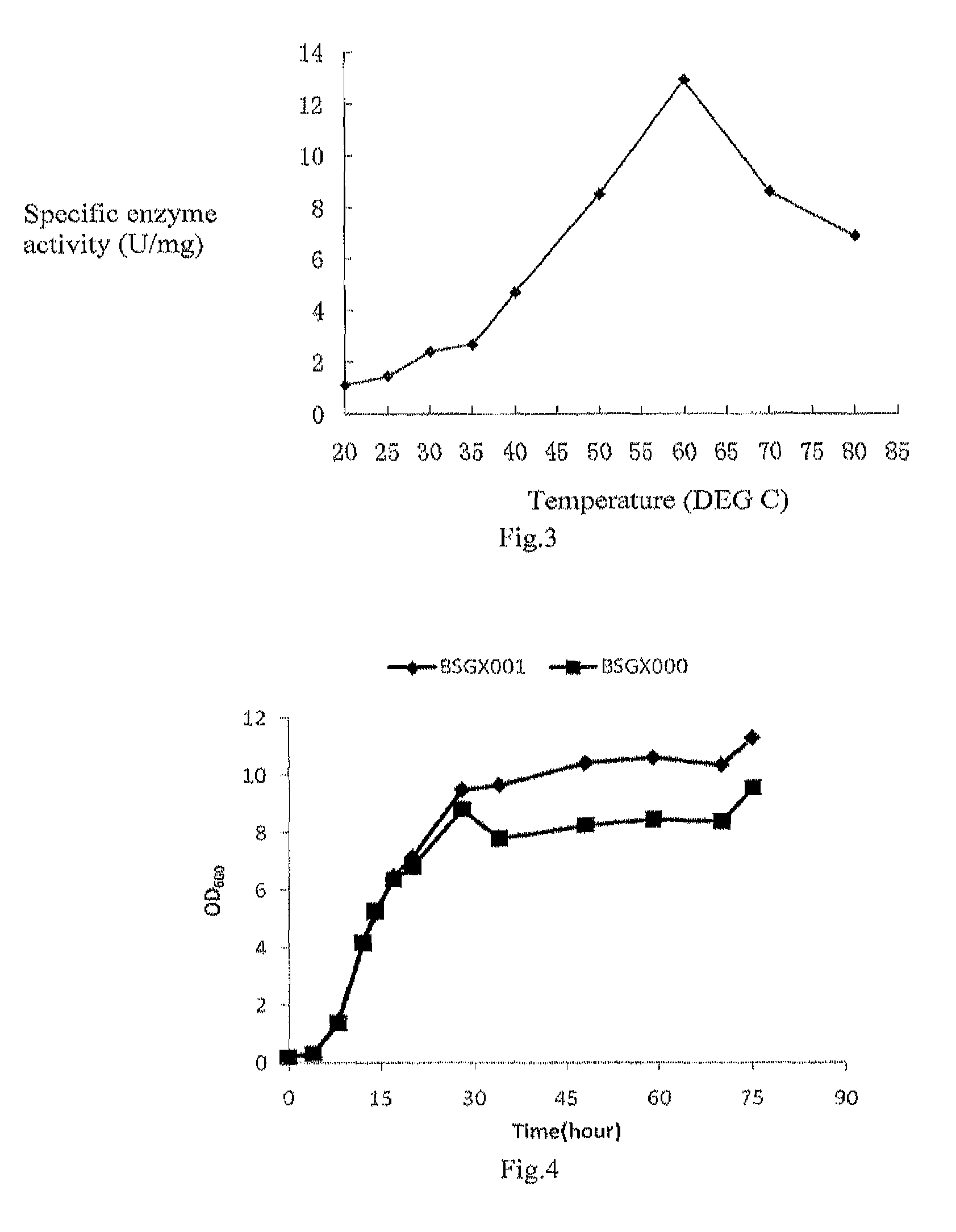
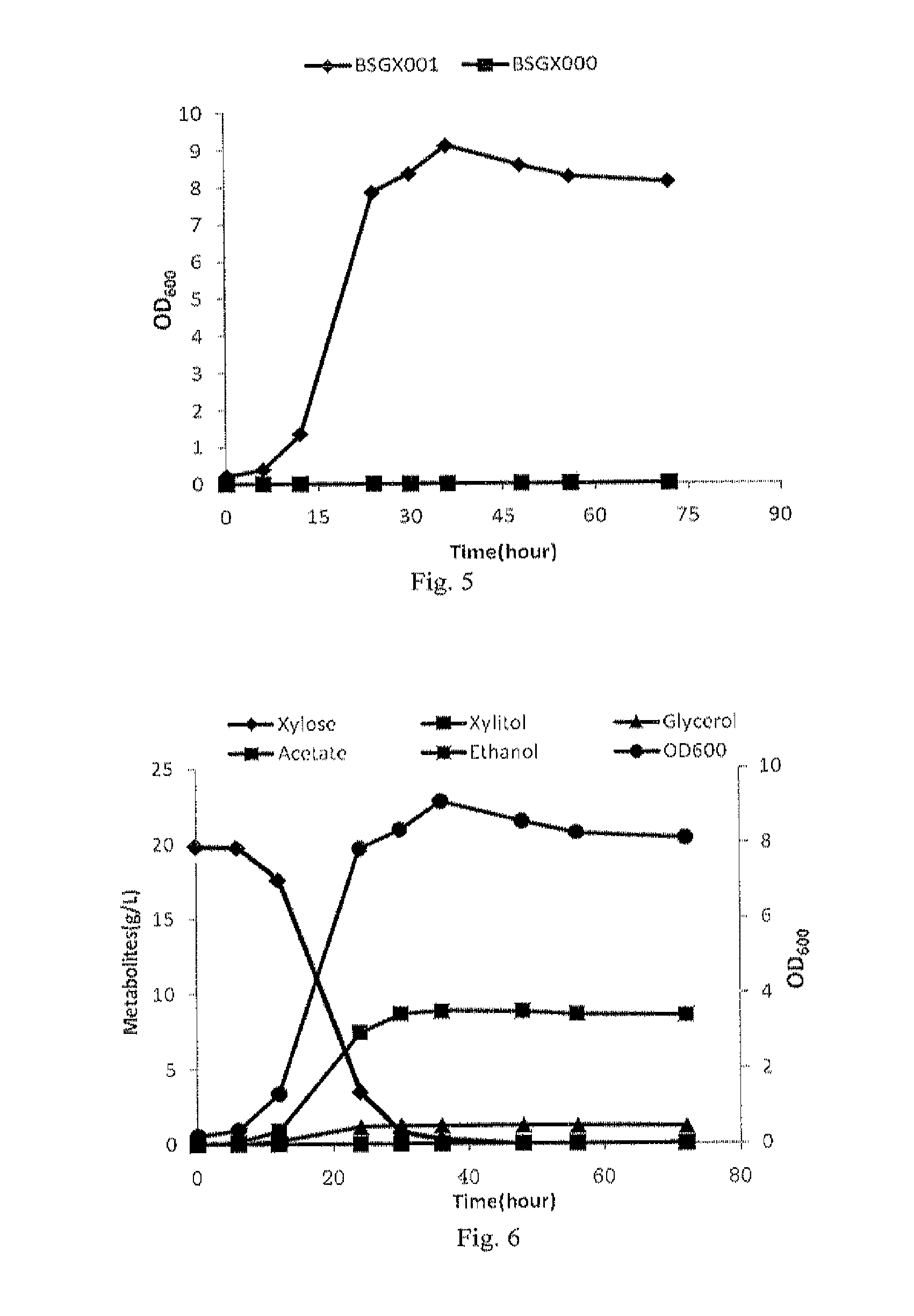
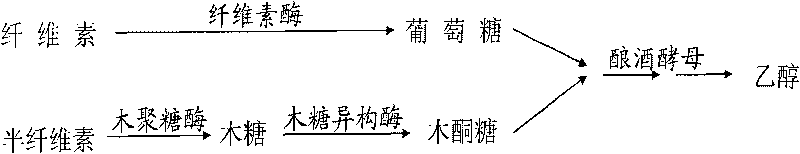
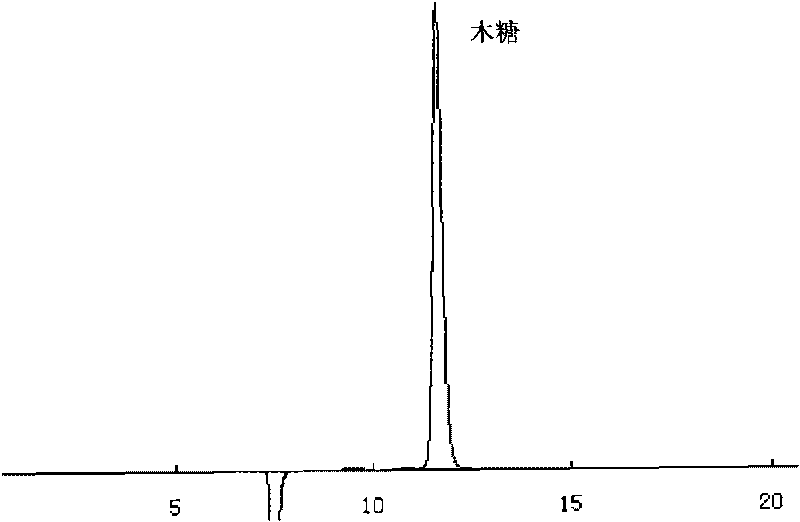
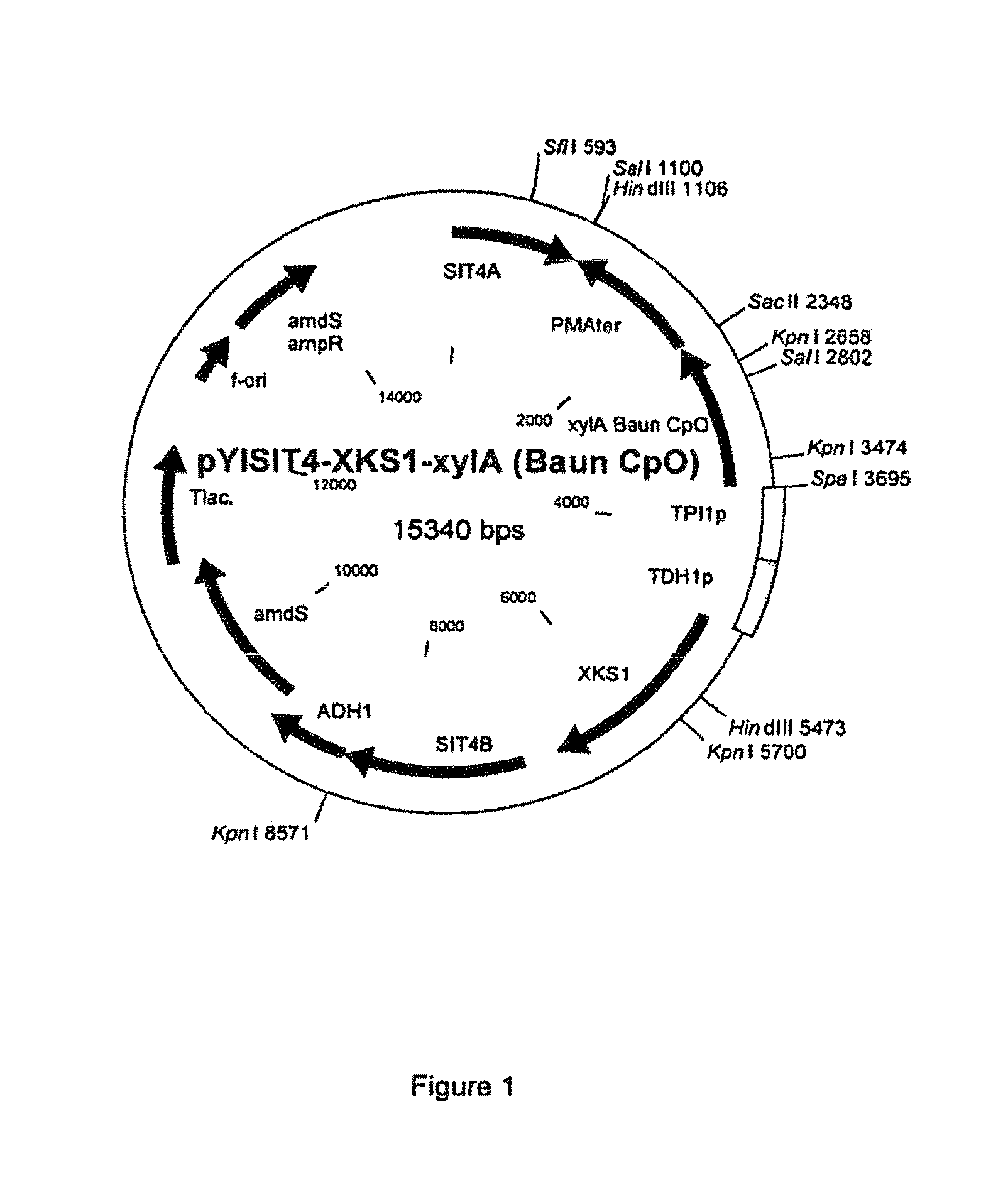
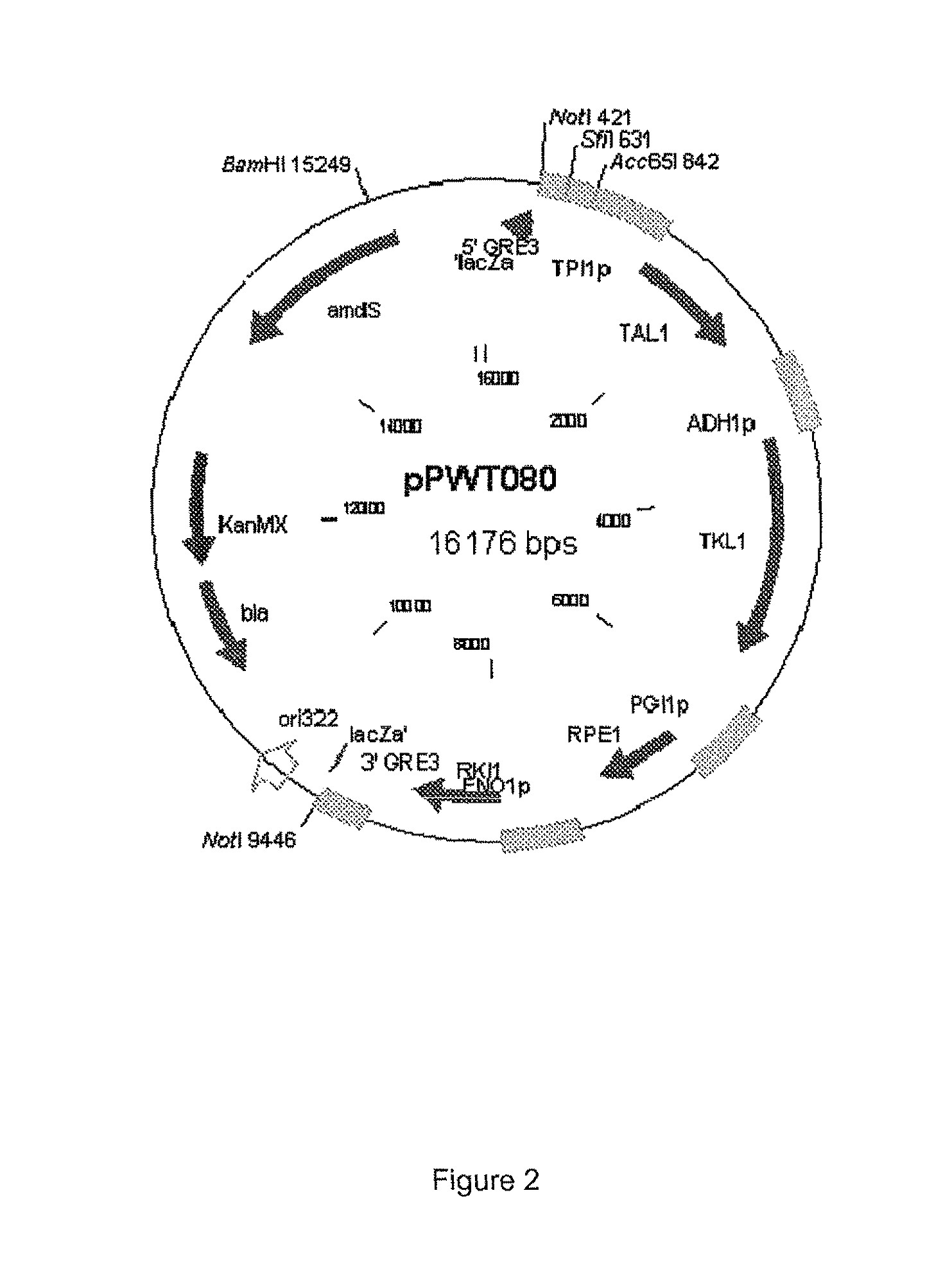
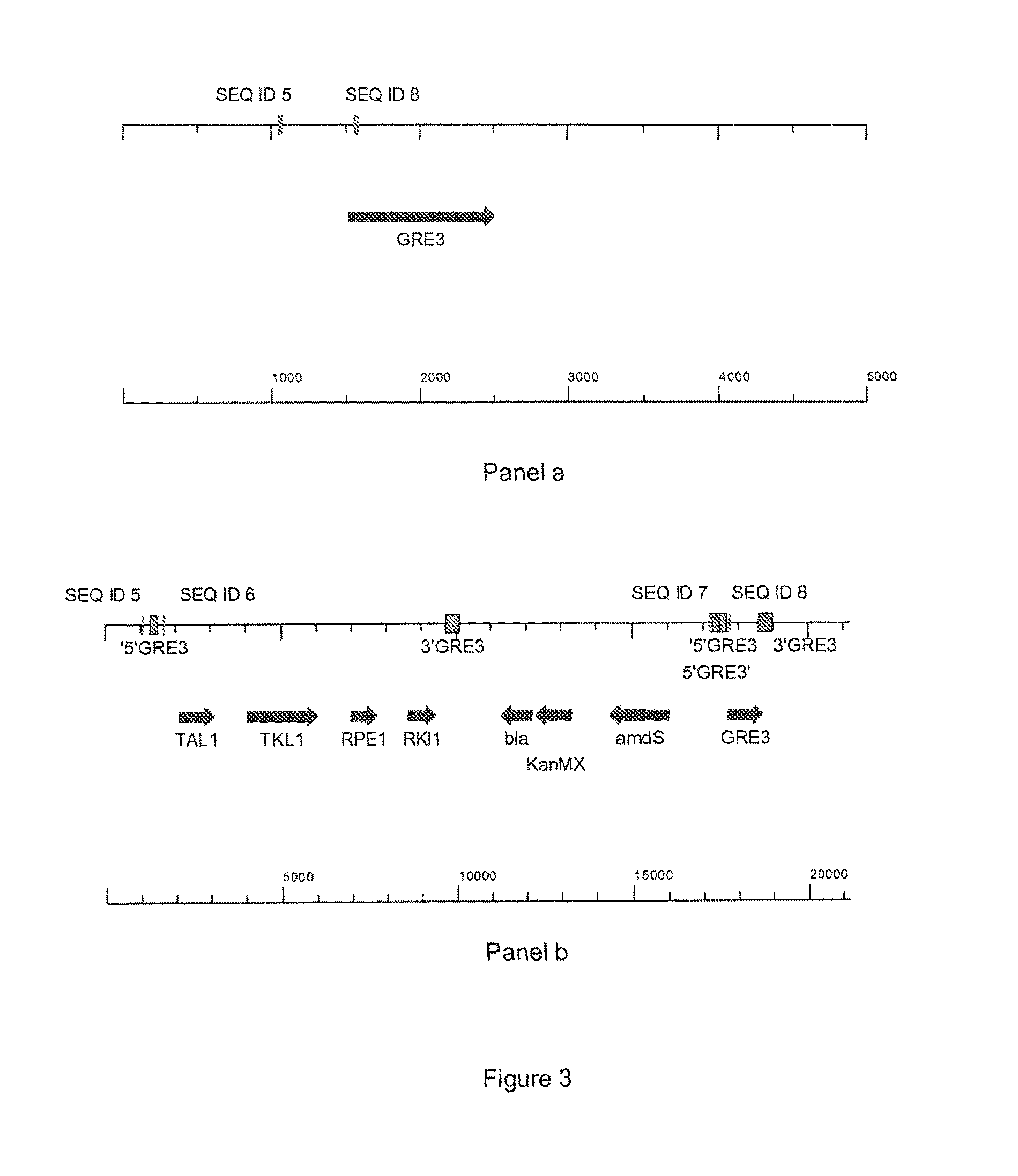
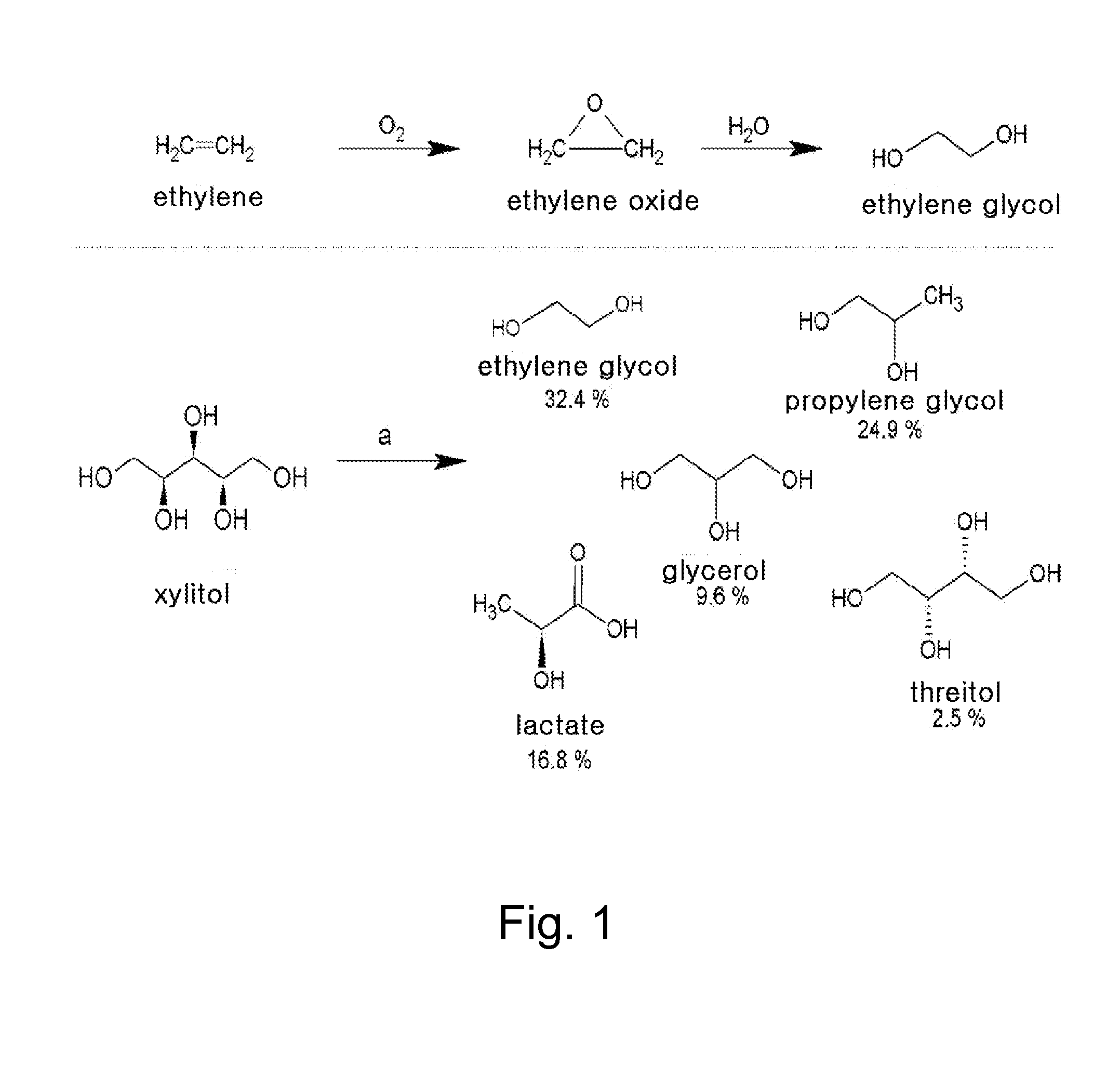
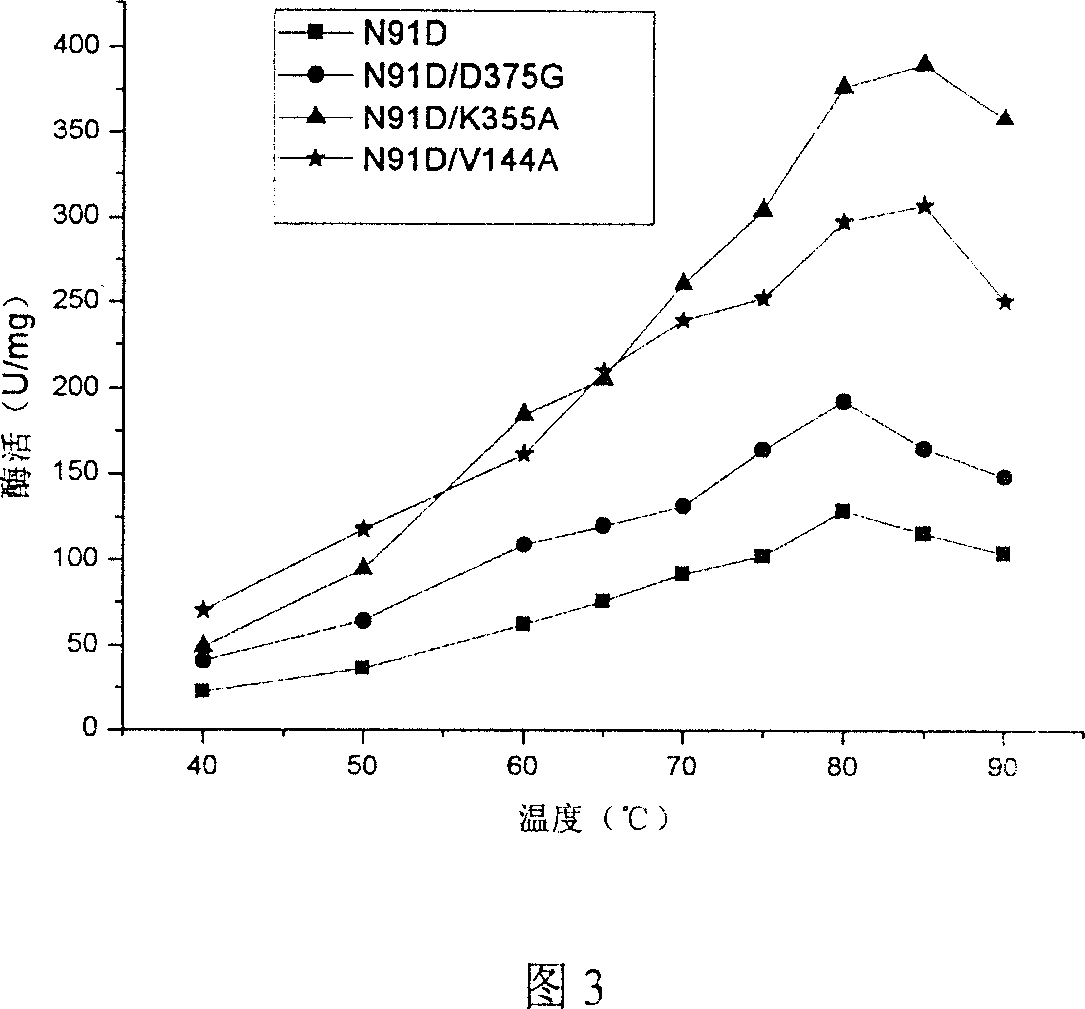
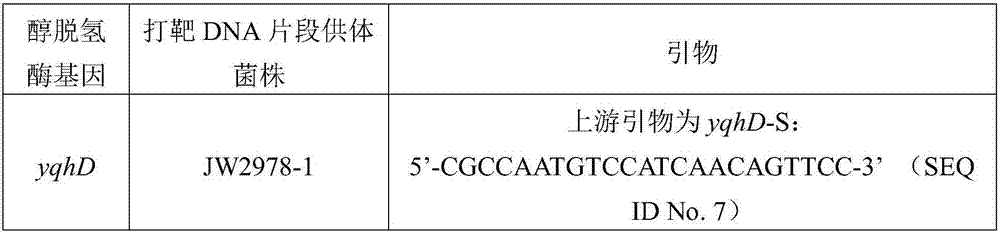
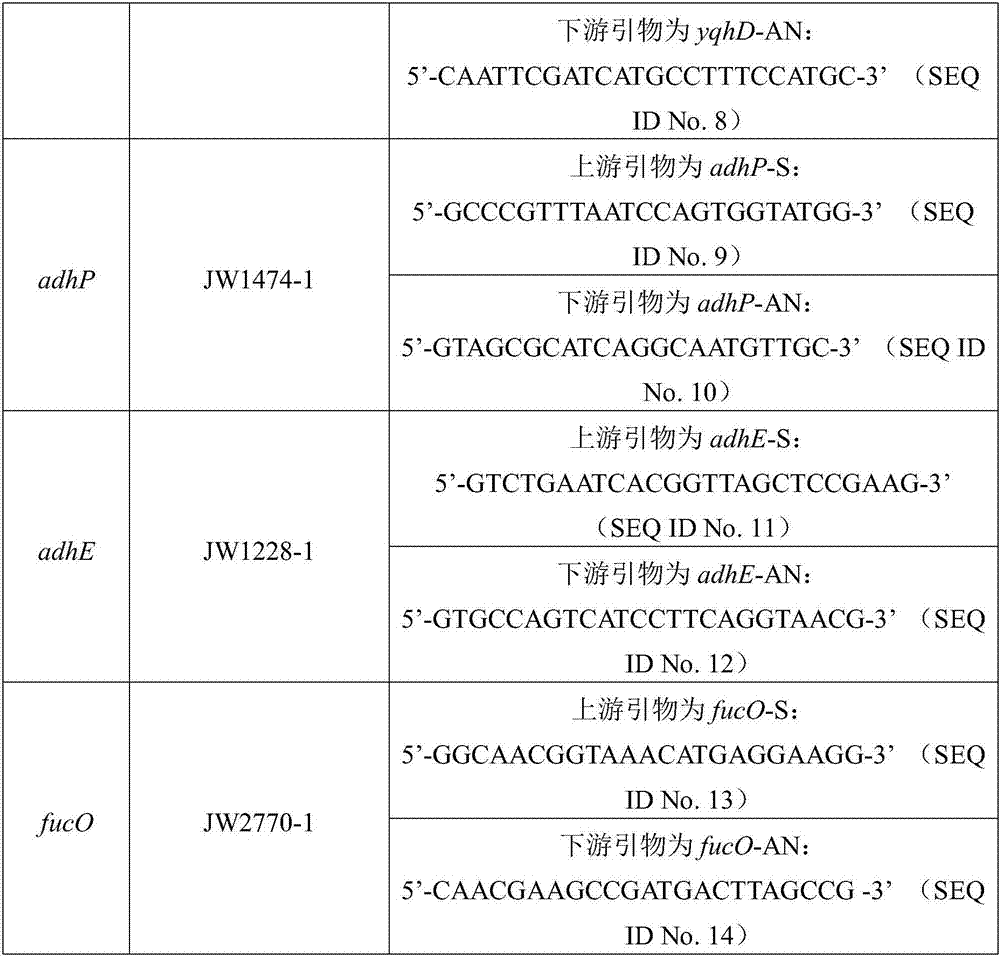
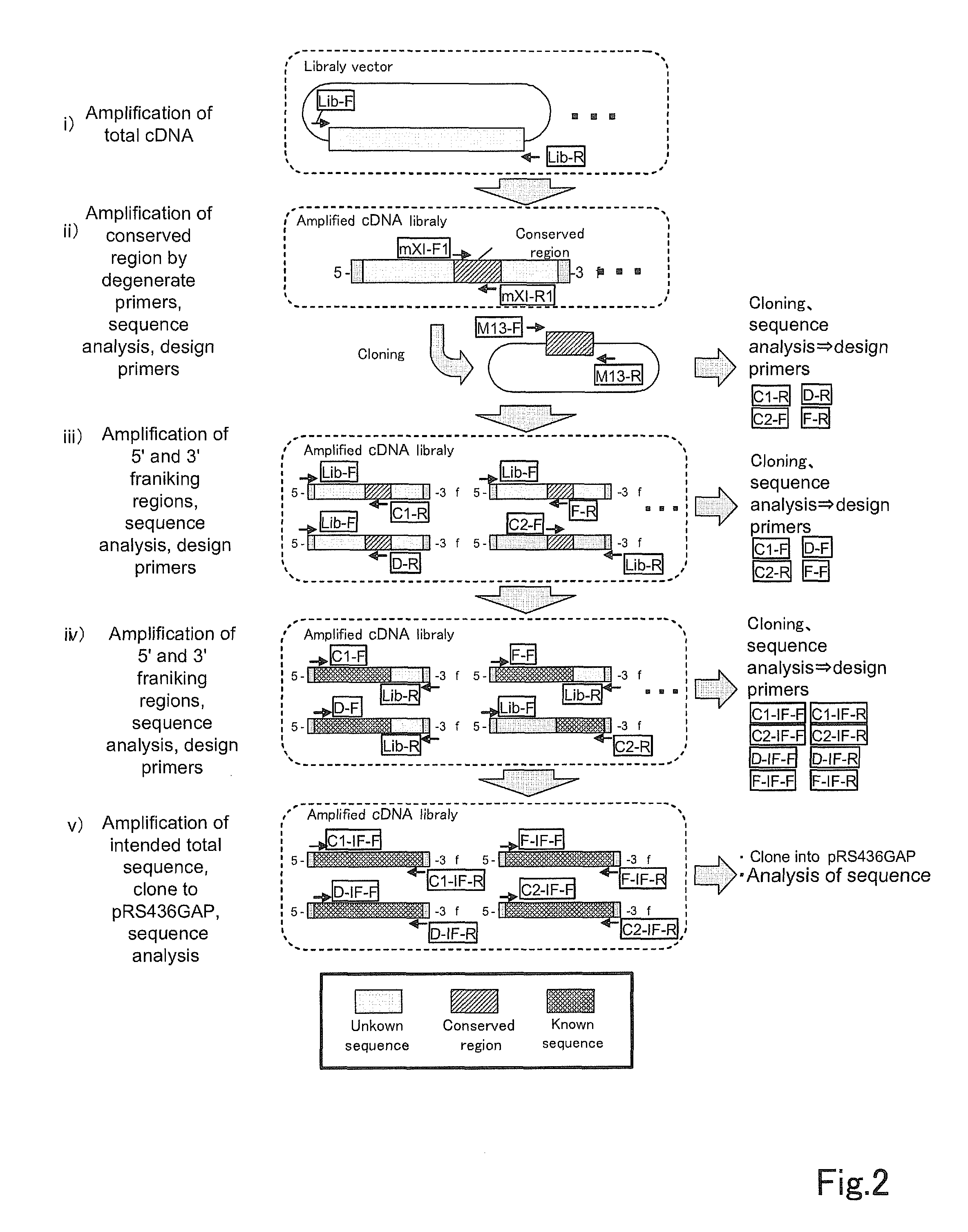
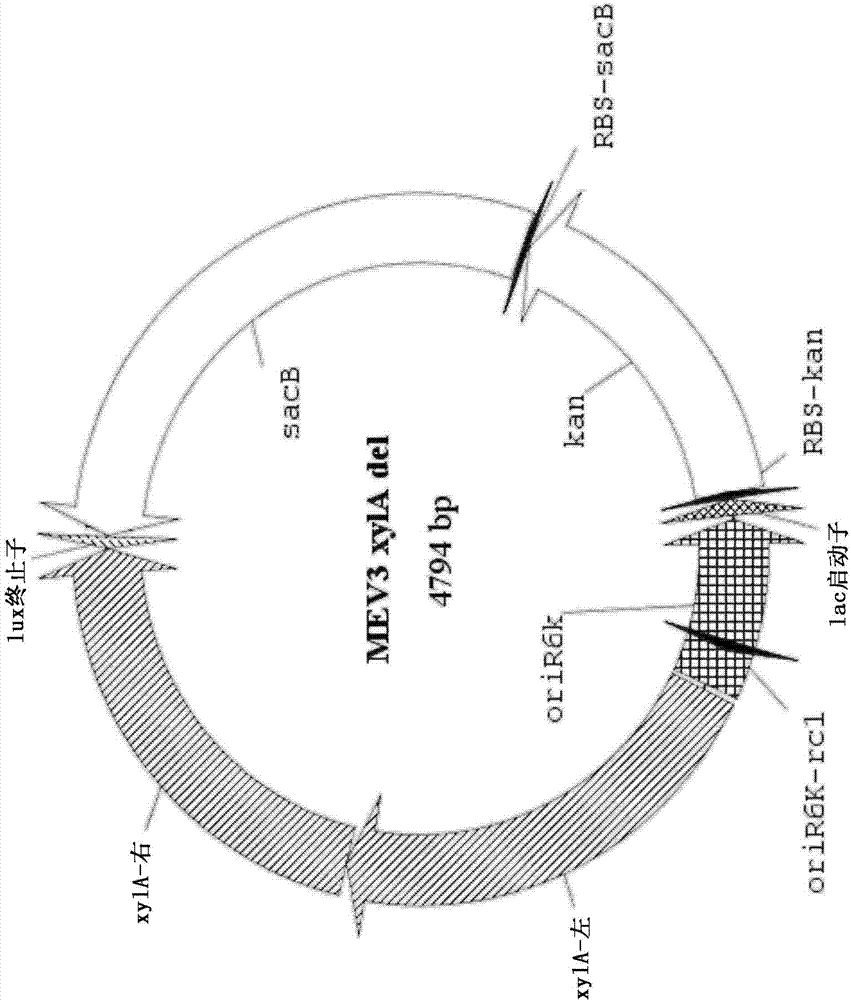
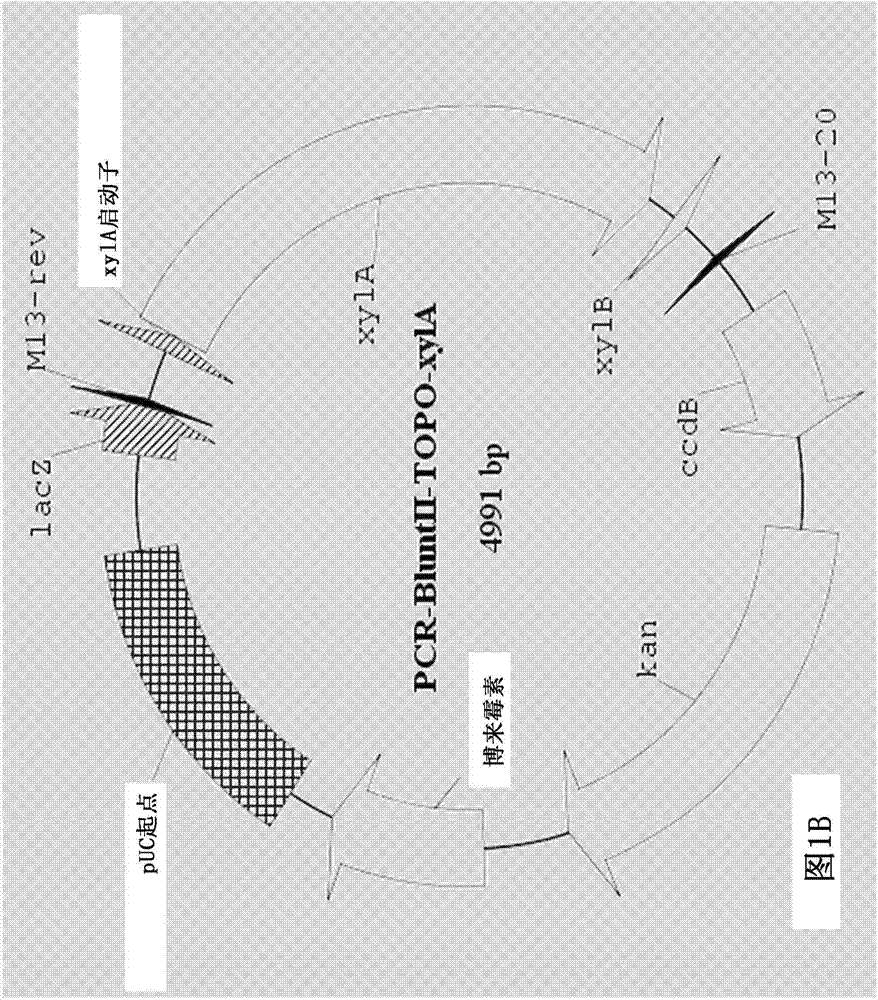
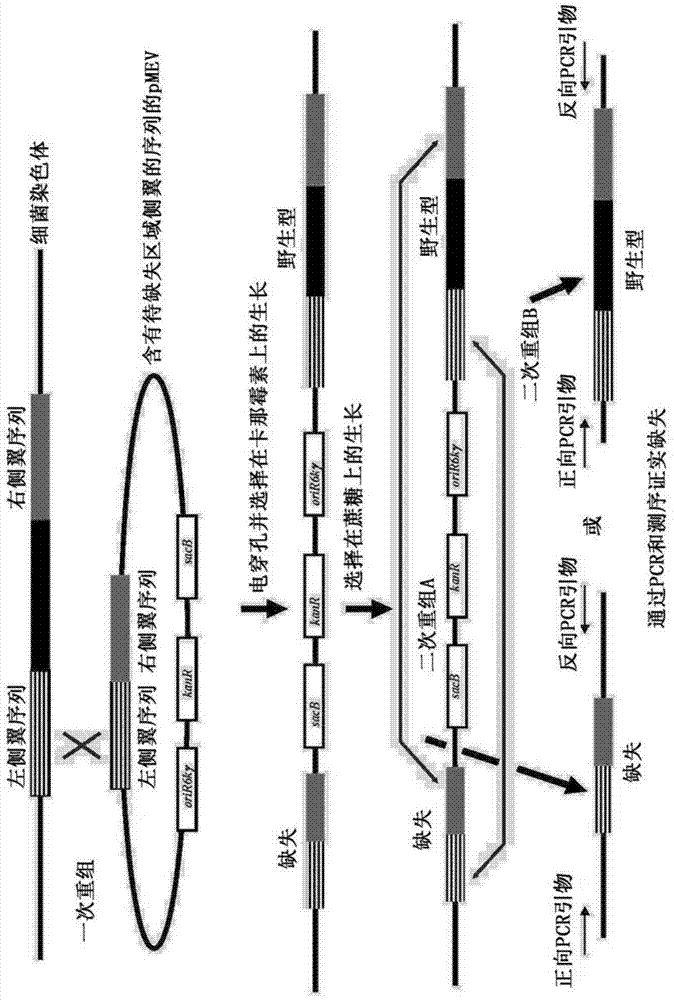
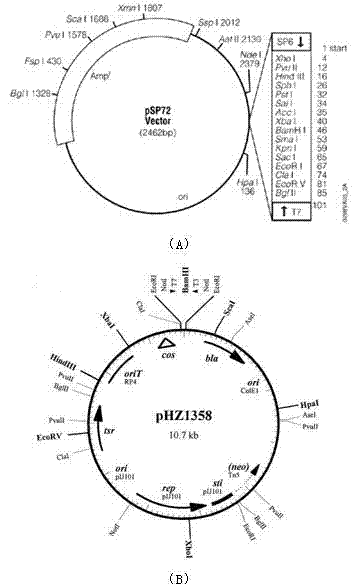
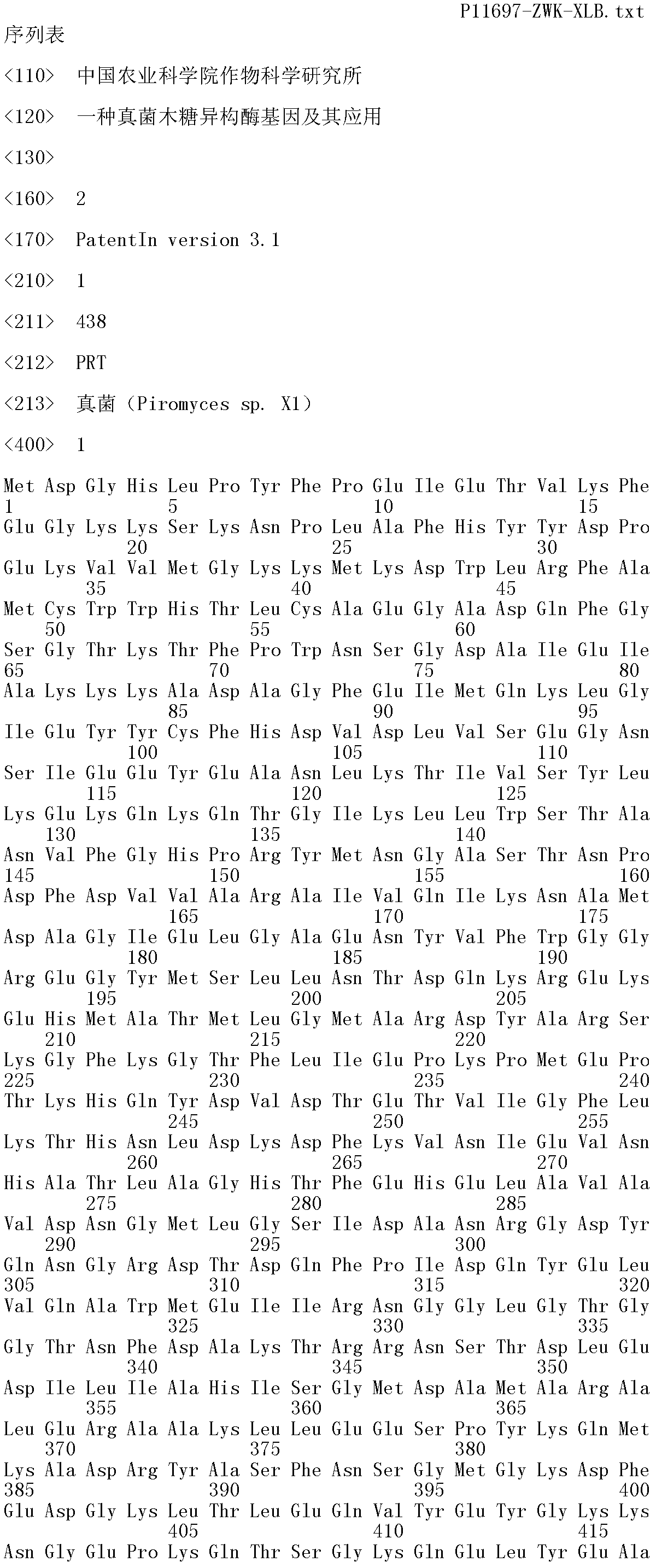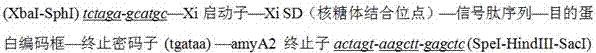Patents
Literature
98 results about "Xylose isomerase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
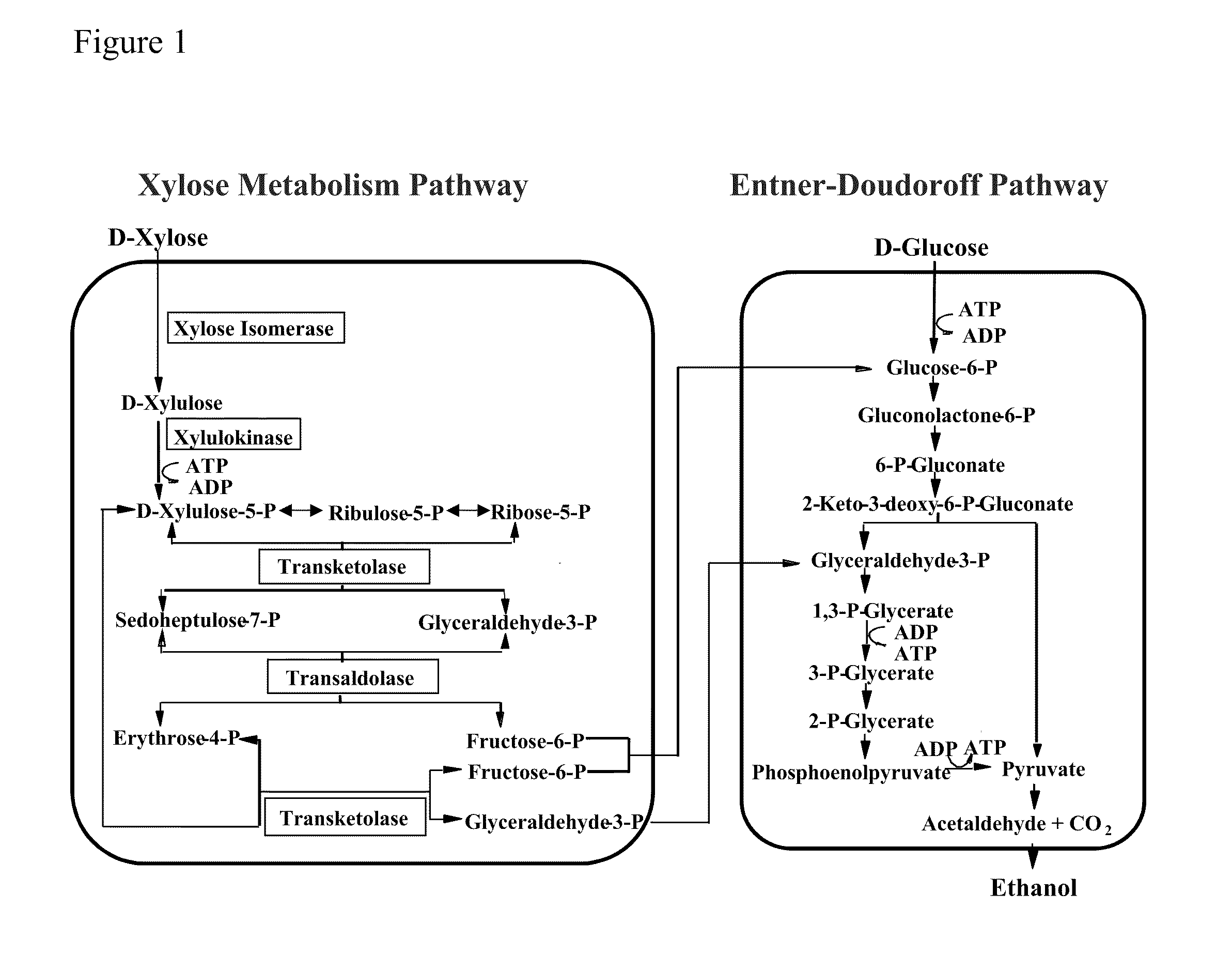
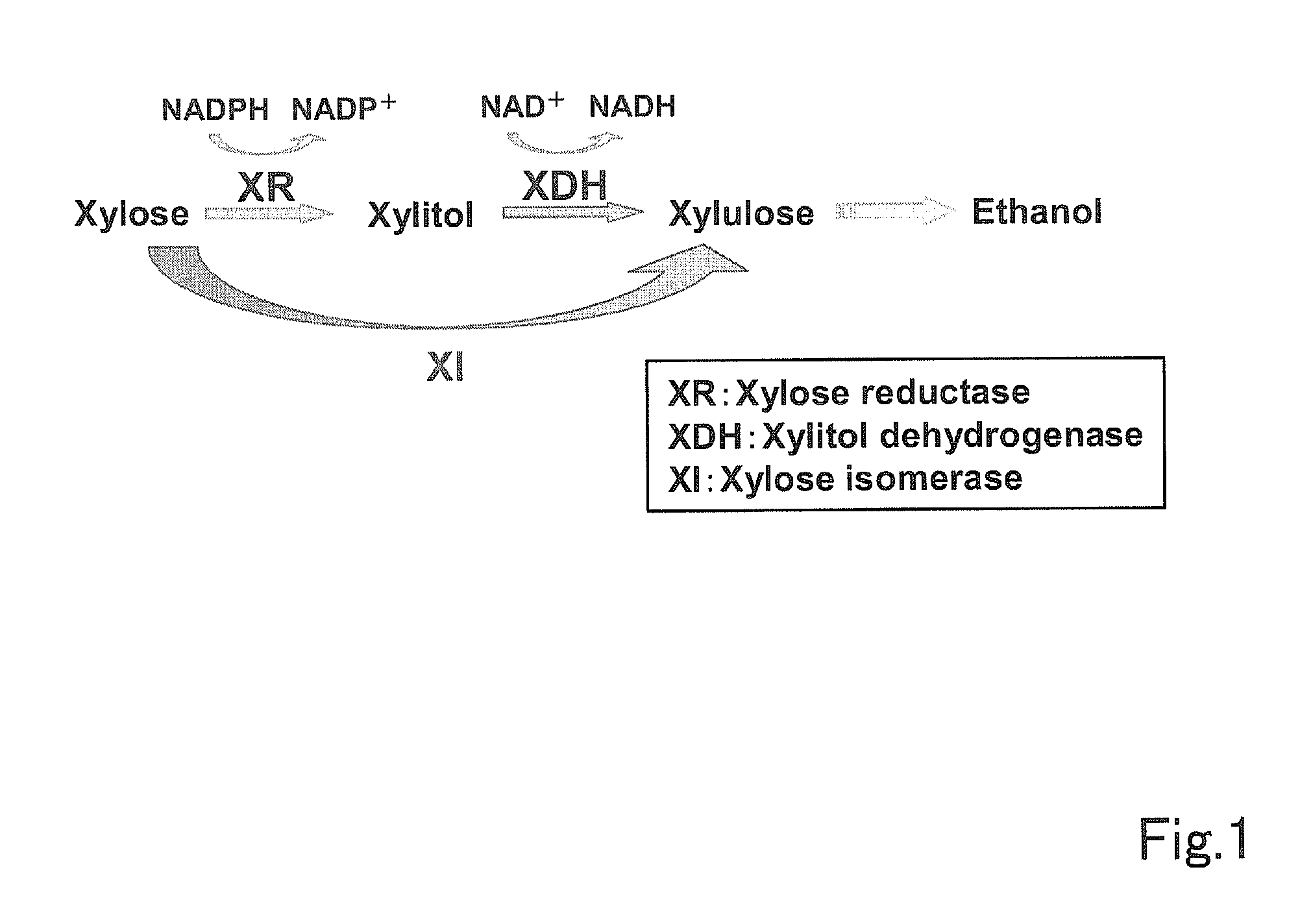
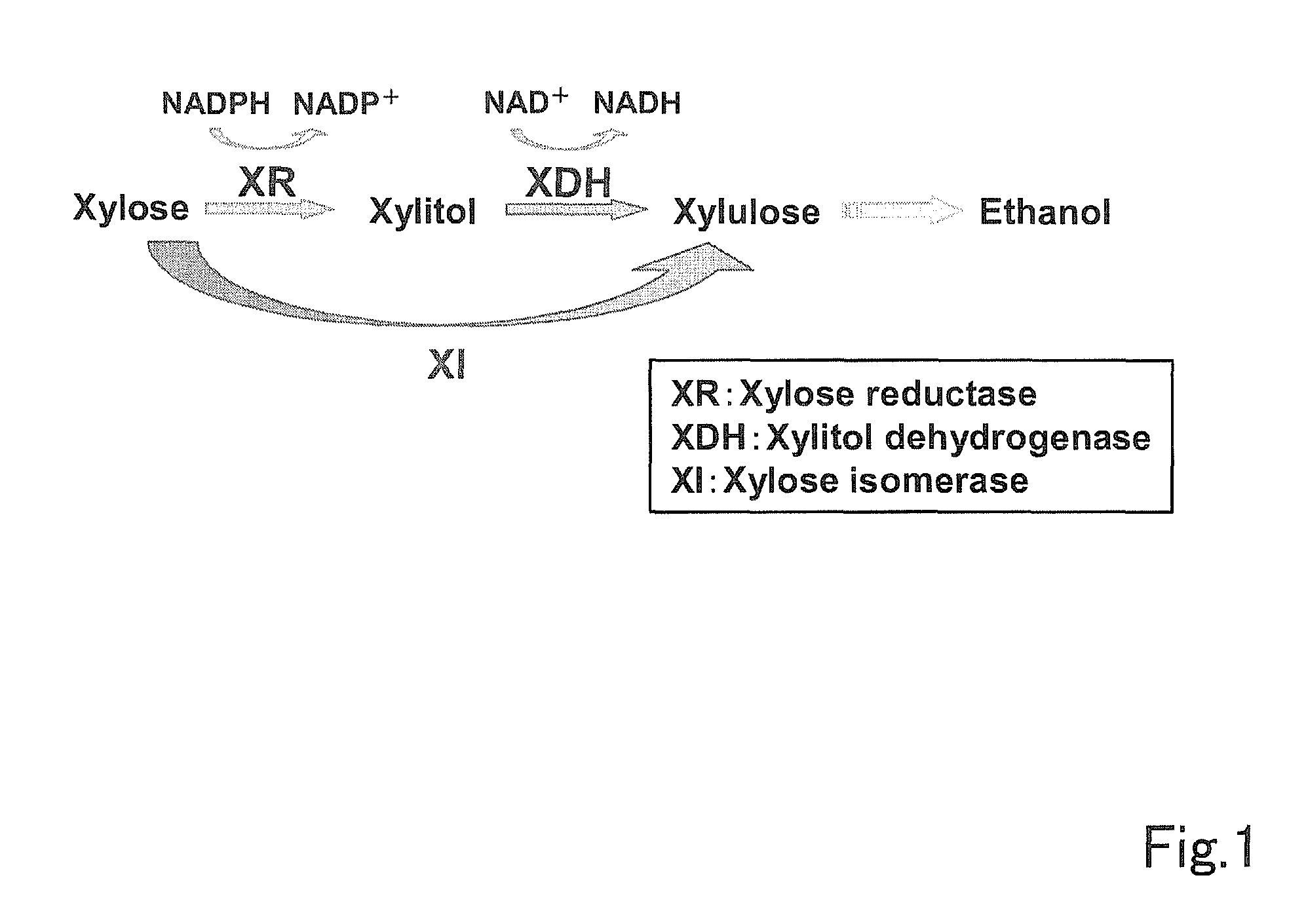
In enzymology, a xylose isomerase (EC 5.3.1.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of D-xylose and D-xylulose. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically those intramolecular oxidoreductases interconverting aldoses and ketoses. The isomerase has now been observed in nearly a hundred species of bacteria. Xylose-isomerases are also commonly called fructose-isomerases due to their ability to interconvert glucose and fructose. The systematic name of this enzyme class is D-xylose aldose-ketose-isomerase. Other names in common use include D-xylose isomerase, D-xylose ketoisomerase, and D-xylose ketol-isomerase.
Xylose utilization in recombinant zymomonas
ActiveUS20110318801A1Increase productionImprove utilizationBacteriaBiofuelsHide markov modelMolecular phylogenetics
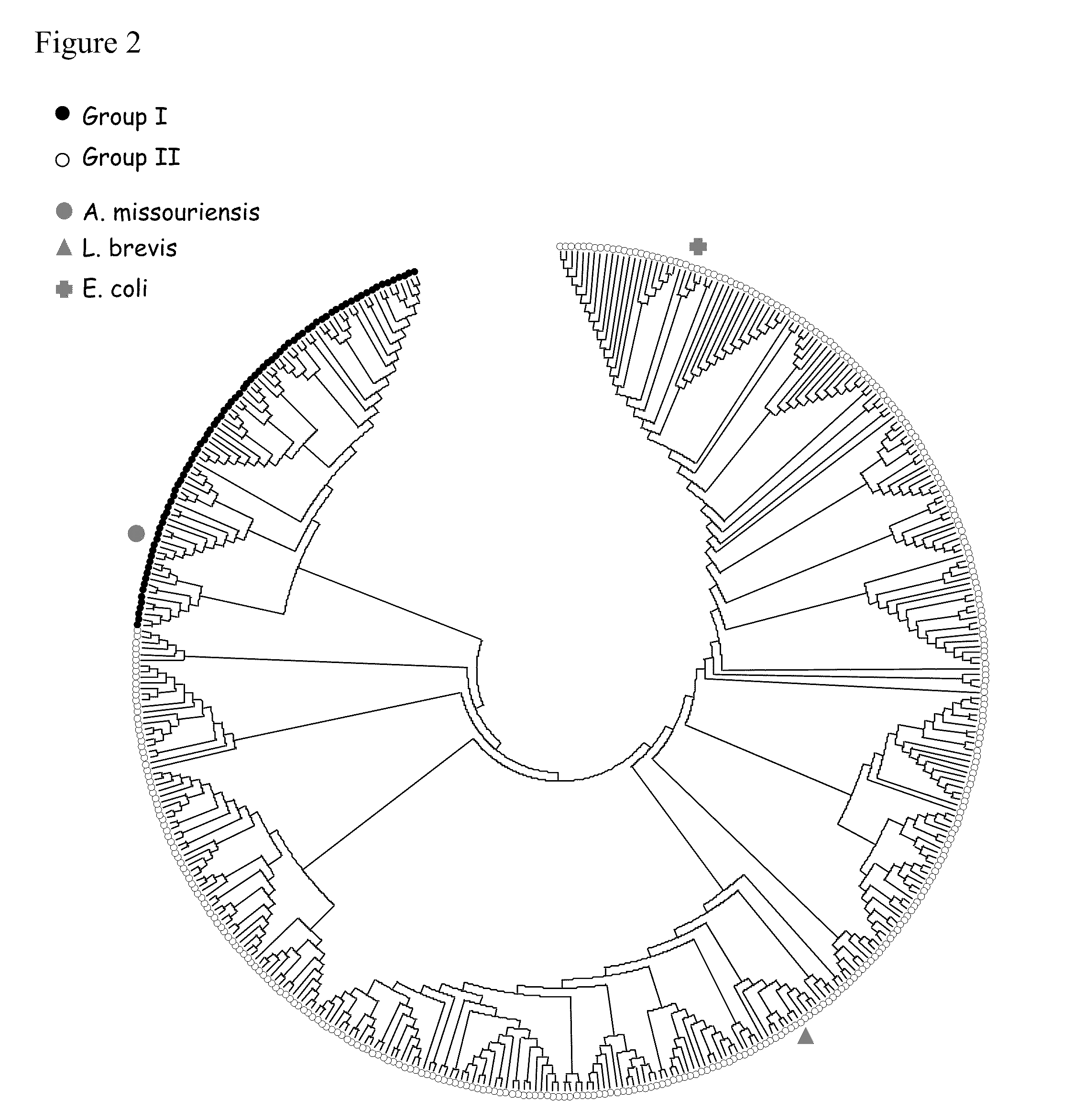
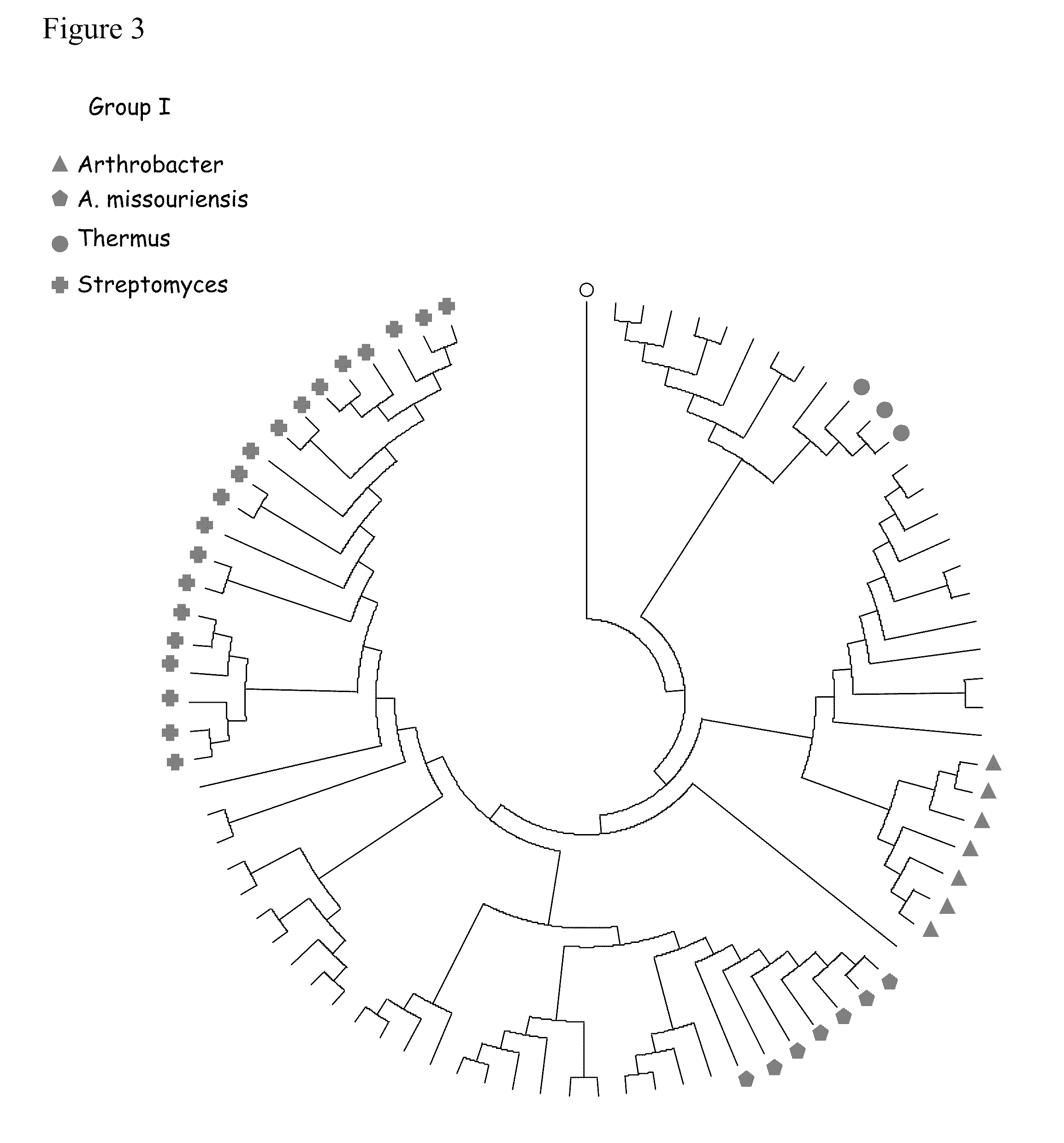
Zymomonas expressing xylose isomerase from A. missouriensis was found to have improved xylose utilization, growth, and ethanol production when grown in media containing xylose. Xylose isomerases related to that of A. missouriensis were identified structurally through molecular phylogenetic and Profile Hidden Markov Model analyses, providing xylose isomerases that may be used to improve xylose utilization.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP
Nucleic acid molecule encoding xylose isomerase and xylose isomerase encoded by the nucleic acid molecule
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
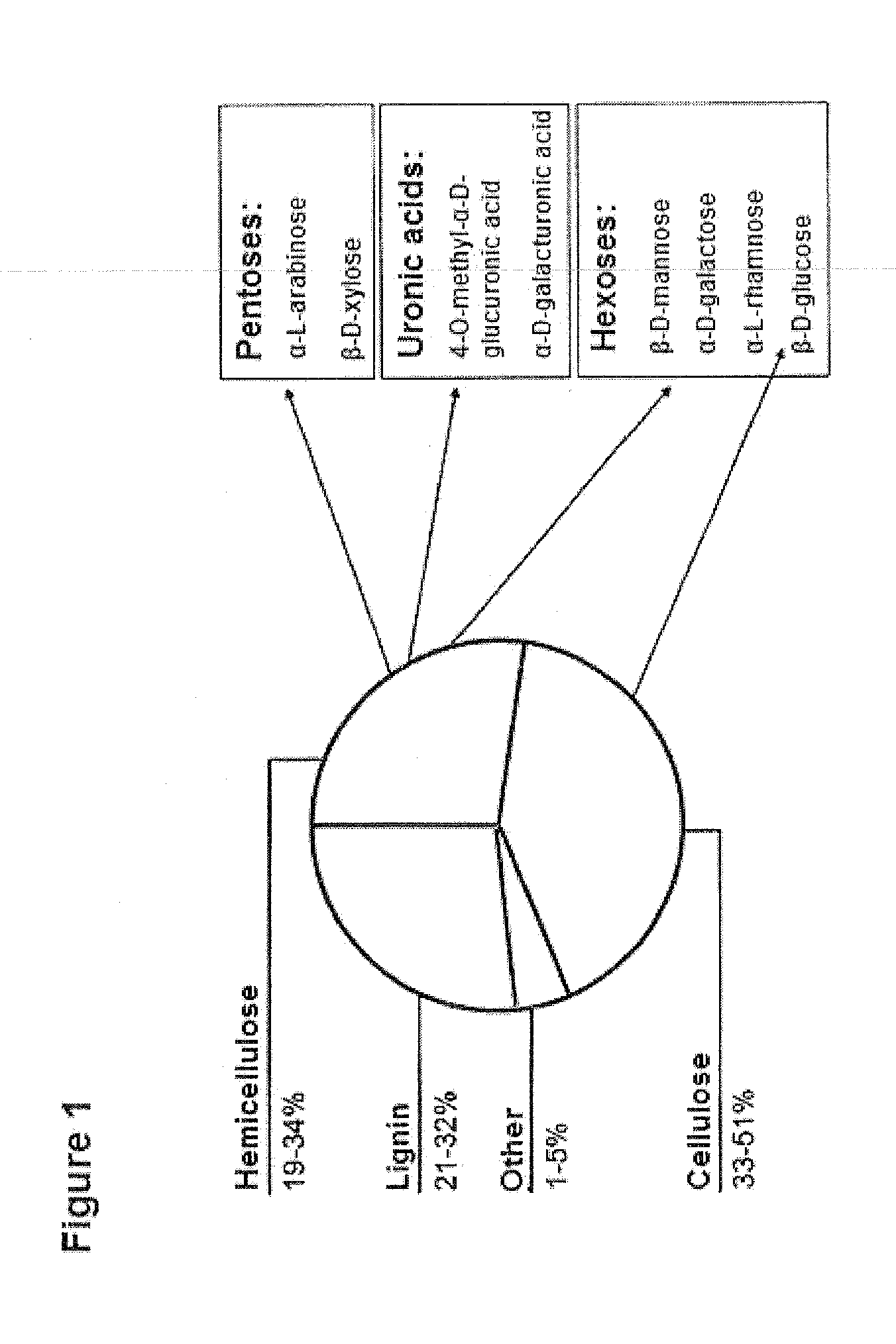
Method for producing ethanol by fermenting straws
ActiveCN101705255AOvercome stabilityOvercoming the deficiency of high residual xyloseBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesIsomerizationXylanase Y
The invention provides a method for producing ethanol by synchronizing saccharification, isomerization and fermentation of lignocellulose. In the method, cellulase, xylanase and xylose isomerase are used to enzymolyze the lignocellulose, and enzymolysis products are fermented to obtain the ethanol. The method adopts the synchronous saccharification, isomerization and fermentation of the lignocelluloses to produce the ethanol, and has the advantages of reducing the negative feedback inhibition of the enzymolysis products on the cellulase and the xylanase, increasing enzymolysis rate, shortening a fermentation period, reducing production cost and the like.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Expression cartridge for the transformation of eukaryotic cells, method for transforming eukaryotic cells, genetically modified organism, method for producing biofuels and/or biochemicals, and thus produced biofuel and/or biochemical
The present invention describes the expression cassette for transforming eukaryotic cell which comprises the peptide encoding non-natural sequence of nucleotides with xylose isomerase feature (SEQ ID NO: 1), optionally also comprising other genes of pentose phosphate route. Additionally, it is described the microorganism filed under the number DSM28739, which, in addition to the above-mentioned modifications, also present genetic modifications from adaptive evolution. The described microorganism shows efficient consumption of xylose and conversion of ethanol when compared to its correspondent without said genetic modifications and mutations from evolution. It is also described the process for producing biofuels e biochemicals, preferably ethanol, mainly from the lignocellulosic portion of the vegetal biomass. Biofuels, preferably ethanol, and biochemicals produced by the process of the invention are also described.
Owner:BIOCELERE AGROIND
Method for preparing an industrial yeast, industrial yeast, and application to the production of ethanol from at least one pentose
The present invention relates to the field of the methods for obtaining yeast strains producing ethanol, of the thereby produced strains, and of the industrial production of ethanol from said strains.More particularly, the present invention describes in its most general aspect, a method for preparing yeasts from Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains by integration into the genome of the yeast of at least one gene coding for xylose isomerase and of at least one gene coding for xylitol dehydrogenase.The strain of the invention is useful for producing ethanol from a medium comprising at least one pentose, preferably xylose or a xylose and arabinose mixture.
Owner:LESAFFRE & CIE
Xylose isomerase, and encoding gene and use thereof
The invention relates to a xylose isomerase and the coded protein and the application thereof, pertaining to the technical field of enzyme genetic engineering. A coded xylose isomerase DNA sequence is obtained from mutation at partial positions of a xylose isomerase gene xylA(Genebank EU643621) in Sorangium cellulosum 157-2. The invention also relates to enzyme coded by the DNA sequence and the application of the coded enzyme in the fields of chemical industry, food and medicine. In addition, compared with the traditional xylose isomerase, the activity of xylose isomerase of the invention in saccharomyces cerevisiae is increased by 2.8 times.
Owner:HENAN TIANGUAN GRP +1
Method for producing ethanol using recombinant yeast
The invention is intended to metabolize acetic acid and to lower acetic acid concentration in a medium at the time of xylose assimilation and ethanol fermentation by a yeast strain having xylose-metabolizing ability. The method for producing ethanol comprises a step of culturing recombinant yeast strains resulting from introduction of a xylose isomerase gene and an acetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene into a medium containing xylose, so as to perform ethanol fermentation.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Pentose sugar fermenting cell
ActiveUS8399215B2Reduce the amount of solutionMicroorganismsBiofuelsBiotechnologyXylose fermentation
The invention relates to a cell which comprises a nucleotide sequence encoding a xylose isomerase, wherein the amino acid sequence of the xylose isomerase has at least about 70% sequence identity to the amino acid sequence set out in SEQ ID NO: 3 and wherein the nucleotide sequence is heterologous to the host. The cell of the invention may be used in a process for producing a fermentation product, such as ethanol. Such a process may comprise fermenting a medium containing a source of xylose with a cell of the invention such that the cell ferments xylose to the fermentation product.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
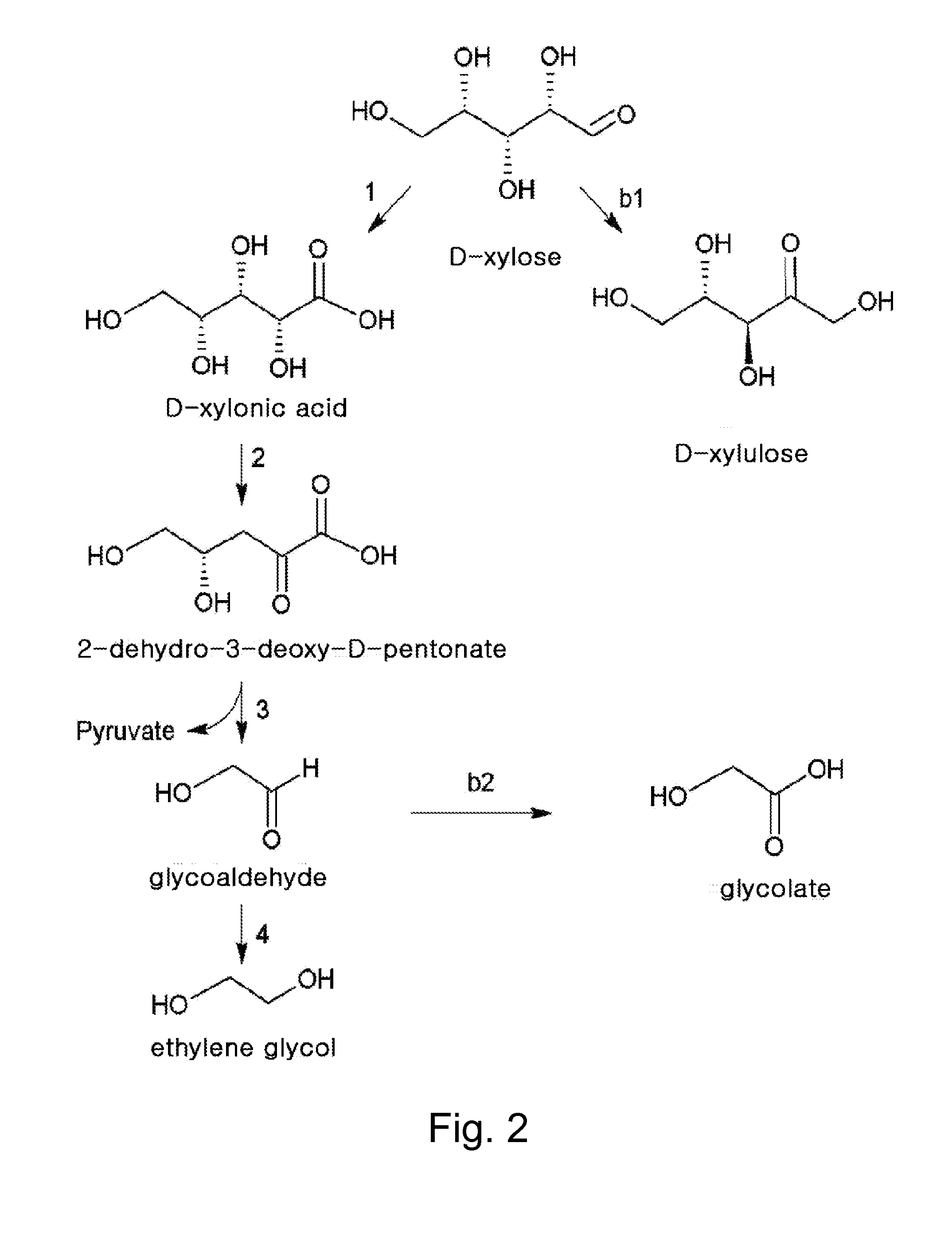
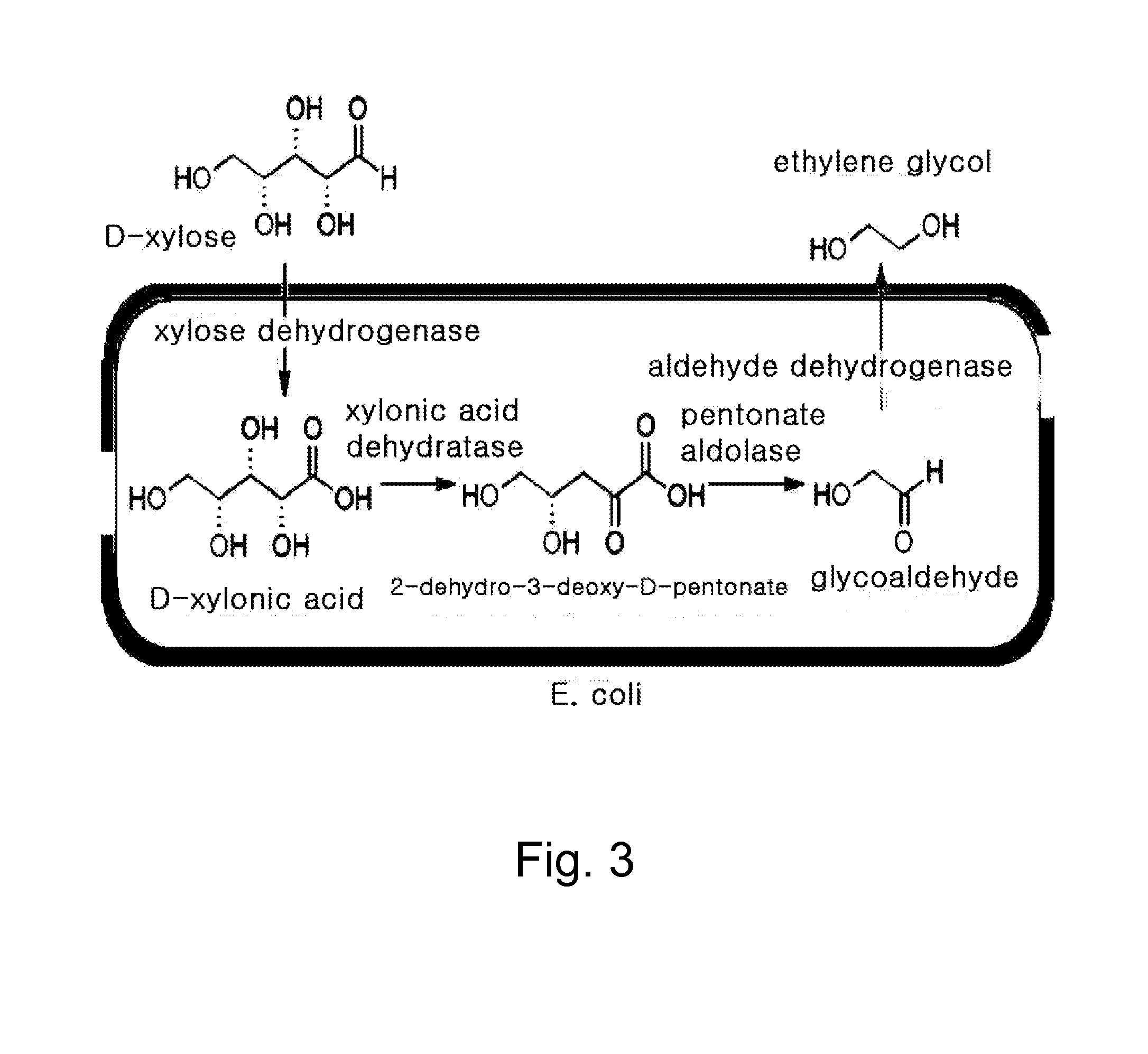
Ethane-1,2-diol producing microorganism and a method for producing ethane-1,2-diol from d-xylose using the same
Disclosed herein is a microorganism capable of producing ethane-1,2-diol from D-xylose, and a method for producing ethane-1,2-diol using the same. More specifically, the present invention relates to an engineered Escherichia coli (E. coli) prepared by knocking out a D-xylose isomerase gene and / or an aldehyde dehydrogenase gene within the genomic DNA of E. coli and transforming an expression vector including a D-xylose dehydrogenase gene into the E. coli, and an efficient method for producing ethane-1,2-diol from D-xylose using the engineered E. coli.
Owner:MYONGJI UNIV IND & ACAD COOPERATION FOUND
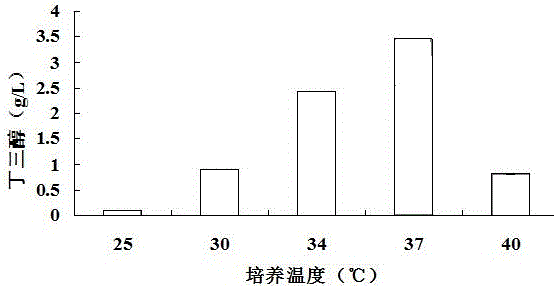
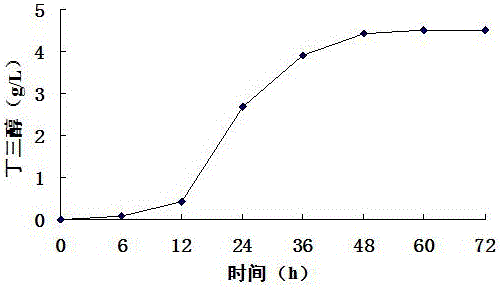
Method for producing D-1,2,4-butantriol through bio-converting cellulosic hydrolyzate
ActiveCN106148429AHigh purityReduce branch pathwaysMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesCelluloseXylonic acid
The invention discloses a method for producing D-1,2,4-butantriol through bio-converting cellulosic hydrolyzate. The method comprises the steps of constructing genes for cloning and expressing 2-keto acid decarboxylase, D-xylitol dehydrogenase, D-xylonic acid dehydrase and D-alcohol dehydrogenase, shifting the constructed genes into cells of host bacteria for knocking out xylose isomerase so as to obtain genetic engineering strains, culturing the genetic engineering strains, inoculating the genetic engineering strains to the cellulosic hydrolyzate, and carrying out fermentation so as to produce the D-1,2,4-butantriol. The method disclosed by the invention is easy and feasible, is high in yield and is applicable to industrialization.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Heat-resistant engineered yeast strains for high-temperature high-efficiency xylose fermentation and application of heat-resistant engineered yeast strains
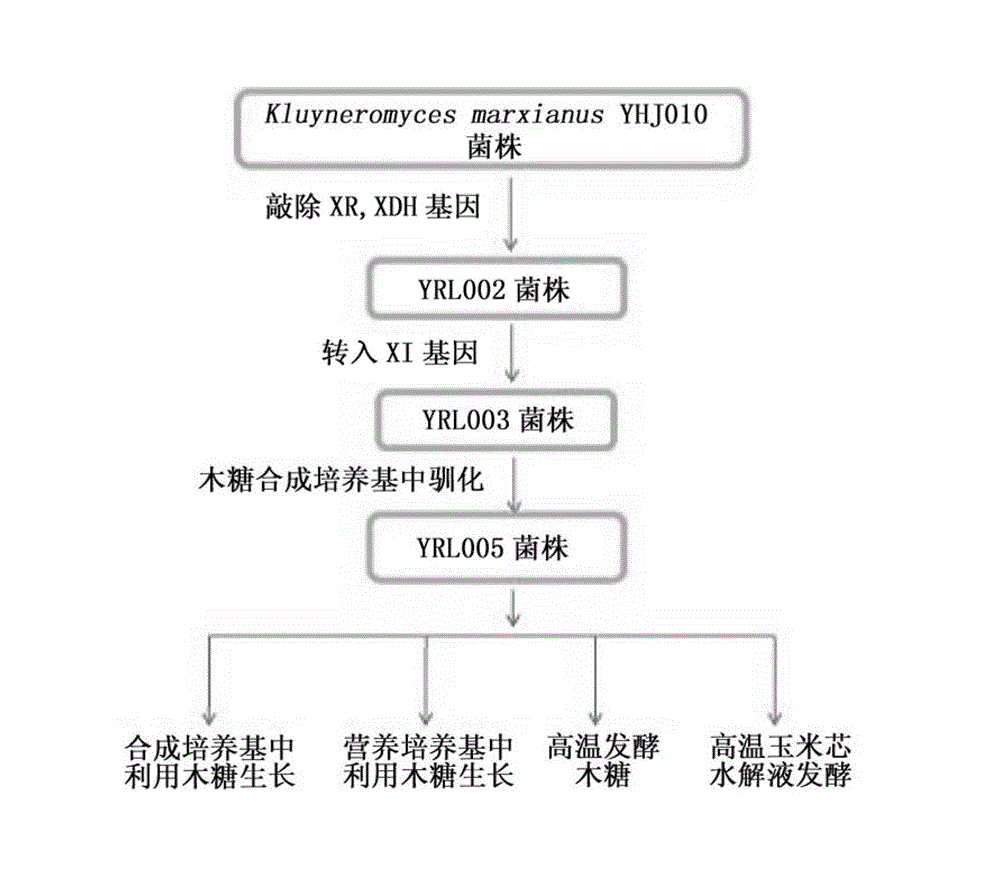
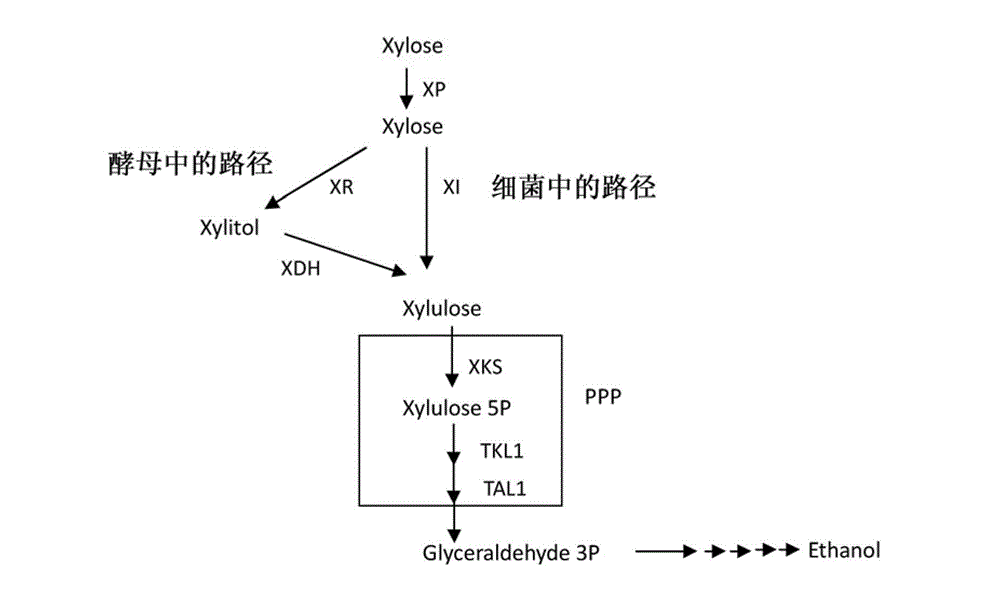
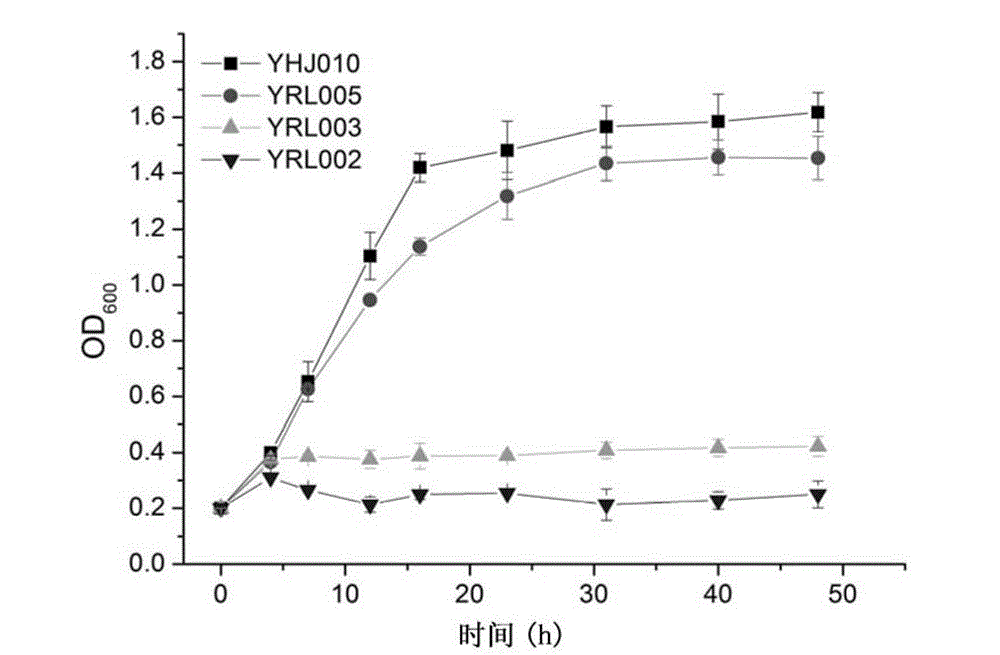
The invention relates to heat-resistant engineered yeast strains for xylose fermentation. A heat-resistant yeast strain Kluyveromyces marxianus in which xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase genes are knocked out is taken as a host, and a heat-resistant yeast expression vector containing a xylose isomerase gene of which a codon is optimized is transformed into the host. The invention also relates to domesticated strains of the heat-resistant engineered yeast strains for the xylose fermentation, a preparation method for the domesticated strains and application of the domesticated strains.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
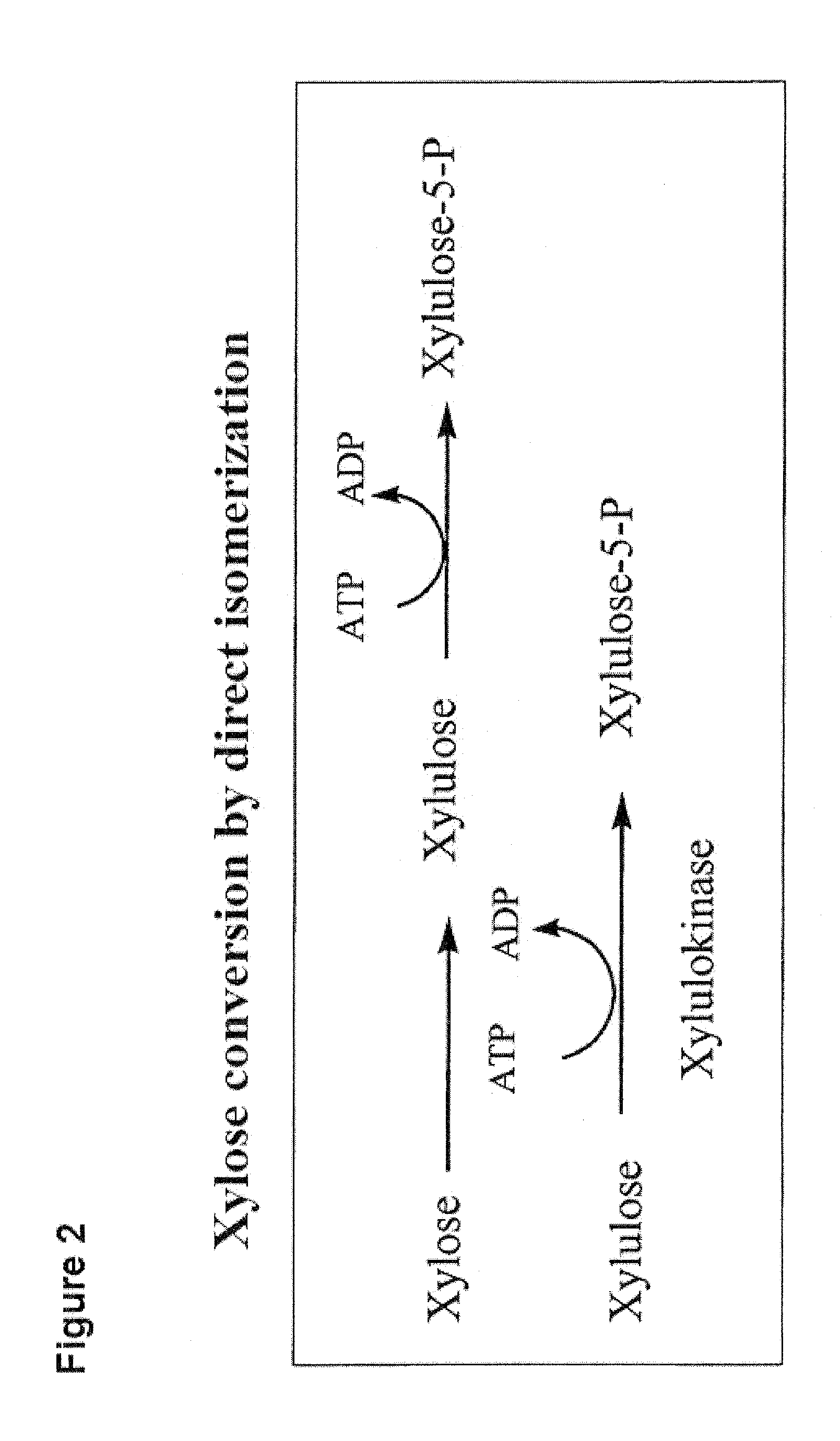
Prokaryotic Xylose Isomerase for the Construction of Xylose Fermenting Yeasts
The present invention relates to the use of nucleic acid molecules coding for a bacterial xylose isomerase (XI), preferably coming from Clostridium phytofermentans, for reaction / metabolization, particularly fermentation, of recombinant microorganisms of biomaterial containing xylose, and particularly for the production of bioalcohols, particularly bioethanol, by means of xylose fermenting yeasts. The present invention further relates to cells, particularly eukaryotic cells, which are transformed utilizing a nucleic acid expression construct which codes for a xylose isomerase, wherein the expression of the nucleic acid expression construct imparts to the cells the capability to directly isomerize xylose into xylulose. Said cells are preferably utilized for reaction / metabolization, particularly fermentation, of biomaterial containing xylose, and particularly for the production of bioalcohols, particularly bioethanol. The present invention also relates to methods for the production of bioethanol, and to methods for the production of further metabolization products, comprising the metabolization of media containing xylose.
Owner:LESAFFRE & CIE
Xylose isomerase and use thereof
It is an object of the disclosure of the present description to provide an eukaryotic cell having xylose utilization ability. The disclosure of the present description provides a novel eukaryotic cell having xylose utilization ability by transforming a yeast or other eukaryotic cell using DNA that codes a xylose isomerase from a termite protist.
Owner:RIKEN +1
Mutant xylose isomerase and its gene and application
The invention discloses mutated xylose isomerase, its coding gene and application. The amino acid sequence of the xylose isomerase is SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.3, SEQ ID NO.5 or SEQ ID NO.7. The xylose isomerase has higher activity than wild one, and can be used for high fructose syrup production. The coding gene of the mutated xylose isomerase can be used for the construction of recombinant bacterium utilizing xylose.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Activity expression and application of thermobifida fusca xylose isomerase in wine brewing yeast
The invention discloses a method for extraction of xylose isomerases by taking brown hot crack loving spore fungus as sources and the activity expression and application of the brown hot crack loving spore fungi xylose isomerases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The molecule weight of the brown hot crack loving spore fungi xylose isomerases is 43 kilodaltons; the most suitable reaction temperature of the xylose isomerases is 80 to 85 DEG C; and the most suitable reaction pH of the xylose isomerases is 7.0. The xylose isomerases can convert xyloses into xyluloses under normal biochemical reaction conditions; genes of the xylose isomerases can be recombined into the Saccharomyces cerevisiae in which the activity expression is realized, and the xyloses or other carbon sources such as lignocellulose hydrolysate and so on can be utilized for production of various fermentation products such as alcohols and so on. The method utilizes the genetic engineering means to expand substrates which are converted by the alcohols and has important theoretical significance and application value on full utilization of lignocellulose resources.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant escherichia coli, preparation method and method for synthesizing 3,4-dihydroxybutyric acid
InactiveCN107312737AAchieve leapfroggingEasy to prepareBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGlycerol
The invention relates to a recombinant escherichia coli, a preparation method and a method for synthesizing 3,4-dihydroxybutyric acid, and belongs to the field of biosynthesis. The recombinant escherichia coli is obtained through knocking out xylose isomerase gene xylA, 2-keto acid aldolase gene yjhH, 2-keto acid aldolase gene yagE and alcohol dehydrogenase gene in escherichia coli, overexpressing xylose dehydrogenase gene and / or 2-keto acid decarboxylase gene, and overexpressing aldehyde dehydrogenases gene. By taking xylose as a basic substrate, a compound substrate can be formed by adding glucose and / or glycerinum on the basis of the xylose, and the 3,4-dihydroxybutyric acid is biologically synthesized through the recombinant escherichia coli; by-products are extremely less, and the formation of the by-products can be interdicted through passage metabolism optimization. The recombinant escherichia coli, the preparation method and the method for synthesizing the 3,4-dihydroxybutyric acid have the advantages that the preparation method is simple, the production cycle is short, the cost is low, later continuous optimizing and transformation are realized, and the good industrial development and application prospect is realized.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Xylose isomerase and use thereof
Owner:RIKEN +1
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing ethanol by xylose fermentation and construction method thereof
The invention provides recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing ethanol by xylose fermentation and a construction method thereof. In the invention, candida boidinii is led to the saccharomyces cerevisiae to metabolize a DNA fragment of a coding gene of related enzymes of the xylose, so that the saccharomyces cerevisiae can secrete and express xylose isomerase the enzymatic reaction conditions of which are close to growth conditions of the saccharomyces cerevisiae, so the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae can effectively utilize the xylose to produce the ethanol, thus solving the technical problem that the saccharomyces cerevisiae can not utilize the xylose to produce the ethanol. The invention lays a foundation for industrial application of the saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing the ethanol by using xylose fermentation, thus having great economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
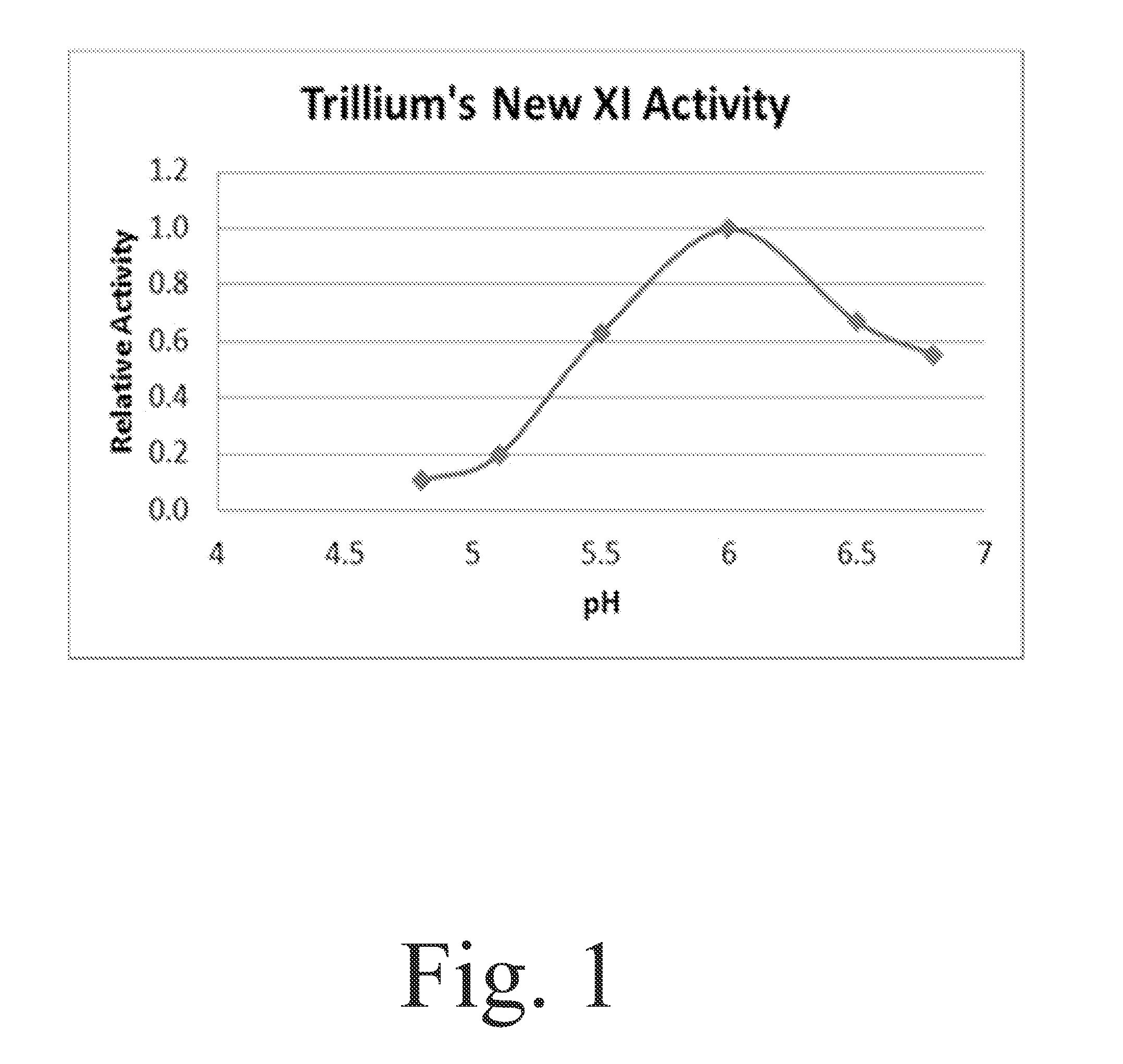
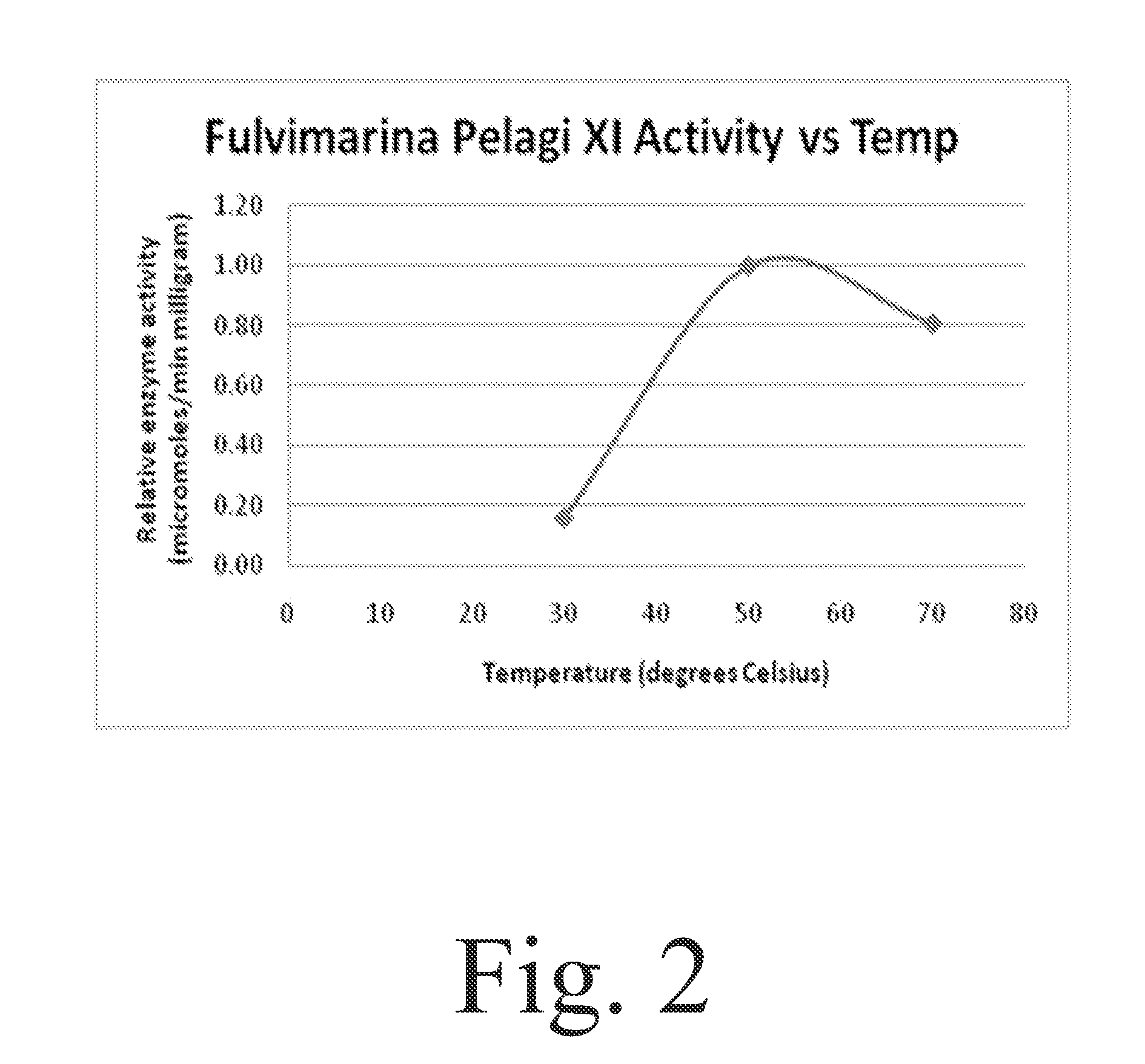
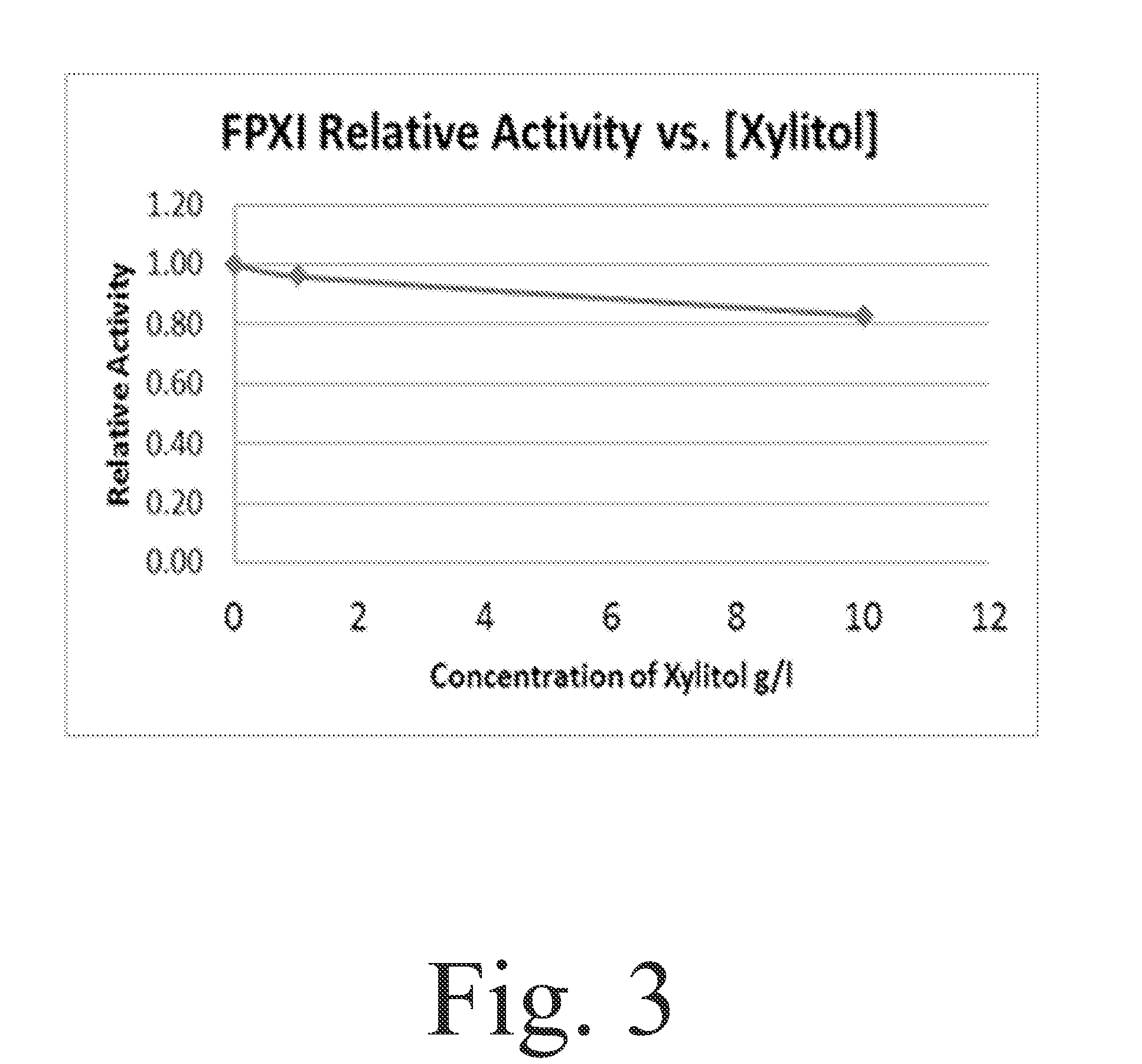
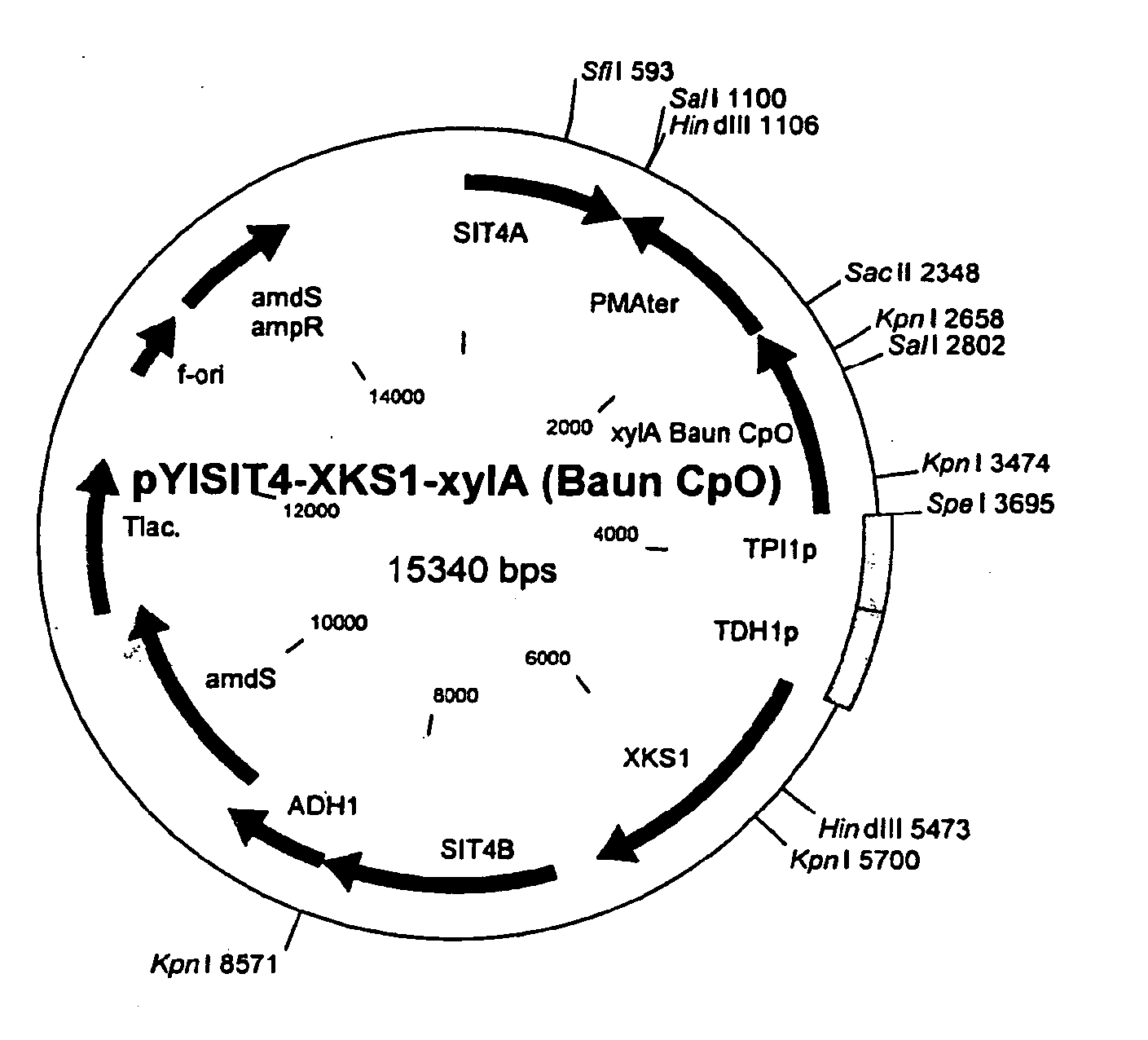
Method enabling isomerization process flows at lower pH, lower temperature, and in the presence of certain inhibiting compounds by using the xylose isomerase enzyme from the microorganism Fulvimarina pelagi
The present invention enables isomerization process flows at lower pH, lower temperature, and in the presence of certain inhibiting compounds by using the xylose isomerase enzyme from the microorganism Fulvimarina pelagi. The xylose isomerase from this marine bacterium not only is very active at the fermentation pH and temperature, it is also tolerant of xylitol and calcium in the amounts generated in biomass fermentation conditions. For the HFCS application, the xylose isomerase from Fulvimarina pelagi is pH compatible with the process and is tolerant of calcium in the amounts found in the HFCS process. The temperature optimum is similar to commercially available amylase / gluco-amylase products.
Owner:BEATTY CHRISTOPHER CHARLES +2
Pentose sugar fermenting cell
The invention relates to a cell which comprises a nucleotide sequence encoding a xylose isomerase, wherein the amino acid sequence of the xylose isomerase has at least about 70% sequence identity to the amino acid sequence set out in SEQ ID NO: 3 and wherein the nucleotide sequence is heterologous to the host. A cell of the invention may be used in a process for producing a fermentation product, such as ethanol. Such a process may comprise fermenting a medium containing a source of xylose with a cell of the invention such that the cell ferments xylose to the fermentation product.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
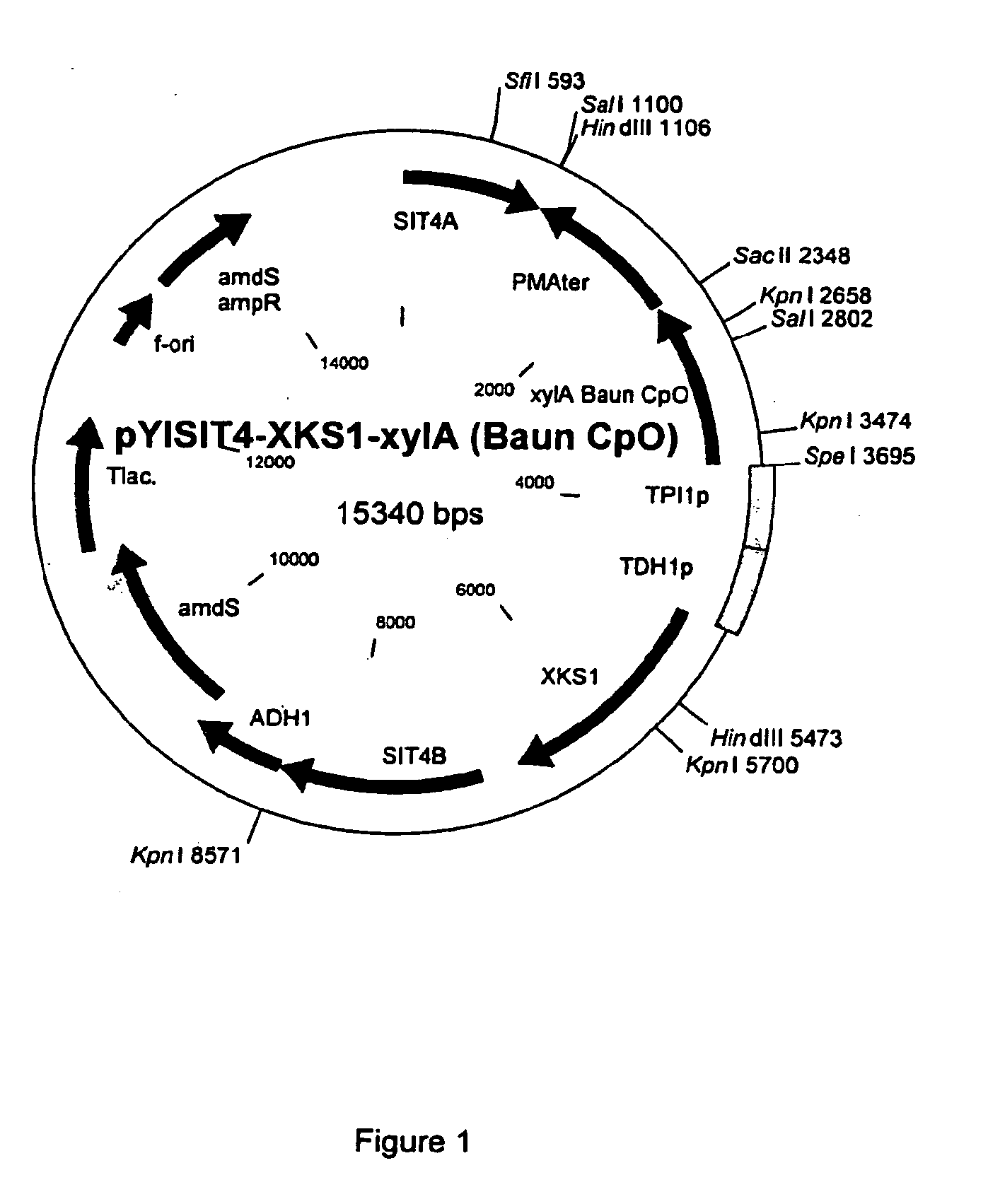
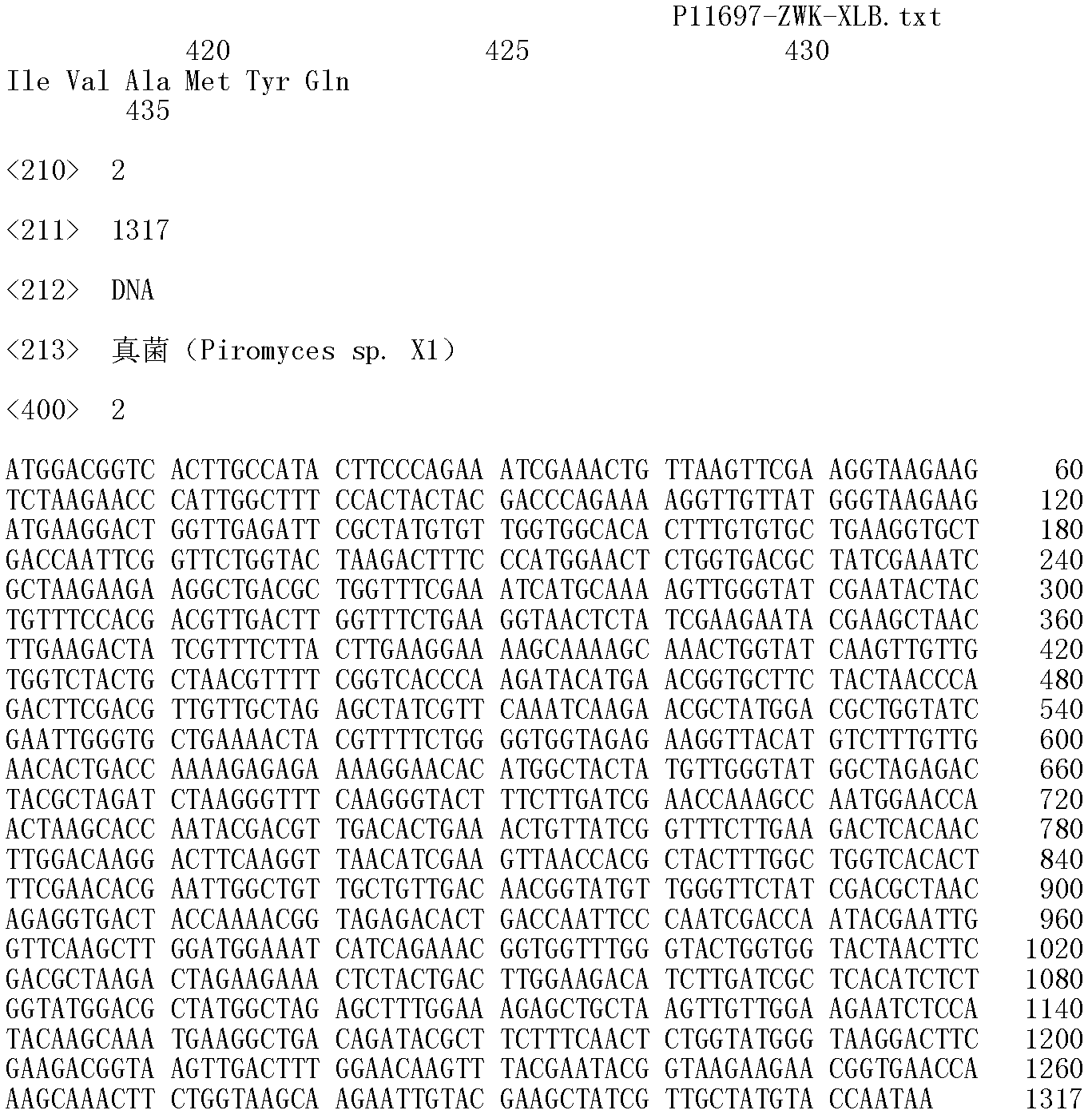
Fungi xylose isomerase gene and application thereof
The invention relates to a novel xylose isomerase gene from fungi, and an application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the xylose isomerase gene is shown as SEQ ID No.2. A novel yeast engineering bacterium is obtained by introducing recombinant plasmids containing the gene into saccharomyces cerevisiae. Experiments demonstrate that the saccharomyces cerevisiae that has no capability for conversing xylose to xylosone originally gains a conversion capability for conversing xylose to xylosone after the gene is expressed in the saccharomyces cerevisiae. The engineering bacterium can prepare ethanol and other fermentation products by fermenting a medium comprising the xylose.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for extracting xylitol and D-galactitol from xylose mother solution
The invention discloses a method for extracting xylitol and D-galactitol from xylose mother solution, which adopts a homologous exchange method to construct a bacillus subtilis 168 xylose isomerase gene (xylA) deficient strain Bsxyl, utilizes the engineering strain Bsxyl to purify xylose mother solution to obtain xylose and D-galactose and further carries out catalytic hydrogenation and crystallization separation to obtain xylitol and galactitol. The Bsxyl strain is already stored in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on March 25, 2010, the strain accession number of the Bsxyl strain is CGMCC No.3692, and the strain can purify xylose mother solution to obtain xylose and D-galactose. The strain can purify fermentation culture solution containing xylose mother solution, so that the total purity of xylose and galactose can reach more than 88.8 percent, and after further catalytic hydrogenation and crystallization separation, obtaining xylitol and D-galactitol the purity of which is more than 98 percent.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV FOR NATITIES
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for expressing xylose isomerase and construction method
ActiveCN105368731AImprove ethanol yieldFast filtrationFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousXylose fermentation
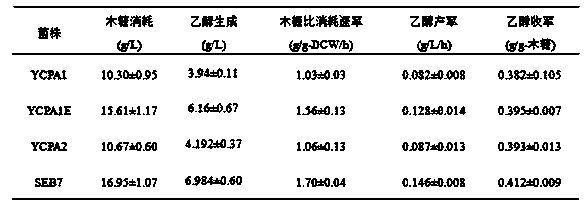
The invention discloses a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for expressing xylose isomerase and a construction method and solves the problem that after heterogenous expression of xylA gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a recombinant bacterium constructed thereby has a low growth rate in xylose, causing the fermentation requirement to be not met. The invention includes a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain SEB7, collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center under CGMCC11327. The invention also provides a construction method of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain SEB7. The strain SEB7 obtained by the invention can generate ethanol 6.98 g / L within a fermenting time of 48 h by using xylose 16.95 g / L, with ethanol yield up to xylose 0.412 g / g; the strain has the advantages such as high xylose fermentation speed and high ethanol yield.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Screening method for using xylose isomerase genes for peanut genetic transformation
InactiveCN102433354AAvoid safety hazardsScreening method safetyMicrobiological testing/measurementHorticulture methodsSucroseSaccharum
The invention provides a screening method for using xylose isomerase genes for peanut genetic transformation. The screening method comprises the following steps of: constructing a recombinant vector with target genes; transforming the recombinant vector into peanut embryo lobule explants; transferring the transformed embryo lobule explants to an induction culture medium with sucrose and xylose for culturing until embryos are induced; transferring the embryos to a germination culture medium for culturing until seedlings are induced; performing PCR(polymerase chain reaction) detection on regrowth to obtain transgene positive plants; and transplanting the transgene positive plants to fields by a grafting method. According to the screening method, the culture medium with the 5 g / L of sucrose and the 10 g / L of xylose is used for culturing, so that the transgene plants can be screened, and hidden danger possibly caused by screening by using antibiotics is avoided, and the transformation efficiency is high, and the screening method is a safe and high-efficient screening method.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Mutant xylose isomerase and its gene
The invention discloses a discontinuous xylo-pfan isomerase and its genes. The discontinuous xylo-pfan isomerase selects form Thermus thermophilus and its amino acid sequence is indicated by SEQ ID NO.2. The said discontinuous xylo-pfan isomerase has improved specificity to the substrate D-wood sugar without changing original heat endurance. The discontinuous xylo-pfan isomerase can be used in miscible liquids including wood sugar and amylaceum to specially detect the wood sugar content and can be used in constructing recombination bacteria with wood sugar.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Xylose isomerases and their uses
This disclosure relates to novel xylose isomerases and their uses, particularly in fermentation processes that employ xylose-containing media.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Function and application of xylose isomerase gene of non-glutinous rice
The invention discovers that a xylose isomerase gene of non-glutinous rice has the function of converting xylose into xylulose. According to the invention, a recombinant plasmid containing the gene is constructed and is introduced into saccharomyces cerevisiae to obtain new engineered saccharomyces cerevisiae. Experiments prove that the saccharomyces cerevisiae which does not have the function ofconverting xylose into xylulose obtains the conversion capacity after the xylose isomerase gene is expressed in a host cell.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Construction method for streptomycete expression plasmids and production method for keratinase
InactiveCN102533833AIncrease productionHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionAmylaseSrc family kinase
The invention relates to a construction method for streptomycete expression plasmids and a production method for keratinase. The construction method for streptomycete expression plasmids includes the following steps: a promoter Xi of actinoplanes missouriensis xylose isomerase and a terminator of streptomycete avermitilis amylase are sleeved, and the promoter-shine-dalgarno (SD) sequence comes from 90 to 269bp of an actinoplanes missouriensis xylose isomerase gene; a cloned src family kinases (sfks) gene is inserted in a construction expression frame structure of a synthetic Xi promoter-SD-amyA2 terminator fragment, and then a conventional method is used for constructing the streptomycete expression plasmids. The production method for keratinase includes: leading the streptomycete expression plasmids into an expression host of streptomycete lividans TK24 through conjugal transfer, performing recombinant expression and generating the keratinase. Specific activity of a crude enzyme solution is 1700 U / mg after expression of the expression plasmids in the streptomycete lividans TK24 and is improved by 50 times compared with specific activity of starting strain streptomycete fradiae varieties S-221, and yield of the keratinase is much higher than starting strains after the expression.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Xylose isomerase producing method
InactiveCN102747063AWide reaction temperature rangeWide reaction pH rangeMicroorganism based processesIsomerasesEscherichia coliGenus Thermus
The invention discloses a xylose isomerase producing method and belongs to the technical field of biology. The xylose isomerase producing method includes: firstly, cloning xylose isomerase genes of thermus, streptomyces and escherichia coli; secondly, constructing a pichia pastoris expression vector, a saccharomyces cerevisiae expression vector and a bacillus subtilis expression vector which include three xylose isomerase gene expression cassettes, and transforming the vectors to corresponding host bacteria respectively; thirdly, respectively screening recombinants of over-expression xylose isomerases as engineering bacteria; and finally, fermenting the pichia pastoris engineering bacteria, the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria and the bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria to produce a recombinant mixed xylose isomerase. Different from a traditional single-gene-coded xylose isomerase, the recombinant mixed xylose isomerase is wide in suitable reaction temperature and pH (potential of hydrogen) range and suitable for various purposes, and yield of the xylose isomerase expressed by the engineering bacteria including the polygene expression cassettes is obviously higher than that of the xylose isomerase expressed by engineering bacteria including single genes, so that production cost is reduced.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Method for expressing xylose isomerase by applying pGAP regulation of Pichia pastoris
InactiveCN101698840AReduce manufacturing costEase of mass productionMicroorganism based processesIsomerasesBiotechnologyYeast
The invention relates to a method for expressing xylose isomerase by applying pGAP regulation of Pichia pastoris, belonging to the biotechnology field. Firstly, pGAP promoters are amplificated in Pichia pastoris, a Pichia pastoris expression vector of which xylose isomerase is regulated by the pGAP is built, and then the Pichia pastoris expression vector is transformed into Pichia pastoris genome. High copy recons are selected as engineering bacterial strain according to resistance genes on the Pichia pastoris expression vector, and the engineering bacterial strain is inoculated into liquid culture medium containing carbon source to ferment engineering bacteria for secreting and expressing the xylose isomerase. The invention has the advantages of low production cost and short fermenting period. The using of the pGAP regulation of Pichia pastoris to express the xylose isomerase is favorable to purifying the product, and the problems of high production cost and hard product purification caused by using natural bacterial strains produced xylose isomerase to produce xylose isomerase can be solved. The invention is favourable for mass production of xylose isomerase.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com