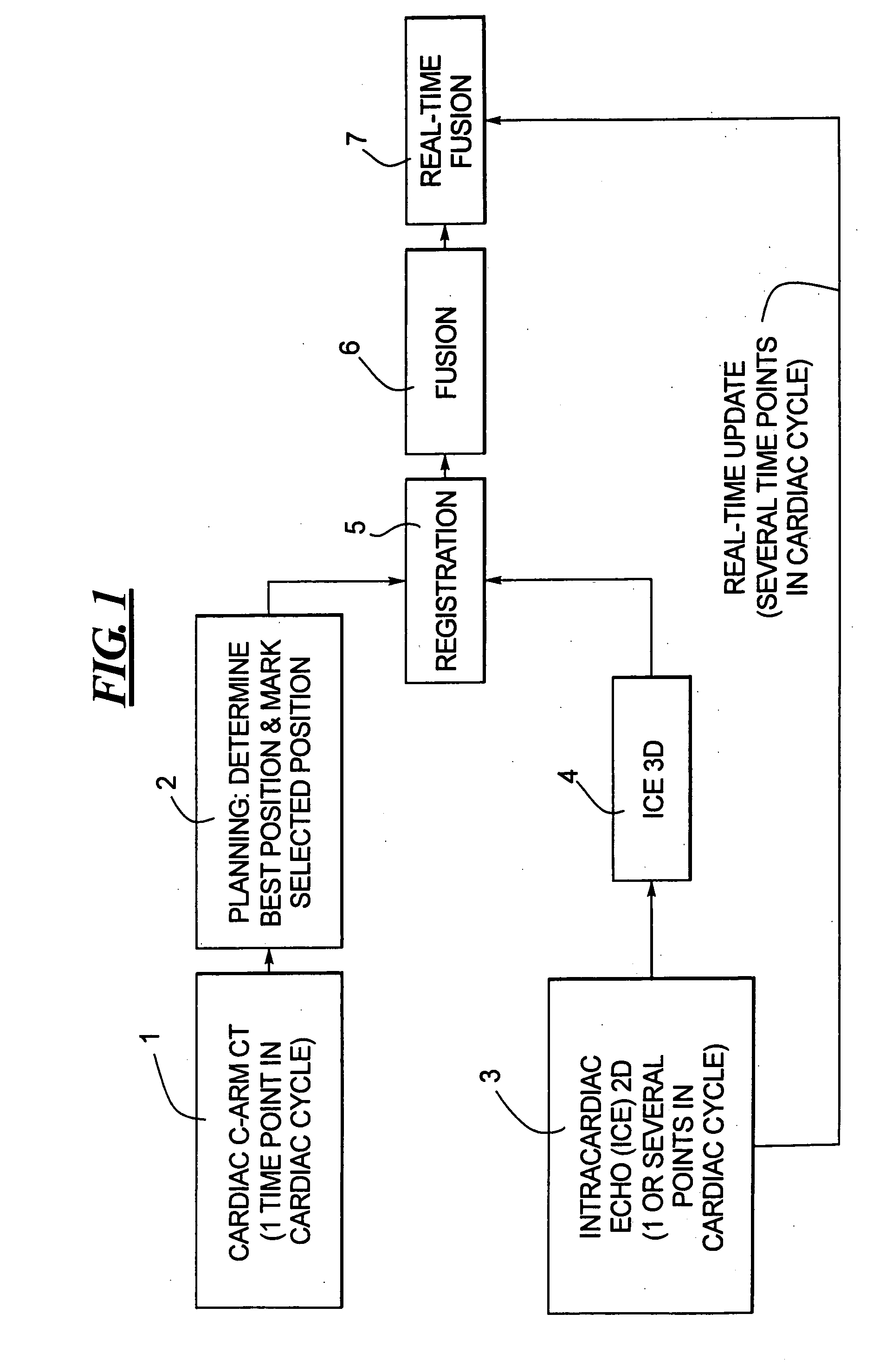
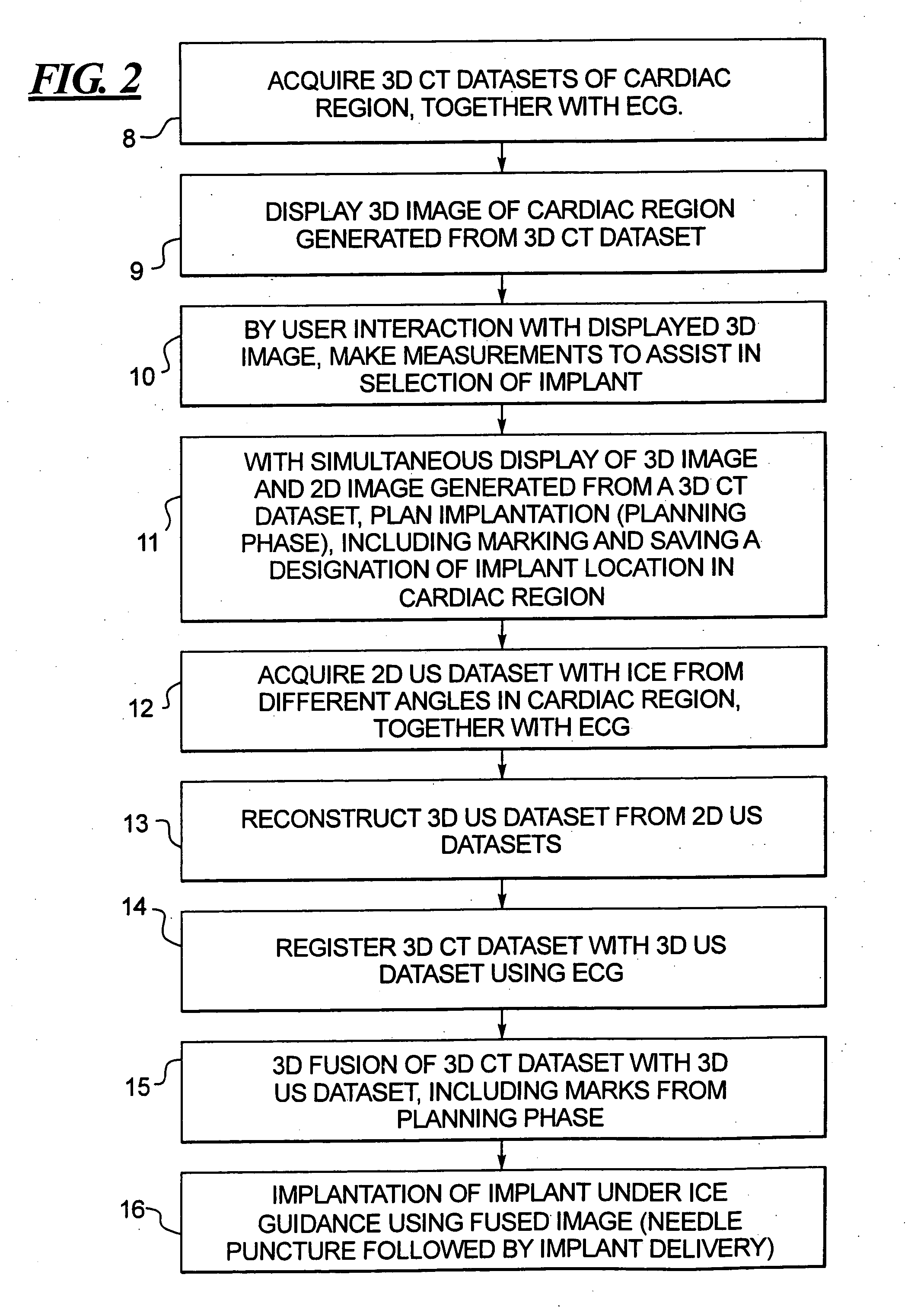
In a method for implanting a cardiac implant, a 3D CT dataset of a cardiac region of interest at which an implant is to be implanted, is displayed and the implantation procedure is planned, which includes the physician electronically marking a best implantation site in the displayed image. This marking is then included in the 3D CT dataset. A 3D ultrasound dataset of the region of interest is acquired, and is brought into registration with the 3D CT dataset that incorporates the marking, and a fused image is produced therefrom. The fused image is displayed during the implantation procedure, and is updated with multiple real-time 2D ultrasound images obtained using the catheter that is employed to deliver the implant to the implantation site.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Laparoscopic Ultrasound Robotic Surgical System
ActiveUS20170128145A1Easy to useImprove efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapies2d ultrasoundVirtual fixture
A LUS robotic surgical system is trainable by a surgeon to automatically move a LUS probe in a desired fashion upon command so that the surgeon does not have to do so manually during a minimally invasive surgical procedure. A sequence of 2D ultrasound image slices captured by the LUS probe according to stored instructions are processable into a 3D ultrasound computer model of an anatomic structure, which may be displayed as a 3D or 2D overlay to a camera view or in a PIP as selected by the surgeon or programmed to assist the surgeon in inspecting an anatomic structure for abnormalities. Virtual fixtures are definable so as to assist the surgeon in accurately guiding a tool to a target on the displayed ultrasound image.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Laparoscopic Ultrasound Robotic Surgical System
ActiveUS20170128041A1Easy to useImprove efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapies2d ultrasoundVirtual fixture
A LUS robotic surgical system is trainable by a surgeon to automatically move a LUS probe in a desired fashion upon command so that the surgeon does not have to do so manually during a minimally invasive surgical procedure. A sequence of 2D ultrasound image slices captured by the LUS probe according to stored instructions are processable into a 3D ultrasound computer model of an anatomic structure, which may be displayed as a 3D or 2D overlay to a camera view or in a PIP as selected by the surgeon or programmed to assist the surgeon in inspecting an anatomic structure for abnormalities. Virtual fixtures are definable so as to assist the surgeon in accurately guiding a tool to a target on the displayed ultrasound image.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
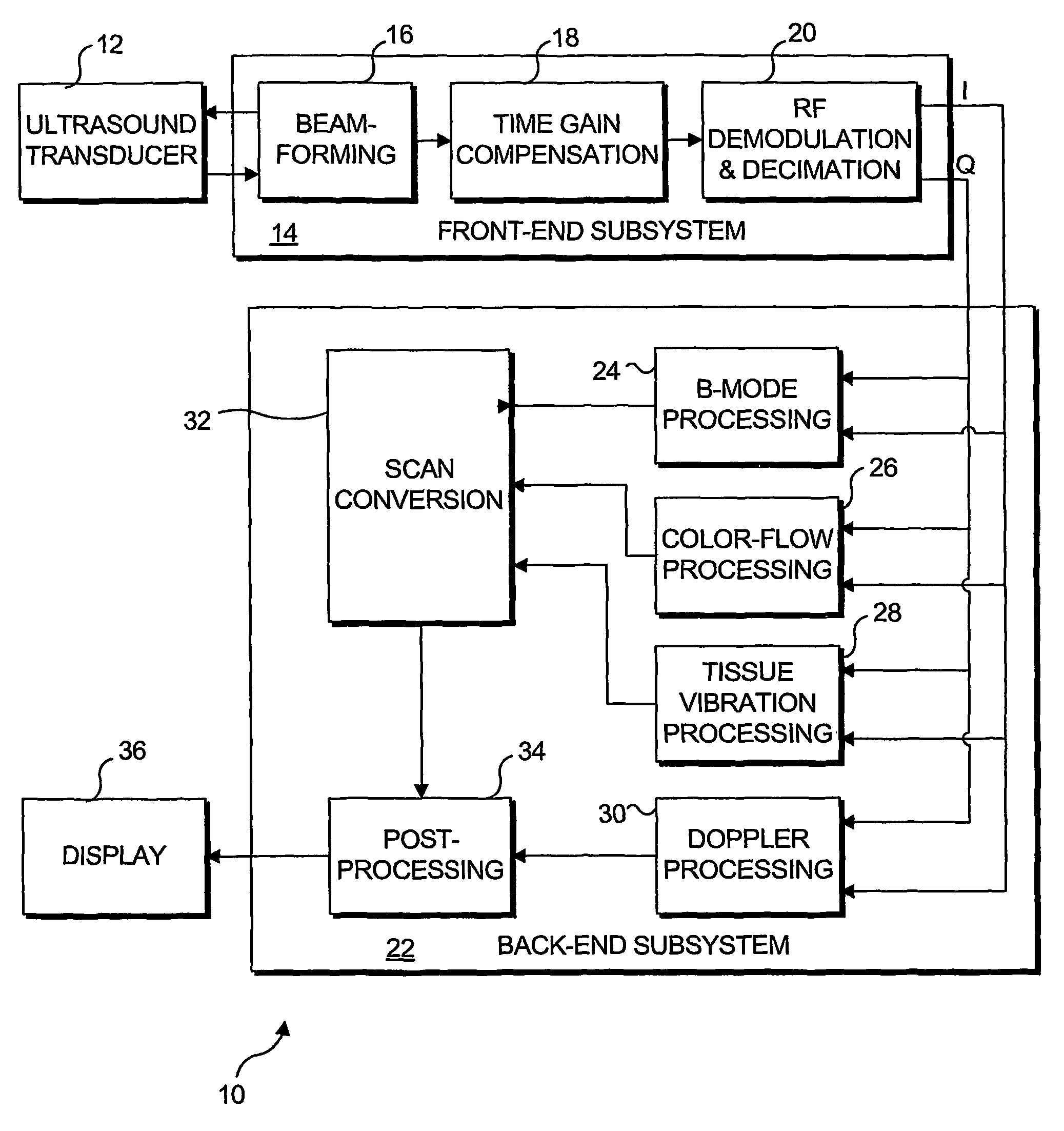
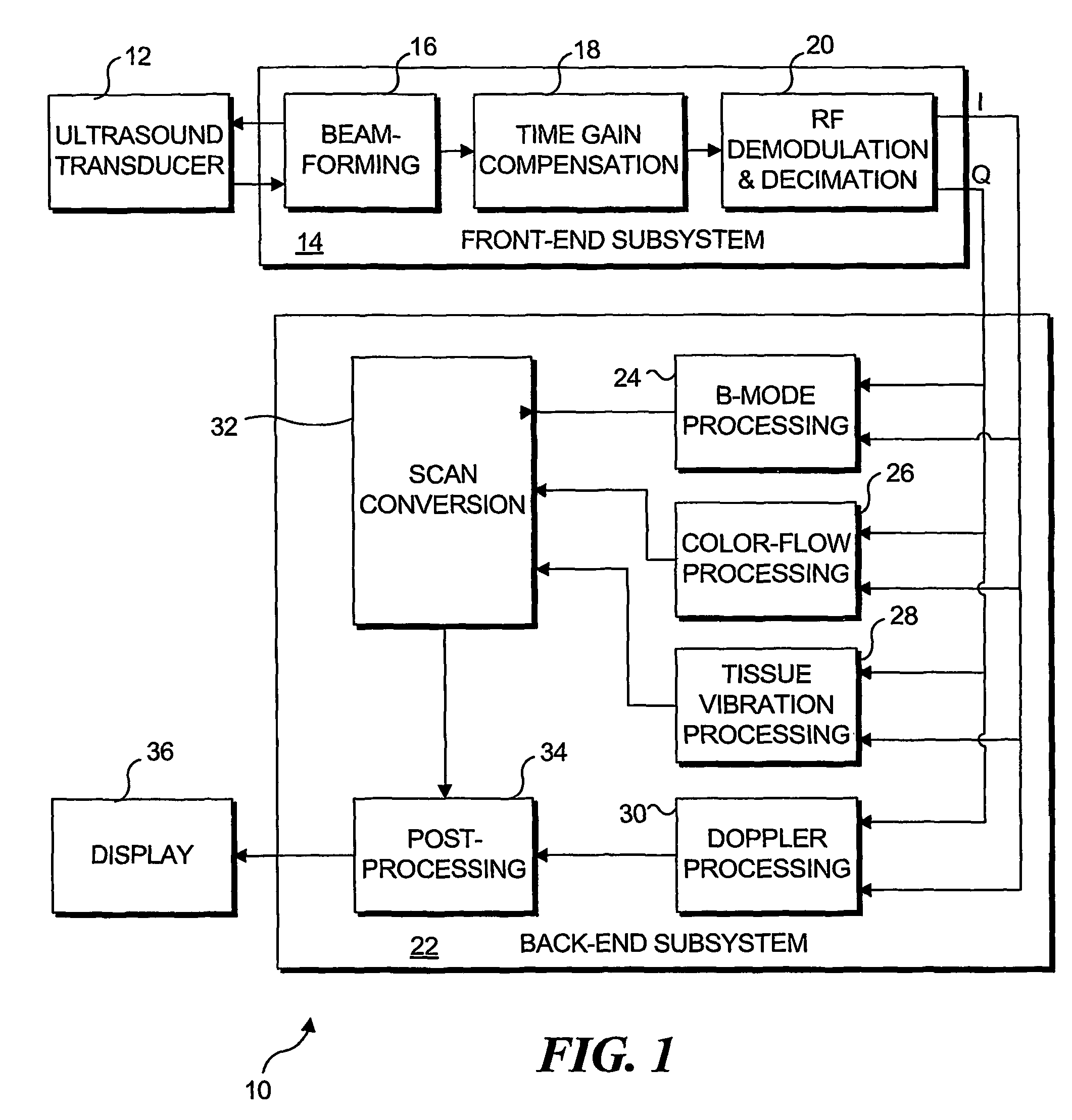
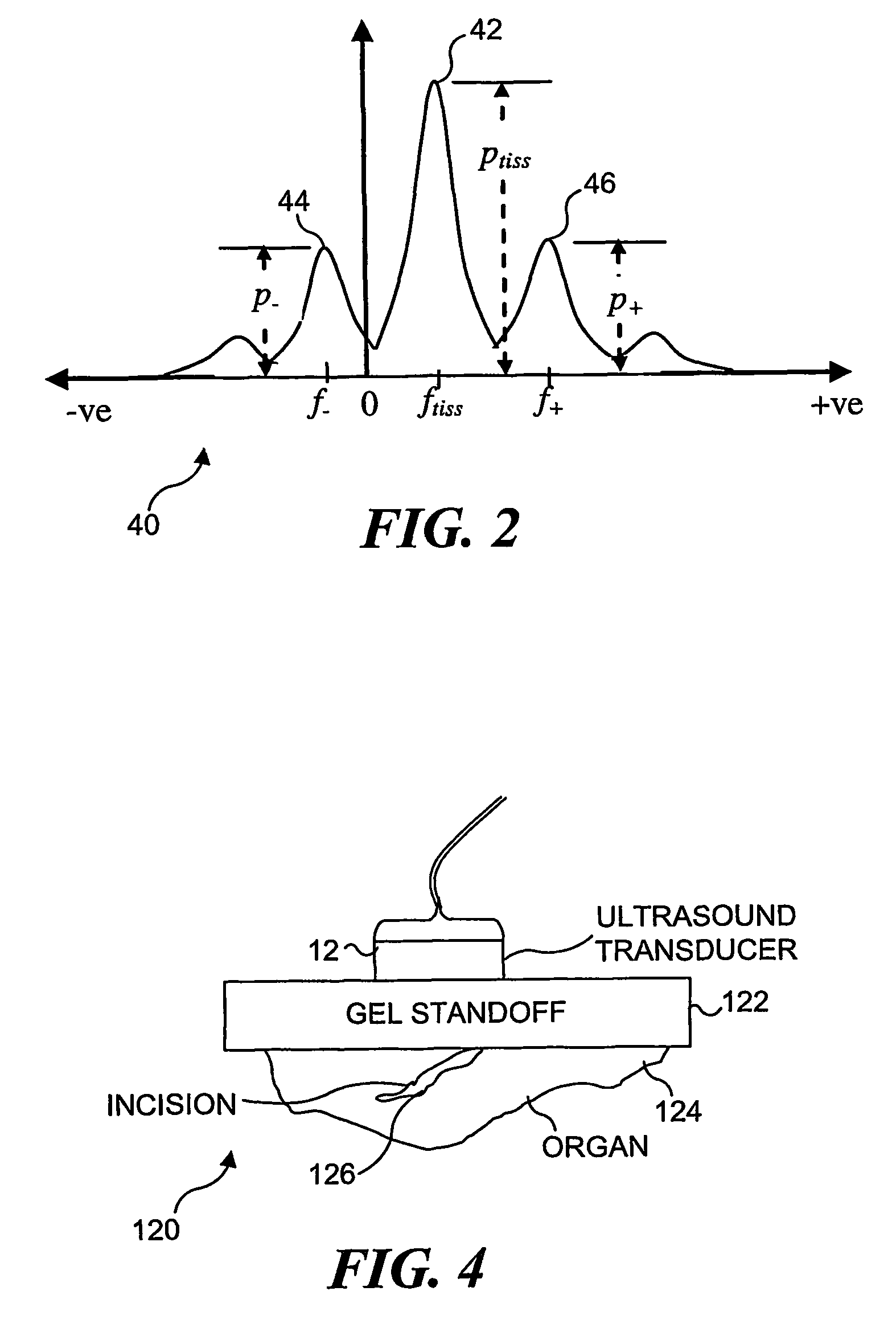
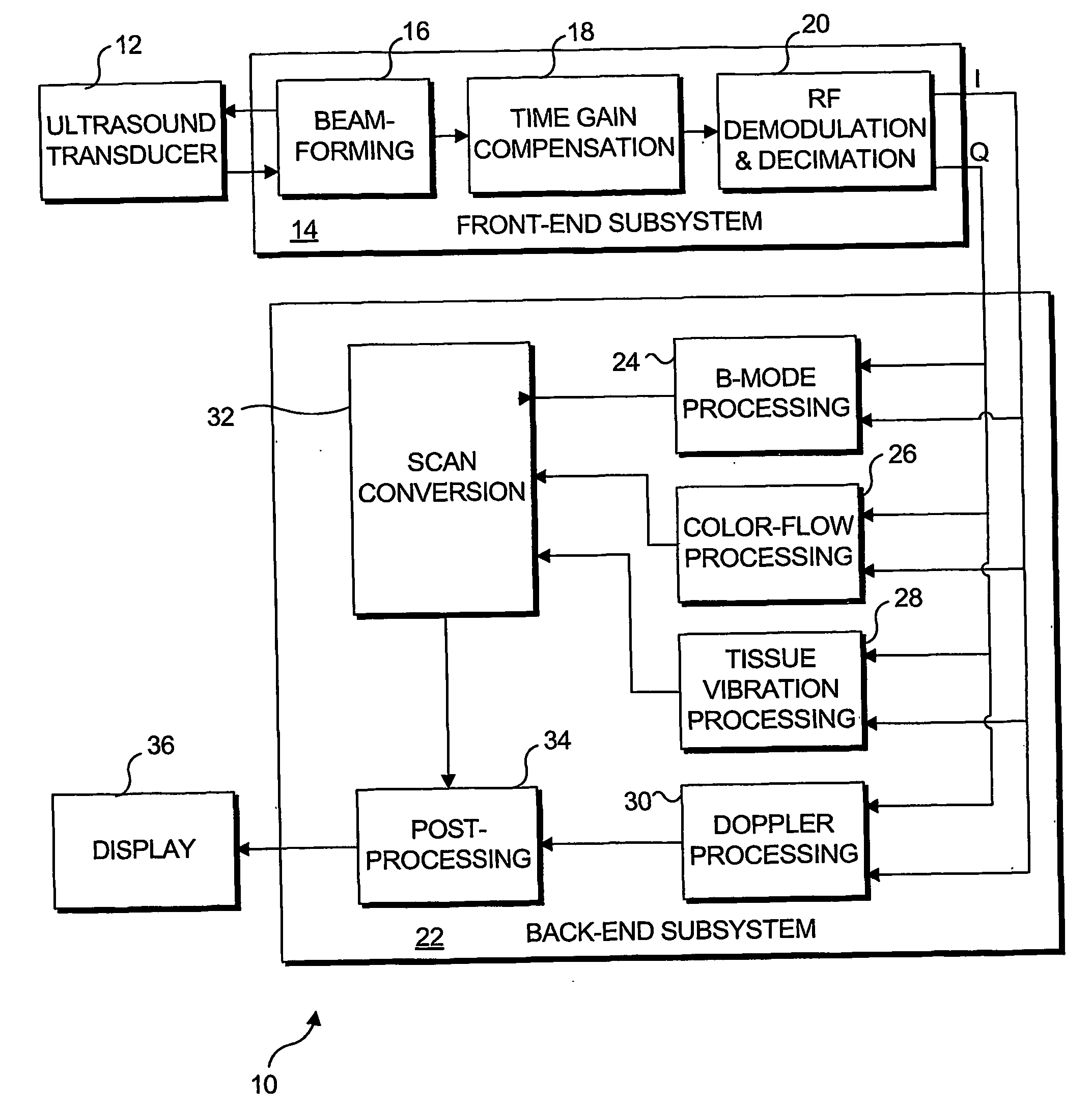
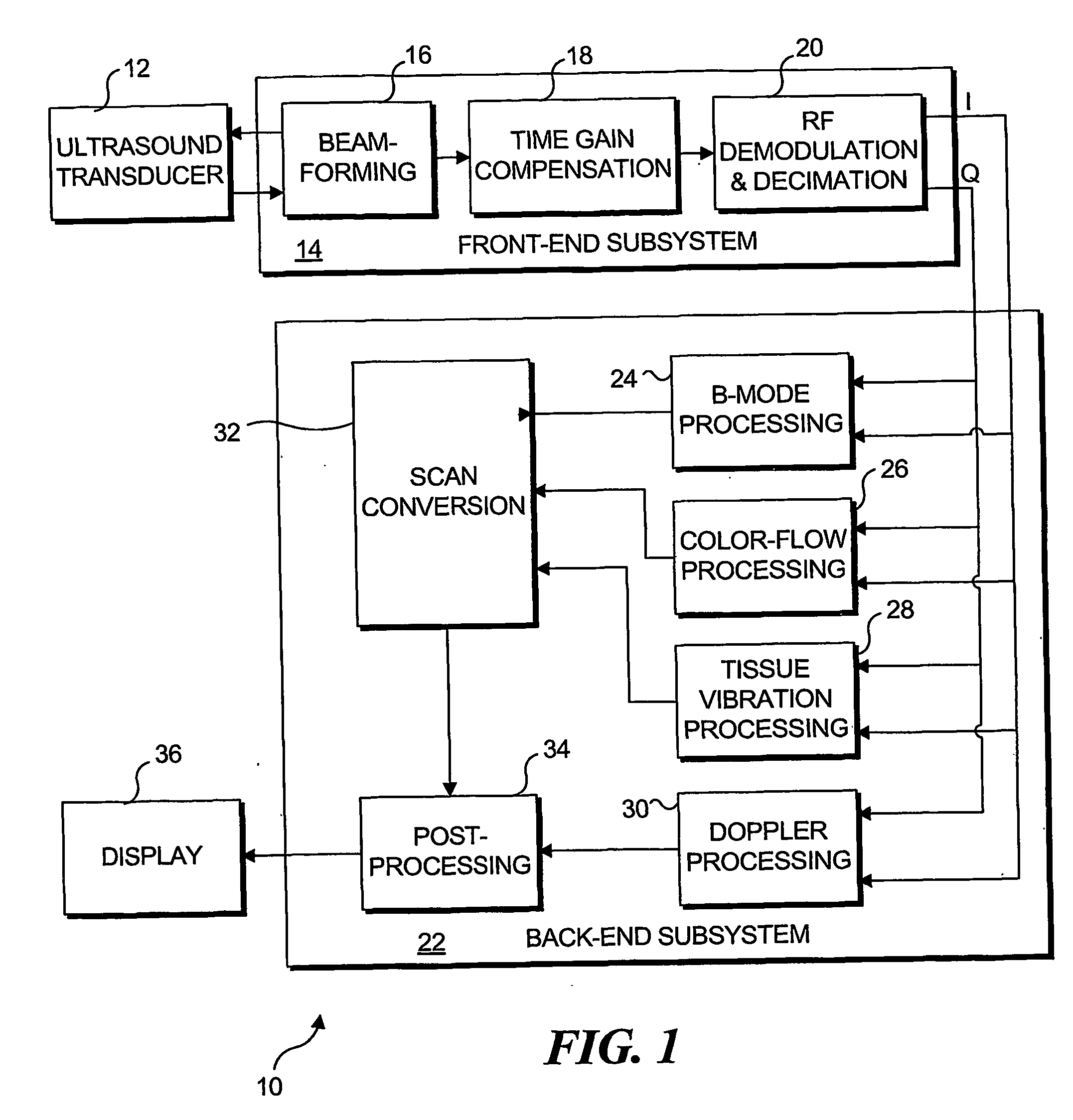
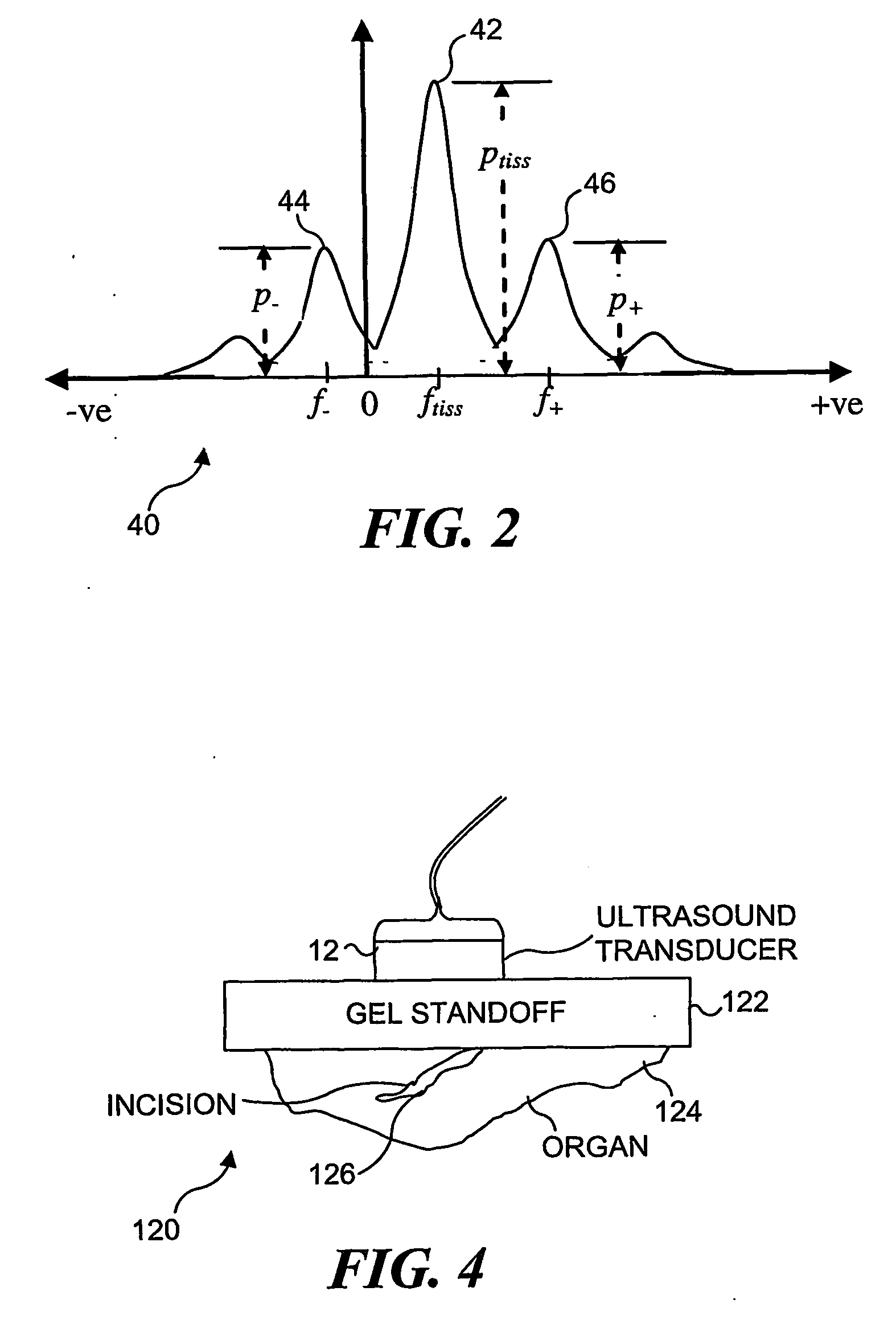
Transcutaneous localization of arterial bleeding by two-dimensional ultrasonic imaging of tissue vibrations
InactiveUS7803116B2Improve visualizationLocalize a bleeding site quickly and non-invasivelyBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsVibration amplitudeSonification
An ultrasound based technique for detecting and imaging vibrations in tissue caused by eddies produced during bleeding through punctured arteries or from organs. A clutter signal, normally suppressed in conventional color flow imaging, is employed to detect and characterize local tissue vibrations, to detect internal bleeding in an image, or as an audible or palpable signal, or a readout. Using a tissue vibration image, the origin and extent of vibrations relative to the underlying anatomy and blood flow can be visualized in real time, enabling measurements of vibration amplitude, frequency, and spatial distribution. Bleeding rate can be determined from the frequency and amplitude of the vibrations. Signal processing algorithms usable to identify tissue vibrations from an ensemble of 2D ultrasound data include those based on phase decomposition, spectral estimation using eigendecomposition, and spectral estimation using autoregressive modeling for isolating vibrations from clutter, blood flow, and noise.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Transcutaneous localization of arterial bleeding by two-dimensional ultrasonic imaging of tissue vibrations
InactiveUS20070066895A1Improve visualizationAugment duplex ultrasoundBlood flow measurement devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringVibration amplitudeFrequency spectrum
An ultrasound based technique for detecting and imaging vibrations in tissue caused by eddies produced during bleeding through punctured arteries or from organs. A clutter signal, normally suppressed in conventional color flow imaging, is employed to detect and characterize local tissue vibrations, to detect internal bleeding in an image, or as an audible or palpable signal, or a readout. Using a tissue vibration image, the origin and extent of vibrations relative to the underlying anatomy and blood flow can be visualized in real time, enabling measurements of vibration amplitude, frequency, and spatial distribution. Bleeding rate can be determined from the frequency and amplitude of the vibrations. Signal processing algorithms usable to identify tissue vibrations from an ensemble of 2D ultrasound data include those based on phase decomposition, spectral estimation using eigendecomposition, and spectral estimation using autoregressive modeling for isolating vibrations from clutter, blood flow, and noise.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Laparoscopic Ultrasound Robotic Surgical System
InactiveUS20170128144A1Easy to useImprove efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapies2d ultrasoundVirtual fixture
A LUS robotic surgical system is trainable by a surgeon to automatically move a LUS probe in a desired fashion upon command so that the surgeon does not have to do so manually during a minimally invasive surgical procedure. A sequence of 2D ultrasound image slices captured by the LUS probe according to stored instructions are processable into a 3D ultrasound computer model of an anatomic structure, which may be displayed as a 3D or 2D overlay to a camera view or in a PIP as selected by the surgeon or programmed to assist the surgeon in inspecting an anatomic structure for abnormalities. Virtual fixtures are definable so as to assist the surgeon in accurately guiding a tool to a target on the displayed ultrasound image.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC +1
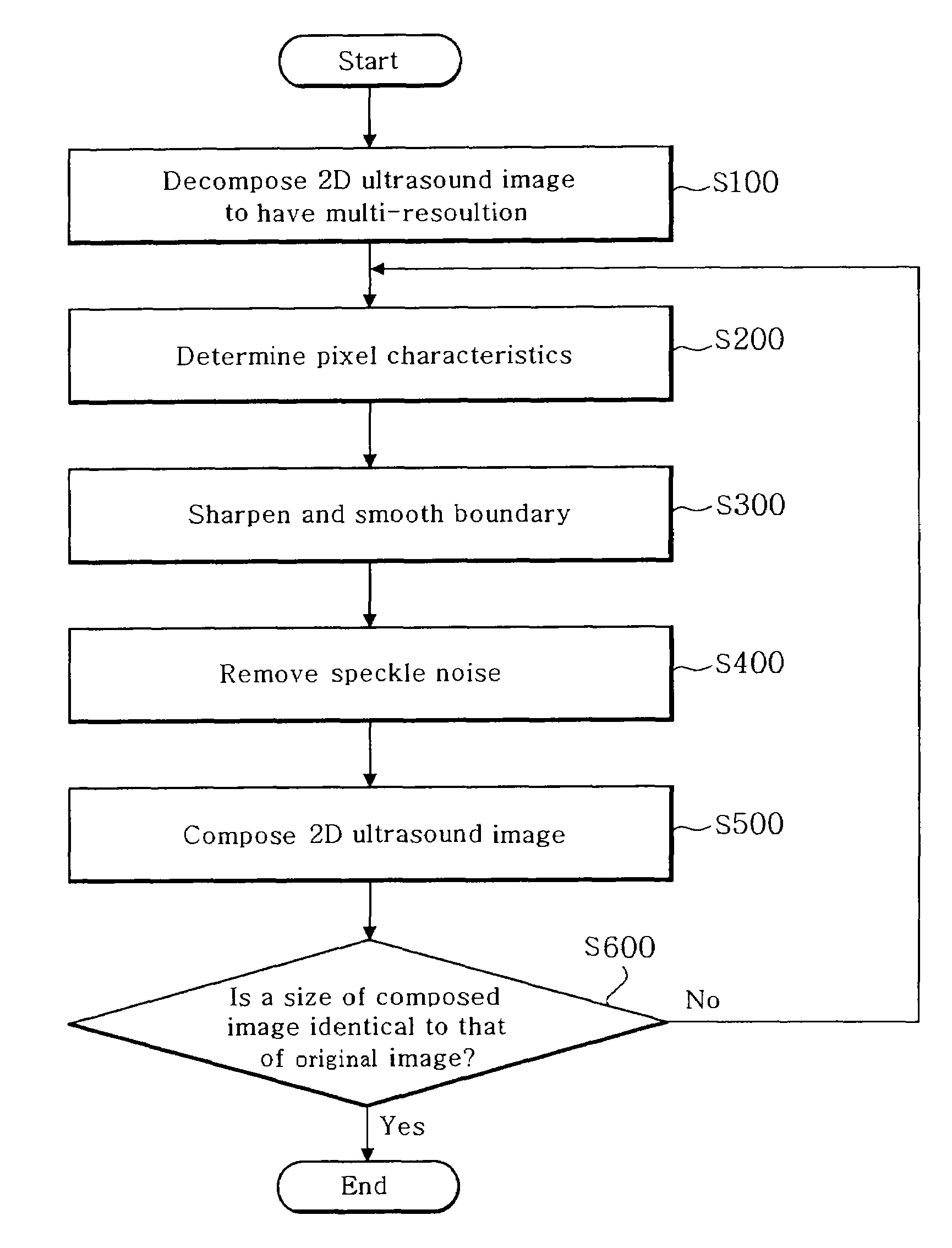
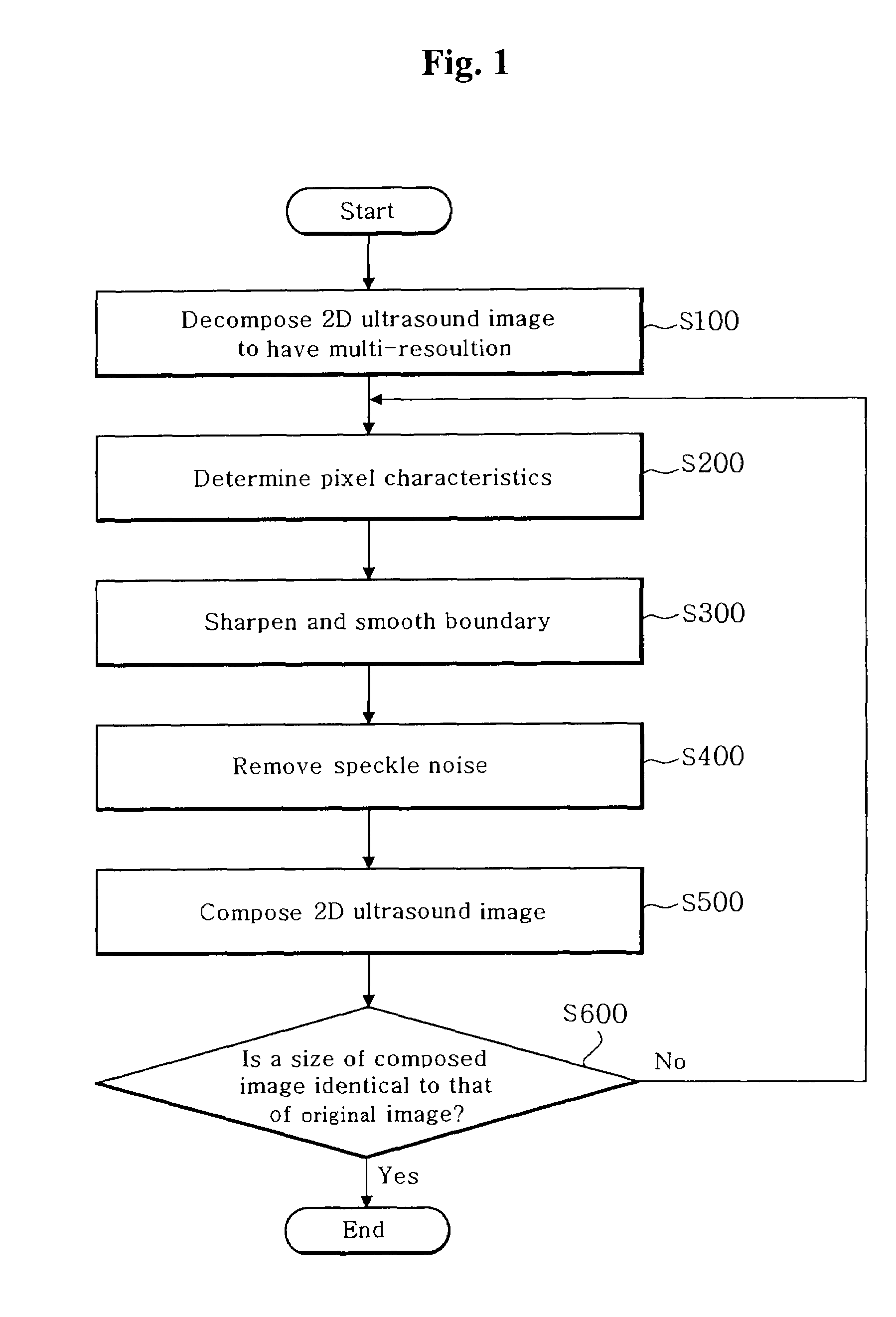
Method and apparatus for enhancing image quality of a two-dimensional ultrasound image
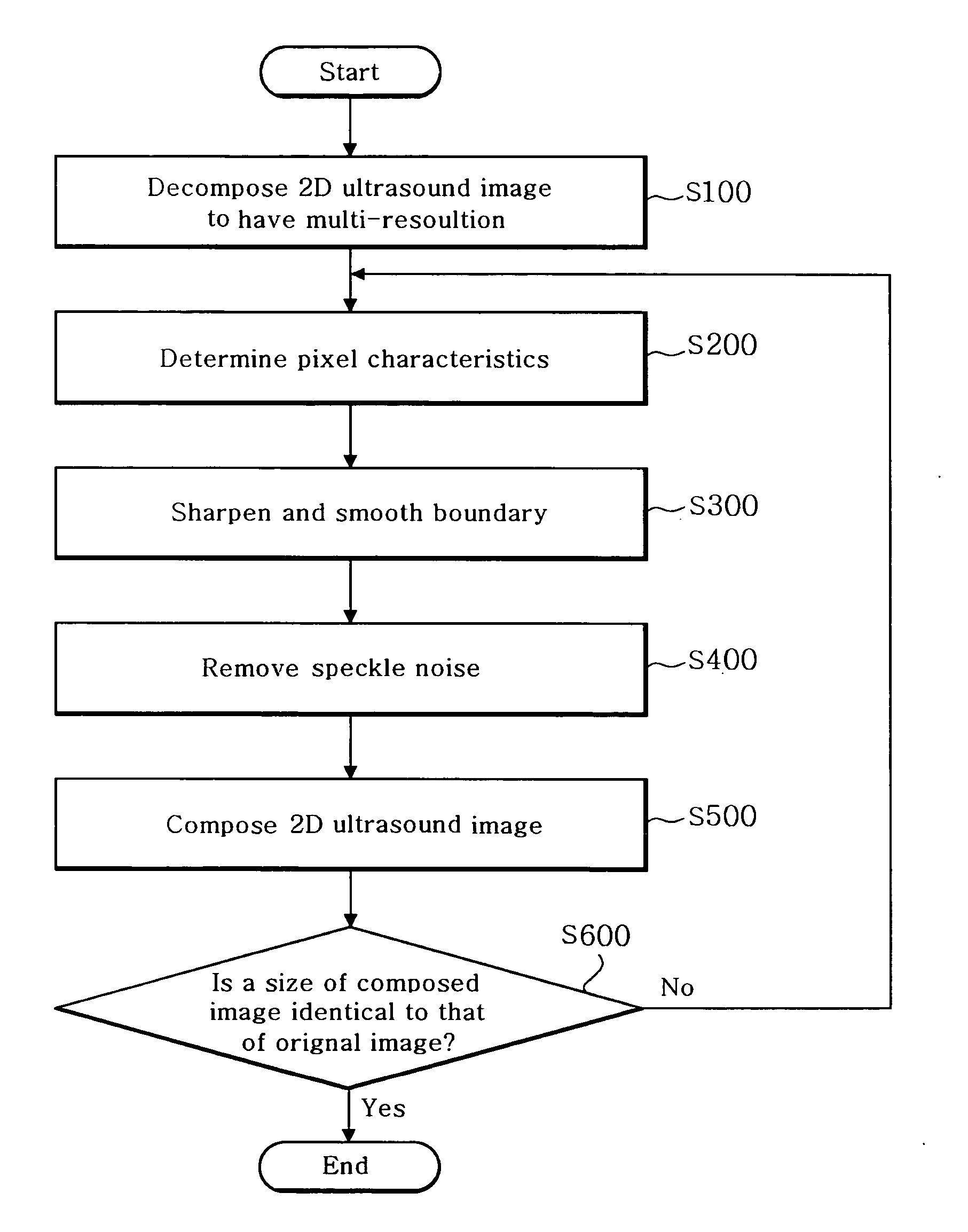
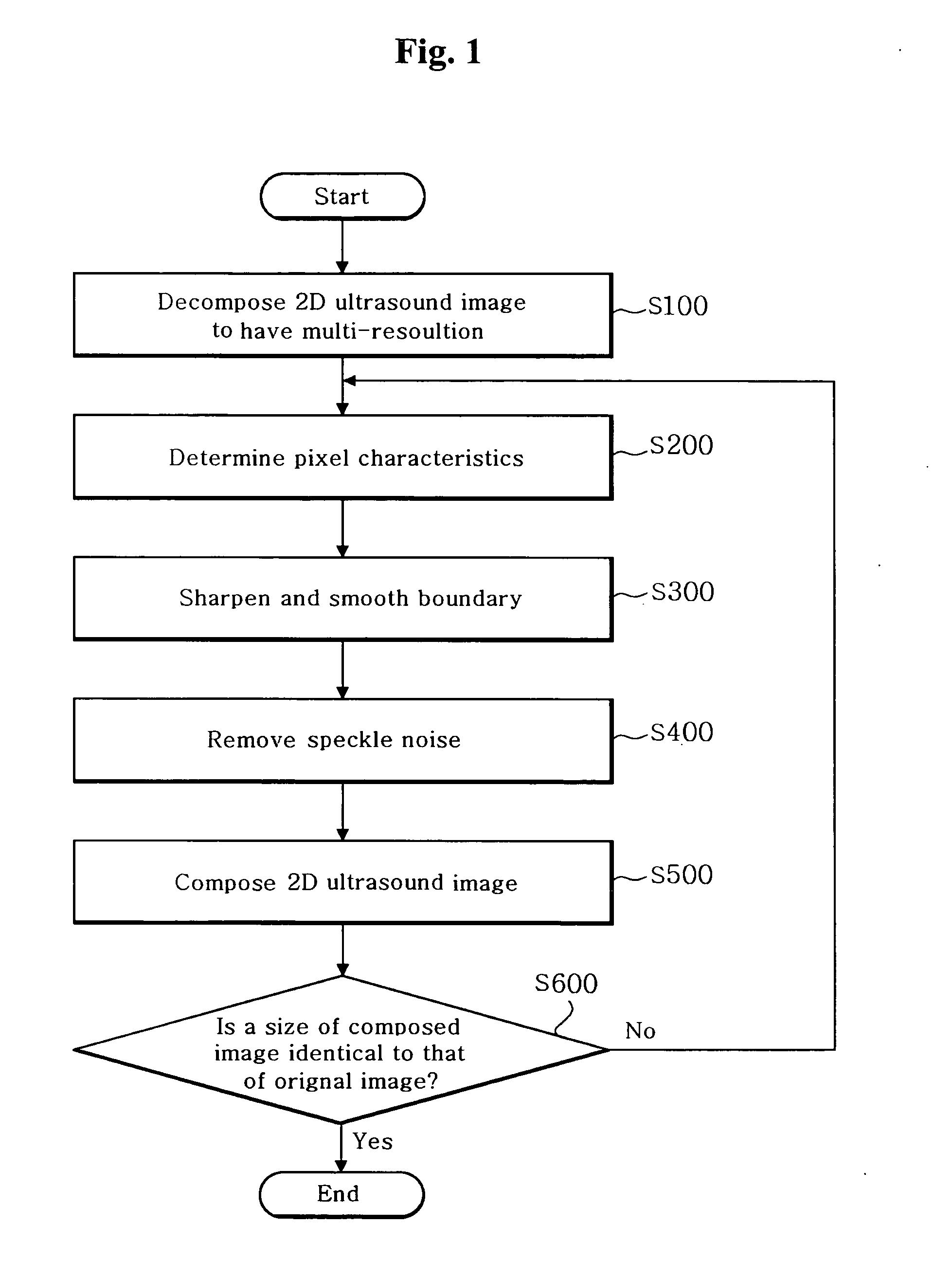
ActiveUS20060084869A1Improve image qualityRemove speckle noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancement2d ultrasoundImaging quality
The present invention relates a method and an apparatus for enhancing ultrasound image quality through a post-processing. A method for enhancing an image quality of a two-dimensional (2D) ultrasound image, comprises the steps of: a) decomposing the 2D ultrasound image into a plurality of images having a multi-resolution by N levels, wherein N is a positive integer; b) determining characteristics of each pixel in the decomposed image; c) performing an enhancement process for the decomposed image based on the pixel characteristics; d) performing 1st-level composition for the decomposed image; and e) repeatedly performing steps b) to d) until a size of the composed image is identical to that of the 2D ultrasound image.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Apparatus and method for forming 3D ultrasound image
ActiveUS7507204B2Reduce errorsReduce time consumptionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgerySonification2d ultrasound
The present invention relates to a 3D ultrasound diagnostic forming a 3D ultrasound image only with volume data exiting within contour by automatically detecting the contour of a target object, comprising: a first unit for generating a region of interest (ROI) box on a 2D ultrasound image; a second unit for detecting a contour of a target object in the ROI box; and a third unit for forming a 3D ultrasound image by rendering volume data existing in the detected contour.
Owner:MEDISON CO LTD
Method and apparatus for processing ultrasound image
ActiveUS20130018265A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancement2d ultrasoundComputer vision
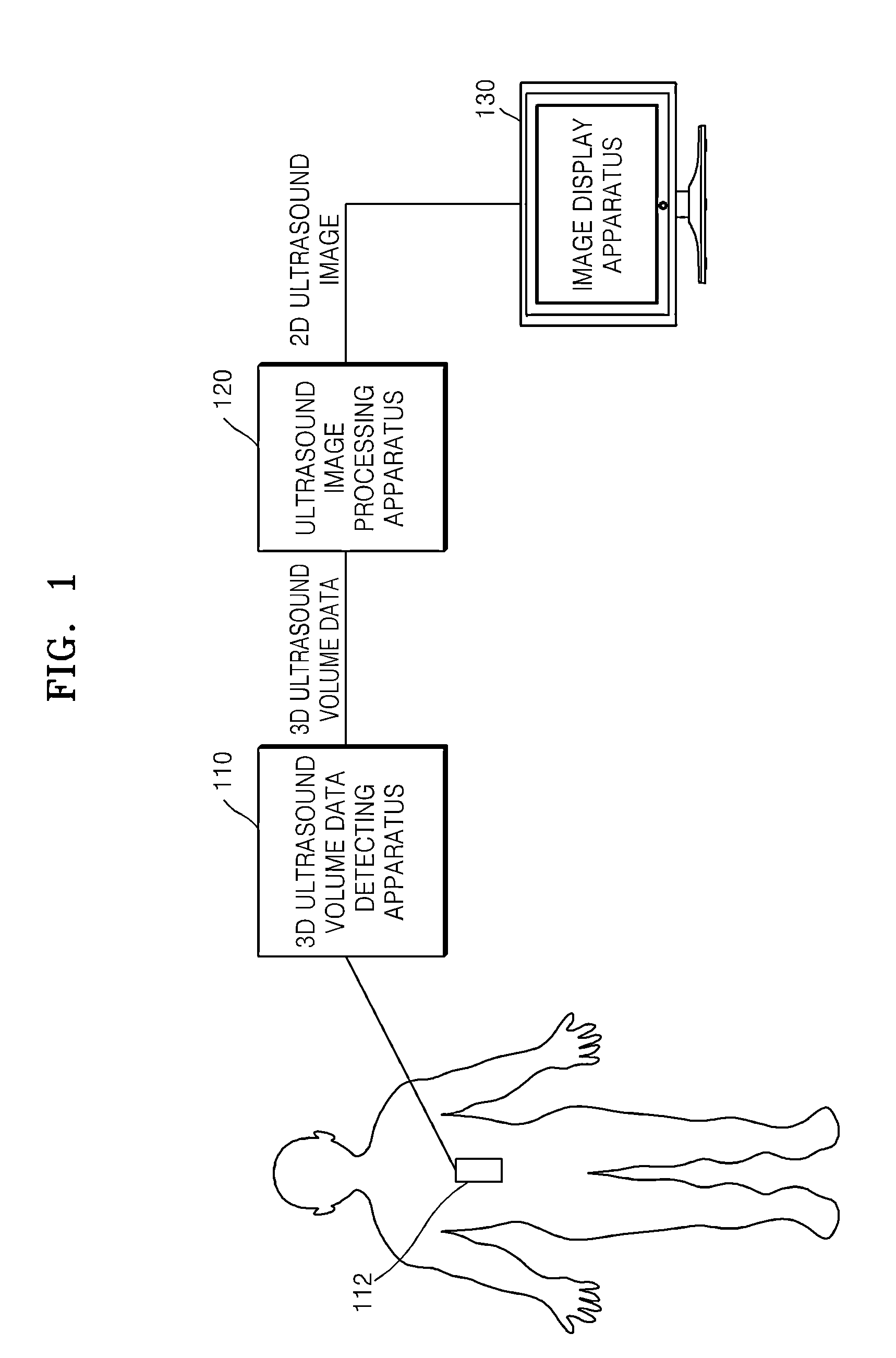
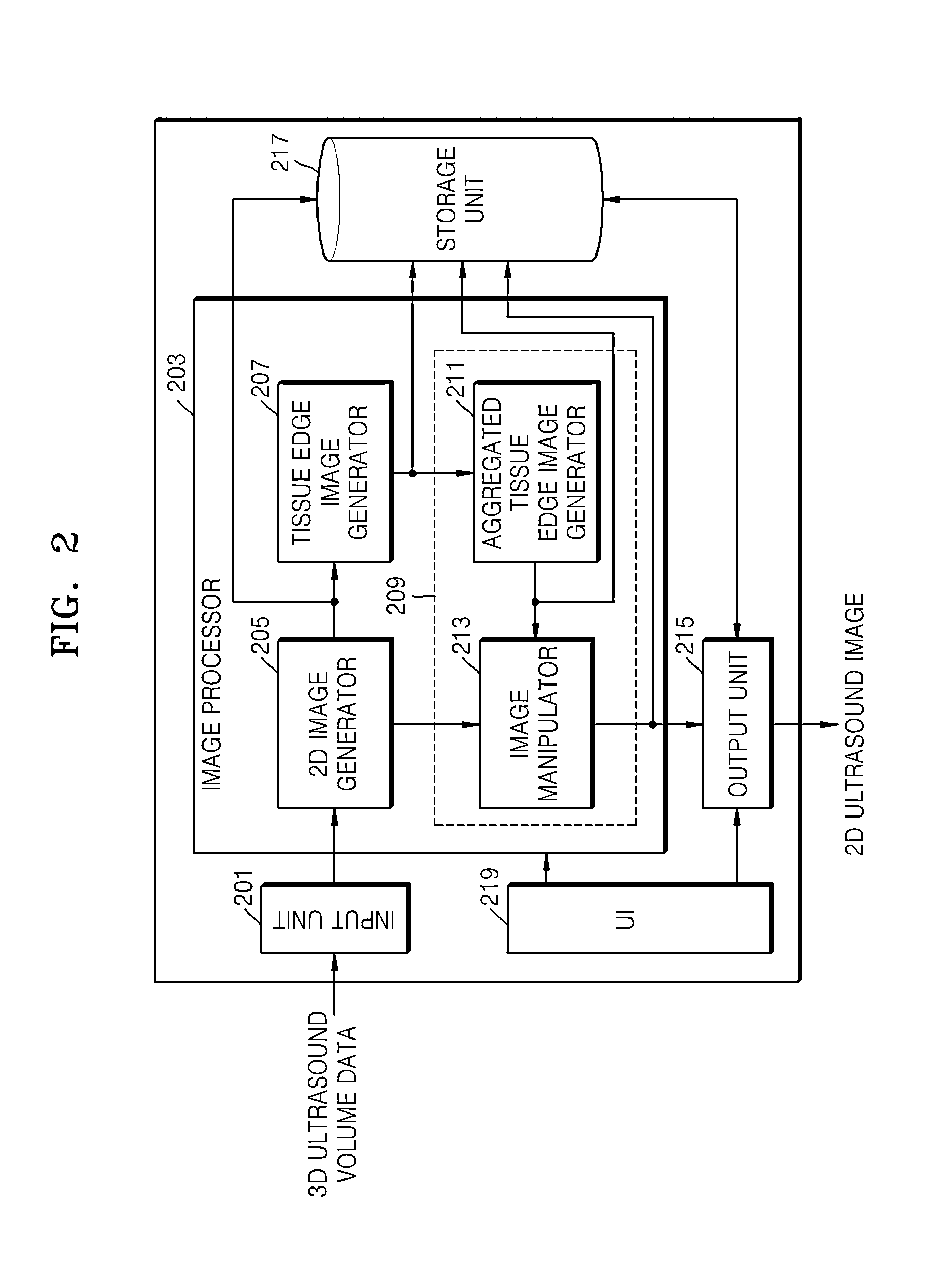
A method of processing an ultrasound image includes generating a plurality of two-dimensional (2D) ultrasound images from three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound volume data of an object to be diagnosed, generating a plurality of tissue edge images of an edge of at least one tissue component in the object to be diagnosed based on values of a plurality of pixels forming each of the 2D ultrasound images generated from the 3D ultrasound volume data, and generating a 2D ultrasound image from which a noise component has been removed by discriminating the edge of the at least one tissue component from a position of the noise component based on a difference between a similarity of the edge of the at least one tissue component in the tissue edge images and a similarity of the noise component in the tissue edge images.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for measuring a volume of an organ of interest
In an embodiment of the subject matter described herein a system is provided. The system includes a portable host system having one or more processors and a memory for storing a plurality of applications. The one or more processors configured to execute programmed instructions of a select application by performing one or more operations, which include obtain a set of frames of 2D ultrasound images, develop a prospect model indicating a likelihood that frames within the set include an organ of interest (OOI), identify primary and secondary reference frames from the set of the frames based on the prospect model, determine a characteristic of interest in the primary reference frame, select a candidate shape for the OOI based on the character of interest in the primary reference frame, and adjust the candidate shape based on the secondary reference frames to form a resultant shape for the OOI.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
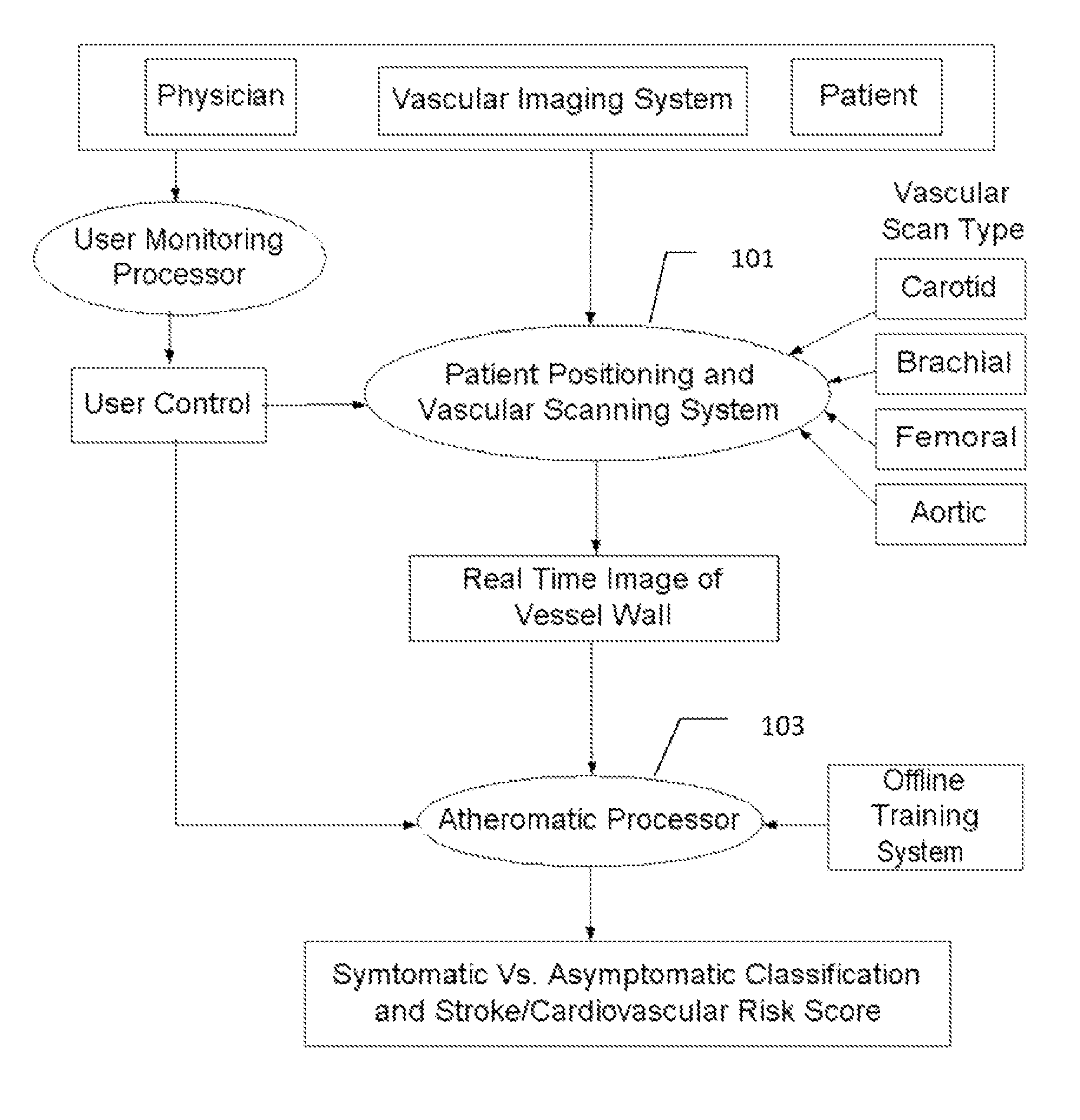
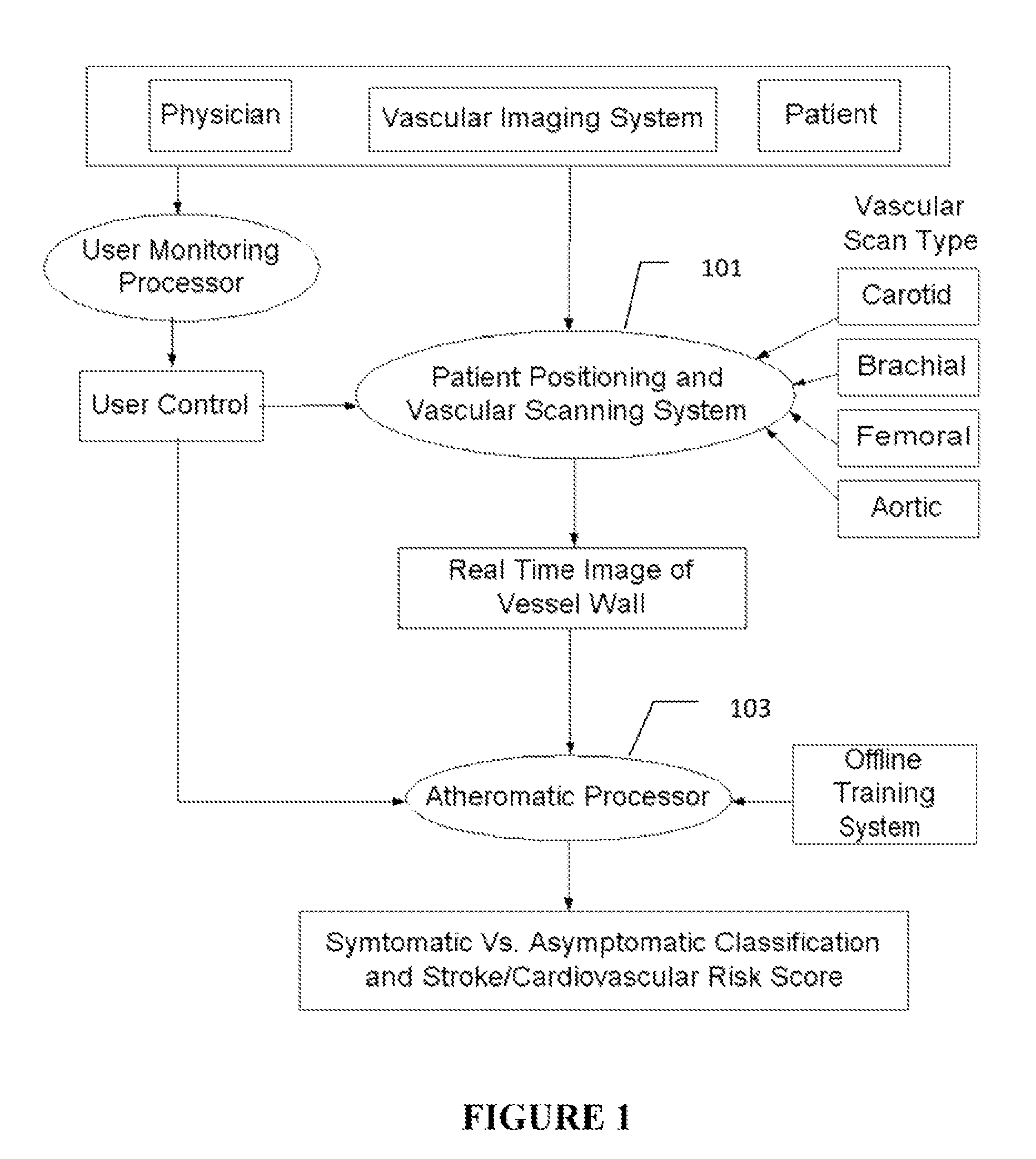
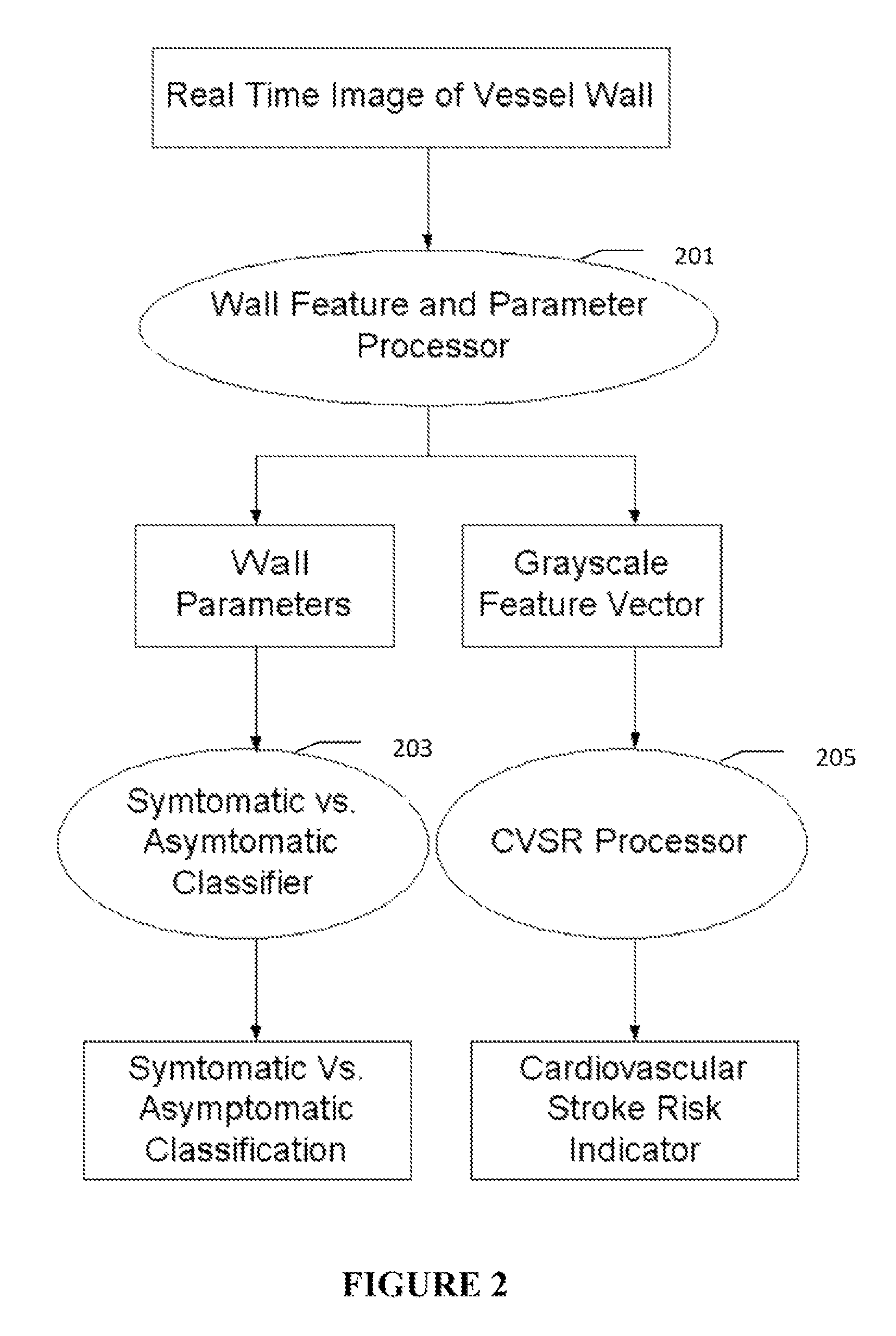
Imaging based symptomatic classification using a combination of trace transform, fuzzy technique and multitude of features
InactiveUS8532360B2Improve accuracyMaximum accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsCarotid atherosclerosis2d ultrasound
Owner:ATHEROPOINT
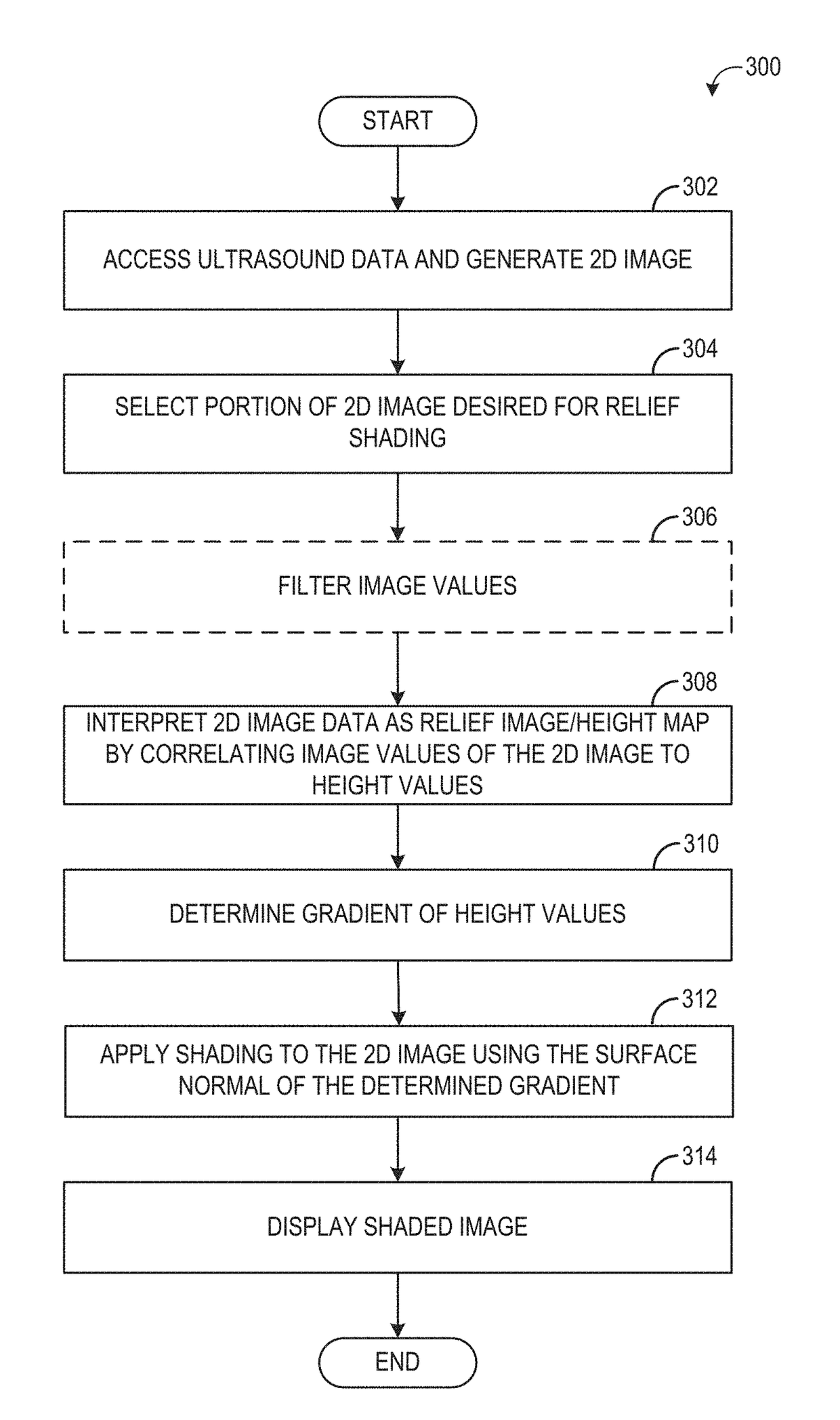
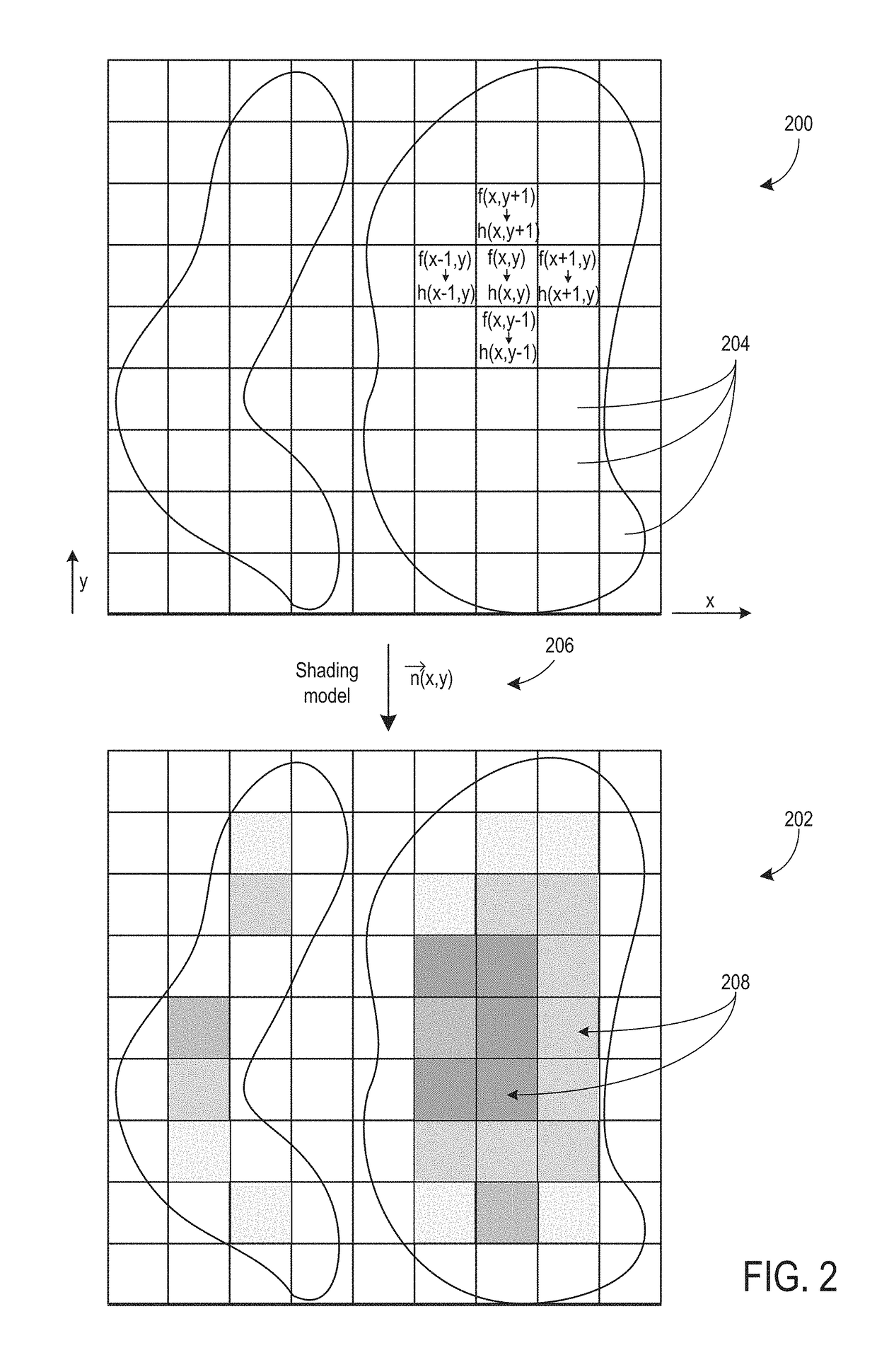
Methods and system for shading a two-dimensional ultrasound image
Various methods and systems are provided for shading a 2D ultrasound image, generated from ultrasound data, using a gradient determined from scalar values of the ultrasound image data. As one example, a method includes correlating image values of a dataset acquired with an ultrasound imaging system to height values; determining a gradient of the height values; applying shading to a 2D image generated from the dataset using the determined gradient; and displaying the shaded 2D image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for co-registration and navigation of three-dimensional ultrasound and alternative radiographic data sets
A co-registration and navigations system in which 3D and / or 2D ultrasound images are displayed alongside virtual images of a patient and / or CT or MRI scans, or other similar imaging techniques used in the medical field.
Owner:SAVITSKY ERIC +2
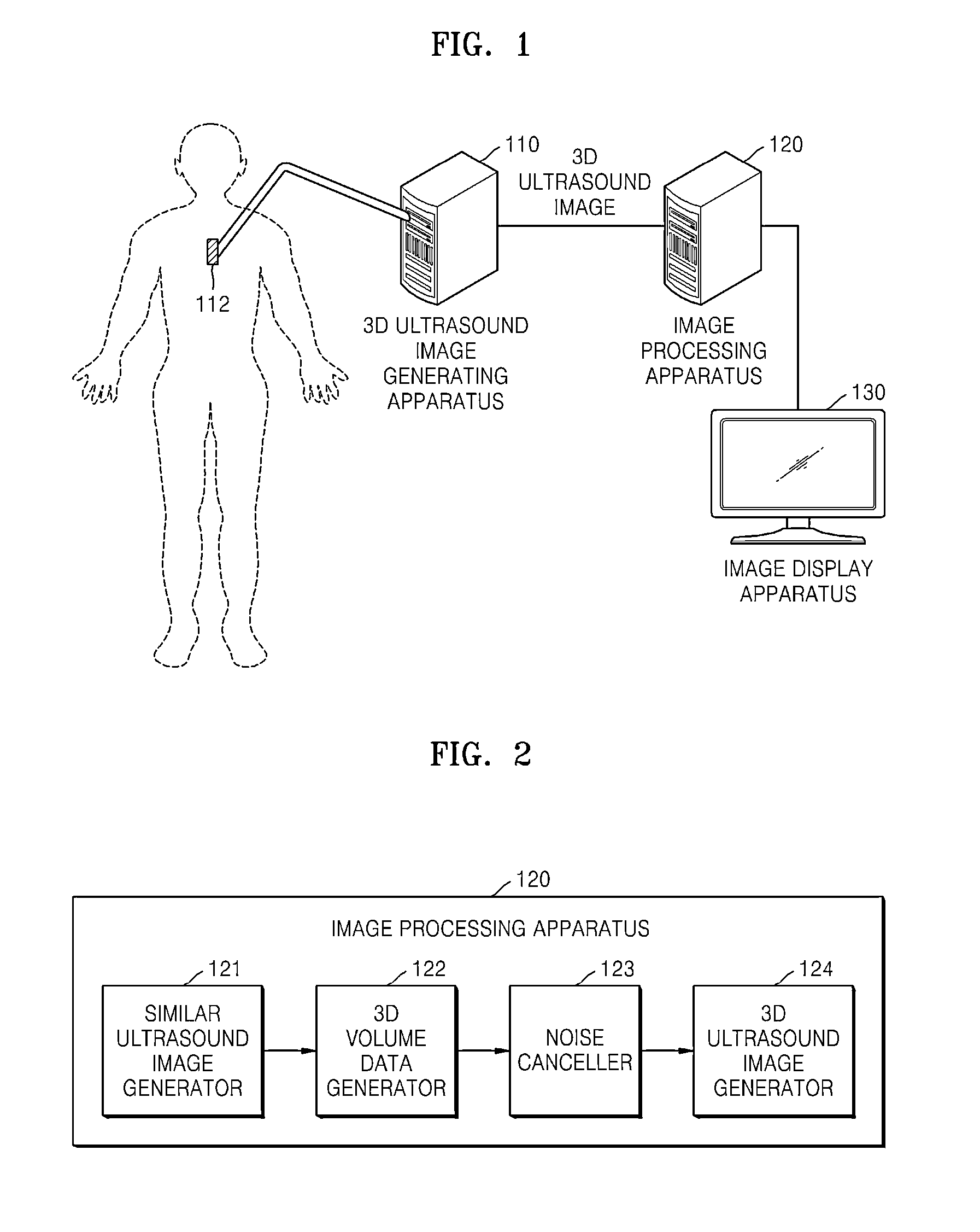
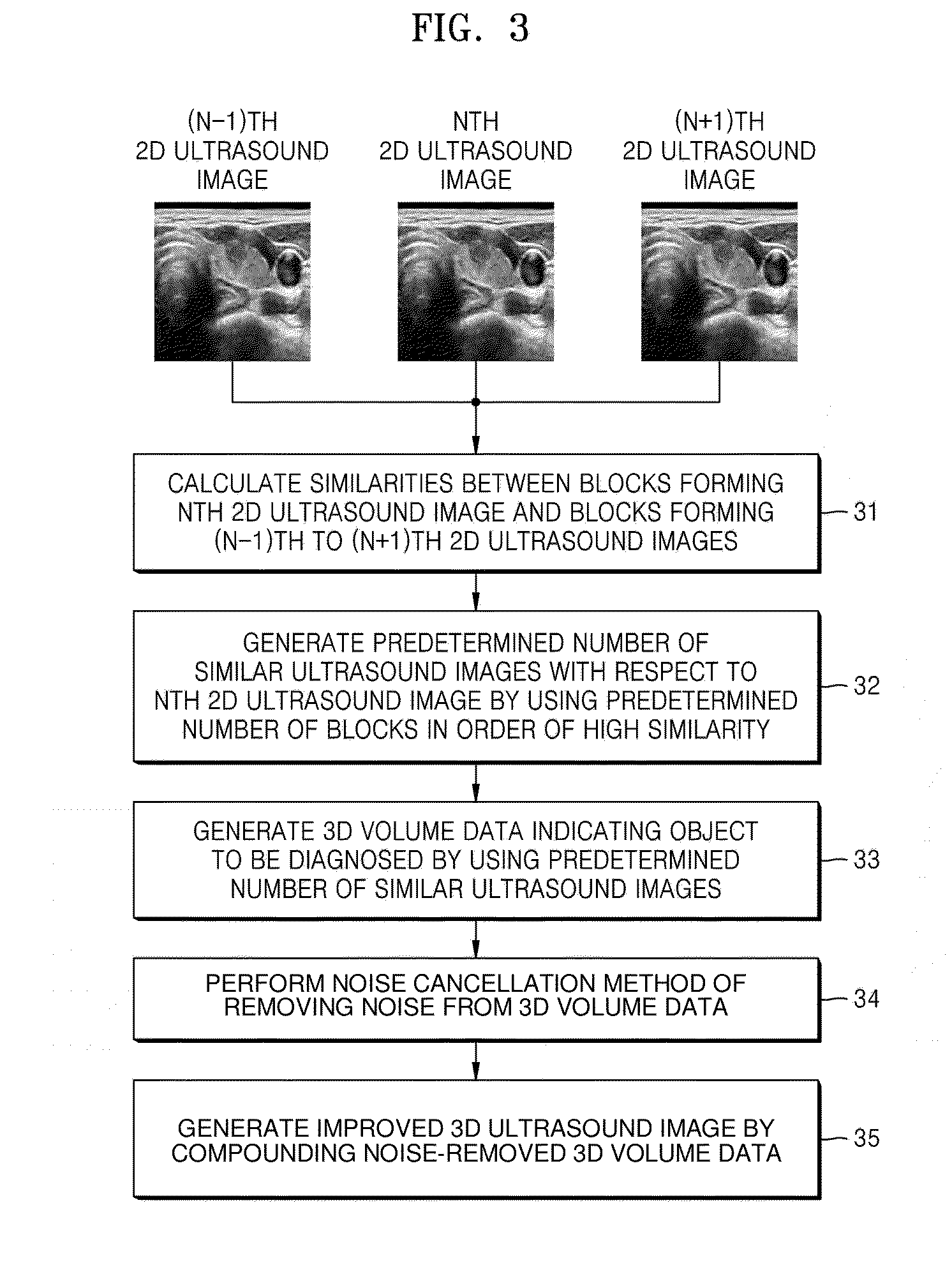
Method and apparatus for processing ultrasound image
A method and apparatus for processing an ultrasound image are provided. The method includes determining similarities between a first two-dimensional (2D) ultrasound image, among 2D ultrasound images of a three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound image, and the 2D ultrasound images. The method further includes generating a predetermined number of similar ultrasound images with respect to the first 2D ultrasound image based on the similarities. The method further includes generating 3D volume data based on the predetermined number of the similar ultrasound images. The method further includes removing noise from the 3D volume data. The method further includes generating another 3D ultrasound image based on the noise-removed 3D volume data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
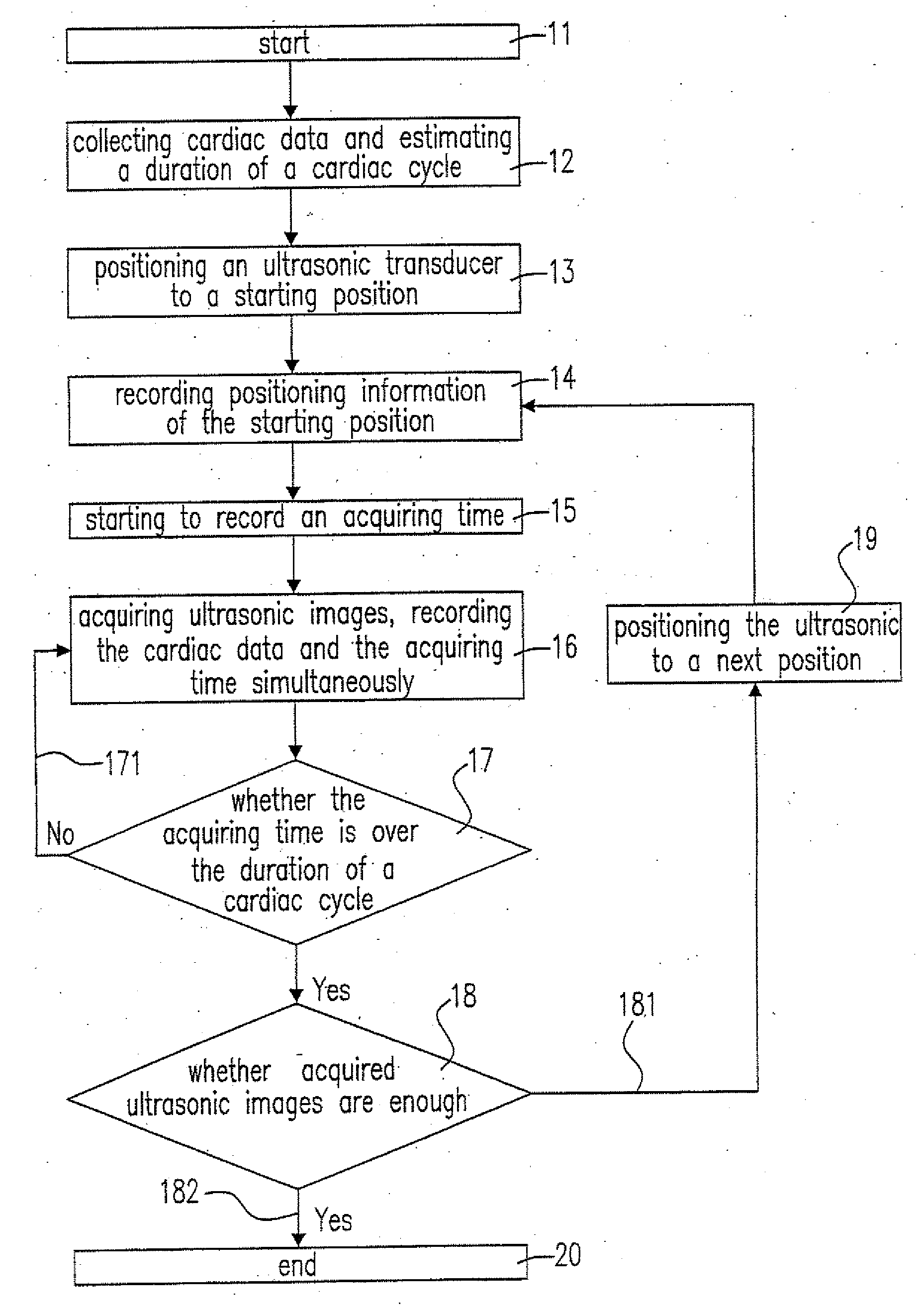
Quantitative Elastography with Tracked 2D Ultrasound Transducers
A method is described for acquiring 3D quantitative ultrasound elastography volumes. In one embodiment, the method comprises using a 2D ultrasound transducer to scan a volume of tissue through which shear waves are created using an external vibration source, the synchronized measurement of tissue motion within the plane of the ultrasound transducer with the measurement of the transducer location in space, the reconstruction of tissue displacements in time and space over a volume from this synchronized measurement, and the computation of one or several mechanical properties of tissue from this volumetric measurement of displacements. The tissue motion in the plane of the transducer may be measured at a high effective frame rate in the axial direction of the transducer, or in the axial and lateral directions of the transducer. The tissue displacements over the measured volume may be interpolated over a regular grid in order to make the computation of mechanical properties easier.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
2d ultrasound transducer for radial application and method
ActiveCN101291744AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical vibrations separationUltrasonic sensorAcoustic array
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for obtaining a 3D image in radial applications, typically endorectal imaging where the object of interrogation is the rectal wall, in particular, the present invention is related a two dimensional (2D) acoustic array transducer that is wrapped around a cylindrically shaped probe so that the 2D array is capable of steering the beam radially and axially to obtain a precise 3D data acquisition of the object of interrogation.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method for real-time ultrasound guided prostate needle biopsy based on biomechanical model of the prostate from magnetic resonance imaging data
A method and system for real-time ultrasound guided prostate needle biopsy based on a biomechanical model of the prostate from 3D planning image data, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data, is disclosed. The prostate is segmented in the 3D ultrasound image. A reference patient-specific biomechanical model of the prostate extracted from planning image data is fused to a boundary of the segmented prostate in the 3D ultrasound image, resulting in a fused 3D biomechanical prostate model. In response to movement of an ultrasound probe to a new location, a current 2D ultrasound image is received. The fused 3D biomechanical prostate model is deformed based on the current 2D ultrasound image to match a current deformation of the prostate due to the movement of the ultrasound probe to the new location.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Apparatus and method for providing a dynamic 3D ultrasound image
InactiveUS20100174191A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringSonificationUltrasonic sensor
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method and apparatus for enhancing image quality of a two-dimensional ultrasound image
ActiveUS7664301B2Improve image qualityRemove speckle noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonification2d ultrasound
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com