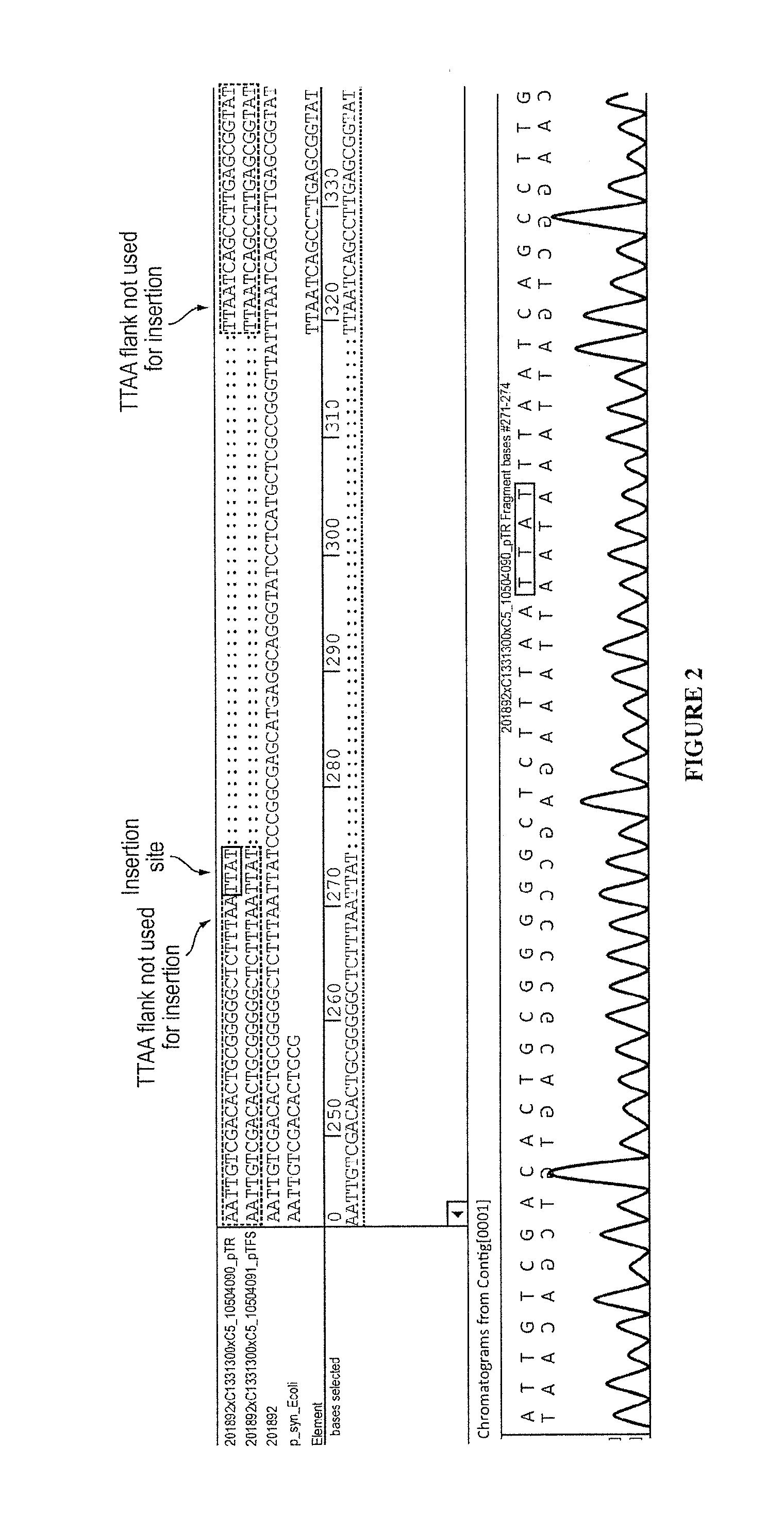
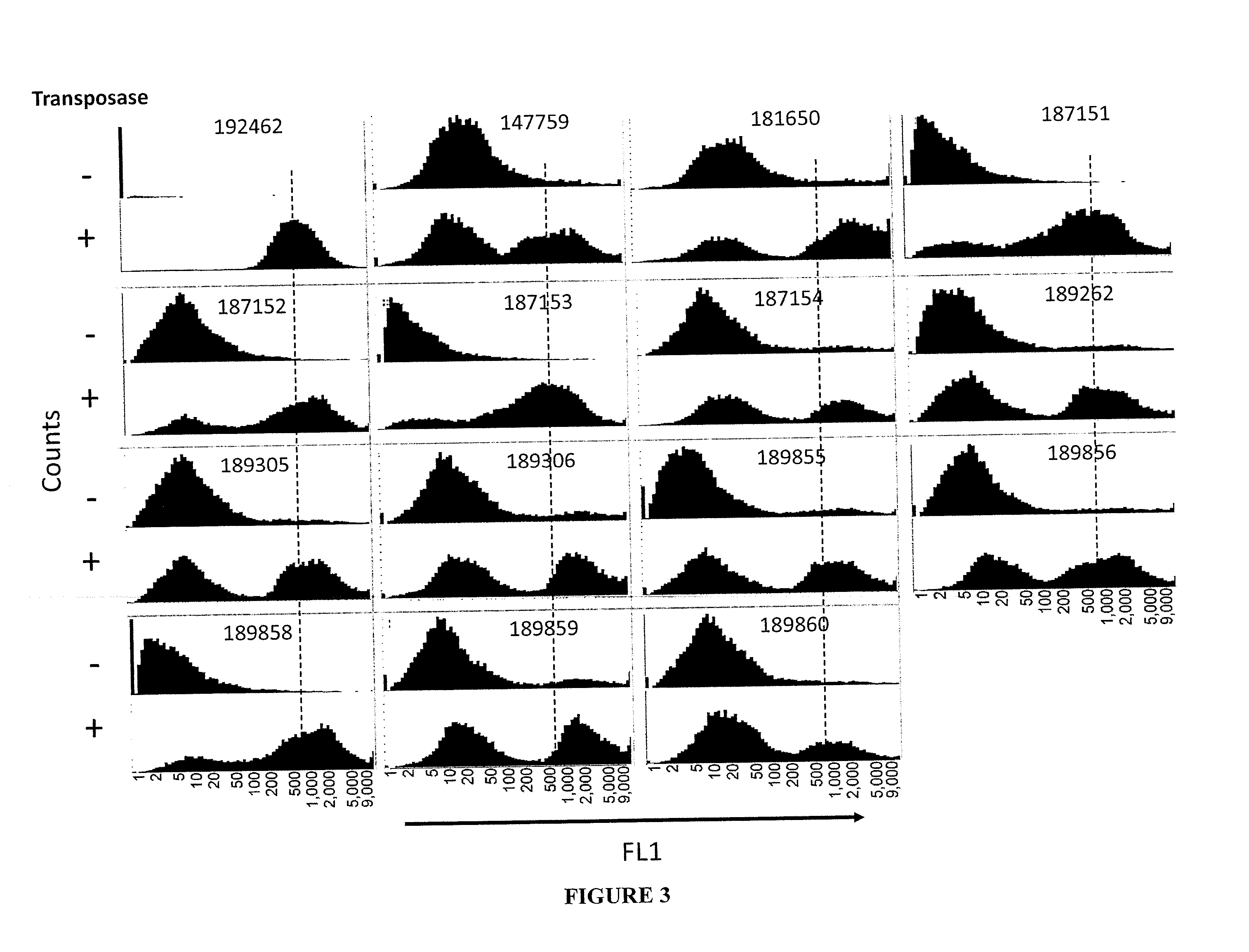
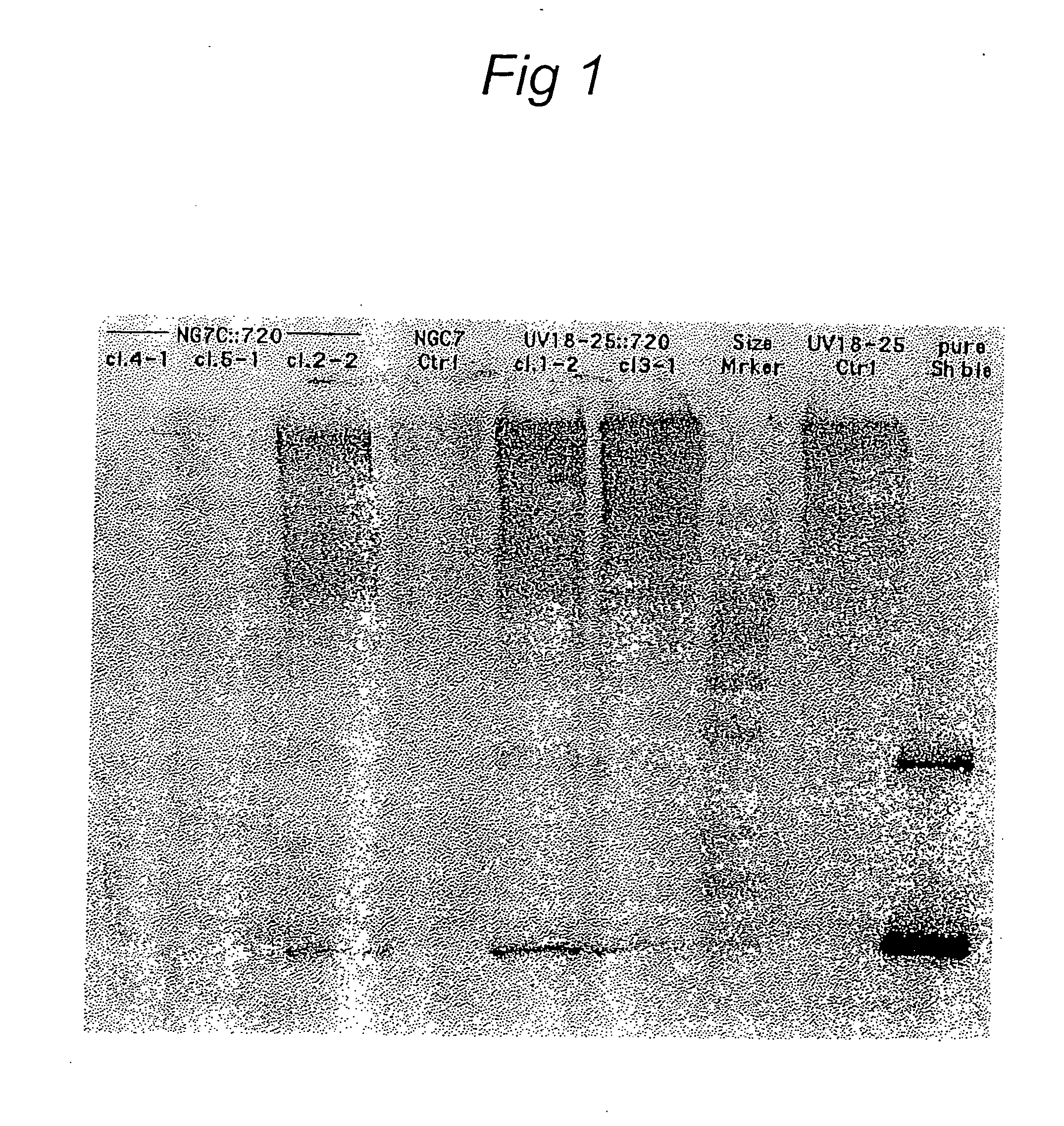
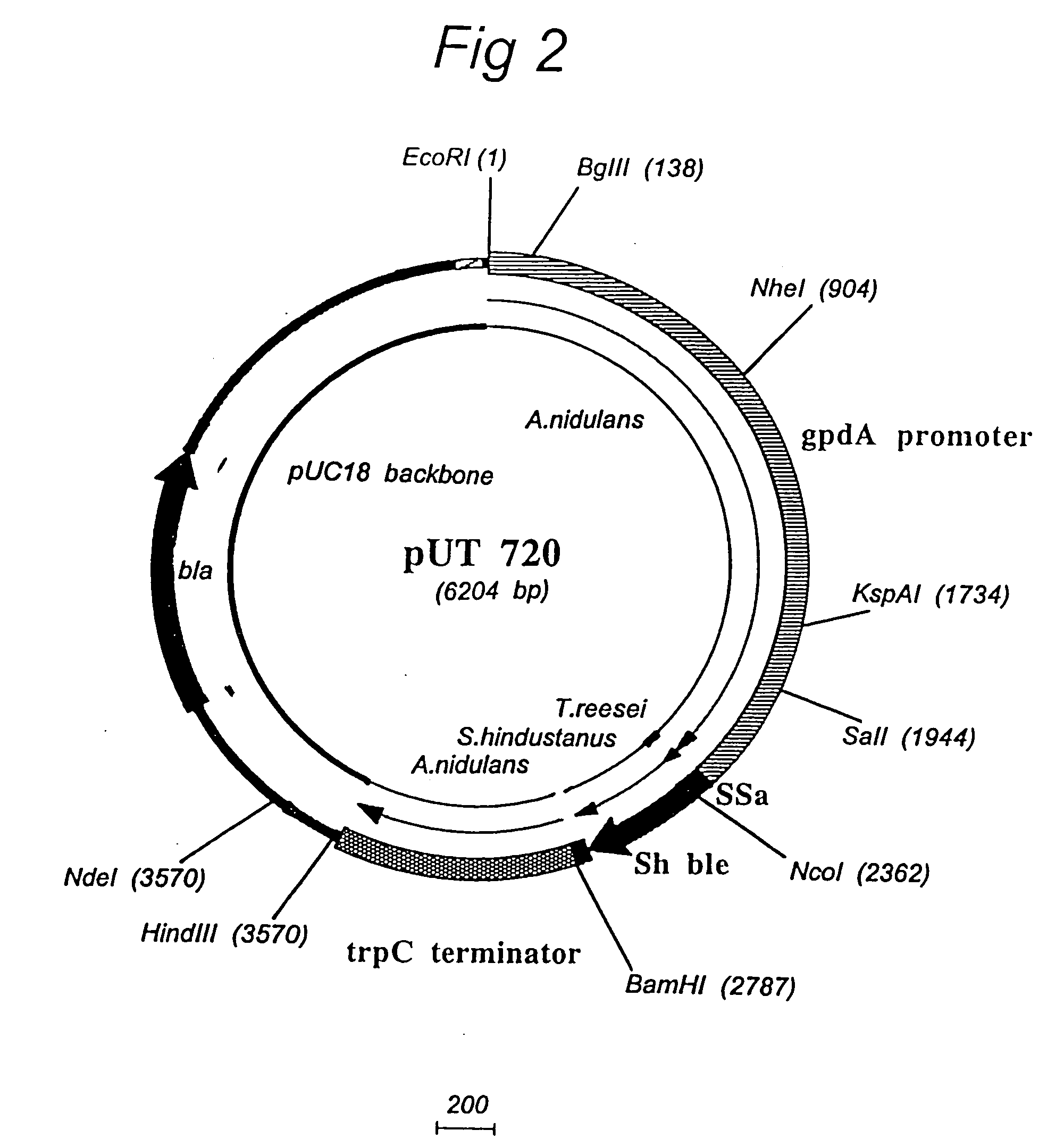
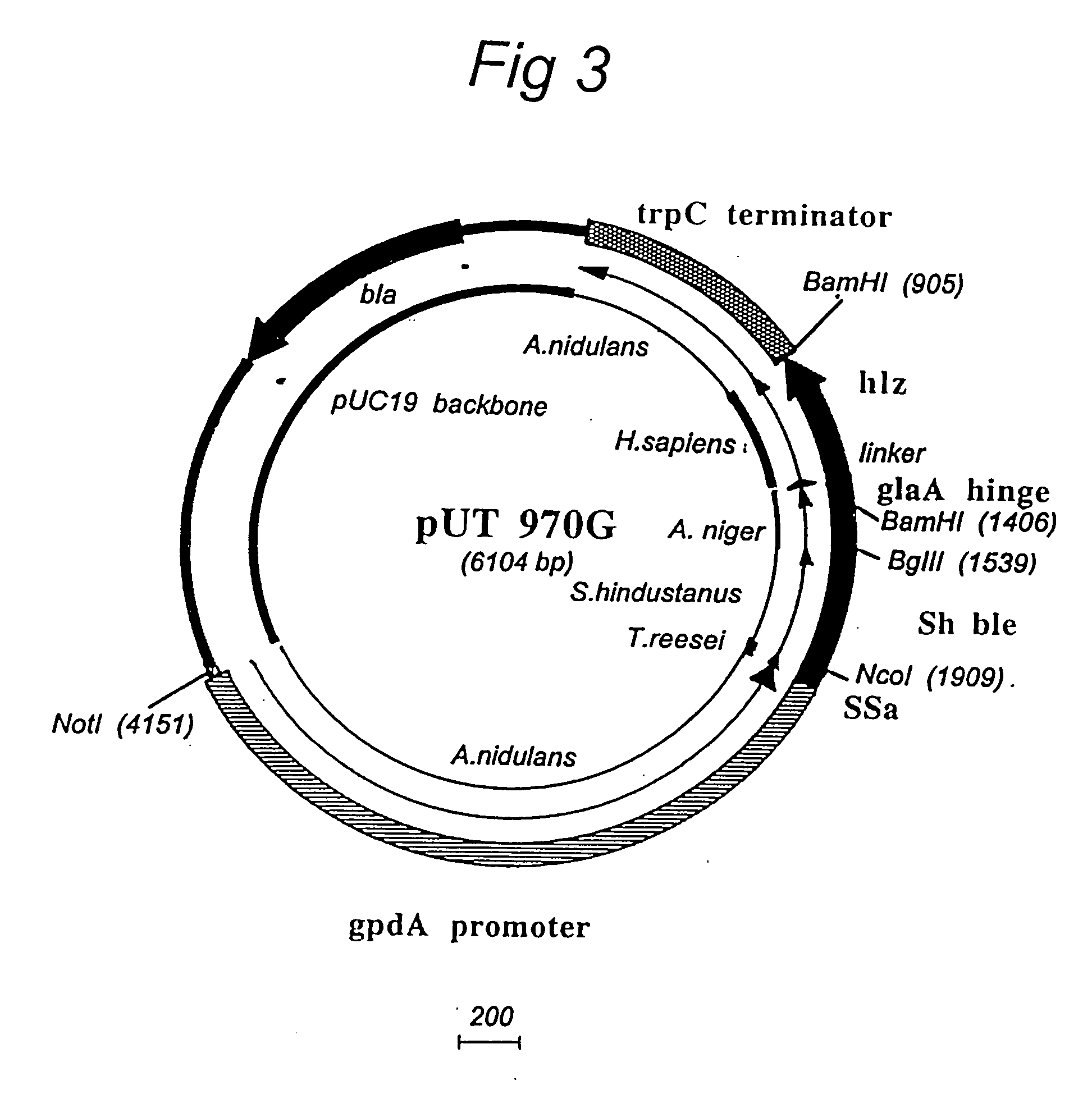
Patents
Literature
81 results about "Eukaryotic gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genes that are expressed usually have introns that interrupt the coding sequences. A typical eukaryotic gene, therefore, consists of a set of sequences that appear in mature mRNA (called exons) interrupted by introns. The regions between genes are likewise not expressed, but may help with chromatin assembly,...
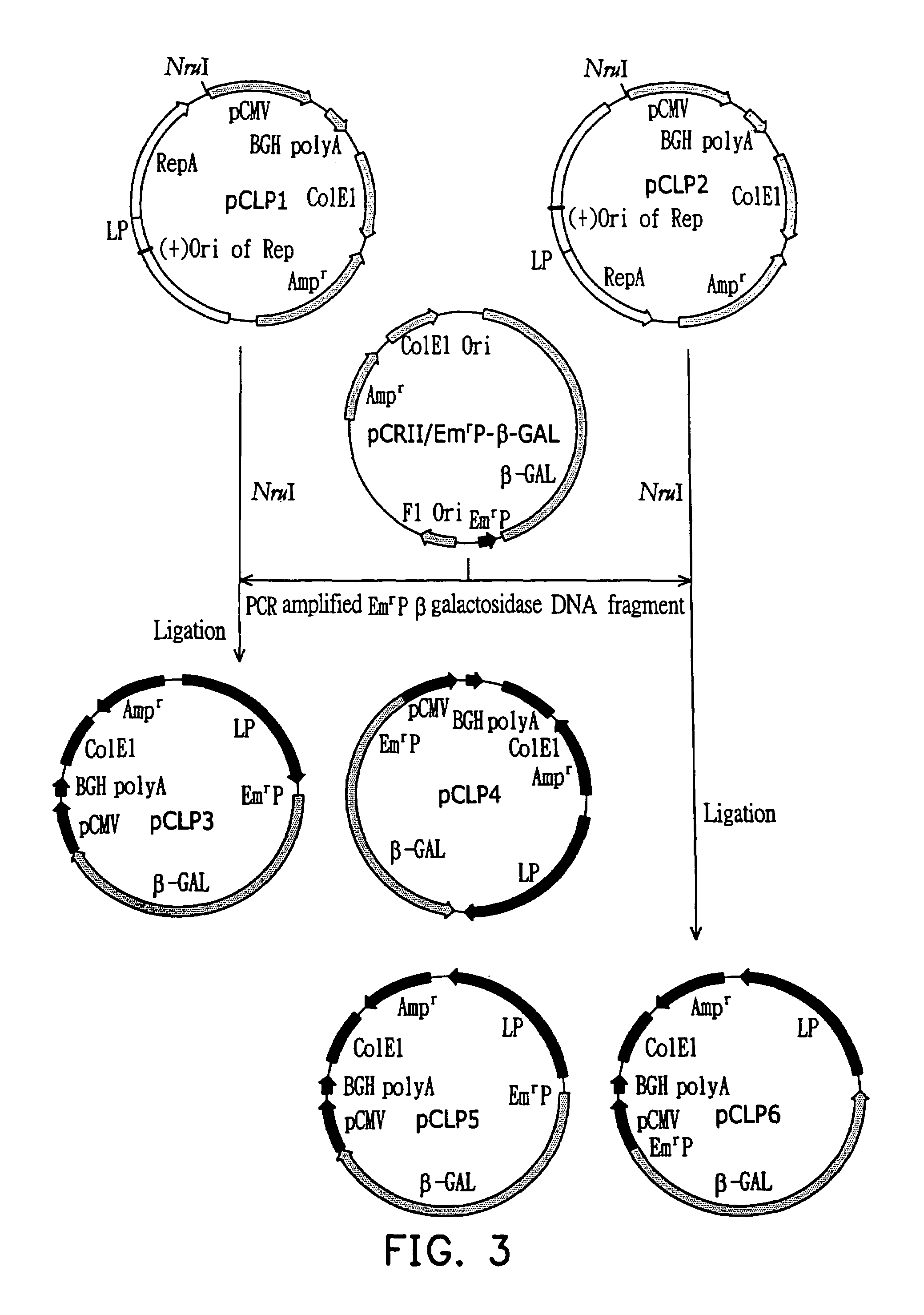
Synthetic 5'UTRs, Expression Vectors, and Methods for Increasing Transgene Expression
ActiveUS20100293625A1Increase transgene expressionImprove stabilityVectorsSugar derivativesReticulum cellIntein
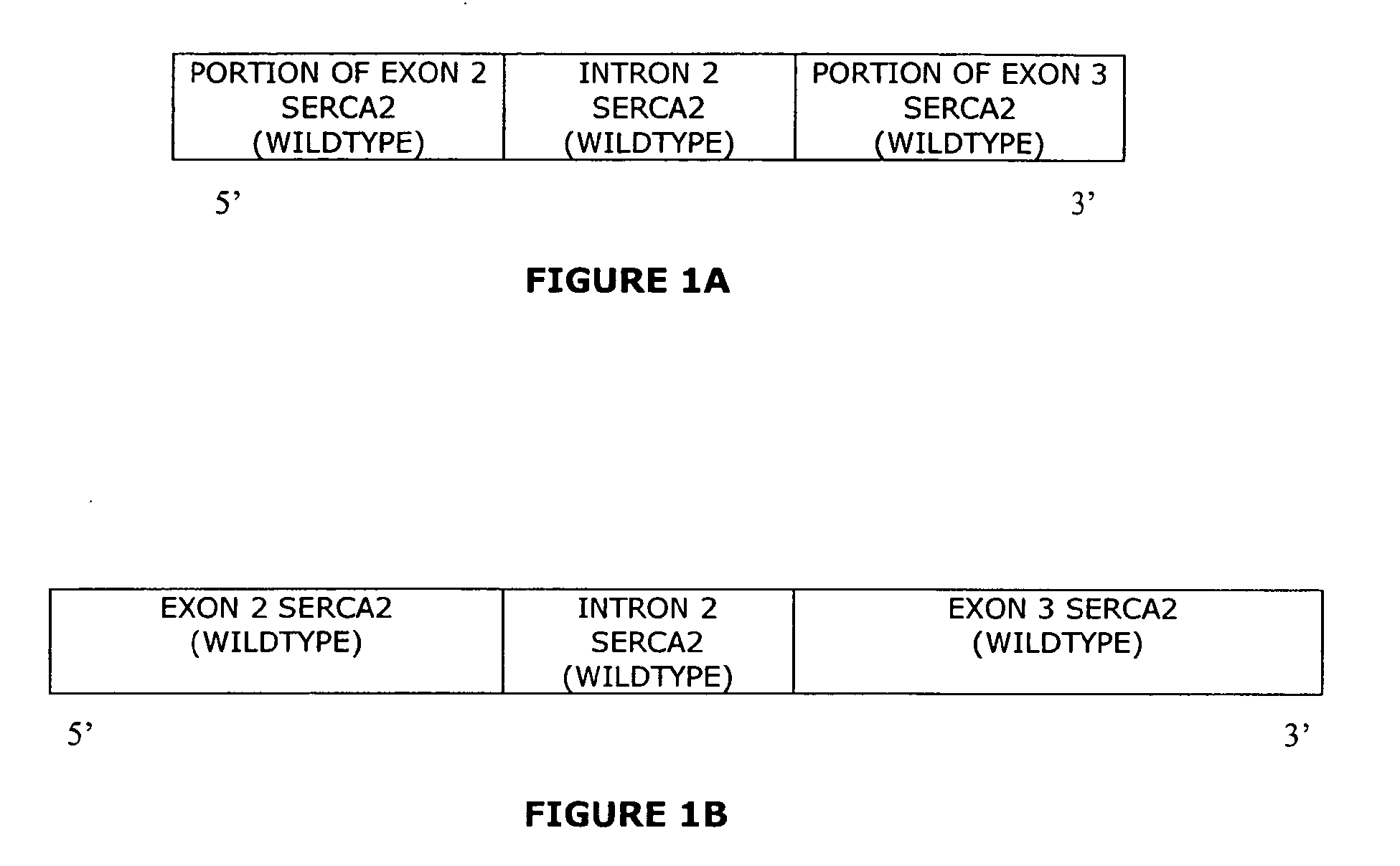
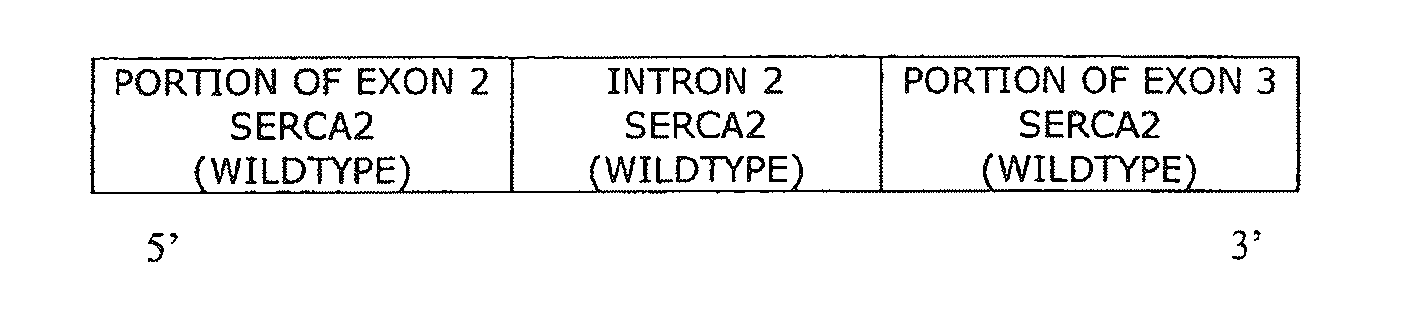
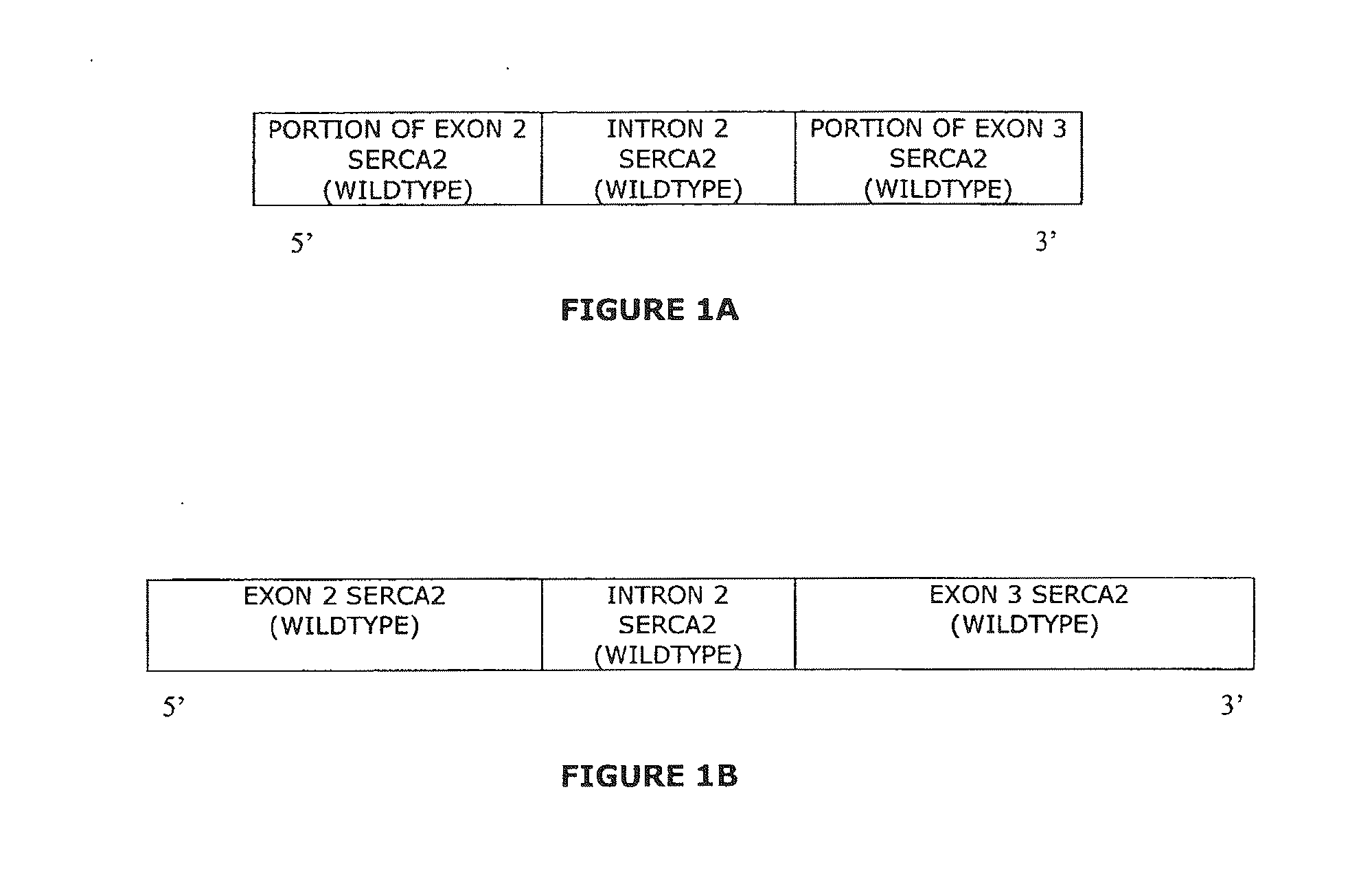
The present invention provides synthetic 5′UTRs comprising a first polynucleotide fragment and a second polynucleotide fragment, wherein the first polynucleotide fragment comprises at least one splice site of a first eukaryotic gene, the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of 5′ untranslated region of a second eukaryotic gene, and the first polynucleotide fragment is located 5′ of the second polynucleotide fragment. In one embodiment, the first polynucleotide fragment comprises the second intron of a sarcoplasmic / endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase gene and the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of the 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR) of a eukaryotic casein gene. The synthetic 5′UTRs are useful for increasing the expression of a transgene when positioned between a promoter and a transgene within an expression vector. The present invention also provides vectors comprising synthetic 5′UTRs and methods for increasing the expression of a transgene using synthetic 5′UTRs.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Targeted gene discovery
InactiveUS6139833AEnhancing general accessibilityRaise the possibilityBiocideBacteriaGenomic DNAIn vivo
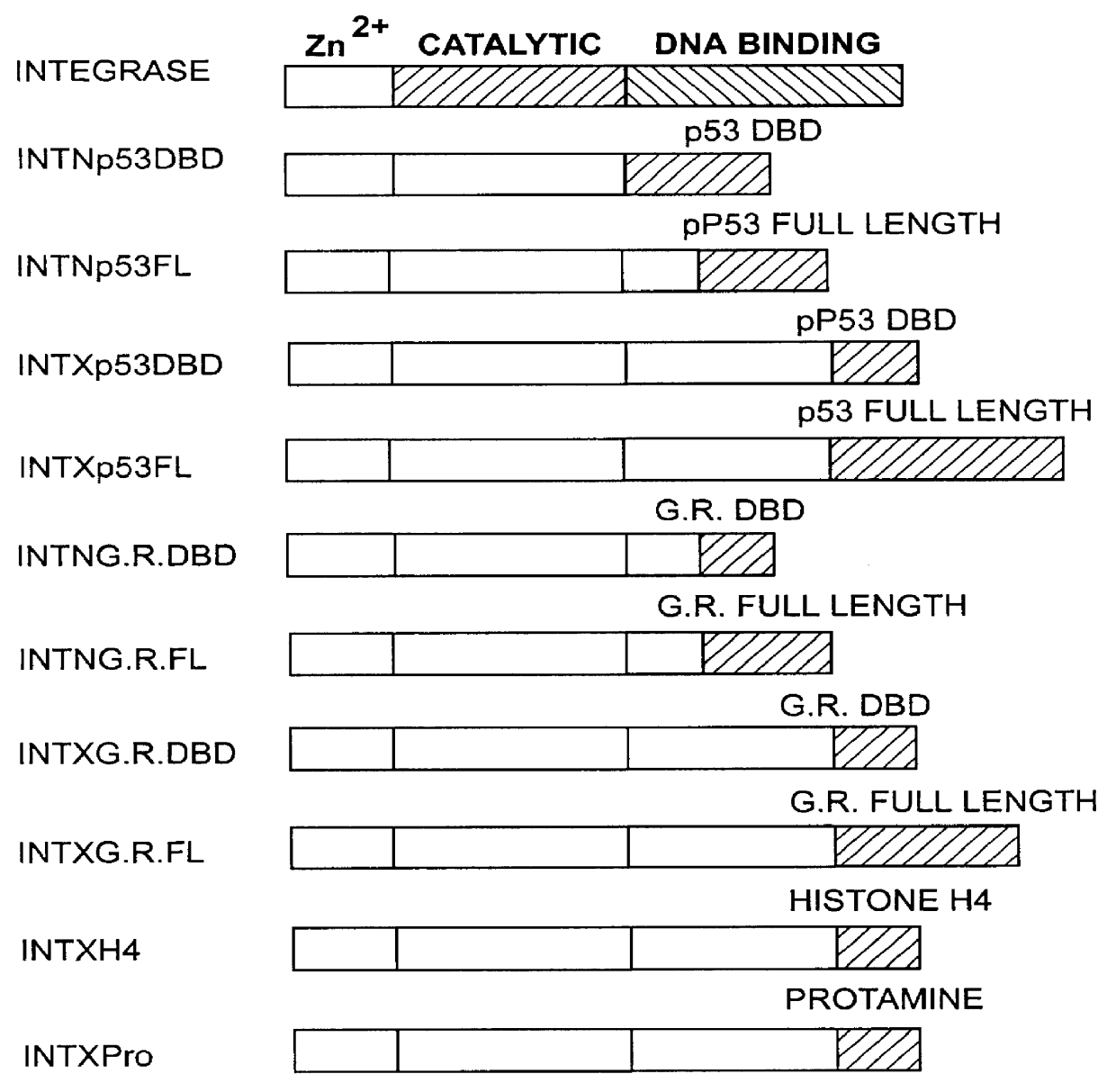
The present invention describes a comprehensive system for gene discovery using retrovirus that have been engineered to exhibit increased accessibility to genomic DNA, or to mutate and identify the chromosomal target sequences of DNA binding proteins. The strategy employs the combination of retroviral integrase / DNA binding protein fusion constructs and gene-trapping methodologies. This novel technology provides the ability to establish proviral integration at any location within the genome. In addition, it allows for the generation of a collection of eukaryotic cells in which each cell contains a mutation in a target gene or sequence for a known DNA binding protein which also allow for rapid in vivo functional analysis. Sequence information obtained for genes identified using the described methods identify a collection of eukaryotic genes related by, or directly or indirectly regulated by, a given DNA binding protein.
Owner:LEXICON PHARM INC
Synthetic 5'UTRs, Expression Vectors, and Methods for Increasing Transgene Expression
InactiveUS20110247090A1High expressionImprove stabilitySugar derivativesFermentationNucleotideReticulum cell
The present invention provides synthetic 5′UTRs comprising a first polynucleotide fragment and a second polynucleotide fragment, wherein the first polynucleotide fragment comprises at least one splice site of a first eukaryotic gene, the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of 5′ untranslated region of a second eukaryotic gene, and the first polynucleotide fragment is located 5′ of the second polynucleotide fragment. In one embodiment, the first polynucleotide fragment comprises the second intron of a sarcoplasmic / endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase gene and the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of the 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR) of a eukaryotic casein gene. The synthetic 5′UTRs are useful for increasing the expression of a transgene when positioned between a promoter and a transgene within an expression vector. The present invention also provides vectors comprising synthetic 5′UTRs and methods for increasing the expression of a transgene using synthetic 5′UTRs.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Eukaryotic gene editing method based on gene cas7-3 in I type CRISPR-Cas system
PendingCN107557378AEasy gene editingGene editing fastStable introduction of DNAVector-based foreign material introductionEukaryotic geneEucoenogenes
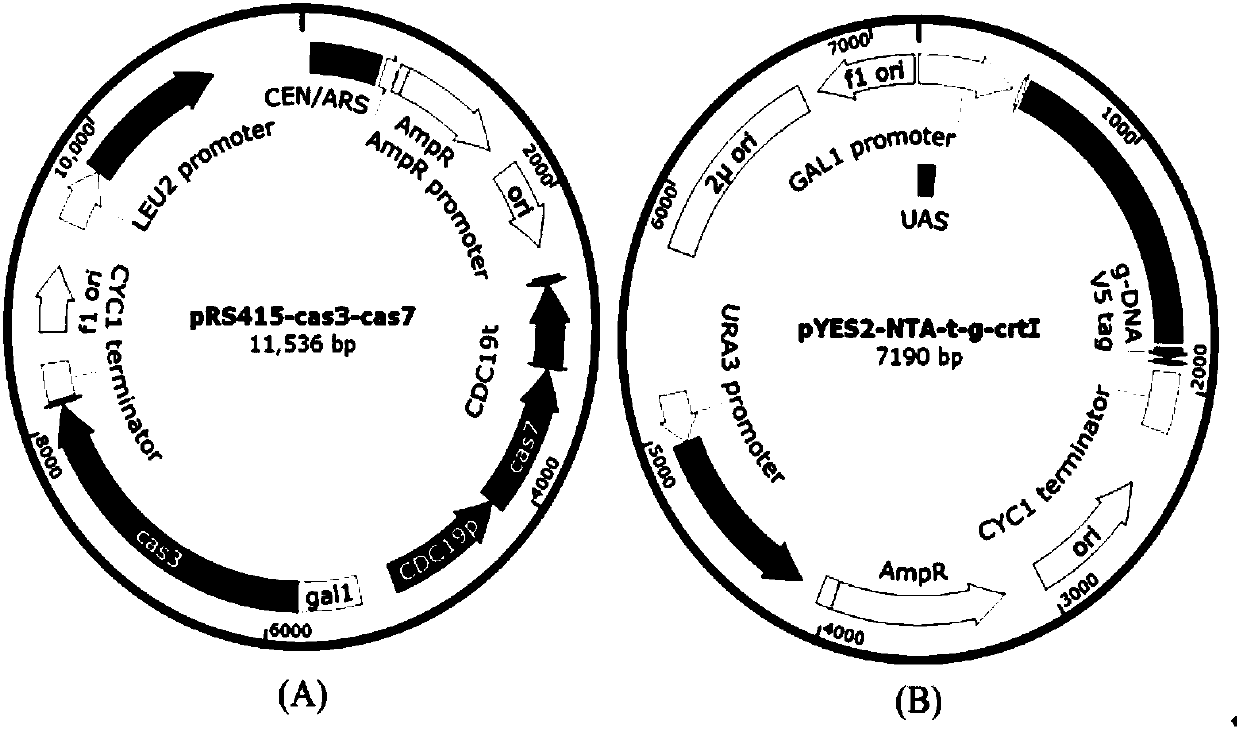
The invention discloses gene knockout and gene insertion on eukaryotic genomes carried out by two Cas proteins (Cas7 and Cas3) in a 1 class I type CRISPR-Cas system for the first time. The developmentof the method breaks the limitation of dependence on single-gene cas9 and cpf1, and provides a new perspective for performing gene editing on the eukaryotes by multi-gene. By applying the system, thegene editing can be conveniently, rapidly and effectively carried out on eukaryote brewer's yeast genomes. The optimized tool is expected to be widely used in the gene editing of other eukaryotes.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
High-throughput screening of expressed DNA libraries in filamentous fungi
InactiveUS7122330B2Minimizes and eliminates formationLow culture viscosityHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyCDNA library
The invention provides a method for the expression of exogenous DNA libraries in filamentous fungi. The fungi are capable of processing intron-containing eukaryotic genes, and also can carry out post-translational processing steps such as glyclosylation and protein folding. The invention provides for the use of fungi with altered morphology, which permits high-throughput screening and directed molecular evolution of expressed proteins. The same transformed fungi may be used to produce larger quantities of protein for isolation, characterization, and application testing, and may be suitable for commercial production of the protein as well.
Owner:DANISCO US INC +1
Method and system for predicting splice variant from DNA chip expression data
InactiveUS20020029113A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingEukaryotic geneMessenger RNA
A system and method predict alternative splicing transcripts using DNA chip expression data as a primary data source. The system and method may perform prediction of alternative splicing of pre-messenger RNA that may be used, for example, for regulating eukaryotic gene expression.
Owner:WARNER-LAMBERT CO
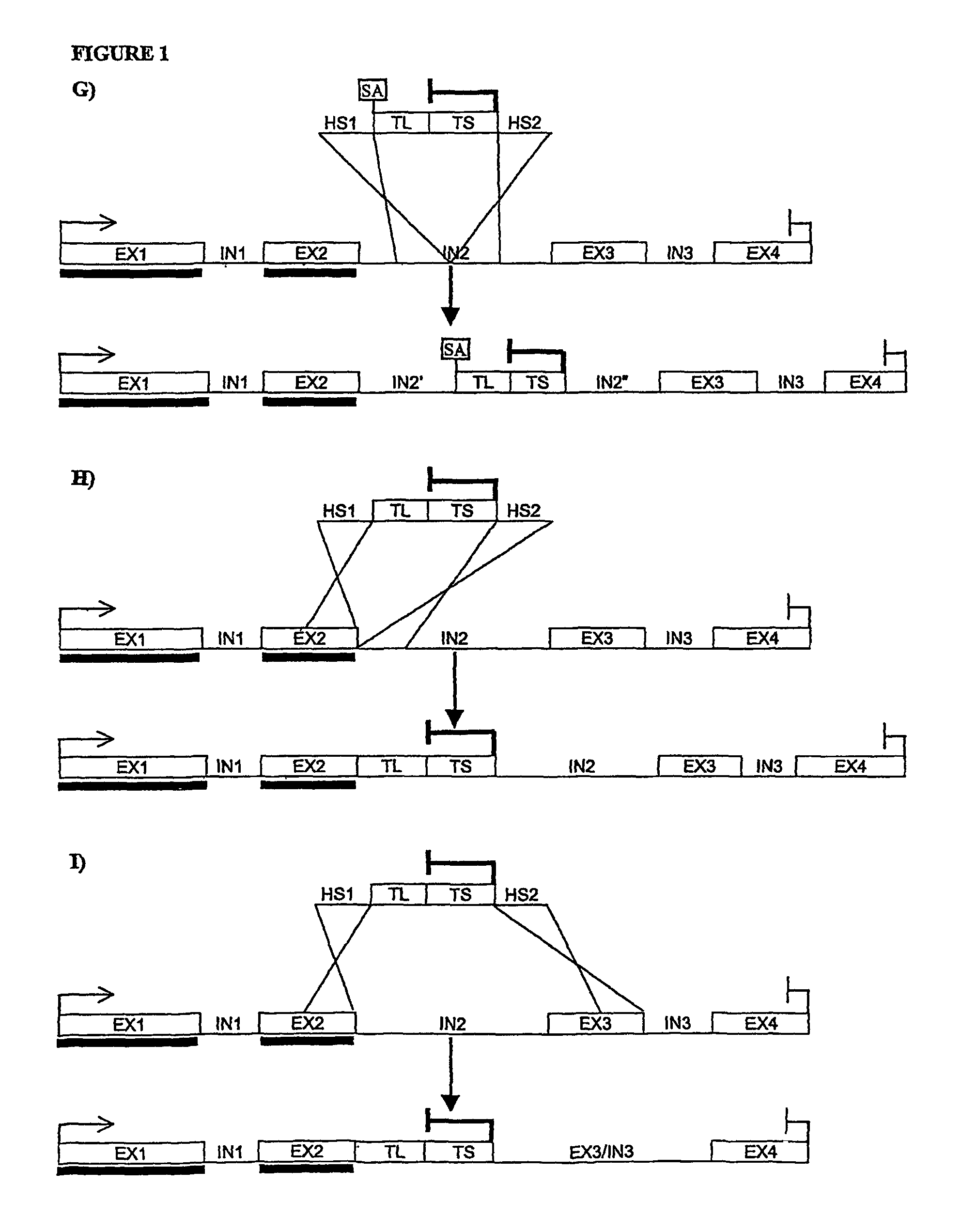
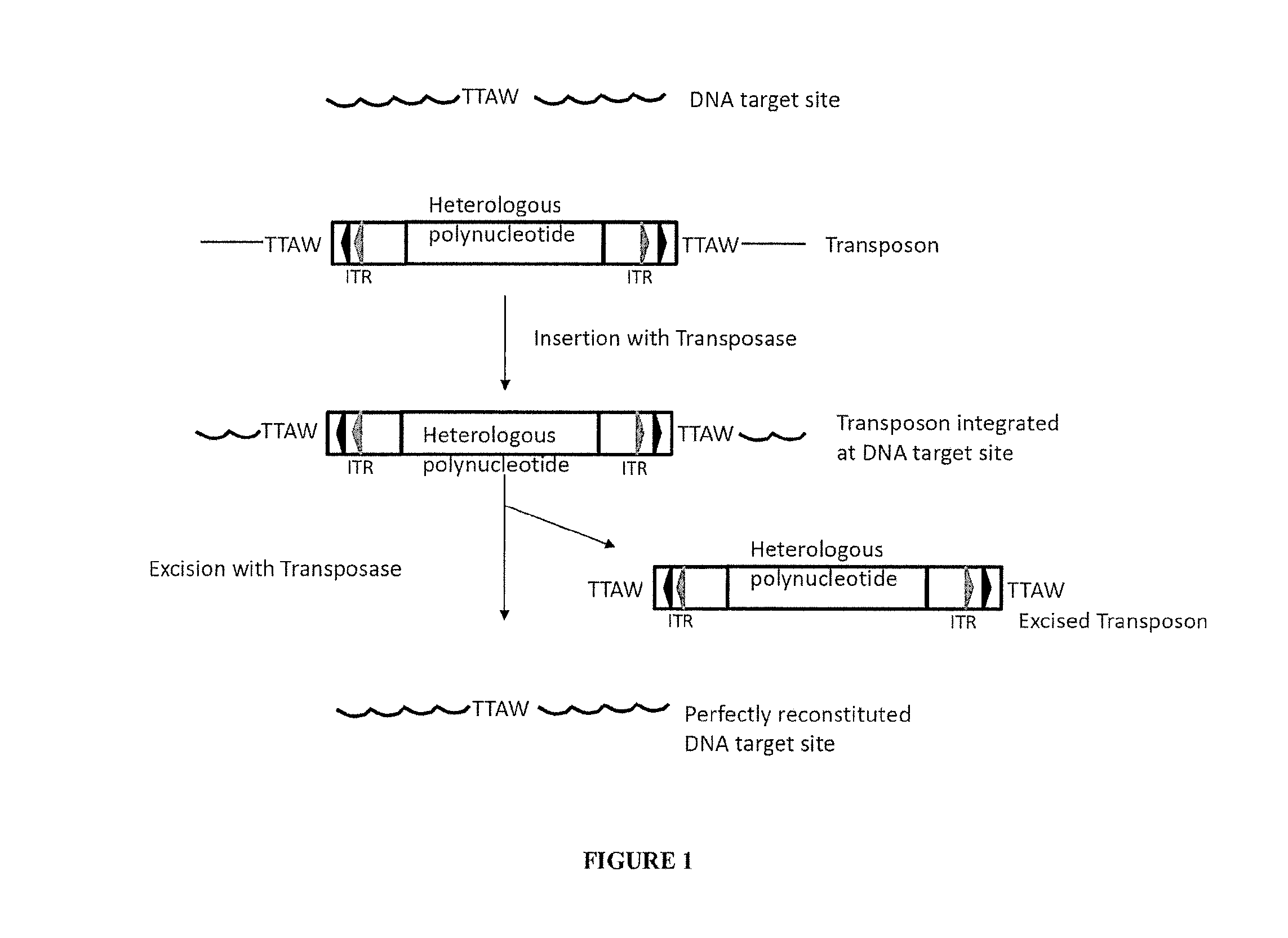
Enhanced nucleic acid constructs for eukaryotic gene expression
ActiveUS9428767B2High expressionReduce interferencePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsHeterologousEukaryotic gene
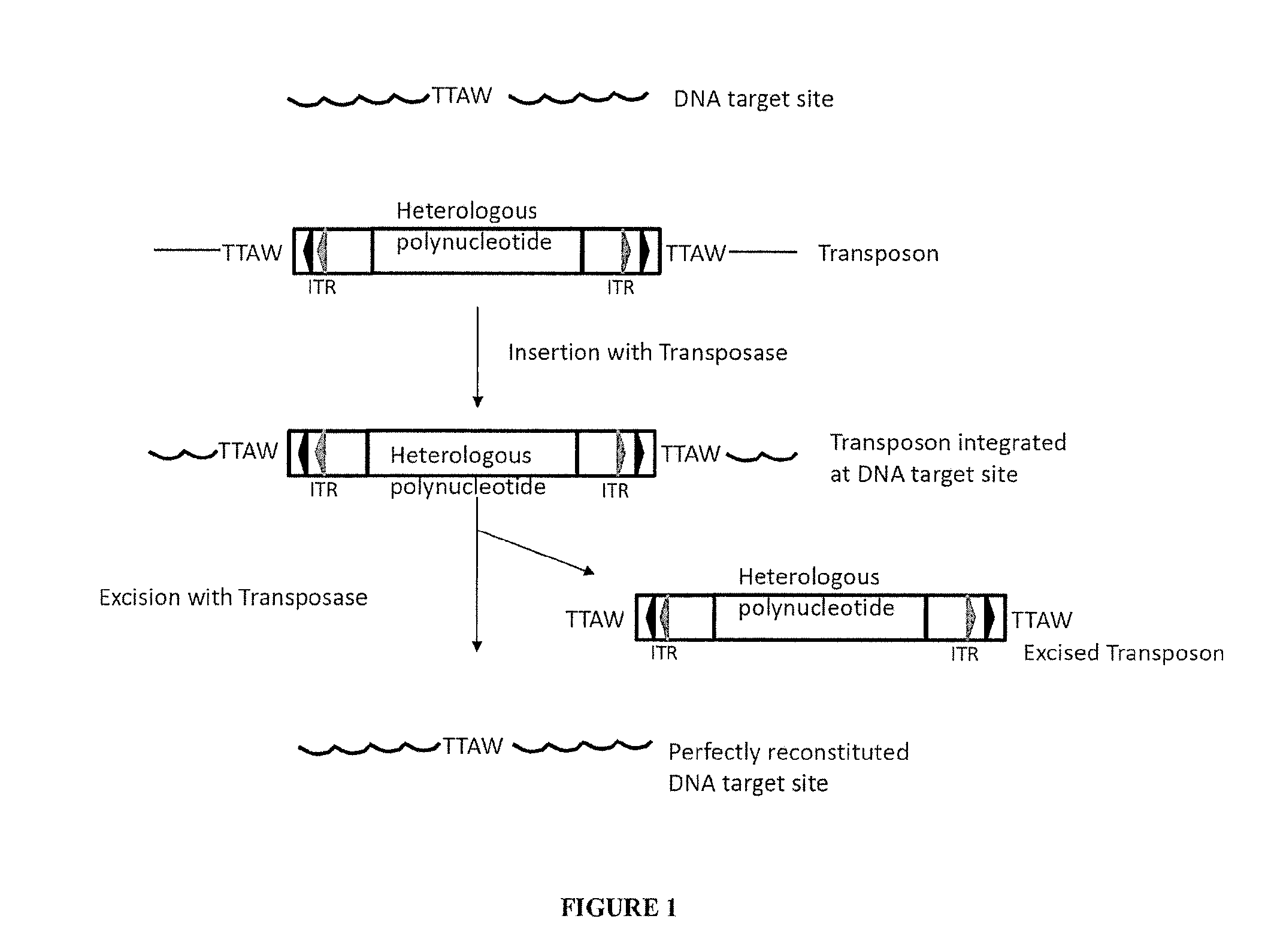
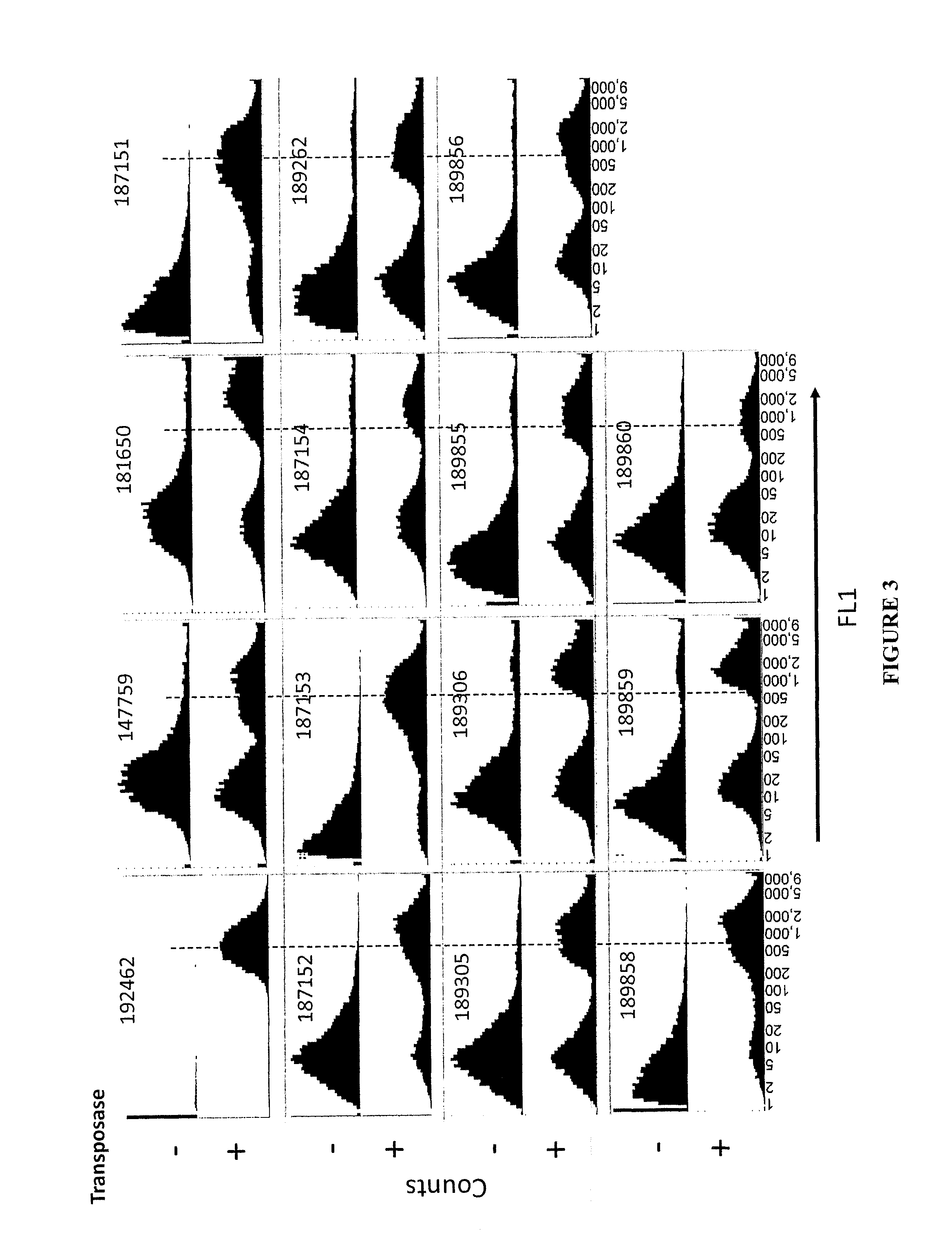
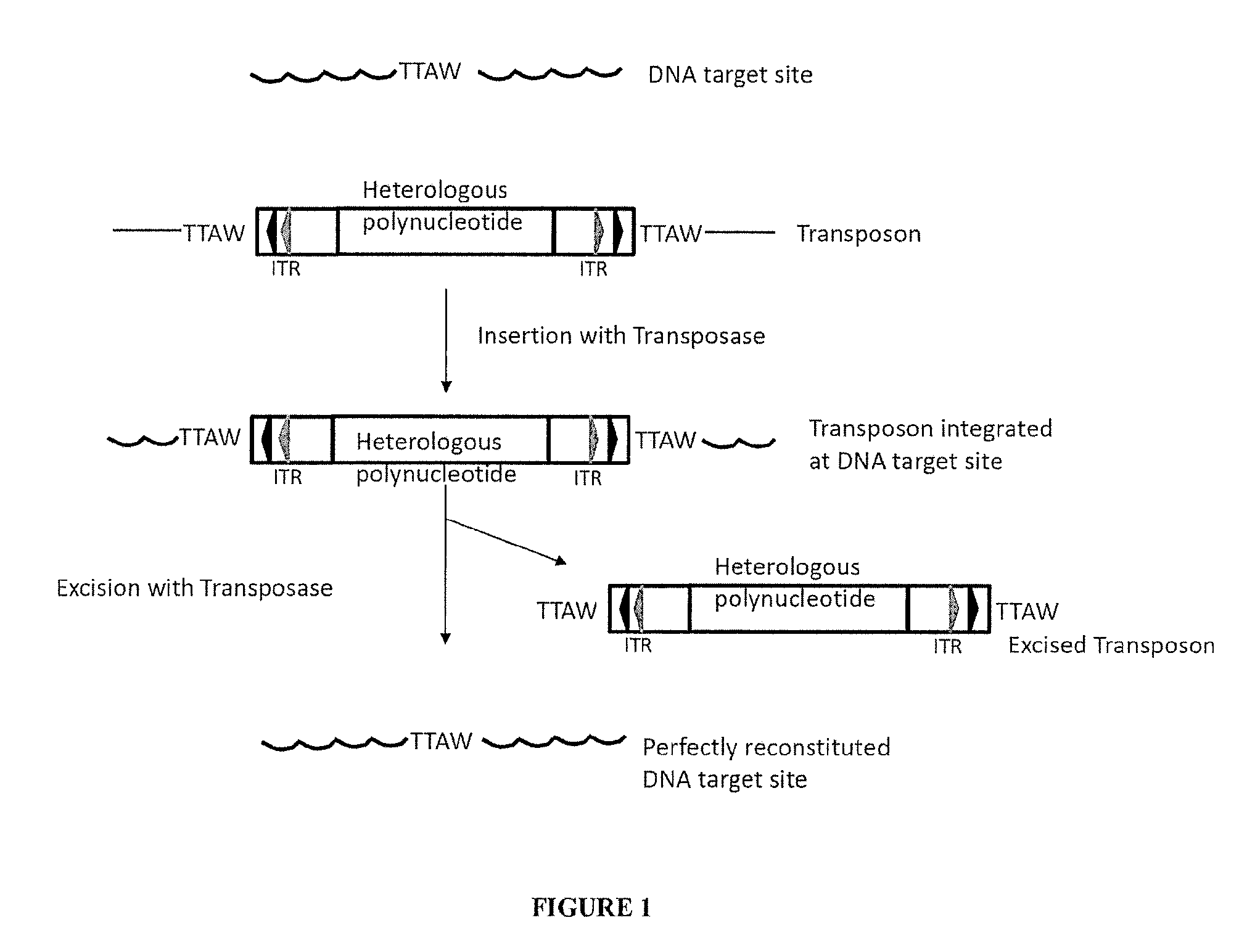
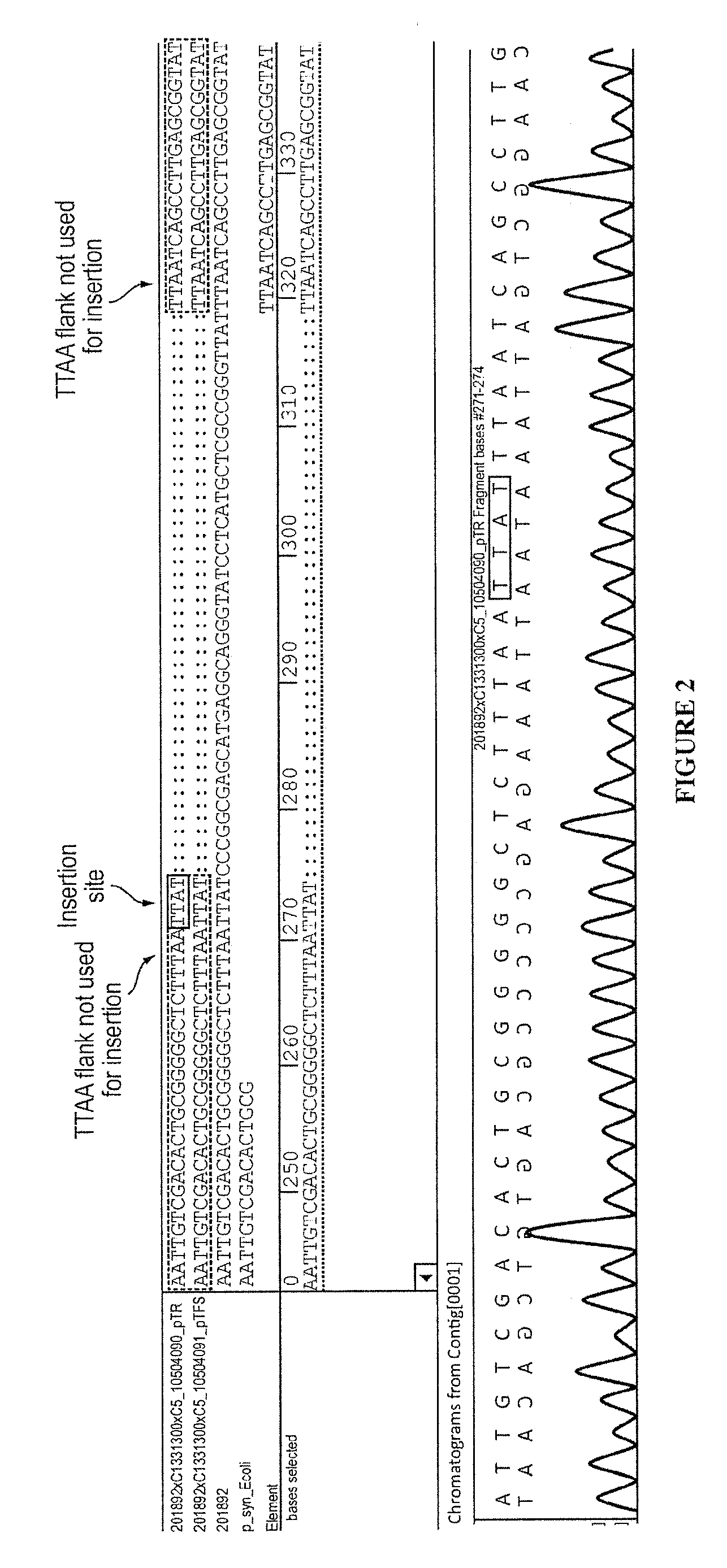
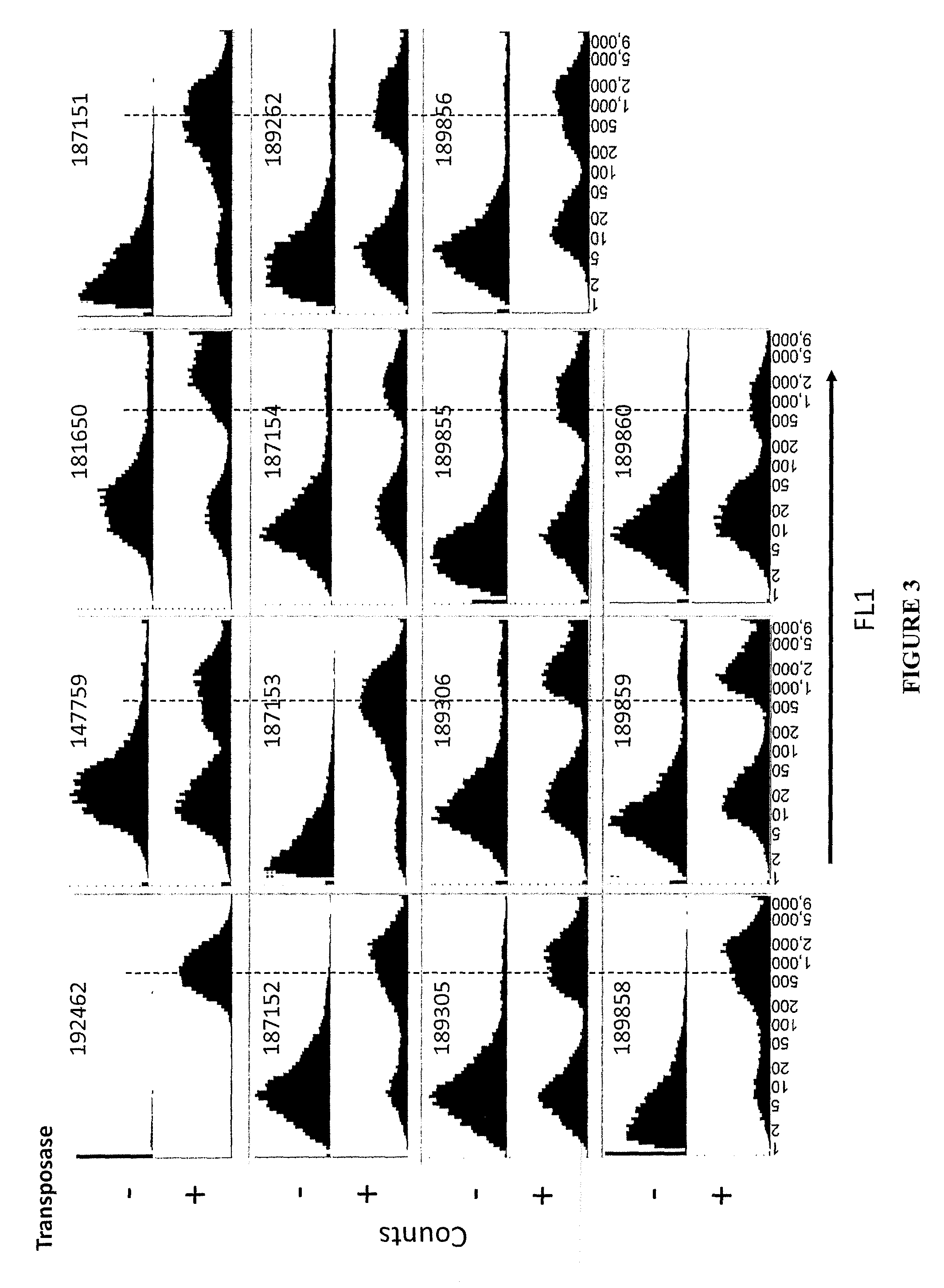
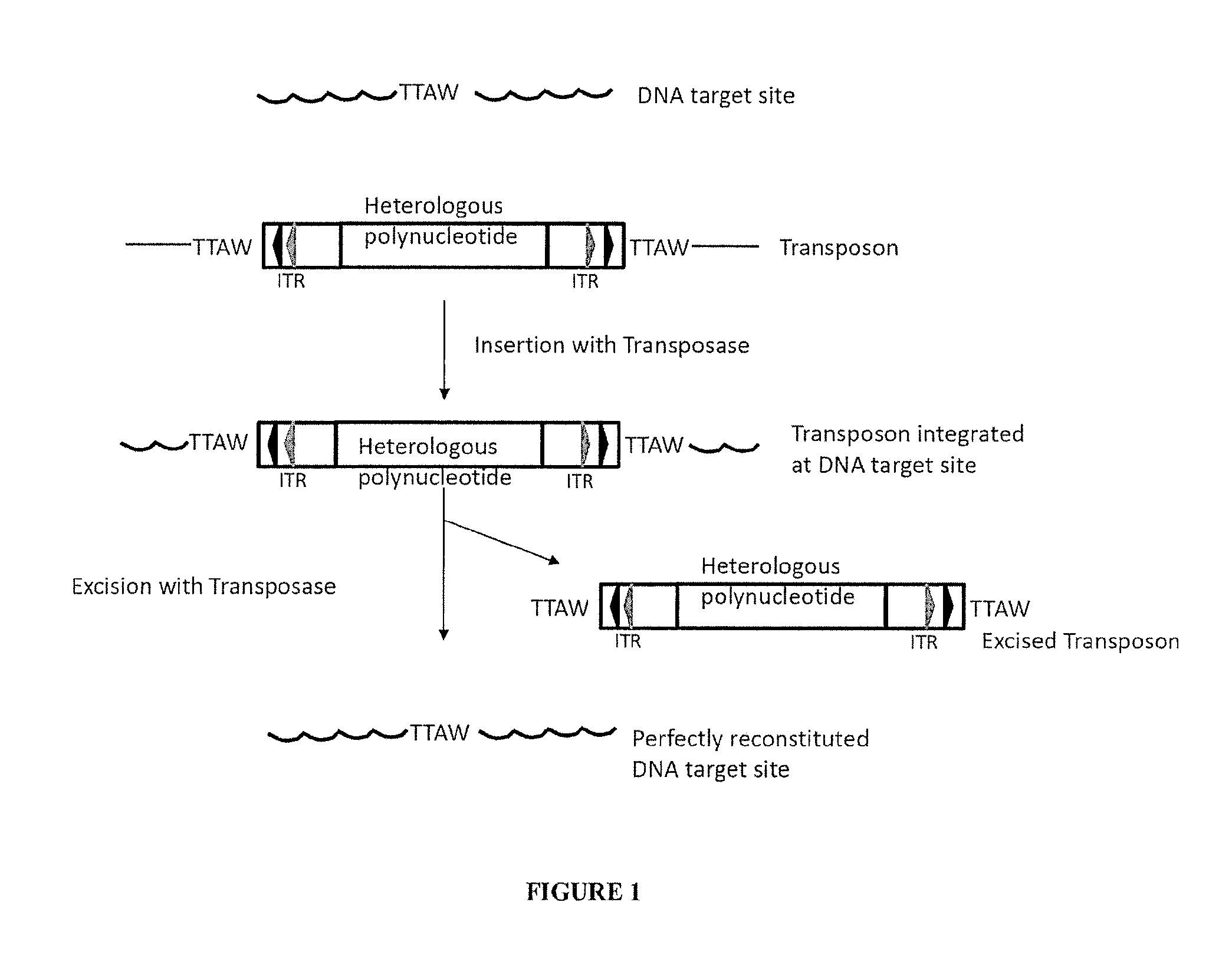
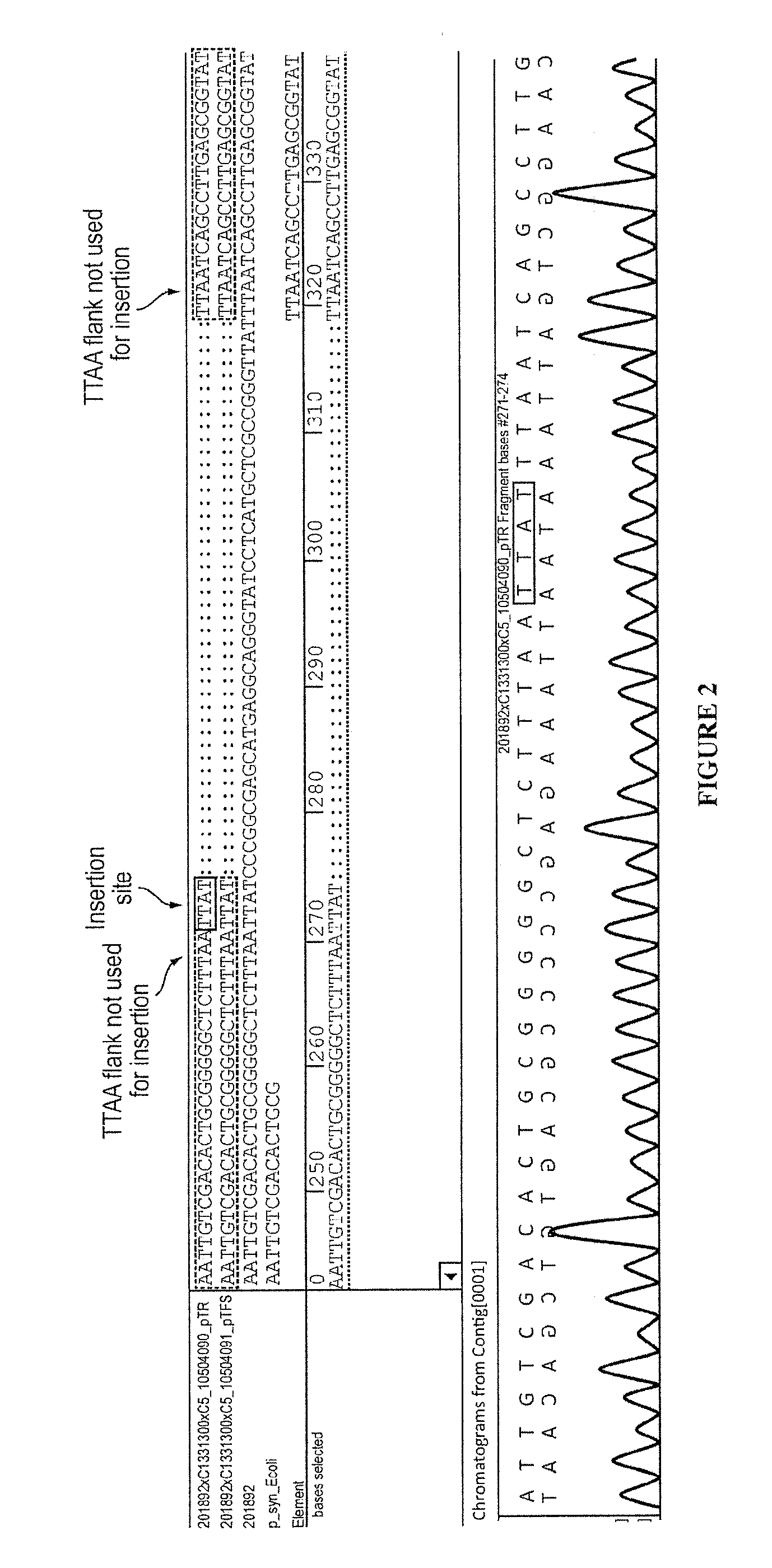
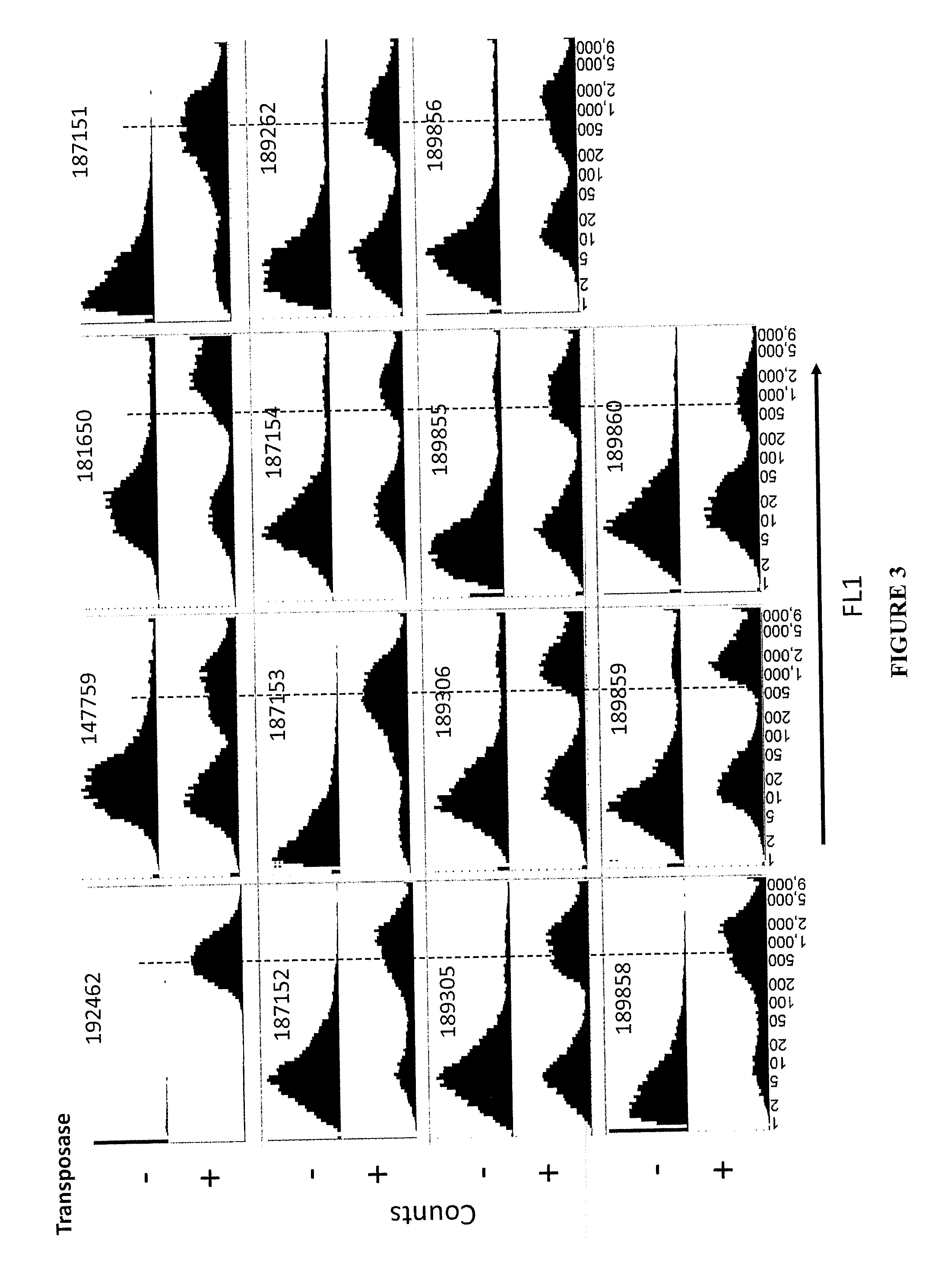
The present invention provides polynucleotide vectors for high expression of heterologous genes, and methods for constructing such vectors. Some vectors further comprise novel transposons and transposases that further improve expression. Further disclosed are vectors that can be used in a gene transfer system for stably introducing nucleic acids into the DNA of a cell. The gene transfer systems can be used in methods, for example, but not limited to, gene expression, gene therapy, insertional mutagenesis, or gene discovery.
Owner:DNA2 0
Enhanced nucleic acid constructs for eukaryotic gene expression
InactiveUS20150291975A1High expressionReduce interferenceOrganic active ingredientsFusion with DNA-binding domainHeterologousEukaryotic gene
The present invention provides polynucleotide vectors for high expression of heterologous genes, and methods for constructing such vectors. Some vectors further comprise novel transposons and transposases that further improve expression. Further disclosed are vectors that can be used in a gene transfer system for stably introducing nucleic acids into the DNA of a cell. The gene transfer systems can be used in methods, for example, but not limited to, gene expression, gene therapy, insertional mutagenesis, or gene discovery.
Owner:DNA2 0
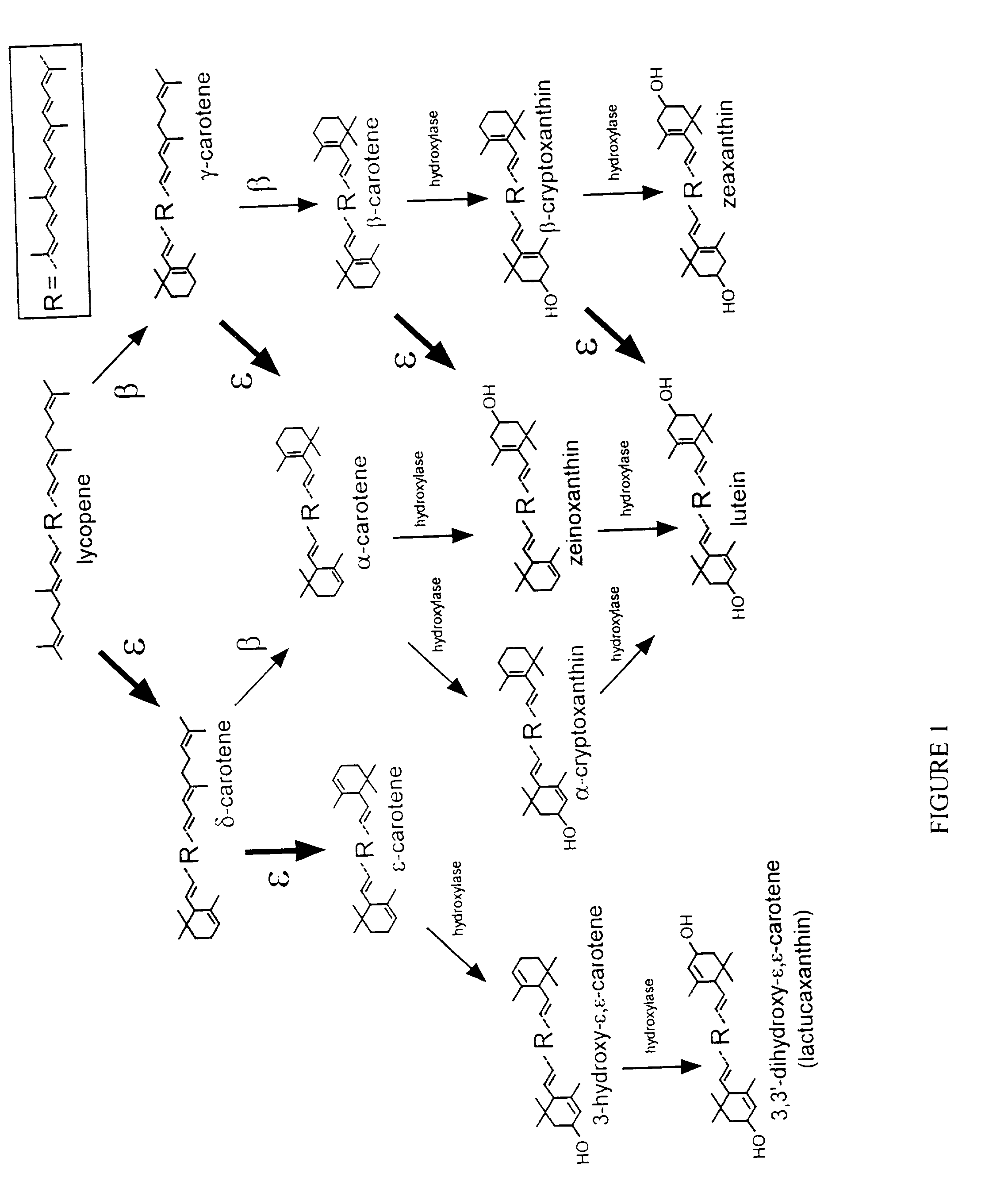
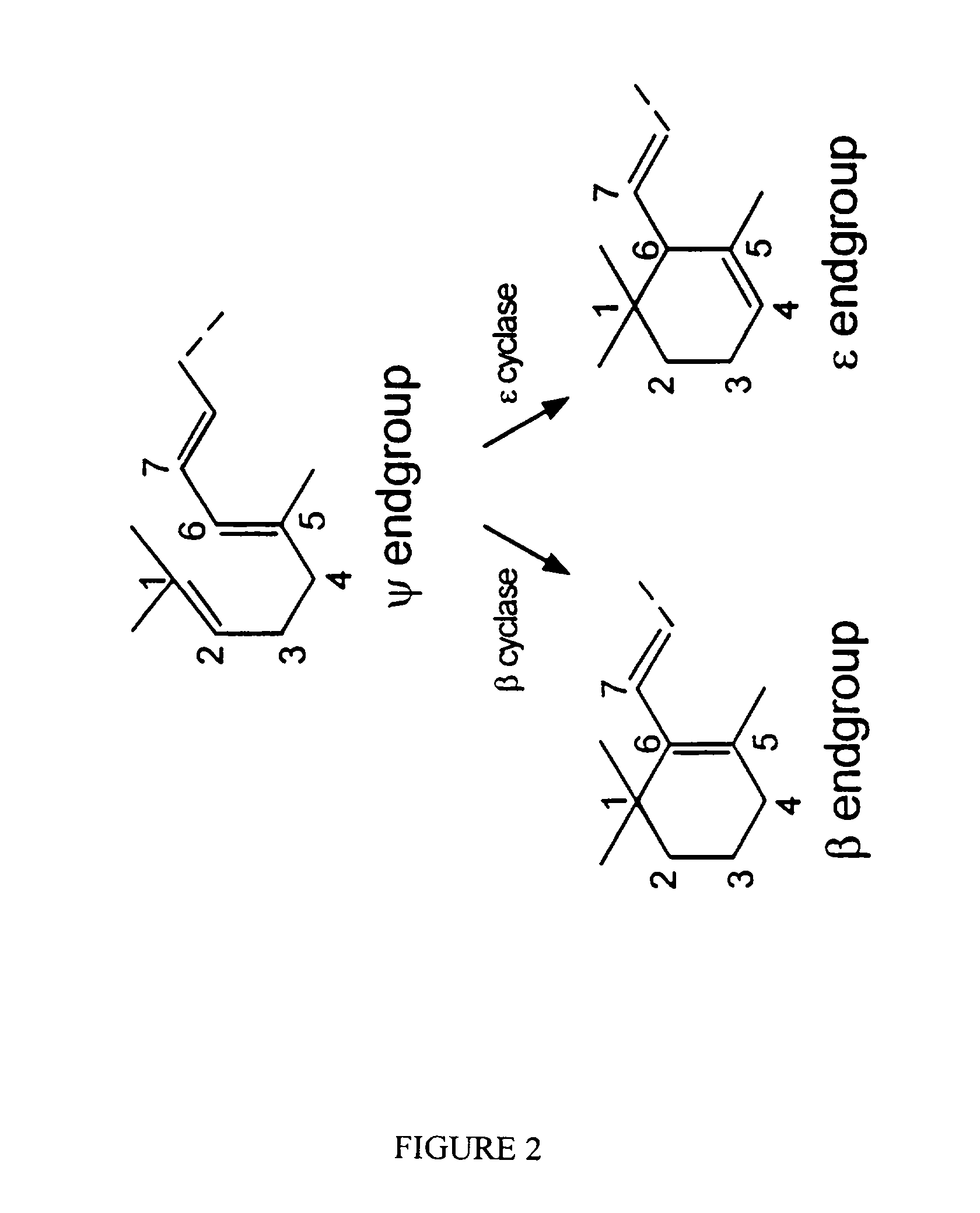
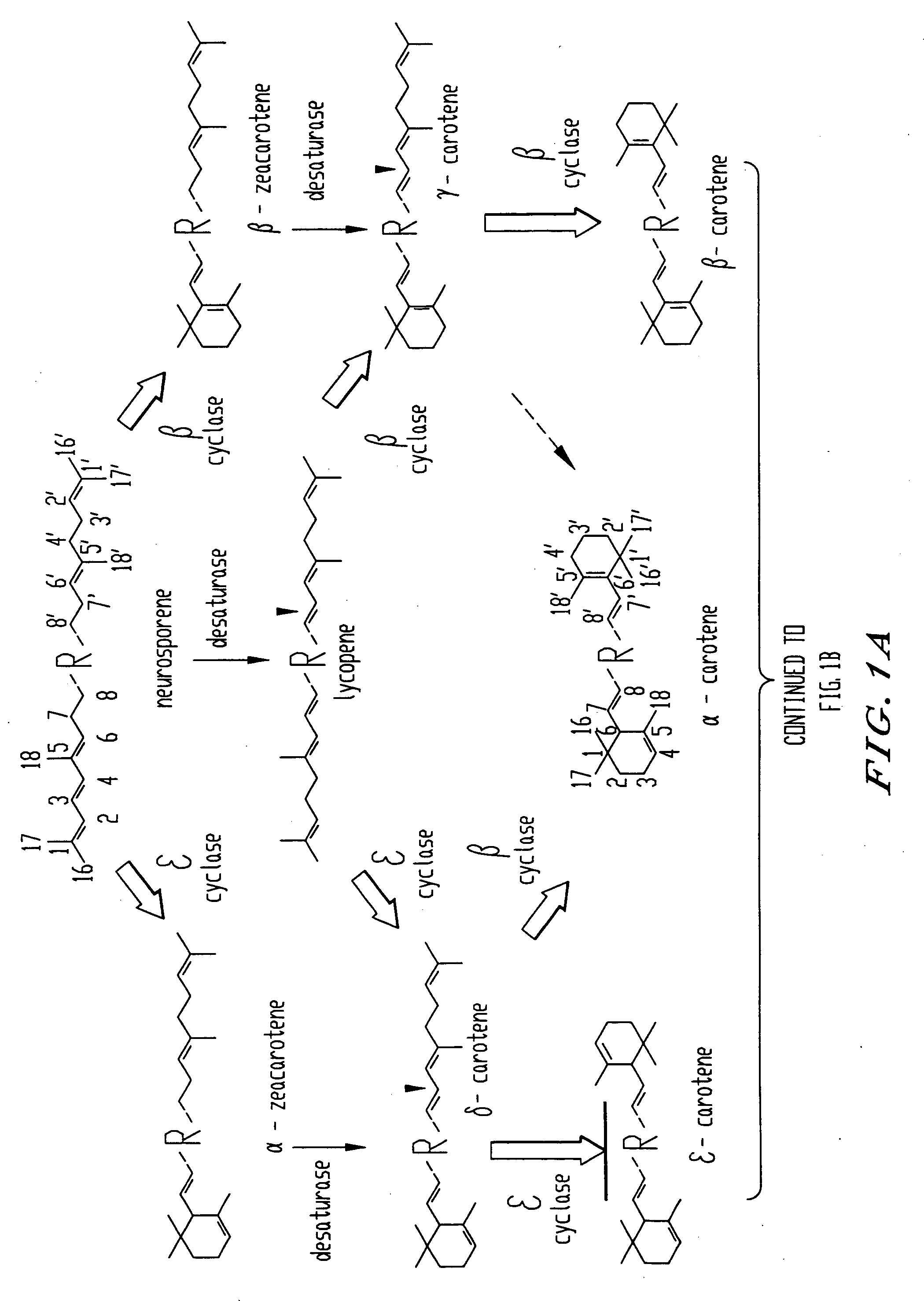
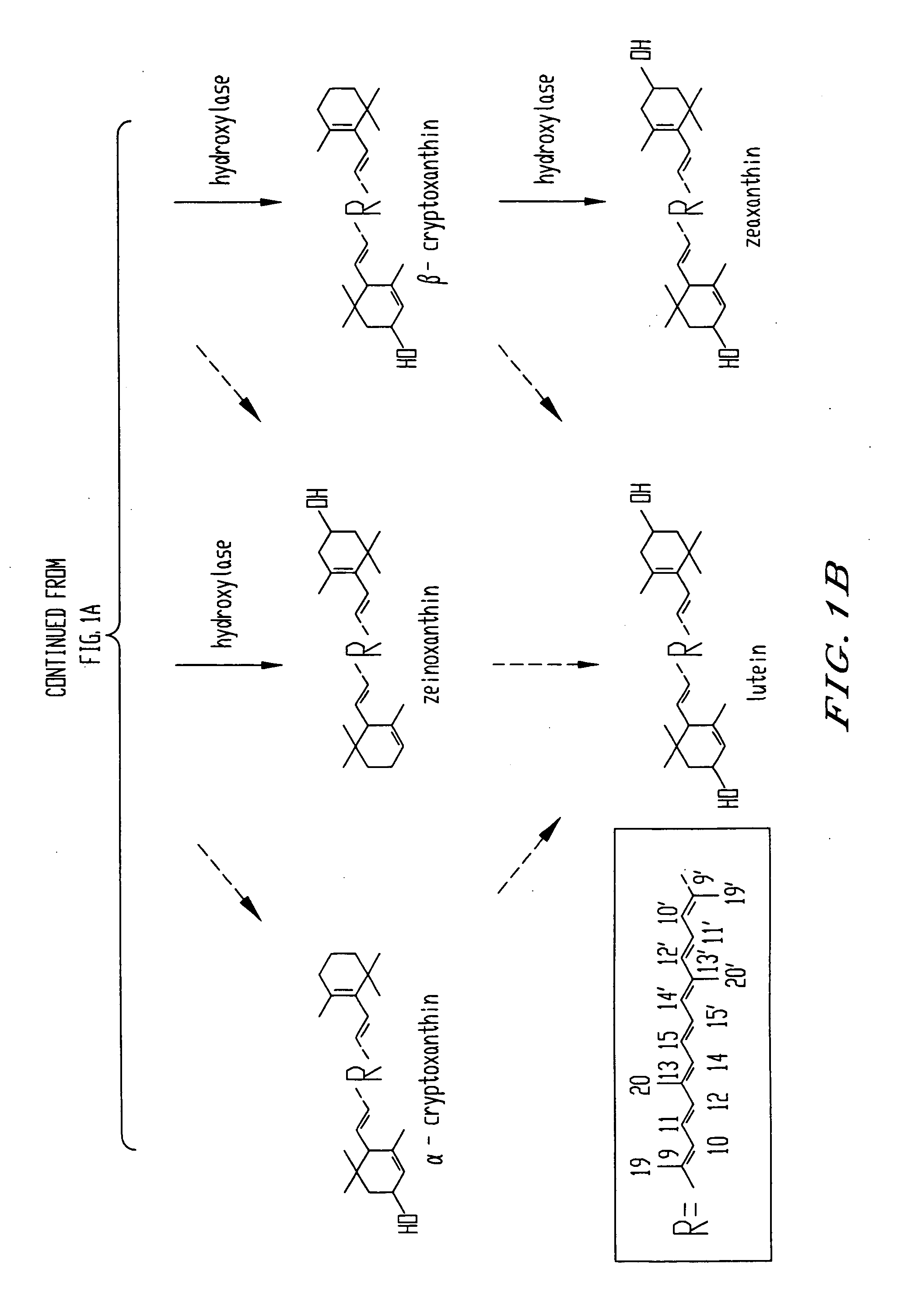
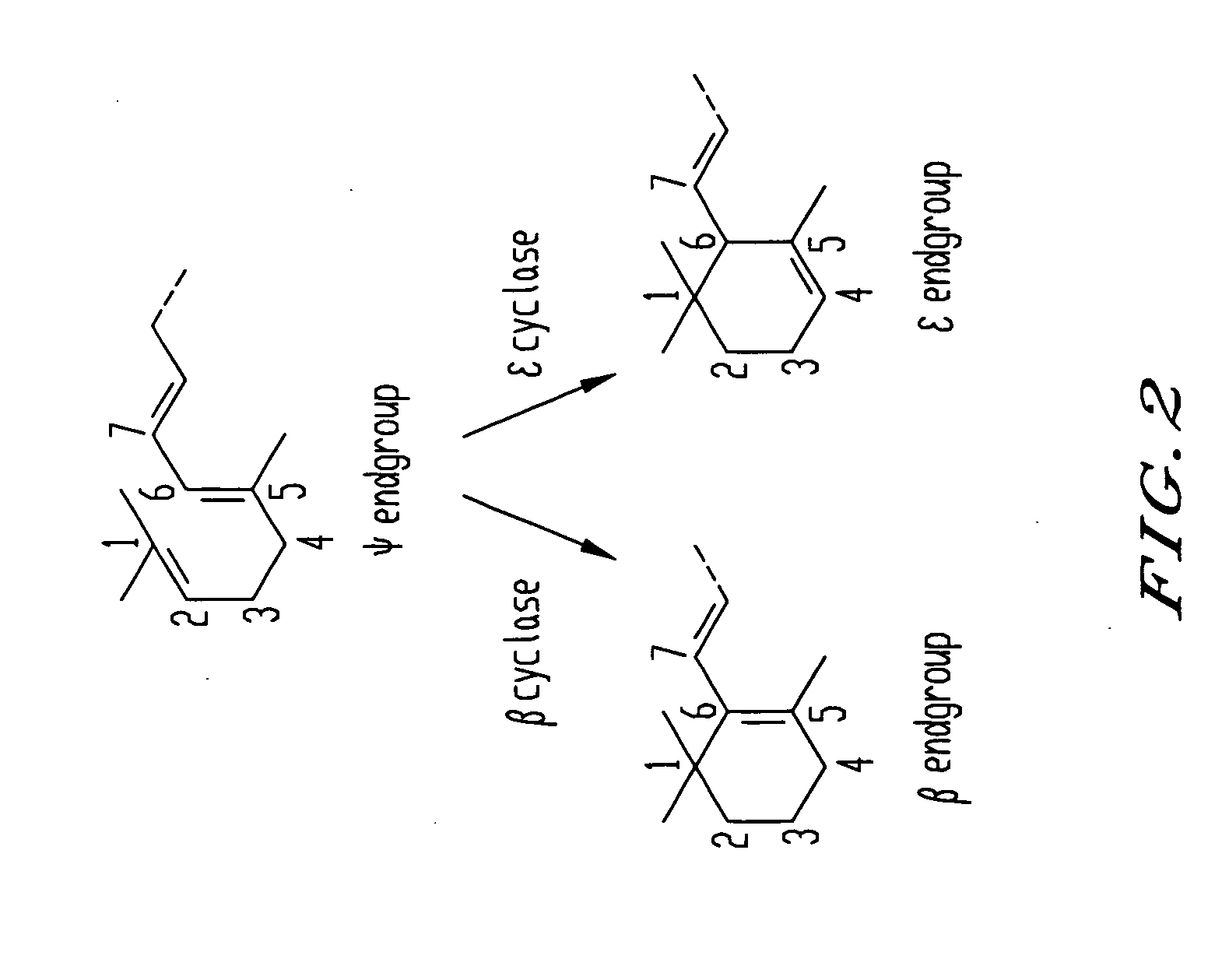
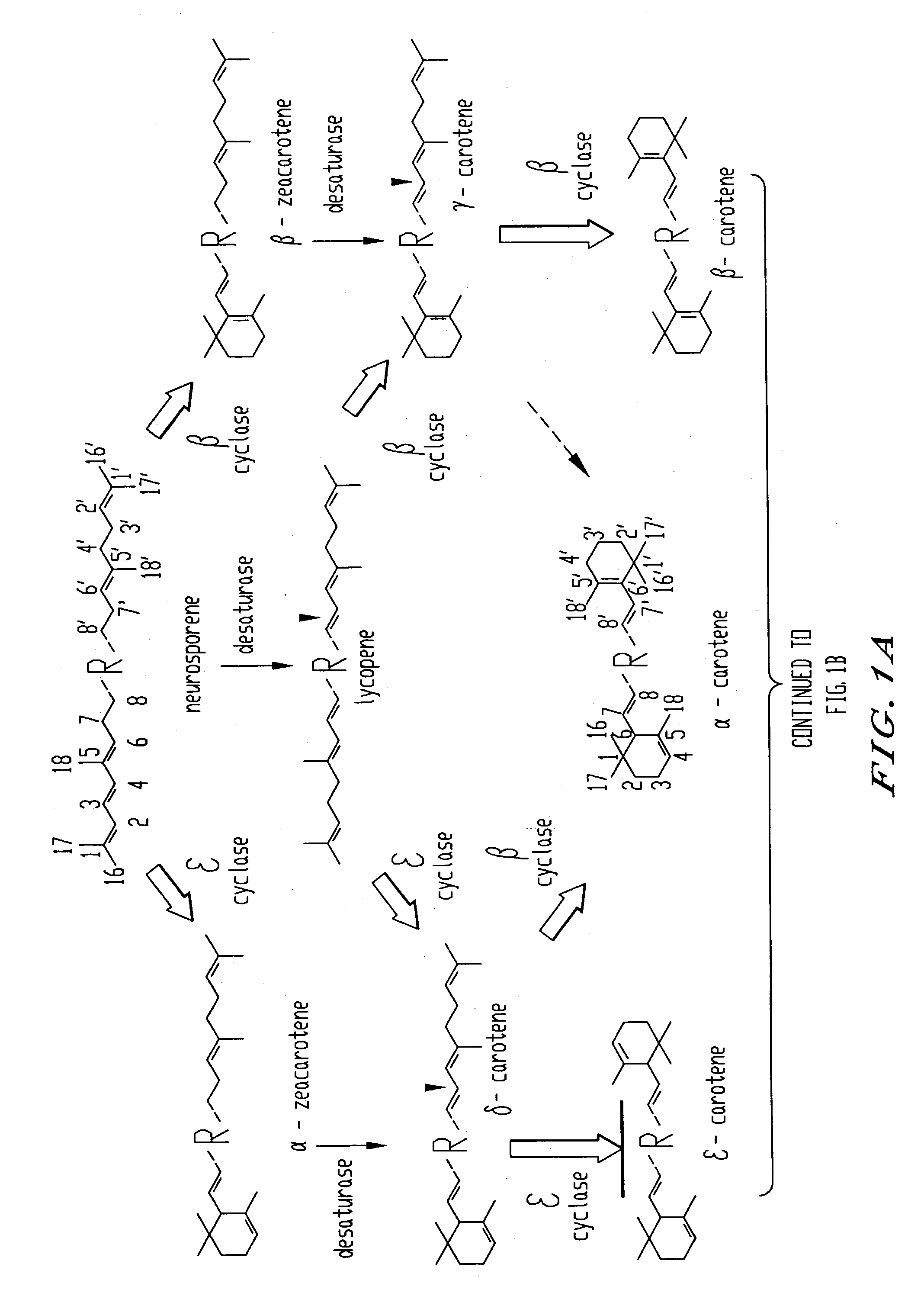
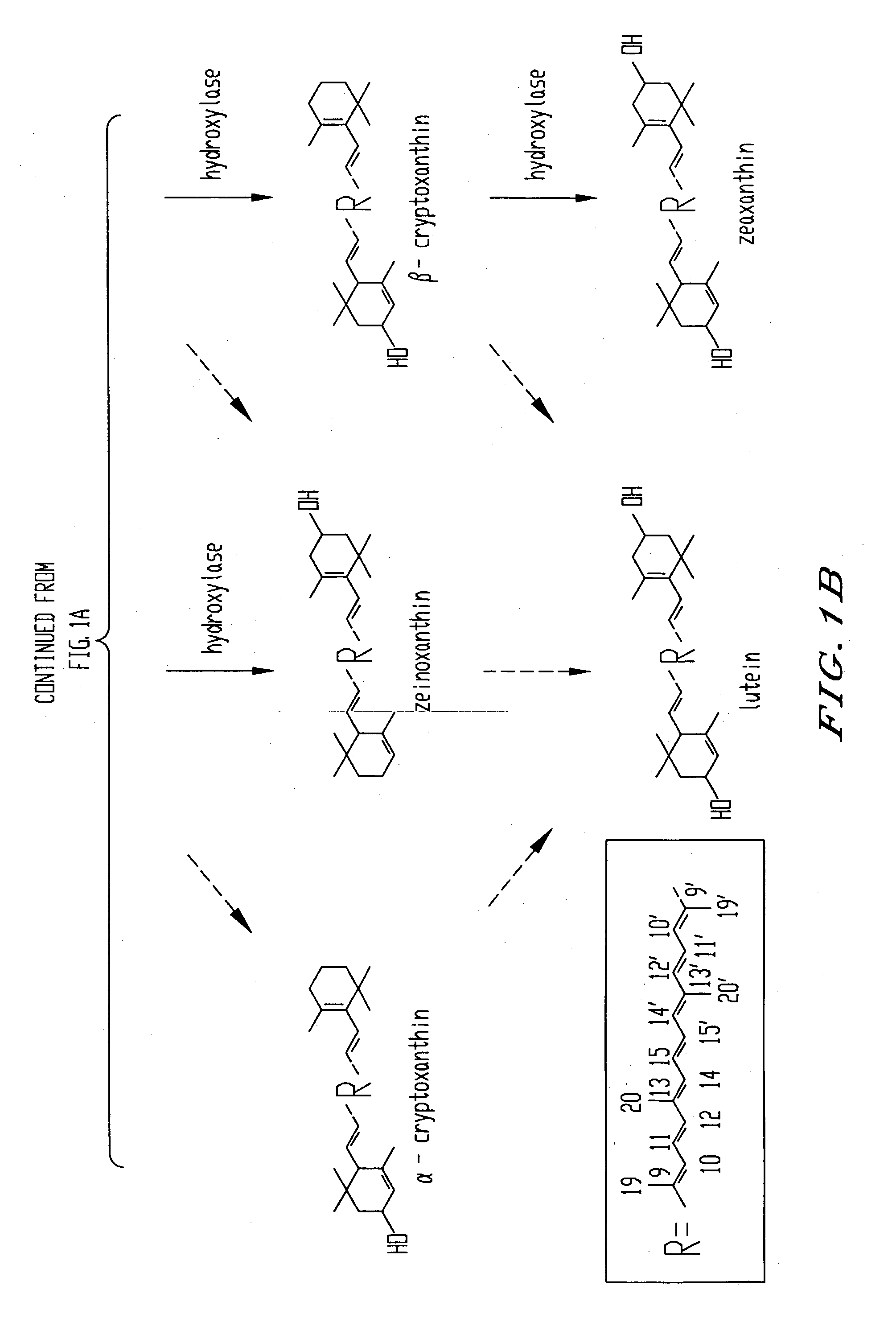
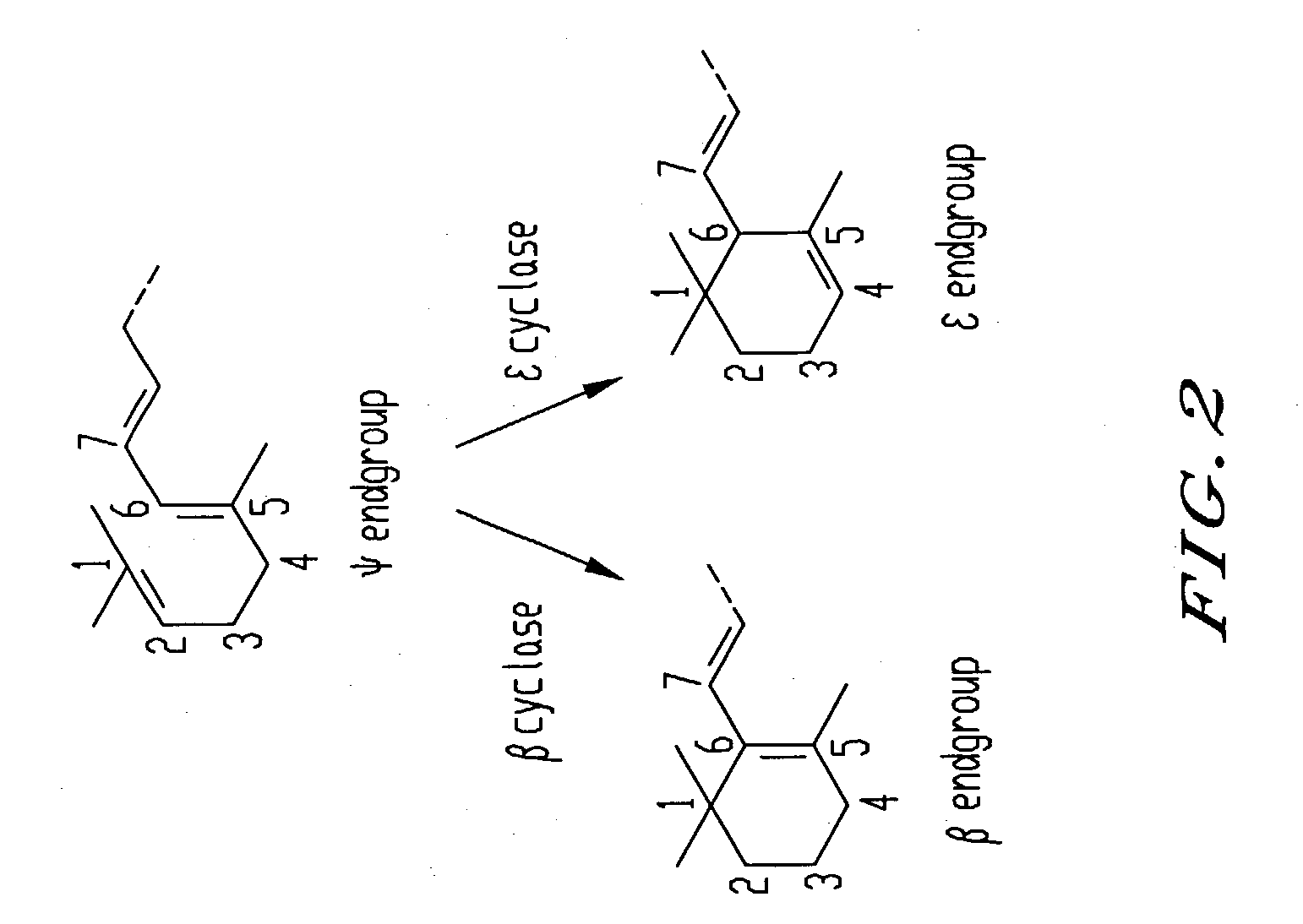
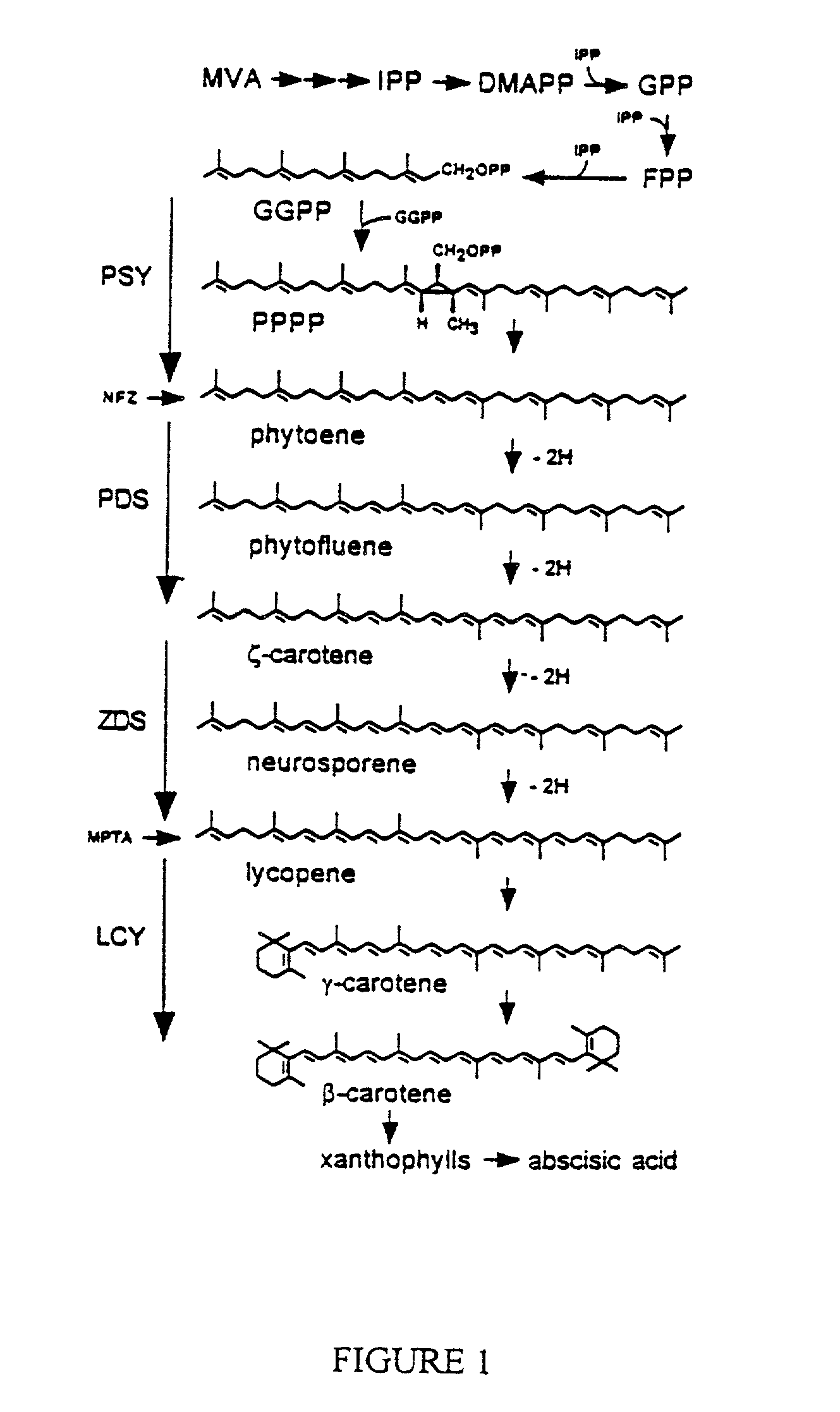
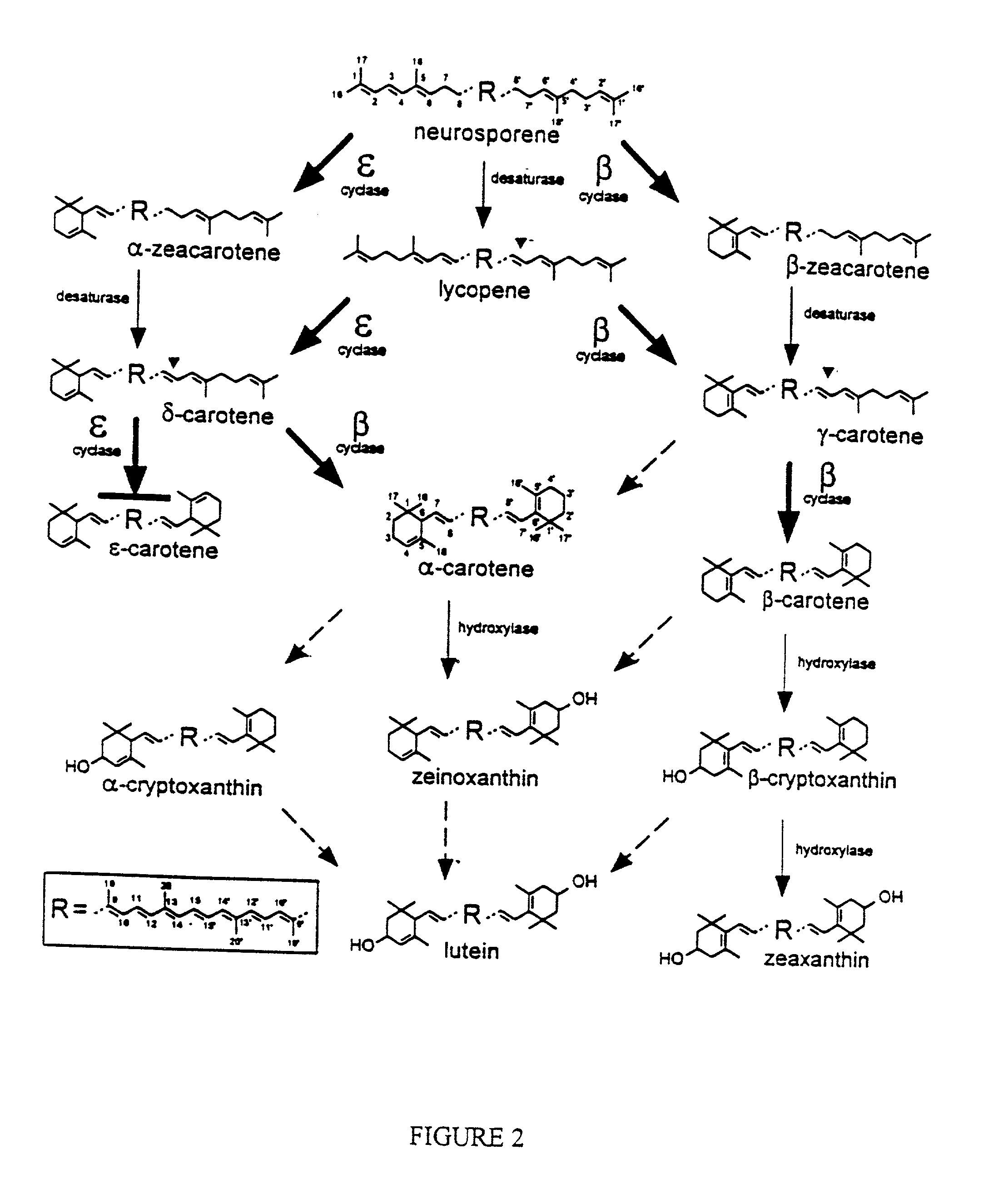
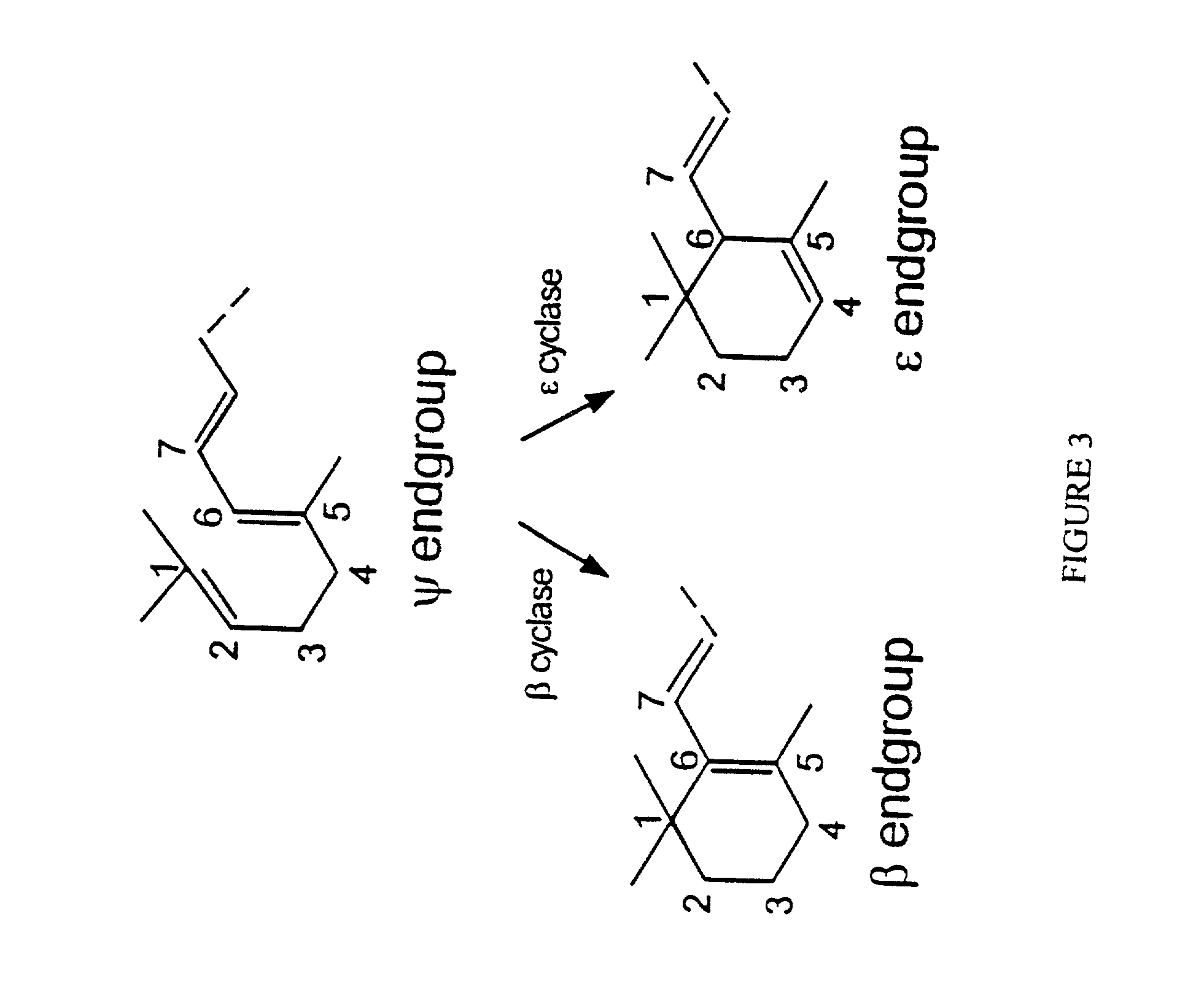
Genes encoding epsilon lycopene cyclase and method for producing bicyclic carotene
The present invention relates to the DNA sequence for eukaryotic genes encoding epsi cyclase isolated from romaine lettuce as well as vectors containing the same and hosts transformed with said vectors. The present invention provides methods for controlling the ratio of various carotenoids in a host and to the production of novel carotenoid pigments. The present invention also provides a method for treating disease by administering carotenoids obtained from transformed hosts, or by administering a composition containing the transformed hosts.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Genes encoding epsilon lycopene cyclase and method for producing bicyclic epsilon carotene
The present invention relates to the DNA sequence for eukaryotic genes encoding ε cyclase isolated from romaine lettuce as well as vectors containing the same and hosts transformed with said vectors. The present invention provides methods for controlling the ratio of various carotenoids in a host and to the production of novel carotenoid pigments. The present invention also provides a method for treating disease by administering carotenoids obtained from transformed hosts, or by administering a composition containing the transformed hosts.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
DNA encoding an epsilon, epsilon-lycopene cyclase from romaine lettuce
The present invention relates to the DNA sequence for eukaryotic genes encoding epsilon cyclase isolated from romaine lettuce as well as vectors containing the same and hosts transformed with said vectors. The present invention provides methods for controlling the ratio of various carotenoids in a host and to the production of novel carotenoid pigments. The present invention also provides a method for treating disease by administering carotenoids obtained from transformed hosts, or by administering a composition containing the transformed hosts.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Genes of carotenoid biosynthesis and metabolism and methods of use thereof
Nucleic acid sequences encoding ∈-cyclase, isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase and beta-carotene hydroxylase as well as vectors containing the same and hosts transformed with the vectors. Methods for controlling the ratio of various carotenoids in a host and for the production of novel carotenoid pigments. The present invention also provides a method for screening for eukaryotic genes encoding carotenoid biosynthesis, and for modifying the disclosed enzymes.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
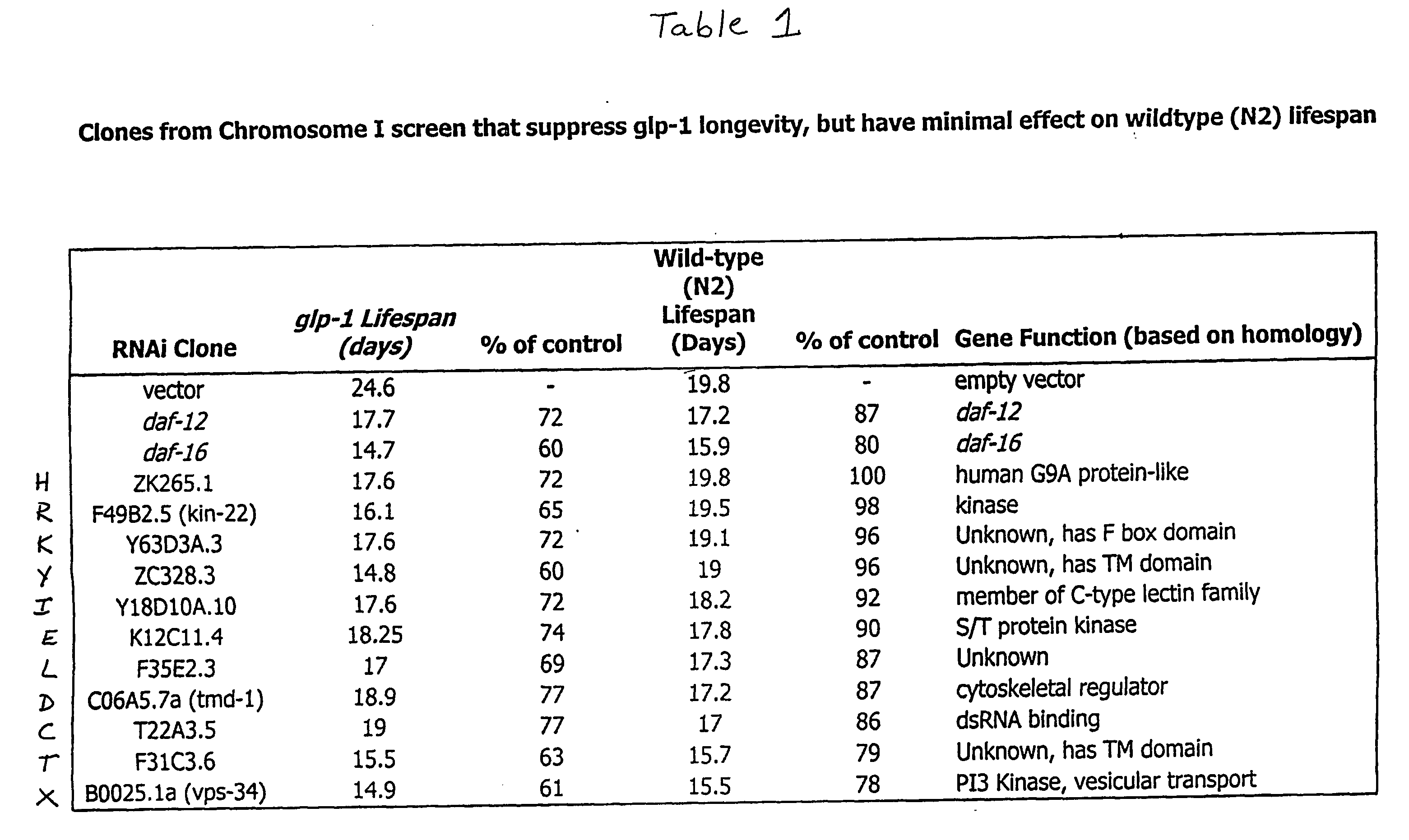
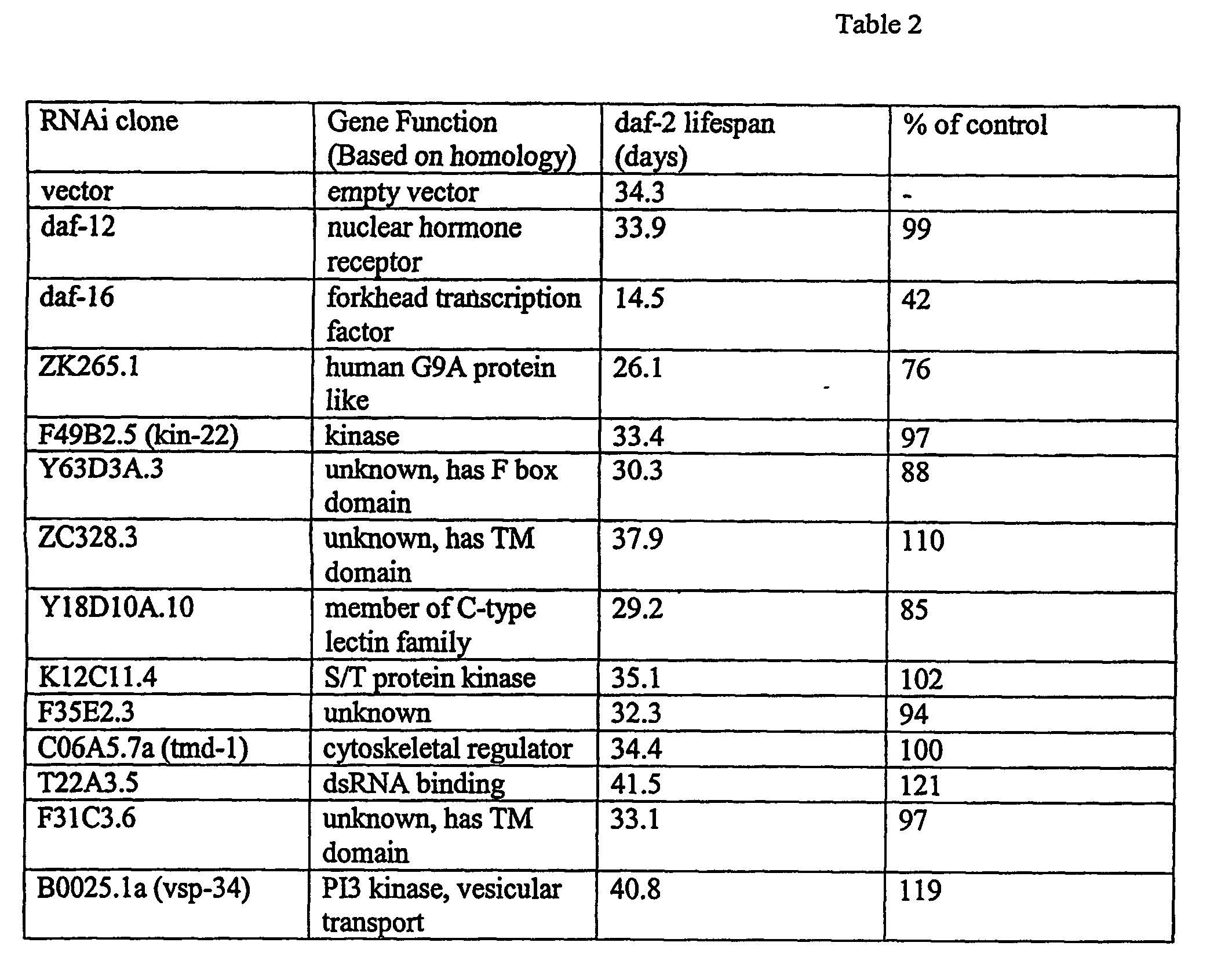
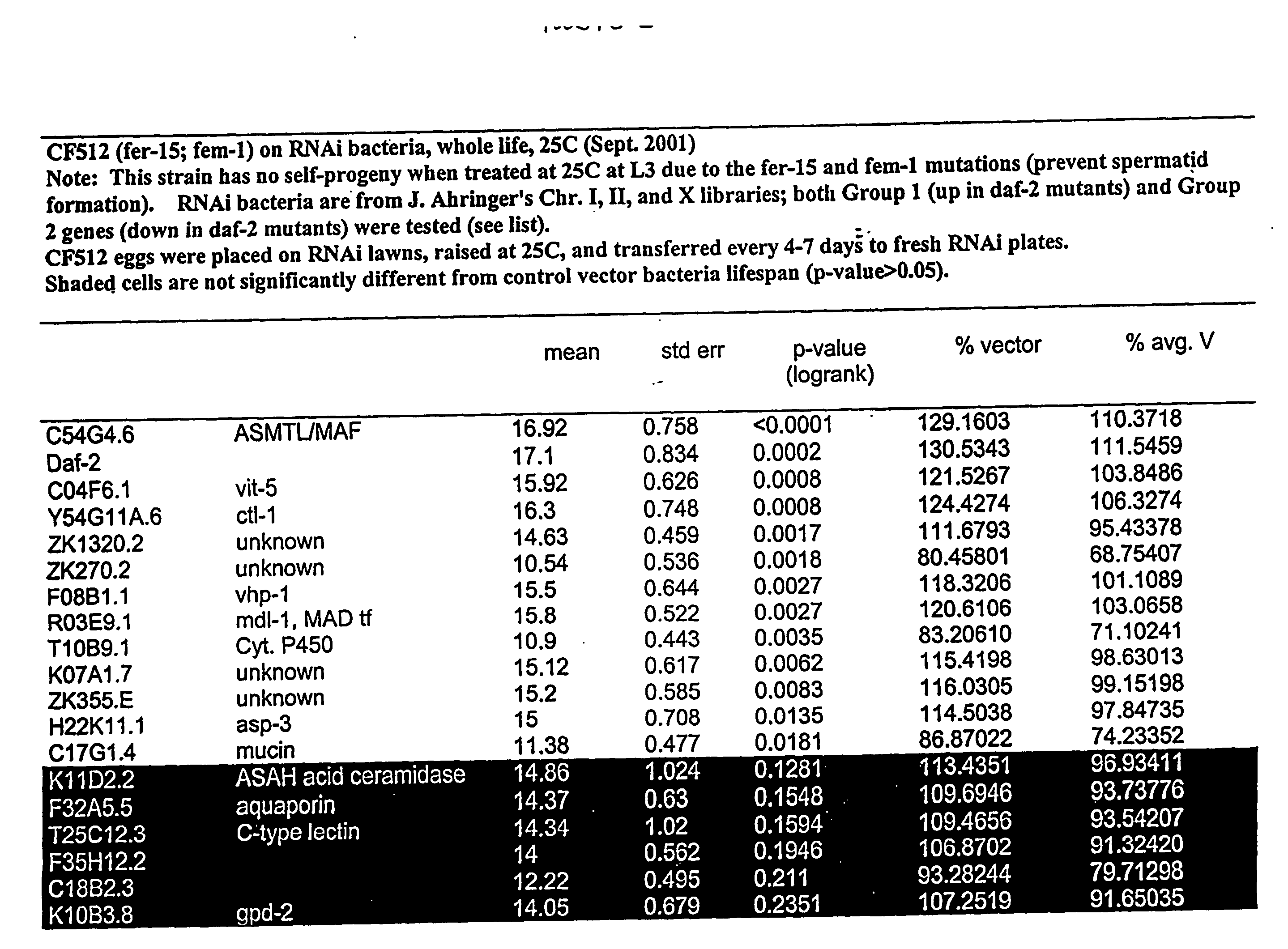
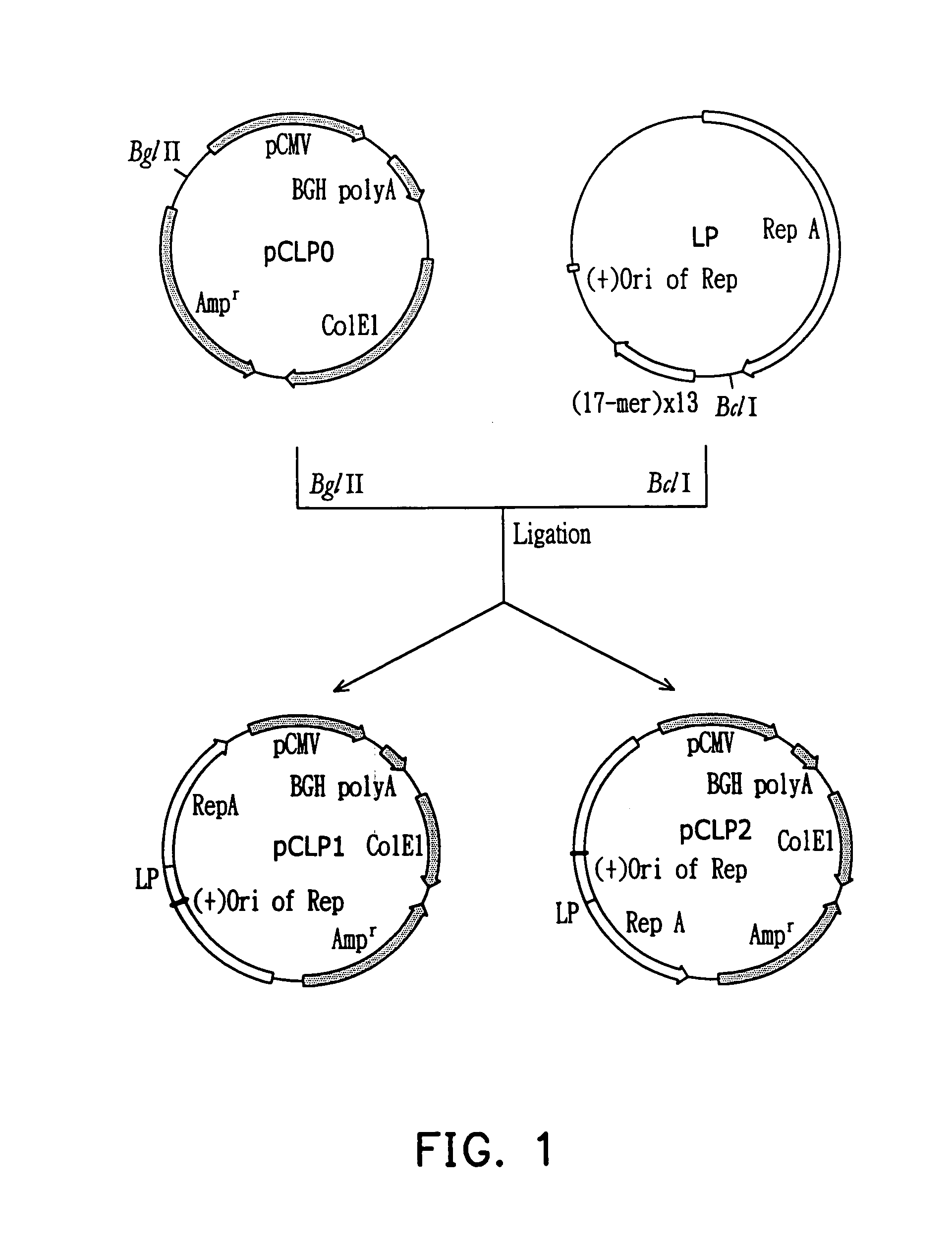
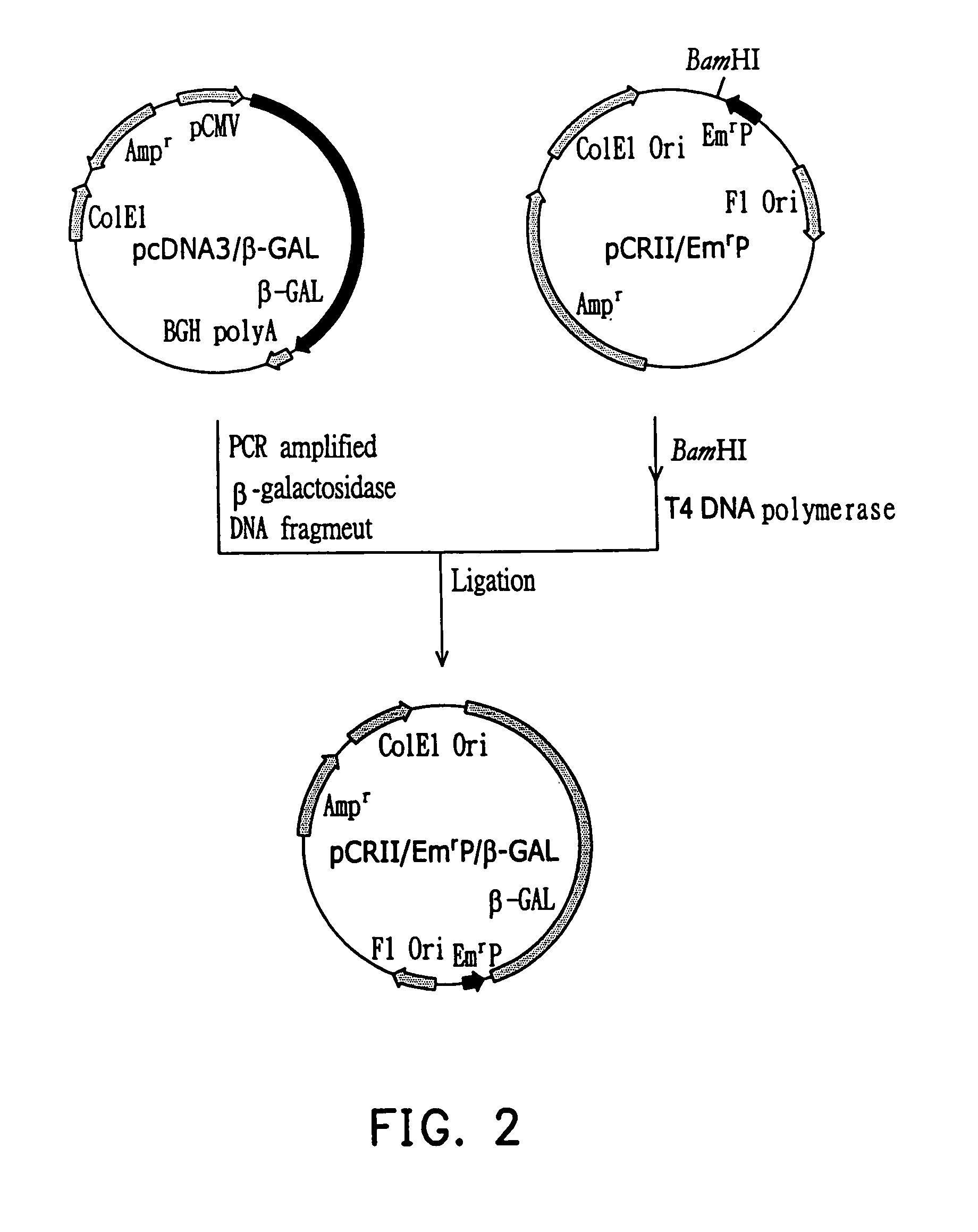
Eukaryotic genes involved in adult lifespan regulation
InactiveUS20060228707A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingAntiendomysial antibodiesAntisense nucleic acid
The present invention relates to regulation of lifespan in eukaryotes. More particularly, one aspect of the present invention is the identification of genes, gene products, and genes in pathways controlled by such genes and gene products, using RNAi and microarray analysis, that regulate lifespan (e.g., extend or truncate adult lifespan) in eukaryotes such as invertebrates (e.g., C. elegans), plants, and mammals, e.g., humans. The invention further relates to methods for identifying and using agents, including small molecule chemical compositions, antibodies, antisense nucleic acids, and ribozymes, that regulate, e.g., enhance, adult lifespan via modulation of aging associated proteins; as well as to the use of expression profiles, promoters, reporter genes, markers, and compositions in diagnosis and therapy related to lifespan extension, life expectancy, and aging. The present invention also relates to gene therapy involving lifespan associated genes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Eukaryotic gene expression cassette and uses thereof
An expression cassette comprising a herpes simplex virus latency-associated transcript P2 region, a promoter and a heterologous gene operably linked in that order. The expression cassette is incorporated into herpes simplex virus vectors to allow for delivery of heterologous genes to mammalian cells for long-term expression.
Owner:BIOVEX LTD
Lac shuttle vectors
The invention discloses a Lac shuttle vector, comprising at least (a) a region which regulates a plasmid copy number; (b) an eukaryotic gene expression cassette, which comprises at least an eukaryotic gene transcriptional promoter sequence, a multiple cloning site and a transcriptional terminator sequence; (c) a lactic acid bacteria plasmid sequence, which comprises a plus origin of replication, and a nucleic acid sequence encoding for a protein which relates to the lactic acid bacteria plasmid replication; and (d) a non-antibiotic resistance selection gene and the promoter sequence thereof. The Lac shuttle vector features a non-antibiotic resistance gene as a selection marker, which is useful in pharmaceuticals and foods.
Owner:ANAWRAHTA BIOTECH
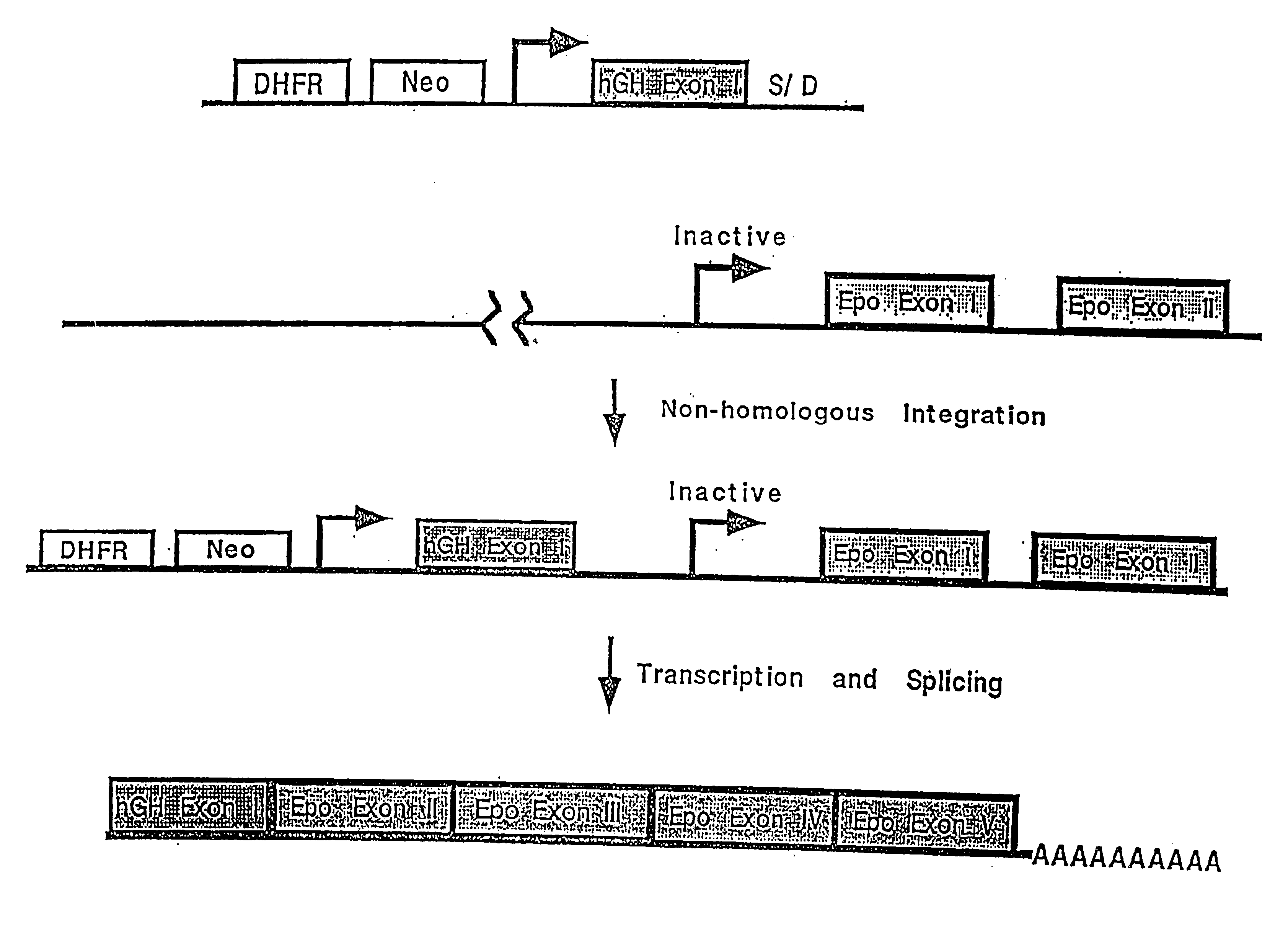
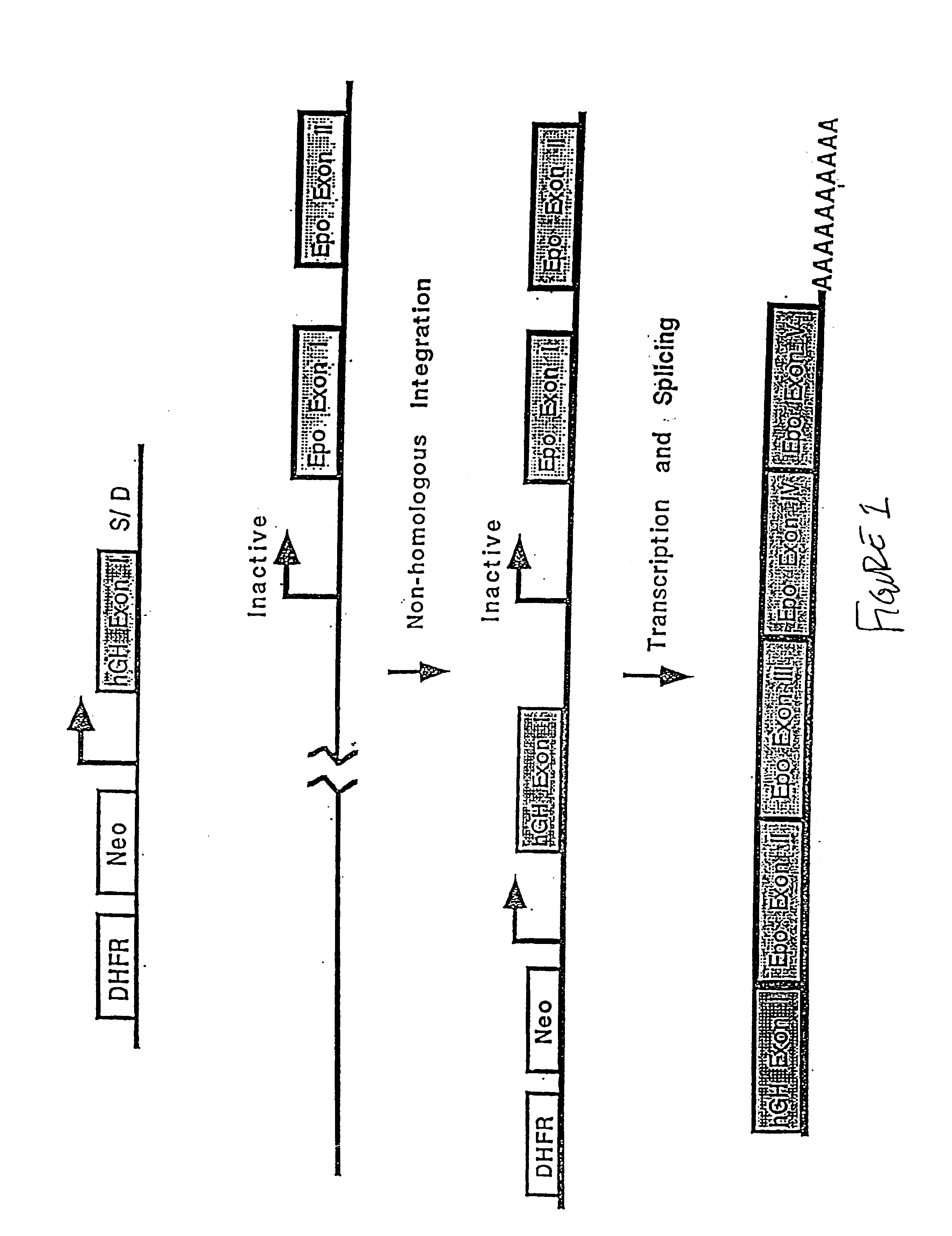
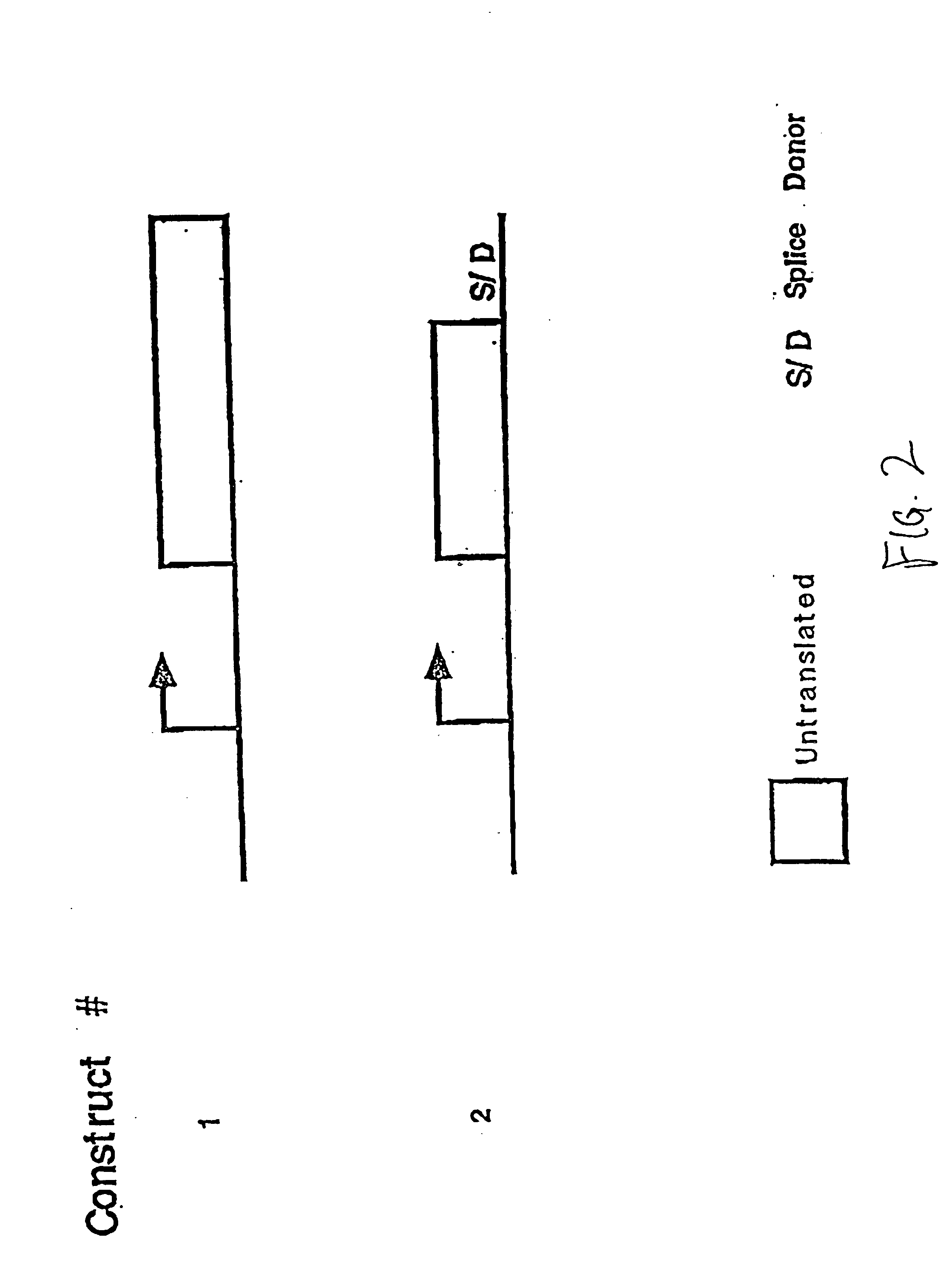
Compositions and methods for non-targeted activation of endogenous genes
InactiveUS6897066B1Improve purification effectAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsEukaryotic geneGene product
The field of the invention is activating gene expression or causing over-expression of a gene by recombination methods in situ. The invention relates to expresssing an endogenous gene in a cell at levels higher than those normally found in the cell. Expression of the gene is activated or increased following integration, by non-homolgous or illegitimate recombination, of a regulatory sequence that activates expression of the gene. The method allows the identification and expression of gene undiscovered by current methods since no target sequence is necessary for integration. Thus, gene products associated with human disease and development are obtainable from gene that have not been sequenced and indeed, whose existence is unknown, as well as from well characterized genes. The methods provide gene products from such genes for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. In one embodiment the vector comprises a promoter, an exon, and an unpaired splice donor sequence, the exon being derived from a eukaryotic gene.
Owner:ATHERSYS
Enhanced nucleic acid constructs for eukaryotic gene expression
ActiveUS20150291977A1Heterologous gene expression can be improvedHigh expressionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsHeterologousEukaryotic gene
The present invention provides polynucleotide vectors for high expression of heterologous genes, and methods for constructing such vectors. Some vectors further comprise novel transposons and transposases that further improve expression. Further disclosed are vectors that can be used in a gene transfer system for stably introducing nucleic acids into the DNA of a cell. The gene transfer systems can be used in methods, for example, but not limited to, gene expression, gene therapy, insertional mutagenesis, or gene discovery.
Owner:DNA2 0
Engineering systhesized gene cry LC of pests-killing crytal protein of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner
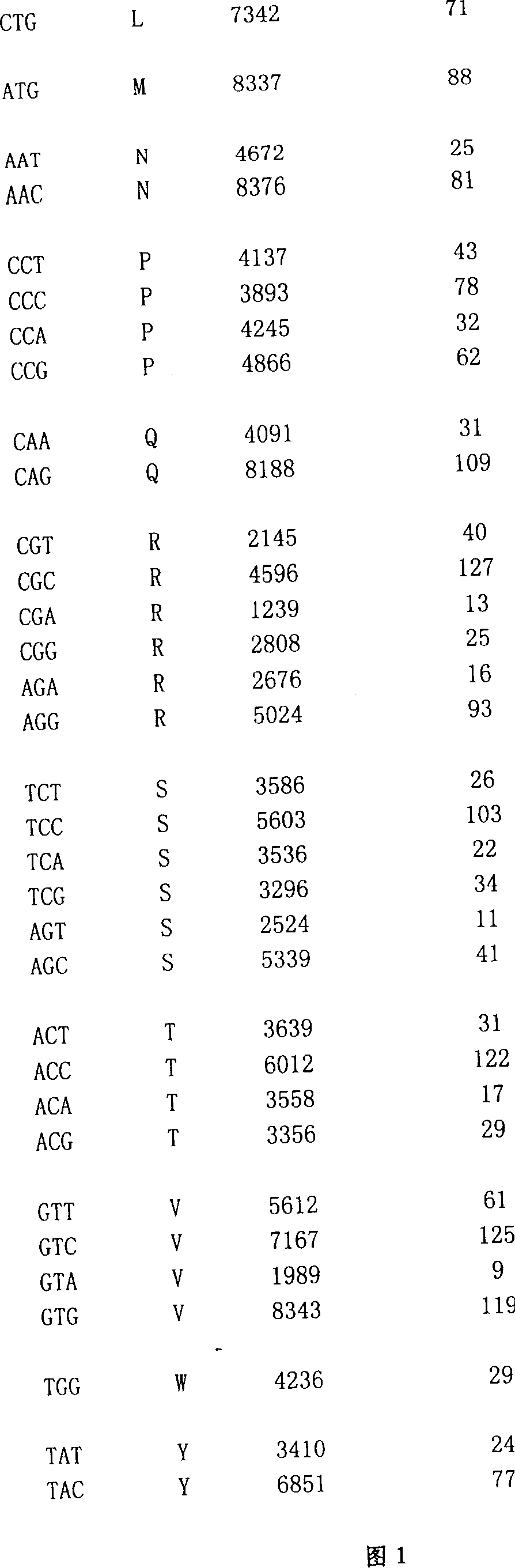
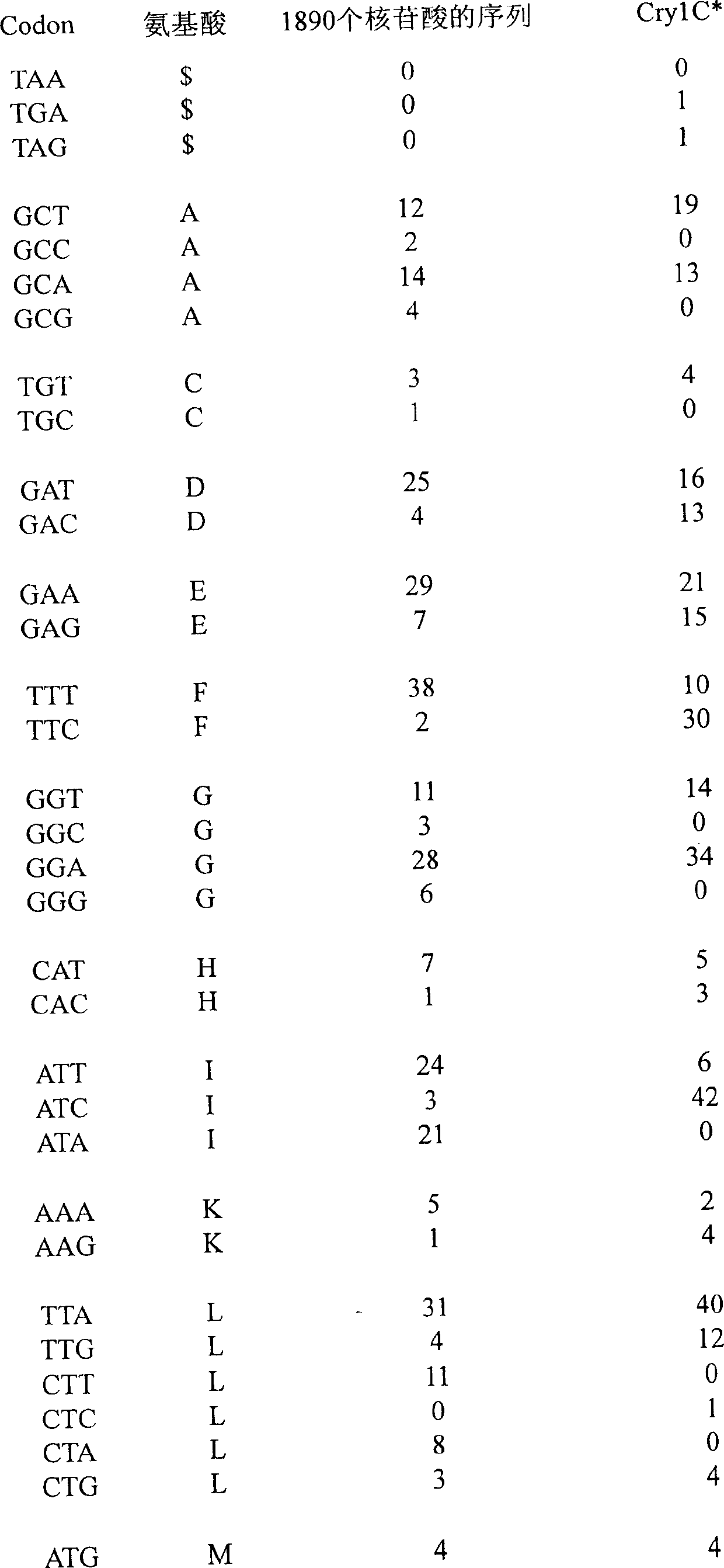
The present invention is characterized by that it utilizes a series method to design and synthesize a bacillus thuringiensis Berlinear insecticidal protein gene CrylC. As compared with sequence of 1890 nucleotides of 5' end of original CrylCa5 gene the amino acid composition of said gene coded protein is not changed, but the richly-contained AT sequence, existed invented repeats and undefined eukaryotic gene intron sequence in the original gene are eliminated, C+G content is 44.64%, and the homology with original sequence is 84.0%, on the 5' end of coding sequence the guide sequence (SEQ ID No:3) is added and on the 3' end the tailing identification signal sequence (SEQ ID No.4) is added.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Complementation trap
Methods and DNA constructs are provided for detection and manipulation of a target eukaryotic gene whose expression is restricted to certain tissues or specialized cell types. The methods include transforming a cell with a first indicator component under the control of a promoter selected for its restricted expression in a particular cell or tissue. The cell is also transformed with a gene trap vector encoding a second indicator component. The cell is allowed to differentiate to produce specialized cell or tissue which is monitored for expression of both the first and second indicator components, thereby detecting a gene into which the trap vector has integrated which is expressed in the same cell or tissue type as the selected promoter.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Triticum aestivum farnesyl phosphate synthase (TaFPS) gene as well as isolation colonizing and enzyme activity measuring method thereof
InactiveCN102433349AIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesEnzyme GenePhosphate
The invention belongs to molecular biology and relates to a technology for isolation colonizing of a triticum aestivum farnesyl phosphate synthase (TaFPS) gene as a key enzyme gene participating in isoprene-like substances such as wheat chlorophyll, carotenoid and the like as well as prokaryotic expression of enzyme protein, separated purification of the enzyme protein and detection in vitro of the enzyme activity. The invention provides important technical storage for further constructing a eukaryotic gene expression vector of the TaFPS gene and converting the eukaryotic gene expression vector into a corresponding crop, particularly obtaining plants with important commercial value by means of secondary metabolism, discussing the relationships between the overexpression of the TaFPS gene in a receptor plant and important economical characters such as a secondary metabolite, the seed size of crops, the grain weight and the like, further improving the yield of the crops, analyzing the structures of an introne, an exon and a promoter of the TaFPS gene, researching the functions of the promoter and developing a relevant molecular marker.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Antimicrobial peptide gene of portunus trituberculatus and clone method
InactiveCN101508992AReduce savingsQuality improvementFermentationAnimals/human peptidesAquaculture industryComplete sequence
The invention provides a Portunus trituperculatus antibacterial peptide gene and a cloning method thereof. The Portunus trituperculatus crustin antibacterial peptide gene cDNA is 565nt except poly A, and contains 5' non-coding region (5' UTR) of 75nt, a reading frame of 330nt, and 3' non-coding region (3' UTR) of 160nt, wherein the sequence number of GenBank is FJ467931. The method successfully clones complete sequence of Portunus trituperculatus crustin cDNA, can construct pronucleus or eucaryon gene engineering strain through a gene engineering mode, efficiently express recombinant protein with physiological activity, and can be produced in scale. As a feed immunity additive, the gene can replace certain antibiotics in the traditional feed for seaculture industry, thereby realizing green culture, reducing and even eliminating accumulation of the antibiotics in aquatic products, and improving quality of the aquatic products; the gene can also be used as an effective substitute of certain drug resistance antibiotics for the medicine of preventing and treating drug resistance bacteria in seaculture.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
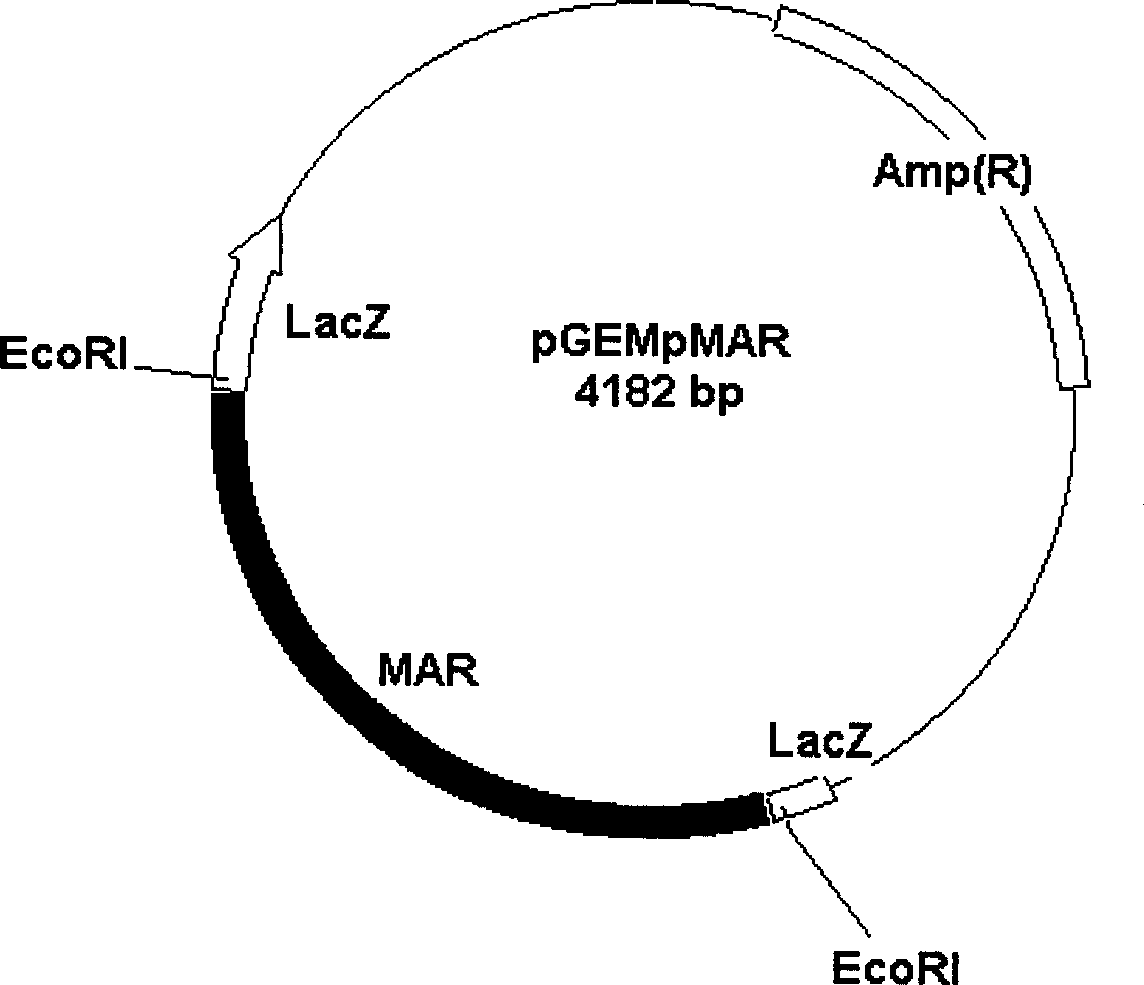
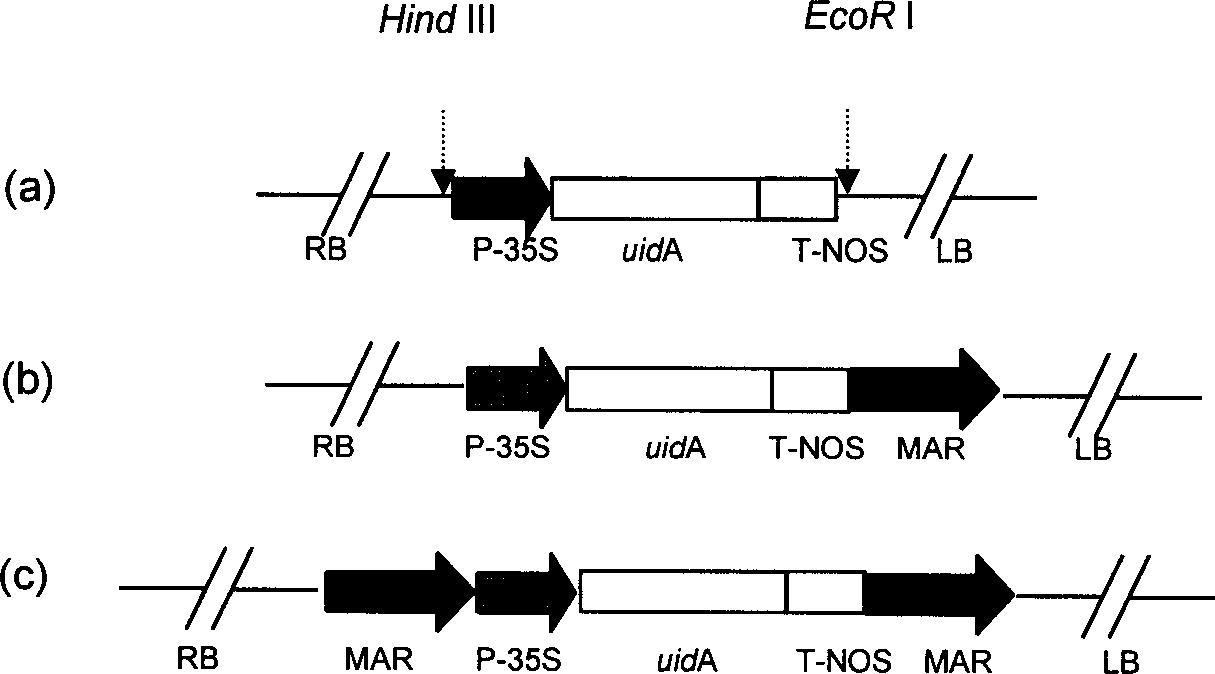
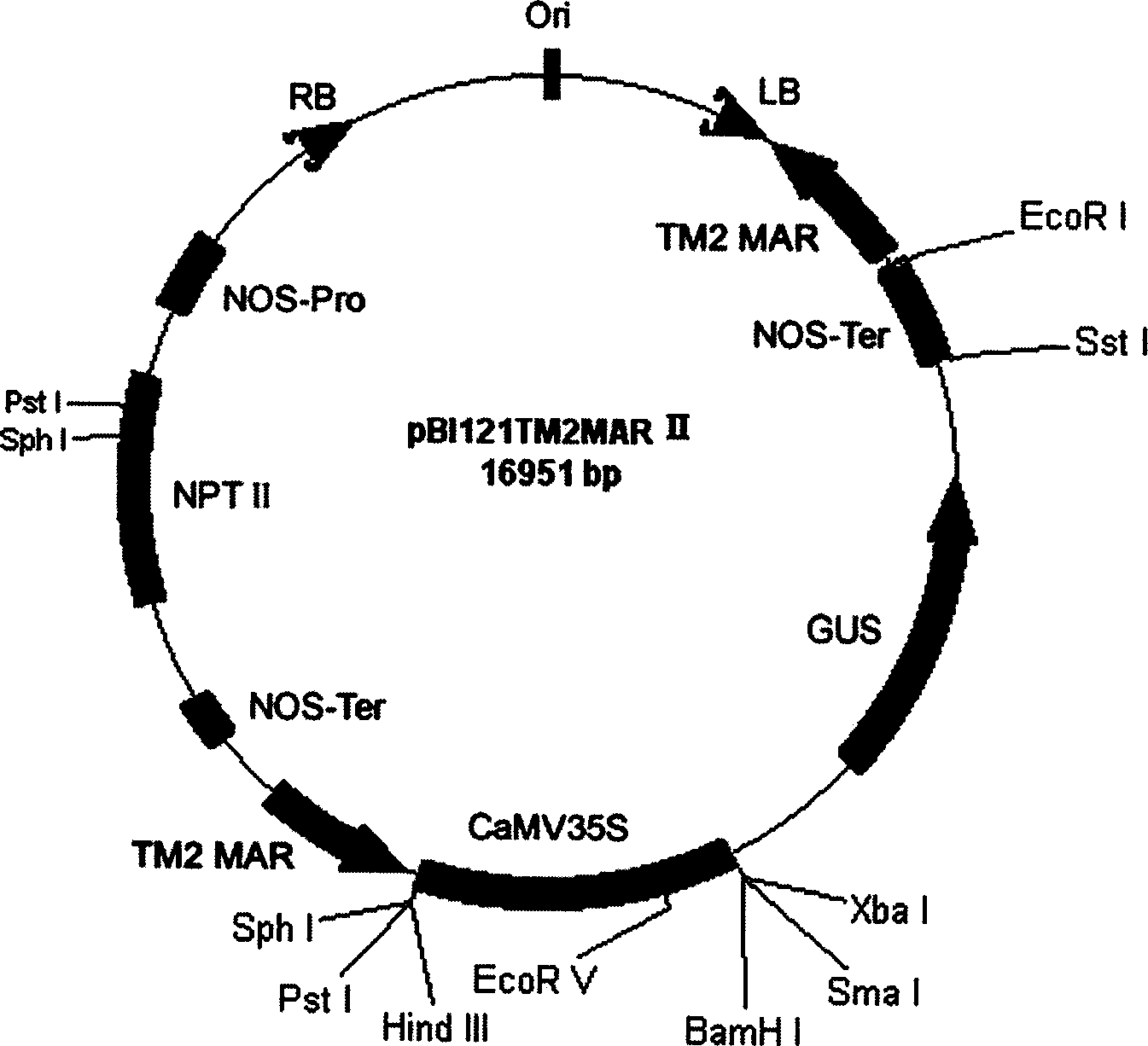
Tobacco strong nuclear matrix binding sequence, separating identification method and use thereof
InactiveCN1401790AIncrease productionImprove expression levelMicrobiological testing/measurementNuclear matrixPlant genetic engineering
A strong nuclear matrix binding sequence (MAR) of tobacco and its separating and assay method and application are disclosed. A novel strong MAR sequence is separated from the tobacco genom and has the typical characteristics of MAR sequence and the stronger speicfic binding power with nuclear matrix in vitro. Said MAR sequence can be used to construct plant gene expression vector, that is, antrorsly constructing it at both sides of the gene expression cassette of expression vector pBI121 gus. It can increase the average expression level of exogenous gus gene by 5 times, and used in genetic engineering.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Eukaryotic gene expression cassette and uses thereof
The present invention provides an expression cassette comprising, operably linked, (i) a myosin light chain enhancer, (ii) a promoter selected from a myosin heavy chain promoter and a viral promoter and (iii) a polynucleotide sequence of interest. The expression cassette can be used in methods of medical treatment and vaccination.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE OF LONDON
Method of producing functional protein domains
The present invention provides a method of producing functional protein domains, which are fragments of primary translational products consisting of one or more distinct protein domains encoded by specific subsets of exonic sequences. The method is based on the integration, by a single homologous recombination event, of a regulatory unit into the eukaryotic gene coding for the primary translational product at the level of the intronic genomic region immediately adjacent to the exonic sequences which code for the functional protein domain.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
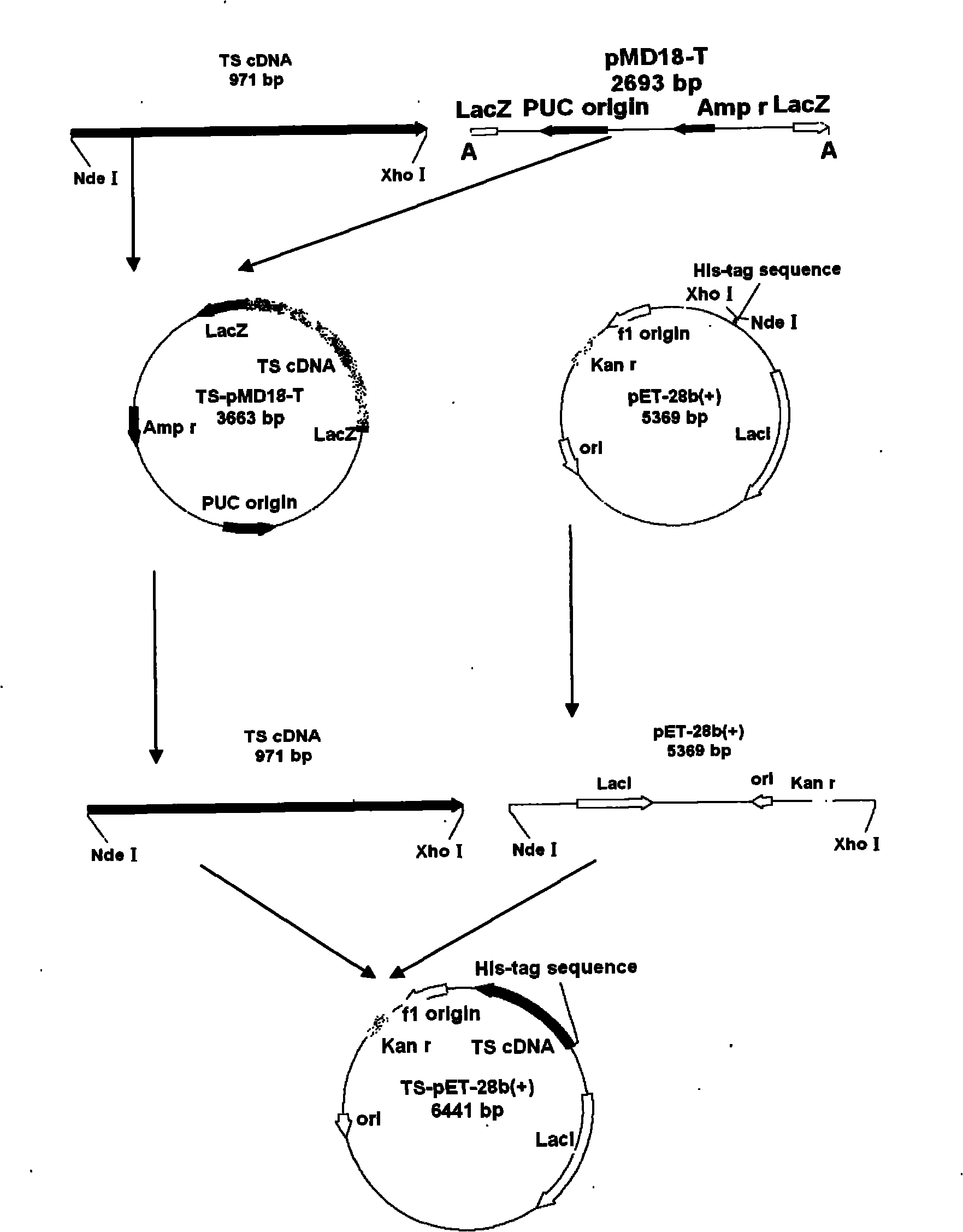
Overexpression of thymidylate synthase in colon bacillus
The invention relates to a new method of overexpression of thymidylate synthase in colon bacillus. TS (Thymidylate Synthetase) is a necessary enzyme for synthetizing catalytic thymidylate in vivo, repression of TS activity in rapidly proliferating cells can hander DNA synthesis to cause cell death, TS is an important target for cancer chemotherapy for the past many years, and research on enzymatic properties thereof contributes to the development of new anti-cancer drugs. Human TS gene is eukaryotic gene and contains a large number of prokaryote rare codons, and pure enzyme is less and the operating volume is large with the traditional expression method. According to the invention, colon bacillus expression plasmids TS-pET-28b(+) containing wild type human thymidylate synthase gene is constructed by adopting a molecular biology method, transferred to a bacterial strain Rosetta (DE3) containing the eukaryote rare codons, and are efficiently expressed through optimization of fermentation conditions, thus, the system has the characteristics of high expression level, low cost, and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Enhanced nucleic acid constructs for eukaryotic gene expression
ActiveUS20150291976A1Heterologous gene expression can be improvedHigh expressionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsHeterologousEukaryotic gene
The present invention provides polynucleotide vectors for high expression of heterologous genes, and methods for constructing such vectors. Some vectors further comprise novel transposons and transposases that further improve expression. Further disclosed are vectors that can be used in a gene transfer system for stably introducing nucleic acids into the DNA of a cell. The gene transfer systems can be used in methods, for example, but not limited to, gene expression, gene therapy, insertional mutagenesis, or gene discovery.
Owner:DNA2 0
High-throughput screening of expressed DNA libraries in filamentous fungi
InactiveUS20060257923A1Minimizes and eliminates formationLow culture viscosityHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyPost translational
The invention provides a method for the expression of exogenous DNA libraries in filamentous fungi. The fungi are capable of processing intron-containing eukaryotic genes, and also can carry out post-translational processing steps such as glyclosylation and protein folding. The invention provides for the use of fungi with altered morphology, which permits high-throughput screening and directed molecular evolution of expressed proteins. The same transformed fungi may be used to produce larger quantities of protein for isolation, characterization, and application testing, and may be suitable for commercial production of the protein as well.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
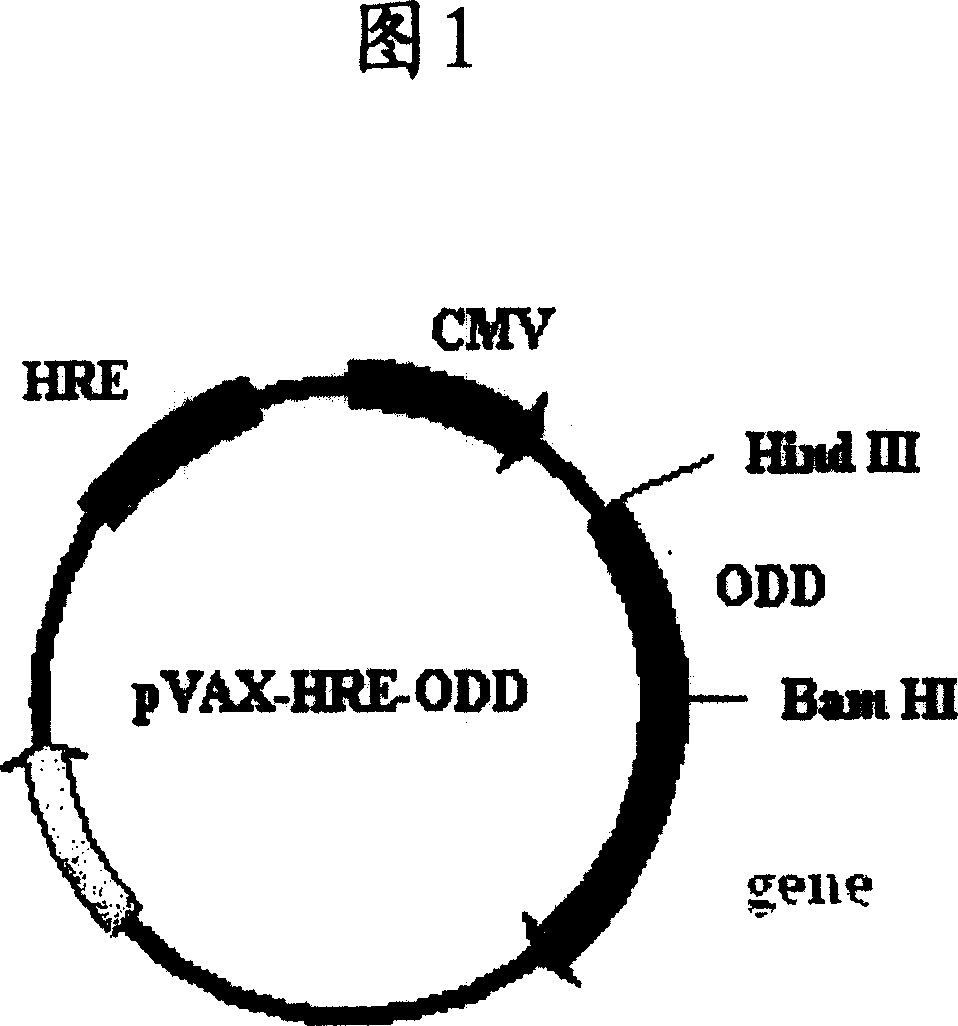
Strict hypoxia targeting carrier and uses thereof
The present invention provides a novel eukaryotic gene construct. HRE is inserted in a promoter upstream, and ODD is inserted in front of an effector, thus resulting that the gene construct has rigid hypoxic targeting effect. The present invention also provides a carrier which contains the gene construct. In addition, the present invention relates to a drug combination which contains the gene construct.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
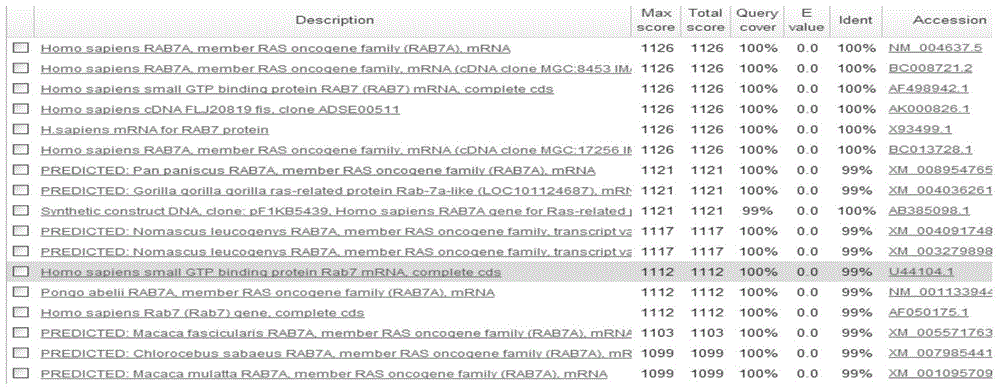
Lentiviral vector of fusion green fluorescent protein with over expression of RAB7A and EGFP genes, building method and application thereof
ActiveCN104531762AIntuitive observation of position changesSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGreen fluorescent proteinEukaryotic gene
The invention discloses a lentiviral vector of fusion green fluorescent protein with over expression of RAB7A and EGFP genes, a building method and application thereof. The vector takes a lentiviral vector LV11 as a skeleton vector, wherein an EGFP gene segments and RAB7A gene segments are inserted behind a CMV promoter of the vector LV11 in a direction from 5' to 3'. By virtue of the lentiviral vector of fusion green fluorescent protein with over expression of RAB7A and EGFP genes, the problem that over-expression vector is effective and intuitive in the study of RAB7A genes can be solved. The vector takes CMV as the promoter, so that the high-efficiency expression of eukaryotic gene can be ensured; EGFP is used as a marker, the autophagy and endocytosis degree of cells and the effect of RAB7A genes in cell hypoxia process can be judged by intuitively observing the intensity of the expressed fluorescence; a good tool is provided for studying the functions of the RAB7A genes; the basis is provided for the subsequent correlation studies of RAB7A.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Myzus persicae resistance associated CYP6CY3 promoter and activity analysis
InactiveCN103820448AImprove the level ofStable expressionVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationEukaryotic geneMyzus persicae
The invention discloses a myzus persicae resistance associated CYP6CY3 promoter and activity analysis, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The sequence of the promoter is represented by SEQ ID NO: 1; the regions from -1bp to -2230bp of the SEQ ID NO: 1 represent a DNA sequence of the myzus persicae resistance relevant CYP6CY3 promoter; the regions from +1bp to +71bp of the SEQ ID NO: 1 represent a DNA sequence of a 5' non-translating region of a gene CYP6CY3 of myzus persicae P450. The myzus persicae resistance associated CYP6CY3 promoter can be used for high-efficiency expression of a eukaryotic gene and is applied to a research on acquisition of low-abundance genes, so that high-level and stable expression can be obtained; an active significance is realized for the research on a target function.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com