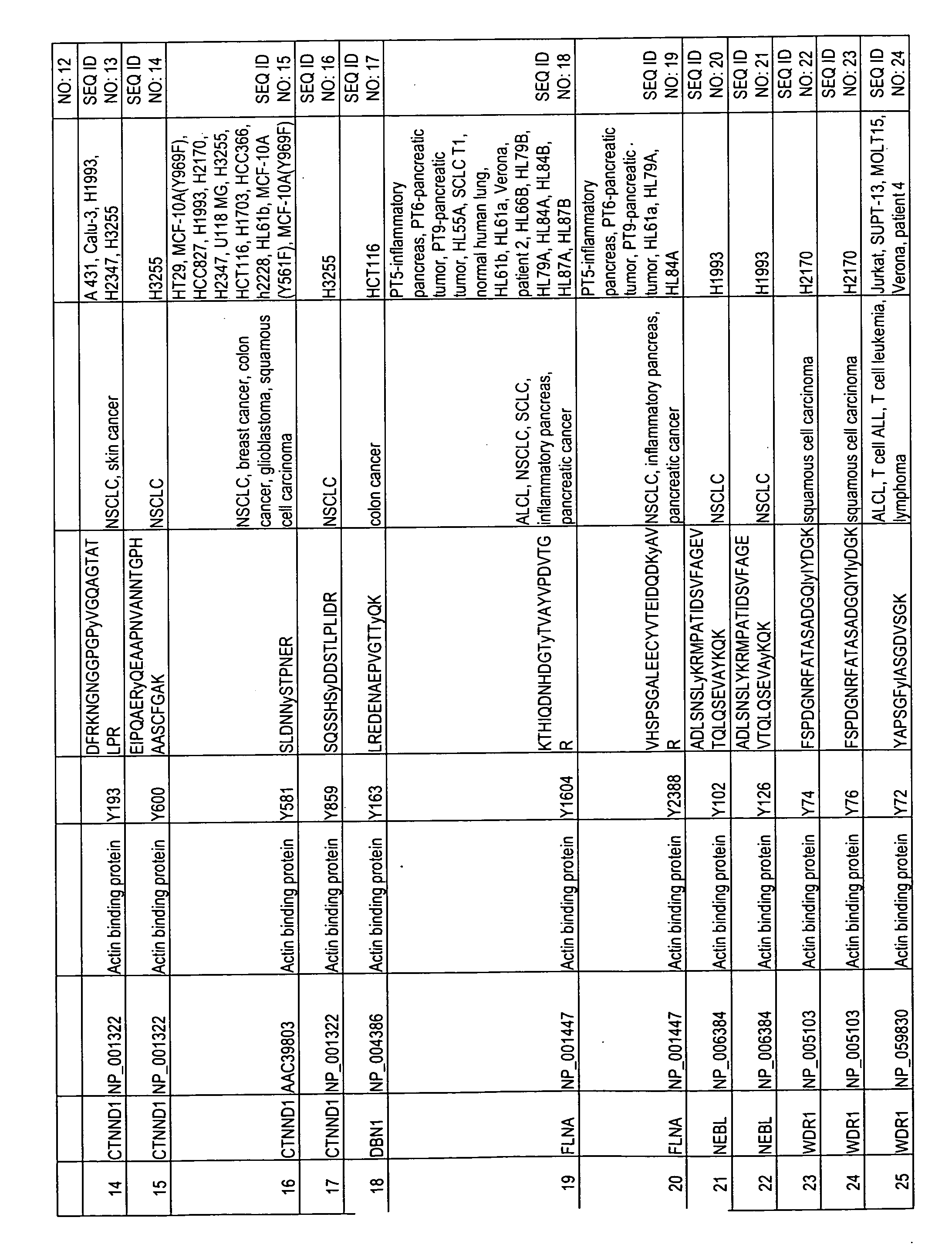
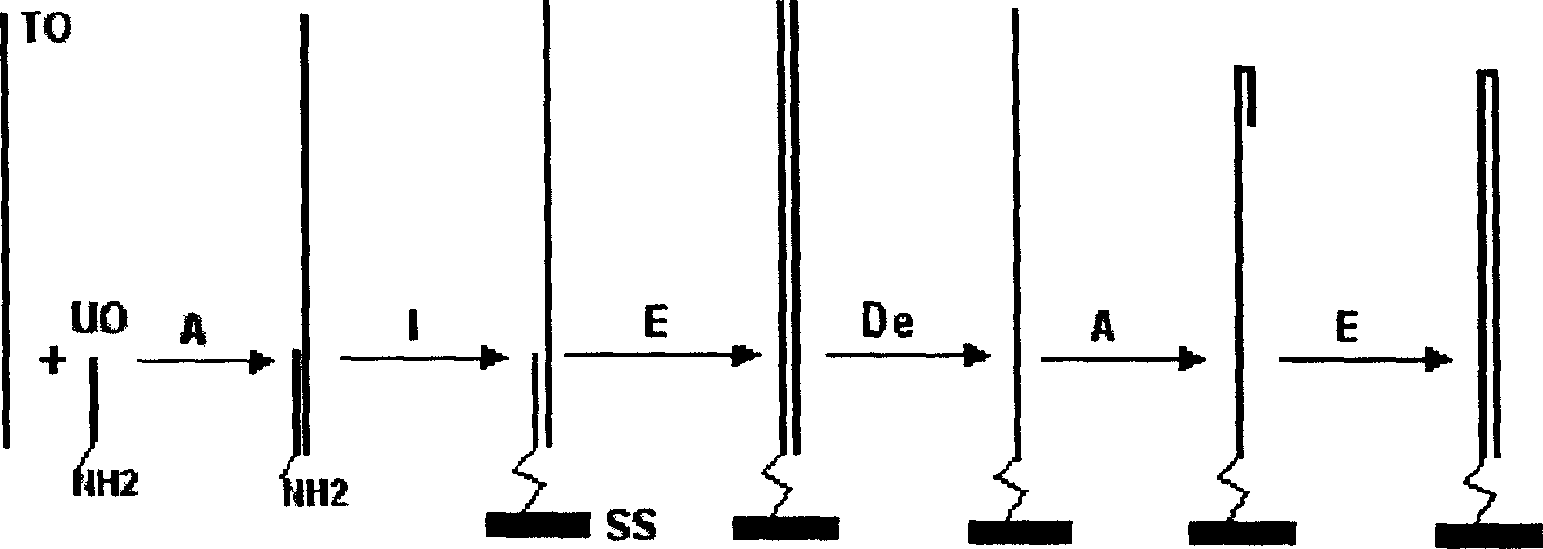
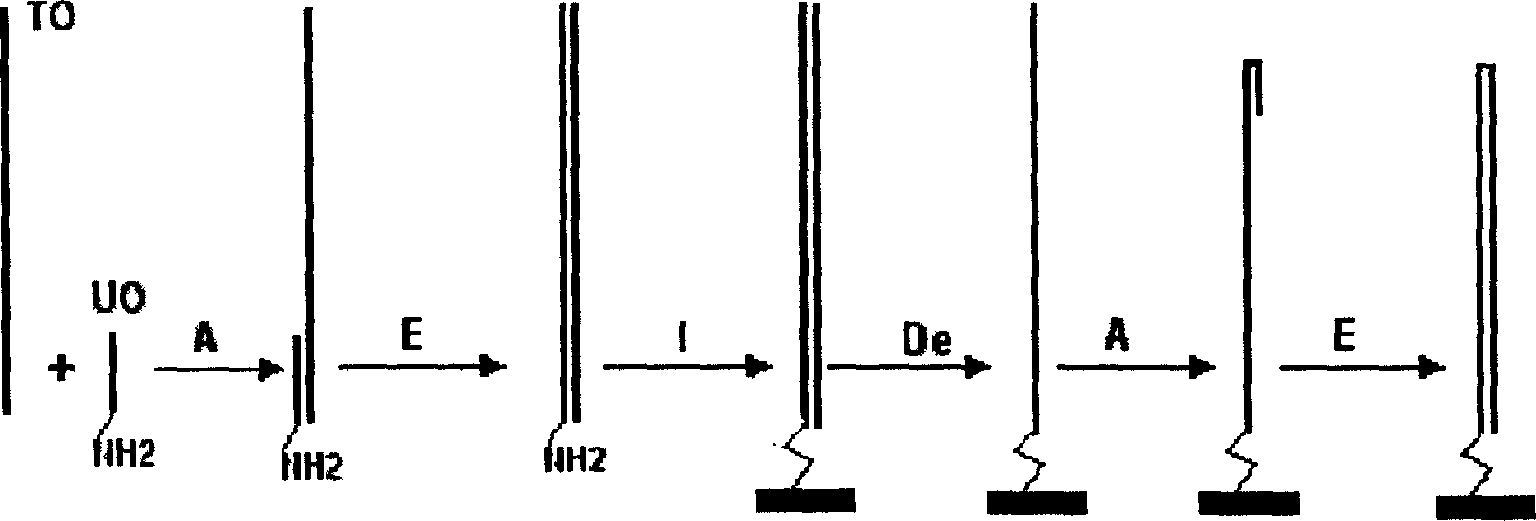
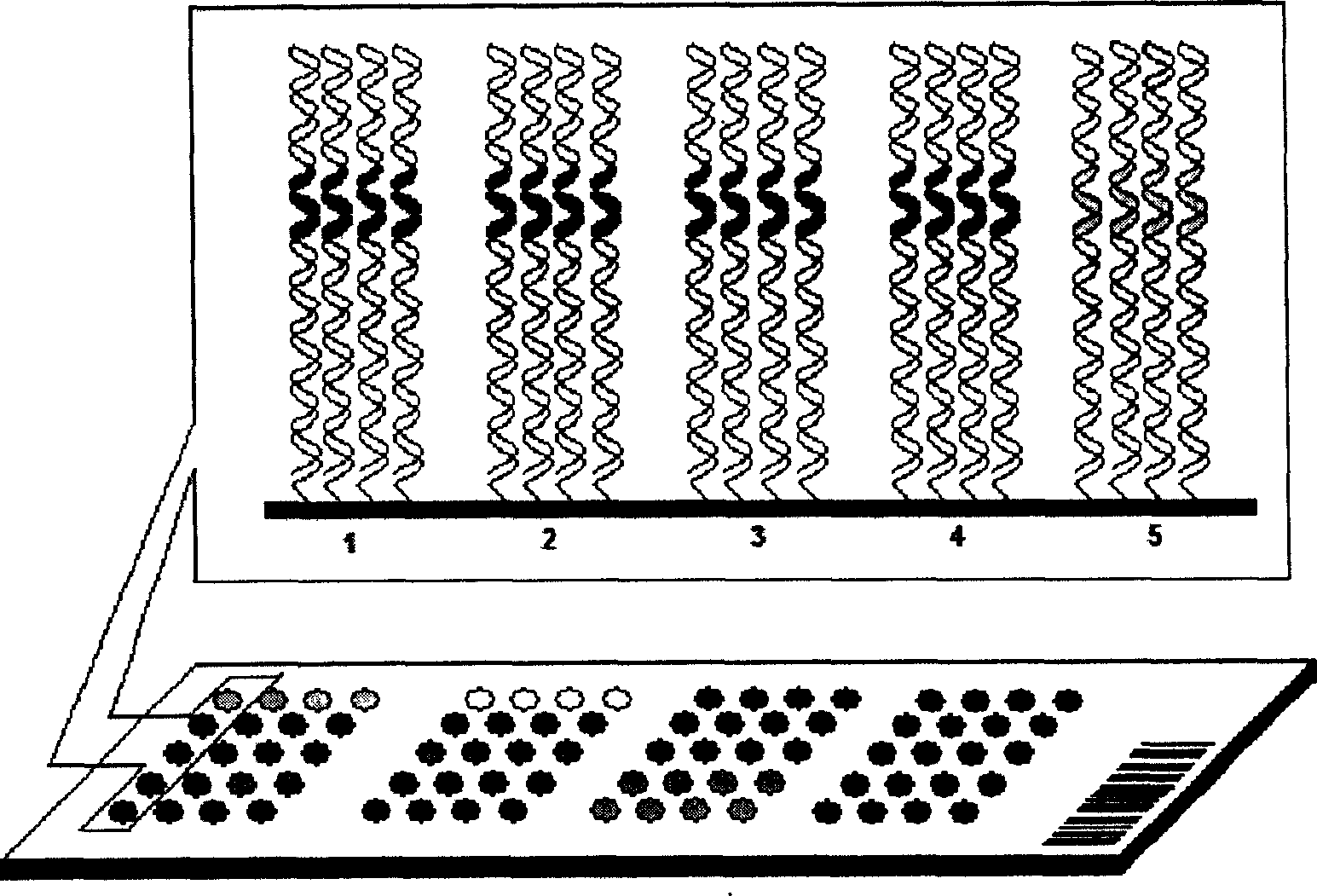
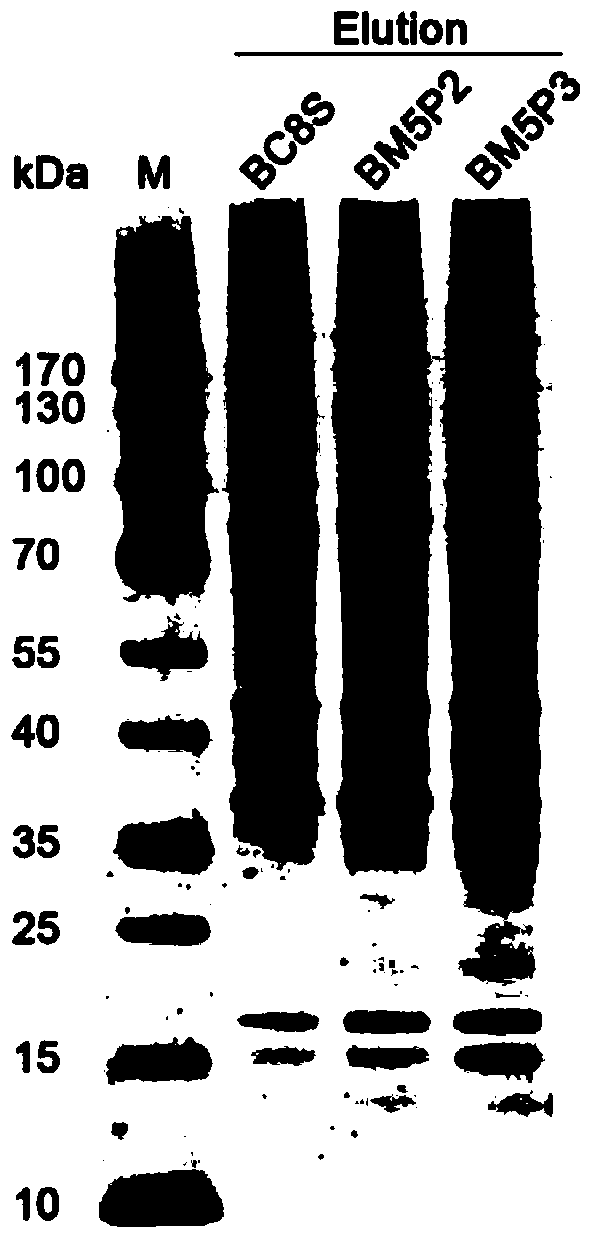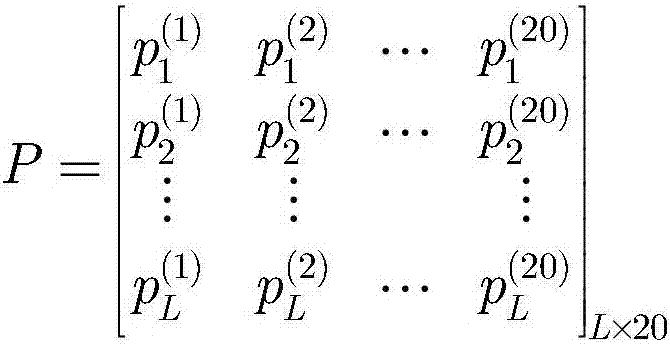Patents
Literature
150 results about "DNA-binding protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
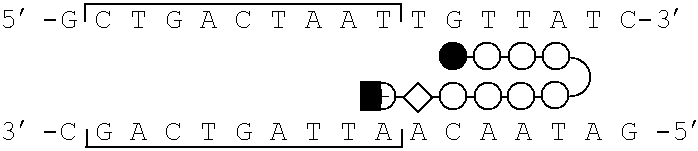
DNA-binding proteins are proteins that have DNA-binding domains and thus have a specific or general affinity for single- or double-stranded DNA. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the major groove of B-DNA, because it exposes more functional groups that identify a base pair. However, there are some known minor groove DNA-binding ligands such as netropsin, distamycin, Hoechst 33258, pentamidine, DAPI and others.
Nucleic acid binding proteins
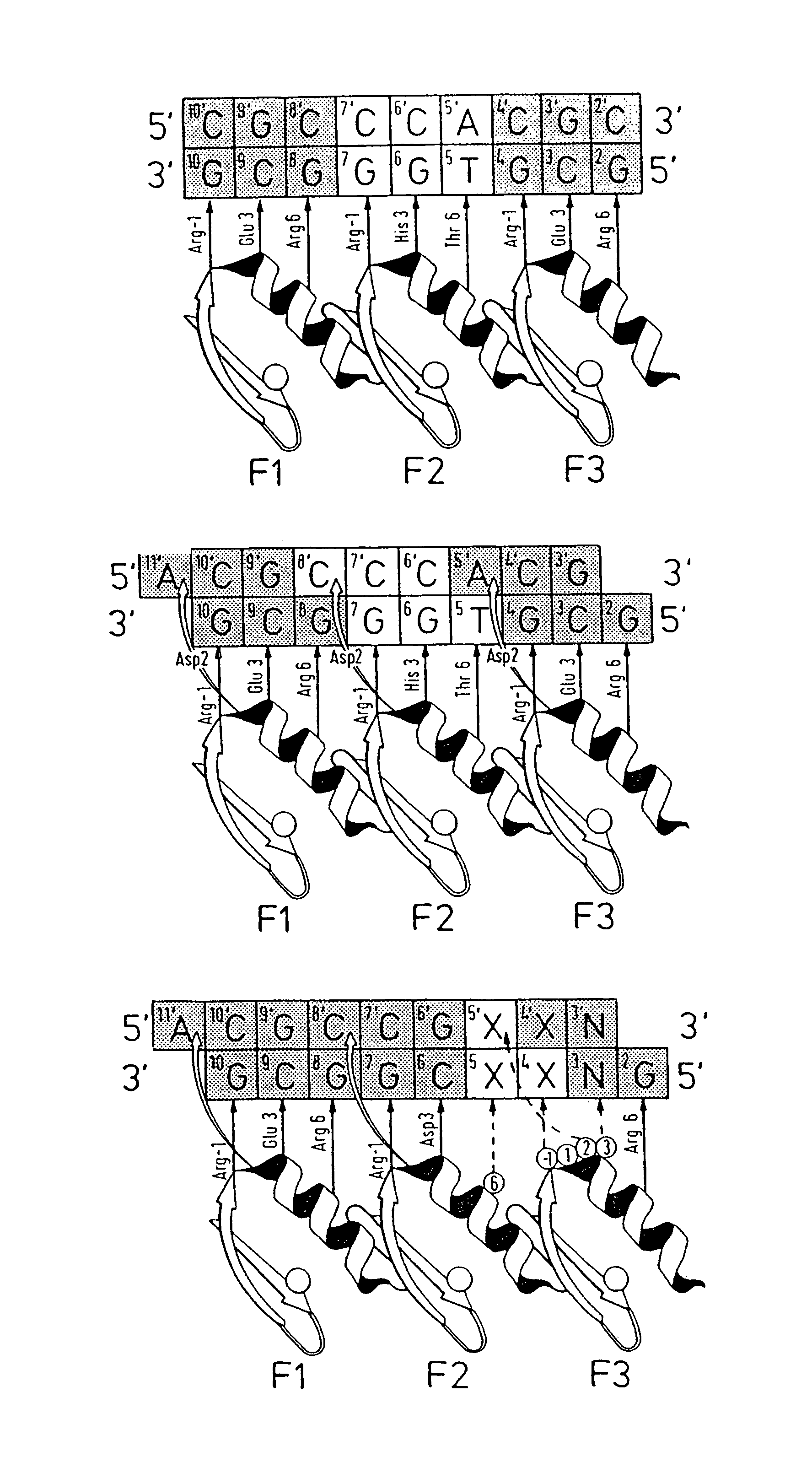
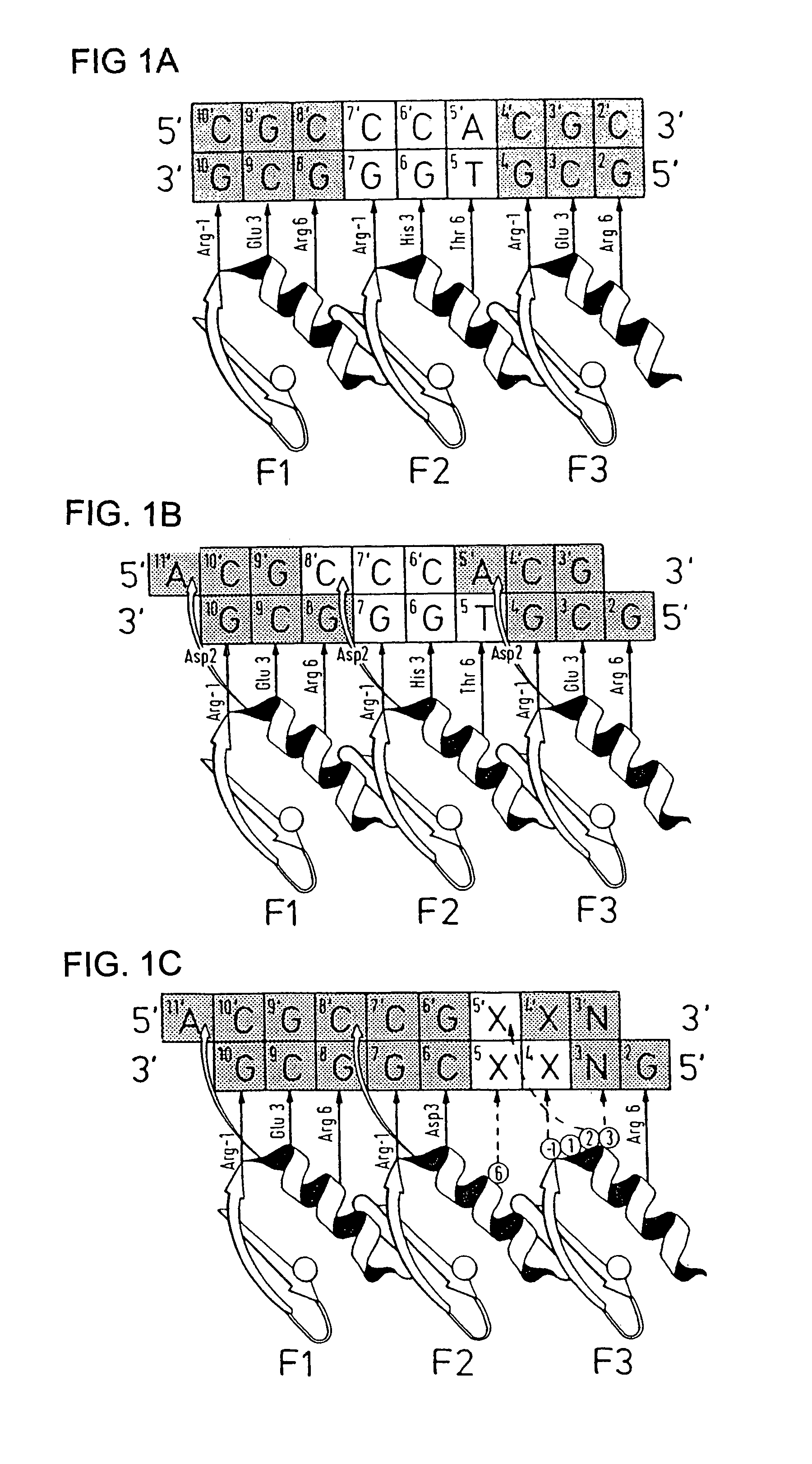
Disclosed herein are methods for designing DNA binding proteins comprising a plurality of zinc fingers and methods for binding the proteins to target nucleotide sequences in cells.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Targeted gene discovery
InactiveUS6139833AEnhancing general accessibilityRaise the possibilityBiocideBacteriaGenomic DNAIn vivo
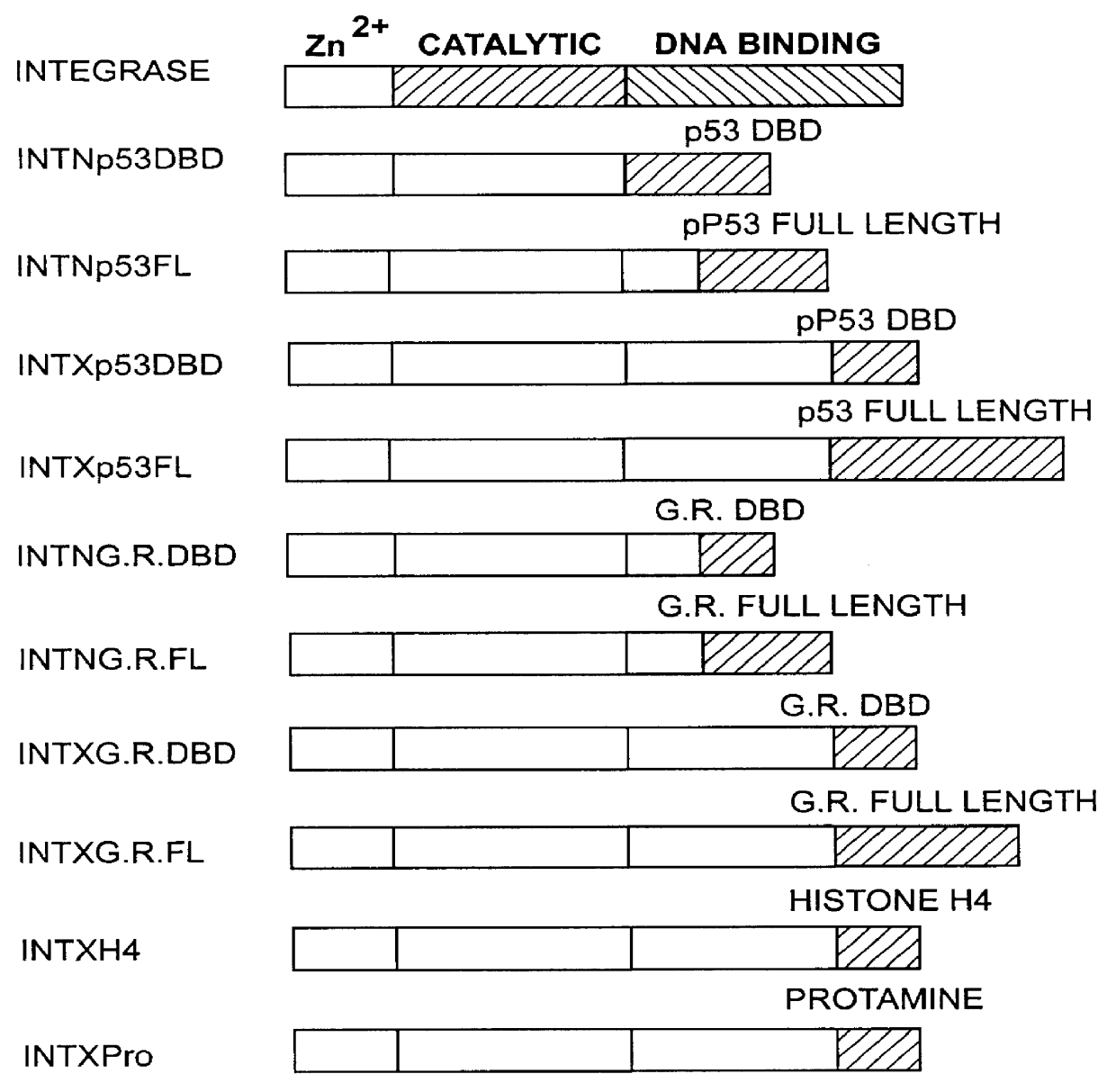
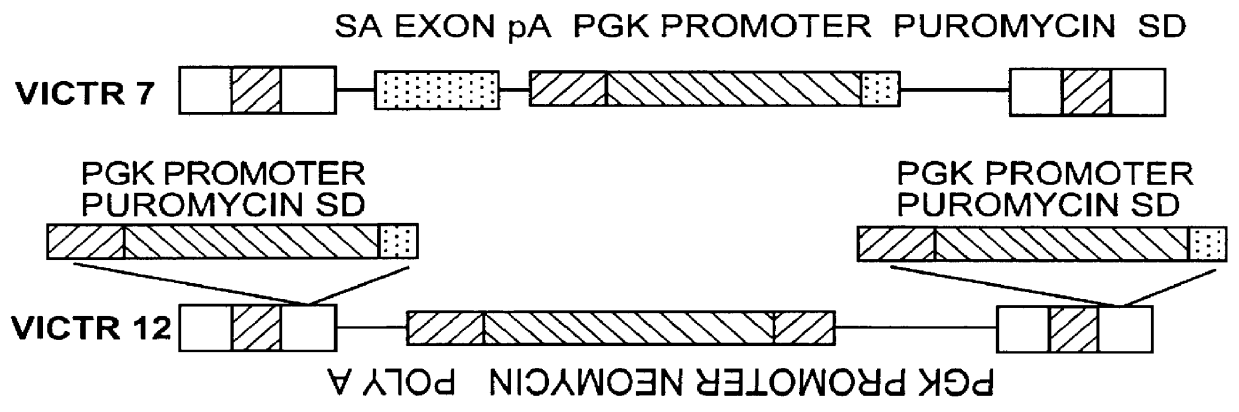
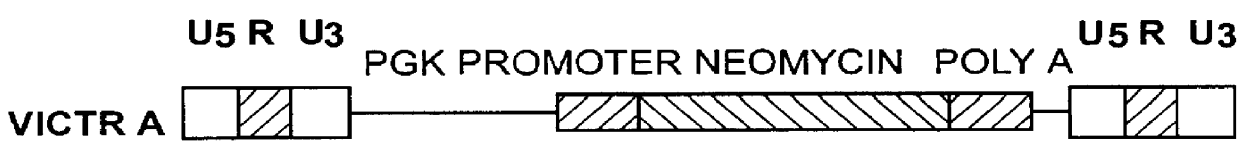
The present invention describes a comprehensive system for gene discovery using retrovirus that have been engineered to exhibit increased accessibility to genomic DNA, or to mutate and identify the chromosomal target sequences of DNA binding proteins. The strategy employs the combination of retroviral integrase / DNA binding protein fusion constructs and gene-trapping methodologies. This novel technology provides the ability to establish proviral integration at any location within the genome. In addition, it allows for the generation of a collection of eukaryotic cells in which each cell contains a mutation in a target gene or sequence for a known DNA binding protein which also allow for rapid in vivo functional analysis. Sequence information obtained for genes identified using the described methods identify a collection of eukaryotic genes related by, or directly or indirectly regulated by, a given DNA binding protein.
Owner:LEXICON PHARM INC
Isolated human cytomegalovirus polypeptides and uses thereof
InactiveUS6120989APeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIgm antibodyHuman cytomegalovirus
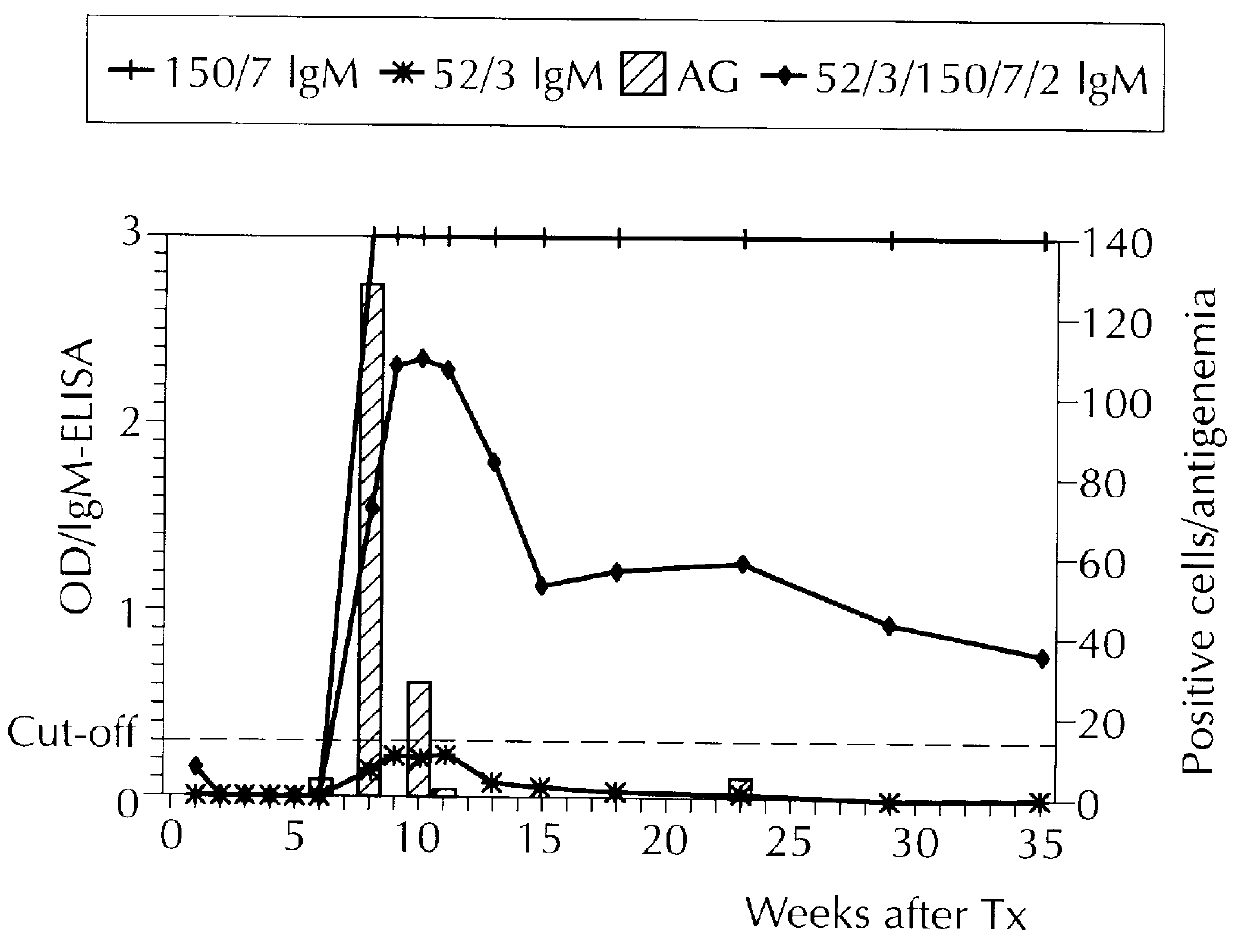
Diagnostically relevant polypeptides and fusion proteins comprising an amino acid sequence which originates from cytomegalovirus and corresponds to a region of the major DNA-binding protein or of the C-terminal region of the tegument protein pp150 fused with at least one further fragment from another antigenic protein of cytomegalovirus are disclosed. The major DNA-binding protein is encoded by the reading frame UL57. The poly-peptides and fusion proteins according to the invention can be used in an advantageous manner in diagnostic tests and methods for the detection of IgM antibodies against cytomegalovirus.
Owner:BIOTEST SERUM INST GMBH
Compositions and methods for inducing gene expression
InactiveUS7053062B2High expressionIncreased formationVirusesFusion with DNA-binding domainA-DNABiological activation
The present invention provides recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding a chimeric transactivator protein including a DNA binding domain of a DNA binding protein and a protein domain capable of transcriptional activation. The present invention also provides recombinant viral and non-viral vectors that are able to infect and / or transfect and sustain expression of a biologically active chimeric transactivator proteins in mammalian cells. Also provided are host cell lines and non-human transgenic animals capable of expressing biologically active chimeric transactivator proteins. In another aspect, compositions and methods for treating or preventing ischemic damage associated with hypoxia-related disorders are provided.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
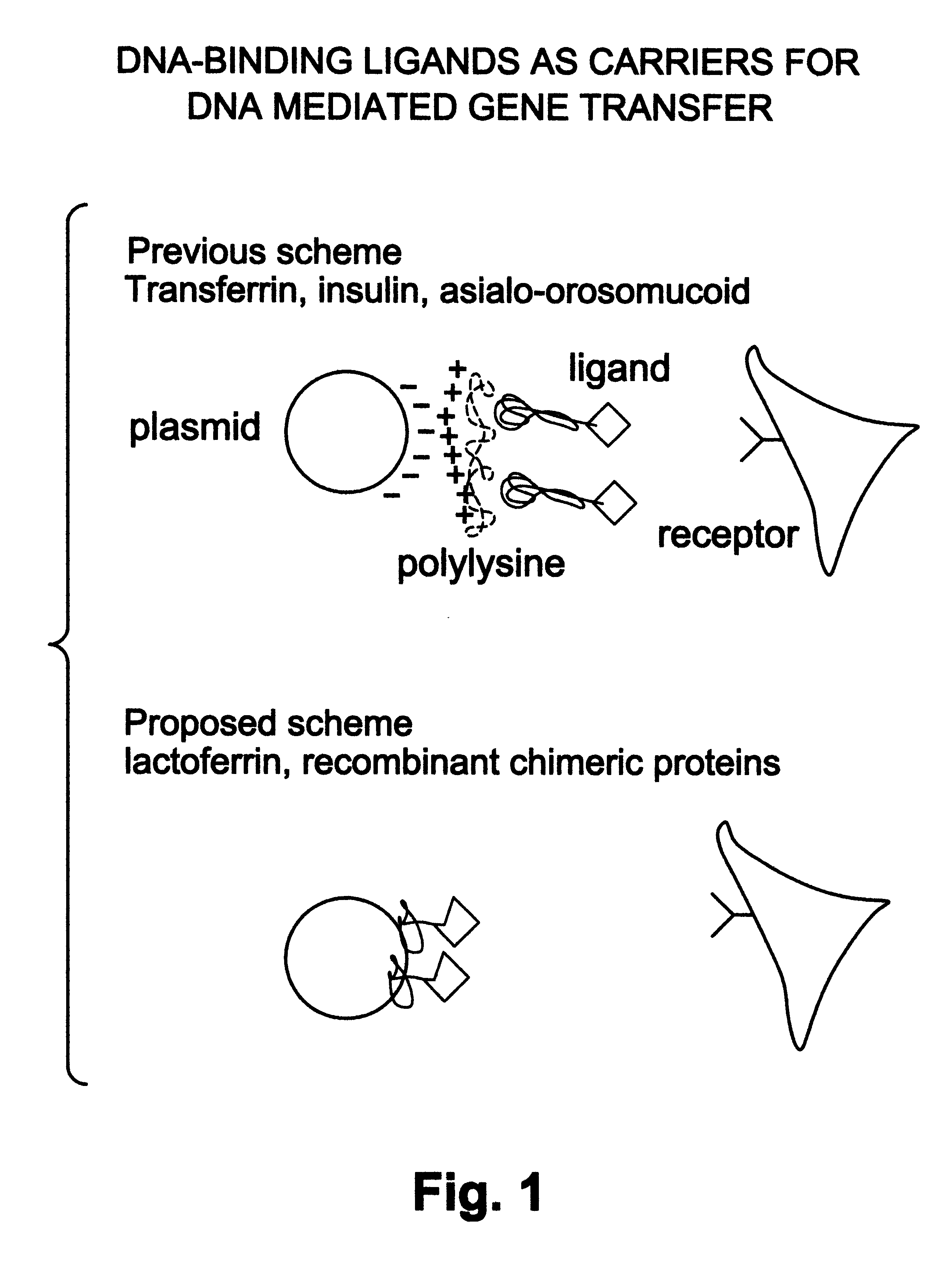
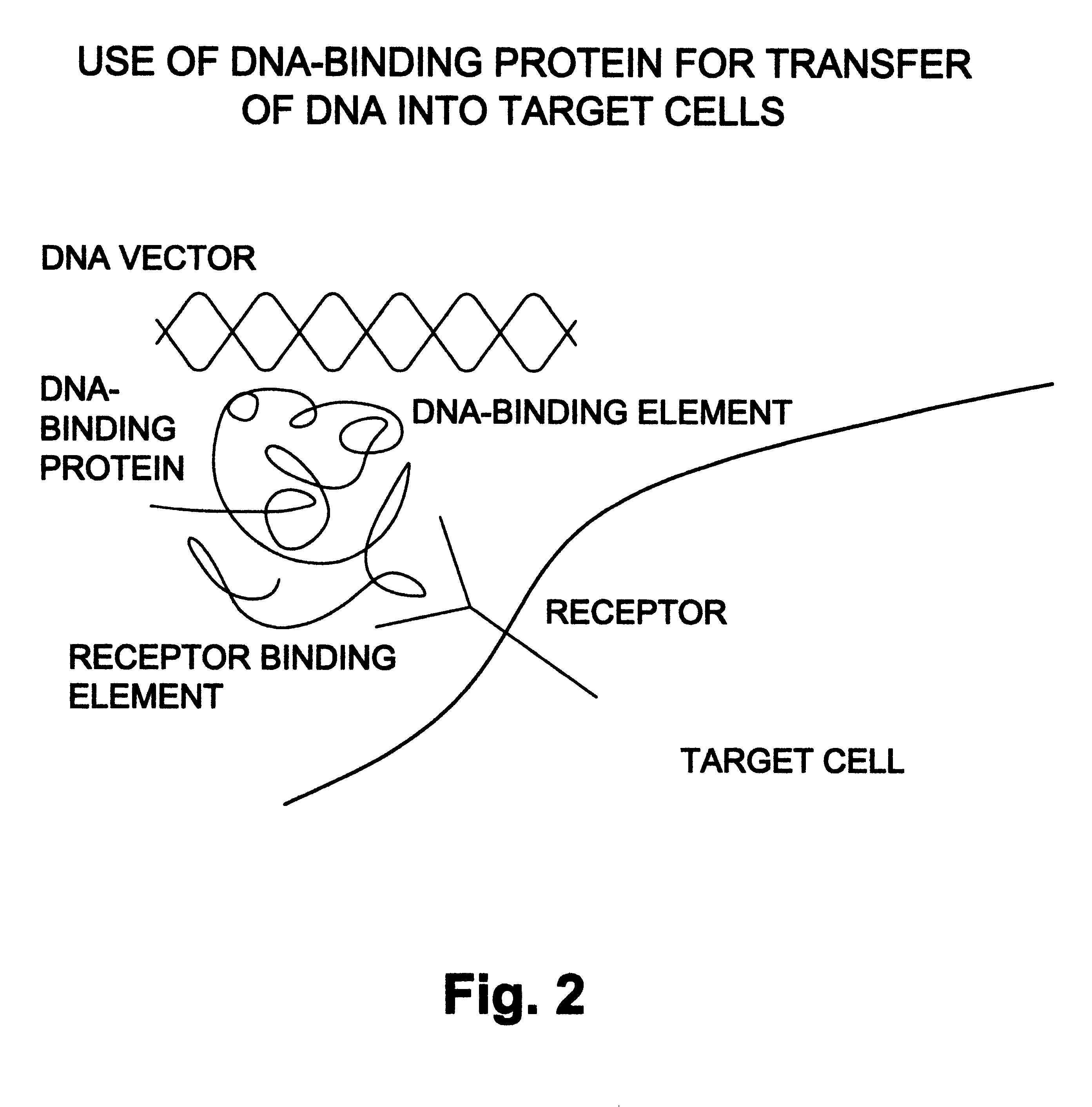
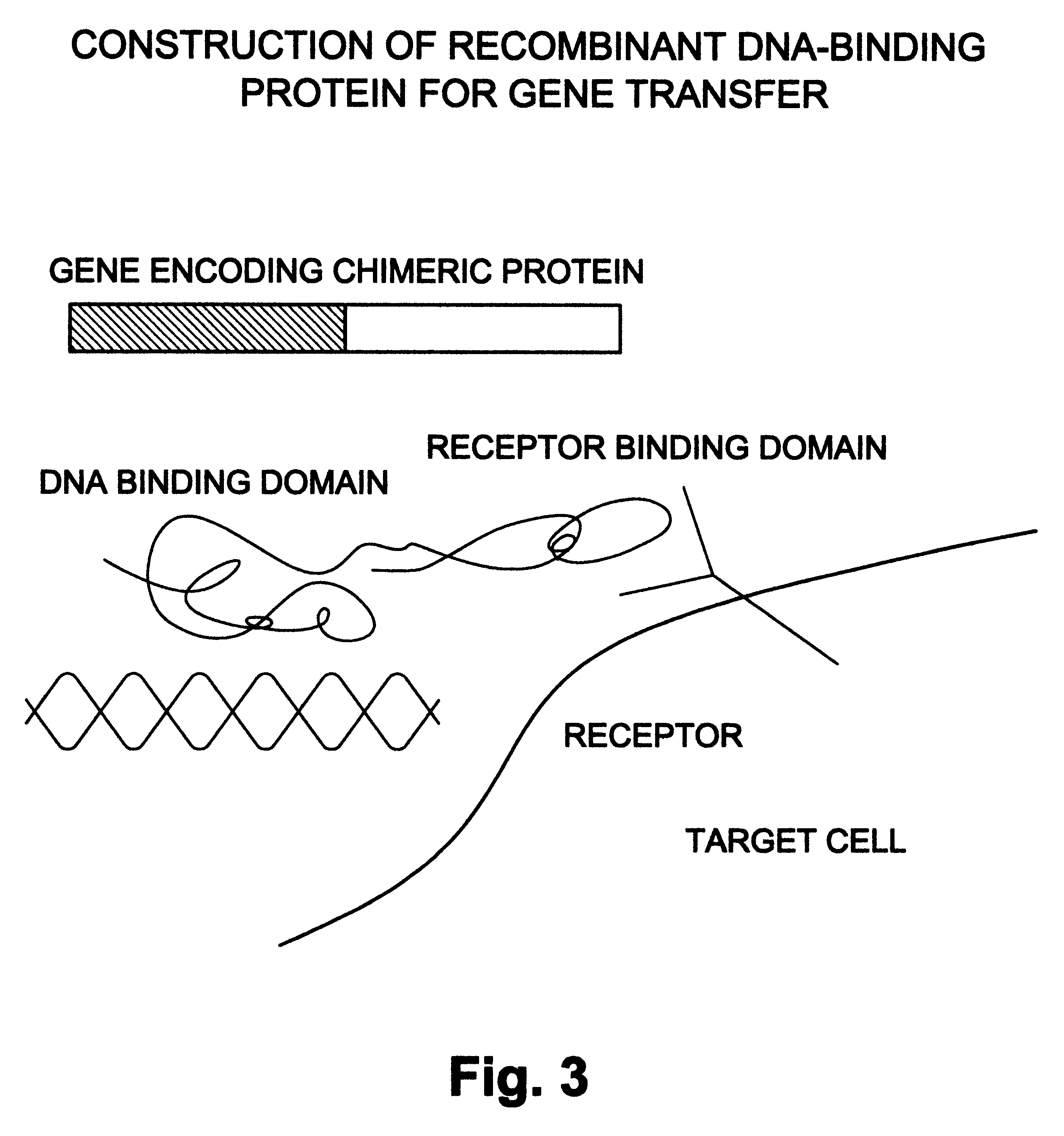
Natural or recombinant DNA binding proteins as carriers for gene transfer or gene therapy
InactiveUS6191257B1Increase entryImprove protectionSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseProtein containing complex
A complex for gene transfer a DNA molecule specifically and non-specifically bound to DNA binding protein. Additionally, it can include a chimeric compound for gene transfer. The chimeric compound has a DNA-binding element and a ligand binding element. The chimeric recombinant DNA can also include a binding protein which has a first element for binding to a receptor, a second element for binding to DNA, a third element for destabilizing endosomes and a fourth element for directing the traffic in a protein containing complex in the nucleus of a cell. The complex will be used for the treatment of a variety of diseases.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Inhibition of major groove DNA binding proteins by modified polyamides
This invention provides improved polyamides comprising a positive patch for contacting the phosphate backbone or major groove of a DNA molecule. As such, the improved polyamides are capable of inhibiting the function or binding of a DNA-binding protein to a DNA molecule. The improved polyamide provides for more efficient function of the polyamide.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Mapping of proteins along chromatin by chromatin cleavage
ActiveUS7790379B2Accurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein insertionProtein C
The present invention is directed to a method for localizing, in chromatin or DNA, the binding loci of a chromatin or DNA binding protein comprising the following steps:a) tethering, directly or indirectly, an enzyme with regulatable activity to said chromatin binding protein,b) transiently activating the regulatable enzymatic activity bound to the targeted chromatin andc) mapping the enzymatically-modified genomic sites introduced by the enzyme into the chromatin.According to an embodiment of the invention, the regulatable enzyme is a regulatable protease. The mapping step may be carried out on specific DNA fragments, or on a chromosome-wide scale or a genome-wide scale.The present invention is also directed to kits for carrying out the methods of the invention.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
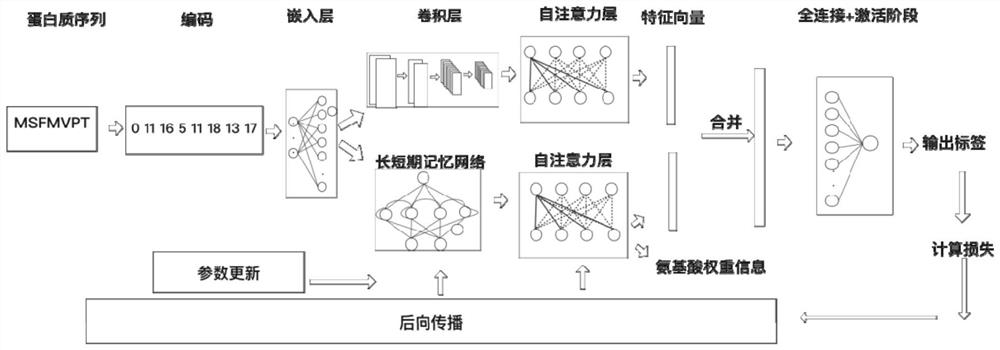
DNA binding protein identification and function annotation deep learning method based on self-attention mechanism
The invention discloses a DNA binding protein identification and function annotation deep learning method based on a self-attention mechanism. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a data set from a protein database, training and testing a constructed deep learning model by using the selected data set, and predicting whether protein can be combined with DNA by using the trained deeplearning model, wherein the deep learning model comprises a coding layer, an embedding layer, a long short-term memory neural network layer (LSTM), a convolutional neural network layer (CNN) and a self-attention layer (Self-Attention). Through a deep learning model based on a self-attention mechanism, whether the protein has a function of combining with DNA or not can be predicted according to primary sequence information of the protein, and an area with a combining function is found out.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Ensemble learning method for predicting DNA protein binding site
PendingCN108763865AGood effectReduce imbalanceNeural architecturesSpecial data processing applicationsBinding siteA-DNA
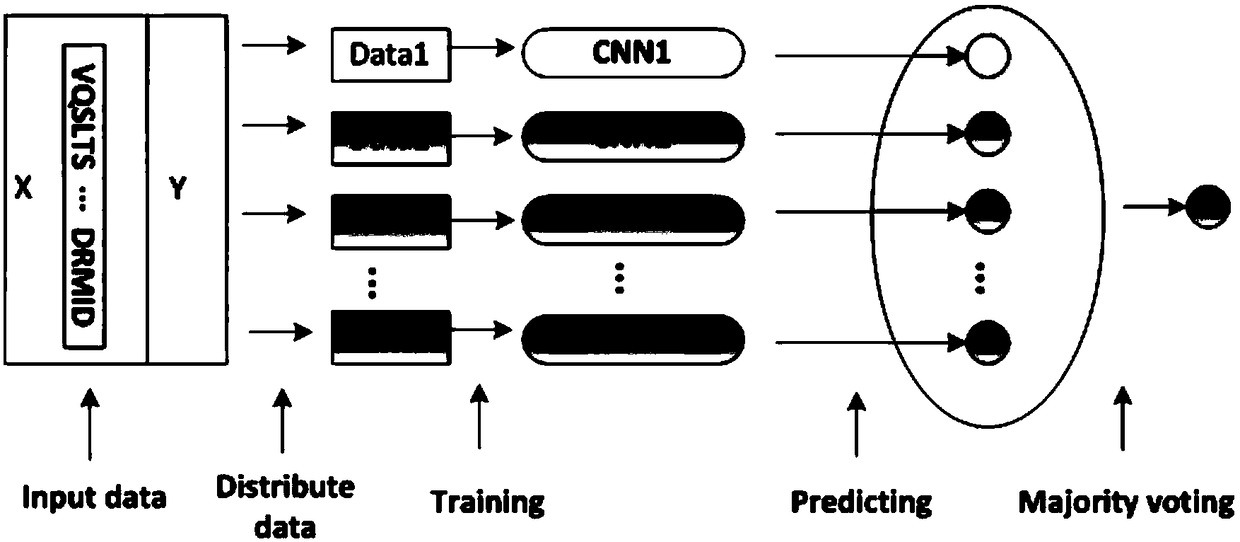
The invention relates to an ensemble learning method for predicting a DNA protein binding site. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining protein sequence data of the DNA protein binding site; preprocessing the protein sequence data of the DNA protein binding site; establishing input data in a one-hot coding mode; combining extracted features, establishing features of amino acid on each protein sequence, and taking the features as the input data; carrying out oversampling on positive sample data through utilization of an SMOTE algorithm; dividing negative sample data into a plurality of parts according to the positive sample quantity, and combining each part of negative samples with the positive samples to form a new data subset, thereby obtaining N data subsets; training eachdata subset through utilization of convolutional neural networks; and integrating results of N convolutional neural networks through utilization of a majority voting method, thereby obtaining a predicting result. According to the method, the DNA protein binding site predicting problem under the imbalance data condition is solved, and the predicting accuracy is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
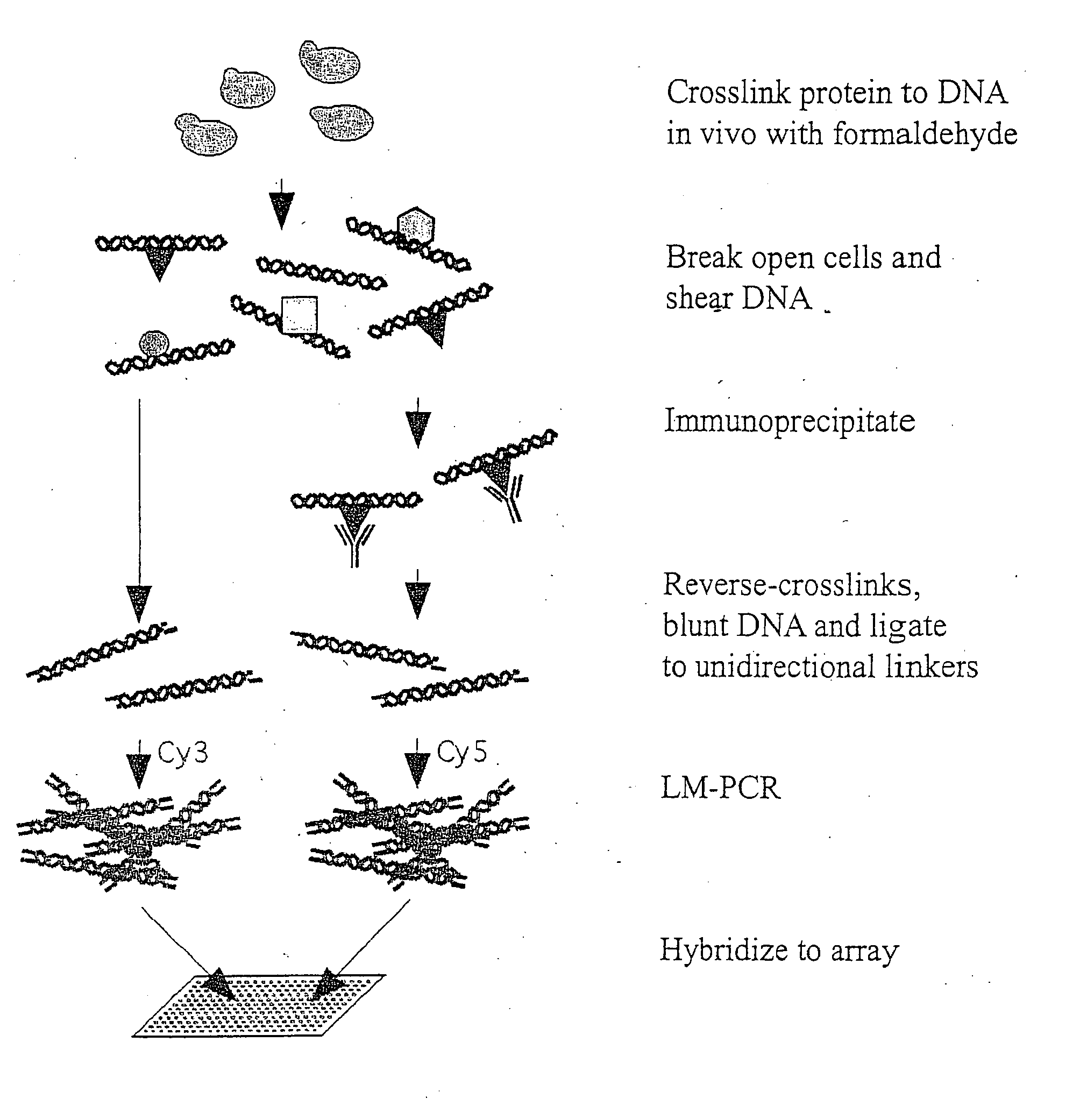
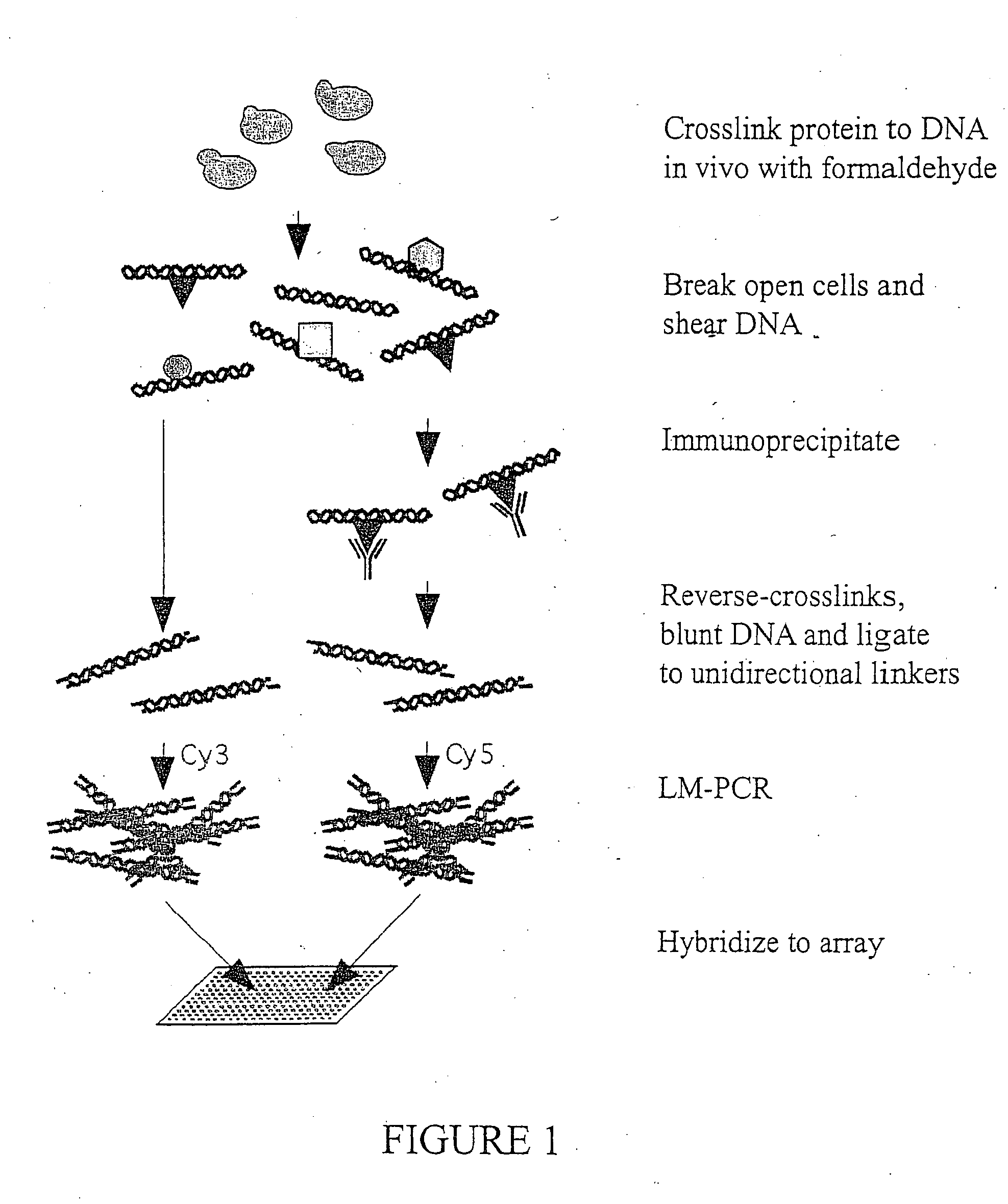
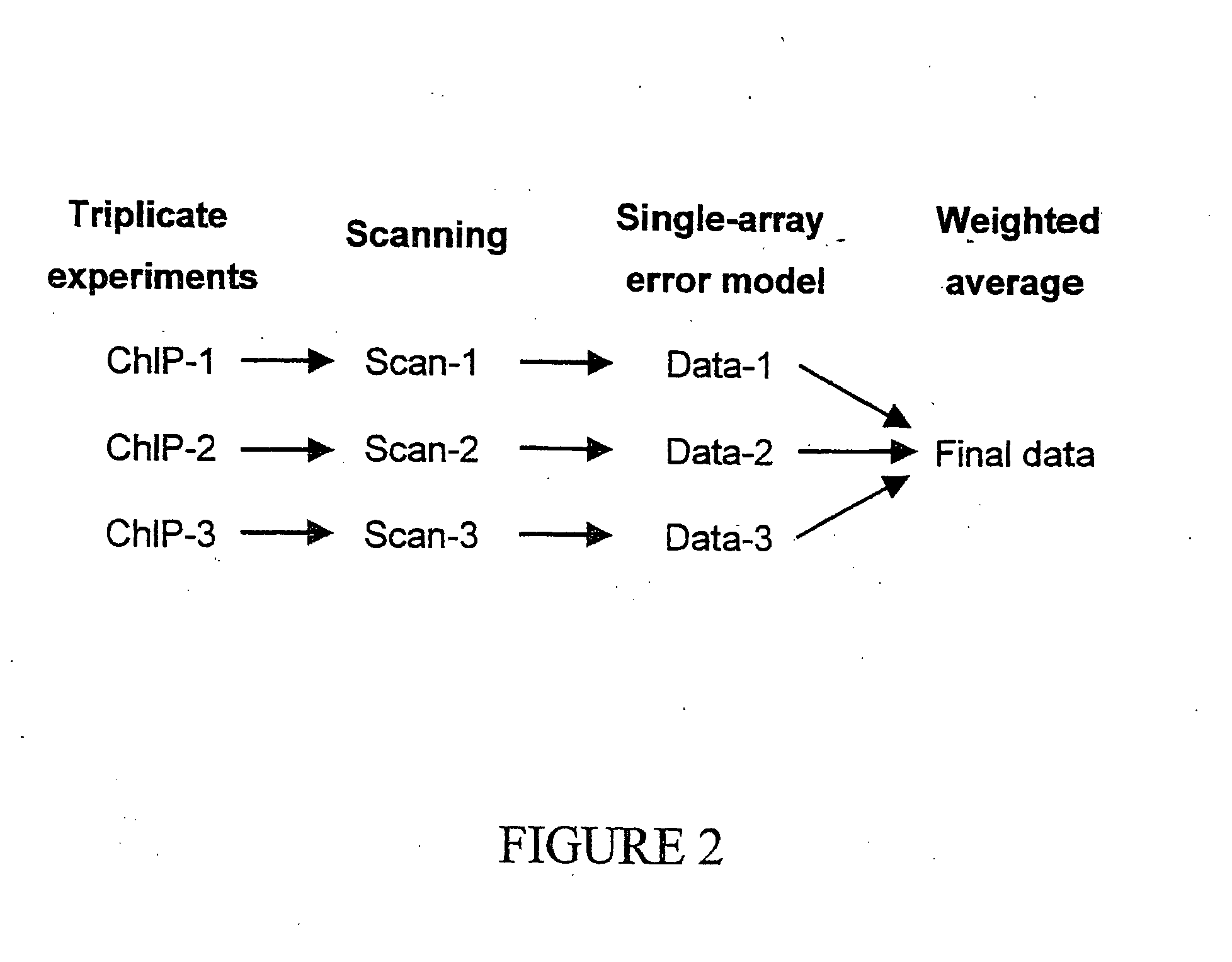
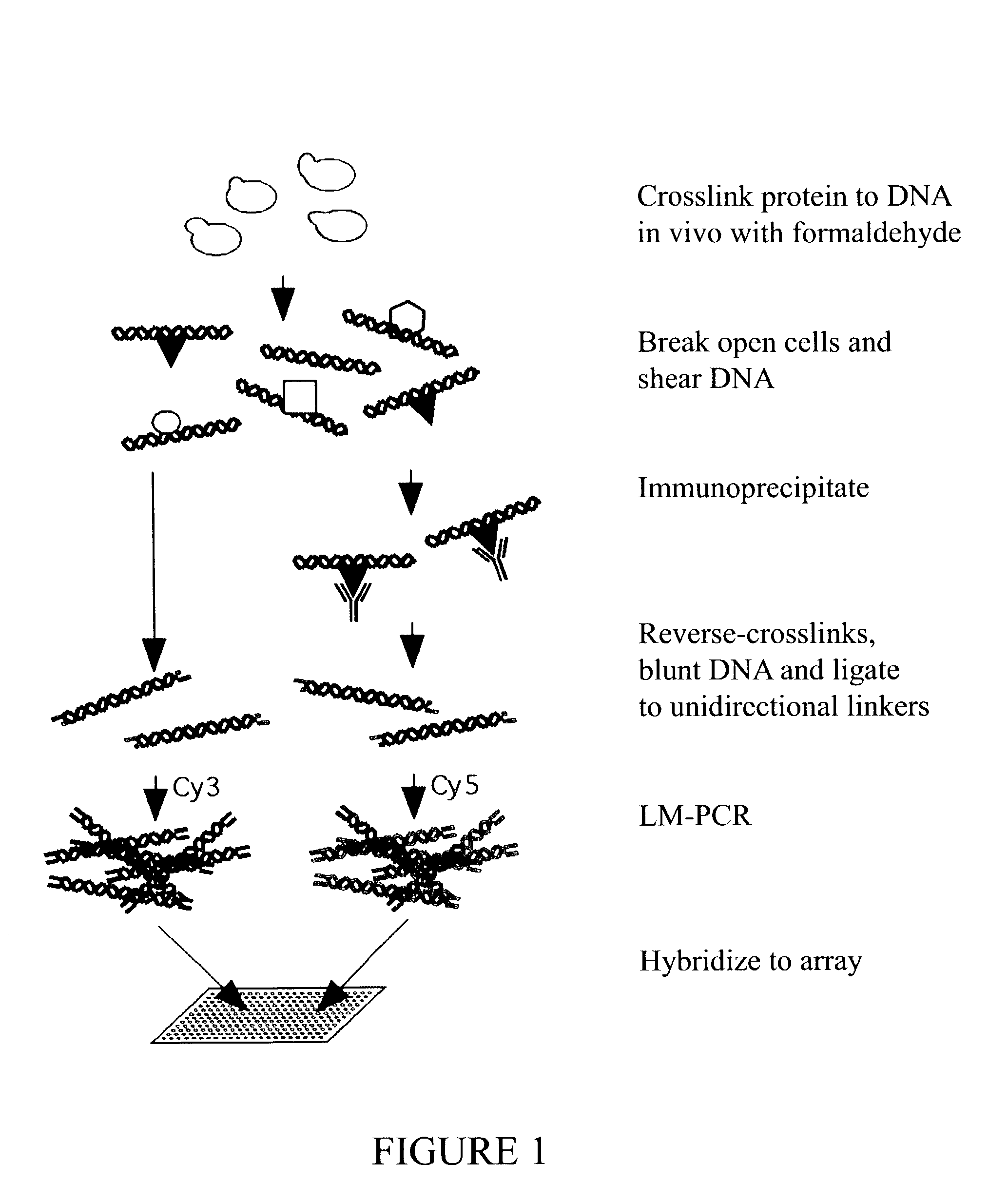
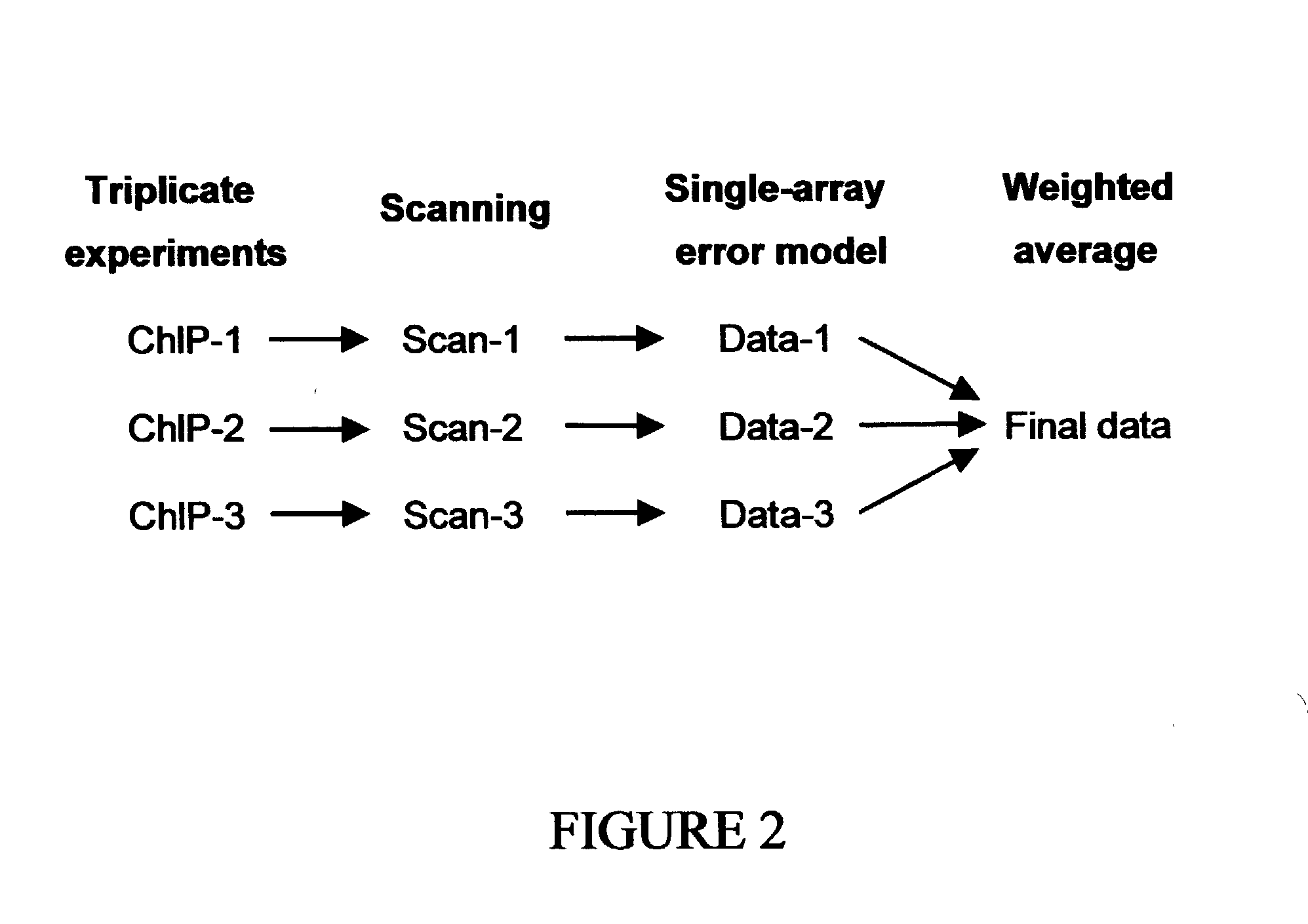
Genome wide location and function of DNA binding proteins
InactiveUS20080125328A1Easy to dissectAid in identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenomic DNAGenome
The present invention relates to a method of identifying a region (one or more) of a genome of a cell to which a protein of interest binds. In the methods described herein, DNA binding protein of a cell is linked (e.g., covalently crosslinked) to genomic DNA of a cell. The genomic DNA to which the DNA binding protein is linked is removed and combined or contacted with DNA comprising a sequence complementary to genomic DNA of the cell under conditions in which hybridization between the identified genomic DNA and the sequence complementary to genomic DNA occurs. Region(s) of hybridization are region(s) of the genome of the cell to which the protein of binds. A method of identifying a set of genes where cell cycle regulator binding correlates with gene expression and of identifying genomic targets of cell cycle transcription activators in living cells is also encompassed.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
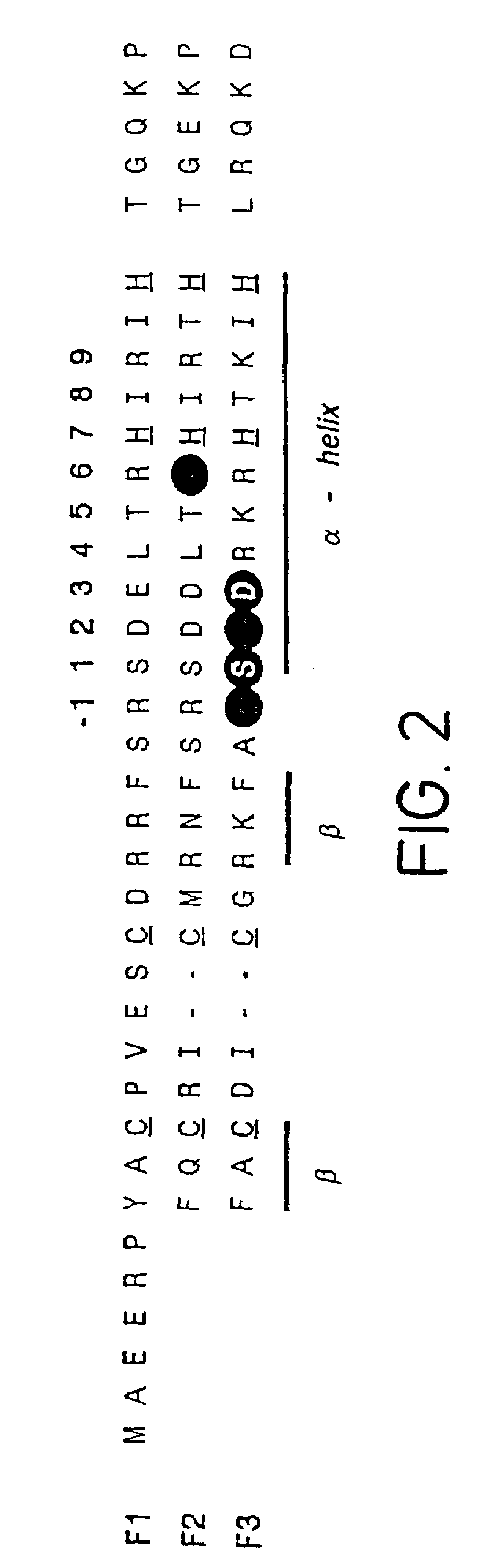
Zinc finger protein derivatives and methods therefor
InactiveUS20050084885A1Modulate it functionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainBiological activationTransgene
Zinc finger proteins of the Cys2His2 type represent a class of malleable DNA binding proteins which may be selected to bind diverse sequences. Typically, zinc finger proteins containing three zinc finger domains, like the murine transcription factor Zif268 and the human transcription factor Spl, bind nine contiguous base pairs (bp). To create a class of proteins which would be generally applicable to target unique sites within complex genomes, the present invention provides a polypeptide linker that fuses two three-finger proteins. Two six-fingered proteins were created and demonstrated to bind 18 contiguous bp of DNA in a sequence specific fashion. Expression of these proteins as fusions to activation or repression domains allows transcription to be specifically up or down modulated within cells. Polydactyl zinc finger proteins are broadly applicable as genome-specific transcriptional switches in gene therapy strategies and the development of novel transgenic plants and animals. Such proteins are useful for inhibiting, activating or enhancing gene expression from a zinc finger-nucleotide binding motif containing promoter or other transcriptional control element, as well as a structural gene or RNA sequence.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
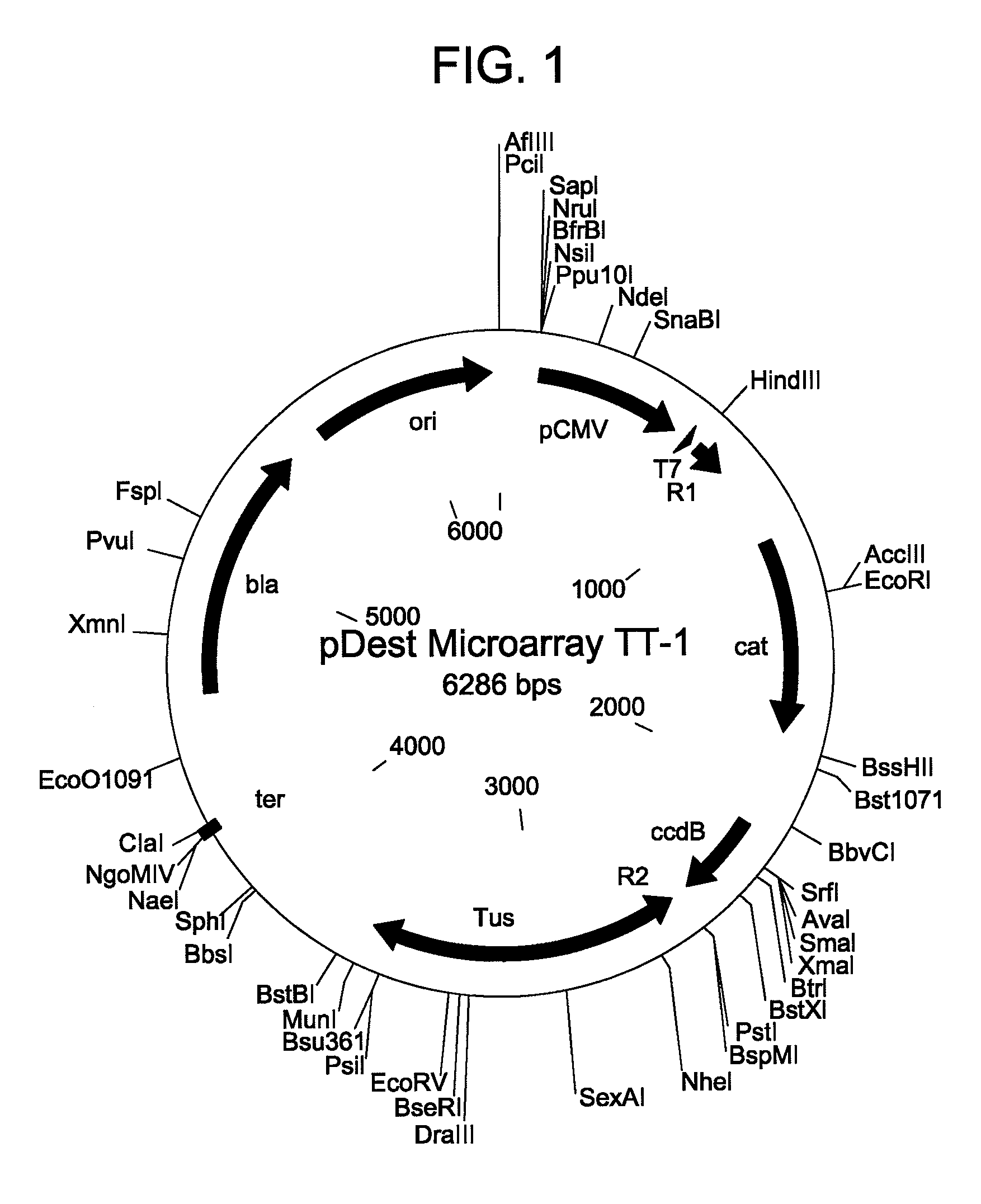
In situ assembly of protein microarrays
The invention provides a microarray and methods for producing a protein microarray. The array comprises multiple nucleic acid molecules immobilized on a substrate, each comprising (i) a protein-binding domain and (ii) a nucleic acid sequence encoding a fusion protein comprising a polypeptide of interest and a DNA-binding protein that binds the protein-binding domain, and one or more fusion proteins produced from the multiple nucleic acid molecules. Each fusion protein is immobilized on the substrate via binding to a nucleic acid sequence comprising the protein-binding domain present on the nucleic acid molecule from which the fusion protein is produced or on the substrate. The invention also provides a method of analyzing protein interactions with, for example, other proteins, lipids and drugs.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC
High-sensitivity high-flux DNA binding protein detection method
InactiveCN101591705AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein targetSingle strand
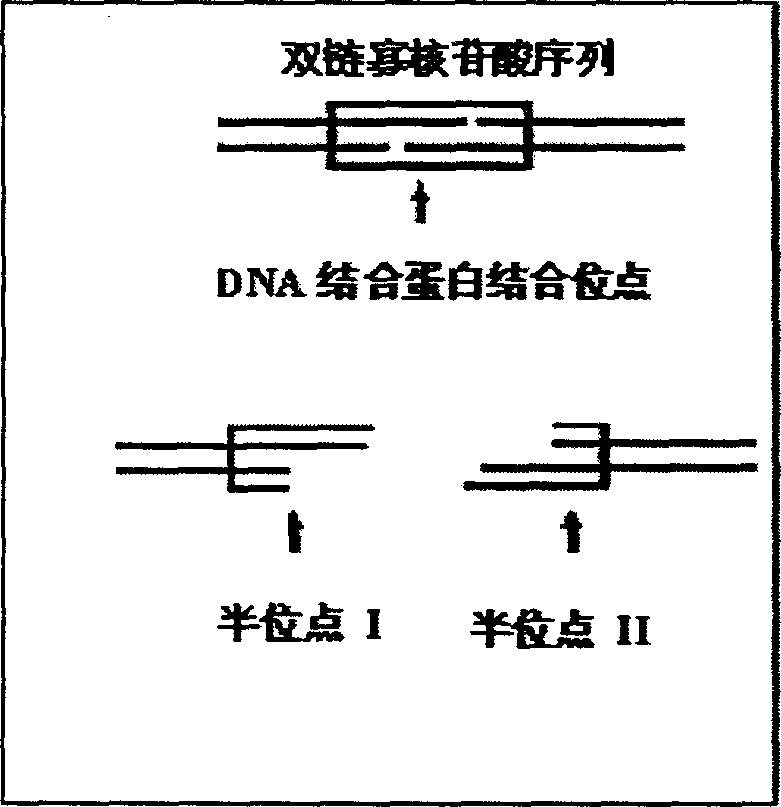
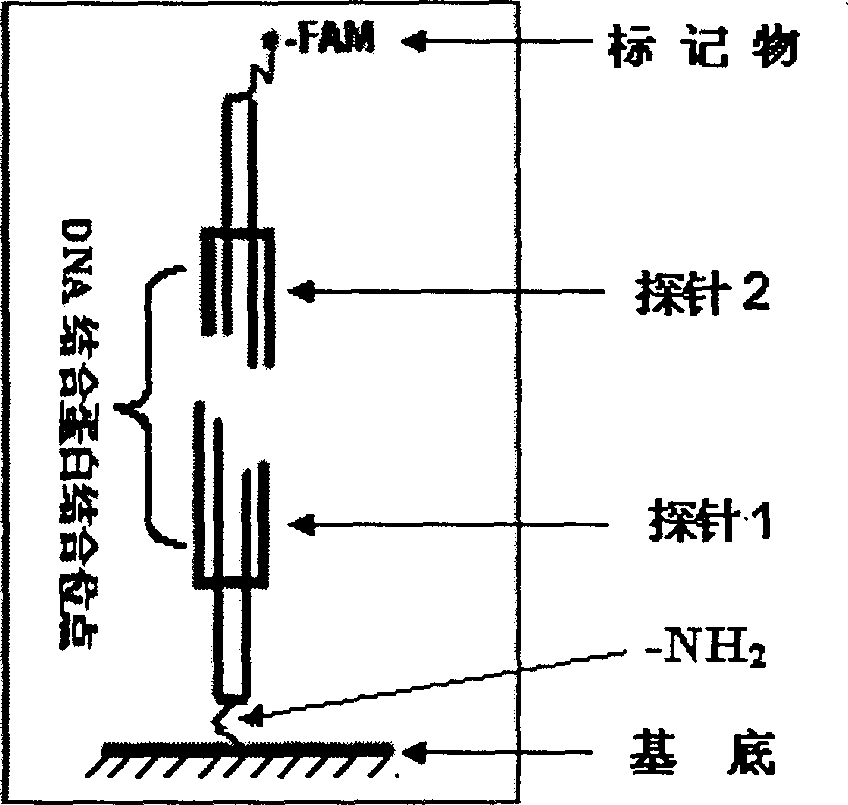
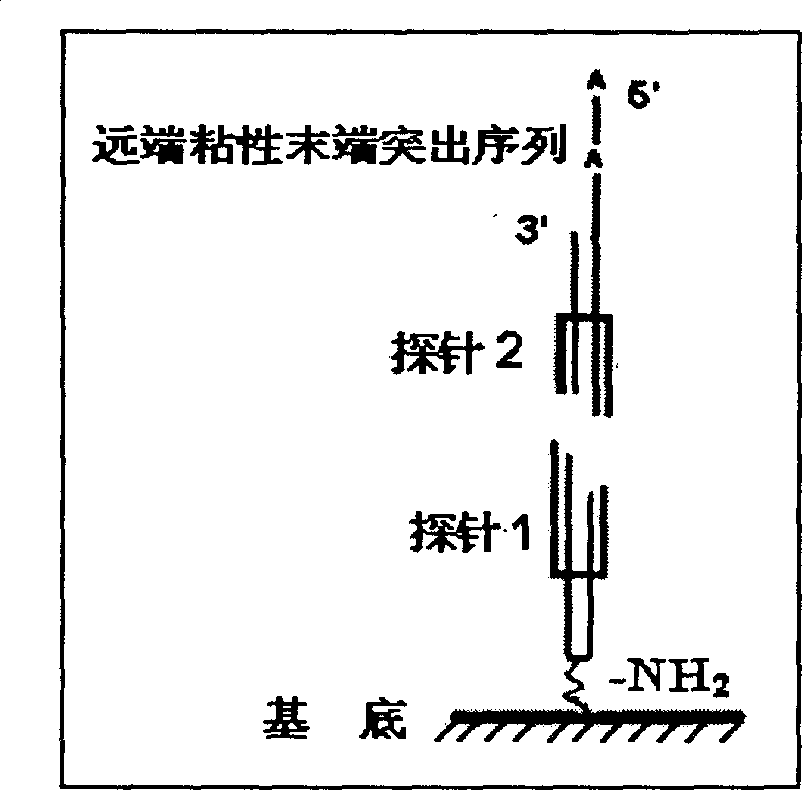
The invention belongs to microarray chip based DNA binding protein detection technology, and in particular relates to high-sensitivity high-flux DNA binding protein detection technology by a microarray chip. Double-stranded or single-stranded oligonucleotides are fixed on the chip, and a cell crude extract to be screened and the chip are directly incubated; then exonuclease is put into the system for incubation; and finally, a circular probe is added into the system for rolling circle amplification. Specific lattice sequences of the chip capable of combining a target protein can be taken as an extension primer for the rolling circle amplification; and sequences not combined with the protein are digested by the exonuclease, and cannot perform the rolling circle amplification, and finally amplified products and universal fluorescent probes are hybridized. The existence of the DNA binding protein can be detected according to the existence of specific array dot signals on the chip; and the intensity of the lattice fluorescence can quantitatively detect the content of the target protein. The chip can realize the detection of the DNA binding protein with super sensitivity, low cost, high specificity and high flux, and can be widely applied to scientific research and clinical detection and diagnosis.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
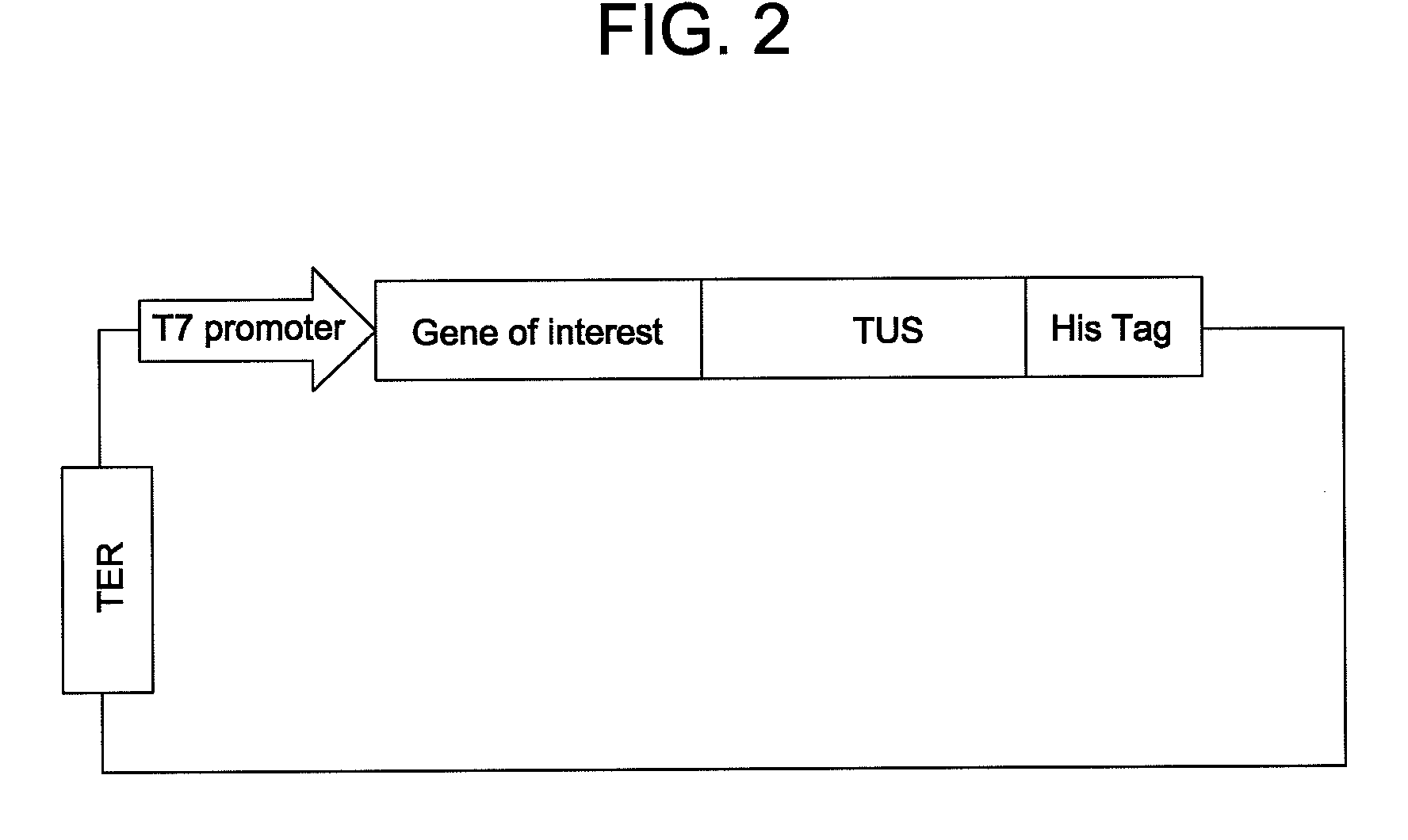
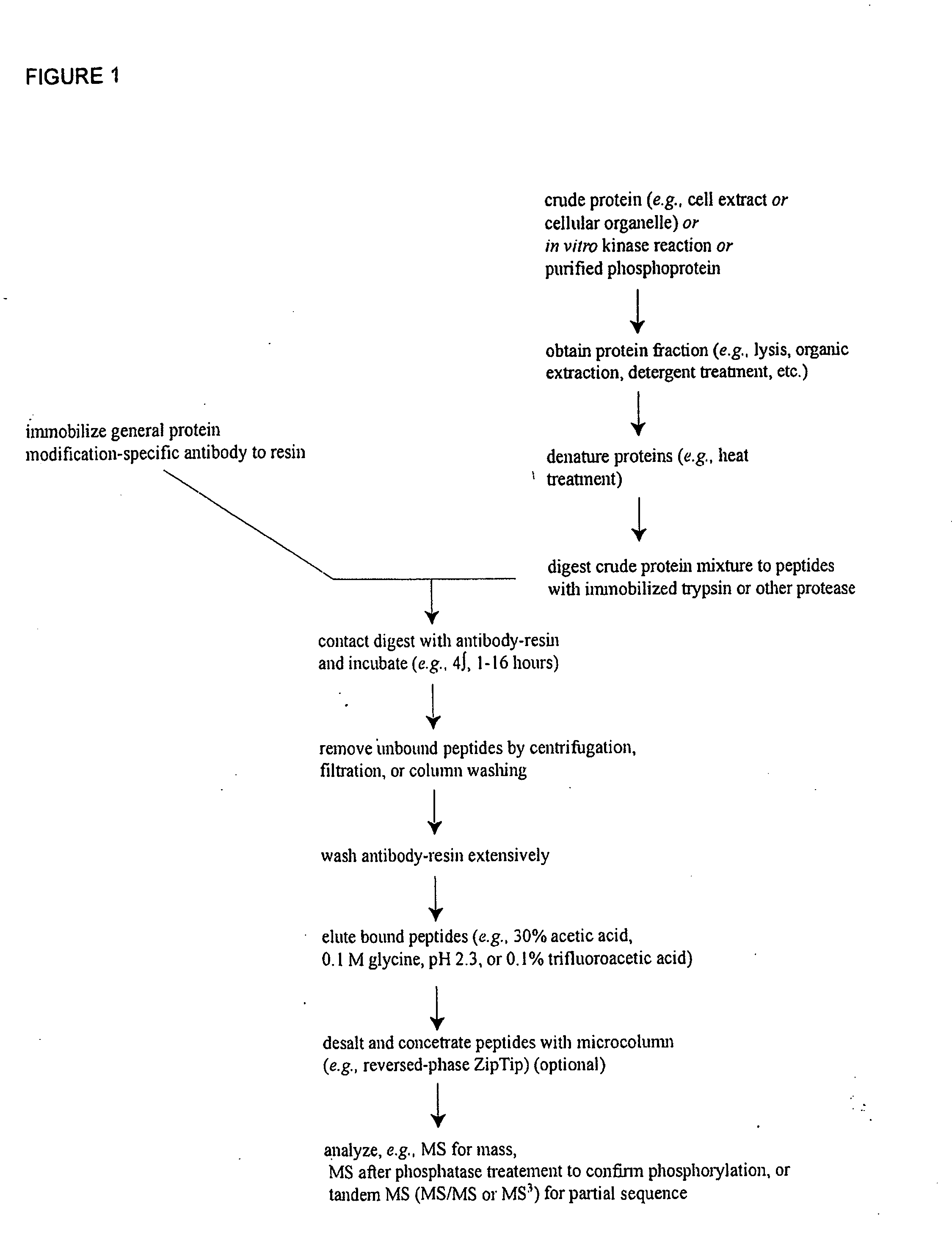
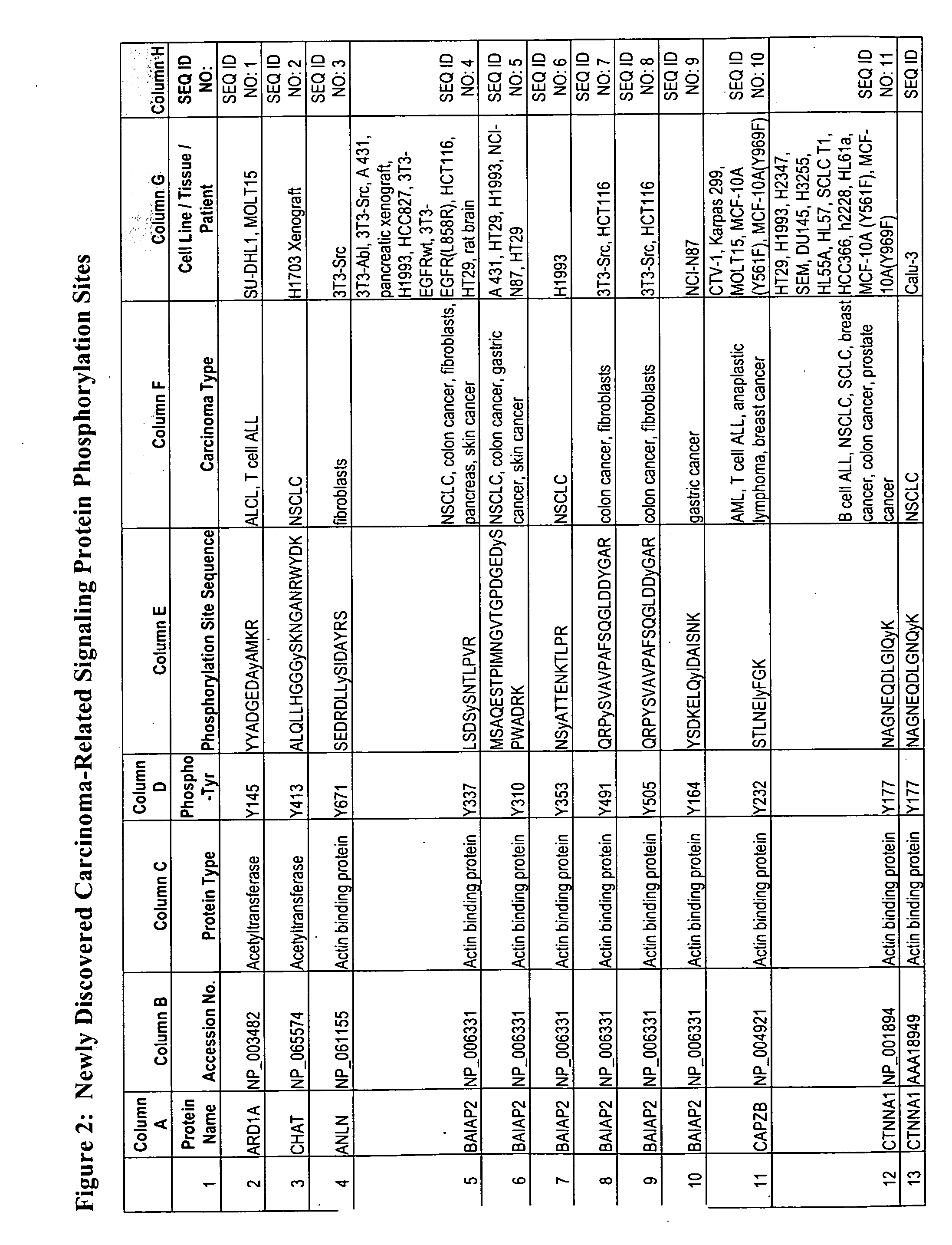
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090258442A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationPhospholipaseADAMTS Proteins
The invention discloses nearly 474 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Kinase, Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Phosphatase, G protein Regulator / Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors / GTPase Activating Proteins, Cytoskeleton Proteins, DNA Binding Proteins, Phospholipase, Receptor Proteins, Enzymes, DNA Repair / Replication Proteins, Adhesion Proteins, and Proteases, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Single molecule dsDNA microarray chip preparation method
InactiveCN1590559APromote commercial applicationReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological studiesPolymerase L
A process for preparing the unimolecular ds DNA microarray on the surface of solid carrier includes chemically synthesizing target oligonucleotide and universal oligonucleotide, renaturation of them, linking them to the surface of solid carrier to become oligonucleotide microarray, on-chip polymerase elongation reaction to become bimolecular dsDNA microarray, modifying to become ssDNA microarray, renaturation to form hairpin structure, and on-chip polymerase elongation reaction.
Owner:王进科 +2
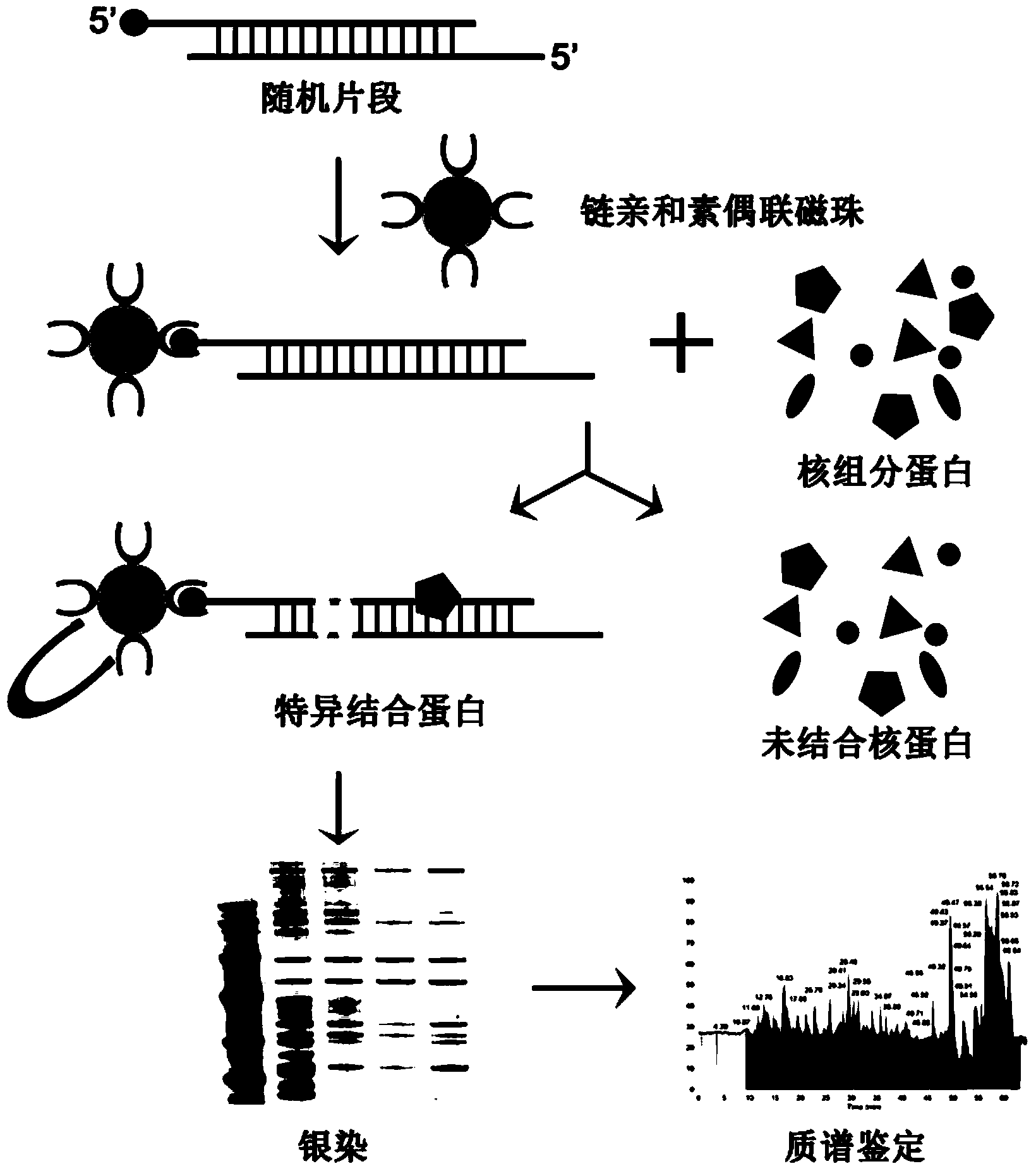
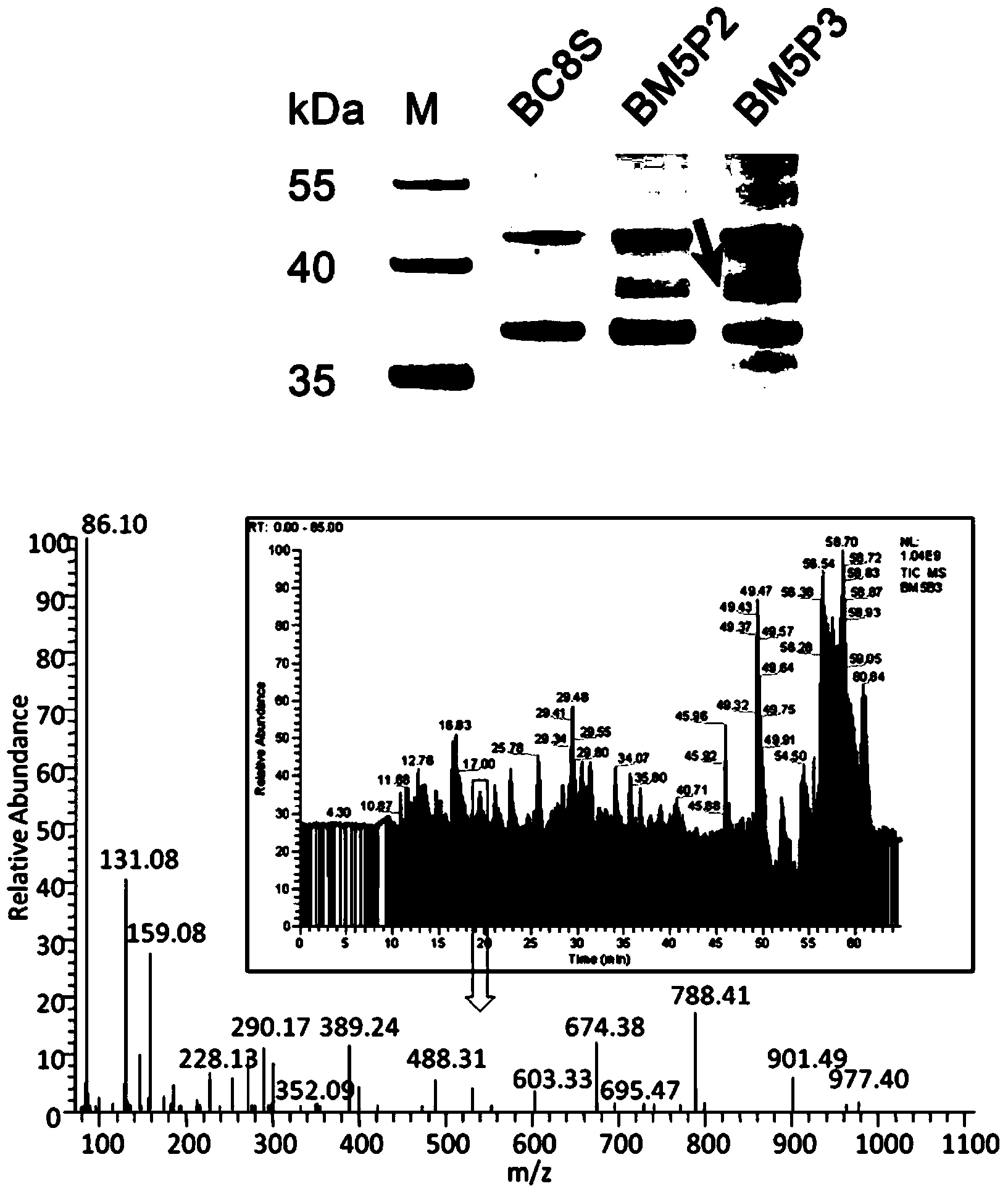
Methods for separating and identifying DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) binding protein through DNA co-immunoprecipitation
ActiveCN103739664AImprove experimental efficiencyImprove stabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPeptide preparation methodsMolecular oncologyAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to methods for separating and identifying DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) binding protein, in particular to methods for separating and identifying DNA binding protein through a DNA co-immunoprecipitation technology. The separating method comprises the steps of extracting nucleoprotein of a cell, mixing a target DNA molecule and nucleoprotein, adding a molecular entity capable of being bound with the target DNA molecule, separating to obtain a nucleoprotein ingredient bound with the target DNA molecule, further separating the obtained nucleoprotein ingredient, and obtaining the DNA binding protein. The identifying method further comprises the step of identifying the DNA binding protein obtained by separating. The methods have the characteristics of good stability and repeatability, and significantly improve the experiment efficiency of identifying the unknown DNA binding protein. The methods provide beneficial help for subjects such as molecular behavioristics, molecular oncology, cytobiology and biochemistry deeply researching into cytogene transcriptional control and genetic transcription.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI +1
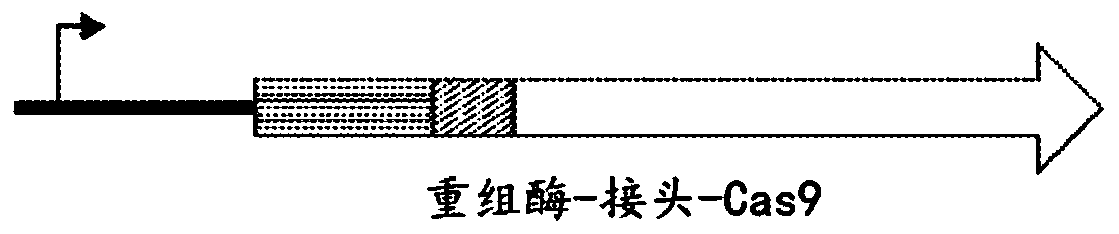
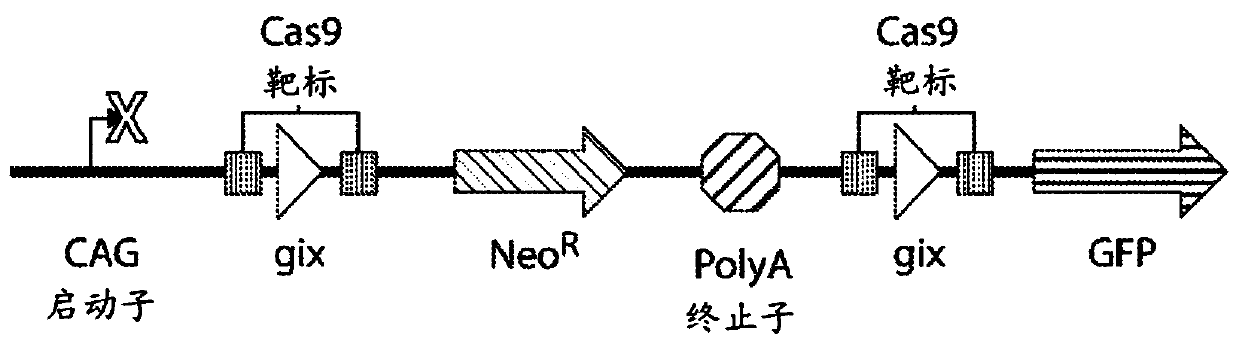
Programmable cas9-recombinase fusion proteins and uses thereof
Some aspects of this disclosure provide a fusion protein comprising a guide nucleotide sequence-programmable DNA binding protein domain (e.g., a nuclease-inactive variant of Cas9 such as dCas9), an optional linker, and a recombinase catalytic domain (e.g., a tyrosine recombinase catalytic domain or a serine recombinase catalytic domain such as a Gin recombinase catalytic domain). This fusion protein can recombine DNA sites containing a minimal recombinase core site flanked by guide RNA-specified sequences. The instant disclosure represents a step toward programmable, scarless genome editing inunmodified cells that is independent of endogenous cellular machinery or cell state.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Genome-wide location and function of DNA binding proteins
InactiveUS20080241822A1Easy to dissectAid in identification of gene functionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenomic DNALiving cell
The present invention relates to a method of identifying a region (one or more) of a genome of a cell to which a protein of interest binds. In the methods described herein, DNA binding protein of a cell is linked (e.g., covalently crosslinked) to genomic DNA of a cell. The genomic DNA to which the DNA binding protein is linked is removed and combined or contacted with DNA comprising a sequence complementary to genomic DNA of the cell under conditions in which hybridization between the identified genomic DNA and the sequence complementary to genomic DNA occurs. Region(s) of hybridization are region(s) of the genome of the cell to which the protein of binds. A method of identifying a set of genes where cell cycle regulator binding correlates with gene expression and of identifying genomic targets of cell cycle transcription activators in living cells is also encompassed.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
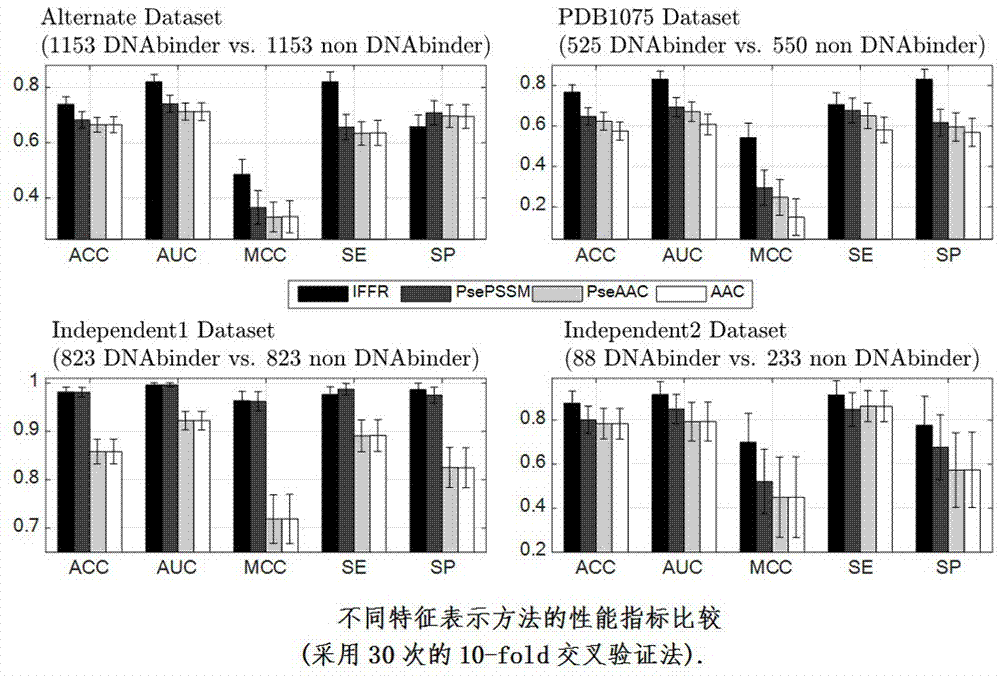
Characteristic extraction and classification method and device for DNA (Deoxyribo-Nucleic Acid) binding protein sequence information
InactiveCN108875310AImplement function annotationsAchieve classification goalsSpecial data processing applicationsData setProtein insertion
The invention relates to a characteristic extraction and classification method and device for DNA (Deoxyribo-Nucleic Acid) binding protein sequence information. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, carrying out theory argumentation, and analyzing and arranging collected data to obtain a reliable dataset with a biological meaning and a statistical meaning; then, extracting effective protein sequence data characteristic parameters from a complex protein three-dimensional structure as a key link which is a way of converting sequence character information into digital characteristic information, designing a reasonable classification algorithm for extracted characteristic data, and screening the characteristics favorable for classification for realizing target classification;and finally, adopting a reasonable and fair evaluation system, including testing methods, checking means, evaluation index selection and the like, for classification performance. By use of the method, requirements on high-flux protein sequencing function annotation can be met, automated DNA binding protein sequence function annotation can be realized, and meanwhile, the characteristics which areput forward can assist biologists in carrying out experimental analysis and research on the DNA binding protein sequence.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Chip for non-label detecting DNA bindin, preparation and use method thereof
InactiveCN1435492AAvoid lossHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDNABioinformatics
A chip for the non-label detection of DNA bindin has the dual-chain oligonucleotide probes designed according to the specific DNA recognizing sequence for the DNA bindin to be detected. The probe A is fixed to the substrate, and a label is introduced to the probe B. The probe B and the solution of the DNA bindin are inculated together and then hybridized with chip. If DNA bindin exists, the probes A and B have very high binding efficiency and the label of probe B can be detected at the position of probe A.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
High-temperature-resistant Pyrolobus polymerase and efficient expression plasmid and application thereof
InactiveCN102392000AImprove efficiencyEfficient synthesisBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliAgricultural science
The present invention discloses high-temperature-resistant Pyrolobus polymerase and efficient expression plasmid and application thereof. The Pyrolobus polymerase is YP_004780419.1 protein, and Sso7dDNA binding protein connected through a linker sequence GGSG exits at the carbon end of the Pyrolobus polymerase, wherein the sequence of the Pyrolobus polymerase is shown as Sequence 1 in the sequence table. The present invention improves the efficiency of polymerase by connecting DNA binding protein to the end of the polymerase, and synthetizes and recombines Pyrolobus polymerase with DNA modified through in vitro synthesis suitable to express in colibacillus. The enzyme has the same polymerase activity as products in the markets, and can synthetize large segments of DNA more effectively. In addition, the Pyrolobus polymerase has strong high-temperature resistance, and is still active even after being processed for 5h at 98 DEG C. The enzyme will be widely applied to the fields of DNA synthesis, sequencing, labeled probe synthesis and the like.
Owner:李志茹
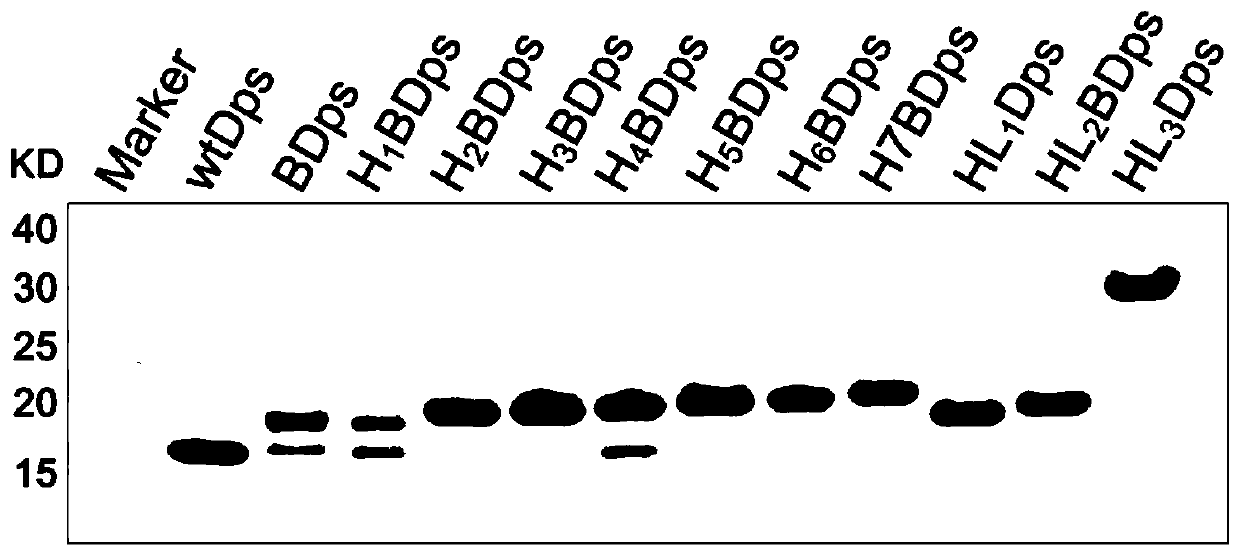
Transmembrane Dps (starvation-induced DNA binding protein) and application
ActiveCN110283251AEasy to purifyHigh yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsAntioxidant proteinBiocompatibility Testing
The invention belongs to the field of bioscience, and particularly relates to transmembrane Dps (starvation-induced DNA binding protein) and an application. By means of rational design of a protein nanocage derived from prokaryotes, the protein nanocage is enabled to be an antioxidant protein nanomaterial which can be applied to mammalian cells. The protein nanomaterial is characterized in that transportation across mammalian cell membranes of Dps is realized by fused expression of His-tag and Avitag (LNDIFEAQKIEWHE) at the N-terminal of Dps; the cells can be protected from being damaged by ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species); meanwhile, the protein nanomaterial is good in biocompatibility, simple to design, easy to prepare, high in yield and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
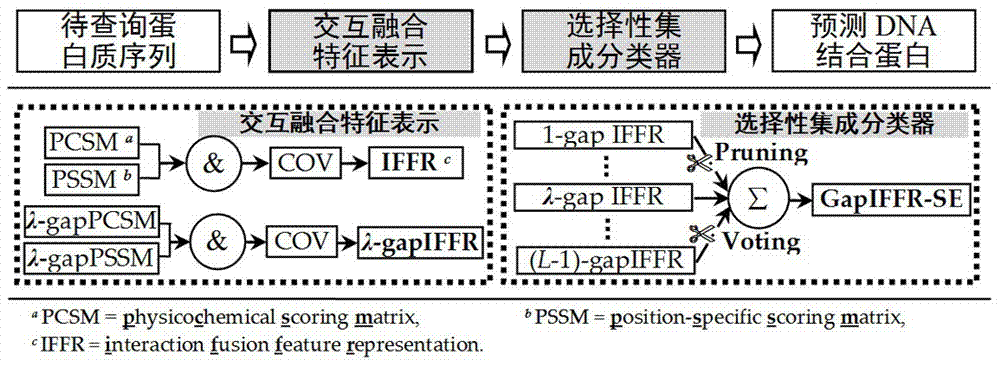
DNA-binding protein identification method of interactive fusion characteristic representations and selective integrations
ActiveCN107463799AAccurate predictionImprove generalization abilityBiostatisticsSequence analysisA-DNAComputer science
The present invention relates to a DNA-binding protein identification method of interactive fusion characteristic representations and selective integrations. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the present invention has more excellent performance, which indirectly shows that in the method provided by the present invention, the interactive fusion characteristic representations can generate characteristics that carry strong discrimination information, and at the same time selective integration can further improve the generalization of the overall learner, so that accurate prediction of DNA-binding protein can be ensured finally.
Owner:FUQING BRANCH OF FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
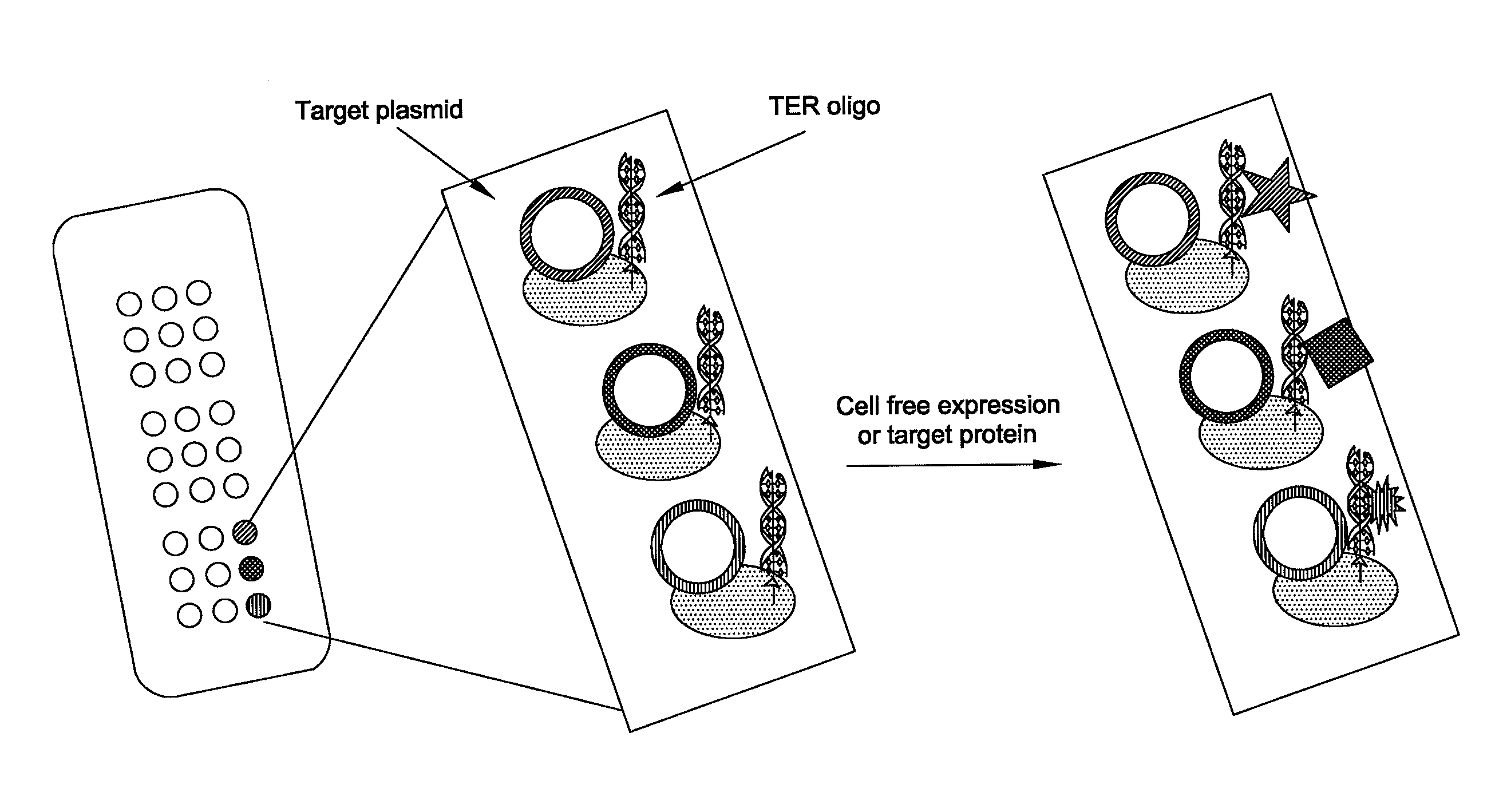
Method for forming a stable complex comprising a transcription product and translation product of a dna encoding a desired polypeptide, a nucleic acid construct used for the method, a complex formed by the method, and screening of a functional protein and mrna or dna encoding the protein using the method
InactiveUS20050191626A1Without reducing sequence varietyLinkage stabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotypeA-DNA
A stable linkage between a genotype and a phenotype in a cell-free system was successfully achieved by using interaction between a RNA-binding protein and RNA, between a DNA-binding protein and DNA, or by using a protein that inactivates a ribosome. Furthermore, it was found that functional proteins could be selected by using these stable linkages.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Polypeptide targeting to mitochondria
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
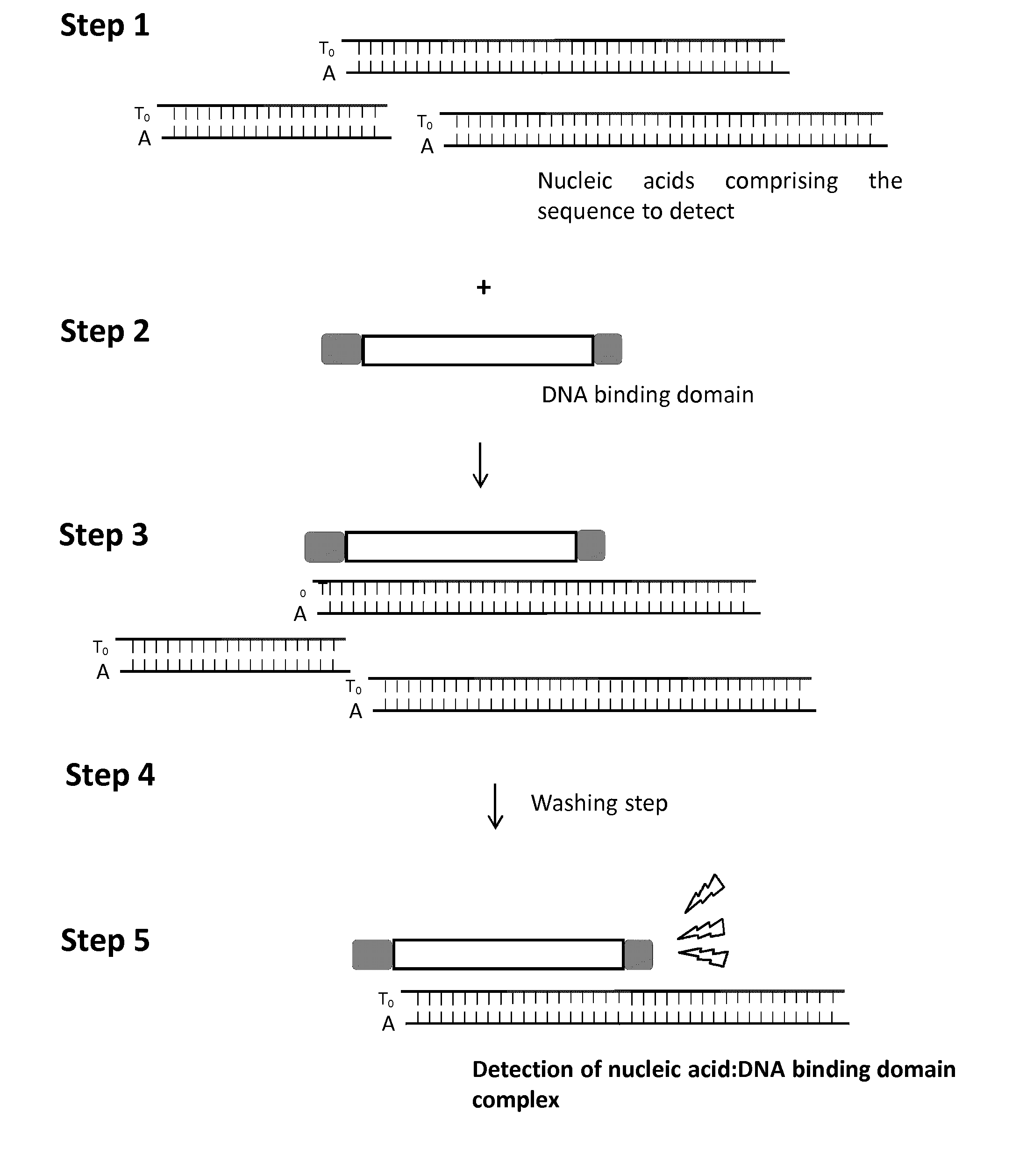
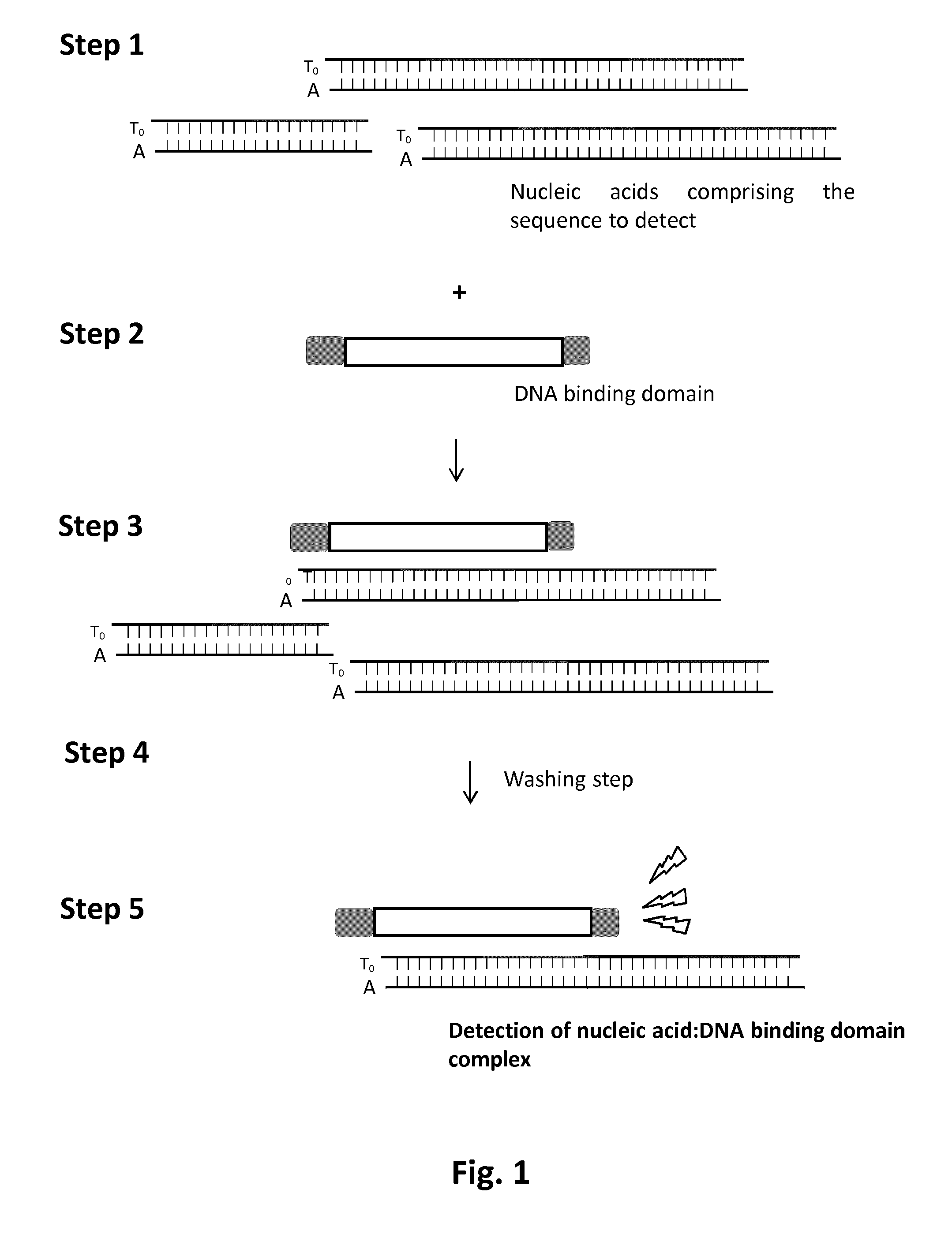
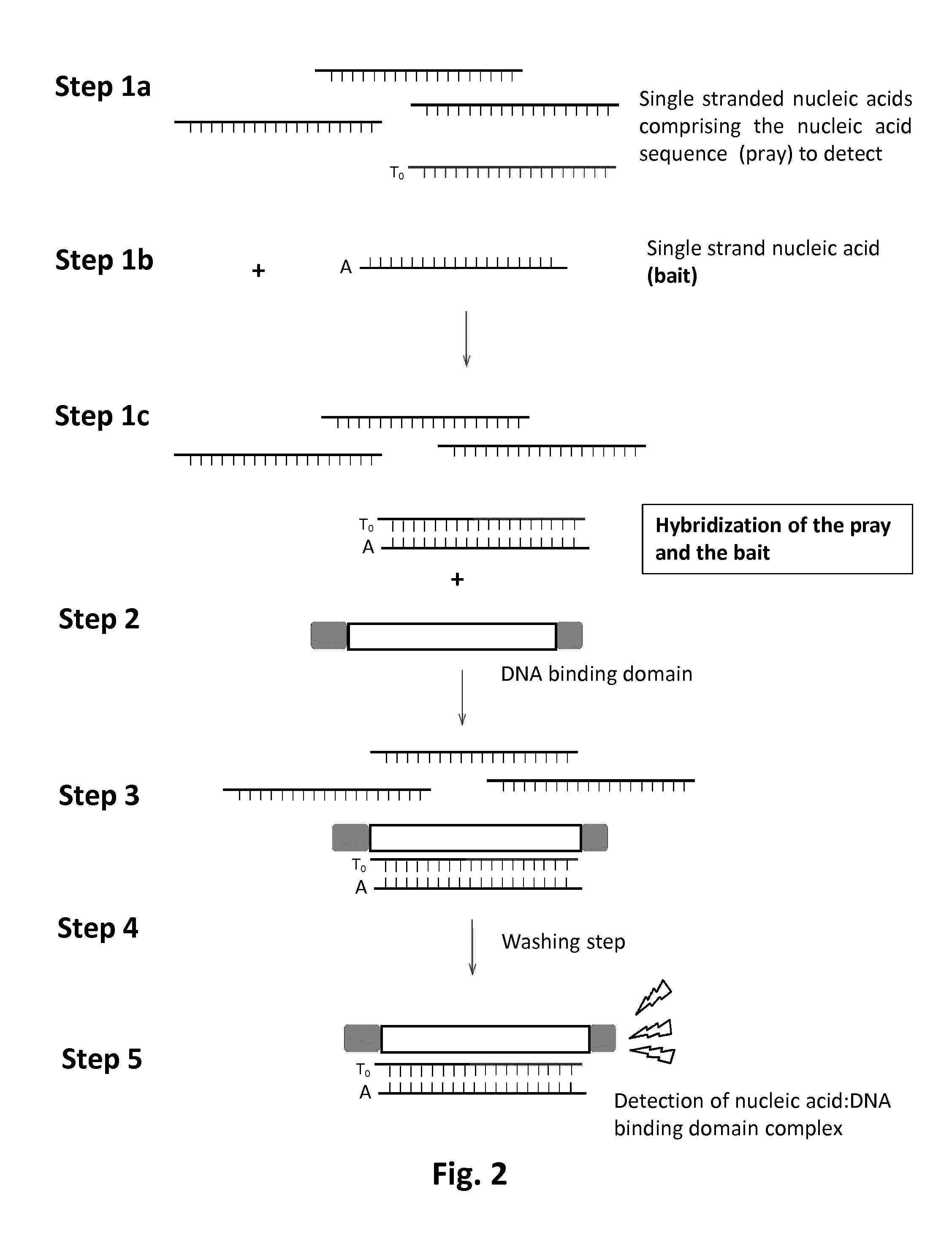
Methods and kits for detecting nucleic acid sequences of interest using dna-binding protein domain
InactiveUS20160355875A1Rapid diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDNA-binding domainNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to a method for the detection of a specific nucleic acid. Specifically, the invention provides a method and kits for detecting the presence of a specific nucleic acid using engineered DNA-binding domains such as Transcription Activator Like-Effector (TALE) domain or modular base-per-base binding domains (MBBBD). The method of the invention is particularly useful for in vitro diagnostic application.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
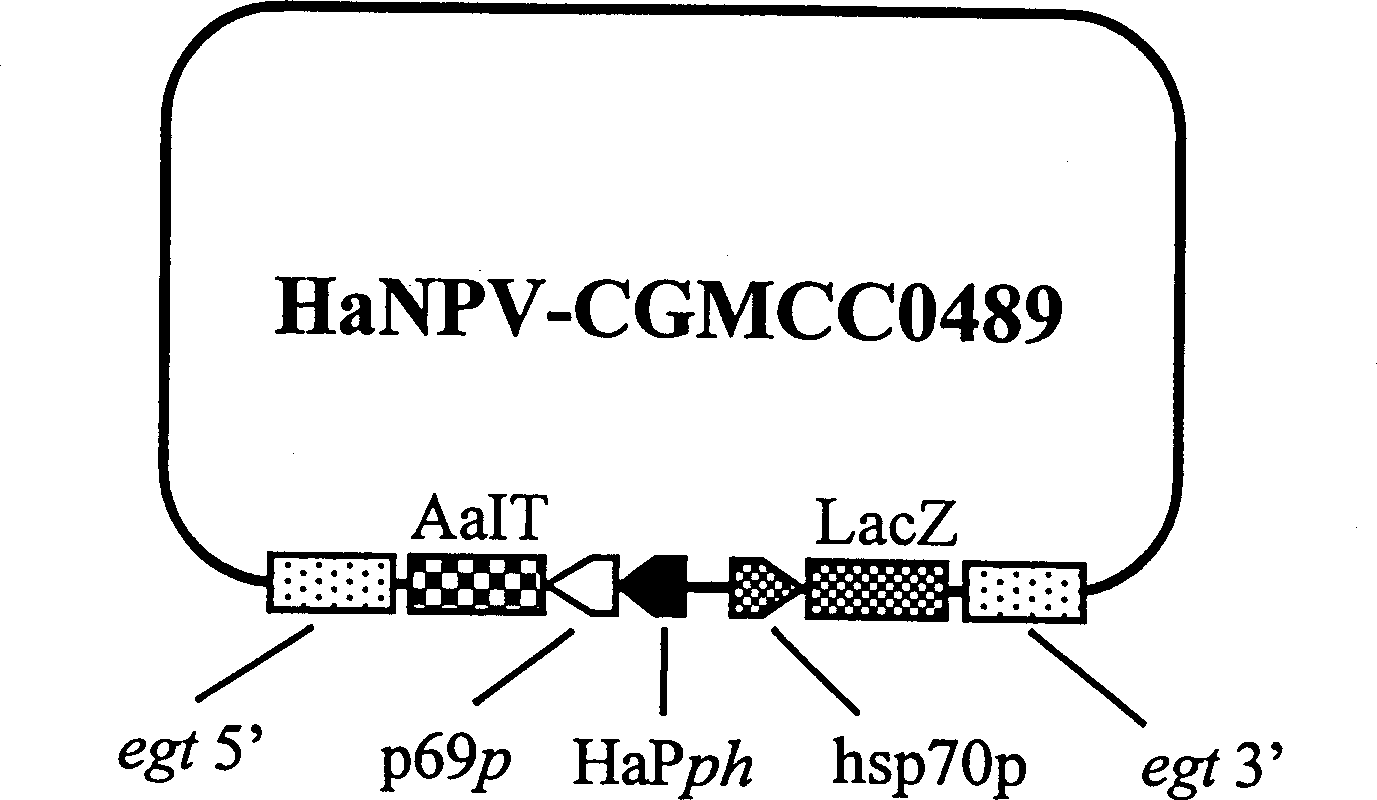
Genetically engineered virus of Chinese ballworm
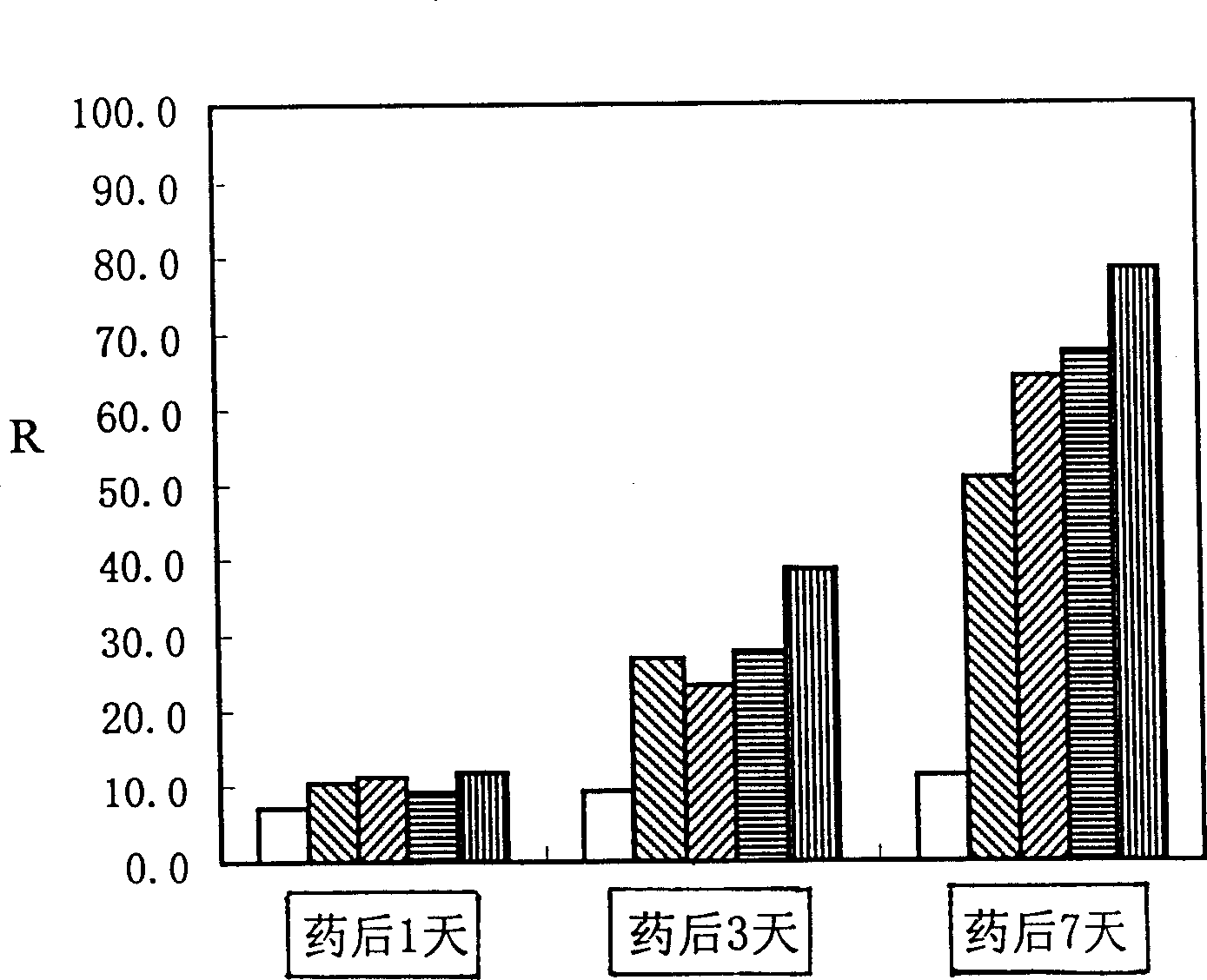
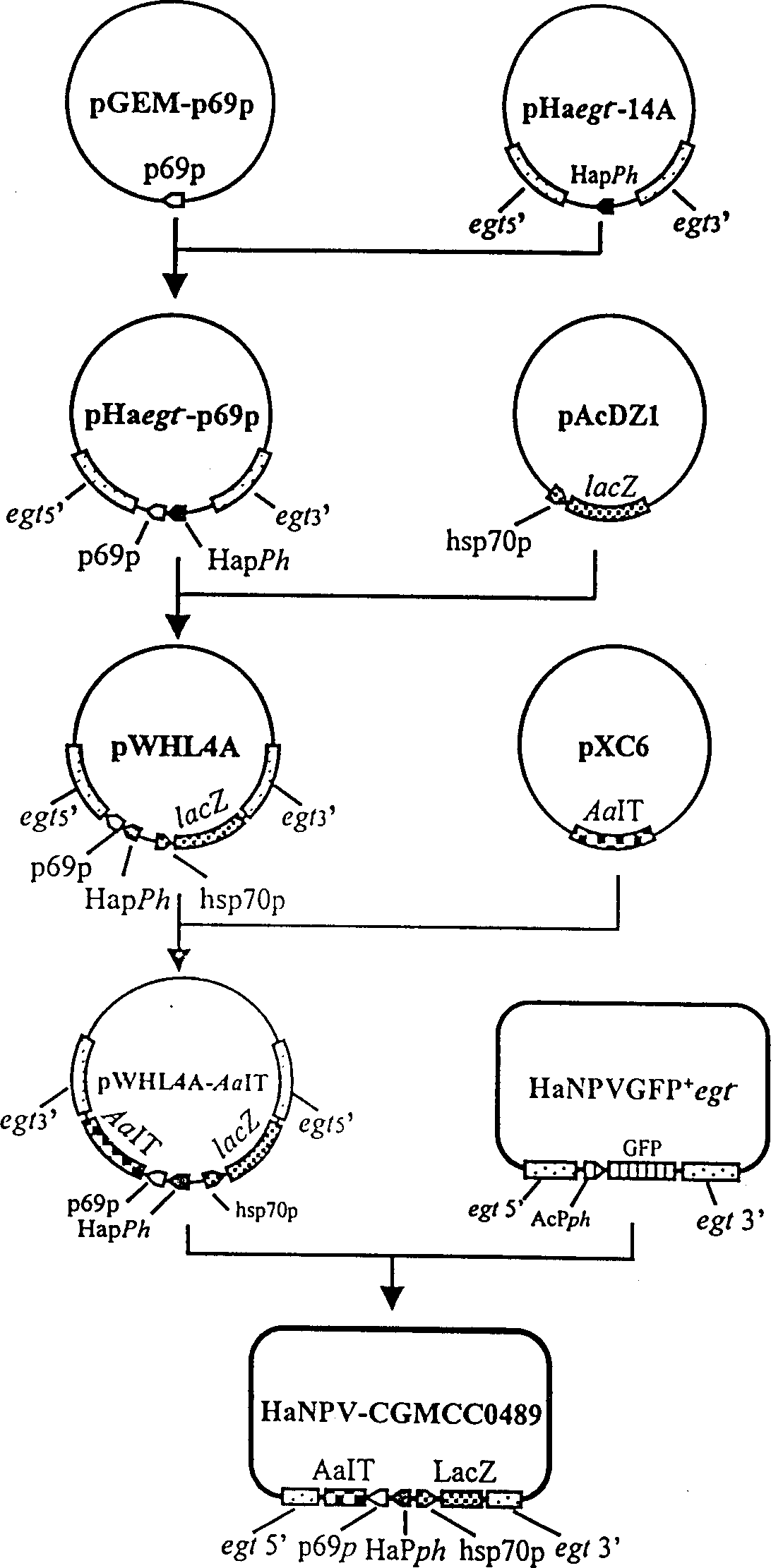
InactiveCN1109105CFast insecticideGood field application effectBiocideViruses/bacteriophagesWild typeEngineered genetic
A genetically engineered virus of Chinese ballworm is obtained by double recombination of wild virus. Its genome is deficient is egt gene. At the position deficient in egt gene, the insect-specific neurotoxic AaIT gene controlled by the promoters of Chinese ballworm virus' alkaline DNA binding protein gene (p6.9) and polyhedrin protein gene (ph) and the beta-galactosidase (LacZ) gene controlled by the promoter of heat shock protein gene (hsp70) are inserted. Its advantages are higher insecticiding speed and better application effect.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
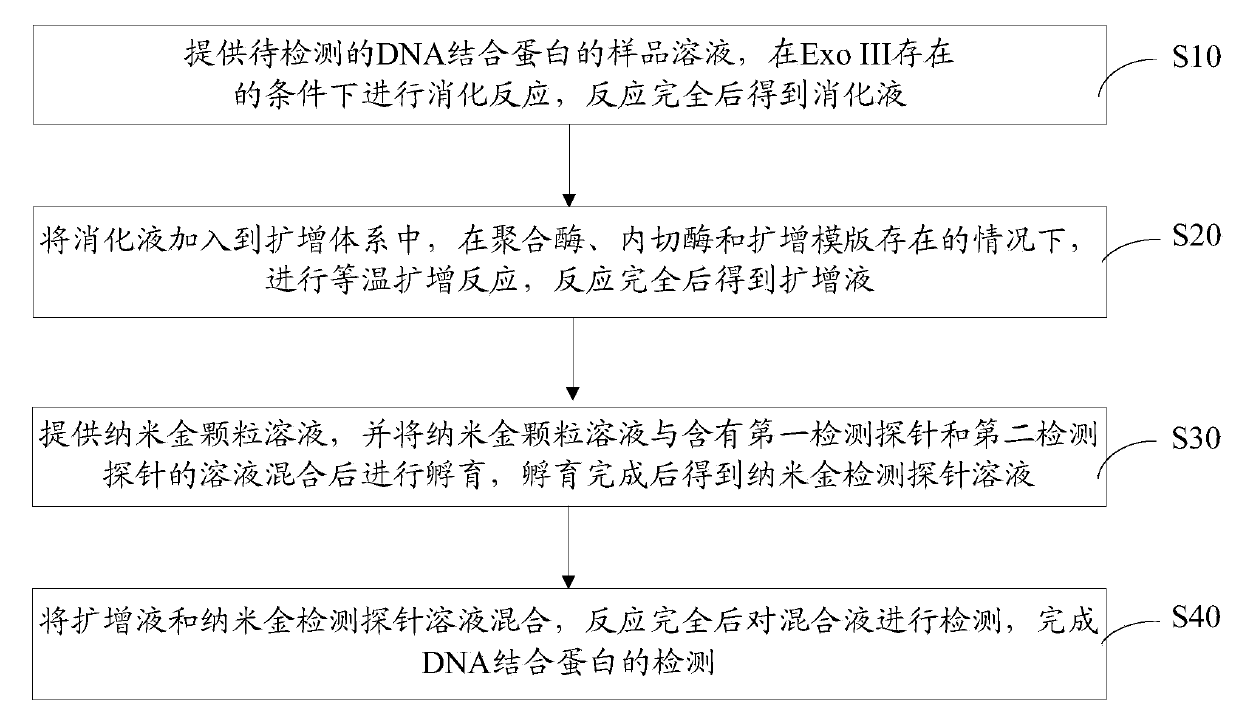
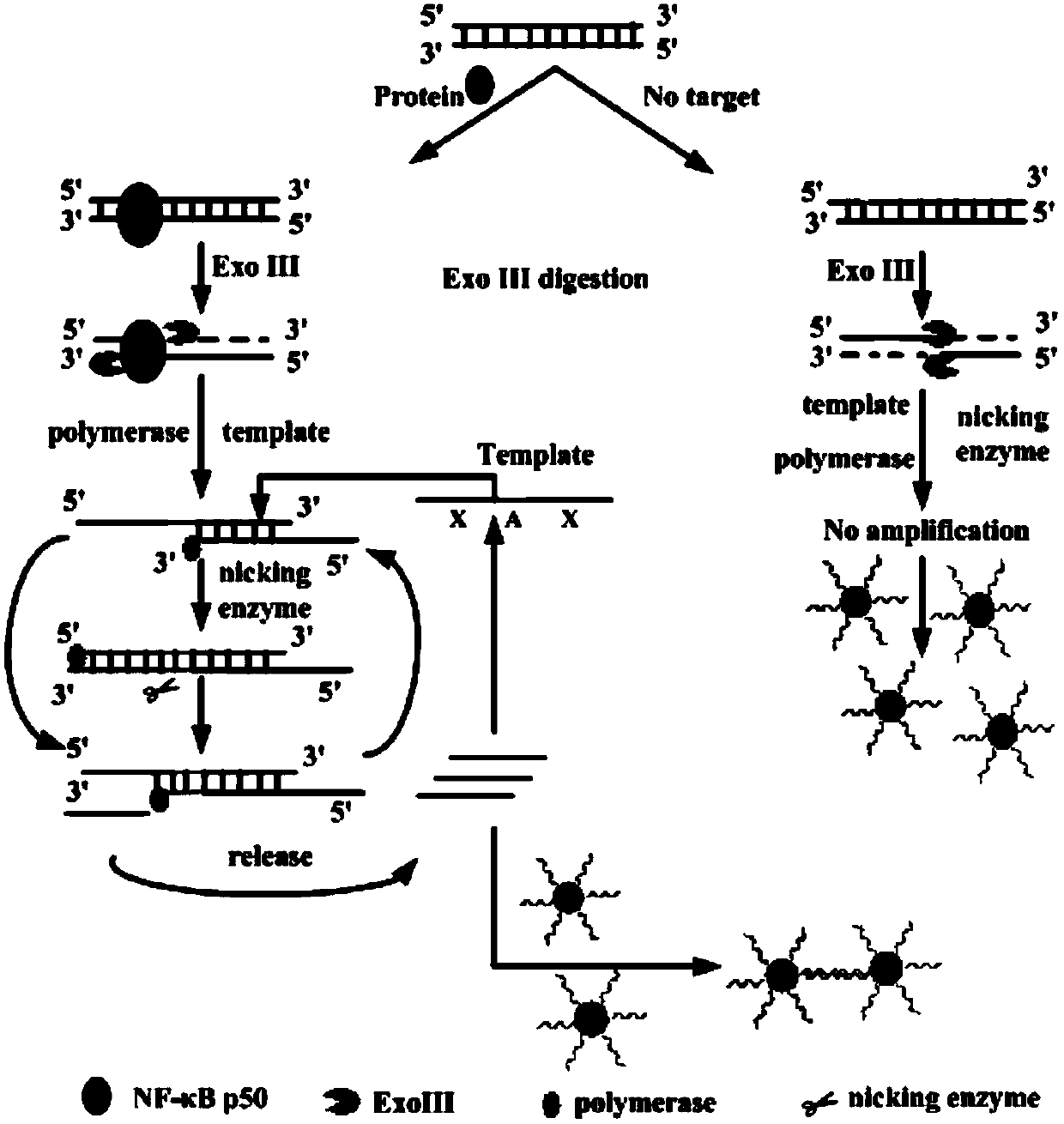
Method for detecting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) binding protein
The invention discloses a method for detecting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) binding protein. The method comprises the following steps: providing a sample solution of the DNA binding protein to be detected, and carrying out digestion reaction under the condition that Exo III exists, thus obtaining a digestive juice after complete reaction; adding the digestive juice in an amplification system, carrying out isothermal amplification reaction under the condition that a polymerase, an incision enzyme and an amplification template exist to obtain an amplification solution; mixing a gold nanoparticle solution with a solution containing a first detection probe and a second detection probe and then carrying out incubation to obtain a nano gold detection probe solution; mixing the amplification solution with the nano gold detection probe solution and then detecting a mixed solution to complete the detection for the DNA binding protein. The first detection probe and the second detection probe are combined with a target DNA in an amplification product so that gold nanoparticles of the detection probes gather to cause that the color of the mixed solution changes, thus the method is visual in phenomenon and high in sensitivity.
Owner:深圳柏垠生物科技有限公司
Method for separating DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) binding protein and accurately positioning DNA binding site
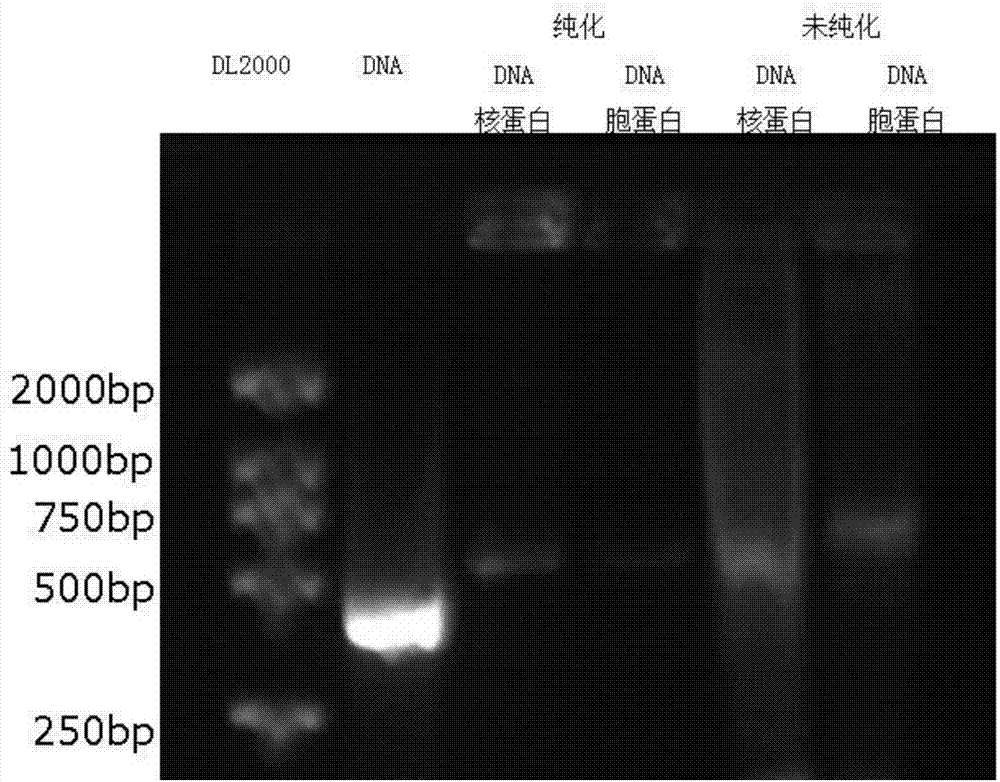
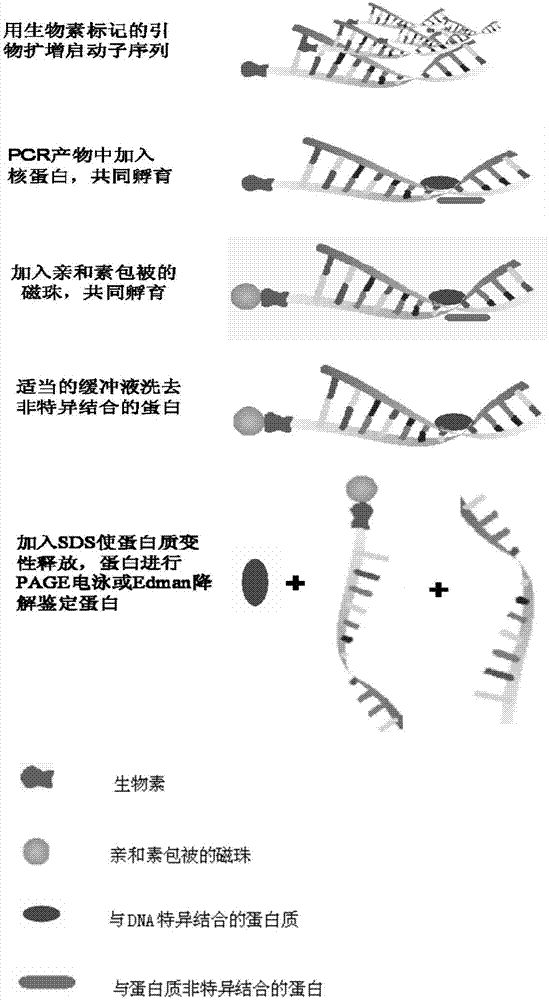
InactiveCN104725465AAccurately locate the site of actionEasy to introduceMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsMagnetic beadBinding site
The invention provides a method for separating DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) binding protein and accurately positioning DNA binding site, which comprises the following steps: DNA binding protein separation: carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on a DNA segment to be researched by using biotin-labeled primers, sequentially adding nucleoprotein or cytoplast protein and avidin-coated magnetic beads, co-incubating, washing off nonspecific binding protein, and adding SDS (sodium dodecylsulfate) to denature and release the protein; and protein DNA binding site positioning: by using the DNA segment to be researched as a template, carrying out PCR reaction by using different primers to obtain overlapping DNA segments, and positioning the DNA binding site of the isolated protein according to the affinity difference of the overlapping DNA segments for the isolated protein.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com