A method for detecting dna methyltransferase activity based on strand displacement amplification and dnazyme amplification
A technology of methyltransferase and strand displacement reaction, applied in the field of enzyme detection, can solve problems such as low sensitivity, and achieve the effects of wide application, good selectivity and specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] M.SssI, HaeIII, HhaI and AluI methyltransferases, HpaII restriction endonuclease, Klenow Fragment (3′–5′exo-) polymerase, Nb.BbvCI cutter and S-adenosylmethionine from Purchased from NEB. 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich. Four deoxyribonucleic acid (dNTPs) and HEPES were purchased from Shanghai Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd. All chemicals used in the experiments were of analytical grade and used without further purification. All solutions were prepared with ultrapure water (>18.25MΩ·cm). The oligonucleotides in this work were synthesized and purified by Shanghai Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd., and their sequences are listed in Table 1.
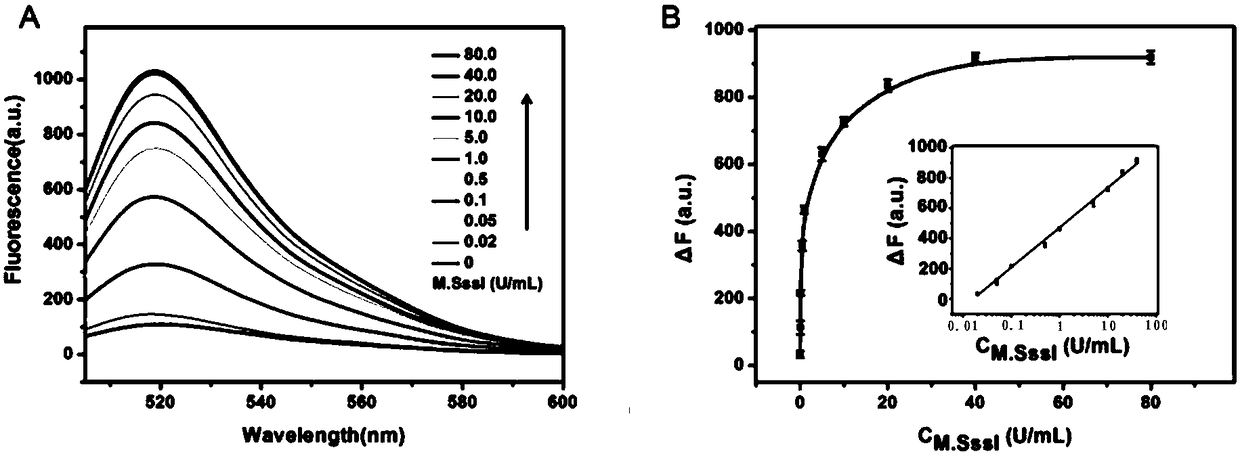
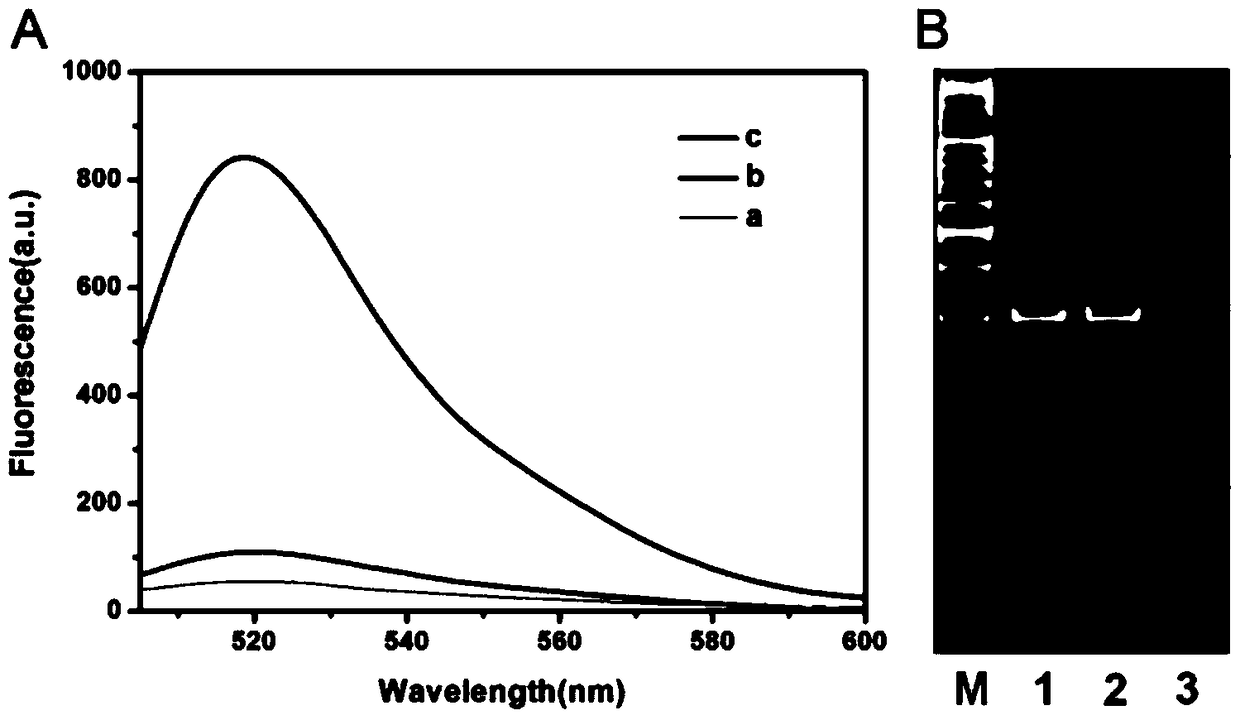
[0042] The fluorescence spectra of all samples were measured on a Hitachi F-7000 fluorescence spectrophotometer. The emission spectrum ranges from 505 to 600 nm, and the excitation wavelength is 494 nm. The fluorescence intensity at 518 nm was used to evaluate the performance of this sensing...
Embodiment 2
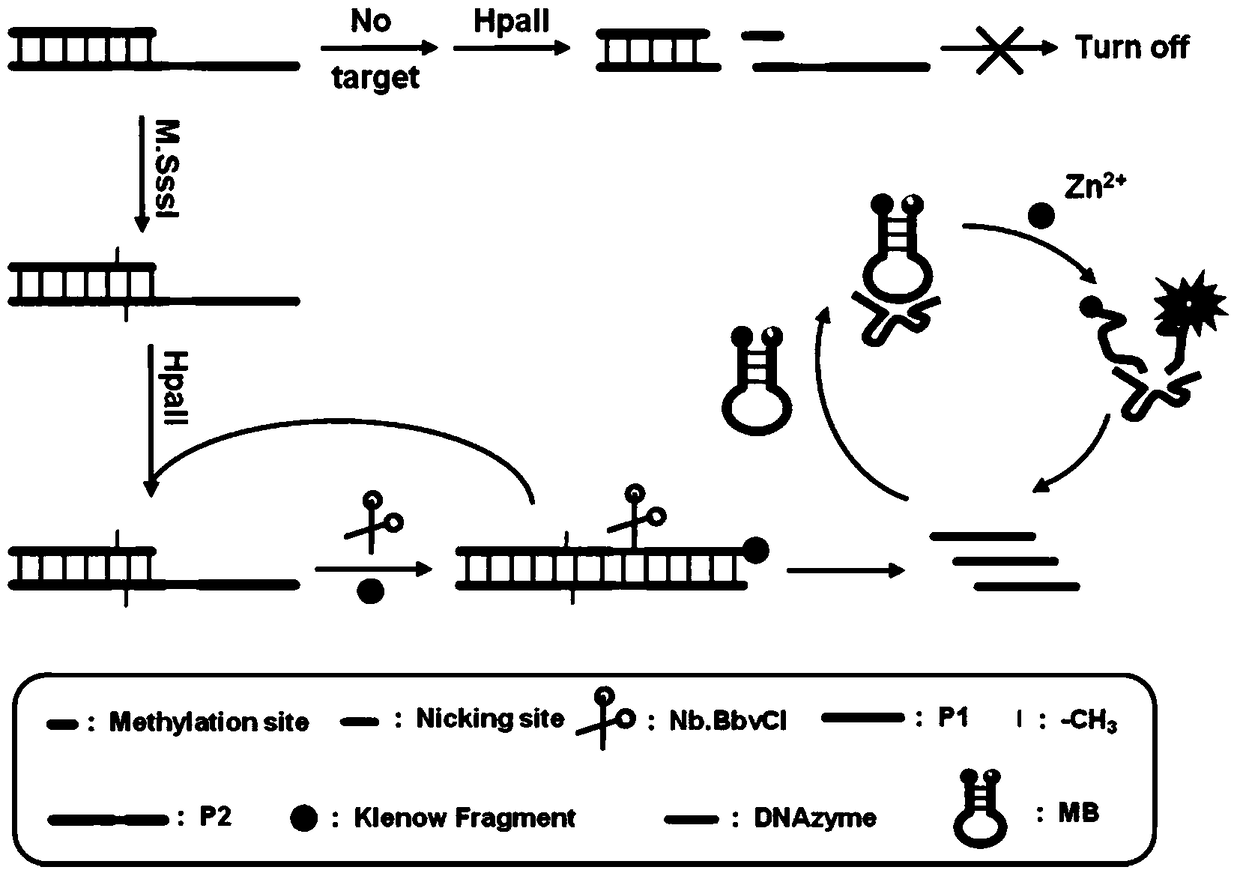
[0055] Principle analysis
[0056] The proposed rationale for the assay of methyltransferase activity is as follows: figure 1 shown. We designed a trifunctional dsDNA probe, including a methylation site for DNA methyltransferase recognition, an 8–17 DNAzyme complementary sequence for DNAzyme synthesis, and a cleavage site for nickase cleavage. First, M.SssI methyltransferase specifically recognizes and catalyzes the methylation of the trifunctional dsDNA probe to form methylated dsDNA. Subsequently, the HpaII restriction enzyme specifically cleaves residual unmethylated dsDNA. Subsequently, under the action of Klenow Fragment polymerase and dNTPs, P1 in the methylated dsDNA acts as a primer to initiate the polymerization reaction, forming a complete DNA double strand with a cleavage site. Next, Nb.BbvCI cleaves the complete DNA duplex, creating a new replication site for the next stage of polymerization. Through this repeated polymerization and cleavage reaction, a large n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com