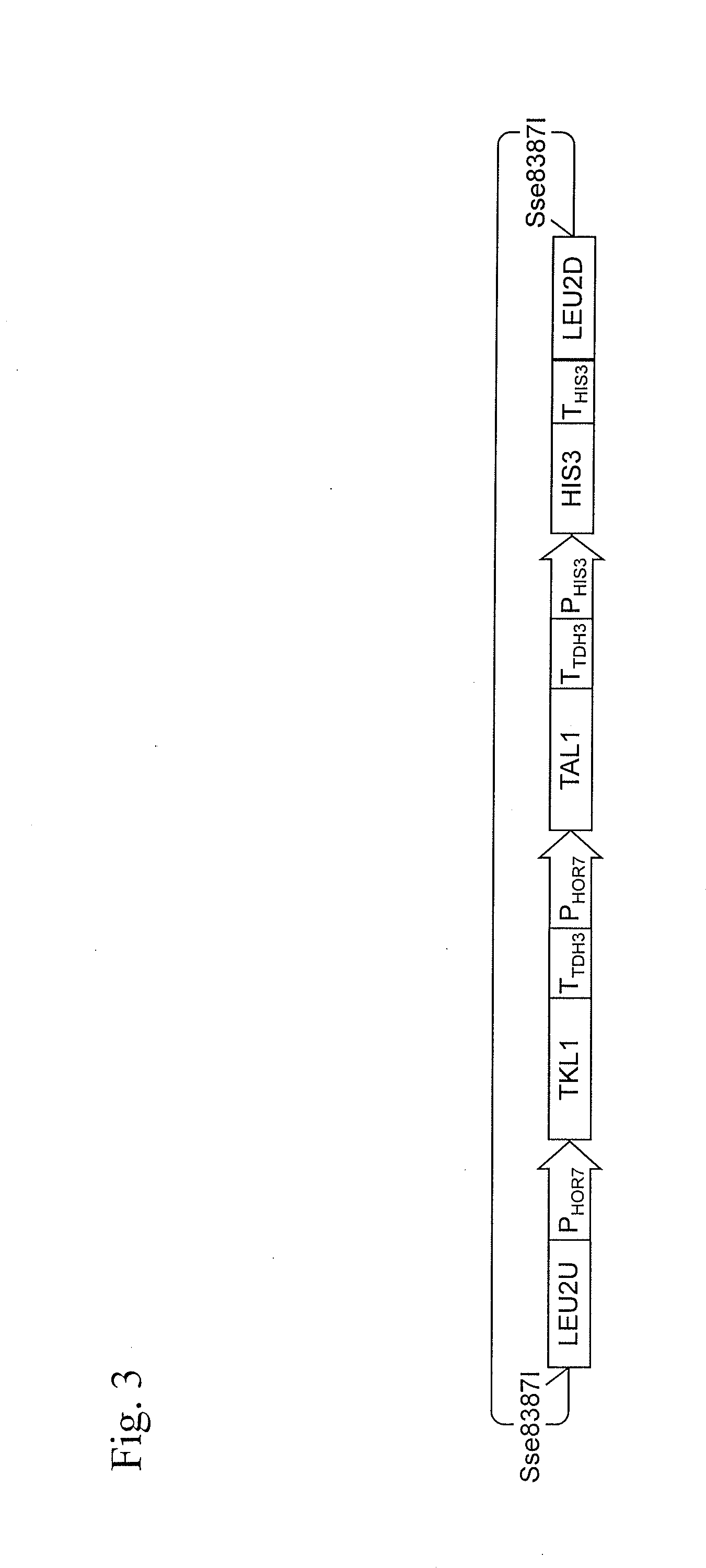
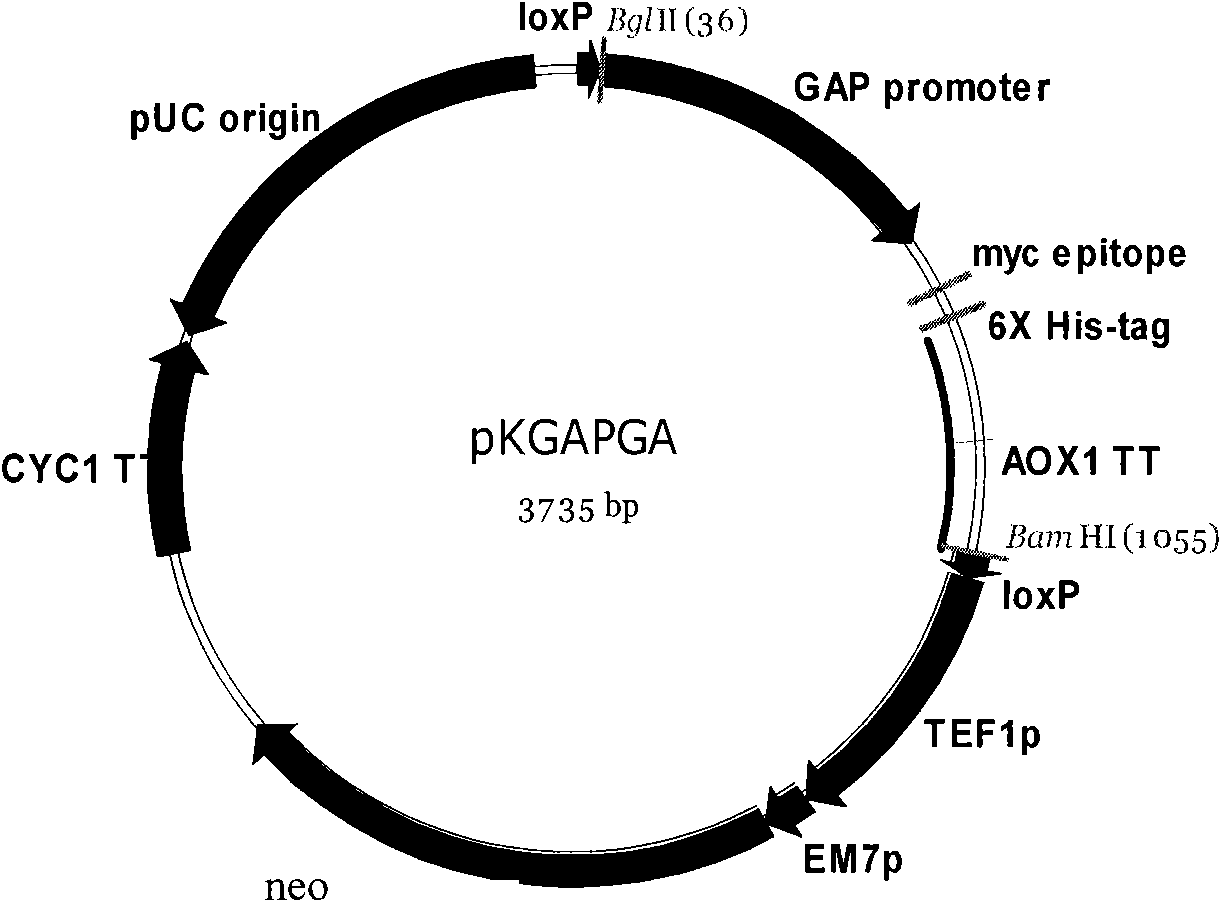
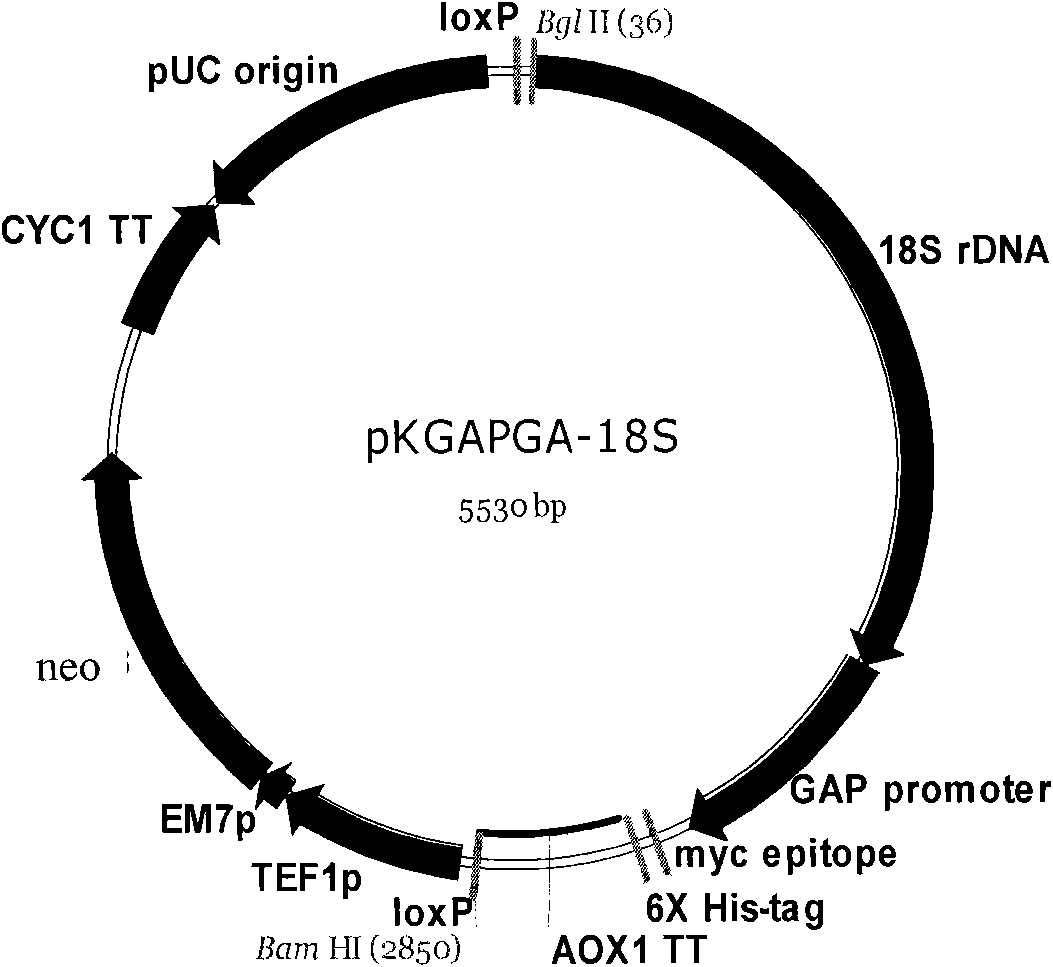
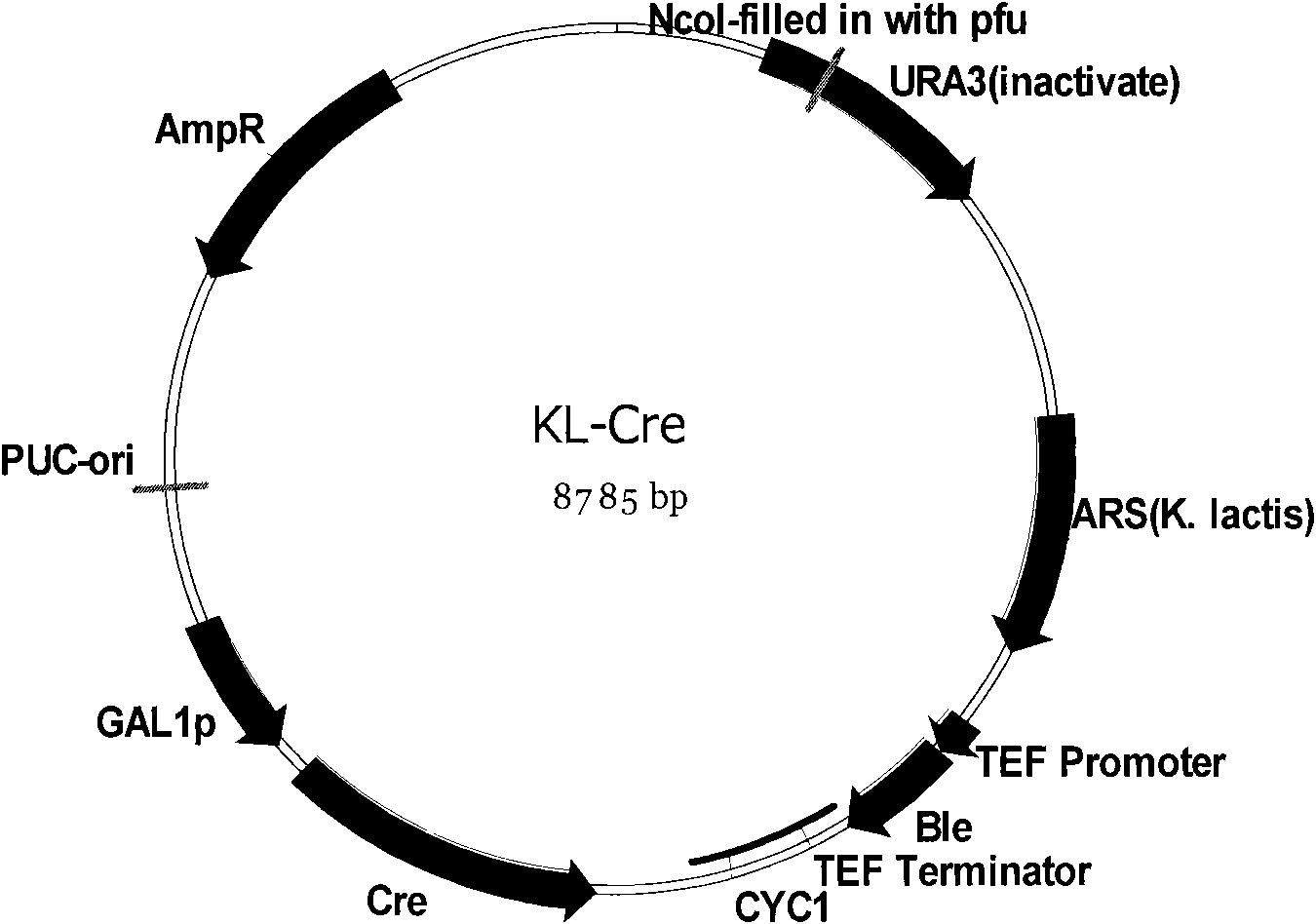
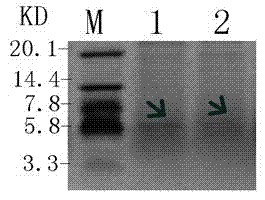
Patents
Literature
127 results about "Recombinant zymomonas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
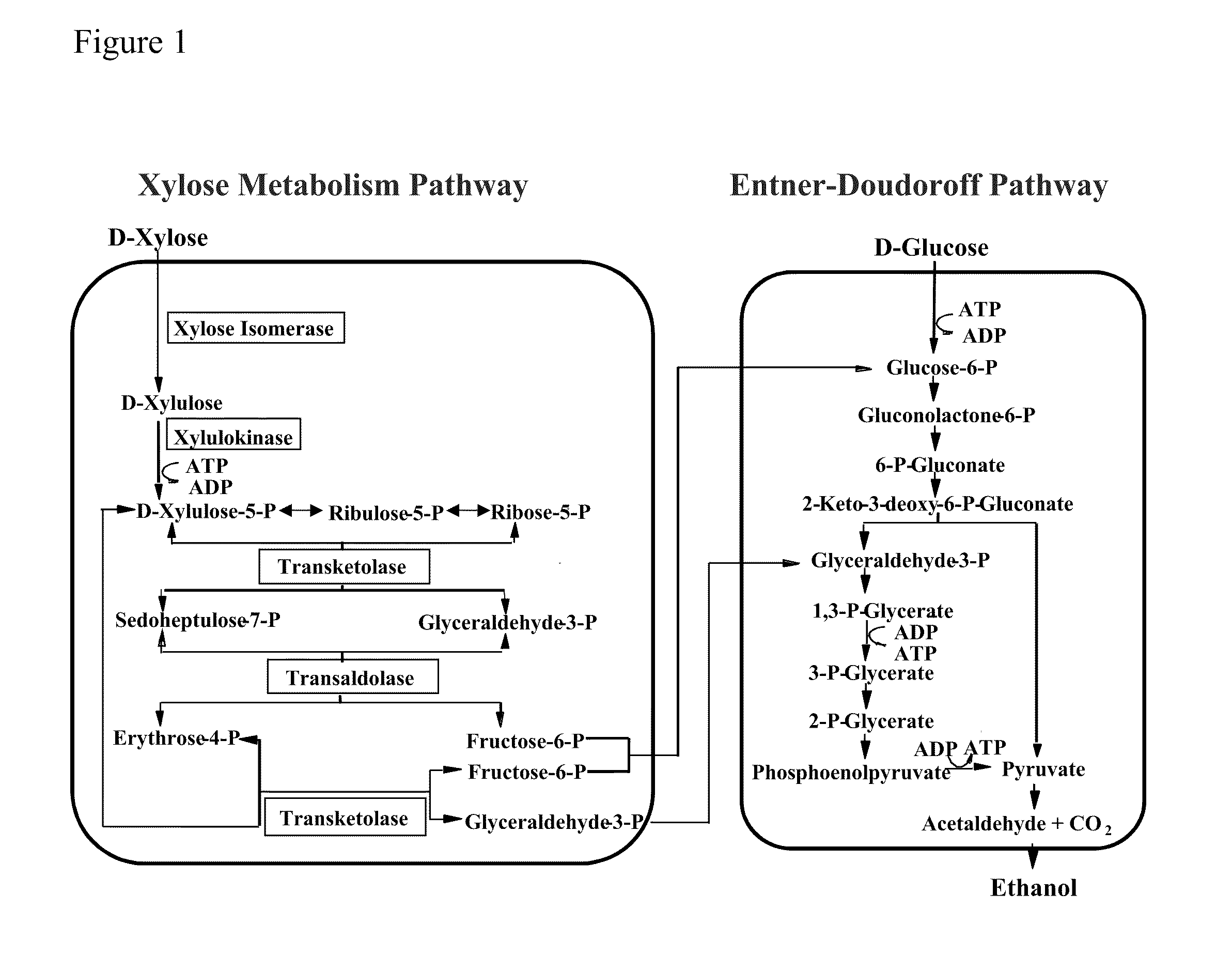
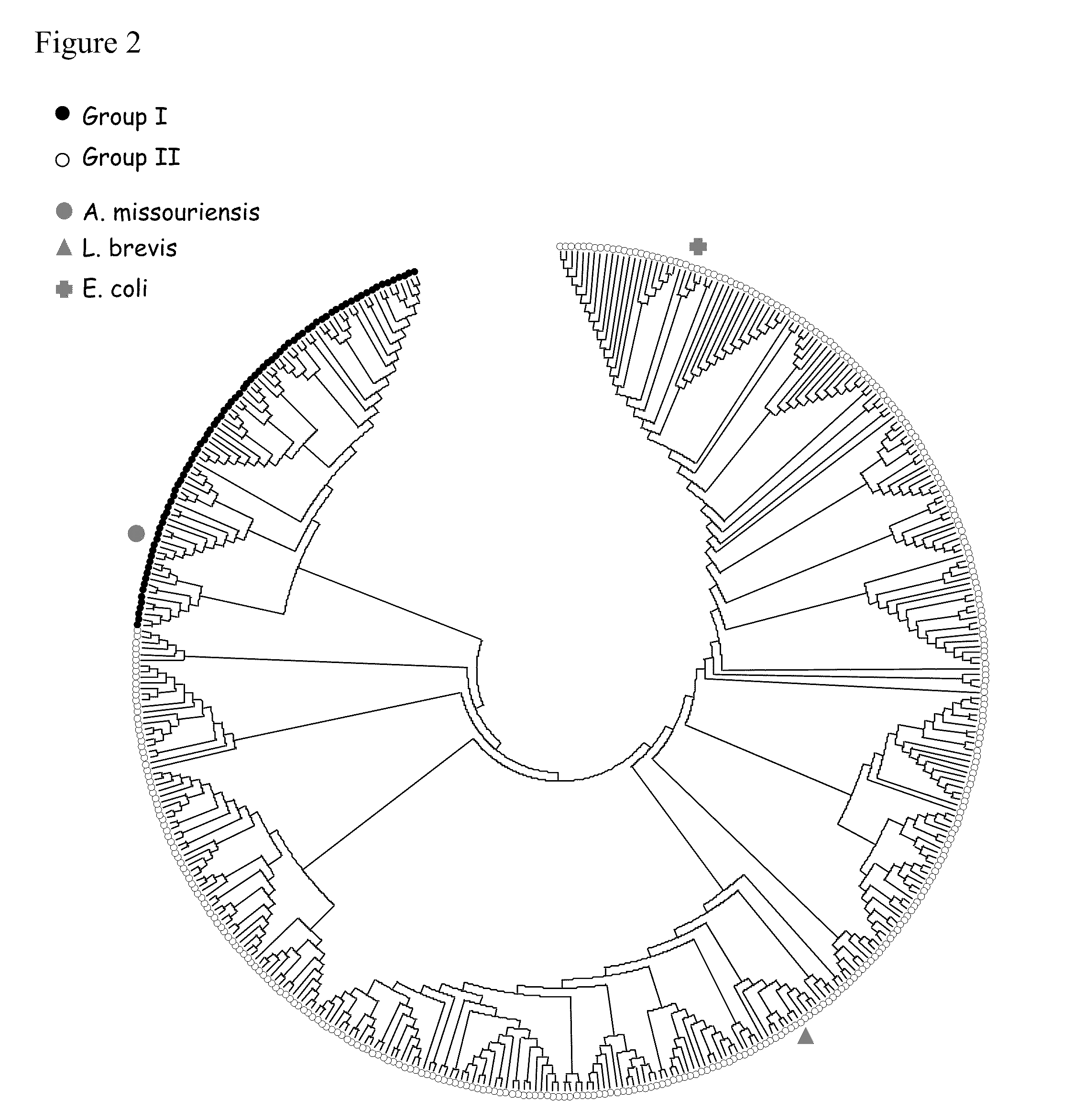
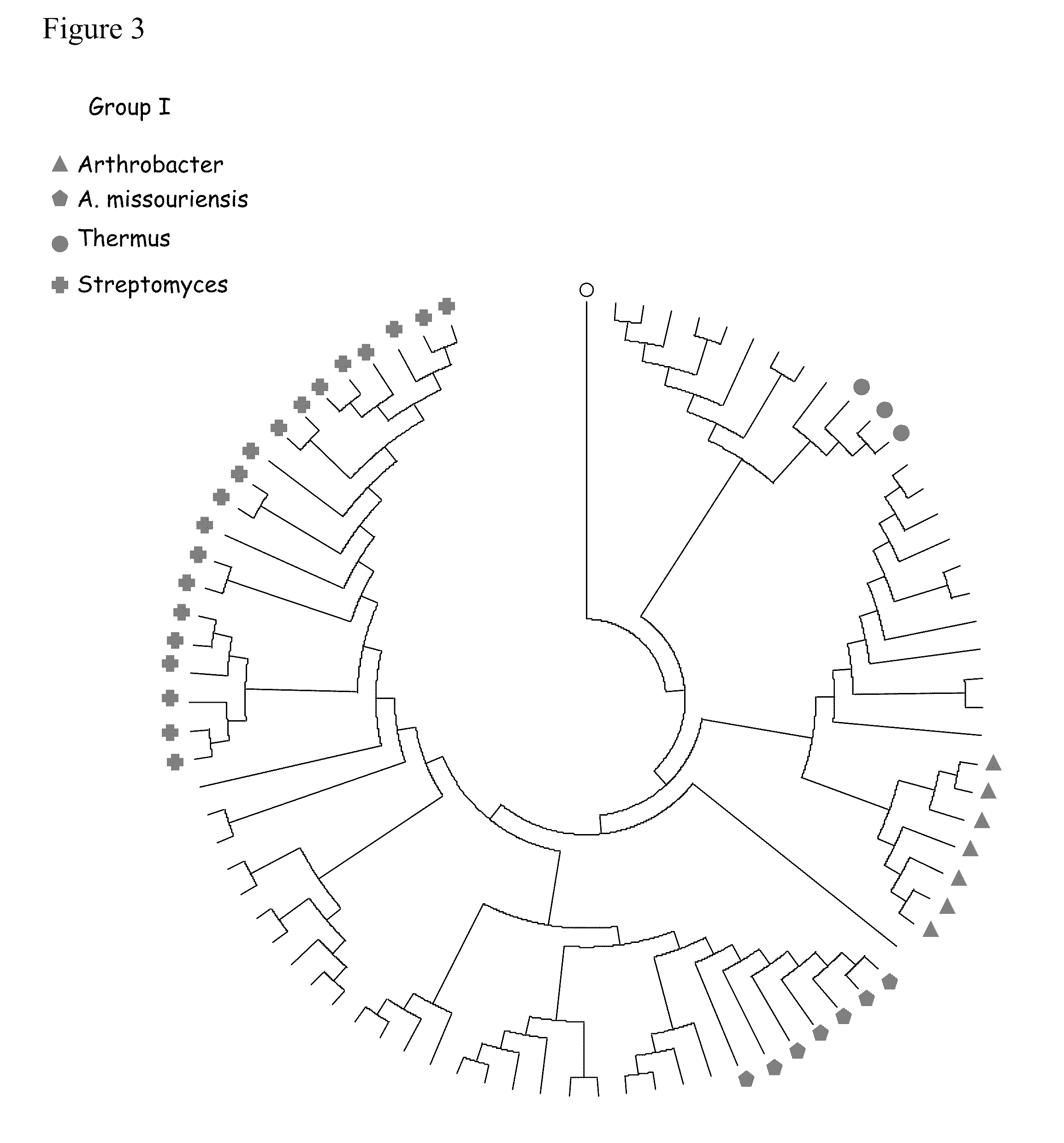
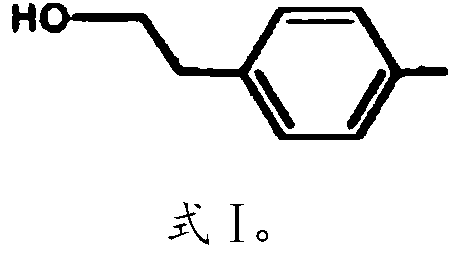
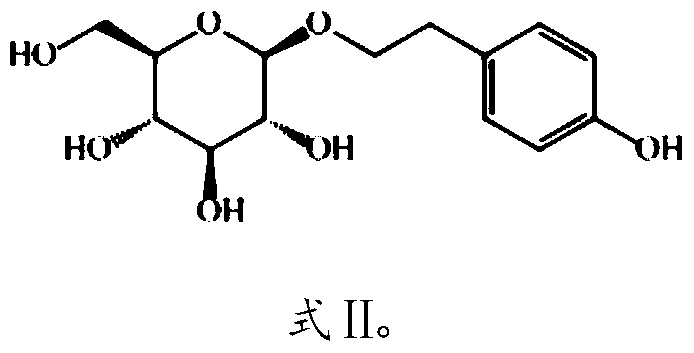
Xylose utilization in recombinant zymomonas
ActiveUS20110318801A1Increase productionImprove utilizationBacteriaBiofuelsHide markov modelMolecular phylogenetics
Zymomonas expressing xylose isomerase from A. missouriensis was found to have improved xylose utilization, growth, and ethanol production when grown in media containing xylose. Xylose isomerases related to that of A. missouriensis were identified structurally through molecular phylogenetic and Profile Hidden Markov Model analyses, providing xylose isomerases that may be used to improve xylose utilization.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP
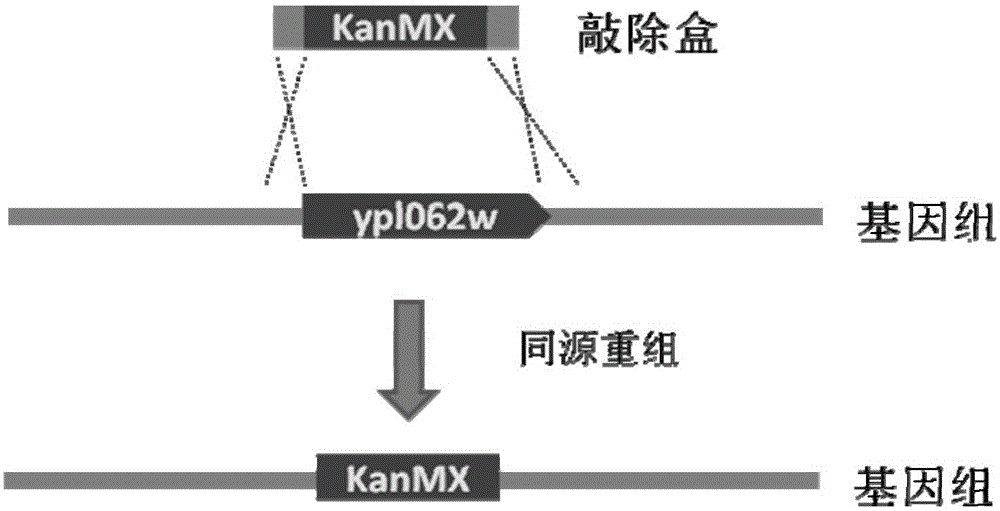
Recombinant yeast strain as well as construction method and application thereof
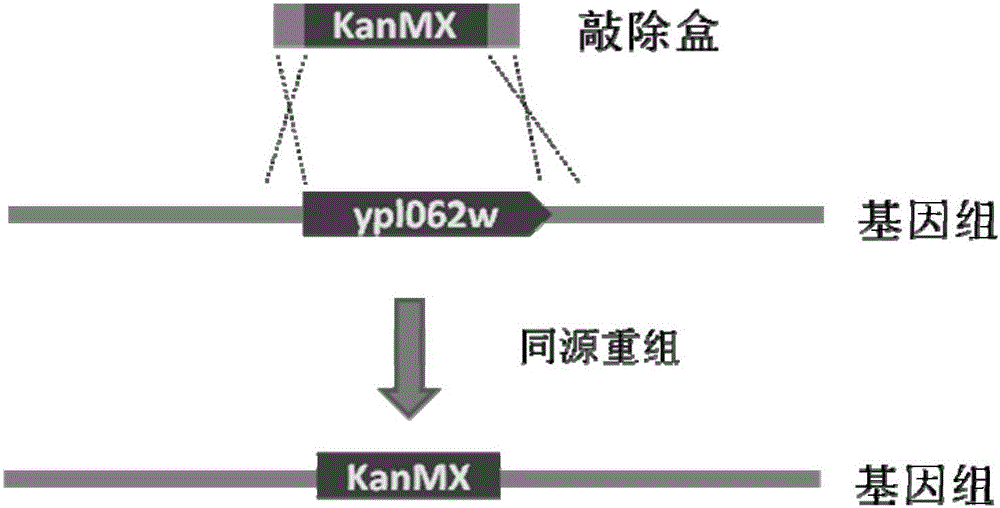
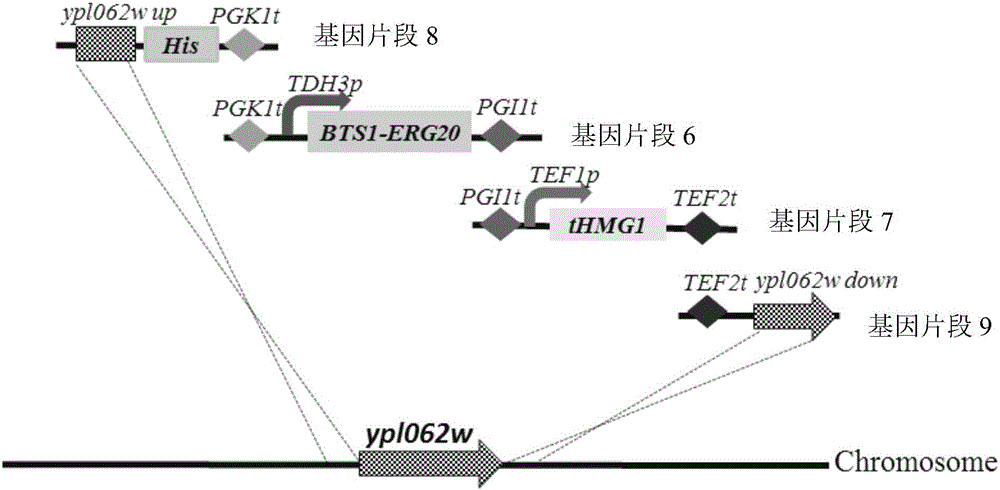
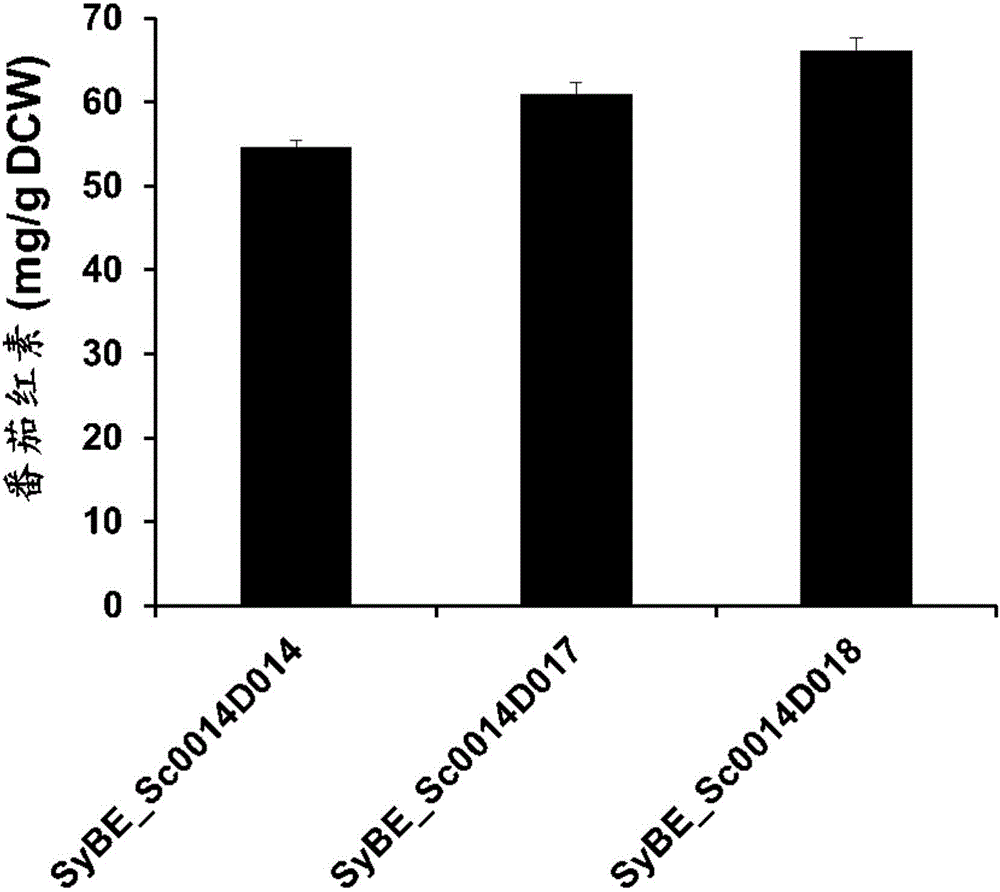
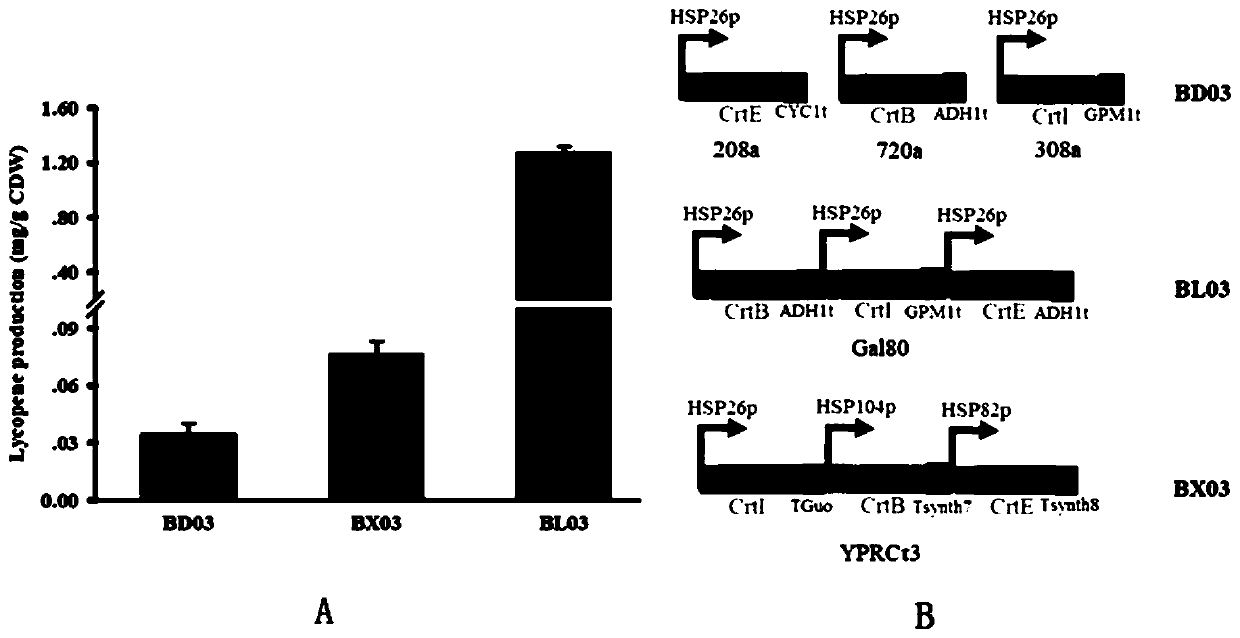
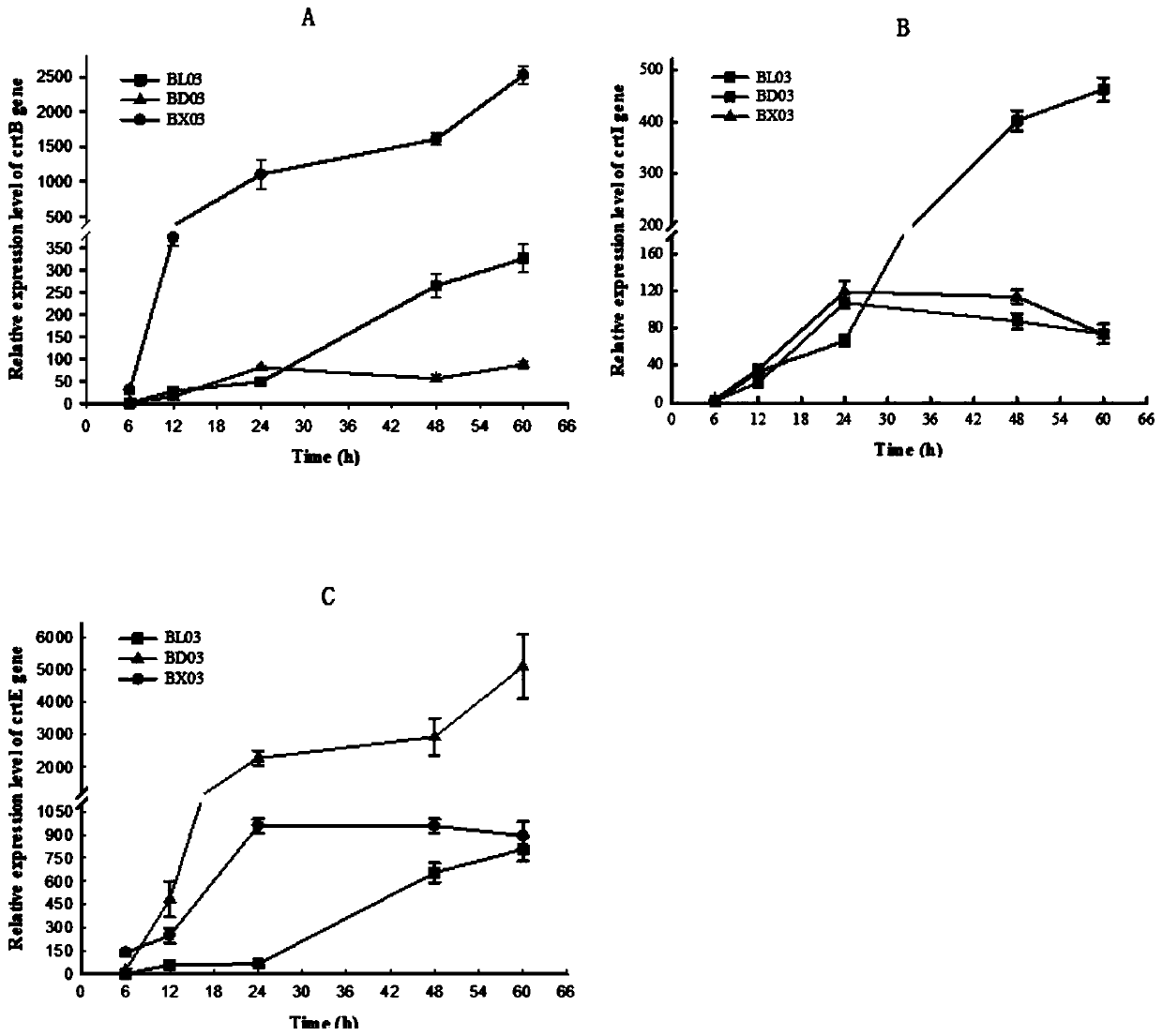
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering, and discloses a recombinant yeast strain as well as a construction method and an application thereof. The recombinant yeast strain has the knockout gene gal1, gal7, gal10 or gal80, and the knockout gene ypl062w, and contains 2-4 gene segments integrated to the genome through the yeast homologous recombination. According to the invention, the yeast strain with the knockout genes is established, an optimized host cell is provided for producing lycopene, and functional genes crtE, crtB and crt I with different sources for synthetizing lycopene, and the specific yeast endogenous genes are selected, and integrated to the genome of the yeast strain with the knockout gene through the modular design, and thus a brand-new recombinant strain with high yield of lycopene is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Recombinant yeast strain, and construction method and application thereof
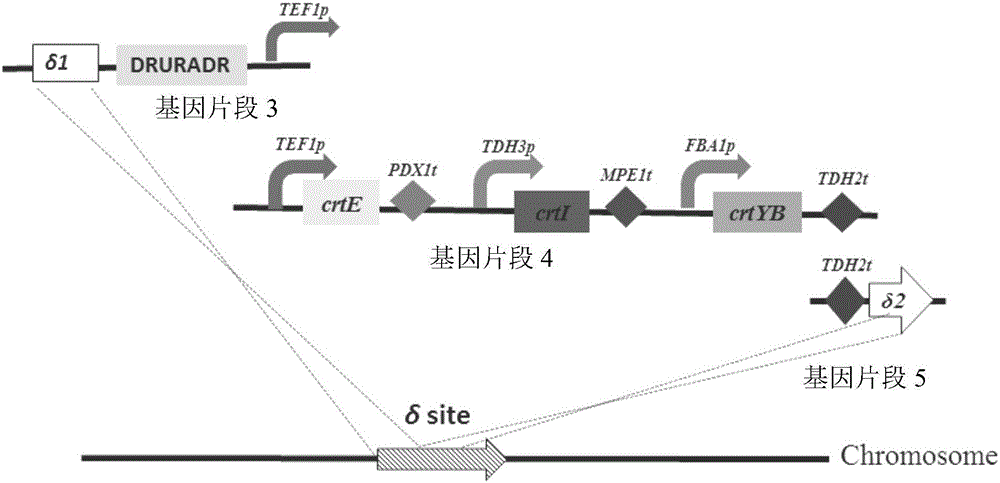
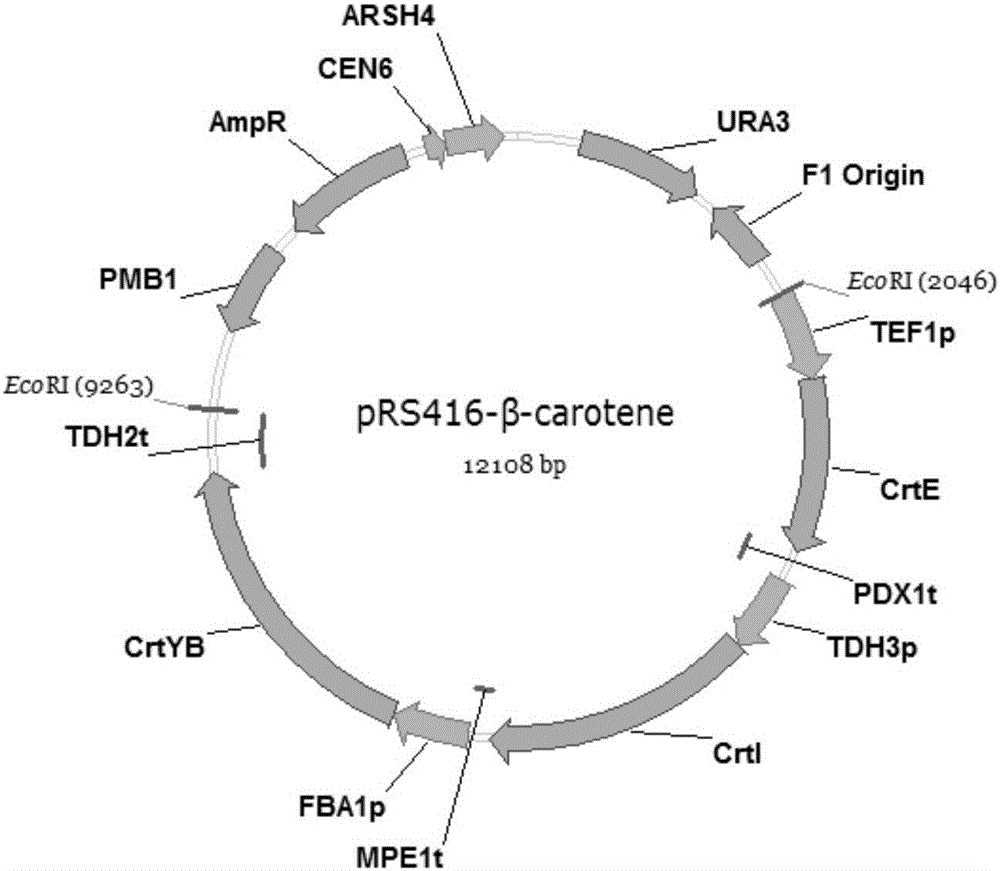
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and discloses a recombinant yeast strain, and a construction method and application thereof. In the recombinant yeast strain, gal1, gal7, gal10 and ypl062w genes are knocked out, and the recombinant yeast strain comprises 9 gene segments which are integrated to the genome by yeast homologous recombination. The construction method comprises the following steps: constructing a four-knock-out yeast strain to provide an optimized host cell for producing beta-carotin, selecting lycopene cyclases crtY from different sources, and carrying out modular design to integrate functional genes crtE crtB and crtI of the specific-source synthetic lycopene, specific yeast endogenous genes and the like to the four-knock-out yeast strain genome, thereby obtaining a brand-new recombinant strain capable of producing beta-carotin at high yield.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Recombinant yeast strain, and construction method and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and discloses a recombinant yeast strain, and a construction method and an application thereof. The recombinant yeast strain is obtained through the following steps: knocking out gal1, gal7, gal10 and ypl062w genes, integrating three gene fragments a genome through yeast homologous recombination, further knocking out an rox1 gene, and further integrating two gene fragments to the yeast genome. The gene knockout yeast strain constructed in the invention provides optimized host cells for production of lycopene; and combined functional genes crtE, crtB and crtI having specific sources and used for synthesizing the lycopene and specific yeast endogenous genes are selected and are integrated to the gene knockout strain genome through modular designing, so the brand new recombinant strain for highly yielding lycopene is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Recombinant yeast strain, and building method and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and discloses a recombinant yeast strain, and a building method and application thereof. The recombinant yeast strain includes two specific gene segments recombined and integrated onto a genome in a homologous way through yeast. By selecting the specific group for forming a promoter combination and matching phaffia rhodozyma sourced phytoene synthetase and lycopene cyclase dual-function enzyme gene CrtYB, GGPP synthase CrtE, phytoene desaturase CrtI and specific yeast endogenous gene and the like, the substances are integrated onto the yeast strain genome through modular design; the yp1062w gene is knocked away through homologous recombination; one strain of fire-new recombinant yeast without an inducing agent is obtained; the high yield of the beta-renieratene is ensured.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
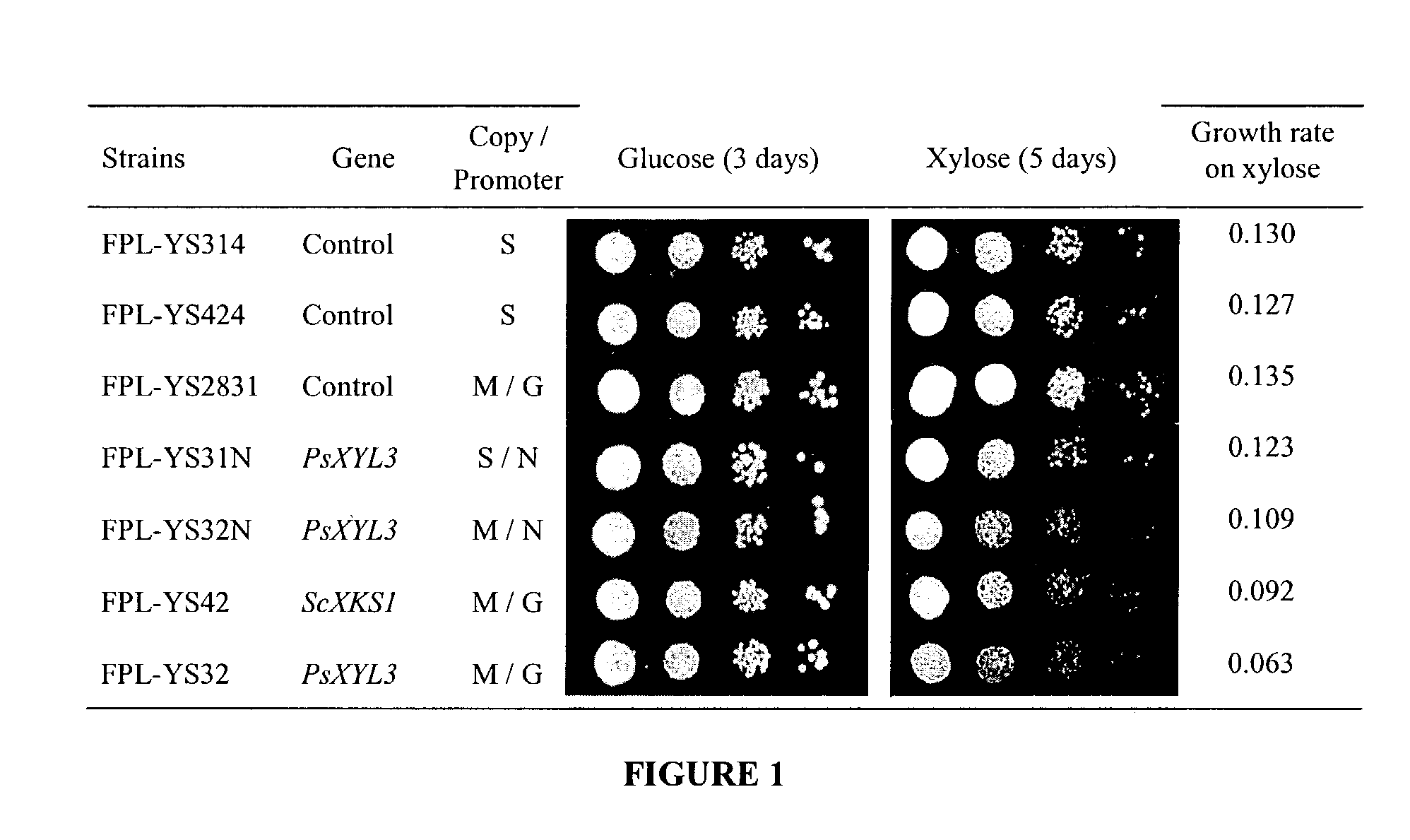
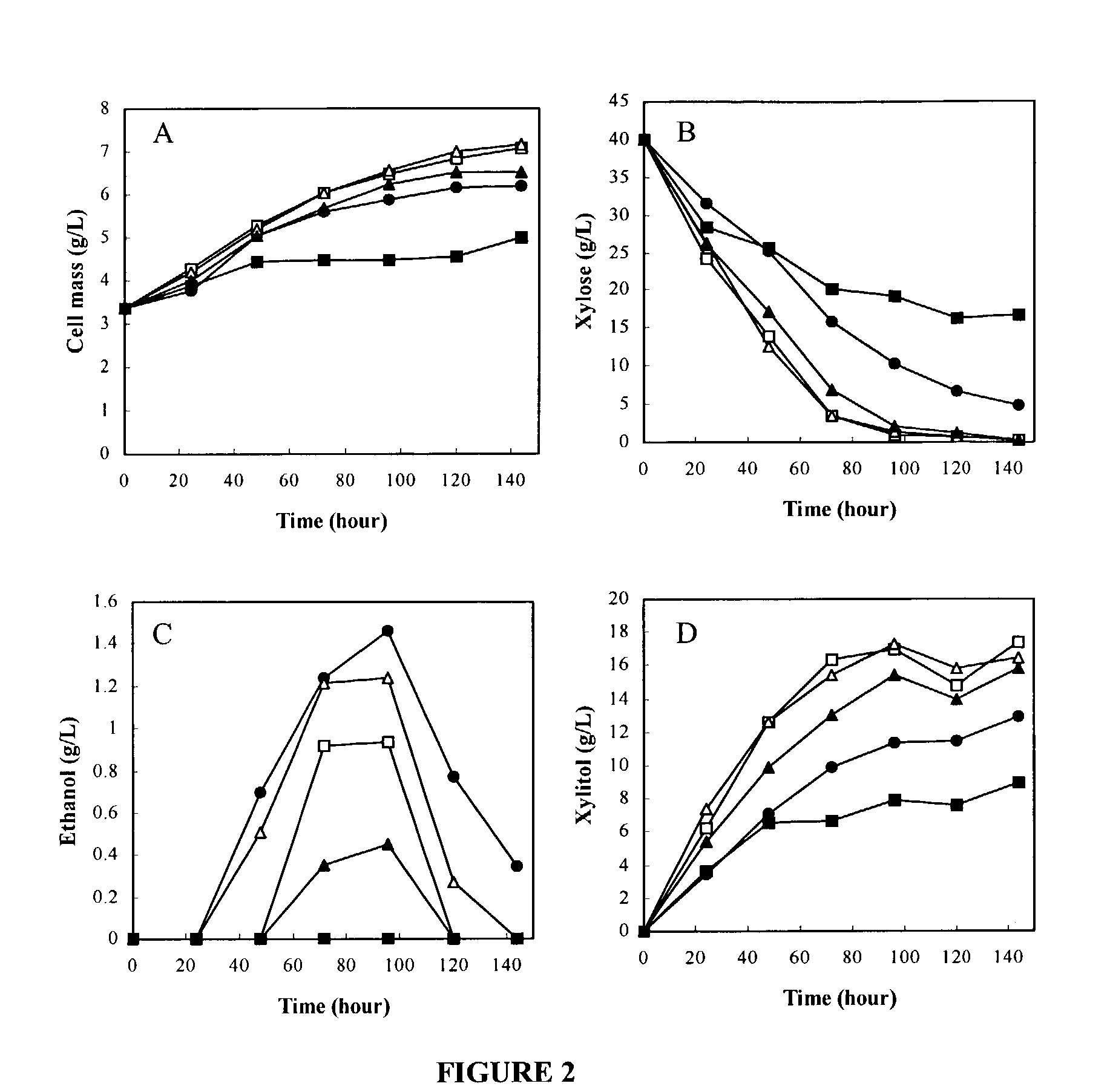
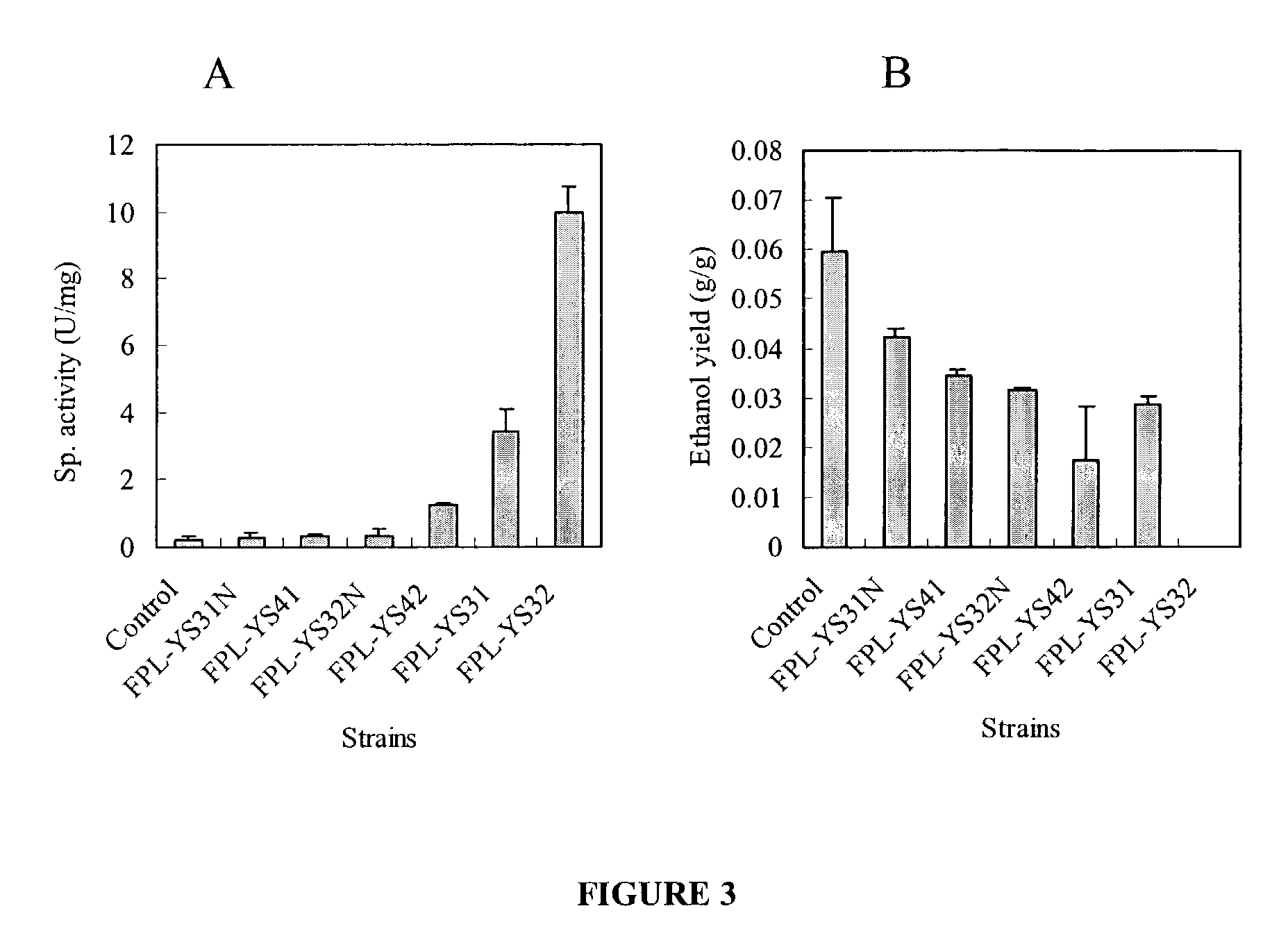
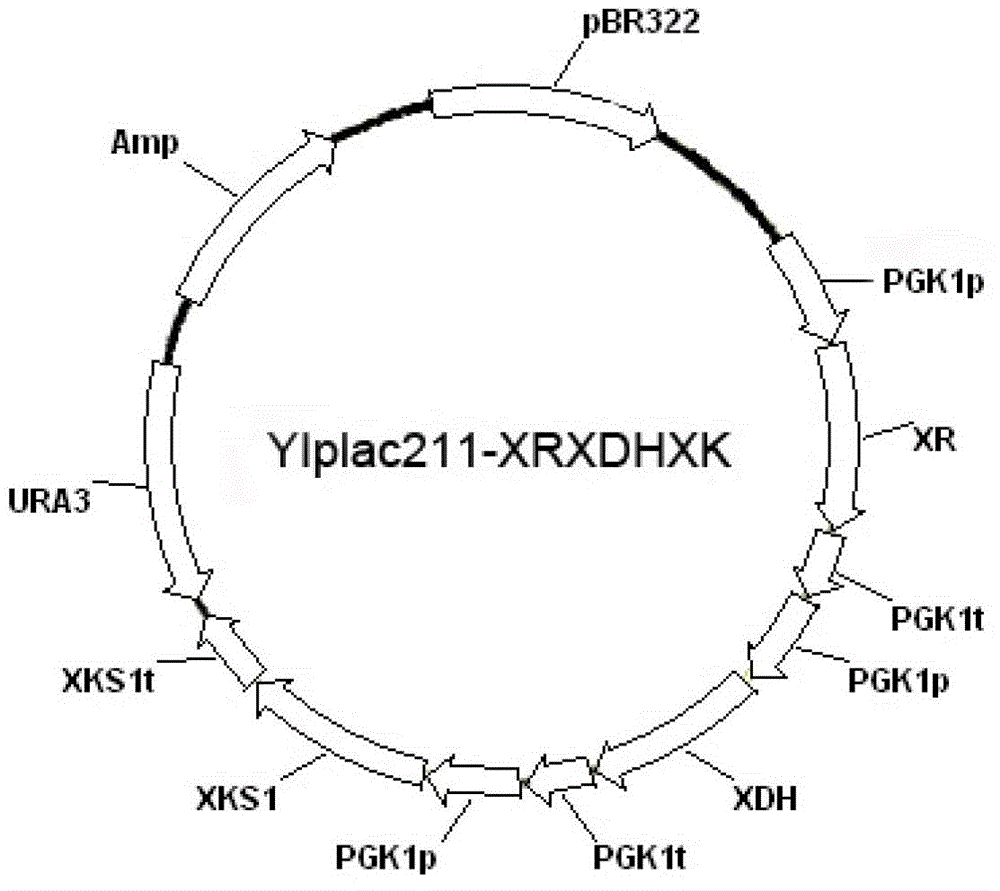
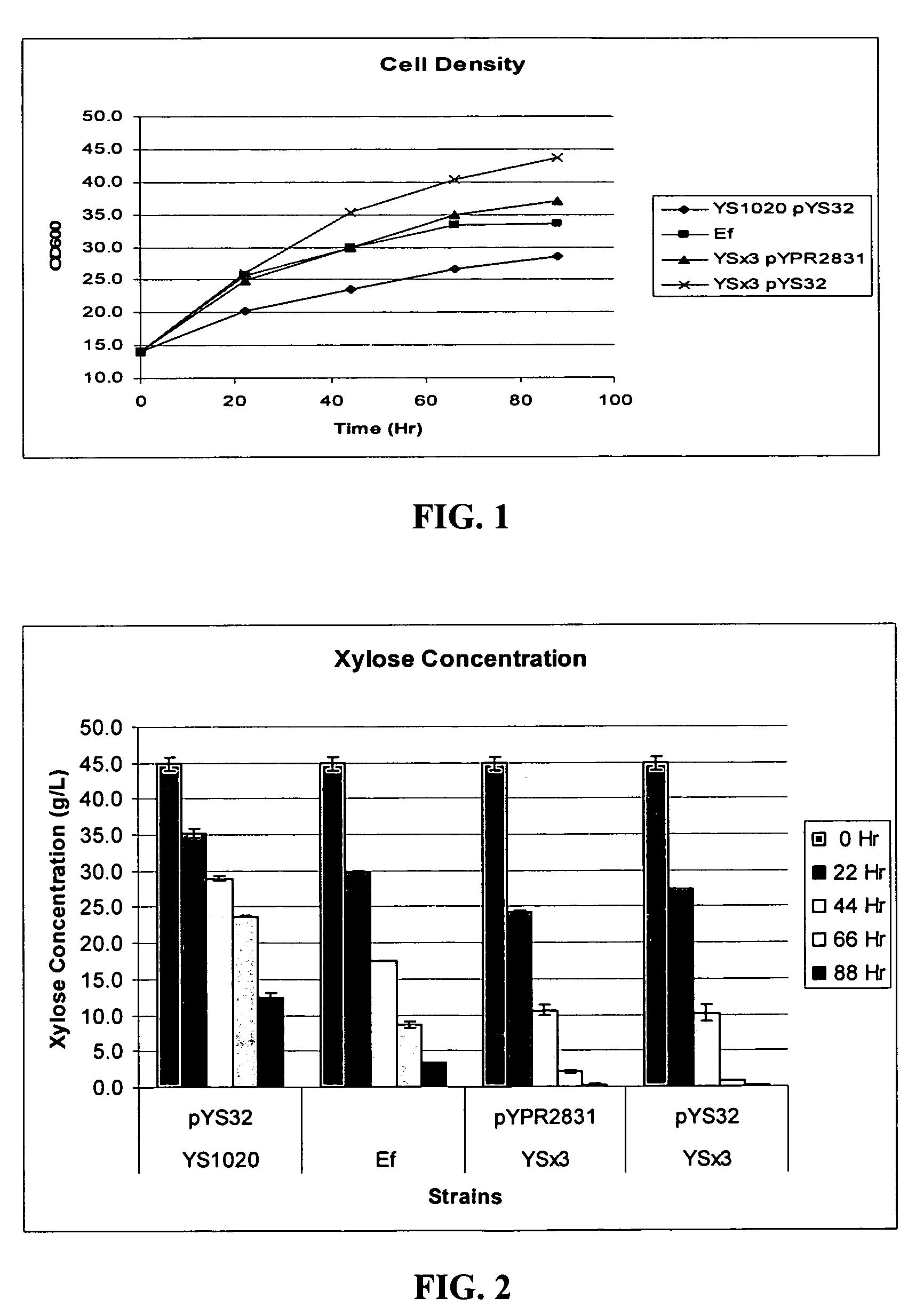
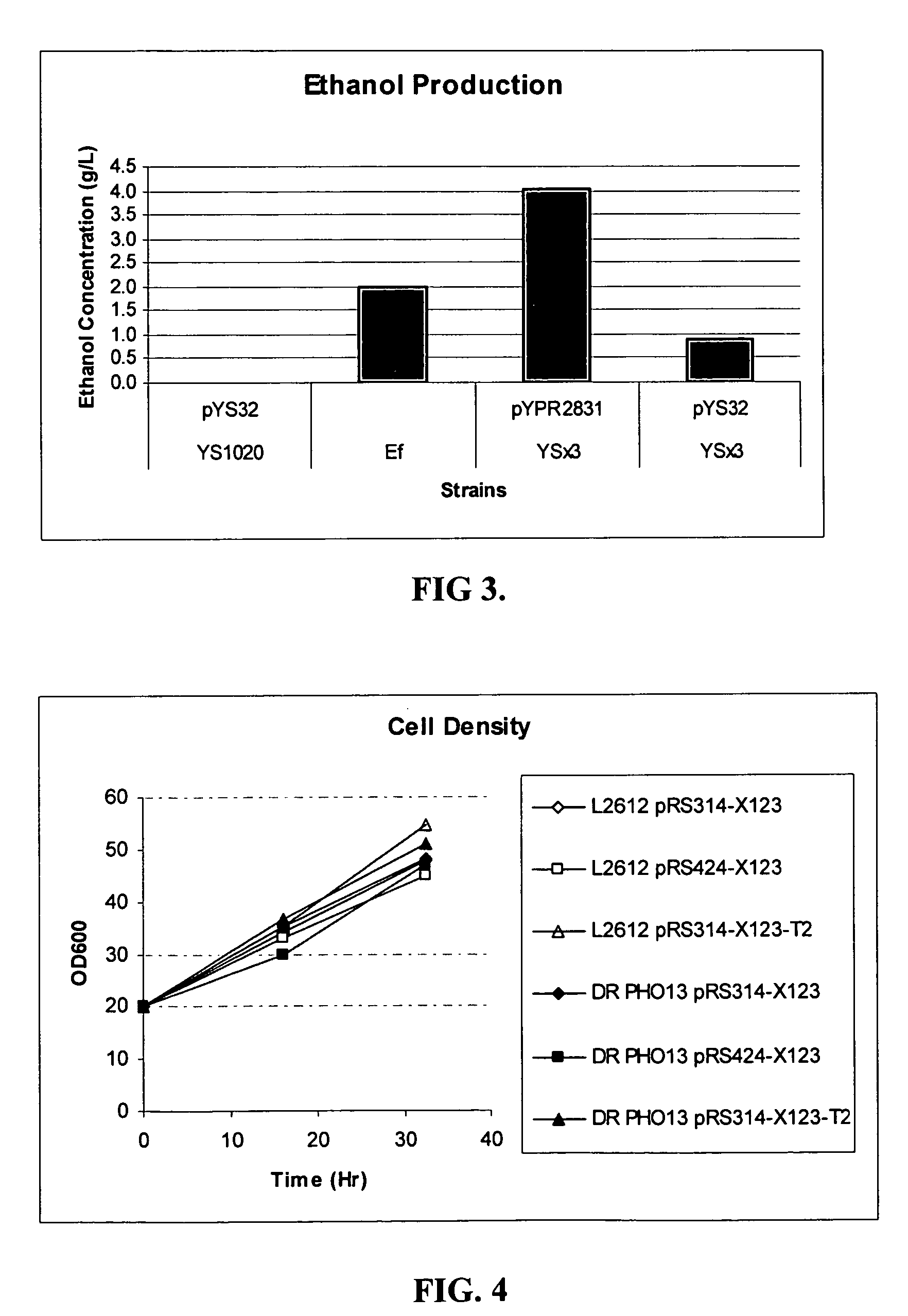
Xylose-fermenting recombinant yeast strains
Disclosed are xylose-fermenting recombinant yeast strains comprising heterologous PsXYL1, Ps XYL2, and PsXYL3, as well as methods of fermenting xylose to obtain ethanol using the recombinant yeast strain.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Recombinant yeast strain capable of efficiently metabolizing xylose and application thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant yeast strain (Saccharomyces cerevisiae)) capable of efficiently metabolizing xylose, which is named SyBE005. The recombinant yeast strain has been collected in Common Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, the collection number is CGMCC No.6634, and the recombinant yeast strain has the capacity of efficiently metabolizing xylose to produce ethanol. The recombinant yeast strain SyBE005 can effectively ferment xylose to generate ethanol. The ethanol yield reaches 64% of the theoretical yield, and the yield of the byproduct xylitol is lower than 12%; and thus, the recombinant yeast strain can efficiently convert xylose into ethanol, and is an excellent strain utilizing cellulose hydrolysate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
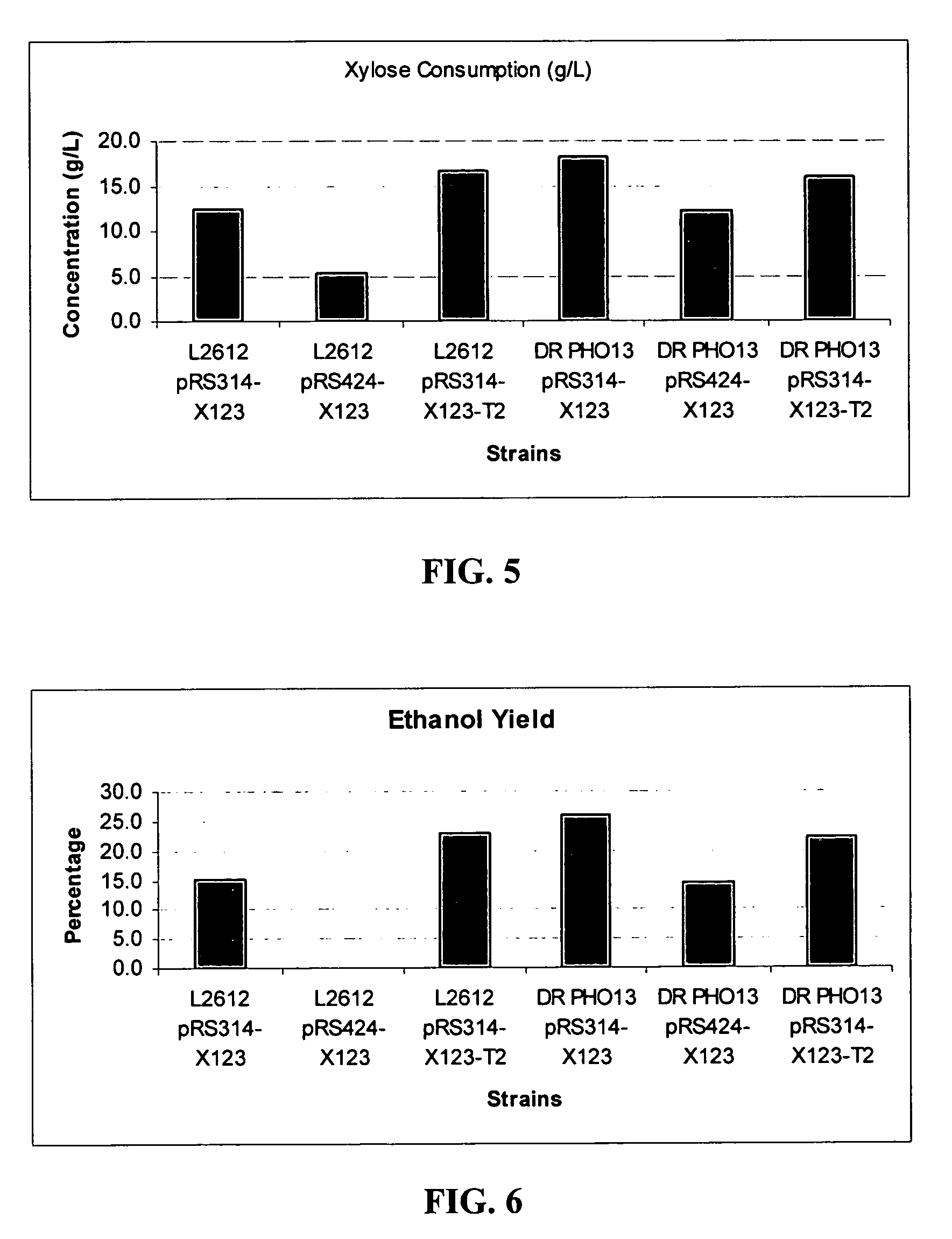
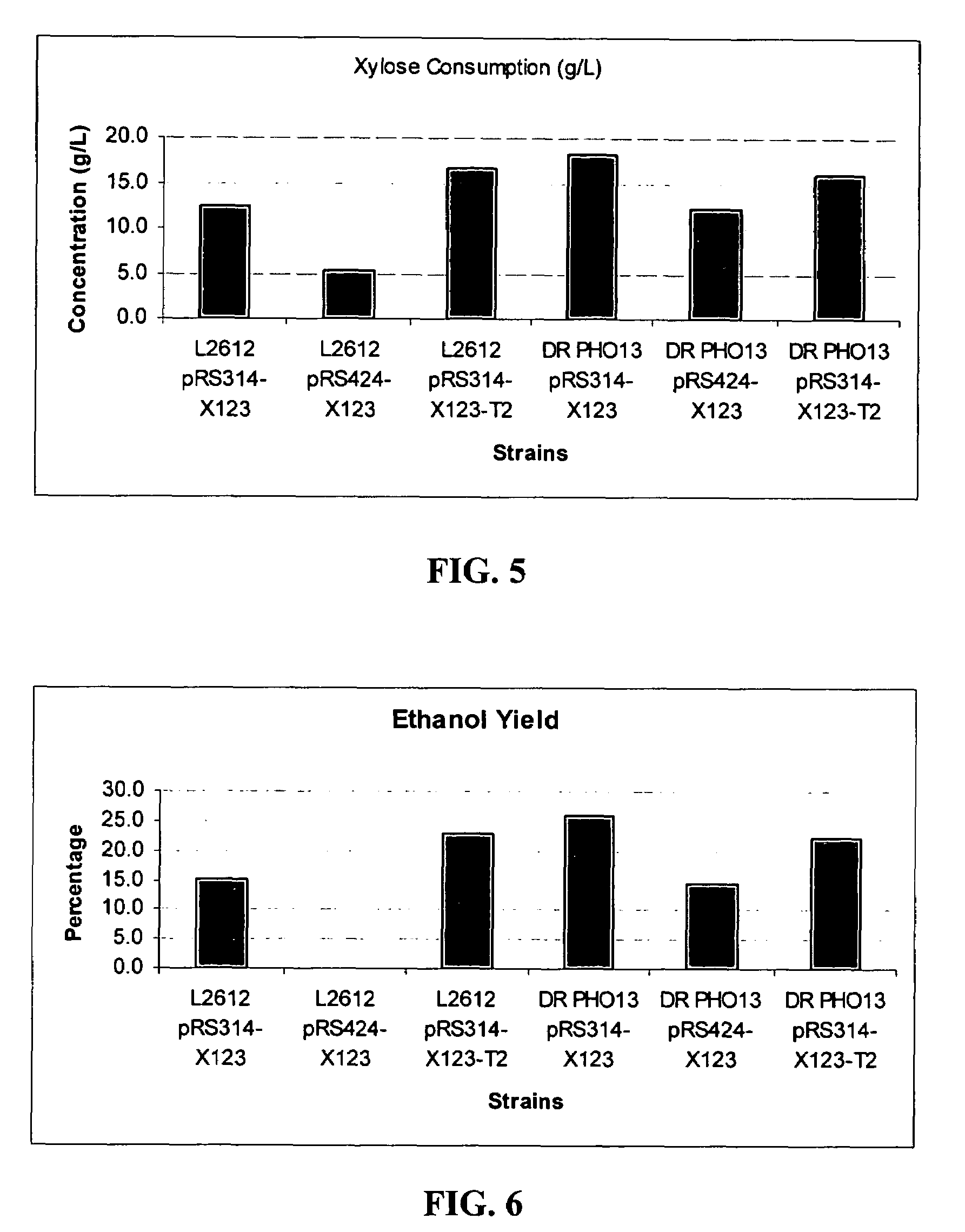
Xylose-fermenting recombinant yeast strains
Disclosed are xylose-fermenting recombinant yeast strains expressing xylose reductase, xylitol dehydrogenase, and xylulokinase and having reduced expression of PHO13 or a PHO13 ortholog, as well as methods of fermenting xylose to obtain ethanol using the recombinant yeast strains.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Xylose-fermenting recombinant yeast strains
Disclosed are xylose-fermenting recombinant yeast strains expressing xylose reductase, xylitol dehydrogenase, and xylulokinase and having reduced expression of PHO13 or a PHO13 ortholog, as well as methods of fermenting xylose to obtain ethanol using the recombinant yeast strains.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Recombinant yeast strain, construction method and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and discloses a recombinant yeast strain, a construction method thereof and the application thereof. In the recombinant yeast strain, gal1, gal7, gal10 and ypl062w genes are knocked out, and the recombinant yeast strain comprises 6 gene segments which are integrated to the genome through yeast homologous recombination. On the above basis, the recombinant yeast strain is further integrated onto one gene segment of a yeast genome, so that a better recombinant yeast is obtained. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the yeast strain is constructed based on gene knock-out, and an optimized host cell for producing lycopene is provided. Meanwhile, functional genes crtE crtB and crtI of a specific source combination and used for the synthesis of lycopene, specific yeast endogenous genes and specific exogenous genes are selected. The above selected genes are integrated to the gene knock-out genome of the yeast strain, and then a brand-new recombinant strain capable of producing high-yield lycopene is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
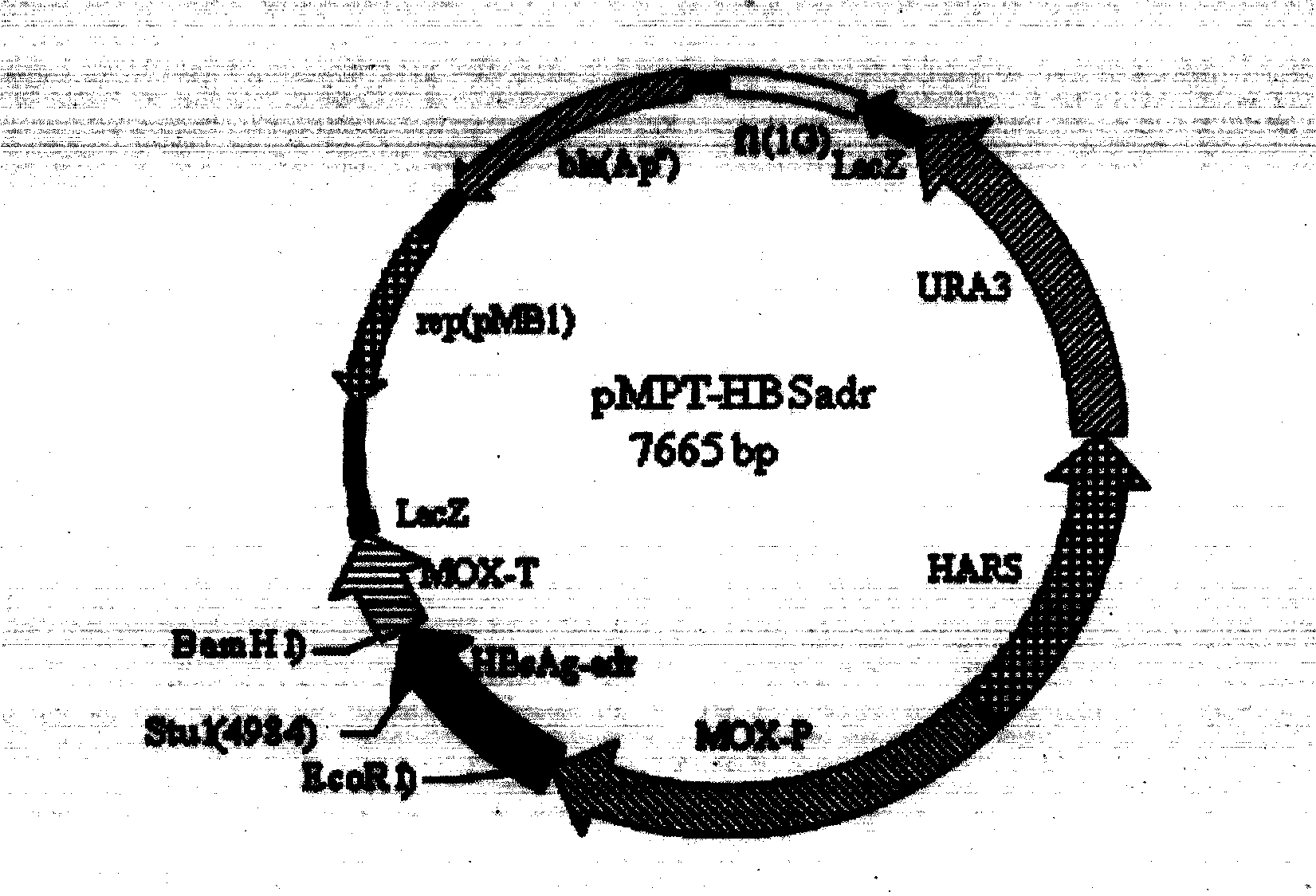
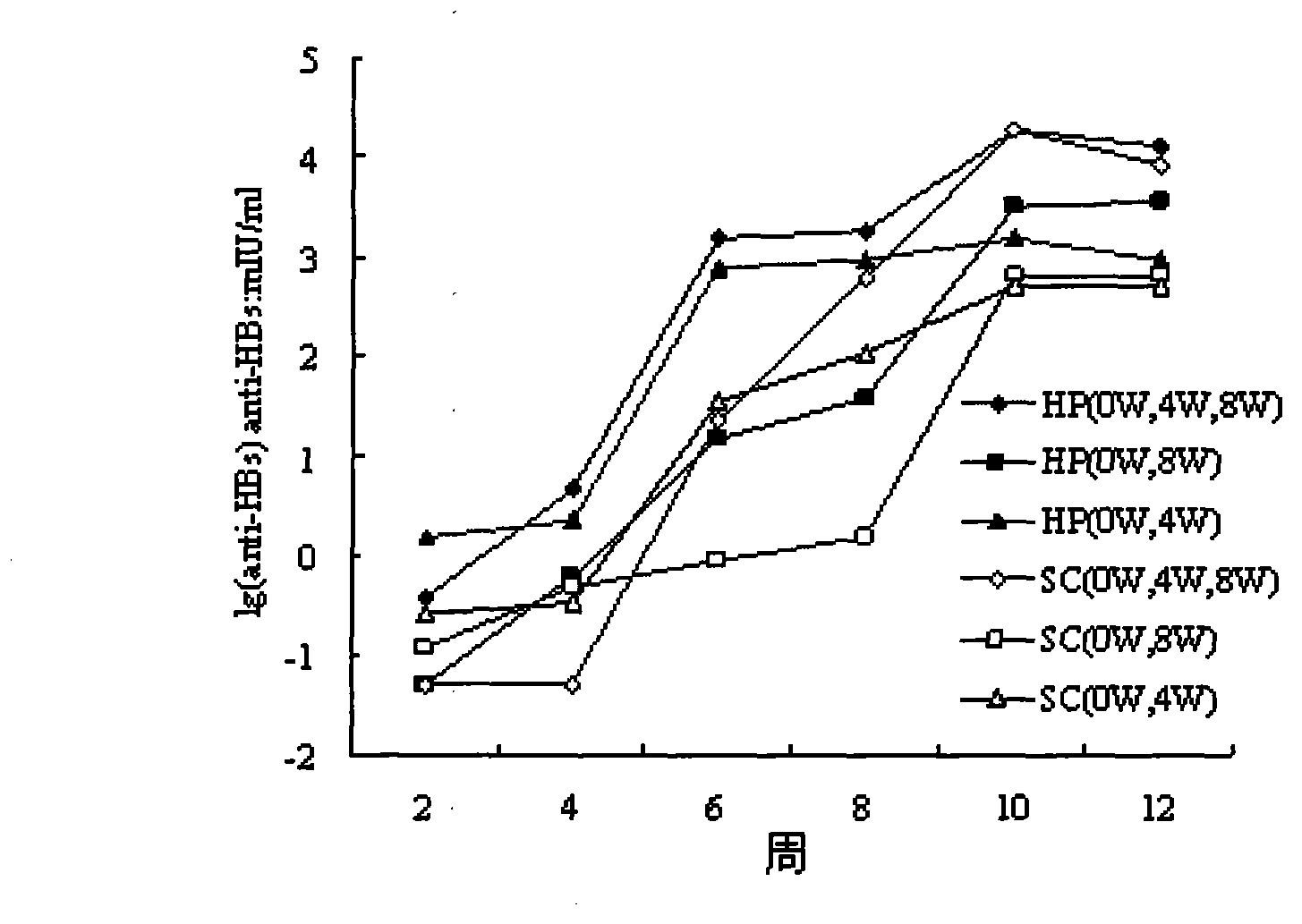
Recombinant DNA sequence, hansenula polymorpha, preparation method for hepatitis B surface antigen, and hepatitis B vaccine
InactiveCN104232661AImprove expression levelSplit genetic stability is highFungiMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisHigh cell
The invention provides a recombinant DNA sequence, hansenula polymorpha, a preparation method for hepatitis B surface antigen, and a hepatitis B vaccine. The recombinant DNA sequence is obtained by codon optimization of coding genes of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen according to codon usage frequency of the hansenula polymorpha. The invention also provides the hansenula polymorpha comprising the recombinant DNA sequence, a method for preparing adr sub-type hepatitis B surface antigen by using the recombinant DNA sequence, and the hepatitis B vaccine. The adr sub-type hepatitis B surface antigen has high expression level of the recombinant DNA sequence. The recombinant hansenula polymorpha is fast in growth speed, has high HBsAg yield, can be fermented in high cell density by using a cheap chemically synthetic medium, has low fermentation contamination rate and is beneficial to large-scale production; and HBsAg adr vaccine provided by the invention has high trend of Th1 and Th2 type cellullar immunologic response.
Owner:北京天坛生物制品股份有限公司
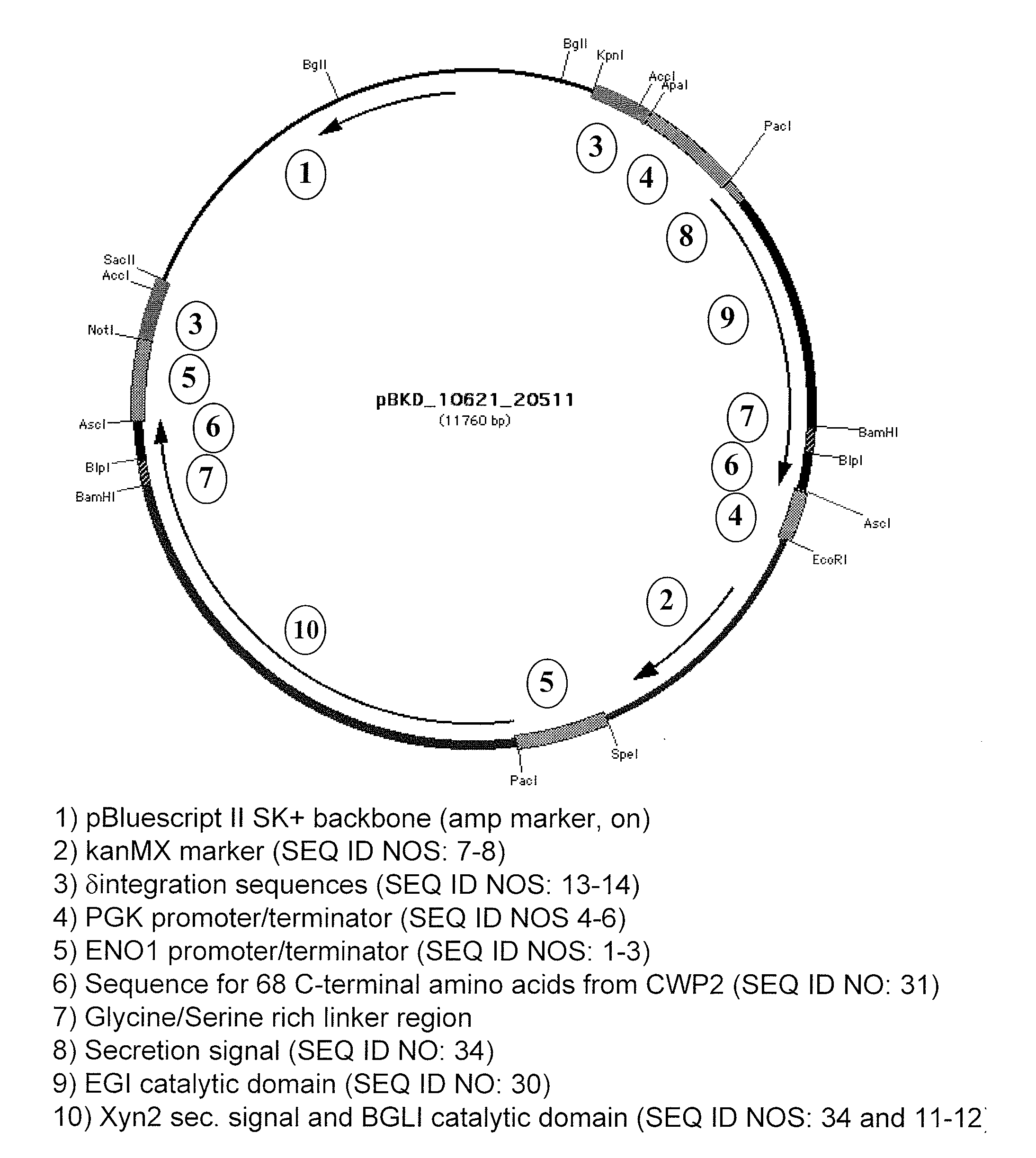
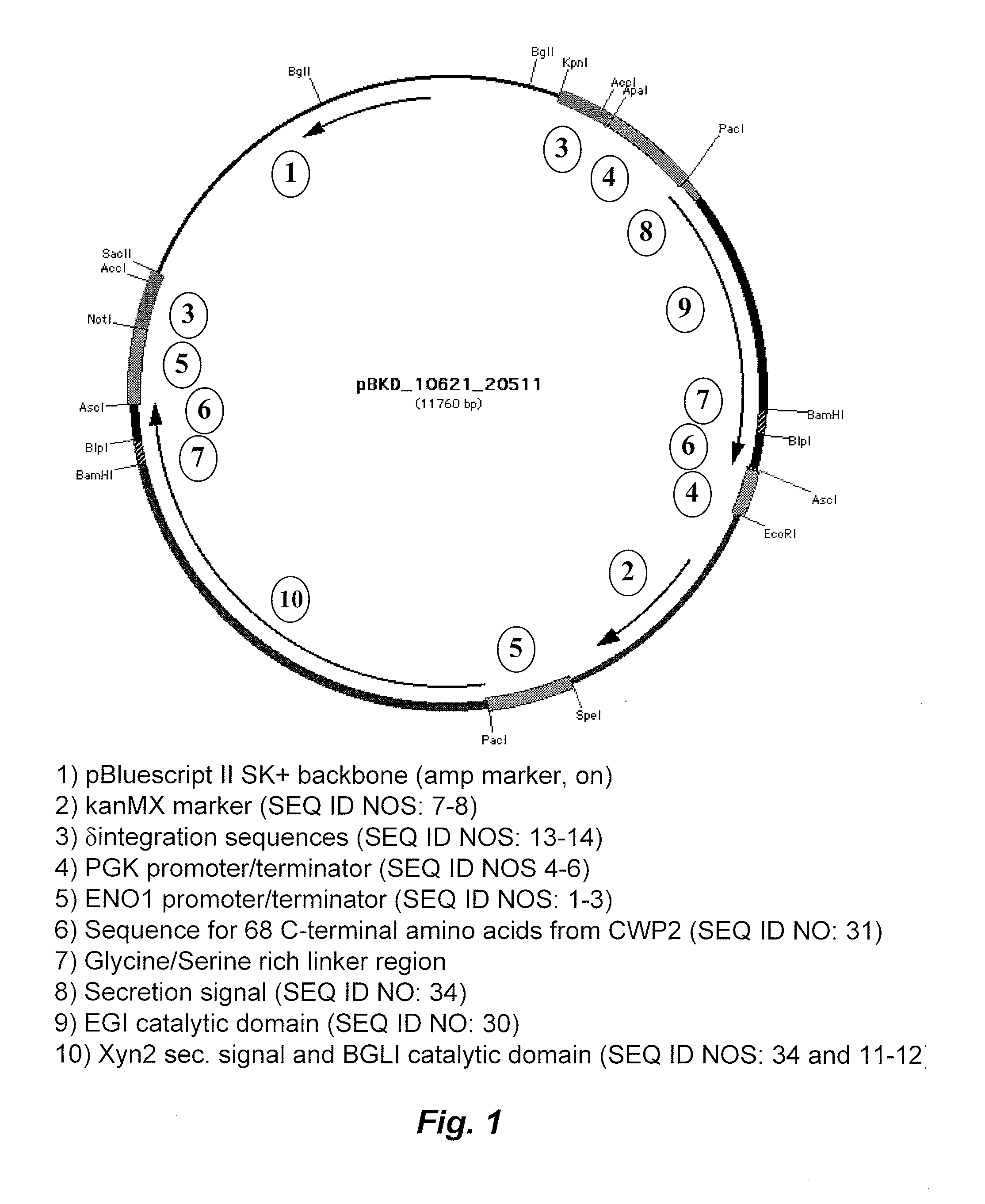
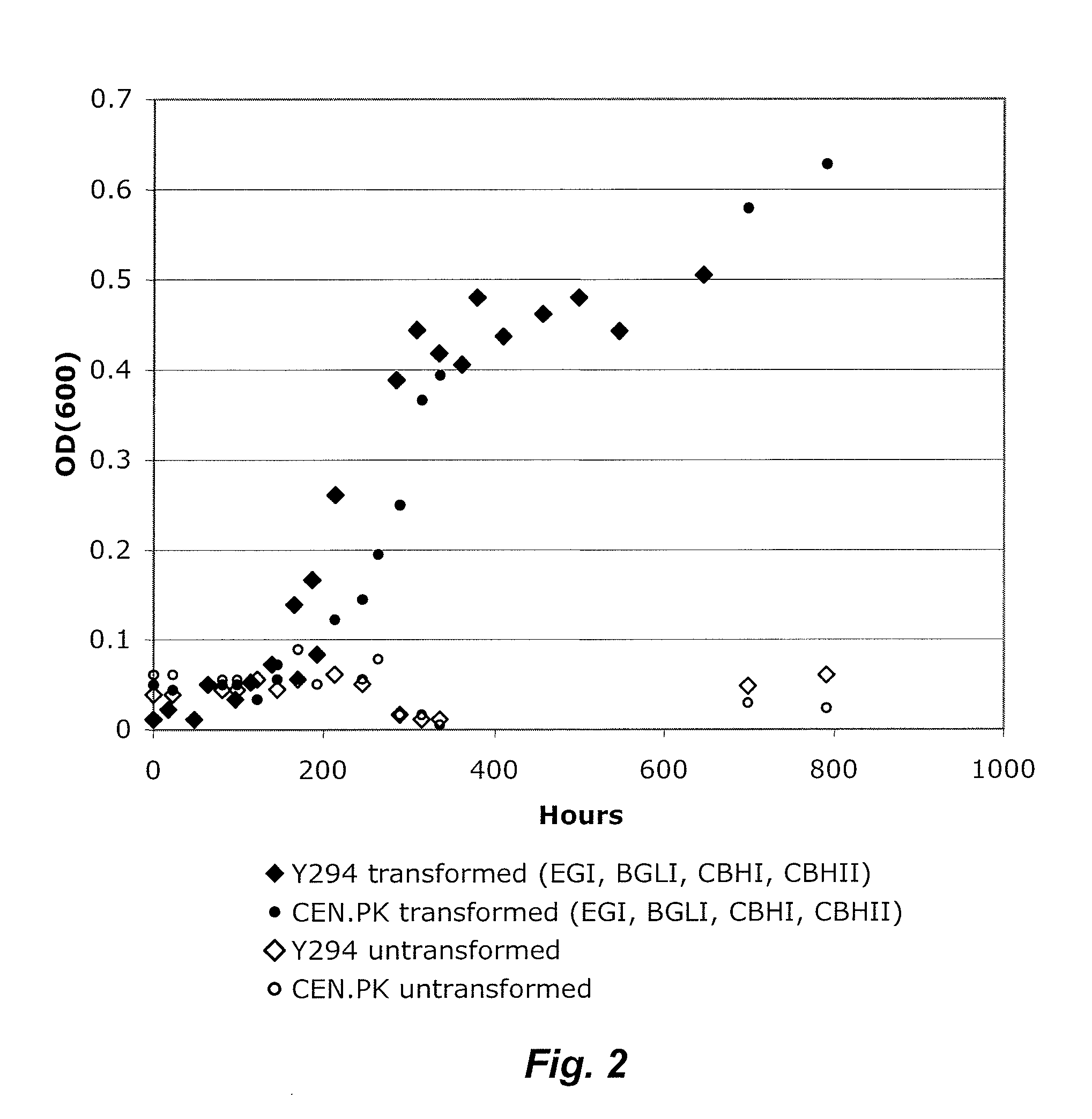
Recombinant Yeast Strains Expressing Tethered Cellulase Enzymes
InactiveUS20100075363A1High binding affinityReduction in supernatant optical densityFungiSugar derivativesYeastBiotechnology
Recombinant yeast strains that saccharify, ferment and grow on insoluble and crystalline forms of cellulose are disclosed herein. The yeast strains express tethered cellulases including cellobiohydrolase, endoglucanase and β-glucosidase. The recombinant organisms are particularly suited for consolidated bioprocessing.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Engineering lactobacilli for producing plant flavonoid to synthesize related enzymes, construction and application thereof
The invention discloses engineering lactobacilli for producing plant flavonoid to synthesize related enzymes, construction and application thereof, belonging to the field of lactobacillus reformation of genetic engineering. The engineering lactobacilli is produced by the steps of: synthesizing flavonoid completely from Chinese locally planted soybeans (Glycine max(L.)Merr.) into related enzyme genes PAL, 4CL, CHS and CHI which are connected into a polycistron structure PLA-4CL-CHS-CHI; then constructing the polycistron structure onto a reformed lactobacillus expression vector pMG26e to form a recombinant vector pMG26e-4GS; and then electrically shocking and converting the pMG26e-4GS into lactobacilli to obtain the engineering lactobacilli for producing plant flavonoid to synthesize related enzymes. The preservation number of the recombinant lactobacilli is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.4086, and the engineering lactobacilli has more abundant physiological functions compared with original lactobacilli and can be applied to the field of food. Through fermentation, the flavonoid output of the obtained recombinant strain is in the level of mg / l, which is higher than the fermentation levels of like recombinant escherichia coli and recombinant yeast.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Applications of glycosyltransferase and related materials thereof in construction of engineering bacteria for producing ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1
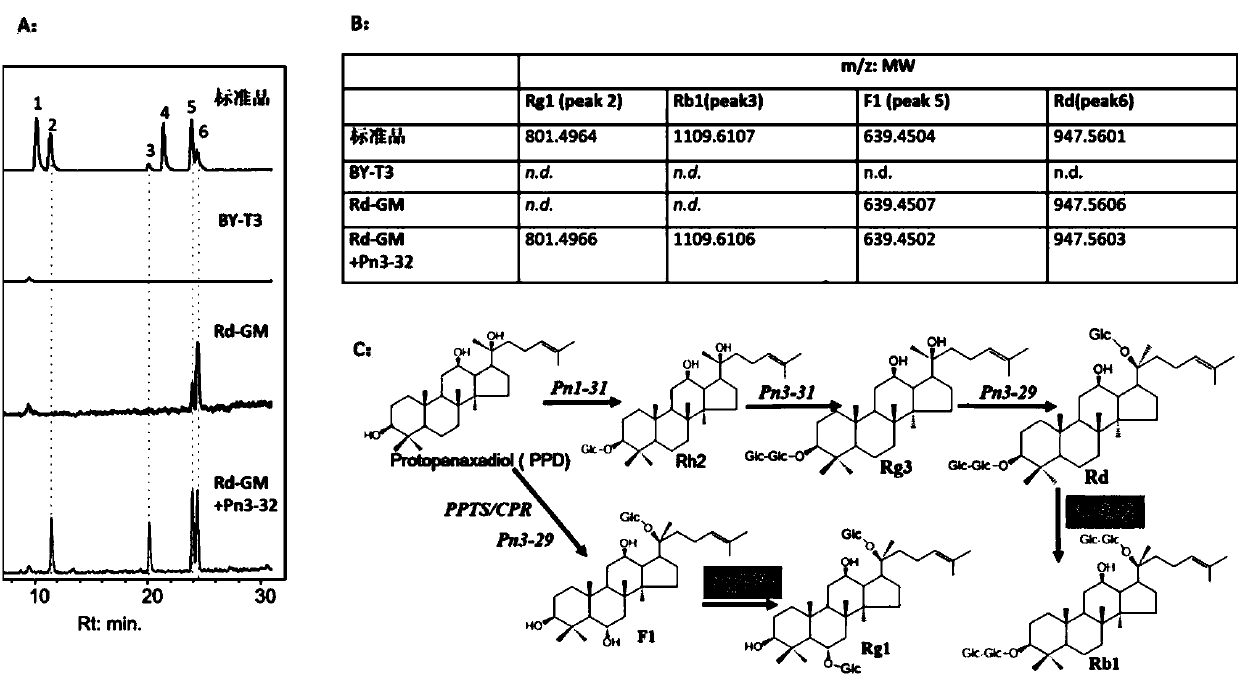
The invention discloses applications of glycosyltransferase and related materials thereof in the construction of engineering bacteria for producing ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1. A glycosyltransferase genePn3-32 which can catalyze ginsenoside Rd to generate ginsenoside Rb1 can be successfully identified through a synthetic biological method; and the gene can simultaneously catalyze ginsenoside F1 to generate ginsenoside Rg1 and construct recombinant yeast producing the ginsenoside Rb1 and the ginsenoside Rg1. Through experiments, the constructed recombinant yeast producing the ginsenoside Rb1 and the ginsenoside Rg1 can simultaneously generate the ginsenoside Rb1 and the ginsenoside Rg1. Pn1-31, Pn-3-29, Pn3-31 and Pn3-32 glycosyltransferase genes in medicinal plant radix notoginseng are firstly utilized to continuously catalyze protopanaxadiol and protopanaxatriol to synthetize the ginsenoside Rb1, the ginsenoside Rg1 and corresponding intermediates, so that novel cases can be provided formicrobial strains to produce natural products.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for producing antigen protein in use for hog cholera vaccine
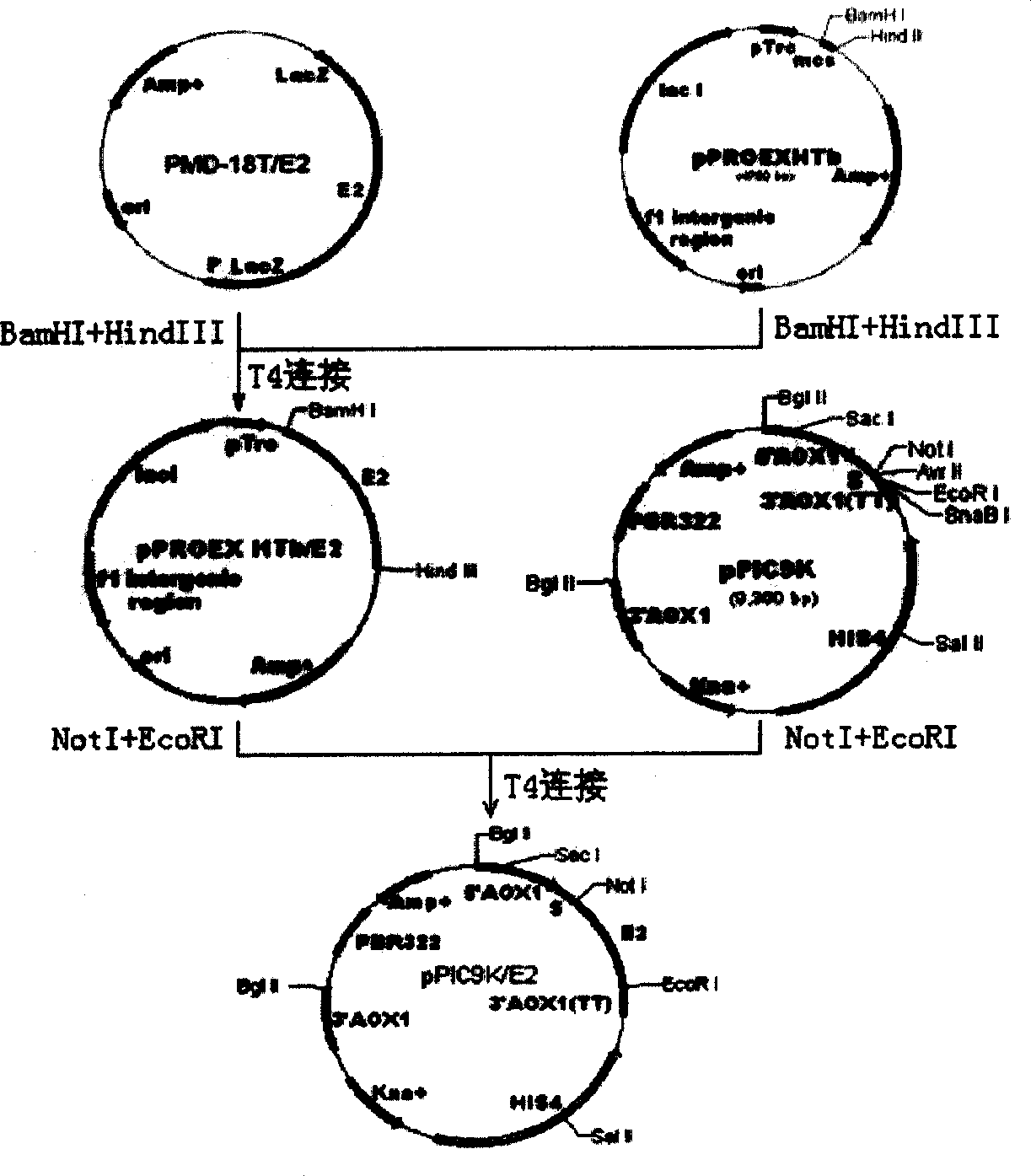
A process for preparing the antigen protein used for hog cholera vaccine includes extracting hog cholera virus RNA, reverse transcription to obtain the immune gene E2 of hog cholera virus, using E2 as template for PCR while inserting them to expression carrier of Bichia yeast, introducing the recombinant expression carrier to Bichia yeast, screening the recombinant Bichia yeast, discriminating its expression product testing its immunoactivity, determining the chosen recombinant yeast, testing and analyzing its culture condition, choosing the optimal culture condition, culturing the recombinant yeast and preparing the antigen protein of said vaccine.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
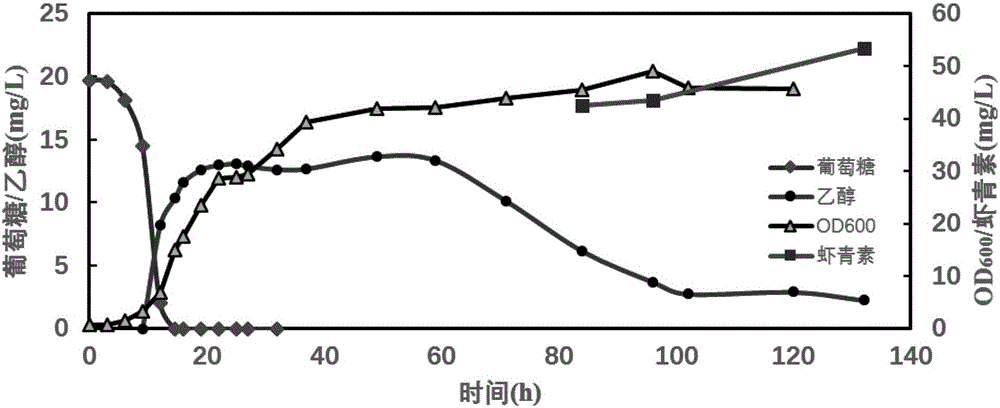
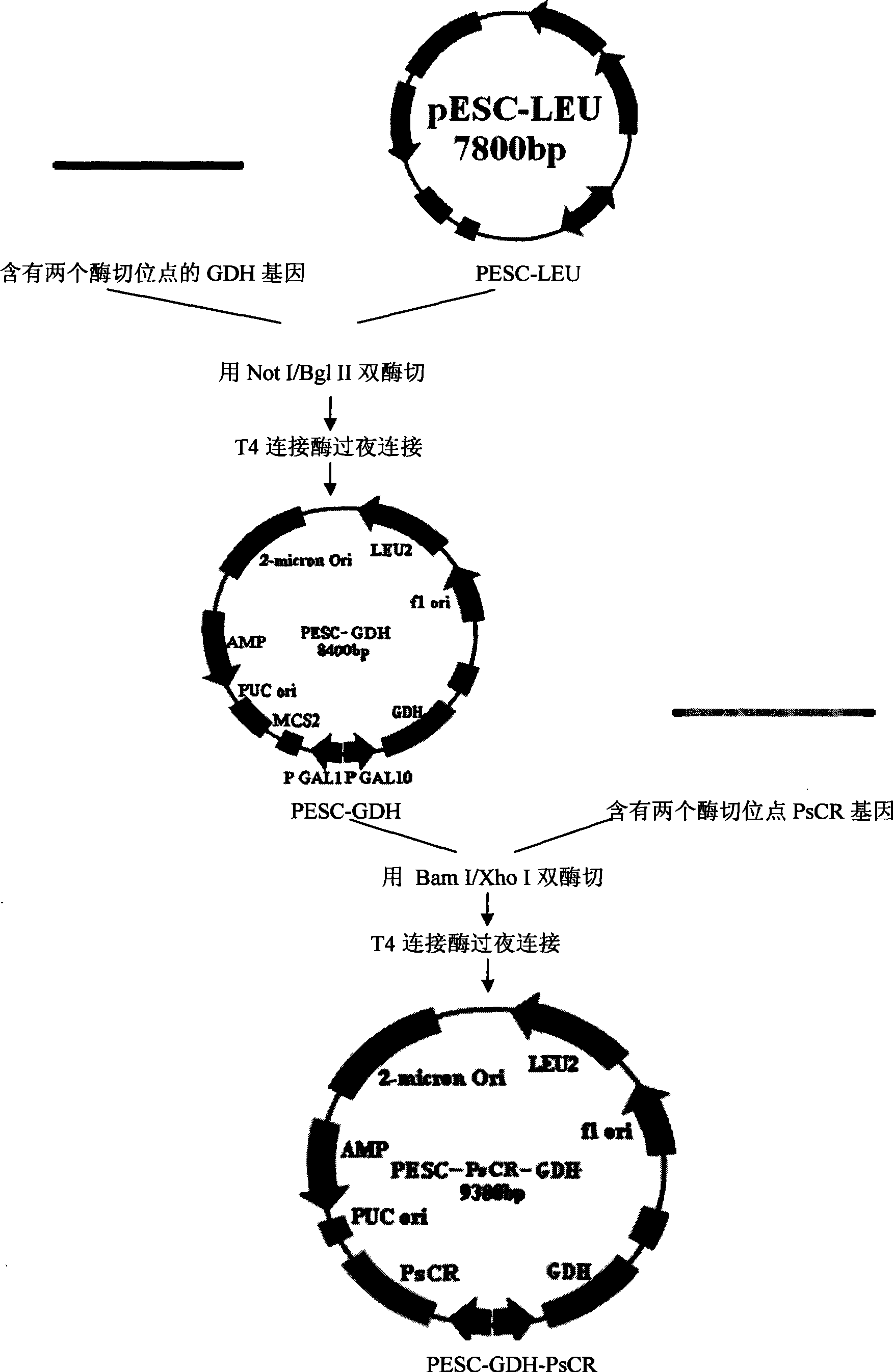
Recombinant zymomonas mobilis capable of producing ethanol by using xylose and fermentation method thereof
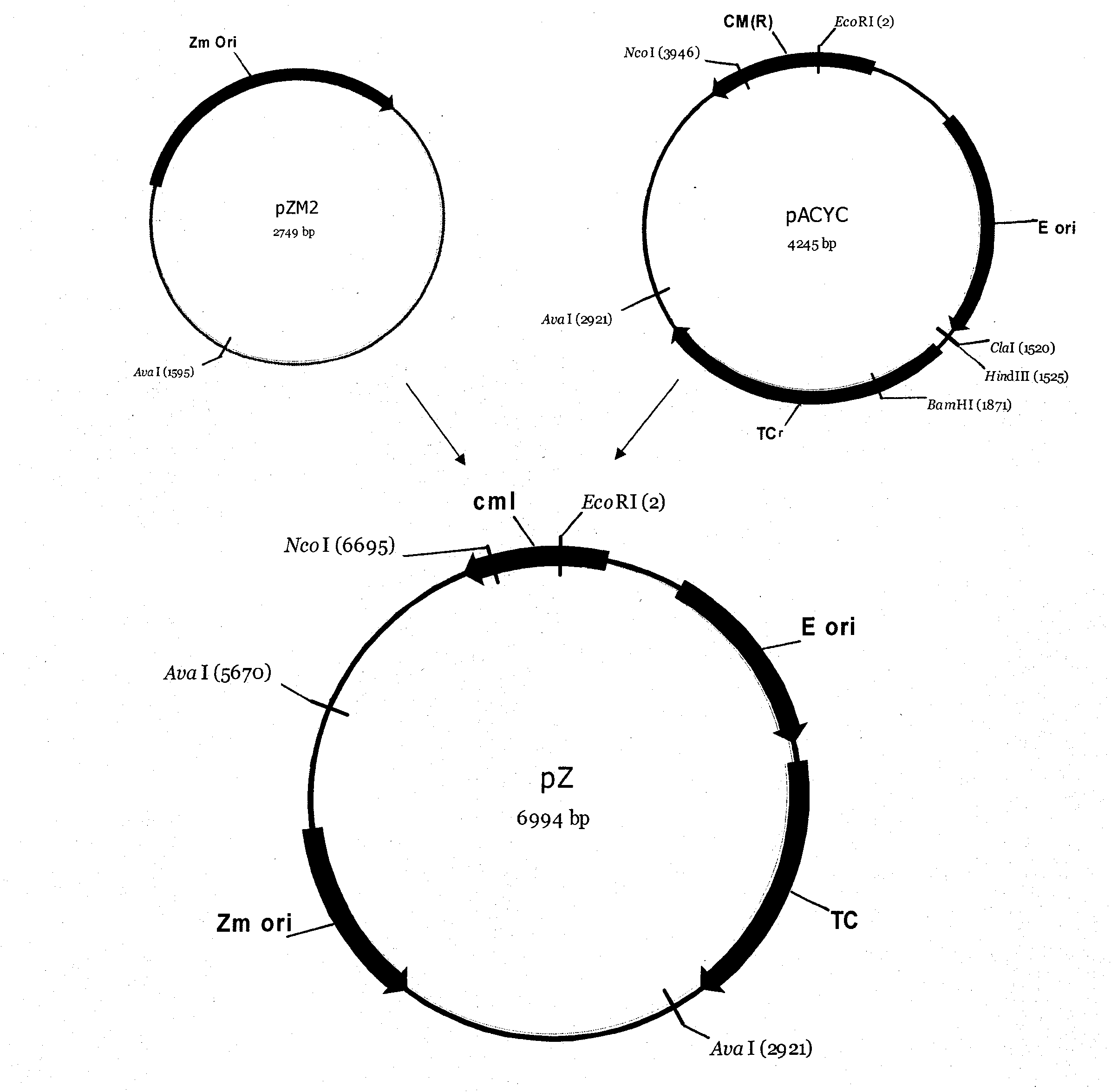
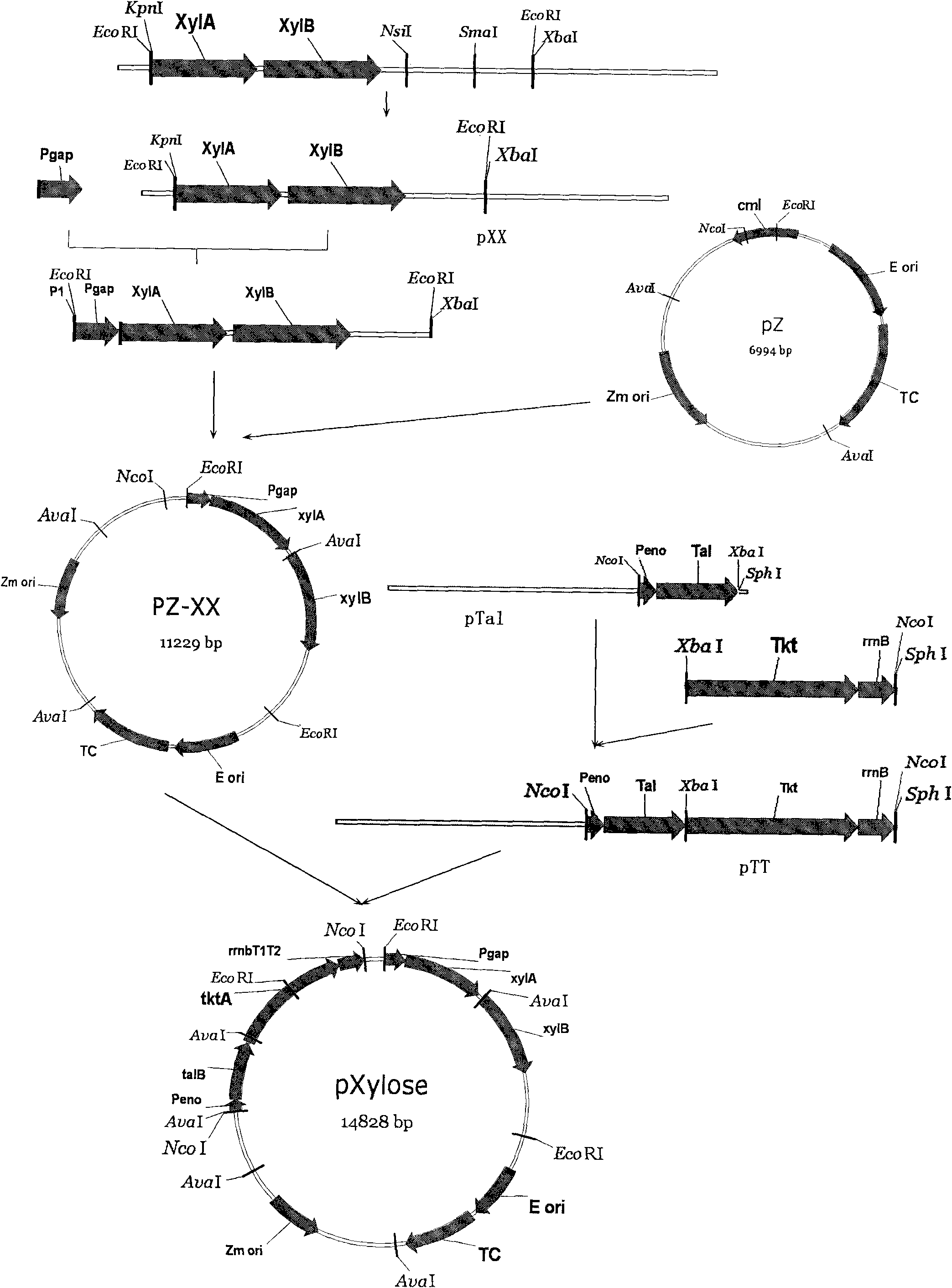
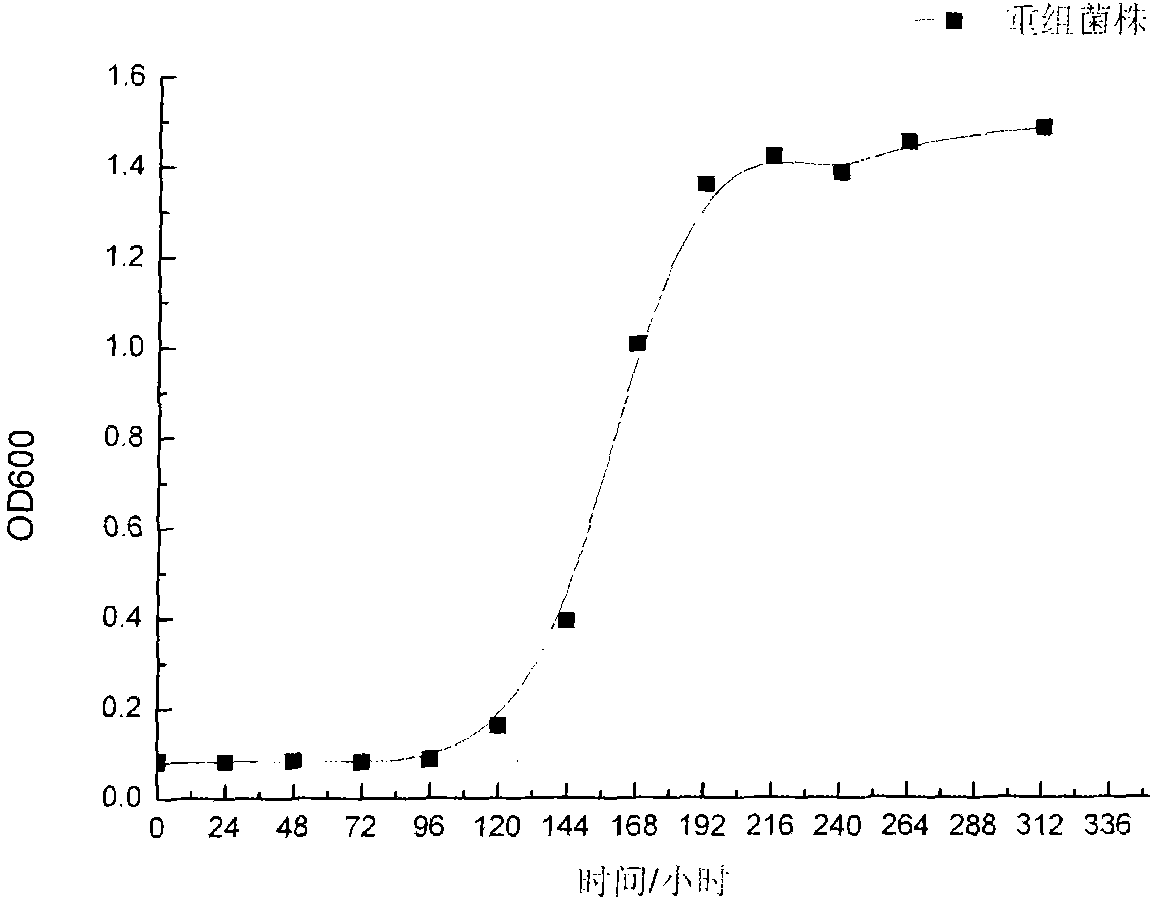
The invention discloses recombinant zymomonas mobilis capable of producing ethanol by using xylose and a fermentation method thereof. The recombinant zymomonas mobilis GX1 capable of producing the ethanol by using the xylose is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and has a preservation number of CGMCC 3438. The controlling elements of Escherichia coli rrnB and related genes of xylose metabolism are fused to build plasmids with artificially fused operons for the first time; and recombinant zymomonas mobilis strains capable of producing the ethanol by using the xylose are obtained through a method of electrotransformation and acclimatization. The recombinant zymomonas mobilis can efficiently express exogenous genes, can efficiently produce the ethanol by using glucose and the xylose to ferment together at the temperature of between 30 and 34 DEG C, and can produce the ethanol by using corncob hydrolysate containing the xylose and the glucose. The strains have important significance for producing clean energy by effectively using waste lignocellulose and solving the current energy crisis.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
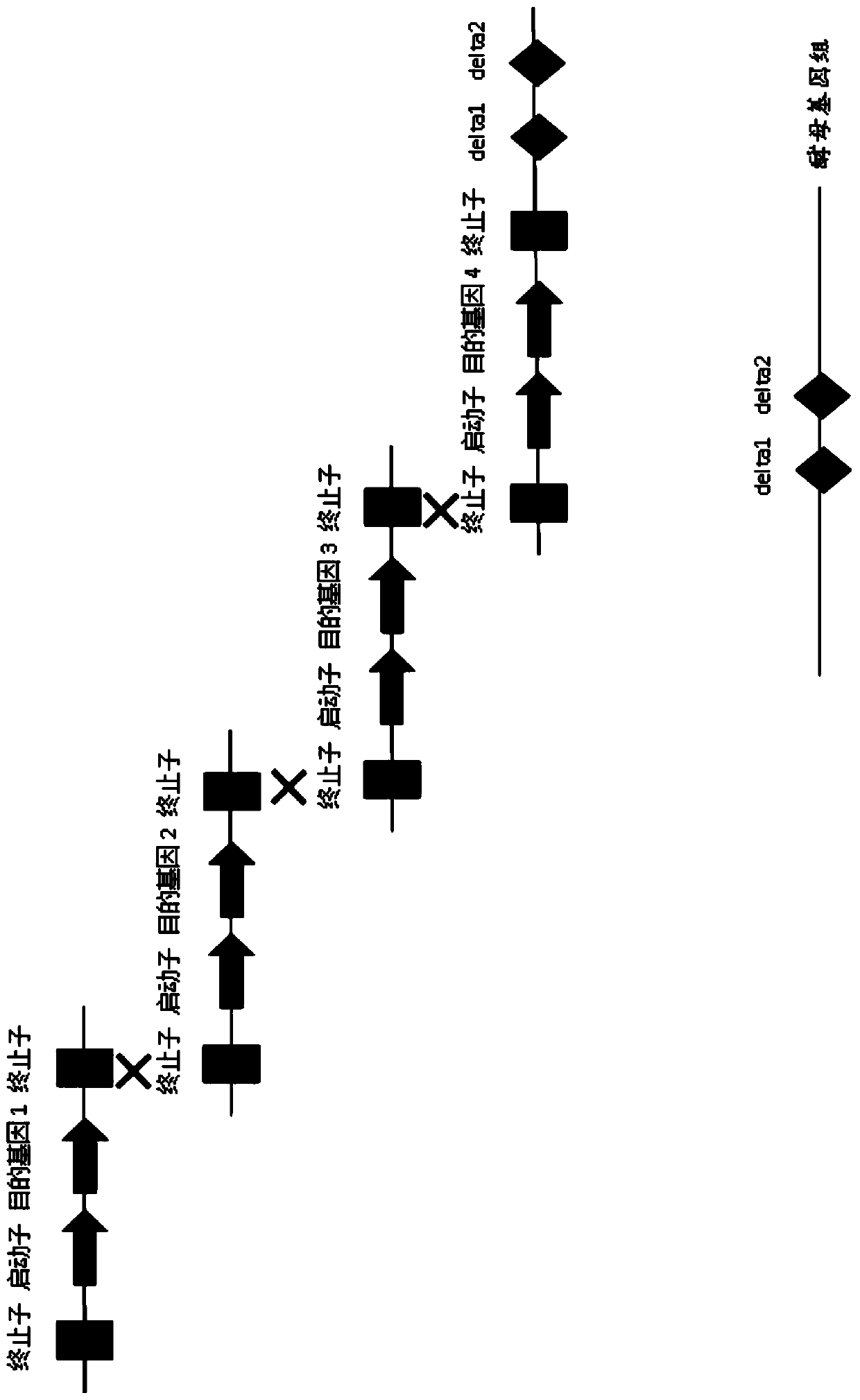
Recombinant plasmid and recombinant yeast strain and establishing method and application thereof
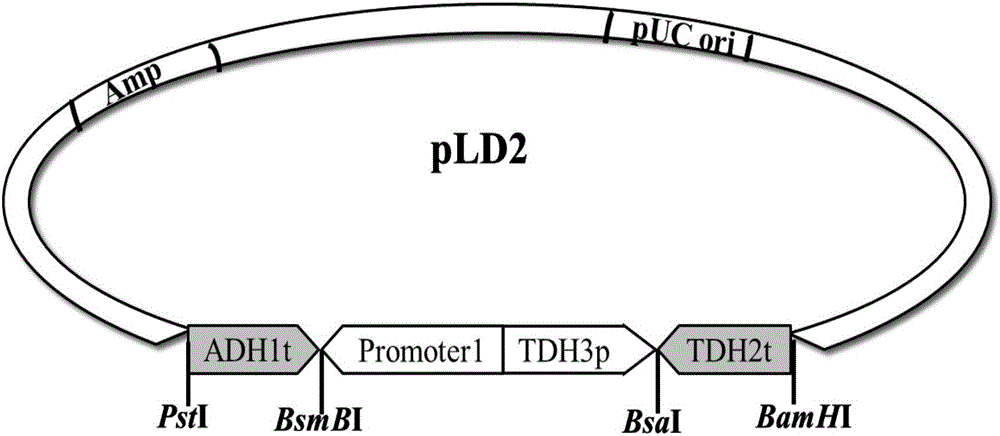
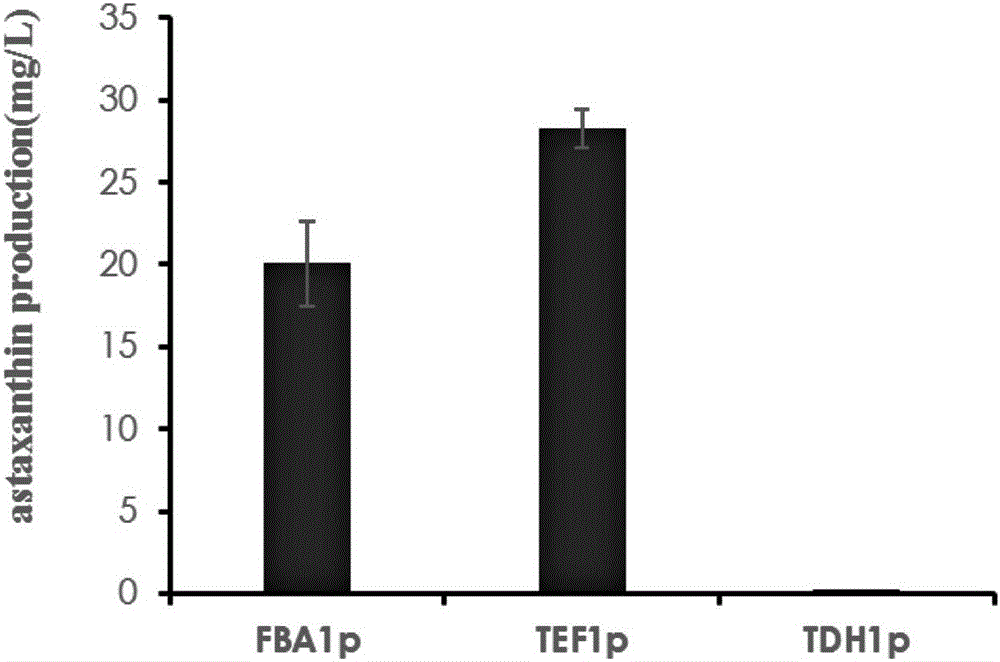
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and discloses a recombinant plasmid and a recombinant yeast strain and an establishing method and application thereof. The recombinant plasmid comprises a gene segment which is formed by sequentially splicing a terminator ADH1t, a beta-carotene hydroxylase gene crtZ, a promoter FBA1p or TEF1p, a promoter TDH3p, a beta-carotene ketolase gene crtW and a terminator TDH2t. By selecting the specific terminators, the specific promoters and the exogenous genes crtZ and crtW, the gene segment capable of producing astaxanthin is formed; thus, the recombinant plasmid is obtained and converted into the specific brewing yeast strain, the high yield of astaxanthin is ensured, and a more economical, more efficient and simpler mode is provided for heterologous microorganism production of astaxanthin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Engineering bacterium for high yielding of salidroside and/or tyrosol and application of engineering bacterium
ActiveCN110499260AHigh economic valueThe fermentation process is simpleFungiMicroorganism based processesGlycineBio engineering
The invention relates to the field of bioengineering, in particular to an engineering bacterium for high yielding of salidroside and / or tyrosol and application of the engineering bacterium. The engineering bacterium for high yielding of the salidroside is recombinant yeast obtained by processing saccharomyces cerevisiae in such a way that a codon for coding an amino acid at a 229th site in an ARO4gene is mutated into a codon for coding leucine, a codon for coding glycine at a 141st site in an ARO7 gene is mutated into a codon for coding serine, and a codon for coding lysine at a 222nd site inan ARO3 gene is mutated into a codon for coding leucine. The invention further discloses fermentation for preparing the salidroside through the engineering bacterium. The engineering bacterium can produce the salidroside and / or the tyrosol at the high yield, and has high economic value and good industrial application prospects.
Owner:成都薇合生物科技有限公司
Method for producing ethanol using recombinant yeast
The invention is intended to metabolize acetic acid and to lower acetic acid concentration in a medium at the time of xylose assimilation and ethanol fermentation by a yeast strain having xylose-metabolizing ability. The method for producing ethanol comprises a step of culturing recombinant yeast strains resulting from introduction of a xylose isomerase gene and an acetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene into a medium containing xylose, so as to perform ethanol fermentation.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Recombinant yeast and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses recombinant yeast and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) transferring an expression vector I into host yeast to obtain recombinant yeast transferred into the expression vector I, and recording the recombinant yeast as yeast A; and (2) transferring an expression vector II into the yeast A to obtain recombinant yeast transferred into the expression vector I and the expression vector II, and recording the recombinant yeast of the expression vector I and the expression vector II as yeast B. Experiments prove that the recombinant yeast prepared by the preparation method does not carry any resistance genes; the transferred expression vectors have multiple copy numbers between 5 and 50, and the copies are all integrated into a genome of the host yeast; and exogenous gene products expressed by the recombinant yeast are safe food-grade products. The preparation method has the advantages of simple operation, time saving, labor saving and low cost, and thus the recombinant yeast and the preparation method thereof are suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing ethyl alcohol through crop stalks by use of recombinant zymomonas mobilis
InactiveCN105368882AIncrease productionImproving the Efficiency of Using Straw to Produce EthanolMicroorganismsBiofuelsTrichoderma sp.Alcohol production
The invention provides a method for producing ethyl alcohol through crop stalks by use of recombinant zymomonas mobilis. According to the method, the crop stalks are used as a base material, aspergillus niger and trichoderma are mixed and fermented to produce a crude enzyme solution containing cellulase, the crop stalks are processed through the crude enzyme solution to enable cellulose in the crop stalks to be decomposed to produce reducing sugar, and finally recombinant zymomonas mobilis is used for fermenting the enzymatically-decomposed reducing sugar to produce ethyl alcohol. In the method, fermentation products of aspergillus niger and trichoderma are mixed according to the ratio of 1: 1 to obtain the cellulase crude enzyme solution, so that the product feedback inhibition is effectively controlled, and the cellulase crude enzyme with higher activity and yield is obtained. As zymomonas mobilis is inoculated in the enzymatically-decomposed fermentation liquor containing reducing sugar, the ethyl alcohol production efficiency through the crop stalks by use of zymomonas mobilis is greatly improved, and defects that the use range of a zymomonas mobilis substrate is narrow, and the crop stalks cannot be effectively utilized are overcome. According to the method, the conversion rate of ethyl alcohol through the crop stalks is 5%, that is, 100 g of the crop stalks can produce 5 g of ethyl alcohol.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant yeast strain capable of producing conjugated linoleic acid and application thereof
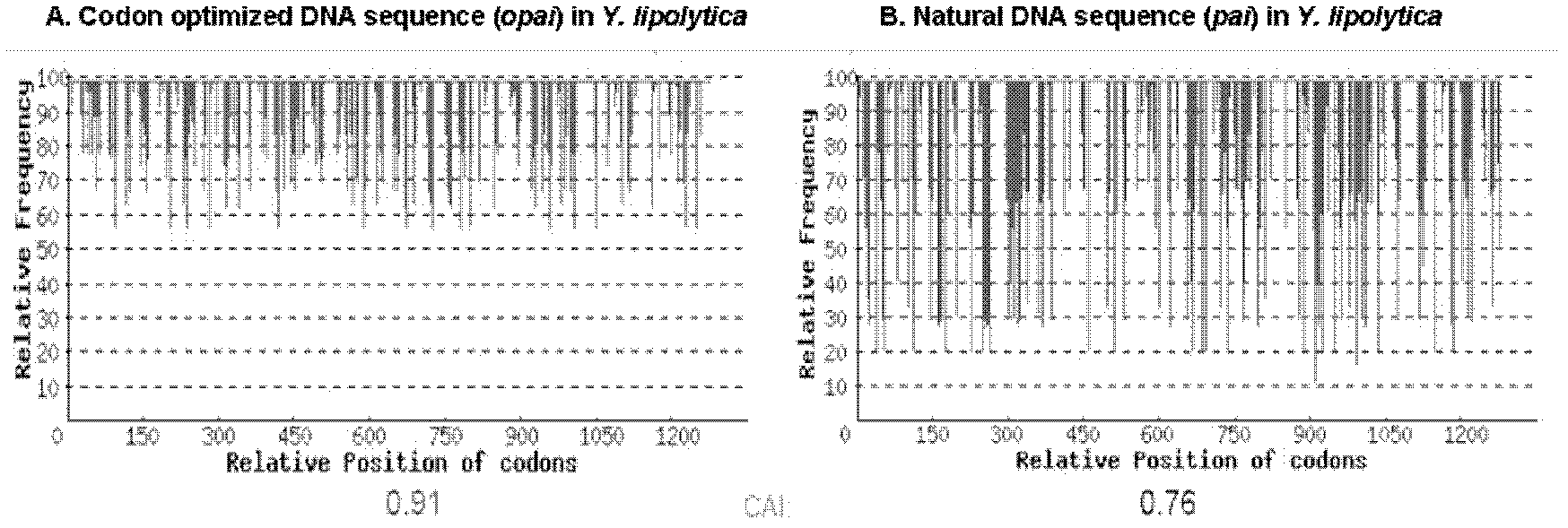
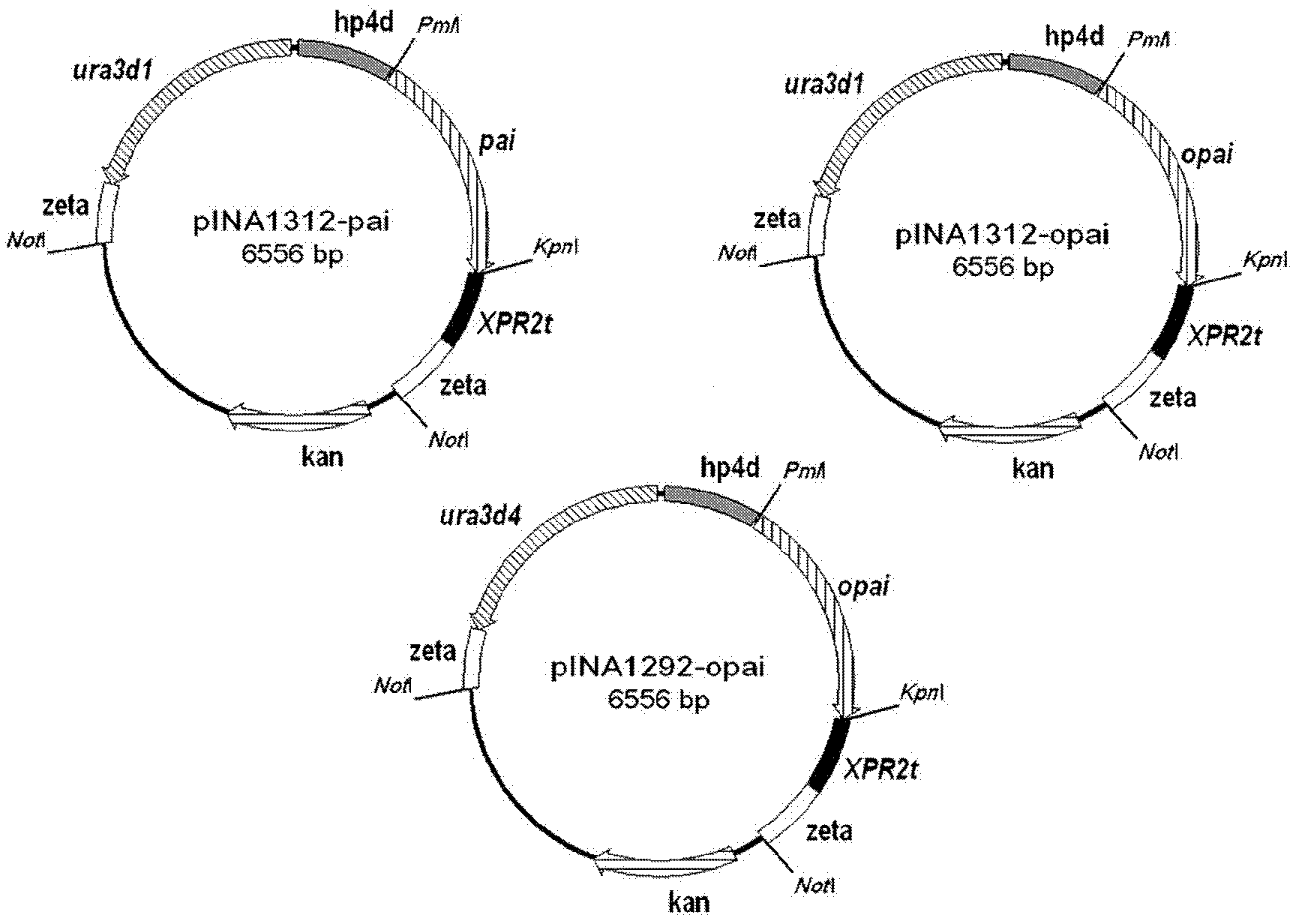
The invention relates to a recombinant yeast strain capable of producing conjugated linoleic acid and an application thereof. In the invention, codon optimization is carried out on linoleate isomerase in propionibacterium acnes (PAI) gene to obtain an optimized gene opai, recombinant expression plasmid and recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica bacterium which contain the opai gene are prepared, and therecombinant Yarrowia lipolytica bacterium which expresses the opai gene is utilized to produce conjugated linoleic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Efficient production method and application of antimicrobial peptide PR-39 of pig small intestine in pichia pastoris
InactiveCN102229934AAvoid degradationLess purification workAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyAntimicrobial peptides
The invention discloses an efficient manufacturing method and application of antimicrobial peptide PR-39 of pig small intestine in pichia pastoris. The efficient manufacturing method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: synthesizing a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) for coding PR-39 according to the feeding preference of the pichia pastoris; connecting an expression vector pGAPZalphaA, constructing a pGAPZalphaA-PR-39 eukaryotic expression vector; transforming a recombinant expression vector into a host cell and constructing an expression engineering bacterium; fermenting and culturing recombinant saccharomycete and expressing. The method provided by the invention can be used for efficiently expressing the antimicrobial peptide PR-39 in the host cell of the pichia pastoris by utilizing a gene engineering technology, has the advantages of high expression efficiency, simple separation and purification, low production cost, easiness in amplification and good stability, is suitable for large-scale industrial production and has a wide application prospect in the fields of preparing antibacterial medicines, fodder additives or food preservatives.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Preparation method and purification method of recombinant human-derived III type collagen
ActiveCN107033238AHigh purityReduce generationConnective tissue peptidesPeptide preparation methodsPurification methodsCollagen VI
The invention relates to the technical field of collagen extraction and discloses a preparation method and a purification method of recombinant human-derived III type collagen. According to the purification method of the recombinant human-derived III type collagen, by thermal treatment of fermentation liquid, obtained by fermentation of recombinant saccharomycetes capable of giving expression to the recombinant human-derived III type collagen, at a temperature of 65-75 DEG C, degradation of the recombinant human-derived III type collagen in the fermentation liquid into small-molecule peptides is effectively prevented, endotoxins in the fermentation liquid can be reduced, and accordingly purity of the recombinant human-derived III type collagen is greatly improved to meet requirements of cosmetic raw materials, medical instruments and medical high-purity collagen. The recombinant human-derived III type collagen prepared according to the method is high in purity and low in endotoxin content and meets requirements of cosmetic raw materials, medical instruments and medical high-purity collagen.
Owner:山东多美康生物医药有限公司
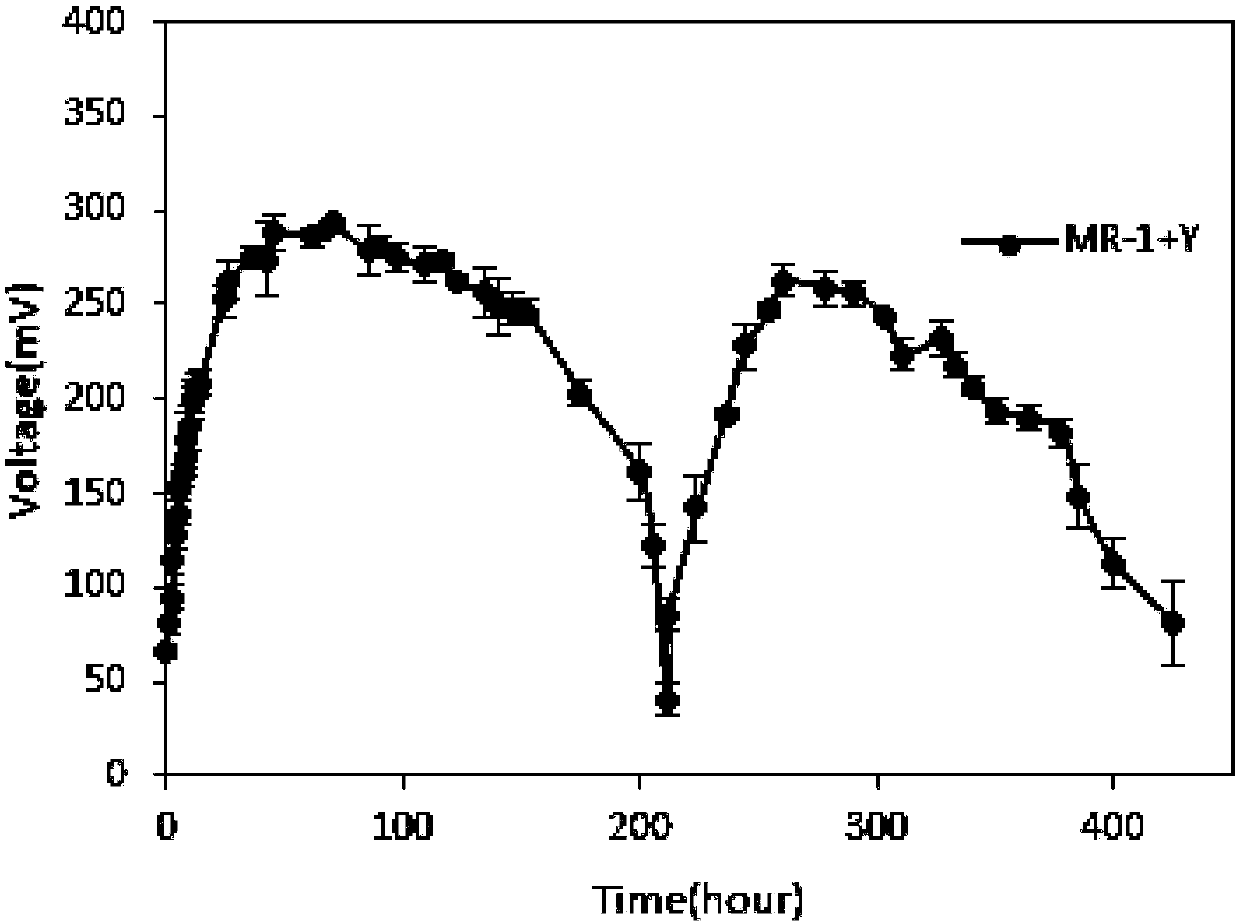
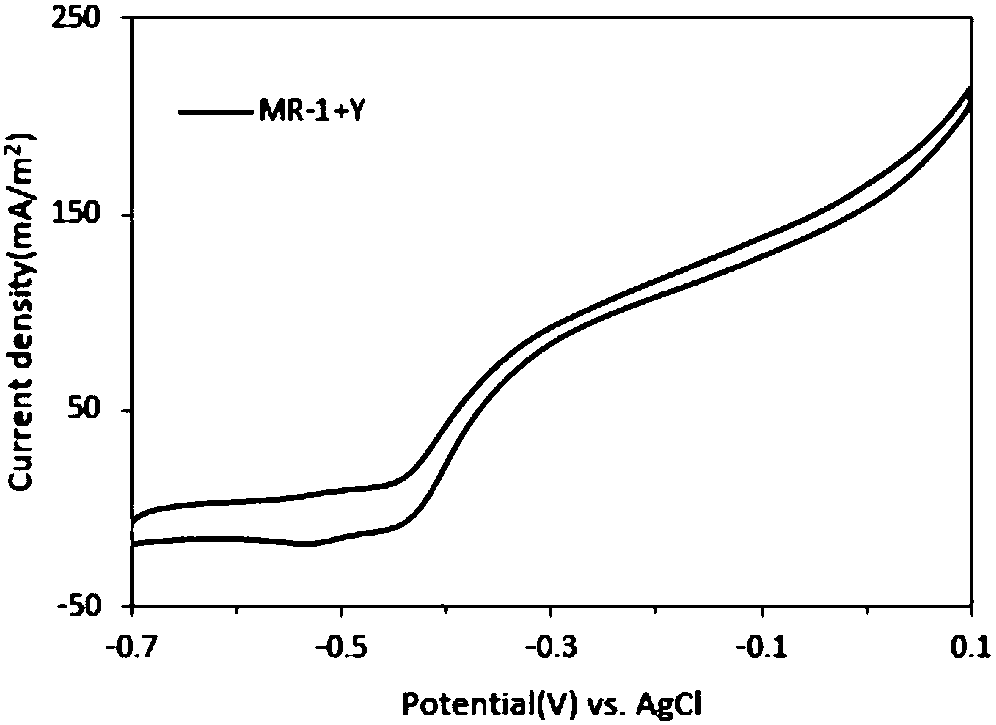
Recombinant yeast strain and microbial mixed bacteria electricity generation method
ActiveCN107916235AAdd carbon source spectrumLower internal resistanceFungiBacteriaNew energyElectron donor
The invention relates to the technical field of bio-energy and discloses a recombinant yeast strain and a microbial mixed bacteria electricity generation method. According to the recombinant yeast strain disclosed by the invention, genes PDC1, PDC5, PDC6, ADHI and ADH4 are knocked-out, and genes LDH, XR, XDH and XKS are inserted. Meanwhile, a yeast-Shewanella mixed bacteria system taking glucose and xylose as a carbon source is constructed, and by modifying brewer's yeasts, the glucose and xylose can be metabolized to produce lactic acid, and the carbon source and electron donors are providedfor shewanella in the MFC, so that available carbon source spectrums of the shewanella are increased, and the recombinant yeast strain has excellent performance on the electrochemical effect and laysa foundation for researching biomass by human beings and identifying new energy conversion manners.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
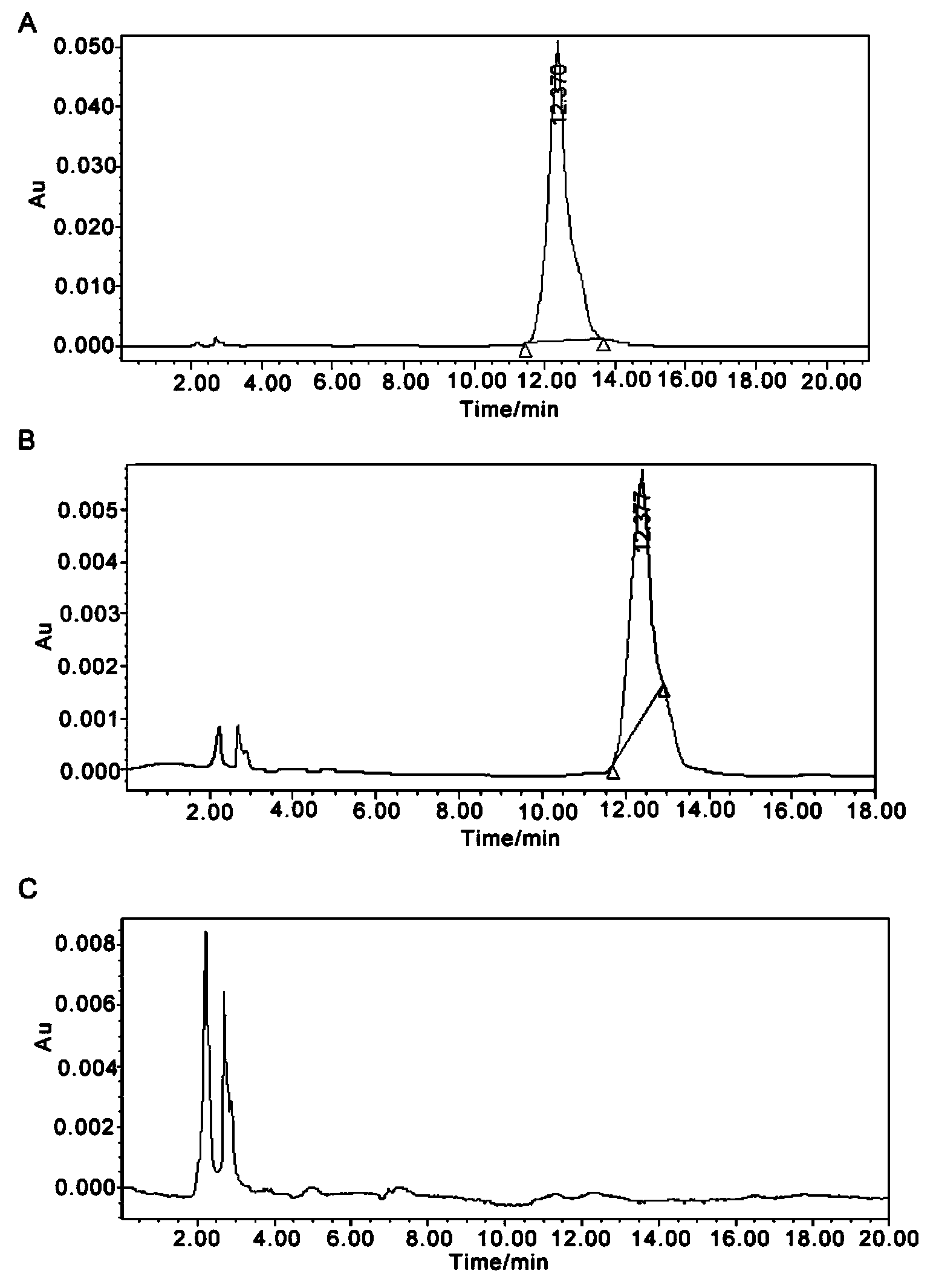
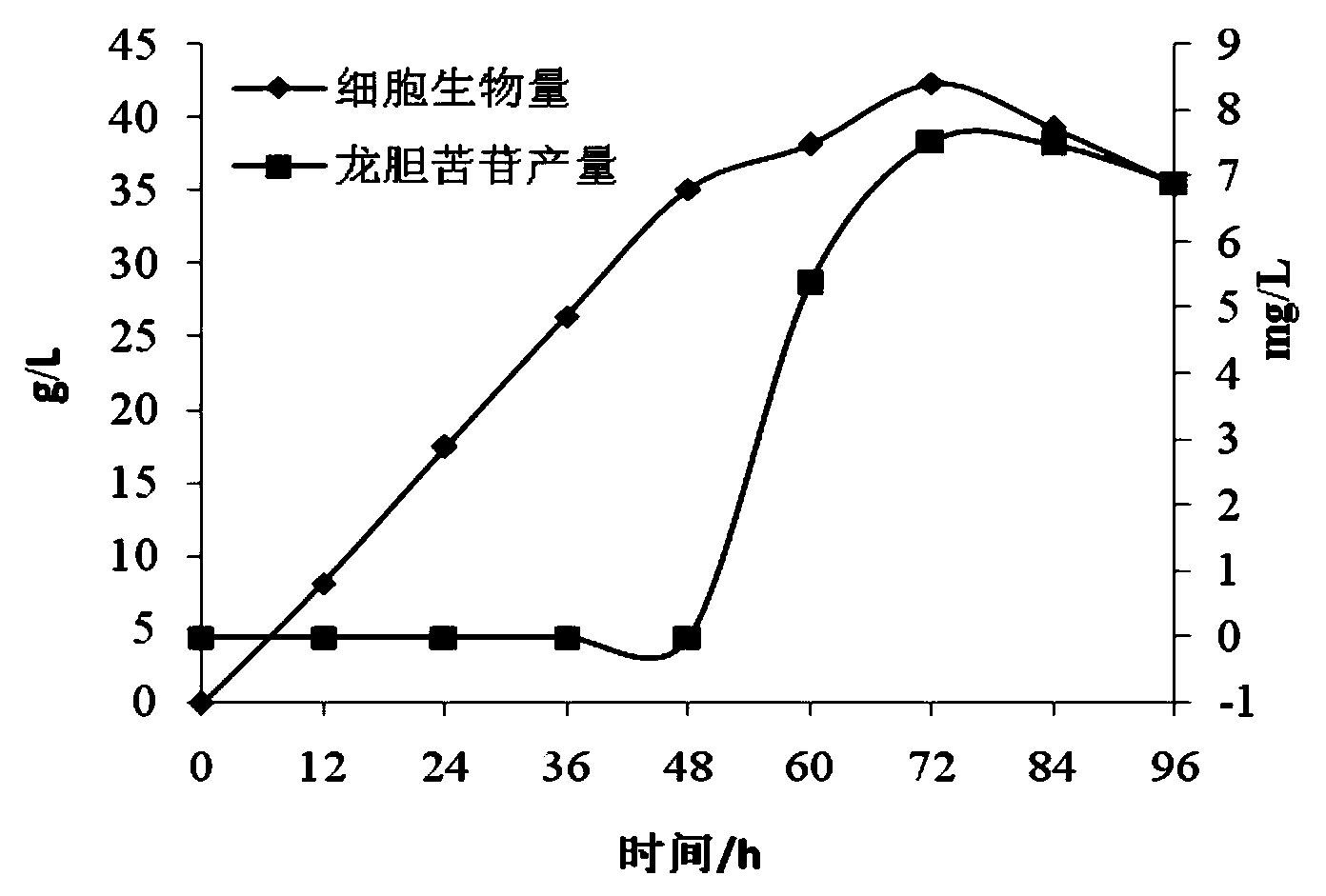
Hansenula polymorpha recombination strain and application thereof in biosynthesis of gentiopicroside
ActiveCN103966112AEasy to separate and extractEasy to ferment at high densityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFermentation
The invention provides a hansenula polymorpha recombination strain and application thereof in the biosynthesis of gentiopicroside. A recombination saccharomycete used for producing gentiopicroside is obtained by a method for conversion of low energy ion implantation mediated gentiana macrophylla genome total DNA in the saccharomycete, and is named as hansenula polymorpha of which the preservation number is CGMCC.No.8998. The hansenula polymorpha recombination strain and the application realize the technical breakthrough in the aspect of using the recombination saccharomycete to be subjected to biological fermentation to produce gentiopicroside, solves the source shortage of gentiopicroside, protects the gentianaceae plant resources of our country, and provides a new way for sustainable development of the gentianaceae plant resources.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Recombinant yeast for unsymmetrical conversion and preparation of (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoate and construction method and use thereof
InactiveCN101392225AImprove conversion rateHigh optical activityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses recomposed yeast for asymmetrically transforming and preparing (S)-4-chlorine-3-hydroxy-ethylbutyrate, which is Saccharomyces cerevisiae for reducing enzyme gene and glucose dehydrogenase gene by the introduction of carbonyl. The invention further discloses a composition method of the recomposed yeast. The method for preparing (S)-4-chlorine-3-hydroxy-ethylbutyrate by using the recomposed yeast is that: 4-chloracetyl-ethyl-acetate is used as a substrate, glucose is used as an auxiliary substrate, and the recomposed yeast is used for the transformation reaction so as to prepare (S)-4-chlorine-3-hydroxy-ethylbutyrate. The recomposed yeast, without adding any auxiliary enzyme, can effectively catalyze 4-chloracetyl-ethyl-acetate into (S)-4-chlorine-3-hydroxy-ethylbutyrate, with optical purity e.e value larger than 98 percent and the transformation ratio to the substrate larger than 95 percent, thus reducing the production cost. Compared with other strains without the need to add expensive auxiliary enzyme, the recomposed yeast has high transformation ratio to the substrate and high optical activity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant yeast strain and application thereof
ActiveCN109943492AHigh expression activityAvoid enteringFungiBiofuelsBiotechnologyLycopene synthesis
The invention discloses a recombinant yeast strain and application thereof. The recombinant yeast strain expresses lycopene synthesizing genes crtE, crtB and crtI, the genes crtE, crtB and crtI come from deinococcus gobiensis, and all the genes are put under a growth-coupling dynamic controlling element HSP26 promoter, and are integrated onto a saccharomyces cerevisiae genome in a series mode; anHMGR gene is dynamically controlled through the overexpression rate-limiting step of the recombinant yeast strain, the HMGR gene is put under a growth-coupling dynamic controlling element Cit1 promoter, a competitive metabolic pathway ERG9 promoter is replaced with a growth-coupling dynamic controlling element PDC1 promoter, an HMG1 gene promoter and a control area of the HMG1 promoter are replaced with the growth-coupling dynamic controlling element Cit1 promoter, and an Ald6 gene is knocked out. The recombinant yeast strain can be applied to synthesis of carotenoid.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Oral vaccine for preventing H7N9 virus infection and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109609538AImproving immunogenicityExert immune effectSsRNA viruses negative-senseFungiYeastVirus
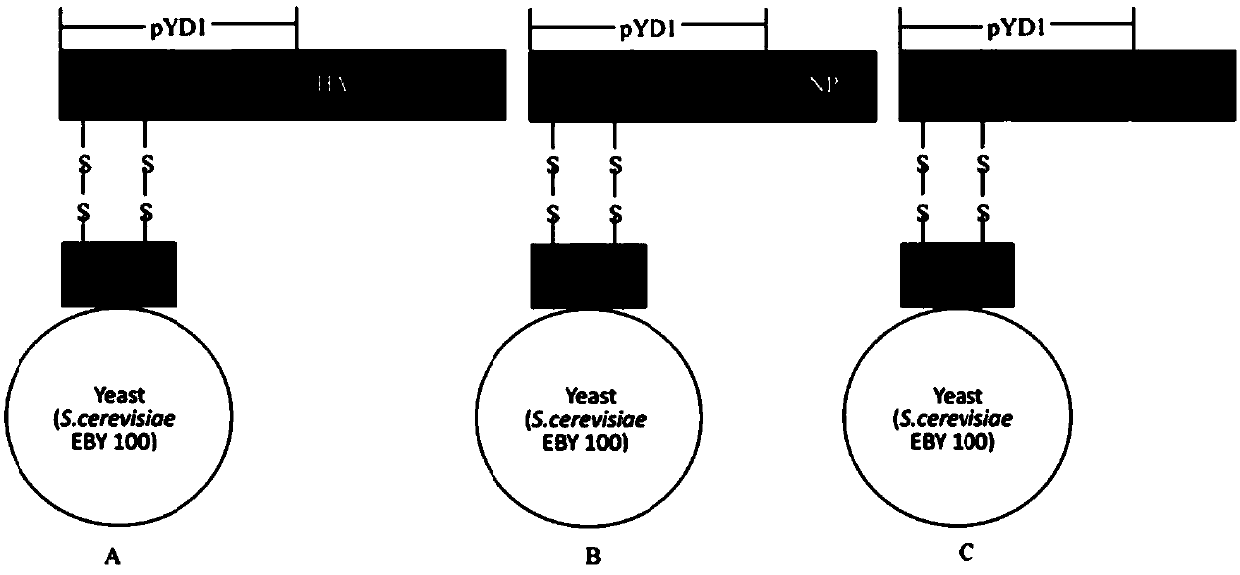
The invention discloses an oral vaccine for preventing H7N9 virus infection and a preparation method thereof. Specifically, the present invention discloses a recombinant plasmid, and also discloses recombinant yeast comprising the recombinant plasmid, and an application of the recombinant yeast in preparing the vaccine for preventing H7N9 virus infection. The present invention successfully establishes the recombinant yeast EBY100 / pYD1-HA comprising partial gene segments of H7N9 virus, confirms that HA can be efficiently expressed in yeast, and further proves that the recombinant yeast has goodimmunoprotective effect against the H7N9 virus, can be prepared into the oral vaccine, and has excellent application prospects.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Yeast strains for the expression and secretion of heterologous proteins at high temperatures
ActiveUS20180265853A1Restoring and increasing high-temperature robustnessImprove robustnessBiofuelsDepsipeptidesBiotechnologyYeast
The present disclosure relates to recombinant yeast strains capable of maintaining their robustness at high temperature as well as recombinant proteins expressed therefrom. The present disclosure also provides methods for using the recombinant yeast strain for making a fermentation product. The present disclosure further process a process for making recombinant yeast strains capable of maintaining their robustness at high temperature.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com