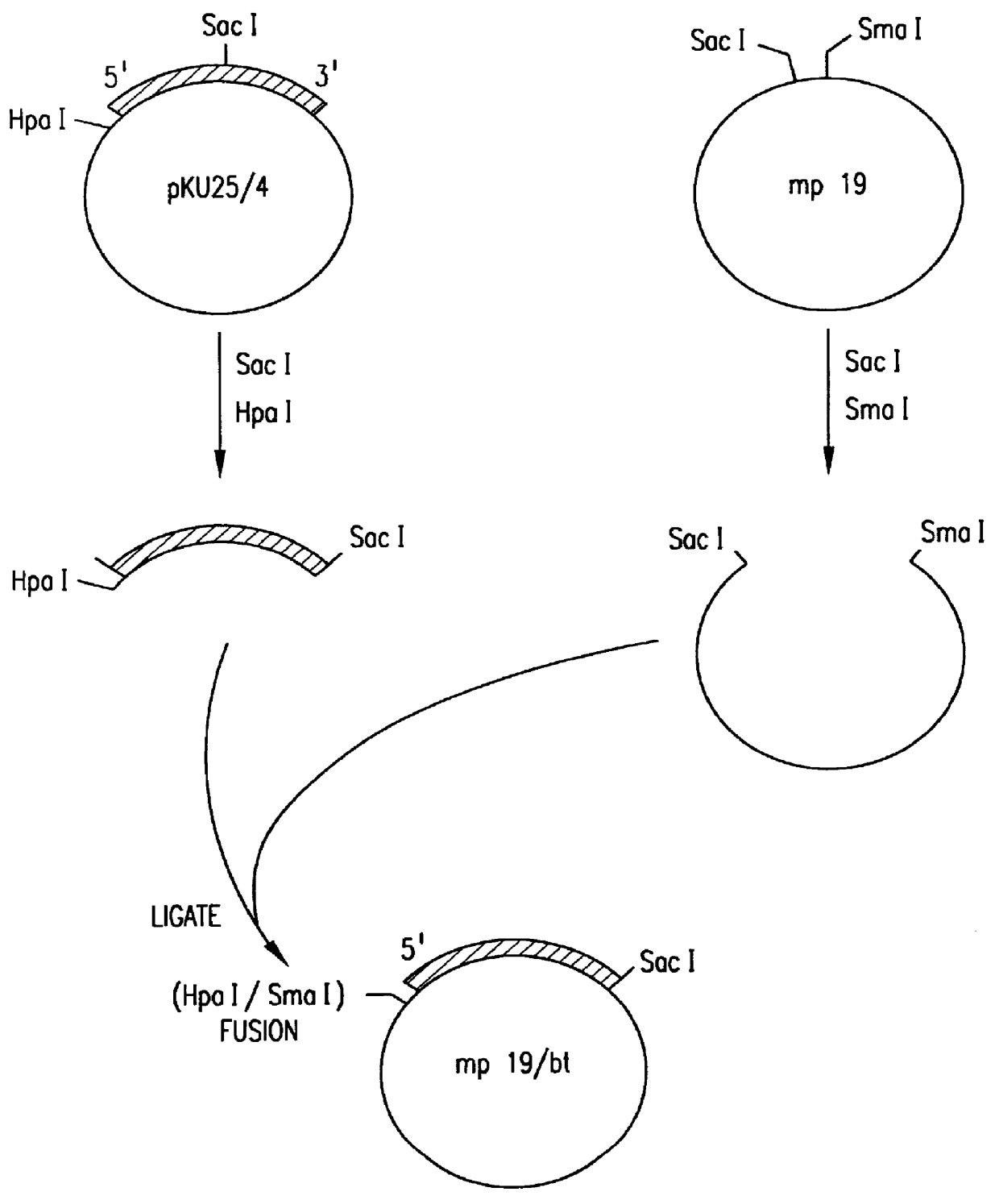
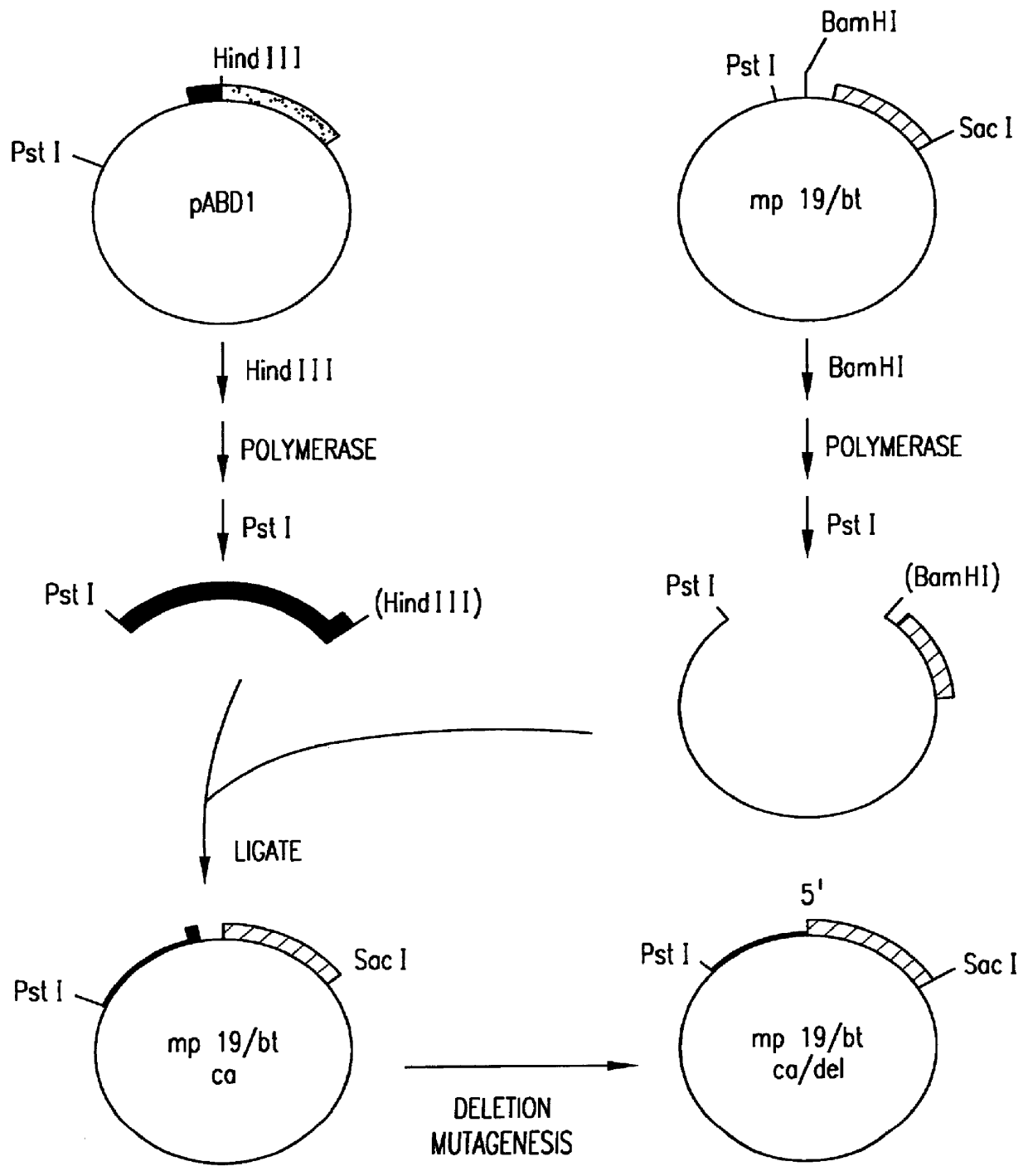
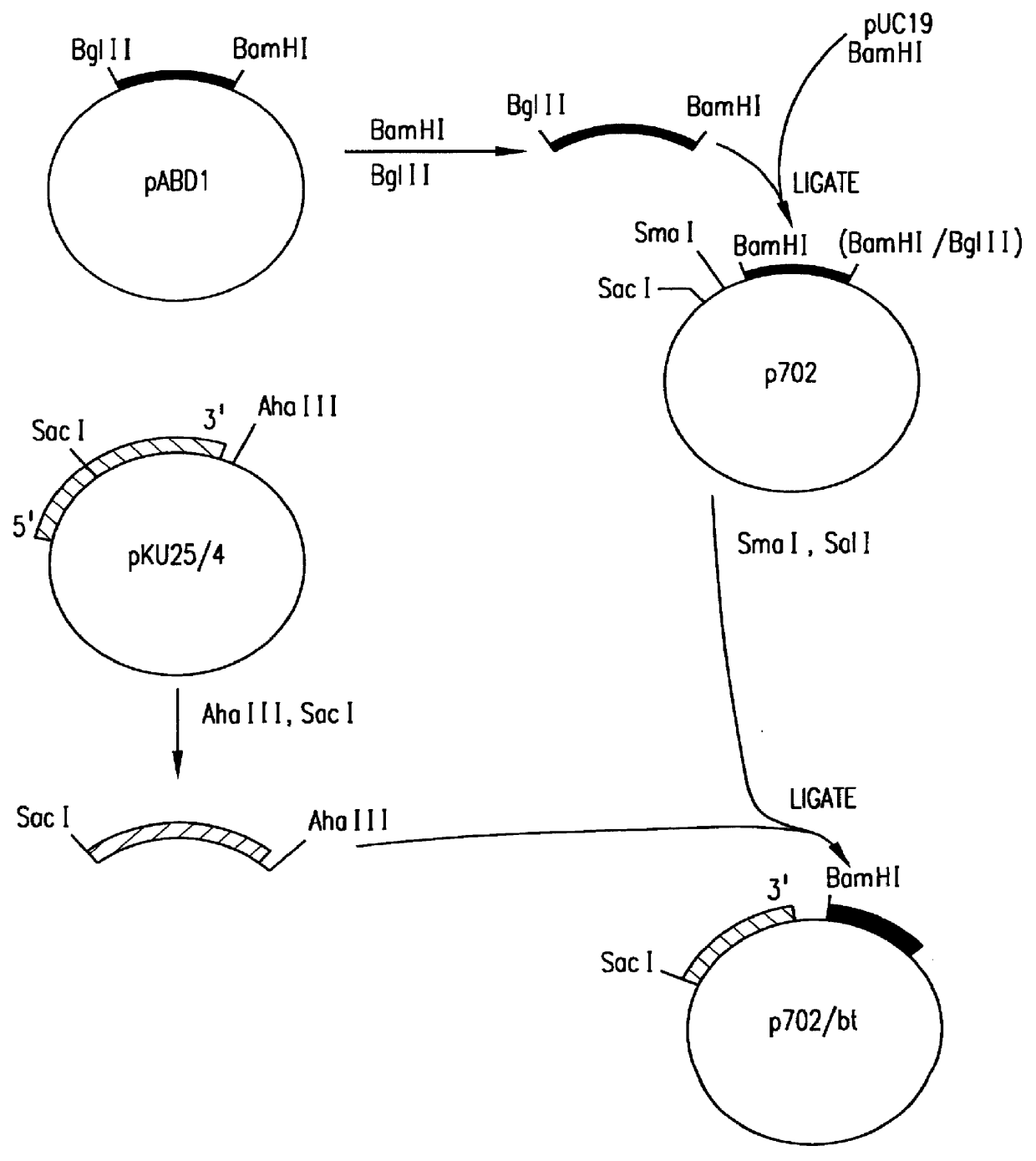
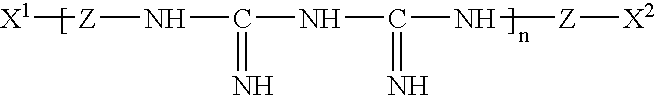
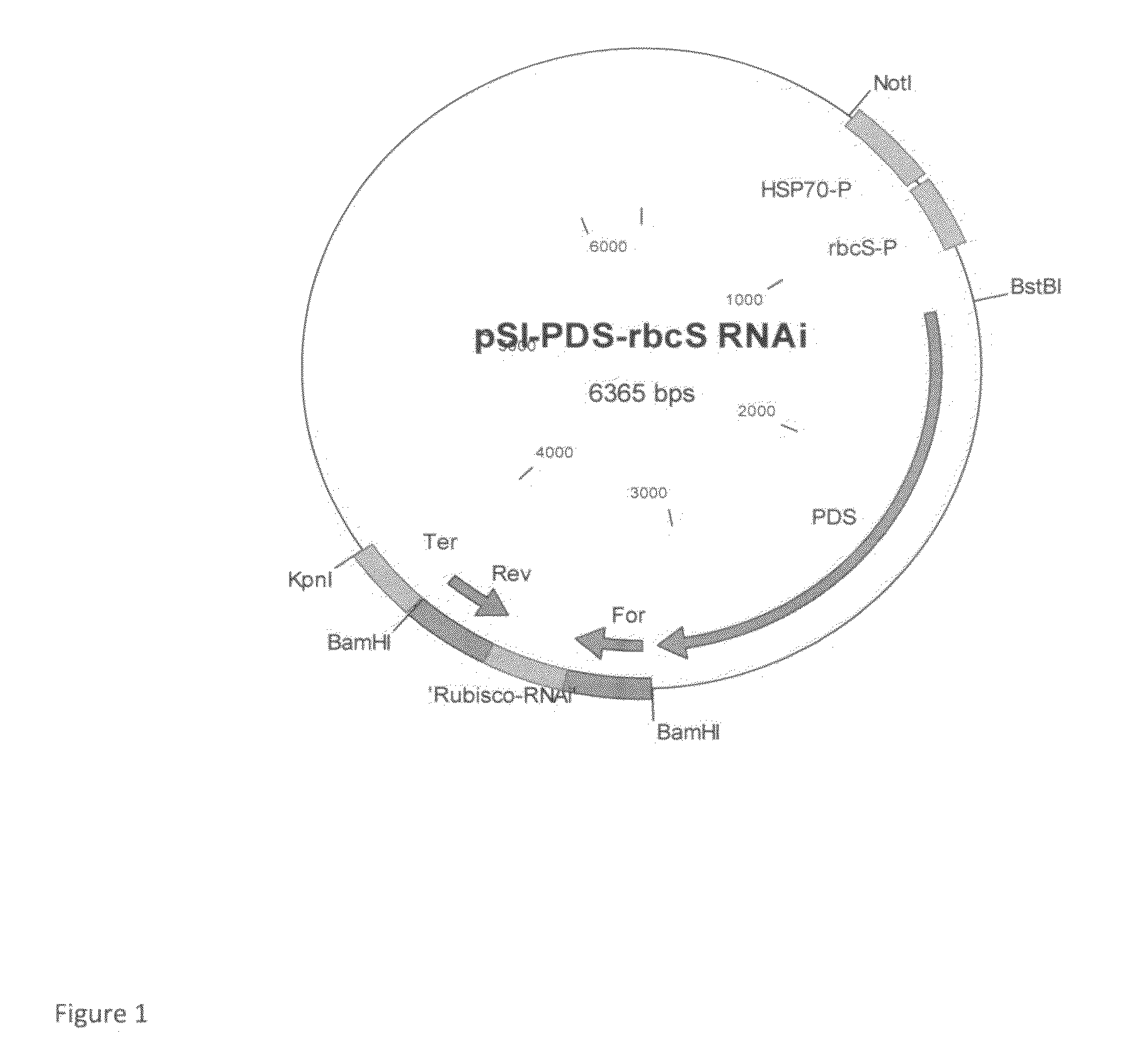
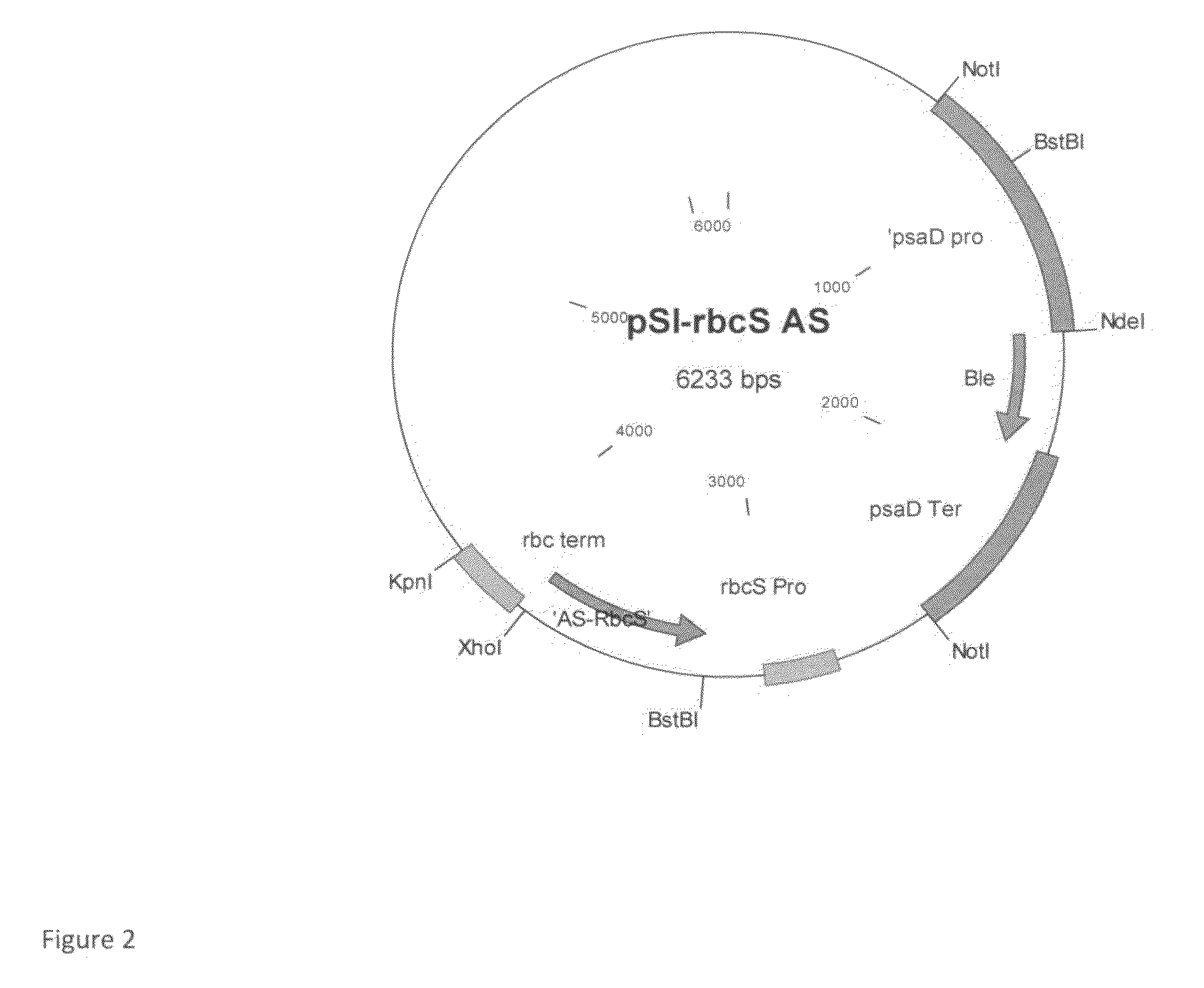
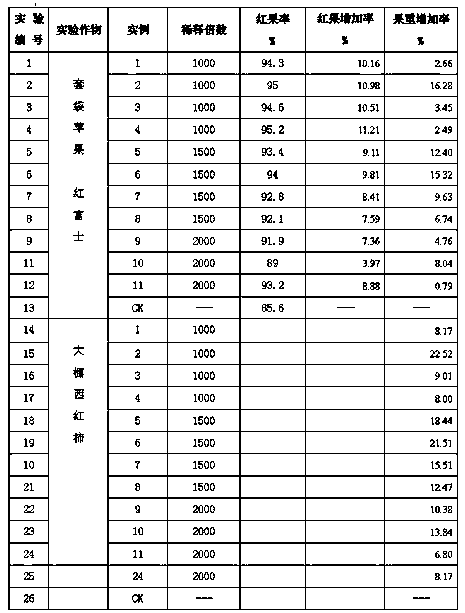
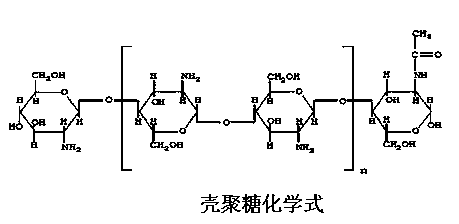
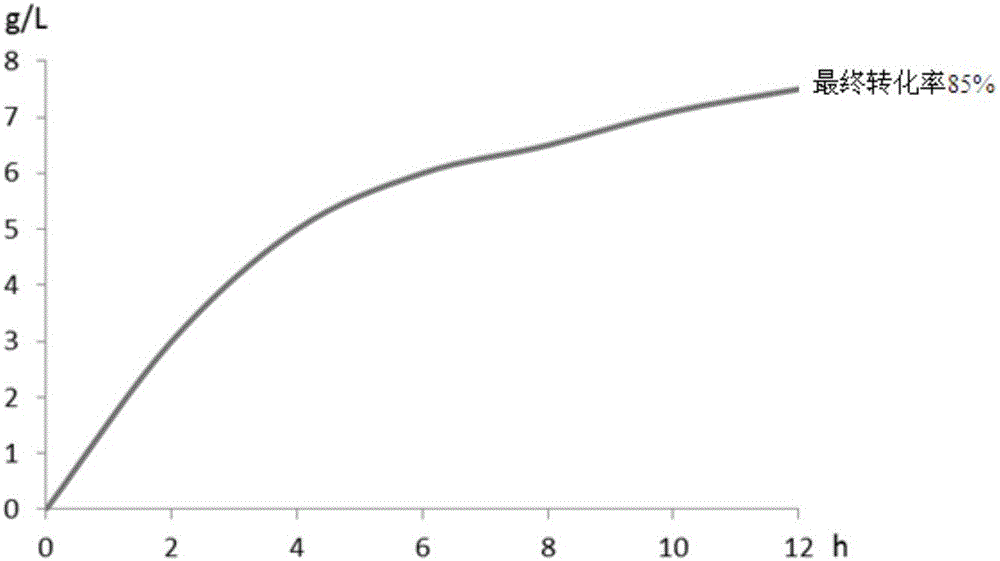
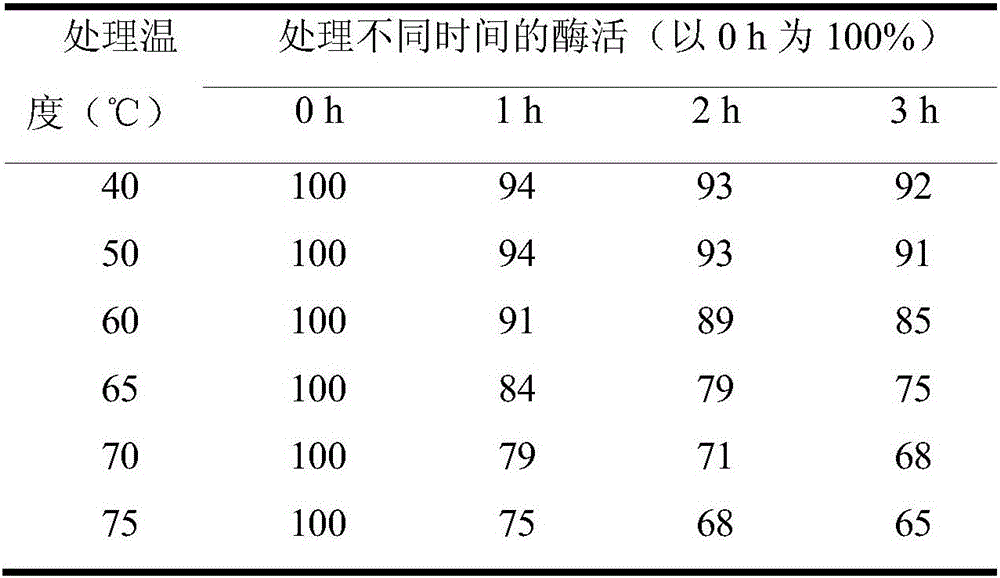
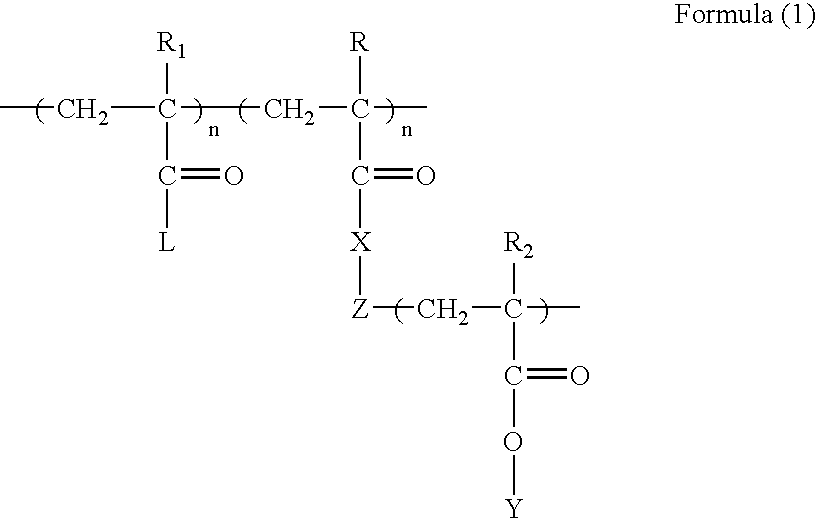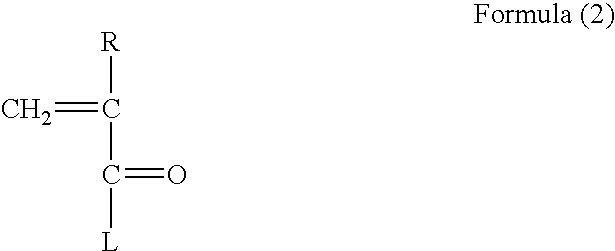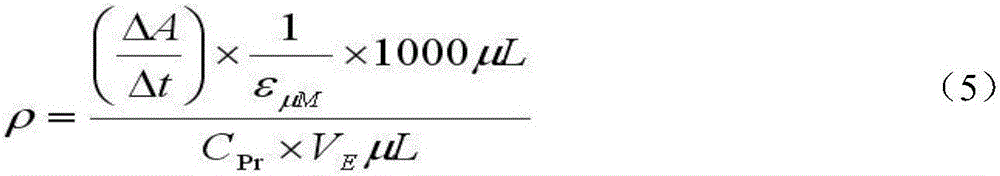Patents
Literature
106 results about "Ribulose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
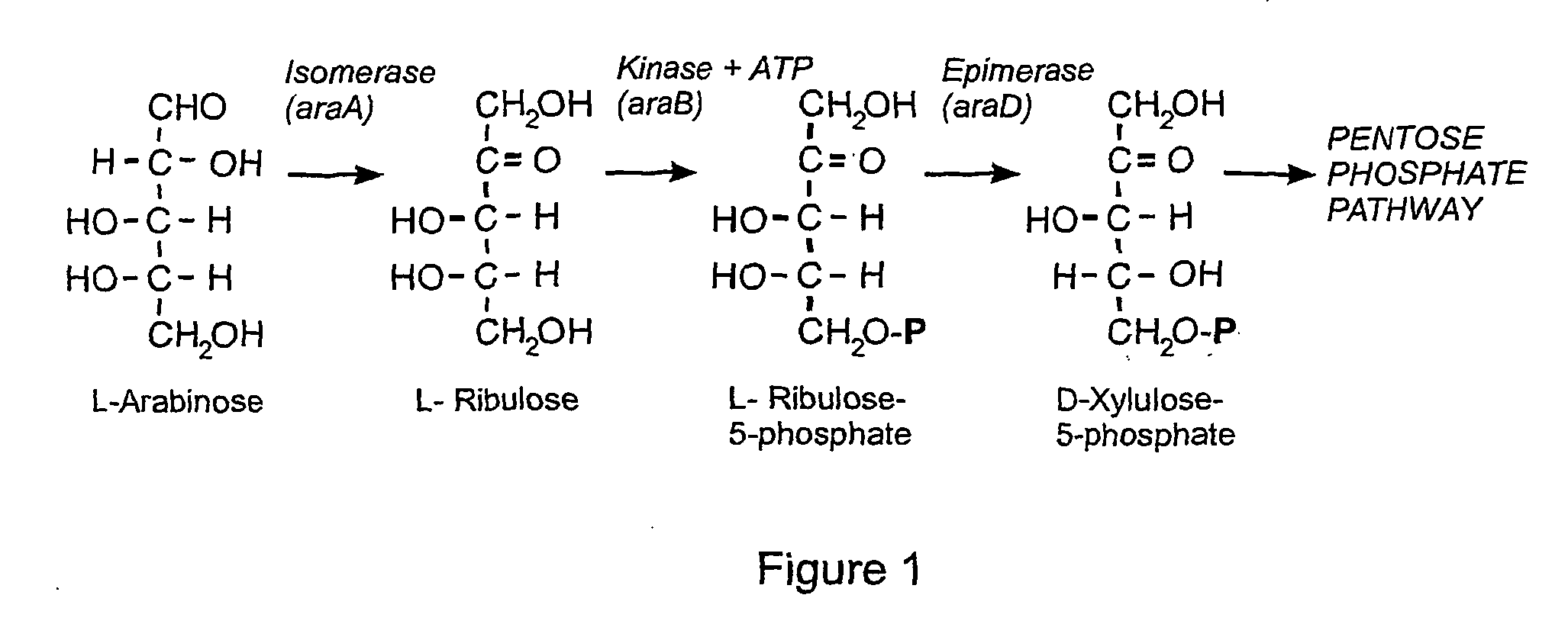
Ribulose is a ketopentose — a monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms, and including a ketone functional group. It has chemical formula C₅H₁₀O₅. Two enantiomers are possible, d-ribulose (d-erythro-pentulose) and l-ribulose (l-erythro-pentulose). d-Ribulose is the diastereomer of d-xylulose.
Cotton promoter
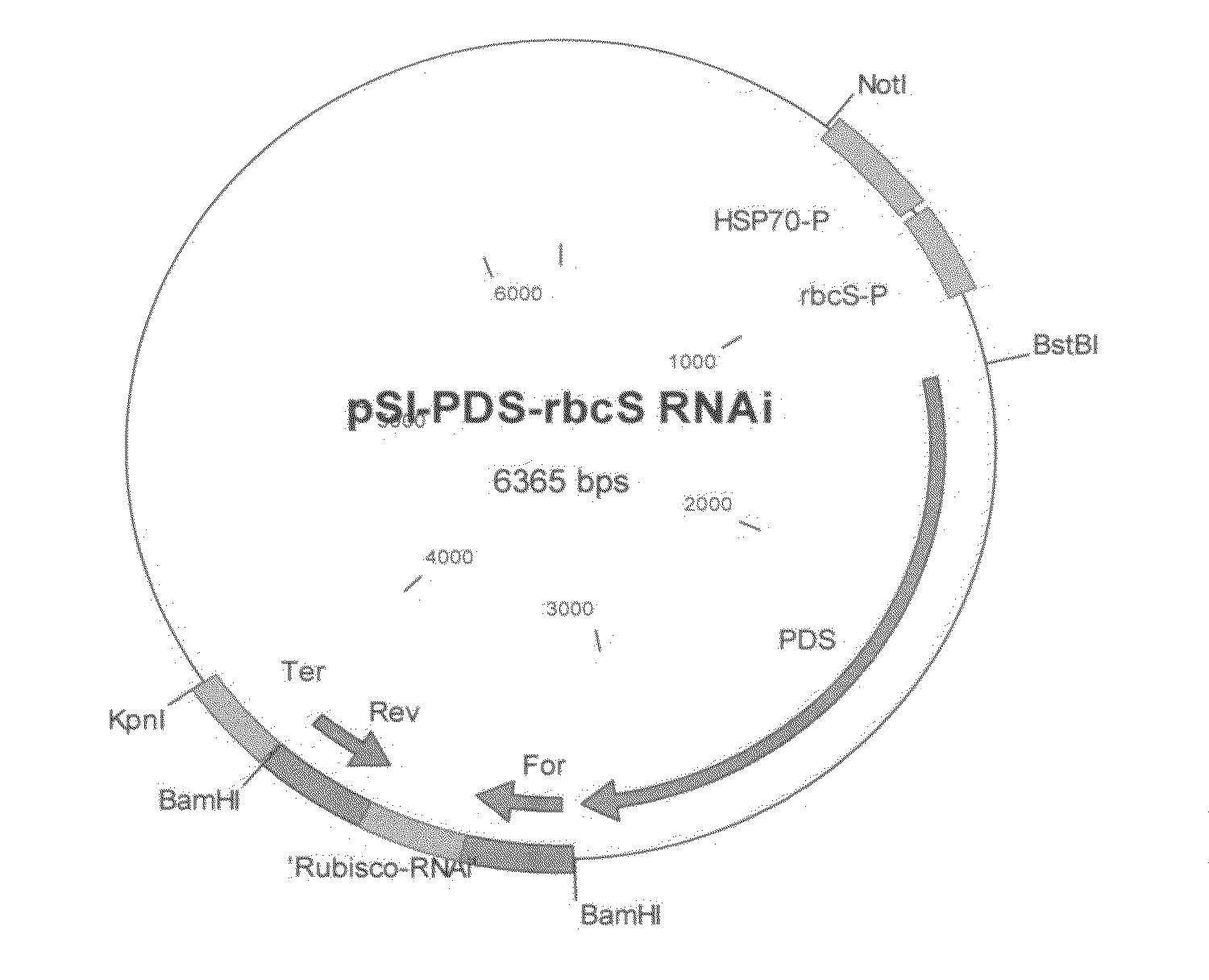
A promoter isolated from a cotton gene encoding the small subunit of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase is described. The isolated promoter is operably linked to a coding sequence of interest to make a chimeric gene.
Owner:NOVARTIS FINANCE
Ophthalmic and contact lens solutions containing simple saccharides as preservative enhancers
InactiveUS20070098818A1Effective preservationDegree of reductionBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsTagatoseSucrose
The present invention relates to an ophthalmic solution comprising 0.00001 to 10.0 weight percent of a simple saccharide, at least 0.00001 weight percent of a preservative, and not more than about 0.2 percent by weight chloride. The simple saccharide is chosen from the group consisting of: inositol; mannitol; sorbitol; sucrose; dextrose; glycerin; propylene glycol; ribose; triose; tetrose; erythrose; threose; pentose; arabinose; ribulose; xylose; xylulose; lyxose; hexose; allose; altrose; fructose; galactose; glucose; gulose; idose; mannose; sorbose; talose; tagatose; adlose; ketose; heptose; sedoheptulose; monosaccharides; disaccharides; sugar alcohols; xylitol; and polyol.
Owner:FXS VENTURES LLC
Novel arabinose-fermenting eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20100304454A1Improve stabilityAvoid recombinationFungiHydrolasesPropanoic acidGlucose repression
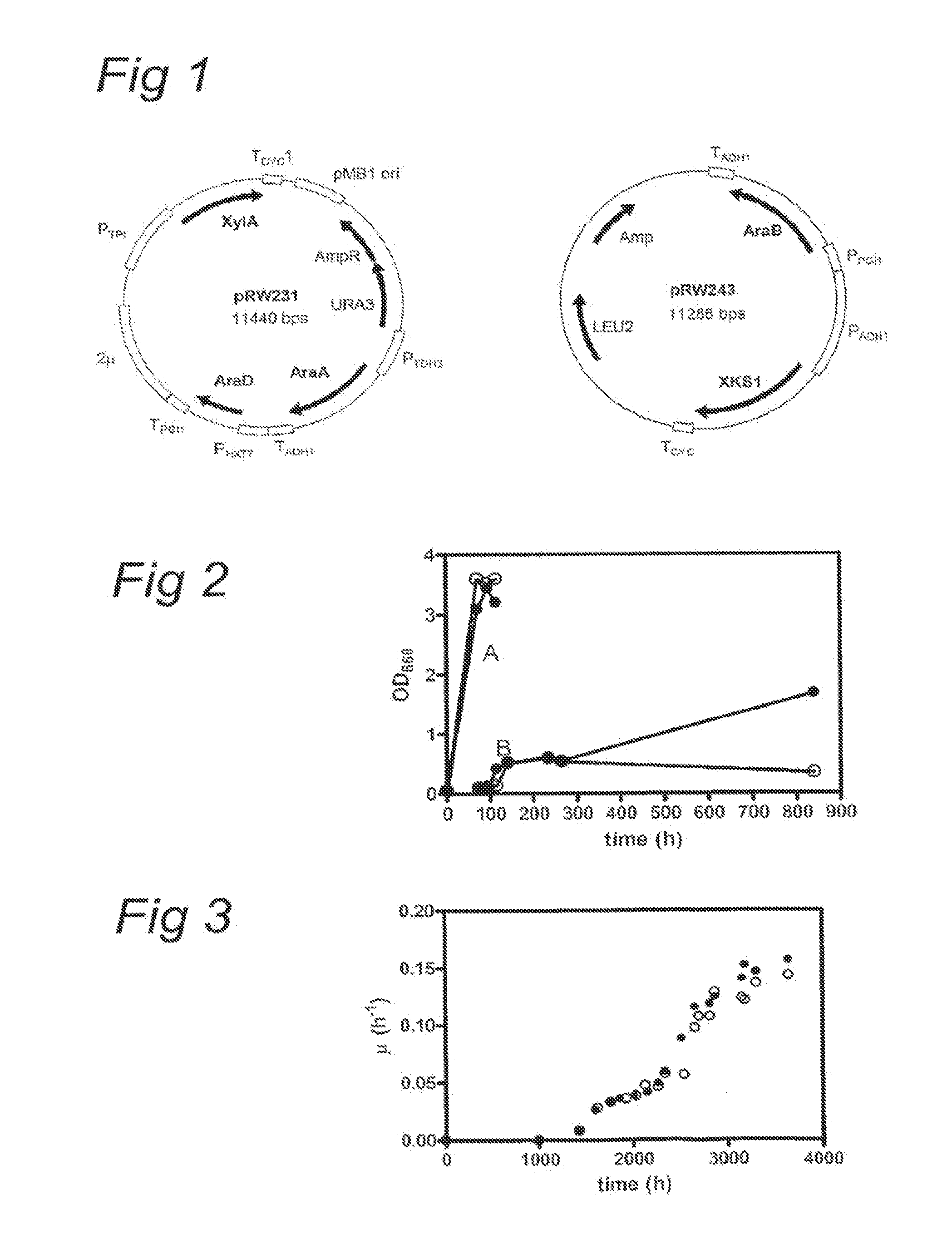
The present invention relates to eukaryotic cells which have the ability to convert L-arabinose into D-xylulose 5-phosphate. The cells have acquired this ability by transformation with nucleotide sequences coding for an arabinose isomerase, a ribulokinase, and a ribulose-5-P-4-epimerase from a bacterium that belongs to a Clavibacter, Arthrobacter or Gramella genus. The cell preferably is a yeast or a filamentous fungus, more preferably a yeast is capable of anaerobic alcoholic fermentation. The may further comprise one or more genetic modifications that increase the flux of the pentose phosphate pathway, reduce unspecific aldose reductase activity, confer to the cell the ability to directly isomerise xylose into xylulose, increase the specific xylulose kinase activity, increase transport of at least one of xylose and arabinose into the host cell, decrease sensitivity to catabolite repression, increase tolerance to ethanol, osmolarity or organic acids; and / or reduce production of by-products. The cell preferably is a cell that has the ability to produce a fermentation product such as ethanol, lactic acid, 3-hydroxy-propionic acid, acrylic acid, acetic acid, succinic acid, citric acid, amino acids, 1,3-propane-diol, ethylene, glycerol, -lactam antibiotics and cephalosporins. The invention further relates to processes for producing these fermentation products wherein a cell of the invention is used to ferment arabinose into the fermentation products.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV +1
Metabolic engineering of arabinose-fermenting yeast cells
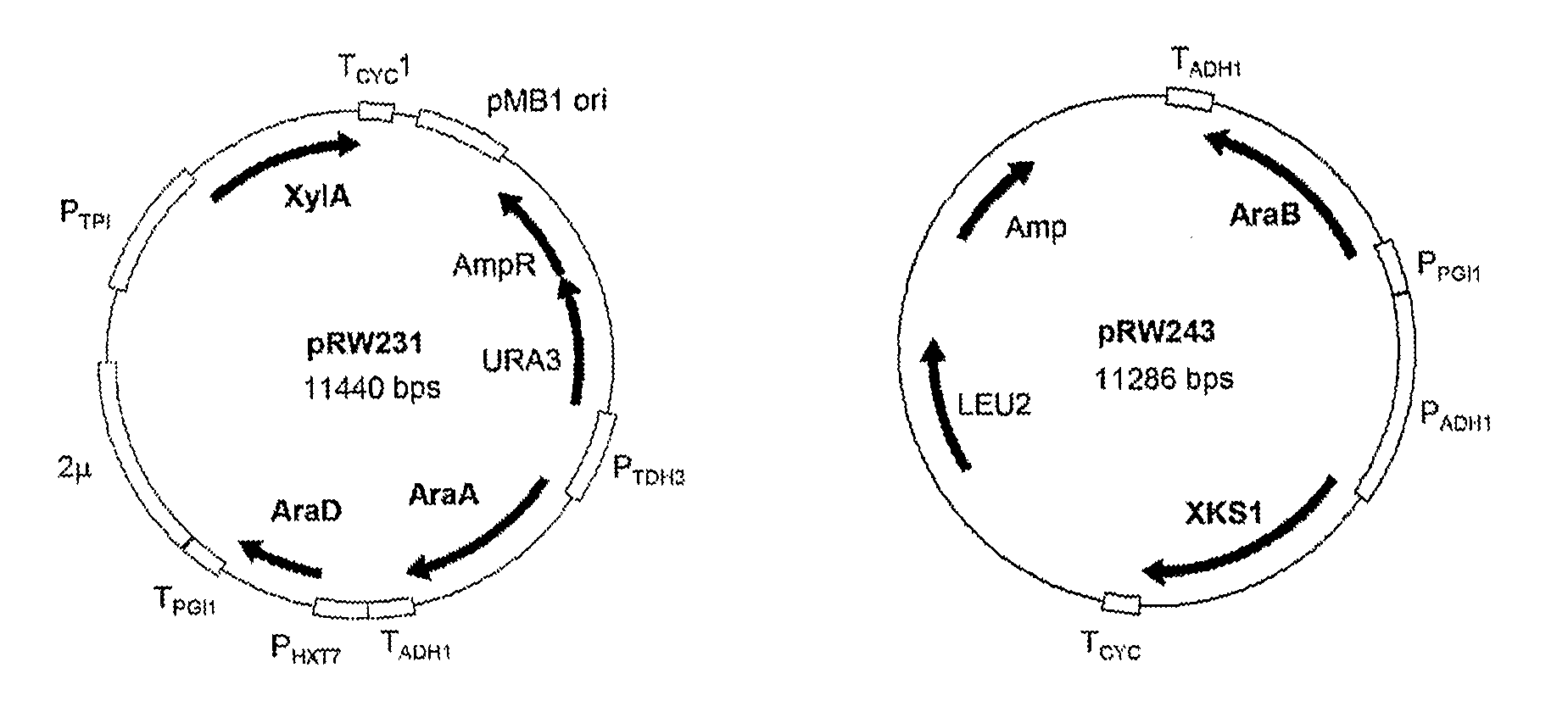
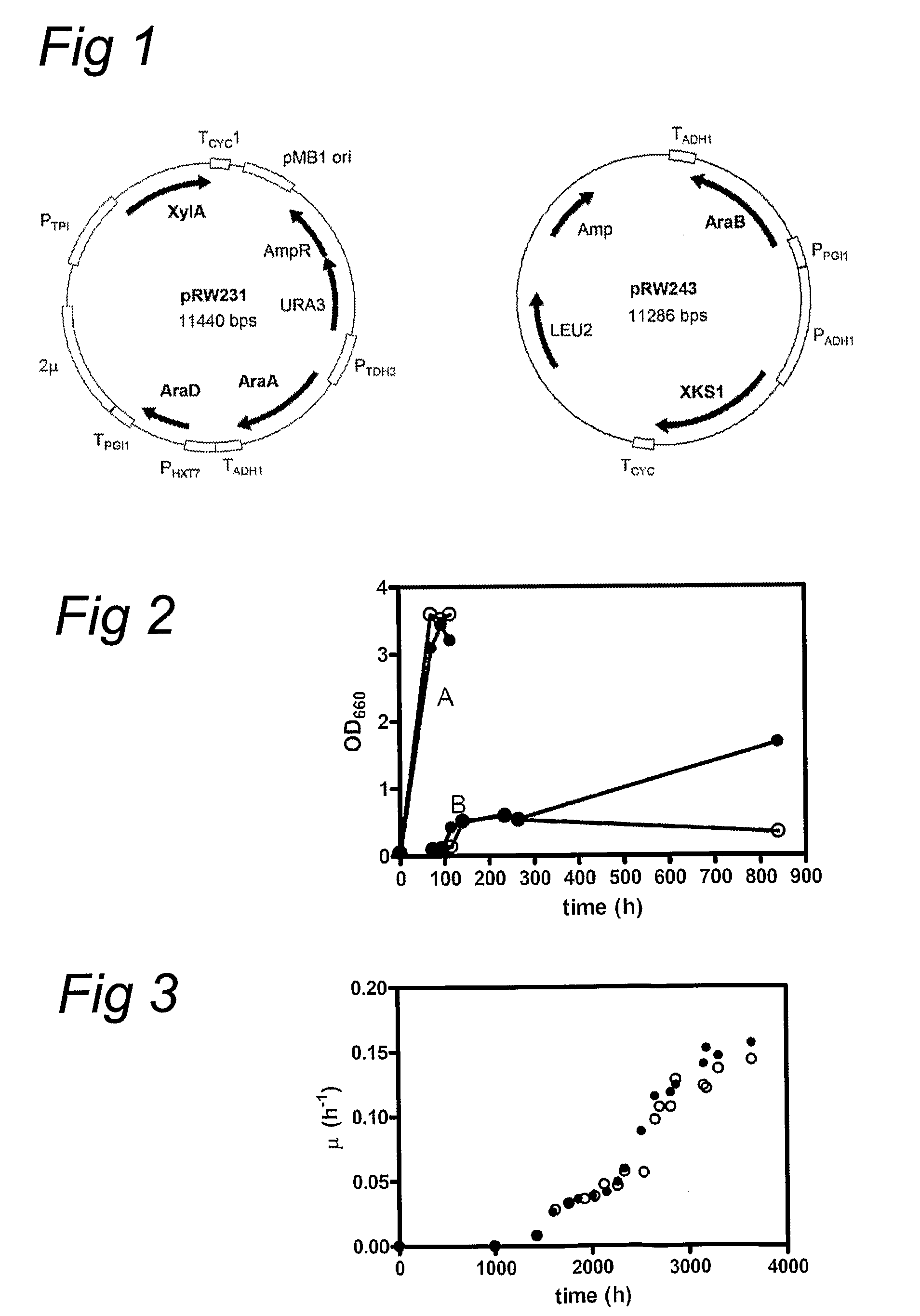
The invention relates to an eukaryotic cell expressing nucleotide sequences encoding the ara A, ara B and ara D enzymes whereby the expression of these nucleotide sequences confers on the cell the ability to use L-arabinose and / or convert L-arabinose into L-ribulose, and / or xylulose 5-phosphate and / or into a desired fermentation product such as ethanol. Optionally, the eukaryotic cell is also able to convert xylose into ethanol.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Decreasing RUBISCO content of algae and cyanobacteria cultivated in high carbon dioxide
InactiveUS20100081177A1Increase storage capacityImprove capacity utilizationBacteriaHydrolasesPhylum CyanobacteriaBiotechnology
Algae and cyanobacteria are genetically engineered to have lower RUBISCO (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase / oxygenase) content in order to grow more efficiently at elevated carbon dioxide levels while recycling industrial CO2 emissions back to products, and so as not to be able to grow outside of cultivation.
Owner:TRANSALGAE
Modified yeast consuming L-arabinose
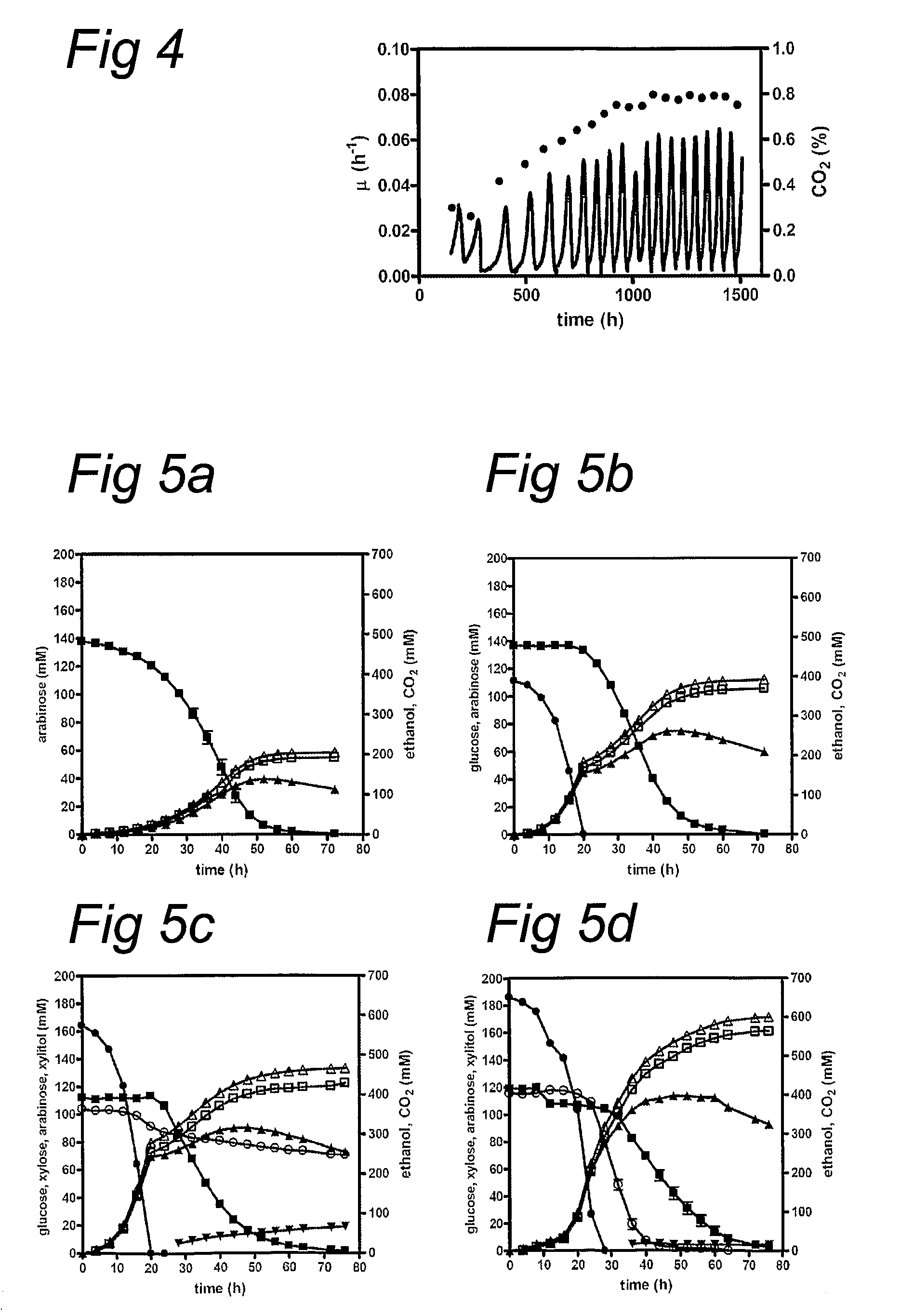
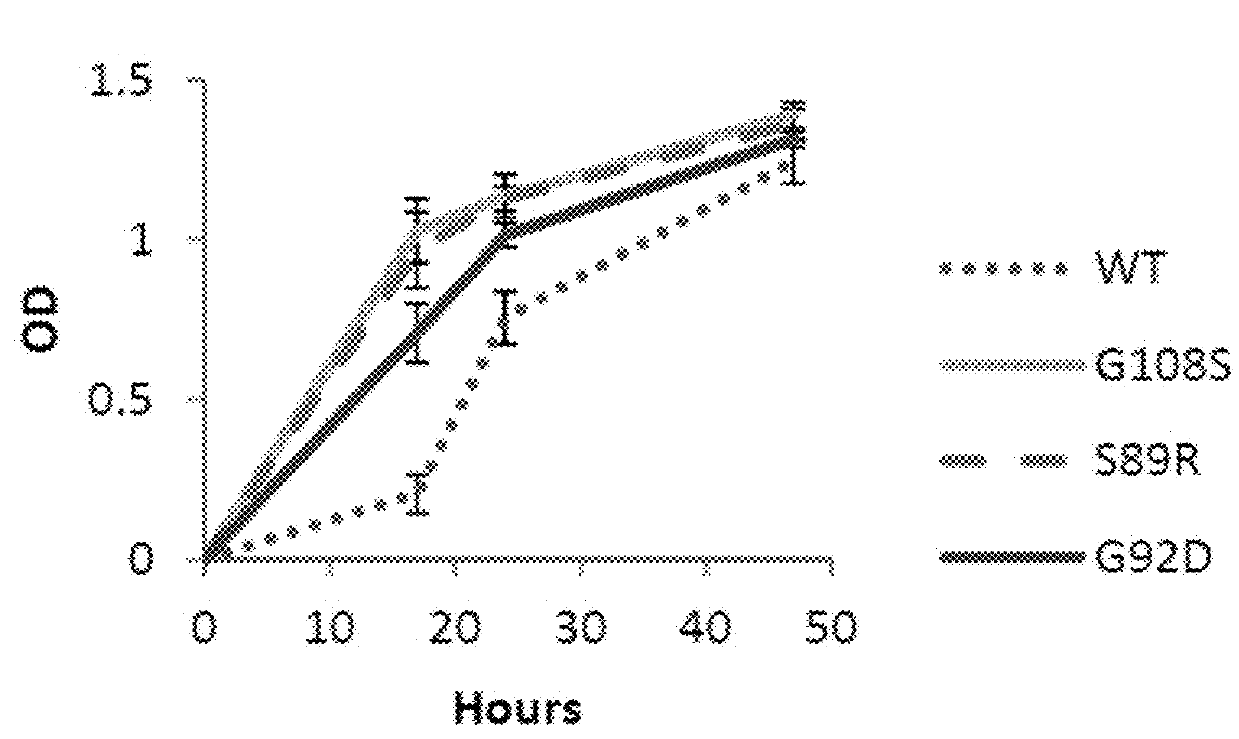
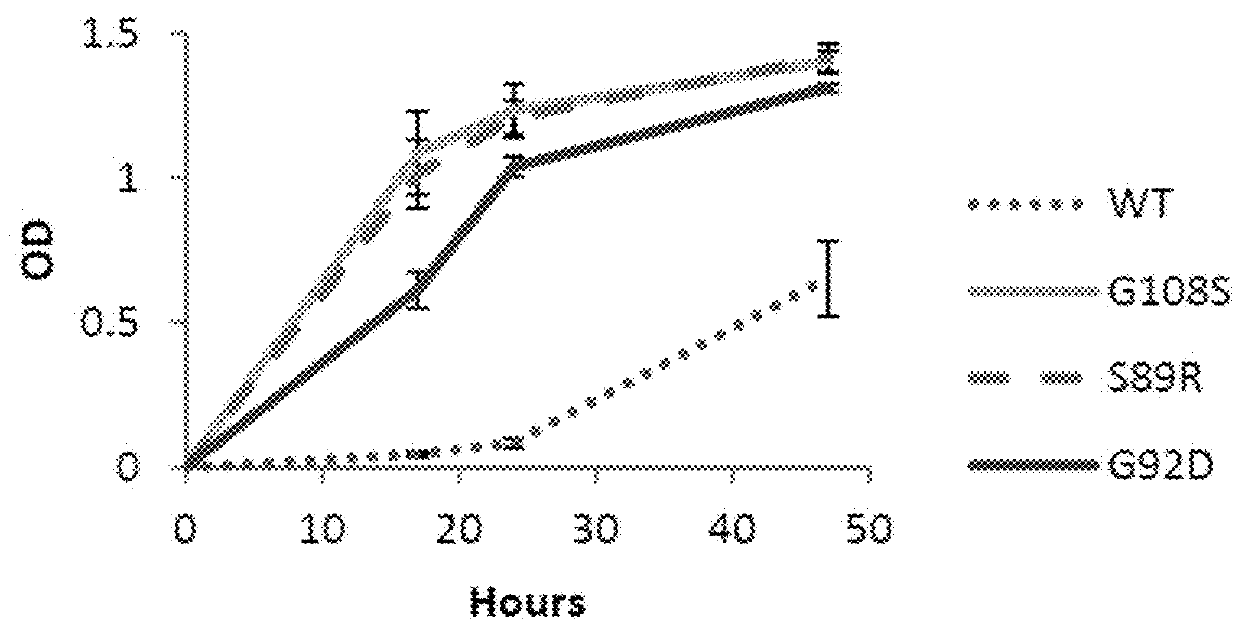
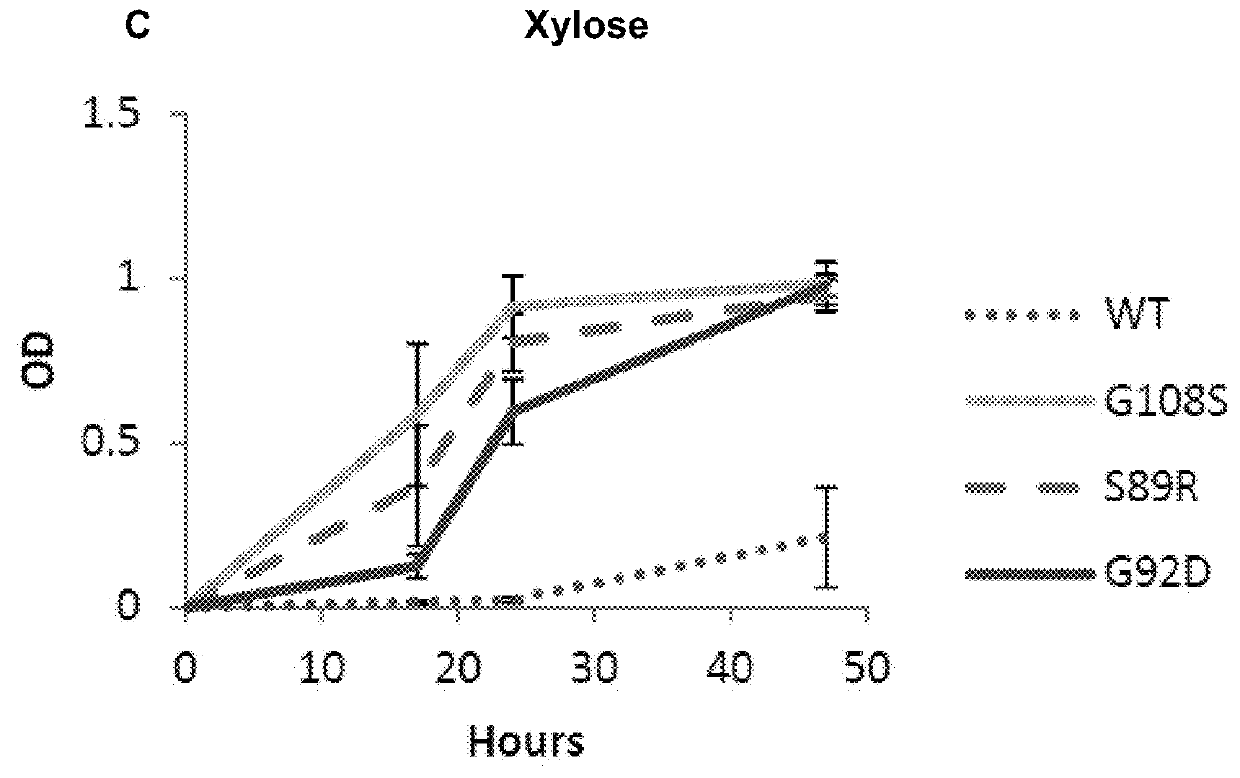
The present invention relates to a method for producing a L-arabinose utilizing yeast strain for the production of ethanol, whereby a yeast strain is modified by introducing and expressing araA gene (L-arabinose isomerase), araB gene (L-ribulokinase D121-N) and araD gene (L-ribulose-5-P 4-epimerase) and carrying additional mutations in its genome or overexpressing a TAL1 (transaldolase) gene, enabling it to consume L-arabinose, to use it as the only carbon source, and to produce ethanol, as well as a method for producing ethanol using such a modified strain.
Owner:FORSKARPATENT I SYD AB
Foliar fertilizer used for enhancing photosynthesis of plants, and its preparation method
ActiveCN103819270AAvoid accumulationSolve the problem of poor color and low qualityFertilizer mixturesPhosphateSodium bisulfate
The invention relates to a foliar fertilizer used for enhancing the photosynthesis of plants, and its preparation method. The foliar fertilizer which is a composition comprises a part A and a part B, the part A comprises 1-3% of chitosan, 1-3% of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase, 5% of a surfactant, 1-5% of an antifreeze agent, 5-10% of acetic acid, 10% of ethanol, 0.1-0.2% of a stabilizer, and the balance water, and the pH value of the part A is 4-6; the part B comprises 5-5% of sodium bisulfate, 5-10% of biochemical fulvic acid, 1-5% of the antifreeze agent, 5% of the surfactant, 5-10% of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 5-10% of urea, 1-3% of magnesium sulfate, 0.1-0.2% of a stabilizer, and the balance water, and the pH value of the part B is 7-8; a ratio of the part A to the part B is 1:1; and materials of the part A and materials of the part B are uniformly stirred and mixed at normal temperature to form the composition, and the composition is diluted to 1000-2000 times aqueous solution spray when the composition is used. The foliar fertilizer can effectively solve the problems of bad color and low quality caused by possible-meeting of bad natural environment after too late bag removal of bagged apples.
Owner:SHAANXI PUCHENG MEIERGUO AGROCHEM
Synthesis method of sugar via extracellular enzyme catalysis
The invention discloses a synthesis method of sugar via extracellular enzyme catalysis, comprising steps that: formaldehyde is reacted with 5-ribulose phosphate under the enzyme catalysis to produce 6-fructose phosphate; the 6-fructose phosphate is converted to the sugar under the enzyme catalysis, or connects glycosyl to an amylum chain or a cellulose chain. The formaldehyde can be produced by hydrogenating or electrolyzing carbon dioxide via the enzyme catalysis or chemical catalysis. The synthesis method also can comprise the step of using the 6-fructose phosphate to regenerate the 5-ribulose phosphate, so as to continuously produce the sugar. The synthesis method of the sugar via the extracellular enzyme catalysis uses a simple reactor, and can adopt the energy-fixed carbon dioxide to industrially produce the sugar.
Owner:黄卫东
Rice Rubisco large-subunit antigen epitope, large-subunit antibody and applications of antibody
InactiveCN103952389AHigh potencyHigh affinitySerum immunoglobulinsBiological material analysisEpitopeOxygenase
The invention rice photosynthesis key enzyme-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase / oxygenase (Rubisco) large-subunit antigen epitope, a polyclonal antibody resisting rice Rubisco large-subunit, and a preparation method and applications of the antibody. The amino acid sequence of the rice Rubisco large-subunit specific antigen epitope is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The preparation method comprises the following steps: synthesizing a polypeptide; coupling the polypeptide with carrier protein; preparing antiserum from an immune animal; and performing affinity chromatography for purification, thereby obtaining the polyclonal antibody resisting rice Rubisco large-subunit. The polyclonal antibody is high in titer, remarkable in affinity, excellent in specificity, low in preparation cost and high in yield, and can generate specific binding reaction with rice Rubisco large-subunit; an important tool is supplied for the fundamental research on the rice Rubisco large-subunit as well as the research on the relevant physiological functions of the rice Rubisco large-subunit.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
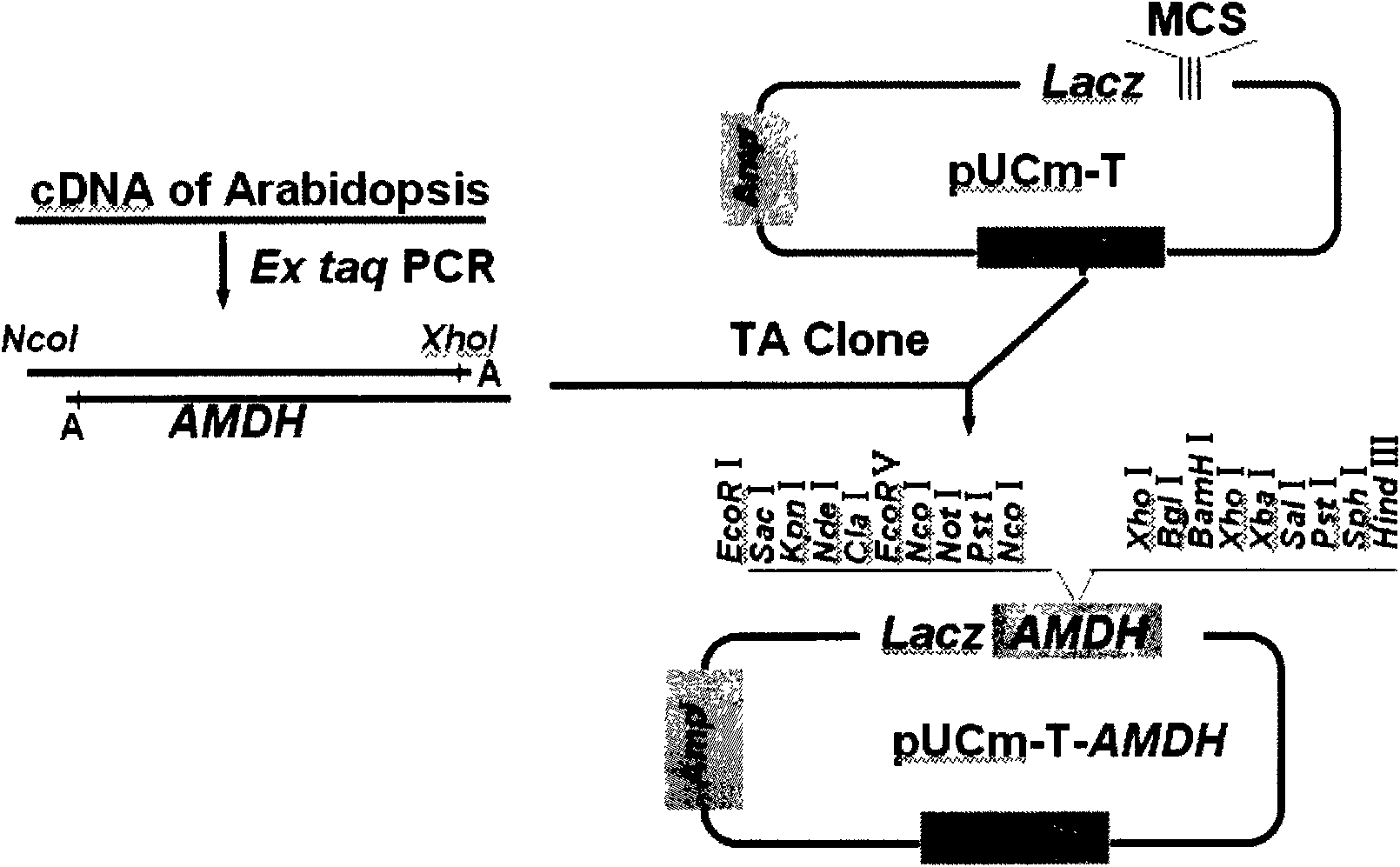
Plant expression vector of arabidopsis thaliana cytosolic malate dehydrogenase gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101586116ADetoxifyImprove the ability to resist aluminum poisoningFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumWild type
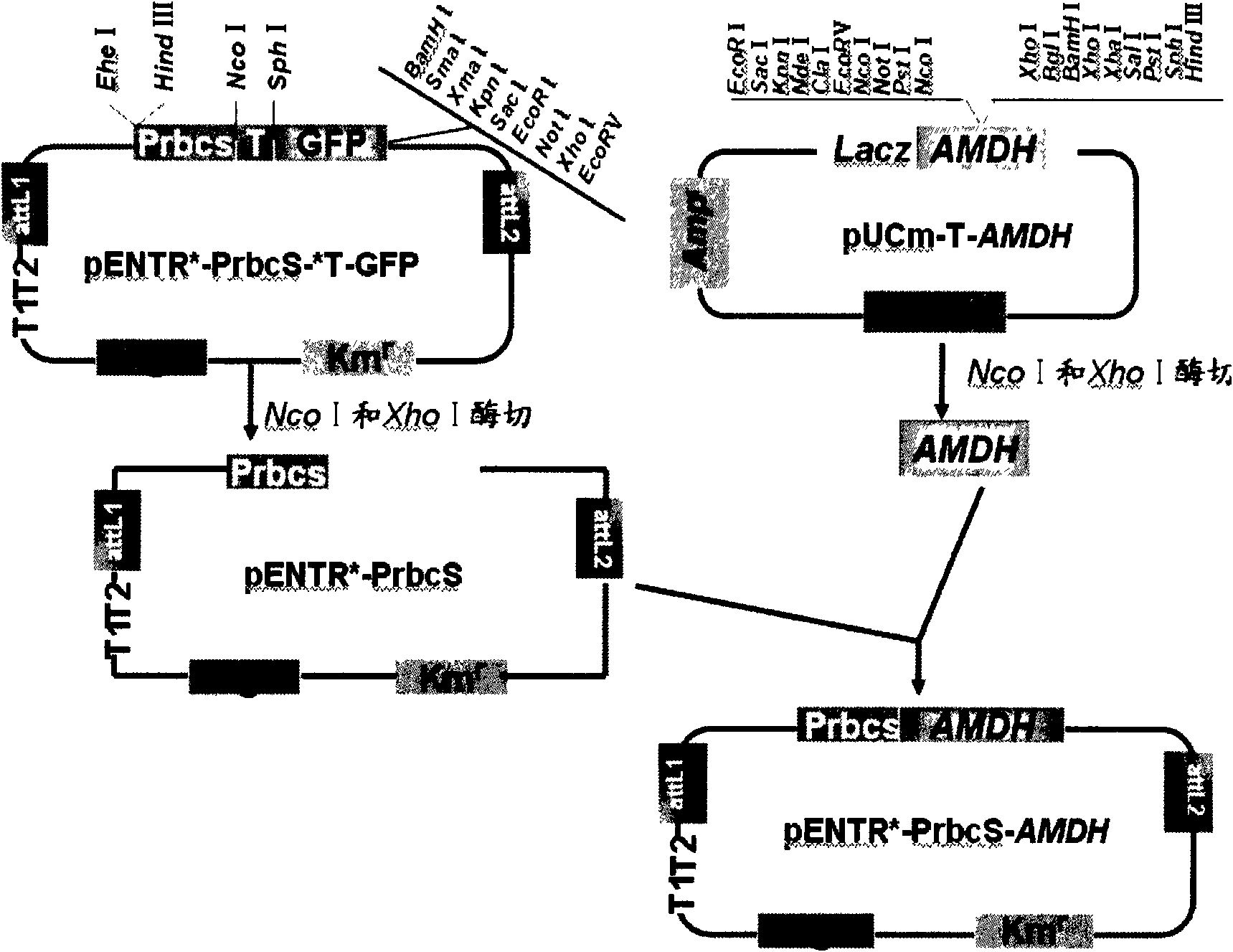
The invention in particular relates to a plant expression vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-AMDH for improving the aluminum toxicity resistance of plants, a construction method and application thereof, which belong to the field of plant gene engineering. The special vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-AMDH for improving the aluminum toxicity resistance of the plants is the plant expression vector containing a photoinducible promoter (PrbcS) of a rubulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase (RubIsco) small subunit gene and an arabidopsis thaliana cytosolic malate dehydrogenase gene (AMDH). The AMDH gene is cloned from arabidopsis thaliana, the photoinducible promoter is used to control the overexpression of the AMDH gene in tobacco, malic acid is synthesized, and the malic acid is secreted out of cells so as to strengthen the resistance of the plants on aluminum toxicity in acid soil. Experimental results show that the activity of malate dehydrogenase of trans-AMDH genic tobacco leaves is 1.4 times of that of wild tobacco. Under the stress of 30 mu M of aluminum toxicity, trans-AMDH genic tobacco can secrete more organic acid, and has better root system growth; and the growth condition under the stress of the aluminum toxicity shows that the plant height and the green leaf number of the trans-AMDH genic tobacco are higher than those of the wild tobacco.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Yeast expressing a synthetic calvin cycle
InactiveCN111133097AIncrease cell densityIncreased space-time yieldPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiHeterologousYeast
Owner:UNIV FUR BODENKULTUR WIEN
Selection system containing non-antibiotic resistance selection marker
InactiveUS20070036822A1Easy to useAvoid problemsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaEscherichia coliL-ribulose-5-phosphate 4-epimerase
A selection system free of antibiotic resistance genes, which is based on the use of an araD gene as a selection marker carried on a vector which is inserted in a bacterial strain deficient of the araD gene. The araD gene from E. coli encodes the L-ribulose-5-phosphate-4-epimerase. A method of selecting the cells transformed with a plasmid, which contains the araD gene. The non-antibiotic selection marker makes the system suitable for producing therapeutics. The araD gene is not essential for growth of the host but manipulation of it affects the growth under certain selective conditions. Deletion of araD leads to accumulation of substance which is toxic to the host but not to humans. The araD gene is relatively small and therefore a small plasmid may be constructed, which requires less energy for replication, and leads to increased growth rate and yield.
Owner:FIT BIOTECH OY PLC
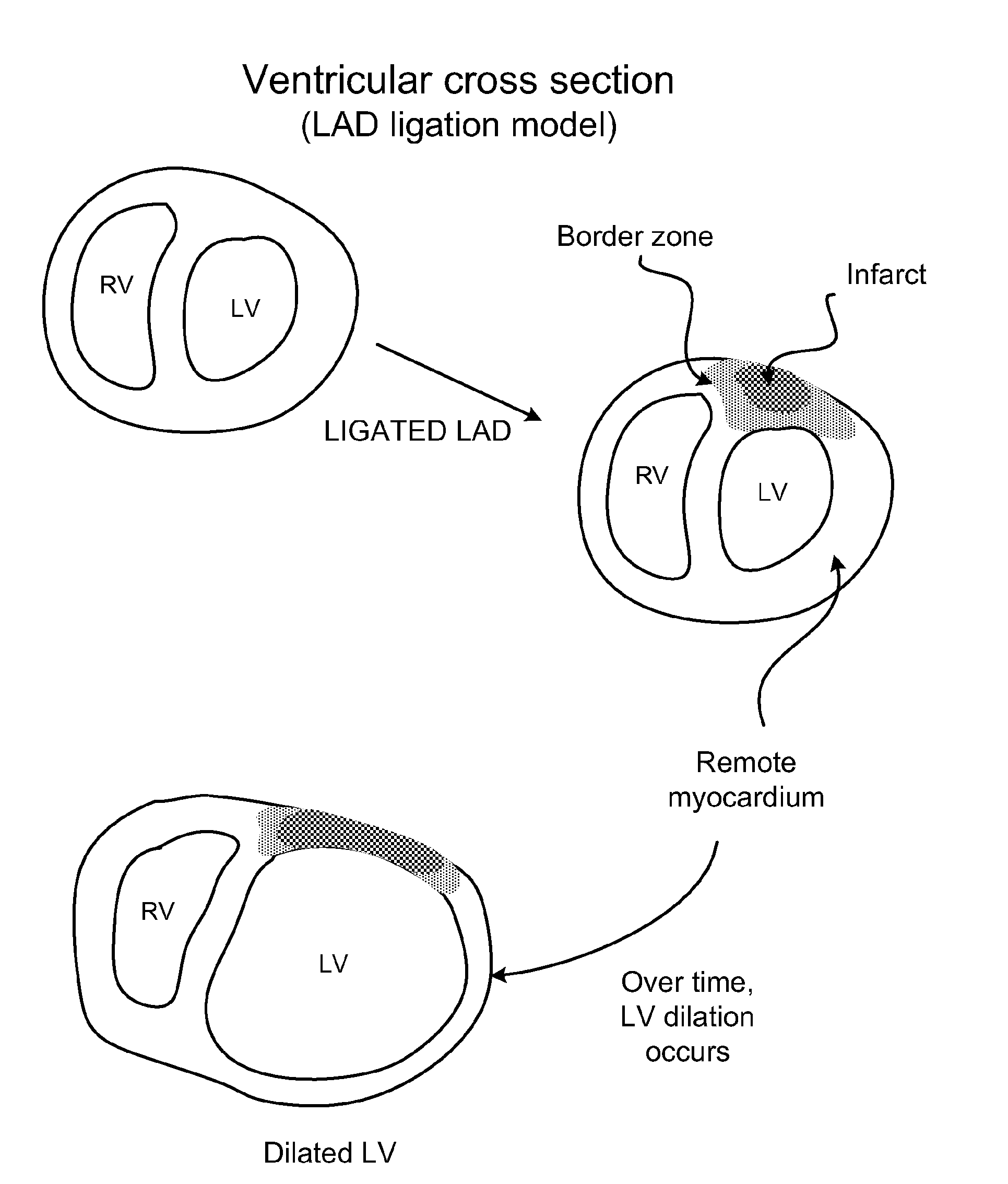
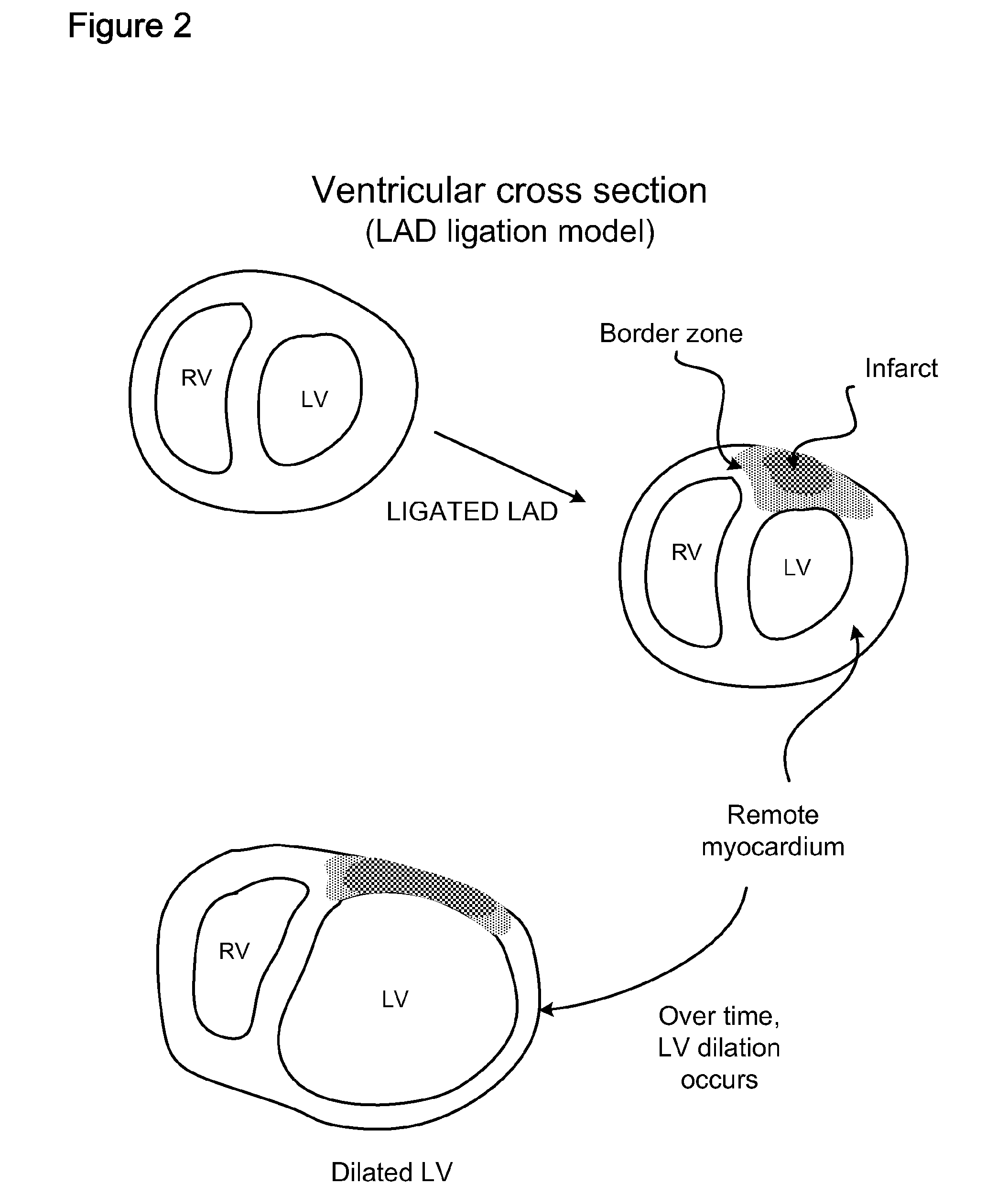
Methods and compositions for inhibiting progression to chronic cardiac failure
InactiveUS20110053869A1Reducing ultimate sizeProgressive damageBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsRate limitingDisease
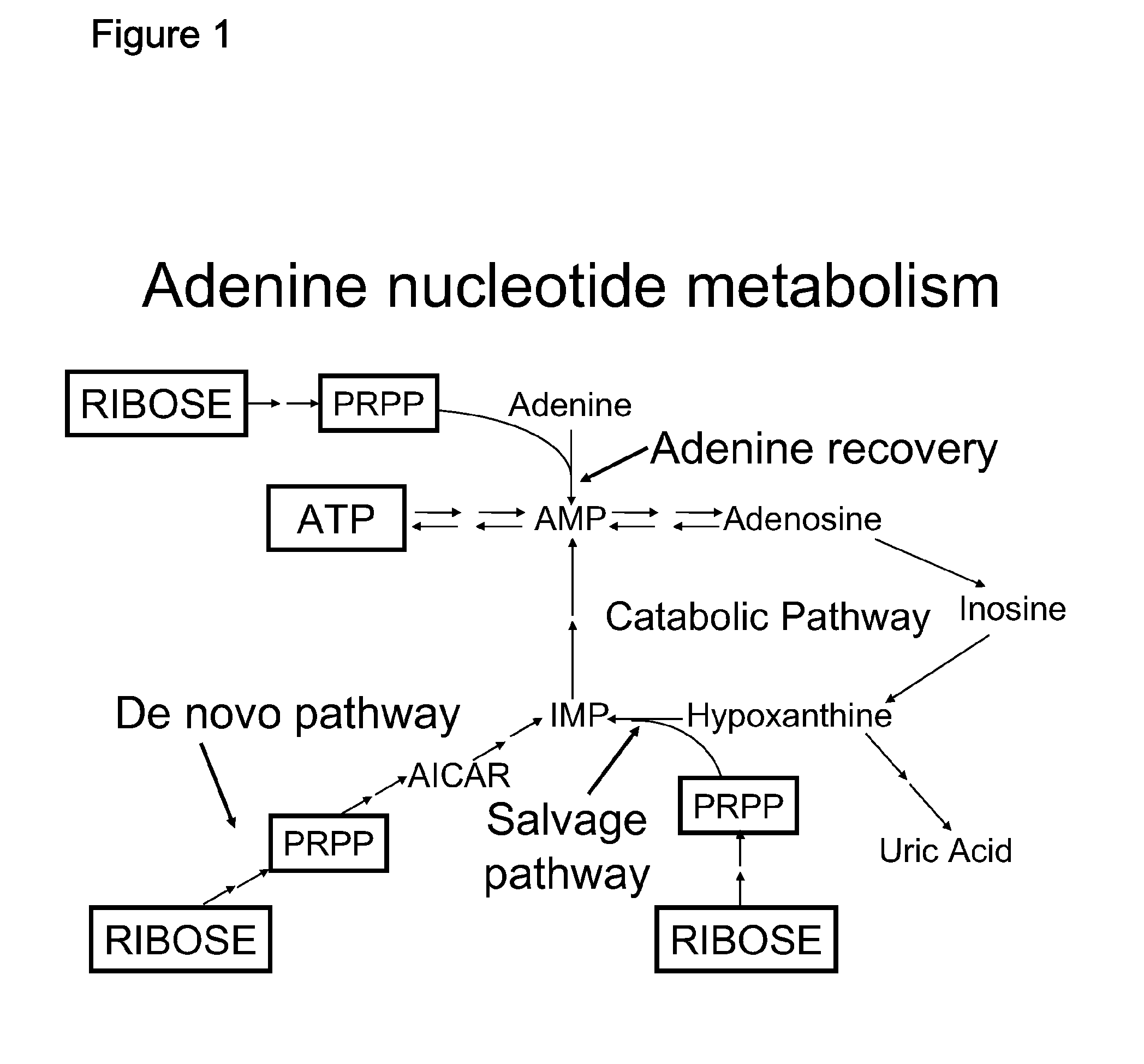
The present invention is provides methods and formulations for preventing or ameliorating progression to chronic heart failure subsequent to cardiac stress, including as a consequence of myocardial infarction (MI), coronary artery disease, hypertension, cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, valvular regurgitation, severe lung disease, and / or severe anemia of chronic disease, by administration of one or more rate-limiting precursors to the synthesis of ATP. In one embodiment the ATP precursor is a pentose selected from one or more of ribose, D-ribose, ribulose, xylitol, xylulose, and a 5-carbon precursor of ribose.
Owner:FOKER JOHN E
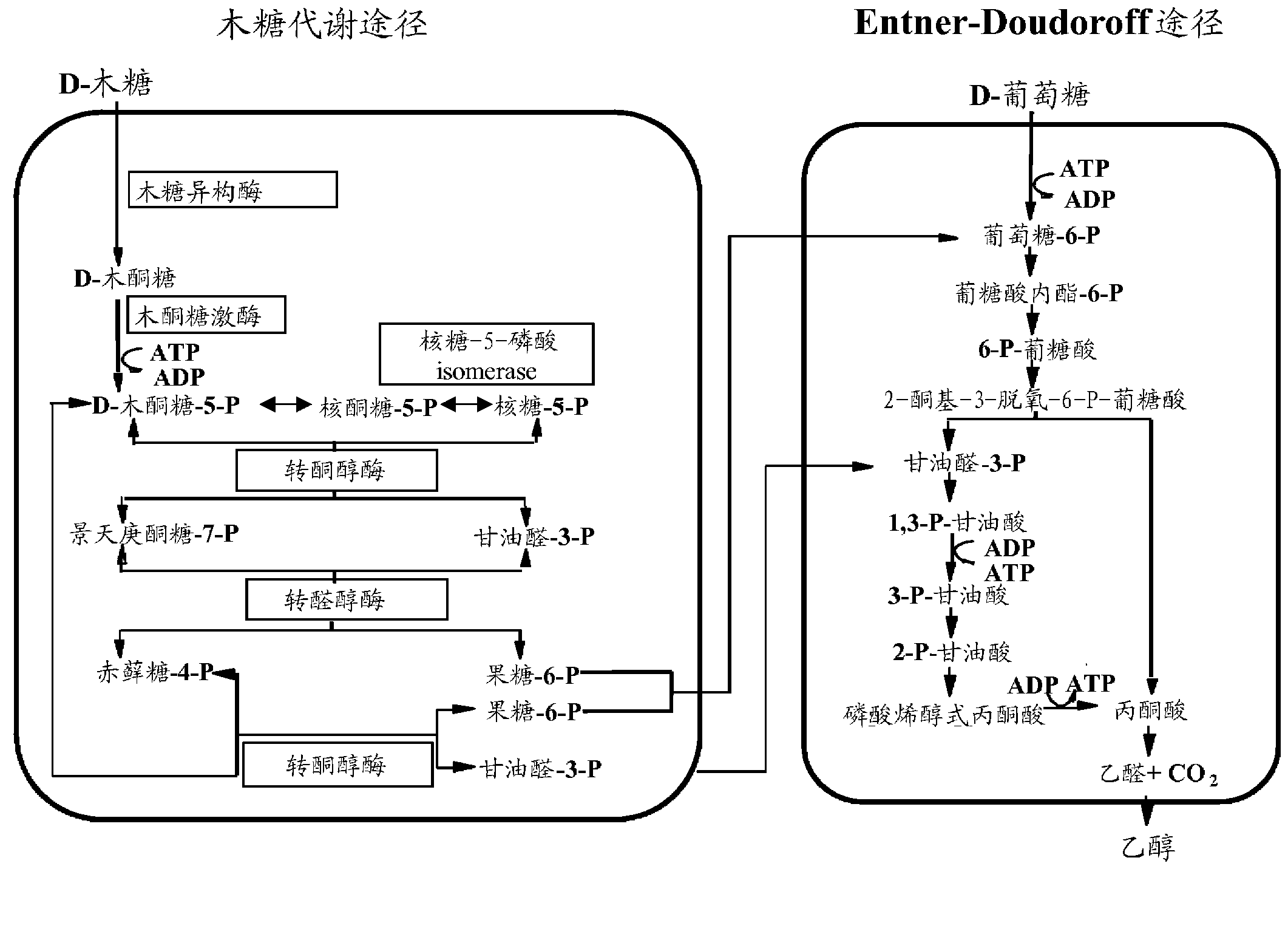
Improved xylose utilization in recombinant zymomonas having increased ribose-5-phosphate activity
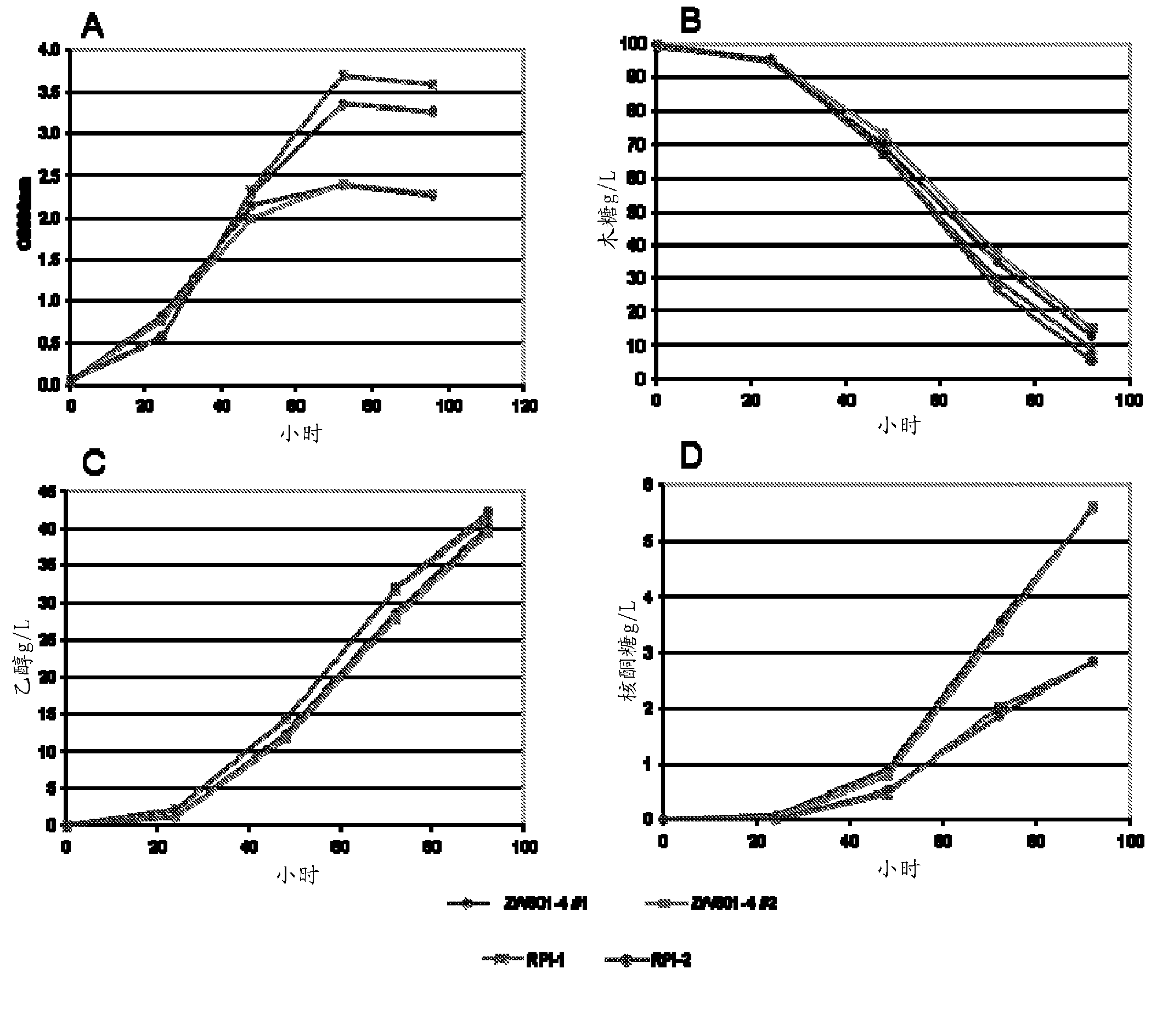
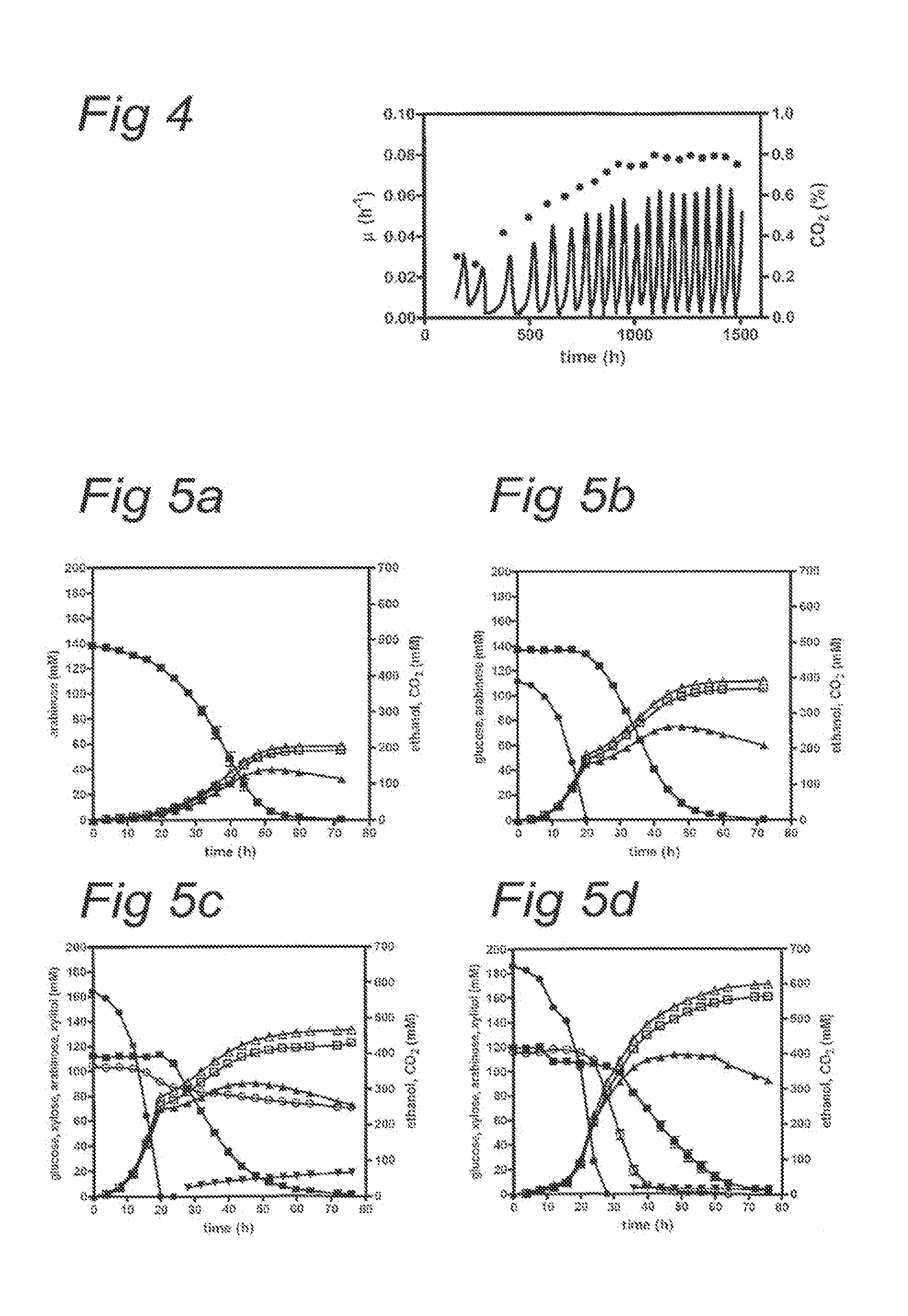
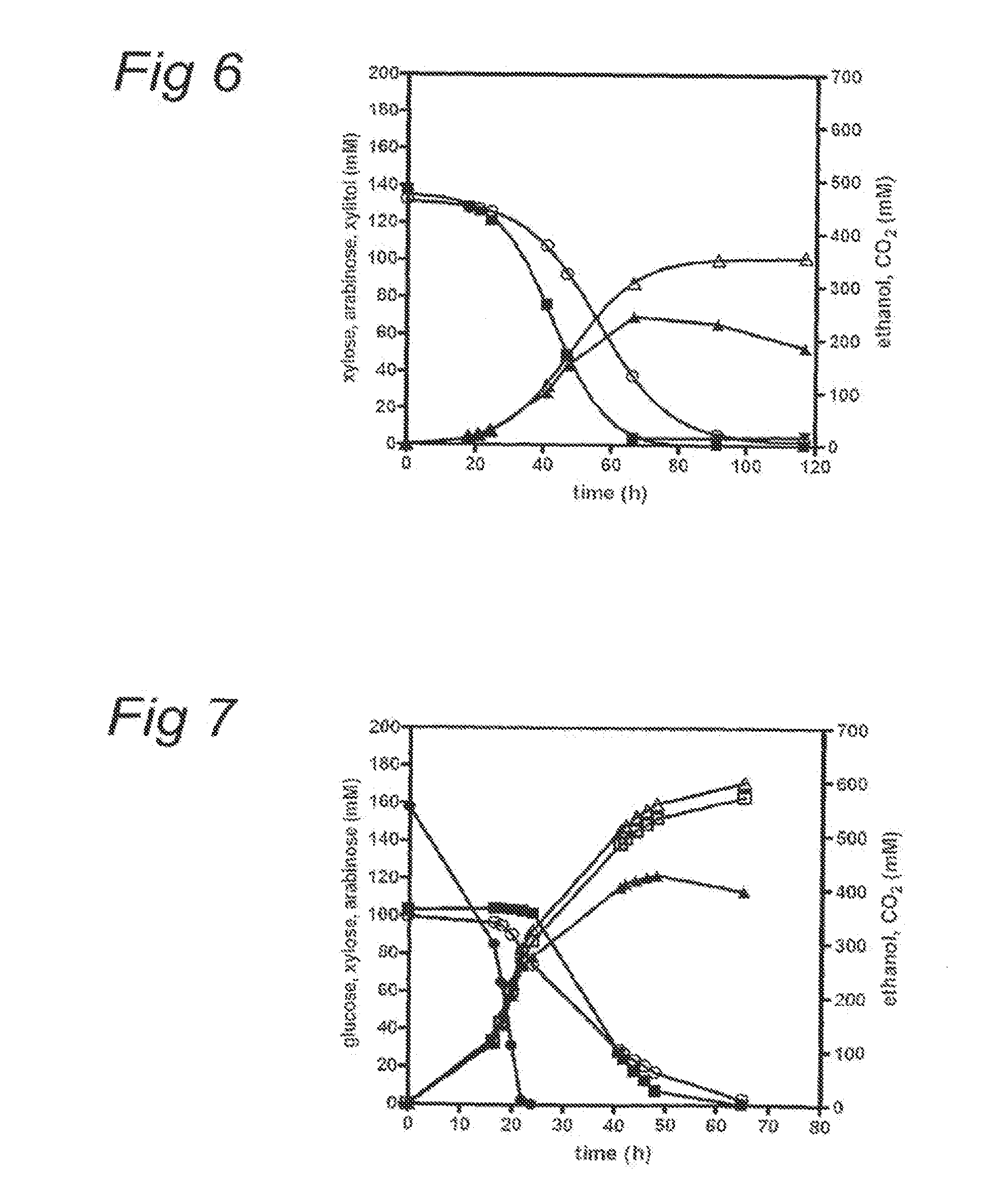
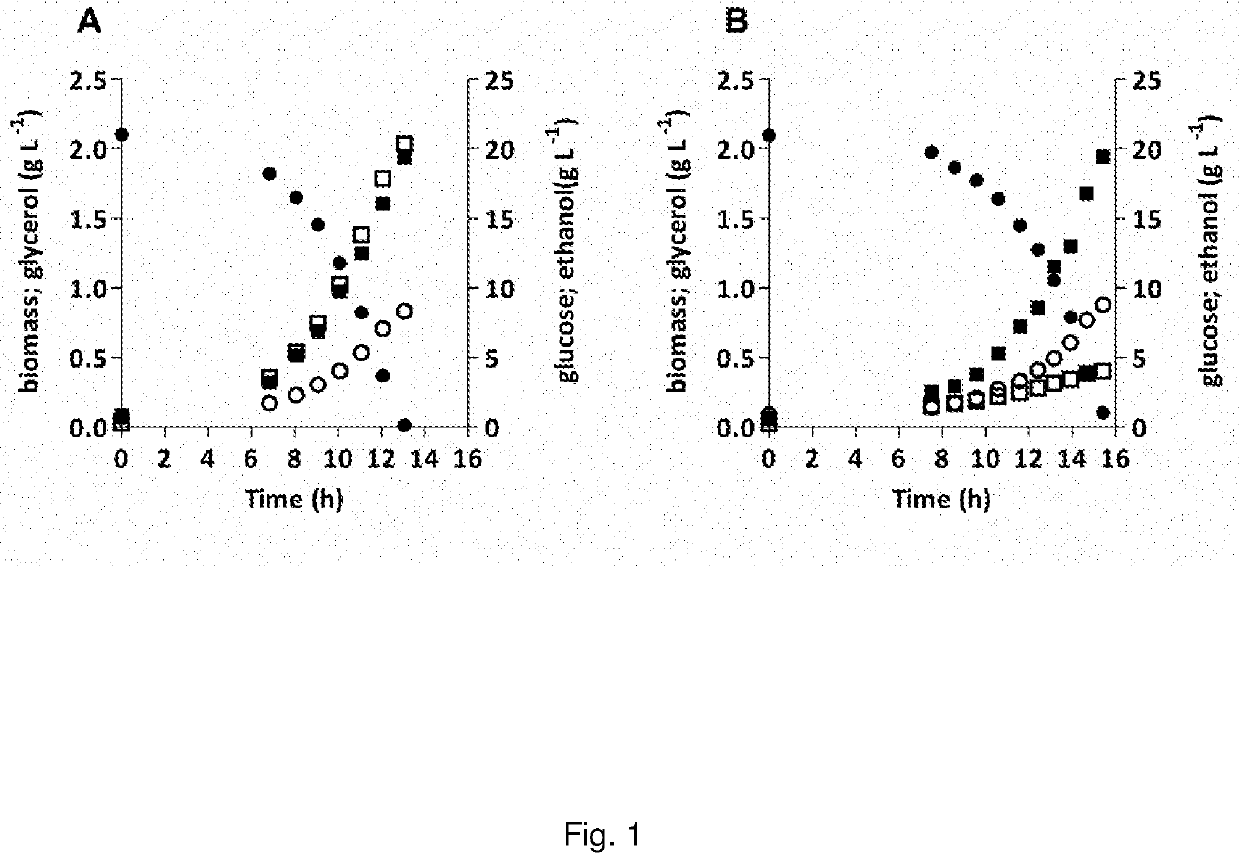
Xylose-utilizing Zymomonas strains studied were found to accumulate ribulose when grown in xylose-containing media. Engineering these strains to increase ribose-5-phosphate isomerase activity led to reduced ribulose accumulation, improved growth, improved xylose utilization, and increased ethanol production.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
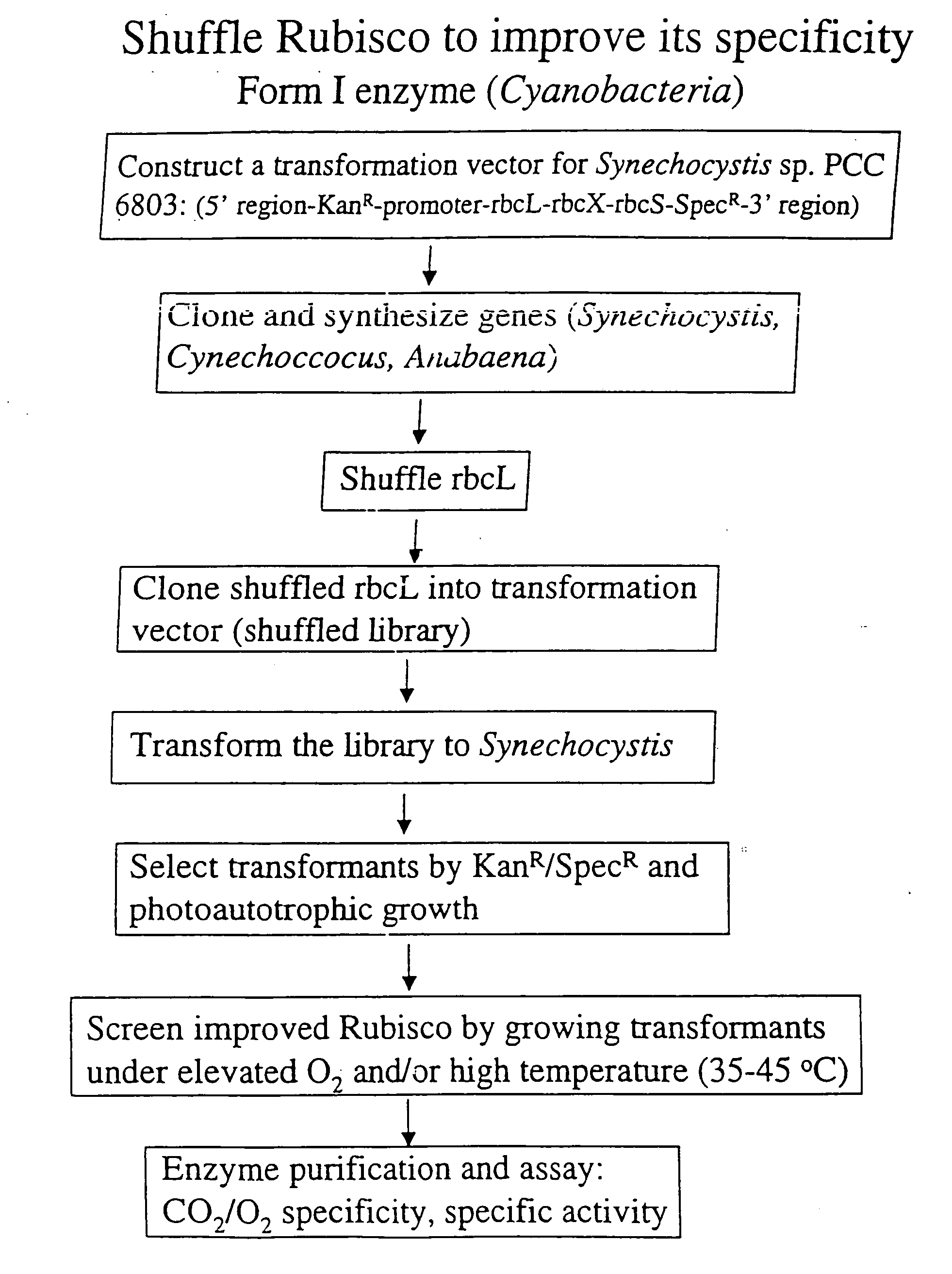
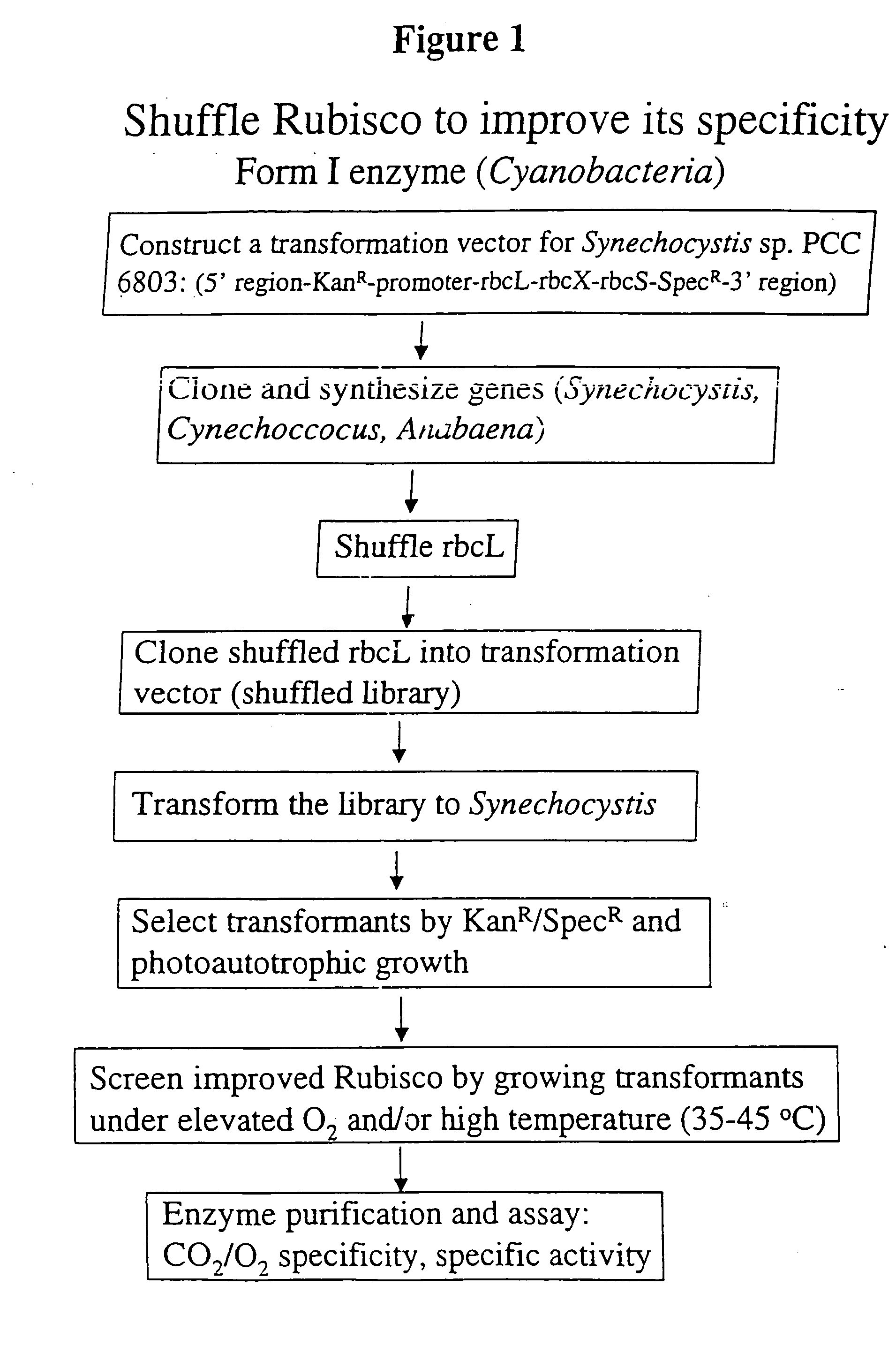
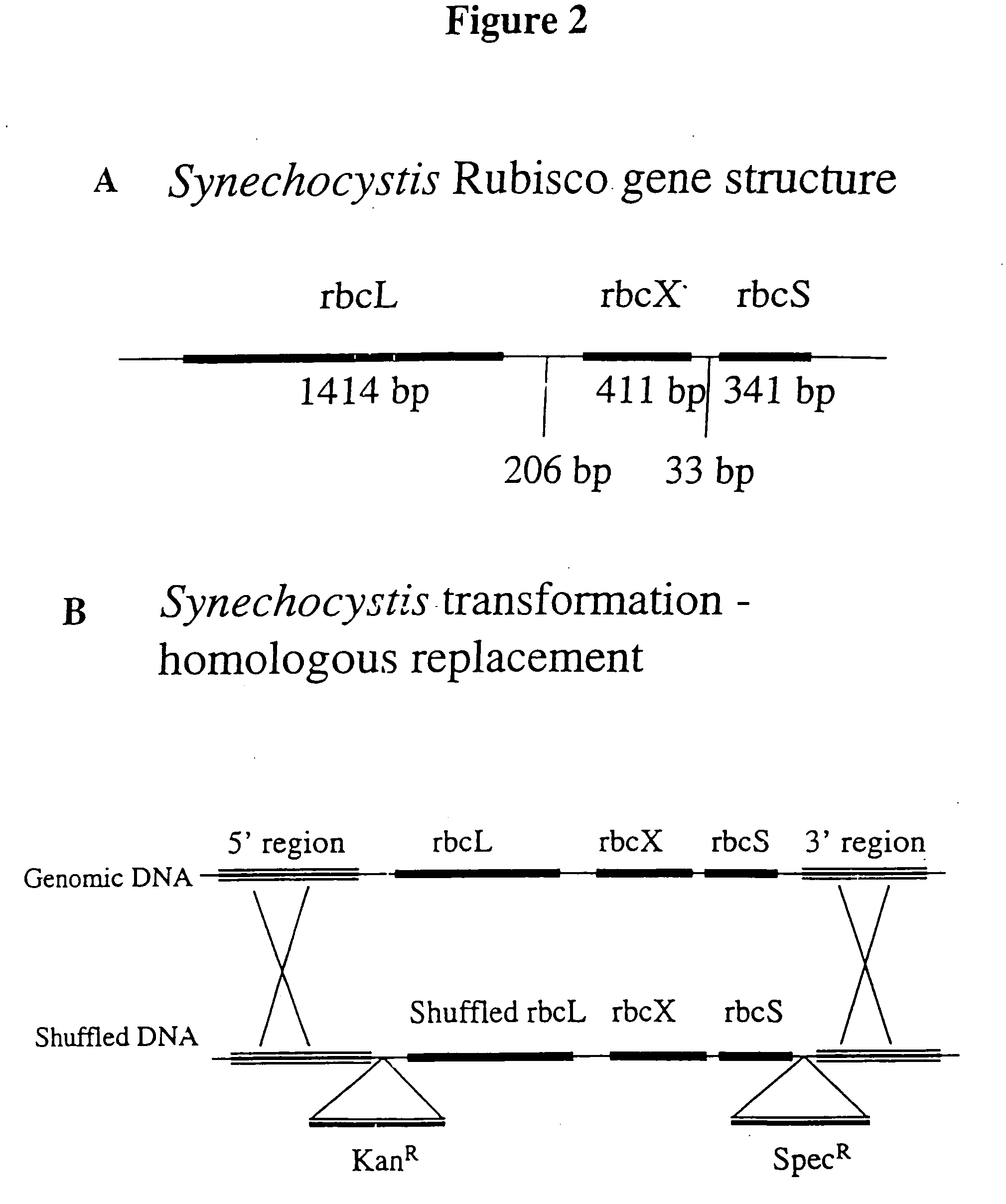
Modified ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase for improvement and optimization of plant phenotypes
InactiveUS20060117409A1Elevated carbon fixation activityIncrease catalytic rateMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesENCODERibulose
The invention relates to methods and compositions for generating, modifying, adapting, and optimizing polynucleotide sequences that encode proteins having Rubisco biosynthetic enzyme activities which are useful for introduction into plant species, agronomically-important microorganisms, and other hosts, and related aspects.
Owner:MAXYGEN
Recombinant yeast cell
ActiveUS10689670B2Improve production yieldReduce formationFungiTransferasesHeterologousPhosphoribokinase
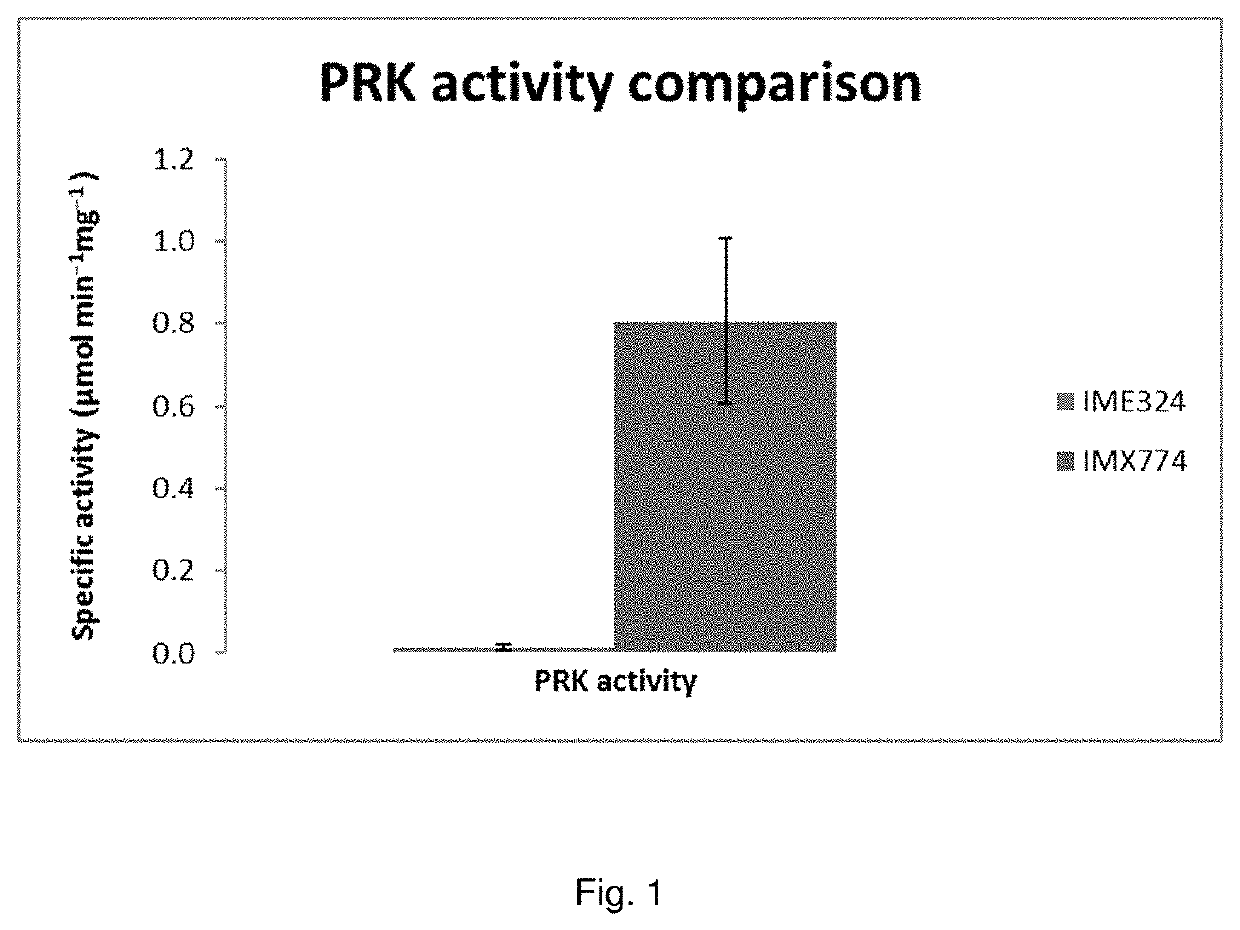
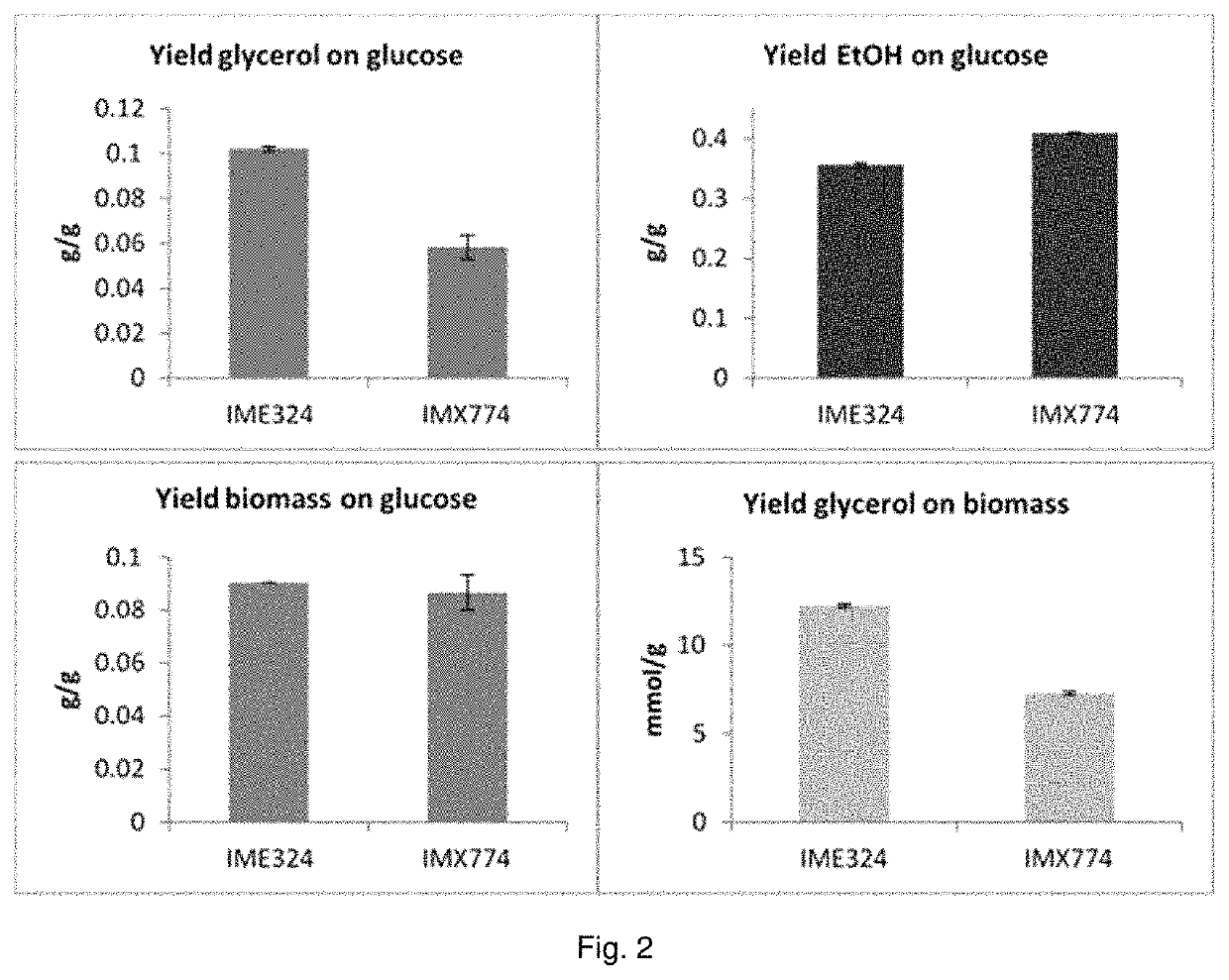
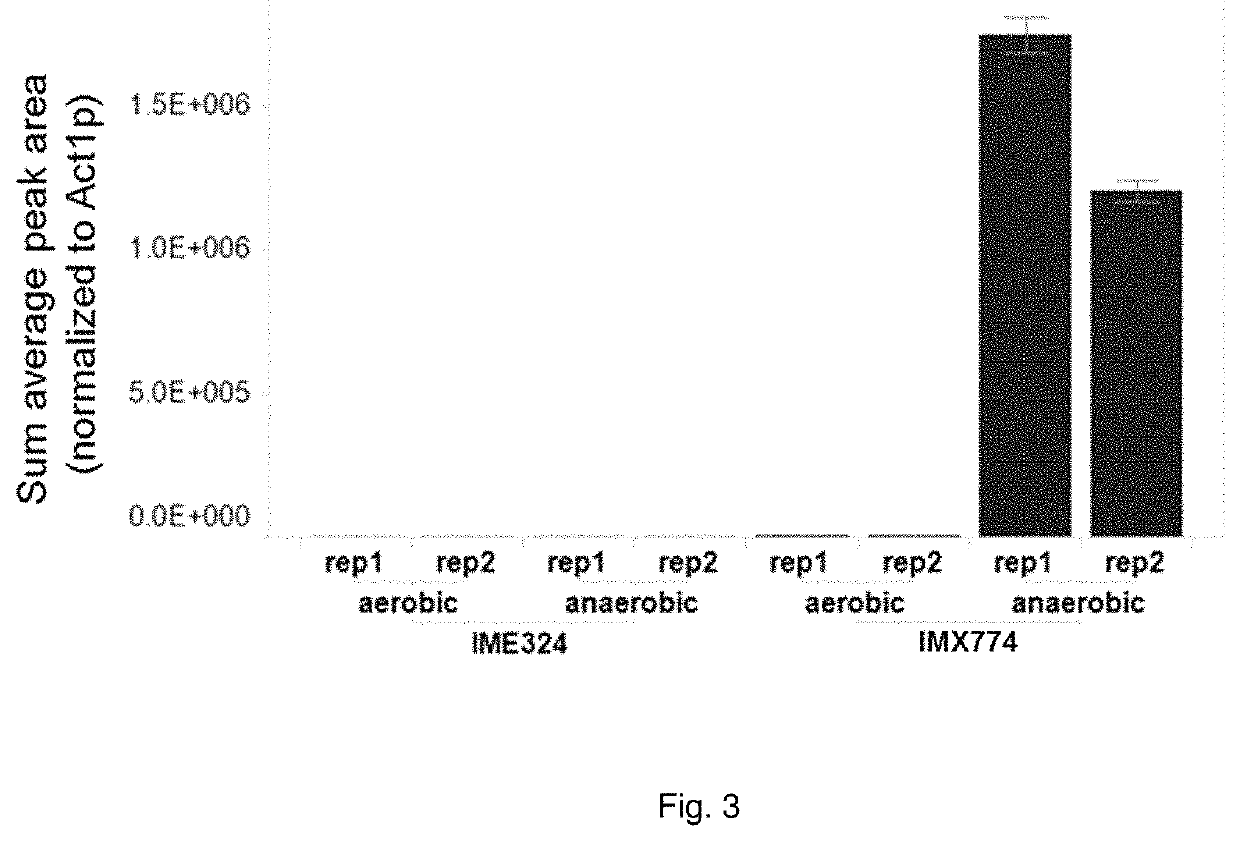
The present invention describes a recombinant yeast cell functionally expressing one or more heterologous nucleic acid sequences encoding for ribulose-1,5-phosphate carboxylase / oxygenase (EC4.1.1.39; Rubisco), and optionally one or more molecular chaperones for Rubisco, and one or more phosphoribulokinase (EC2.7.1.19; PRK), wherein the phosphoribulokinase is under control of a promoter (the “PRK promoter”) that enables higher expression under anaerobic conditions than under aerobic conditions.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Modified rubisco large subunit n-methyltransferase useful for targeting molecules to the active-site vicinity of ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate
InactiveUS20090070901A1Improve efficiencyImprove productivityTransferasesImmunoglobulinsGrowth plantAntibody conjugate
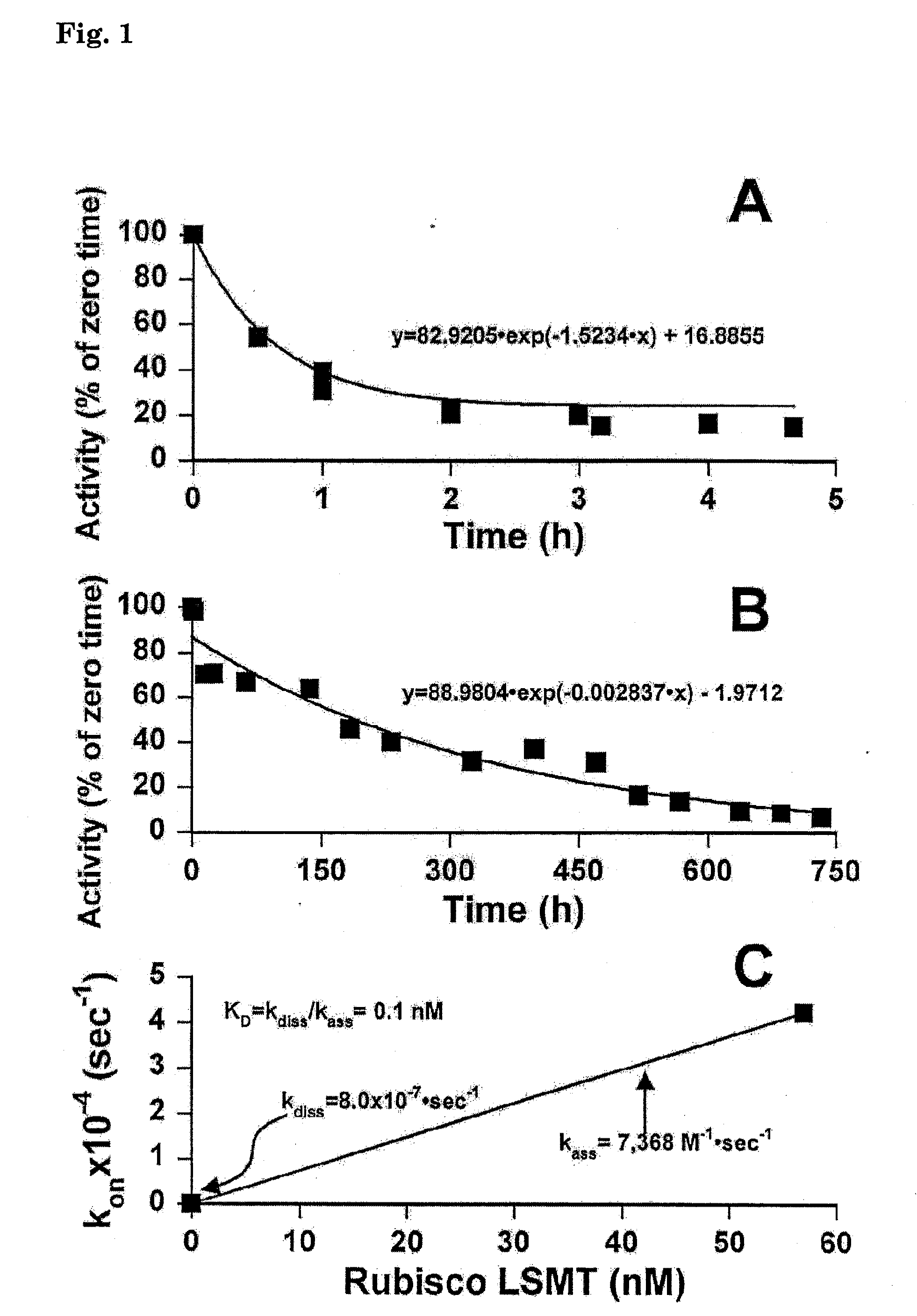
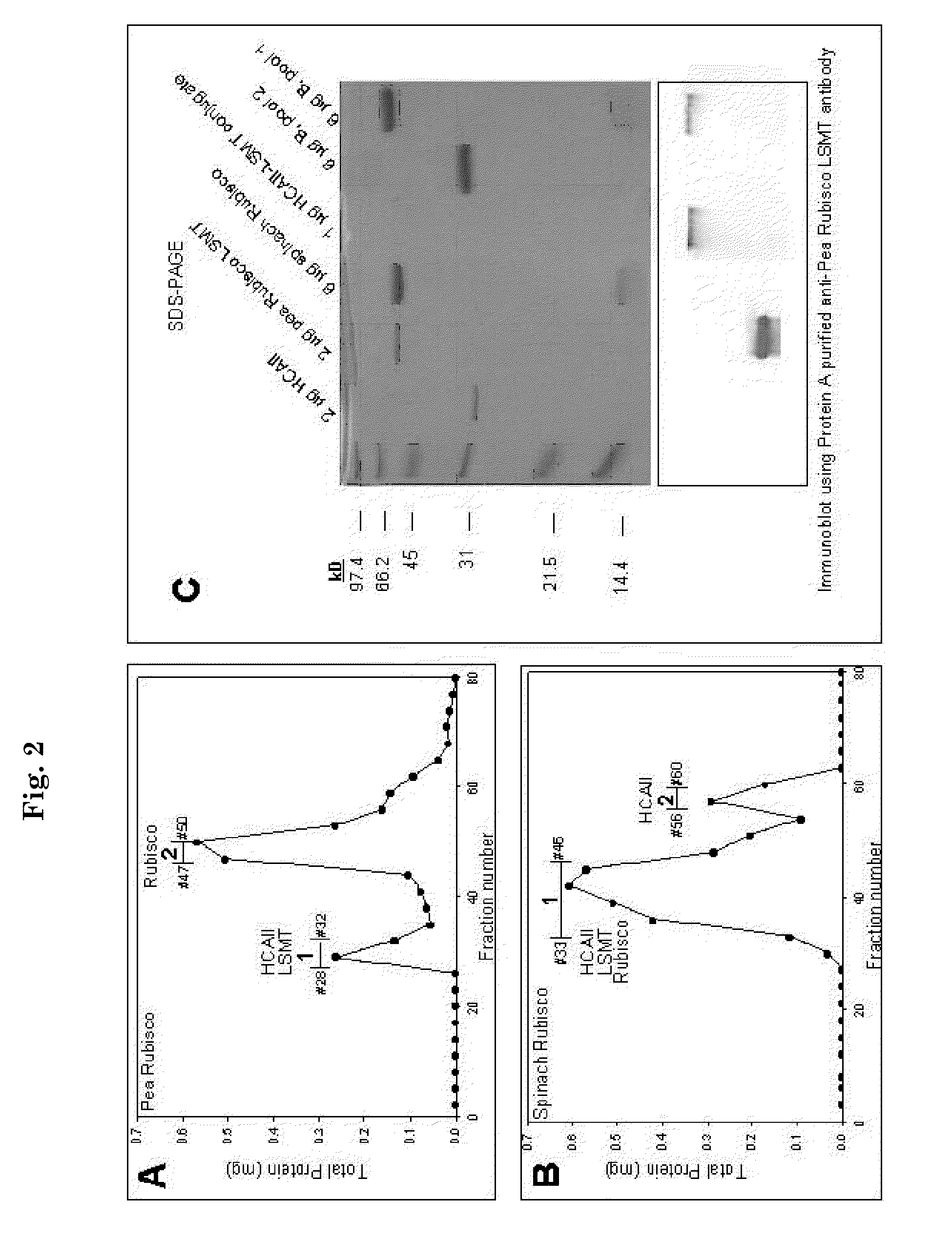
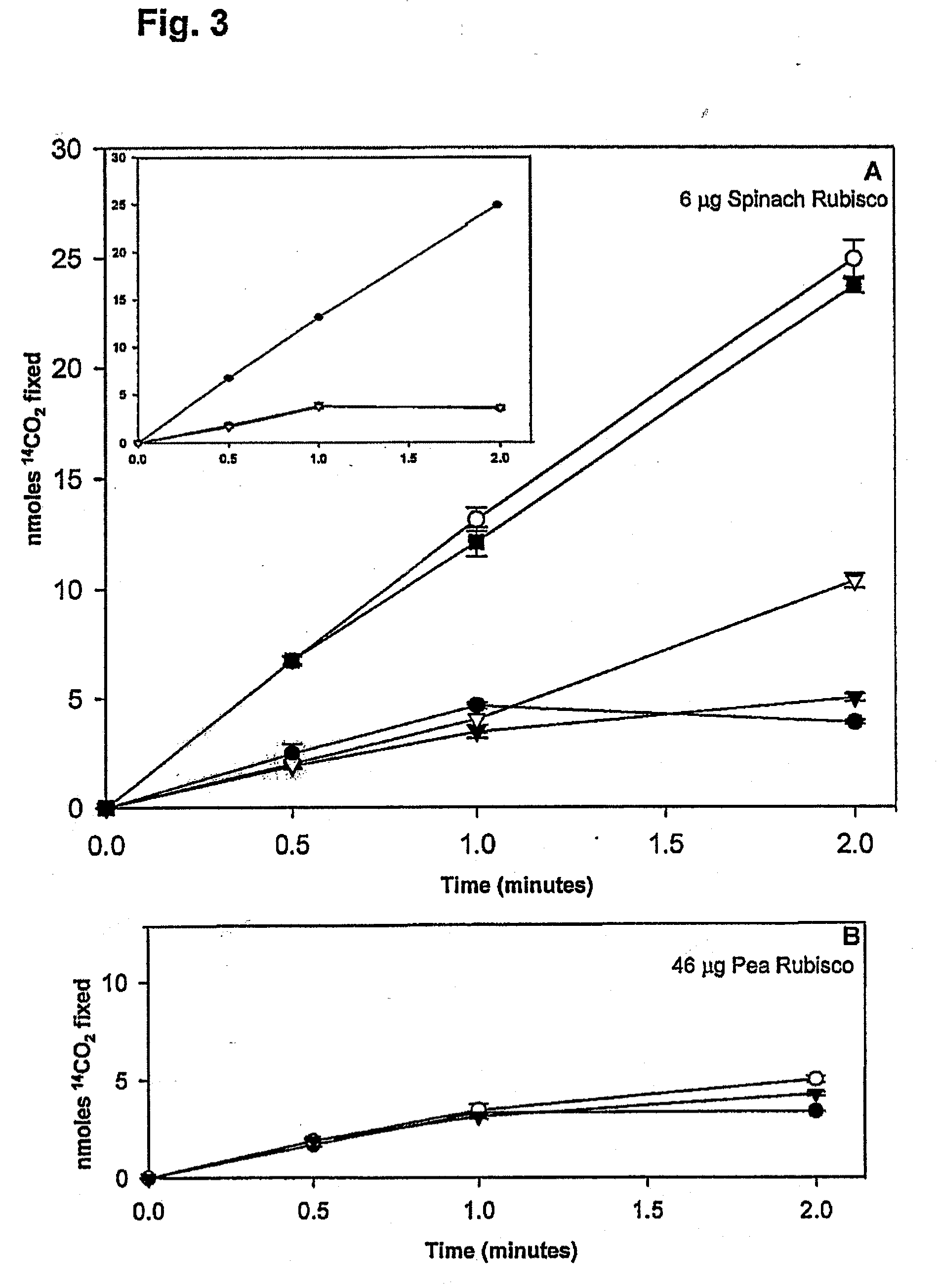
The present invention generally relates to a modified Rubisco large subunit εN-Methyltransferase (Rubisco LSMT, or RLSMT). The present invention also relates to a modified RLSMT-carbonic anhydrase (RLSMT-CA). This modified RLSMT-CA improves the efficiency of the reduction of CO2 during photosynthesis, which may increase plant growth rates. The present invention also relates to nucleic acids encoding the modified RLSMT-CA or modified RLSMT. Also, the present invention relates to cells including the modified RLSMT-CA or modified RLSMT, plants containing the modified RLSMT-CA or modified RLSMT, and methods using compositions of the present invention. In addition, the present invention relates to antibodies conjugated to CA which may bind to Rubisco, and antibodies which bind a modified RLSMT-CA. The invention also relates to modified forms of the LS and SS of Rubisco where the modified forms are fusions with CA or biologically active fragments thereof. The present invention provides methods of altering Rubisco carboxylase activity and altering plant growth.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Recombinant escherichia coli for producing pentamethylene diamine and application of recombinant escherichia coli
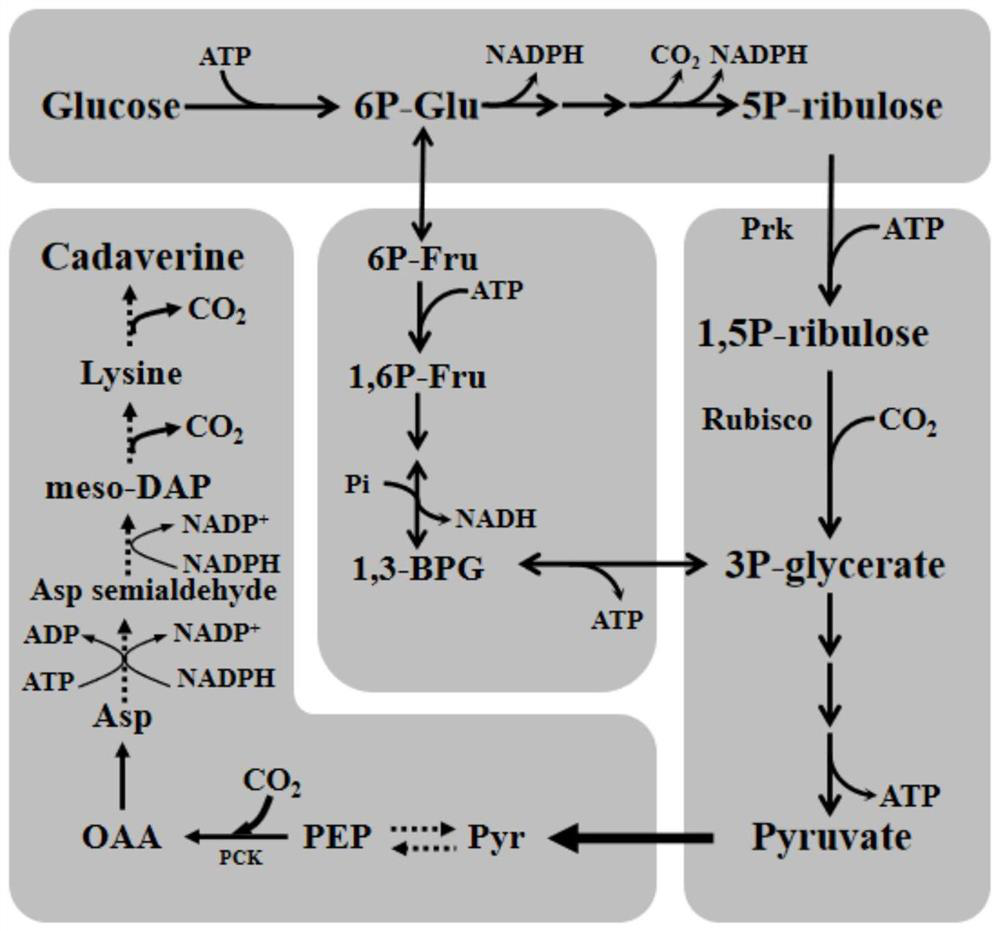
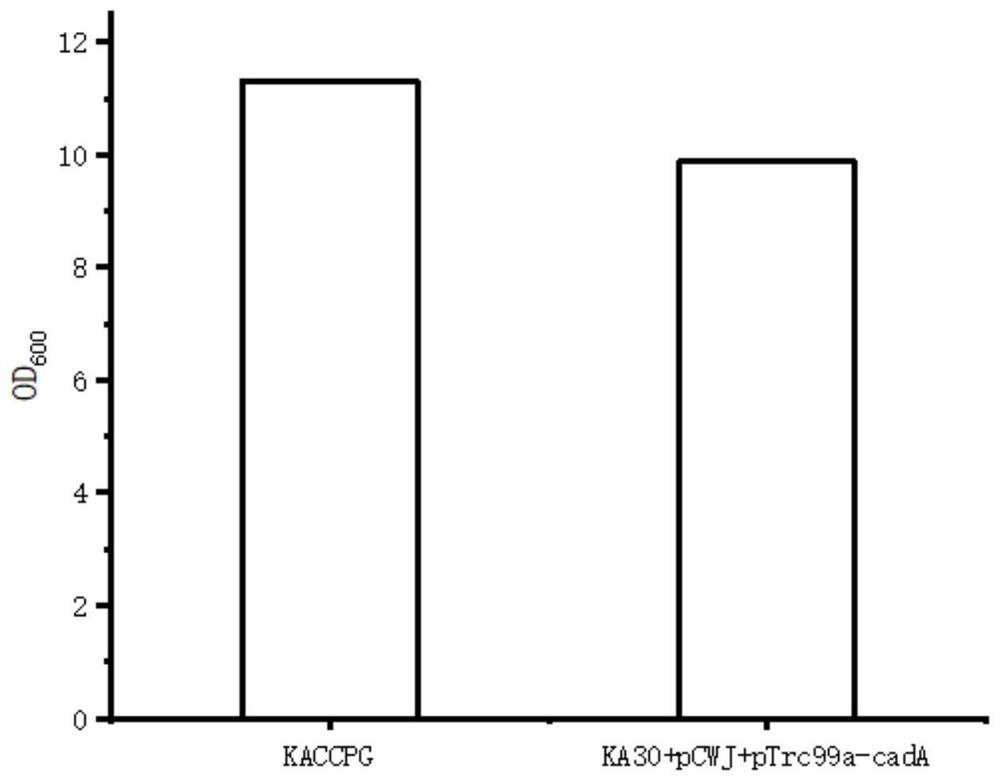
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli for producing pentamethylene diamine and application of the recombinant escherichia coli. A ribulose diphosphate carboxylase gene in rhodospirillum, a ribose phosphate kinase gene and a lysine decarboxylase gene in spinach are synthesized from the beginning, PCR copy an escherichia coli molecular chaperone gene to construct a plasmid pTrc99a-cadA-cbbM and a plasmid pCWJ-prkA-GroEL / GroES, the double-plasmid recombinant bacteria grow well in a specific culture medium, and glucose is efficiently utilized. According to the recombinant escherichia coli, inducers arabinose and IPTG are respectively added in different time periods, the heterologous gene expression is stable, the reaction system is simple, the condition is mild, the period is short, few byproducts are produced, the method is clean and pollution-free, the method is a simple, rapid and efficient production way, and the fermentation result shows that the yield of the recombinant escherichia coli KACCPG is obviously improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Host cells and methods for producing 1-deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) and/or a DXP derived compound
The present invention provides for a genetically modified host cell capable of producing 1-deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate or 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) (12), and optionally one or more DXP derived compounds, comprising: (a) a mutant RibB, or functional variant thereof, capable of catalyzing xylulose 5-phosphate and / or ribulose 5-phosphate to DXP, or (b) a YajO, or functional variant thereof, and a XylB, or functional variant thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Metabolic engineering of arabinose-fermenting yeast cells
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Polyvalent imprinted polymer and process of preparation thereof
InactiveUS7041762B2Enhanced interactionInhibitory concentrationOther chemical processesCelluloseOctanoic Acids
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Tobacco reference genes screened by use of gene chip and combination of real time PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and method thereof
The invention discloses tobacco reference genes screened by use of a gene chip and combination of a real time PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and a screening method thereof. By use of the screening method, the new tobacco reference genes comprising tobacco ribulose phosphate kinase gene and tobacco digalactosyl diacylglycerol synthase gene, the stability of the tobacco ribulose phosphate kinase gene is higher than that of all reported tobacco reference genes in the prior art, and the stability of the tobacco digalactosyl diacylglycerol synthase gene is next only to that of reported tobacco reference gene EF-1-a.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI RES INST
L-ribose isomerase and application thereof for biologically preparing L-ribose
InactiveCN105779425AImprove catalytic performanceHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRibose isomeraseRibose
The invention discloses an L-ribose isomerase.The amino acid sequence of the L-ribose isomerase is shown in SEQ ID NO.1.The nucleotide sequence of the L-ribose isomerase is shown in SEQ ID NO.2.The L-ribose isomerase has the good thermal stability and pH stability, and the catalytic efficiency for L-ribulose can reach 85% or above.The invention further discloses recombinant bacteria comprising the L-ribose isomerase and a construction method of the recombinant bacteria.The catalytic efficiency of the recombinant bacteria for L-ribulose can reach 81% or above.The L-ribose isomerase has the good application prospect and economic value for industrial production of L-ribose.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Transient expression vector carrying NtRBSC1 gene
InactiveCN107058373APrecise positioningEasy for in-depth developmentVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and in particular relates to a recombinant transient expression vector carrying a small subunit gene of tobacco ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. One transient expression vector NtRBSC1-pFF19-GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein) is constructed by utilizing a tobacco NtRBSC1 gene; after tobacco cells are transformed through the vector, fused protein of fluorescence labeled gene GFP and NtRBSC1 can be transformed into tobacco protoplasts, so that NtRBSC1 protein is subjected to sub-cellular localization by detecting the position of the fused protein through a laser confocal microscope; the position of chloroplast is displayed. Overall, the manner is a simple and accurate method for localizing in living cells and accurate reference evidence can be provided for research on the chloroplast of the tobacco cells and related genes; research on the tobacco NtRBSC1 gene and deep development of functions of the tobacco NtRBSC1 gene are convenient to realize.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Plants with improved photosynthetic carbon fixation capacity
InactiveUS20190376077A1Improving the assimilation of carbon in a plantIncrease probabilityHydrolasesClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyMetabolic enzymes
Owner:BASF SE
Radioactive Diagnostic Imaging Agent
InactiveUS20080193379A1Low puritySugar derivativesRadioactive preparation carriersTagatoseImaging agent
It is intended to provide a radioactive diagnostic imaging agent comprising a radioactive halogen-labeled compound as an active ingredient, in which the active ingredient is prevented from radiolysis and its stability is improved. This is achieved by adding a biologically-acceptable sugar or sugar alcohol to the radioactive diagnostic imaging agent in an amount effective to prevent radiolysis. The amount of the sugar or sugar alcohol to be added is preferably 10 (mmol / L) / GBq / mL or more, and more preferably 50 (mmol / L) / GBq / mL or more. The sugar is preferably selected from the group consisting of erythrose, threose, ribose, arabinose, xylose, lyxose, allose, altrose, glucose, mannose, gulose, idose, galactose, talose, erythrulose, ribulose, xylulose, psicose, fructose, sorbose, and tagatose. The sugar alcohol is preferably selected from the group consisting of erythritol, xylitol, sorbitol, and mannitol.
Owner:NIHON MEDI PHYSICS CO LTD
Productivity and Bioproduct Formation in Phototropin Knock/Out Mutants in Microalgae
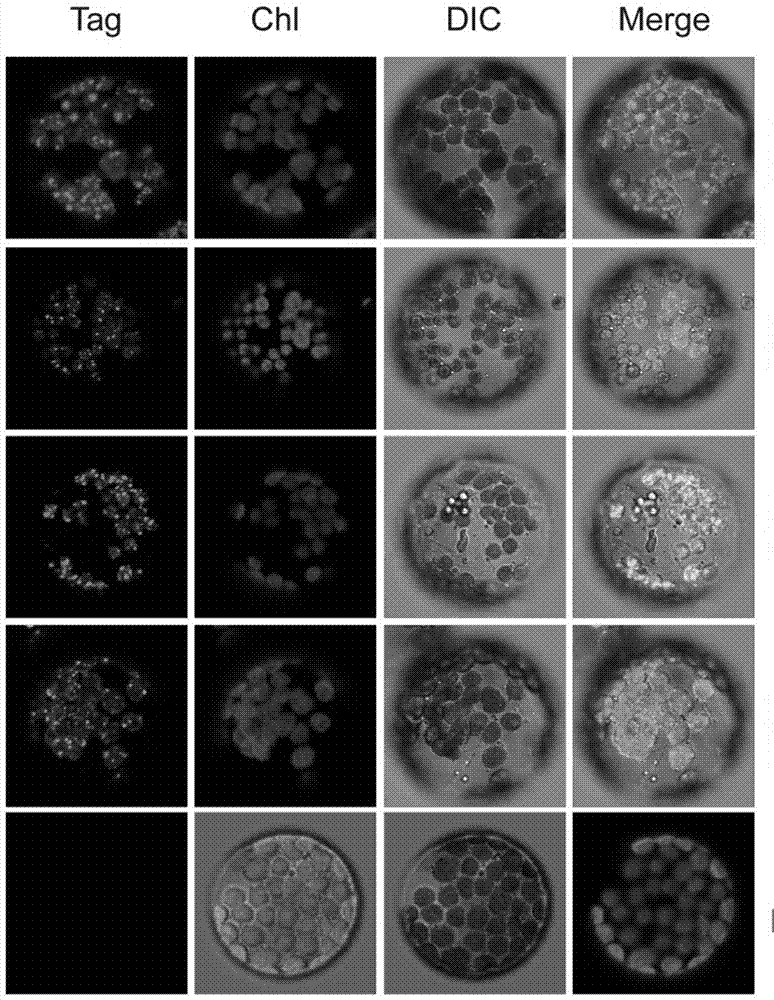
ActiveUS20180187170A1Reduced PHOT expressionHigh genetic stabilityHydrolasesUnicellular algaeElectron micrographsChlamydomonas reinhardtii
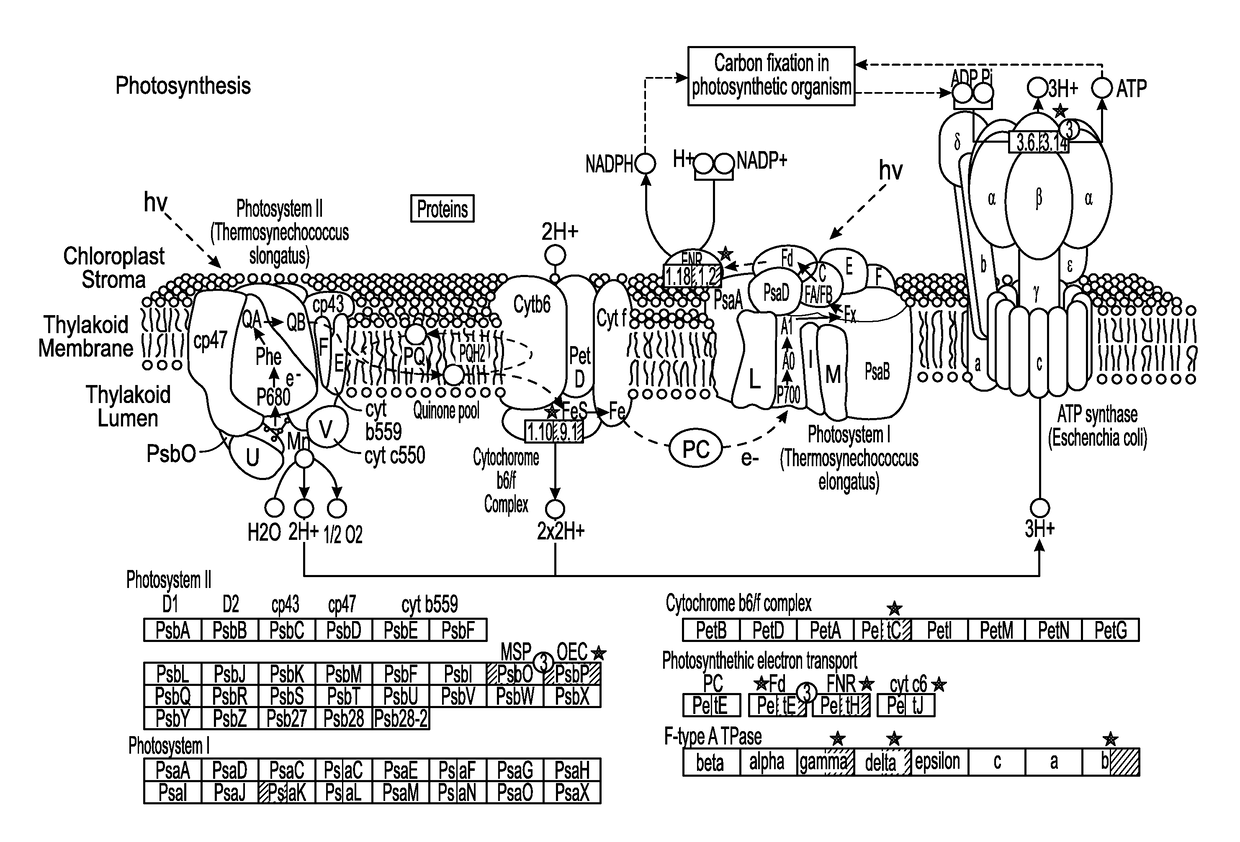
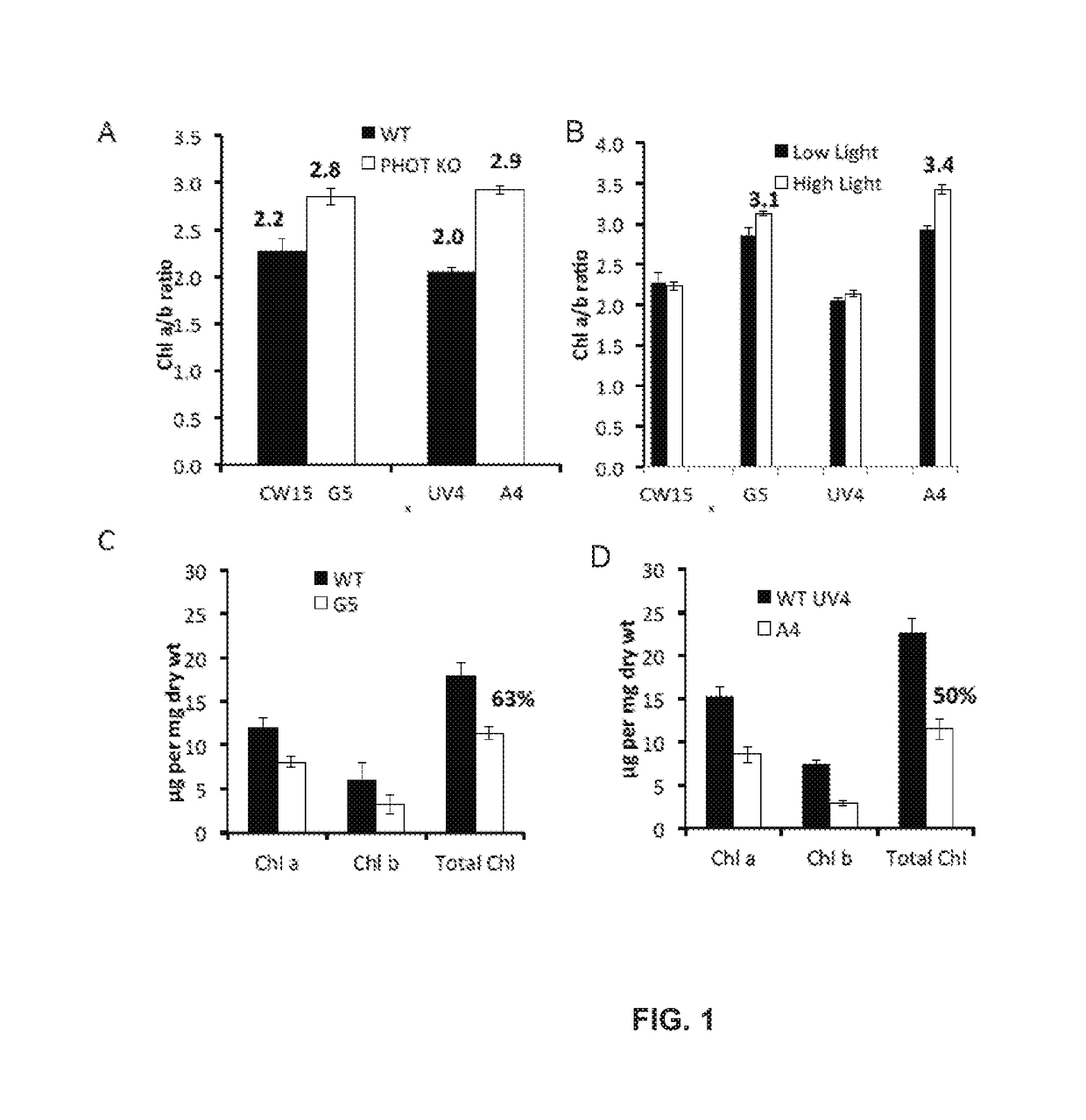
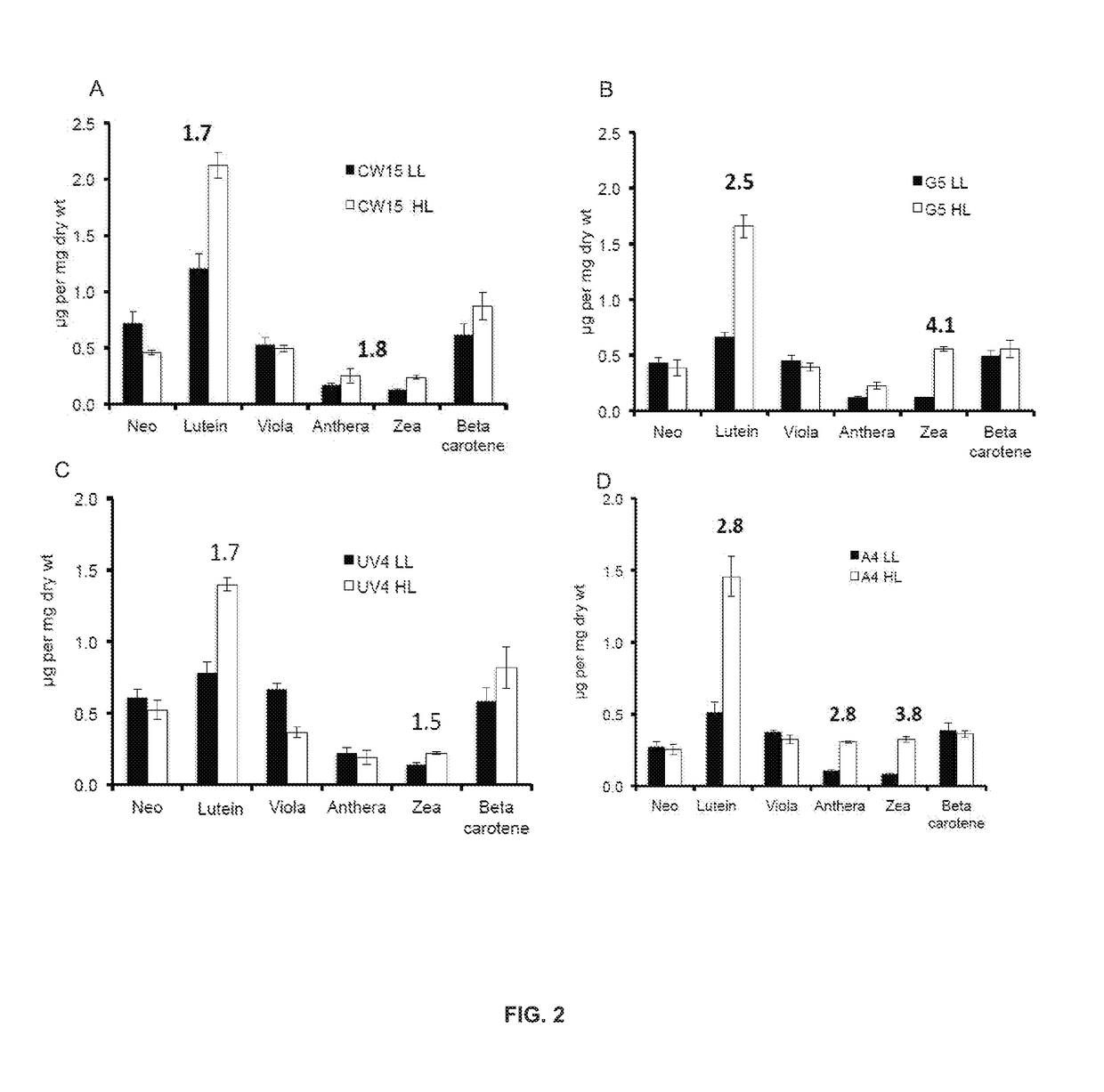
Phototropin is a blue light receptor, which mediates a variety of blue-light elicited physiological processes in plants and algae. In higher plants these processes include phototropism, chloroplast movement and stomatal opening. In the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, phototropin plays a vital role in progression of the sexual life cycle and in the control of the eye spot size and light sensitivity Phototropin is also involved in blue-light mediated changes in the synthesis of chlorophylls, carotenoids, chlorophyll binding proteins. We compared the transcriptome of phototropin knock out (PHOT KO) mutant and wild-type parent to analyze differences in gene expression in high light grown cultures (500 μmol photons m−2 s−1). Our results indicate the up-regulation of genes involved in photosynthetic electron transport chain, carbon fixation pathway, starch, lipid, and cell cycle control genes. With respect to photosynthetic electron transport genes, genes encoding proteins of the cytochrome b6f and ATP synthase complex were up regulated potentially facilitating proton-coupled electron transfer. In addition genes involved in limiting steps in the Calvin cycle Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase / oxygenase (RuBisCO), Sidoheptulose 1,7 bisphosphatase (SBPase), Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (3PGDH) and that mediate cell-cycle control (CDK) were also up regulated along with starch synthase and fatty acid biosynthesis genes involved in starch and lipid synthesis. In addition, transmission electron micrographs show increased accumulation of starch granules in PHOT mutant compared to wild type, which is consistent with the higher expression of starch synthase genes. Collectively, the altered patterns of gene expression in the PHOT mutants were associated with a two-fold increase in growth and biomass accumulation compared to wild type when grown in environmental photobioreactors (Phenometrics) that simulate a pond environment. In conclusion, our studies suggest that phototropin may be a master gene regulator that suppresses rapid cell growth and promotes gametogenesis and sexual recombination in wild type strains.
Owner:NMC INC +1
Recombinant yeast cell
The present invention describes a recombinant yeast cell functionally expressing one or more heterologous nucleic acid sequences encoding for ribulose-1,5-phosphate carboxylase / oxygenase (EC4.1.1.39; Rubisco), and optionally one or more molecular chaperones for Rubisco, and one or more phosphoribulokinase (EC2.7.1.19; PRK), wherein one or more genes of the non-oxidative branch of the pentose phosphate pathway are overexpressed and / or wherein said yeast cell comprises a deletion or disruption of a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD) gene.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Method for quantitative determination of regeneration capability of 1,5-ribulose diphosphate
ActiveCN106092944AComparableStable and reliable share of glycolytic pathwayColor/spectral properties measurementsNon destructiveQuantitative determination
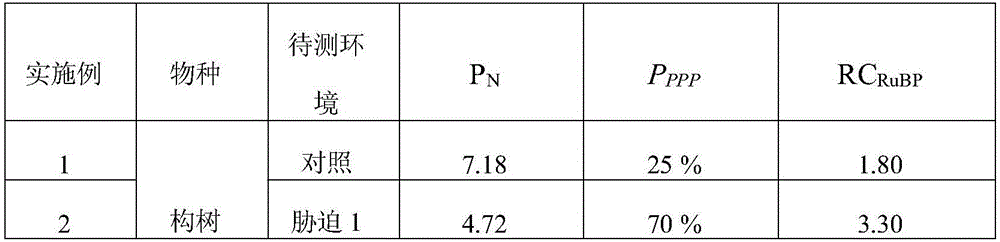
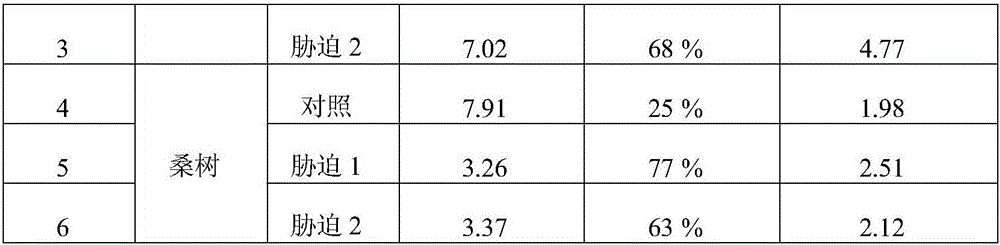
The invention discloses a method for quantitative determination of regeneration capability of 1,5-ribulose diphosphate. The method comprises the following steps: selecting the second, the third and the fourth completely spread leaves, performing non-destructive determination on apparent photosynthesis rate, taking a mean value of three leaves to represent the apparent photosynthesis rate PN of the plant; then taking the leave which has measured apparent photosynthesis rate, shearing the leave and fully mixing the leave, taking 0.1 g of the material for enzyme liquid extraction; respectively determining the phosphofructokinase vitality and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme vitality expressed by the change value at unit volume and unit time in the extracted enzyme liquid, calculating phosphopentose pathway proportion in the glycometabolism according to a formula, and then multiplying by the apparent photosynthesis rate of the plant leave to obtain the regeneration capability of 1,5-ribulose diphosphate. The method can realize rapid quantitative determination of the regeneration capability of 1,5-ribulose diphosphate, and has the advantages of less step, simple calculation, and comparability and reliability of the determination result.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Modified yeast consuming L-arabinose
The present invention relates to a method for producing a L-arabinose utilizing yeast strain for the production of ethanol, whereby a yeast strain is modified by introducing and expressing araA gene (L-arabinose isomerase), araB gene (L-ribulokinase D121-N) and araD gene (L-ribulose-5-P 4-epimerase) and carrying additional mutations in its genome or overexpressing a TALl (transaldolase) gene, enabling it to consume L-arabinose, to use it as the only carbon source, and to produce ethanol, as well as a method for producing ethanol using such a modified strain.
Owner:SCANDINAVIAN TECH GRP AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com